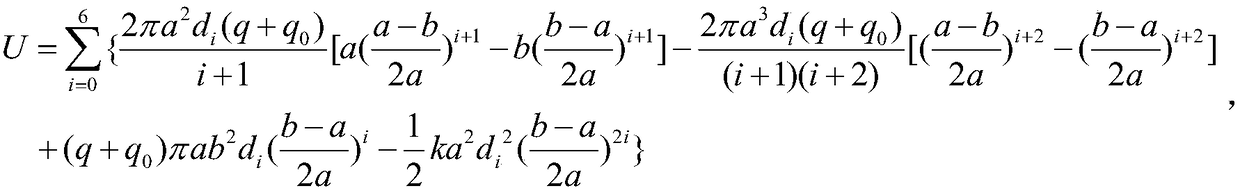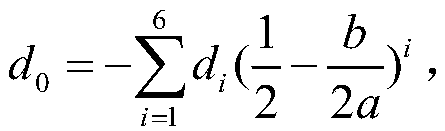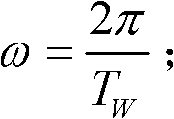Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
317 results about "Stiffness coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
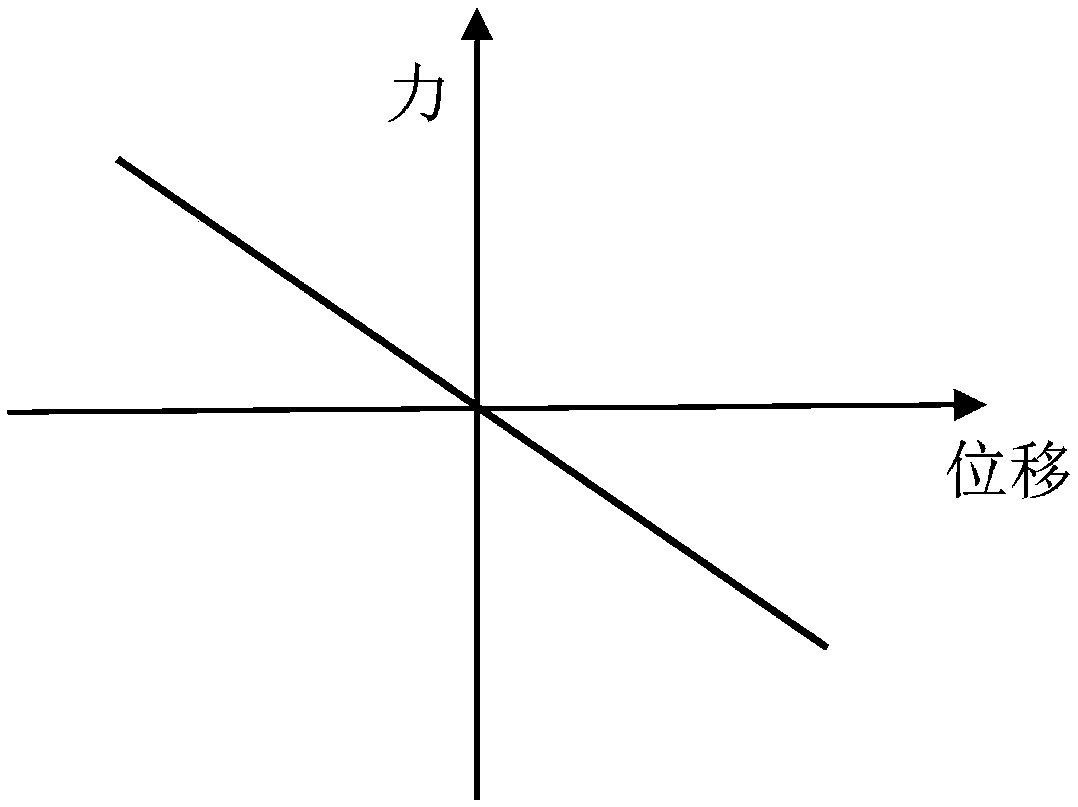
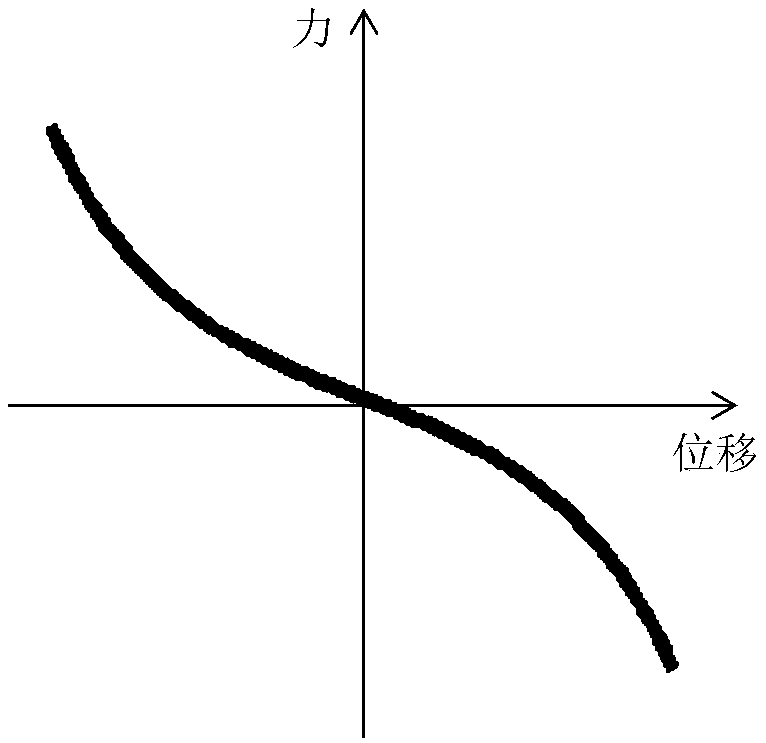
Stiffness coefficient. [′stif·nəs ‚kō·i‚fish·ənt] (mechanics) The ratio of the force acting on a linear mechanical system, such as a spring, to its displacement from equilibrium.
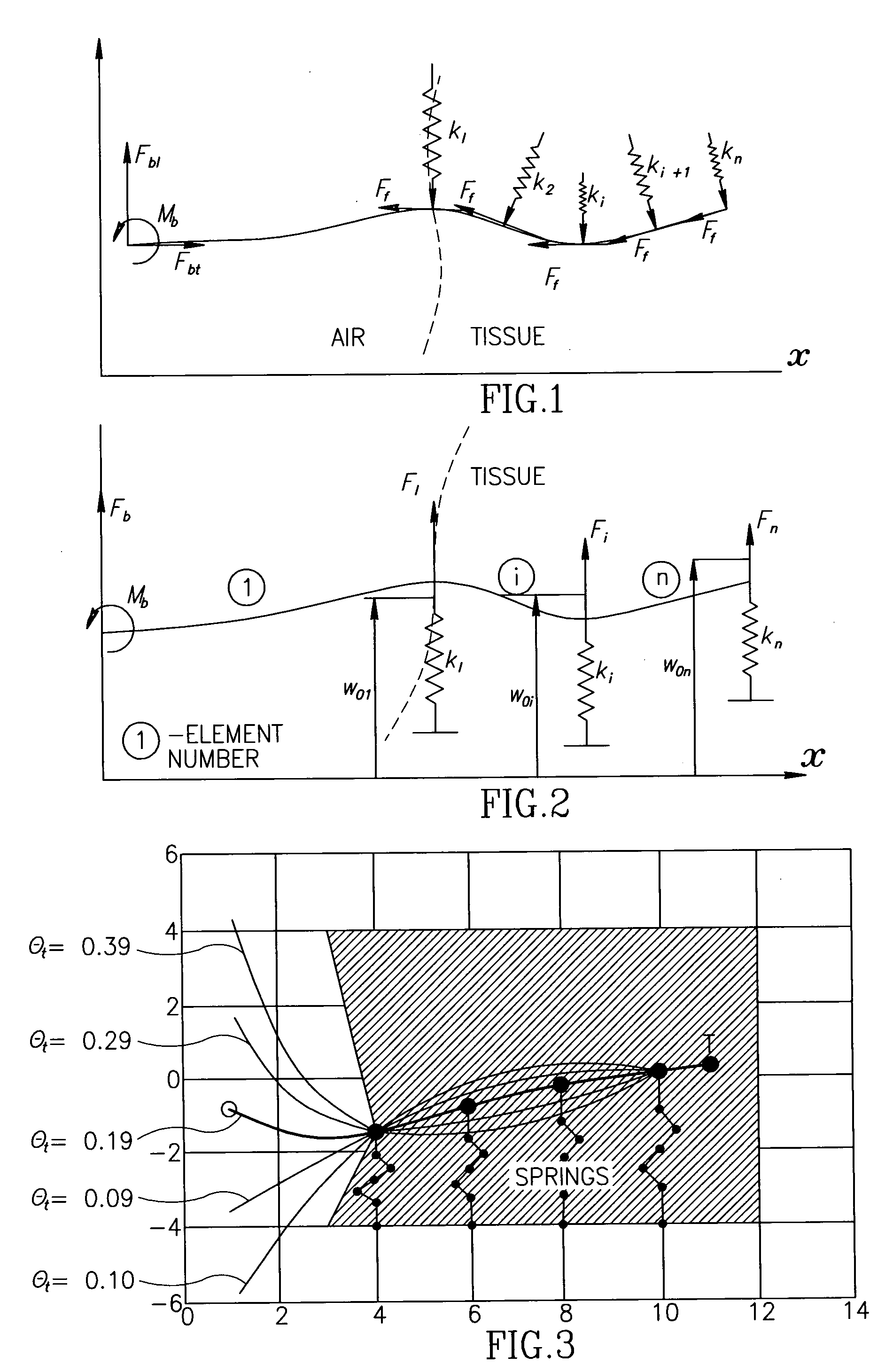
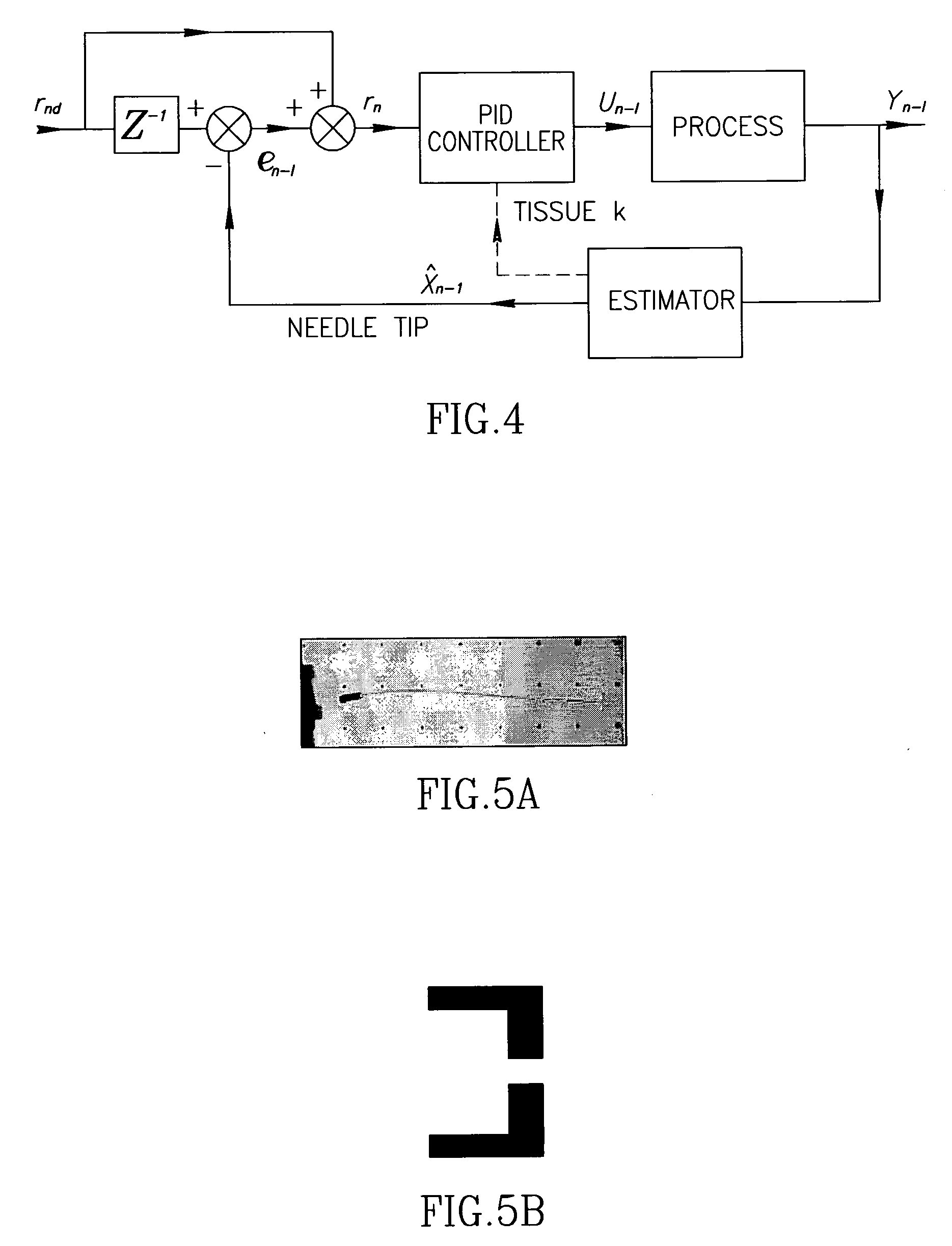
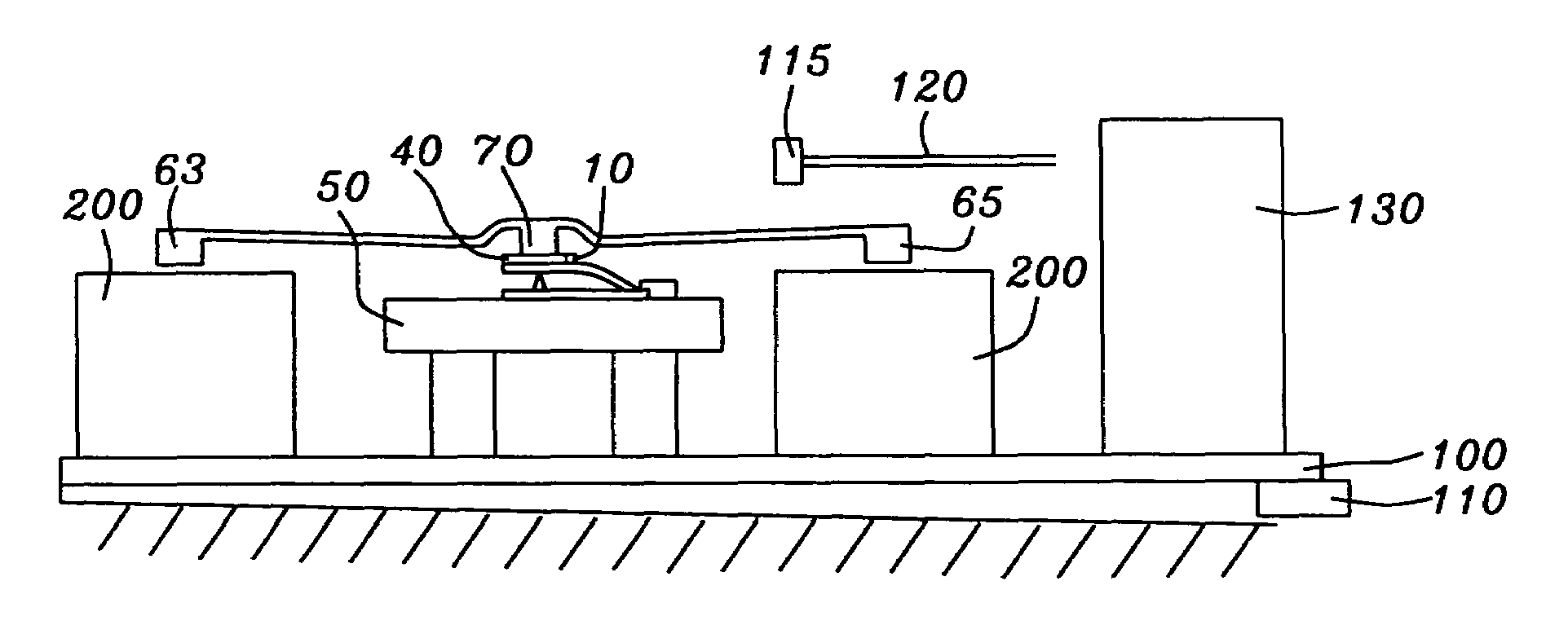
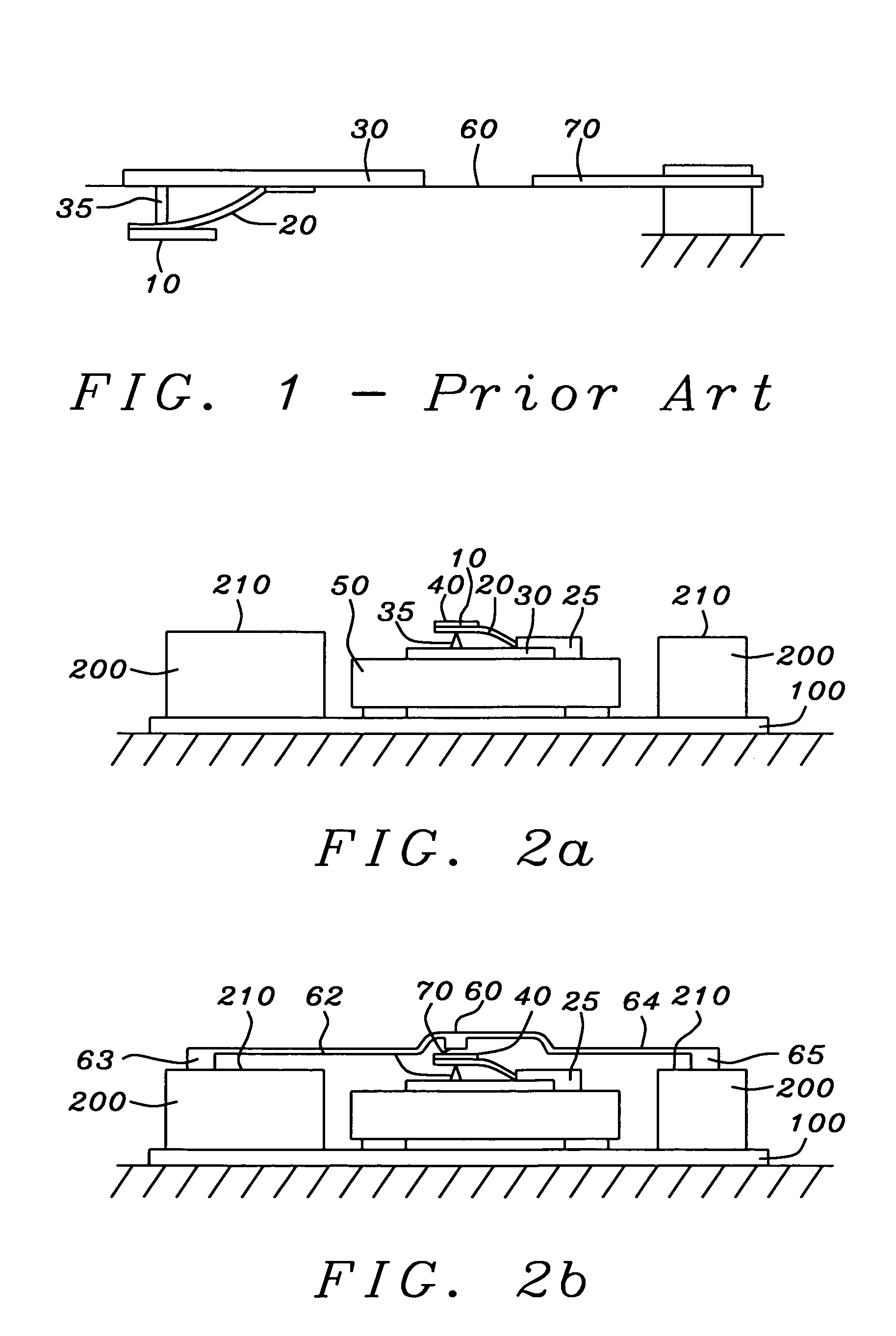
Controlled steering of a flexible needle
ActiveUS20090149867A1Avoid obstaclesReduce in quantitySurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsStiffness coefficientRobotic systems
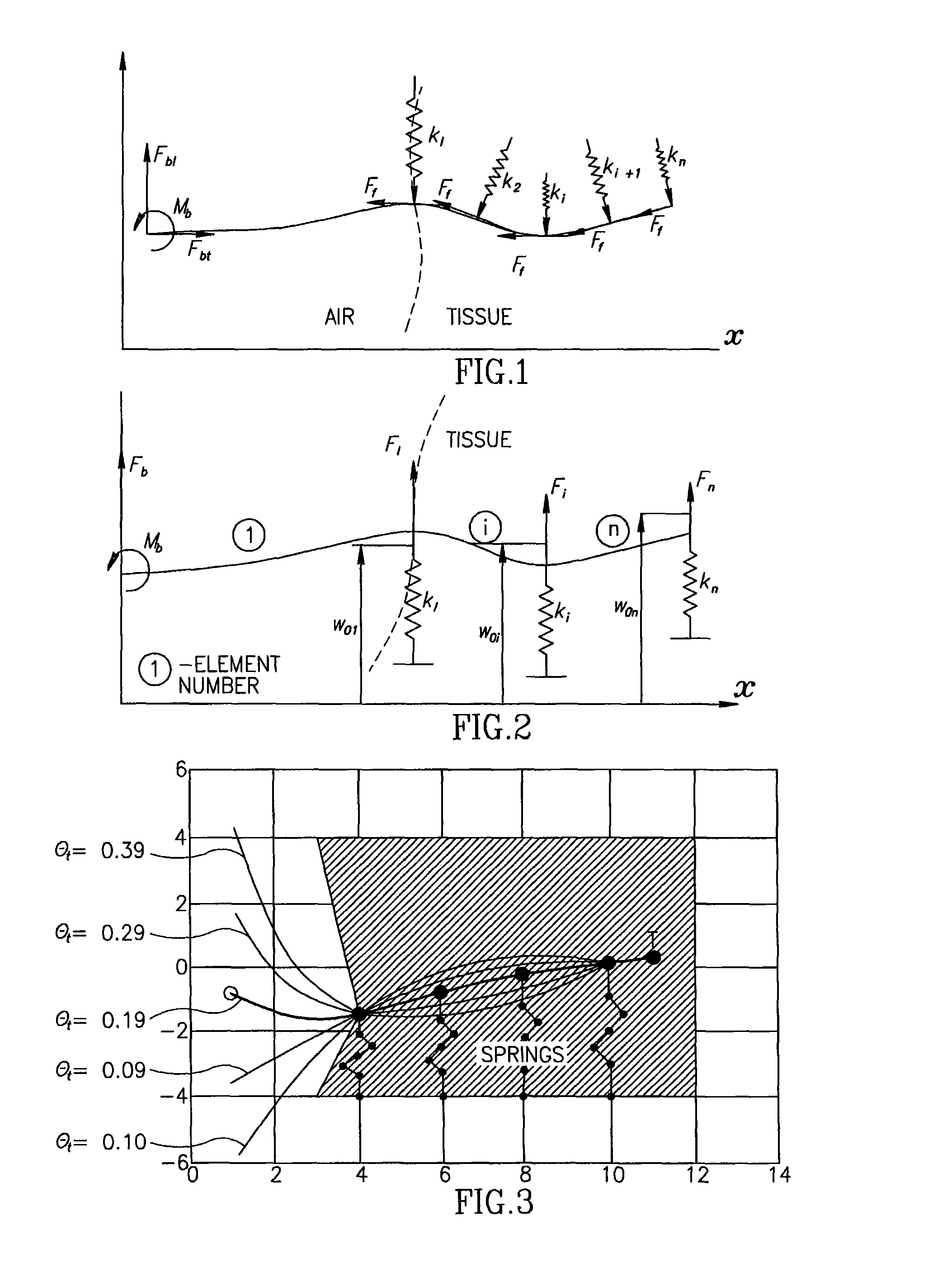
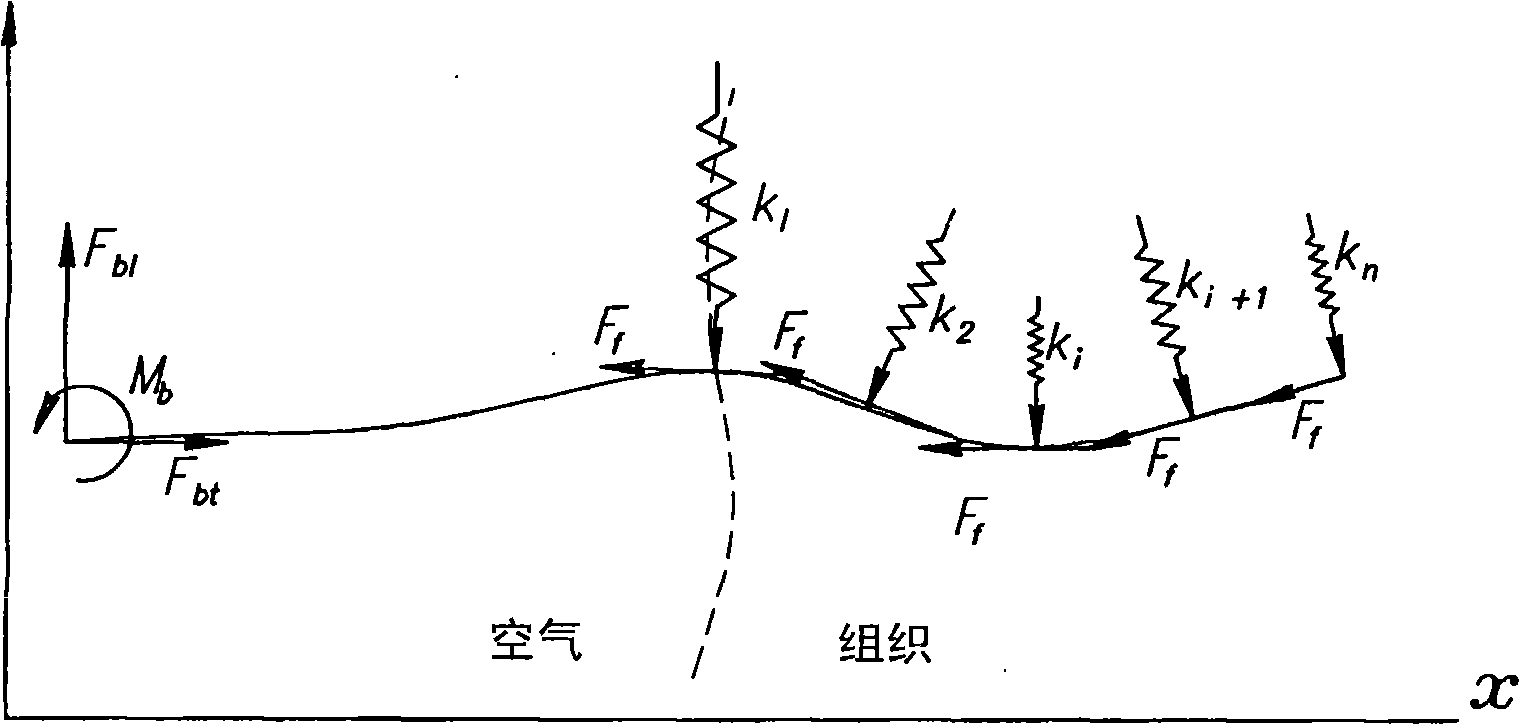
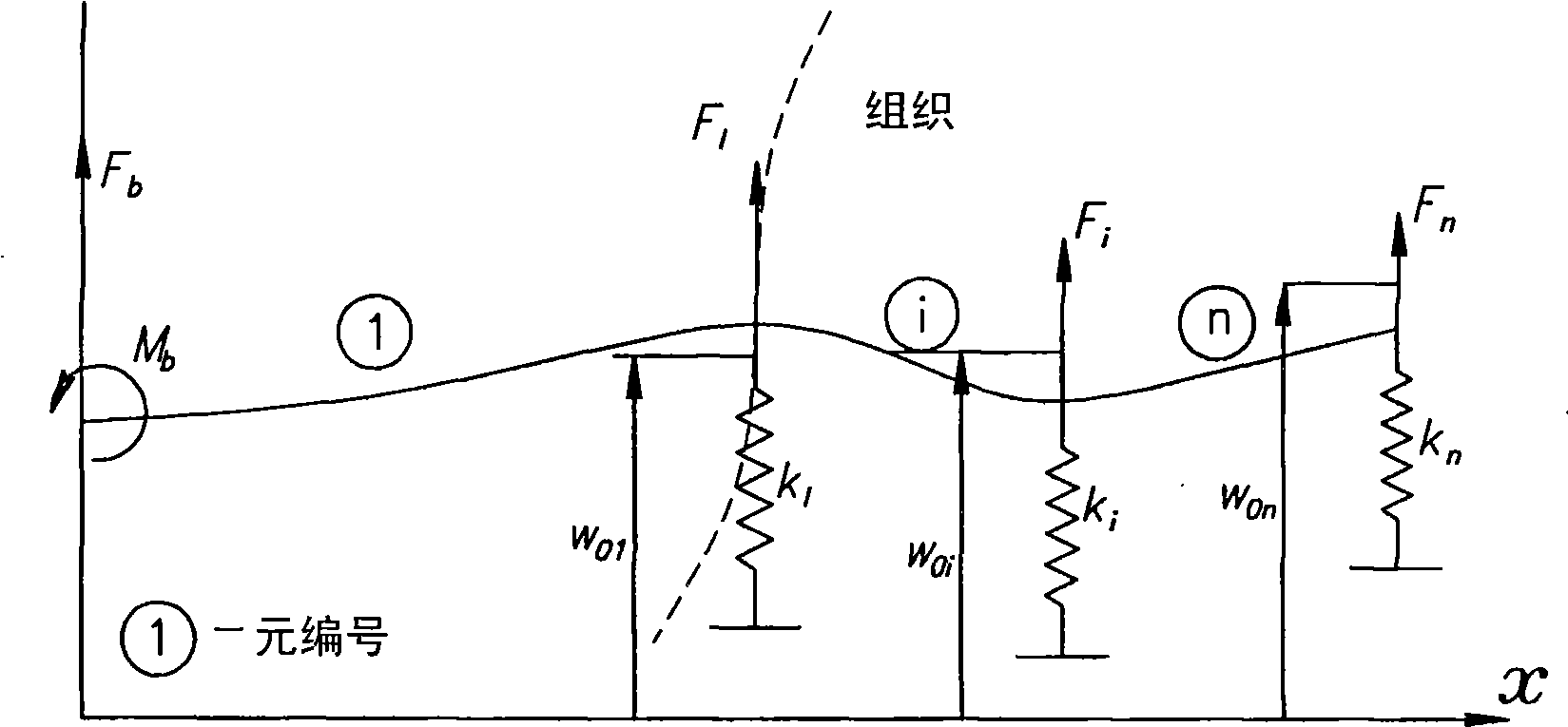
A robotic system for steering a flexible needle during insertion into soft-tissue using imaging to determine the needle position. The control system calculates a needle tip trajectory that hits the desired target while avoiding potentially dangerous obstacles en route. Using an inverse kinematics algorithm, the maneuvers required of the needle base to cause the tip to follow this trajectory are calculated, such that the robot can perform controlled needle insertion. The insertion of a flexible needle into a deformable tissue is modeled as a linear beam supported by virtual springs, where the stiffness coefficients of the springs varies along the needle. The forward and inverse kinematics of the needle are solved analytically, enabling both path planning and correction in real-time. The needle shape is detected by image processing performed on fluoroscopic images. The stiffness properties of the tissue are calculated from the measured shape of the needle.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Anti-vibration bracket for tubular motor
InactiveUS20060086874A1Decrease their propagationHorizontal stiffness is lowSpringsShutters/ movable grillesStiffness coefficientCoil spring
A bracket includes a rigid member that can be fastened to a fixture such as a wall, and flexible elements depend downwardly from the rigid member and are engaged with a tubular motor assembly of a window covering, awning, projector screen, or the like, to couple the motor assembly to the fixture while attenuating the propagation of vibrations from the tubular motor assembly to the fixture. This reduces noise in the room. The flexible elements may be flexible strings, elastic strings, or coil springs and have horizontal stiffness coefficients much lower than the vertical stiffness coefficient.
