Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106results about "Specific heat investigation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
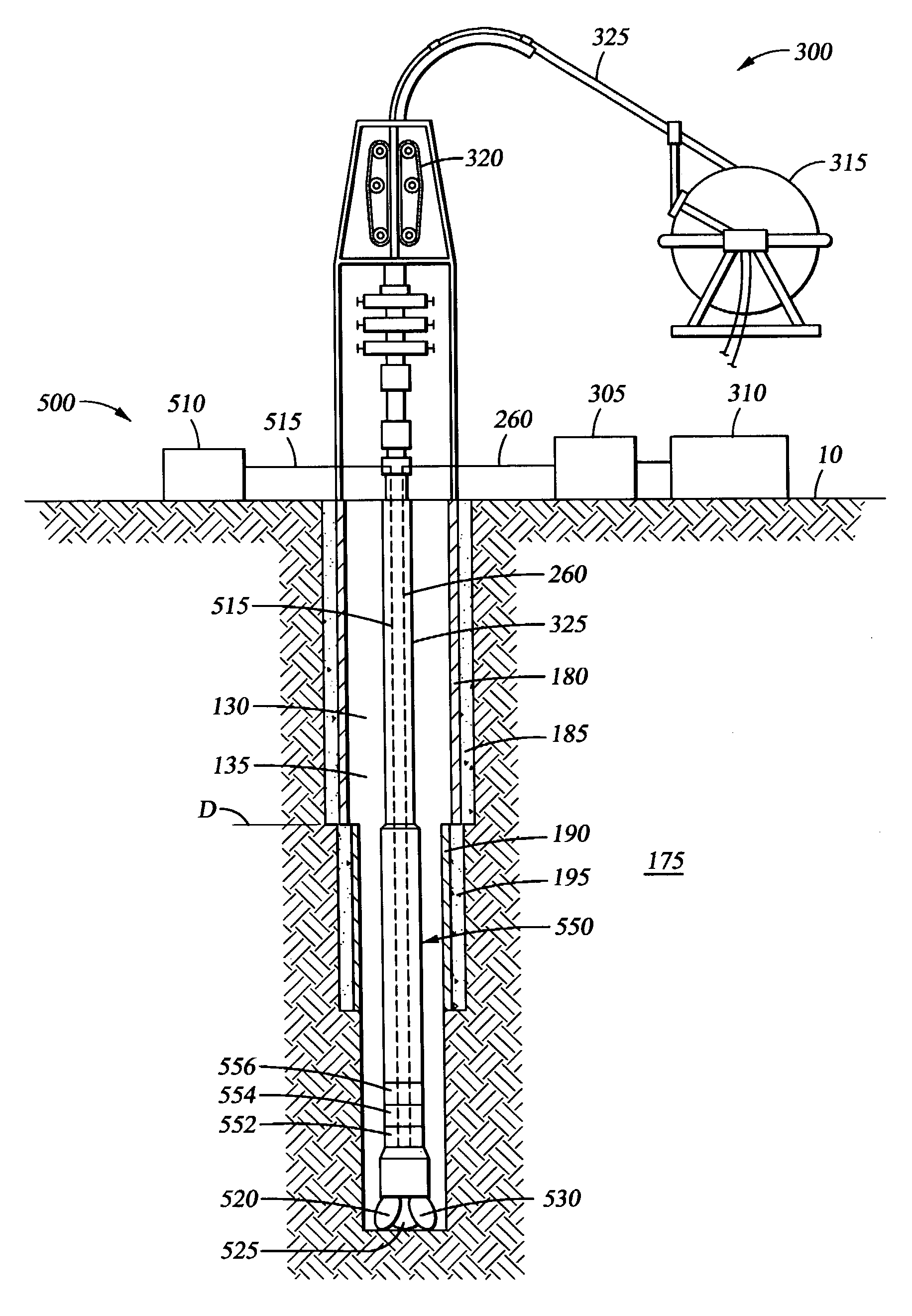
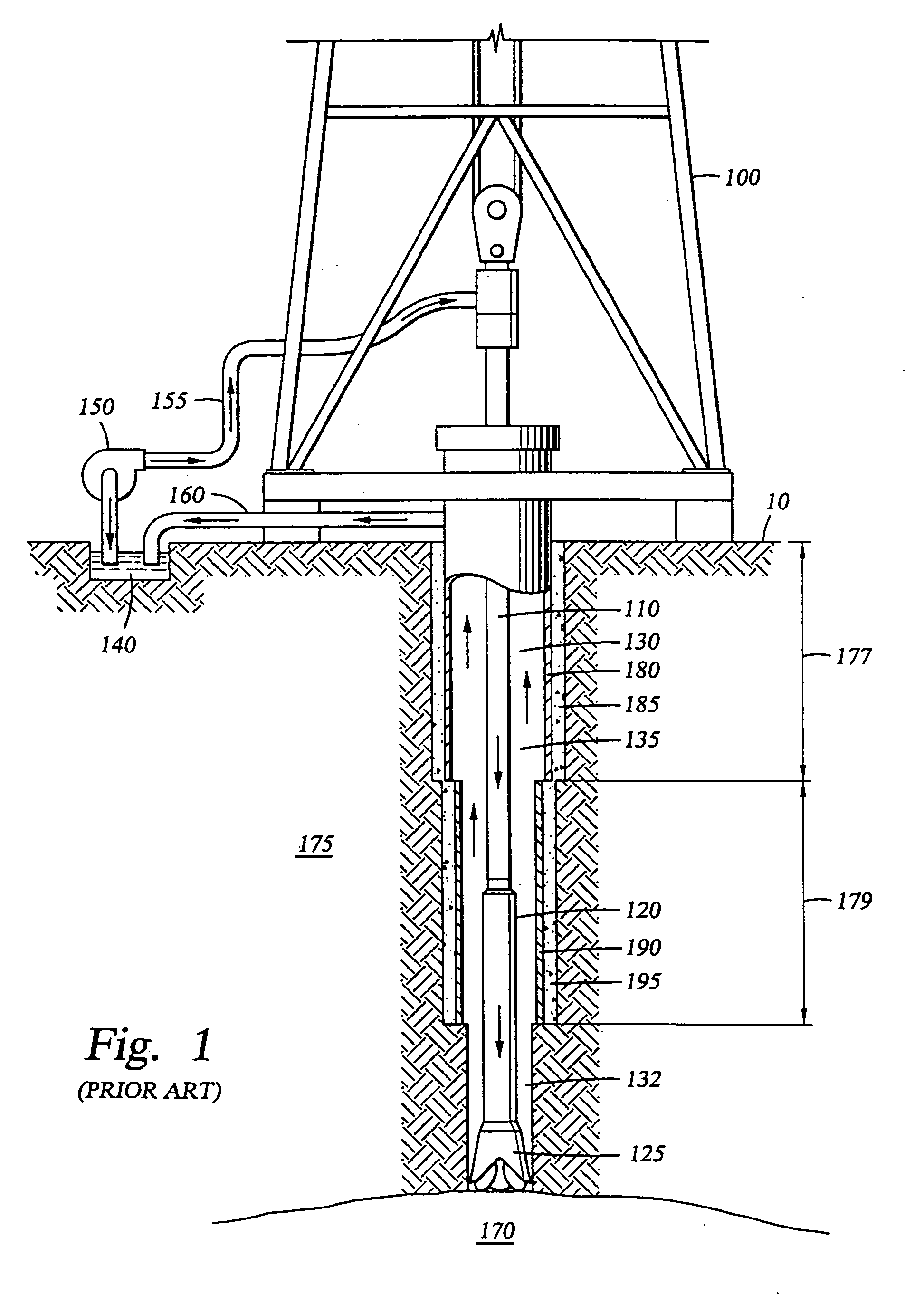
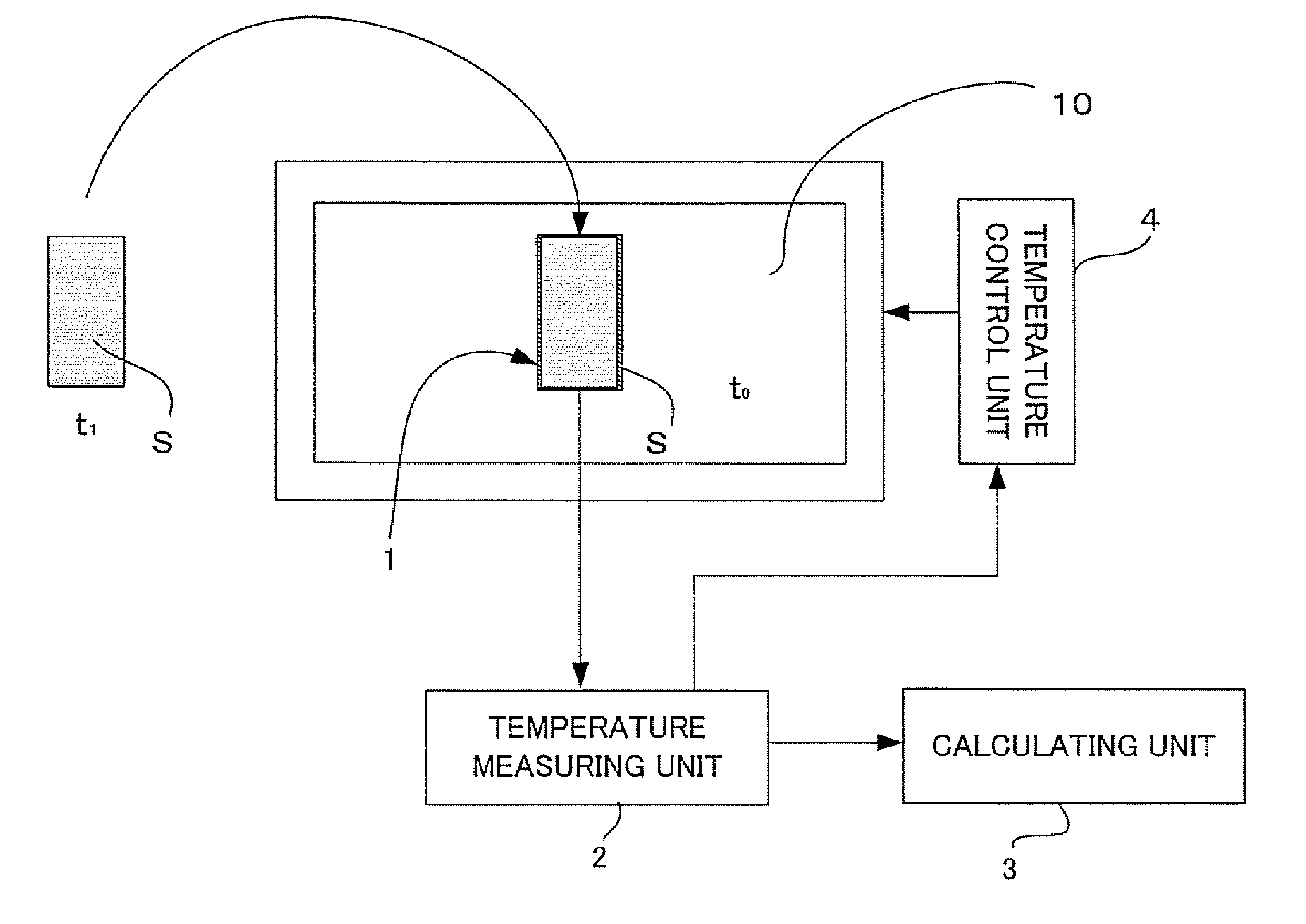
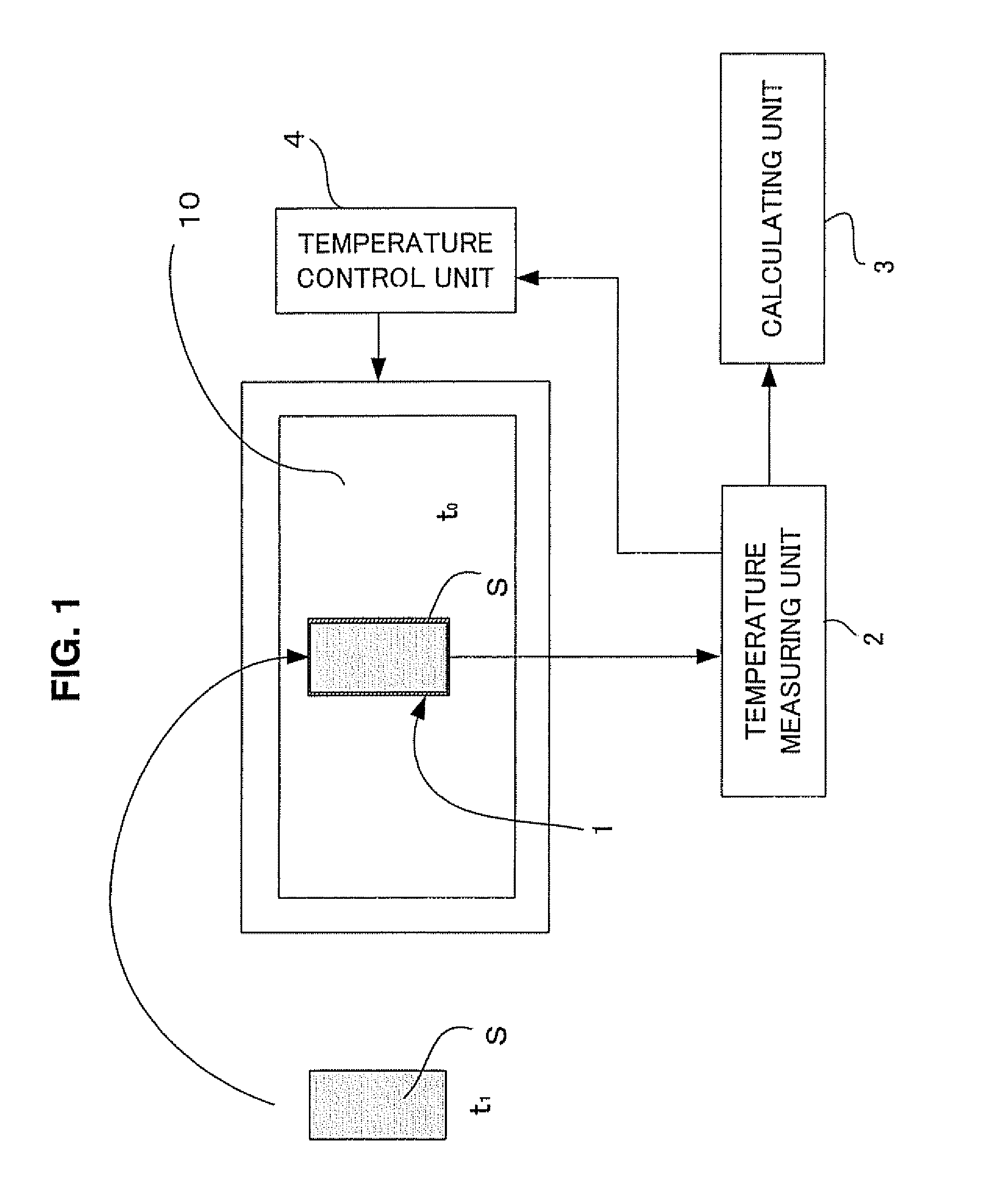
Determination of thermal properties of a formation
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for making in situ thermal property determinations utilizing a heat source employed in wellbore stabilization procedures, well drilling, or well perforating, for example. In particular, using a heat source, such as a laser driller, to enable formation temperature measurements. Based on these measurements, thermal properties of the formation may be inferred.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
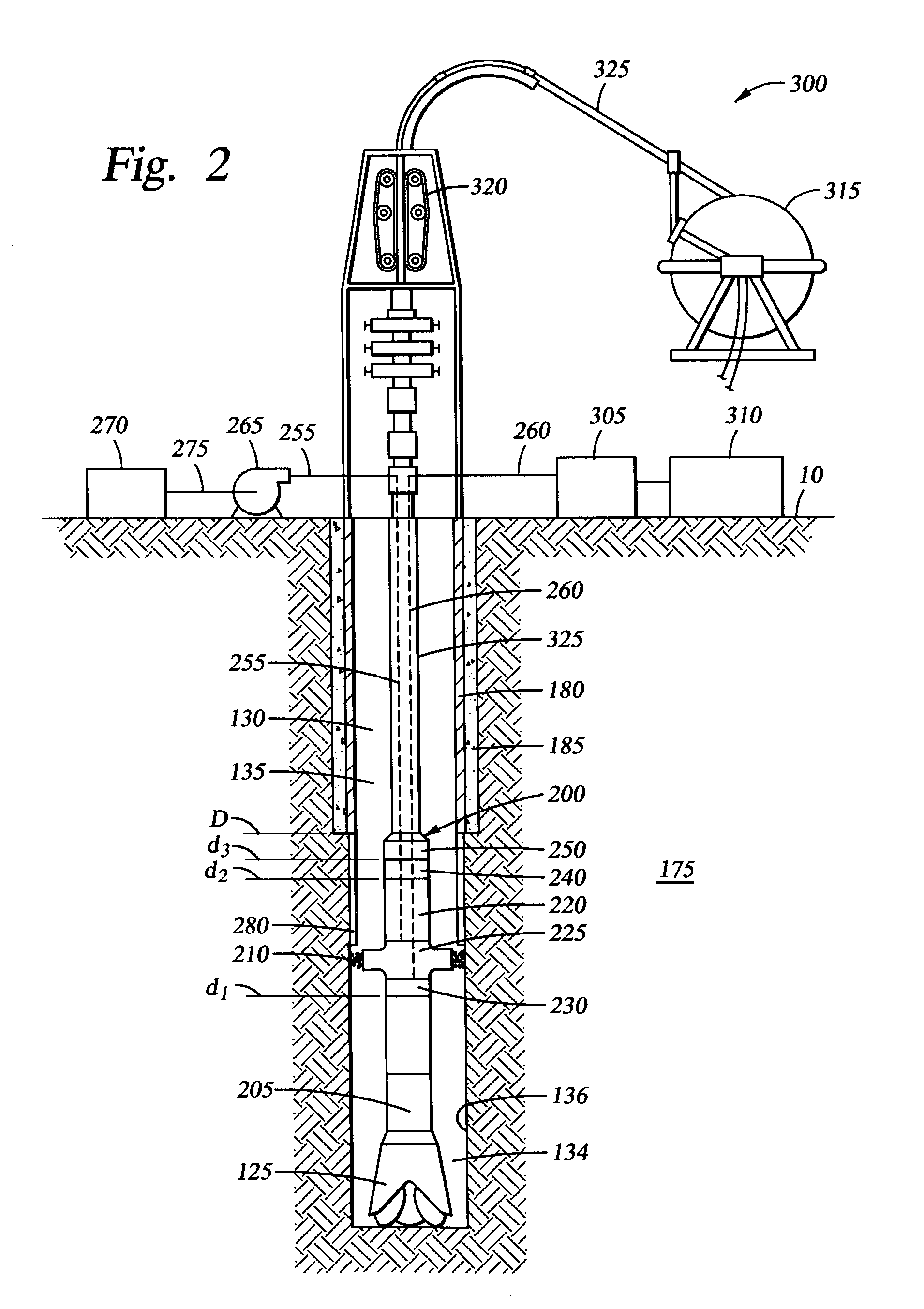
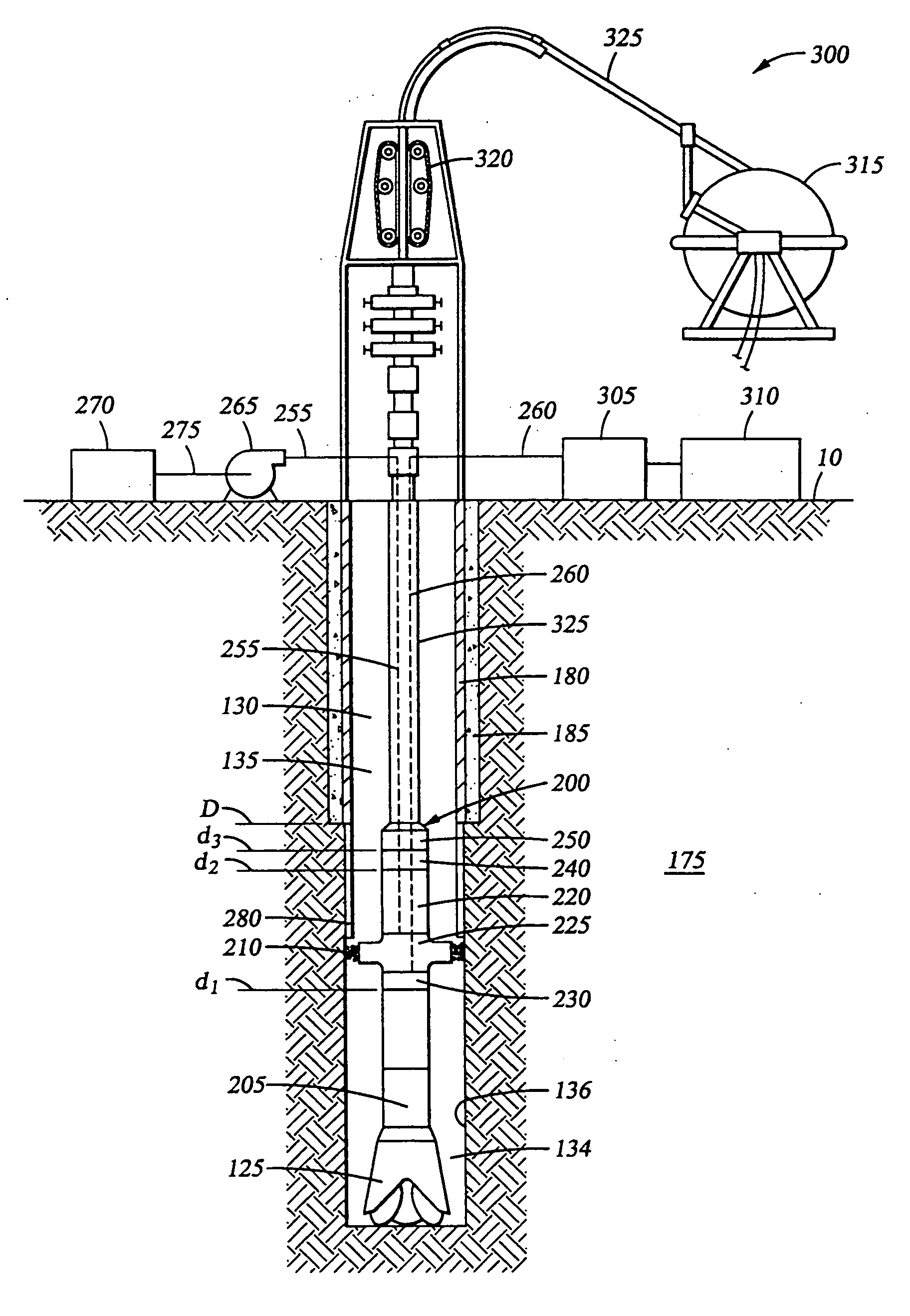
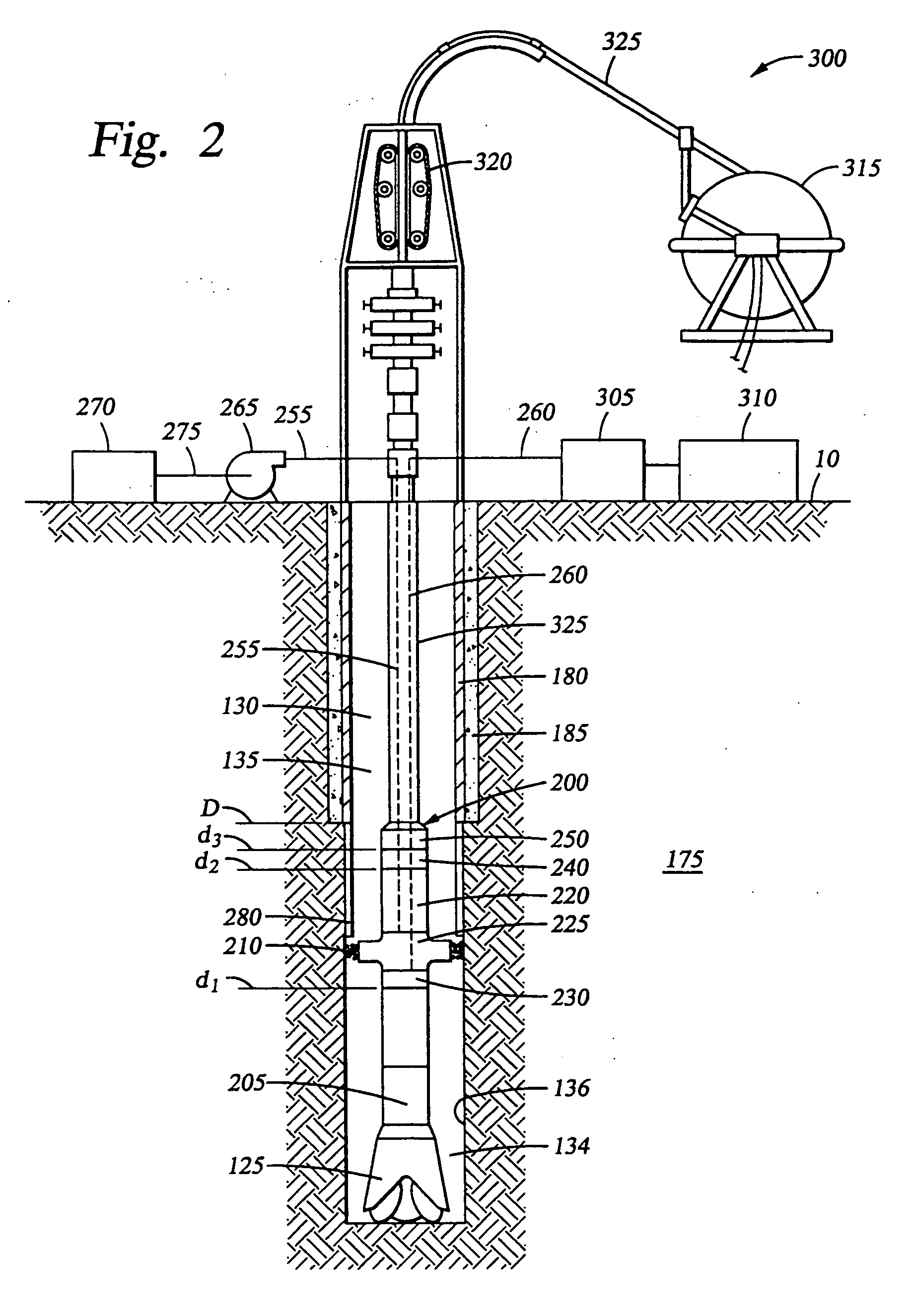
Assembly and method for determining thermal properties of a formation and forming a liner
A method comprises heating a formation adjacent a selected depth level within a wellbore extending into the formation, forming a temporary liner in the wellbore, measuring a first temperature of the formation at the selected depth level at a first time after heating the formation, measuring a second temperature of the formation at the selected depth level at a second time after heating the formation, and combining the temperature measurements to derive an indication of thermal properties of the formation. An apparatus comprises a coiled tubing drillstring extending into a wellbore, an assembly supported by the drillstring, the assembly comprising an extruder that extrudes a liner material onto a wall of the wellbore, a heat source that heats the liner material and a formation, and at least one temperature sensor that measures a temperature of the formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
