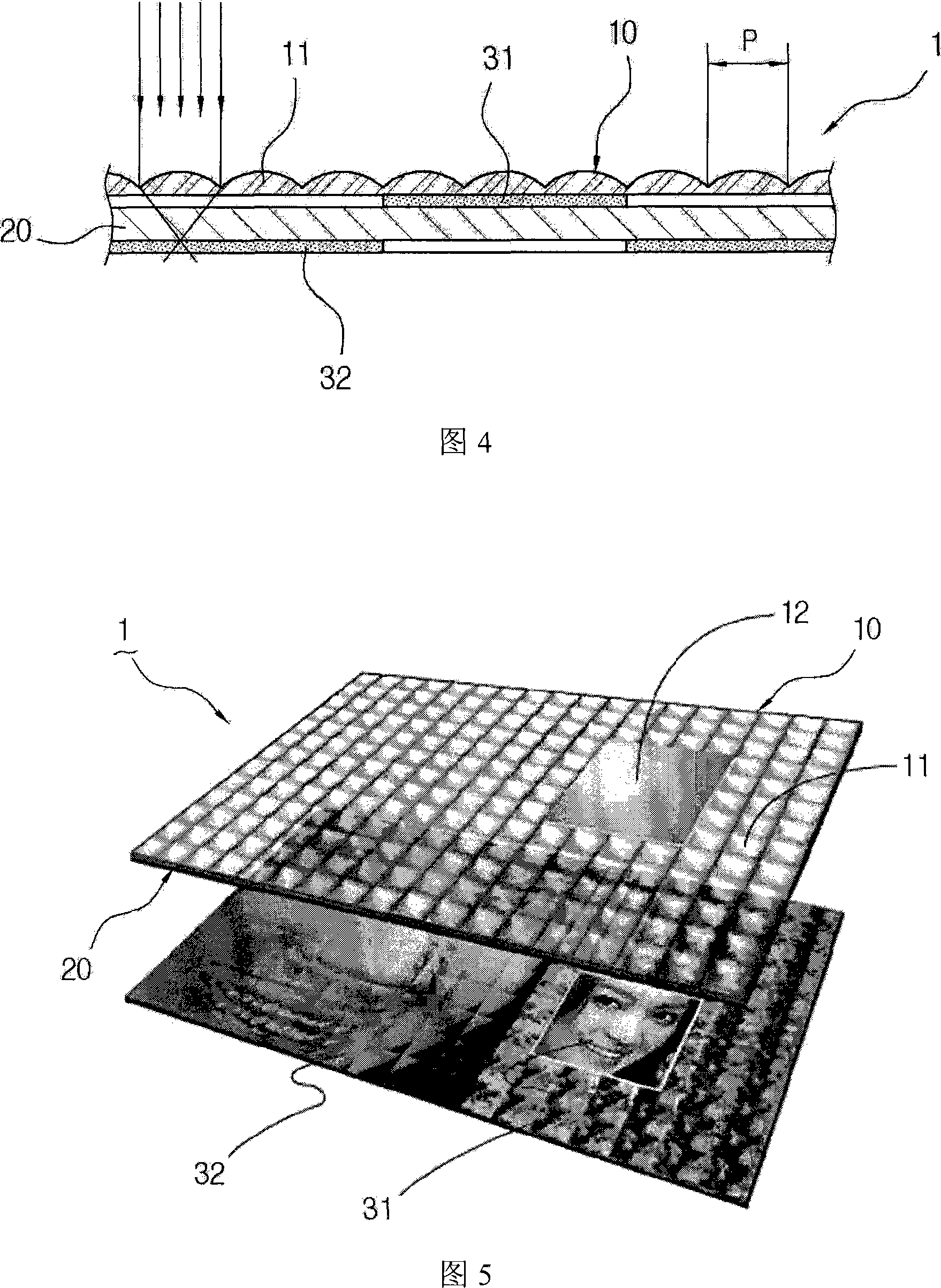
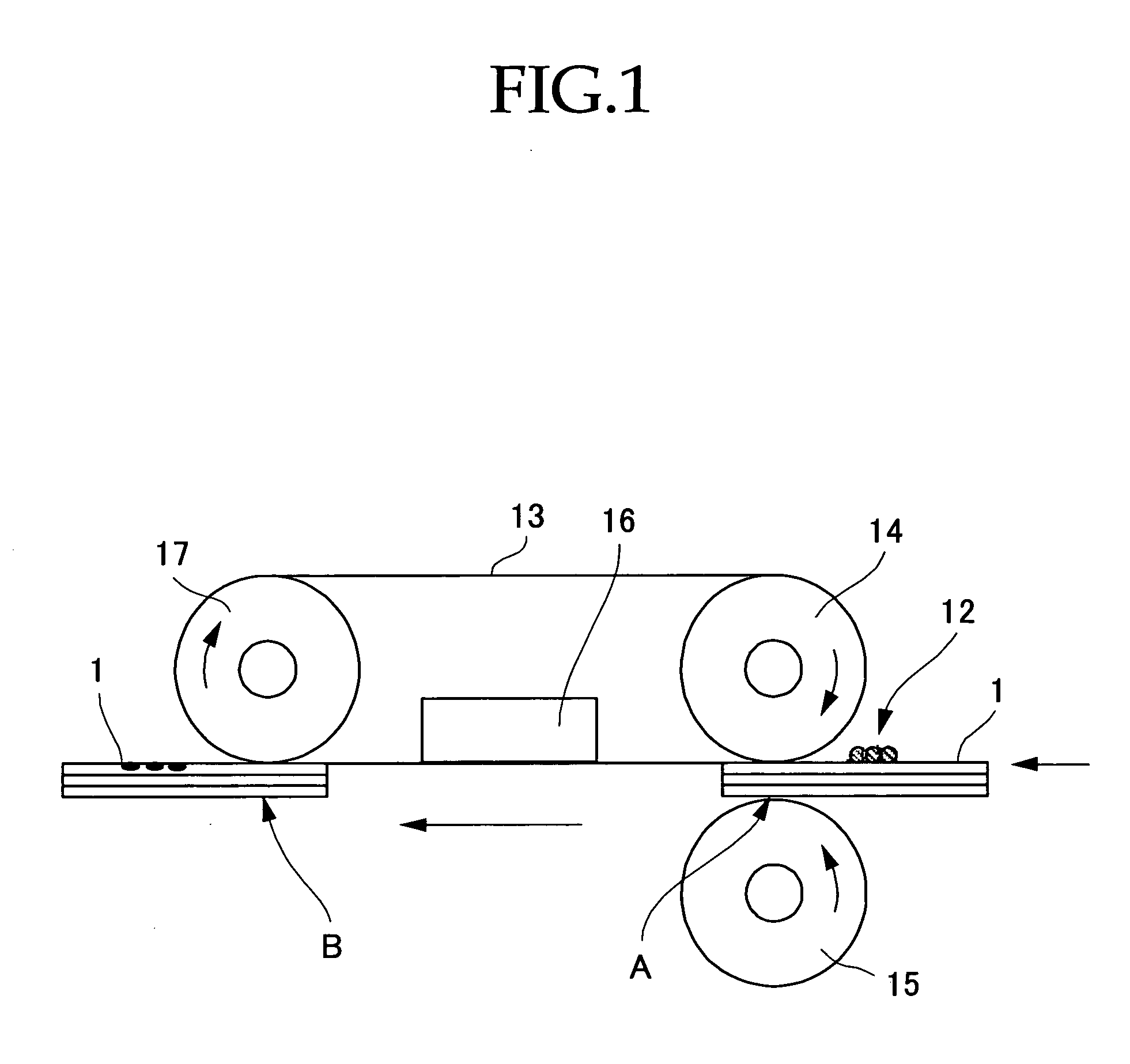
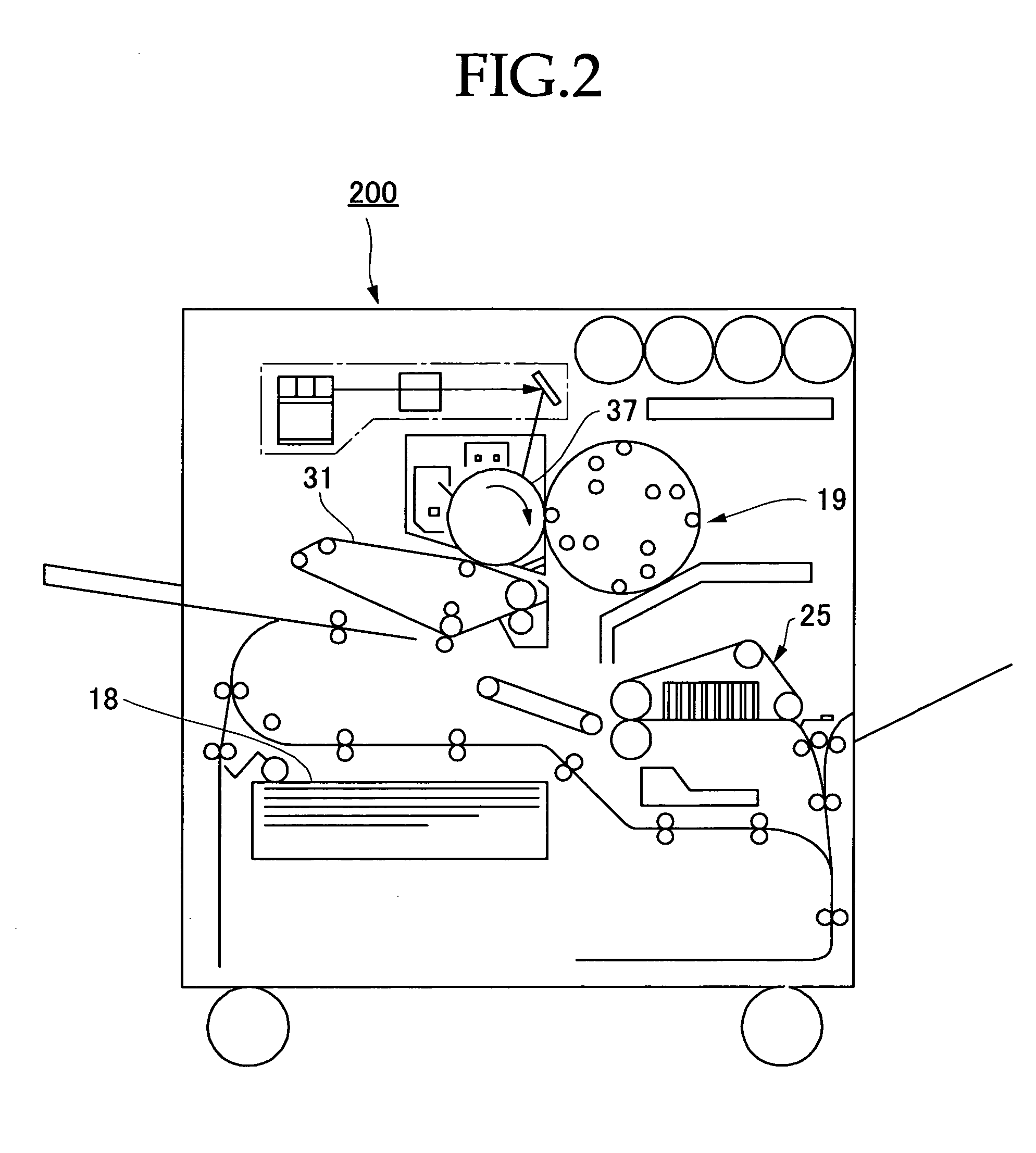
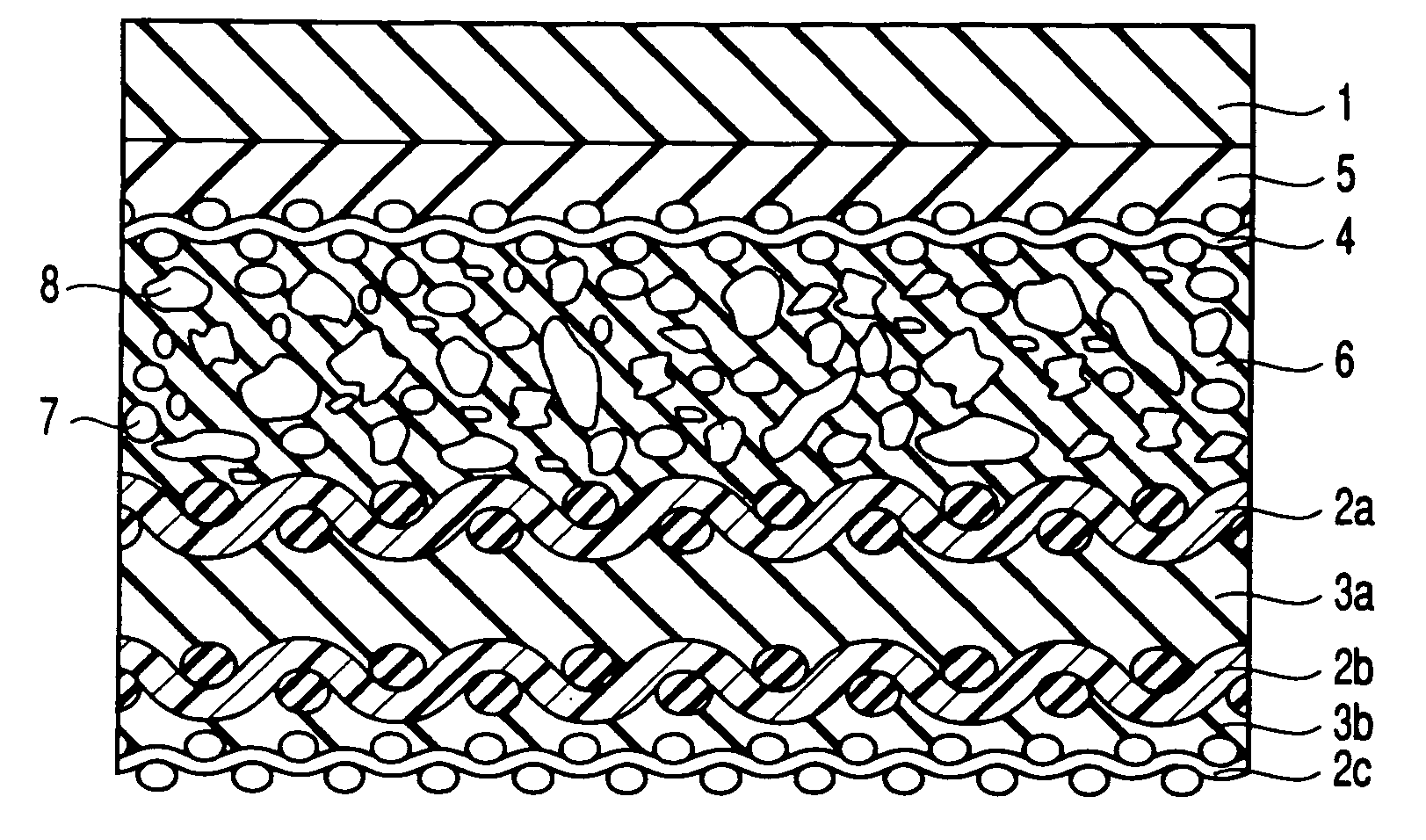
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
120results about "Photographic equipment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
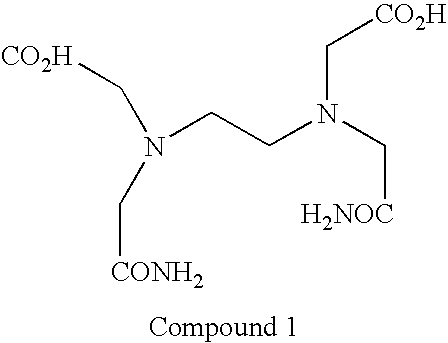
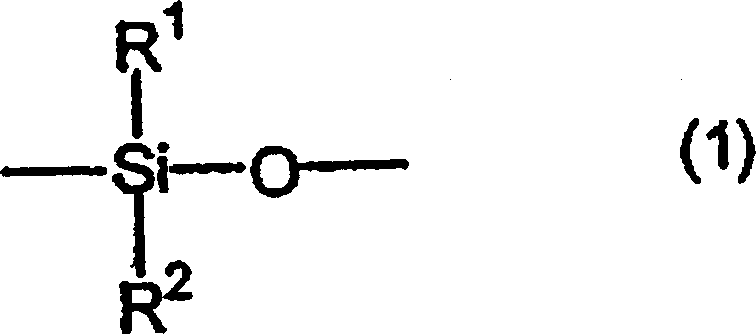
Resin composition
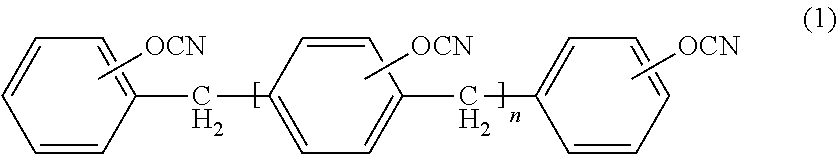
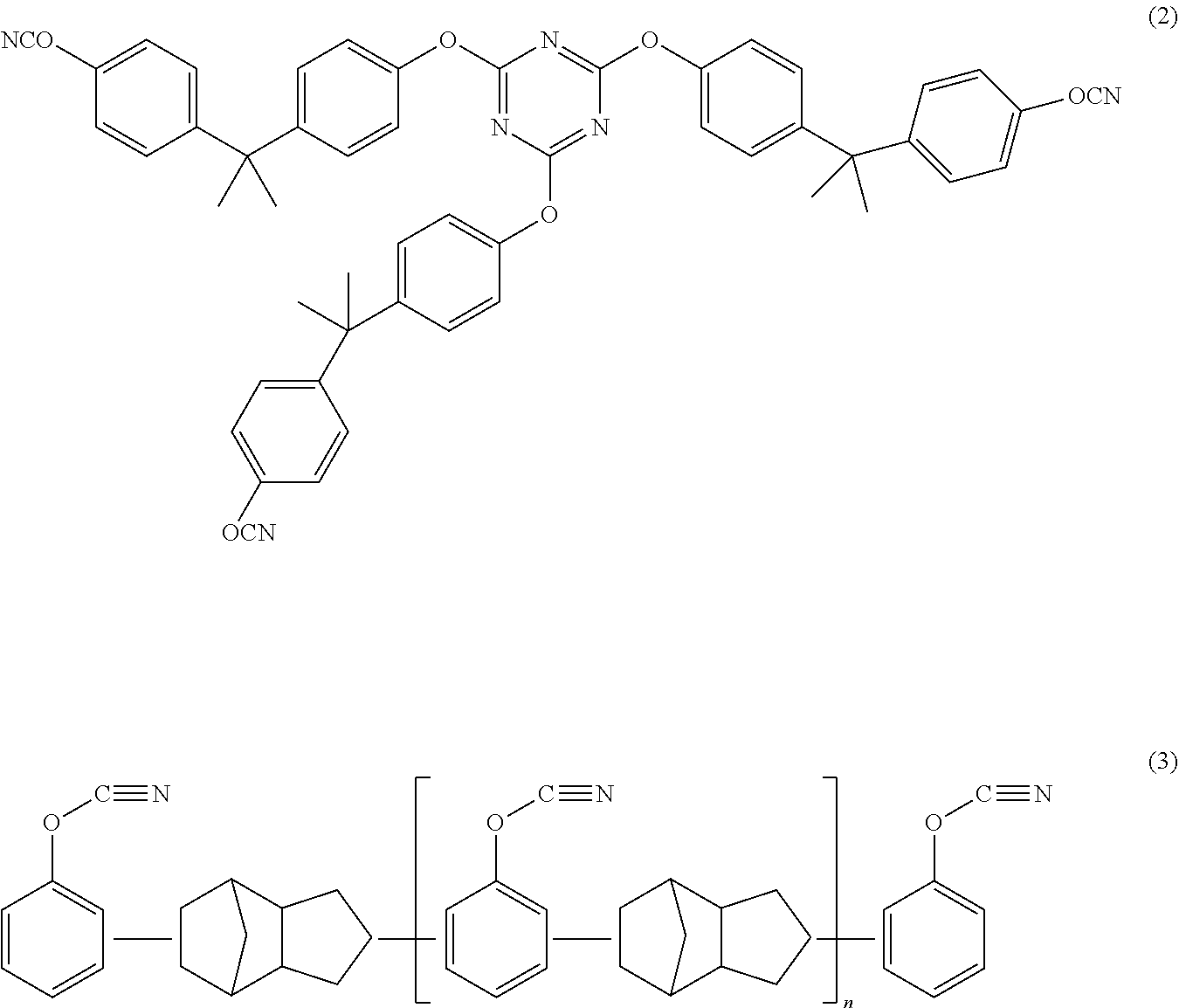
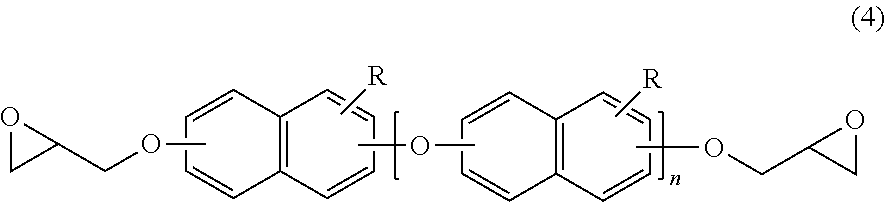
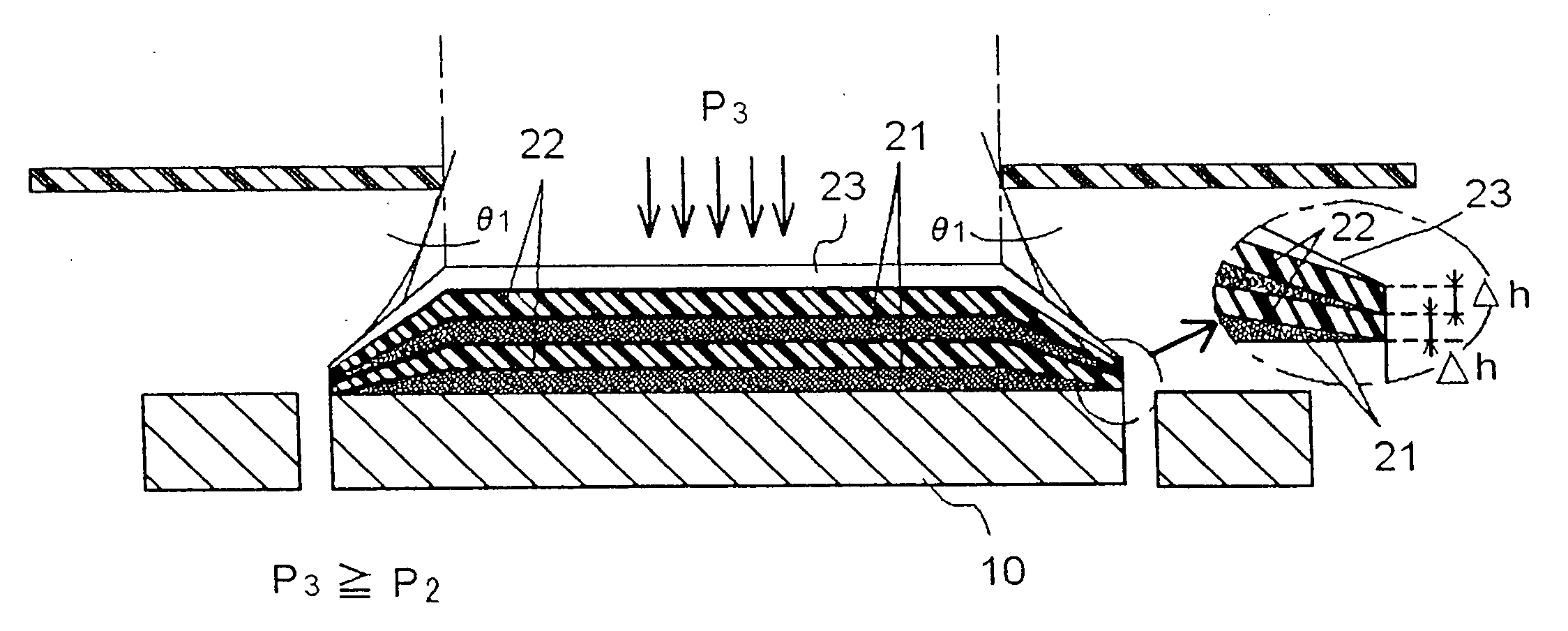
A resin composition which is low in a roughness of an insulating layer surface and capable of forming thereon a plated conductor layer having a sufficient peel strength in a wet roughing step and which is excellent in dielectric characteristics and a coefficient of thermal expansion, is disclosed. The resin composition contains a cyanate ester resin and a specified epoxy resin.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Density filter, method of forming the density filter and apparatus thereof
A film coating method enables, when forming film layers in response to optical characteristics on a substrate, to coat gradation range layers of decreasing thickness without distributions, and to coat films on a plurality of substrates at the same time. The gradation range layer is formed by sputtering evaporation targets of dielectric substances with an introduction gas, followed by forming the films with compounds generated by applying a reactive gas to the films.
Owner:NISCA KK
Temporary Adhesive Camera Mount
InactiveUS20150177597A1Transportation and packagingSynthetic resin layered productsAdhesiveEngineering
A removable adhesive base mount is structured to couple a camera mount system to a capture surface such as a sports board, a helmet, a vehicle, and the like. An upper camera mount component securing a camera couples to a lower camera mount component, which in turn couples to the removable adhesive base mount. The removable adhesive mount includes a base mount component, a foam component, a separating component and an adhesive component. Stretching the adhesive component decouples the adhesive component from the capture surface and the separating component thereby decoupling the removable adhesive base mount from the capture surface.
