Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97results about How to "Service is blocked" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
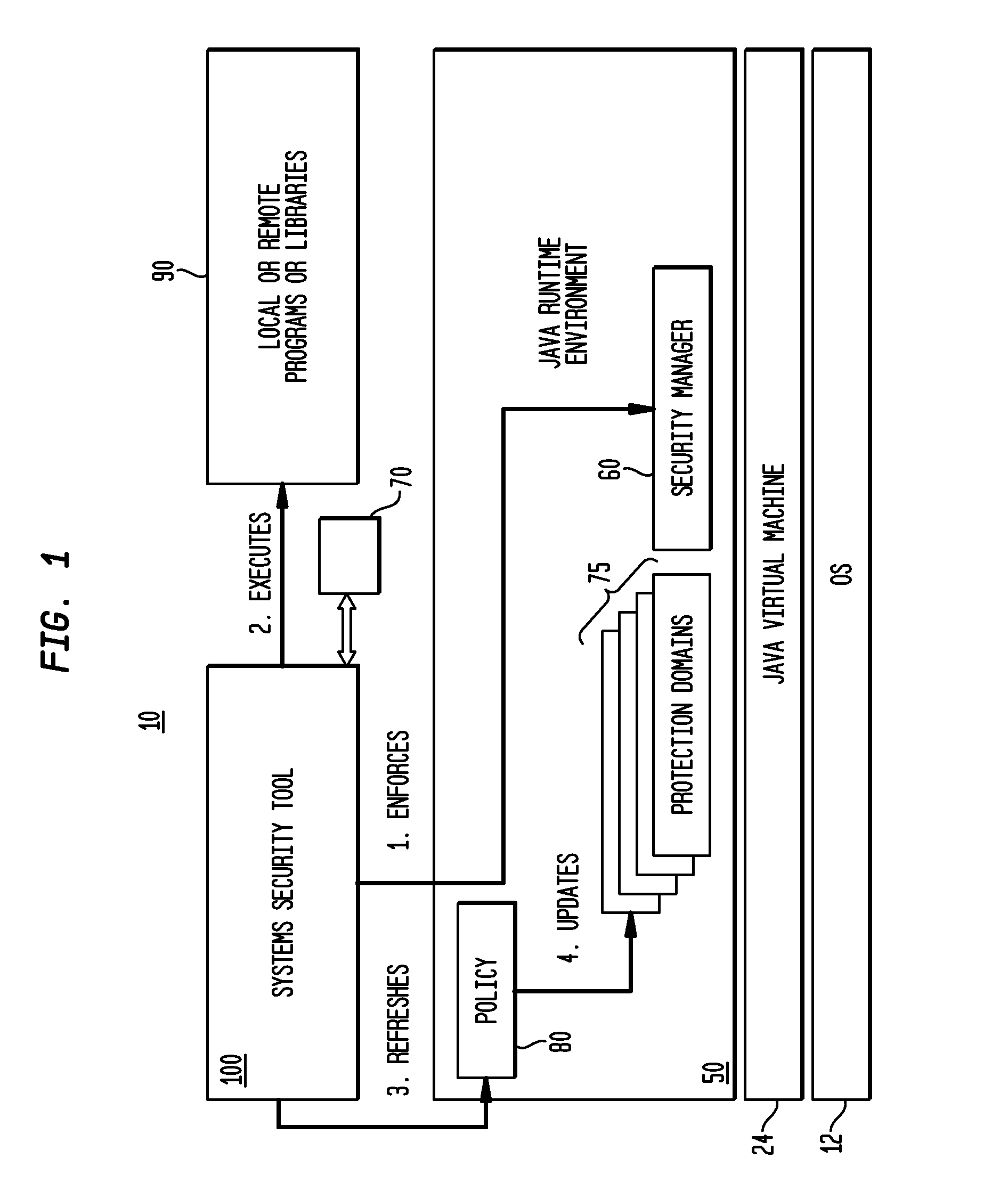
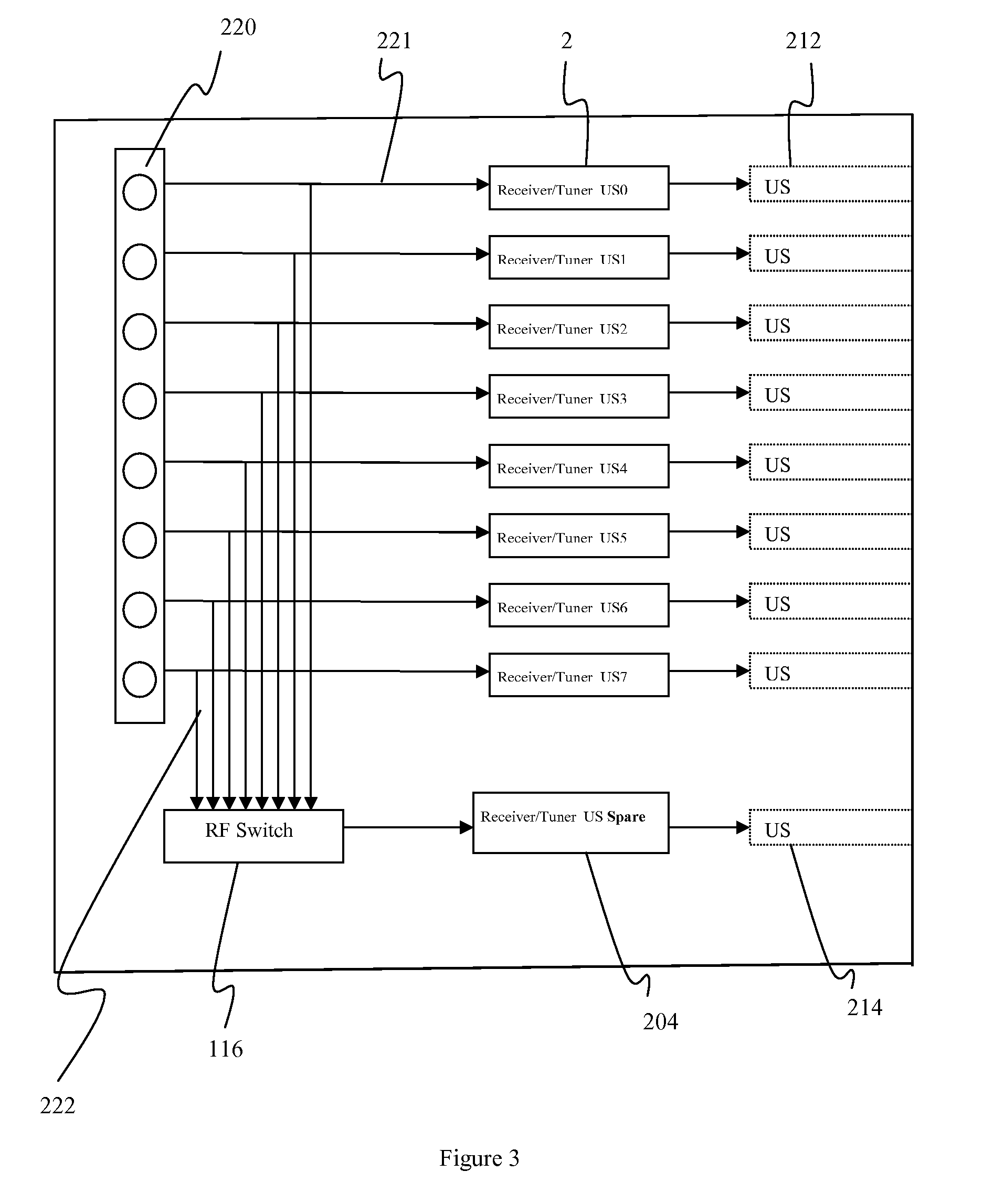
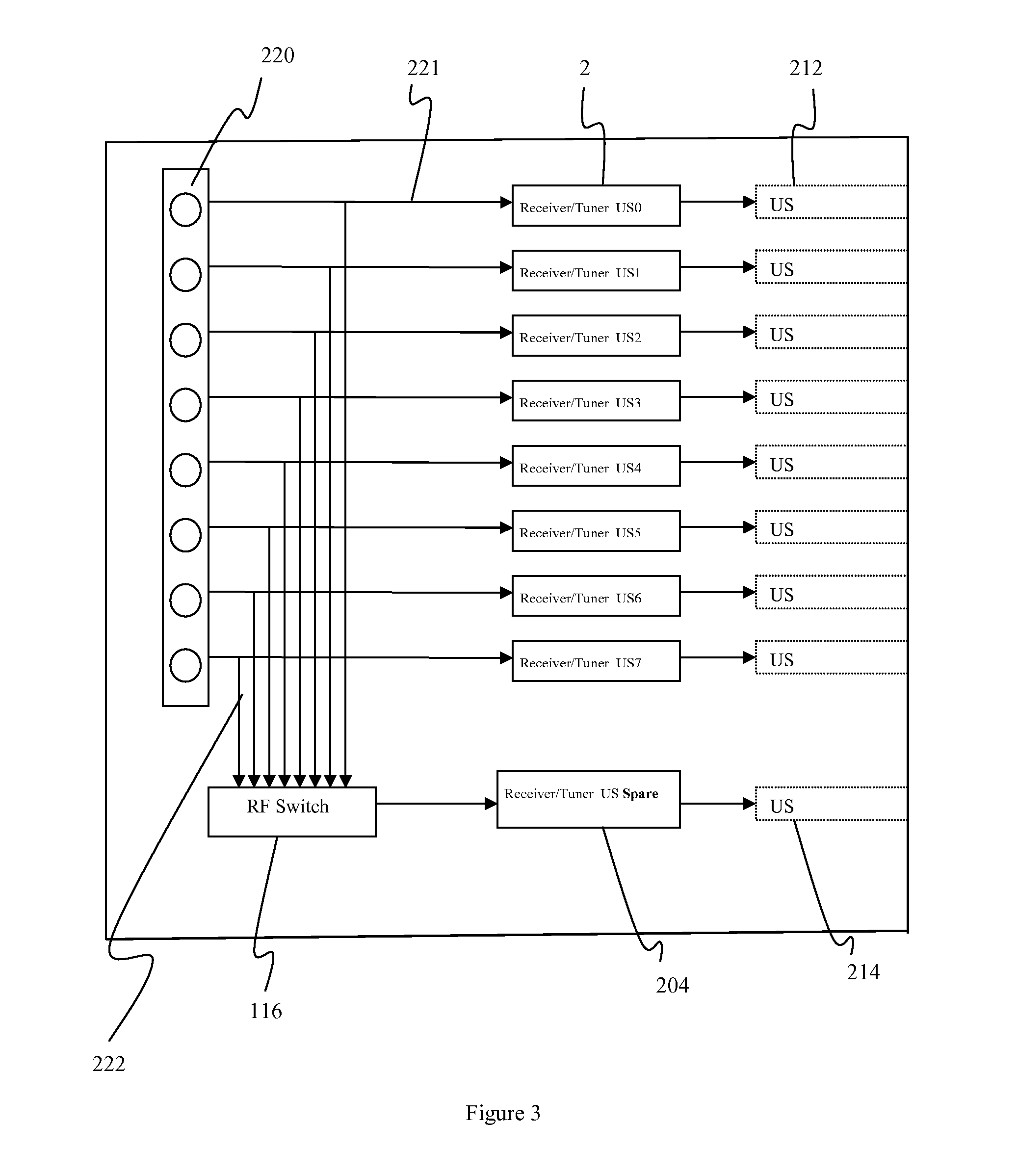
Load balancing system
InactiveUS20050102400A1Prevent reduction of service performanceLower performance requirementsResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram planningDistributed computing
A load balancing system having a plurality of service servers and a load balancer which prevents a service performance from being reduced by an overload of requests on the service servers. The system includes a load balancer and a administration server, the load balancer outputs an access log relating to an access to the service server, and the administration server performs statistical operation over the access log. The administration server prepares a service server run schedule on the basis of a result of the statistical operation and informs the load balancer of it. The load balancer controls distribution of a request to the service server according to the informed run schedule.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
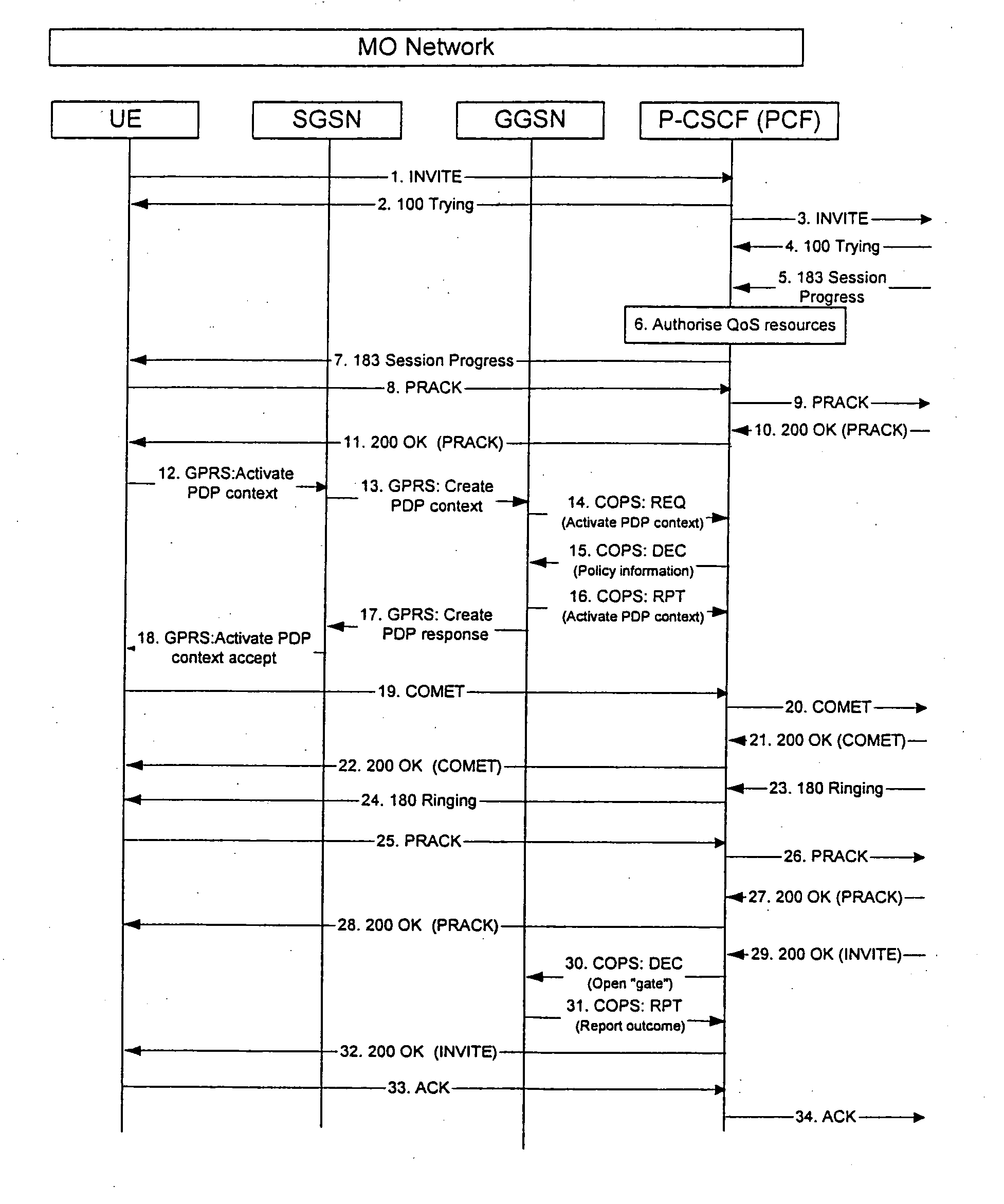
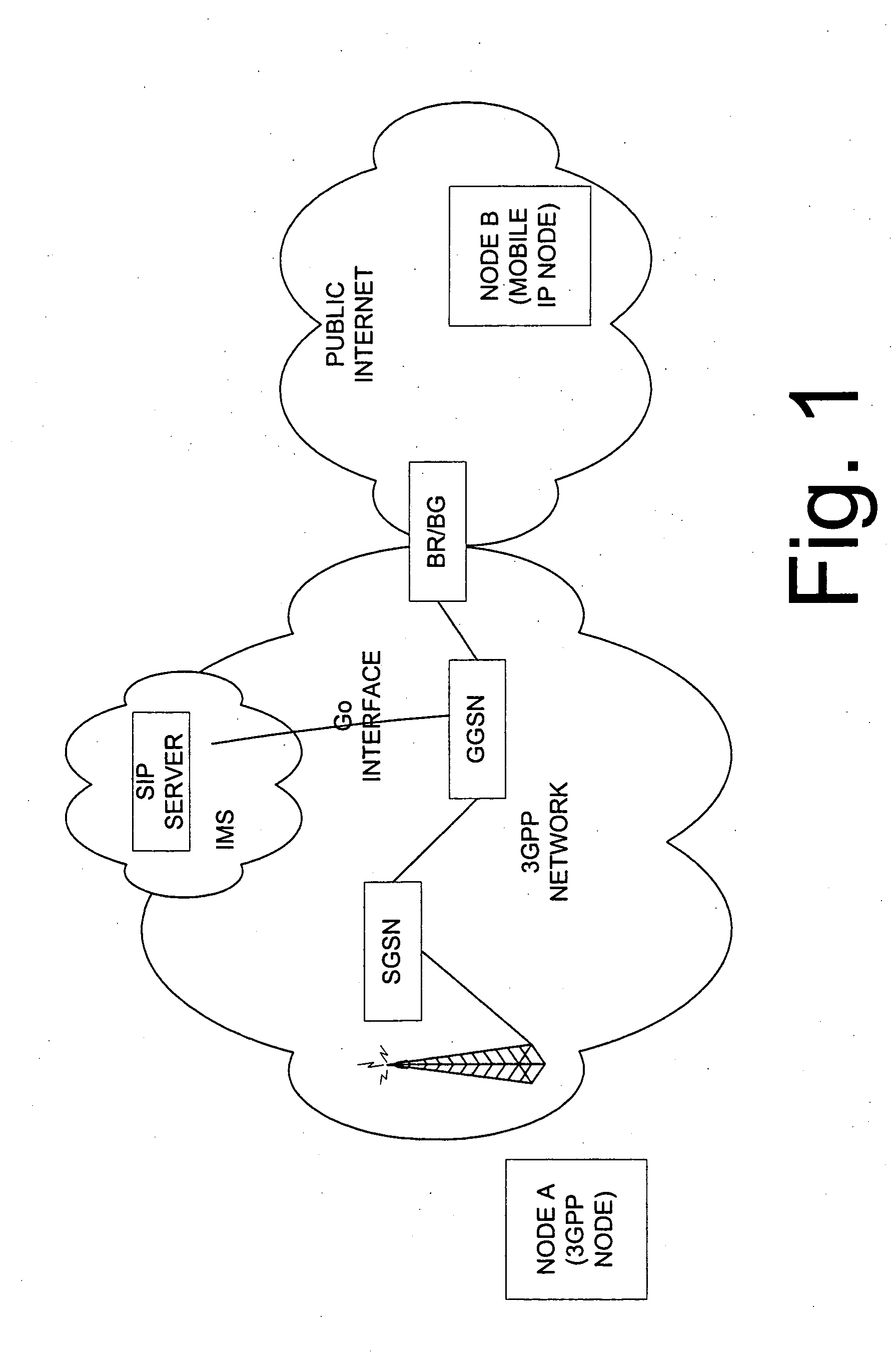
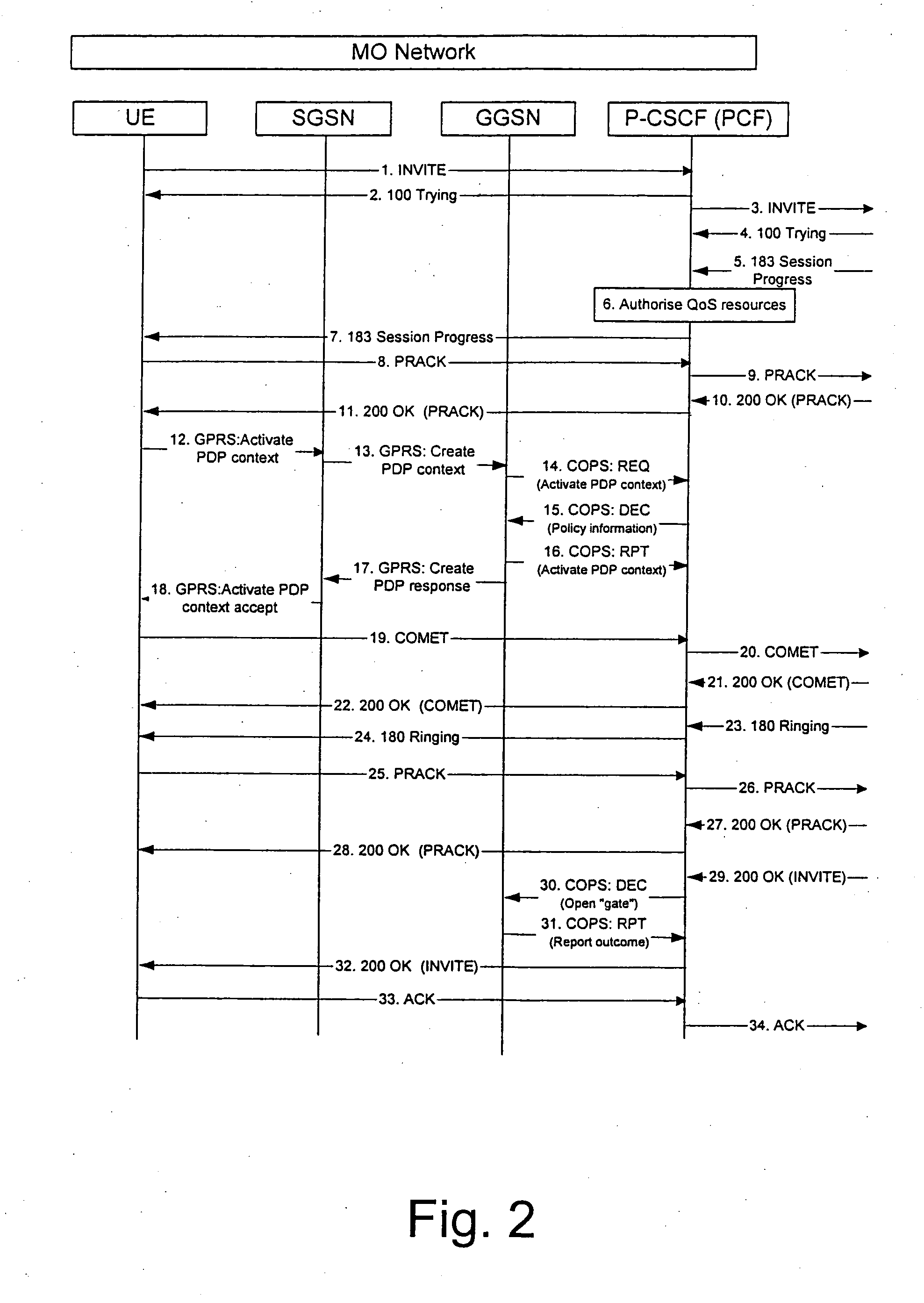
Method to support mobile IP mobility in 3GPP networks with SIP established communications
InactiveUS20050165917A1Service is blockedAvoid attackMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionNetwork elementNetworked system
The invention proposes a method for controlling a connection between a first network node and a second network node, wherein the connection is controlled by a packet filtering function filtering packets such that a packet is discarded in case a source address and / or a destination address do not comply with a filtering rule, wherein the packet filtering function is configured at a connection set up, and at least one of the first or second network node is adapted to change its address, the method comprising the steps of informing, the packet filtering function about the new address of the network node having changed its address, and updating the packet filter of the packet filtering function by using the new address of the network node having changed its address. The invention also proposes a corresponding network system comprising at least a network node and a packet filtering network element. Furthermore, the invention proposes a corresponding packet filtering network device.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
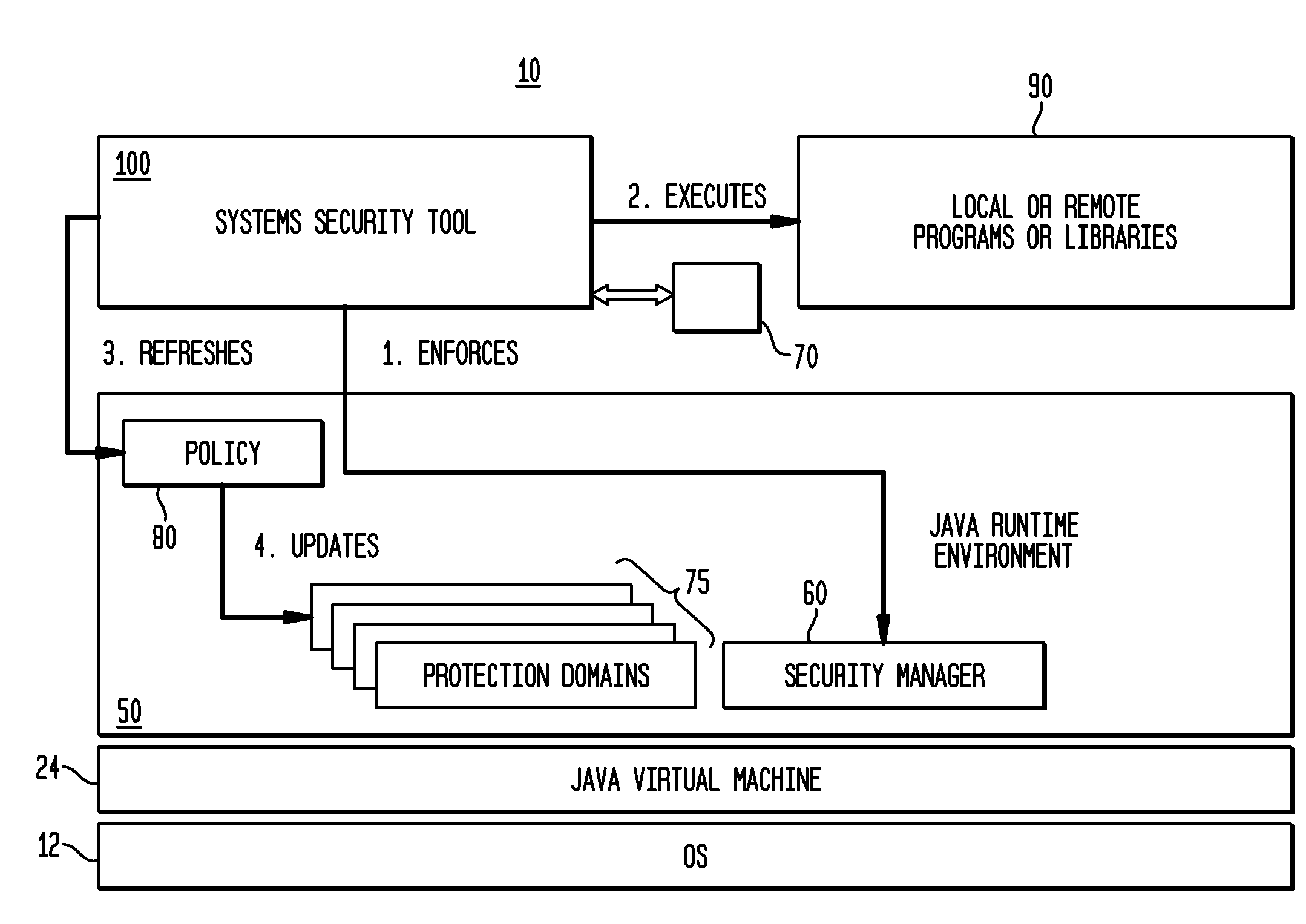
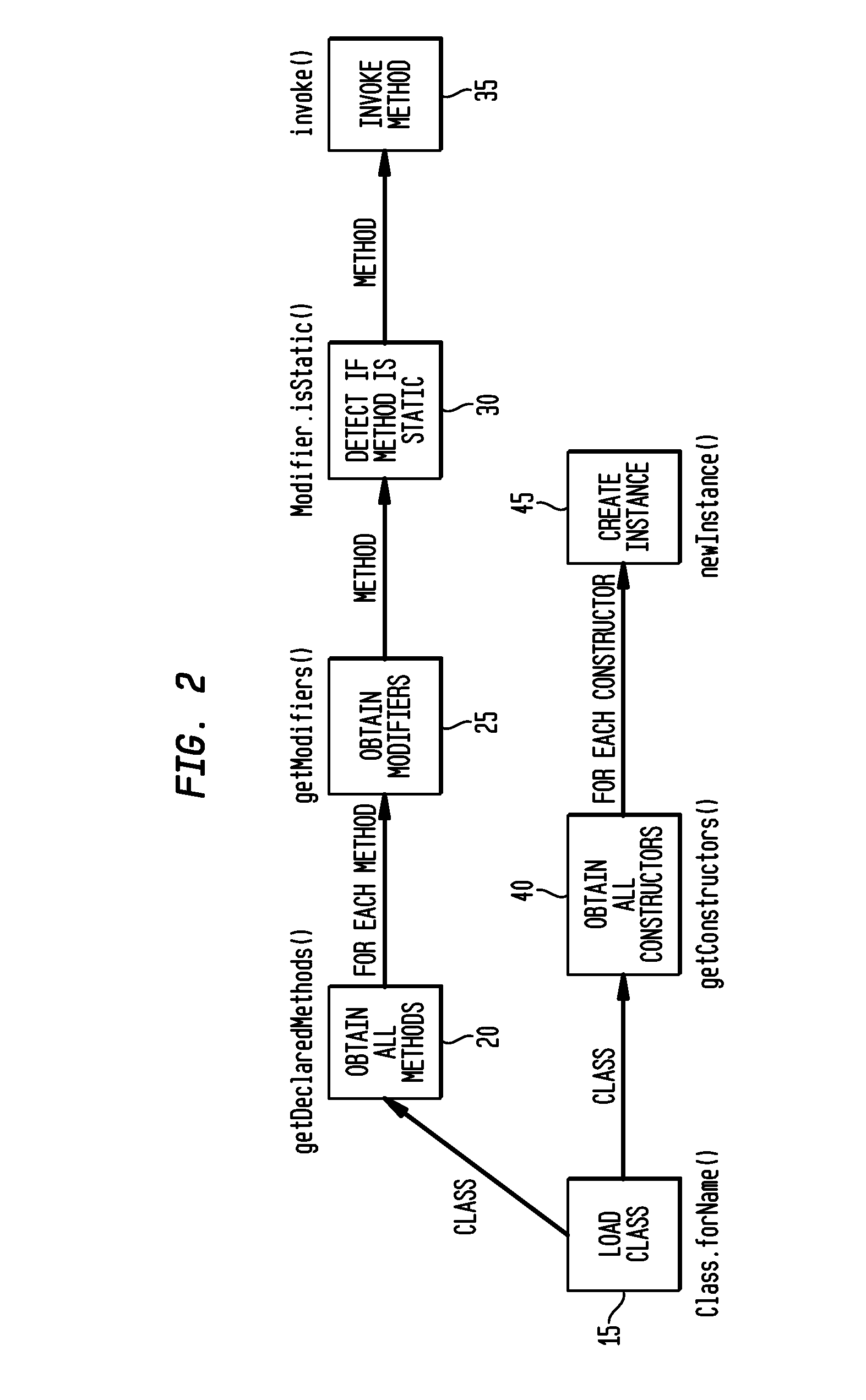
Method and system for run-time dynamic and interactive identification of software authorization requirements and privileged code locations, and for validation of other software program analysis results
ActiveUS20090007223A1Service is blockedOptimizationComputer security arrangementsTransmissionSystems approachesSecurity policy
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Filtering subscriber traffic to prevent denial-of-service attacks
ActiveUS7379423B1Service is blockedError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityIp address