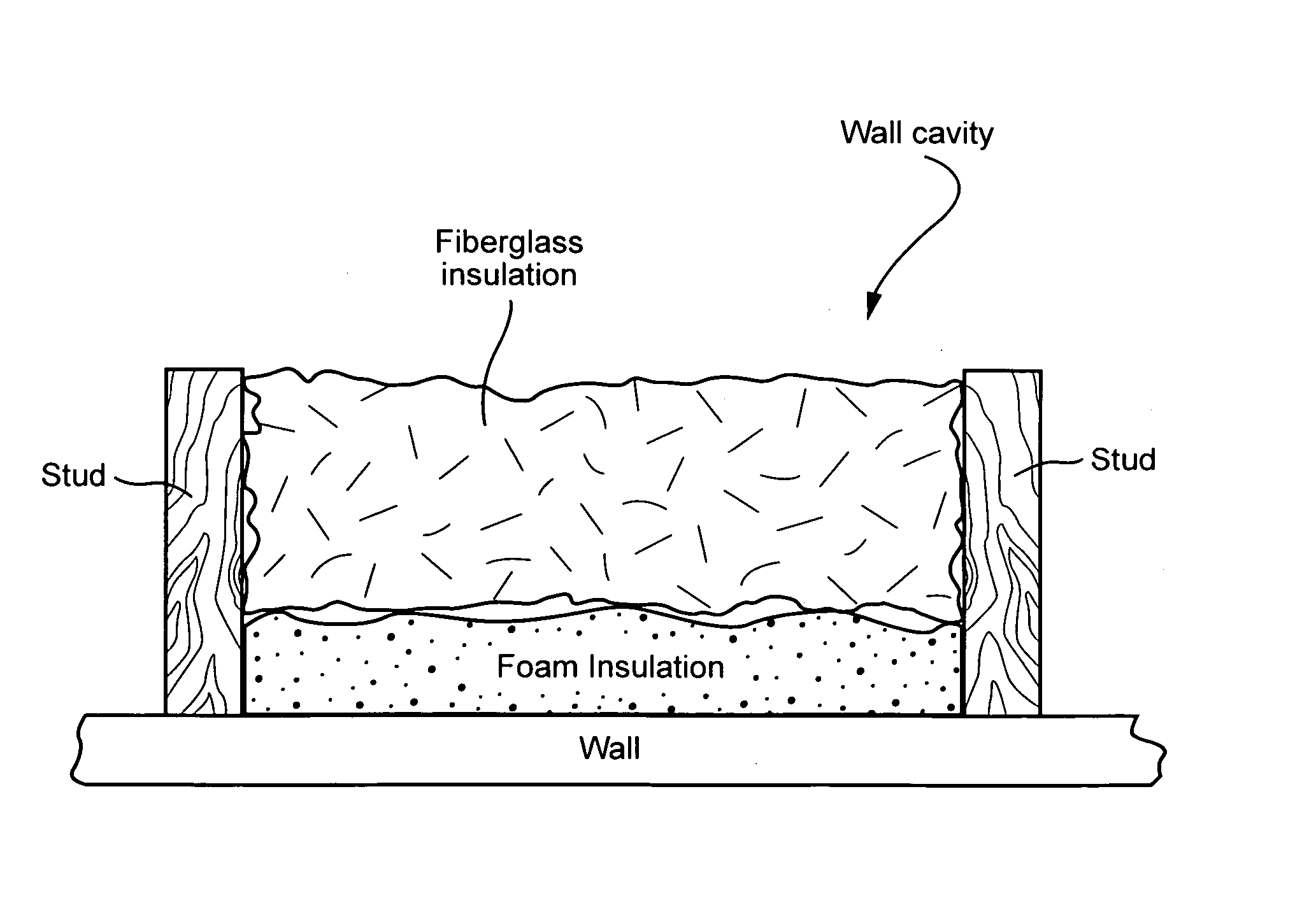
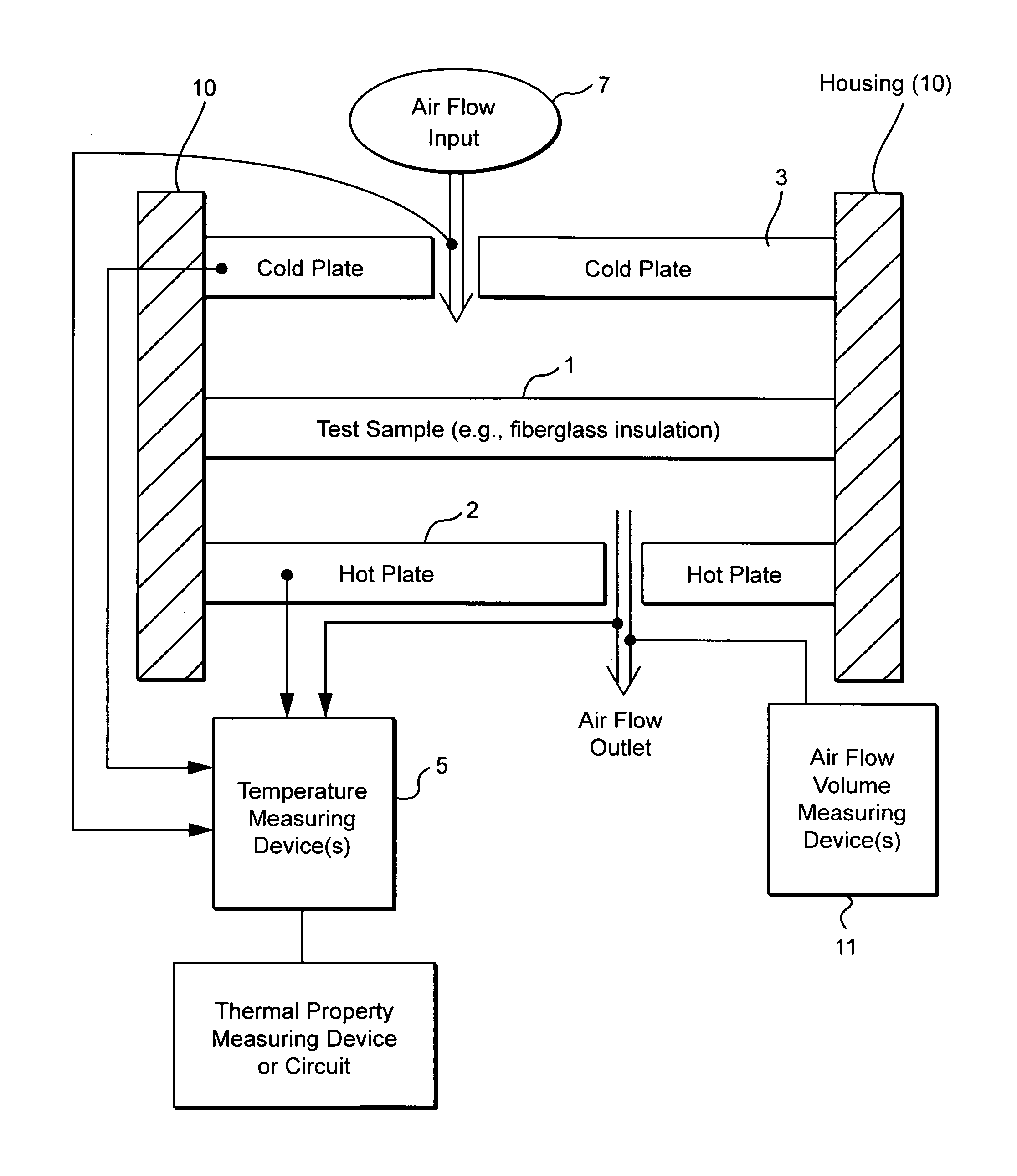
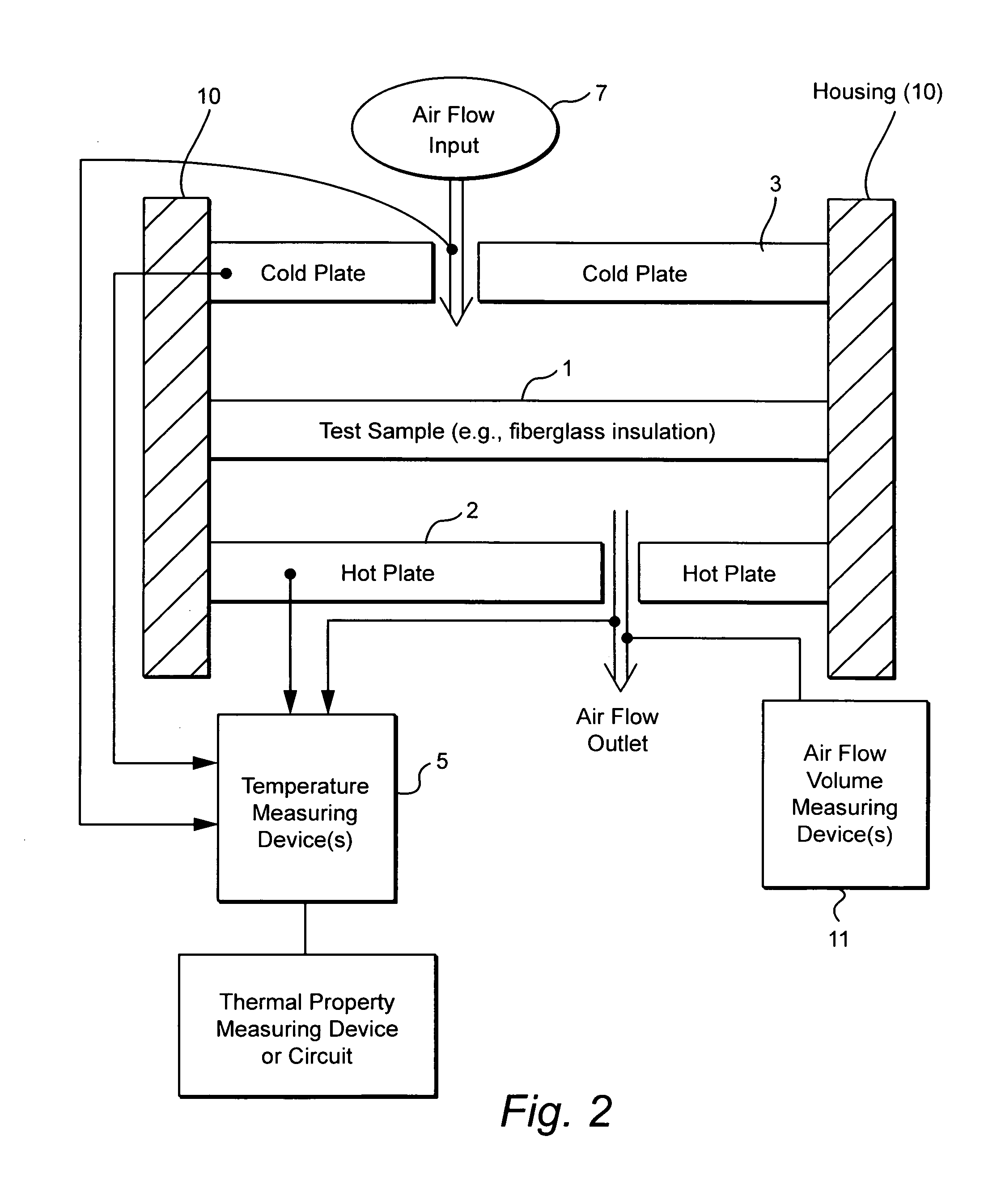
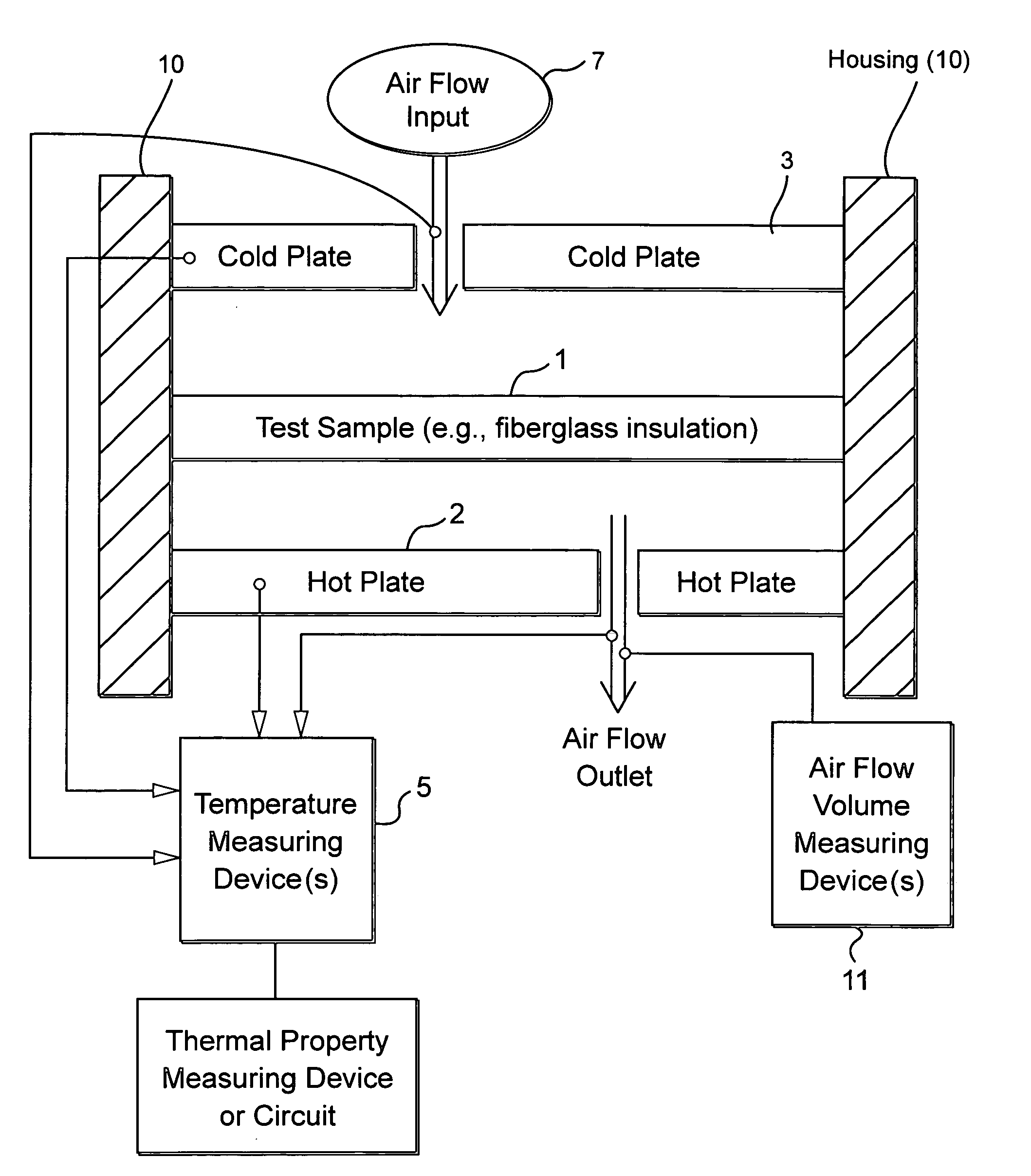
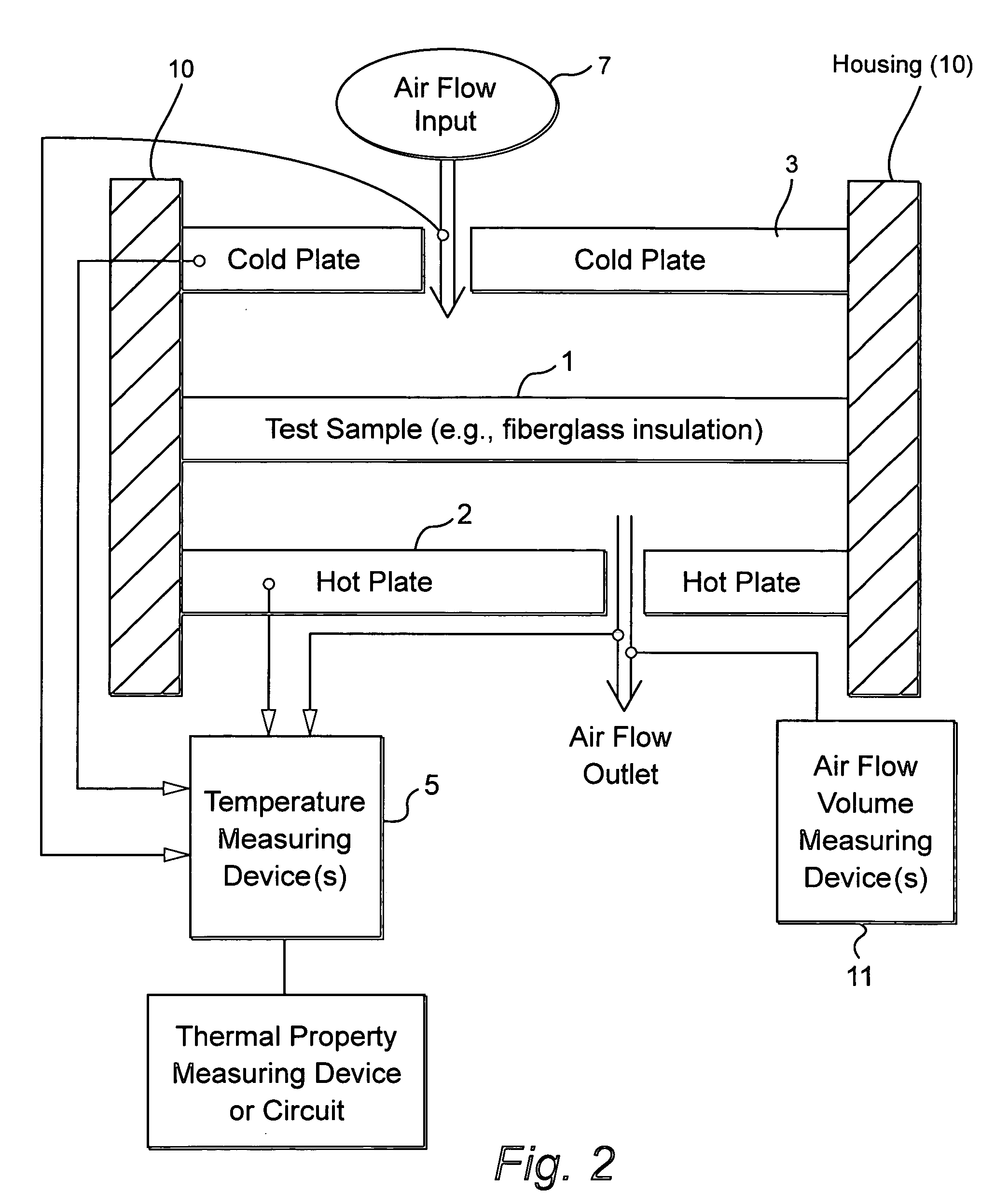
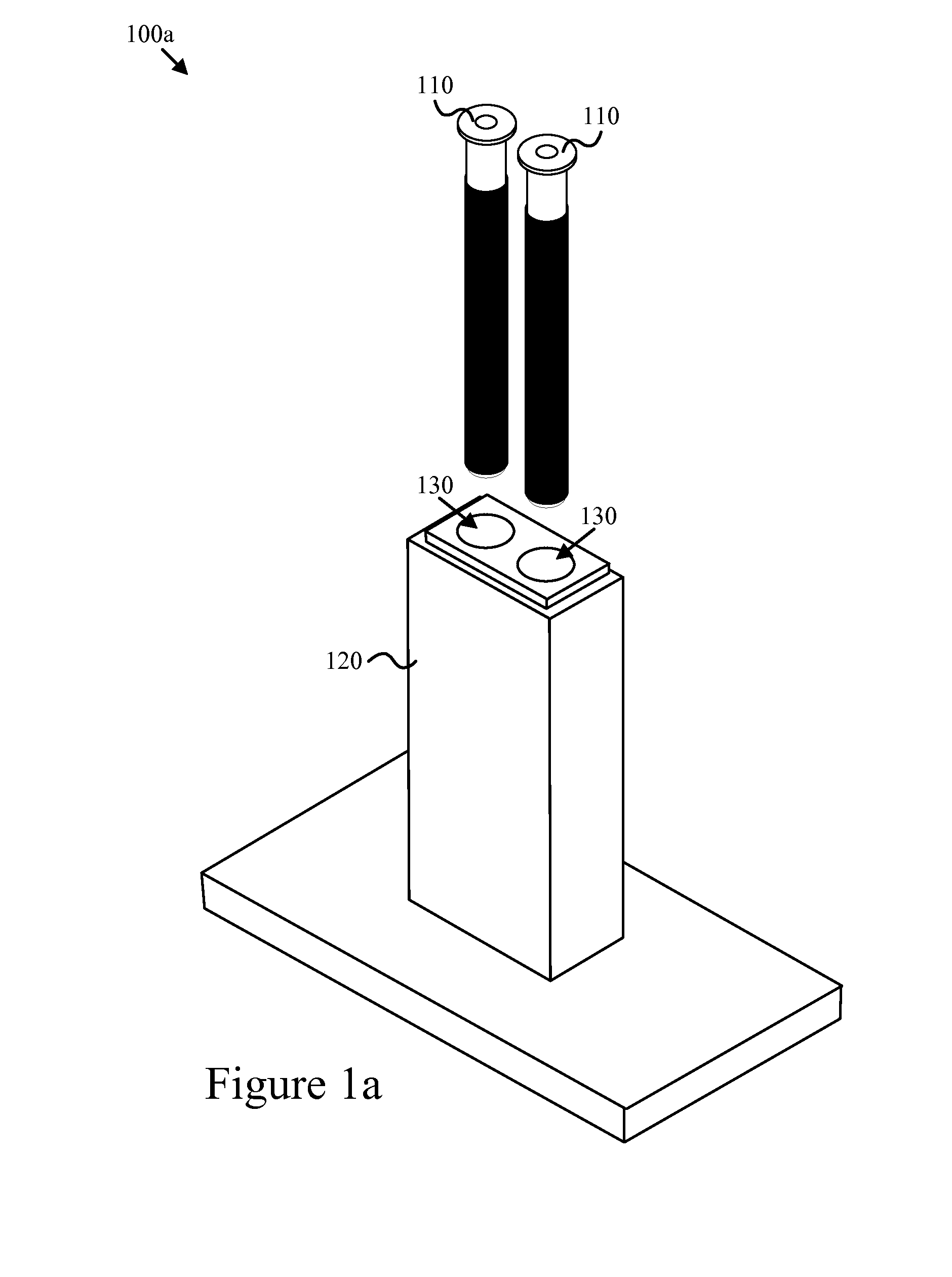
Method and/or system for compensating for effects of heat flow and/or air flow through fiberglass insulation
InactiveUS20060272280A1Reduce the amount requiredSufficient amountThermometer detailsMaterial thermal conductivityGlass fiberHeat flow
A method and / or system is provided that compensates for the flow of air through fiberglass insulation. In certain example embodiments, a dynamic heat flow meter or the like is provided for measuring and / or determining any detrimental effects of air flow through insulation such as fiberglass insulation. Once the possible detrimental effects are recognized, an insulation system is adapted (e.g., by providing a foam based insulation in a wall cavity in addition to the fiberglass insulation) to compensate, or substantially compensate, for the effects of air flow through the fiberglass. For instance, a sufficient amount of foam insulation may be provided in a cavity adjacent fiberglass, where the foam blocks or substantially blocks air from flowing through the cavity, thereby compensating for the effects of air flow through fiberglass and permitting the intended R-value to be maintained or substantially maintained.
Owner:KNAUF INSULATION LLC
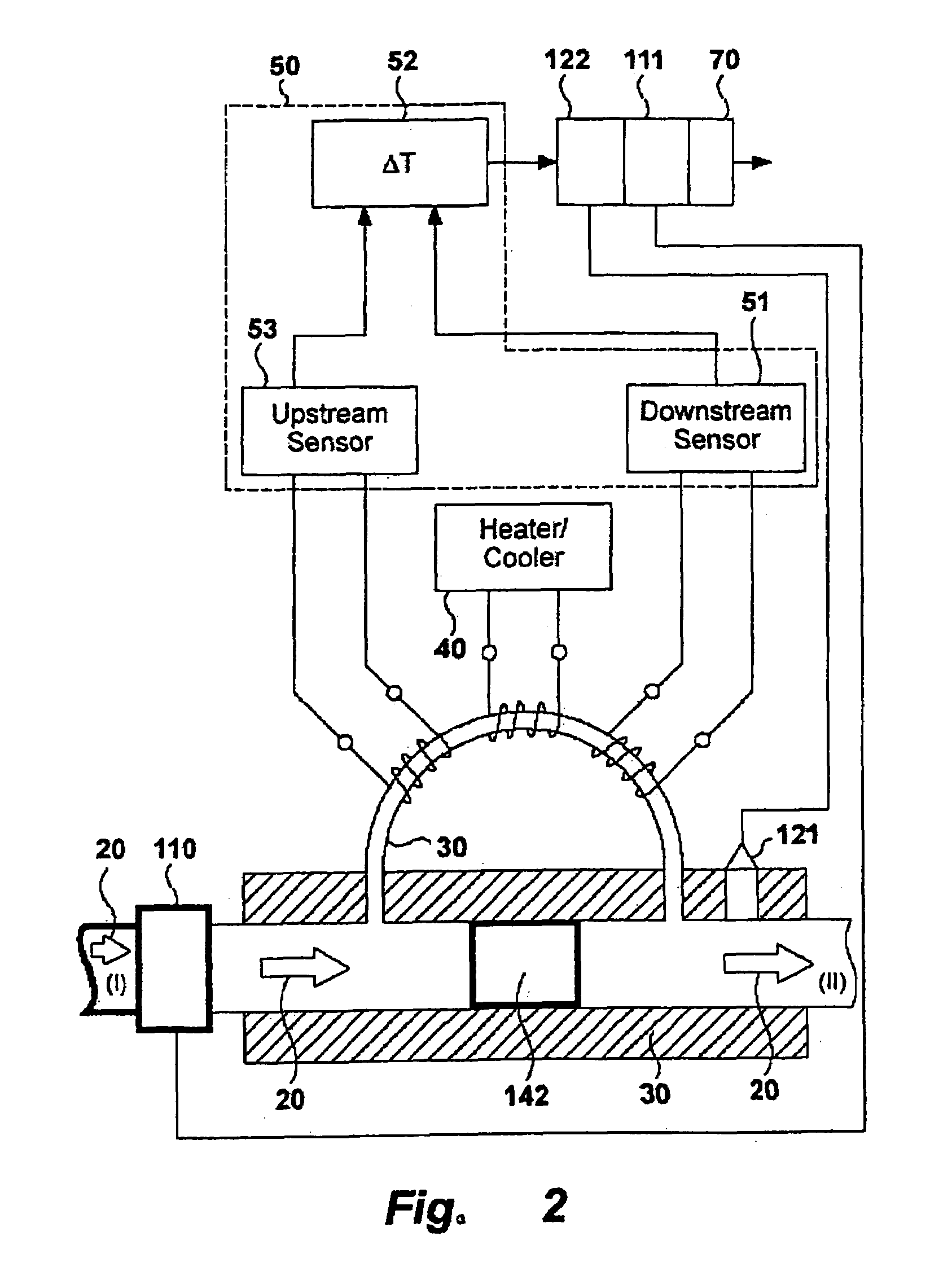
Method and device for determining a charcteristic value that is representative of the condition of a gas
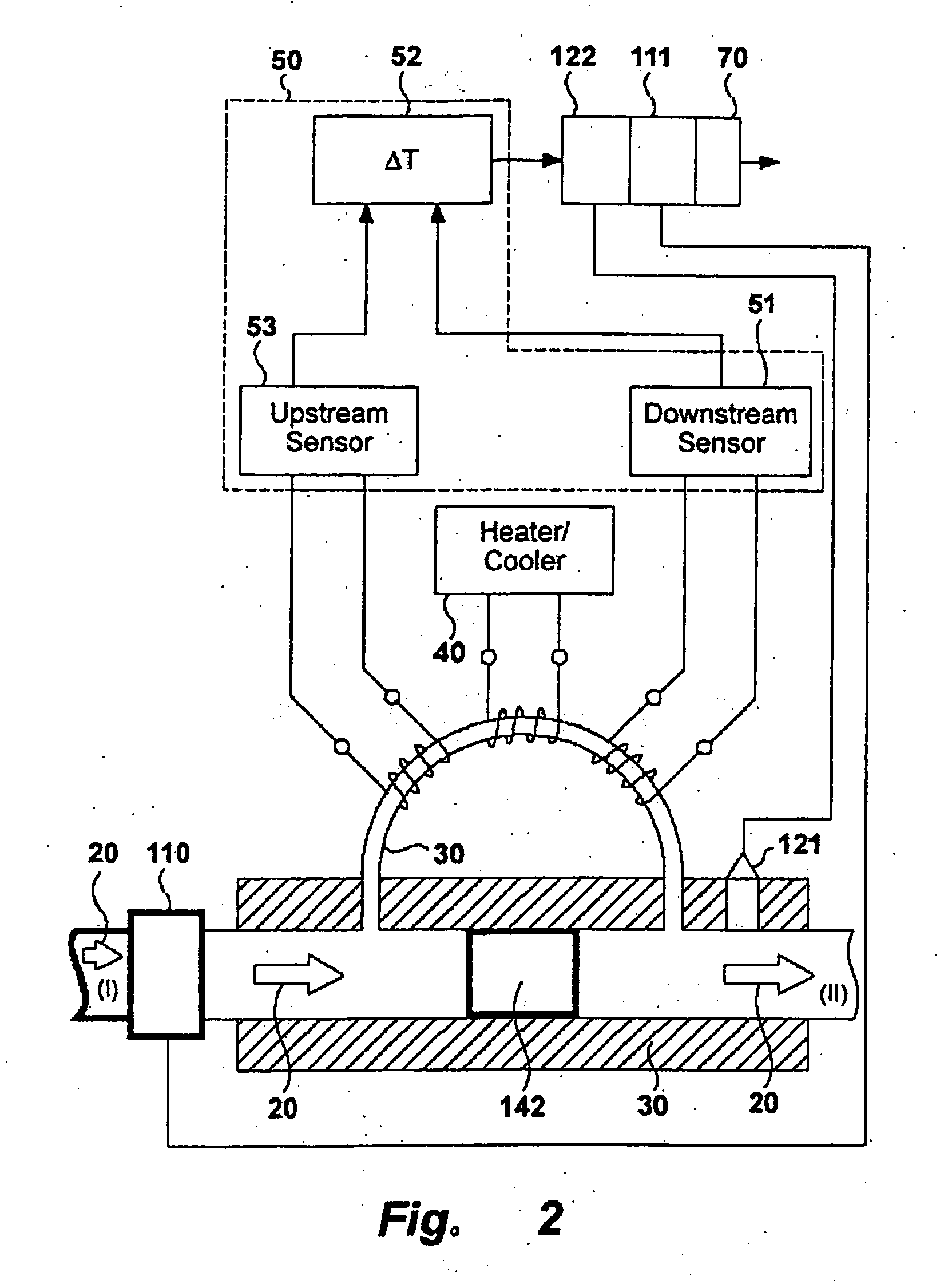
