Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
637results about How to "Preventing Image Quality Deterioration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
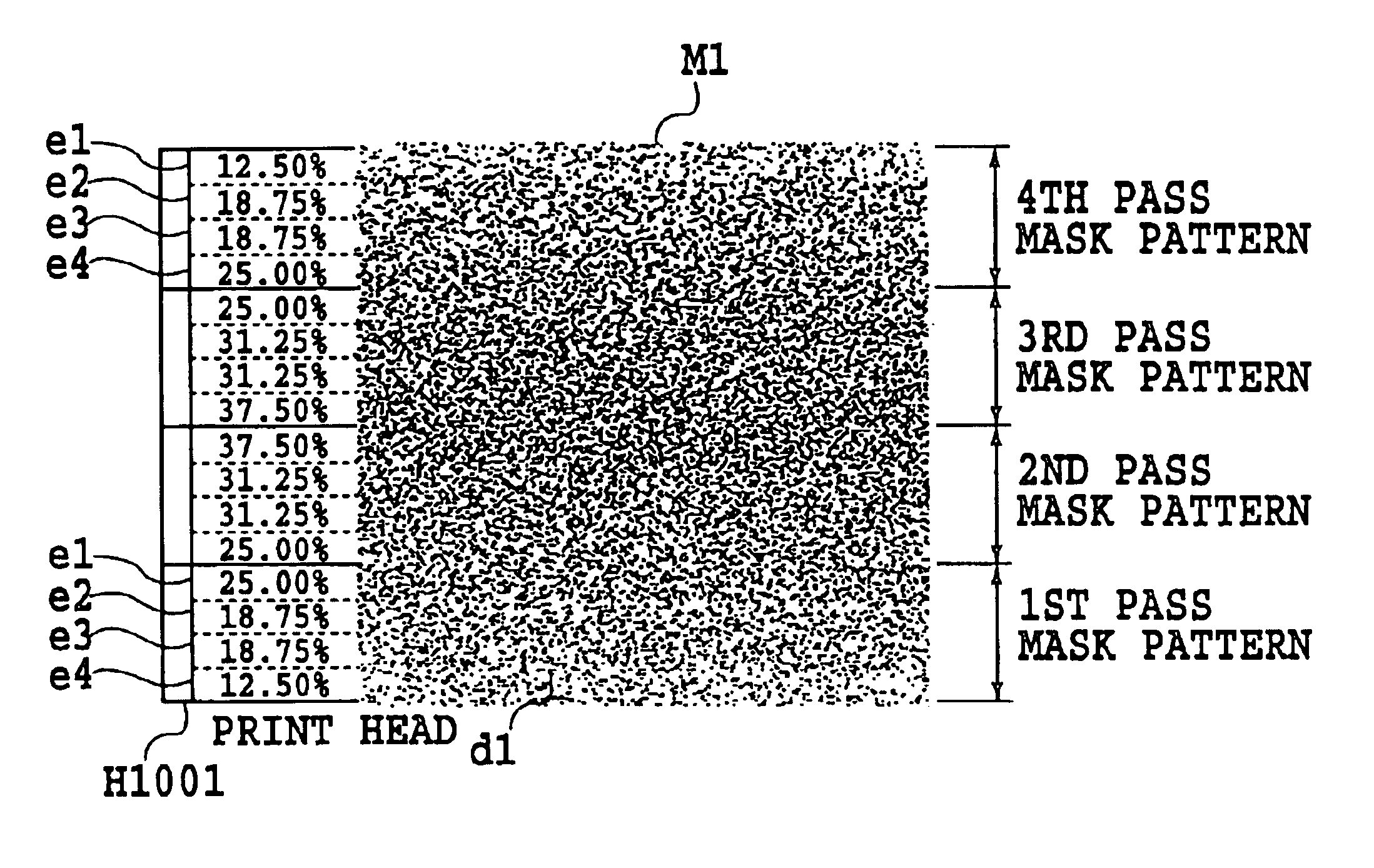
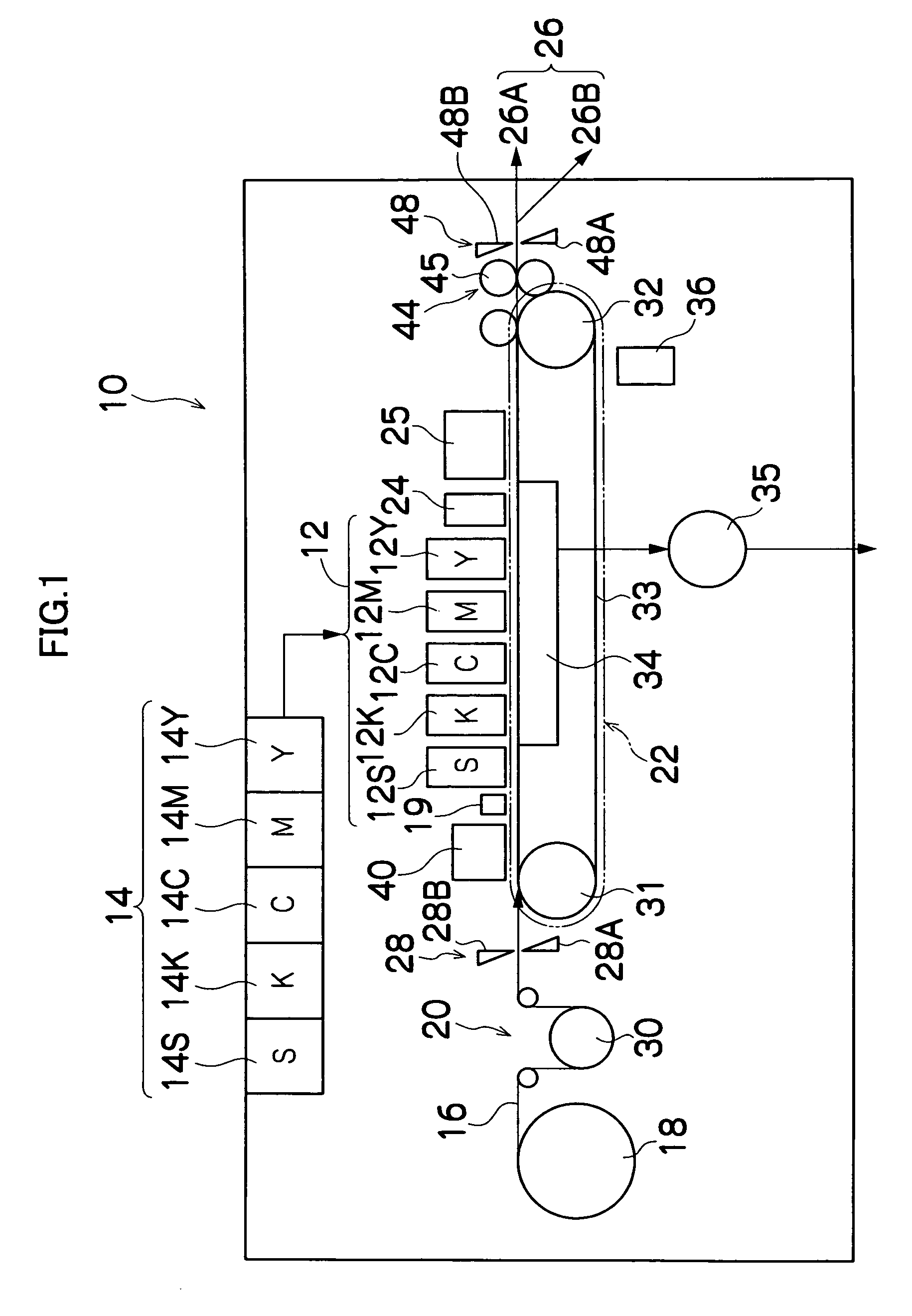
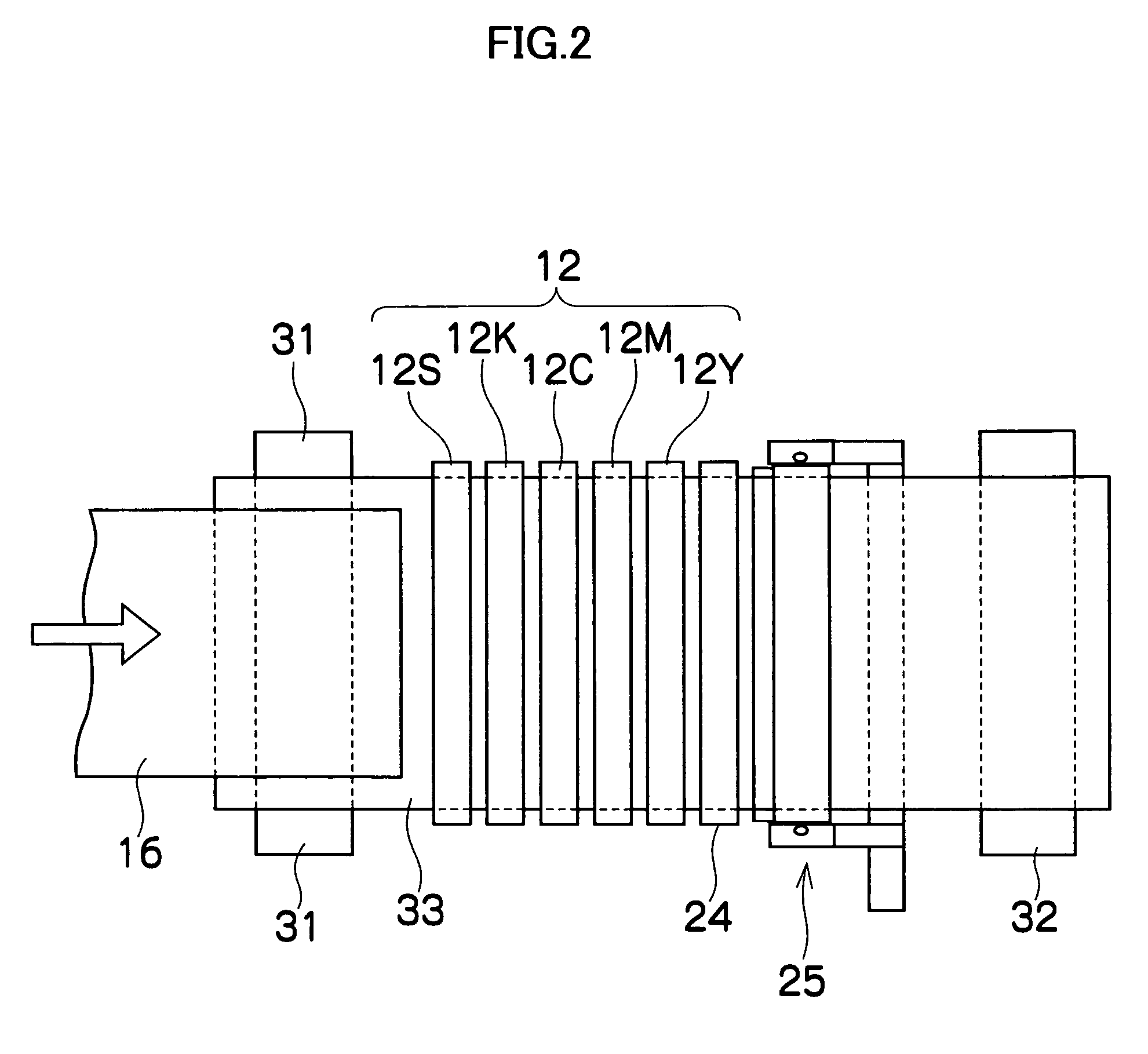
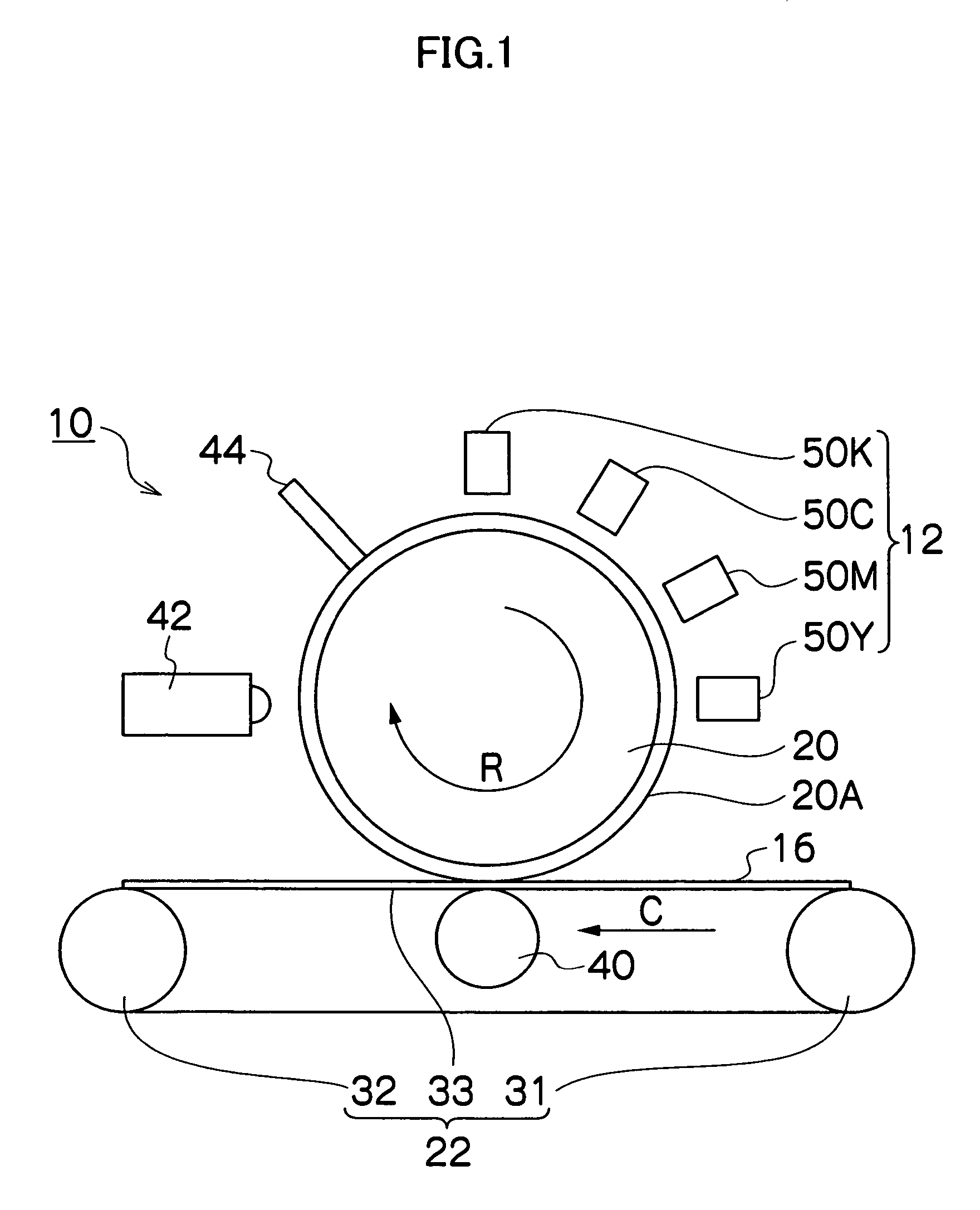
Ink jet printing apparatus and ink jet printing method for forming an image on a print medium
InactiveUS6874864B1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationIncrease speedVisual representation by matrix printersOther printing apparatusImaging qualityVolumetric Mass Density
An apparatus and method are provided to enable high speed printing of an image with high resolution while suppressing degradation of image quality due to white stripes and density variations. In an ink jet printing apparatus using a multi-pass printing system, the same scan print area is divided at a predetermined pitch and the printing duties of the divided areas determined by the thinning out mask pattern are set to different values. In regard to the same scan print area formed by a plurality of the main scans, the divided areas corresponding to the ends of the print head have their printing duties set smaller than those of the divided areas on the inner side of the ends of the print head.
Owner:CANON KK
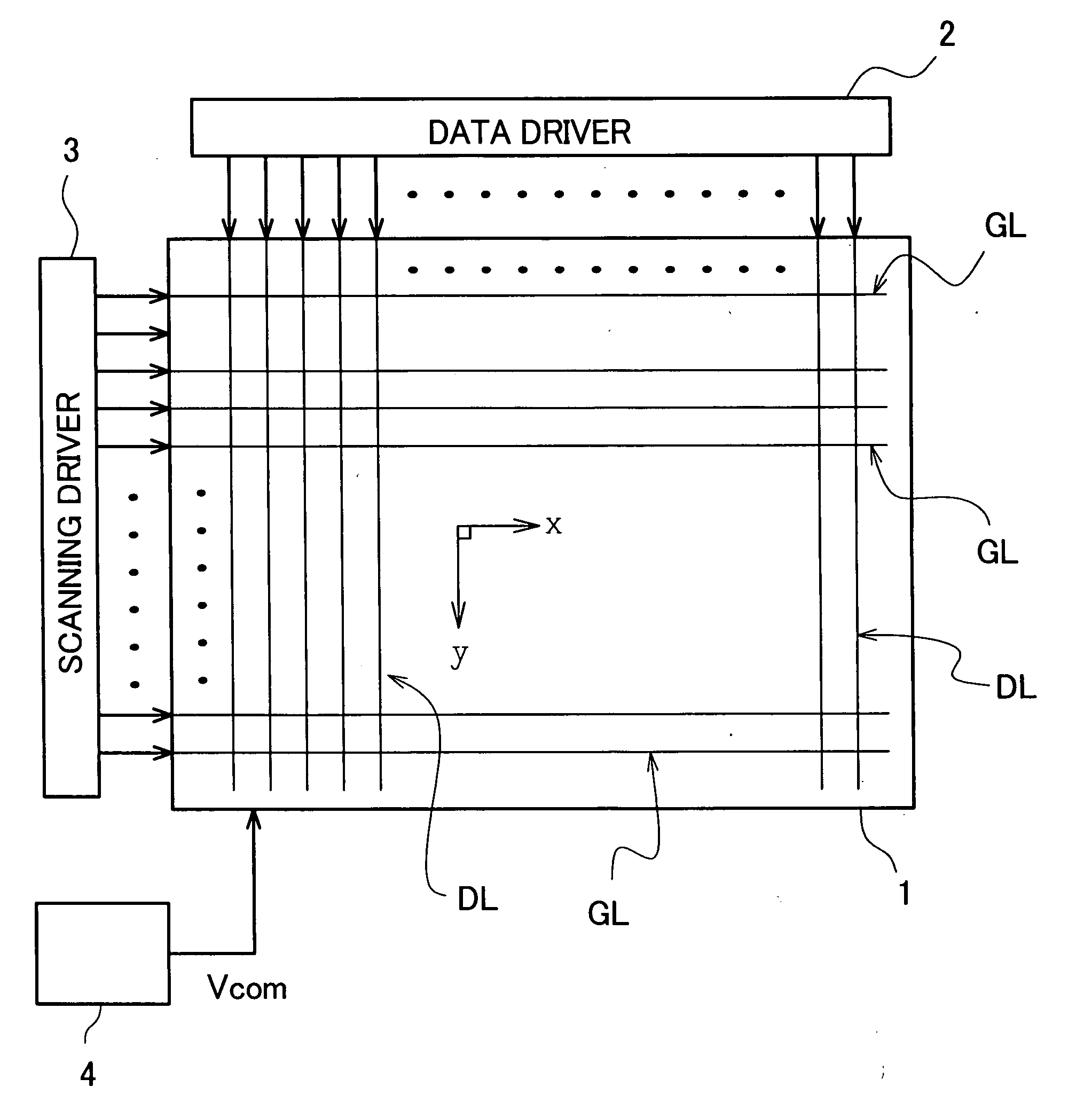
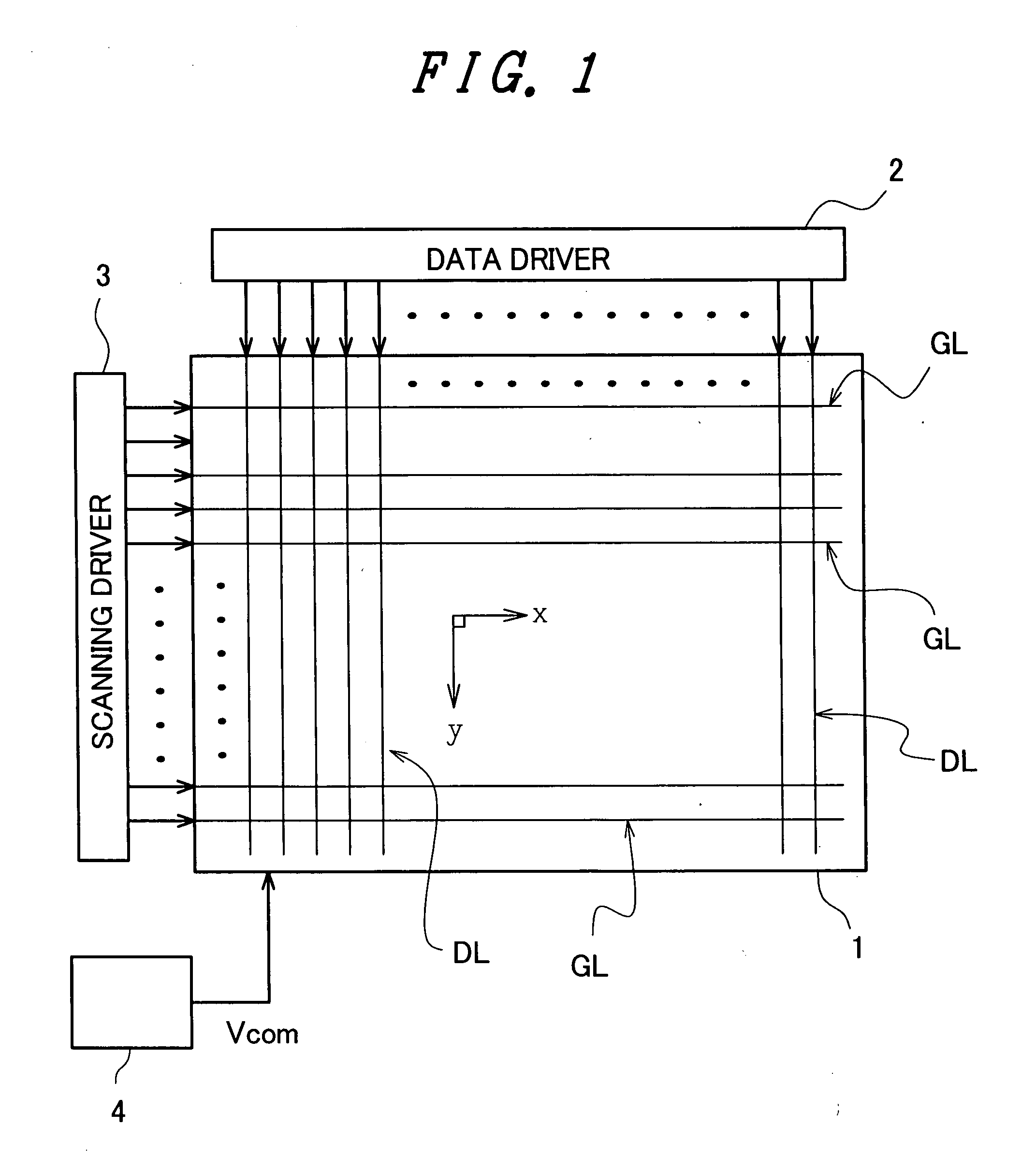
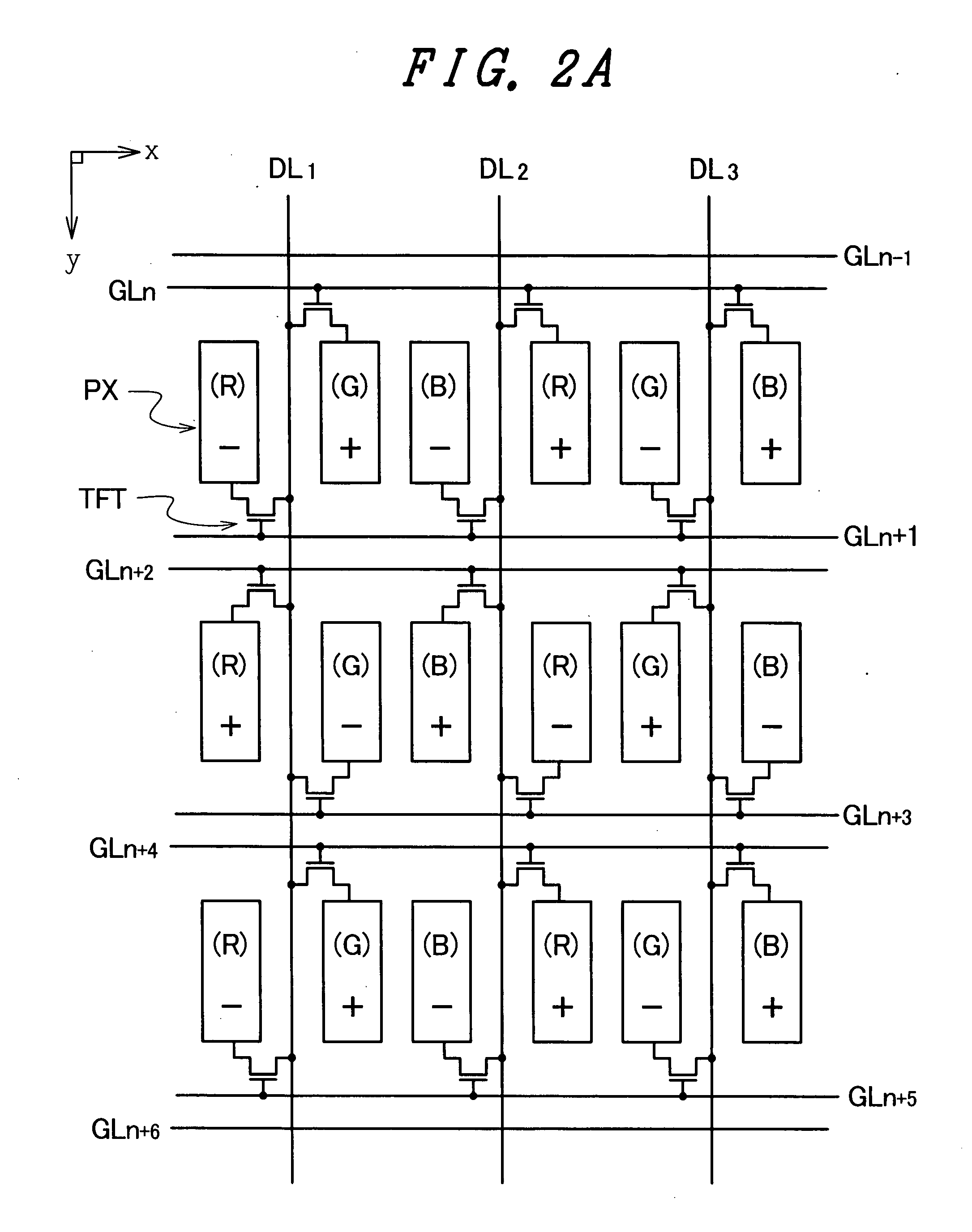
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20080068516A1Inhibit deteriorationLower heating valueTelevision system scanning detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayImaging quality
The present invention prevents deterioration of image quality by lowering a heat value of a data driver connected to a liquid crystal display panel. In a liquid crystal display device, a pixel which connects a TFT thereof to one of two neighboring scanning signal lines and a pixel which has a TFT thereof connected to the other scanning signal line are alternately arranged in the extending direction of the scanning signal lines, two pixels which are arranged close to each other with one video signal line sandwiched therebetween have respective TFTs connected to the video signal line, and the connection relationship between the TFT of each pixel and the scanning signal line is inverted for every pair of two pixels arranged in the extending direction of the video signal lines. Here, each time the scanning signal line to which a scanning signal is inputted is changed, a potential of a common voltage is alternately changed over between a first potential and a second potential higher than the first potential, a video signal of a potential higher than the first potential is inputted to the video signal lines when the common voltage of the first potential is inputted to the common electrode, and a video signal of a potential lower than the second potential is inputted to the video signal lines when the common voltage of the second potential is inputted to the common electrode.