Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
113 results about "Waveguide sensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
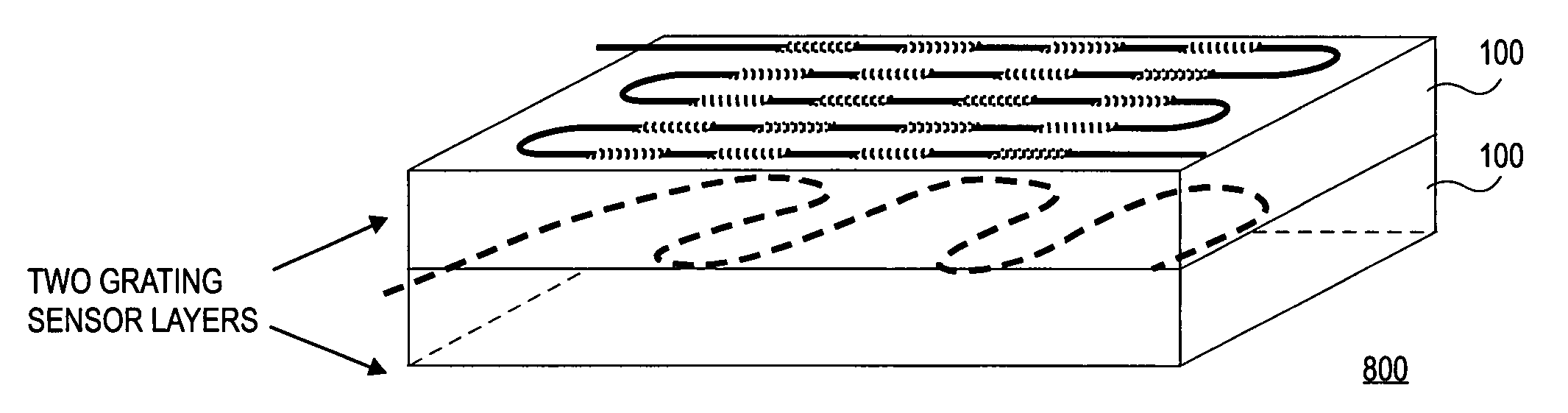
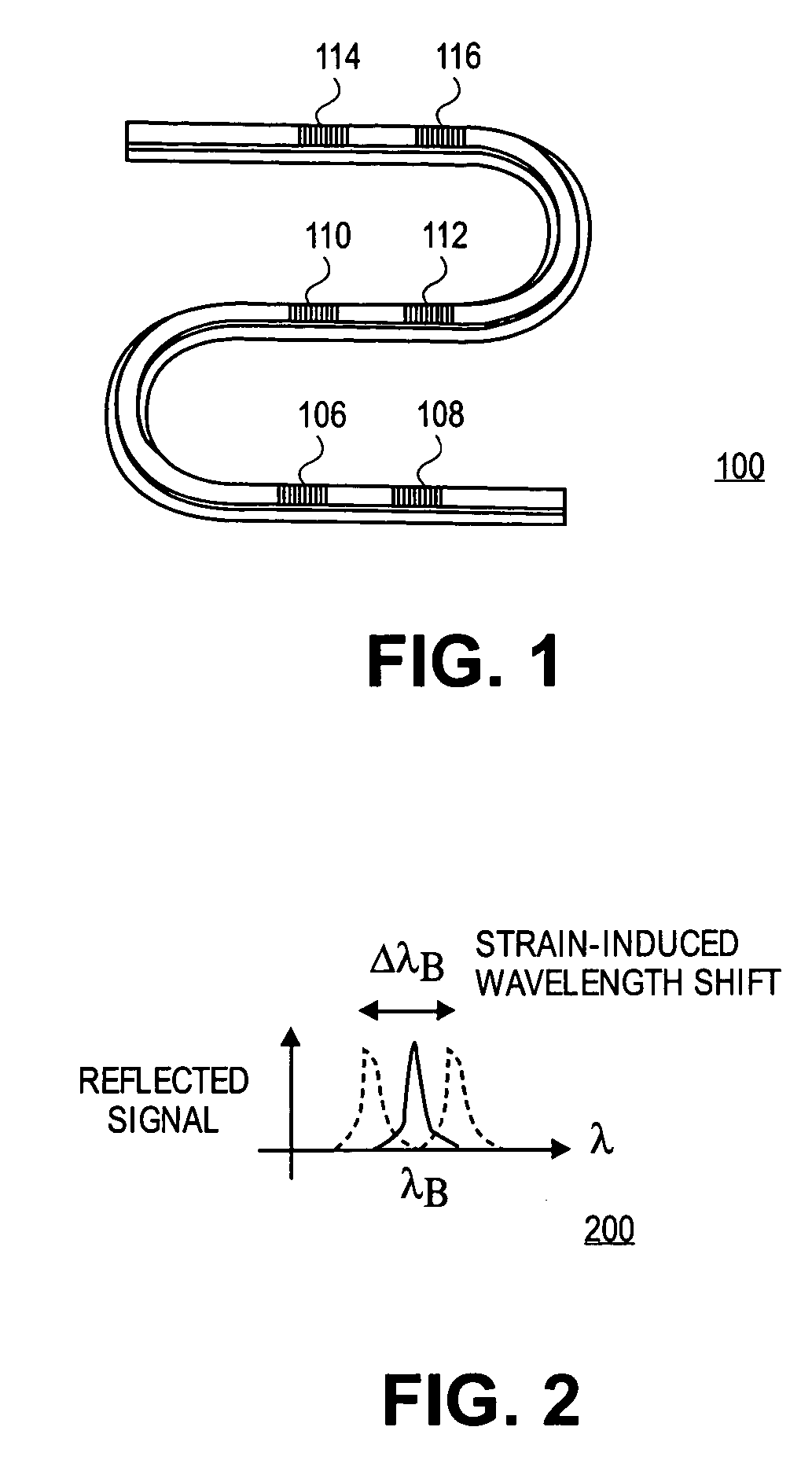
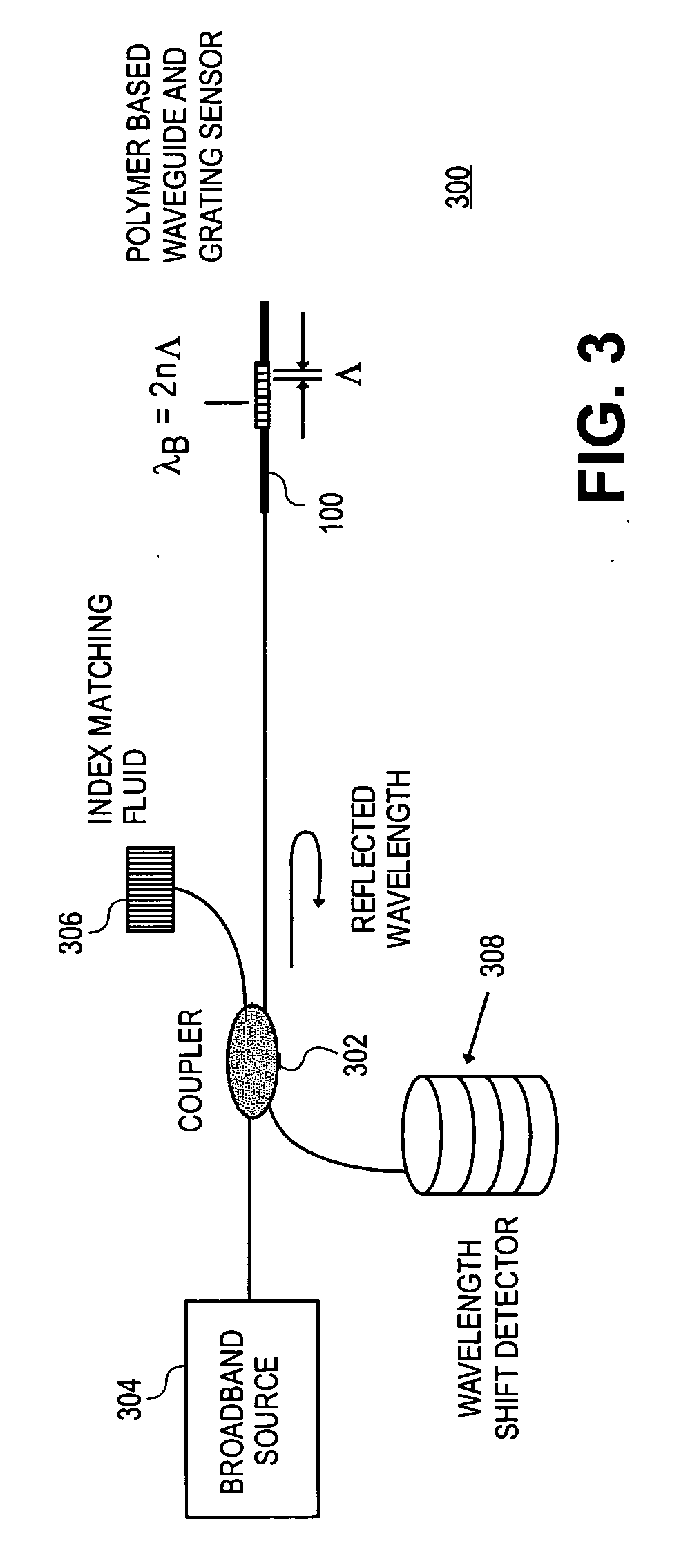
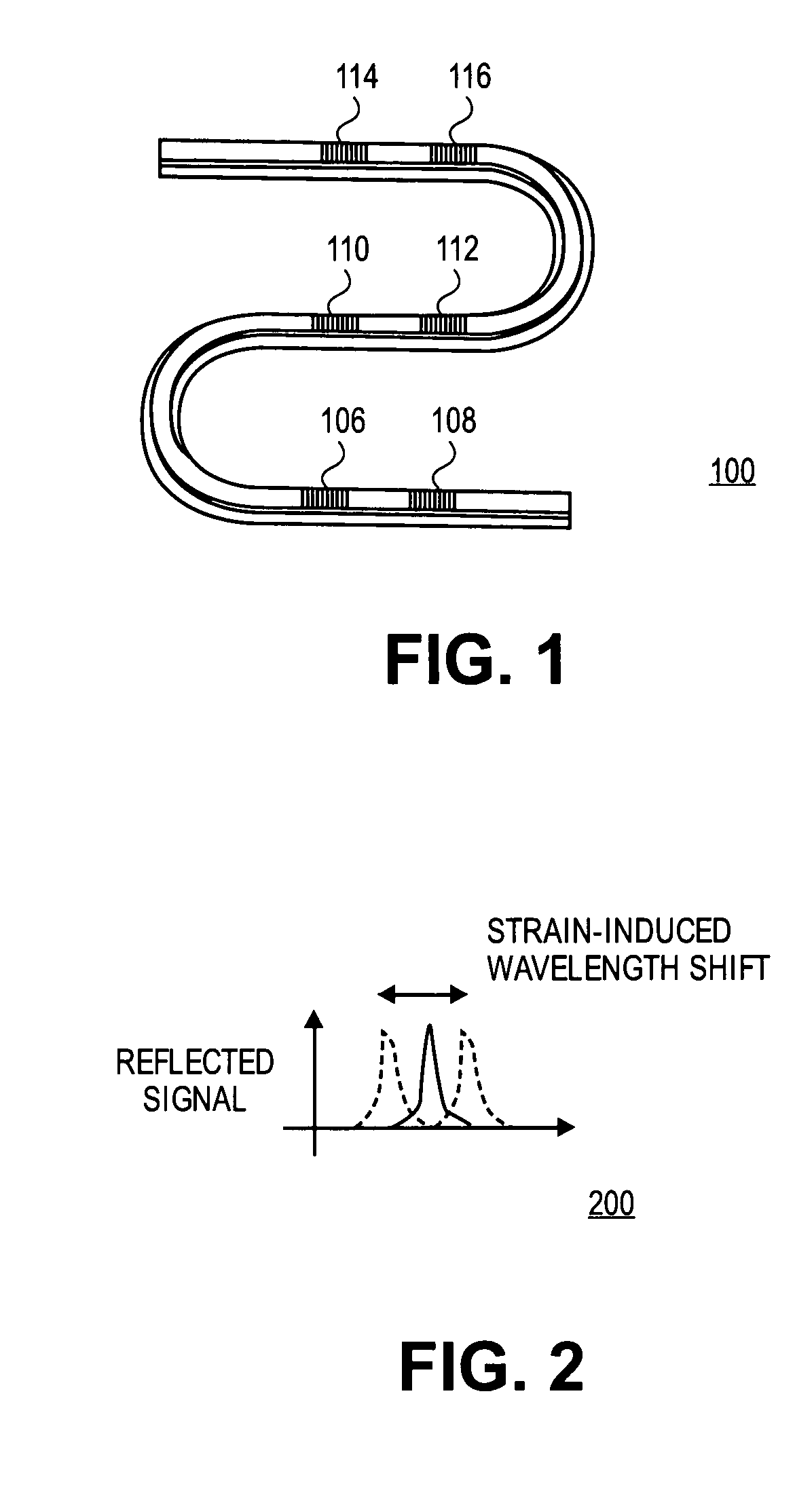
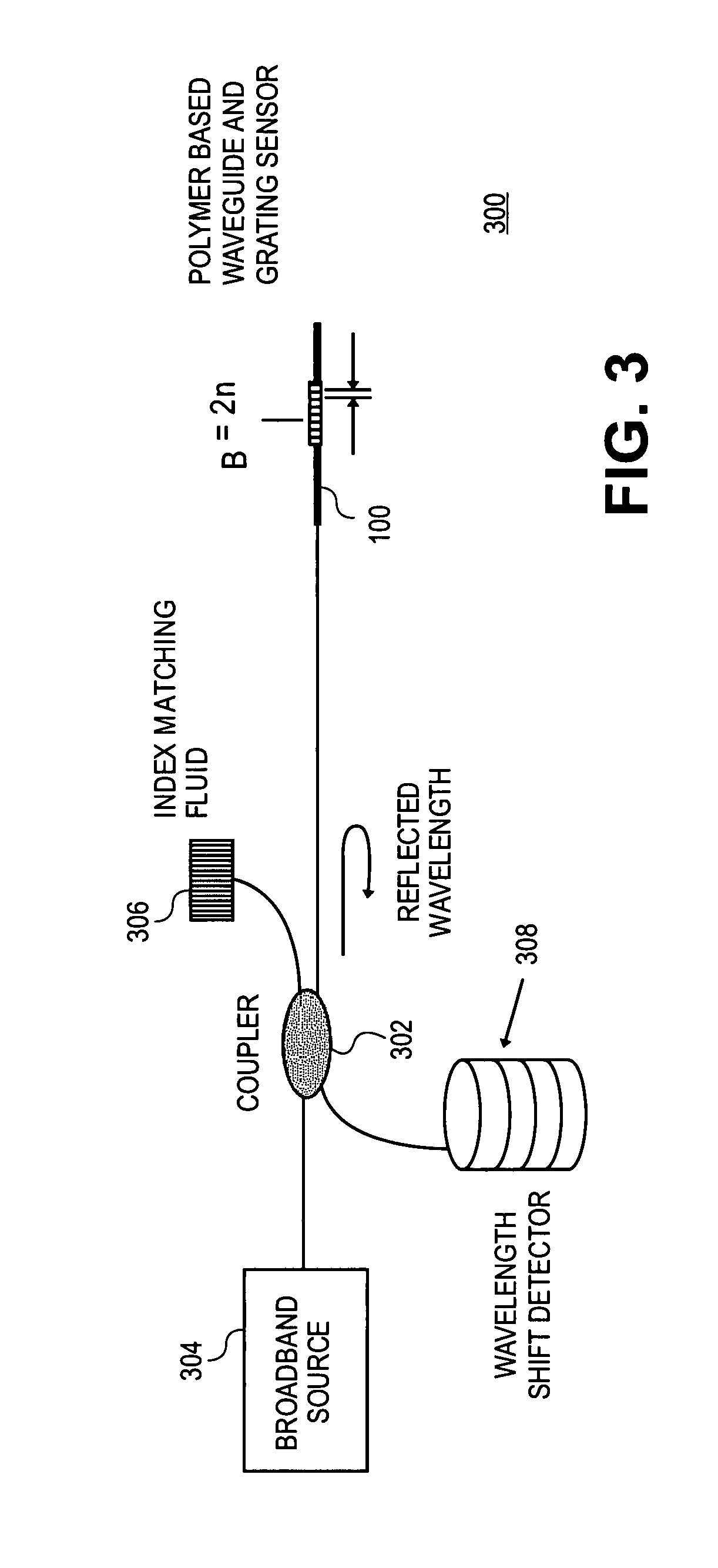
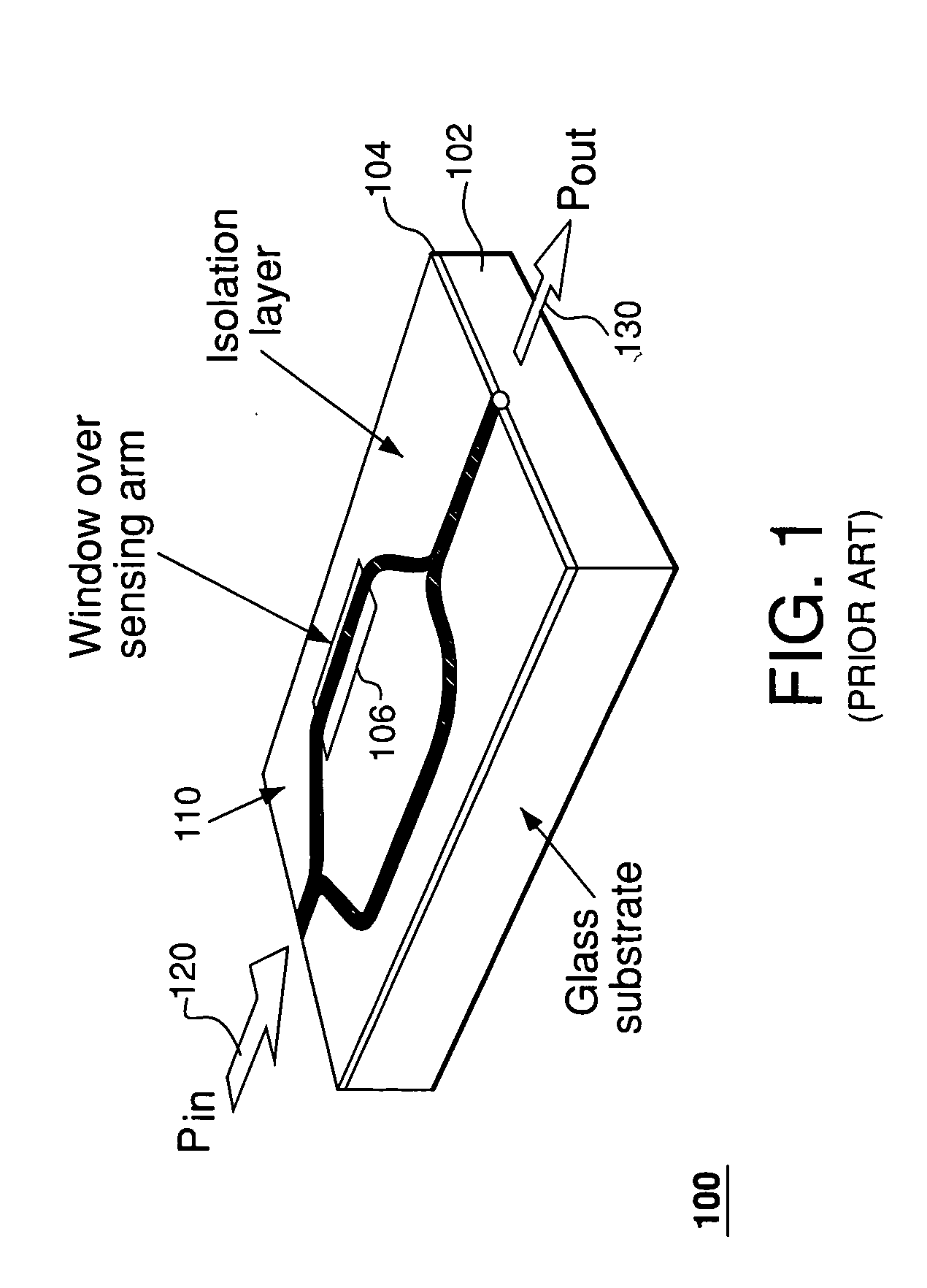
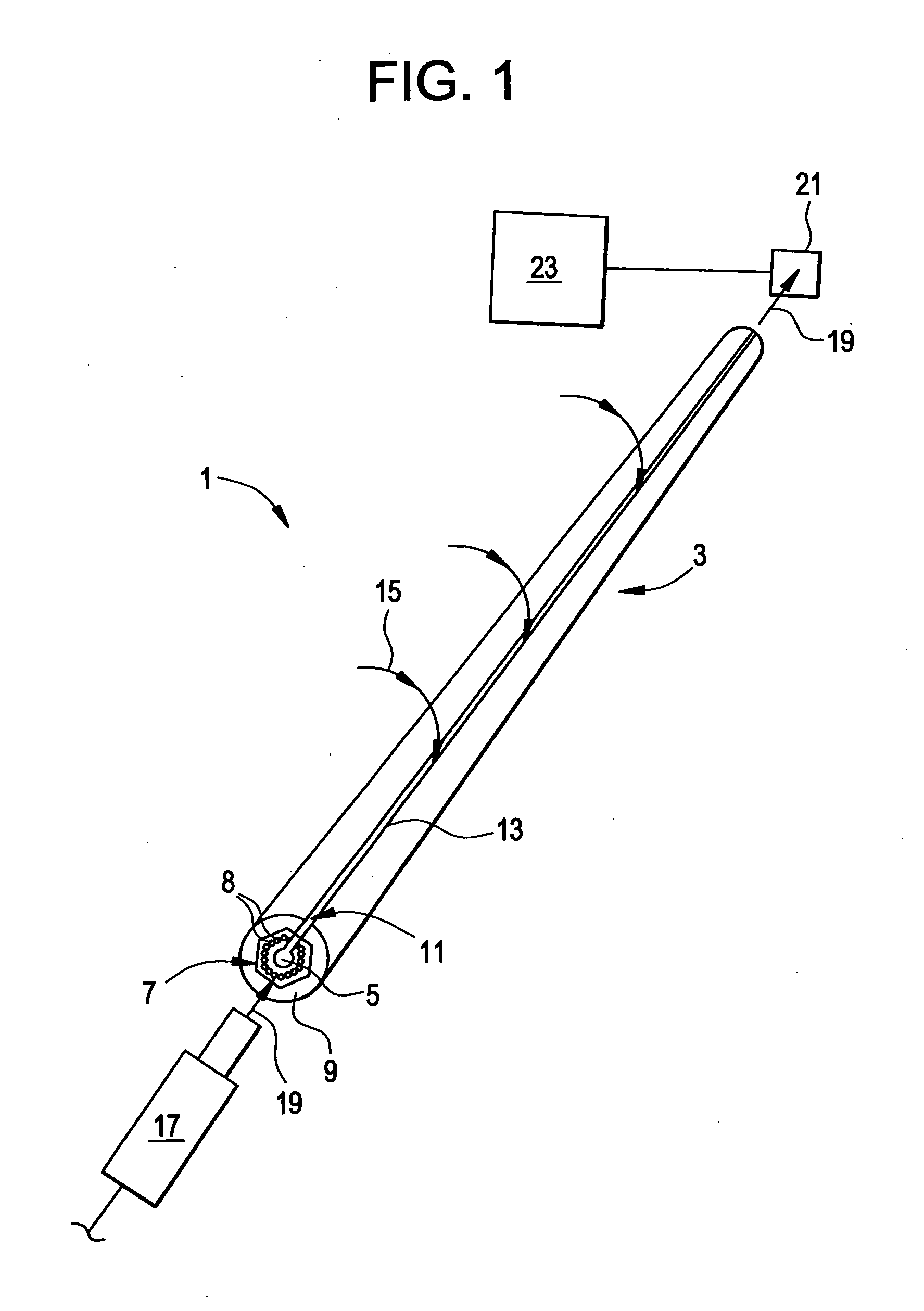
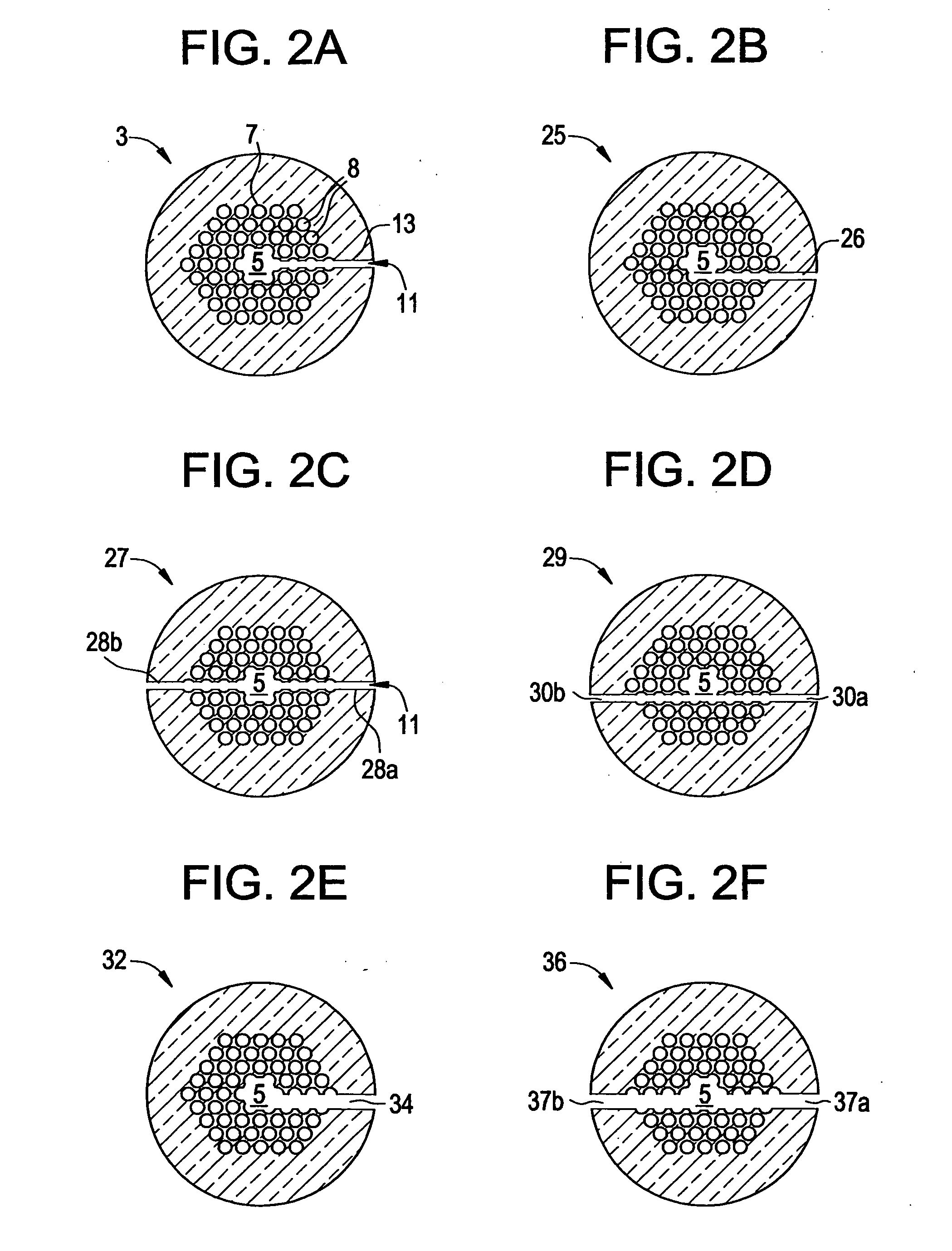
Polymer based distributive waveguide sensor for pressure and shear measurement
InactiveUS20050232532A1Improve spatial resolutionCladded optical fibreStrain gaugeGratingShear stress
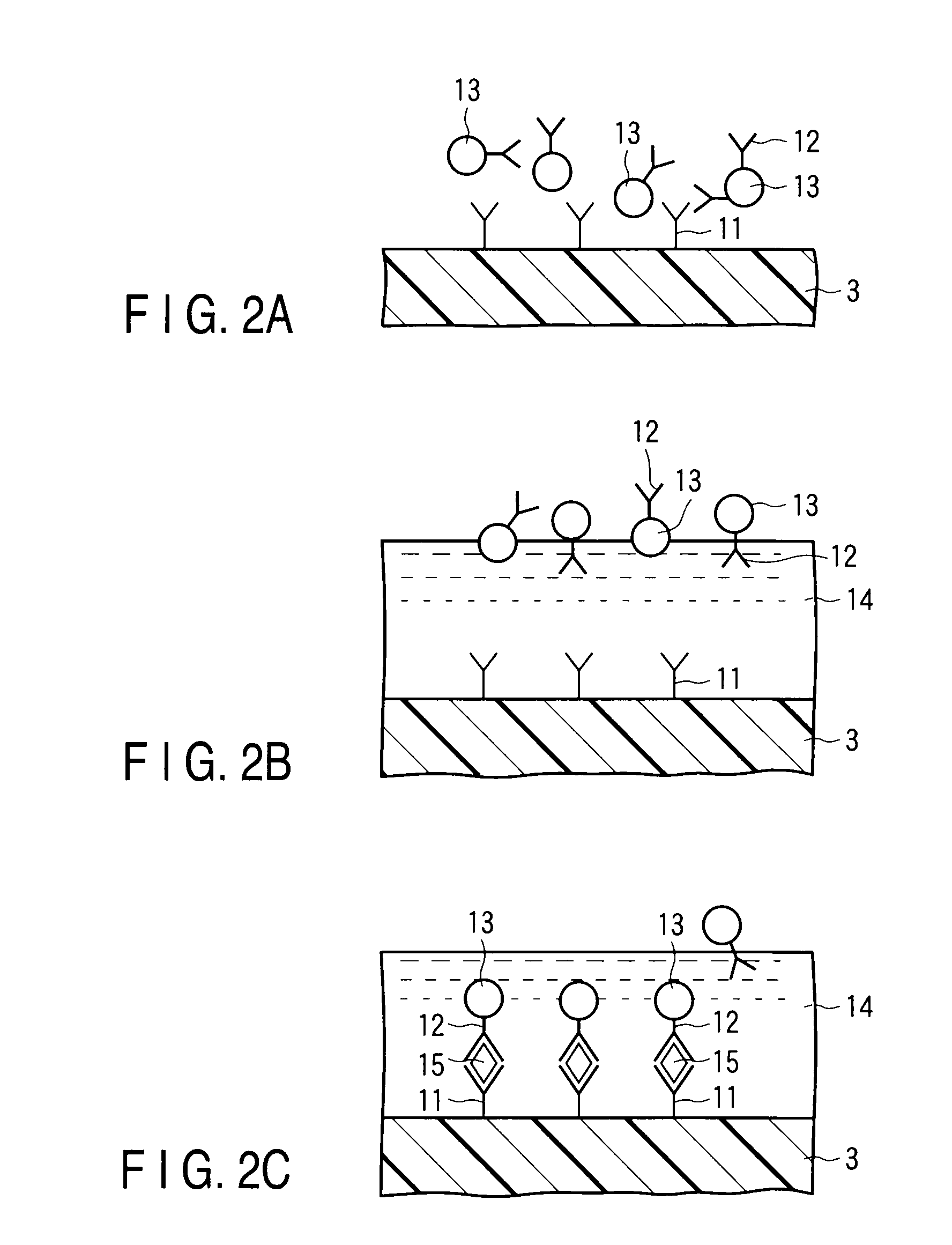
