Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
102 results about "Tangential contact" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
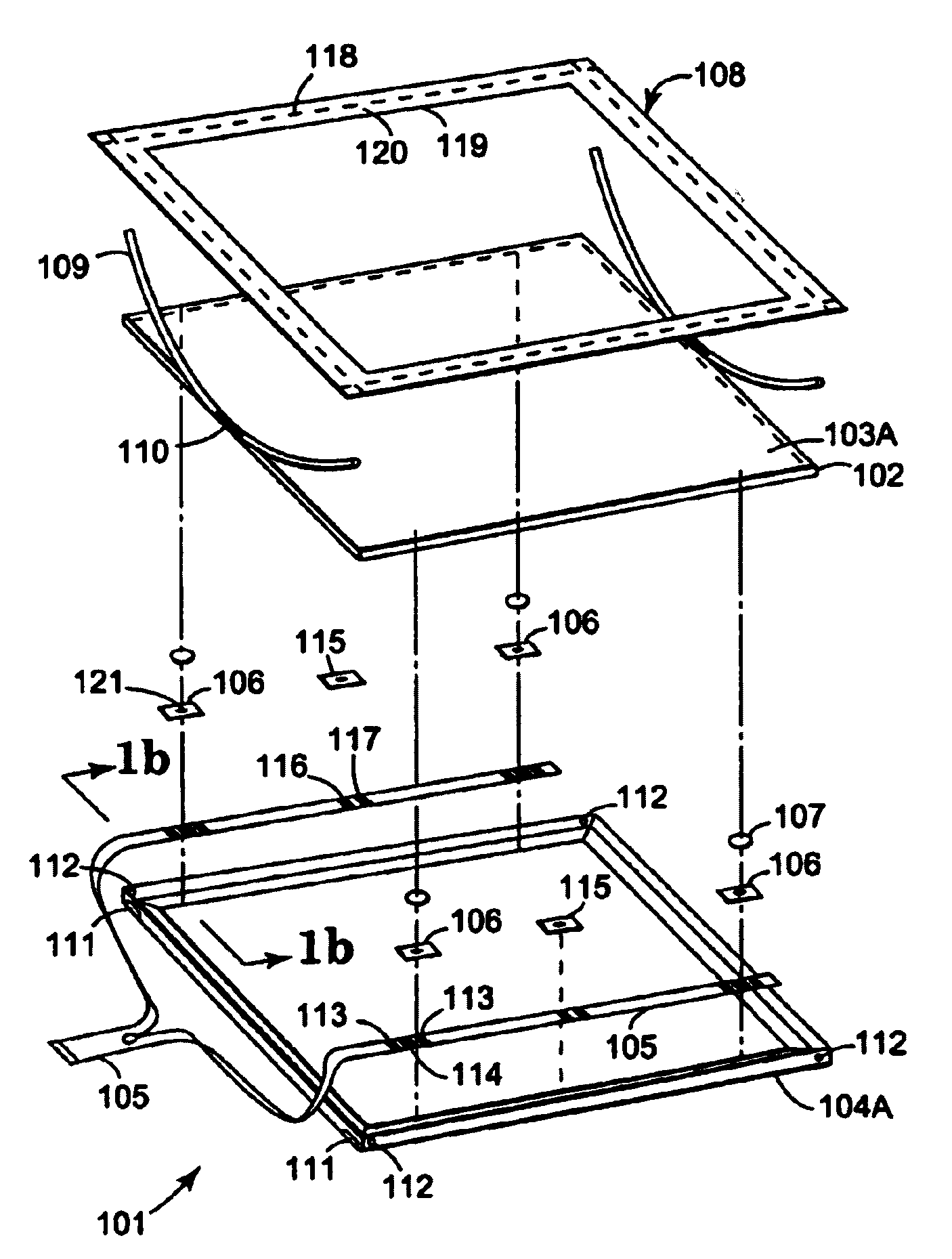
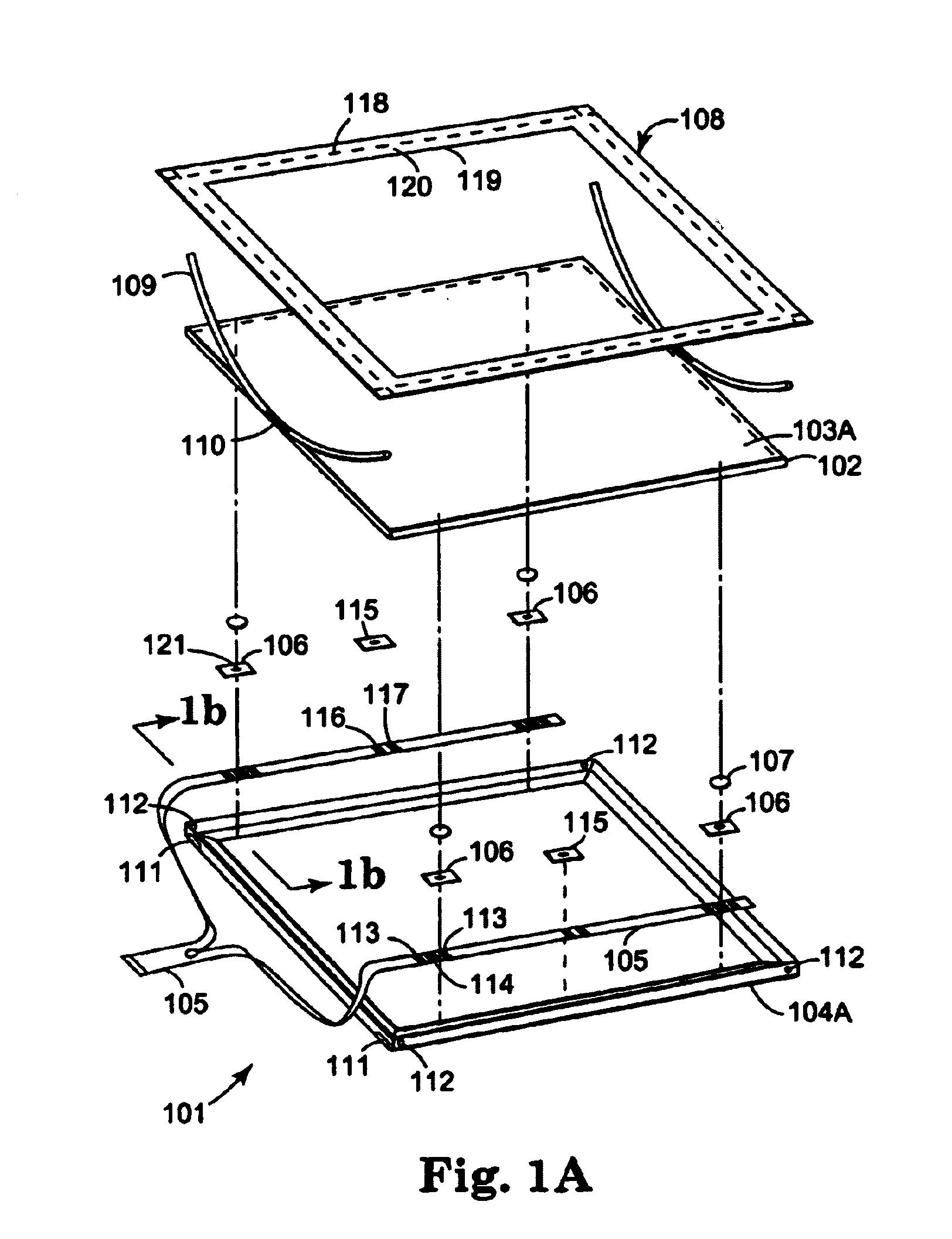
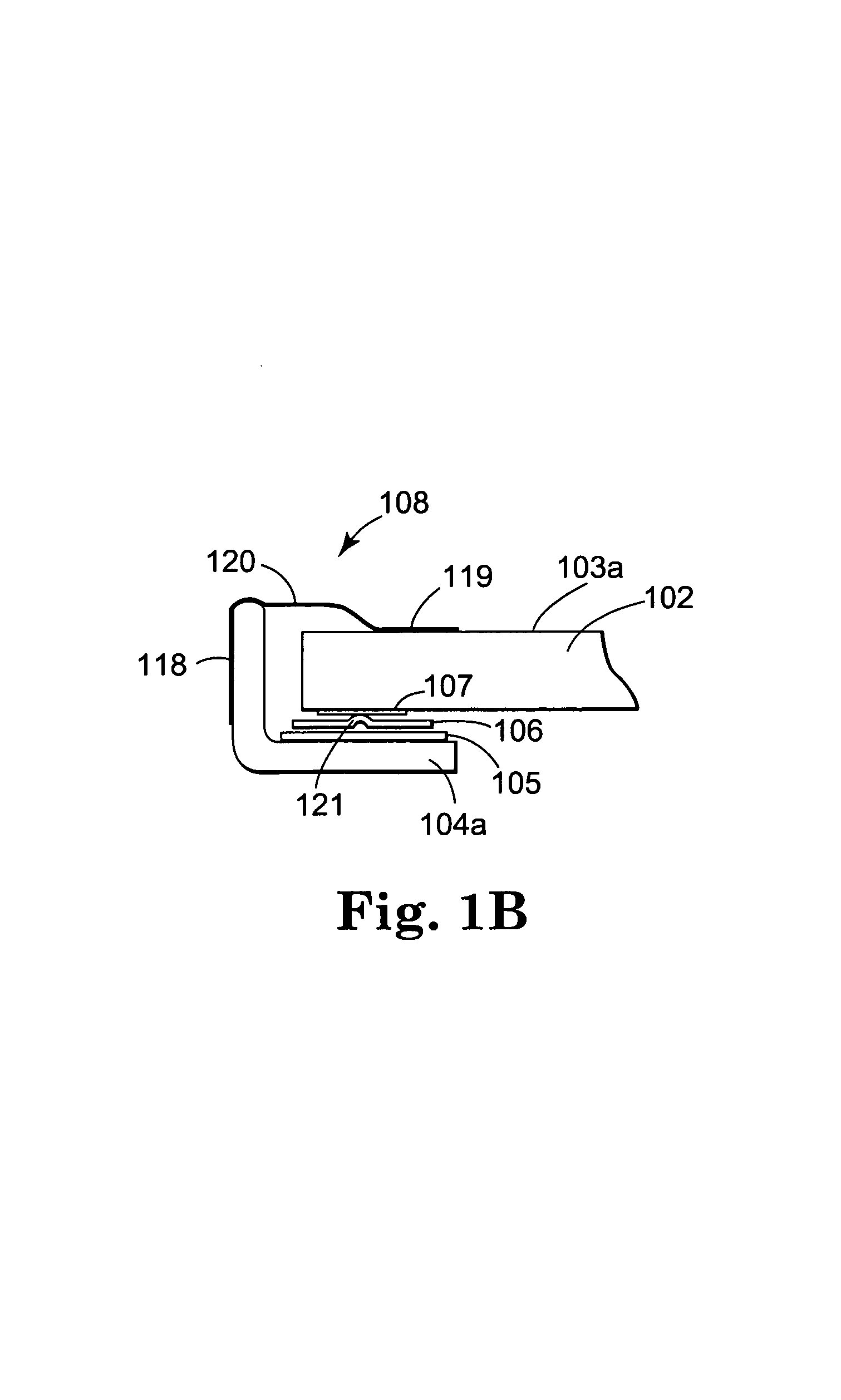
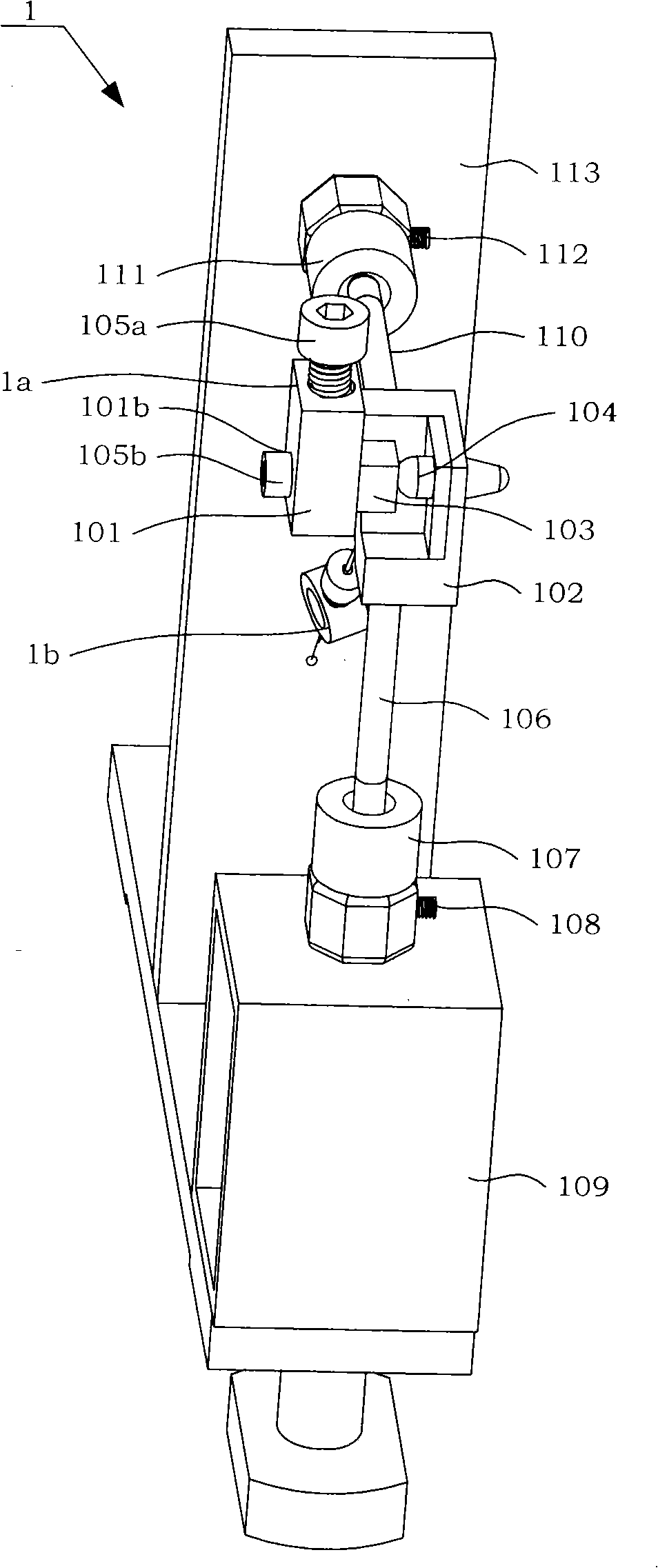
Tangential force control in a touch location device
ActiveUS7183948B2Reduce transmissionEffective applicationElectronic switchingGraph readingTangential forceTangential contact
Various techniques are provided for reducing the impact of tangential forces on touch location in a touch location device. For example, in one aspect, shunt connections are provided that impede lateral motion of the touch surface structure at the level of the touch plane, thereby reducing to insignificant magnitude reactions to tangential force passing through the sensing connections. In another aspect, sensing connections incorporate elastic means so adjusted as to turn that connection's reaction to tangential touch force perpendicular to its axis of sensitivity. In another aspect, sensing connections incorporate sensing means so adjusted as to turn that connection's axis of sensitivity perpendicular to its reaction to tangential force.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
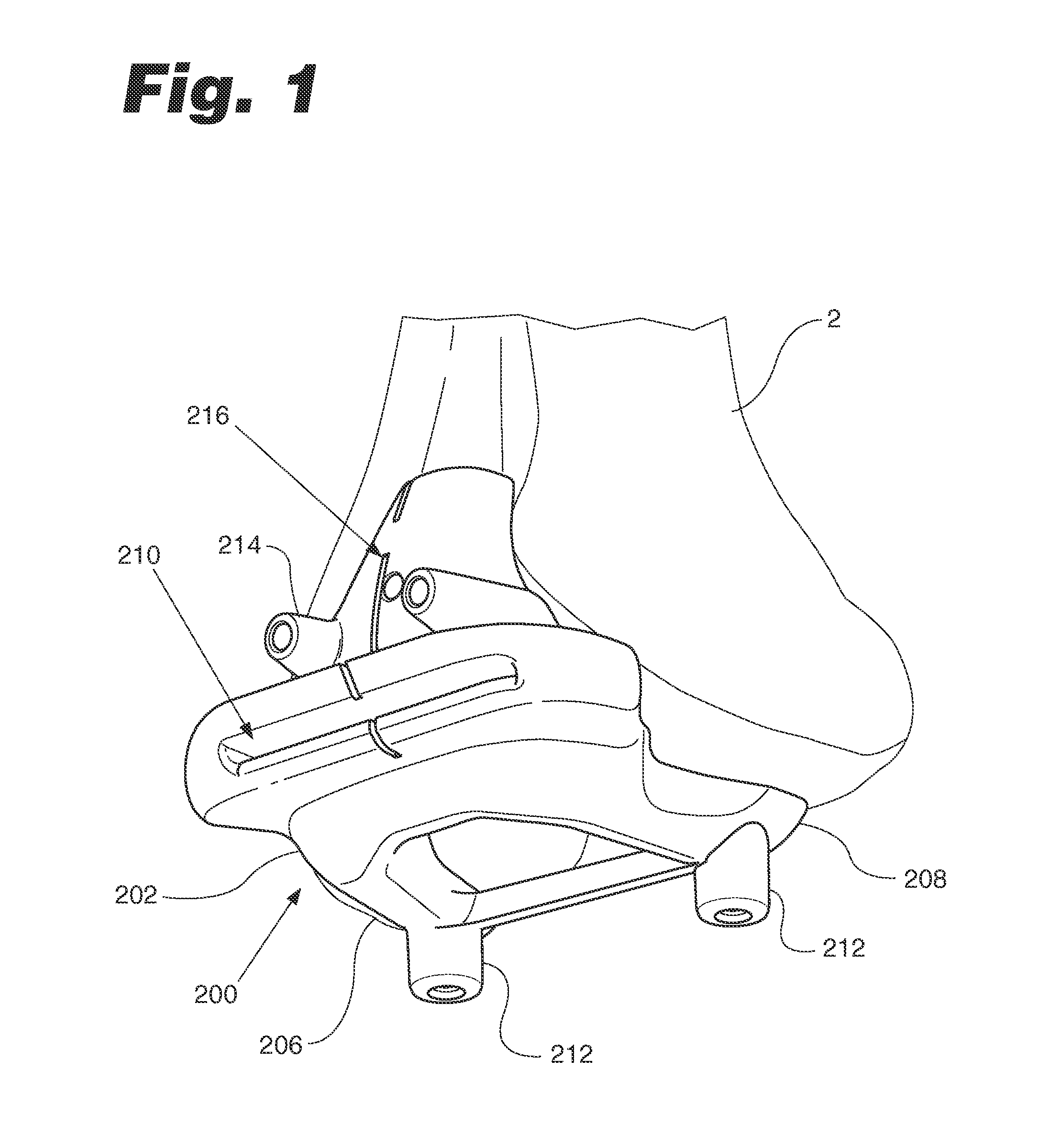
Patient match instrument
InactiveUS20140018813A1Good repeatabilityGood reproducibilitySurgical sawsProsthesisTangential contactTrochlear groove