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
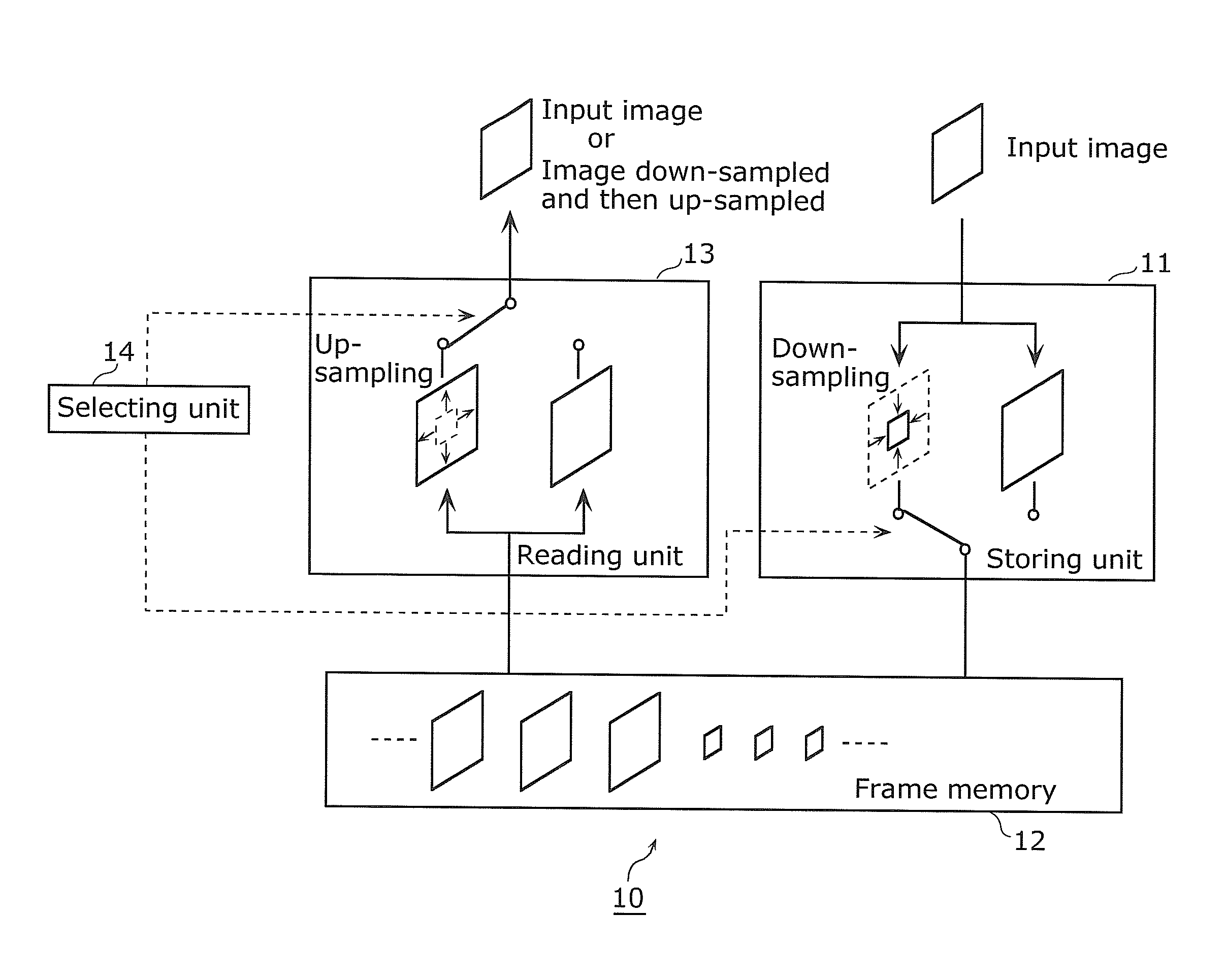
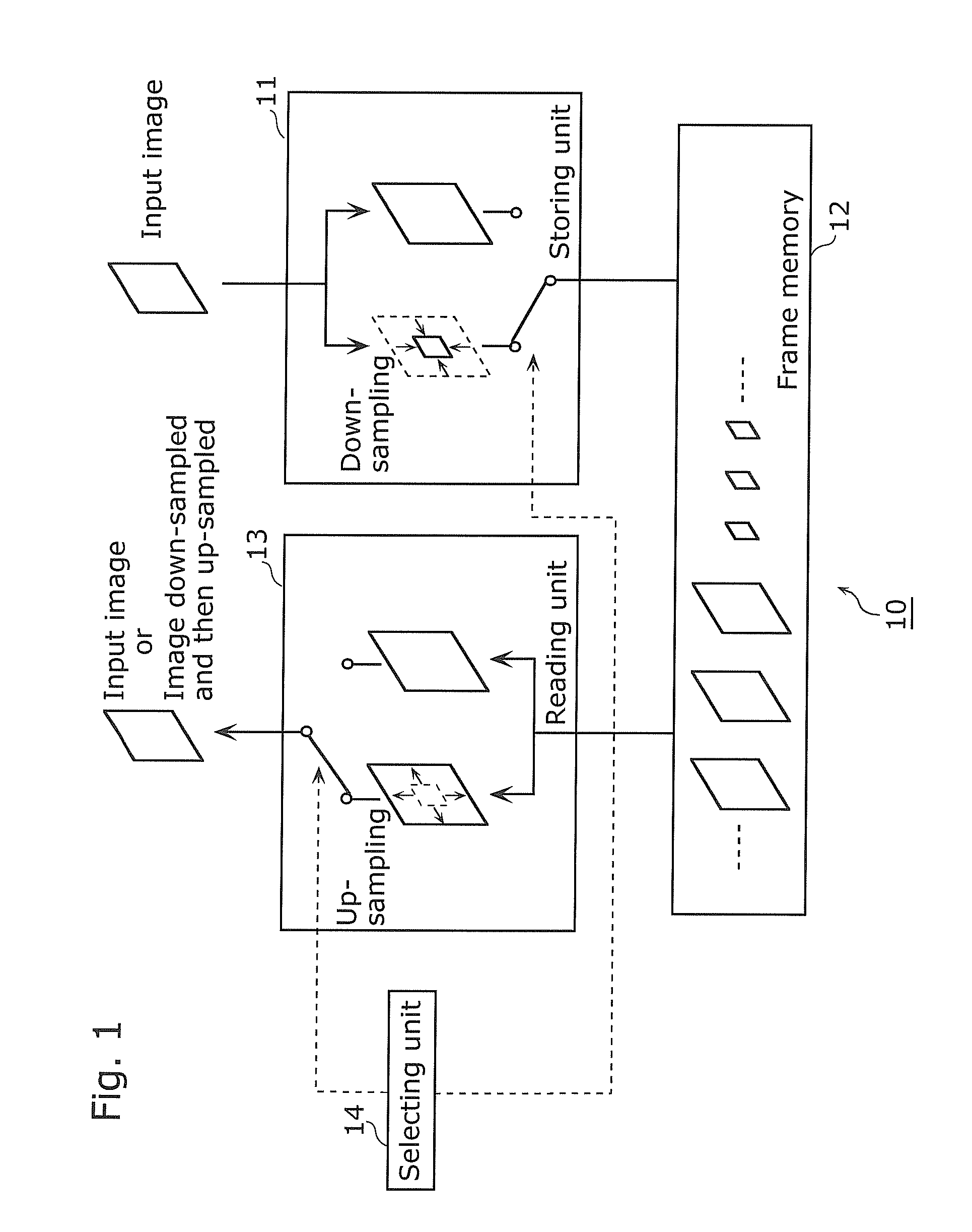
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, program and integrated circuit
InactiveUS20110026593A1Attenuation bandwidthReduce capacityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionIntegrated circuitImage quality degradation
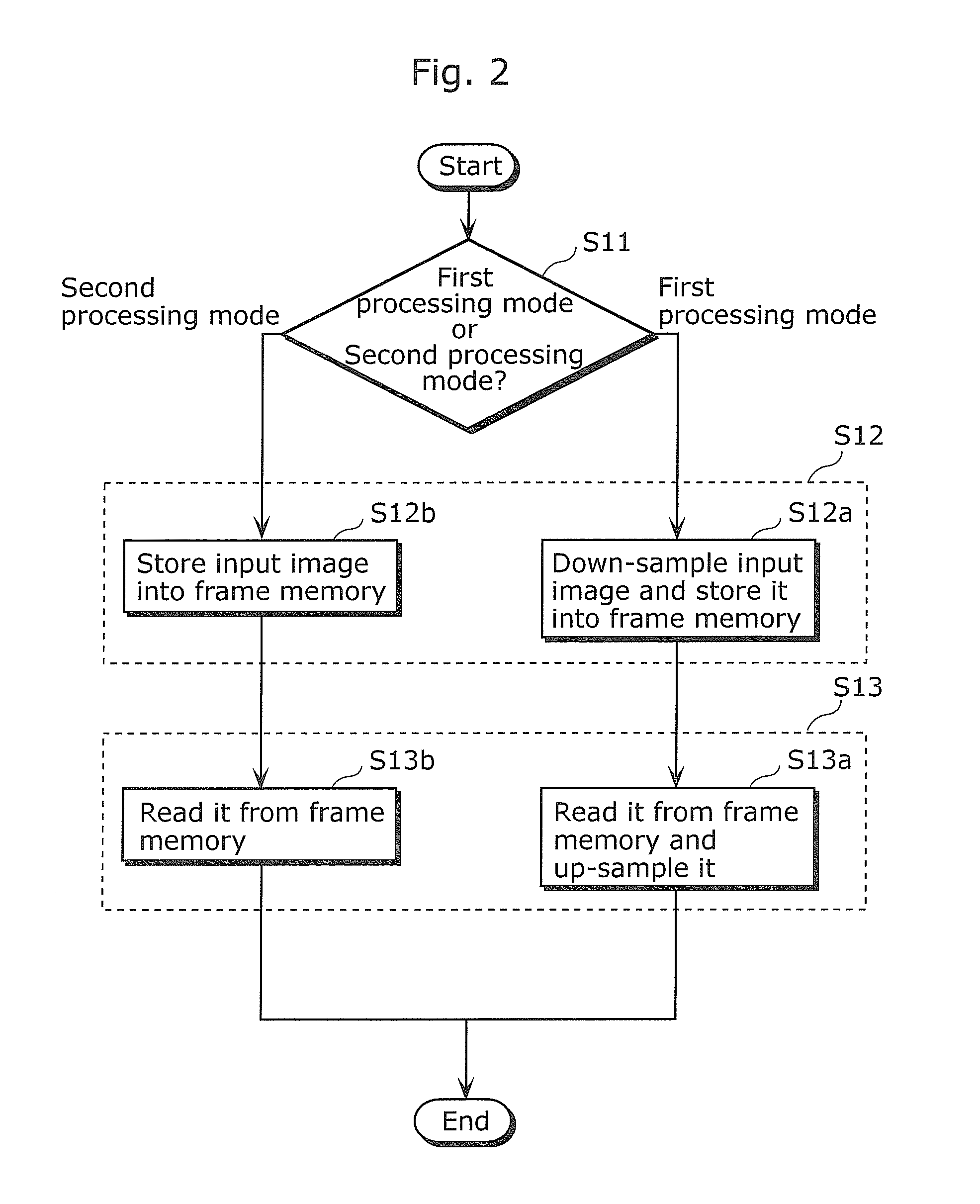
An image processing apparatus (10) capable of reducing the bandwidth and capacity required for a frame memory and preventing image quality degradation includes: a selecting unit (14) that selectively switches between first and second processing modes, a frame memory (12); a storing unit (11) that (i) down-samples an input image by deleting predetermined frequency information included in the input image and stores the input image as a down-sampled image in the frame memory (12) when the switching unit switches to the first processing mode, and (ii) stores the input image without down-sampling in the frame memory (12) when the switching unit switches to the second processing mode; and a reading unit (13) that (i) reads out the down-sampled image from the frame memory (12) and up-samples the down-sampled image when the switching unit switches to the first processing mode, and (ii) reads out the input image without down-sampling from the frame memory (12) when the switching unit switches to the second processing mode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20040201564A1Improve image qualityPrevent degradationStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsData controlHysteresis
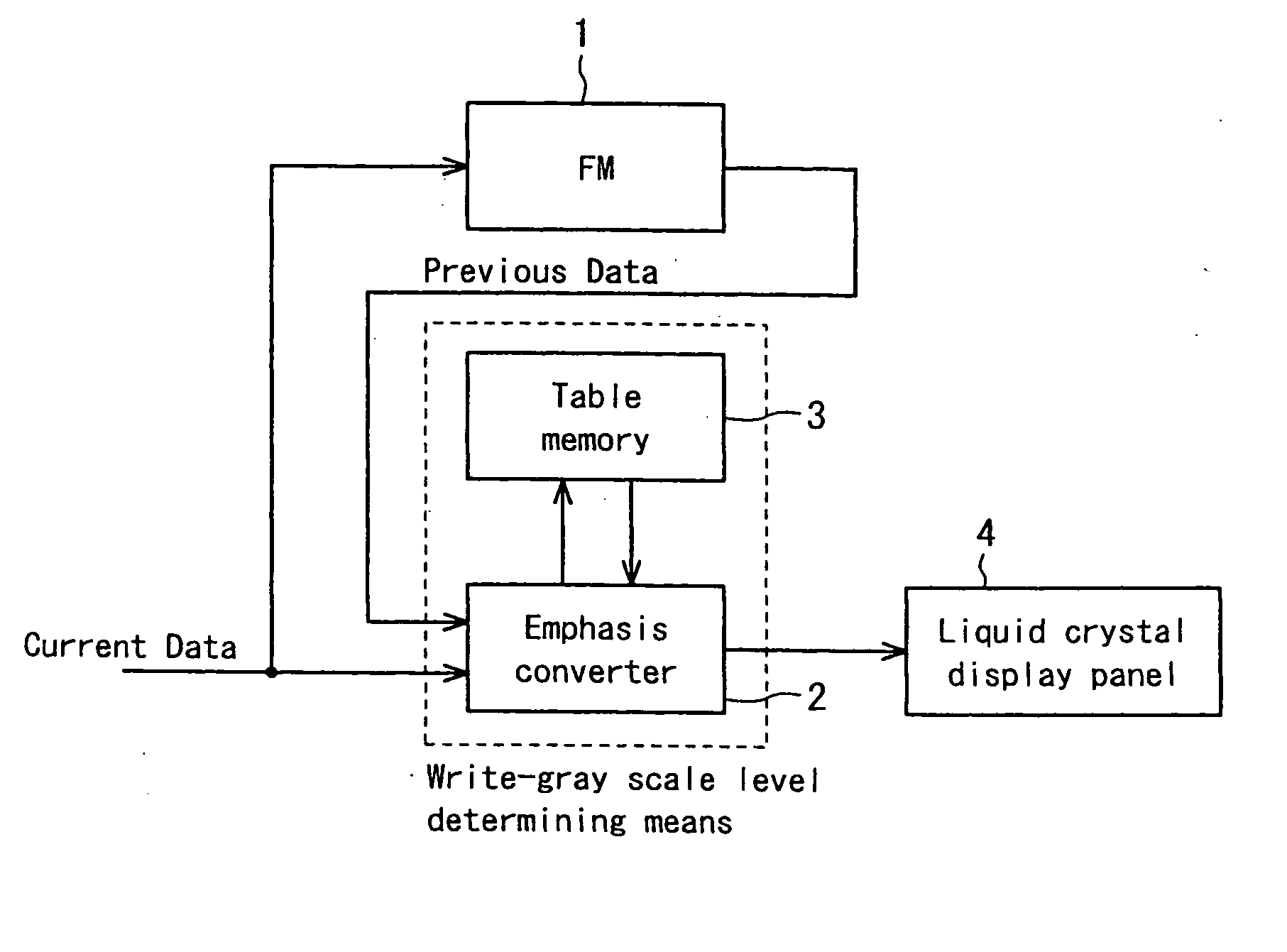
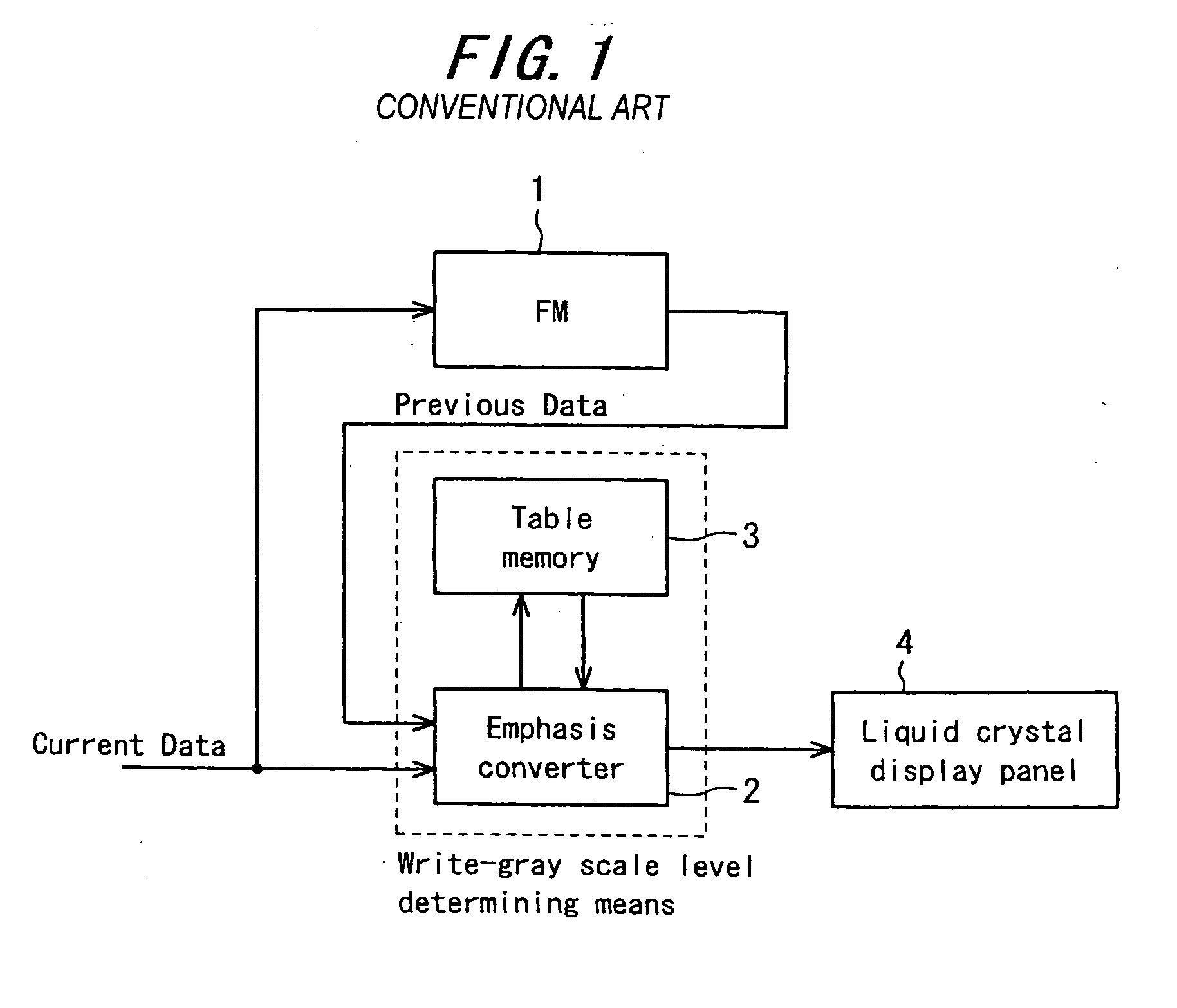
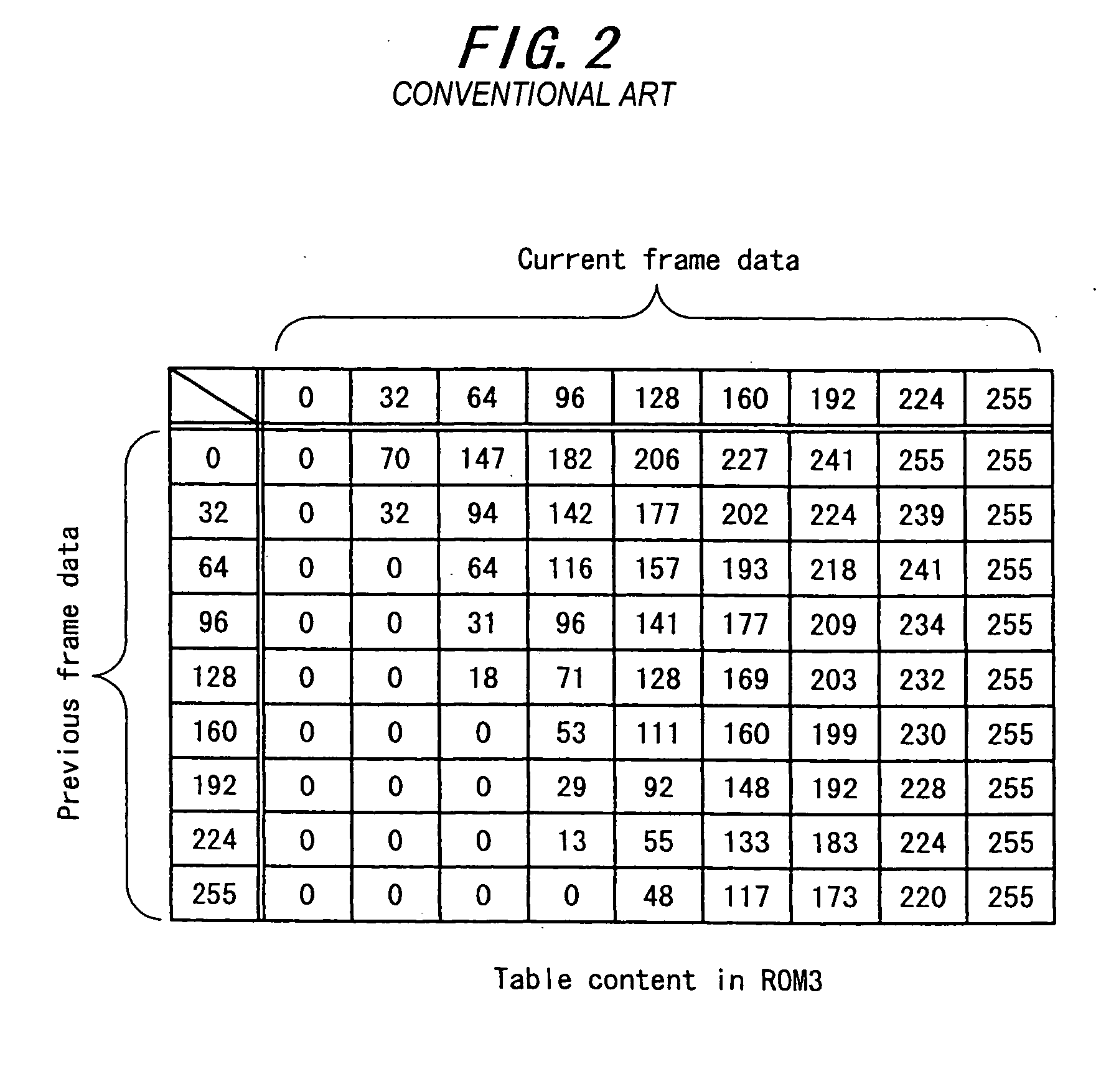
An emphasis converter 52 compares the image data of the current vertical period with the image data of the previous vertical period and controls the input image data to a liquid crystal display panel 4 based on the emphasis conversion parameters stored in tables of ROMs 3a to 3c so as to achieve accelerated drive. A microcomputer 38 is able to realize stable control of selecting emphasis conversion parameters by adding hysteresis to the detected temperature from a thermistor 37 even when the detected temperature fluctuates up and down crossing the temperature threshold.
