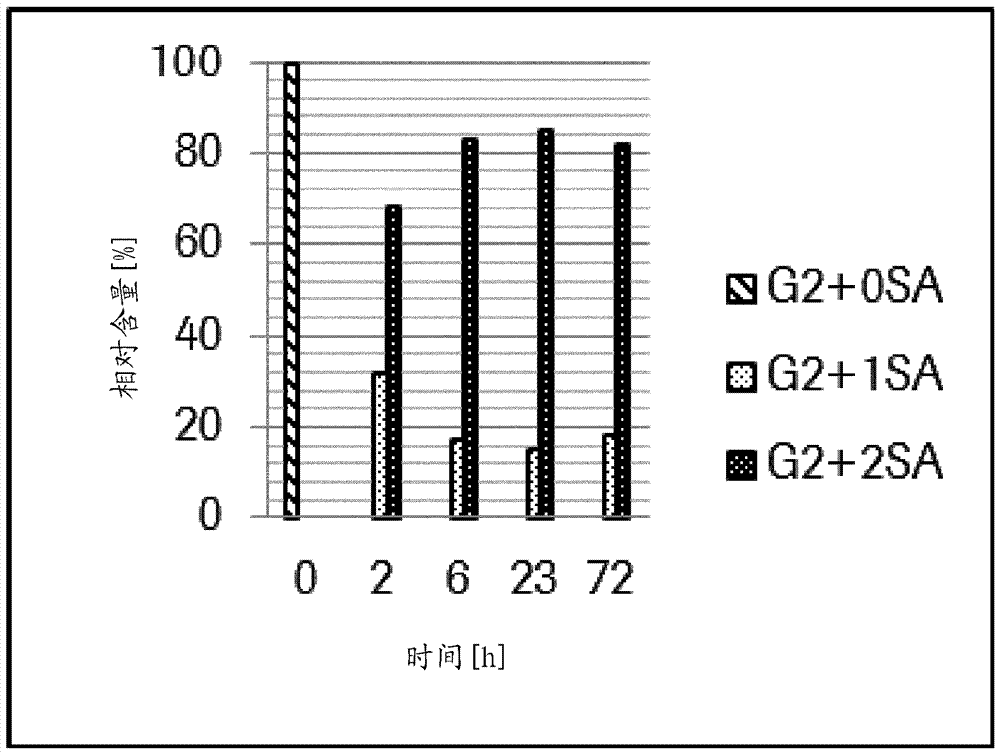
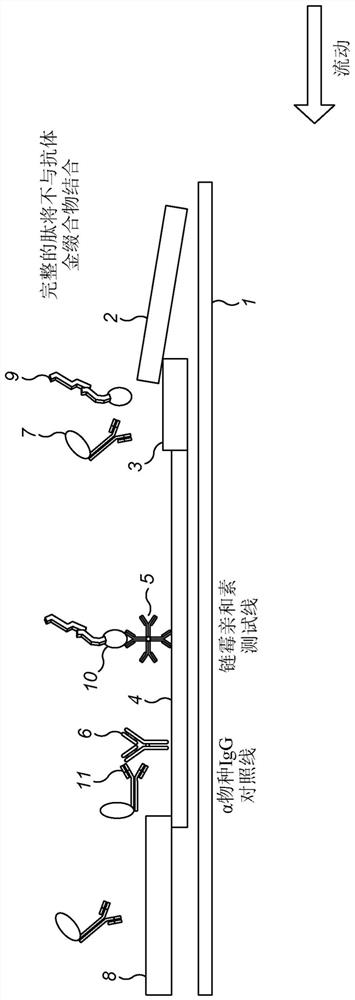
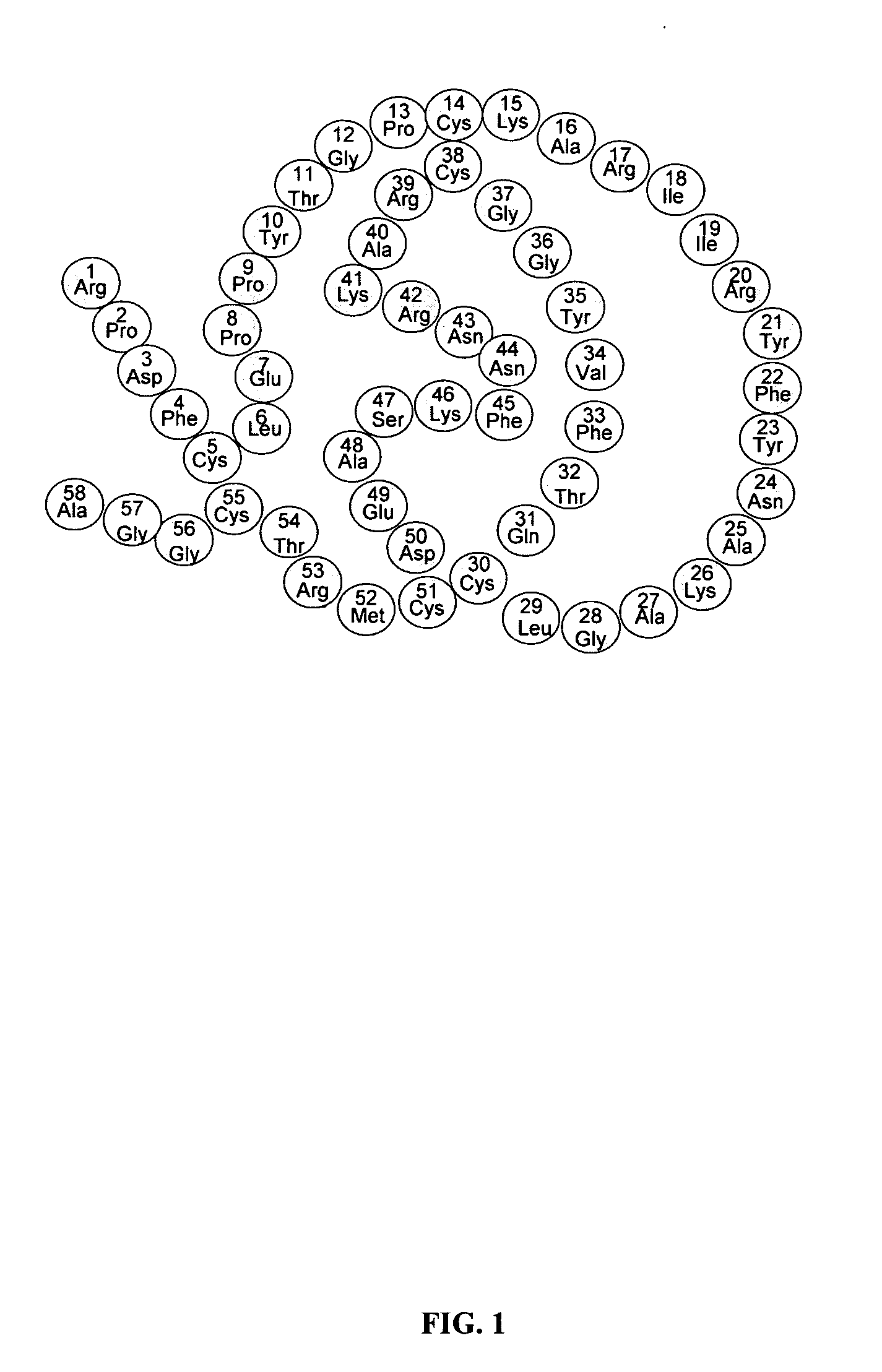Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Sialidase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Novel class of therapeutic protein based molecules
ActiveUS20050112751A1Prevent and inhibit adhesion and functionInhibitory responseAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderTherapeutic proteinViral infection
The present invention provides new compositions and methods for preventing and treating pathogen infection. In particular, the present invention provides compounds having an anchoring domain that anchors the compound to the surface of a target cell, and a therapeutic domain that can act extracellularly to prevent infection of a target cell by a pathogen, such as a virus. The present invention also comprises therapeutic compositions having sialidase activity, including protein-based compounds having sialidase catalytic domains. Compounds of the invention can be used for treating or preventing pathogen infection, and for treating and reducing allergic and inflammatory responses. The invention also provides compositions and methods for enhancing transduction of target cells by recombinant viruses. Such compositions and methods can be used in gene therapy.
Owner:ANSUN BIOPHARMA
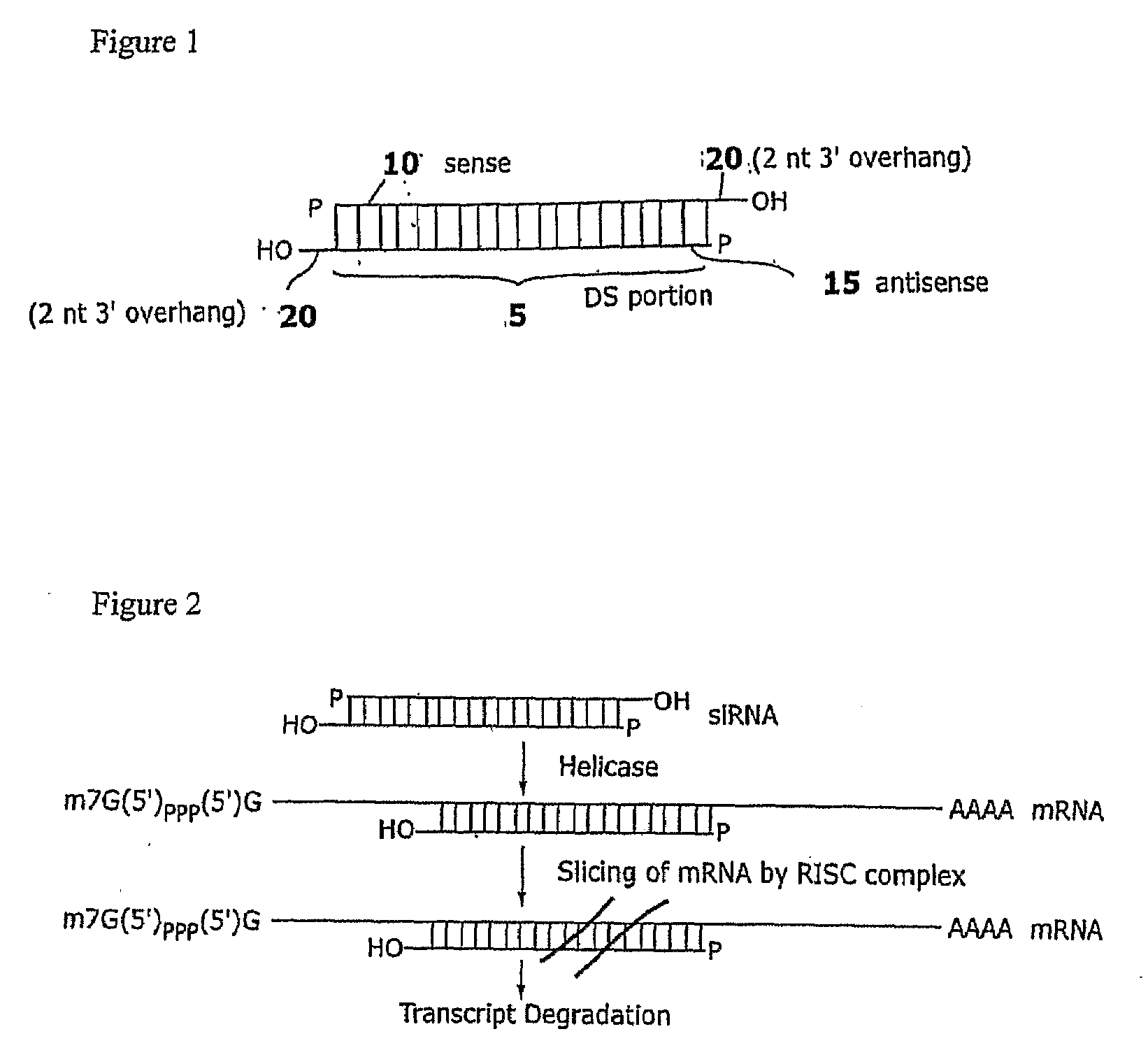
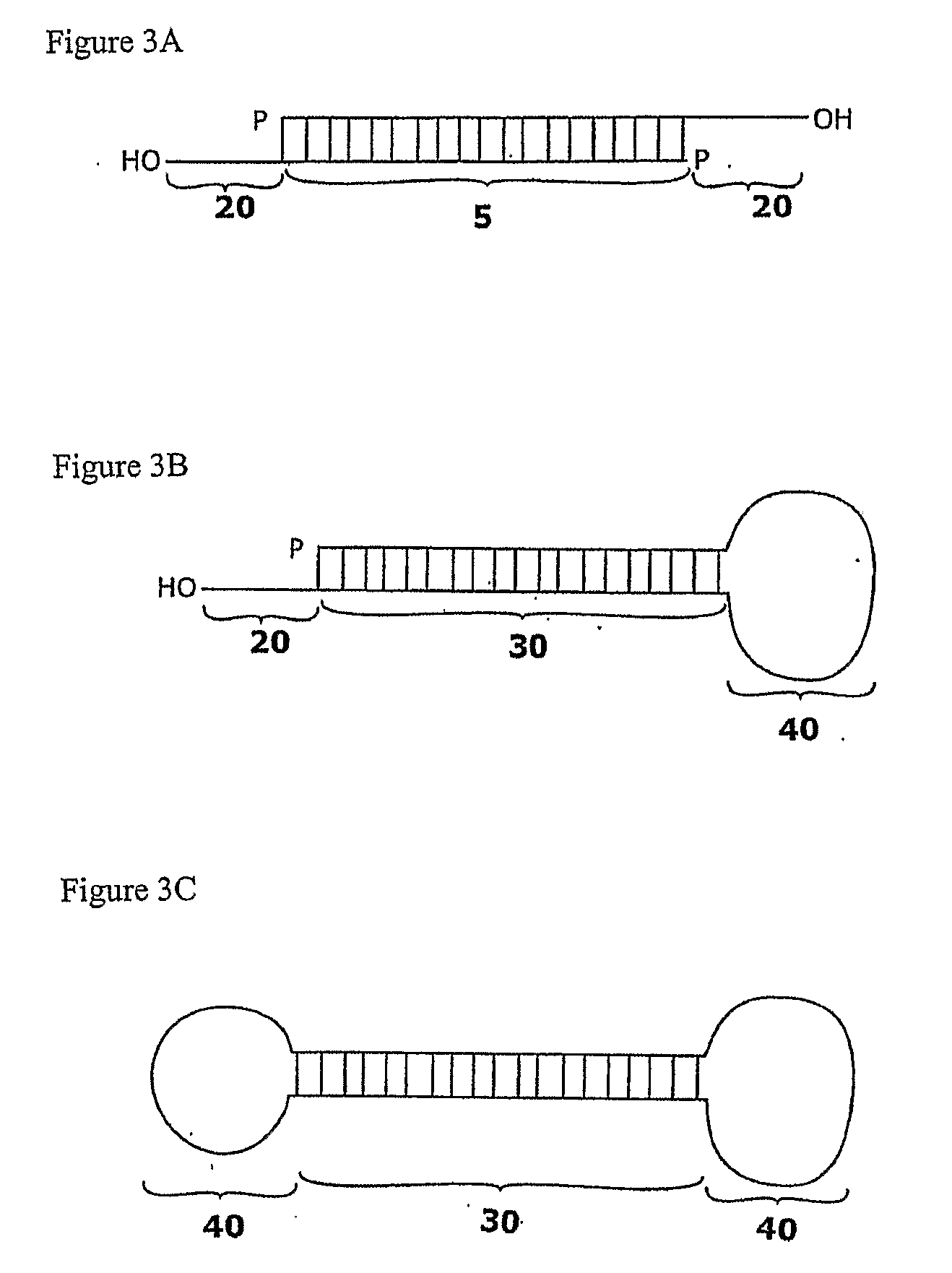
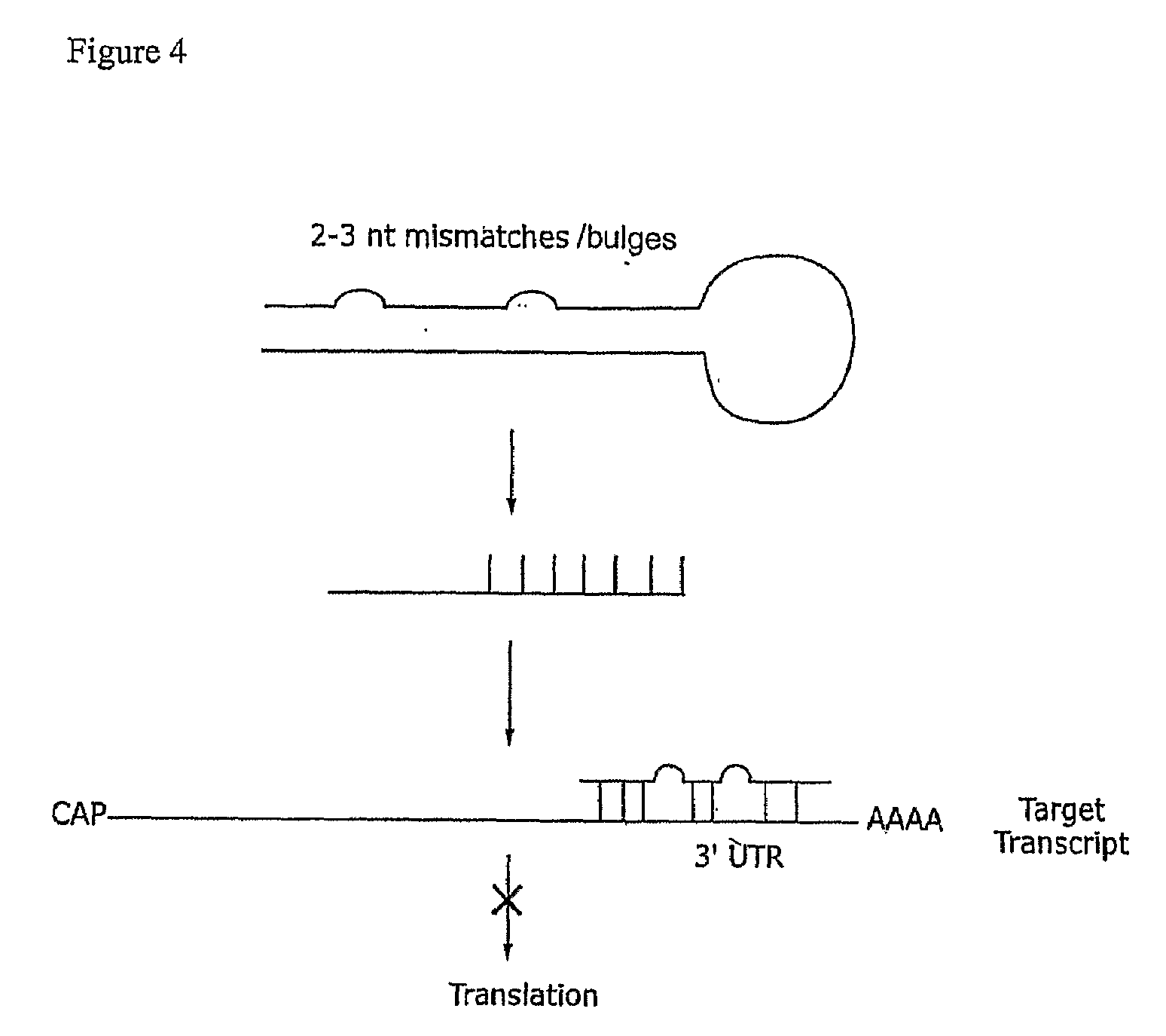
Compositions and methods for RNA interference with sialidase expression and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090203055A1Reducing sialidase activityReduce decreaseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSialic acidControl cell
The present invention provides RNAi agents targeted to sialidase. The RNAi agents include siRNA, shRNA, and expression vectors that comprise a template for transcription of an siRNA or shRNA. The invention further provides cells and cell lines that comprise an RNAi agent targeted to sialidase. The cells and cell lines