Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53 results about "Xml processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
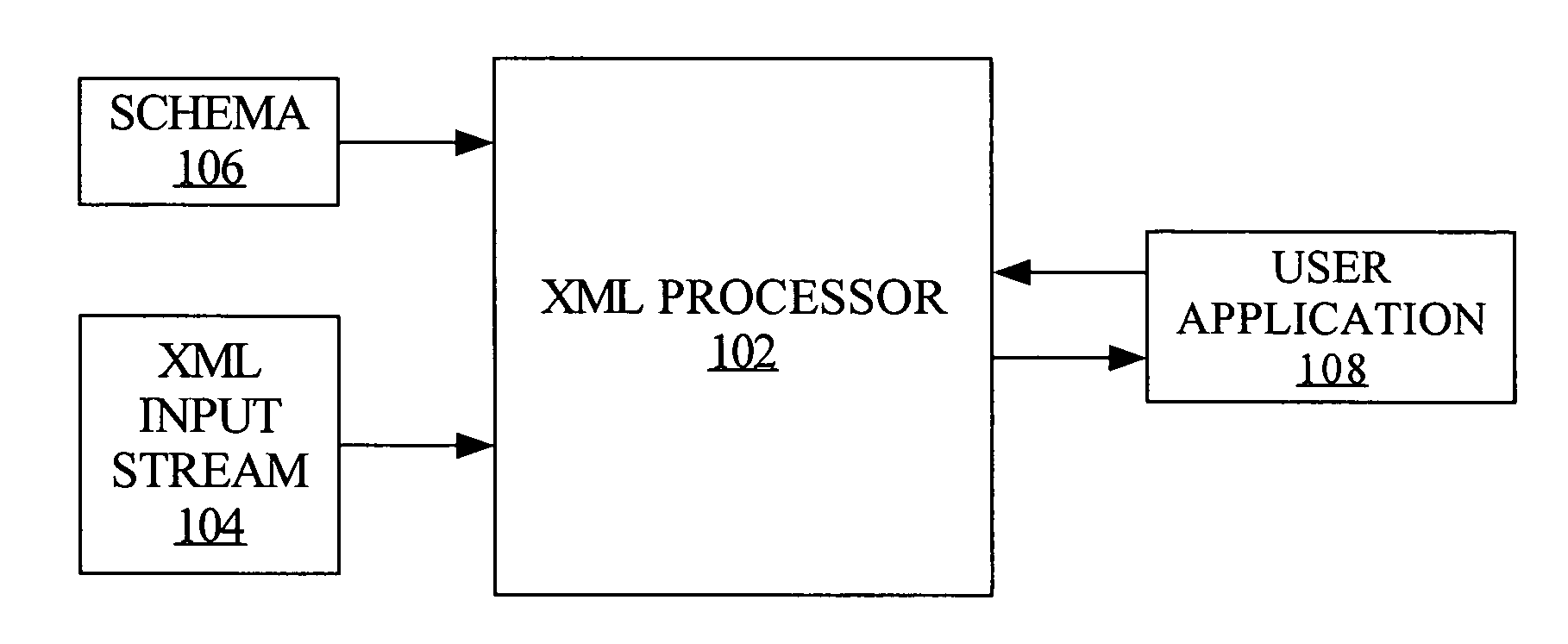
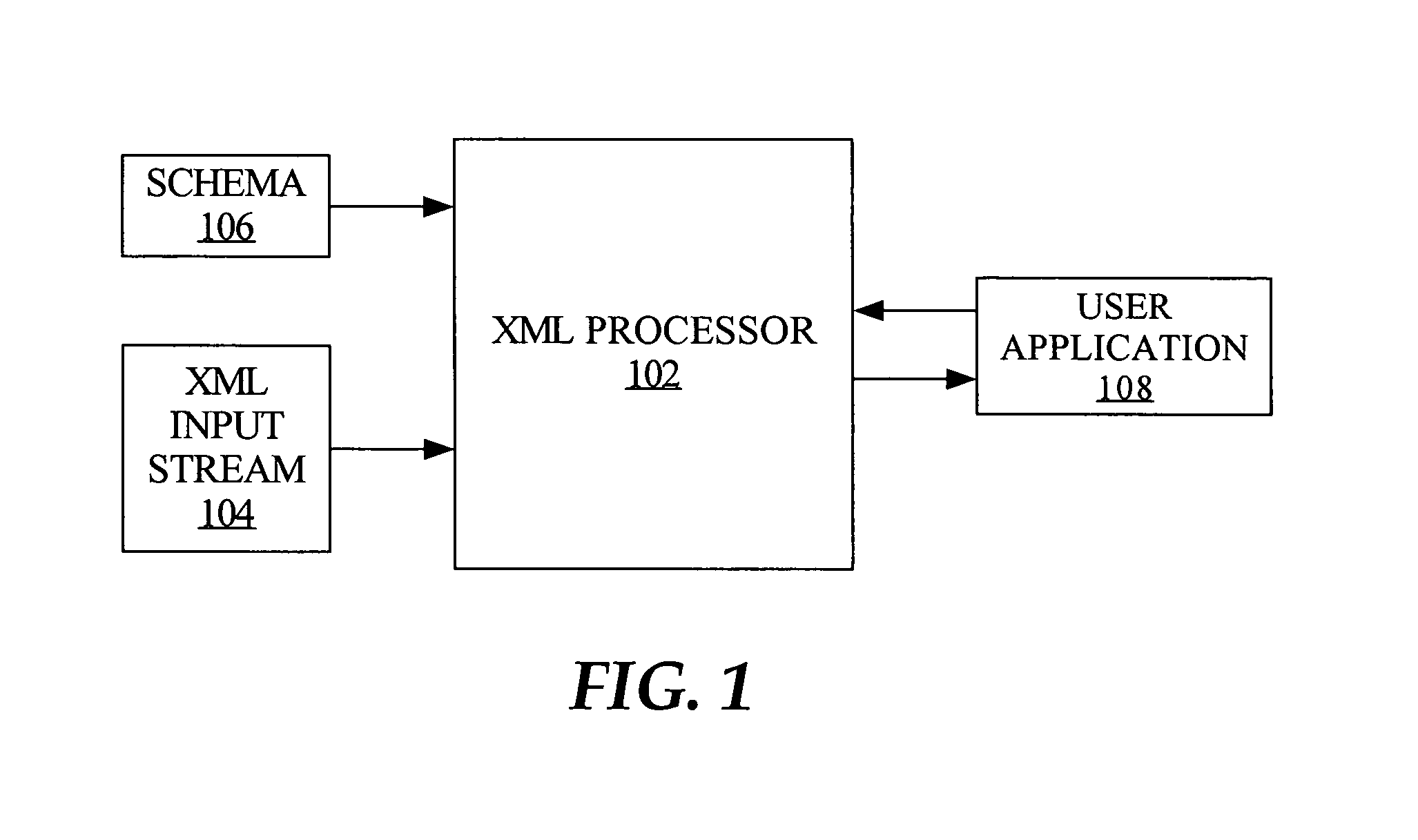
XML - Processors. When a software program reads an XML document and takes actions accordingly, this is called processing the XML. Any program that can read and process XML documents is known as an XML processor. An XML processor reads the XML file and turns it into in-memory structures that the rest of the program can access.
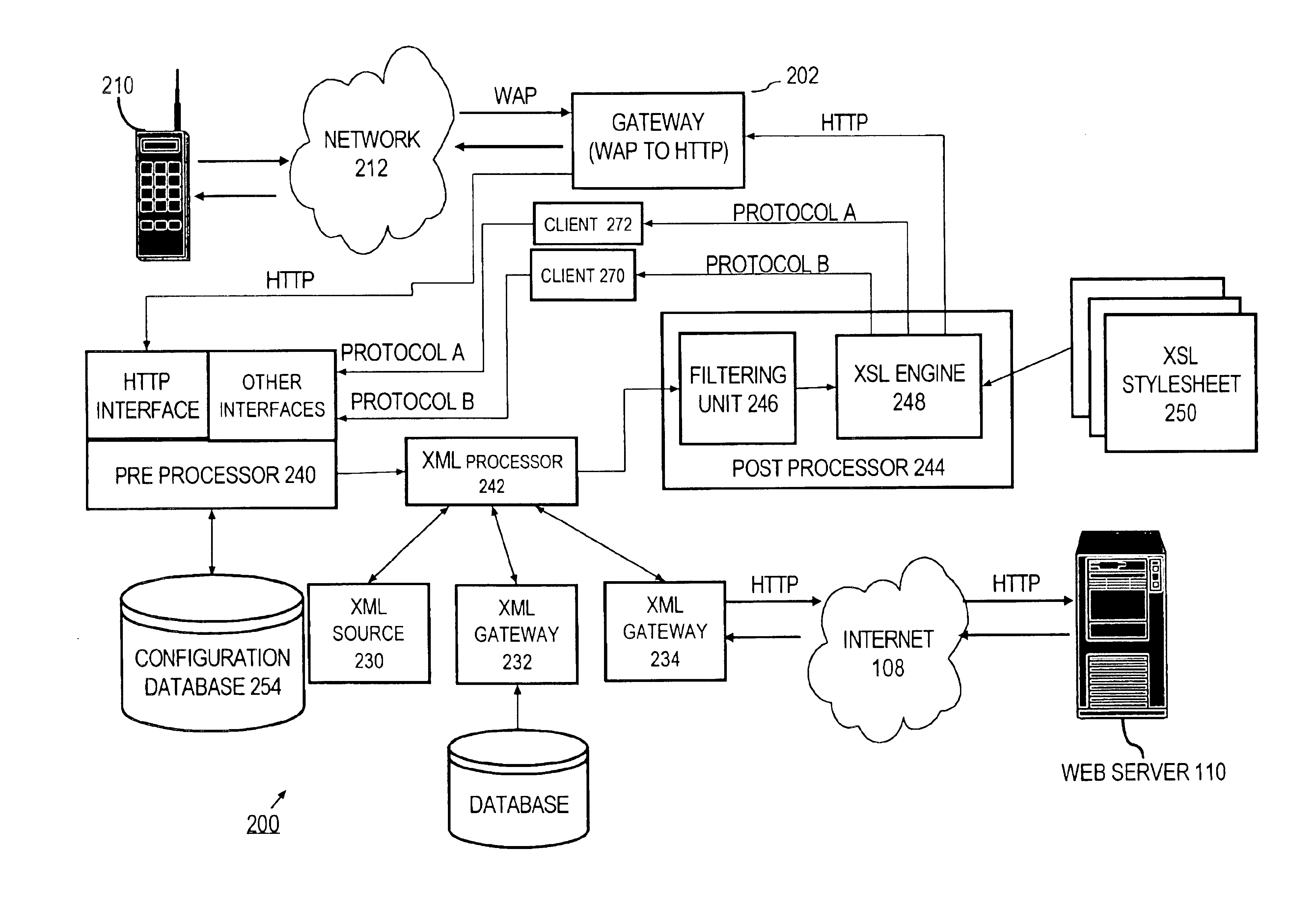
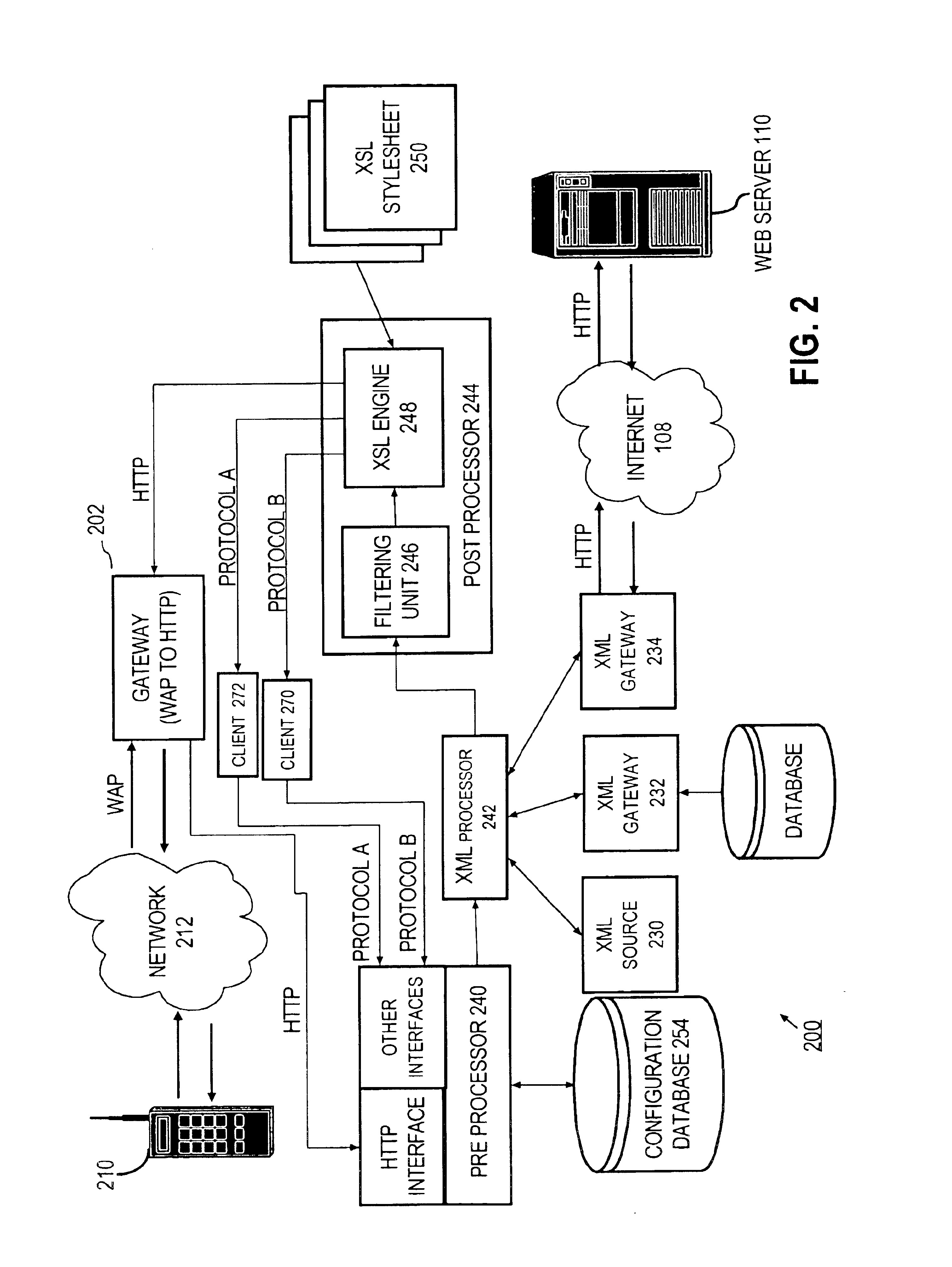
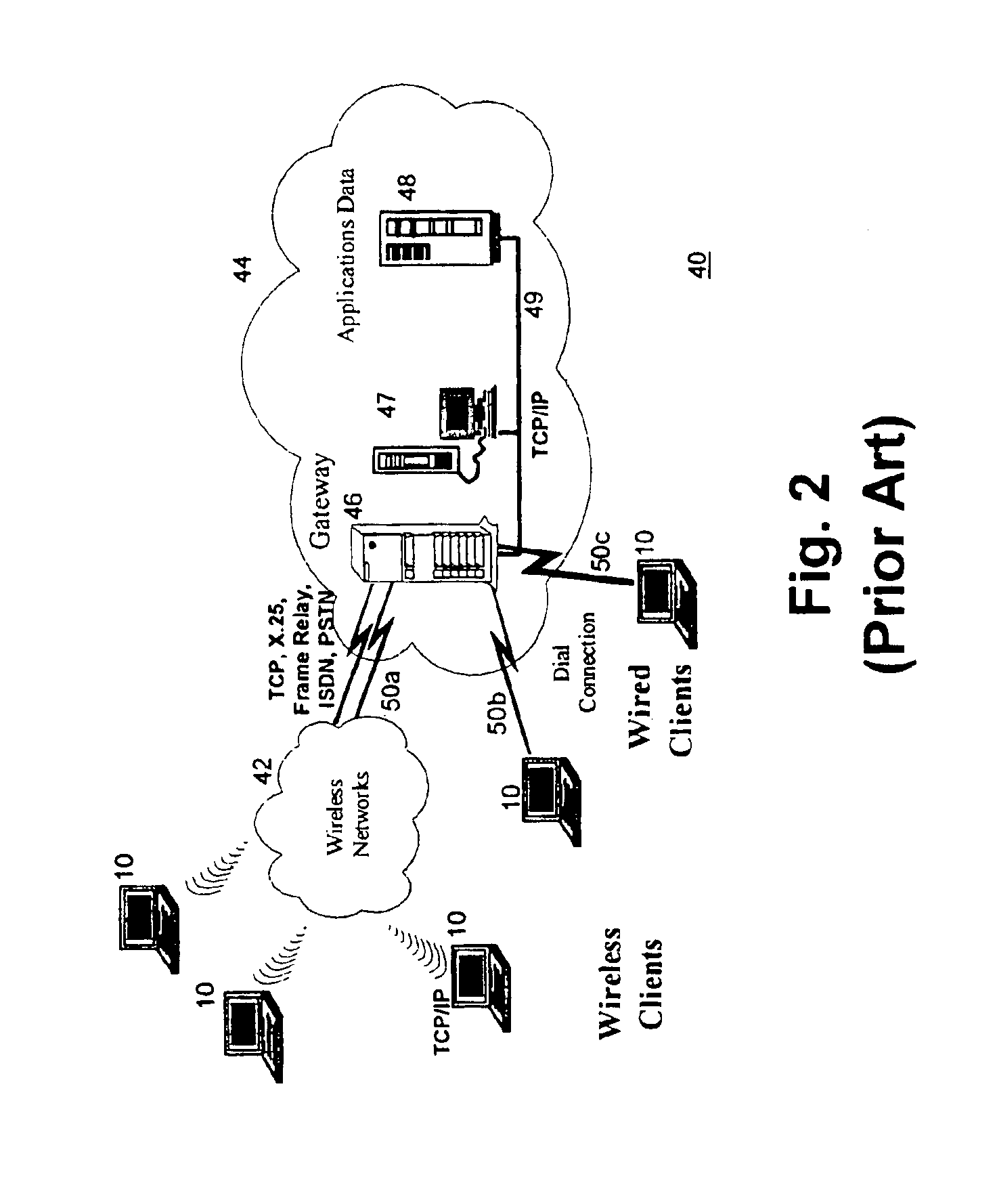
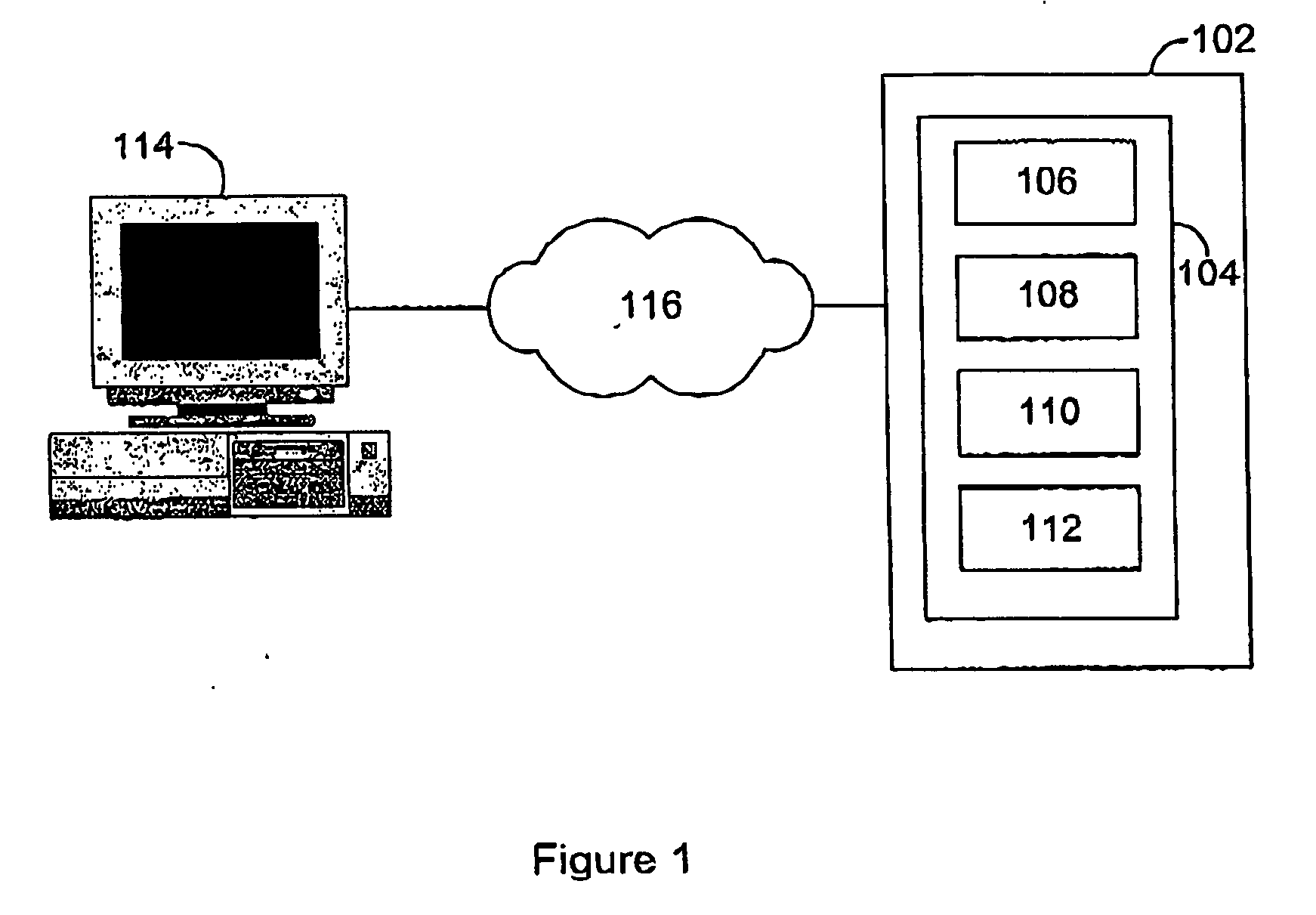
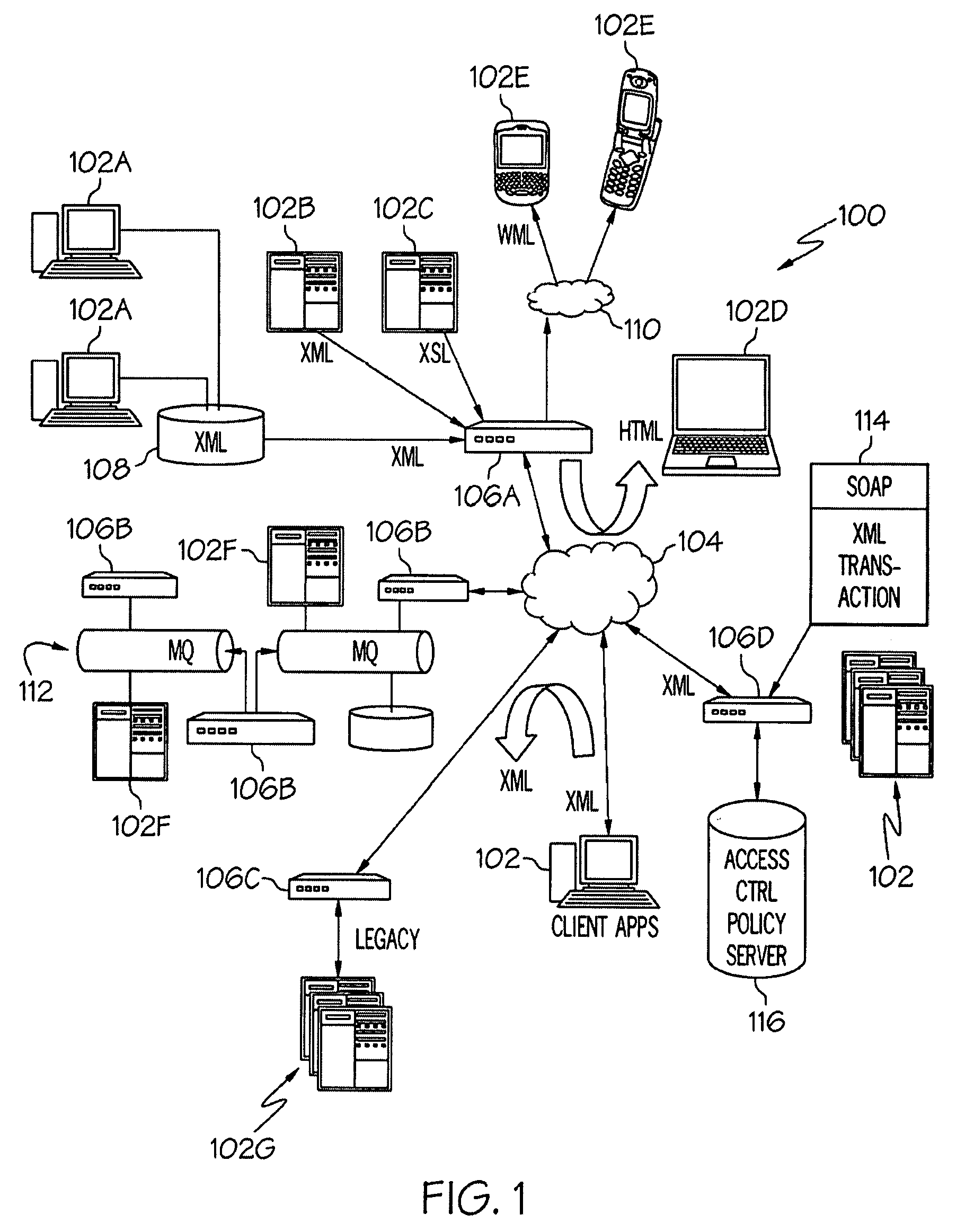
Providing clients with services that retrieve data from data sources that do not necessarily support the format required by the clients
InactiveUS6826597B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalPost processorData source
A method and system for allowing clients to retrieve data from data sources that do not necessarily support the same protocols and formats as the clients. The clients issue service requests. A pre-processor responds to the requests by generating XML-structured request objects with unresolved links to the data sources that have information required by the clients. An XML processor resolves the links by issuing requests through one or more gateways. The gateways convert the responses received from the data sources into XML, which the XML processor uses to create XML composite response documents. A post-processor filters the XML response documents, and applies XSL stylesheets to transform the XML composite response documents into client-specific responses that conform to the format required by the clients. The client-specific responses are then sent to the clients.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
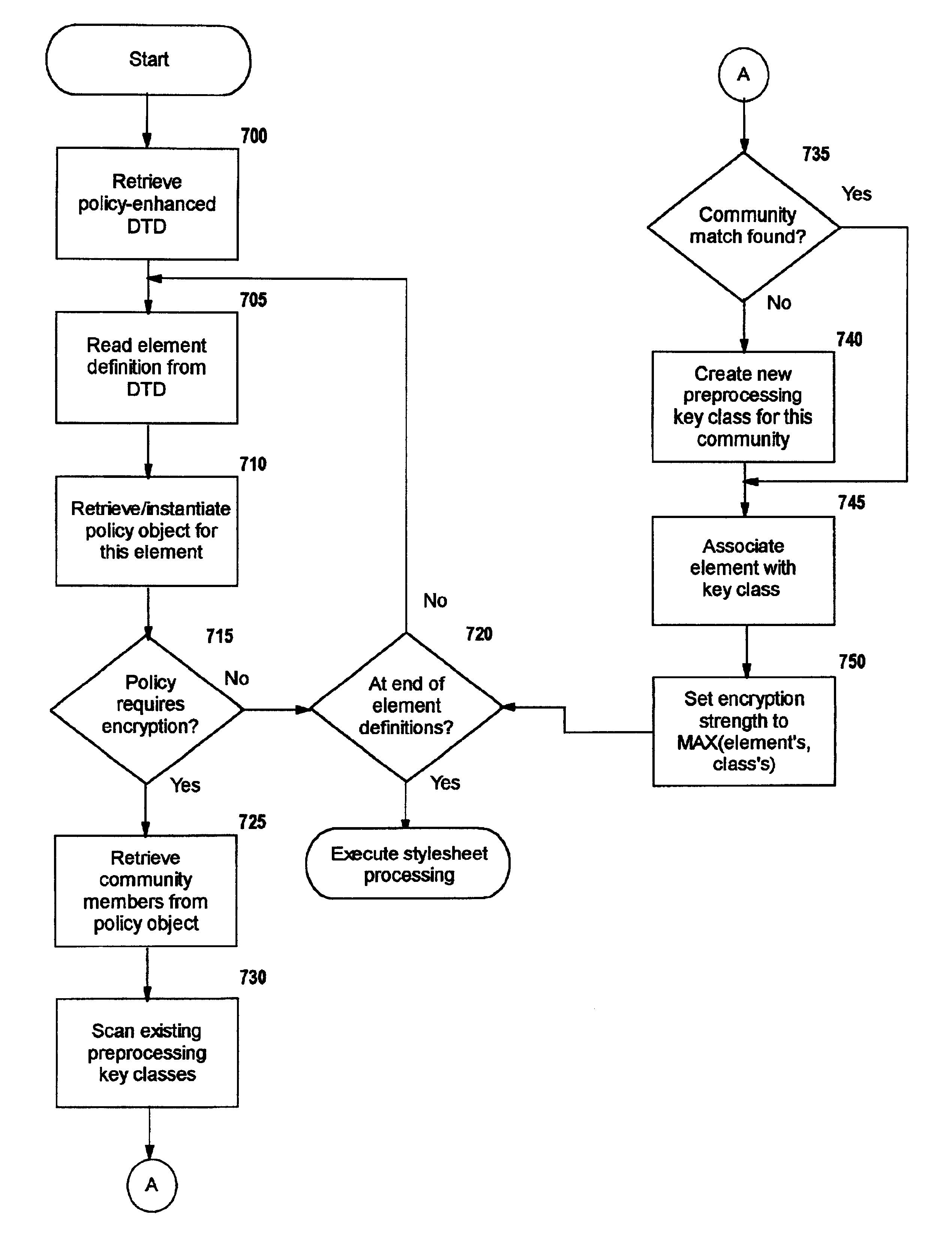
Selective data encryption using style sheet processing
InactiveUS6931532B1Security policy efficientlyEfficiently enforcedKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEngineeringExtensible markup
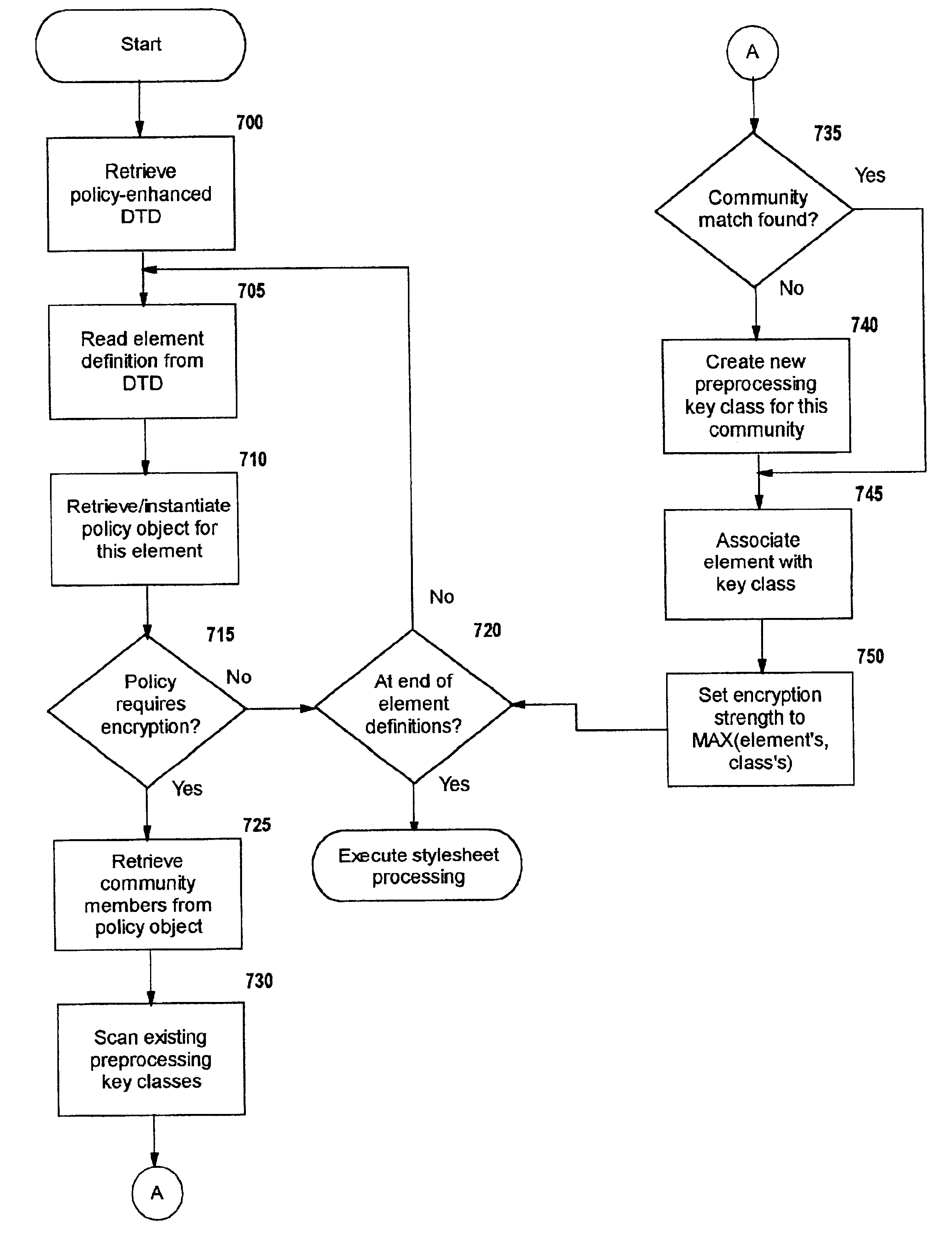
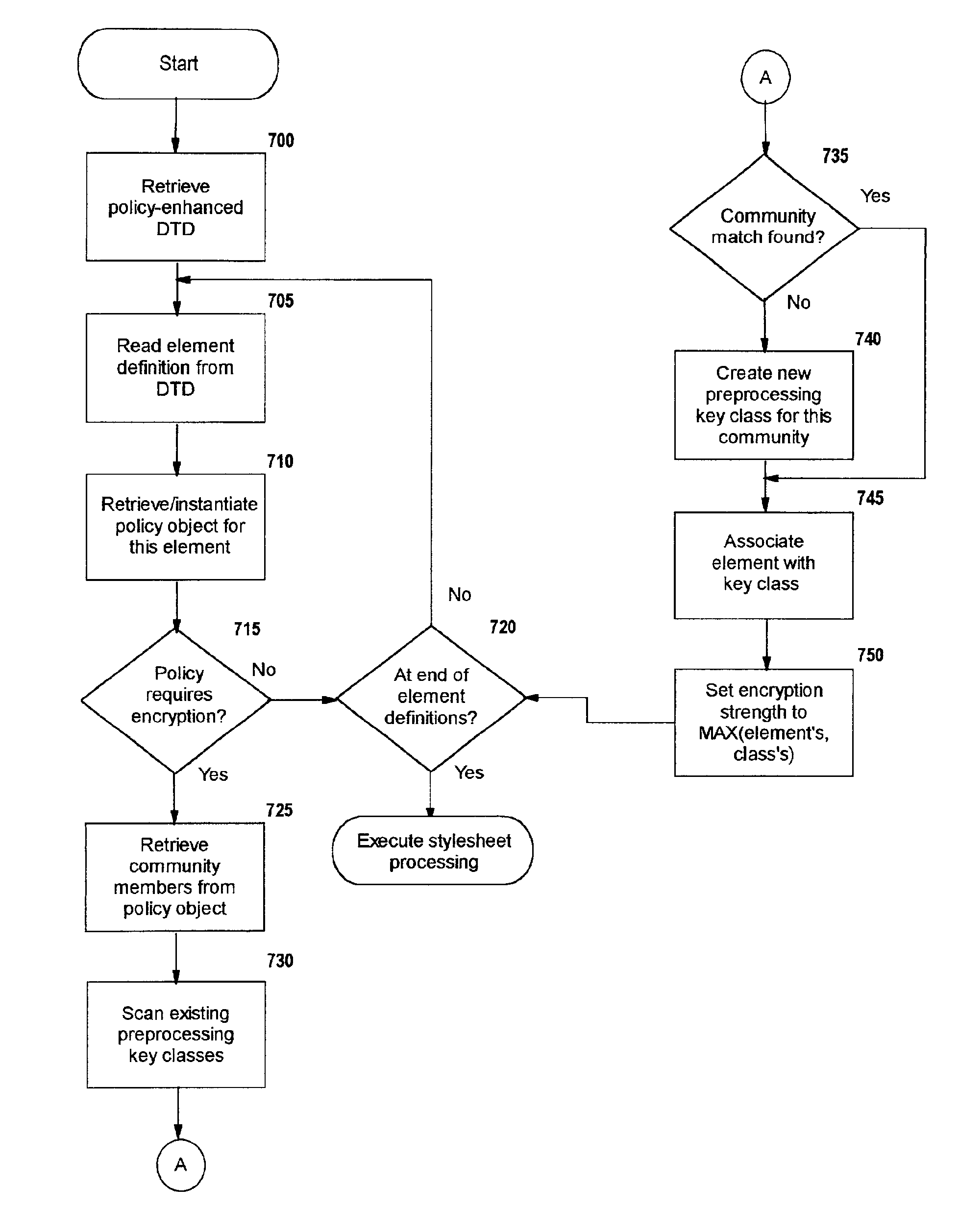
A method, system, and computer program product for selectively encrypting one or more elements of a document using style sheet processing. Disclosed is a policy-driven augmented style sheet processor (e.g. an Extensible Stylesheet Language, or “XSL”, processor) that creates a selectively-encrypted document (e.g. an Extensible Markup Language, or “XML”, document) carrying key-distribution material, such that by using an augmented document processor (e.g. an augmented XML processing engine), an agent can recover only the information elements for which it is authorized. The Document Type Definition (DTD) or schema associated with a document is modified, such that the DTD or schema specifies a reference to stored security policy to be applied to document elements. Each document element may specify a different security policy, such that the different elements of a single document can be encrypted differently (and, some elements may remain unencrypted). The key distribution material enables a document to be encrypted for decryption by an audience that is unknown at the time of document creation, and enables access to the distinct elements of a single encrypted document to be controlled for multiple users and / or groups of users. In this manner, group collaboration is improved by giving more people easier access to information for which they are authorized, while protecting sensitive data from unauthorized agents. A key recovery technique is also defined, whereby the entire document can be decrypted by an authorized agent regardless of how the different elements were originally encrypted and the access protections which were applied to those elements.
Owner:IBM CORP
Selective data encryption using style sheet processing for decryption by a client proxy
InactiveUS6978367B1Security policy efficientlyEfficiently enforcedKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDocumentation procedureDocument preparation
A method, system, and computer program product for selectively encrypting one or more elements of a document using style sheet processing. Disclosed is a policy-driven augmented style sheet processor (e.g. an Extensible Stylesheet Language, or “XSL”, processor) that creates a selectively-encrypted document (e.g. an Extensible Markup Language, or “XML”, document) carrying key-distribution material, such that by using an augmented document processor (e.g. an augmented XML processing engine), an agent can recover only the information elements for which it is authorized. The Document Type Definition (DTD) or schema associated with a document is modified, such that the DTD or schema specifies a reference to stored security policy to be applied to document elements. Each document element may specify a different security policy, such that the different elements of a single document can be encrypted differently (and, some elements may remain unencrypted). The key distribution material enables a document to be encrypted for decryption by an audience that is unknown at the time of document creation, and enables access to the distinct elements of a single encrypted document to be controlled for multiple users and / or groups of users. In this manner, group collaboration is improved by giving more people easier access to information for which they are authorized, while protecting sensitive data from unauthorized agents. A key recovery technique is also defined, whereby the entire document can be decrypted by an authorized agent regardless of how the different elements were originally encrypted and the access protections which were applied to those elements.