Owner:SHARP KK
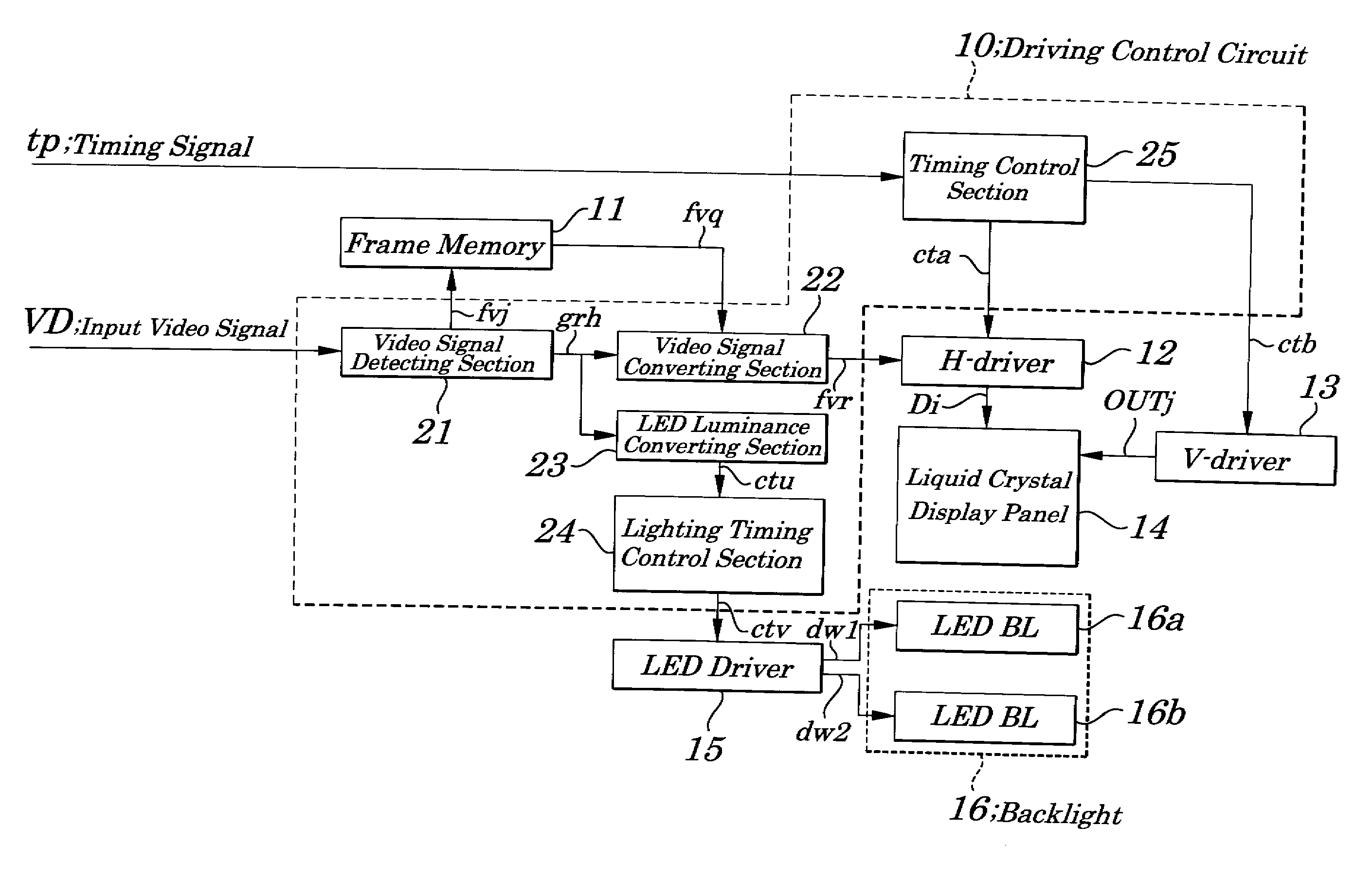
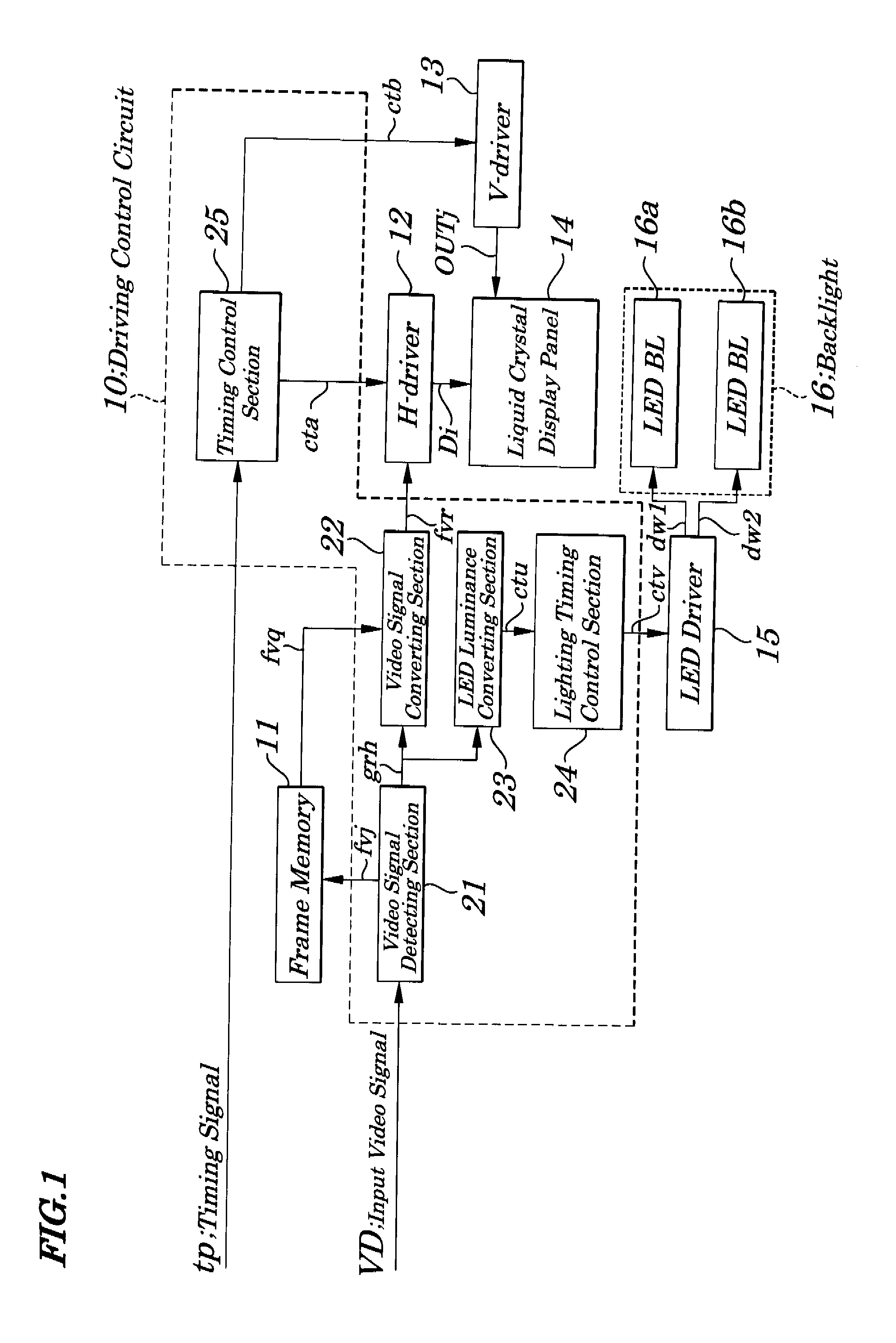
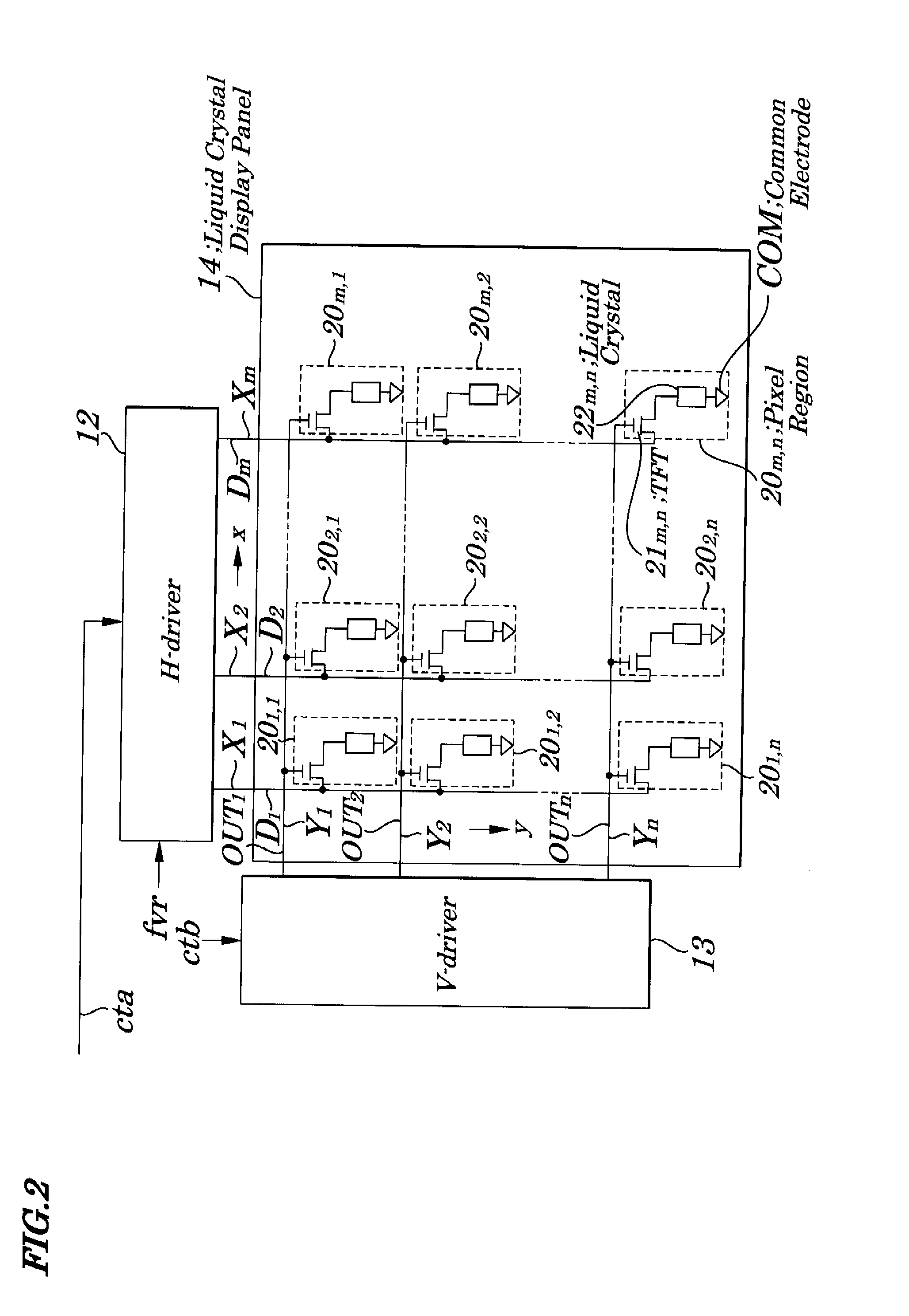
Liquid crystal display device, driving control circuit and driving method used in same device
ActiveUS20080007512A1Improve resolutionPreventing Image Quality DeteriorationStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayLiquid crystal
A liquid crystal display device capable of improving quality of moving images is provided. Each LED (Light Emitting Diode) block is turned ON according to a response of a liquid crystal corresponding to a light emitting region and the brightest gray level is detected for each of red (R), green (G) and blue (B) of an input video signal in every frame period and an input video signal is converted into a value obtained by being multiplied by an upper limit gray level and then by being divided by the brightest gray level and a gray level voltage corresponding to the converted value is applied to each data electrode and, during a lighting period of LED blocks, each LED block is made to flash at a duty corresponding to a rate of the brightest gray level to the upper limit gray level.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
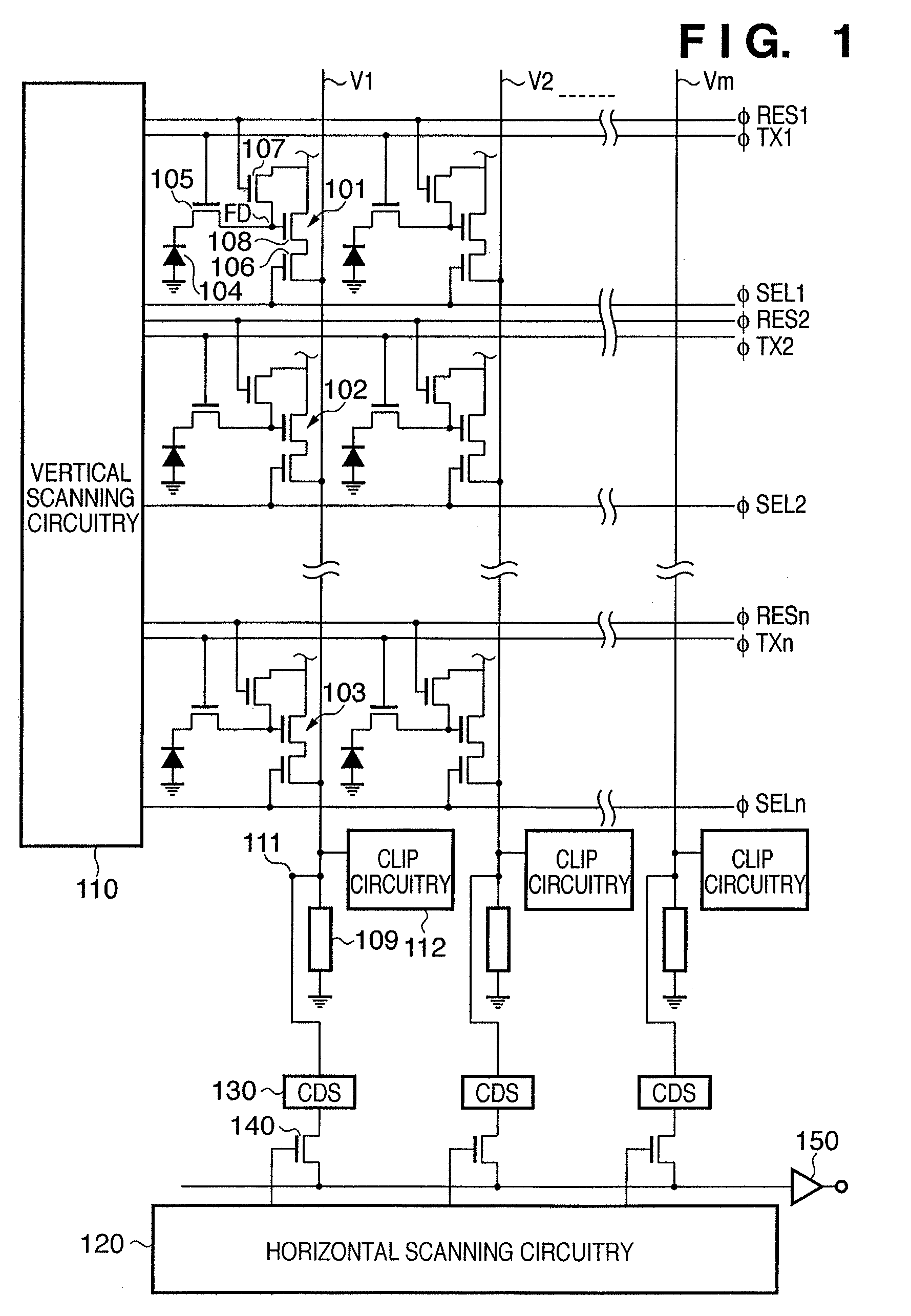
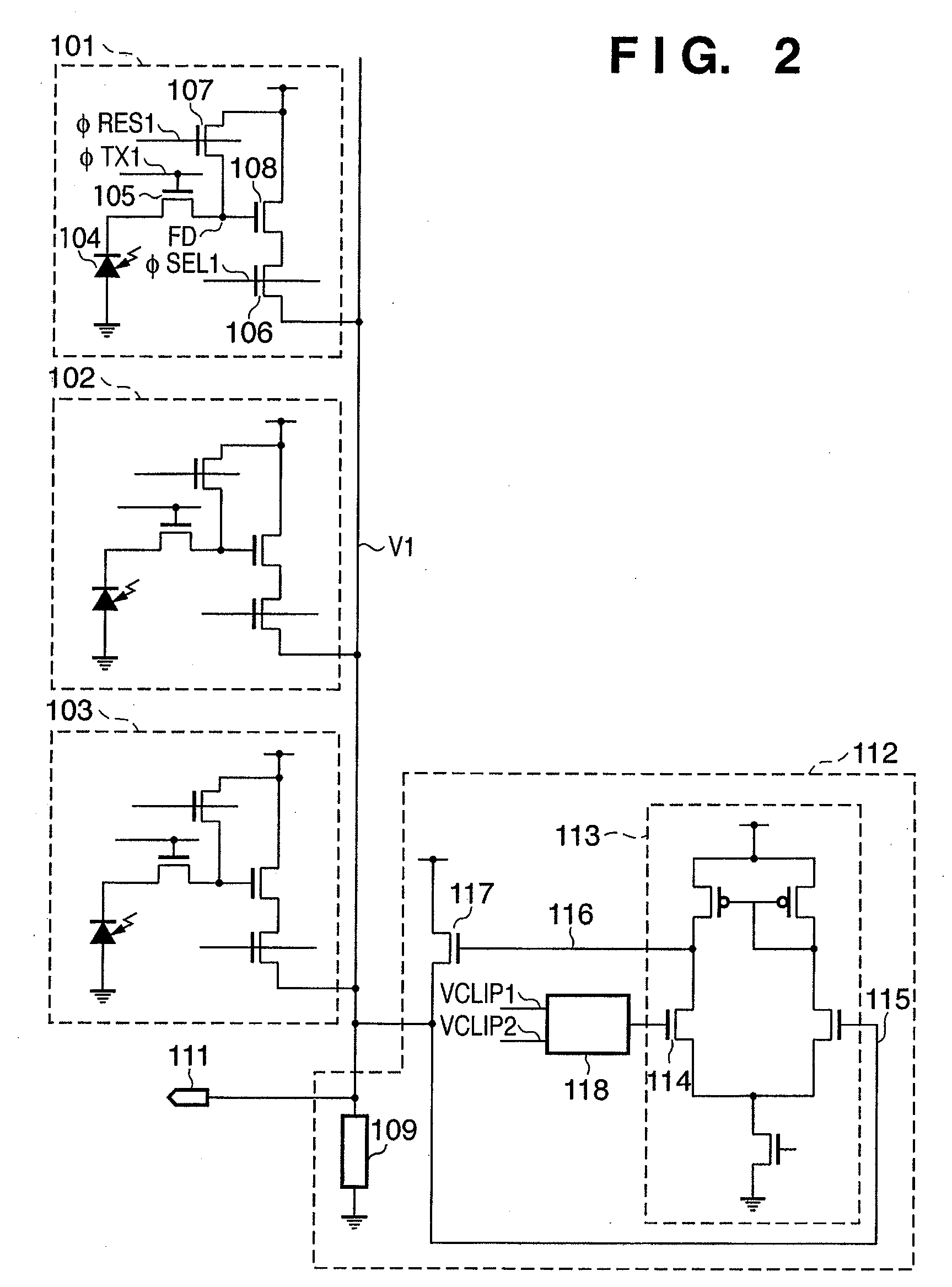
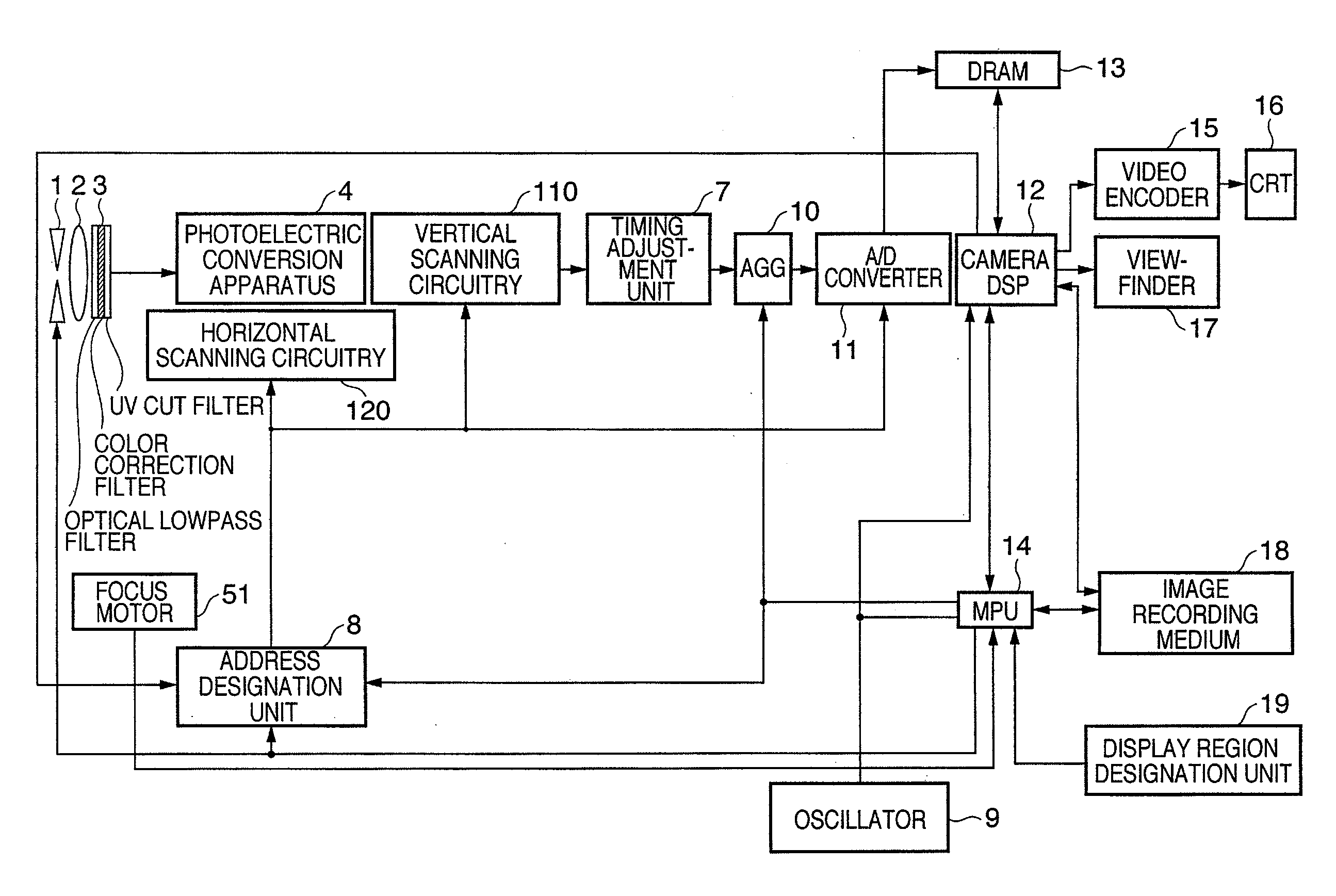
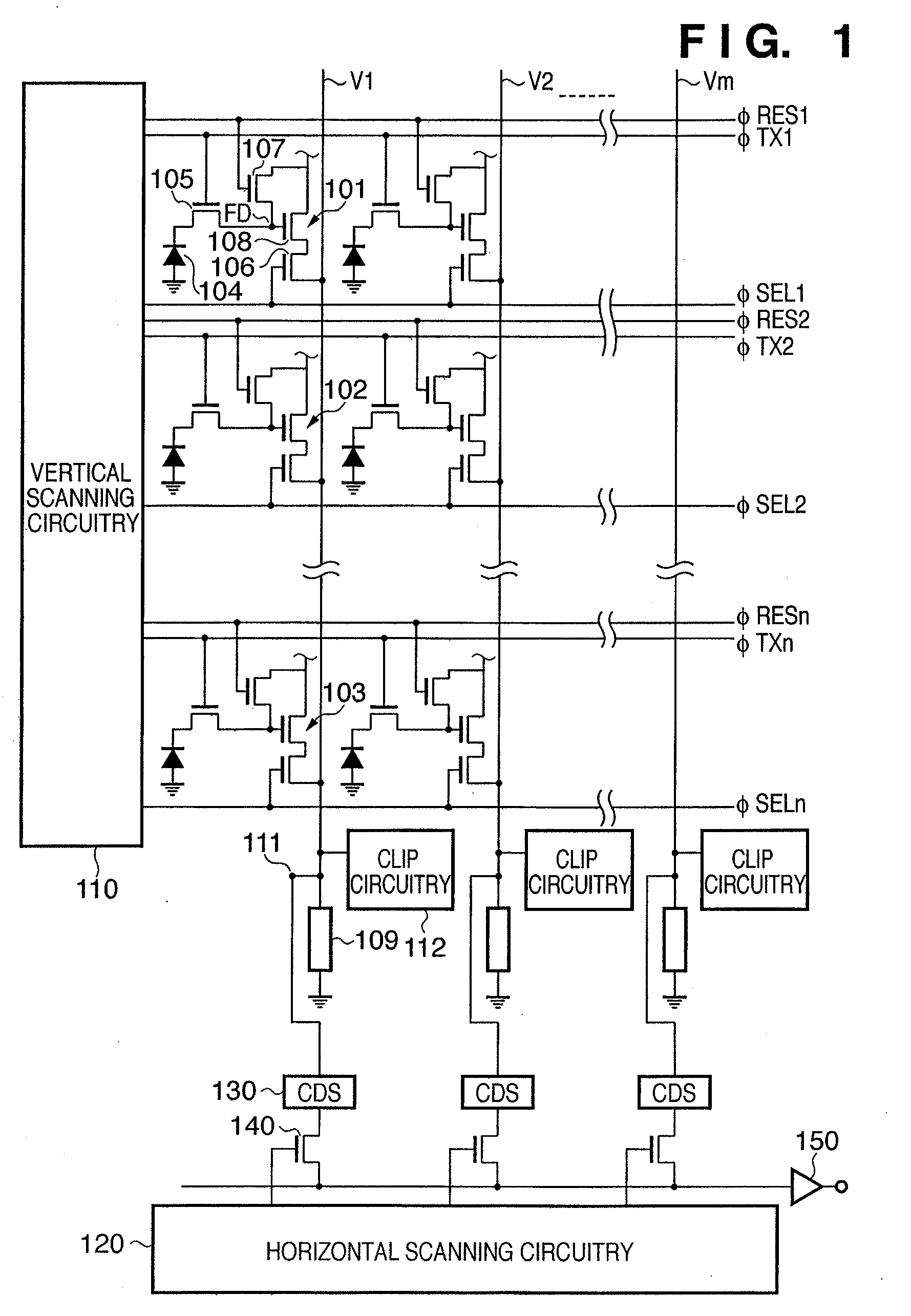
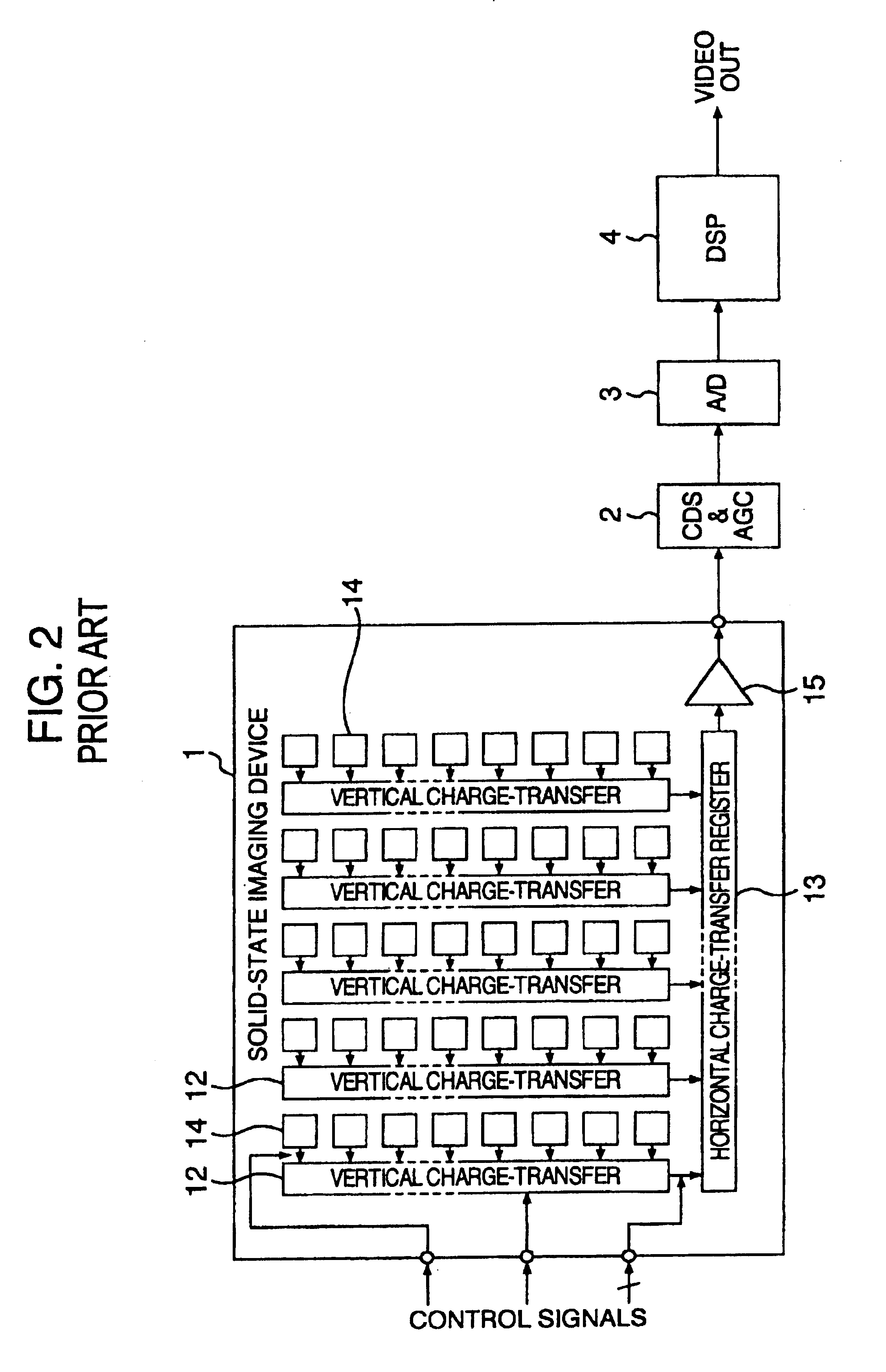
Photoelectric conversion apparatus, control method thereof, imaging apparatus, and imaging system
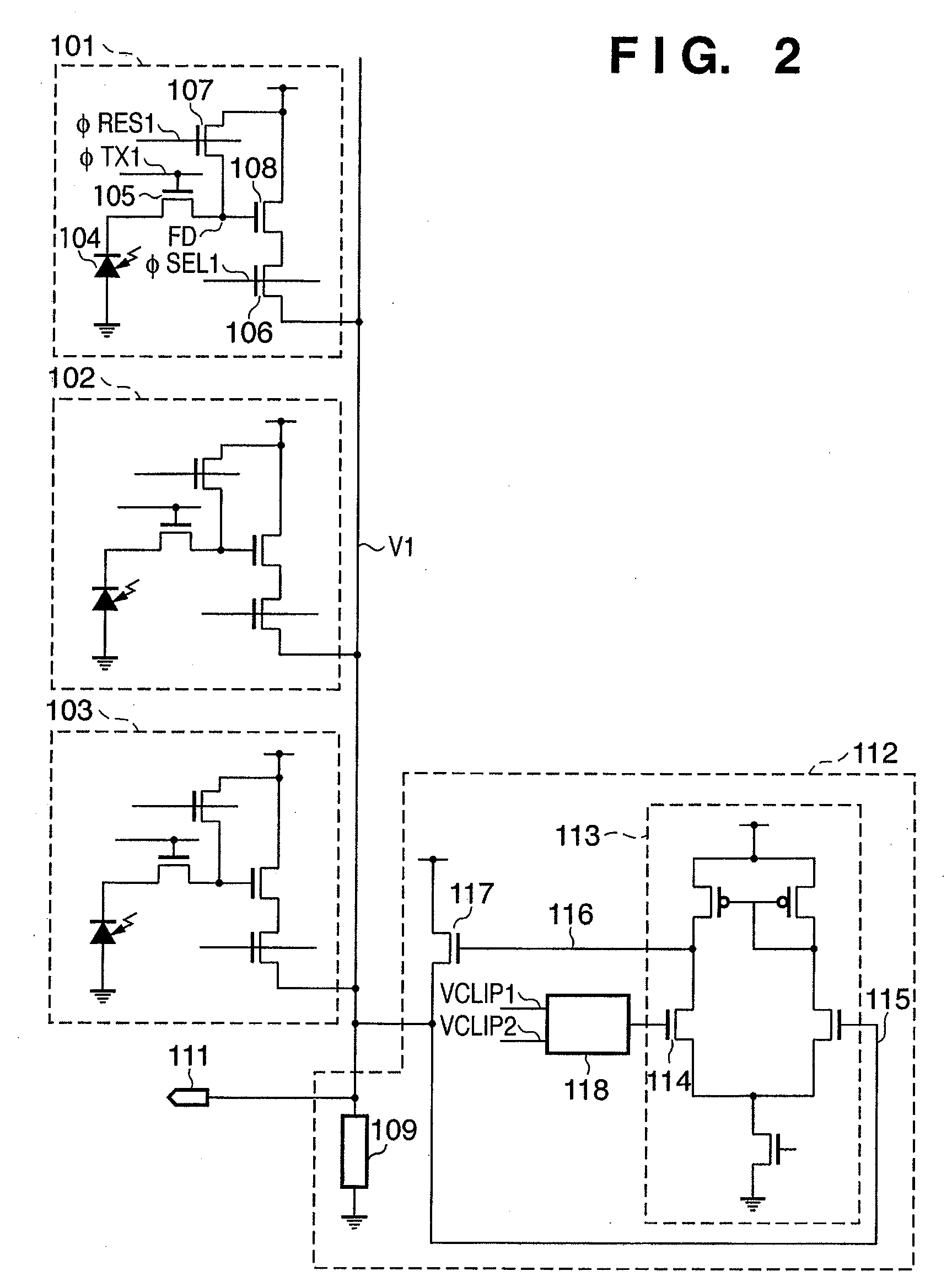
ActiveUS7817199B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationImprove featuresTransistorTelevision system detailsPhotoelectric conversionImage system
Owner:CANON KK
Photoelectric conversion apparatus, control method thereof, imaging apparatus, and imaging system
ActiveUS20080036890A1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationImprove featuresTransistorTelevision system detailsPhotoelectric conversionElectric potential
Each pixel has a photoelectric conversion unit configured to convert light into electrical charges and to store the electrical charges, an amplifying unit configured to amplify a signal based on the electrical charges stored in the photoelectric conversion unit and to output the signal to an output line, and a reset unit configured to reset a input part of the amplifying unit. A clip unit, which is configured to limit an electric voltage of the output line, includes an amplifying circuitry for amplifying a signal based on the electric voltage of the output line and an MOS transistor for limiting the electric voltage of the output line based on the difference in electric potential between the gate and source. The clip unit controls the electric potential of the gate of the MOS transistor by the amplifying circuitry.
