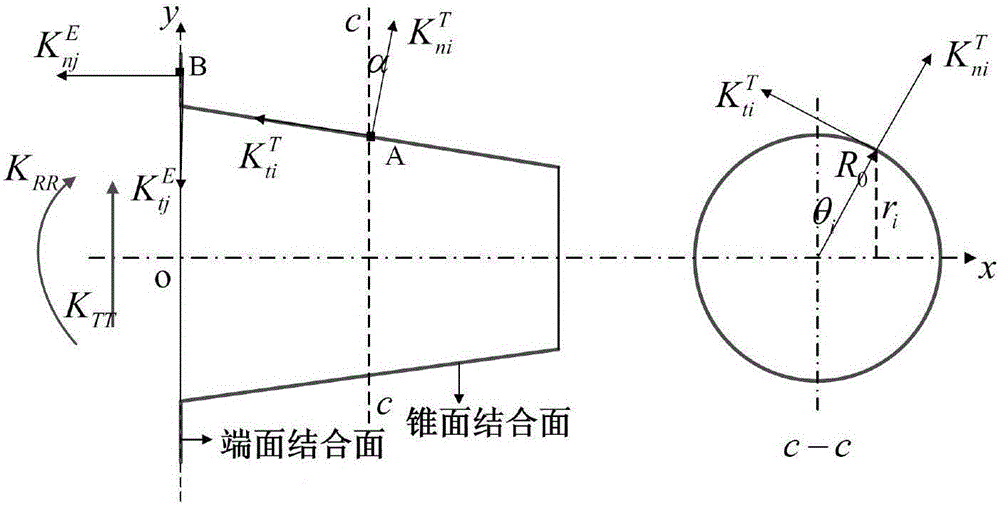
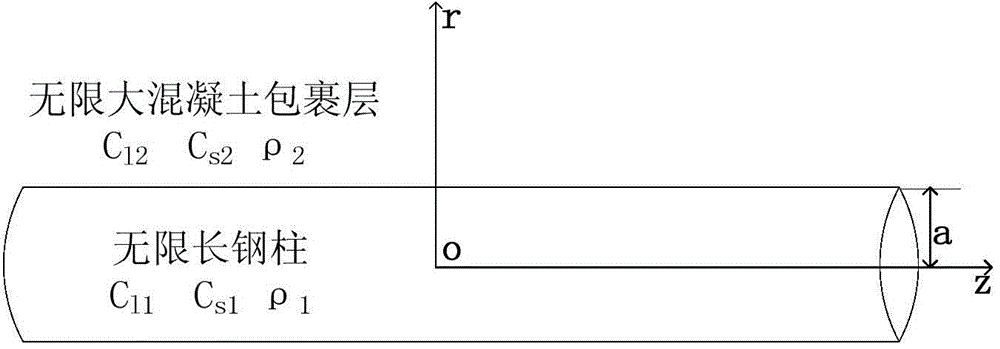
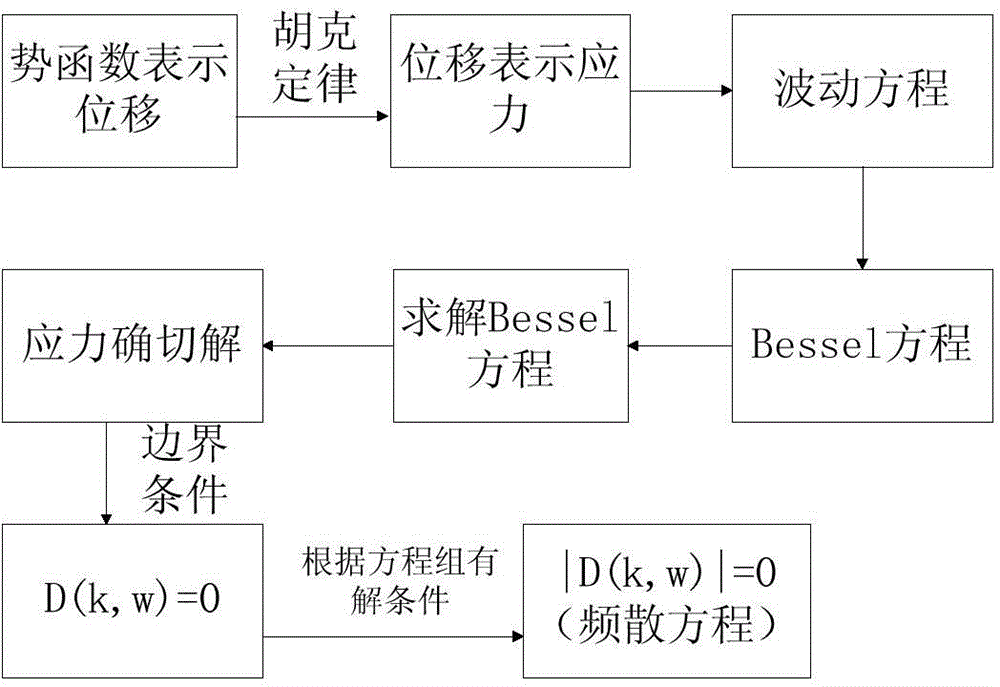
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Tangential stiffness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
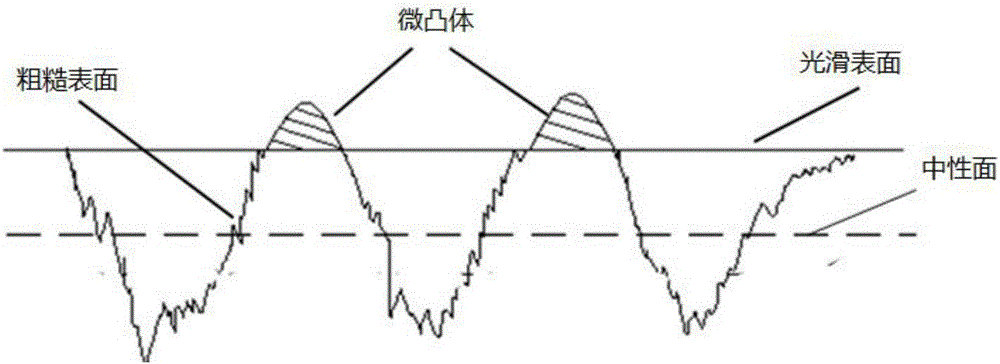
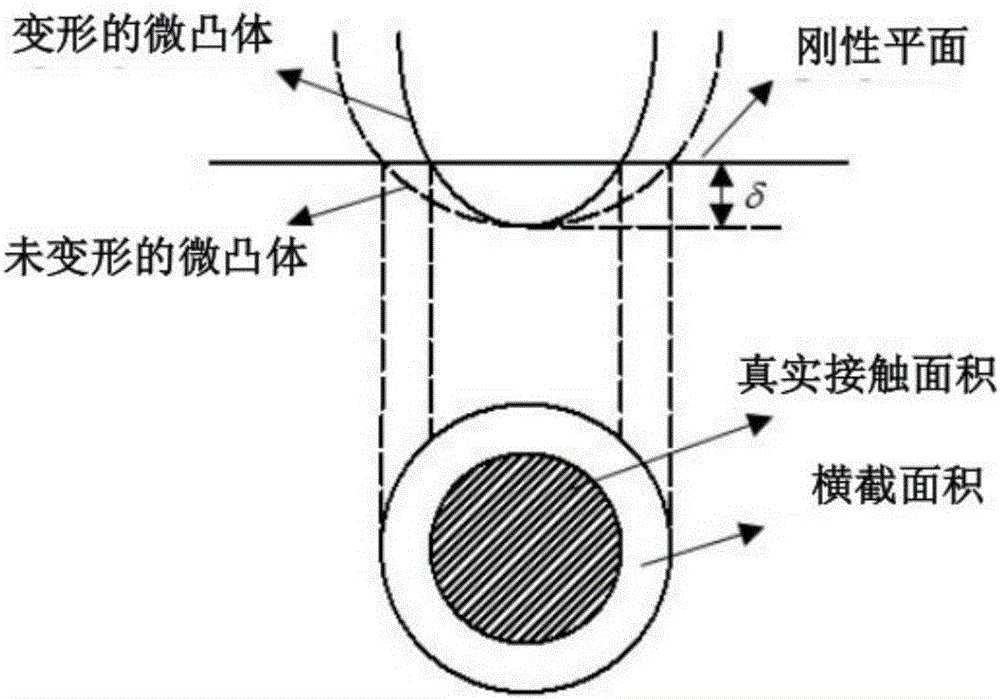
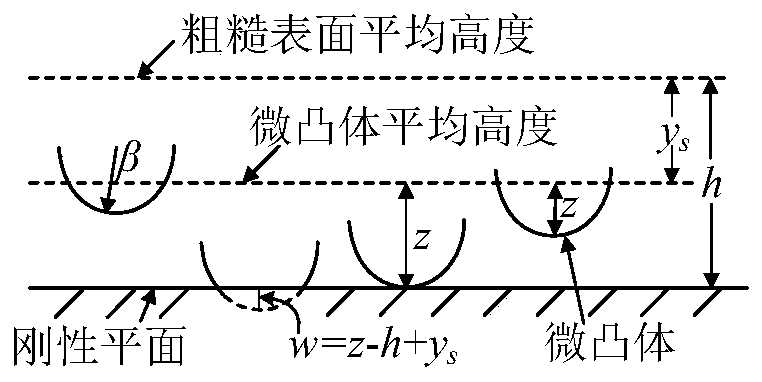
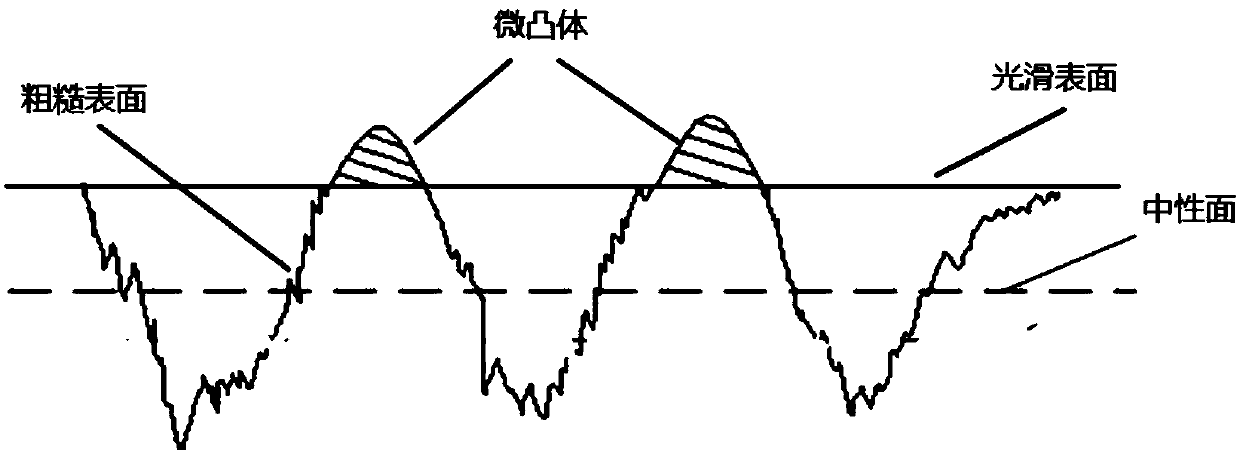
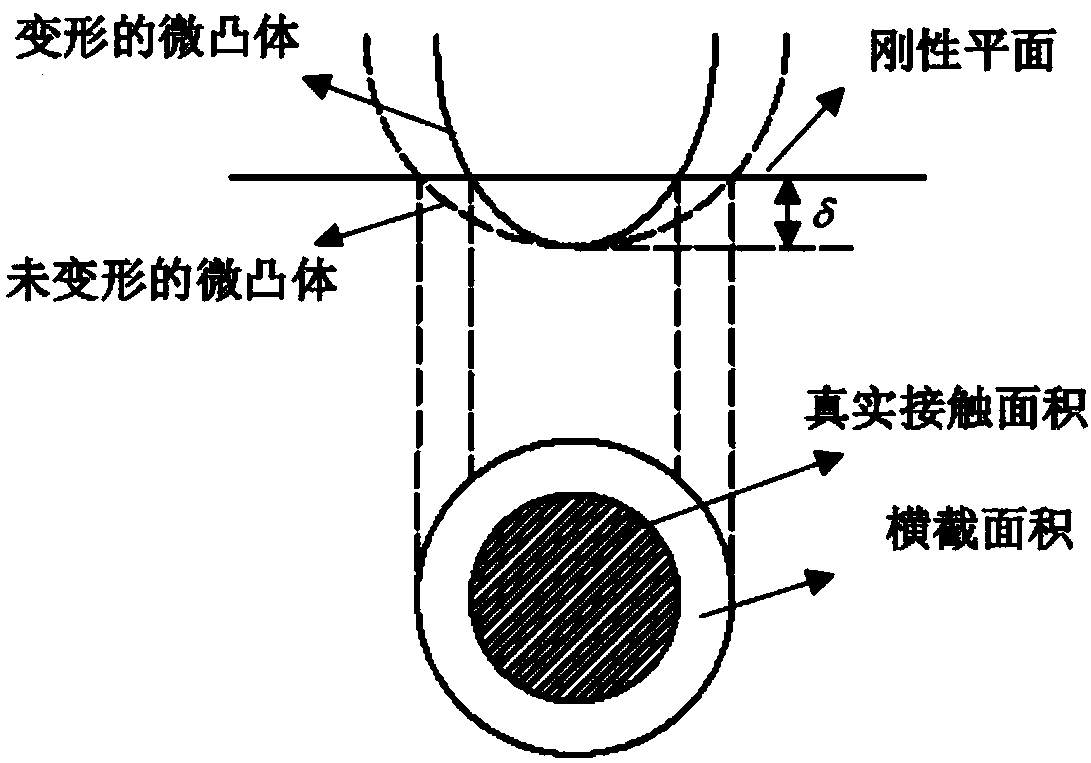
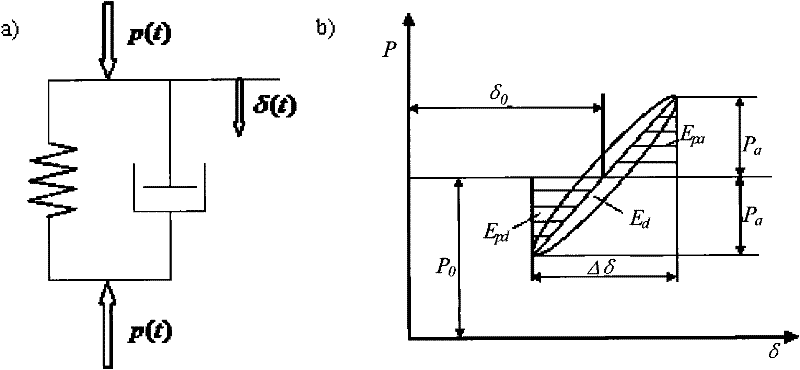
The tangential contact stiffness or shear stiffness for joint interfaces is always considered constant during moving contact. However, the real process of moving contact for rough surfaces is composed of three states: adhesion, transition and sliding.