InactiveUS20060123892A1Accurate and reproducible temperature difference measurementReliable characterisationAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting/calibration apparatusEngineeringTemperature difference
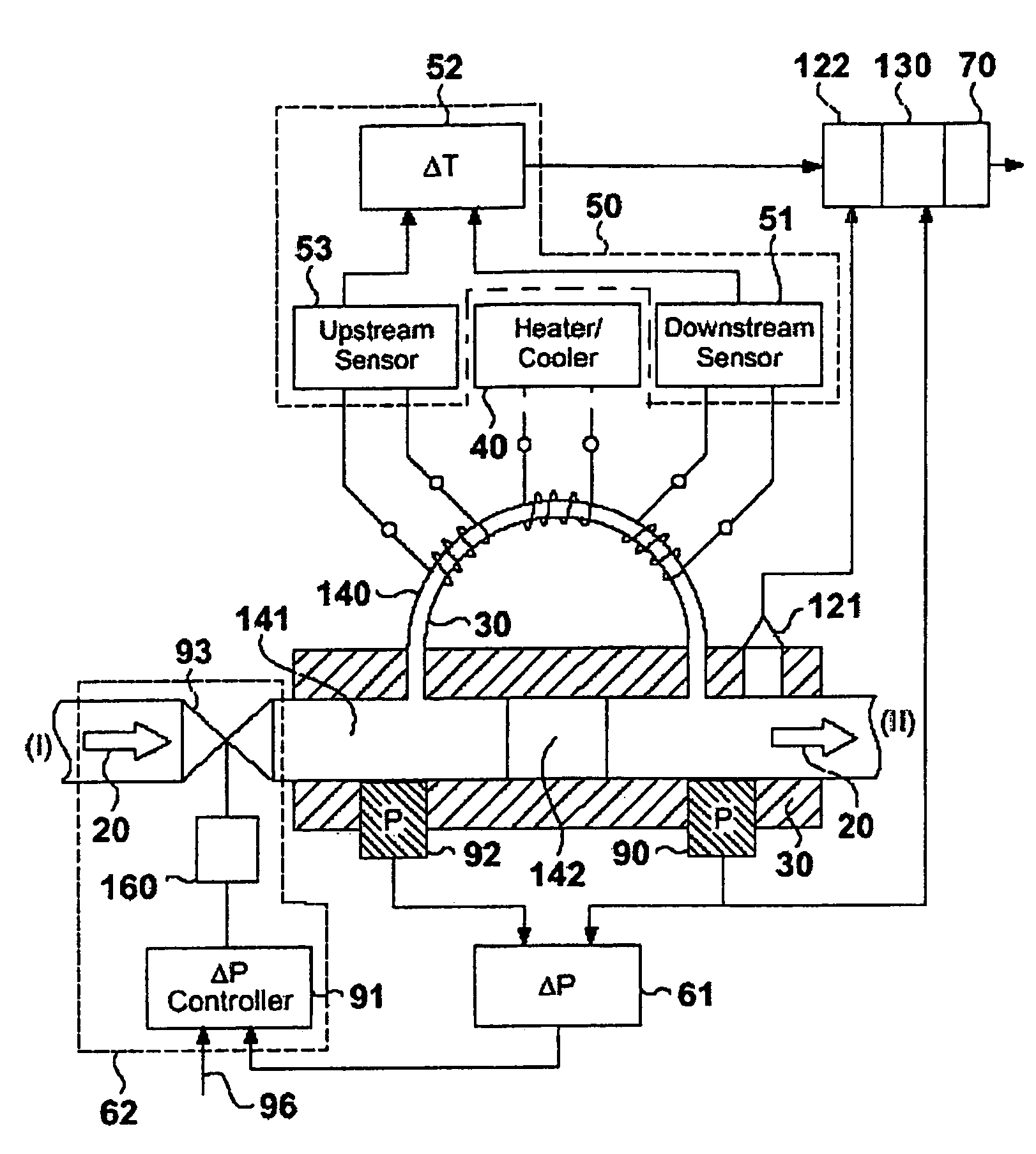
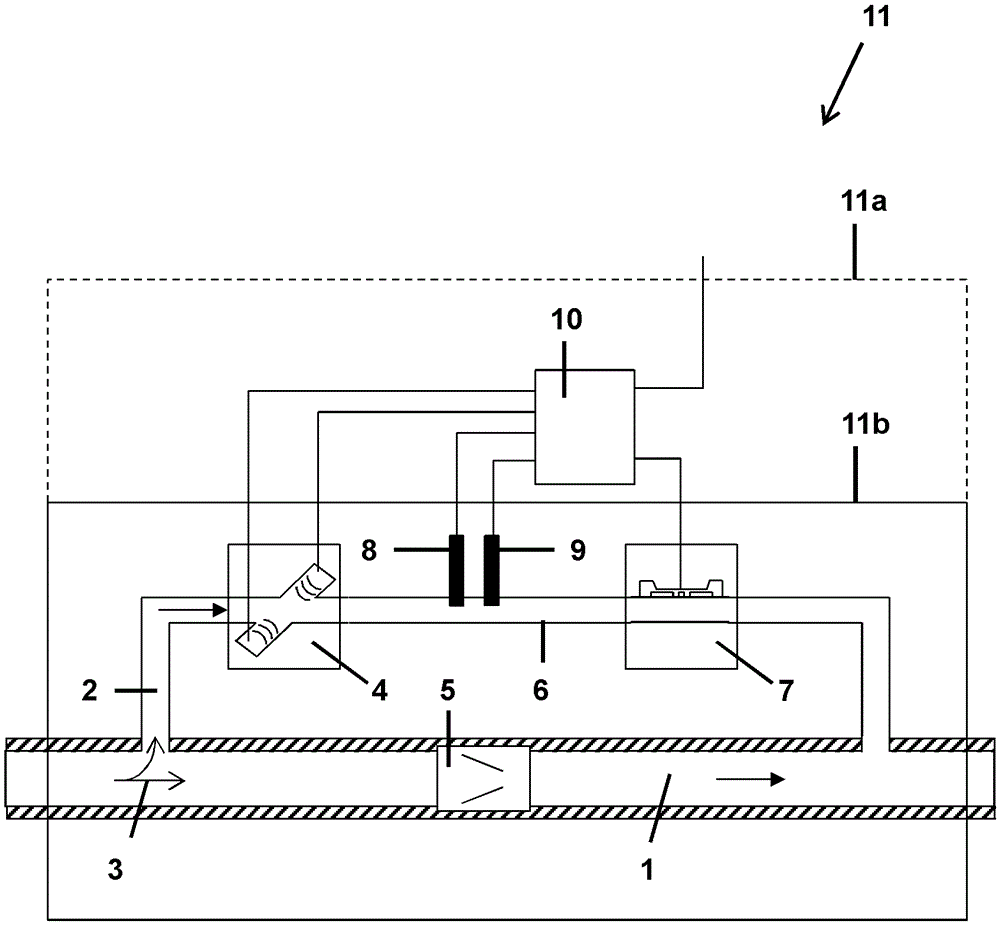
The invention relates to a device and methods for the characterisation of a flowing substance, liquid or gas. Particular embodiments of the invention relates to the use of the device for the identification of a flowing substance for controlling the flow of a fuel or combustion gas to deliver a controlled heat of combustion and for measuring the heat capacity of a gas. Further embodiments of the invention relate to a flow control device for controlling the flow rate of a flowing substance and a method for the combustion of a fuel or combustion gas. The device for the characterisation of a flowing substance comprises: a transport duct on which is mounted a heating or a cooling element; a temperature difference sensor comprising a first temperature measurement cell downstream of the heating or cooling element and means to determine a temperature difference in the flowing substance upstream and downstream of the heating or cooling element; flow control means comprising flow measurement means for measuring a mass flow characteristic and flow correction means for correcting for measured mass flow variations; and evaluation means for evaluating a characterising feature of the flowing substance comprising a function relating temperature differences measured on one or more calibration substances to one or more characterising features of the flowing substance. The device is relatively simple and cheap and gives a quick but accurate and reliable characterisation of a flowing substance, gas or liquid, that can be used in a flow control device to control the flow rate of unknown substances.