Owner:CANON KK
Display device
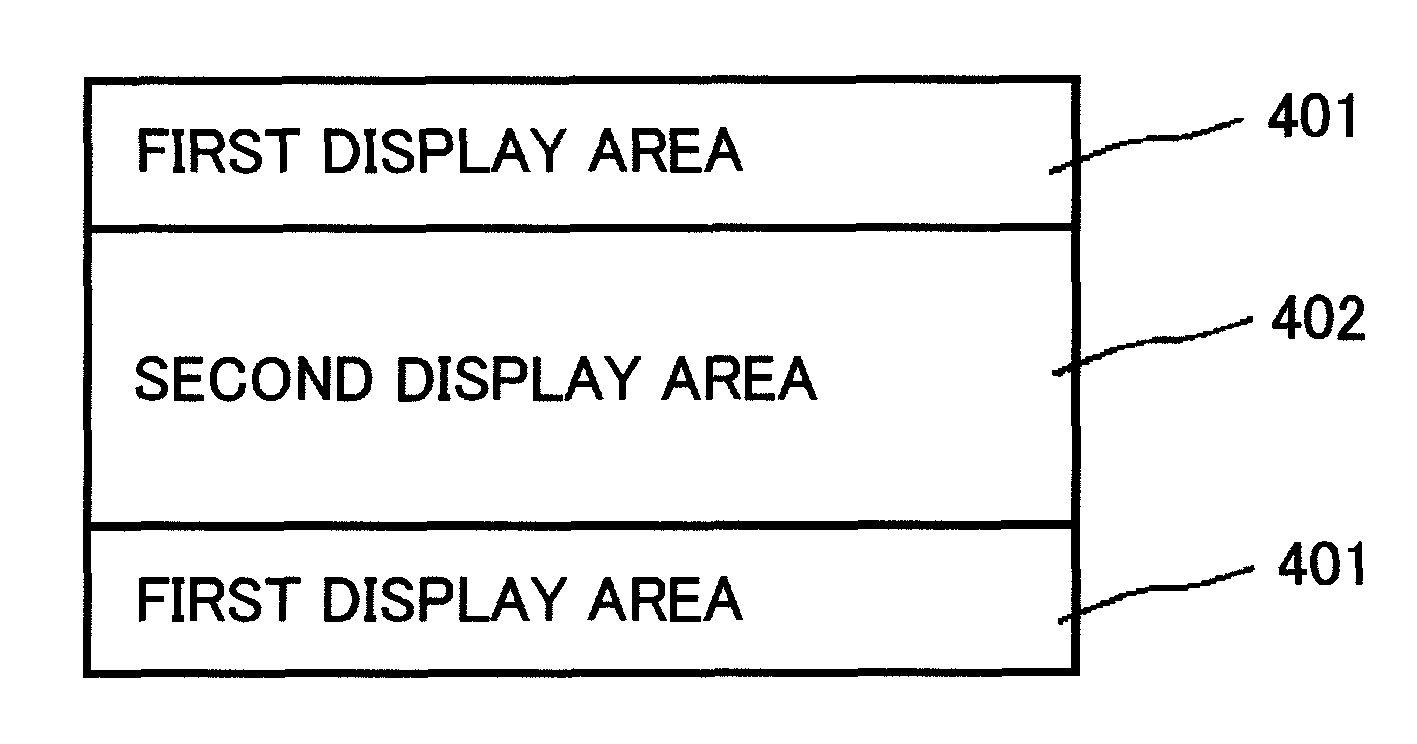
ActiveUS20110032231A1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingFrequency conversionDisplay device
A display device includes a frame frequency conversion circuit configured to convert a frame frequency of an input display data and a timing control circuit configured to control a first drive circuit and a second drive circuit based on a frame frequency after the conversion. The display device generates at least two display areas on the display panel. The at least two display areas display images at different frame frequencies. The display device further includes a switch unit configured to display an image at the frame frequency before the conversion at one of the at least two display areas and configured to display an image at the frame frequency after the conversion at another one of the at least two display areas. At least one of a boundary position and a size of the at least two display areas varies with time.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
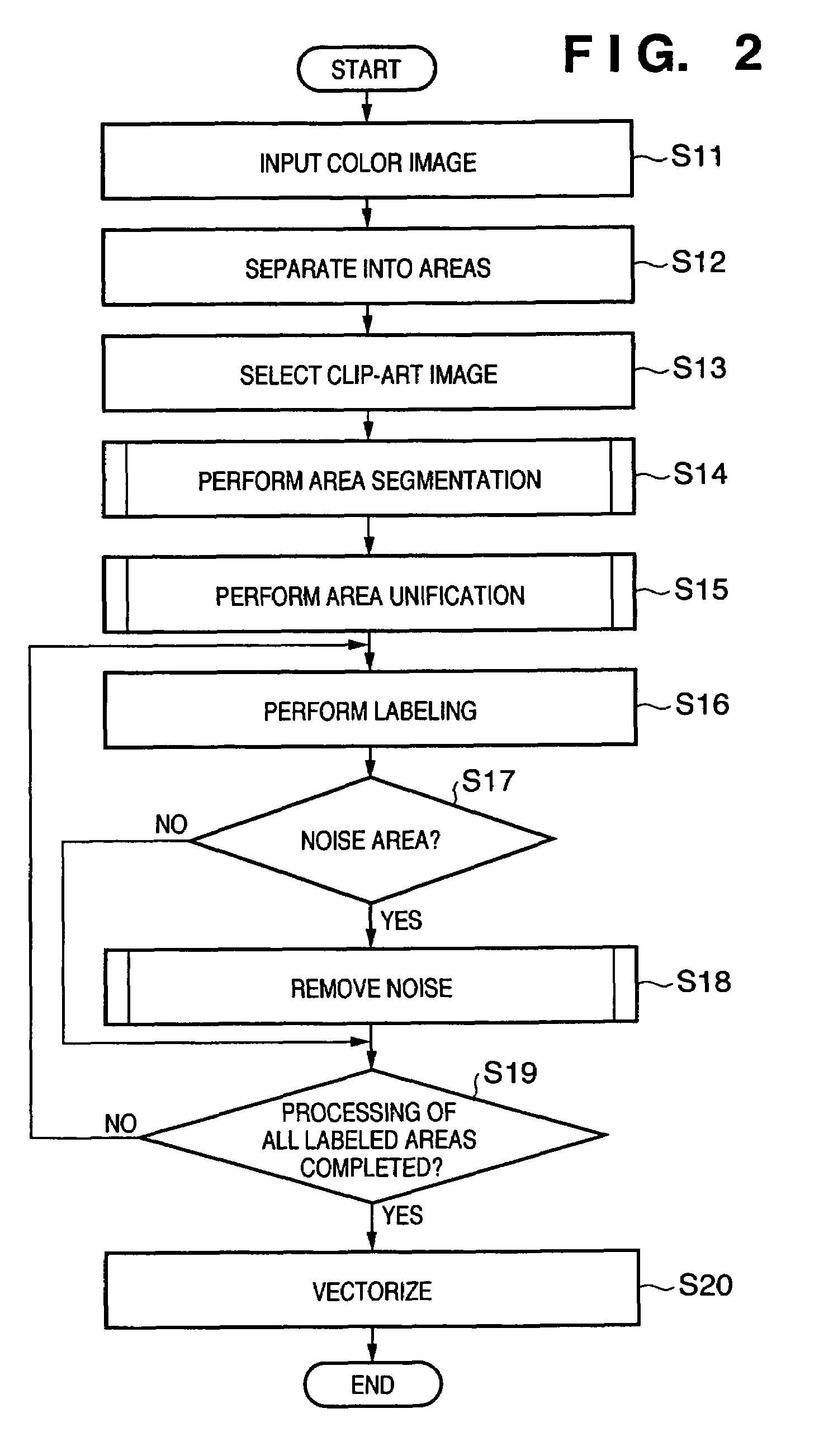
Image processing method and apparatus
InactiveUS20070025617A1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationReduce data volumeCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging processing
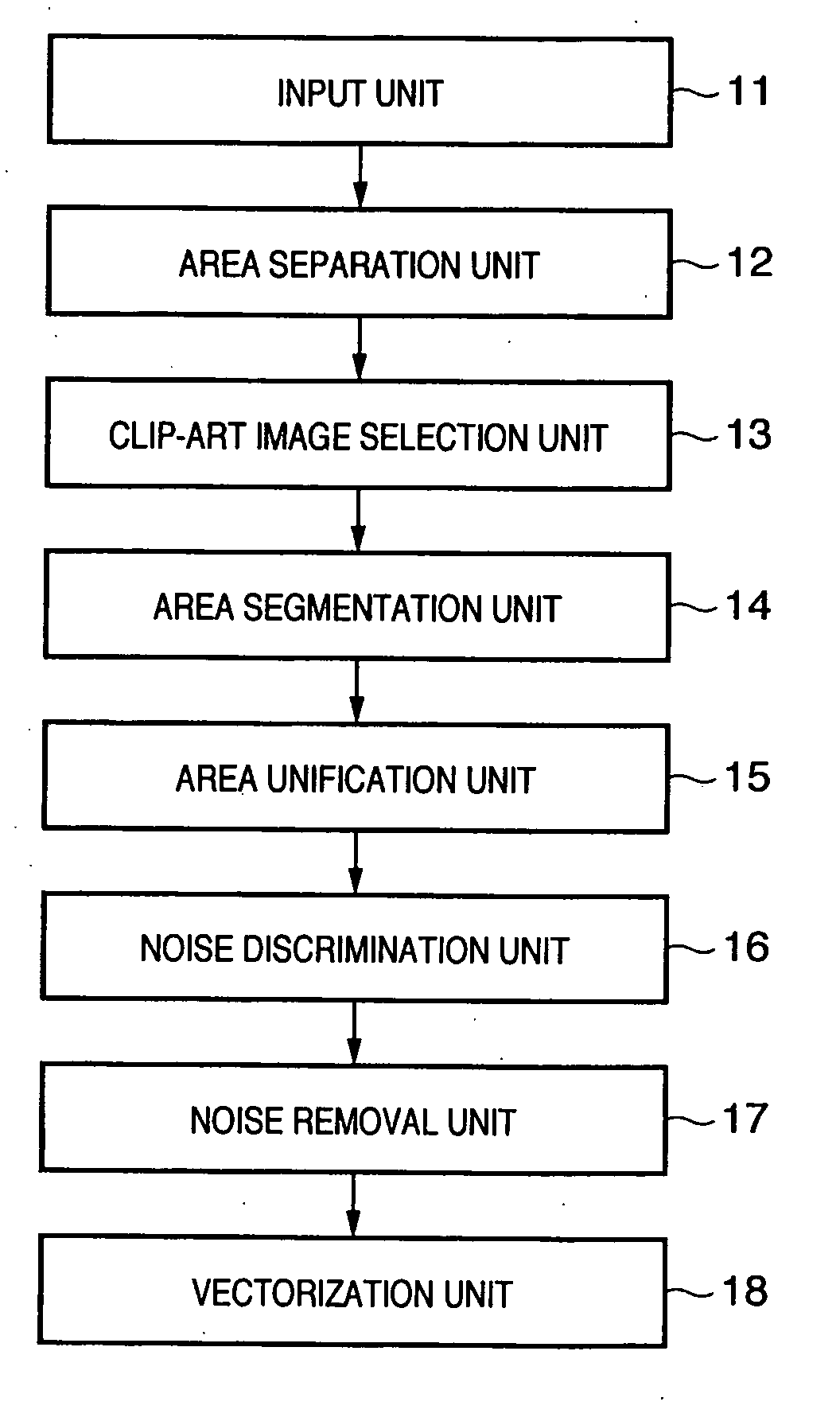
Disclosed is an image processing apparatus in which vector data from which noise has been removed and amount of data reduced can be generated in ideal fashion with regard to an illustration area selected from a document image. The document image is input to the apparatus and is segmented into a plurality of areas. A clip-art image is selected from these areas and a plurality of clusters are generated with regard to this image area. When a small area included in the plurality of clusters is determined as a noise, the noise is eliminated by combining the small area with a adjacent cluster. After noise is removed, the cluster group eventually obtained is converted to vector data.
Owner:CANON KK
Image recording method and image recording apparatus
InactiveUS20070222811A1Reduce pile heightPrevent ink bleedingMaterial nanotechnologyDuplicating/marking methodsImage recordingComputer science
The image recording method for forming an image on a recording medium, includes the step of applying droplets of stimulus-responsive ink which responds to a stimulus so that the stimulus-responsive ink converts from a sol state to a gel state, on the recording medium, wherein each of the droplets of the stimulus-responsive ink has a volume of 0.5 pl to 2.5 pl.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image pick-up apparatus
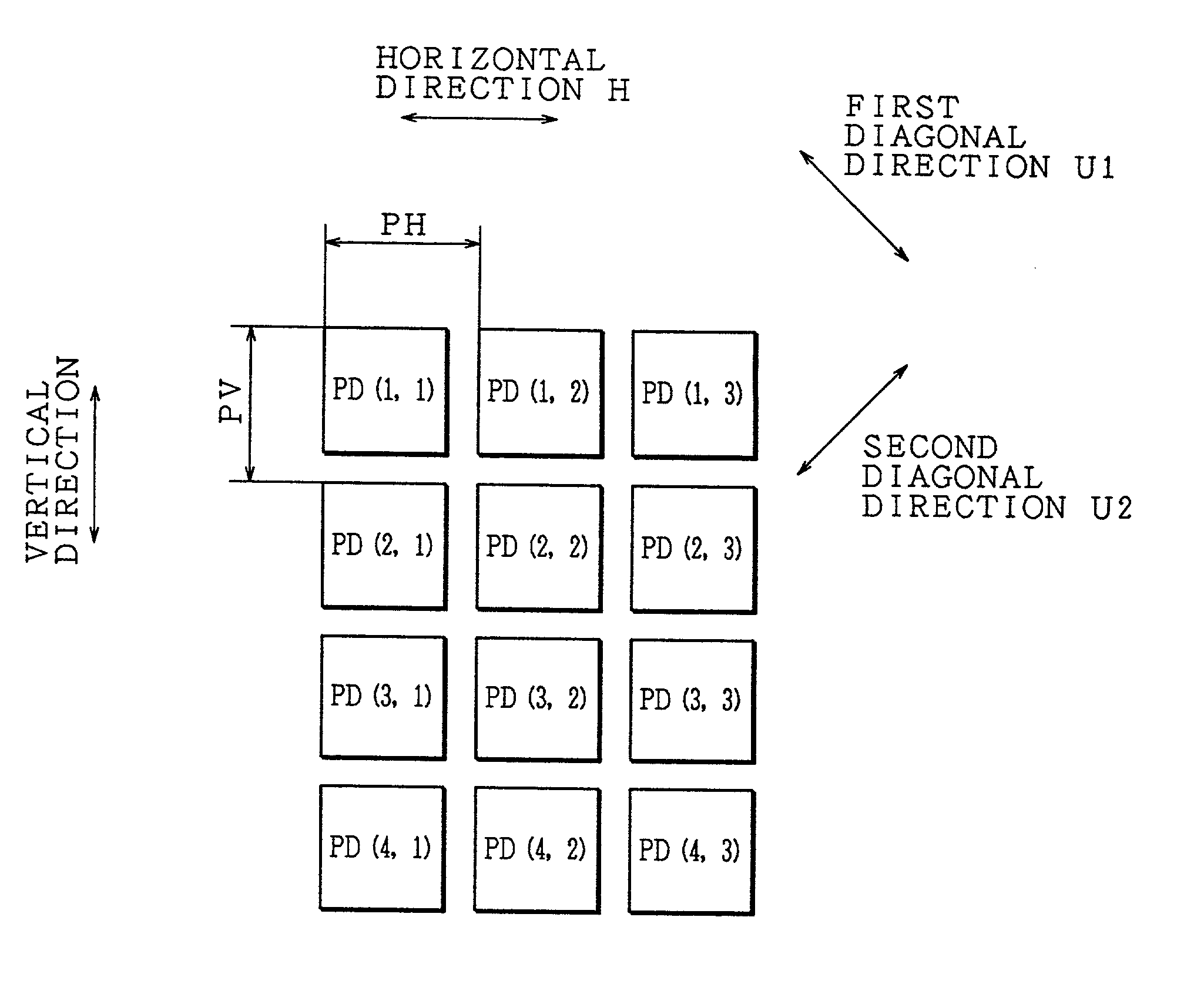
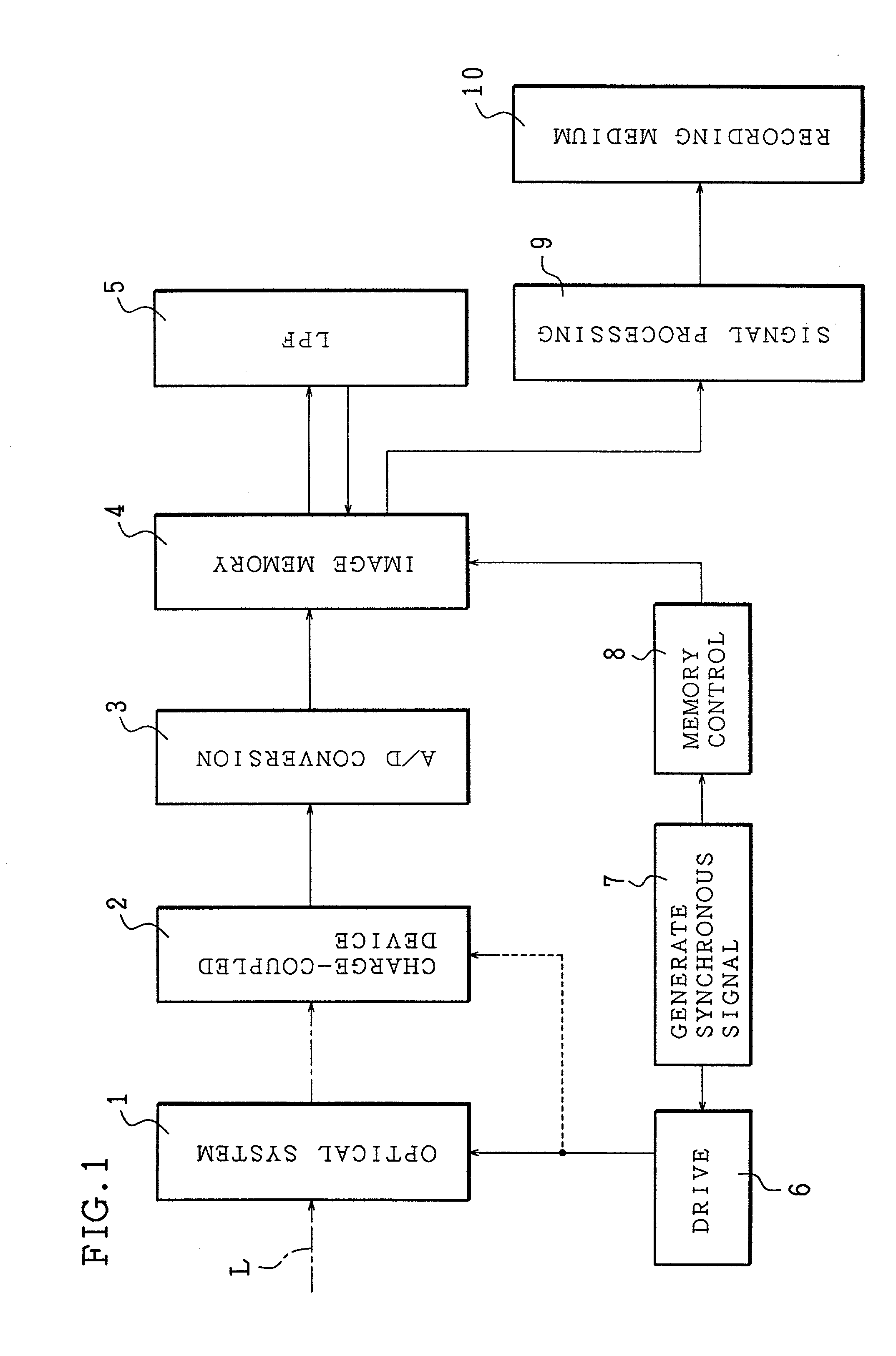
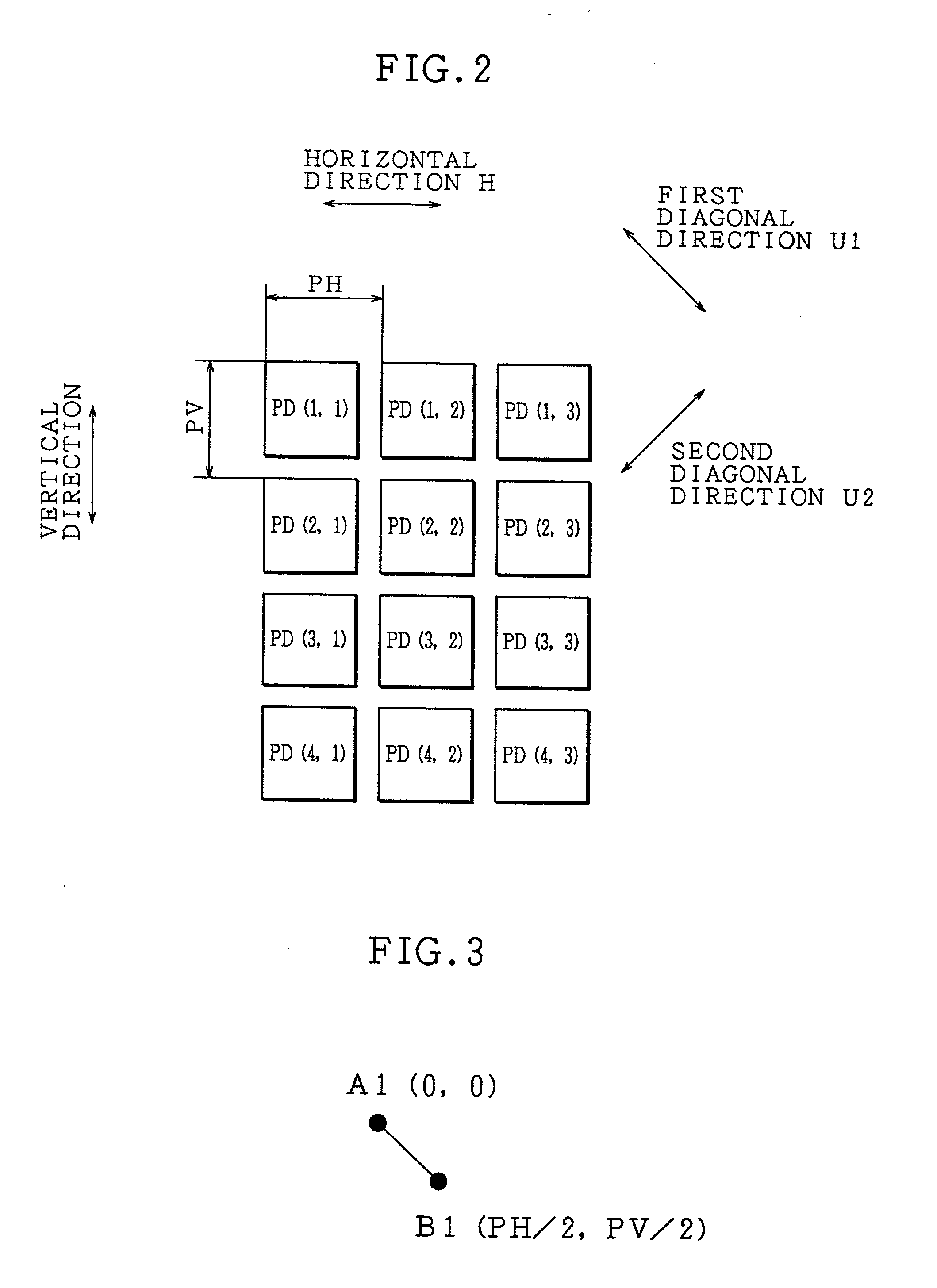
InactiveUS20020126209A1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationReduce the amount requiredTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging qualityComputer science
An image pick-up apparatus is provided with: a charge-coupled device for picking up imaging light from a subject and forming image data; an image-shift mechanism for shifting the charge-coupled device to a plurality of relative positions with respect to the imaging light so as to allow the charge-coupled device to form the image data at the relative positions; an LPF constituted by a filter for removing a spatial frequency component that appears due to a light-quantity difference between a plurality of pieces of image data generated by the charge-coupled device through the image-shift mechanism; and a memory control section for combining the plurality of image data. With this arrangement, it is possible to suppress a striped pattern due to the light-quantity difference, and consequently to improve the image quality.
