Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
114results about How to "Seek miniaturization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
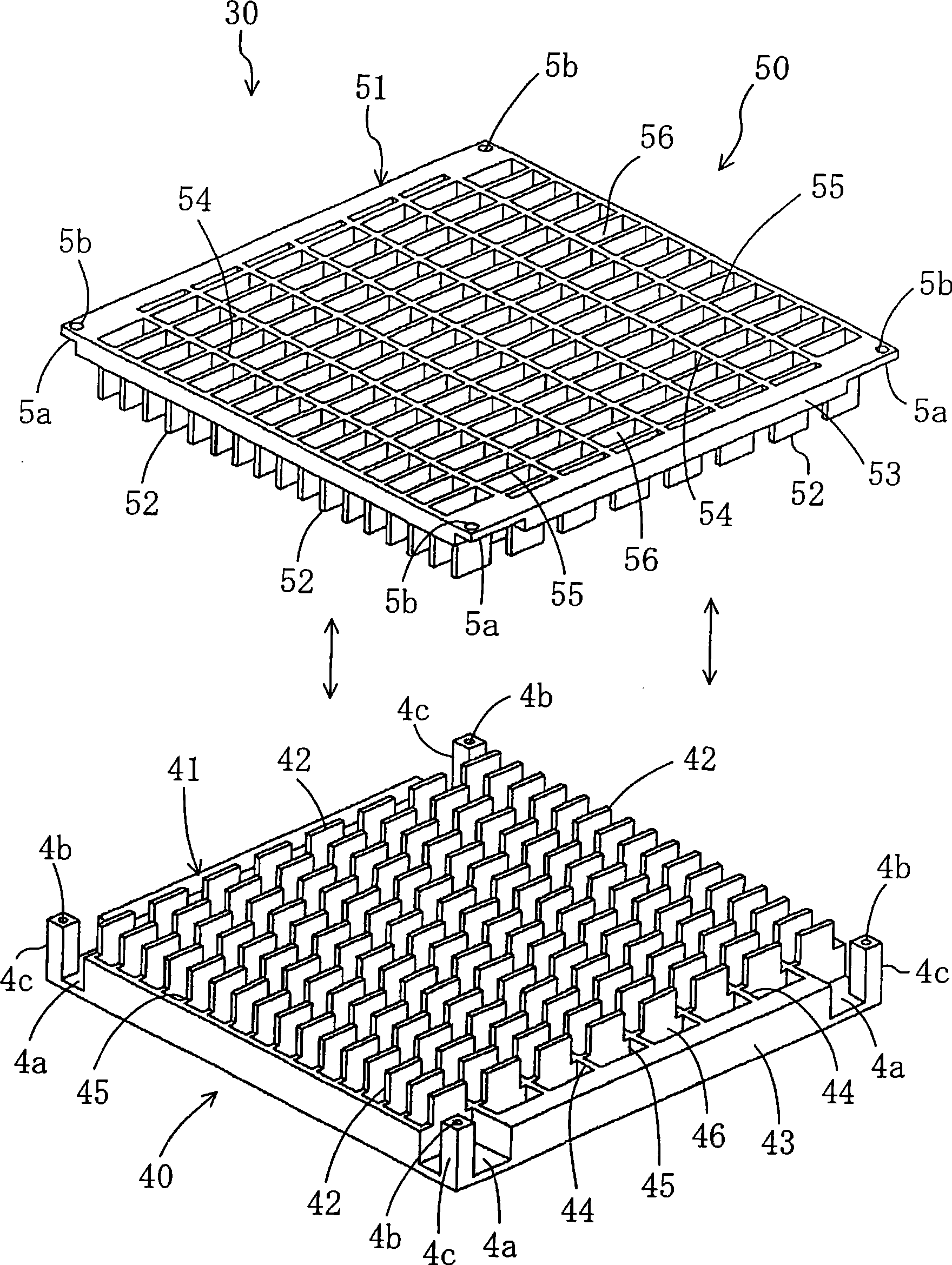
Brushless motor
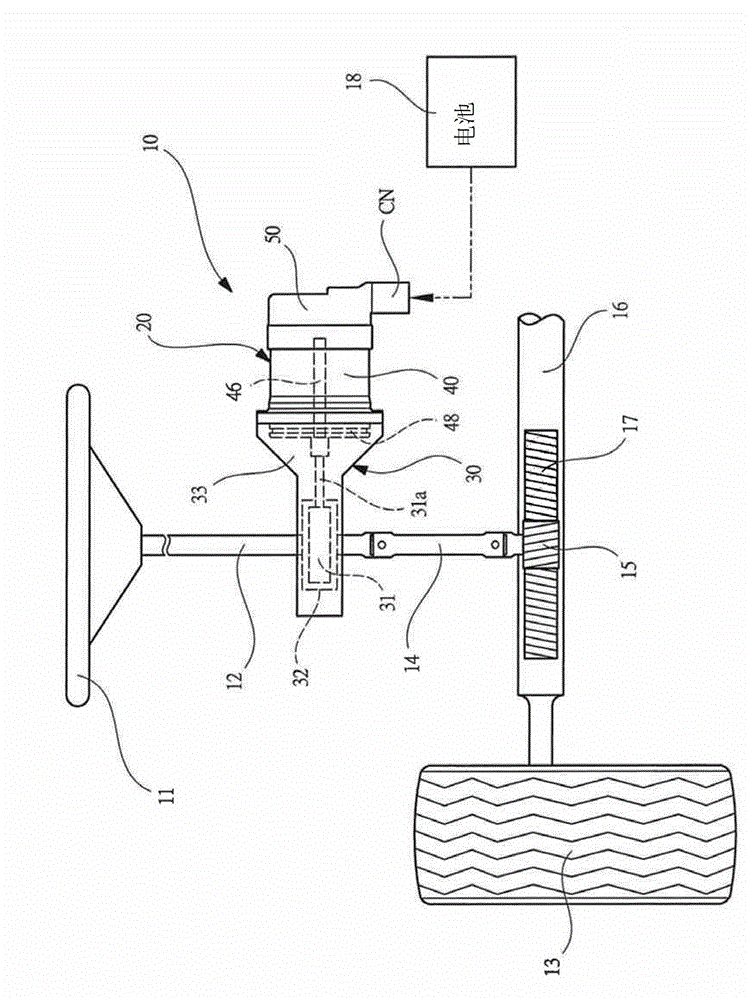
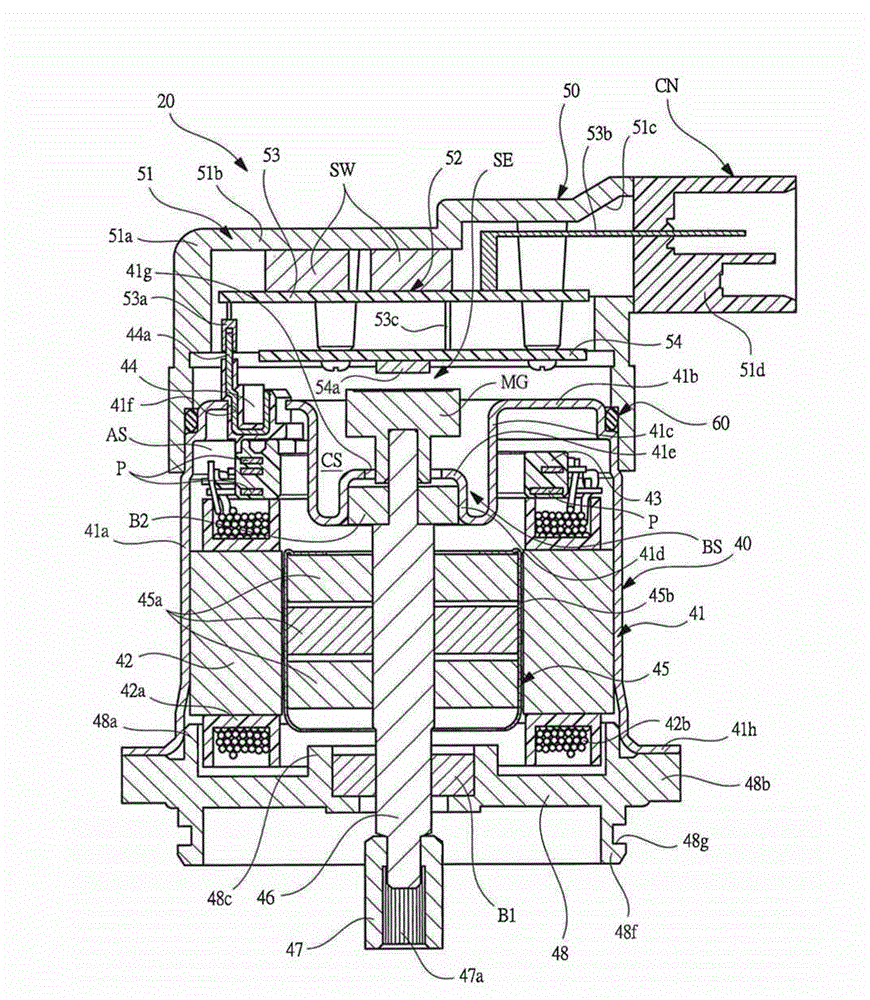
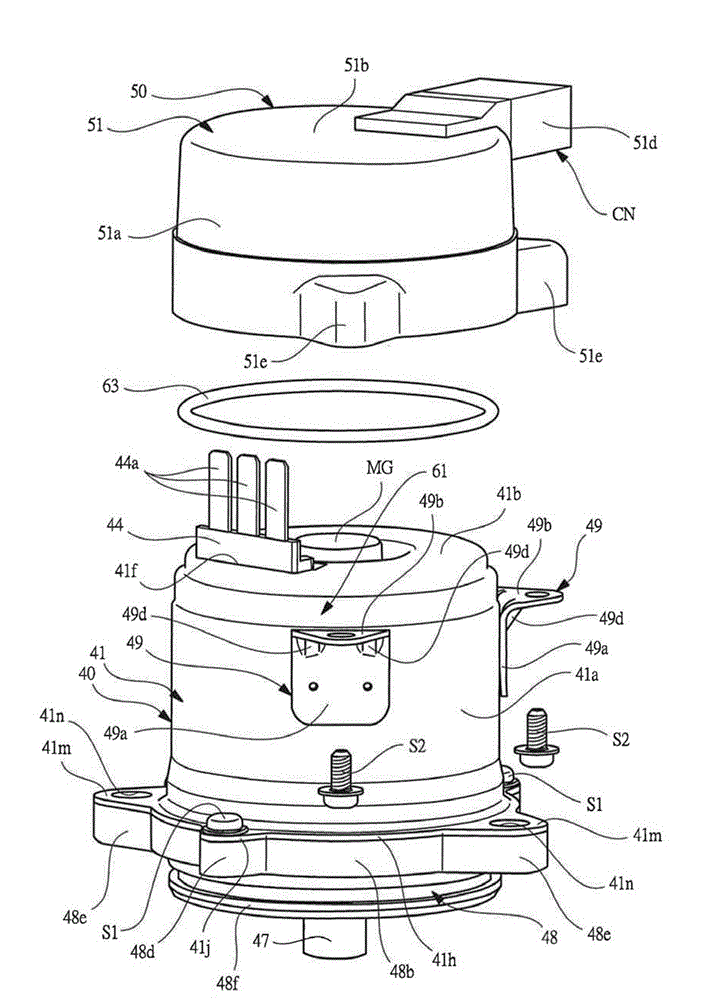
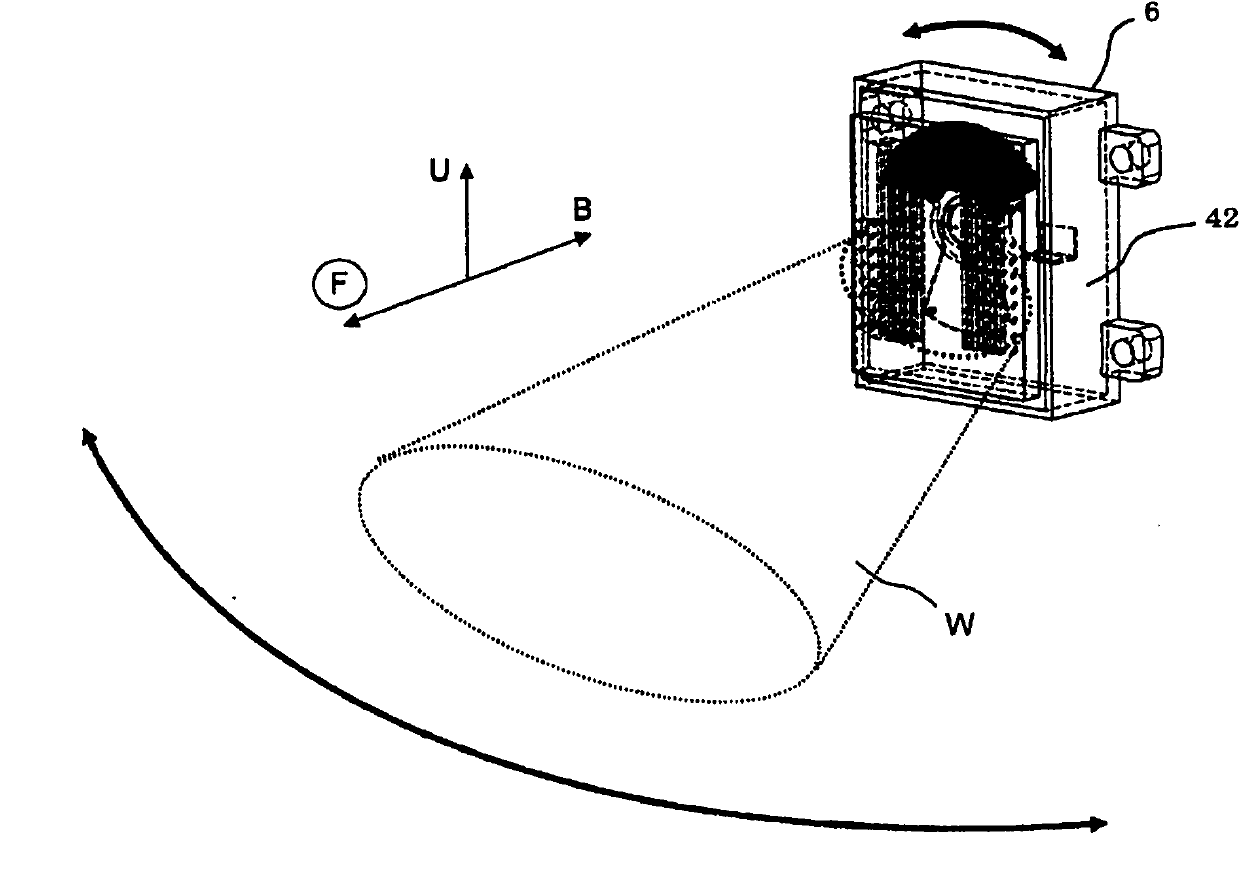
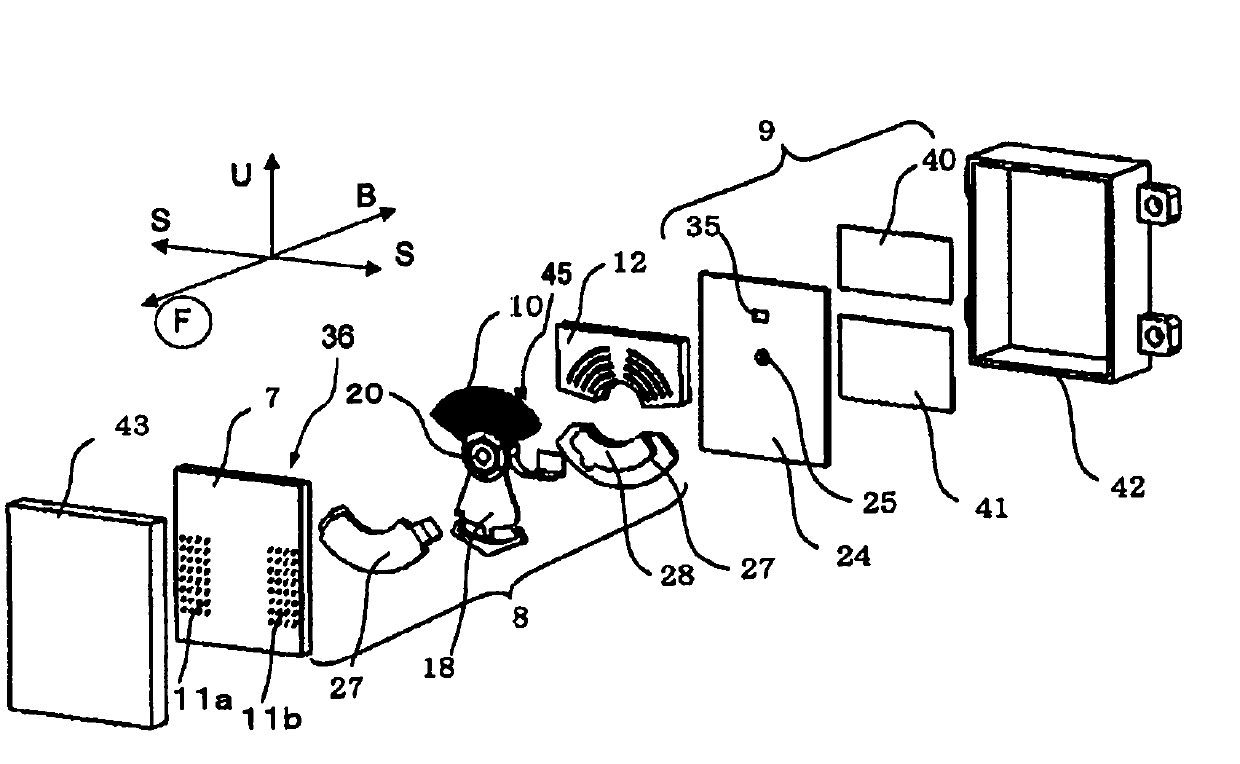
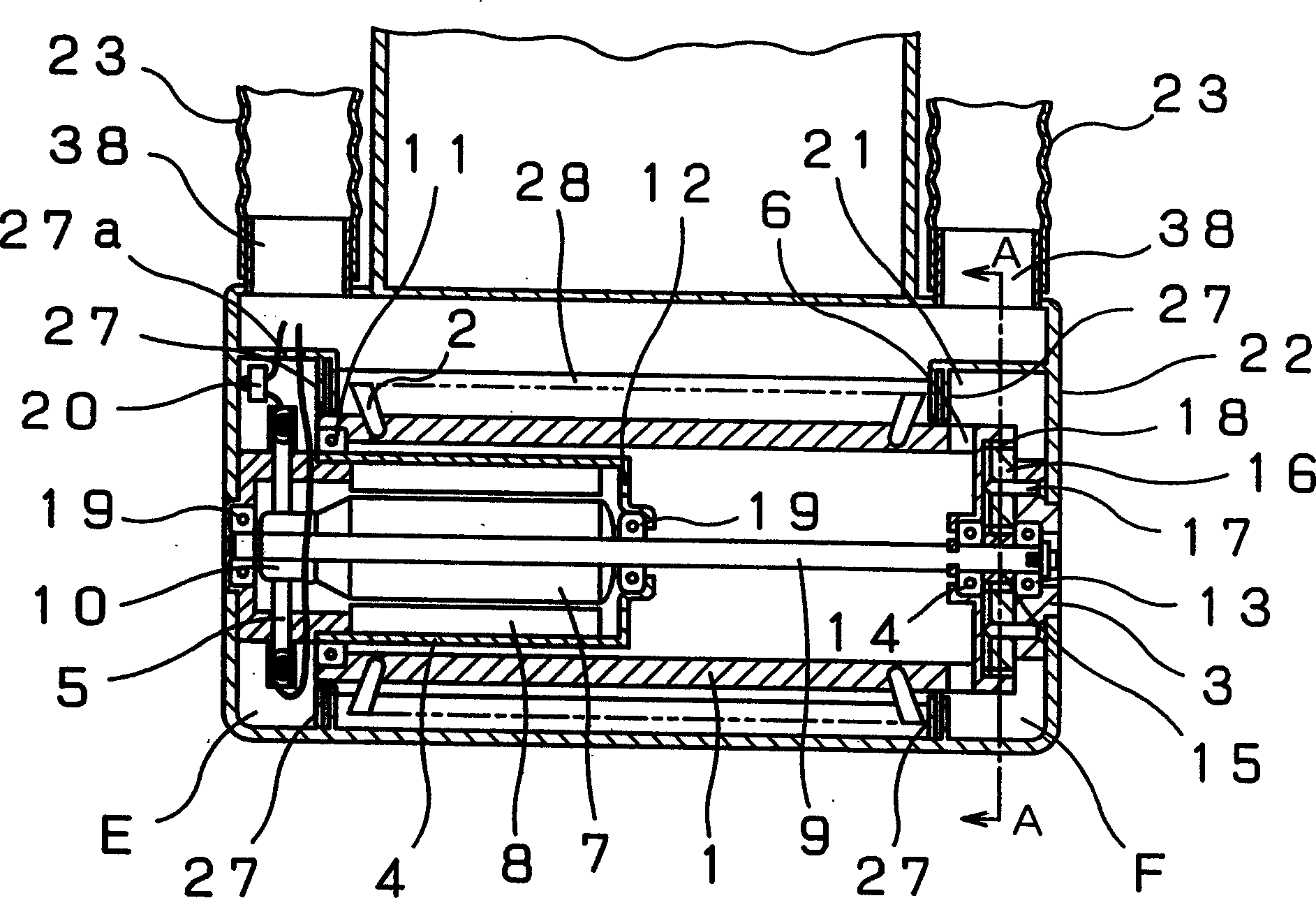
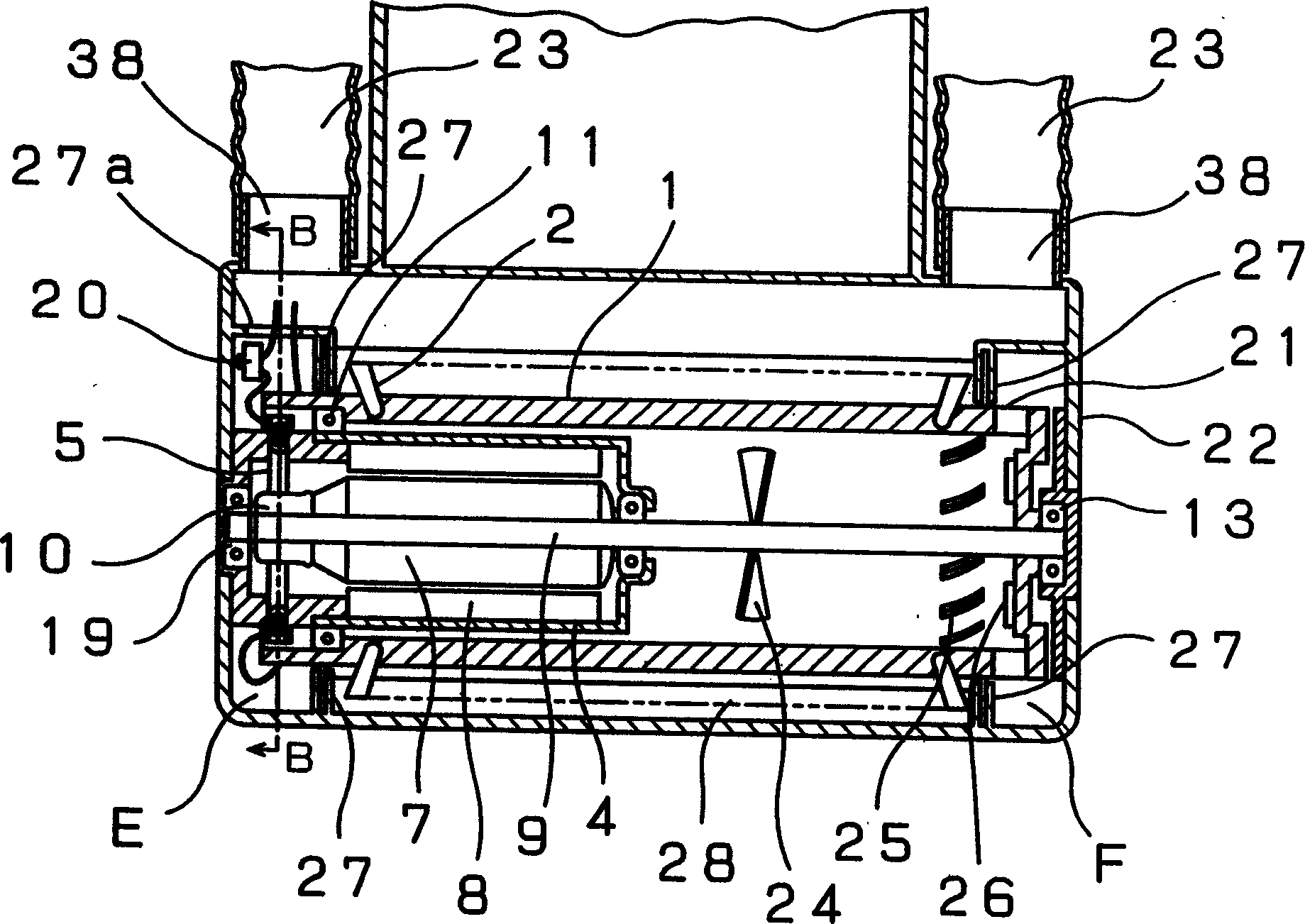
InactiveCN103066787ASeek miniaturizationGuaranteed cooling effectAssociation with control/drive circuitsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesBrushless motorsManufacturing cost reduction
The invention discloses a brushless motor which can ensure heat dissipation of a control device and meanwhile manufacturing process is simplified, manufacturing cost is reduced, and the brushless motor is minimized and has light weight. the brushless motor includes: a motor case 41 in which a cylindrical stator core 42 formed from steel plate by press molding is secured; a bracket 48 on one side in an axial direction of a motor case, a tip side of a rotary shaft 46 secured to a rotor 45 being rotatably supported by the bracket; and a housing member 51 on the other side in the axial direction of the motor case, a control device 52 for controlling the rotation of the rotor being accommodated in the housing member, the control device having a power-related circuit board 53 disposed on the side of a bottom 51b of the housing member and a control-related circuit board 54 disposed on the side of an opening of the housing member, semiconductor switching devices SW being disposed on the power-related circuit board in contact with the housing member.
