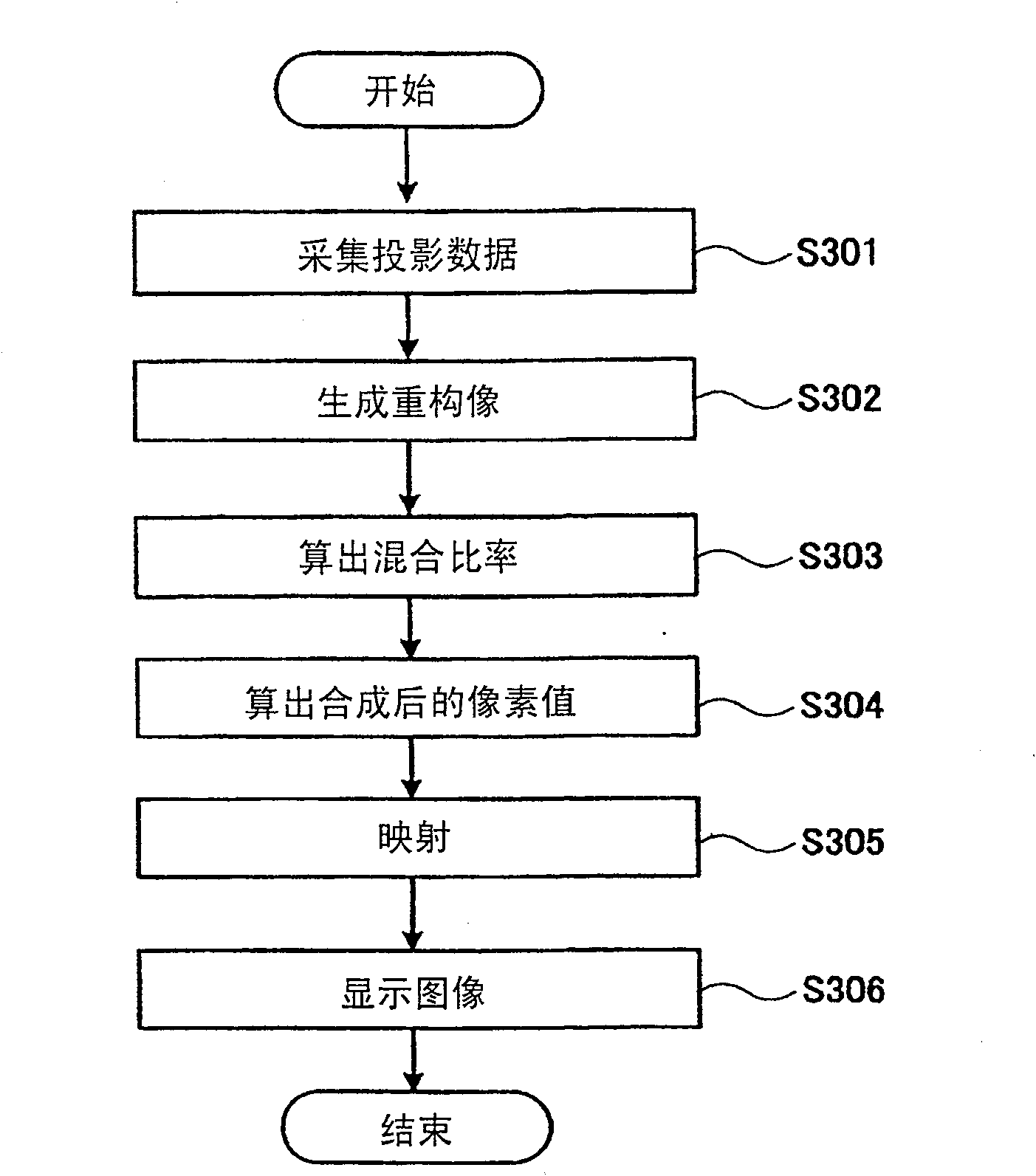
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Synthetic projection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
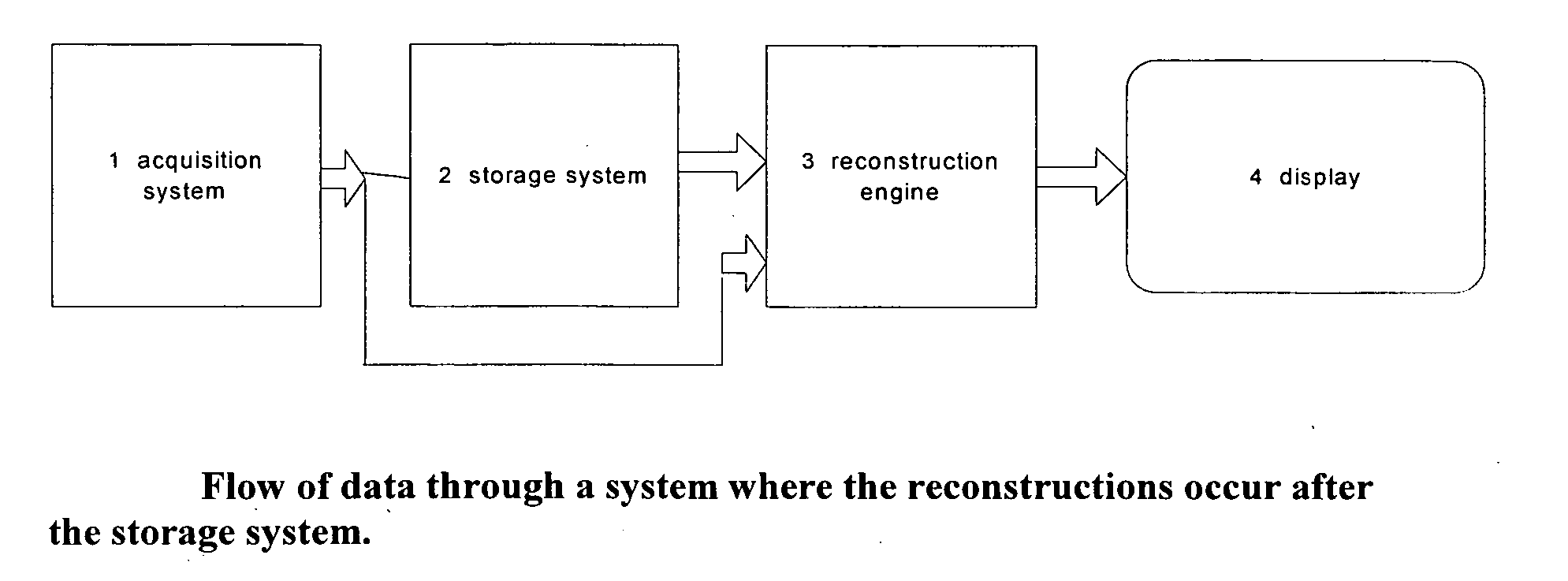
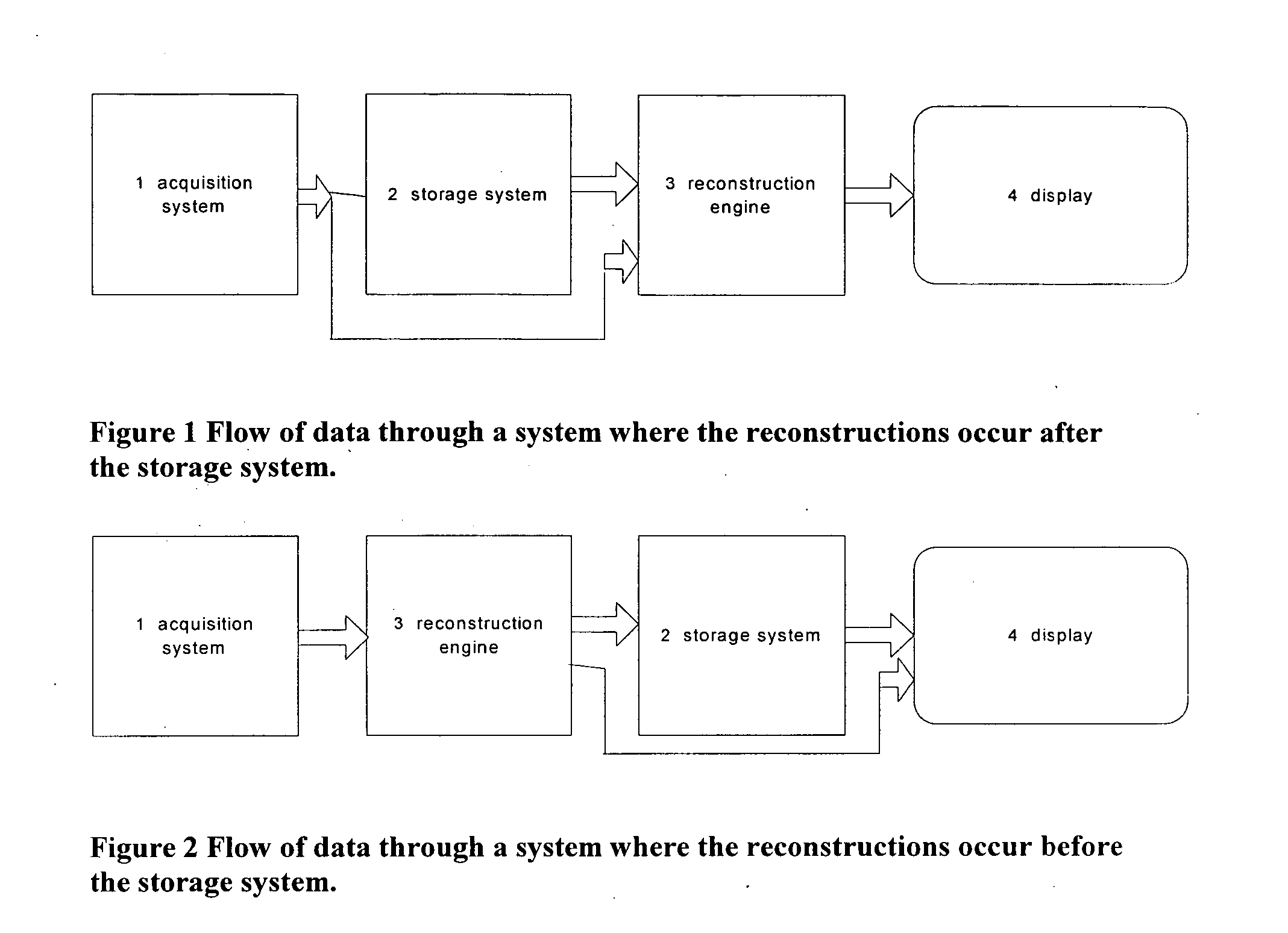
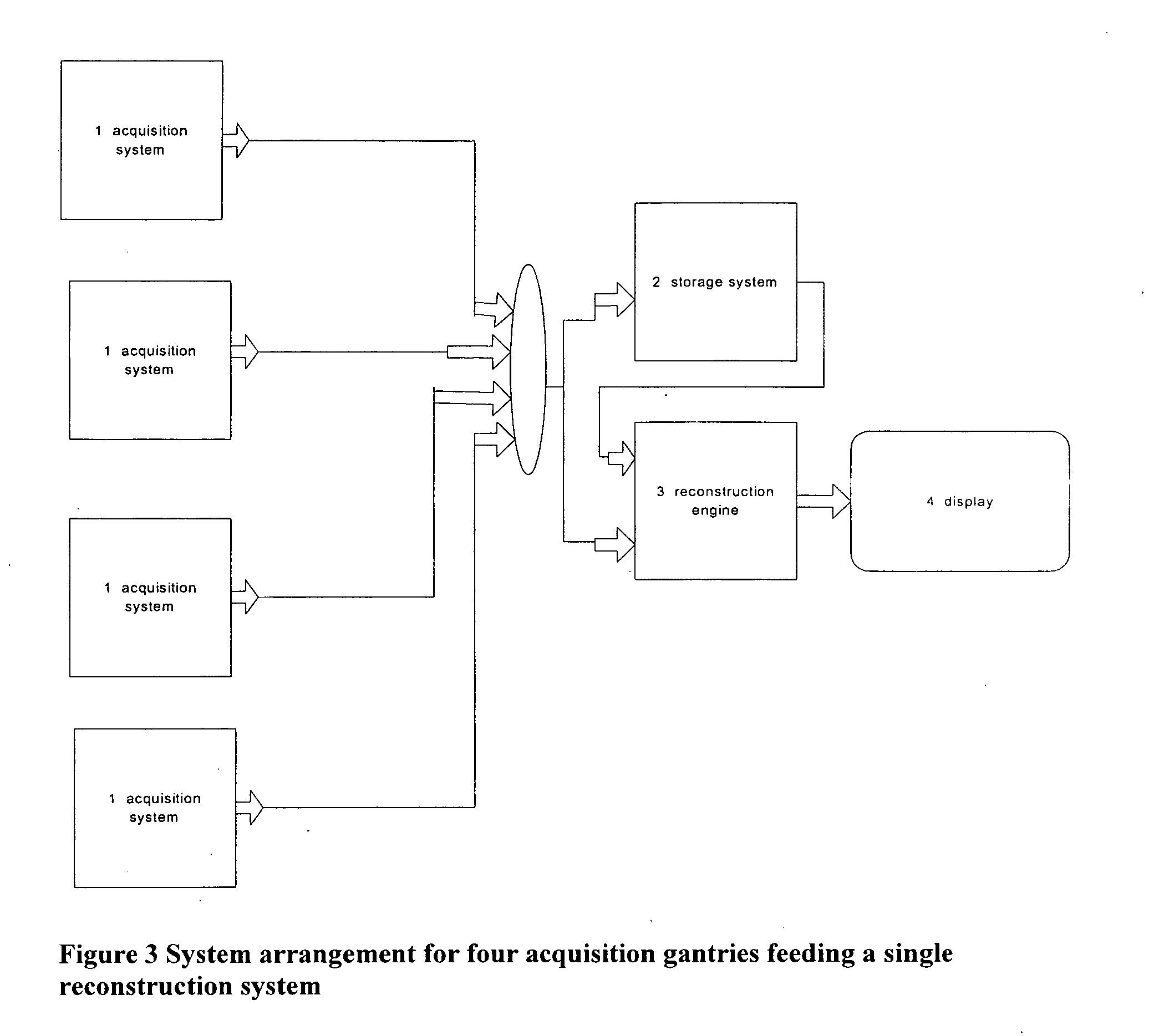
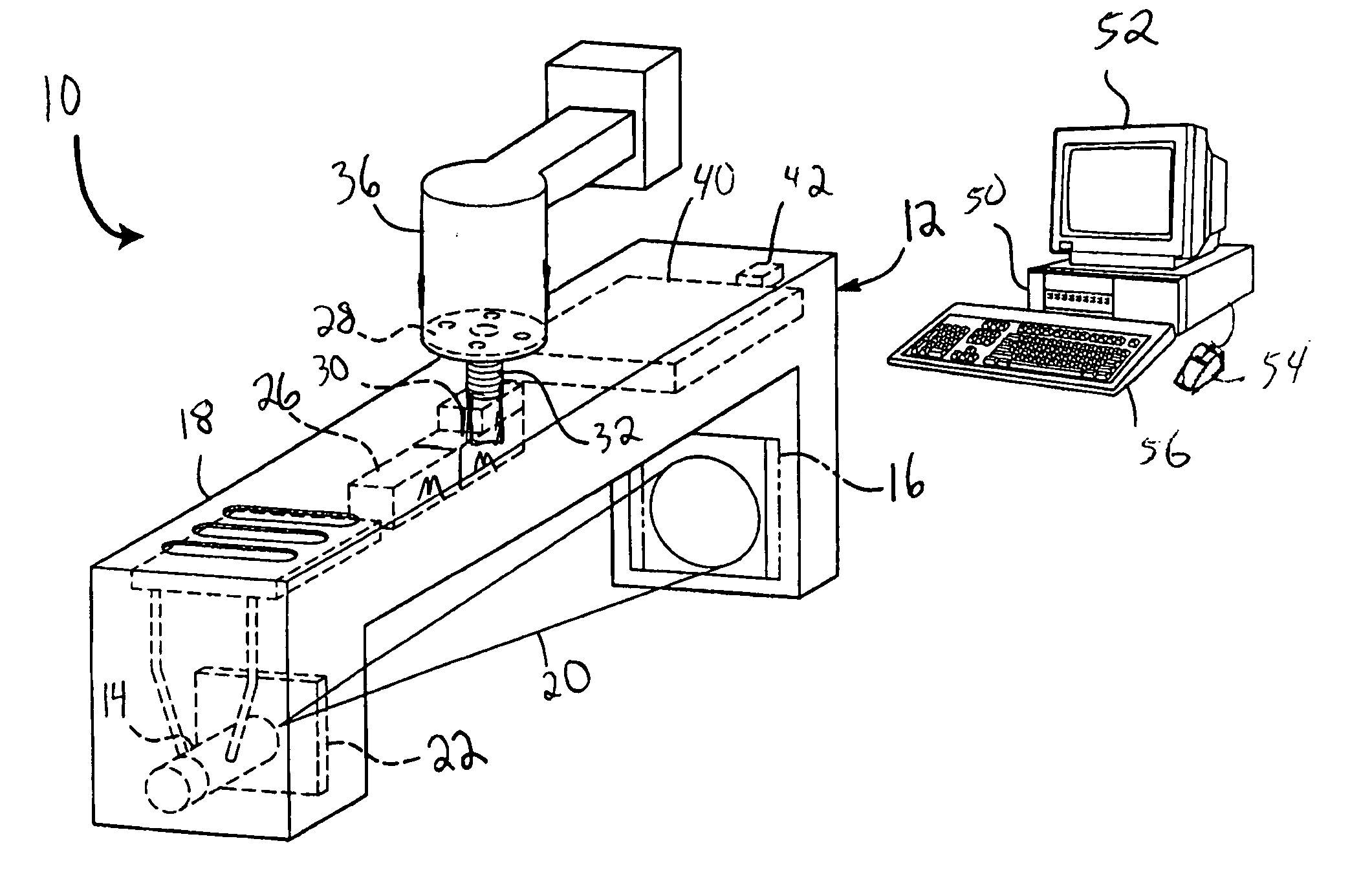
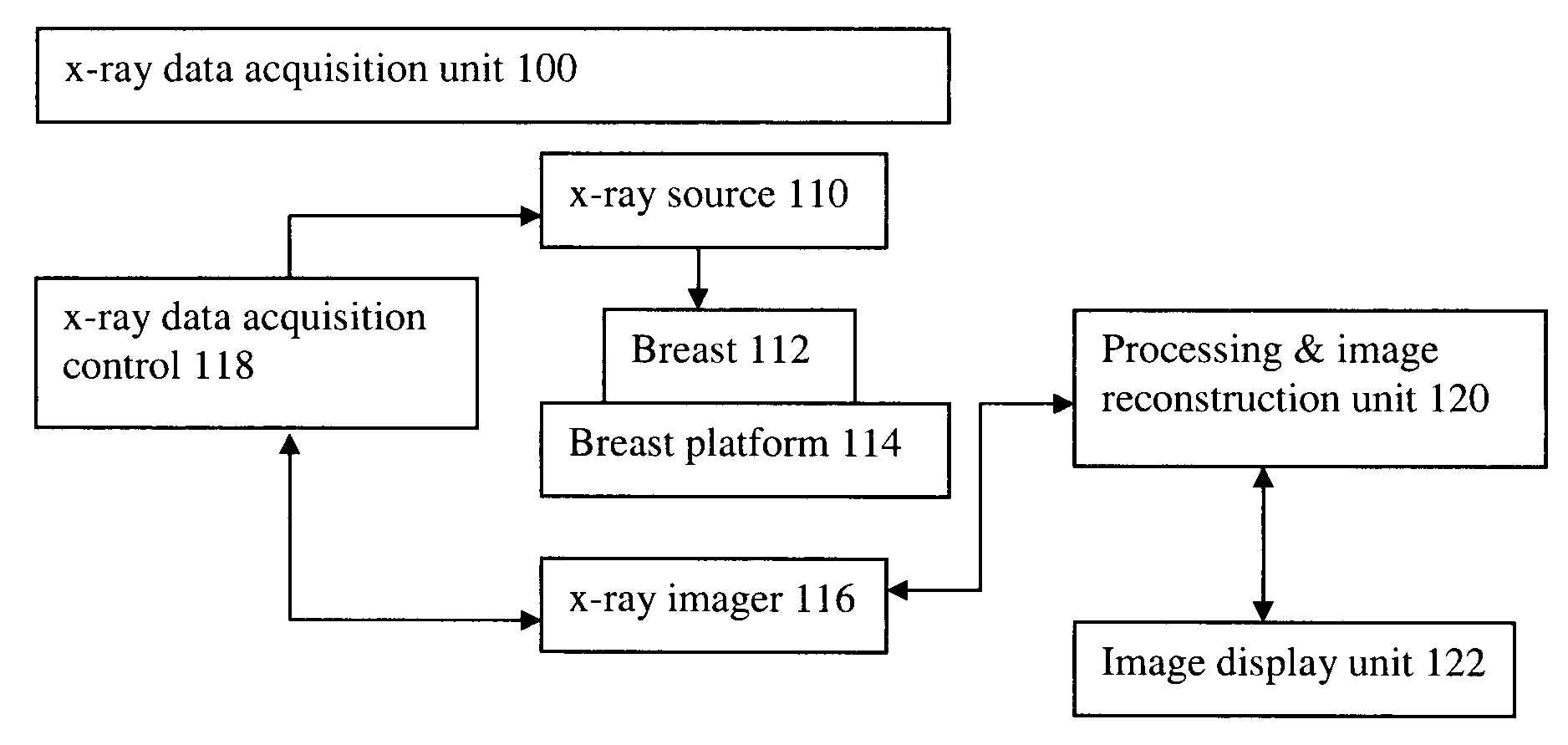
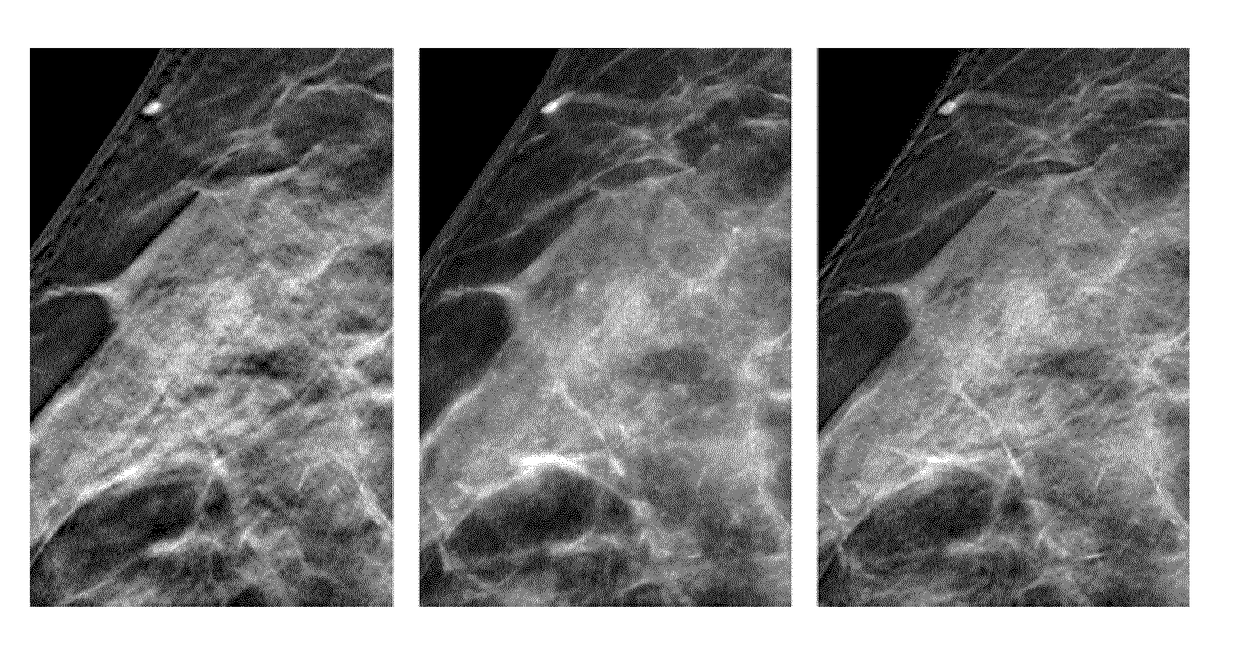
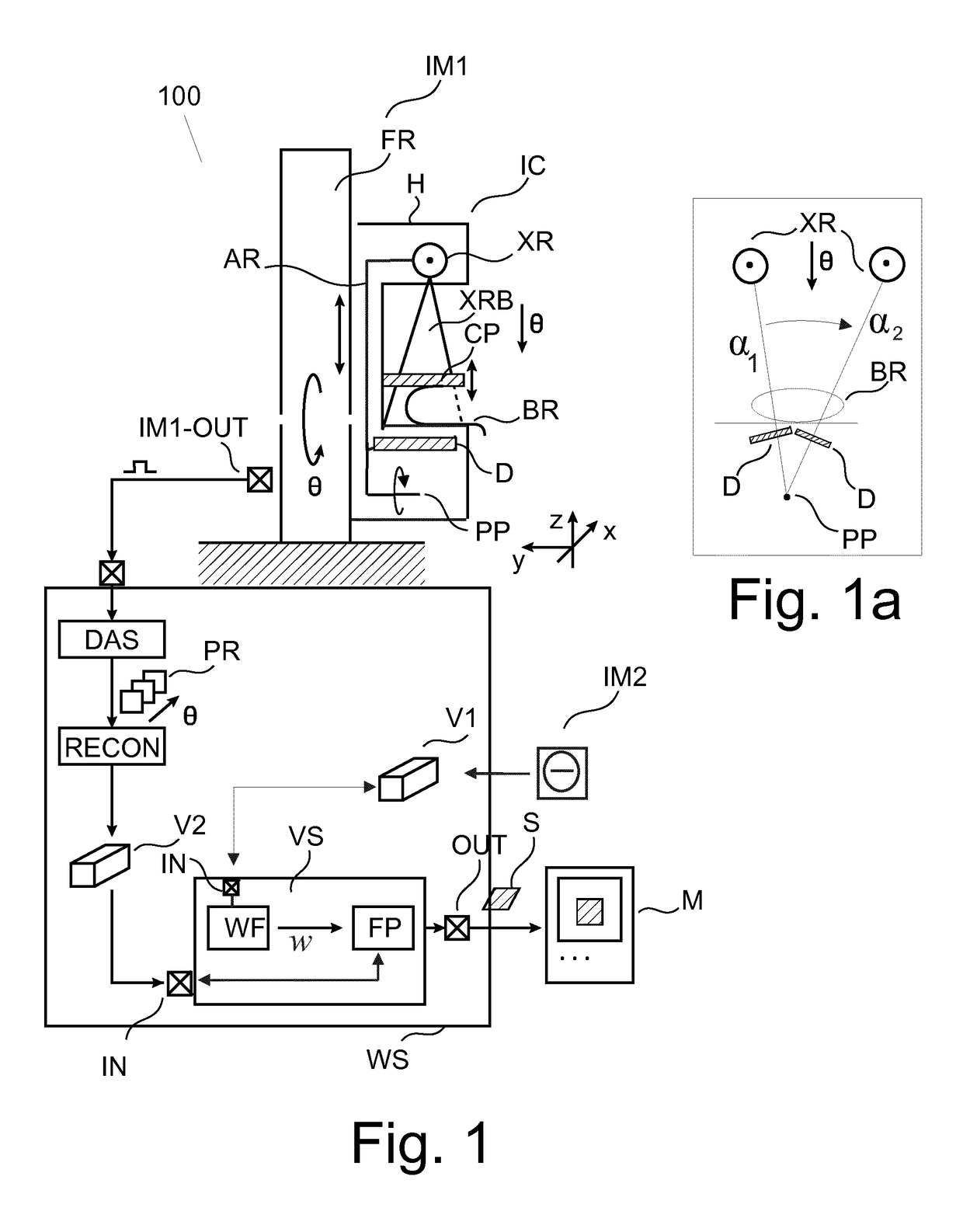
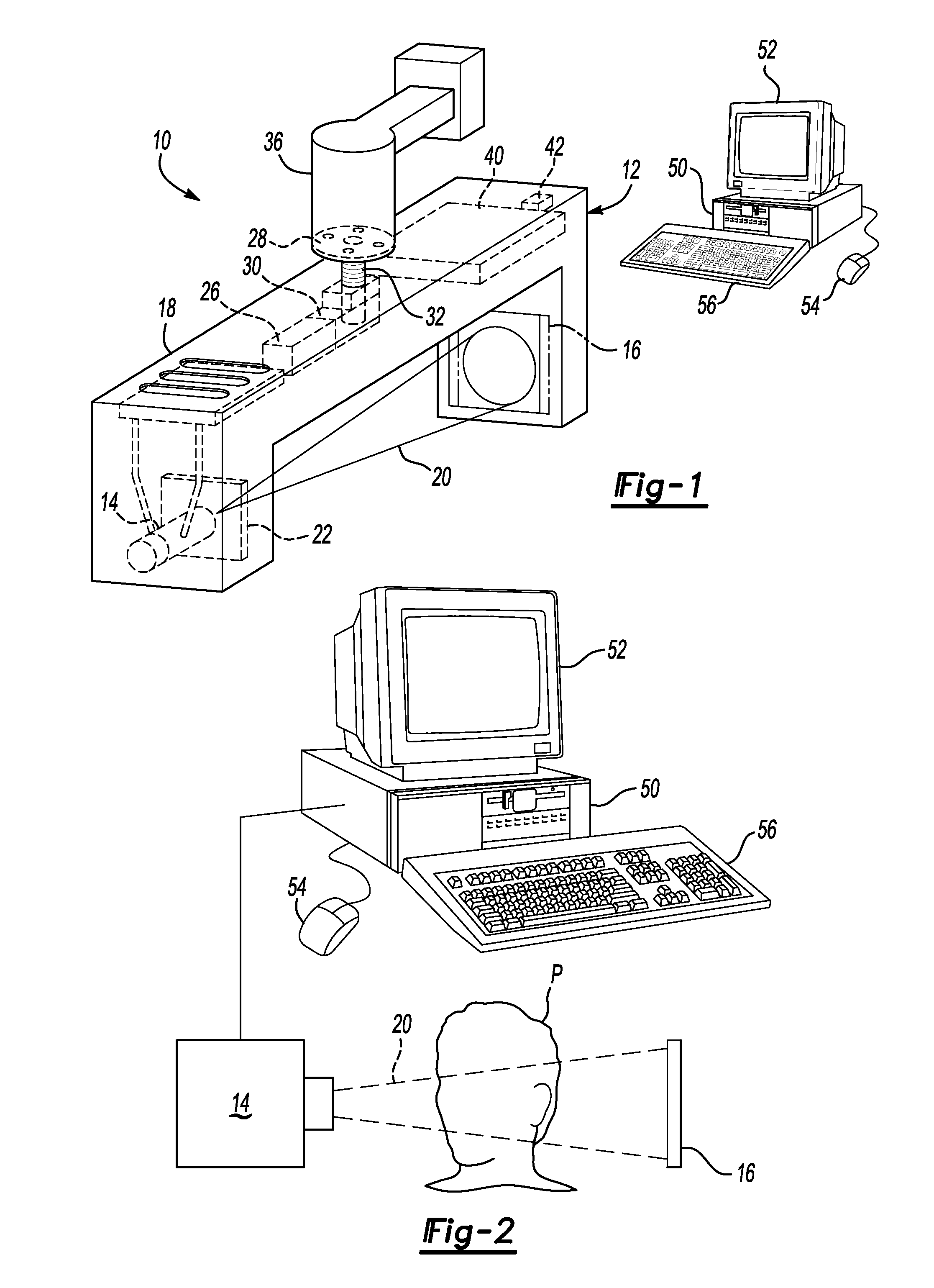
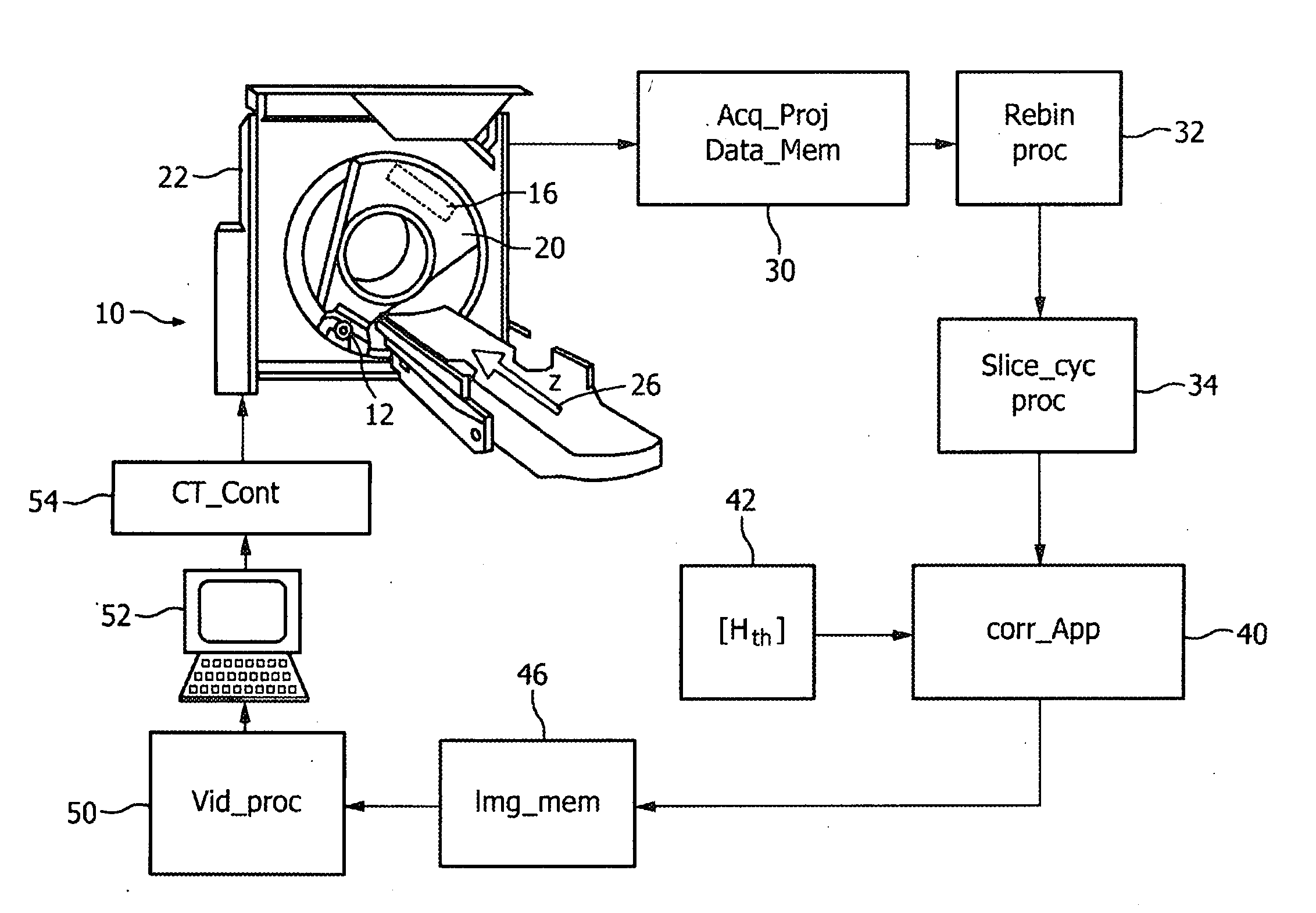
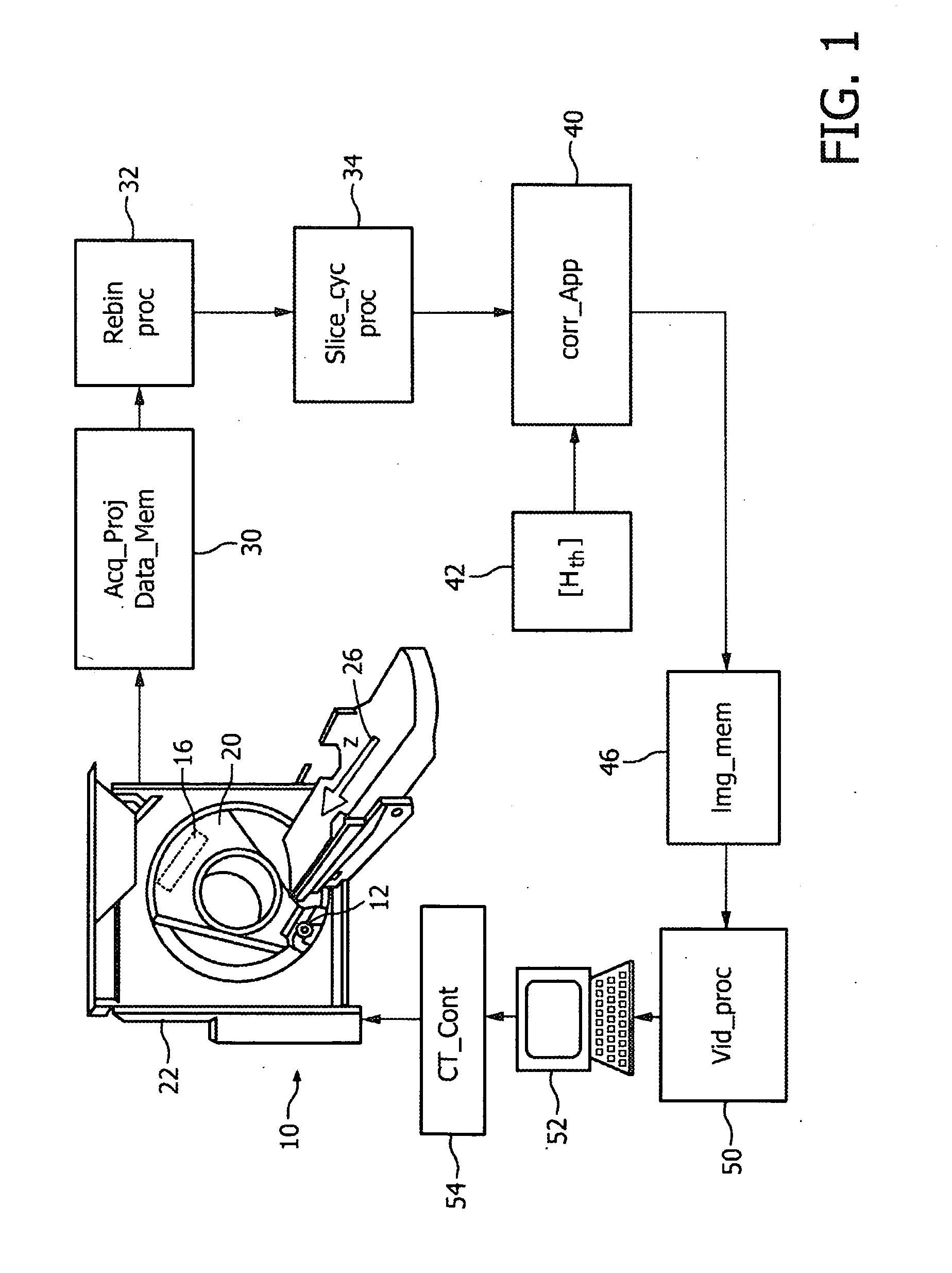
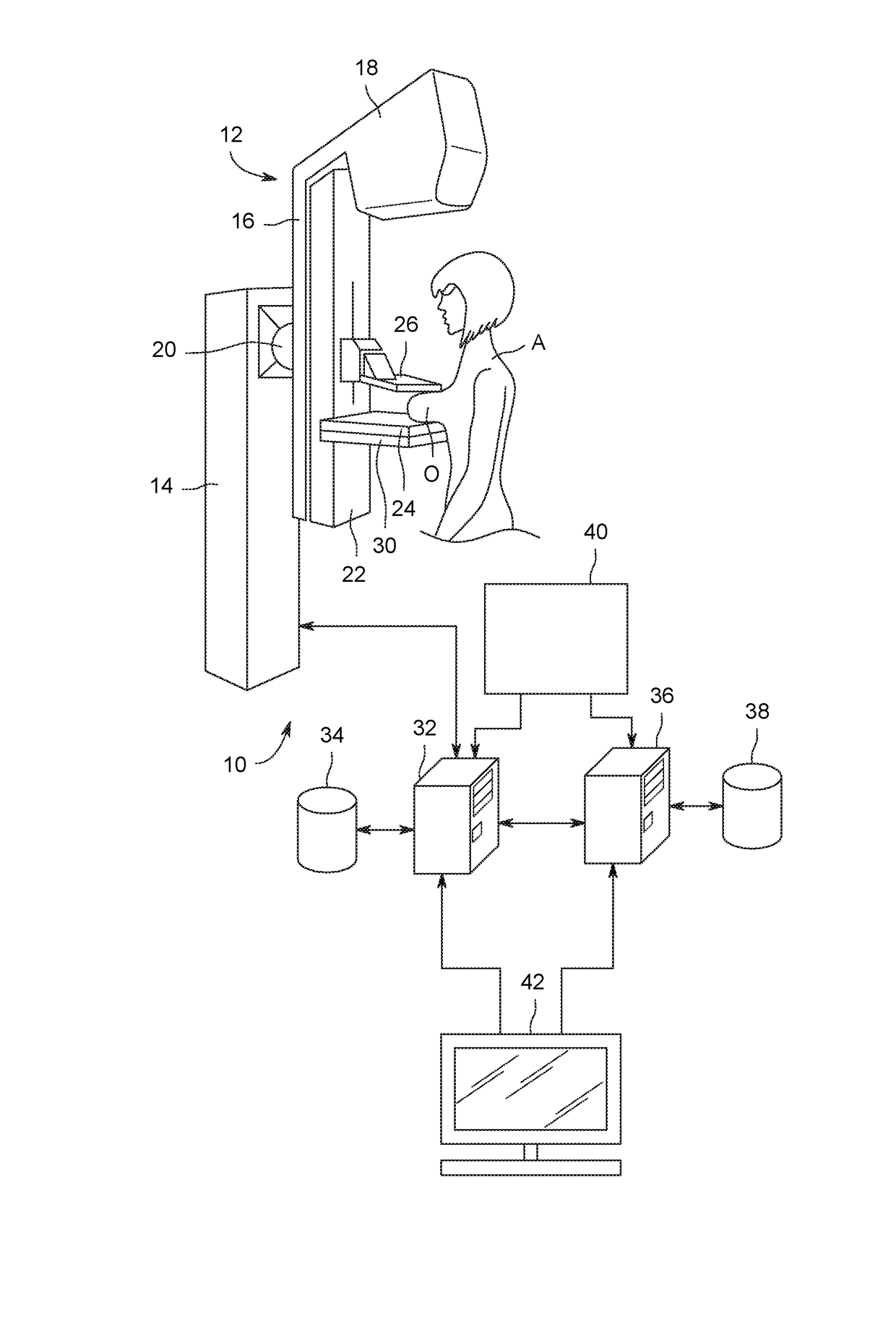
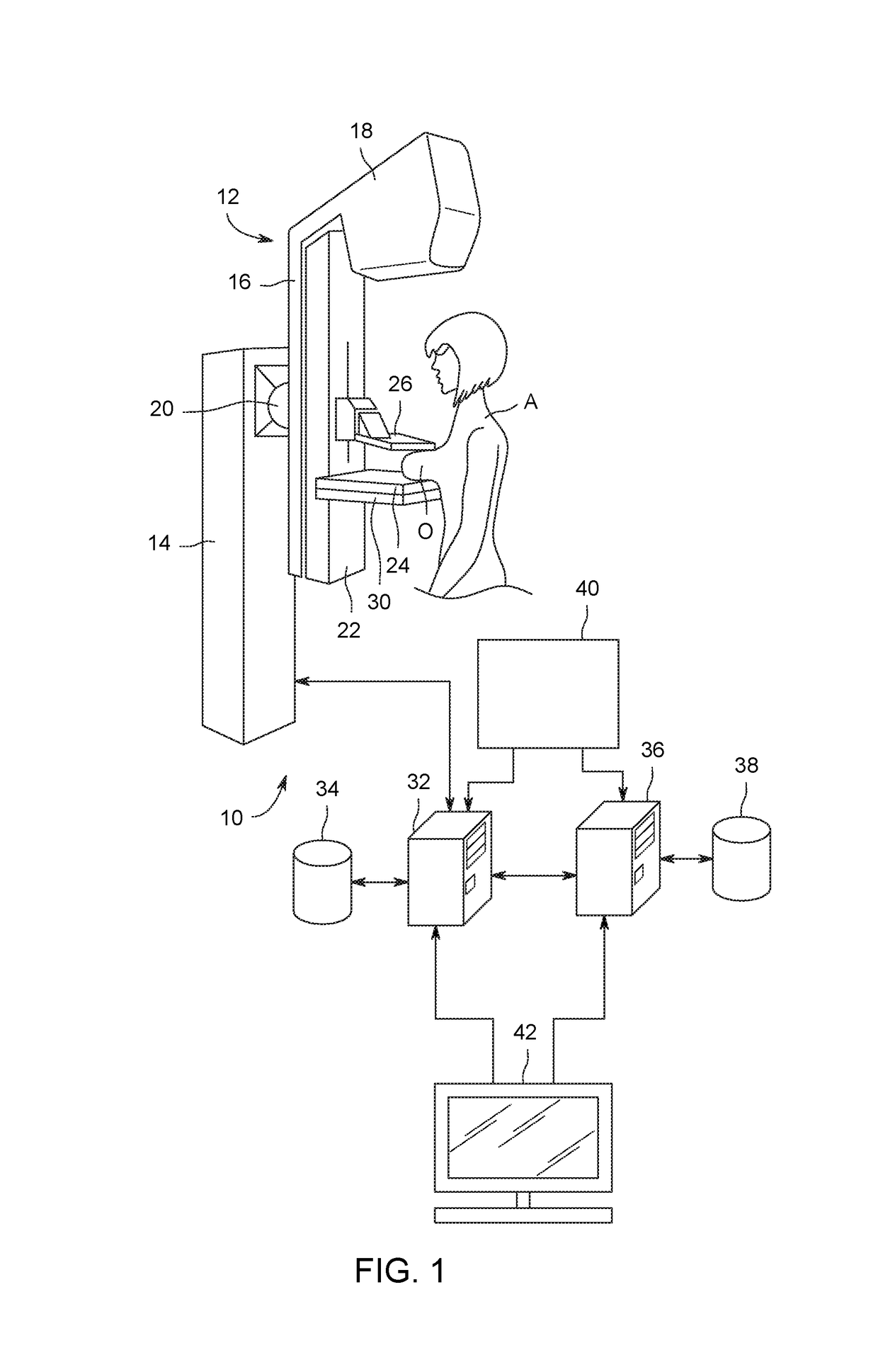
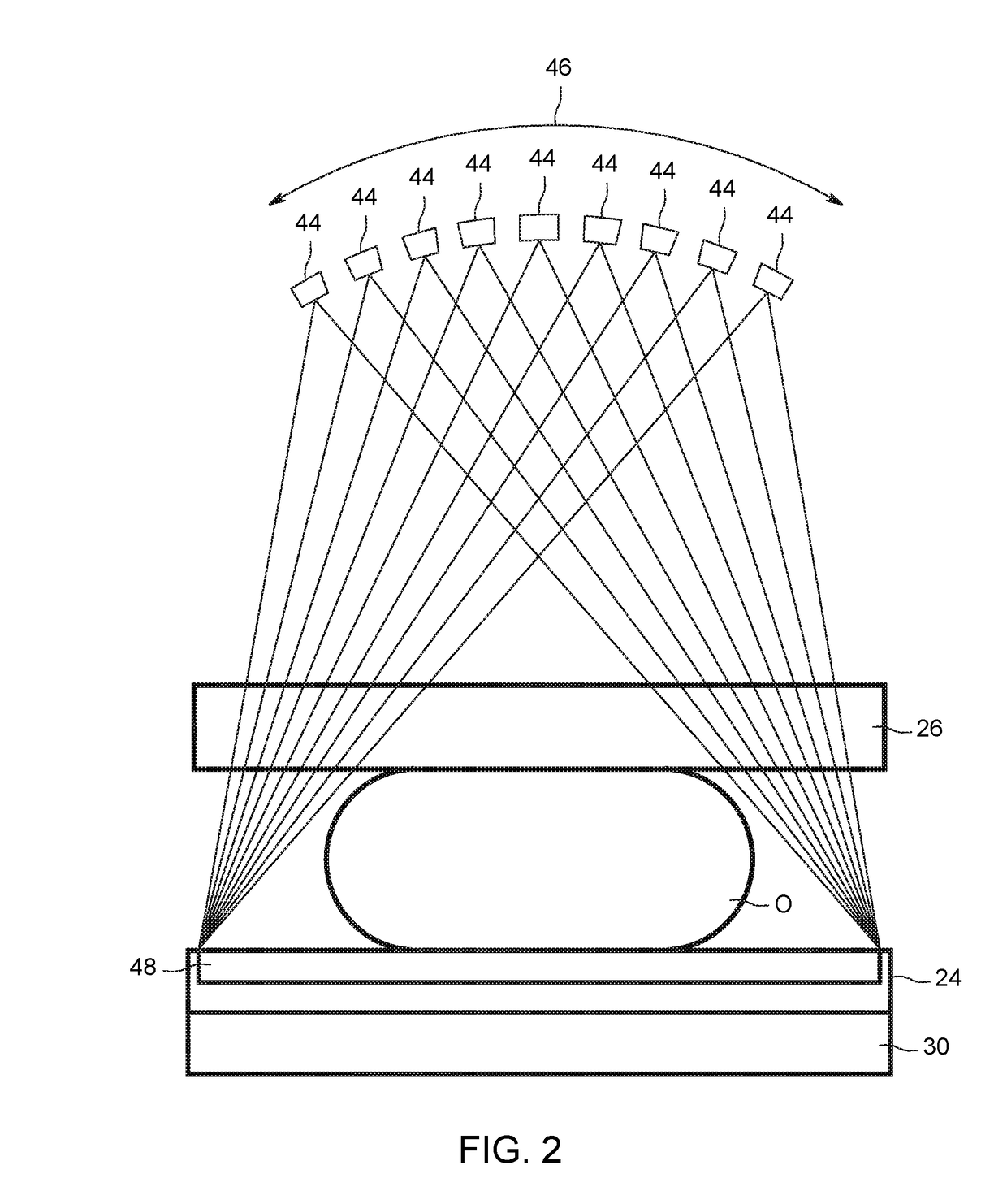
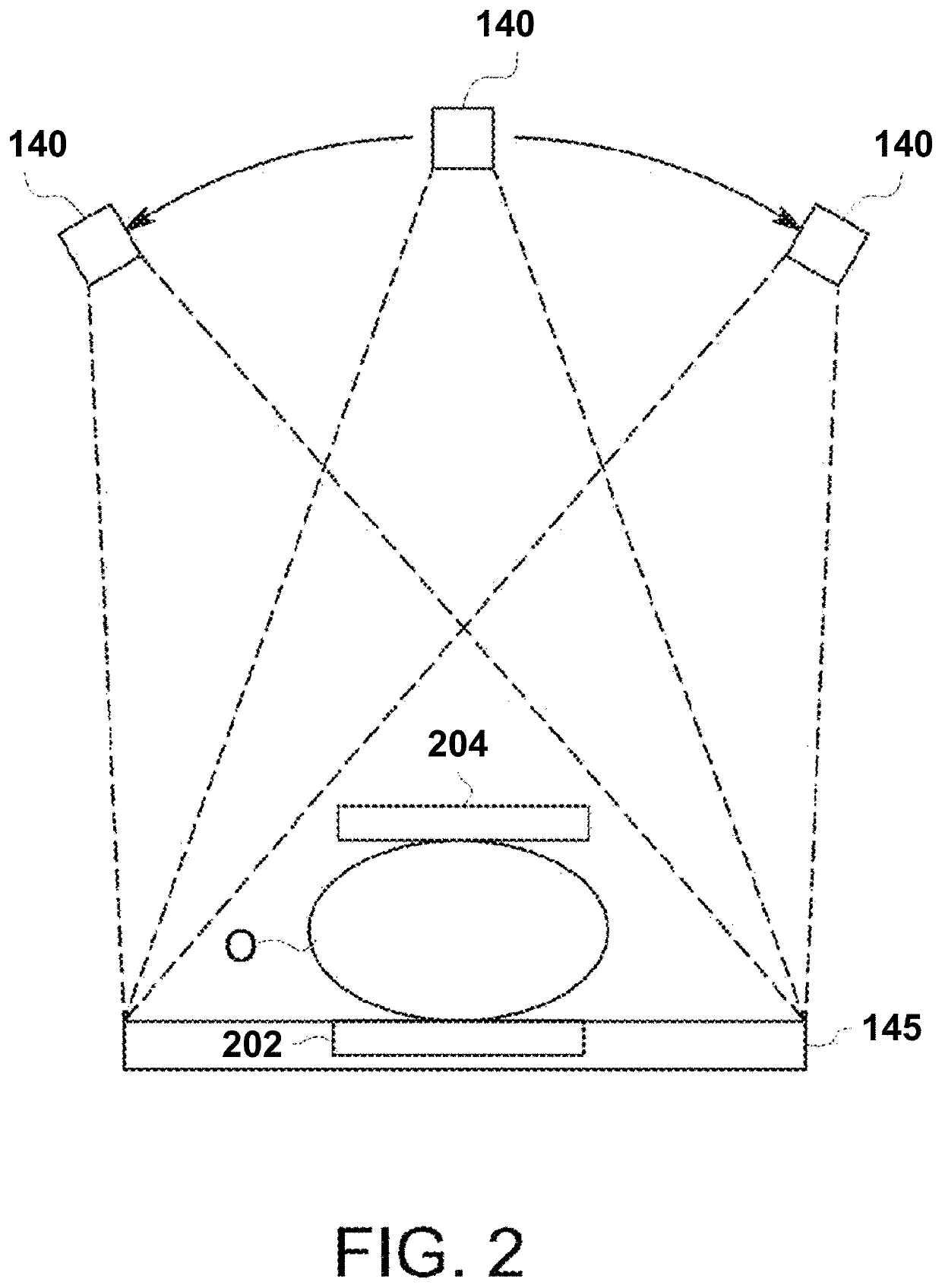
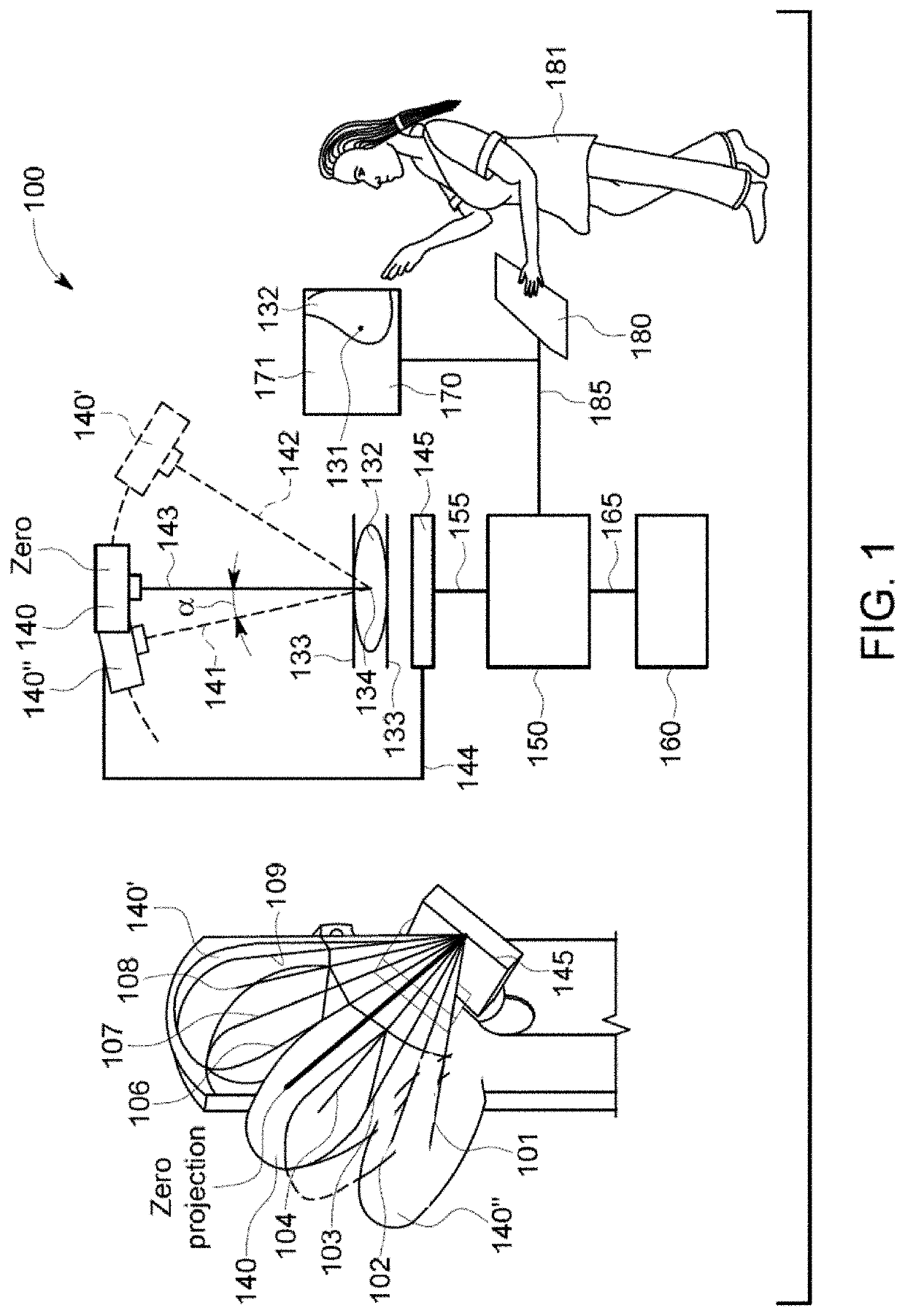
Image handling and display in X-ray mammography and tomosynthesis
InactiveUS20060098855A1Facilitate analysis and storageImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionProjection imageTomosynthesis
A method and system for acquiring, processing, storing, and displaying x-ray mammograms Mp tomosynthesis images Tr representative of breast slices, and x-ray tomosynthesis projection images Tp taken at different angles to a breast, where the Tr images are reconstructed from Tp images
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
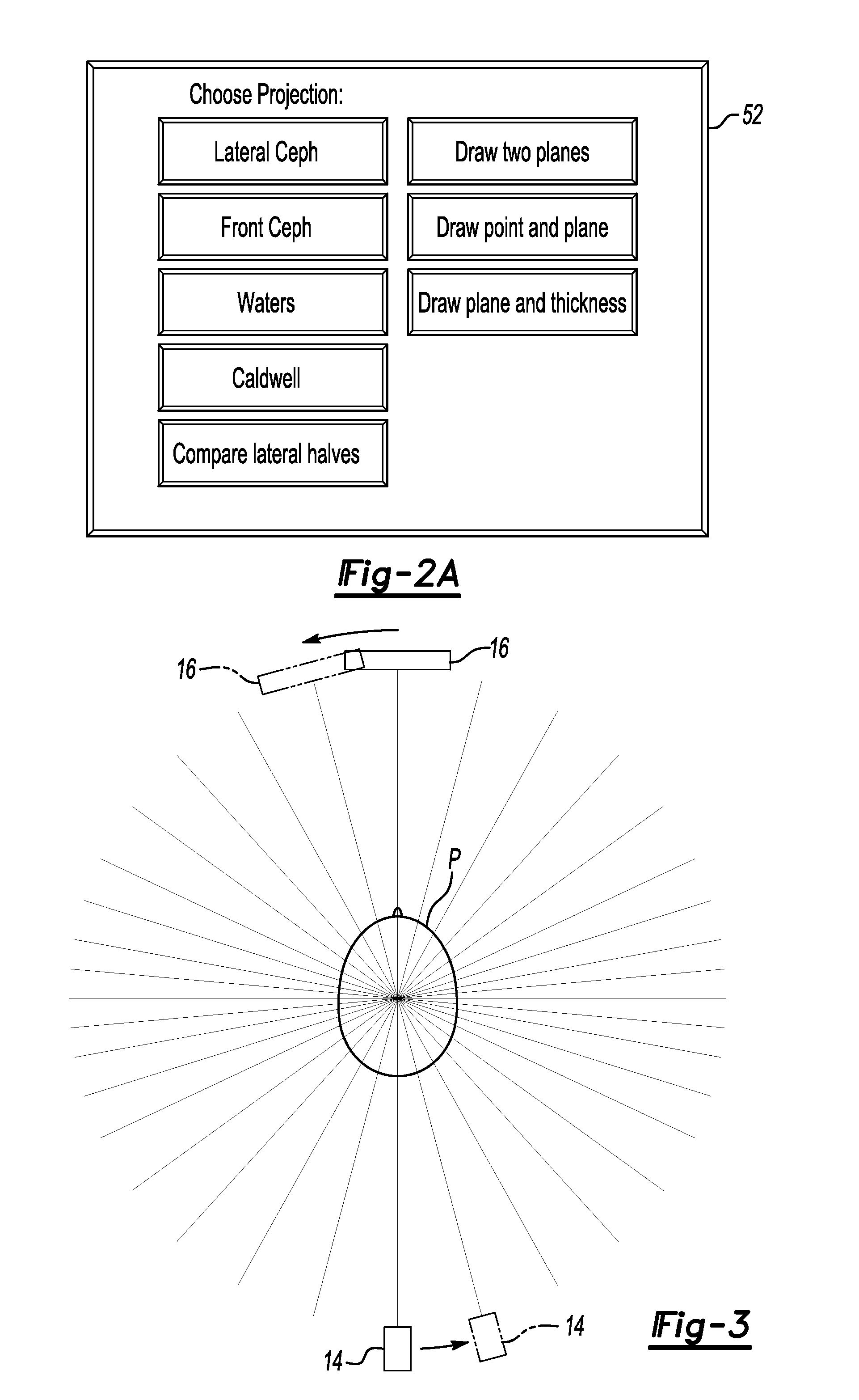
CT system with synthetic view generation
ActiveUS20060239400A1Reduce doseQuality improvementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputer graphics (images)Ct scanners
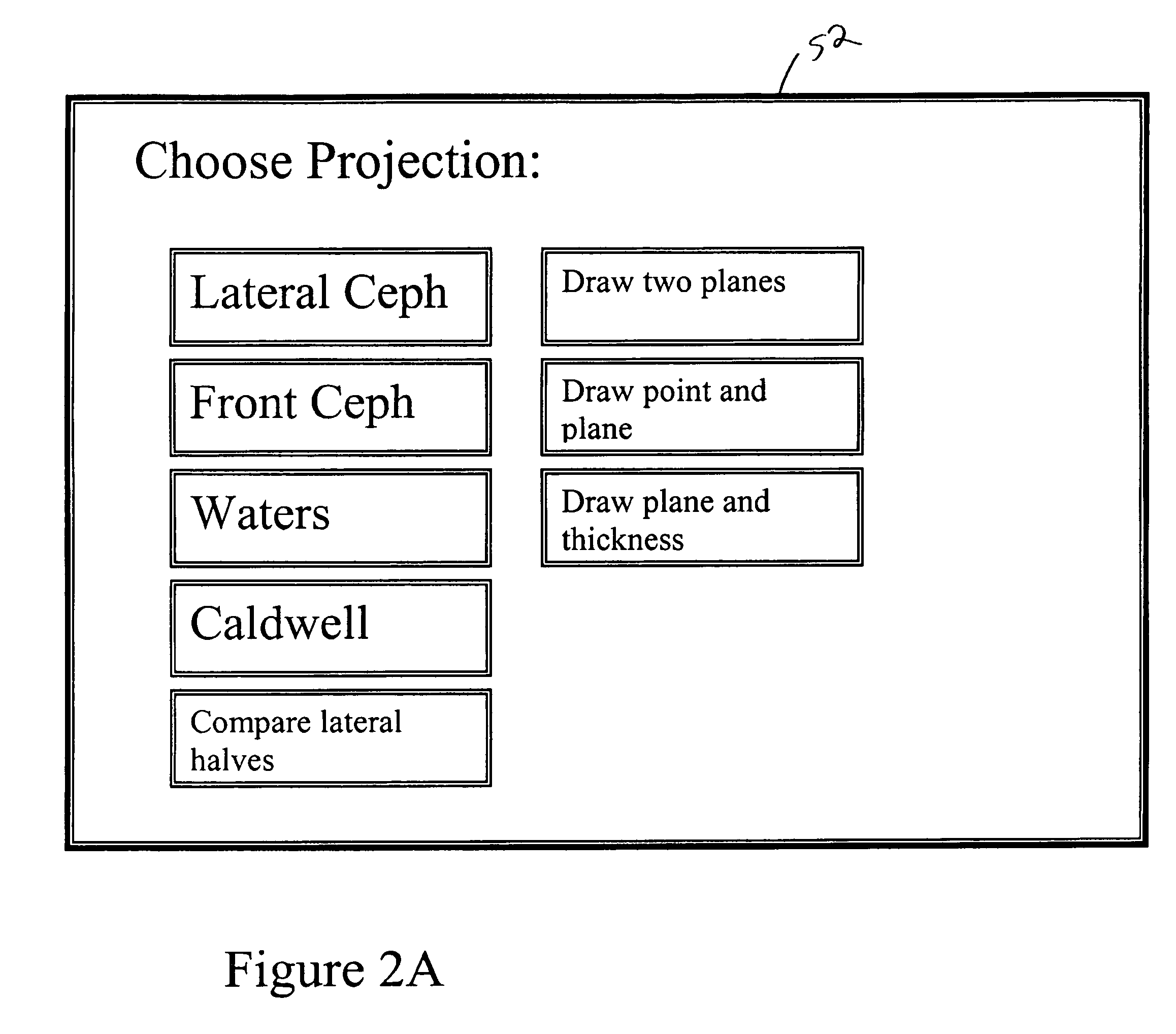
A CT scanner system provides projection-like images of a patient volume. After a CT scan is obtained and a three-dimensional model of the patient is created, any synthetic view can be generated by choosing any array of projection lines, e.g. between a point and a surface (a flat plane, curved plane, spherical, etc) or between two surfaces (parallel or not) and summing across the projection lines. The synthetic projections can mimic certain traditional views, such as a ceph scan, Water's view, Caldwell's projection, etc or can provide a new view that is impossible or impractical with traditional x-ray equipment, such as a perfect parallel projection, or a projection that does not pass all the way through the patient.
Owner:XORAN TECH
Image Handling and Display in X-Ray Mammography and Tomosynthesis
A method and system for acquiring, processing, storing, and displaying x-ray mammograms Mp tomosynthesis images Tr representative of breast slices, and x-ray tomosynthesis projection images Tp taken at different angles to a breast, where the Tr images are reconstructed from Tp images
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
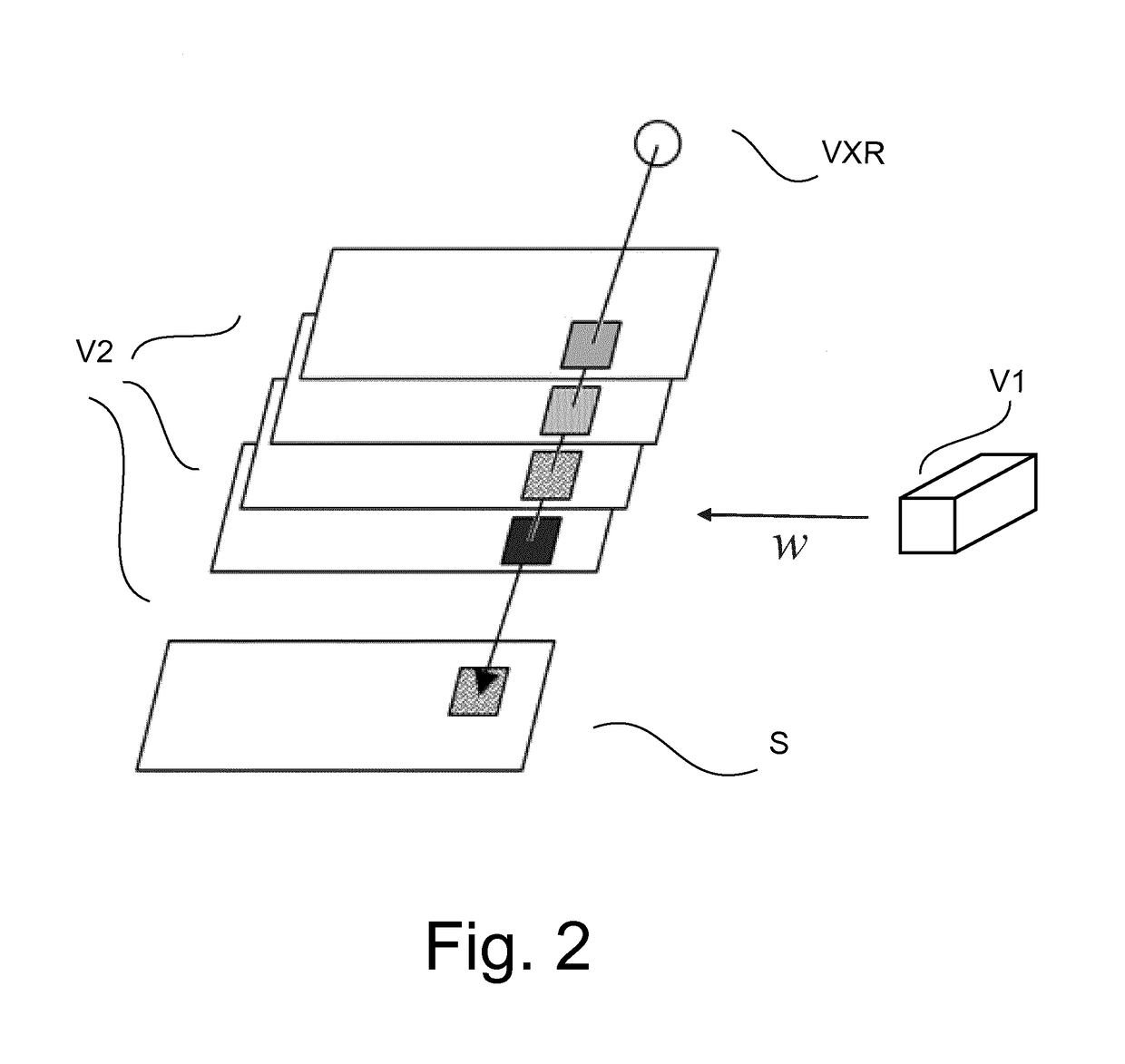
Method for generation of synthetic mammograms from tomosynthesis data
ActiveUS20170316588A1Enhance image structureBetter visibleReconstruction from projectionImage generationTomosynthesisProjection image