A patient matched instrument for a patient's femur is disclosed. The instrument includes a body having a cutting slot and a patient matched surface that mates with the patient's trochlear groove, a first leg portion extending from the body, a second leg portion extending from the body; and each leg portion has a contacting pad for tangential contact with the patient's femoral medial and lateral condyles.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
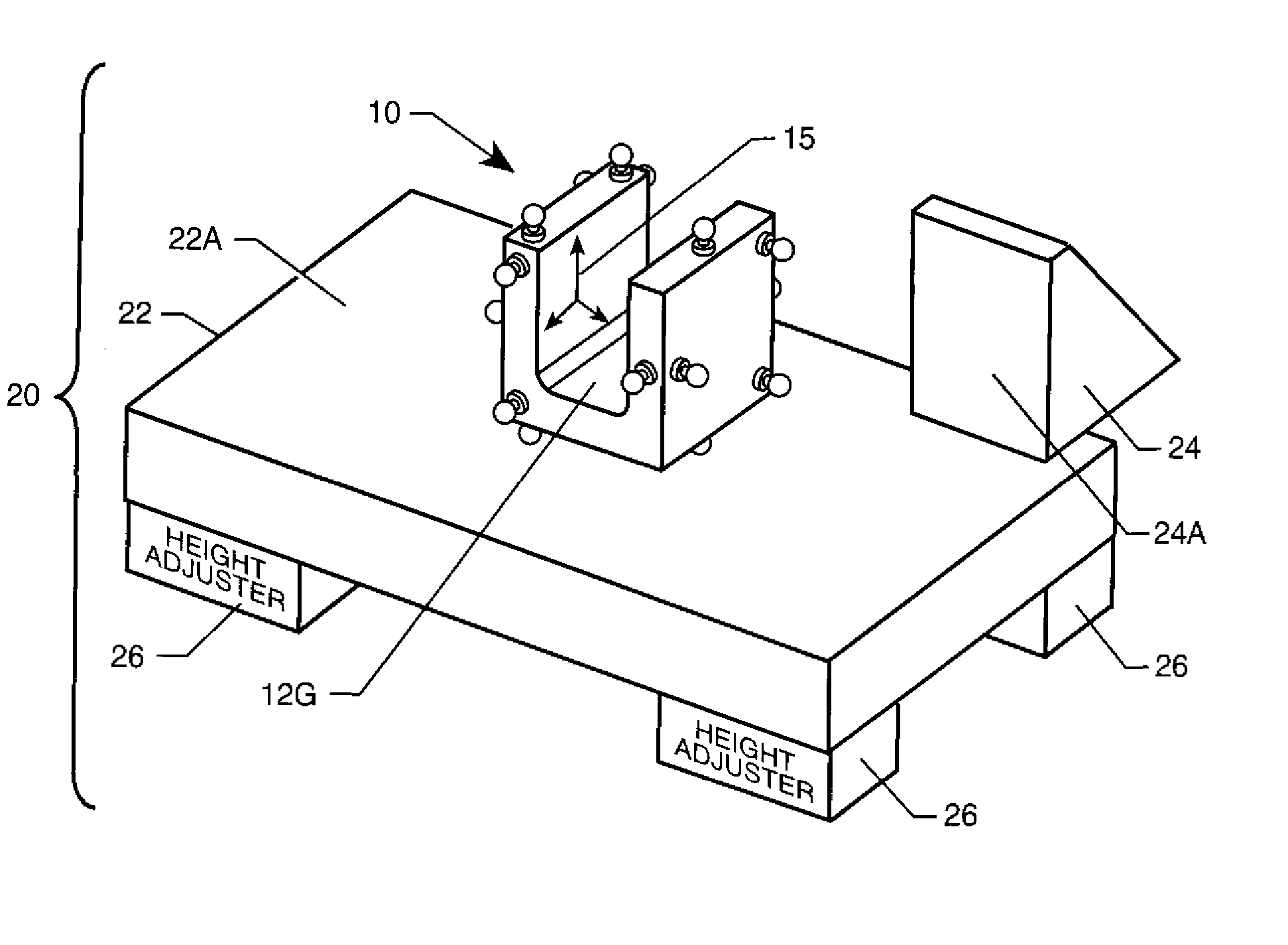
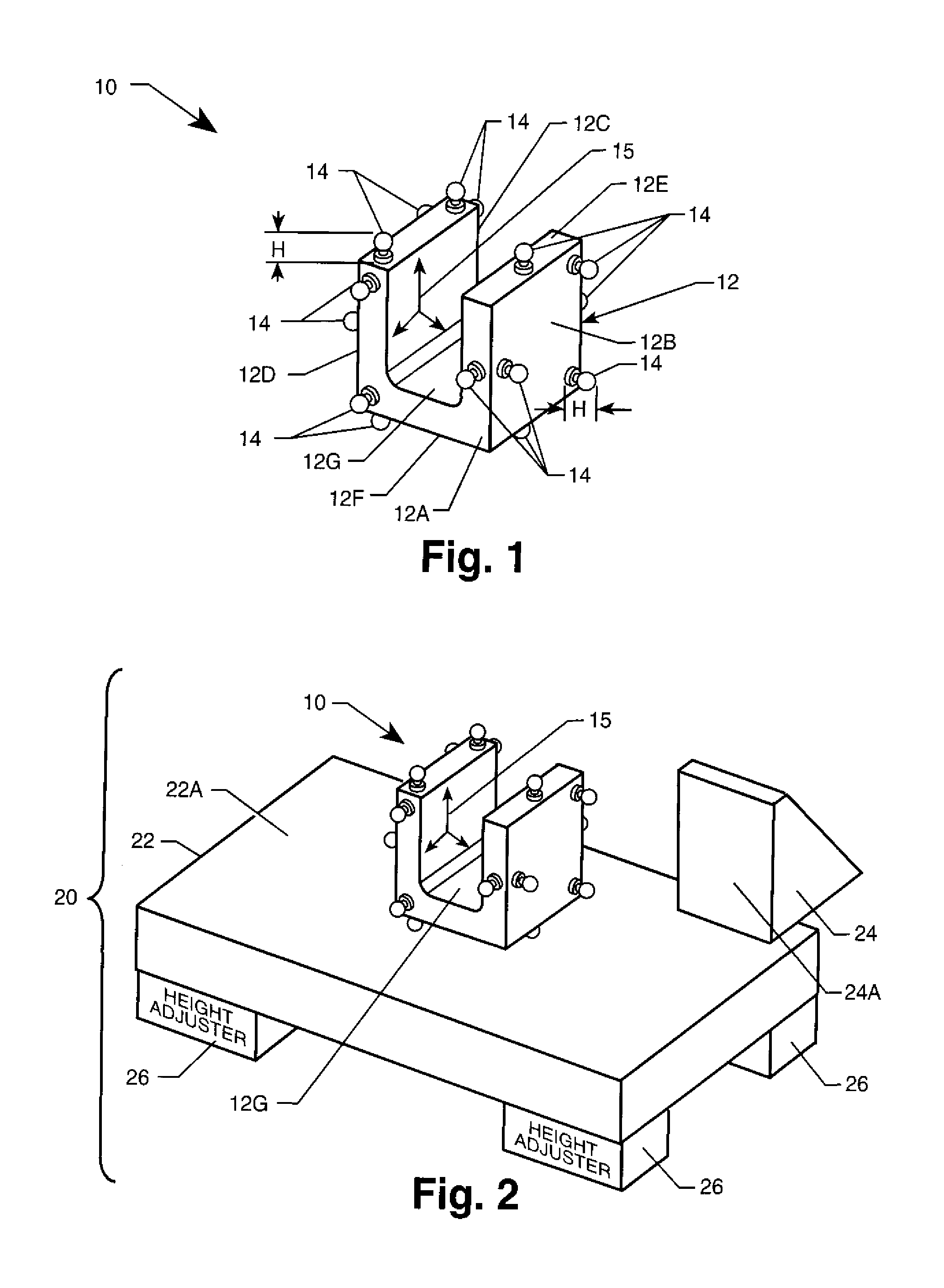
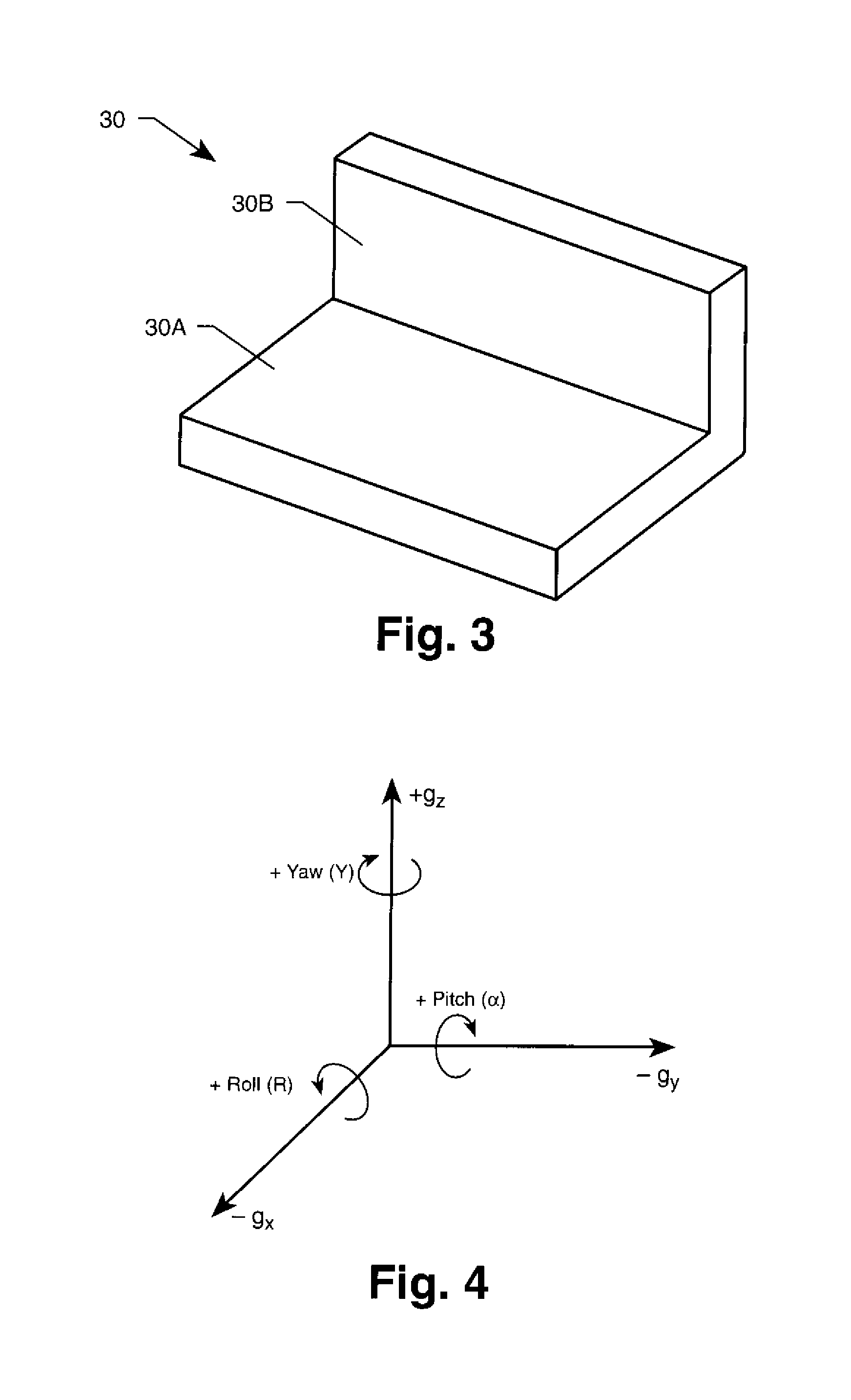
Positioning System For Single Or Multi-Axis Sensitive Instrument Calibration And Calibration System For Use Therewith
InactiveUS20080202199A1Simple procedureWave based measurement systemsCalibration apparatusReference fieldTangential contact
A positioning and calibration system are provided for use in calibrating a single or multi axis sensitive instrument, such as an inclinometer. The positioning system includes a positioner that defines six planes of tangential contact. A mounting region within the six planes is adapted to have an inclinometer coupled thereto. The positioning system also includes means for defining first and second flat surfaces that are approximately perpendicular to one another with the first surface adapted to be oriented relative to a local or induced reference field of interest to the instrument being calibrated, such as a gravitational vector. The positioner is positioned such that one of its six planes tangentially rests on the first flat surface and another of its six planes tangentially contacts the second flat surface. A calibration system is formed when the positioning system is used with a data collector and processor.