According to embodiments of the present invention, a distributed pressure and shear stress sensor includes a flexible substrate, such as PDMS, with a waveguide formed thereon. Along the waveguide path are several Bragg gratings. Each Bragg grating has a characteristic Bragg wavelength that shifts in response to an applied load due to elongation / compression of the grating. The wavelength shifts are monitored using a single input and a single output for the waveguide to determine the amount of applied pressure on the gratings. To measure shear stress, two flexible substrates with the waveguide and Bragg gratings are placed on top of each other such that the waveguides and gratings are perpendicular to each other. To fabricate the distributive pressure and shear sensor, a unique micro-molding technique is used wherein gratings are stamped into PDMS, for example.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
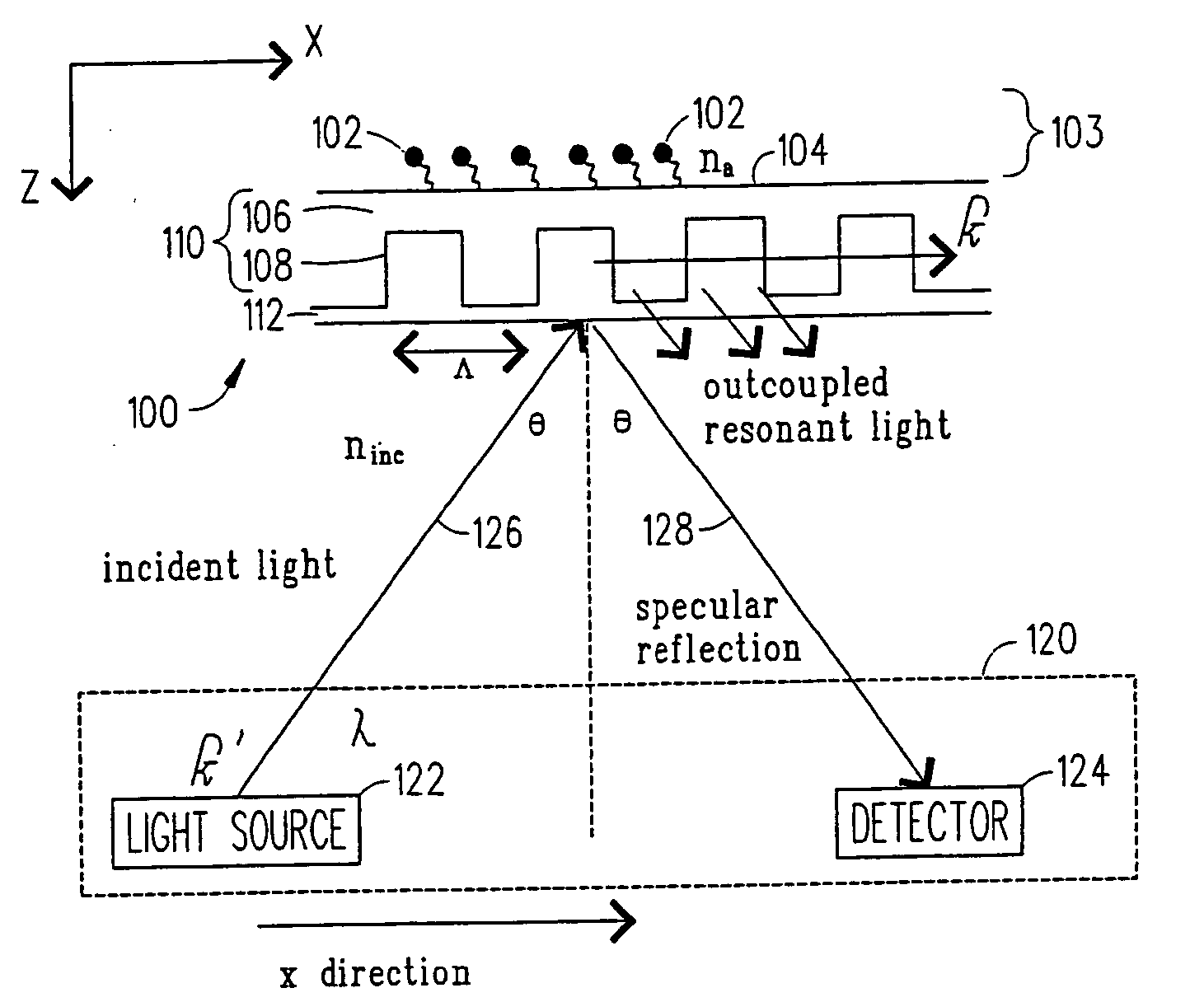
Double resonance interrogation of grating-coupled waveguides
InactiveUS20050070027A1High sensitivityReduce sensitivityScattering properties measurementsImmunoassaysGratingChemical reaction
A method for using a double resonance effect within a grating-coupled waveguide (GCW) sensor, as generated from a light beam with a given span of wavelengths or angles, is provided. The method can be used for label-independent detection of biological and chemical agents, to interrogate biological-binding events or chemical reactions within a sensing region at increased sensitivity, and with decreased sensitivity to environmental perturbations. Also described is an optical interrogation system incorporating the method.
