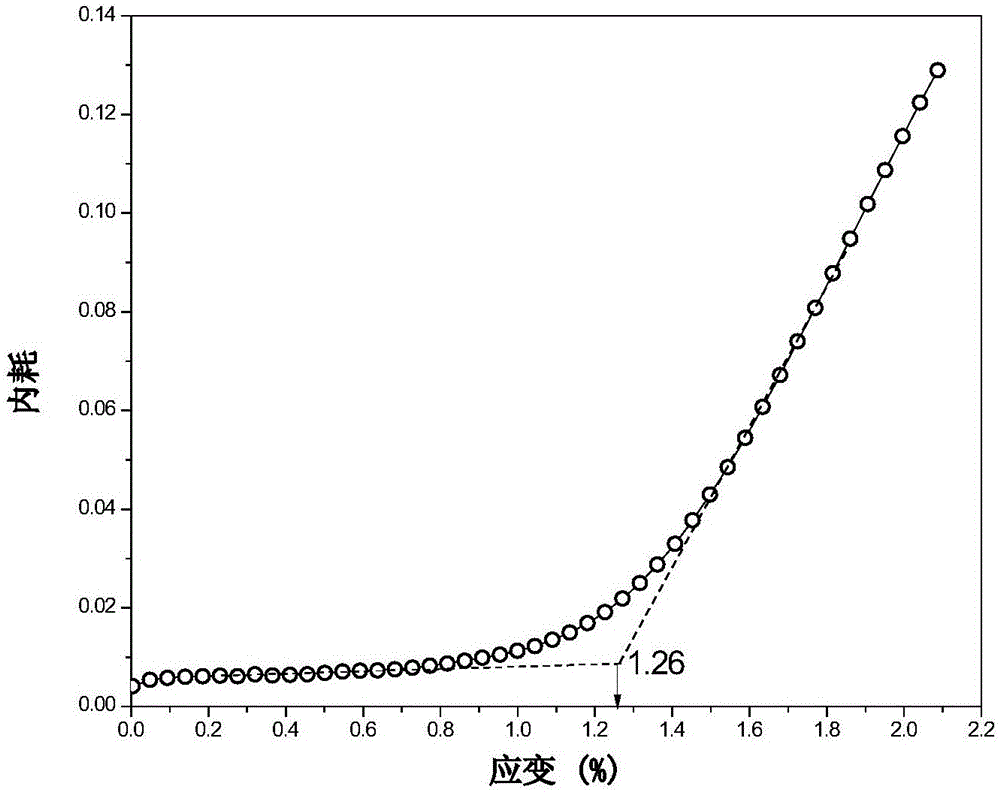
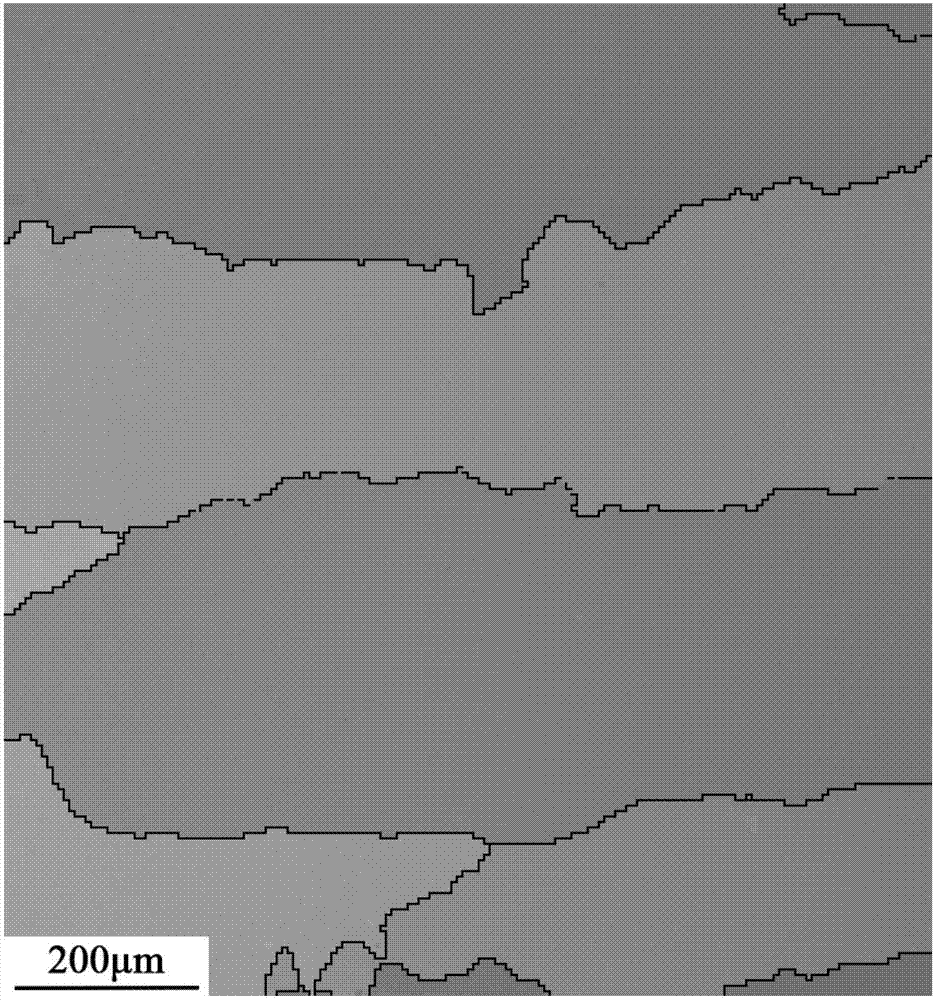
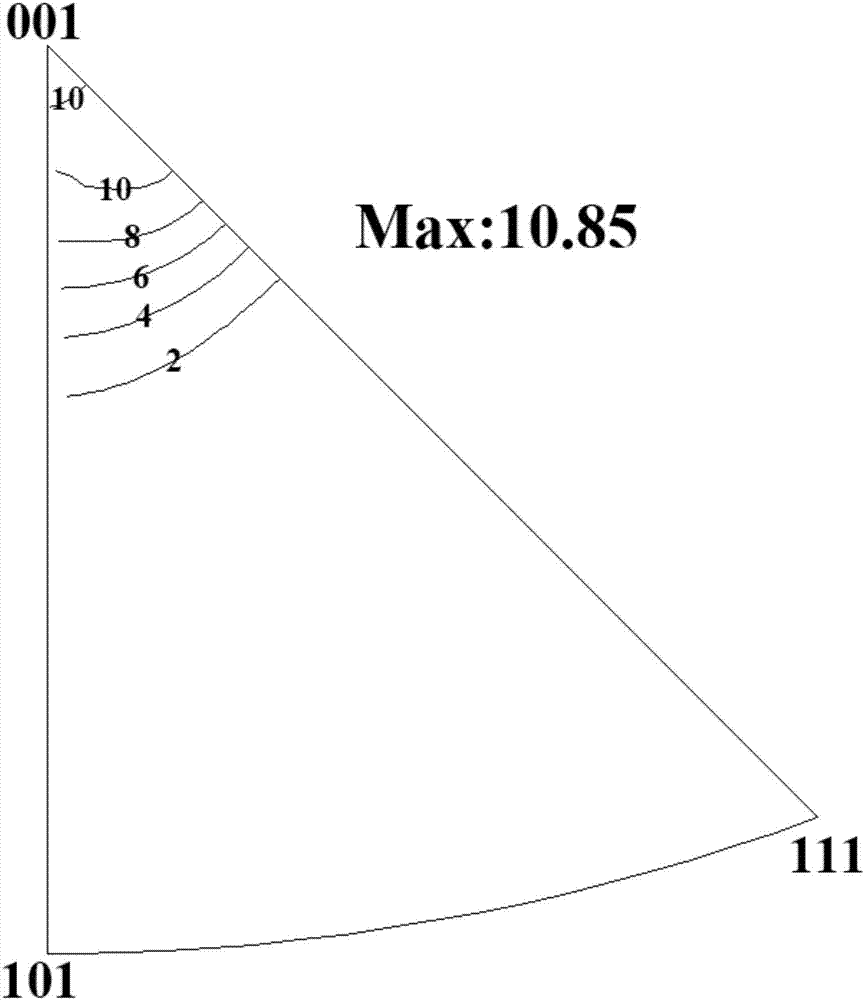
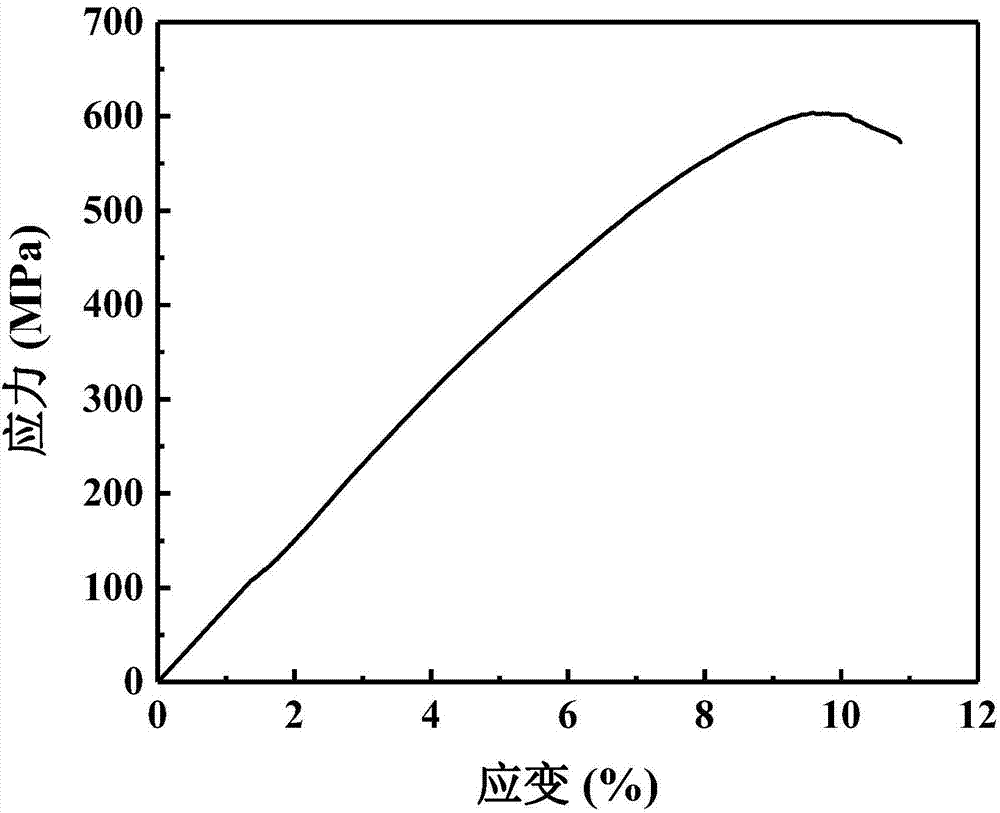
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Stress induced martensite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
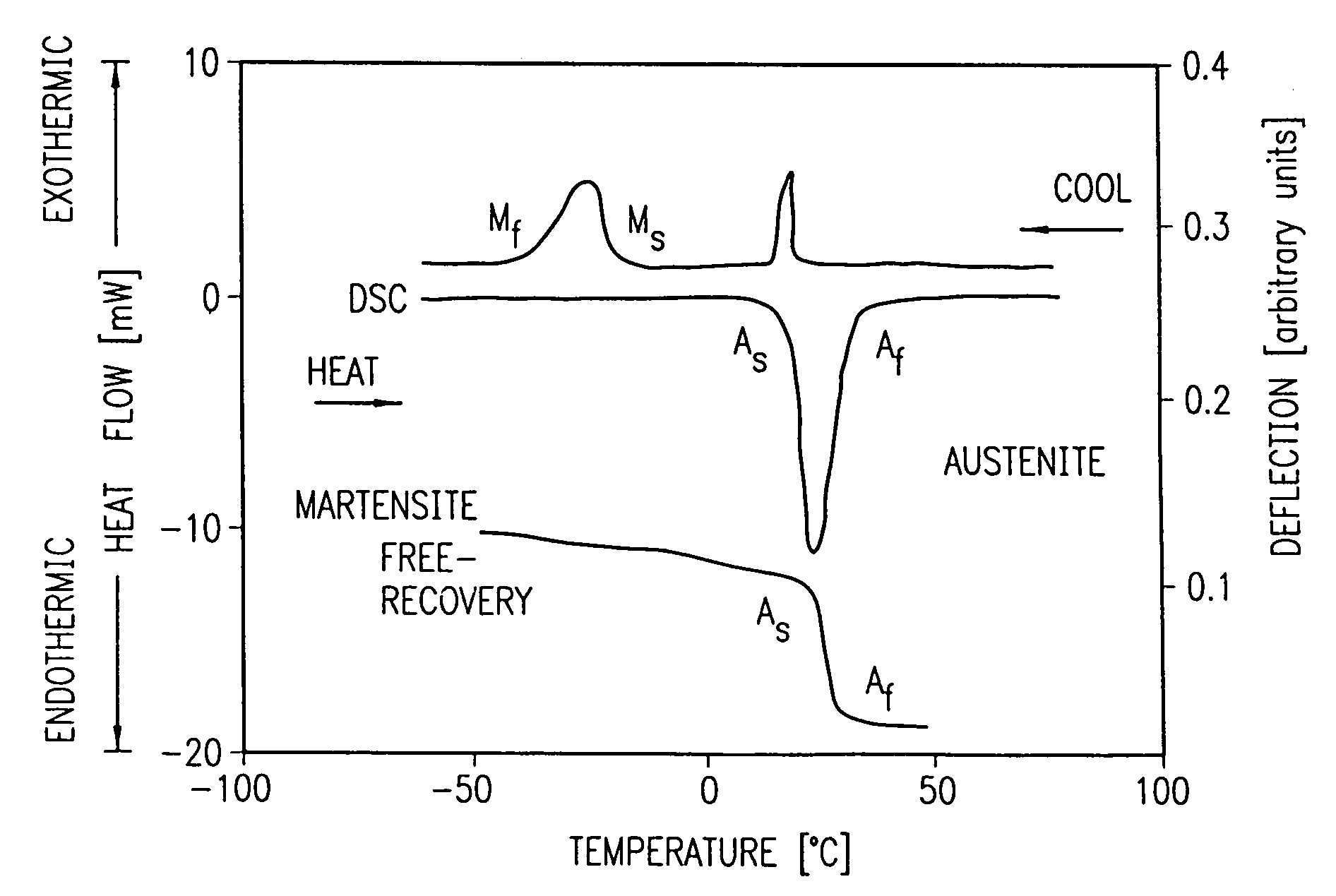
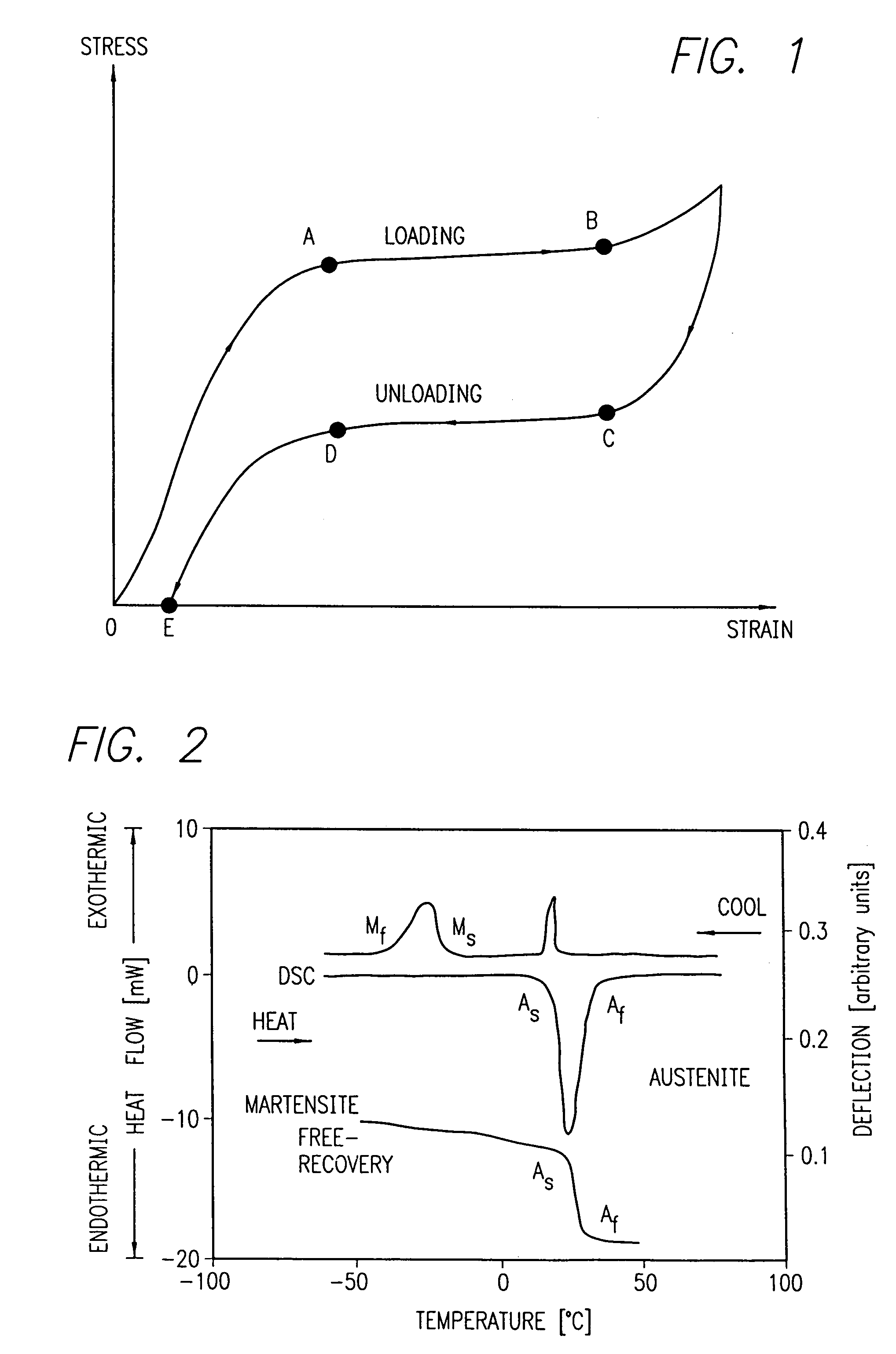
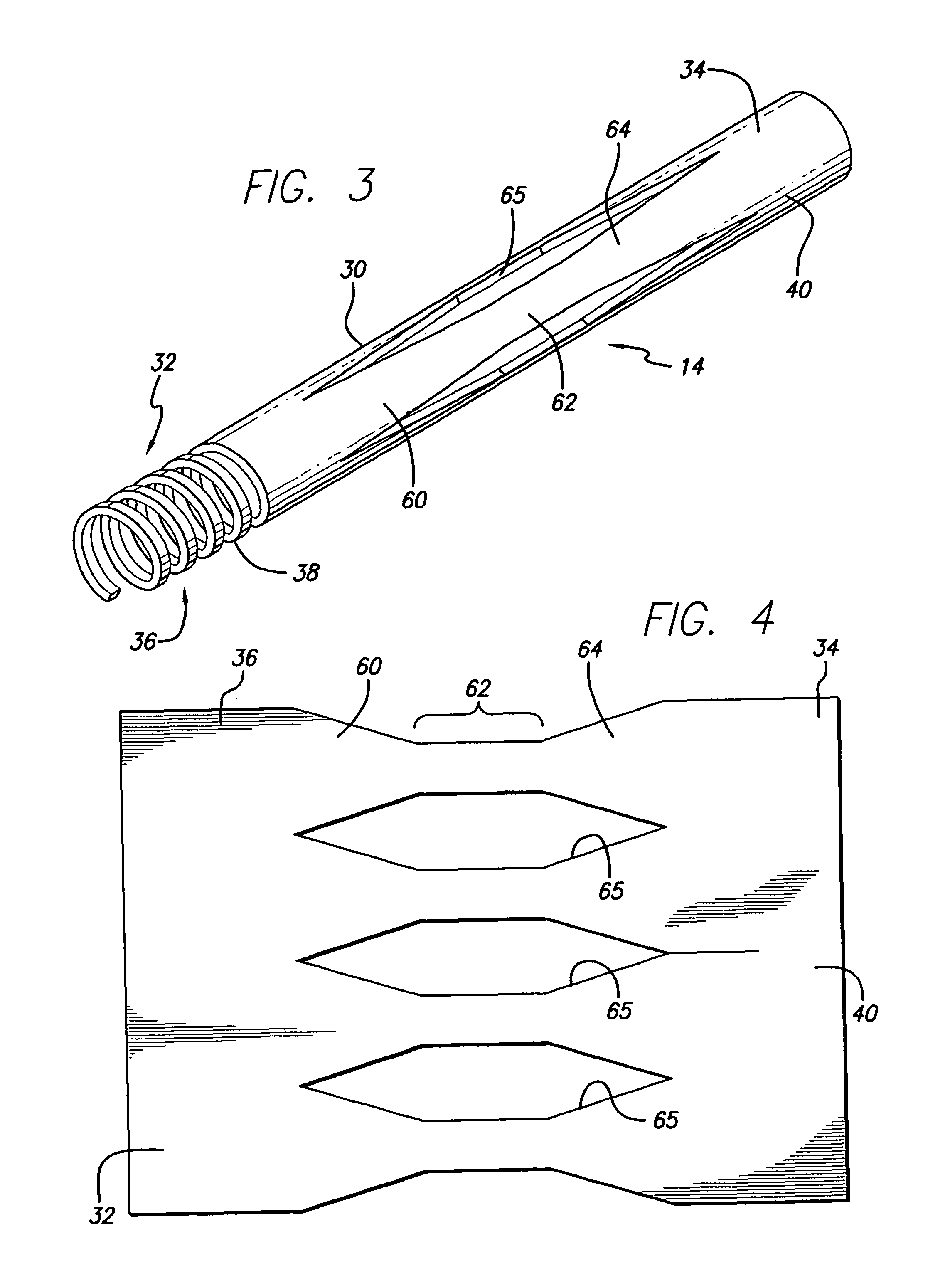
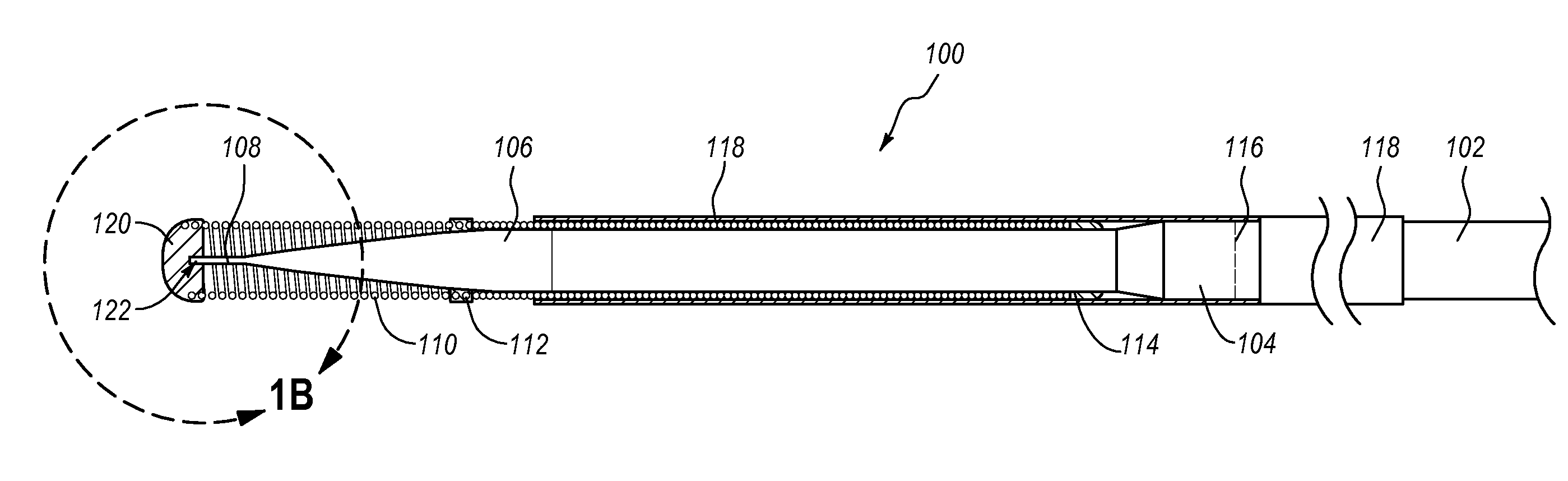
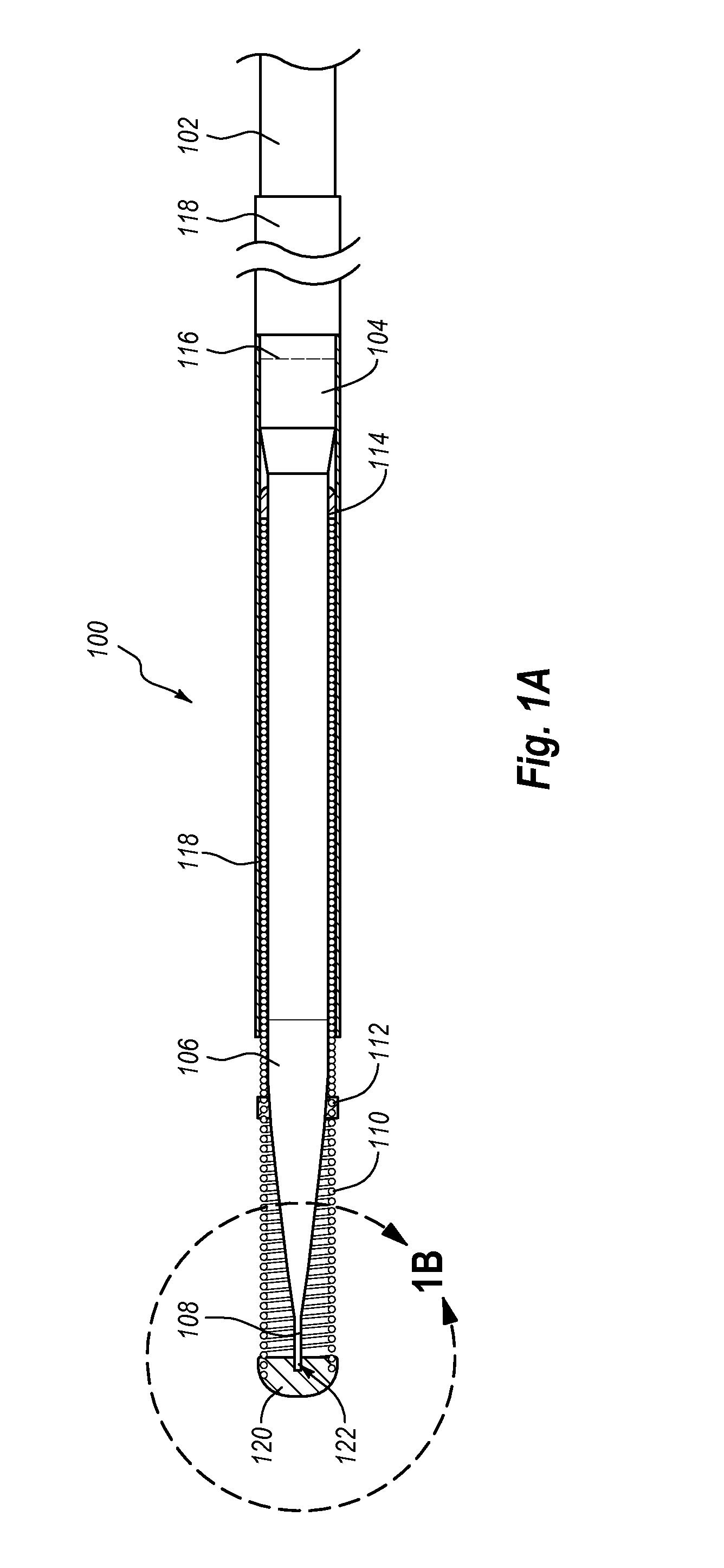
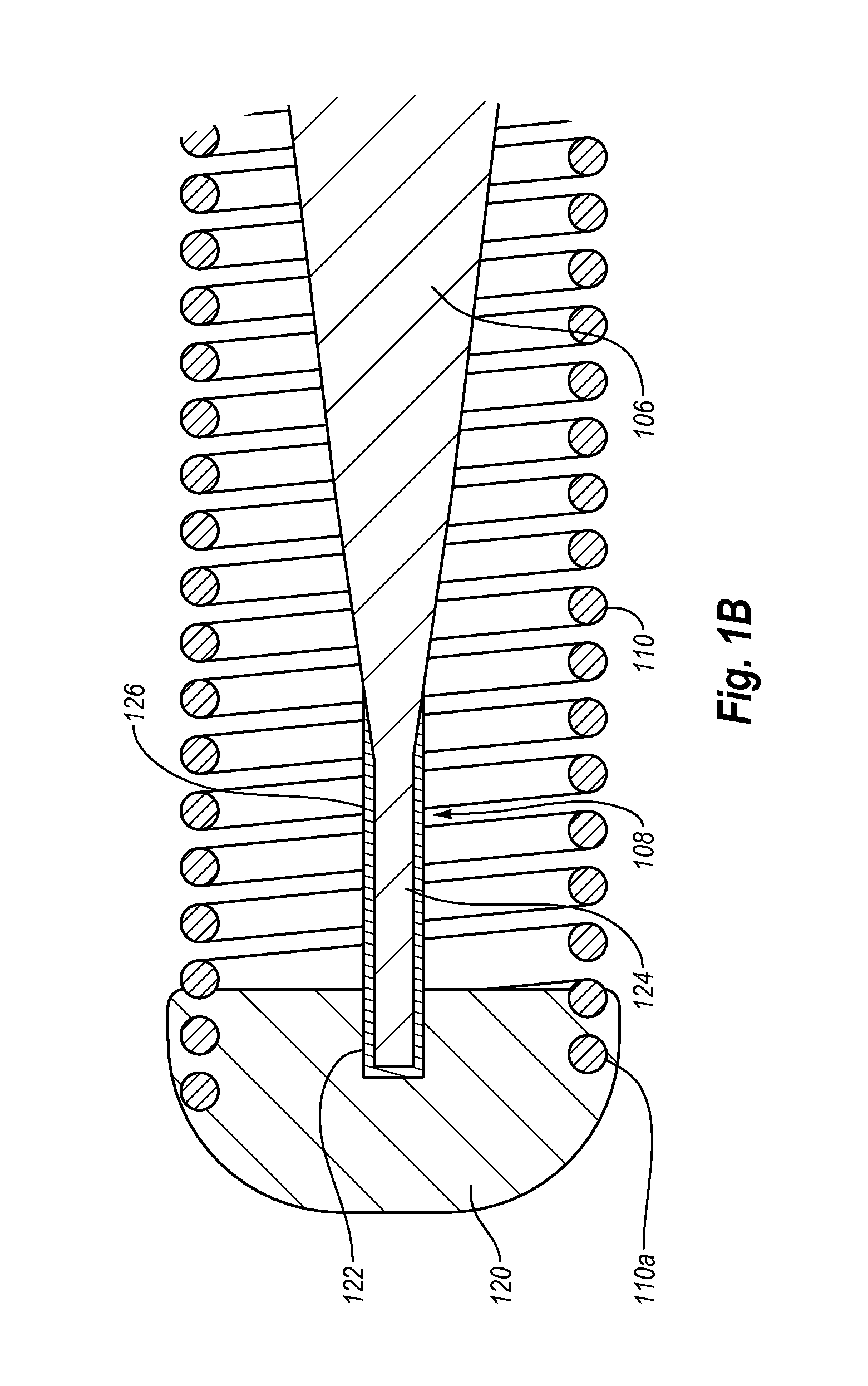
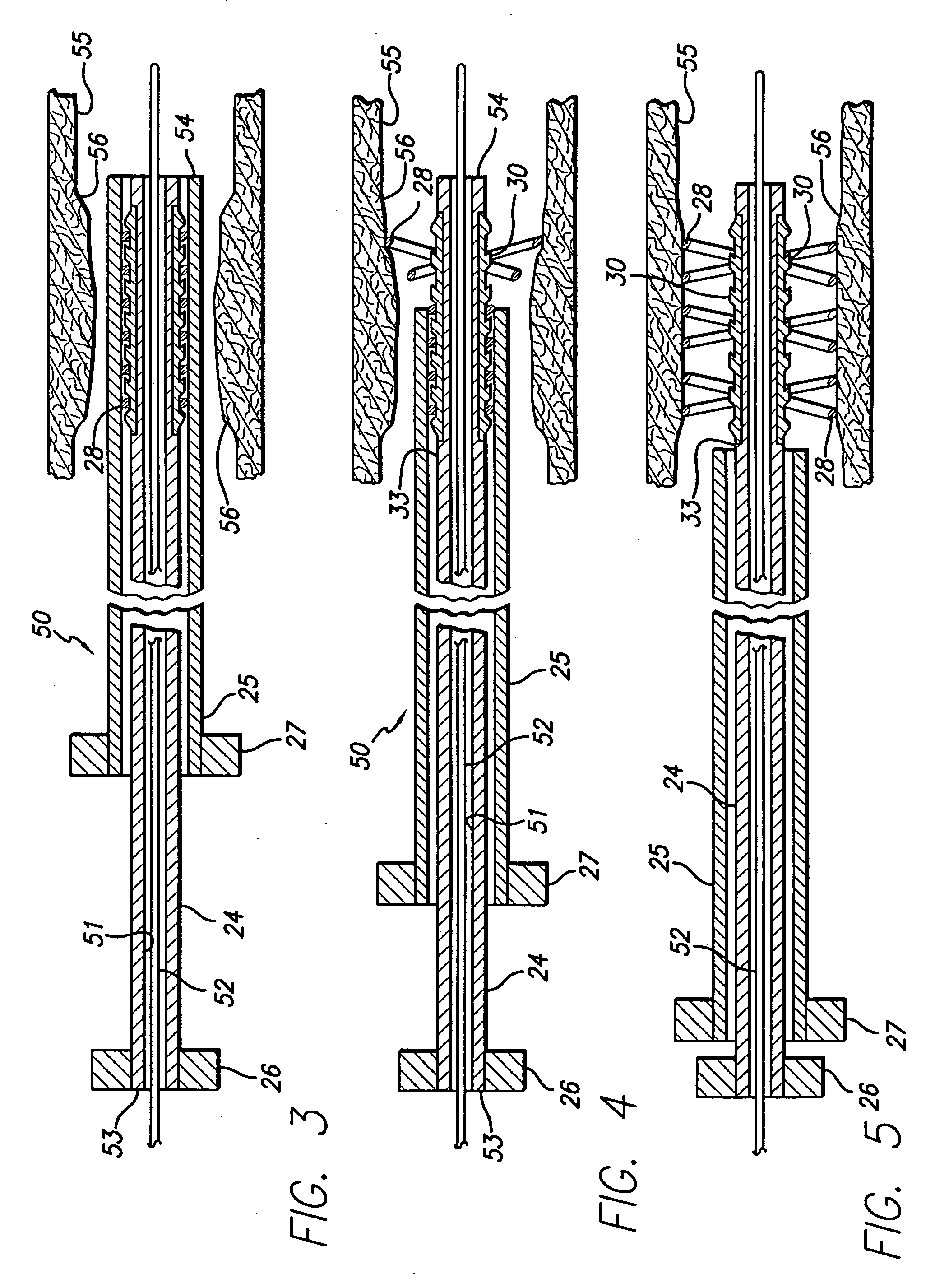
Avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation in nickel titanium alloys used in medical devices
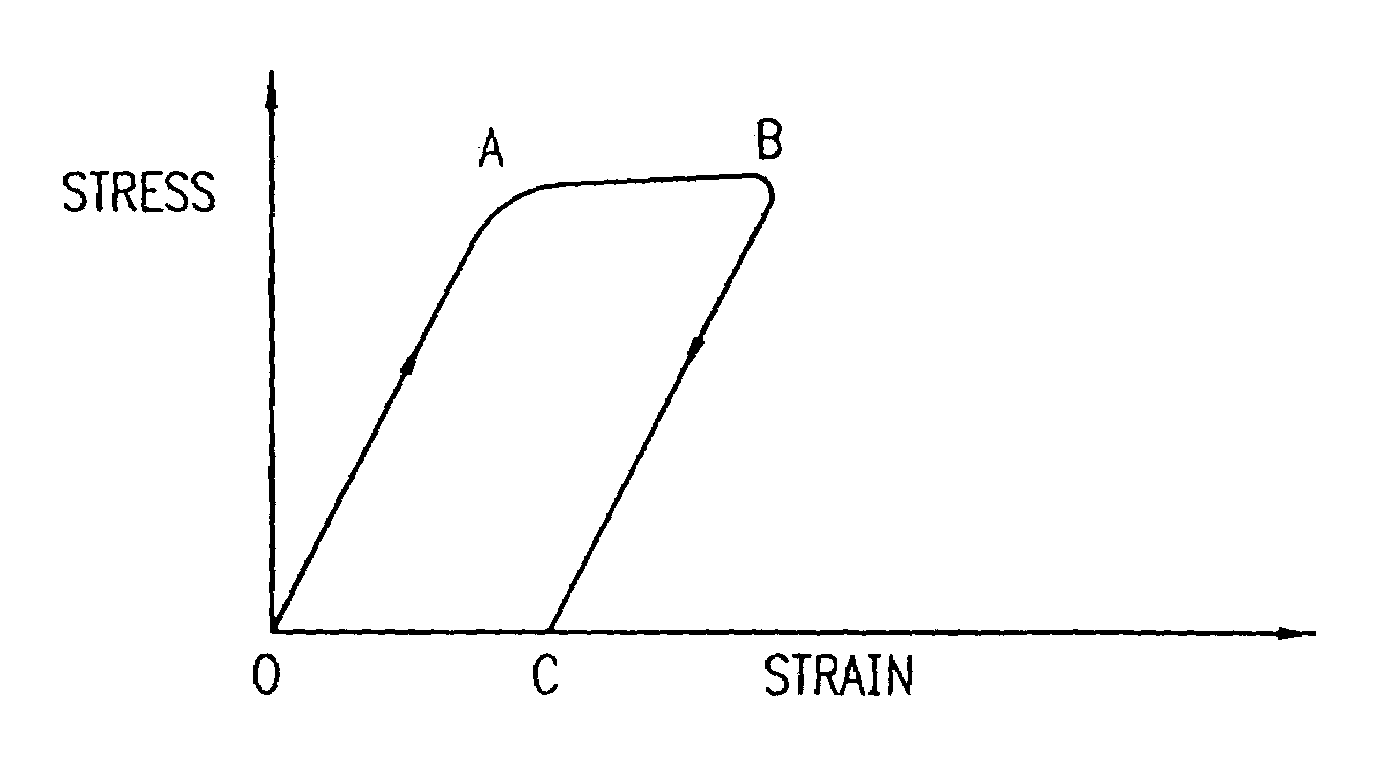
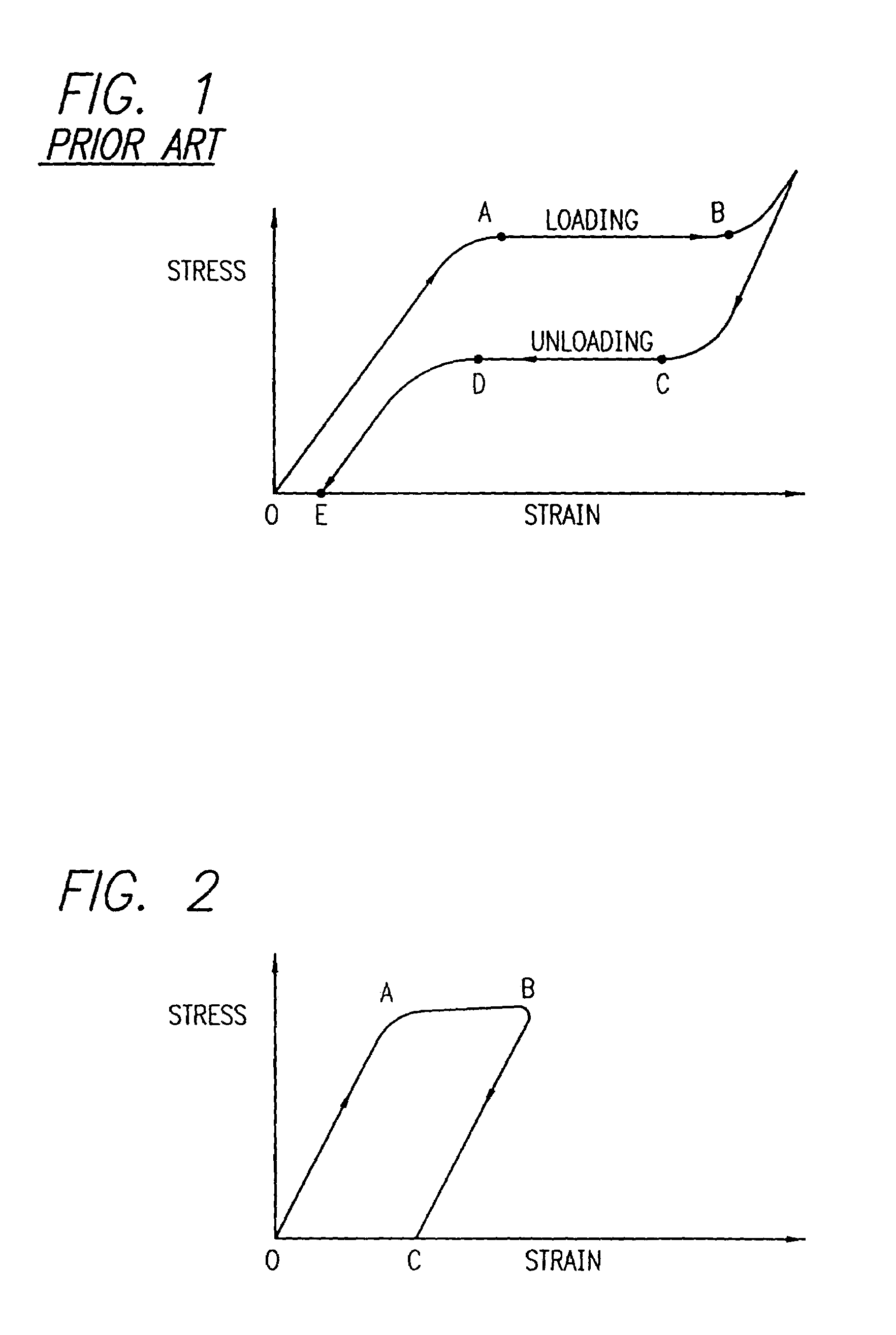
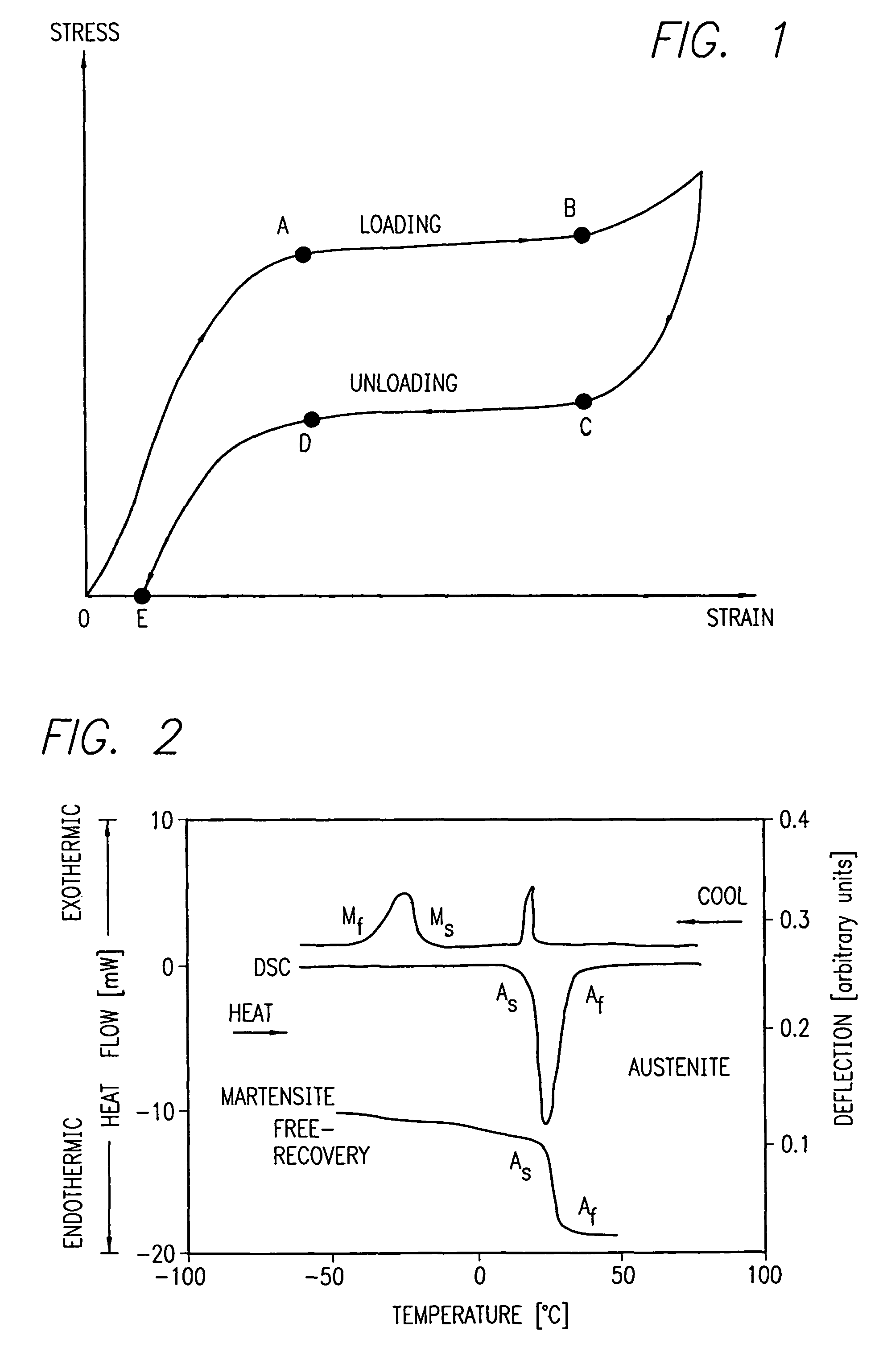
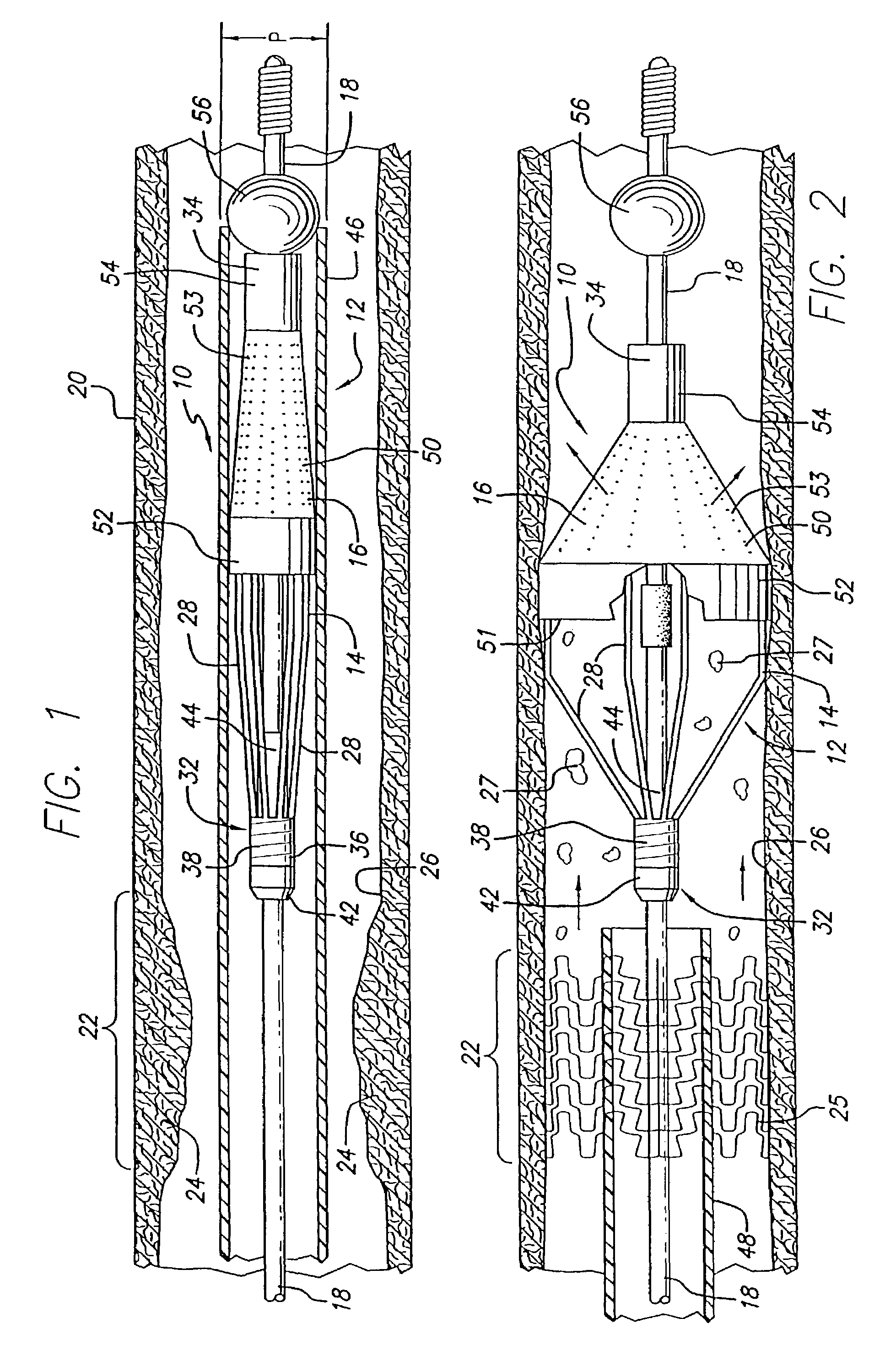
A process for assembling a medical device made from a nickel-titanium alloy for use in a mammalian body while avoiding the formation of stress-induced martensite and a medical device used in combination with a delivery system for deployment into the mammalian body are disclosed. By heating the nickel-titanium alloy of the medical device to a temperature above Md, and deforming and installing the device into a delivery system or holding capsule, it is possible to avoid the formation of stress-induced martensite in the stent, which stays in the austenitic phase throughout.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
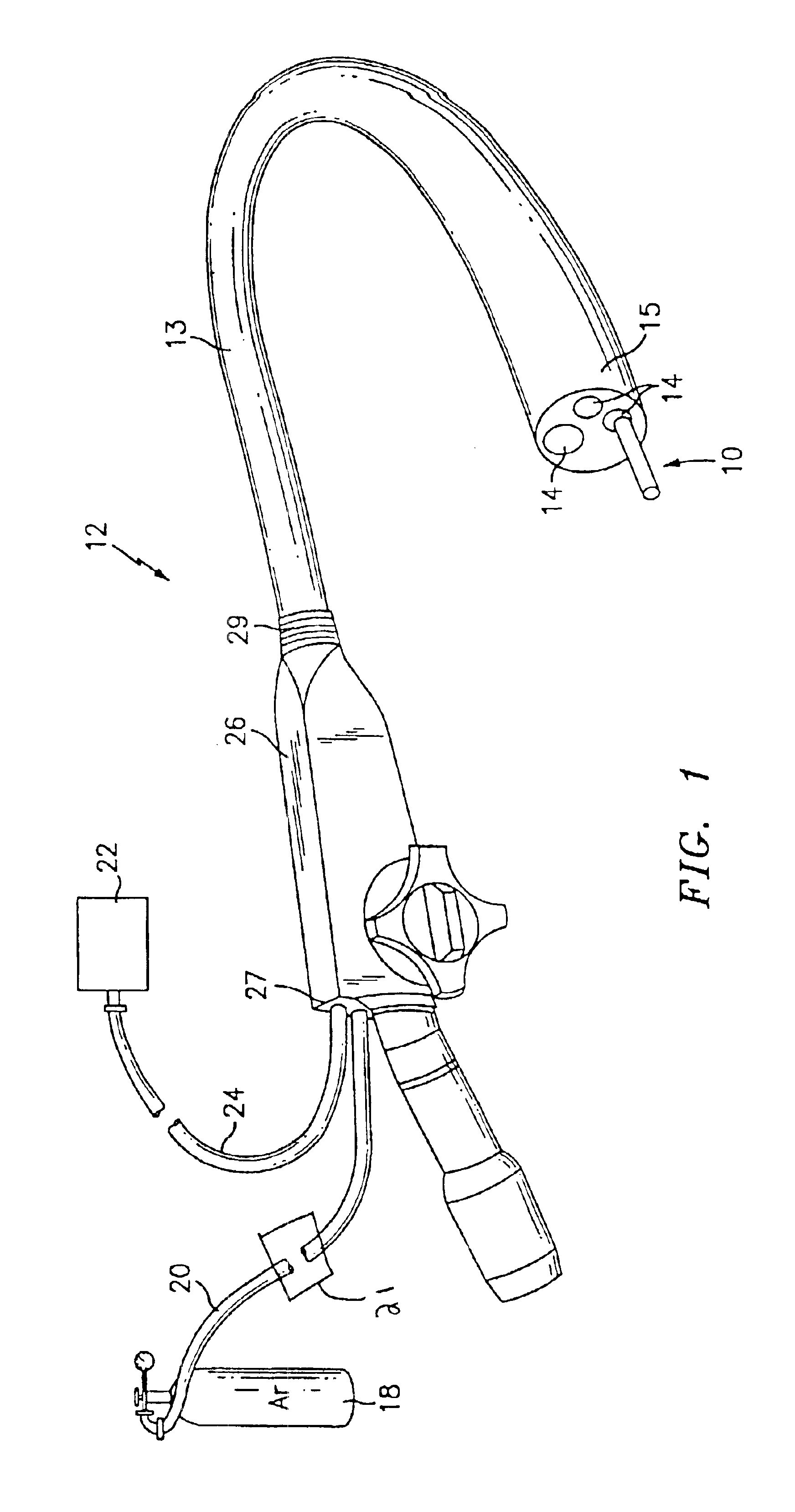
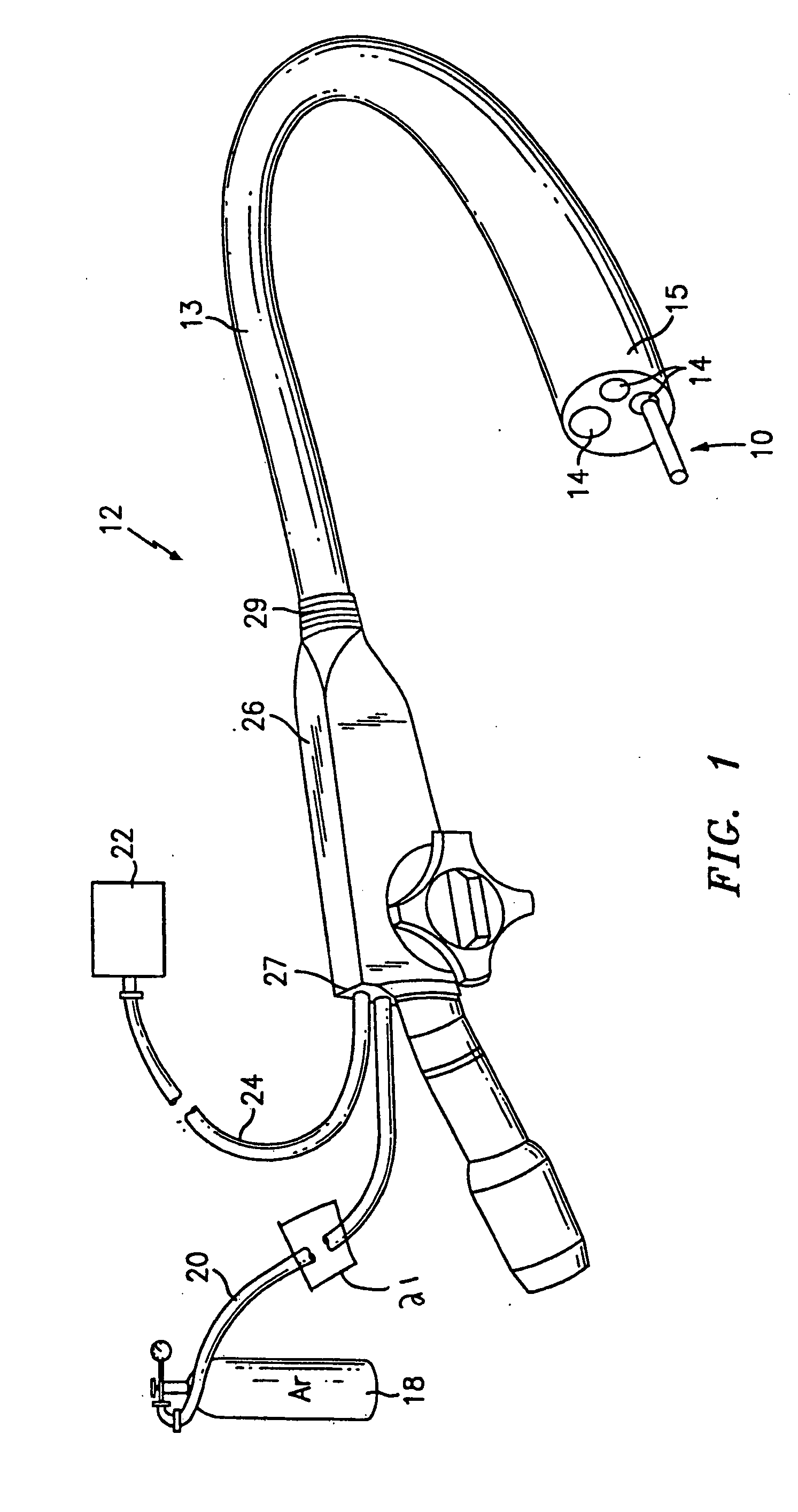
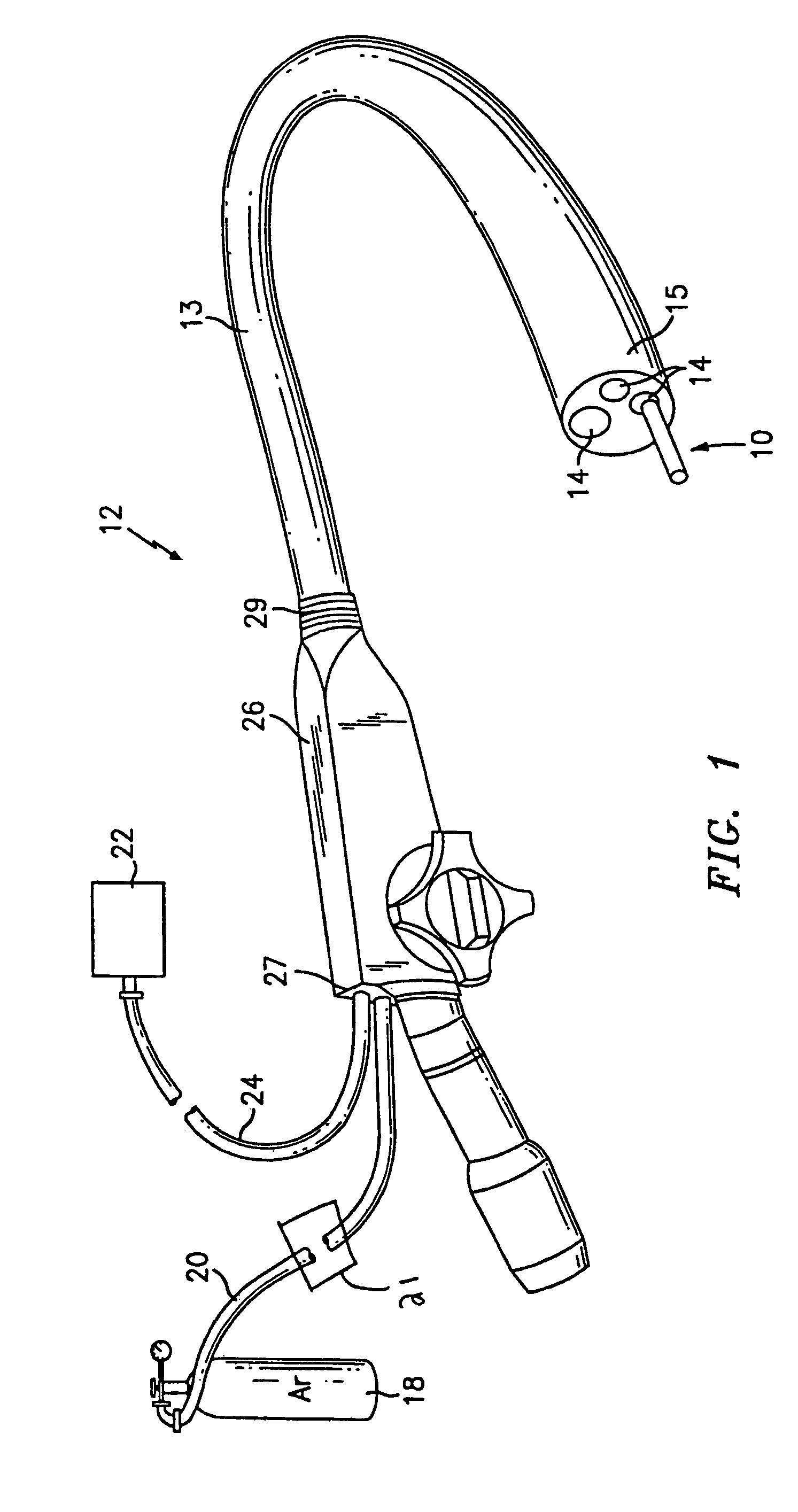
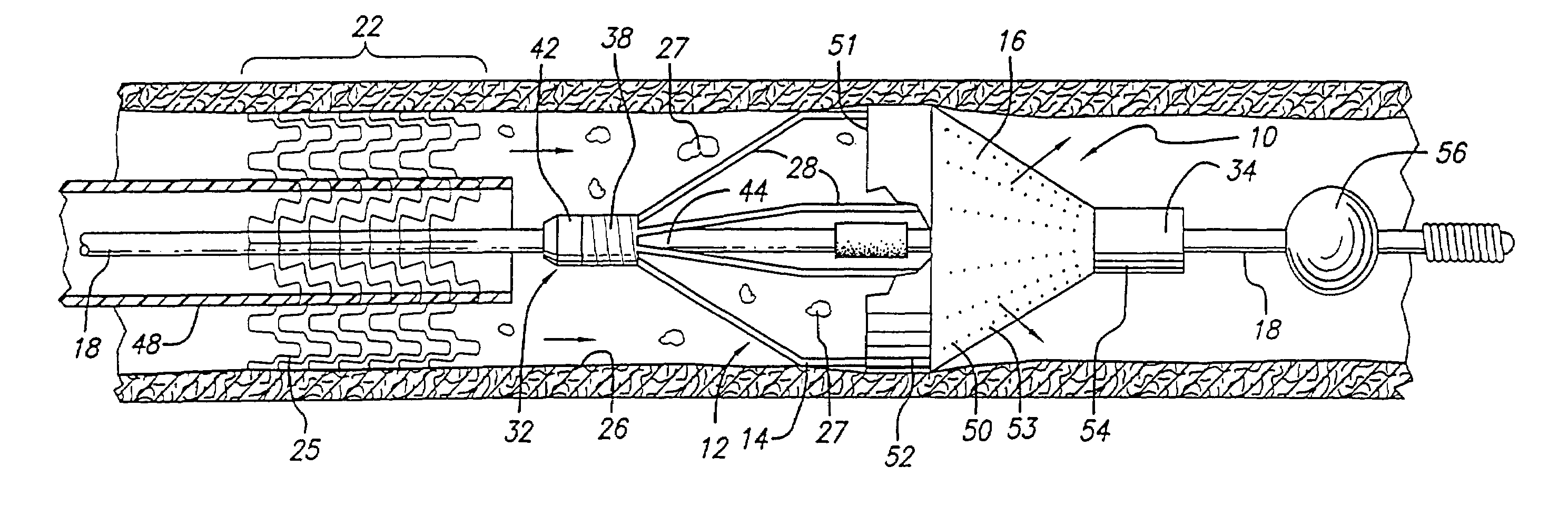
Articulating ionizable gas coagulator
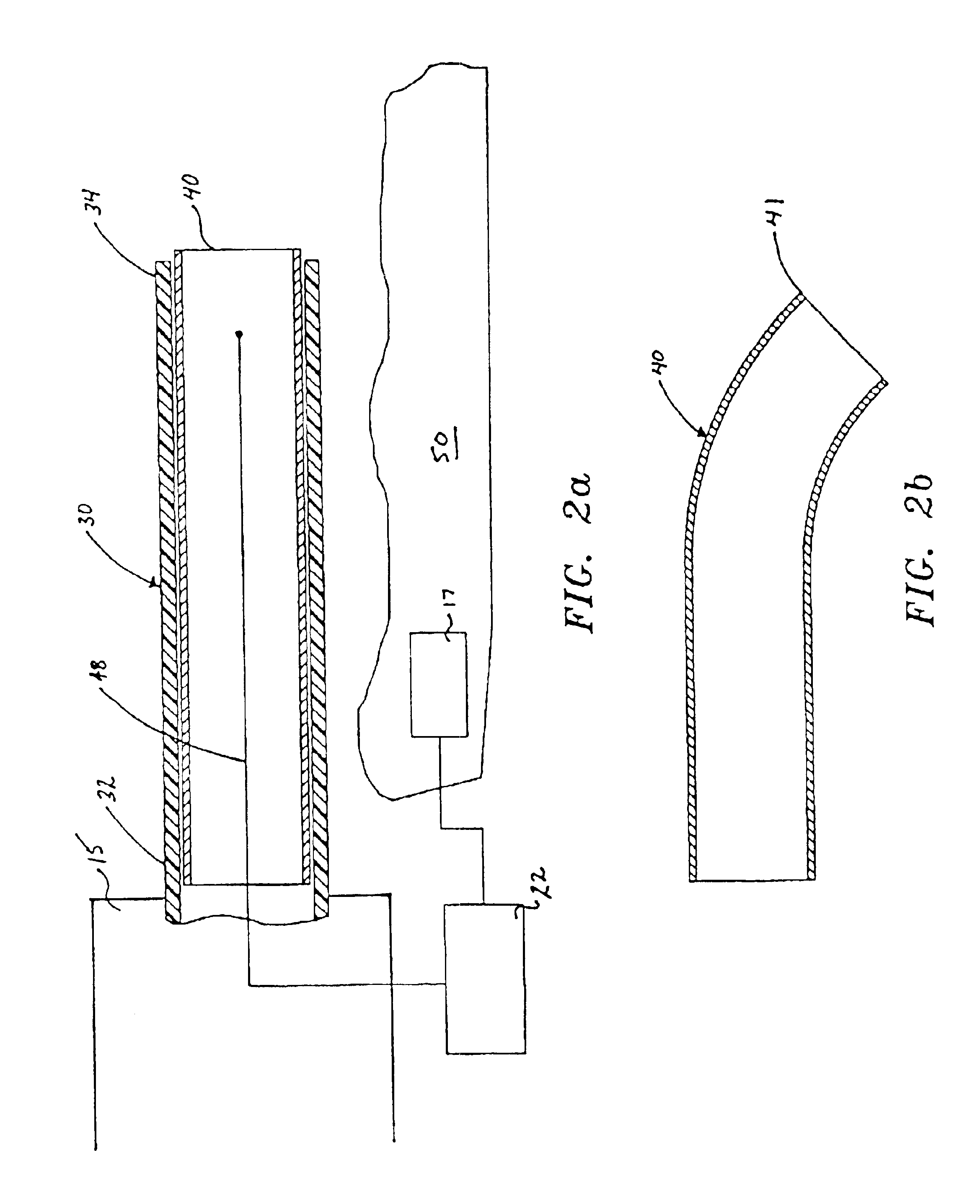
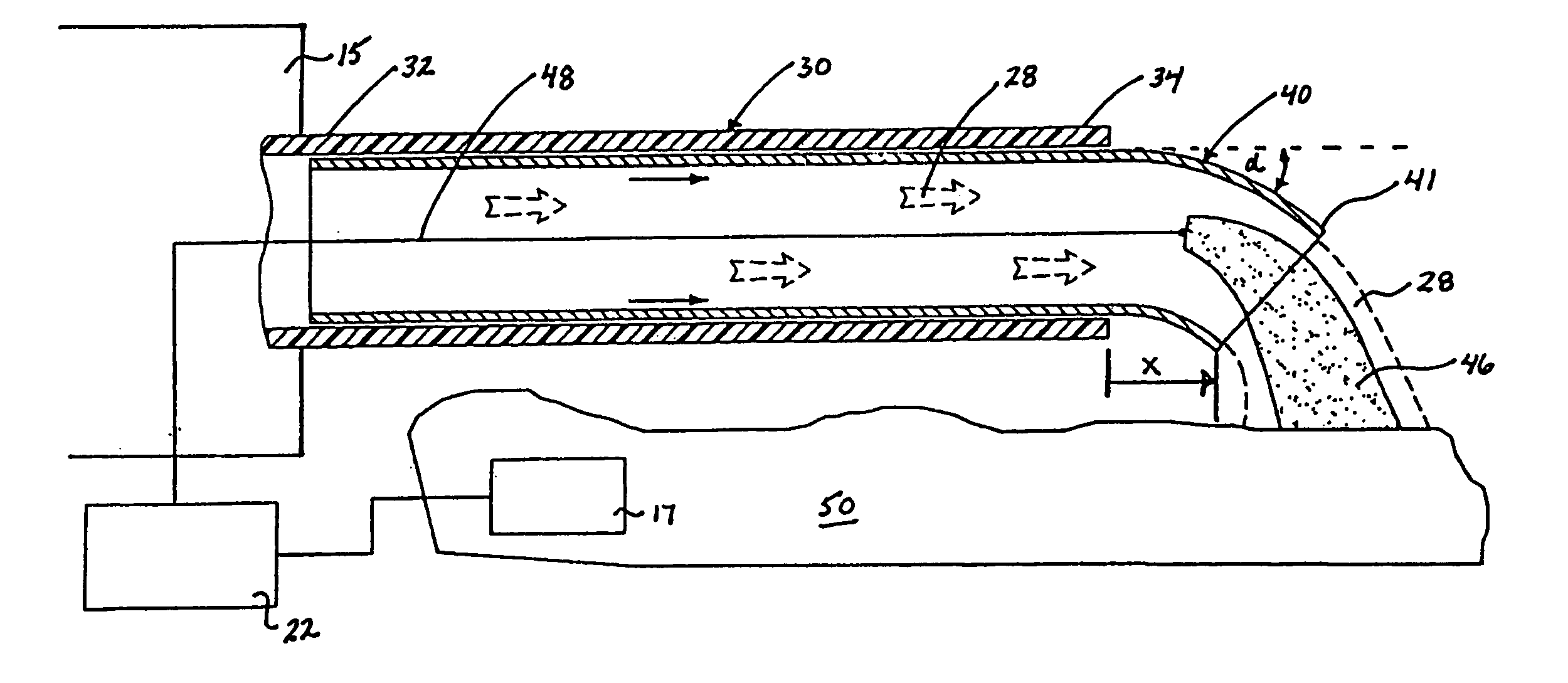
InactiveUS6911029B2Avoid arcingSurgical instruments for heatingShape-memory alloyStress induced martensite
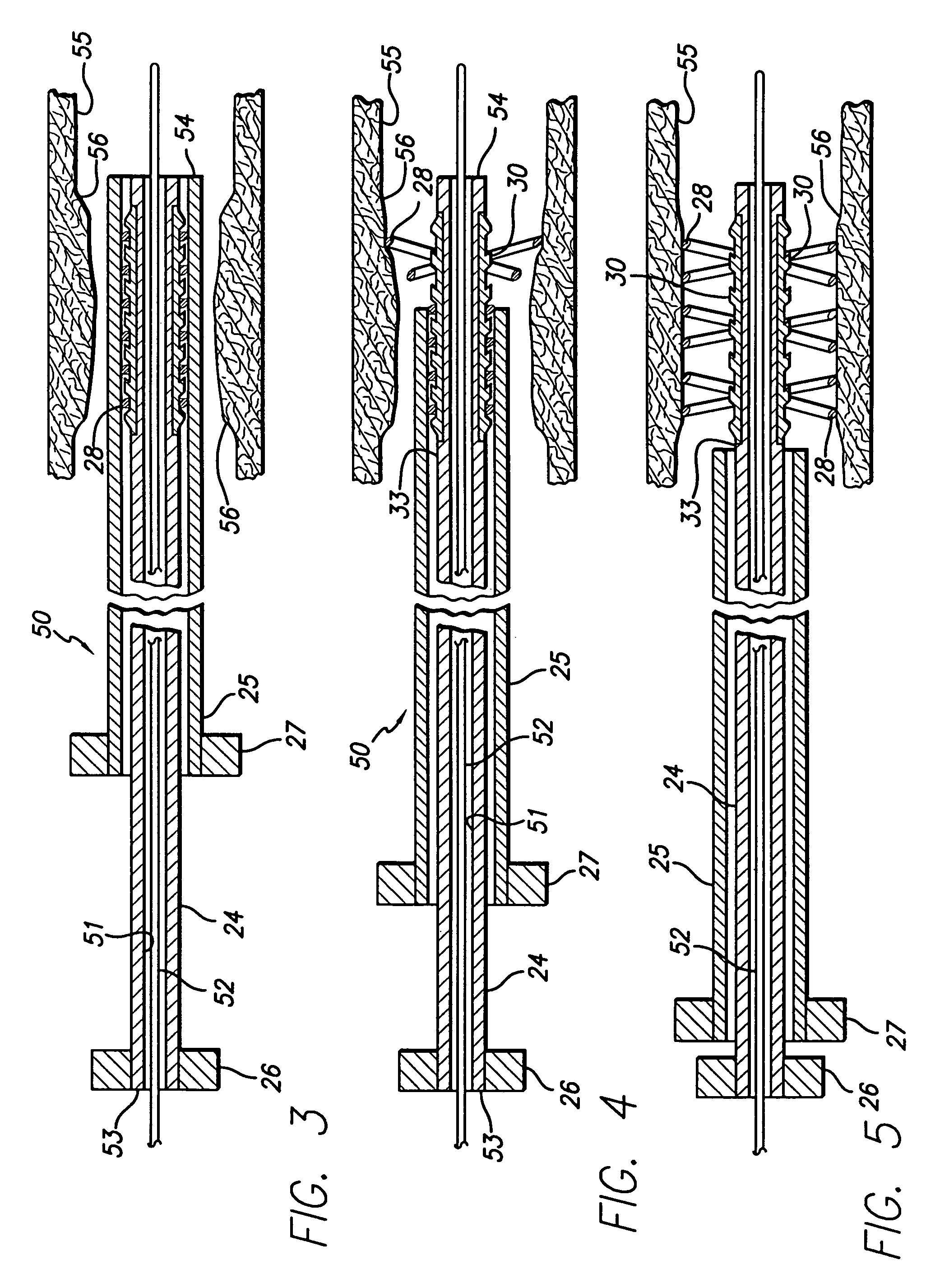
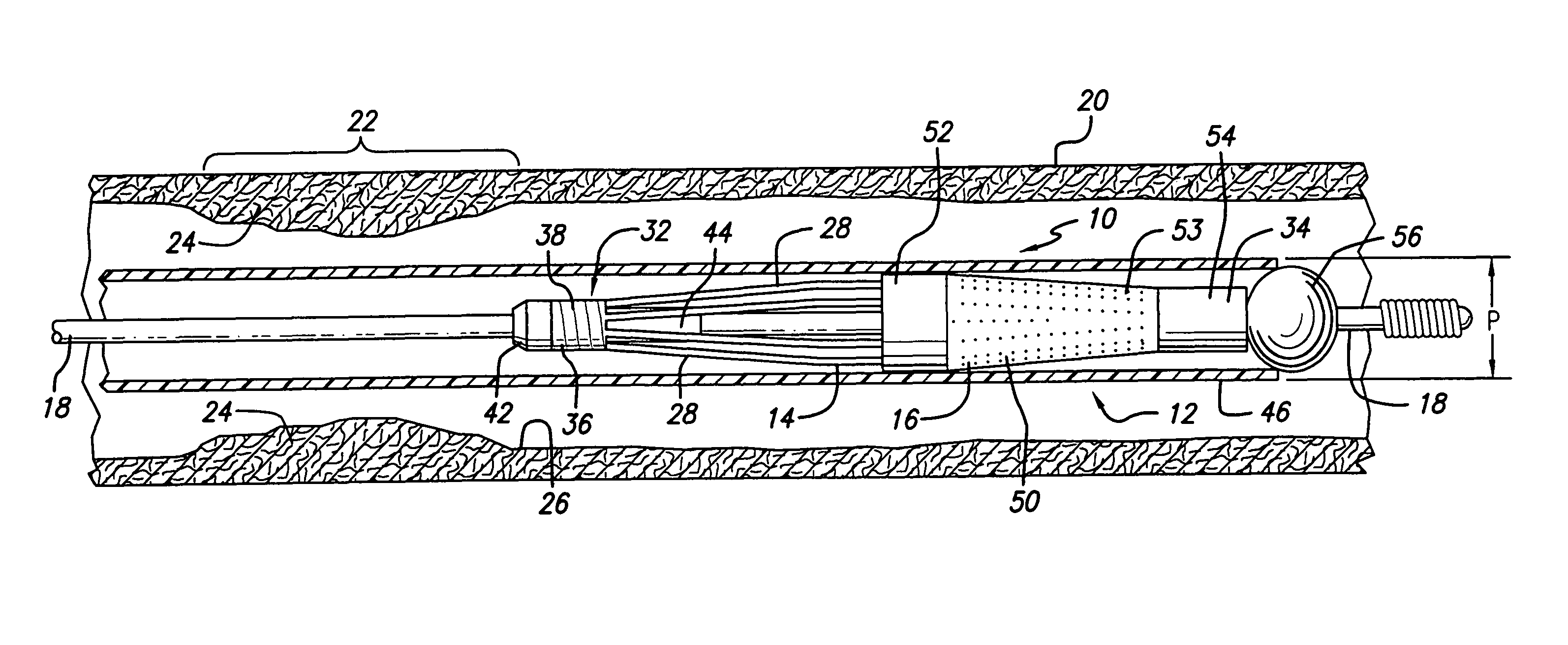
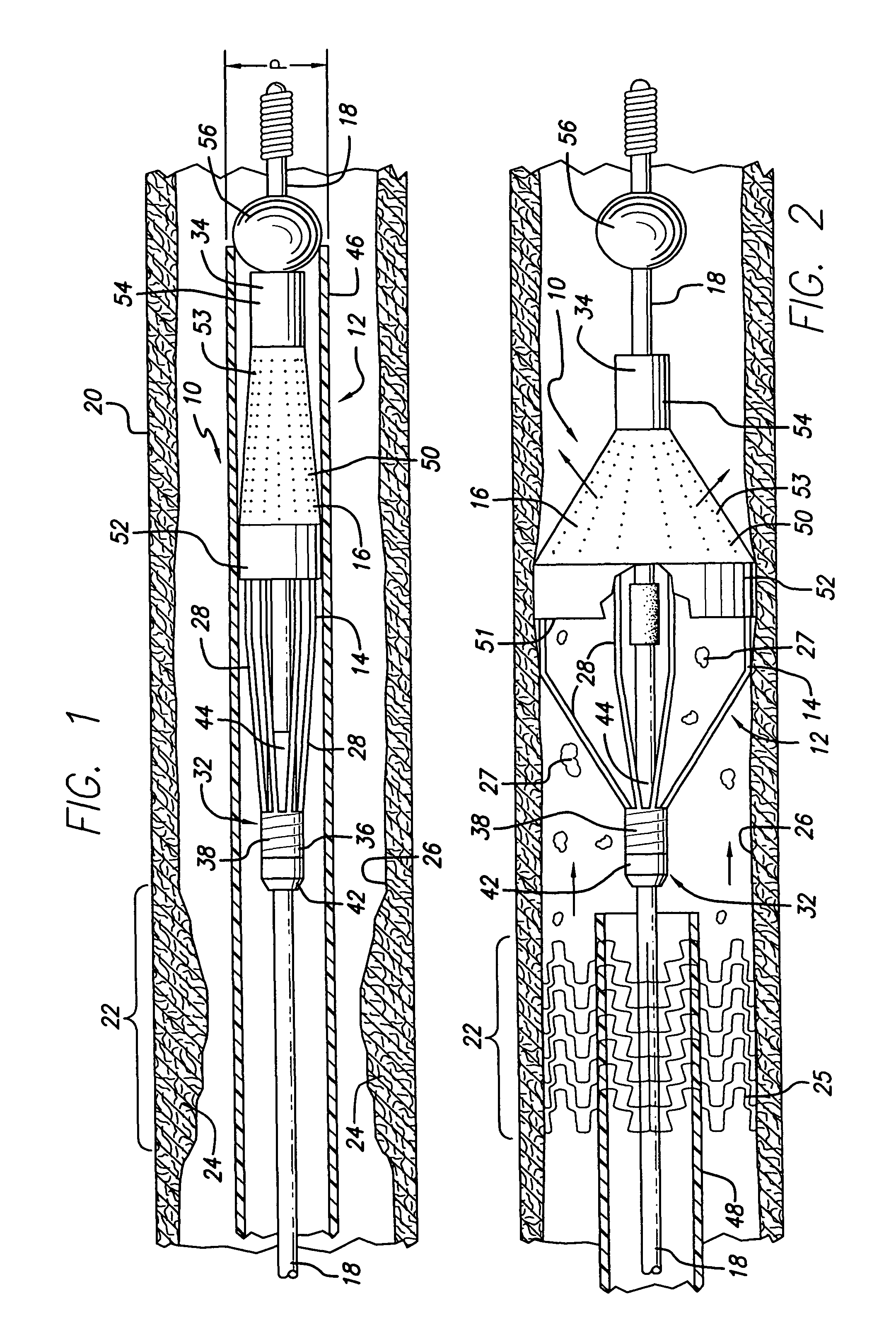
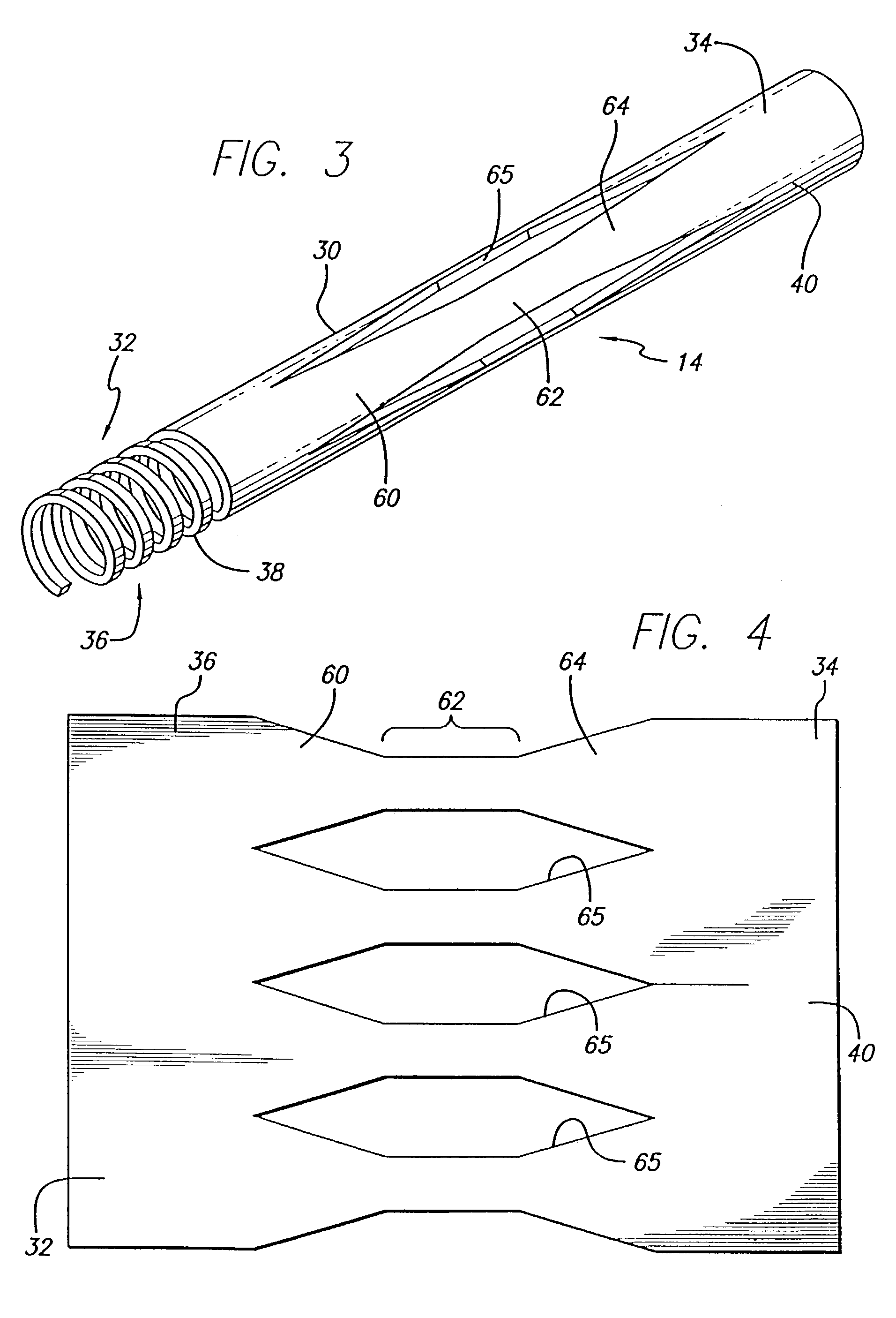