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
Imaging device
InactiveCN101154013ASeek miniaturizationTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisEngineering
An imaging device for making camera shake compensation by relatively moving an imaging optical system and an imaging element in directions perpendicular to an optical axis direction, includes first to third actuators and a moving member. The first actuator relatively moves the imaging optical system and the imaging element in a first direction perpendicular to the optical axis direction. The second actuator 6 relatively moves the imaging optical system and the imaging element in a second direction which is perpendicular to the optical axis direction and which intersects the first direction. The second actuator is attached to the moving member. The moving member is moved by an action of the first actuator and an action of the second actuator in the first direction and the second direction. The third actuator relatively moves the imaging optical system and the moving member in the optical axis direction.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Cover member and power supply device equipped with this cover member
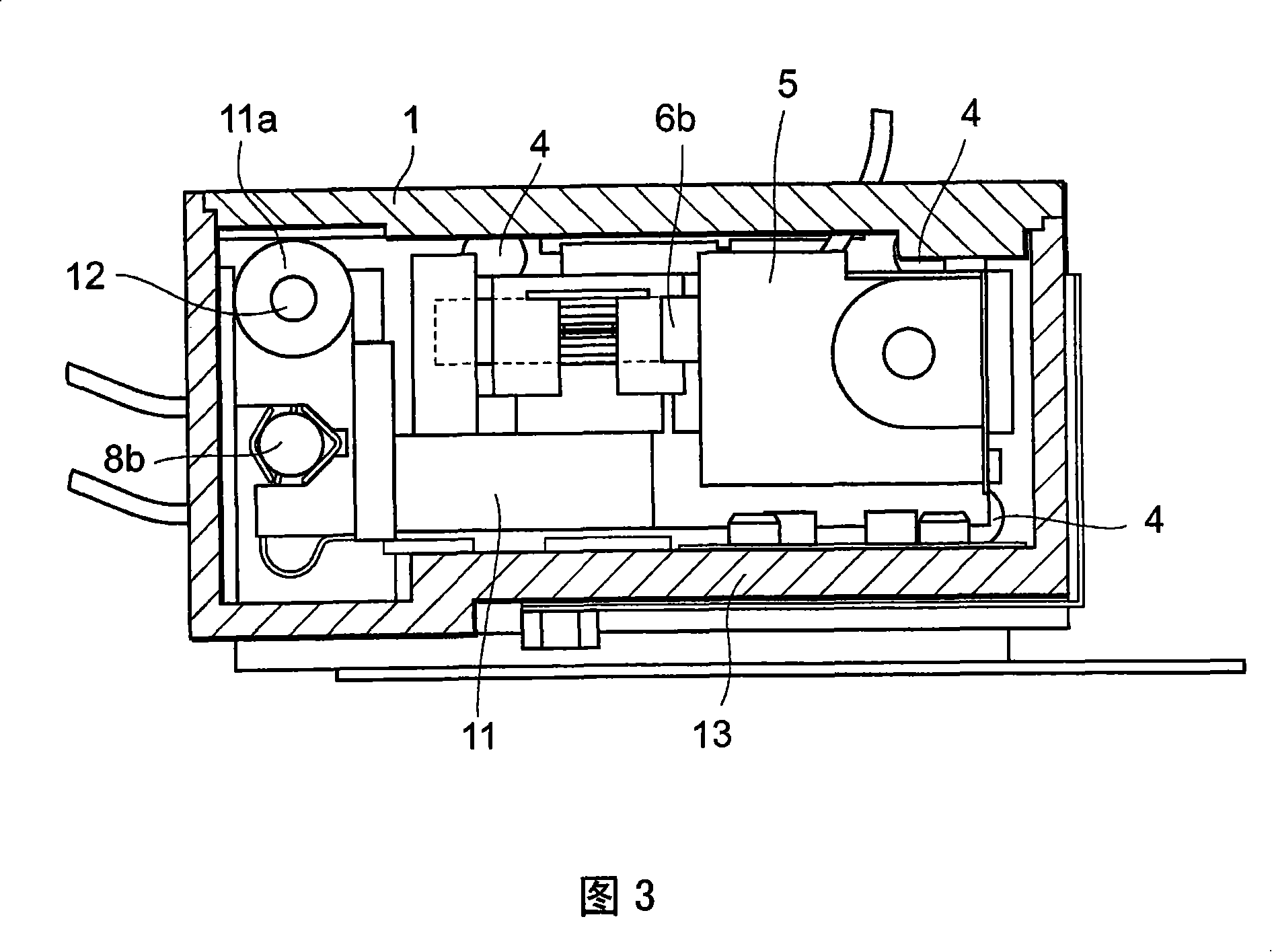
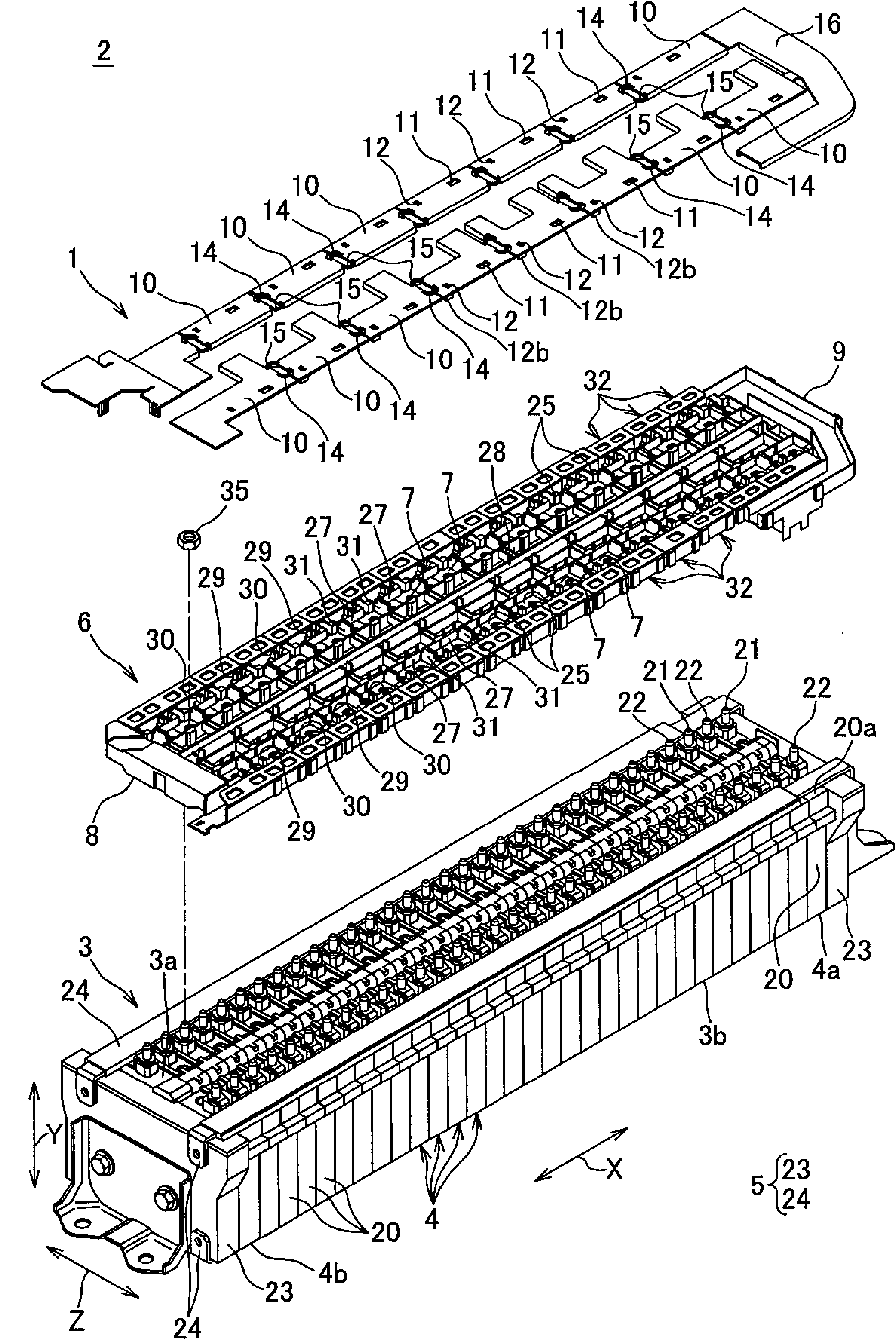
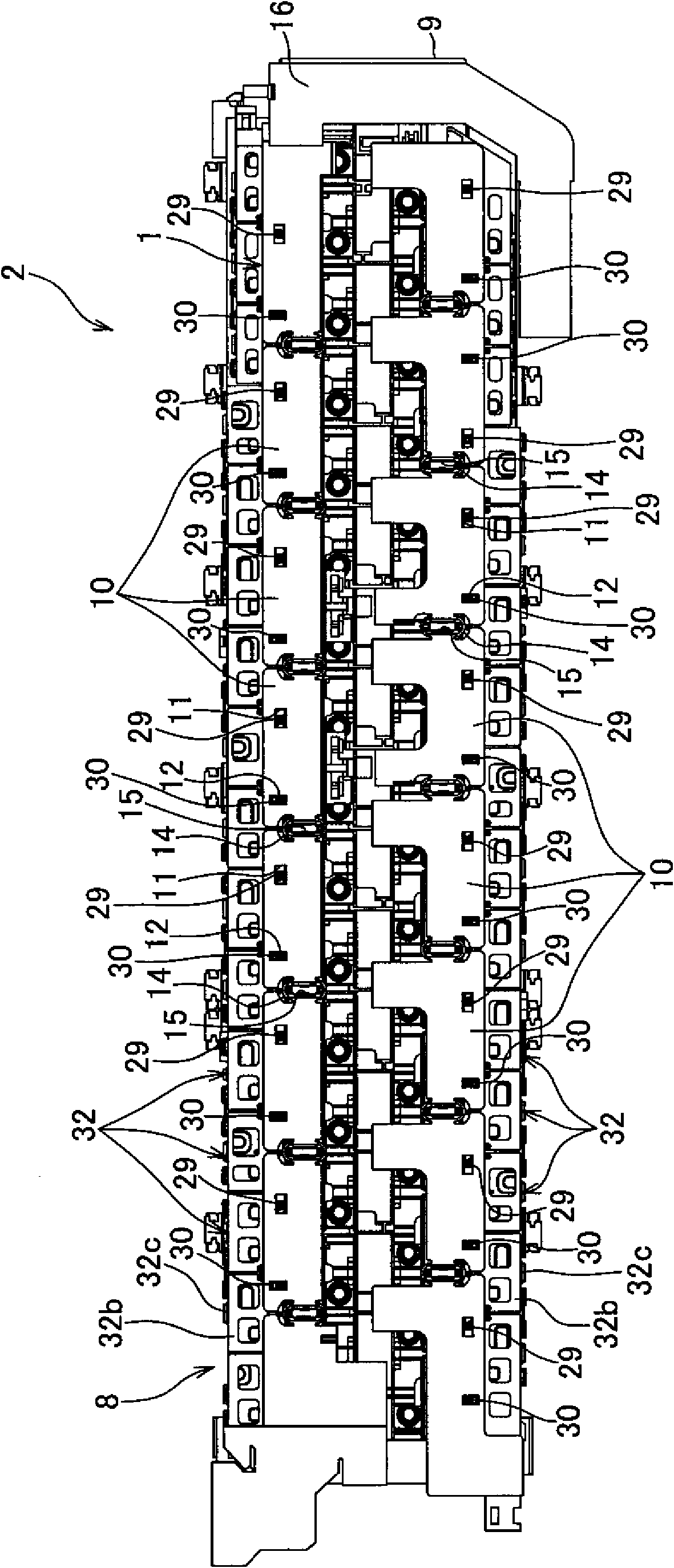
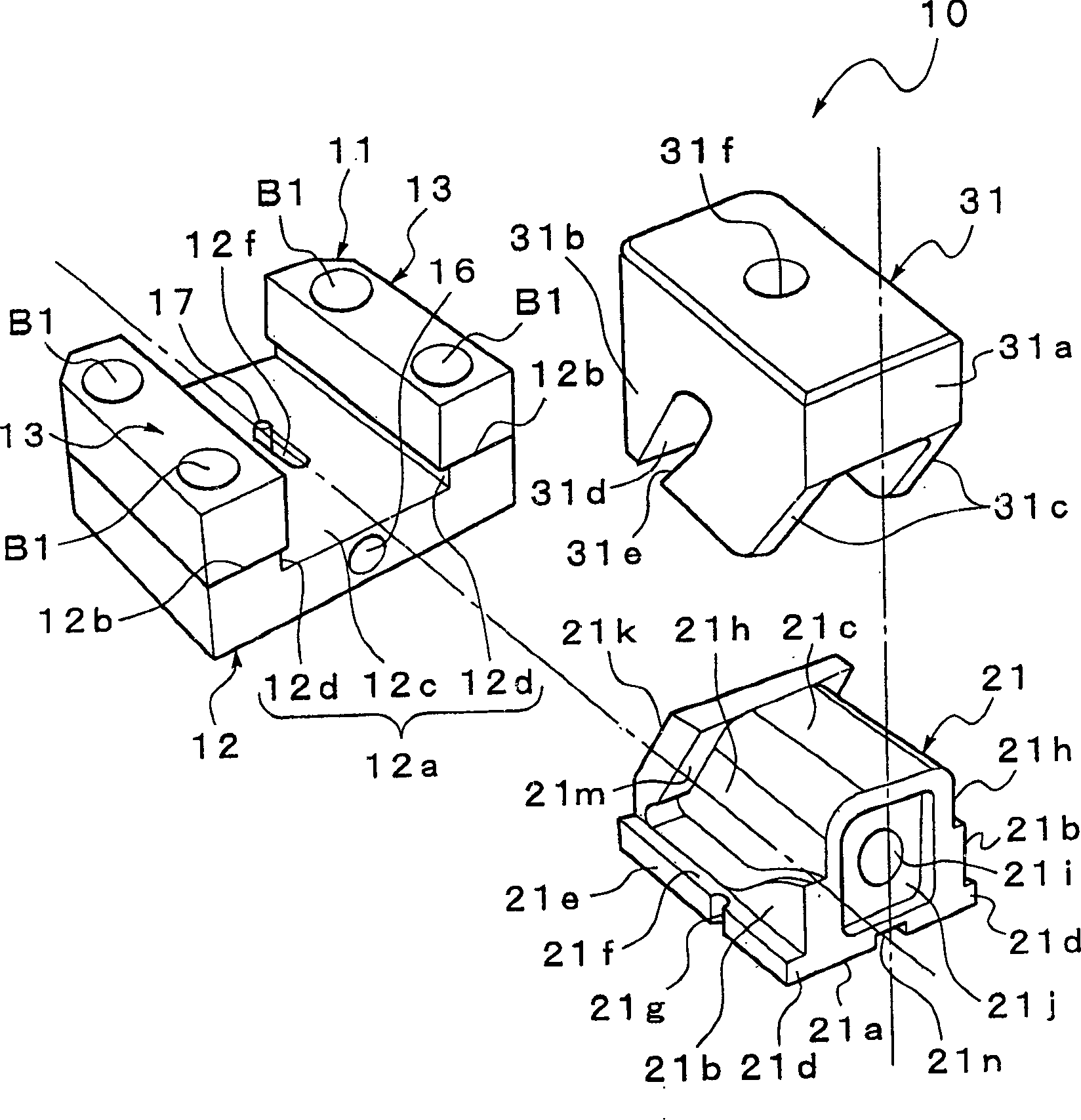
ActiveCN102576843AEasy to installEasy to processCell lids/coversElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
In a power supply device, there has been a problem that when a bus bar module to which batteries are connected varies in length, it becomes difficult to attach a cover member. The bus bar module (6) comprises: a plurality of bus bars for connecting adjacent batteries in a battery assembly body to each other, the battery assembly body being formed by stacking a plurality batteries; a main body portion (8) having the bus bars attached thereto and being stacked on the battery assembly body; a plurality of alignment projections (29) provided on the main body portion; and a plurality of locking portions (30). The cover member (1) is installed adjacent to the bus bar module along the stacked direction (X) of the batteries and comprises: a plurality of cover portions (10) for covering each of the bus bars; and an elastic deformation portion (14) for coupling the adjacent cover portions so as to be able to be mutually displaced. Each of the cover portions comprises: an alignment opening (11) into which each of the alignment projections is inserted; and a locking receiving portion (12) by which each of the locking portions is locked. The alignment opening is shaped so as to be able to be inserted even when the positions of the alignment projections move along the direction (X), thereby solving the above problem.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Slide core unit
InactiveCN1564731AReduce maintenance costsSteady back movementDomestic articlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:竹元 通则 +1
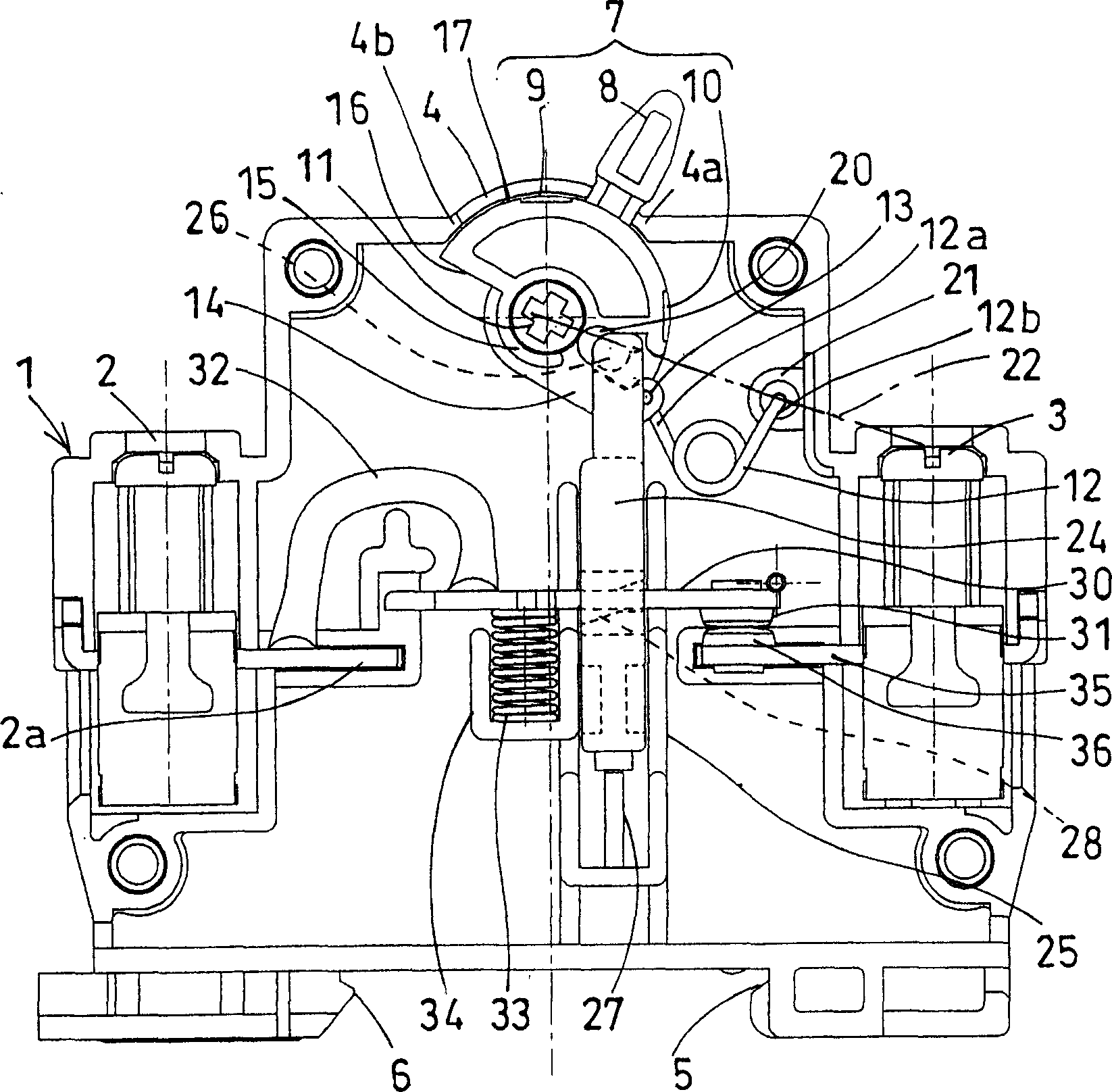
Brake cylinder device and disc brake device
InactiveCN102985718ASave configuration spaceGreat driving forceAxially engaging brakesBrake actuating mechanismsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Disclosed is a compact brake cylinder device which, while avoiding increases in the size of the device, is capable of increasing the braking force outputted from a brake output unit which moves together with a rod. A rod (22) is provided inside of a cylinder body (20) so as to freely move in the advancing and retracting directions of the cylinder shaft direction. A piston (24) partitions a pressure chamber (44) inside of the cylinder body (20), surrounding the circumference of the rod (22), and moves in a linear direction parallel to the movement direction of the rod (22). By supplying a pressure fluid to the pressure chamber (44), the piston (24) resists the biasing force of a biasing spring (23) and moves in the retracting direction relative to the cylinder body (20). At that time, a force-multiplication mechanism (25) converts the linear direction drive force generated by the piston (24) to a rotational direction, moves the rod (22) in the advancing direction, and multiplies the drive force from the piston (24) to act on the rod (22). A brake output unit (21) moves together with the rod (22) in the advancing direction and outputs a braking force.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP
Dust collector
ActiveCN101472682AIncrease dust collection areaSpark suppressionExternal electric electrostatic seperatorElectrode constructionsElectricityEngineering
A dust collector includes a charging part (12) for charging dust with electricity and a dust collecting part (30). Each of a dust collecting electrode (40) and a high-voltage electrode (50) that constitute the dust collecting part (30) includes: a base (41, 51) with a rectangular grid structure having a large number of vent holes (46, 56) formed therein; and projections (42, 52) extending into the vent holes (56, 46) of the opposed electrode (50, 40). The dust collector collects dust by generating an electric field between the dust collecting electrode (40) and the high-voltage electrode (50).