Owner:CORNING INC
Polymer based distributive waveguide sensor for pressure and shear measurement
InactiveUS20070258674A1Improve spatial resolutionCladded optical fibreStrain gaugeShear stressGrating
According to embodiments of the present invention, a distributed pressure and shear stress sensor includes a flexible substrate, such as PDMS, with a waveguide formed thereon. Along the waveguide path are several Bragg gratings. Each Bragg grating has a characteristic Bragg wavelength that shifts in response to an applied load due to elongation / compression of the grating. The wavelength shifts are monitored using a single input and a single output for the waveguide to determine the amount of applied pressure on the gratings. To measure shear stress, two flexible substrates with the waveguide and Bragg gratings are placed on top of each other such that the waveguides and gratings are perpendicular to each other. To fabricate the distributive pressure and shear sensor, a unique micro-molding technique is used wherein gratings are stamped into PDMS, for example.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
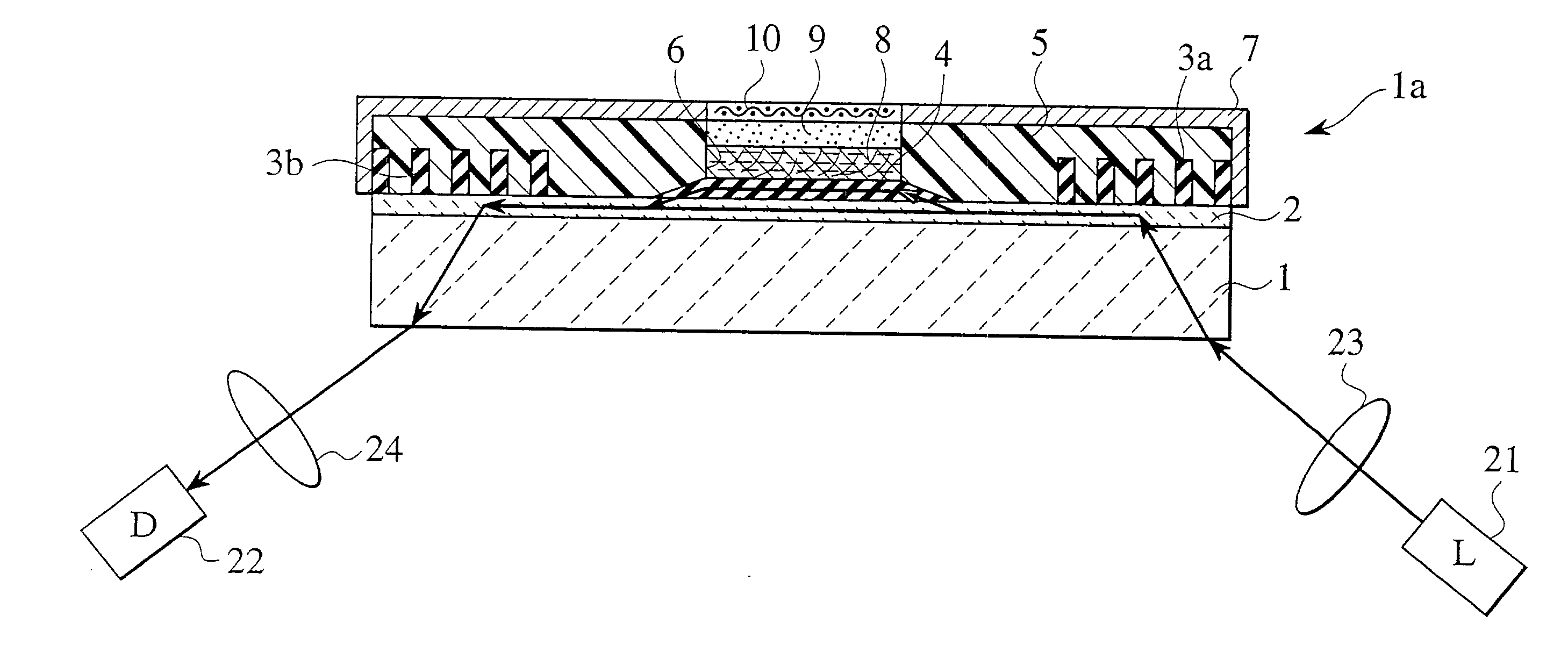
Biosensor with evanescent waveguide and integrated sensor
InactiveUS20100055666A1Luminescence signal can be reducedEffect to sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementElectricityWaveguide
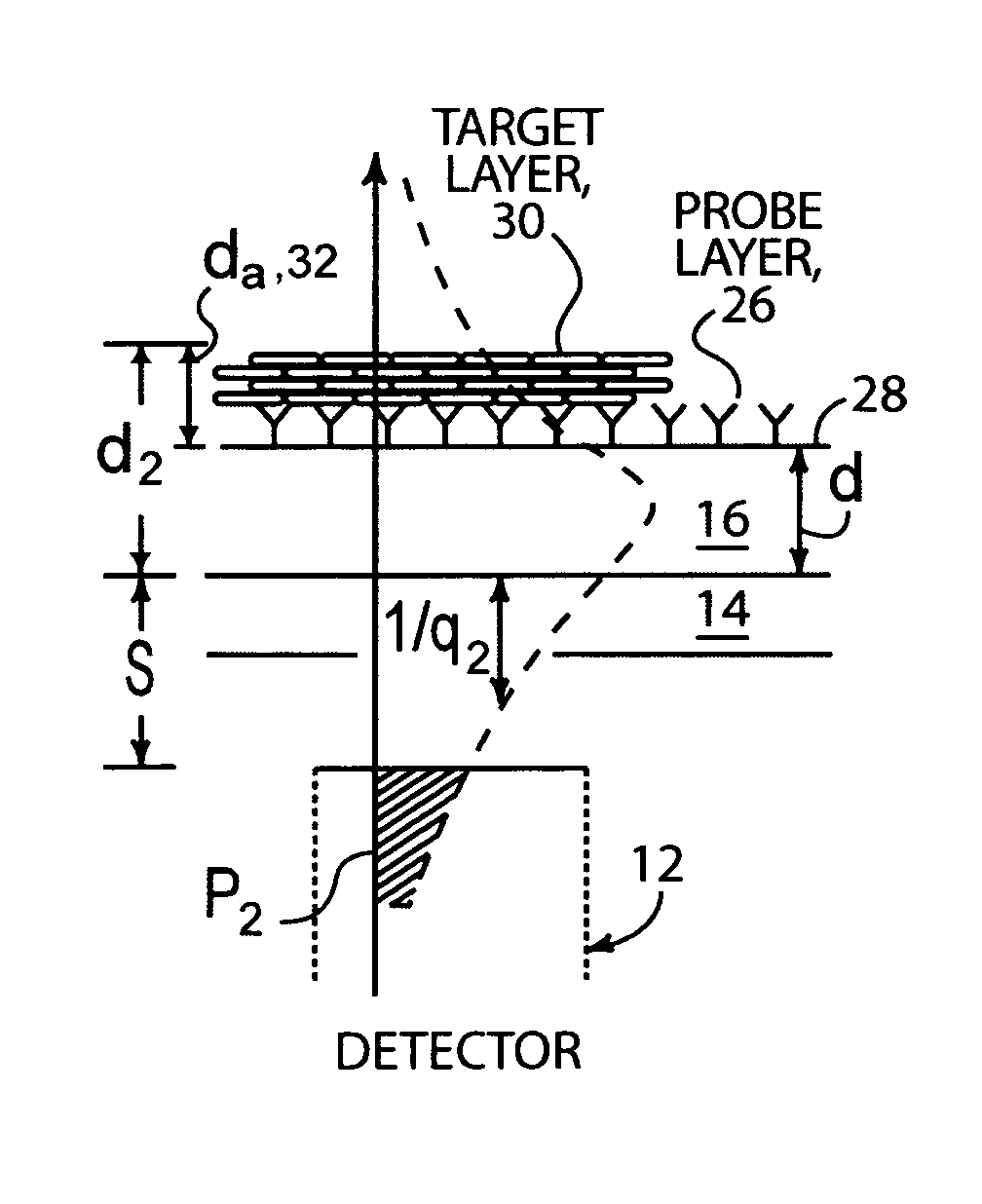
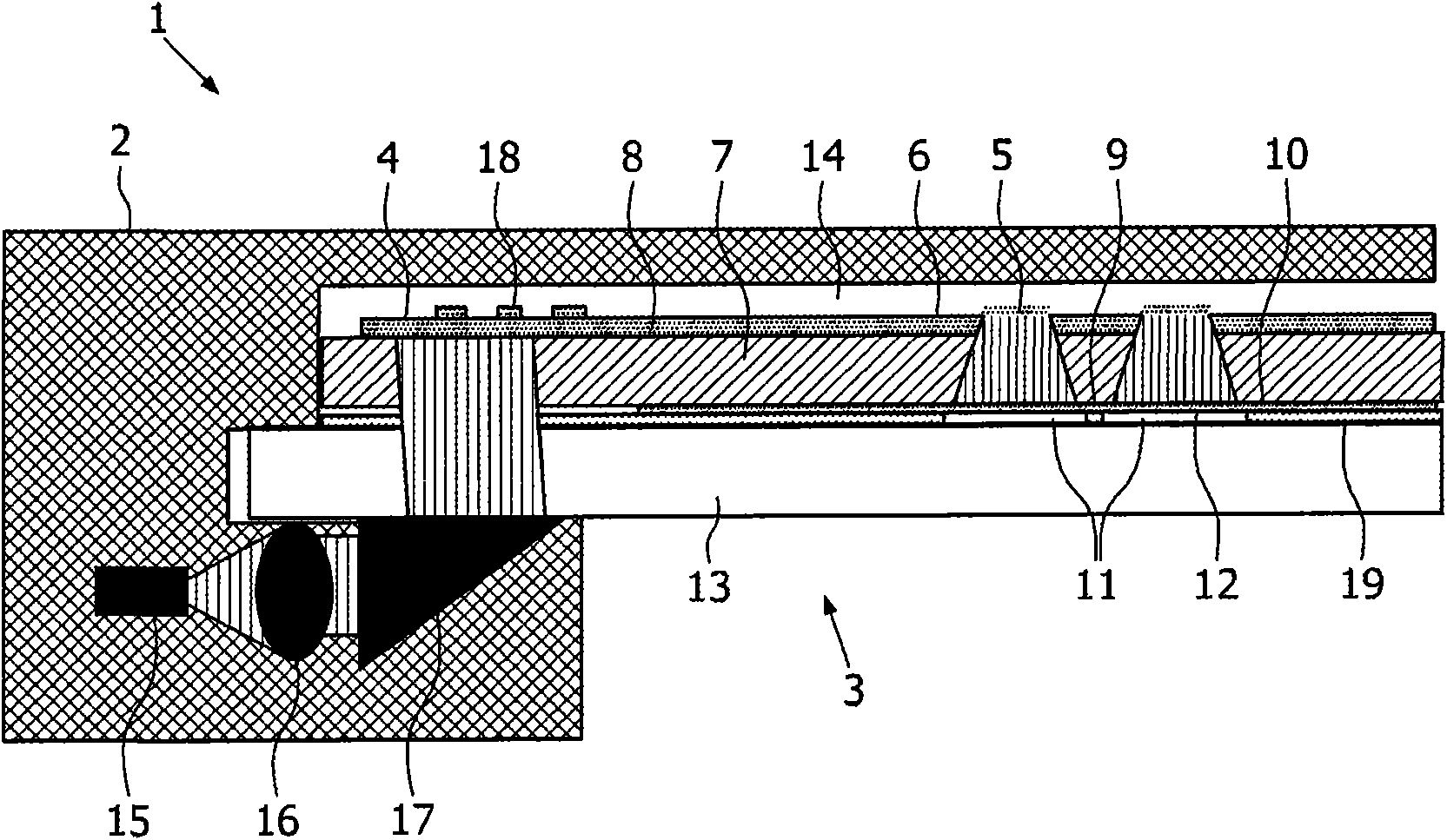
The present invention is directed to a waveguide sensor as well as to an evanescent field induced evanescent field induced sensor system for use in diagnostic housing and an integrated waveguide sensor comprising: a waveguide layer,—capture compounds applied on the upper surface of said waveguide layer for 5 specific bonding to target substances,—a cladding layer surface of said waveguide layer,—a filter which is transmitting for luminescent radiation while absorbs and / or reflects radiation of excitation radiation, wherein the filter is arranged below the lower 10 surface of said cladding layer, at least one detector for sensing luminescent radiation, wherein the detector is arranged below the lower surface of said filter, a substrate that is connected with the detector and comprises the electrical interface of said detector; wherein 15 between the upper surface of the waveguide layer and along at least a lower surface section of the housing a channel is formed for receiving a fluidic probe; and the luminescent radiation is generated by luminescent tag bound to target substances as a result of their excitation by the evanescent field. This provides an improved sensitivity of the evanescent field induced sensor 20 system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Side-hole cane waveguide sensor
A side-hole optical cane for measuring pressure and / or temperature is disclosed. The side-hole cane has a light guiding core containing a sensor and a cladding containing symmetrical side-holes extending substantially parallel to the core. The side-holes cause an asymmetric stress across the core of the sensor creating a birefringent sensor. The sensor, preferably a Bragg grating, reflects a first and second wavelength each associated with orthogonal polarization vectors, wherein the degree of separation between the two is proportional to the pressure exerted on the core. The side-hole cane structure self-compensates and is insensitive to temperature variations when used as a pressure sensor, because temperature induces an equal shift in both the first and second wavelengths. Furthermore, the magnitude of these shifts can be monitored to deduce temperature, hence providing the side-hole cane additional temperature sensing capability that is unaffected by pressure. Additionally, the side-hole cane can be used to measure a differential pressure between a first pressure ported to the side-holes and a second external pressure.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Substrate-Integrated Hollow Waveguide Sensors
ActiveUS20130081447A1Cladded optical fibreColor/spectral properties measurementsLight guideHollow waveguide