Owner:IBM CORP
Selective data encryption using style sheet processing for decryption by a key recovery agent
InactiveUS6941459B1Security policy efficientlyEfficiently enforcedKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDocumentation procedureExtensible markup
A method, system, and computer program product for selectively encrypting one or more elements of a document using style sheet processing. Disclosed is a policy-driven augmented style sheet processor (e.g. an Extensible Stylesheet Language, or “XSL”, processor) that creates a selectively-encrypted document (e.g. an Extensible Markup Language, or “XML”, document) carrying key-distribution material, such that by using an augmented document processor (e.g. an augmented XML processing engine), an agent can recover only the information elements for which it is authorized. The Document Type Definition (DTD) or schema associated with a document is modified, such that the DTD or schema specifies a reference to stored security policy to be applied to document elements. Each document element may specify a different security policy, such that the different elements of a single document can be encrypted differently (and, some elements may remain unencrypted). The key distribution material enables a document to be encrypted for decryption by an audience that is unknown at the time of document creation, and enables access to the distinct elements of a single encrypted document to be controlled for multiple users and / or groups of users. In this manner, group collaboration is improved by giving more people easier access to information for which they are authorized, while protecting sensitive data from unauthorized agents. A key recovery technique is also defined, whereby the entire document can be decrypted by an authorized agent regardless of how the different elements were originally encrypted and the access protections which were applied to those elements.
Owner:PHONENICIA INNOVATIONS LLC SUBSIDIARY OF PENDRELL TECH
Selective data encryption using style sheet processing for decryption by a group clerk
InactiveUS6961849B1Security policy efficientlyEfficiently enforcedKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEngineeringExtensible markup
A method, system, and computer program product for selectively encrypting one or more elements of a document using style sheet processing. Disclosed is a policy-driven augmented style sheet processor (e.g. an Extensible Stylesheet Language, or “XSL”, processor) that creates a selectively-encrypted document (e.g. an Extensible Markup Language, or “XML”, document) carrying key-distribution material, such that by using an augmented document processor (e.g., an augmented XML processing engine), an agent can recover only the information elements for which it is authorized. The Document Type Definition (DTD) or schema associated with a document is modified, such that the DTD or schema specifies a reference to stored security policy to be applied to document elements. Each document element may specify a different security policy, such that the different elements of a single document can be encrypted differently (and, some elements may remain unencrypted). The key distribution material enables a document to be encrypted for decryption by an audience that is unknown at the time of document creation, and enables access to the distinct elements of a single encrypted document to be controlled for multiple users and / or groups of users. In this manner, group collaboration is improved by giving more people easier access to information for which they are authorized, while protecting sensitive data from unauthorized agents. A key recovery technique is also defined, whereby the entire document can be decrypted by an authorized agent regardless of how the different elements were originally encrypted and the access protections which were applied to those elements.
Owner:IBM CORP
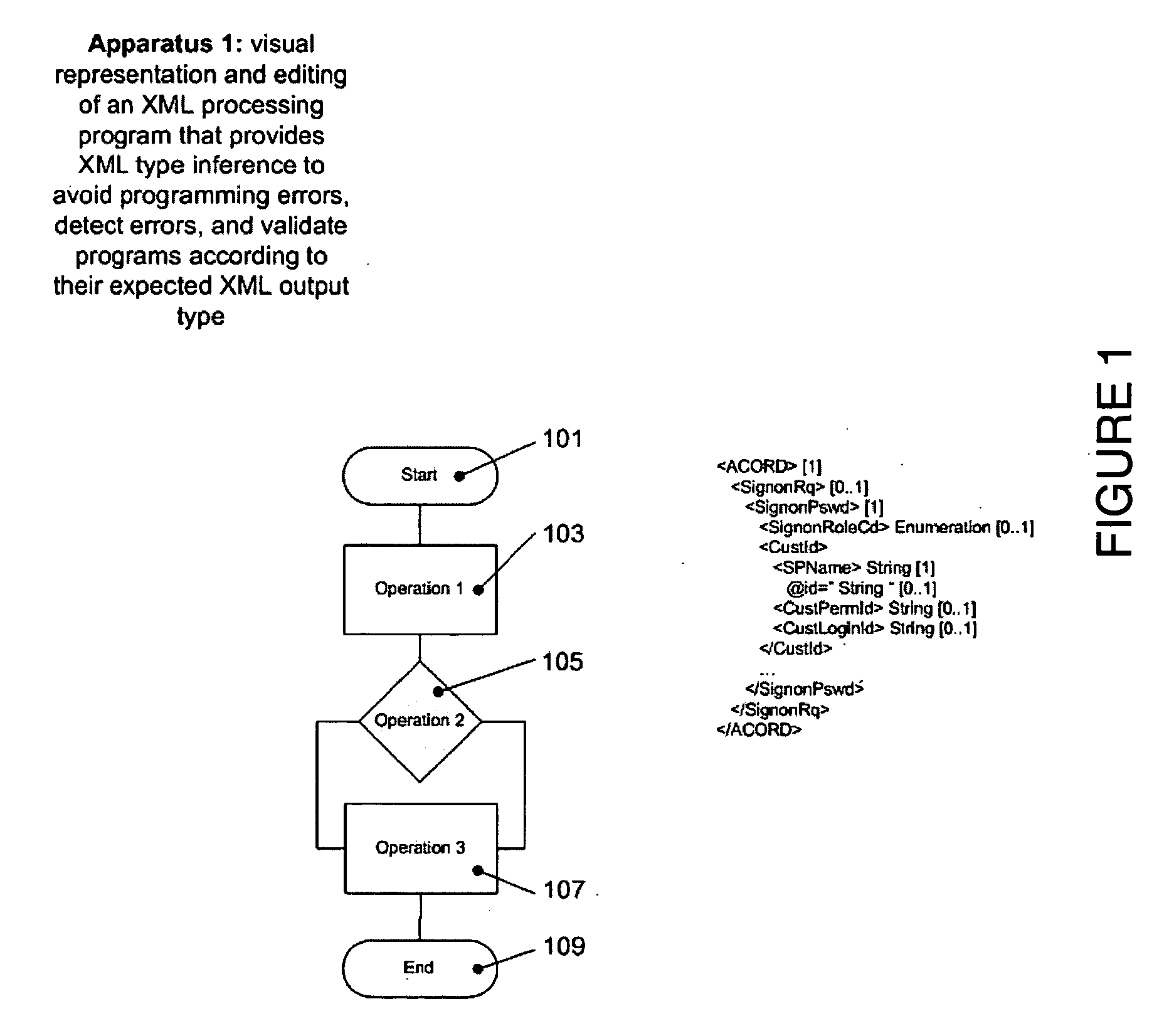
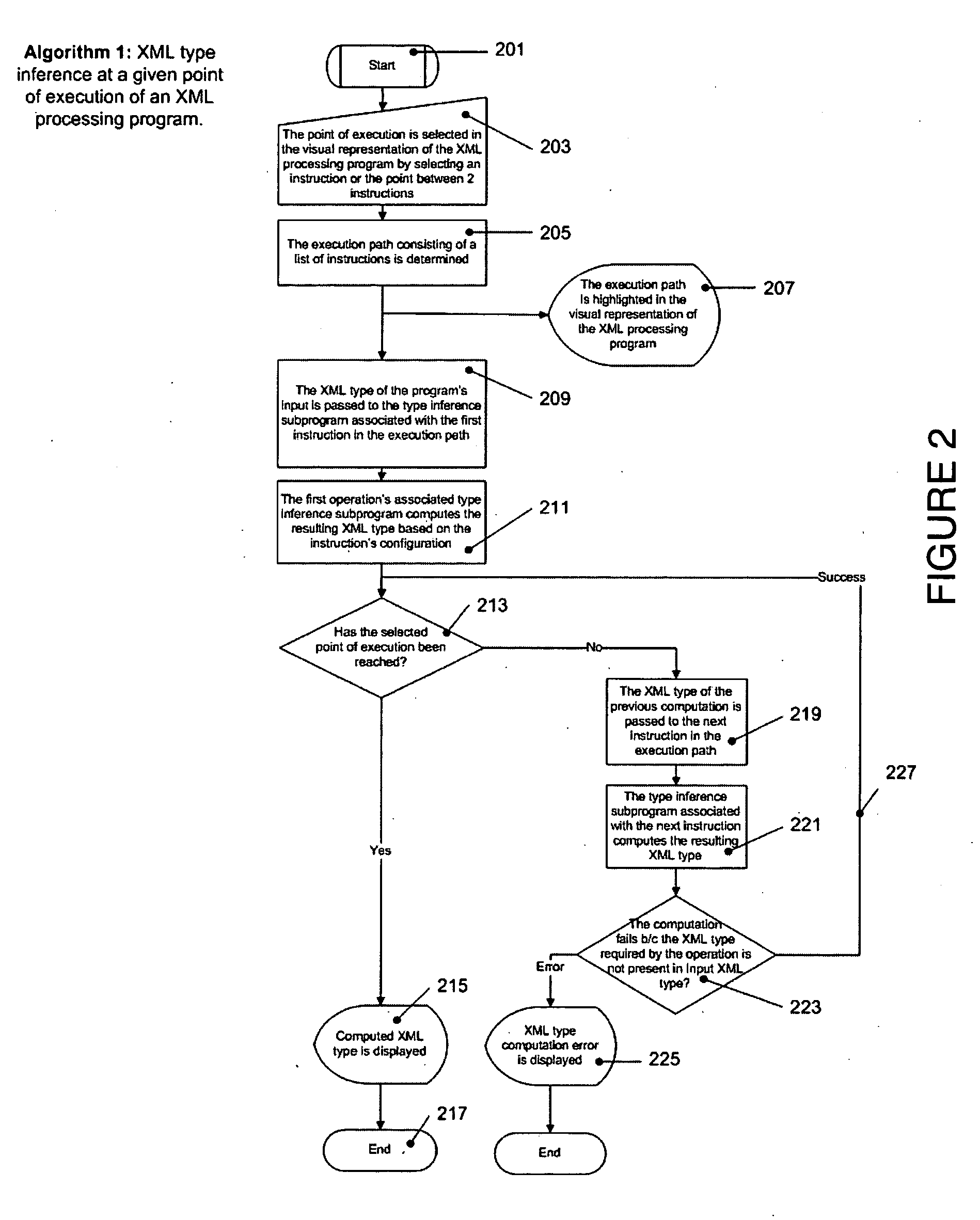
Graphical XML programming system and engine where XML processing programs are built and represented in a graphical fashion
ActiveUS20060075387A1Fix bugsDesign errorNatural language data processingVisual/graphical programmingChange managementWeb service
A system and methods are provided for operating and building graphically XML processing programs, guiding the user in development of the program, preventing and detecting development errors as the program is being designed, ensuring that the program is valid, i.e. satisfies required input and output constraints at all times, i.e. from the time it is developed to when it is deployed in a production environment, ensuring the automated change management if the internal logic of the Web service, or data sources called by the service or the schema that underlies the Web service are modified. The system includes a graphical XML Programming system where XML processing programs are built and represented in a graphical fashion, a real-time metadata computation and visualization method for each selected execution point in the visual program that provides guided programming, error prevention and detection, and change impact analysis and change management, and, an automated execution path exploration method that enables overall program validation and error identification. The system and methods allow a user to reduce by at least a factor of 2 the costs of development and maintenance of reliable XML processing programs such as Web Services.
