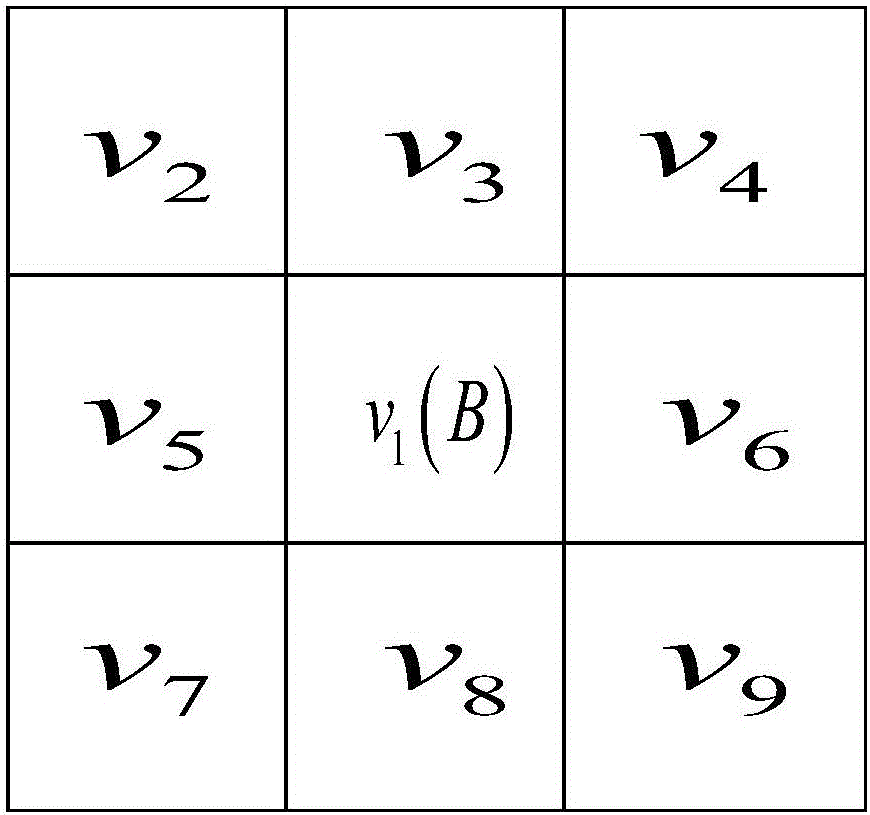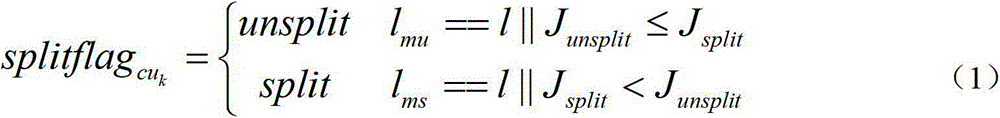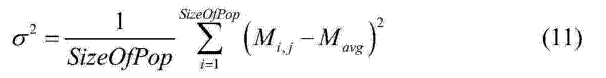Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
229 results about "Sum of absolute differences" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
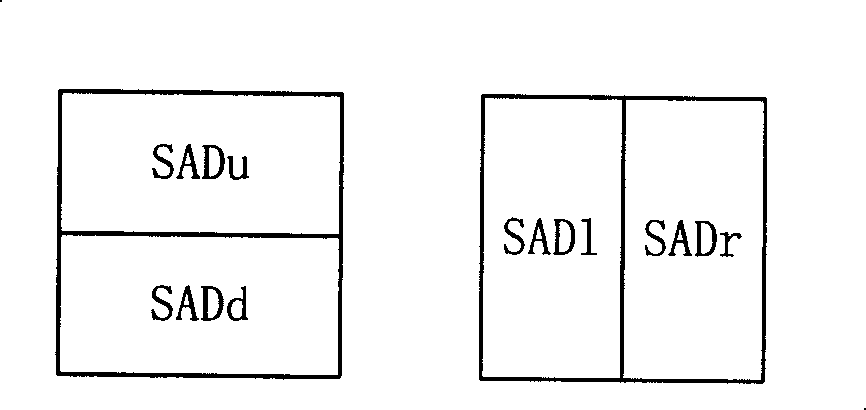
In digital image processing, the sum of absolute differences (SAD) is a measure of the similarity between image blocks. It is calculated by taking the absolute difference between each pixel in the original block and the corresponding pixel in the block being used for comparison. These differences are summed to create a simple metric of block similarity, the L¹ norm of the difference image or Manhattan distance between two image blocks.
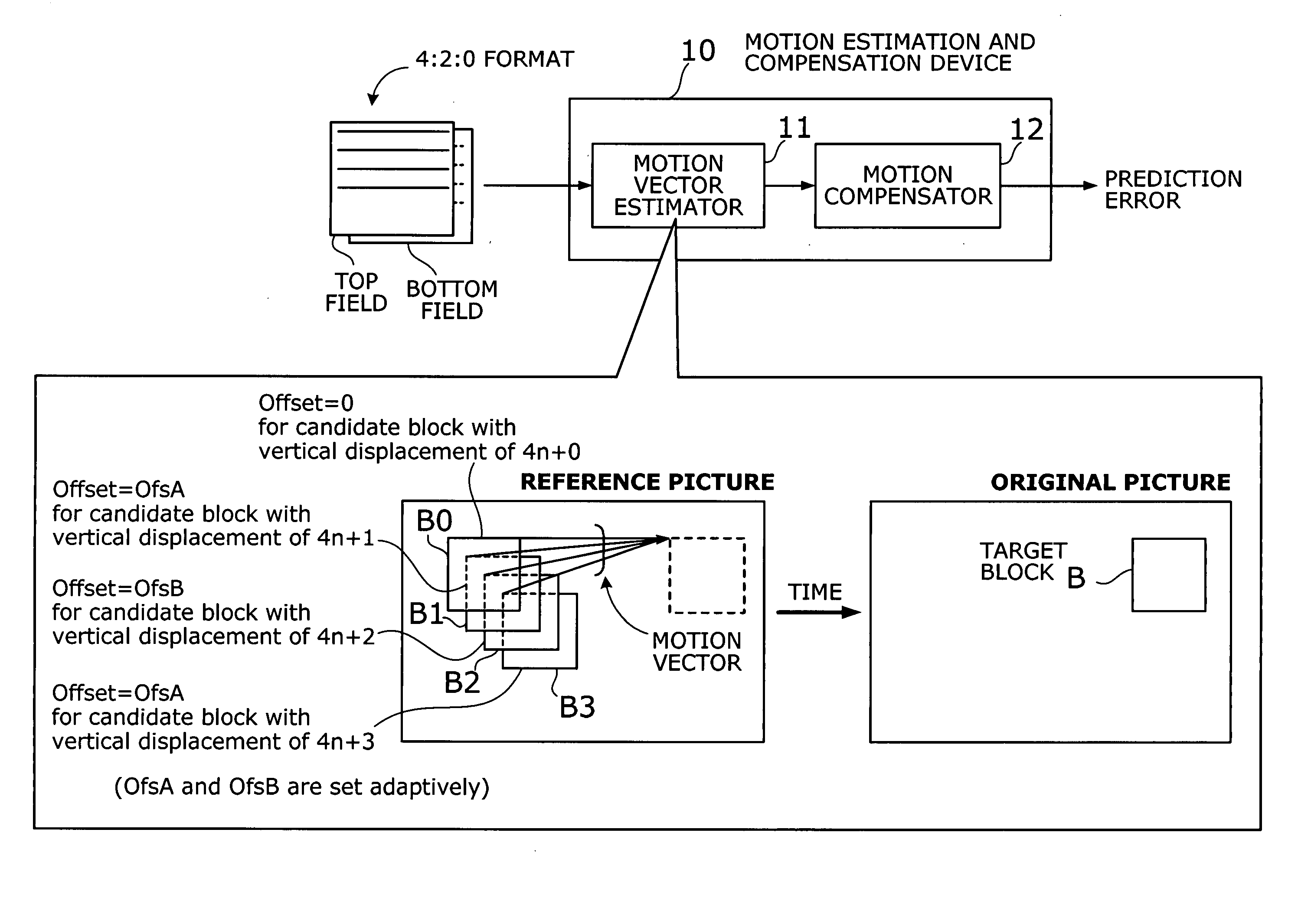
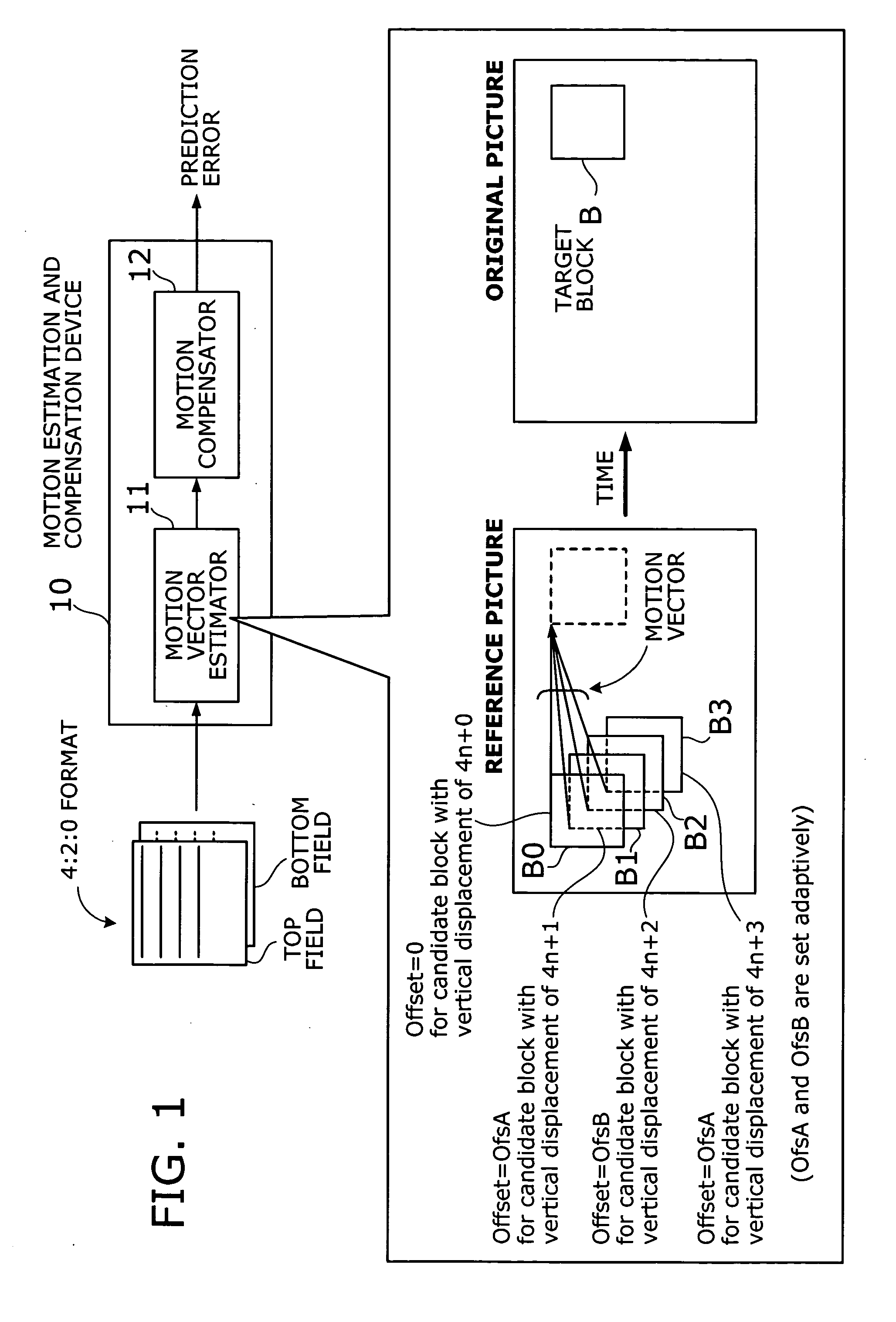
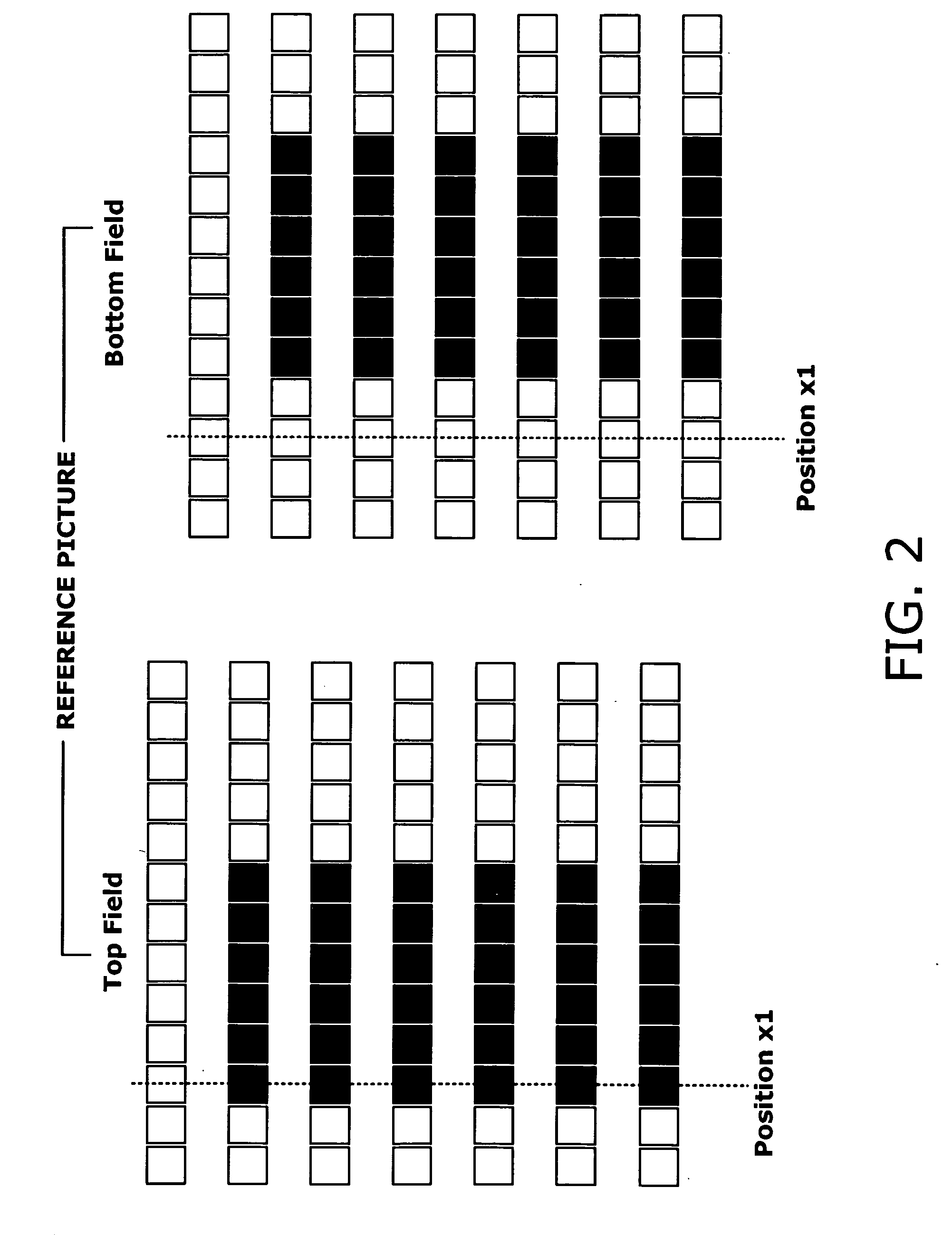
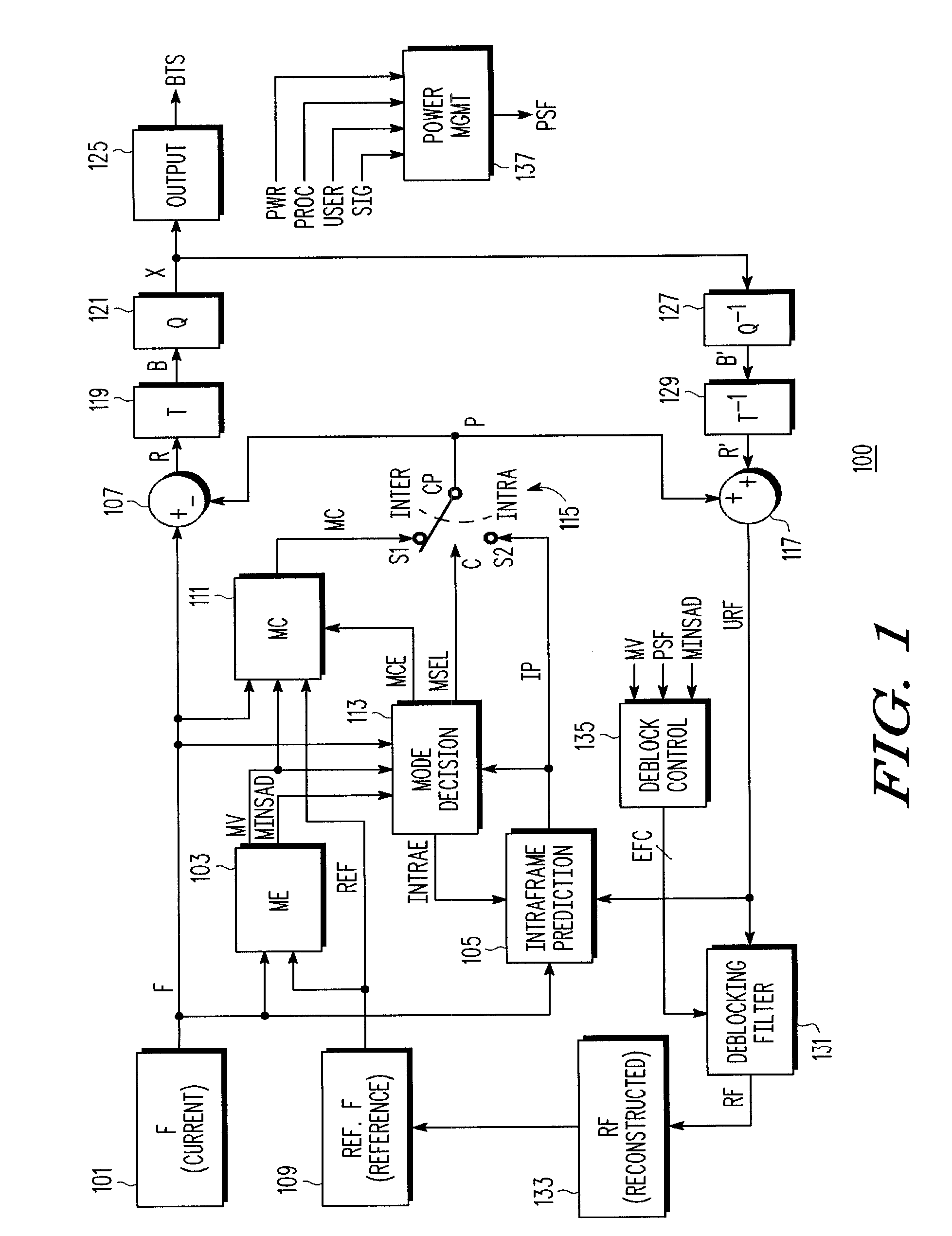
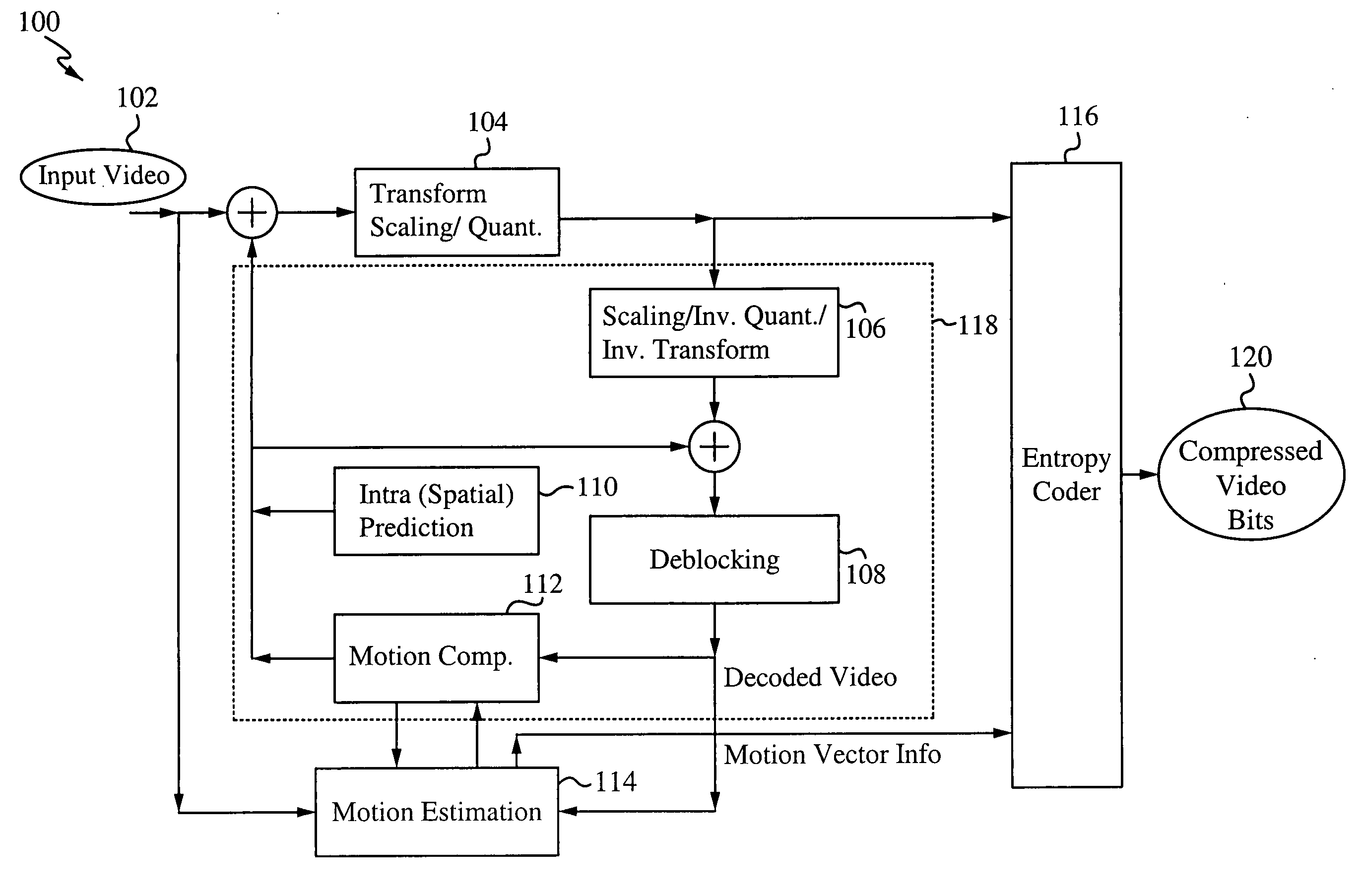
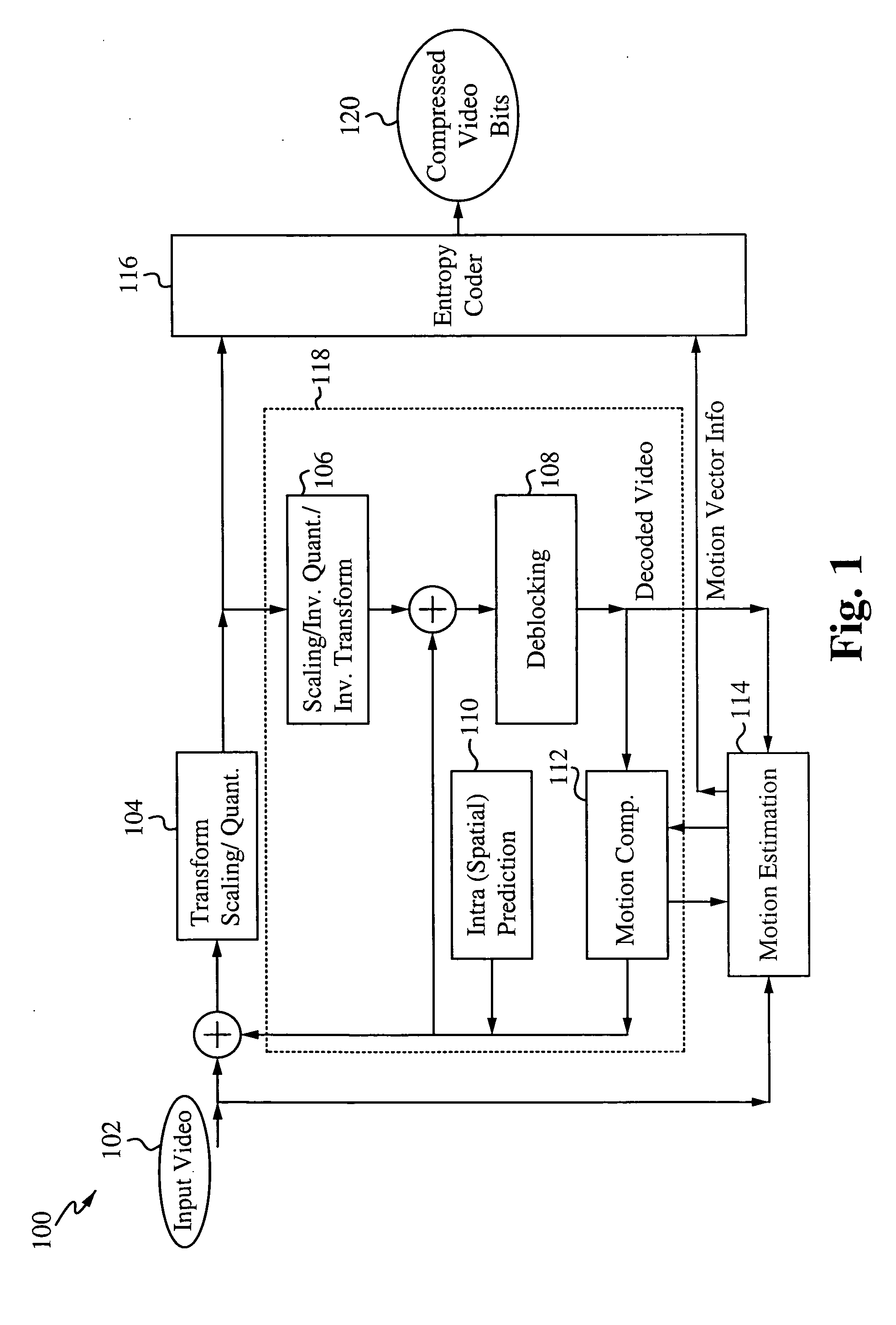
Motion estimation and compensation device with motion vector correction based on vertical component values
InactiveUS20060023788A1Color television with pulse code modulationImage analysisMotion vectorErrors and residuals
A motion estimation and compensation device that avoids discrepancies in chrominance components which could be introduced in the process of motion vector estimation. The device has a motion vector estimator for finding motion vectors in given interlace-scanning chrominance-subsampled video signals. The estimator compares each candidate block in a reference picture with a target block in an original picture by using a sum of absolute differences (SAD) in luminance as similarity metric, chooses a best matching candidate block that minimizes the SAD, and determines its displacement relative to the target block. In this process, the estimator gives the SAD of each candidate block an offset determined from the vertical component of a corresponding motion vector, so as to avoid chrominance discrepancies. A motion compensator then produces a predicted picture using such motion vectors and calculates prediction error by subtracting the predicted picture from the original picture.