Owner:SOMFY SAS
Controlled steering of a flexible needle
ActiveUS8348861B2Reduce in quantitySurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsStiffness coefficientRobotic systems
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Underwater topographic mapping and correcting method adopting AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) equipped with multi-beam sonar
ActiveCN106123850AReduce mistakesRealize topographic mapping tasksNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsProfile tracingOcean bottomStiffness coefficient
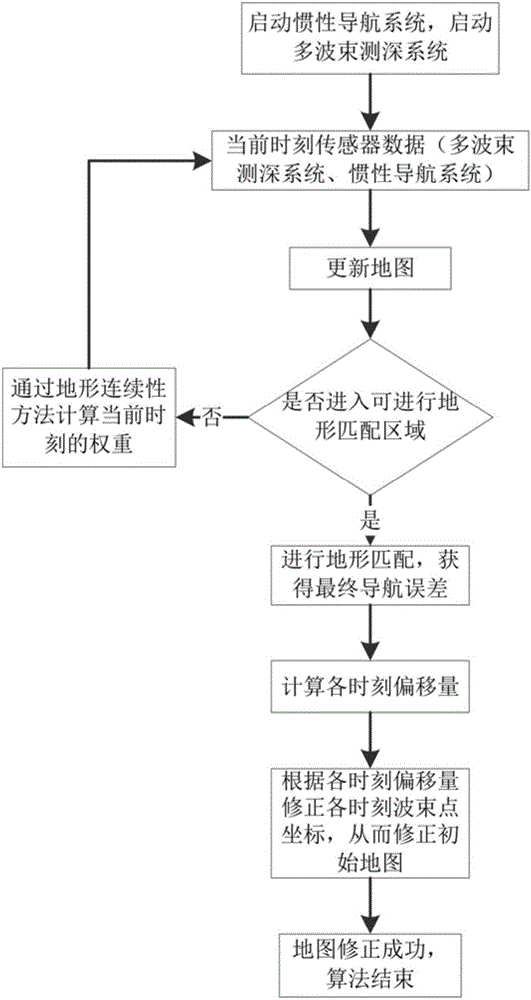
The invention provides an underwater topographic mapping and correcting method adopting an AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) equipped with multi-beam sonar. The method comprises steps as follows: multi-beam sonar and a depth gauge are started to collect data, and each ping is corrected according to sound velocity information collected by a sound velocity section plotter; an accurate relative position between two moments is determined with a topographic matching method, so that a final navigation error of an inertial navigation system is obtained; the inertial navigation system is simplified into a spring model, a relationship between each node error and an actual final navigation error is calculated according to a stiffness coefficient formula of a spring; weight of each time node relative to the final error is determined with a topography continuity method; a final moment error is distributed to each time node. The method is independent of GPS (global position system) information in a submarine topographical map establishing process, the multi-beam sonar can be carried by the AUV for completing submarine topographic mapping of a deeper sea area, the consistency of an established map is better, the time node error is small, and the submarine topographical map can be taken as a priori topography map to be applied to the underwater topographic matching navigation.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Controlled steering of a flexible needle
A robotic system for steering a flexible needle during insertion into soft-tissue using imaging to determine the needle position. The control system calculates a needle tip trajectory that hits the desired target while avoiding potentially dangerous obstacles en route. Using an inverse kinematics algorithm, the maneuvers required of the needle base to cause the tip to follow this trajectory are calculated, such that the robot can perform controlled needle insertion. The insertion of a flexible needle into a deformable tissue is modeled as a linear beam supported by virtual springs, where the stiffness coefficients of the springs varies along the needle. The forward and inverse kinematics of the needle are solved analytically, enabling both path planning and correction in real-time. The needle shape is detected by image processing performed on fluoroscopic images. The stiffness properties of the tissue are calculated from the measured shape of the needle.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Laminating manufacture method for symmetric laminated plate
InactiveCN102521435AImproved quasi-uniformityImprove uniformitySpecial data processing applicationsIn planeStiffness coefficient
The invention relates to a laminating manufacture method for a symmetric laminated plate. The laminating manufacture method comprises the following steps of: under the condition of quasi-uniform quasi-isotropy, setting up a relational expression between a regularization in-plane stiffness coefficient formula (shown as a drawing) and a flexural stiffness coefficient formula (shown as a drawing) according to the geometric model of the symmetric laminated plate; with appointed number p of directional single layers, adopting a regularization stiffness coefficient method to carry out optimized adjustment on a laminating sequence by taking the quadratic sum of a formula (shown as a drawing) as an evaluation function; and obtaining the symmetric laminated plate with quasi-uniform quasi-isotropy.According to the laminating manufacture method, the theoretical-equation-based regularization stiffness coefficient method is adopted to design and optimize the laminating sequence, and the optimal laminating sequence under a certain number of directional single layers is directly obtained through calculation, so that the obtained symmetric laminated plate has optimal quasi-isotropy for in-plane stiffness, and the quasi-isotropy for the flexural stiffness of the obtained symmetric laminated plate is optimal with the appointed number of directional single layers. A carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite reflecting mirror formed by using the laminating sequence has less asymmetric deformation under active deformation, and thus, the surface shape accuracy of the reflecting mirror after being actively controlled is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for propagating pseudo acoustic quasi-p waves in anisotropic media
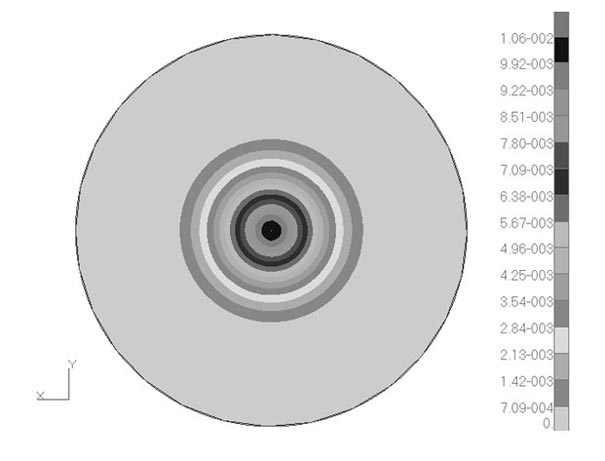
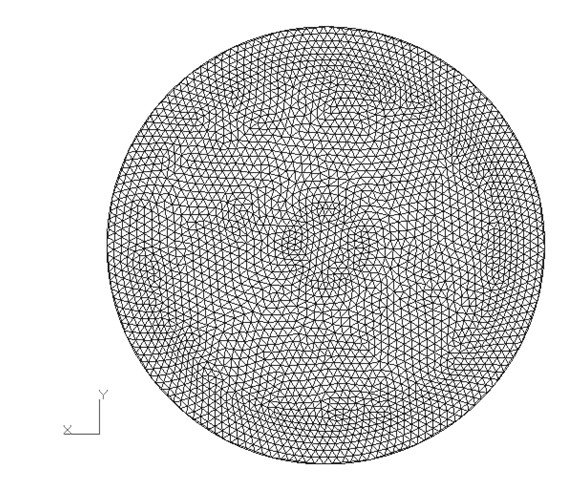
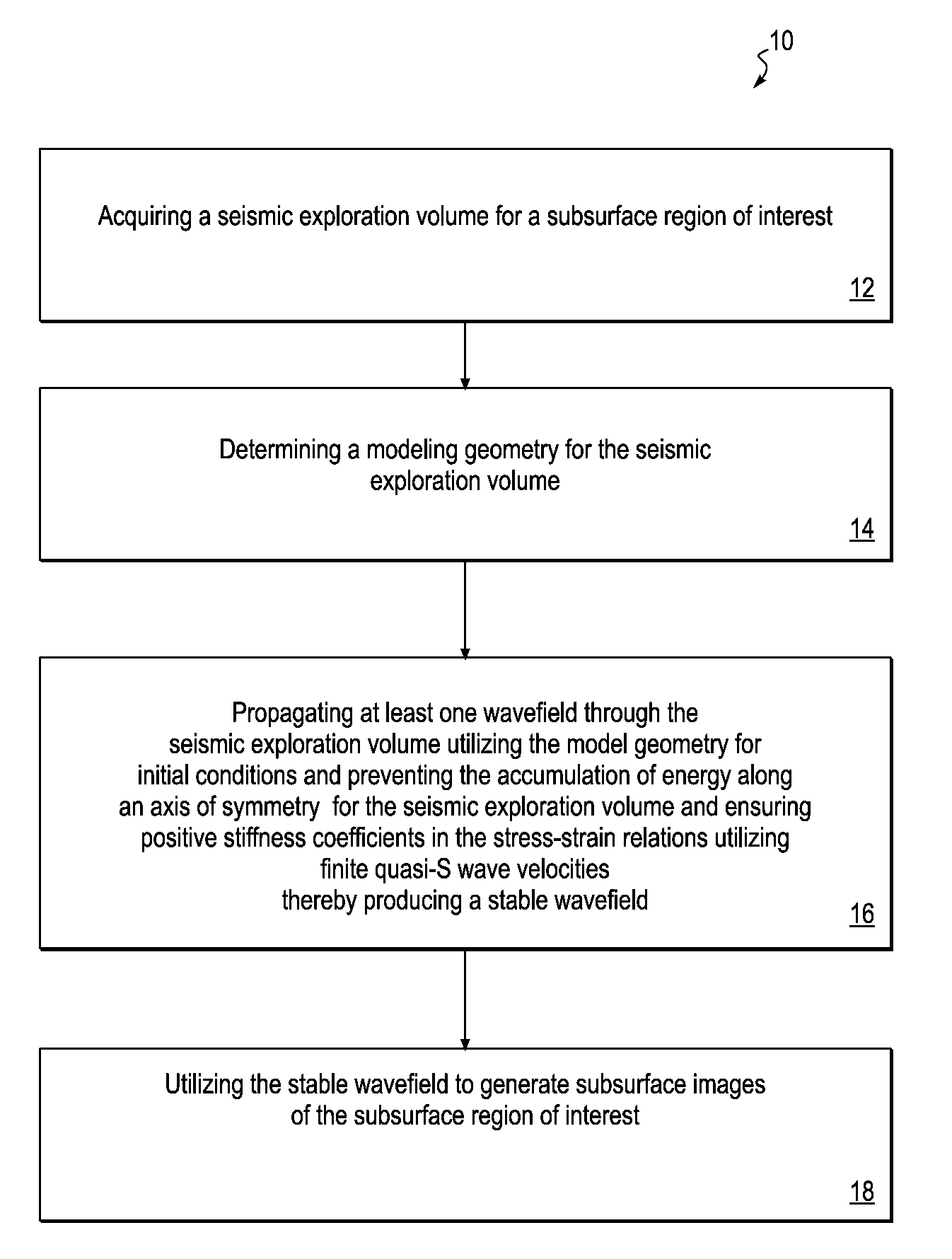
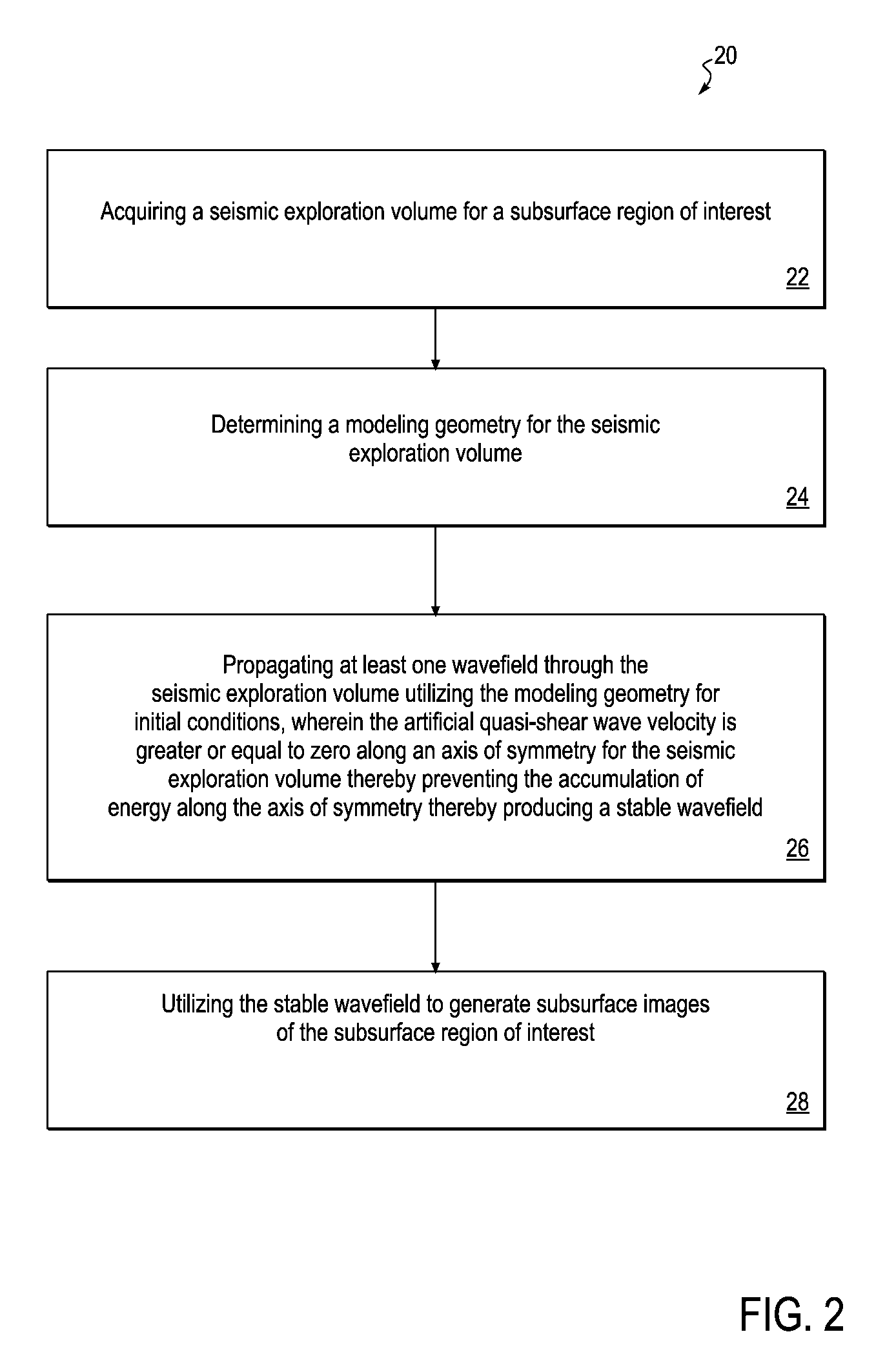
ActiveUS20110007604A1Avoid energy accumulationStable wavefieldMechanical area measurementsDigital computer detailsStiffness coefficientAxis of symmetry
A computer-implemented method for pseudo acoustic quasi-P wave propagation which remain stable in anisotropic media with variable tilt and is not limited to weak anisotropic conditions. The method includes acquiring a seismic exploration volume for a subsurface region of interest, and determining a modeling geometry for the seismic exploration volume. The method further includes propagating at least one wavefield through the seismic exploration volume utilizing the modeling geometry and initial conditions and preventing the accumulation of energy along the axis of symmetry of the seismic exploration volume and ensuring positive stiffness coefficients in the stress-strain relations through the use of finite quasi-S wave velocities thereby producing a stable wavefield. The method includes utilizing the stable wavefield to generate subsurface images of the subsurface region of interest.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Computation of shapes of three-dimensional linkage structures based on optimization techniques
InactiveUS6662148B1Person identificationAnalogue computers for chemical processesStiffness coefficientHuman body
Spinal modeling is based on a concept called spinal energy which assumes that the spine assumes a shape to minimize spinal energy. Spinal energy depends on parameters called stiffness coefficients. These parameters can be determined from human data which, by hypothesis, are universal for a large class of humans. The method adapts Newton's method to the manifold SO(3)<n >to find a solution of model of the human spine. Where basins of attraction are small in Newton's method, homotopy methods are introduced to move from known solutions to unknown solutions. By setting the gradient of the spinal energy to zero, Newton's method is used to solve the inverse problem of finding stiffness coefficients from human data. A new approach to improving deformed spines uses the modeling method based on spinal energy. This approach preserves maximally the range of motion of the spine. The technique used is vertebraplasty; i.e., adding and / or subtracting material surgically from various vertebral bodies without fusing or altering soft tissue. An interactive process is used to determine the surgery to be performed to improve spinal shape.