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
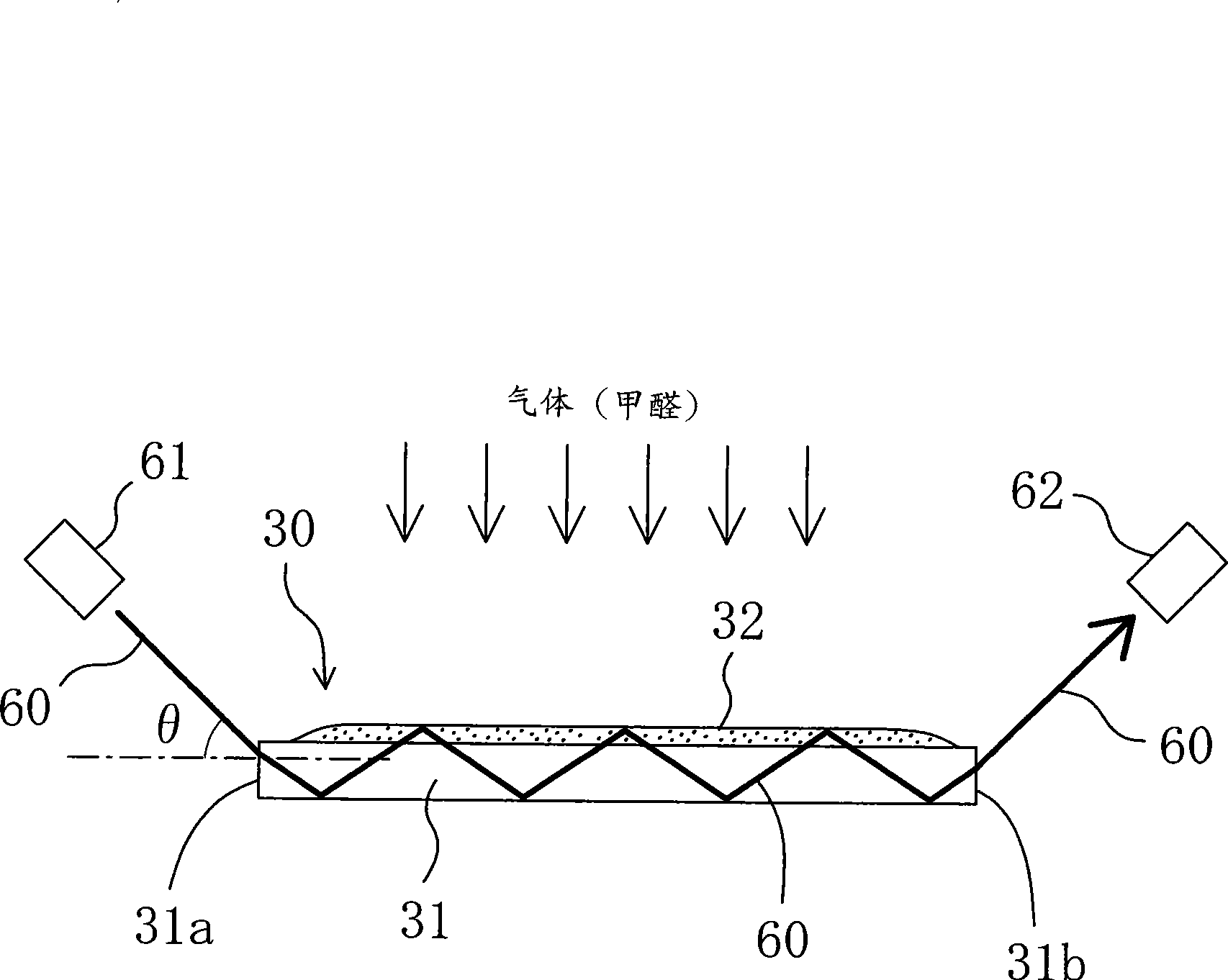
Formaldehyde detecting material, formaldehyde detector, formaldehyde detecting method and formaldehyde detecting reagent
InactiveCN101535798AShort reaction timeMake sure to reactAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorOptical propertyLight signal
A formaldehyde detector (10) provided with a detecting reagent which develops a color in response to formaldehyde. The detector (10) comprises a detection element (30) having a base material (31) which constitutes an optical waveguide transmitting light via repeated total reflection and a mesoporous layer (32) which serves as the surface of the base material (31), is formed by laminating on at least a part of the light reflecting face and carries the detecting reagent as described above. Furthermore, it has a light emitting material which emits an incident light on the base material (31) and a light receiving material which receives the light outgoing from the base material (31). Furthermore, it has a signal processing section wherein the light signal from the light receiving material is received and a change in the optical properties based on the color development due to the reaction of formaldehyde with the detecting reagent is detected to thereby detect formaldehyde and measure its concentration from the change in the optical properties.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
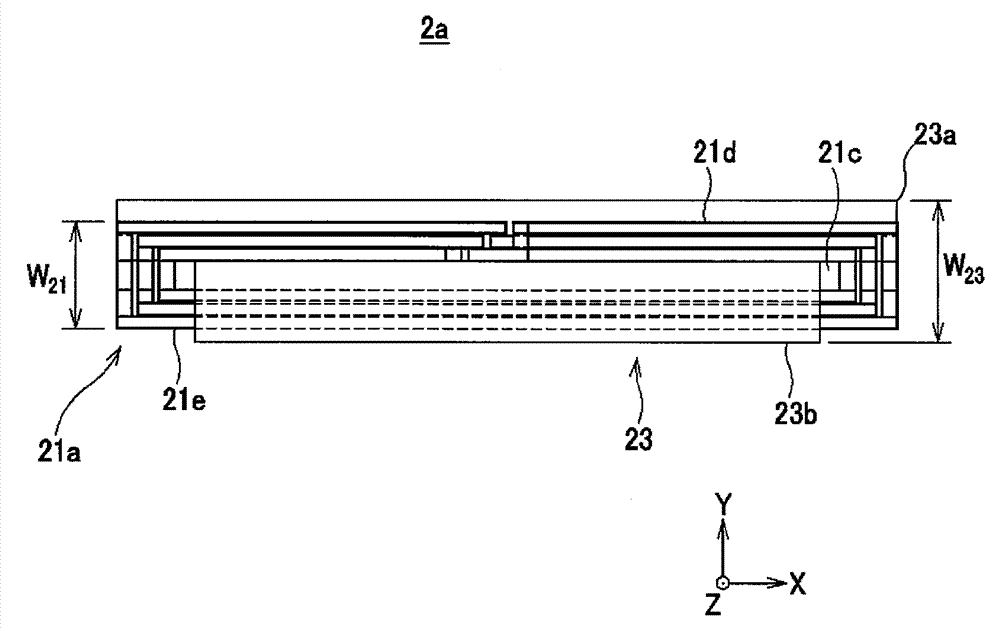
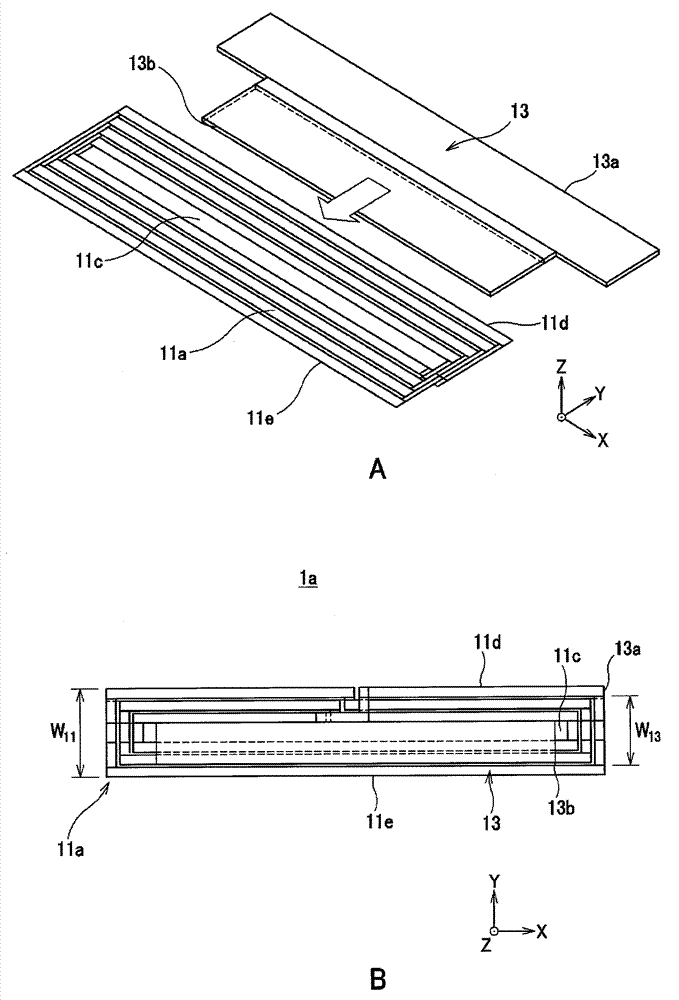
Antenna apparatus and communication apparatus
ActiveCN103947043ASeek miniaturizationSeeking thinnerLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna substrateEngineering
Provided is a communication apparatus, with which, while maintaining communication characteristics, a housing of an electronic apparatus can be reduced in size and thickness when the communication apparatus is assembled to the electronic apparatus. The communication apparatus is provided with: an antenna substrate (11) having an antenna coil (11a) formed thereon, said antenna coil to be inductively coupled with a reader writer (120); and a magnetic sheet (13), which draws a magnetic field to the antenna coil (11a), said magnetic field having been transmitted from the reader writer (120). In the direction in which the magnetic sheet (13) is inserted into a center portion (11c) of the antenna coil (11a) formed on the antenna substrate (11), both the end portions (13a, 13b) of the magnetic sheet (13) are positioned further toward the center portion (11c) than both the end portions (11d, 11e) of the antenna coil (11a).
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Ferrite composition and electronic component
InactiveCN104557005AHigh Q valueSeek miniaturizationTransformersInorganic material magnetismCopper oxideElectronic component
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Substrate dividing device
InactiveCN103803787AShorten working timeSeek miniaturizationGlass severing apparatusGlass productionEngineeringMechanical engineering
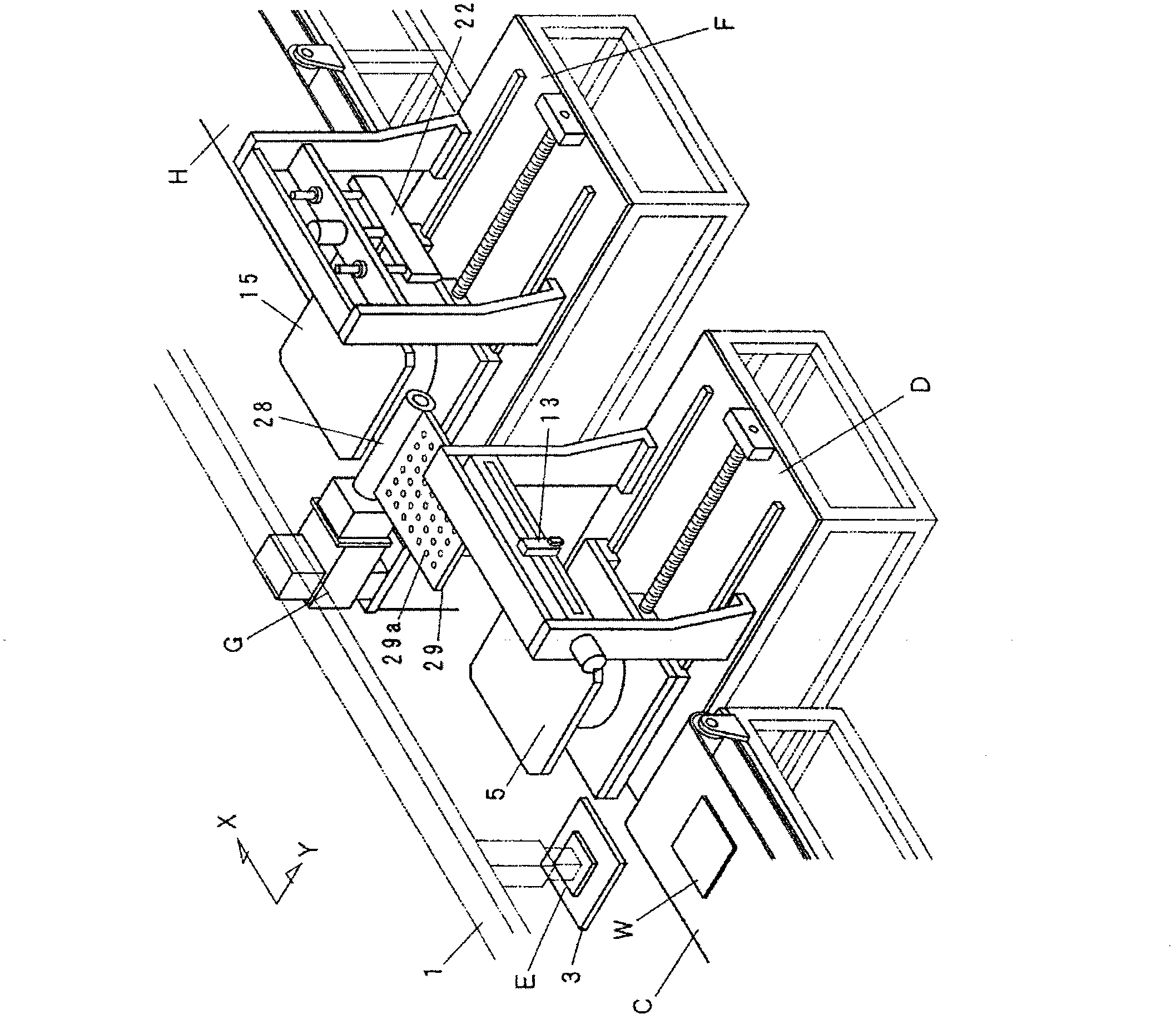
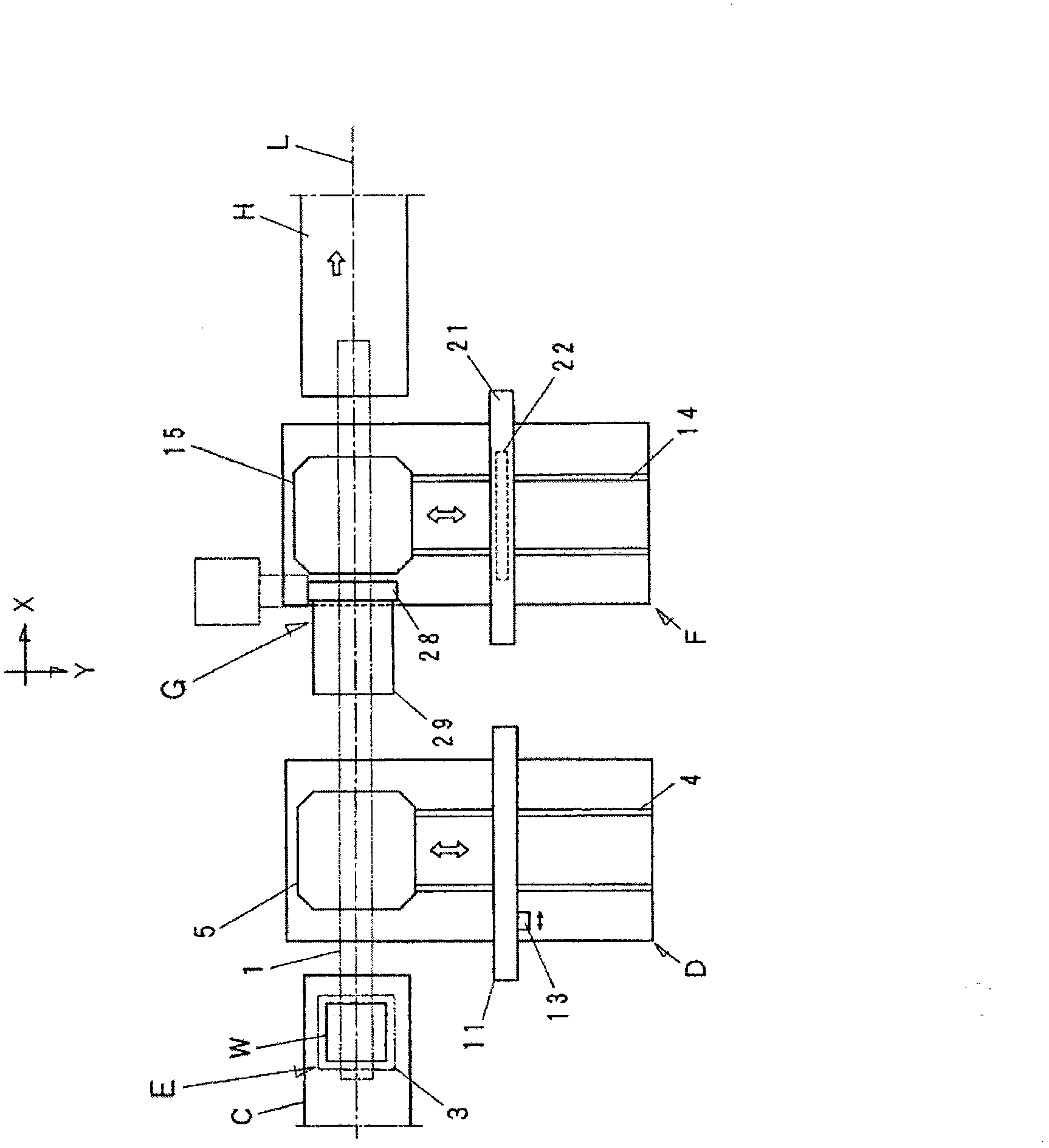
The invention discloses a substrate dividing device, comprising an etching device (D) forming etching lines on the surface of brittle material substrate (W); a conveying mechanism (E) which transmits the etched substrate (W) to an absorbing inversion mechanism (G); the absorbing inversion mechanism (G) which has an absorbing plate (29) which can be inversely rotated up and down through a rotating shaft (28), and which takes the substrate (W) from the conveying mechanism (E) and enables the substrate (W) to be inversely rotated up and down and to be placed on a platform (15) of a breaking device (F); and the breaking device (F) which breaks the substrate (W) taken from the absorbing inversion mechanism (G). The rotating shaft (28) of the absorbing plate (29) of the absorbing inversion mechanism (G) is disposed at the end part of the absorbing plate (29) in an extending manner along a direction approximately orthogonal to the conveying direction of the substrate (W). The absorbing plate (29) absorbed with the substrate (W) is inversely rotated with the rotating shaft (28) being the fulcrum. The rotating shaft (28) is disposed near the platform (15) of the breaking device (F) in a manner that the inversely-rotated substrate (W) can be disposed on the platform (15) of the breaking device.