Owner:EMERSON ELECTRIC CO
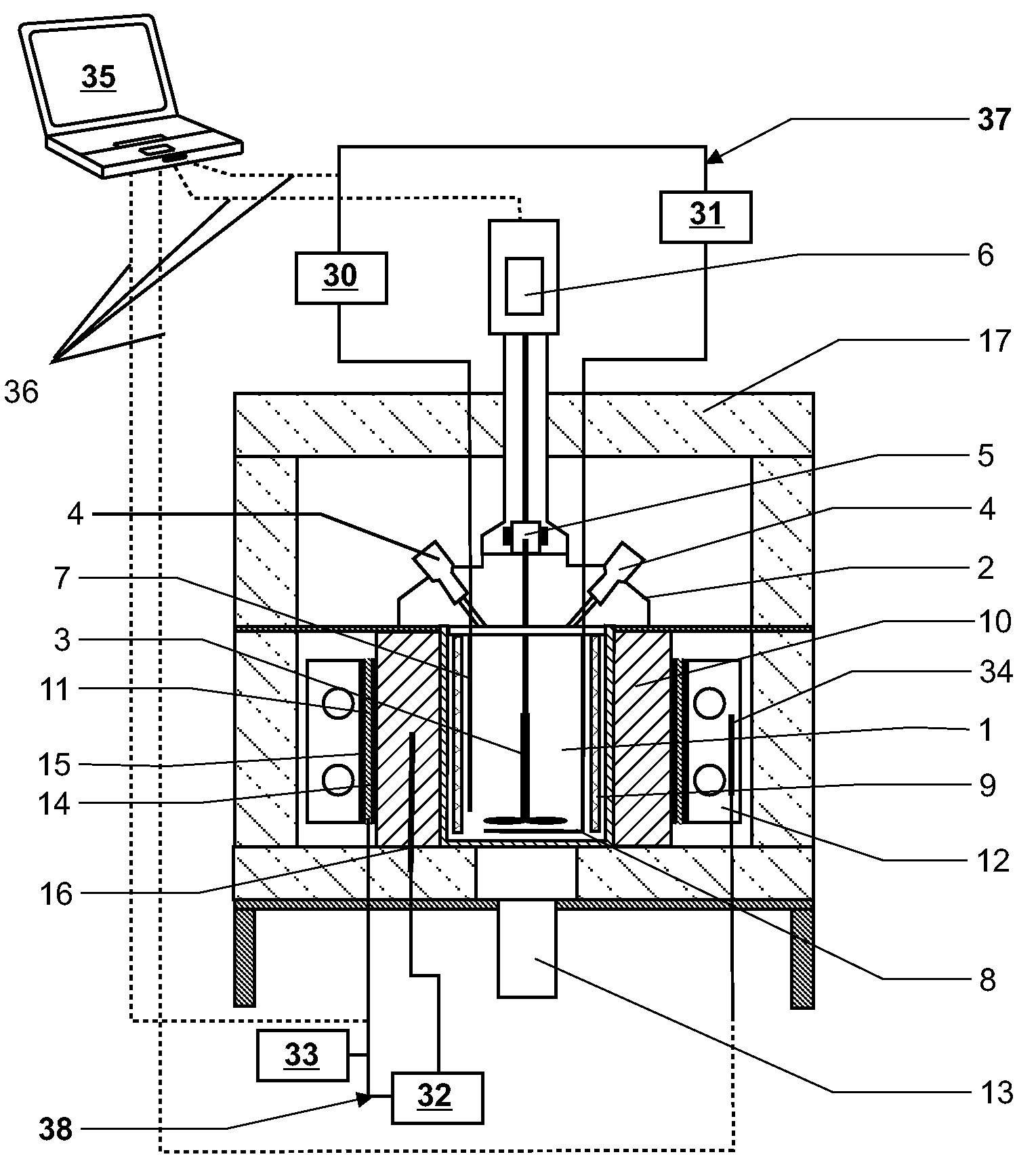
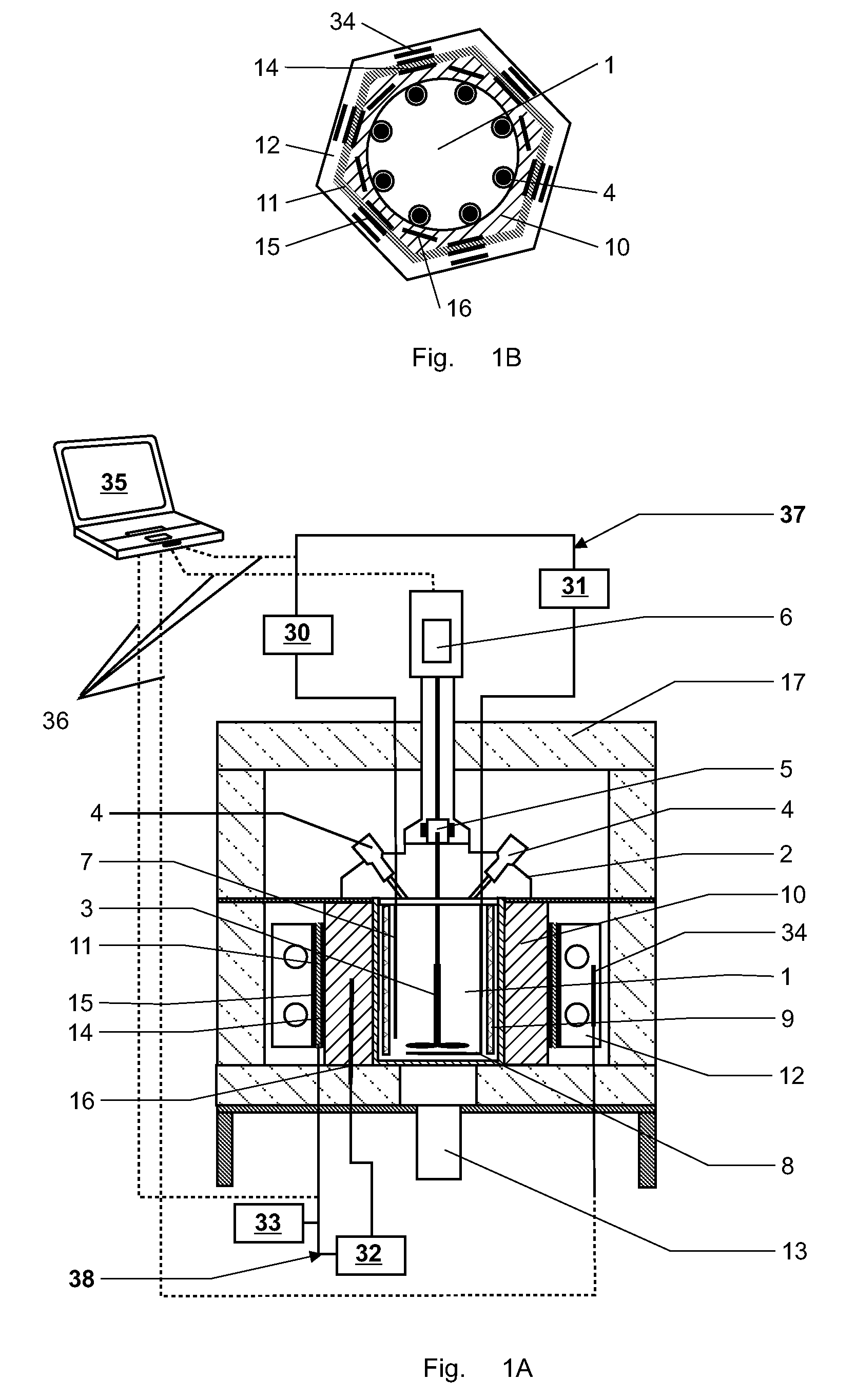
Method and device for determining specific heat capacity
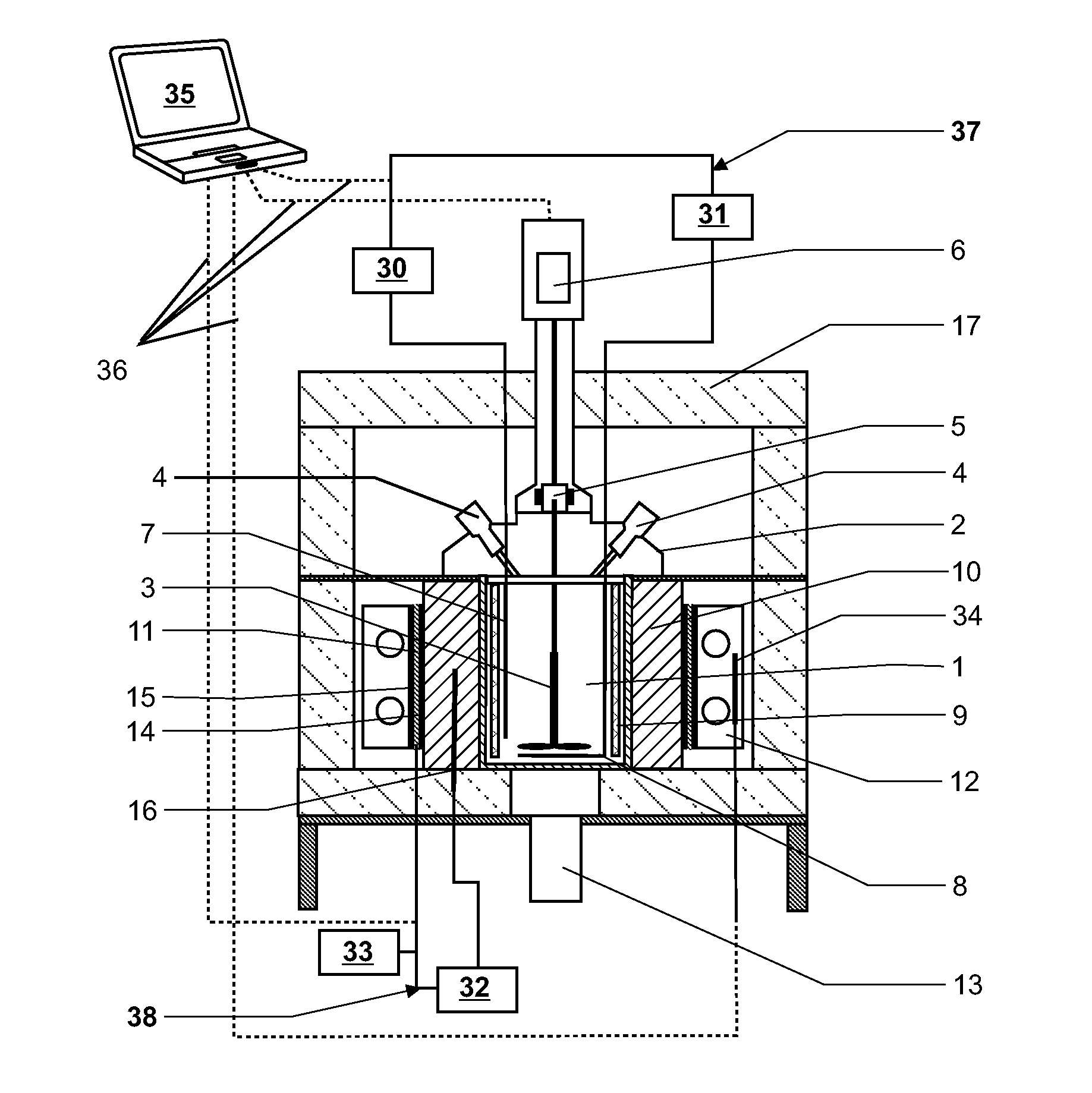
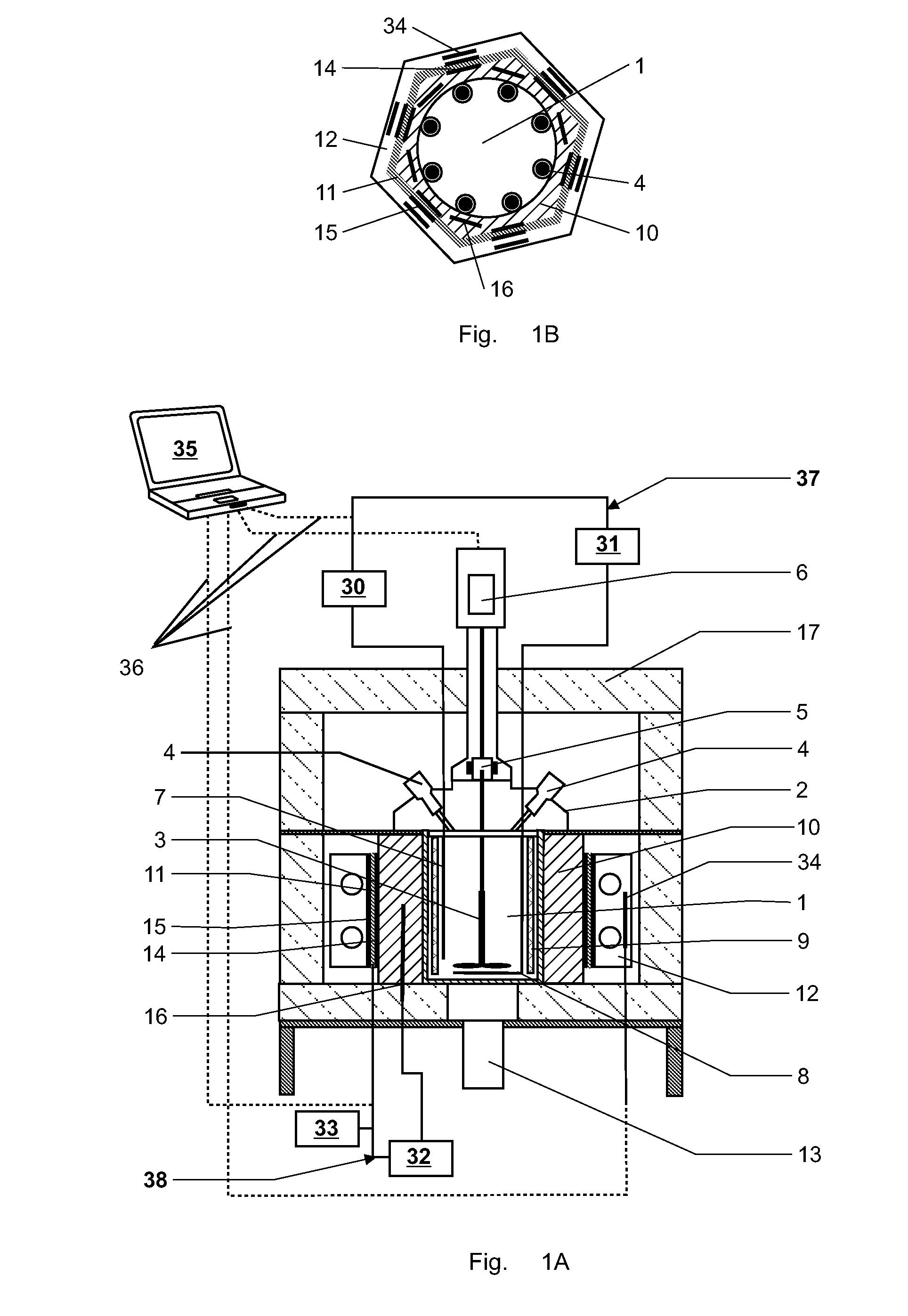
ActiveUS20090154520A1Improve accuracyEasy to exportMaterial heat developmentDigital computer detailsEnergy variationEngineering
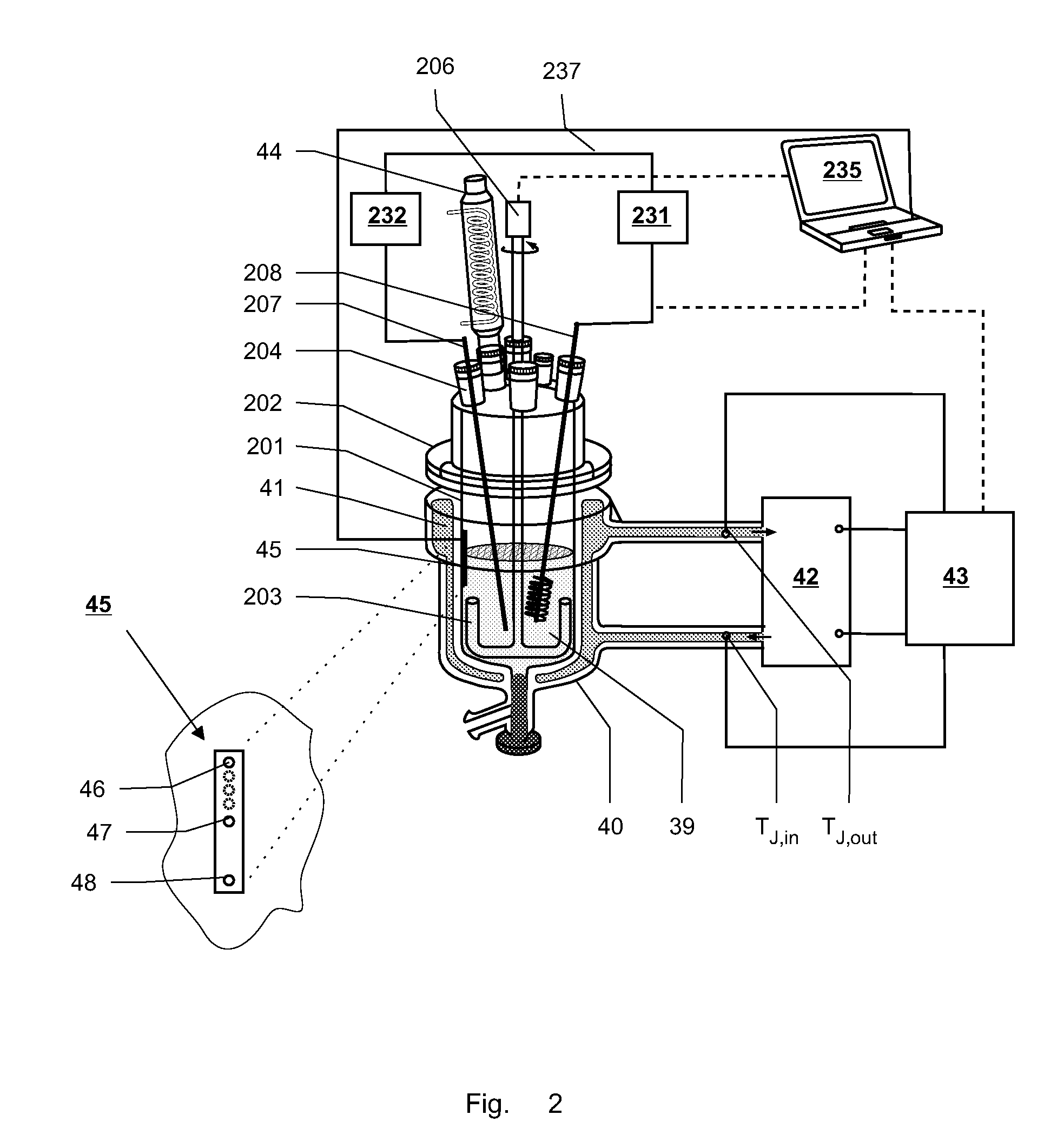
The specific heat capacity (cp) of a medium is determined using a calorimeter with a reactor (1), a stirrer (3), a first thermostat for providing an inner heat balance, a second thermostat, means for providing an outer heat balance and a central control unit (35). The method uses the steps of: applying a modulated energy profile to the medium, inside the reactor (1), under near isothermal conditions; monitoring the resulting energy changes of: the medium, the reactor (1), the first thermostat, the second thermostat and / or the outer heat balance means as a function of time; determining the respective inner and outer heat balances independently from each other at predefined time intervals; and calculating the overall heat transfer coefficient (UA) and the specific heat capacity of the medium (cp) simultaneously and independently from each other as a function of time from the inner and outer heat balances.