Owner:PENDRAGON NETWORKS
Voice coil motor for driving liquid lens and lens assembly with voice coil motor
ActiveCN109975973AControl displacementControl deformationAssociation with control/drive circuitsProjector focusing arrangementStiffness coefficientOptical axis
The invention provides a voice coil motor for drives a liquid lens and a lens assembly with the voice coil motor. The voice coil motor comprises a number of sub-motor parts which are independently controllable. Each sub-motor part comprises a fixed part, a movable part movable relative to the fixed part along the optical axis direction, and a connection elastic piece which is connected with the liquid lens and the movable part. The movable part drives the connection elastic piece to press the liquid lens when the movable part is subjected to a force in the optical axis direction. The connection elastic piece is a leaf spring, and the stiffness coefficient in the optical axis direction is greater than the stiffness coefficient of the connection elastic piece in a direction perpendicular tothe optical axis. The voice coil motor further comprises a driving circuit part which controls the moving distance of the movable part. The voice coil motor provided by the technical scheme can accurately achieve autofocus and optical anti-vibration of the liquid lens at the same time.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Seismic control bearing device and seismic control system including the same
InactiveUS20070283635A1Reduce vibrational energyNon-rotating vibration suppressionBridge structural detailsStiffness coefficientDamping factor
Provided are a seismic control bearing device capable of absorbing and / or blocking vibration energy transmitted to structures due to earthquakes, and so on, as well as actively controlling various dynamic behaviors generated from the structures with low power and without additional equipment, and a seismic control system including the same. The seismic control bearing device is installed between a ground base and a structure constructed on the ground base to reduce vibration energy applied to the structure, and includes a plurality of deposition members spaced apart from each other; and a plurality of magneto-sensitive members disposed between the deposition members and formed of a magneto-sensitive material. The properties including a stiffness coefficient and an damping coefficient of the magneto-sensitive material are varied depending on a variation of a magnetic field formed around the magneto-sensitive member.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
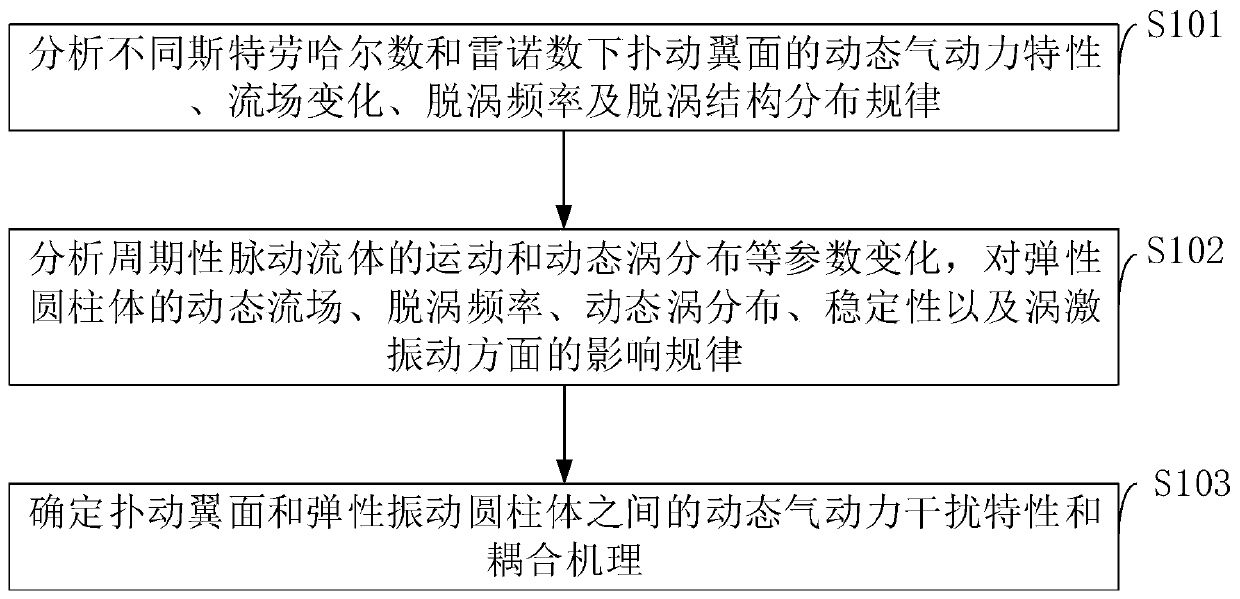
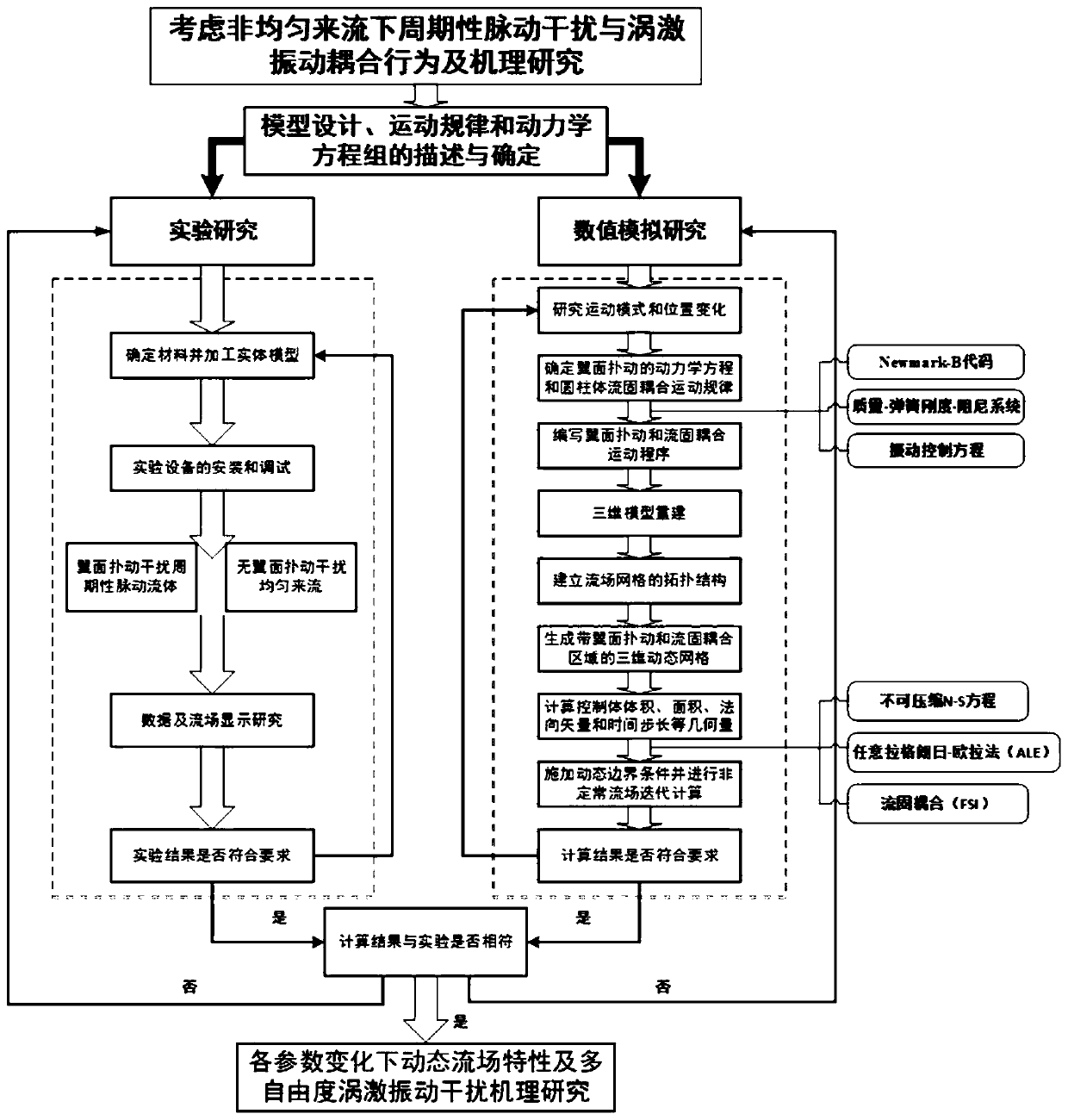
Elastic cylinder vortex-induced vibration rule and coupling mechanism determination method
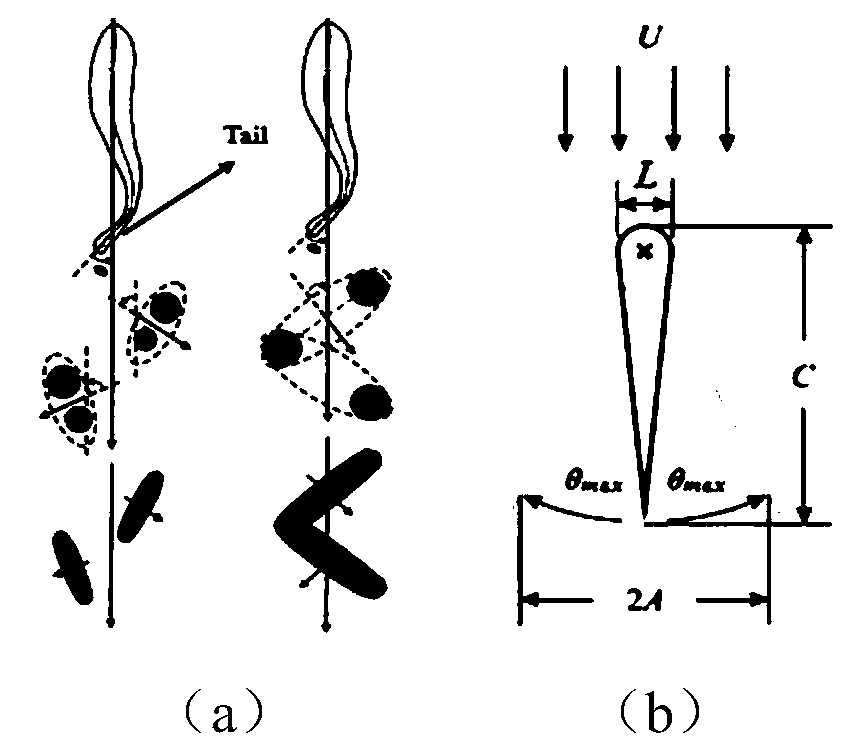
The invention belongs to the technical field of fluid and structure, and discloses an elastic cylinder vortex-induced vibration rule and coupling mechanism determination method. According to the method, rules of influence to dynamic flow field, vortex shedding frequency, dynamic vortex distribution, stability and vortex-induced vibration of elastic are determined as well as unsteady aerodynamic force interference characteristic and coupling mechanism between flapping wings and the elastic-vibration cylinders by analyzing unsteady aerodynamic force characteristics, flow field variation, vortexshedding frequency and vortex shedding structure distribution rule of the flapping wings. The dynamic fluid characteristics, vortex shedding frequency and vortex shedding structure distribution rule of the flapping wings under variation of parameters such as different flapping angle, flapping frequency and Reynolds number is defined; the vortex-induced vibration vibration rule and coupling mechanism of the elastic cylinders under different flapping angle, flapping frequency, mass ratio, damping ratio, spring stiffness coefficient, flow parameters under different degrees of freedom, and dynamicvortex distribution parameter along with motion of the flapping wings is determined.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
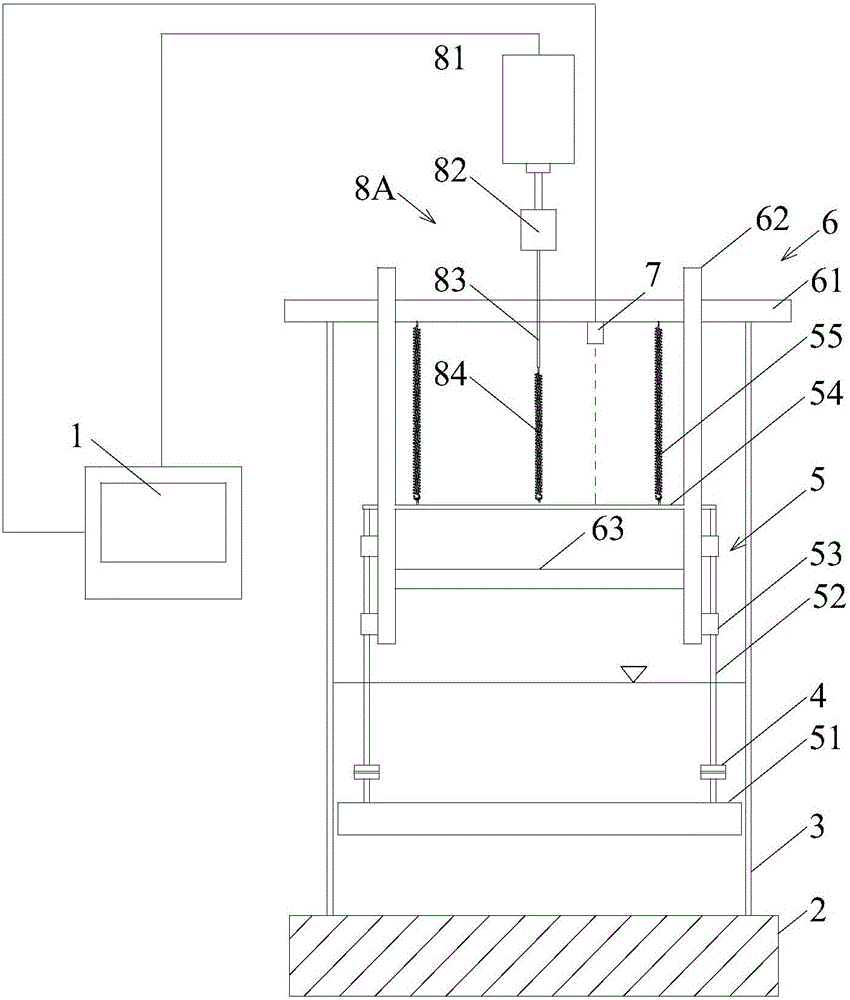
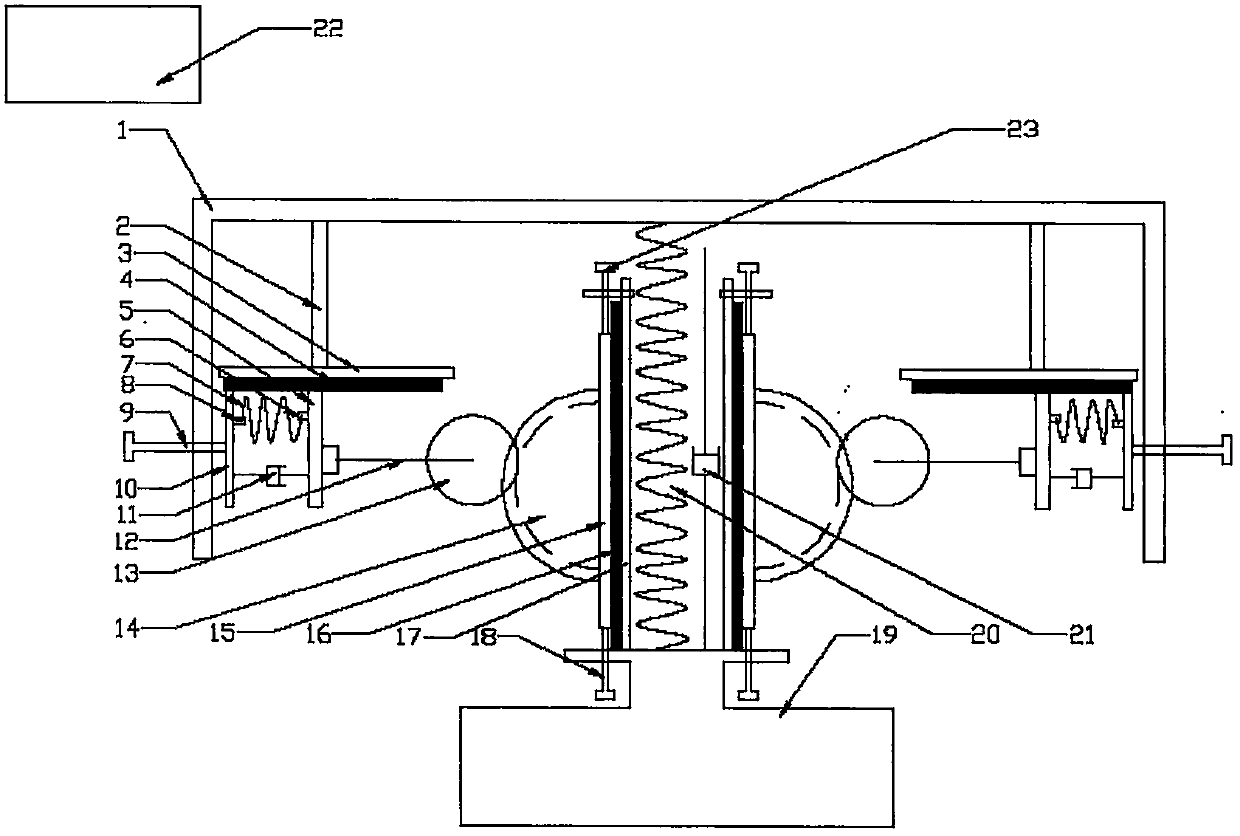
Simulation device for vortex-induced vibration of submarine pipeline and experimental method
ActiveCN106679791AEasy post-processingIncrease varietySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansDamping factorStiffness coefficient
The invention discloses a simulation device for vortex-induced vibration of a submarine pipeline and an experimental method. The simulation device comprises a water tank, a rectangular support frame, a pipeline model movement mechanism and a test system. The support frame is set up on the water tank. The pipeline model movement mechanism includes a simulation pipeline, two linear guide rails and a cross bar which constitute a rectangle. The two linear guide rails are mounted on the support frame respectively through guide rail blocks, and the cross bar is arranged on the top and connected to an upper beam of the support frame by means of two main springs. Test instruments in the test system are installed and then connected with a control host. The vortex-induced vibration of the pipeline under controllable damping can be simulated for the structure by installing a damping control device. When an experiment is carried out by the device, the instrument is calibrated first, and the damping coefficient of a free vibration system and the stiffness coefficient of the springs are measured by the device in a water injecting experiment. The device can be used to systematically study the vortex vibration trigger and amplitude and other issues, and the results can be referred to in the engineering design of a submarine pipeline.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolator with horizontal damper
PendingCN109973571ASuppress resonanceSimple structureSpringsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsStiffness coefficientResonance