Owner:DIEBOLD NIXDORF
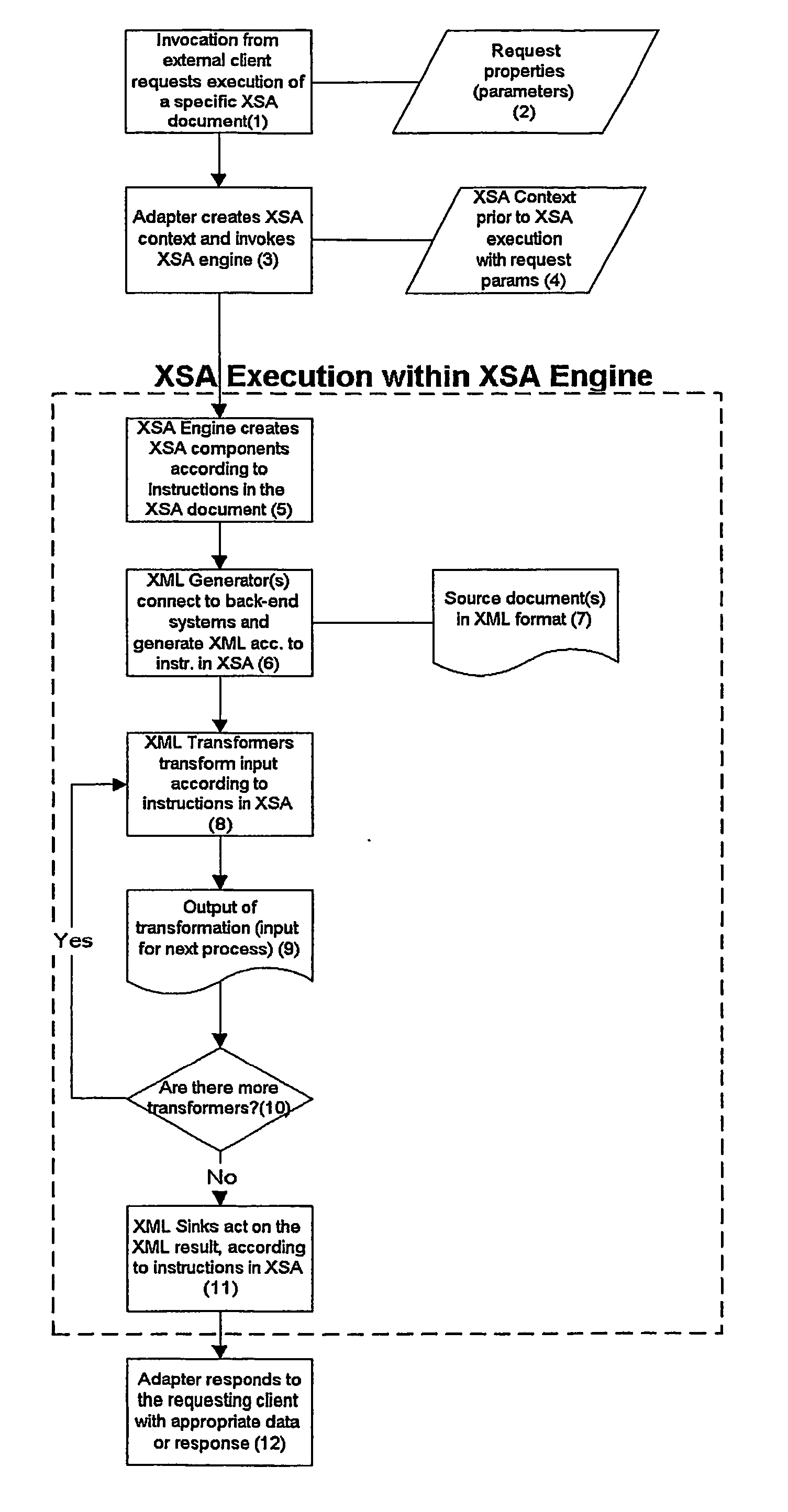
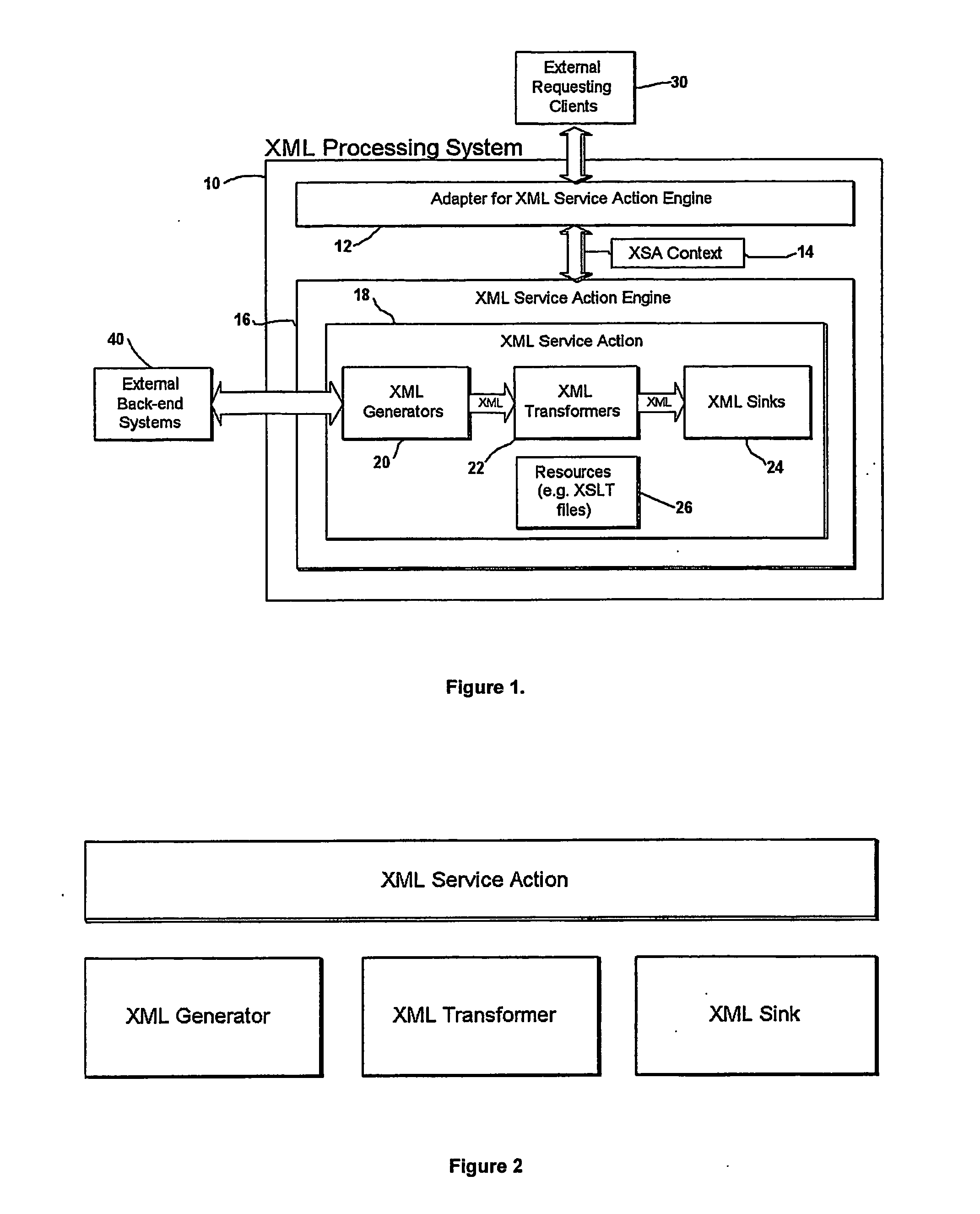
System and method for a context-independent framework for management and execution of xml processing tasks
InactiveUS20060155529A1Diminishes and even needReduce needNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsGeneral purposeElectronic document
A system for a context-independent framework for management and execution of XML processing tasks is provided. The XML processing tasks are executed by a module, herein referred to as the XSA Engine, according to a predefined set of instructions provided as electronic documents written in a special purpose, XML-based, programming language. The instruction sets contain references to, and control the execution of, instances of three classes of processing modules, which independently accomplish an XML processing subtask and jointly accomplish an XML processing task. The framework is decoupled from any specific execution context, meaning that standardized XML processing can be applied in almost any desired application. The special purpose programming language enhances productivity for development of XML processing tasks as compared to using general purpose programming languages, and diminishes the need for writing custom code to link different types of XML processing subtasks to accomplish an XML processing task.
Owner:TEAMWARE GROUP
Document assembly system
ActiveUS20060036612A1Digital data processing detailsNatural language data processingXML schemaData source
A document assembly or document automation system includes an assembler for generating an instance document on the basis of a source document and one or more logic source documents referenced by the source document. The source document and logic source documents are XML documents including at least one XML processing instruction. The source document and logic source documents are valid with respect to XML schema. The system generates an instance document in HTML, PDF or RTF format by resolving variables in the source document and / or logic sources using one or more data sources. This may involve performing one or more interview rounds with a user of the system, access to a database, and / or evaluation of a function defined in one of the documents. The system includes an editor for creating and maintaining source documents and logic source documents whilst maintaining their validity with respect to the appropriate XML schema.
Owner:SPEEDLEGAL HLDG
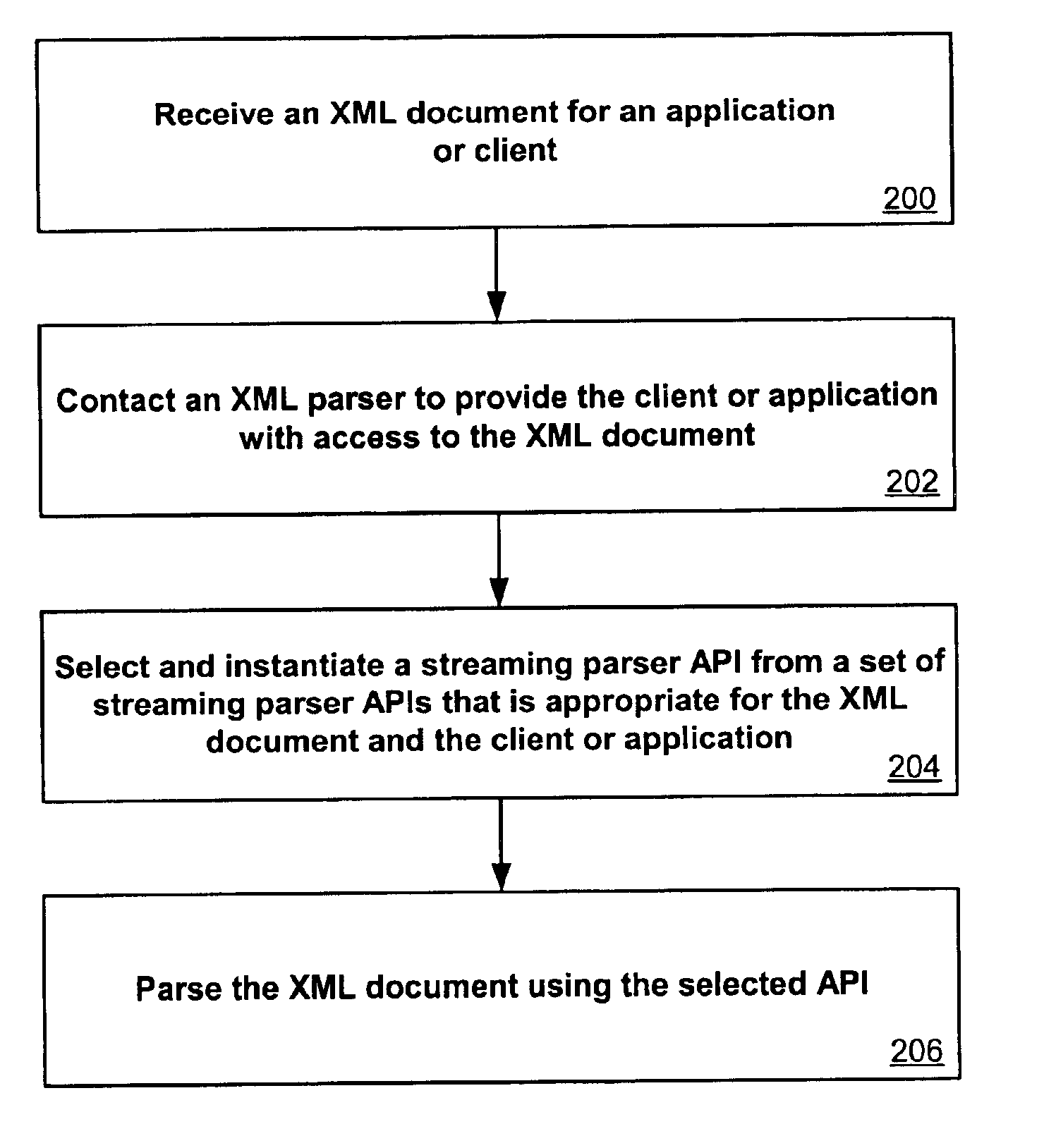
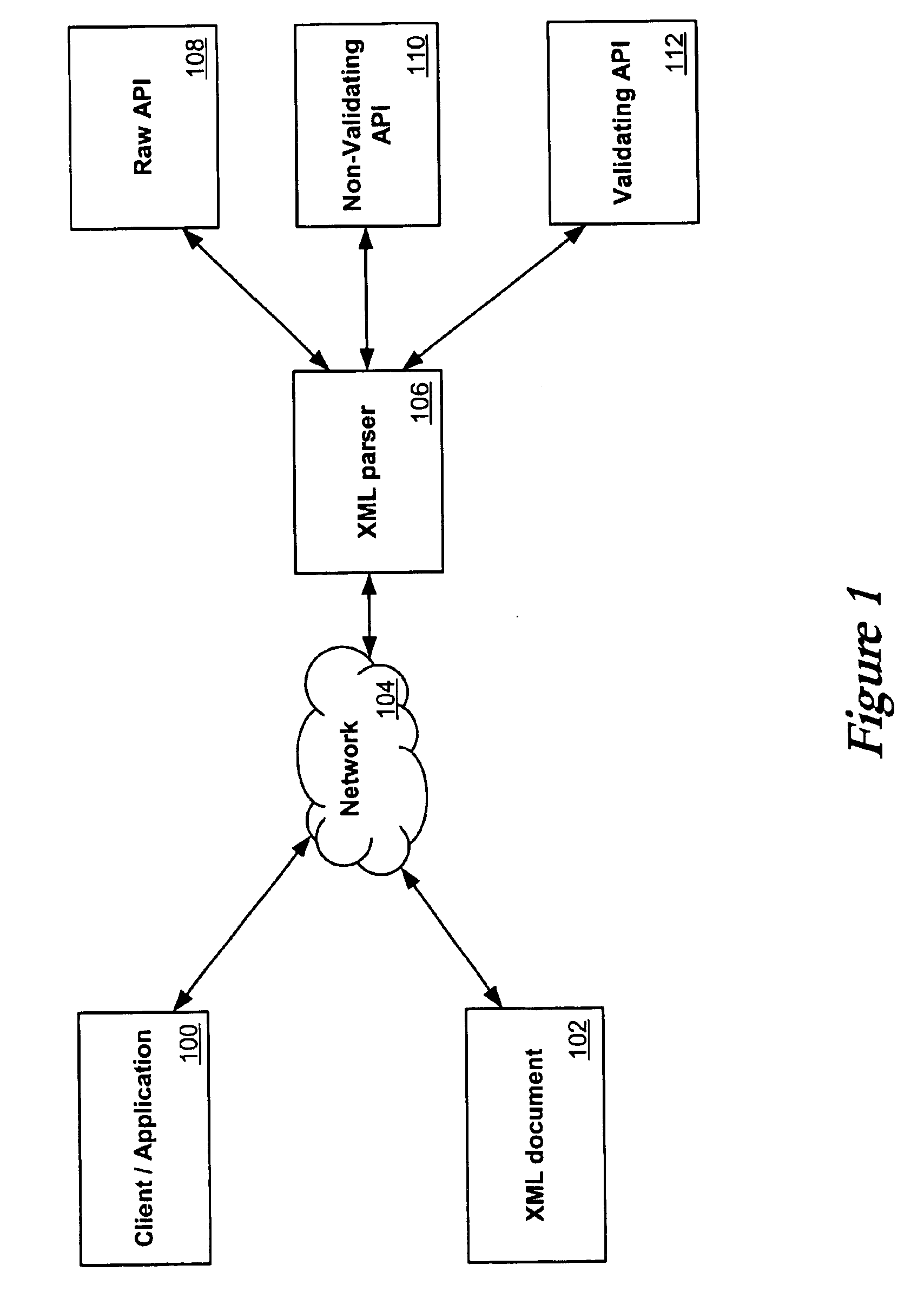
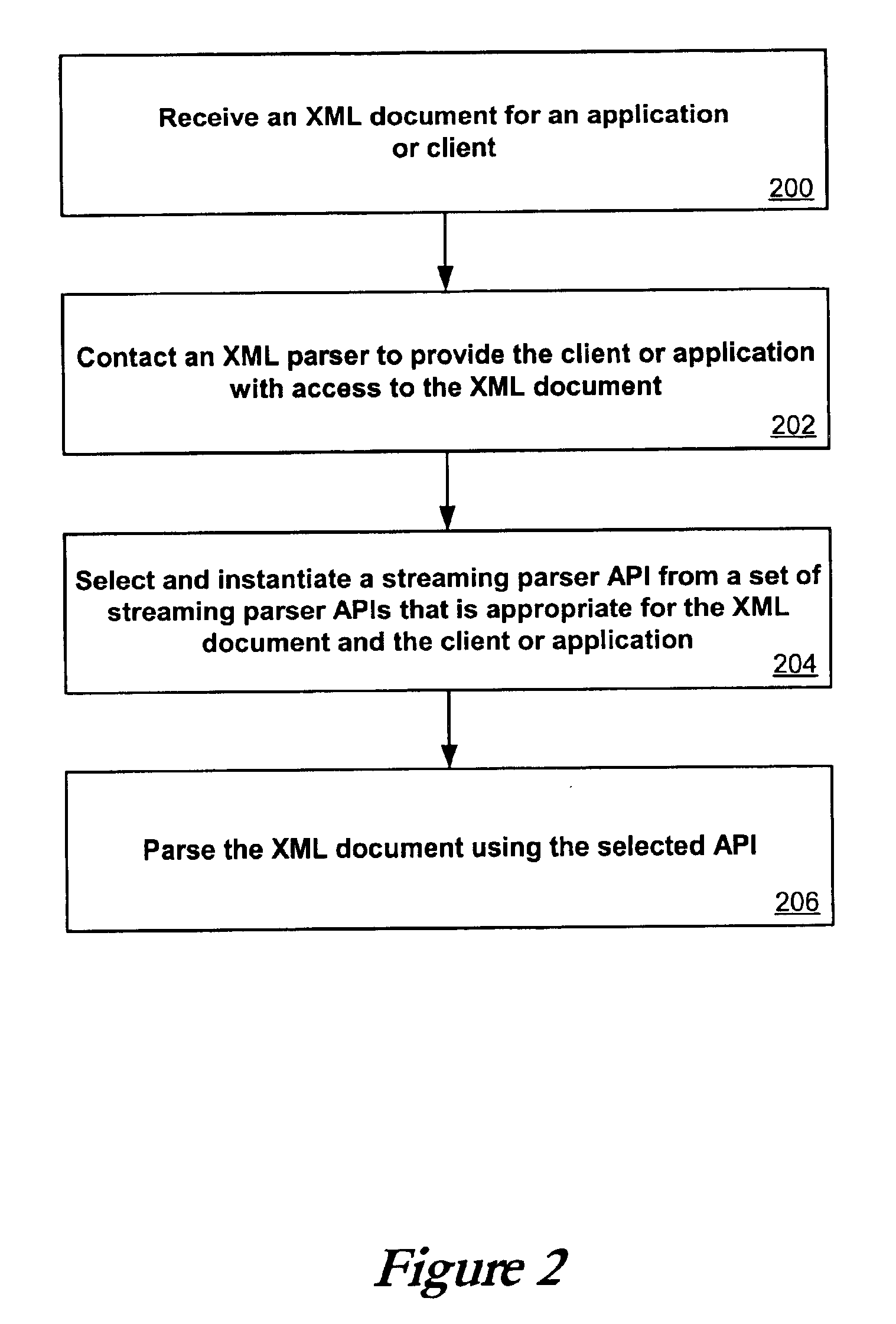
System and method for XML parsing
InactiveUS6880125B2Solid parsing supportIncrease speedDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingClient-sideApplication software
Broad XML support is obtained through use of a set of streaming parser APIs. An application or client needing access to an XML document can contact an XML parser, XML processor, or XML reader in order to gain access to the document. The XML processor selects and instantiates a streaming parser API that is appropriate for the XML document and the client or application. Streaming parser APIs include raw streaming parser APIs, non-validating streaming parser APIs, and validating streaming parser APIs. The XML parser can then provide a variety of types of access to the application or client that does not require the entire document to be read into memory, including providing an XML stream, pulling XML information, and skipping unwanted XML from the document.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
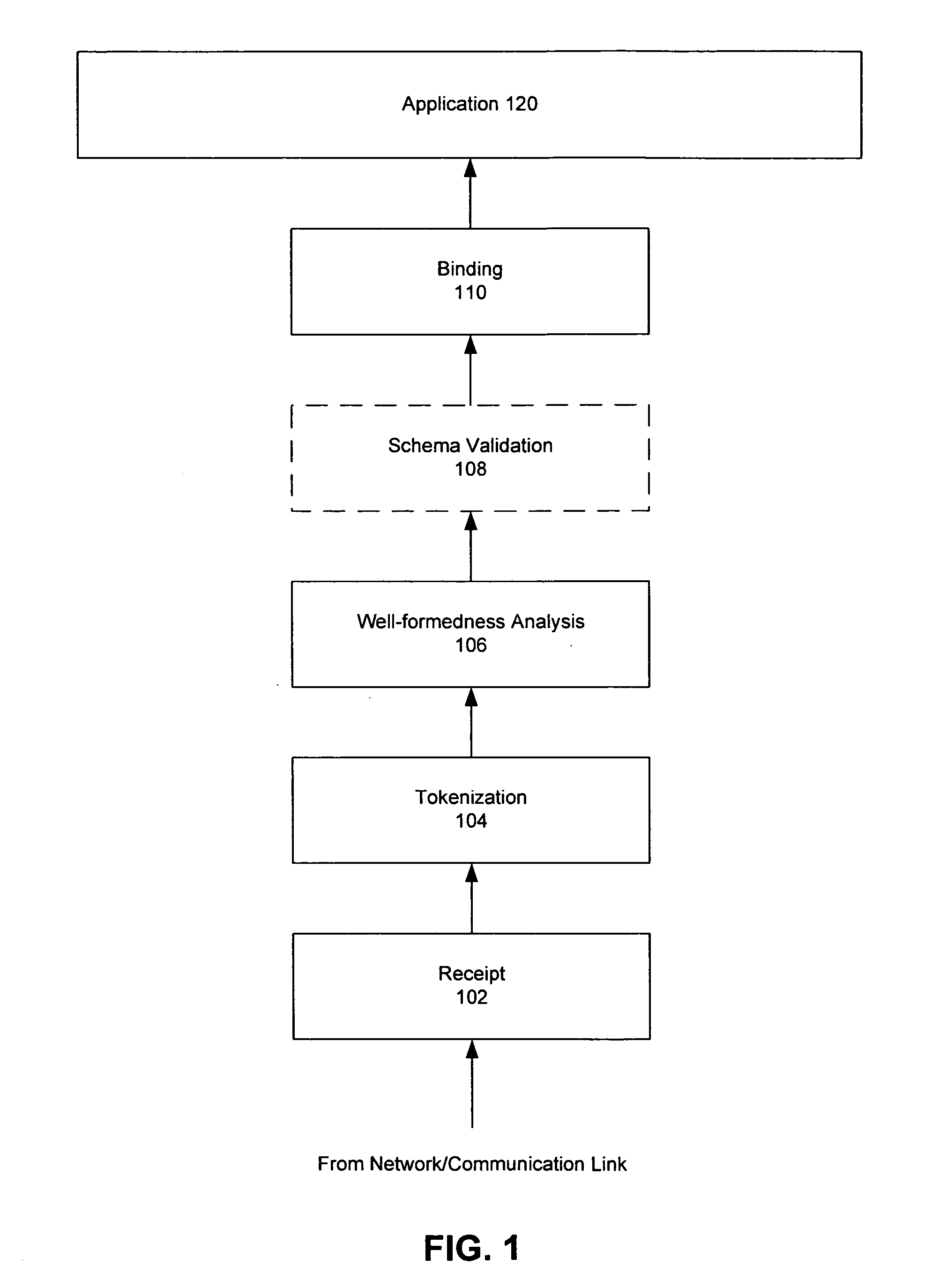
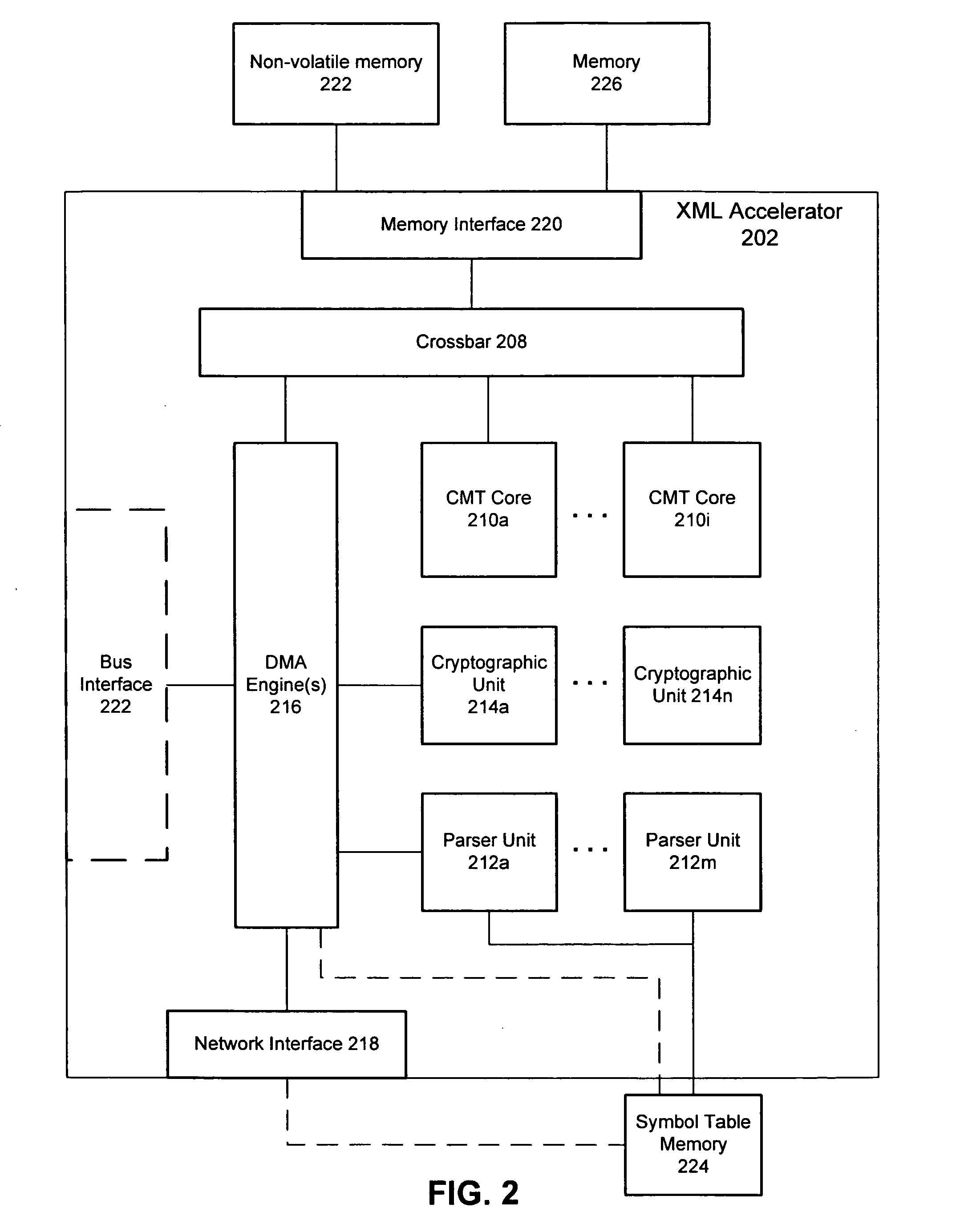
Method and apparatus for hardware XML acceleration
ActiveUS20070113171A1Improved processing security throughputReduce latencyDigital computer detailsProgram controlTerm memoryPaper document
A method and apparatus for accelerating processing of a structured document. A hardware XML accelerator includes one or more processors (e.g., CMT processors), one or more hardware XML parser units, one or more cryptographic units and various interfaces (e.g., to memory, a network, a communication bus). An XML document may be processed in its entirety or may be parsed in segments (e.g., as it is received). A parser unit parses a document or segment character by character, validates characters, assembles tokens from the document, extracts data, generates token headers (to describe tokens and data) and forwards the token headers and data for consumption by an application. A cryptographic unit may enforce web security, XML security or some other security scheme, by providing encryption / decryption functionality, computing digital signatures, etc. Software processing, bus utilization and latencies (e.g., memory, bus) are greatly reduced, thereby providing significantly improved XML processing and security processing throughput.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
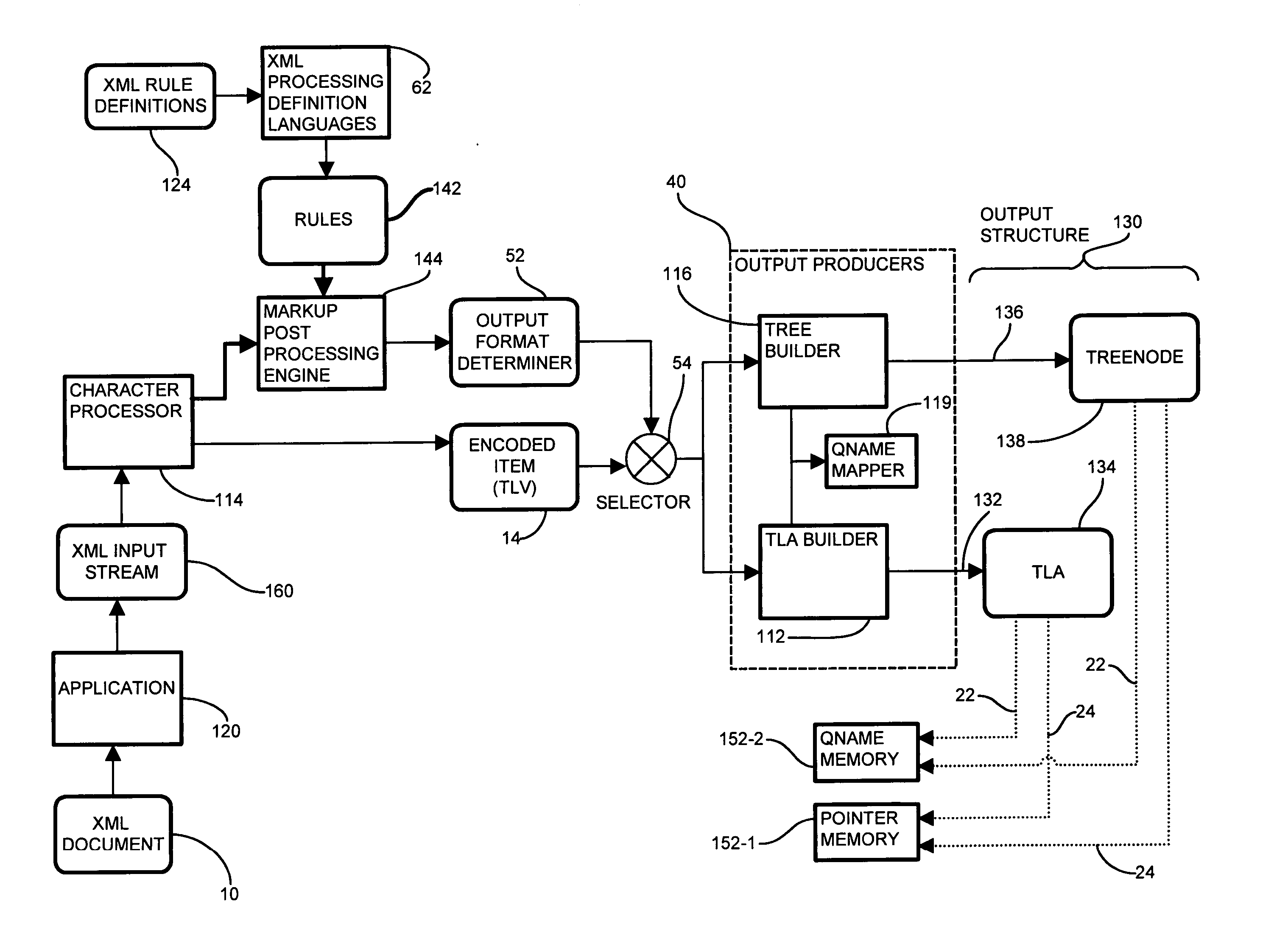
Method and apparatus for processing markup language information
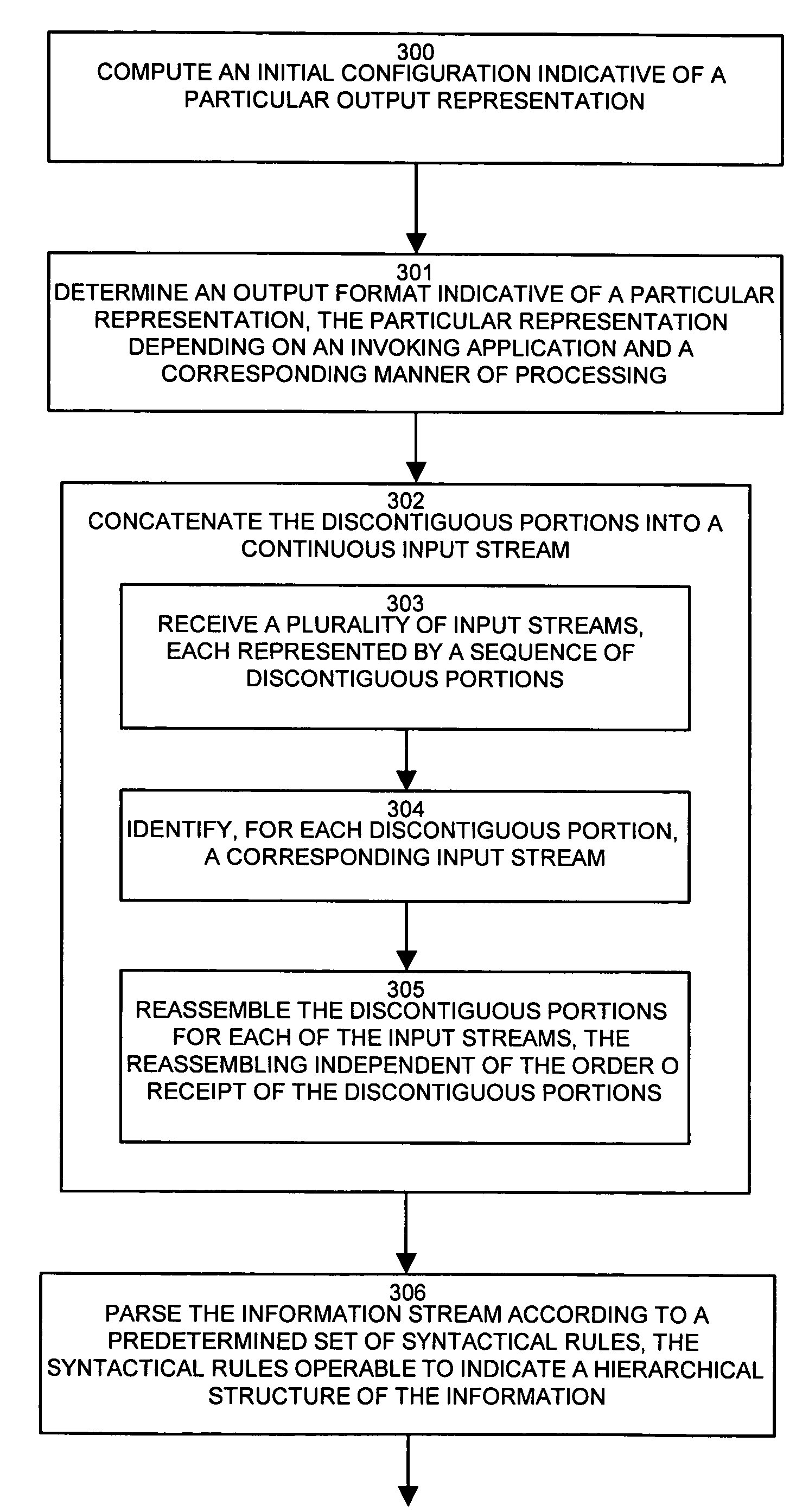
InactiveUS20060236224A1Improve abilitiesRapid parsing and processingNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsData streamApplication software