Owner:SHARP KK
Motion picture encoding device and motion picture encoding processing program
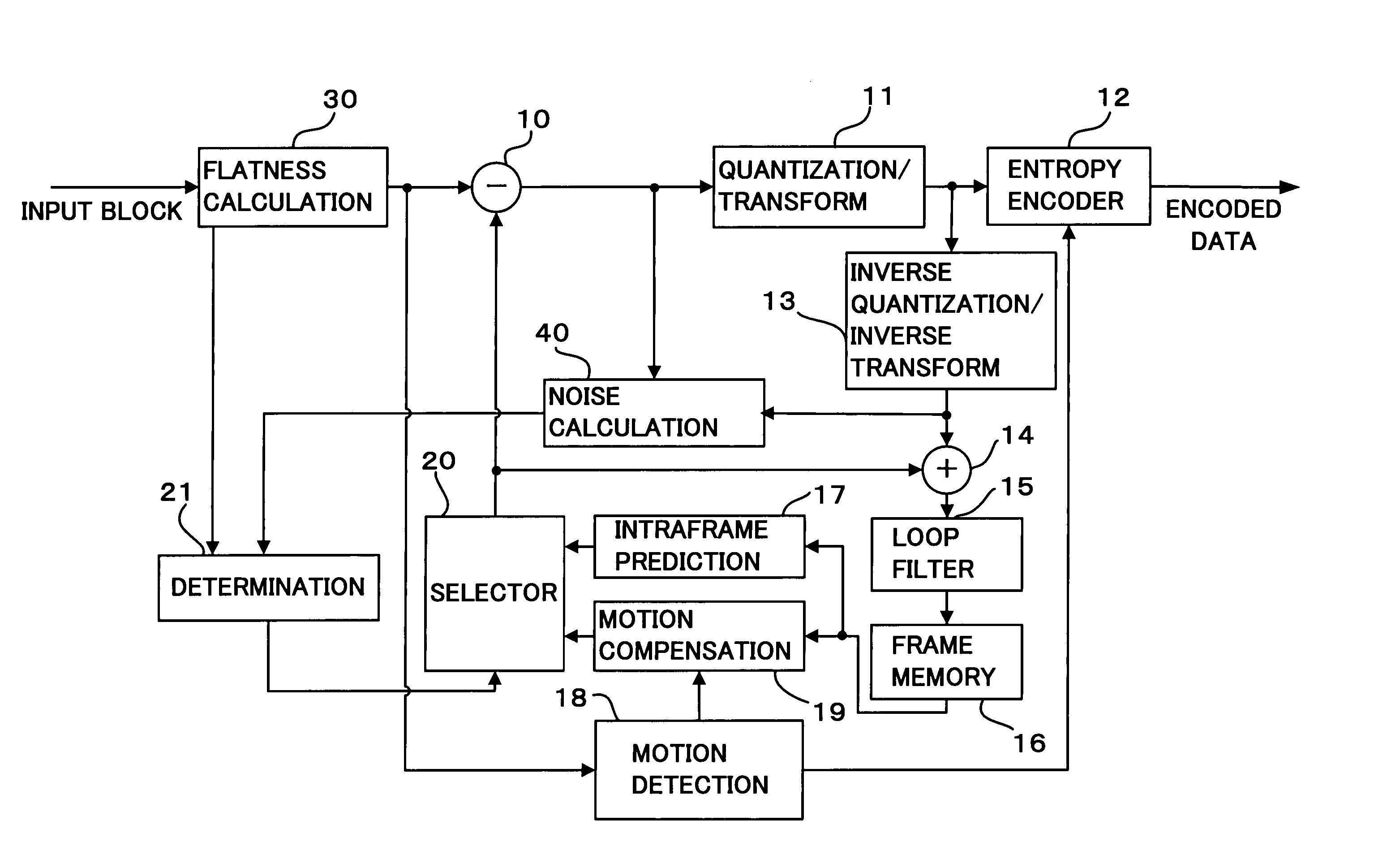
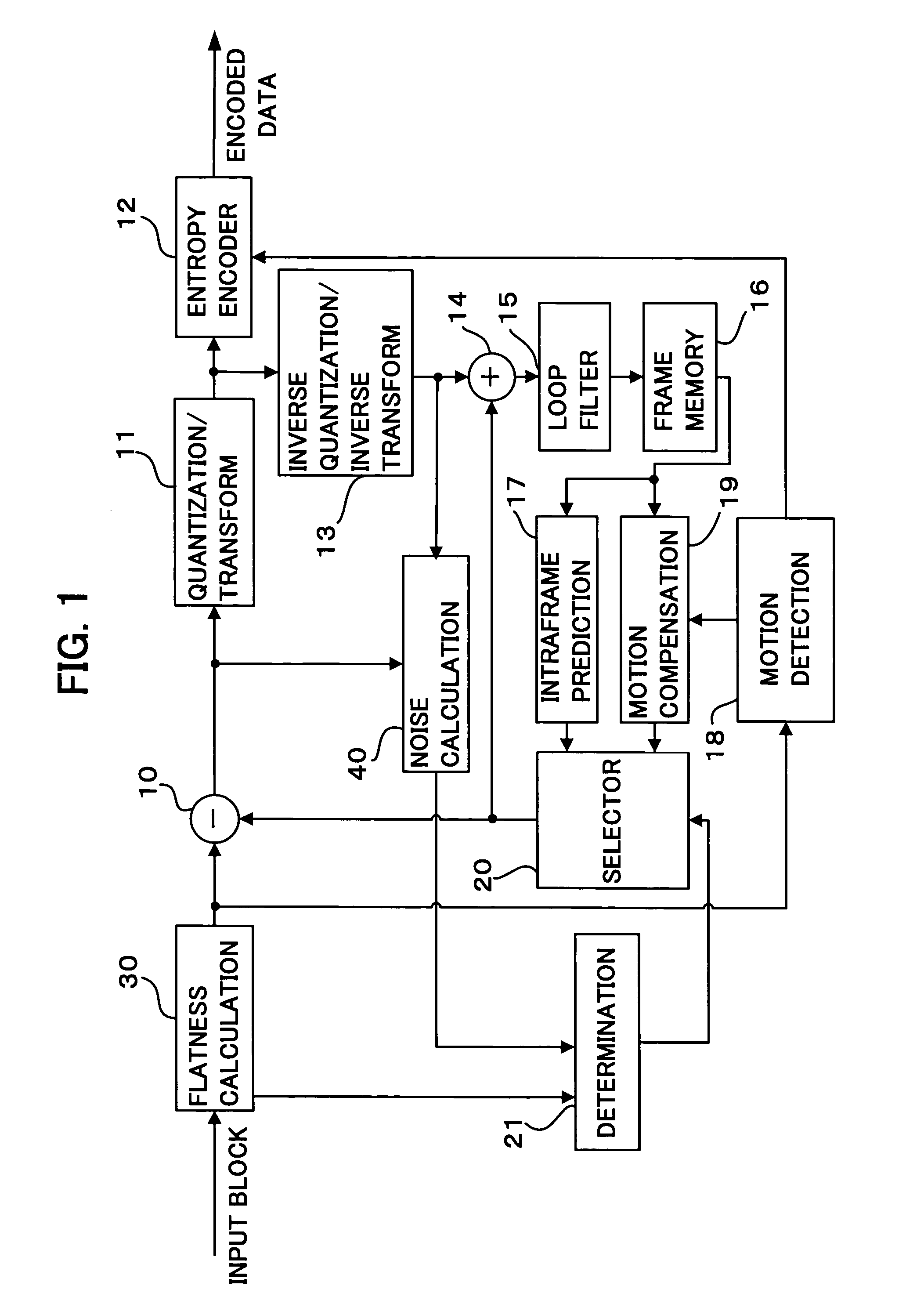
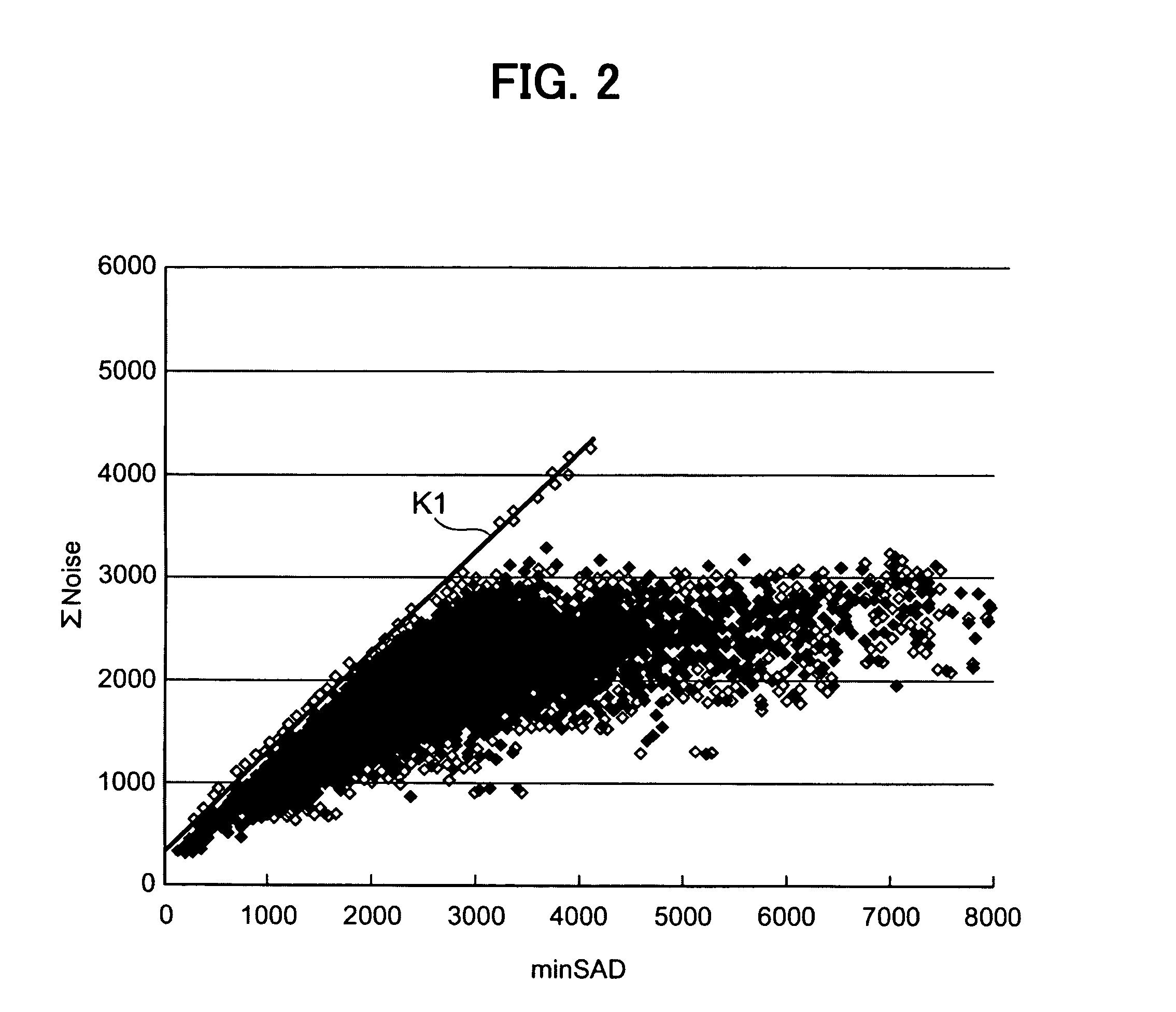
ActiveUS20070019729A1Faster speedImage quality be avoidColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSum of absolute differencesMacroblock
The minimum Sum of Absolute Differences obtained by a motion vector search roughly judges the magnitude of quantization error by whether or not exceeding a predetermined threshold value. When the quantization error is lower, whether or not visually noticeable noise exists in some of the pixels of the current macroblock is judged based on the amount of flatness and noise detected in each of the 4x4 pixel blocks of the current macroblock partitioned into 16 sub-macroblocks. If there is visually noticeable noise, intra-frame coding is selected. When the quantization error is higher, whether or not visually noticeable noise exists in the current macroblock is judged while considering the magnitude of the motion vector. If there is visually noticeable noise, intra-frame coding is selected.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060221166A1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationSuppressing the adherence of an image forming bodyOther printing apparatusPrinting after-treatmentFree energiesSurface roughness
The image forming apparatus comprises: an ejection head which ejects liquid onto a recording medium to form a desired image on the recording medium; a conveyance device which moves at least one of the recording medium and the ejection head so as to move the recording medium in a conveyance direction relatively to the ejection head; and a contact device which makes contact with the liquid on the recording medium and is arranged on a downstream side of the ejection head in the conveyance direction, the contact device having surface properties satisfying at least one of the following conditions: that a surface roughness of the contact device is greater than a surface roughness of the recording medium; that a surface free energy of the contact device is smaller than a surface free energy of the recording medium; and that a contact angle of the liquid on the contact device is smaller than a contact angle of the liquid on the recording medium.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image processing method and apparatus
InactiveUS7623712B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationReduce data volumeCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging processing
Disclosed is an image processing apparatus in which vector data from which noise has been removed and amount of data reduced can be generated in ideal fashion with regard to an illustration area selected from a document image. The document image is input to the apparatus and is segmented into a plurality of areas. A clip-art image is selected from these areas and a plurality of clusters are generated with regard to this image area. When a small area included in the plurality of clusters is determined as a noise, the noise is eliminated by combining the small area with a adjacent cluster. After noise is removed, the cluster group eventually obtained is converted to vector data.
Owner:CANON KK
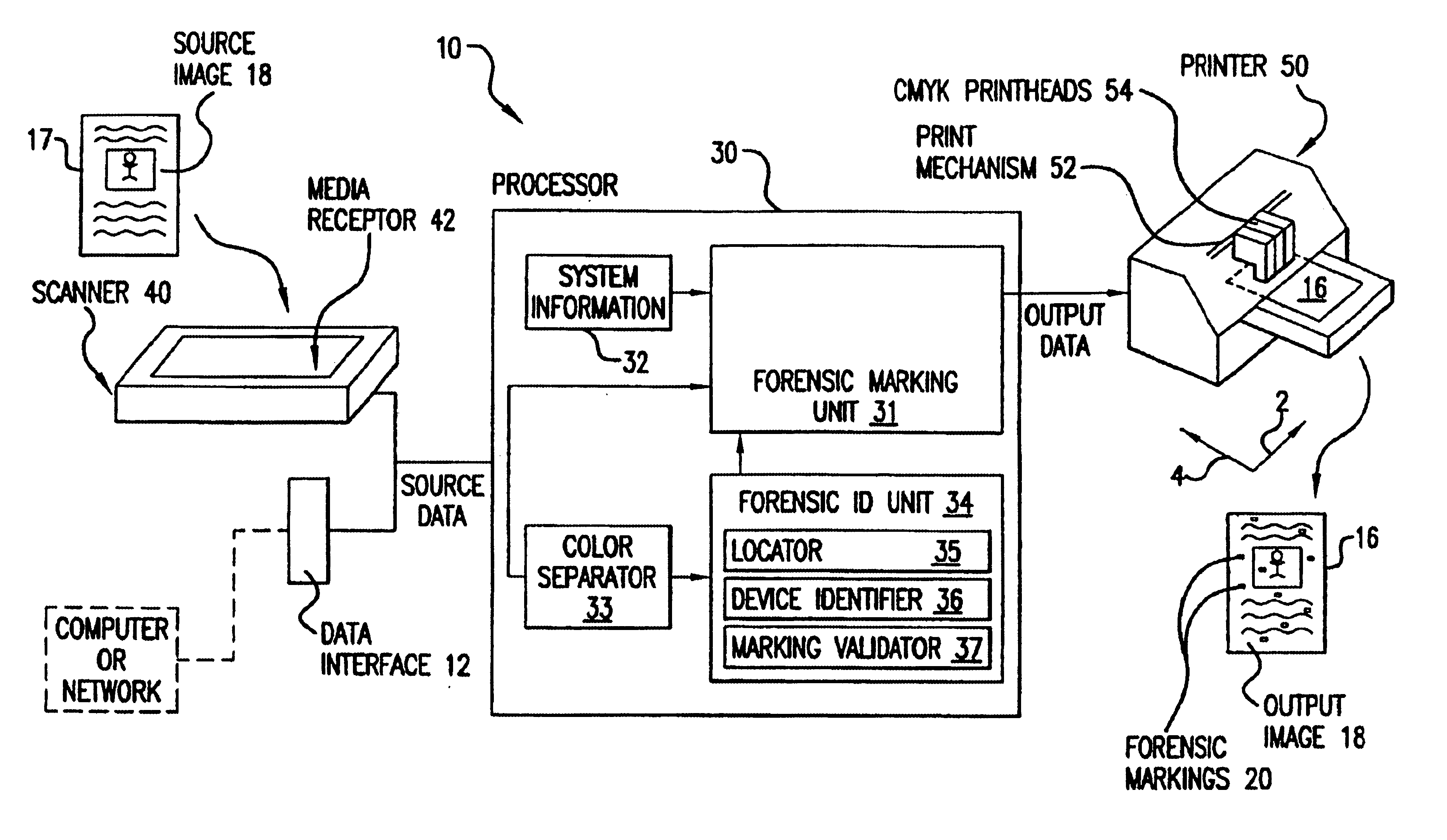
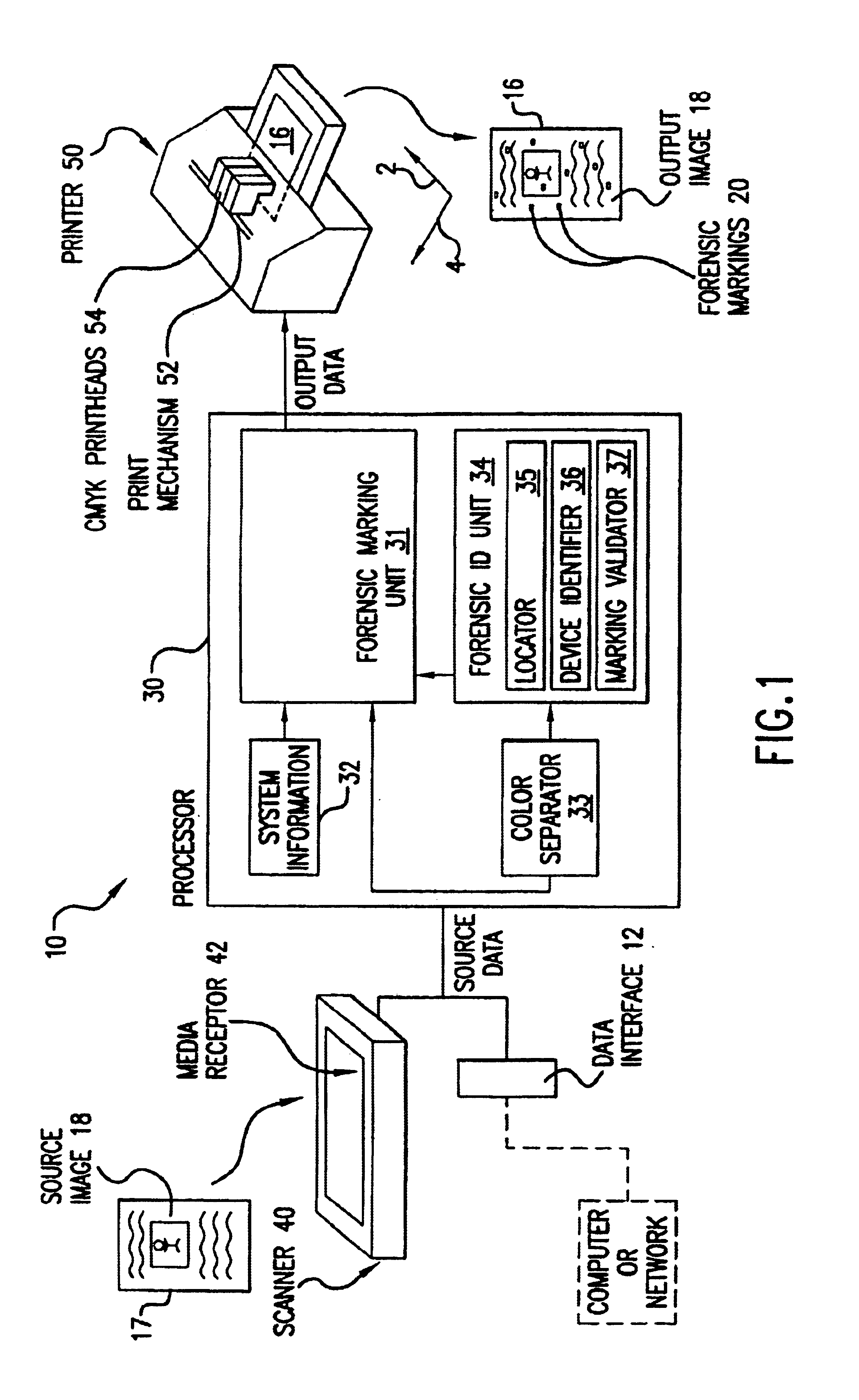
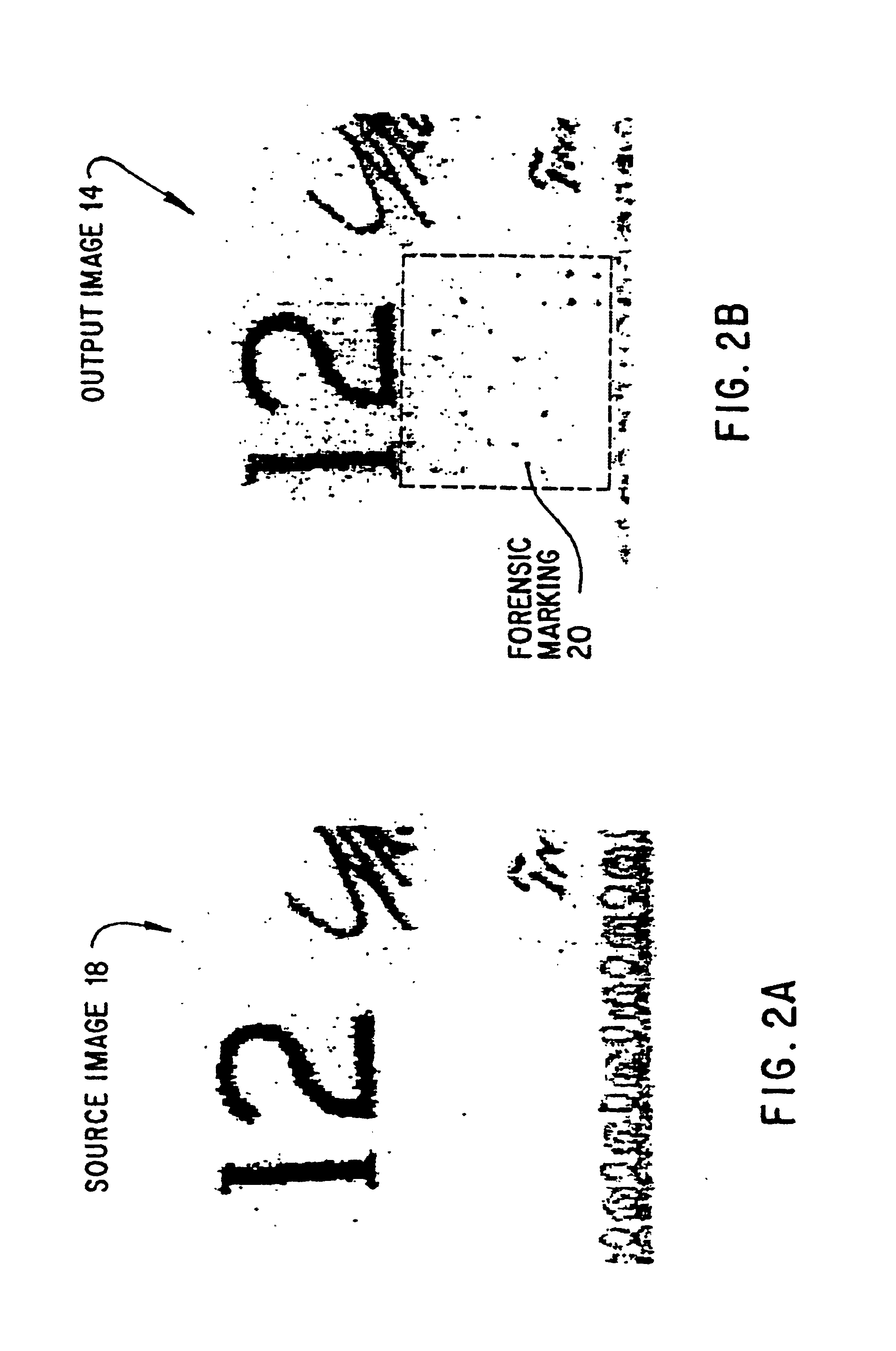
High reliability forensic color marking system
InactiveUS7002710B1High precisionAccurate identificationPaper-money testing devicesVisual presentation using printersPattern recognitionHigh density
A forensic marking system and method for identifying the printing device on which a medium was printed. Encoded forensic markings which identify the device but are of low perceptibility to the human eye are superimposed on the printed image. The markings have a color, size, density, and repetition pattern that only minimally affect print quality while providing highly accurate identification of the printing device, even if the printed medium contains high-density image content.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
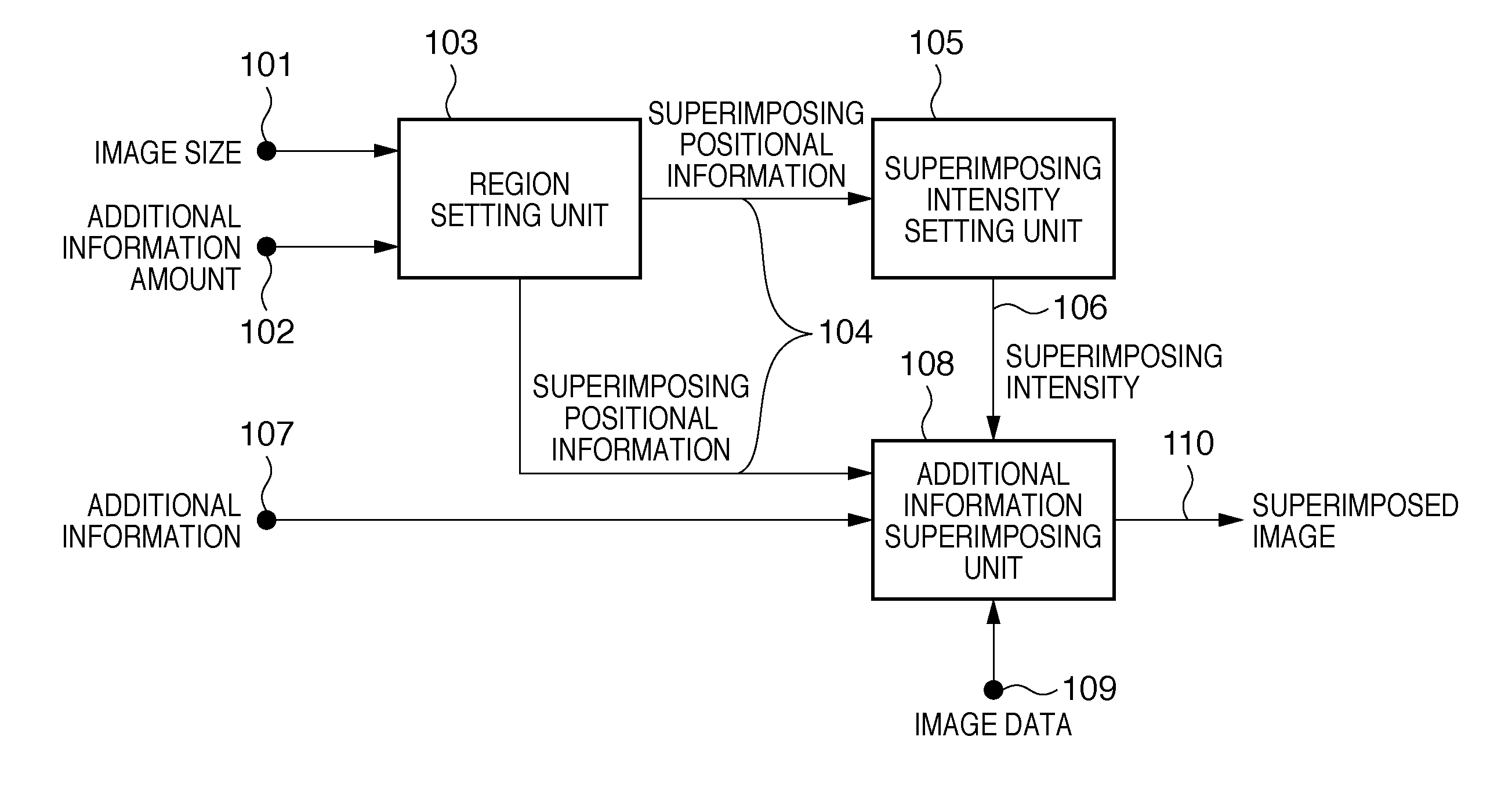
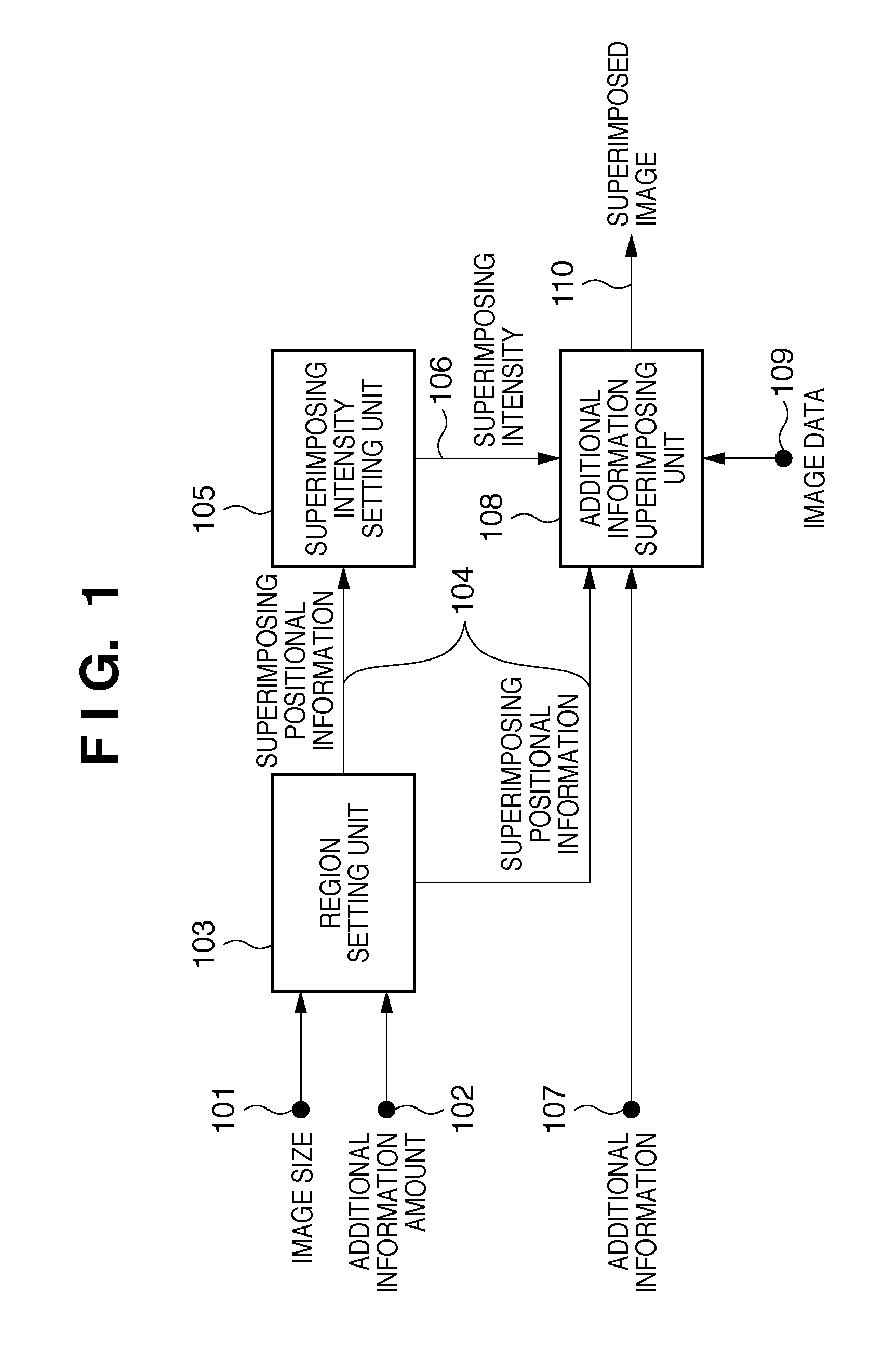
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and medium storing program thereof
ActiveUS8300925B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing apparatus that superimposes additional information on image data, the apparatus sets, in the image data, a main region in which the superimposing intensity for superimposing the additional information is constant, and a superimposing intensity change region in which the superimposing intensity for superimposing the additional information is not constant, sets, the superimposing intensity according to the target pixel in the superimposing intensity change region, and superimposes the additional information on image data using the set superimposing intensity.