The invention discloses a quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolator with a horizontal damper. Two sets of cam-roller-spring mechanisms are horizontally and symmetrically arranged to serve as a negativestiffness structure, the horizontal damper is additionally arranged, and then the negative stiffness structure, the horizontal damper and a vertical positive stiffness spring structure are connected in parallel to form a quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolation mechanism jointly. The matched stiffness coefficients of vertical springs and horizontal springs are selected, the height of cams and thepre-compression amount of the horizontal springs are adjusted according to the mass of an object subjected to vibration isolation and the stiffness of the vertical springs, the centers of the cam androllers are made horizontally flush, and the system has the quasi-zero-stiffness feature at the balanced position. On the basis of the certain vertical damping, the horizontal damping of the system isreasonably designed, and the resonance phenomenon of the system can be restrained or even eliminated. The vibration isolator has the high-static and low-movable stiffness feature, can achieve low-frequency vibration isolation, is simple in structure and convenient to maintain, and can be widely applied to low-frequency vibration management projects.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL INST OF LABOUR PROTECTION +1
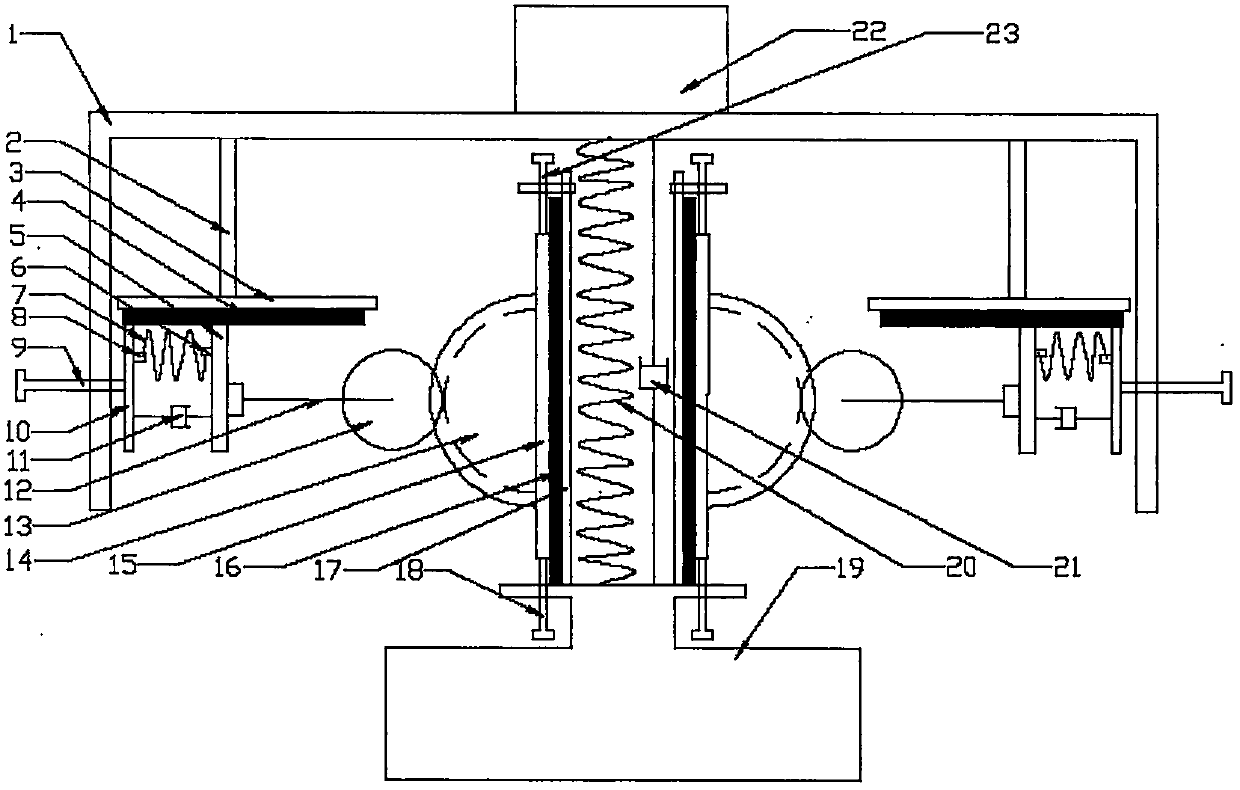
Tensioner with multiple spring rates
ActiveUS20150247559A1Reduce tensionHigh tensionSprings/dampers functional characteristicsGearingStiffness coefficientEngineering
In a first aspect, a tensioner is provided which includes: an arm, including a pivot mount; a pulley rotatably mounted to the arm; and a strut pivotally connected to the arm. The strut includes: a base, having a pivot mount; a first body moveable relative to the base; a first resilient element connected between the base and the first body, the first resilient element having a first stiffness coefficient; a second body moveable relative to the first body, the second body having a pivot mount; a second resilient element connected between the first body and the second body, the second resilient element having a second stiffness coefficient that is lower than the first stiffness coefficient; and an actuator, connected to the base and first body, for selectively moving the first body towards the base and compressing the first resilient element.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
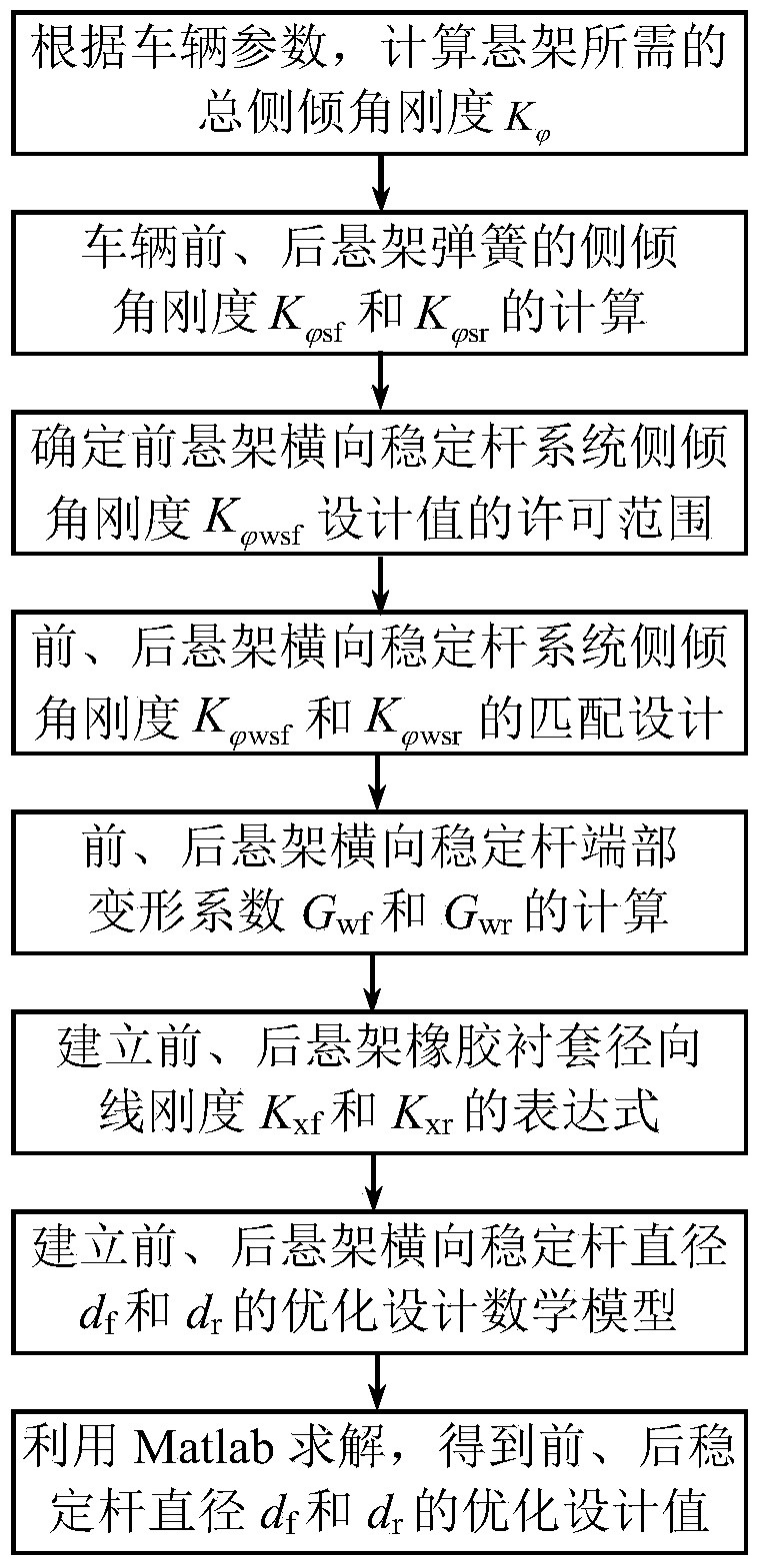
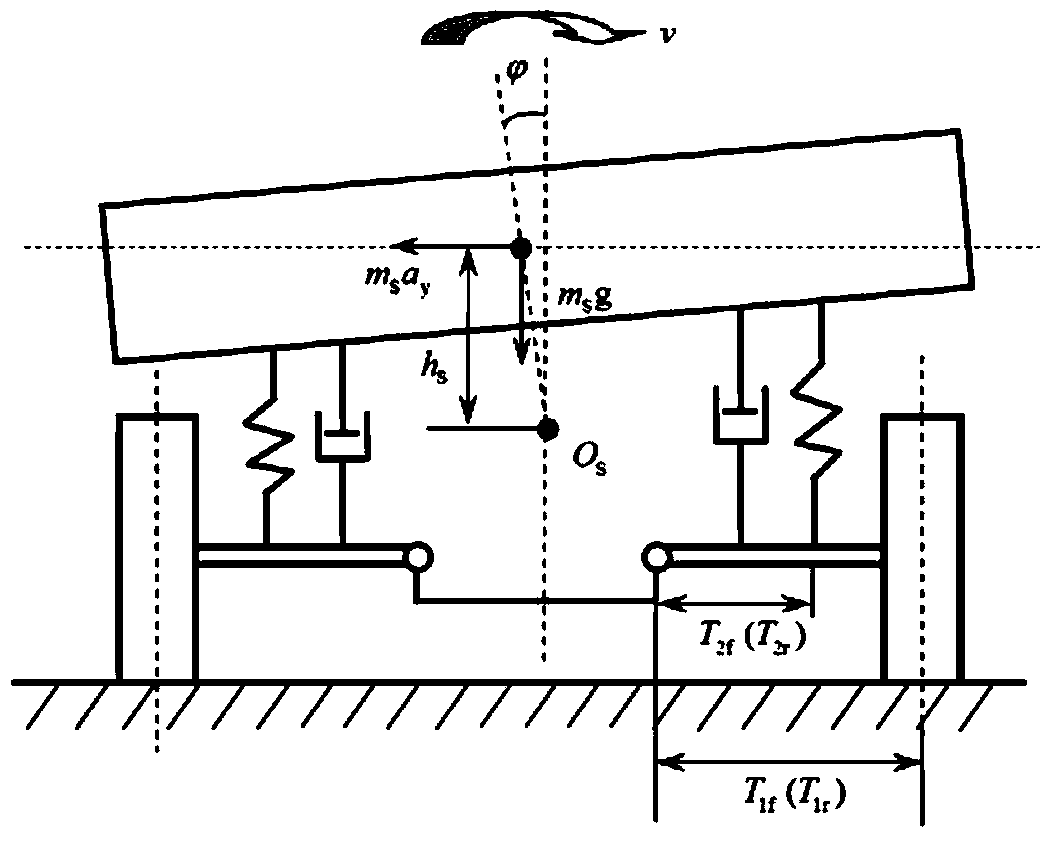
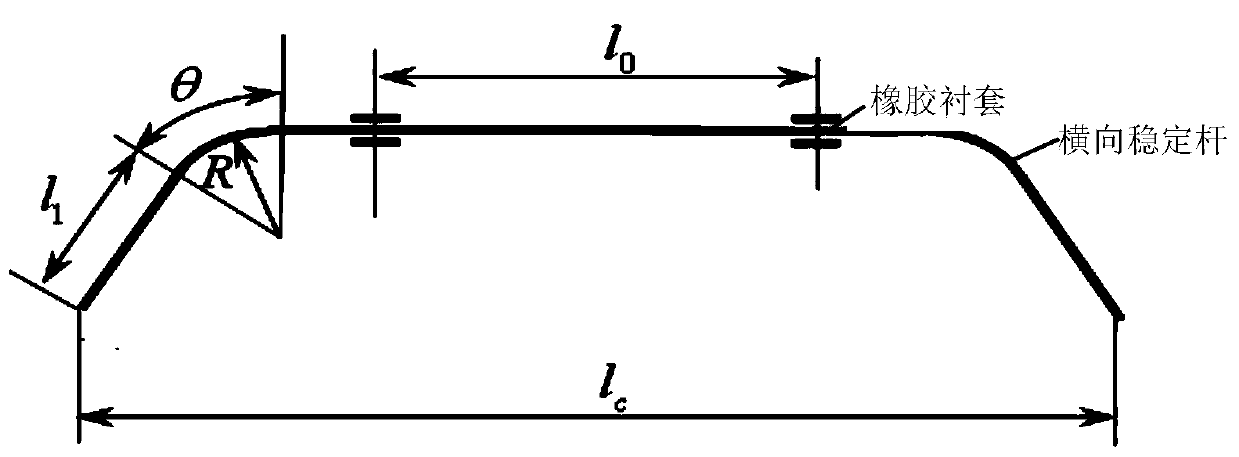
Design method for stiffness matching and diameter of vehicle suspension stabilizer bars
InactiveCN104200040AAccurate design methodRobust Design MethodInterconnection systemsSpecial data processing applicationsStiffness coefficientOptimal design
The invention relates to a design method for stiffness matching and diameter of vehicle suspension stabilizer bars and belongs to the technical field of vehicle suspensions, aiming to fill a gap of the reliable optimal design method for diameter of the stabilizer bars due to limitation of radial deformation analytic analysis and inter-coupling of the stabilizer bars and rubber bushings. The design method is characterized by including the steps of firstly, performing matching design on stiffness of angle of roll of a front suspension stabilizer bar system and a rear suspension stabilizer bar system according to vehicle parameters and roll models; secondly, building an optimal design mathematical model of the stabilizer bar diameter d according to the matching design value of stiffness of the angle of roll, the radial stiffness coefficient Kx of the rubber bushings and the deformation coefficient expression Gw of ends of the stabilizer bars so as to obtain the accurate and reliable optimal design value of the stabilizer bar diameter d by means of a Matlab program. By the design method, design level and performance of the suspensions and the stabilizer bars can be improved, riding comfort and safety of vehicles can be improved, and meanwhile, design speed for product development can be increased and cost for design and test can be reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
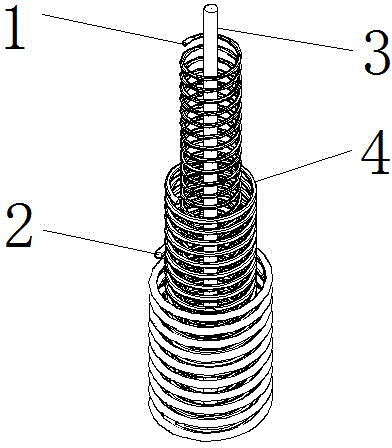
Multilayer buffer spring
InactiveCN104895978ASimple structureIncrease frictionVibration dampersWound springsStiffness coefficientEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a multilayer buffer spring which comprises an inner spring, a middle spring and an outer spring. The middle spring is mounted inside the outer spring, the inner spring is mounted inside the middle spring, a fixing rod is mounted inside the inner spring, the height of the middle spring is twice that of the outer spring, the height of the inner spring is three times that of the outer spring, the diameter of the inner spring is smaller than that of the middle spring, the diameter of the middle spring is smaller than that of the outer spring, the bottoms of the inner spring, the middle spring and the outer spring are positioned on the same horizontal plane, and the centers of the fixing rod, the inner spring, the middle spring and the outer spring are positioned on the same straight line. The multilayer buffer spring is simple in structure and has high economic benefits and wide application prospects, the free height and stiffness coefficient can be adjusted, a fastening component applies pressure to one peripheral side of the outer spring to increase friction force between a cavity and the inner spring, and positional fixity of the inner spring and the outer spring is ensured.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGYANG METAL PROD
Preparation method of graphene/aluminum composite material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene / aluminum composite material. The preparation method specifically includes the following steps that graphene oxide powder is evenly dispersed in an alcohol solution, and a graphene oxide alcoholic solution is prepared after emulsification and ultrasonic treatment; aluminum powder is slowly added under stirring, temperature is controlled to be not higher than room temperature, stirring speed is controlled to be 100-1000 r / min, stirring time lasts for 1-5 h, and the uniform graphene oxide alcoholic solution containing the aluminum powder is obtained; solid and liquid separation is performed through the filtering technology and the centrifugal technology, and graphene oxide / aluminum dry powder is obtained after separated paste solid is frozen and dried; and the dry powder is subjected to heat reduction under Ar / H2 mixed atmosphere, and finally the graphene / aluminum composite material is prepared. The graphene / aluminum composite material prepared through the method has the beneficial effects of being high in strength, low in heat expansion coefficient and the like, and the specific stiffness coefficient and the special strength coefficient are remarkably increased. The method is simple in technology and efficient, industrialized production and application can be easily achieved.