Information represented in text-based markup languages, such as XML, is often a large, highly nested structure corresponding to complex patterns of metadata and / or data. Parsing such data streams via conventional software mechanisms rapidly exhibits degrading performance as the size, or volume, of data increases. Further, such do not perform dynamic modification to the output in response to feedback based on the data being parsed. An adaptive XML processing hardware apparatus processes an XML document in a manner suited to the invoking application, and processes the incoming XML into an optimal structure based on the type of data and a set of rules relating the type of the data to the output format. It also dynamically augments the output information stream based on the data, at the option of the invoking system. The generated output may take a tree form, adaptable for efficient traversal of the hierarchical structure represented by the input XML, or may involve an attribute approach, in which the XML takes the from of a stream of fixed length cells containing optimized representations of input data, or may take a combination of the two approaches, based on configuration and XML input stream.
Owner:IBM CORP
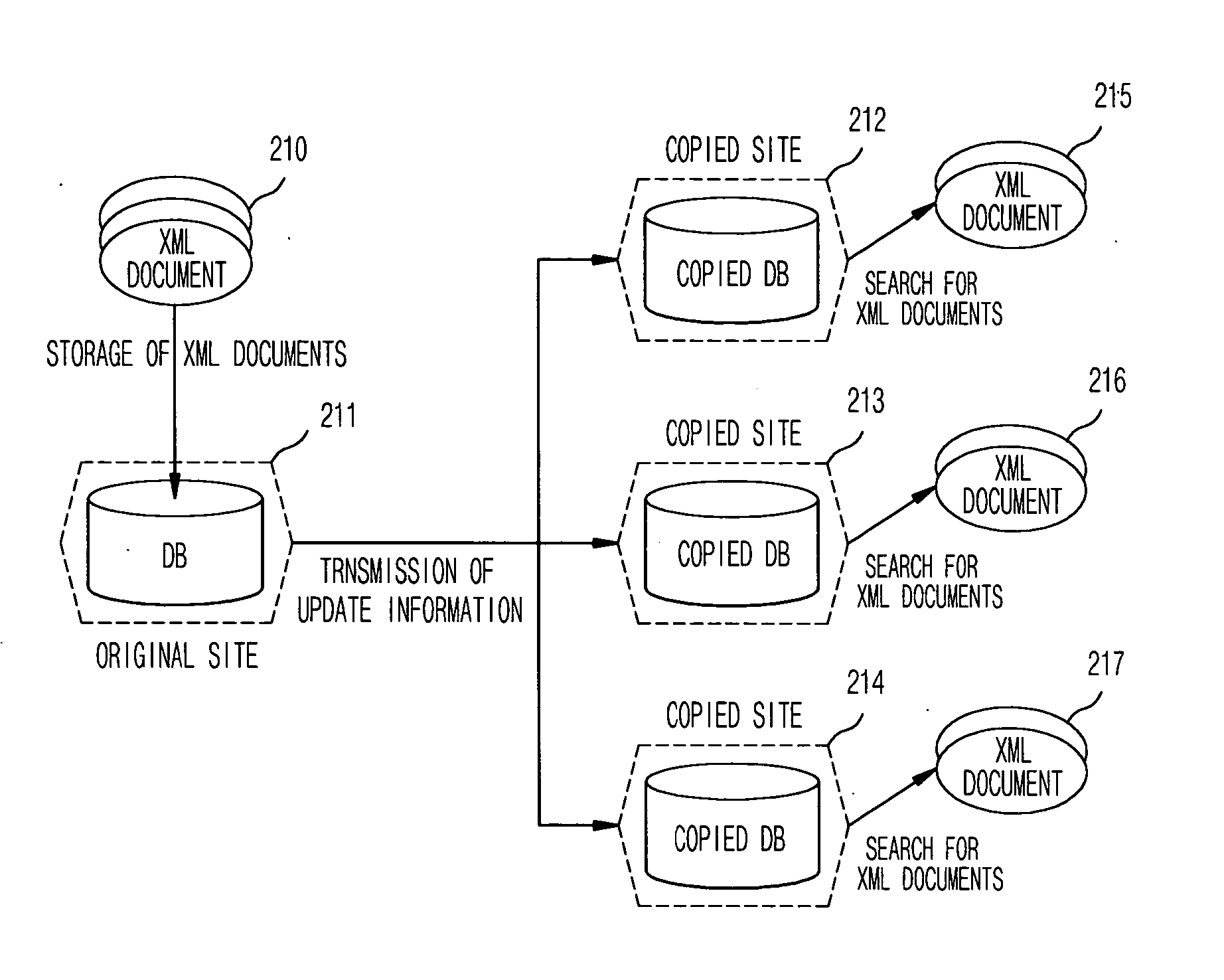
XML database duplicating apparatus for copying XML document to remote server without loss of structure and attribute information of XML document and method thereof
InactiveUS20050138048A1Keep in syncMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsThe InternetXML database
Disclosed is an XML database duplicating apparatus and method capable of providing an effective application service without interruption at a low cost in the diverse Internet environments by copying an XML document of a database system mounting an XML processing technique to another remote server. When the XML document stored in a database of the original server is copied to databases of copied servers, the structure and attribute information included in the XML document are maintained as they are, and thus the respective copied servers can support the searches based on the contents and the attribute provided by an XML query language and disperse users' queries concentrated to the original server to the respective copied servers, so that the service request for application programs can be processed.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
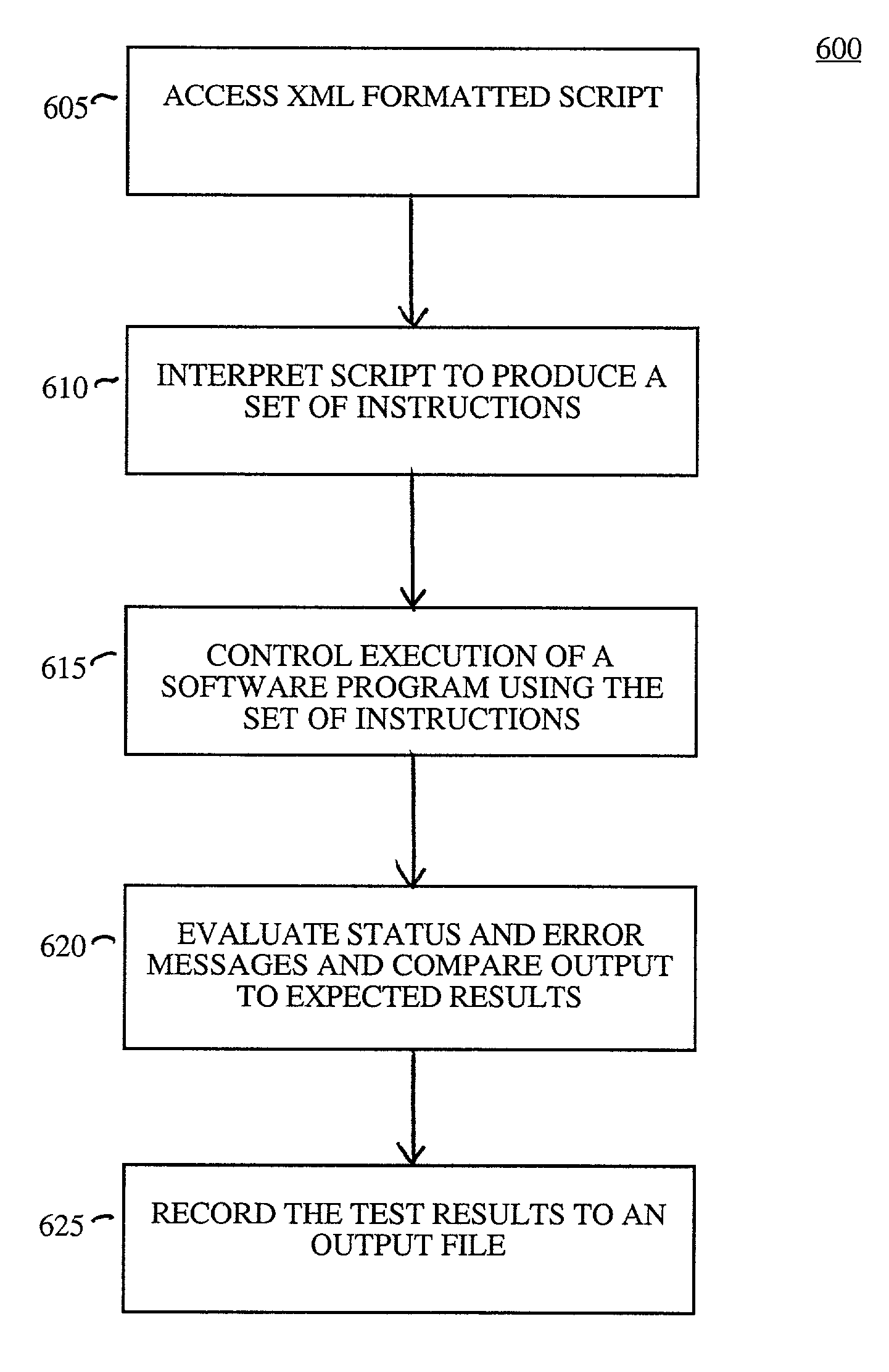
System and method for software testing with extensible markup language and extensible stylesheet language
ActiveUS7127641B1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsScripting languageSoftware engineering
A system and method for using Extensible Markup Language (XML) as a scripting language to drive testing of a software program. XML is used to define a markup language in a script that provides commands that are interpreted by a test control processor. The test control processor includes an XML processor for processing the script. Using the script, the test control processor submits instructions to a software program and extracts the behavior of the software program. The software program behavior is tested by submitting multiple sets of instructions and comparing the results. Information regarding the software program behavior and test results is written to an output log file by the test control processor.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
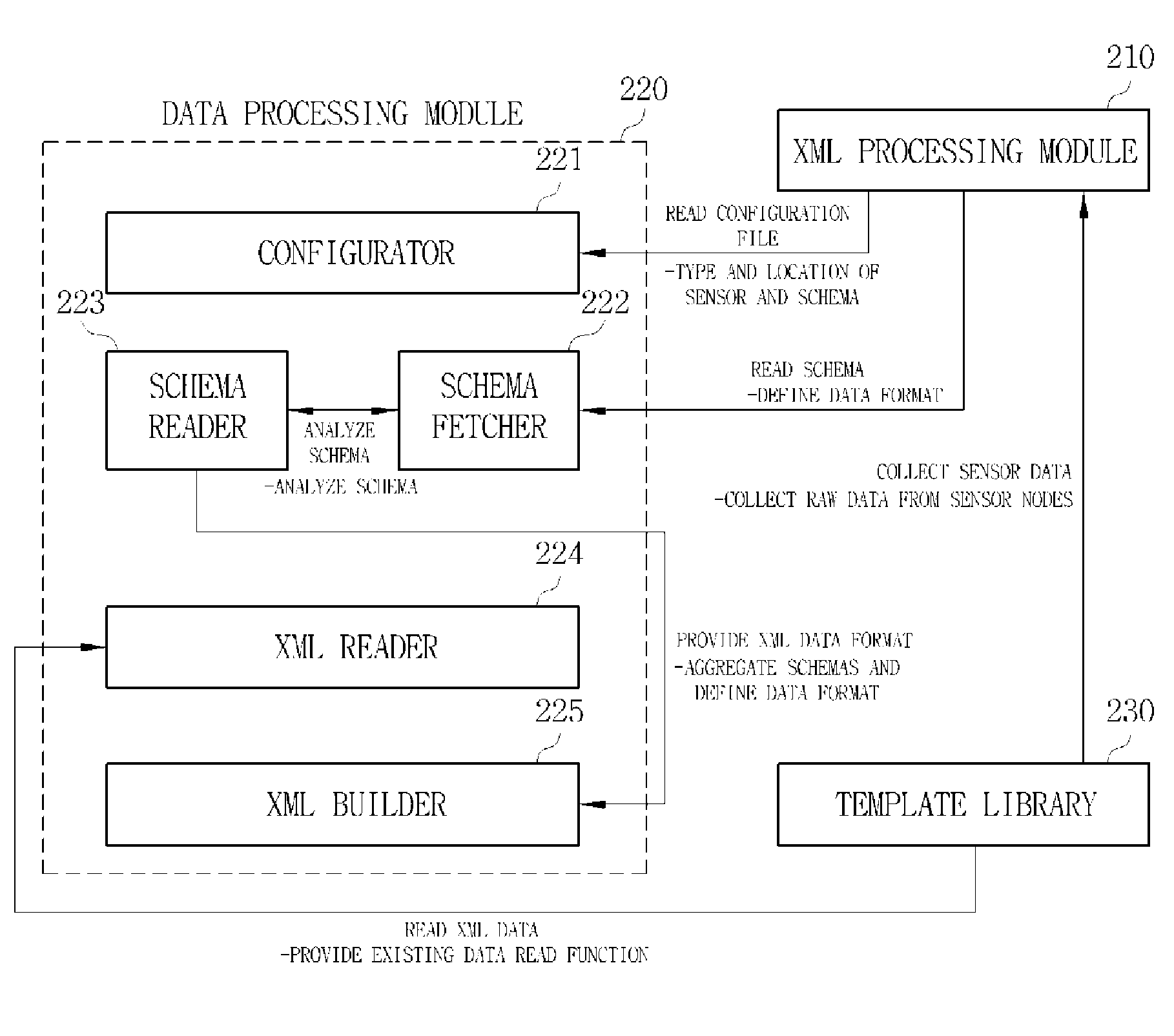
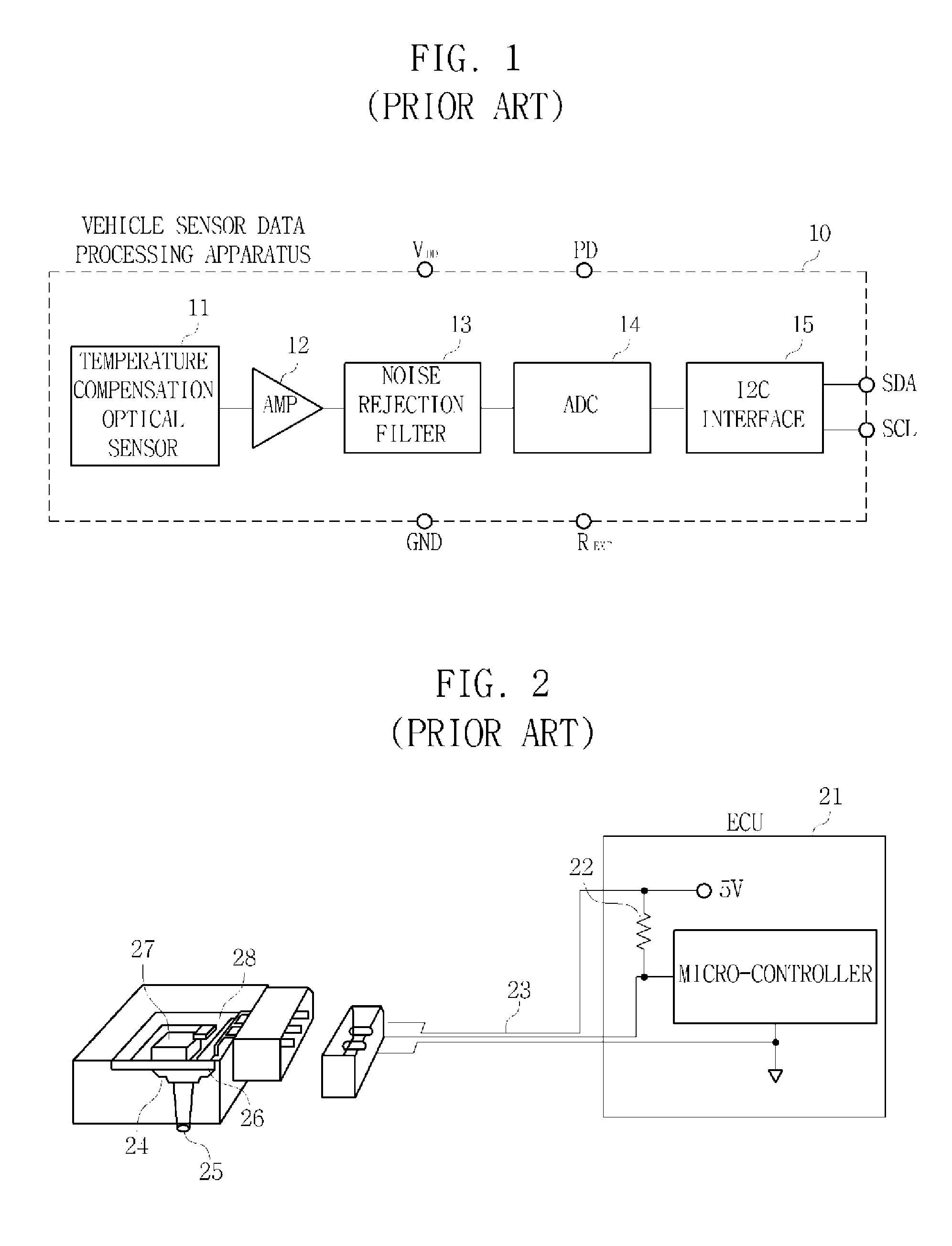
Apparatus and method for processing sensor data for vehicle using extensible markup language
InactiveUS20110161804A1Easy to optimizeSimple processCode conversionTransmissionBatch processingExtensible markup
An apparatus and a method for processing sensor data for a vehicle using an unified data format eXtensible Markup Language in process of data communication between various vehicle sensors and a vehicle application system, which facilitates transmit and receive data processing in terms of a vehicle network of the sensors and the application system are provided. The apparatus for processing the sensor data for the vehicle using the XML includes a plurality of vehicle sensors installed inside the vehicle for detecting a change of physical quantity and providing a detection signal; a sensor transducer for converting the detection signal of the vehicle sensors to an electrical analog signal; a signal conditioning unit for amplifying the electrical analog signal to a measurable signal; an Analog / Digital Converter (ADC) for converting the amplified analog signal to sensor data of a digital signal; a frame generator for generating and providing the sensor data converted to the digital signal per frame; and a sensor data converter comprising a Dynamic data Exchange Channel (DEC) for batch-processing the sensor data input from the frame generator per frame, in an XML format. The DEC of the sensor data converter defines a structure of the sensor data using a schema of the XML and converts the sensor data format to the XML format at the same time.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRONICS TECH INST
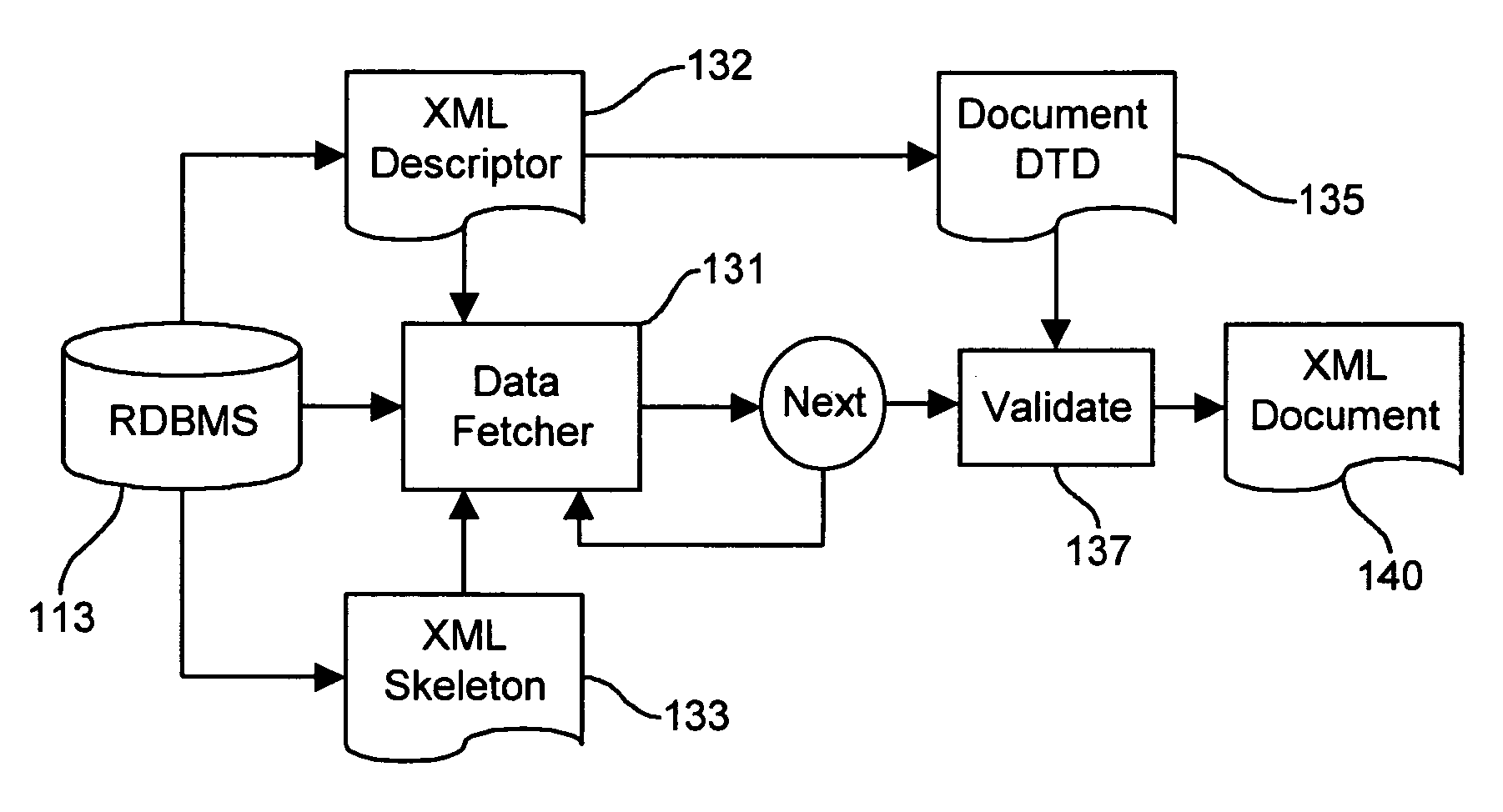
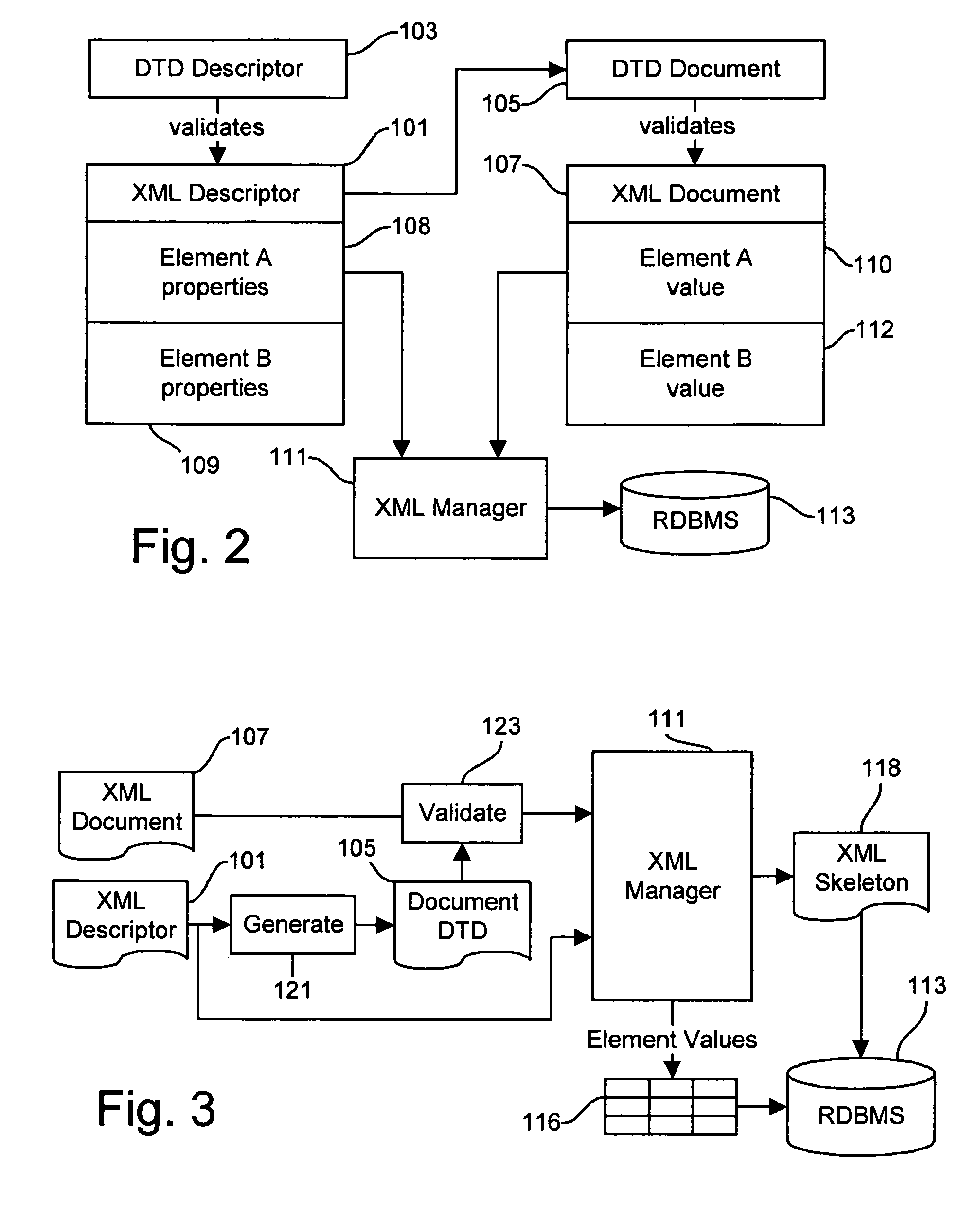
Dynamic XML processing system
InactiveUS7287216B1Power capacityData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExtensible markupDocument preparation
