Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
220 results about "Weep" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
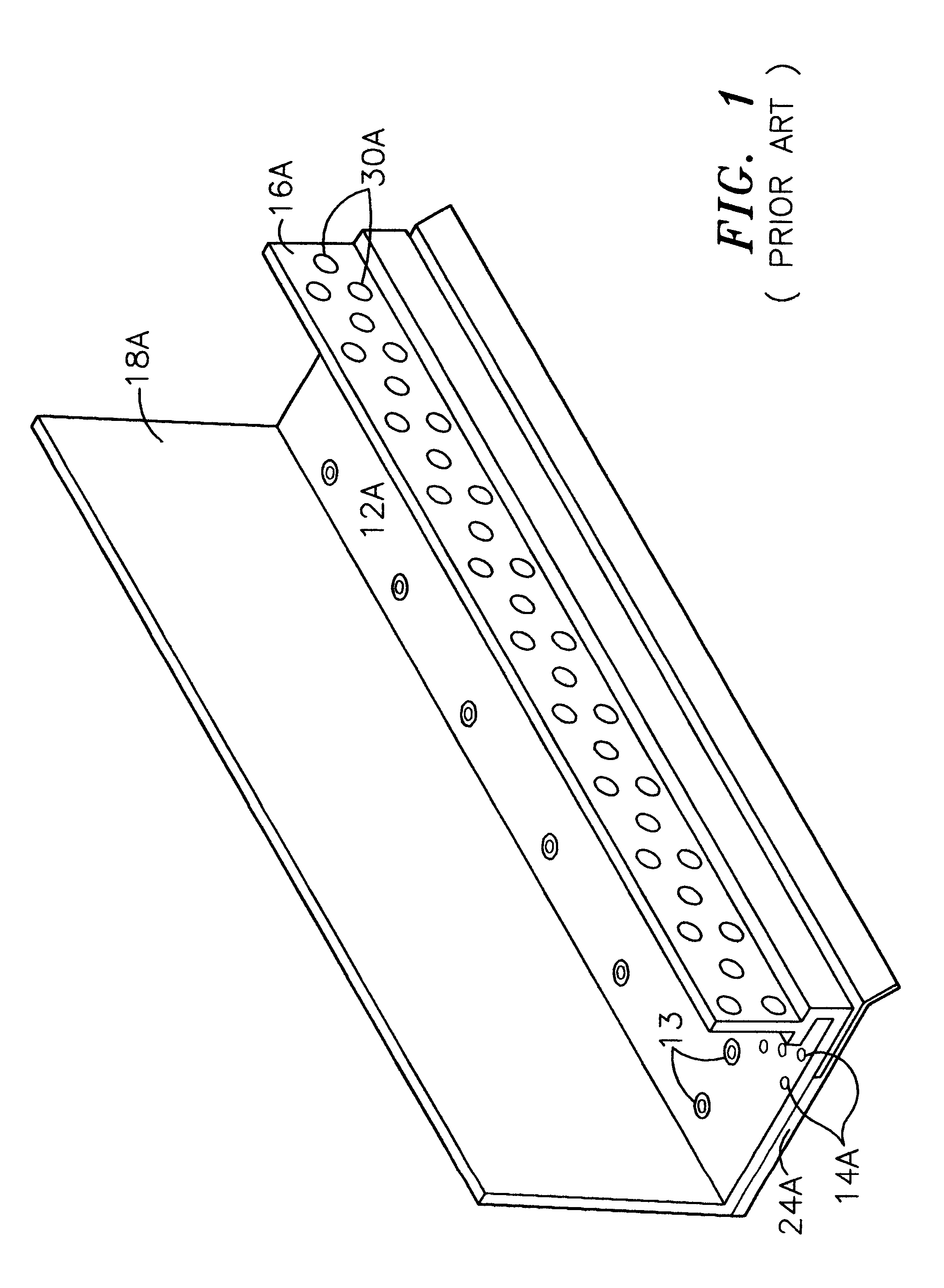
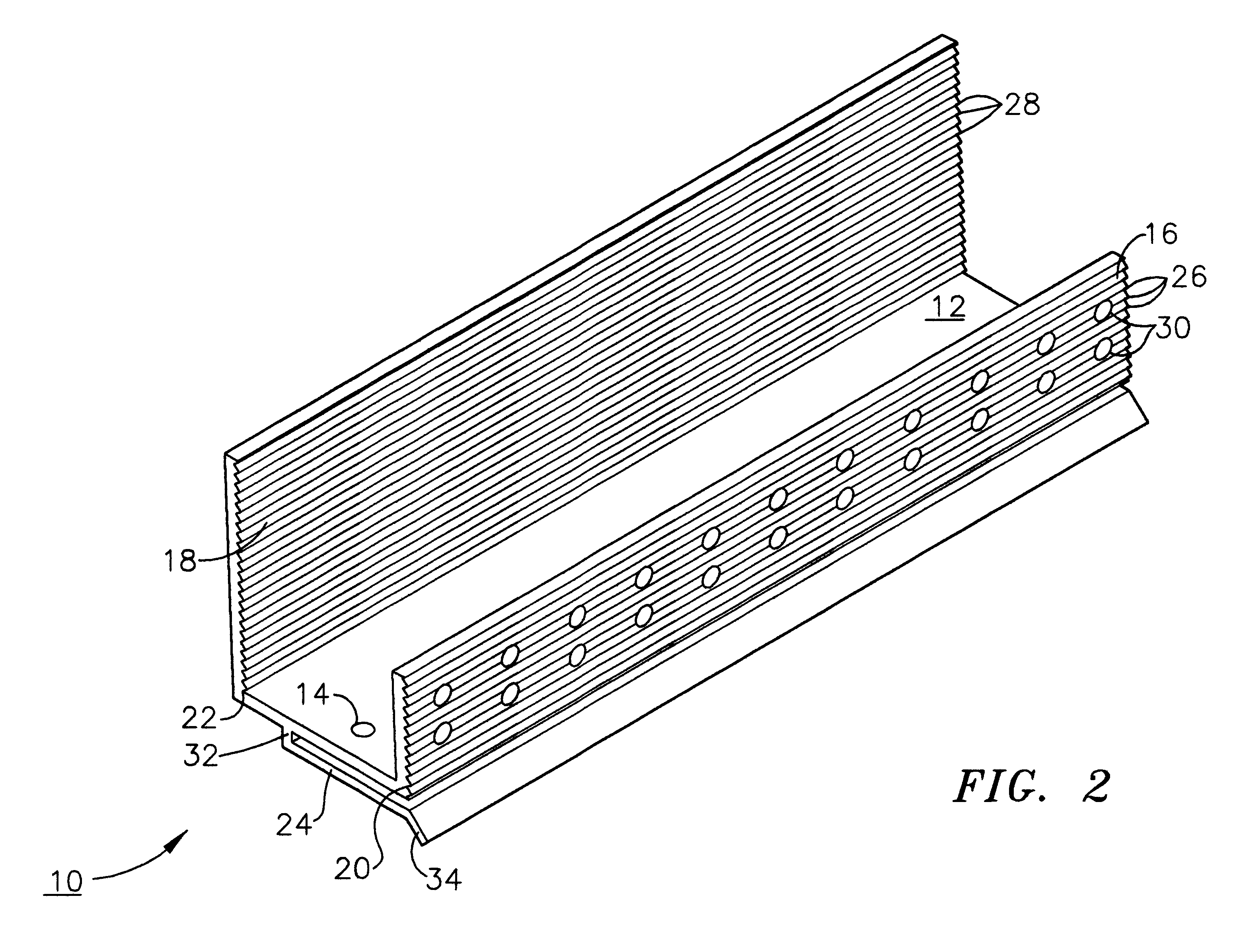
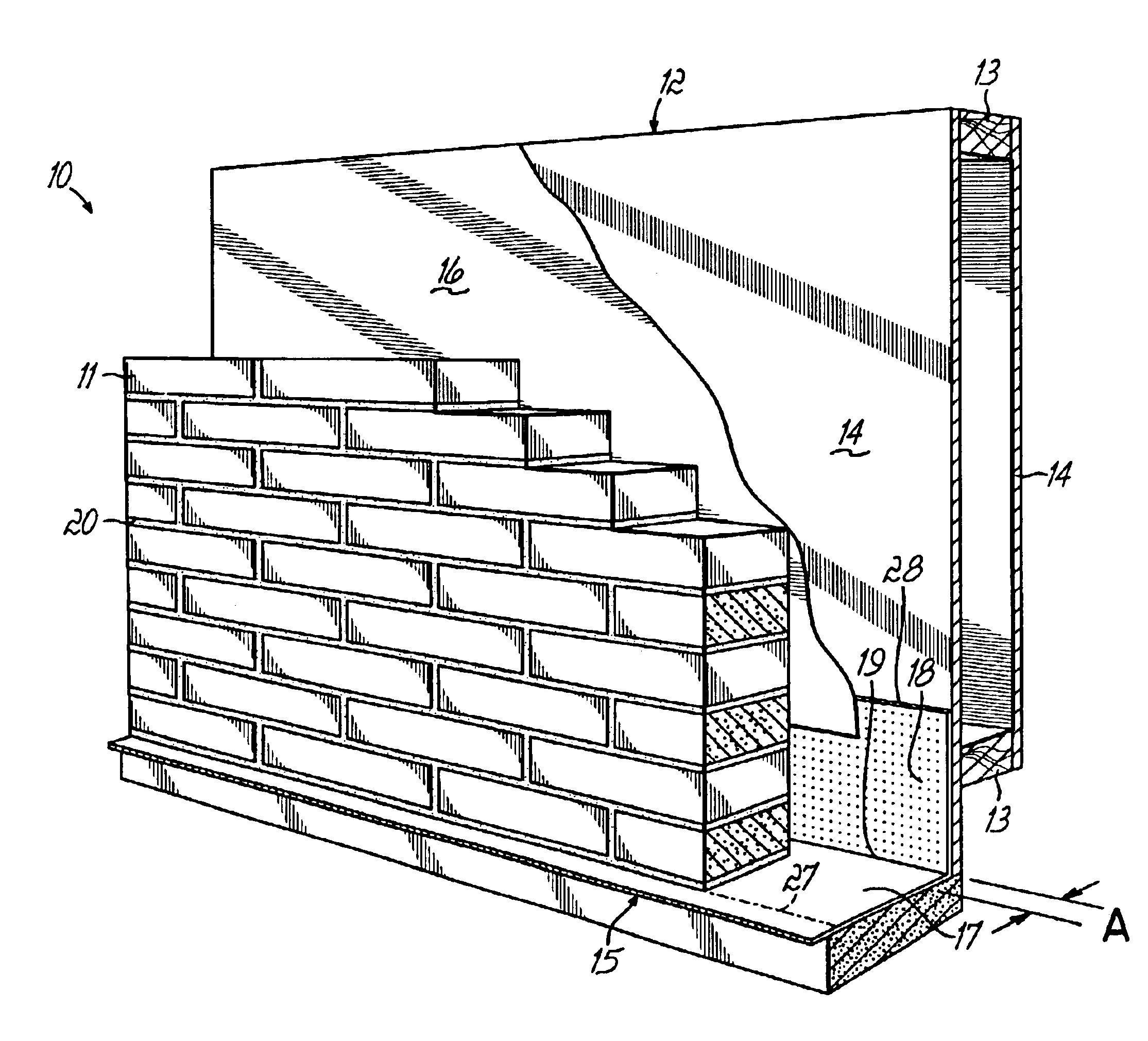
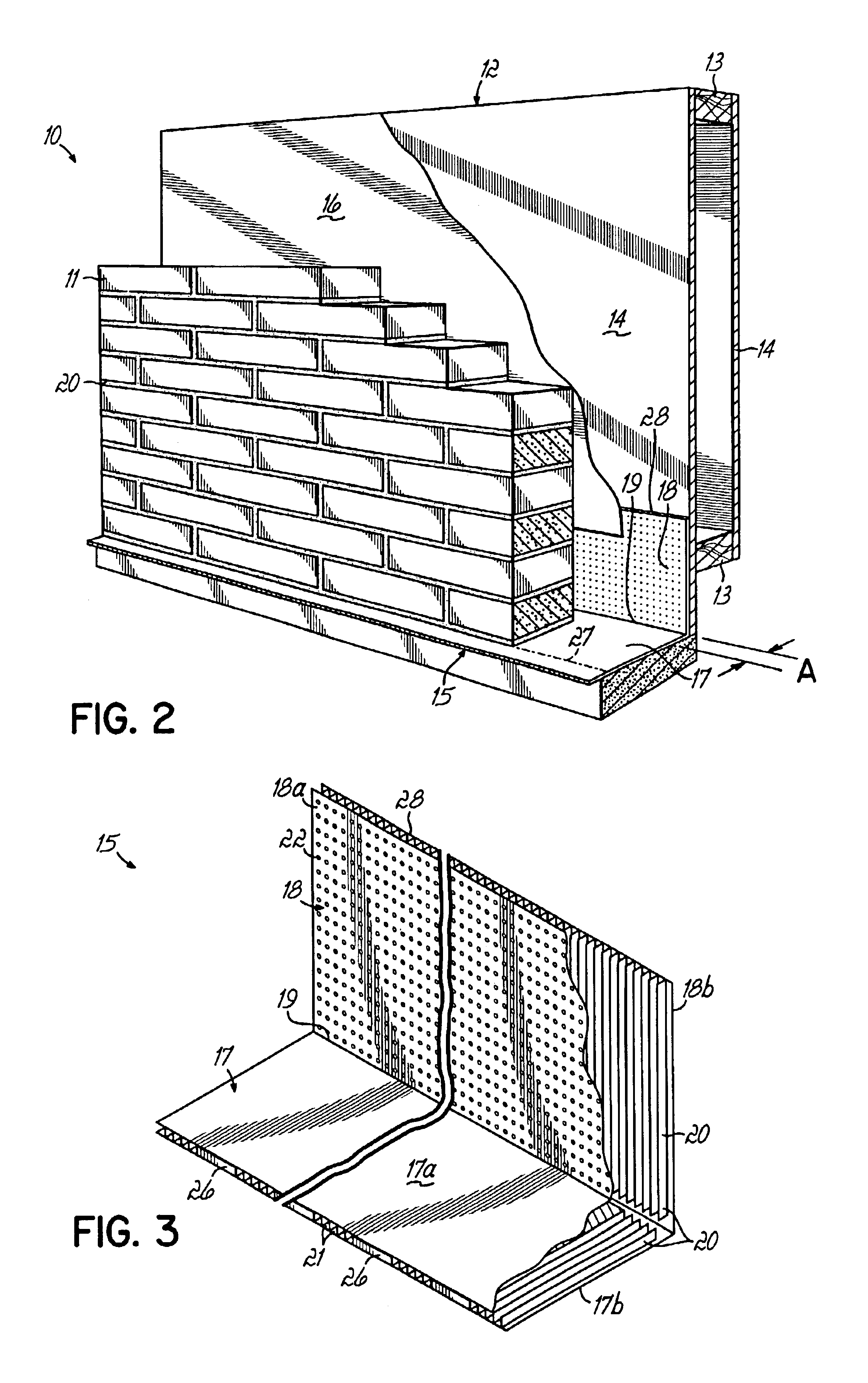
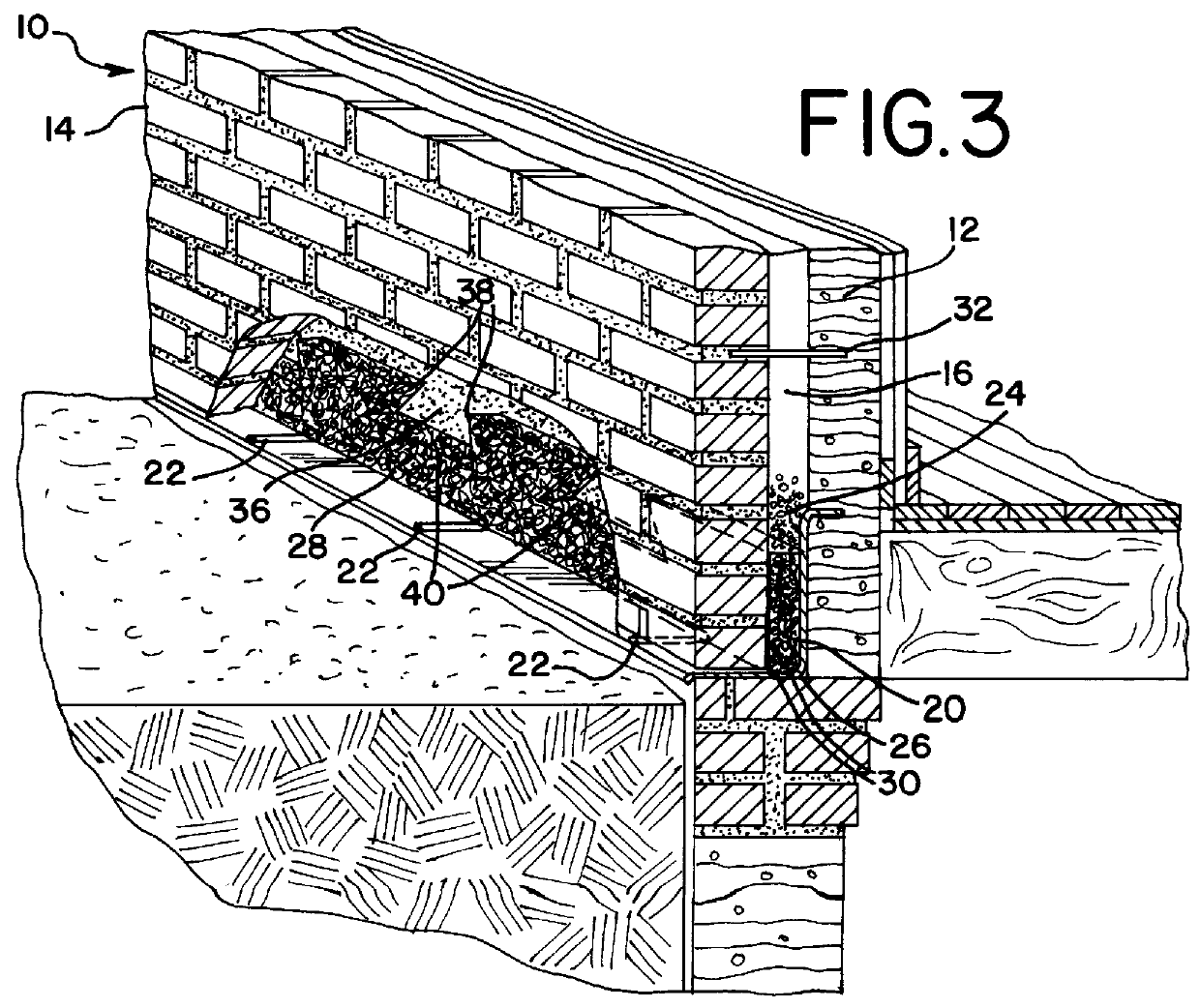
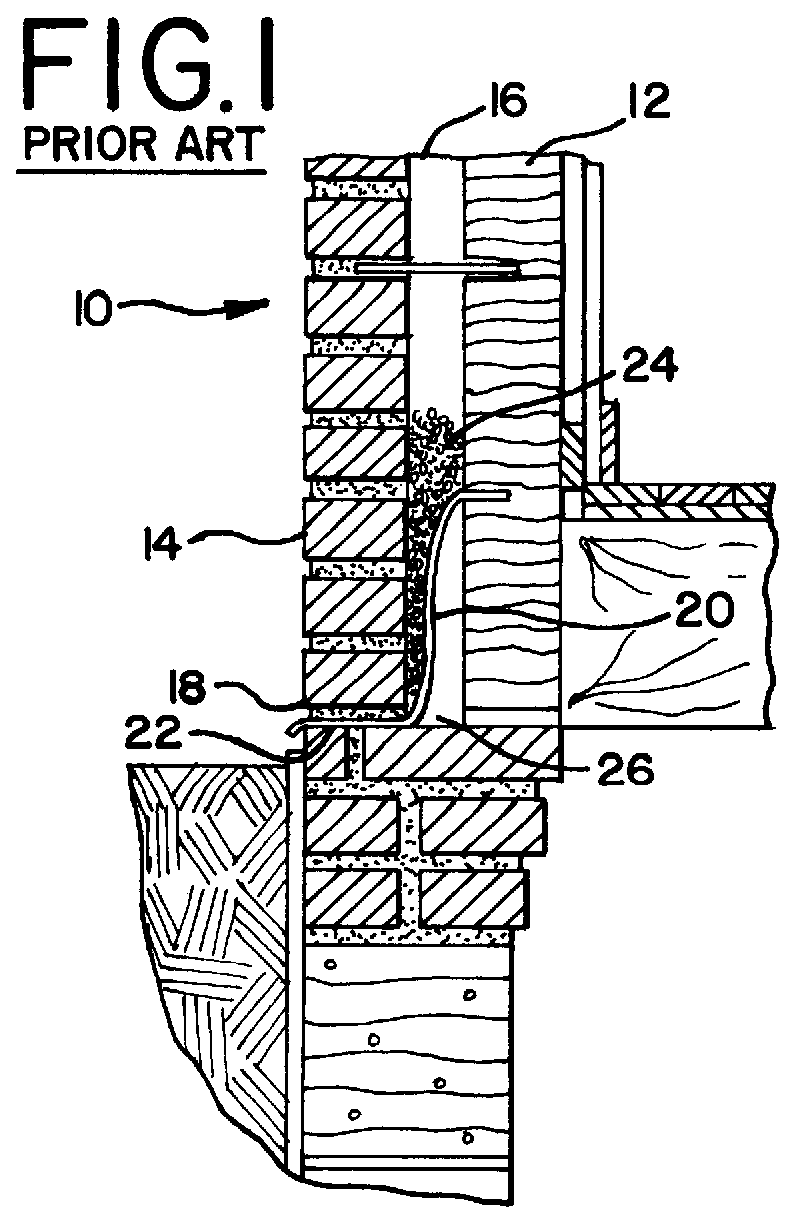
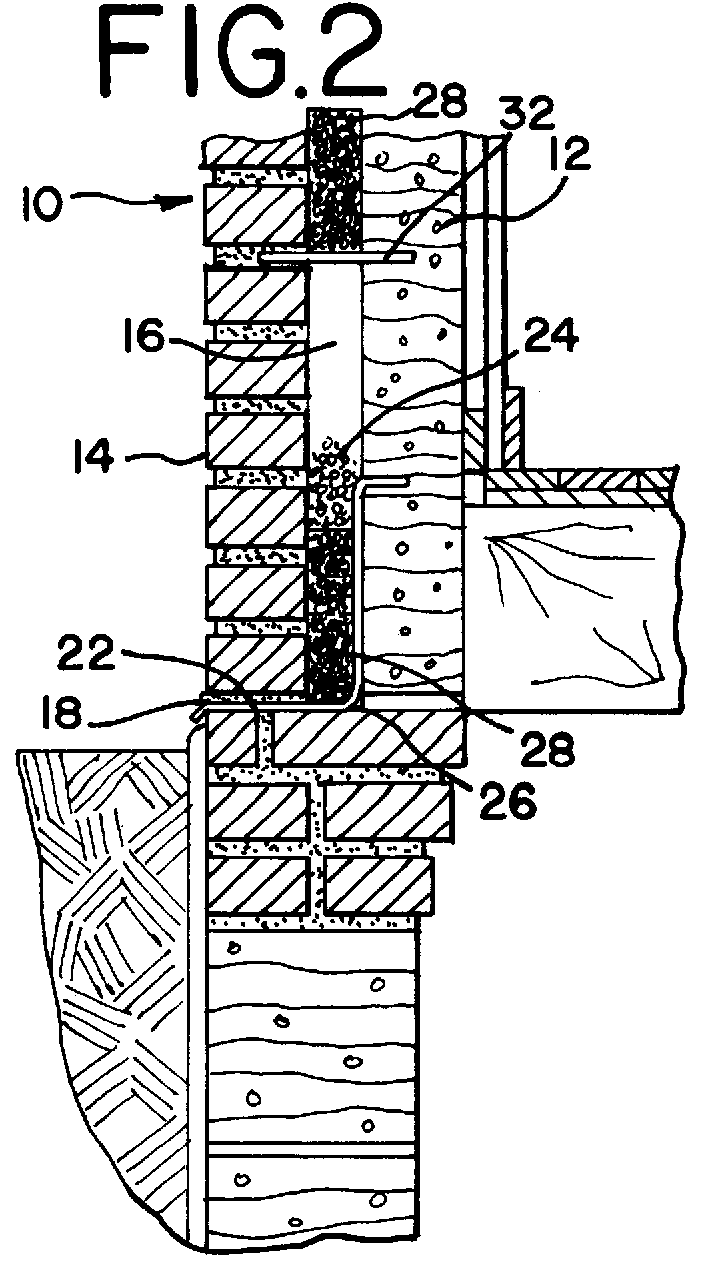
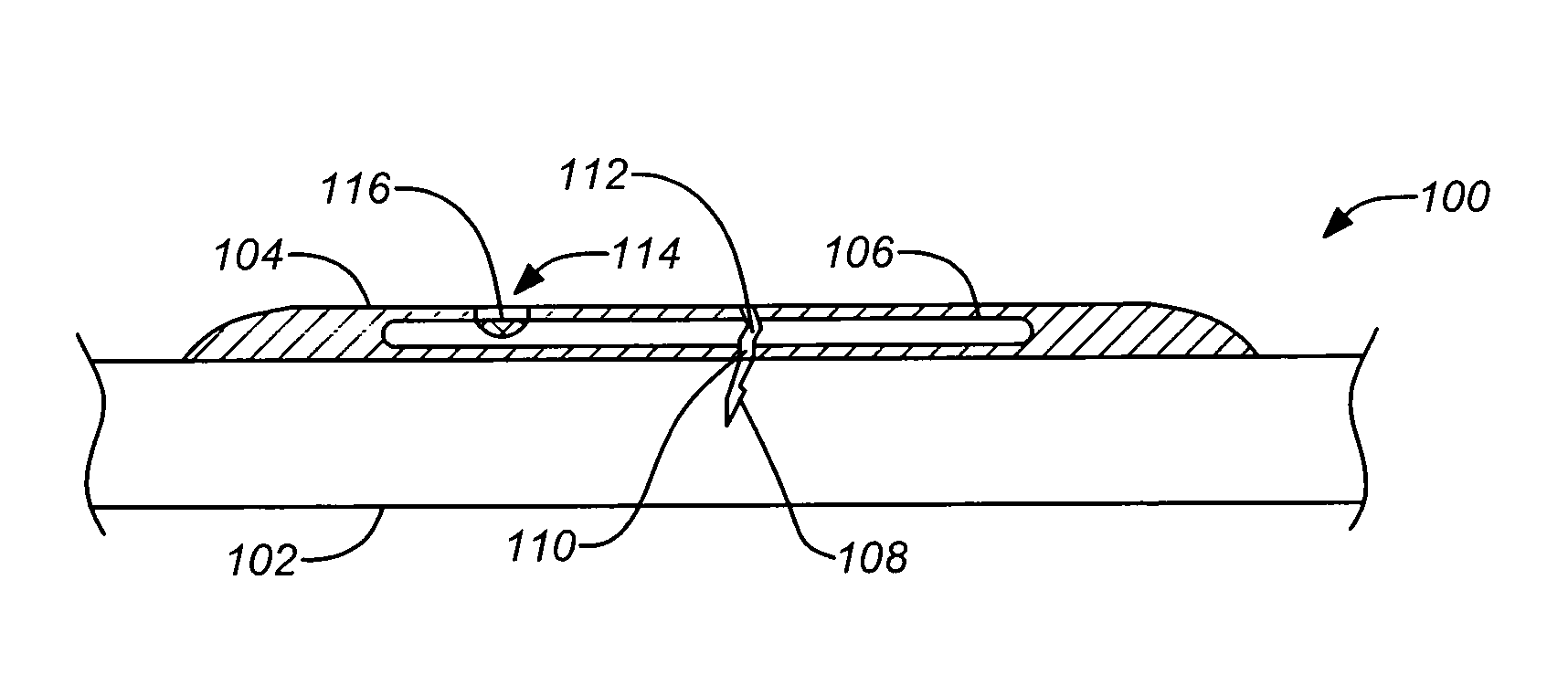
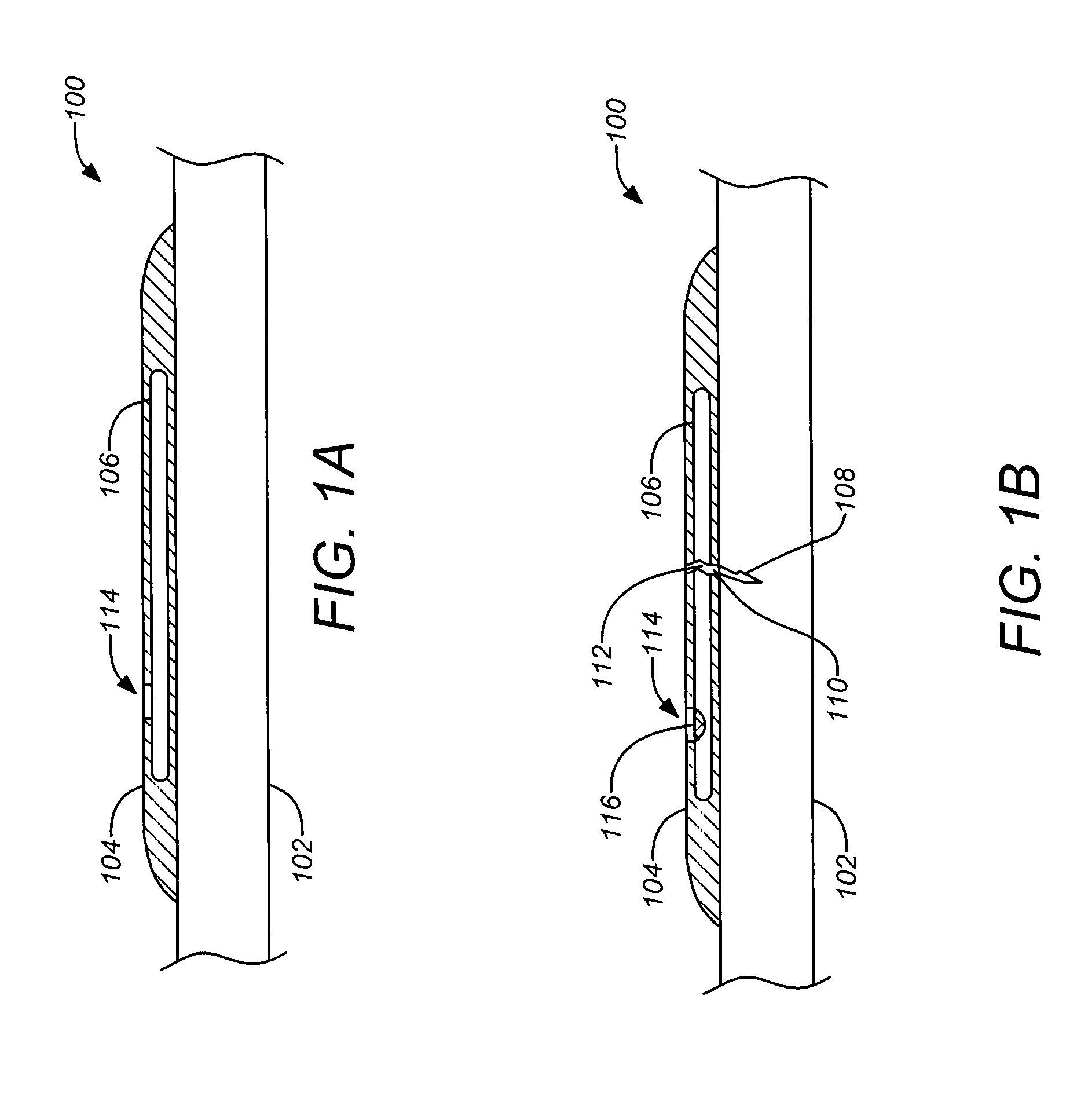
A weep, a weep hole, or a weep-brick is a small opening that allows water to drain from within an assembly. Weeps are located at the bottom of the object to allow for drainage; the weep hole must be sized adequately to overcome surface tension.