Owner:FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS LTD
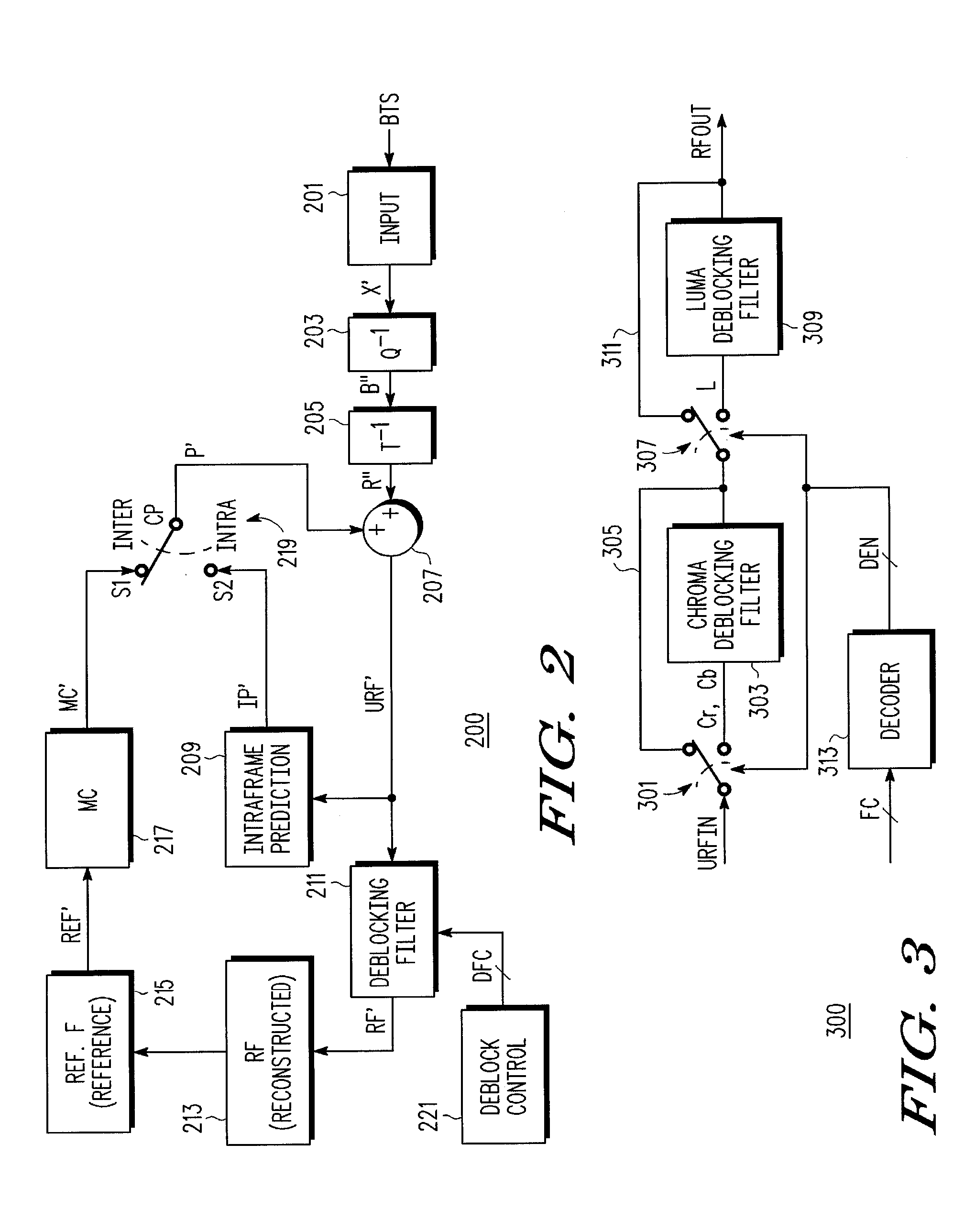
Adaptive disabling of deblock filtering based on a content characteristic of video information
ActiveUS20080137752A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionInformation processing
A method of adaptively disabling deblock filtering of video information including determining a content characteristic of the video information, and adaptively disabling deblock filtering of the video information based on the content characteristic. The content characteristic may be a content complexity, such as an average of minimum sums of absolute differences of pixel values determined during motion estimation, or the mean square error of the video information, or the number of bits used for coding the video content. The content characteristic may be other than complexity, such as motion vector information. A video information processing system including a video processing circuit which processes video information and which determines a content characteristic of the video information, and a deblocking filter circuit which adaptively disables deblock filtering of the video information based on the content characteristic.
Owner:NXP USA INC
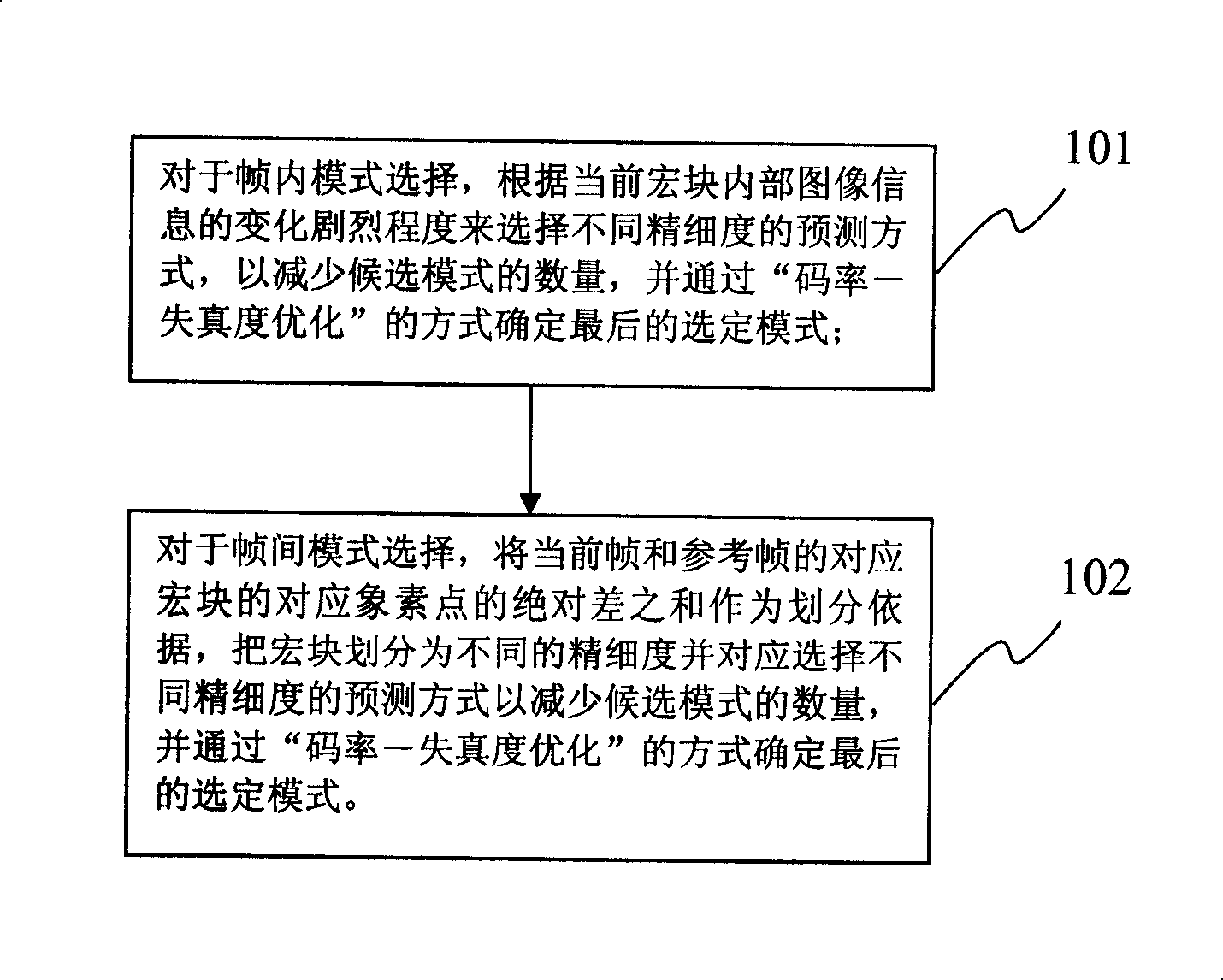
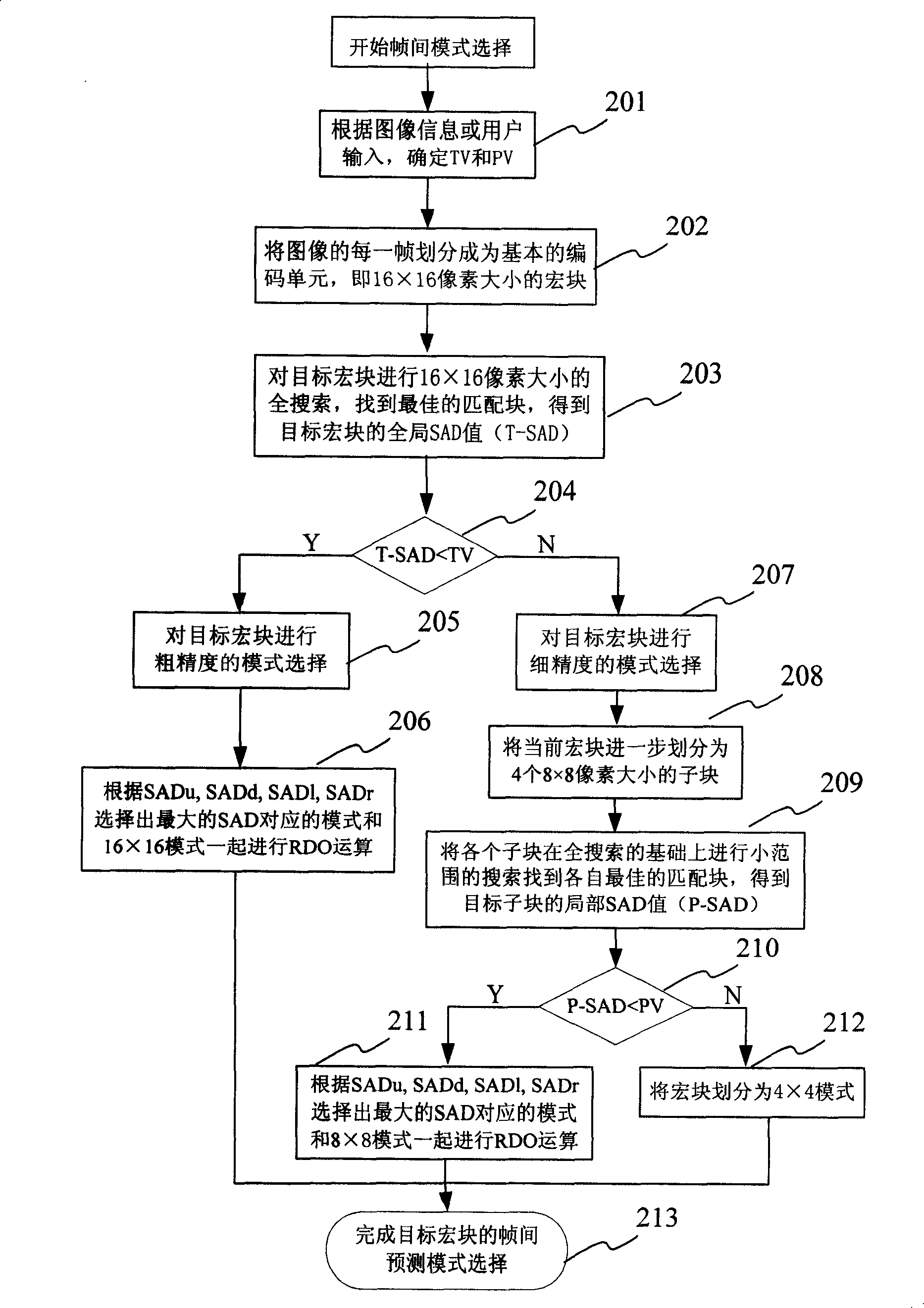
Method and apparatus for fast mode selecting of H264 video coding
InactiveCN101207810AReduce in quantityReduce computationTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationRound complexityAbsolute difference
The invention discloses a quick mode selection method and a device of an H264 video coding. The method comprises the selection of a mode in frames and the selection of the mode between the frames, wherein, for the selection of the mode in the frames, a prediction method with different fineness is chosen according to the dramatic degree of the image information changes in the prior macro block, thereby decreasing the number of the model to be chosen and confirming the final selection mode through the method of code rate-distortion factor optimizing; for the selection of the mode between the frames, the sum of the absolute difference of the corresponding pixel point of the corresponding macro block of the prior frame and the reference frame is used as a dividing basis to divide the macro block into different fineness and to correspondingly choose a prediction method with different fineness for decreasing the number of the model to be chosen and confirming the final selection mode through the method of code rate-distortion factor optimizing. The invention can decrease the number of the model to be chosen and solve the application limited problems caused by over-complicated code, over-loaded operation and over time consumption in the prior art.
Owner:车主邦(北京)科技有限公司
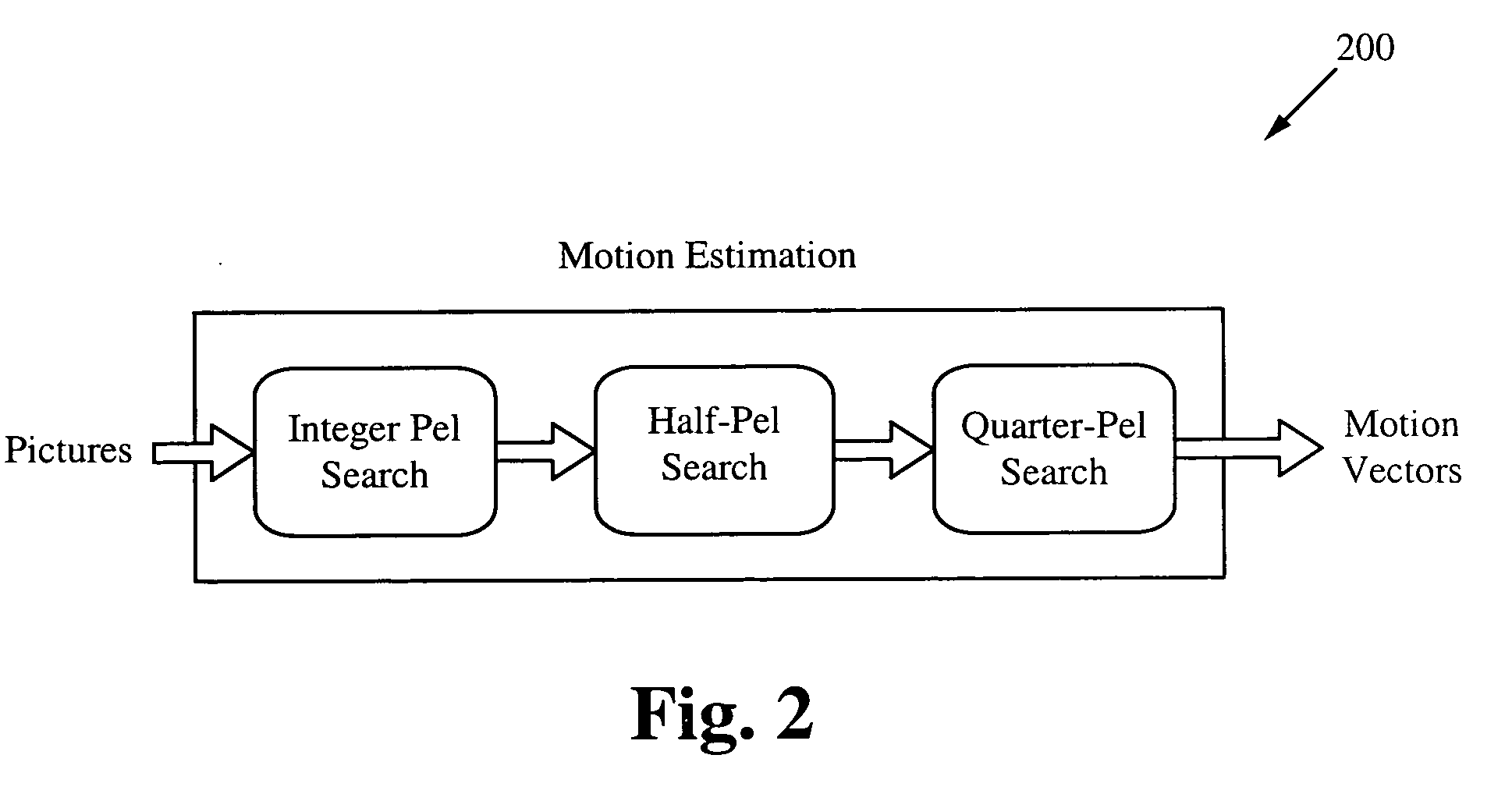
Motion estimation technique for digital video encoding applications
InactiveUS20100177826A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationPattern recognitionDigital video
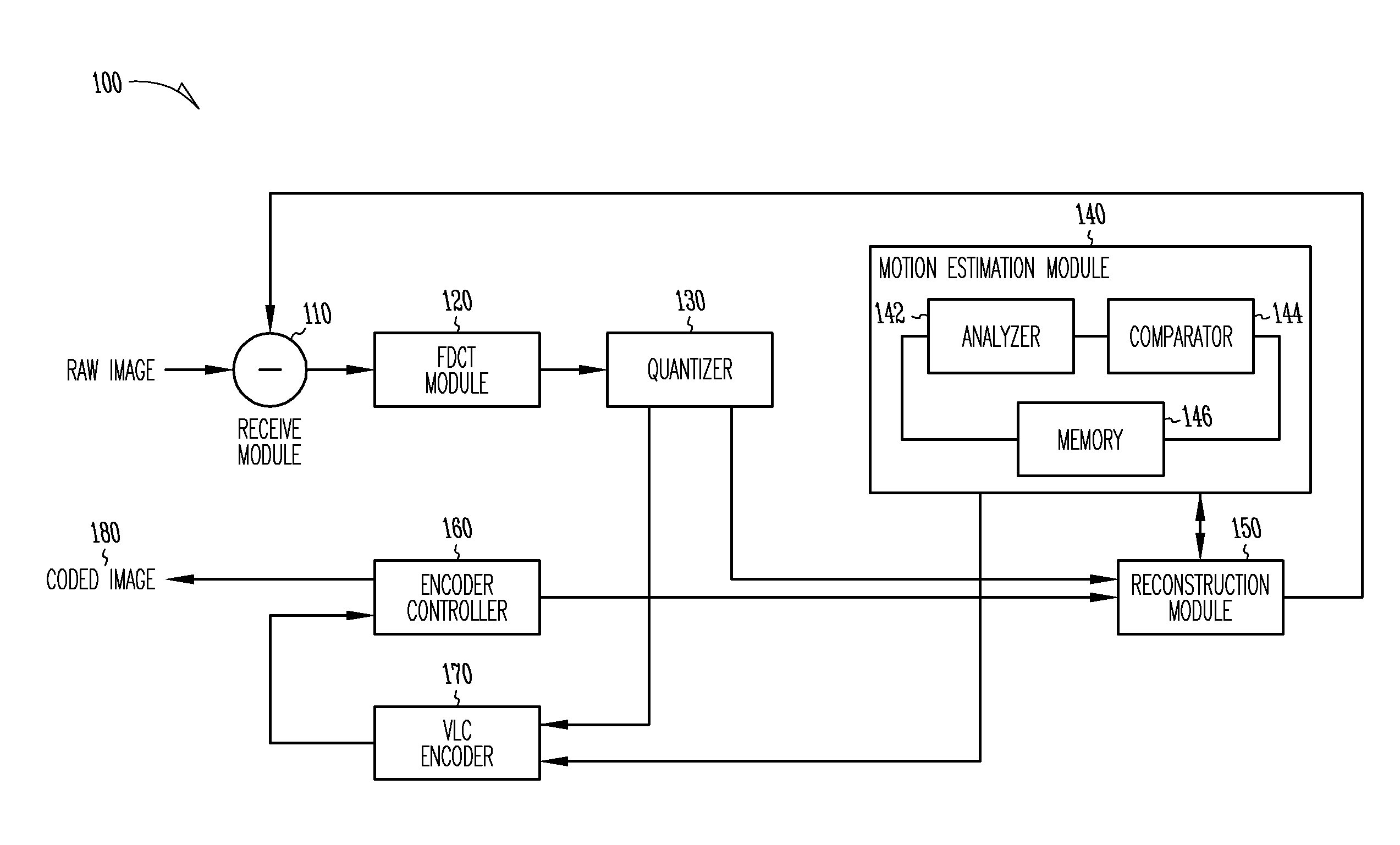
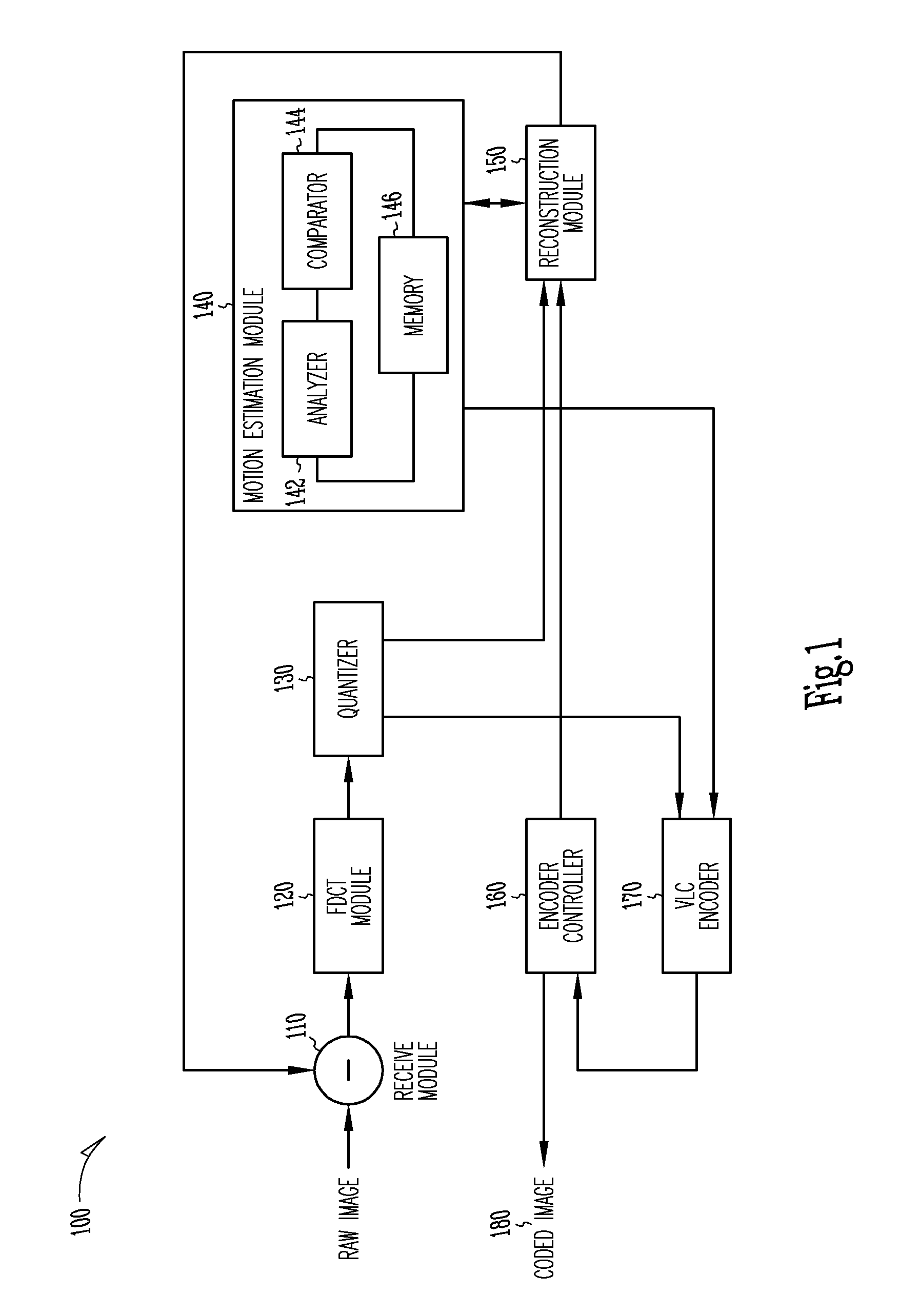
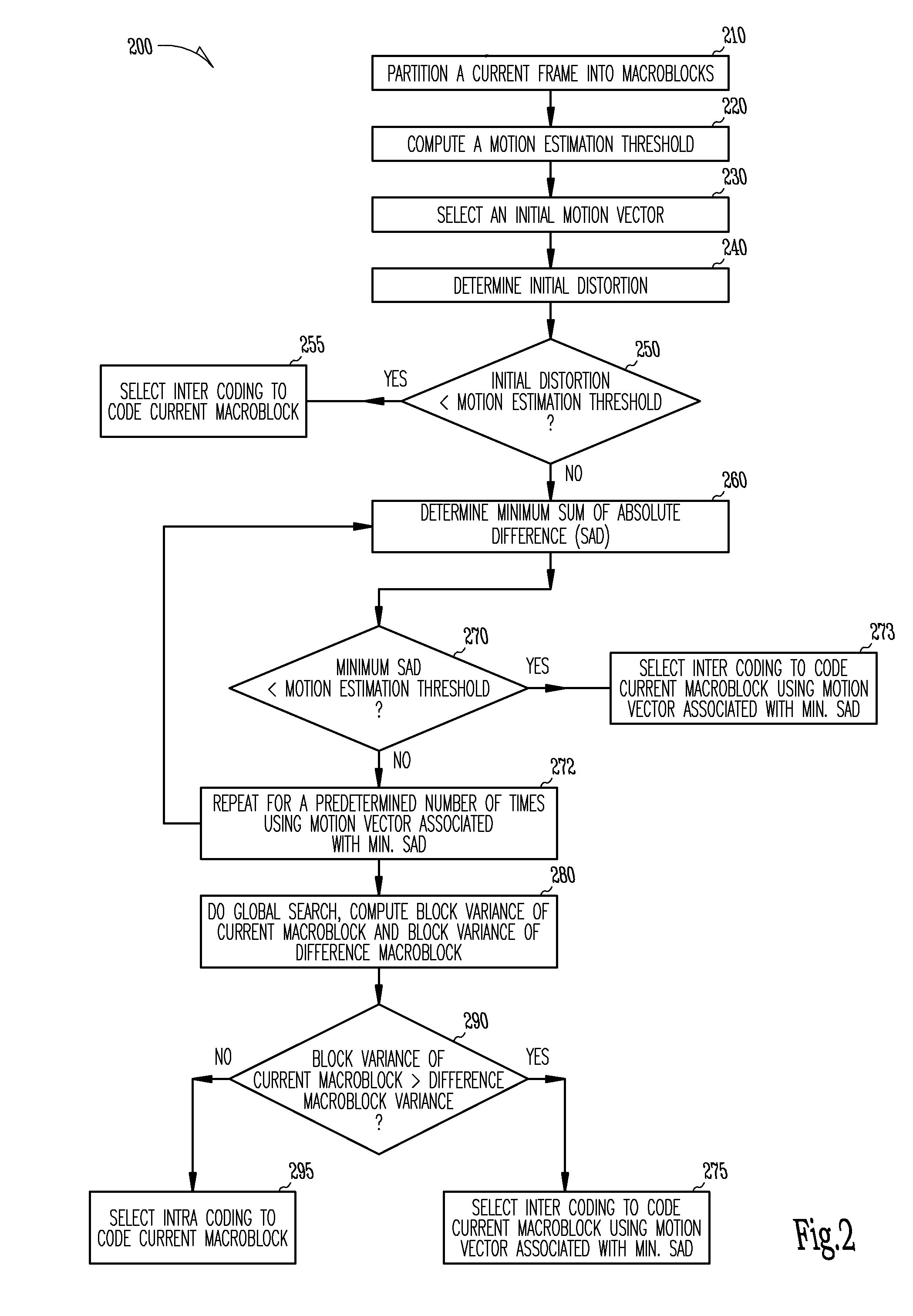
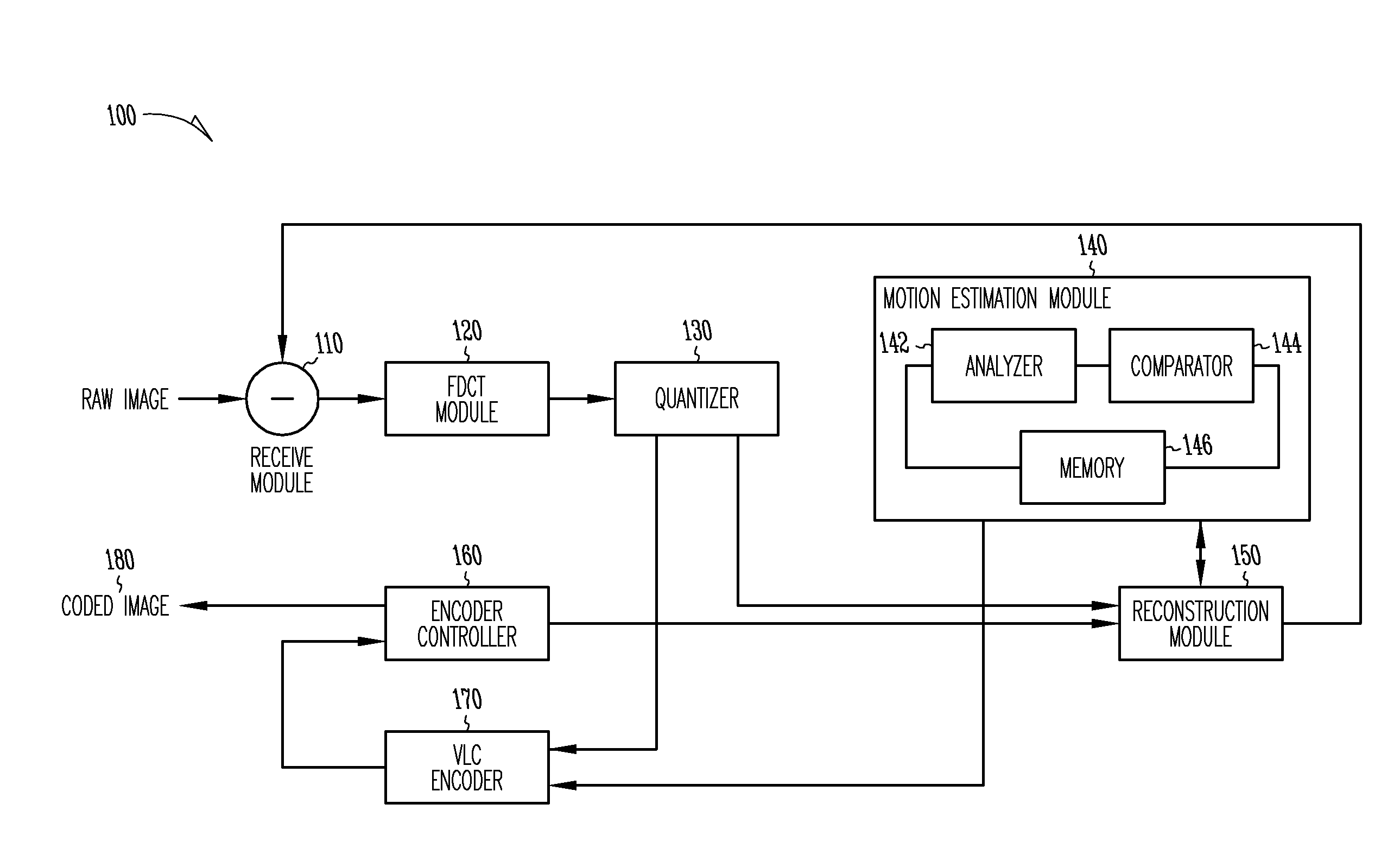
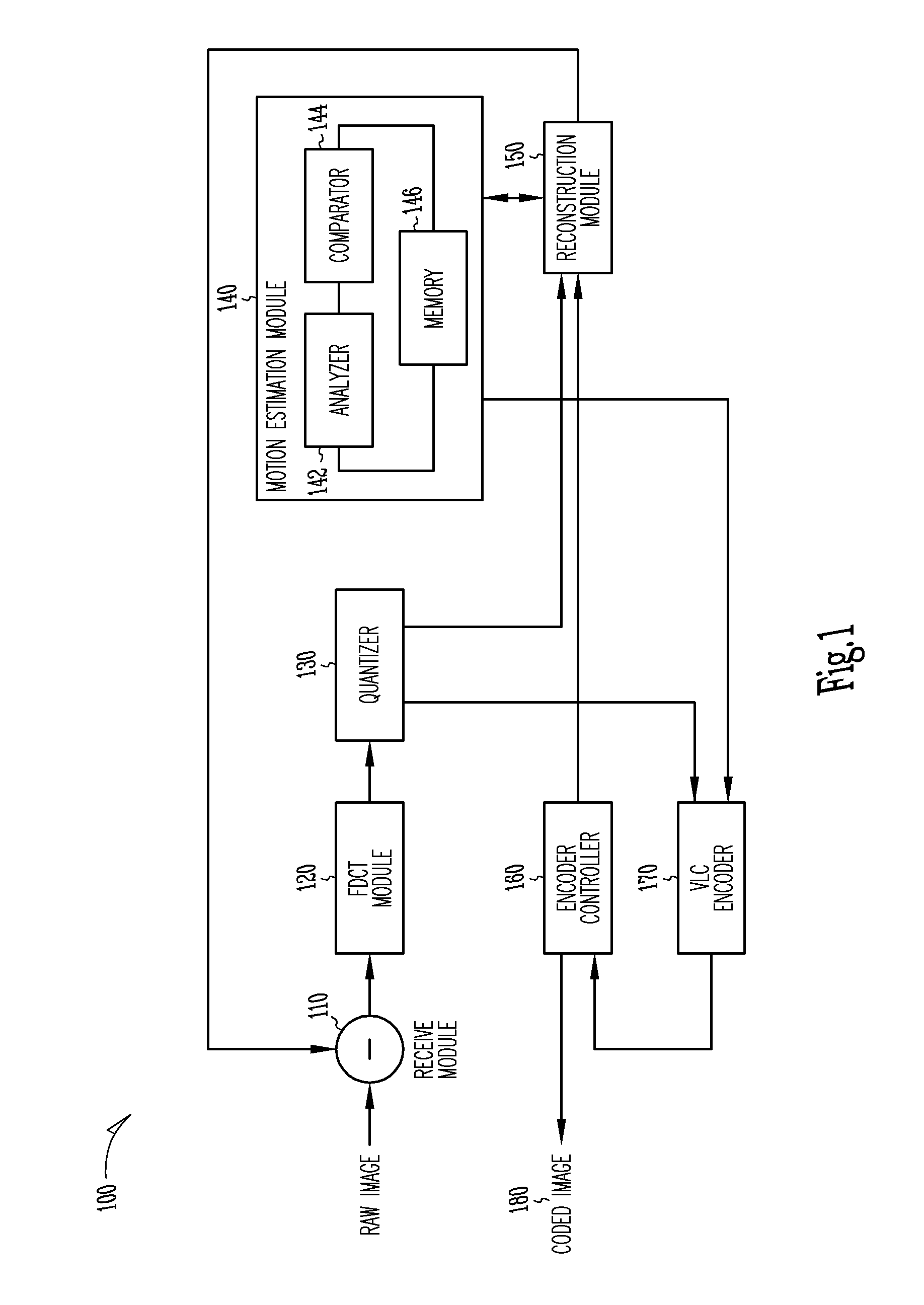
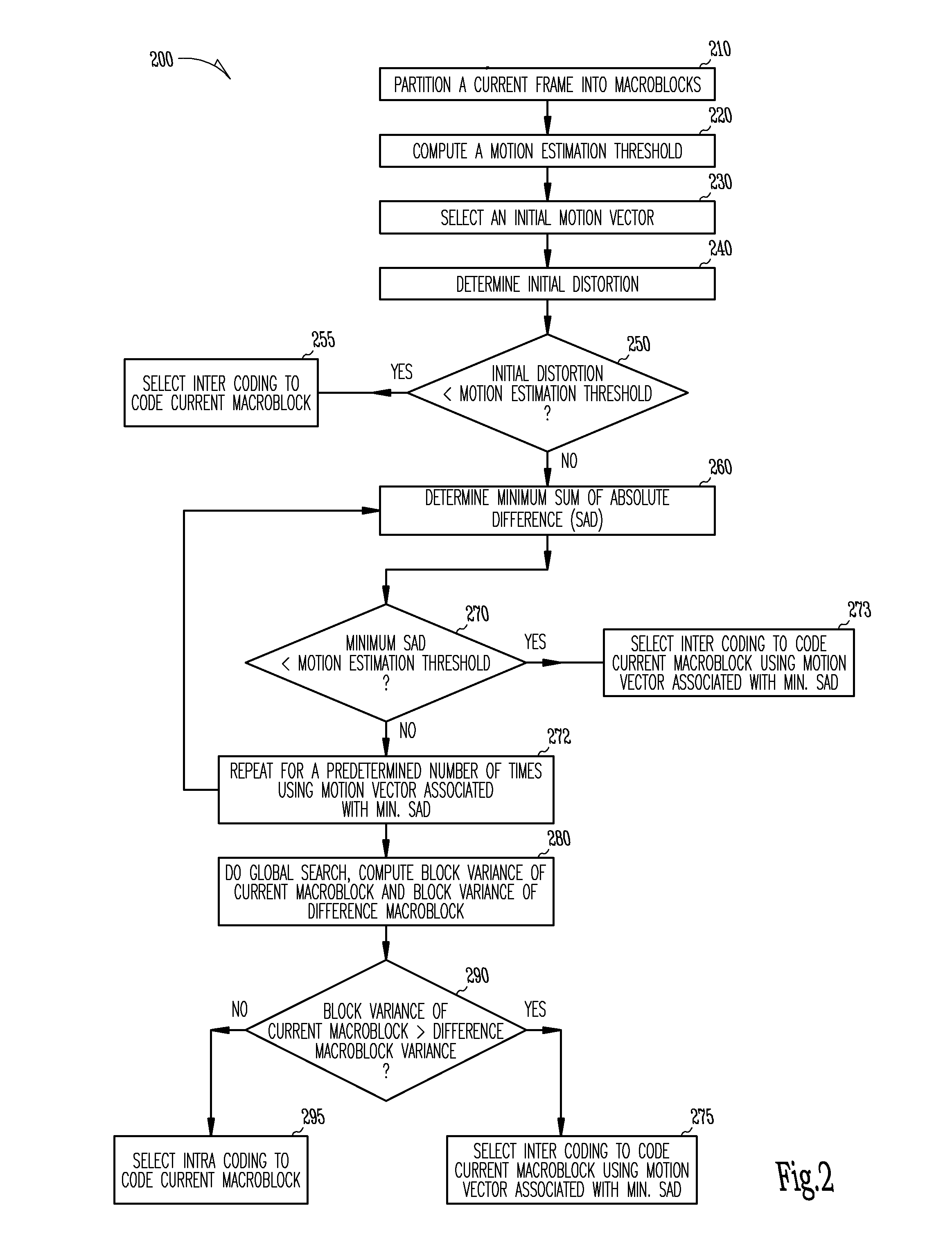
The present invention provides an improved motion estimation encoder for digital video encoding applications. In one example embodiment, the improved encoder receives a raw image in the form of a current frame and estimates the macroblock motion vector with respect to a reference frame. The encoder then performs an initial local search around an initial motion vector candidate derived from spatio-temporal neighboring macroblock parameters. The encoder then compares the user-defined complexity scalable sum of absolute difference between the original and the associated reference macroblock against an adaptive threshold value for motion estimation convergence. The encoder introduces a global full search around a candidate from a coarser level, in case an initial local search fails. The encoder then selects an inter encoding mode for coding the current macroblock, when the first local search is successful, otherwise the encoder selects the inter or intra encoding mode for encoding the current macroblock by comparing variances of the original and difference macroblocks.