A system for storing and dynamically updating data represented in the Extensible Markup Language (XML) which separates the data values in at least some of the elements of an XML document and places those data values in relational database tables where they may be processed using conventional RDBMS techniques. The hierarchical structure of the XML document is saved separately in an XML skeleton object from which element data other than primary key values has been removed. The XML documents document type definition (DTD) is stored, along with additional property data used the RDBMS, in an XML Definition object. The additional property information includes the identification of primary key data values which are used to link the structural definition data to the value data stored in the tables, the designation of data types used for more efficient storage of data from predetermined XML elements, the designation of selected element data for indexing and for column storage, and the designation or relational integrity constraints which help insure that logically connected data is not inappropriately deleted or updated. The XML data as stored in the relational tables can be retrieved as a complete XML document, or selected XML elements can be retrieved by themselves, by merging the table data into the XML skeleton.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for providing graphical representation and development of a processing application
ActiveUS7512840B2Good serviceError detection/correctionNatural language data processingChange managementWeb service
A system and methods are provided for operating and building graphically XML processing programs, guiding the user in development of the program, preventing and detecting development errors as the program is being designed, ensuring that the program is valid, i.e. satisfies required input and output constraints at all times, i.e. from the time it is developed to when it is deployed in a production environment, ensuring the automated change management if the internal logic of the Web service, or data sources called by the service or the schema that underlies the Web service are modified. The system includes a graphical XML Programming system where XML processing programs are built and represented in a graphical fashion, a real-time metadata computation and visualization method for each selected execution point in the visual program that provides guided programming, error prevention and detection, and change impact analysis and change management, and, an automated execution path exploration method that enables overall program validation and error identification. The system and methods allow a user to reduce by at least a factor of 2 the costs of development and maintenance of reliable XML processing programs such as Web Services.
Owner:DIEBOLD NIXDORF
Method and apparatus for processing markup language information
InactiveUS7287217B2Improve abilitiesRapid parsing and processingDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingData streamDocument preparation
Information represented in text-based markup languages, such as XML, is often a large, highly nested structure corresponding to complex patterns of metadata and / or data. Parsing such data streams via conventional software mechanisms rapidly exhibits degrading performance as the size, or volume, of data increases. Further, such do not perform dynamic modification to the output in response to feedback based on the data being parsed. An adaptive XML processing hardware apparatus processes an XML document in a manner suited to the invoking application, and processes the incoming XML into an optimal structure based on the type of data and a set of rules relating the type of the data to the output format. It also dynamically augments the output information stream based on the data, at the option of the invoking system. The generated output may take a tree form, adaptable for efficient traversal of the hierarchical structure represented by the input XML, or may involve an attribute approach, in which the XML takes the from of a stream of fixed length cells containing optimized representations of input data, or may take a combination of the two approaches, based on configuration and XML input stream.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for implementing database application while guaranteeing independence of software modules
InactiveUS20060277158A1Reduce context switchingGuaranteed independenceDigital data protectionProgramming languages/paradigmsSoftware engineeringProcessing element
Provided are a system and method for implementing a database application while guaranteeing the independence of software modules. The system includes an XML processing unit, an SQL information unit, an object pool, and a scheduler. The system can ensure the independence of software modules and the flexibility of developing a database application, reduce the development and maintenance cost of software programs, and guarantee the independence of software programs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
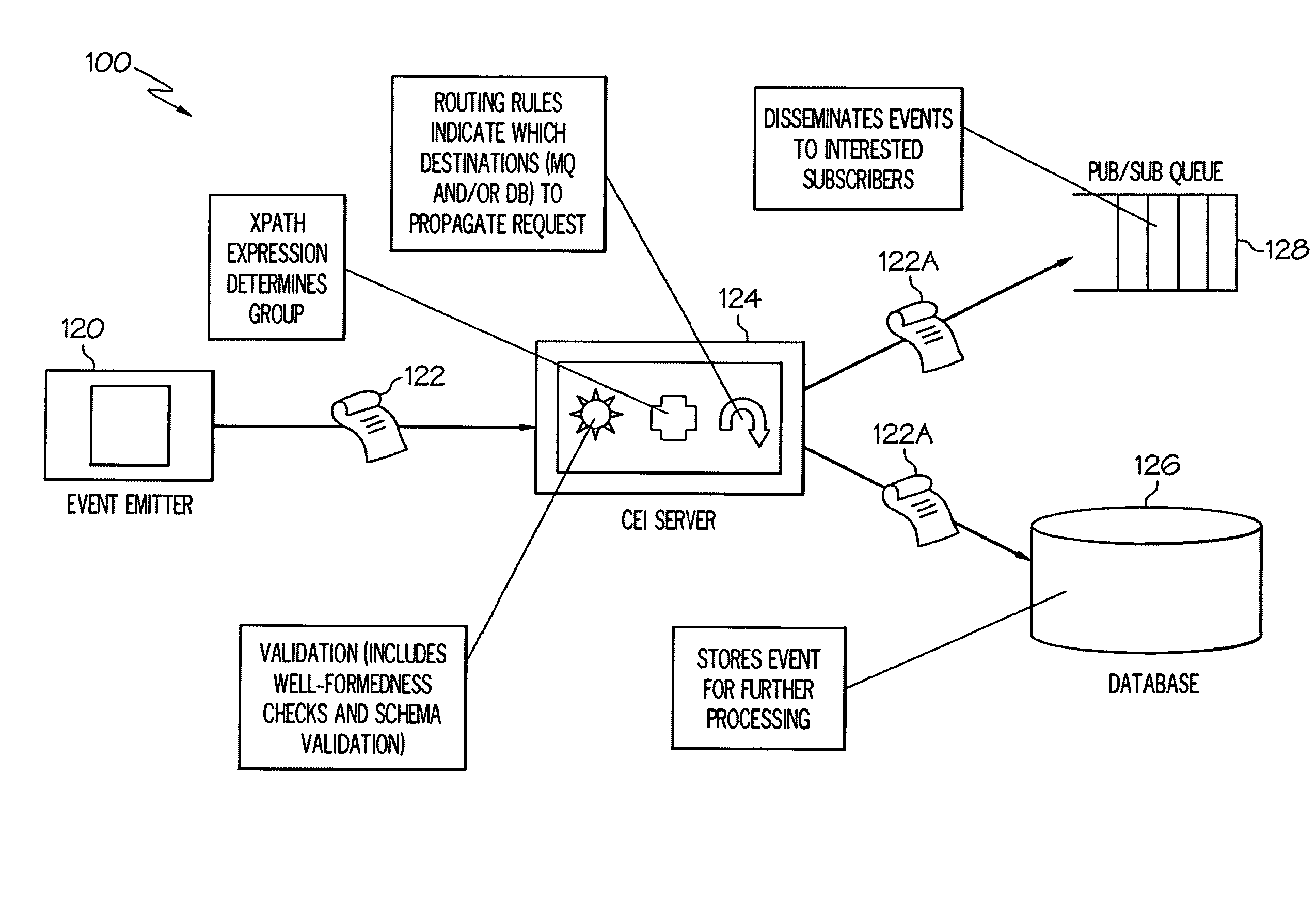
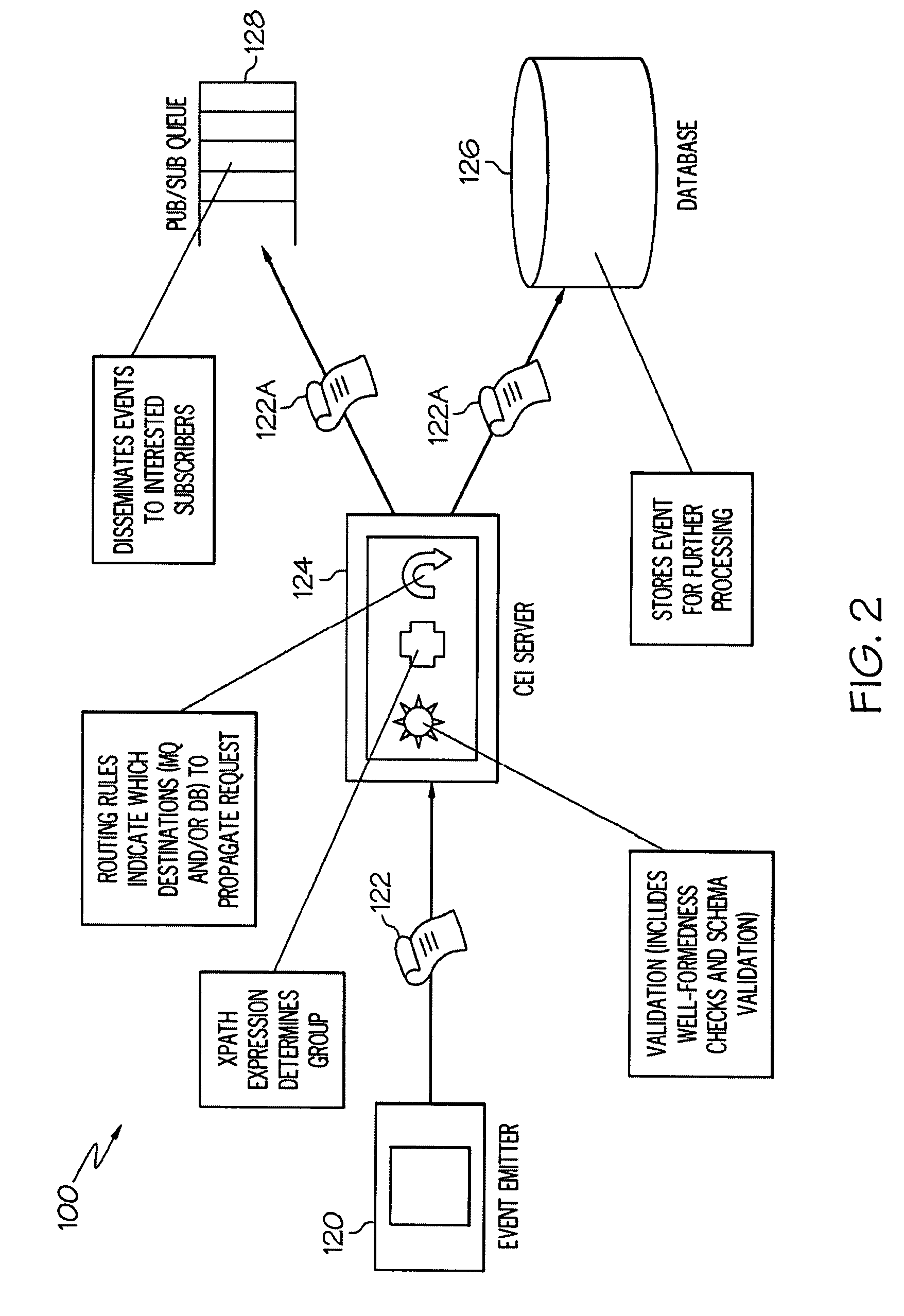
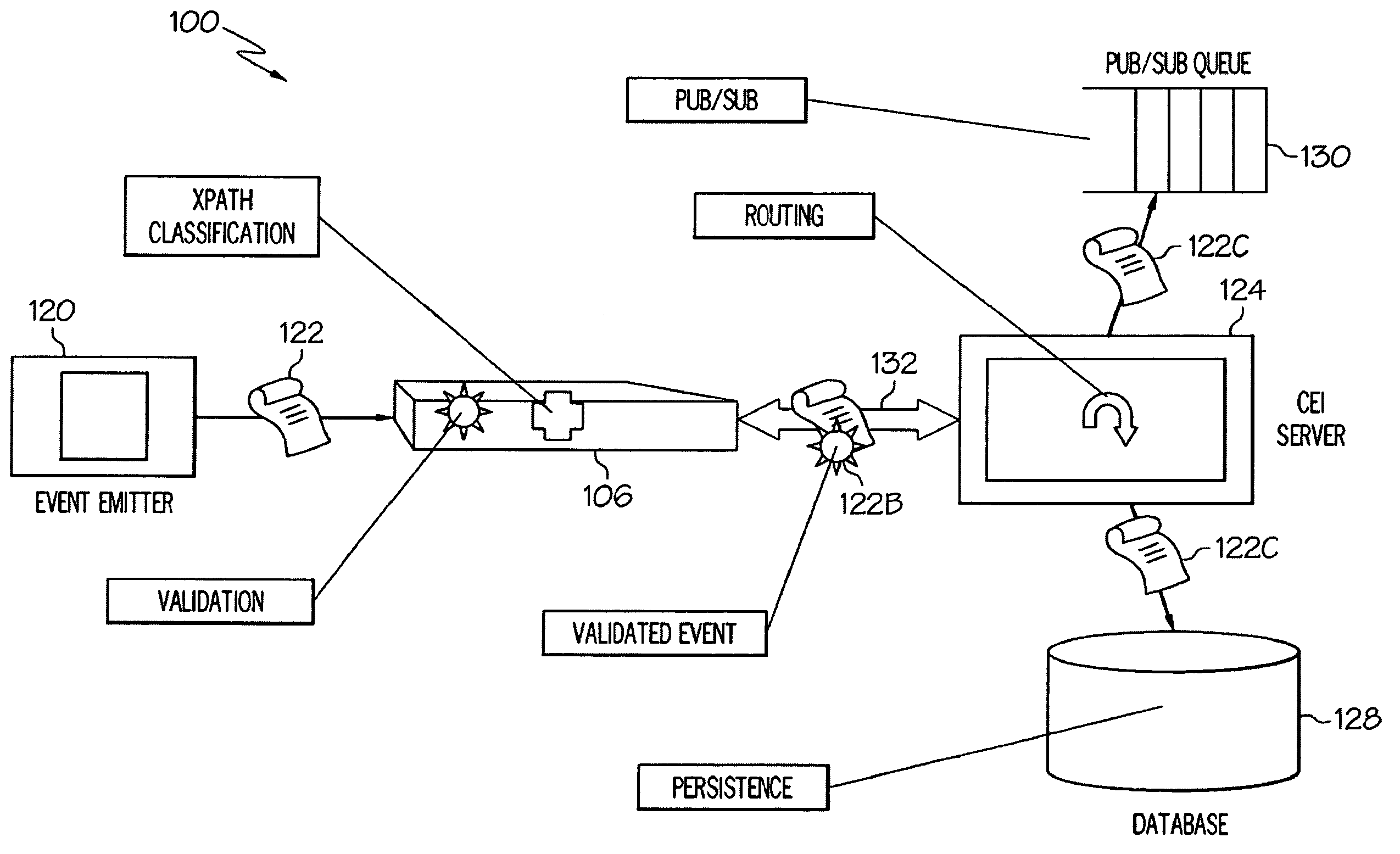
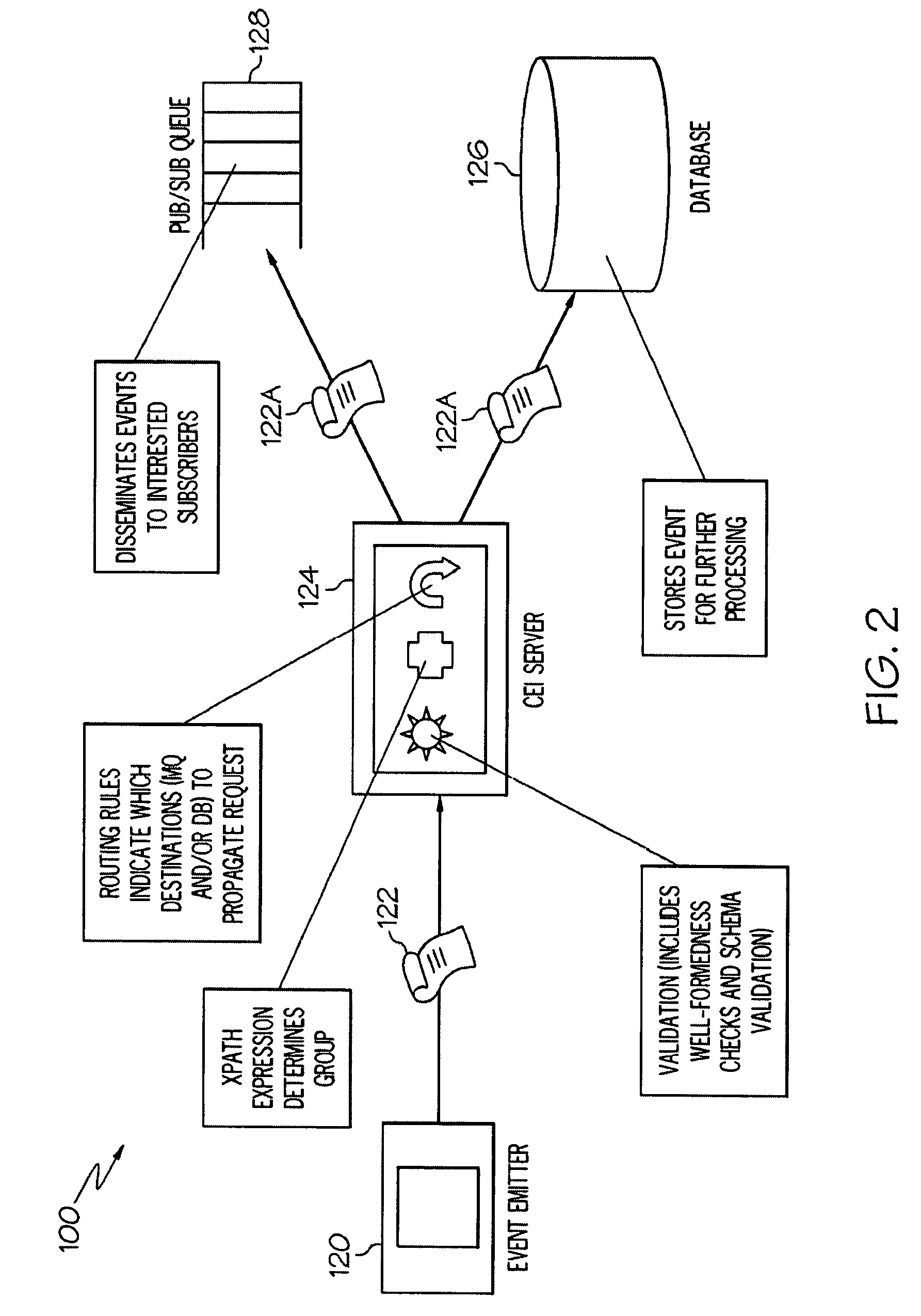
High-Performance XML Processing in a Common Event Infrastructure
InactiveUS20090064185A1Easy to deployNeed can be addressedMultiprogramming arrangementsResourcesProcess functionXml processing
Delegation of processing functions to specialized appliances in an enterprise is provided. An appliance typically comprises a combination of hardware and resident firmware that addresses needs in a computing environment, such as by providing common message transformation, integration, security, filtering and other functions. Delegation is carried out by specifying at least one XML function for front-process offloading from a server to a corresponding appliance configured to receive messages pushed towards the server, communicating management directives to the appliance for configuring the appliance to perform the specified XML function(s) according to specific requirements dynamically specified by the server and communicating instructions to the appliance so that the appliance augments received event messages with intermediate processing information based upon the front-process offloading, as received event messages pass through the appliance.