Owner:NASA
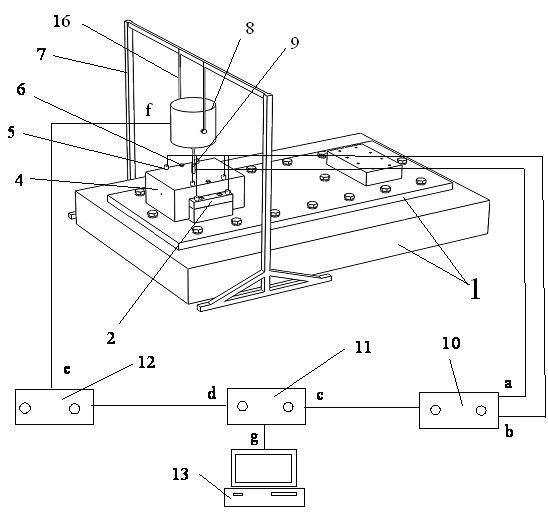
Device for testing dynamic characteristic parameters of fixed joint surface and testing method thereof
InactiveCN102072806AEasy to Accurately AcquireAccurate acquisitionVibration testingEngineeringVibration exciter
The invention relates to a device for testing dynamic characteristic parameters of a fixed joint surface of a single-degree-of-freedom system. The device comprises a base, a lower experimental plate, an experimental sample wafer, an upper experimental plate, a piezoelectric acceleration transducer, a bolt, a bracket, a vibration exciter, an impedance head, a charge amplifier, a digital analyzer, a power amplifier, an electronic computer, a normal coupling bolt hole, a lower experimental plate coupling bolt, a tangential coupling bolt hole and a flexible rope. Compared with the prior art, the device has the remarkable advantages of compact structure and clear testing principle; the dynamic characteristic parameters of a normal contact surface and a tangential contact surface can be simultaneously measured; the dynamic characteristic parameters of the contact surfaces in different load states can be measured by adjusting the pre-tightening force of the coupling bolt of the upper experimental plate and the lower experimental plate; the excitation force passes through the center of gravity of the upper experimental plate during measurement; vibration signals of the upper experimental plate and the lower experimental plate are simultaneously measured; the influence of the vibration signal of the base is eliminated during the calculation of a frequency response function of the system; and the device has the characteristics of high efficiency, stability and accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
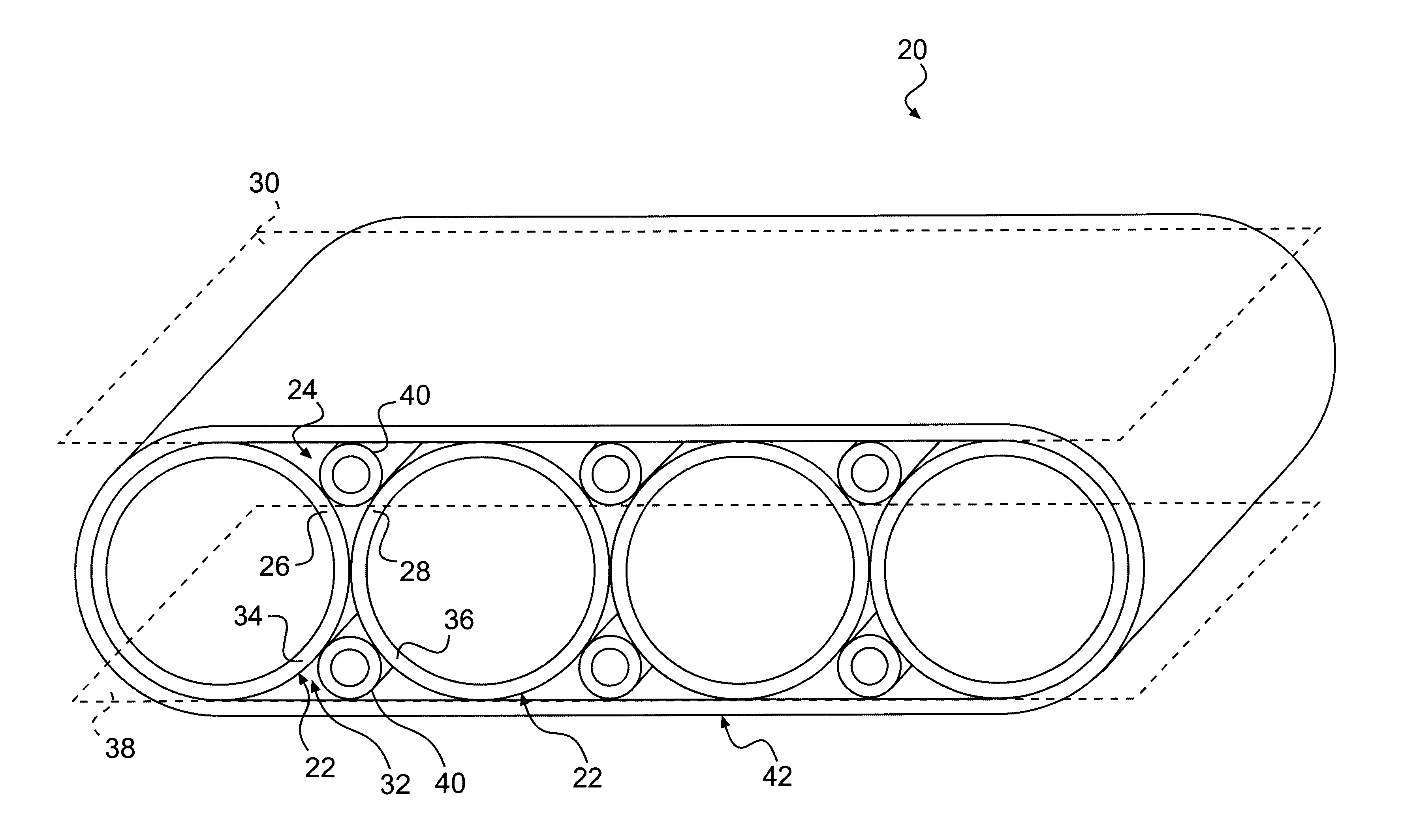
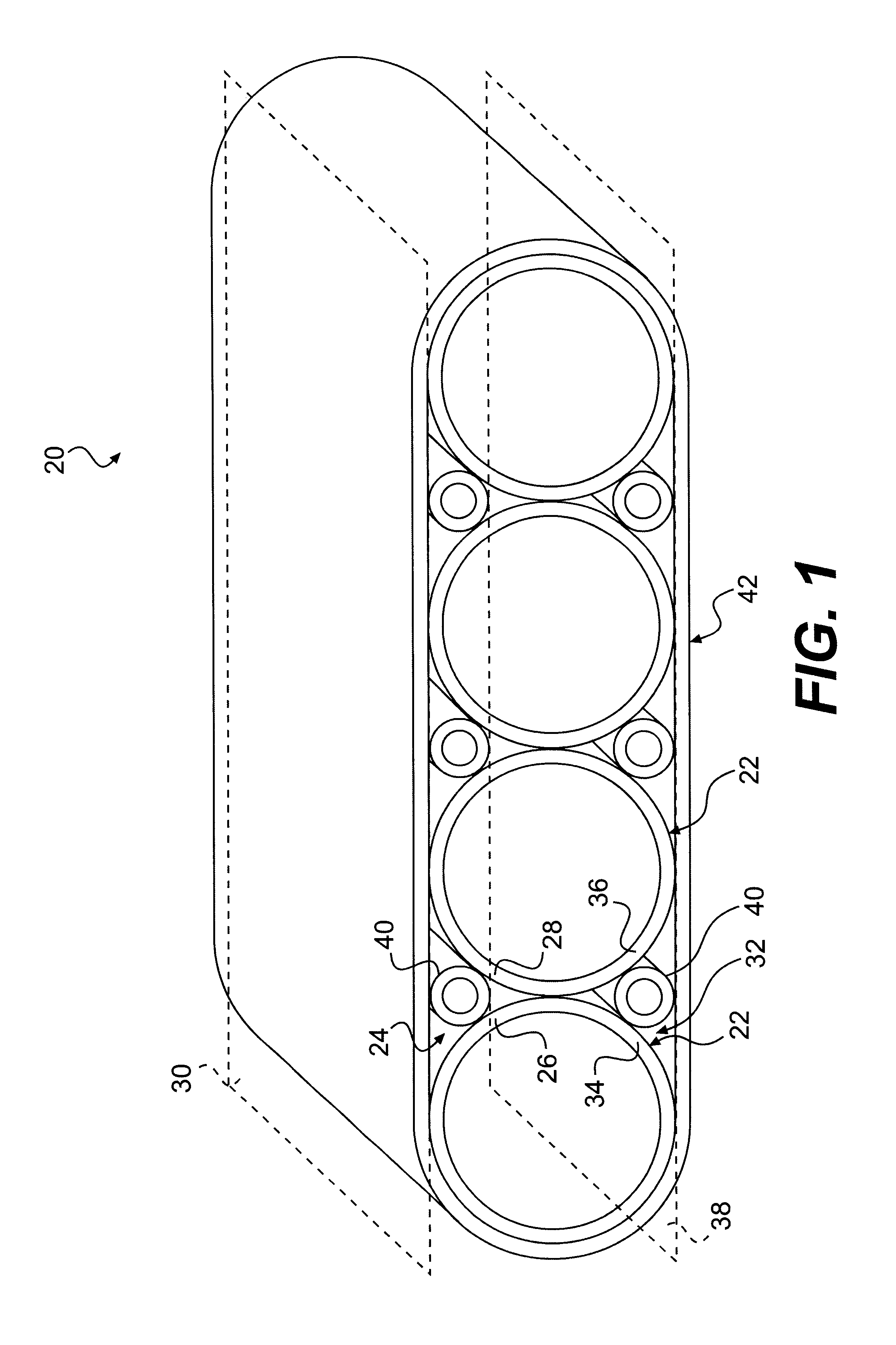
Pipe assembly for collecting surface water runoff and associated methods
The present invention includes a pipe assembly for collecting water runoff. The pipe assembly includes a plurality of elongated primary pipes disposed in adjacent contact along their lengths. Each pair of adjacent elongated primary pipes define upper and lower elongated voids between adjacent pipe haunches and upper and lower imaginary planes tangential thereto. An elongated secondary pipe is disposed in each void in tangential contact along its length with the two adjacent elongated primary pipes defining the void. A material transversely encompasses the plurality of elongated primary pipes and elongated secondary pipes. The pipe assembly may be used in a water storage system and methods for installing such a system. The pipe assembly may also be used in a method for collecting surface water. The pipe assembly may be used in a system for use in a water flow path.
Owner:ADVANCED DRAINAGE SYST
Device for placing sleeves on traveling articles
ActiveUS20100037556A1Eliminate riskRegular cut edgeWrappers shrinkageWrapping material feeding apparatusTangential contactEngineering
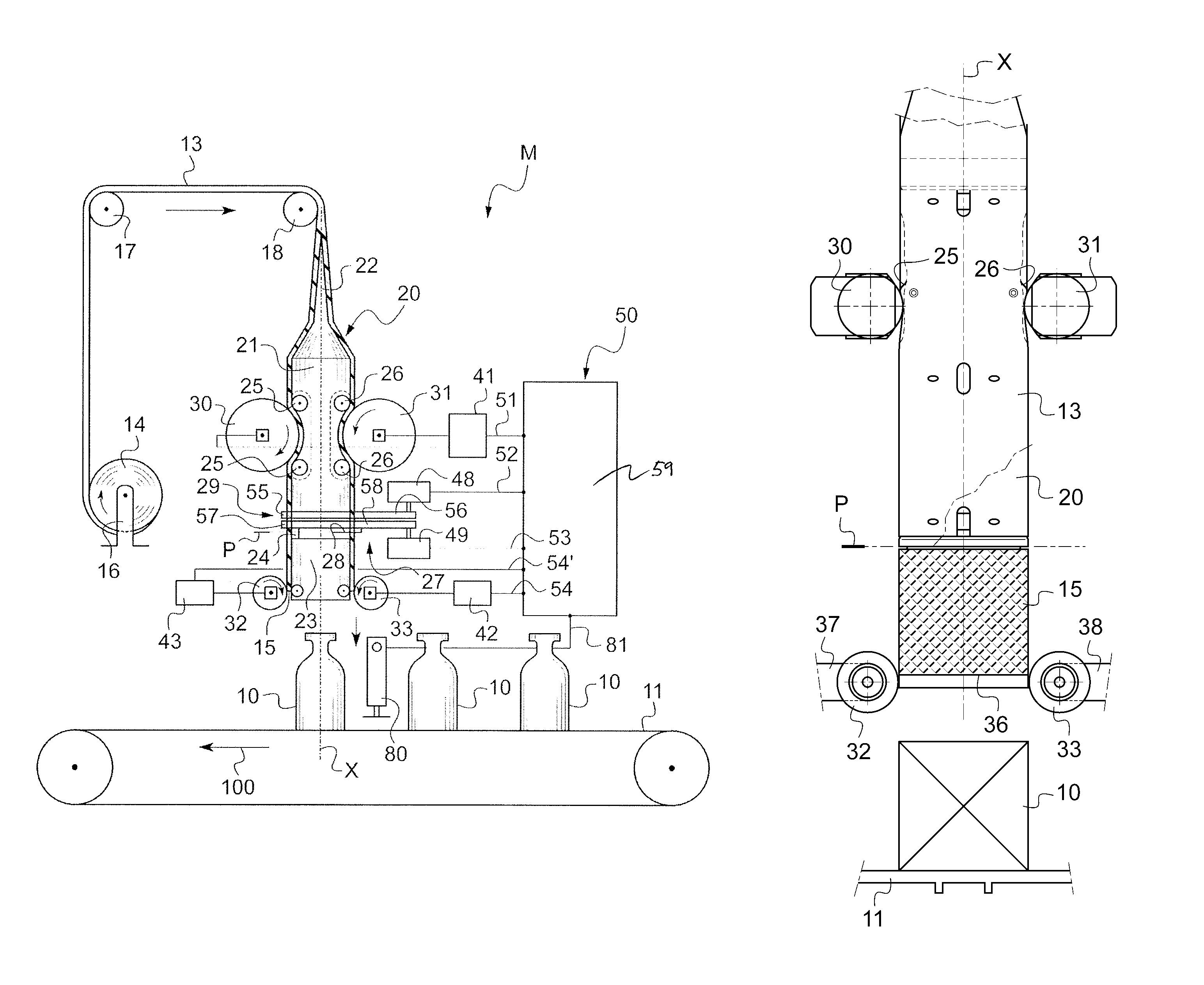
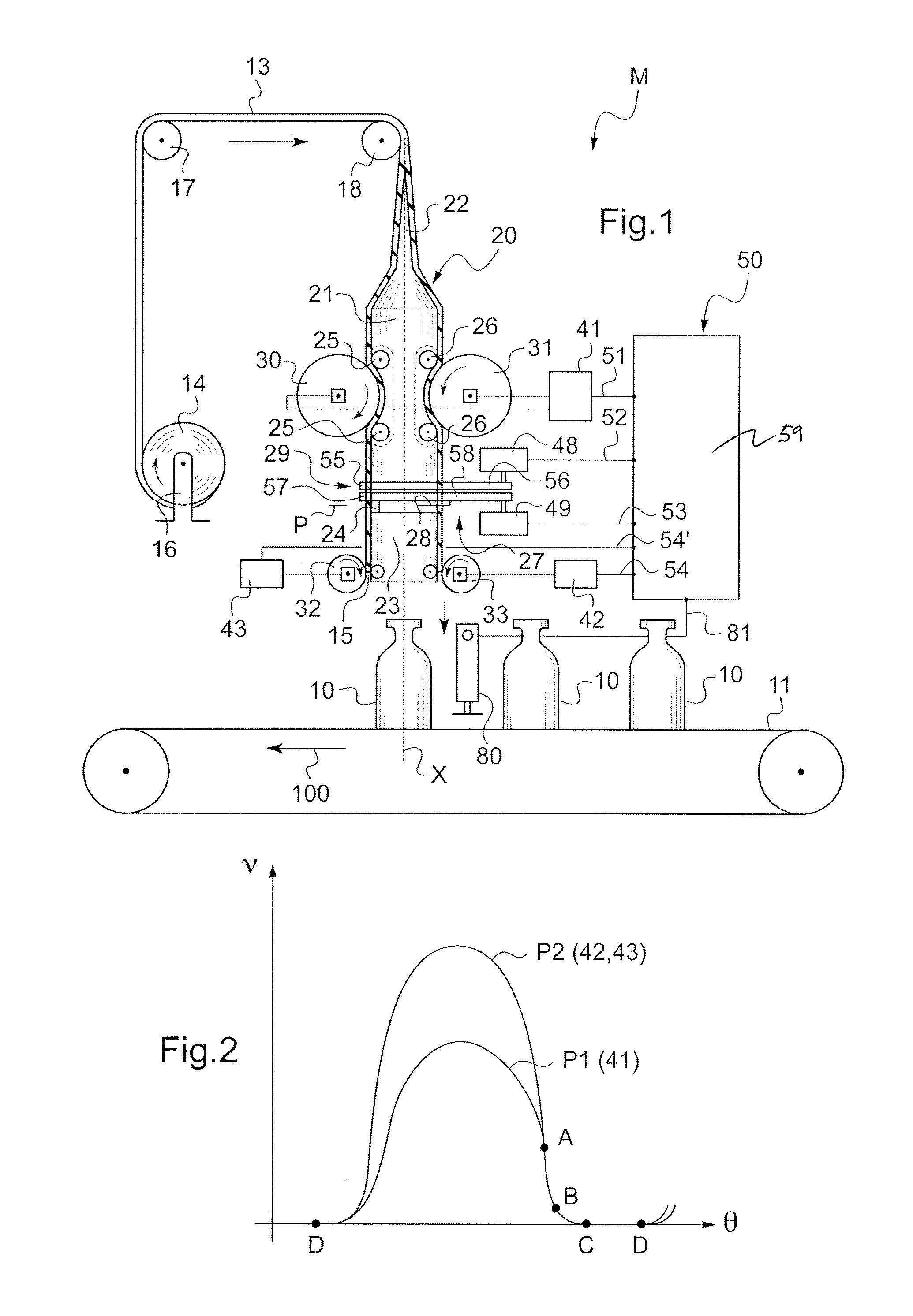
The invention relates to a device for placing sleeves on traveling articles, said sleeves being cut from a continuous sheath passing over a sheath-opening shaper, first outer wheels serving to advance the sheath along the shaper, and second outer wheels being provided downstream from cutter means for the purpose of ejecting the cut-off sheath segment, said wheels being driven in rotation by associated electric motors controlled synchronously by a virtual-shaft common electronic programmer. In accordance with the invention, the programmer is arranged to determine a continuous profile of speed variation for the associated electric motors, said profiles being bell-shaped and having a common end segment in which the profiles coincide, this corresponding to the motors having identical speeds, the length of the common end segment being selected so that the sheath is advanced beyond the point of tangential contact with the second wheels so that said sheath is pinched by said second wheels prior to being held stationary for the cutting and ejection pass.