An electrosurgical apparatus for coagulating tissue includes an elongated flexible tube having a proximal end, a distal end and a source for supplying pressurized ionizable gas to the proximal end of the tube. The apparatus also includes a hollow sleeve made from a shape memory alloy having a generally curved austenite state and displaying stress-induced martensite behavior. The hollow sleeve is restrained in a deformed stress-induced martensite configuration within the tube and partial extension of a portion of the hollow sleeve from the tube transforms the portion of the sleeve from the deformed configuration to the generally curved austenite configuration such that the gas is directed transversely at the issue. An electrode ionizes the gas in the region between the sleeve and the tissue. Other embodiments of the present disclosure also include a wire connected to the distal end of the tube which movable from a first position wherein the tube is disposed in a generally rectilinear, parallel fashion relative to the tissue to a second retracted position wherein the distal end of the tube flexes at an angle to direct the gas towards the tissue. Still other embodiments of the present disclosure include a corona electrode for inducing ignition of the gas.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Articulating ionizable gas coagulator
InactiveUS20050197658A1Avoid arcingSurgical instruments for heatingShape-memory alloyStress induced martensite
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Manufacturing and application methods for laser cladding powder of iron-base alloy
InactiveCN103056355AReduce residual stressImprove fatigue strengthMetallic material coating processesStress induced martensiteWear resistance
The invention discloses a design manufacturing method and an application method for laser cladding powder. The design manufacturing method includes preparing Fe-Mn-Si memory alloy powder and putting the memory alloy powder into a ball grinder to process powder mixing. The application method includes processing a vacuum drying treatment before the cladding, presetting the cladding powder on base materials, and processing the cladding with laser which is 1.5-3 Kw in laser power, 400-1000 mm / min in scanning speed and 3 mm in laser diameter. By the stress of the laser cladding layer of the Fe-Mn-Si memory alloy, martensitic transformation and the martensitic deformation compatibility are induced so as to effectively remove the residual stress of the cladding layer and improve the fatigue strength of the cladding layer with no need of adding extra processing. The laser cladding powder of the iron-base alloy has the advantages of being simple in preparation technology, applicable to mass production, good in wear resistance, low in residual stress, high in fatigue strength, and the like.