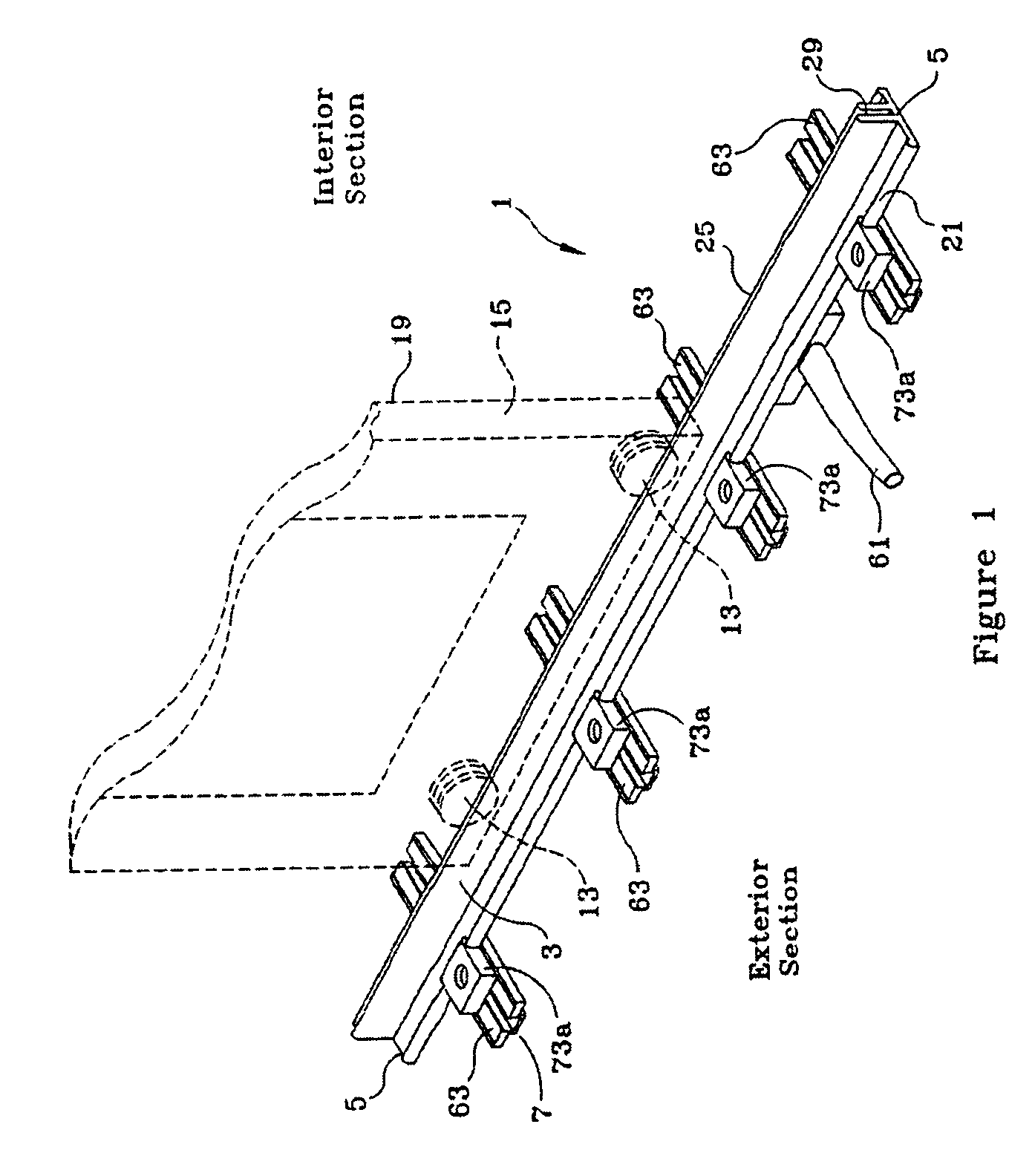
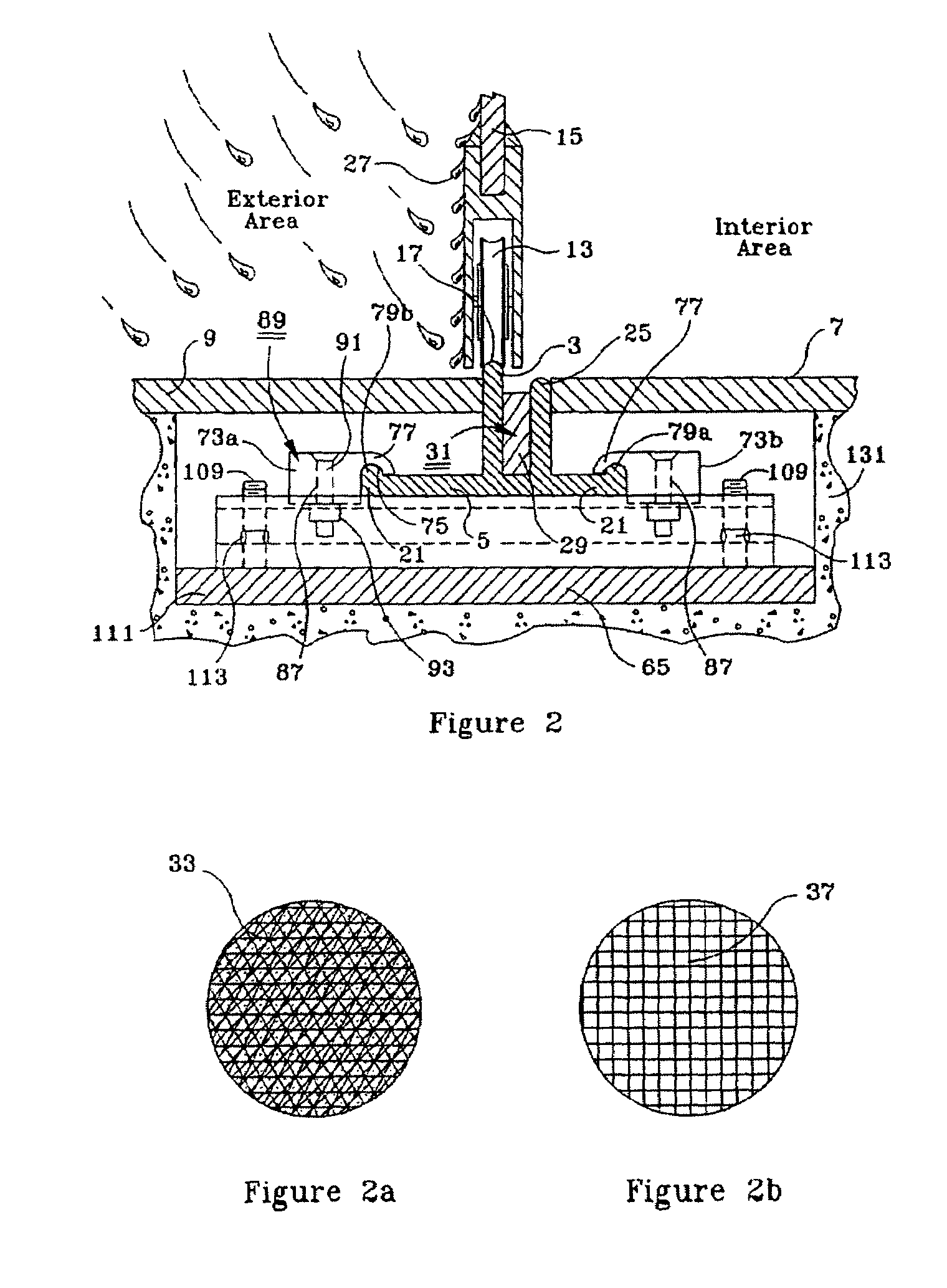
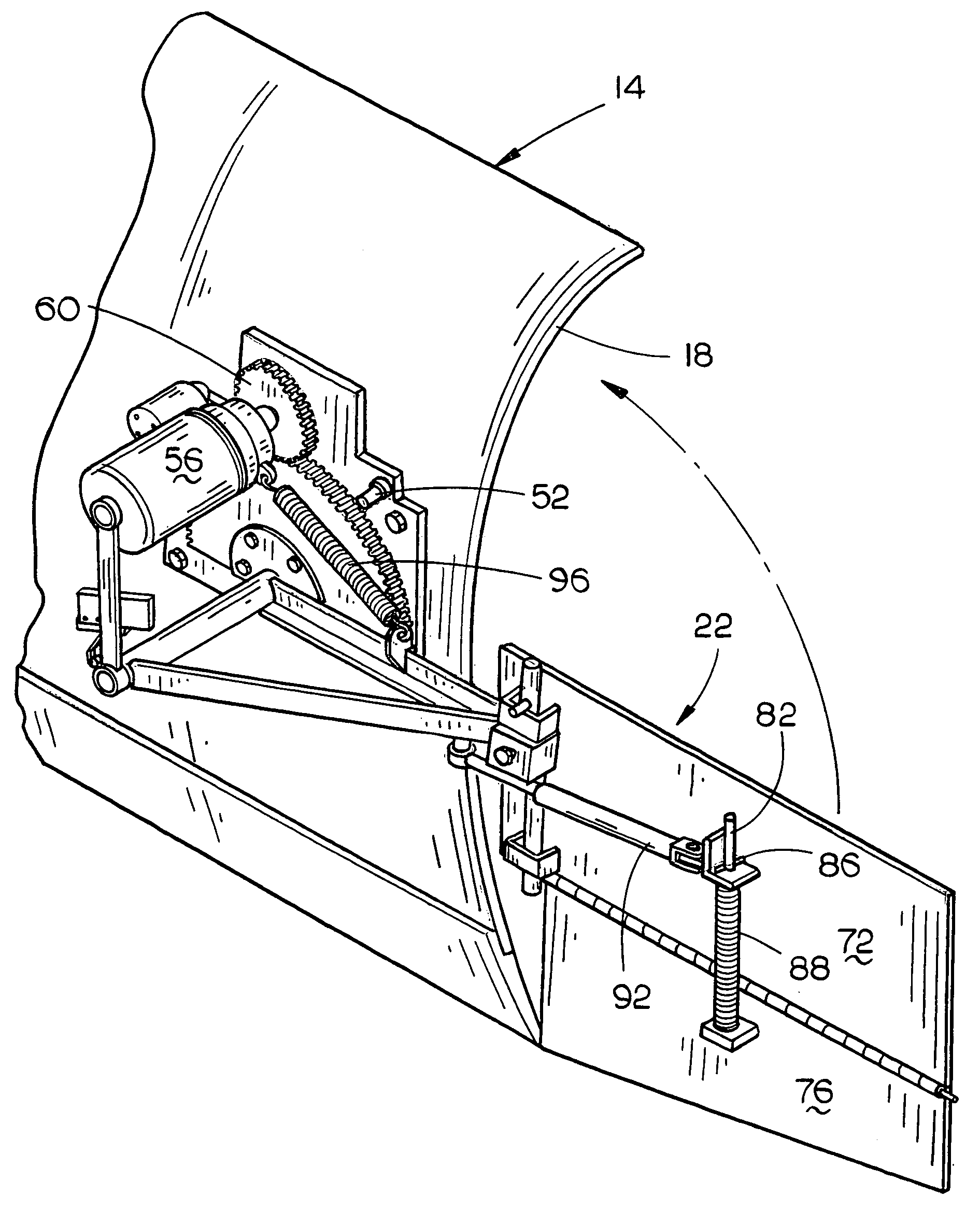
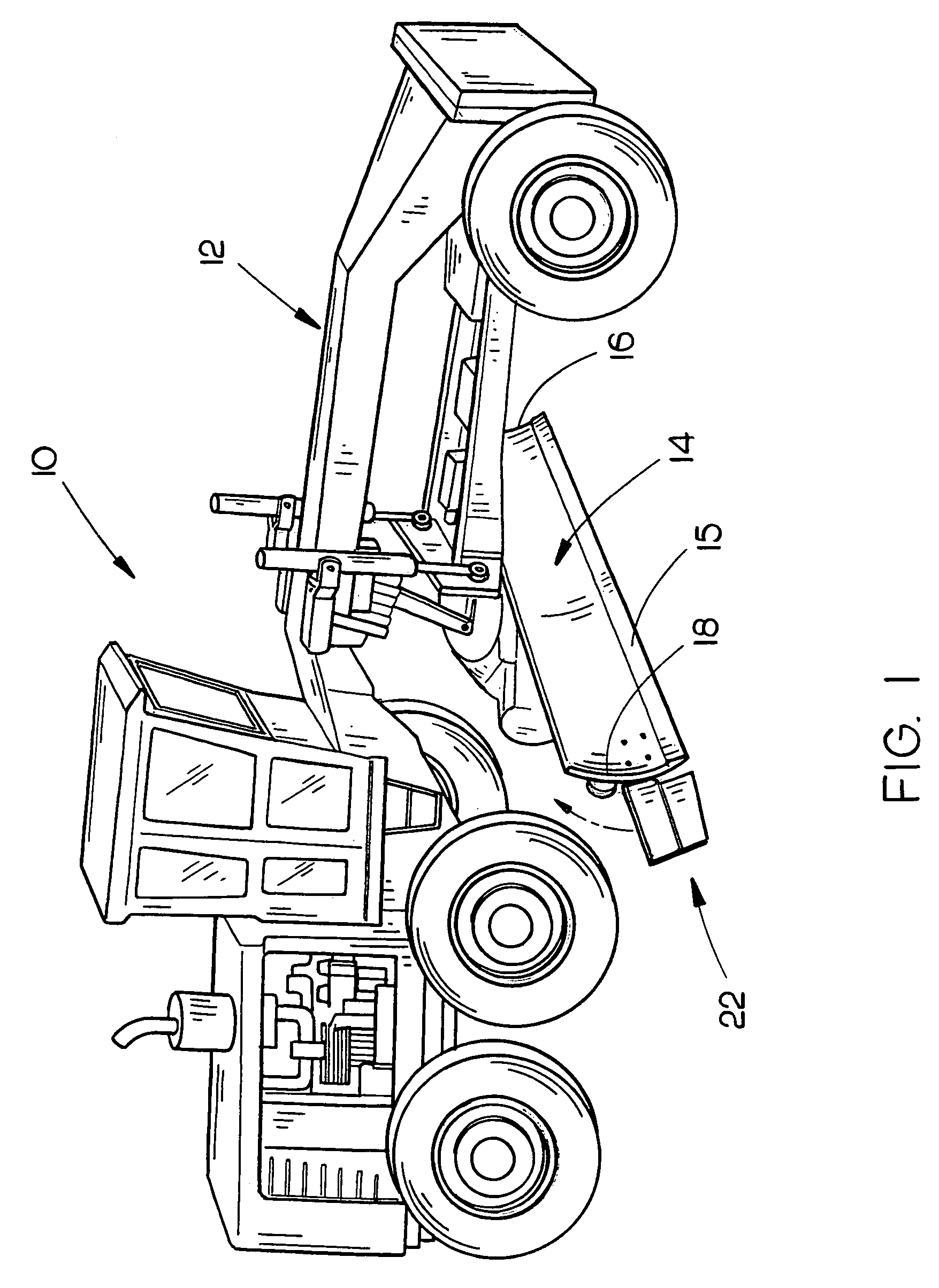
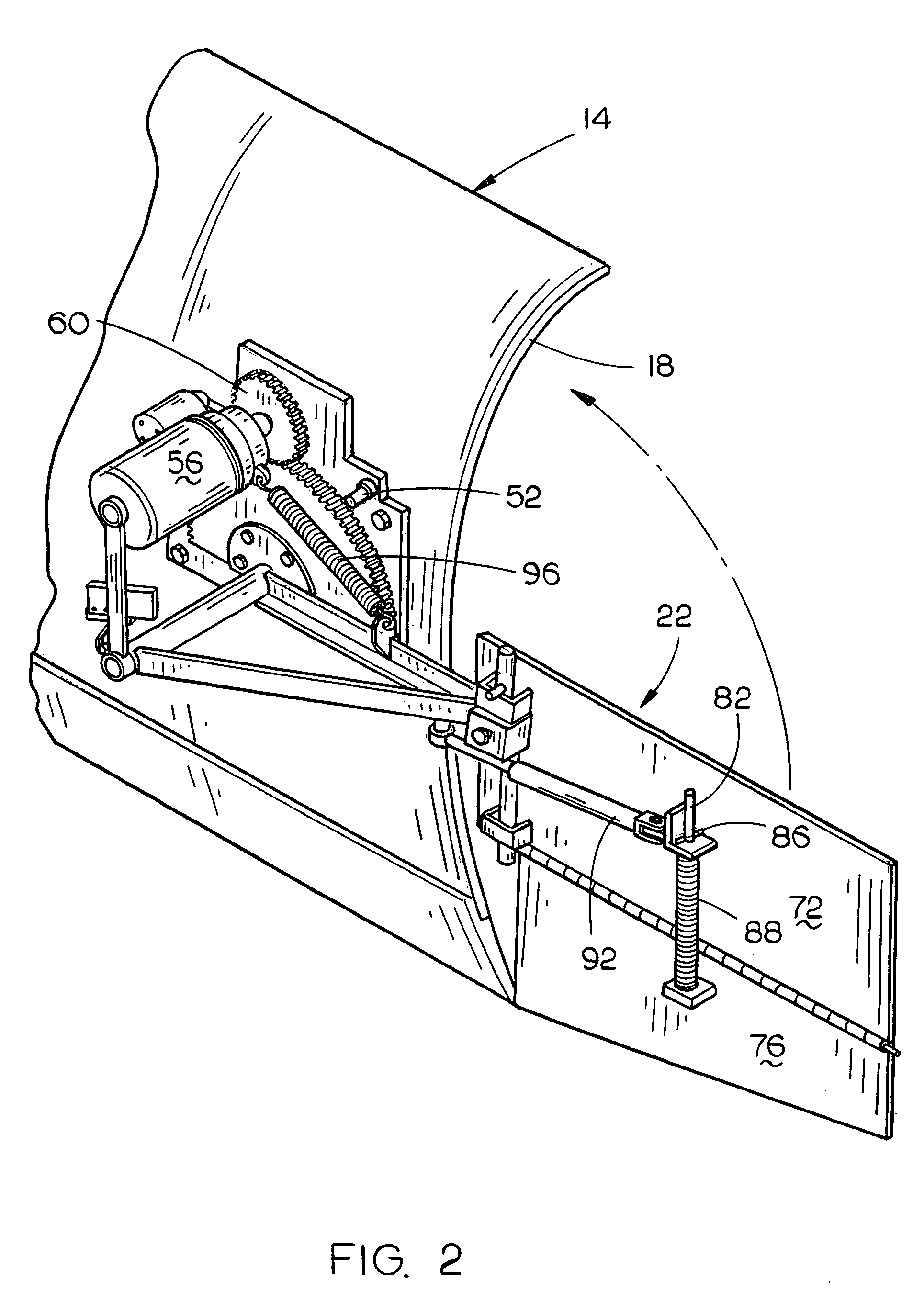
Moisture management system
InactiveUS6470638B1Improve adhesionImprove moisture managementBuilding roofsRoof covering using slabs/sheetsAdhesiveEngineering
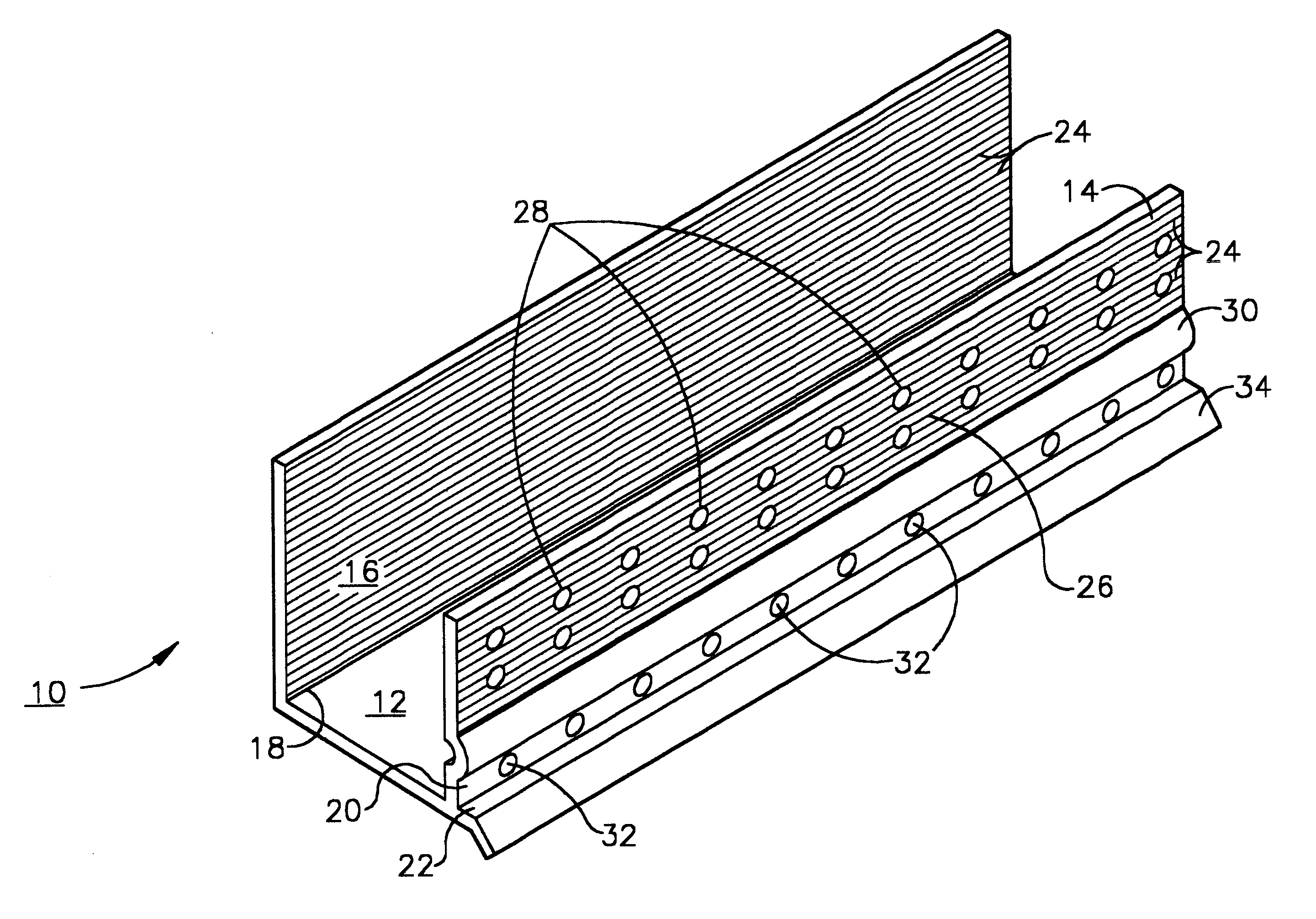
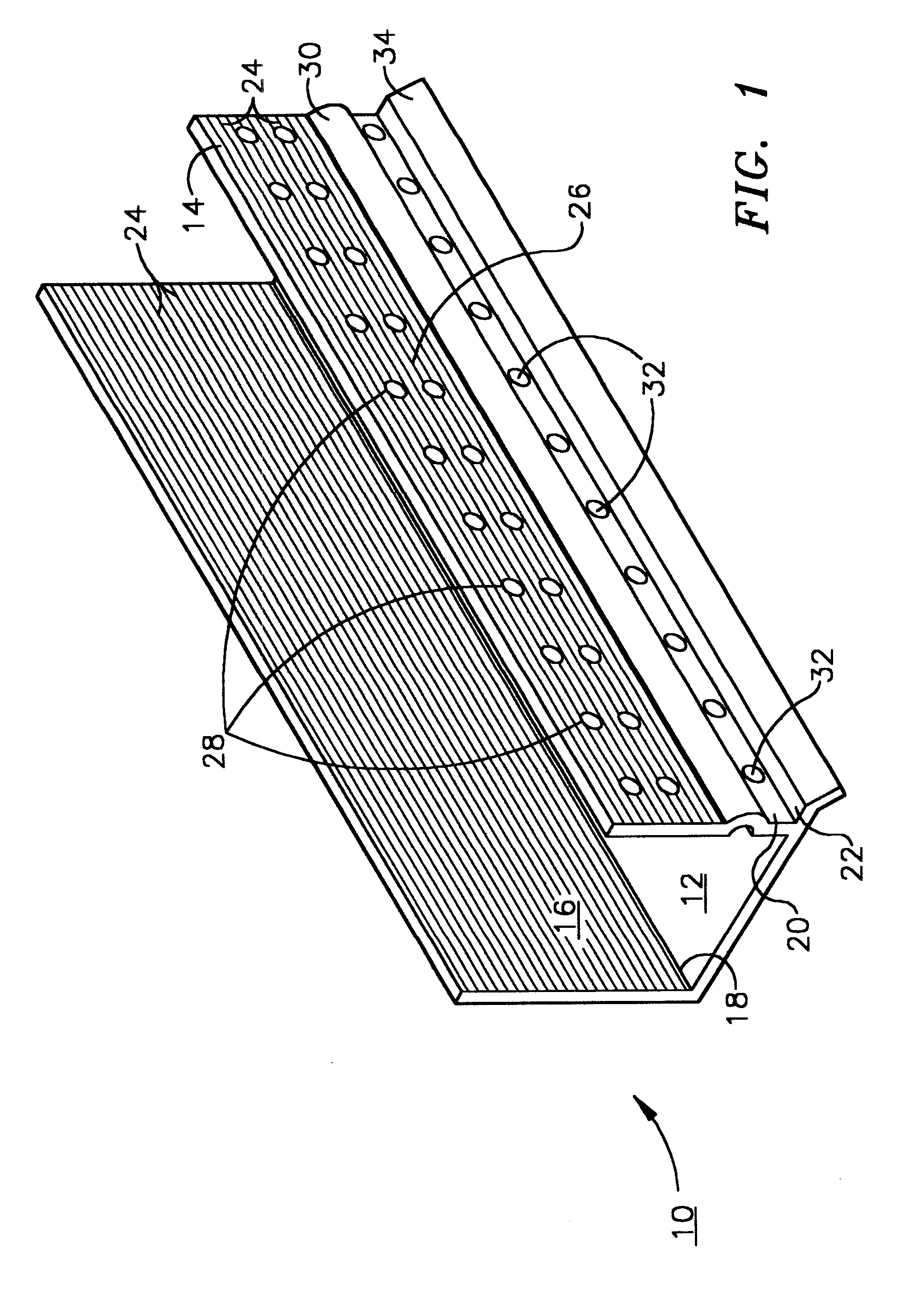
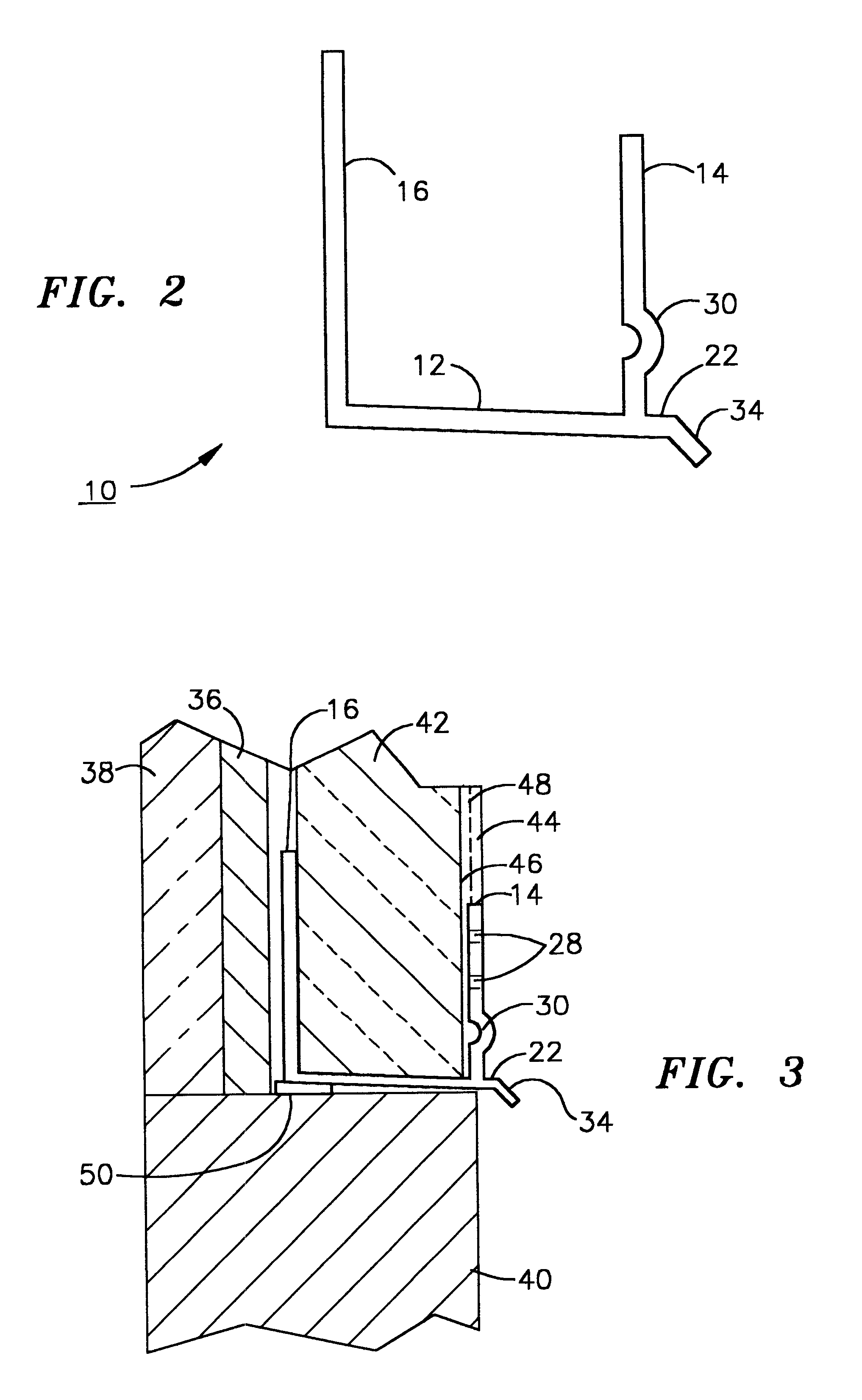
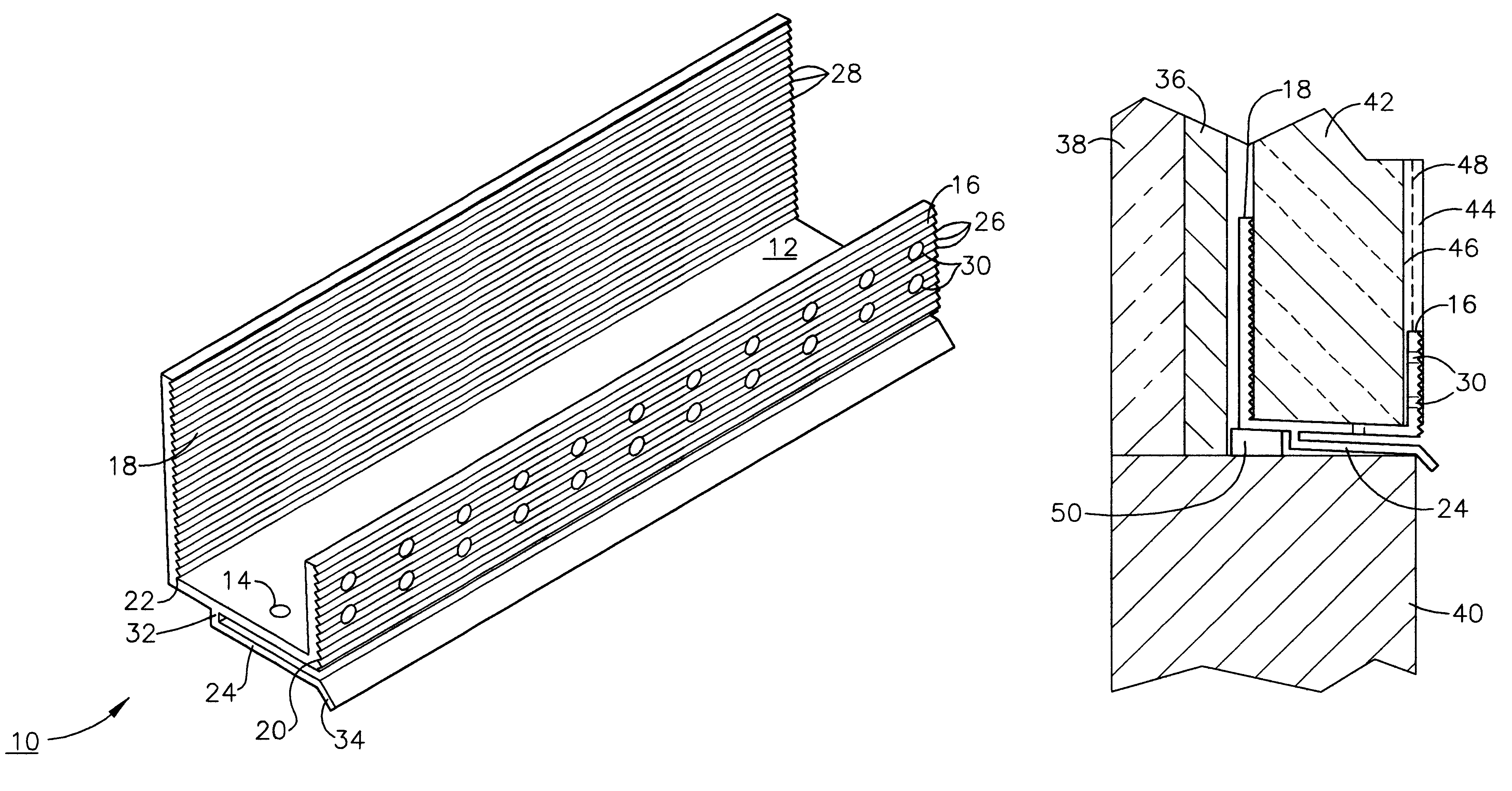
An improved moisture management system for installation over doors and windows in buildings that included exterior, stucco-covered, curtain walls comprising an integrally formed, three sided, elongated track including a base, an upright front wall that includes at its base weep holes for the removal of entrained moisture as well as a longitudinal forward extending finish stop above the weep holes, and an upright rear wall at opposing elongated edges of the base, and, extending angularly downward from the outside of the base, and integrally formed therewith, a drip plate that permits ready drainage of water exiting the moisture management system through the weep holes in the upright front wall. Preferably, elongated striations in the front faces of both the front and rear upright walls as well as holes in the upright front wall above the finish stop provide improved adherence of sealants and adhesives used in the installation process.