Owner:SASKEN COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES
Method for analyzing object motion in multi frames
ActiveUS20120250945A1Inhibition effectInhibitionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionObject motion
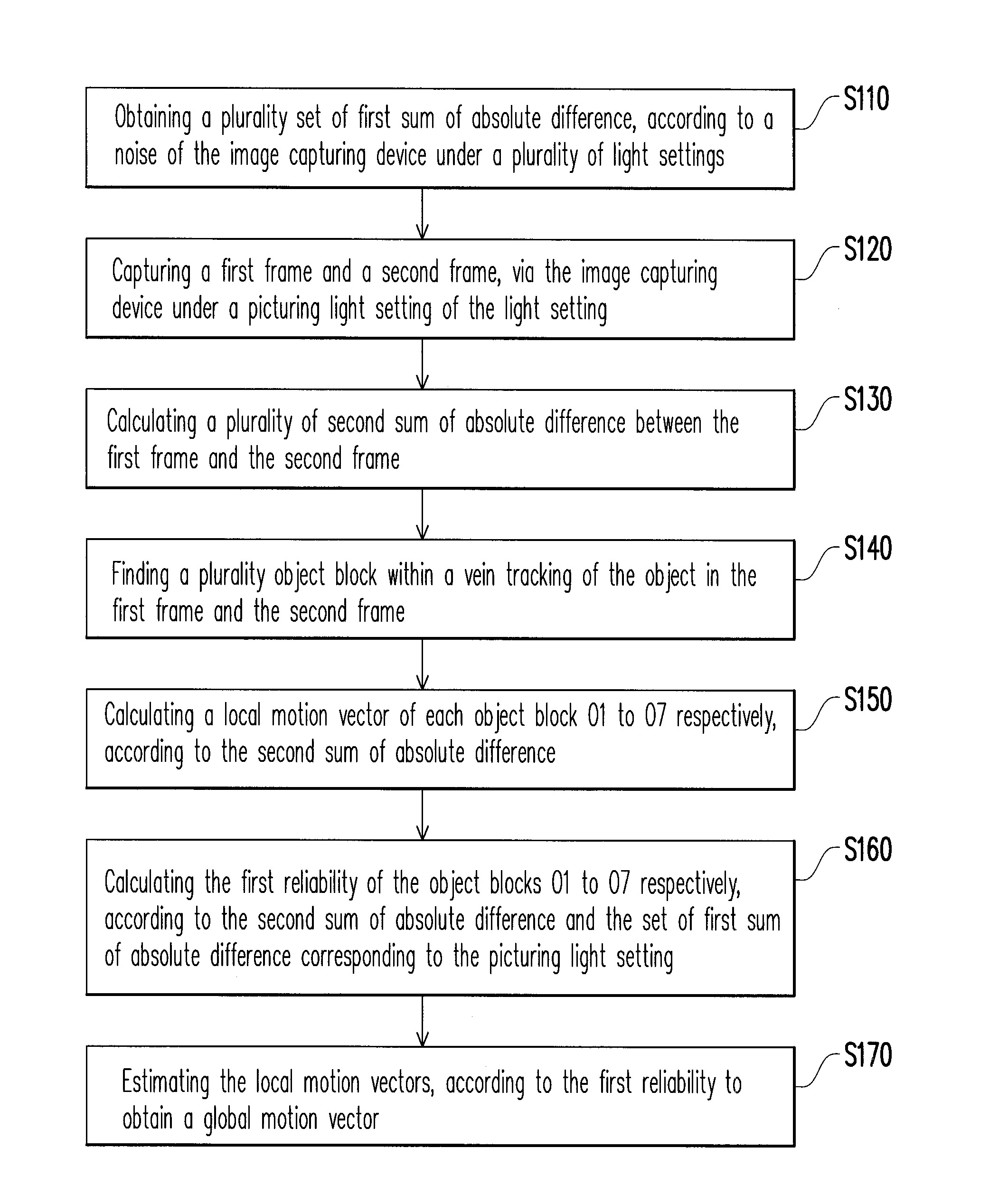
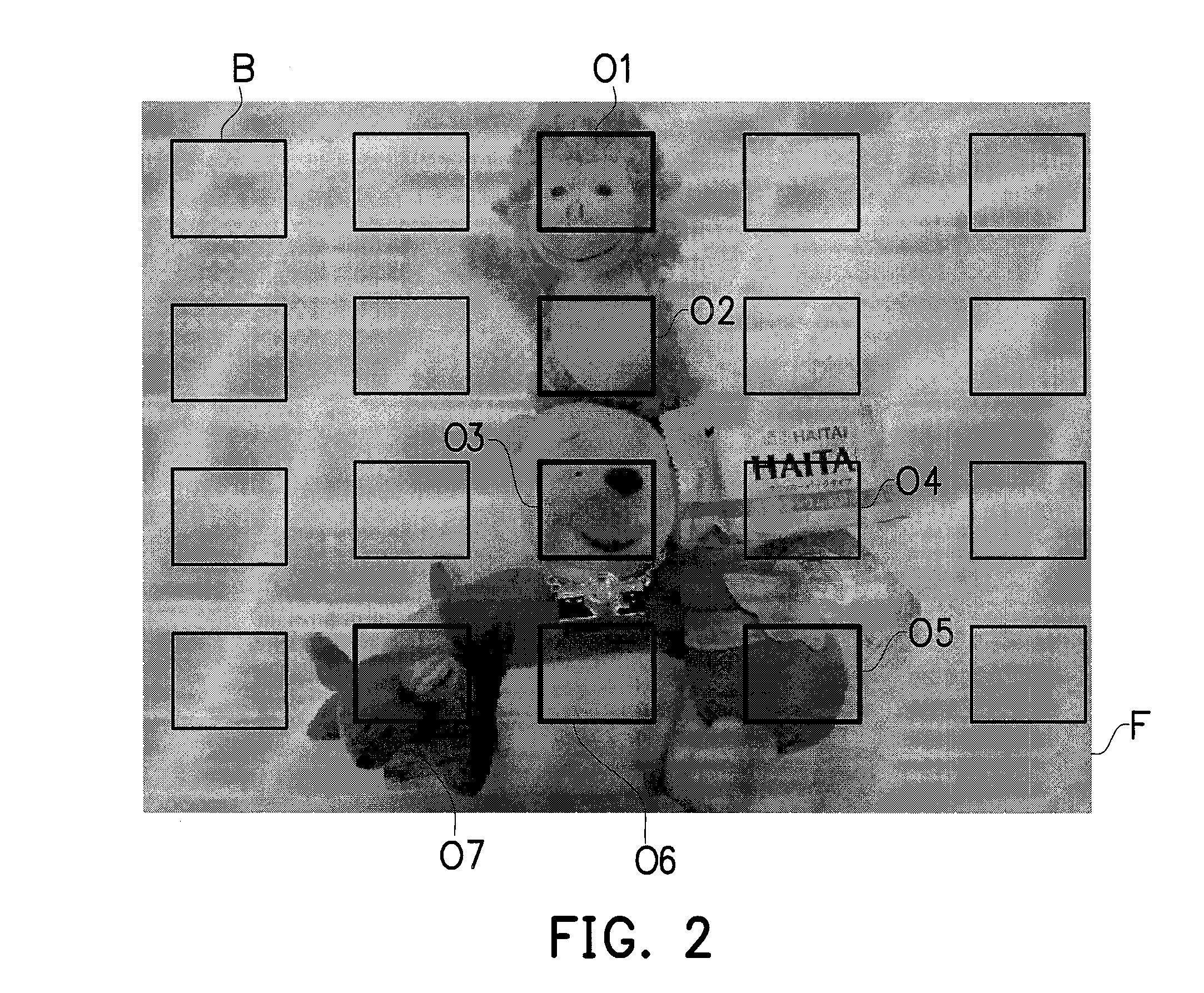
A method for analyzing object motion in multi frames adapted to an image capturing device is provided. Firstly, a plurality set of first sum of absolute difference (SAD) are obtained according to noise of the image capturing device under a plurality of light settings. Next, two frames are captured under a picturing light setting of the light settings. Then, a plurality of second SAD between the two frames are calculated. Afterwards, a plurality of object block within vein tracking of the object are found. Next, a local motion vector of each object block is respectively calculated according to the second SAD. Then, a first reliability of each object block is respectively calculated according to the second SAD and the set of the first SAD corresponding to the picturing light setting. Afterwards, the local motion vectors are estimated according to the first reliability to obtain a global motion vector.
Owner:ALTEK CORP
Deinterlacing apparatus and method
ActiveUS7057665B2Improve image qualityLow costPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern detectionSelf adaptive
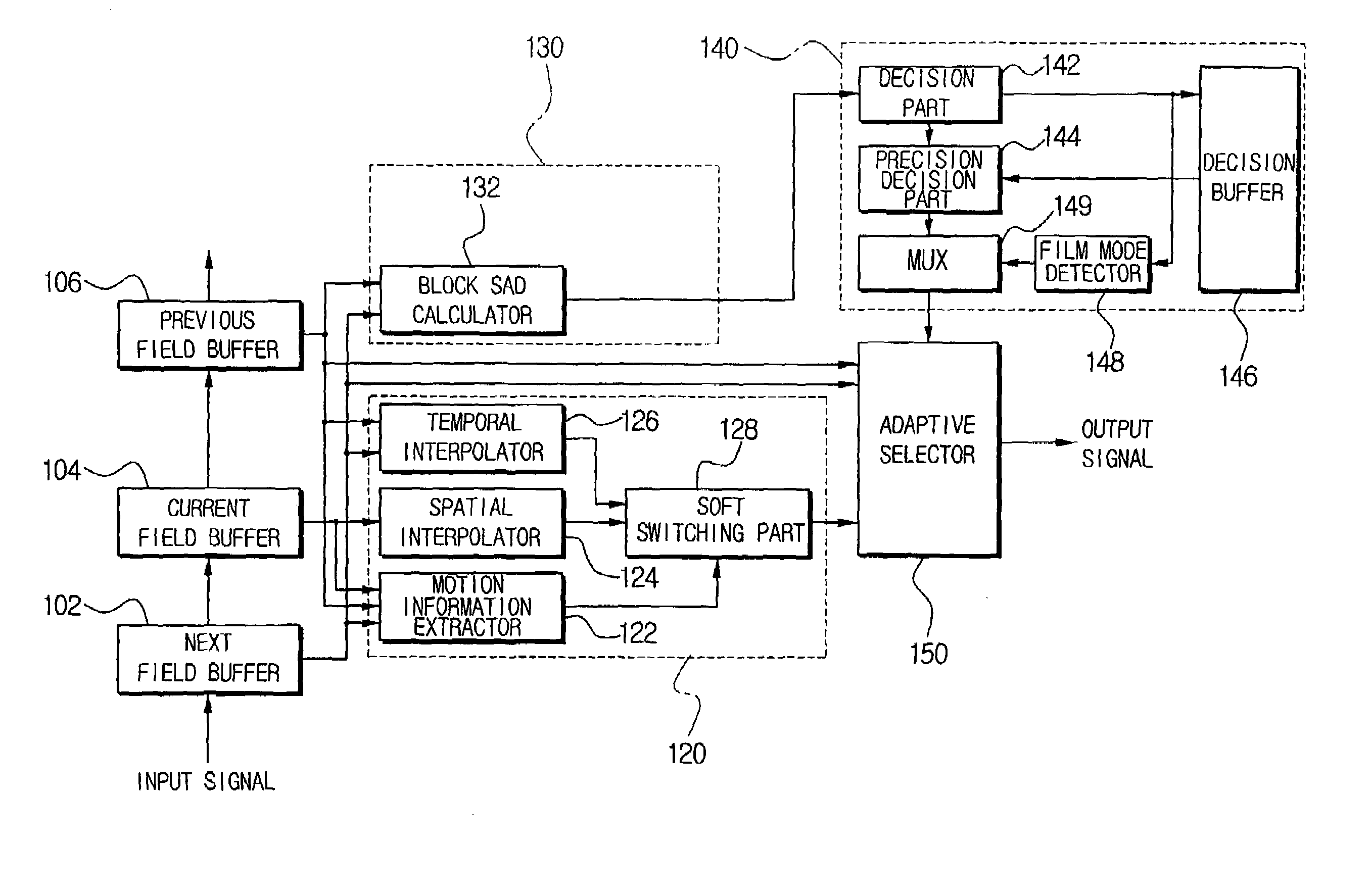
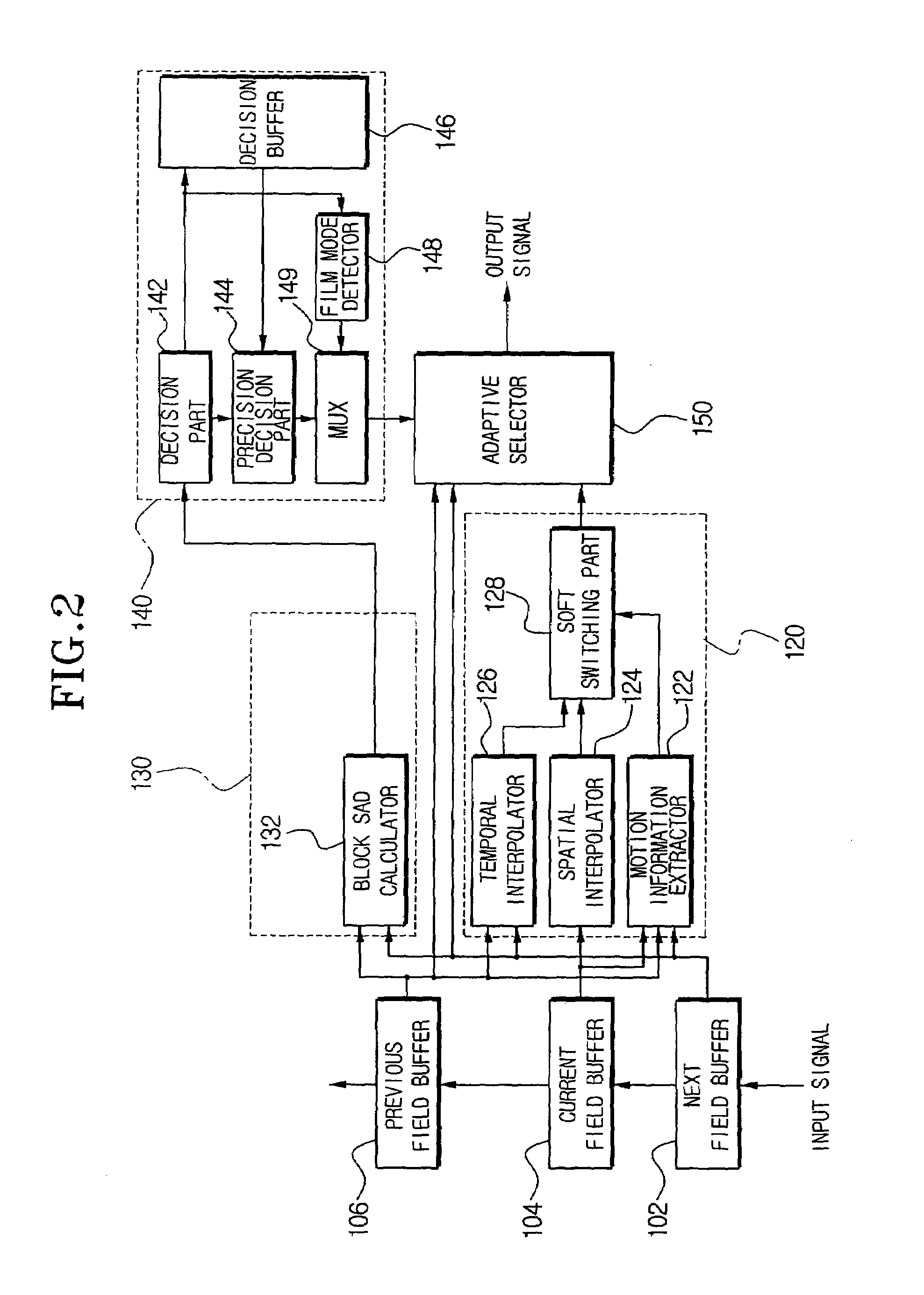
A deinterlacing apparatus and method use a buffer unit having a previous field buffer, a current field buffer, and a next field buffer to store, sequentially, individual fields of an image signal; calculate a Sum of Absolute Difference (SAD) value of a predetermined search region unit with reference to a next field stored in the next field buffer and a previous field stored in the previous field buffer; determine whether the predetermined search region is a still region and whether a source of the image signal is a film based on the SAD value; uses a 3D interpolation unit to output adaptively a temporal interpolation value and a spatial interpolation value based on motion information; and adaptively select a deinterlacing result based on the previous field, the next field, and an output of the 3D interpolation unit according to a signal outputted from the still region / film mode detection unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-Directional Motion Estimation Using Parallel Processors and Pre-Computed Search-Strategy Offset Tables
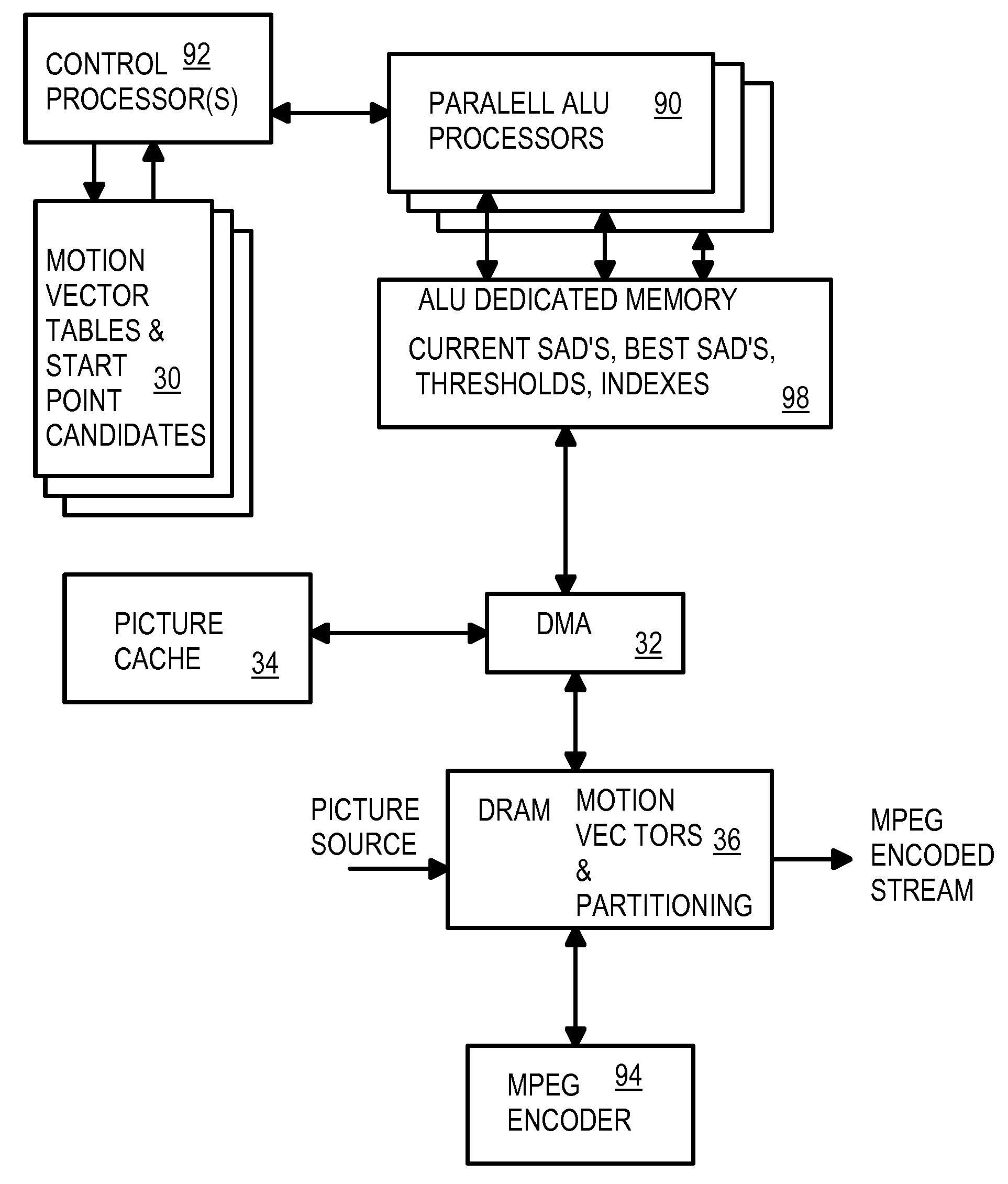
A motion estimator uses many parallel Arithmetic-Logic-Unit (ALU) processors to simultaneously perform searches in many directions from a starting point. Each processor follows a different path outward from the starting point, generating sum-of-absolute differences (SADs) for each point in the path. A best SAD for the path is kept, along with an index into motion vector tables containing X,Y points for all paths. Current and best SAD's, thresholds, and indexes are stored in an ALU dedicated memory. When the number of best SAD's meeting thresholds exceeds a target, the current search-level ends. The index of the overall best SAD locates a new starting point, and a next-denser search-level is performed in the same manner, but over a smaller search area. Each processor calculates SAD's for one 16×16 macroblock, four 8×8 blocks, and 16 4×4 blocks and the net best SAD of these 3 types determines partitioning.