Owner:SLEEVER INT
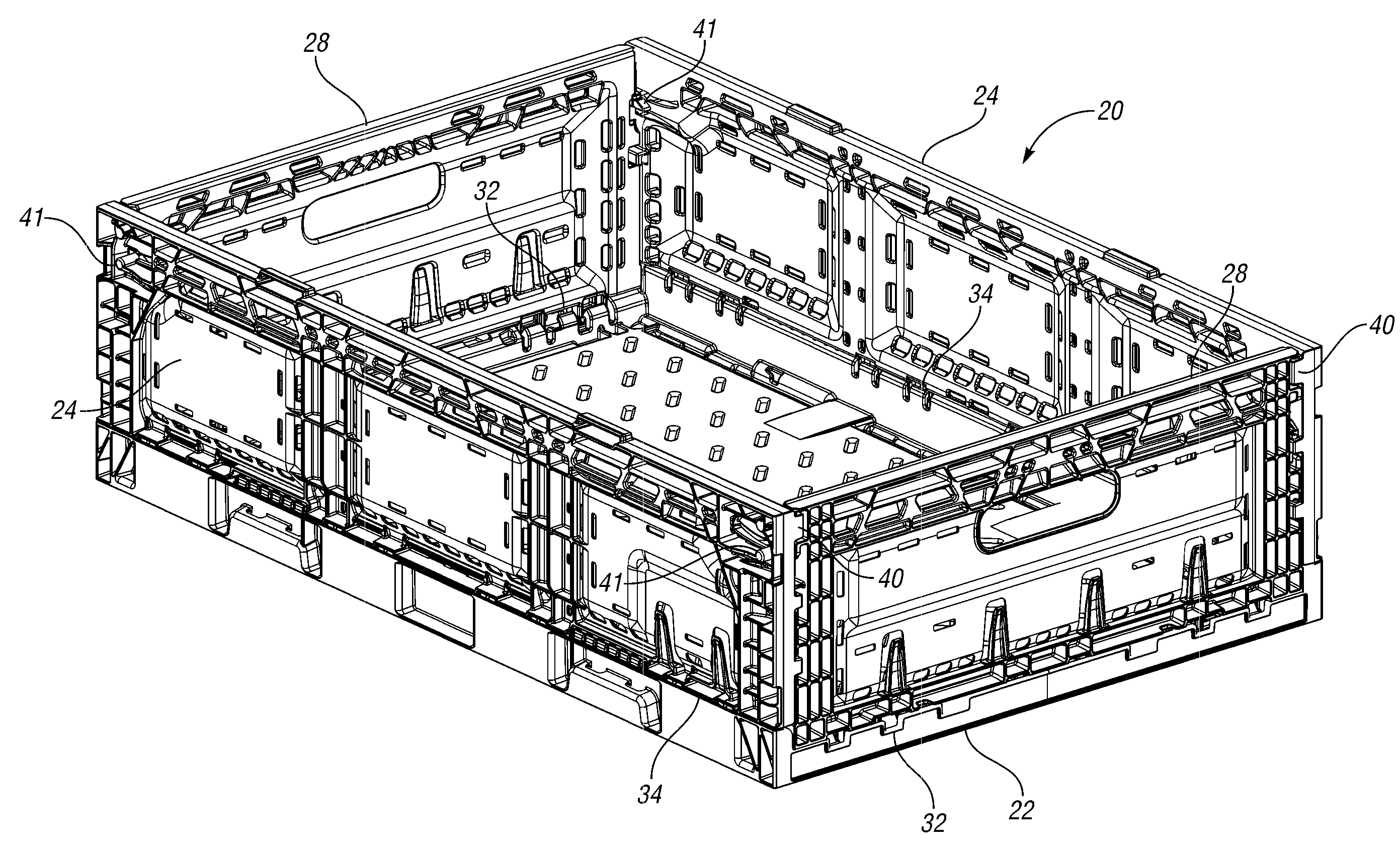
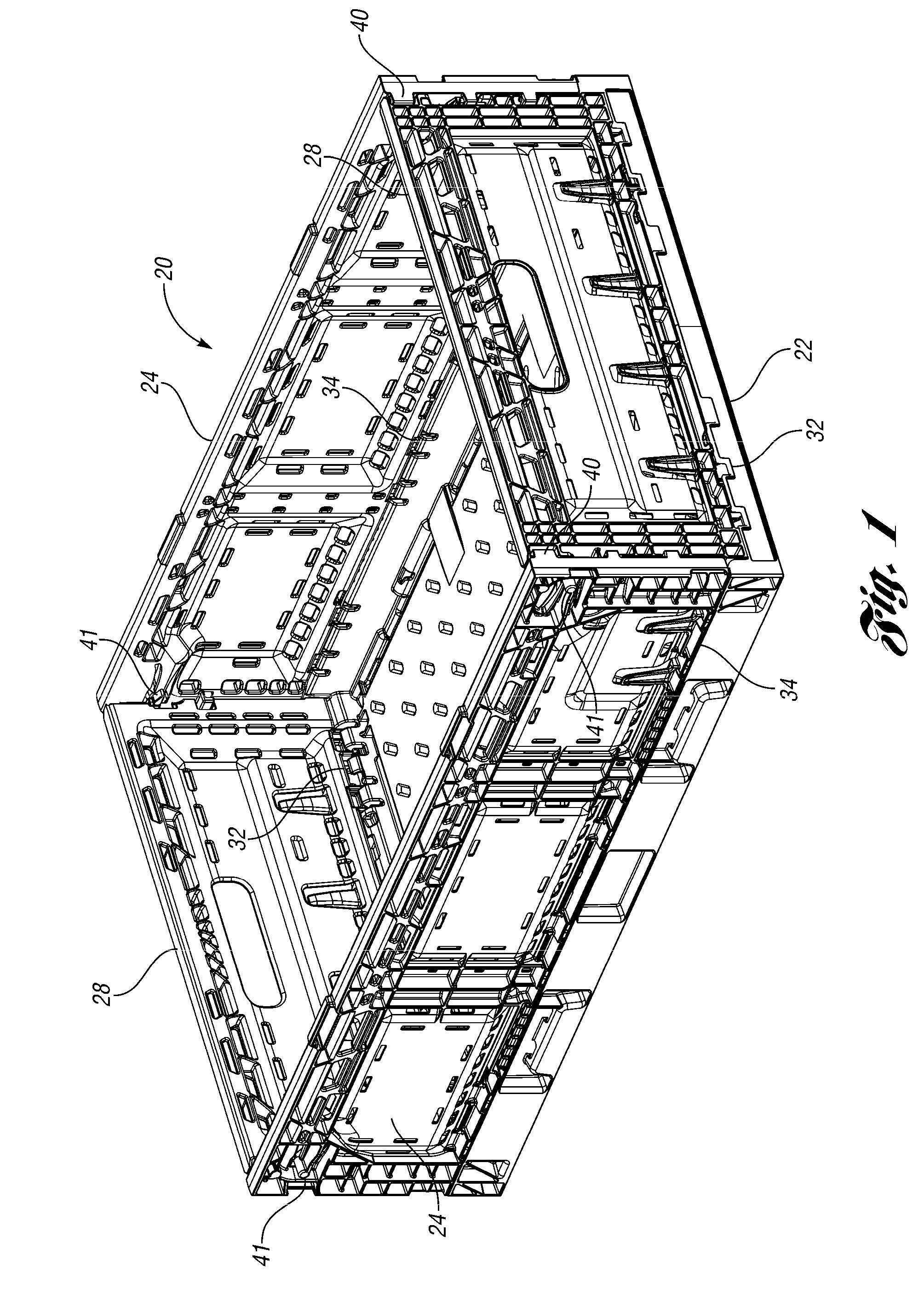
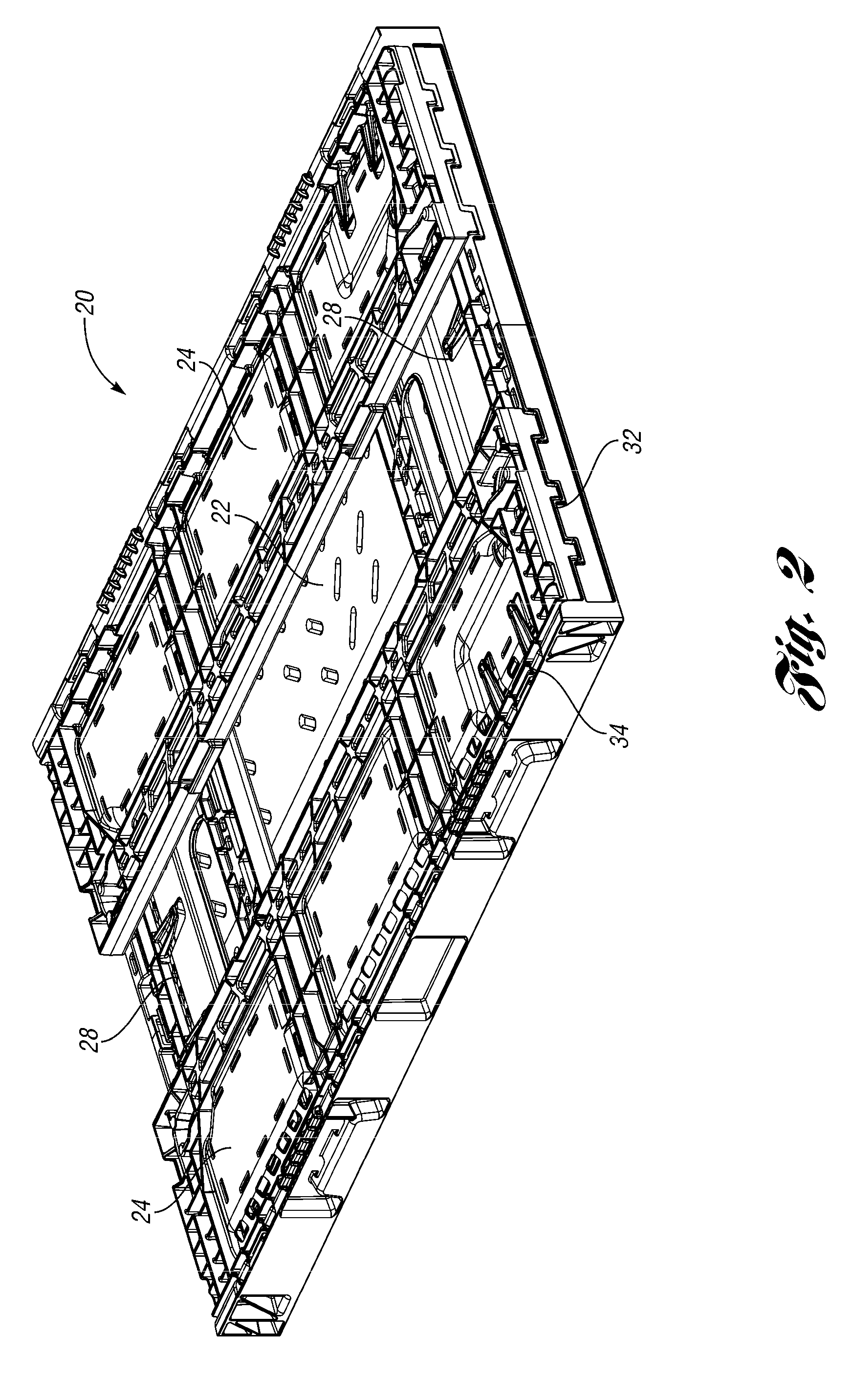
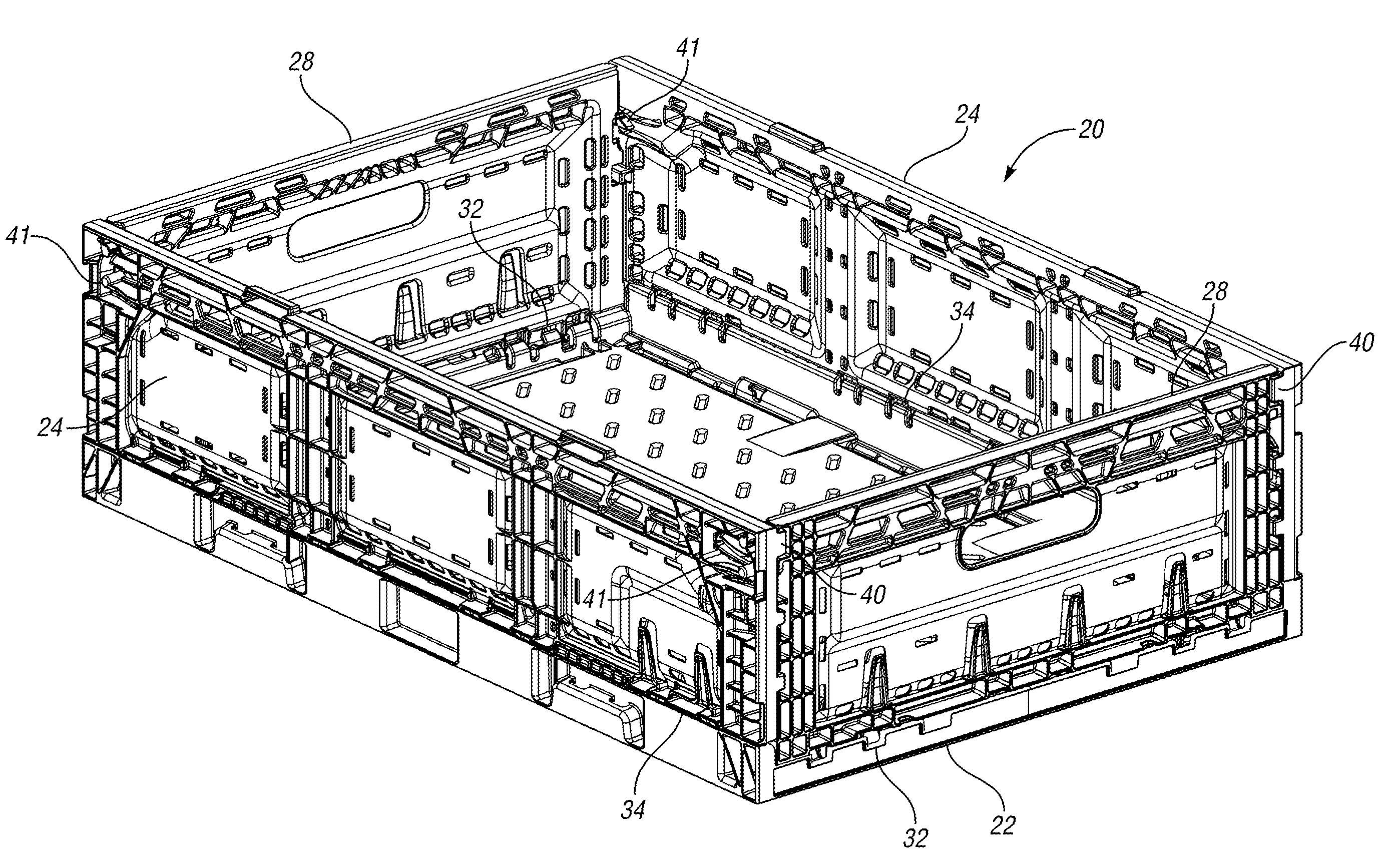
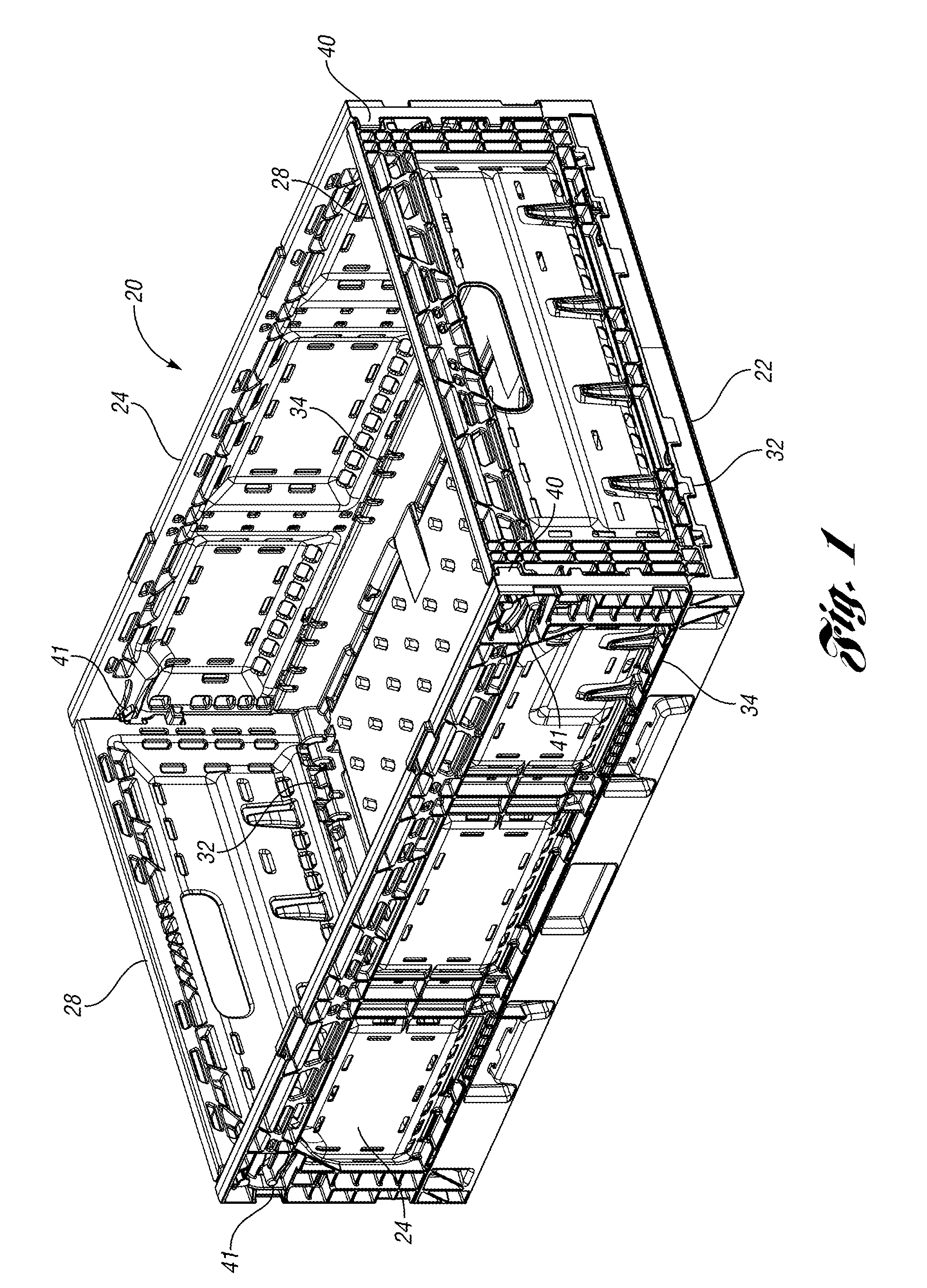
Collapsible container
Owner:REHRIG PACIFIC CO INC
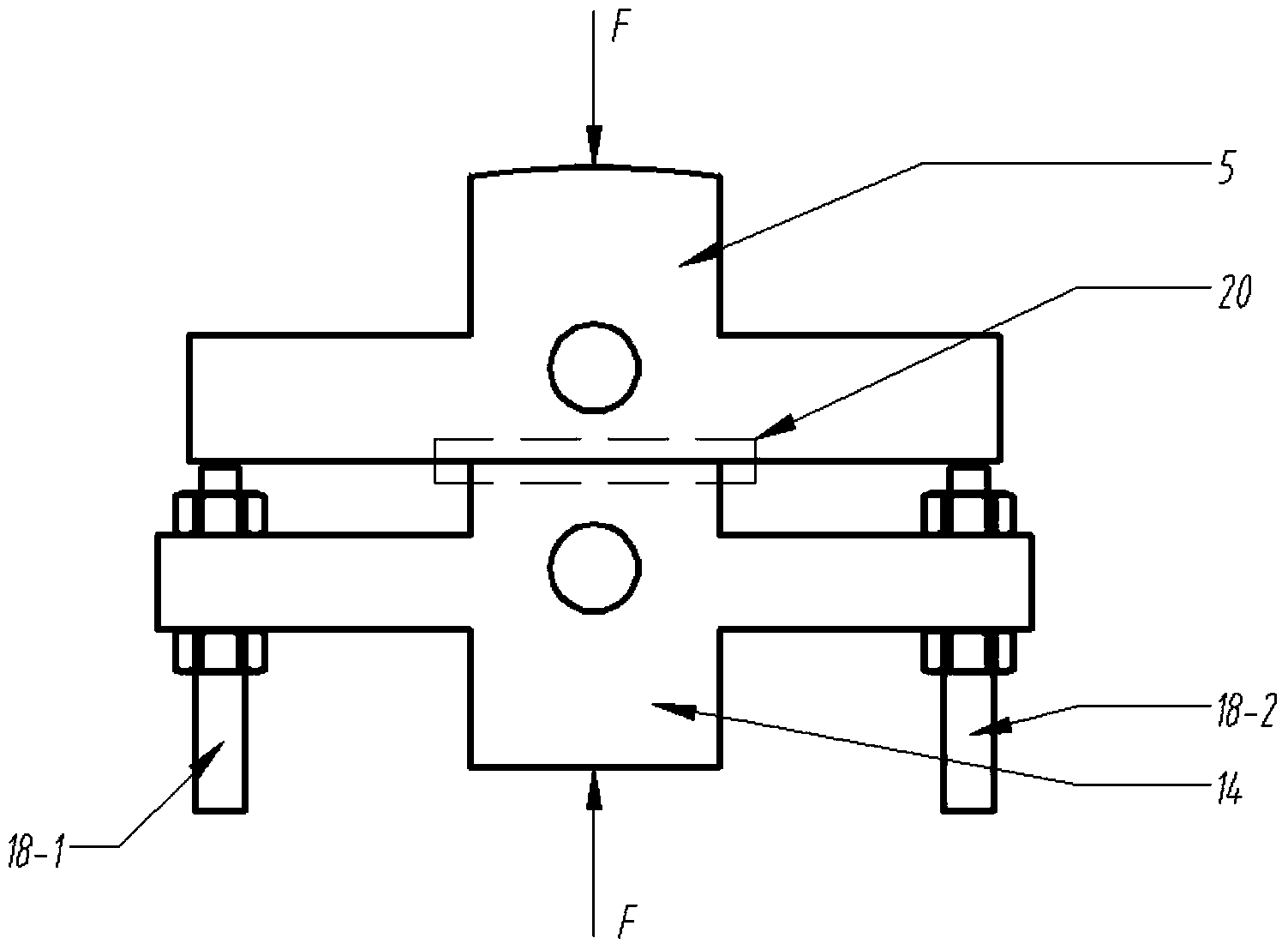
Comprehensive experiment table for measuring normal and tangential contact rigidity of mechanical junction surface
InactiveCN103913385AReduce duplicationReduce processing costsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesTest efficiencyTangential contact
The invention relates to a comprehensive experiment table for measuring normal and tangential contact rigidity of a mechanical junction surface, wherein upper and lower support plates are connected into a whole by a stand column, a jack is fixed in the lower support plate, a pressure sensor and a lower test piece are arranged on the jack, an upper test piece is arranged right above the lower test piece, a lower tangential rigidity test pad is clung to two side faces of the upper test piece and the lower test piece and is connected by bolts and nuts, a bolt pretightening force measuring sensor is lined under a bolt head, an eddy current sensor is fixed on two beams extending forwards and backwards of the lower test piece and just faces to two beams extending forwards and backwards of the upper test piece, an adjusting screw is screwed into a screw guide sleeve by virtue of thread, the upper test piece is embedded into a test piece fixing sleeve, a circular arc surface is formed above the upper test piece, a surface corresponding to the circular arc surface, of the test piece fixing sleeve, is a plane, and by changing the assembly relationship of test pieces, the normal contact rigidity and the tangential contact rigidity of the test piece are realized in the same device, the equipment utilization rate is improved, the cost is saved, and the testing efficiency is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
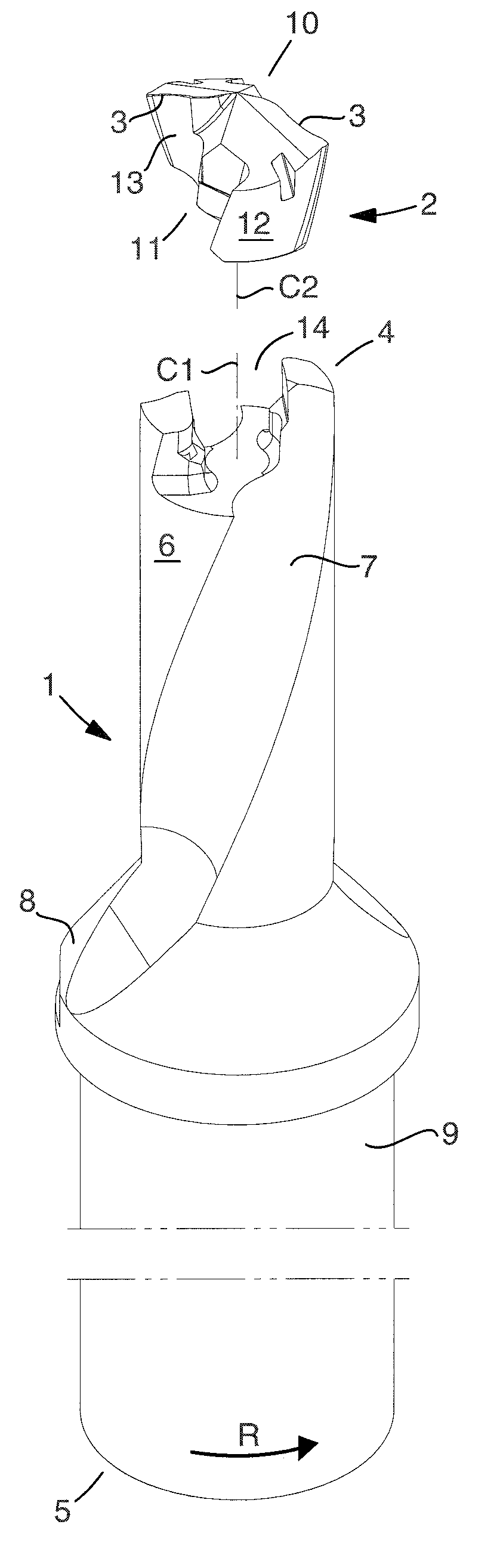
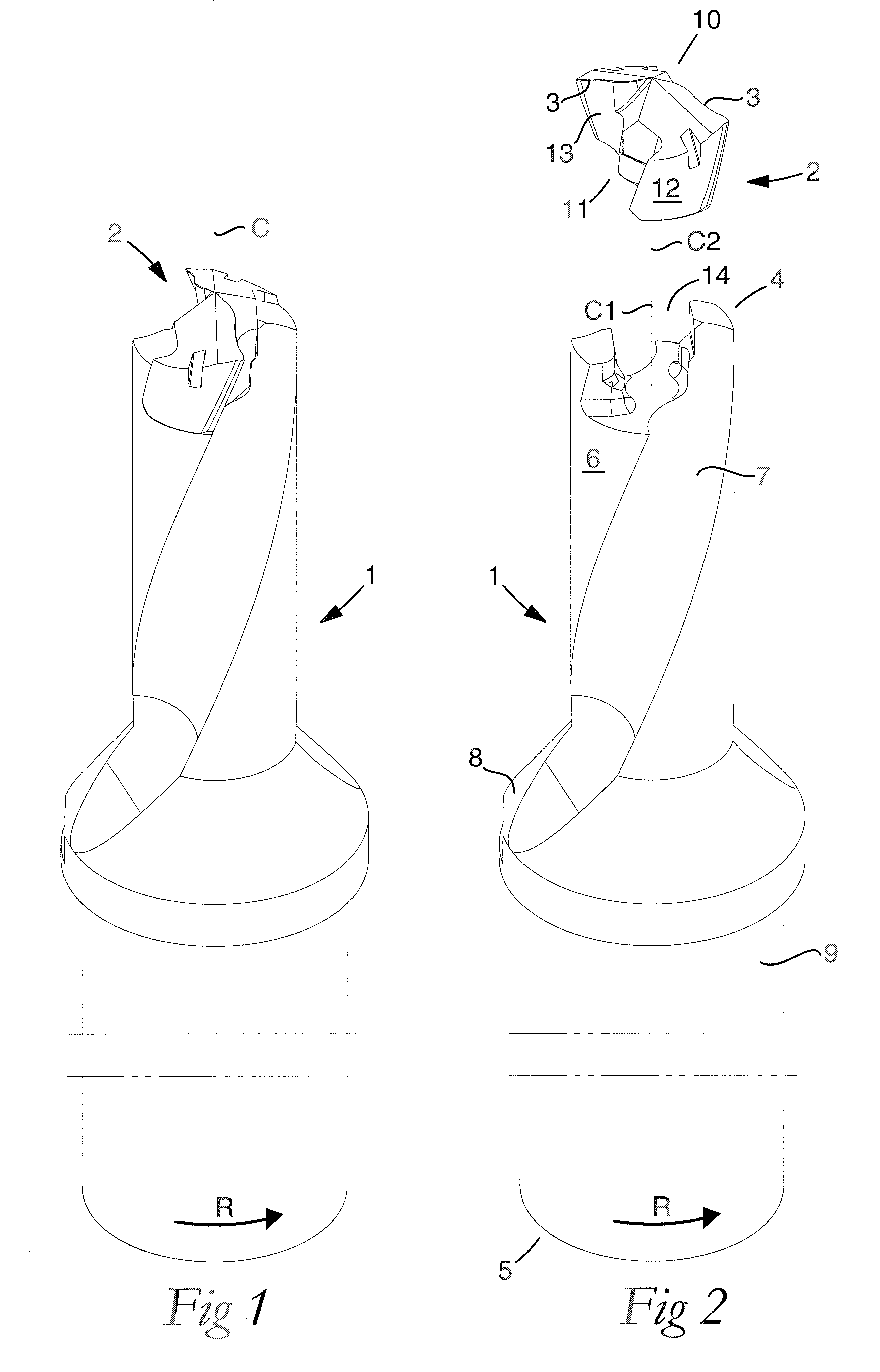
Drilling tool for chip removing machining as well as a loose top and a basic body therefor
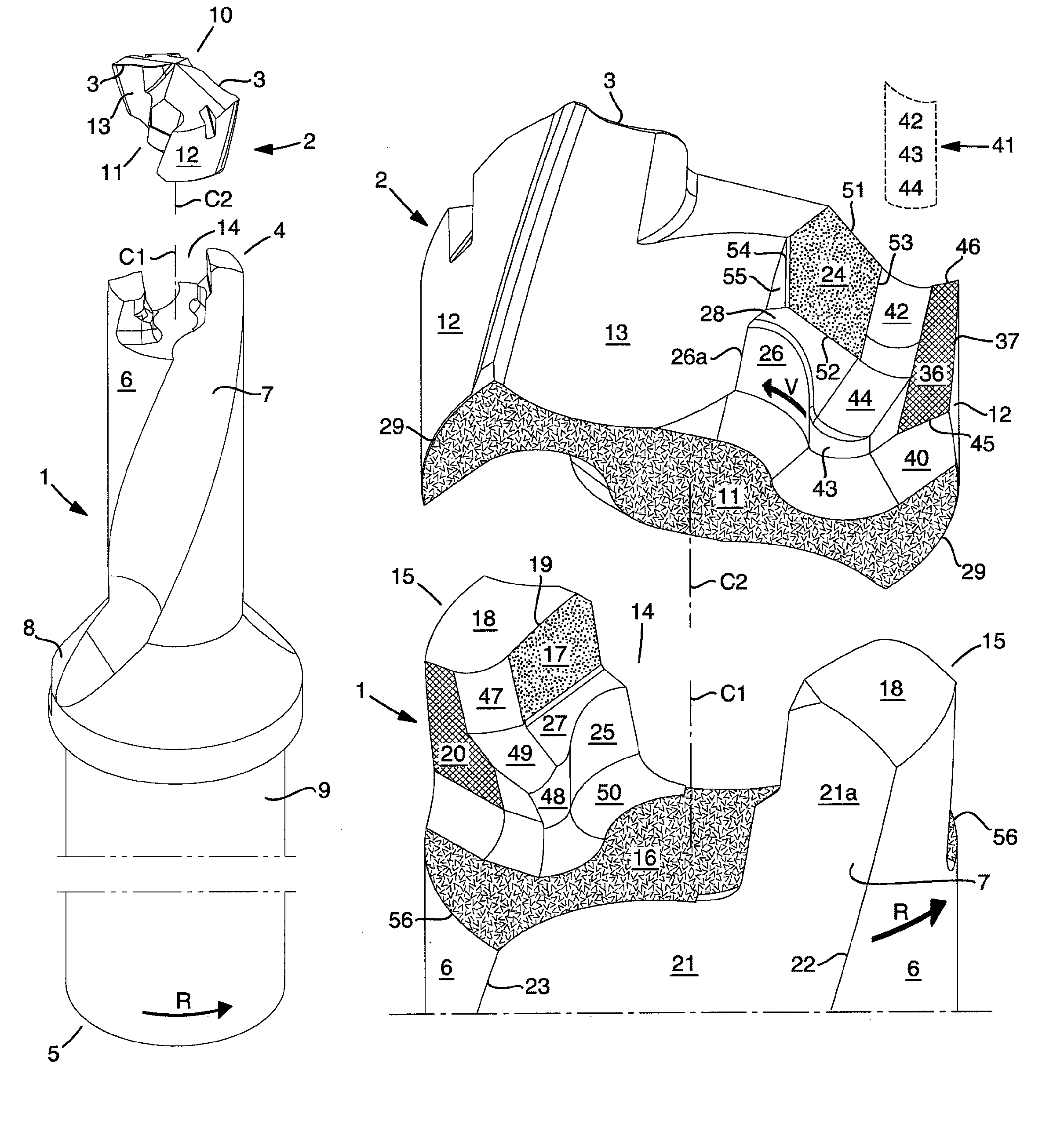
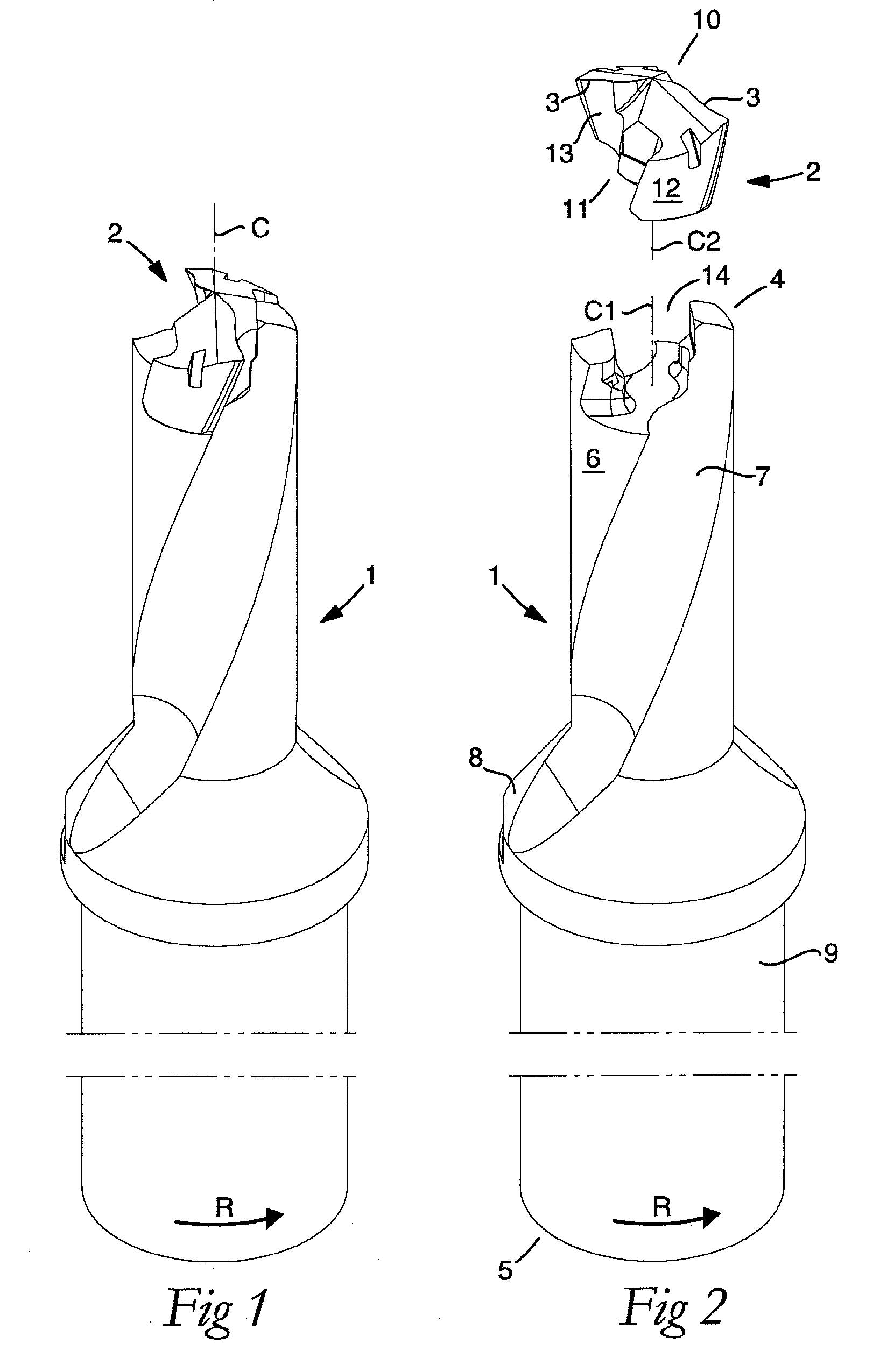
ActiveUS20100322729A1Easy transferThread cutting toolsThread cutting machinesFluteTangential contact
A loose top for drilling tools, including front and rear ends, a pair of envelope part surfaces concentric with a center axis, and two chip flutes countersunk in relation to the pair of envelope part surfaces between which two bars project radially from a central core, the front end including a cutting edge and at least one clearance surface positioned rotationally behind the cutting edge, the rear end forming an axial contact surface. The loose top includes two opposite side contact surfaces against which elastically bendable branches of a tool basic body are pressed in use, a pair of convex guide surfaces situated axially behind the side contact surfaces, the guide surfaces being concentric with the center axis and radially spaced-apart from the center axis at a distance that is less than the radial distance between the center axis and a respective side contact surface, and a pair of torque-carrying tangential contact surfaces that are situated radially inside the envelope part surfaces and outside the side contact surfaces. The axial contact surface extends perpendicular to the center axis between borderlines adjacent to the two envelope part surfaces.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Belt type precise seed-metering device
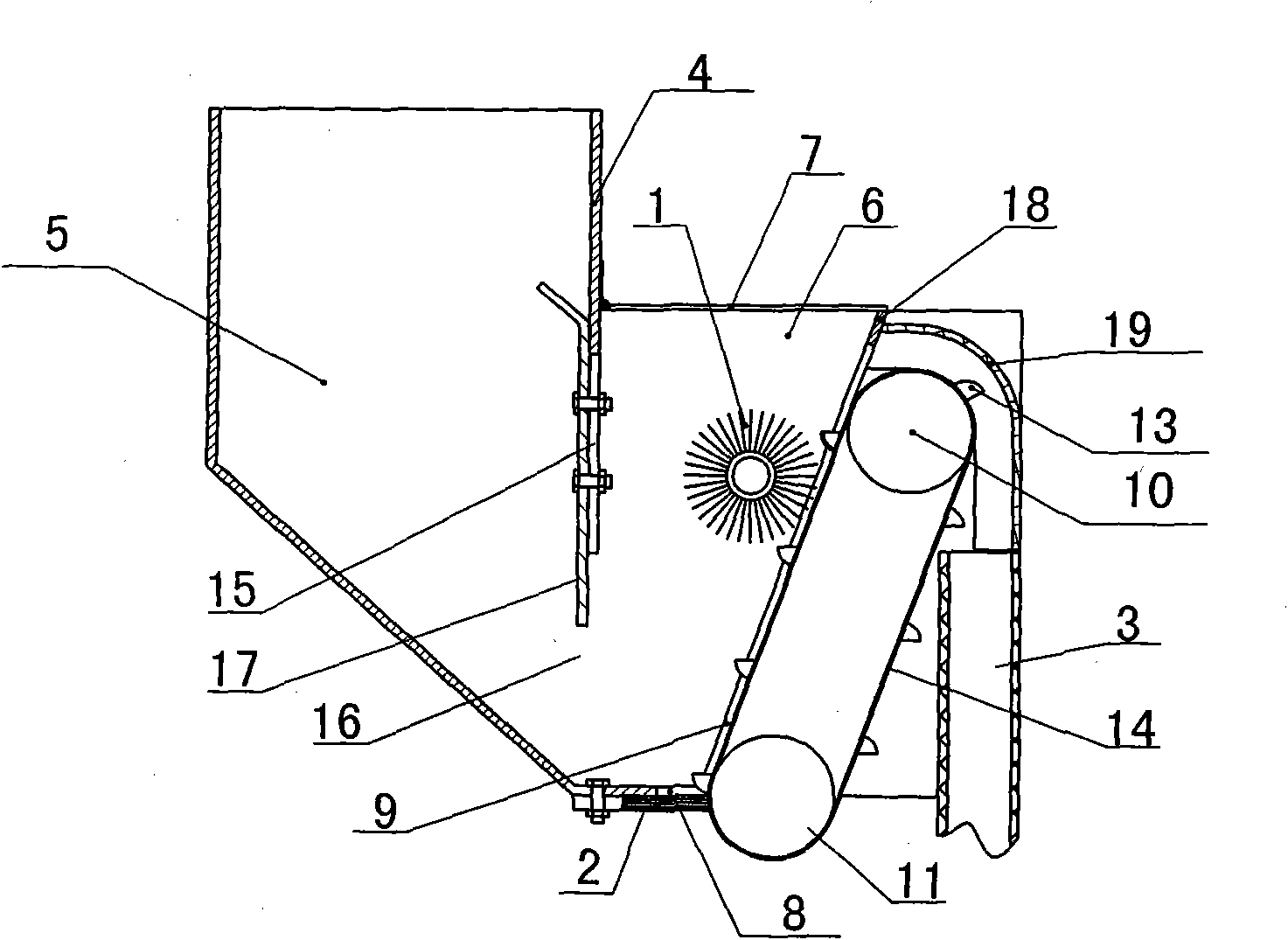
InactiveCN101855960AImprove reliabilityNot easy to fall offSeed depositing seeder partsSingle grain seedersDrive wheelTangential contact