A method of storing address lease information including a Media Access Control (MAC) address, an IP address, and a port for a subscriber in a database coupled to a network edge device when an address lease is associated with the subscriber, receiving subscriber packets on at least one port of the network edge device, comparing source address information from packets purportedly transmitted by the subscriber with address lease information associated with the subscriber, and forwarding those of the packets if source address information from the packets, including source MAC and IP addresses, corresponds to address lease information associated with the subscriber.
Owner:CALIX
Terminal, method and computer program product for validating a software application
ActiveUS20060101408A1Service is blockedDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionOperational systemSoftware
A terminal for validating a software application includes a processor capable of operating an operating system (OS) platform (e.g., Symbian™ OS platform), and capable of operating at least one software application above the OS platform. The software application(s) are associated with a permission record that includes permissions identifying services the software application is authorized to receive from the OS platform. The OS platform is capable of receiving a request, from a software application, for a service of the OS platform. The OS platform can determine if the software application is authorized to receive the requested service based upon the associated permission record. And if the software application is authorized, the OS platform is capable of providing the requested service to the software application.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for utilizing portable e-mail addresses
InactiveUS20070260693A1Improve efficiencyImprove securityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionEmail addressAddress resolution
A signal bearing medium tangibly embodies a program of machine-readable instructions executable by a digital processing apparatus to perform operations comprising receiving an email message having an extended email address encoded virtual address, resolving said address to an actual email address, replacing the virtual address with the actual email address, and transmitting said email message.
Owner:IBM CORP
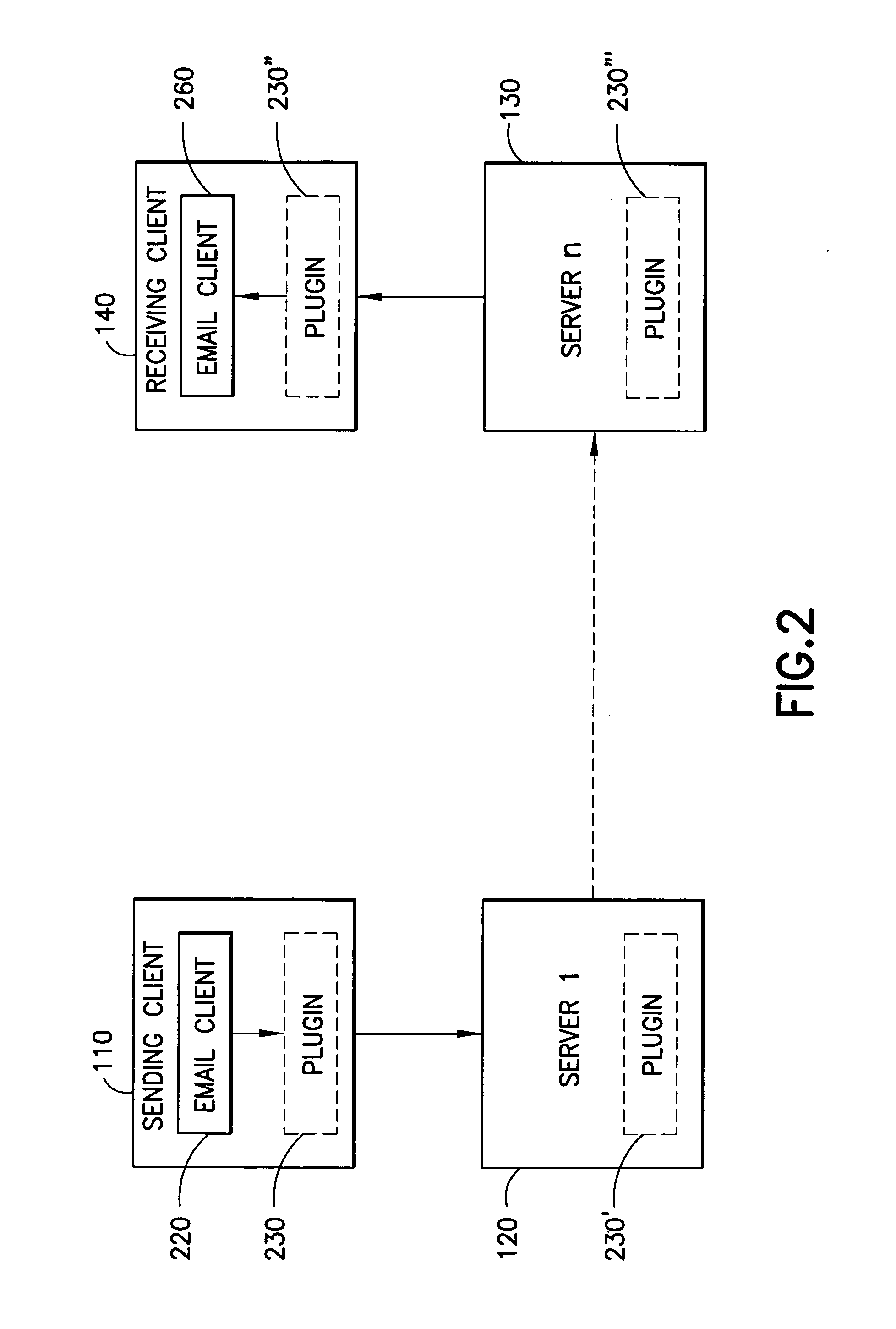
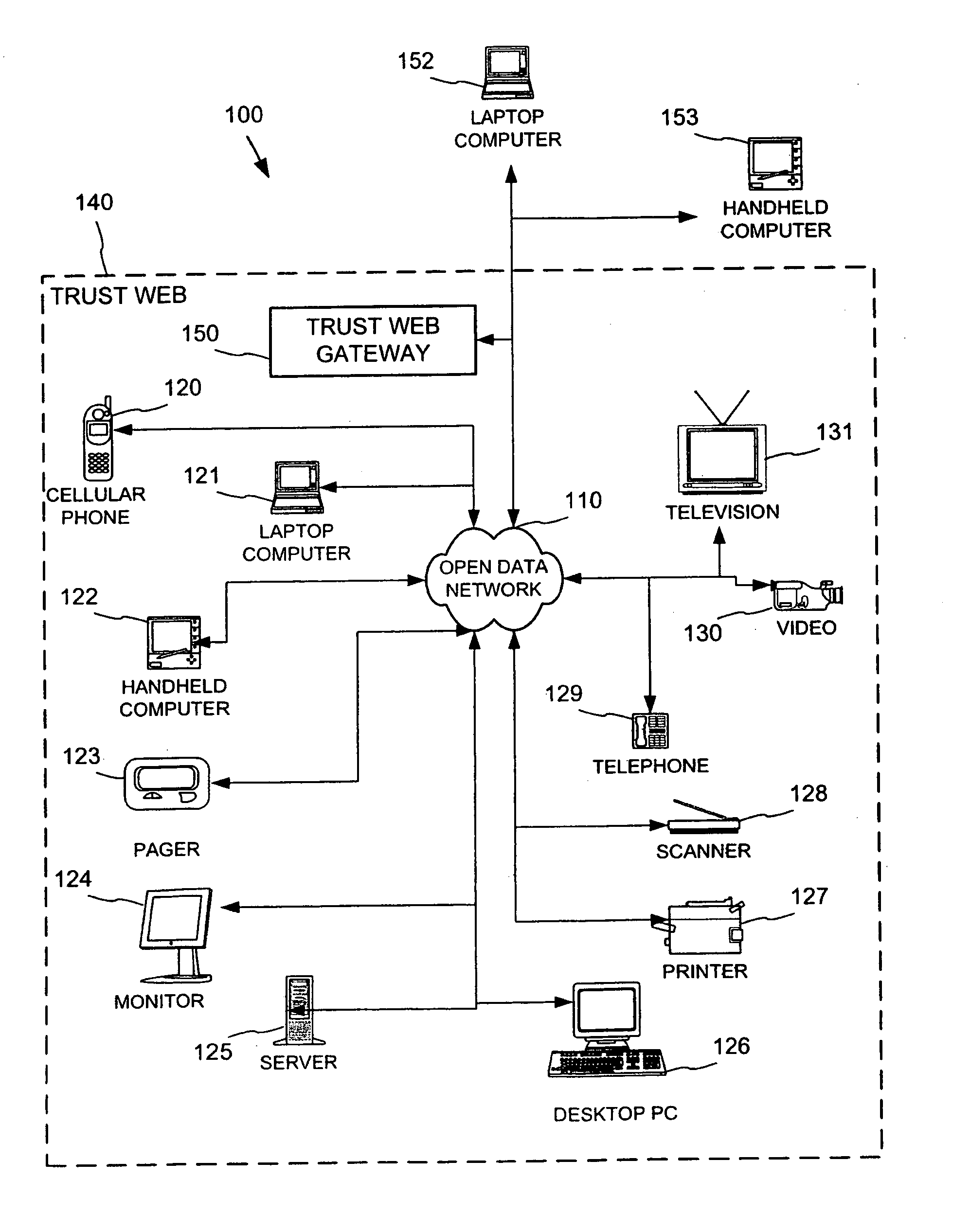
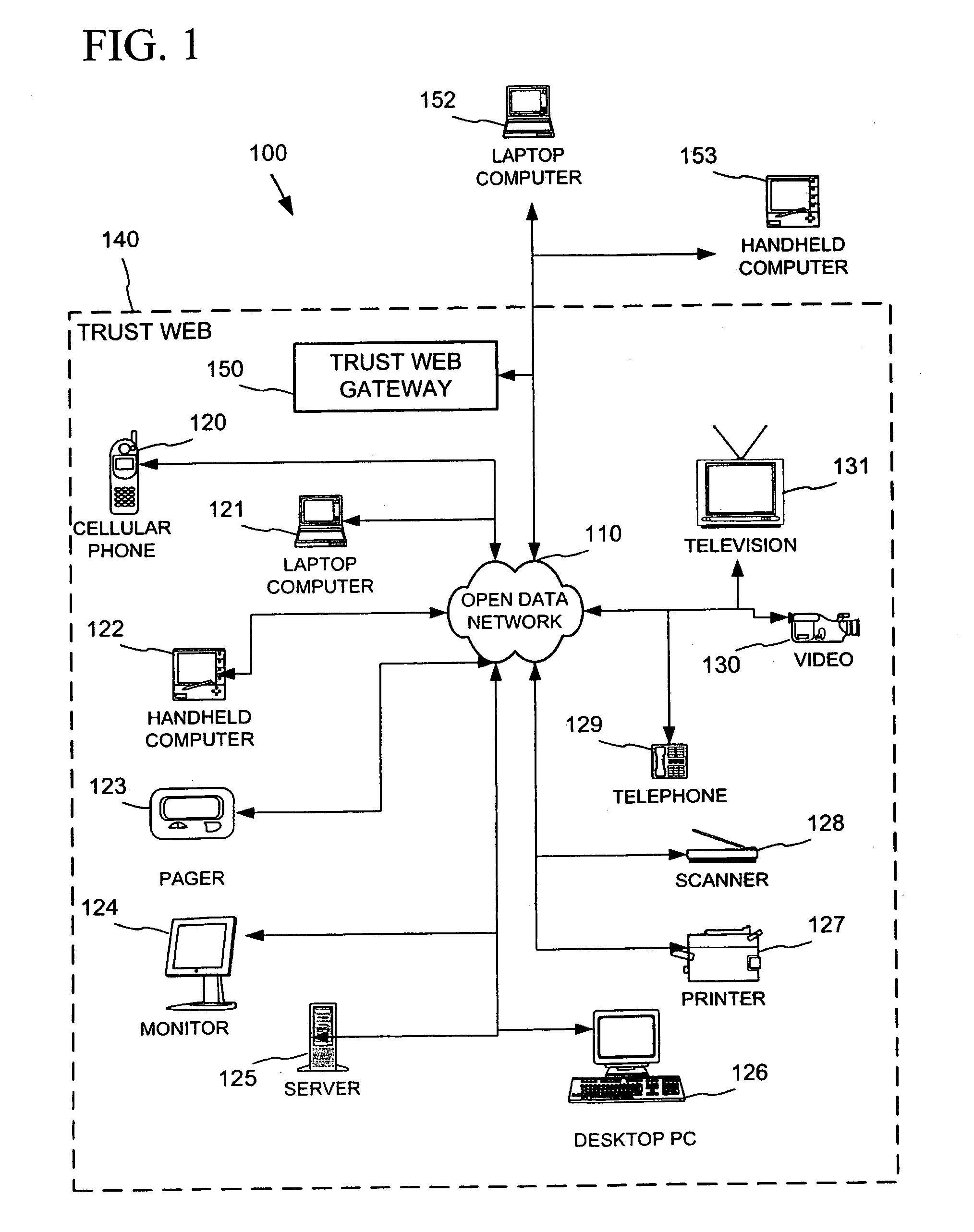
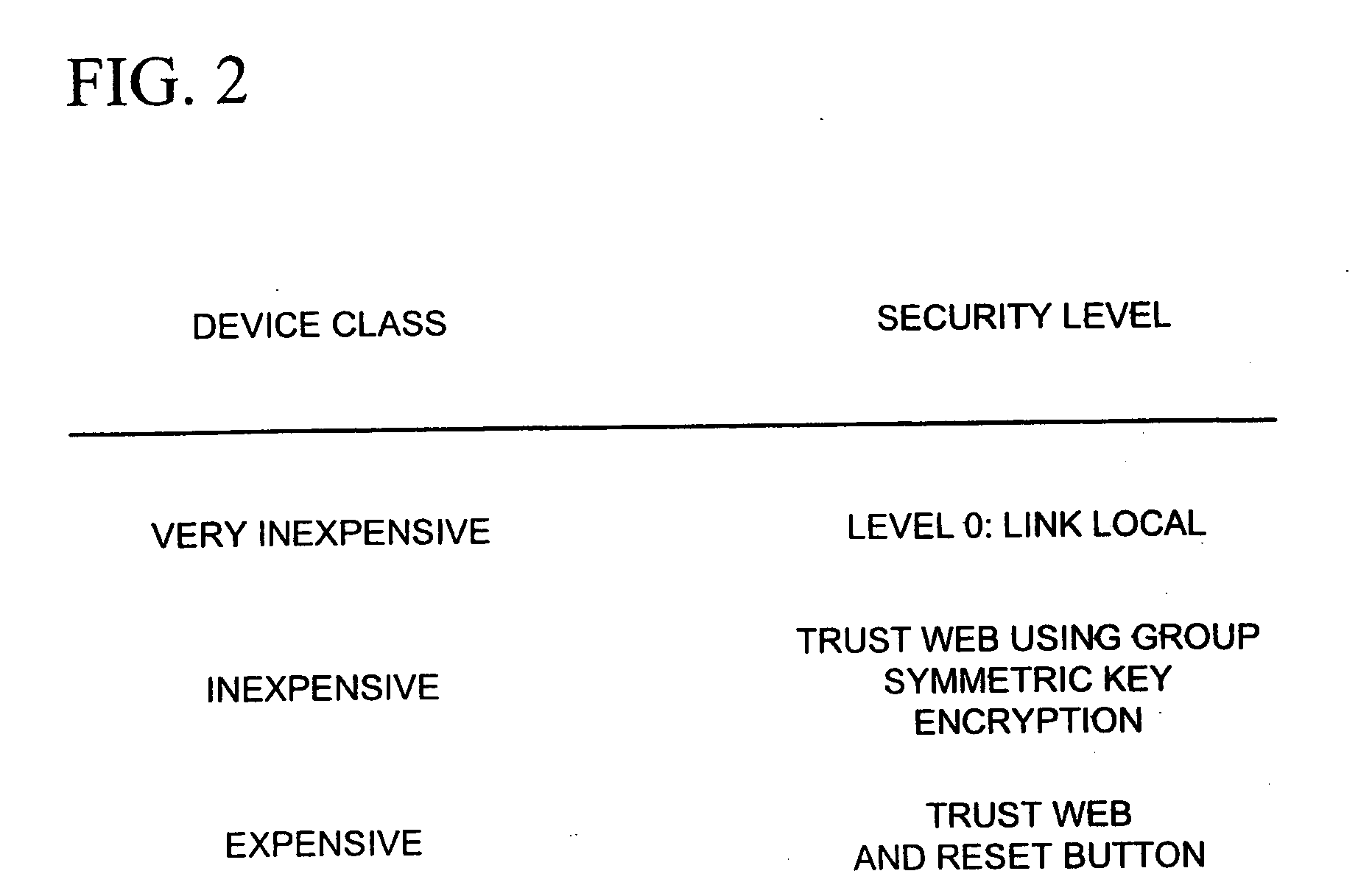
Establishing secure peer networking in trust webs on open networks using shared secret device key
InactiveUS7082200B2CostImprove connectivityKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsS/KEYVia device
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Communication connection control mechanism in a core network ordered access change scenario
InactiveUS20060221903A1Stable serviceStable connection quality levelData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAccess networkControl communications