Owner:CANON KK
Display device and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20070222380A1Lower on-resistanceImage quality can be hinderedDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceDisplay device
A display device in which variations in luminance due to variations in characteristics of transistors are reduced, and image quality degradation due to variations in resistance values is prevented. The invention comprises a transistor whose channel portion is formed of an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor, a connecting wiring connected to a source electrode or a drain electrode of the transistor, a light emitting element having a laminated structure which includes a pixel electrode, an electro luminescent layer, and a counter electrode, an insulating layer surrounding an end portion of the pixel electrode, and an auxiliary wiring formed in the same layer as a gate electrode of the transistor, a connecting wiring, or the pixel electrode. Further, the connecting wiring is connected to the pixel electrode, and the auxiliary wiring is connected to the counter electrode via an opening portion provided in the insulating layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS7708371B2Inhibit deteriorationPreventing Image Quality DeteriorationOther printing apparatusImage formationImage correction
The image forming apparatus comprises: an image forming device which includes an intermediate transfer body having a transfer surface on which an image is formed according to a first image data, the image forming device performing a transfer of the image onto a recording medium from the transfer surface; a transfer state determination device which determines a state of the transfer surface after the transfer of the image onto the recording medium has been performed; and an image correction device which corrects a second image data corresponding to an image formed on the transfer surface, according to the state of the transfer surface determined by the transfer state determination device.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
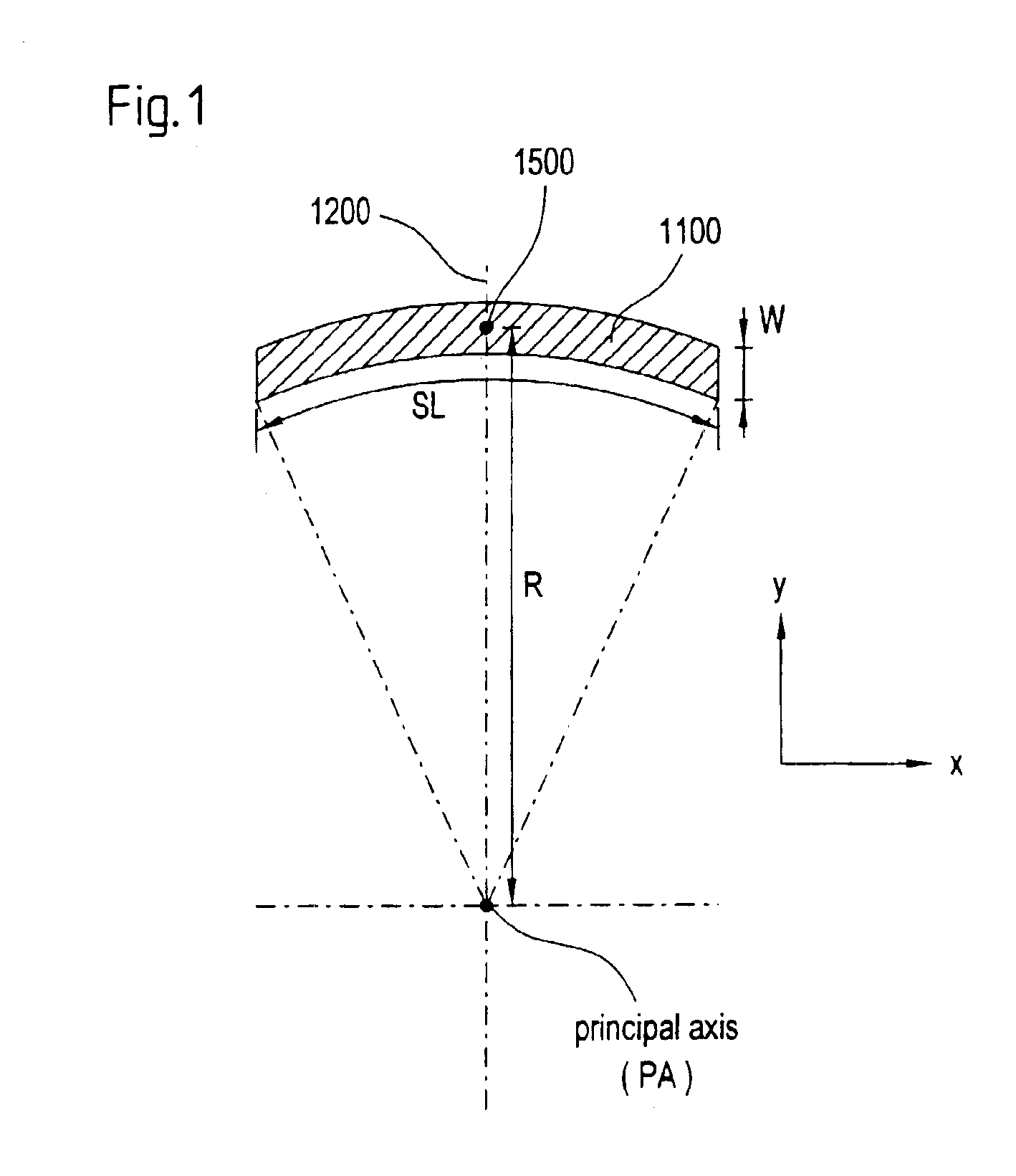
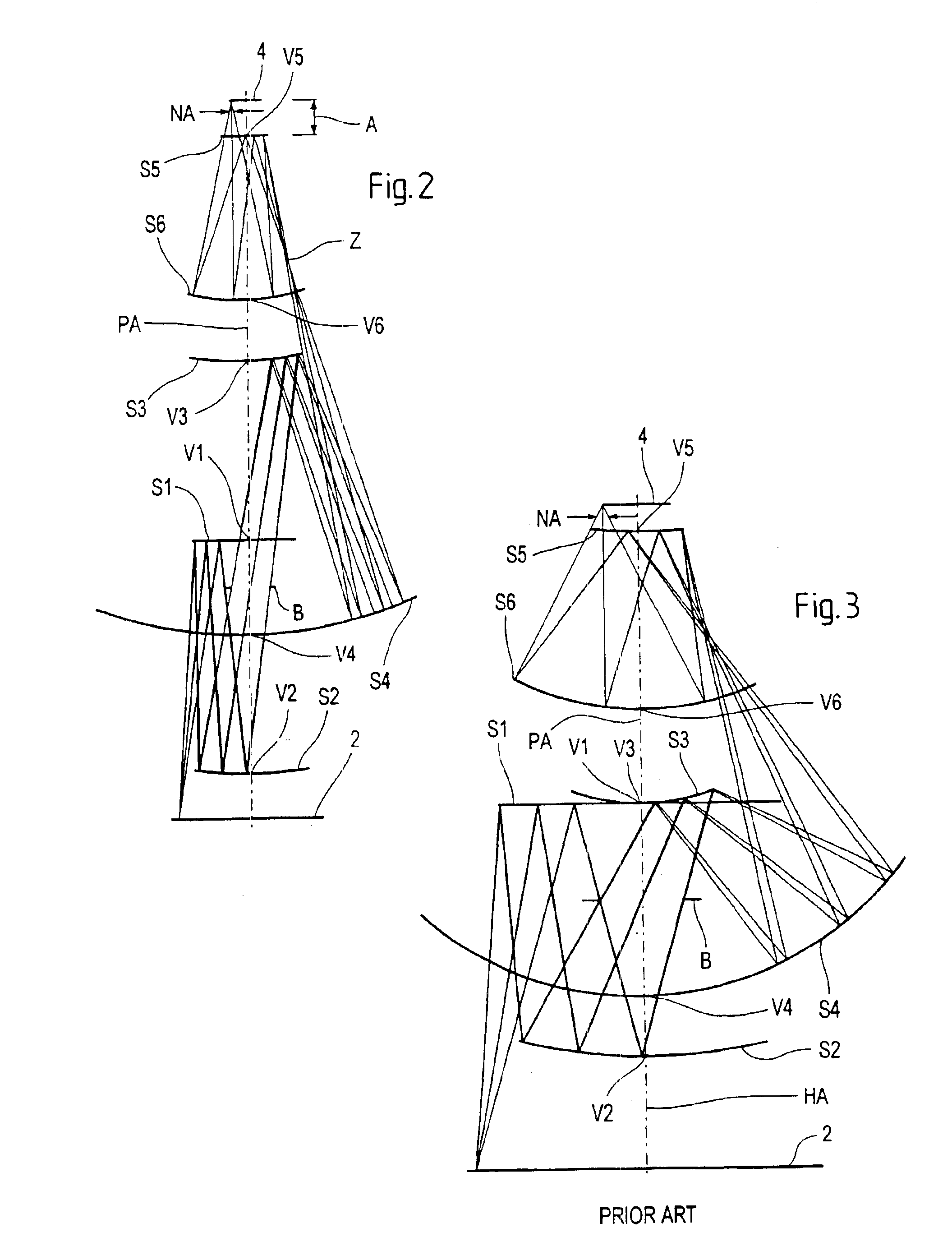
Microlithography reduction objective and projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS6902283B2Efficiently maskedThe implementation process is simpleMirrorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusImage planePhysics
A projection objective formed from six mirrors arranged in a light path between an object plane and an image plane is provided. The projection objective, in some examples, is characterized by having a physical distance between the vertexes of adjacent mirrors that is large enough to allow for the six mirrors to have sufficient thickness and stability properties to prevent surface deformations due to high layer tensions. In some embodiments, mirror thickness are such that surface deformations are prevented with mirrors having layer tensions lower than 350 MPa. Mirror surfaces may comprise multilayer systems of Mo / Be or Mo / Si layer pairs. In some examples, the physical distance between a vertex of the third mirror and a vertex of the sixth mirror (S3S6) satisfies the following relationship: 0.3×(a used diameter of the third mirror S3+a used diameter of the sixth mirror S6)<S3S6. In some examples, a ratio of a physical distance between a vertex of the first mirror and a vertex of the third mirror (S1S3) to a physical distance between the vertex of the first mirror and a vertex of the second mirror (S1S2) is within the range of: 0.5<S1S3 / S1S2<2. In some examples, the physical mirror surfaces of the mirrors have a rotational symmetry with respect to a principal axis (PA). In some examples, all physical mirror surfaces are aspherical. In some examples, at most five physical mirror surfaces are aspherical. Other examples are provided, along with microlithography projection exposure apparatuses and processes for producing a microelectronic device.
Owner:CARL ZEISS STIFTUNG
Stereoscopic viewing device and stereoscopic viewing method
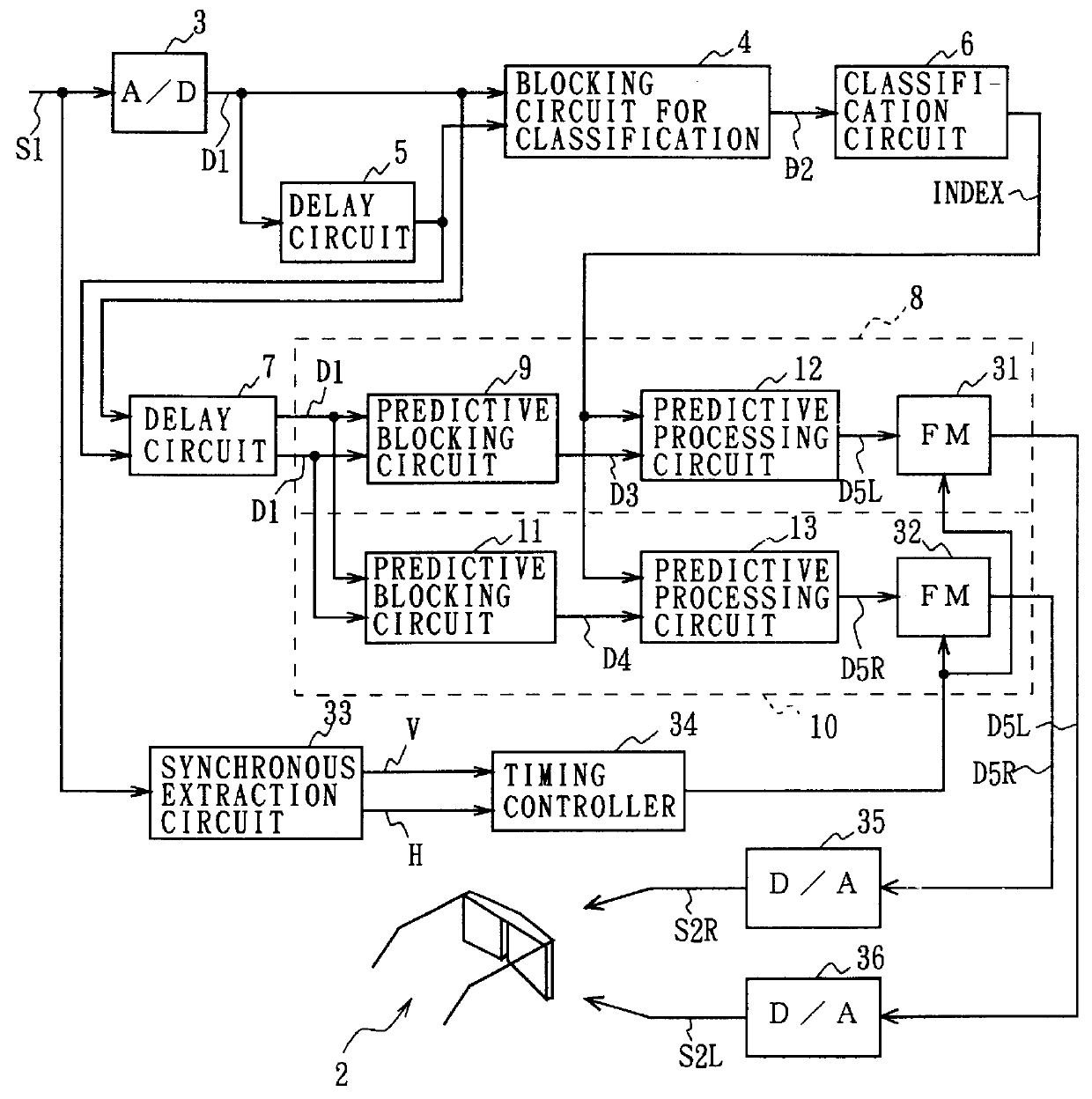
InactiveUS6078352APreventing Image Quality DeteriorationInhibit deteriorationClosed circuit television systemsDigital video signal modificationTemporal RegionsImaging quality
This invention concerns a stereoscopic viewing device and a stereoscopic viewing method, and makes it possible to provide a satisfactory stereoscopic image without increasing of the quantity of recorded information and the quantity of transmitted information. According to the invention, the input television signal is classified respectively on the basis of the level distribution pattern for every pixel in the spatio-temporal region whose center is lying on each attentional pixel, and the input television signal is blocked for every pixel in the spatio-temporal region whose center is lying on each attentional pixel respectively so as to generate the pixel data for predictive calculation, and the predictive calculation of the predictive calculating pixel data is processed utilizing the predictive coefficient which is corresponding to the result of classification obtained from the classifying means out of the predictive coefficients of each set which have been previously prepared, so as to generate the video signal for left eye and the image signal for right eye respectively, and then the stereoscopic image is displayed on the basis of the video signal for left eye and the video signal for right eye; in this way a stereoscopic image can be projected on the displaying means such that a flicker is eliminated and a deterioration of the image quality is prevented.
Owner:SONY CORP
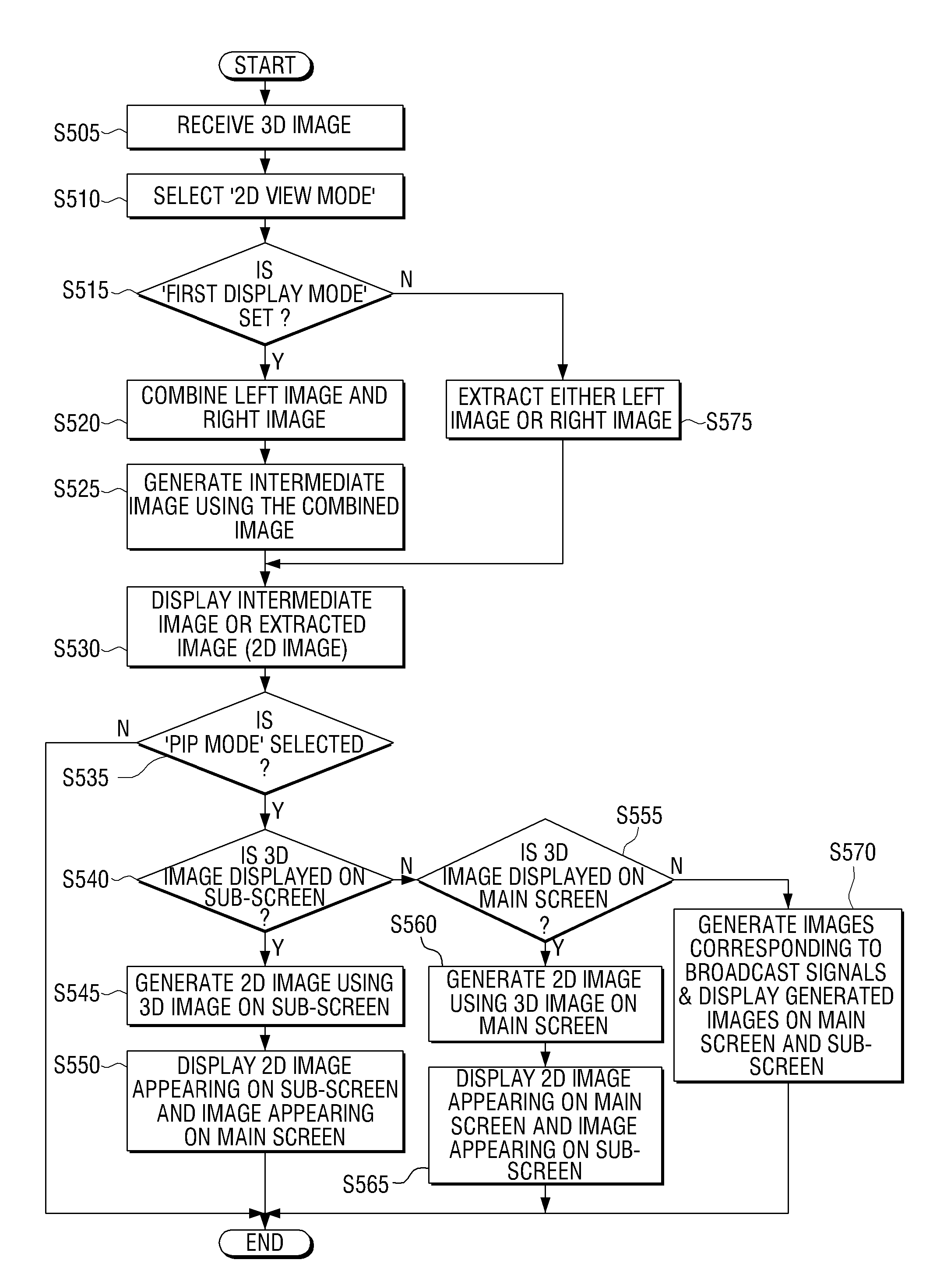
Broadcast display apparatus and method for displaying two-dimensional image thereof
InactiveUS20100091091A1Prevent degradation of image qualityPreventing Image Quality DeteriorationTelevision system detailsColor television details3d image2d images
A broadcast display apparatus and a two dimensional (2D) image display method of the broadcast display apparatus are provided. The 2D image display method includes selecting a 2D display mode; generating a 2D image using at least one of a left image and a right image of a three dimensional (3D) image; and displaying the 2D image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
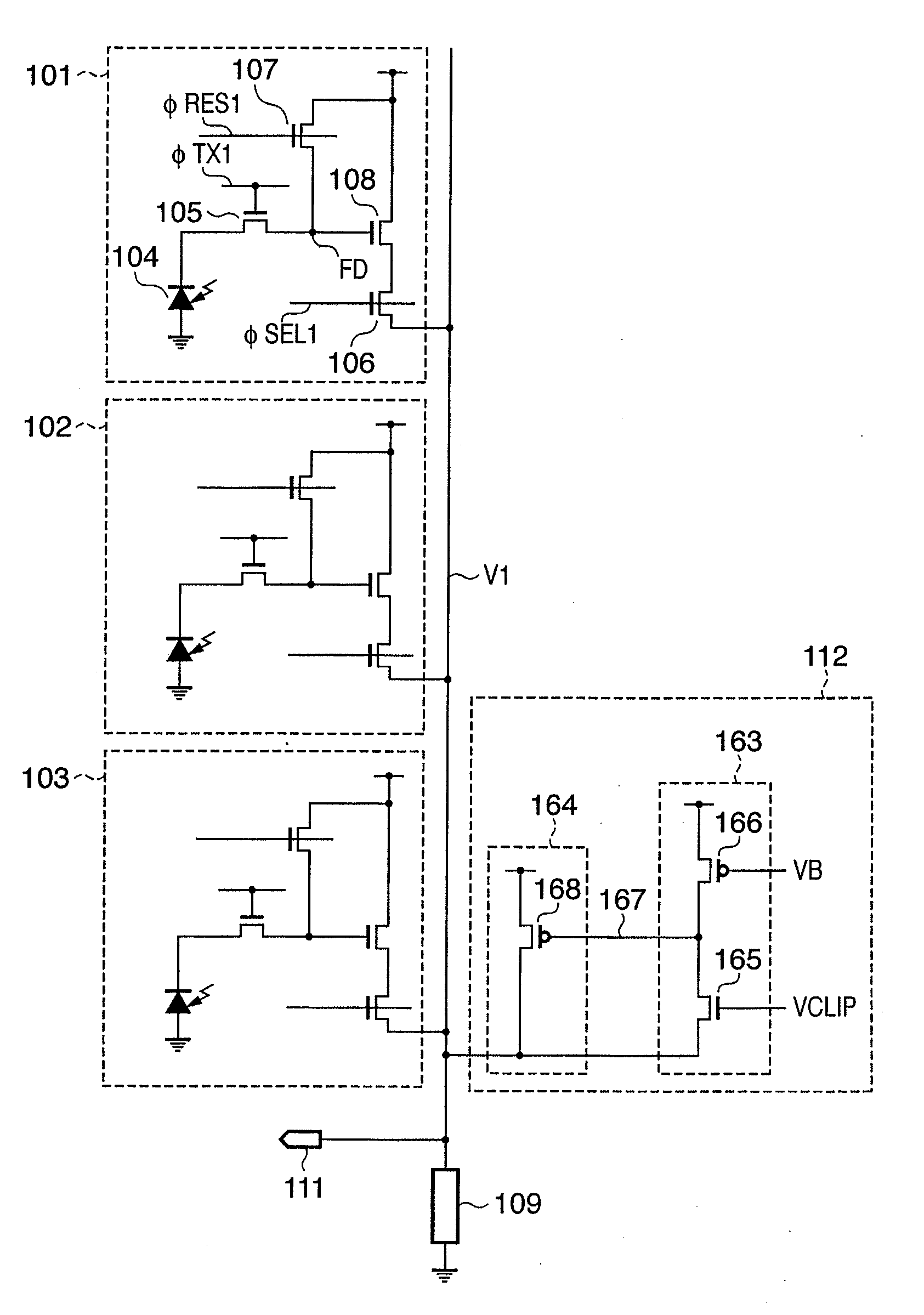
Photoelectric conversion apparatus which avoids certain shading effects
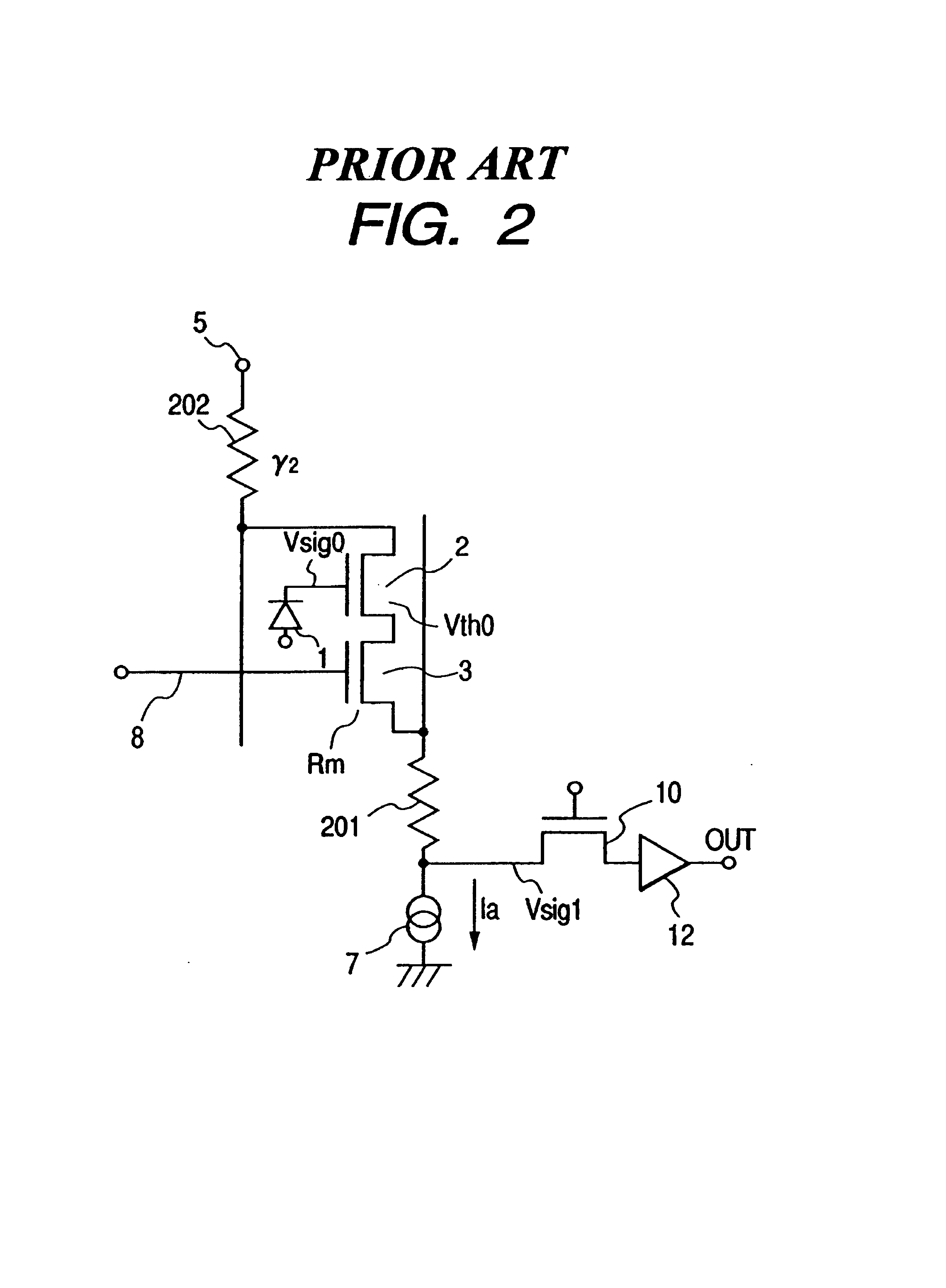
InactiveUS7221397B1Quality improvementPreventing Image Quality DeteriorationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceImaging quality
In order to solve the problem in which voltages Vsig1 read in units of rows have differences to cause vertical shading, thereby degrading image quality, and the problem in which the dynamic ranges of source follower circuits are different in units of rows because finite resistances are distributed in the power supply lines, a photoelectric conversion apparatus includes photoelectric conversion portions placed in a plurality of rows, an amplification section including a load section arranged in units of vertical output lines to amplify signal charges accumulated in the photoelectric conversion portions placed in a plurality of rows, a vertical scanning section for sequentially scanning signals amplified by the amplification section to read the signals onto the vertical output lines, and a horizontal scanning section for sequentially scanning the signals amplified by the amplification section to read the signals onto horizontal output lines, wherein the load sections are located on a side vertically opposite to the direction of signal output from the amplification section.