Owner:GOPRO
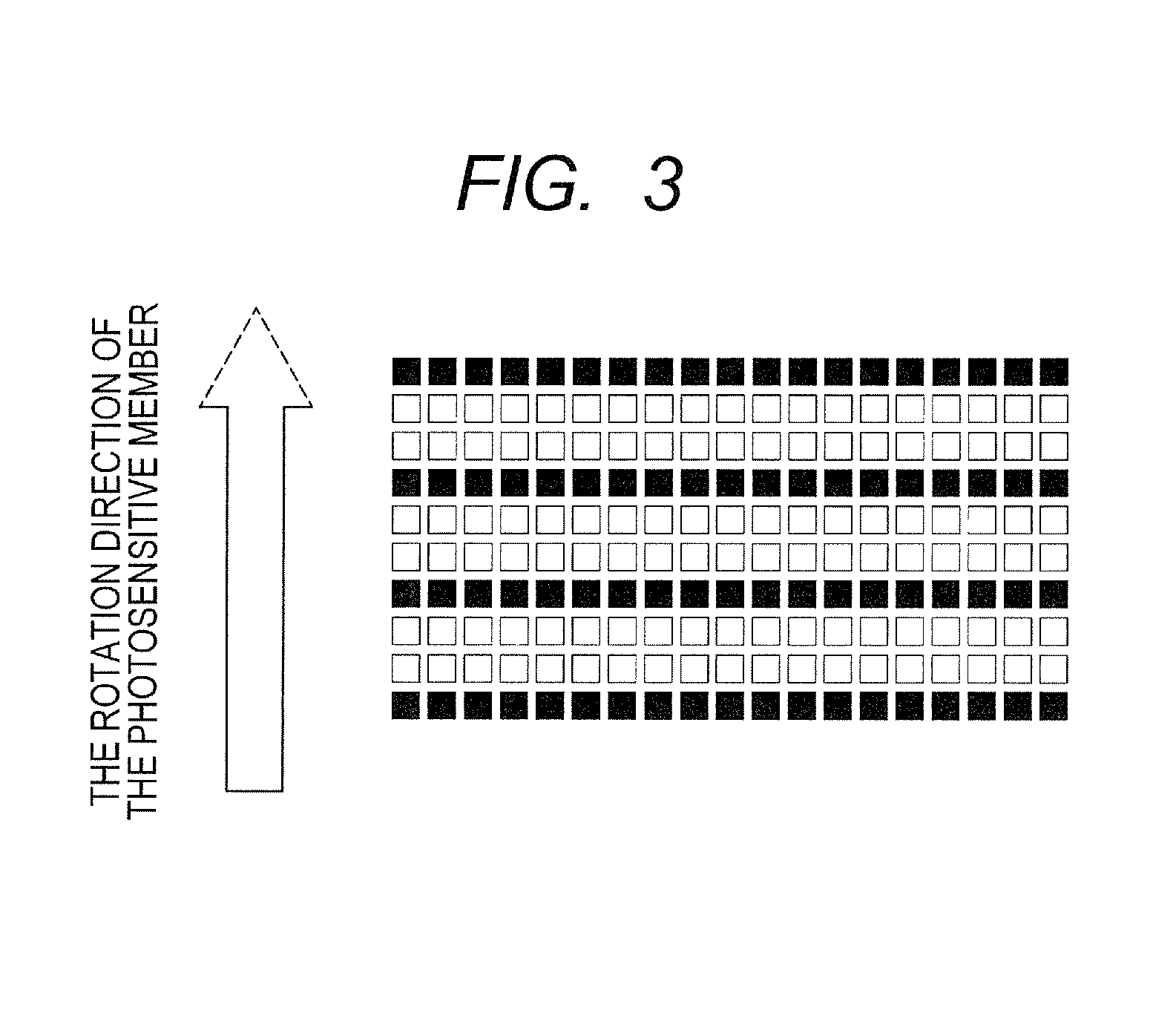
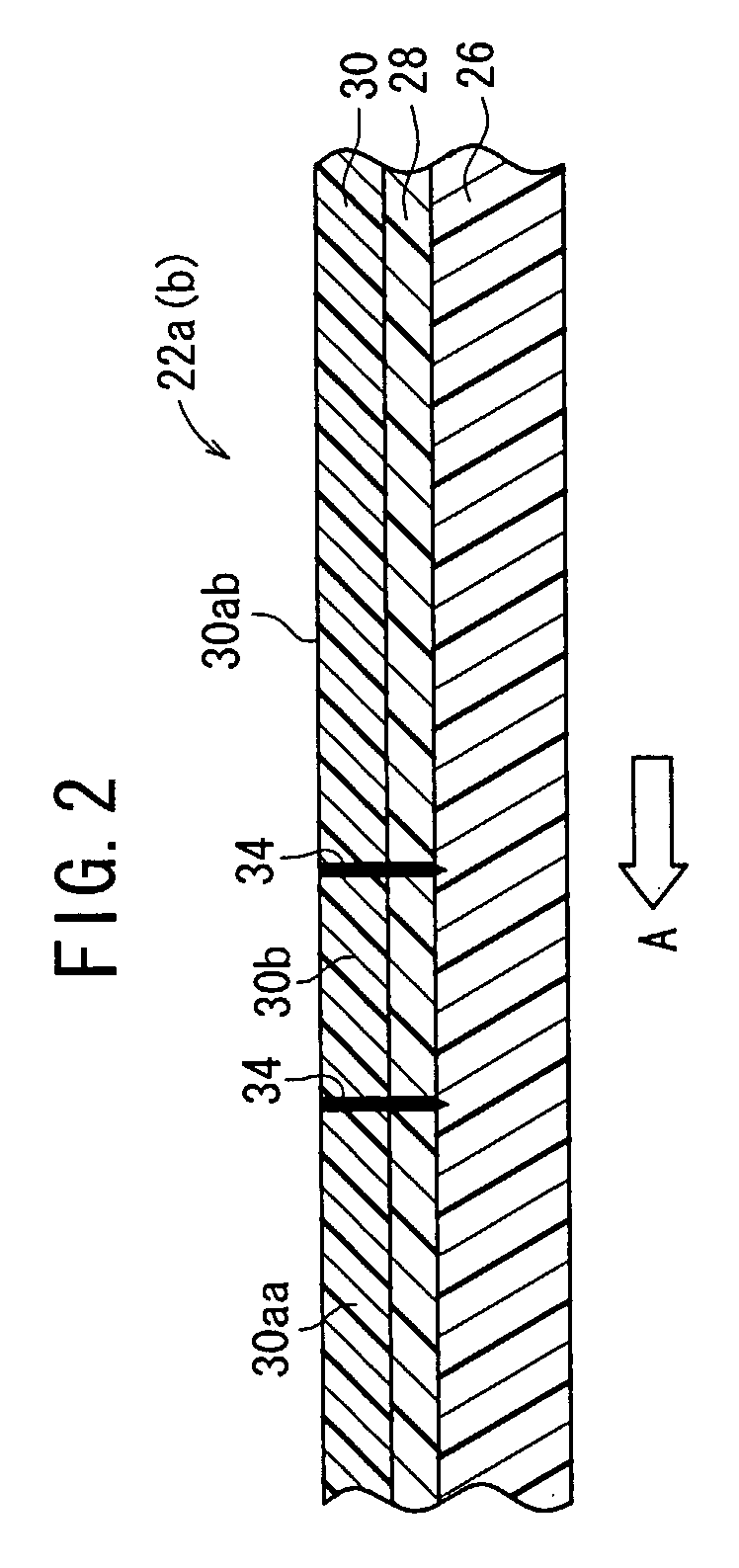
Member for electrophotography, process cartridge and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS9360789B1Synthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageSurface layerSurface distance
It is intended to provide a member for electrophotography that can inhibit the adhesion of dirt to the outer surface. The member for electrophotography has a substrate, an elastic layer on the substrate, and a surface layer on the elastic layer. The surface layer contains a binder resin and first particles, the surface of the surface layer has first convexes derived from the first particles, the first particles resulting in the first convex has an average inter-particle surface distance of 50 nm or less, the first particles have a number-average particle diameter of 200 nm or more and 1000 nm or less, and the surface of the surface layer has a universal hardness of 1.0 N / mm2 or more and 7.0 N / mm2 or less.
Owner:CANON KK
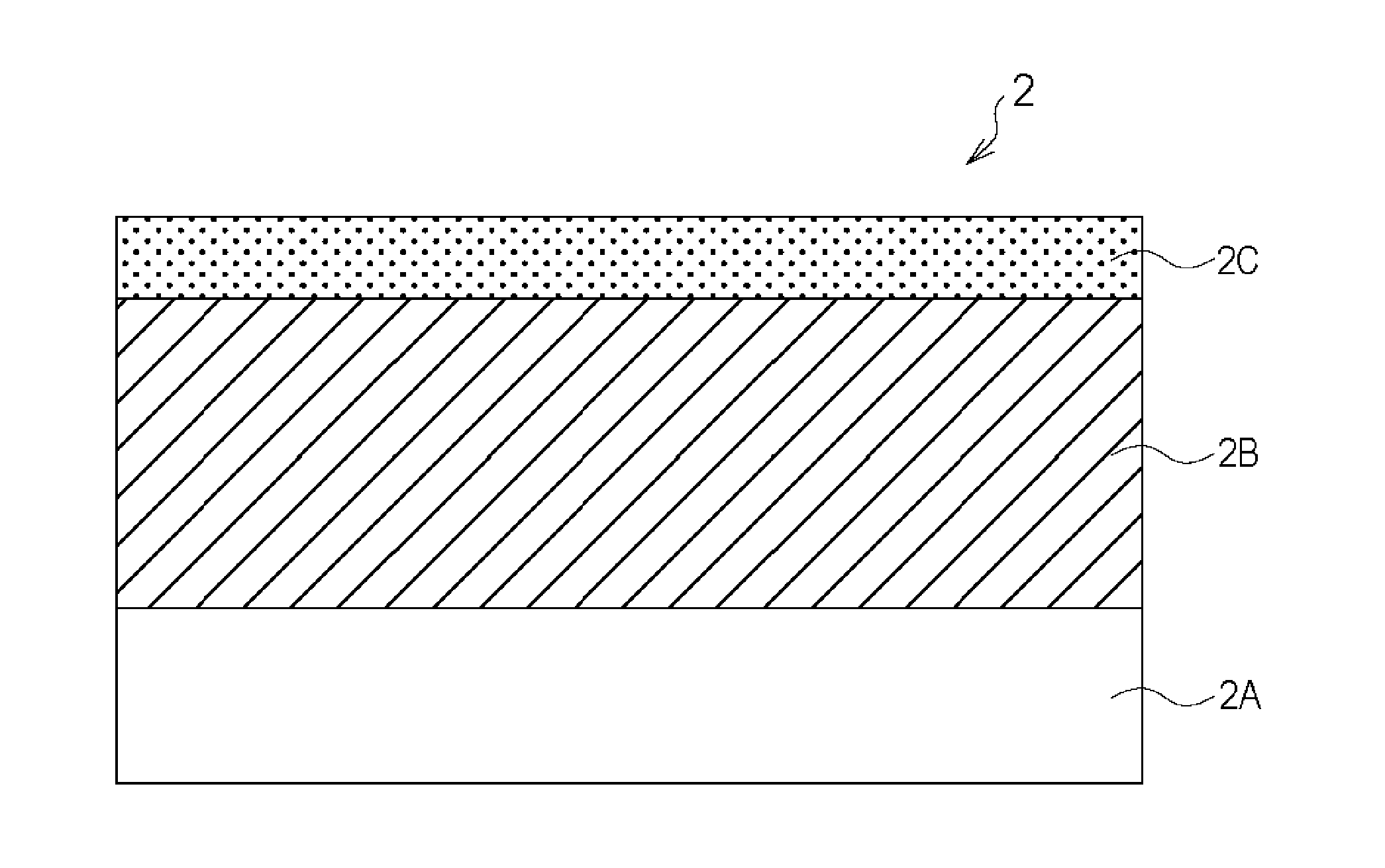
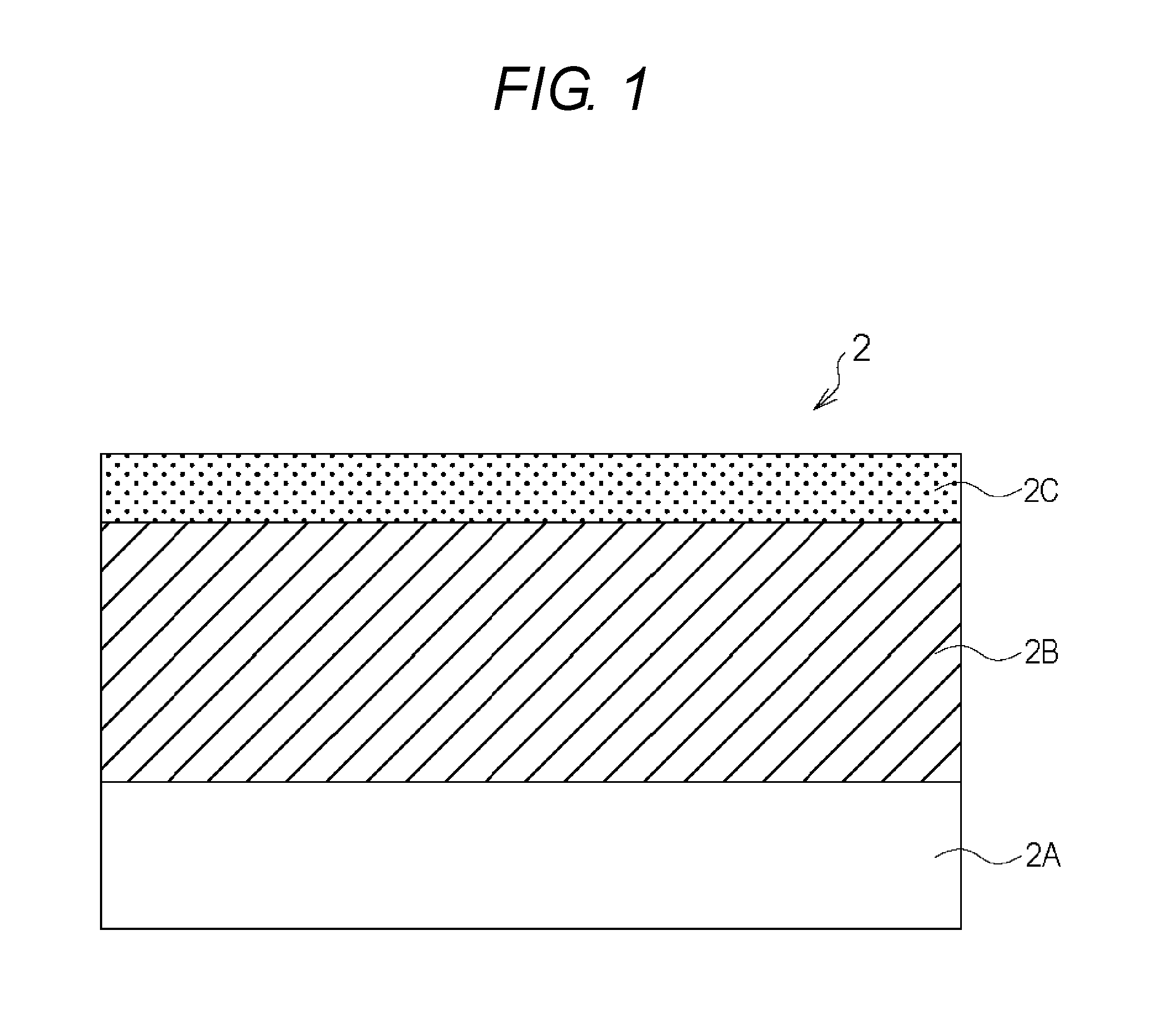
Member for electrophotography, method for producing the same, and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS9442408B2Synthetic resin layered productsElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEpichlorohydrin
A member for electrophotography for use in forming a high quality electrophotographic image for a long period is provided. The member for electrophotography includes a support, an elastic layer on the support, and a surface layer on the elastic layer. The elastic layer includes a quaternary ammonium salt and an epichlorohydrin rubber. The surface layer includes a material having a specific structure. A universal hardness a surface of the surface layer is 1.0 N / mm2 or more and 5.0 N / mm2 or less.