Owner:NEOMAGIC
Field programmable object array having image processing circuitry
ActiveUS20100020880A1Improve performanceReduce Design ComplexityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningData compressionImaging processing
A field programmable object array integrated circuit has video data compression capability. The integrated circuit comprises an array of programmable objects and a video compression co-processor communicatively coupled to the array of objects. The video compression co-processor comprises a set of search engines and a subpixel engine. The subpixel engine can interpolate subpixels from integer pixels and shift the integer pixels by a predetermined number of subpixels. The search engines can perform a plurality of sum of absolute differences (SAD) computations between search window pixels and macroblock pixels to locate the best SAD value using either integer pixels and / or the interpolated subpixels.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
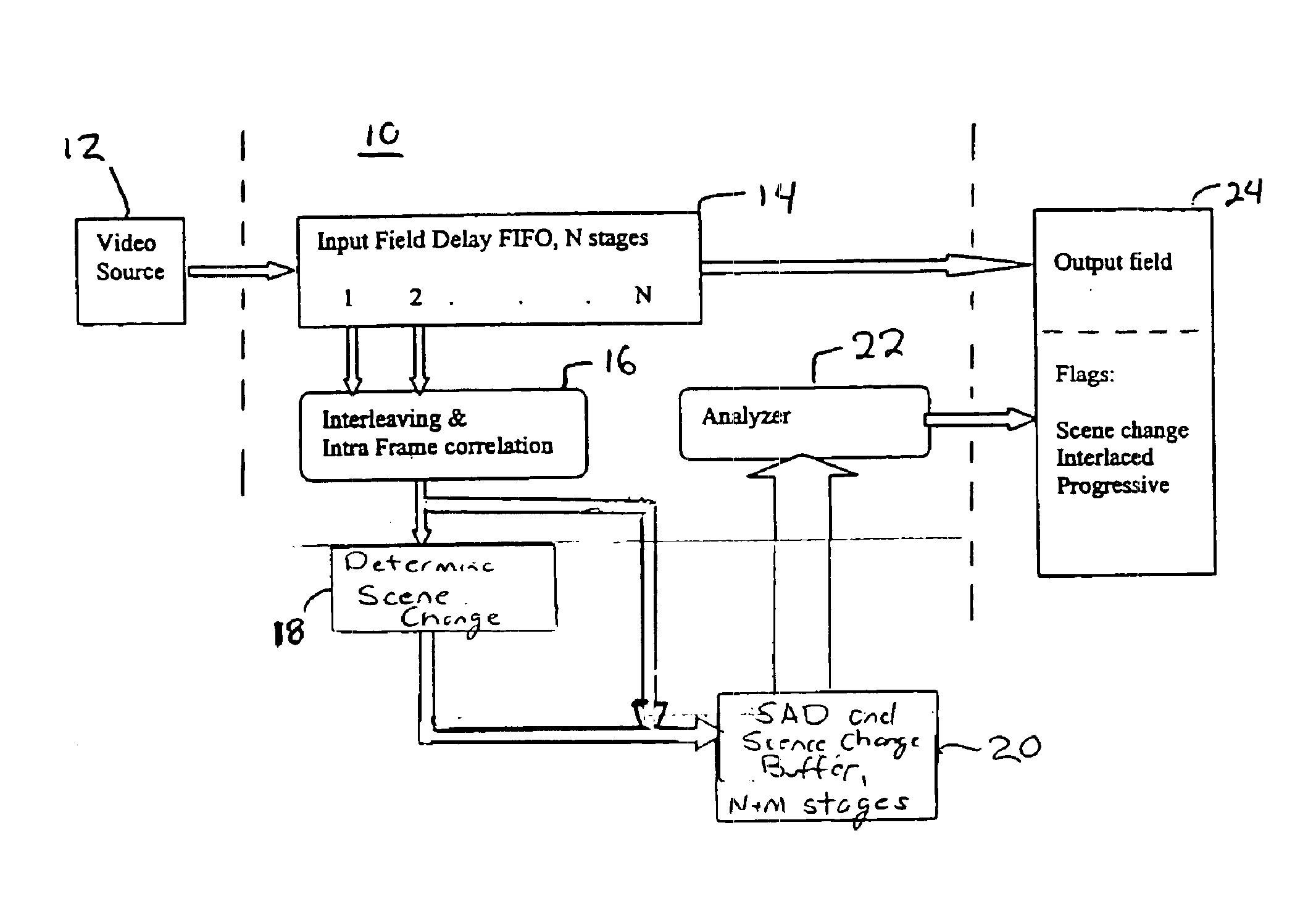
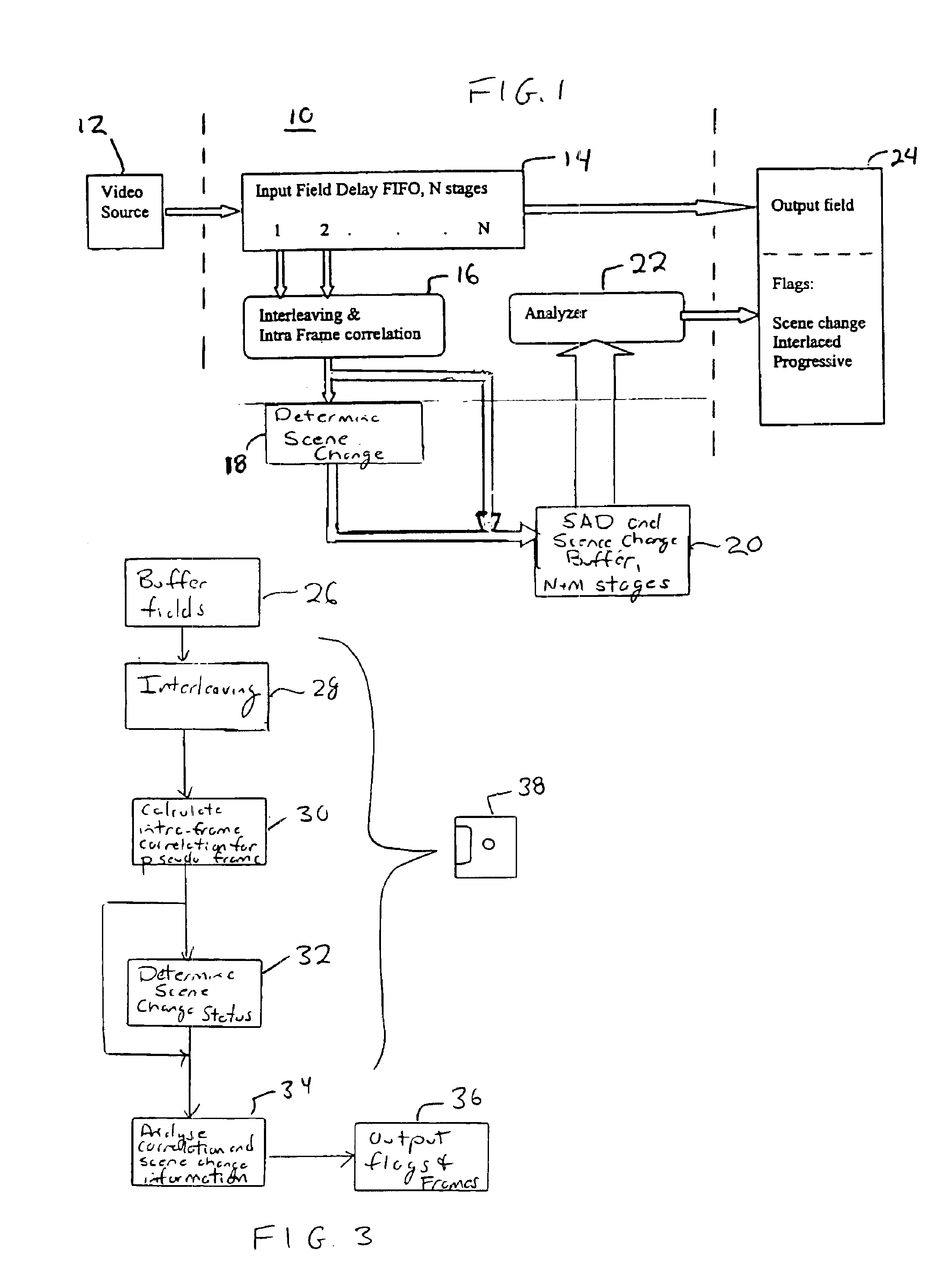
Apparatus for detecting mixed interlaced and progressive original sources in a video sequence
A method and apparatus of identifying the source of materials in a video sequence is disclosed. A series of pseudo frames is formed, for example by interleaving, from fields in adjacent frames. A correlation value is calculated for each of the pseudo frames. The correlation value may be a sum of absolute difference (SAD) of luminance values of every neighboring scan line accumulated over the entire pseudo frame. Scene changes may be determined, for example, based on the correlation values. Frames and repeated fields are identified based on the correlation values and the scene changes. Finally, the source of each frame in the series is identified based on the identification of frames and repeated fields.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
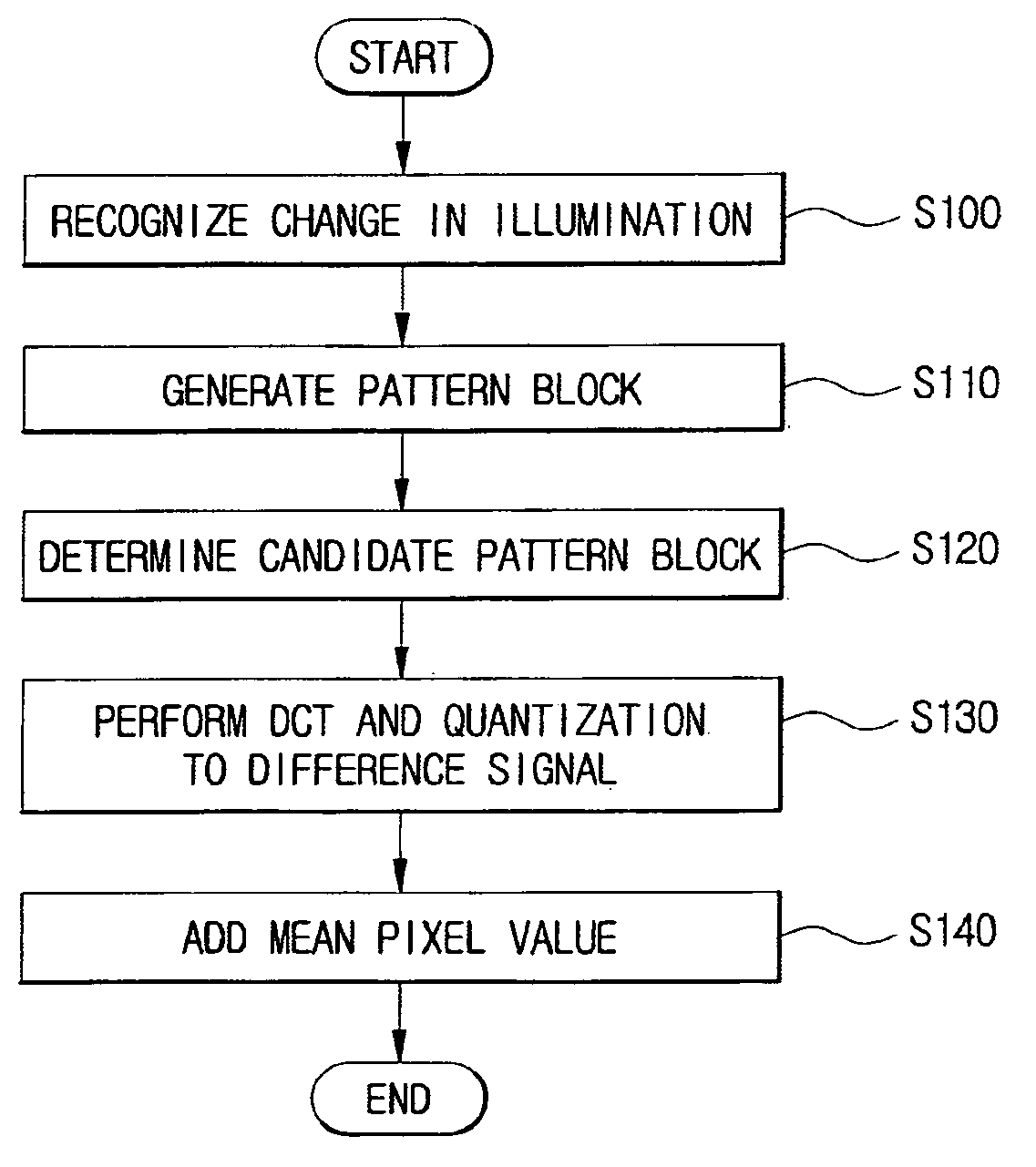
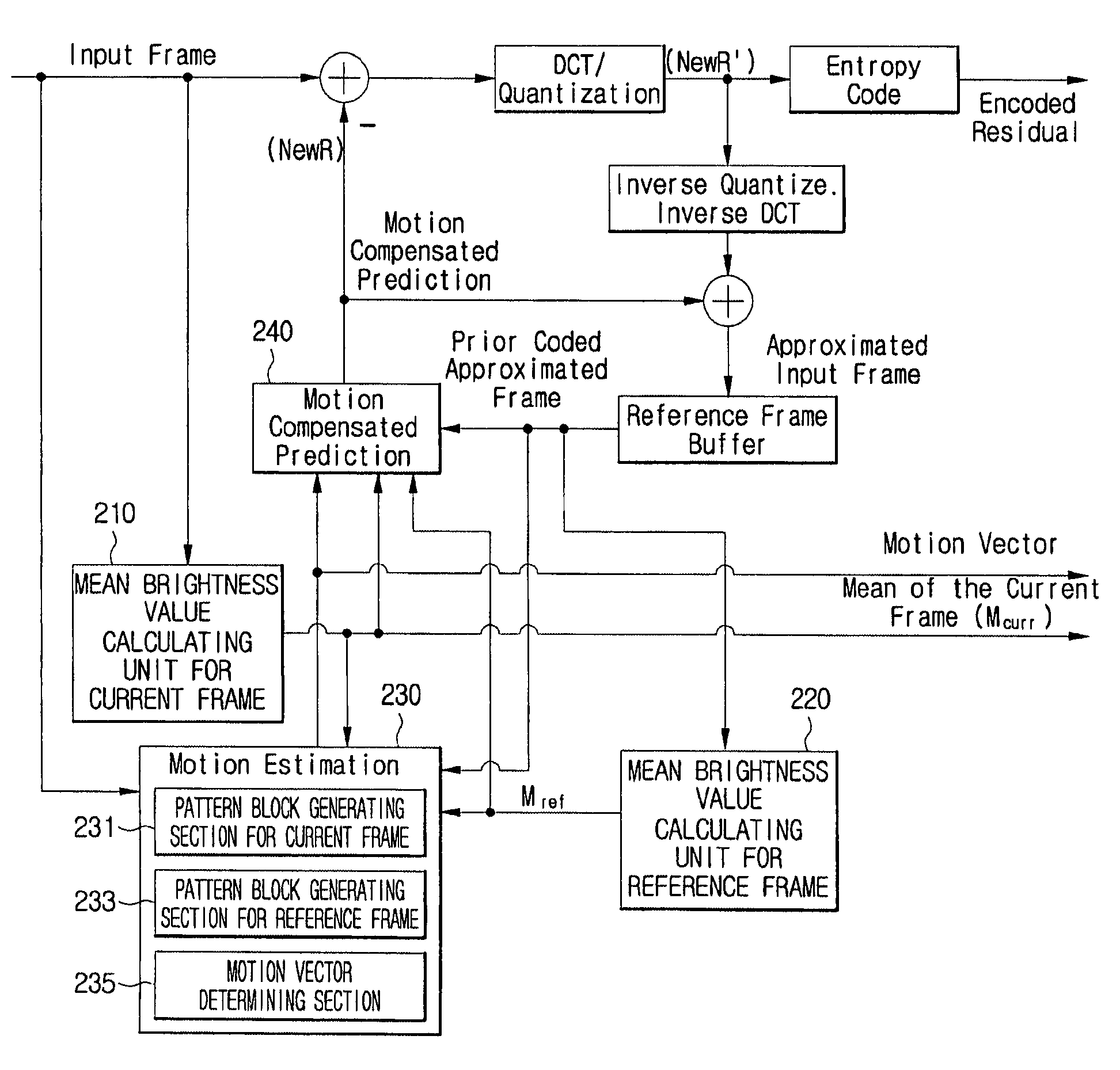
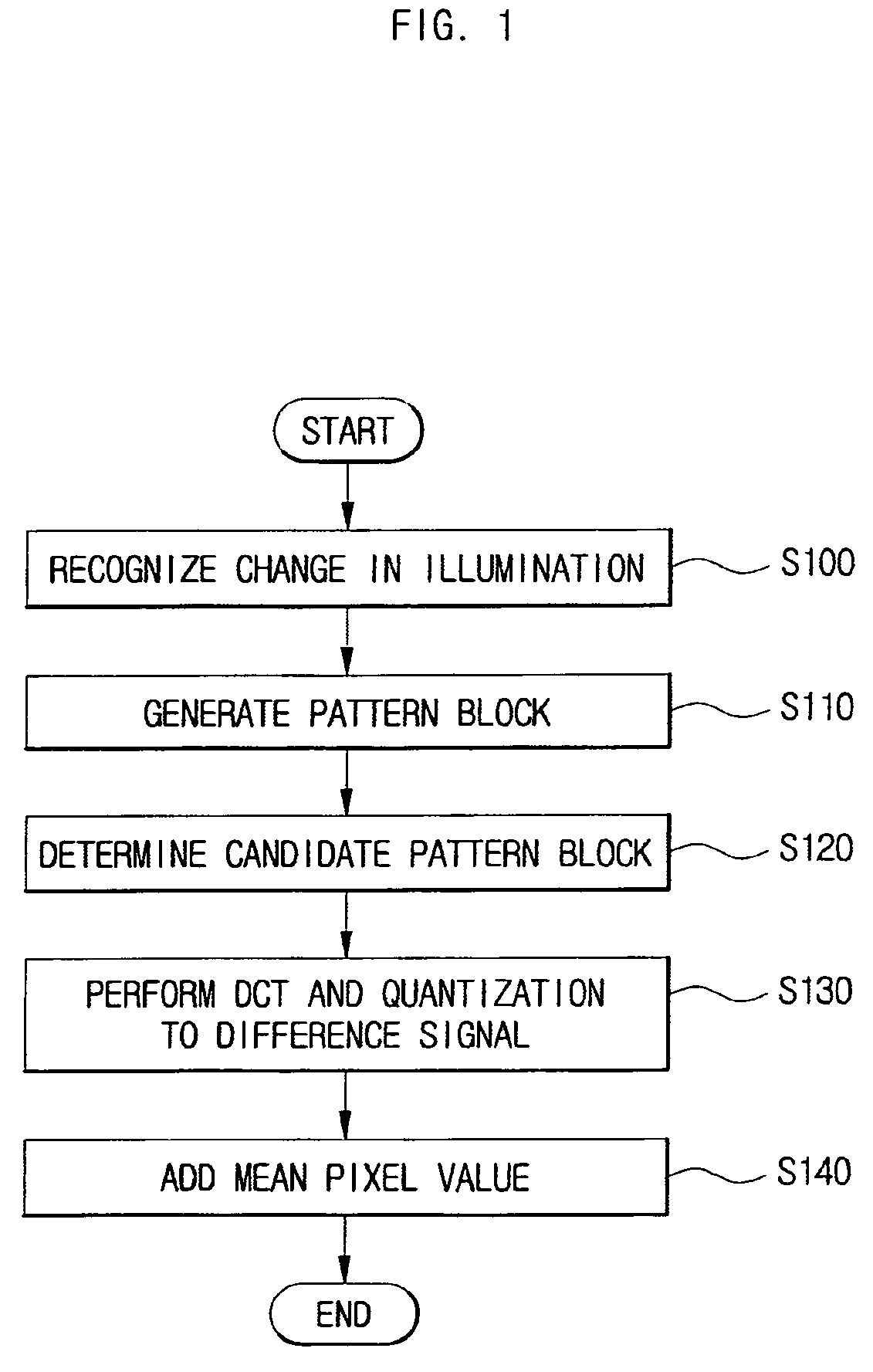
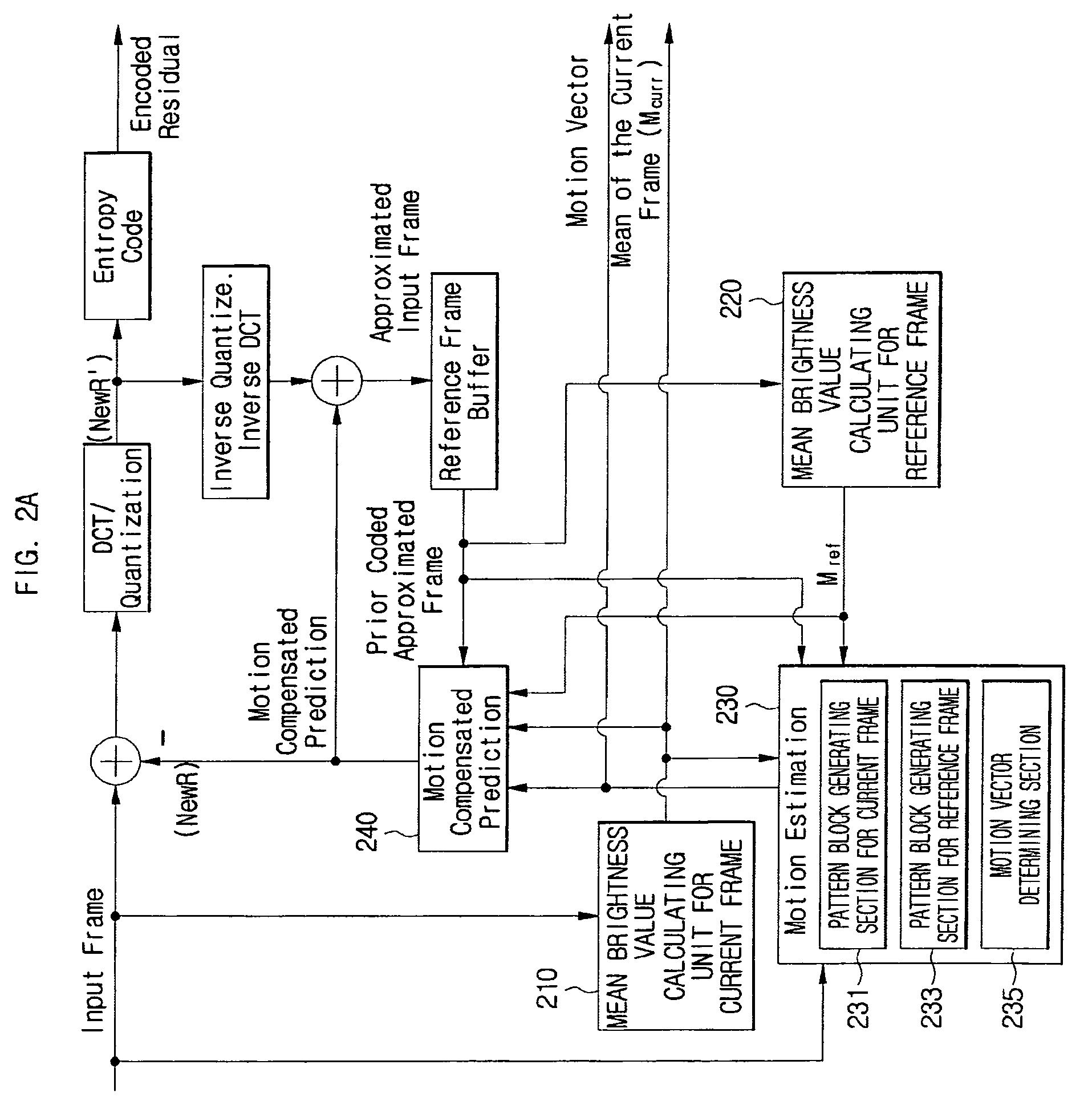
Motion estimation and compensation method and device adaptive to change in illumination
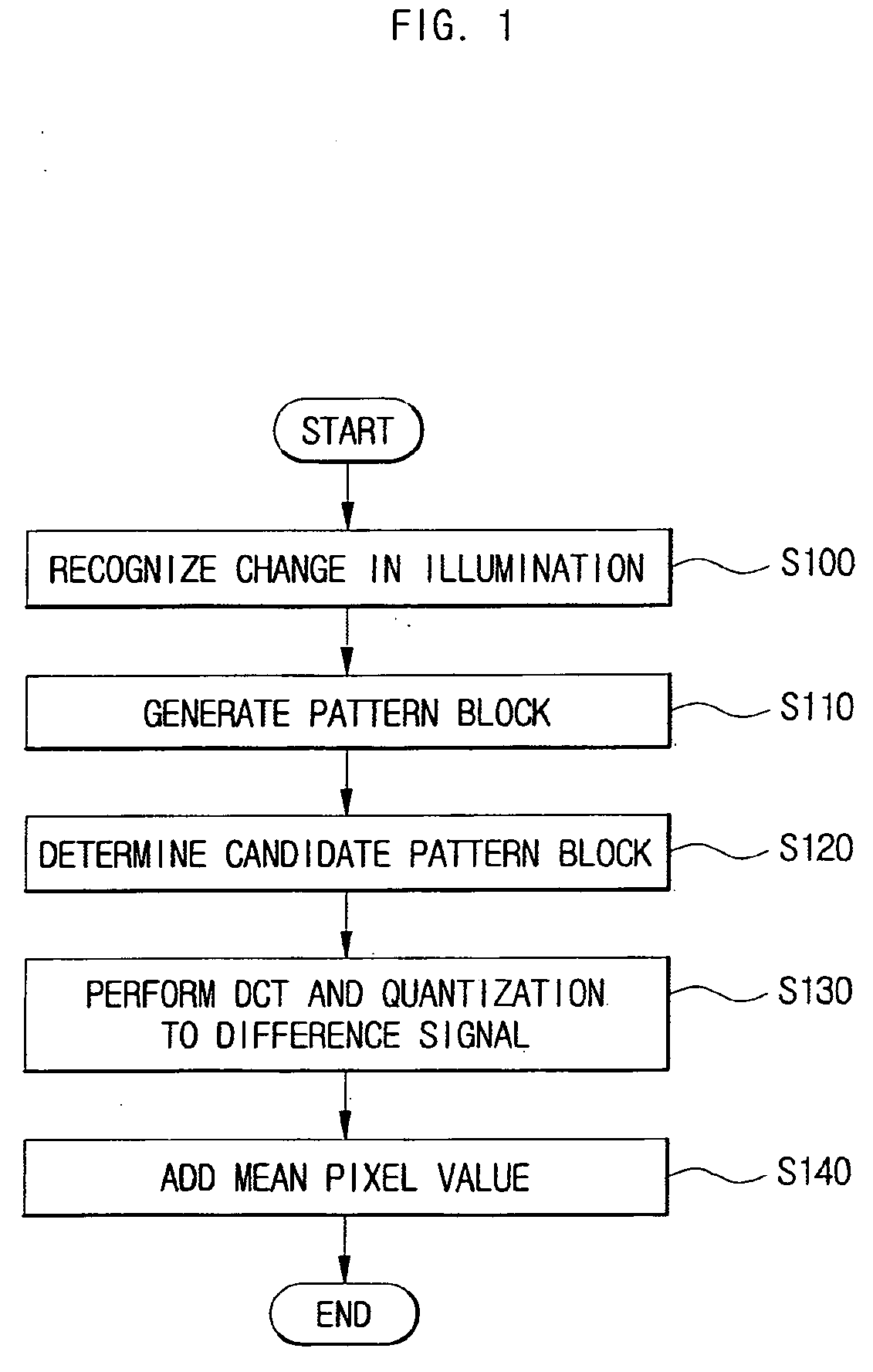
InactiveUS20060133501A1Efficiently encodeEfficient decodingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionMotion vector
Provided are a motion estimation device and method adaptive to change in illumination. The motion estimation method includes the steps of: generating a current frame pattern block for a current frame block and a reference frame pattern block for a reference frame block; calculating the sum of absolute differences (SAD) for candidate pattern blocks corresponding to the current frame pattern block among the reference frame pattern blocks and determining the candidate pattern block corresponding to the SAD satisfying a predetermined condition among the calculated SADs as a motion vector; encoding the current frame block, by generating a residual signal using a difference signal between the candidate pattern block corresponding to the motion vector and the current frame pattern block then performing discrete cosine transform and quantization to the residual signal with a predetermined encoding mode; and adding flag information indicating the addition of a mean pixel value applied to the encoded current frame block and identification information on the encoding mode as header information corresponding to the encoded current frame block. By omitting insertion of a mean pixel value for some fields, it is possible to minimize the amount of bit streams transmitted to a decoder.