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Maraging stainless steel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses maraging stainless steel and a preparation method thereof. The maraging stainless steel comprises 9.0-13.0 wt% of Cr, 11.0-15.0 wt% of Ni, 1.5-4.0 wt% of Mo, no more than 2.5 wt% of Cu, 1.2-1.9 wt% of Ti, no more than 2.0 wt% of Mn, no more than 2.0 wt% of Al, no more than 1.0 wt% of Si, less than 0.03 wt% of C, and the balance Fe. When an alloy is subjected to complete austenitizing and rapidly cooled to the room temperature, the alloy is in a supercooled austenite state, the material is in stress-induced martensite phase transformation to be transformed into a martensite state during cold machining, and the Vickers hardness increment Hv can reach 250-300 after aging treatment is conducted. The stainless steel is especially suitable for manufacturing small-sectional-area products like fishing hooks and medical suture needles.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Austenitic nitinol medical devices
InactiveUS7128758B2StrongHoop strength of was so lowStentsSurgeryStress induced martensiteTitanium alloy
A medical device for use within a body lumen that is made from a binary nickel-titanium alloy that remains in its austenitic phase throughout its operational range is disclosed. The medical device, such as an intraluminal stent, is made from superelastic nickel-titanium and may optionally be alloyed with a ternary element. By adding the ternary element and / or through heat treatment, it is possible to lower the phase transformation temperature between the austenitic phase and the martensitic phase of the nickel-titanium alloy. By lowering the phase transformation temperature, the martensite deformation temperature is likewise depressed. It is possible then to depress the martensite deformation temperature below body temperature such that when the device is used in a body lumen for medical treatment, the nickel-titanium device remains completely in the austenitic phase without appearance of stress-induced martensite even if the device is placed under stress.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation in nickel titanium alloys used in medical devices