There is proposed a mechanism for controlling a communication connection of a user equipment in a communication network. The communication network comprises at least a core network subsystem having at least one core network control element, and a first access network subsystem and at least a second access network subsystem. On one hand, when it is detected that at least one connection parameter of a communication connection of the user equipment can not be maintained by the first access network subsystem, a connection modification message is sent to the core network control element. The core network control element responds with an acknowledgement message the acknowledgement message comprising an instruction parameter for instructing that the communication connection of the user equipment is to be changed to the second access network subsystem being determined to having the capability to provide the connection parameter. On the other hand, when a change of a communication connection of the user equipment from the first access network subsystem to the second access network subsystem is to be performed, it is checked whether or not the cell change is executable. On the basis of the result of the checking step, a message is sent to the core network control element comprising an information element about the execution of the change of the access network subsystem.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Shared interrupt controller for a multi-threaded processor
InactiveUS20080091867A1Service is blockedSimple and efficientRegister arrangementsDigital computer detailsEmbedded system
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
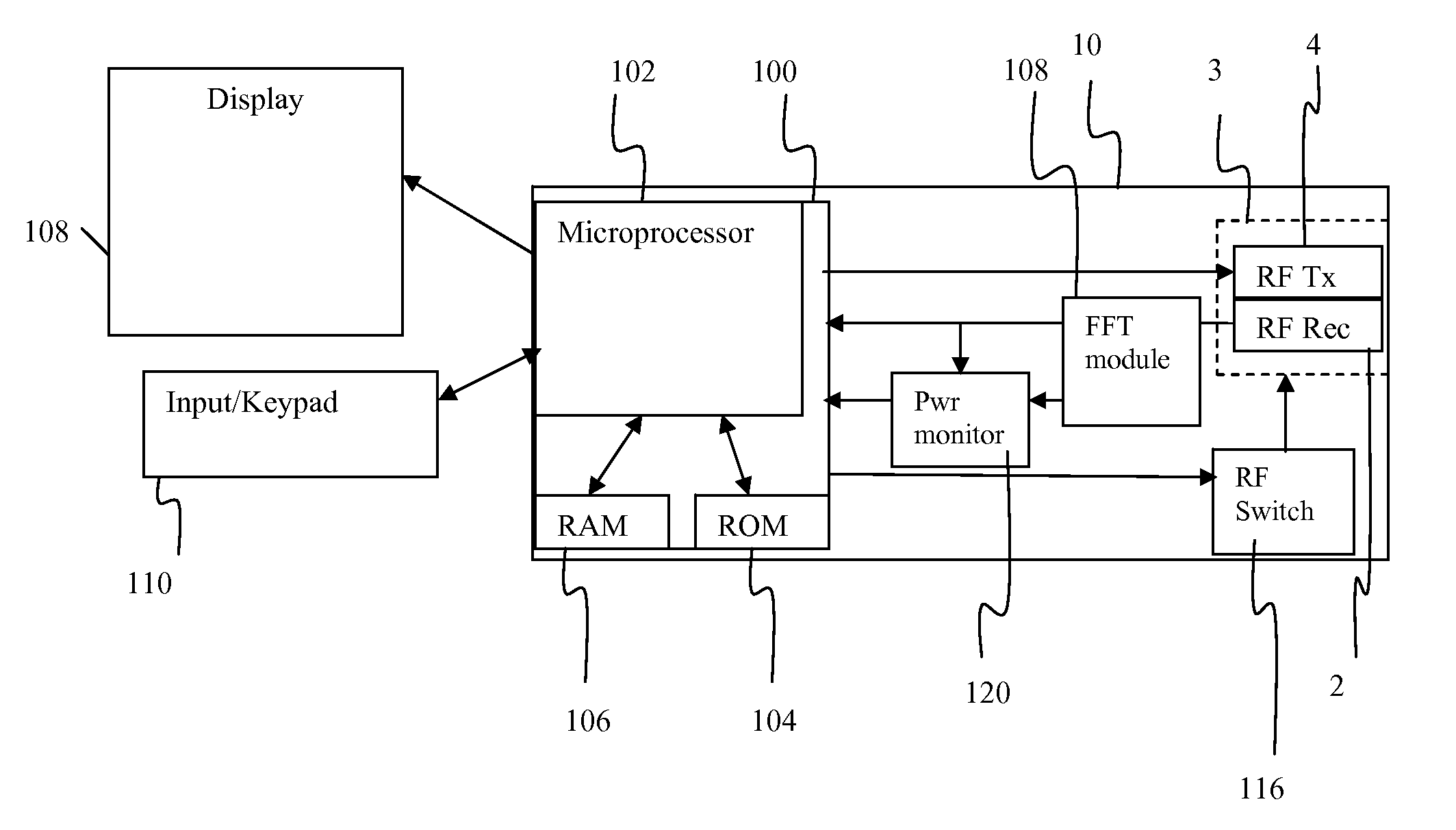
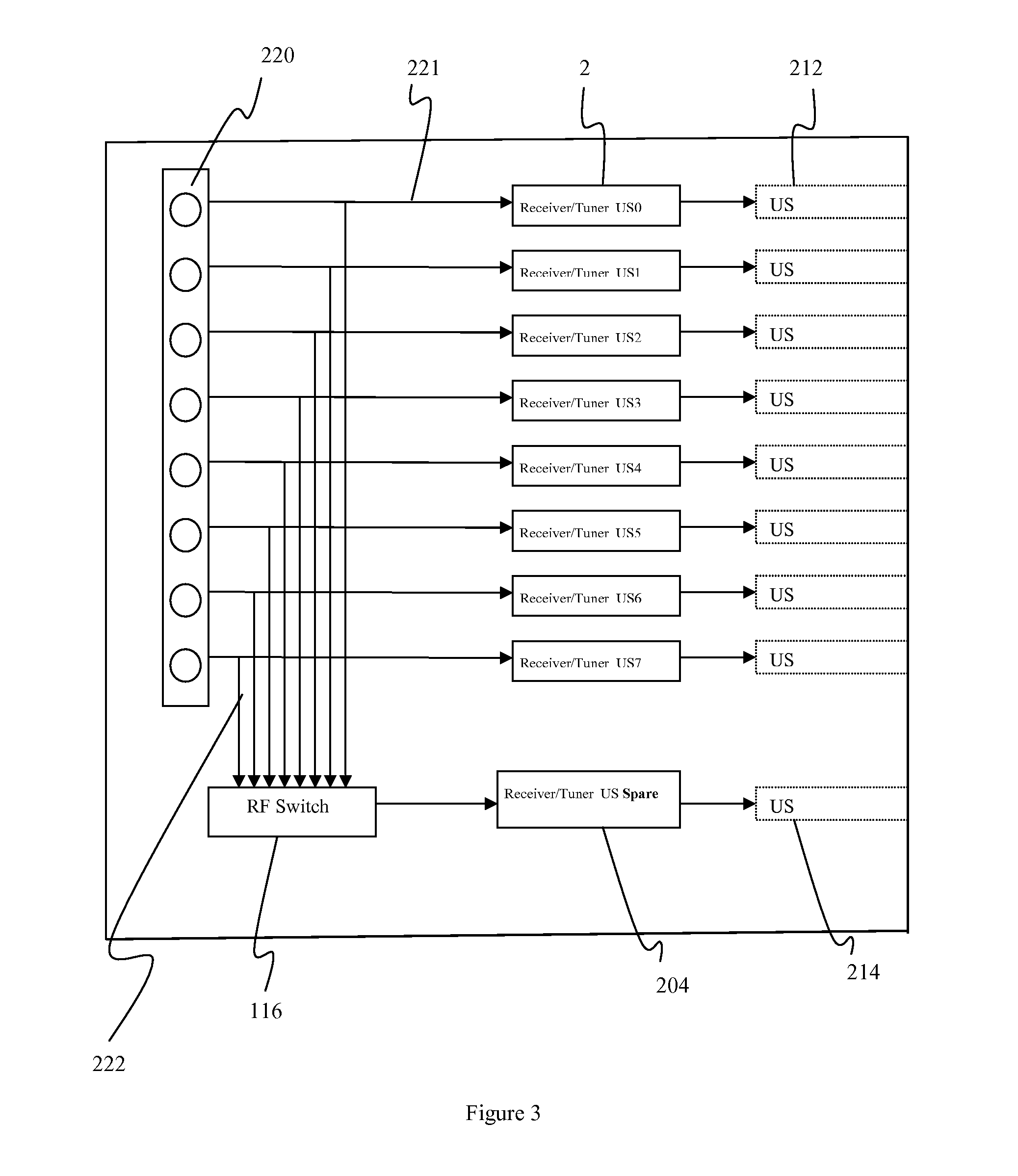
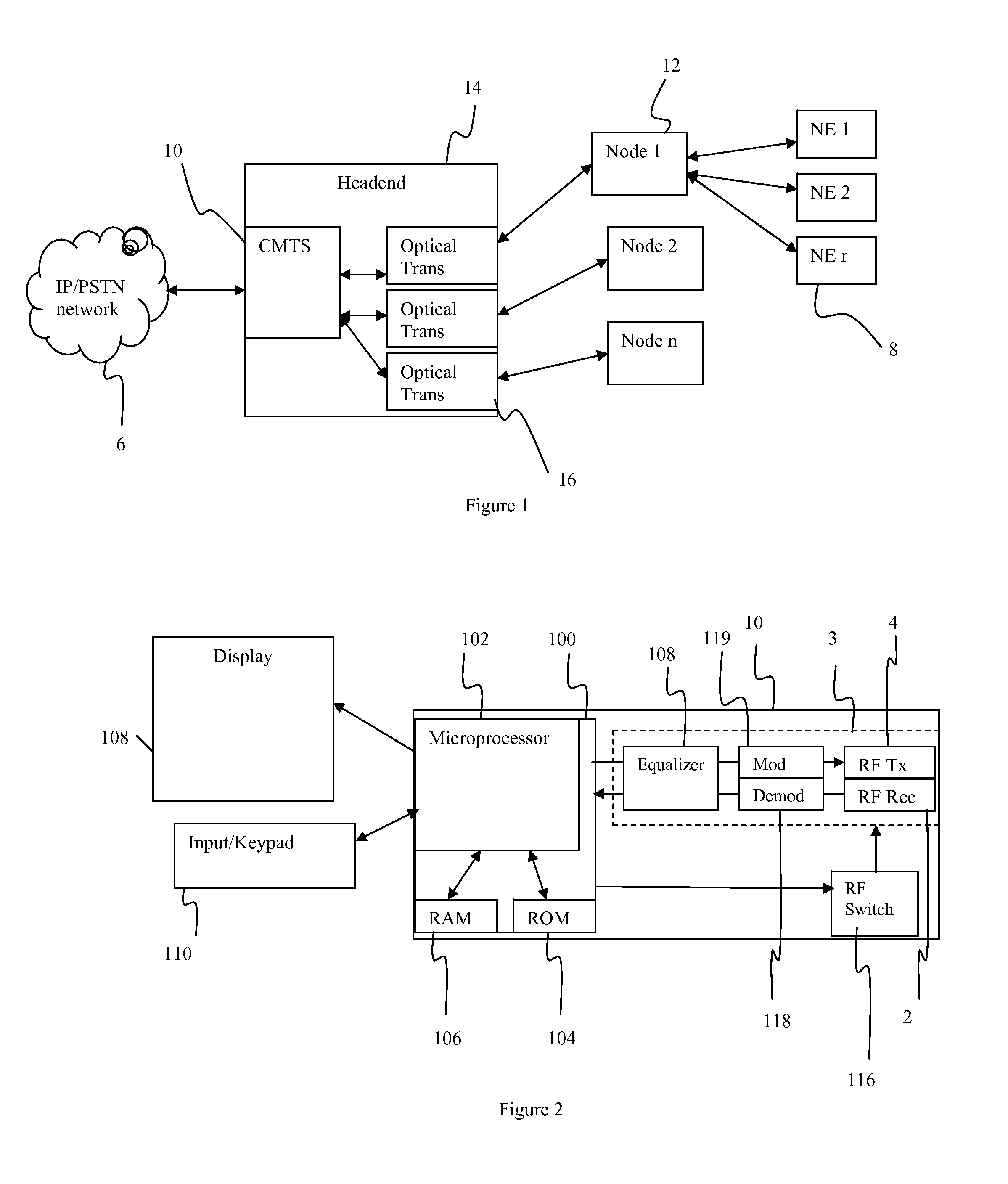
Method and Apparatus for Determining the Dynamic Range of an Optical Link in an HFC Network
ActiveUS20070223920A1Avoid impactService is blockedBroadcast transmission systemsTransmission monitoringNetwork elementPower level
The dynamic range of an optical link in a network is determined by simultaneously transmitting signals from two network elements at first and second frequencies, which create a combined signal at a third frequency. The transmission power levels of selected network elements is successively increased until the measured power from the third frequency no longer changes in a predicatable manner, at which point the upper limit of the dynamic range of the optical link is determined.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
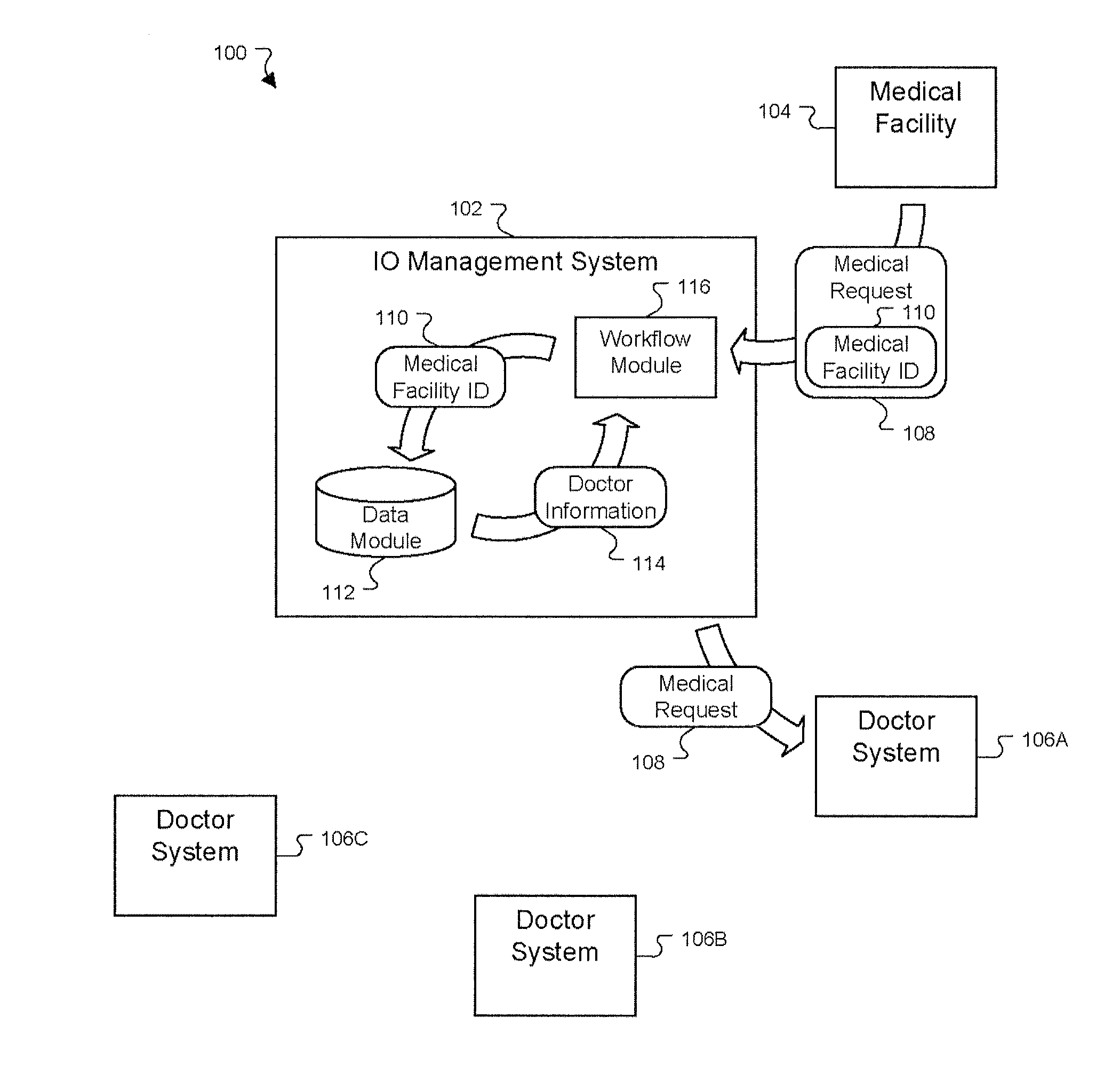
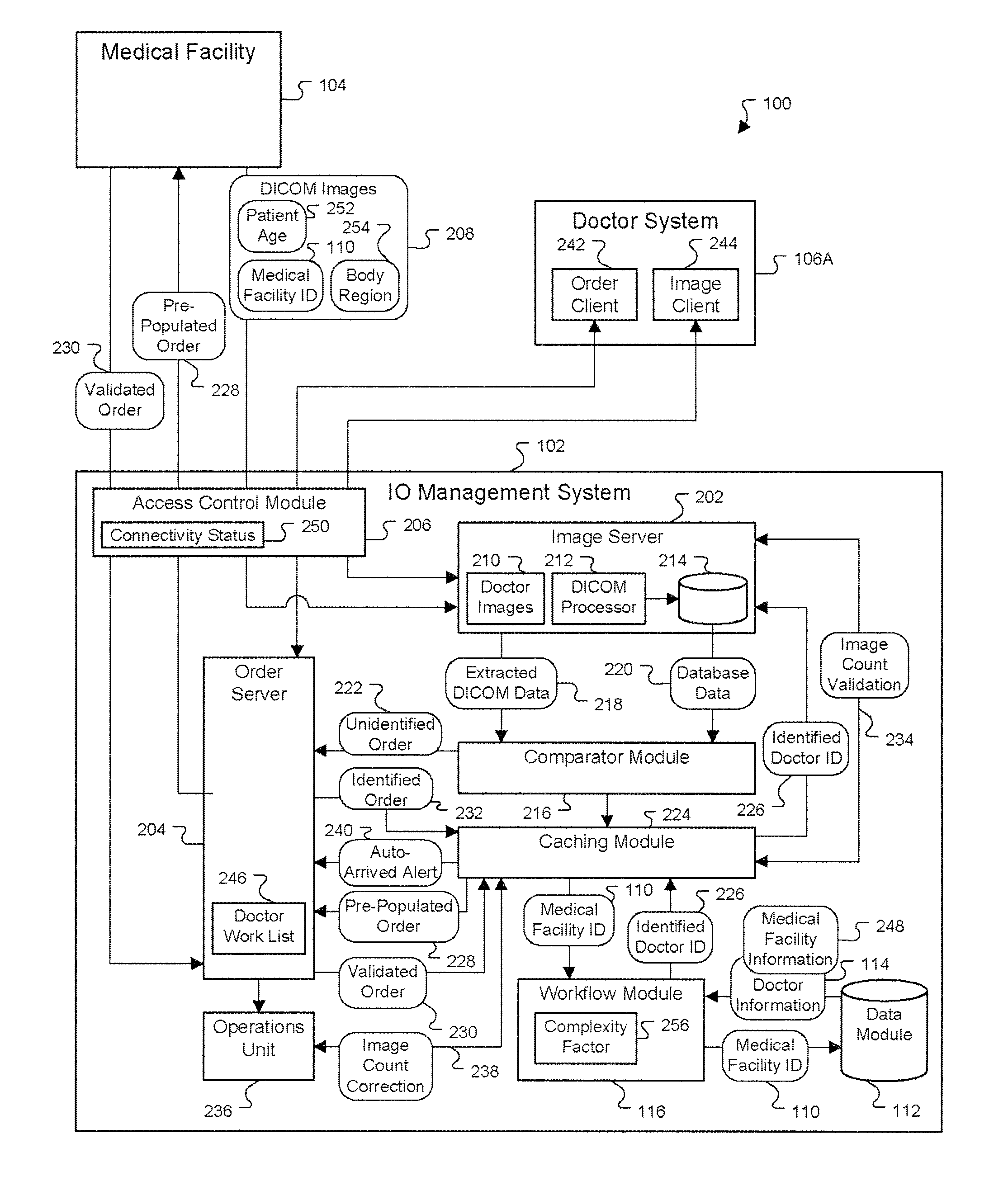
Enhanced multiple resource planning and forecasting
ActiveUS20110066449A1Avoid service interruptionAccurate volumeHospital data managementHealthcare resources and facilitiesSystem configurationResource efficiency
A system configuration and techniques for optimizing schedules and associated use predictions of a multiple resource planning workflow are disclosed herein, applicable to environments such as radiologist scheduling in a teleradiology workflow. In one embodiment, a series of computing engines and components are provided to allow detailed forecasting and the generation of customized recommendations for scheduling and other resource usage scenarios. This forecasting can factor resource efficiencies, changes in resource demand volume, resource specialties, resource usage preferences, expected future events such as the removal or addition of resources at future times, and other resource availability or usage changes. The forecasts may be further enhanced through the use of historical data models and estimated future data models. Additionally, a calendar and other tools may be presented through a user interface to allow forecast and scenario customization based on selection of a series of future dates.