Owner:HUMAX CO LTD
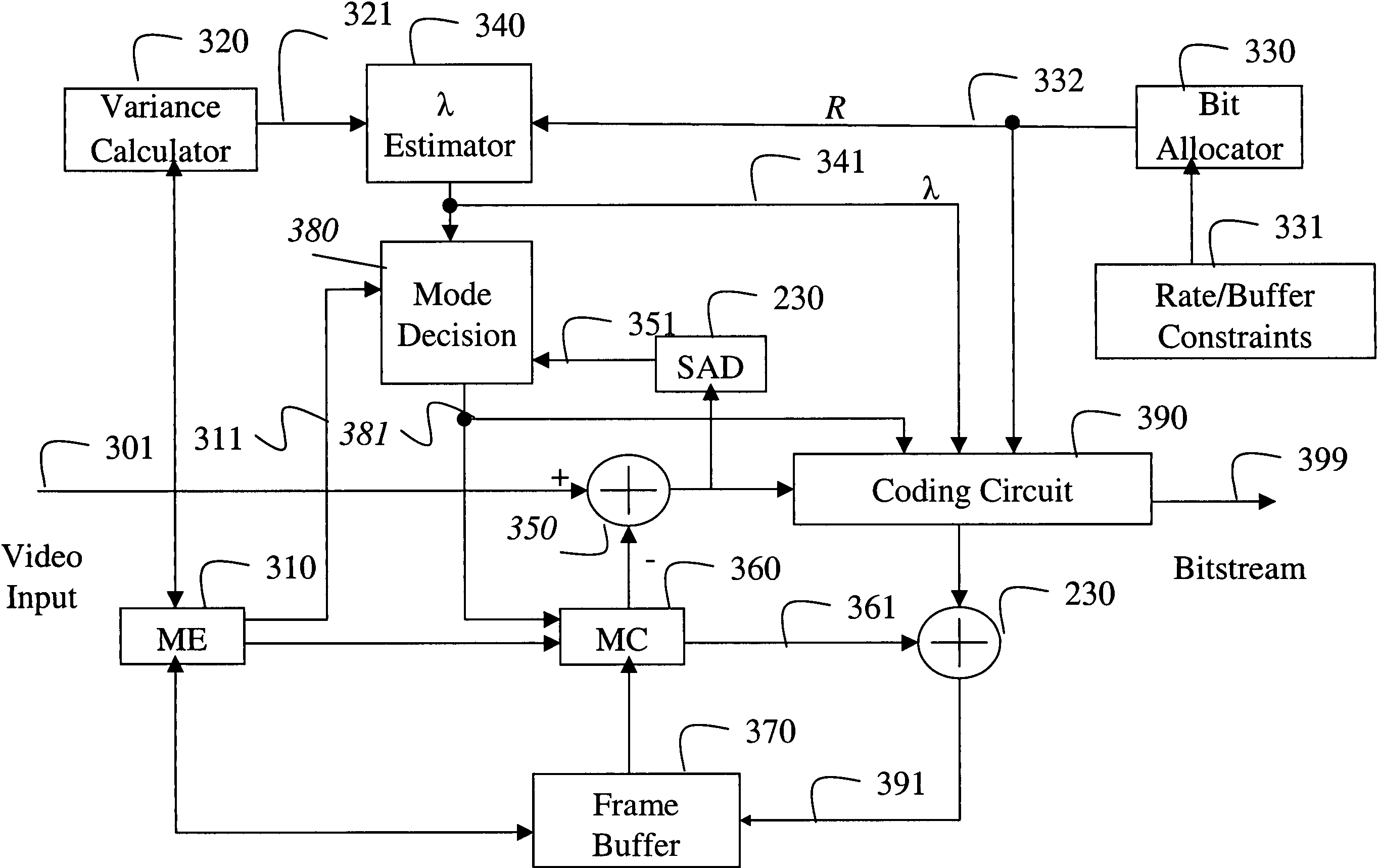
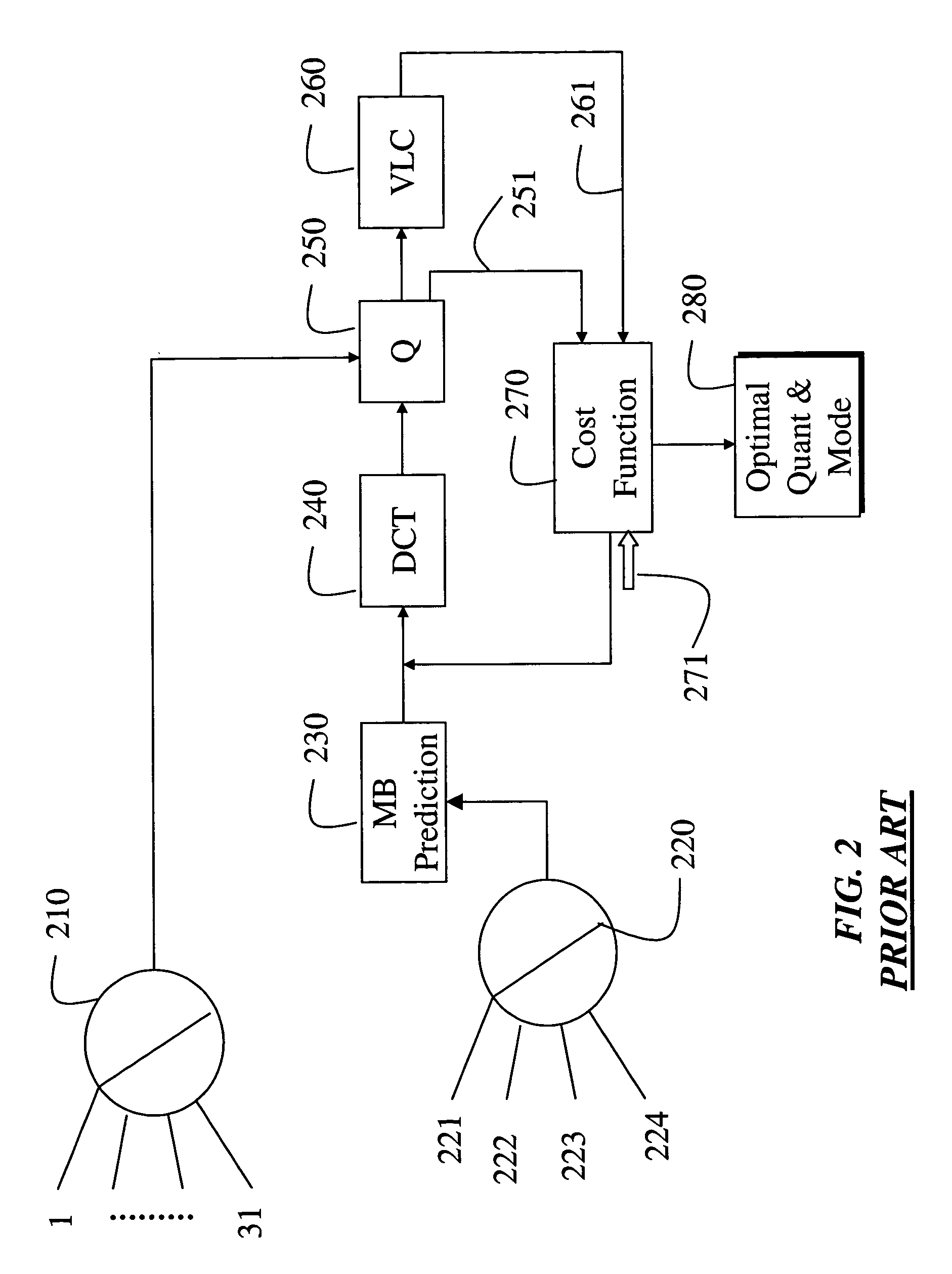
System and method for determining coding modes, DCT types and quantizers for video coding
InactiveUS7280597B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionFrame based
A method encodes a video by first measuring a variance of pixel intensities in a current frame. A number of bits to encode the current frame is assigned according to rate and buffer fullness constraints. A multiplier value is determined directly as a function of only the variance and the number of bits assigned to the current frame. Motion vectors between a reference frame and the current frame are estimated, and a sum of absolute difference (SAD) is based on a motion compensated residual between the reference frame and the current frame. An encoding mode is determined for each macro block in the current frame based on the sum of absolute difference, the motion vectors and the multiplier value. Then, the motion compensated residual is encoded based on the encoding mode, multiplier value and the number of allocated bits.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH CENT AMERICA ITA
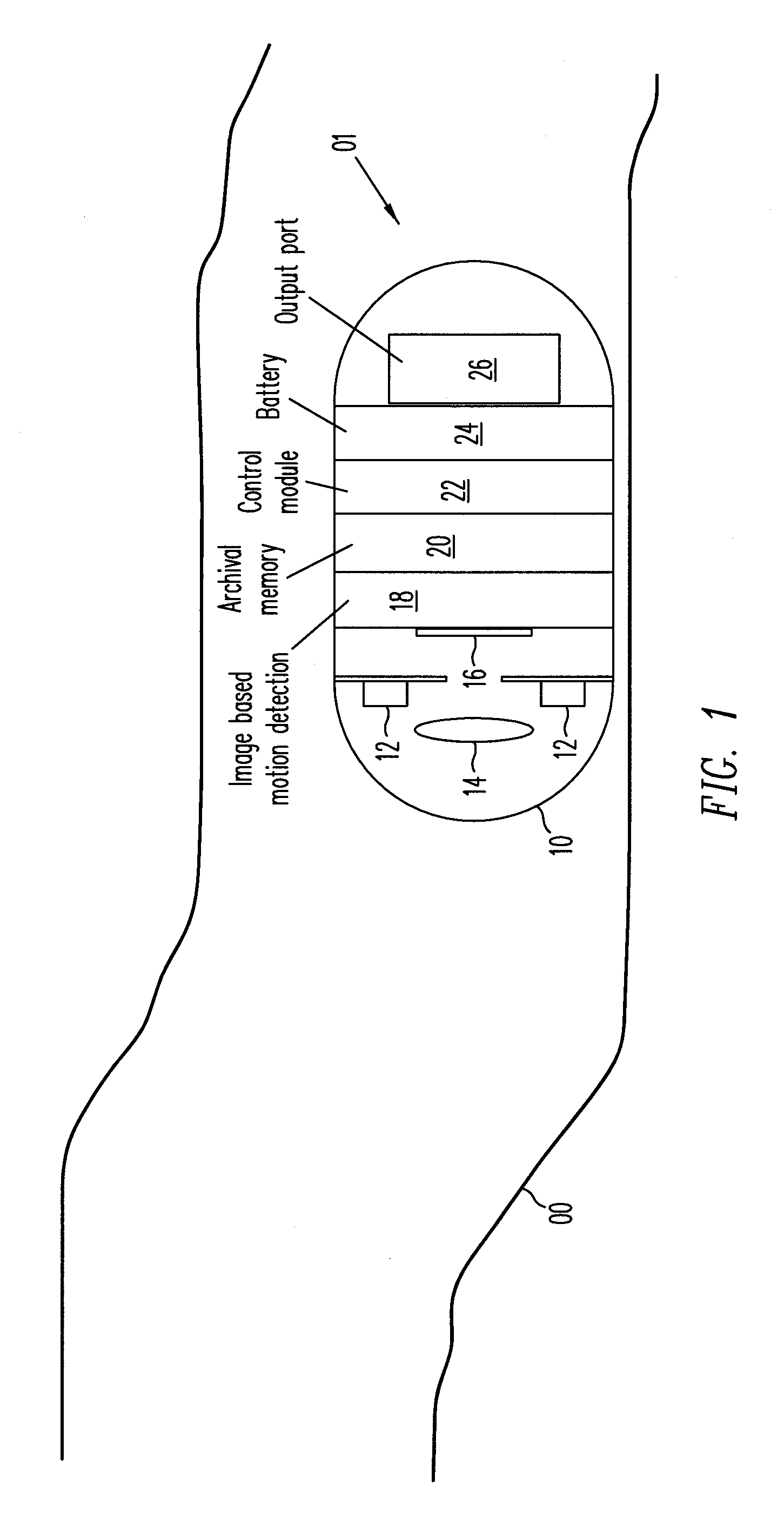
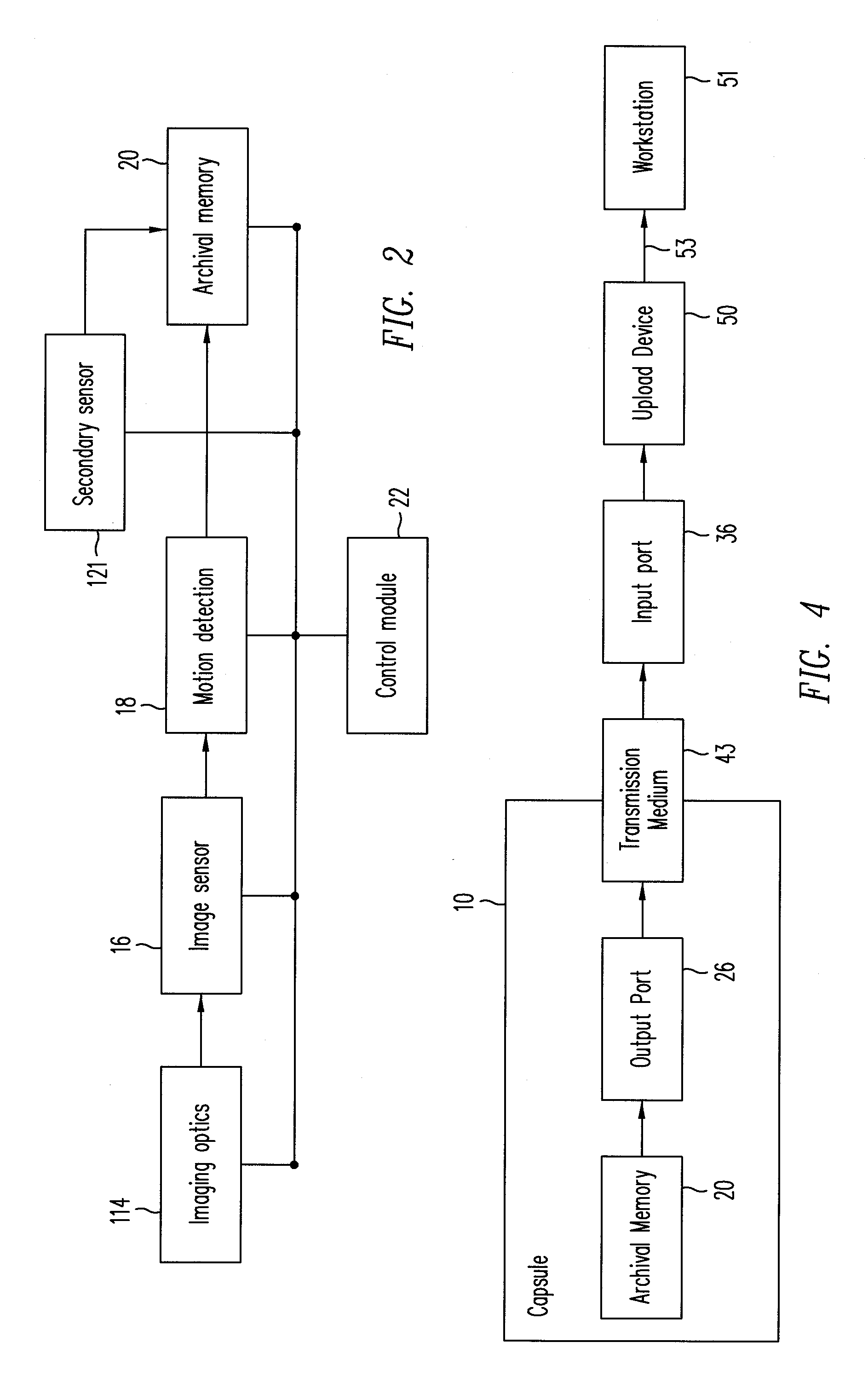
Movement detection and construction of an "actual reality" image
InactiveUS20080117968A1Minimize cost functionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesEndoscopesComputer graphics (images)Image compression
A method for intraframe image compression of an image is combined with a method for reducing memory requirements for an interframe image compression. The intraframe image compression includes (a) dividing the image into blocks; (b) selecting a block according to a predetermined sequence; and (c) processing each selected block by: (1) identifying a reference block from previously processed blocks in the image according to an activity metric; and (2) using the reference block, compressing the selected block. The selected block may be compressed by compressing a difference between the selected block and the reference block, where the difference may be offset by a predetermined value. The difference is compressed after determining that an activity metric of the difference block. The activity metric depends on elements of a difference block, which is a block in which elements are each a difference between an element of the current image frame and a corresponding element of the reference frame. The activity metric is a function of the sum of (a) the sum over all rows of all differences between two successive consecutive elements of each row of the difference block; and (b) the sum over all columns of all differences between two consecutive elements of each column of the difference block. The reference block is identified by minimizing a cost function based on the activity metric and either a sum of absolute differences function or a sum of square differences function. The cost function may be a weighted sum of the activity metric and either a sum of absolute differences function or a sum of square differences function, or a weighted sum of the activity function and either a sum of absolute differences function or a sum of square differences function.
Owner:CAPSO VISION INC
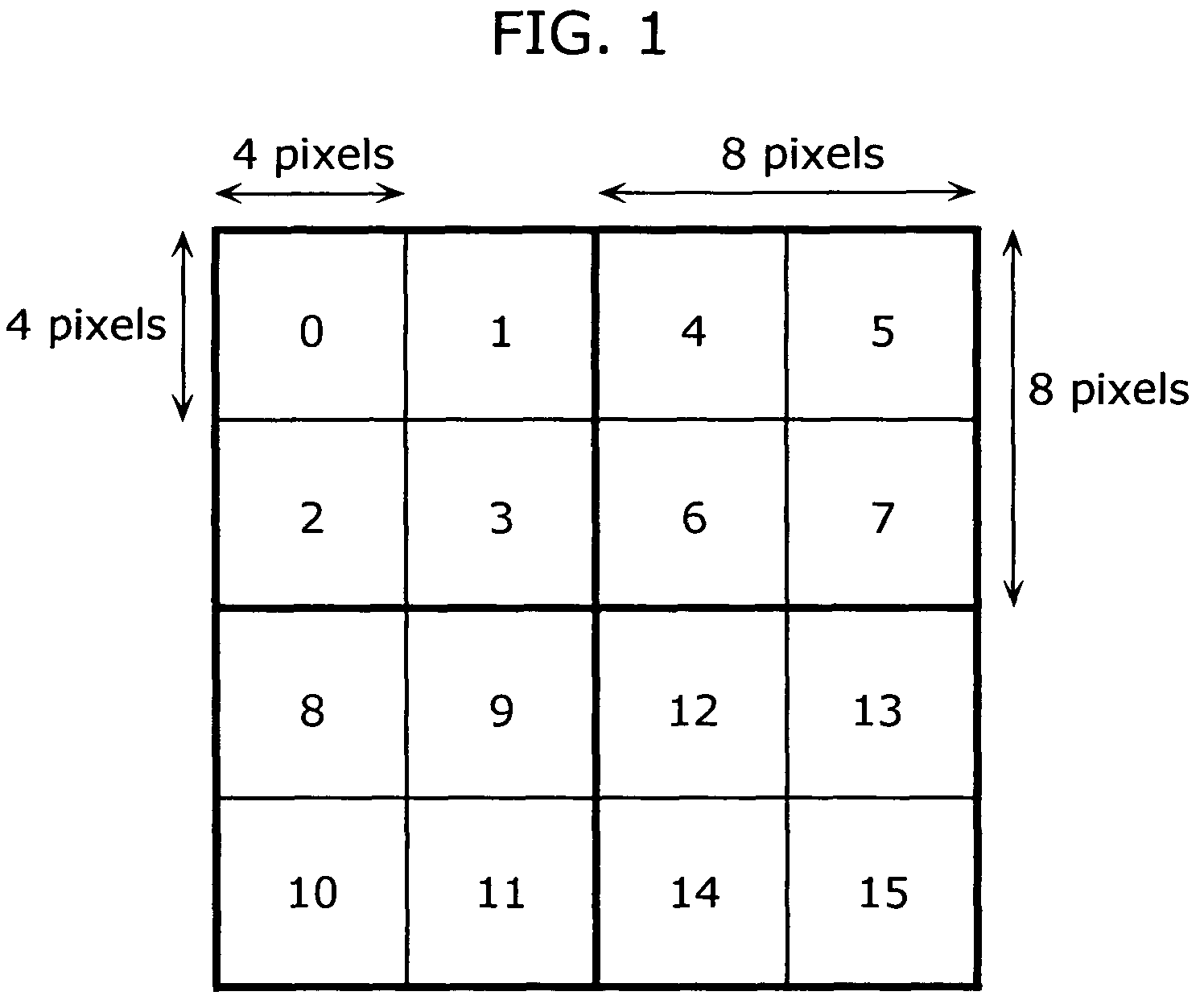
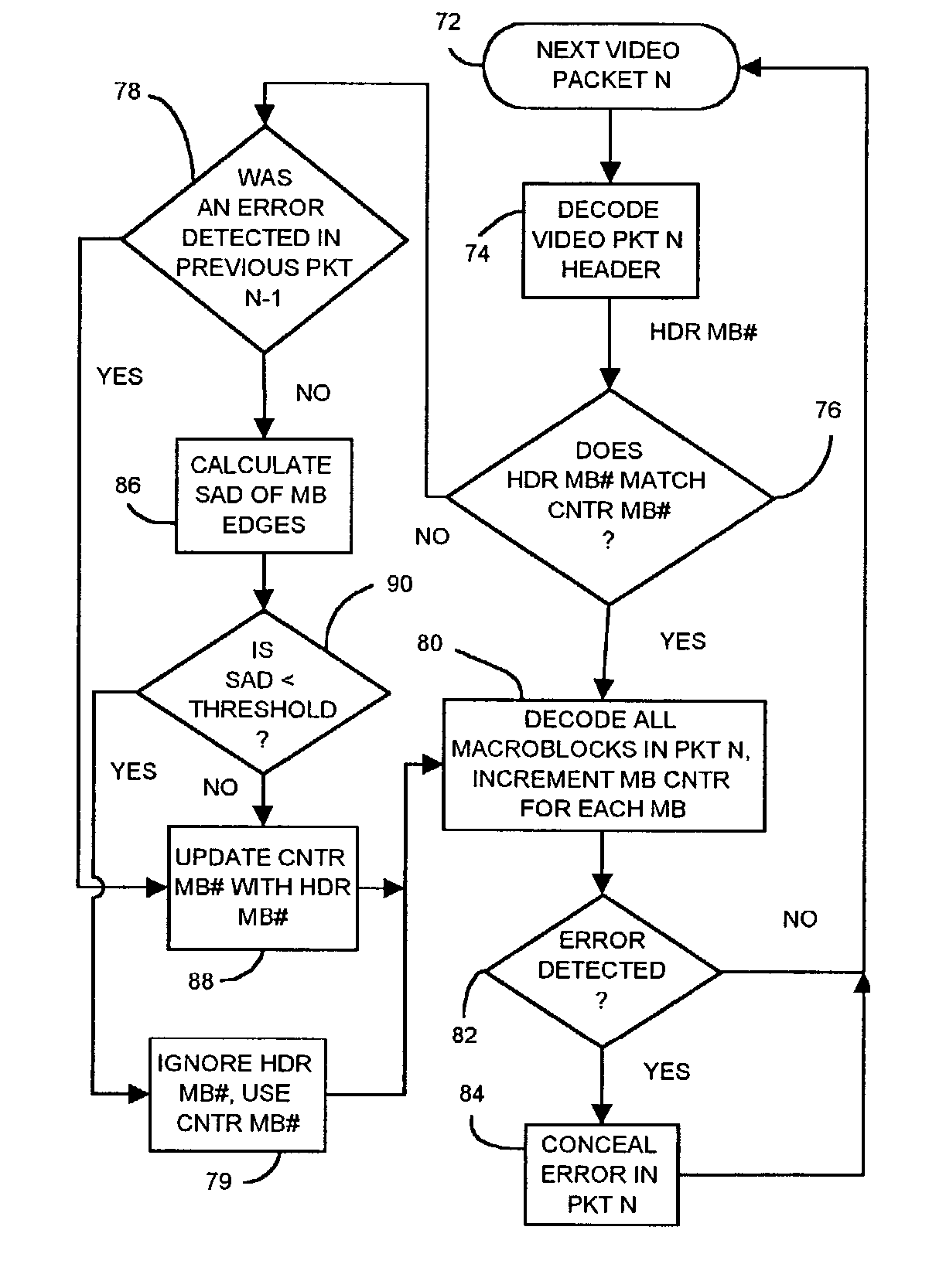
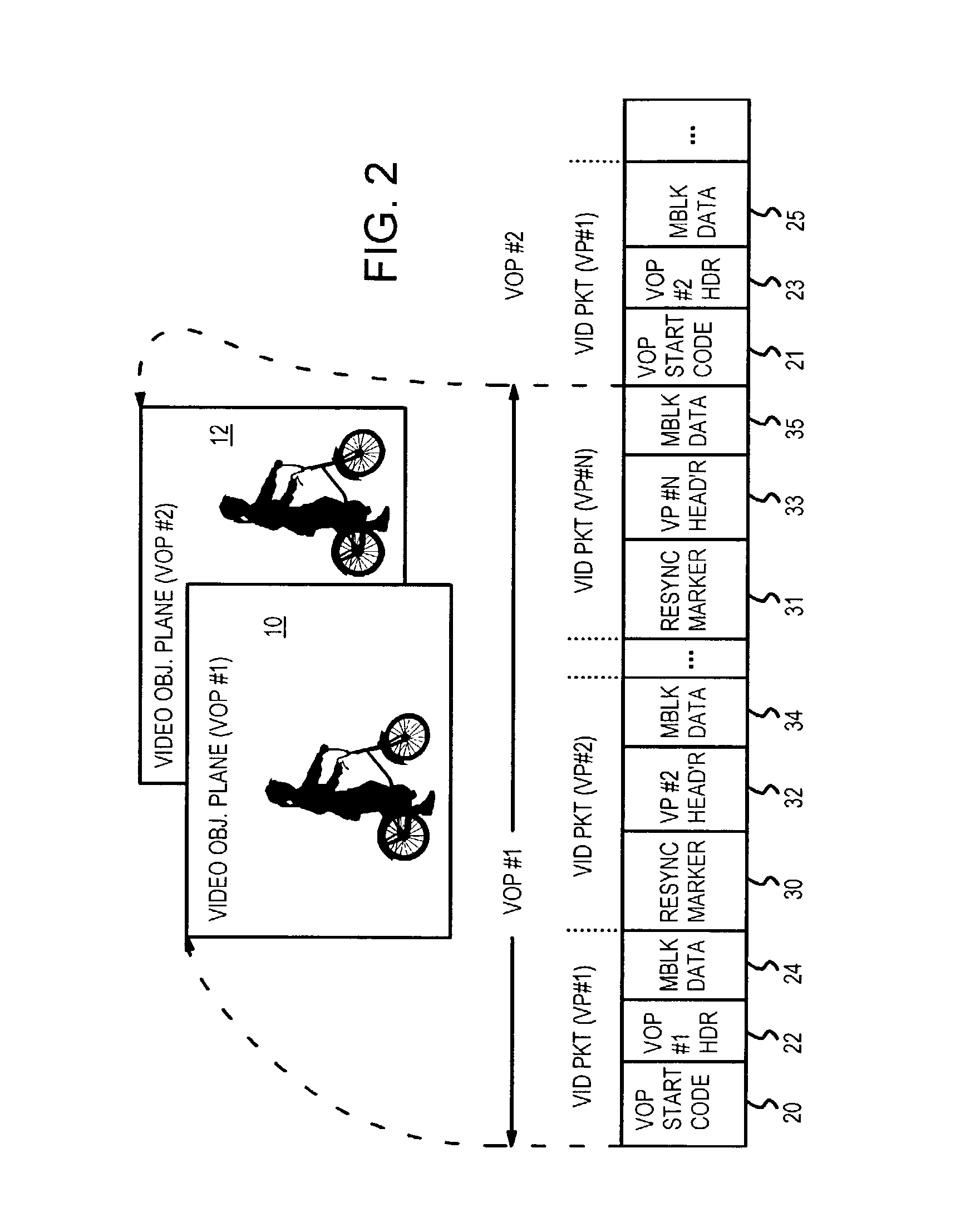
Sum-of-absolute-difference checking of macroblock borders for error detection in a corrupted MPEG-4 bitstream
InactiveUS20040071217A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAbsolute differenceSum of absolute differences
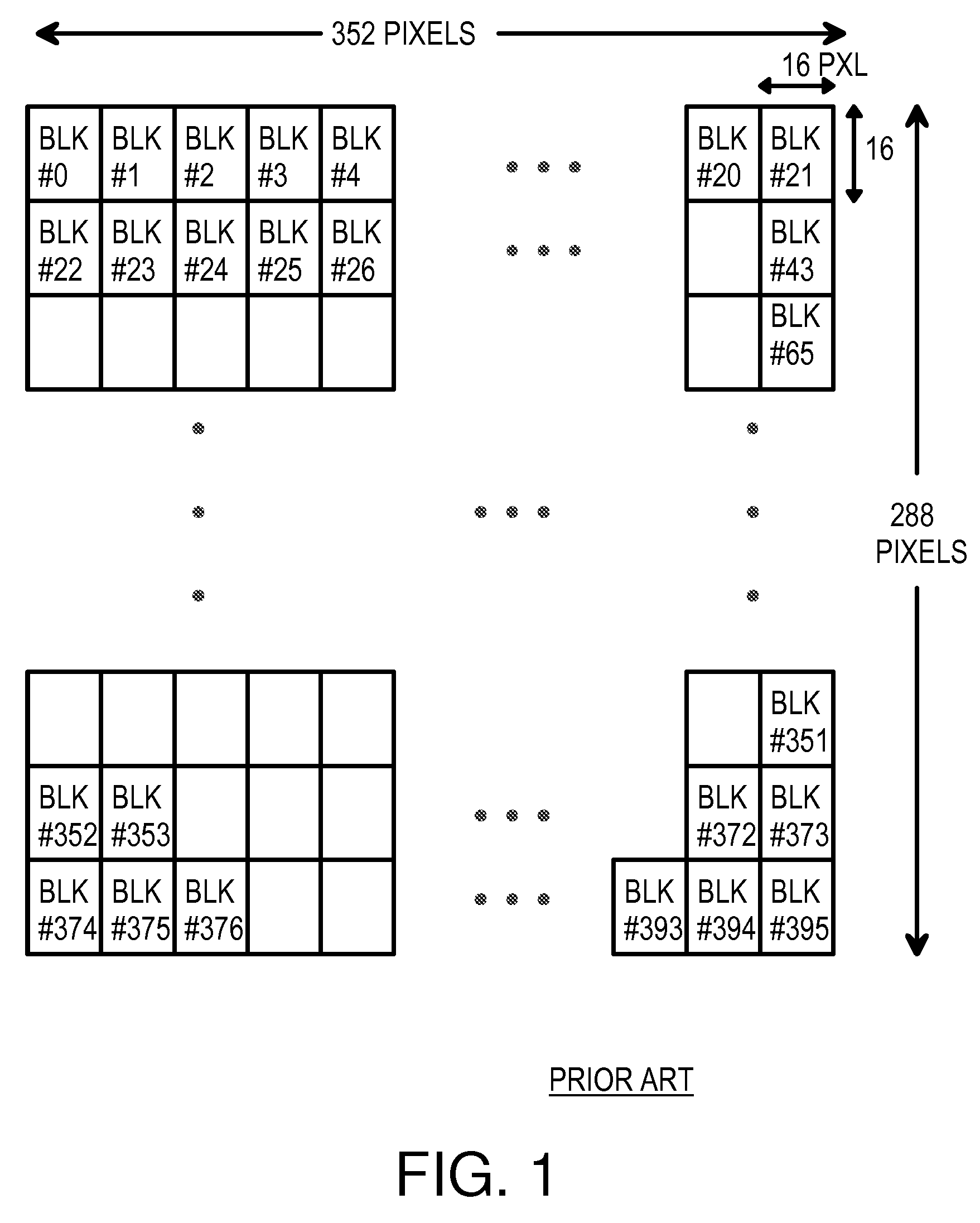
An MPEG decoder verifies a previous video packet by calculating the sum-of-the-absolute differences (SAD) for macroblock boundaries. When a macroblock counter goes off count, the macroblocks can be placed in the wrong relative locations in a frame. Image shapes are sliced when macroblock misplacement occurs, creating many new bisecting edges along macroblock boundaries. These image discontinuities along macroblock boundaries have a large SAD for pixels on either side of the macroblock boundary. The SAD is generated along the left and upper edges of a current macroblock, and a maximum SAD of all macroblocks in the previous video packet is generated. When the maximum SAD is above a threshold, the macroblock counter is likely to be in error, and the macroblock counter is reloaded with the header macroblock number from the next packet header. When the SAD is below threshold, a mis-matching header macroblock number is ignored.