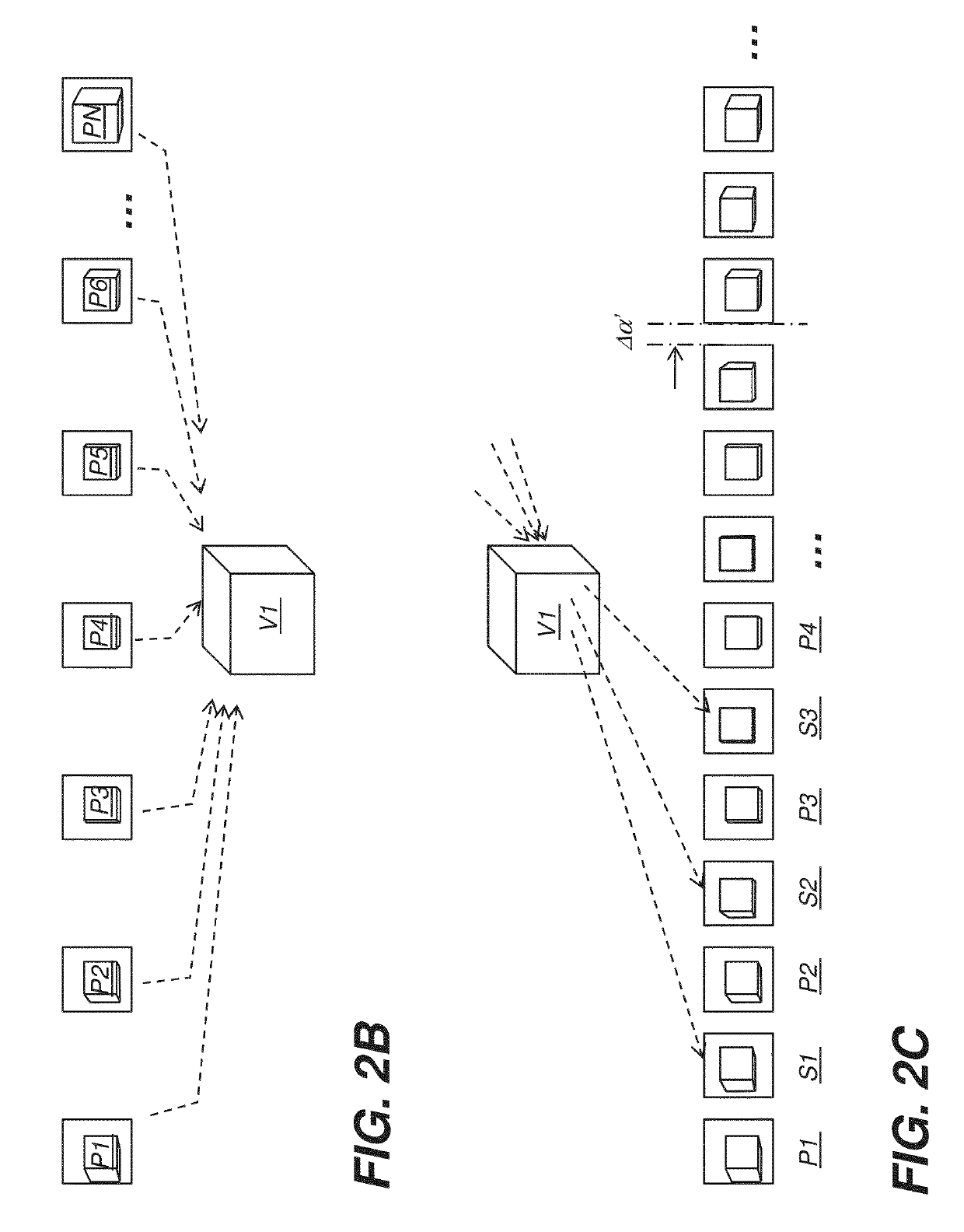
A method and related apparatus (VS) for synthesizing a projection image (S), in particular for use in mammography. It is proposed to compute a weight function from one image volume (V1) and is then used to implement a weighted forward projection through another image volume block to compute a synthesized projection image (S) across block (V2).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
CT system with synthetic view generation
ActiveUS7397890B2Reduce doseQuality improvementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersComputer graphics (images)
Owner:XORAN TECH
Methods for generation of edge=preserving synthetic mammograms from tomosynthesis data
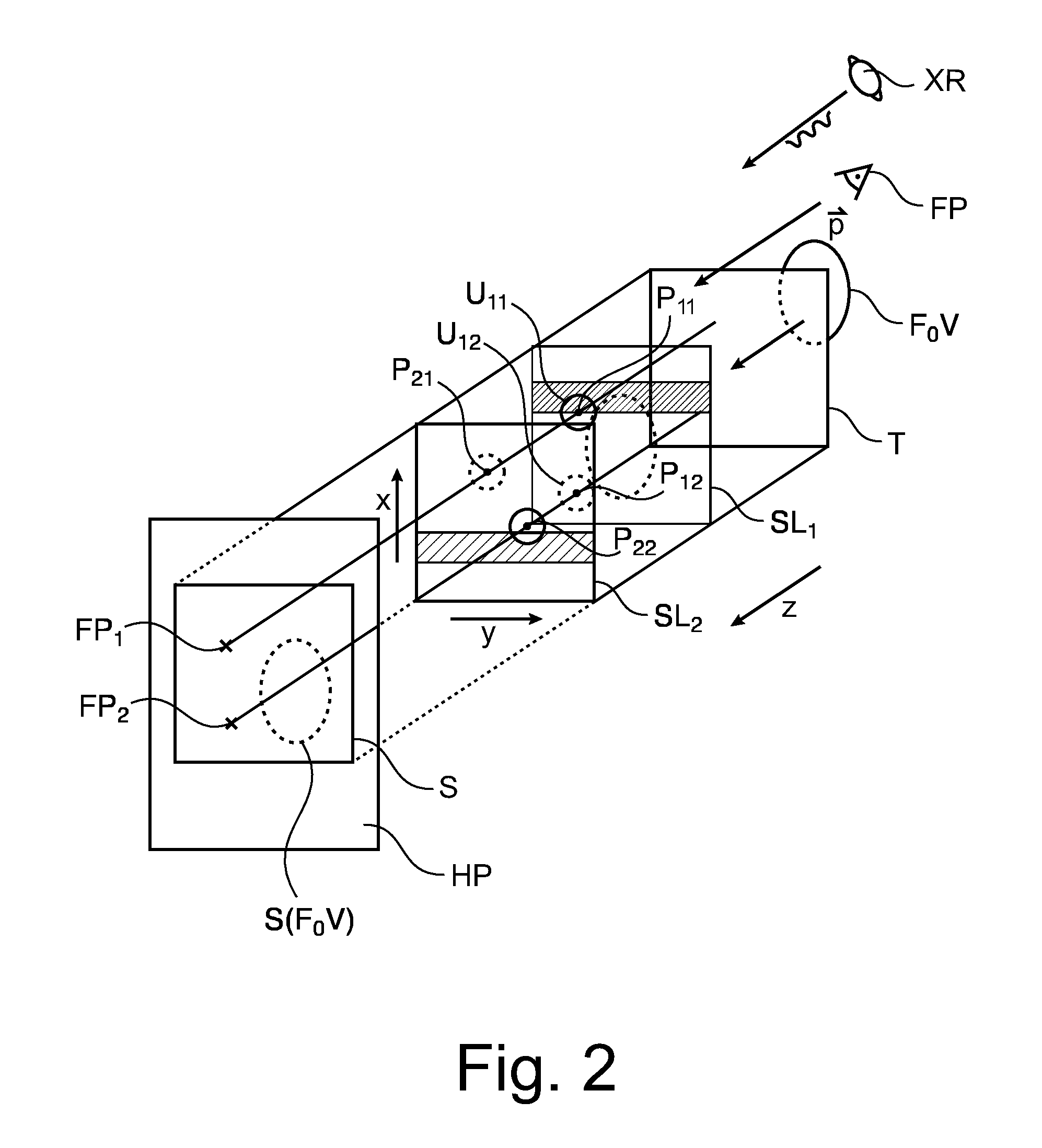
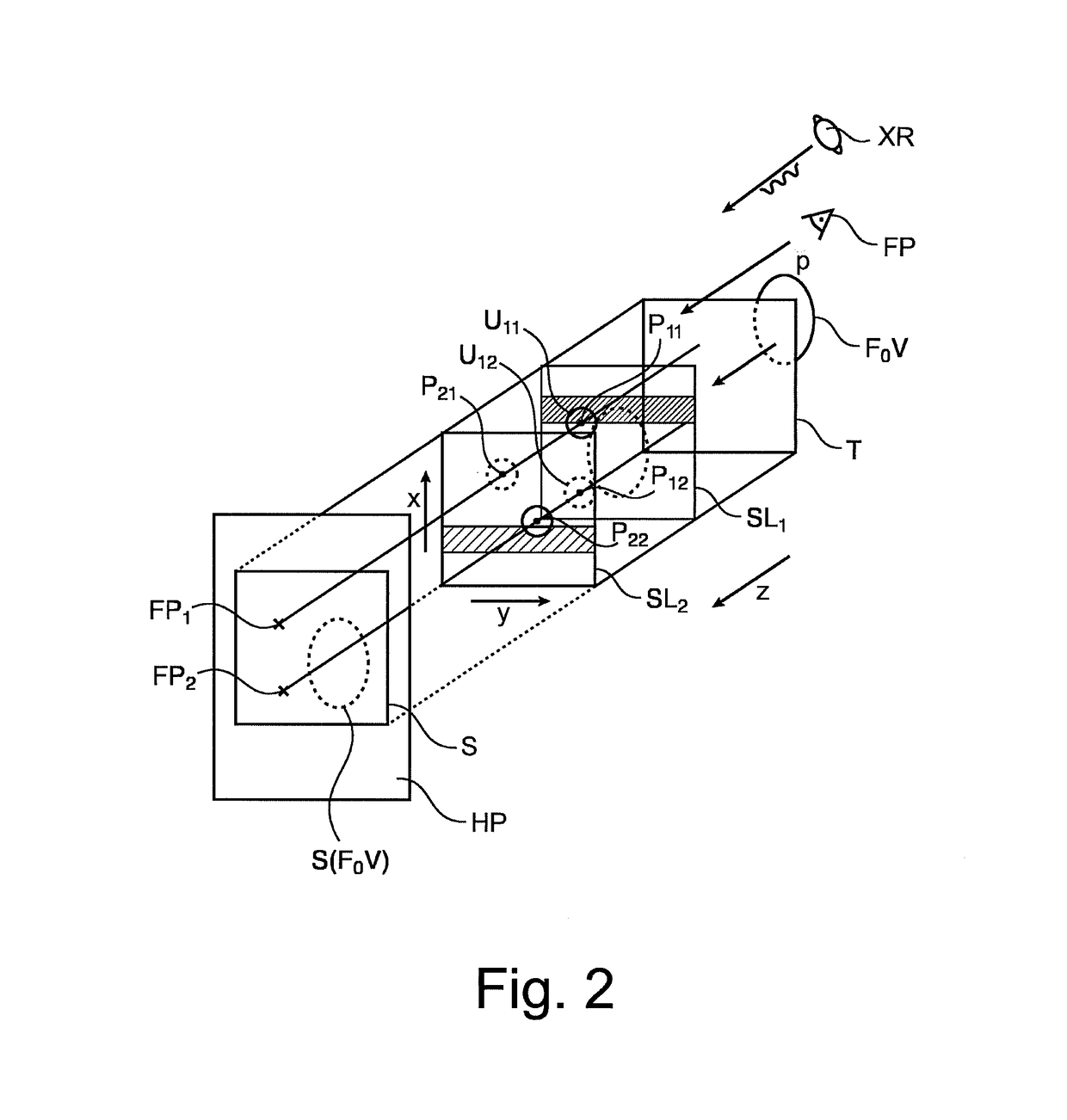
A method and related apparatus (VS) for synthetic projection images, in particular synthetic 2D mammograms (S) formed from a 3D image volume T made up of slices (SL). It is proposed to compute a forward projection (FP) using a weighted average function that is implemented by a filter (FL). The filter function (FL) is configured such that that voxels in a slice with maximum sharpness are assigned highest weights thereby avoiding blurring by averaging with structurally less relevant slices.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
System and Method for Generating Enhanced Density Distribution in a Three Dimenional Model of a Structure for Use in Skeletal Assessment Using a Limited Number of Two-Dimensional Views
ActiveUS20110231162A1Low costReduce exposureMedical simulationReconstruction from projectionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
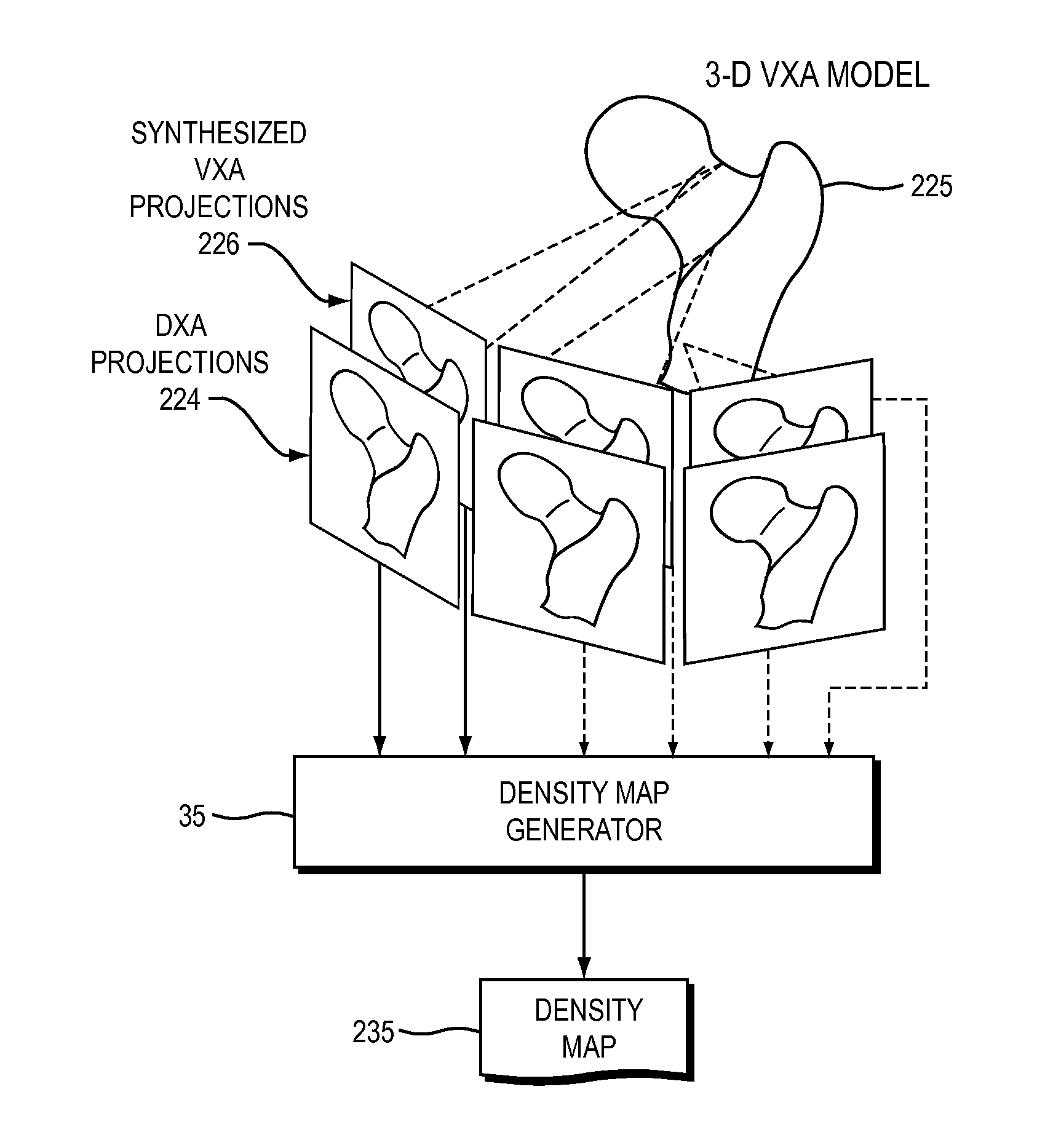
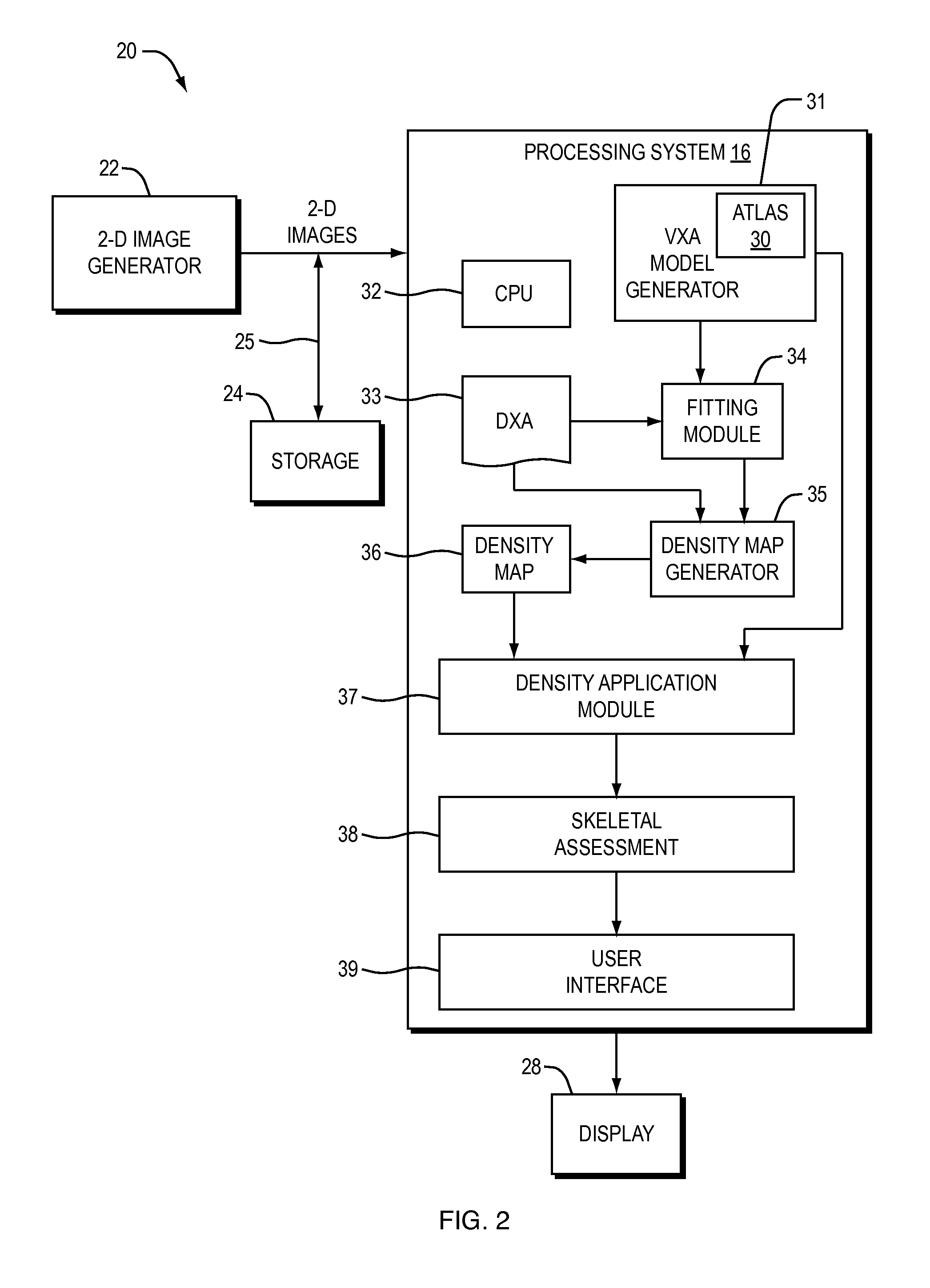
A method of generating a density enhanced model of an object is described. The method includes generating a customized a model of an object using a pre-defined set of models in combination with at least one projection image of the object, where the customized model is formed of a plurality of volume elements including density information. A density map is generated by relating a synthesized projection image of the customized model to an actual projection image of the object. Gains from the density map are back-projected into the customized model to provide a density enhanced customized model of the object. Because the density map is calculated using information from the synthesized projection image in combination with actual projection images of the structure, it has been shown to provide spatial geometry and volumetric density results comparable to those of QCT but with reduced patient exposure, equipment cost and examination time.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Apparatus, method and computer program for producing a corrected image of a region of interest from acquired projection data
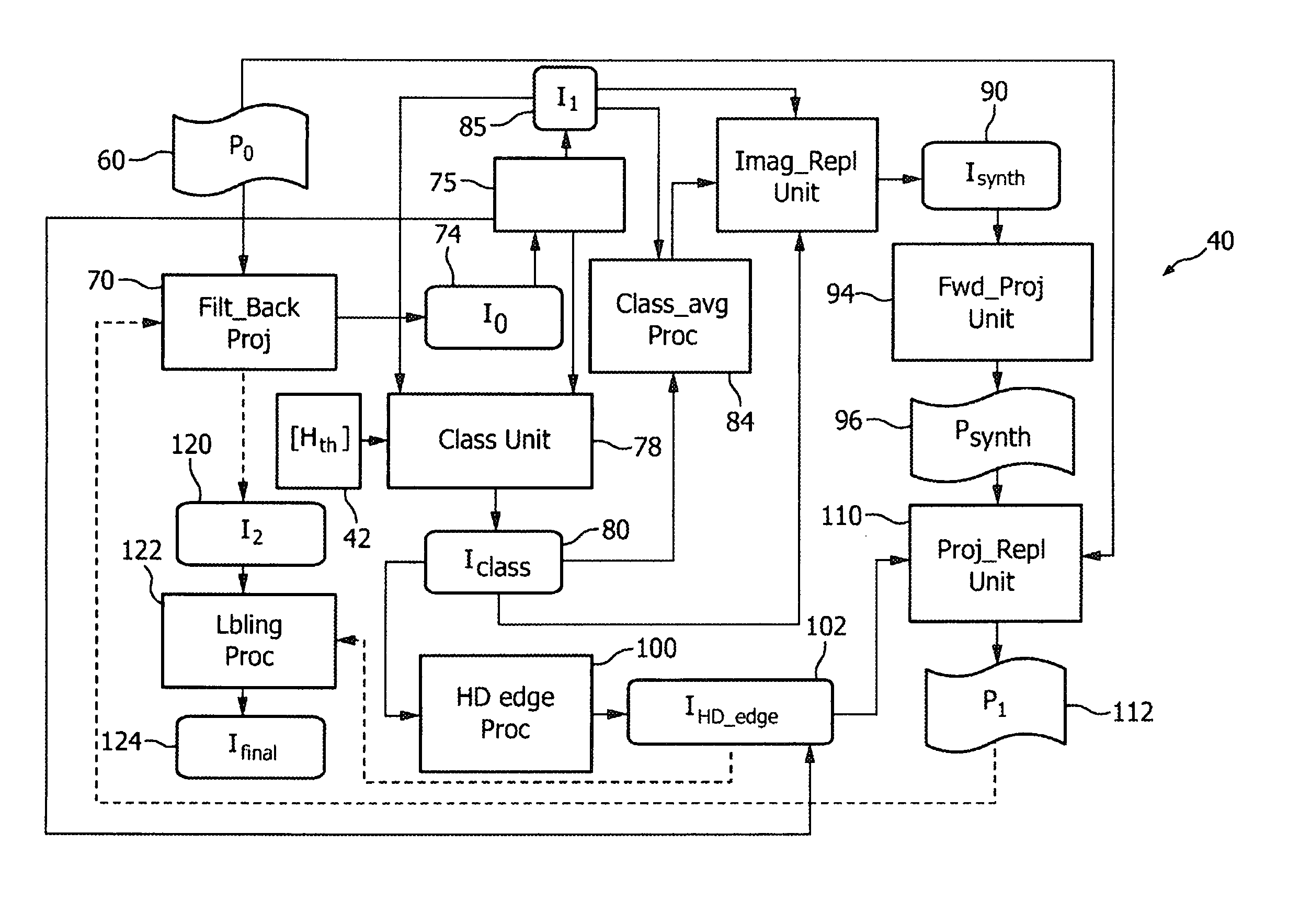
InactiveUS8582855B2Easy to correctHigh densityReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionHigh densityIntermediate image