Owner:CANON KK
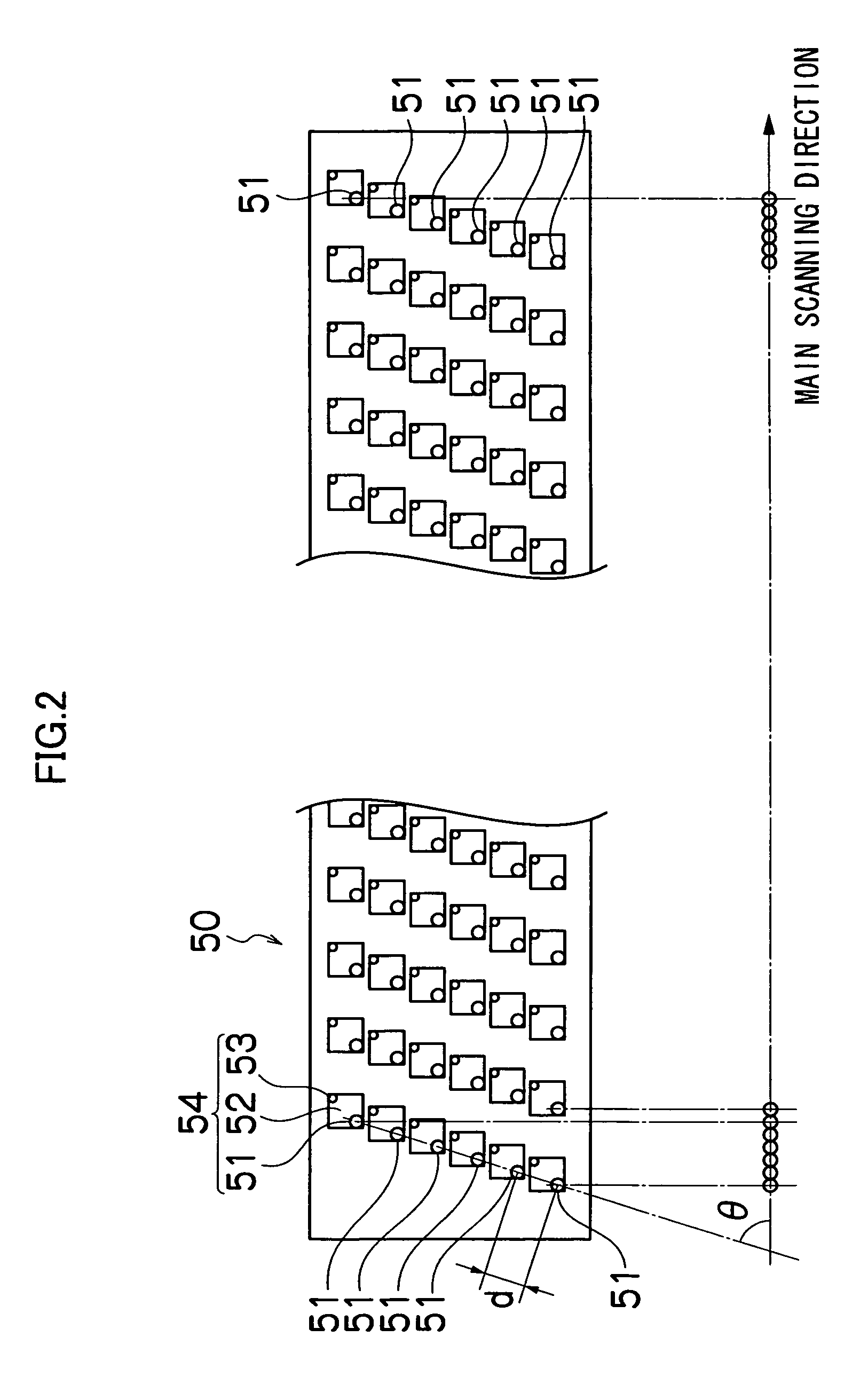
Adjustment method of printing positions, a printing apparatus and a printing system
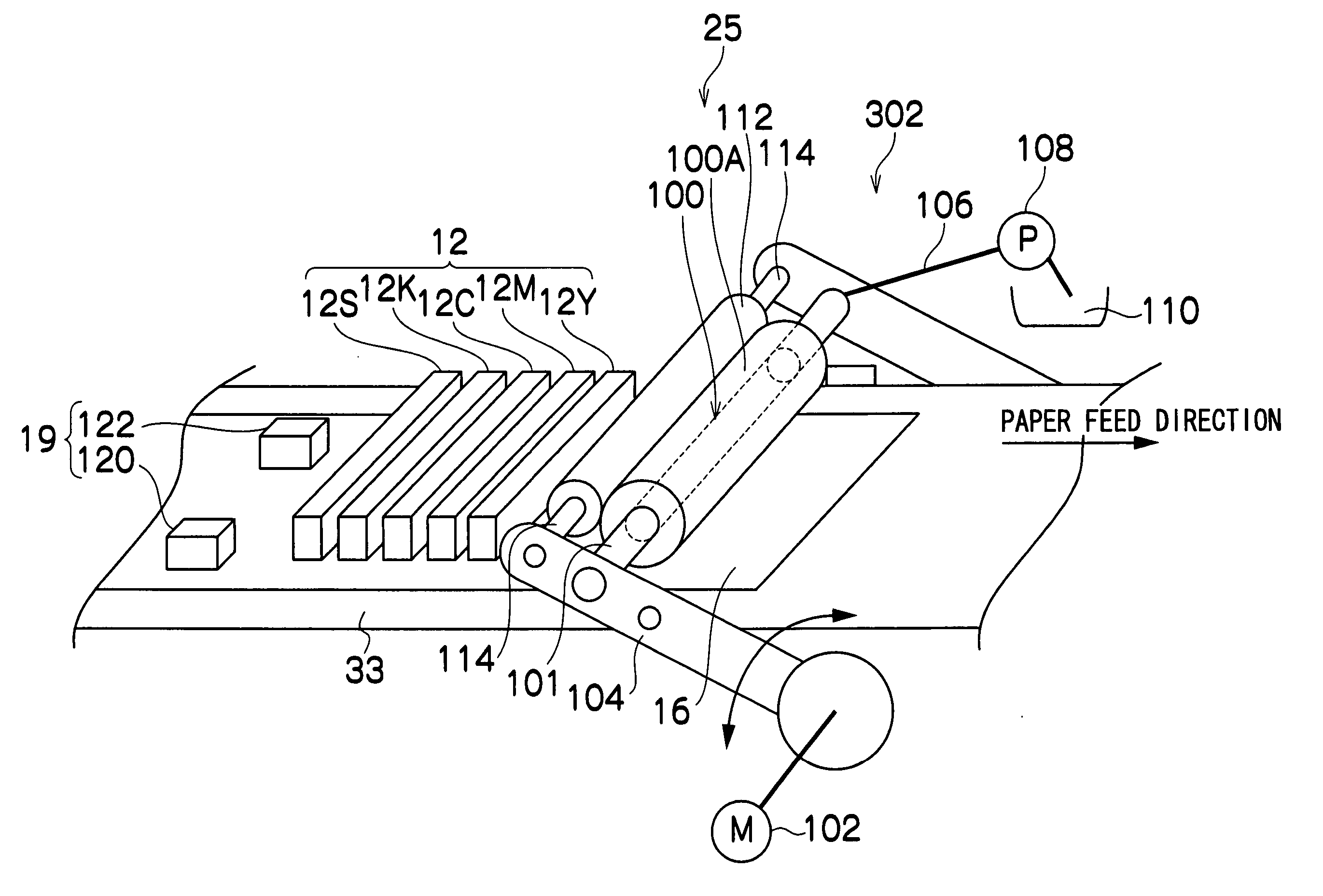
InactiveUS20060044334A1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationQuality improvementSpacing mechanismsOther printing apparatusGratingImage resolution
By using an ink jet head, which has for each color two parallel columns of nozzles arranged side by side in the main scan direction and shifted from each other by one-half the pitch at which the nozzles are arranged in each column, odd-numbered rasters and even-numbered rasters making up an image are printed by the two nozzle columns. The registration between the odd- and even-numbered rasters is secured during the printing to produce an image with high print quality. For that purpose, the ink ejection timing between the two raster groups is shifted by a predetermined interval to form a plurality of adjustment patterns; the adjustment patterns printed are checked and, according to the check result, an adjustment value for the ink ejection timing between the two ink nozzle columns is entered, and the entered adjustment value is stored to be reflected on the actual printing operation. To facilitate the adjustment pattern check, the plurality of adjustment patterns have a dot distribution with a blue noise characteristic at a resolution at which the printing apparatus can print.
Owner:CANON KK
Projection system for EUV lithography
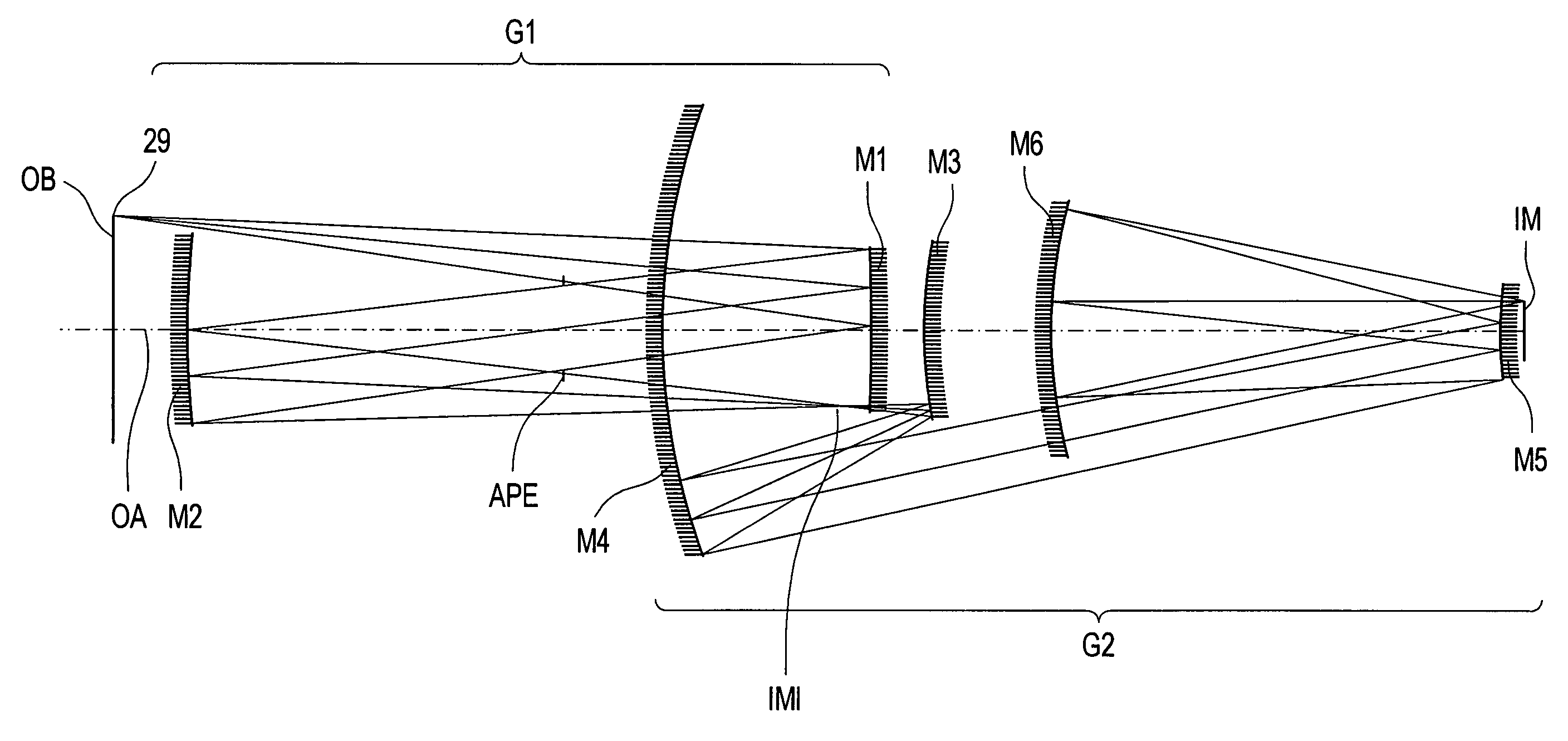
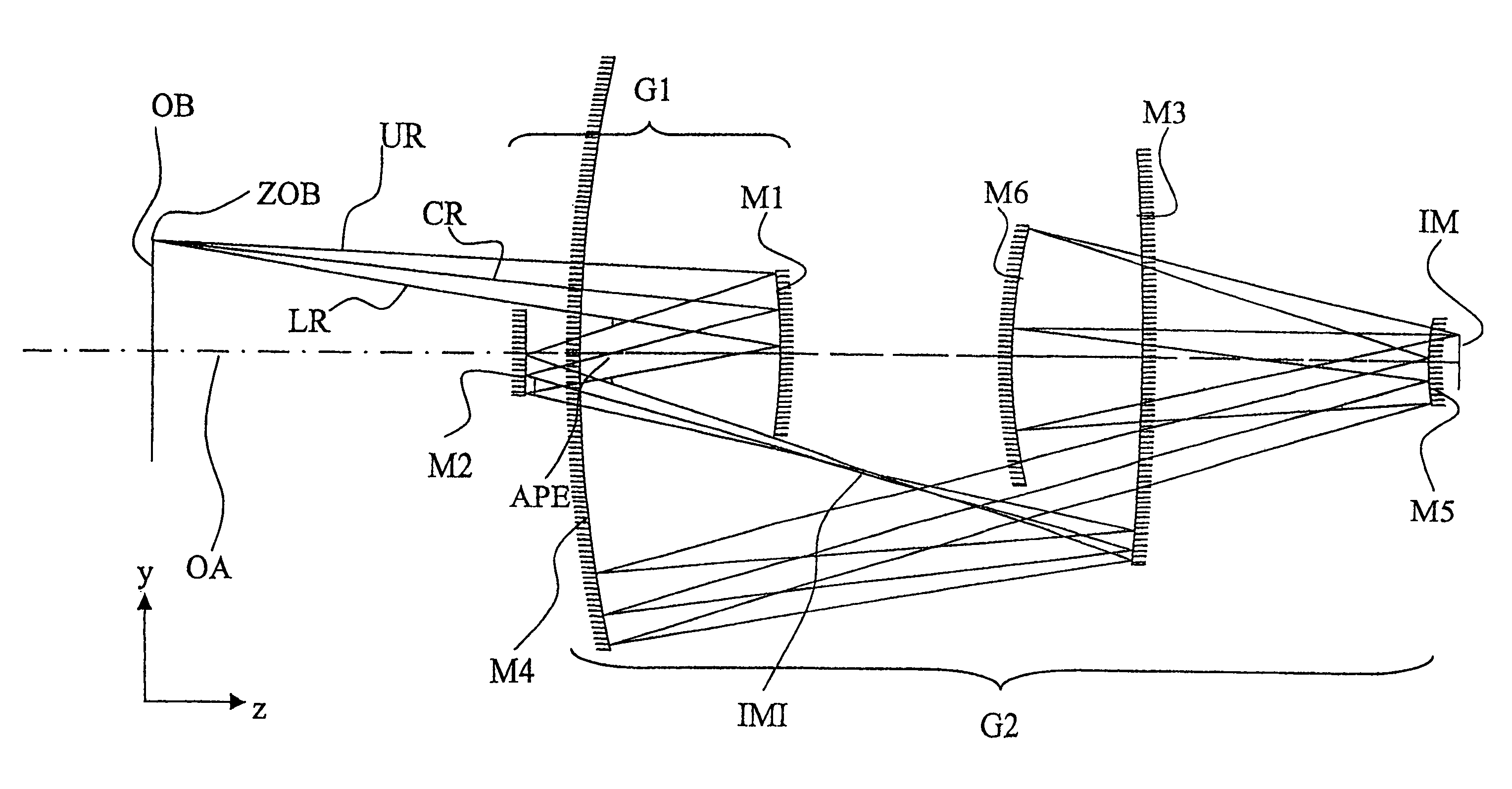
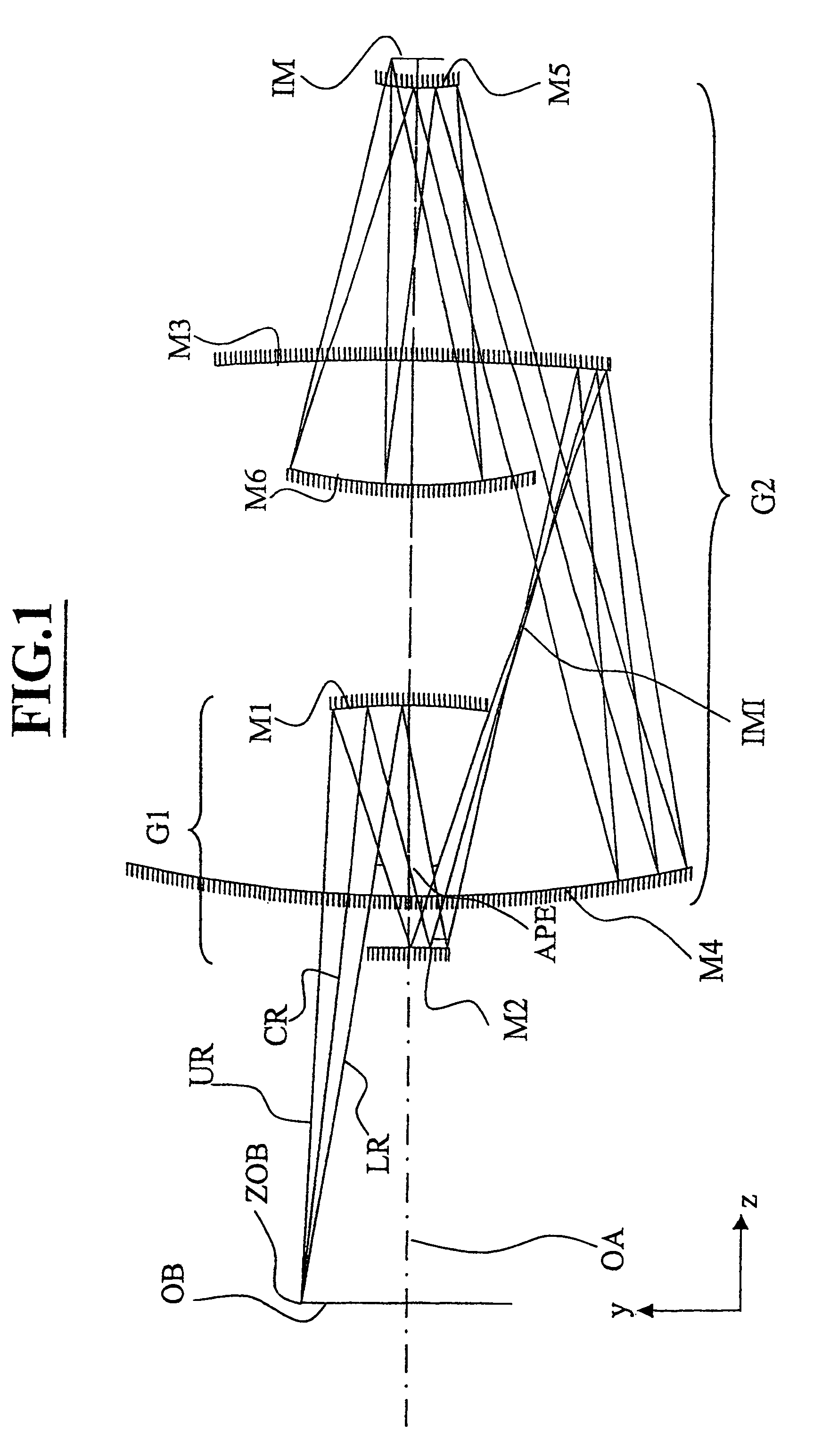
InactiveUS6985210B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationEasy mounting and adjustingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageOptical axis
An EUV optical projection system includes at least six reflecting surfaces for imaging an object (OB) on an image (IM). The system is preferably configured to form an intermediate image (IMI) along an optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between a secondary mirror (M2) and a tertiary mirror (M3), such that a primary mirror (M1) and the secondary mirror (M2) form a first optical group (G1) and the tertiary mirror (M3), a fourth mirror (M4), a fifth mirror (M5) and a sixth mirror (M6) form a second optical group (G2). The system also preferably includes an aperture stop (APE) located along the optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between the primary mirror (M1) and the secondary mirror (M2). The secondary mirror (M2) is preferably concave, and the tertiary mirror (M3) is preferably convex. Each of the six reflecting surfaces preferably receives a chief ray (CR) from a central field point at an incidence angle of less than substantially 15°. The system preferably has a numerical aperture greater than 0.18 at the image (IM). The system is preferably configured such that a chief ray (CR) converges toward the optical axis (OA) while propagating between the secondary mirror (M2) and the tertiary mirror (M3).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Digital micro-mirror device (DMD) assembly for an optical projection system
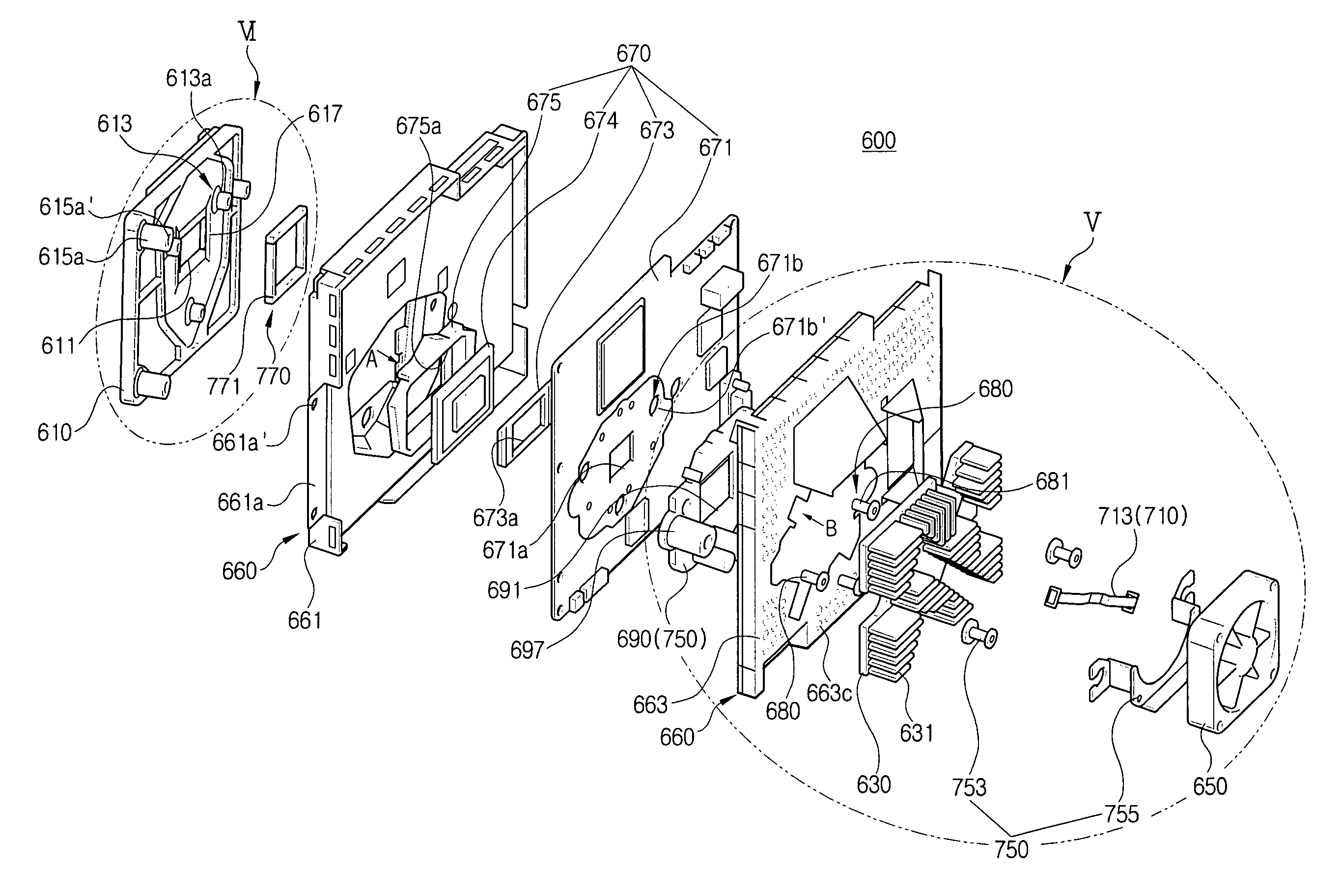
InactiveUS20060227514A1Easy to assembleImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsKitchen equipmentDigital micro mirror deviceOptical mount
A digital micro-mirror assembly for an optical projection system includes a DMD module with a control board. The control board is provided with a first fixing member, and a DMD is mounted on one side of the control board. A DMD holder resiliently supports a perimeter of the DMD, and an optical holder is provided with a second fixing member to support the DMD module. A fastening member is engaged with the first and the second fixing members to integrally connect the DMD module and the optical holder.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Pixel and organic light emitting display device using the same
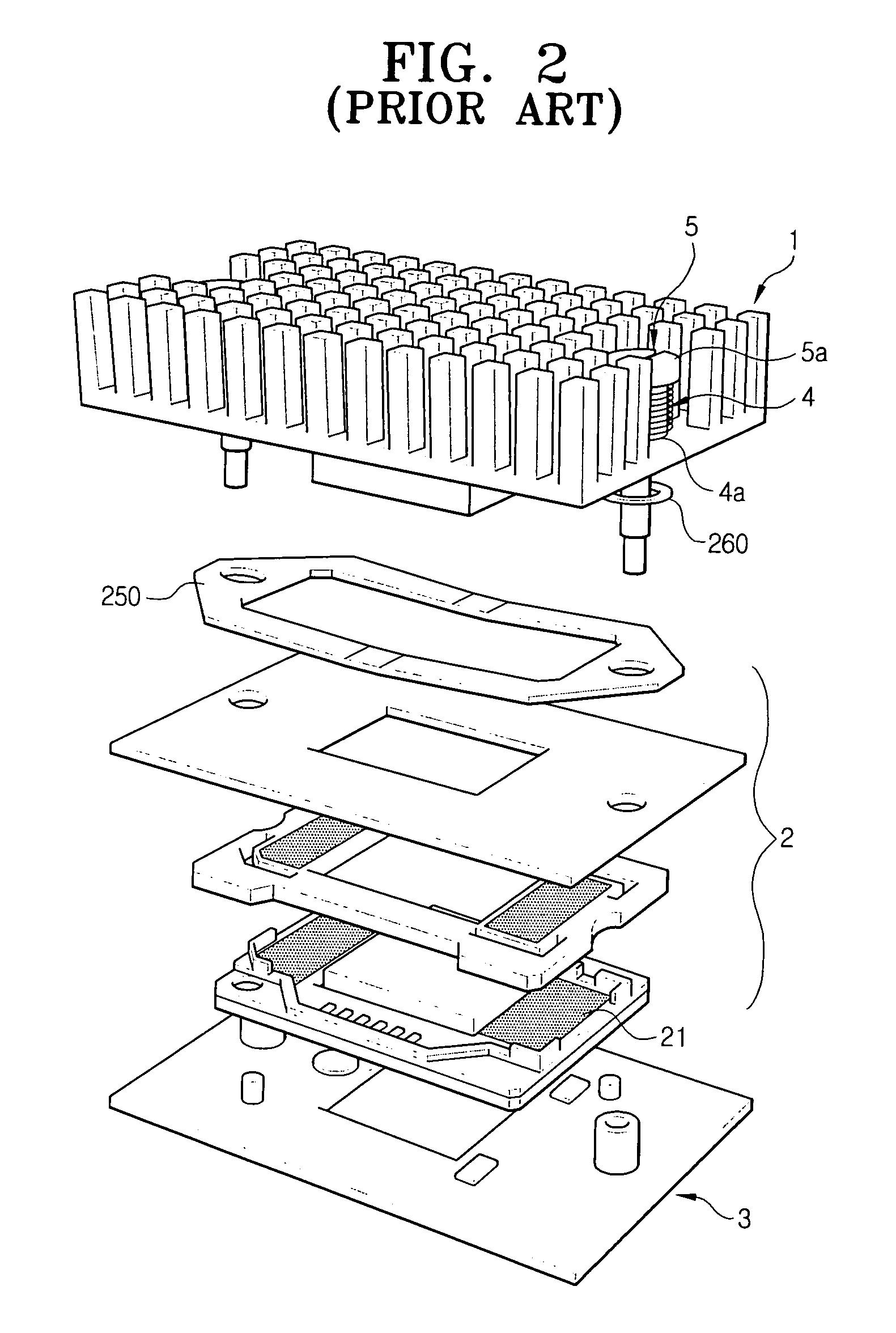
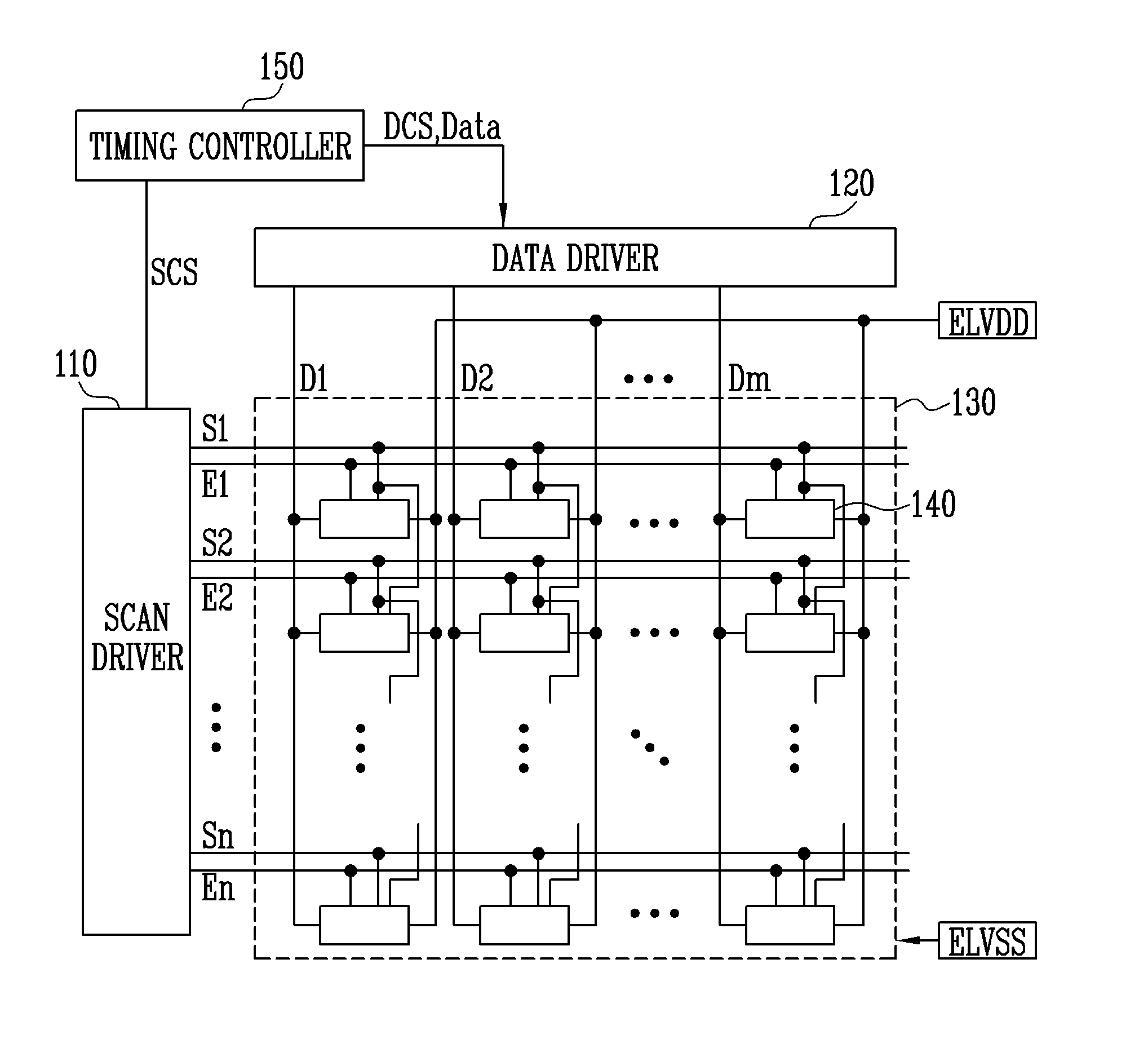
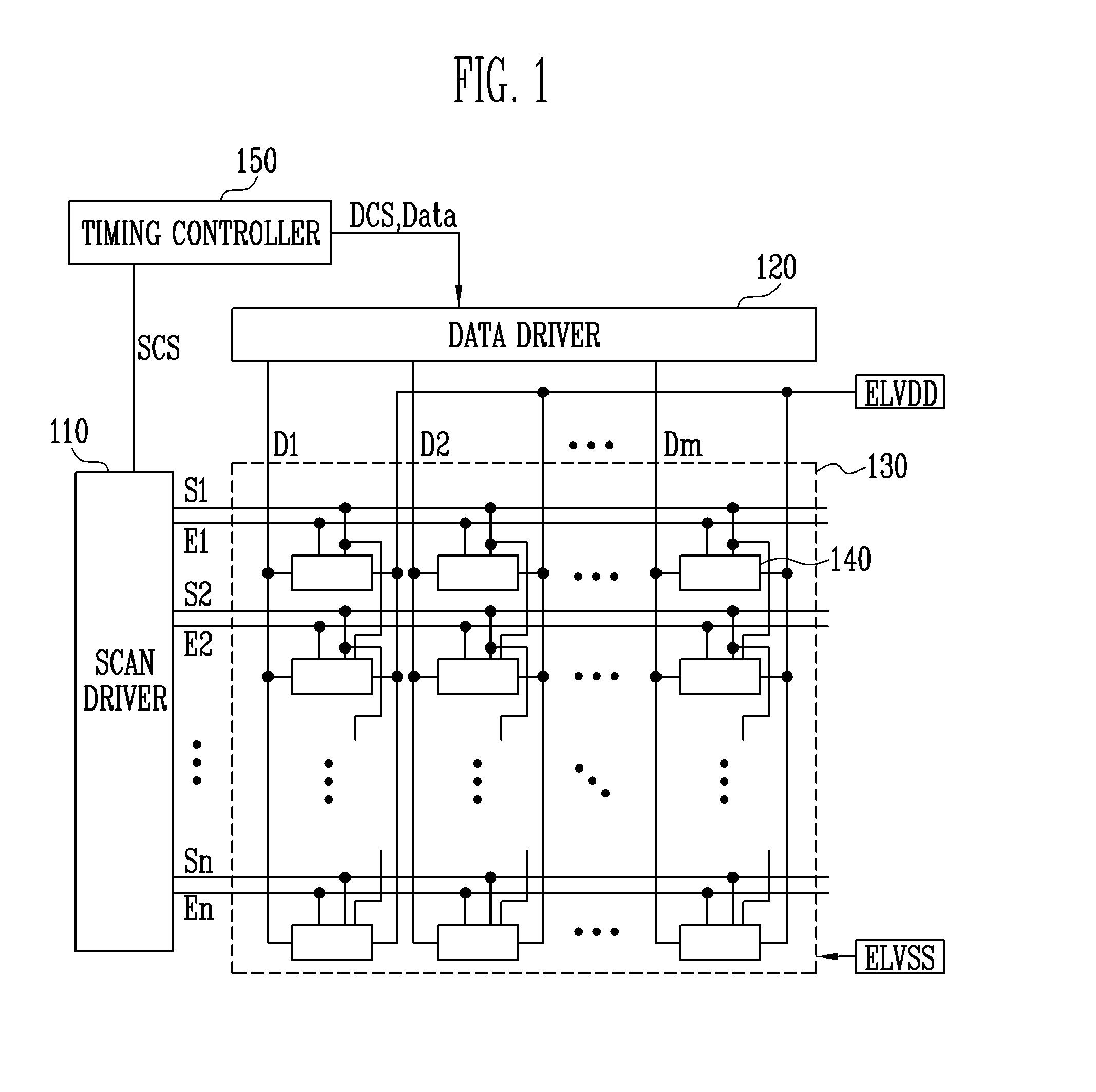
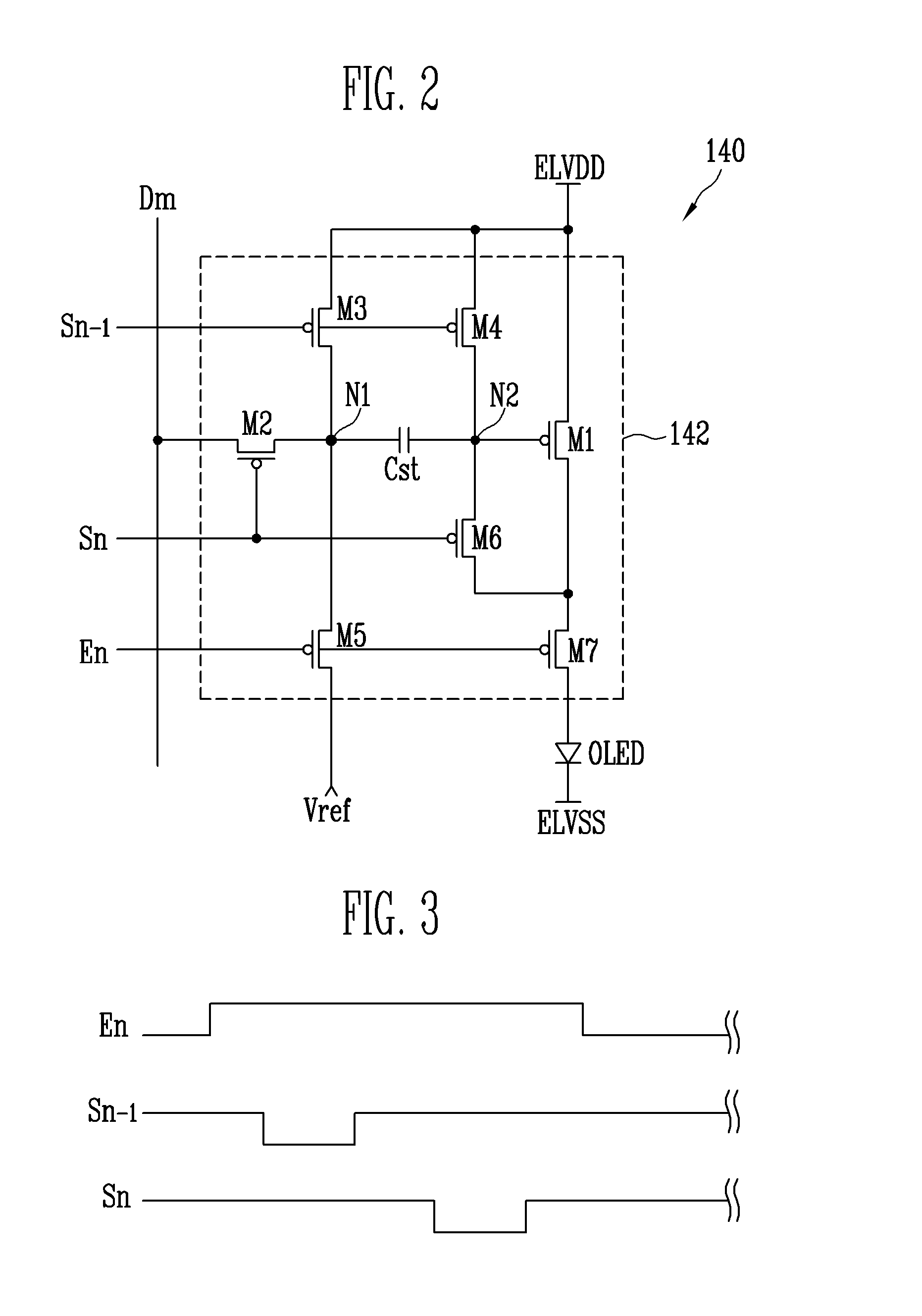
ActiveUS20140168180A1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationImprove image qualityElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor lamp usageScan lineDisplay device
A structure of a pixel and an organic light emitting display device using the same are provided. The pixel includes an organic light emitting diode; a first transistor controlling the amount of current supplied from a first power source to the organic light emitting diode depending on a voltage applied to a second node; a second transistor coupled between a data line and a first node, and turned on when a scan signal is supplied to a first scan line; a third transistor coupled between the first power source and the first node, and turned on when the scan signal is supplied to a second scan line; a fourth transistor coupled between the first power source and the second node, and turned on when the scan signal is supplied to the second scan line; and a storage capacitor coupled between the first and second nodes.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Image processing apparatus, method of processing images, and printing apparatus to which image processing method is applied