A process for assembling a medical device made from a nickel-titanium alloy for use in a mammalian body while avoiding the formation of stress-induced martensite and a medical device used in combination with a delivery system for deployment into the mammalian body are disclosed. By heating the nickel-titanium alloy of the medical device to a temperature above Md, and deforming and installing the device into a delivery system or holding capsule, it is possible to avoid the formation of stress-induced martensite in the stent, which stays in the austenitic phase throughout.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
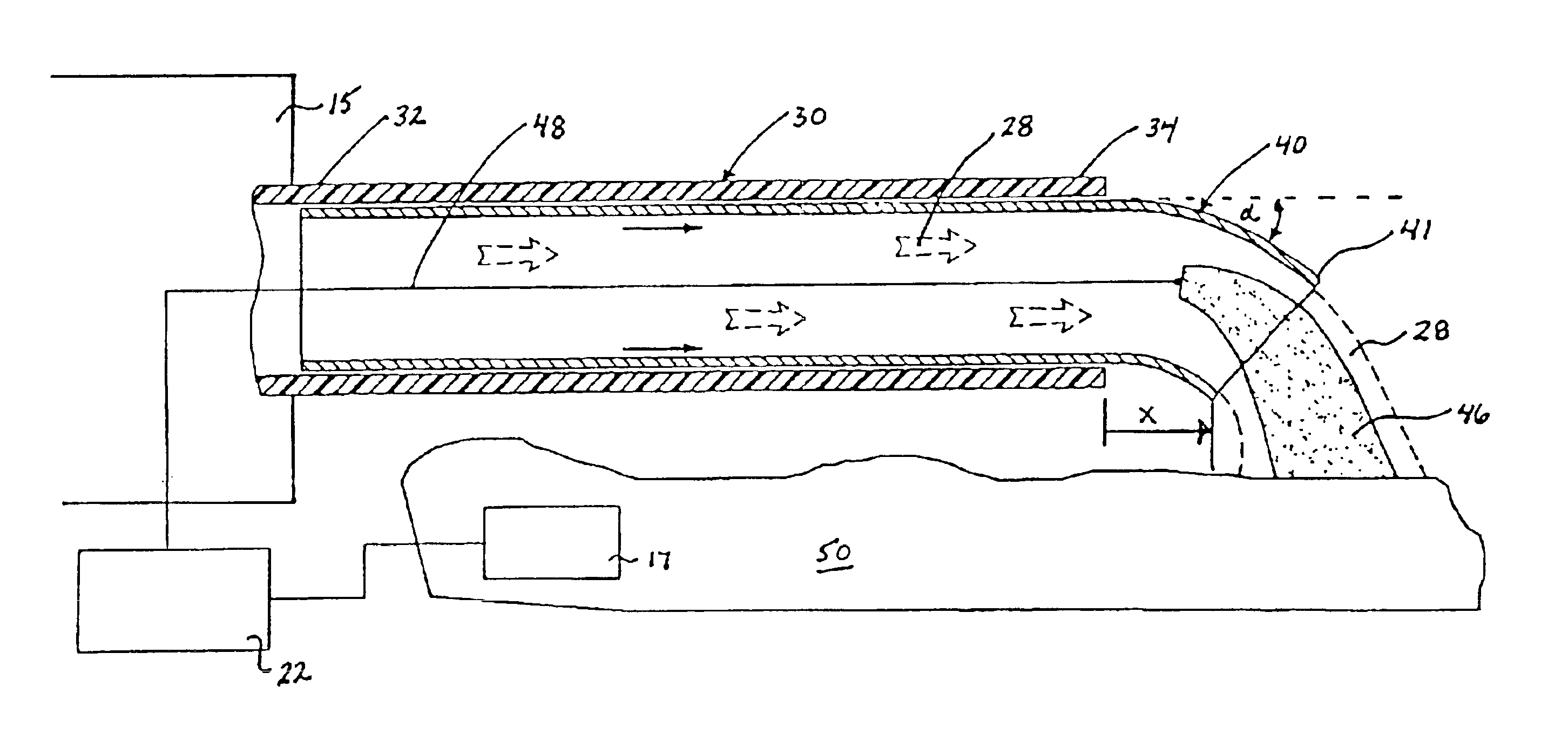
Heat treatment for cold worked nitinol to impart a shape setting capability without eventually developing stress-induced martensite
InactiveUS7976648B1High mechanical strengthMore storage capacityGuide wiresSurgeryEmbolic Protection DevicesStress induced martensite
Cold worked nickel-titanium alloys that have linear pseudoelastic behavior without a phase transformation or onset of stress-induced martensite as applied to a medical device having a strut formed body deployed from a sheath. In one application, an embolic protection device that employs a linear pseudoelastic nitinol self-expanding strut assembly with a small profile delivery system for use with interventional procedures. The expandable strut assembly is covered with a filter element and both are compressed into a restraining sheath for delivery to a deployment site downstream and distal to an interventional procedure. Once at the desired site, the restraining sheath is retracted to deploy the embolic protection device, which captures flowing emboli generated during the interventional procedure. Linear pseudoelastic nitinol is used in the medical device as distinct from non-linear pseudoelastic (i.e., superelastic) nitinol.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method for improving function stability of nickel-titanium shape memory alloy
