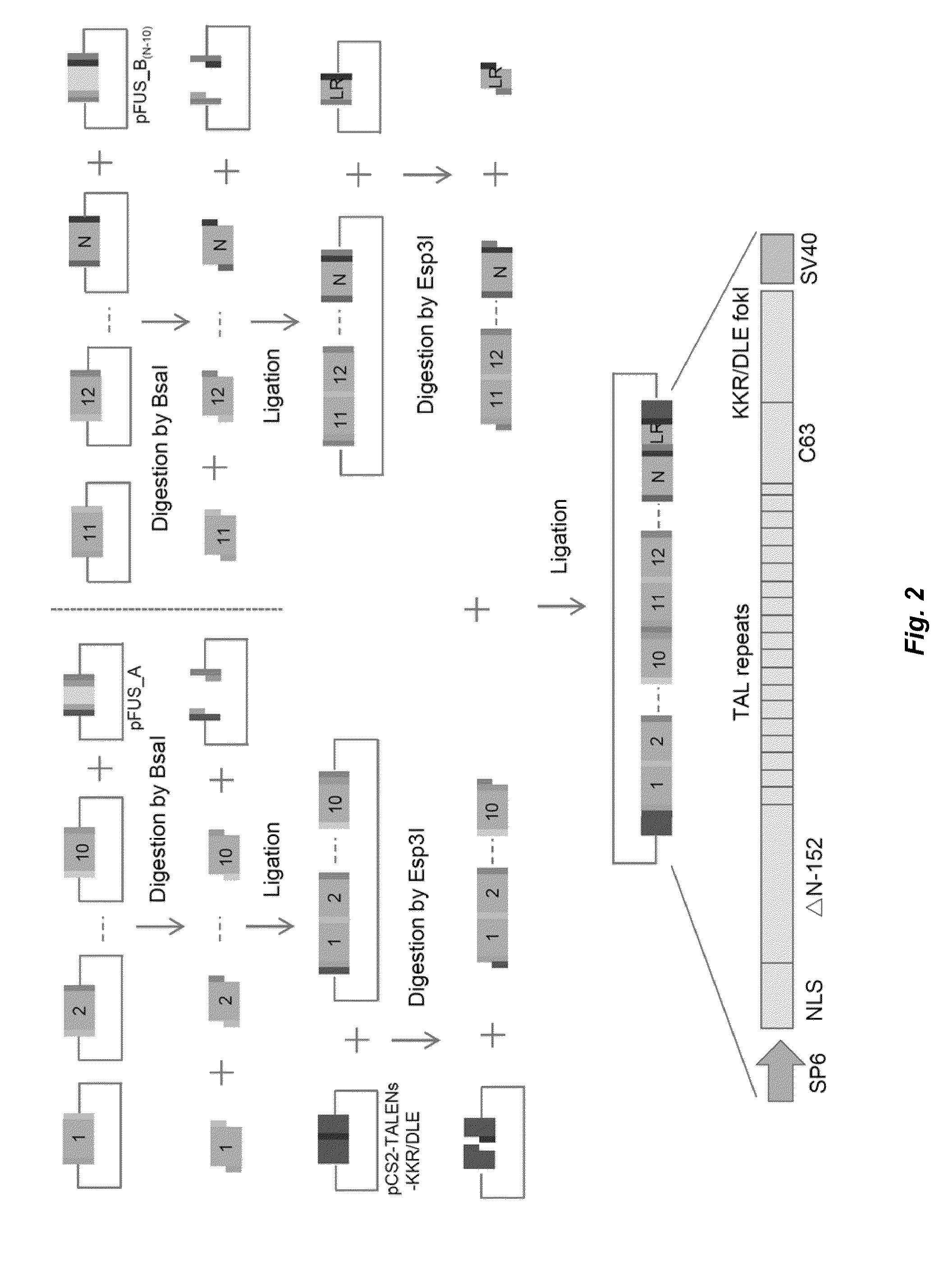
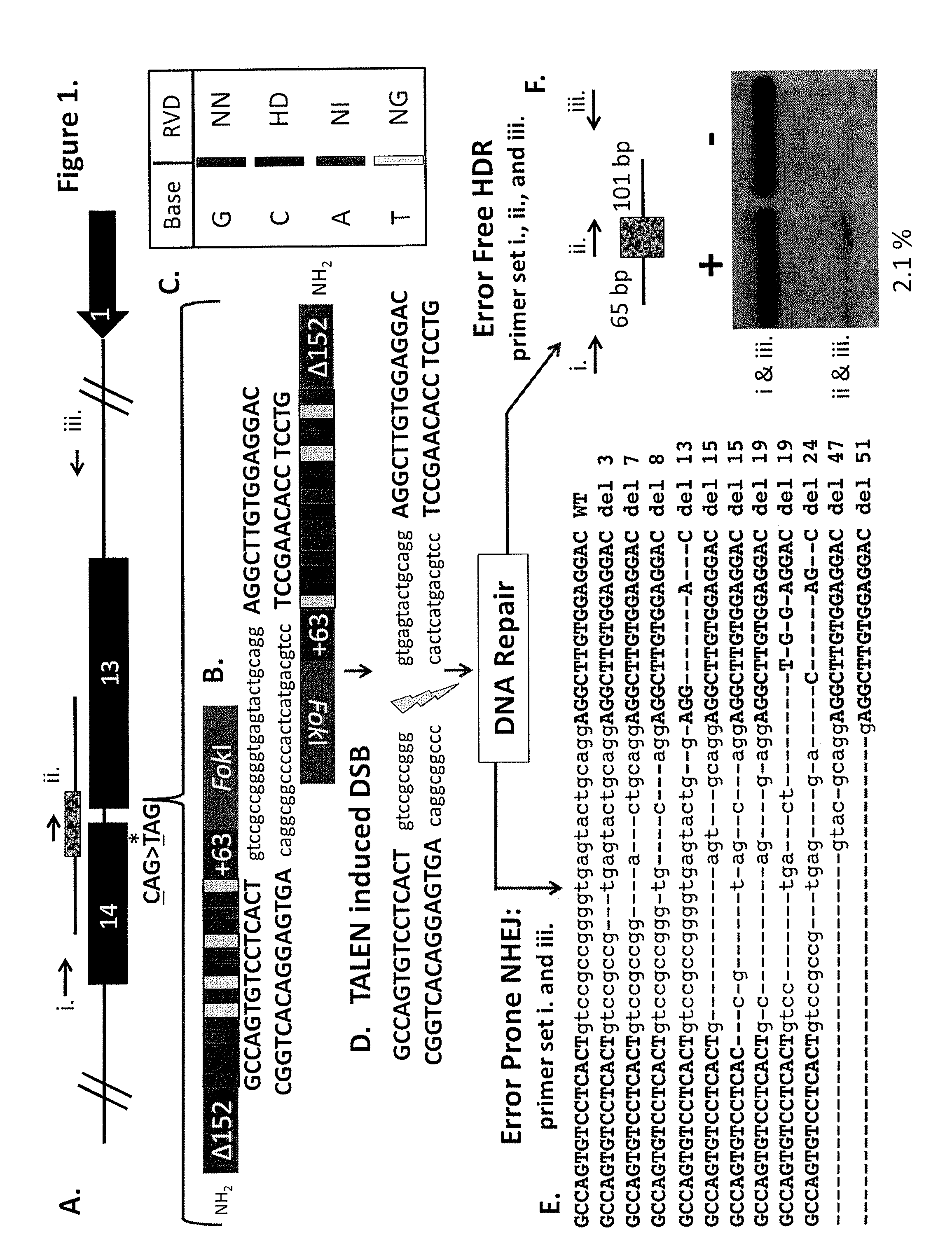
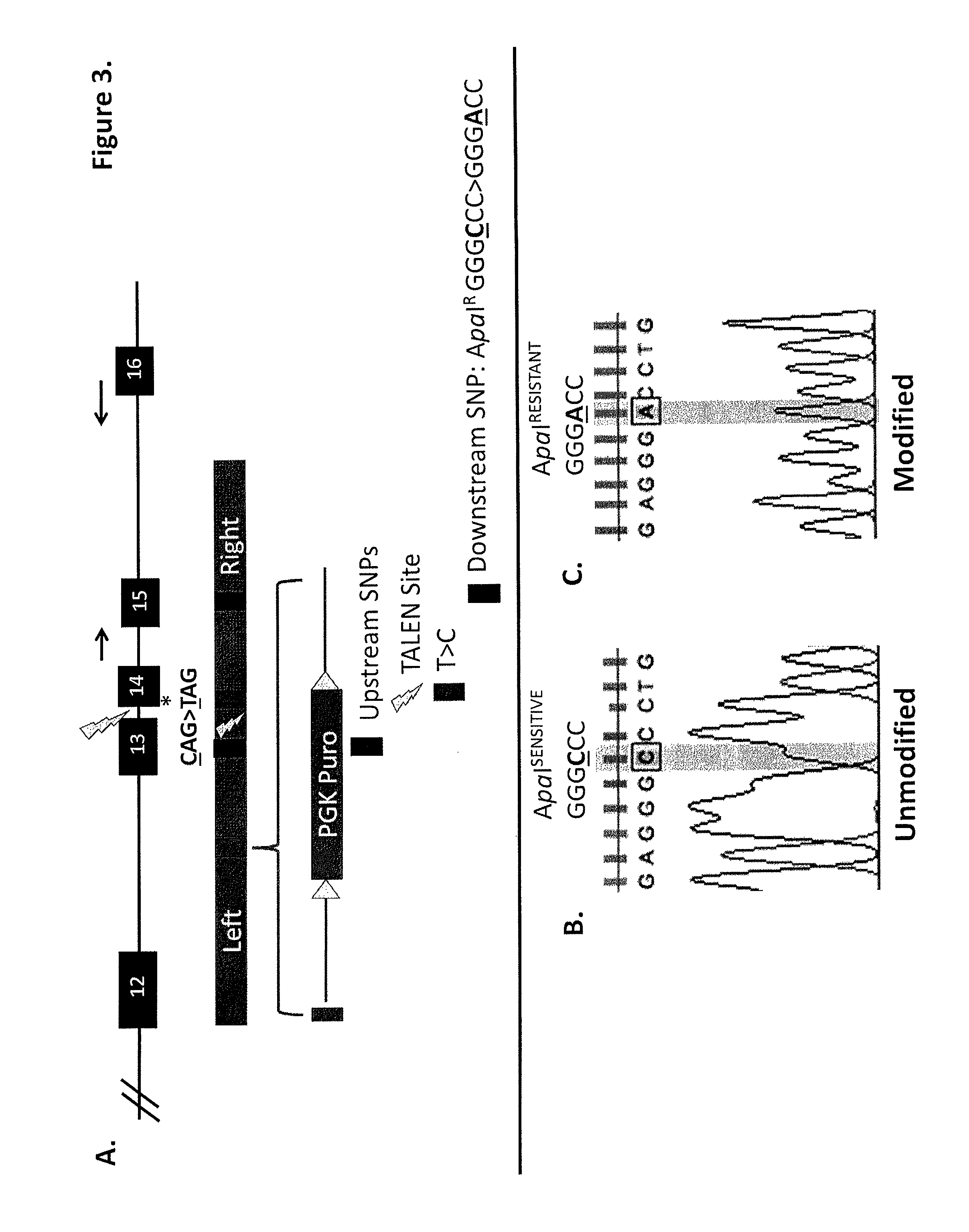
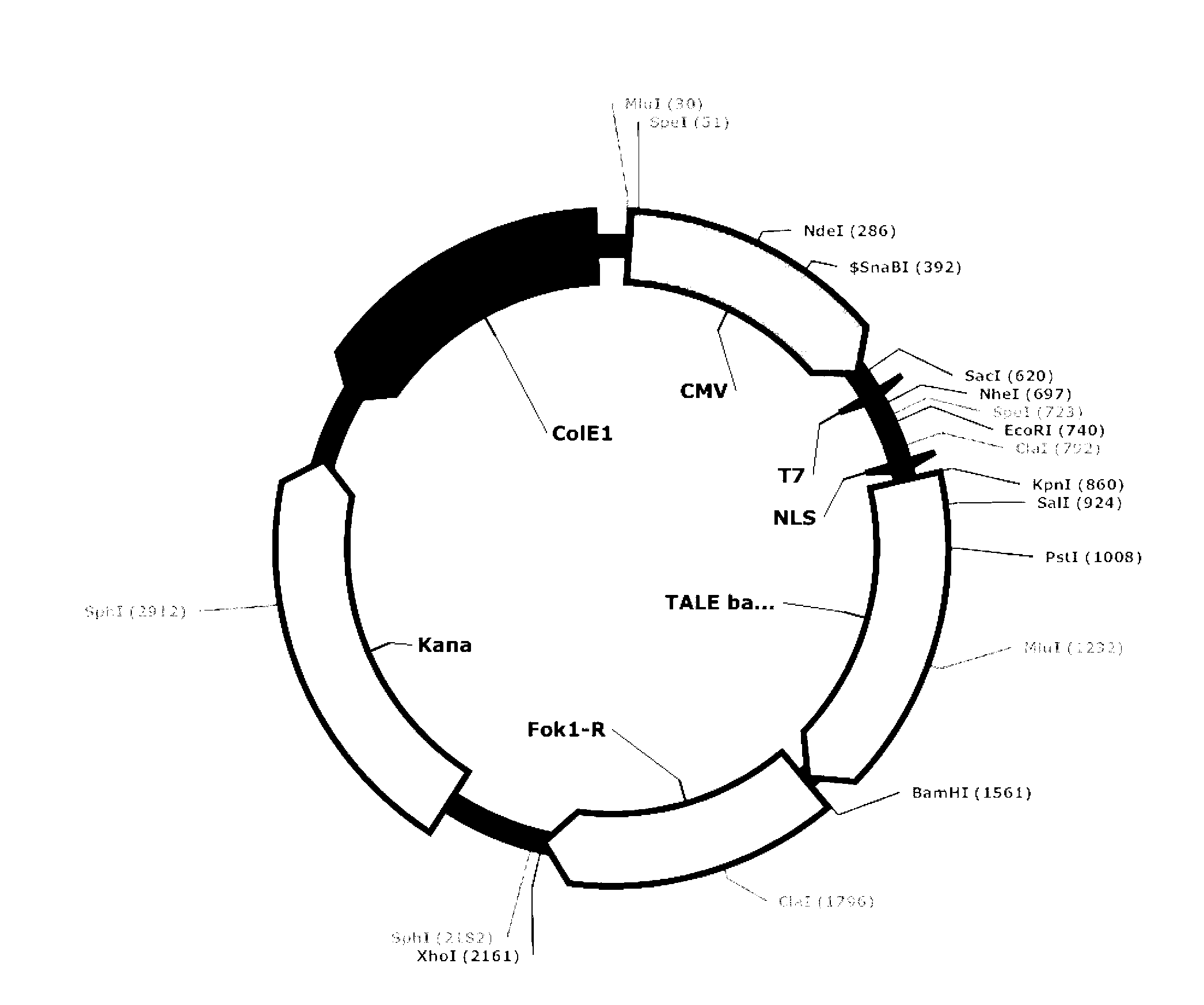
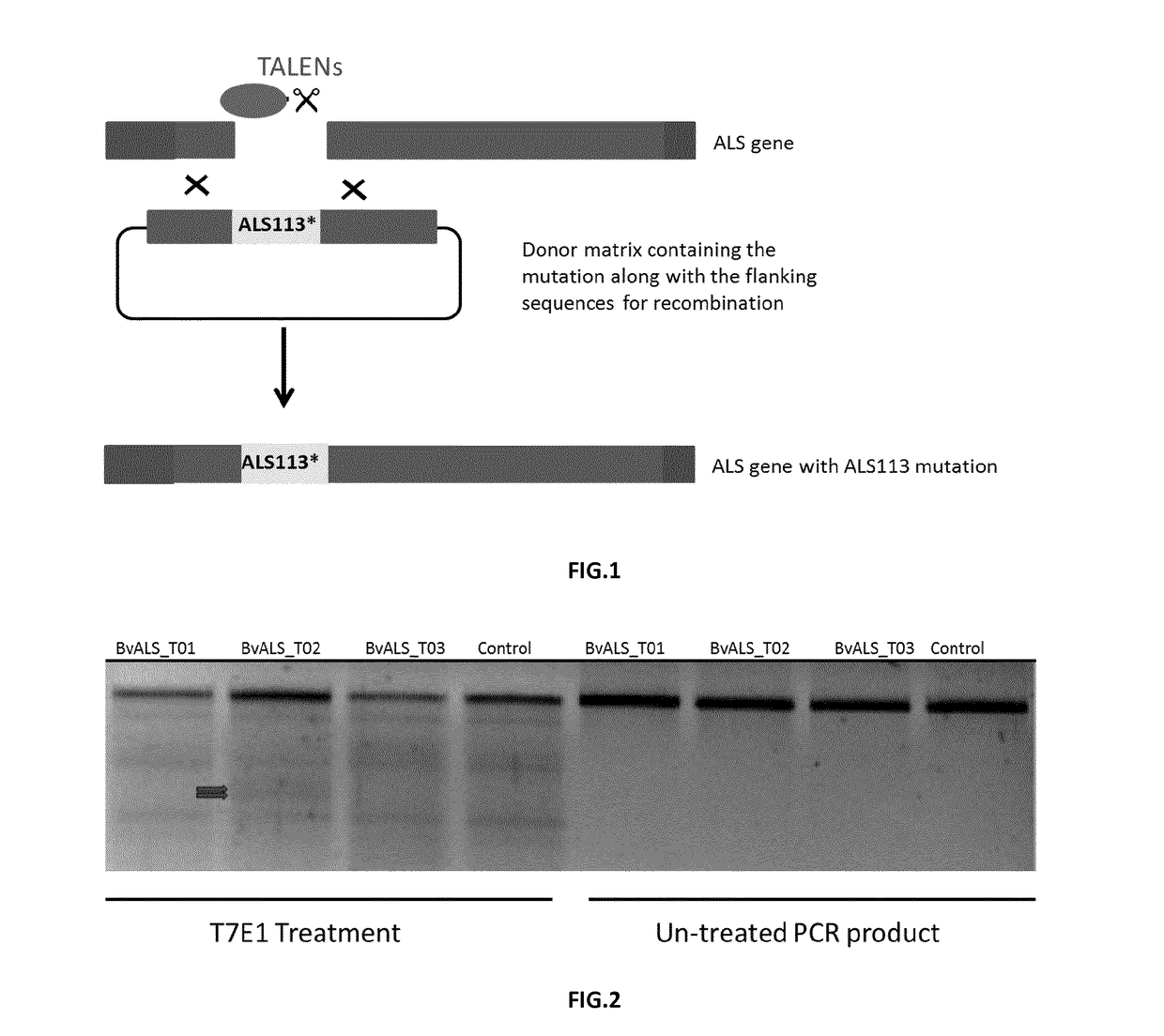
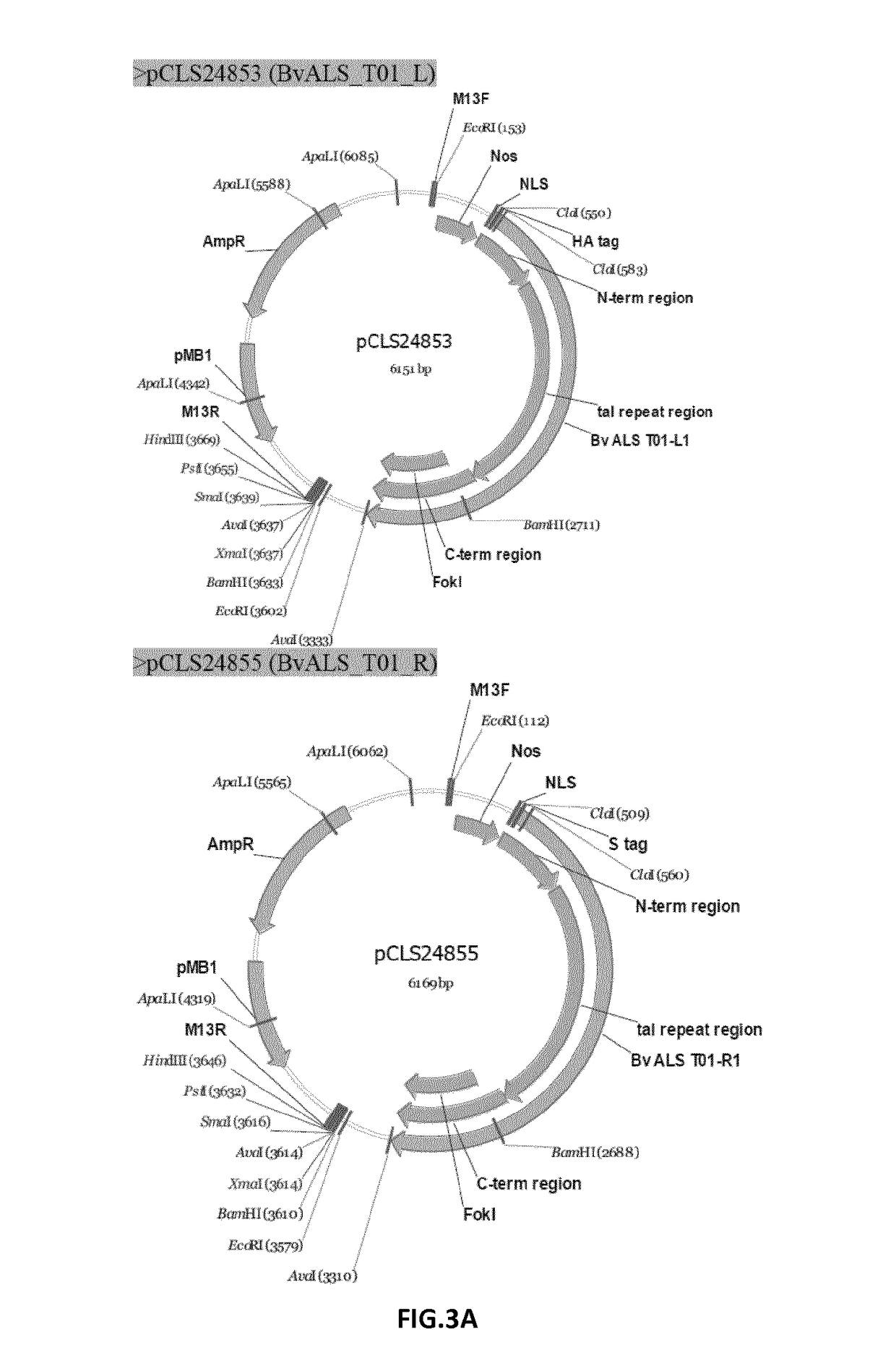
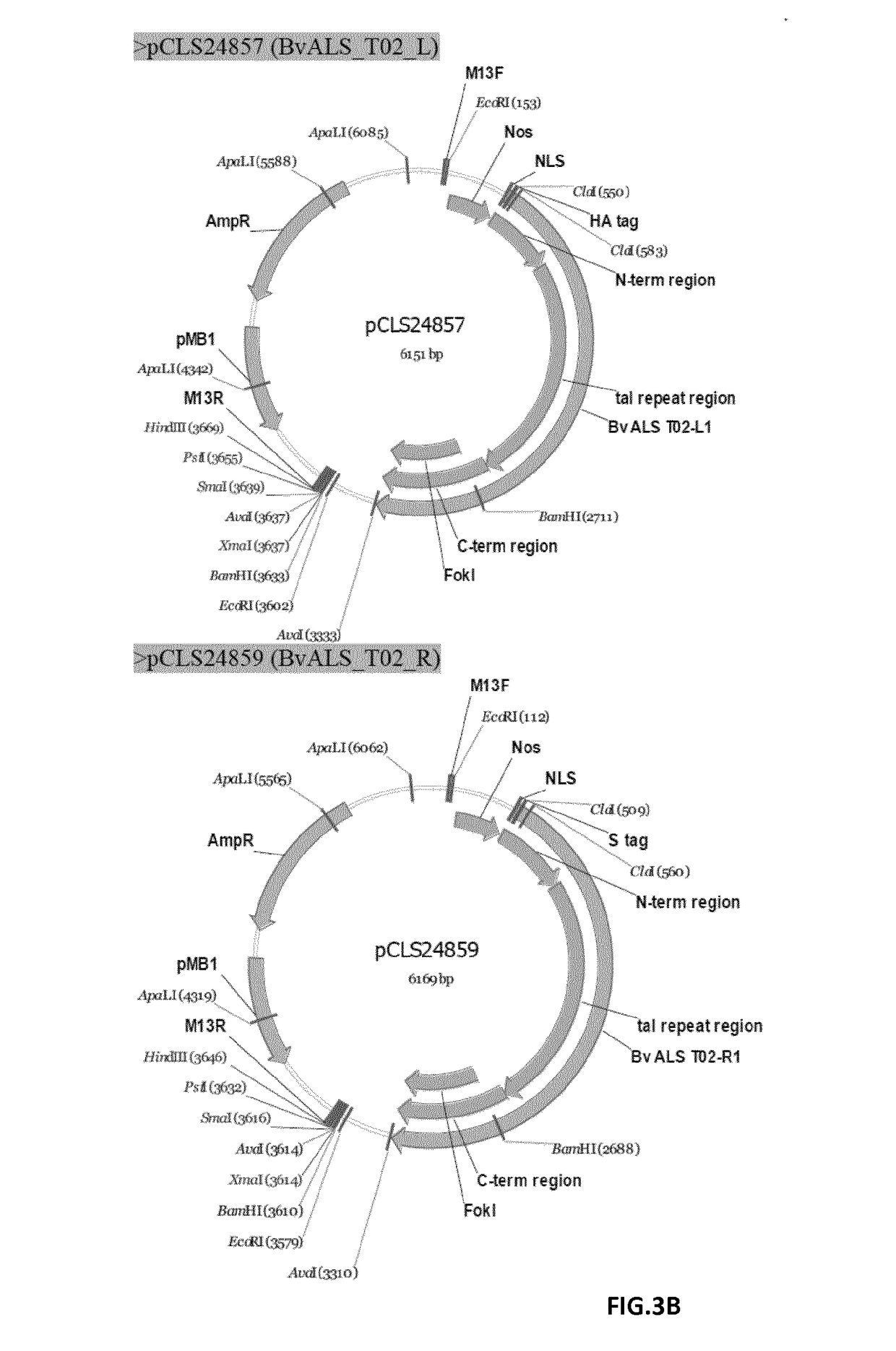
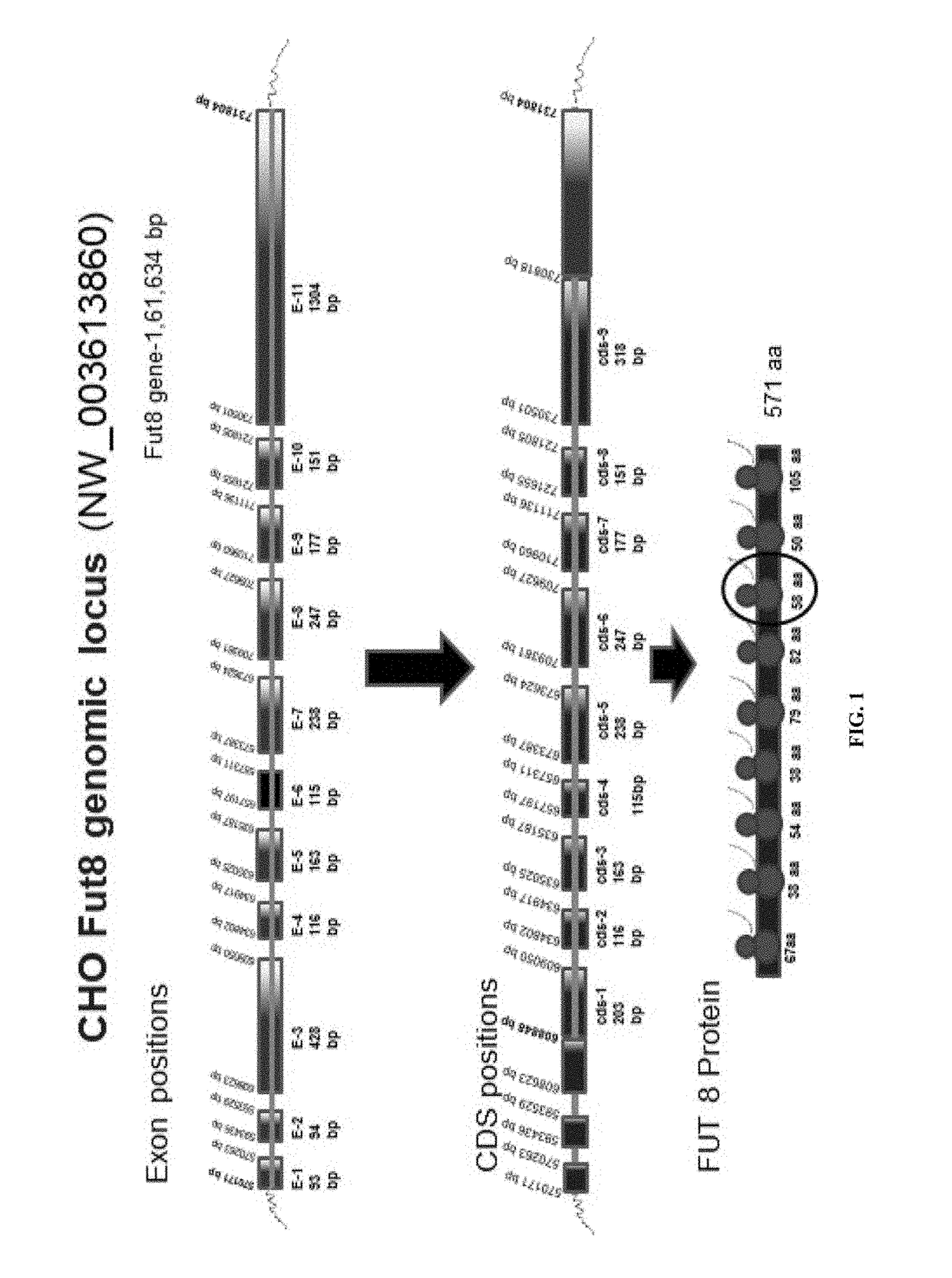
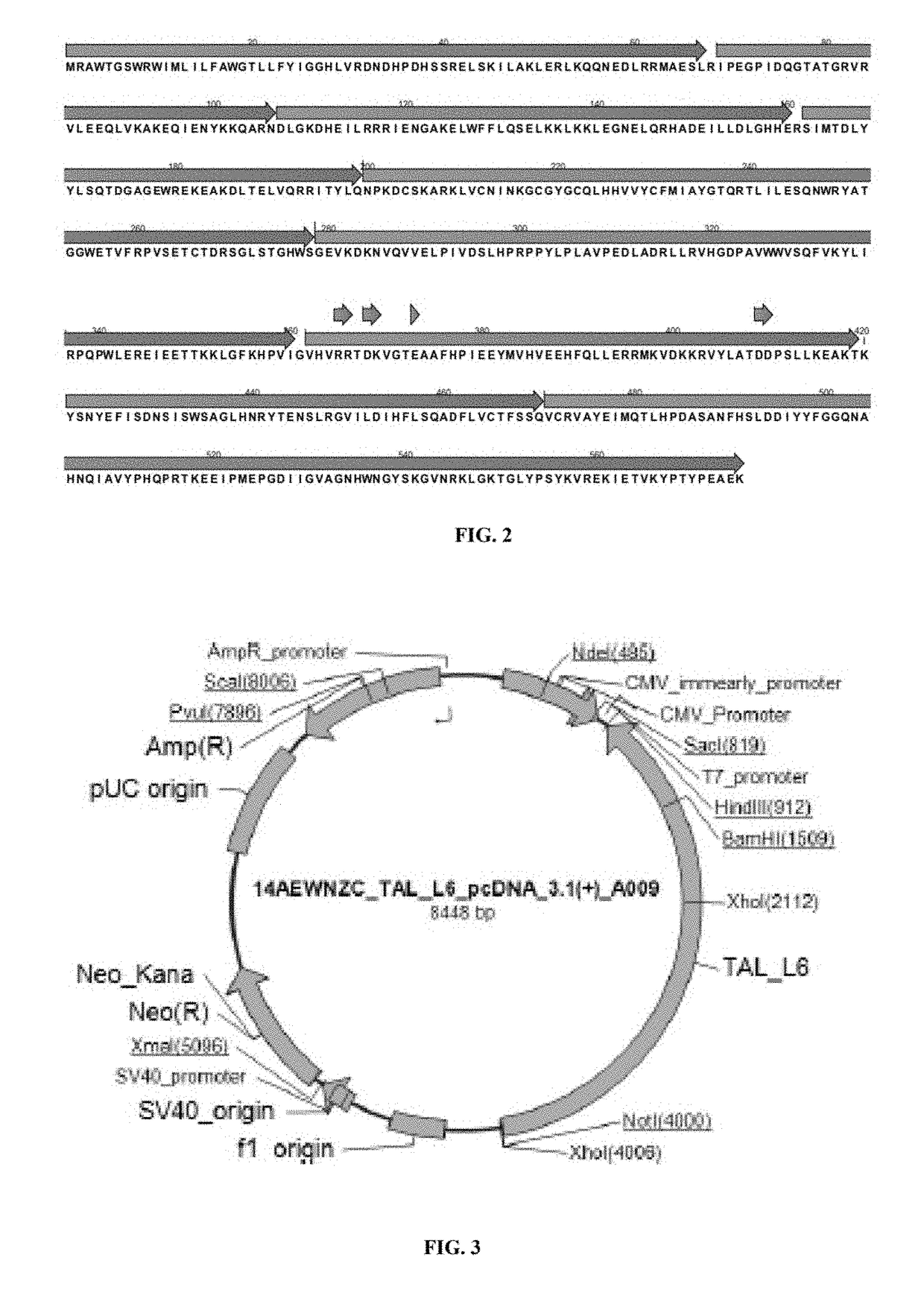
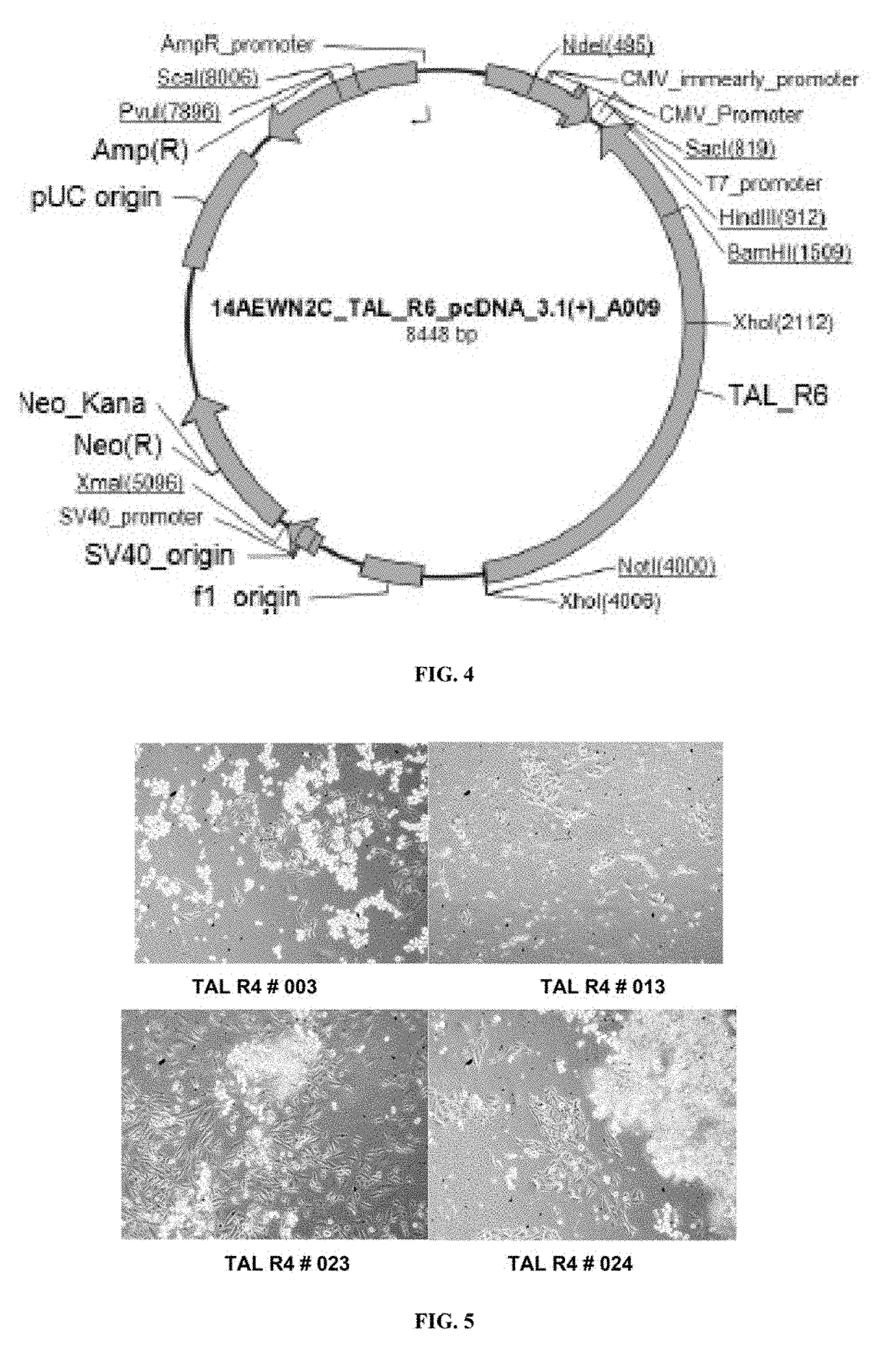
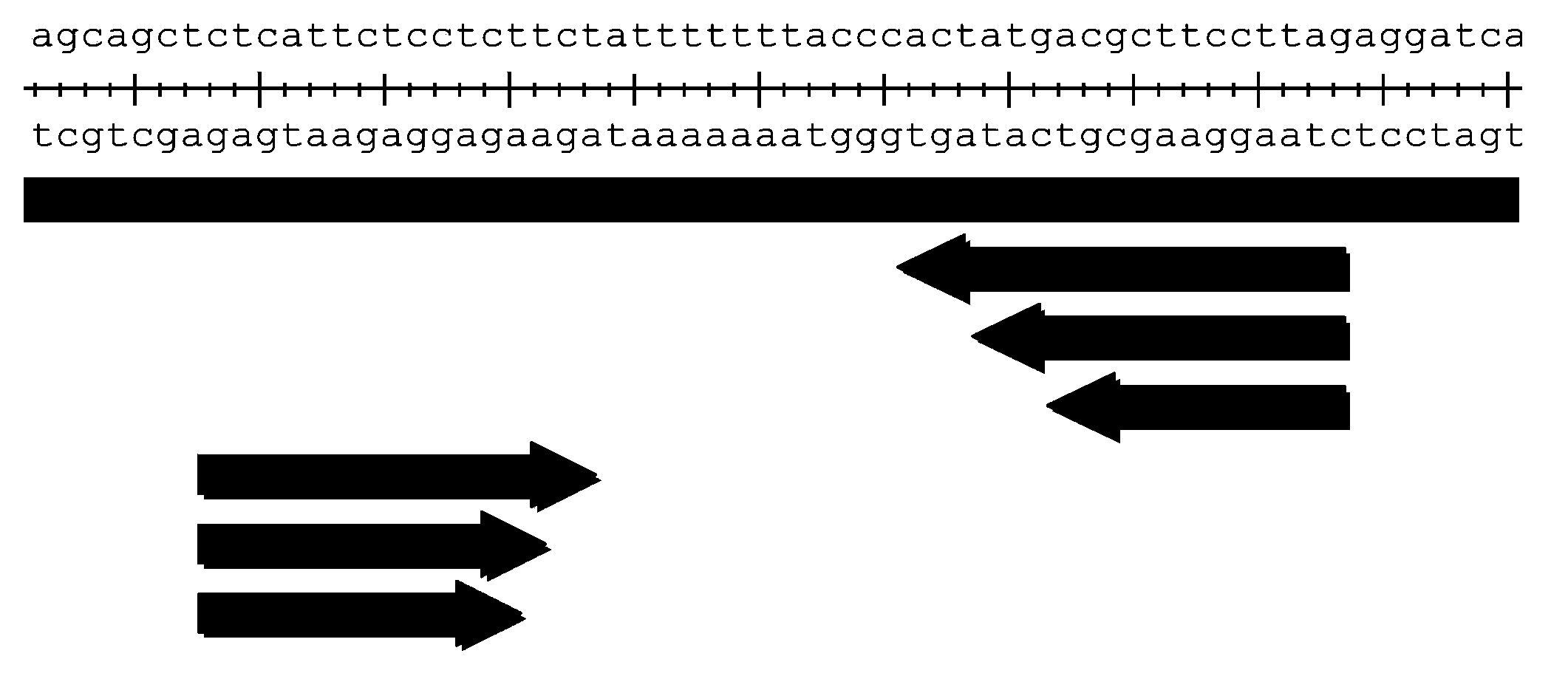
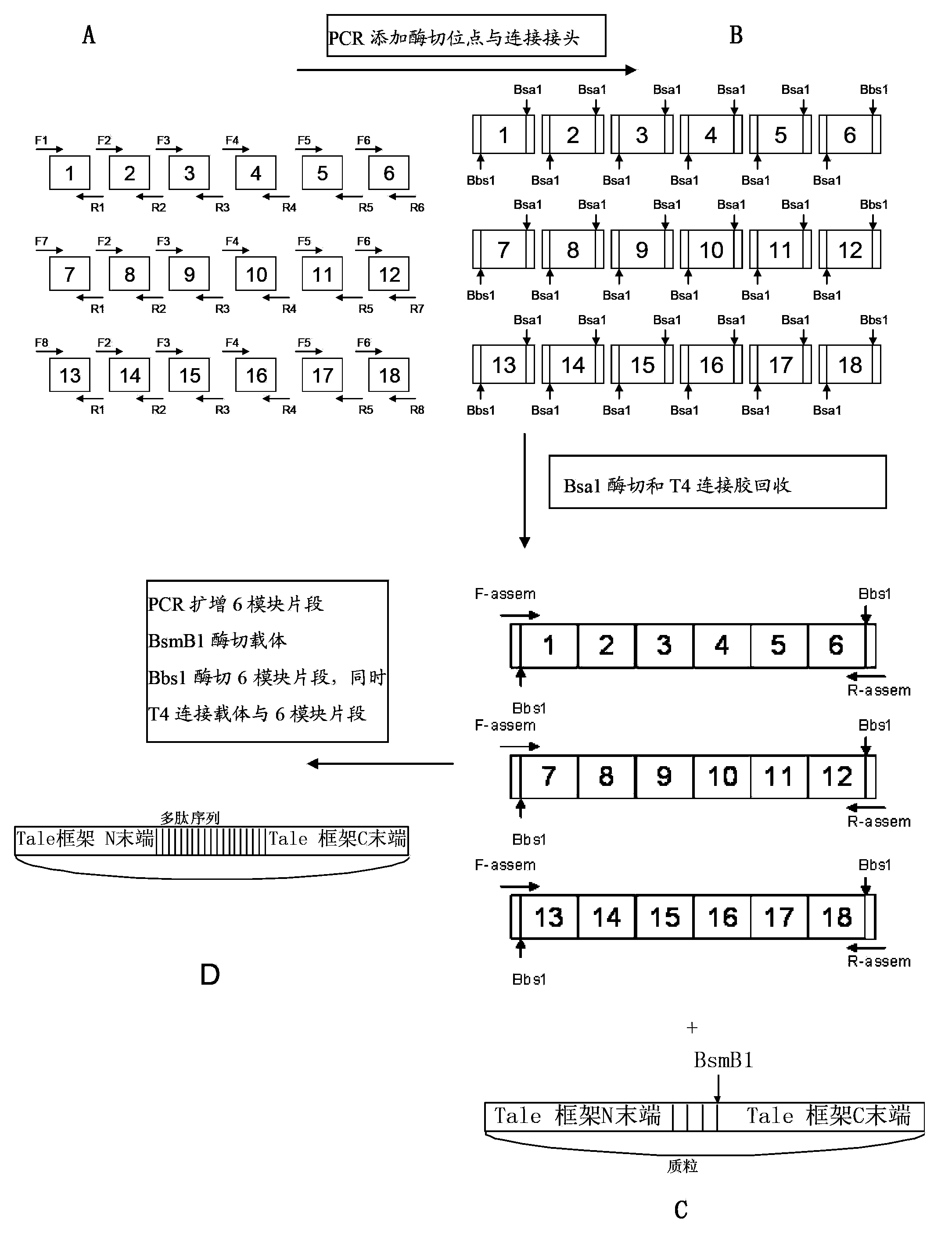