Owner:CANON KK
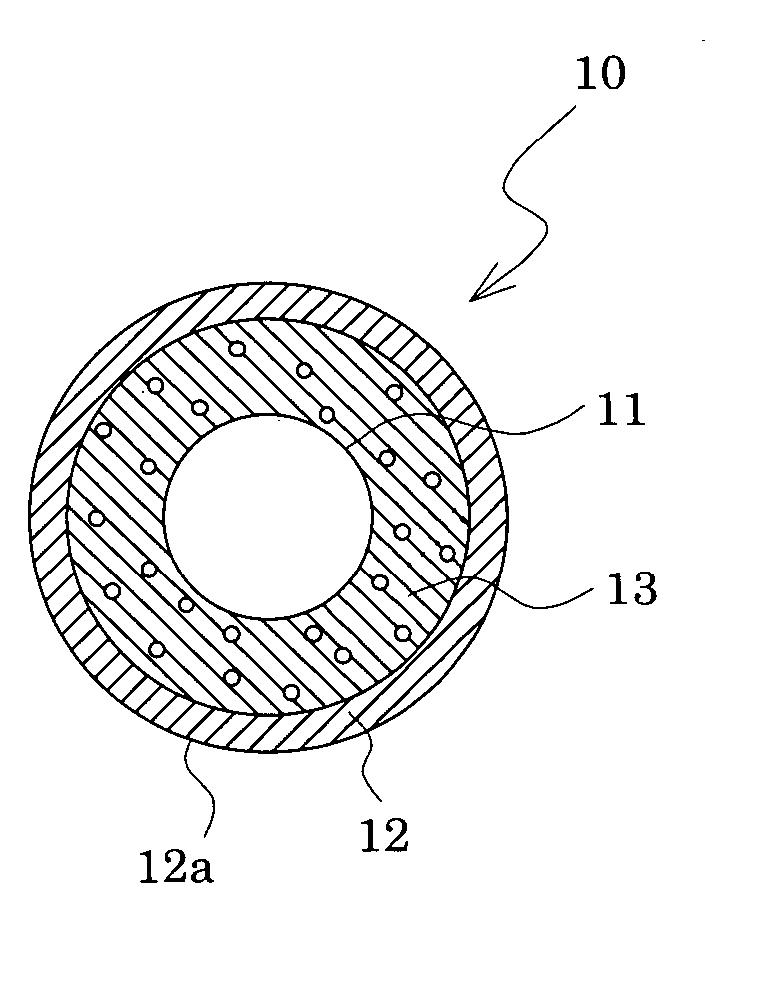
Conductive rubber member
InactiveUS20070110936A1Easy to processLow costClosuresClosure using stoppersOrganic solventAcrylonitrile
A conductive rubber member having at least one conductive elastic layer, wherein the conductive elastic layer, which is at least an outermost layer, in contact with an opposing member during use is a curing product of a rubber composition having a conductivity imparting agent incorporated into a rubber base material containing acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR); and a superficial portion of the conductive elastic layer is a surface treatment layer formed by impregnating the conductive elastic layer with a surface treating solution containing at least an isocyanate component and an organic solvent.
Owner:SYNZTEC
Support for image recording material and image recording material
InactiveUS20090202753A1Improve imaging clarityImprove smoothnessSynthetic resin layered productsPaper/cardboard layered productsImage recordingRecording layer
A support for an image recording material for receiving at least an image recording layer. The center surface average roughness SRa of the support surface to be provided with an image recording layer is 0.15 μm or less when measured under a condition of a cutoff of 0.02 to 0.5 mm, and is 0.45 μm or less when measured under a condition of a cutoff of 1 to 3 mm. An image recording material having an image recording layer on the support. The center surface average roughness SRa of the surface of the image recording material which surface is to be provided with an image is 0.1 μm or less when measured under a condition of a cutoff of 0.02 to 0.5 mm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
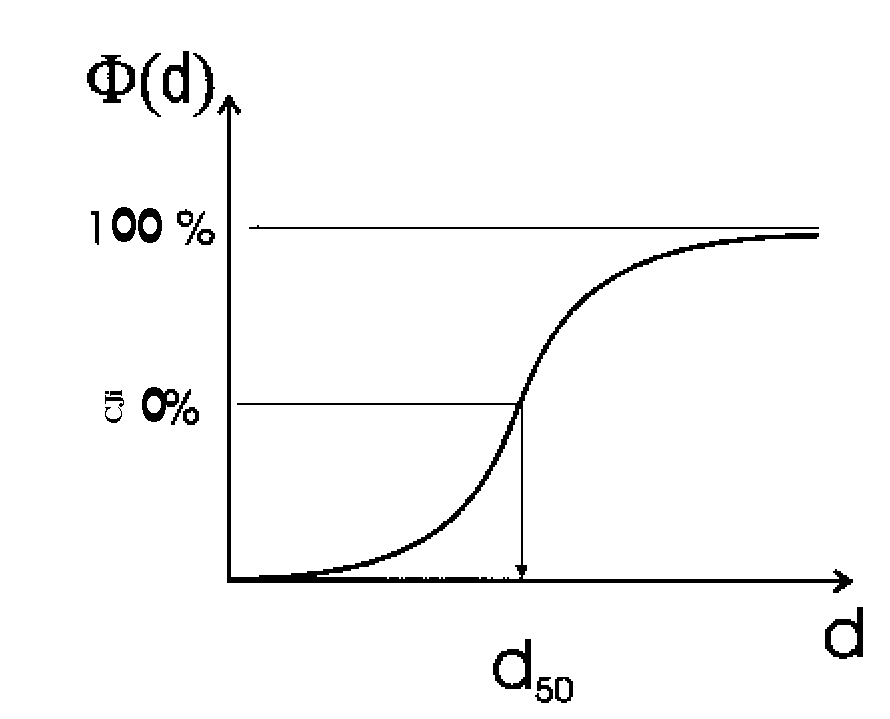
Multilayer, white polyester film
InactiveUS20070240075A1Improve propertiesEase of productionPhotosensitive materialsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterPolymer science
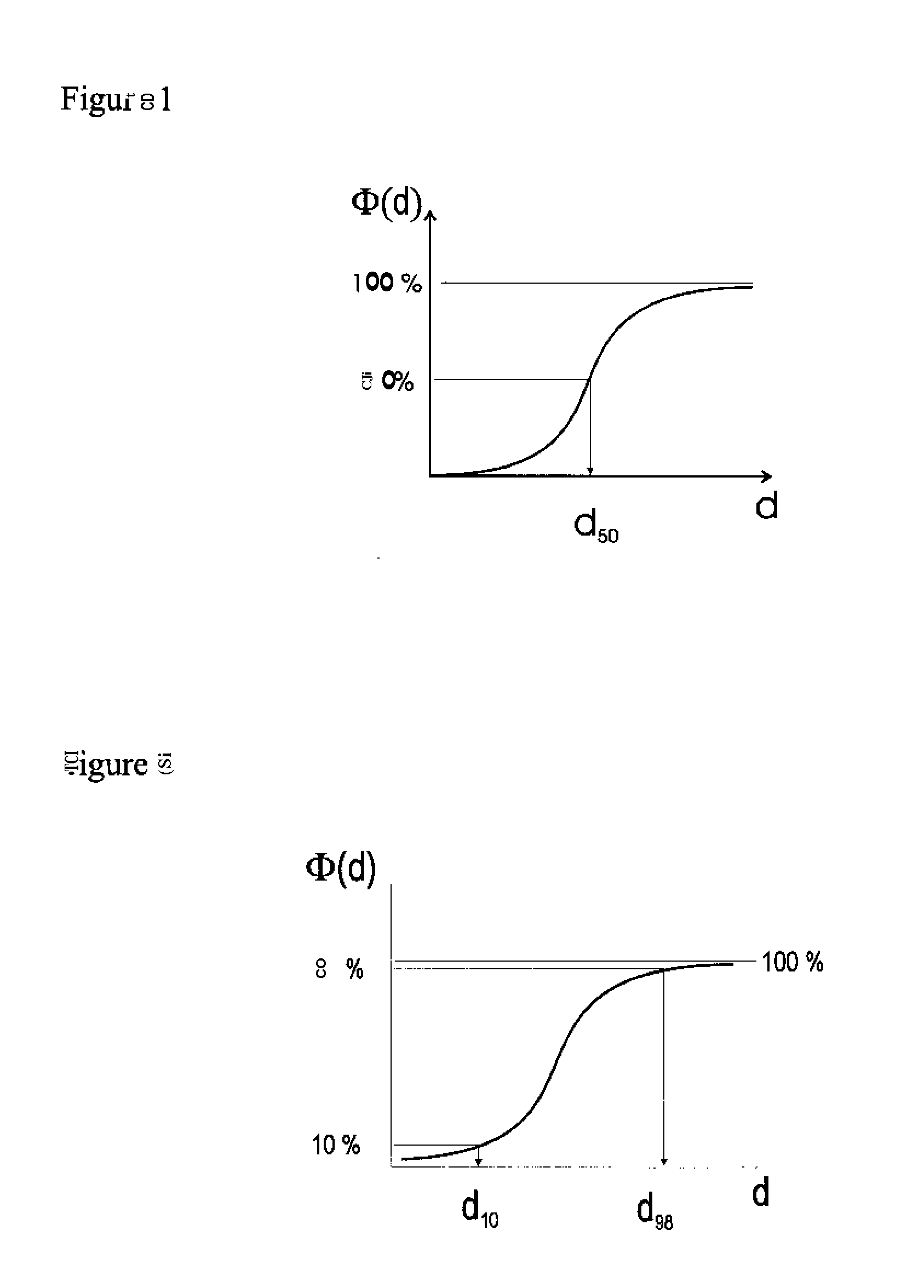
The invention relates to a multilayer, white, biaxially oriented polyester film, which has a base layer B and at least one outer layer (A), wherea) the base layer (B) includes, as sole whitening pigment, a concentration of from 5 to 25% by weight of barium sulfate, andb) the outer layer (A) includes, as sole whitening pigment, a concentration of from 5 to 25% by weight of barium sulfate, and also includes from 0.01 to 4% by weight of antiblocking agent whose median diameter (d50 value) is from 2 to 8 μm.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POLYESTER FILM
Liquid resin composition, cured film and laminate
InactiveUS20070172646A1Simple processImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsRefractive indexSolvent
A liquid resin composition containing (A) fluorine-containing polymer, (B) curable compound, (C) metal oxide particles having a number average particle size of 100 nm or less and (D) a solvent. When the composition is cured, the metal oxide particles (C) are distributed unevenly, the refractive index changes in the thickness direction by 0.05 to 0.8, so that there can be produced a cured film having a bilayer structure substantially consisting of a low-refractivity layer and a high-refractivity layer.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Conductive rubber member
ActiveUS20070104906A1Easy to processLow costClosuresClosure using stoppersOrganic solventEngineering
A conductive rubber member having at least one conductive elastic layer, wherein the conductive elastic layer, which is at least an outermost layer, in contact with an opposing member during use is a curing product of a rubber composition having a conductivity imparting agent incorporated into a rubber base material containing chloroprene rubber; and a superficial portion of the conductive elastic layer is a surface treatment layer formed by impregnating the conductive elastic layer with a surface treating solution containing at least an isocyanate component and an organic solvent.