The present invention relates to an apparatus for producing a corrected image of a region of interest from acquired projection data (60), wherein an uncorrected intermediate image (74) is reconstructed. The uncorrected intermediate image (74) is corrected and image elements of the corrected intermediate image (85) are classified. Image elements of the corrected 5 intermediate image (85) that are of a high density or low density class are replaced by image elements having values depending on values of the low density class to generate a synthetic image (90). Synthetic projection data (96) are generated by forward projecting the synthetic image (90), and acquired projection data contributing to the high density class are replaced by corresponding synthetic projection data (96) to generate corrected projection data (112). 10 The corrected projection data (112) are used for reconstructing the corrected image.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Apparatus, method and computer program for producing a corrected image of a region of interest from acquired projection data
InactiveUS20100322514A1Easy to correctHigh densityReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionIntermediate imageHigh density
The present invention relates to an apparatus for producing a corrected image of a region of interest from acquired projection data (60), wherein an uncorrected intermediate image (74) is reconstructed. The uncorrected intermediate image (74) is corrected and image elements of the corrected intermediate image (85) are classified. Image elements of the corrected 5 intermediate image (85) that are of a high density or low density class are replaced by image elements having values depending on values of the low density class to generate a synthetic image (90). Synthetic projection data (96) are generated by forward projecting the synthetic image (90), and acquired projection data contributing to the high density class are replaced by corresponding synthetic projection data (96) to generate corrected projection data (112). 10 The corrected projection data (112) are used for reconstructing the corrected image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
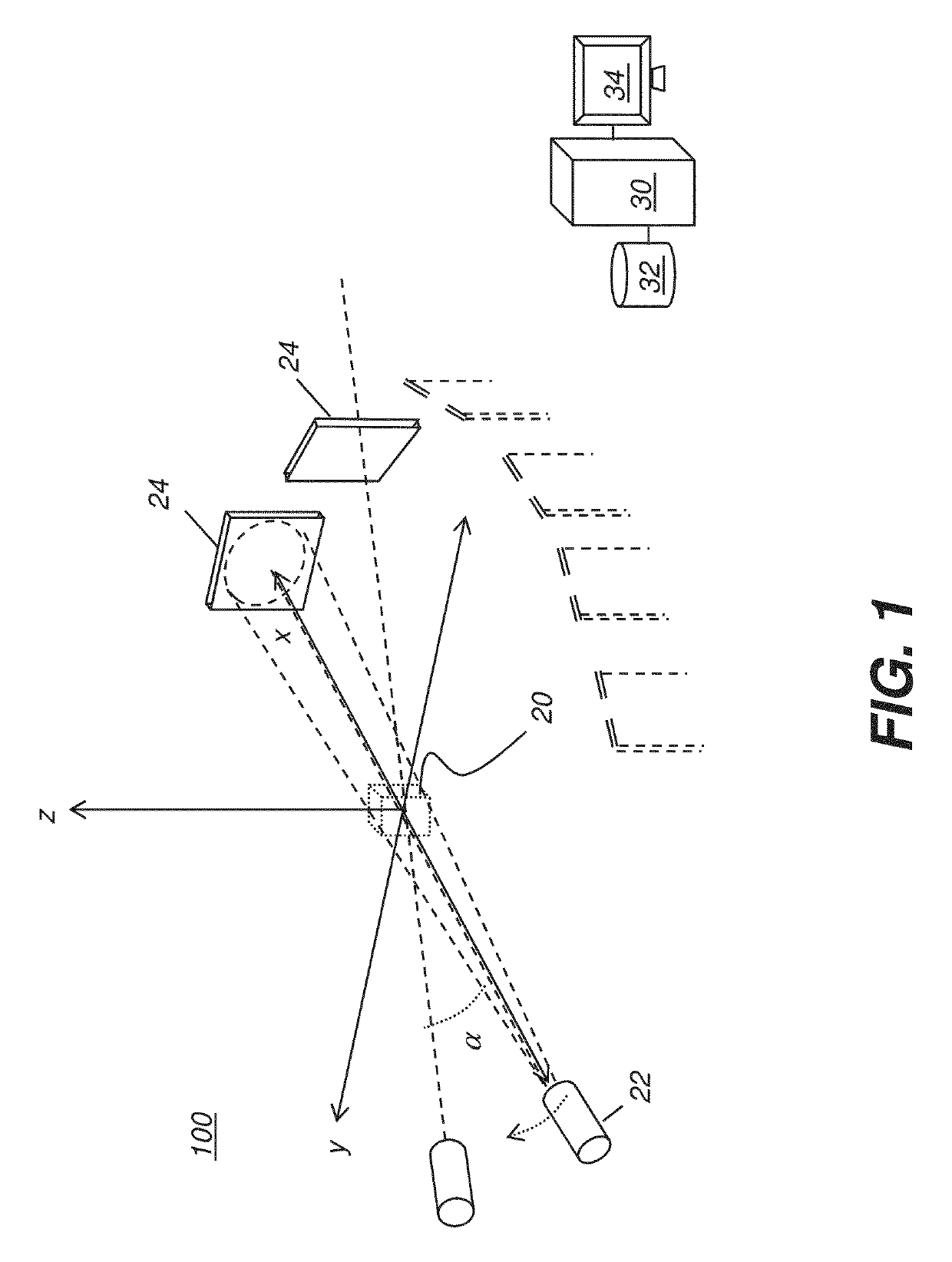
Projector, projection system, and method for generating pixel value in projector
InactiveUS7918560B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationProjectorsColor photographyImage formationProjection system
A projector includes an illuminator; a first image formation unit including a first optical unit having a light modulation element that modulates the light from the illuminator, the first image formation unit using the first optical unit to output first image light; a second image formation unit including a second optical unit having a light modulation element that modulates the light from the illuminator, the second image formation unit using the second optical unit to output second