Owner:MITSUBOSHI DIAMOND IND CO LTD
Power supply
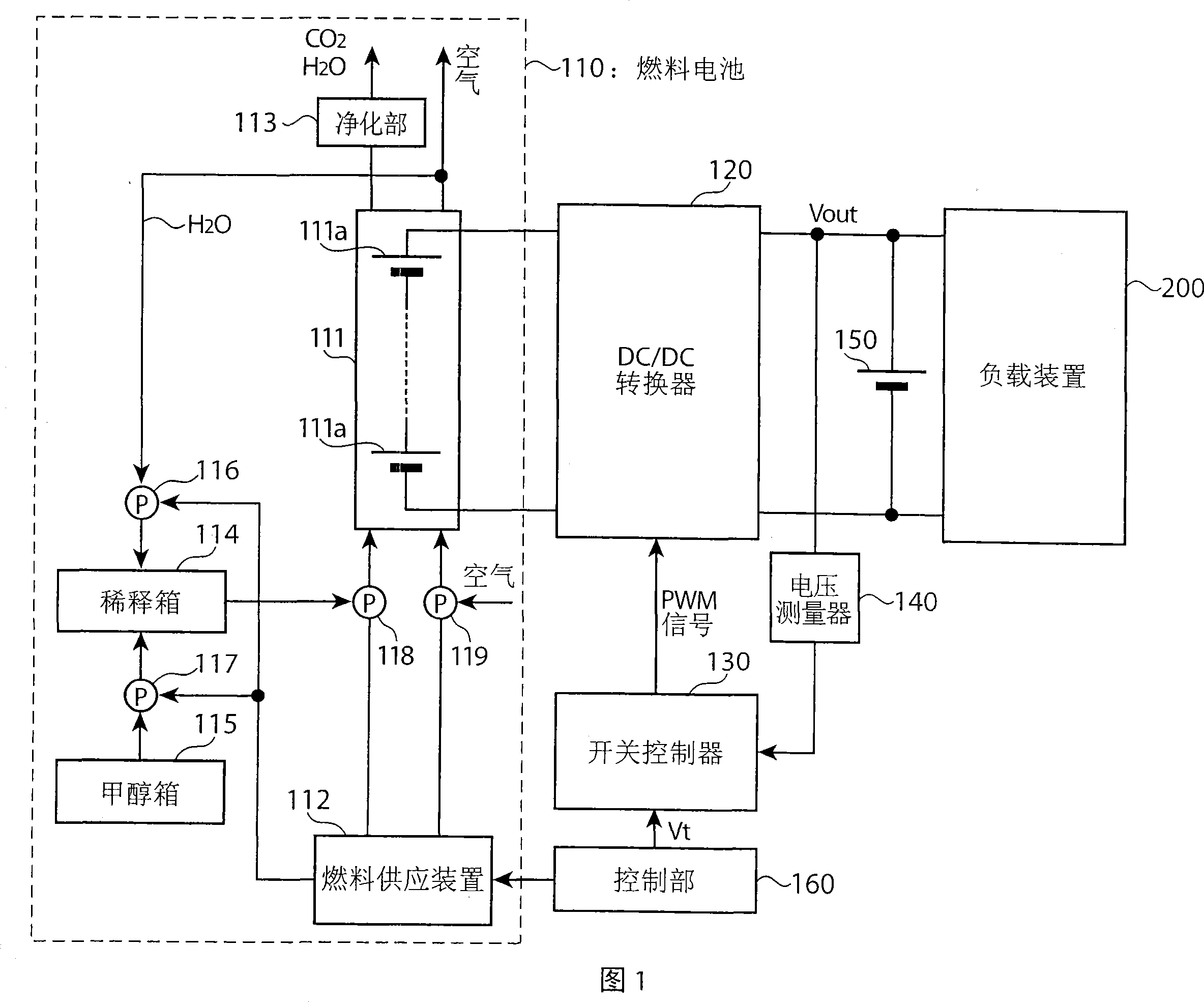
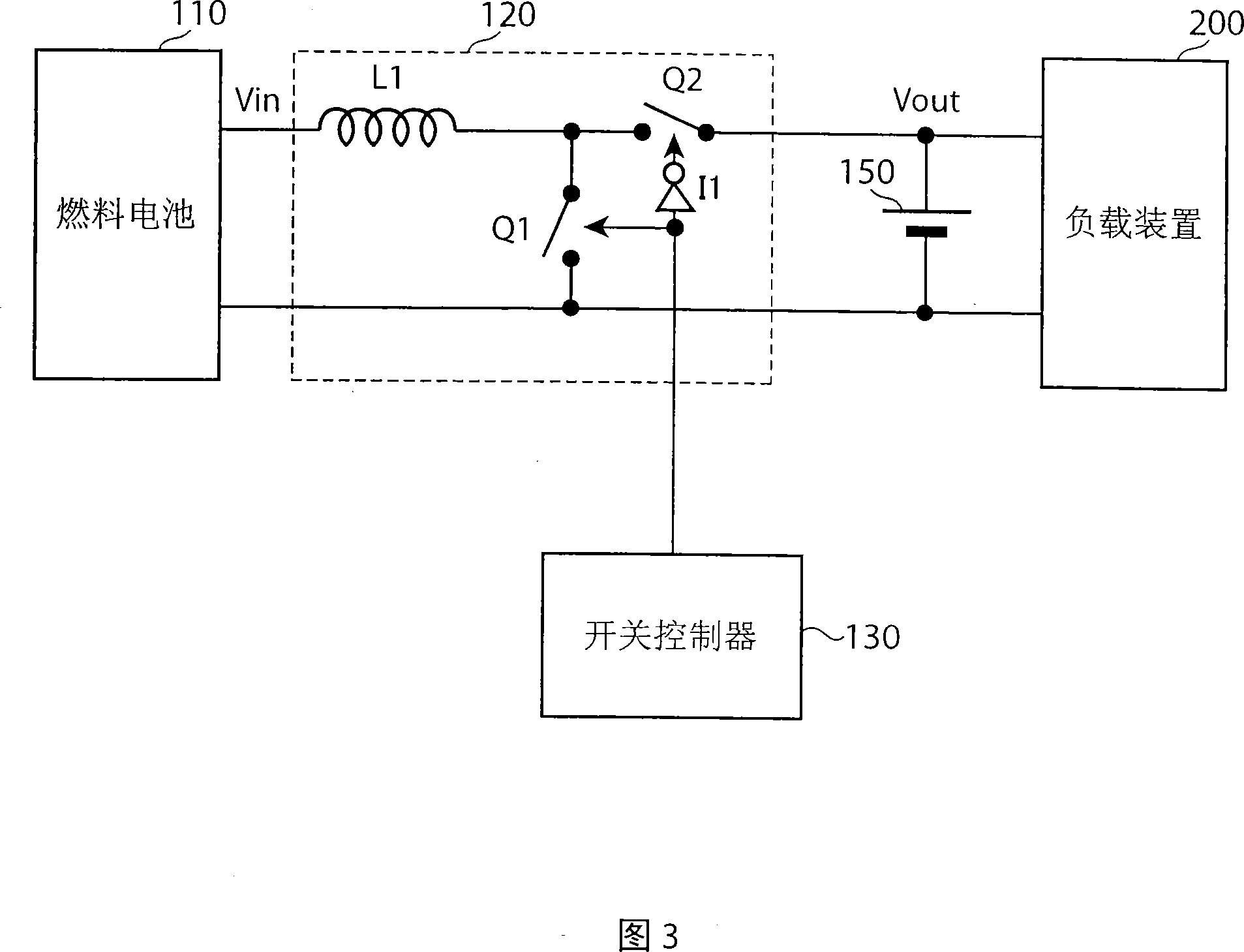
InactiveCN1989644AStable power generationAvoid oscillationBatteries circuit arrangementsFuel cell auxillariesNegative feedbackPower flow
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Canister layout structure in motorcycle
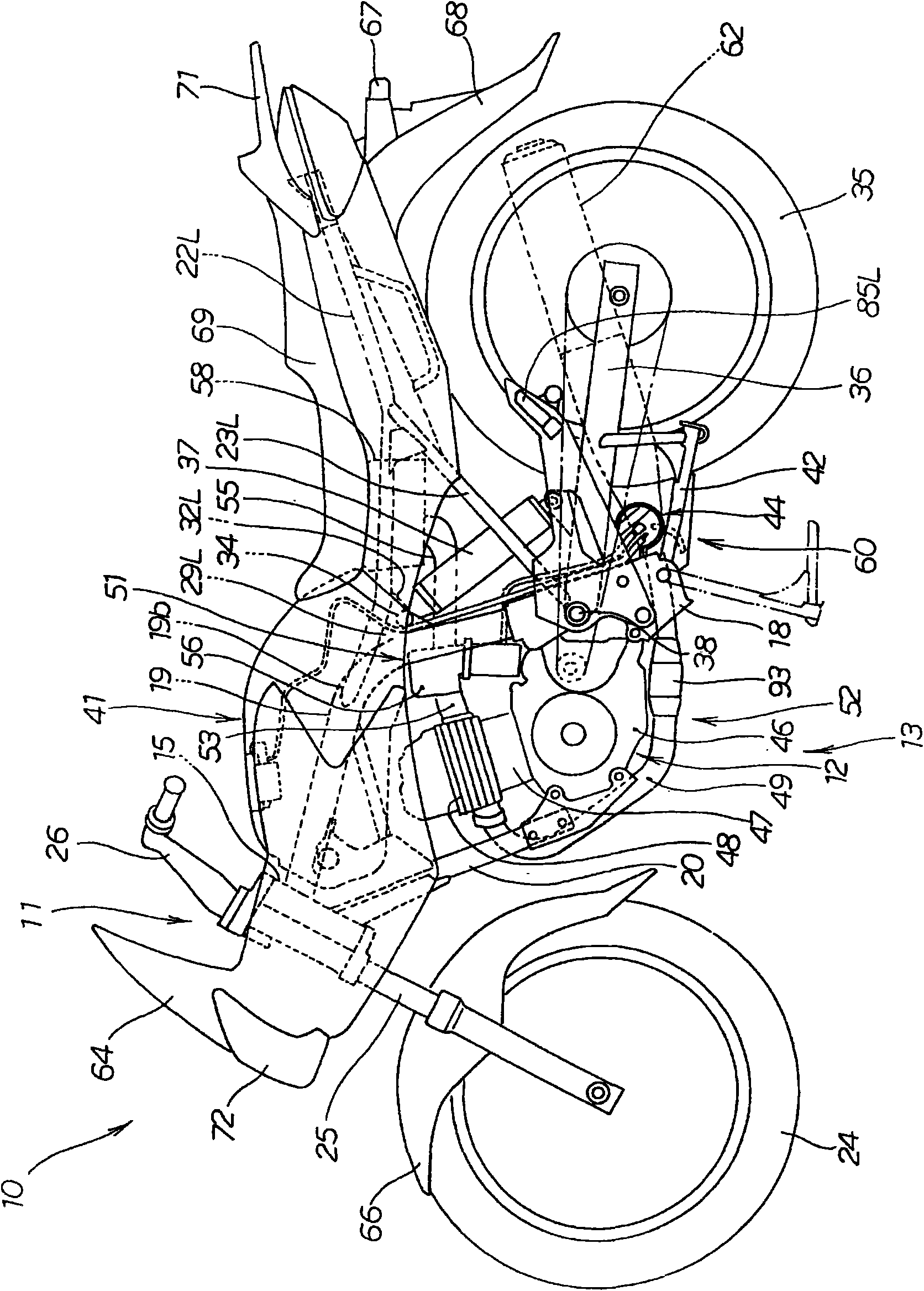
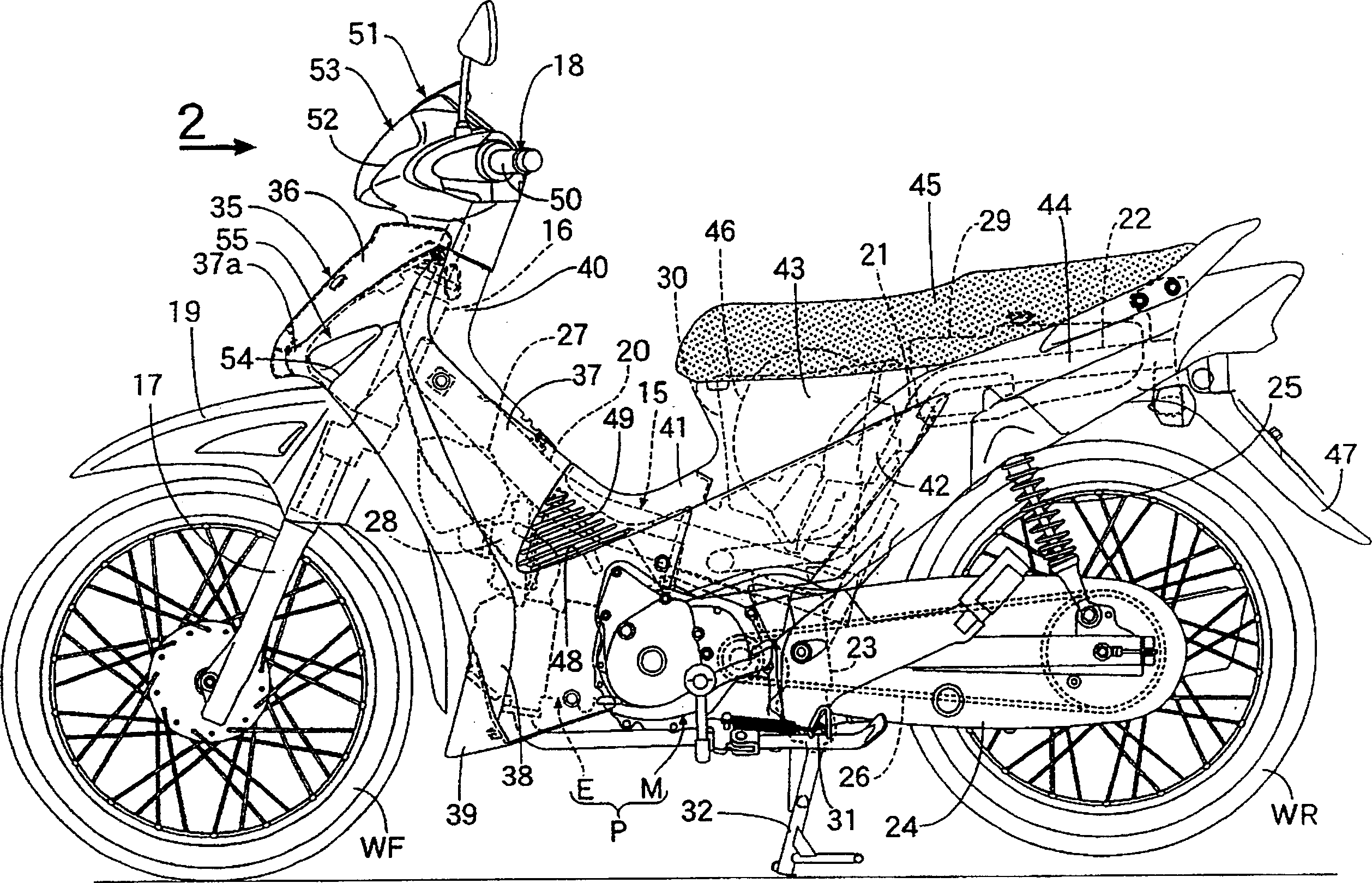
ActiveCN101659297AReduce the number of piecesSeek lightweightAxle suspensionsFuel tanksVehicle frameFuel tank
It is an object of the present invention to provide a technique which can reduce the number of parts and the weight of a vehicle body in a motorcycle having a canister at a lower portion of the vehicle body. A canister layout structure in a motorcycle includes a swing arm vertically swingably supported to a rear portion of a body frame and supporting a wheel, a canister located below the swing arm for trapping an evaporative fuel evaporated in a fuel tank, and a center stand pivotably supported to a lower portion of the body frame for making the body frame stand on a road surface when parking. The center stand is retractable to keep a horizontal position substantially parallel to a road surface during running. The canister is located above the center stand in its retracted condition.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Handle cover apparatus for a motorcycle
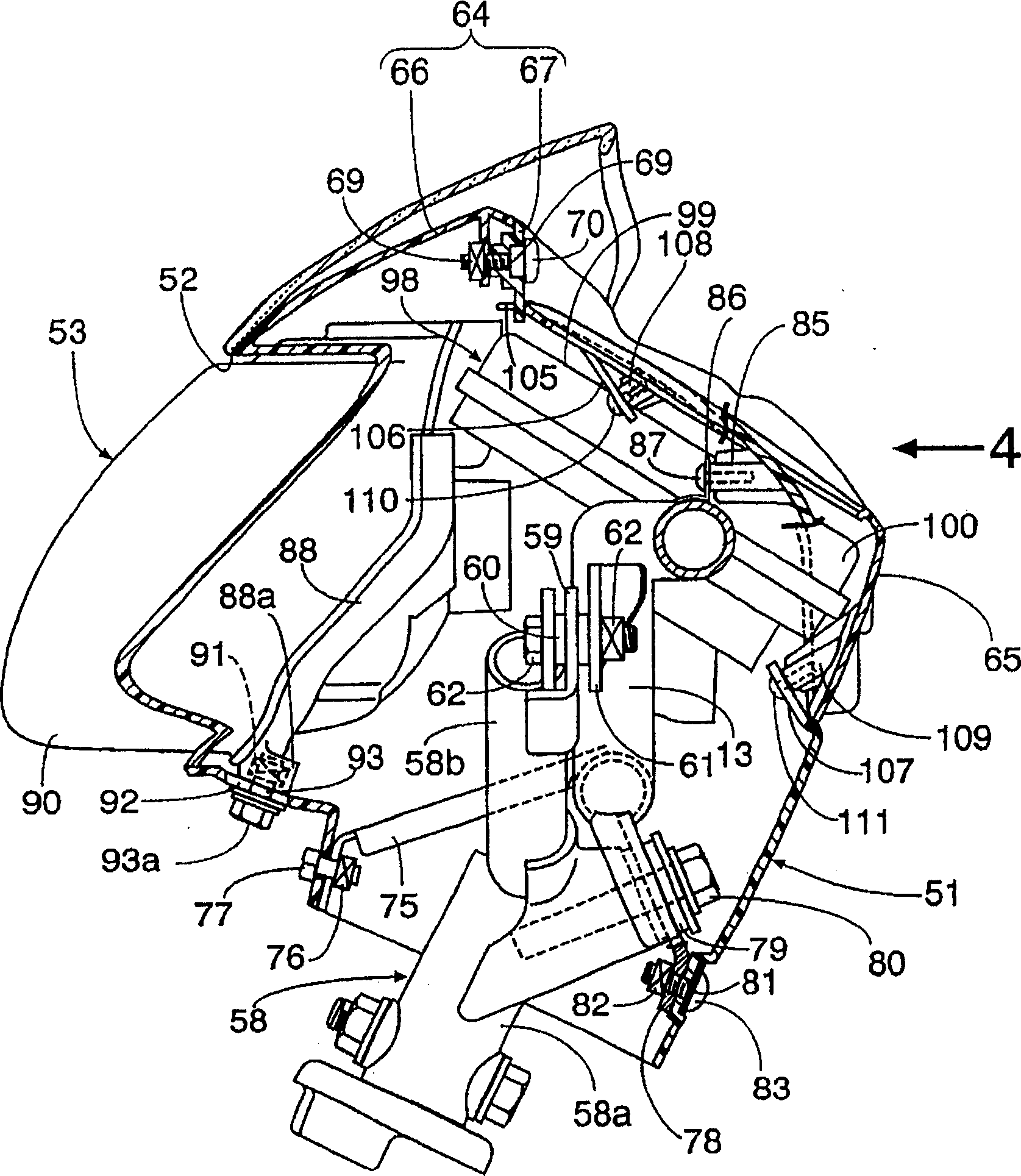
InactiveCN1754749ALow costEasy to replaceMotorised scootersSteering deviceEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
High frequency waveguide, antenna device, and electronic apparatus with antenna device
InactiveCN102017284AWide detection angleSeek miniaturizationWaveguide type devicesAntenna detailsLength waveWaveguide
A waveguide structure (8) includes a movable waveguide body (10) and a fixed waveguide body (12) opposed to the movable waveguide body (10) at a predetermined distance apart. At least the movable waveguide body or the fixed waveguide body, a groove or grooves (13, 29) are formed in the opposite surfaces of the waveguide bodies. Outside at least one of the grooves (13, 29), projections (44) having a height of approximate Lambada / 4 (Lambada is the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave used) are provided.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Rotary brush device and dust cleaner using same
InactiveCN1507829ASeek miniaturizationEasy to operateSuction nozzlesElectric equipment installationElectric machineGear wheel
A motor is incorporated in a cylindrical body which is a rotary brush. Rotation of a rotor of the motor, directly or via a speed reduction mechanism, drives the rotary brush. Cooling air runs through the cylindrical body so that the motor is cooled and protected. A rotary brush and an electric apparatus using this rotary brush can be therewith reduced in size.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Tire sensor device and tire information transmission method
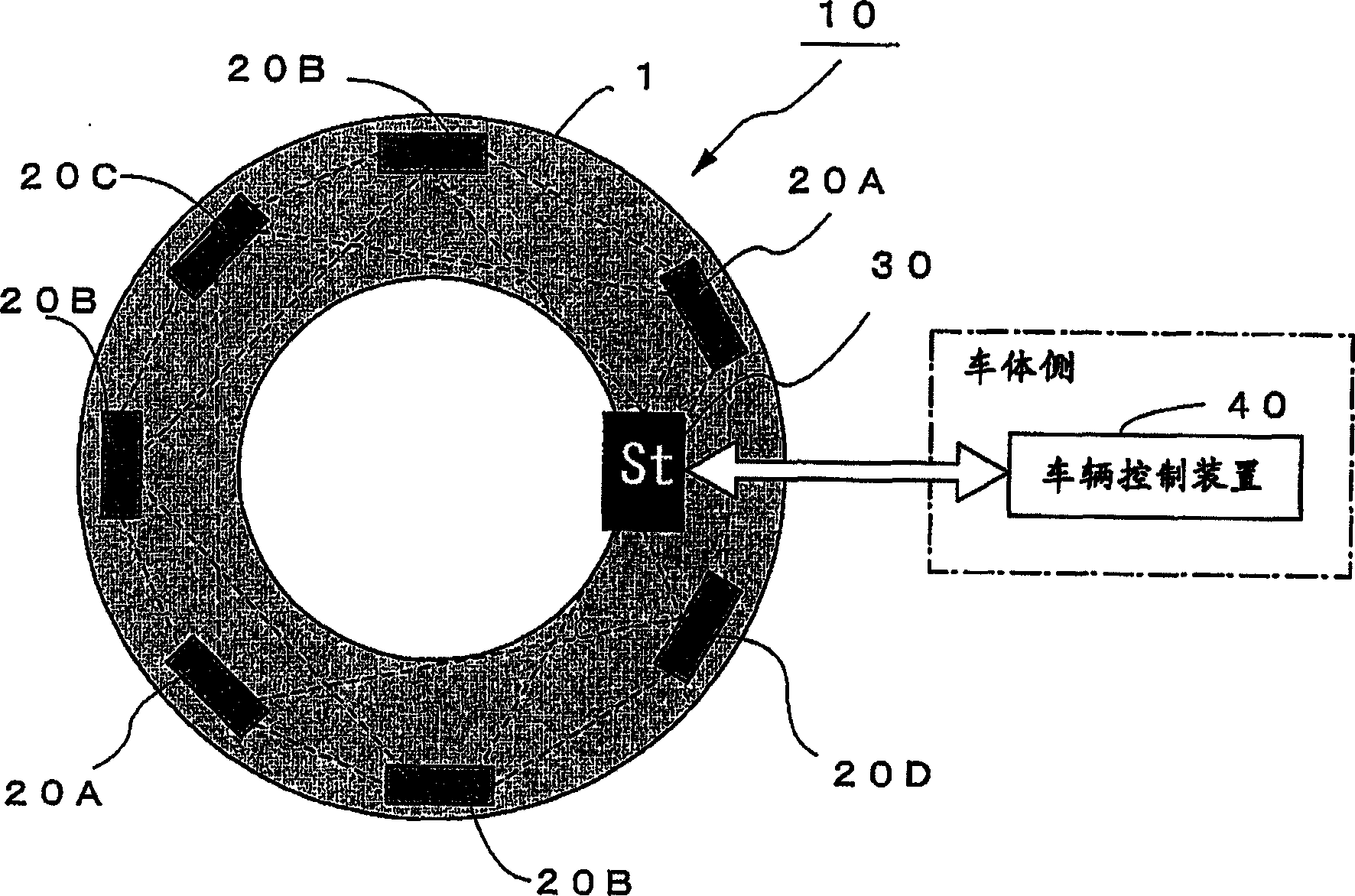
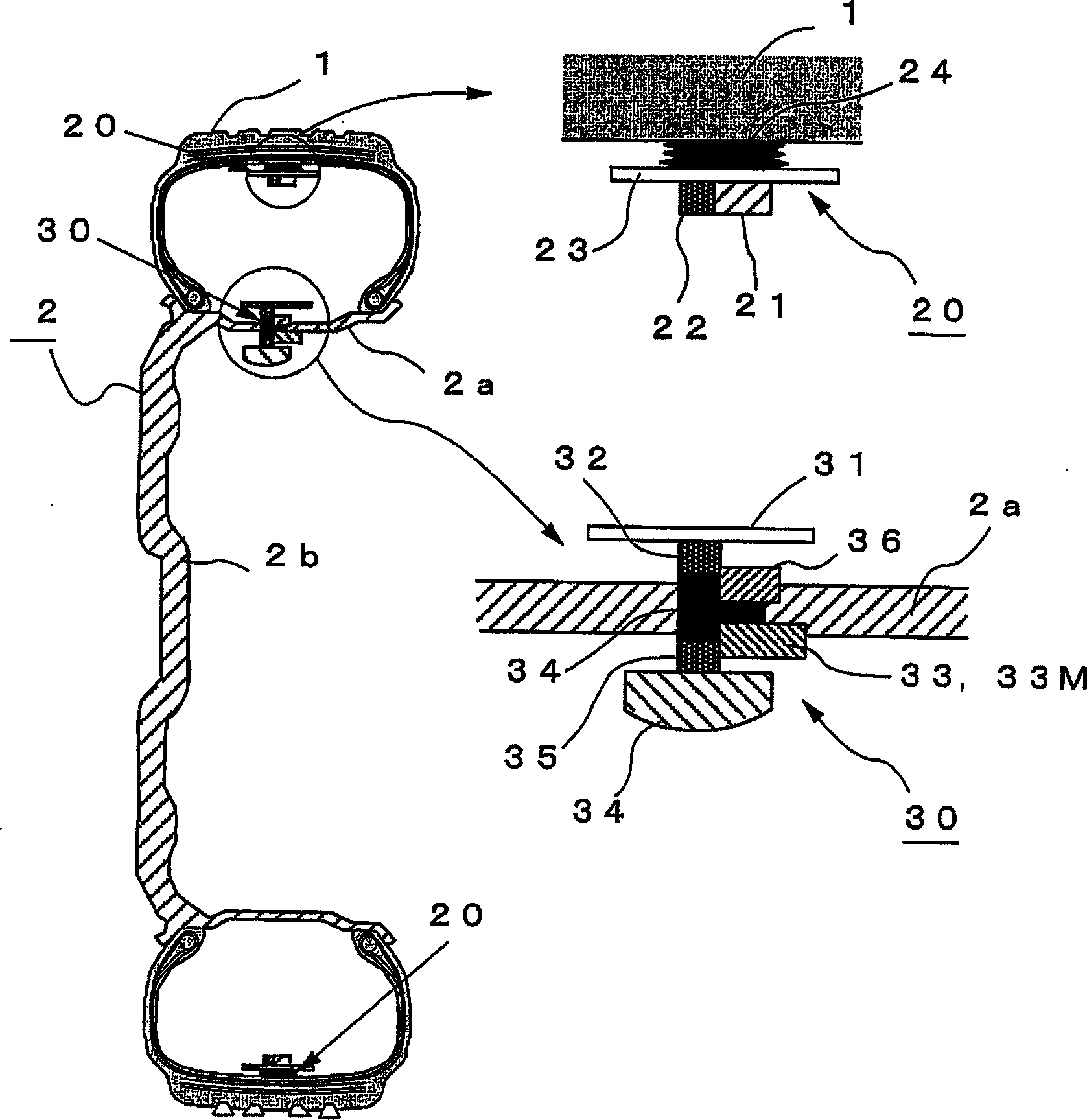
InactiveCN1875387AExtended service lifeGuaranteed non-interferenceTransmission systemsTyre measurementsEmbedded systemVIT signals
In a tire, there are arranged a plurality of sensor modules (20A-20D) each including a sensor, a communication module having a communication function and a power regeneration circuit, and an antenna; and a base station (30) including an internal communication device for performing communication with the sensor modules (20A-20D), an information processing device for processing tire information signals from the sensor modules, an external communication device for communicating with a vehicle control device (40) of the vehicle body side, and a power source. The sensor modules (20A-20D) and the base station (30) constitute an in-tire LAN. Tire information signals transmitted from the sensor modules (20A-20D) are processed at the base station (30) and transmitted to a vehicle control device (40). Thus, it is possible to obtain appropriate tire information while reducing the size of the sensor device and power consumption.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