The invention relates to a method for improving the function stability of a nickel-titanium shape memory alloy, and belongs to the field of nickel-titanium shape memory alloys. According to the method, dislocations and other defects are introduced into the nickel-titanium shape memory alloy, the dislocations serve as activity position points for promoting second phase nucleation, then, fine and evenly-distributed nano reinforcement phases are formed in a matrix structure of the nickel-titanium shape memory alloy through later aging treatment, accordingly, the matrix strength of the nickel-titanium shape memory alloy is obviously improved, and then the function stability of the alloy is improved. Meanwhile, in the method, only temperature martensite phase change induction circulation or stress martensite phase change induction circulation need to be conducted on a nickel-titanium shape memory alloy component before aging treatment, and operation is simple and convenient; and the methoddoes not have the requirement for the shape of the nickel-titanium shape memory alloy component, and the method is adaptive to the complex nickel-titanium shape memory alloy component and capable of effectively improving the function stability of the complex nickel-titanium shape memory alloy component.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
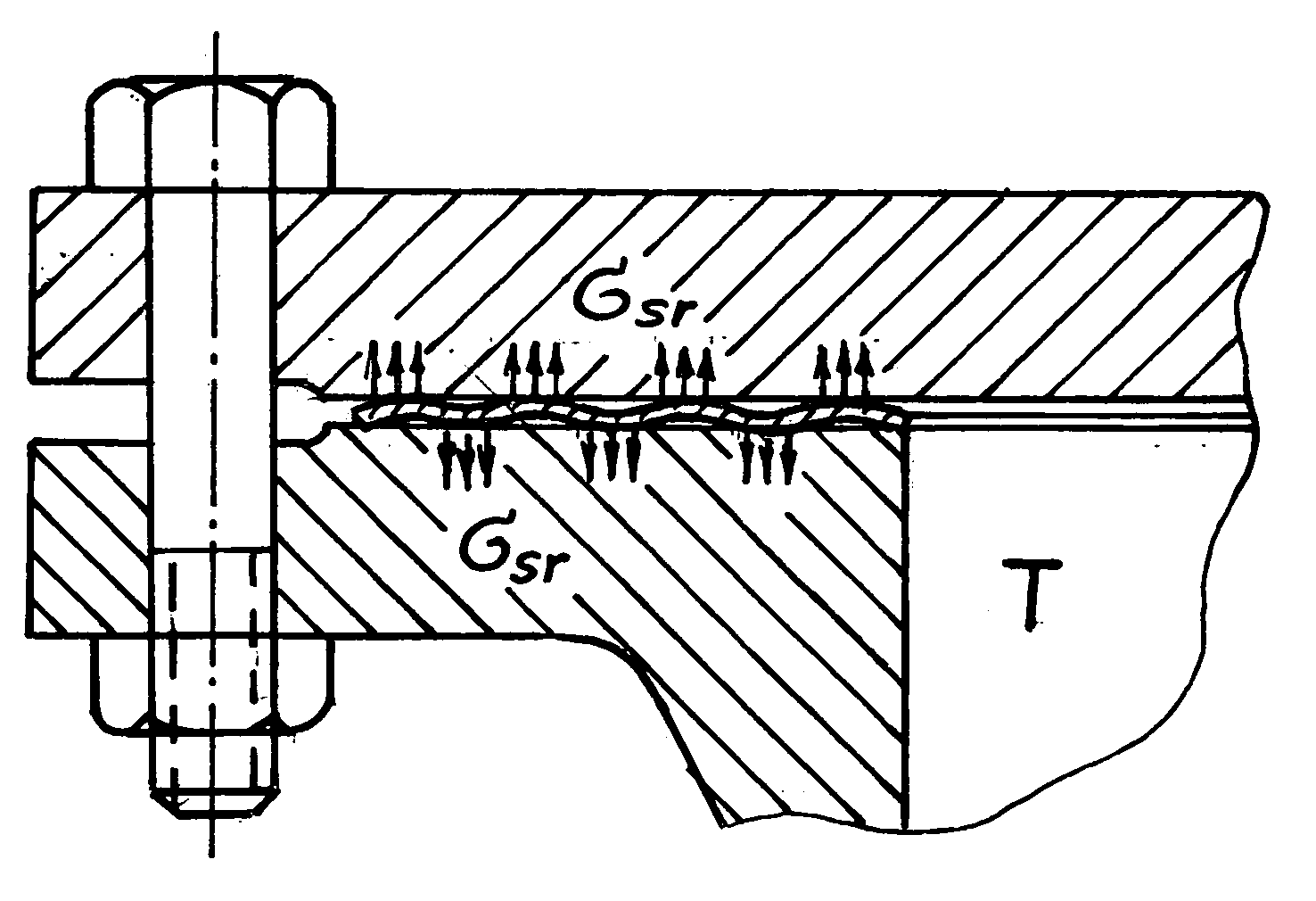
Negative creep corrugated gasket and methods of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20120286480A1Regain shapeReduce the temperatureEngine sealsFlanged jointsMartensite transformationShape-memory alloy
A “negative creep” corrugated gasket of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) for Bolted Flanged Connections (BFCs) operates under temperatures that are within the temperature interval of reverse martensitic phase transformation from martensite to austenite of the SMA. Gasket corrugation is shape-memorized to operating “swelling” at temperature of direct martensitic phase transformation from austenite to martensite of the SMA being compressed to obtain some quantity of residual contraction corresponding to stress-induced martensite formation. A free “swelling” of deformed gasket corrugation at operating temperature defines the “negative creep” effect of the gasket, and it is blocked by rigid flanges with appearance of reactive shape-recovering stresses between the gasket corrugation and flange surfaces. The reactive shape-recovering stresses have direction inverse to the direction of operating creep of the gasket providing leak-tight, multiple, automatic and continuous seal between the flanges of the BFC. Methods of manufacturing of “negative creep” corrugated gasket are disclosed.