exhibit reduced sialidase activity relative to control cells that do not comprise an RNAi agent targeted to sialidase. Certain of the cell lines stably express the RNAi agent. The invention further provides methods of producing the cells and cell lines. The invention further provides methods for producing a glycoprotein in cells that comprise an RNAi agent targeted to sialidase. The glycoproteins exhibit an improved sialic acid profile relative to glycoproteins produced by cells that do not comprise an RNAi agent targeted to sialidase. The invention further provides glycoproteins, e.g., therapeutic glycoproteins, produced in the cells.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
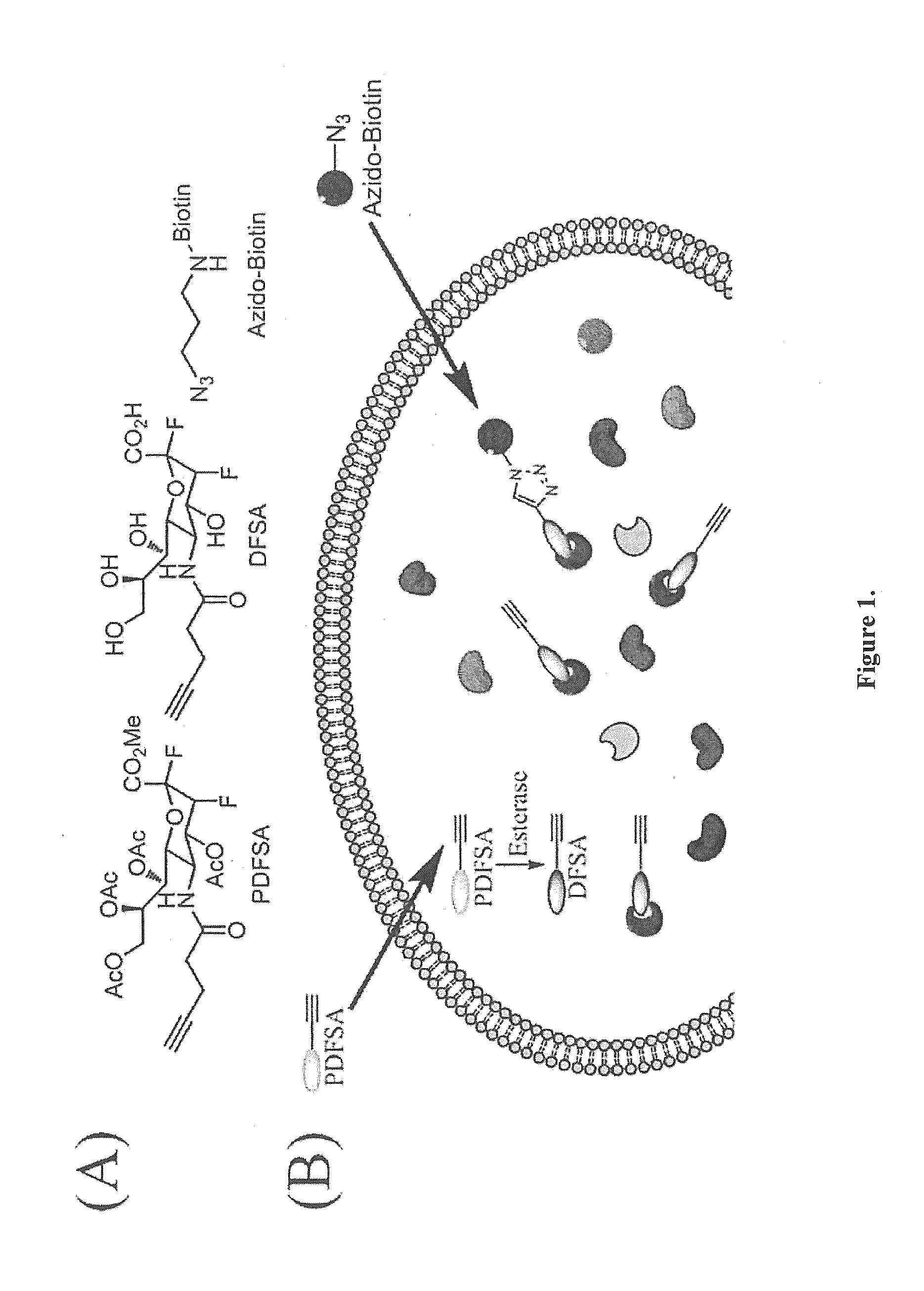
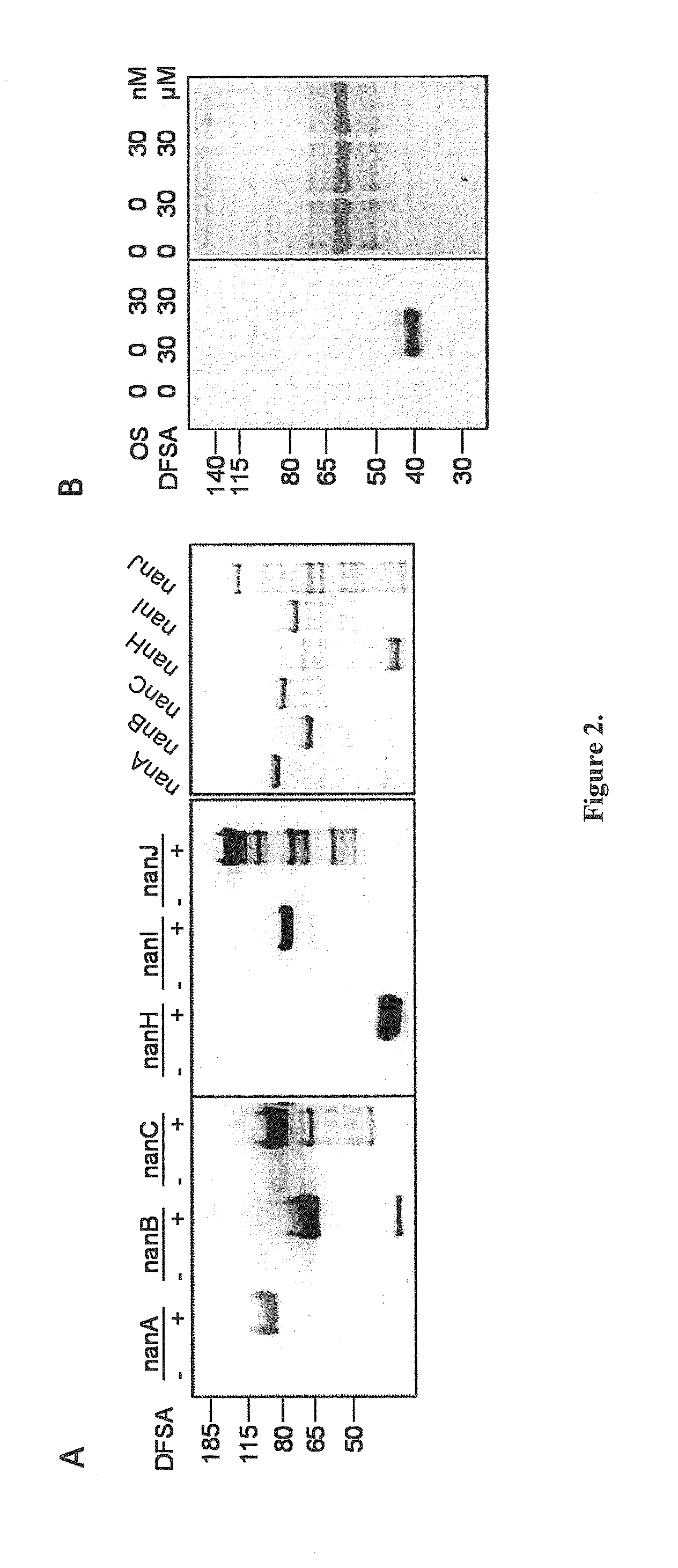
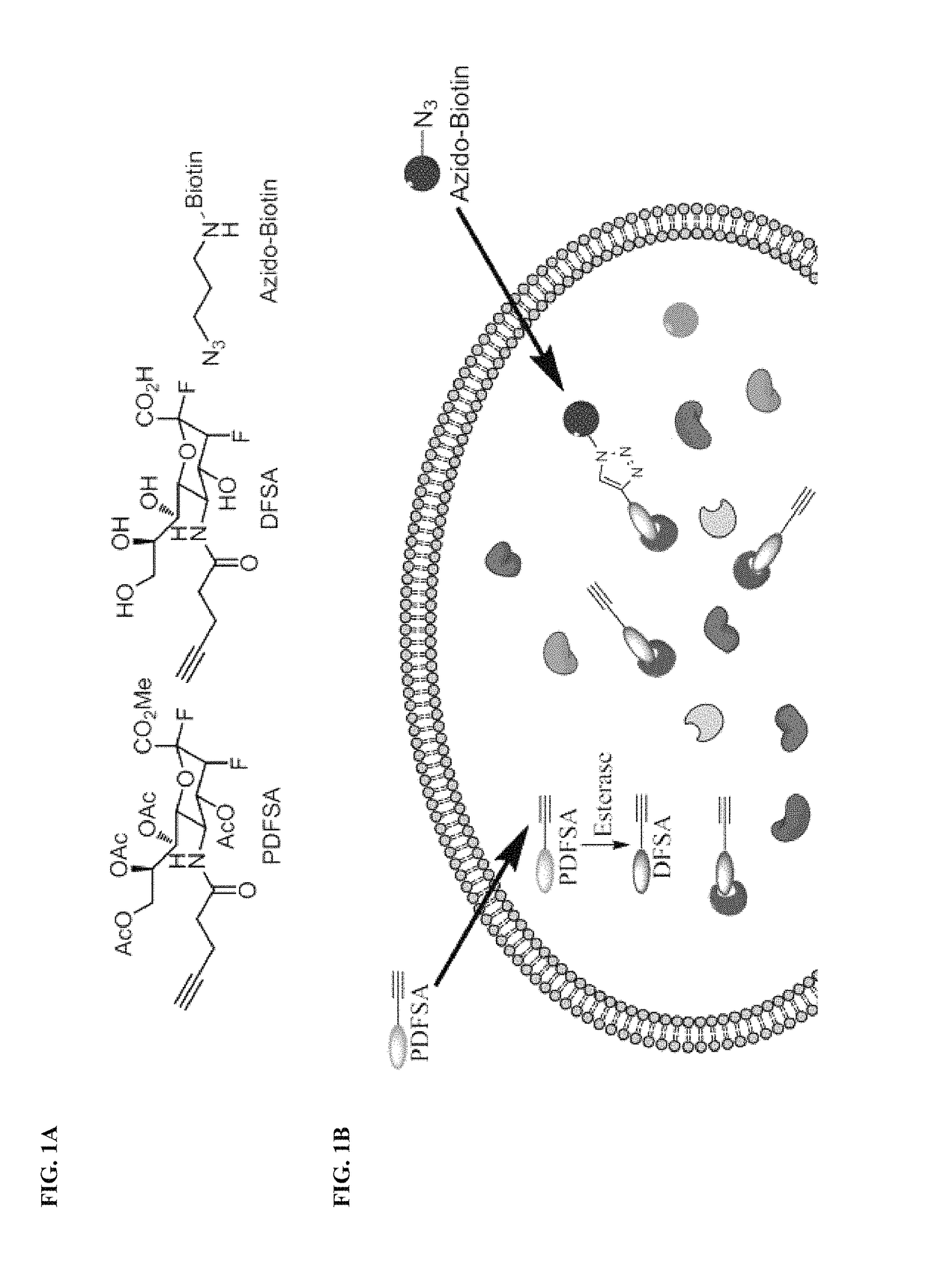
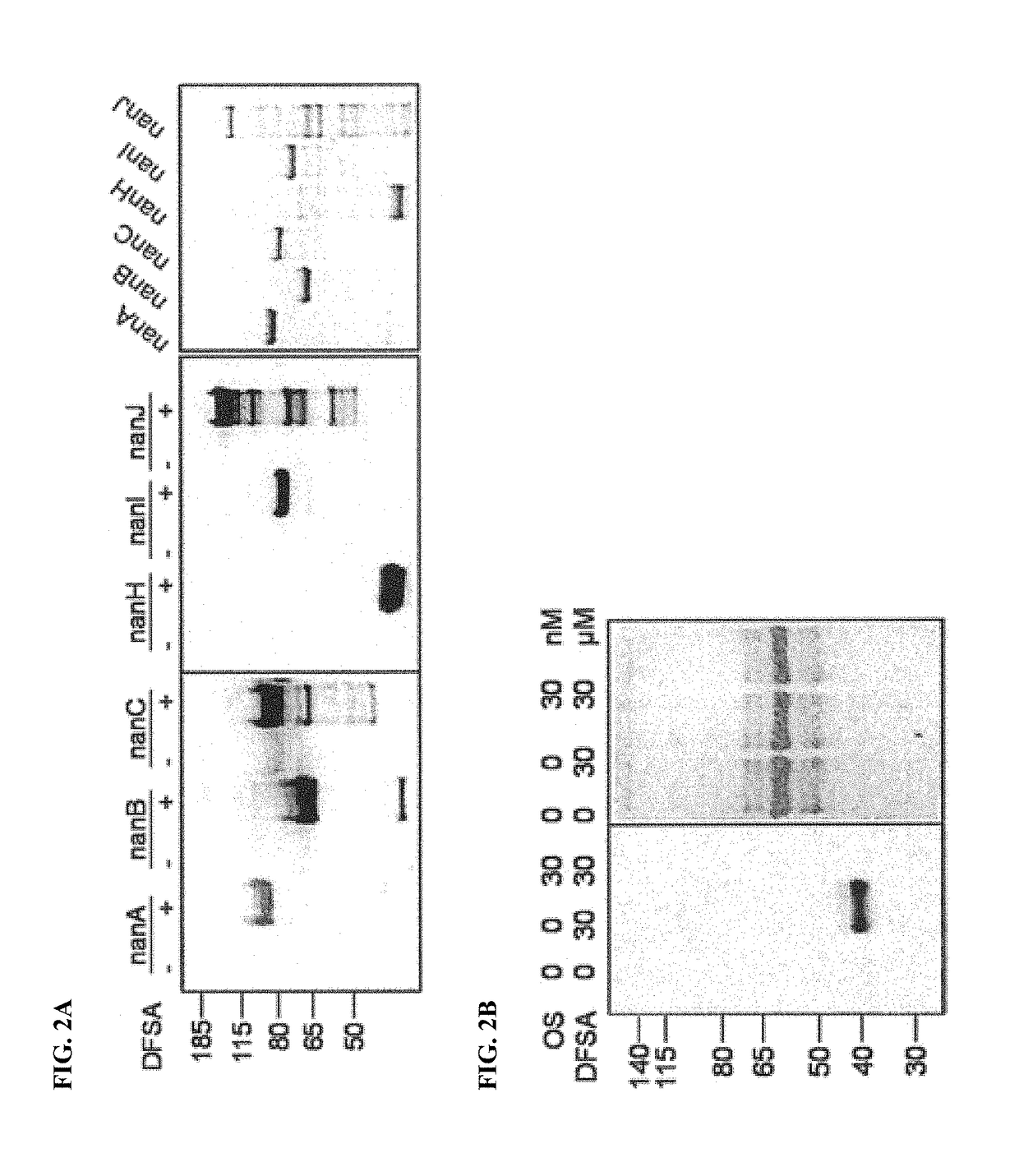
Cell-permeable probes for identification and imaging of sialidases
Provided herein are novel irreversible sialidase inhibitors. These compounds can be conjugated with a detectable tagging moiety such as azide-annexed biotin via CuAAC for isolation and identification of sialidases. The provided compounds and the corresponding detectable conjugates are useful for detecting sialidase-containing pathogens and imaging in situ sialidase activities under physiological conditions.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Class of therapeutic protein based molecules
InactiveUS7645448B2Prevent and inhibit adhesion and functionInhibitory responseAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseTherapeutic proteinViral infection
The present invention provides new compositions and methods for preventing and treating pathogen infection. In particular, the present invention provides compounds having an anchoring domain that anchors the compound to the surface of a target cell, and a therapeutic domain that can act extracellularly to prevent infection of a target cell by a pathogen, such as a virus. The present invention also comprises therapeutic compositions having sialidase