Owner:REDROCK SEMICON
Floating point execution unit for calculating packed sum of absolute differences
ActiveUS20140149720A1Less logicReduce power consumptionInstruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesParallel computingExecution unit
A method and circuit arrangement provide support for packed sum of absolute difference operations in a floating point execution unit, e.g., a scalar or vector floating point execution unit. Existing adders in a floating point execution unit may be utilized along with minimal additional logic in the floating point execution unit to support efficient execution of a fixed point packed sum of absolute differences instruction within the floating point execution unit, often eliminating the need for a separate vector fixed point execution unit in a processor architecture, and thereby leading to less logic and circuit area, lower power consumption and lower cost.
Owner:IBM CORP
Speculative start point selection for motion estimation iterative search
InactiveUS20100014588A1Improve efficiencyQuality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionIterative searchMotion vector
A speculative start point selection for motion estimation iterative search improves the efficiency and quality of the integer-pel motion estimation iterative search by speculatively selecting the start position of the iteration. The start position is selected by comparing the Sum of Absolute Differences (SAD) value of a 0 motion vector, a predicted motion vector and a global motion vector (GMV) and selecting the position with the smallest SAD value. A refinement scheme with a threshold improves the efficiency and quality of the motion estimation iterative search by performing several comparisons to ensure the proper motion vector is selected. Applications of this improved motion estimation search include stabilizing an image as well as many other applications where motion vectors are used.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
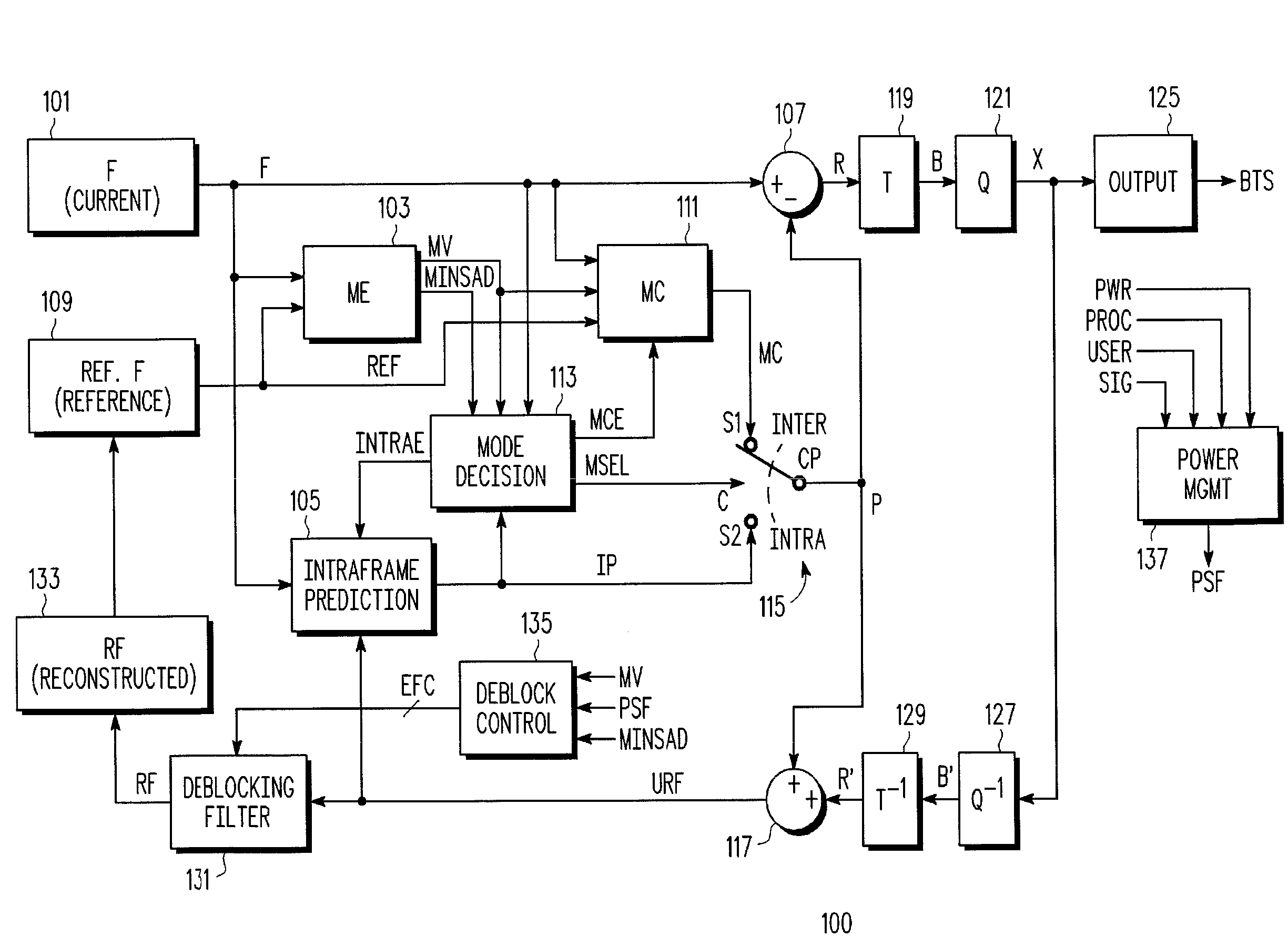
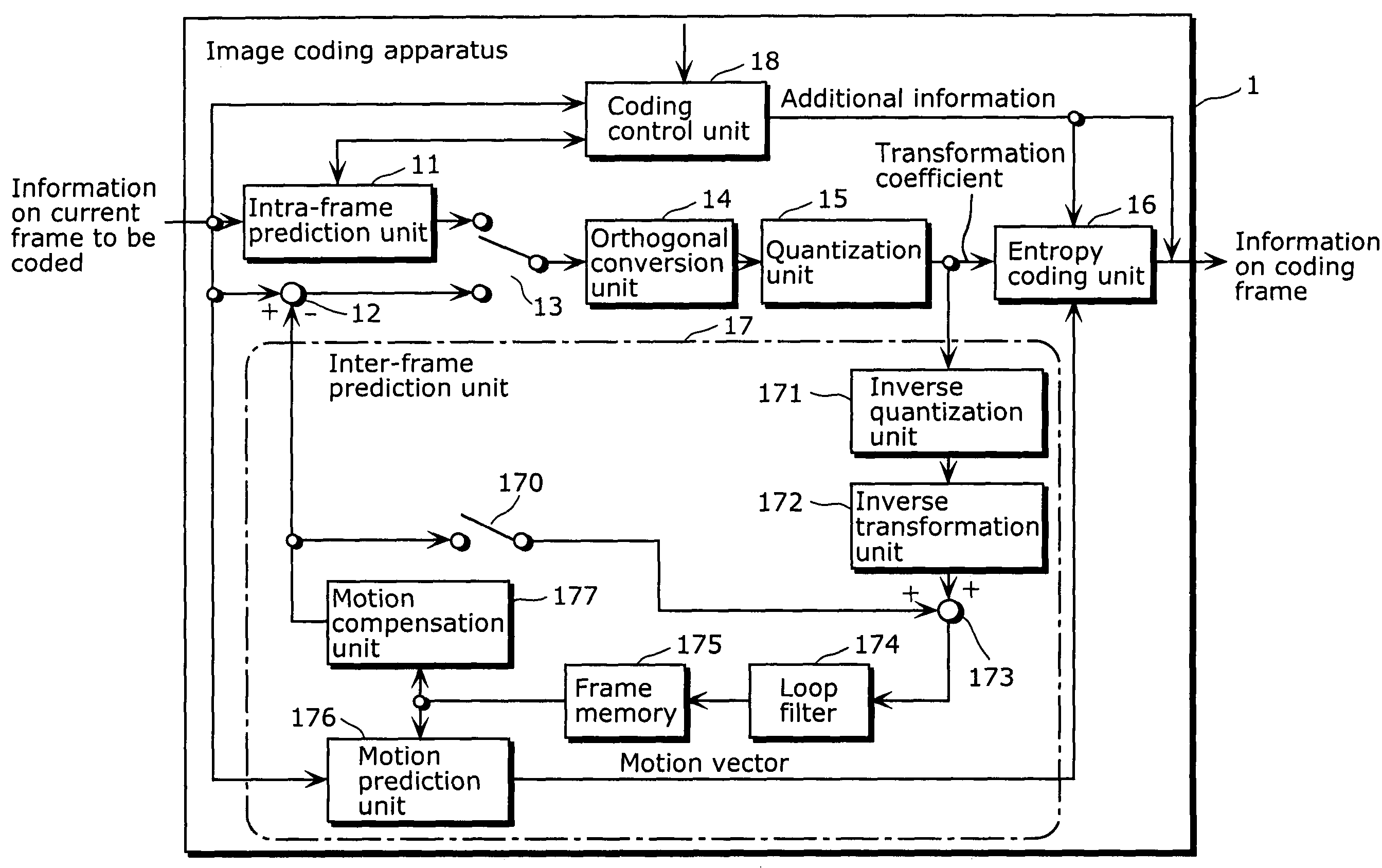
Image coding apparatus and image coding method
InactiveUS7881377B2Reduce computationImprove processing speedPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionCoding blockAlgorithm
An image coding apparatus executes intra-frame prediction with a predetermined intra-frame prediction mode for a certain block. A block selection unit judges that the current block to be coded is a prediction error calculation block or a non-prediction error calculation block. In the case where the current block is a prediction error calculation block, a mode error value calculation unit calculates the prediction error by the sum of absolute differences and for all of the intra-frame prediction modes, an inter-mode comparison unit compares the prediction errors, and as a result of the comparison, an intra-frame prediction mode having the minimum prediction errors is determined as the intra-frame prediction mode. In the case where the current block is a non-prediction error calculation block, the prediction error is not calculated. As an alternative, a prediction mode estimation unit determines the intra-frame prediction mode based on the neighboring prediction mode information stored in a storage unit.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Sum-of-absolute-difference checking of macroblock borders for error detection in a corrupted MPEG-4 bitstream
InactiveUS7027515B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAbsolute differenceComputer science
An MPEG decoder verifies a previous video packet by calculating the sum-of-the-absolute differences (SAD) for macroblock boundaries. When a macroblock counter goes off count, the macroblocks can be placed in the wrong relative locations in a frame. Image shapes are sliced when macroblock misplacement occurs, creating many new bisecting edges along macroblock boundaries. These image discontinuities along macroblock boundaries have a large SAD for pixels on either side of the macroblock boundary. The SAD is generated along the left and upper edges of a current macroblock, and a maximum SAD of all macroblocks in the previous video packet is generated. When the maximum SAD is above a threshold, the macroblock counter is likely to be in error, and the macroblock counter is reloaded with the header macroblock number from the next packet header. When the SAD is below threshold, a mis-matching header macroblock number is ignored.
Owner:REDROCK SEMICON
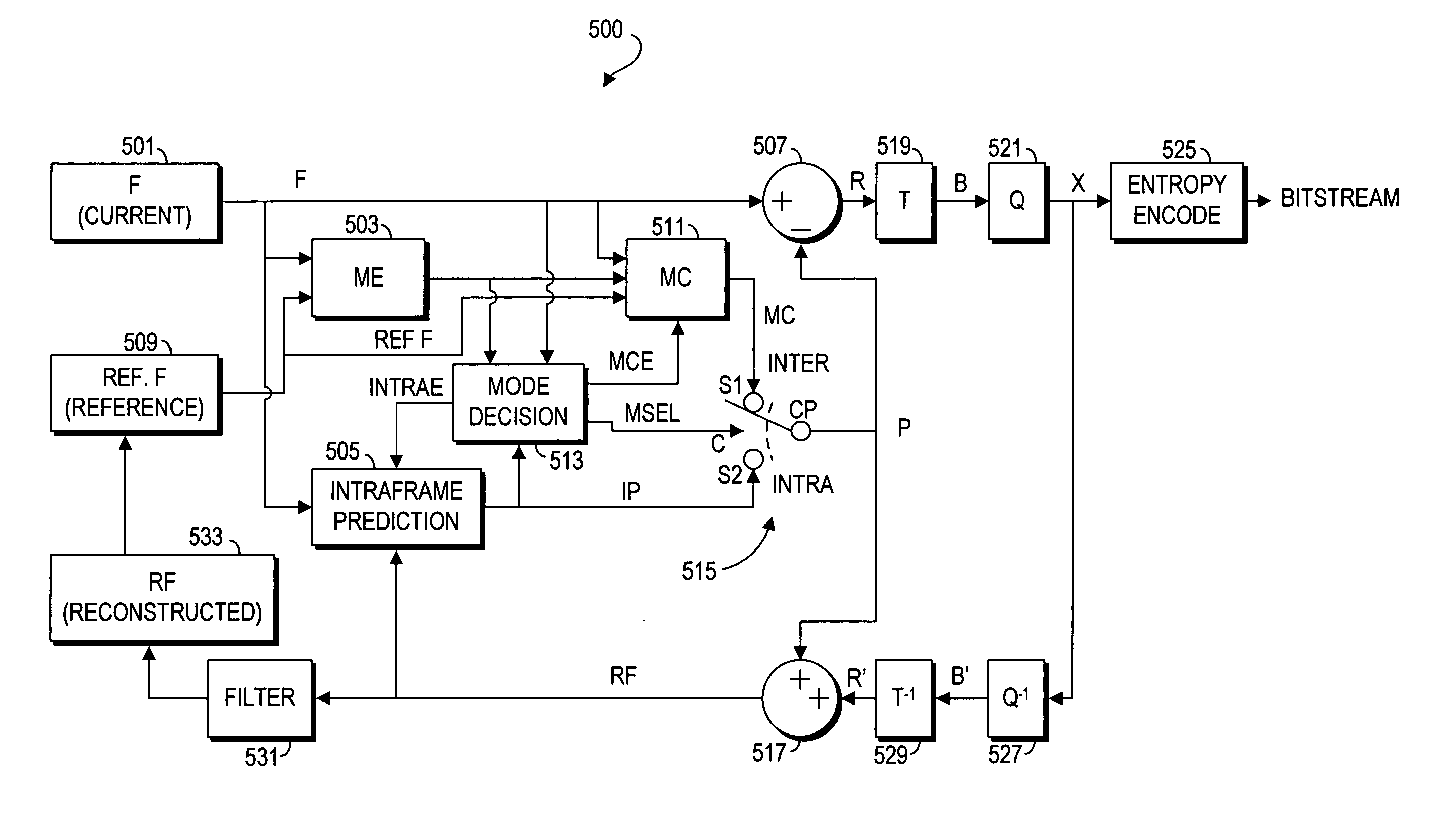
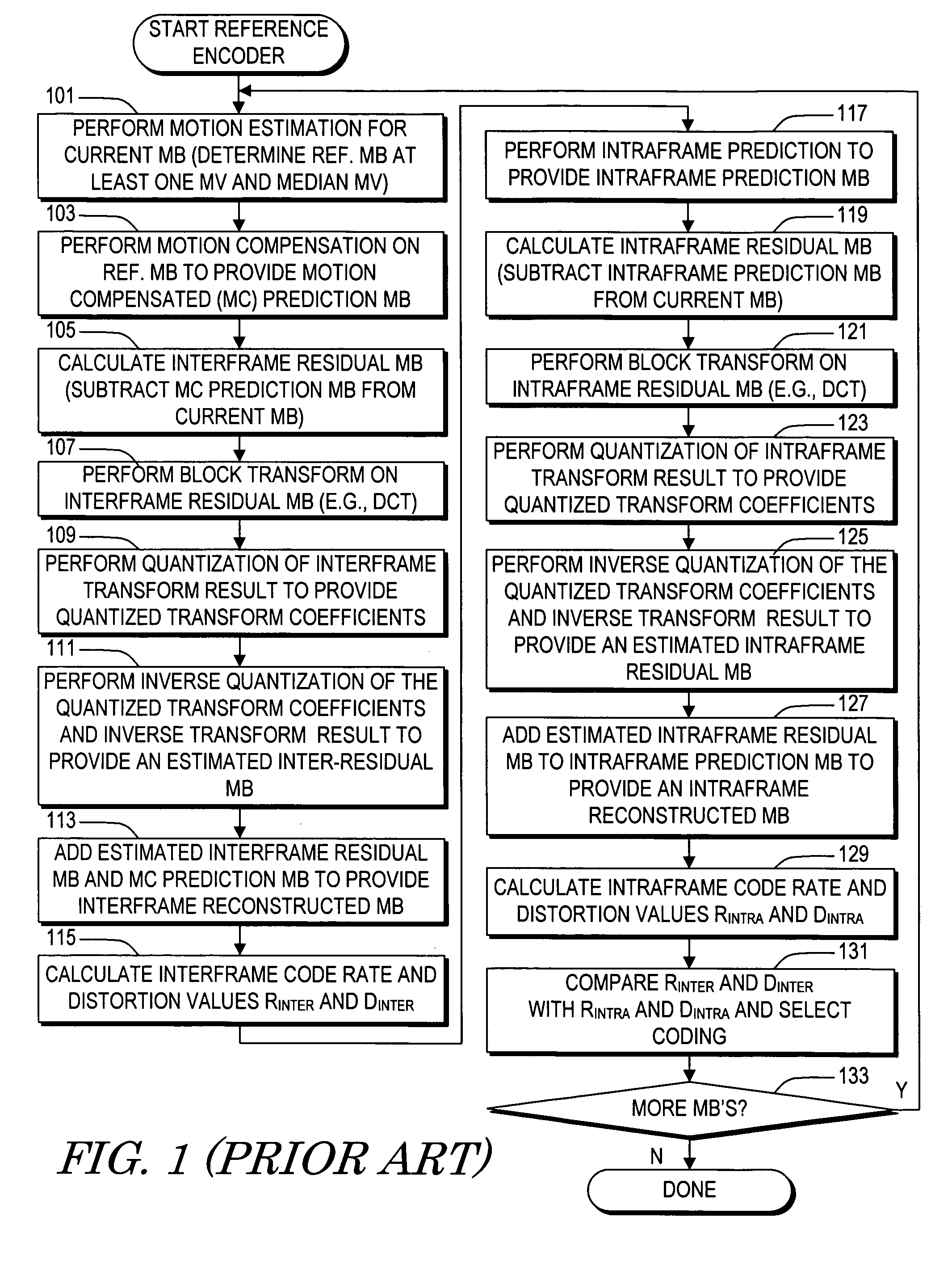
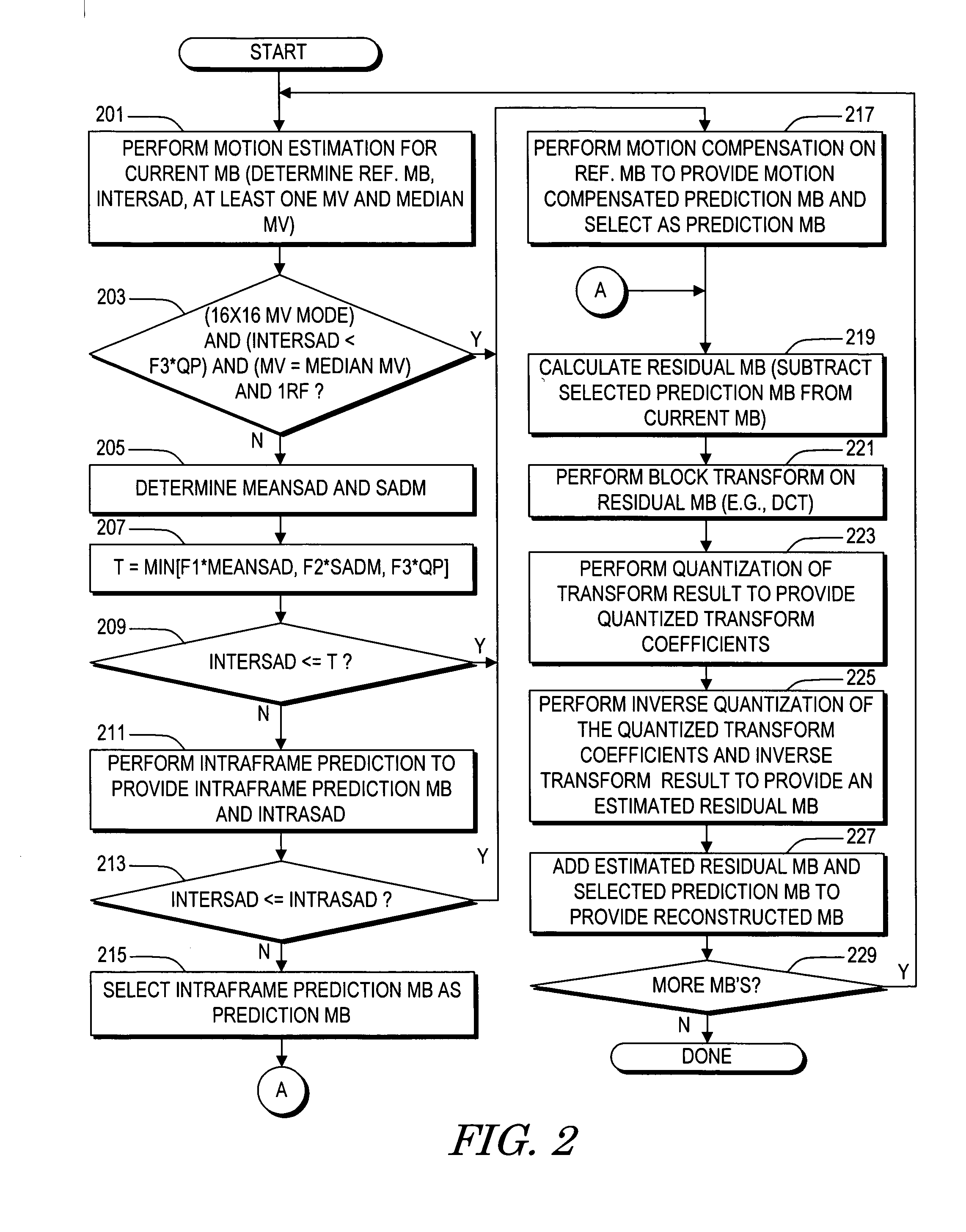
System and method of coding mode decision for video encoding
InactiveUS20070086523A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSum of absolute differencesMacroblock