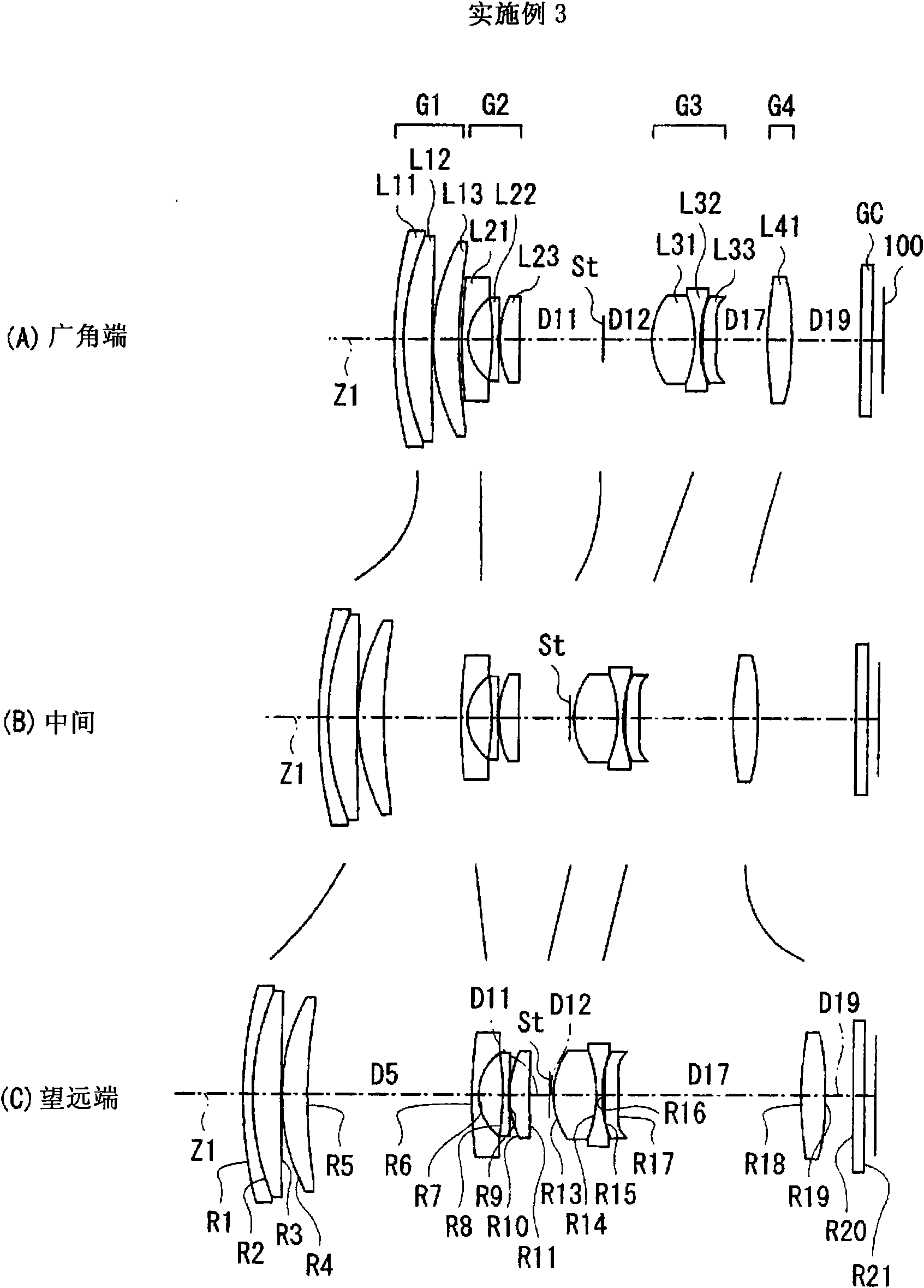
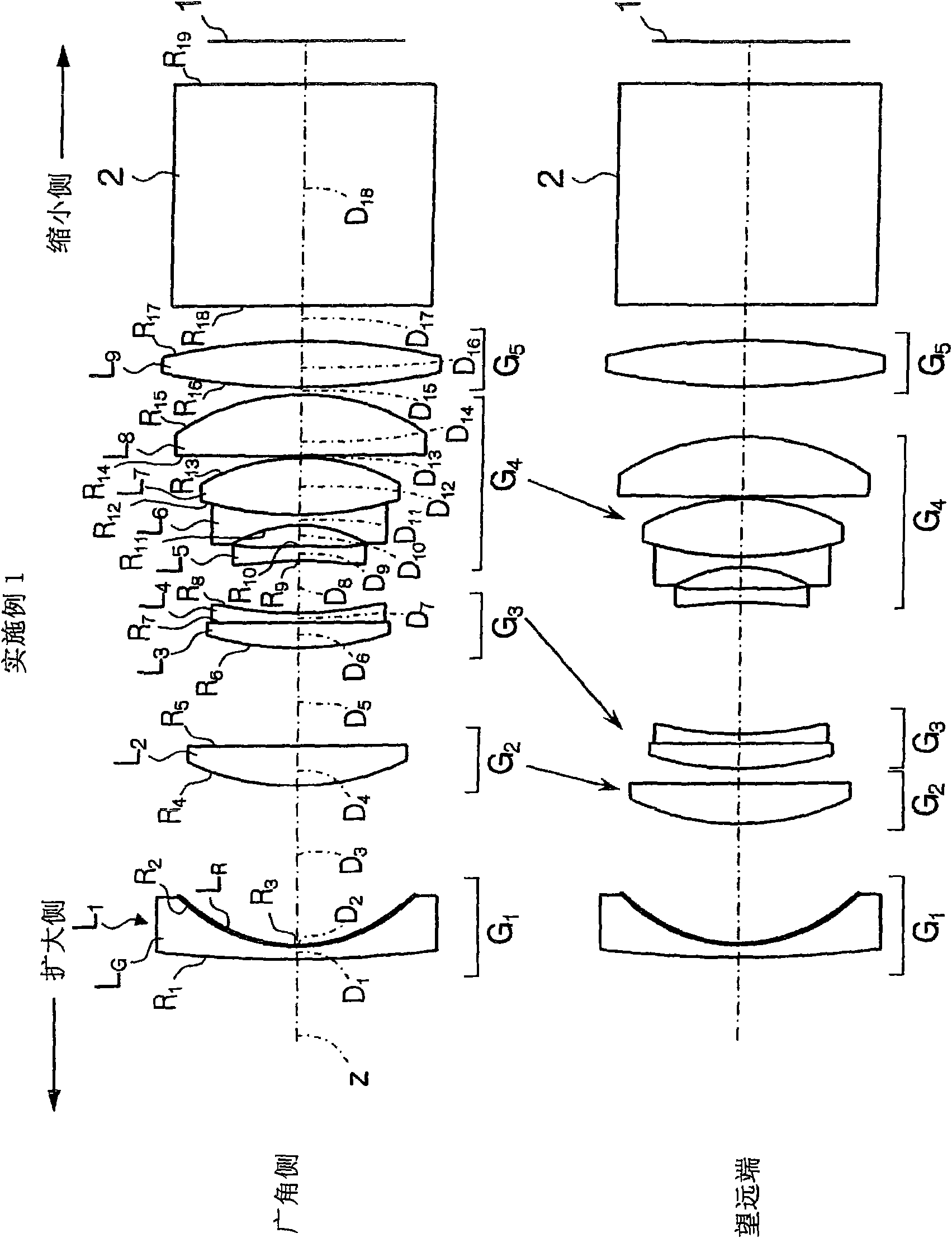
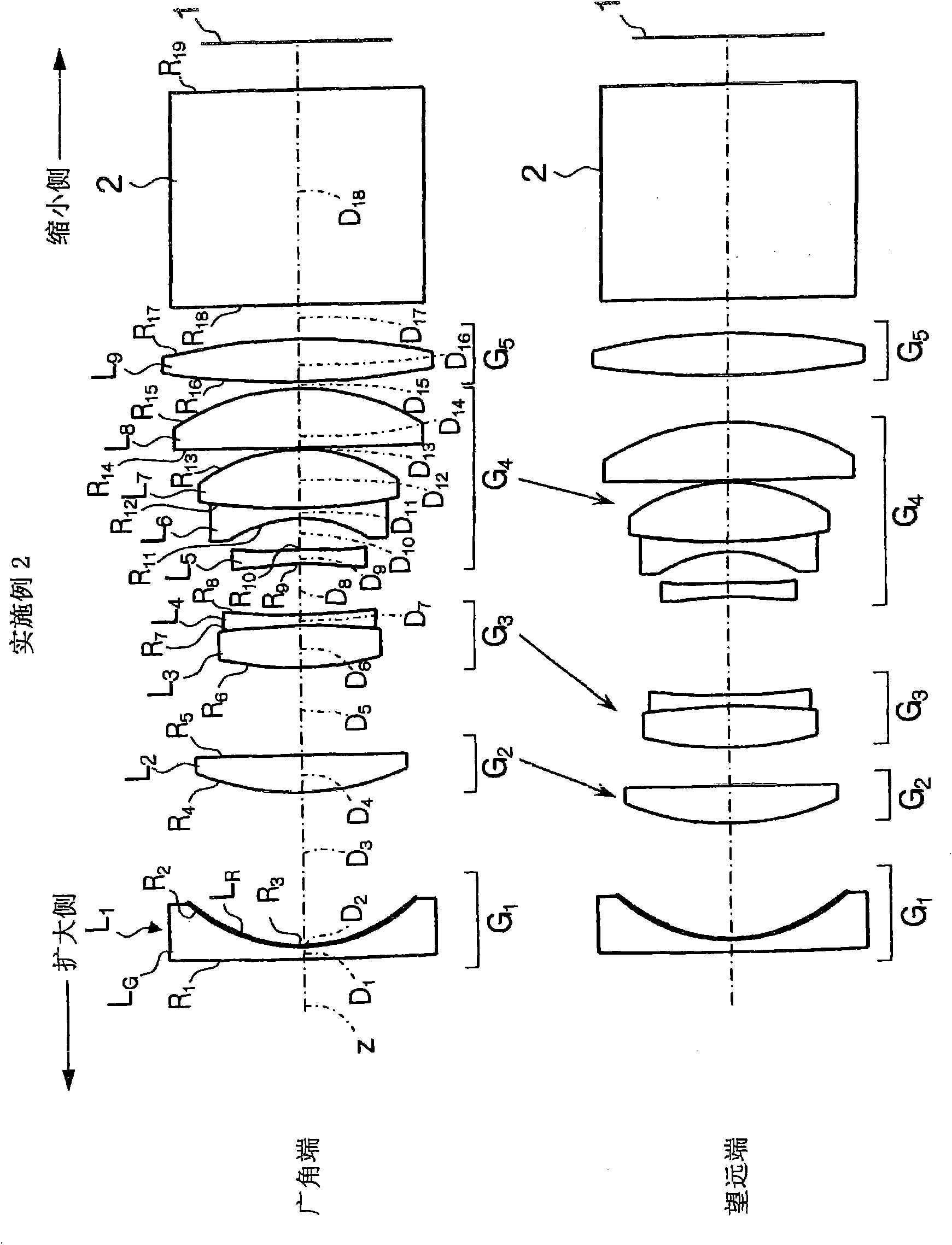
Zoom lens system and imaging apparatus
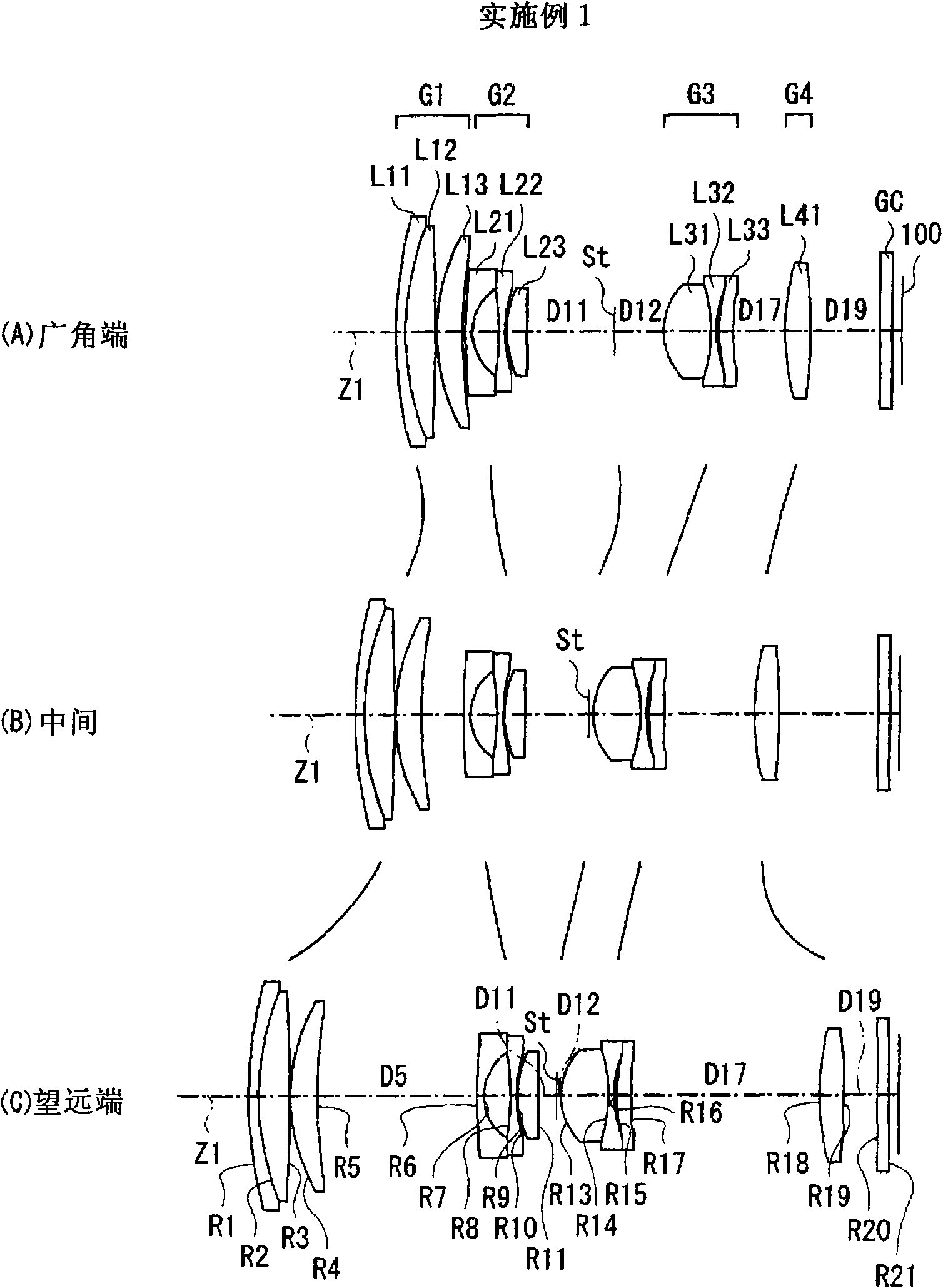
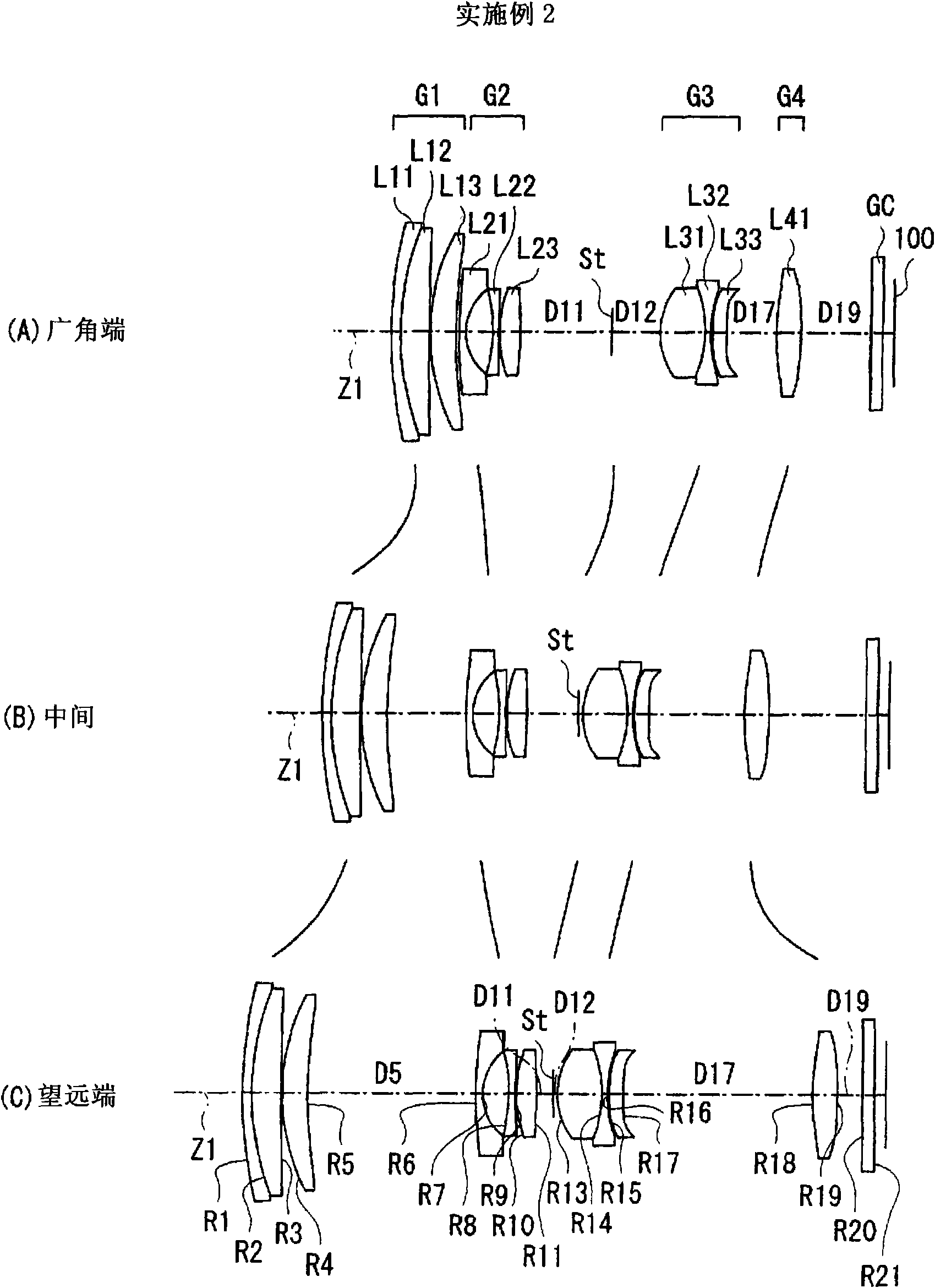
InactiveCN101571624ASeek miniaturizationHigh zoom ratioTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisMiniaturization
A positive first lens group G1, a negative second lens group G2, an aperture diaphragm St, a positive third lens group G3, and a positive fourth lens group G4 are sequentially arranged, and a movement of the lens groups and the aperture diaphragm St during zooming is optimized in combination with an appropriate conditional expression. During zooming, a position of the aperture diaphragm St on an optical axis at a wide-angle end is closer to an image plane than that at a telephoto end, and a space on the optical axis at the wide-angle end between the aperture diaphragm St and the third lens group G3 is larger than that at the telephoto end, thereby suppressing the length of the whole lens. Also, heights of rays passing through the first lens group G1 are lowered, thereby suppressing the lens diameter of the first lens group G1. The following conditional expression is satisfied: 0.4<(Pt-Pw) / fw<0.9 (1), where fw denotes a focal length of the whole system at the wide-angle end, Pw denotes a distance on the optical axis at the wide-angle end between the image plane and the stop, and Pt denotes a distance on the optical axis at the telephoto end between the image plane and the stop, thereby realizing a high variable power ratio and a small size as a whole.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
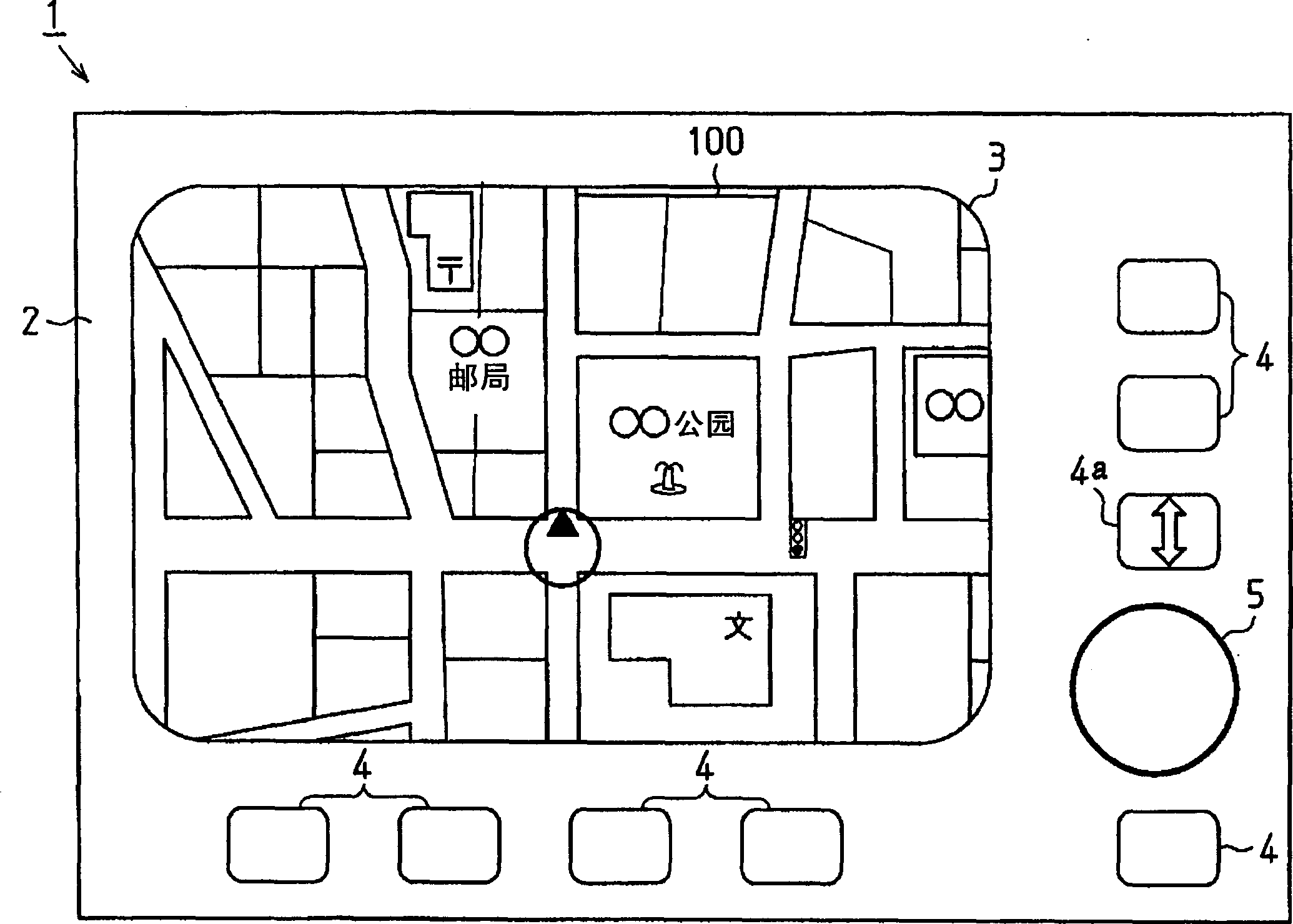
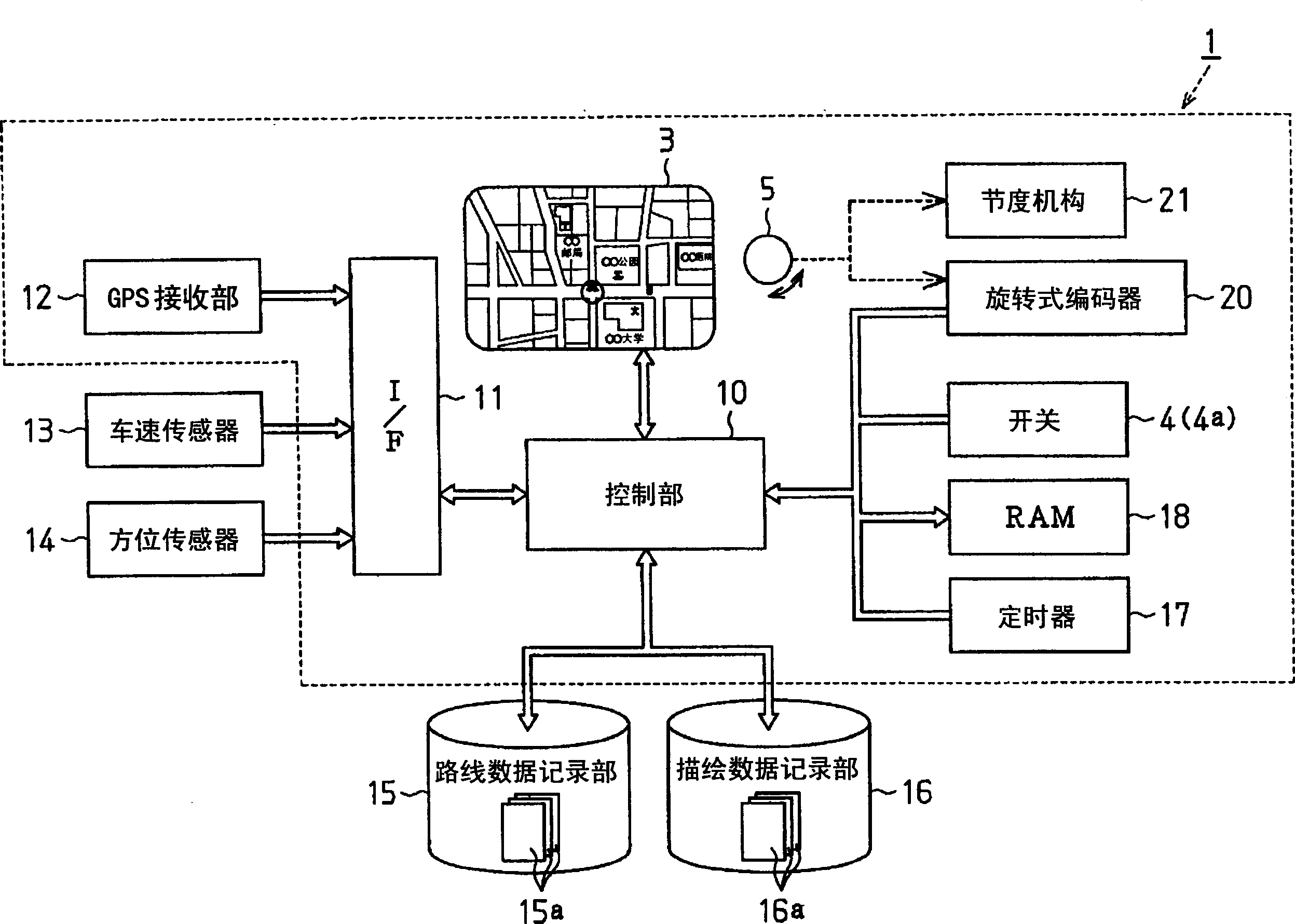
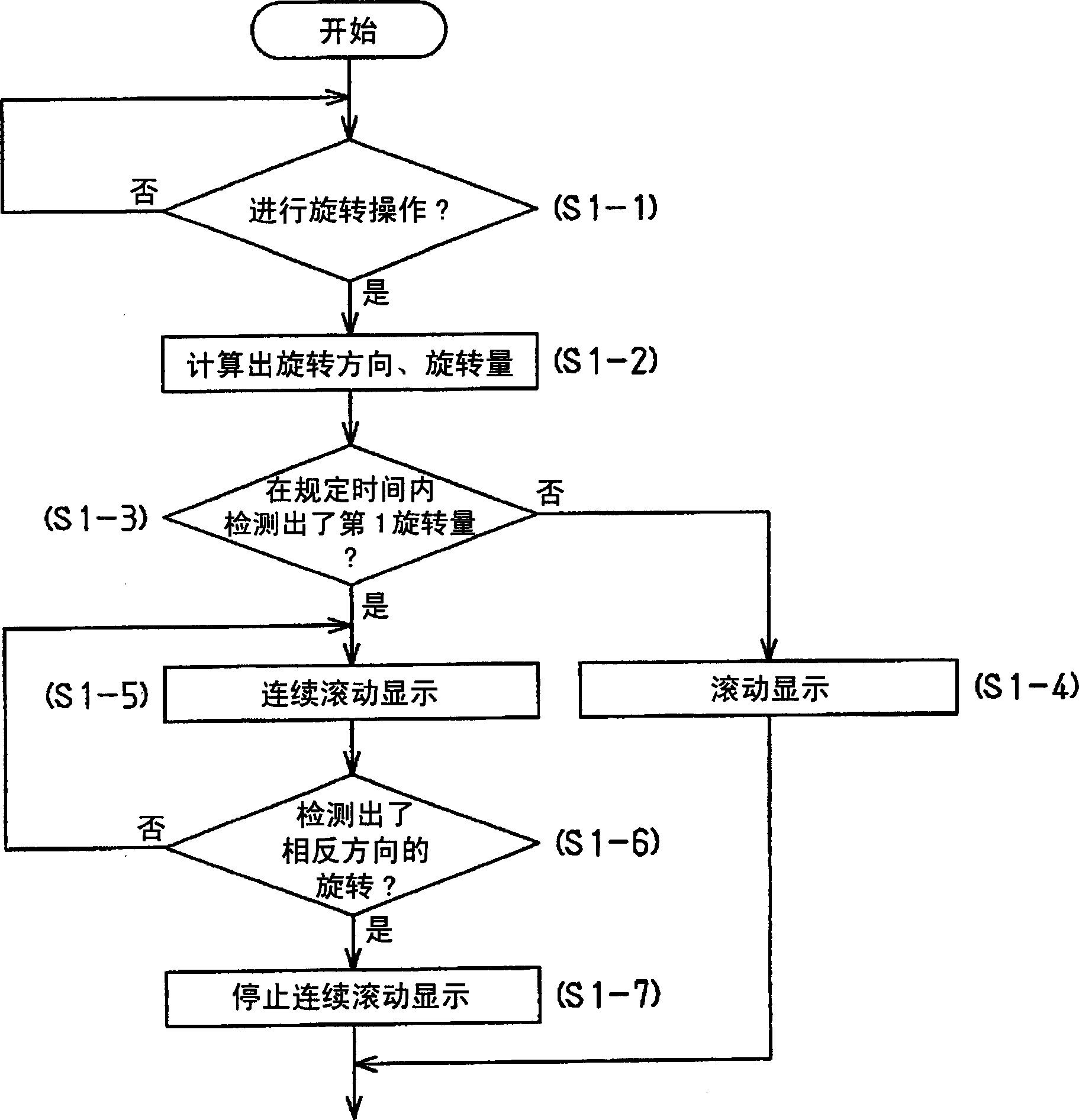
Navigation system, display changeover method, and display device
InactiveCN1776369AEasy to operateAvoid misuseRoad vehicles traffic controlMaps/plans/chartsComputer hardwareMedicine
Provided are a navigation device, a display switching method, and a display device capable of improving operability when performing continuous scrolling display. A navigation device (1) includes a display (3), an operation unit (5) for rotating the operation unit (5), and a control unit (10) for detecting the rotation amount and the rotation direction of the operation unit (5). The control unit (10) calculates the displacement of the map drawing data corresponding to the rotation amount and rotation direction of the operation unit (5), determines a display area of the map drawing data based on the displacement, and outputs the display area to the display. In addition, when the control unit (10) detects that the operation unit (5) has rotated more than a first rotation amount in one direction within a predetermined period of time, it continuously shifts the display area of the map drawing data and displays it on the display (3). Scrolls the display continuously.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Head lamp
ActiveCN102606970AReduce the numberPrevent deviationLight fasteningsFixed installationEngineeringLight source
The invention provides a head lamp easy to manufacture, wherein the number of parts is reduced and the position deviation of a light shielding member relative to a lens is prevented. Therefore, dusts hardly enter the gap between the light shielding member and the lens. The head lamp (10) includes a light source such as a bulb (74), a lens in front of the bulb (74), and a light shielding member (77) arranged at the outer side of the lens (76) and provided for covering part of the light emitted from the bulb (76). The lens (76) is provided with a concave part (88) consistent with the light shielding member (77) in shape, so that the light shielding member (77) can be detachably fixed in the concave part (88).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
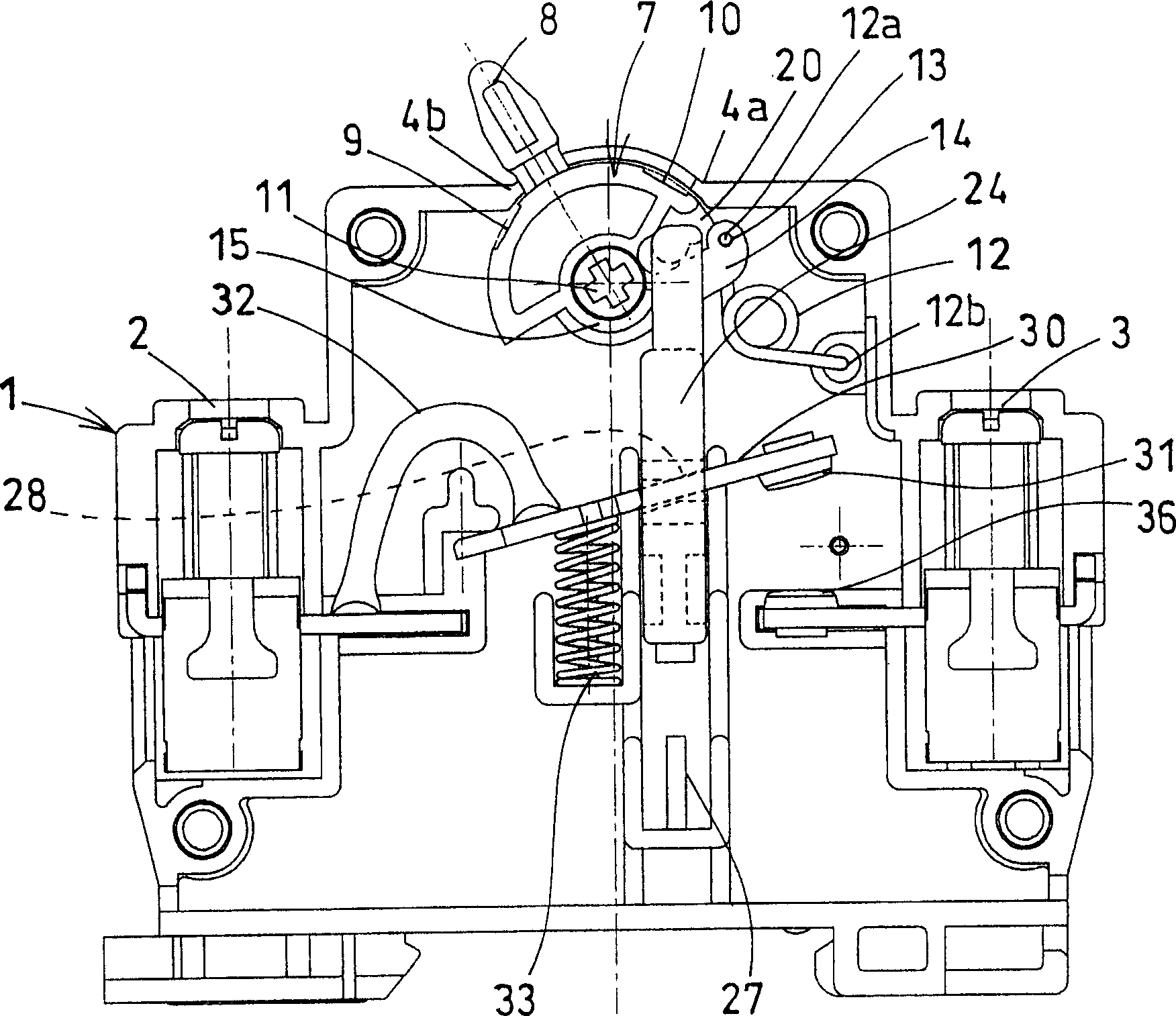
Brake cylinder device and disk brake device
ActiveCN102713333ANot easily affectedImprove space efficiencyAxially engaging brakesBrake wear compensation mechanismEngineeringGuide tube