Owner:PLASTIC COMPONENTS
Moisture management system
InactiveUS6293064B1Improve water resistanceImprove featuresRoof covering using slabs/sheetsRoof covering using tiles/slatesAdhesiveEngineering
A moisture management system for installation over doors and windows in buildings that included exterior, stucco-covered, curtain walls comprising an integrally formed, three sided, elongated track including a base having weep holes therein, an upright front wall and an upright rear wall at opposing elongated edges of the base, and, extending angularly downward from the outside of the base, and integrally formed therewith, a drip plate that permits ready drainage of water entering the moisture management system through the weep holes in the base. Elongated striations in the front faces of both the front and rear upright walls as well as holes in the front upright wall provide adherence of sealants and adhesives used in the installation process.
Owner:PLASTIC COMPONENTS
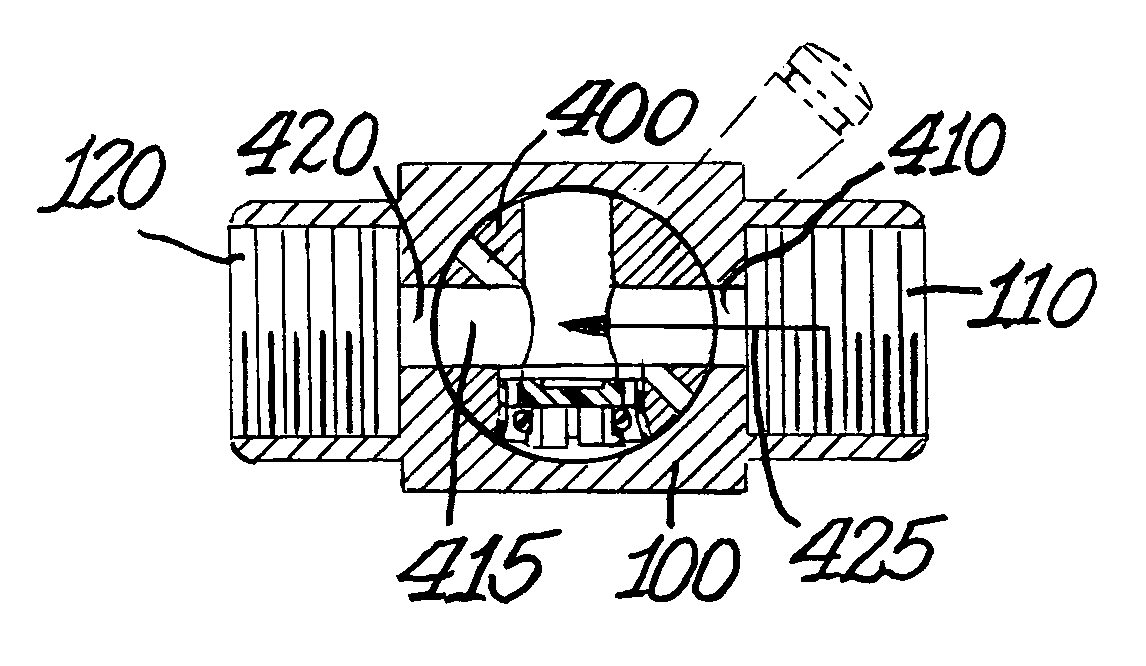
Flow control apparatus
InactiveUS7503345B2Facilitate water conservationQuickly and easily adjustPlug valvesBathsWater flowEngineering
The invention is a flow controller attachable to a water supply. The controller has a body with inlet and outlet connections and a control element positioned between the inlet and outlet. The controller has an actuator extending from the control element that permits selection of three different settings. The first setting aligns a set of openings in the control element with the inlet and outlet of the body permitting unimpeded full flow of water. A second setting aligns another set of openings, which form a weep hole, in the control element to substantially impede flow from the inlet to the outlet. A third setting aligns a third set of openings in the control element with a flow control device, to partially impede flow from the inlet to the outlet, creating a low flow.
Owner:SPEAKMAN
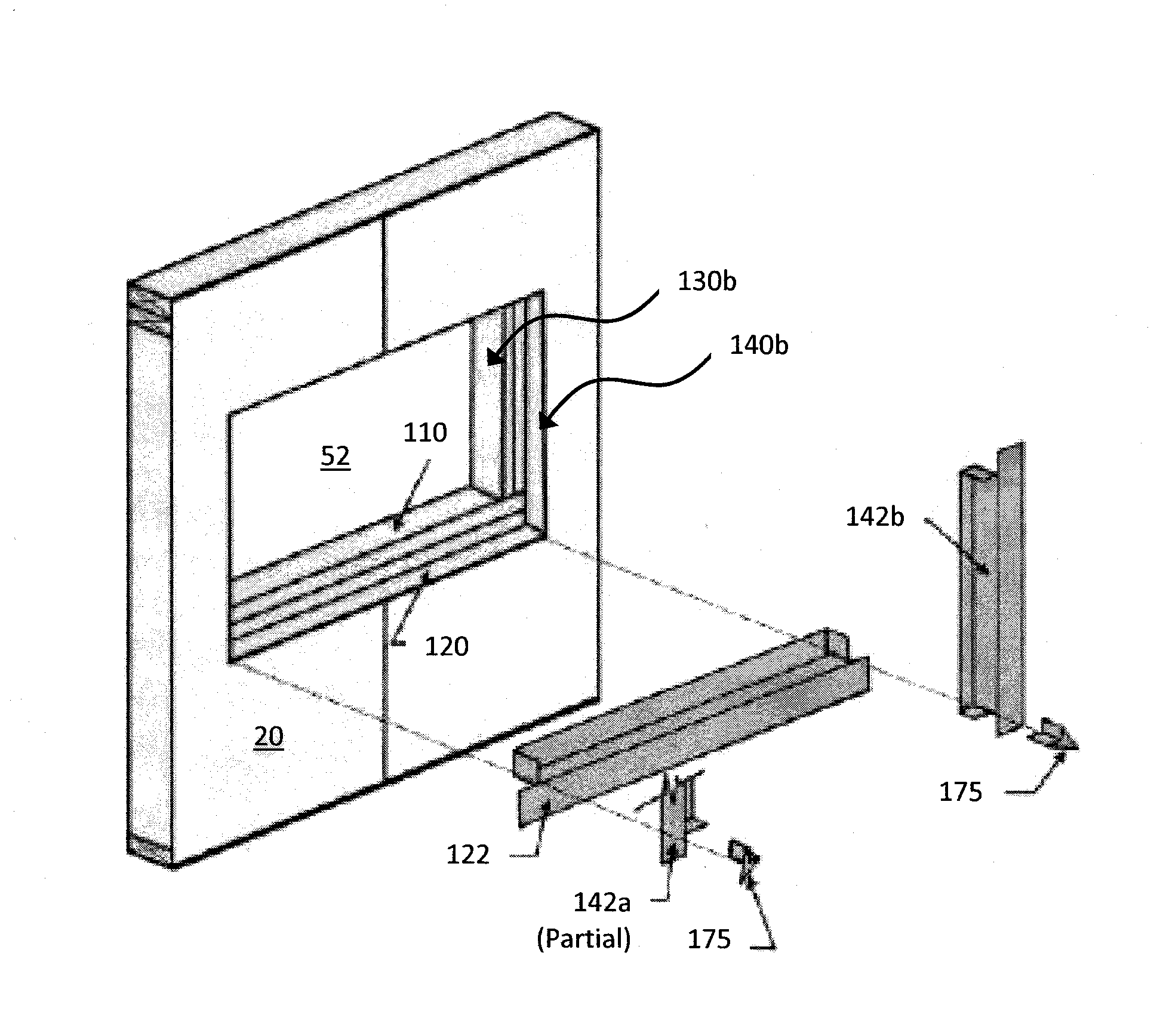
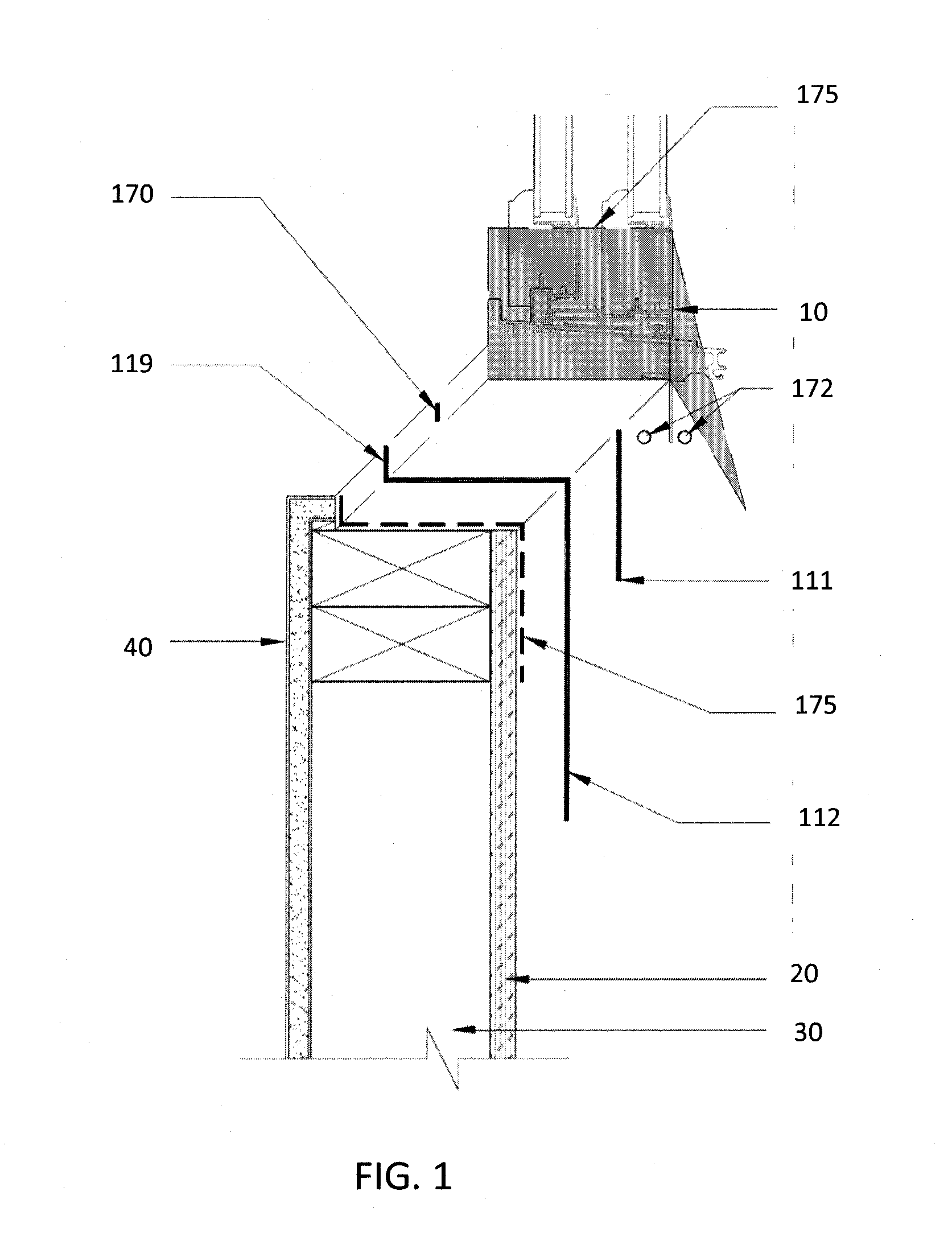
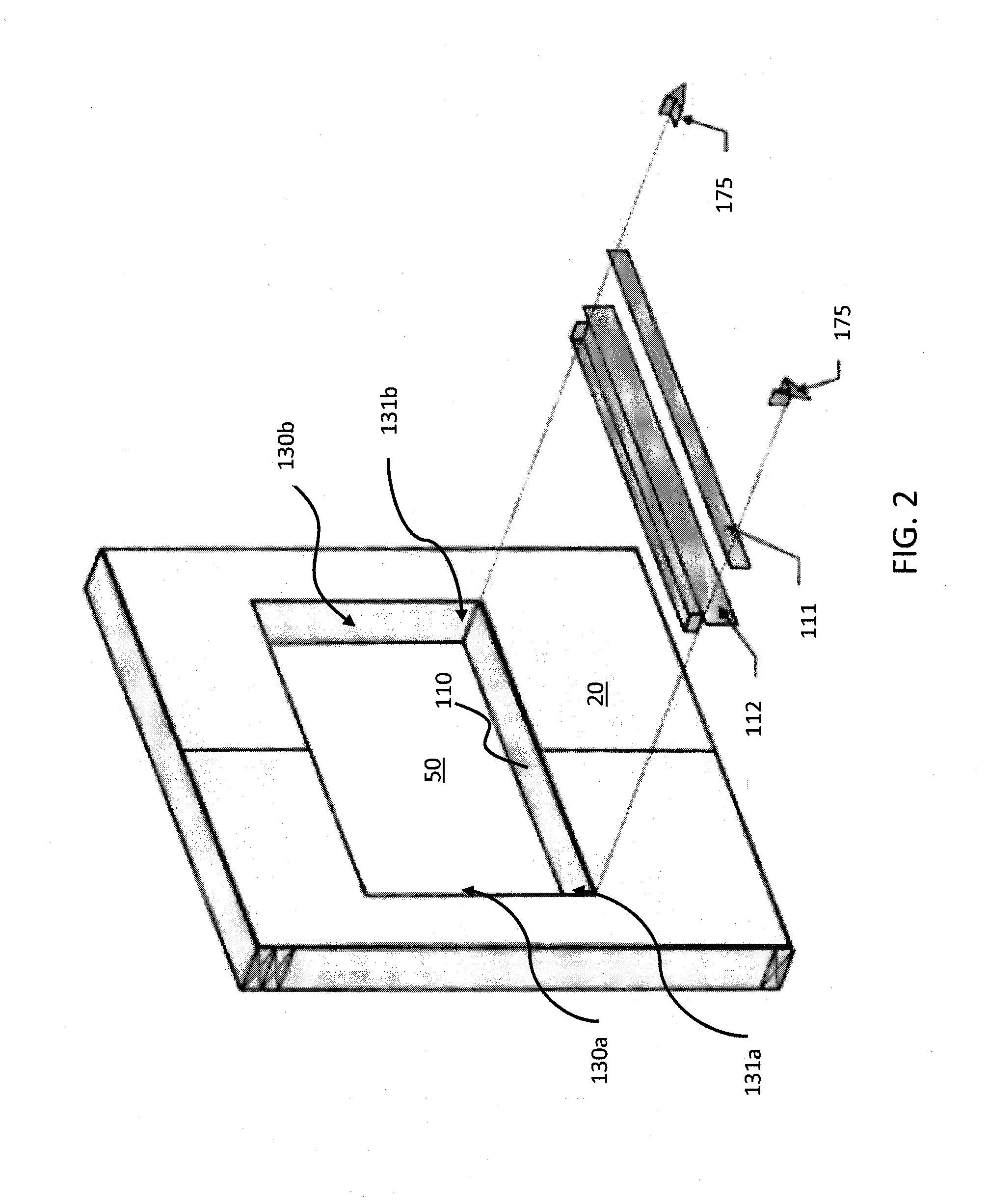
Fiber optic cable assemblies with furcation bodies having features for manufacturing and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20100202740A1Prevent rotationPrevent lateral movementMetal rolling stand detailsFibre mechanical structuresFiberEngineering
Fiber optic cable assemblies having furcation bodies with features that are advantageous for manufacturing are disclosed along with methods of making the same. The furcation body include at least one anti-rotation feature for mounting the furcation body and a viewing portion and / or weep hole. The viewing portion is advantageous since it allows the observation during filling of the cavity with an epoxy, adhesive, or the like to strain relieve components of the fiber optic cable assembly within the furcation body. Simply stated, the viewing portion is translucent or clear for observing the filling of the furcation body and detecting if an air bubbles / air pockets are formed so that they can be reduced and / or eliminated. The furcation body may also have a weep hole for allowing air bubbles / air pockets to escape. Additionally, the furcation body of the fiber optic cable assembly may be secured within a clip or other suitable structure for mounting the same.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
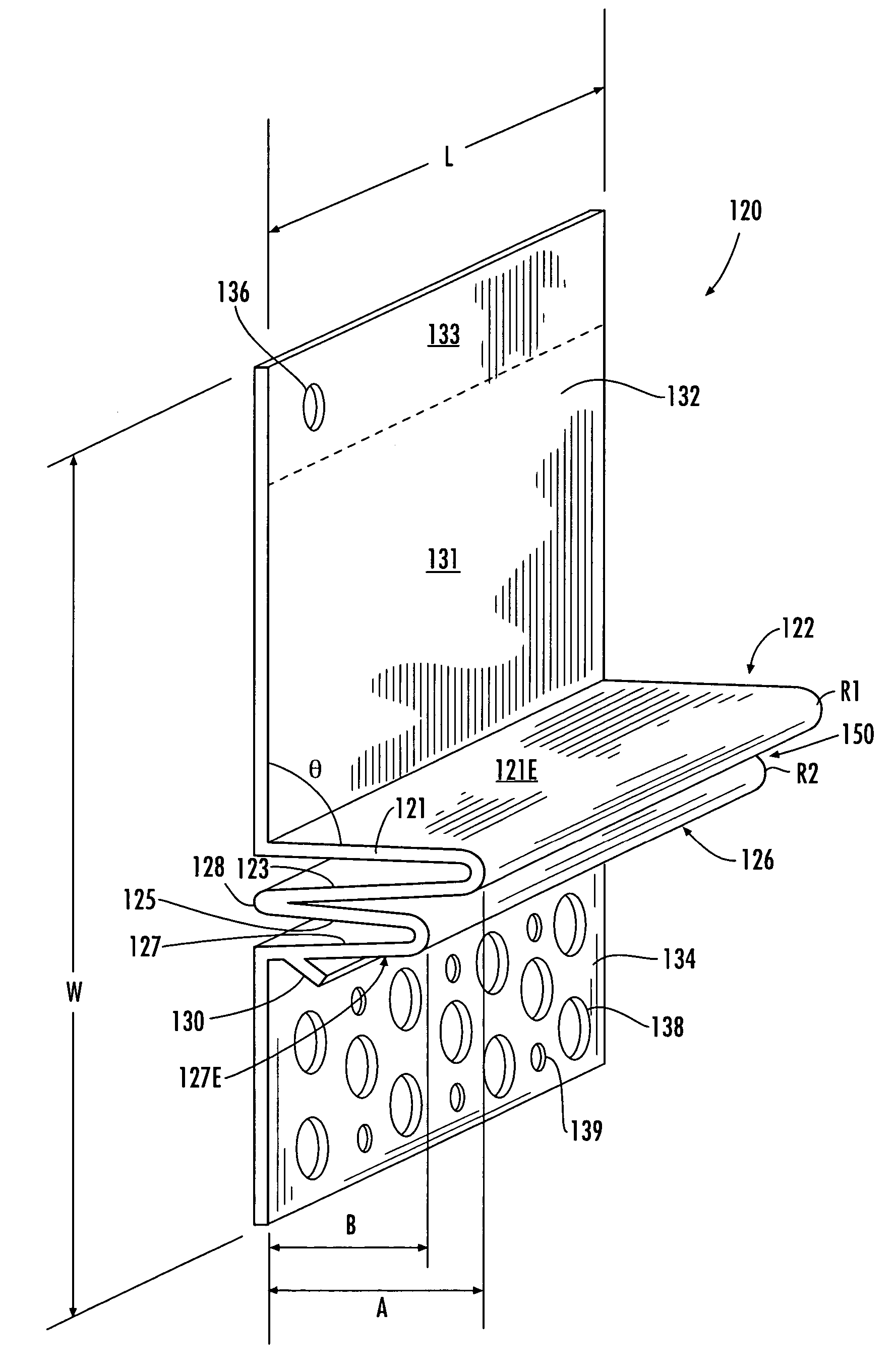
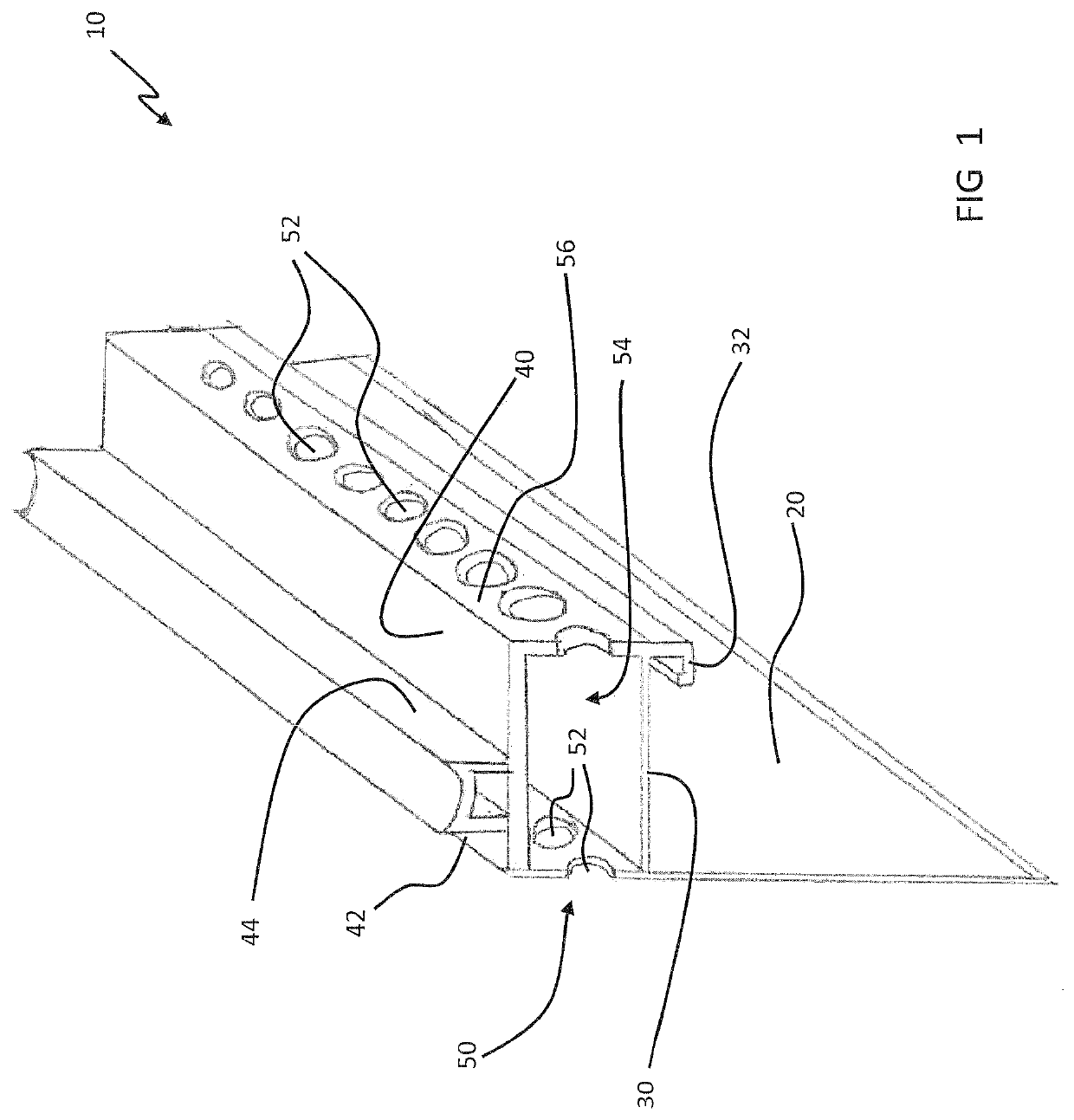
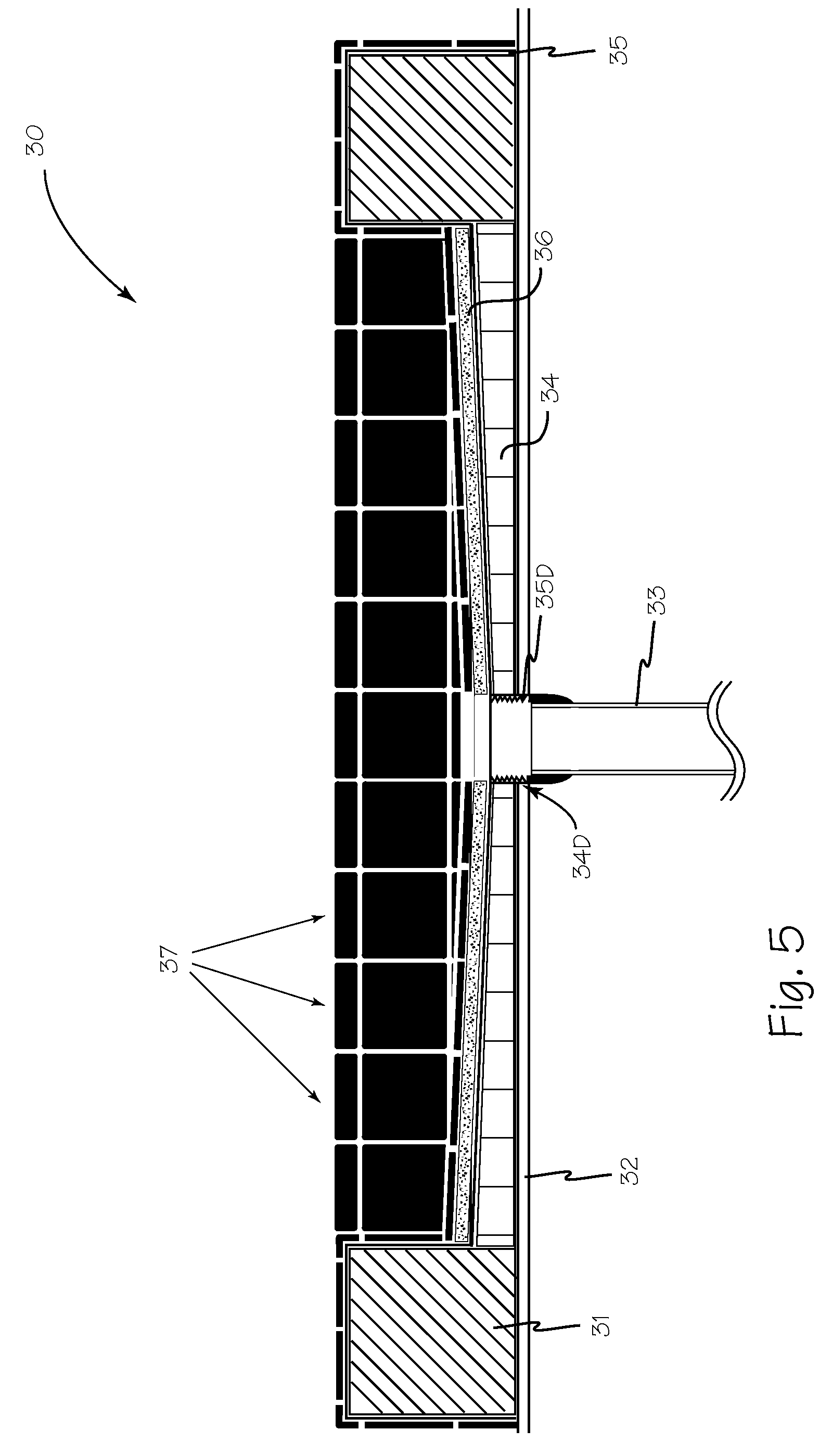
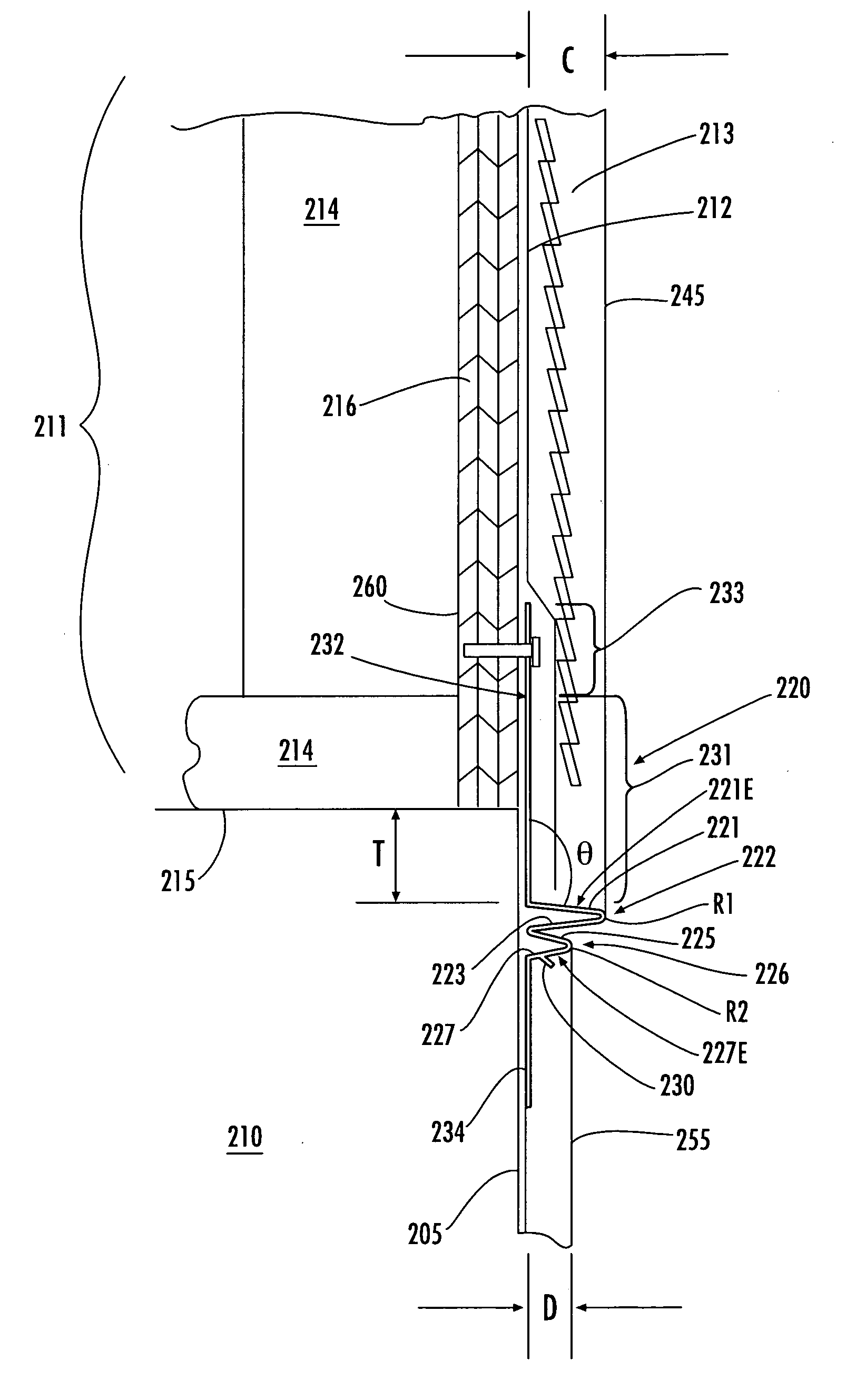
Flashing and weep apparatus for masonry wall window and door installations
ActiveUS6964136B2Easy to installEasy to implementRoof covering using slabs/sheetsRoof covering using tiles/slatesCavity wallMoisture
A flashing and weep apparatus allows for simple installation and accurate placement windows and doors in cavity wall construction. In a first embodiment, the flashing and weep apparatus is a two-panel extrusion that has a flashing panel that acts as a non-porous support for the masonry veneer. This embodiment also includes a second panel which is joined at a generally right angle to the first panel to be juxtaposed against the outer face of the inner wall in the cavity wall construction. Weep channels are formed between the two panels and allow for the drainage and dissipation of water and other moisture in the cavity wall system. In a second embodiment, membrane is initially attached to and draped along the lower portion of the inner wall immediately above the sill or lintel. The membrane extends across the cavity spacing between the walls to underlie the masonry components forming the outer veneer. Weep channels on the membrane communicate and transmit water and moisture from the cavity between the walls to the exterior of the veneer. The weep channels are positioned at the joint between adjacent bricks. The membrane extending beyond the mortar joint at the masonry veneer is trimmed during the installation process so as not to extend beyond the outer veneer wall while still providing an easily installed and implemented flash and weep system.
Owner:TY DAS BUILDING PROD LLC
Mortar and debris collection device and system
InactiveUSRE36676E1Promote full dispersionAvoid Waterlogging ProblemsStrutsFoundation engineeringPorosityWater channel
A mortar and debris collection device for a cavity wall construction has a non-water absorbent body formed with circuitous paths therethrough making the body water-permeable. The collection device has a porosity sufficient to permit water to pass therethrough but insufficient to permit mortar and other debris to pass therethrough to weep holes or other water channels covered by the collection debris. The device may be freely placed on the wall base within the cavity to cover the opening of a weep hole, or may also be placed on existing wall ties within the cavity.
Owner:MORTAR NET USA
Shower pan drain assembly system
InactiveUS20100043136A1Prevent leakageAvoid cloggingSewerage structuresBathsEngineeringWater seepage