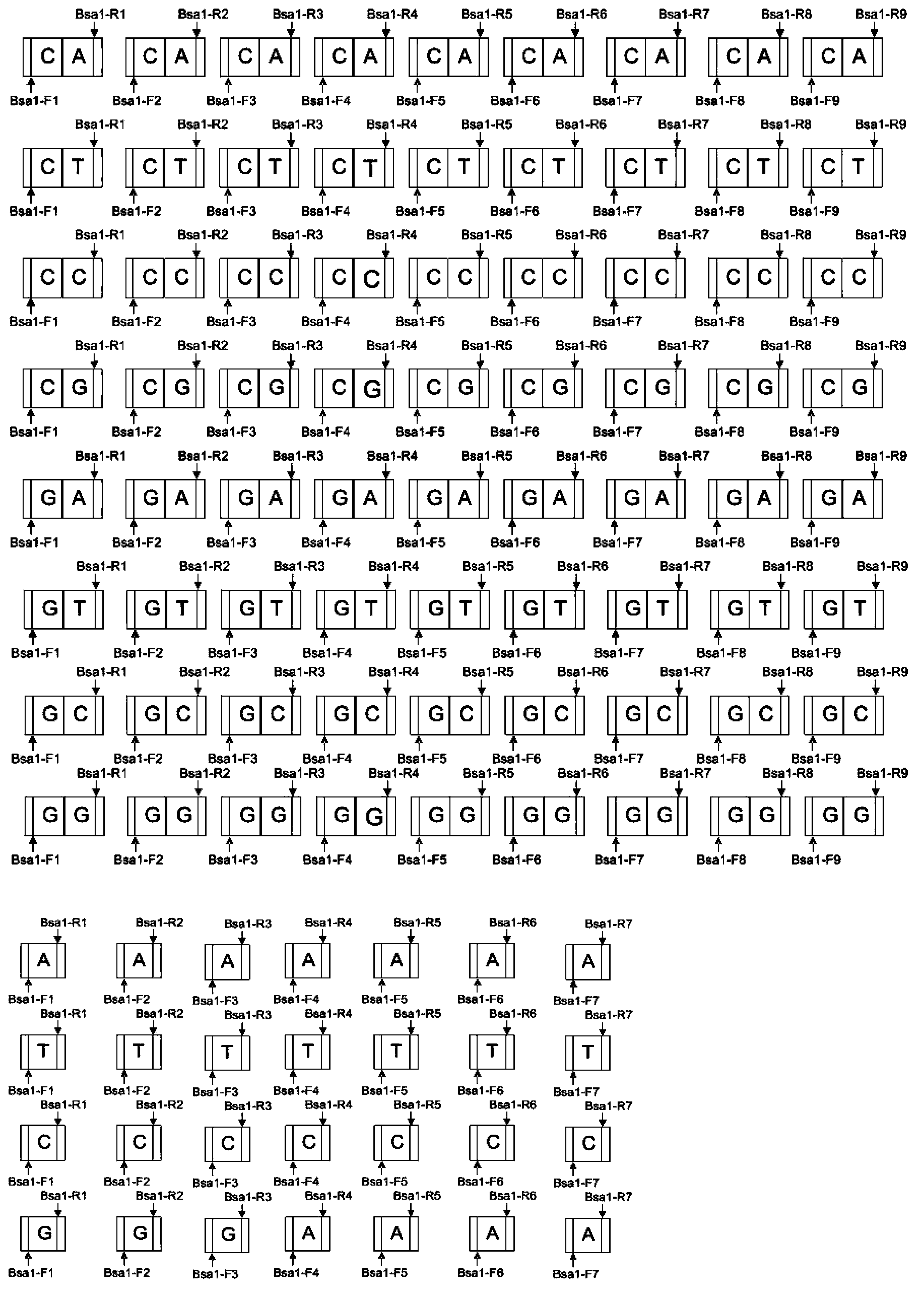Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Transcription activator-like effector nuclease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
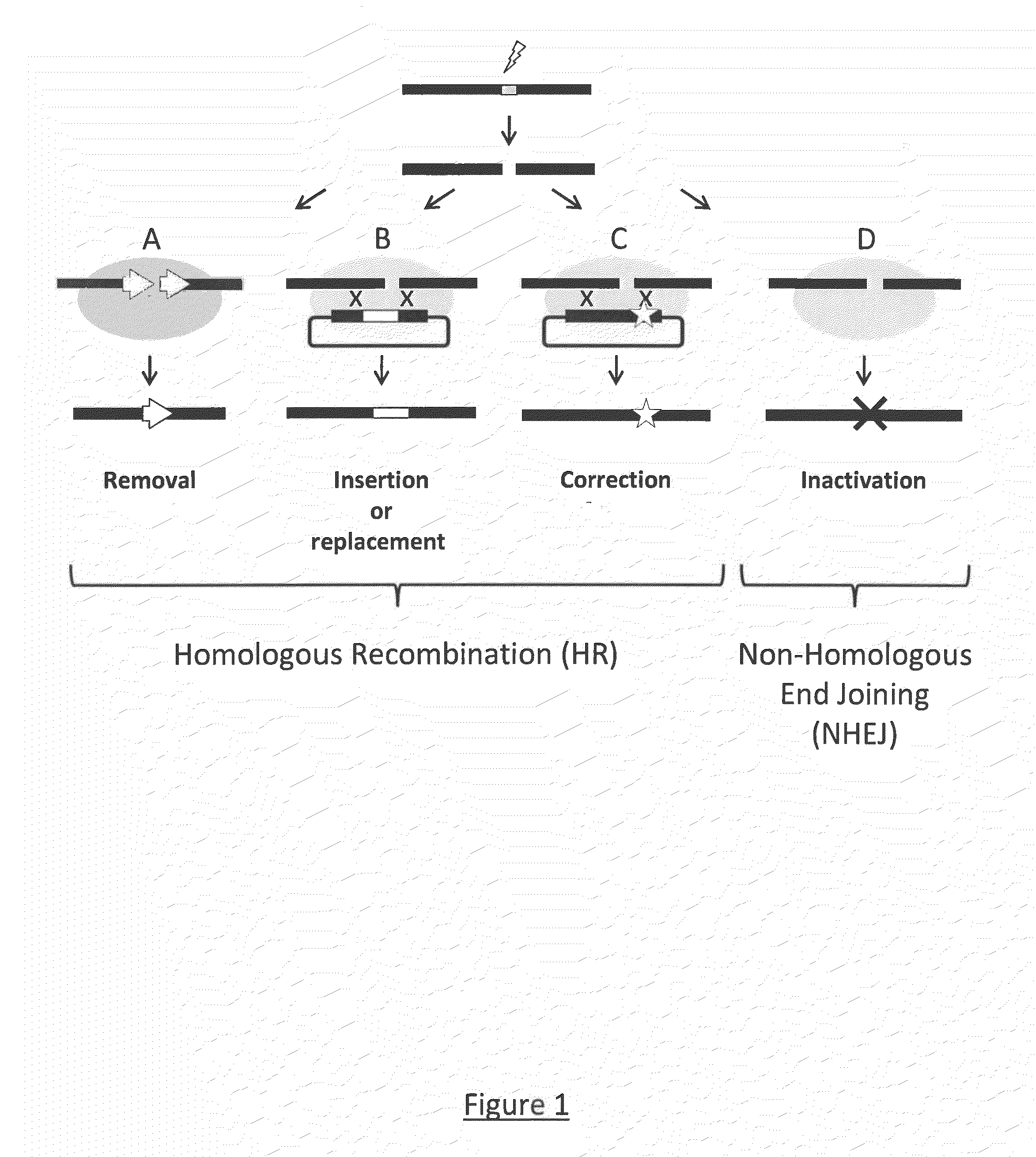
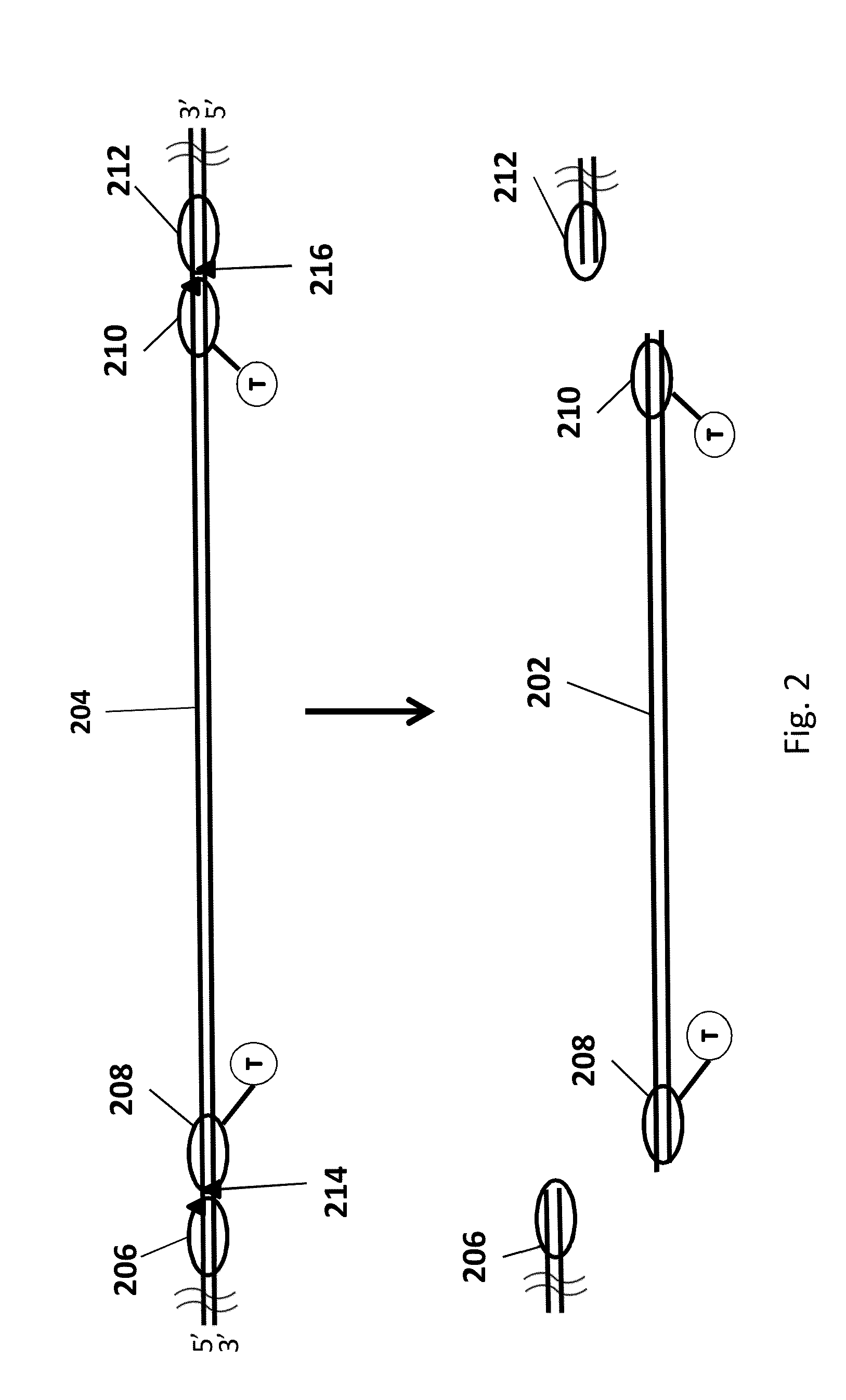
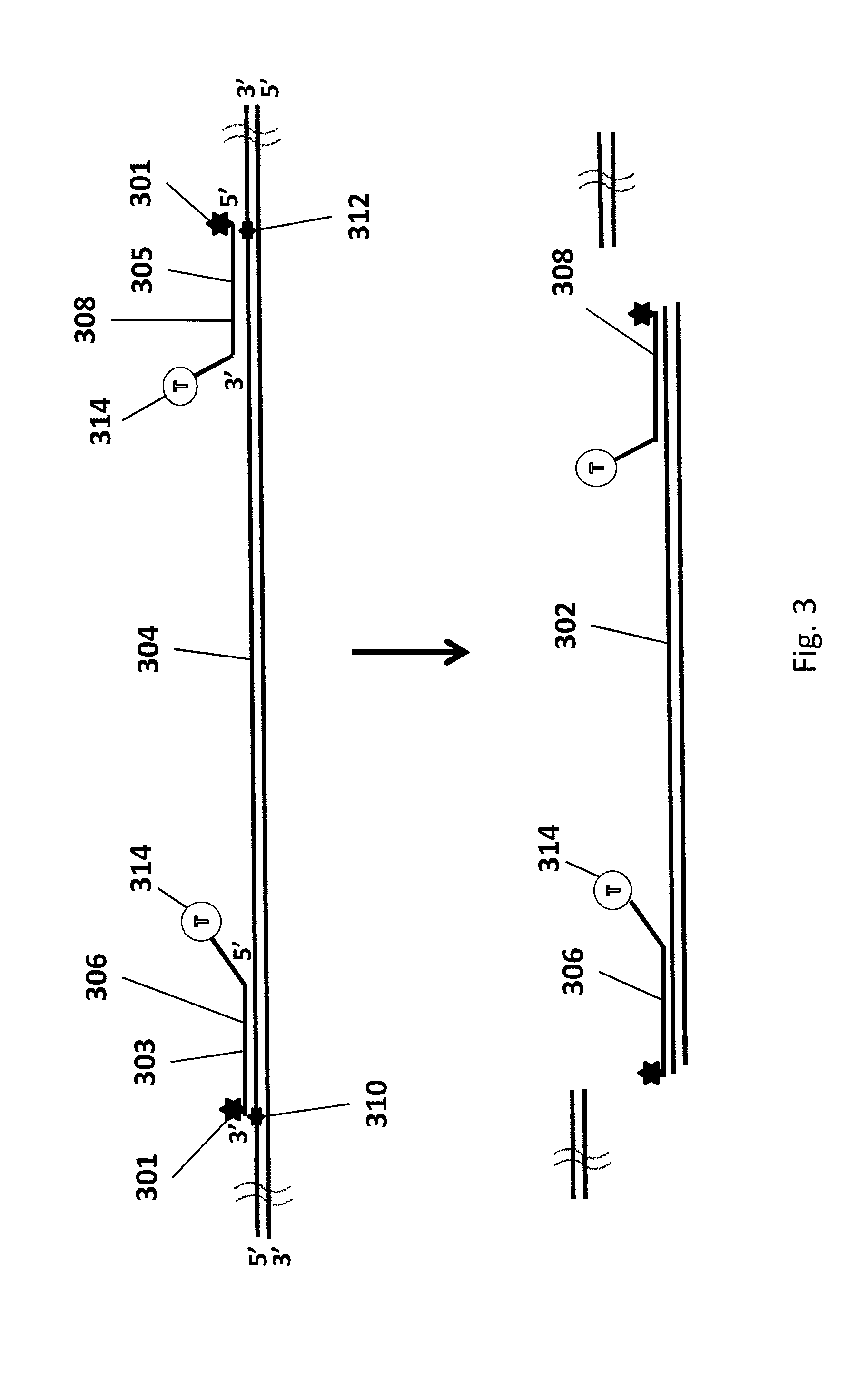
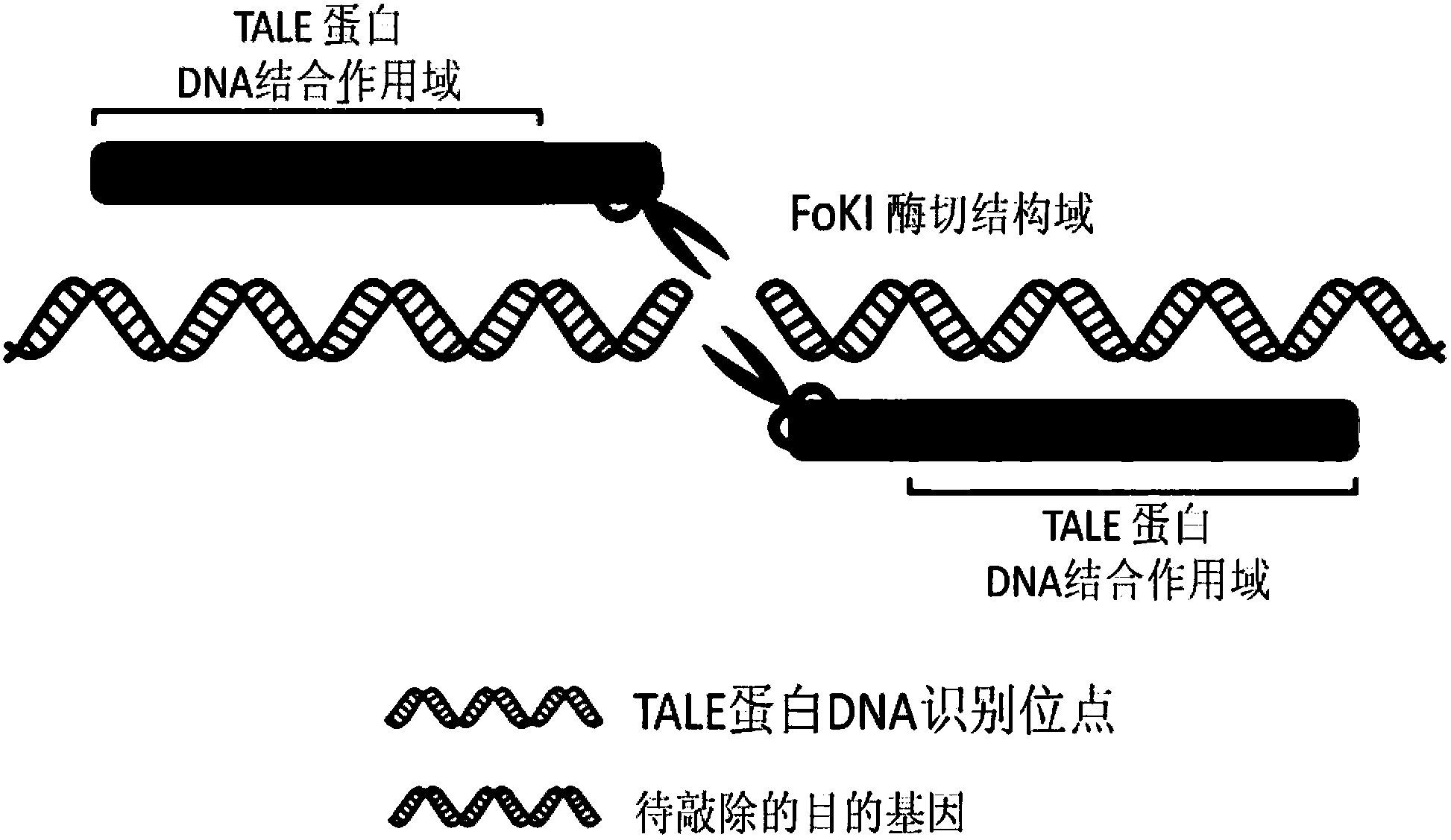
Transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN) are restriction enzymes that can be engineered to cut specific sequences of DNA. They are made by fusing a TAL effector DNA-binding domain to a DNA cleavage domain (a nuclease which cuts DNA strands). Transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs) can be engineered to bind to practically any desired DNA sequence, so when combined with a nuclease, DNA can be cut at specific locations. The restriction enzymes can be introduced into cells, for use in gene editing or for genome editing in situ, a technique known as genome editing with engineered nucleases. Alongside zinc finger nucleases and CRISPR/Cas9, TALEN is a prominent tool in the field of genome editing.