activity, including protein-based compounds having sialidase catalytic domains. Compounds of the invention can be used for treating or preventing pathogen infection, and for treating and reducing allergic and inflammatory responses. The invention also provides compositions and methods for enhancing transduction of target cells by recombinant viruses. Such compositions and methods can be used in gene therapy.
Owner:ANSUN BIOPHARMA
Cell-permeable probes for identification and imaging of sialidases
Provided herein are novel irreversible sialidase inhibitors. These compounds can be conjugated with a detectable tagging moiety such as azide-annexed biotin via CuAAC for isolation and identification of sialidases. The provided compounds and the corresponding detectable conjugates are useful for detecting sialidase-containing pathogens and imaging in situ sialidase activities under physiological conditions.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Novel Class of Therapeutic Protein Based Molecules
InactiveUS20090142327A1High transduction efficiencyInhibit the inflammatory responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsTherapeutic proteinViral infection
The present invention provides new compositions and methods for preventing and treating pathogen infection. In particular, the present invention provides compounds having an anchoring domain that anchors the compound to the surface of a target cell, and a therapeutic domain that can act extracellularly to prevent infection of a target cell by a pathogen, such as a virus. The present invention also comprises therapeutic compositions having sialidase activity, including protein-based compounds having sialidase catalytic domains. Compounds of the invention can be used for treating or preventing pathogen infection, and for treating and reducing allergic and inflammatory responses. The invention also provides compositions and methods for enhancing transduction of target cells by recombinant viruses. Such compositions and methods can be used in gene therapy.