The invention provides a belt type precise seeding-metering device which comprises a seed taking device, a seed cleaning hairbrush, a driving belt wheel, a sealing hairbrush, a seed guiding pipe and a seed box. The device is characterized in that a partition plate is added, and the seed box is longitudinally spaced into a large seed box and a small seed box which are communicated through lower parts; the bottom of the small seed box is provided with a rectangular opening, and the sealing hairbrush is horizontally blocked on the rectangular opening; the rear wall of the small seed box, away from the large seed box, is an inclined plane, and the bottom of the rear wall is upwards provided with a long and narrow rectangular opening; the seed taking device is positioned on the rear part of the small seed box and comprises a driving wheel, a driven wheel and a flat belt with a seed taking scoop; the axial line of the driven wheel is parallel and level to the bottom of the small seed box, and the flat belt is blocked on the long and narrow rectangular opening and in tangential contact with the sealing hairbrush; the highest operation position of the seed taking scoop is lower than the upper end of the long and narrow rectangular opening; the seed cleaning hairbrush is cylindrical and positioned in the small seed box, and the excircle surface of the seed cleaning hairbrush is tangential with the flat belt; and an opening of the seed guiding pipe is positioned right below the seed taking scoop when the seed taking scoop turns. The device has high sowing precision, less breakage and convenient seed filling.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Collapsible Container
A collapsible container with latches provides a more consistent knockdown force in more situations. At least one of the engaging surfaces of the latch is curved outwardly toward the other engaging surface. This provides substantially tangential contact between the surfaces, even when the wall is deformed slightly by the knockdown force. The tangential contact provides consistent frictional force resisting the knockdown force.
Owner:REHRIG PACIFIC CO INC
Method for cell alignment and identification and calibration of robot tool
InactiveUS6356808B1CalibrationQuick and inexpensiveProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsTangential contactEngineering
A method for cell alignment, identification and calibration of part of a robot tool, preferably a part of the robot tool, is positioned close to a detector, whereupon it is moved repeatedly past the limit of the area of detection of the detector. During the movement, the pose of the robot is registered each time the surface of said robot tool comes into tangential contact with the area of detection, and an over determined system of equations is formed, consisting of a correlation between the registered poses and unknown parameters regarding the detection area of the detector and the location of the robot part in space. An error vector is introduced into the system of equations, which is then solved while minimizing the error vector, preferably in the least square sense, in order to thus identify said unknown parameters and the error vector.
Owner:ROBOTKONSULT
Rough surface-based three-dimensional contact stiffness calculation method for spur gear
ActiveCN106844818APrecise contact stiffnessSolve the disadvantages of smooth contactGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationContact pressureEngineering
The invention discloses a rough surface-based three-dimensional contact stiffness calculation method for a spur gear. The method comprises the steps of firstly by adopting hexahedral mesh generation, requiring all square meshes on a tooth surface to be equal in area; calculating contact pressure distribution of the smooth tooth surface based on a finite element method, and extracting node pressure intensity of a contact region; calculating normal contact stiffness and tangential contact stiffness of a single square mesh based on a fractal theory; and calculating the contact stiffness of the tooth surface. According to the method, the precision of a gear contact stiffness calculation model is further improved; the defect of smooth contact according to a Hertz theory in an original calculation process is overcome; an influence law of a roughness parameter on a gear stiffness characteristic in a rough tooth surface contact process and a calculation method are disclosed; and meanwhile, a finite element-based three-dimensional contact stiffness calculation model is more accurate than an original two-dimensional calculation model or calculation formula, and the influence of errors in actual assembling and manufacturing processes of the gear is considered, so that the gear contact stiffness is more accurate and a foundation is laid for gear dynamics analysis.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device for storing and dispensing in single units objects in the form of sheets or thin strips