Owner:VIRTUAL RADIOLOGIC
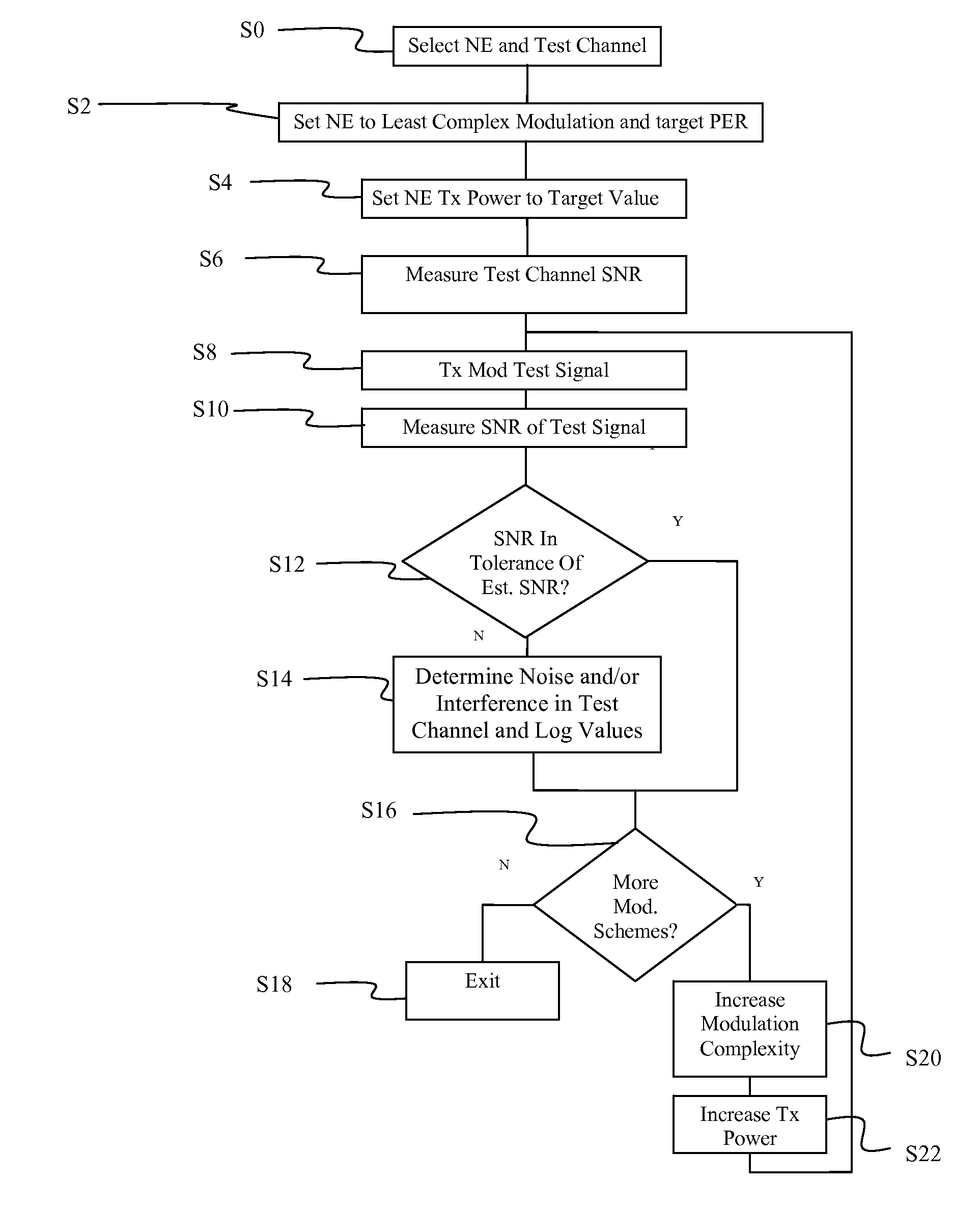
Method and Apparatus for Characterizing Modulation Schemes in an HFC Network
InactiveUS20080101210A1Service is blockedEffective resourcesFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsTest channelPhase noise
The available modulation schemes of a network are analyzed to determine which ones contain excessive phase noise or narrowband interference. A network element is selected and assigned to a test channel at a first modulation scheme at a predetermined power level to achieve a predetermined PER. The network element transmits a test signal and the network controller measures the signal to noise ratio (SNR) in the received test signal. If the SNR is not within a predetermined tolerance range of an estimated SNR for the modulation scheme at the predetermined PER, the modulation scheme is determined to have excessive phase noise or narrowband interference. Each available modulation scheme is tested by instructing the network element to transmit the test signal using each modulation scheme and assigning the power level of each modulation scheme. The suitable modulation schemes may be determined.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for enhanced security in a broadband telephony network
InactiveUS7035410B1Prevent theftPrivacy protectionDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsSecure communicationBroadband
The broadband telephony interface is provisioned by receiving information authenticating a provisioning server, establishing a communication channel between the user and the provisioning server over which is transmitted authorization information from the user to the provisioning server, and encrypting and transmitting a cryptographic key associated with the user to the provisioning server. The cryptographic key can be a symmetric key or a public key corresponding to a private key stored in the broadband telephony interface. The cryptographic key can be utilized to generate other keys which are utilized to secure communication channels for the telephony service. The broadband telephony interface advantageously can be implemented as untrusted hardware or software that is installed by a customer.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Power-on-reset of elevator controllers
ActiveUS7350626B2Reduce in quantityLow costComputer controlElevatorsPower-on resetControl engineering
An elevator (9) includes remote elevator monitoring equipment (10) connected by a communication linkage (12) to a central elevator monitoring and control station (11). Main, drive, and door controllers (16-18) are interconnected (19-21) with the monitor lines. Power-on-reset (POR) of controllers may be caused internally or by remotely-operable power relays (23-25) which interrupt power to the controllers. Maintenance personnel at the remote station (11) may order a POR through the communication linkage. In another embodiment, the remote elevator monitor (10) determines presence of a malfunction which a POR may cure and causes a POR internally or by a power relay. In another embodiment, the controller (16a) includes, in its program routines, elevator diagnostics (50) which can recognize an elevator malfunction which a POR may cure, and either cause the relay to interrupt power for an interval or cause an internal POR.