Owner:ANSUN BIOPHARMA
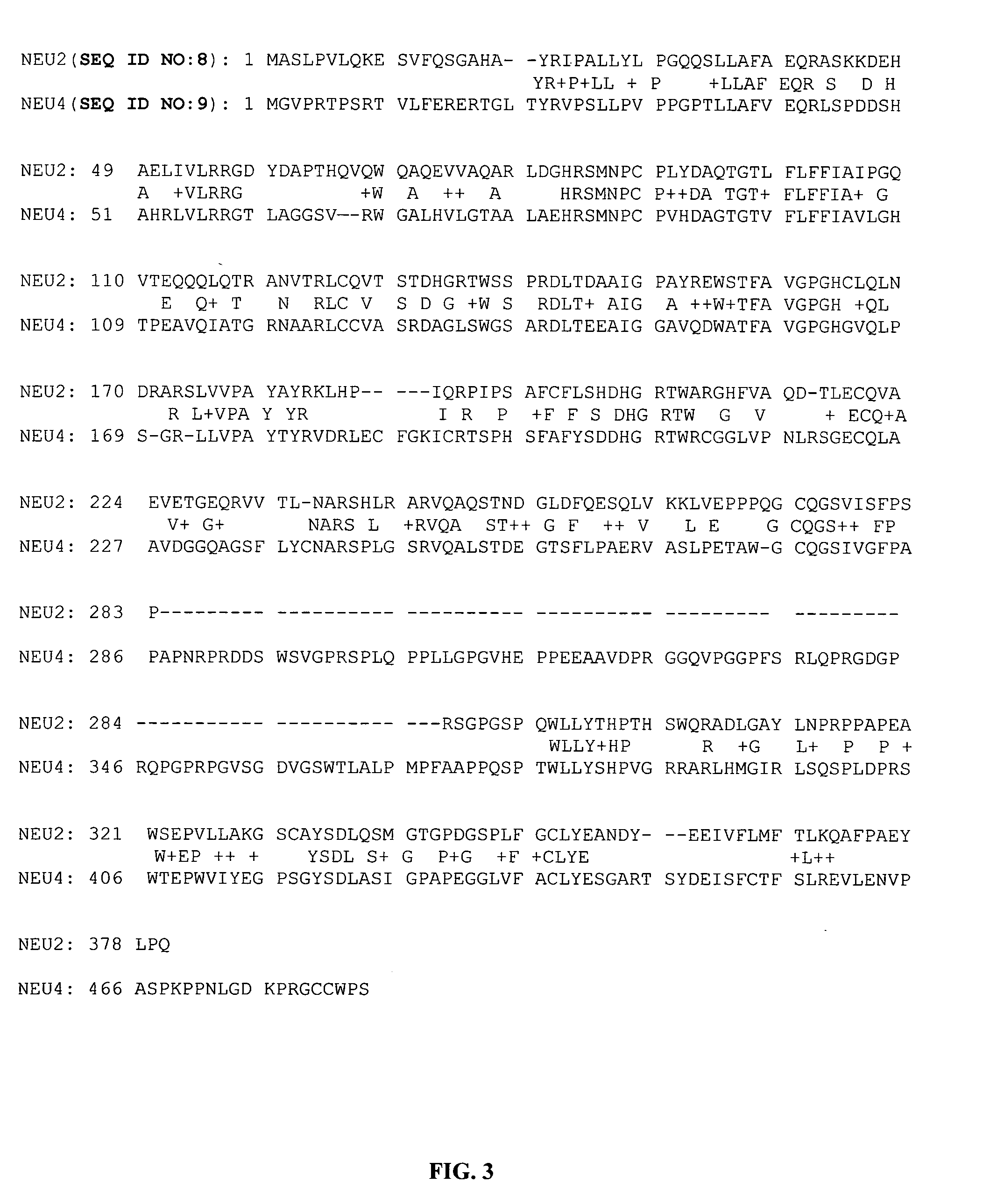
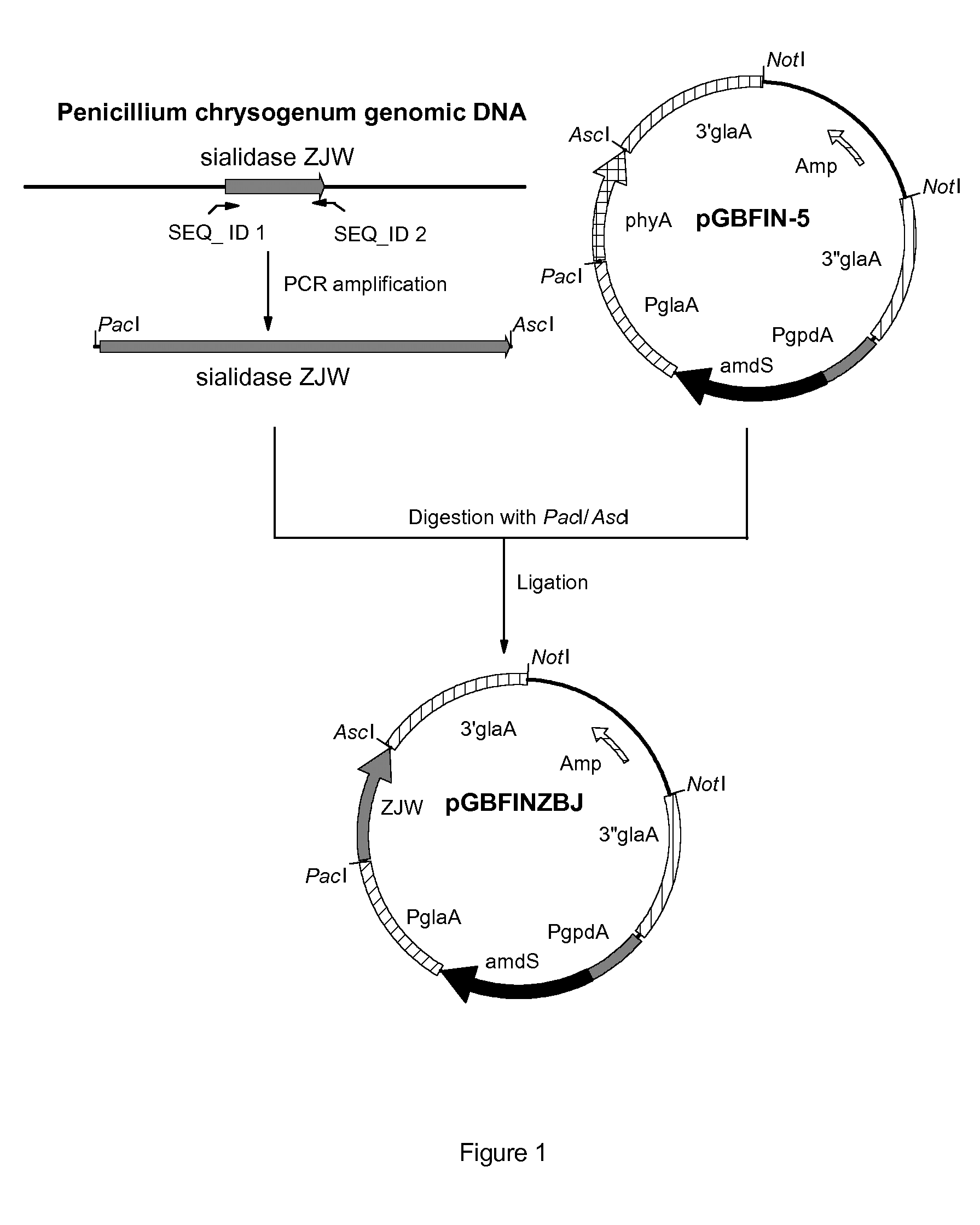
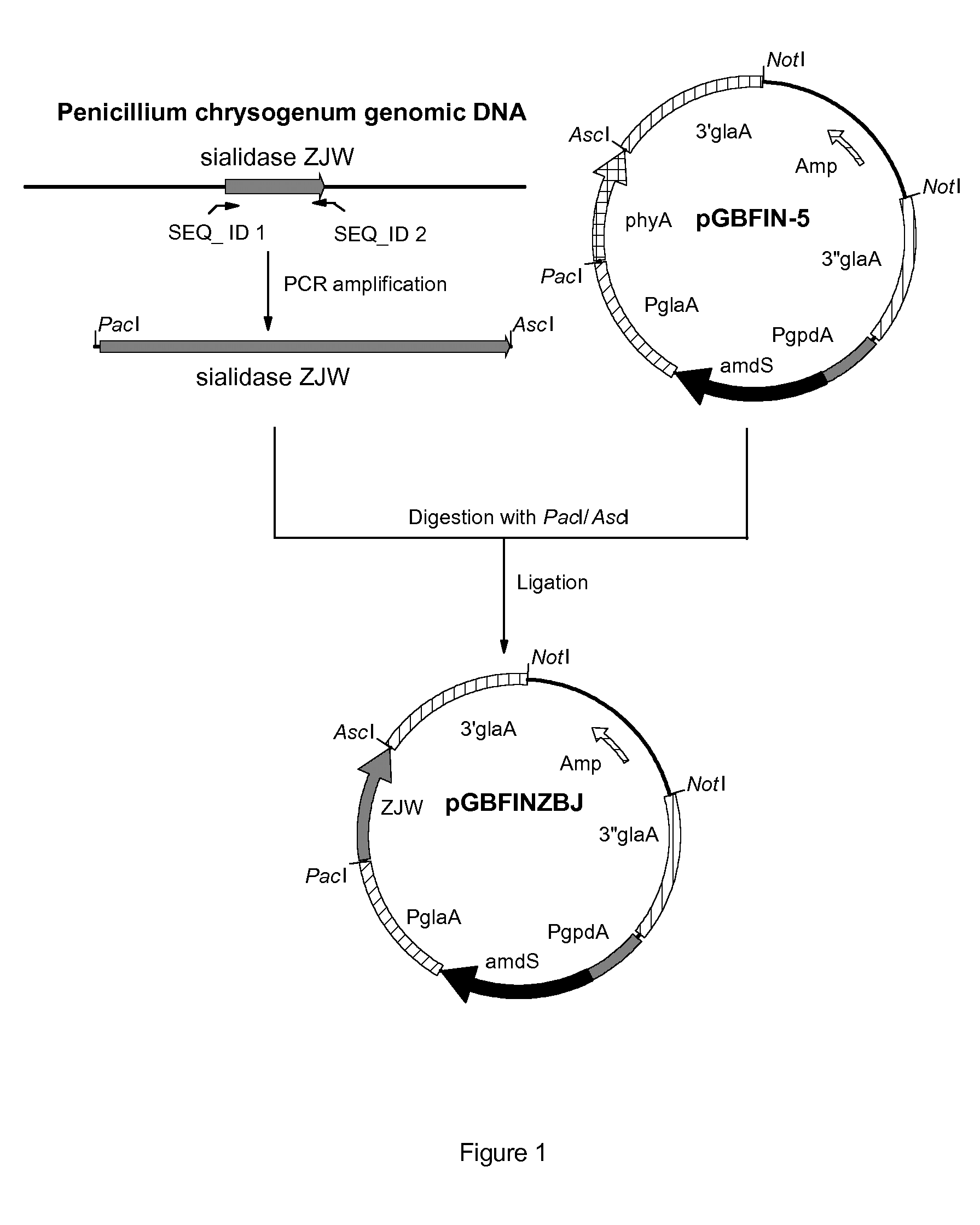
Sialidases
Isolated polypeptide having sialidase activity and having an amino acid sequence which has at least 90% amino acid sequence identity with amino acids 34 to 407 of SEQ ID NO: 3.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
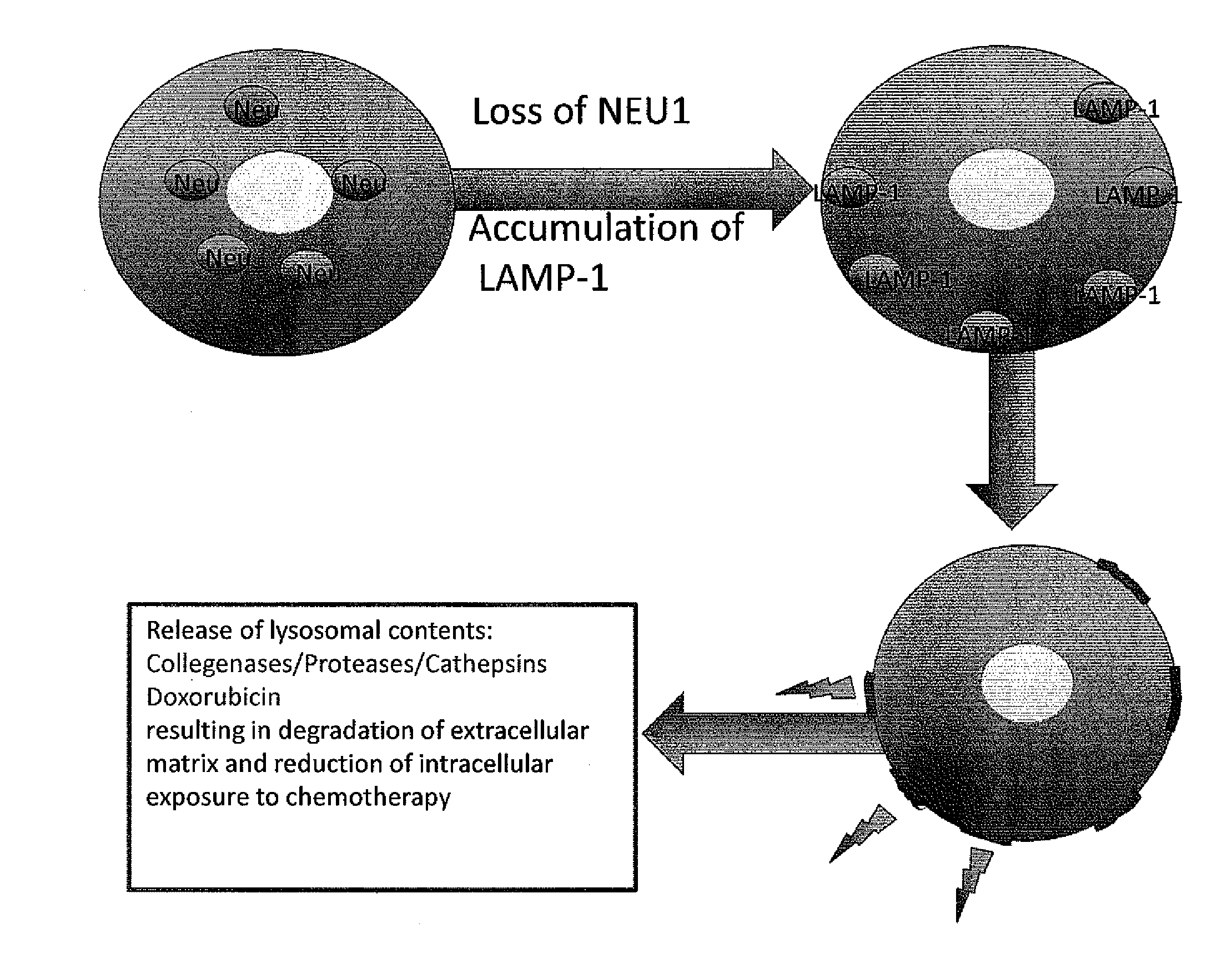
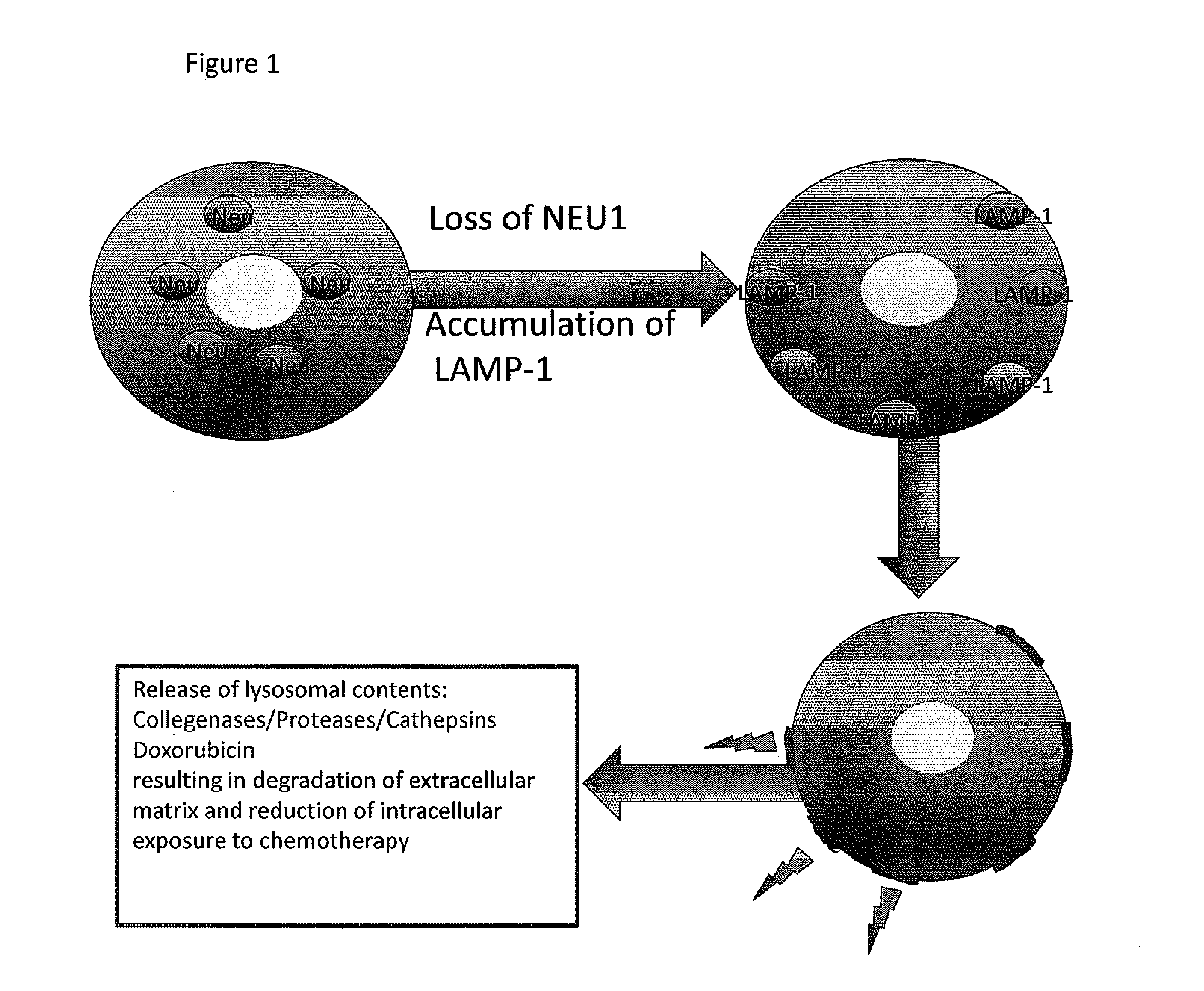
Methods and compositions to detect the level of lysosomal exocytosis activity and methods of use
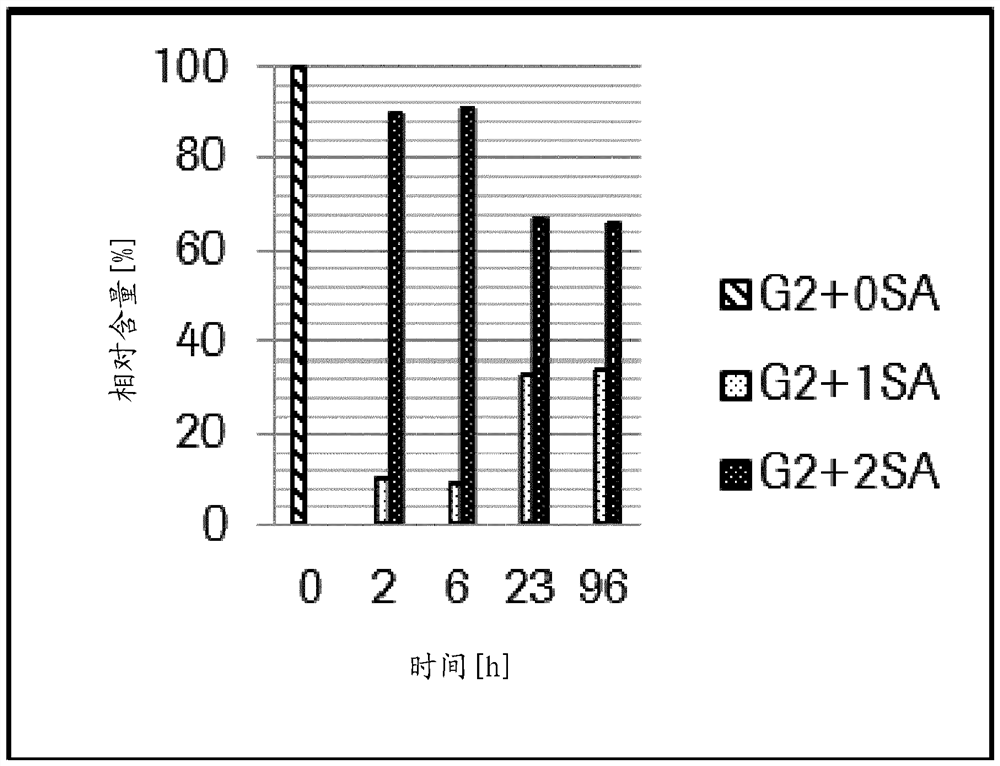
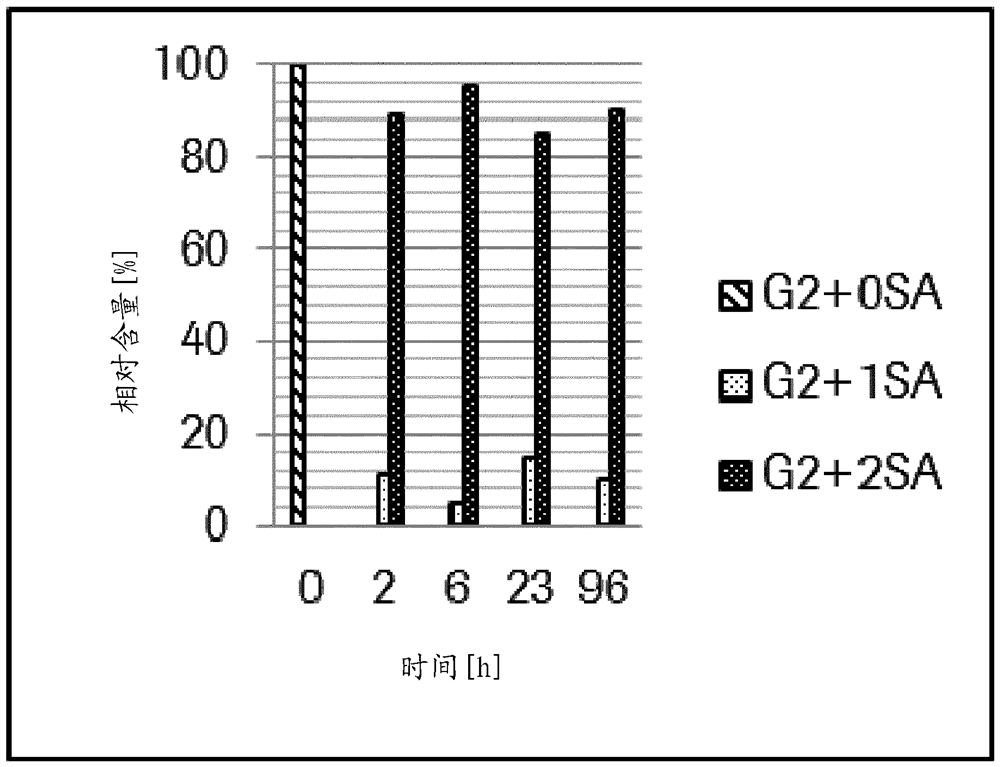
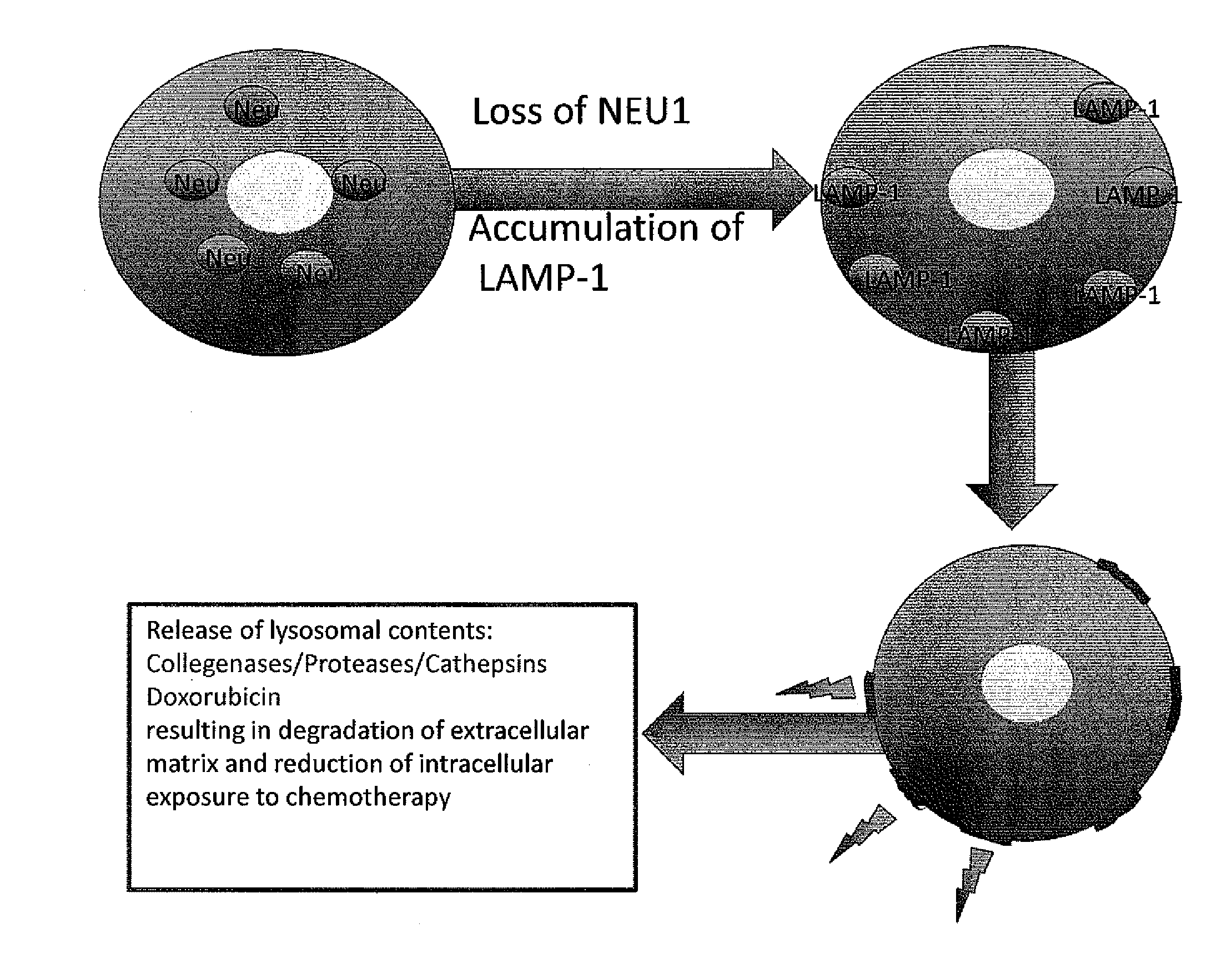
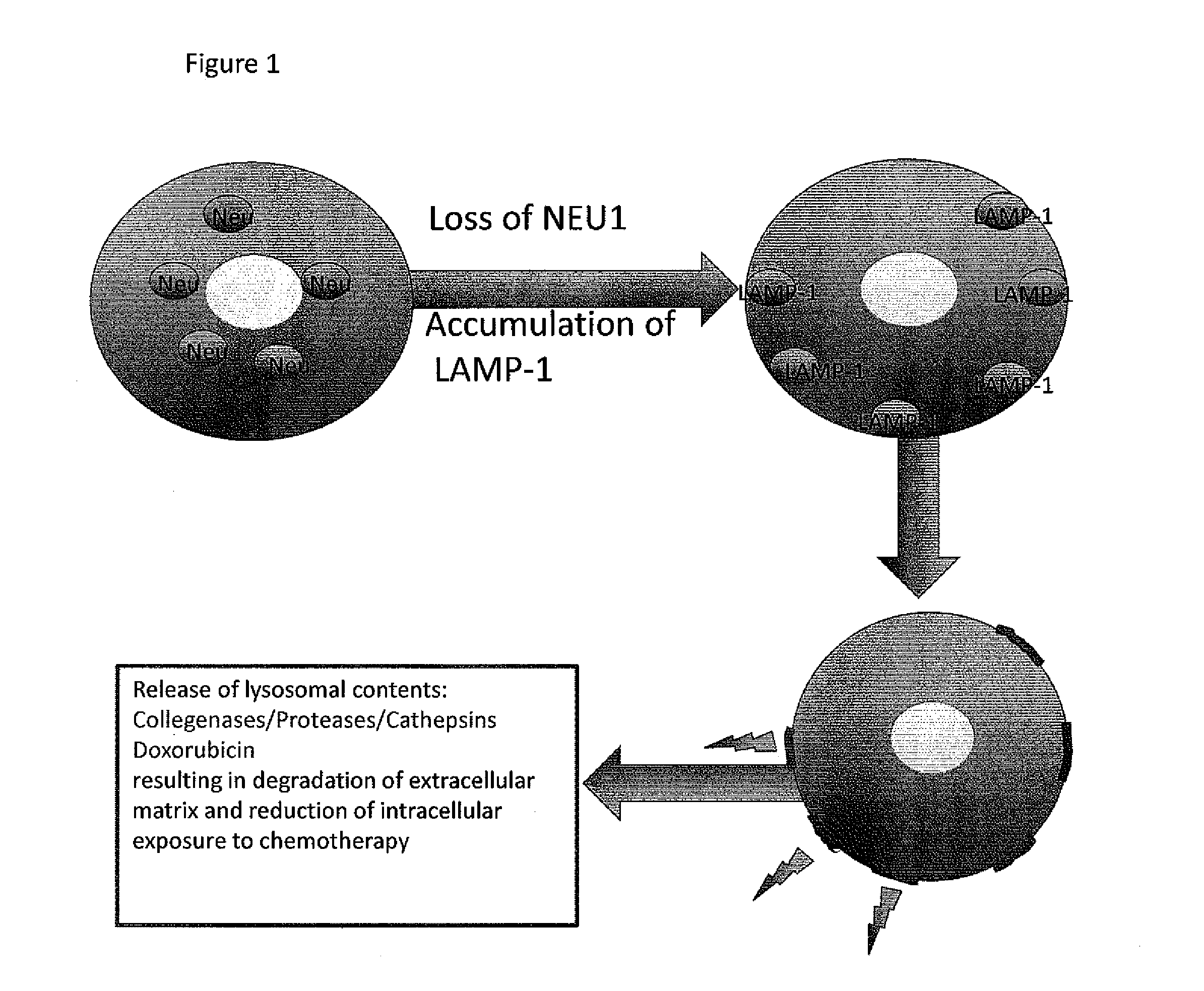
ActiveUS20140193392A1Low lysosomal sialidase activityNervous disorderVirusesSialic acid aldolaseState dependent
Methods are provided for the prognosis, diagnosis and treatment of various pathological states, including cancer, chemotherapy resistance and dementia associated with Alzheimer's disease. The methods provided herein are based on the discovery that various proteins with a high level of sialylation are shown herein to be associated with disease states, such as, cancer, chemotherapy resistance and dementia associated with Alzheimer's disease. Such methods provide a lysosomal exocytosis activity profile comprising one or more values representing lysosomal exocytosis activity. Also provided herein, is the discovery that low lysosomal sialidase activity is associated with various pathological states. Thus, the methods also provide a lysosomal sialidase activity profile, comprising one or more values representing lysosomal sialidase activity. A lysosomal sialidase activity profile is one example of a lysosomal exocytosis activity profile. As such, the level of lysosomal exocytosis activity and / or lysosomal sialidase activity is predictive of a diagnosis and / or prognosis of cancer, chemotherapy resistance or dementia associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Novel class of therapeutic protein based molecules
ActiveUS20110182875A1High transduction efficiencyInhibit the inflammatory responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteriaTherapeutic proteinViral infection
The present invention provides new compositions and methods for preventing and treating pathogen infection. In particular, the present invention provides compounds having an anchoring domain that anchors the compound to the surface of a target cell, and a therapeutic domain that can act extracellularly to prevent infection of a target cell by a pathogen, such as a virus. The present invention also comprises therapeutic compositions having sialidase activity, including protein-based compounds having sialidase catalytic domains. Compounds of the invention can be used for treating or preventing pathogen infection, and for treating and reducing allergic and inflammatory responses. The invention also provides compositions and methods for enhancing transduction of target cells by recombinant viruses. Such compositions and methods can be used in gene therapy.