InactiveUS7050194B1Improve picture qualityPreventing Image Quality DeteriorationDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingError diffusion
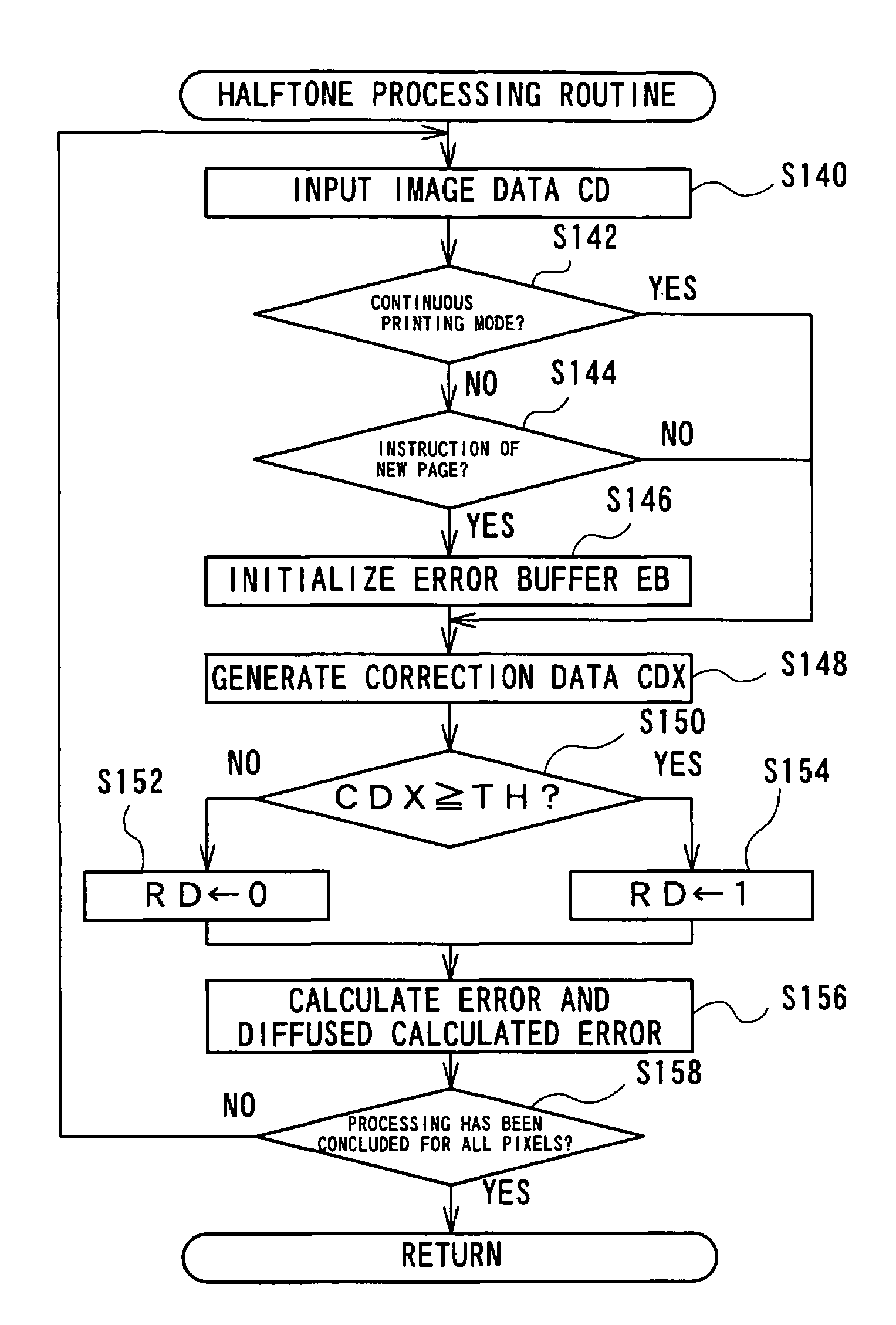
A printing apparatus of the present invention prints an image corresponding to image data, which are divided into a plurality of pages and supplied from an application program, on a roll of machine glazed paper without any margin set between the adjoining pages. This arrangement enables printing on a large-sized printing medium, such as a banner. A printer driver incorporated in the printing apparatus causes the image data divided into the plurality of pages to be subjected to halftone processing according to an error diffusion method. When a standard printing mode is specified, an error buffer is initialized on every instruction of a new page. When a continuous printing mode is specified, on the other hand, the error buffer is not initialized. This causes an error occurring in a certain pixel included in one page to be diffused to pixels included in a next page in the continuous printing mode. The arrangement of the present invention enables the image data divided into a plurality of pages to be collectively processed by the halftone processing and thereby improves the picture quality of the image especially in the vicinity of a boundary between the adjoining pages.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Projection system for EUV lithography
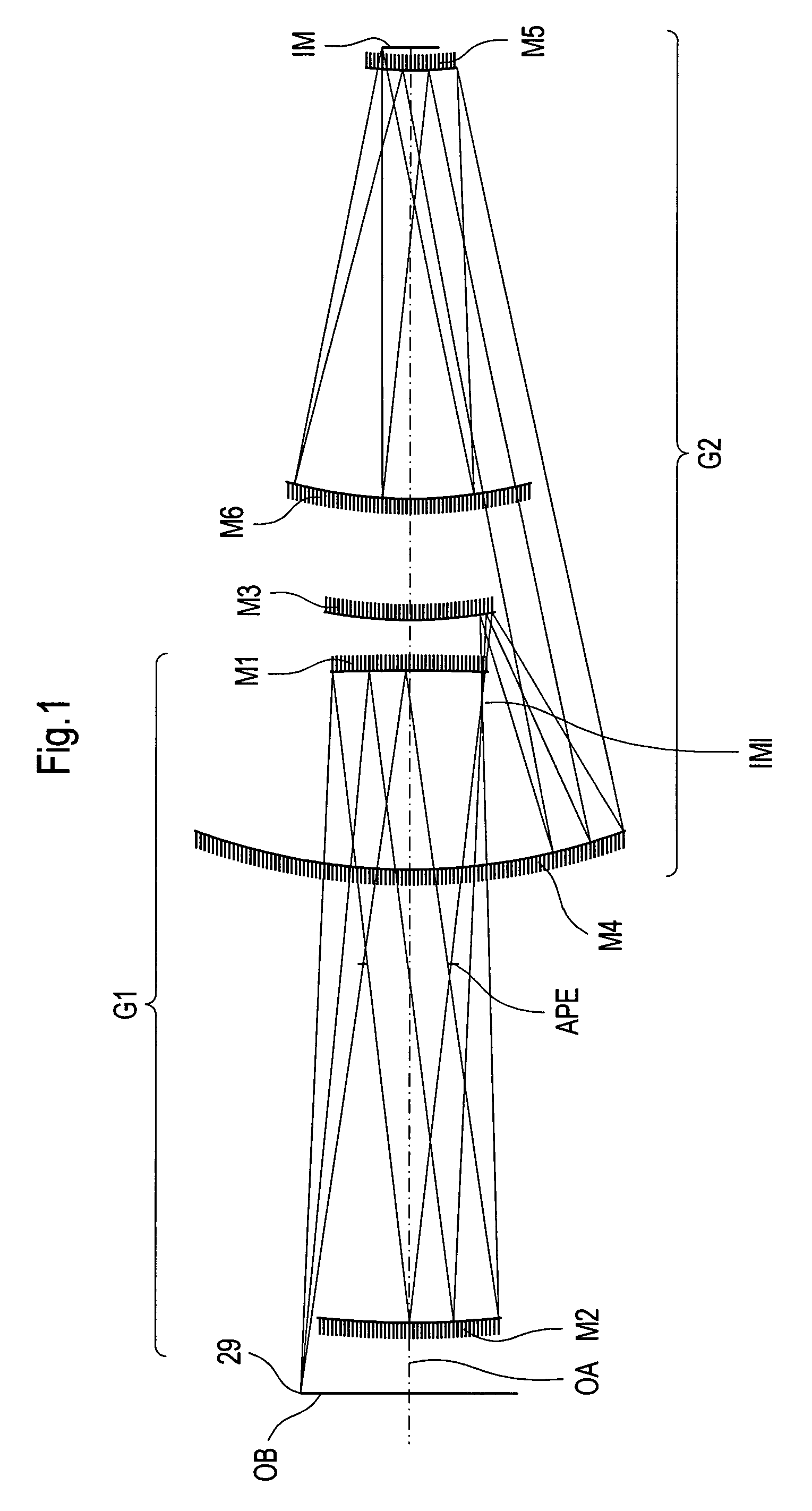
InactiveUS7151592B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationEasy mounting and adjustingMirrorsMicroscopesLithographic artistIntermediate image
An EUV optical projection system includes at least six mirrors (M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6) for imaging an object (OB) to an image (IM). At least one mirror pair is preferably configured as an at least phase compensating mirror pair. The system is preferably configured to form an intermediate image (IMI) along an optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between a second mirror (M2) and a third mirror (M3), such that a first mirror (M1) and the second mirror (M2) form a first optical group (G1) and the third mirror (M3), a fourth mirror (M4), a fifth mirror (M5) and a sixth mirror (M6) form a second optical group (G1). The system also preferably includes an aperture stop (APE) located along the optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between the first mirror (M1) and the second mirror (M2). The second mirror (M2) is preferably convex, and the third mirror (M3) is preferably concave. The system preferably forms an image (IM) with a numerical aperture greater than 0.18.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Lens barrel and image pickup unit
InactiveUS8102609B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationImprove accuracyMountingsOptical axisPhysics
Disclosed herein is a lens barrel including: a plurality of lenses arranged in a state of being separated from each other in a direction of an optical axis; and a lens retaining body for retaining the lenses; wherein a print pattern that has a light shielding function and is partly in contact with the lens retaining body to adjust an interval between the lenses in the direction of the optical axis is formed on at least one of the plurality of lenses.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method of processing image signal from solid-state imaging device, image signal processing apparatus, image signal generating apparatus and computer program product for image signal processing method
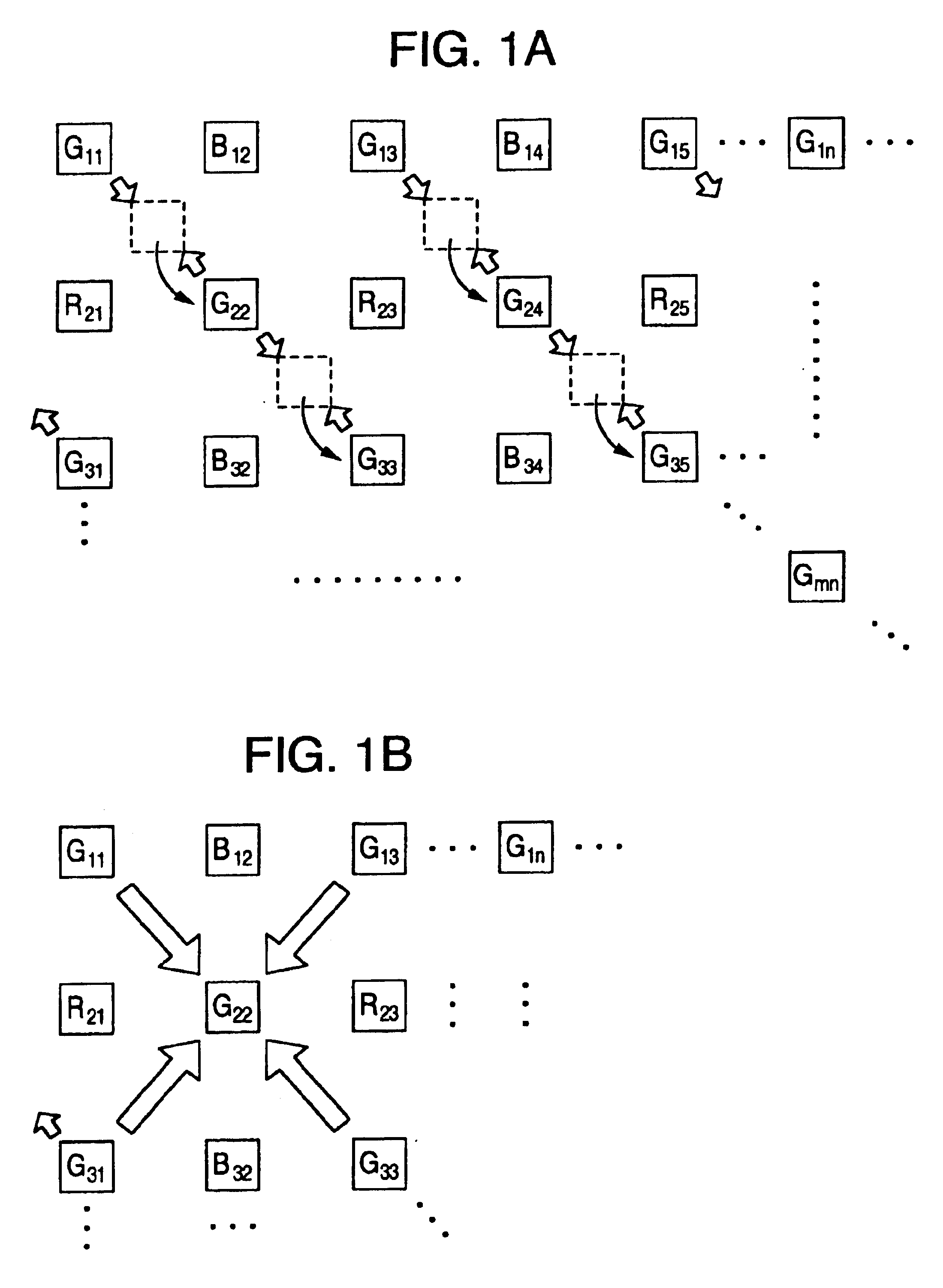
InactiveUS6900838B1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationAvoid height differenceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsGreen-lightComputer science
An image signal processing method and an image signal processing apparatus for processing the color component signal obtained from a solid-state image pickup device including an arrangement of a plurality of photoelectric elements and a color filter arranged in the light receiving section of each pixel corresponding to the photoelectric element, an image signal generating apparatus and a computer program product for the image signal processing method. A color component signal is fetched from a designated pixel corresponding to the photoelectric element having a filter that can transmit the green light on a line of the solid-state image pickup device. A color component signal is also fetched from a pixel corresponding to the photoelectric element having a filter for transmitting at least the green light on another line, which pixel is located in the neighborhood of the designated pixel. Further, based on a plurality of the color signals fetched in the foregoing steps, the value of the color component signal of the designated pixel having the filter for transmitting at least the green light is determined.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com