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Method and apparatus for characterizing modulation schemes in an HFC network
InactiveUS7876697B2Service is blockedEffective resourcesTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTest channelPhase noise
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
System and method for auctioning services over an information exchange network
InactiveUS20080208733A1Reduce competitionEncouraging fierce price competitionFinanceCommerceRating systemService provision
Owner:PRINTVISION
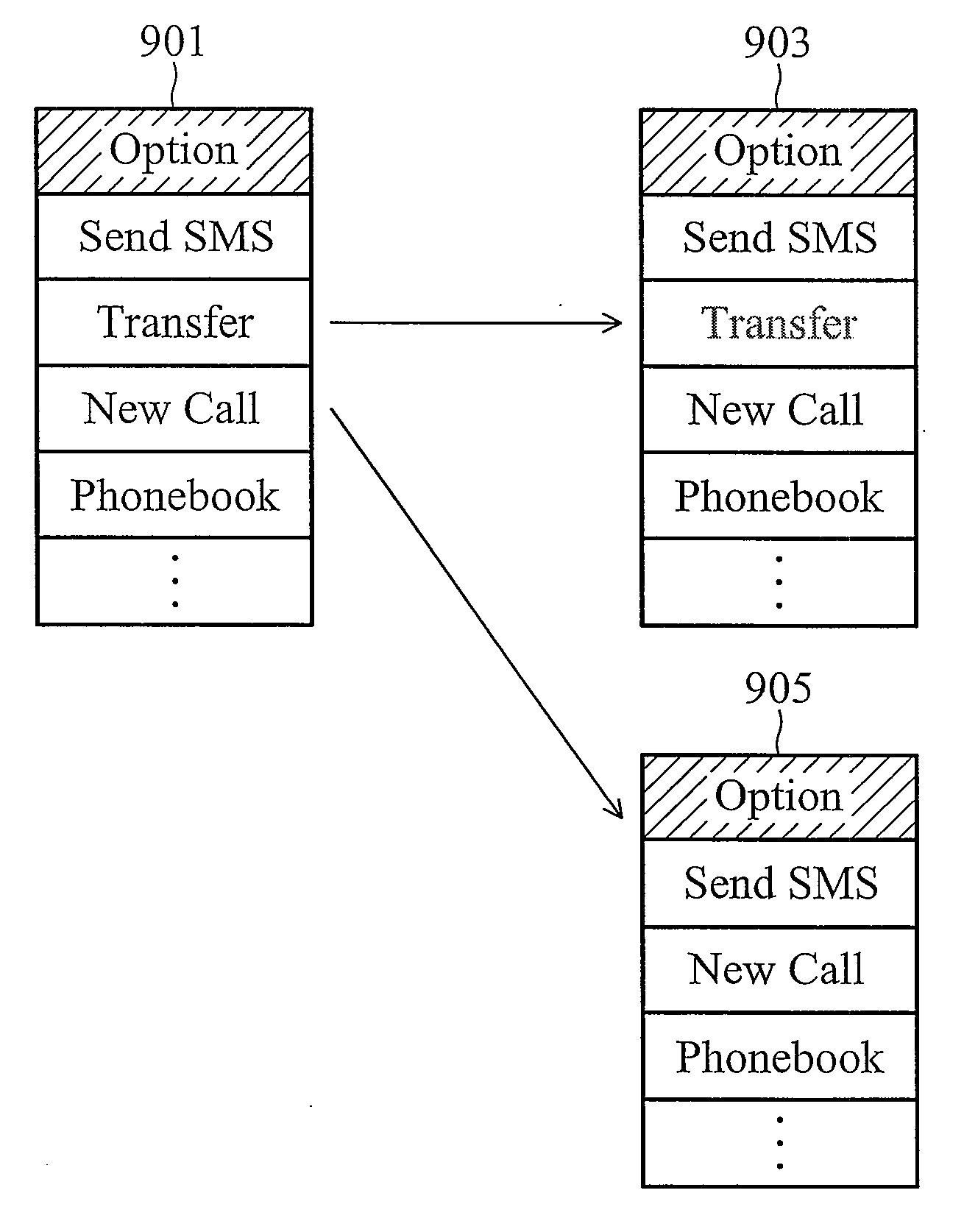
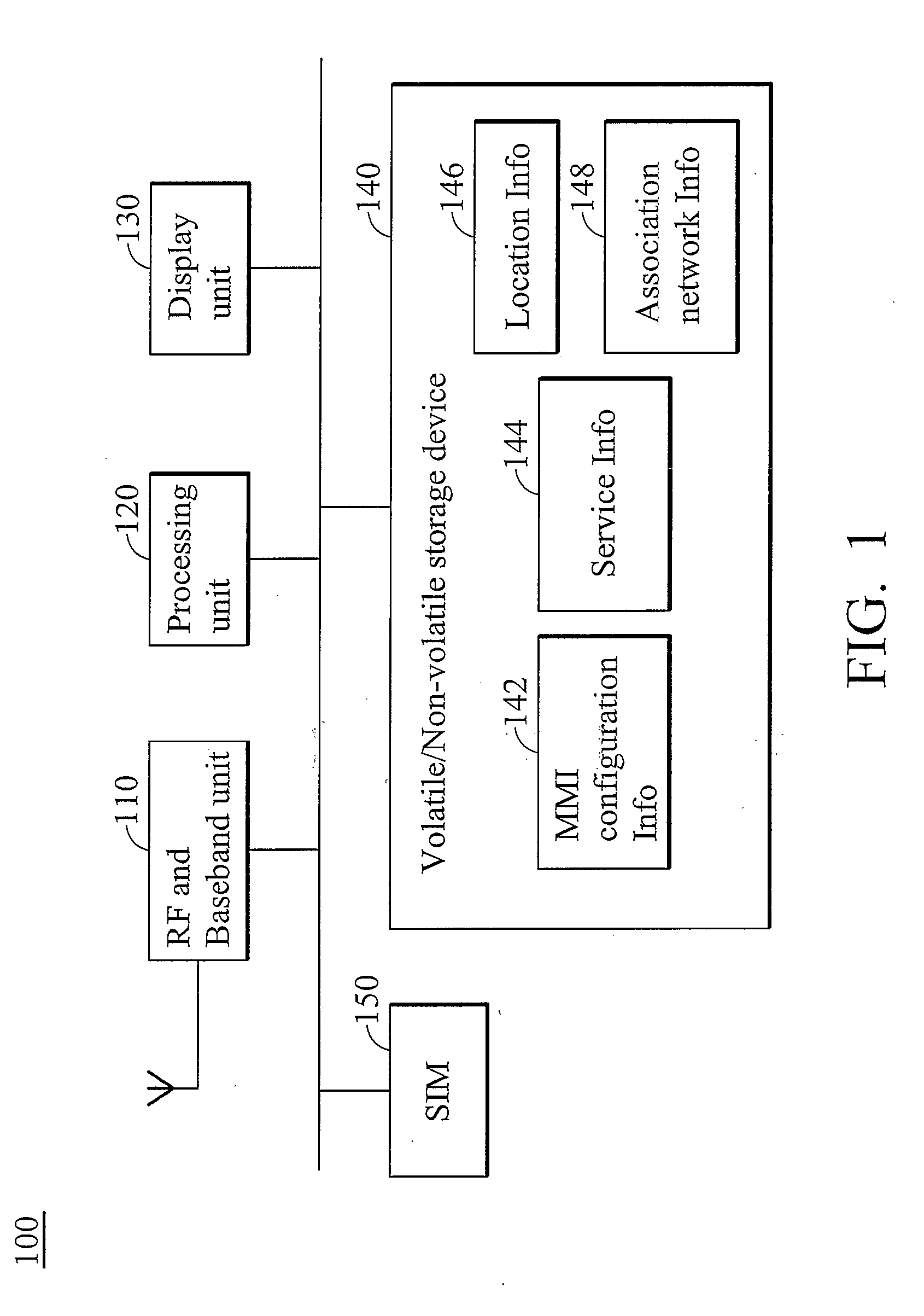
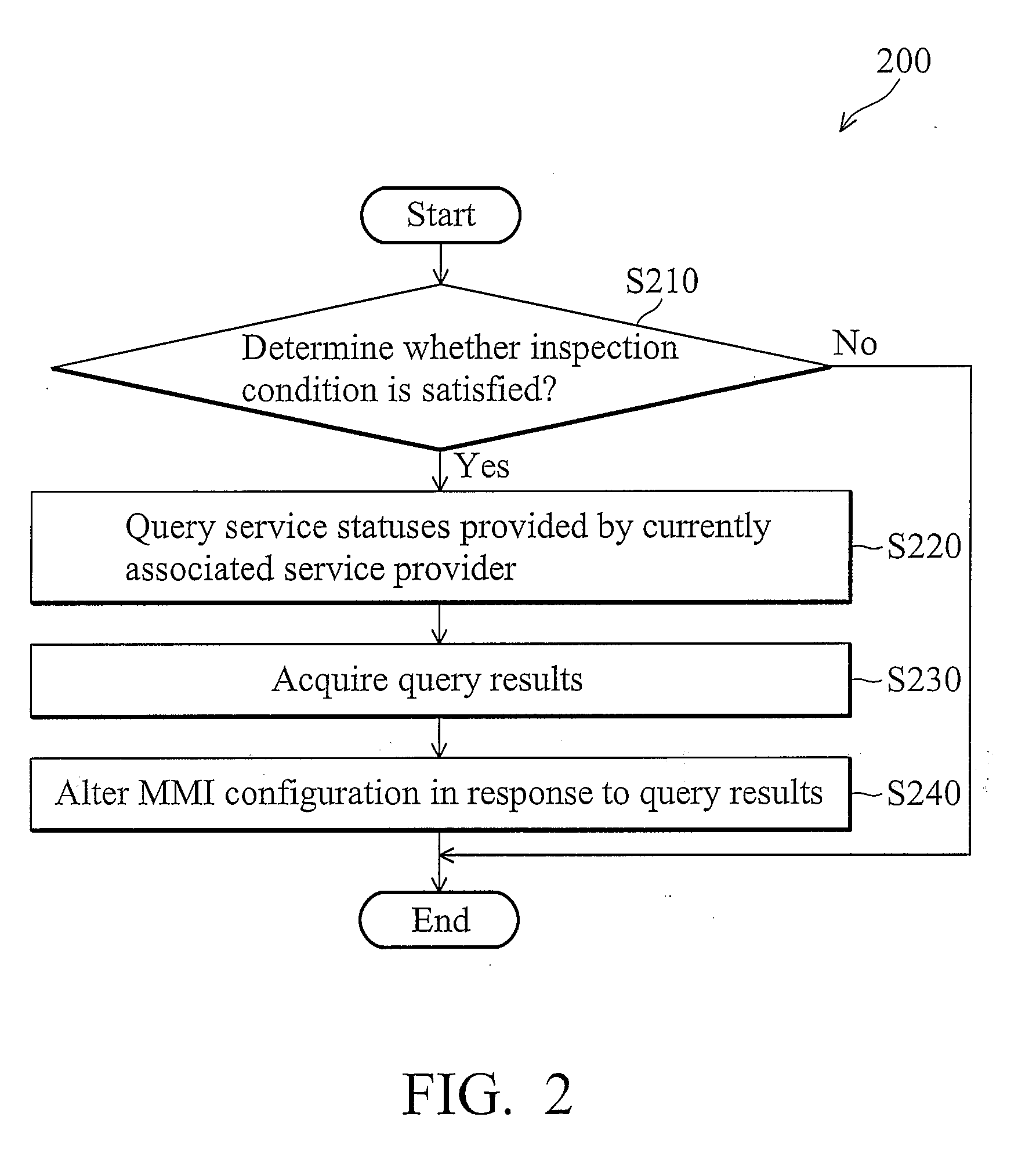
Methods and devices for dynamic menu update
ActiveUS20090178005A1Service is blockedAvoid unnecessary consumptionSubstation equipmentTransmissionMan machineHuman–computer interaction
A method for altering man machine interface (MMI) configurations for use in a device is provided. The method comprises the following steps. A status of a service is queried after detecting that an inspection condition is satisfied. The queried status is acquired from the currently associated network. A menu item of a service menu is enabled when the queried status indicates that the service is available. Otherwise, the menu item of the service menu is disabled or the menu item is removed from the service menu when the queried status indicates that the service is unavailable, preventing a user from requesting the service via the menu item.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method for mobile telecommunication security in a mobile communication network and therefor device
ActiveUS20090017863A1Easy to implementEffective preventionUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionData taking preventionTelecommunicationsMobile communication network
A method of operating a mobile communication device in a mobile communication network, the method comprising the steps of the mobile communication device: receiving a non integrity-protected message with a parameter value included therein to be implemented on the mobile communication device; using a predetermined value stored on the mobile communication device instead of the parameter value received.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Reducing core network traffic caused by migrant users
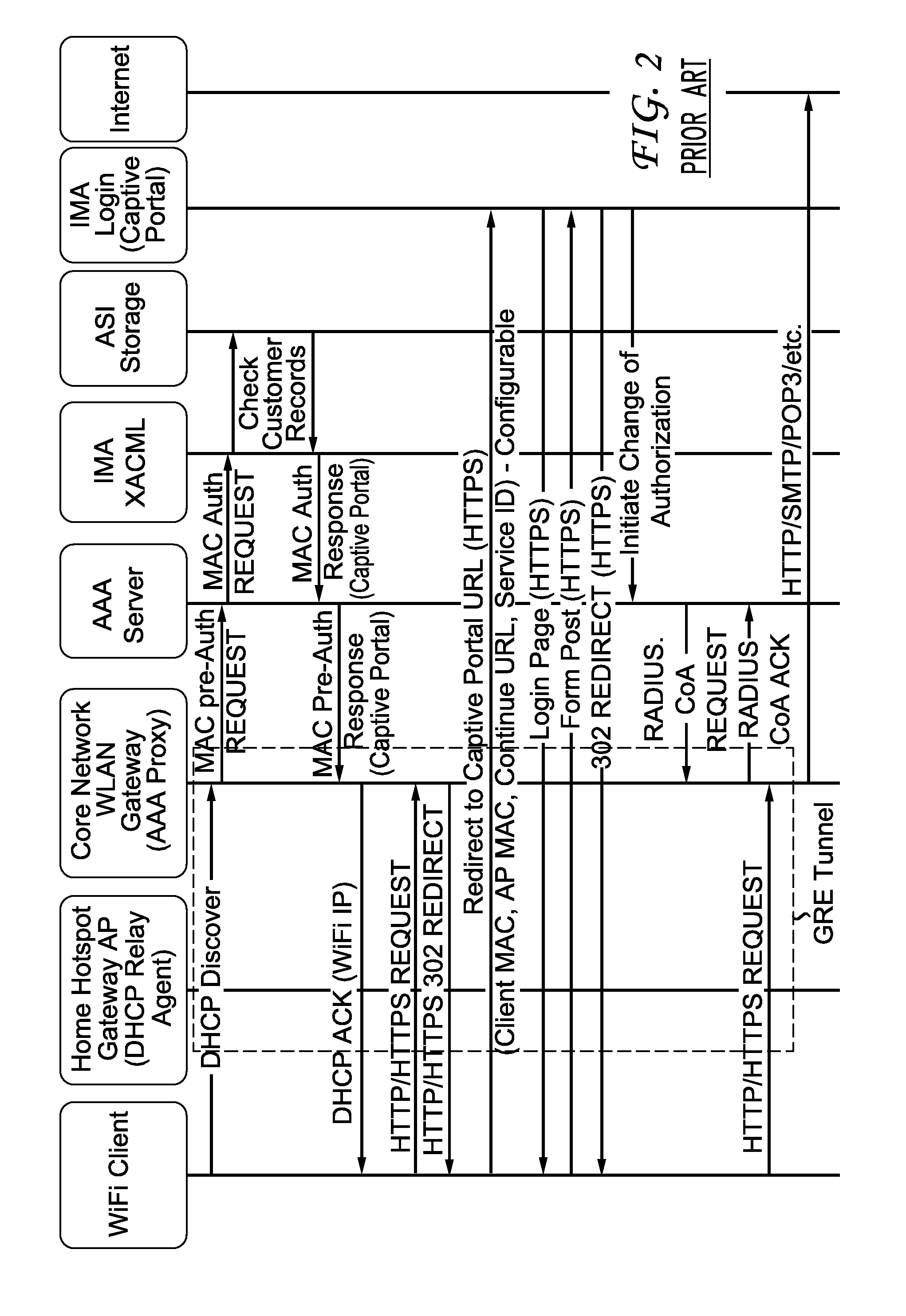
ActiveUS20150237527A1Reduce core trafficService is blockedNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital data processing detailsIp addressHypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer
A method and apparatus for reducing core network traffic caused by migrant users of a public wireless network are described including receiving a DHCP discover request from a wireless client device, determining if there are enough IP addresses available to assign one of the plurality of IP addresses to the wireless client device, transmitting a DHCP acknowledgement including the assigned IP address and a lease duration to the wireless client device, determining if a lease timeout has occurred, releasing the assigned IP address if the lease timeout has occurred, receiving a first hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) request or first hypertext transfer protocol secure (HTTPS) request from the wireless client device, transmitting a media access control (MAC) pre-authentication request from the wireless client to an authentication, authorization and accounting (AAA) server, receiving a MAC pre-authentication response from the AAA server and providing access to the Internet via the wireless client device.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
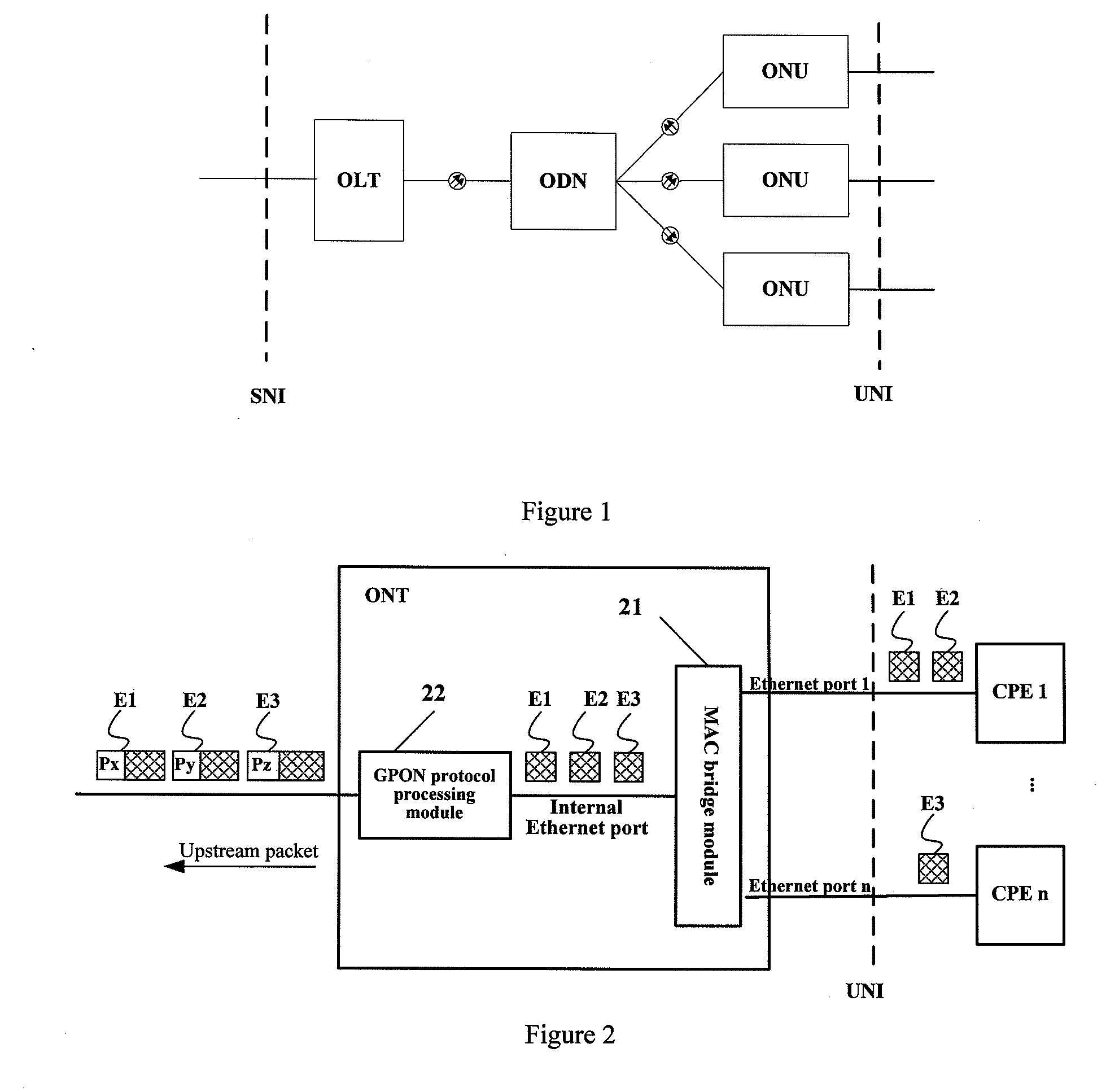
Optical network terminal, method for configuring rate limiting attributes of ports, and method for processing packets
ActiveUS20090022494A1Service is blockedAvoid attackMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexNetwork terminationTraffic capacity
The present invention relates to an optical network terminal (ONT), a method for configuring rate limiting attributes of ports, and a method for processing packets. The ONT includes a passive optical network (PON) protocol processing module, and a user network interface (UNI) module, which are connected through an internal interface. The ONT also includes a port rate limiting module connected to a UNI. The port rate limiting module stores rate limiting attributes, and the ONT uses these attributes to control the traffic of the UNI. The port rate limiting attributes are configured for the ONT through an ONT management and control interface (OMCI) message of an optical line terminal (OLT). In this way, when the ONT receives data from the UNI, it can control the traffic of the UNI according to the port rate limiting attributes. The present invention enables the port rate limiting function for the ONT, prevents overflow of the internal receiving buffer of the ONT, and prevents denial of service (DoS) attacks from illegal users.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Enhanced multiple resource planning and forecasting
ActiveUS20130066646A1Service is blockedAccurate volumeForecastingHospital data managementTime scheduleSystem configuration
A system configuration and techniques for optimizing schedules and associated use predictions of a multiple resource planning workflow are disclosed herein, applicable to environments such as radiologist scheduling in a teleradiology workflow. In one embodiment, a series of computing engines and components are provided to allow detailed forecasting and the generation of customized recommendations for scheduling and other resource usage scenarios. This forecasting can factor resource efficiencies, changes in resource demand volume, resource specialties, resource usage preferences, expected future events such as the removal or addition of resources at future times, and other resource availability or usage changes. The forecasts may be further enhanced through the use of historical data models and estimated future data models. Additionally, a calendar and other tools may be presented through a user interface to allow forecast and scenario customization based on selection of a series of future dates.