Owner:EFREMOV ANATOLY IVANOVICH
Articulating ionizable gas coagulator
InactiveUS7578818B2Avoid arcingSurgical instruments for heatingShape-memory alloyStress induced martensite
An electrosurgical apparatus for coagulating tissue includes an elongated flexible tube having a proximal end, a distal end and a source for supplying pressurized ionizable gas to the proximal end of the tube. The apparatus also includes a hollow sleeve made from a shape memory alloy having a generally curved austenite state and displaying stress-induced martensite behavior. The hollow sleeve is restrained in a deformed stress-induced martensite configuration within the tube and partial extension of a portion of the hollow sleeve from the tube transforms the portion of the sleeve from the deformed configuration to the generally curved austenite configuration such that the gas is directed transversely at the tissue. An electrode ionizes the gas in the region between the sleeve and the tissue. Other embodiments of the present disclosure also include a wire connected to the distal end of the tube which movable from a first postion wherein the tube is disposed in a generally rectilinear, parallel fashion relative to the tissue to a second retracted position wherein the distal end of the tube flexes at an angle to direct the gas towards the tissue. Still other embodiments of the present disclosure include a corona electrode for inducing ignition of the gas.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
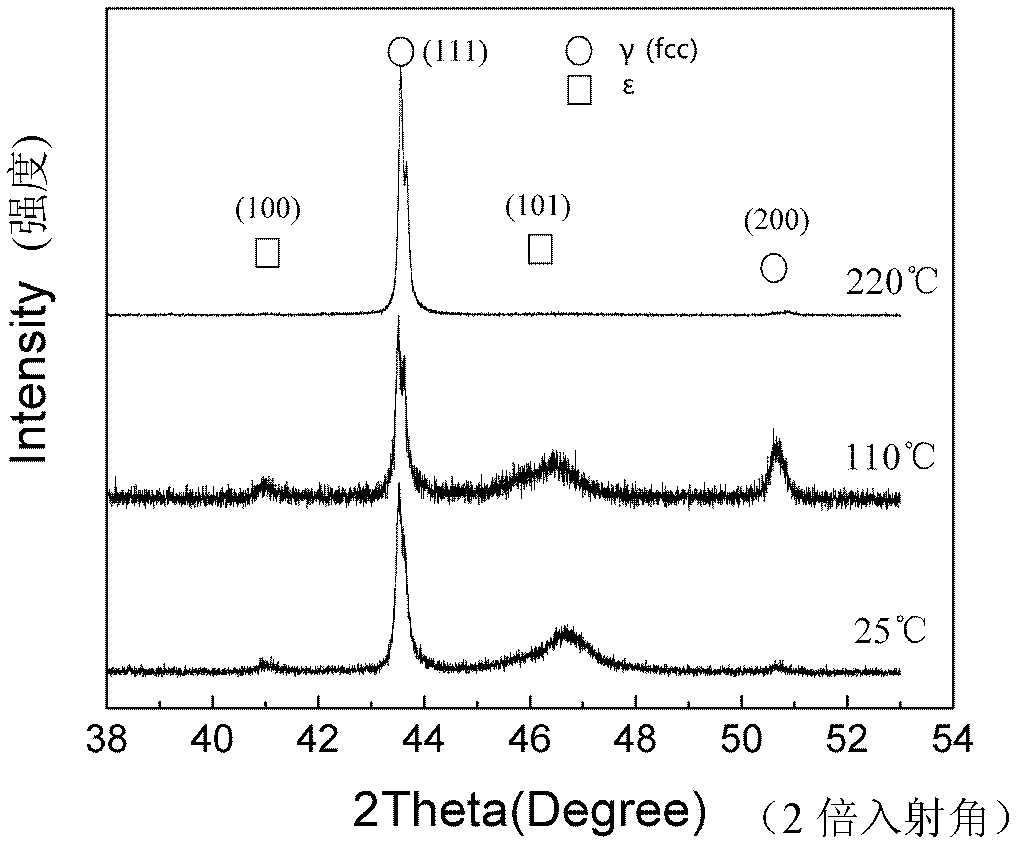
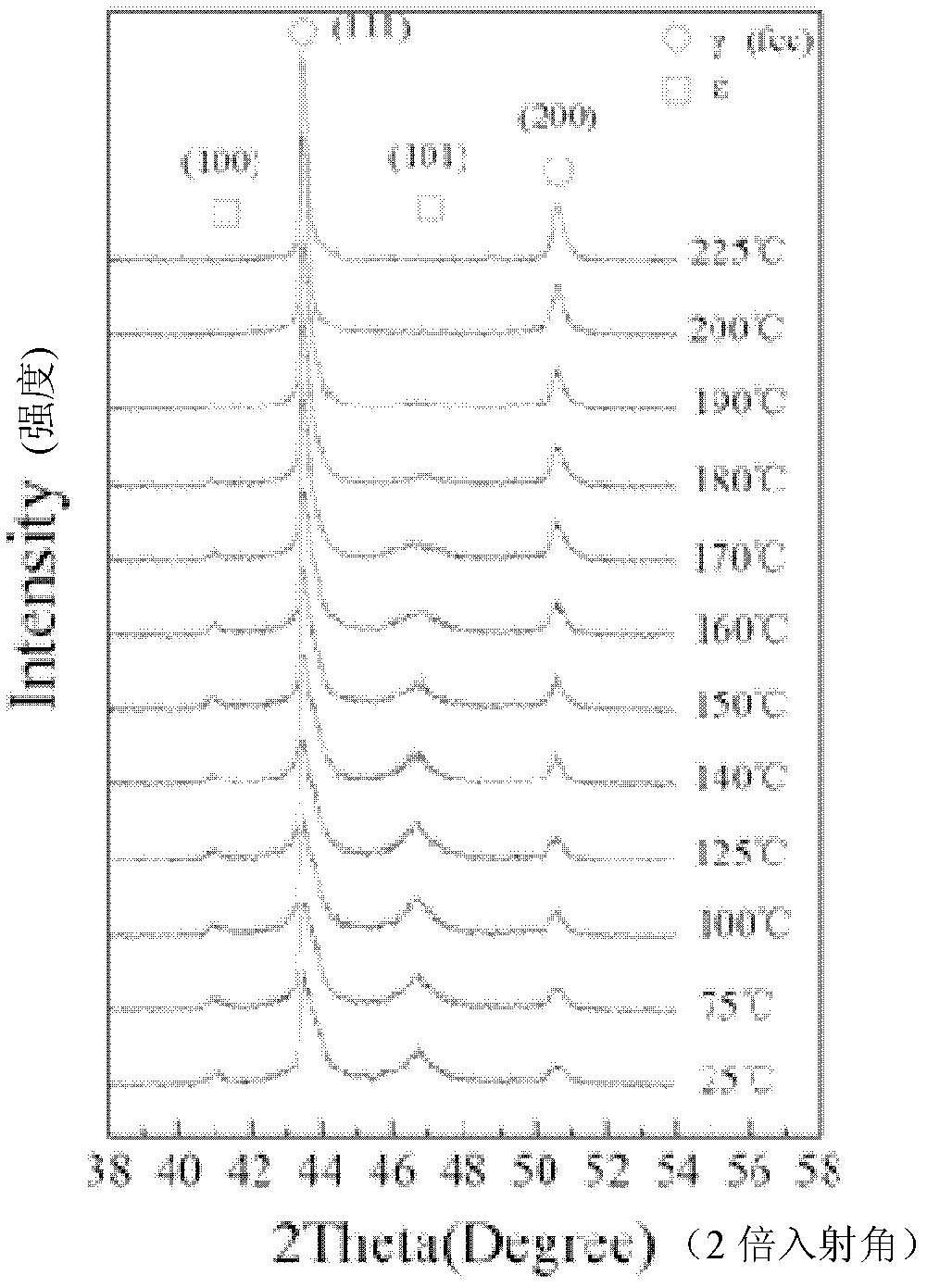
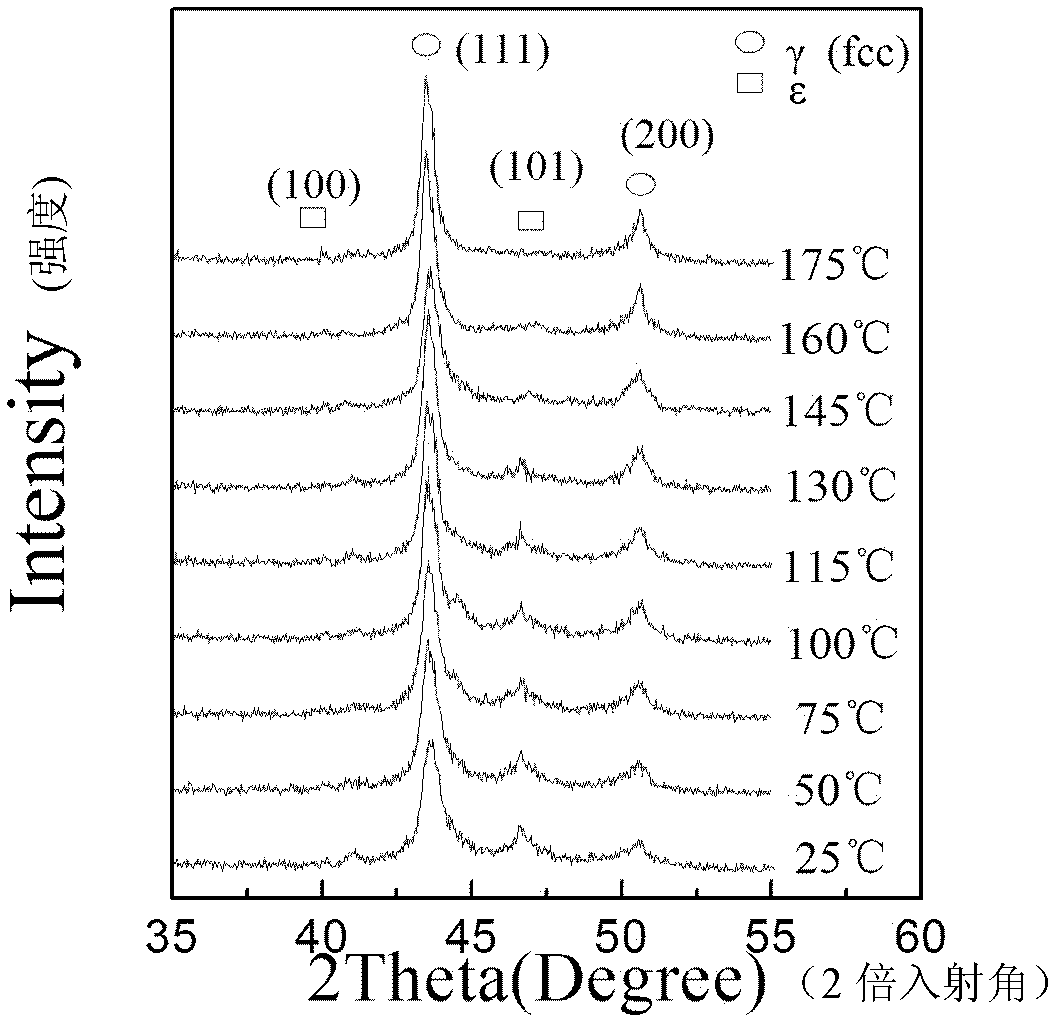
Method for representing recovery characteristics of Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy by in-situ X-ray diffraction
InactiveCN102435624AWill not characterize outcome effectsReduce measurement errorPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayAlloy
The invention discloses a method for representing recovery characteristics of a Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy by in-situ X-ray diffraction. In the method, in-situ X-ray diffraction analysis is introduced to the inverse phase change process of the Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy, thus phase change characteristics of conversion from martensite to austenite under stress induction in the heating shape recovery process of the Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy can be represented synchronously in real time through high-temperature in-situ X-ray diffraction. The method mainly comprises the steps of: pretreating a sample and carrying out X-ray diffraction on the pretreated sample by utilizing a high-temperature in-situ sample platform so as to obtain an in-situ X-ray diffractogram representing the shape memory recovery characteristics of the Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy. By using the method disclosed by the invention, phase change characteristics of the Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy can be presented from a macroscopic perspective, and the change of structure in the recovery process is synchronously, in situ and visually researched through diffraction pattern analysis.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Laser additive manufacturing shear type phase change crack resistance method
ActiveCN111151753AInhibition of microcracksAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMartensite transformationCrack resistance
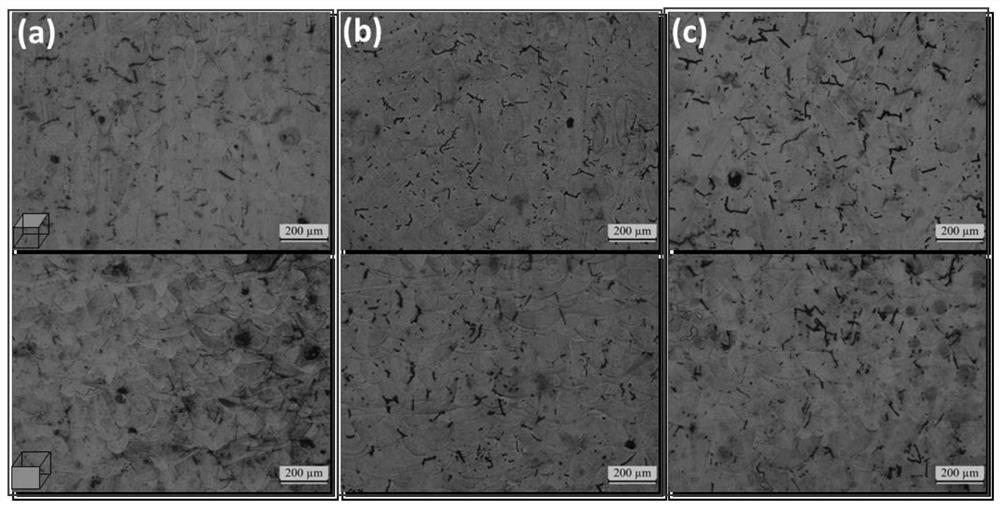
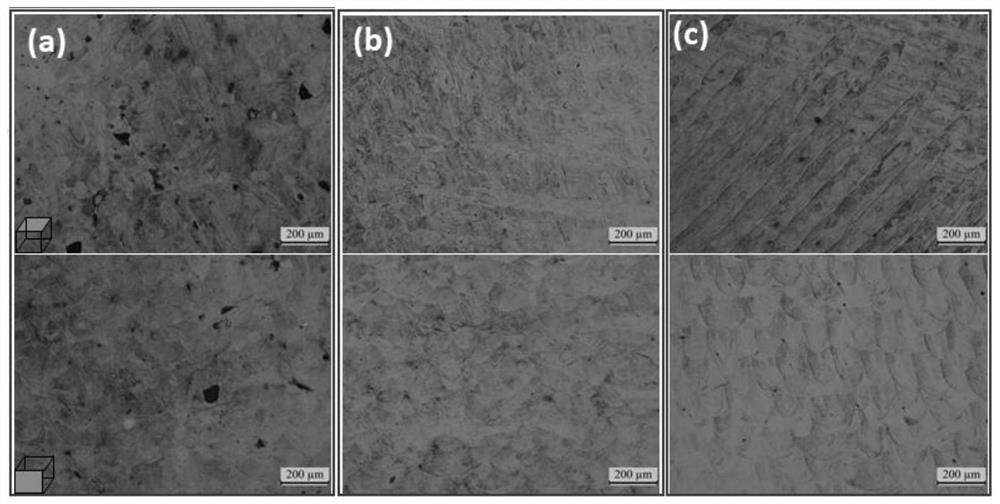
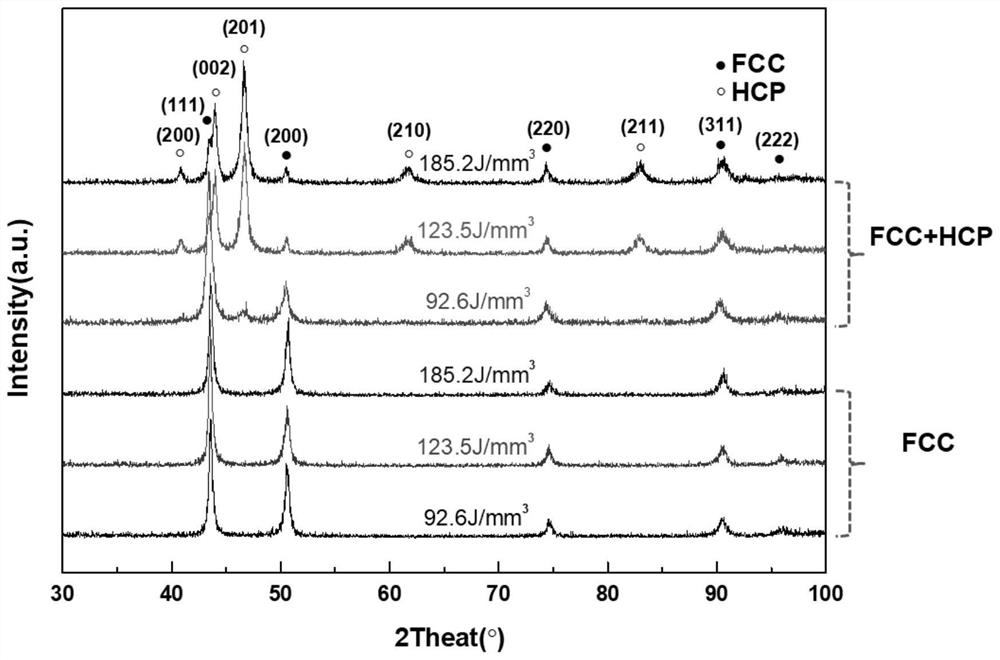
The invention discloses a laser additive manufacturing shear type phase change crack resistance method. The method comprises the steps of adopting a laser additive manufacturing technology and takinghigh-entropy alloy powder with FCC-HCP martensite phase change as additive manufacturing special powder; drying the metal powder in a vacuum drying oven for 12 hours at a drying temperature of 120 DEGC; and carrying out additive manufacturing and printing on the dried high-entropy alloy powder, wherein the printing parameters are as follows: the laser power is 400 W, the scanning speed is 800-1600 mm / s, the scanning distance is 0.09 mm, the powder laying thickness is 0.03 mm, and the substrate preheating temperature is 100 DEG C. The problem of metallurgical defects such as thermal crack deformation and the like are caused by high temperature and high stress gradient in a molten pool in the traditional laser additive manufacturing process is solved. On the basis of the study, the idea ofsuppressing hot cracks in additive manufacturing alloys by stress-induced martensitic transformation is extended to other additive manufacturing alloy systems, and a new method is provided for additive manufacturing of crack-free alloys.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Shape memory alloy check nut and manufacturing technique
The invention relates to a shape memory alloy blocking nut and its preparing process. The raw materials for the nut comprise the following components(in % by weight): C 0.01-0.05, Mn 15.0-17.0, Si 4.8-5.2, Cr8.5-9.5, Ni 6.5-7.5, P 0.01-0.03, S 0.01-0.02, N 0.03-0.05, and Fe 60.65-65.05. The preparing process comprises: (1) preparing the raw materials and rolling to obtain the iron-base shape memory alloy rod stocks with outside hexagon strip and inner circular hole; (2) solution treatment for the rod stocks: keeping the temperature of 950K. to 1150K. for 30 min to 60 min; (3) shape memory training for the rod stocks; (4) cutting the rod stocks to nut blanks, and processing the inner circular hole according to the given size of 94% to 96%; (5) reaming the nut to given size for completing the stress induced martensitic transformation of the nut; (6) fine machining for the internal thread; (7) pre-tightening the nut according to the estimated force moment, keeping the temperature of 500K to 800K for 15min to 45min, and carrying out the annealing treatment.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG RAILWAY INST
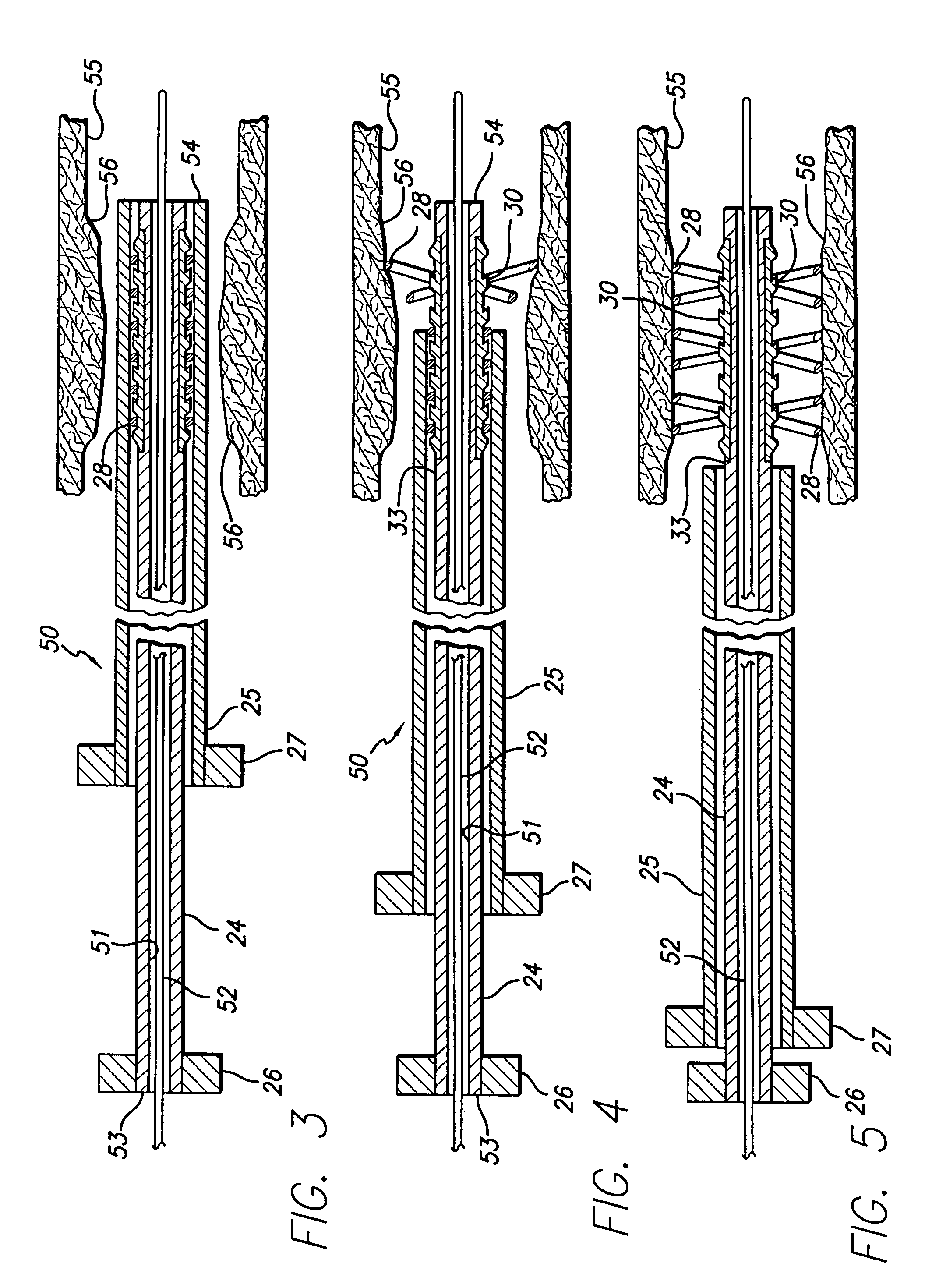
Guide Wire Device Including a Solderable Linear Elastic Nickel-Titanium Distal End Section and Methods Of Preparation Therefor
ActiveUS20130006149A1Increased durabilityEasy to guideGuide wiresDiagnostic recording/measuringHigh stiffnessAlloy
Shapeable guide wire devices and methods for their manufacture. Guide wire devices include an elongate shaft member having a shapeable distal end section that is formed from a linear pseudoelastic nickel-titanium (Ni—Ti) alloy that has linear pseudoelastic behavior without a phase transformation or onset of stress-induced martensite. Linear pseudoelastic Ni—Ti alloy, which is distinct from non-linear pseudoelastic (i.e., superelastic) Ni—Ti alloy, is highly durable, corrosion resistant, and has high stiffness. The shapeable distal end section is shapeable by a user to facilitate guiding the guide wire through tortuous anatomy. In addition, linear pseudoelastic Ni—Ti alloy is more durable tip material than other shapeable tip materials such as stainless steel.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Devices configured from heat shaped, strain hardened nickel-titanium
InactiveUS7938843B2High mechanical strengthMore energy storageEar treatmentGuide wiresEmbolic Protection DevicesStress induced martensite
Cold worked nickel-titanium alloys that have linear pseudoelastic behavior without a phase transformation or onset of stress-induced martensite as applied to a medical device having a strut formed body deployed from a sheath is disclosed. In one application, an embolic protection device that employs a linear pseudoelastic nitinol self-expanding strut assembly with a small profile delivery system for use with interventional procedures is disclosed. The expandable strut assembly is covered with a filter element and both are compressed into a restraining sheath for delivery to a deployment site downstream and distal to an interventional procedure. Once at the desired site, the restraining sheath is retracted to deploy the embolic protection device, which captures flowing emboli generated during the interventional procedure. Linear pseudoelastic nitinol is used in the medical device as distinct from non-linear pseudoelastic (i.e., superelastic) nitinol.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method for determining stress-induced martensitic transformation critical point of shape memory alloy composite damping material
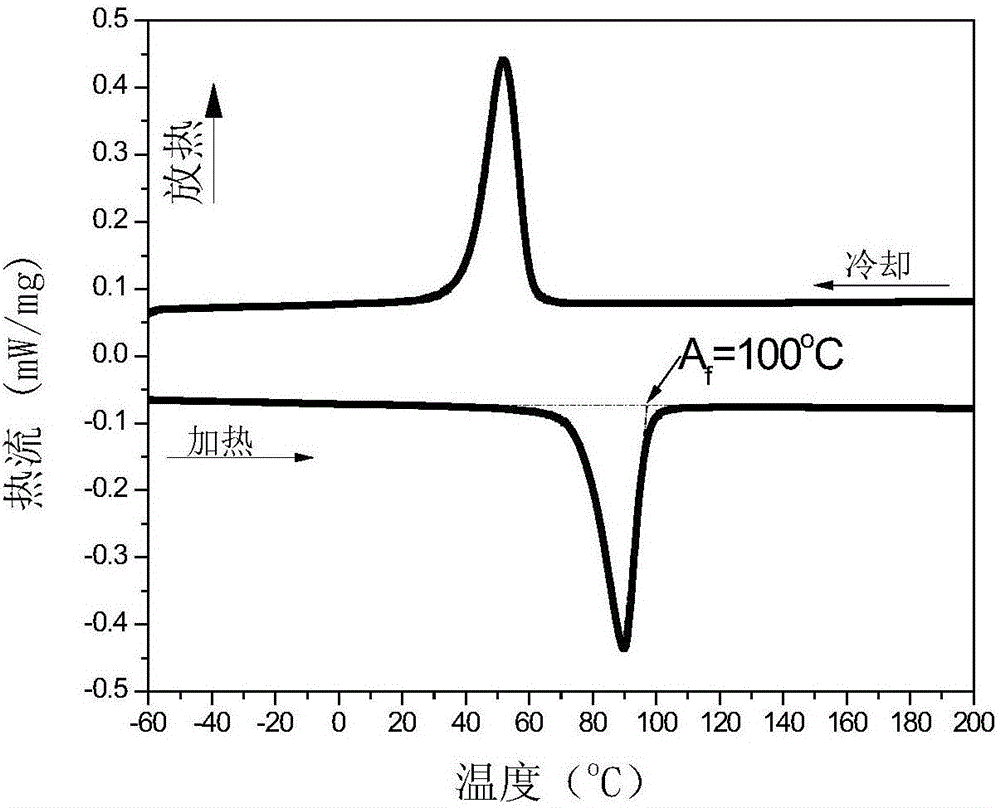
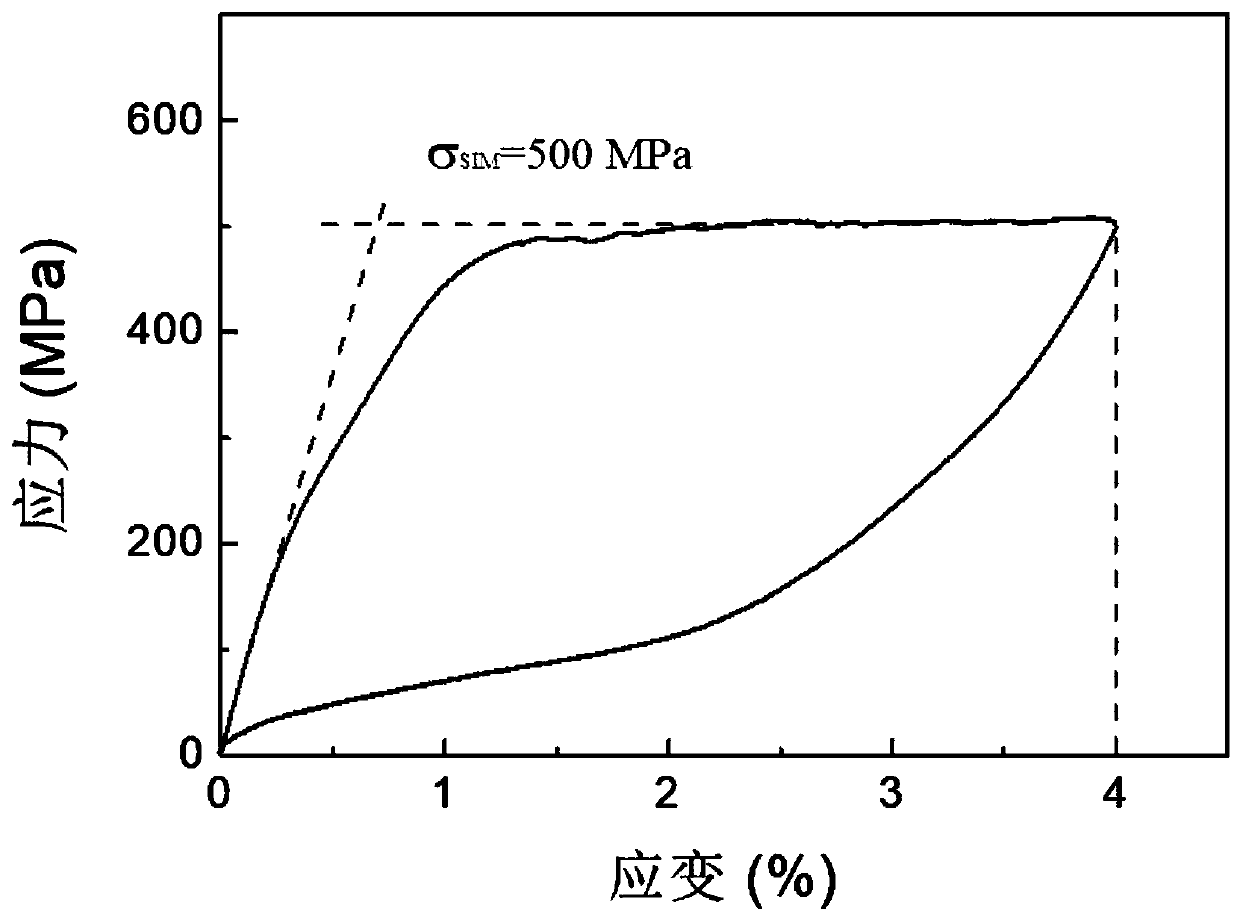