Method for the generation of compact tale-nucleases and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130117869A1Simple processSimple and efficient vectorizationFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesDNA-binding domainNuclease
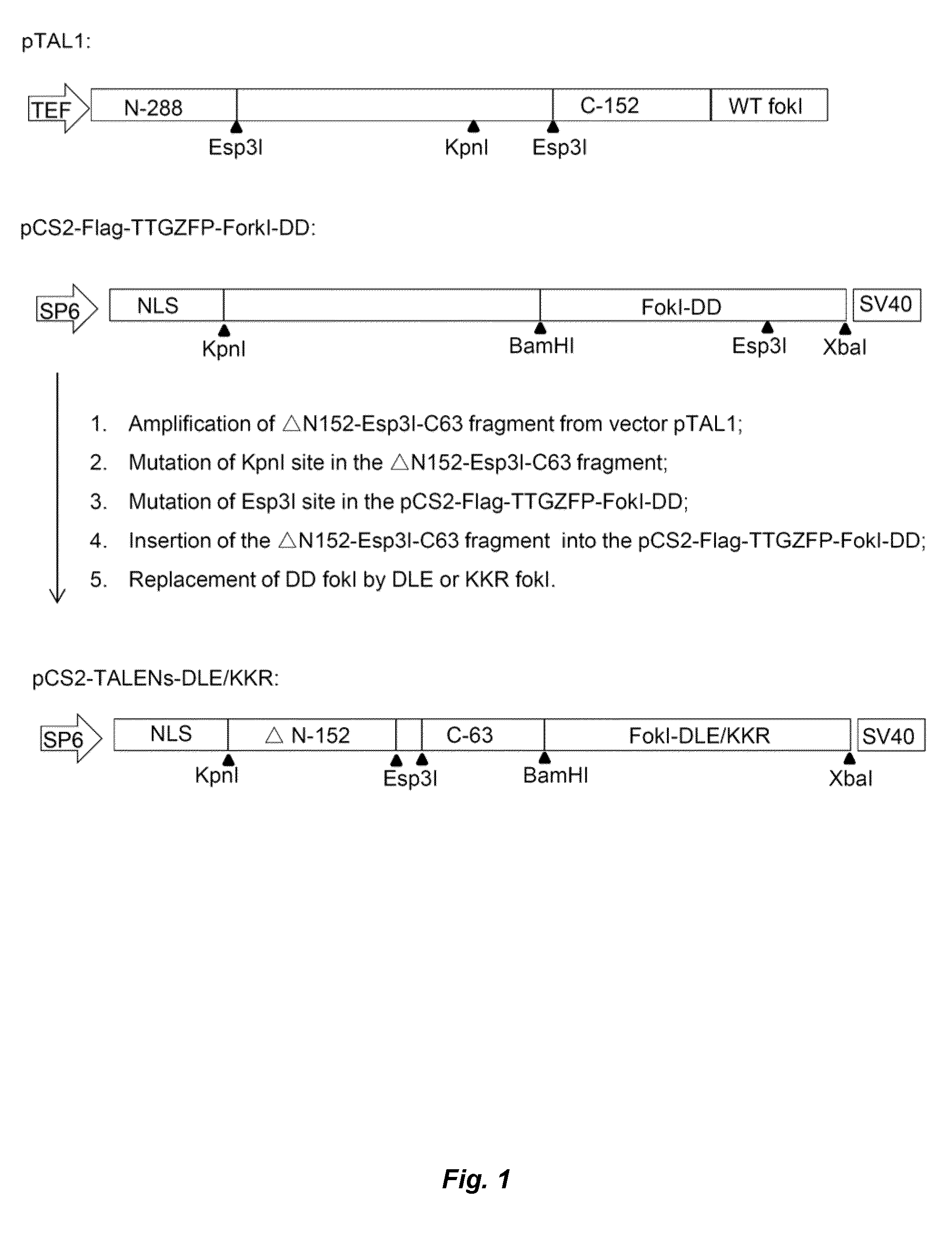
The present invention relates to a method for the generation of compact Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALENs) that can efficiently target and process double-stranded DNA. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for the creation of TALENs that consist of a single TALE DNA binding domain fused to at least one catalytic domain such that the active entity is composed of a single polypeptide chain for simple and efficient vectorization and does not require dimerization to target a specific single double-stranded DNA target sequence of interest and process DNA nearby said DNA target sequence. The present invention also relates to compact TALENs, vectors, compositions and kits used to implement the method.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Gene targeting system
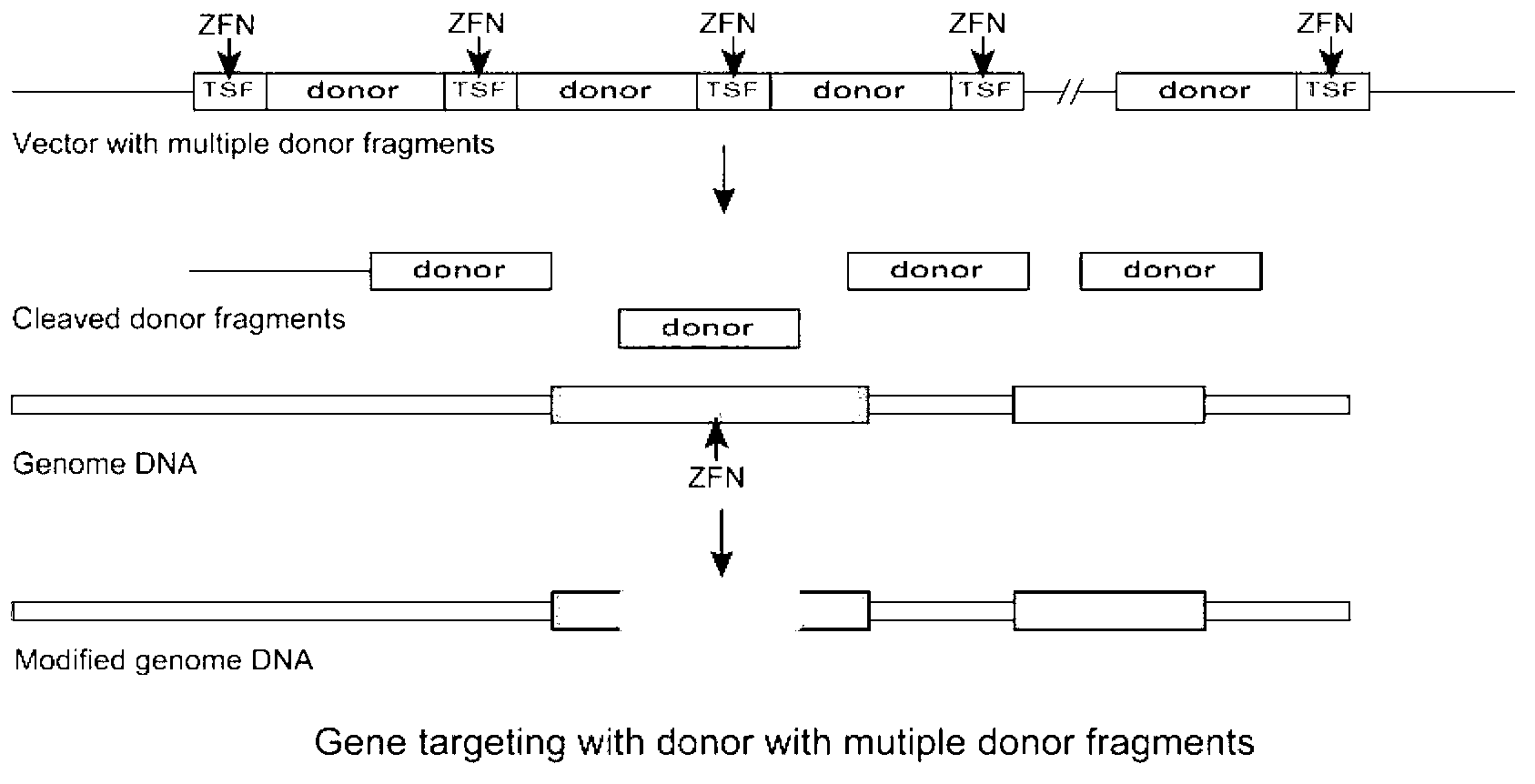
InactiveCN103224947AImprove the level ofHigh target shooting efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionGene targetsZinc finger nuclease
The invention relates to a gene targeting system, which comprises two parts such as a site-specific cleavage nuclease expression vector and a targeting vector, wherein the targeting vector contains 2-10 donor DNA fragments, 5' ends and 3' ends of every donor DNA fragment are respectively inserted into recognition sequences of the site-specific cleavage nuclease, the donor DNA comprises an upstream homologous arm, a downstream homologous arm and an exogenous DNA sequence positioned between the upstream homologous arm and the downstream homologous arm, and the site-specific cleavage nuclease expression vector is any one selected from an expression vector carrying zinc finger nuclease, a transcription activator-like effector nuclease expression vector, and a RNA-mediated nuclease RNA:Cas9 expression vector.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Transcription activator-like effector nucleases (talens)
ActiveUS20140087426A1Sugar derivativesHydrolasesPolynucleotideTranscription Activator-Like Effectors
This application provides transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs), polynucleotide sequences encoding the TALENs, expression cassettes for producing TALENs to target cleavage of nucleic acids, and methods of producing and using the TALENs.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
TALEN-based gene correction
ActiveUS9393257B2Accurate expressionOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesHuman DNA sequencingHuman cell
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Talen-based gene correction
ActiveUS20140256798A1Restores correct gene expressionOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesHuman DNA sequencingHuman cell
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Genomic enrichment method, composition, and reagent kit
InactiveUS20140038241A1Improve efficiencyStrong specificityHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingEnrichment methods
By using engineered sequence specific DNA nuclease (“SSDN”), the composition, reagent kit and method of the present invention can cut and release a DNA sequence of interest 1×104-1×107-base pairs long from a source DNA as large as the whole genome. The SSDN further includes an affinity tag or is bound to a solid support that facilitates the isolation of the DNA sequence of interest. The SSDN can include a RecA and Ref combination, a transcription activator like effector nuclease, or a sequence specific chemical nuclease. When applied to genomic sequencing, specific region(s) of interest in the genome can be cut and isolated. Because the irrelevant part of the genome is removed from the sequencing reaction, the speed, cost, and accuracy of genomic sequencing can be improved.
Owner:ZHOU ZHAOHUI +1
Monopterus albus gene editing method
The invention discloses a monopterus albus gene editing method. The monopterus albus gene editing method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring an artificially inseminated monopterus albus 1-cell stage embryo by establishing an indoor eel whole artificial propagation technology; 2, establishing a transcription activator-like effector nuclease gene editing vector of a target gene, performing in-vitro transcription to synthesize mRNA, and transferring the mRNA into the monopterus albus 1-cell stage fertilization embryo by adopting a microinjection method; 3, screening to obtain a monopterus albus with a mutant target gene through a three-primer detection method, and determining the mutation type of the target gene through sequencing. According to the method, a micromanipulation technology for a monopterus albus embryo is established for the first time, a precise monopterus albus endogenous gene editing technology is established for the first time, and powerful technological means is provided for performing function research on a monopterus albus gene and genetic improvement of monopterus albus breeding variety.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
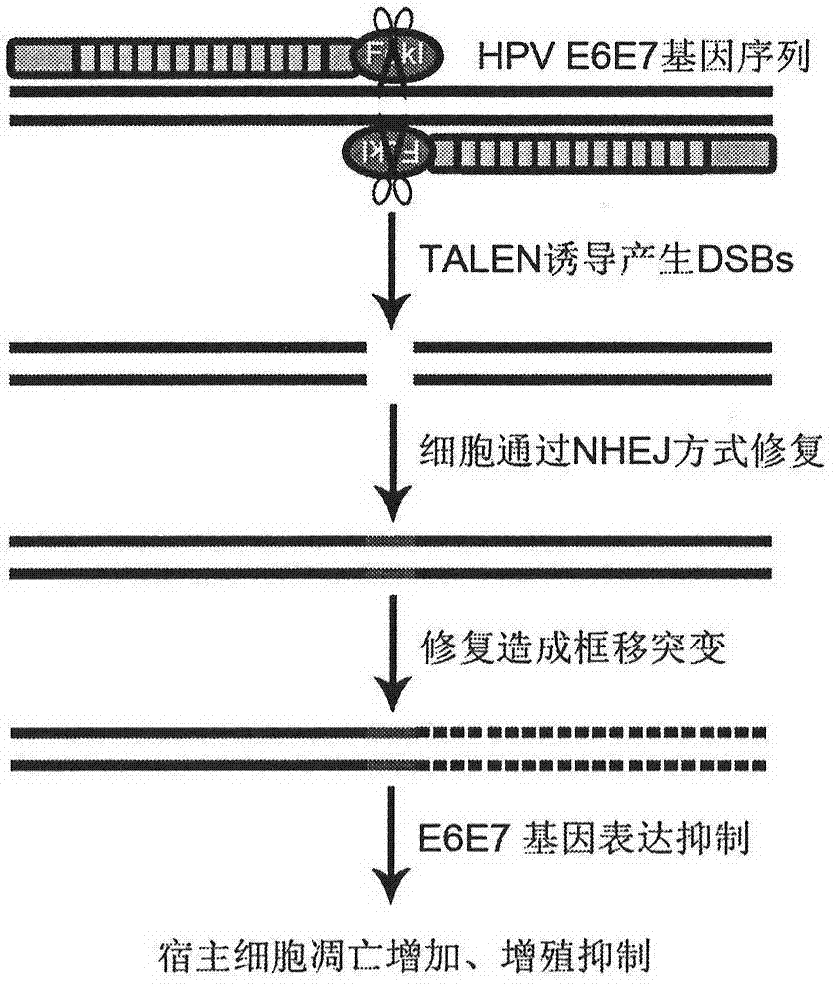
Method for knocking out HPV (human papilloma virus) E6E7 oncogene by use of TALEN (transcription activator-like effector nuclease)
The invention relates to the field of gene therapy and discloses a fixed-point knockout system for high-risk HPV (human papilloma virus) E6E7 gene, namely targeted cutting of TALENs (transcription activator-like effector nucleases) of HPV E6E7 gene, wherein a TALENs expression vector of the target specific site is designed according to the high-risk HPV E6E7 gene sequence, and the HPV E6E7 gene sequence in the cells are cut in a targeted manner so as to knock out the target gene and induce the apoptosis increase and proliferation inhibition of corresponding subtype cells while the TALENs do not act on the HPV positive or HPV negative cells of other subtypes. By transfecting the TALEN expression vector in a subcutaneous tumor model of HPV positive cervical cancer cells, the growth of subcutaneous tumor can be obviously inhibited, and the tumor weight is reduced. According to the method for targeted knockout of high-risk HPV E6E7 gene using TALEN provided by the invention, the virus oncogene can be efficiently broken on the DNA level so as to cause apoptosis and proliferation inhibition of the HPV infected cells, and the method is of tremendous therapeutic value on HPV infection related diseases and particularly precancerous lesions such as cervical intraepithelial neoplasias.
Owner:武汉雅马生物工程有限公司
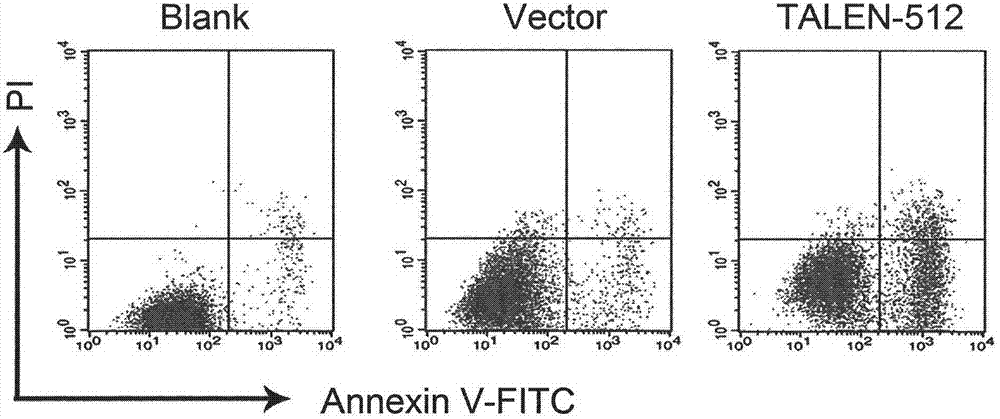
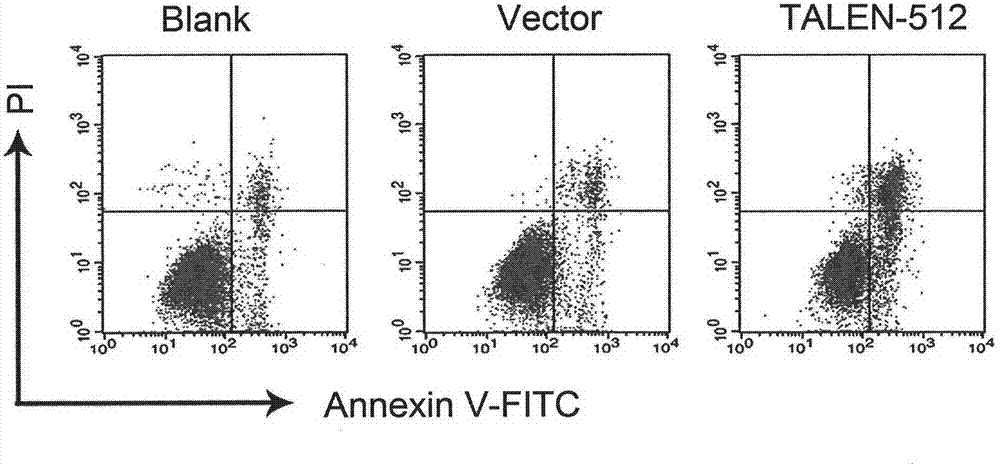
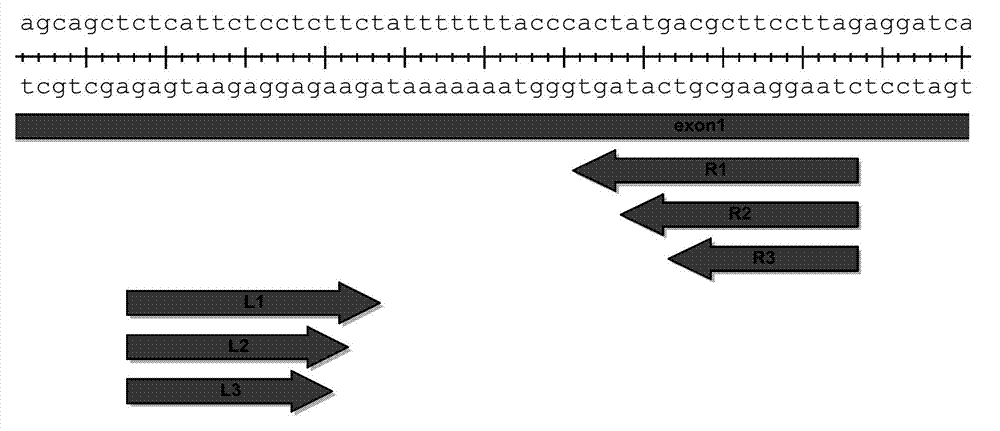
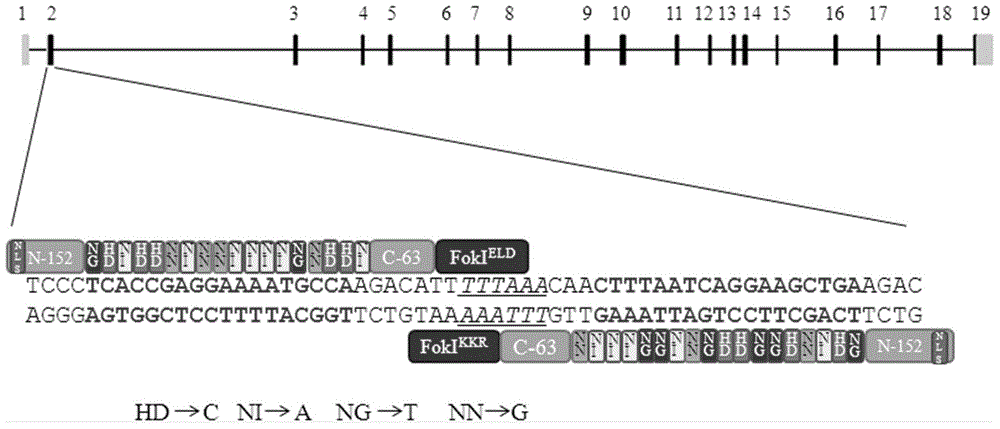
A pair of transcription activator like effector nucleases of L3 and R1 and a coding gene and an application thereof
The invention discloses a pair of transcription activator like effector nucleases, a coding gene and an application thereof. The pair of transcription activator like effector nucleases (TALEN) is obtained by respective fusion of a pair of DNA recognins with two heterogenous subunits of a Fok1 DNA endonuclease, and can specifically recognize two adjacent loci on human RHD or RHCE gene exon1. When the pair of transcription activator like effector nucleases is simultaneously transferred to a host cell, targeting of the exon1 loci of the host cell gene can be realized; the targeted loci are subject to gene mutation; therefore, targeting modification of the human RHCE or RHD gene is realized, and advantages of strong specificity, high targeting efficiency, high accuracy and the like are provided.