An integrated shower base designed for improving the drainage of a tile shower is disclosed. The shower pan may be custom fabricated and molded with a depression surrounding a drainage opening for receiving a one piece floor drain. The pan and floor drain are welded together to prevent leaking. The floor drain contains weep holes so that water that seeps through the mortar on the shower floor and into the shower pan can drain properly without leaking. The floor drain also contains a reservoir for holding water that drains through the regular shower drain and also for water that seeps through the shower floor. A mortar guard is placed over the weep holes to prevent the holes from becoming clogged. A drainage mat is placed over the shower pan to help water seepage flow to the floor drain.
Owner:MICHAEL BORIS
Cooking fume remover
InactiveCN1908527AReduce pollutionImprove filtering effectDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusWater circulationSoot
The invention relates to an environment-friendly range hood with simple structure, low cost and capable of effectively separating oil fume, which includes a chassis, a suction channel, an exhaust channel, a fan and a switch, and is characterized in that the fan is located between the suction channel and the exhaust channel Between them, the suction channel and the exhaust channel form a flue; the flue is provided with a number of cooling fins inclined downward along the air inlet direction, and the surface of the cooling fins facing away from the air inlet direction is a water tank set from top to bottom , the lower end of the water tank is connected with the water collection tank, and each cooling fin forms a row of cooling grids on the same plane along the radial direction of the flue, and there is a tuyere between adjacent cooling fins, and a leaking pipe is fixed on the upper part of the cooling fin, and the leaking pipe There are water leakage holes corresponding to the water tanks of each cooling fin; the water tank, water pump, leaking pipe, cooling fin water tank and water collection tank fixed in the chassis form a water circulation loop.
Owner:麦广海
Irrigation device and system
InactiveUS6901698B2Reduce lossesMinimizing installation timeRoot feedersWatering devicesEngineeringIrrigation
The present invention is directed to an irrigation device and irrigation system. More specifically, the present invention is directed to a weep or tear type irrigation device and irrigation system.
Owner:MANNING HAROLD
Fiber optic cable assemblies with furcation bodies having features for manufacturing and methods of making the same
InactiveUS8290333B2Prevent rotationPrevent lateral movementMetal rolling stand detailsCoupling light guidesEpoxyFiber
Fiber optic cable assemblies having furcation bodies with features that are advantageous for manufacturing are disclosed along with methods of making the same. The furcation body include at least one anti-rotation feature for mounting the furcation body and a viewing portion and / or weep hole. The viewing portion is advantageous since it allows the observation during filling of the cavity with an epoxy, adhesive, or the like to strain relieve components of the fiber optic cable assembly within the furcation body. Simply stated, the viewing portion is translucent or clear for observing the filling of the furcation body and detecting if an air bubbles / air pockets are formed so that they can be reduced and / or eliminated. The furcation body may also have a weep hole for allowing air bubbles / air pockets to escape. Additionally, the furcation body of the fiber optic cable assembly may be secured within a clip or other suitable structure for mounting the same.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Process for concurrently molding semiconductor chips without void and wire weep and molding die used therein
InactiveUS6200121B1Tailstocks/centresSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShell moldingSemiconductor chip
A molding die used for concurrently packaging semiconductor chips in a large piece of synthetic resin has a cavity rectangular in cross section and having two long peripheral lines and two short peripheral lines for accommodating a circuit panel where the semiconductor chips are mounted, melted synthetic resin is supplied through a gate extending along one of the long peripheral lines to the cavity so that the melted synthetic resin smoothly flows over the cavity, and the smooth flow prevents the molded product from voids and a wire weep.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Movement control screed
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to a movement control screed that is structured for installation between first and second masonry coatings applied adjacent to a building wall. The movement control screed is structured as a control joint for absorbing movement between the first and second masonry coatings and also as a weep screed for accommodating drainage of water from behind the masonry coatings. The movement control screed comprises first and second flanges provided on opposite sides of first and second ribs.
Owner:ALABAMA METAL INDS
In-floor, adjustable, multiple-configuration track assembly for sliding panels with built-in weep system
InactiveUS7007343B2Low costCurtain suspension devicesCondensed water drain-offEngineeringMechanical engineering
In-floor, adjustable, track assembly for sliding panels with a build-in weep system, including a track, extending upward from a base, for engaging the undercarriage of a vertically-oriented panel, and supporting rectilinear motion therealong, an upright splash guard, parallel to and spaced slightly apart from one side of the upright track and forming, with the track, a channel therebetween with the base, for directing moisture from the bottom of the panel into the channel, at least one collection pan mounted under the channel and accessible through an aperture to collect moisture from the channel, and a hose for drawing off the moisture from the channel.