Owner:IBM CORP
XML (extensive makeup language) processing method and device for graph structure
ActiveCN102831167AReduce computational complexityReduce the difficulty of modificationSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a graph structure storage method based on XML. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring drawn graph structure information, and each graph element inside the graph structure and graph element information of each element; using the acquired graph structure information, and each graph element and graph element information of each graph element to generate an XML file for describing the drawn graph structure based on the predetermined XML limiting rule; and storing the generated XML file in a storage device. The graph structure storage method is used for describing an association relationship of a plurality of sides reaching the same node, so that the graph structure can be applicable to a wider scene. Besides, the XML can be directly modified, so that the modifying difficulty of the graph structure is greatly reduced, and the graph structure is easy to maintain.
Owner:NEUSOFT CORP
XML metadata objectification analytic method and system
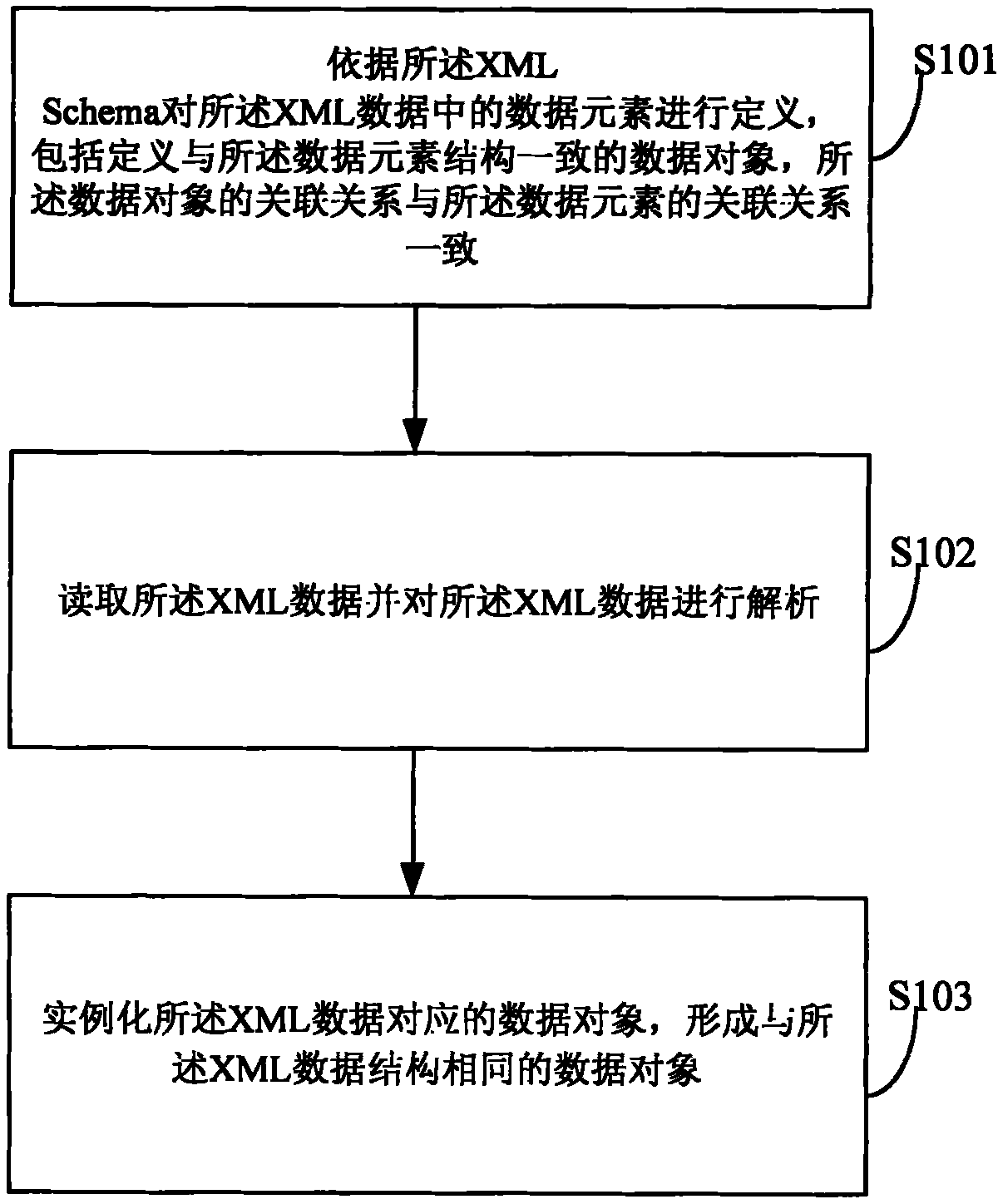
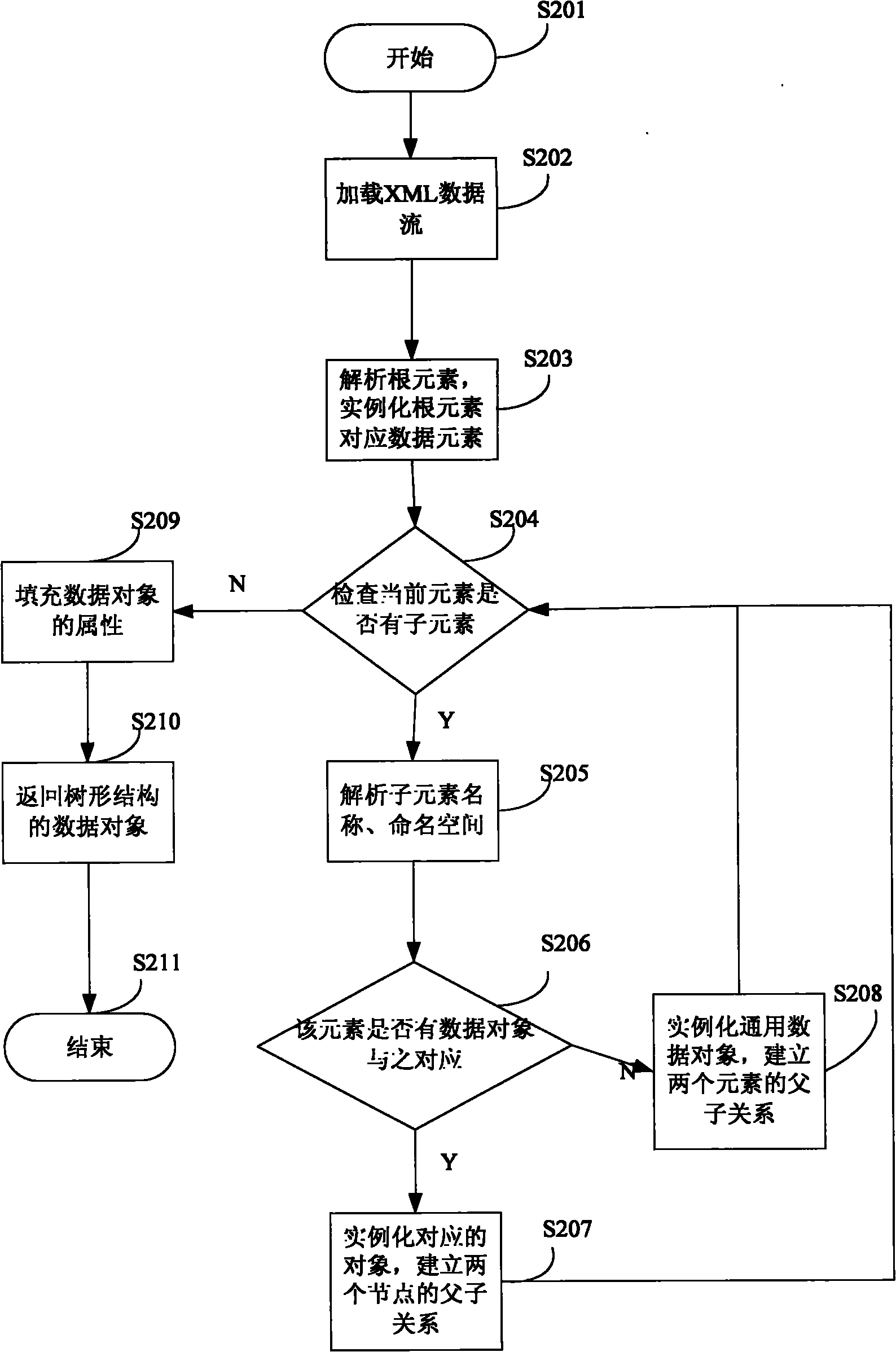
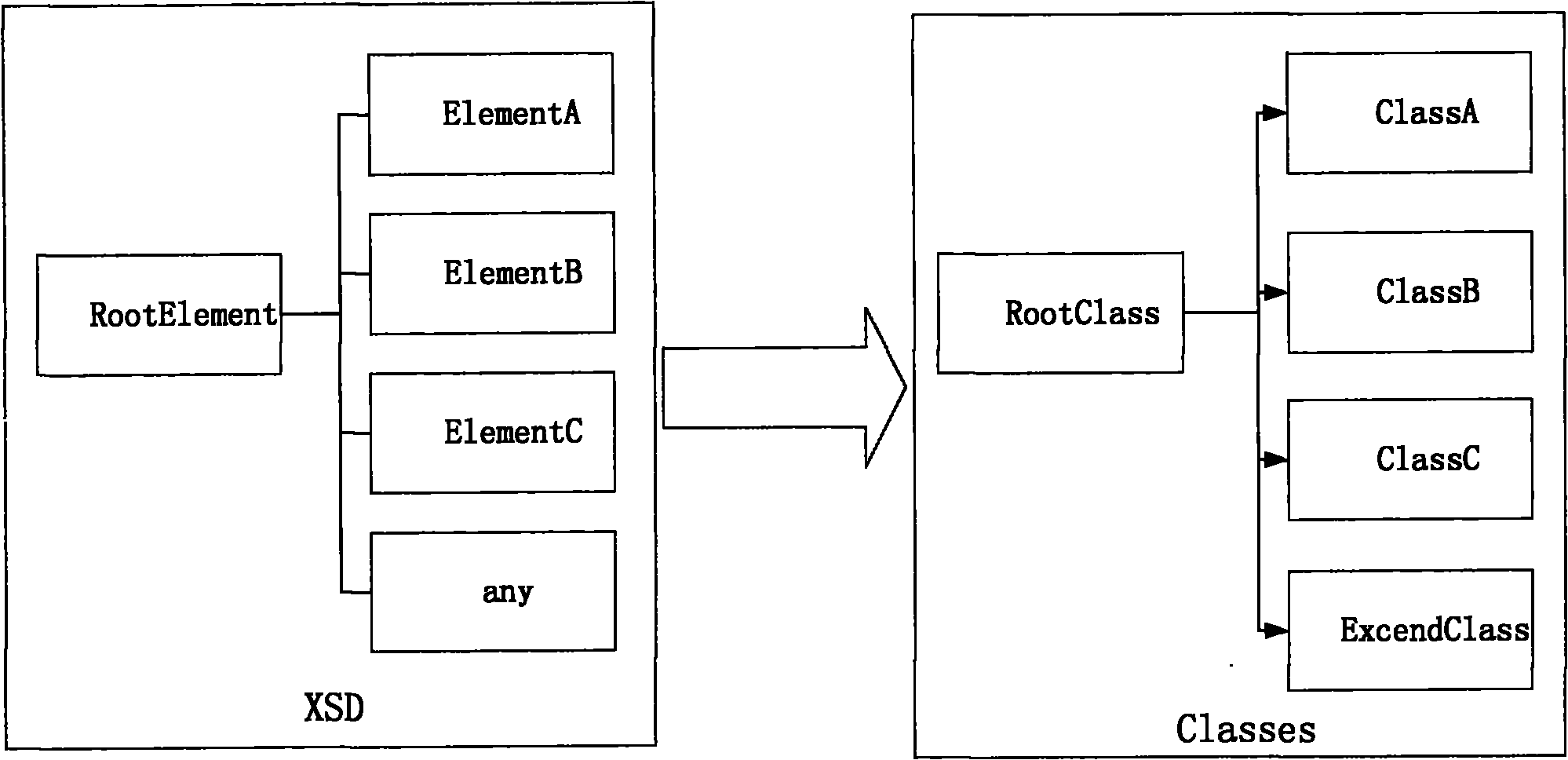
The invention discloses an XML metadata objectification analytic method, a data element in XML data is defined according to an XML Schema. The method comprises the following steps: a data object which is consistent with the structure of the data element is defined, wherein the incidence relations of the data object and the data element are consistent; the XML data are read and analyzed; the data object corresponding to the XML data is instantiated, and the data object of the same structure as the XML data is formed. The XML metadata objectification analytic method and a system predefine the XML Schema of the structure of the XML data, the XML Schema defines the attribute name, type, default, incidence relation of father and son elements and the like of each element, and the embodiment of the invention uses the data directly to establish a corresponding Java type, thus solving the problems in the existing XML processing mode.
Owner:山东中创软件商用中间件股份有限公司
Techniques for streaming validation-based XML processing directions
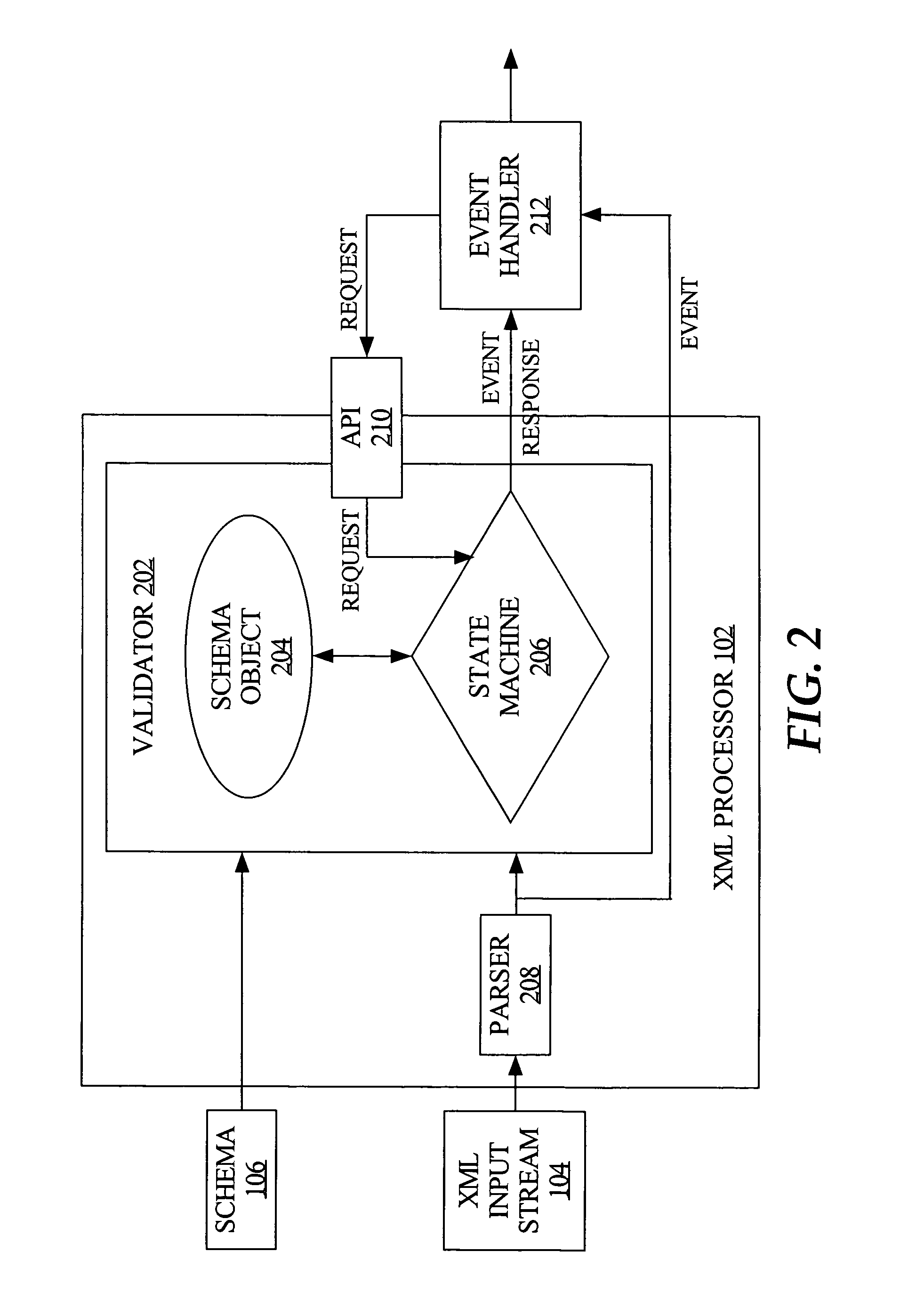
ActiveUS7587667B2Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsData validationProcessing type
An XML processing model enables applications that use an XML stream to perform metadata-based or other processing of data during a data validation operation while preserving a streaming processing model. For example, while an XML node is being validated, requests can be received regarding the status of the validation and any processing that may be required with the node in order to conform it to requirements of an external application. A validator exposes public APIs that allow such validation-time requests from an event handler that is associated with an external application and that is registered with the XML stream. Messages that identify schema annotation definitions are provided to an external application to direct the type of processing to be performed on nodes at application runtime. Thus, applications can process a node according to the annotation definition concurrently with validation of the given node by the validator.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
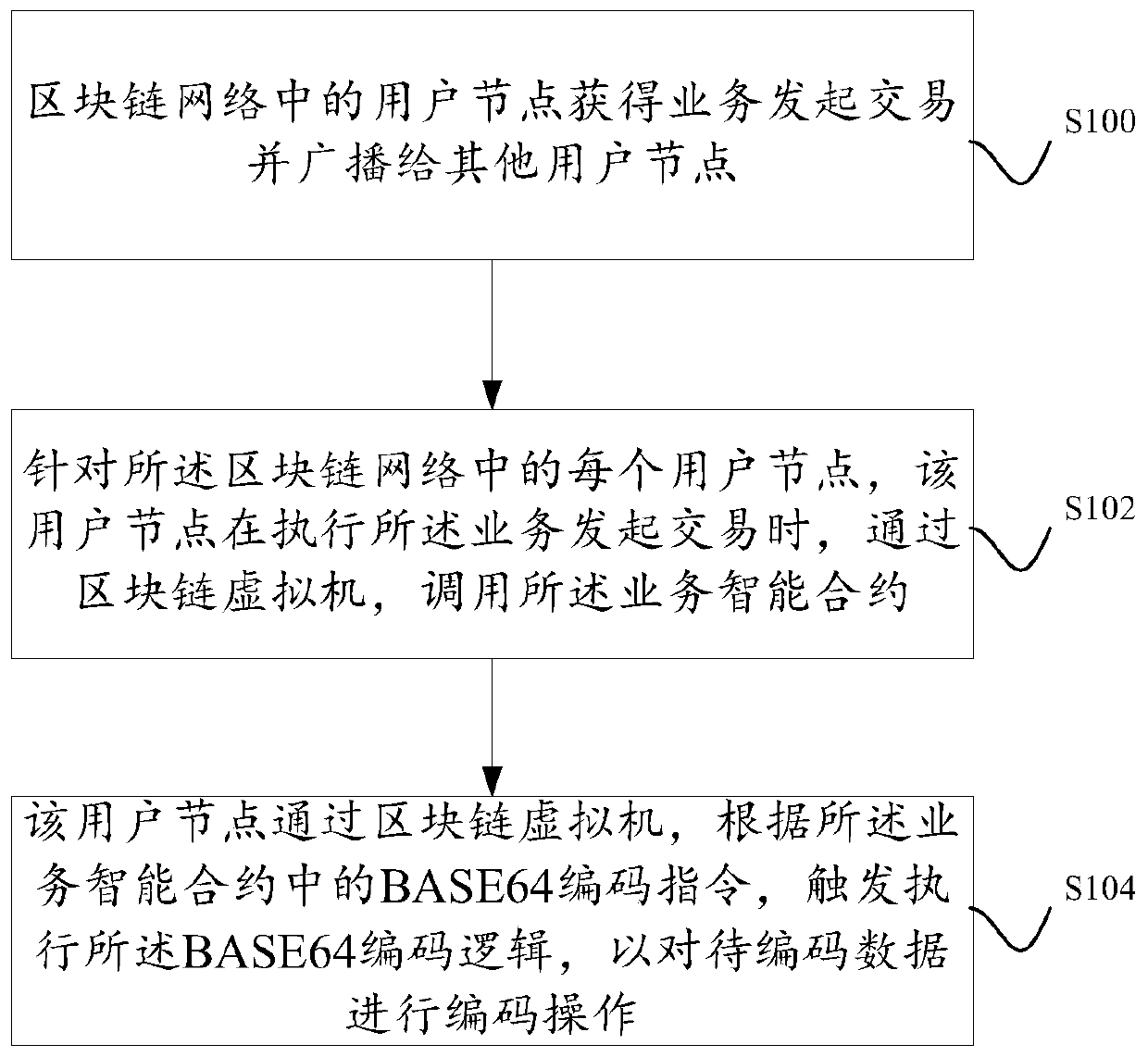
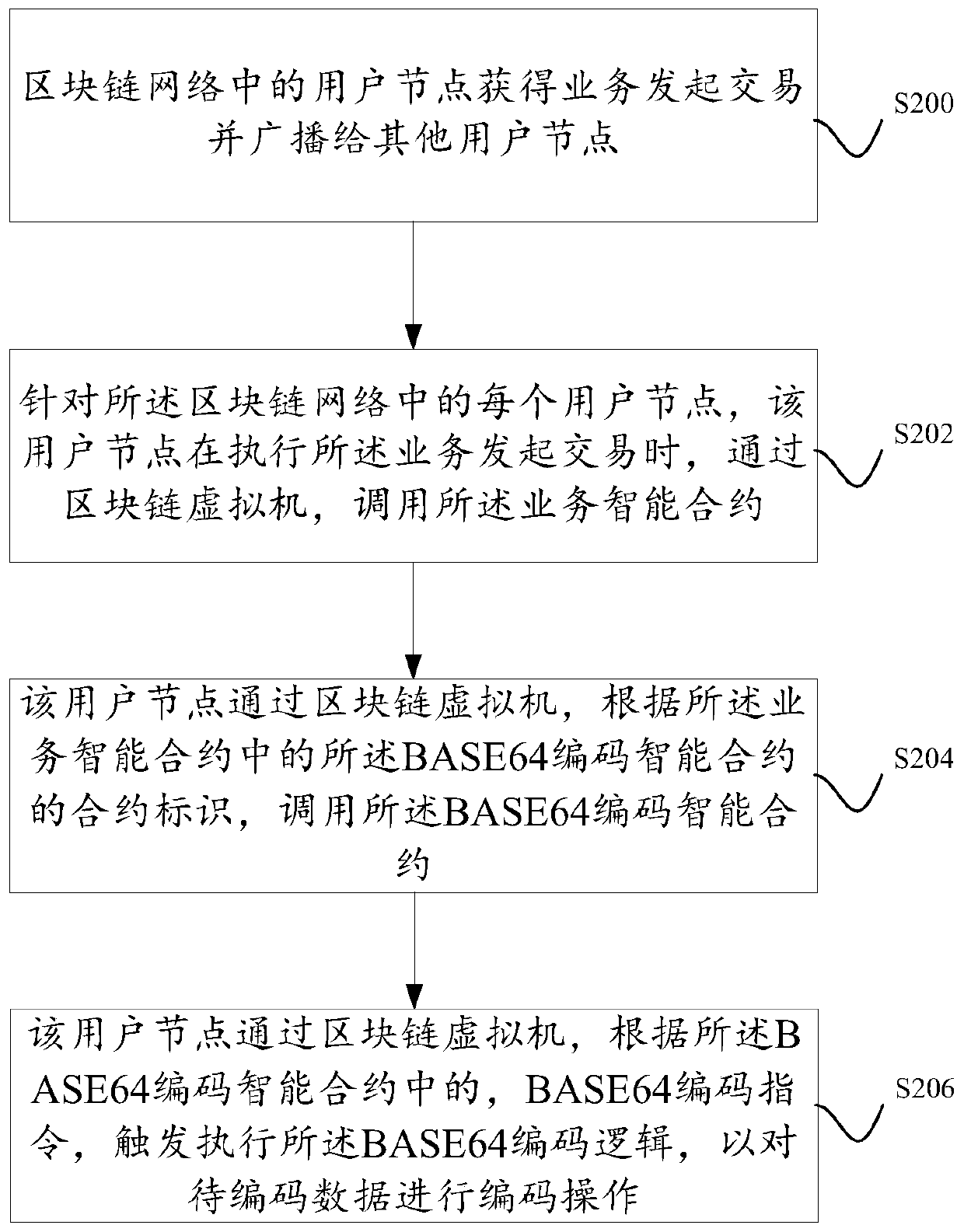