Owner:浙江煦顼技术有限公司
Transcription activator like effector nuclease and application thereof
InactiveCN105524897AEfficient screeningScreening treatment is fast and effectiveHydrolasesFermentationGrowth Hormone Receptor GeneGrowth hormone receptor
The invention provides a transcription activator like effector nuclease and application thereof. Growth hormone receptor gene is recognized based on specificity of the transcription activator like effector nuclease. The transcription activator like effector nuclease is used for effectively realizing fixed-point gene knockout to animal growth hormone receptor (GHR) so as to effectively interfere with growth axis path of animals.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST +1
Recombinant transcription activator like effector, transcription activator like effector nuclease, as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102702335AAchieve targeted modificationStrong specificityHydrolasesBacteria peptidesA-DNAInsulin Gene
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering and discloses a pair of polypeptides and encoding genes thereof, with sequences shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 to 4. The pair of polypeptides is used for establishing a pair of a recombinant transcription activator like effector (TALE) and a transcription activator like effector nuclease (TALEN); the TALEN is a fusion protein formed by fusing a pair of DNA recognizing proteins with a DNA severing protein respectively; and the TALEN can perform targeted severing on a target site of a human insulin gene so as to achieve targeted modification on the human insulin gene, with the characteristics of strong specificity, high efficiency and high accuracy.
Owner:浙江煦顼技术有限公司
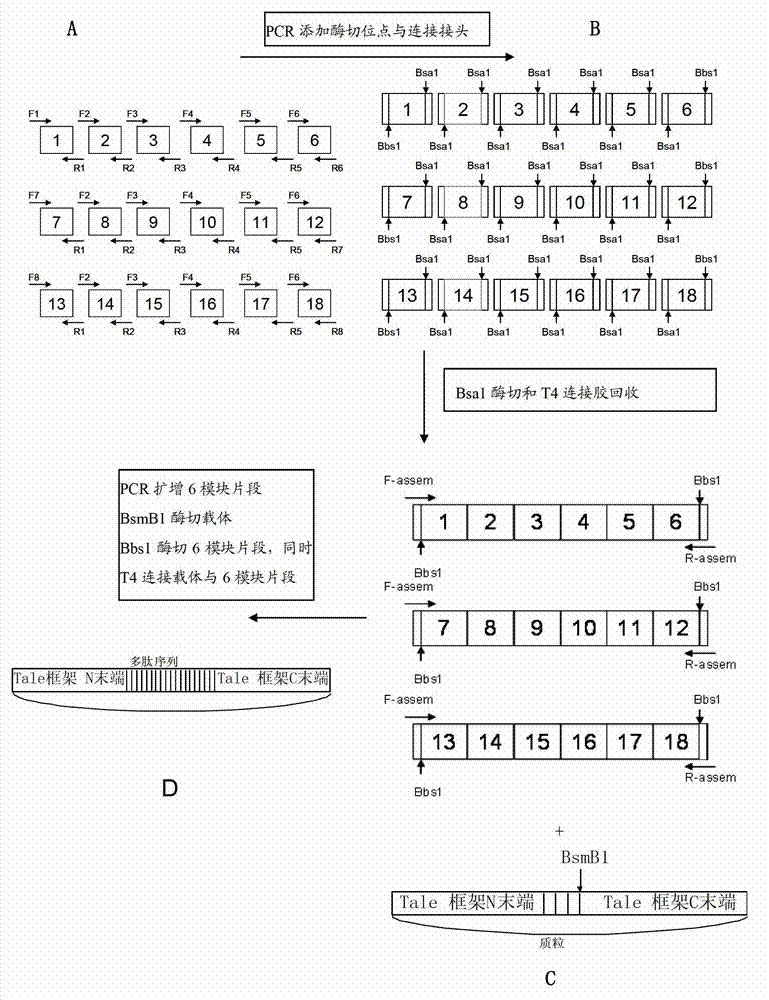
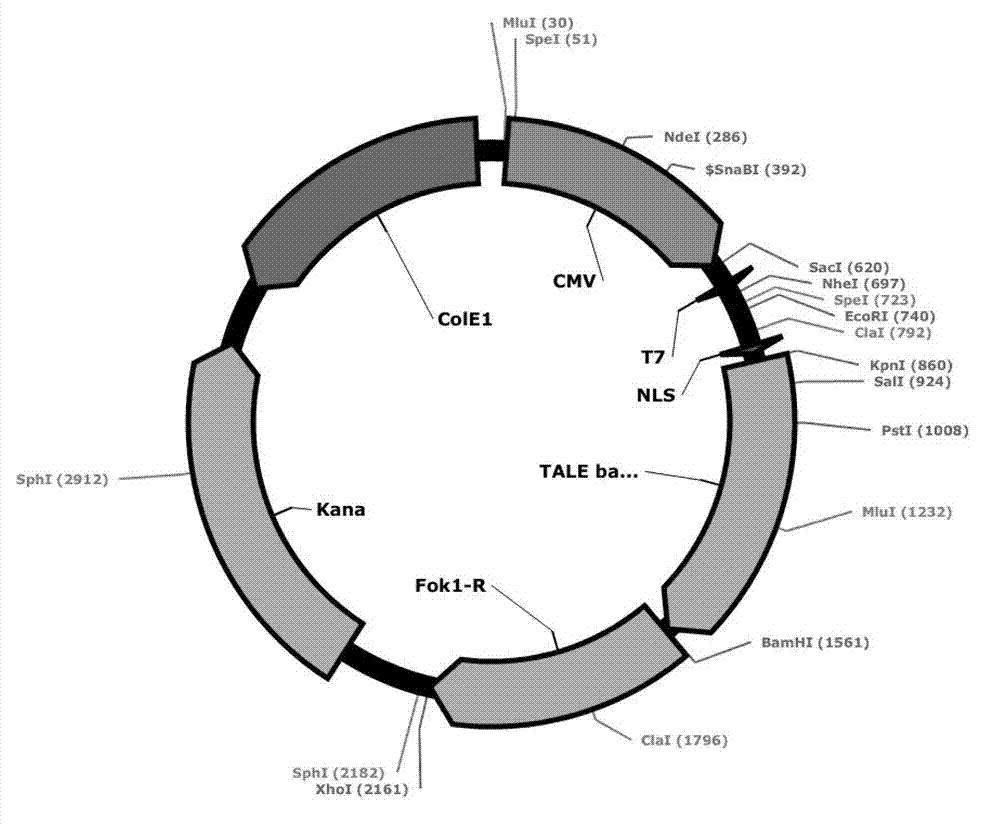
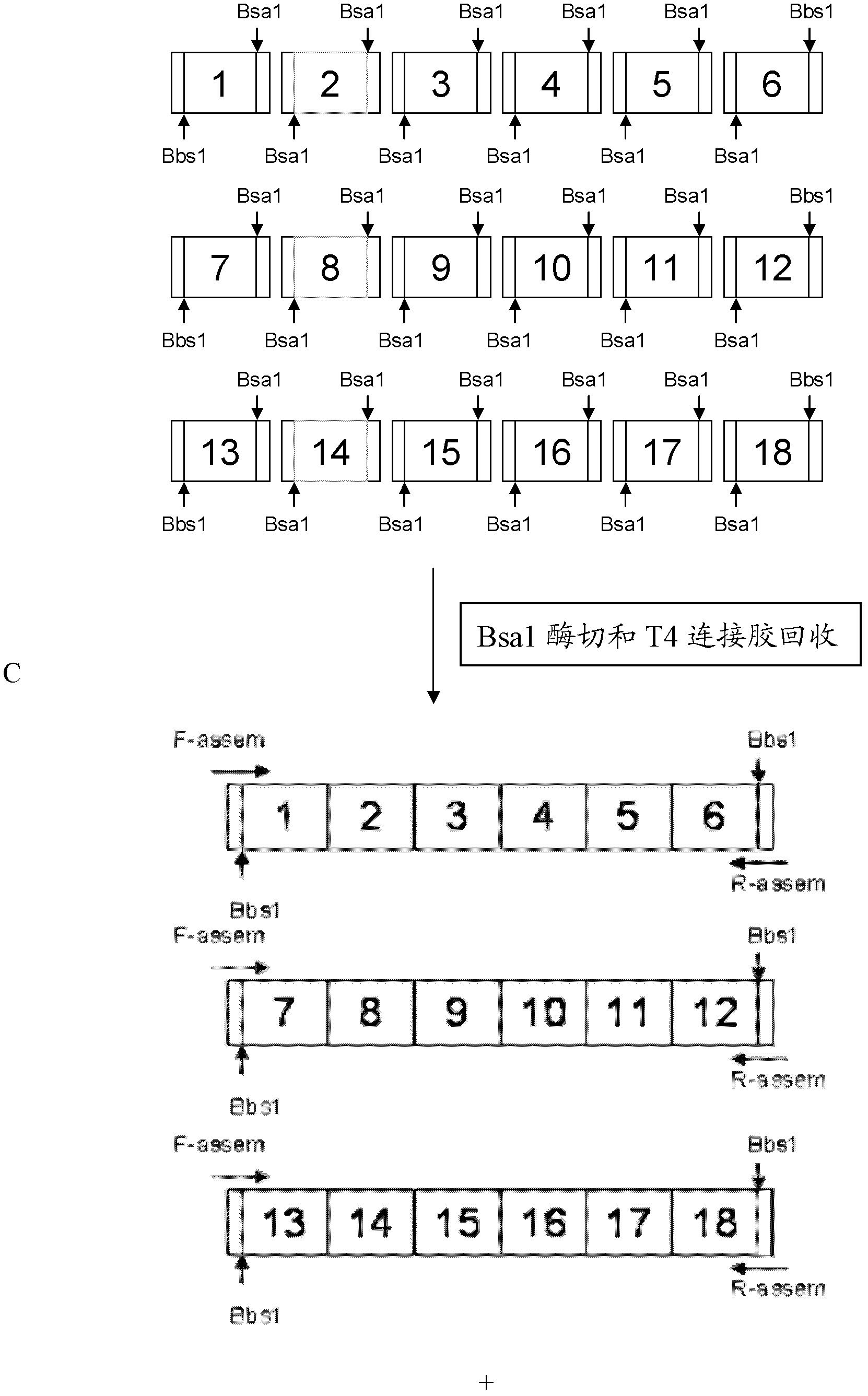
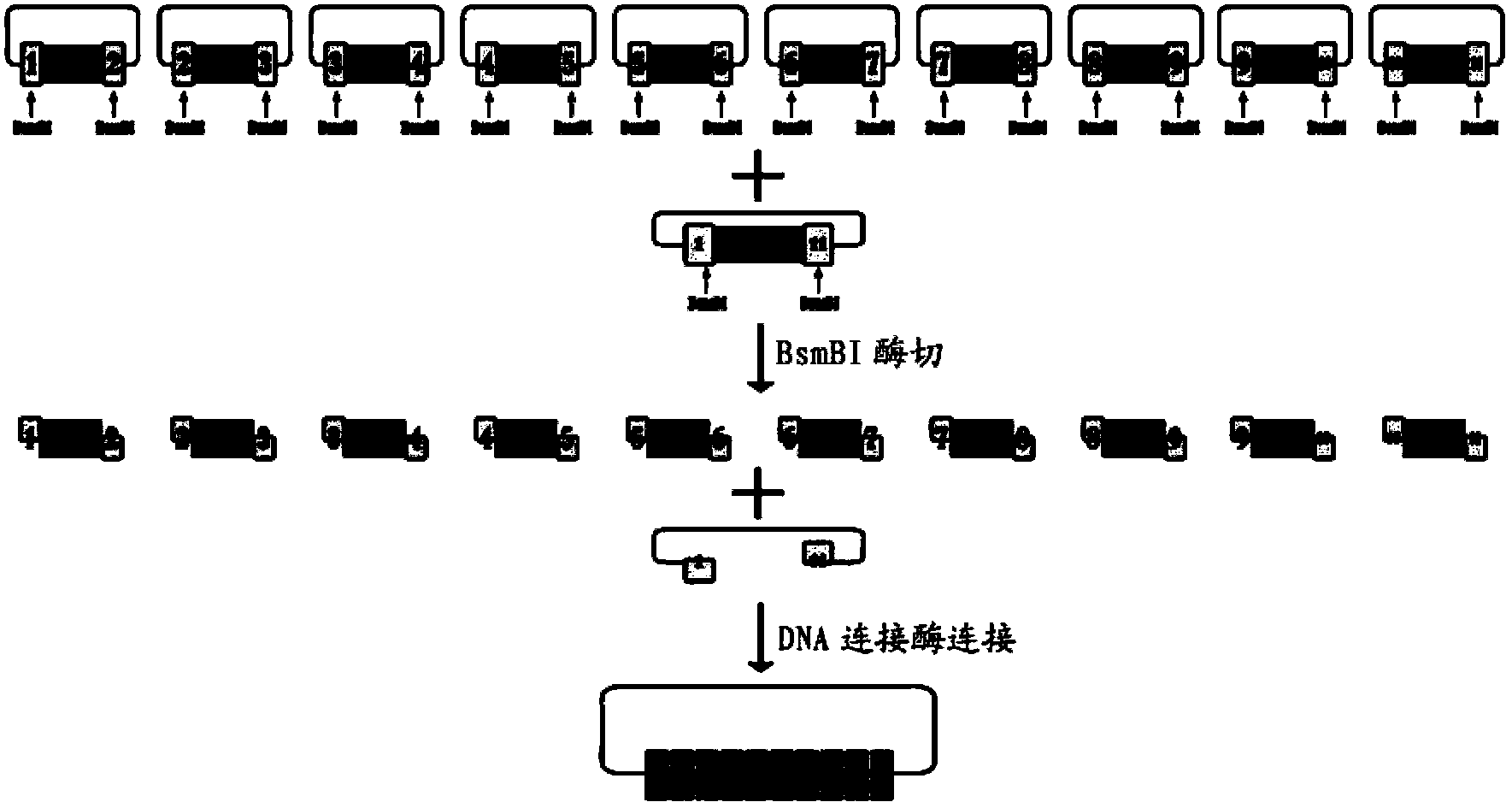