Owner:WEILAND SLIDING DOORS & WINDOWS
Wall planting system
ActiveUS8281517B2Improve aestheticsImprove thermal efficiencyWatering devicesAgriculture gas emission reductionLine tubingEngineering
Owner:HORTECH
Cyclone with in-situ replaceable liner system and method for accomplishing same
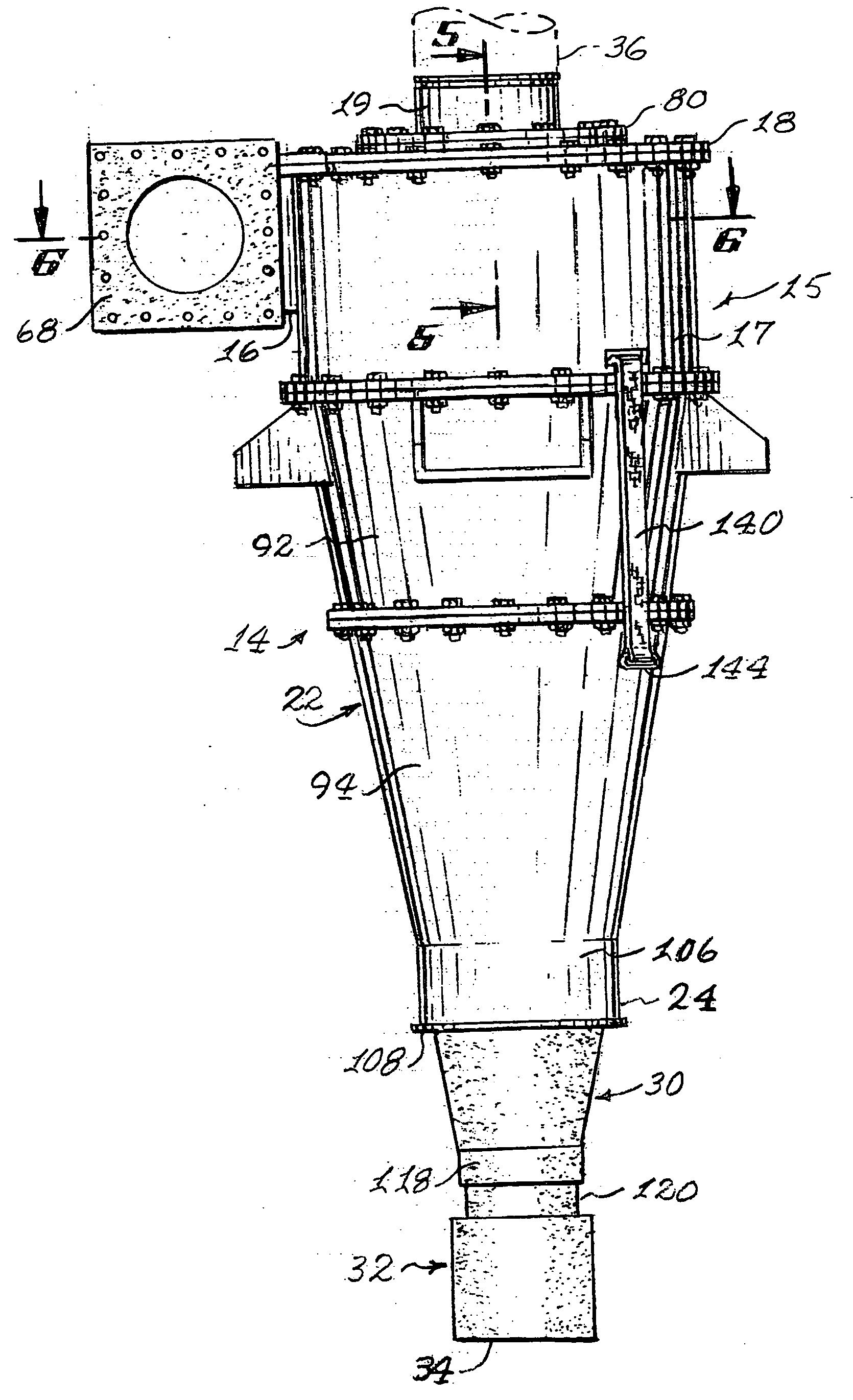
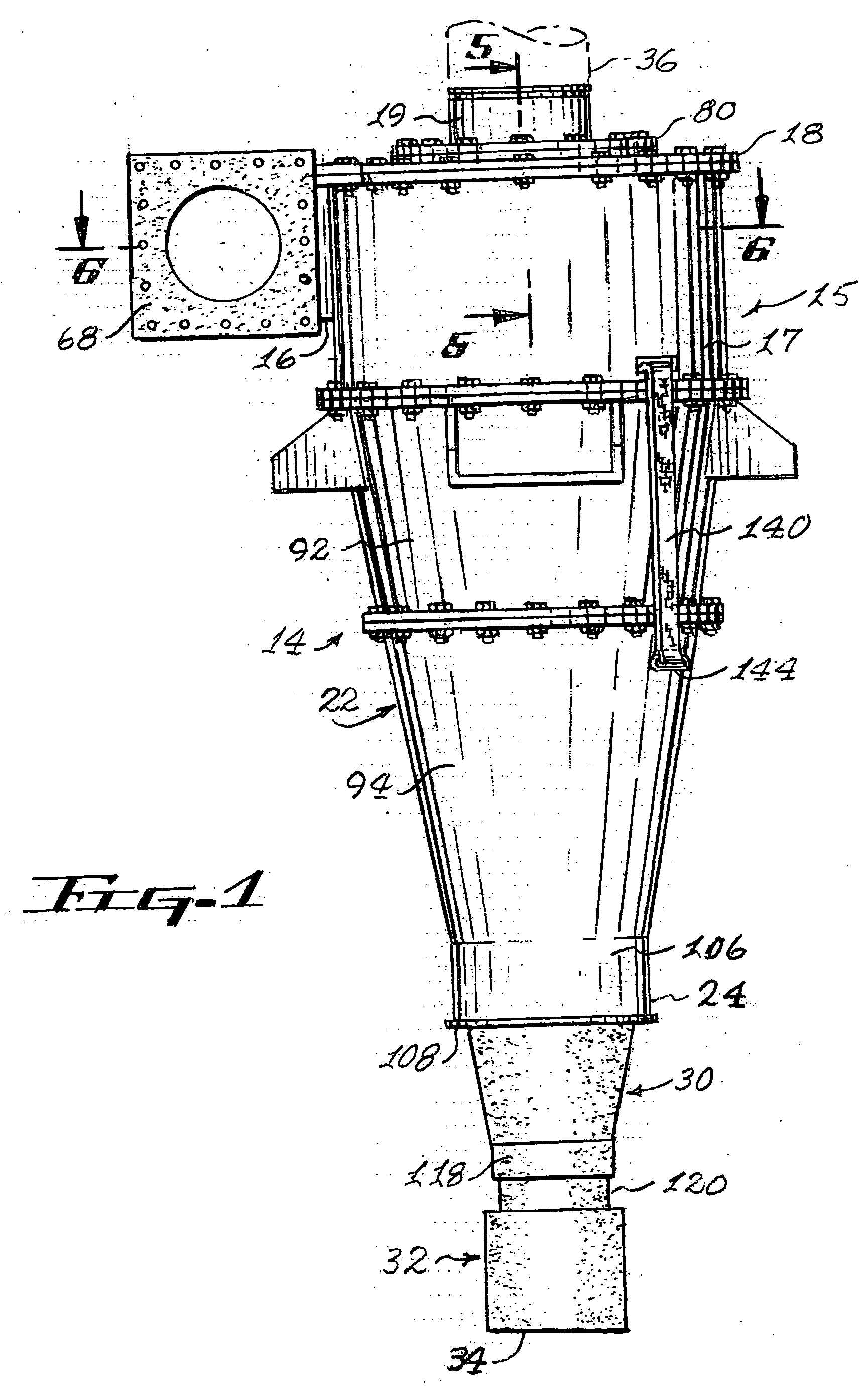
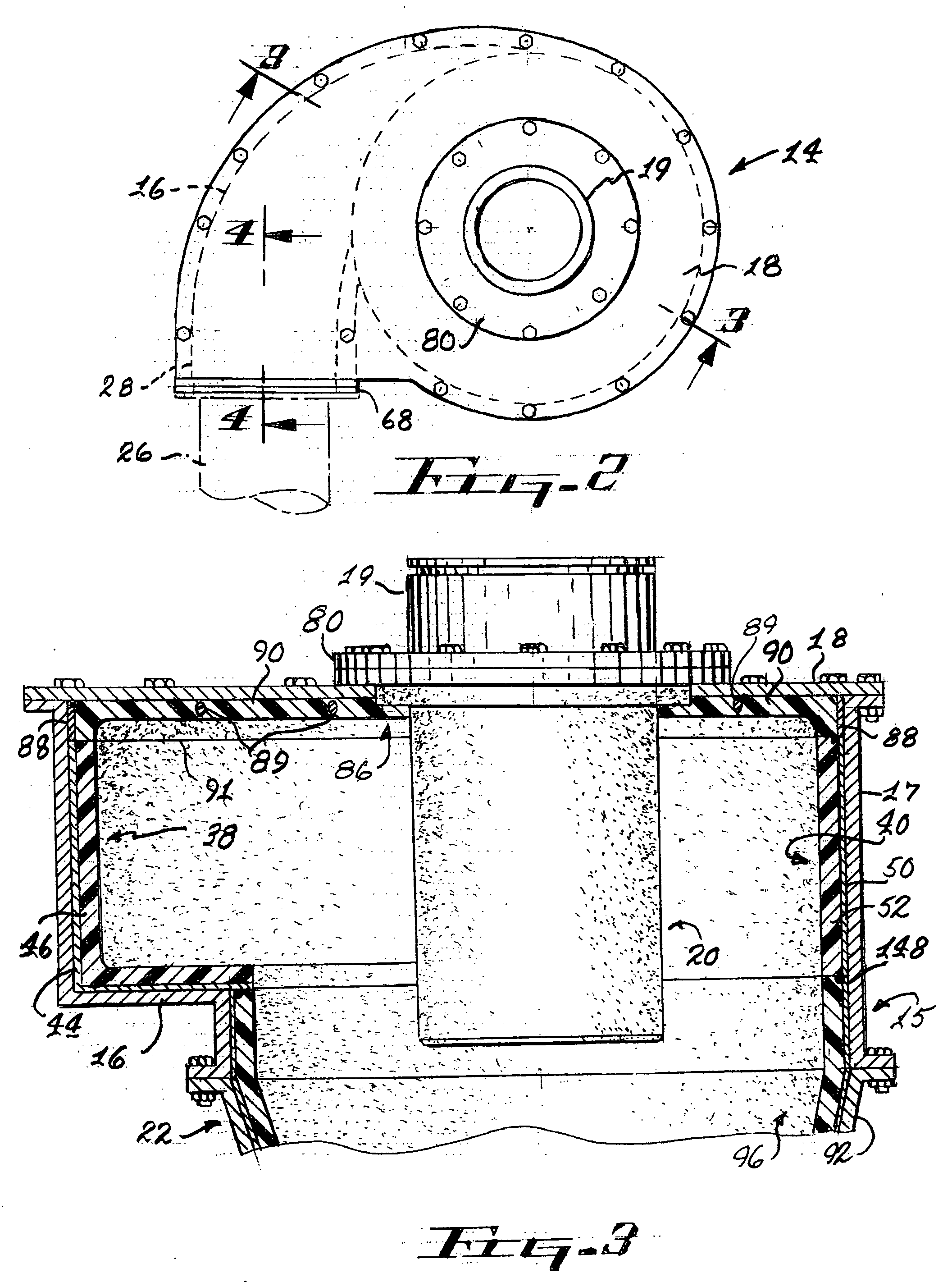
ActiveUS20050103691A1Eliminate needReversed direction vortexDispersed particle separationCycloneClassical mechanics
Cyclones having abrasion resistant liners with a system and method for replacing the liners when they worn out due to the destructive nature of the materials being classified in the cyclone. The cyclone includes segmented inlet housing liners which are separately removable through the opened top of the cyclone housing. A lifting ring in the bottom of a conical housing has an apex cone and plural cone liners supported in a stacked array thereon within the conical housing and hoisting straps are used to lift the lifting ring, the apex cone and the array of cone liners out of the opened top of the cyclone housing without having to remove the cyclone from its operating position and completely disassemble the cyclone. Wear detector bolts attach the inlet head liners and a cage-like conical housing allows direct viewing of wear detecting weep holes provided in the liners mounted therein.
Owner:GIW IND
Toolbox structure of construction machine
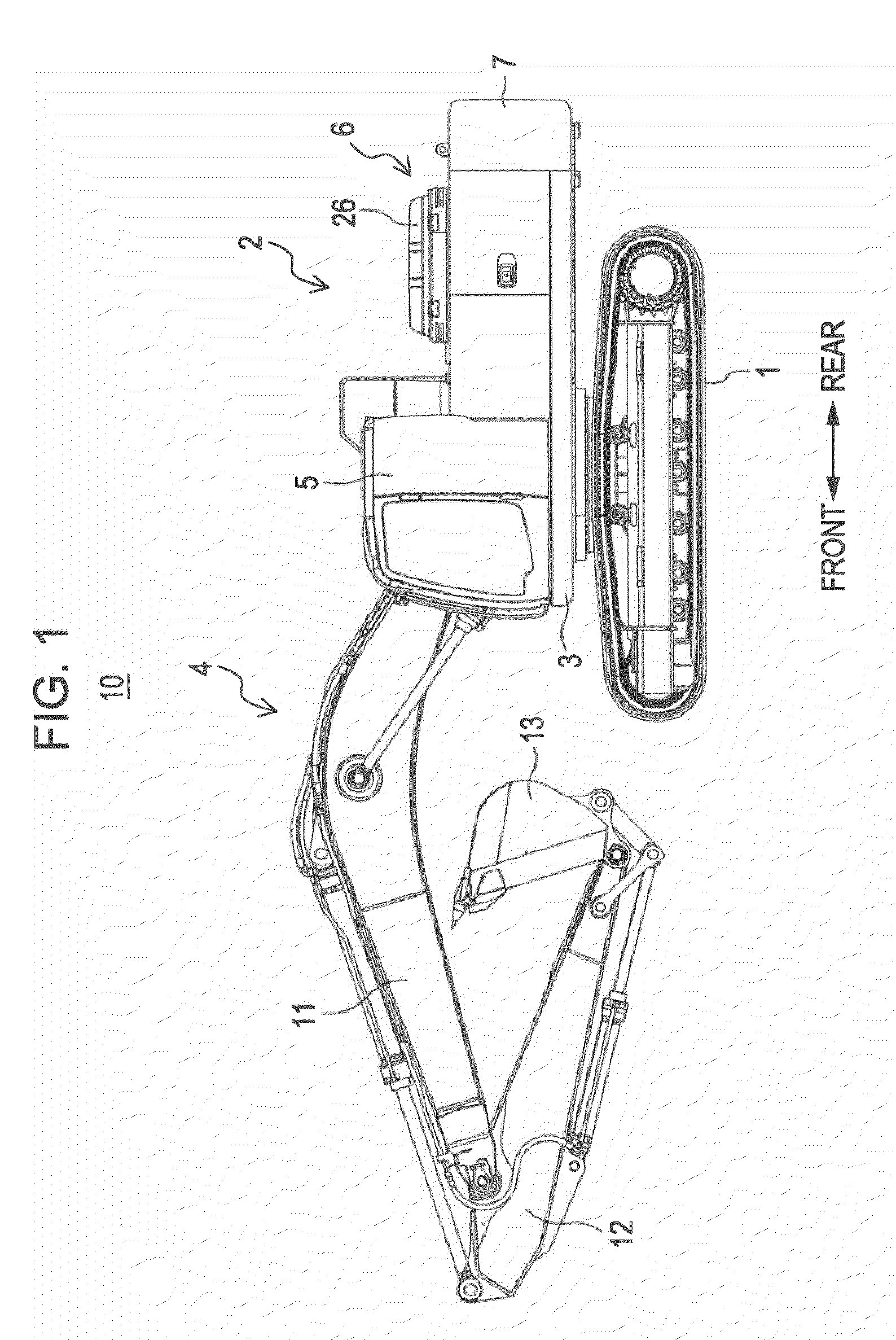
ActiveUS20100206927A1Prevent rustSimple structureSoil-shifting machines/dredgersOptical signallingArchitectural engineeringToolbox
An illumination device is installed in a box body of a toolbox of a construction machine, and is protected by a protective cover. Water that flows into the box body through a weep hole formed in a lid is received by the protective cover and is guided to a water drain hole formed in a bottom plate of the box body. Then, the water is drained to the outside of the box body.
Owner:KOBELCO CONSTR MASCH CO LTD
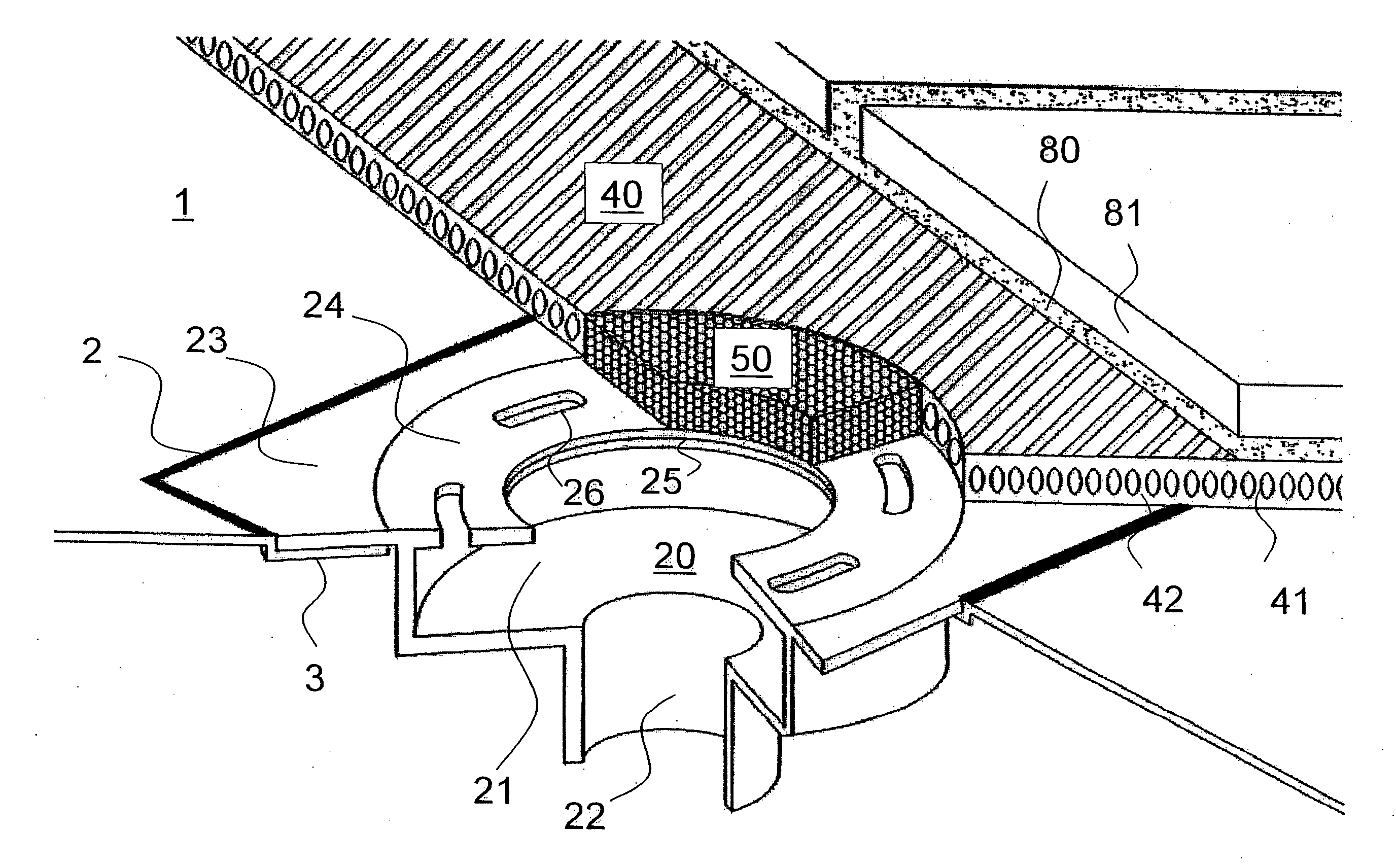
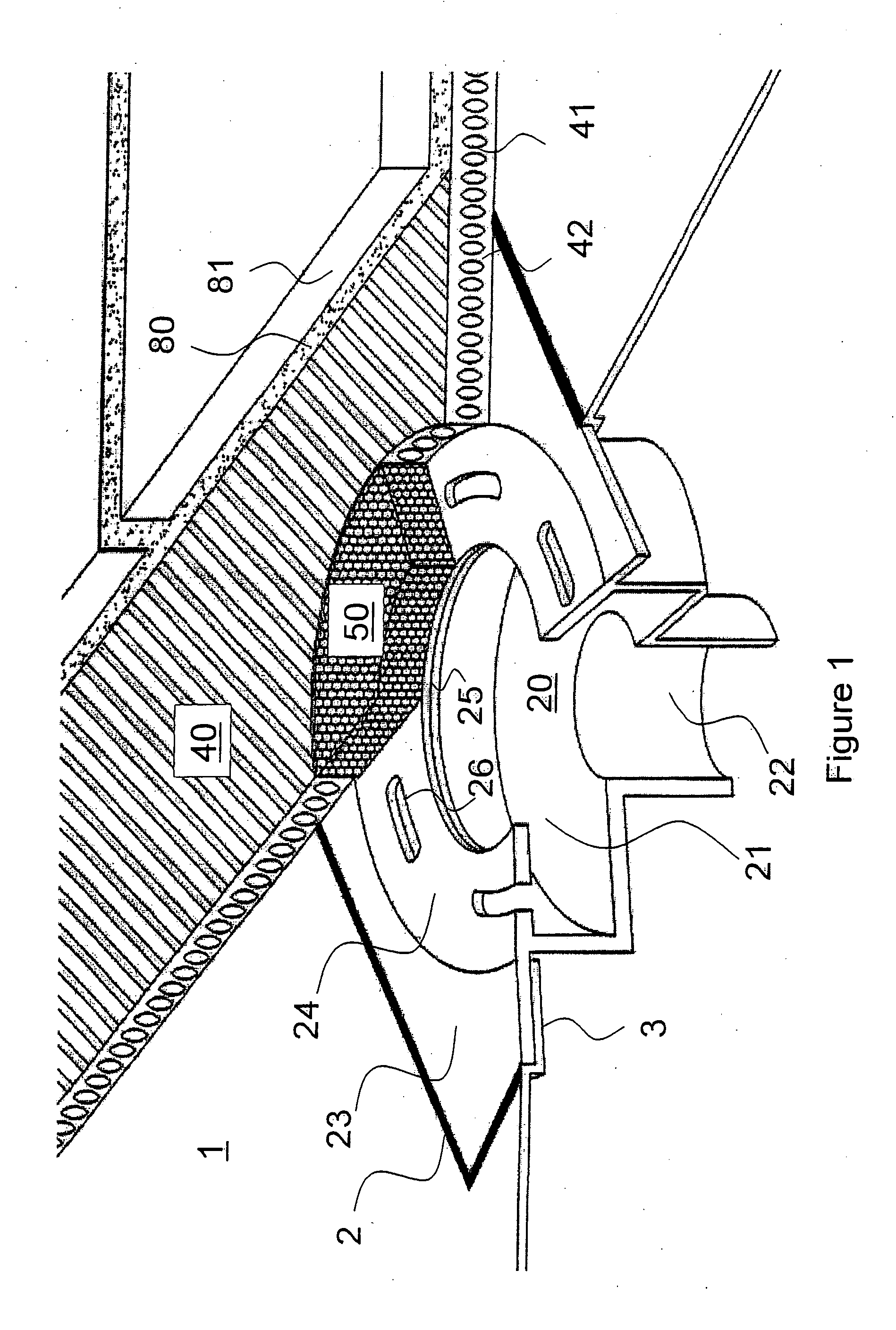
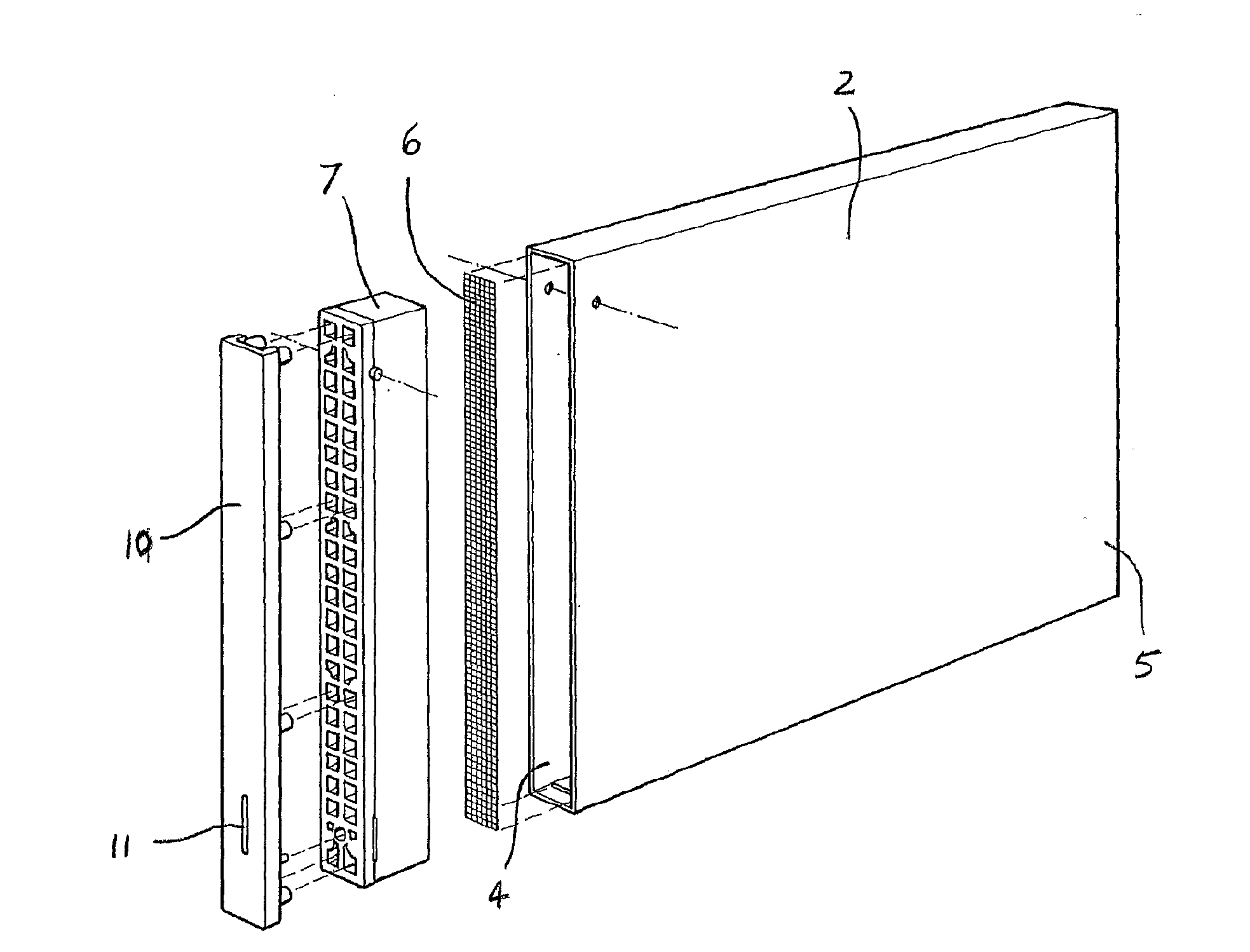
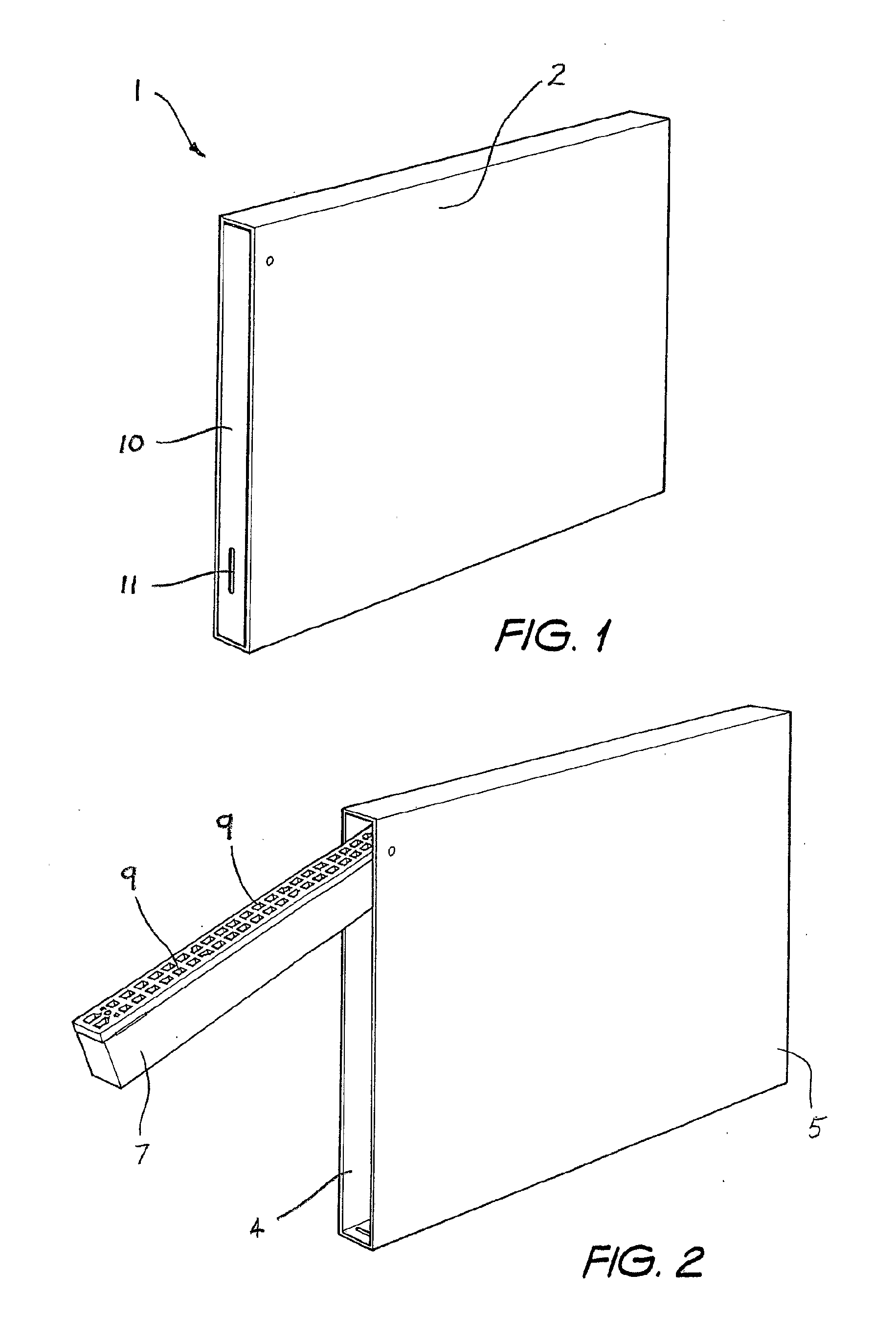
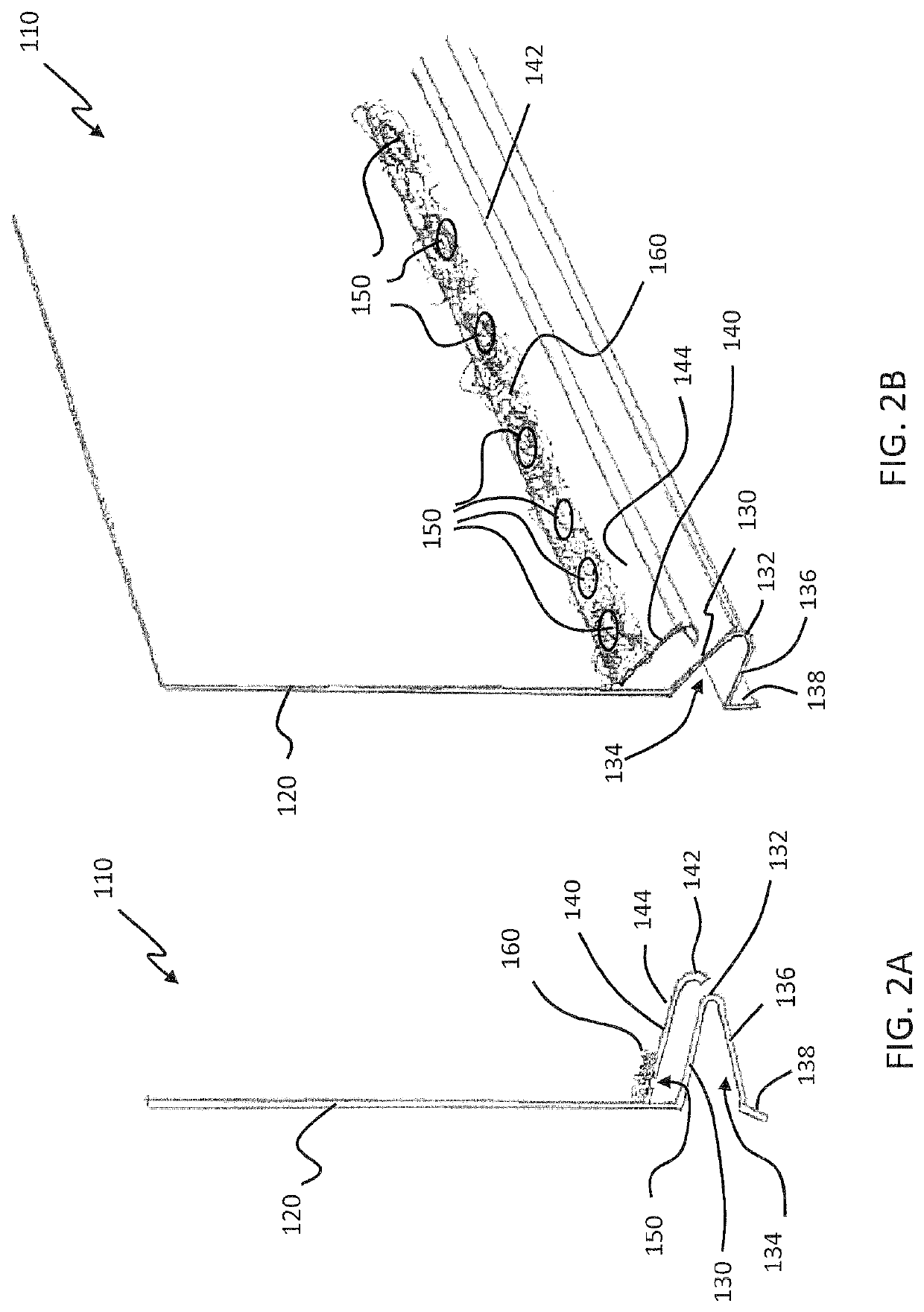
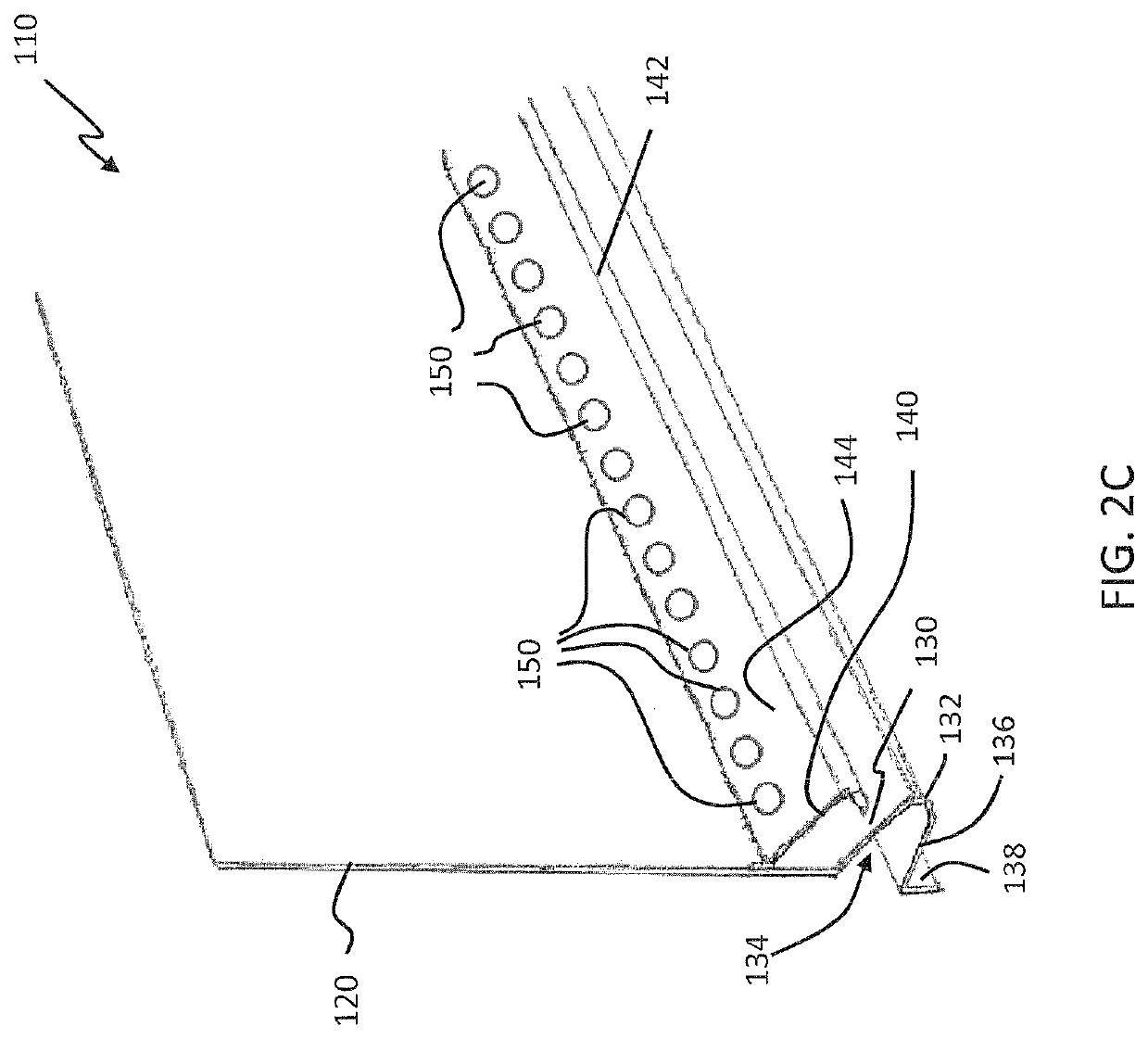
Insert for a Weep Hole Opening in a Masonry Wall
ActiveUS20080276556A1Avoid passingBuilding roofsRoof covering using slabs/sheetsEngineeringGuide tube
An insert (1) for a weep hole opening in a masonry wall is disclosed. The insert (1) includes a hollow body (2) defining an air flow conduit (3) and including a first open end (4) and a second open end (5). A stainless steel mesh screen (6) extends across the conduit (3) near the first open end (4) and is adapted to prevent fire brands and sparks from passing through the body (2). A locating member, in the form of a grate (7), is hingedly connected to the body (2) adjacent the first open end (4). The screen (6) is located in a recess (8) in the rear of the grate (7) and friction between the screen (6) and the grate (7) retains the screen (6) in the recess (8). The grate (7) is formed from a material that substantially retains its spatial integrity when exposed to the heat flux profile generated by a typical forest fire, such that the grate (7) continues thereafter to locate the screen (6). The grate (7) also has a plurality of ventilation apertures (9) to allow air to pass through the air flow conduit (3). A mortar guard (10) releasably snap-lockingly engages the grate (7) to cover the ventilation apertures (9) to prevent mortar clogging the apertures (9) during rendering.
Owner:FLINT +1
Passive water management fuel cell
InactiveUS6794077B2Easy to manufactureImprove toleranceFuel cells groupingWater management in fuel cellsFuel cellsWater channel
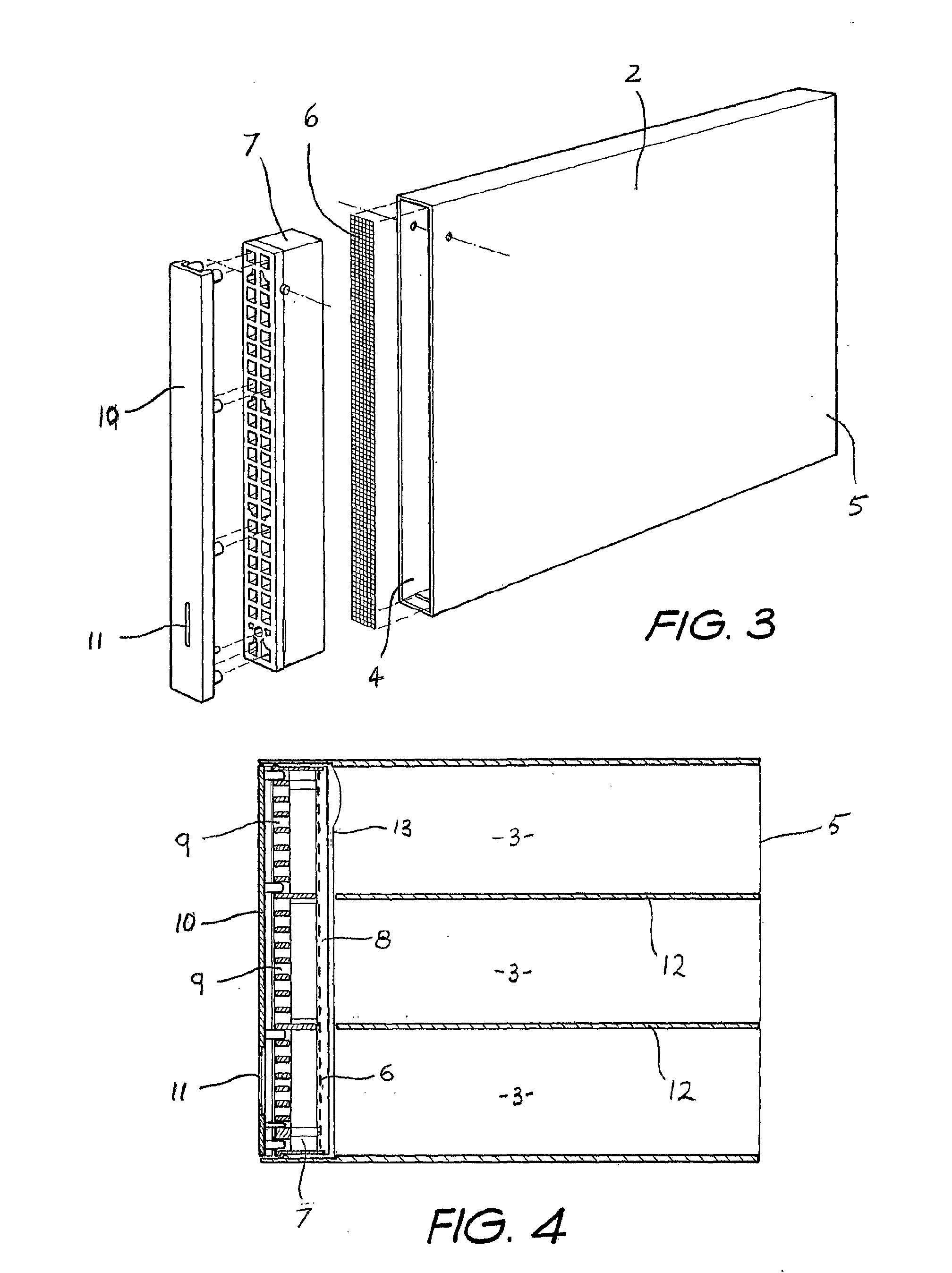
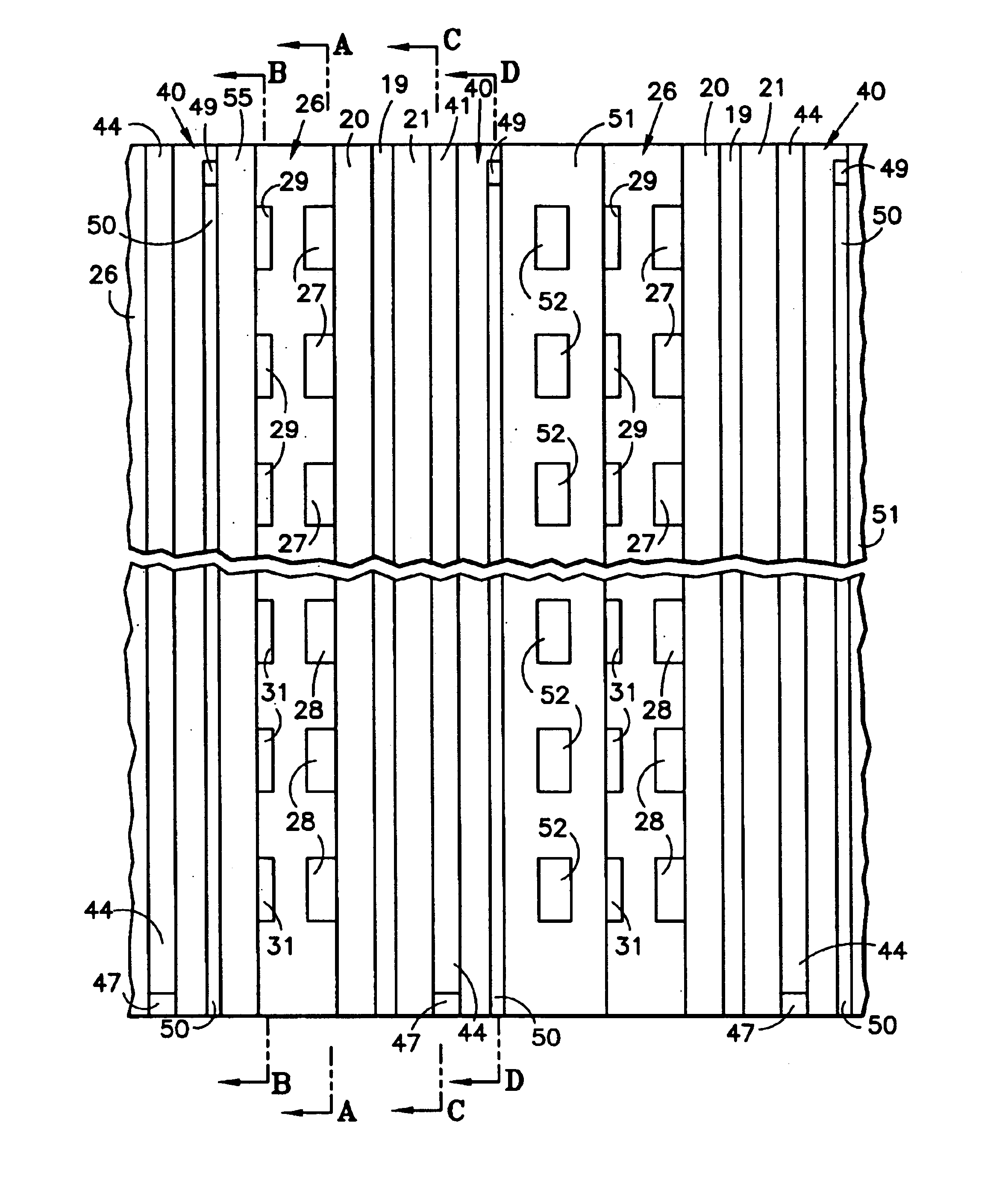
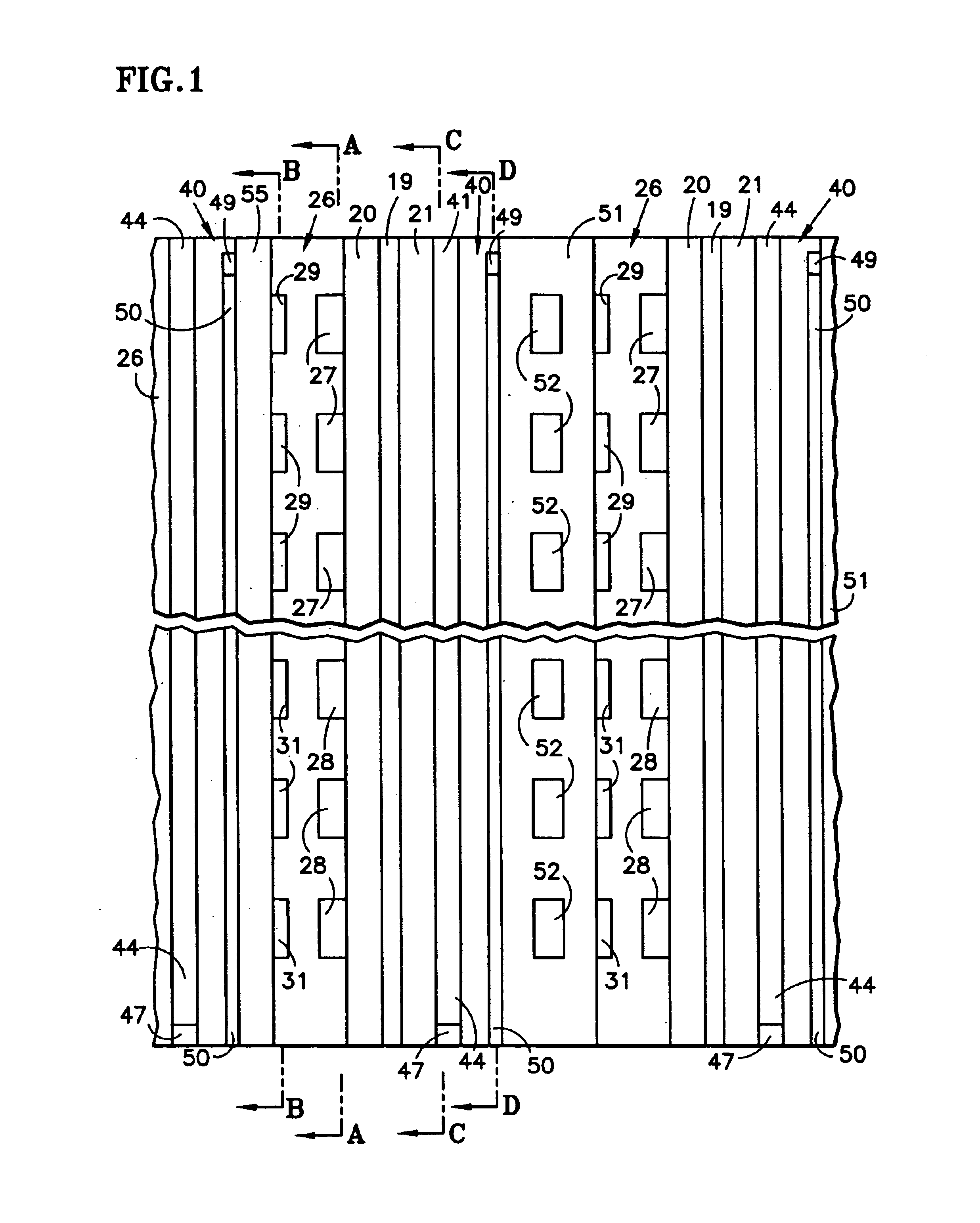
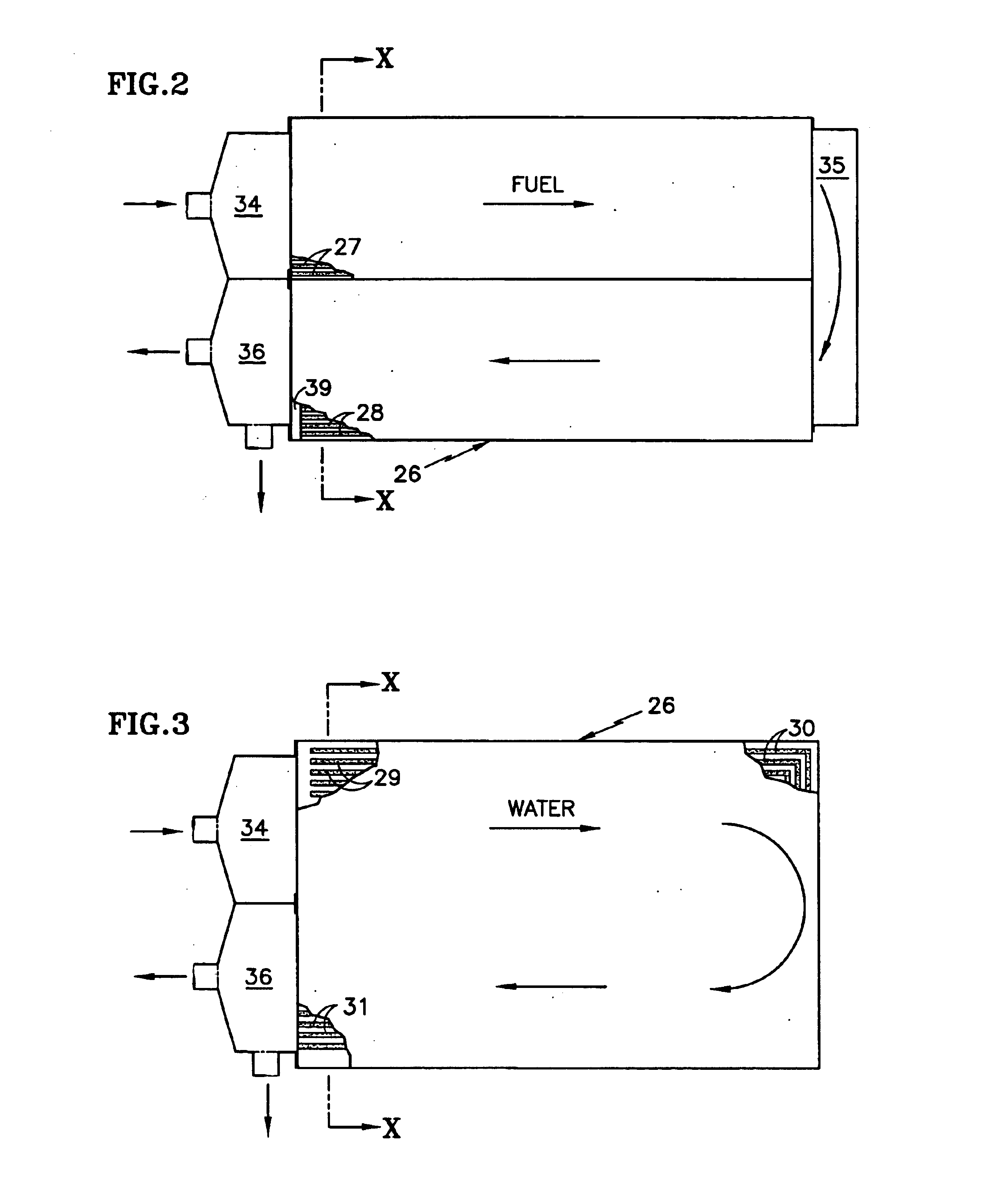
A proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell includes fuel and oxidant flow field plates (26, 40) having fuel and oxidant channels (27, 28; 41, 44), and water channels, the ends (29, 48) of which that are adjacent to the corresponding reactant gas inlet manifold (34, 42) are dead ended, the other ends (31, 50) draining excess water into the corresponding reactant gas exhaust manifold (36, 45). Flow restrictors (39, 47) maintain reactant gas pressure above exit manifold pressure, and may comprise interdigitated channels (65, 66; 76, 78). Solid reactant gas flow field plates have small holes (85, 88) between reactant gas channels (27, 28; 41) and water drain channels (29, 30; 49, 50). In one embodiment, the fuel cells of a stack may be separated by either coolant plates (51) or solid plates (55) or both. In a second embodiment, coolant plates (51a) have weep holes (57) that inject water into the ends (29) of the reactant gas water channels which are in the region of the inlet manifold (34), thereby assuring humidification of the reactants.
Owner:AUDI AG
Vented stop bead apparatus, vented weep screed apparatus, and related systems and methods thereof
Owner:E Z BEAD
Weep hole screen device and method
InactiveUS6176048B1Easy to cleanPrevent excess moisture build-upBuilding repairsPasturing equipmentMechanical engineeringSilicone sealant
A screen device to prevent animal entry into weep holes of foundation walls is formed from flexible, polymeric materials such as nylon or other conventional plastics. The screen device includes a frame having inner and outer sections with a porous barrier therebetween. The method of installing the screen device over a foundation wall weep hole includes the step of sealing the edges of the outer frame section with a standard silicone sealant, and thereafter inserting a porous barrier into the outer frame section. The porous barrier is releasably held in place with an inner frame section which is lastly placed in and connected to the outer frame section.
Owner:BERGER BRUCE B
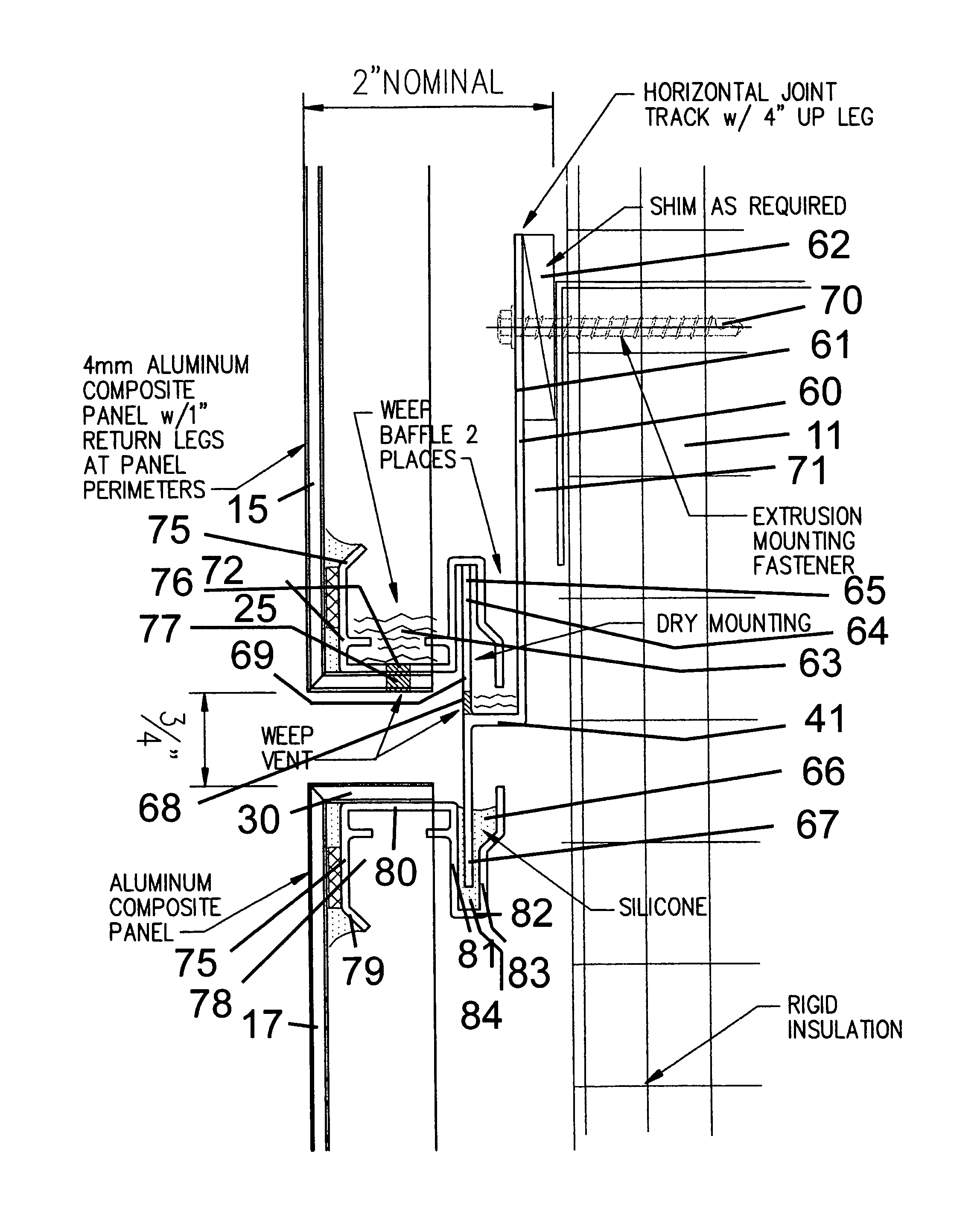
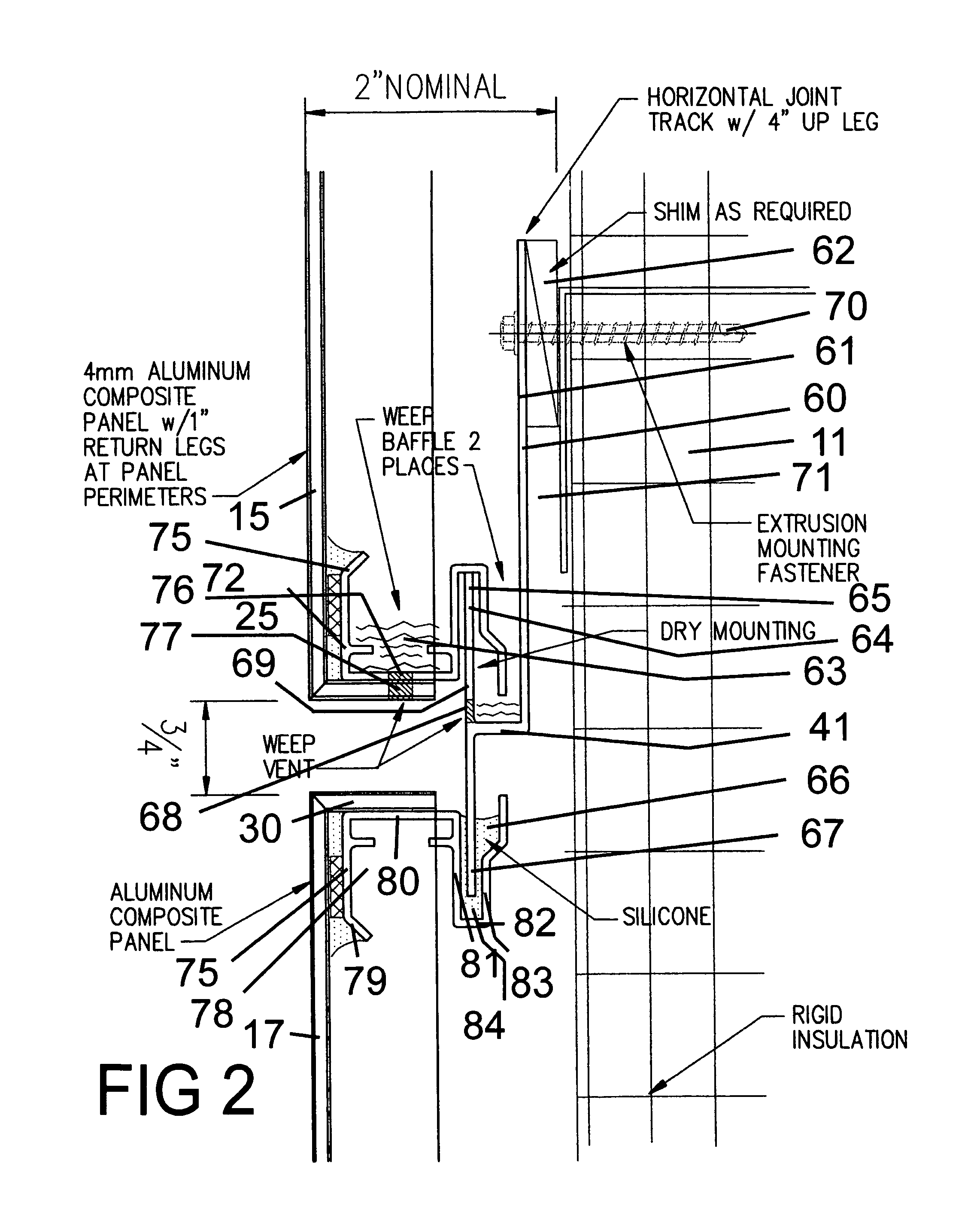
Rain screen system
A rain screen system for attaching an array of panels to the outside of a building, by means of a track system. The track system includes a series of horizontal mounting tracks that extend across the entire width of the panel array. Each horizontal mounting track has an upturned building-side leg that forms both a mounting flange, through a local shim, to the building, as well as the building side of a water tight, continuous, self draining gutter system. Each track also has an upturned panel-side leg that forms both a mounting flange for the lower edge of a panel and the panel side of the gutter system. Each track also forms a water seal at the top edge of the panel. The gutter system has a weep holes on the panel side of the gutter system, adapted so that drainage is fed to the top of the lower panel.
Owner:SMITH STEWART +1
Means for creating weep holes in a ridge of roadway material
ActiveUS7051819B1Good lookingReduce manufacturing costMechanical machines/dredgersRoad cleaningDeep holeRidge
Owner:SCHENK DOUGLAS G
Movement control screed
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to a movement control screed that is structured for installation between first and second masonry coatings applied adjacent to a building wall. The movement control screed is structured as a control joint for absorbing movement between the first and second masonry coatings and also as a weep screed for accommodating drainage of water from behind the masonry coatings. The movement control screed comprises first and second flanges provided on opposite sides of first and second ribs.
Owner:ALABAMA METAL INDS
Sliding door assembly
ActiveUS8381444B1Improve reliabilitySimple designCondensed water drain-offRain/draught deflectorsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A sliding door assembly has a frame with a movable panel and a fixed panel. The movable panel has a pair of rollers that roll along a header located above the panels with the rollers attached to the movable panel via posts that pass through a channel on the header. The posts pass through a curved section of the channel whenever the movable panel is proximate its closed position and a straight section of channel when the movable panel is traveling laterally. The movable panel presses against a gasket located on the frame components surrounding the movable panel wherein one or more latches press the movable panel against the gasket whenever this panel is in the closed position. Valve is positioned within a weep hole on the threshold in order to prevent water from seeping into the building via the bottom of the door assembly.