Rough surface-based three-dimensional contact stiffness calculation method for spur gear
ActiveCN106844818APrecise contact stiffnessSolve the disadvantages of smooth contactGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationContact pressureEngineering
The invention discloses a rough surface-based three-dimensional contact stiffness calculation method for a spur gear. The method comprises the steps of firstly by adopting hexahedral mesh generation, requiring all square meshes on a tooth surface to be equal in area; calculating contact pressure distribution of the smooth tooth surface based on a finite element method, and extracting node pressure intensity of a contact region; calculating normal contact stiffness and tangential contact stiffness of a single square mesh based on a fractal theory; and calculating the contact stiffness of the tooth surface. According to the method, the precision of a gear contact stiffness calculation model is further improved; the defect of smooth contact according to a Hertz theory in an original calculation process is overcome; an influence law of a roughness parameter on a gear stiffness characteristic in a rough tooth surface contact process and a calculation method are disclosed; and meanwhile, a finite element-based three-dimensional contact stiffness calculation model is more accurate than an original two-dimensional calculation model or calculation formula, and the influence of errors in actual assembling and manufacturing processes of the gear is considered, so that the gear contact stiffness is more accurate and a foundation is laid for gear dynamics analysis.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
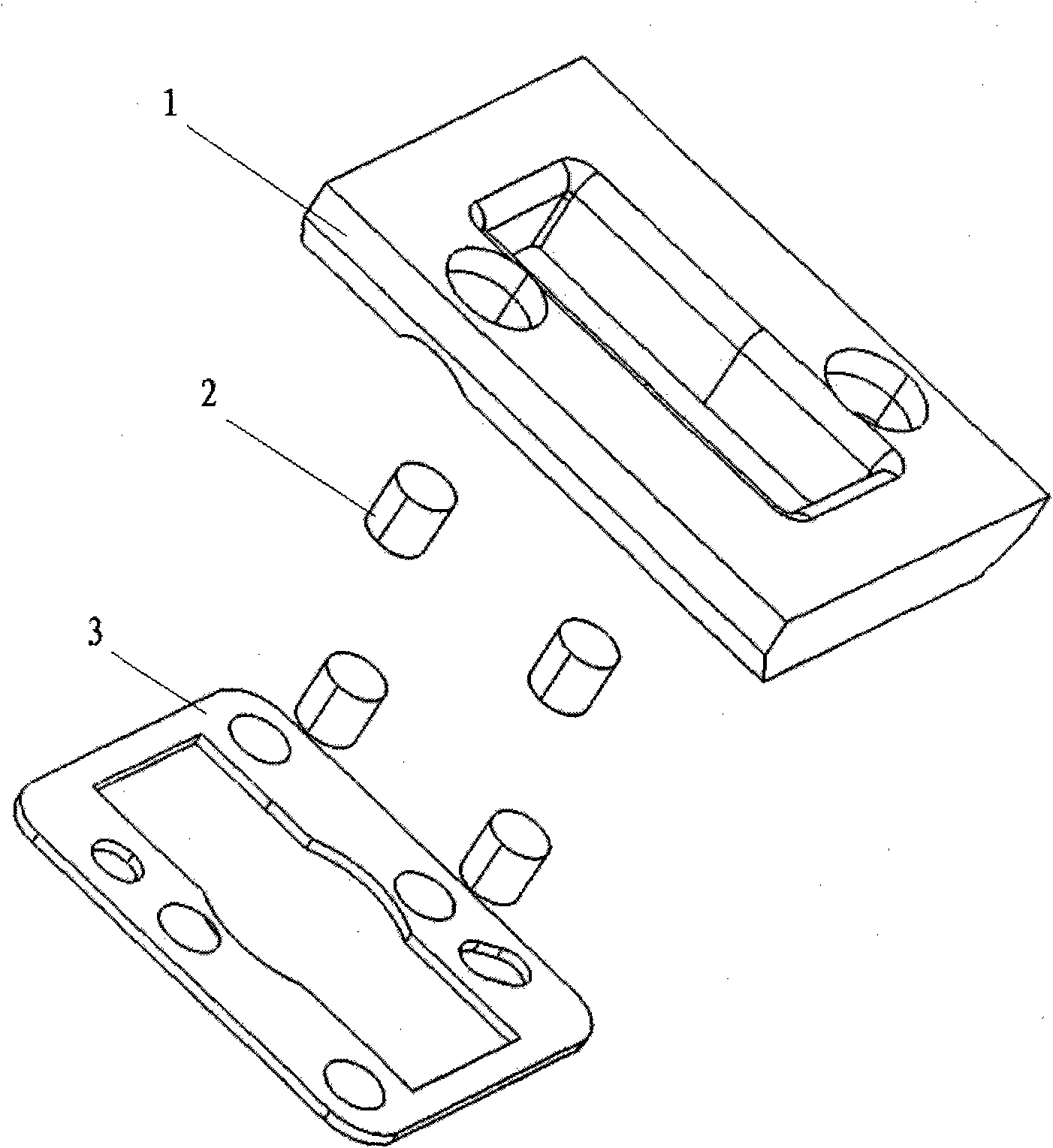
Automobile shock absorber
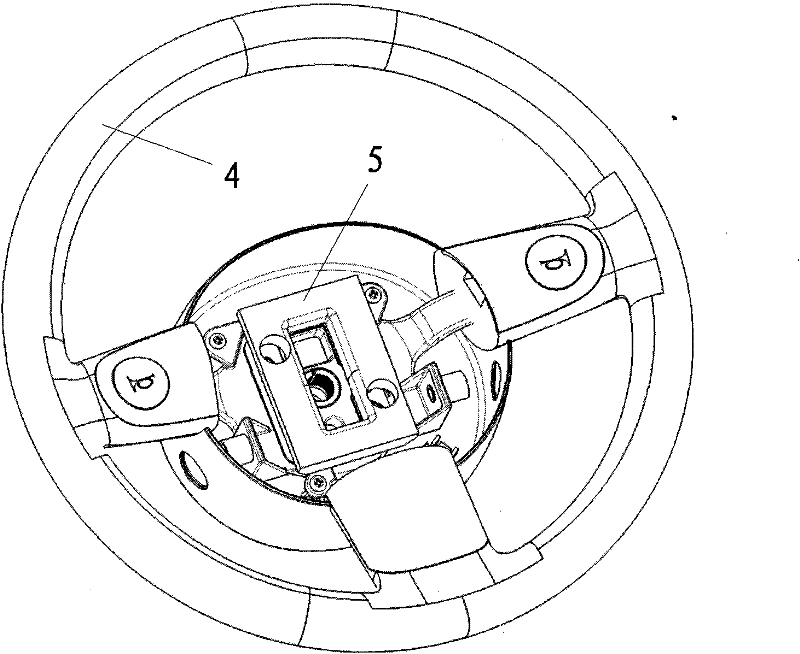
ActiveCN101900179ASolve idle vibration problemLow costHand wheelsElastic dampersSteering wheelResonance
The invention discloses an automobile shock absorber and belongs to the field of automobiles. The automobile shock absorber is arranged inside an automobile steering wheel and comprises a mass block and a rubber column under the mass block, wherein the rubber column is used for supporting the mass block; and the mass block is fixedly connected with the rubber column, and the tangential inherent frequency of the automobile shock absorber is allowed to be close to the idle-speed vibration frequency of the automobile steering wheel so as to form resonance. The automobile shock absorber of the invention effectively utilizes the inner space of the steering wheel and the tangential stiffness property of rubber and adopts a shock absorbing structure comprising the mass block and the rubber column, so that a small-size and low-frequency power shock absorber is designed and manufactured, the idle-speed vibration problem of the steering wheel is solved, and the first application of shock absorber technology in solving the vibration problem of the idle-speed steering wheel in China is realized. Comparing with the prior art, the automobile shock absorber has the advantages of simple structure, simple and convenient processing and manufacturing, short development period, low cost and convenient popularization.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
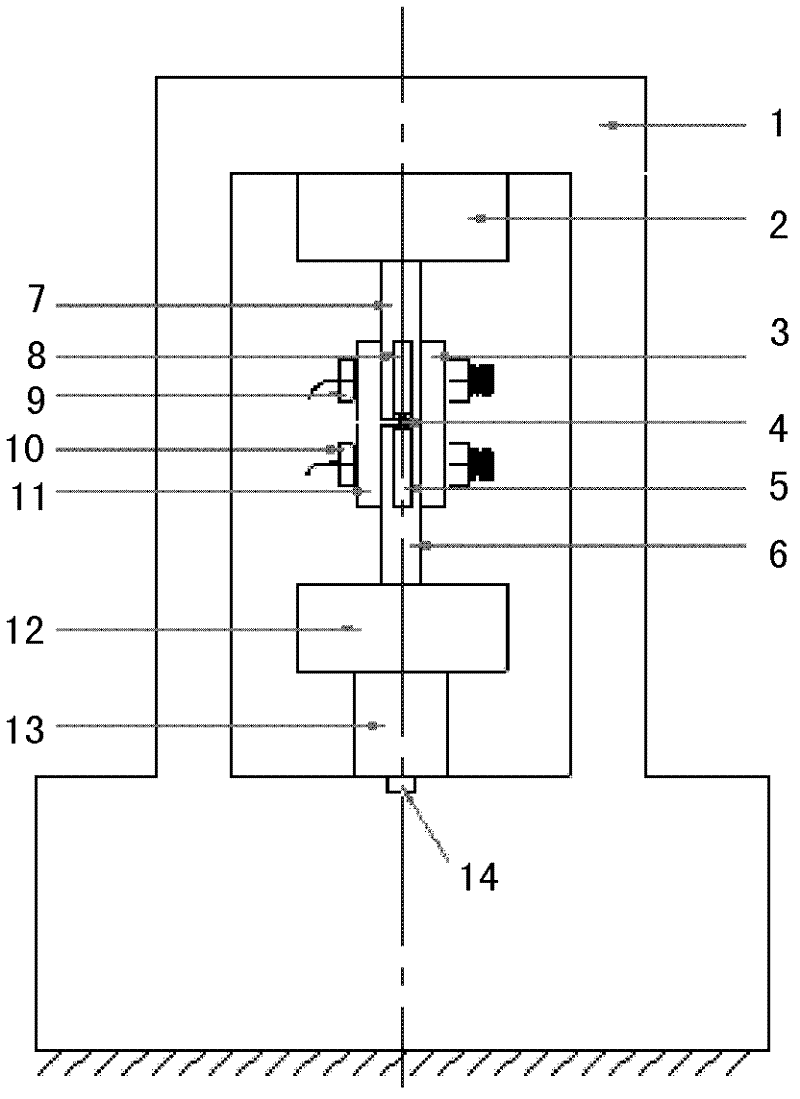
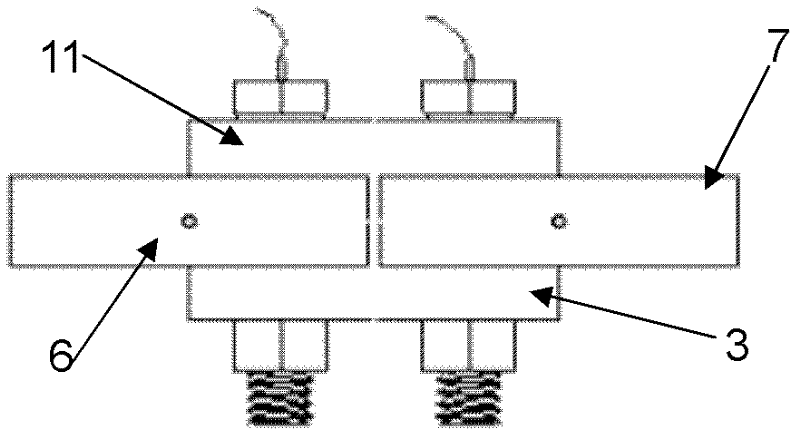
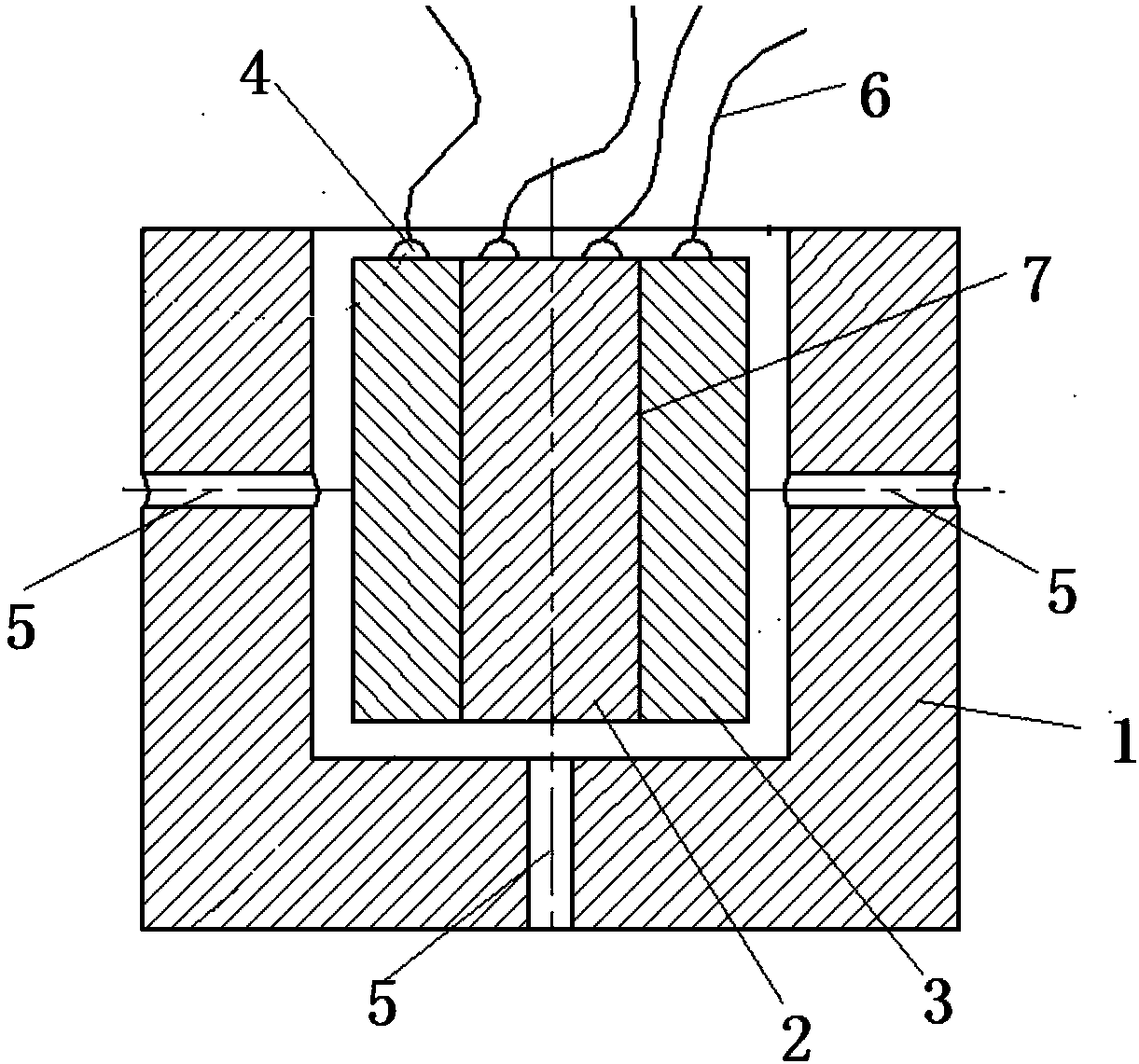
Device for testing tangential stiffness property of joint surface
InactiveCN102393330AEasy to processEasy to installMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesTangential displacementHigh intensity
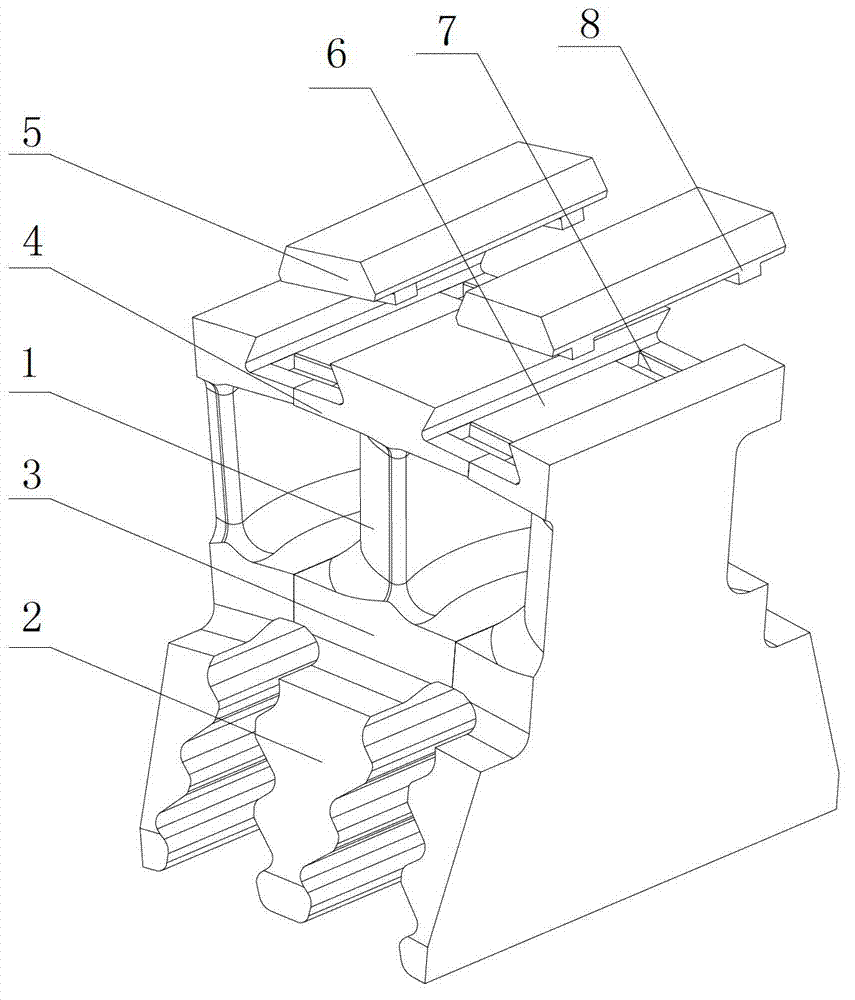
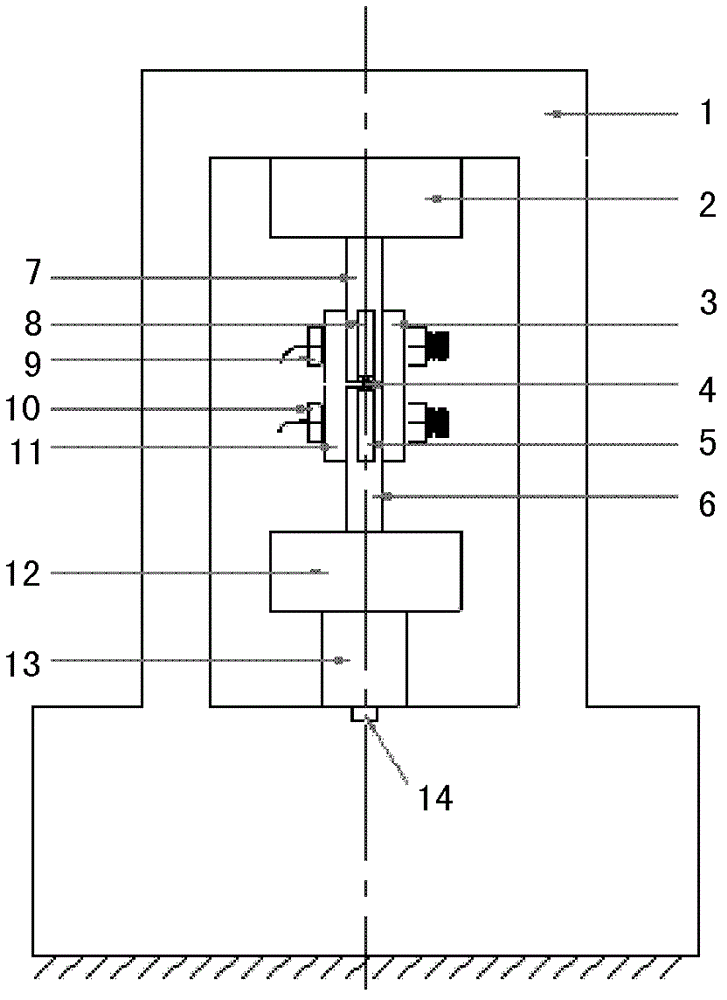
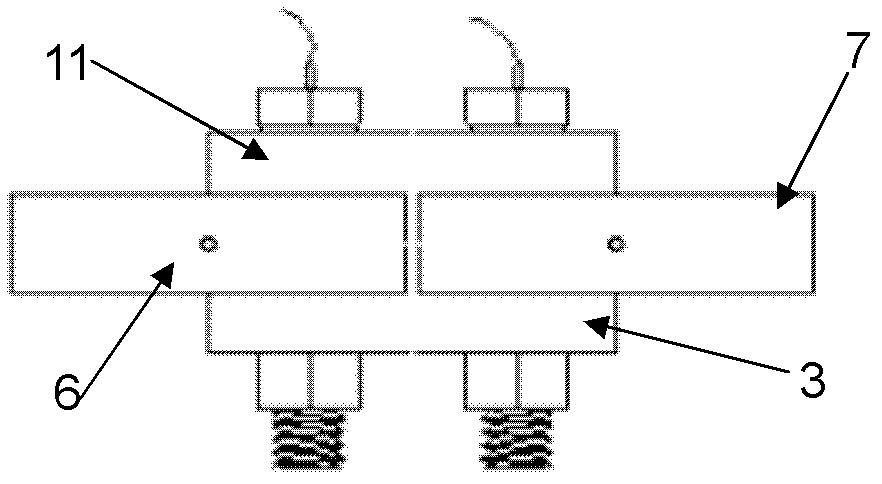
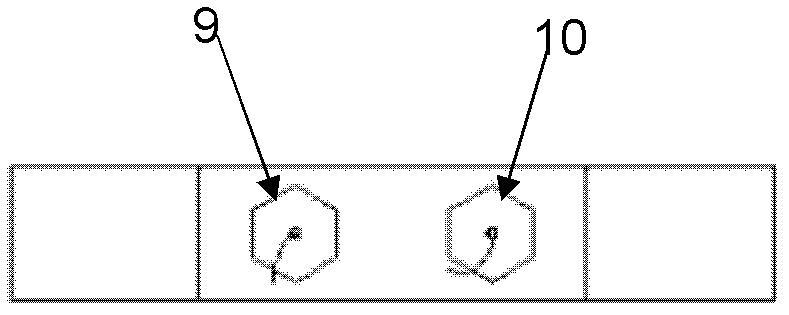
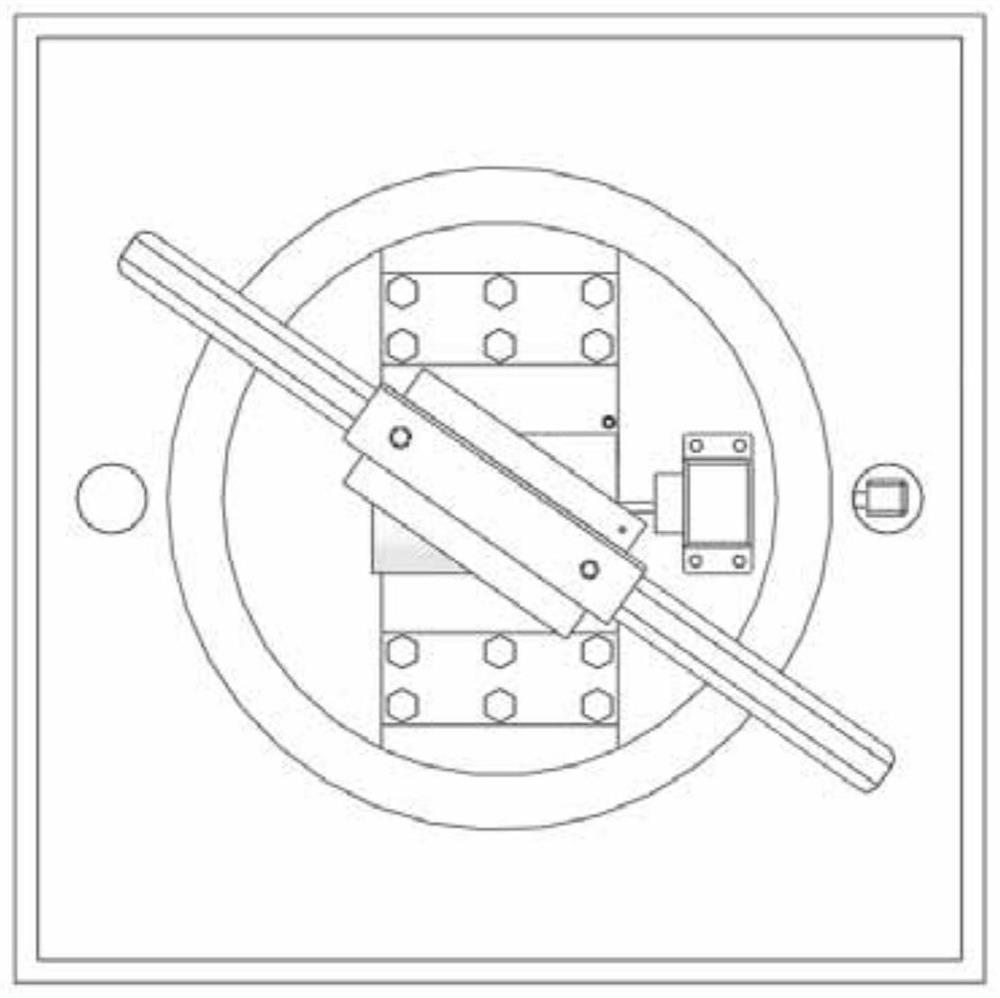
The invention discloses a device for testing a tangential stiffness property of a joint surface, and belongs to the fields of mechanical design and manufacture. The device consists of a test loading device (1) and a tangential test assembly. An upper test piece (7) is butted with a lower test piece (6), and a gap is reserved at the joint; a pressing plate (3) and a pressing plate (11) are arranged on two surfaces vertical to the test piece butting surface, and are fixedly connected through two high-strength bolts (9) and (11) to form the tangential test assembly; the high-strength bolts (9) and (11) are symmetrical about the gap of the joint of the upper and lower test pieces; brackets (8) and (5) are arranged on two sides of the gap of the joint for accommodating an eddy current displacement sensor (4); and a force sensor (14) for measuring loading force signals and the eddy current displacement sensor (4) for measuring the tangential displacement variation of the joint surface are connected to a signal acquisition system. The device has the advantages of simple machining, convenience for clamping, high universality, high controllability of the parameters and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