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO GMBH
Method and measuring apparatus for determining specific quantities for gas quality
ActiveUS20160138951A1Preciser valueGood correlationMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial thermal conductivityStreamflowThermal conductivity
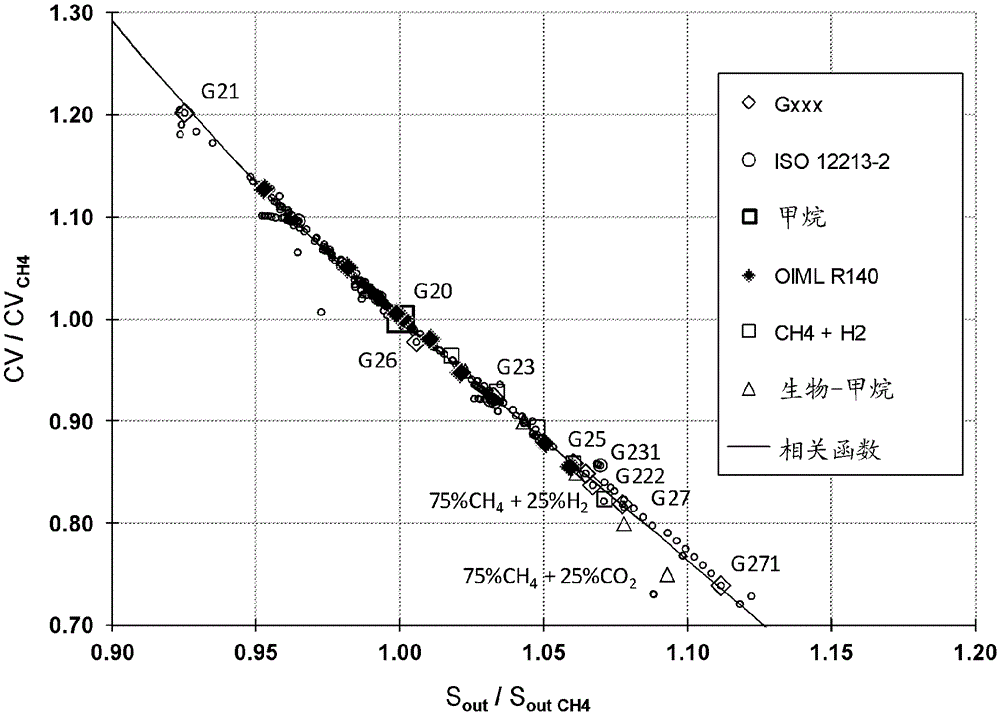
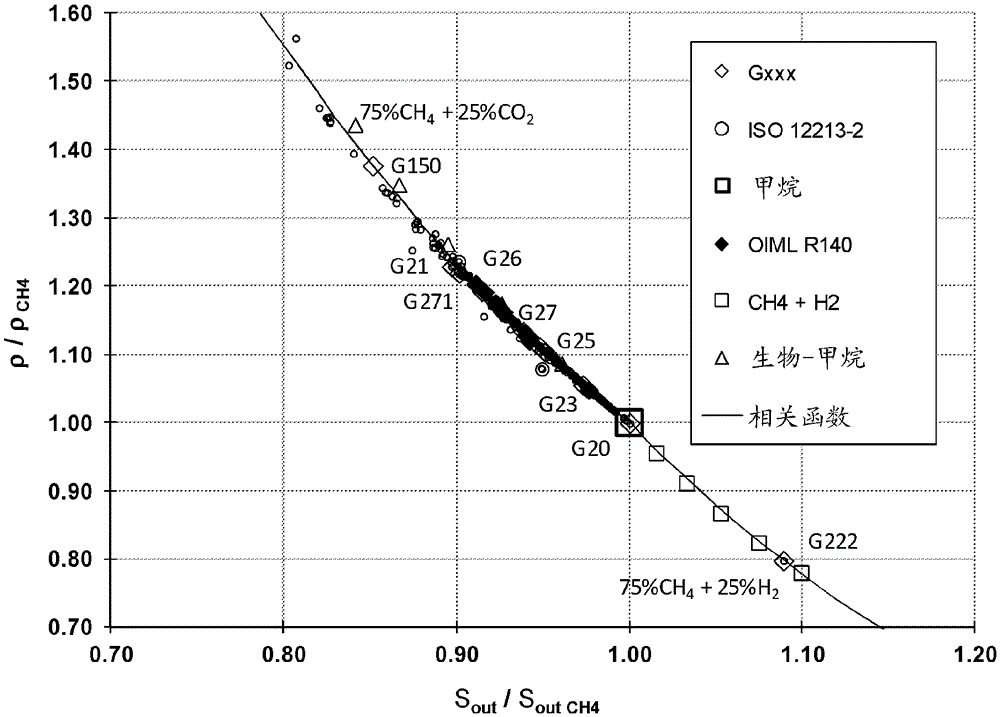
A method and a measuring apparatus for determining specific quantities for the gas quality in which the gas or gas mixture flows through an ultrasonic flow sensor as well as through a microthermal sensor, and the former is used for determining the sound and flow velocity and the latter for determining the thermal conductivity and the thermal capacity of the gas or gas mixture. The sound velocity, the thermal conductivity and the thermal capacity are subsequently used for the correlation of the specific quantities for the gas quality.
Owner:MEMS
Method for acquiring thermal efficiency of a boiler
InactiveUS20190113417A1Accuracy satisfiedReal-time capability satisfiedFluid heatersElectric testing/monitoringEngineeringThermal efficiency
The present invention discloses a method for acquiring thermal efficiency of a boiler, comprising: acquiring effective output heat and total output heat of the boiler, and obtaining the thermal efficiency of the boiler according to the effective output heat and total output heat. In the method provided by the present invention, by acquiring the thermal efficiency of the boiler according to the obtained effective output heat and total output heat, the thermal efficiency of the boiler can be acquired without performing coal quality testing, thus the thermal efficiency of the boiler is conveniently obtained, and the real-time capability and accuracy are satisfied.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER COMAPNY +1
Method and/or system for compensating for effects of heat flow and/or air flow through fiberglass insulation
InactiveUS7748197B2Sufficient amountCompensation effectThermometer detailsMaterial thermal conductivityGlass fiberHeat flow
A method and / or system is provided that compensates for the flow of air through fiberglass insulation. In certain example embodiments, a dynamic heat flow meter or the like is provided for measuring and / or determining any detrimental effects of air flow through insulation such as fiberglass insulation. Once the possible detrimental effects are recognized, an insulation system is adapted (e.g., by providing a foam based insulation in a wall cavity in addition to the fiberglass insulation) to compensate, or substantially compensate, for the effects of air flow through the fiberglass. For instance, a sufficient amount of foam insulation may be provided in a cavity adjacent fiberglass, where the foam blocks or substantially blocks air from flowing through the cavity, thereby compensating for the effects of air flow through fiberglass and permitting the intended R-value to be maintained or substantially maintained.
Owner:KNAUF INSULATION LLC
Method and device for determining a characteristic value that is representative of the condition of a gas
InactiveUS7377152B2Accurate temperature differenceReliable characterisationTesting/calibration apparatusMaterial thermal conductivityEngineeringTemperature difference
The invention relates to a device and methods for characterizating flowing substances, liquid or gas. The device includes: a transport duct with a heating or a cooling element; a temperature difference sensor having a temperature measurement cell downstream of the heating or cooling element and means to determine a temperature difference in the flowing substance upstream and downstream of the heating or cooling element; a flow control means having flow measurement means for measuring a mass flow characteristic and a flow correction means for correcting for measured mass flow variations; and an evaluation means for evaluating a characterizing feature of the flowing substance comprising a function relating temperature differences measured on one or more calibration substances to one or more characterizing features of the flowing substance. Various embodiments relate to the related use and methods of the device for identification and control of the flowing substance.
Owner:EMERSON ELECTRIC CO
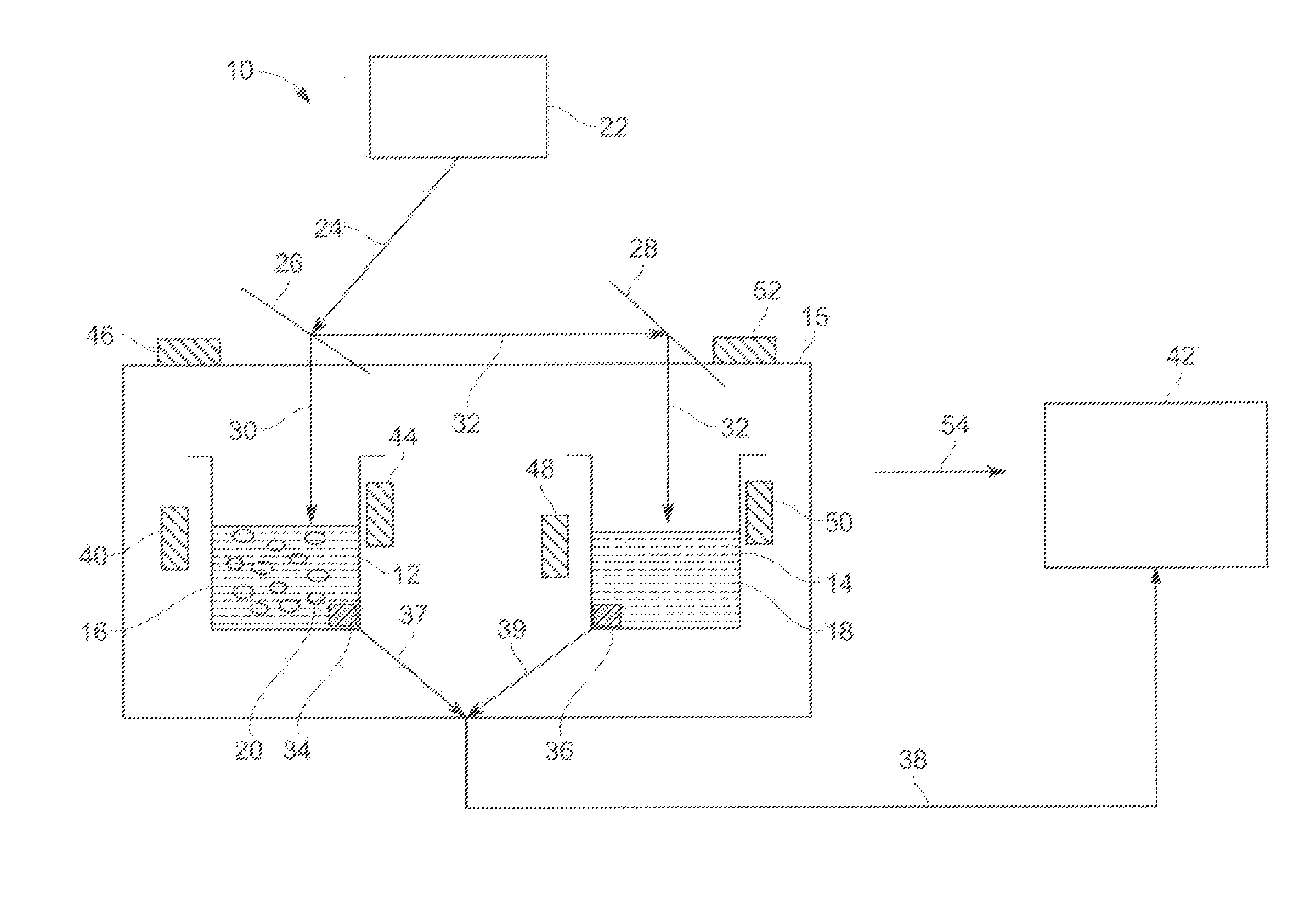
Method and device for dissolved gas analysis
ActiveUS20140165704A1Material analysis by optical meansSpecific heat investigationThermodynamicsElectromagnetic radiation
A system, comprising at least one source for irradiating electromagnetic radiation into a sample fluid and a reference fluid resulting in a change in a temperature of the sample fluid and a change in a temperature of the reference fluid, and a processing subsystem that monitors and determines a concentration of a gas of interest dissolved in the sample fluid based upon a difference between the change in the temperature of the sample fluid and the change in the temperature of the reference fluid, wherein the reference fluid does not contain the gas of interest, and the electromagnetic radiation has a wavelength range corresponding to a spectral absorption range of the gas of interest.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for obtaining furnace thermal efficiency
ActiveCN106845089AEasy accessElectric testing/monitoringHardware monitoringEngineeringThermal efficiency
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER COMAPNY +3
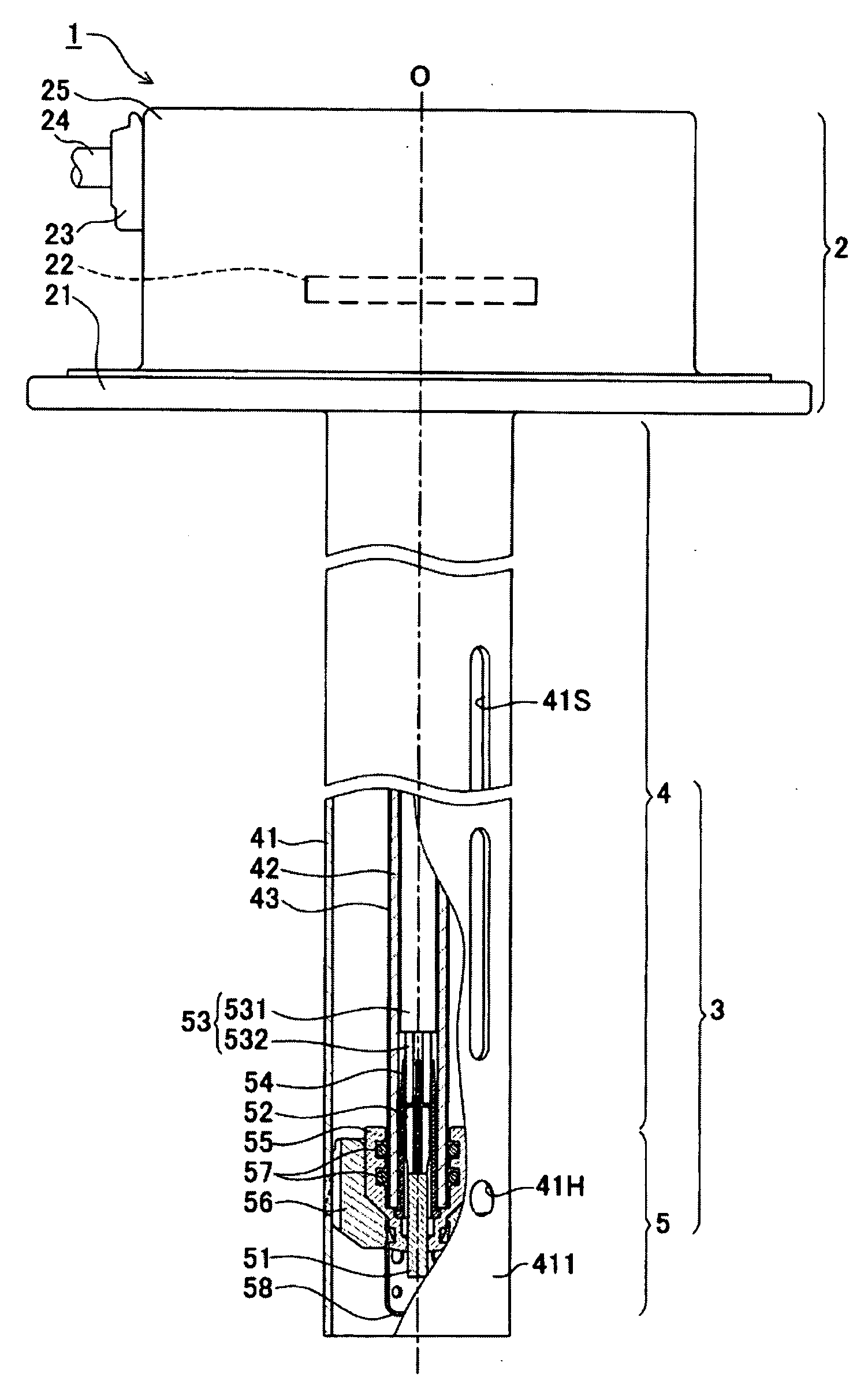
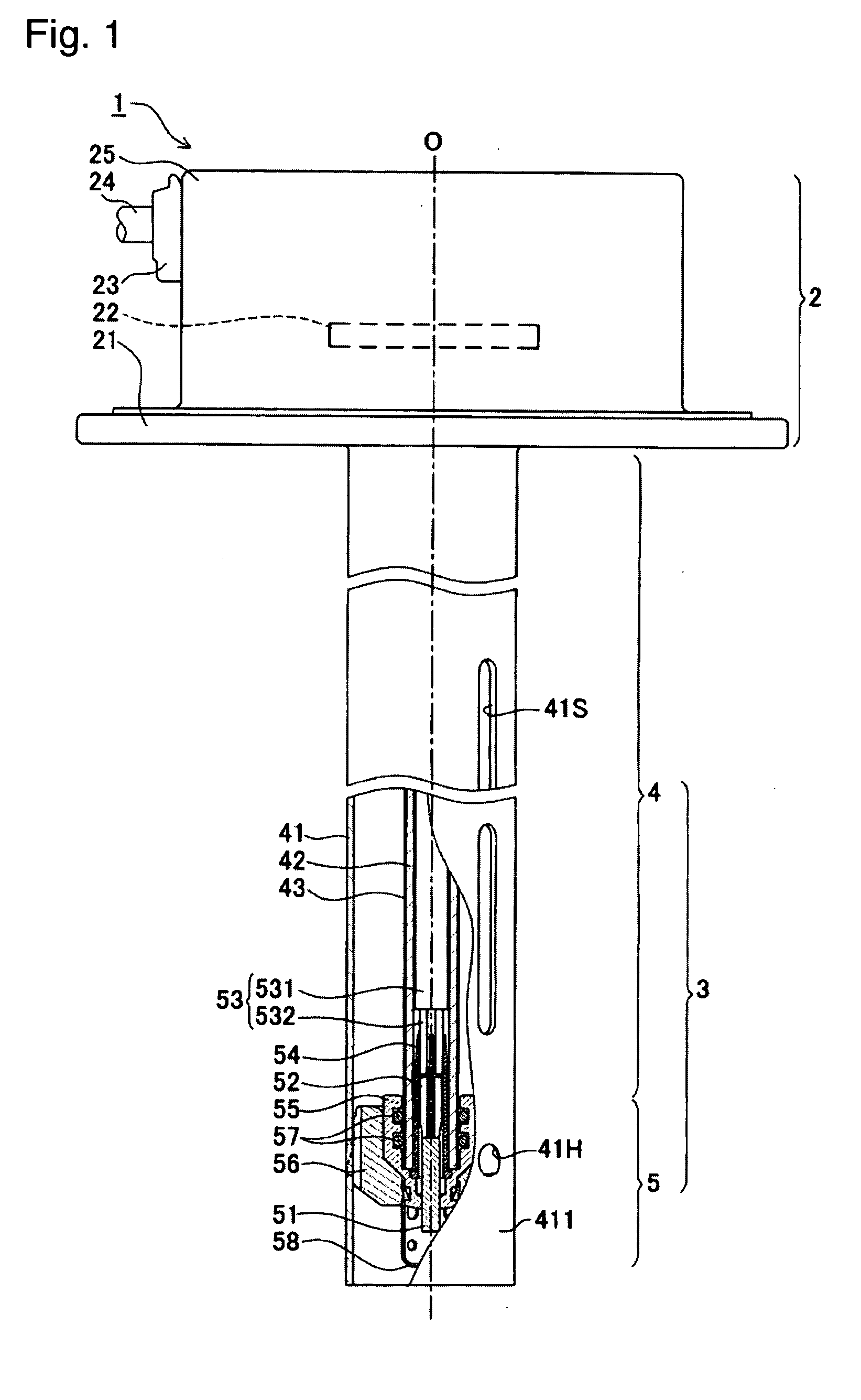
Liquid-condition detection sensor
InactiveUS20070169544A1Guaranteed to continue to useAvoid problemsSamplingExhaust apparatusLiquid stateEngineering
A liquid-condition detection sensor (1) including a sensor element (51), at least a portion of which contacts a urea aqueous solution; connection terminals (52) fixedly attached to the sensor element (51); connection cables (53) which electrically communicate with the concentration sensor element (51) via the connection terminals (52); an inner tube (42) which holds the concentration sensor element (51) at a distal end portion (421) by use of a holder member (55) and surrounds a portion of the connection cables (53) and the entire connection terminals (52); and a separator formed from a material having rubberlike elasticity (54) including a terminal-inner-tube-insulating portion (542) which intervenes between the connection terminals (52) and the inner tube (42) to thereby insulate the connection terminals (52) and the inner rube (42) from one another.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Method and measuring apparatus for determining specific quantities for gas quality
ActiveCN105606786AAccurate mass flow valueHigh precisionMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial thermal conductivityMeasurement deviceStreamflow
A method and a measuring apparatus for determining specific quantities for the gas quality in which the gas or gas mixture flows through an ultrasonic flow sensor as well as through a microthermal sensor, and the former is used for determining the sound and flow velocity and the latter for determining the thermal conductivity and the thermal capacity of the gas or gas mixture. The sound velocity, the thermal conductivity and the thermal capacity are subsequently used for the correlation of the specific quantities for the gas quality.