InactiveUS20090302048A1Not cause riskReduce coefficient of frictionCoin-freed apparatus detailsFlat article dispensingTangential contactEngineering
The invention concerns a device, such as a box, for storing and dispensing in single-units objects in the form of sheets, wafers, thin strips or platelets, with planar geometry in particular square, rectangular, polygonal, circular, elliptical, enabling said objects to be dispensed individually in single units, comprising: a) storage means such as a container with a lid, containing the objects to be dispensed, stored stacked on one another on a storage surface, said storage means including a surface for guiding the objects to be dispensed and a dispensing opening enabling the objects to be dispensed individually in single units; b) dispensing means bade of a flexible, deformable, mobile driving element, having one of its ends in contact with the object to be driven, along at least one transverse tangential contact line, and whereof the longitudinal cross-section is S- or nearly U-shaped.
Owner:AIRSEC S
Feed unit for strip wrapping material
A strip of wrapping material is advanced by a feed unit that includes a gumming device composed of a gumming roller and a transfer roller contrarotating about horizontal and parallel axes and in tangential contact one with another along an area coinciding with a straight line generator common to both. At least one of the two rollers is maintained at a given temperature by a fluid directed through a circuit of which a first portion extends along a shaft supporting and driving the roller and a second portion is located internally of the roller itself; the circuit includes valves operating respectively along a flow branch and a return branch of the circuit, associated both with the drive shaft and with the respective roller and interposed between the first and second portions so that these can be opened and closed when required, whilst the first portion is connected to an inlet duct and to an outlet duct rigidly associated with a frame and connected to the circuit by way of a hydraulic or pneumatic rotary coupling.
Owner:GD SPA
Device for placing sleeves on traveling articles
ActiveUS8146334B2Eliminate riskRegular cut edgeWrappers shrinkageWrapping material feeding apparatusTangential contactEngineering
The invention relates to a device for placing sleeves on traveling articles, said sleeves being cut from a continuous sheath passing over a sheath-opening shaper, first outer wheels serving to advance the sheath along the shaper, and second outer wheels being provided downstream from cutter means for the purpose of ejecting the cut-off sheath segment, said wheels being driven in rotation by associated electric motors controlled synchronously by a virtual-shaft common electronic programmer. In accordance with the invention, the programmer is arranged to determine a continuous profile of speed variation for the associated electric motors, said profiles being bell-shaped and having a common end segment in which the profiles coincide, this corresponding to the motors having identical speeds, the length of the common end segment being selected so that the sheath is advanced beyond the point of tangential contact with the second wheels so that said sheath is pinched by said second wheels prior to being held stationary for the cutting and ejection pass.
Owner:SLEEVER INT
Rounded shoe and position brake assembly for the counterbalance system of a tilt-in window
ActiveUS7966770B1Wear minimizationPrevents the brake shoe housing from bindingBuilding braking devicesWing openersTangential contactActuator
A counterbalance assembly for counterbalancing a tilt-in window sash within a guide track of a window frame. A brake shoe housing is provided having a face section and a rear section defined between a top edge, a bottom edge, and two side edges. At least one of the two side edges is a curved surface having a convex curvature. A curl spring is provided having a free end. The free end of the curl spring engages the brake shoe housing, therein applying a turning torque to the brake shoe housing that cocks the brake shoe housing and moves the curved surface into tangential contact with the guide track. A cam actuator is interposed between the face section and the rear section that spreads these sections into contact with the guide track when the tilt-in window sash is tilted forward.