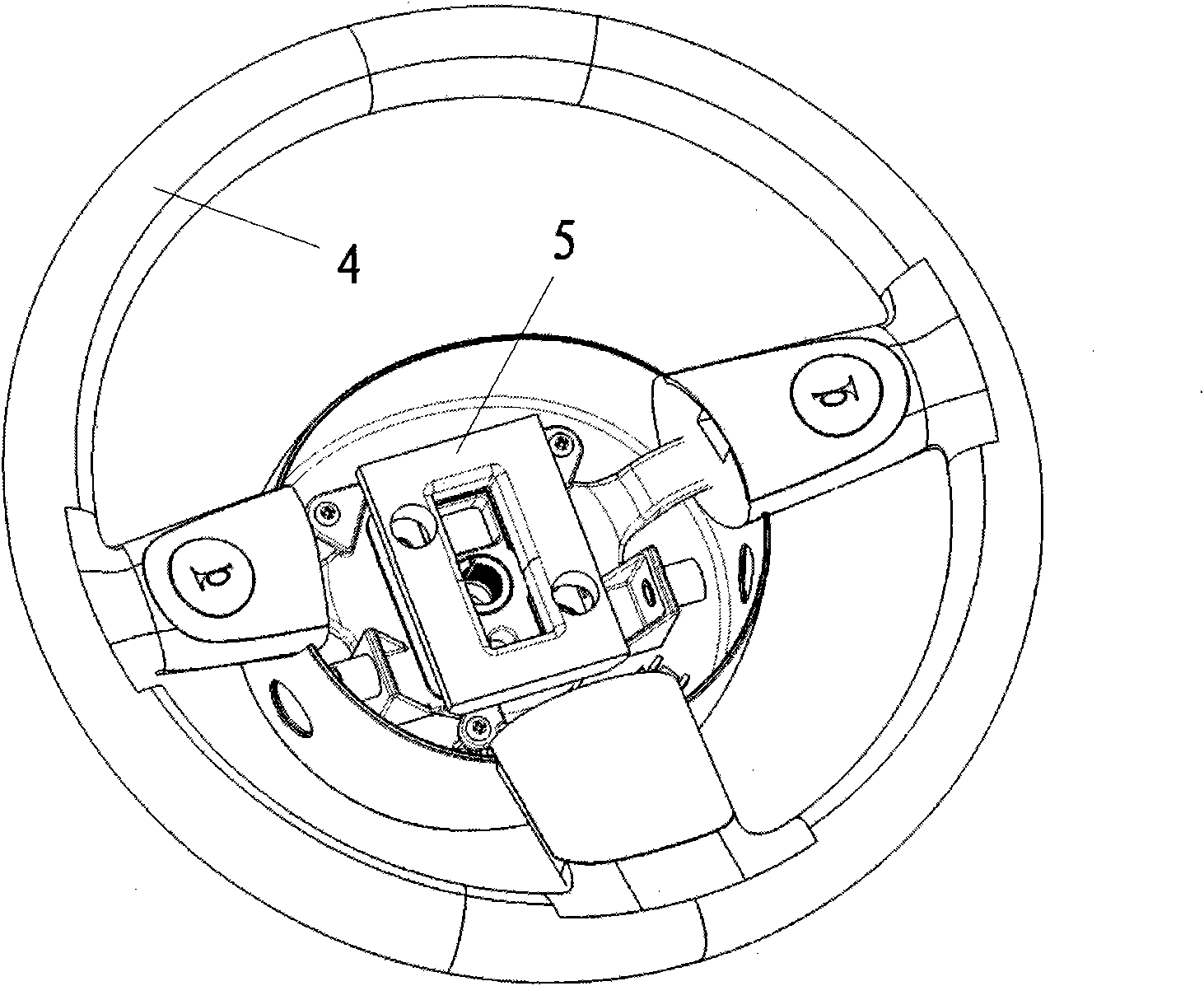
Steering system dynamic vibration absorber and design method thereof
ActiveCN101699098ASimple structureLow costNon-rotating vibration suppressionSteering controlsSteering columnSteering wheel
The invention aims to provide a steering system dynamic vibration absorber with simple structure, low cost and convenient installation and a design method thereof so as to solve the problem of steering wheel vibration when idling and improve vehicle riding comfort. The steering system dynamic vibration absorber comprises a platelike mounting base and a mass block which are connected by a plurality of rubber columns; by adjusting the mass of the mass block and the rubber column tangential stiffness, the tangential inherent frequency of the dynamic vibration absorber when the dynamic vibration absorber is installed in a steering system is similar to the main exciting frequency when the motor idles; the vibration of the motor when the vehicle idles is transmitted to the dynamic vibration absorber via a steering column or the steering wheel to cause the mass block to carry out sympathetic vibration and convert into heat quantity to be dissipated, thus greatly lowering vibration transmitted to the steering wheel and improving vehicle riding comfort. The absorber has small improvement of the original vehicle, has simple structure, low cost and convenient installation and is suitable for being applied to produced or designed and shaped vehicle types.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
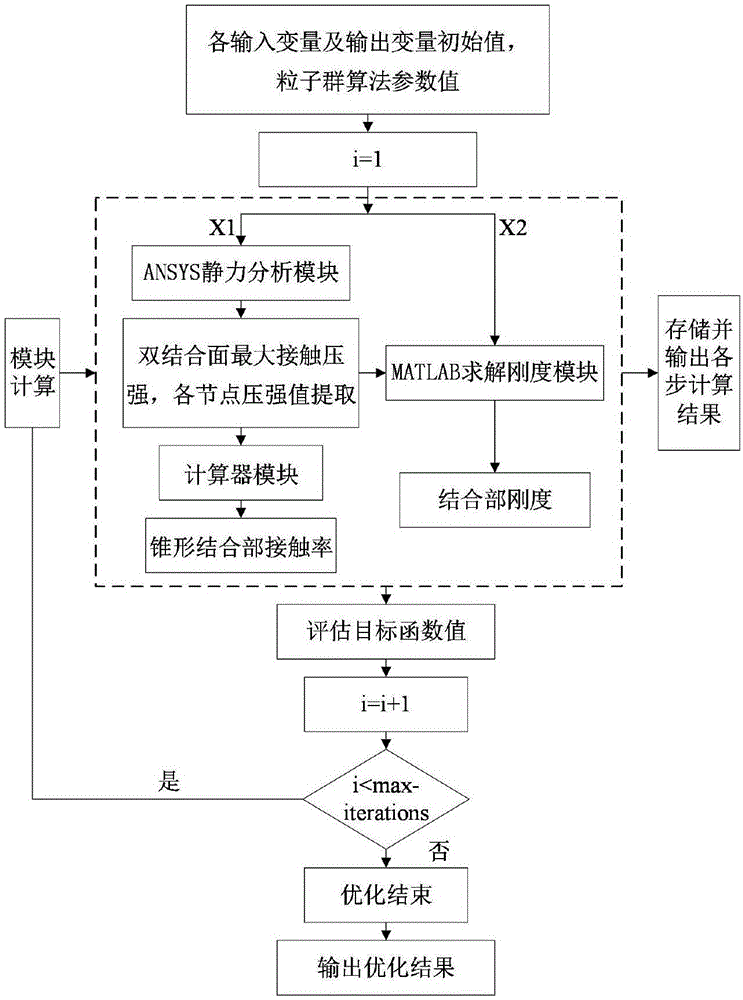
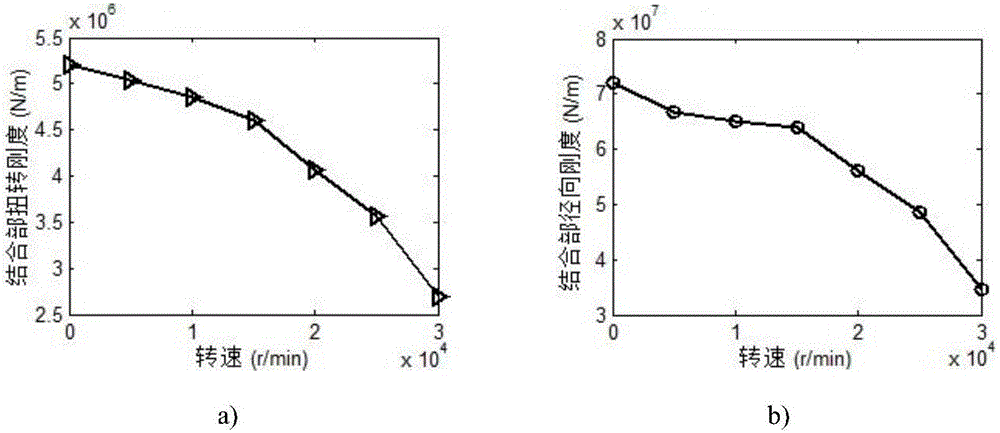
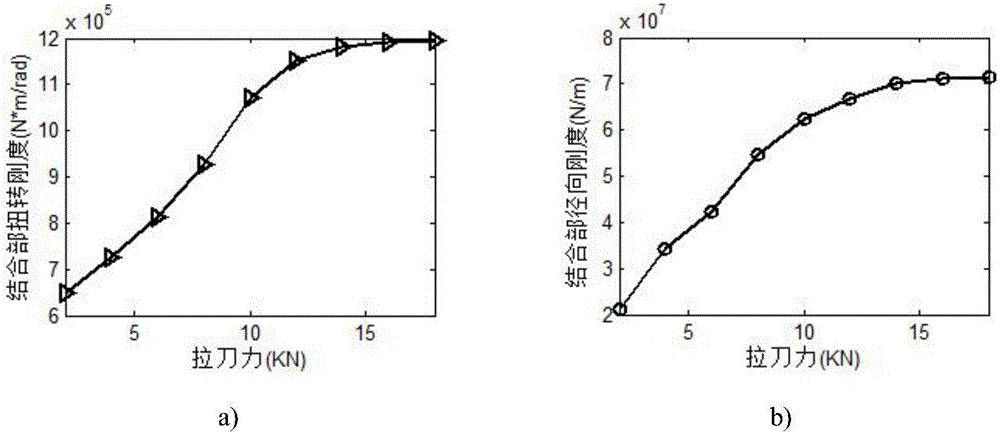
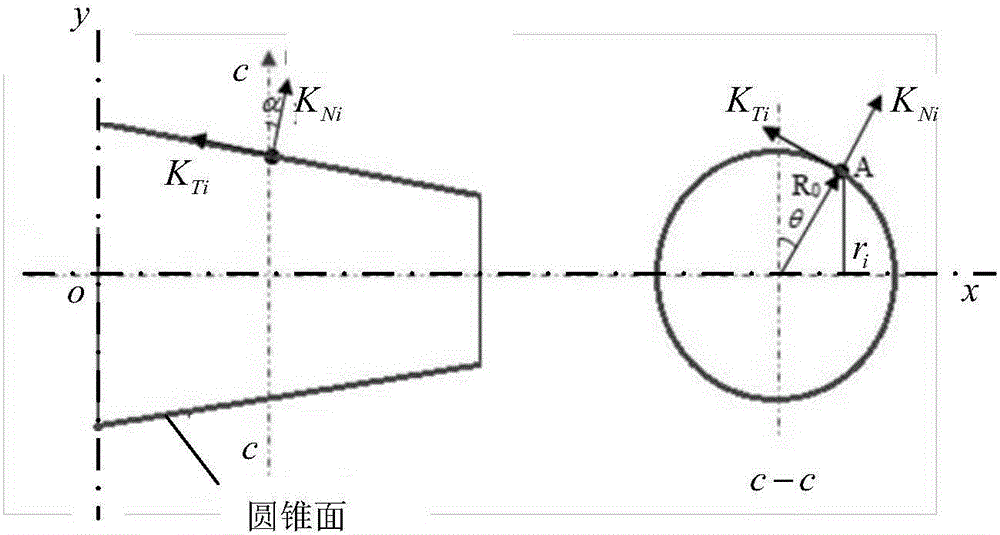
Dual-face locking knife handle-spindle system joint part stiffness characteristic optimization method based on particle swarm optimization
The invention discloses a dual-face locking knife handle-spindle system joint part stiffness characteristic optimization method based on particle swarm optimization. The dual-face locking knife handle-spindle system joint part stiffness characteristic optimization method based on particle swarm optimization adopts knife handle-spindle structural technological parameters and joint surface fractal parameters as optimization variables. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a three-dimensional fractal normal and shear stiffness model and a joint part torsion and radial stiffness model are built, and MATLAB programs are written separately; secondly, a contact-considering three-dimensional geometrical model is built for the dual-face locking knife handle-spindle system and static analysis is performed, so that an APDL file is obtained, and finally integration in Isight software and iterative optimization based on the particle swarm optimization are achieved. According to the method, the combination of the three-dimensional fractal micro contact stiffness modeling theory and finite element static analysis is adopted, the dual-face locking knife handle-spindle system joint part torsion and radial stiffness can be calculated under the high-speed condition, and the knife handle-spindle system optimization process on the Isight software platform based on the particle swarm optimization is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
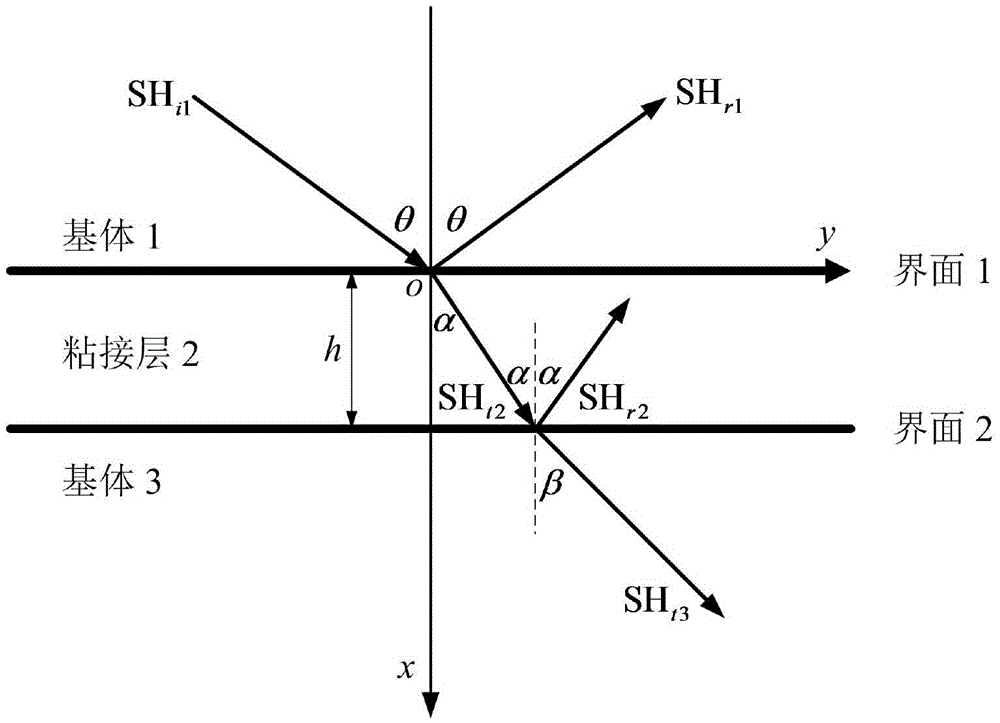
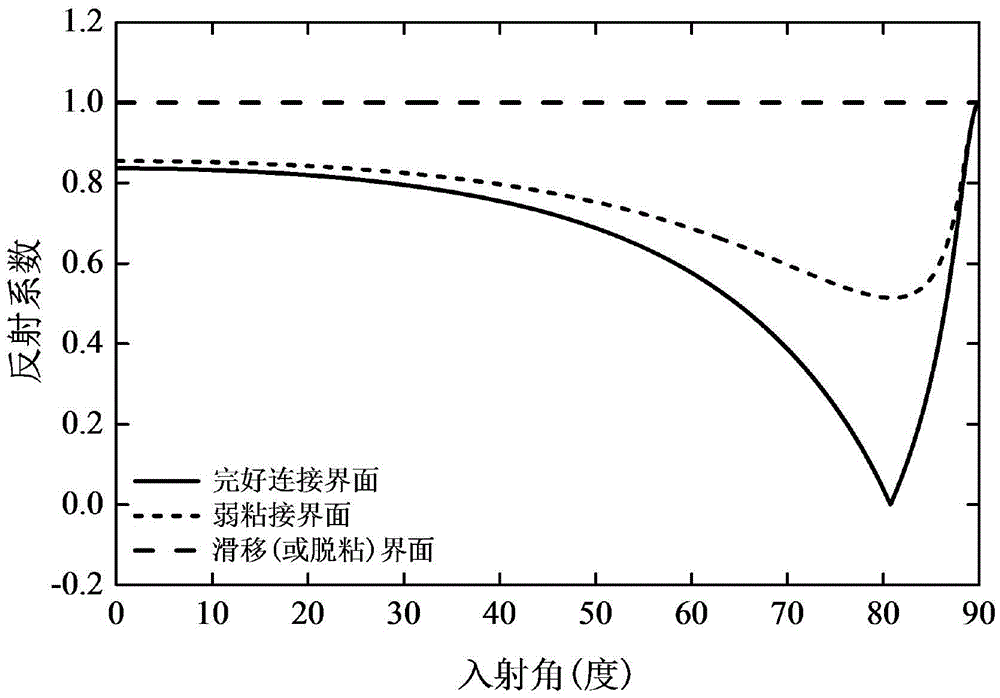
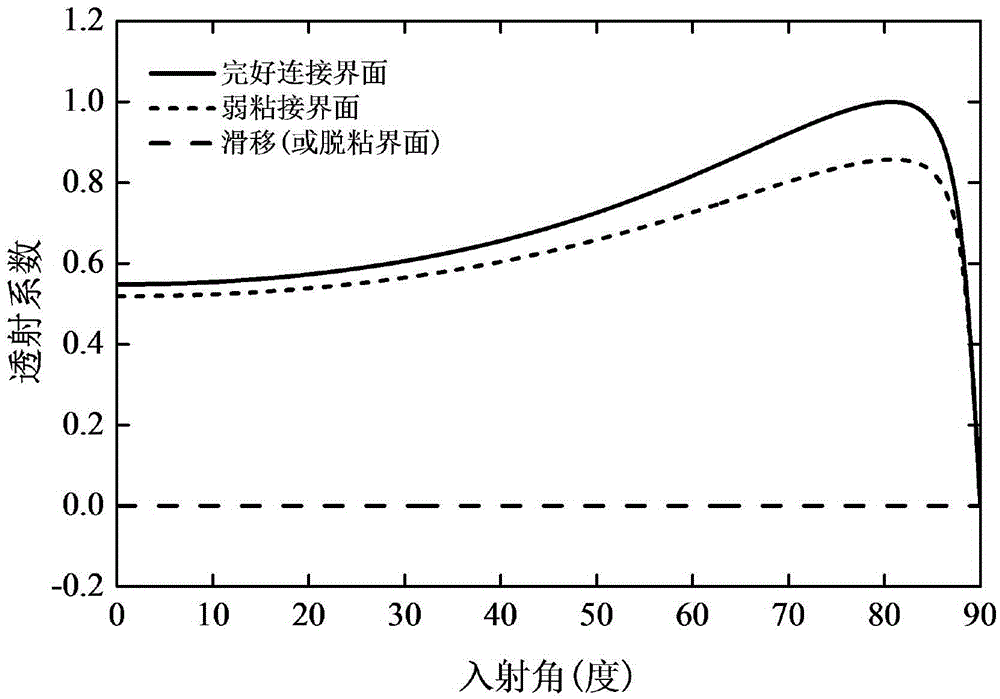
SH guided wave detection method for interfacial state of bonded structure
ActiveCN105486747AEasy to calculateQuick calculationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEpoxyWave detection
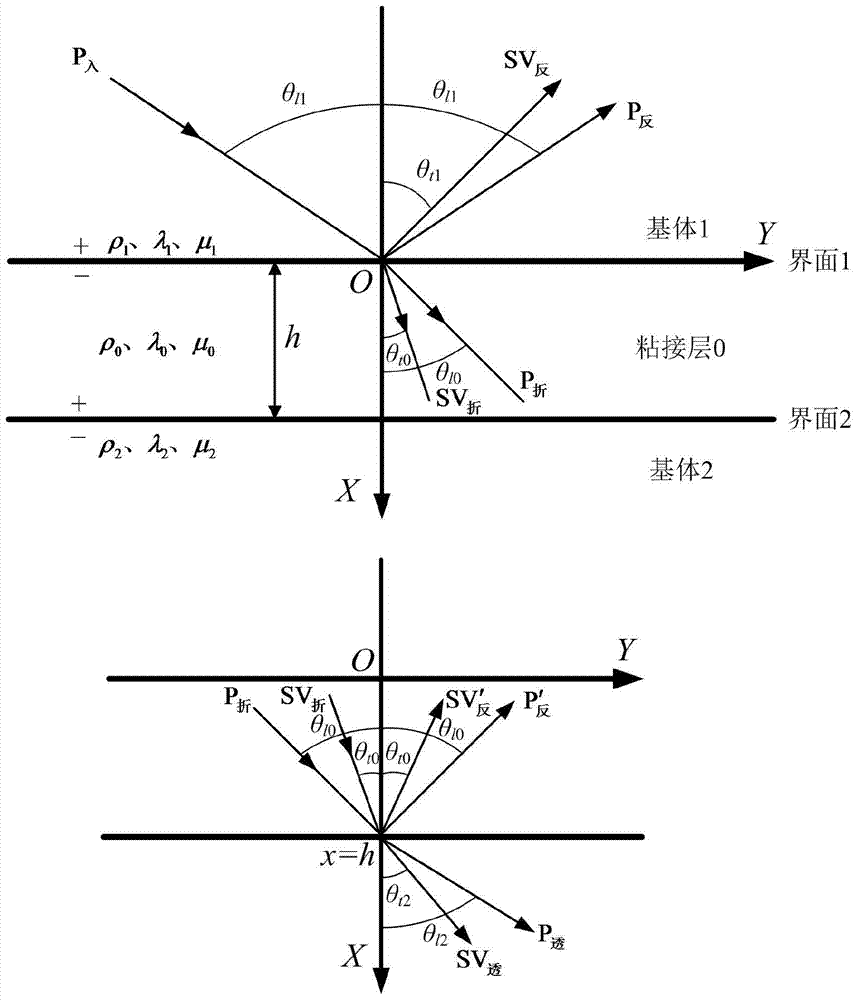
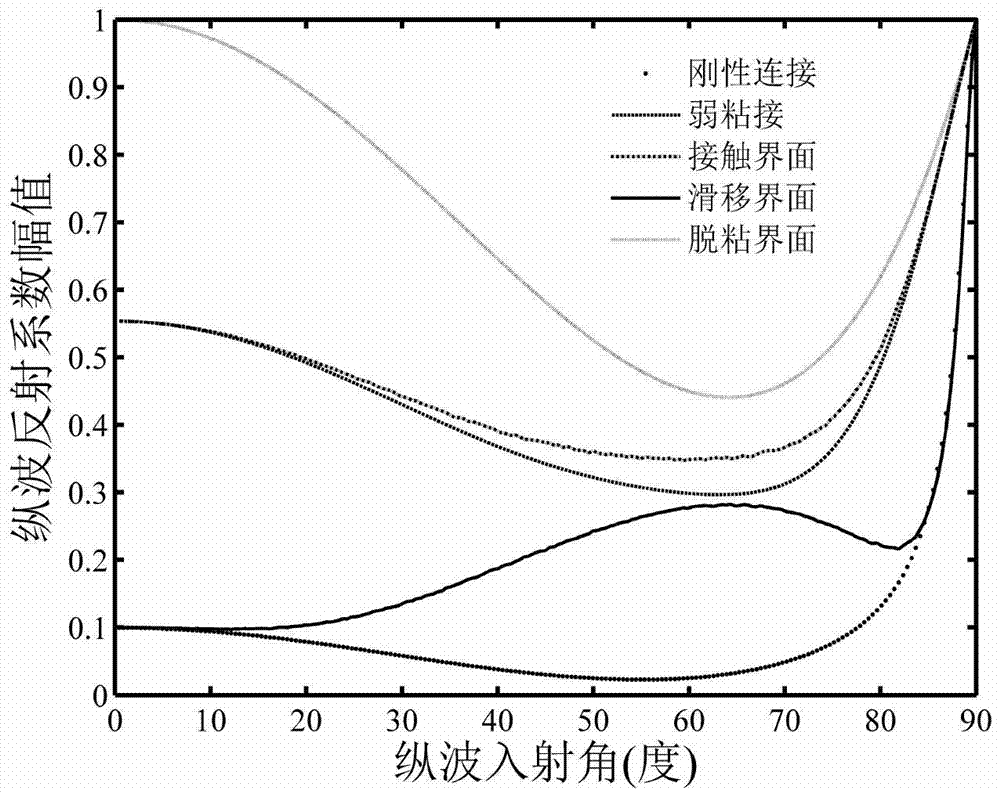
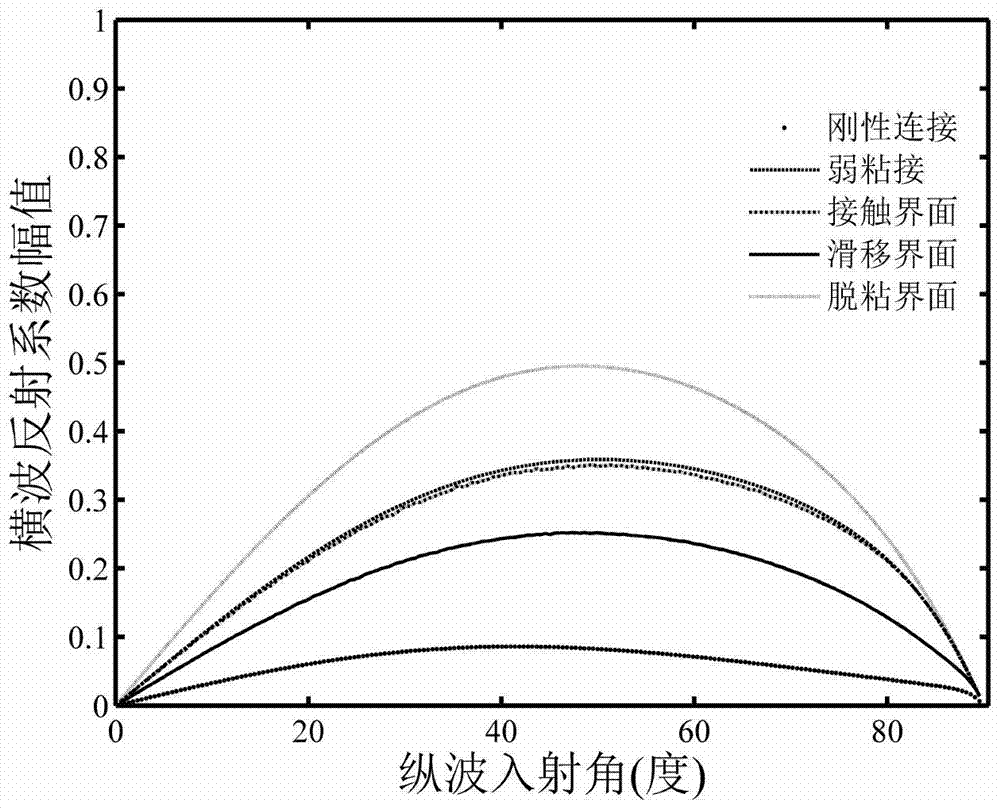