Owner:MEMS
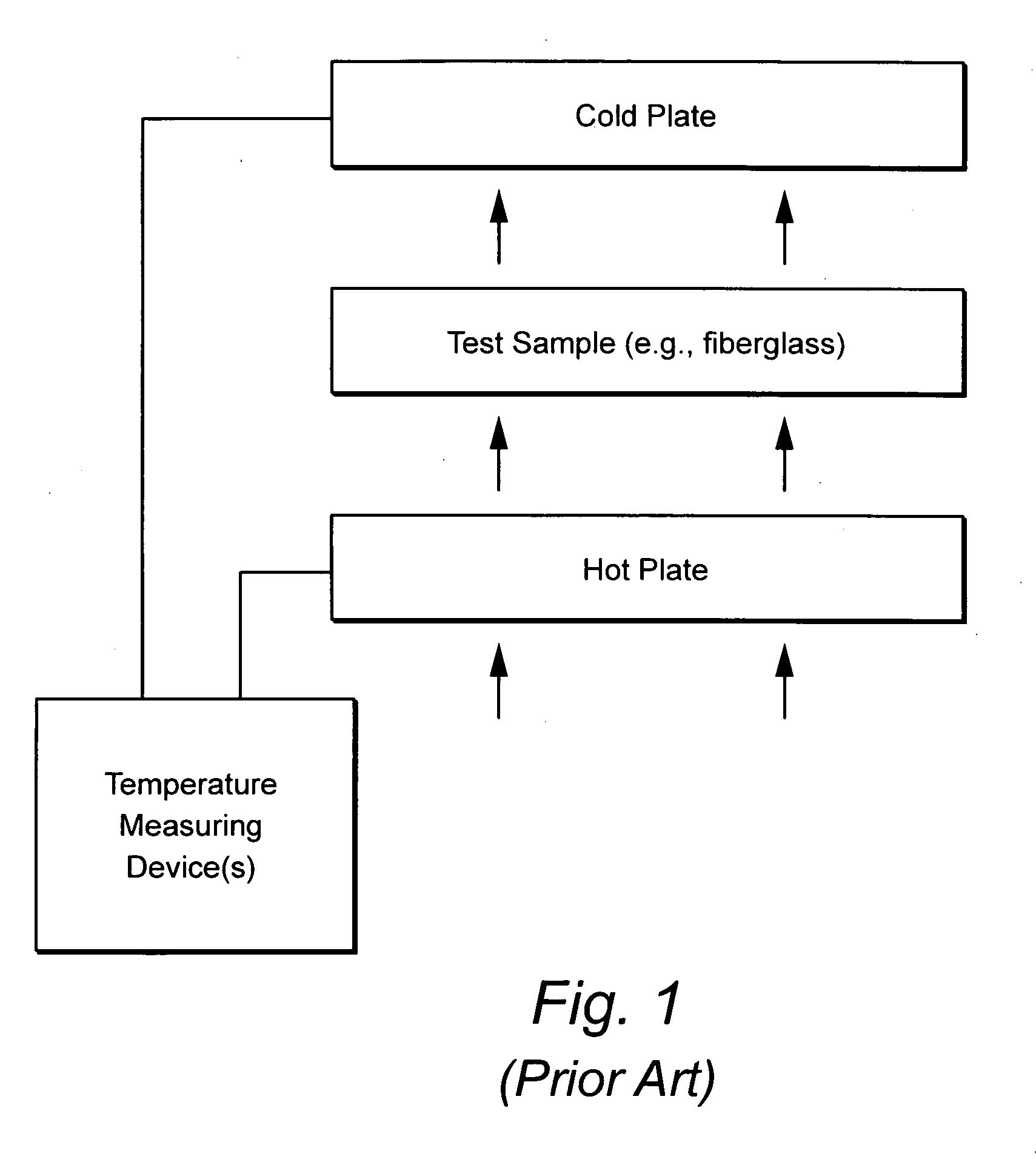
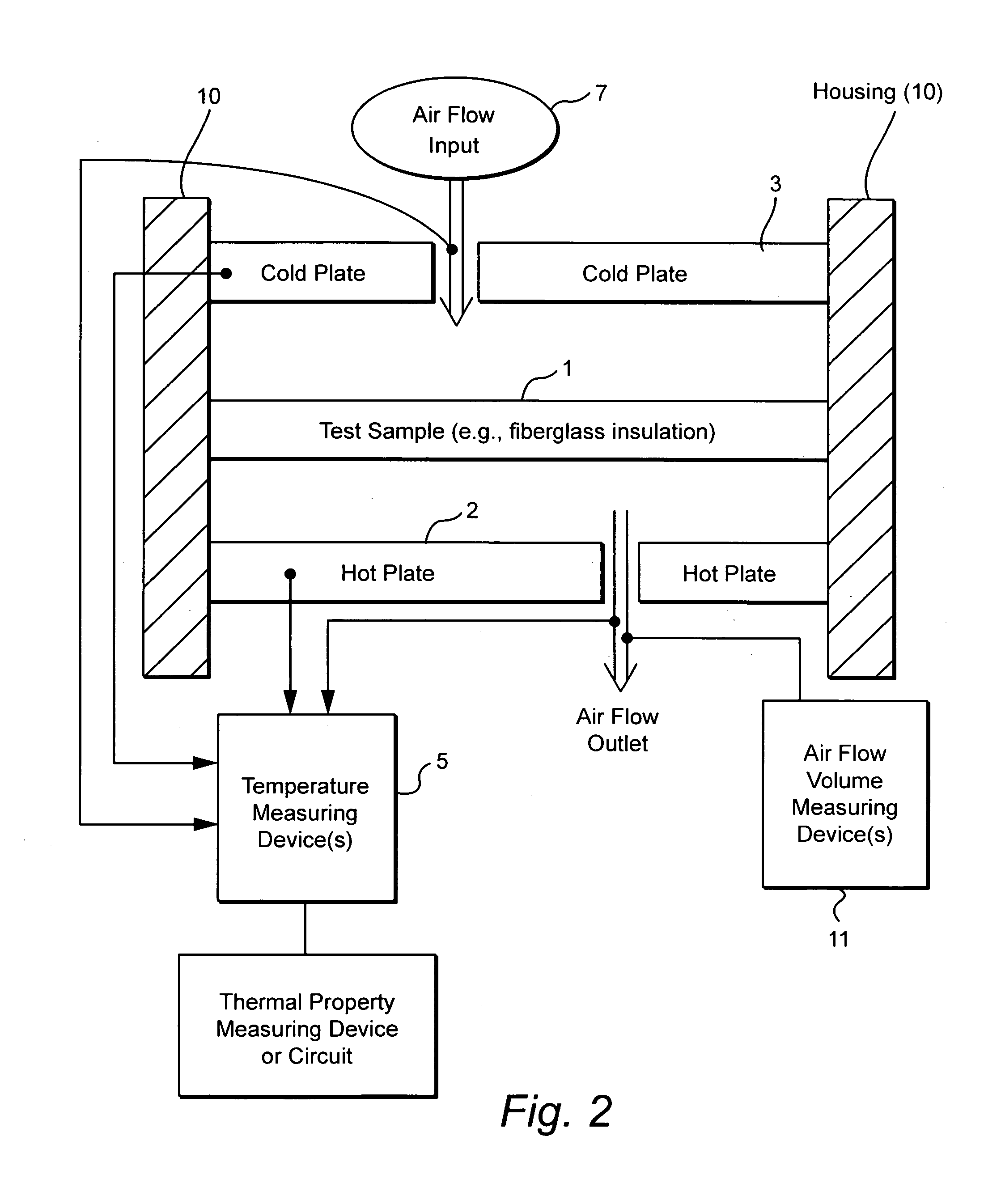
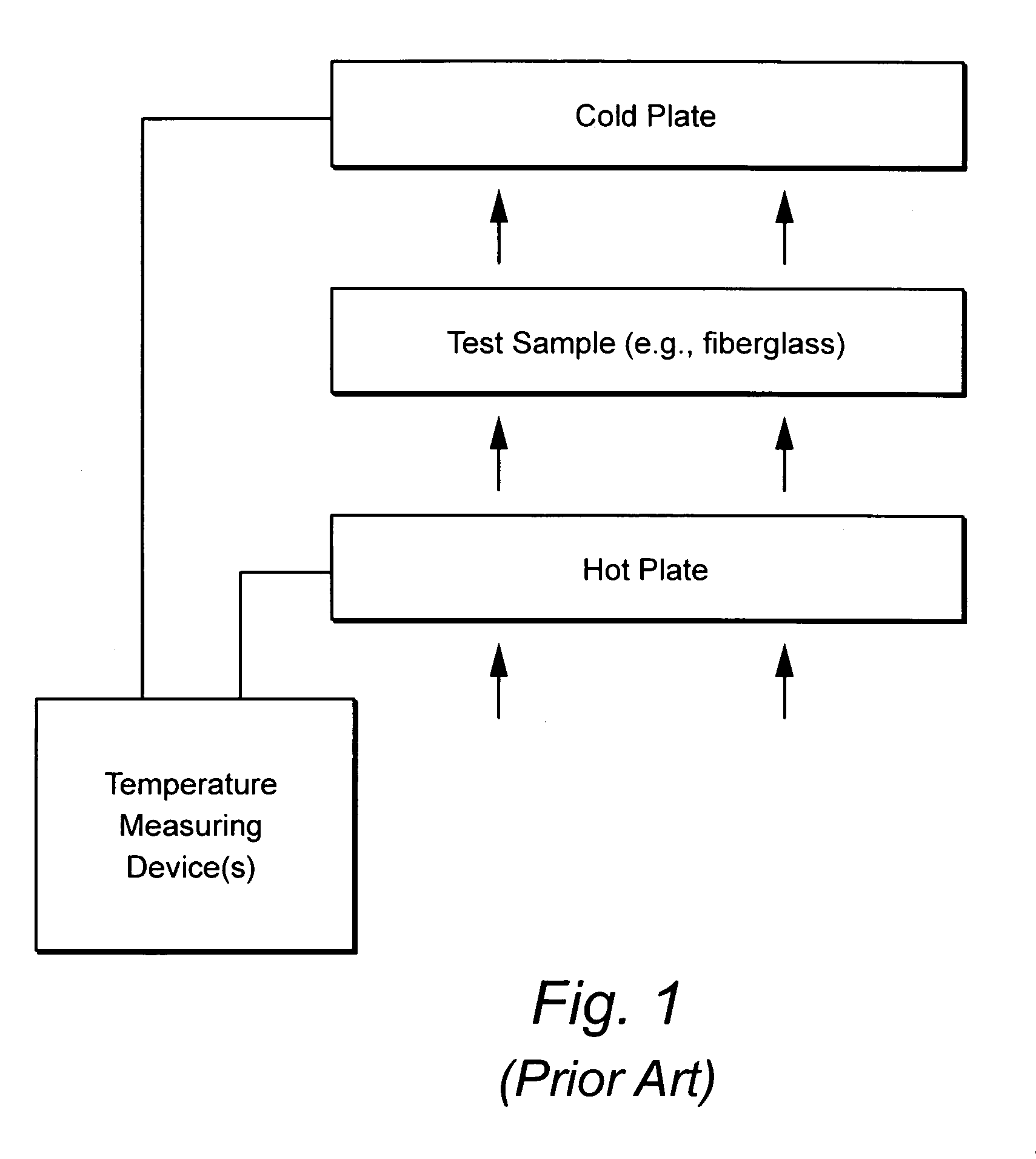
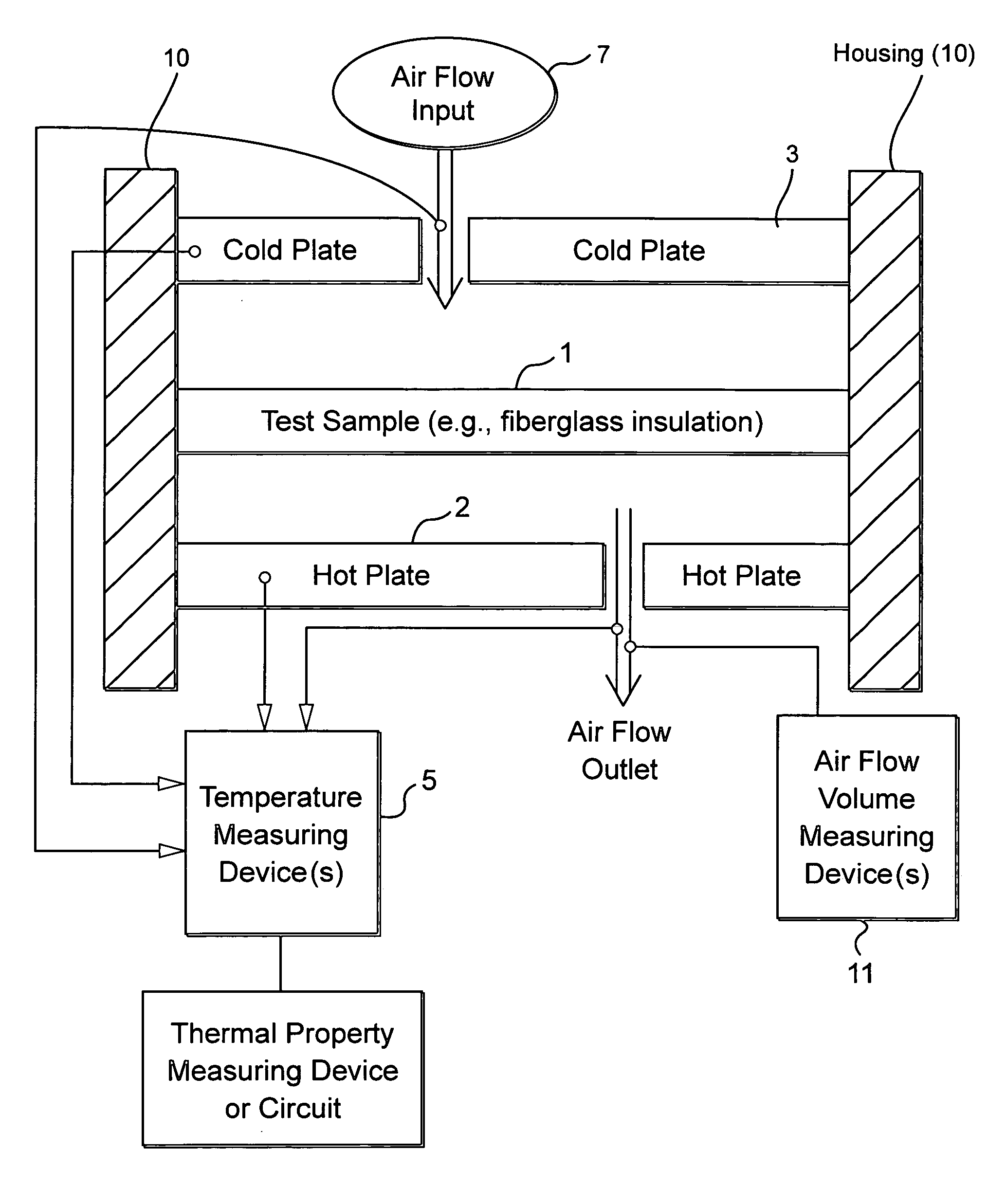
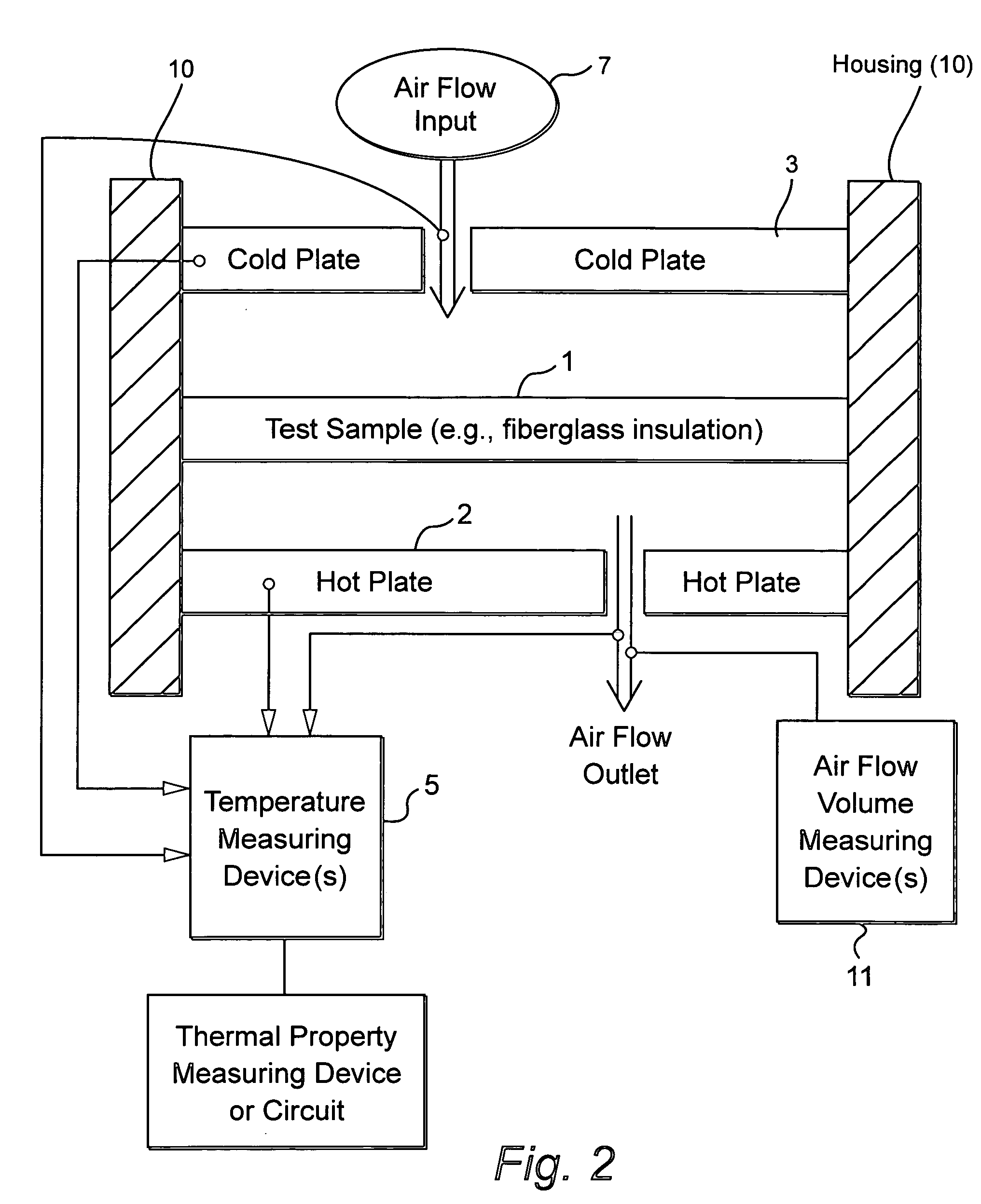
Dynamic heat flow meter for measuring thermal properties of insulation or the like, and corresponding method
A dynamic heat flow meter is provided which introduces a measured air flow into the system adjacent the test sample (e.g., insulation product), for which thermal properties are to be measured. The heat flow meter then measures thermal properties (e.g., thermal conductivity and / or heat capacity) of the test sample taking into account air flow through and / or adjacent the test sample.
Owner:KNAUF INSULATION LLC
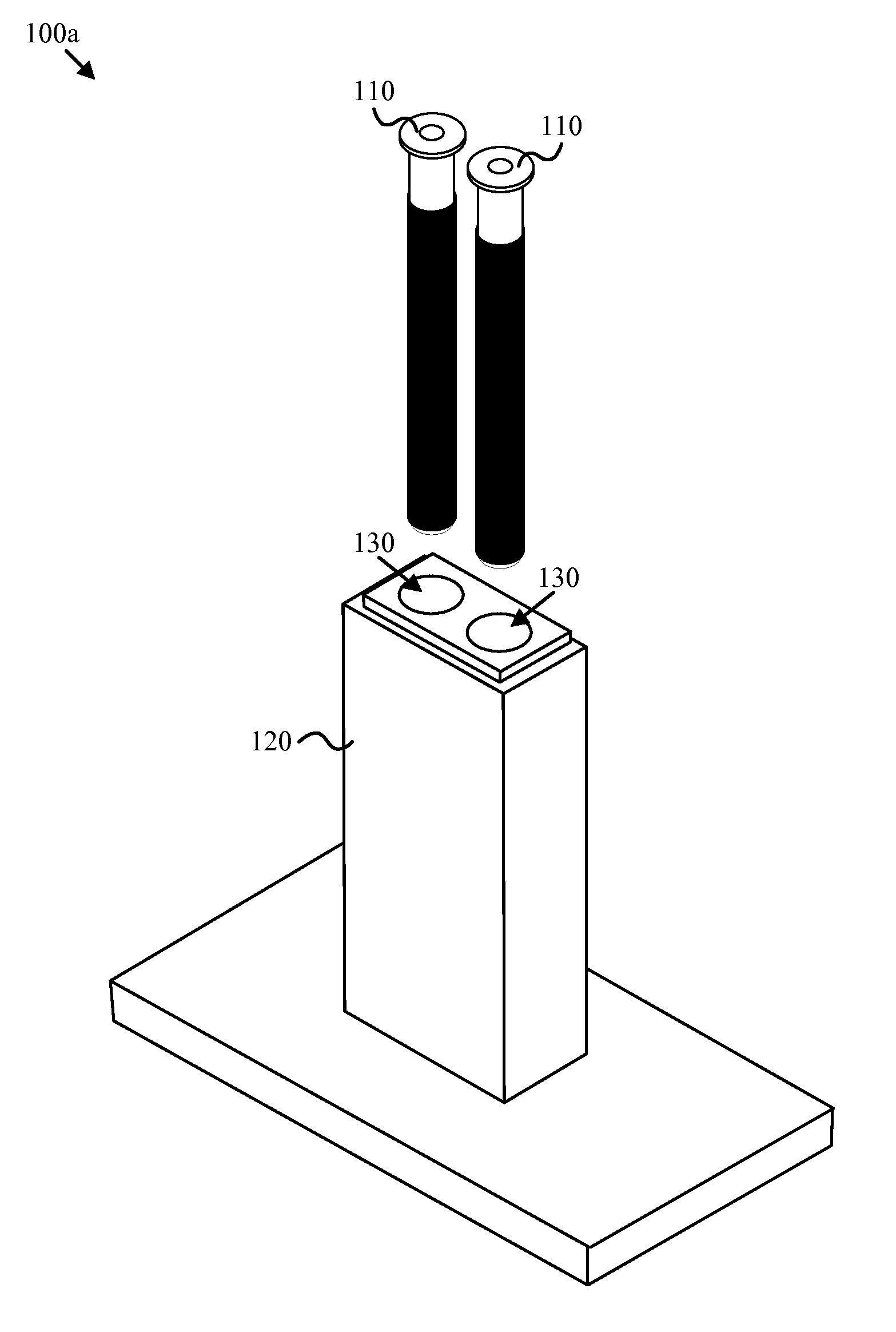
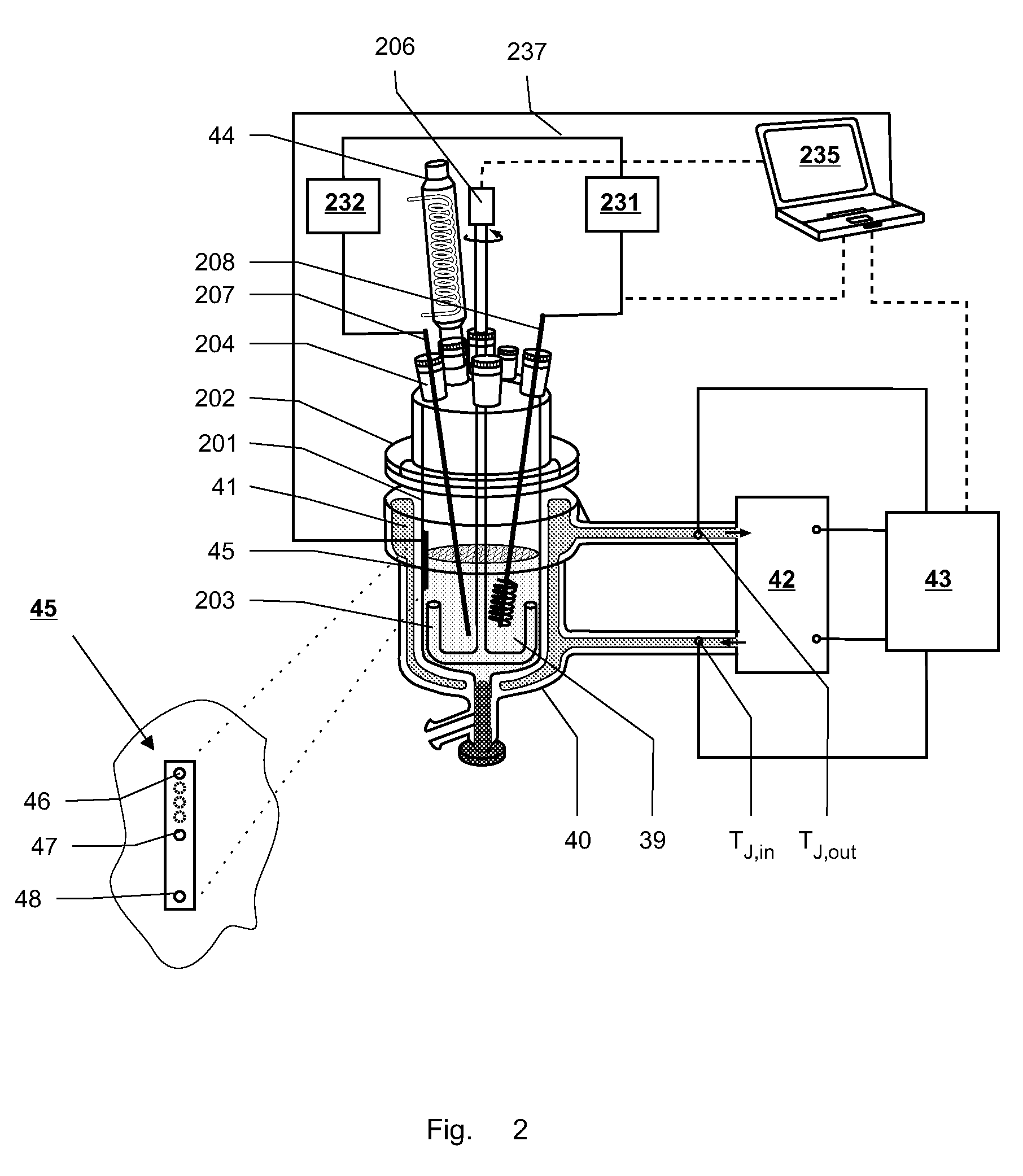
Apparatus and method for determining denaturation thermograms of blood plasma or serum
InactiveUS20140362888A1Thermometers using value differencesMaterial heat developmentEngineeringBlood plasma
An apparatus for determining thermograms of blood plasma or serum includes two or more reaction vessels that each comprise a temperature sensing coil and a heating coil that is coaxial with and exterior to, or interleaved with, the temperature sensing coil. The apparatus also includes a heat conductive body having two or more cavities formed therein for receiving the reaction vessels. A corresponding method includes activating the heating coils of the reaction vessels and collecting temperature data for the reaction vessels with the temperature sensing coils.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Dynamic heat flow meter for measuring thermal properties of insulation or the like, and corresponding method
A dynamic heat flow meter is provided which introduces a measured air flow into the system adjacent the test sample (e.g., insulation product), for which thermal properties are to be measured. The heat flow meter then measures thermal properties (e.g., thermal conductivity and / or heat capacity) of the test sample taking into account air flow through and / or adjacent the test sample.