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) library and method for constructing transcription activator like effector nuclease plasmids
ActiveCN103668470AAvoid destructionAvoid degradationSugar derivativesHydrolasesEnzyme digestionComputer module
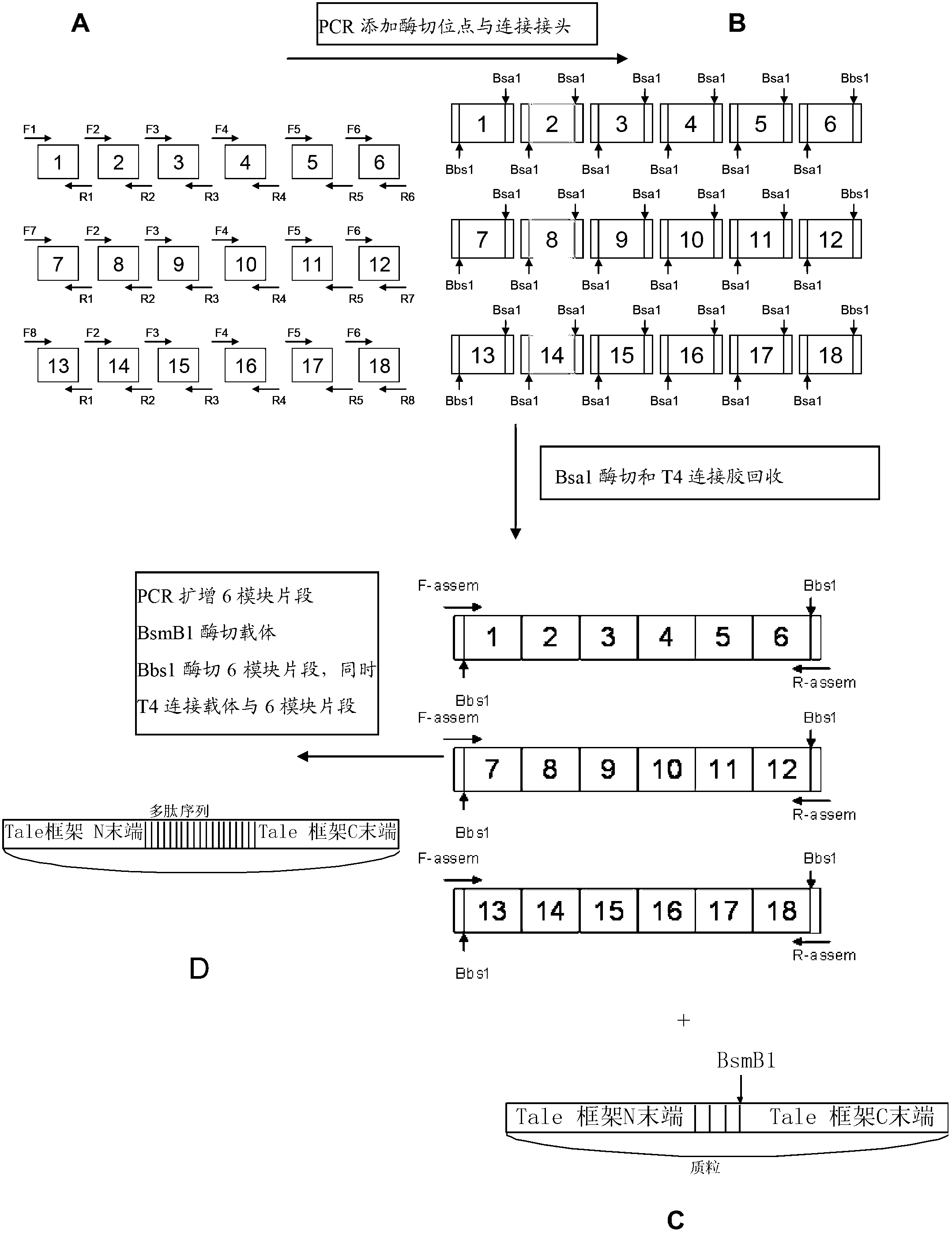
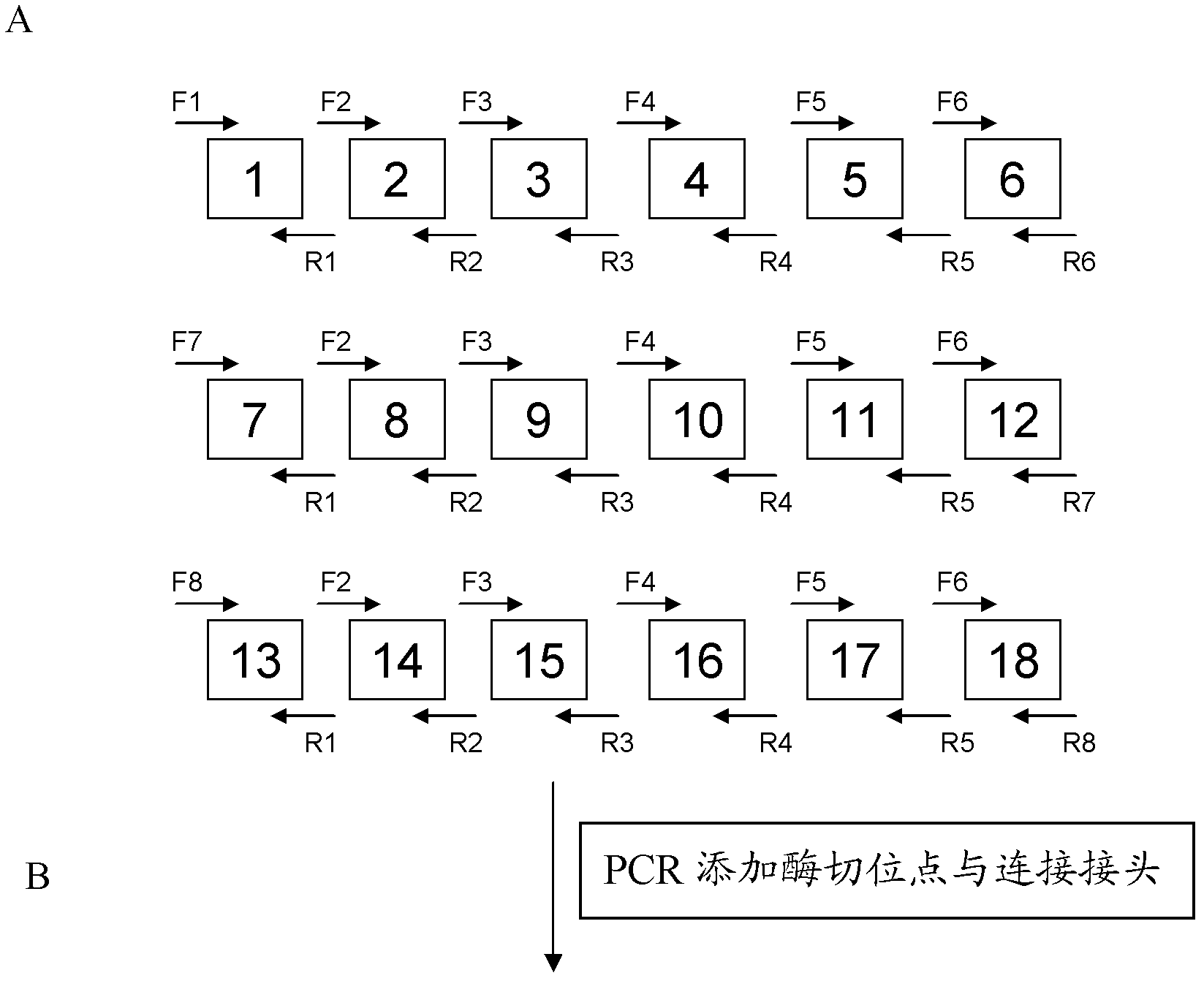
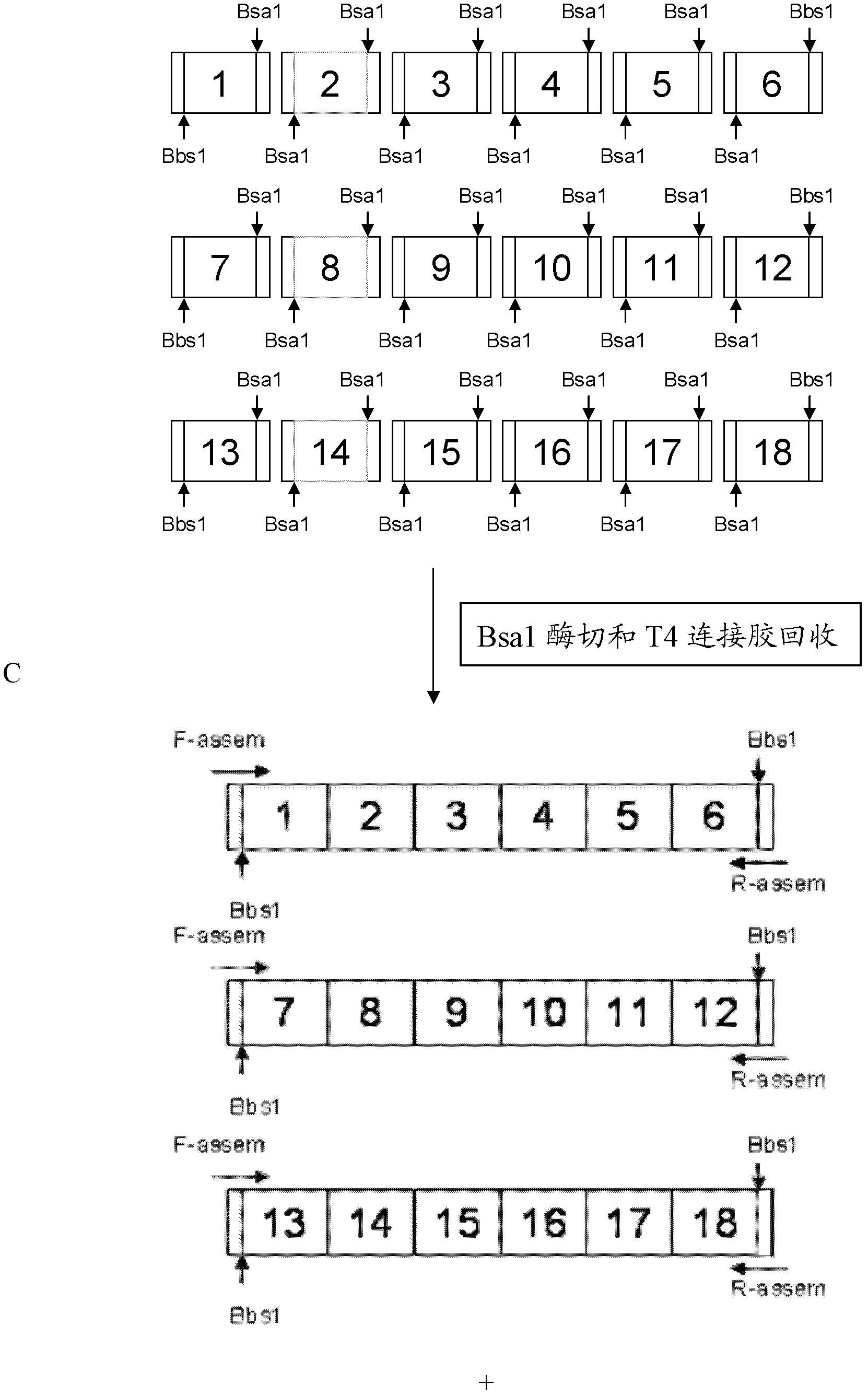
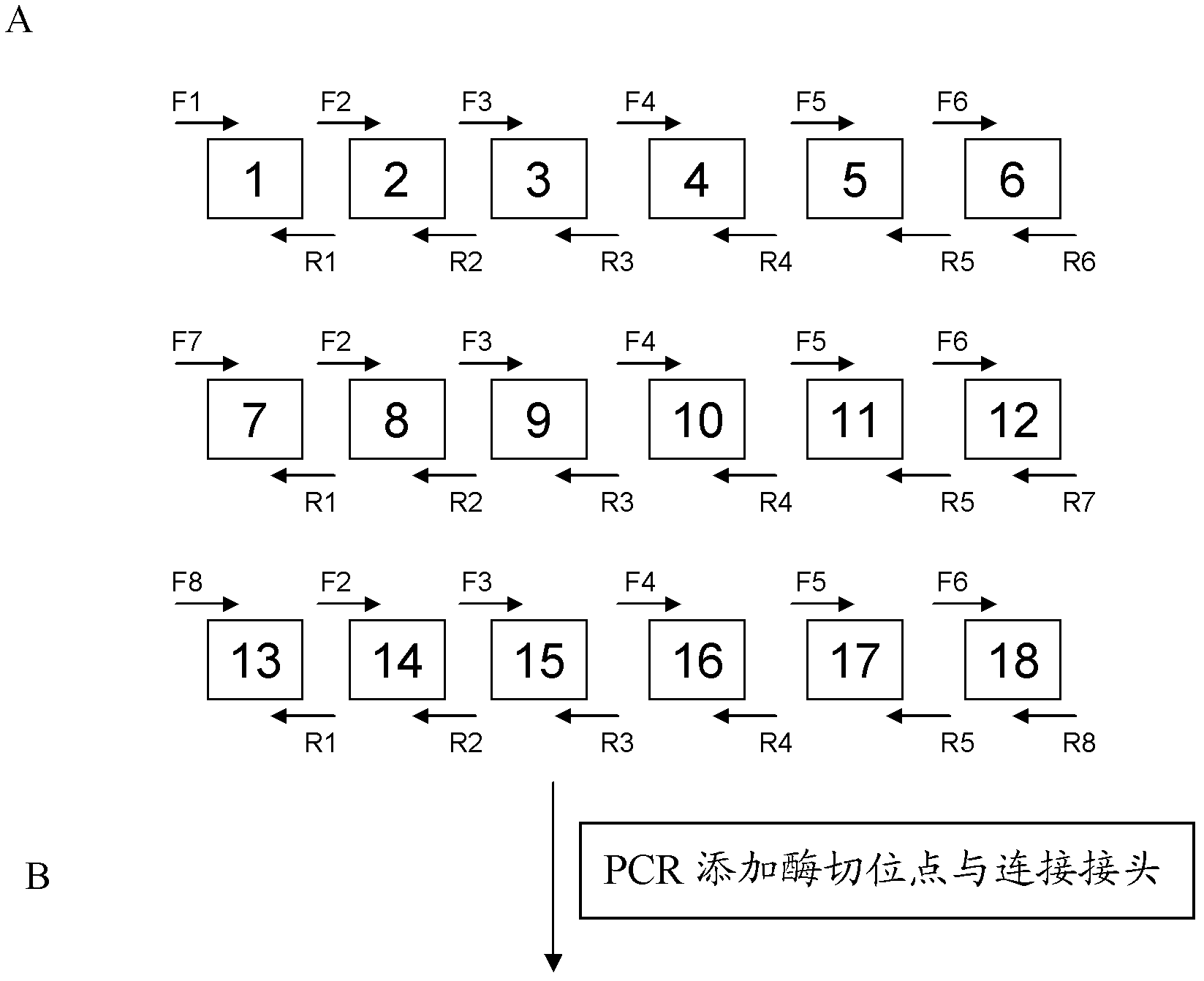
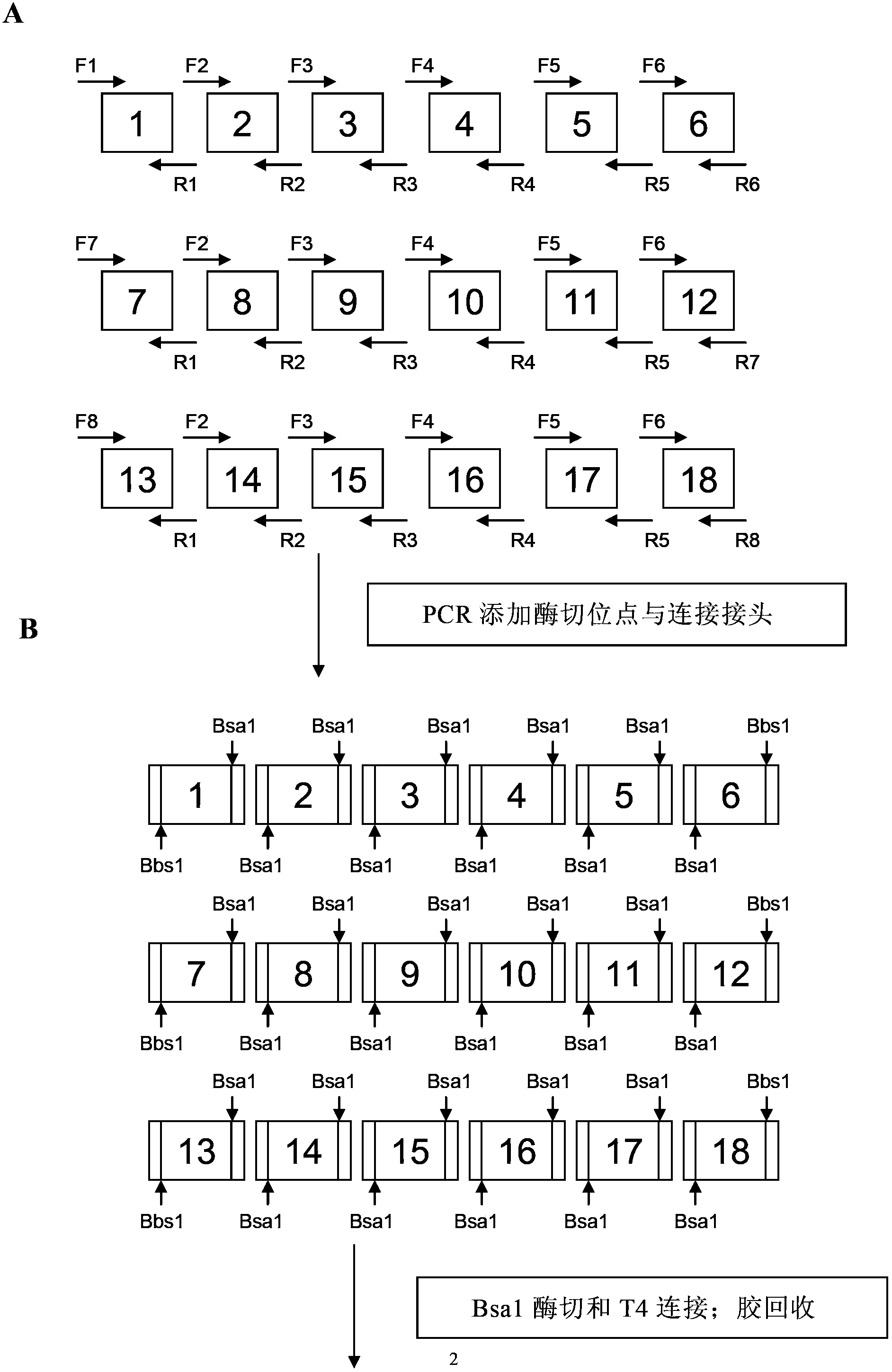
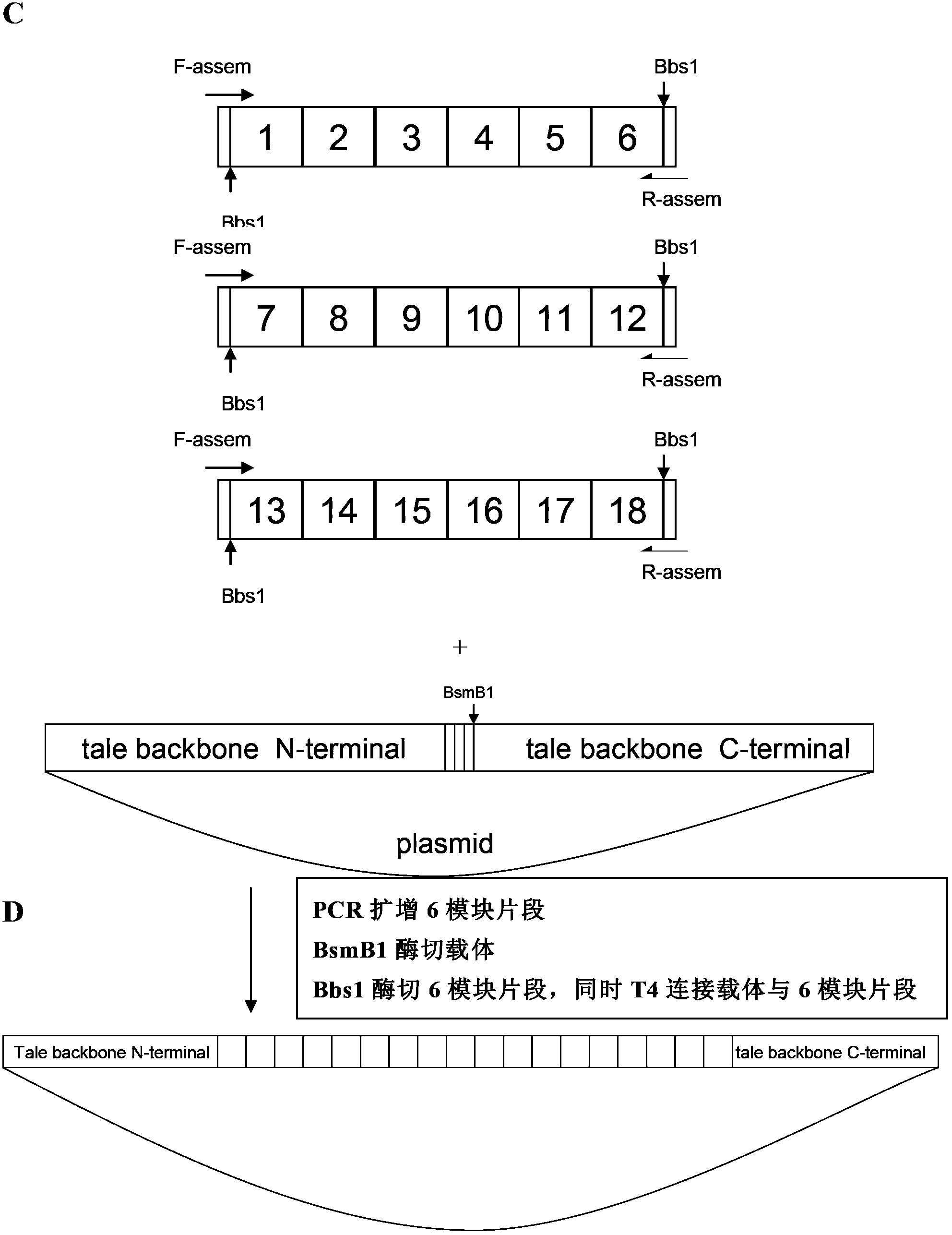
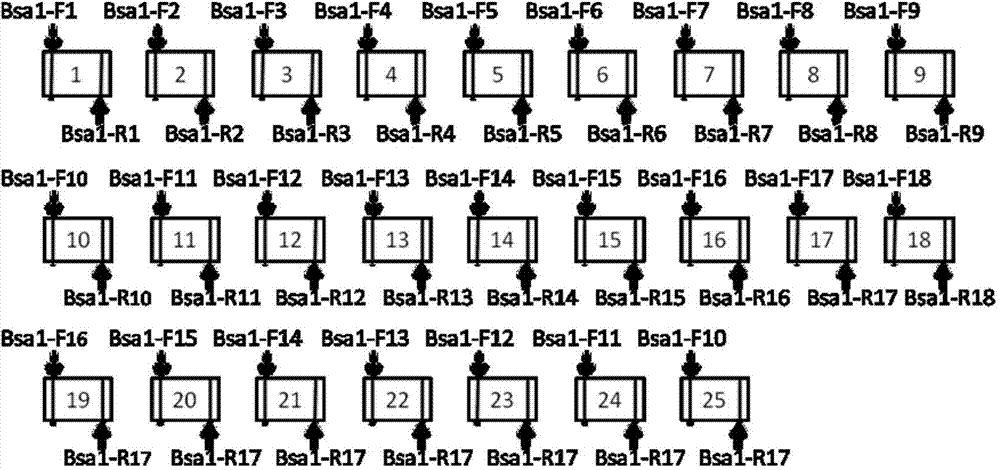
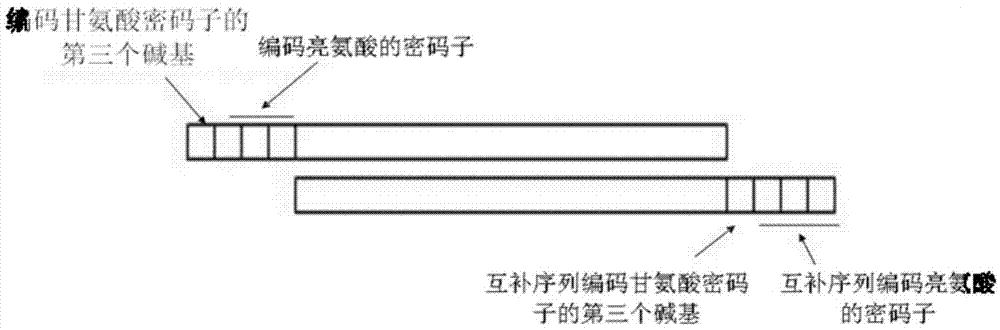
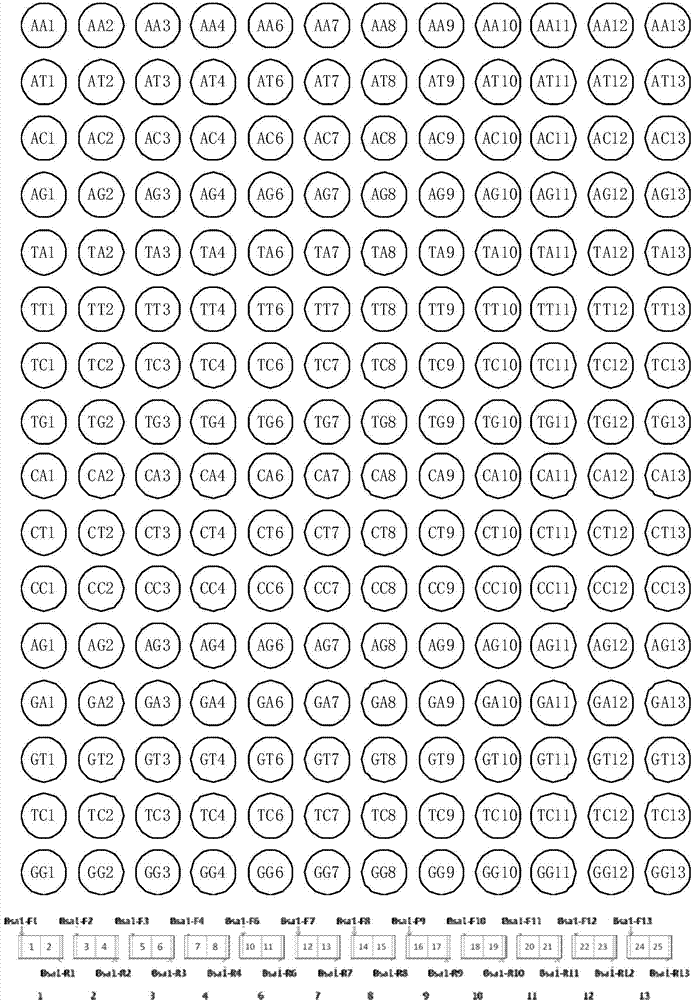
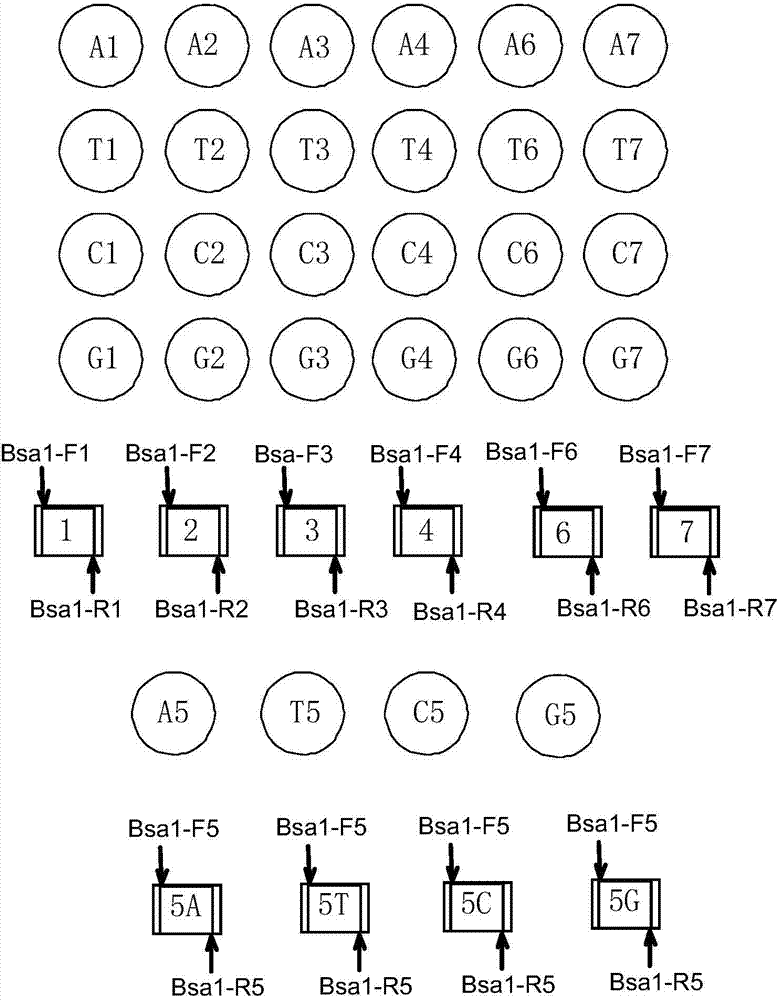
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) library and a method for constructing transcription activator like effector nuclease plasmids. A Tale connecting cell library comprises 16 groups*n double-base identifying modules and 4 groups*n single-base identifying module; and a first viscous tail end and a second viscous tail end which are formed by enzyme digestion of two restriction enzymes are arranged on two tail ends of each double-base identifying module or each single-base identifying module; the DNA library comprises plasmids which are as many as connecting units of the Tale connecting cell library; each plasmid comprises a connecting unit with mutually different base sequences; and Bsa I enzyme digestion sites are provided at junctions of the two tail ends of each connecting unit and an original carrier. The DNA library disclosed by the invention is adopted to construct transcription activator like effector nuclease plasmids; enzyme digestion and connection of the identifying modules can be carried out in one reaction, so that 12-19 identifying modules can be further connected, and therefore, the method is quick in speed, high in efficiency, simple to operate, easy for storing materials and low in cost.