The invention provides an SH guided wave detection method for the interfacial state of a bonded structure. An expression containing a tangential rigidity coefficient K<T> for the reflection and transmission coefficients of a minimum-grade SH guided wave mode (SH<0>) in a plate-shaped bonded structure is deduced based on the governing equation of wave propagation. Taken an aluminum / epoxy resin / aluminum bonded structure as an example, the relation between incident angles and reflection or transmission characteristics of SH guided waves in different interfacial states is analyzed when the incident frequency f of the SH guided waves and the thickness h of a bonding layer are respectively set at specific values. Meanwhile, the influence of the product of frequency and thickness on reflection or transmission characteristics of the SH guided waves is discussed when the incident angles of the SH guided waves are set to be 0 DEG and 50 DEG C. How to discriminate interfacial states is also elaborated. Compared with other detection methods, the SH guided wave detection method for the interfacial state of the bonded structure has the advantages of easiness, effectiveness and practicability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device and method for testing tangential rigidity of junction surface of wheel disc
InactiveCN107153029ASimple structureEasy to operateMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringUniversal testing machine
The invention relates to a device and a method for testing tangential rigidity of a junction surface of a wheel disc. The device comprises a universal testing machine, a pull rod rotor, a digital dial gauge I, a digital dial gauge II and a computer, wherein a pressure sensor arranged on the universal testing machine is connected with the computer by a data line; the universal testing machine further comprises a rack; an upper press head is arranged on the top of the rack; the digital dial gauge I and the digital dial gauge II are respectively positioned at two sides of the upper press head; a movable cross beam is arranged in the middle of the rack; two support blocks are arranged on the cross beam at an interval; the pull rod rotor is horizontally erected on the two support blocks; the pull rod rotor is positioned just under the upper press head. After the technical scheme is adopted, the technical problem that a device and a method which are used for testing the tangential rigidity of the junction surface of the wheel disc are lacked in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Full-waveform information test method for joint rigidity of rock mass
ActiveCN103792289AFull Coverage GuaranteedReduce thicknessAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalReflected wavesFull waveform
The invention relates to a full-waveform information test method for the joint rigidity of rock mass. The method comprises data test and data analysis. The test comprises the following two steps: (1) testing the physical mechanics parameter of the rock mass within a test region, and (2) testing the normal rigidity and the tangential rigidity of the joint in the field; the data analysis comprises the following five steps: (1) building a time-domain analysis model when wavelet is propagated within the joint, (2) decomposing transmitted wave by the wavelet, (3) computing a wavelet system of incident wave and reflected wave, (4) computing time-domain wave form at an incident side which is in parallel with the joint trend and is vertical to the joint trend, and (5) computing the normal rigidity and the tangential rigidity of the joint. The test method is used for analyzing the rigidity of the joint based on the full-waveform information, a structural surface has the function of controlling the mechanical property of the rock mass, the exact acquisition of the normal rigidity and the tangential rigidity of the joint of the rock mass has important meaning on the design, the construction, the stability evaluation and the rock mass reinforcement of the rock mass engineering, According to the method, the operation is simple and quick, and the test cost is low, and a test result comprehensively reflects the complexity of the mechanical property.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Blocked analysis method for large-size machine tool structural member
InactiveCN107589670AImprove dynamic performanceGuide designSpecial data processing applicationsAdaptive controlEngineeringThree dimensional model