Provided is a brake cylinder device such that there exists a gap adjustment mechanism, that it is possible to prevent, at low cost, susceptibility to the influence of ambient environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, and that the radial dimensions of a cylinder body can be made compact. A threaded shaft (24) connected to a brake output section (21) is placed inside a guide tube (25) installed in a piston (22). A pressure spring (26) applies force to the threaded shaft (24) in the braking direction. A clutch nut (27) threadably engages with the tip portion of the threaded shaft (24). A front clutch (28) and a rear clutch (29) are disposed in such a way as to be capable of abutting the front side and the rear side, respectively, of the clutch nut (27). A stop (30) is disposed in such a way as to be capable of moving relative to the clutch nut (27) and the guide tube (25) along the axial direction of the threaded shaft (24), and the movable range is restricted with respect to the cylinder body (20). An adjustment spring (31) is provided in such a way that one end thereof abuts the stop (30), and that it is possible to apply force to the clutch nut (27) in the anti-braking direction.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP
Manufacturing system of optical display device and manufacturing method
ActiveCN103907051AShrink the frameSeek to expandPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsOptical bondingBand shape
A manufacturing system of an optical display device of the present invention is a manufacturing system of an optical display device that bonds an optical material to an optical display component and is provided with a primary bonding device that bonds a first surface of a plurality of optical display components to the primary optical material sheet while unwinding a band-shaped primary optical sheet from a primary whole roll where the sheet has a larger width than the width of the display region of an optical display component in the width direction of the component perpendicular to the transport direction of the optical display components for a plurality of optical display components transported on a line; a primary cutting device that cuts out a primary optical bonding body that includes a single optical display component and the primary optical material overlapping the single optical display component from a bonding sheet by cutting the part opposite the primary optical component sheet facing the display region and the remaining part positioned on the outside of the opposite part, and cuts out the primary optical material as the optical material having a size corresponding to the display region from the primary optical component sheet; and a secondary bonding device that bonds secondary optical parts to the second surfaces of the optical display components in the bonding part of the primary optical bonding material while transporting the plurality of secondary optical materials with a separator sheet as the carrier after the band-shaped secondary optical component sheet having a width corresponding to the display region in the width direction of a component for a plurality of bonding bodies of primary optical parts transported on the line is wound out together with the separator sheet from the secondary whole roll; cutting is performed along the width direction each time the secondary optical component sheet is unrolled to the length corresponding to the display region in the secondary optical component sheet; and the secondary optical materials are formed as optical parts having sizes corresponding to that of the display region.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Display driver, electro-optical device, and control method for display driver
InactiveCN1595478AReduce sizeReduce power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsIdentification meansValue setProcessor register