Owner:TANGSHAN JIANHUA TECH DEV
Method for determining elastic energy of circular film under condition that maximum deflection is limited by elasticity
ActiveCN109323923AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStiffness coefficientYoung's modulus
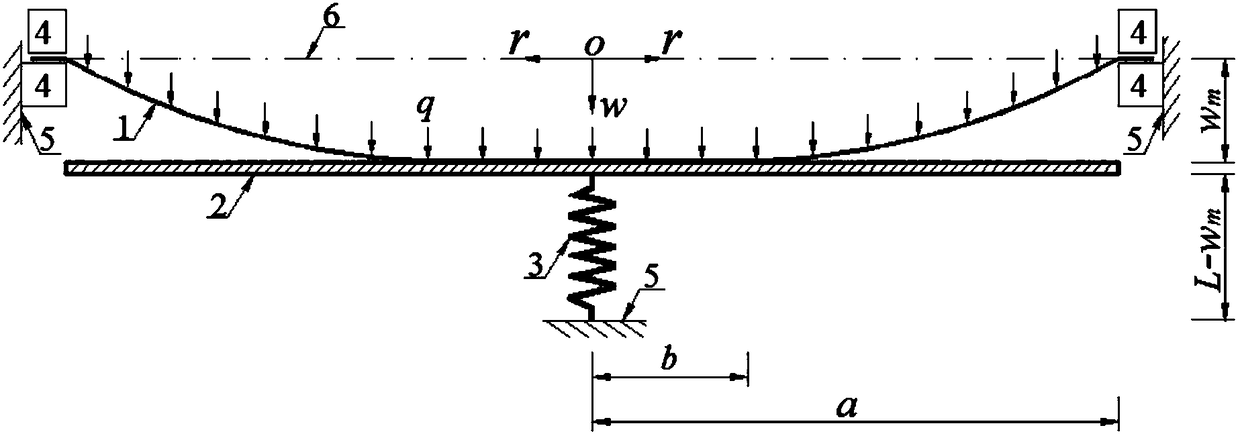
The invention discloses a method for determining elastic energy of a circular film under condition that maximum deflection is limited by elasticity. The method comprises the following steps of: applying a uniform load q to a circular film with a Young's modulus of E, a Poisson's ratio of v, a thickness of h, a radius of a, and a self-weight of q0 per unit area, which is initially flat and fixedlyclamped at the periphery, to enable the circular film to produce axisymmetric deformation; pushing a rigid circular plate which has a radius of a and a center on the same axis as the center of the circular film, is always parallel to the circular film which is flat at the middle, and has a smooth surface to move a distance of wm in parallel; forming an contact area with a radius b between the axisymmetrically deformed circular film and the rigid circular plate; compressing a spring having a stiffness coefficient of k from the original length L by wm by the parallelly moving rigid circular plate; and after ignoring the self-weight of the rigid circular plate, using the measured value of the load q to determine the elastic energy U of the axisymmetrically deformed circular film based on a static balance analysis of the axisymmetrically deformed circular film.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Plate strip rolling thickness control method based on mill spring characteristic curve
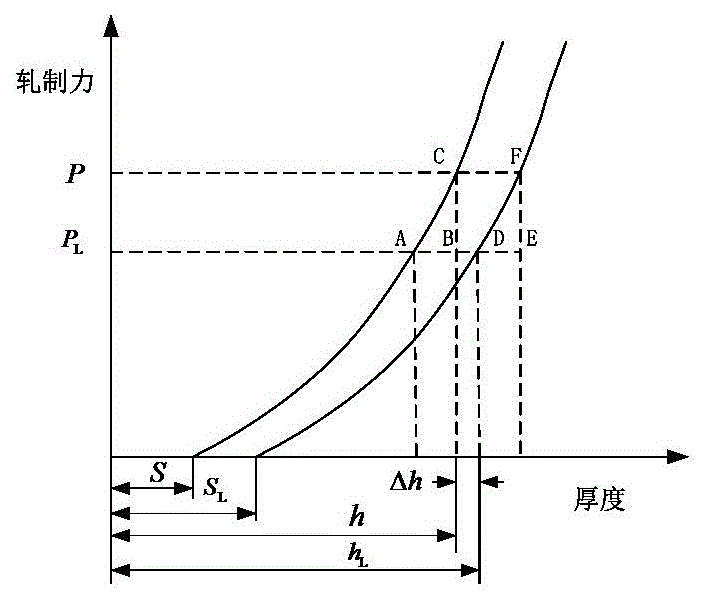
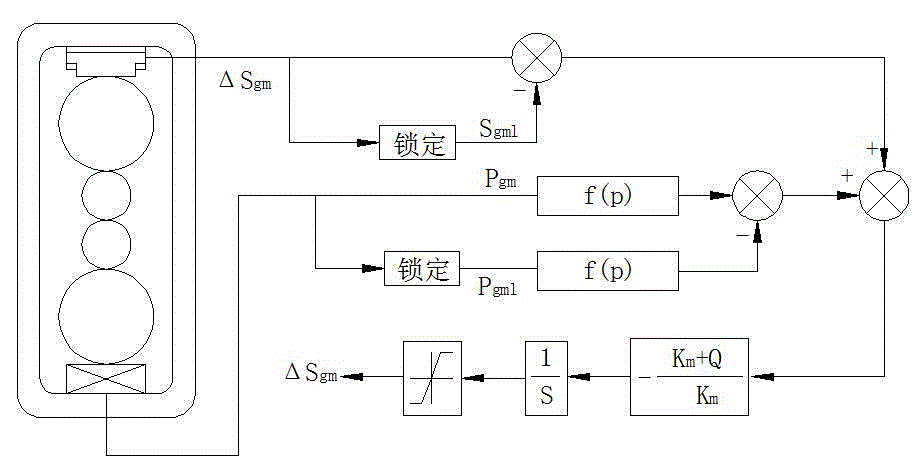
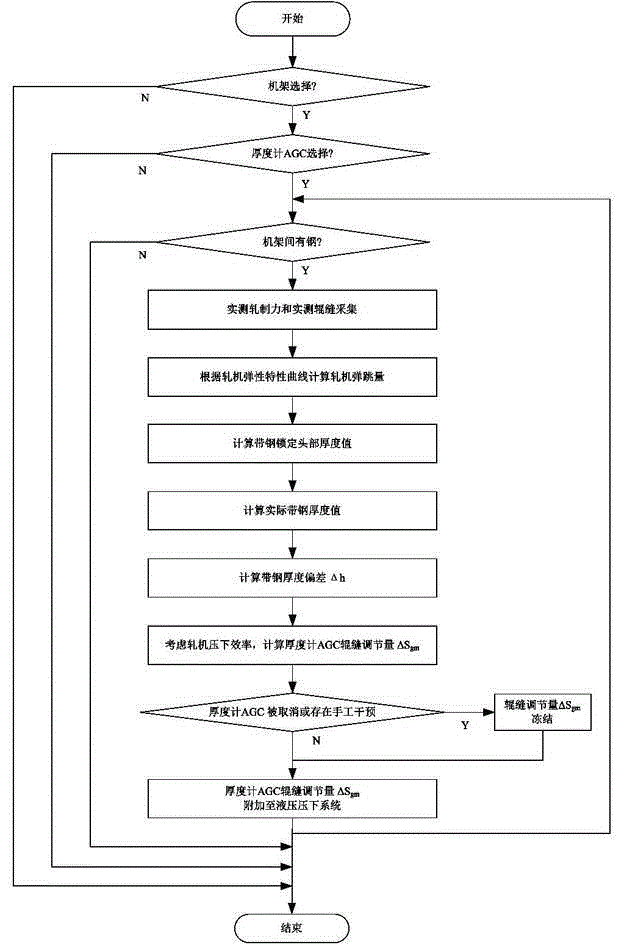
InactiveCN105127210ATroubleshoot thickness datum calculationsHigh thickness accuracyRoll mill control devicesMetal rolling arrangementsStiffness coefficientAutomatic control
The invention discloses a plate strip rolling thickness control method based on a mill spring characteristic curve and belongs to the technical field of automatic control of plate strip rolling. The control method for determining thickness gage AGC (automatic gage control) comprises steps as follows: 1, inputting a stiffness coefficient Km of a mill and a plasticity coefficient Q of a plate strip, and determining a proportionality coefficient K of a thickness control object; 2, acquiring a rolled arch spring characteristic curve through a forced-contract experiment, regressing rolled piece spring curve according to off-line data, acquiring a total mill spring characteristic curve equation, and determining a mill spring amount Str; 3, determining a thickness deviation value delta h of a mill outlet according to actually measured rolling force, an actually measured roll seam, locking rolling force and a locking roll seam on the basis of the mill spring amount Str determined in the prior step and in the principle of thickness gage AGC of the mill spring characteristic curve; 4, determining an adjustment amount delta Sgm of thickness gage AGC with the consideration of the pressing efficiency of the mill. The influence of the stiffness coefficient of the mill on the spring equation is effectively avoided, and the thickness accuracy of plate strip rolling in the automatic control process is improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Piezoresistive acceleration sensor and manufacturing method thereof
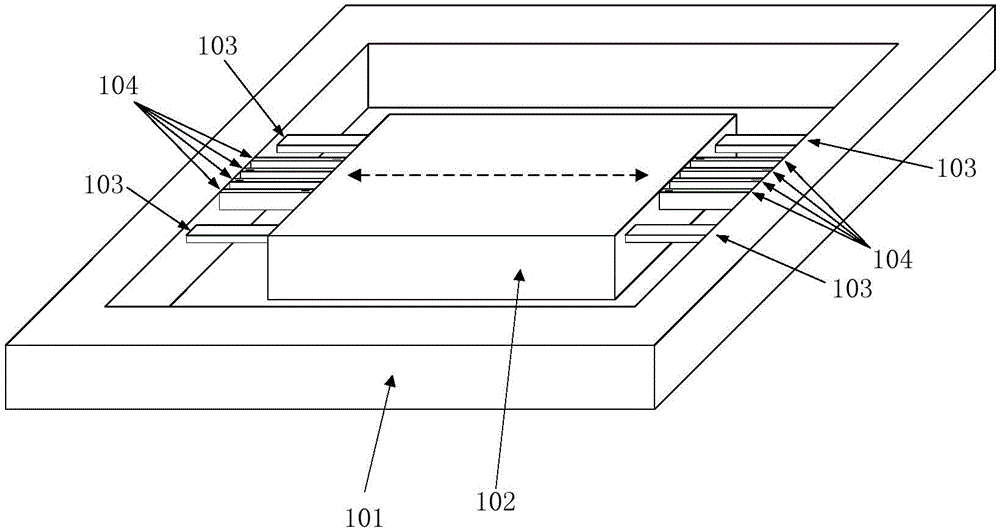
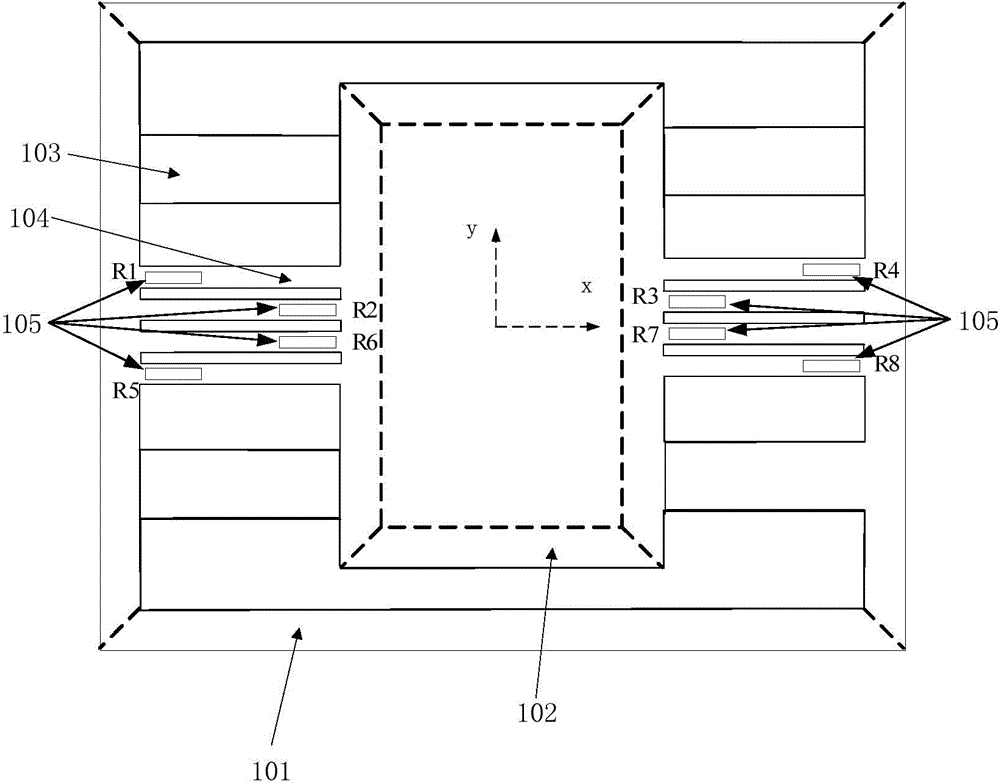
ActiveCN105785073AThe overall thickness is thinThin sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesStress concentrationStiffness coefficient
The invention provides a piezoresistive acceleration sensor and a manufacturing method thereof. The sensor is improved by comprising a sensitive structure part. The left and right sides of a mass block in the sensitive structure are symmetrically provided with four mutually independent sensitive girders. Each sensitive girder is provided with a force-sensitive resistor. The two sides of the four sensitive girders are respectively provided with one support girder for supporting the mass block. The force-sensitive resistors are arranged on the mutually independent sensitive girders, so that the widths of the sensitive girders are reduced. Therefore, the influence of the sensitive girders on the stiffness coefficient of the sensitive structure is significantly reduced, so that the high sensitivity and the high figure of merit are realized. The sensitive girders are arranged closer to the centerline of the mass block, thus being smaller in deflection. The paraxial sensitivity is reduced. The support girders are closer to the edge of the mass block, thus being large in the arm of force. Therefore, the twist of the mass block, caused by the paraxial acceleration, can be better inhibited. The upper surfaces of the support girders are lower and are free of any oxidation layer. Therefore, the structural deflection, caused by the stress of the oxidation layer, can be reduced. The thickness of the sensitive girders is larger than the thickness of the support girders, so that the stress concentration can be achieved. As a result, the sensitivity and the figure of merit are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Internal force calculation method taking shear deformation of closed frame and rigid joints into consideration
ActiveCN105631136AIncrease credibilityPowerfulDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALStiffness coefficient
The invention provides an internal force calculation method taking shear deformation of a closed frame and rigid joints into consideration. The method comprises the following steps of determining a structure, determining a calculation diagram, determining a calculation model, limiting the freedom degree of the model, restraining lateral sway, determining a shear-resisting rigidity coefficient, adjusting the calculation model and carrying out structural calculation and analysis. Precision of the calculation result meets the standard requirement, the fast and accurate purpose is achieved, powerful functions and operation convenience of a structural mechanics solver are fully utilized, reliability of the calculation result is high, and the method is convenient to apply and popularize.