Owner:KNAUF INSULATION LLC
Method for measuring thermophysical properties of phase change material
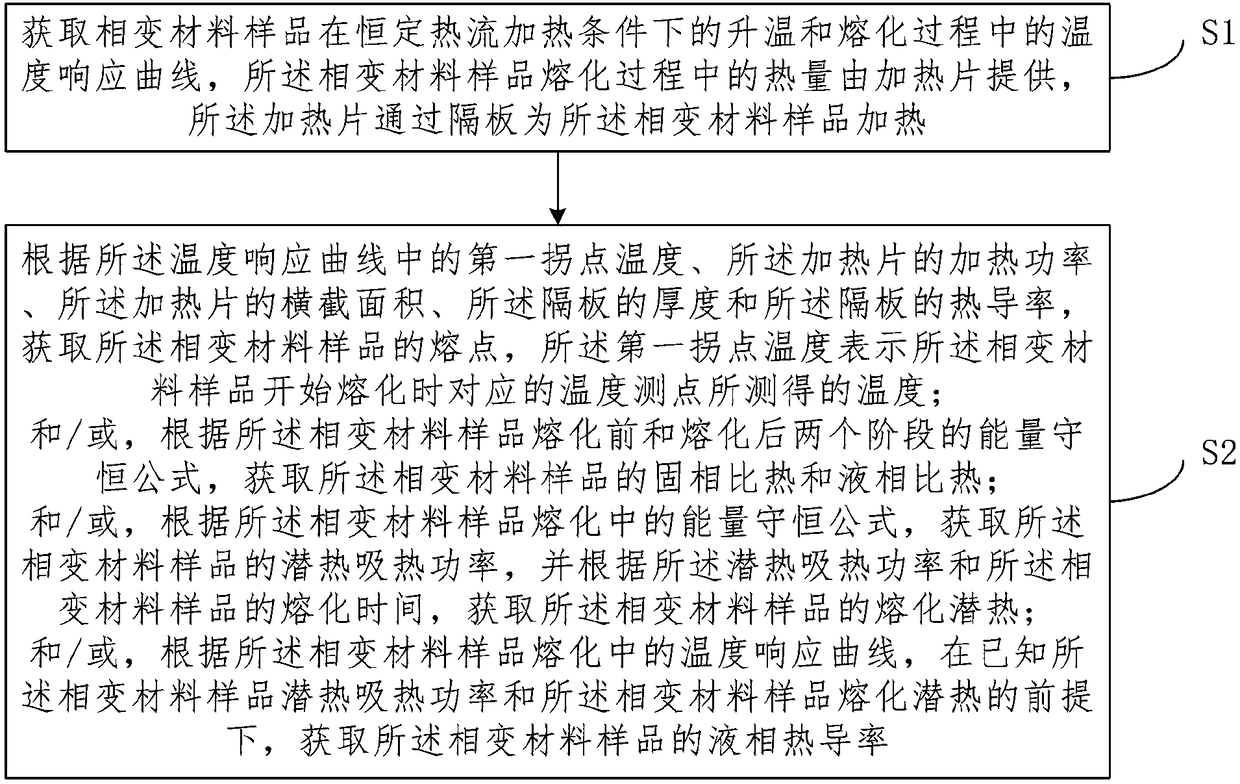
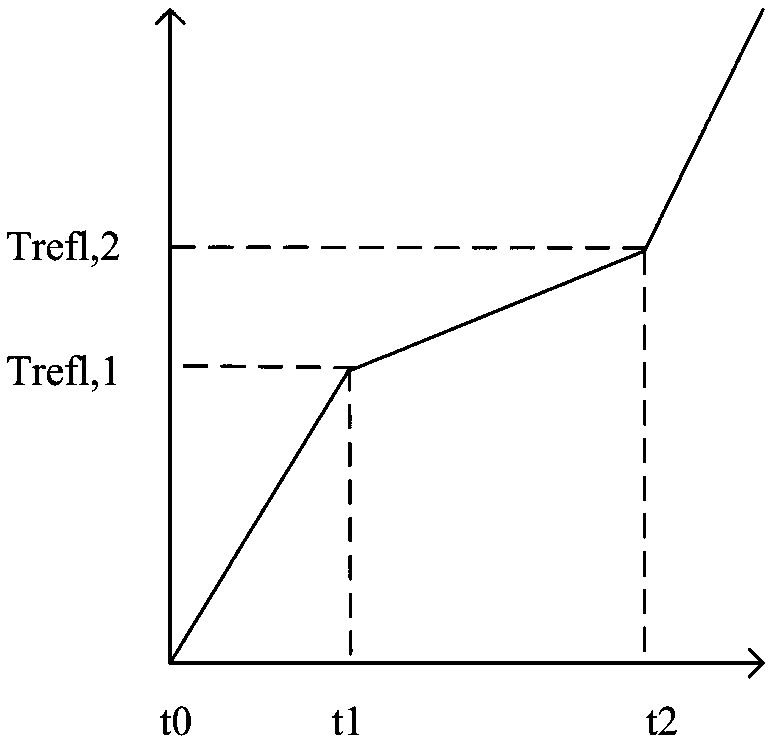
ActiveCN109030543ASimple test methodLow costMaterial heat developmentSpecific heat investigationTemperature responseLarge sample
The invention provides a method for measuring thermophysical properties of phase change material. The method comprises: establishing a theoretical analysis model for a one-dimensional constant heat flow melting process of the phase change material; obtaining a temperature response curve of the phase change material sample during heating and melting process under constant heat flow heating conditions; and using the theoretical analysis model to calculate the thermophysical properties of the phase change material. The thermophysical properties comprises melting point, solid phase specific heat capacity, liquid phase specific heat capacity, latent heat of fusion and thermal conductivity. According to the method for measuring thermophysical properties of phase change material has the advantages of simple device and low cost; the test speed is fast, and the test can be completed in about 10 minutes; the macroscopic large sample can be tested to obtain the macroscopic equivalent thermophysical properties of the composite anisotropic phase change material; a number of important thermophysical data which comprising melting point, solid phase specific heat capacity, liquid phase specific heat capacity, latent heat of fusion and thermal conductivity can be obtained by one measurement.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thermal analysis method for determining content of each phase state ingredient of half crystallization high molecular material
InactiveCN106770427AAccurate and reversible specific heat capacityAccurate Glass Transition TemperatureSpecific heat investigationInvestigating phase/state changeChemistryPhase state
The invention provides a thermal analysis method for determining the content of each phase state ingredient of a half crystallization high molecular material. According to the method, conventional and step type temperature rise modes are respectively used for heating a sample; a StepScan DSC curve is resolved into a reversible specific heat capacity curve and an irreversible specific heat capacity curve; the glass transition position is determined through the discontinuous mutation of the specific heat capacity on the reversible specific heat capacity curve; then, the content of different phase state ingredients of half crystallization molecules is determined according to the specific heat capacity increase and the melting enthalpy on the DSC curve. Through an SSDSC technology, the glass transition is separated out from a dynamic process to obtain the parameters such as the reversible specific heat capacity, the glass transition temperature and the melting enthalpy in the test sample temperature rise process; the glass transition temperature of the half crystallization high molecular material can be obtained; the reversible specific heat capacity corresponding to different temperatures can be accurately obtained; meanwhile, the content of different phase states such as the crystallization state, the flowing amorphous state and the hard amorphous state in the half crystallization high molecular test sample can be calculated according to the specific heat capacity and the melting enthalpy.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Device for testing thermophysical parameters of soil mass sample
InactiveCN106353359APrecise control over the initial stateHigh precisionMaterial heat developmentPreparing sample for investigationThermal probeSoil mass
The invention discloses a device for testing thermophysical parameters of a soil mass sample. The device comprises a sample preparation system and a testing system, wherein the sample preparation system is used for completing preparation of the soil mass sample, and the testing system is used for completing the testing on the thermophysical parameters of the soil mass sample under different thermal loads; the sample preparation system comprises a mini-type compacting device, a metal bar, a sample preparation tube and an external extension tube, and the mini-type compacting device is formed by a base and a compacting hammer; the testing system is formed by high / low temperature alternating humidity-temperature test chamber, a thermal probe and a KD2 Pro thermal characteristic analyzer, and a stainless steel support is arranged at the inner part of the high / low temperature alternating humidity-temperature test chamber and is used for placement of the sample preparation tube filled with the soil mass sample. Actual simulation under different thermal load environments is realized through the device, and the thermophysical parameters of the soil mass sample are accurately tested. According to the device disclosed by the invention, the structure is simple, the operation is convenient, the precision of a testing result is higher, convenience can be provided for research and application of a geotechnical engineering thermoanalysis field, and engineering application and large-scale promotion are facilitated.
Method and device for determining specific heat capacity
ActiveUS7712956B2Improve accuracyEasy to exportMaterial heat developmentDigital computer detailsEnergy variationThermostat
The specific heat capacity (cp) of a medium is determined using a calorimeter with a reactor (1), a stirrer (3), a first thermostat for providing an inner heat balance, a second thermostat, means for providing an outer heat balance and a central control unit (35). The method uses the steps of: applying a modulated energy profile to the medium, inside the reactor (1), under near isothermal conditions; monitoring the resulting energy changes of: the medium, the reactor (1), the first thermostat, the second thermostat and / or the outer heat balance means as a function of time; determining the respective inner and outer heat balances independently from each other at predefined time intervals; and calculating the overall heat transfer coefficient (UA) and the specific heat capacity of the medium (cp) simultaneously and independently from each other as a function of time from the inner and outer heat balances.
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO GMBH
Detection of Carbon Nanotubes by Microwave-Induced Heating
ActiveUS20130259085A1Material analysis using microwave meansSpecific heat investigationCarbon nanotubeMicrowave irradiation
The present invention includes a method, systems and devices for the detection of carbon nanotubes in biological samples by providing a sample suspected of having one or more carbon nanotubes; irradiating the sample with a microwave radiation, wherein the carbon nanotubes absorb the microwave radiation; and detecting and measuring the one or more thermal emissions from the carbon nanotubes.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
Method and measuring apparatus for determining specific quantities for gas quality
ActiveUS10101186B2High densityImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial thermal conductivityMeasurement deviceStreamflow
Owner:MEMS
Liquid-condition detection sensor
A liquid-condition detection sensor (1) including a sensor element (51), at least a portion of which contacts a urea aqueous solution; connection terminals (52) fixedly attached to the sensor element (51); connection cables (53) which electrically communicate with the concentration sensor element (51) via the connection terminals (52); an inner tube (42) which holds the concentration sensor element (51) at a distal end portion (421) by use of a holder member (55) and surrounds a portion of the connection cables (53) and the entire connection terminals (52); and a separator formed from a material having rubberlike elasticity (54) including a terminal-inner-tube-insulating portion (542) which intervenes between the connection terminals (52) and the inner tube (42) to thereby insulate the connection terminals (52) and the inner rube (42) from one another.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
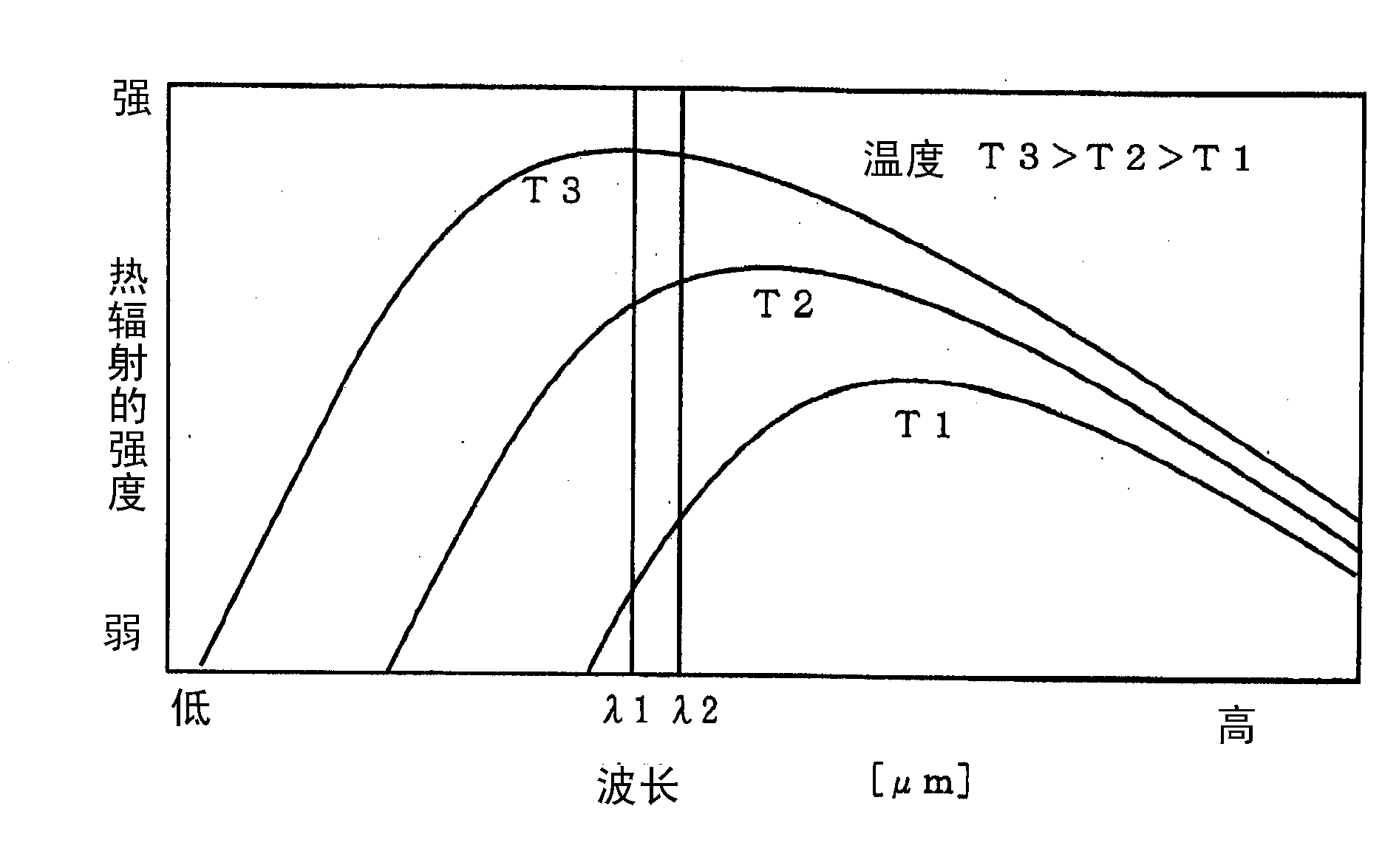
Specific Heat Measuring Method and Instrument
ActiveUS20080025365A1Reduce instrument costSimple configurationMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentVolumetric Mass DensityInstrumentation
In order to measure specific heat, the measurement time is very long and the instrument is very expensive. The specific heat may be calculated based on the thermal time constant obtained from the change of the sample temperature when the predetermined amount of sample with known density at the first temperature is introduced in the environment at the second temperature. This measuring method can use the oscillatory densitometer. The predetermined amount corresponds to the volume of the sample to be introduced in the oscillatory densitometer, the density is a measurement result of the oscillatory densitometer, and the thermal time constant corresponds to the time constant of the oscillation period of the oscillatory densitometer.