A method of making a coding mode decision for a current macroblock of a current video frame including determining an INTERSAD value, selecting at least one video characteristic associated with the current video frame, comparing the INTERSAD value with a corresponding range of each selected video characteristic, selecting interframe coding if the INTERSAD value is within the corresponding range of each selected video characteristic, performing intraframe prediction to provide an intraframe prediction macroblock and determining an INTRASAD value if the INTERSAD value is an outlier of any selected video characteristic, selecting intraframe coding if the INTERSAD value is greater than the INTRASAD value and otherwise selecting interframe coding. The video characteristics may be based on any combination of an average of interframe differential sums, a sum of absolute differences between each pixel value of the current macroblock and a mean pixel value of the current macroblock, and a quantization parameter.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Apparatus for motion estimation of video data
InactiveUS20060120455A1Efficient motion estimationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorComputer science
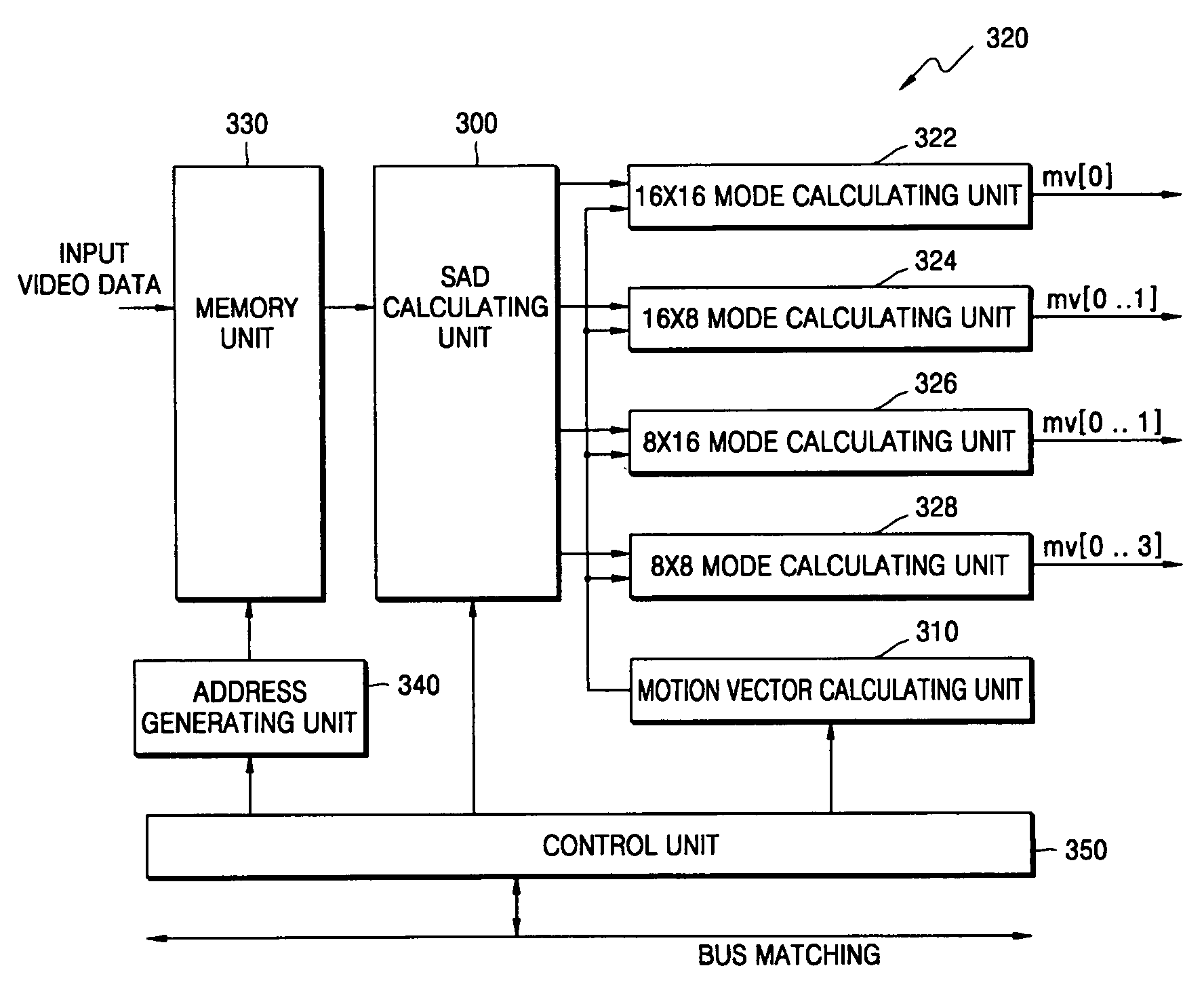
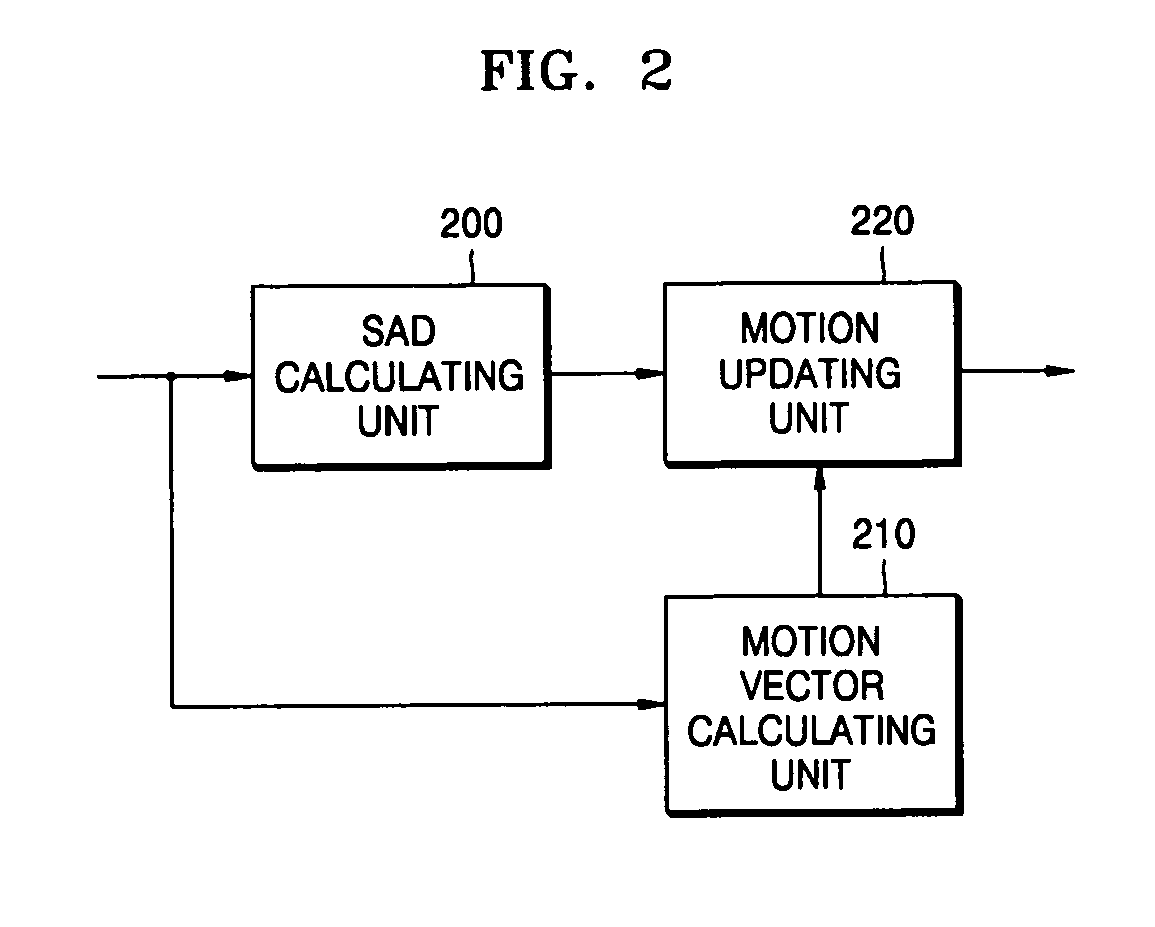
Provided is an apparatus for motion estimation of video data. The apparatus includes a sum of absolute difference (SAD) calculating unit which receives video data and calculates an SAD for each frame of the video data, a motion vector calculating unit which divides each frame of the video data into macroblocks or sub-macroblocks having a predetermined size and calculates a motion vector estimation value using motion vectors or prediction vectors of macroblocks or sub-macroblocks adjacent to each macroblock or sub-macroblock, and a motion updating unit which performs motion estimation on the video data using an SAD calculated by the SAD calculating unit for the macroblocks or the sub-macroblocks adjacent to each macroblock or sub-macroblock having the predetermined size and the motion vector estimation value of the motion vector calculating unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
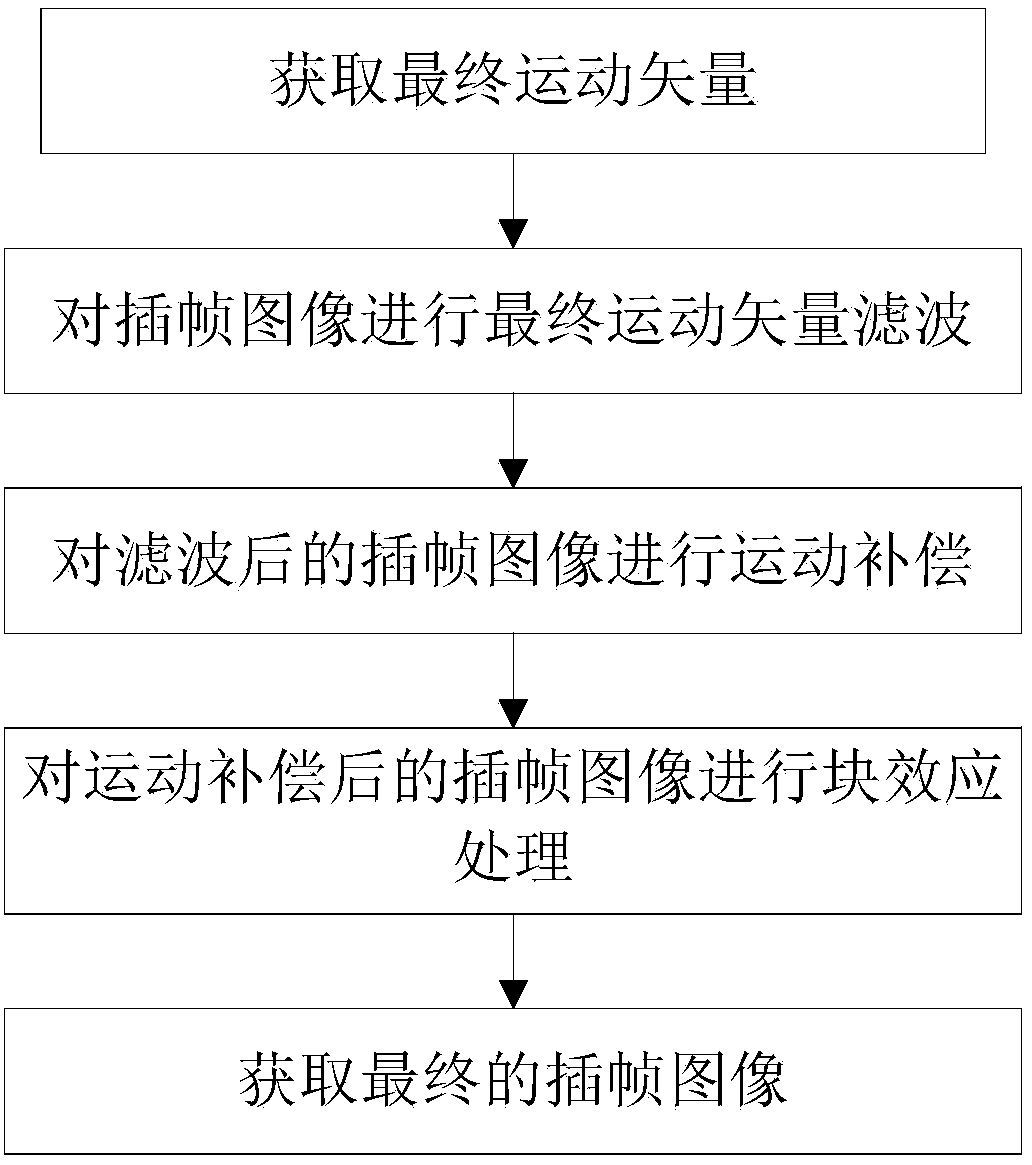
Motion vector post-processing based frame rate up-conversion method
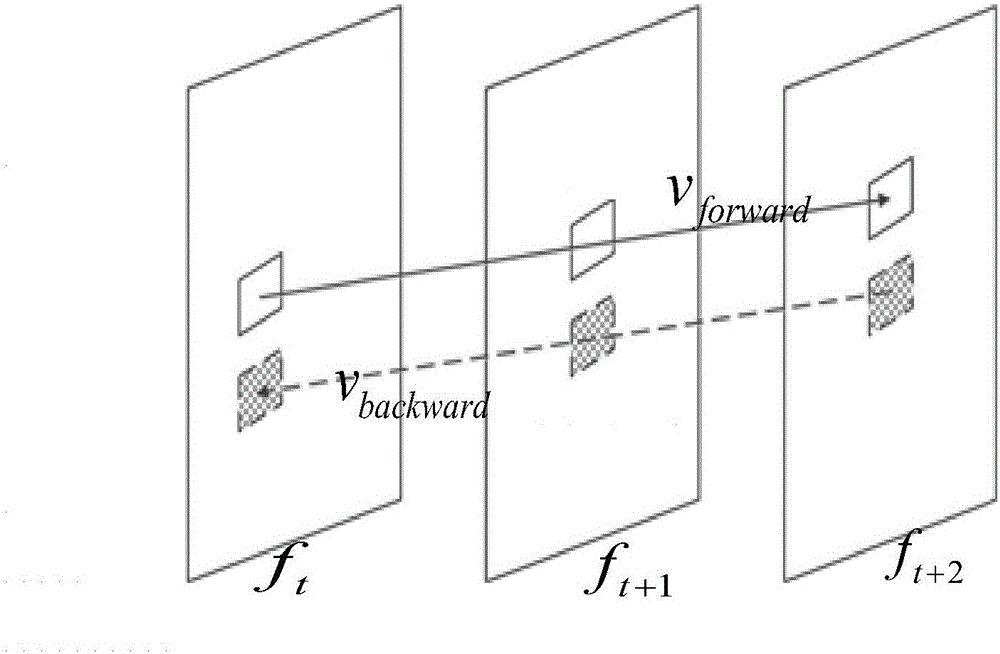
ActiveCN105100807ASolve voidSolve occlusionDigital video signal modificationMotion vectorVisual perception
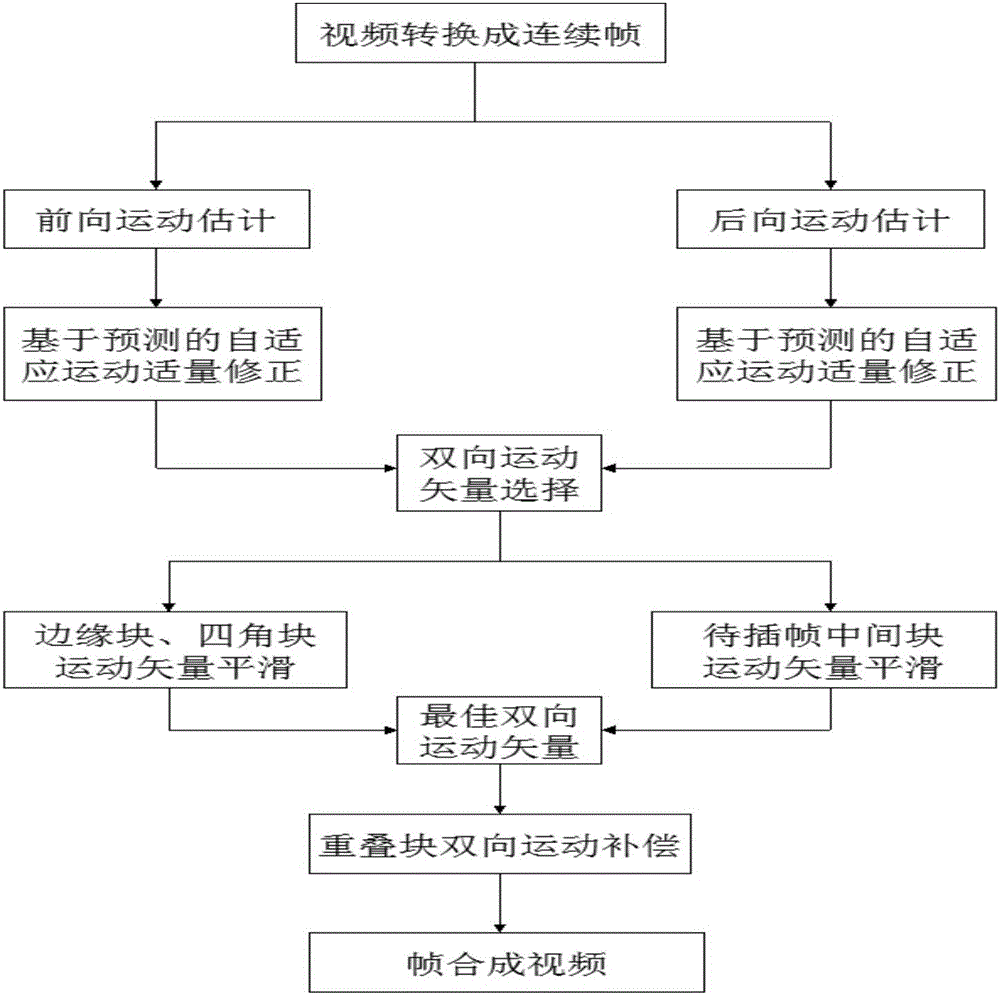
The invention provides a motion vector post-processing based frame rate up-conversion method. According to the method, firstly, forward and backward motion estimations are performed on an original video frame, so as to obtain a forward motion vector and a backward motion vector, and abnormal values of the forward motion vector and the backward motion vector are modified based on prediction; bidirectional candidate motion vectors are selected based on minimum sum of absolute differences (SAD); then, different smoothing methods are adopted for bidirectional motion vectors of different positions; vector extrapolation is performed on an edge block and four corner blocks firstly, a distance-based weighting smoothing method is adopted for unreliable motion vectors , the candidate vectors of a middle block are selected based on the direction and magnitude of the motion vector of an adjacent block, and a final vector of a to-be-interposed block is selected from the candidate vectors based on the minimum SAD; and finally, an interpolation frame is obtained by use of bidirectional motion compensation of overlapped blocks. Through adoption of the frame rate up-conversion method, the problems of holes and shielding of the interpolation frame can be solved effectively, phenomena of motion blur and shaking can be eliminated, and the visual effect of the constructed interpolation frame is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Bidirectional motion estimating method and video frame rate up-converting method and system
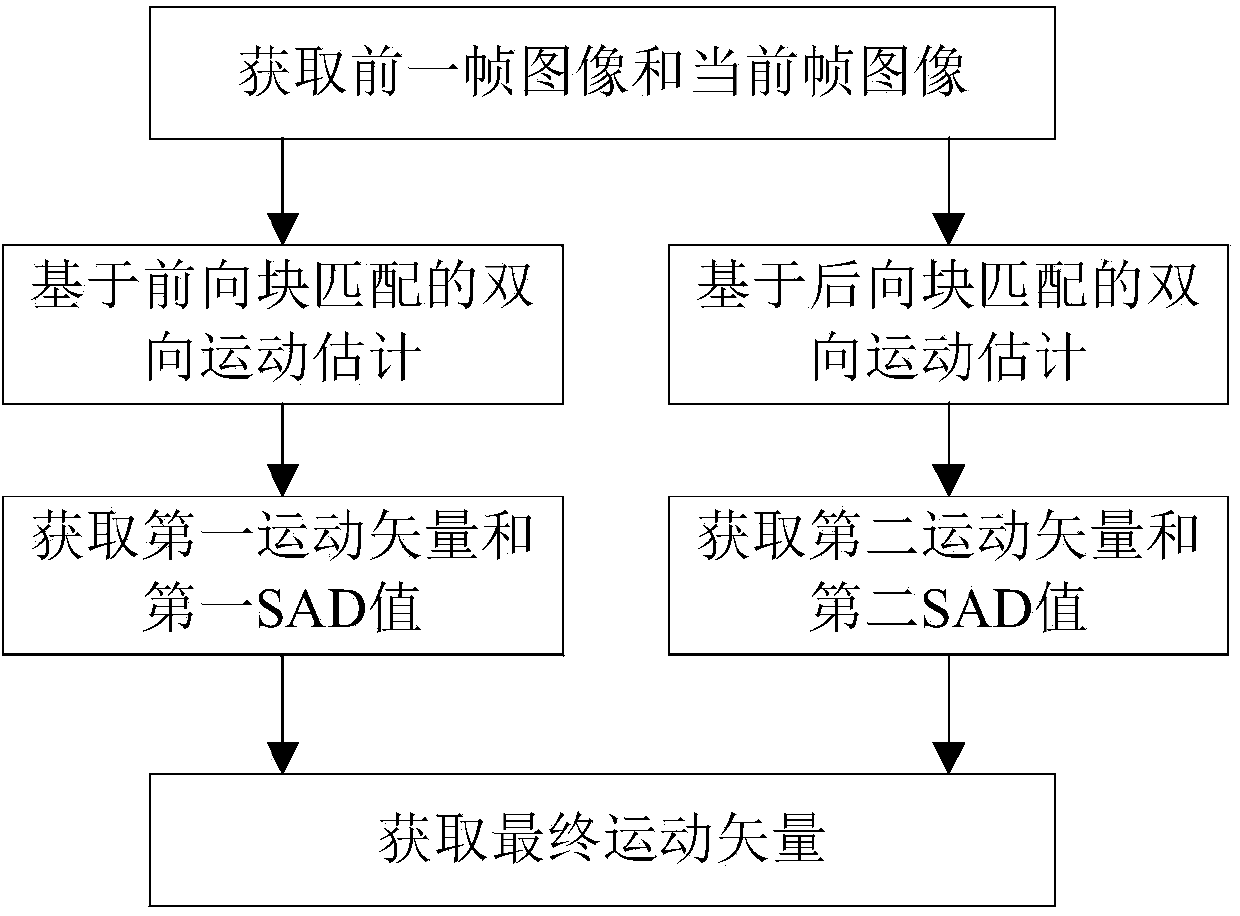
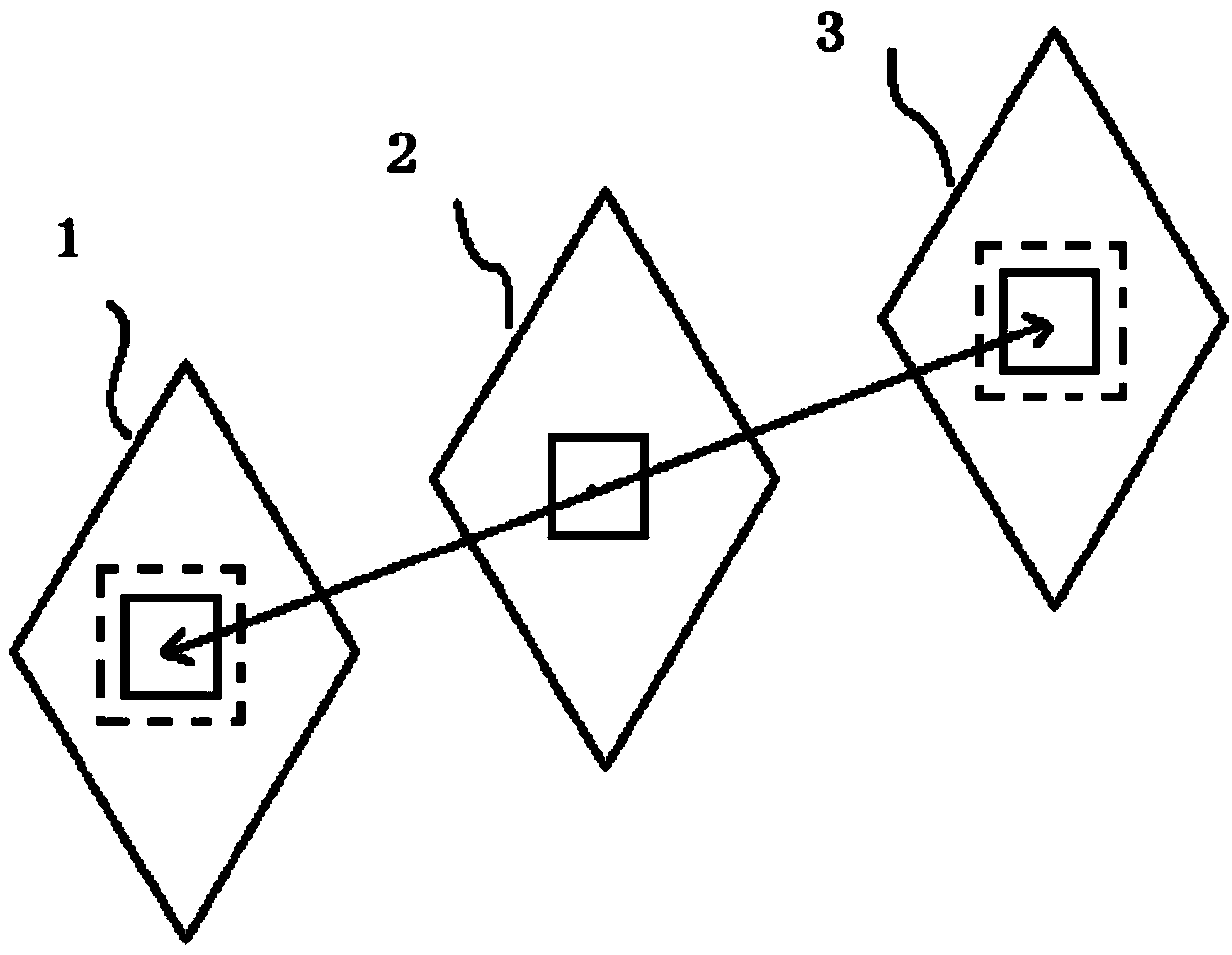
ActiveCN104219533AAccurately describe the movementResolve confusionDigital video signal modificationImaging qualityMotion vector
The invention provides a bidirectional motion estimating method and system. The method comprises, after a prior frame image and a current frame image are obtained, performing bidirectional motion estimation based on forward block matching and backward block matching respectively; then according to the minimum SAD (sum of absolute difference) value and the corresponding motion vector which are obtained respectively, obtaining a final motion vector, wherein the obtained final motion vector can accurately describe the motion status of a moving object and accordingly solve the confusion between the moving object and the background due to inaccuracy of the motion vector. The invention also provides a video frame rate up-converting method and system. The method comprises obtaining the final motion vector according to the bidirectional motion estimating method and system and then performing motion vector filtering, motion compensation and blocking effect treatment; the finally obtained interpolated frames can eliminate confusion between the moving object and the background and blocking effects, improves the image quality of interpolated images, reduces the problems such as smoothness and continuity of video images and improves the visual effects of videos.