Methods and apparatuses are provided that greatly expand the utility of conventional hollow waveguide-based sensors via either straight, substrate-integrated channels or via meandering (e.g., circuitous, curved or folded optical paths) waveguide sensor designs. Full- or hybrid-integration of the meandering hollow waveguide with light source, detector, and light-guiding optics facilitates compact yet high-performance gas / vapor and / or liquid sensors of the substrate-integrated hollow waveguide sensor.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Optical substance analyzer
ActiveUS20050135723A1Advantageously high sensitivityLarge differential phase shiftMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhase-affecting property measurementsGratingDifferential phase
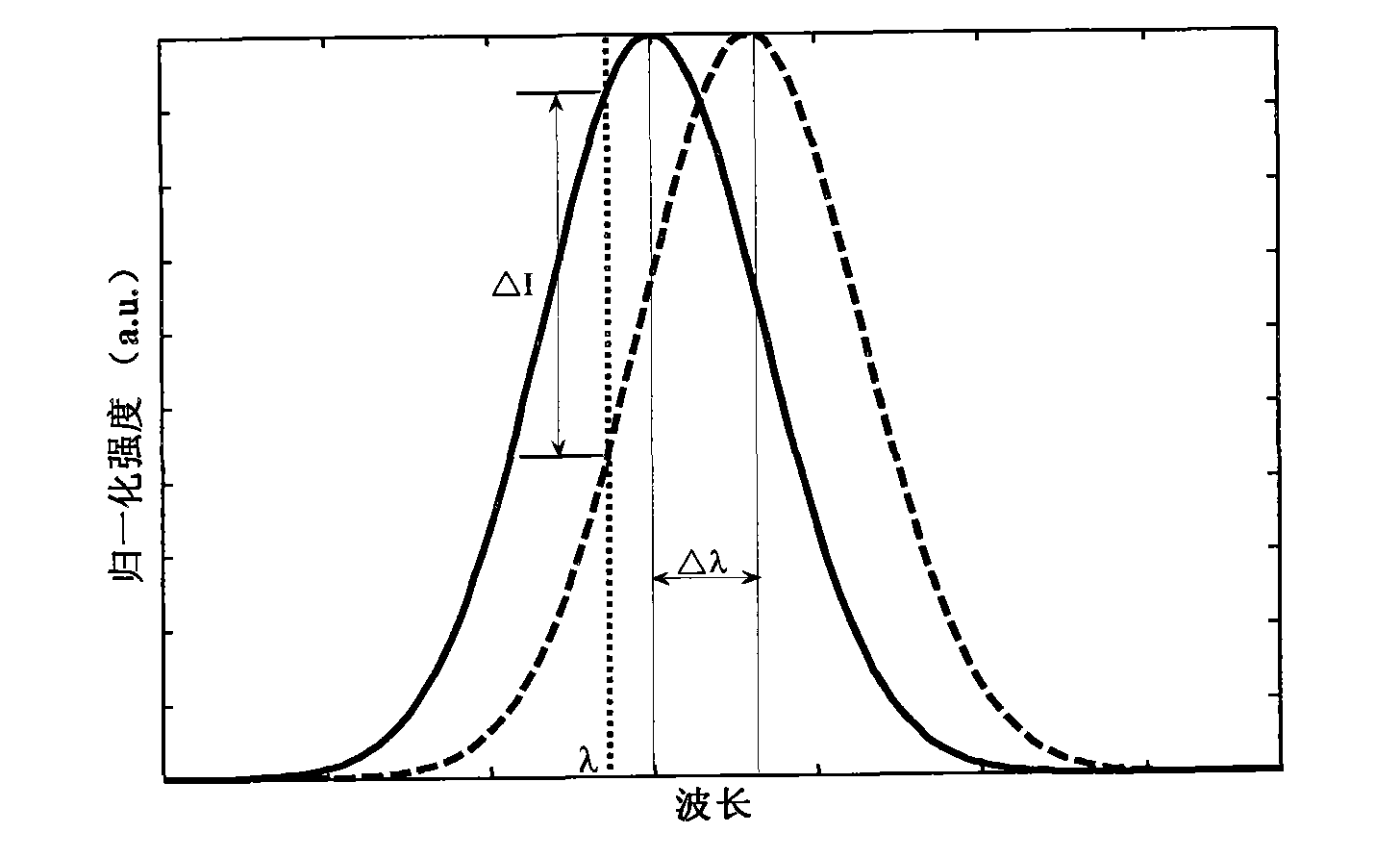
A portable waveguide sensor having one or more gratings. In one embodiment, the sensor has a waveguide, wherein a plurality of grooves imprinted onto the waveguide form a Bragg grating. The surface of the grooves has a functional layer adapted to bind a substance of interest, e.g., a biological pathogen. When the pathogen binds to the functional layer, the binding shifts the spectral reflection band corresponding to the Bragg grating such that a probe light previously reflected by the grating now passes through the grating, thereby indicating the presence of the pathogen. In another embodiment, the sensor has a Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI), one arm of which has a resonator formed by two Bragg gratings. The surface of the resonator between the gratings has a functional layer whereas the Bragg gratings themselves do not have such a layer. Due to multiple reflections within the resonator, light coupled into the MZI interacts with the bound pathogen over a relatively large effective propagation length, which results in a relatively large differential phase shift and therefore advantageously high sensitivity to the pathogen.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
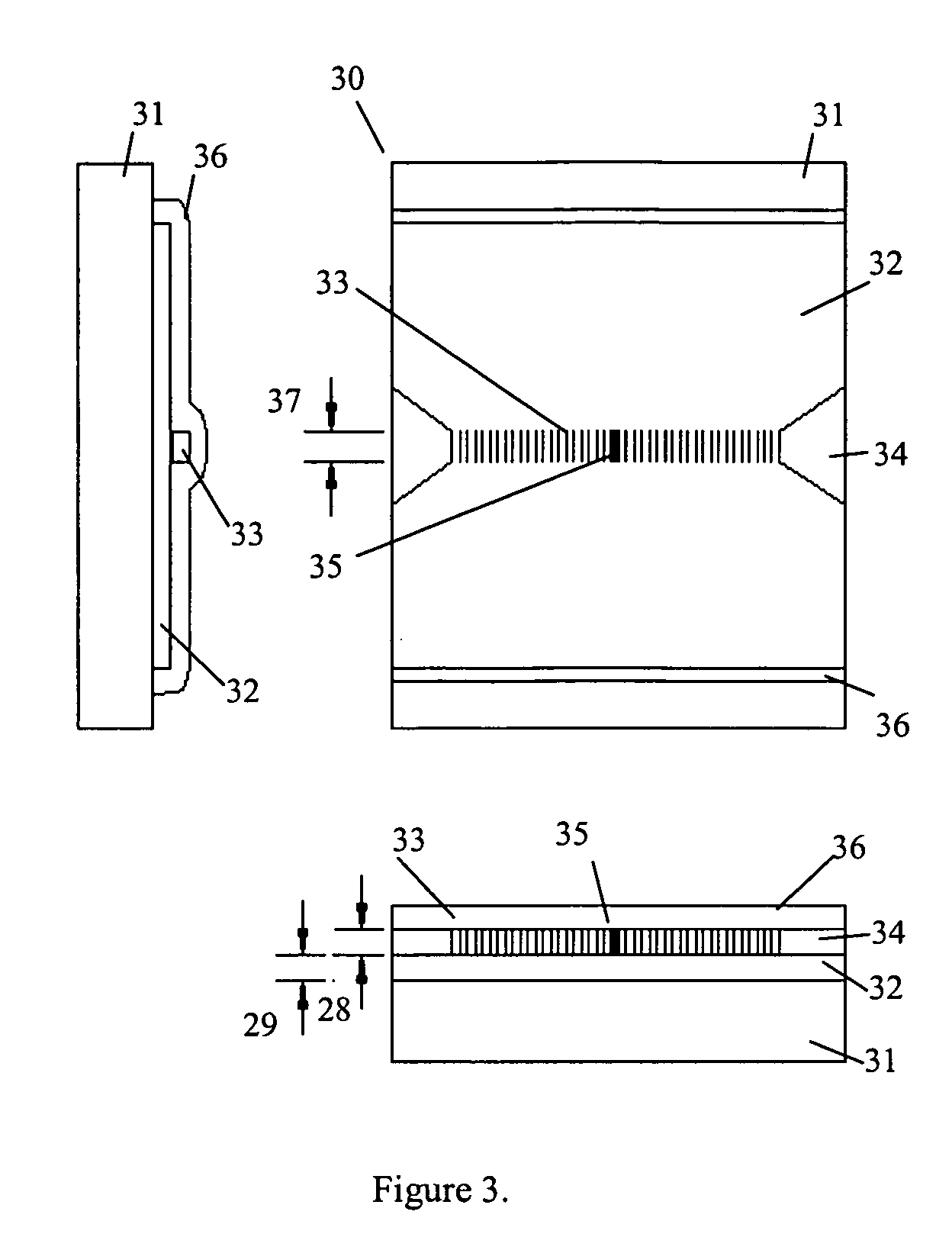
Optical waveguide sensor, device, system and method for glucose measurement
An optical waveguide sensor for glucose measurement comprises a substrate, a first optical waveguide layer formed on a surface of the substrate, an entrance grating and an exit grating which are formed contacting with the first optical waveguide layer and being spaced from each other, a second optical waveguide layer located between the entrance grating and the exit grating while being in contact with the first optical waveguide layer, the second optical waveguide layer having a higher refractive index that that of the first optical waveguide layer, and a functioning layer containing an enzyme and a coloring reagent which is formed on the second optical waveguide layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Integrated Optical Waveguide Sensors With Reduced Signal Modulation
InactiveUS20080298740A1Reduce amount of incident lightIncrease the amount of lightMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorOptical waveguide light guideGratingWaveguide
The invention provides an integrated optical waveguide sensor module (200) with reduced signal modulation and increased sensitivity. An optical waveguide sensor module (200) comprises an optically transparent substrate (210) having a first and a second interface and an optical waveguide film (220) disposed on the substrate (210) with the first interface (225) therebetween, wherein the film (220) comprises at least one grating pad (235) that is optically coupled therewith. The substrate (210) and the optical waveguide film (220) are configured to reduce parasitic interference within the substrate.
Owner:CIPHERGEN BIOSYSTEMS INC
Magneto-optical resonant waveguide sensors
InactiveUS20060103380A1High measurement sensitivityImprove resolutionOptical light guidesMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsFiberWaveguide
A waveguide magneto-optic sensor provides a signal indicative of the value and / or direction of a detected magnetic field by a spectral shift of the characteristic resonant spectral feature of the sensor is disclosed. The sensor does not suffer from vibrations, fiber bending or other light intensity noise and provides an absolute self-referencing signal. The sensor elements can easily be coupled to optical fibers and read with scanning spectrometers or scanning lasers calibrated against NIST-traceable gas absorption standards.