The invention discloses a blocked analysis method for a large-size machine tool structural member. The method comprises the steps of establishing a combining surface rigid model based on a three-dimensional fractal contact theory, and identifying a normal stiffness and lateral stiffness; performing parameter modeling of the large-size structural member (crossbeam) based on a definite element method, and integrating the identified normal stiffness and the lateral stiffness into a large-size structural member three-dimensional model; and utilizing a parameter blocked designing method and a particle swarm optimization method, optimizing the dynamic performance of the large-size structural member (crossbeam), and designing the optimized large-size structural member (crossbeam) three-dimensional model by means of an optimization result. A re-manufacturing factor is taken into a designing period so that the structural member not only can satisfy function and performance requirement of a product and furthermore facilitates manufacturing, transportation, assembling and re-manufacturing. The blocked analysis method for the large-size machine tool structural member is deeply understood, thereby better guiding designing and application of the large-size machine tool structural member.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for predicting interface failure and mesoscopic crack propagation of composite material under hydraulic osmotic load
ActiveCN112487557ASimulation is accurateGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCrazingClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a method for predicting interface failure and microscopic crack propagation of a composite material under a hydraulic osmotic load. The method comprises the following steps: representing a fracture state and interface distribution of a model by using a fracture phase field and an interface phase field; combining a phase field method and a Biot pore elastic medium theory inthe simulation and prediction process, calculating distribution of a displacement field and a liquid pressure field of the model under a hydraulic load, calculating the influence of the displacement field on the fracture phase field, and therefore achieving simulation of crack growth of a composite material under the mesoscopic scale when the composite material is subjected to the hydraulic load.According to the method, the interface normal rigidity and tangential rigidity are considered in a cohesion interface model. According to the phase field method model, the growth and bifurcation of the microscopic cracks of the composite material can be accurately simulated.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Joint rigidity analyzing method for bi-side locking handle-main shaft under high rotating speed conditions
ActiveCN106525418APrecise 3D Fractal TheoryMachine gearing/transmission testingExpansion factorElement analysis
The invention discloses a joint rigidity analyzing method for a bi-side locking handle-main shaft under high rotating speed conditions, specifically to a joint portion rigidity modeling method taking non-uniform distribution of bi-joint-side pressure, and the system joint rigidity under high rotating speed conditions is analyzed based on the method. The method includes the steps of establishing a three-dimensional fractal normal and tangential rigidity model, analyzing to obtain pressure values of each node on a bi-joint side based on static force, calculating the equivalent rigidity value corresponding to the nodes, and obtaining the torsion and radial rigidity value through a confirmation model, and finally revealing the influence trend of broaching tool force, disk spring rigidity and disc spring pretightening force on the rigidity of the joint portion under different rotation speed and high rotation speed. The method is characterized in that the influence of elasto-plastic deformation and domain expansion factor are taken into consideration in the fractal theory, and nonuniformity of the pressure distribution on the joint surface is considered in the finite element analysis, thereby conducting accurate modeling and analyzing the joint rigidity of T40 handle-main shaft under high rotating speed conditions.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Analytical method of single-faced contact handle-main shaft combination part stiffness based on three-dimensional modified fractal theory
InactiveCN106777463ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisEngineering
The invention discloses an analytical method of a single-faced contact handle-main shaft combination part stiffness based on a three-dimensional modified fractal theory, and particularly relates to an accurate rigidity model of the combining part considering about uneven distribution of pressure of system combining face; based on the model, the rigidity of the combining part is analyzed under the high rotate speed condition. The method includes steps of firstly establishing three-dimensional modified fractal normal and tangential stiffness models; acquiring pressure intensity of every node of a contact face through static analysis, and calculating the equivalent nominal and tangential rigidities corresponding to every node on the basis of the pressure intensity; through conversion and link in parallel, acquiring the torsional and radial stiffness value of the combining part; finally, the influence tendency of the broach force under different rotate speeds and high rotate speed on the rigidity of the combining part is disclosed, the reasonable value scale of the limit rotate speed and the broach force is confirmed. The method considers about uneven distribution of pressure in a finite element analysis, thereby carrying out the accurate modeling and analysis on the BT40 handle-main shaft combination part stiffness under the high rotate speed condition.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for judging connecting compactness of interface by using spring stiffness coefficient
InactiveCN104458570AFew parametersAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing mechanical meansStiffness coefficientSignal on
The invention discloses a method for judging the connecting compactness of an interface by using a spring stiffness coefficient. The method is mainly used for ultrasonic nondestructive testing of the interface compactness and comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a corresponding model according to actual conditions, and arranging a spring model at the interface; (2) deducing out a frequency dispersion equation of guided wave propagation according to a wave equation and boundary conditions; (3) drawing out a changing curve of phase velocity along with the tangential stiffness coefficient Kt under the condition that the normal stiffness coefficient Kn is infinitely great so as to obtain a tangential stiffness coefficient value with relatively sensitive phase-velocity change and a corresponding frequency-dispersion characteristic curve; (4) determining peeling-degree percentage values corresponding to different Kt values by simulation; (5) exciting and receiving ultrasonic guided wave signals on a tested object; (6) extracting parameters from actual testing signals to carry out inversion and further determine corresponding Kt values; and (7) judging the compactness degree of the interface by the tangential spring stiffness coefficient value. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the connecting condition of the interface of a bonding part can be relatively well obtained and the quality monitoring and the maintenance can be carried out on the bonding part in a relatively effective manner.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
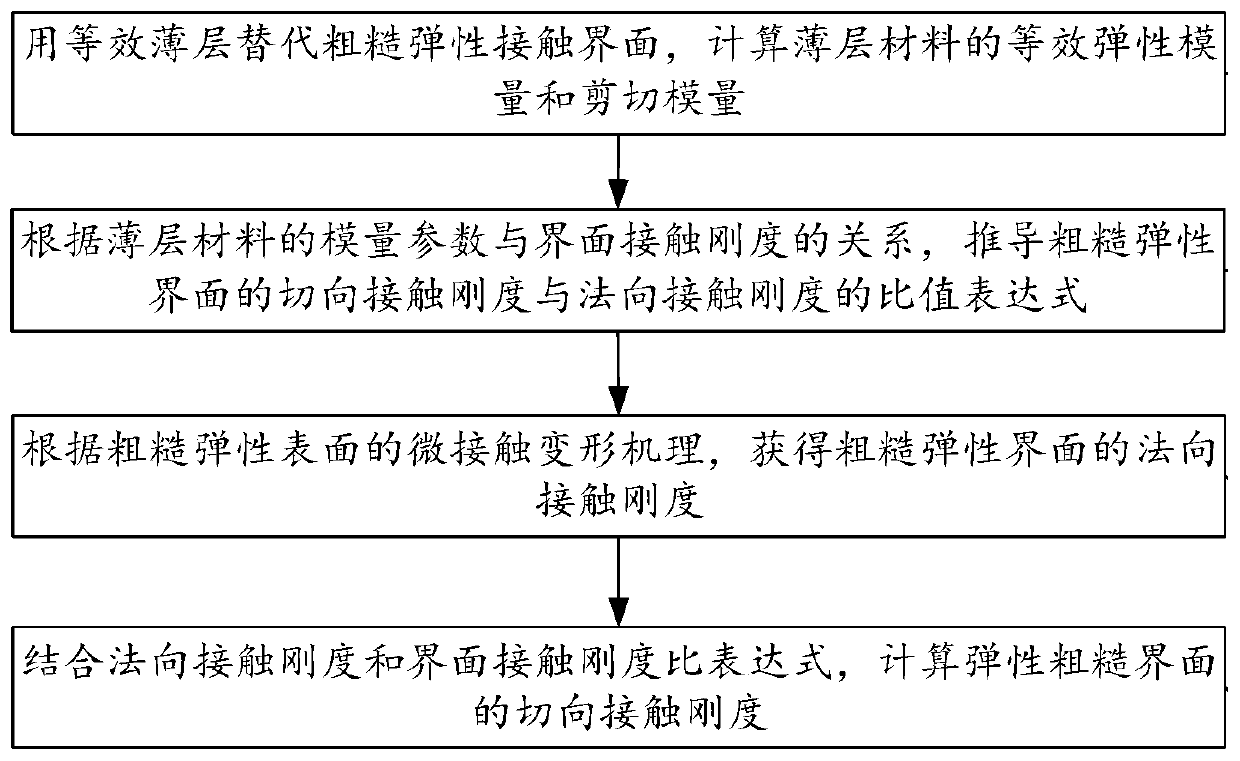
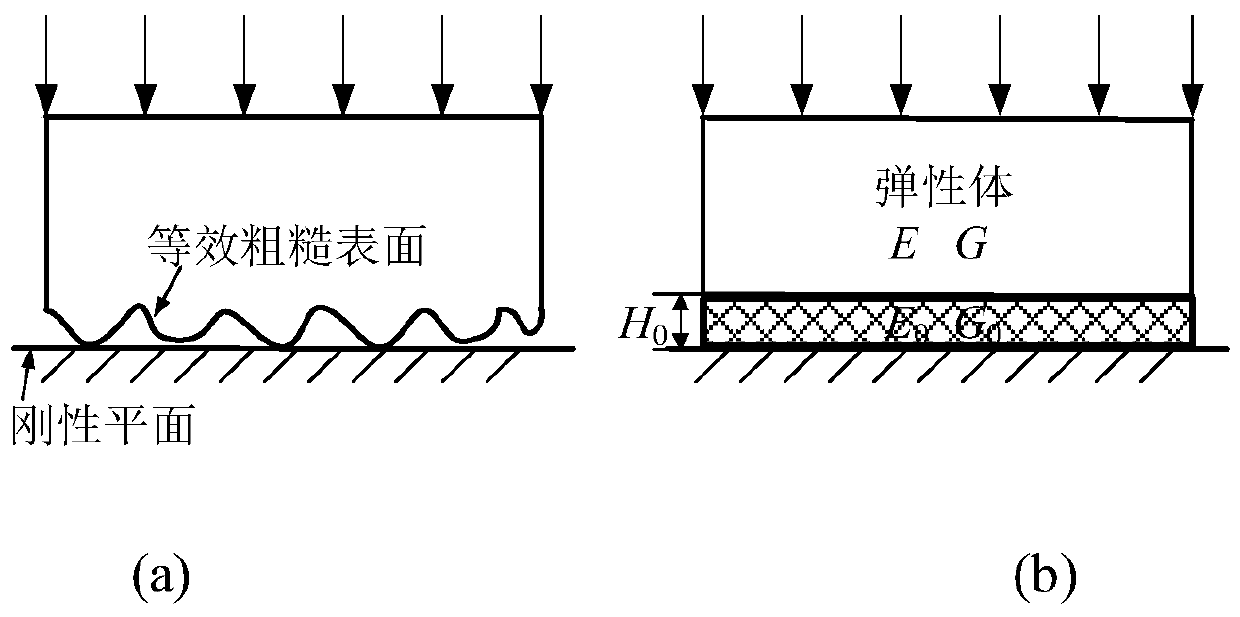
Method for calculating the tangential contact stiffness of a rough elastic interface
ActiveCN109829224AThe result is accurateOvercome limitationsSpecial data processing applicationsShear modulusTangential contact
The invention provides a method for calculating the tangential contact stiffness of a rough elastic interface, and belongs to the technical field of interface contact stiffness calculation. The methodcomprises the steps that firstly, an equivalent thin layer is used for replacing a rough contact interface, and elasticity modulus and shear modulus of a thin layer material are calculated; secondly,representing the contact stiffness of the rough elastic interface based on the modulus parameters of the thin-layer material, and deducing a specific value expression of the tangential contact stiffness and the normal contact stiffness of the rough elastic interface; obtaining the normal contact stiffness of the rough elastic interface according to the micro-contact deformation mechanism of the rough elastic interface; and finally, calculating the tangential contact stiffness of the rough elastic interface by combining the normal contact stiffness and the interface contact stiffness ratio expression. The invention provides the novel method for calculating the tangential contact stiffness of the rough elastic interface, the tangential contact stiffness characteristic of the rough elastic interface is disclosed, the calculation result is accurate, and a theoretical basis is provided for the tangential contact dynamics analysis of the rough elastic interface.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Vibration damping support structure, compressor and air conditioner
PendingCN110242541AIncrease contact areaIncrease radialPositive displacement pump componentsNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringVibration isolation