Owner:SYNZTEC
Intermediate transfer member, imaging apparatus, and method
ActiveUS20120171494A1Need be improveSynthetic resin layered productsElectrographic process apparatusUV curingElectron
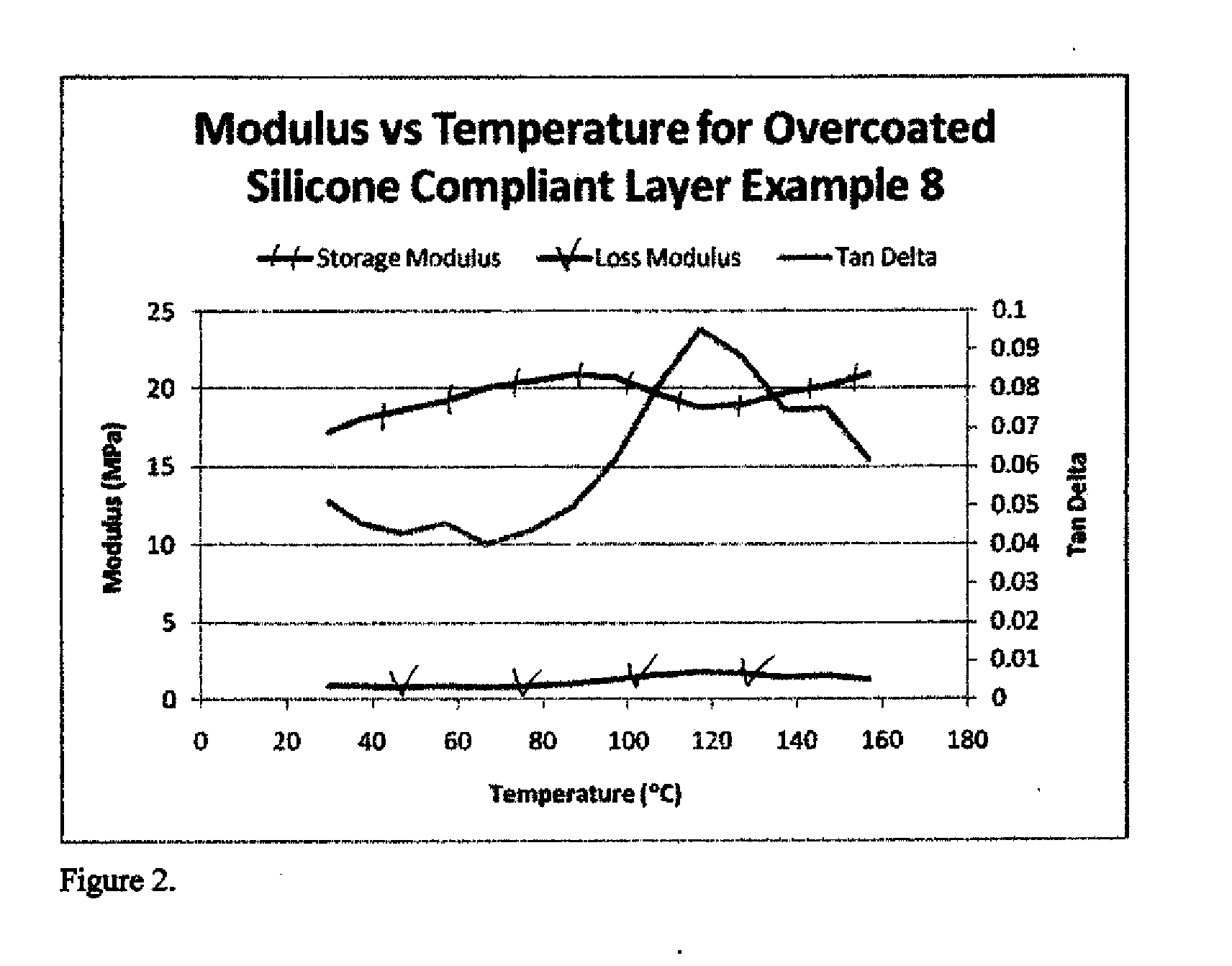
An intermediate transfer member for electrophotography includes a substrate, a cured static dissipative silicone compliant layer comprising crosslinked silicone polymer formed from a UV light curable siloxane and a UV curing catalyst, and an outermost surface ceramer layer. This intermediate transfer member can be incorporated into a suitable imaging apparatus for forming a toned image on a receiver element.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
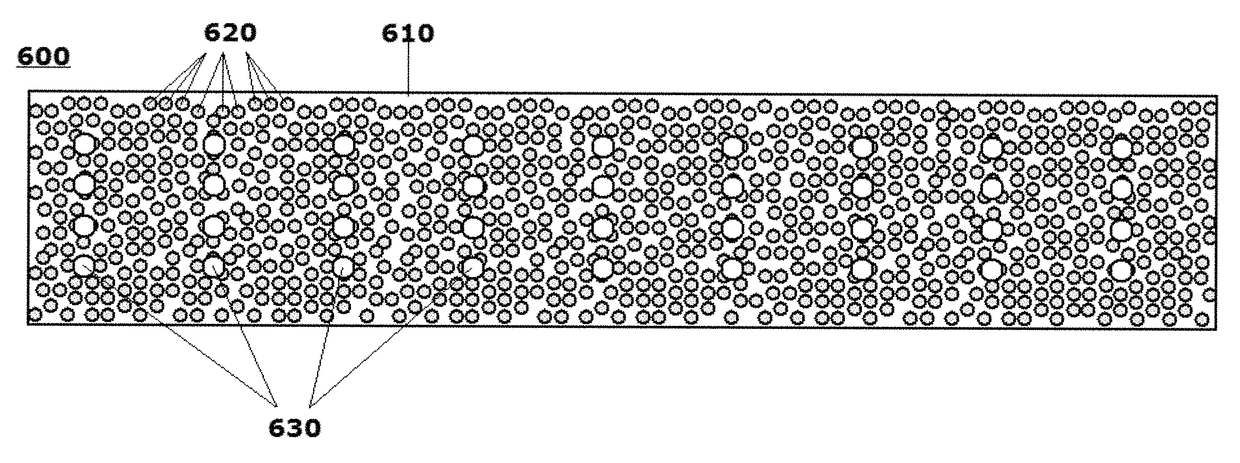
Systems and methods for implementing selective electromagnetic energy filtering objects and coatings using selectably transmissive energy scattering layers
ActiveUS9726790B2Good lookingDiffusing elementsDigital data processing detailsShutterIncident energy
Owner:FACE INT
Electrophotographic endless belt, process for producing electrophotographic endless belt, and electrophotographic apparatus
InactiveUS7201967B2Easy transferImprove uniformitySynthetic resin layered productsElectrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisCommon logarithmPolyamide
In an electrophotographic endless belt having a resin layer formed of a resin composition containing a polyamide, the resin composition further contains a copolymer obtained by copolymerization of an olefin and an oxygen-containing heterocyclic compound, a curve (T-log10 η curve) showing the relationship between temperature T (° C.) and common logarithm log10 η of melt viscosity η (Pa·s), of the resin composition has, in the range of log10 η of from log10 1,000 to log10 8,000, a gently inclined region the inclination Δ log10 η / ΔT of which is from −0.02 to 0, and the gently inclined region has a temperature range of 10° C. or more, and the resin layer has a thickness the maximum thickness of which is 115% or less of the average value of the thickness of the resin layer and the minimum thickness of which is 85% or more of the average value of the thickness of the resin layer. Also disclosed is a process for producing the above electrophotographic endless belt.
Owner:CANON KK
Protected polycarbonate films having thermal and UV radiation stability, and method of making
A composite film is disclosed, comprising a protective layer comprising an adhesion-modified polyolefin film, a coating layer comprising the reaction product of a crosslinkable compound, an initiator, and a binder; and a polycarbonate layer; wherein the coating layer is disposed between the protective layer and the polycarbonate layer, and the peel strength between the protective layer and the polycarbonate layer, as measured both before and after thermal treatment or a combination of thermal and UV treatment of the composite film, is about 1 to about 20 centi-Newtons per centimeter measured using 180° angle peel measured at a peel rate of 25.4 cm / min. A method for forming a composite film, and an article comprising the composite film, are also disclosed.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Transfer medium, production method thereof, and transferred matter
InactiveUS20120156444A1Improve discharge stabilityHigh resolutionDecorative surface effectsLayered productsEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Polyester compounds having enhanced hydrophobic surface properties
ActiveUS20160130411A1Improved anti-graffiti propertyOptimize timingSynthetic resin layered productsBagsPolyesterMasterbatch
A masterbatch having reactive silicone as a hydrophobic additive, the polyester compound that the silicone-containing masterbatch has been let down into, and the plastic articles and films from such compounds having enhanced hydrophobic properties are disclosed. Films having a Water Contact Angle of at least 76° (ASTM D7490-08) are exemplified.
Owner:AVIENT CORP
Systems and methods for producing objects incorporating selectably active electromagnetic energy filtering layers and coatings
ActiveUS9726791B2Good lookingDiffusing elementsDigital data processing detailsElectricityIncident energy
A system and method are provided for forming body structures including energy filters / shutter components, including energy / light directing / scattering layers that are actively electrically switchable. The filters or components are operable between at least a first mode in which the layers, and thus the presentation of the shutter components, appear substantially transparent when viewed from an energy / light incident side, and a second mode in which the layers, and thus the presentation of the energy filters or shutter components, appear opaque to the incident energy impinging on the energy incident side. The differing modes are selectable by electrically energizing, differentially energizing and / or de-energizing electric fields in a vicinity of the energy scattering layers, including electric fields generated between a pair of transparent electrodes sandwiching an energy scattering layer. Refractive indices of transparent particles, and the transparent matrices in which the particles are fixed, are tunable according to the applied electric fields.
Owner:FACE INT
Liquid resin composition, cured film and laminate
ActiveCN1791635ASimplify the manufacturing processExcellent adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsRefractive indexSolvent
A liquid resin composition comprising (A) a fluoropolymer, (B) a curable compound, (C) metal oxide particles having a number average particle diameter of 100 nm or less, and (D) a solvent. Once this composition is cured, metal oxide particles (C) can be segregated, the refractive index can be changed by 0.05 to 0.8 in the film thickness direction, and the cured material has a substantially two-layer structure of a low refractive index layer and a high refractive index layer. membrane.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Systems and methods for producing laminates, layers and coatings including elements for scattering and passing selective wavelengths of electromagnetic energy
PendingUS20160306078A1Increasing potential available energy collection energyIncreasing energy energy harvesting capacityDigital data processing detailsDiffusing elementsRefractive indexLight excitation
A system and method are provided for forming electromagnetic energy transmissive layers, which are particularly configured to selectively scatter specific and selectable wavelengths of electromagnetic energy, while allowing remaining wavelengths to pass therethrough. Processes are provided by which to form, or otherwise incorporate, one or more energy scattering layers, including uniquely implementing optical light scattering techniques in such energy scattering layers, and to objects, object portions, wall plates, lenses, filters, screens and the like that are formed of, or that otherwise incorporate, such transmissive energy-scattering layers. Refractive indices of particles fixed in a matrix are tunable in order that the finished layers provide an opaque appearance when viewed from an energy-incident excited by light in the visible spectrum. A color, pattern, texture or image of the scattering layer may be rendered according to an individual user's desires, the layers being substantially-transparent to light passing through layers.
Owner:FACE INT
Image transfer sheet with laser, led, or dye-sublimination printed image and methods of making and using
An multilayer image transfer sheet for non-thermally transferring an image to a receiving object includes, in the following order with respect to each other, a backing sheet; a water-releasable sacrificial layer disposed on the backing sheet; a printed image layer disposed over the water-releasable sacrificial layer; and an adhesive layer disposed over the printed image layer and configured and arranged for permanent attachment of the printed image layer to a receiving object. The printed image layer comprises toner or dye printed using a laser printer, LED printer, or dye-sublimation printer.
Owner:BROTHER INT
Conductive rubber member
InactiveUS7638196B2Easy to processLow costClosuresClosure using stoppersOrganic solventAcrylonitrile
A conductive rubber member having at least one conductive elastic layer, wherein the conductive elastic layer, which is at least an outermost layer, in contact with an opposing member during use is a curing product of a rubber composition having a conductivity imparting agent incorporated into a rubber base material containing acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR); and a superficial portion of the conductive elastic layer is a surface treatment layer formed by impregnating the conductive elastic layer with a surface treating solution containing at least an isocyanate component and an organic solvent.