Owner:TIMOTHY J MCDONALD TECH
Large Vessel Closure Sheath
InactiveUS20130006297A1Reduce capacityImprove sealingSurgical veterinaryWound clampsLarge vesselVascular closure device
A vascular closure device for closing vessels of the body following percutaneous access via an introducer sheath that is similar in size to the vessel lumen. The vascular closure device has an anchor that is inflated using a polymerizable polymer. The anchor is attached to a plug that also can be inflated with a polymer. The anchor and plug can be introduced into the body via a positionable introducer sheath that is also used for the therapeutic procedure. A weep hole in the introducer sheath is positionable adjacent the arteriotomy site.
Owner:DRASLER WILLIAM JOSEPH
Irrigation device and system
InactiveUS20050145716A1Reduce lossesMinimize timeSelf-acting watering devicesHeat exhanger conduitsEngineeringIrrigation
Owner:MANNING HAROLD
Fracture detecting structural health sensor
ActiveUS7621193B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceMeasurement/indication equipmentsElectrical conductorStructural health monitoring
A sensor device for monitoring and testing the integrity of structural elements is disclosed. A frangible membrane including a thin breakable conductor sense loop is bonded to a structural element to be tested. A fracture in the bonded structural element induces a disruption in the both the frangible membrane and the thin breakable conductor sense loop. Measured electrical property change of the disrupted conductor sense loop reveals the fracture in the structural element. Connection to the sensor device may be through a connector or using a wireless reader which remotely energizes the sensor device. The sensor may also be implemented as a gasket and / or employ weep holes to the breakable conductor to reveal possible corrosion as well.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Anchor-spraying concrete for treating water and support
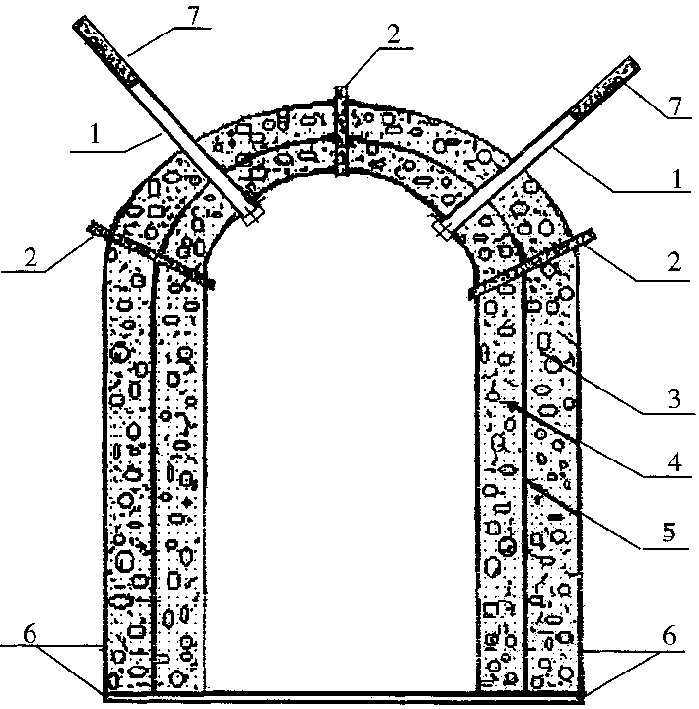
InactiveCN1381651ASolve construction technical problemsAchieve governanceArtificial islandsUnderground chambersShotcreteUltimate tensile strength
An anchoring-sprayed prop for controlling water in constructing underground engineering features direct use of anchorage and spraying concrete. Its construction technology includes such steps as drilling weep holes, setting up weep pipes, primary spraying, drilling anchor holes, installing anchor rods, hanging net, spraying again, blocking drainage pipes, and curing. If the bed rock encounters fault, it is necessary to spray concrete for the third time.
Owner:王衡
Method for flashing a window or door opening
ActiveUS20150047269A1Simple methodRoof covering using slabs/sheetsRoof covering using tiles/slatesEngineeringSealant
A method for flashing an opening defined by a bottom sill, a pair of side jambs, and a top header includes forming a sill diverter dam at the bottom sill to receive a backside of a door or window frame with an adhesive strip placed along the sill diverter dam. The method further includes applying a sheet of flexible membrane at each intersection of the bottom sill and each side jamb, attaching a strip of weep flashing to the wall overlapping the diverter dam at the bottom sill, applying sealant along an upper edge of the door or window frame, attaching a jamb diverter sheet to the wall at each side jamb, applying sealant to the door or window frame, placing the door or window frame in the opening, applying additional sealant along the top header, and attaching a header diverter sheet to the wall along the top header.
Owner:MESSENGER GARY WILLIAM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com