image light; a polarization combining system that combines the first image light outputted from the first image formation unit and the second image light outputted from the second image formation unit; a projection system that projects the image light combined by the polarization combining system; projection position adjusters that optically adjust the projection positions of the light modulation elements on a projection surface; and a pixel value generator that generates the pixel value for each pixel contained in the light modulation elements, the projection positions of which have been adjusted by the projection position adjusters, based on the projection position of the light from the pixel.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
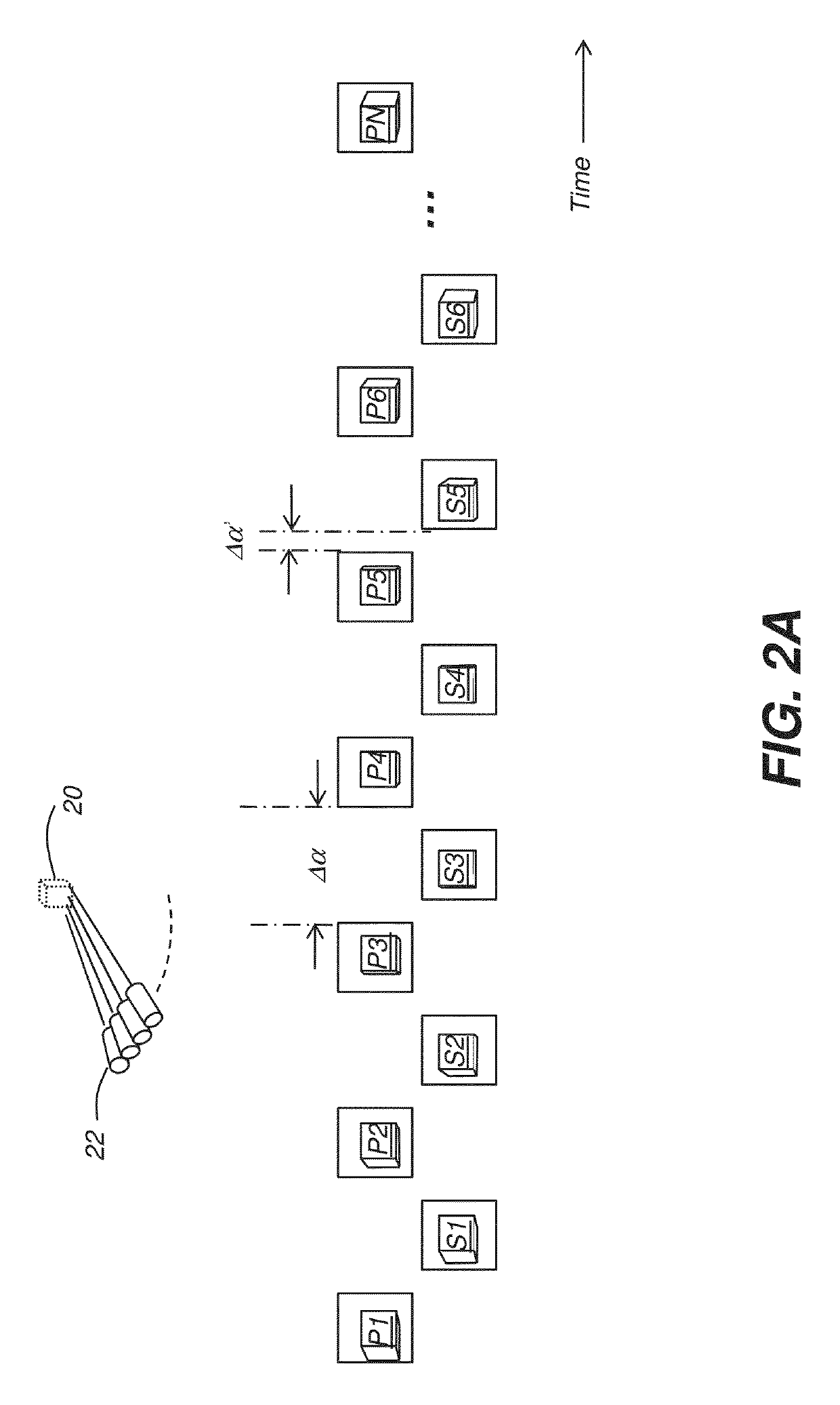
Interpolated tomosynthesis projection images
ActiveUS20180114312A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisSynthetic projection
Systems and methods of medical imaging includes acquiring a plurality of projection images. A first projection image and a second projection image from the plurality of projection images are selected that are adjacent to a received focal point. A first set of object locations in the first projection image and a second set of object locations in the second projection image are identified that contribute to a pixel of the synthetic projection image. A value for the pixel of the synthetic projection image is calculated from the pixels of the first set of object locations and the pixels of the second set of object locations. The synthetic projection image is created with the calculated value.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Generating synthesized projection images for 3D breast tomosynthesis or multi-mode x-ray breast imaging
ActiveUS20200085393A1Eliminate needImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionSynthetic projectionMedical imaging
Methods and systems for medical imaging including synthesizing virtual projections from acquired real projections and generating reconstruction models and images based on the synthesized virtual projections and acquired real projections. For example, first x-ray imaging data is generated from a detected first x-ray emission at a first angular location and second x-ray imaging data is generated from a detected second x-ray emission at a second angular location. Based on at least the first x-ray imaging data and the second x-ray imaging data, third x-ray imaging data for a third angular location relative to the breast may be synthesized. An image of the breast may be displayed or generated from the third x-ray imaging data.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
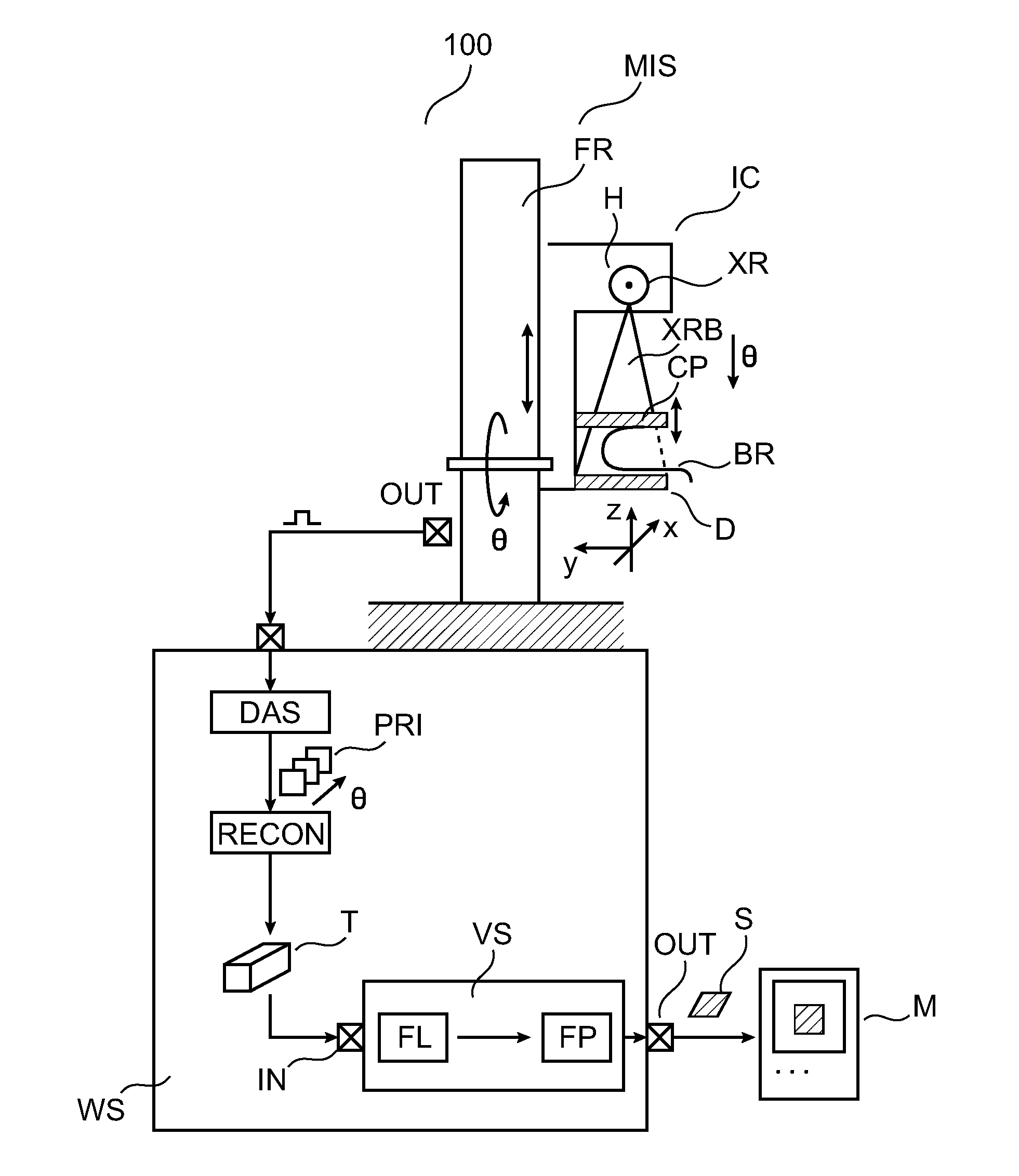
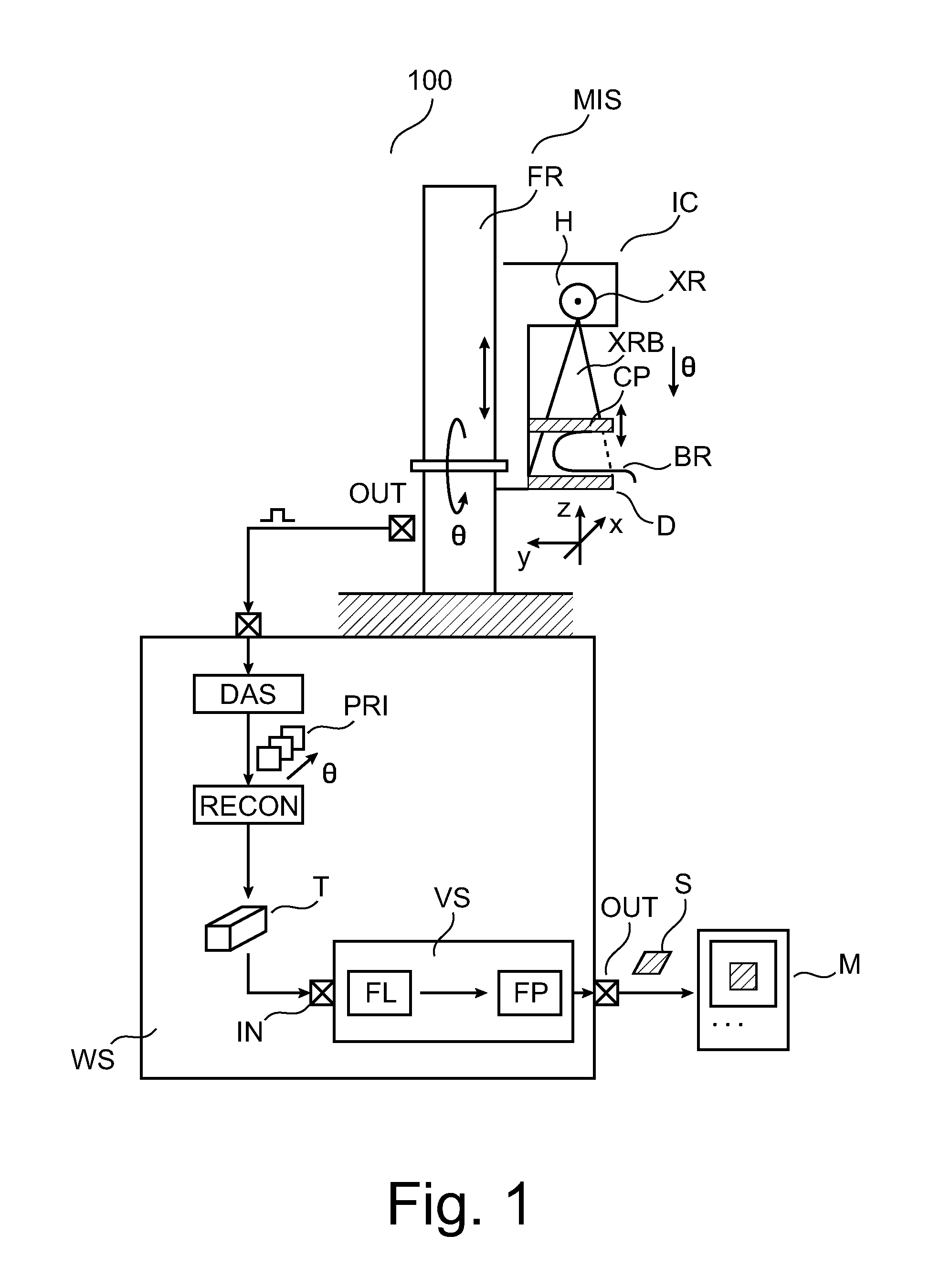
Computed-tomography system and method for determining volume information for a body
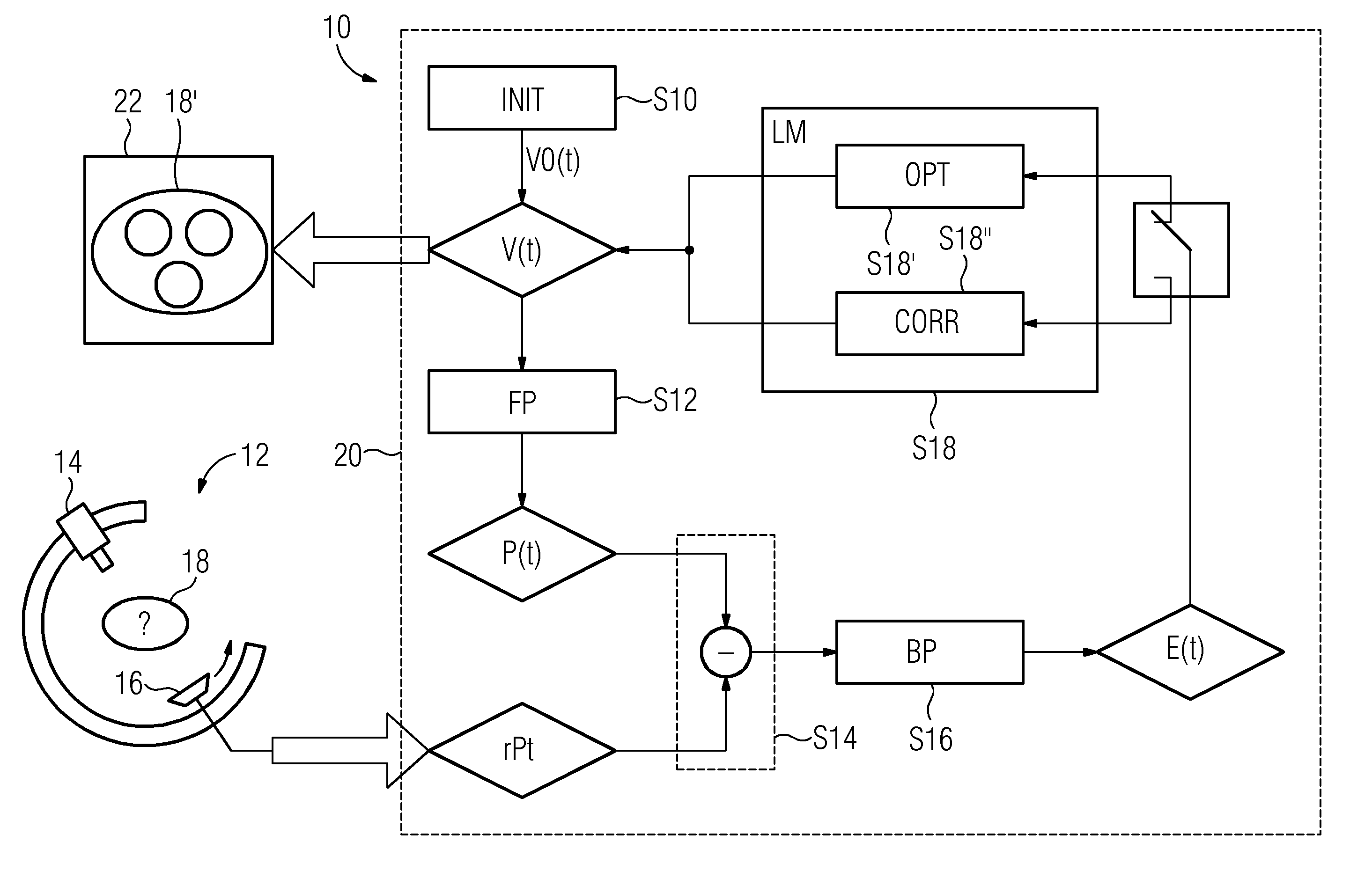
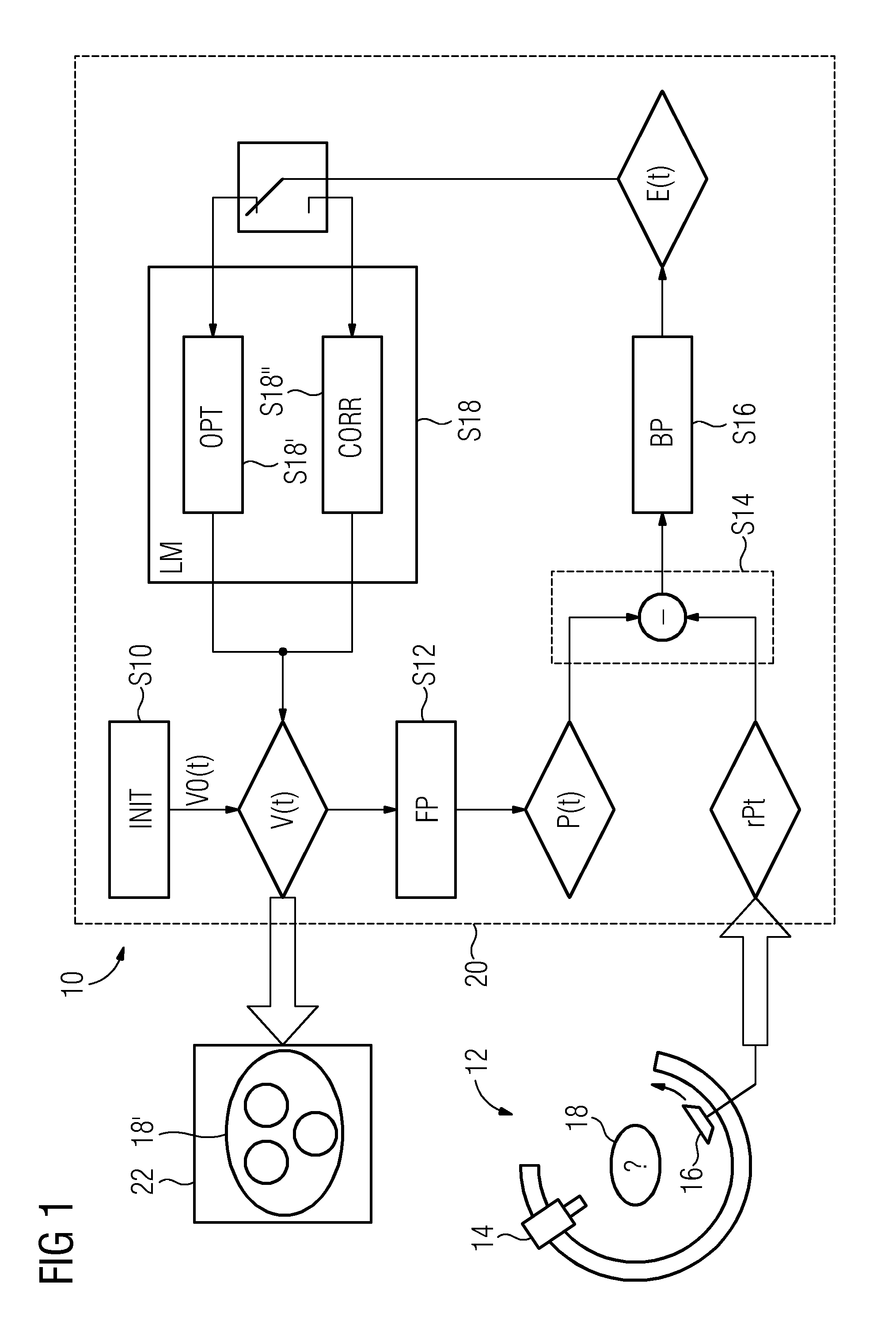
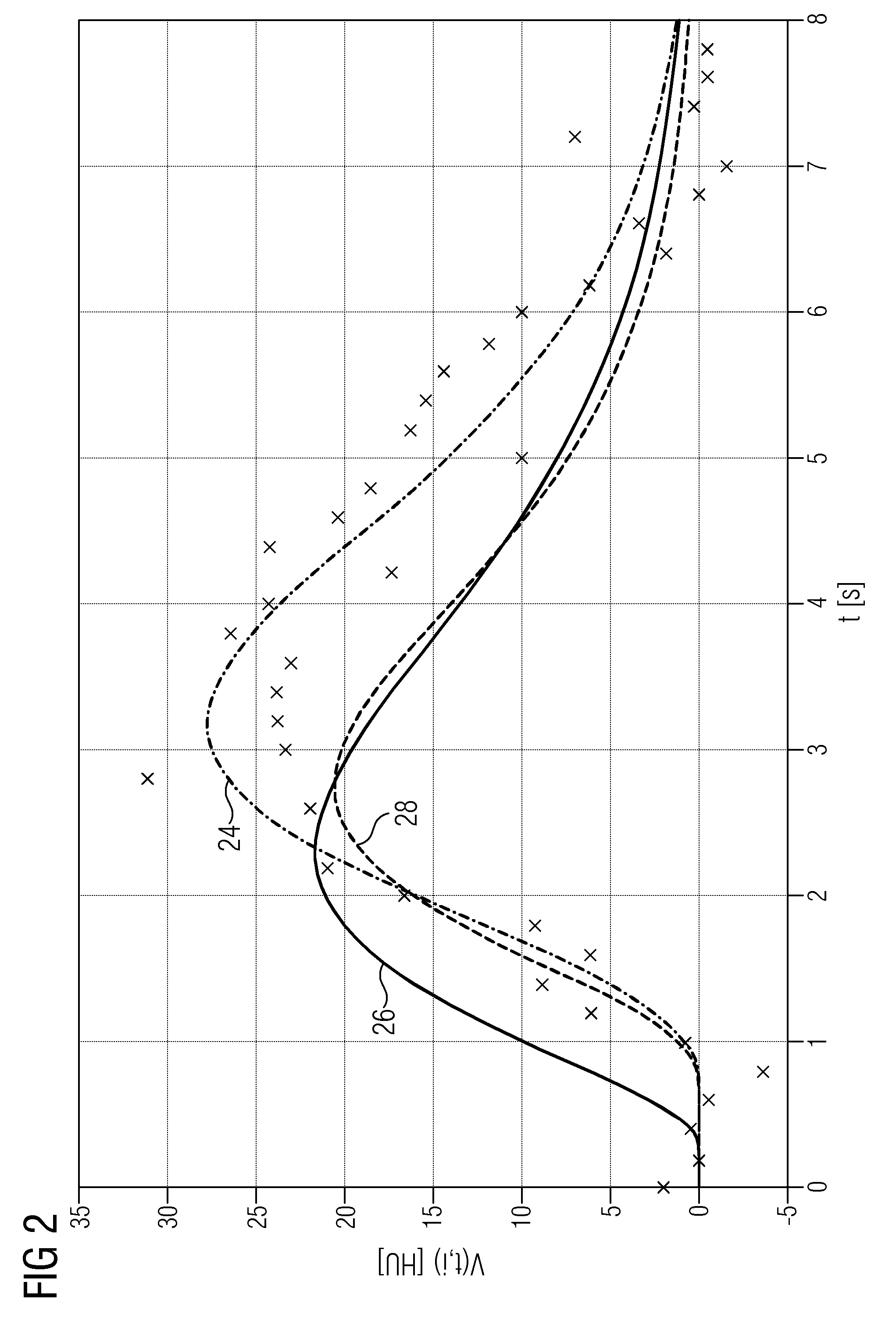