A display driver includes: a data input section to which display data or command data is input; a display processing section which includes a data line driver section driving the data lines based on the display data input through the data input section; a control register for controlling the display processing section; a command signal generation section which generates a command signal which changes at a predetermined timing and is used to identify the command data; a command extraction section which extracts the command data from data such as the display data input through the data input section based on the command signal; and a decoder which decodes the command data extracted by the command extraction section. A value corresponding to a decoding result of the command data is set in the control register. The display processing section is controlled based on the value set in the control register.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Projection zoom lens and projection type display apparatus
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
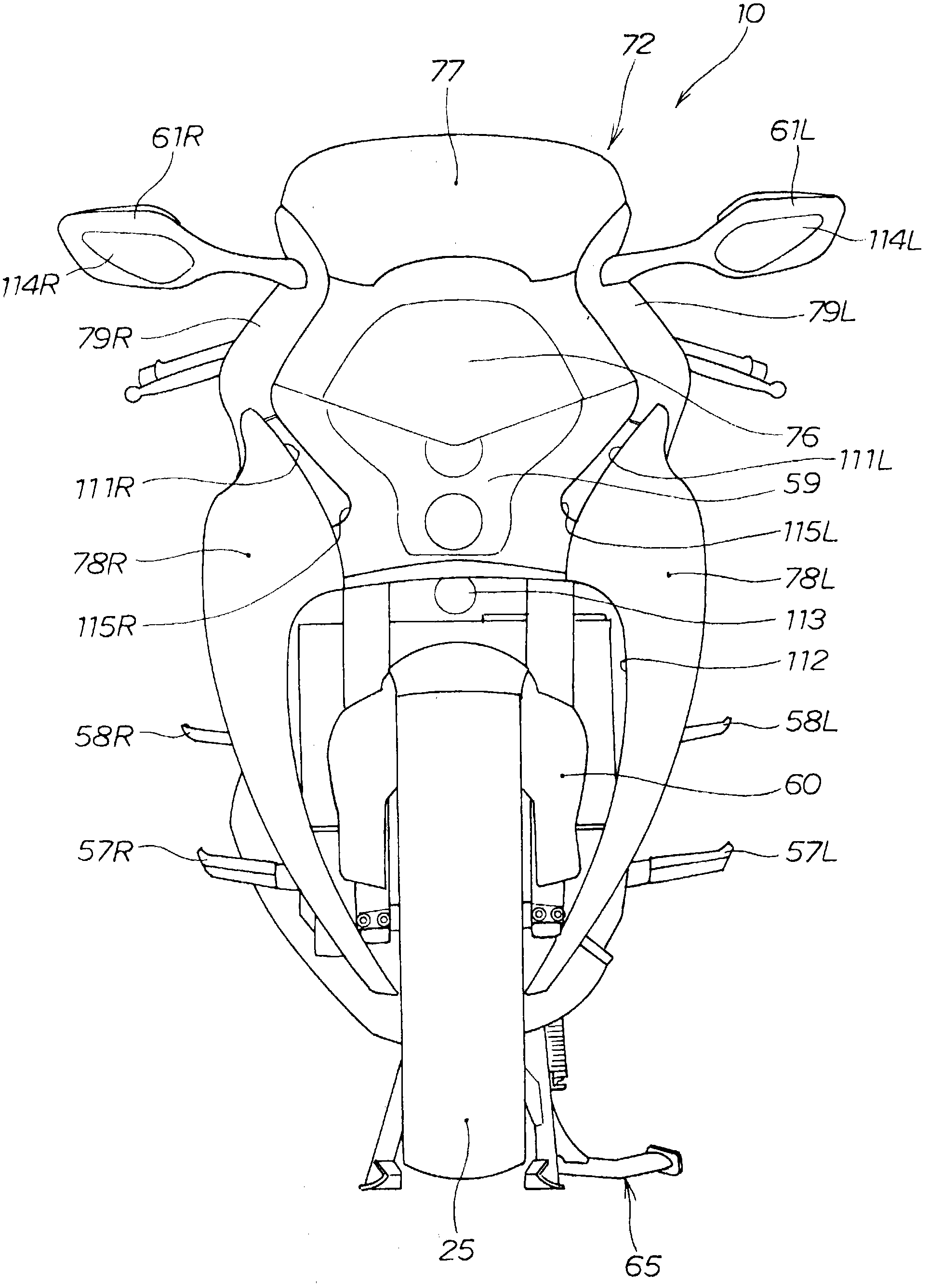
Vehicle
InactiveCN102143882ASmall light emitting areaReduce the width of the vehicleCycle standsOptical signalAutomotive engineeringBody frame
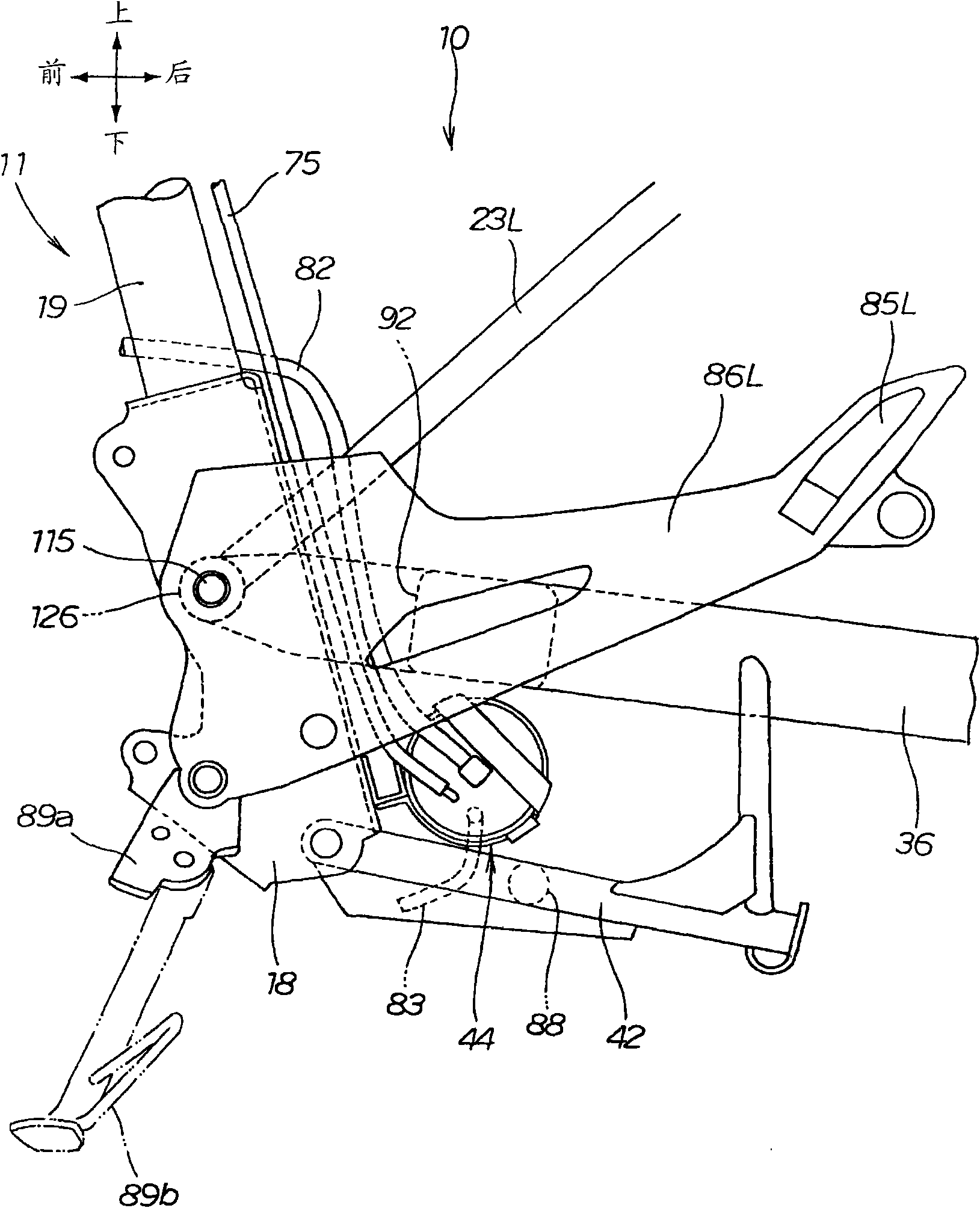
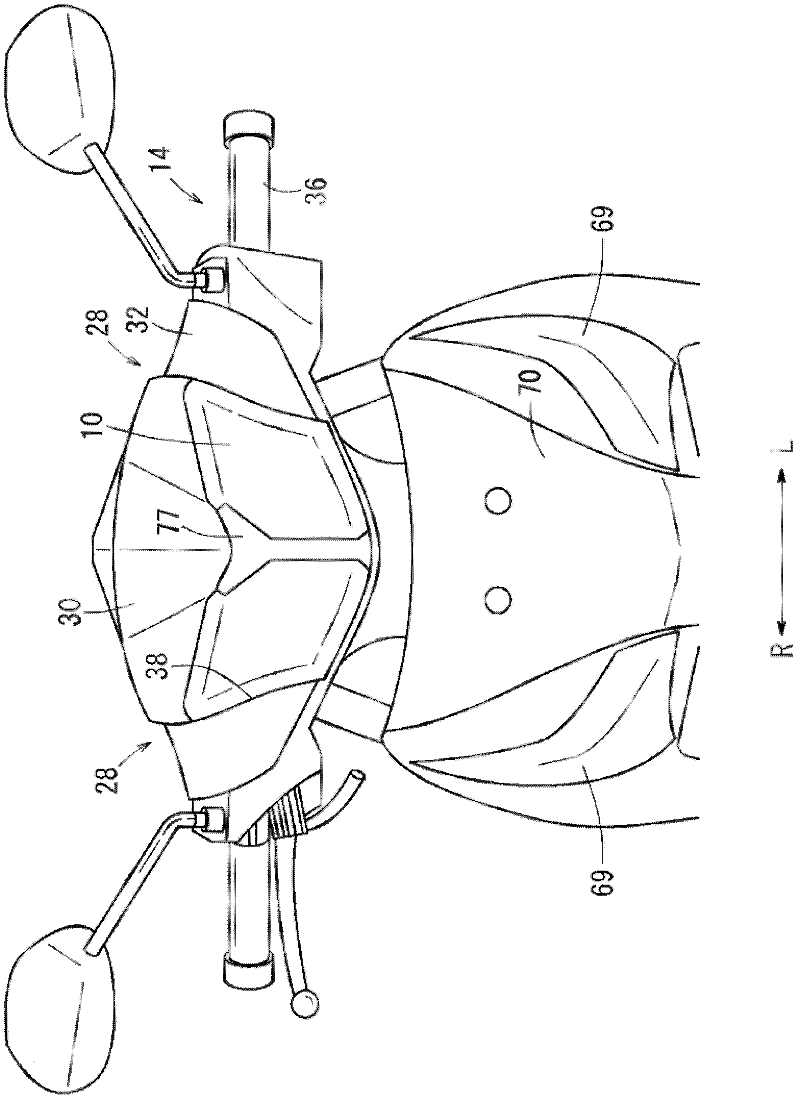
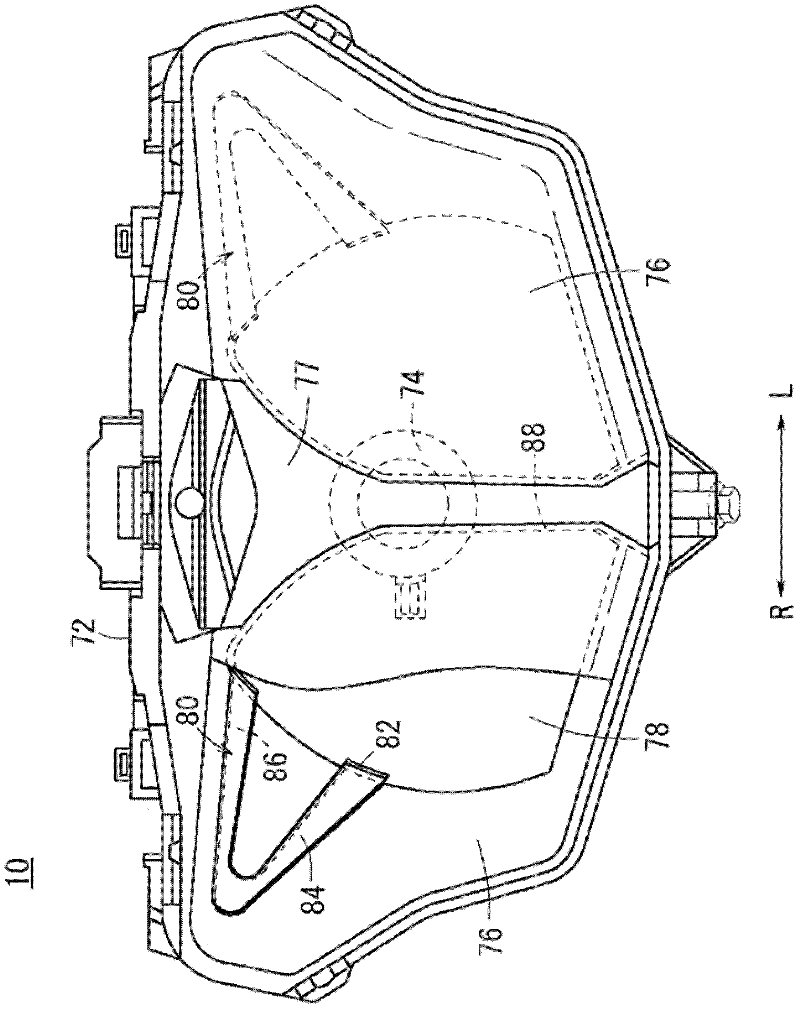
A vehicle comprising a vehicle body frame (11), a front cowl (72) provided in front of the vehicle body frame, and a headlight unit (59) mounted within the width, in the vehicle's lateral direction, of the front cowl. The headlight unit has, on the opposite sides thereof, recesses (115L, 115R) recessed inward in the vehicle's lateral direction. Air intake openings (111L, 111R) for introducing air in front of the front cowl into the inner side of the front cowl are formed between the headlight unit and the front cowl.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
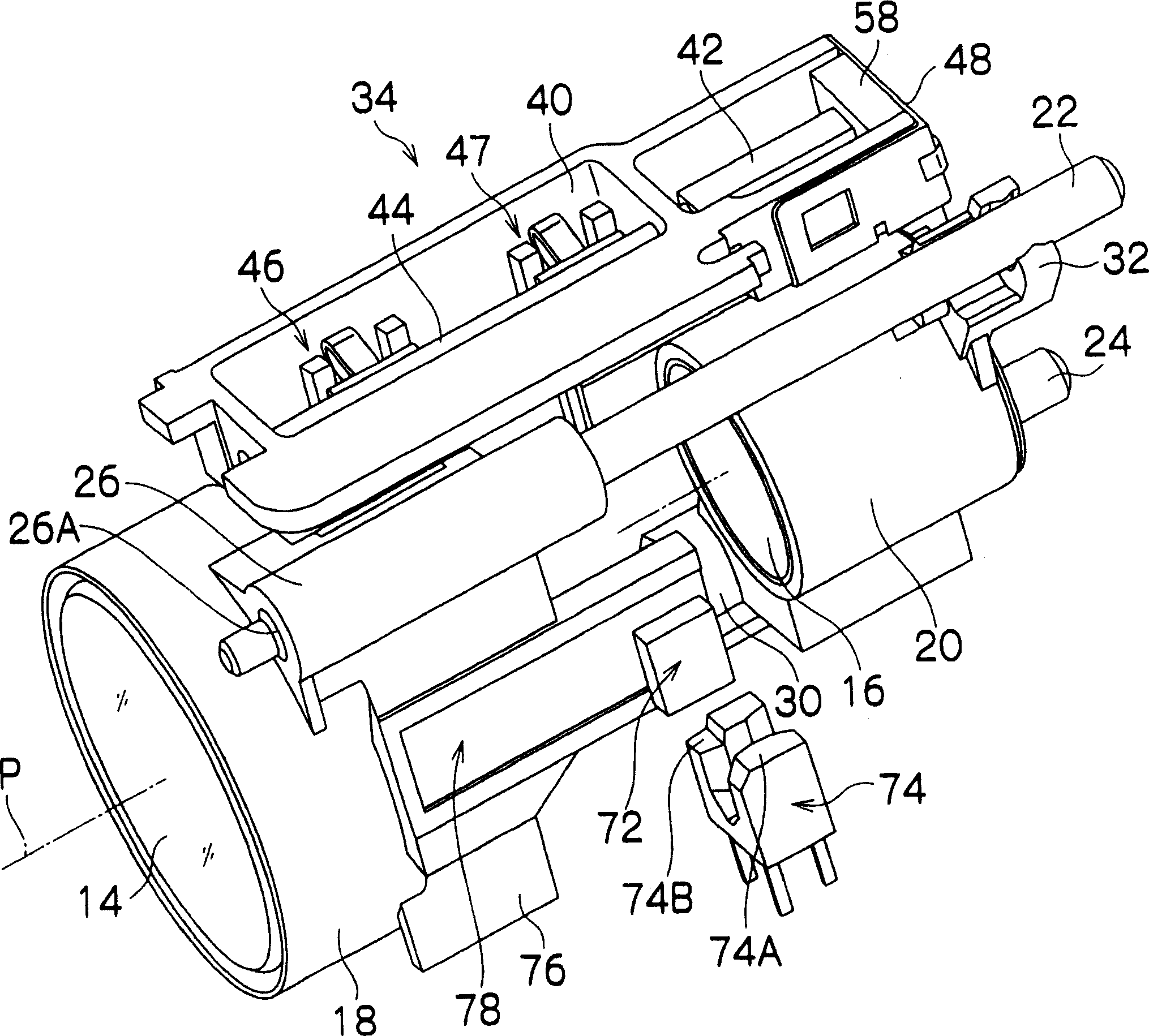
Actuator
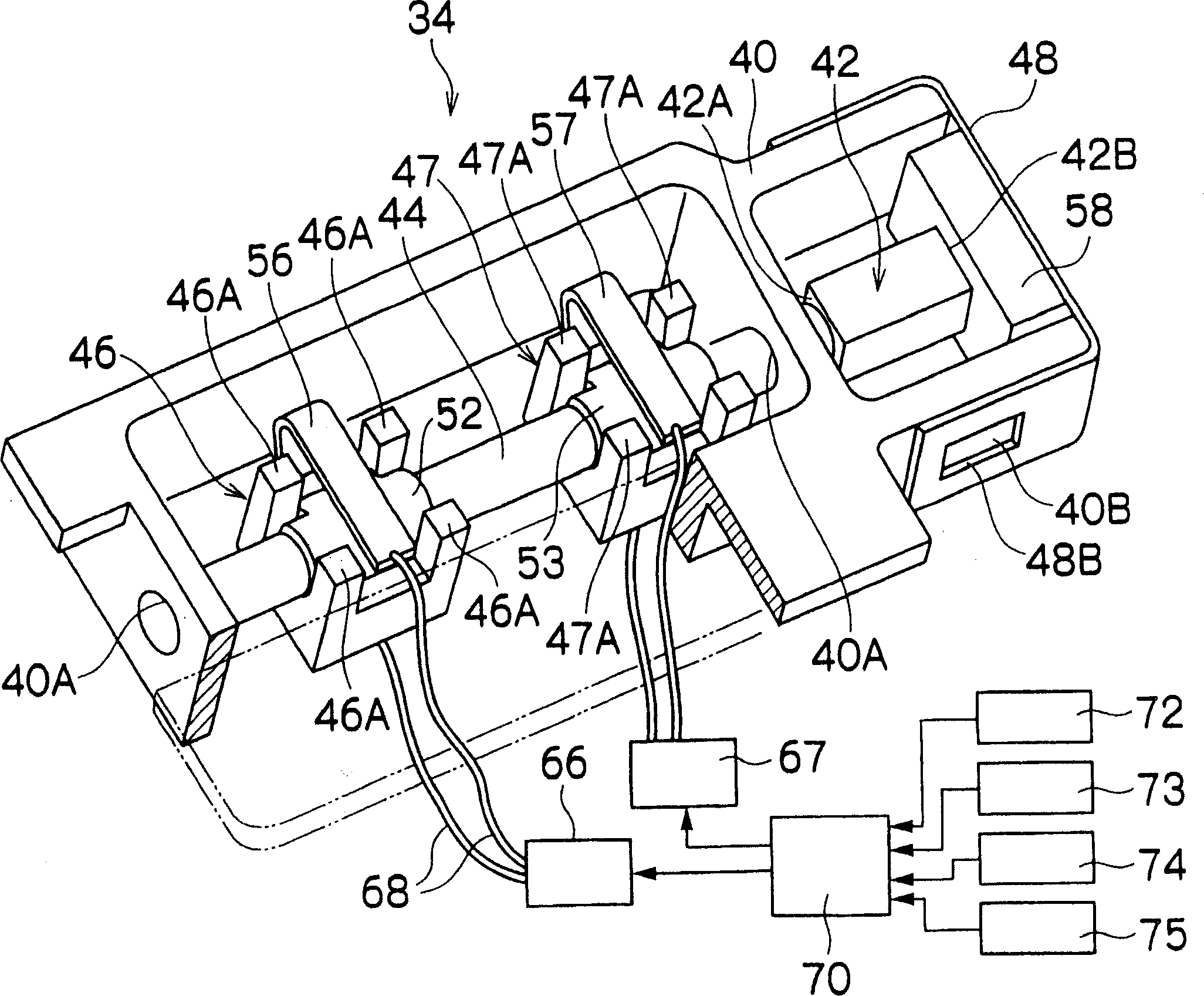
InactiveCN1913326AReduce the numberSeek miniaturizationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMountingsDrive shaftShape-memory alloy
The invention provides a miniature actuator in which a plurality of driven members can be driven with common drive friction member and electromechanical conversion element. The actuator 34 comprises a piezoelectric element 42, a drive shaft 44 fixed to the displacement surface 42A of the piezoelectric element 42, coupling pieces 46 and 47 friction-engaged with the drive shaft 44, and presser springs 56 and 57 for biasing the coupling pieces 46 and 47 individually. The presser springs 56 and 57 are composed of a shape memory alloy and when they are heated by means of heaters 66 and 67, the presser springs 56 and 57 deform to regulate the biasing force individually.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Plate type apparatus for producing fresh water
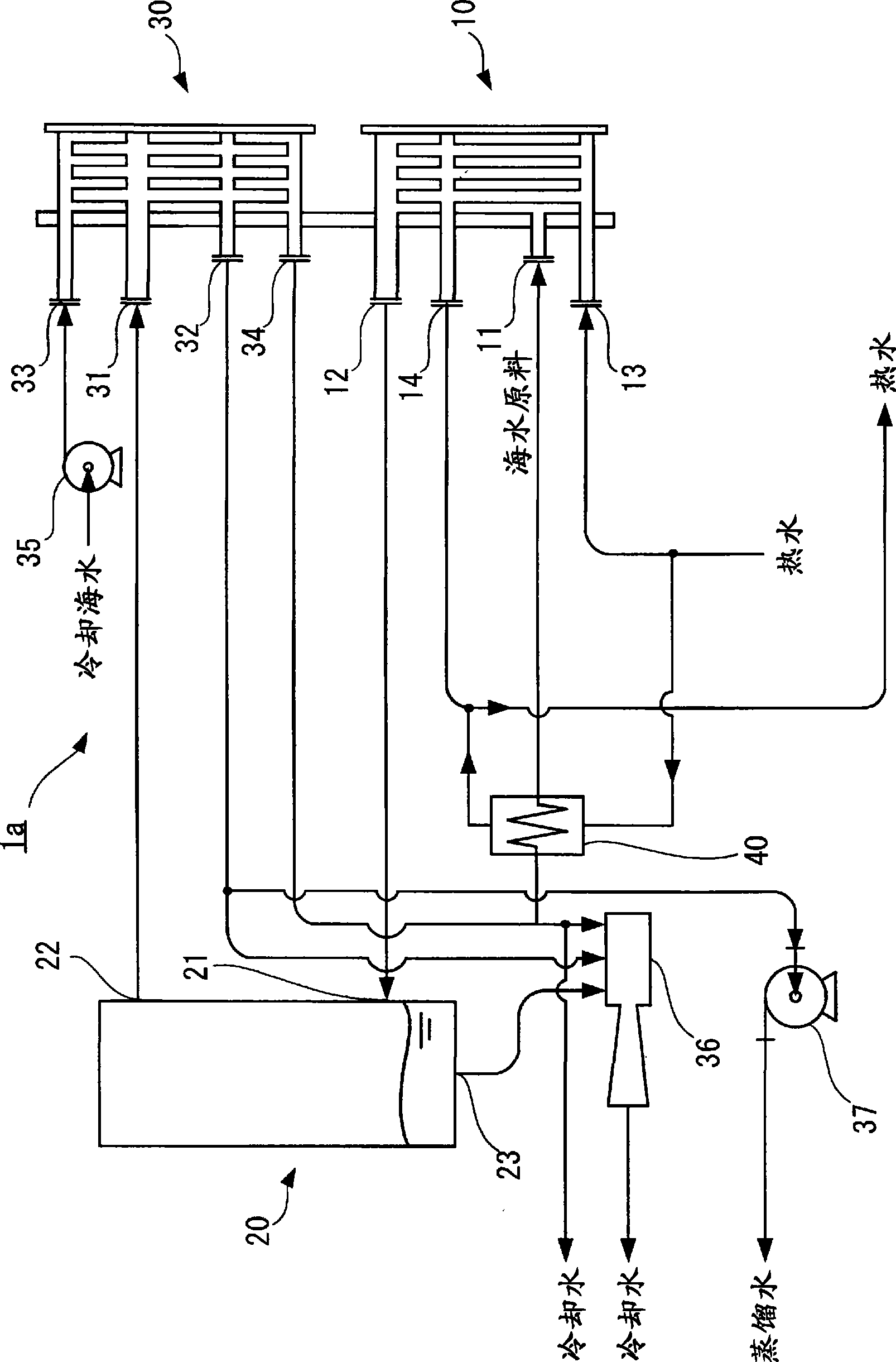
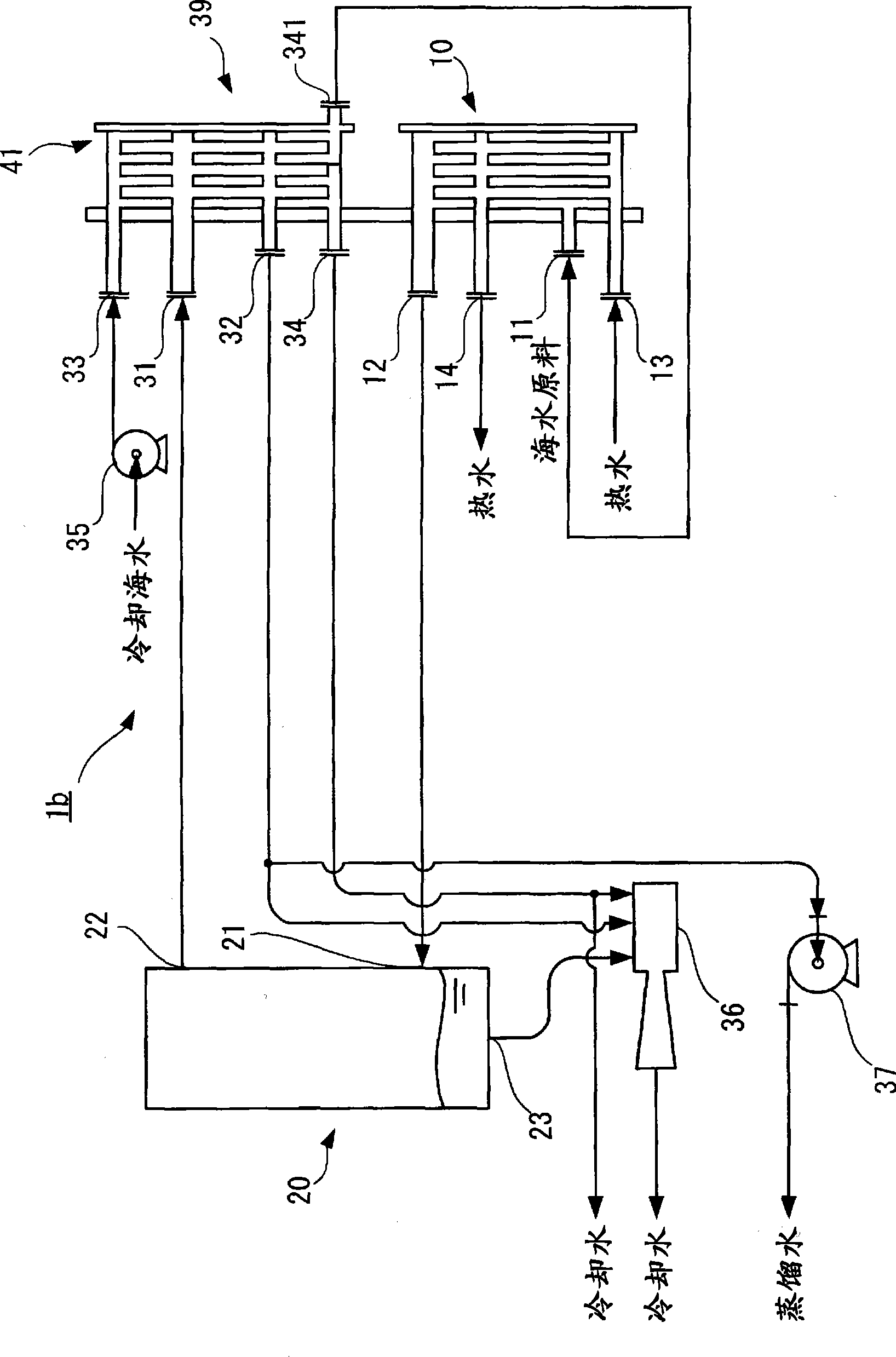
ActiveCN101479195ALow costSeek miniaturizationVapor condensationSteam/vapor condensersWater dischargeWater vapor
A plate type water making apparatus including heater (10) for heating raw seawater by hot water to thereby produce steam and condenser (30) for cooling the produced steam by cooling water to thereby produce distilled water, characterized by further including preheating means (40) for heating portion of cooling water discharged from the condenser (30) so as to introduce the same in the heater (10) as raw seawater. In this plate type water making apparatus, heating evaporation of raw seawater can be efficiently performed, so that there can be attained downsizing and cost reduction.
Owner:SASAKURA ENG CO LTD
Bottom cover structure of a saddle type vehicle
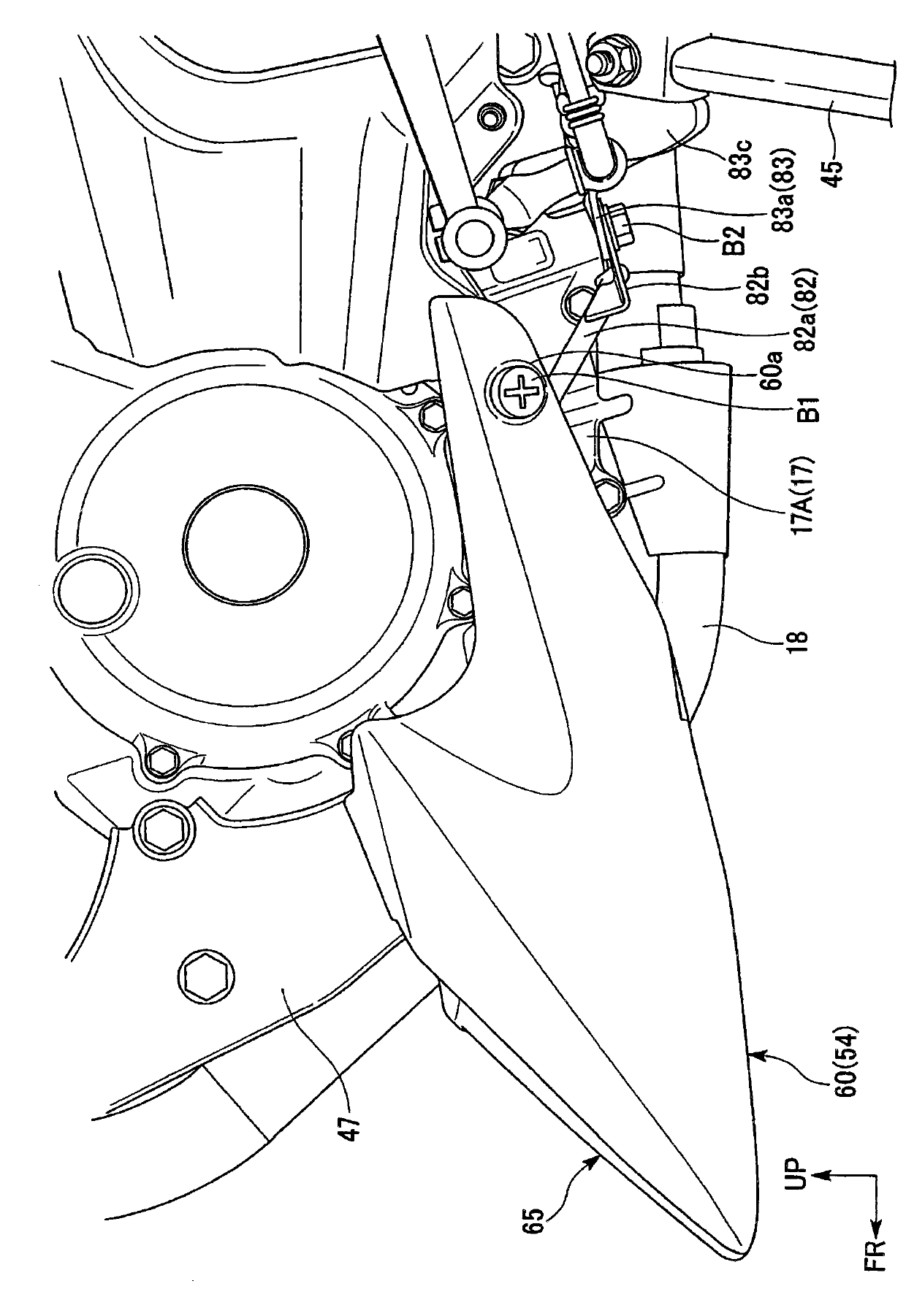