Owner:浙江煦顼技术有限公司
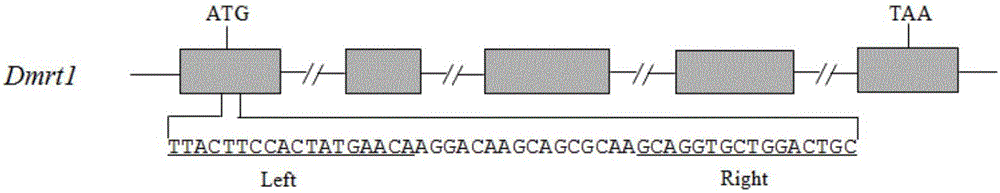
Goat MSTN (myostatin) gene fixed-point modification system and application thereof
The invention discloses a goat MSTN (myostain) gene fixed-point modification system and an application method thereof. The goat MSTN gene fixed-point modification system can effectively identify and modify transcription activator like effector nucleases (TALENs) of a goat MSTN gene target sequence, the TALENs provided by the invention is composed of nucleases TALEN-R and TALEN-L which can respectively identify identification modules TALMEX-1F and TALMEX-1R; the nuclease TALEN-L is a protein coded by a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 or SEQ ID NO.3, and the nuclease TALEN-R is a protein coded by a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.4 or SEQ ID NO.5.The invention also discloses a method for obtaining a muted cell line by carrying out targeted modification on a goat cell MSTN gene by adopting the knock-out system. According to the goat MSTN gene fixed-point modification system, the goat MSTN gene is knocked out or modified for obtaining a new variety with a high high-quality meat factor, so that the goat MSTN gene fixed-point modification system has an important application value on mechanism study of an MSTN gene regulation and control mechanism.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Pair of transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN), encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102702331AAchieve targeted modificationStrong specificityHydrolasesDepsipeptidesHeterologousDna recognition
Owner:上海煦顼技术有限公司
Site-directed mutagenesis system of mustard genome and application of site-directed mutagenesis system
InactiveCN103865897ARich genetic resourcesFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesSite-directed mutagenesisNuclease
The invention relates to a site-directed mutagenesis system of a mustard genome and an application of the site-directed mutagenesis system' and belongs to the technical field of biology. The site-directed mutagenesis system of the mustard genome is characterized by comprising two transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN) in two target sequences of a specifically-recognized target gene, wherein the target sequences include a first target sequence and a second target sequence, the first target sequence is located at a 5'-terminal of the target gene, and the second target sequence is located at a 3'-terminal of the target gene; the two transcription activator-like effector nucleases include transcription activator-like effector nucleases TALEN-L and TALEN-R which can specifically recognize the first target sequence and the second target sequence. The invention further discloses an application of a deletion system. According to the application, rich breeding materials can be provided, and the site-directed mutagenesis system has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
A pair of transcription activator-like effector nucleases and coding engines as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102627692AAchieve targeted modificationStrong specificityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesHeterologousPRNP
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Pair of transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and coding genes and application thereof
InactiveCN102627690AAchieve targeted modificationStrong specificityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesHeterologousPRNP
The invention discloses a pair of transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and coding genes and application thereof. The pair of TALENs are obtained through a pair of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) recognition proteins which are respectively merged with two heterogenous subunit of a Fokl DNA incision enzyme, and can specifically recognize two adjacent loci of a goat or sheep prion protein (PRNP) gene exon 2. When the pair of TALENs enters a host cell, the pair of TALENs can target at exon 2 loci of the PRNP gene of the host cell and can enable the targeted loci to be genetically mutated to realize the targeted modification of the goat or sheep PRNP gene. The pair of TALENs has the advantages of high specificity, high targeting efficiency, high accuracy and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for constructing spontaneous hyperuricemia mouse model and application of mouse model
InactiveCN104388467AProlong survival timeAbsence of fatal hyperuricemiaMicroinjection basedAnimal husbandryWild typeBlood urate level
The invention discloses a method for constructing a spontaneous hyperuricemia mouse model. The method for constructing the spontaneous hyperuricemia mouse model provided by the invention comprises the following step: knocking out urate oxidase genes of a target mouse by utilizing transcription activator-like effector nuclease to obtain a homozygote mouse from which the urate oxidase genes are knocked out, namely the spontaneous hyperuricemia mouse model. Experiments prove that the serum uric acid level of the spontaneous hyperuricemia mouse model obtained by the method disclosed by the invention is 3-4 times that of a wild type mouse and achieves the hyperuricemia level, and the pathogenesis of spontaneous hyperuricemia is better simulated. In addition, as the serum uric acid level of the mouse model obtained by the method disclosed by the invention is lower than the ultrahigh-level serum uric acid value reported in the previous literature, the lethal hyperuricemia does not exist, and the survival time of the mouse is long, so that long-term experiment of the mouse is facilitated.
Owner:李长贵
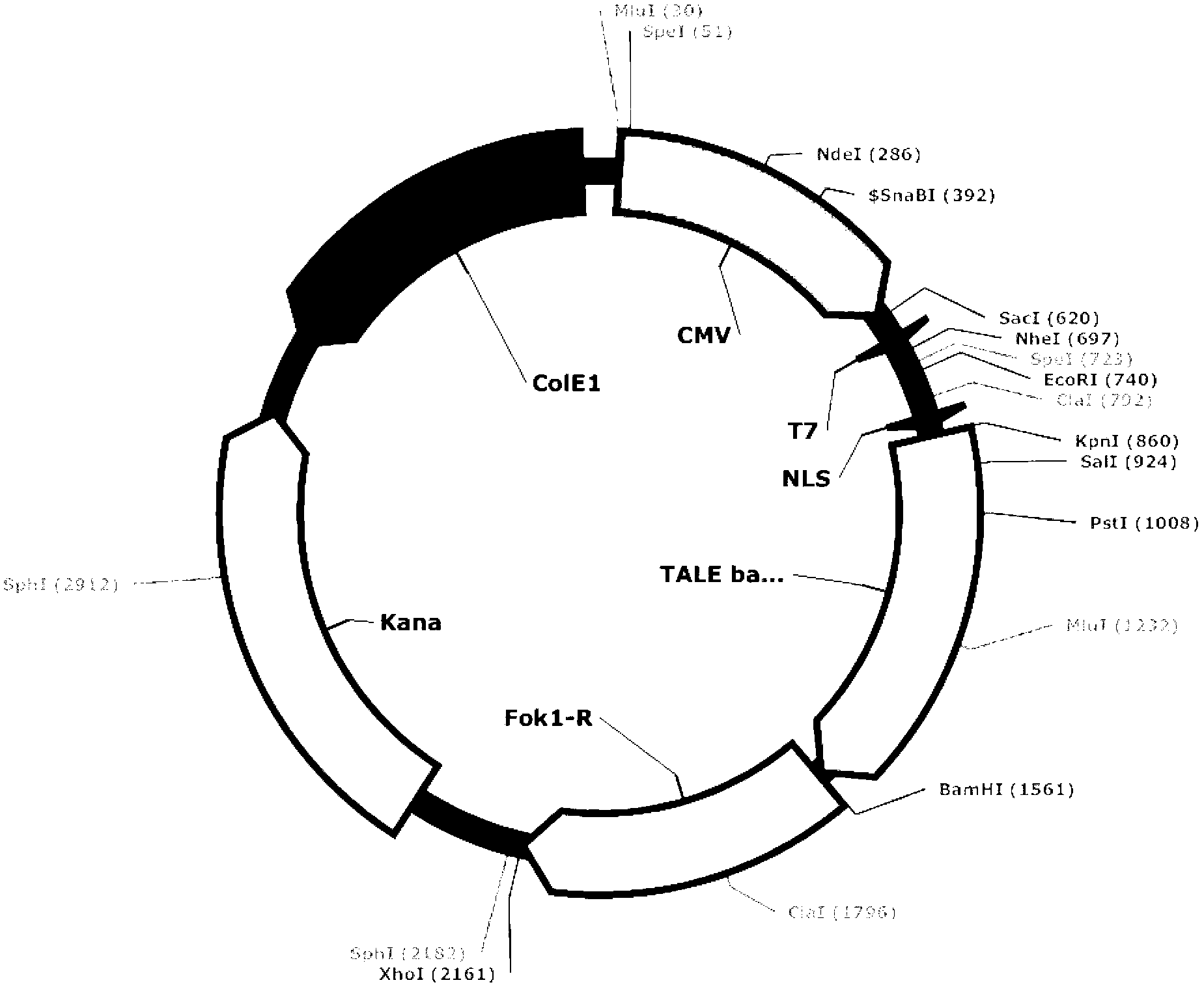
Method of achieving protein expression vector capable of genome site-specific modification
ActiveCN103898099AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationAnimal geneIndividual animal
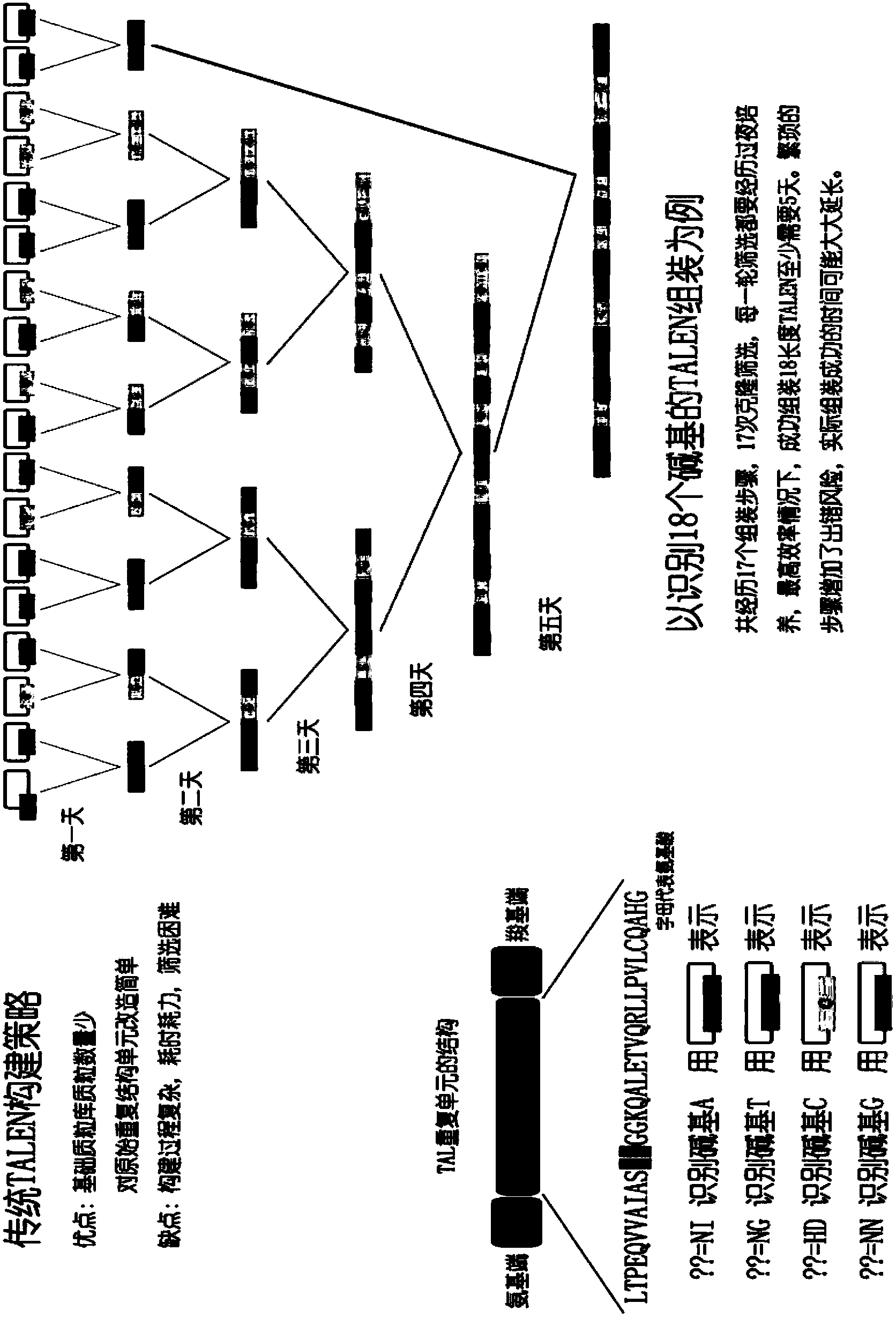
The invention relates to a biological gene clone expression technology, and particularly relates to a method of rapidly and efficiently constructing an expression vector of a transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN). The method is particularly suitable for constructing an expression vector aiming at higher animal genome genetic modification in large scale so as to study functions of animal genes.
Owner:BEIJING PERCANS ONCOLOGY CO LTD
A pair of transcription activator-like effector nucleases and coding sequence and application thereof
The invention discloses a transcription activator-like effector nuclease mediating targeted knockout of a colitis related gene Ace2, a coding sequence and an application of the nuclease. The transcription activator-like effector nuclease disclosed by the invention comprises a pair of transcription activator-like effector proteins and a monomer or a catalytic subunit of a DNA incision enzyme, wherein the monomer or the catalytic subunit are separately fused with the proteins. The transcription activator-like effector proteins have the functions of separately identifying and cutting two adjacent loca of an Ace2 gene of a mouse to efficiently and specifically realize targeted knockout of the Ace2 gene so as to quickly obtain a colitis model of the mouse, thereby providing a good genetic resource for research on colitis.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST +1
ZMIZ1-mediated targeting knockout transcription activator-like effector nuclease, preparation method and applications
InactiveCN103421093AHigh target shooting efficiencyHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideZMIZ1 Gene
The invention relates to ZMIZ1-mediated targeting knockout transcription activator-like effector nuclease, a preparation method and applications, and concretely relates to an artificially synthetic method for a transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) gene which can target human endogenous ZMIZ1 gene efficiently, and a directed targeting method of recombinant plasmids containing the TALEN gene. The transcription activator-like effector nuclease contains a pair of transcription activator-like effector (TALEs) proteins and catalytic subunits, of DNA endonucleases, which are fused with the proteins respectively, and has functions of identifying and cutting two adjacent loca of the human ZMIZ1 gene respectively. Based on the design of the amino acid sequence of TALEs, the nucleotide sequence coding the TALEN is synthetized and the carrier containing the nucleotide sequence is constructed. Through transfection of cells by utilization of TALENs plasmids, the targeting efficiency of cells can be raised greatly.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
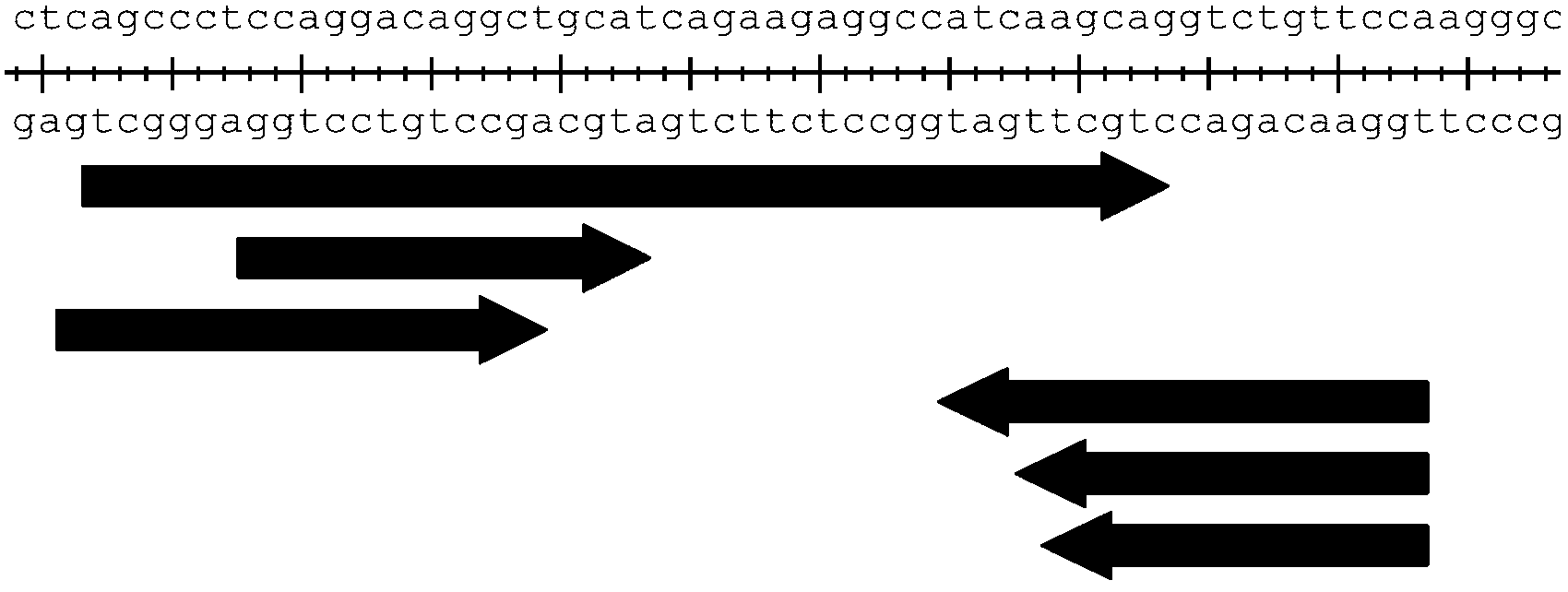
Single-module DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) library and connecting method for TALENs (transcription activator-like effector nucleases) identification modules
ActiveCN103497966AAvoid purification processAvoid the reconnection stepNucleotide librariesVector-based foreign material introductionDNA fragmentationA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) library, a construction method for TALENs (transcription activator-like effector nucleases) plasmids and a connecting cell library for TALEs (transcription activator-like effectors). The DNA library comprises all TALE connecting cells in the TALE connecting cell library. The construction method comprises the following steps of determining identification modules according to a target sequence of a target gene, and selecting a DNA fragment corresponding to each identification module from the DNA library; recombining and connecting the connecting cells in each DNA fragment into a TALENs vector by adopting type-two restriction enzymes and DNA ligases in the same system; and performing digestive treatment by using linear DNA digestion enzymes to obtain the TALENs plasmids. Compared with the prior art, the DNA library, the construction method and the connecting cell library have the advantages that the DNA library is used for constructing the TALENs plasmids, and 12 to 19 identification modules can be connected at one time, so that high speed, high efficiency, simplicity in operation and low cost are ensured, and materials are easy to store.