Owner:ANSUN BIOPHARMA
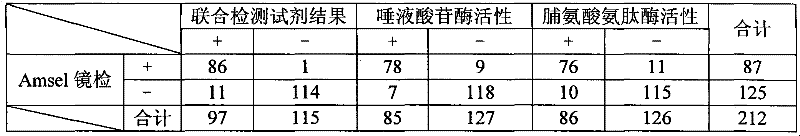
Joint detection reagent for bacterial vaginosis
InactiveCN101748188AAvoid missing detectionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacterial vaginosisP-Nitroaniline
The invention relates to a joint detection reagent for bacterial vaginosis, which comprises a sialidase activity detection reagent and a praline aminopeptidase activity detection reagent, wherein the sialidase activity detection reagent consists of the following substances: 0.5-2.5g / l enzyme substrate A, 30-60g / l carbohydrate and 1-2g / l citric acid; the enzyme substrate A is 5-bromine-4-chlorine-3-indol-N-acetyl-alpha-sialic acid glycosides, nitrobenzene-N-acetyl-alpha-sialic acid glycosides or naphthol-N-acetyl-alpha-sialic acid glycosides; the praline aminopeptidase activity detection reagent consists of the following substances: 2-5g / l enzyme substrate B, 0.1-0.3mol / l Tris-hydrochloric acid buffer solution and 10-20g / l N-glycylglycine; and the enzyme substrate B is L-proline-paranitroaniline, L-proline-alpha-naphthylamine or L-proline-beta-naphthylamine. The reagent is used conveniently, special devices such as a microscope and the like are not required in detection, the detection speed is high, the sensitivity and the specificity are high, BV detection miss caused by merely detecting the activity of one enzyme is effectively avoided, and the reagent is popularized easily.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