The invention provides a vibration damping support structure, a compressor and an air conditioner. The vibration damping support structure includes a support leg and a vibration damping pad, the support leg includes a flat plate with a hole and a reinforcing pipe, and the reinforcing pipe is arranged in the hole in a penetrating manner; and the reinforcing pipe is arranged in the vibration damping pad. The reinforcing pipe is arranged in the flat plate of the support leg in the penetrating manner, the contact area between the support leg and the vibration damping pad is increased, the radial or tangential stiffness is increased, greater force can be borne, the requirement for the large rigidity required by low frequency vibration is met, and the effects of reducing vibration and increasing the vibration isolation rate are achieved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
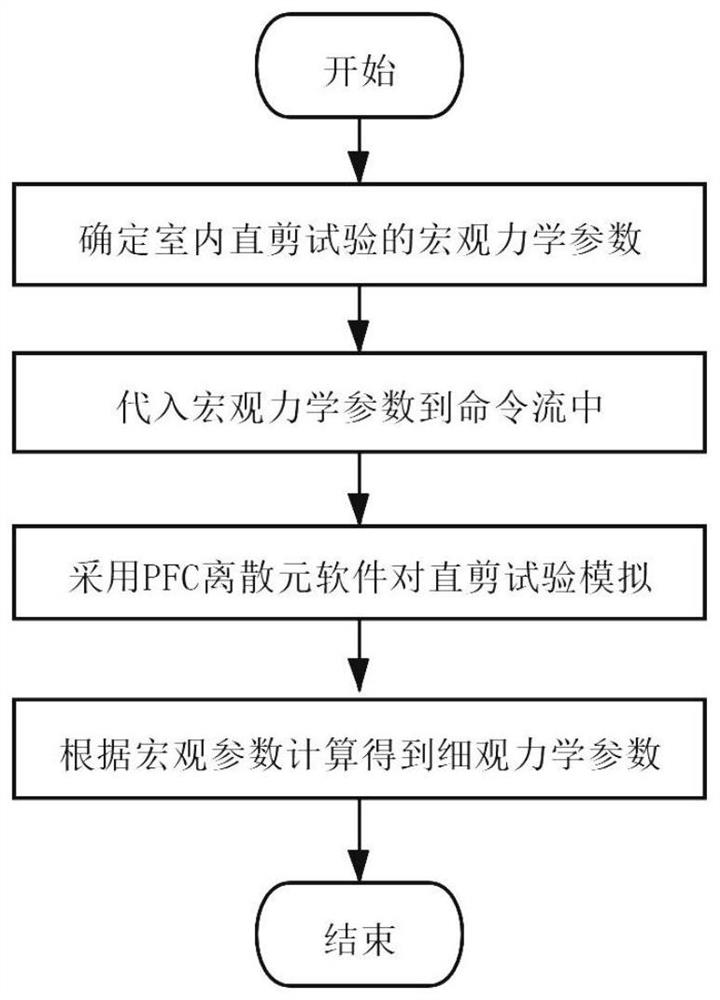
Method for calculating micro-mechanical parameters of reinforced tailings based on PFC discrete element
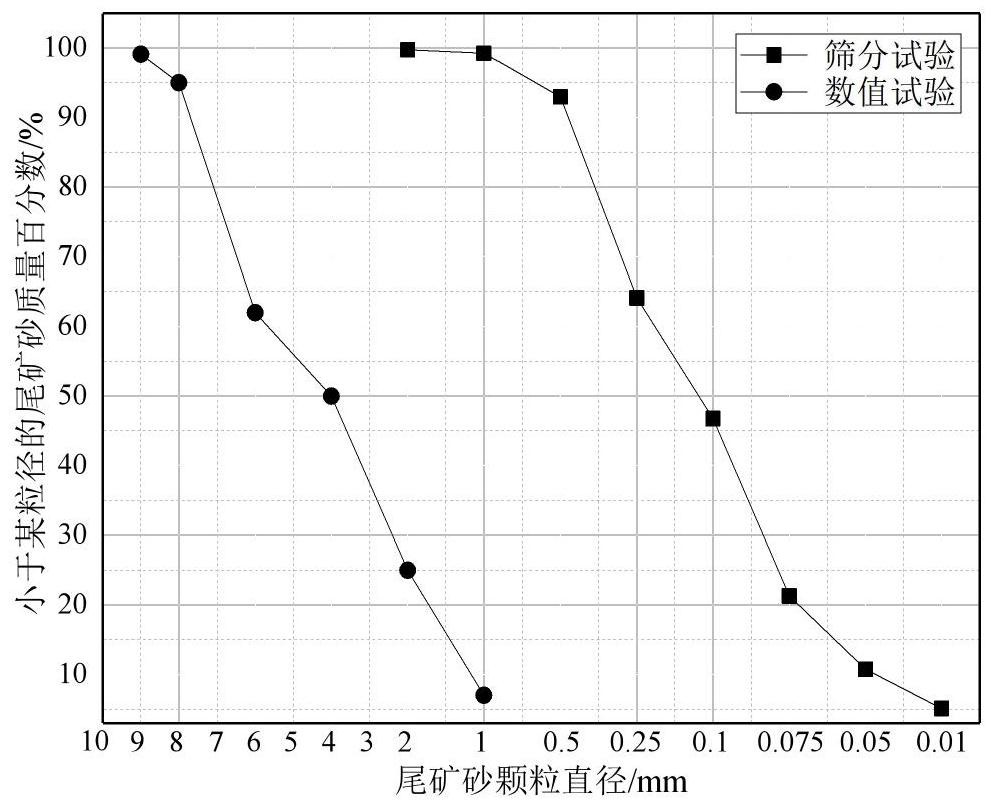
PendingCN113868933AImproved correlation calculation methodImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingMacroscopic scaleFrictional coefficient
The invention relates to a method for calculating micro-mechanical parameters of reinforced tailings based on PFC discrete elements. The method comprises the following specific steps: obtaining macromechanical parameters through a geogrid and tailing sand indoor direct shear test; by utilizing PFC discrete element software, establishing a direct shear test numerical model, determining an overlying load by adjusting servo confining pressure in the model, and before the direct shear test of the model is started, substituting macro mechanical parameters such as peak shear stress intensity, density, apparent cohesive force, an internal friction angle and a friction coefficient calculated by the test into a command; and, after the program is started and the operation is completed, obtaining the numerical values of the normal stiffness and the tangential stiffness of the mesomechanics parameters in the model shear test process. The method has the advantages that: macroscopic mechanical parameters are obtained through indoor tests, mesoscopic mechanical parameters can be obtained through numerical simulation calculation, a macroscopic and mesoscopic parameter relevance calculation method is improved, calculation efficiency is higher, results are more accurate, important mesoscopic mechanical parameter indexes can be provided for safety and stability calculation of the reinforced tailing fill dam, and the contact state of the tailings particles is clearly described in numerical simulation, so that a numerical simulation result is closer to an actual working condition.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Damp lashing strip structure of industrial steam turbine high load short vane
ActiveCN103089322AMeet the strength vibration performanceIncrease the circumferential lengthBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesWedge angleShear stiffness
The invention relates to a damp lashing strip structure of an industrial turbine high load short vane. Each vane is composed of a vane body, a vane root and a middle connecting body. A whole circle of vanes are evenly installed on a rotor from the vane root along the peripheral direction. A lashing strip is arranged at the top of the vane body. The lashing strips at each two adjacent vanes are arranged in a tightly adhesive mode. An axial wedged groove is formed in a matching face of each of the two adjacent lashing strips in a milling mode. A wedged damping block is arranged in each wedged groove. Two ends of the bottom of each wedged groove are respectively provided with a sealing groove along the peripheral direction. Sealing shoulders are arranged on the position, corresponding to the sealing grooves, on each wedged damping block. According to the damp lashing strip structure of the industrial turbine high load short vane, the peripheral length of each wedged damping block can be increased as large as possible in the condition that a wedge angle is controlled well so that centrifugal force is increased and damping effect is good. Shear stiffness of the damp lashing strip is large so that the effect of bunching the vanes can be achieved, and therefore dynamic stress can be effectively reduced and short vane strength vibration performance is achieved in the condition of large load and high temperature.