Owner:CHINA POWER CONSRTUCTION GRP GUIYANG SURVEY & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Vibration diaphragm and loudspeaker provided with same
ActiveCN105376679ALarge stiffness coefficient distribution spaceImprove acoustic performanceNon-planar diaphragms/conesStiffness coefficientEngineering
The invention discloses a vibration diaphragm and a loudspeaker provided with the same and belongs to the electro acoustic product technical field. The vibration diaphragm comprises a frame; the frame is provided with an edge portion, a folding ring portion and a center portion which are distributed from outside to inside sequentially and are connected with one another to form an integrated body; a plurality of open holes are distributed in the folding ring portion; the outer side of the frame is provided with a film coated layer; the frame and the film coated layer are both made of polymer materials; the material hardness of the fame is greater than that of the film coated layer; and the material of the film coated layer has elasticity. With the vibration diaphragm and the loudspeaker provided with the same of the invention adopted, technical problems such as little possibility of realizing smoothness adjustment of a vibration diaphragm in the prior art can be solved. The smoothness adjustment of the vibration diaphragm of the invention is flexible; the stiffness coefficient distribution space of the vibration diaphragm is large; the stability and reliability of the vibration diaphragm are higher; and therefore, with the vibration diaphragm adopted, the acoustic performance of the loudspeaker can be excellent, the sound quality of the loudspeaker is high, and the service life of the loudspeaker is long, and people's requirements for high sound quality of electronic equipment can be satisfied.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Method for on-line drafting elastic curve of rolling mill
InactiveCN101470428AProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersStiffness coefficientReturn-to-zero
The invention discloses a method of on-line drawing an elastic curve for rolling mills. Based on the principle of the known pressing process, the method utilizes the pressing process to measure relative data of roll-gap spring rate and rolling force, collects the data measured on-line in real time to store in a digital control system PLC, utilizes the tracing point method to analog an elastic curve of a rolling mill in the digital control system PLC, and then operates stiffness coefficient and spring rate of the rolling mill under any roll-force through a piecewise linear method by aid of the elastic curve of the rolling mill. The method of on-line drawing an elastic curve for rolling mills not only finish the conventional pressing return-to-zero work, but can fast on-line analog the elastic curve of the rolling mill and precisely compensate the spring rate of the rolling mill in real time, thereby overcoming the defects of poor precision and low efficiency of the known pressing process.
Owner:上海欧达电气成套设备工程有限公司 +1
Adhesion safety detecting method of tower crane
InactiveCN102323073AImprove flexibilityStructural/machines measurementVibration amplitudeStiffness coefficient
The invention provides an adhesion safety detecting method of a tower crane. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a force transmission relation between a tower roof system of the tower crane and the position of the tower body connected with an adhesion device through establishing a mathematical structural model of the tower crane, wherein the vibration parameter of the tower system is tested in the construction site to obtain a fixed vibration frequency of the tower crane and a maximum vibration amplitude of a hoisting weight in the vertical direction so that the stiffness coefficient of the adhesion system and the stress situation of the position of the tower body connected with the adhesion device can be obtained according to the force transmission relation between the tower roof system of the tower crane and the position of the tower body connected with the adhesion device; thus, the safety of the adhesion device of the tower crane is judged. By using the method provided by the invention, the possible dangerous working condition of the tower can be analyzed to find parts of the tower body and the adhesion device that may exceed the limit value so as to take responsive measures immediately; and effective guaranteeing effect can be generated on the safe use of the tower temporarily designed with the adhesion device.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Modeling method of liquid sloshing in microgravity environment of spherical tank
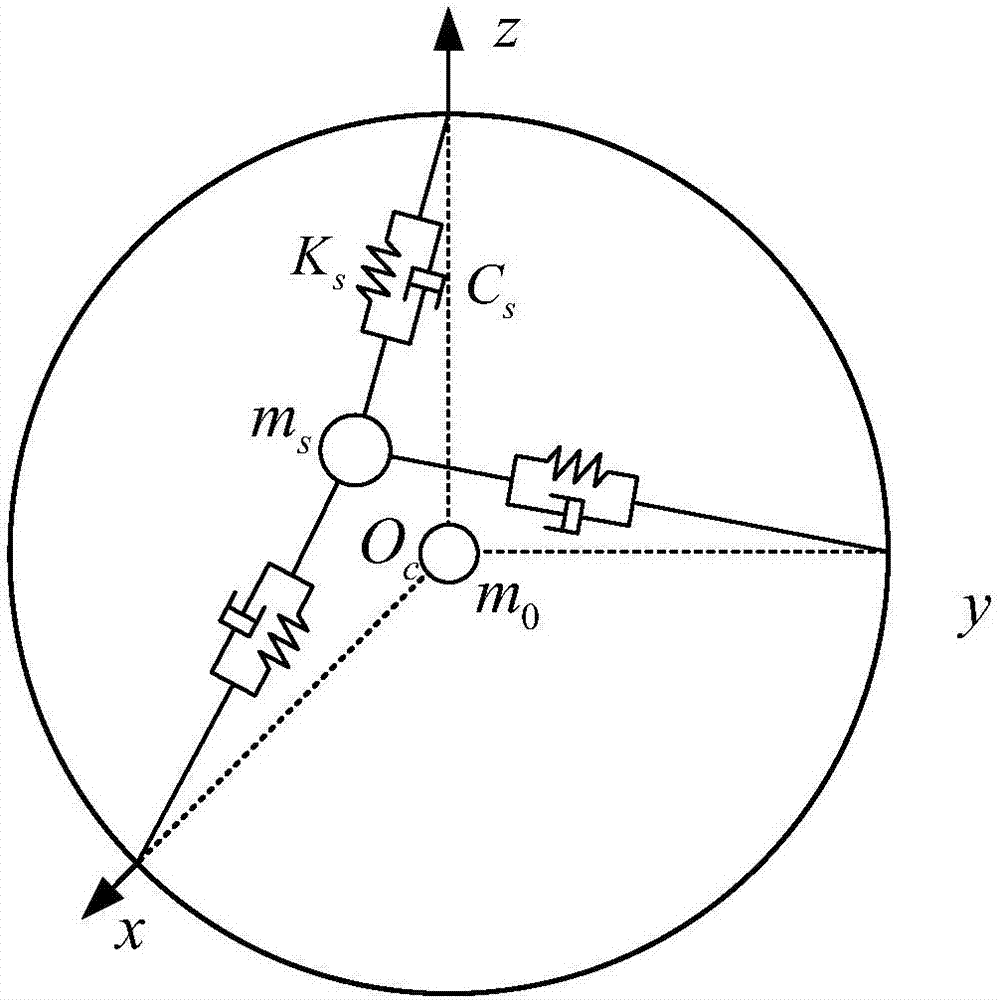
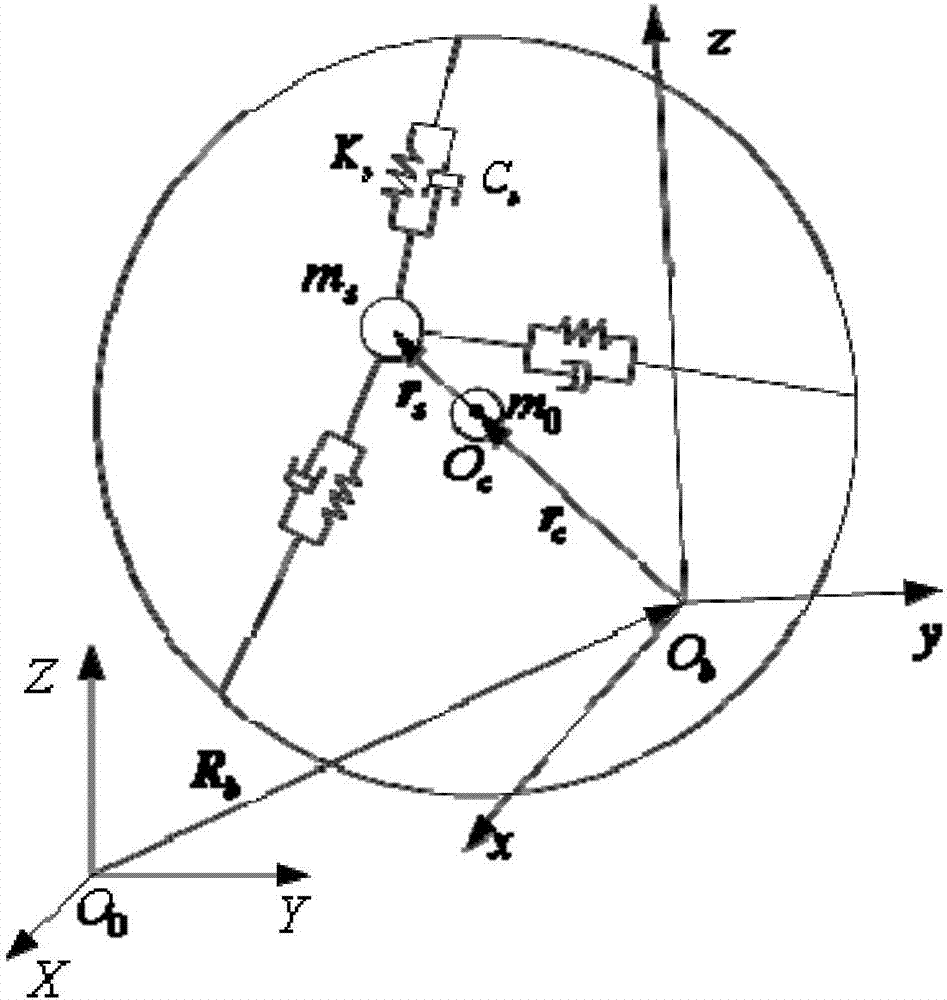
The invention provides a modeling method of liquid sloshing in a microgravity environment of a spherical tank. Firstly, an equivalent mechanical model of liquid sloshing under the microgravity environment of a spherical tank is established. The equivalent mechanical model is a three-axis spring-mass equivalent mechanical model which contains the rest mass m0 and the sloshing mass ms, wherein the rest mass m0 is located in the center of the spherical tank, the sloshing mass is connected with the tank by three spring dampers with a stiffness coefficient of Ks and a damping coefficient of Cs. When the sloshing mass is in the equilibrium position, the directions of the three spring dampers are respectively overlapped with the three axes of the spherical tank. Then, the n-order natural frequency [omega]0i and the modal [phi]i of the liquid sloshing in the zero-gravity environment of the spherical tank are calculated. Finally, based on the force of the liquid applied to the wall of the tank and the kinetic energy of the sloshing liquid relative to the tank, the force of the equivalent mechanical model and the kinetic energy equivalent principle, the sloshing mass ms and the rest mass m0 of the equivalent mechanical model are obtained by calculation.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
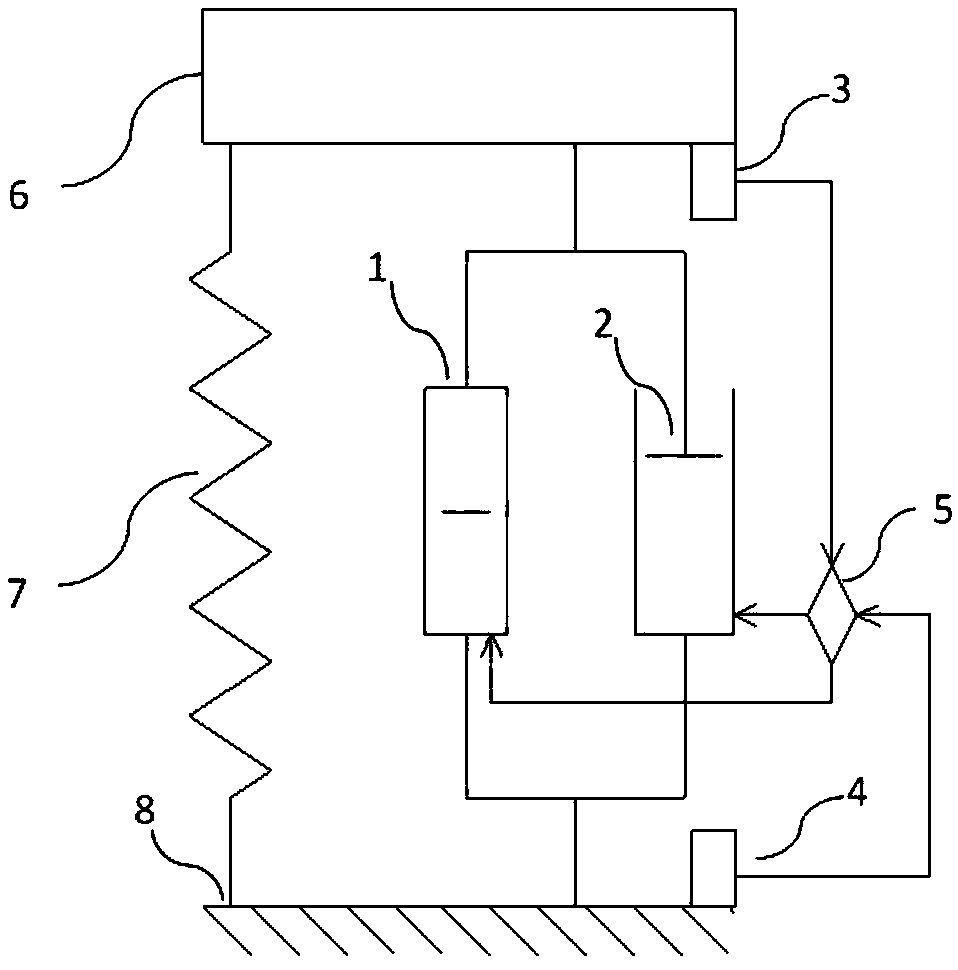
Mixed vibration control device and method based on negative stiffness and variable damping and application
ActiveCN111336210AImprove reliabilityLow costSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionStiffness coefficientVibration control