Owner:KYOTO ELECTRON MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for determining acceptance/rejection of fine diameter wire bonding
ActiveCN102918384AImprove reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementInfraredEmissivity
Owner:JTEKT CORP
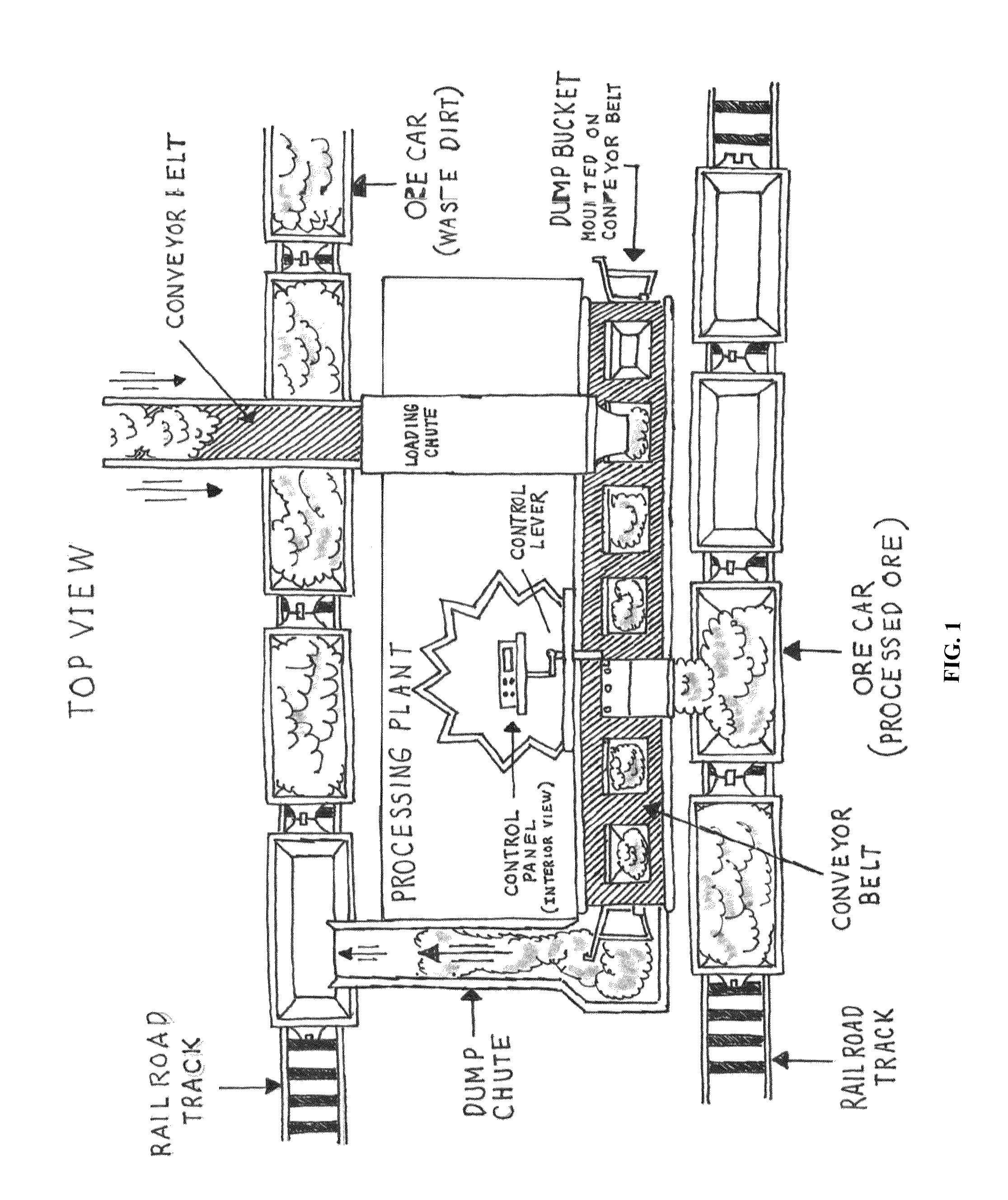
Mineral processing
Owner:A N ENTERPRISES
Determination of fluid parameters
ActiveUS20180038811A1Compact and cost efficient designEfficiently determinedMaterial heat developmentFuel testingEngineeringHeat capacity
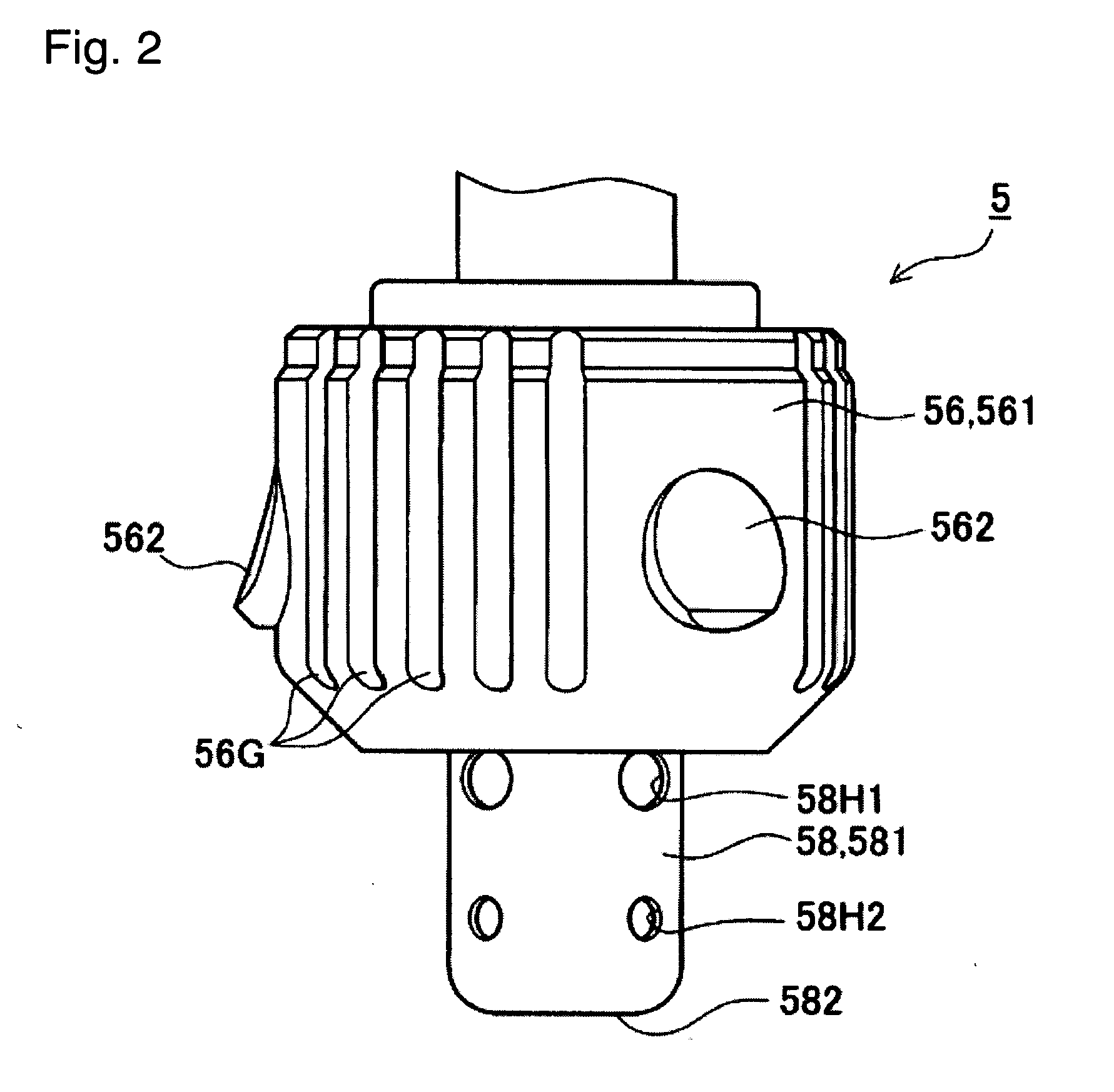
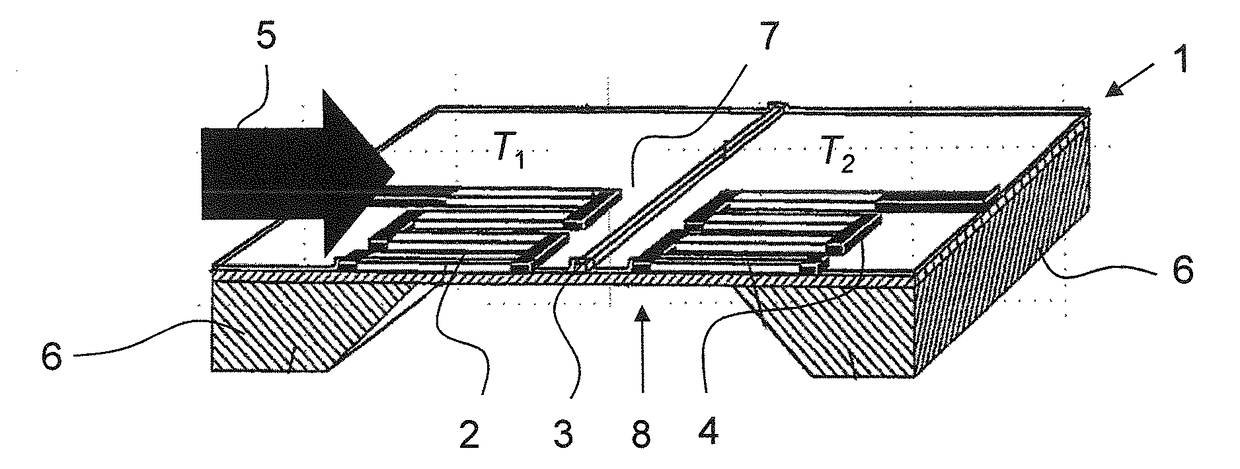
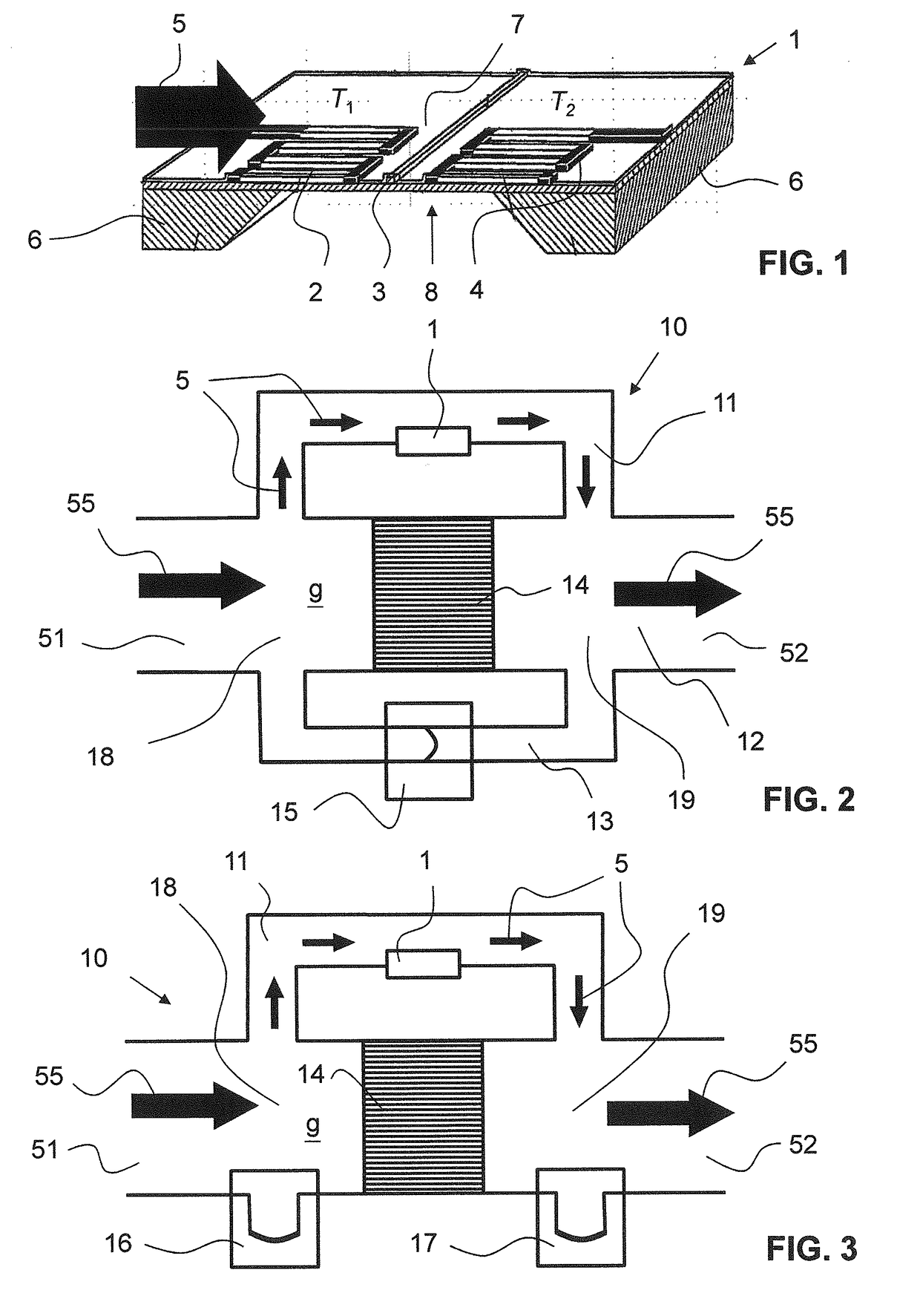
A method for determining fluid parameters, such as a heat capacity cpp, a calorific value Hp, a methane number MN, and / or a Wobbe index WI, of an unknown fluid (g). An unknown flow (55) of the fluid (g) is set in a sensor device (10), the sensor device (10) comprising a thermal flow sensor (1) and a pressure sensor device (15) for measuring at least one temperature value T1, T2, a further parameter, and differential pressure value Δρ over a flow restrictor (14). Using these measurement parameters T1, T2, Δp and calibration data, the calorific value Hp, and / or the Wobbe index WI, or parameters indicative thereof, of an unknown fluid (g) are calculated. The invention also relates to such a sensor device (10) and to a computer program product for carrying out such a method.
Owner:SENSIRION AG
Batch and continuous methods for evaluating the physical and thermal properties of films
ActiveUS20180066940A1Fast and reliableIncrease competitionMaterial thermal conductivityPermeability/surface area analysisEngineeringThermal methods
Thermal methods and systems are described for the batch and / or continuous monitoring of films and / or membranes and / or electrodes produced in large-scale manufacturing lines. Some of the methods described include providing an energy input into a film, measuring a thermal response of the film, and correlating these to one or more physical properties and / or characteristics of the film.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
Test method capable of simulating thermophysical parameters of soil mass under different thermal loads
InactiveCN106442603APrecise control over the initial stateConvenient researchMaterial heat developmentPreparing sample for investigationThermal probeTest fixture
The invention discloses a test method capable of simulating thermophysical parameters of a soil mass under different thermal loads. A test device is arranged and comprises a sample preparation system and a test system, wherein the sample preparation system comprises a small compactor, a sample preparation tube, a metal rod and an external extension tube, the sample preparation tube is processed from a PVC tube and has the inner diameter being 55.0 mm, the height being 90.0 mm and the wall thickness being 3.0 mm. A test system comprises a high / low-temperature cyclic damp heat test box, a thermal probe and a KD2 Pro thermal characteristic analyzer. By the aid of the device, real simulation in different thermal load environments is realized and the thermophysical parameters of a soil mass sample are tested accurately. The method adopts a simple principle, is convenient to operate, easy to master, capable of simulating different thermal load working conditions and can bring convenience for research and application in the geotechnical engineering thermal analysis field, the test result accuracy is higher, and engineering application and mass popularization are facilitated.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
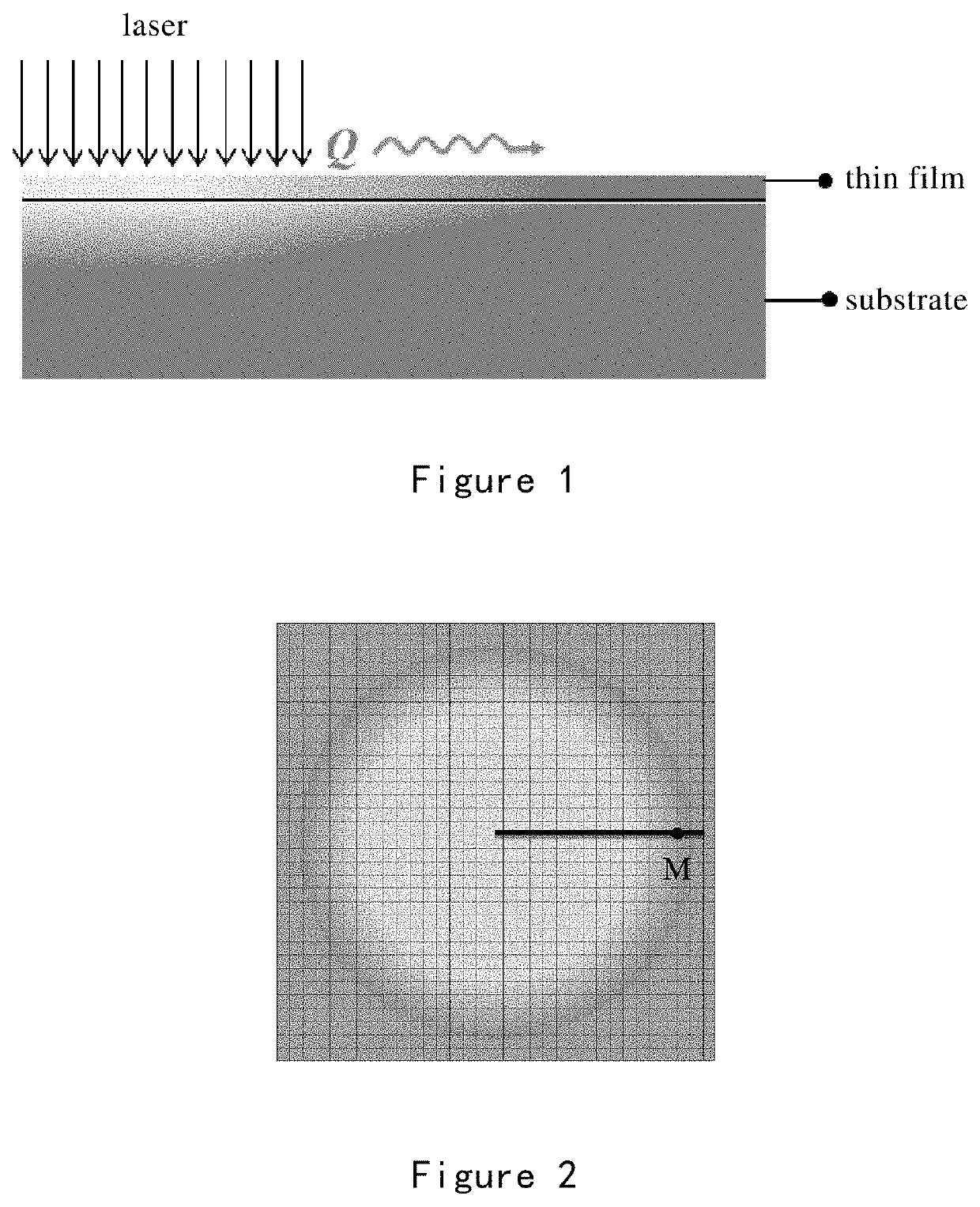
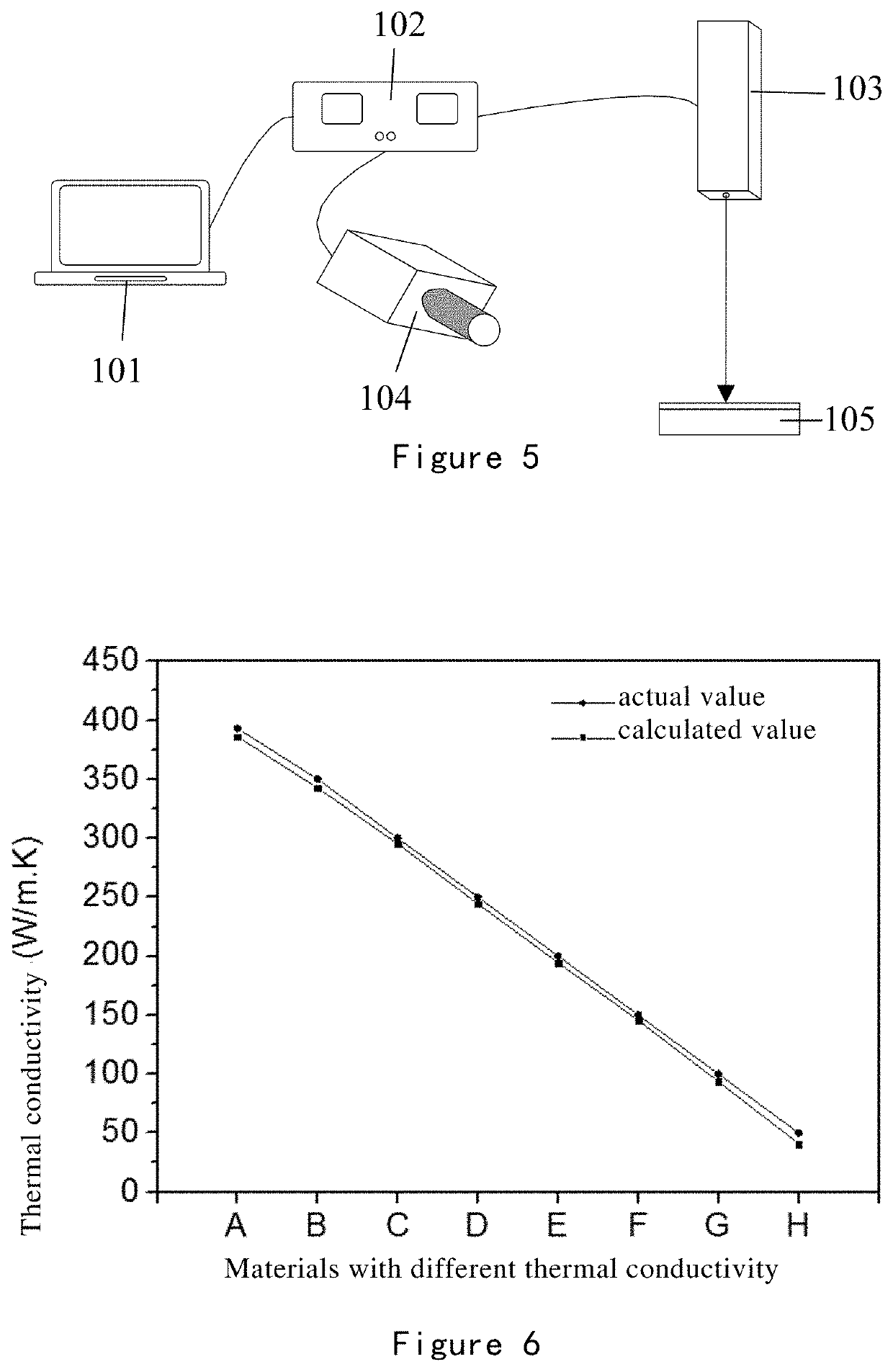
Method and apparatus for rapid measurement of thermal conductivity of a thin film material
ActiveUS20190391095A1Quick measurementSimple structureThermometer detailsMaterial thermal conductivityFast measurementLaser light
The invention discloses a method and a apparatus for rapid measurement of thermal conductivity of a thin film material. The apparatus comprises a control device, a clock synchronizer, a laser, a rapid thermometer and a thermal conductivity output device; the control device and the clock synchronizer are signally connected, and the clock synchronizer is simultaneously signally connected with the laser and the rapid thermometer; in the working state, the control device sends a start signal to the clock synchronizer, and the laser and the rapid thermometer coordinately cooperate, and the laser emits laser light to the surface of the sample; at the same time, the rapid thermometer captures the surface temperature of the sample at the same specified position at different time points during the heating of the sample, and inputs the measured data into the thermal conductivity output device to obtain the thermal conductivity parameter. The apparatus of the invention has simple structure. The method of the invention is efficient and accurate. It can provide reliable parameter data for the thermal properties of various current ultra-thin semiconductor films.
Owner:INFINITE MATERIALS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com