Owner:SUZHOU KEDA TECH +2
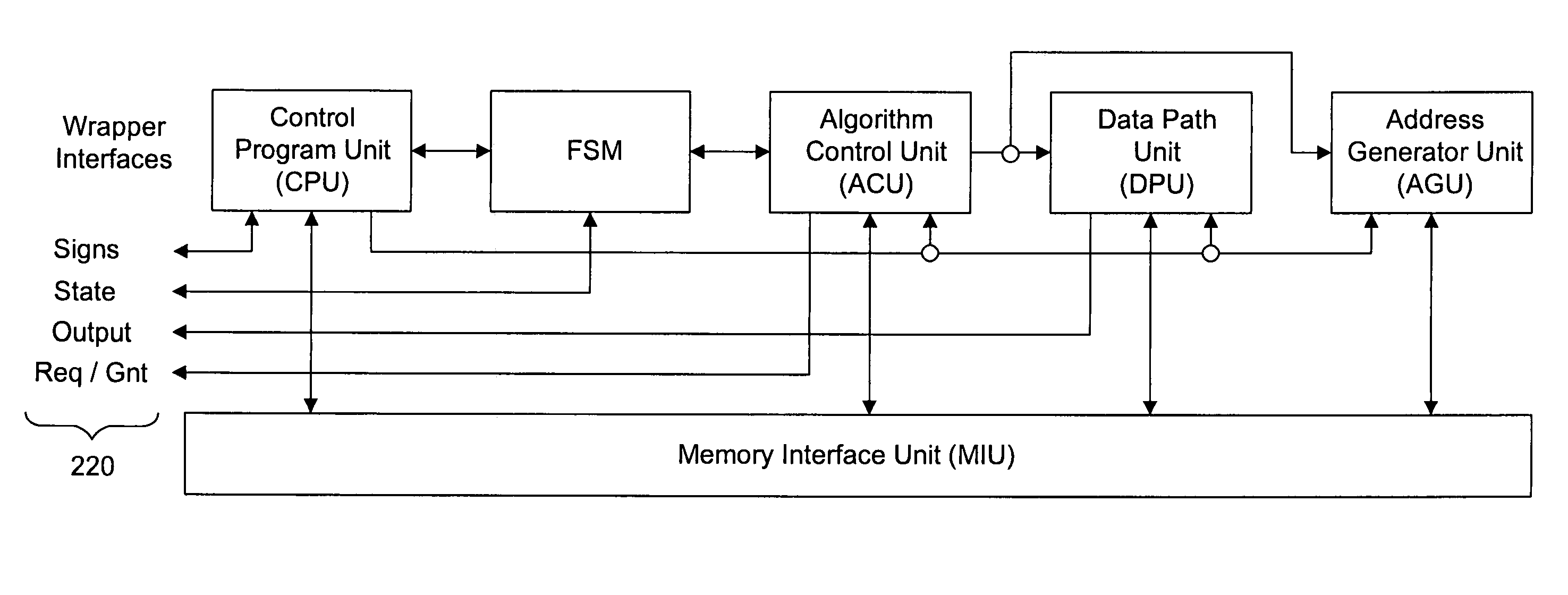
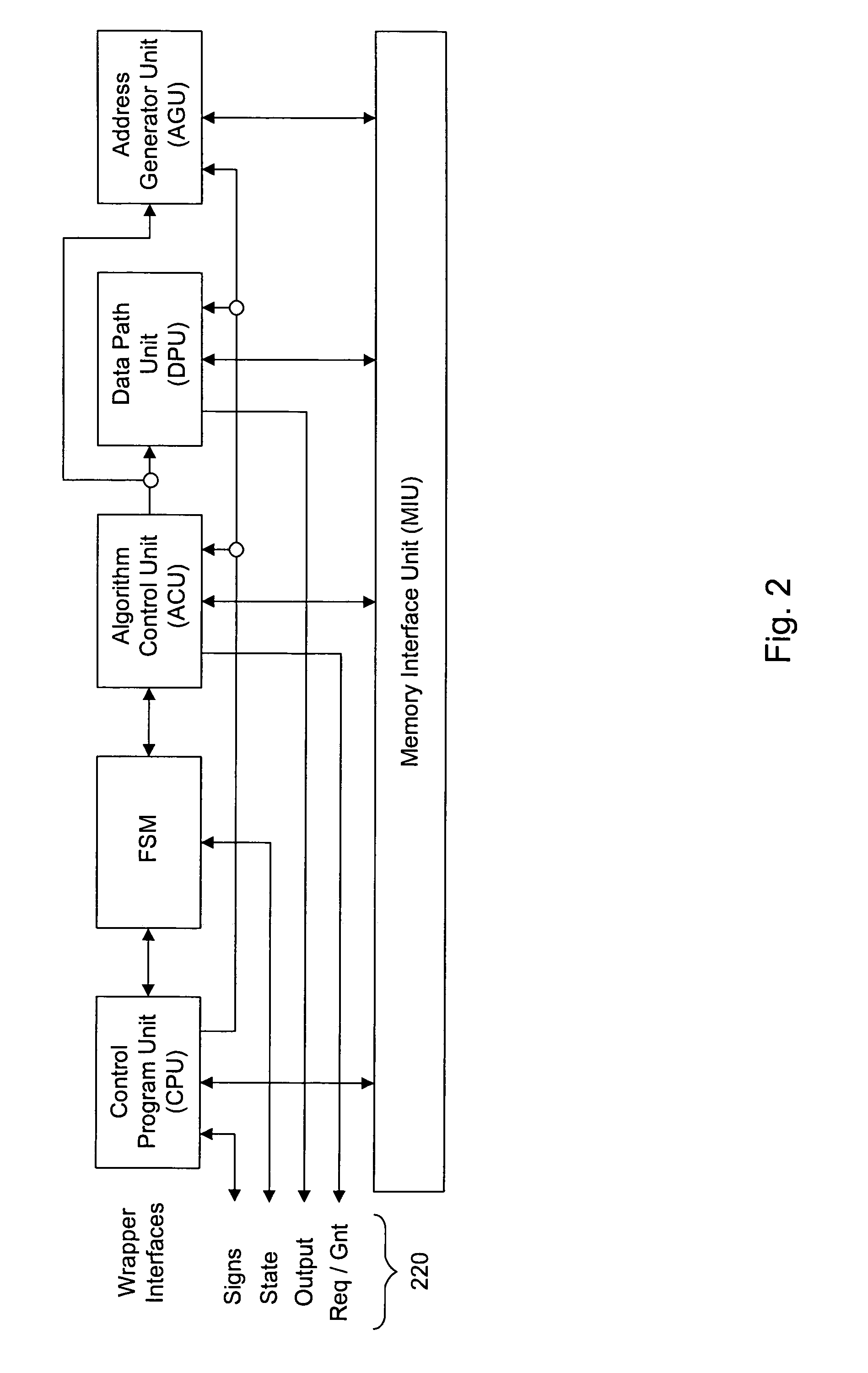
Processing architecture for a reconfigurable arithmetic node
ActiveUS7433909B2Improve performanceArchitecture with single central processing unitComplex mathematical operationsFast Fourier transformParallel computing
A computational unit, or node, in a adaptable computing system is described. A preferred embodiment of the node allows the node to be adapted for use for any of ten types of functionality by using a combination of execution units with a configurable interconnection scheme. Functionality types include the following: Asymmetric Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Filter, Symmetric FIR Filter, Complex Multiply / FIR Filter, Sum-of-absolute-differences, Bi-linear Interpolation, Biquad Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) Filter, Radix-2 Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) / Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (IFFT), Radix-2 Discrete Cosign Transform (DCT) / Inverse Discrete Cosign Transform (IDCT), Golay Correlator, Local Oscillator / Mixer.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method for obtaining parallax by using region-based local stereo matching
ActiveCN102665086AThe result is accurateGood window shapeSteroscopic systemsPattern recognitionParallax
The invention discloses a method for obtaining parallax by using region-based local stereo matching. The method comprises the steps of selecting a plurality of searching pixels in a second channel of viewpoint images for a current pixel of a first channel of viewpoint images; obtaining a first matching cost value and a second matching cost value between the current pixel and a certain searching pixel by respectively using a sum of absolute differences (SAD) algorithm and a Rank transformation algorithm; determining a first matching weight and a second matching weight according to numbers of edge pixels in a set region around pixels corresponding to the current pixel in binaryzation edge images of the first channel of viewpoint images; regarding the sum of the product of the first matching cost value and the first matching weight and the product of the second matching cost value and the second matching weight as a final matching cost value between the current pixel and the searching pixel; obtaining other final matching cost values and choosing the smallest matching cost value in all the final matching cost values and obtaining a vector difference which is a first parallax of the current pixel between a searching pixel which corresponds to the smallest matching cost value and the current pixel.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Telecine conversion detection for progressive scan playback
ActiveUS7391468B2Reduce overheadTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsMoving averageData stream
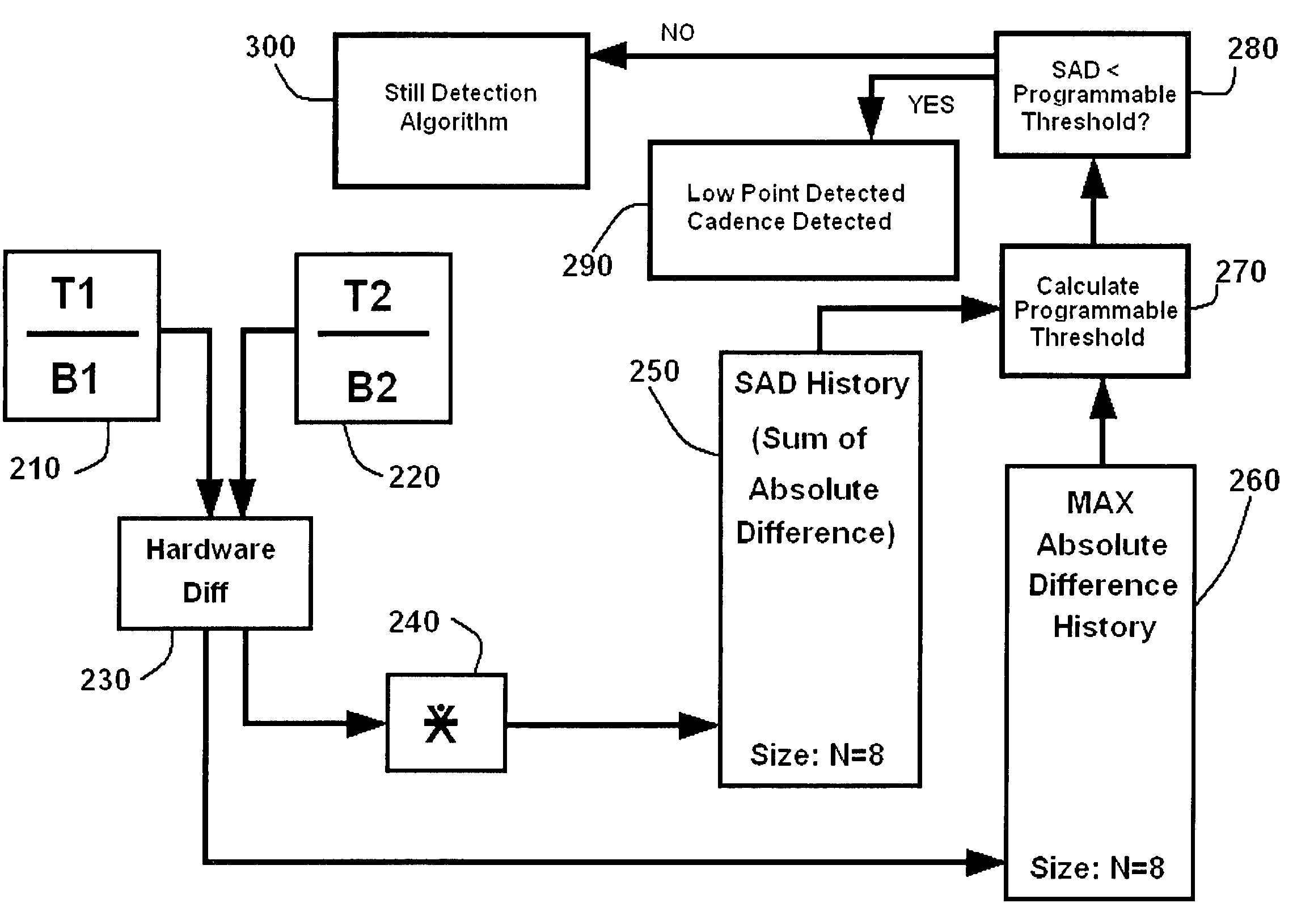
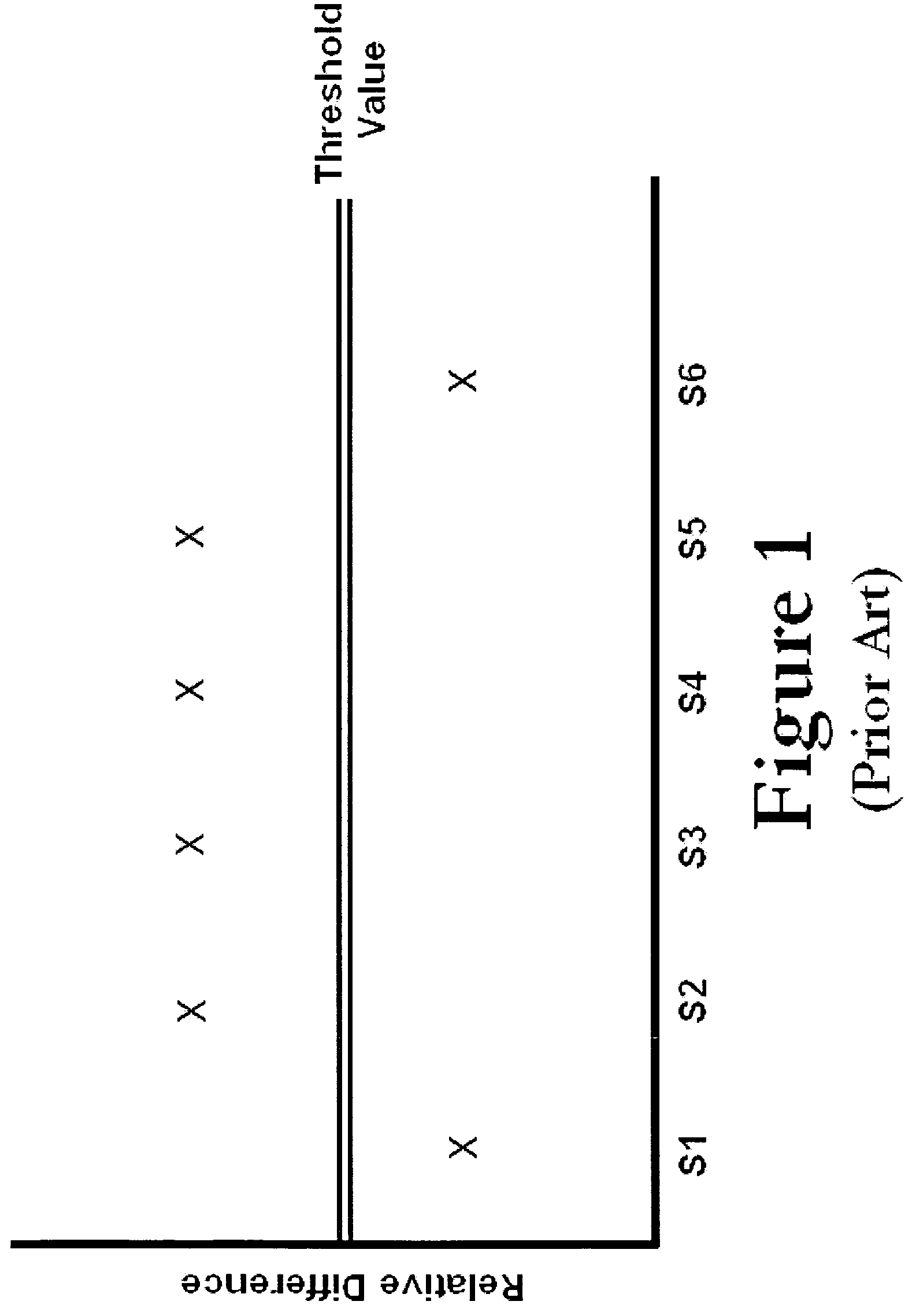
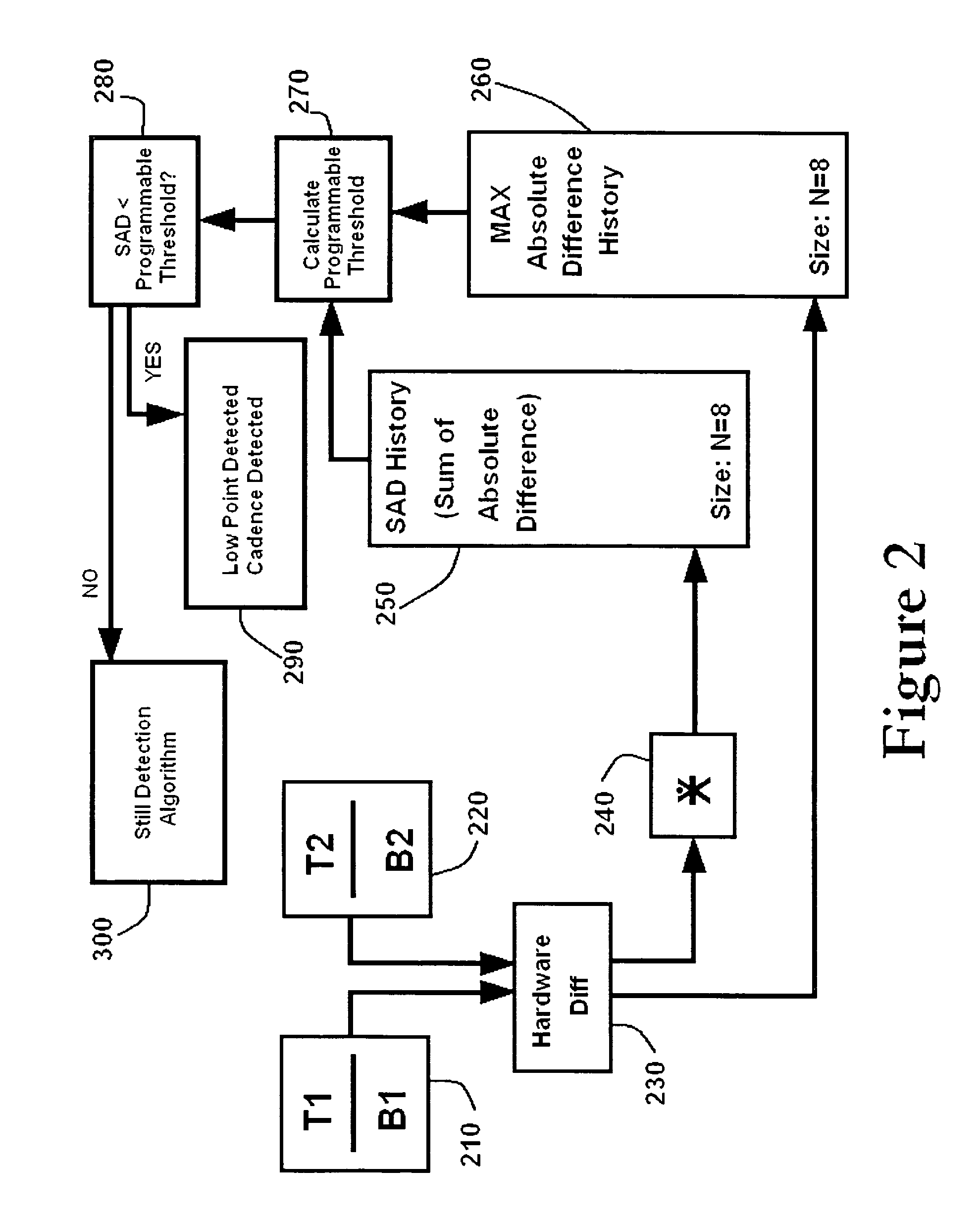
A moving average filter with a weighting factor calculates a continuously programmable threshold to determine whether fields could be considered identical or not. This decision is used to detect the cadence of a TELECINE encoded video signal. This moving average filter is also used for detecting the presence of still images in the video data stream by detecting total difference in Y (luminance) of the fields and then calculating the average difference in luminance (Y) of the field. This average difference in luminance value indicates a degree of difference between fields. For two frames of data input to the system, each having two fields, a difference is calculated between the luminance values of the two top fields for each frame. From this difference value a maximum absolute difference history is stored, along with the Sum of Absolute Differences (SAD). The programmable threshold is then calculated by summing the saturated SAD history over time. If the present SAD is less than the program threshold, then a low point is detected (e.g., small difference between two fields) and if it follows TELECINE pattern, then the cadence of TELECINE is indicated.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Method for quickly selecting HEVC (high-efficiency video coding) inframe coding units
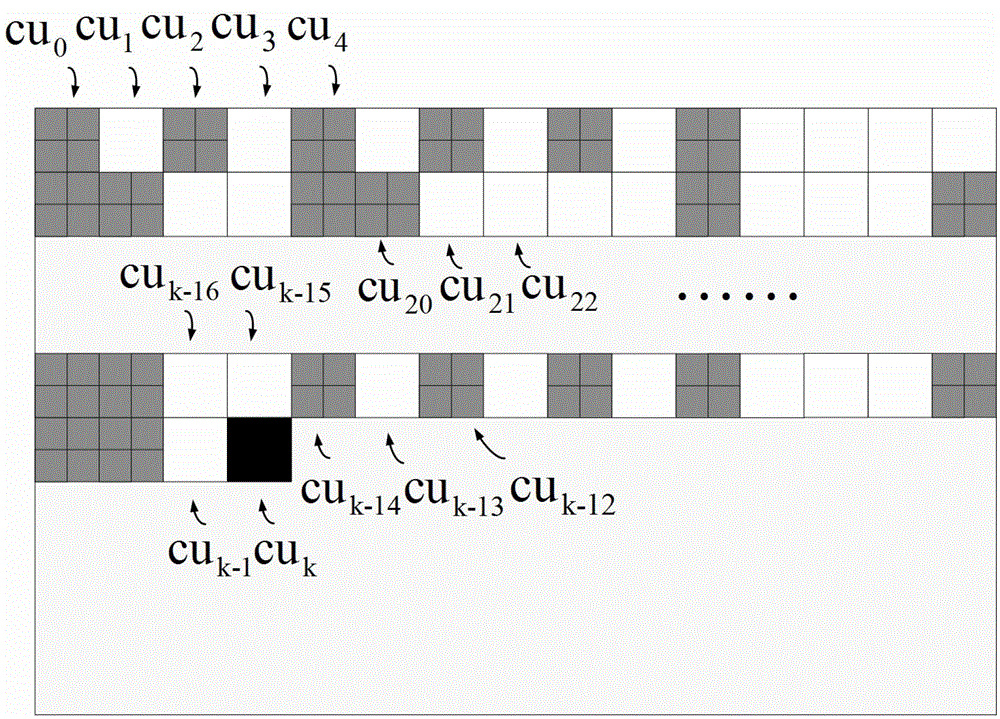
InactiveCN102917225AReduce time complexityReduce computational complexityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationTemplate matchingRate distortion
The invention provides a method for quickly selecting HEVC (high-efficiency video coding) inframe coding units. Rate-distortion cost of each CU (coding unit), obtained by absolute error and SAD (sum of absolute difference) approximately, is related to non-uniformized gradient histogram of each CU. The higher the similarity degree of the non-uniformized gradient histograms of two equal-scale CUs is, the more possibly equal splitflags are. The method is a method for realizing quick selection of the CUs by utilizing the template matching mode on the basis of the non-uniformized gradient histograms, and accordingly, improving coding speed of the HEVC inframe prediction method. Whether each CU is required to be split into four smaller CUs or not is judged by utilizing the non-uniformized gradient histograms as features. On the condition of meeting template matching requirements, a step of comparing rate distortion cost of codes one by one is omitted.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
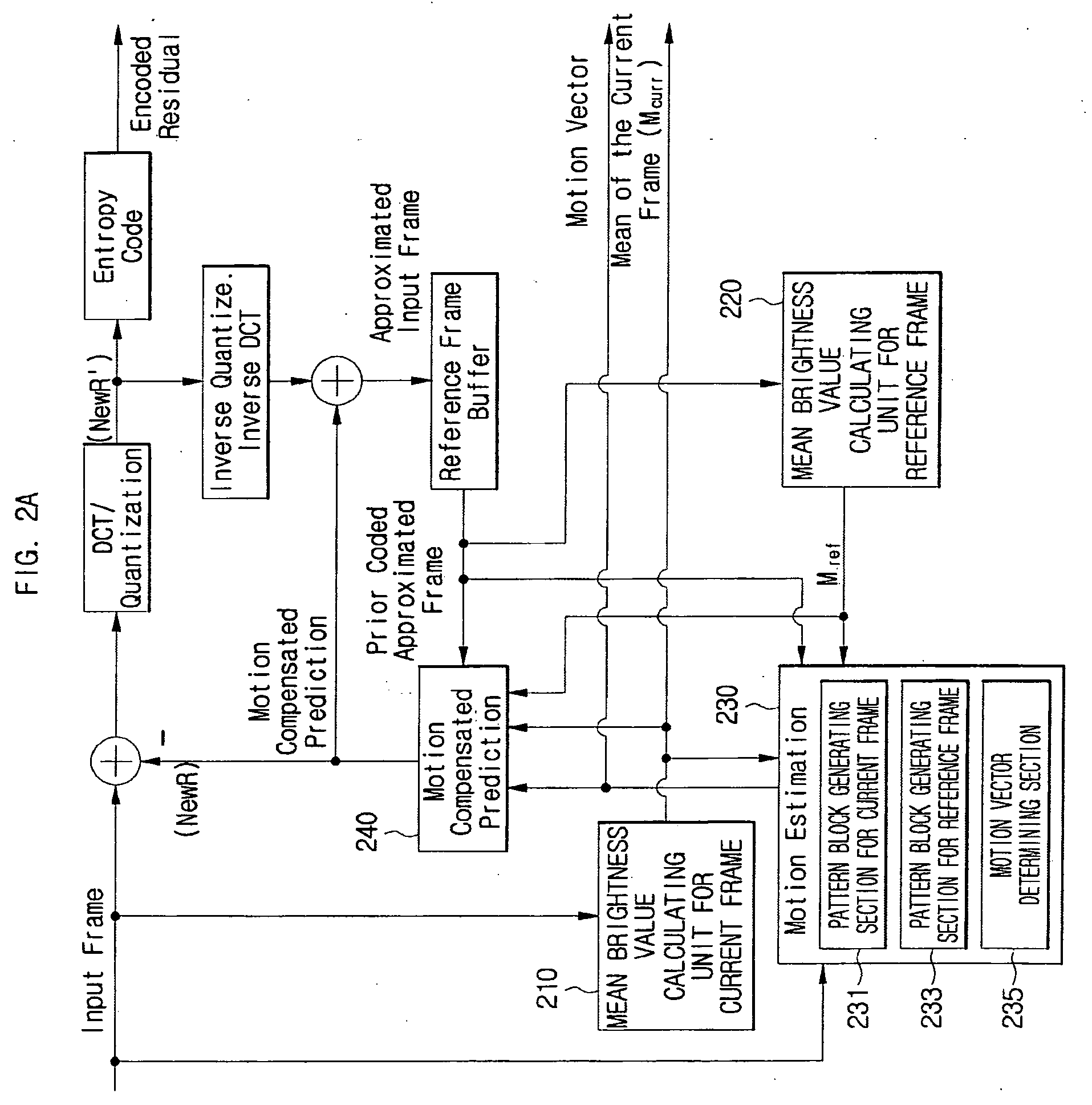
Motion estimation and compensation method and device adaptive to change in illumination
InactiveUS7924923B2Efficiently encodeEfficient decodingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionMotion vector
Provided are a motion estimation device and method adaptive to change in illumination. The motion estimation method includes the steps of: generating a current frame pattern block and a reference frame pattern block for a reference frame block; calculating the sum of absolute differences (SAD) for candidate pattern blocks and determining the candidate pattern block corresponding to the SAD satisfying a predetermined condition among the calculated SAD as a motion vector; encoding the current frame block, and adding flag information indicating the addition of a mean pixel value applied to the encoded current frame block and identification information on the encoding mode as header information corresponding to the encoded current frame block.
Owner:HUMAX CO LTD
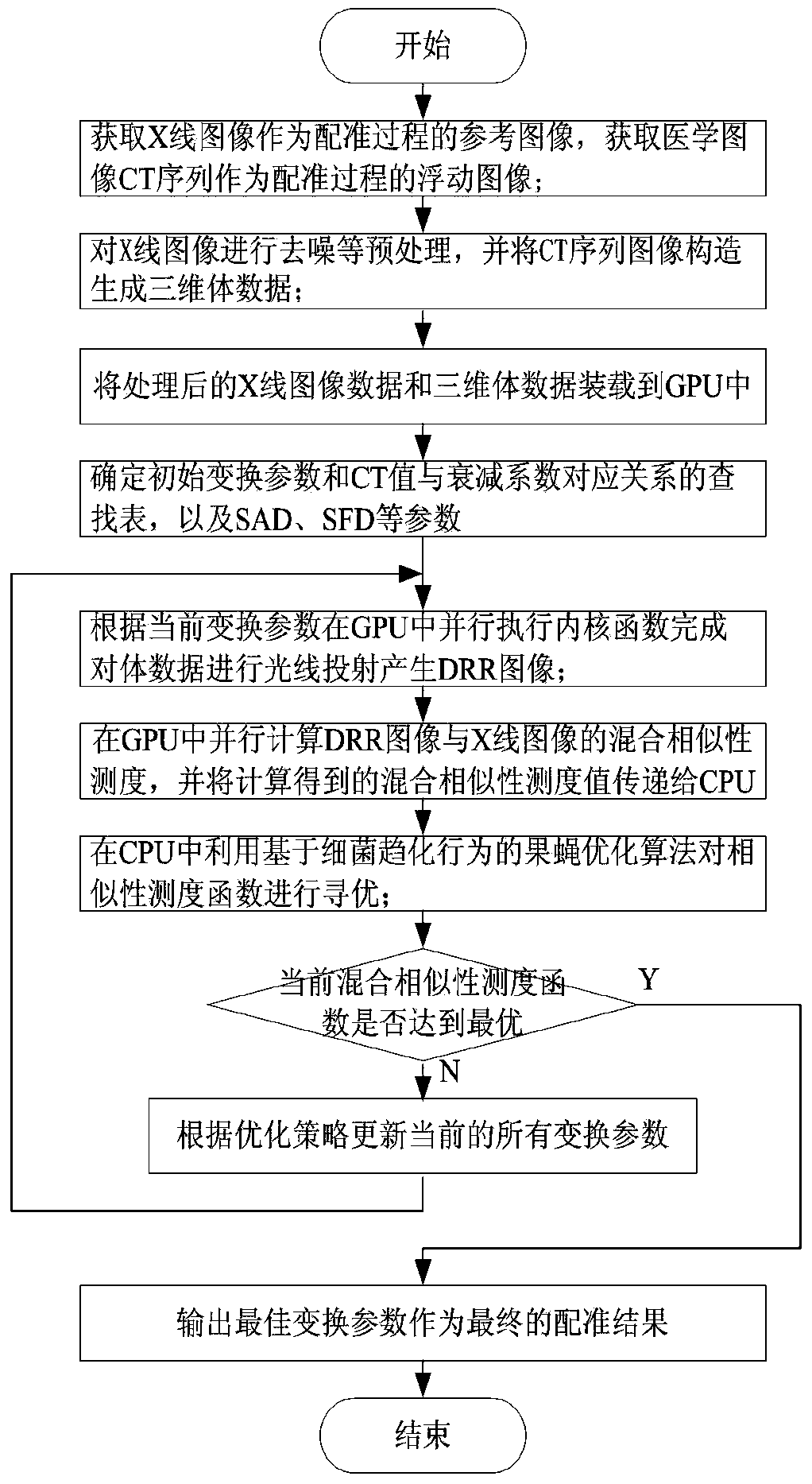
2D-3D medical image parallel registration method based on combination similarity measure
InactiveCN104134210ASimple calculationHigh precisionImage analysisGeneration processParallel programming model
The invention discloses a 2D-3D medical image parallel registration method based on combination similarity measure. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, using a CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) parallel computing model to finish a quick generation process of a DRR (Digitally Reconstructed Radiograph) image; combining a SAD (Sum of Absolute Difference) with PI (pattern intensity) as new similarity measure to carry out parallel computation on GPU (Graphics Processing Unit); and finally, transferring a combination similarity measure value to CPU (Central Processing Unit), and adopting a fruit fly optimization algorithm based on bacterial chemotaxis behaviors to optimize for looking for an optimal registration parameter. An experiment verifies the performance of the method to show that the execution speed of the method is effectively improved since DRR high-speed generation and the mixed similarity measure are realized in the GPU. Meanwhile, compared with the single similarity measure, the invention adopts the mixed similarity measure to improve the accuracy of a registration result.
Owner:LANZHOU JIAOTONG UNIV
Transcoding method from H.264/SVC(scalable video coding) to H.264/AVC(advanced video coding) based on video on demand system of P2PVoD
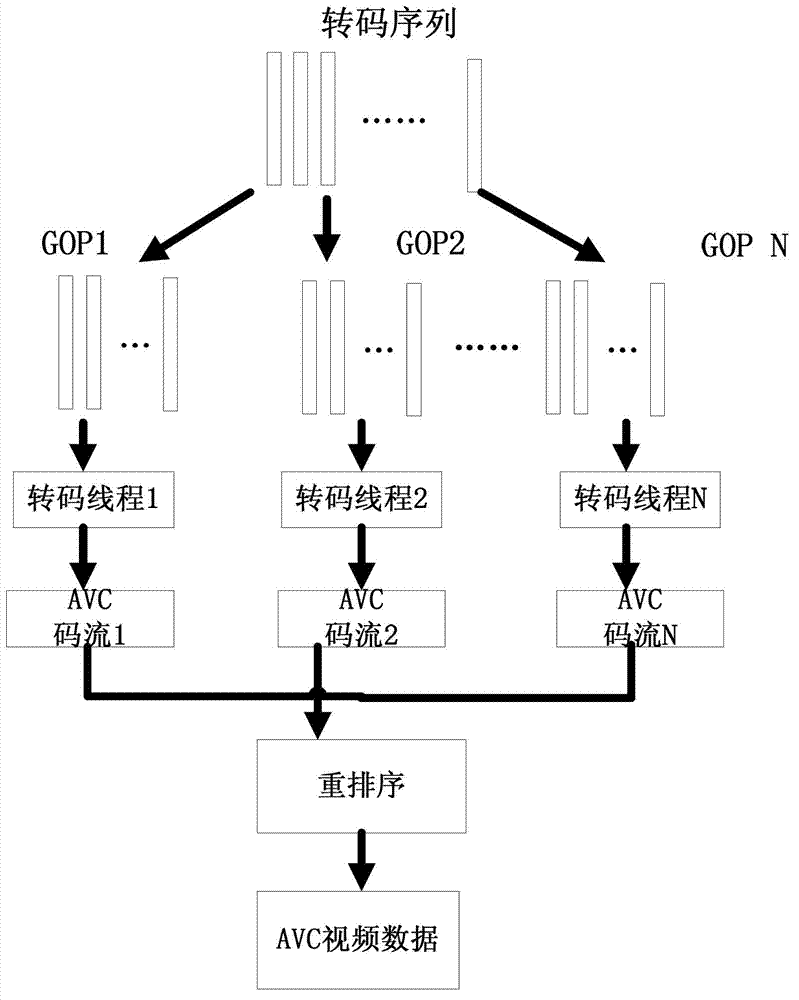
InactiveCN102790905AReduce time overheadReduce time complexitySelective content distributionComputation complexityGroup of pictures
The invention provides a transcoding method from H.264 / SVC(scalable video coding) to H.264 / AVC(advanced video coding) based on a video on demand system of P2PVoD, belonging to the field of video transcoding. With the adoption of SVC self-adapting transcoding, an SVC document is divided into independent multi-layer documents according to layers by a separator, before transcoding, a space layer and a quality layer are subjected to a self-adaption process according to the terminal ability, layers not needed are abandoned to enable the transcoding process to effectively reduce unnecessary time consumption, and the video quality matching with the ability of a client end is provided for the client end; with the adoption of a method combining a pixel region and an alternation region, time complexity is lowered, and error shift is effectively controlled; with the adoption of an encoding control optimized algorithm based on Lagrangian, when an average distortion function is being solved, a sum of absolute difference (SAD) is used for substituting a sum of squared difference (SSD), and the calculation complexity is simplified; and with the adoption of a processing mechanism by parallel threads based on GOP (group of pictures), the single-encoded GOP is processed by parallel threads, and thus the transcoding time is greatly reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Motion estimation technique for digital video encoding applications
InactiveUS20100172417A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationDigital videoPattern recognition
The present invention provides an improved motion estimation encoder for digital video encoding applications. In one example embodiment, the improved encoder receives a raw image in the form of a current frame and estimates the macroblock motion vector with respect to a reference frame. The encoder then performs an initial local search around an initial motion vector candidate derived from spatio-temporal neighboring macroblock parameters. The encoder then compares the user-defined complexity scalable sum of absolute difference between the original and the associated reference macroblock against an adaptive threshold value for motion estimation convergence. The encoder introduces a global full search around a candidate from a coarser level, in case an initial local search fails. The encoder then selects an inter encoding mode for coding the current macroblock, when the first local search is successful, otherwise the encoder selects the inter or intra encoding mode for encoding the current macroblock by comparing variances of the original and difference macroblocks.
Owner:SASKEN COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES
Image coding apparatus and image coding method
InactiveCN1819657AReduce the amount of processing operationsProcessing speedTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationAlgorithmIntra-frame
The image coding apparatus does not determine the intra-frame prediction mode based on the prediction error of the entire blocks included in a macro block, but executes intra-frame prediction with the predetermined intra-frame prediction mode for a certain block. The block selection unit judges that the current block to be coded is a prediction error calculation block or a non-prediction error calculation block. In the case where the current block is a prediction error calculation block, the mode error value calculation unit calculates the prediction error by the sum of absolute differences and the like for all of the intra-frame prediction modes, the inter-mode comparison unit compares the prediction errors, and as a result of the comparison, the intra-frame prediction mode having the minimum prediction errors is determined as the intra-frame prediction mode. In the case where the current block is a non-prediction error calculation block, the prediction error is not calculated. As an alternative method the prediction mode estimation unit determines the intra-frame prediction mode based on the neighboring prediction mode information stored in the storage unit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com