Owner:HANGZHOU STEAM TURBINE
Detection method of interface morphology of multilayer bonded structure
ActiveCN104820017BHigh precisionReduce mistakesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalEpoxyBond interface
Disclosed is a method of detecting interfacial configuration of a multilayer adhesive structure. On the basis of a control equation of wave propagation, mechanical characteristics of an adhesive interface are represented via nominal and tangential rigidity coefficients so as to deduce an expression of reflection and transmission coefficients of longitudinal and transverse waves in the multilayer adhesive structure at the time of incoming of the ultrasonic longitudinal wave; taking an aluminum-epoxy resin-aluminum adhesive structure as an example, when incoming frequency f of the longitudinal wave and thickness h of an adhesive layer are of certain fixed values, the relation of the incoming angle to the reflection and transmission characteristics of the longitudinal and transverse waves in different interfacial configurations is analyzed; similarly, under the condition of the incoming angles 0 DEG and 30 DEG of the longitudinal wave, the influence of a frequency-thickness product upon reflection and transmission characteristics of the acoustical wave is discussed; meanwhile, which manner is taken to identify the interfacial configuration is explained. Compared with other detection methods, the method which is simple, effective and practicable is suitable for identifying the interfacial configurations of the adhesive structures.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Mechanical joint surface tangential rigidity dynamic measuring device and measuring method
InactiveCN108318197AAvoid vibration effectsImprove accuracyMachine part testingElasticity measurementShear stressJoint surface
The invention discloses a mechanical joint surface tangential rigidity dynamic measuring device comprising a cylindrical tank which is internally provided with a shaft core. The external wall of the shaft core is sleeved by a shaft sleeve, and a gap is reserved between the external wall of the shaft sleeve and the internal wall of the tank. A joint surface is formed between the shaft core and theshaft sleeve. An acceleration measuring device is connected on the upper surface of the shaft core and the shaft sleeve, and each acceleration measuring device is connected with signal acquisition equipment through a lead. The center of the bottom part and the external wall of the two sides of the tank are provided with air inlets. The problems that the influence of other joint surfaces and othersurrounding factors cannot be eliminated in the measuring process of the present joint surface rigidity measuring device and the measuring result is not accuracy because of the fact that the uniform shear stress cannot be applied can be solved. According to the measuring method, measurement of the single joint surface can be realized so that joint surface tangential rigidity measurement is enabledto have high accuracy and practical value, and the measuring method is easy.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Steering system dynamic vibration absorber and design method thereof
ActiveCN101699098BSimple structureLow costNon-rotating vibration suppressionSteering controlsSteering columnSteering wheel
The invention aims to provide a design method of a steering system dynamic vibration absorber with simple structure, low cost and convenient installation so as to solve the problem of steering wheel vibration when idling and improve vehicle riding comfort. The steering system dynamic vibration absorber comprises a plate like mounting base and a mass block which are connected by a plurality of rubber columns; by adjusting the mass of the mass block and the rubber column tangential stiffness, the tangential inherent frequency of the dynamic vibration absorber when the dynamic vibration absorber is installed in a steering system is similar to the main exciting frequency when the motor idles; the vibration of the motor when the vehicle idles is transmitted to the dynamic vibration absorber via a steering column or the steering wheel to cause the mass block to carry out sympathetic vibration and convert into heat quantity to be dissipated, thus greatly lowering vibration transmitted to the steering wheel and improving vehicle riding comfort. The absorber has small improvement of the original vehicle, has simple structure, low cost and convenient installation and is suitable for being applied to produced or designed and shaped vehicle types.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Method for acquiring dynamic stiffness of rock joint
PendingCN113432977AThe solution is not easy to determineSolve the inability to take joint normals into accountMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansUniaxial compressionDynamic stiffness
The invention relates to a method for acquiring the dynamic stiffness of a rock joint, and belongs to the technical field of rock mass measurement. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a rock sample containing the joint, carrying out a uniaxial compression test on the rock sample, and determining an equivalent normal stress sigma n and an equivalent tangential stress sigma t on a plane where the joint is located according to an applied compression external load sigma 0; shooting an image of the rock in the compression process, and determining a displacement field and a strain field in the rock test process according to the shot image; determining the thickness of the joint according to the strain field, selecting a plurality of characteristic sections in the length direction of the joint, determining displacements of upper and lower edge measuring points of the characteristic sections, and determining an average normal displacement un and an average tangential displacement ut on a plane where the joint is located; and determining the dynamic normal and tangential stiffness of the joint according to a joint stiffness calculation formula.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Automobile shock absorber
ActiveCN101900179BSolve idle vibration problemLow costHand wheelsElastic dampersSteering wheelResonance
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Calculation Method of 3D Contact Stiffness of Spur Gear Based on Rough Surface
ActiveCN106844818BPrecise contact stiffnessSolve the disadvantages of smooth contactGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationRough surfaceContact pressure
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
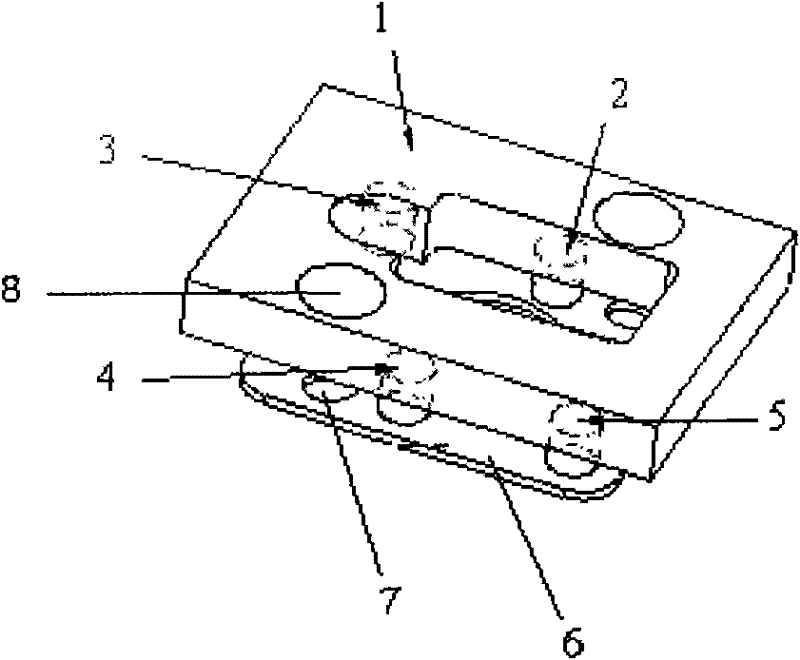
Device for testing tangential stiffness property of joint surface
InactiveCN102393330BEasy to processEasy to installMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesTangential displacementEngineering
The invention discloses a device for testing a tangential stiffness property of a joint surface, and belongs to the fields of mechanical design and manufacture. The device consists of a test loading device (1) and a tangential test assembly. An upper test piece (7) is butted with a lower test piece (6), and a gap is reserved at the joint; a pressing plate (3) and a pressing plate (11) are arranged on two surfaces vertical to the test piece butting surface, and are fixedly connected through two high-strength bolts (9) and (11) to form the tangential test assembly; the high-strength bolts (9) and (11) are symmetrical about the gap of the joint of the upper and lower test pieces; brackets (8) and (5) are arranged on two sides of the gap of the joint for accommodating an eddy current displacement sensor (4); and a force sensor (14) for measuring loading force signals and the eddy current displacement sensor (4) for measuring the tangential displacement variation of the joint surface are connected to a signal acquisition system. The device has the advantages of simple machining, convenience for clamping, high universality, high controllability of the parameters and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Large joint surface experiment device
InactiveCN102053061BSimple structureEasy to installUsing mechanical meansStrength propertiesLarge jointTangential force
The invention relates to a large joint surface experiment device, in particular to a large joint surface normal rigidity and tangential rigidity detection device and method. The device comprises a normal augmentor (1) in a mechanical frame, a normal eddy current sensor (2), an upper test specimen (3), an acceleration sensor (4), a tangential augmentor (5), a lower test specimen (6), a working platform (7), a tangential eddy current sensor (8), a tangential force sensor (9) and an upper computer for calculating the characteristics of a joint surface. In the method, a periodical external force load and the deformation of the joint surface under the periodical external force load are measured in a Kelvin-Voight model, a delaying curve of the periodical process is made, and the rigidity and damping characteristics of the joint surface are obtained. The large joint surface normal rigidity and tangential rigidity detection device can be used for measuring static and dynamic normal rigidities and damps of the large fixed joint surface, and can realize the characteristics of the joint surface when loaded with a positive load, an unbalance load and an impact load.
Owner:天津航天长征技术装备有限公司
Split-type tbm cutter head joint characteristic scaling measurement method and system
ActiveCN110427656BImprove general performanceSame stiffness propertiesDesign optimisation/simulationShear modulusClassical mechanics
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A device and method for testing the tangential stiffness of the joint surface of the wheel disc
InactiveCN107153029BSimple structureEasy to operateMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a device and a method for testing tangential rigidity of a junction surface of a wheel disc. The device comprises a universal testing machine, a pull rod rotor, a digital dial gauge I, a digital dial gauge II and a computer, wherein a pressure sensor arranged on the universal testing machine is connected with the computer by a data line; the universal testing machine further comprises a rack; an upper press head is arranged on the top of the rack; the digital dial gauge I and the digital dial gauge II are respectively positioned at two sides of the upper press head; a movable cross beam is arranged in the middle of the rack; two support blocks are arranged on the cross beam at an interval; the pull rod rotor is horizontally erected on the two support blocks; the pull rod rotor is positioned just under the upper press head. After the technical scheme is adopted, the technical problem that a device and a method which are used for testing the tangential rigidity of the junction surface of the wheel disc are lacked in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
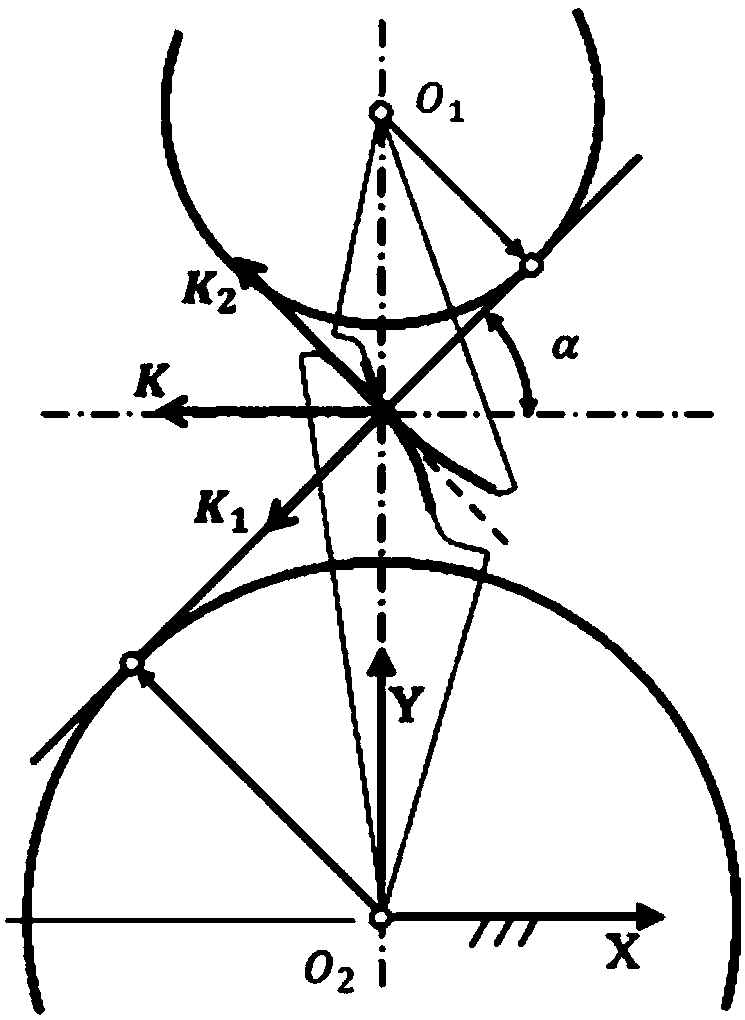
Tangential rigidity measuring device for two crossed parabolic cylinders
ActiveCN114062180ASimple structureEasy to operateInvestigating machinabilitySustainable transportationMeasurement deviceEngineering
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A method for calculating dynamic frequency of self-locking blade of industrial steam turbine
ActiveCN109408922AEasy to useGuaranteed uptimeGeometric CADSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementContact pressureSelf locking
A method for calculating dynamic frequency of self-locking blade of industrial steam turbine is a finite element method, First, the static strength of the blade considering contact is calculated, thetorsion angle of the blade tip and the contact pressure between the adjacent blade shroud are obtained. A spring element (MATRIX 27) is established between nodes in a region where the contact pressureis greater than 30 MPa, in lieu of that contact unit, Let the normal stiffness kn of these elements be the same. The tangential stiffness kt is also the same, and have a certain relationship. The relationship is related to the properties of the material, Resize kt, static strength calculation, Finally, the dynamic frequency of the self-locking blades is calculated according to the obtained valuesof kn and kt. The method has been applied to the dynamic frequency calculation of the last stage blades of an industrial steam turbine used in a large-scale PTA plant. The experimental results show that the dynamic frequency error calculated by this method is less than 4%.
Owner:HANGZHOU STEAM TURBINE
Contact interface tangential rigidity testing device based on cyclic load of piezoelectric actuator
ActiveCN112161765ATangential stiffness determinationMeet the testElasticity measurementPiezoelectric actuatorsEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of mechanical test devices, and provides a contact interface tangential rigidity testing device based on the cyclic load of a piezoelectric actuator. The invention provides a testing machine structure capable of testing the tangential rigidity of a contact interface under the cyclic load. According to the design, the piezoelectric actuator is used for applying a transverse load with a determined size, the generated transverse load is controlled by controlling the input voltage of the piezoelectric actuator, and an equal-size reverse transverse loadis input through the resilience force of a spring. Different from the prior art that only the tangential rigidity under static contact can be tested, the method can provide the cyclic load with a determined amplitude, and can feed back the dynamic tangential force of the contact interface through a force sensor and feed back the dynamic displacement of the contact interface through a laser displacement sensor so as to determine the dynamic tangential rigidity of the contact interface. In addition, test pieces of different sizes can be tested.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com