InactiveCN106404656AHigh precisionLow costUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisMartensite transformationStress induced
The invention discloses a method for determining a stress-induced martensitic transformation critical point of a shape memory alloy composite damping material. A reverse martensitic phase transformation finish temperature Af of a sample is determined through a differential thermal scanning thermal analysis method; the internal friction-strain spectrum of the sample is measured at the temperature higher than the reverse martensitic phase transformation finish temperature Af by means of a dynamic mechanical analyzer; finally, the critical point with the remarkably increasing inner friction in the internal friction-strain spectrum is analyzed through the tangent method, the critical point is the stress-induced martensitic transformation critical point of the shape memory alloy composite damping material, and corresponding strain is stress-induced martensitic transformation critical strain. The method is reliable, quick, high in precision and low in cost. Subtle structure changes of the shape memory alloy composite damping material can be visually reflected, and the transformation critical point is precisely measured. The method is applicable to compact shape memory alloy, porous shape memory alloy and shape memory alloy composite materials.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Nickel-manganese-gallium alloy with high elastic thermal effect and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106906403AElastothermal effect is easyGood reversibilityInorganic material magnetismManganeseStress induced martensite
The invention discloses a nickel-manganese-gallium alloy with a high elastic thermal effect and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the nickel-manganese-gallium alloy and the preparation method thereof. In order to solve the problem that an existing gas refrigerant causes pollution on environment. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: I, weighing; II, manufacturing a casting mould; III, performing a vacuum induction smelting method; IV, performing uniform thermal treatment; and IV, performing ordering treatment. The nickel-manganese-gallium alloy and the preparation method have the advantages that: martensite phase transformation is induced by stress to generate the elastic thermal effect, adiabatic temperature change and reversibility are high, and a stress-induced phase transformation device is easily manufactured. The manufacturing method for a refrigerating device by the elastic thermal effect of the nickel-manganese-gallium alloy has a good prospect. The invention provides the nickel-manganese-gallium alloy with the high elastic thermal effect and the preparation method thereof.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation in nickle titanium alloys used in medical devices
A process for assembling a medical device made from a nickel-titanium alloy for use in a mammalian body while avoiding the formation of stress-induced martensite and a medical device used in combination with a delivery system for deployment into the mammalian body are disclosed. By heating the nickel-titanium alloy of the medical device to a temperature above Md, and deforming and installing the device into a delivery system or holding capsule, it is possible to avoid the formation of stress-induced martensite in the stent, which stays in the austenitic phase throughout.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
NiTi shape memory alloy with functions of energy absorption and vibration reduction, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112080669AChange phase transition temperatureChanging the dislocation densityNiti alloyEnergy absorption
The invention discloses a nickel-titanium shape memory alloy capable of simultaneously realizing the functions of energy absorption and vibration reduction, and a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of NiTi shape memory alloys. A cold-deformed nickel-rich NiTi alloy is used for preparing a hand-shaped structure with a negative poisson ratio characteristic, and the phase change behavior and mechanical property of the NiTi alloy are regulated and controlled through heat treatment to a cold-deformed nickel-rich NiTi alloy component. Thus, stress-inducedmartensitic transformation occurs to the NiTi alloy component in the impact deformation process, and large impact energy is absorbed. The deformed NiTi alloy component is kept in a martensite state, and energy dissipation is promoted due to interaction between martensite variants, so that the component has higher damping performance after completion of impact, and a good damping effect is achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
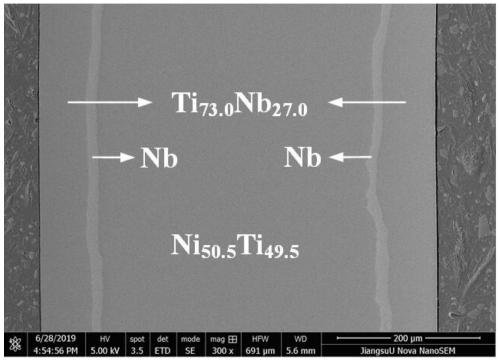
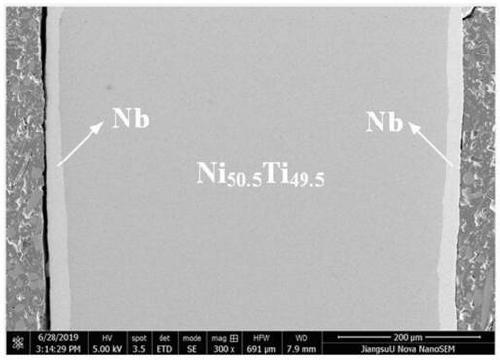
Nb layer-containing TiNb/NiTi memory material and preparation method
ActiveCN111187945AGood biocompatibilityImprove mechanical propertiesTemperature control deviceWork heating devicesMartensite transformationShape-memory alloy
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical shape memory composite materials, in particular to a Nb transition layer-containing TiNb-coated NiTi shape memory composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material prepared by the method has good biocompatibility, relatively high stress-induced martensitic transformation critical stress and large recoverable dependent variable. The Nb transition layer-containing TiNb-coated NiTi shape memory composite material is expected to solve the problems that existing single biomedical shape memory alloys, such as NiTi-based alloys and Ni-free beta-titanium alloys, cannot simultaneously have good biocompatibility, relatively high stress-induced martensite transformation critical stress and large recoverable dependentvariable, and is expected to be applied in the field of biomedicines.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
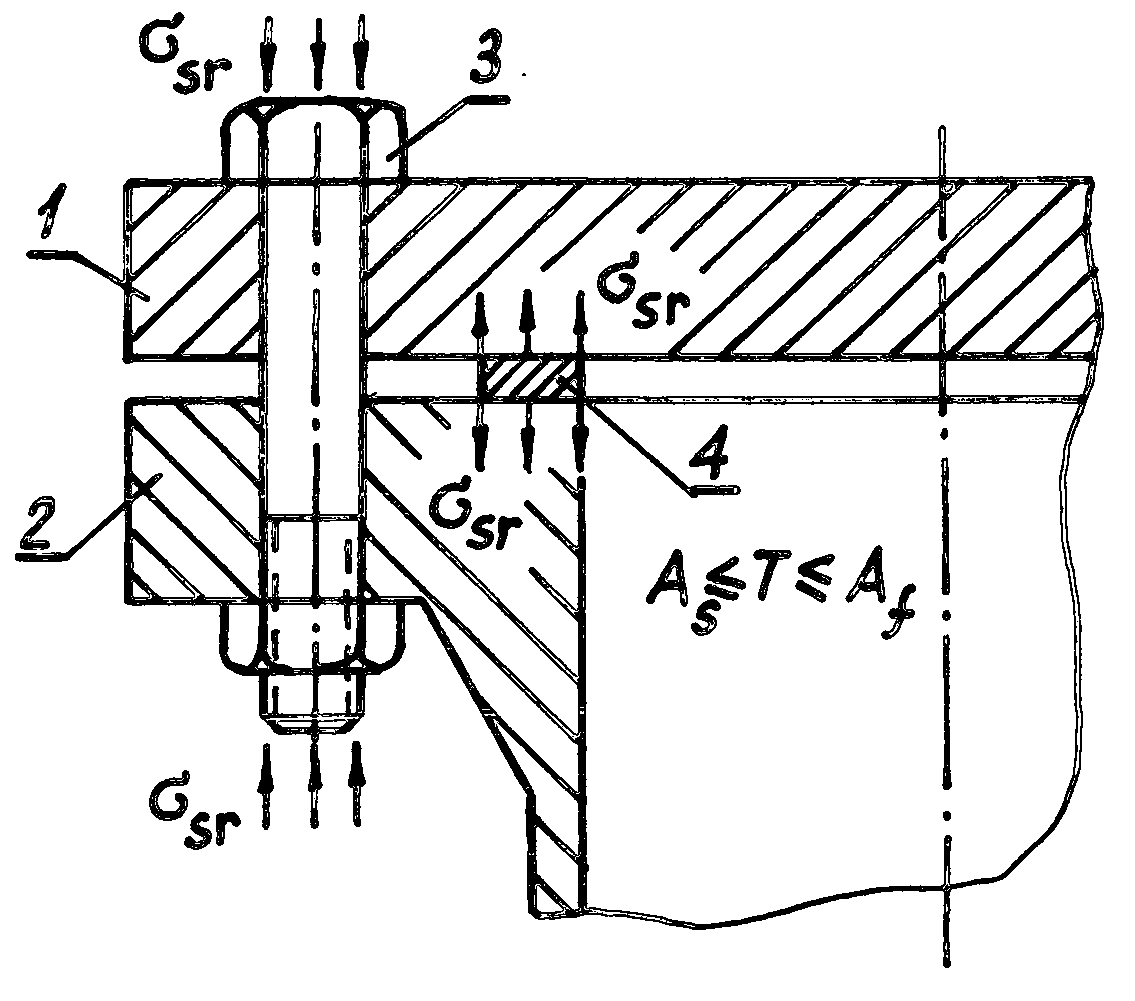
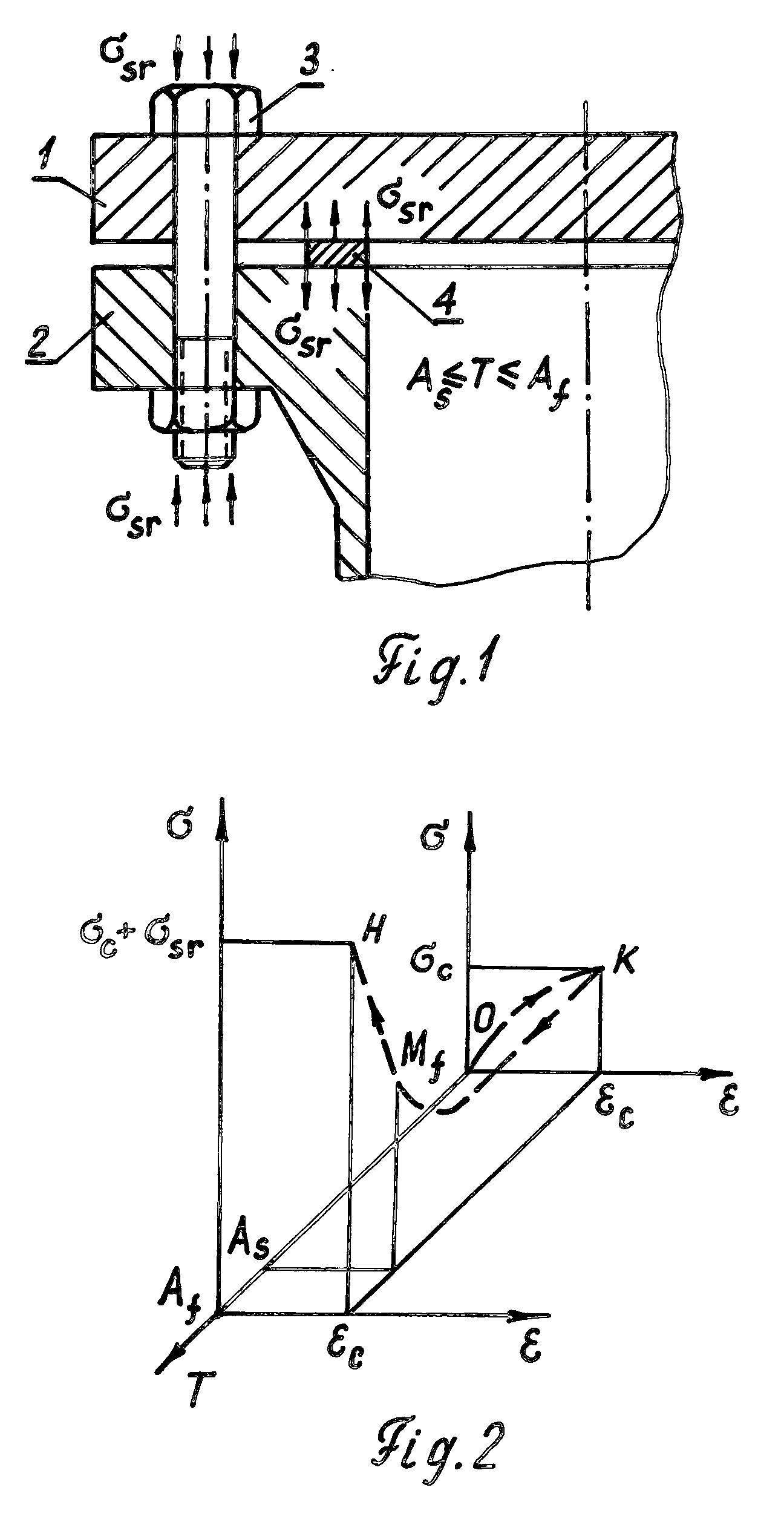
Method to limit a creep of bolts and gaskets of bolted flanged connections
InactiveUS20080199273A1Maximize efficiencyFlanged jointsWashersMartensite transformationShape-memory alloy
A method to limit or exclude operational creep of the bolts and gaskets of Bolted Flanged Connections (BFCs) is disclosed. The method consists in the use of bolts and gaskets manufactured from the same Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) having temperature intervals of reverse martensitic phase transformation close to operational temperatures of the BFCs. These bolts and gaskets of the BFCs are shape-memorized to the compression (bolts) and “swelling” (gaskets) during (1) the formation of stress-induced martensite under temperature of martensite state of the SMAs while bolt preload application, or (2) during the formation of stress-induced martensite while loading-unloading previously stretched bolts and previously compressed gaskets under temperature of martensite state resulting in residual bolt elongations and residual gasket contraction followed by bolt preload application. Constrained shape recovery of initial length of the bolts and initial thickness of the gaskets under operational temperatures of the BFCs is accompanying by appearance of reactive shape-recovering stresses having direction inverse to the direction of operational creep of the bolts and gaskets that limits or excludes their operational creep.
Owner:EFREMOV ANATOLY
Nb coated NiTi shape memory composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111167860AGood biocompatibilityImprove mechanical propertiesMedical devicesAuxillary arrangementsShape-memory alloyStress induced martensite
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical shape memory composite materials, in particular to an Nb coated NiTi shape memory composite material and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, the prepared composite material has good biocompatibility, high stress-induced martensite phase transformation critical stress and large recoverable dependent variable, the problemthat an existing single biomedical shape memory alloy, such as a NiTi-based alloy and a no-Ni beta titanium alloy, cannot has the good biocompatibility, high stress-induced martensite phase transformation critical stress and large recoverable dependent variable at the same time can be solved, and the composite material can be applied to the field of biomedicine.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Nickel-based alloy additive manufacturing method