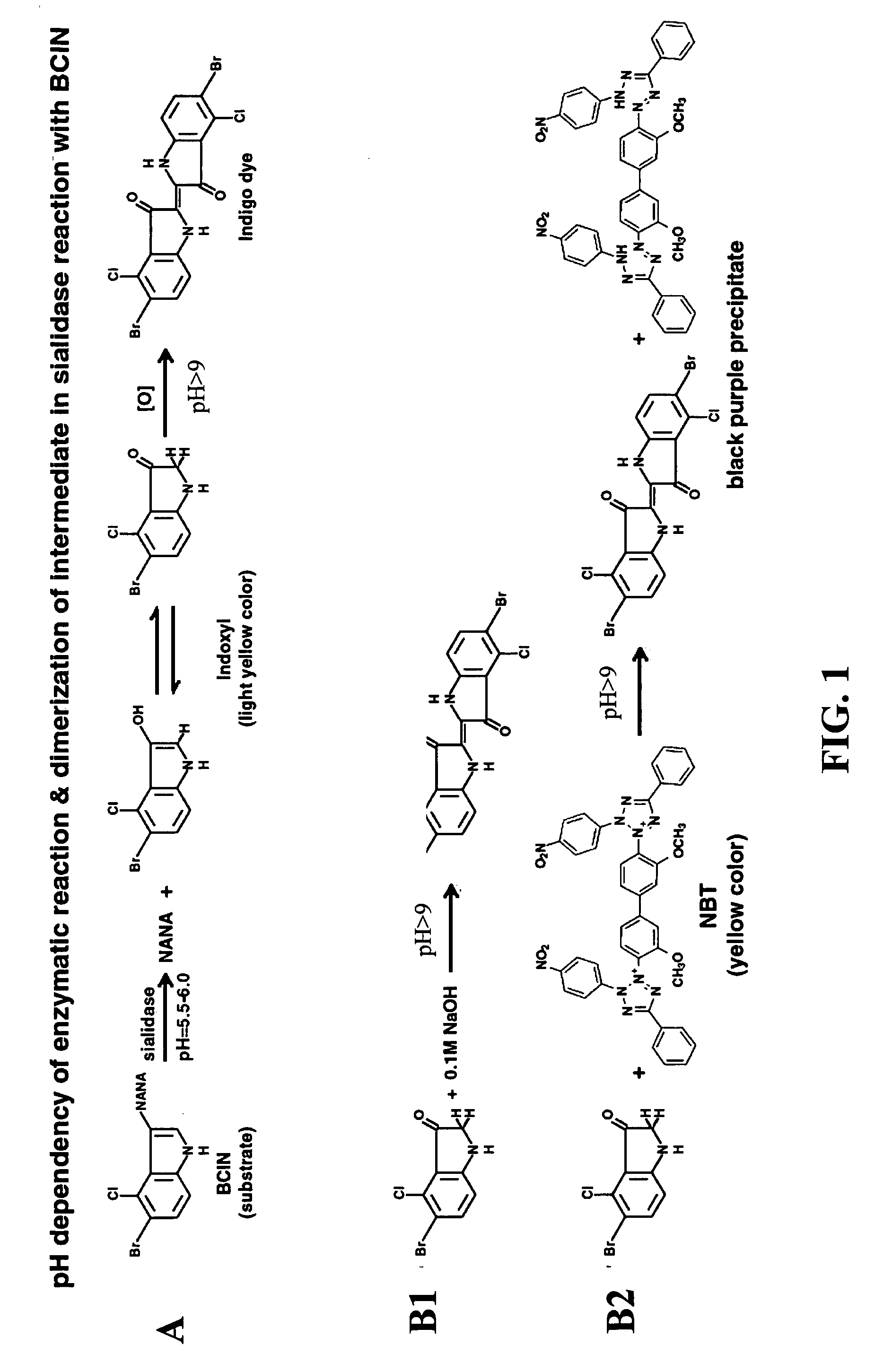
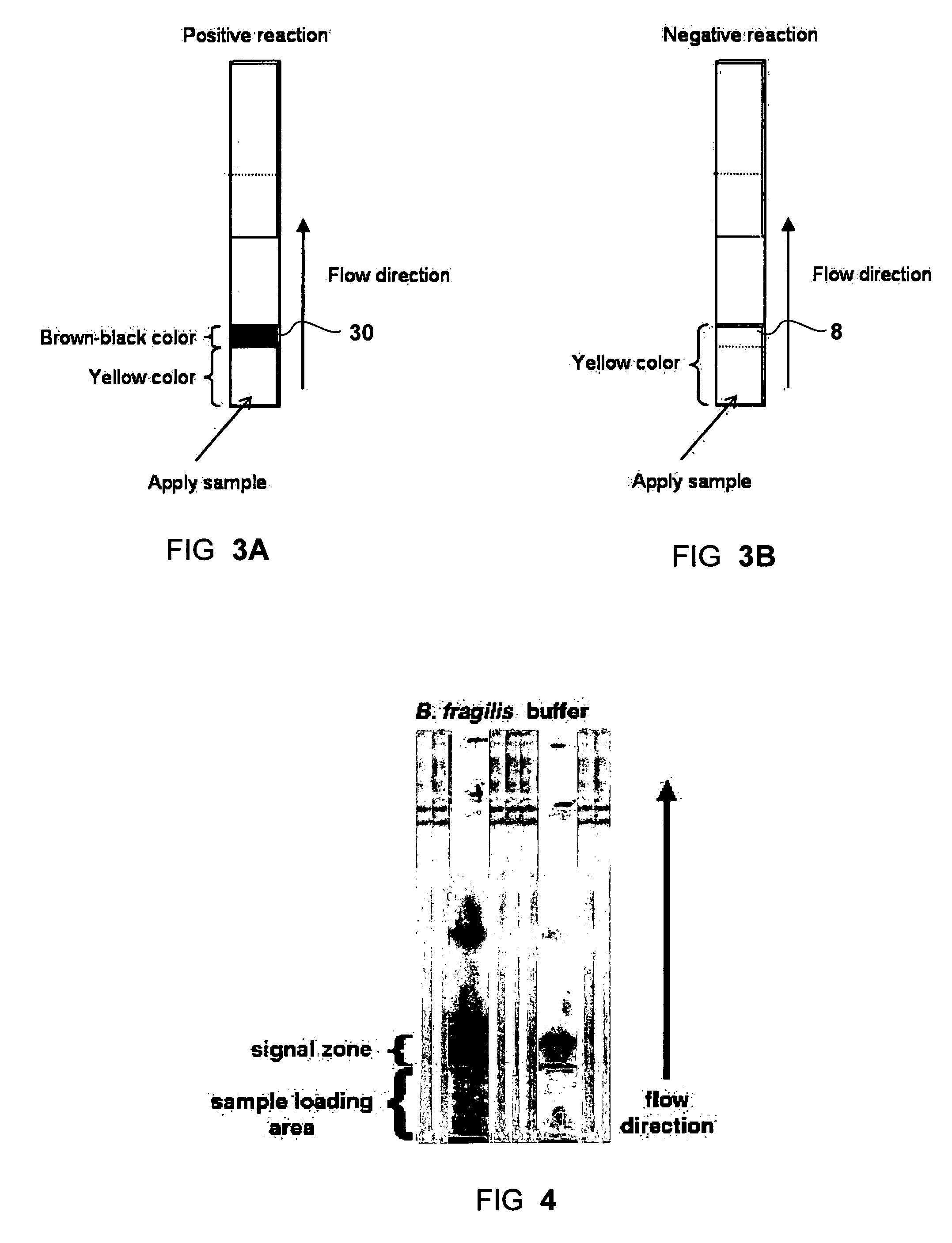
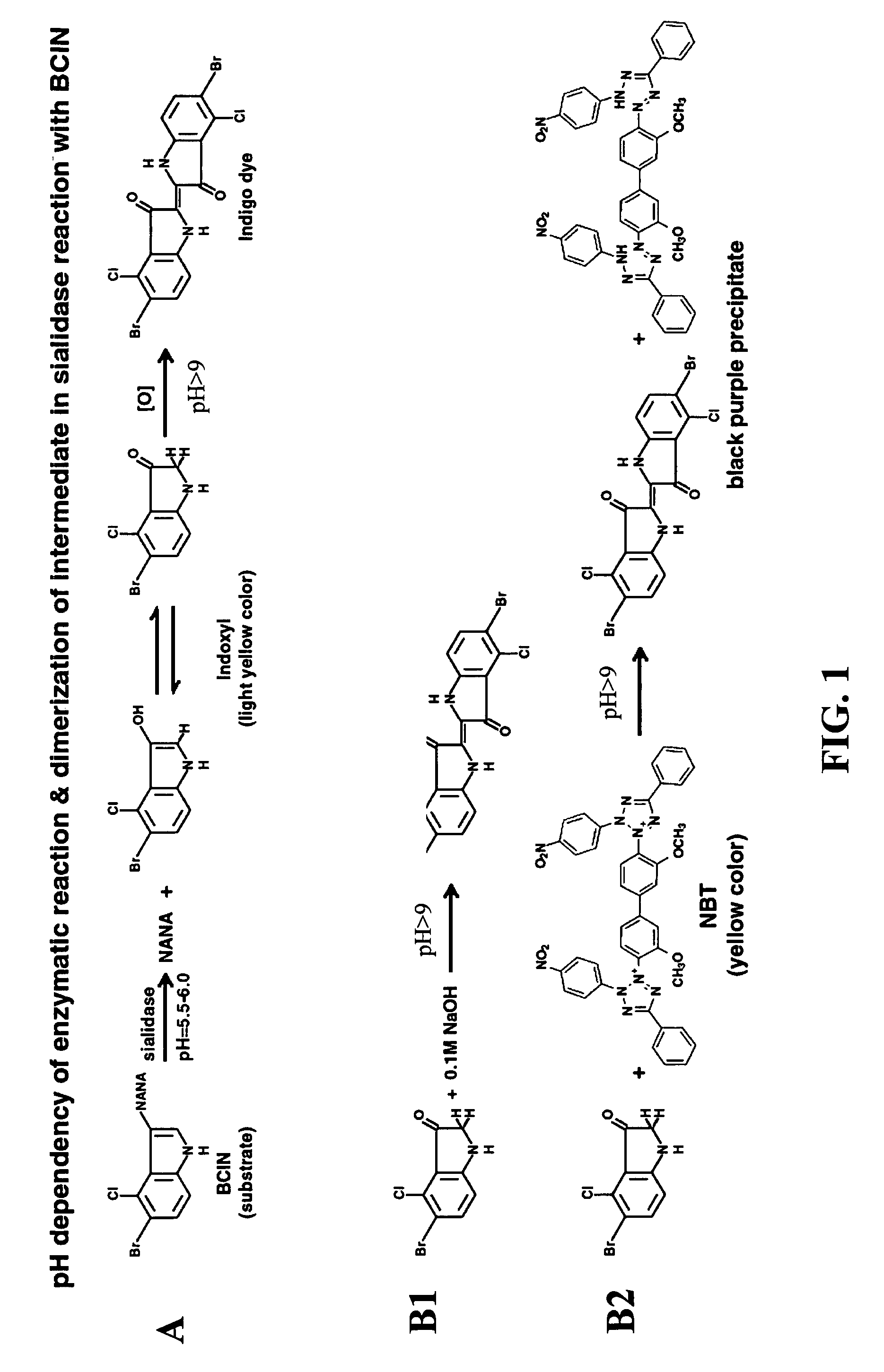
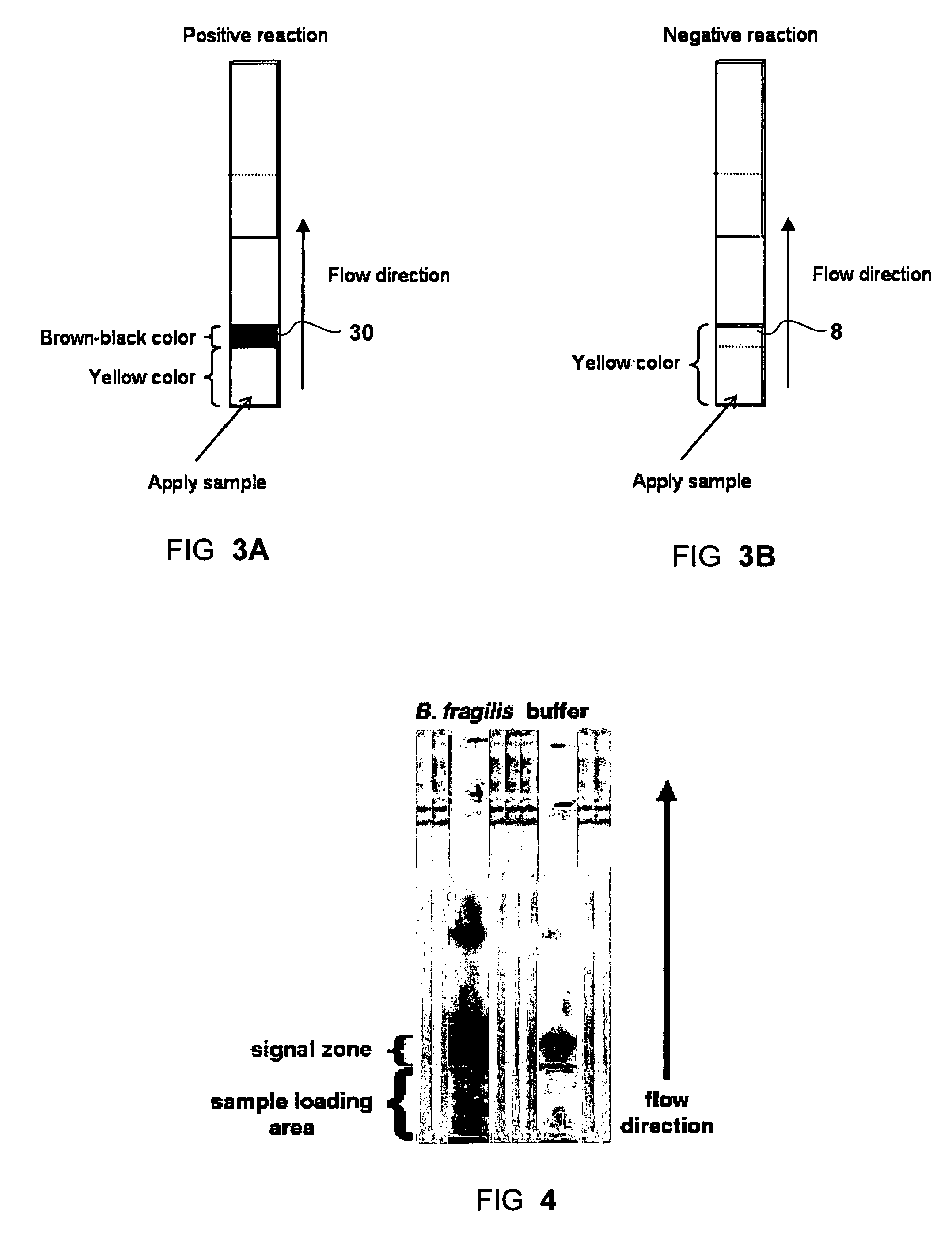
Dry format sialidase assay
InactiveUS20080038766A1Facilitating analyte concentrationFacilitating signal enhancementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAssayColor changes
A solid-phase test device and method for the detection of sialidase activity in a fluid sample. The test device comprises a solid support provided with pre-deposited dry form of a sialidase detecting composition comprising a sialidase substrate and a color-developing reagent, wherein the sialidase substrate when exposed to sialidase yields an intermediate compound which reacts with the color-developing reagent to form a detectable color change.
Owner:ABBOTT RAPID DIAGNOSTICS INT UNLTD
Solid phase test device for sialidase assay
InactiveUS7591978B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementColor changesReagent
A solid-phase test device and a method for the detection of sialidase activity in a fluid sample. The test device includes a solid support provided with a pre-deposited dry form of a sialidase detecting composition. The sialidase detecting composition includes a sialidase substrate and a color-developing reagent. When the sialidase substrate is exposed to sialidase it yields an intermediate compound which reacts with the color-developing reagent to form a detectable color change.