Data processing method and system based on blockchain smart contract
ActiveCN110046023ASupport for XML processing operationsSupport for processing operationsFinancePayment architectureSoftware engineeringChain network
The invention discloses a data processing method and system based on a blockchain smart contract. In the embodiment of the present specification, on one hand, an XML processing instruction is definedand added to an instruction set of a blockchain virtual machine, and on the other hand, an XML processing logic corresponding to the XML processing instruction is deployed in the blockchain virtual machine; and on the other hand, the defined XML processing instruction needs to be added to an instruction set of the intelligent contract compiler, so that the business intelligent contract compiled bythe intelligent contract compiler contains the XML processing instruction. In this way if the business intelligent contract is deployed in the block chain network, the user can simultaneously assignand call the business intelligent contract to execute the business initiation transaction when constructing the business initiation transaction.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
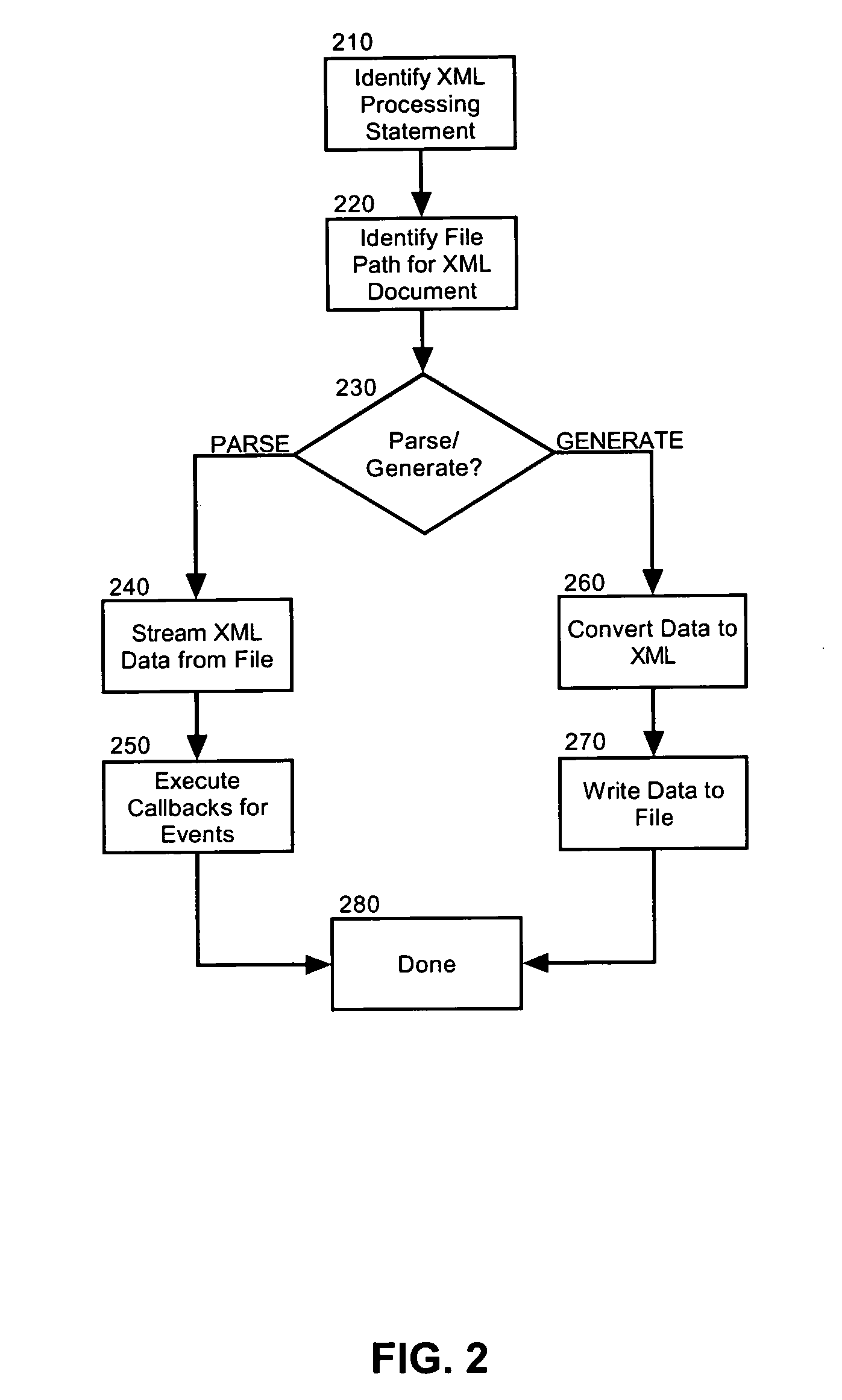
COBOL syntax for native XML file parsing and file generation
InactiveUS20060282820A1Natural language data processingSpecific program execution arrangementsProcessing InstructionObject code
Embodiments of the present invention address deficiencies of the art in respect to XML processing in a COBOL environment and provide a method, system and apparatus for processing a COBOL syntax to allow native XML parsing. In a method of the invention, COBOL source code can be processed and an XML processing directive can be detected in the COBOL source code. In any case, a file path can be extracted from the XML processing directive in the processed COBOL source code. Subsequently, object code can be produced that is configured to process XML data in an XML document stored at a location specified by the file path. Specifically, the object can be configured to parse XML data in an XML document stored at a location specified by the file path, or to generate XML data in an XML document stored at a location specified by the file path.
Owner:IBM CORP
Extensible markup language (XML) performance optimization on a multi-core central processing unit (CPU) through core assignment
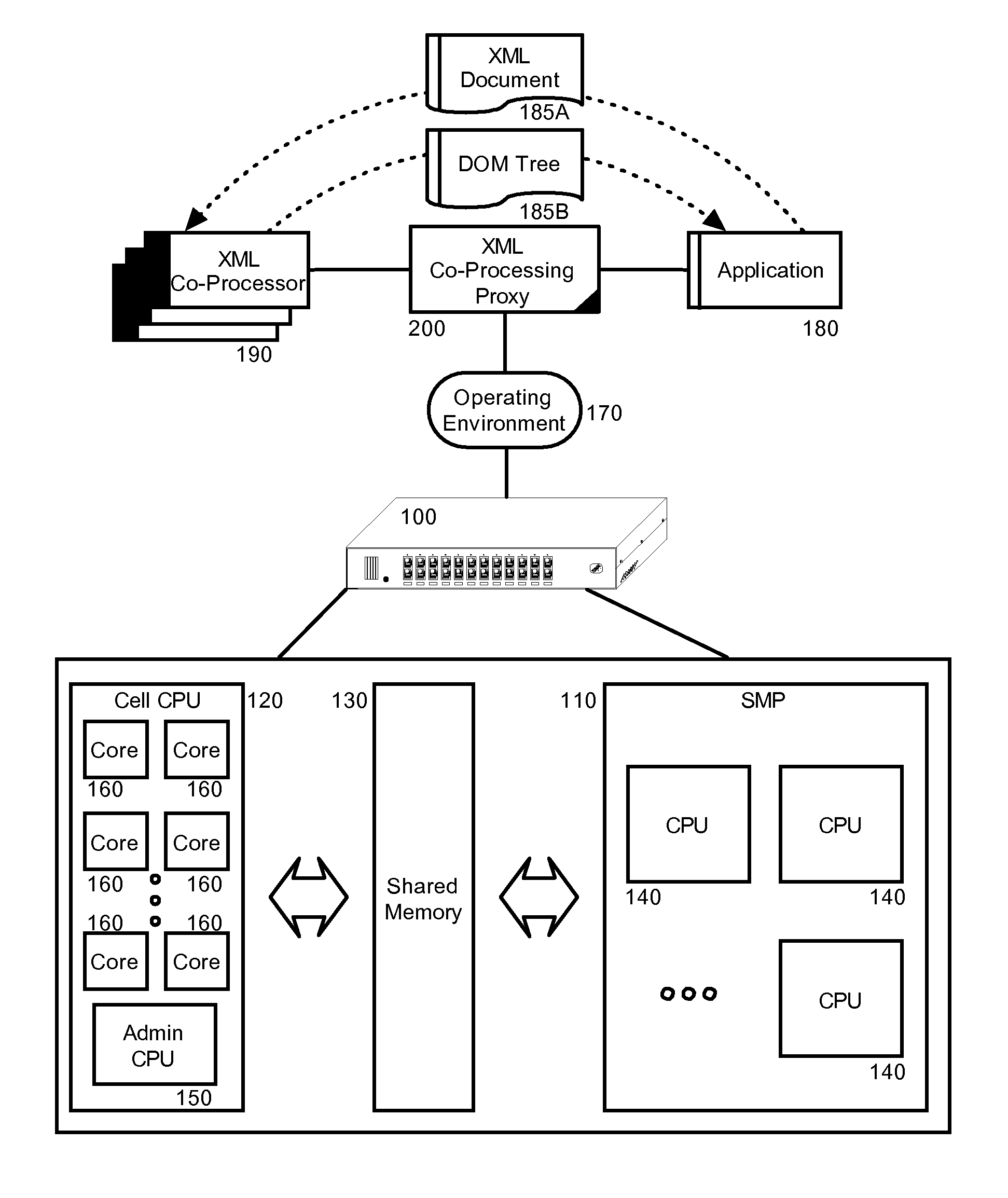
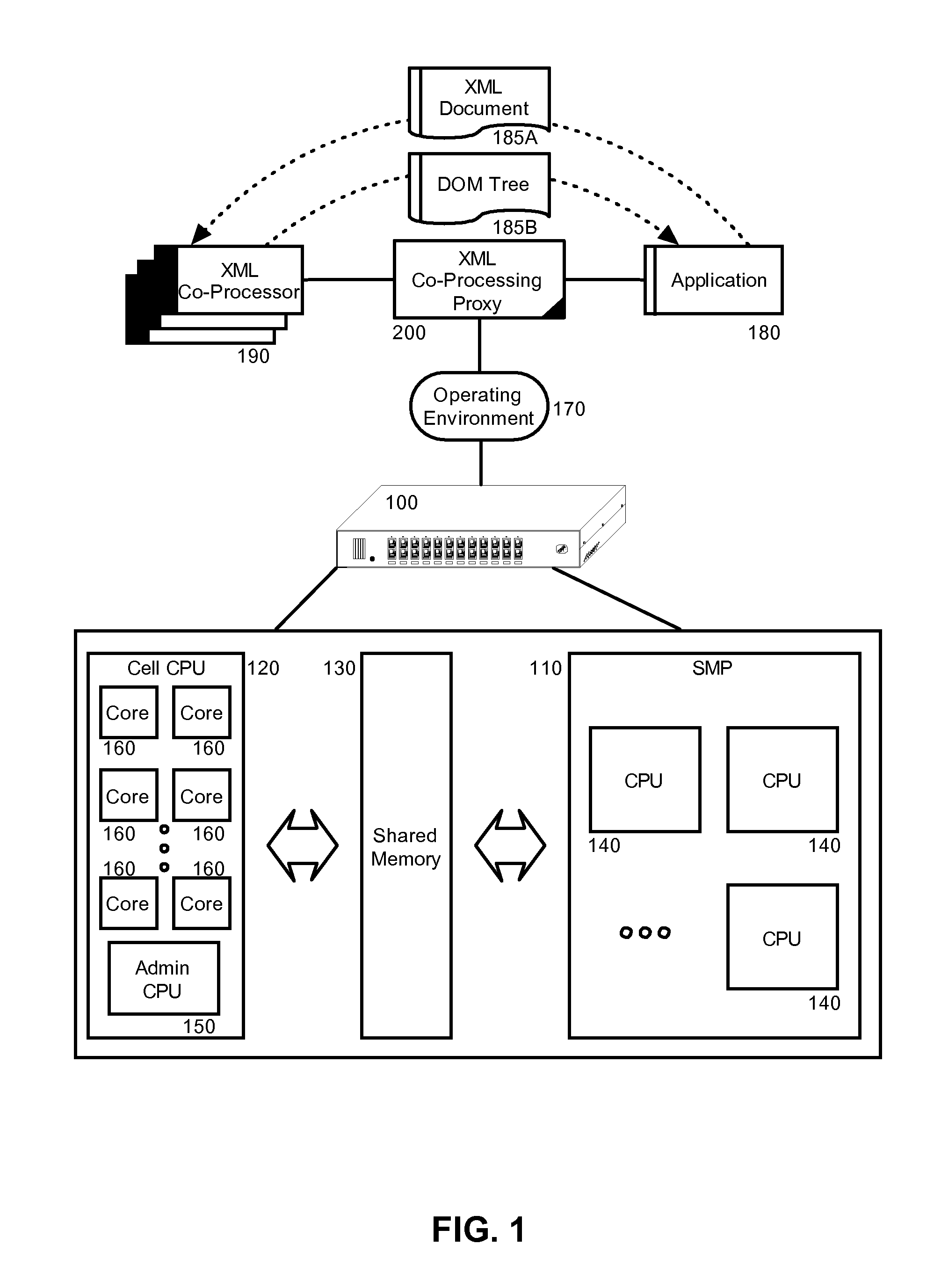
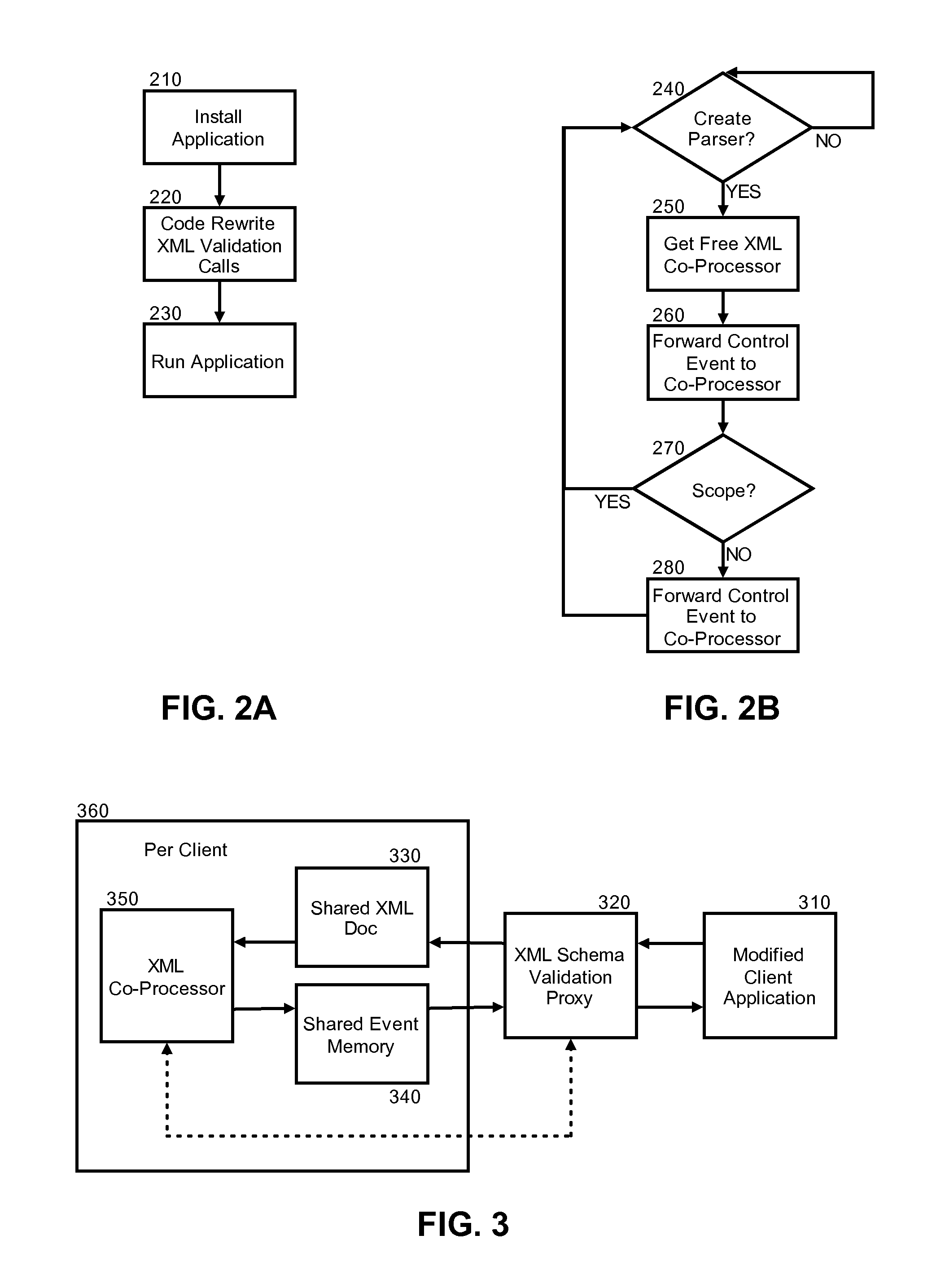
InactiveUS20070266380A1Digital data processing detailsNatural language data processingXML schemaApplication software
Embodiments of the present invention address deficiencies of the art in respect to XML schema validation and provide a method, system and computer program product for optimized XML schema validation and XML document parsing. In one embodiment, an XML data processing system can include shared memory; an XML co-processing proxy comprising program code enabled to receive at least one of XML document schema validation and XML document parsing requests from client applications, and at least one XML processing element coupled to the shared memory. In particular, the XML processing element can be configured to perform the at least one of the XML schema validation and XML document parsing on XML documents provided by the XML co-processing proxy. The XML processing element further can be configured to place results of XML schema validation or the XML document parsing in the shared memory.