Owner:JOHN EVANS SONS INC
Drilling tool for chip removing machining as well as a loose top and a basic body therefor
A loose top for drilling tools, including front and rear ends, a pair of envelope part surfaces concentric with a center axis, and two chip flutes countersunk in relation to the pair of envelope part surfaces between which two bars project radially from a central core, the front end including a cutting edge and at least one clearance surface positioned rotationally behind the cutting edge, the rear end forming an axial contact surface. The loose top includes two opposite side contact surfaces against which elastically bendable branches of a tool basic body are pressed in use, a pair of convex guide surfaces situated axially behind the side contact surfaces, the guide surfaces being concentric with the center axis and radially spaced-apart from the center axis at a distance that is less than the radial distance between the center axis and a respective side contact surface, and a pair of torque-carrying tangential contact surfaces that are situated radially inside the envelope part surfaces and outside the side contact surfaces. The axial contact surface extends perpendicular to the center axis between borderlines adjacent to the two envelope part surfaces.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
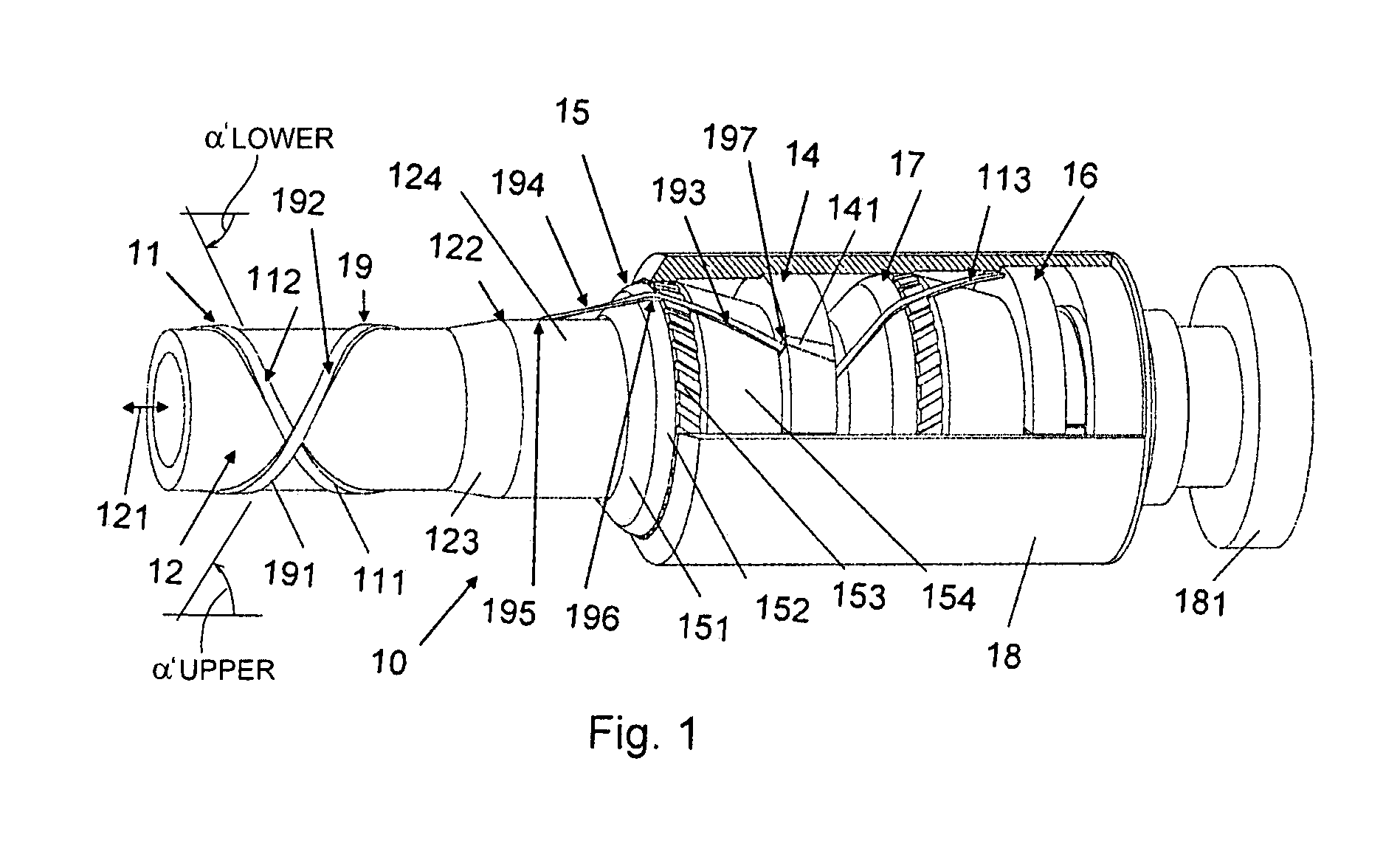
Flexible pipe connected to an end fitting
A pipe structure comprising a length of a flexible pipe connected to an end fitting, the flexible pipe comprising an armour layer and an underlying pipe layer the armour layer, the underlying pipe layer having an outer surface around which armouring wires of an armouring layer are helically wound. The pipe structure provides a coupling between a flexible pipe comprising armouring wires and an end fitting, the coupling exerting a relatively low bending or flexure strain on the wires during normal operation of the flexible pipe. The transition path of an armouring wire between the flexible pipe and the end fitting comprises a straight-line-section between a wire-pipe-exit-point where the wire extends away from its underlying pipe layer and a straight-line-end-point on a support unit of the end fitting where the armouring wire in question has its first tangential point of contact. This has the advantage that in a loaded situation where the armouring wires will elongate elastically leading to a change in the helical angle of the armouring wires, the pipe structure will experience a slight twist and a controlled bending of the armouring wires on the surface of the support unit (due to a possible change in the base point of contact of the armouring wire with the support unit induced by the change of helical angle), thereby avoiding substantial bending of the individual armouring wires, which is of particular importance when the armouring wires are formed of a composite material. The pipe structure may be used in flexible pipes for the off shore transport of fluids (e.g. oil).
Owner:NKT FLEXIBLES IS
Positioning system for single or multi-axis sensitive instrument calibration and calibration system for use therewith
InactiveUS7467536B2Simple procedureWave based measurement systemsCalibration apparatusReference fieldTangential contact
A positioning and calibration system are provided for use in calibrating a single or multi axis sensitive instrument, such as an inclinometer. The positioning system includes a positioner that defines six planes of tangential contact. A mounting region within the six planes is adapted to have an inclinometer coupled thereto. The positioning system also includes means for defining first and second flat surfaces that are approximately perpendicular to one another with the first surface adapted to be oriented relative to a local or induced reference field of interest to the instrument being calibrated, such as a gravitational vector. The positioner is positioned such that one of its six planes tangentially rests on the first flat surface and another of its six planes tangentially contacts the second flat surface. A calibration system is formed when the positioning system is used with a data collector and processor.
Owner:NASA
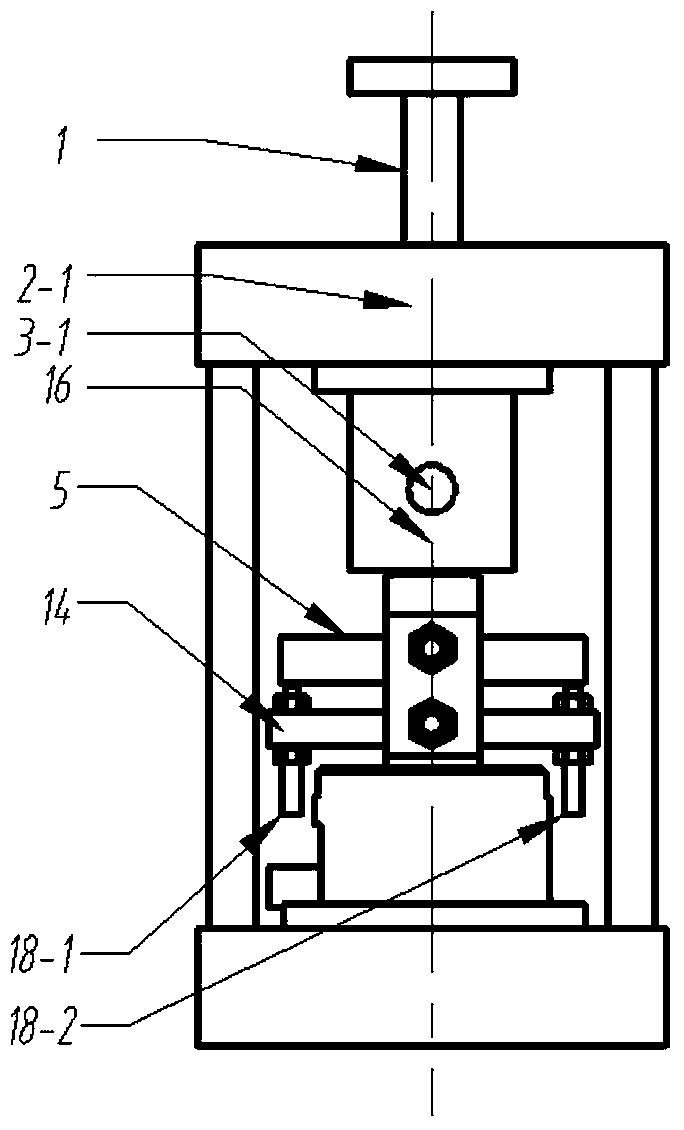
Contact stiffness testing device
InactiveCN101315319ALarge loading rangeAvoid measurement errorsStrength propertiesPositive pressureTangential contact
The invention discloses a device for testing contact rigidity, and comprises a friction force testing component, a positive pressure loading component, freely supported beams, a right support, a left support and a base, wherein the freely supported beams are installed in U-shaped grooves of the right support and the left support; the friction force testing component, the positive pressure loading component, the right support and the left support are arranged on the base. When loaded with an initial positive pressure and a shock excitation load, the device for damping test can test the parameters of the tangential contact rigidity of a contact surface, such as different contact surface shapes, different initial positive pressures, the properties of different experiment sample materials, etc. and analyze the rule of influence of the contact surface shape, the initial positive pressure and the experiment sample material on the contact rigidity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Three-dimensional random convex polygon block discrete element method based on distance potential function
ActiveCN106529146AReduce in quantityImprove accuracyInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsResearch ObjectContact force
The invention discloses a three-dimensional random convex polygon block discrete element method based on a distance potential function. A research object is discretized into a block element system; carrying out contact detection on all block elements according to a nonuniform block discrete element contact detection method provided by the method; defining the distance potential function and carrying out normal contact force calculation on mutually contacting block elements, thereby obtaining normal contact force acting on each target block element and a torque caused by the normal contact force; on the basis of a tangential contact force direction vector calculation method provided by the method, carrying out calculation to obtain tangential contact force of each block element and the torque caused by the tangential contact force according to increment of tangential relative displacement; solving acceleration and angular acceleration of each block element through a rigid motion equation; and calculating velocity and displacement of each block element through a velocity verlet algorithm and describing deformation and motion state of a whole medium according to motion and relative position of each block element.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Measuring device of rigidity and damping of tangential contact
InactiveCN101666782AGuaranteed feasibilityGuaranteed reliabilityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationDynamic methodMeasurement device
The invention relates to a measuring device of rigidity and damping of tangential contact, belonging to the technical field of dynamics measurement and comprising a testing frame, an excitation applying device, a measuring device and a loading device, wherein the measuring device and the loading device are respectively and fixedly arranged in the testing frame; the excitation applying device is fixedly arranged above the testing frame and corresponds to a sample to be measured; the measuring device and the loading device are connected; and the loading device is arranged at the bottom of the testing frame. The measuring device adopts a mode that the same tested samples are respectively arranged at the two ends to clamp another suspended testing sample, so as to lead a vibrational model to be simple, thus guaranteeing feasibility and reliability of dynamic method analysis, realizing reliable measurement of rigidity and damping of tangential contact, easily controlling the size of pretightening force and contact area, and furthest reducing the influence of vibration to measurement.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
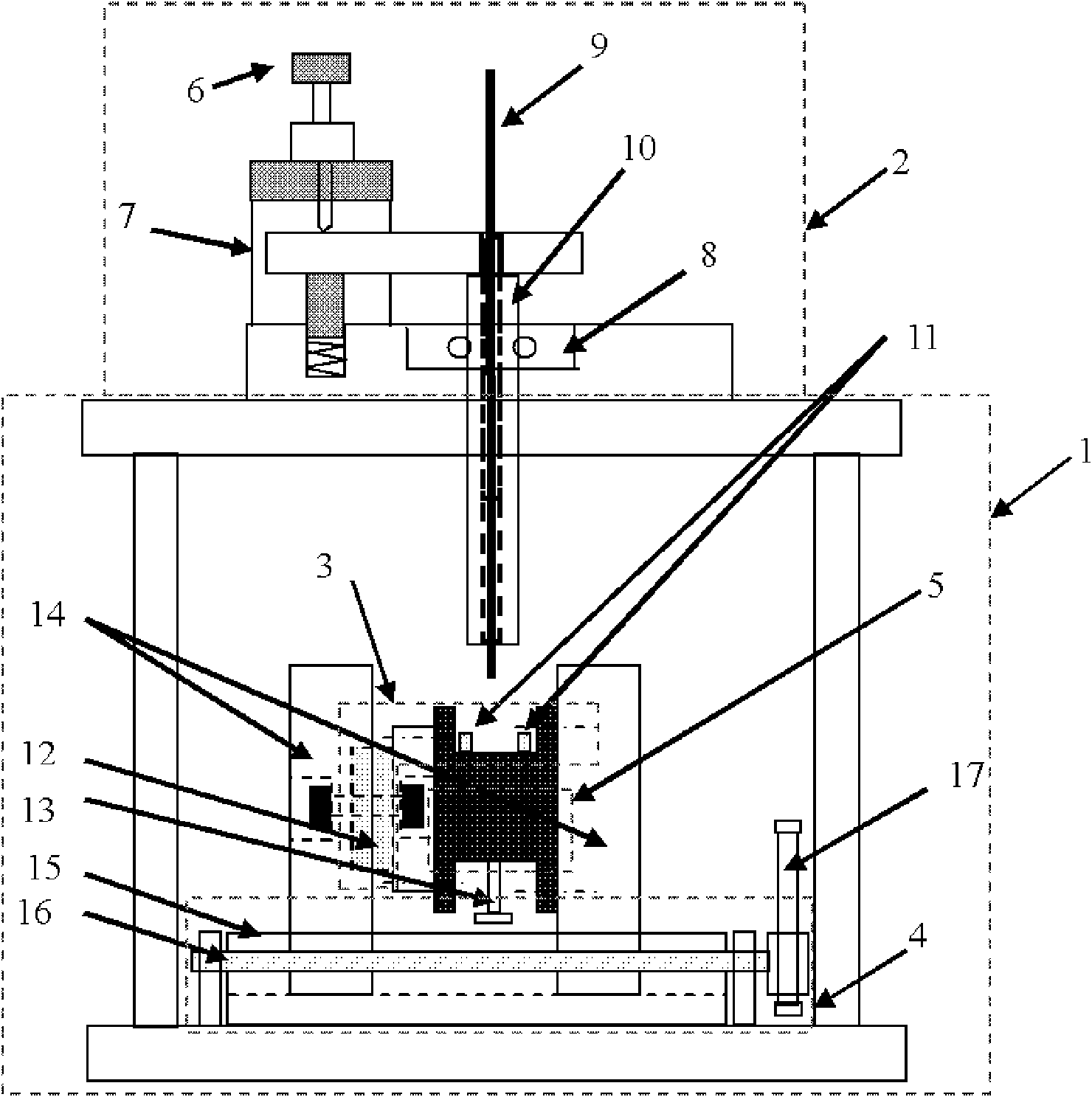
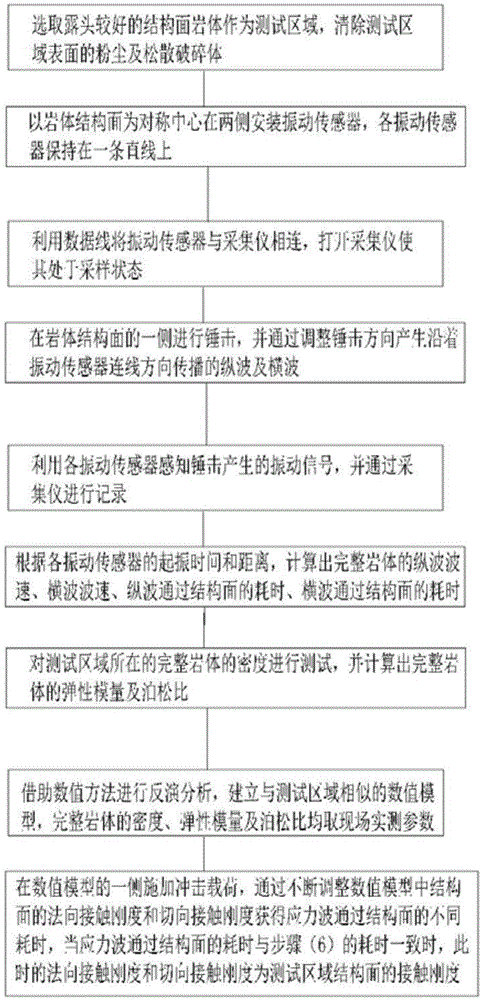
Method for testing contact rigidity of rock discontinuity structural plane, and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN105004662AImprove test accuracyThe testing process is simpleUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisLongitudinal waveClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a method for testing the contact rigidity of a rock discontinuity structural plane. The method comprises the following steps: 1, selecting a test area; 2, installing vibration sensors; 3, starting a collecting instrument to make the collecting instrument in a sampling state; 4, hammering one side of the rock discontinuity structural plane, and adjusting the hammering direction to generate longitudinal waves and transverse waves vibrating along the line direction of the vibration sensors; 5, recording through the collecting instrument; 6, calculating the wave velocity of the longitudinal waves, the wave velocity of the transverse waves, the time consumption of the longitudinal waves passing through the structural plane and the time consumption of the transverse waves passing through the structural plane; 7, calculating the elastic modulus and the Poisson's ratio of a complete rock; 8, carrying out inversion analysis by means of a value technology, and establishing a value model similar to the test area; and 9, applying impact load to one side of the value model, and continuously adjusting the normal contact rigidity and the tangential contact rigidity of the structural plane in the value model to obtain the contact rigidity of the structural plane of the test area. The invention also provides an apparatus adopting the method.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cooling-fin cylindrical battery pack heat dissipation device and method employing composite phase changing material
InactiveCN107623154AImprove cooling effectImprove stabilitySecondary cellsCell component detailsTangential contactEngineering
The invention discloses a cooling-fin cylindrical battery pack heat dissipation device and method employing a composite phase changing material. A cooling fin comprises a main fin and auxiliary fins,wherein the main fin is of a fully-closed shell structure, a phase changing material is packaged in the main fin, the auxiliary fins are expanded towards two sides from a surface of the main fin, andtail ends of the auxiliary fins are in tangential contact with the surface of a battery. Cylindrical batteries in different specification sizes can be adapted by adjusting the size and the distance ofthe fins and the thickness of the phase changing material, and the heat dissipation and the heat preservation performance requirement is met. A fixed base is arranged at the bottom of a battery pack,the battery pack can be reinforced, the shock resistant capability is improved, a fan can be externally connected to improve convection, and the heat dissipation and heat preservation effect is improved. By the heat dissipation device, the advantage of the phase changing material is fully utilized, the temperature uniformity of the battery pack is improved, light requirement is conformed, thermaldisaster is prevented from propagating in a battery stack, the thermal safety of the battery pack is improved, and the heat dissipation device can be widely applied to various fields of automobile and aerospace.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Flexible pipe connected to an end fitting
InactiveUS20060082140A1Small twistLimit bendingFlexible pipesHose connectionsCouplingTangential contact
The invention relates to a pipe structure (10) comprising a length of a flexible pipe connected to an end fitting, the flexible pipe comprising an armour layer (11; 19) and an underlying pipe layer (12; 11) to said armour layer, said underlying pipe layer having an outer surface around which armouring wires (111; 191) of an armouring layer are helically wound. The object of the present invention is to provide a coupling between a flexible pipe comprising armouring wires and an end fitting, the coupling exerting a relatively low bending or flexure strain on the wires during normal operation of the flexible pipe. The problem is solved in that the transition path of an armouring wire between the flexible pipe and the end fitting comprises an straight-line-section (194) between a wire-pipe-exit-point (195) where the wire extends away from its underlying pipe layer and a straight-line-end-point (196) on a support unit (15) of the end fitting where the armouring wire in question has its first tangential point of contact. This ahs the advantage that in a loaded situation where the armouring wires will elongate elastically leading to a change in the helical angle of the armouring wires, a pipe structure according to the invention will experience a slight twist and a controlled bending of the armouring wires on the surface of the support unit (due to a possible change in the base point of contact of the armouring wire with the support unit induced by the change of helical angle), thereby avoiding substantial bending of the individual armouring wires, which is of particular importance when the armouring wires are formed of a composite material. The invention may be used in flexible pipes for the off shore transport of fluids (e.g. oil).