Owner:上海煦顼技术有限公司
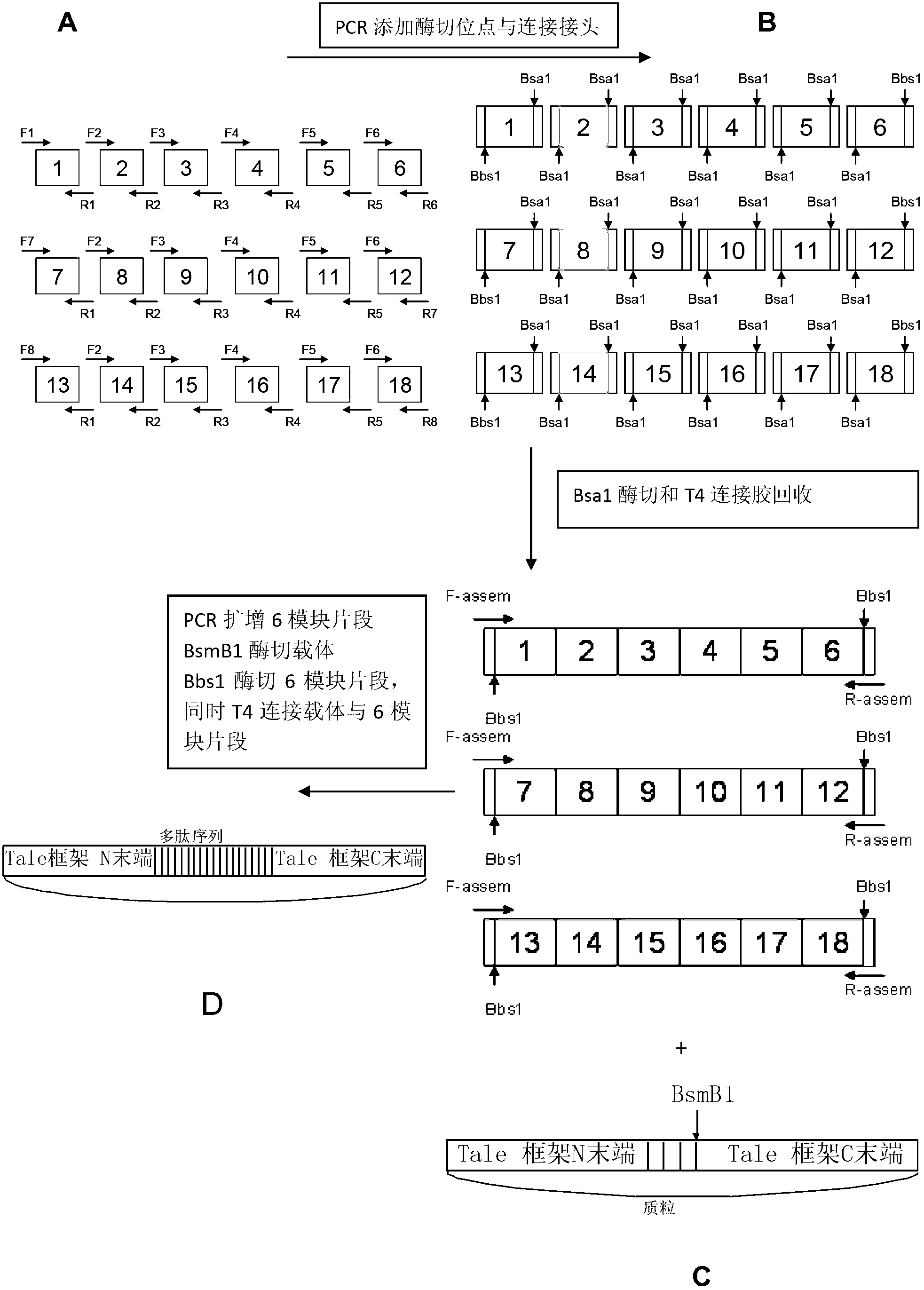
Multi-module DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) library and method for constructing transcription activator like effector nuclease plasmid
ActiveCN103695452AAvoid destructionAvoid degradationVector-based foreign material introductionLibrary creationEnzyme digestionComputer module
The invention discloses a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) library and a method for constructing a transcription activator like effector nuclease plasmid. A transcription activator like effector connection unit library comprises 16 groups*n double-basic group identification modules and 4 groups*m single-basic group identification modules, wherein two tail ends of each double-basic group identification module or single-basic group identification module are both formed into a first cohesive tail end and a second cohesive tail end by being subjected to enzyme digestion through a second class restriction enzyme; n expresses the quantity of each group of double-basic group identification modules, and m expresses the quantity of each group of single-basic group identification modules. The DNA library comprises plasmids, wherein the plasmids are the same as the connection units of the Tale connection unit library in quantity, each plasmid comprises a connection unit with basic group sequences mutually different, the connecting positions of the two tail ends of the connection unit and an original carrier are provided with BsaI enzyme digestion sites. The DNA library disclosed by the invention is used for constructing the transcription activator like effector nuclease plasmid, can realize that 19-26 identification modules are connected for one step by identifying the enzyme digestion of the modules and connecting in same reaction, and has the advantages of high speed, high efficiency, easiness for operation, easiness for material preservation and low cost.
Owner:上海煦顼技术有限公司
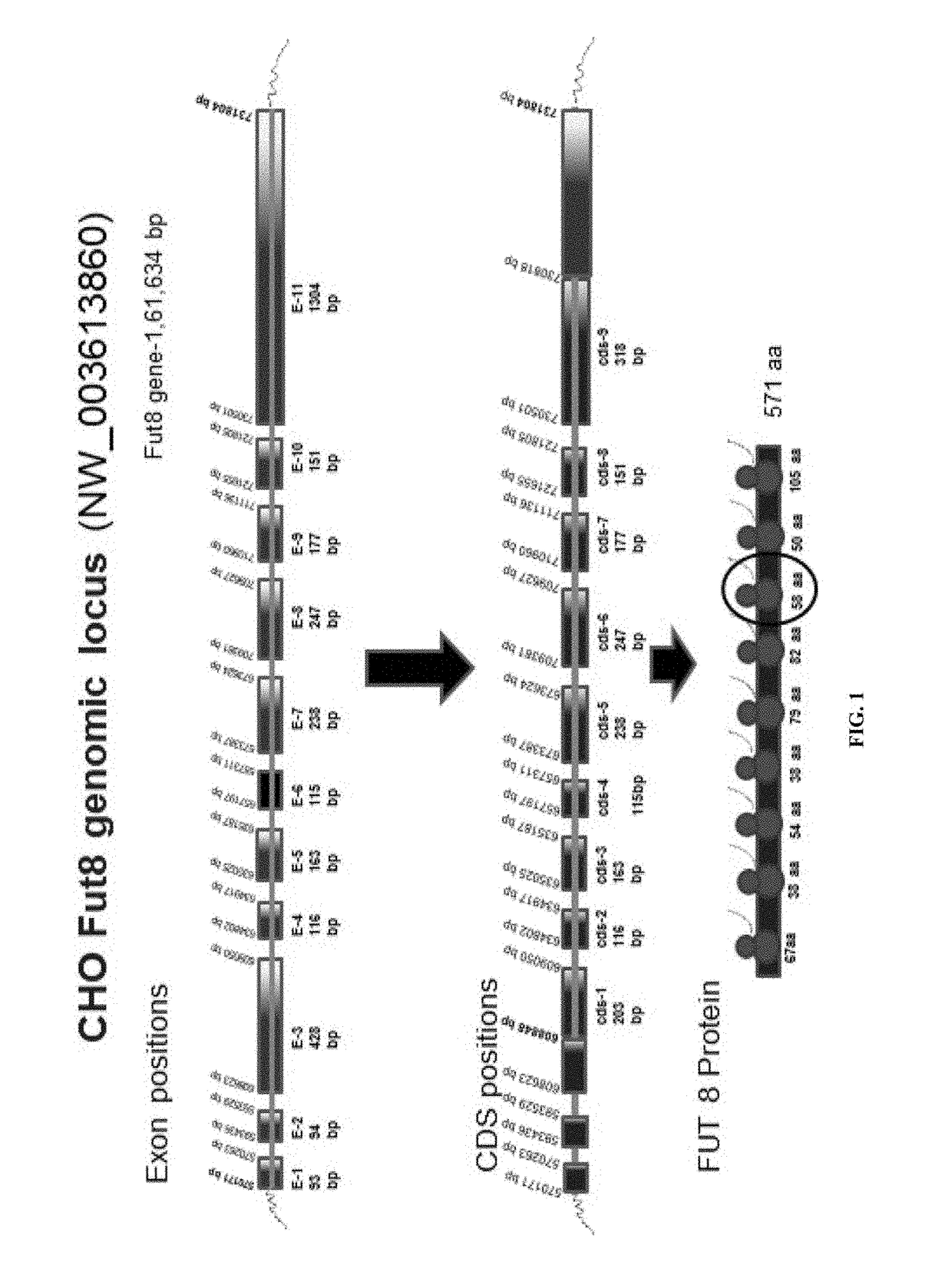
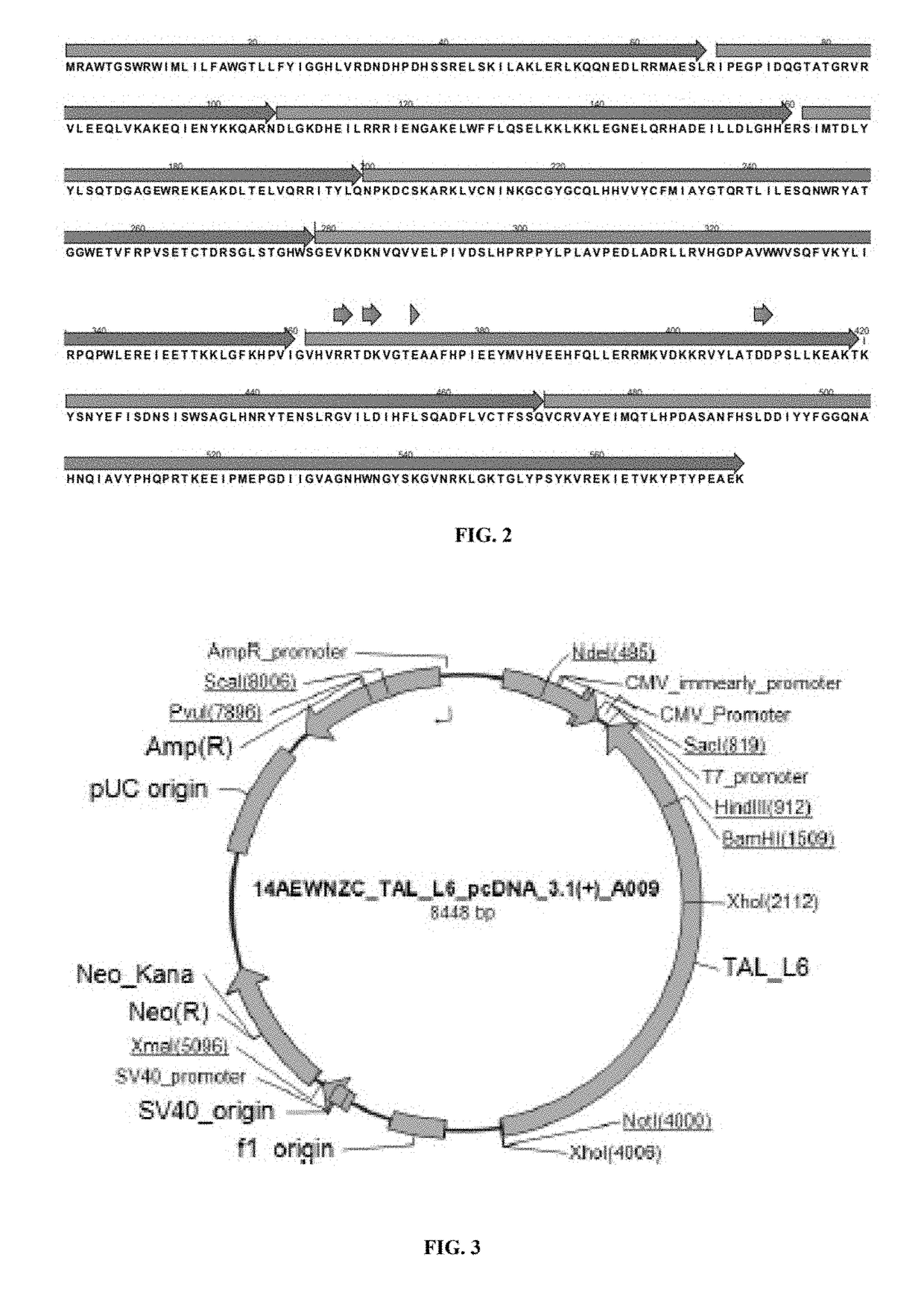
Non-fucosylated protein and methods thereof
Owner:ZUMUTOR BIOLOGICS
A method for gene editing of eels
The invention discloses a monopterus albus gene editing method. The monopterus albus gene editing method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring an artificially inseminated monopterus albus 1-cell stage embryo by establishing an indoor eel whole artificial propagation technology; 2, establishing a transcription activator-like effector nuclease gene editing vector of a target gene, performing in-vitro transcription to synthesize mRNA, and transferring the mRNA into the monopterus albus 1-cell stage fertilization embryo by adopting a microinjection method; 3, screening to obtain a monopterus albus with a mutant target gene through a three-primer detection method, and determining the mutation type of the target gene through sequencing. According to the method, a micromanipulation technology for a monopterus albus embryo is established for the first time, a precise monopterus albus endogenous gene editing technology is established for the first time, and powerful technological means is provided for performing function research on a monopterus albus gene and genetic improvement of monopterus albus breeding variety.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Transformation method of sugar beet protoplasts by talen platform technology
InactiveUS20170121723A1Vector-based foreign material introductionLyasesNucleotideTransformation cell
A method for transformation of sugar beet protoplasts includes obtaining protoplasts from stomatal guard cells isolated from a sugar beet plant. The protoplasts are transformed with a nucleic acid construct including a nucleotide sequence of interest and Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALEN) or one or more vectors including sequences encoding these Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALEN)sequences. The TALEN target and process a target sequence and replace the target sequence through homologous recombination with the nucleic acid construct including the nucleotide sequence of interest, -possibly applying to an in vitroculture of the protoplasts, a medium that is toxic, preferably lethal to the in vitroculture of the protoplasts. Sugar beet plants are regenerated from the cell culture, preferably from the surviving protoplasts having integrated the nucleic acid construct including the sequence of interest that possibly renders the transformed cell resistant to the toxic activity of the applied medium.
Owner:SESVANDERHAVE
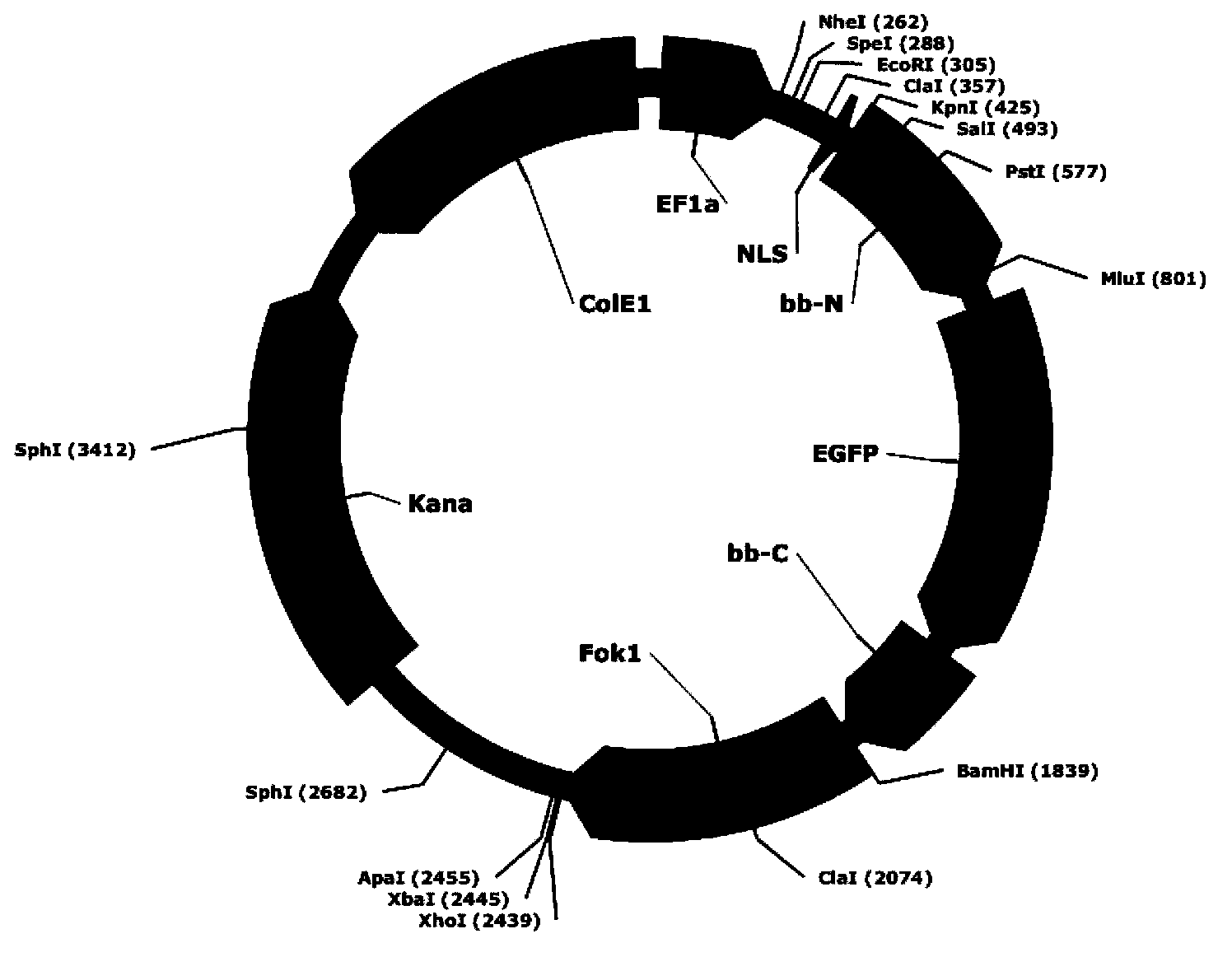
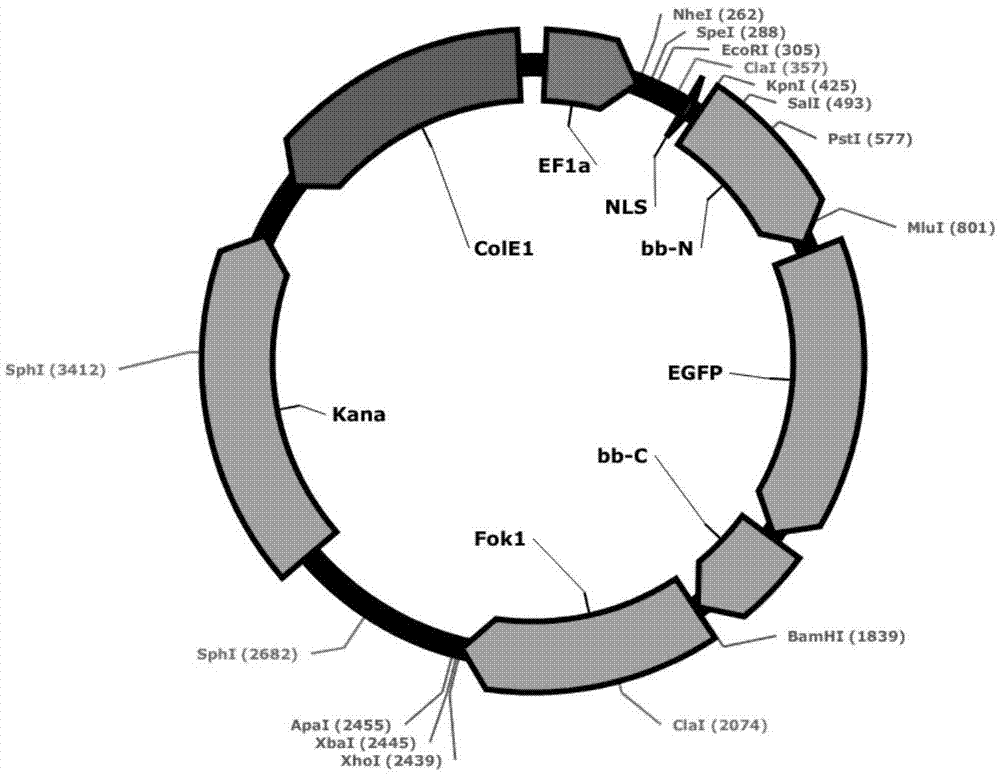
Construction methods and application of fusion protein and vector thereof
The invention discloses construction methods and application of a fusion protein and a vector thereof and aims to provide a method for constructing a fusion protein scientifically and effectively by taking TALEN (transcription activator-like effector nuclease) as a cell strain. The method is technically characterized in that the fusion protein has a structure of EGFP-_mODC_NLS, and an expression vector of the fusion protein comprises the fusion protein with the structure of EGFP-_mODC_NLS and an NLS cutting TALEN plasmid pair of the fusion protein. The fusion protein is used for the NLS cutting TALEN plasmid pair and a prokaryotic expression protein with the structure of EGFP_mODC_NLS_TALEN_R and a protein with the structure of EGFP_mODC_NLS_TALEN_R, and the fusion protein can be used for verifying the transfection efficiency of the TALEN plasmid pair and the activity of the TALEN plasmid pair in cells. The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology.
Owner:广西即泰健康咨询有限公司
Non-fucosylated protein and methods thereof
The present disclosure relates to developing cell lines where specific biological pathways are modified, particularly by modifications in the enzymes of the cell. The present disclosure develops protein expression systems wherein specific modification of glycan chain of the protein is achieved, which produces non-fucosylated proteins, including non-fucosylated antibodies. The non-fucosylated proteins are used in developing therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and biomarkers, and in diagnosis and prognosis of various diseases. The present disclosure employs the Transcription Activator like Effector Nuclease (TALEN) technology for inactivating fucosylation in a cell.
Owner:ZUMUTOR BIOLOGICS
A pair of transcription activator like effector nucleases of L3 and R1 and a coding gene and an application thereof
The invention discloses a pair of transcription activator like effector nucleases, a coding gene and an application thereof. The pair of transcription activator like effector nucleases (TALEN) is obtained by respective fusion of a pair of DNA recognins with two heterogenous subunits of a Fok1 DNA endonuclease, and can specifically recognize two adjacent loci on human RHD or RHCE gene exon1. When the pair of transcription activator like effector nucleases is simultaneously transferred to a host cell, targeting of the exon1 loci of the host cell gene can be realized; the targeted loci are subject to gene mutation; therefore, targeting modification of the human RHCE or RHD gene is realized, and advantages of strong specificity, high targeting efficiency, high accuracy and the like are provided.
Owner:浙江煦顼技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com