Owner:KYTON
Optical waveguide sensor, device, system and method for glucose measurement
An optical waveguide sensor for glucose measurement comprises a substrate, a first optical waveguide layer formed on a surface of the substrate, an entrance grating and an exit grating which are formed contacting with the first optical waveguide layer and being spaced from each other, a second optical waveguide layer located between the entrance grating and the exit grating while being in contact with the first optical waveguide layer, the second optical waveguide layer having a higher refractive index that that of the first optical waveguide layer, and a functioning layer containing an enzyme and a coloring reagent which is formed on the second optical waveguide layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Ferromagnet magnetostrictive effect-based method for testing length of anchor rod
InactiveCN101545755ANo close contactNo need for tight media couplingUsing electrical meansInverse magnetostrictive effectFiltration
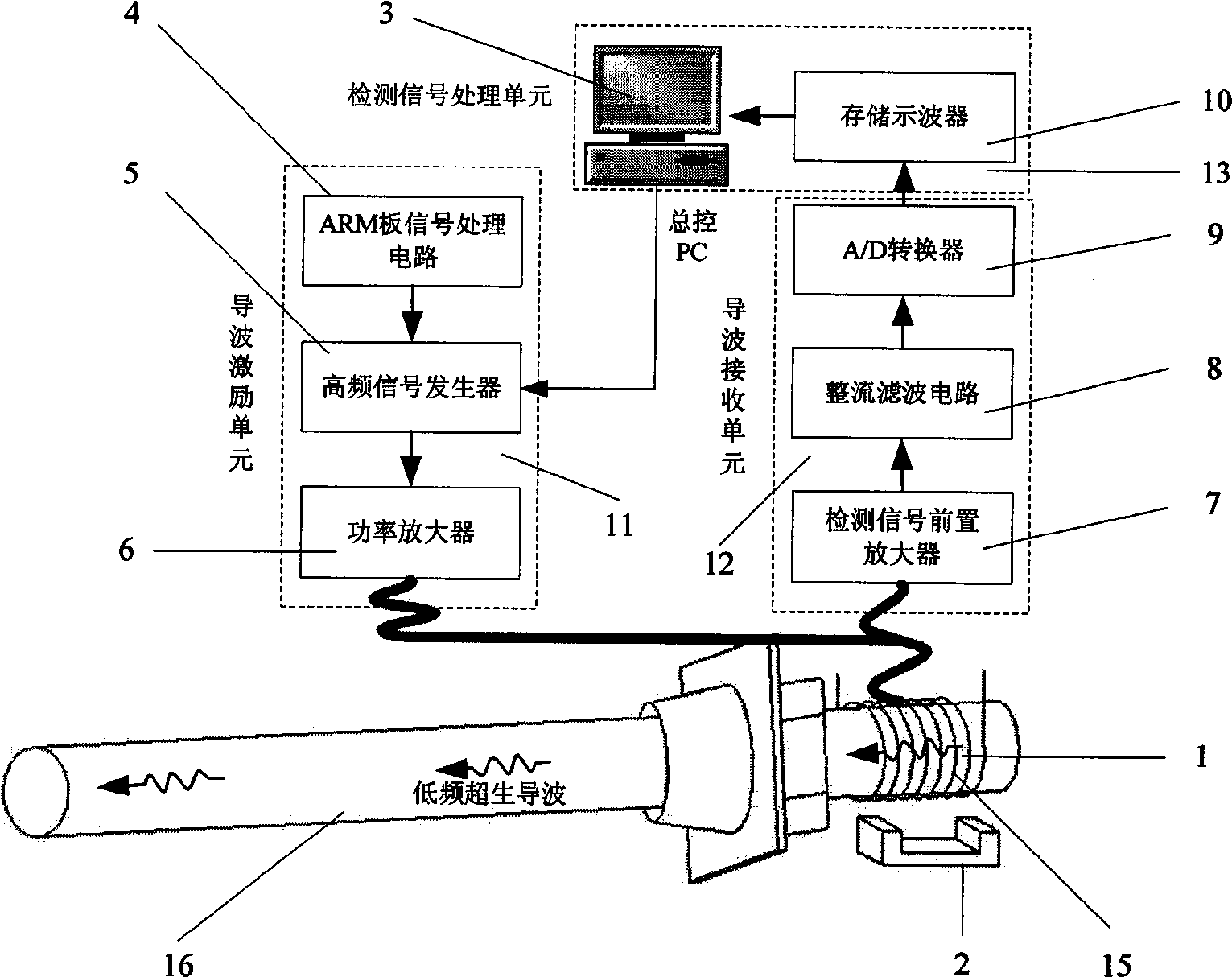
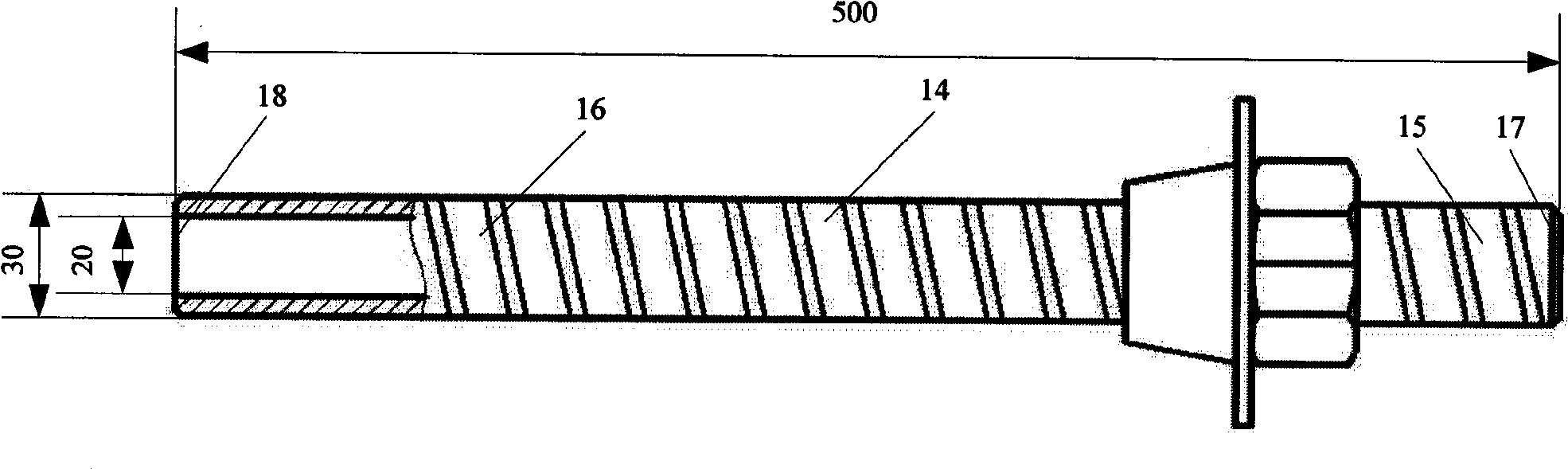
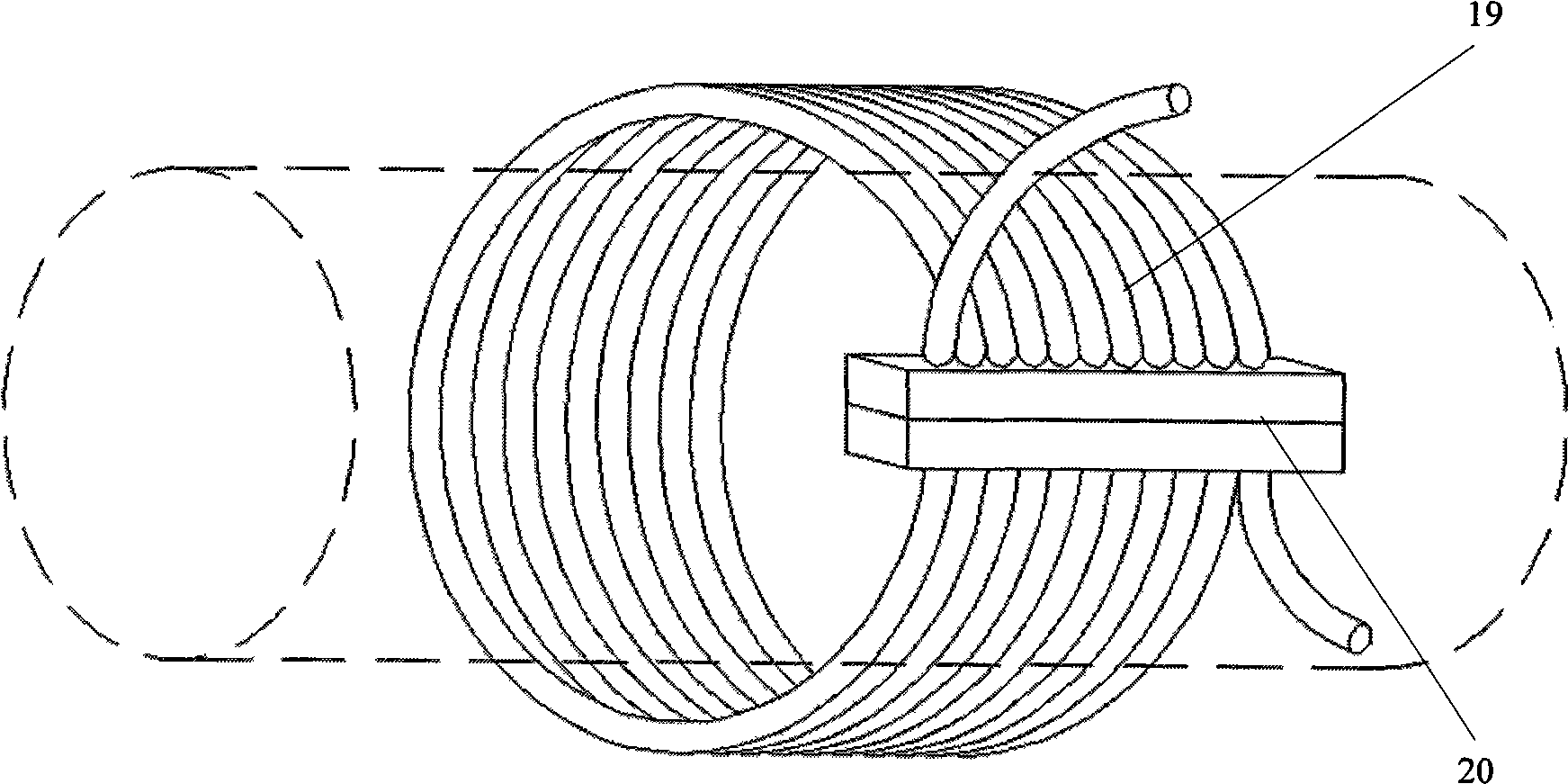
The invention discloses a ferromagnet magnetostrictive effect-based method for testing the length of an anchor rod, which comprises the following steps that: a magnetostrictive waveguide sensor is arranged on the free end of an anchor rod to be tested; a static bias magnetic field is applied at the mounting position of the magnetostrictive waveguide sensor; an exciting pulse signal is applied to the magnetostrictive waveguide sensor to excite mechanical vibration on the free end of the anchor rod; the sizes of the exciting pulse signal, exciting frequency and the static bias magnetic field are set to excite waveguides mainly in a longitudinal mode in the anchor rod; a receiving unit converts an elastic wave signal in a member to be tested into an electrical signal by using an inverse magnetostrictive effect, and after signal amplification, filtration and rectification, signal averaging and A / D conversion treatment, the electrical signal enters a test signal processing unit to test the actual length of the anchor rod to be tested. The method can realize the excitation and detection of ultrasonic waves in the anchor rod. The test signal contains information on the length and defects of the anchor rod and the actual length of a measured anchor rod can be measured accurately through the processing and analysis of a waveguide reflected wave signal.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for enhancing waveguide sensor signal
InactiveUS20090109441A1Increases magnitudeImprove signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansFluorescenceWaveguide
A detection system for a first specific material is provided by which an interferometer, having a reference waveguide segment and a test waveguide segment, is enhanced. The test waveguide segment carries a second capture material for specifically capturing said first specific material that may be present in a fluid specimen. Capture of the first specific material is detected by an interference pattern produced by combining coherent light beams passing through the waveguide segments. To enhance by orders of magnitude the detection limits of the test, the waveguide segments are subjected to an alternating or pulsed electrical or magnetic fields. This same signal is fed to a lock-in amplifier that is associated with computational means by which the interference pattern is interpreted. The invention further includes a waveguide system in which capture of the first specific material is detected by fluorescence. Detection of the fluorescent signal is enhanced relative to noise by subjecting the waveguide segment to alternating or pulsed electrical or magnetic signal.