Owner:VIRTUAL RADIOLOGIC
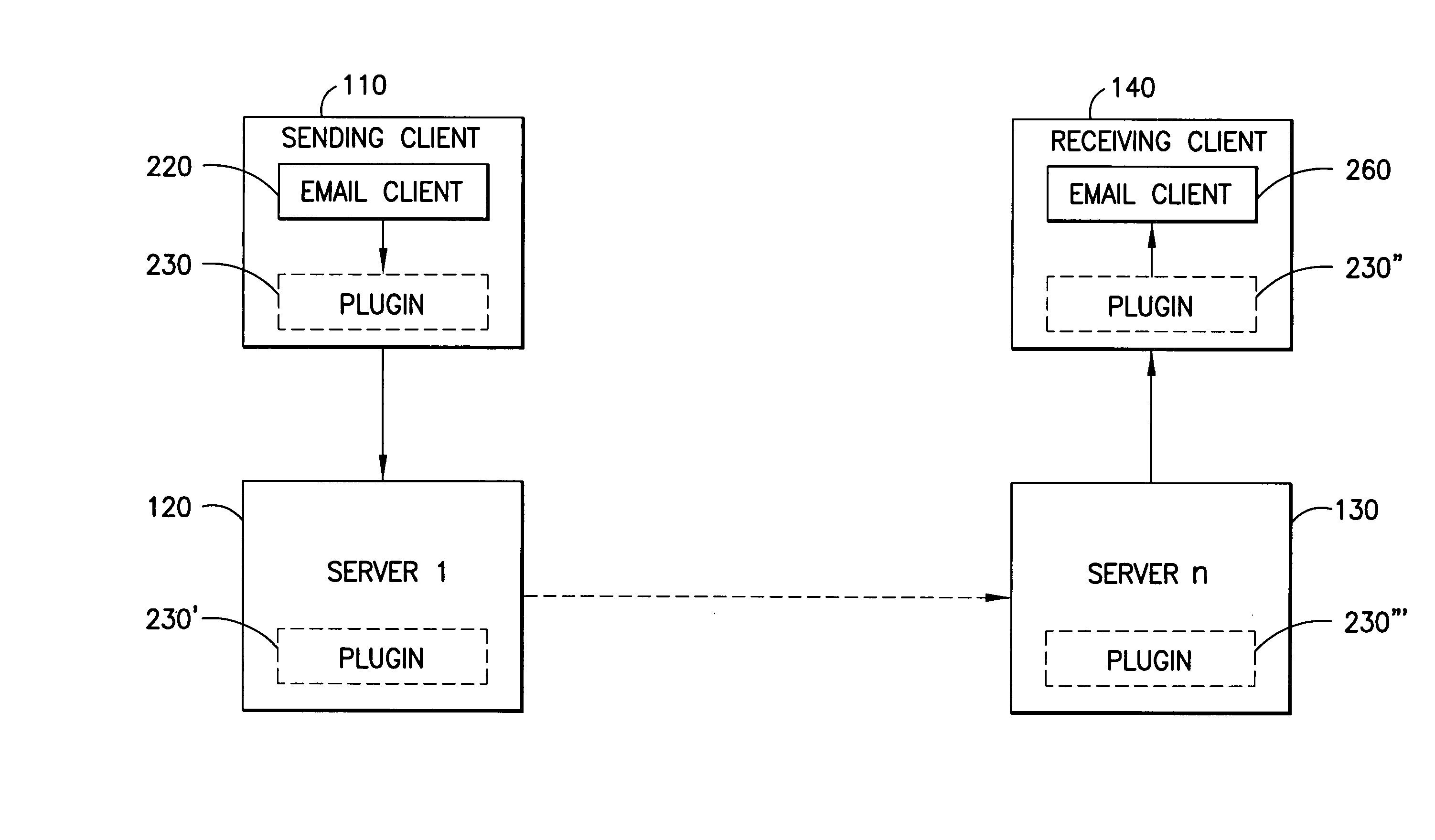
Method for Switching the Serving Services of Virtual Private Lan and a System Thereof
ActiveUS20090154339A1Quick switchService is blockedError preventionTransmission systemsComputer networkPath switching
A method and system for switching the serving services of virtual private LAN is provided. When a fault occurs on a normal service transmission path, a PE device on the secondary path transmits a message including an information of the failure device on the normal service transmission path to the other PE devices on the path to indicate the path switching; the other PE devices replace the faulty PE device corresponding to the transmission path item in VPLS transmission table as the PE device on the secondary path according to the received message for indicating the path switching. Using the present invention, when an access device detects a fault, the VPLS service can switch to the secondary path immediately without affecting other services; because the VPLS messages do not need to be broadcasted during path switching, the network bandwidth will not be wasted.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
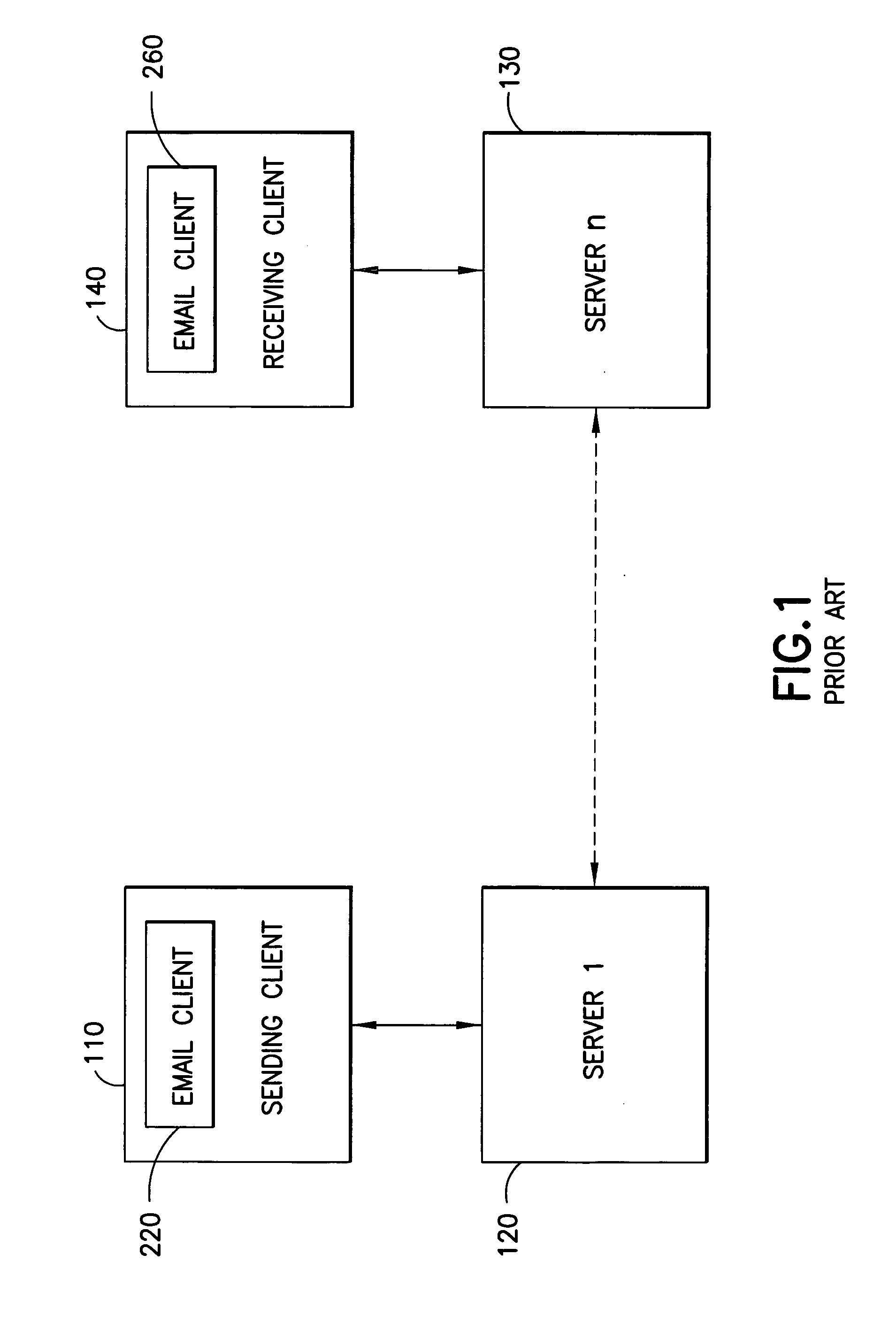
System and method for verifying the legitimacy of requests sent from clients to server
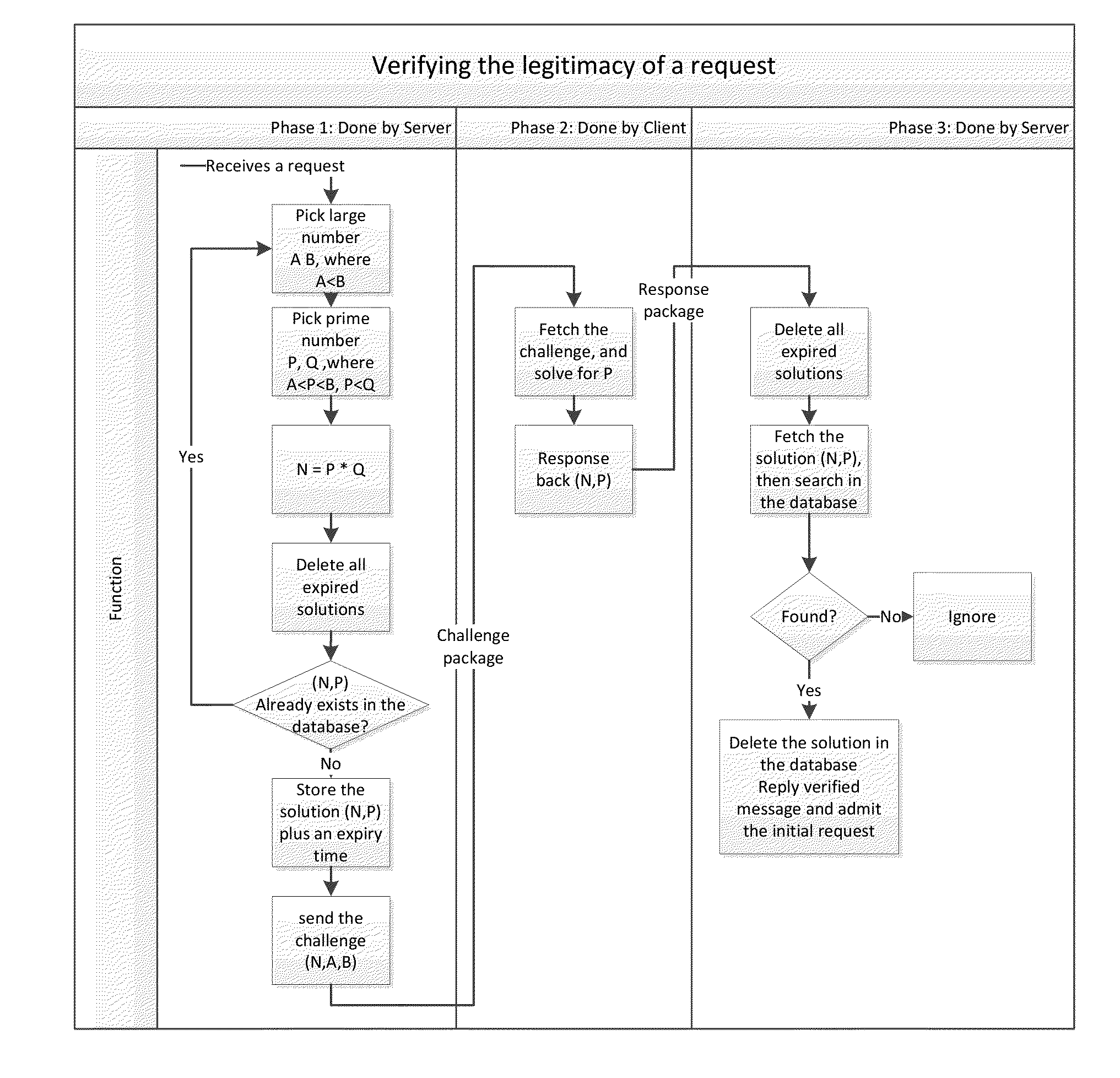
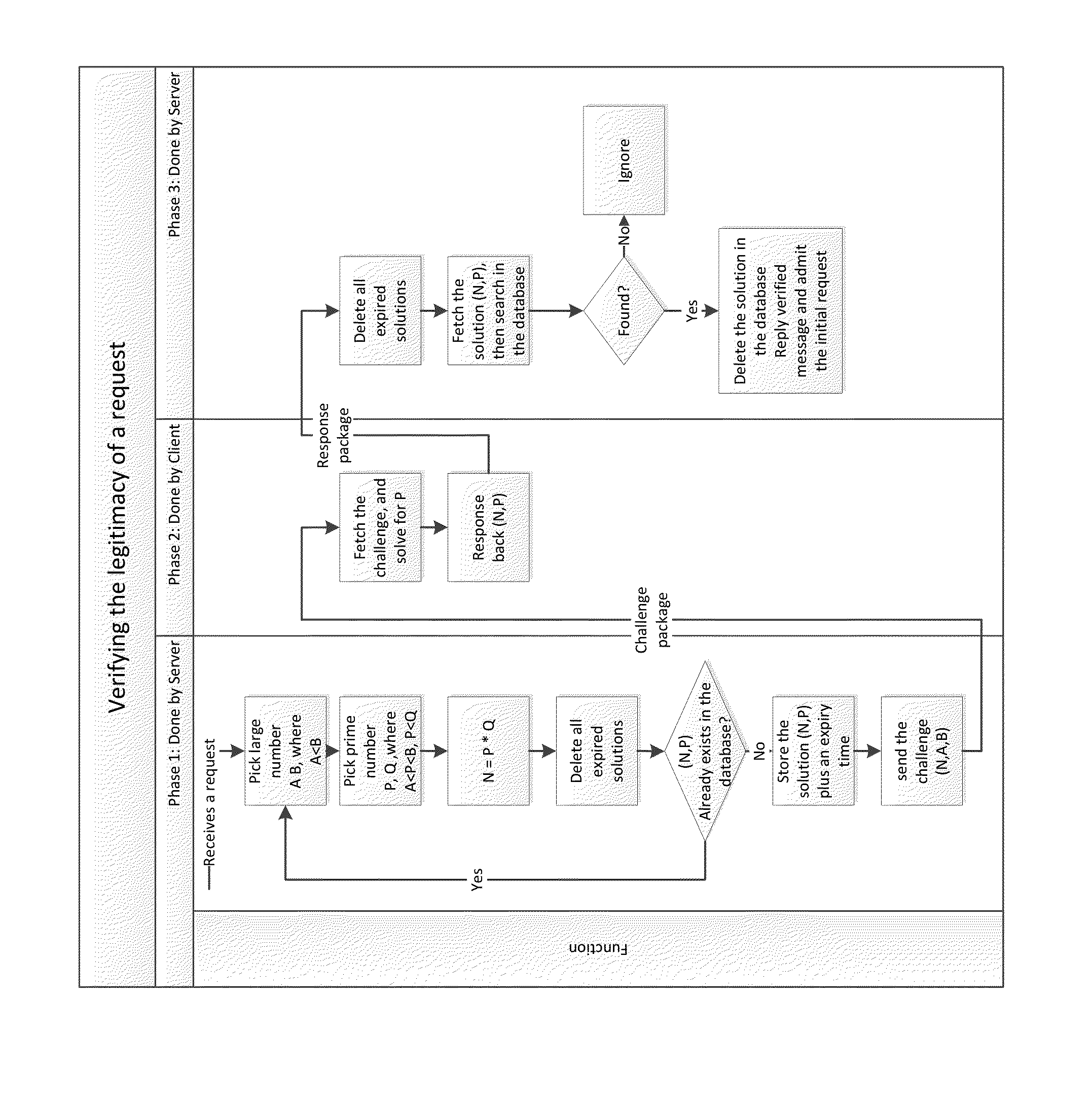
InactiveUS20140380418A1Preventing brute force attack against passwordImprove reliabilityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsBrute forceComputation complexity
Disclosed herein are method and system that can be used for: preventing brute force attacks against passwords; preventing denial of service attacks by flooding; restricting bots from spamming emails, registering resources, and collecting sensitive information; and possibly in other challenge-response tests. It also can be used to replace CAPTCHA in some situations, with advantages of better reliability and spares human participation during the process. This present invention considers a request as legitimate when the requesting client has paid certain amount of computation resource required by the server, in exchange for the server to admit the request. It performs a challenge-response test. The subject challenged is the sincerity of the client to make that request, which is measured by computation resources the client willing to spend in exchange for the service provided by the server. The invention also gives a method to control and guarantee the computation complexity of the challenge problem of the test.