Owner:SYNZTEC
Intermediate transfer belt
InactiveUS20120128953A1Increased durabilityImprove image qualityLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsElastomerSurface layer
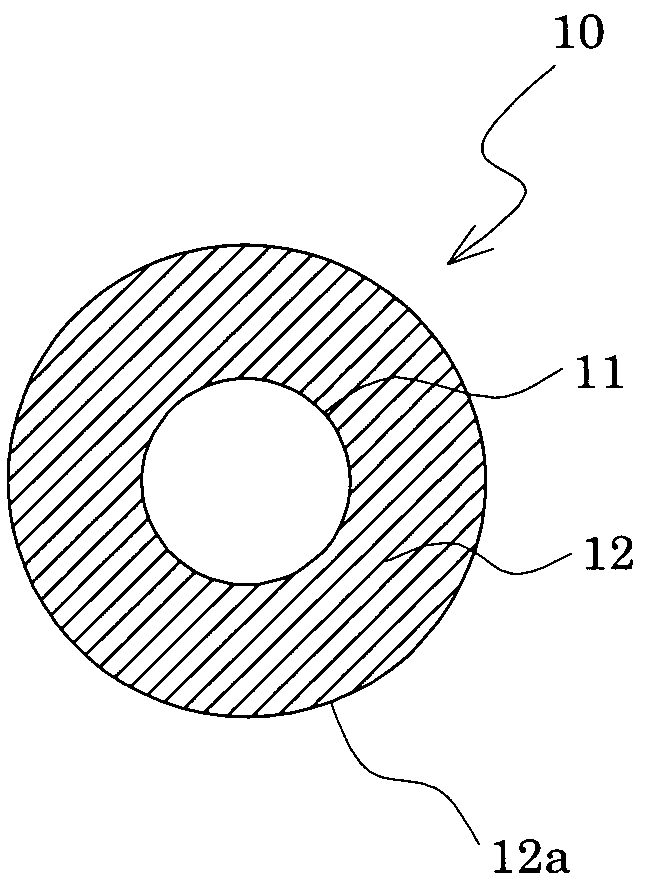
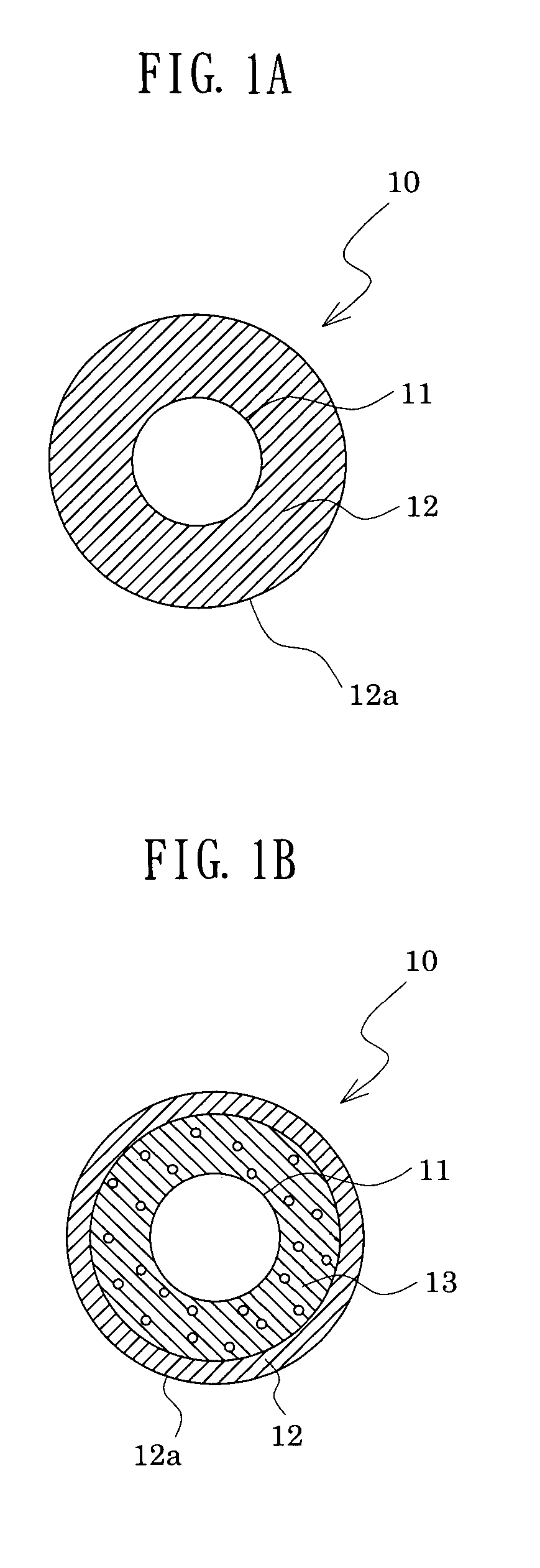
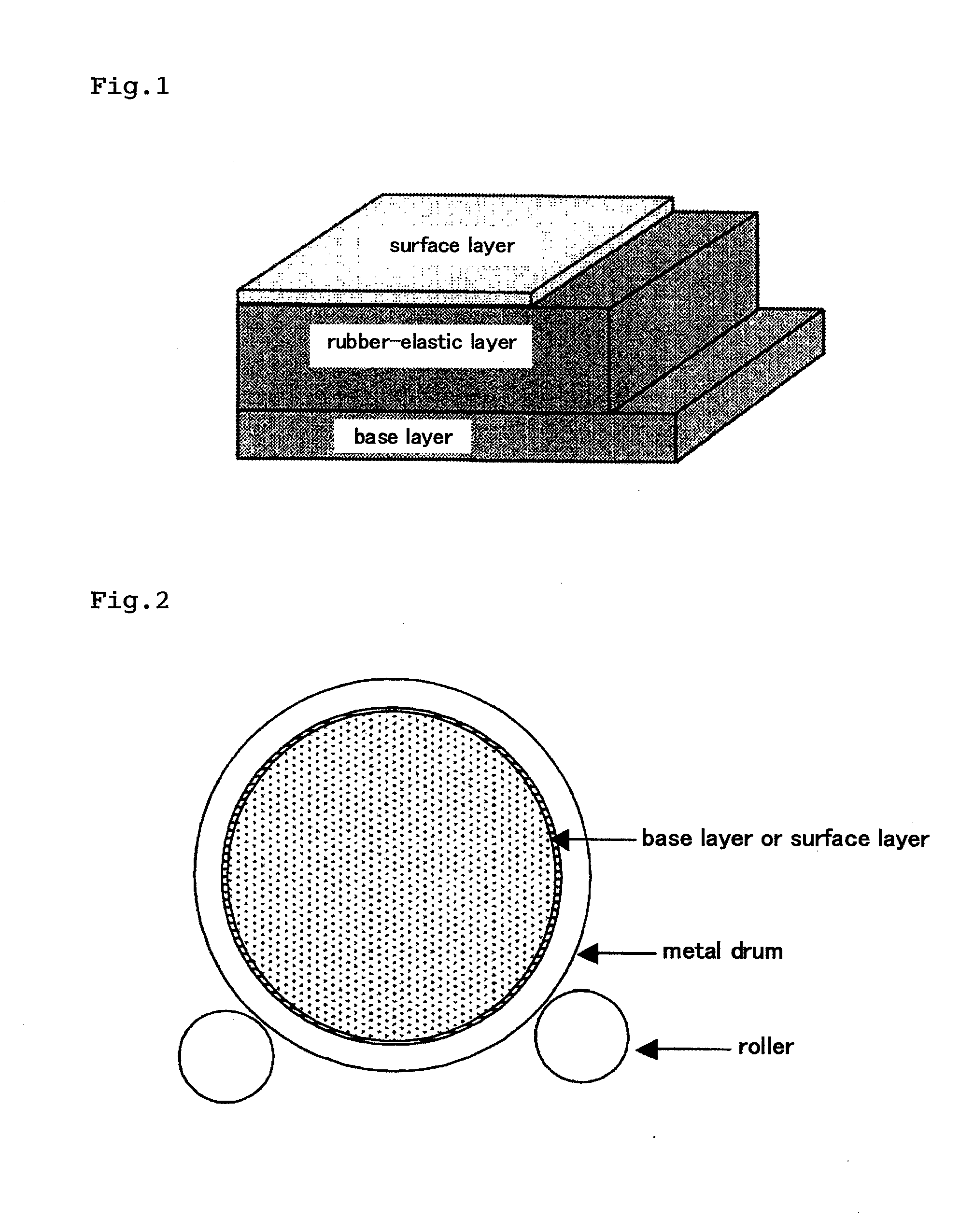
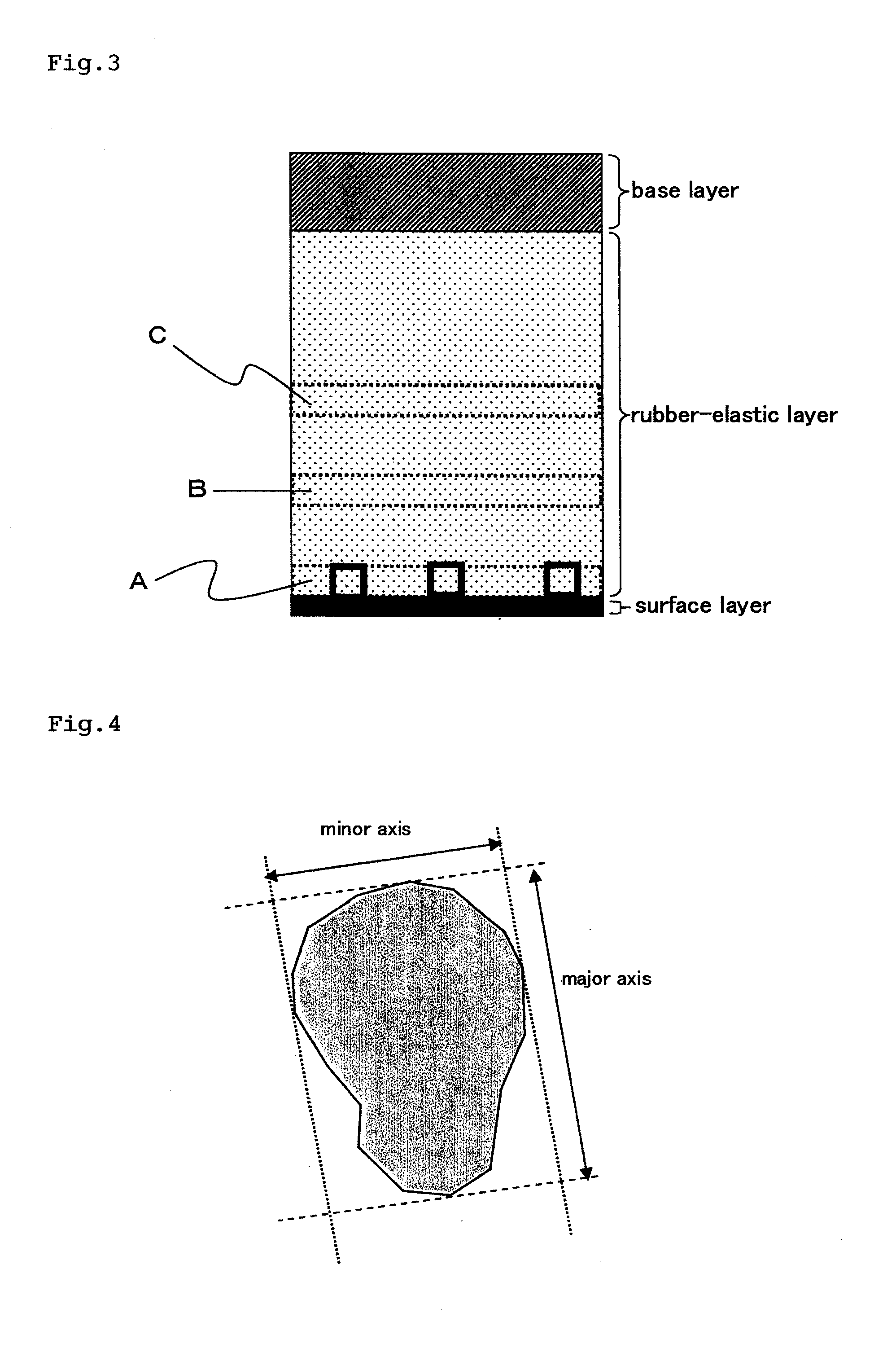
A main object of the present invention is to provide an intermediate transfer belt for image-forming devices and a method for producing the intermediate transfer belt, the intermediate transfer belt having excellent image transfer to rough paper and resistance to abrasion and being free from problems such as filming, by forming a surface layer that has excellent resistance to abrasion and in which defects such as pinholes are not likely to occur even when the surface layer is thinned.An intermediate transfer belt for image-forming devices and a method for producing the same, the intermediate transfer belt comprising at least the following three layers laminated in the described order: (a) a base layer formed from resin, (b) a rubber-elastic layer formed from a rubber or elastomer, having a thickness of 200 to 400 μm and (c) a surface layer formed from resin, having a thickness of 0.5 to 6 μm, wherein the intermediate transfer belt has the following properties: (i) the dynamic ultramicro hardness (ISO14577-1) measured from the surface layer side is 2.5 to 4.5 N / mm2 at the indentation depth of 2 μm, and 1.0 N / mm2 or less at the indentation depth of 10 μm, and / or (ii) the rubber-elastic layer contains a filler in a proportion of 0.4 to 4.0 vol. %, and the ratio (M1 / M3) of the mass concentration M1 of the filler in the region from the interface between the surface layer and the rubber-elastic layer toward the base layer to a depth of 20 μm, to the mass concentration M3 of the filler in the region from 120 μm to 140 μm in depth from the interface between the surface layer and the rubber-elastic layer toward the base layer is 1.3 or higher.
Owner:GUNZE LTD
Acrylic film for lens substrate, lens film using the same lens sheet
InactiveUS7514140B2Good light fastnessFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsOptoelectronicsLens plate
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Method for Defining an Electronically Conductive Metal Structure on a Three-Dimensional Element and a Device Made From the Method
InactiveUS20120094092A1Decorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsCombined useGlass microsphere
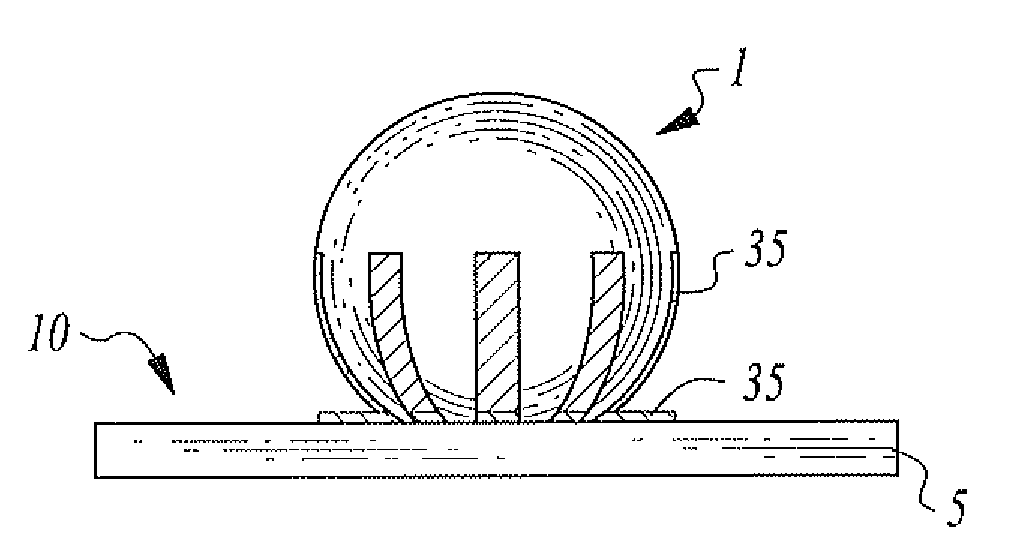
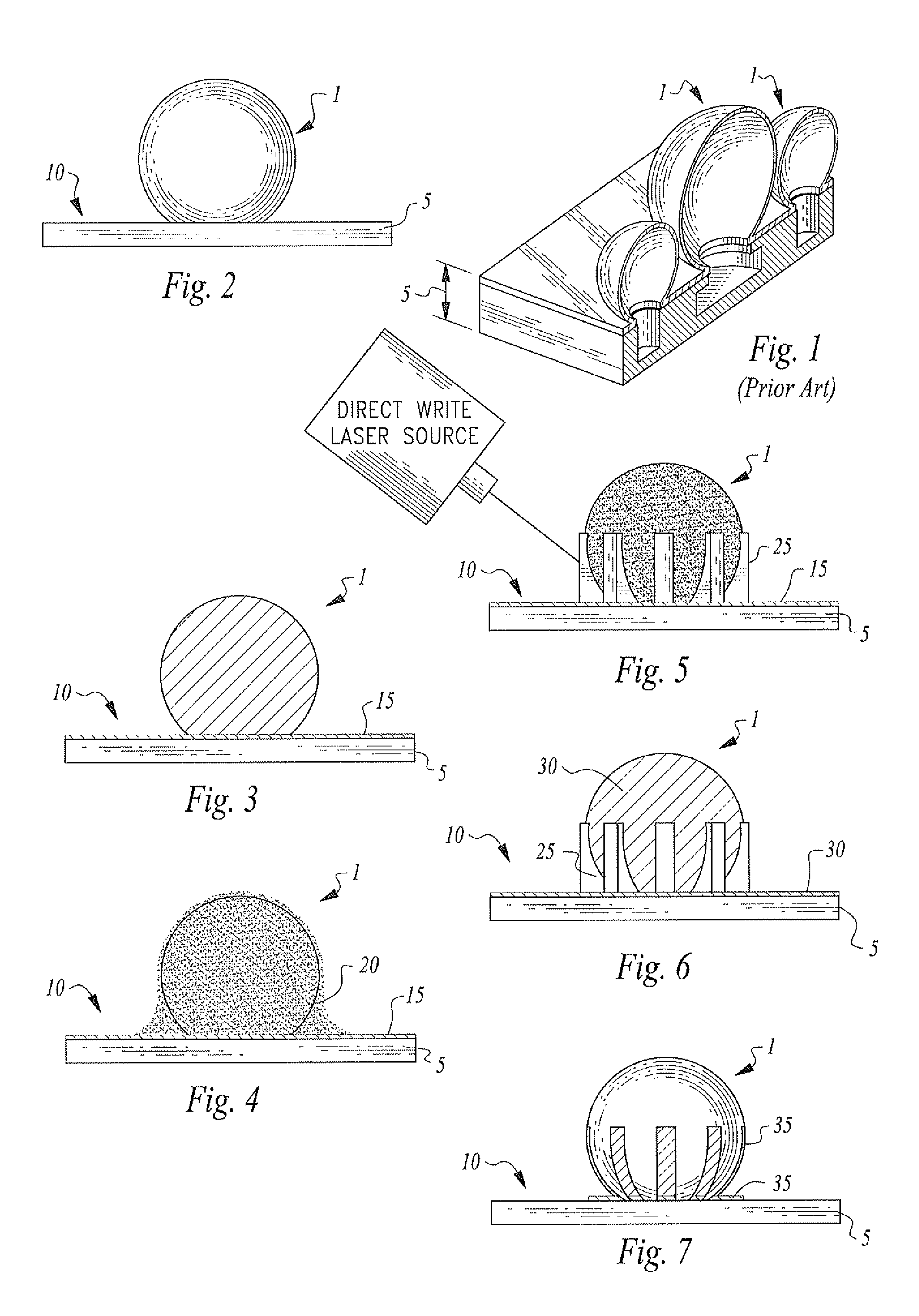
A method for defining an electrically conductive metalized structure, which may comprise an electrode or trace, on the surface of a three-dimensional element. The three-dimensional element may comprise a glass microsphere or shell resonator. A laser direct write grayscale photolithographic process is used in conjunction with electrically conductive metal deposition processes to define one or more electrically conductive metal structures on the surfaces of the three dimensional element.