Owner:MGIMAT
Cascade micro cavities based digital integrated-optical waveguide sensor
InactiveCN101706424ASimple structureSimple designPhase-affecting property measurementsMiniaturizationWaveguide
The invention provides a cascade micro cavities based digital integrated-optical waveguide sensor, comprising a constant micro cavity, an input waveguide, n sensing micro cavities, n connected waveguides, n output waveguides and n sample cells, wherein n is not less than 1. The sensing micro cavities are arranged in the sample cells. The input waveguide is arranged at one side of the constant micro cavity. One end of the input waveguide is coupled with the constant micro cavity and the other end thereof serves as the optical source incoming end of the whole optical waveguide sensor. One end of each connected waveguide is coupled with the constant micro cavity and the other end thereof is coupled with one sensing micro cavity. One end of each output waveguide is coupled with one sensing micro cavity and the other end thereof serves as the sensing signal outgoing end. The optical waveguide sensor has the digital operating mode, features high sensitivity, good anti-noise property and high reliability, is easy to expand to realize regular arrays, is convenient to integrate with integrated spectrometer chips and is conductive to realizing integrated, miniaturized, portable and low-cost sensing system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
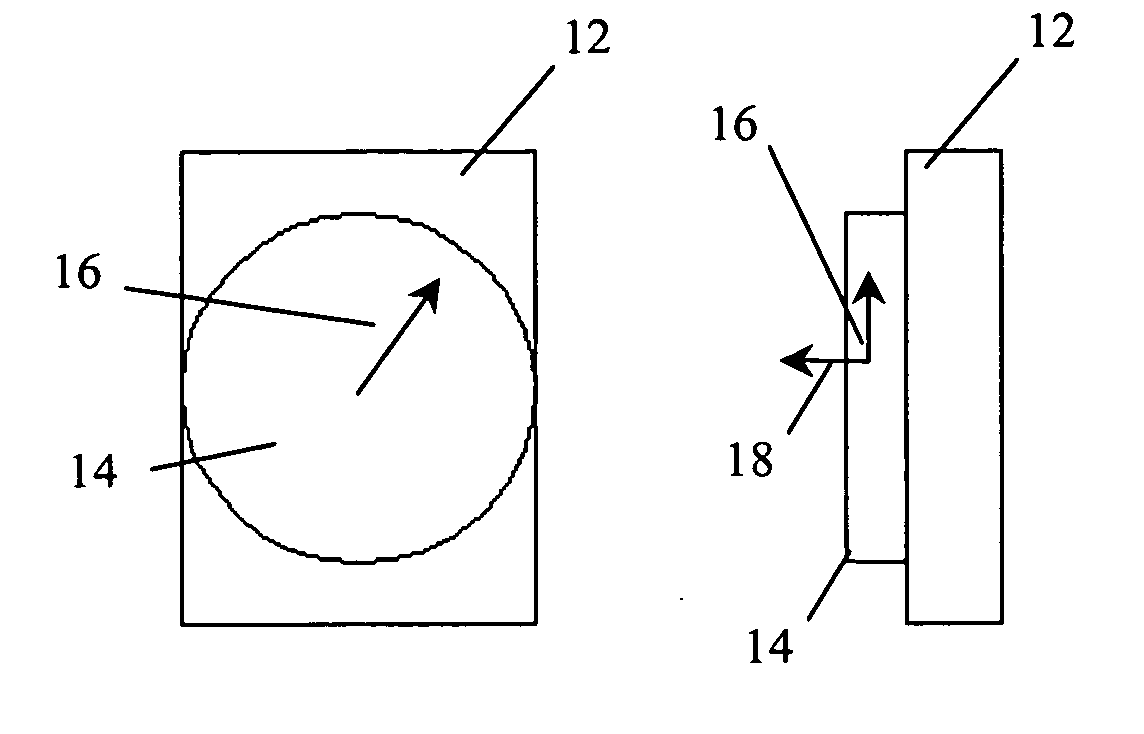
Optical analyte sensor
ActiveUS8349605B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteWaveguide
A waveguide sensor capable of direct, real-time detection and monitoring of analytes in the vicinity of the waveguide surface without requiring the tagging or labeling of the analyte, is described. Analytic and numerical calculations have predicted that by locally detecting either changes in the evanescent field or changes in the light coupled out of the waveguide as a result of the presence of the analyte, high detection sensitivity will be able to be achieved.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
Optical-waveguide sensor chip, method of manufacturing the same, method of measuring substance, substance-measuring kit and optical-waveguide sensor
InactiveUS20090124024A1Analysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBiological testingAnalyteWaveguide
An optical-waveguide sensor chip includes an optical waveguide having a first substance immobilized on the surface thereof, the first substance being specifically reactive with an analyte substance, and fine particles dispersed on the optical waveguide and having a second substance immobilized on the surface thereof, the second substance being specifically reactive with the analyte substance.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Long-range surface plasmon optical waveguide sensor
InactiveUS20100097611A1Effectively control characteristicLoss of an electromagnetic wave is reducedSolid-state devicesScattering properties measurementsMetal stripsSurface plasmon
The present invention provides a long-range surface plasmon optical waveguide sensor which has a reduced loss of an electromagnetic wave, an increased sensitivity and limitation of detection and a high analysis speed, and enables fabrication of a sensor of various sizes such as a small-sized or lightweight system, etc. To this end, the long-range surface plasmon optical waveguide sensor, comprising: a sensor section, wherein the sensor section comprises a substrate, a first dielectric layer stacked on the substrate, a metal thin film stacked on the first dielectric layer, a second dielectric layer stacked on the metal thin film and having a channel penetratingly formed therein in such a fashion that the top surface of the metal thin film is partially exposed into the channel, a metal strip stacked on the second dielectric layer in such a fashion that the underside thereof is partially exposed into the channel, and a third dielectric layer stacked on the metal strip; a light source section for inducing a surface plasmon resonance between the metal thin film and the metal strip; and a detection section for detecting and analyzing a change of light according to the surface plasmon resonance.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Optical waveguide sensor and preparation methods thereof
InactiveCN101832792AImprove efficiencyReduce manufacturing costThermometers using physical/chemical changesCoupling light guidesLaser technologyRefractive index
The invention discloses an optical waveguide sensor and preparation methods thereof. The optical waveguide sensor comprises a structure as follows: an optical waveguide substrate medium consists of heat resisting optical materials and is provided with linear optical waveguides, and in which an optical grating structure is arranged in the linear optical waveguides. The invention further discloses many preparation methods of the structure. Another waveguide sensor comprises a structure as follows: the optical waveguide substrate medium consists of heat resisting optical materials and is provided with linear optical waveguides, and an optical grating structure is further arranged on the surface of the optical waveguide substrate. The invention further discloses many preparation methods of the structure. Because the optical waveguide apparatus has a simple module structure or a structure with few modules, the optical grating on the optical waveguide channel only has a harmonic module or few modules. When the environment temperature is changed, the refractive index of the optical waveguide material and the period of the optical waveguide grating can be changed, therefore, the change of temperature can be measured by measuring the change of wavelength of harmonic wave of the optical grating in the optical waveguide channel on the optical waveguide substrate. Due to the adoption of the laser technology and microelectronic production process, a plurality of optical waveguide grating sensing apparatuses can be further produced on a same substrate with low production cost and high efficiency.
Owner:无锡光芯科技有限公司
High-sensitivity integrated optical waveguide sensor based on digital droplet sample introduction channel
InactiveCN101893562AHigh sensitivityPhase-affecting property measurementsPhotodetectorAlternating current
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity integrated optical waveguide sensor based on a digital droplet sample introduction channel, which comprises a digital droplet sample introduction channel, an input optical waveguide, an output optical waveguide, an integrated planar optical waveguide sensor, a photodetector and a phase-locking amplifier, wherein the integrated planar optical waveguide sensor is coupled with the input and output optical waveguides; the photodetector converts photosignals in the output optical waveguide into electric signals; the phase-locking amplifier is connected with the photodetector; and the integrated planar optical waveguide sensor, which is coupled with the input and output optical waveguides, is arranged in the digital droplet sample introduction channel and below the position after the buffer solution and the substance to be measured are mixed to form droplets. The invention enables the substance to be measured to flow across the sensing region of the integrated optical waveguide sensor in the frequency f, and modulates the optical waveguide output signal output by the sensor in the frequency f, so that the output signal is converted into an alternating current signal; and the effective signals with the frequency f are extracted by the phase-locking amplifier to maximally filter out noise, mainly including white noise which is introduced by the laser device and the photodetector, thereby enhancing the sensitivity of the sensor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Biosensor with evanescent waveguide and integrated sensor
the present invention is directed to a waveguide sensor as well as to an evanescent field induced evanescent field induced sensor systemfor use in diagnostic applications that comprises a housingand an integrated waveguide sensor comprising: a waveguide layer, -capture compounds applied on the upper surface of said waveguide layer for specific bonding to target substances, -a cladding layer contacting arranged on the lower surface of said waveguide layer, -a filter which is transmitting for luminescent radiation while absorbs and / or reflects radiation of excitation radiation, wherein the filter is arranged below the lower surface of said cladding layer, at least one detector for sensing luminescent radiation, wherein the detector is arranged below the lower surface of said filter, a substrate that is connected with the detector and comprises the electrical interface of said detector; wherein between the upper surface of the waveguide layerand along at least a lower surface section of the housing a channel is formed for receiving a fluidic probe; and the luminescent radiation is generated by luminescent tag bound to target substances as a result oftheir excitation by the evanescent field. This provides an improved sensitivity of the evanescent field induced sensor system.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Optical Waveguide Sensor Devices and Methods For Making and Using Them
InactiveUS20080101744A1High sensitivityMany functionsCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHybrid materialElectric devices
The present invention relates to optical waveguide sensor devices. One aspect of the present invention is an optical waveguide sensor device, comprising a substrate; and a device layer disposed on the substrate. The device layer includes one or more sensing optical waveguides, each sensing optical waveguide having a core formed from a polymer material or an organic / silicate hybrid material; and one or more inert inorganic optical waveguides operatively coupled to at least one of the sensing optical waveguides. Another aspect of the present invention is an optical waveguide sensor device, comprising a substrate; and a device layer disposed on the substrate. The device layer includes one or more sensing optical waveguides, each sensing optical waveguide having a core formed from a polymer material or an organic / silicate hybrid material; and one or more electronic devices operatively coupled to at least one of the sensing optical waveguides. The present invention can provide devices having higher sensitivity, smaller size and / or more convenient fabrication than those provided by the prior art.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Waveguide interference sensor
InactiveCN101526373AStable and reliable beam splitting ratioLow costPhase-affecting property measurementsCoupling light guidesFiberMach–Zehnder interferometer
The invention relates to the technical field of waveguide sensors. A novel Michelson interferometer for sensing measurement is designed by using the principle of waveguide nonlinear environment, and has a basic structure that two output ports of a 2*2 waveguide coupler of Mach-Zehnder interferometer are connected by waveguide, wherein the splitting ratio of the waveguide coupler is 1 to 1; or the middle part of a small section of waveguide (fiber) is directly rolled to manufacture a 2*2 waveguide coupler of which splitting ratio is 1 to 1; and the waveguide coupler is connected with another 2*2 waveguide coupler to form the Michelson interferometer. The waveguide interference sensor with low cost and same phase change and reflectivity at two reflection parts is provided with the novel Michelson interferometer structure so as to achieve the effects of improving interference contrast and improving measurement sensitivity.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Photonic crystal and waveguide sensor device
The present invention provides a sensor device for detecting a substance contained in a fluid comprising a first photonic crystal region, a second photonic crystal region, a first channel which is connected to the first photonic crystal region, and passes the fluid containing the substance therein, a second channel which is connected to the second photonic crystal region, and passes a fluid for reference therein, an optical waveguide which is connected to the first photonic crystal region and the second photonic crystal region, and guides light, and a detecting section for detecting a difference between a light which has passed through the optical waveguide and the first photonic crystal region and a light which has passed through the optical waveguide and the second photonic crystal region.