The invention provides a mixed vibration control device and method based on negative stiffness and variable damping and application. The device comprises a negative stiffness component and a variabledamping component connected in parallel between a component on a reed and a component under the reed, a sensor I for measuring vibration of the component on the reed and transferring vibration information, a sensor II for measuring vibration of the component under the reed or a substrate and transferring vibration information, and a controller. The controller receives the vibration information ofthe sensors I and II and adjusts the stiffness coefficient of the negative stiffness component and the damping coefficient of the variable damping component according to attribute parameters of a structure and a control algorithm. The mixed vibration control device solves the problem that semi-active control cannot provide a control force, the direction of which is as same as a vibrating speed direction, so as to execute the control algorithm to obtain the optimum theoretical control force integrally, thereby obtaining a vibration control effect as same as that of active control.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Self-loaded pendulum for slider flexure stiffness measurements
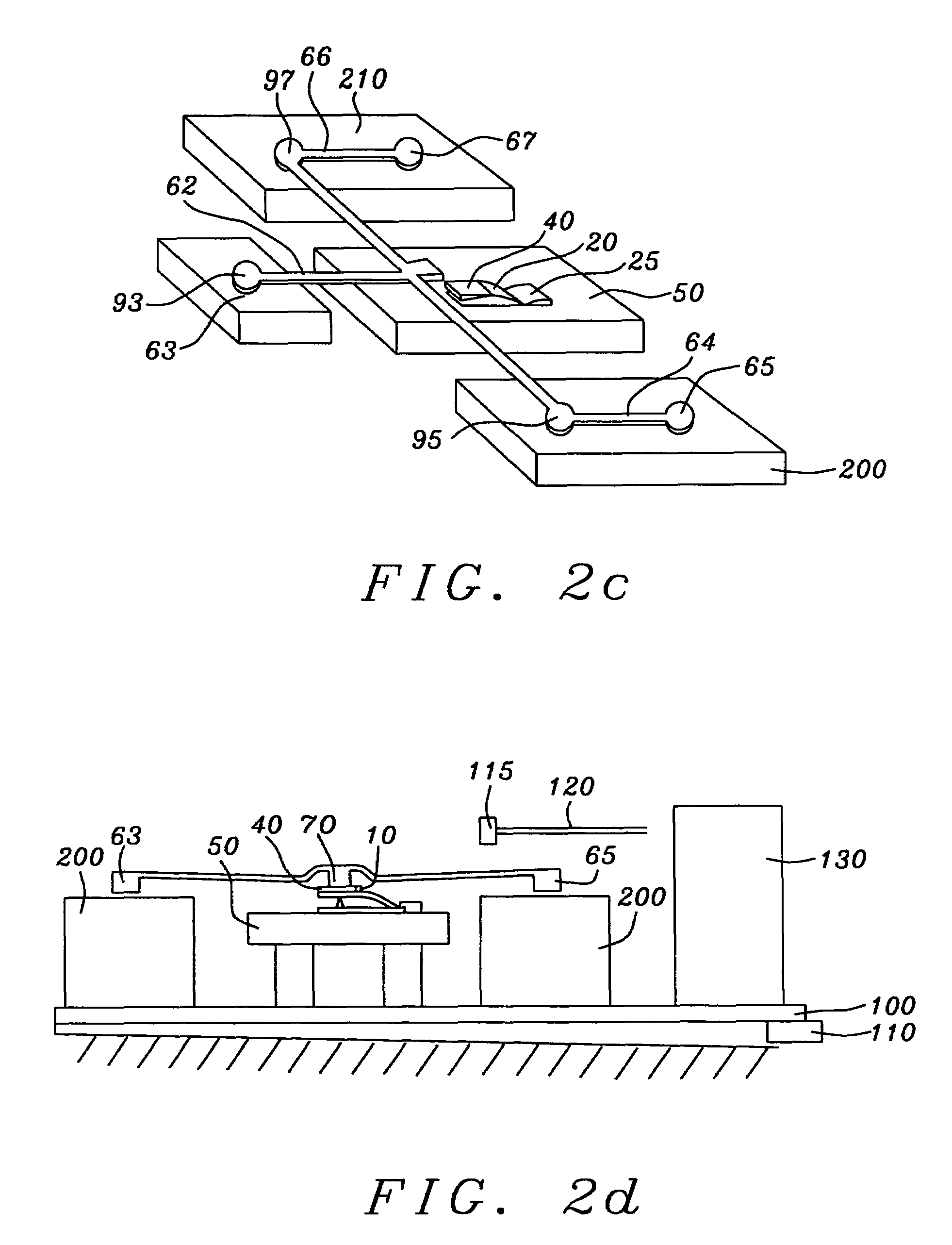
InactiveUS7249520B1Easy to operateFriction freeDisposition/mounting of recording headsForce measurementStiffness coefficientDynamic method
A device is provided by which the stiffness coefficient of a flexure, in either a pitch or roll direction, can be measured while a slider is mounted thereon and while the flexure and slider are in a loaded condition as might be obtained during normal operational conditions of a HGA in a HDA. There are two methods of making the measurement, a static method in which the slider is loaded by an external weight called a pendulum and the angular displacement of the slider is measured, and a dynamical method in which the pendulum is caused to oscillate while in contact with the slider and its natural and loaded frequencies of oscillation are measured.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Piezoelectric type variable stiffness and variable damping dynamic vibration absorber
ActiveCN109780112AAchieving semi-active controlGood vibration dampingInertia force compensationNon-rotating vibration suppressionStiffness coefficientDamping factor
The invention discloses a piezoelectric type variable stiffness and variable damping dynamic vibration absorber. The dynamic vibration absorber comprises an upper bearing platform and a lower bearingplatform; a mass inertia block and a plurality of vibration absorbing units are arranged between the upper bearing platform and the lower bearing platform; the lower bearing platform is fixedly connected with equipment awaiting vibration damping; and each vibration absorbing unit comprises two first piezoelectric elements, a friction lever, a plurality of vertical elastic elements and a second piezoelectric element, wherein the two first piezoelectric elements are arranged on the upper bearing platform and the lower bearing platform correspondingly, the two ends of the friction lever are connected with the two first piezoelectric elements, and the middle part of the friction lever penetrates through the mass inertia block, the two ends of each of the multiple vertical elastic elements areconnected with the mass inertia block and the first piezoelectric elements, and the second piezoelectric element is arranged on the joint face of the friction lever and the mass inertia block. The dynamic vibration absorber disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the stiffness coefficient and the damping coefficient of the vibration absorber can be designed according to the vibration characteristics of the equipment; stiffness and damping can be adjusted by controlling voltage; the dynamic vibration absorber can be effectively applied to architectural and mechanical equipment variedin vibration property; semi-active control over vibration can be realized; and a good vibration damping effect can be achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
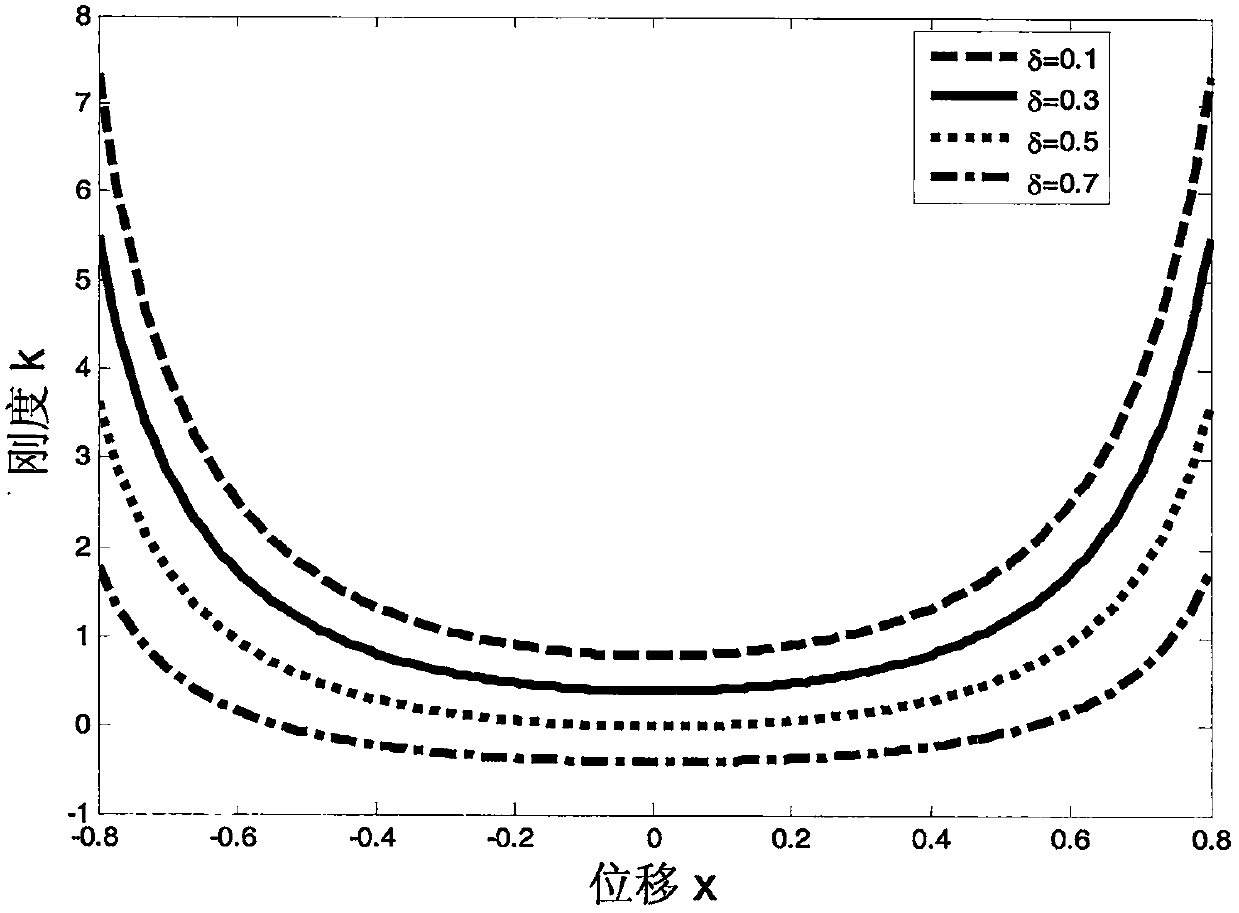
Numerical simulation analysis method for carrying out numerical simulation analysis on nonlinear characteristic of stiffness coefficient of centering disk of loudspeaker
ActiveCN103310052ASpeed up the design processOvercome design gapsSpecial data processing applicationsAxial displacementStiffness coefficient
The invention discloses a numerical simulation analysis method for carrying out numerical simulation analysis on the nonlinear characteristic of stiffness coefficient of a centering disk of a loudspeaker and belongs to the field of loudspeaker design. The method completes static analysis by establishing a geometric model of the centering disk and defining a nonlinear material module and considering the geometric nonlinearity through a finite element method and can obtain axial displacement of the centering disk under the action of different loading forces, so that a changing curve of the stiffness coefficient of the centering disk along with the axial displacement can be obtained by post-processing. By the method, the nonlinear characteristic K(x) of the centering disk can be analyzed and obtained on the initial stage of design, i.e. before a sample is not produced and manufactured, so that the centering disk is rapid and convenient to design and manufacture.
Owner:嘉善恩益迪电声技术服务有限公司 +1
Multi-axial fatigue testing machine
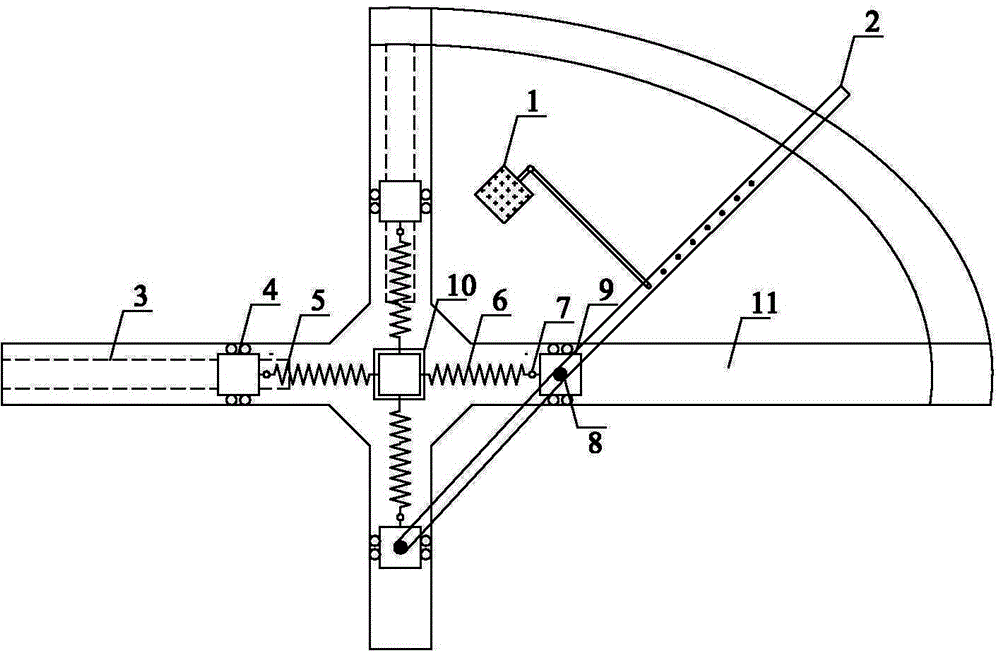
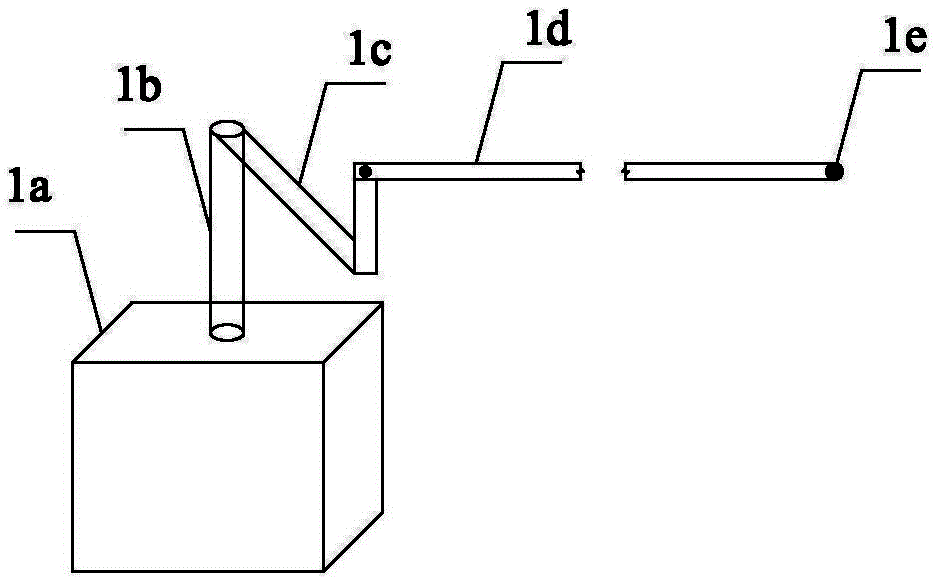
ActiveCN104132857AChange the size of the forceMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesStiffness coefficientEngineering
A multi-axial fatigue testing machine is disclosed. A drive unit is adopted to provide circulation power, and circulation force is transferred through a force transmission arm, a sliding device and a force transmission spring to a test piece such that the test piece is in a multi-axial fatigue stress state. By selecting the drive unit to connect bolt holes at different positions, multi-axial stress amplitude load applied on the test piece is adjusted; by replacing force transmission springs with different stiffness coefficients, stress amplitude load applied on the test piece is adjusted; and by changing moving displacement of a fixed device in a slide, different magnitudes of one-way initial stress or multi-way initial stress are applied. Therefore, the multi-axial fatigue testing machine can carry out a multi-axial fatigue test of a component by selecting reasonable magnitudes of stress amplitude and initial stress according to different force environments.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com