Owner:IBM CORP
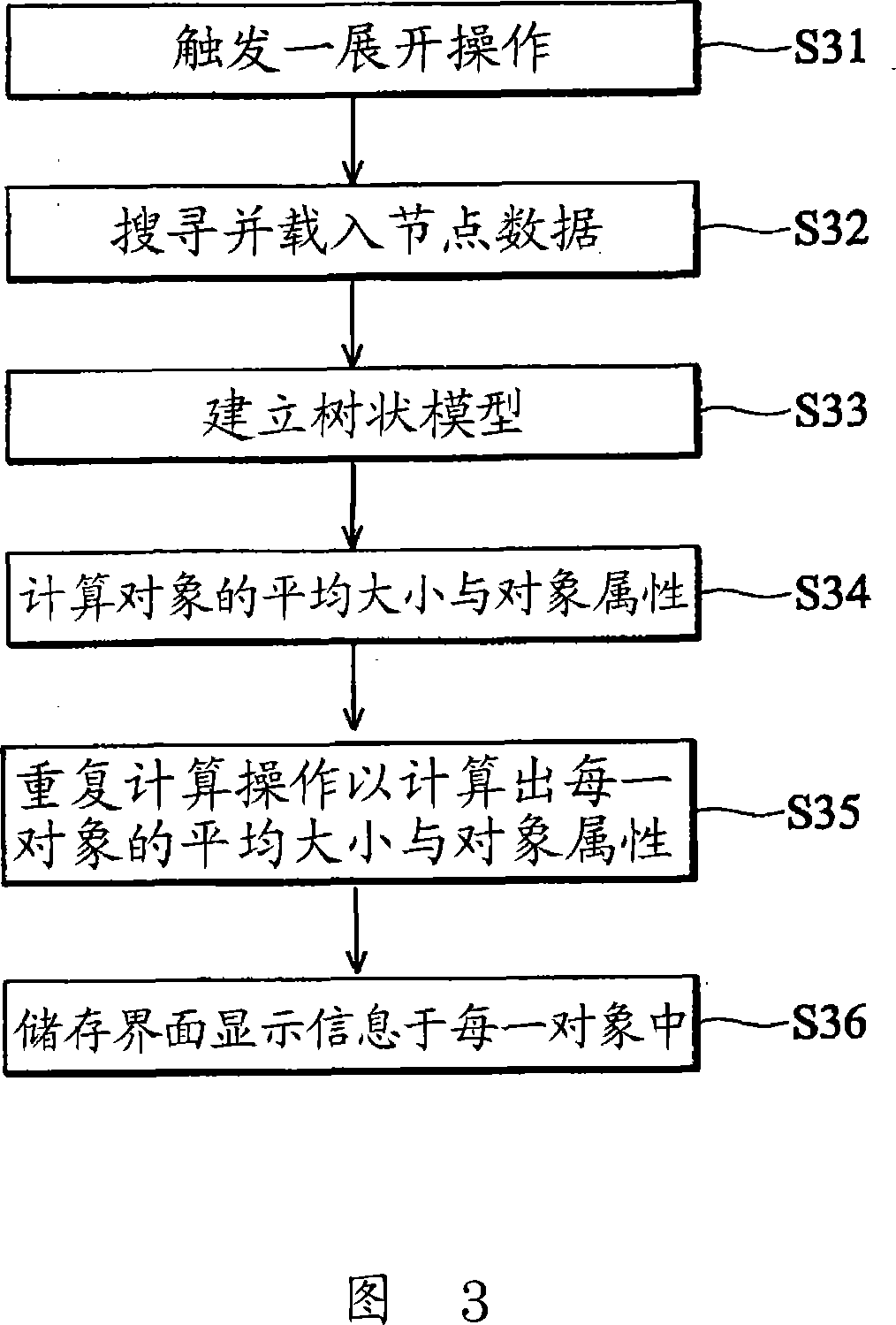
Configurable network interface with horizontal tree structure, its display method and node processing method
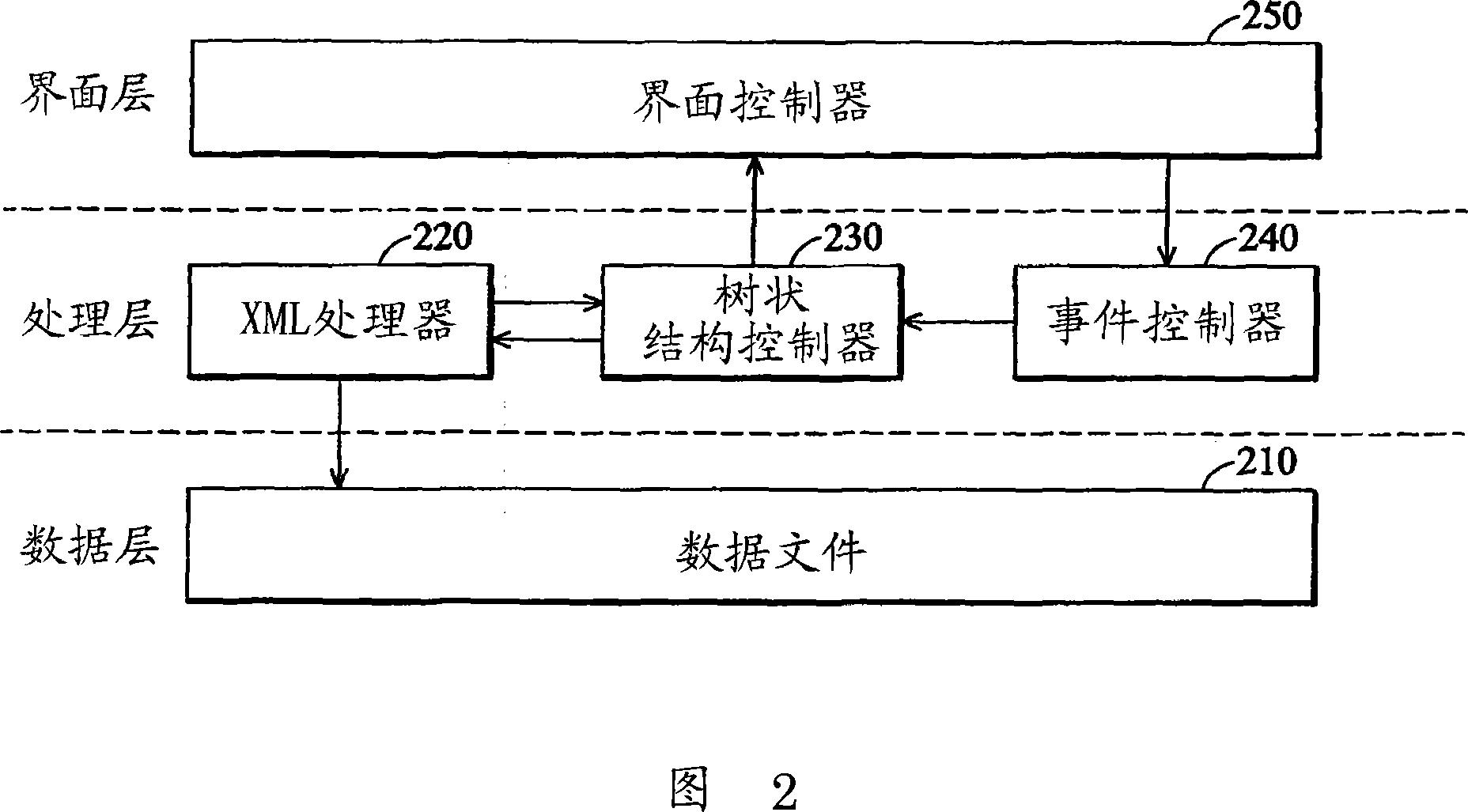
InactiveCN101056303ASave operating timeEasy to useTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsWeb structureData file
Disclosed are a horizontal tree structure configurable web interface and its display method and a node treatment method, wherein said horizontal tree structure configurable web interface comprises a data layer having a data file, a processing layer and an interface layer. The processing layer comprises further a XML processor, a tree structure controller and an event controller, wherein said XML processor is used for reading and resolving said data file, and generating a XML data file on the basis of a presupposed format, said tree structure controller is used for getting the XML data file from the XML processor to generate a tree model and an automatic testing web structure. When an operation command is sensed, said event controller triggers said tree structure controller which is made to read the XML data file through the XML processor. Said interface layer comprises further an interface controller which is used for drawing a horizontal tree structure at an interface and exhibiting property of nodes in the horizontal tree structure.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
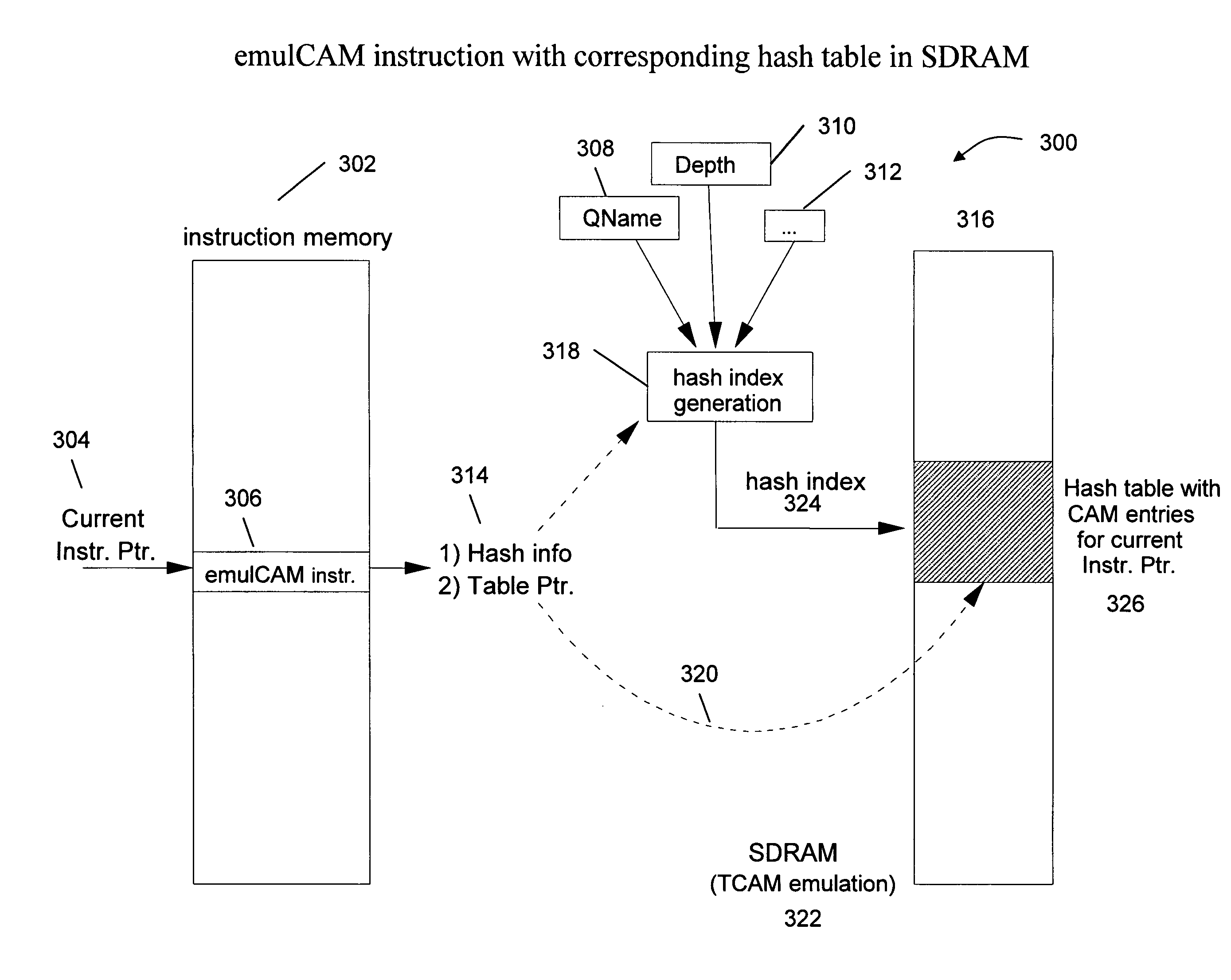
Sdram-based tcam emulator for implementing multiway branch capabilities in an XML processor
InactiveUS20090171651A1Increase the number ofSmall sizeDigital data information retrievalSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationControl vectorMultiway branch
The system and method of the present invention “emulates” the TCAM function using a data structure which is stored in an SDRAM device in such way that the size of emulated TCAM is substantially larger than the original TCAM device, thereby allowing the increase of the number of PPE programs which can be resident in memory. The present invention provides a new “emulCAM” algorithm which builds partially on BaRT, but is extended by providing multiple results per hash table entry with flexible assignment to “match-condition-combinations”, by utilizing MUX control vectors for extracting hash index instead of “index-mask-based extraction”, by moving part of CAM function to invoking emulCAM instruction and by providing “Pathological case handling” using multiple emulCAM instructions.
Owner:IBM CORP
Tiered XML services in a content management system
InactiveUS20120047231A1Powerful and flexibleData processing applicationsSemi-structured data indexingApplication softwareContent management
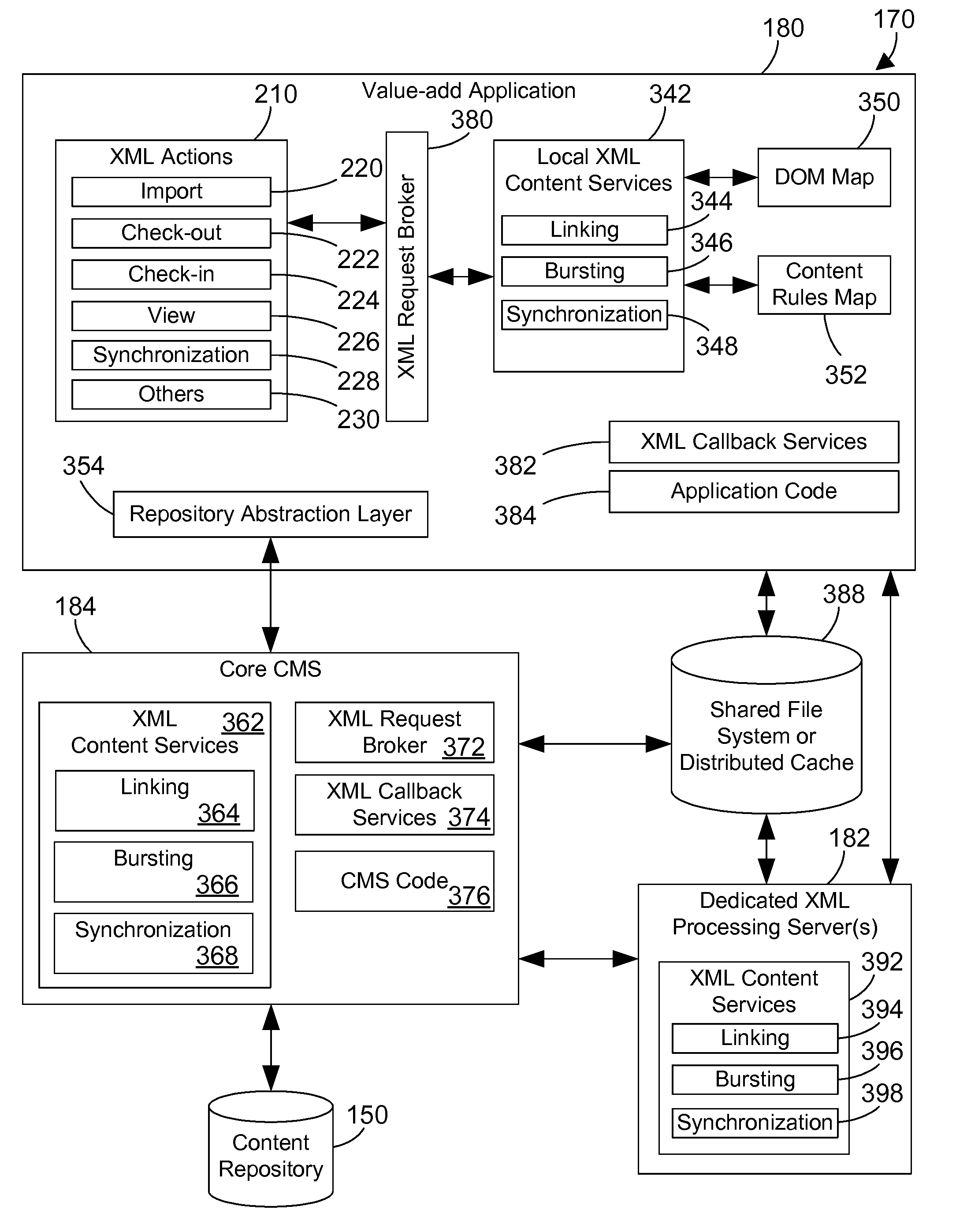
A content management system (CMS) includes a value-add application with a first set of XML content services, one or more dedicated XML processing servers with a second and other sets of XML content services, and a core CMS with a third set of XML content services. The content management system may be designed to provide XML content services at any of these three tiers of processing. A first threshold is defined that allows the value-add application to determine when to offload XML content services to a dedicated XML processing server. A second threshold is defined that allows the core CMS to determine when to offload XML content services to a dedicated XML processing server. Callback services are included that allow each tier of XML content services to send or receive additional information to complete the XML processing. The result is a content management system that is very powerful and flexible.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-performance XML processing in a common event infrastructure
InactiveUS8266630B2Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlProcess functionXml processing
Delegation of processing functions to specialized appliances in an enterprise is provided. An appliance typically comprises a combination of hardware and resident firmware that addresses needs in a computing environment, such as by providing common message transformation, integration, security, filtering and other functions. Delegation is carried out by specifying at least one XML function for front-process offloading from a server to a corresponding appliance configured to receive messages pushed towards the server, communicating management directives to the appliance for configuring the appliance to perform the specified XML function(s) according to specific requirements dynamically specified by the server and communicating instructions to the appliance so that the appliance augments received event messages with intermediate processing information based upon the front-process offloading, as received event messages pass through the appliance.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
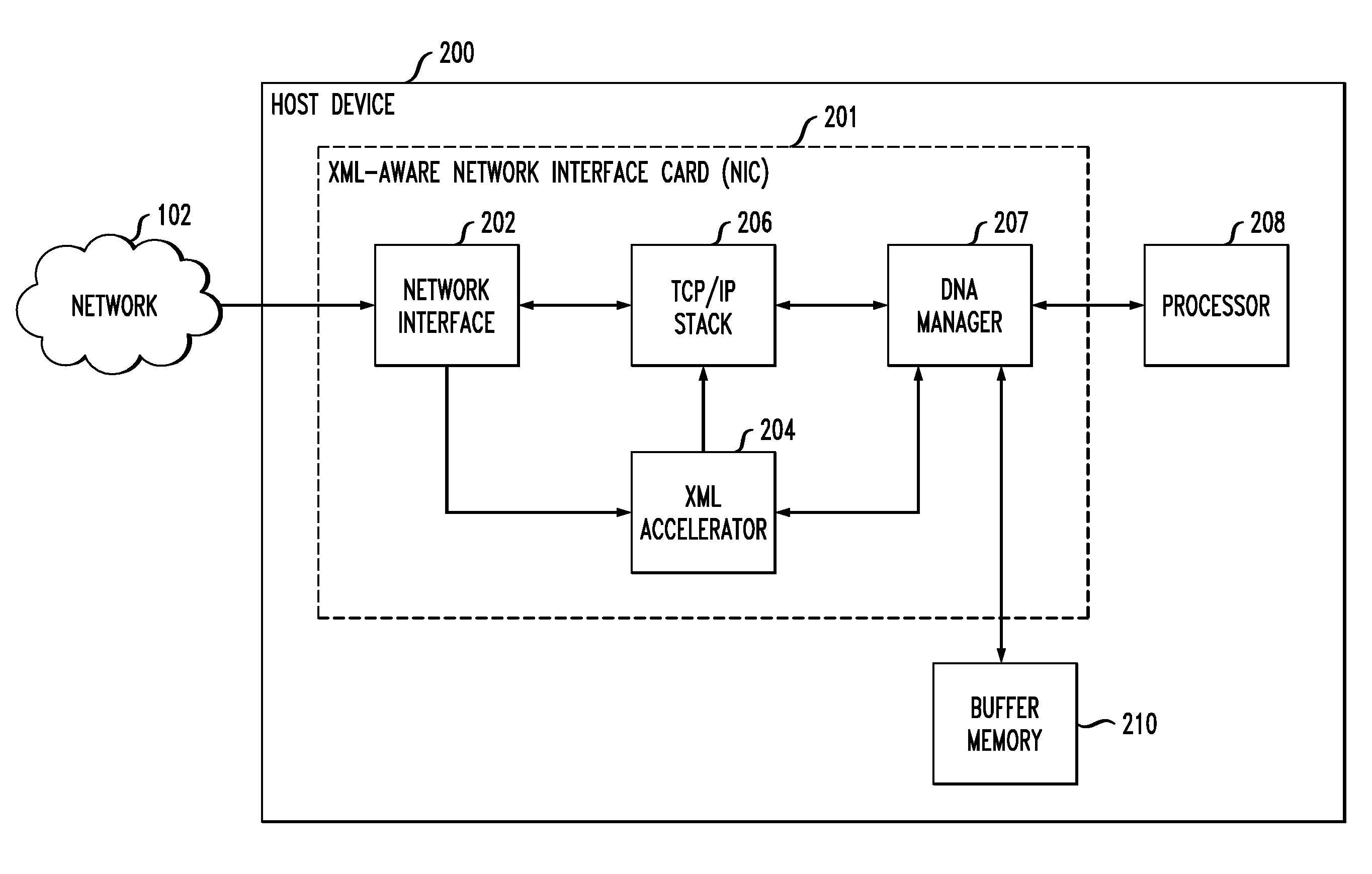
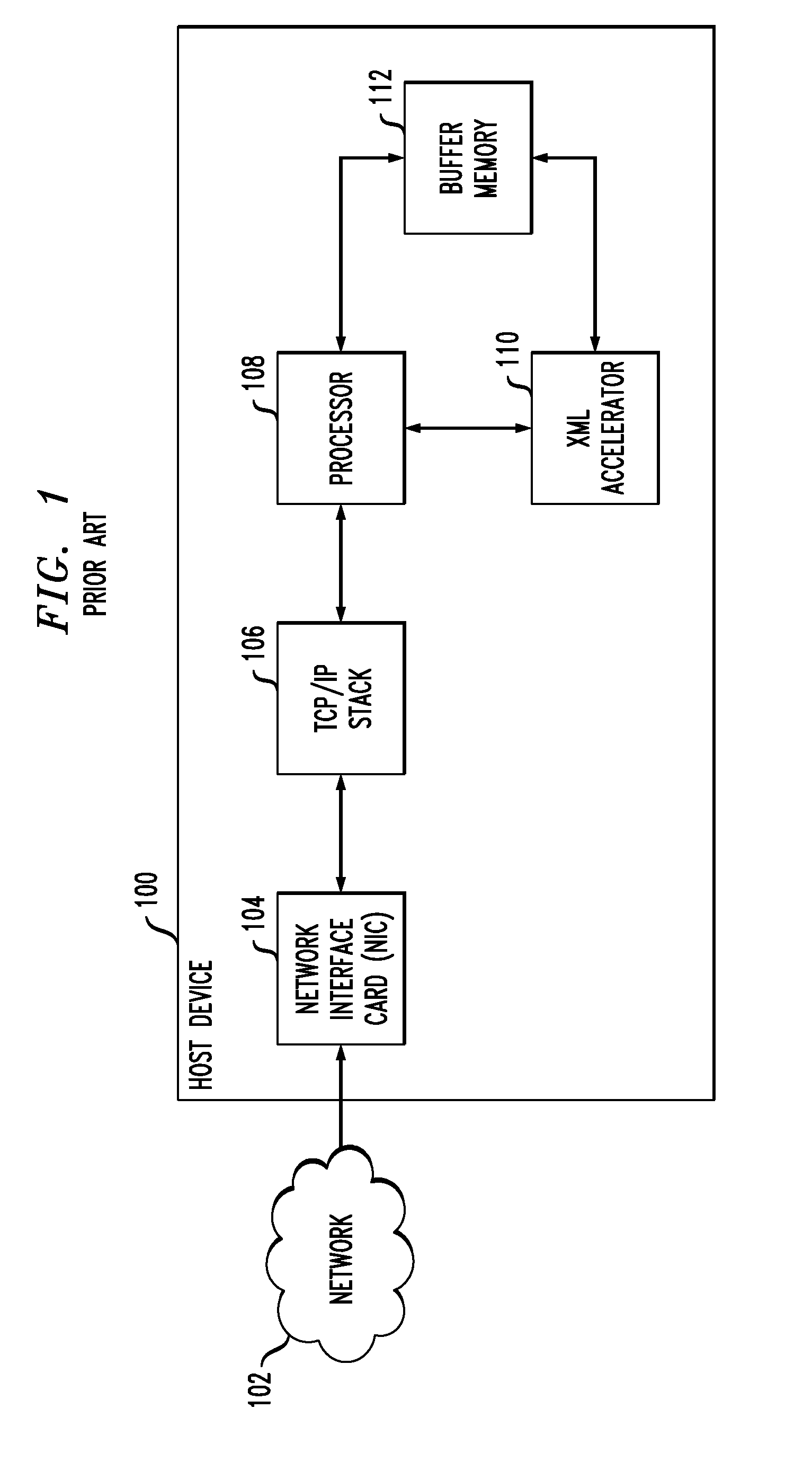
Network Interface for Accelerating XML Processing
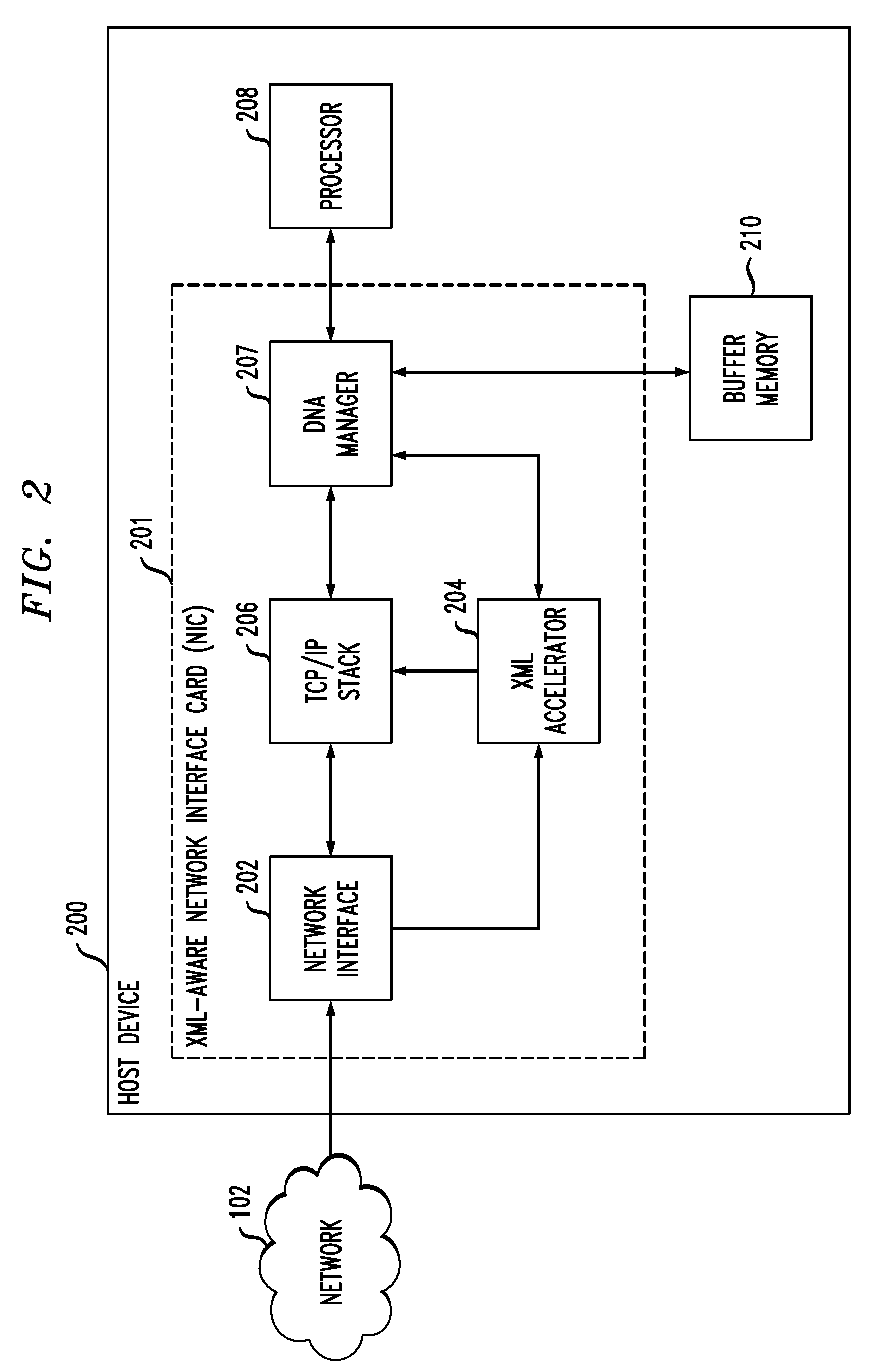
InactiveUS20120041998A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData packComputer engineering
Described embodiments provide a method of processing data packets received at a network interface of a host device. The network interface detects whether a received data packet is an XML packet. If the data packet is an XML packet, the network interface provides the XML packet to an XML accelerator that performs one or more acceleration operations on the XML packet. The XML accelerator provides processed XML data to a buffer memory and provides an indication to a processor of the host device, the indication including a location of the processed XML data in the buffer. The steps of providing the XML packet to the XML accelerator and performing one or more acceleration operations are performed before an XML data stream corresponding to the XML packet is TCP / IP terminated. If the received data packet is not an XML packet, the network interface provides the data packet to a TCP / IP stack.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com