Owner:NKT FLEXIBLES IS
Feed unit for strip wrapping material
A strip of wrapping material is advanced by a feed unit that includes a gumming device composed of a gumming roller and a transfer roller contra-rotating about horizontal and parallel axes and in tangential contact one with another along an area coinciding with a straight line generator common to both. At least one of the two rollers is maintained at a given temperature by a fluid directed through a circuit of which a first portion extends along a shaft supporting and driving the roller and a second portion is located internally of the roller itself; the circuit includes valves operating respectively along a flow branch and a return branch of the circuit, associated both with the drive shaft and with the respective roller and interposed between the first and second portions so that these can be opened and closed when required, while the first portion is connected to an inlet duct and to an outlet duct rigidly associated with a frame and connected to the circuit by way of a hydraulic or pneumatic rotary coupling.
Owner:GD SPA
Directional heat exchanger
A directional heat exchanger system dissipates heat generated by components contained within a thermally insulated antenna mounted atop a periscope tube. A first wall of thermally conductive material has a first face and a second face with the first face being shaped to substantially contact an internal portion of the periscope tube. A plurality of ribs made from thermally conductive material are fixedly coupled to the second face. A second wall of thermally conductive material opposes the second face of the first wall and is in tangential contact with the ribs to form a fluid seal therewith. At least one channel is formed between the first and second walls. The end of each rib is offset from the end of adjacent ribs such that the channel defines a flow path having a first end and a second end. The components generating heat are thermally coupled to a heat pipe positioned partially in the antenna and partially in the periscope tube. A liquid coolant delivery system is coupled to the first and second ends of the flow path to pump a liquid coolant into the first end and recapture the liquid coolant exiting the second end.
Owner:NAVY US SECA OF THE
Clamping device for a cutting insert
InactiveUS20110164933A1Inhibit wearClamp firmlyTurning toolsTool holdersDistal portionTangential contact
An insert clamp secures a cutting insert having a central hole to a tool holder. The clamp includes a forward protrusion to be received in the central hole of the insert, a central body portion provided with a pressing part to press down the upper surface of the insert and a screw hole for a clamping screw to pass through, and a rear protrusion having a rear contact surface to come in contact with a rearward slanting surface of the tool holder. The forward protrusion is formed on the forward end of the insert clamp, an inside surface of the forward protrusion extends downward in a spaced state apart from the inner wall of the central hole of the insert, and a distal portion of the inside surface the forward protrusion is provided with a protuberance of convex curved surface to come in tangential contact with the inner wall of the insert. The pressing part is formed on the bottom surface of the central body portion of the insert clamp, and has convex curved surfaces to come in tangential contact with the upper surface of the insert on both regions of the bottom surface of the central body portion which is bisected by a central line passing through the forward protrusion and the screw hole.
Owner:TAEGUTEC
Vane Fluid Transfer Device
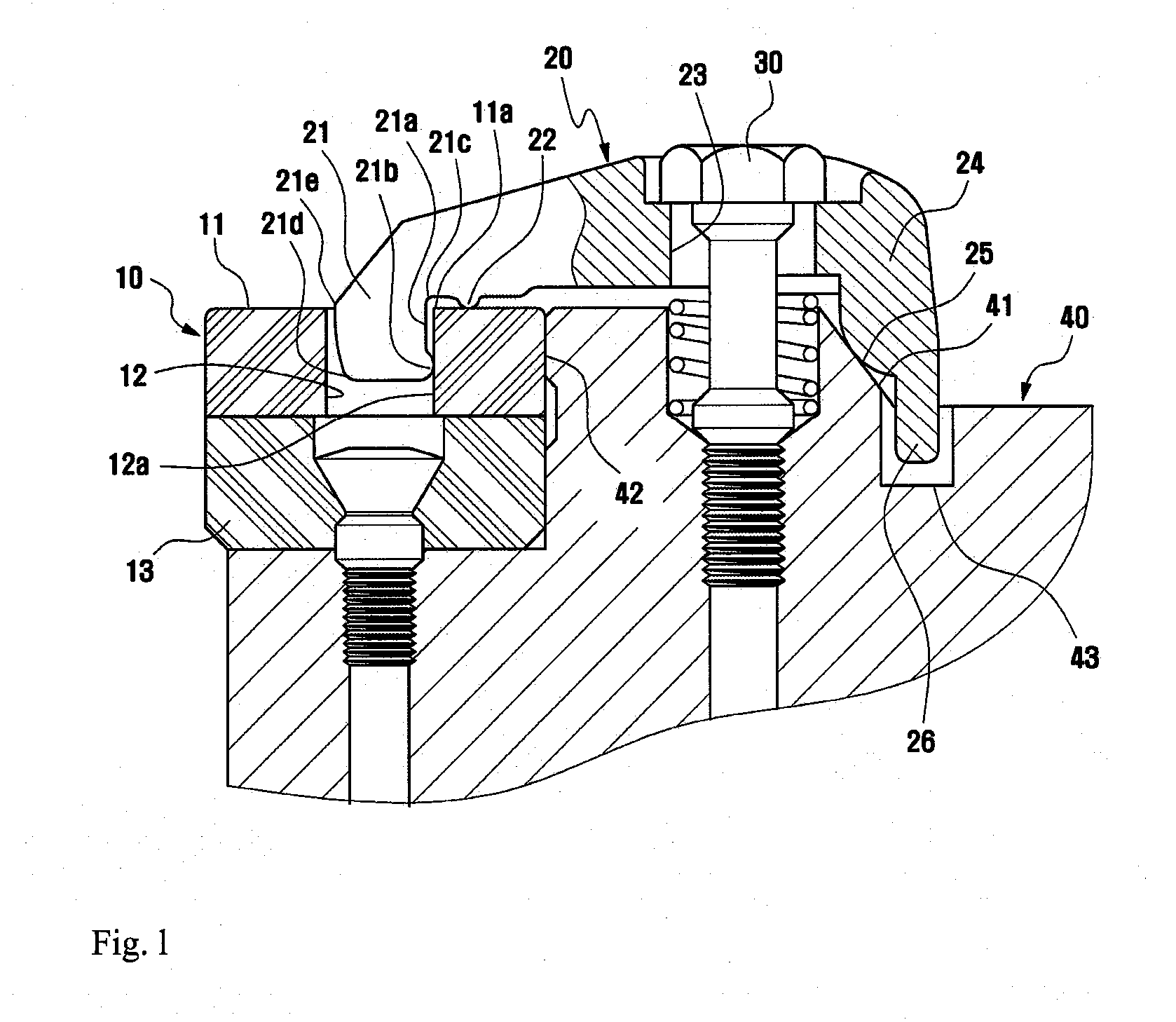
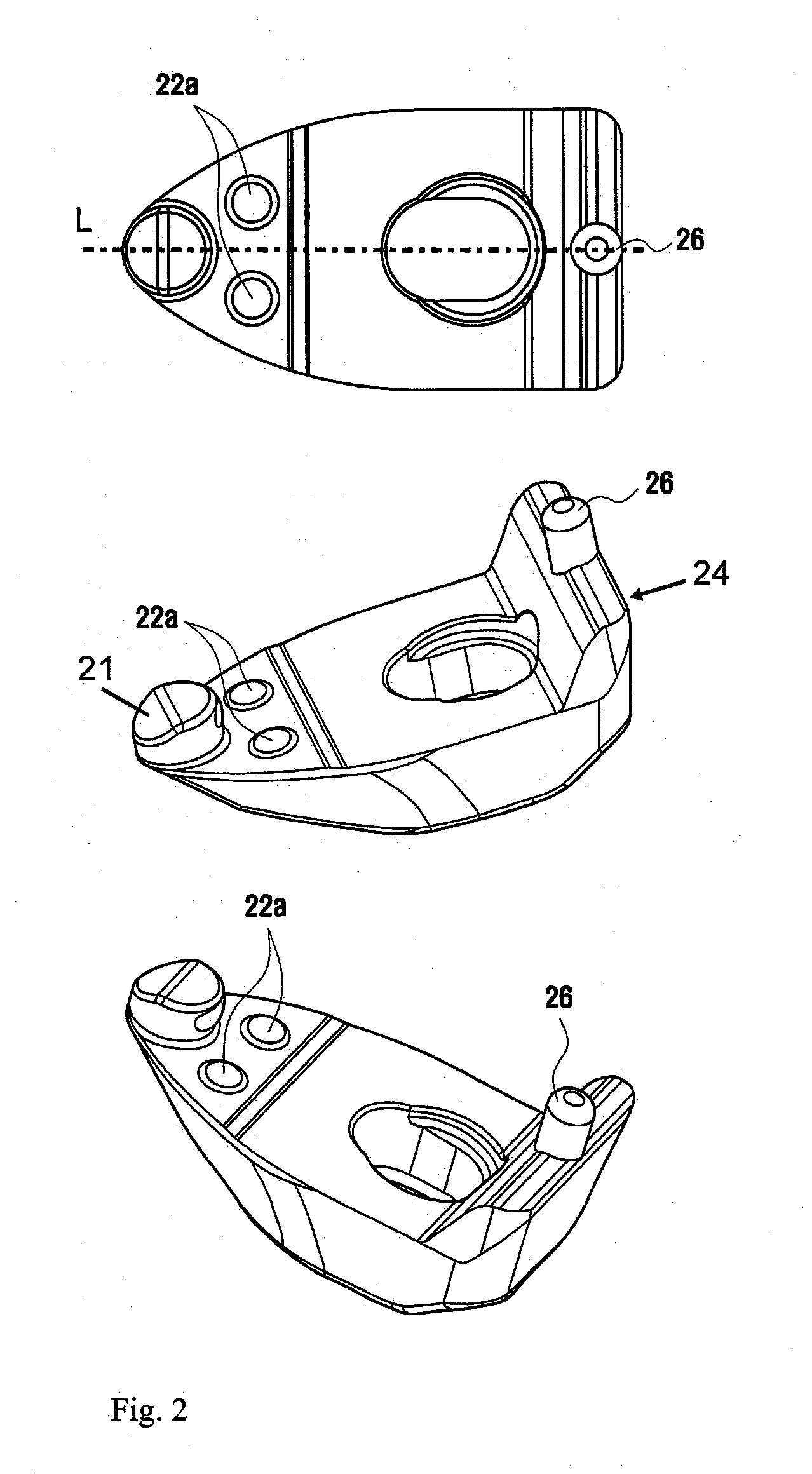
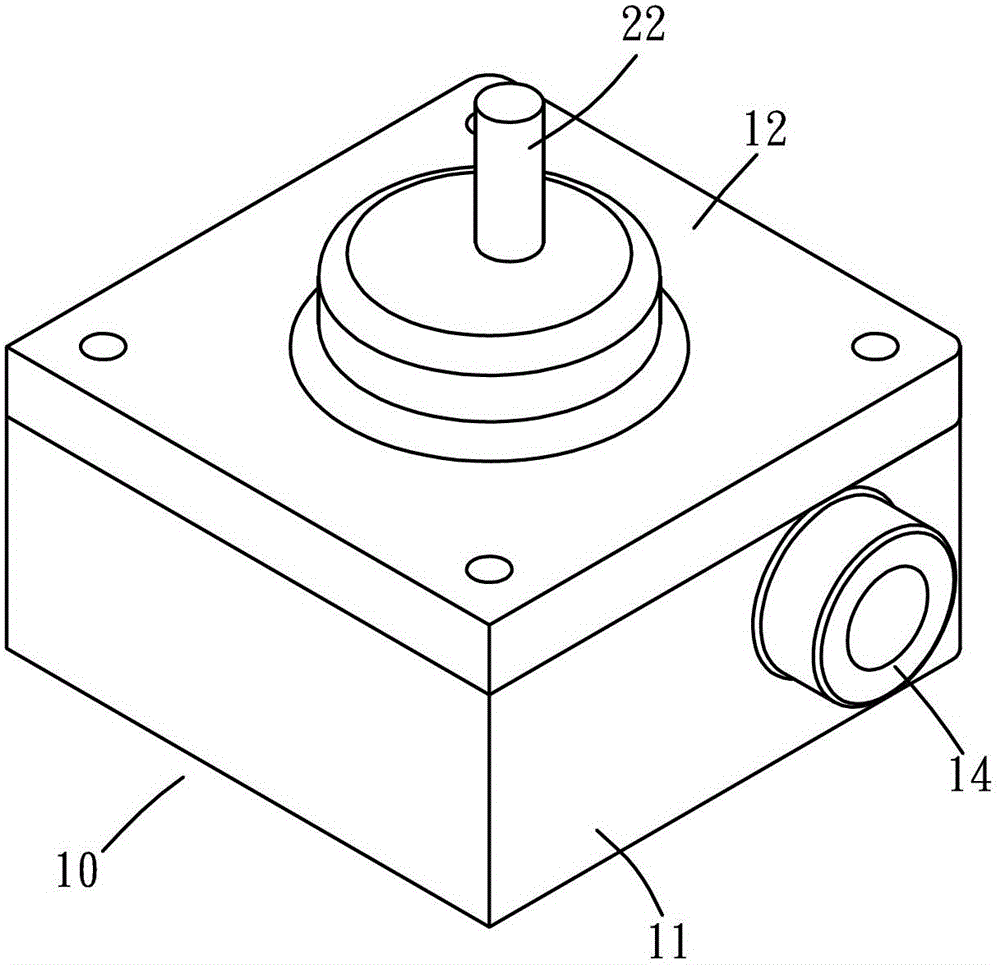
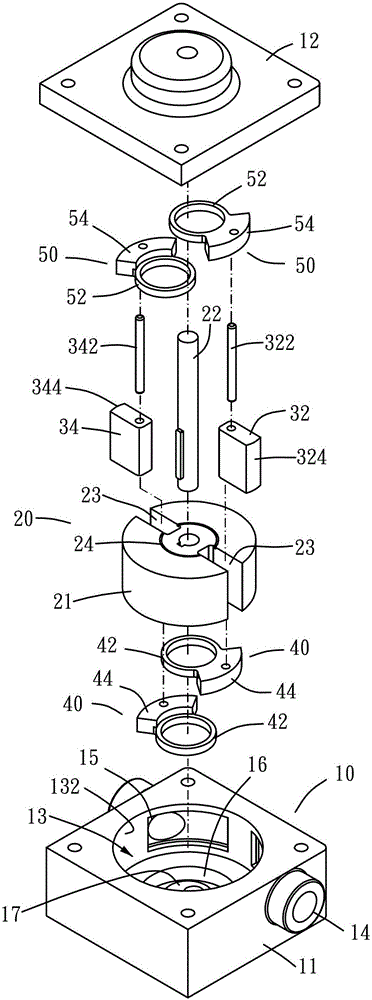
InactiveCN103717837BIncreased efficiency of pumping transfersControl flowRotary piston pumpsRotary piston liquid enginesReciprocating motionTangential contact
A vane type fluid transmission device, comprising a stator (10), a rotor (20), at least one vane (34), at least one first lining (40) and at least one second lining (50), wherein the stator (10) A room (13) is formed inside, and the room communicates with the outside through a flow channel; the rotor (20) includes a body (21) and a main shaft (22), and the main shaft (22) is connected to the main body (21). The body (21) is eccentrically arranged in the chamber (13), and the outer periphery of the body (21) is in tangential contact with the inner wall of the chamber (13). The body (21) has at least one chute (23) along the diameter direction; the blade (34 ) are pivotally embedded in the chute (23), the blades (34) are in contact with the inner wall of the chamber (13), the first and second linings are respectively pivotally embedded in the stator (10), and the first and second linings are respectively connected to the The center of the circle acts as the center, and the blades are pivotally connected with the first and second linings, so that the blades follow the center of the chamber and move back and forth along the chute; the end of the blade in contact with the inner wall of the chamber forms a circle. The arc surface keeps the tip of the vane in tangential contact with the inner wall of the room, thereby improving the efficiency of fluid pumping and transmission, and reducing the difficulty of forming the room by machining the stator.
Owner:杨 进煌 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com