Owner:PFG IP +1
Three-dimensional plastic sheet
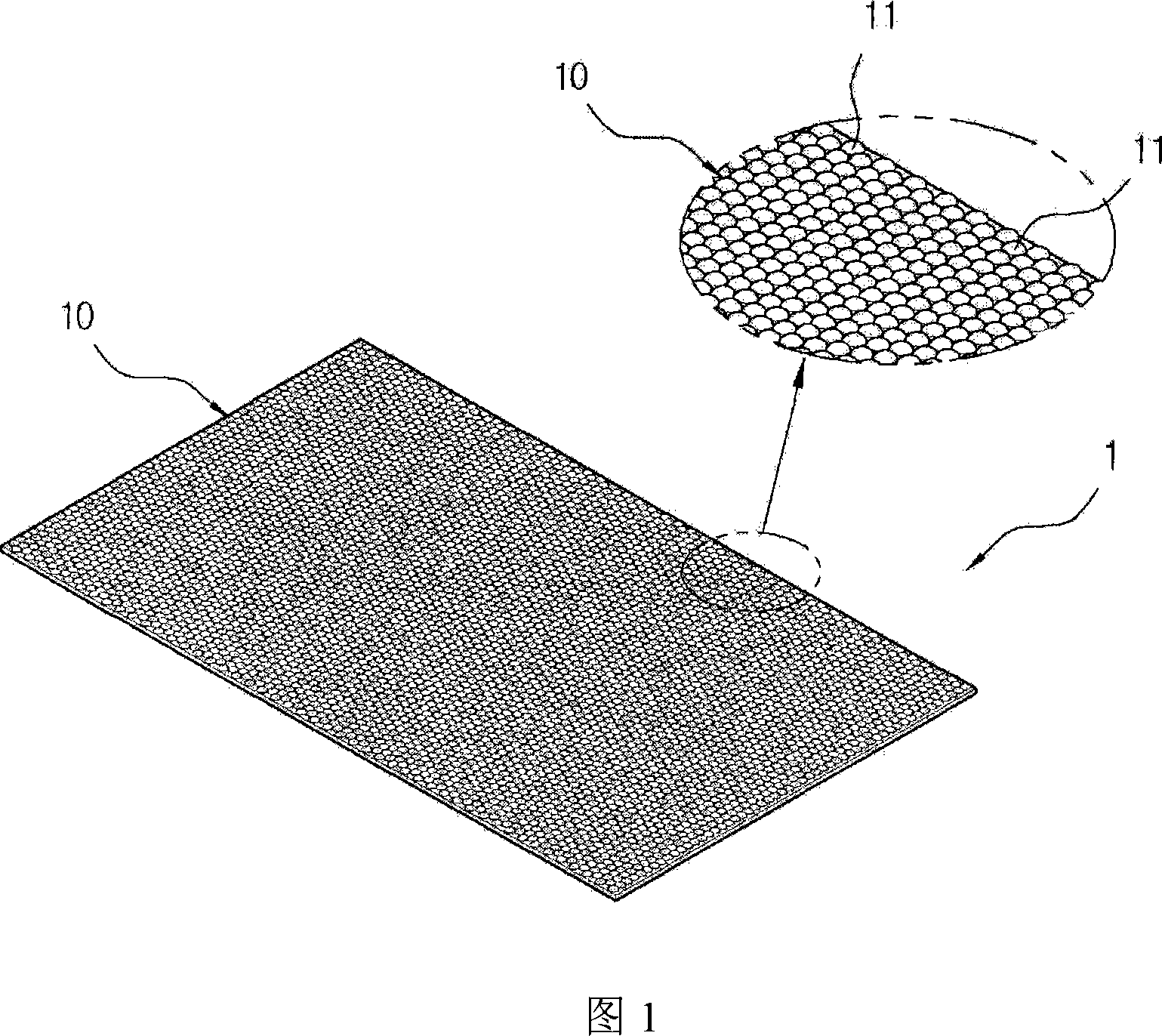
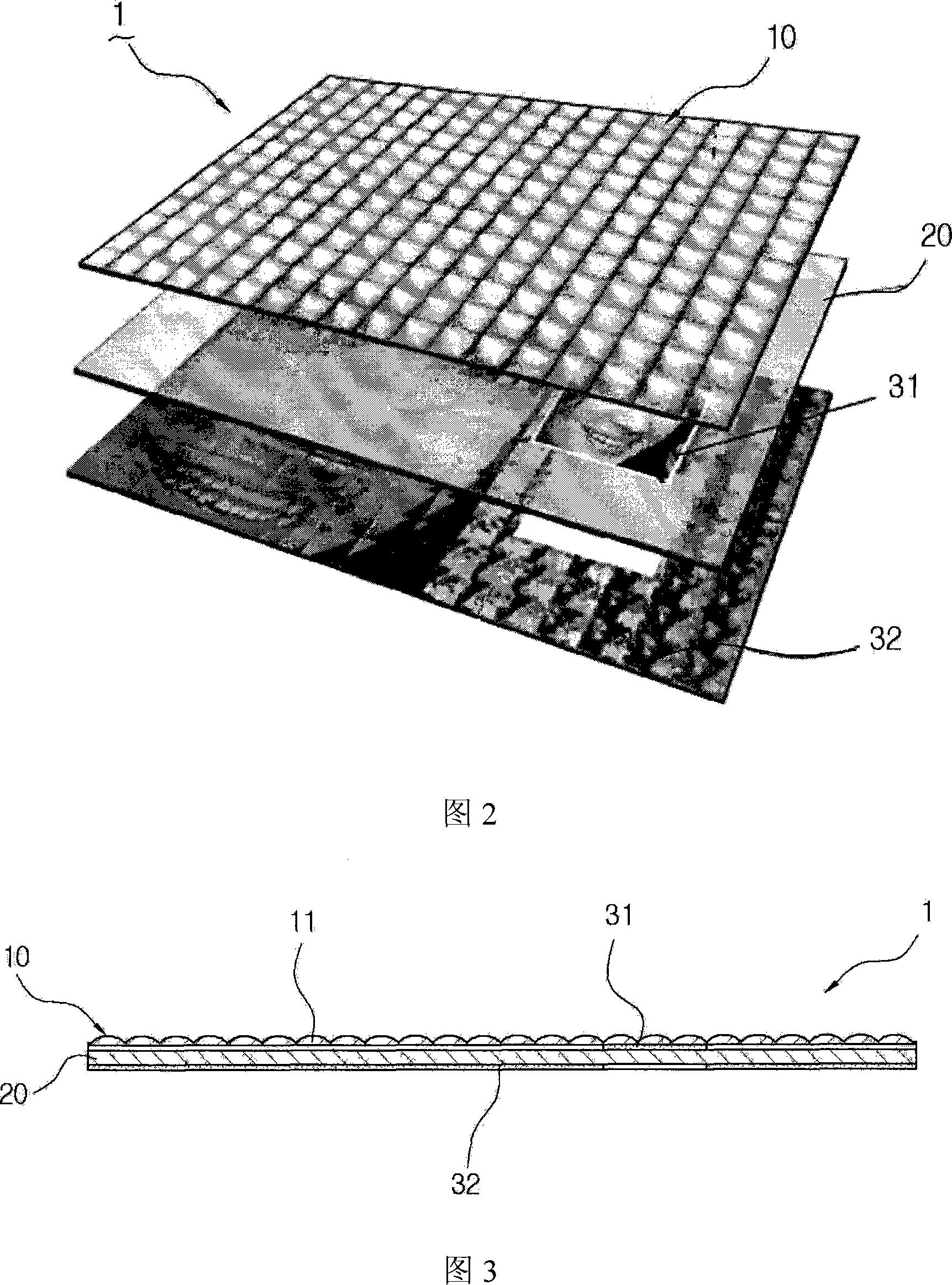
InactiveCN101160208AImprove adaptabilityHigh resolutionSynthetic resin layered productsLight effect designsEngineeringImage segmentation
The present invention relates to a three-dimensional plastic sheet that forms an array of convex lenses having a plurality of semispherical convex lenses arranged horizontally and vertically on the surface thereof, such that a three-dimensional image can be vividly seen even at every positions irrespective of the position or direction of the plastic sheet, while greatly minimizing the generation of moire patterns caused by the interference of different color dots. The three-dimensional plastic sheet includes: a convex lens layer formed of a transparent synthetic resin and having an array of identical semi-spherical convex lenses formed on the top surface thereof; a transparent plate disposed at the bottom surface of the convex lens layer and formed of a synthetic resin plate having a thickness corresponding to a focal distance of each convex lens; a non-focal distance printed layer disposed on the top surface of the transparent plate by means of offset printing for providing a real picture screen thereon; and a focal distance printed layer disposed on the bottom surface of the transparent plate by means of the offset printing for providing a three-dimensional screen thereon through four-color dot printing computed and image-segmented by a computer graphic process.