Owner:WANG HAOXU
Enhanced multiple resource planning and forecasting
ActiveUS8229761B2Service is blockedAccurate volumeHospital data managementResourcesTime scheduleSystem configuration
Owner:VIRTUAL RADIOLOGIC
Techniques for reliable messaging for an intermediary in a network communication environment
ActiveUS20150088999A1Improve reliabilityFacilitates reliable communicationData switching networksReliable messagingNetwork Communication Protocols
The present disclosure relates generally to techniques for improving reliability of message communications. In certain embodiments, techniques are described for facilitating reliable communication of messages between a source (e.g., a client system) and a destination (e.g., a target system) via an intermediary communication handler system. In certain embodiments, a message can include a request to be communicated to a destination for a target service. An intermediary communication handler system can store information indicative of the delivery status for a message to ensure reliable communication. The information indicative of the delivery status for a message can be managed in association with a unique identifier corresponding to the message. The information indicative of the delivery status for a message may also be used to determine whether to retry communication of a message in satisfaction of reliability parameters (e.g., QoS criteria) specified for a communication protocol used for communication of the message.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System, apparatus and method coping with mobile switching node failure
ActiveUS20070281686A1Improve system stabilityAccurate receptionNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer network
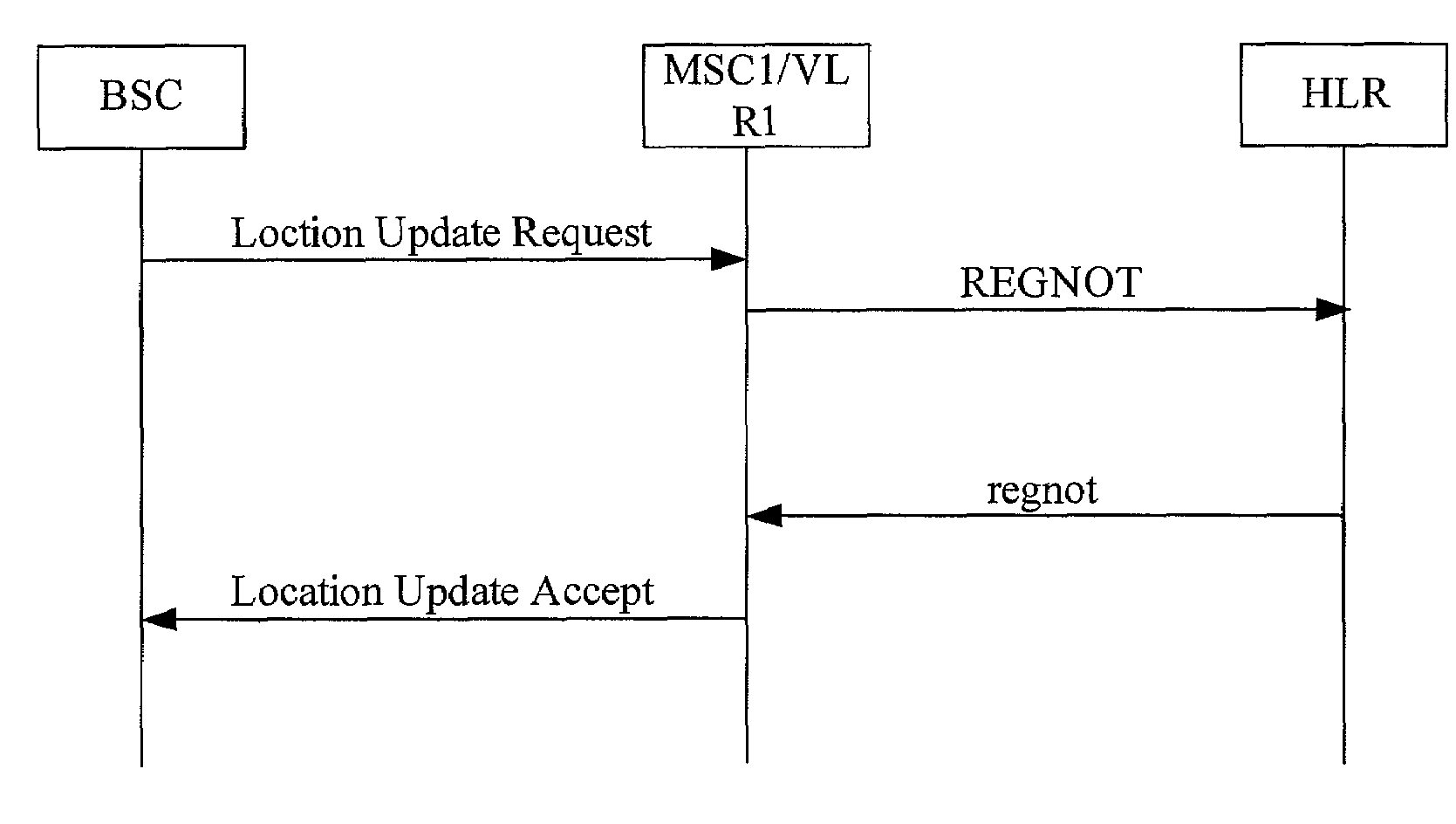
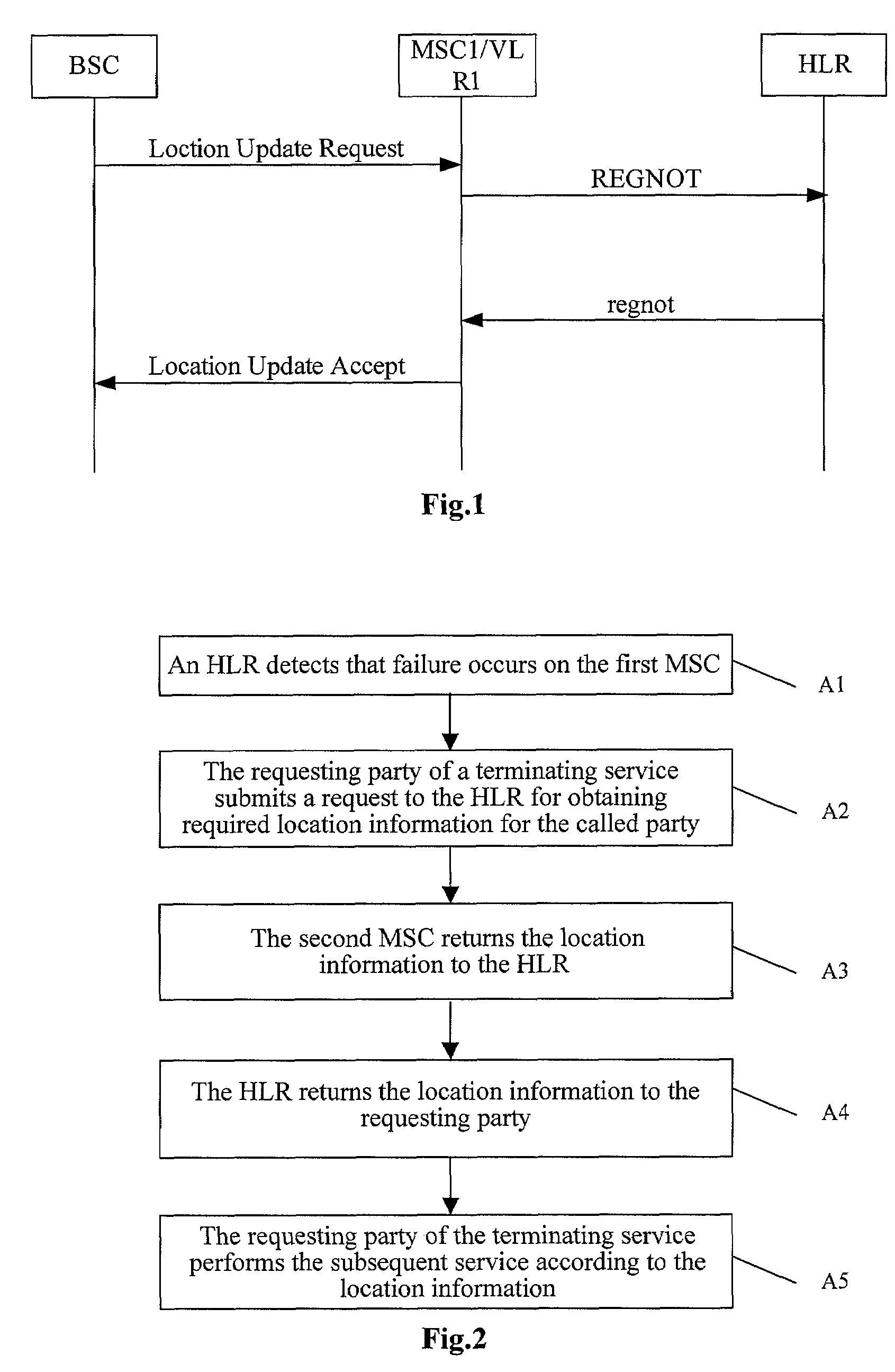
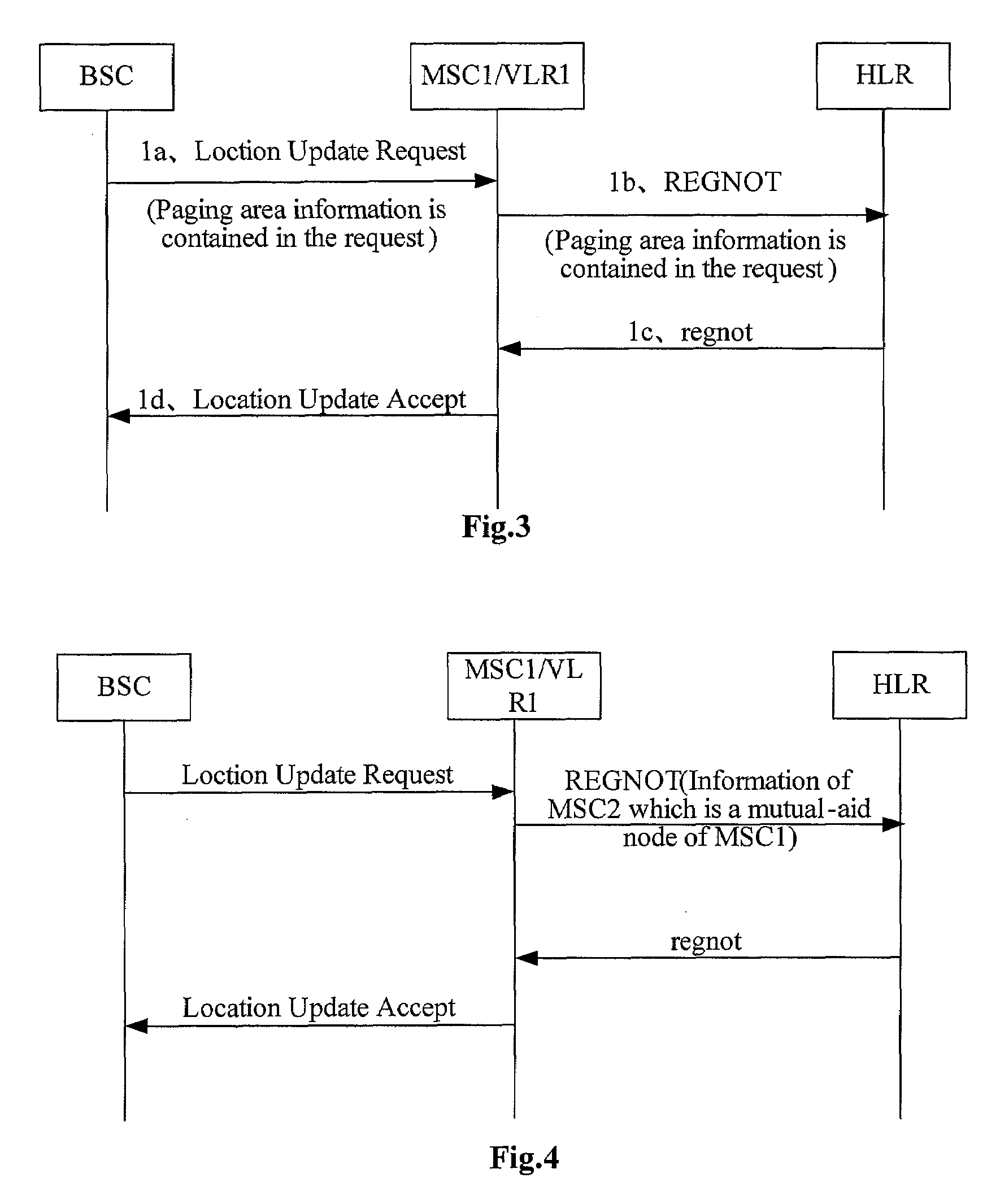
A system, an apparatus and a method for coping with mobile switching node failure are disclosed. The method includes: an HLR (Home Location Register) detects that a first MSC (Mobile Switching Center) is not able to operate; the requesting party of a terminating service submits a request to the HLR for obtaining required location information for a called party registered on the first MSC, and the HLR selects a second MSC for the requesting party and requests for location information from the second MSC; the second MSC returns the location information to the HLR; the HLR returns the location information to the requesting party of the terminating service; and the requesting party of a terminating service performs subsequent service according to the location information.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Cooperative scanning-based cell reselection method and system in wireless communication system
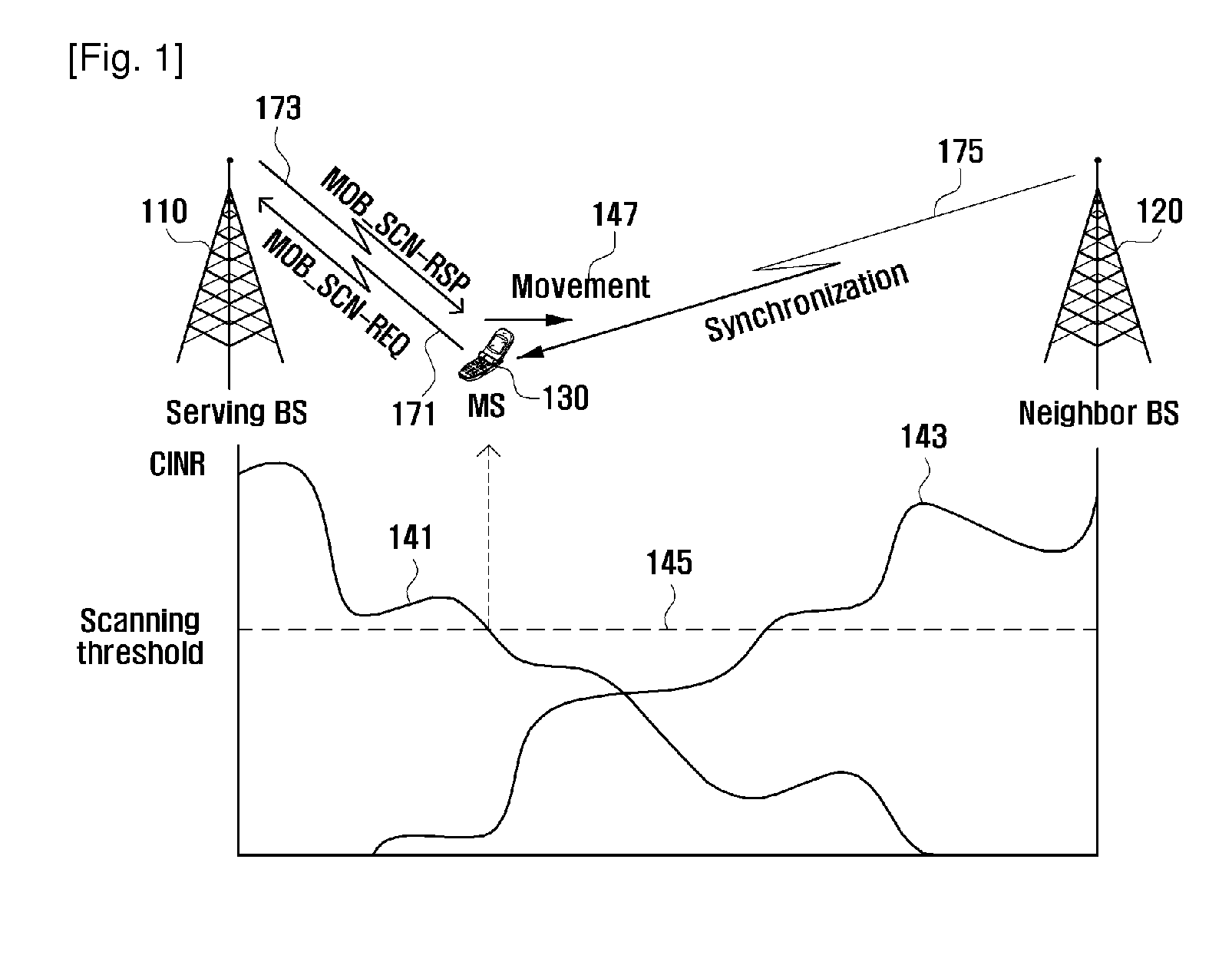
InactiveUS20110230187A1Avoid service interruptionShorten the construction periodAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesCommunications systemMobile relay