PendingCN113403617AReduced crack susceptibilityGrain refinementAdditive manufacturing apparatusMetallic material coating processesAlloyStress induced martensite
The invention belongs to the technical field of nickel-based alloy manufacturing, and discloses a nickel-based alloy additive manufacturing method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a coating on the surface of a nickel-based alloy by adopting a laser cladding method; then, carrying out laser shock processing on the coating; and repeating the laser cladding and laser shock processing processes until a member is repaired or the manufacturing of the member is completed. On one hand, the cladded coating is nickel-based memory alloy powder, has the stress self-adaptive characteristic, can induce epsilon martensite positive and negative phase transformation through stress to relax residual stress in a cladding layer, reduces the cracking sensitivity of the cladding layer and solves the problem of workpiece deformation; and on the other hand, laser shock can refine structure grains of the cladding coating, prefabricate residual compressive stress and improve the bonding performance between the cladding layer and a matrix, so that the strength and hardness of the coating are effectively improved, and the wear resistance is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for representing recovery characteristics of Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy by in-situ X-ray diffraction
InactiveCN102435624BWill not characterize outcome effectsReduce measurement errorPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayAlloy
The invention discloses a method for representing recovery characteristics of a Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy by in-situ X-ray diffraction. In the method, in-situ X-ray diffraction analysis is introduced to the inverse phase change process of the Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy, thus phase change characteristics of conversion from martensite to austenite under stress induction in the heating shape recovery process of the Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy can be represented synchronously in real time through high-temperature in-situ X-ray diffraction. The method mainly comprises the steps of: pretreating a sample and carrying out X-ray diffraction on the pretreated sample by utilizing a high-temperature in-situ sample platform so as to obtain an in-situ X-ray diffractogram representing the shape memory recovery characteristics of the Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy. By using the method disclosed by the invention, phase change characteristics of the Fe-Mn-Si-based memory alloy can be presented from a macroscopic perspective, and the change of structure in the recovery process is synchronously, in situ and visually researched through diffraction pattern analysis.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A method of laser additive manufacturing shear type phase change crack resistance
ActiveCN111151753BInhibition of microcracksAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMartensite transformationCrack resistance
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing shear-type phase change crack resistance by laser additive manufacturing, which includes adopting laser additive manufacturing technology, and using high-entropy alloy powder with FCC→HCP martensitic phase transition as a special powder for additive manufacturing; Dry the metal powder in a vacuum drying oven for 12 hours at a drying temperature of 120°C; perform additive manufacturing printing on the dried high-entropy alloy powder, and the printing parameters are: laser power 400W; scanning speed 800-1600mm / s ; The scanning distance is 0.09mm; the powder coating thickness is 0.03mm; the substrate preheating temperature is 100°C. The invention solves the problem of metallurgical defects such as thermal crack deformation caused by high temperature and high stress gradient in the molten pool in the traditional laser additive manufacturing process. And on the basis of this research, the idea of stress-induced martensitic transformation to suppress hot cracks in additive manufacturing alloys is extended to other additive manufacturing alloy systems, providing a new method for additive manufacturing of crack-free alloys.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Manufacturing and application methods for laser cladding powder of iron-base alloy
InactiveCN103056355BReduce residual stressImprove fatigue strengthMetallic material coating processesStress induced martensiteWear resistance
The invention discloses a design manufacturing method and an application method for laser cladding powder. The design manufacturing method includes preparing Fe-Mn-Si memory alloy powder and putting the memory alloy powder into a ball grinder to process powder mixing. The application method includes processing a vacuum drying treatment before the cladding, presetting the cladding powder on base materials, and processing the cladding with laser which is 1.5-3 Kw in laser power, 400-1000 mm / min in scanning speed and 3 mm in laser diameter. By the stress of the laser cladding layer of the Fe-Mn-Si memory alloy, martensitic transformation and the martensitic deformation compatibility are induced so as to effectively remove the residual stress of the cladding layer and improve the fatigue strength of the cladding layer with no need of adding extra processing. The laser cladding powder of the iron-base alloy has the advantages of being simple in preparation technology, applicable to mass production, good in wear resistance, low in residual stress, high in fatigue strength, and the like.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Shape memory alloy check nut and manufacturing technique
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG RAILWAY INST
High-strength and high-elasticity shape memory alloy chuck for high-carbon steel wire drawing
PendingCN113953338AFlexible loading facilitatesImprove drawing efficiencyDrawing profiling toolsVibration suppression adjustmentsStress concentrationShape-memory alloy
The invention relates to the technical field of high-carbon steel wire machining, and particularly discloses a high-strength and high-elasticity shape memory alloy chuck for high-carbon steel wire drawing. The high-strength and high-elasticity shape memory alloy chuck comprises two chuck main bodies, NiTi shape memory alloy plates are connected to the opposite surfaces of the two chuck main bodies through mounting plates, iron permeating layers are arranged on the opposite surfaces of the two NiTi shape memory alloy plates, and limiting mechanisms are arranged on the opposite surfaces of the two mounting plates. The mechanical characteristic that NiTi shape memory alloy stress induces martensite inverse phase transformation is applied, flexible loading is conducted on the clamped high-carbon steel wire, a stress platform is generated in the loading process, that is, the stress does not change along with the increase of deformation, and therefore it is guaranteed that the high-carbon steel wire does not generate stress concentration at the chuck position, the steel wire is prevented from being broken, the drawing efficiency of the high-carbon steel wire is improved, the iron permeating layer is attached to the surface of the NiTi shape memory alloy plate through a double glow plasma alloying technology, and the surface hardness of the NiTi shape memory alloy plate is improved.
Owner:AOSHENG MAANSHAN STEEL WIRE & WIRE ROPE
A kind of nb-coated niti shape memory composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111167860BGood biocompatibilityImprove mechanical propertiesMedical devicesAuxillary arrangementsShape-memory alloyStress induced martensite
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical shape-memory composite materials, in particular to a Nb-coated NiTi shape-memory composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material prepared by this method has good biocompatibility, high stress-induced martensitic transformation critical stress and large recoverable strain, which is expected to solve the existing single biomedical shape memory alloy, such as NiTi Base alloys and Ni-free β-titanium alloys cannot have good biocompatibility, high stress-induced martensitic transformation critical stress and large recoverable strain at the same time, and are expected to be obtained in the biomedical field application.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com