Owner:MIRECO KOREA
Electrophotographic image-receiving sheet and image-forming method using the same
InactiveUS20060057358A1High quality imagingSimple treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsCrack resistanceImage formation
It is an object of the present invention to provide an electrophotographic image-receiving sheet excellent in both adhesion resistance and cracking resistance, and an image-forming method using the electrophotographic image-receiving sheet. Accordingly, the electrophotographic image-receiving sheet contains a support, and at least two polymer layers disposed on the support, and at least one of the polymer layers containing voids.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
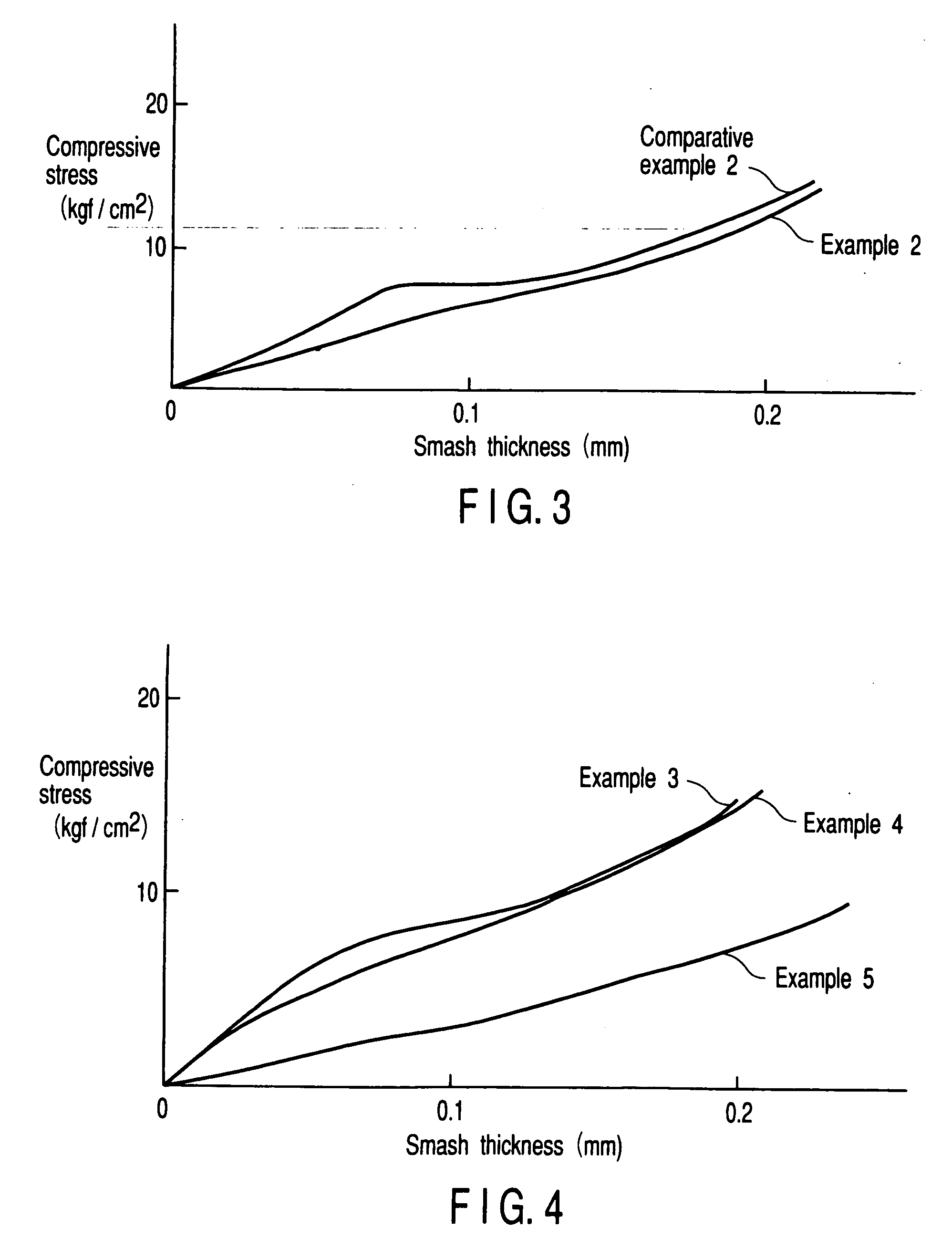
Compressible printing blanket and method of manufacturing a compressible printing blanket
Disclosed is a compressible printing blanket in which voids are formed in the compressible layer by using microballoons, comprising at least two fabric layers, an adhesive layer interposed between adjacent fabric layers, a surface rubber layer, and a compressible layer arranged between the at least two fabric layers and the surface rubber layer and containing spherical voids and voids having a shape other than a sphere in a ratio defined in formula given below: S1:S2=20:80 to 95:5 (1) where, S1 denotes the number of spherical voids per unit area in a cross section of the compressible layer, and S2 denotes the number of voids having a shape other than a sphere per unit area in a cross section of the compressible layer.
Owner:KINOYOSHA CO LTD
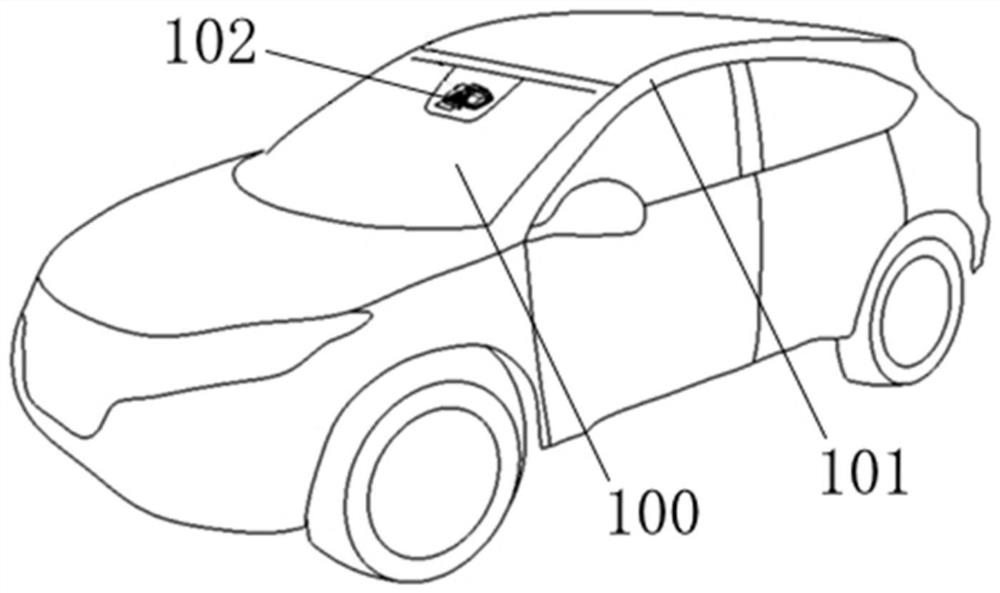
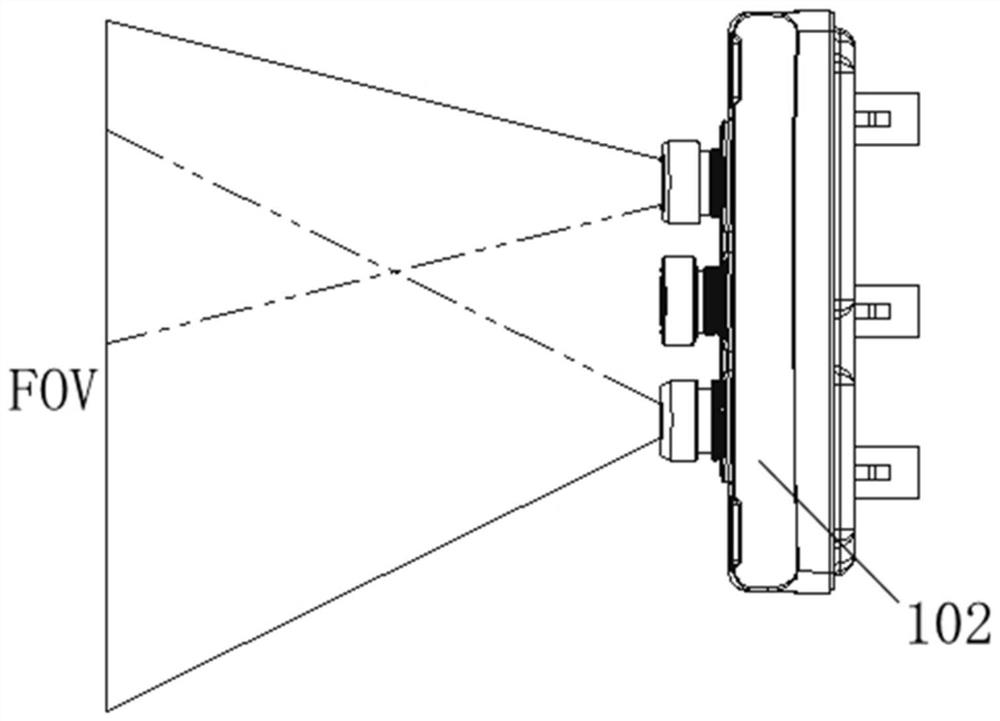
Laminated glass provided with camera
PendingCN112208310AGuaranteed Optical QualityImprove optical qualityWindowsWindscreensTransmittanceLaminated glass
The invention relates to the technical field of glass products, and particularly provides laminated glass provided with a camera. The laminated glass comprises an outer glass plate, an inner glass plate and a middle bonding layer, a support is fixed to the fourth surface of the laminated glass, a camera is installed on the support, an opaque resin layer is further arranged between the fourth surface and the support, and the visible light transmittance of the opaque resin layer is smaller than or equal to 3%. The first surface, the second surface, the third surface and the fourth surface of thelaminated glass are not provided with dark ceramic ink layers in a region range at least 10 mm larger than the periphery of each optical transmission window. The diopter of the area where the opaqueresin layer is located can be smaller than or equal to 200 mdpt, the area with the larger area and the excellent optical quality can be obtained, a camera can collect images easily, the images are clearer, the recognition degree is higher, driving safety is improved, and bonding and fixing of glass accessories such as a camera support and a rain sensor support are facilitated.
Owner:FUYAO GLASS IND GROUP CO LTD
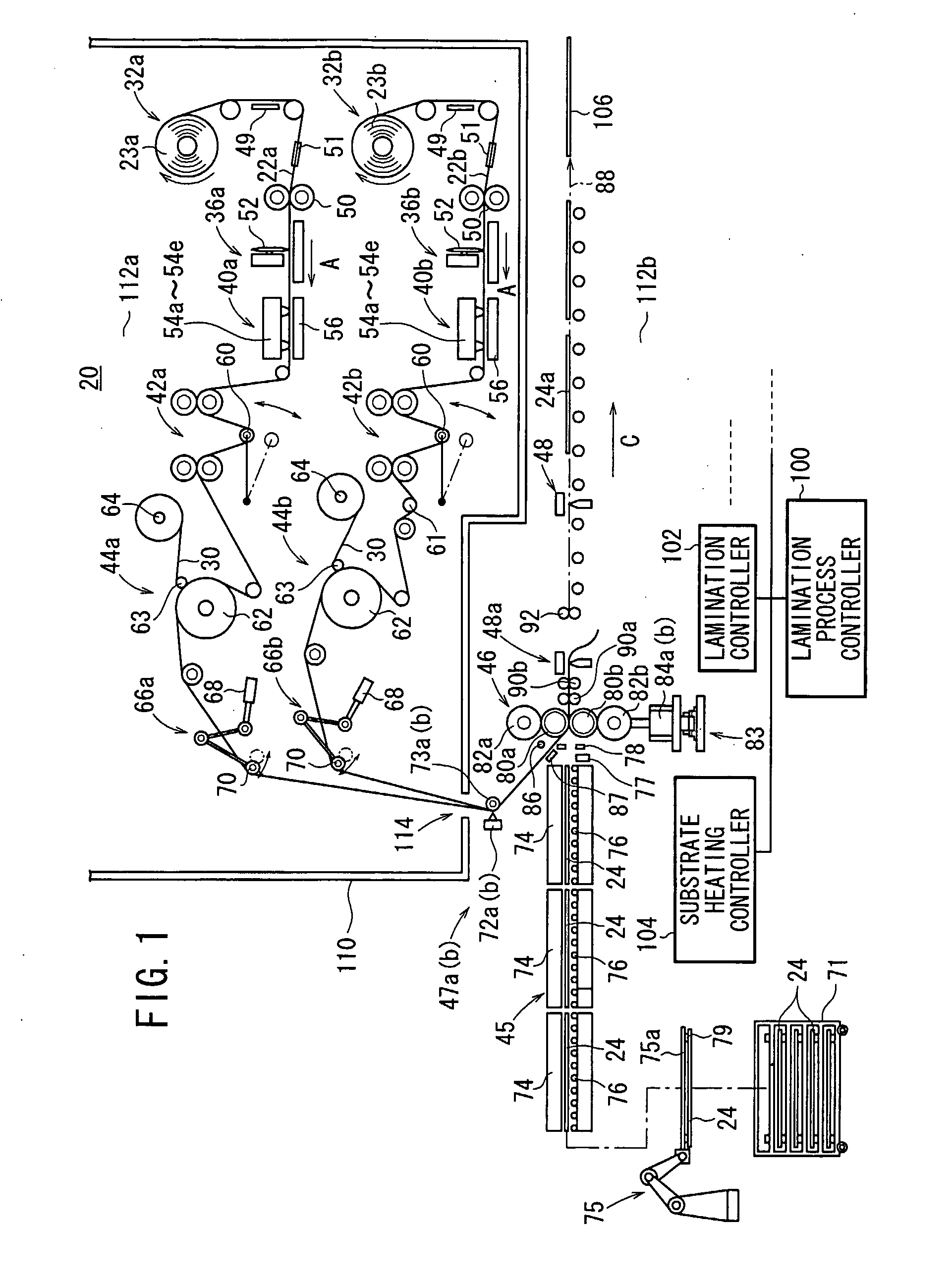
Apparatus for and Method of Manufacturing Photosensitive Laminated Body
InactiveUS20090050261A1Easy to handleEasily and favorably peeled offLamination ancillary operationsDecorative surface effectsTectorial membraneManufactured apparatus
A manufacturing apparatus (20) has first and second reel-out mechanisms (32a, 32b), first and second processing mechanisms (36a, 36b), first and second label bonding mechanisms (40a, 40b), first and second reservoir mechanisms (42a, 42b), first and second peeling mechanisms (44a, 44b), a substrate feed mechanism (45), an attachment mechanism (46), and a base peeling mechanism (186). A cooling mechanism (122) is disposed between the attachment mechanism (46) and the base peeling mechanism (186), for cooling an attached substrate (24a), the attached substrate (24a) being made up of a glass substrate (24) and a photosensitive web (22) attached thereto, from which a protective film (30) has been peeled off, together with a heating mechanism (182) for heating a resin layer, for example a cushion layer (27), inside the cooled attached substrate (24a) to within a predetermined temperature range, which is at or below the glass transition temperature.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Member for electrophotography, image heating apparatus, image forming apparatus, and method for manufacturing member for electrophotography
ActiveUS20160091841A1Improve thermal conductivityIncrease printing speedLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
Provided is a member for electrophotography, where an elastic layer including a silicone rubber and a release layer including a fluorine resin are bonded sufficiently without any adhesive layer interposed therebetween.The member for electrophotography includes a substrate; an elastic layer including a silicone rubber, on the substrate; and a release layer provided in direct contact with the surface of the elastic layer, where the release layer includes a fluorine resin selected from the group consisting of PFA, FEP, PTFE, ETFE, PCTFE, ECTFE, and PVDF, and the elastic layer undergoes a cohesive failure when the release layer is peeled from the elastic layer in accordance with “Determination of peel strength of bonded assemblies. Part 1: 90 degree peel” specified by the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) K 6854-1:1999.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com