A cell reselection method and system based on a cooperative scanning of the mobile relay station and mobile stations is provided for facilitating cell reselection procedure in a Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) system. The cooperative scanning method for a moving wireless network including a mobile relay station and at least one mobile station according to the present invention includes transmitting, at the moving wireless network, a scanning request with cooperative scanning duration to a serving base station; assigning, when a scanning response, neighbor base stations to the mobile relay station and at least one mobile station; scanning, at the mobile relay station and the at least mobile station, the assigned neighbor base stations; and transmitting scanning results to the serving BS station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
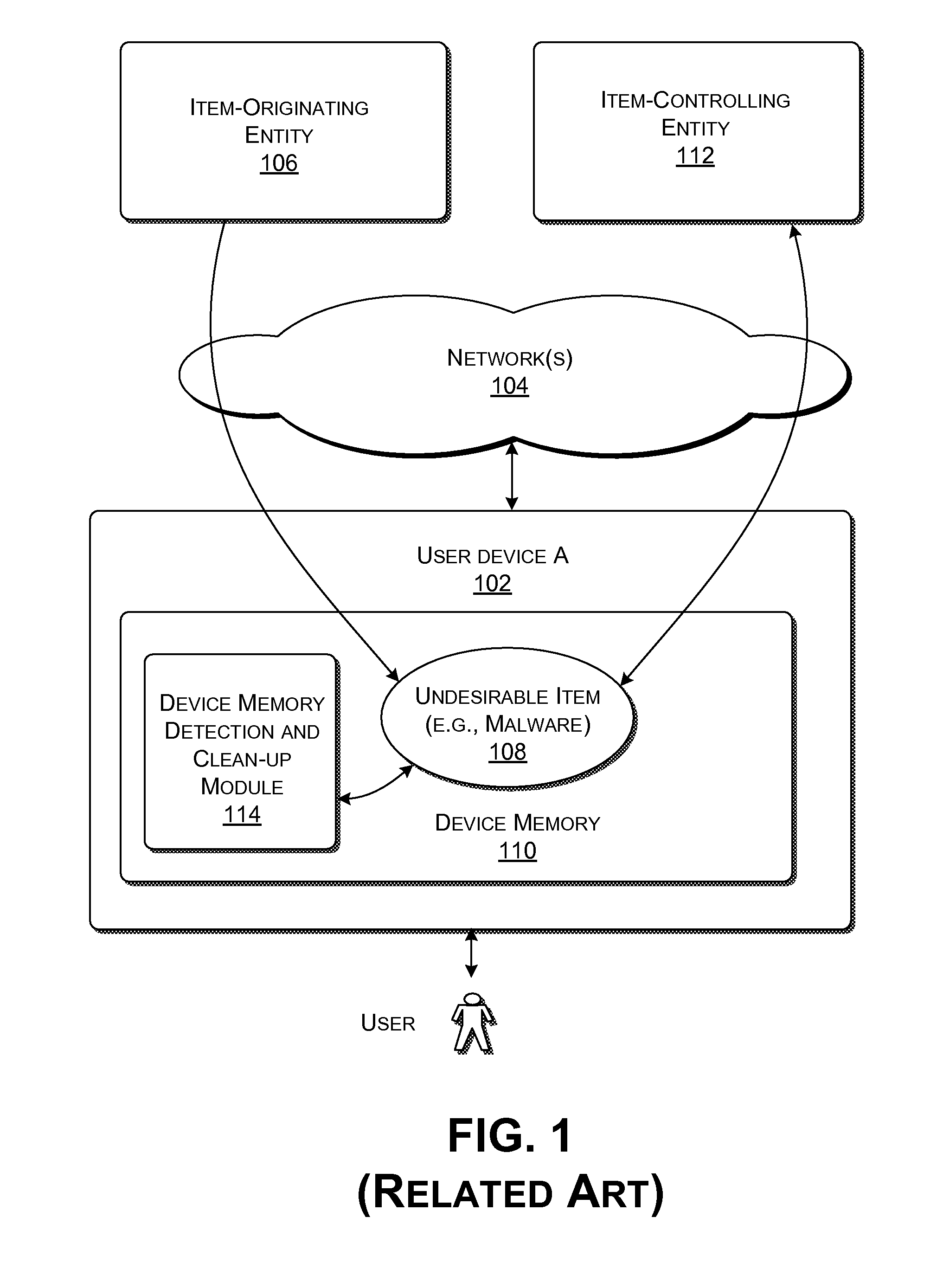
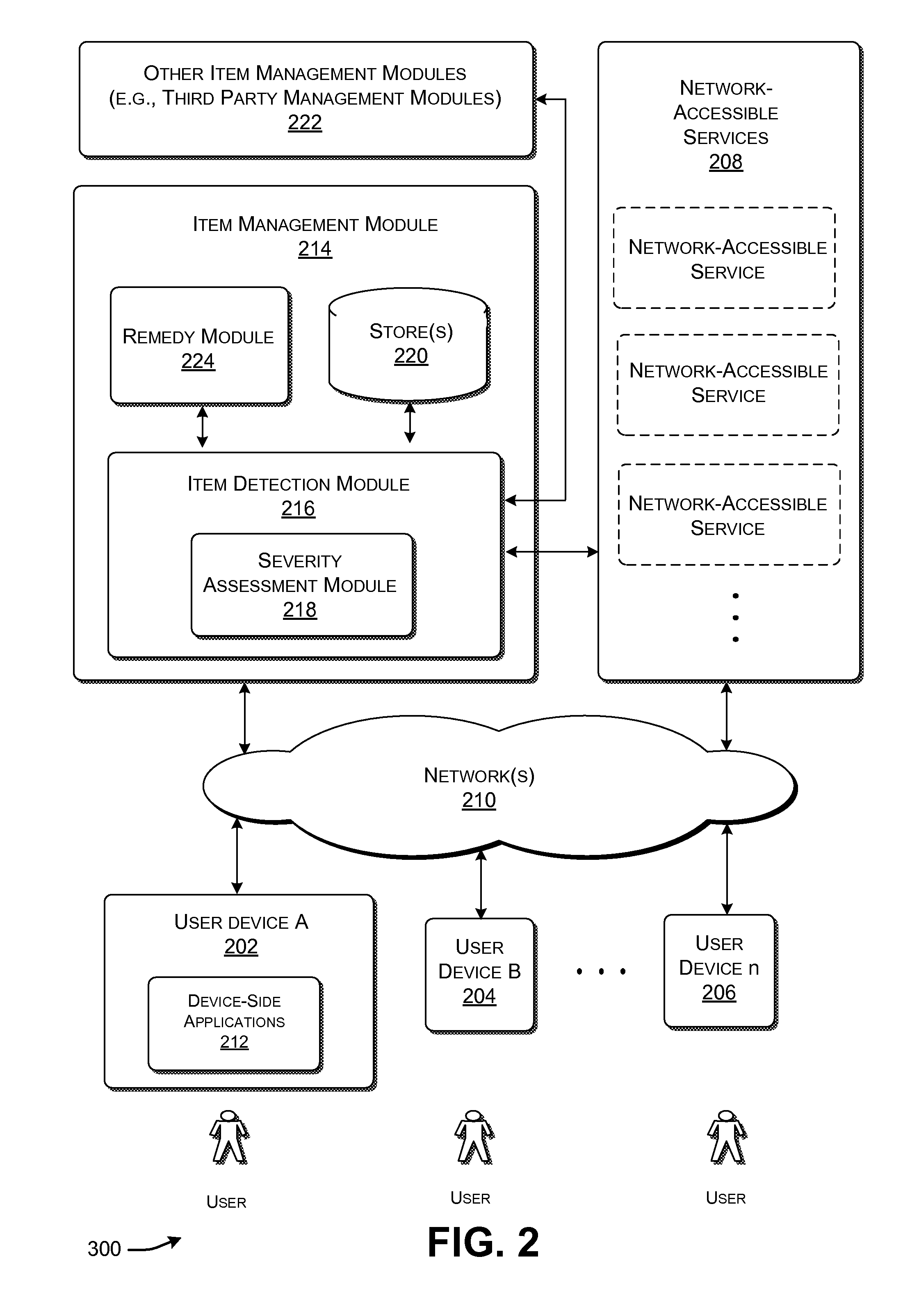
Detection and Removal of Undesirable Items in a Data Processing Environment
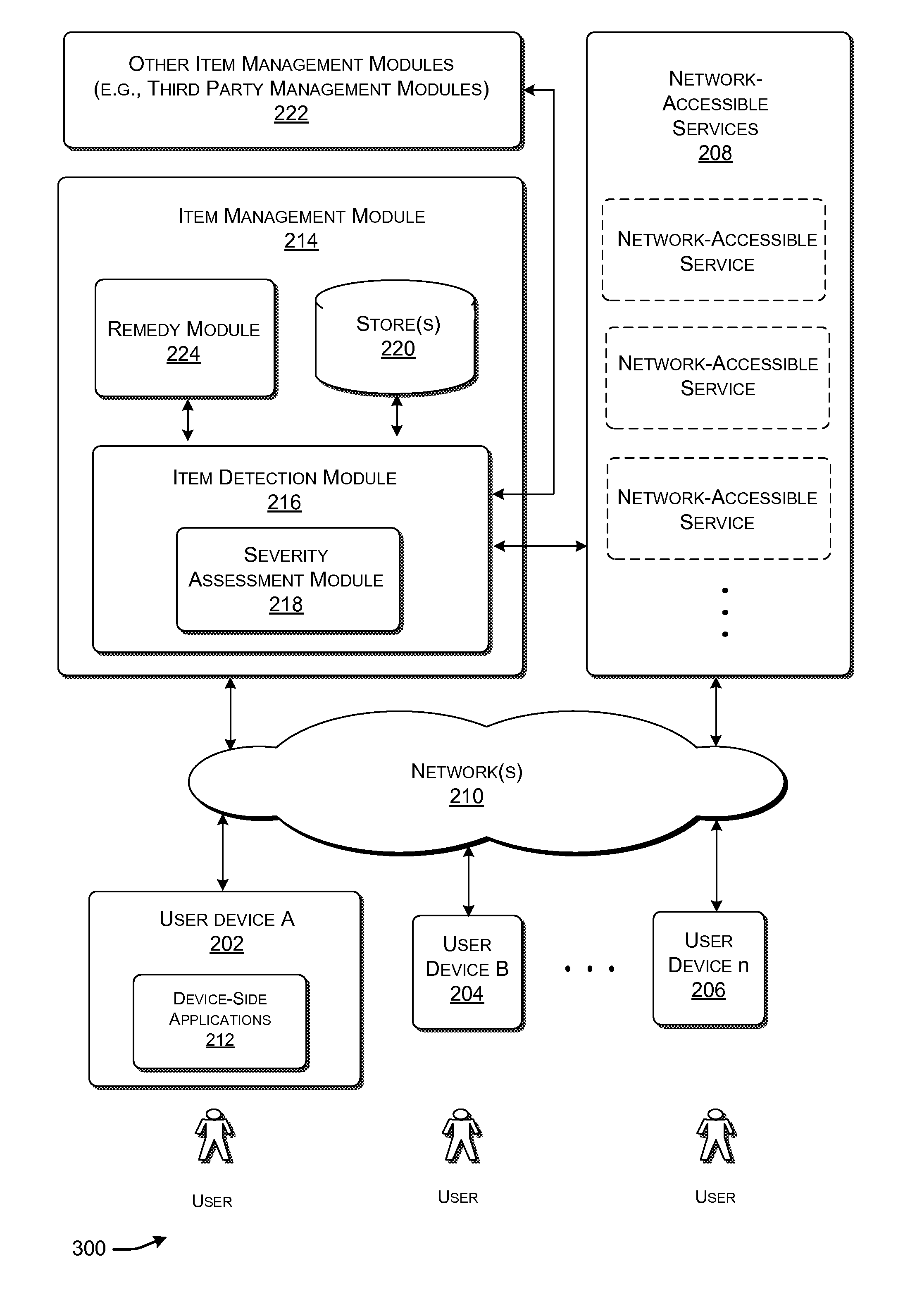
ActiveUS20090006575A1Service is blockedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionData processingUser device
Functionality is described for addressing a threat to the security of a user device that utilizes a network-accessible service. The functionality operates by assessing the likelihood that the user device is infected by the undesirable item. When the user device makes a request to access the network-accessible service, the functionality can interact with the user device in a manner that is governed by the assessed likelihood that the user device is infected by the undesirable item.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Communication apparatus, communication method, and computer program for controlling communication apparatus
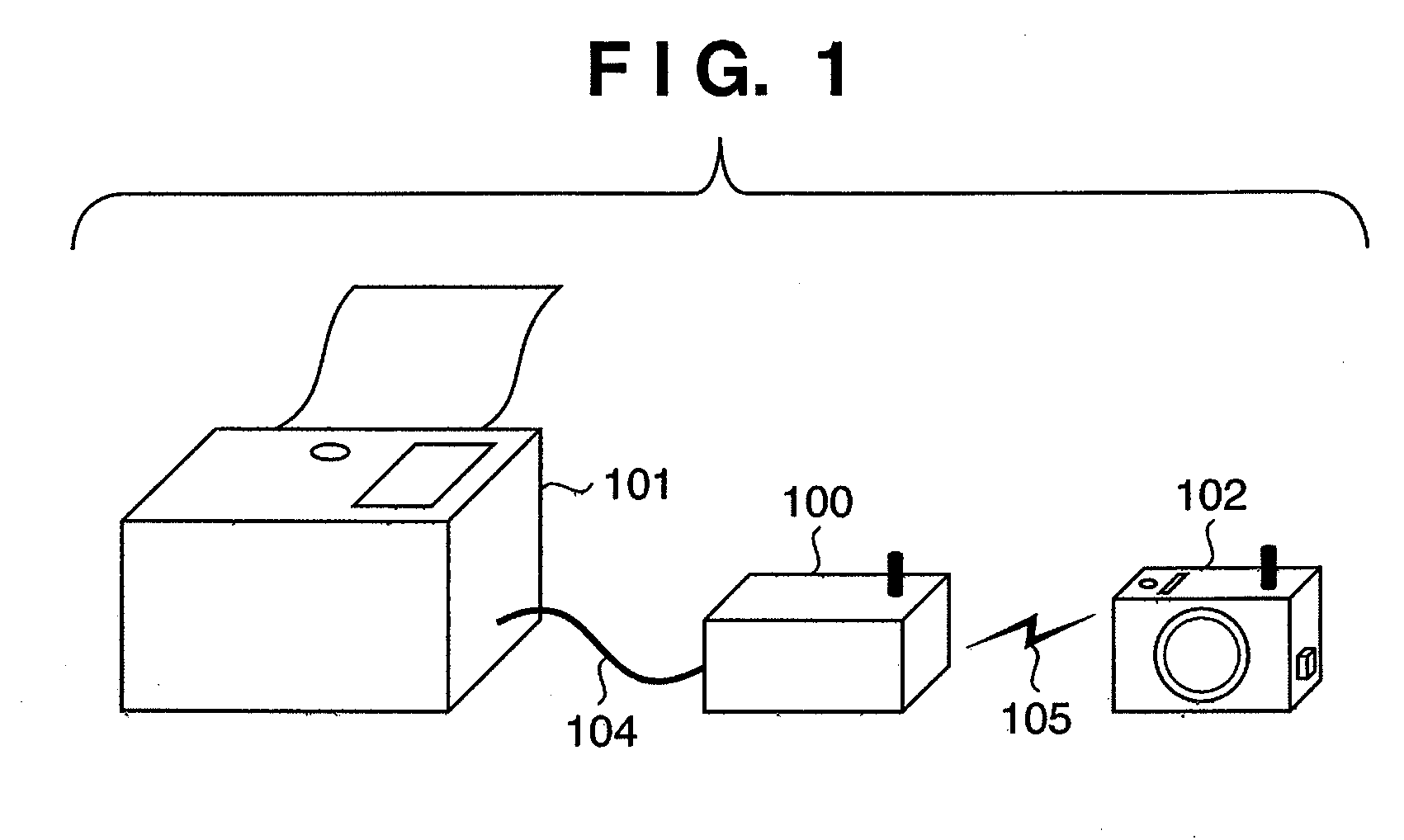
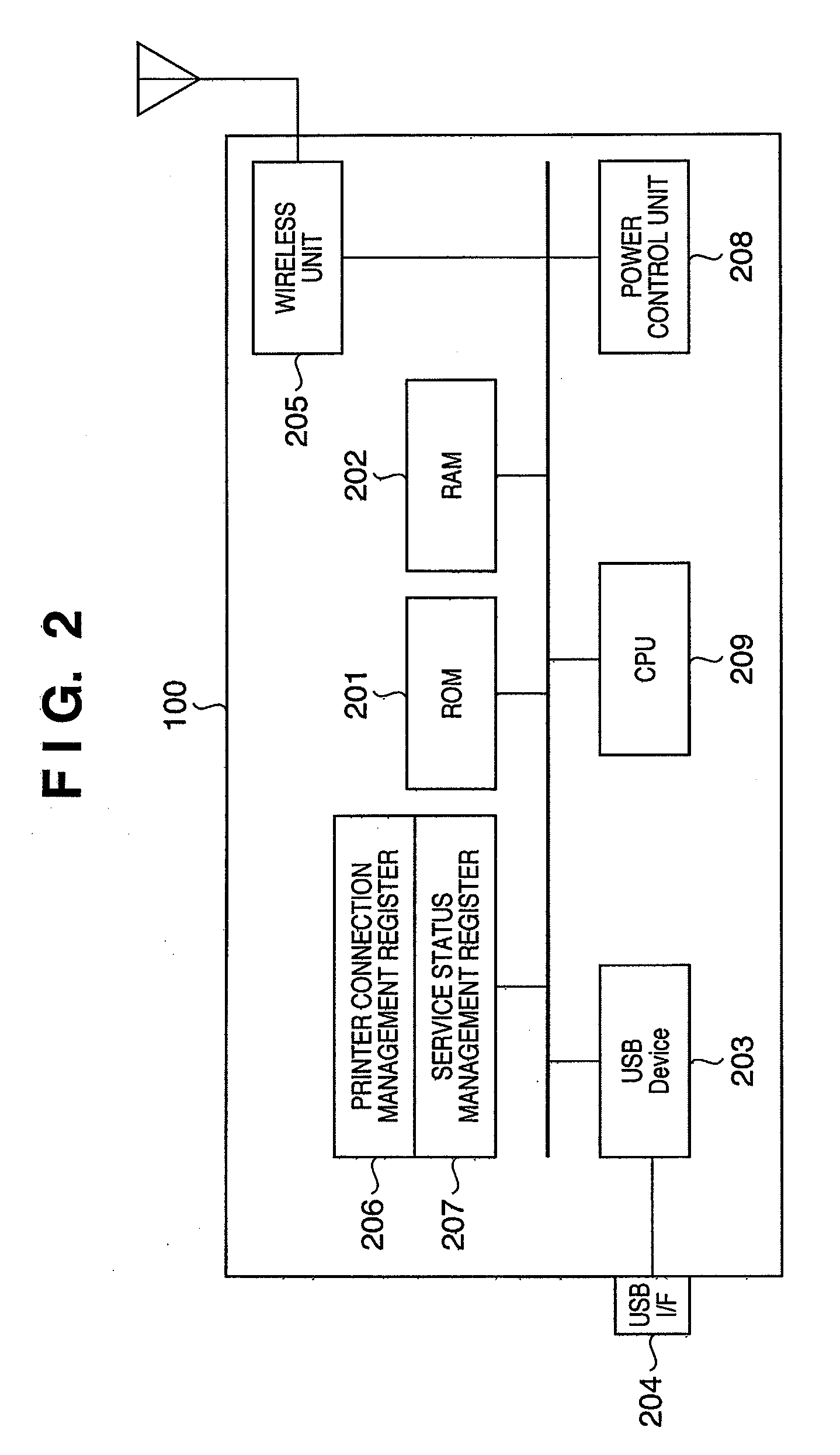
InactiveUS20090075594A1Service is blockedRadio transmissionHome automation networksComputer hardwareControl communications
In a system in which a communication adapter installing UPnP is connected to a printer to provide a print service, the communication adapter notifies a device that the printer joins the network or leaves from it, based on determination whether the printer can provide a service. Hence, the present invention can suppress from issuing a service request to a printer which cannot provide the service.
Owner:CANON KK
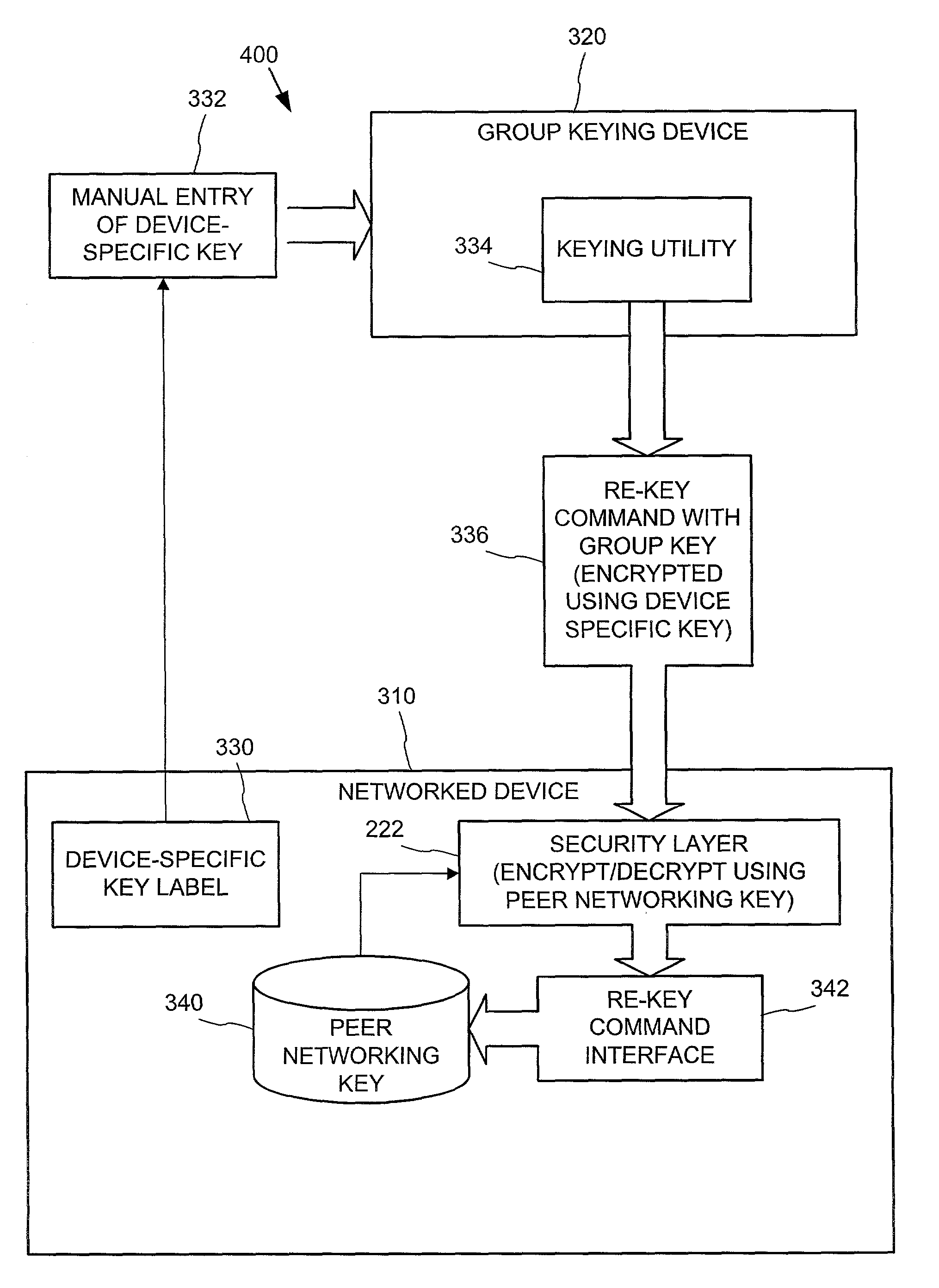
Establishing secure peer networking in trust webs on open networks using shared secret device key
InactiveUS20050286722A1CostInexpensive and reliableData switching networksSecuring communicationRe keyingComputer security
A trust web keying process provides secure peer networking of computing devices on an open network. A device is initially keyed at distribution to an end user or installer with a device-specific cryptographic key, and programmed to respond only to peer networking communication secured using the device's key. The device-specific key is manually entered into a keying device that transmits a re-keying command secured with the device-specific key to the device for re-keying the device with a group cryptographic key. The device then securely peer networks with other devices also keyed with the group cryptographic key, forming a trust web. Guest devices can be securely peer networked with the trust web devices via a trust web gateway.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com