ActiveUS20130129172A1Reduce memory requirementsLess imaging artifactReconstruction from projectionImage analysisVoxelMedicine
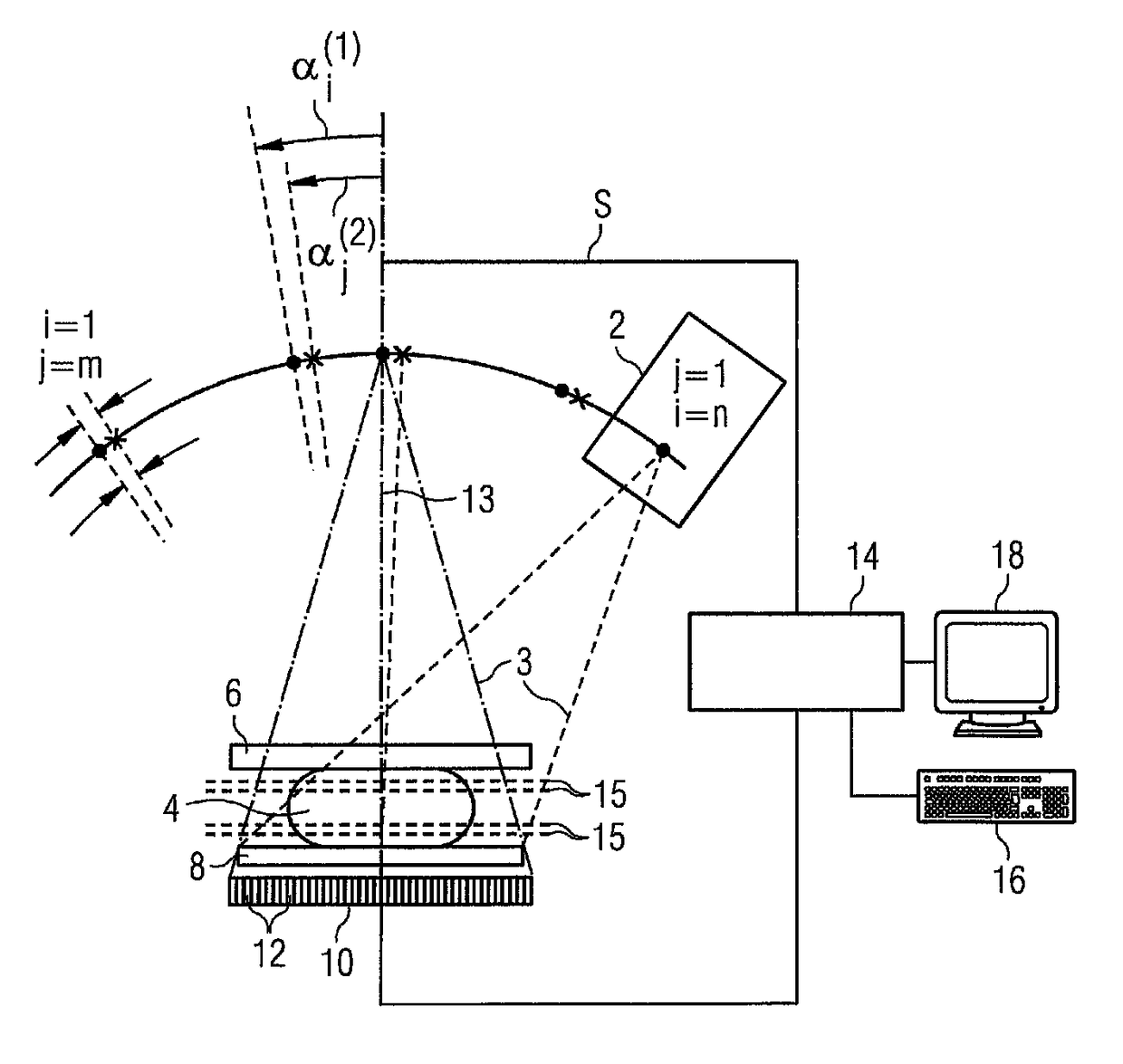
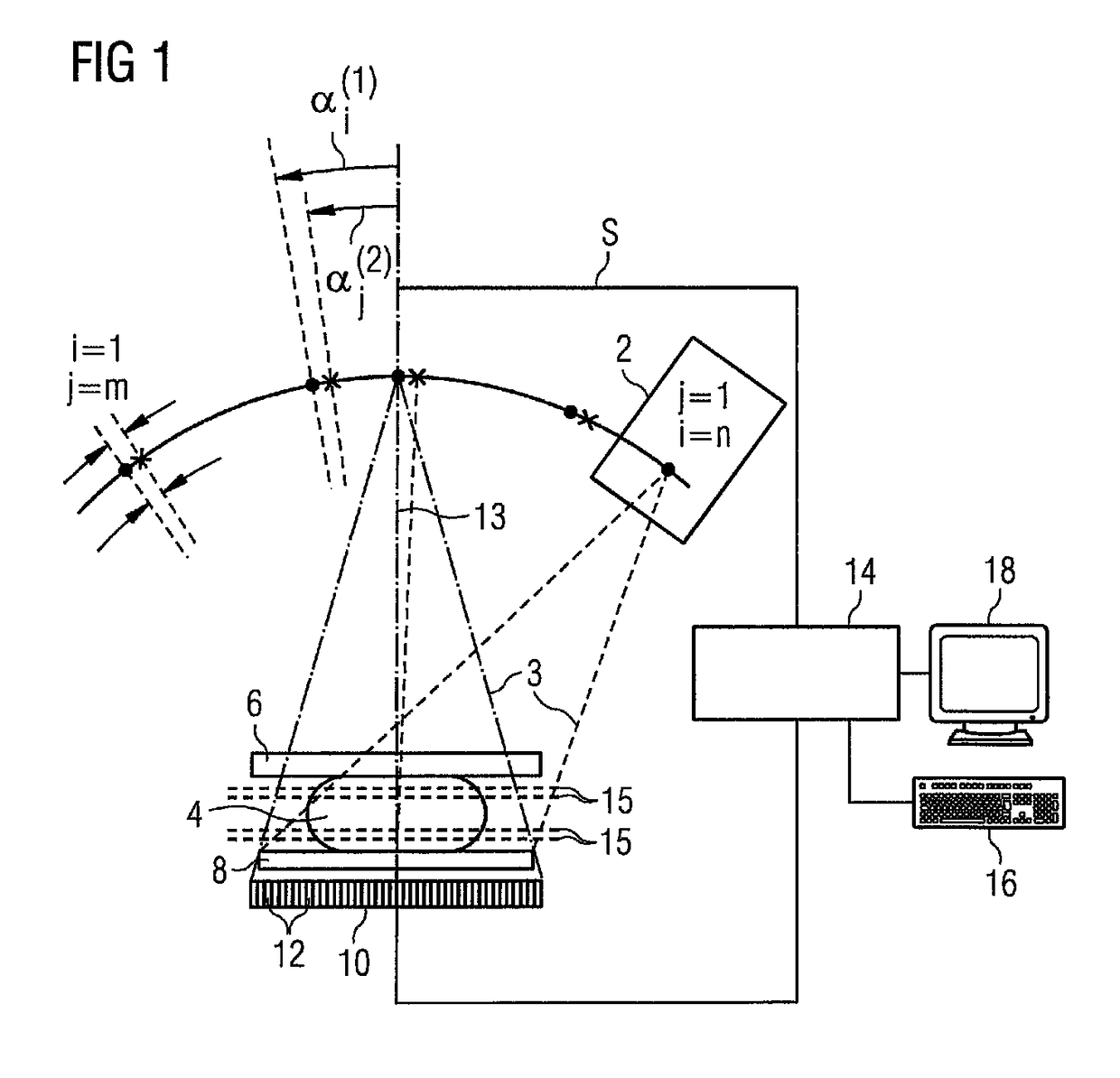
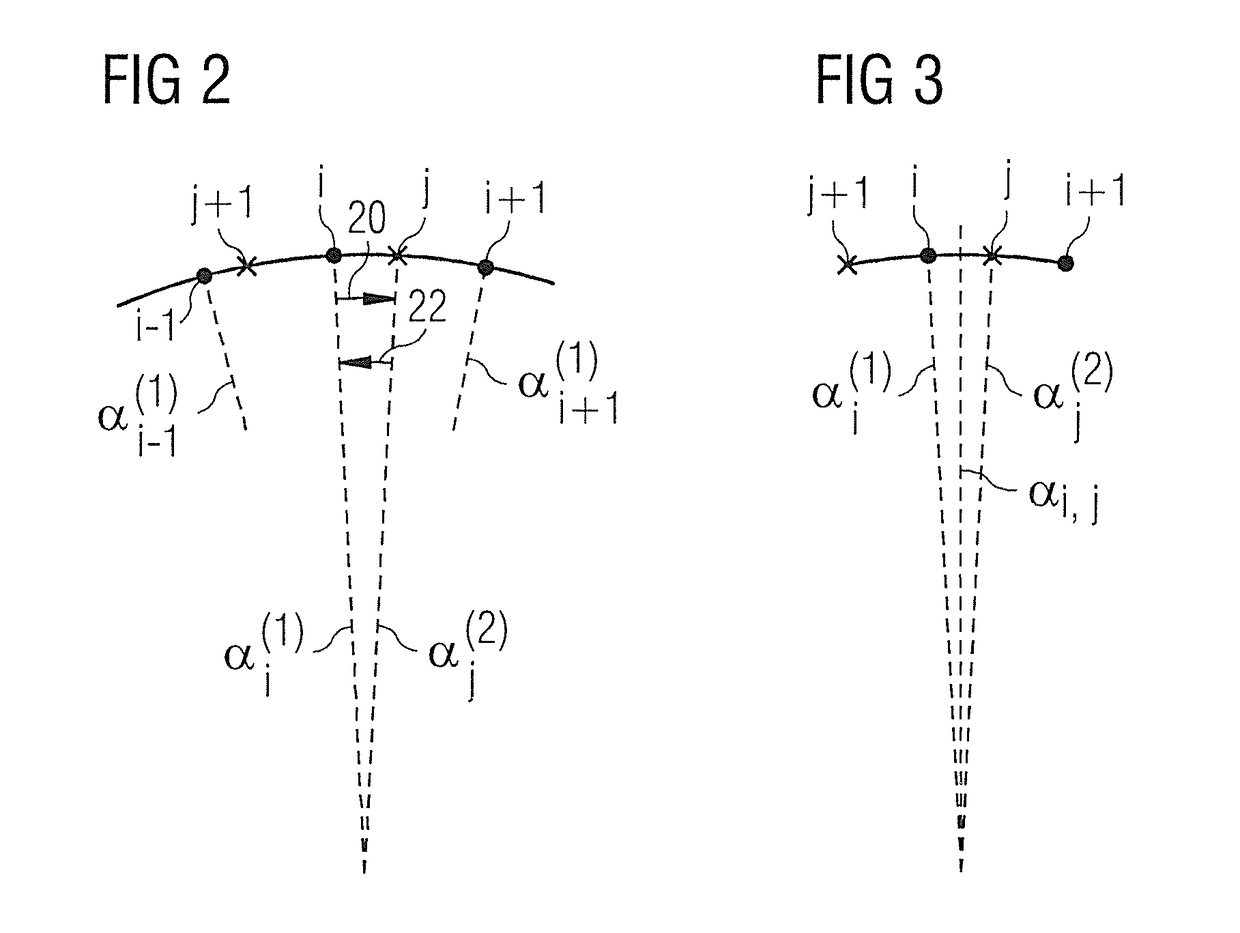
A tomogram of a body is provided. Projection-image data obtained by a radiation-based projection method is used for providing the tomogram. Initial voxel data are first specified for a plurality of voxels of the body. Synthetic projection-image data are generated based upon a projection rule modeling a course of the projection method. Projection-error data is determined by comparing the synthetic projection-image data with the real projection-image data. The projection-error data are imaged on the basis of a back-projection rule dependent on the projection rule so that voxel-error data are produced. Correction data is generated from the voxel-error data by a gradient-based optimizing algorithm, wherein corrected voxel data are generated using the correction data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
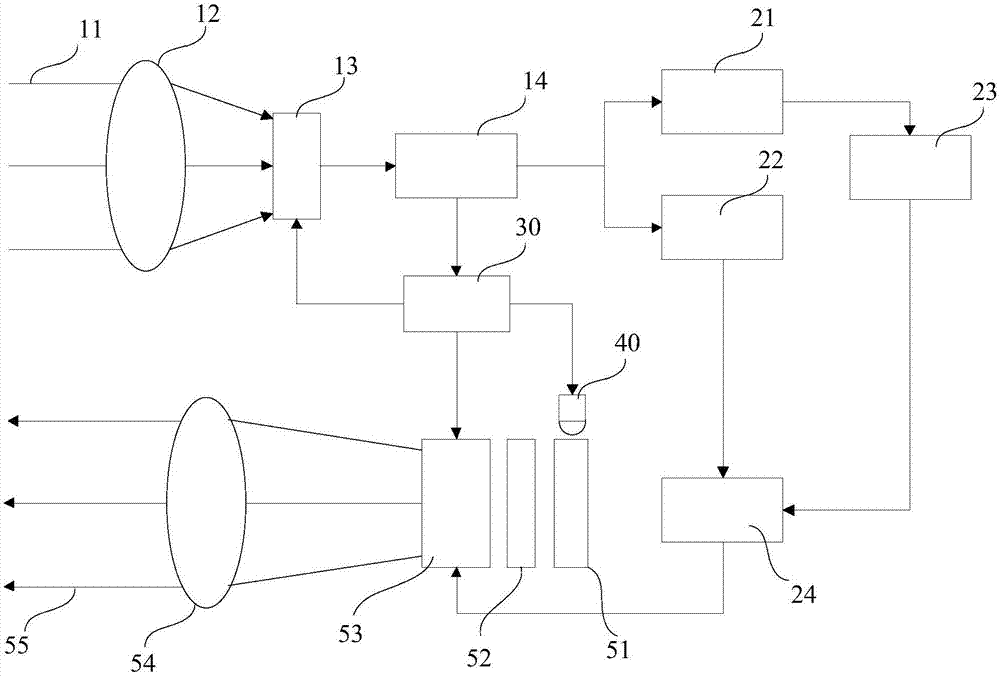
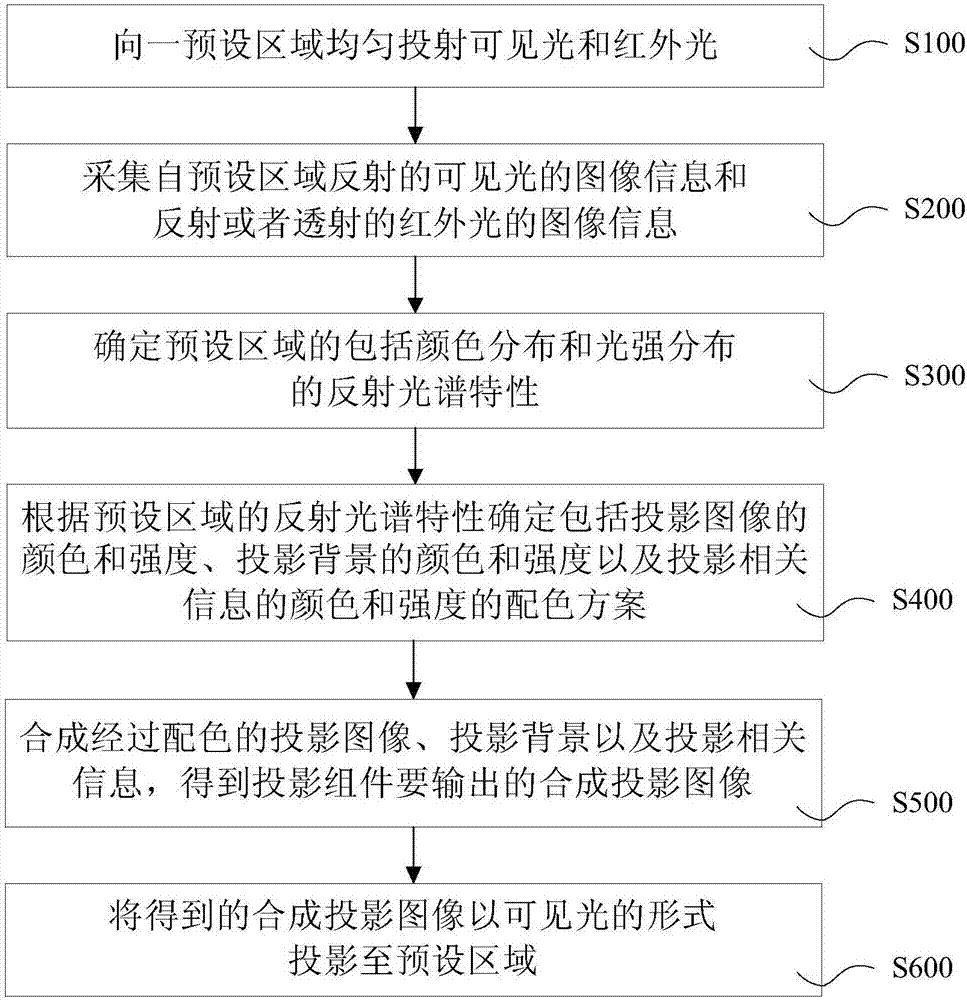
Multi-spectral camera shooting and projecting apparatus and method
PendingCN107411705AIncrease contrastImprove legibilityDiagnostics using spectroscopySensorsComputer graphics (images)Synthetic projection
The invention provides a multi-spectral camera shooting and projecting apparatus and a multi-spectral camera shooting and projecting method. The multi-spectral camera shooting and projecting apparatus comprises a camera shooting assembly, a computing processor assembly and a projecting assembly, wherein the camera shooting assembly collects and outputs image information of light within first-class wavelength range and second-class wavelength range at a preset area; the computing processor assembly selects a color blending scheme comprising the color and intensity of a projection image as well as the color and intensity of the projection background according to the reflection spectrum characteristics of the preset area obtained from the image information of the light within the first-class wavelength range, and synthesizing the image information of the light within the first-class wavelength range and the second-class wavelength range, the projection relevant information and the projection background into the projection image according to the color blending scheme; the projecting assembly projects the synthesized projection image to the preset area in the form of the light within the first-class wavelength range at the projecting stage. According to the apparatus and the method provided by the invention, color blending selection with certain self adaptation or optimization is carried out on the projection image and the projection background, so that the contrast ratio and identifiability of the projection image are enhanced, and a reliable basis is provided for various operations based on the projection image.