Owner:CANON KK
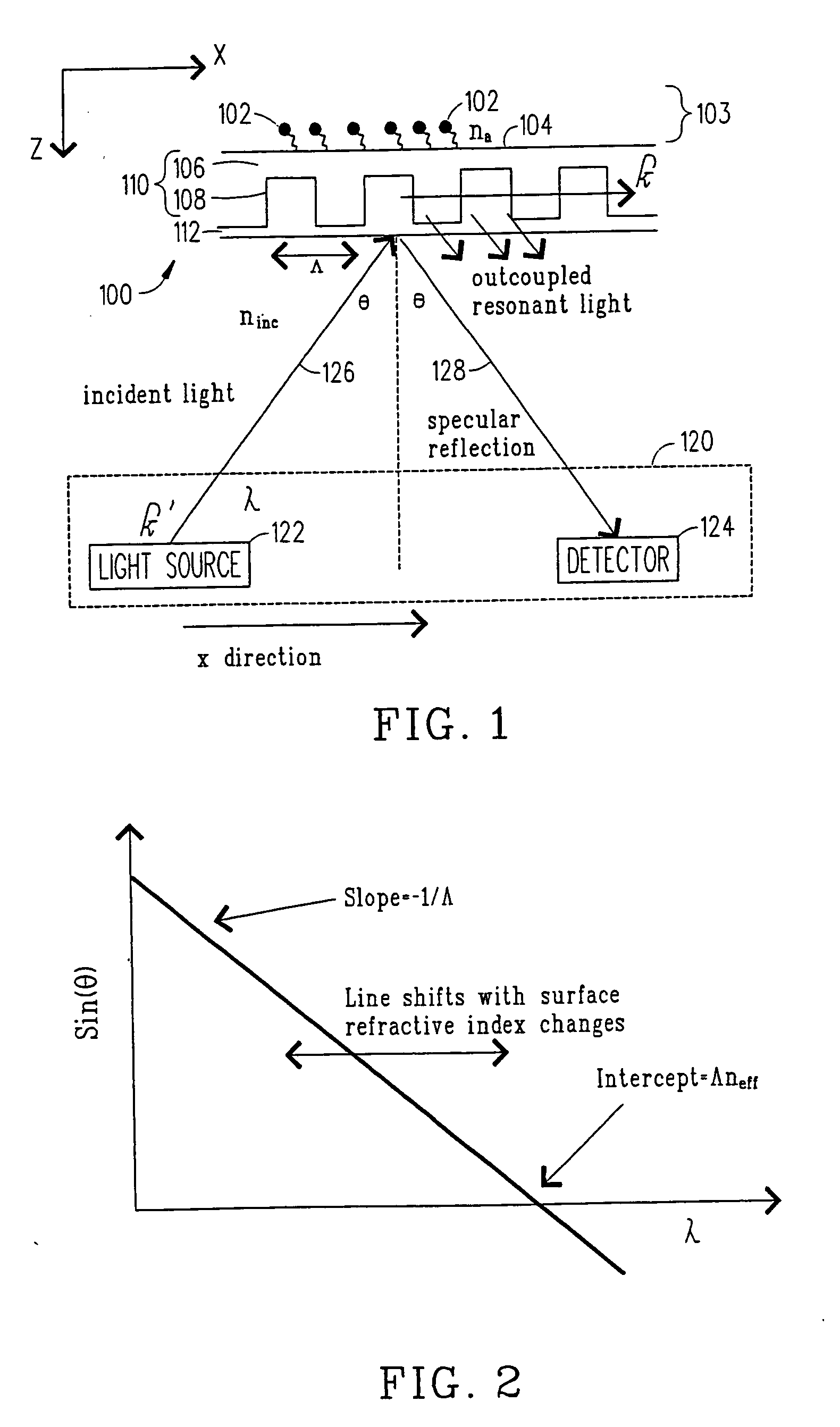
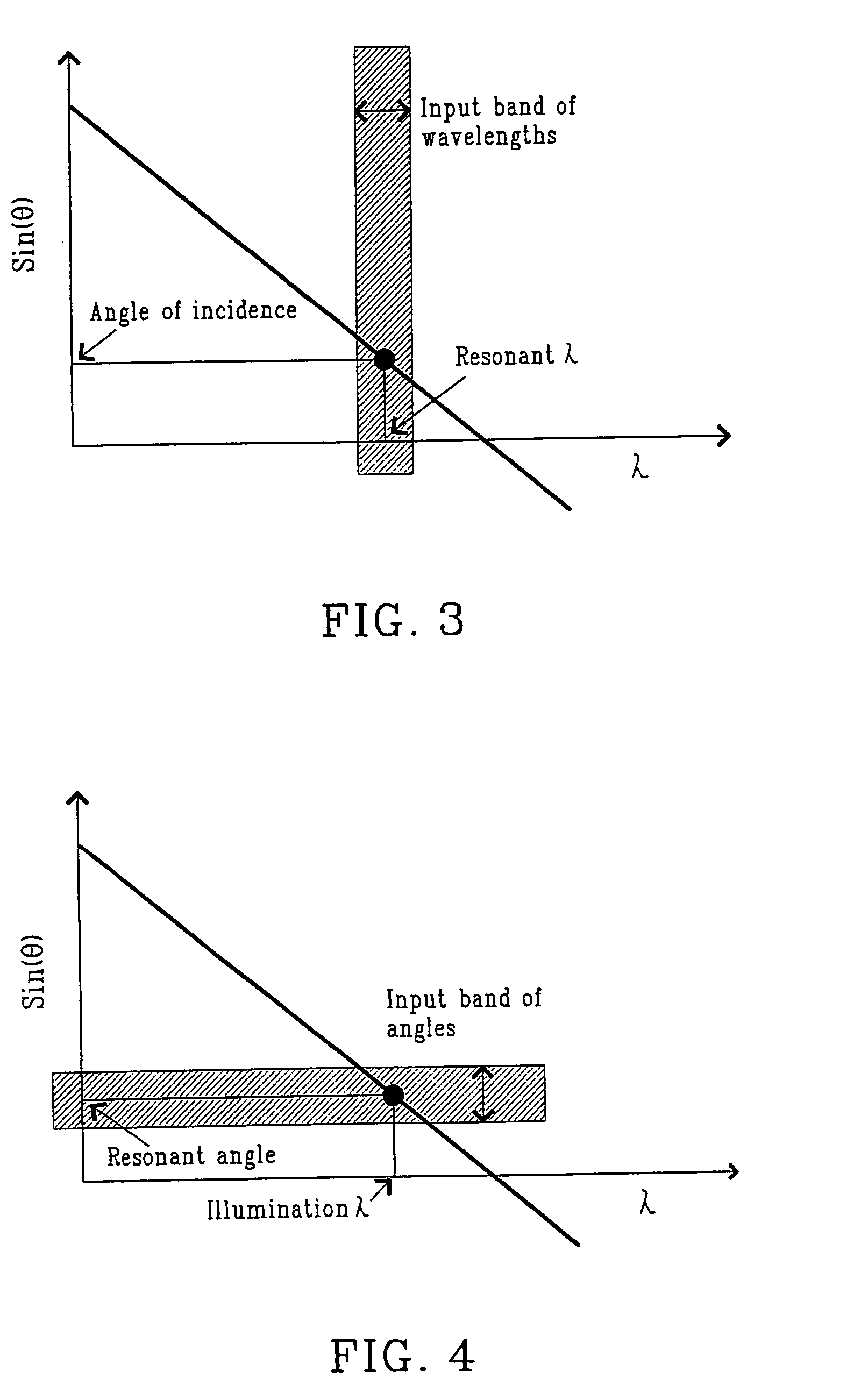
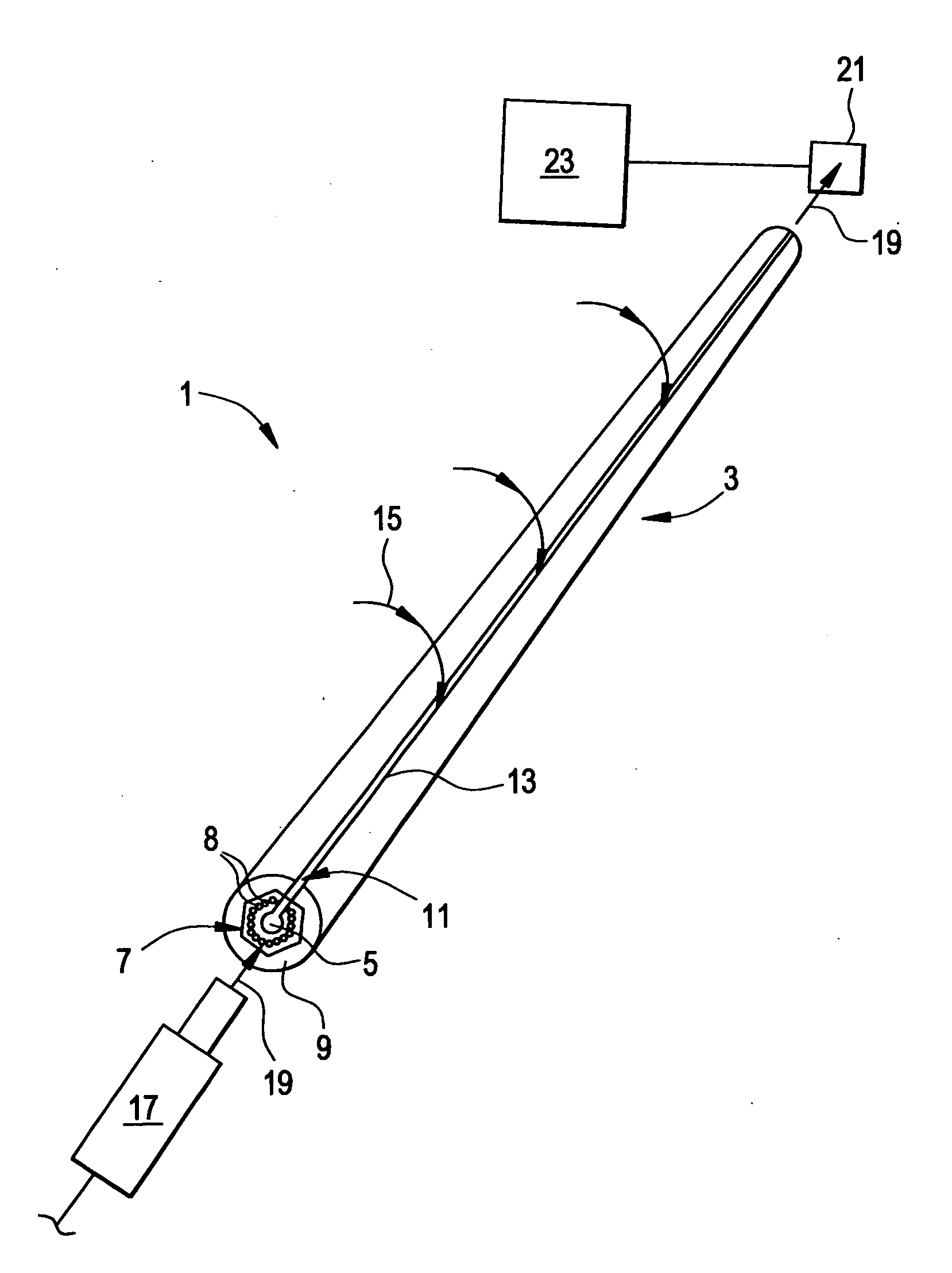
Dynamic optical waveguide sensor
Methods and apparatuses that sense physical parameters, such as pressure and strain, using optical waveguide sensors are described. A light source emits light at a predetermined wavelength along an optical waveguide having a fiber Bragg grating optical sensing element. That sensing element reflects light in accord with a sloped shape function of reflected light amplitude verses wavelength. A receiver converts the reflected light into electrical signals and an analyzer then determines a physical parameter based on changes of amplitude of the reflected light. The analyzer also maintains the wavelength of the light such that the wavelength corresponds to a slope wavelength of the shape function.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Dynamic optical waveguide sensor
Methods and apparatuses that sense physical parameters, such as pressure and strain, using optical waveguide sensors are described. A light source emits light at a predetermined wavelength along an optical waveguide having a fiber Bragg grating optical sensing element. That sensing element reflects light in accord with a sloped shape function of reflected light amplitude verses wavelength. A receiver converts the reflected light into electrical signals and an analyzer then determines a physical parameter based on changes of amplitude of the reflected light. The analyzer also maintains the wavelength of the light such that the wavelength corresponds to a slope wavelength of the shape function.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Apparatus for use in measuring fluid levels
ActiveUS20050127924A1Operating space is limitedEasy to installResistance/reactance/impedenceHollow article cleaningTransceiverMicrowave
A device for use in measuring stratified fluid levels in a container is disclosed. The device has a microwave transceiver sensor head attached to a waveguide sensor rod which is enclosed by a gauge tube. The rod end tubes are comprised of sections which allow them to be assembled or disassembled in a close quarters environment. The tube has a plurality of circumferentially and longitudinally spaced slots providing for the equalization of stratified fluids within the tube. The rod is generally radially centered in the tube by the use of a plurality of spacers which reside in notches in the rod. The spacers are adapted to not penetrate the slots in the tube. The rod can be removed from the tube for cleaning without draining the tank. Additionally, once the rod is removed from the tube, a cleaner brush or scraper can be used to remove any barnacles or other debris from within the tube and the longitudinal slots in the tube.
Owner:OHMARTVEGA
Optical waveguide sensor and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20080205837A1Maximizes exposureMinimize response timeGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingPhotonic bandgapWaveguide
An optical waveguide environmental sensor is provided that is capable of detecting a target gas or liquid in the ambient environment in an advantageously short period of time. The waveguide is preferably in the form of an optical fiber having a cladding that contains a photonic band gap structure which in turn envelopes a light conducting, hollow core portion. The cladding further includes at least one elongated side opening that preferably extends the entire length of the fiber and exposes said hollow core portion to the ambient environment, which provides broad and nearly immediate access of the core portion to gases and liquids in the ambient environment, thereby minimizing sensor response time. The ambient gases or liquids filling the hollow core portion and elongated opening function as a ridge and slab, respectively, of an optical ridge waveguide that effectively supports at least one bound optical mode.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical waveguide sensor and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS20110268385A1High detection sensitivitySmall dimensionCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by optical meansWaveguide sensorWaveguide
An optical waveguide sensor includes a substrate and an optical waveguide. The optical waveguide includes a core and a lateral clad. The core extends in a spiral shape above a surface of the substrate. The lateral clad is disposed in a same layer as the core above the surface of the substrate and is in contact with either side surfaces of the core. At least a part of a surface of the core located opposite from the substrate is a transmission surface from which light leaks and is absorbed by a detected object.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Blood Oxygenation Sensor
InactiveUS20070197888A1Representative measurementHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterRefractive indexOxygen
A planar dielectric waveguide sensor is used to determine the concentrations of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin and other blood constituents such as pH, sugar. The planar waveguide core is in direct contact with the blood such that evanescent field of the light propagating within the core is selectively attenuated at specific wavelengths of interest. The planar waveguide has a construction that promotes strong interaction of the evanescent field with blood cells that contact it. In preferred embodiments, the waveguide is constructed of a low refractive index core to propagate an evanescent wave comparable in size to a red blood cell.
Owner:PHYSICAL LOGIC
Optical substance analyzer
ActiveUS7212693B2Advantageously high sensitivityLarge differential phase shiftMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhase-affecting property measurementsGratingMach–Zehnder interferometer
A portable waveguide sensor having one or more gratings. In one embodiment, the sensor has a waveguide, wherein a plurality of grooves imprinted onto the waveguide form a Bragg grating. The surface of the grooves has a functional layer adapted to bind a substance of interest, e.g., a biological pathogen. When the pathogen binds to the functional layer, the binding shifts the spectral reflection band corresponding to the Bragg grating such that a probe light previously reflected by the grating now passes through the grating, thereby indicating the presence of the pathogen. In another embodiment, the sensor has a Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI), one arm of which has a resonator formed by two Bragg gratings. The surface of the resonator between the gratings has a functional layer whereas the Bragg gratings themselves do not have such a layer.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com