ActiveCN102001384AEasy to shapeIncrease the number ofWeather guardsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a bottom cover structure of a saddle type vehicle. The bottom cover is arranged in the bottom cover structure of the saddle type vehicle arranged before the lower part of an engine behind a front wheel, thus the bottom cover easily forms and the number of the parts is prevented from being increased on the basis of trying for miniaturizing the bottom cover along the vehicle width direction. One side square part (left side square part 60) of left, right side square parts (60,70) gradually protrudes towards the back of the vehicle in a manner of being at the outer side along the vehicle width direction, together with directing towards the back of the vehicle and integrated with a connection part (65). Another side square part (right side square part 70) of the left, right side square parts (60,70) is arranged behind the outer side end (70b) along the vehicle width direction and protrudes towards the back of the vehicle in the manner of comparing with the outer sideend (70b) at the inner side of the vehicle width direction and the left side square part (60) and the connection part (65) are formed in split.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Switch
ActiveCN1835169ASimple structureEfficient use ofSwitch condition indicationDriven elementEngineering
The invention discloses a switcher (1), which comprises handle hole (4). Wherein, the handle (7) has an operate part (8) projected from the handle hole (4), a switch display part (9) near the operate part (8), a clamp hole (13) and nearby hook part (20), which via torsion screw spring (12) is held at the open or close position; the driving element (24) has the projection (26) clamped with the hook part (20), to be supported by the device (1) to move oscillating, and be driven by the switching operation of operate part (8); the movable contact block (30) is held by the driving element (24) with a movable connect point (31) opposite to the fixed connect point (36). The inventive switcher has simple structure, while the handle display part will not be contained into device even when rotating the handle to the close position when melting the connect point.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Screw fastening structure with high-strength self-forming screw
ActiveCN102027244AReduce processing stepsReduce stressSheet joiningScrewsSelf formingMiniaturization
To provide a screw fastening structure for enhancing the strength of a bolt and fatigue strength by reducing the machining process without altering the shape of an associated member, and for achieving downsizing by keeping the fitting length of a thread almost the same as that of the prior art, thus contributing remarkably to weight reduction of a vehicle. A self-forming screw (1) having a strength 14T produced by form rolling before heat treatment is employed as a fastening bolt, and the self-forming screw is driven into a member (4) having an as-cast, nonthreaded rough hole (5). In a screw fastening structure to which a fixing member (6) is fastened, the catch rate of a female screw and a male screw formed by a self-form is 75-90%, the fitting length of the screw and the rough hole is d-2.5d (d is screw diameter), and no clearance appears at the contact surface of the male and female screws because of self-forming screw fastening.
Owner:TOPURA CO LTD
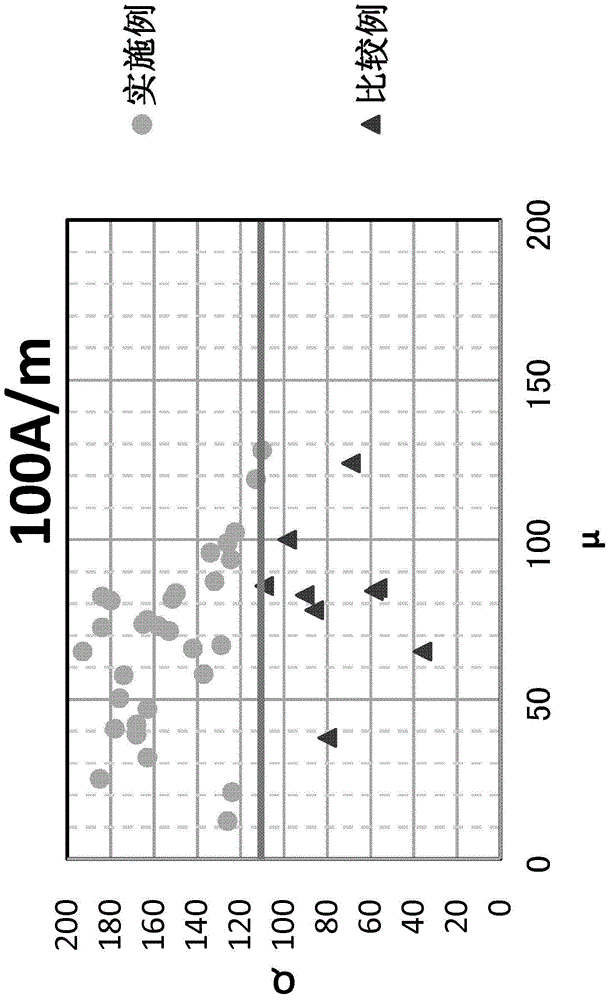
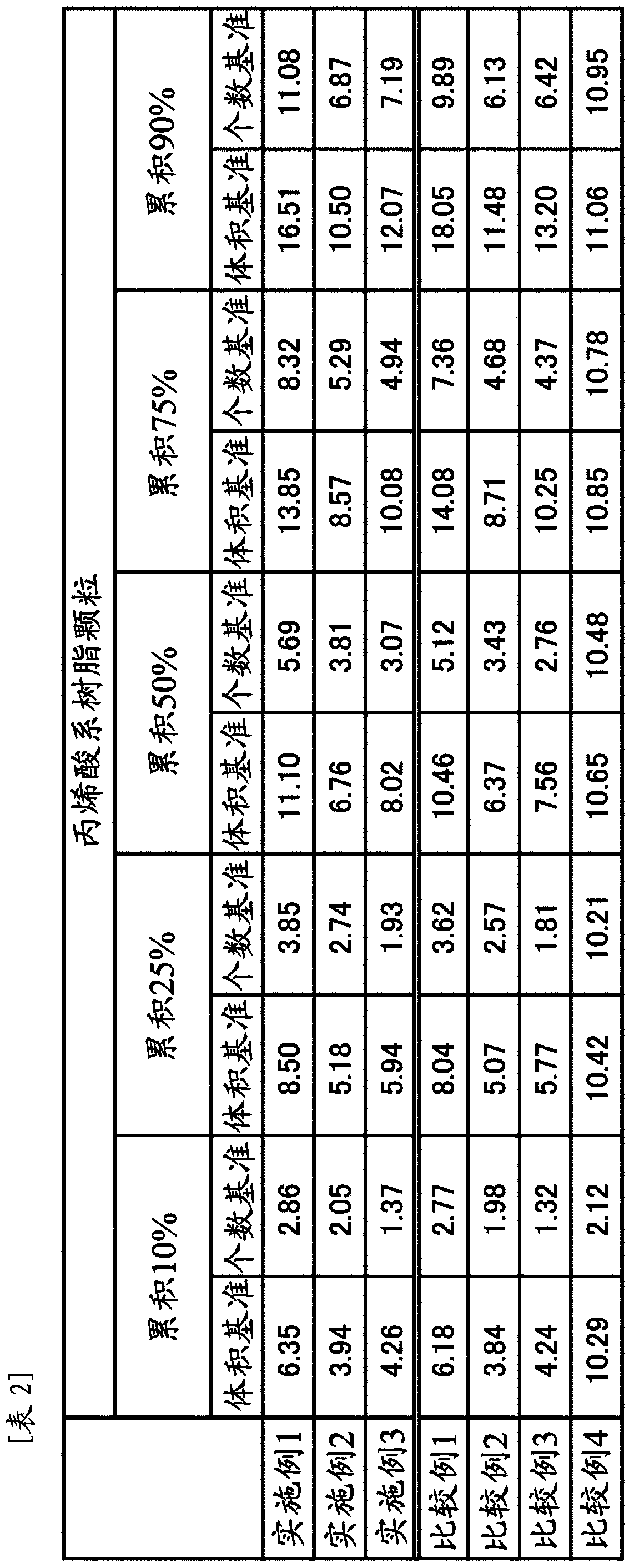
Acrylic acid series resin particle, coating combination and optical material
The invention provides an acrylic acid series resin particle capable of forming an optical material with uniform light diffusion property, a coating combination and the optical material. The acrylic acid series resin particle is characterized in that: value alpha, value gamma and value eta meet a predetermined relationship, and CV value is 30-40%, meanwhile value A is less than 0.75, and value B is 1.1-1.6, wherein the value alpha is cumulative 10% particle size by volume basis / cumulative 10% particle size by count basis, the value gamma is cumulative 50% particle size by volume basis / cumulative 50% particle size by count basis, the value eta is cumulative 90% particle size by volume basis / cumulative 90% particle size by count basis, the CV value is particle size by volume basis, the value A is cumulative 10% particle size by volume basis / cumulative 50% particle size by volume basis, and the value B is cumulative 90% particle size by volume basis / cumulative 50% particle size by volume basis.
Owner:SEKISUI PLASTICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com