Owner:EXPANTRUM OPTOELECTRONICS
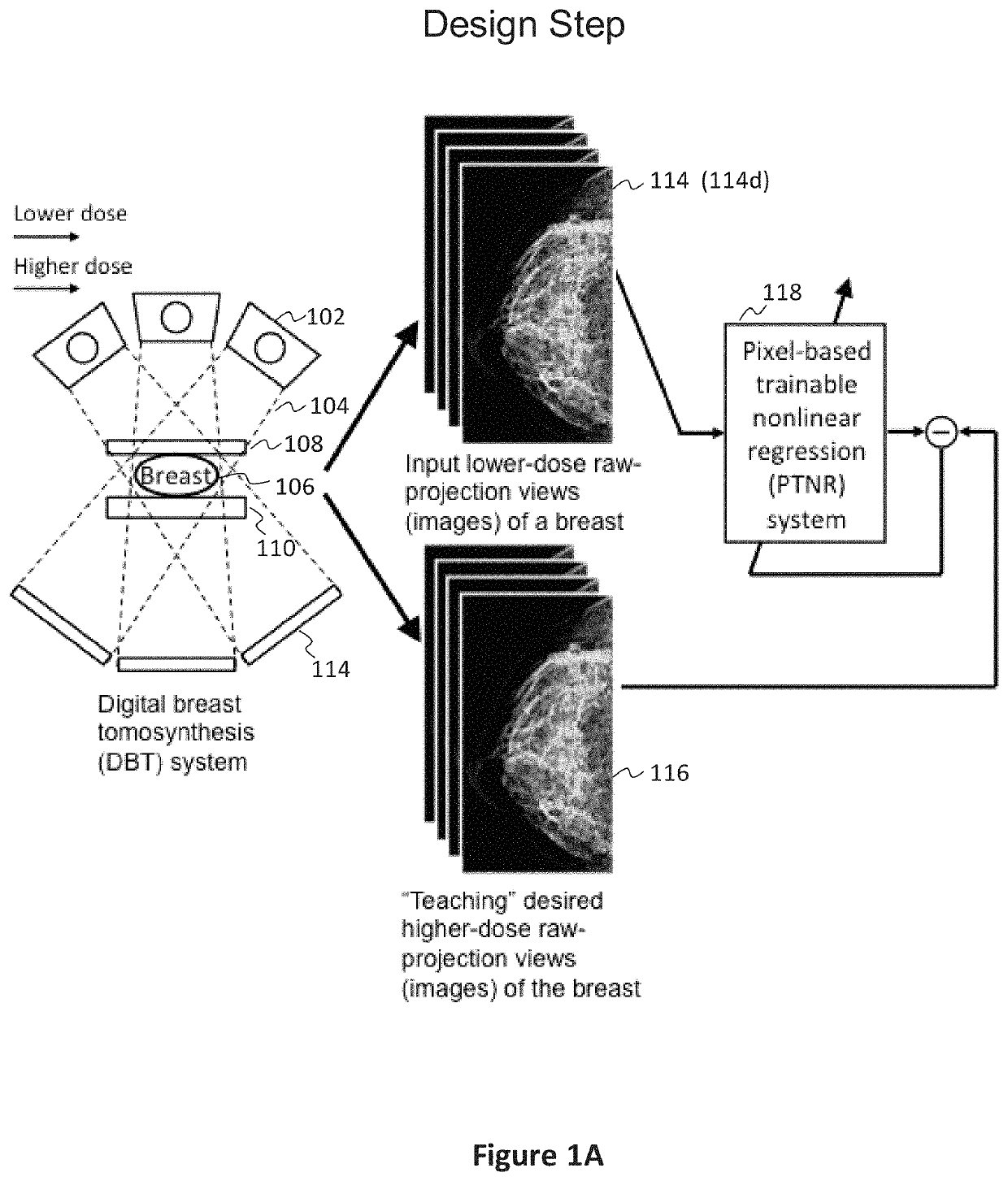
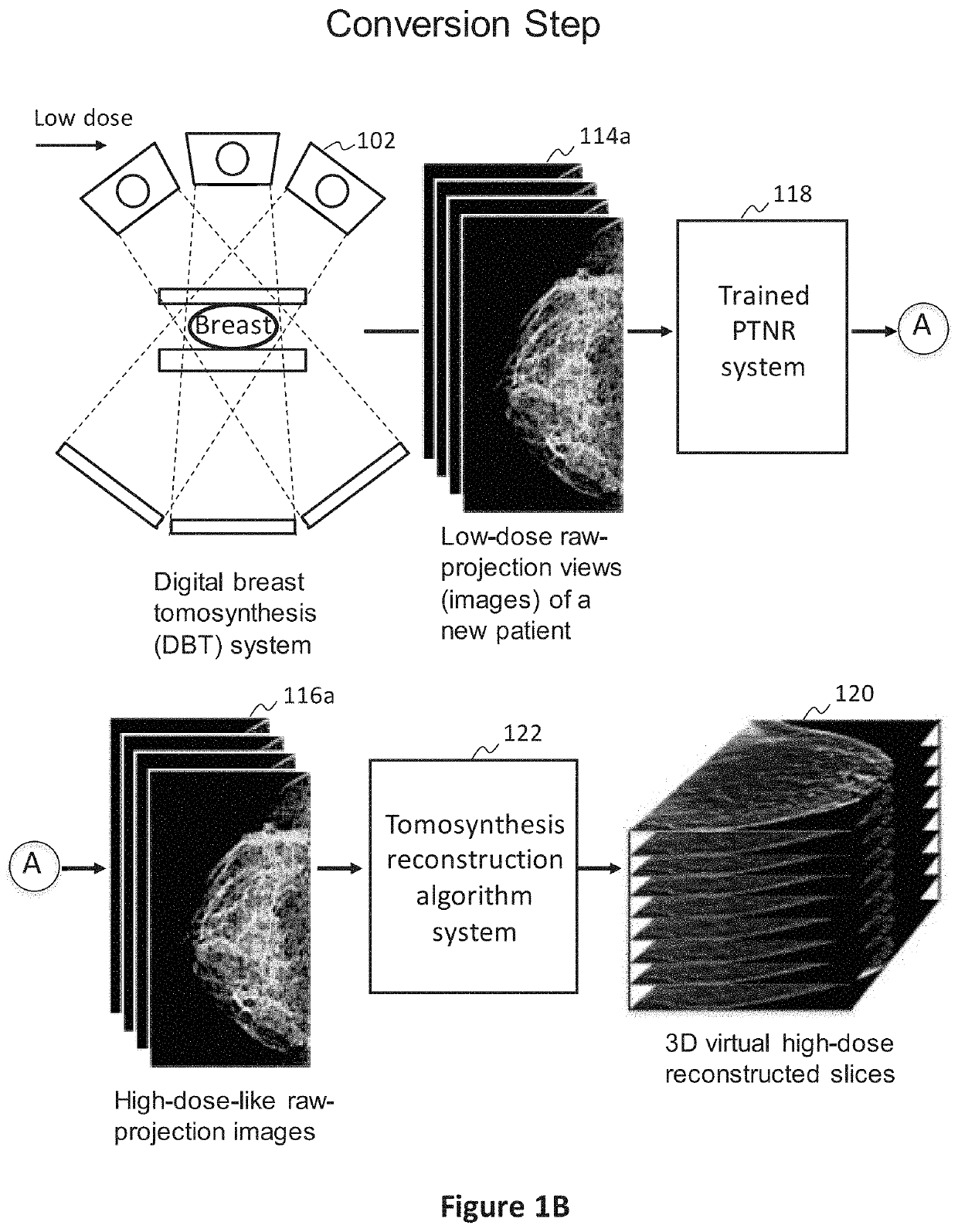
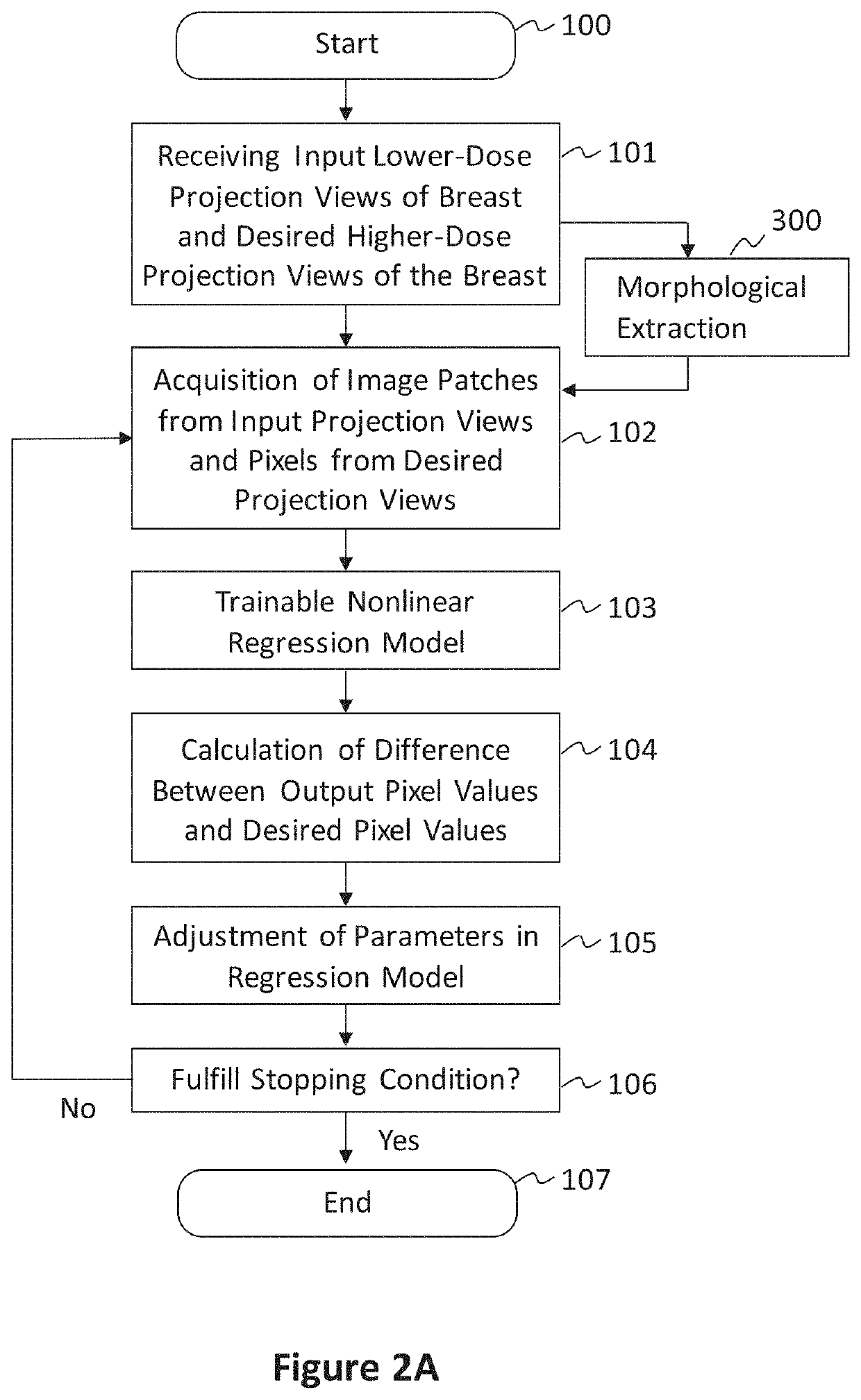
Converting low-dose to higher dose 3D tomosynthesis images through machine-learning processes
A method and system for converting low-dose tomosynthesis projection images or reconstructed slices images with noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like tomosynthesis reconstructed slices, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme called a pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input raw projection views (images) of a breast acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of raw projection views (images together with corresponding desired x-ray radiation dose raw projection views (images) (higher-dose). Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose raw projection images to high-dose-like raw projection images. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose raw projection images anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) raw projection images is entered, the trained PTNR outputs a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it outputs high-dose-like raw projection images where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. Then, from the “high-dose-like” projection views (images), “high-dose-like” 3D tomosynthesis slices are reconstructed by using a tomosynthesis reconstruction algorithm. With the “virtual high-dose” tomosynthesis reconstruction slices, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
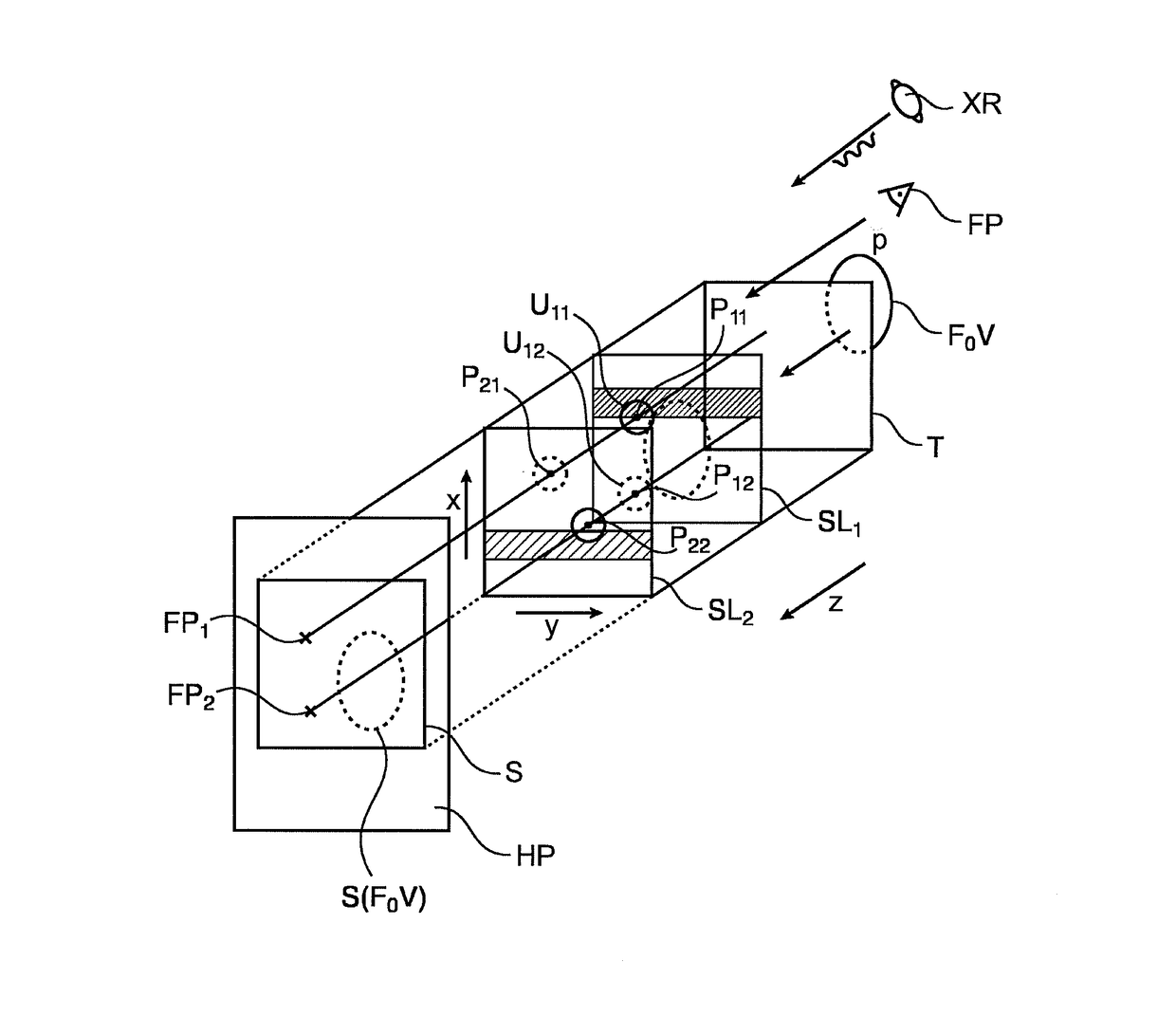
Methods for generation of edge=preserving synthetic mammograms from tomosynthesis data
A method and related apparatus (VS) for synthetic projection images, in particular synthetic 2D mammograms (S) formed from a 3D image volume T made up of slices (SL). It is proposed to compute a forward projection (FP) using a weighted average function that is implemented by a filter (FL). The filter function (FL) is configured such that that voxels in a slice with maximum sharpness are assigned highest weights thereby avoiding blurring by averaging with structurally less relevant slices.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Mammography method and apparatus to generate an X-ray tomosynthesis image of a breast of a patient
ActiveUS9724047B2Reduce exposureReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisTomosynthesisSynthetic projection
In a mammography method and apparatus to generate a tomosynthetic x-ray image of a breast of a patient, two tomosynthesis scans are successively implemented with different x-ray energies. In one of the scans, a synthetic projection image is generated from at least two projection images acquired in this scan, this synthetic projection image corresponding to a projection at a projection angle at which a projection image has been acquired in the other scan. A difference image, used to reconstruct the tomosynthesis x-ray image, is generated from this synthetic projection image and the projection image acquired in the other scan. Alternatively, in each scan a synthetic projection image is generated from at least two projection images acquired in that scan. Each synthetic projection image represents a projection at the same projection angle. A difference image, used to reconstruct the tomosynthesis x-ray image, is generated from these two synthetic projection images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Generating synthesized projection images for 3D breast tomosynthesis or multi-mode x-ray breast imaging
ActiveUS11090017B2Eliminate needImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData displaySynthetic projection
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Computed-tomography system and method for determining volume information for a body
ActiveUS9317915B2Less imaging artifactEfficient implementationReconstruction from projectionImage analysisVoxelComputed tomography
A tomogram of a body is provided. Projection-image data obtained by a radiation-based projection method is used for providing the tomogram. Initial voxel data are first specified for a plurality of voxels of the body. Synthetic projection-image data are generated based upon a projection rule modeling a course of the projection method. Projection-error data is determined by comparing the synthetic projection-image data with the real projection-image data. The projection-error data are imaged on the basis of a back-projection rule dependent on the projection rule so that voxel-error data are produced. Correction data is generated from the voxel-error data by a gradient-based optimizing algorithm, wherein corrected voxel data are generated using the correction data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Error compensation method applicable to rotation axis swing angle of neutron chromatography imaging system
InactiveCN105321206ASolve the problem of shaft deflectionConsistent clarityImage analysis3D modellingSample rotationSynthetic projection
The present invention discloses an error compensation method of a rotation axis swing angle of a neutron chromatography imaging system. The method comprises: based on a projection geometrical symmetry principle of a parallel neutron beam, superimposing projection data within a range of 360 degree rotation of a sample to obtain a synthetic projection image with a unique symmetry axis, wherein, the symmetry axis of the synthetic projection image is a projection line of a rotation axis of the sample; further calculating out a pixel value gradient angle histogram of the synthetic projection image, wherein distribution of the histogram is an even function; and calculating a symmetry center of the even function, wherein a gradient angle corresponding to the symmetry center position is a swing angle of the rotation axis. By using the measured rotation angle as a correction parameter and introducing the correction parameter into a reconstruction algorithm, error compensation for the swing angle of the rotation axis can be realized, so that consistency of a definition of each reconstruction tomography of the sample is ensured, and reconstruction accuracy is effectively improved.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Radiation photography device
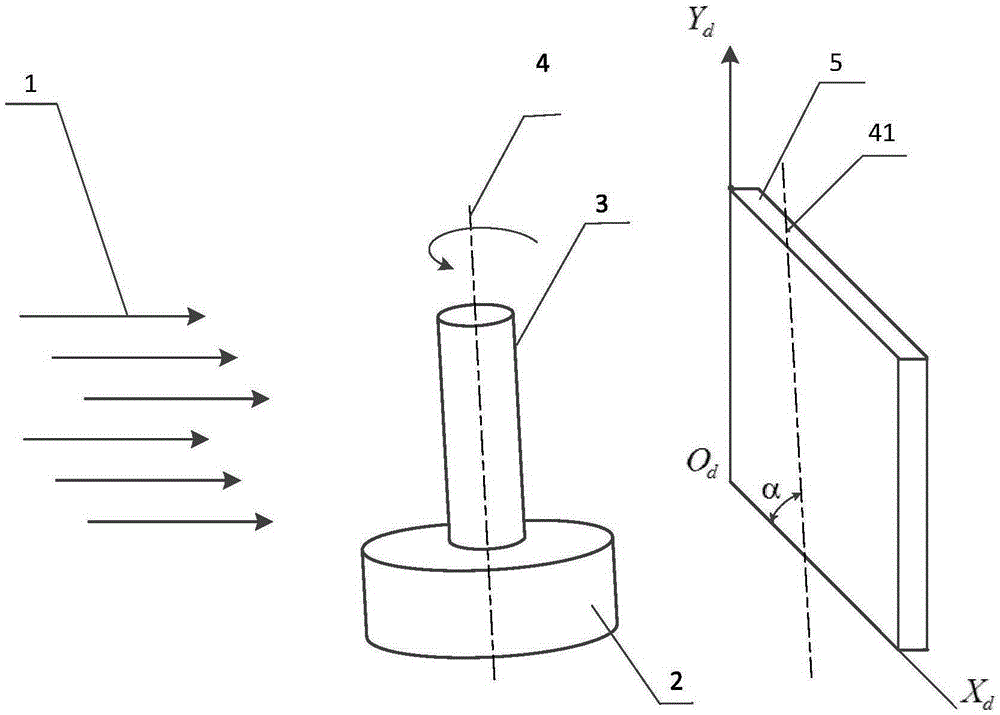
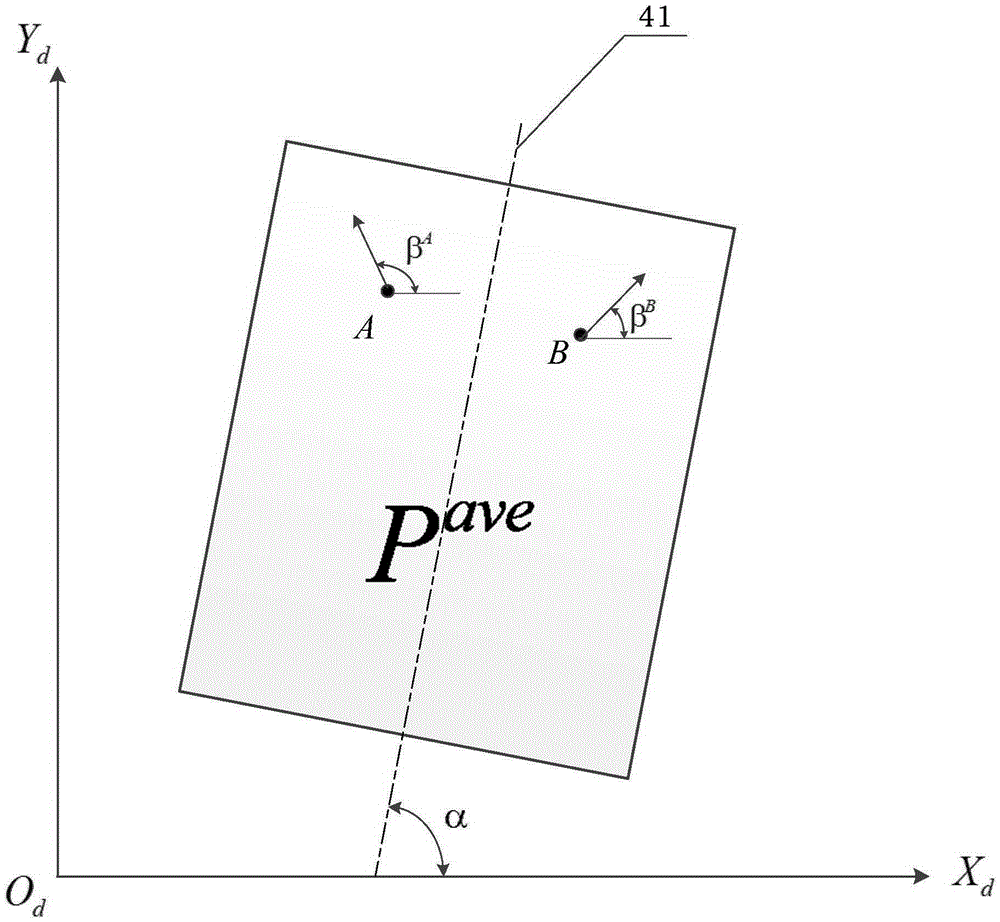
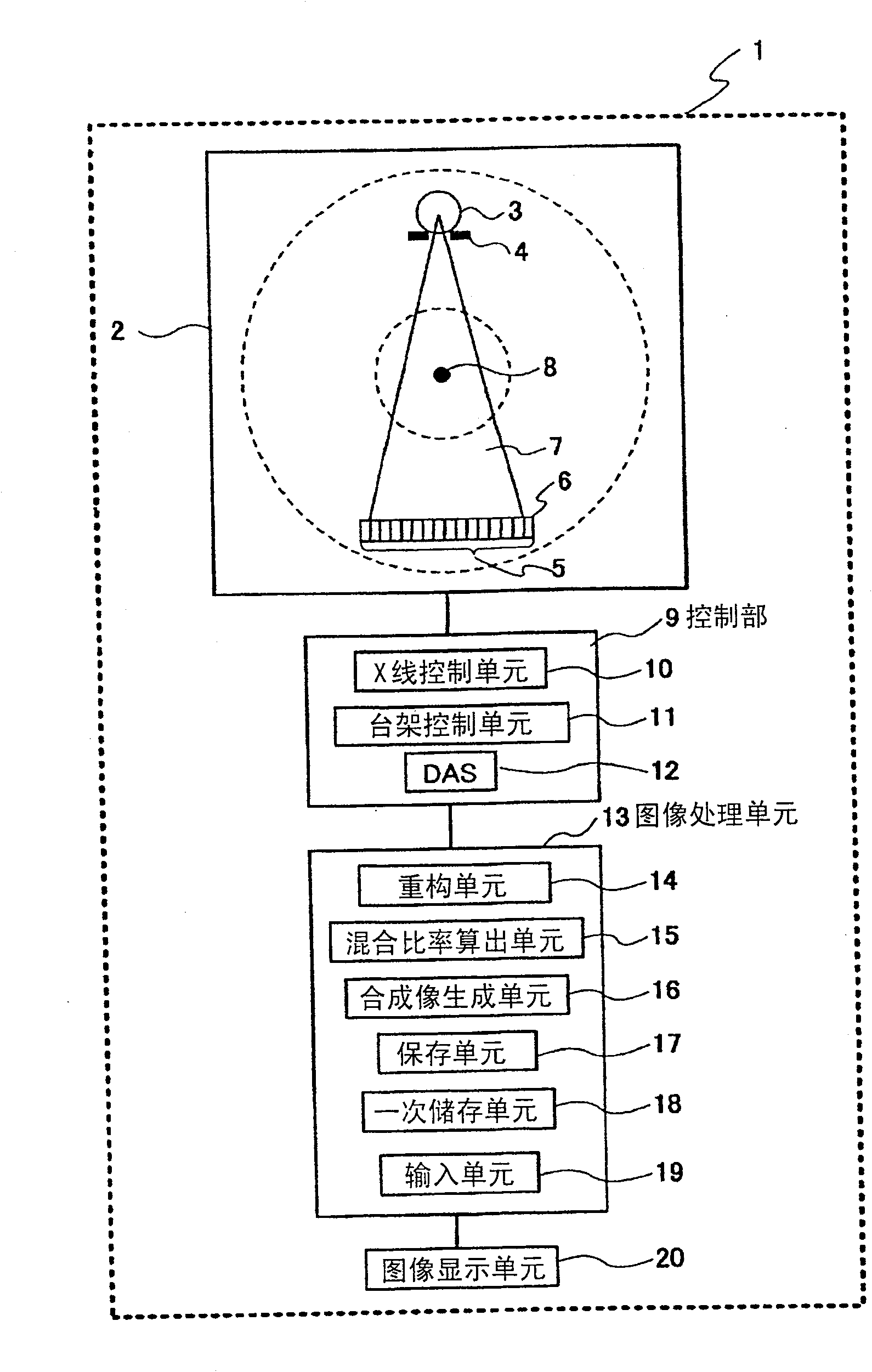
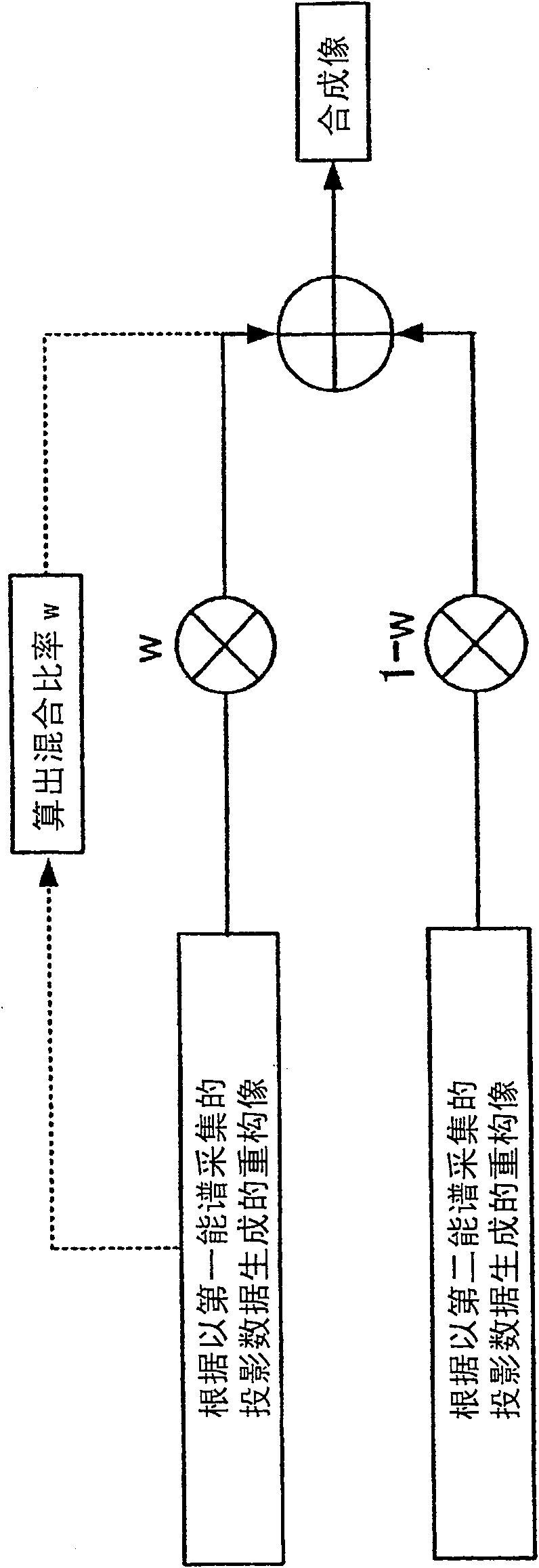
InactiveCN100571634CIncrease contrastComputerised tomographsTomographyImaging processingSynthetic projection
The radiographic apparatus according to the present invention is characterized in that the image processing unit includes: an acquisition unit that acquires projection data of the first energy spectrum and projection data of the second energy spectrum; A first image of projection data of an energy spectrum is synthesized with a second image based on projection data of the second energy spectrum according to prescribed synthesis conditions to generate a composite image; and a display unit displays the generated composite image.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Method for determining a three-dimensional image dataset by an x-ray device
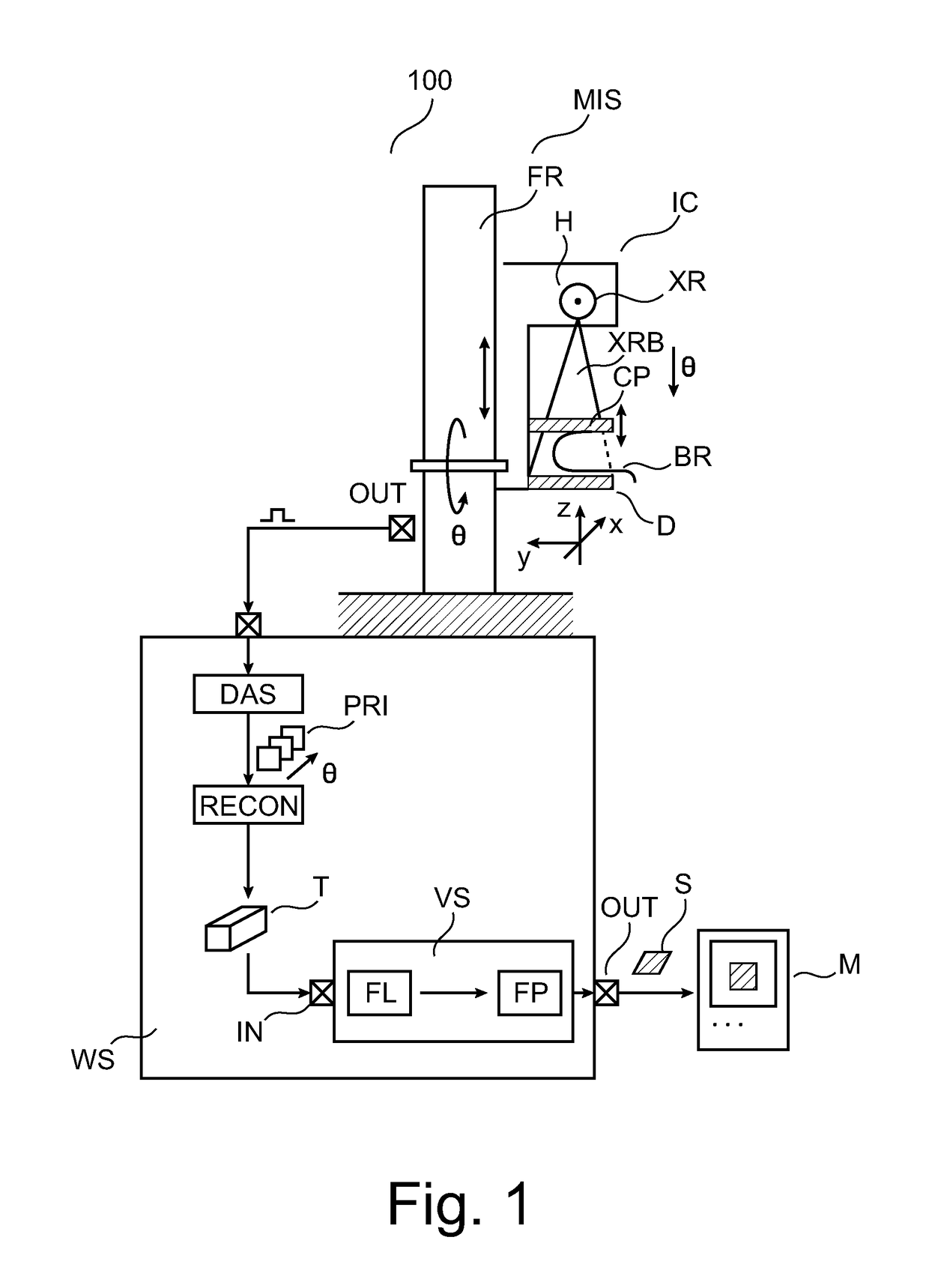
ActiveUS20180098740A1Reduce Image ArtifactsIntuitive evaluationImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionSoft x rayData set
A method for determining a three-dimensional image dataset by an X-ray device is disclosed herein. The method includes recording projection images of an examination object from a plurality of recording angles, and reconstructing the image dataset from the projection images, wherein, for at least one examined projection image, in each case an interference condition is evaluated the fulfillment of which is dependent upon at least parts of the image data of the (respective) examined projection image and / or upon at least one parameter of the radiation source during the recording of the (respective) examined projection image and indicates that the (respective) examined projection image is a projection image with interference during the recording of which arcing has occurred in the radiation source. The method also includes disregarding at least one projection image with interference, or giving the projection image a lower weighting than all the projection images with no interference, or replacing the projection image with a synthetic projection image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Projection lamp
PendingCN112540501AImprove experienceReduce manufacturing costPicture changing apparatusRecord information storageComputer hardwareGrating
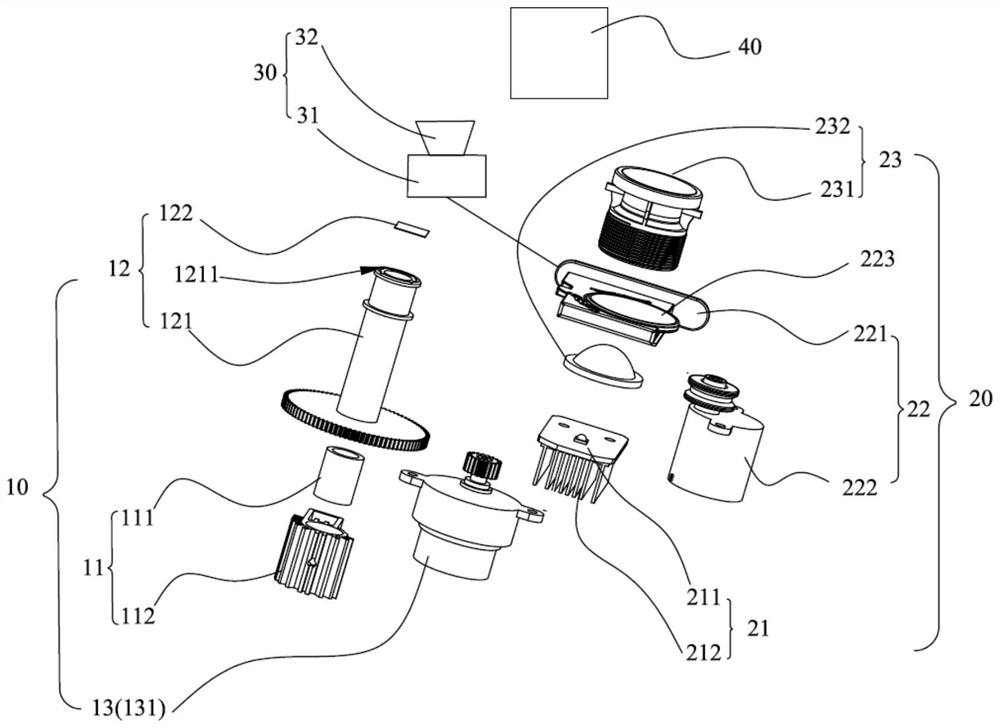
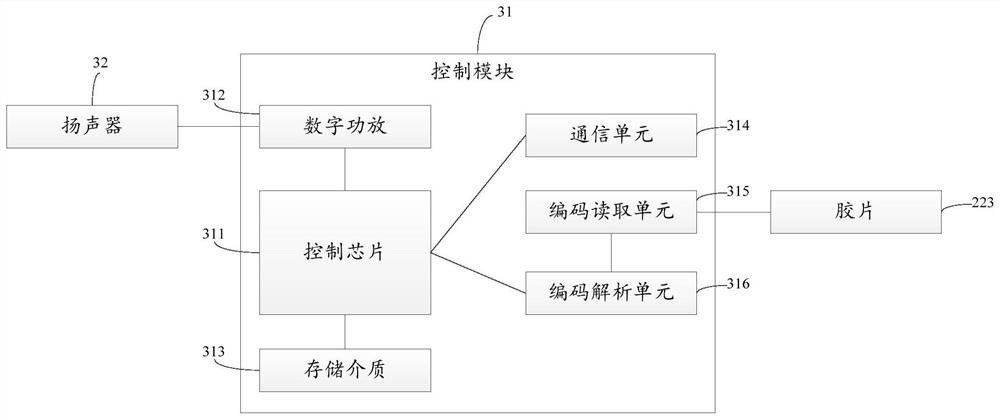
The invention discloses a projection lamp, which comprises a first projection assembly, a second projection assembly and an audio assembly, wherein the first projection assembly is used for projectinga grating sheet, and the second projection assembly is used for projecting a film; the projection area of the first projection assembly coincides with the projection area of the second projection assembly to realize synthetic projection; the audio assembly is used for playing audio according to the film; the first projection assembly comprises a first light source module, a grating module and a driving module; the second projection assembly comprises a second light source module, a film module and an optical lens module; and the audio assembly comprises a control module and a loudspeaker connected with the control module. The projection lamp provided by the invention realizes a dynamic effect, is low in manufacturing cost and simple to use, plays the corresponding audio according to the film, and is good in user experience.
Owner:SHENZHEN CUCO SMART TECH CO LTD
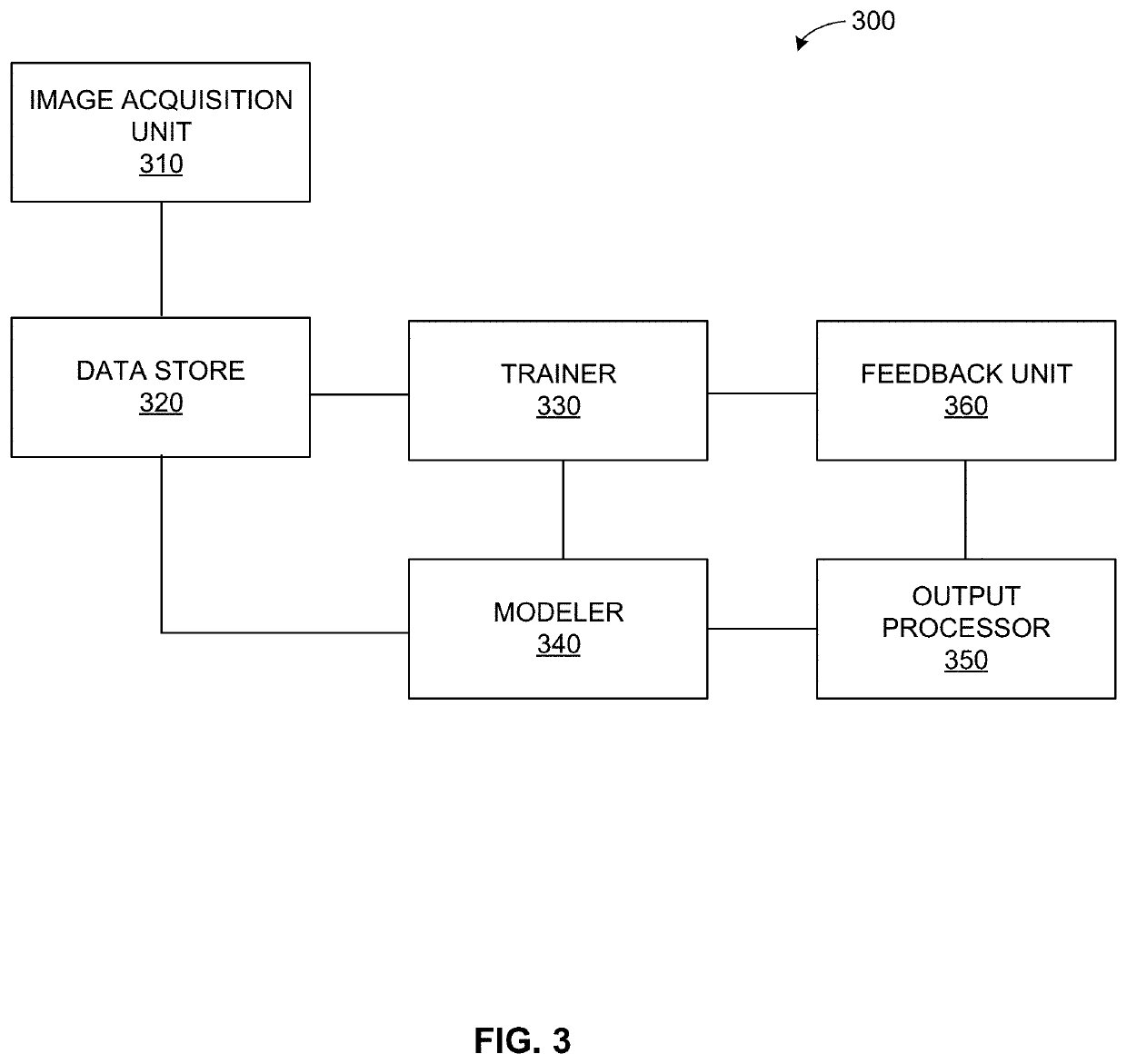
Systems and methods for deep learning-based image reconstruction
Methods, apparatus and systems for deep learning based image reconstruction are disclosed herein. An example at least one computer-readable storage medium includes instructions that, when executed, cause at least one processor to at least: obtain a plurality of two-dimensional (2D) tomosynthesis projection images of an organ by rotating an x-ray emitter to a plurality of orientations relative to the organ and emitting a first level of x-ray energization from the emitter for each projection image of the plurality of 2D tomosynthesis projection images; reconstruct a three-dimensional (3D) volume of the organ from the plurality of 2D tomosynthesis projection images; obtain an x-ray image of the organ with a second level of x-ray energization; generate a synthetic 2D image generation algorithm from the reconstructed 3D volume based on a similarity metric between the synthetic 2D image and the x-ray image; and deploy a model instantiating the synthetic 2D image generation algorithm.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Iterative volume image reconstruction using synthetic projection images
ActiveUS10307114B1Reducing patient exposureReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceSynthetic projection
A method for imaging a subject obtains a first set of acquired projection images of a subject volume, wherein each projection image in the first set has a corresponding acquisition angle and forms an initial reconstructed volume image. A second set of synthetic projection images is generated according to processing of the acquired projection images and combined with the first set to form a combined set of projection images. The method augments the initial reconstructed image to form an improved reconstructed image by at least a first iteration of an iterative reconstruction process using the initial reconstructed image with the combined set of acquired and synthetic projection images and at least a subsequent iteration of the iterative reconstruction process using the first set of acquired projection images and fewer than, or none of, the second set of synthetic projection images. The improved reconstruction image is rendered on a display.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Systems and methods for deep learning-based image reconstruction
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Image processing system, image processing device, image processing method, and program
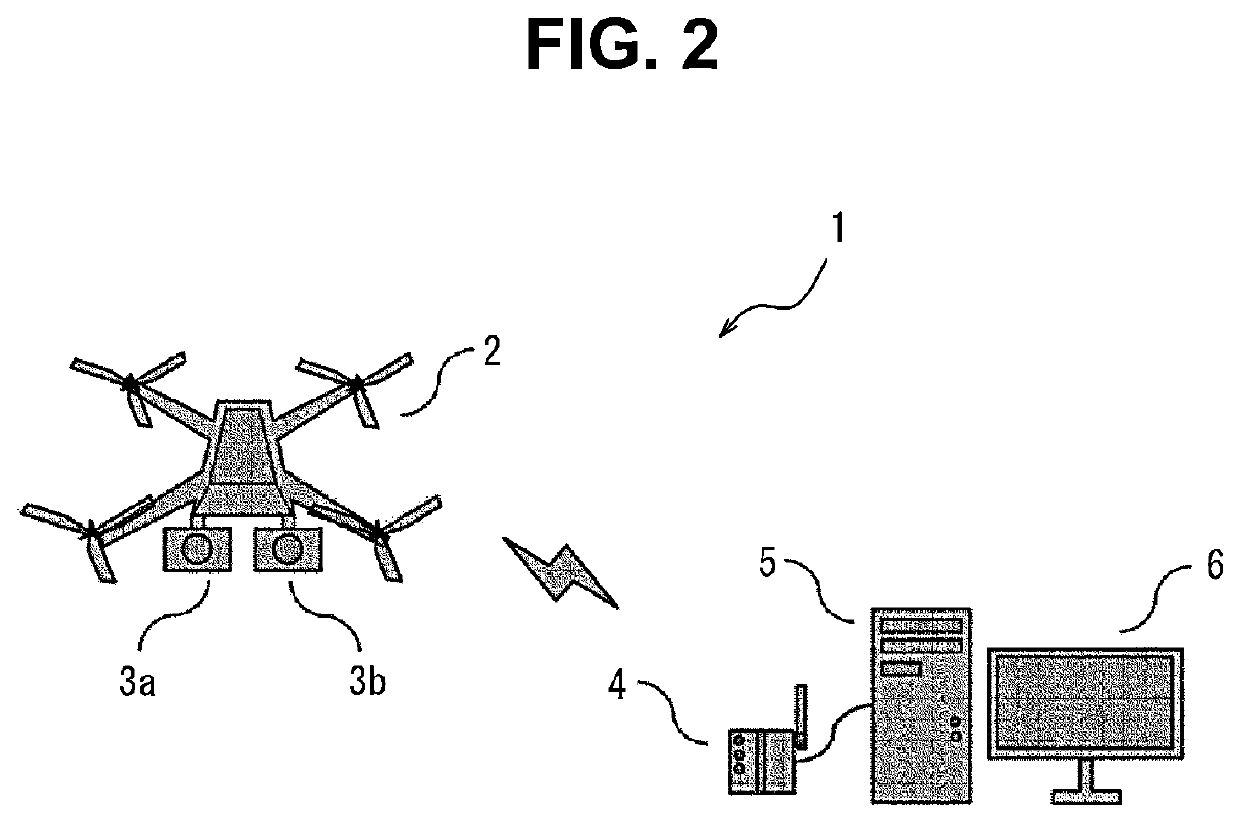
PendingUS20220222834A1Improve accuracyAircraft componentsImage enhancementImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
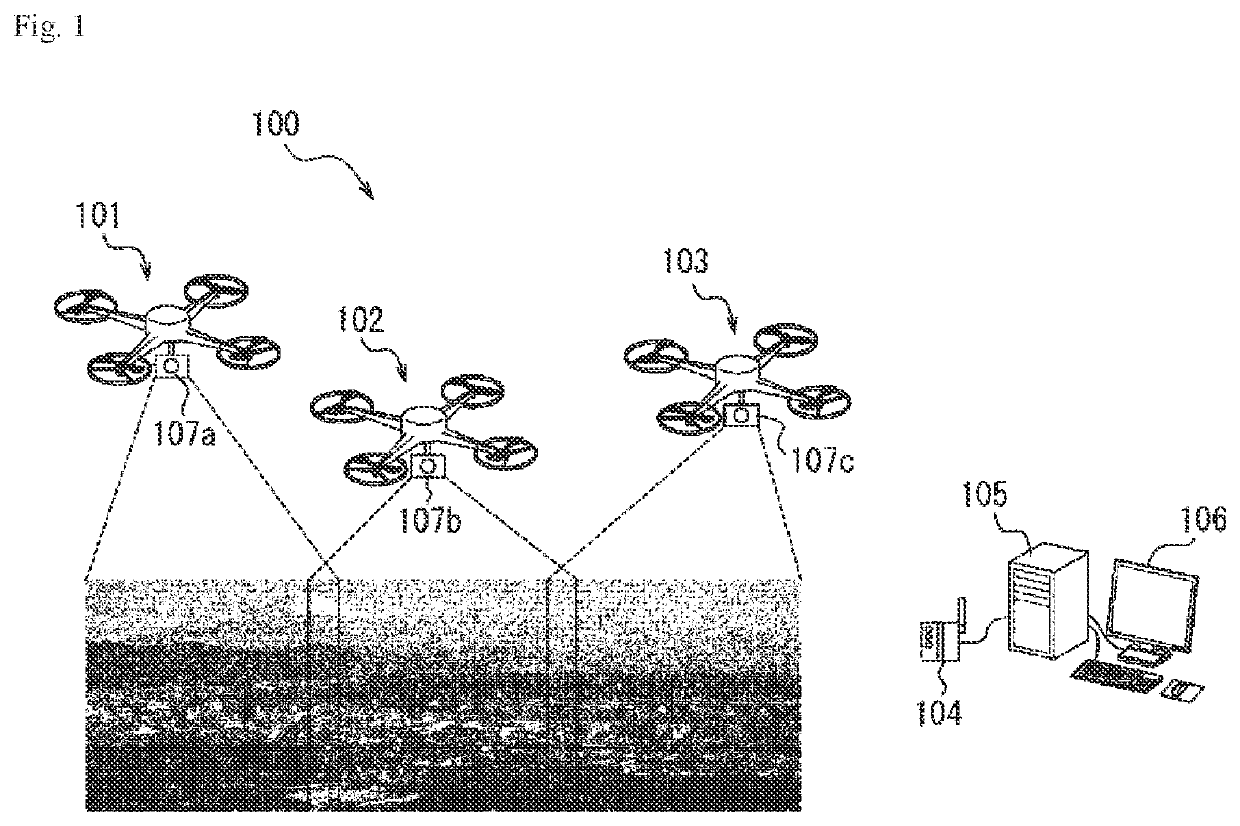
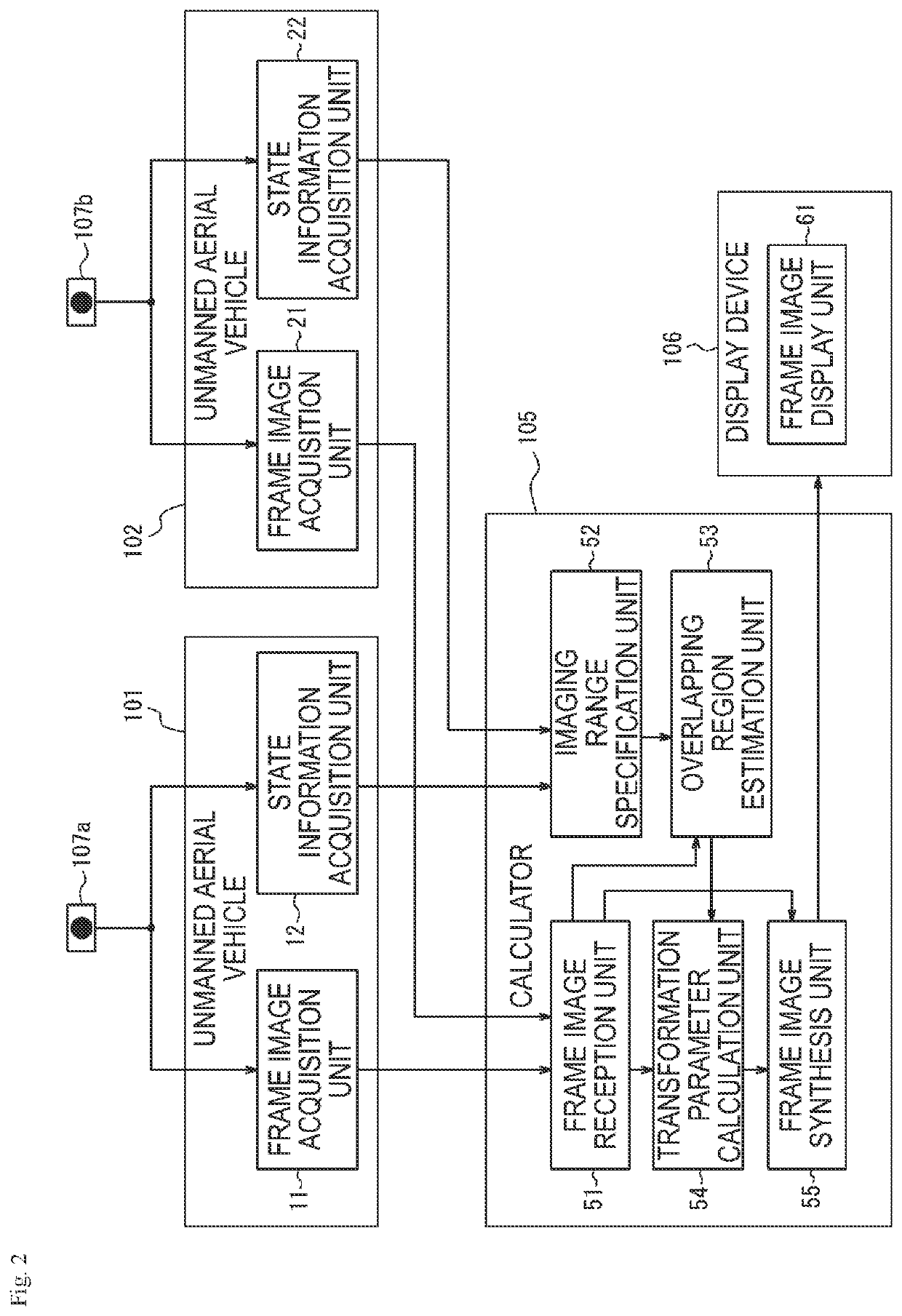
An image processing system (100) includes an imaging range specification unit (52), an overlapping region estimation unit (53), a transformation parameter calculation unit (54), and a frame image synthesis unit (55). The imaging range specification unit (52) specifies first imaging information based on first state information indicating a state of a first unmanned aerial vehicle (101) and second state information indicating a state of a first camera (107a), and specifies second imaging information based on third state information indicating a state of a second unmanned aerial vehicle (102) and fourth state information indicating a state of a second camera (107b). The overlapping region estimation unit (53) calculates a corrected first overlapping region and a corrected second overlapping region in a case where an error of a first overlapping region and a second overlapping region exceeds a threshold. The transformation parameter calculation unit (54) calculates a transformation parameter using the corrected first overlapping region and the corrected second overlapping region. The frame image synthesis unit (55) synthesizes a first frame image after projective transformation and a second frame image after projective transformation.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Image processing method, image processing device, and program
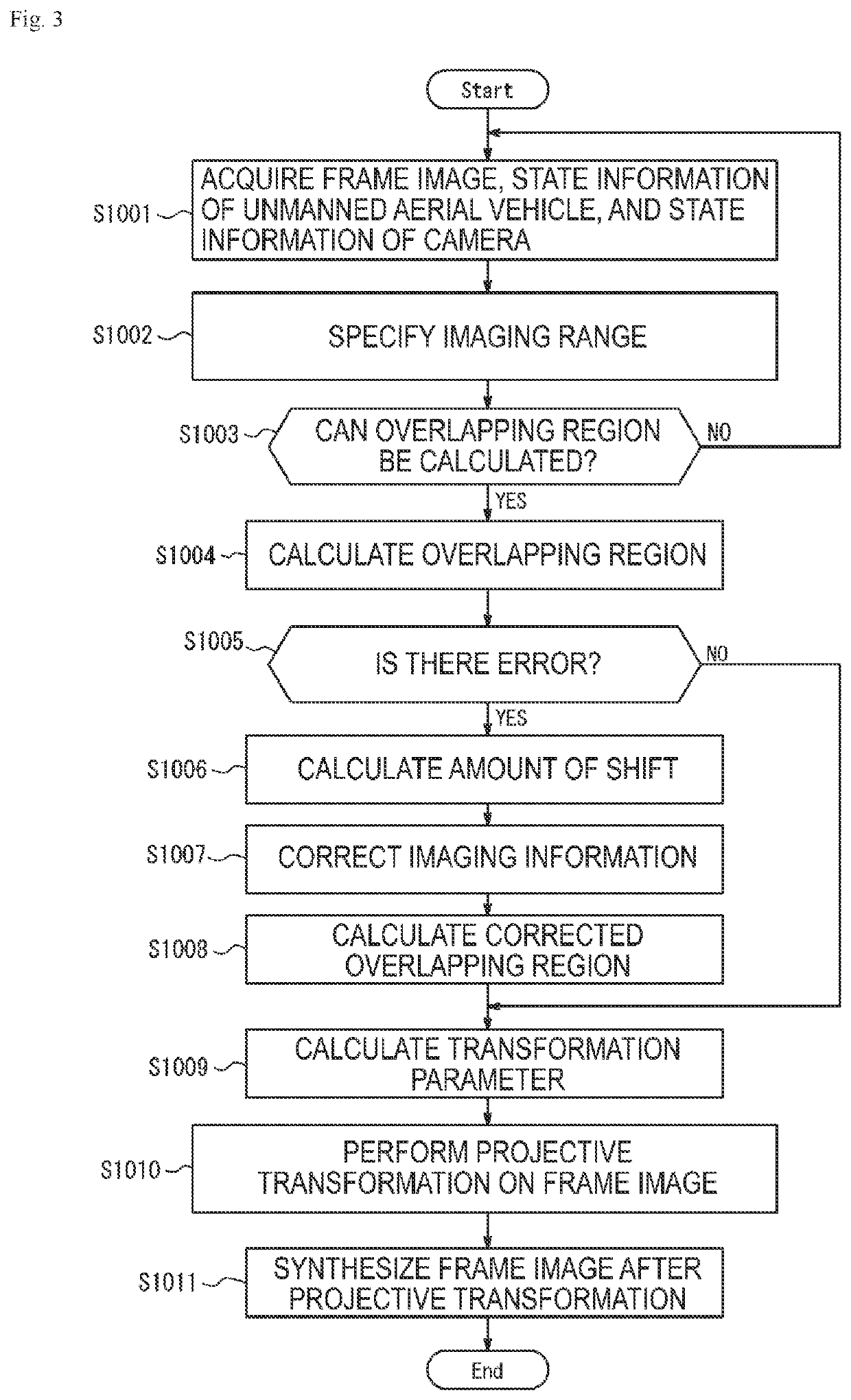
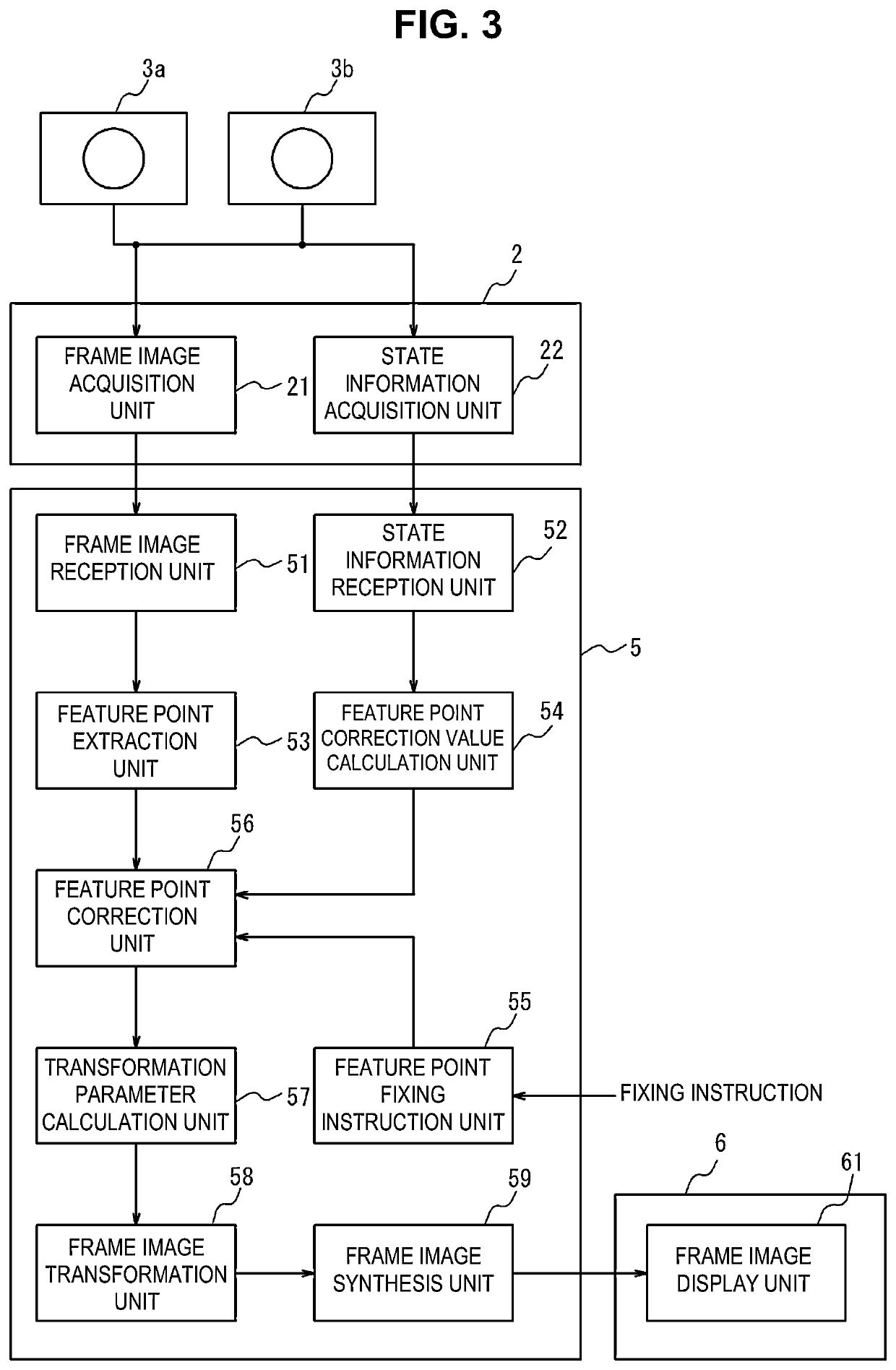
PendingUS20220262094A1Improve accuracyAccuracy of synthesis of frame images shot by cameras mountedImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionImaging processing
An image processing method includes: acquiring first and second frame images shot by cameras; acquiring first state information of an unmanned aerial vehicle and second and third state information of the cameras; extracting feature point groups from the first and second frame images; calculating correction values based on the state information at the first time and state information at a second time; outputting the extracted feature point groups as corrected feature point groups at the first at a predetermined timing, and correcting feature point groups at the second time as the corrected feature point groups at the first time at a timing other than the predetermined timing; calculating a transformation parameter using the corrected feature point groups; performing projective transformation of the first and second frame images based on the transformation parameter; and synthesizing the first and second frame images after the projective transformation.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Image processing apparatus for c-arm
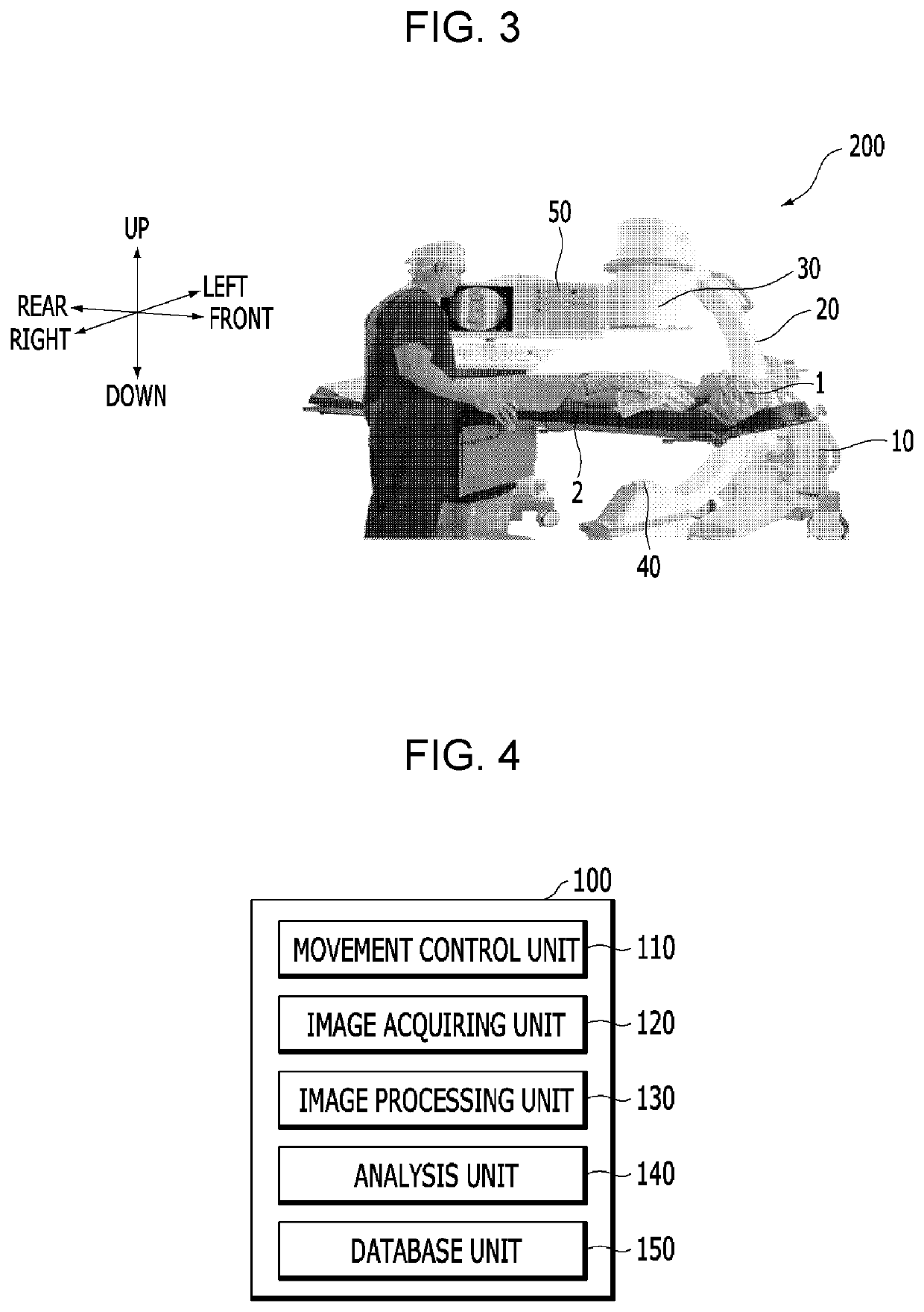
ActiveUS20210353242A1Solve the riskImprove convenienceRadiation diagnostic device controlSurgeryImaging processingRadiology
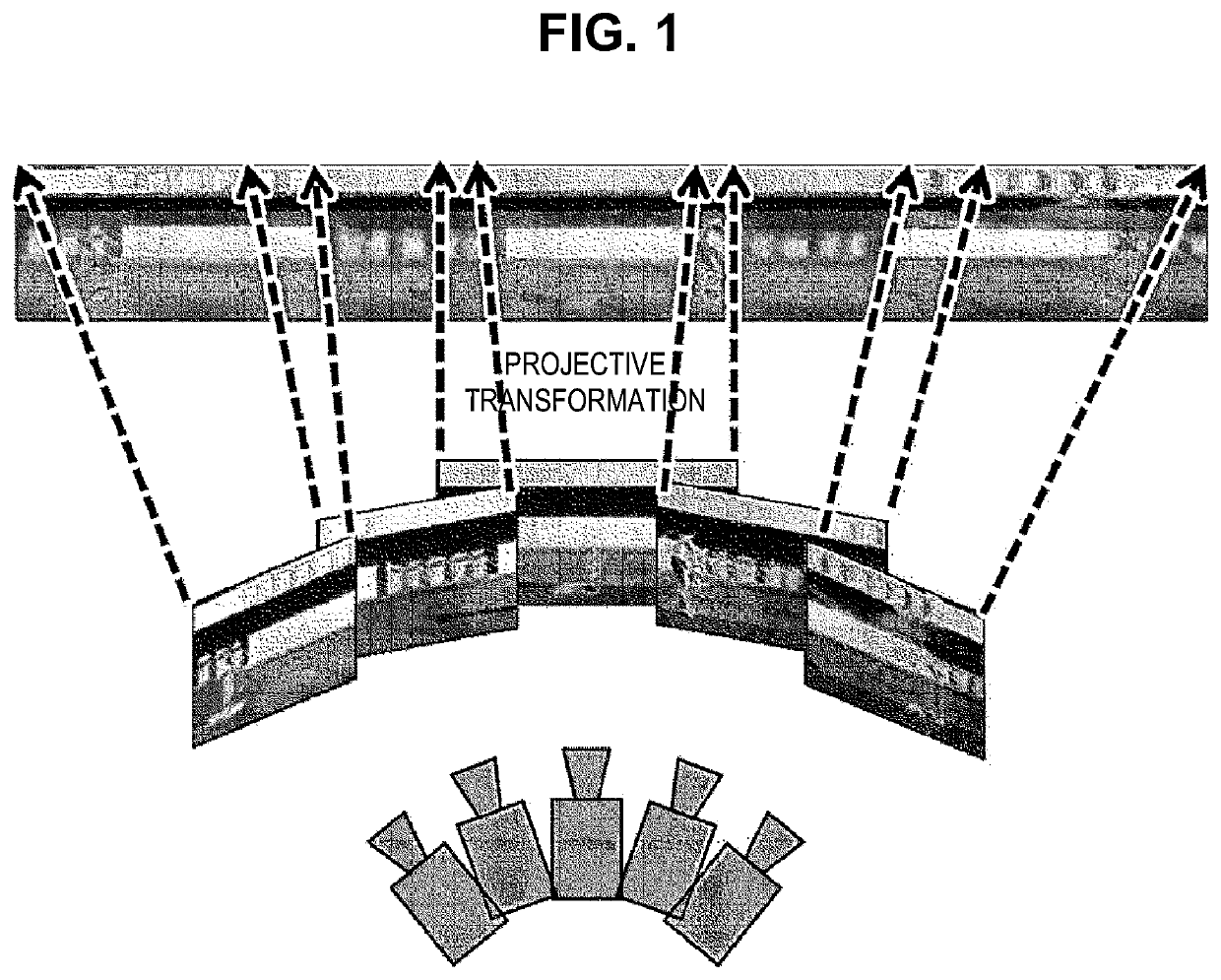
Provided is an image processing apparatus for a C-arm, including: a movement control unit which moves a C-arm which irradiates a radiation onto a bone of a subject located on a table and detects the radiation which penetrates the bone to generate a projection image for the bone, along a predetermined route; an image acquiring unit which acquires a plurality of projection images generated by the moving C-arm at every predetermined interval; and an image processing unit which generates a combined projection image in which the plurality of acquired projection images is combined, and the predetermined interval may be an interval at which a continuous panoramic image may be generated by connecting the plurality of acquired projection images.
Owner:PARK SANG HO
An Error Compensation Method Applicable to the Swing Angle of the Rotation Axis of the Neutron Tomography System
InactiveCN105321206BSolve the problem of shaft deflectionConsistent clarityImage analysis3D modellingRotational axisAxis of symmetry
The invention discloses an error compensation method for neutron tomography rotation axis deflection angle. The method is based on the projection geometric symmetry principle of parallel beam neutron rays, and obtains by superimposing projection data within a 360-degree rotation range of a sample. A composite projected image with a unique symmetry axis, the symmetry axis of the composite projected image is the projection line of the sample rotation axis; the histogram of the pixel value gradient angle of the composite projected image is further calculated, and the histogram distribution is an even function. Find the symmetry center of the even function, and the gradient angle corresponding to the symmetry center position is the yaw angle of the rotation axis. By introducing the measured yaw angle as a correction parameter into the reconstruction algorithm, the error compensation for the yaw angle of the rotation axis can be realized, so as to ensure the consistency of the definition of each reconstructed slice of the sample and effectively improve the reconstruction accuracy.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com