Owner:ABBOTT RAPID DIAGNOSTICS INT UNLTD
Class of therapeutic protein based molecules
The present invention provides new compositions and methods for preventing and treating pathogen infection. In particular, the present invention provides compounds having an anchoring domain that anchors the compound to the surface of a target cell, and a therapeutic domain that can act extracellularly to prevent infection of a target cell by a pathogen, such as a virus. The present invention also comprises therapeutic compositions having sialidase activity, including protein-based compounds having sialidase catalytic domains. Compounds of the invention can be used for treating or preventing pathogen infection, and for treating and reducing allergic and inflammatory responses. The invention also provides compositions and methods for enhancing transduction of target cells by recombinant viruses. Such compositions and methods can be used in gene therapy.
Owner:ANSUN BIOPHARMA
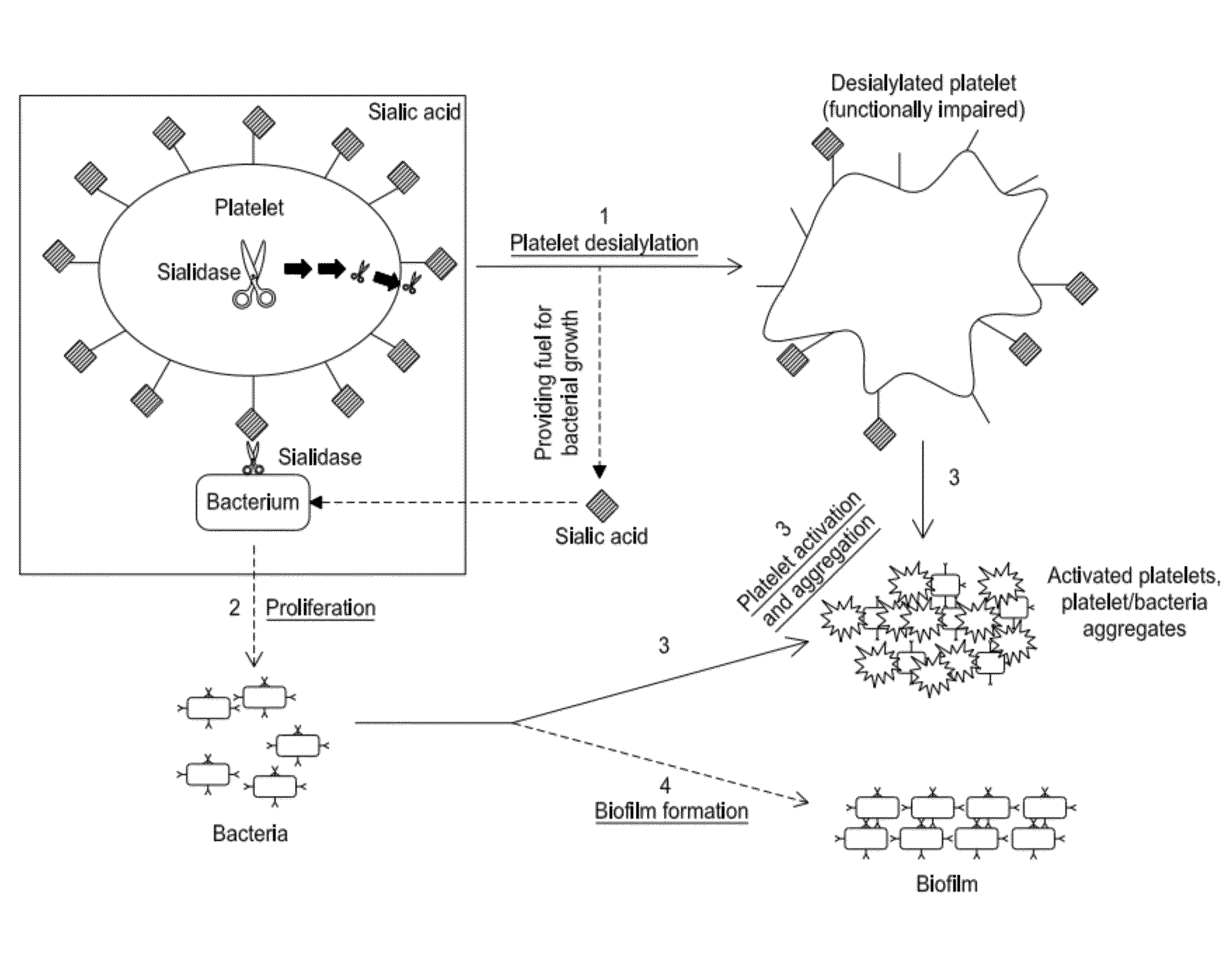
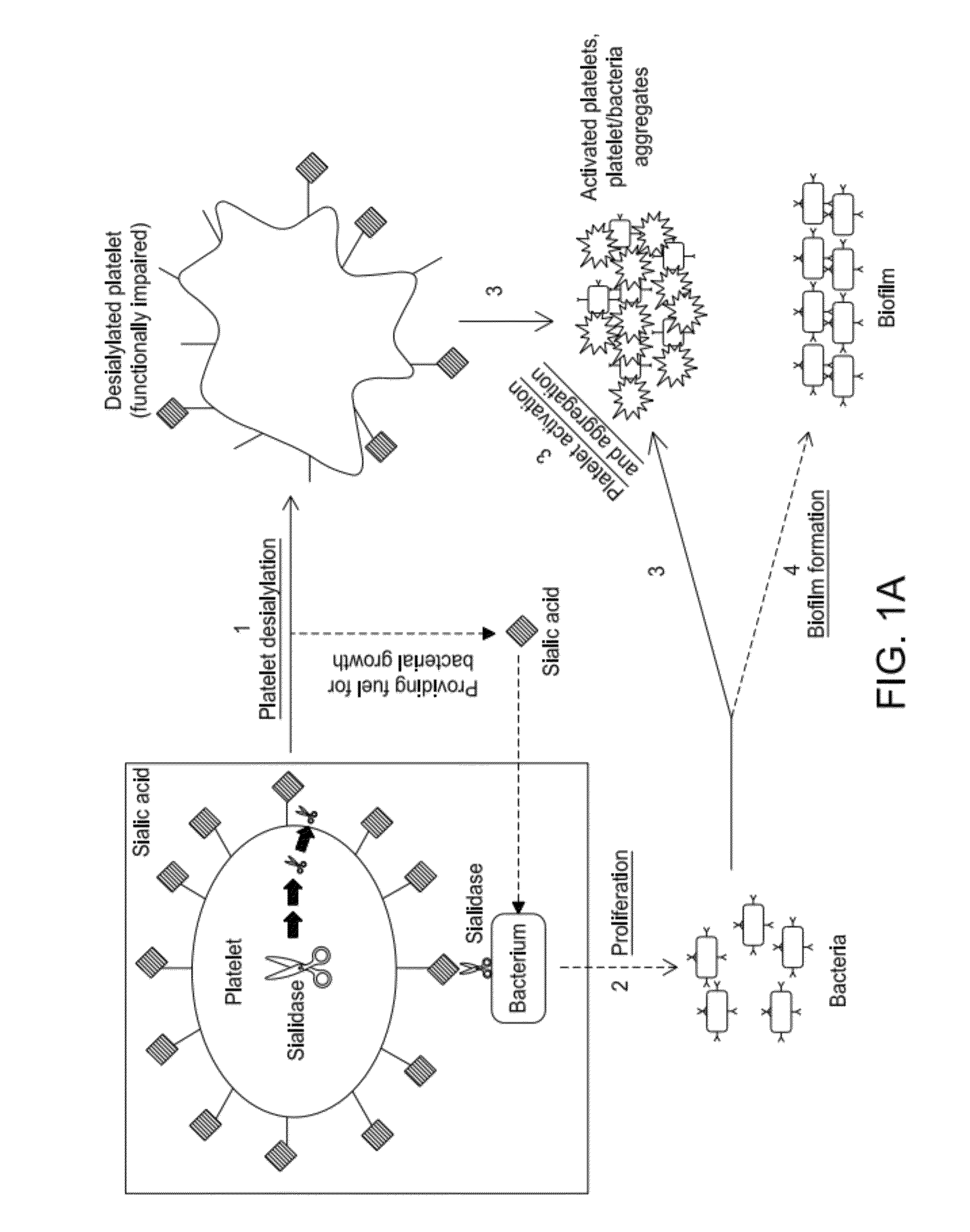
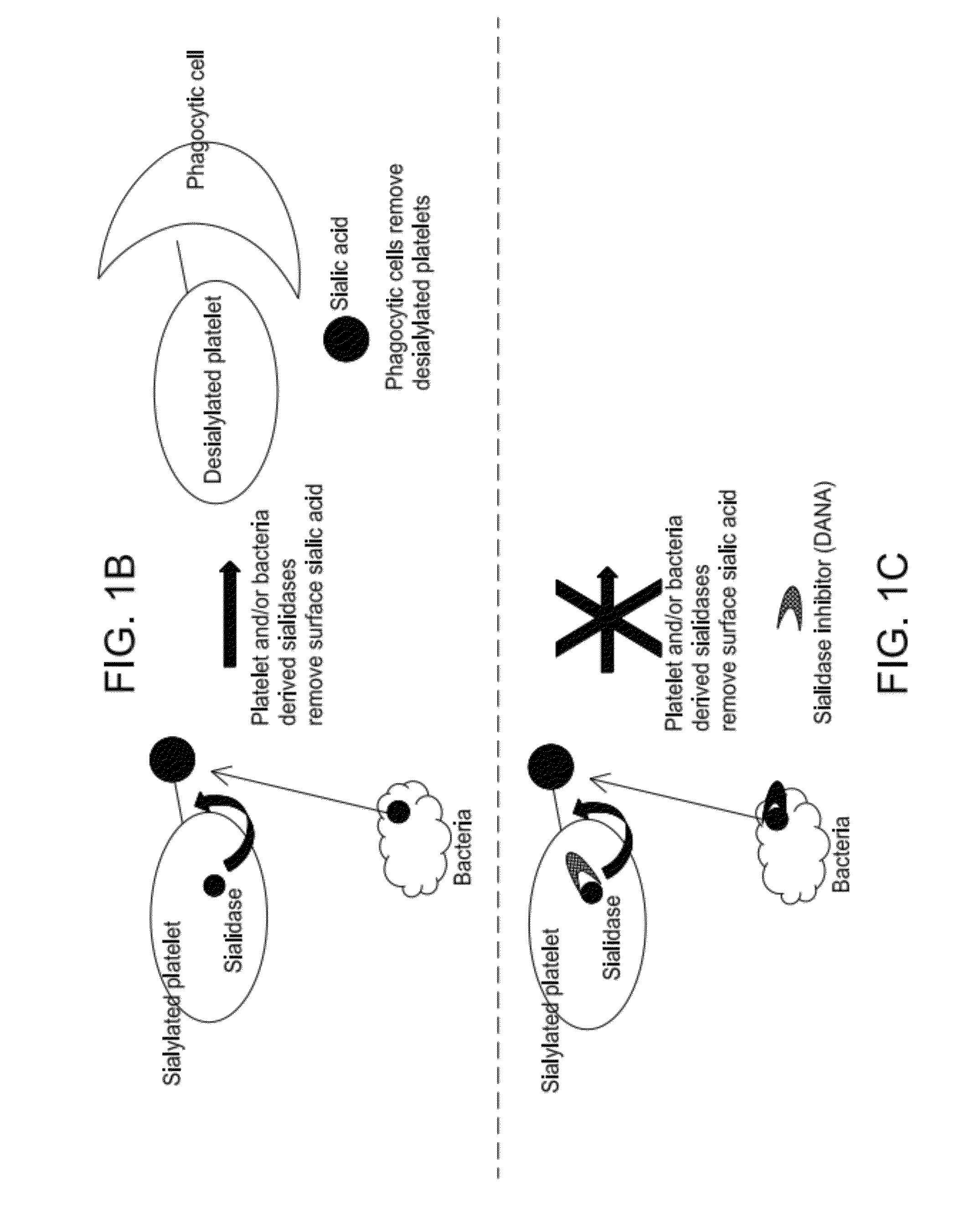
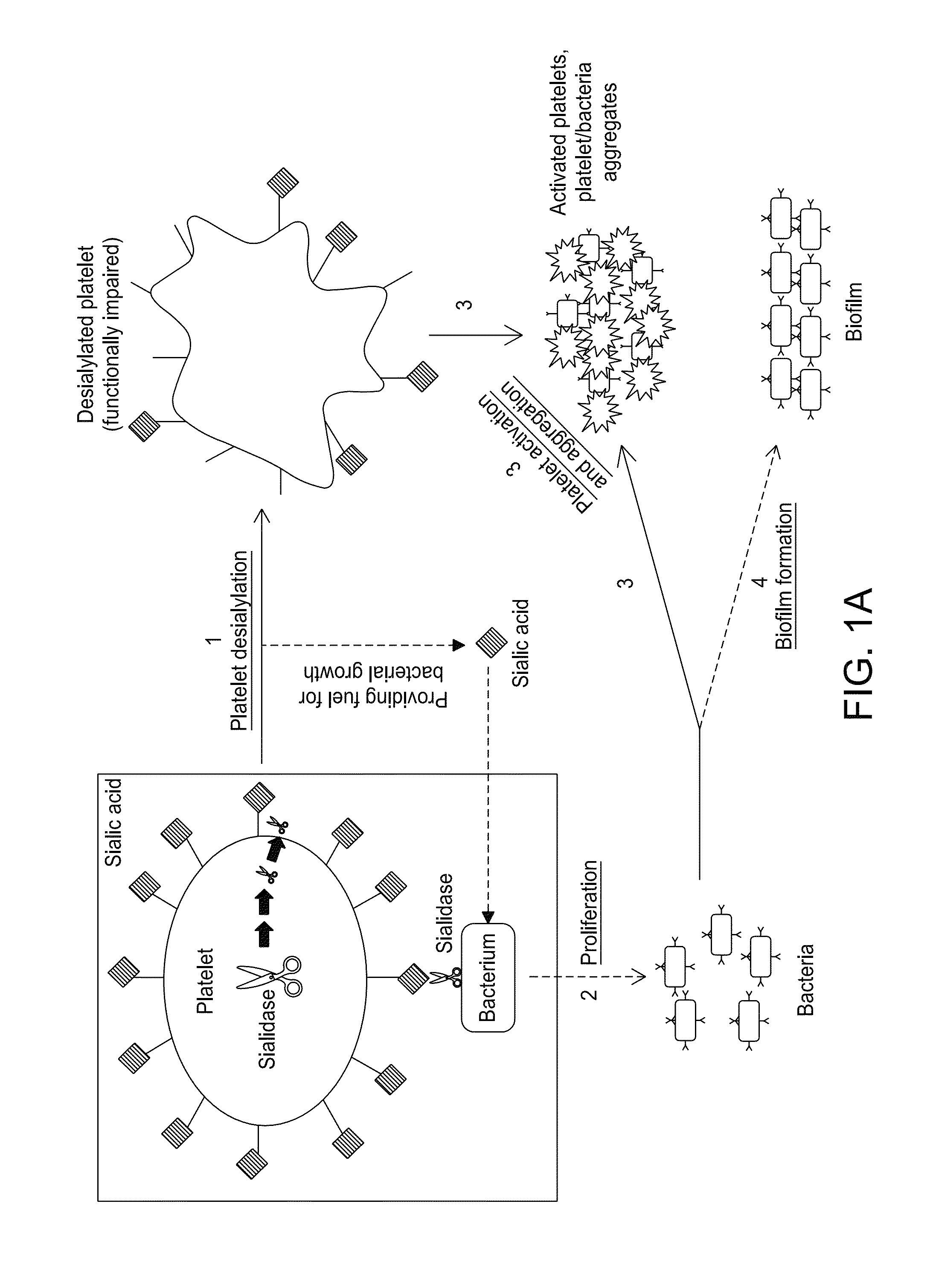
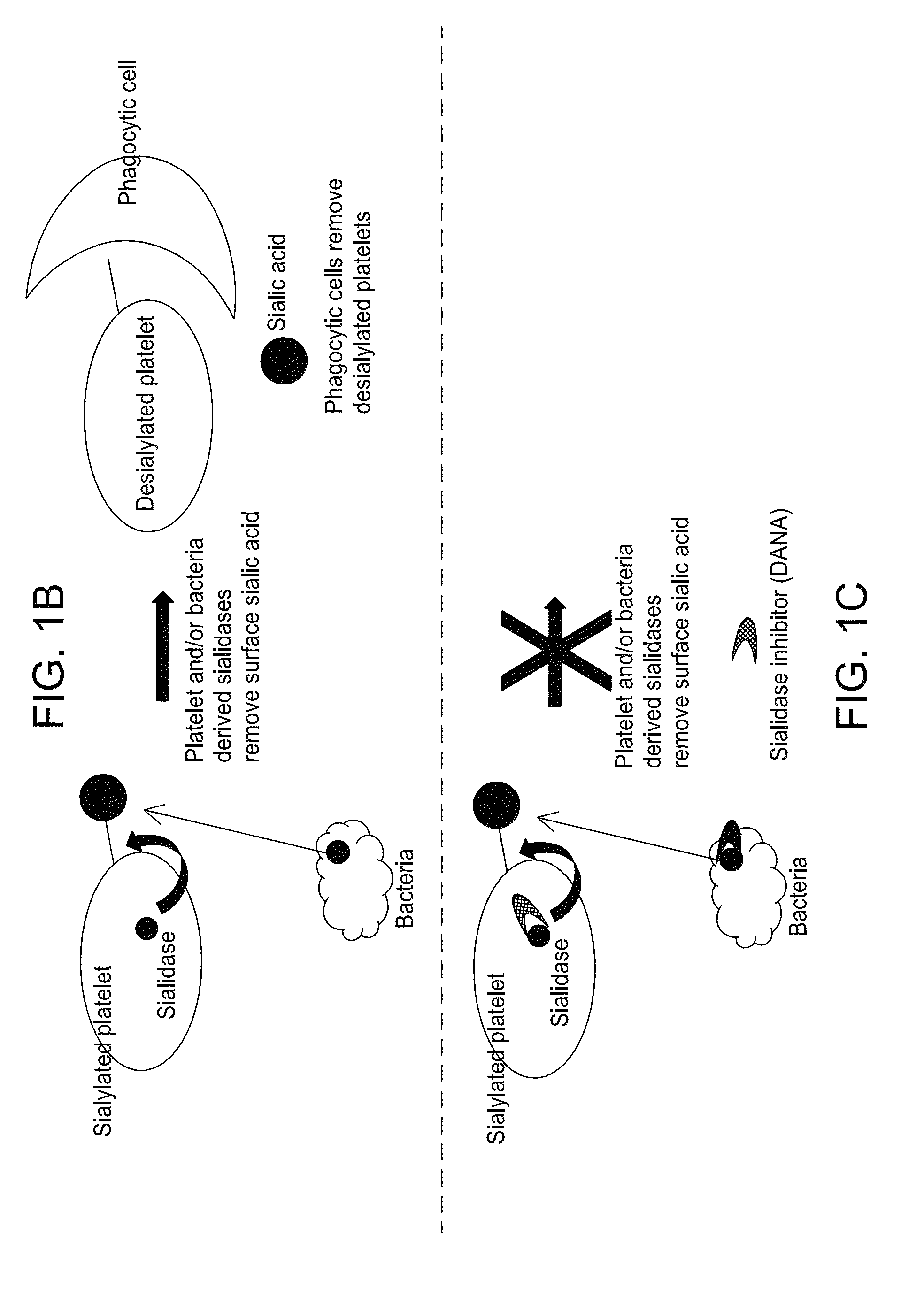
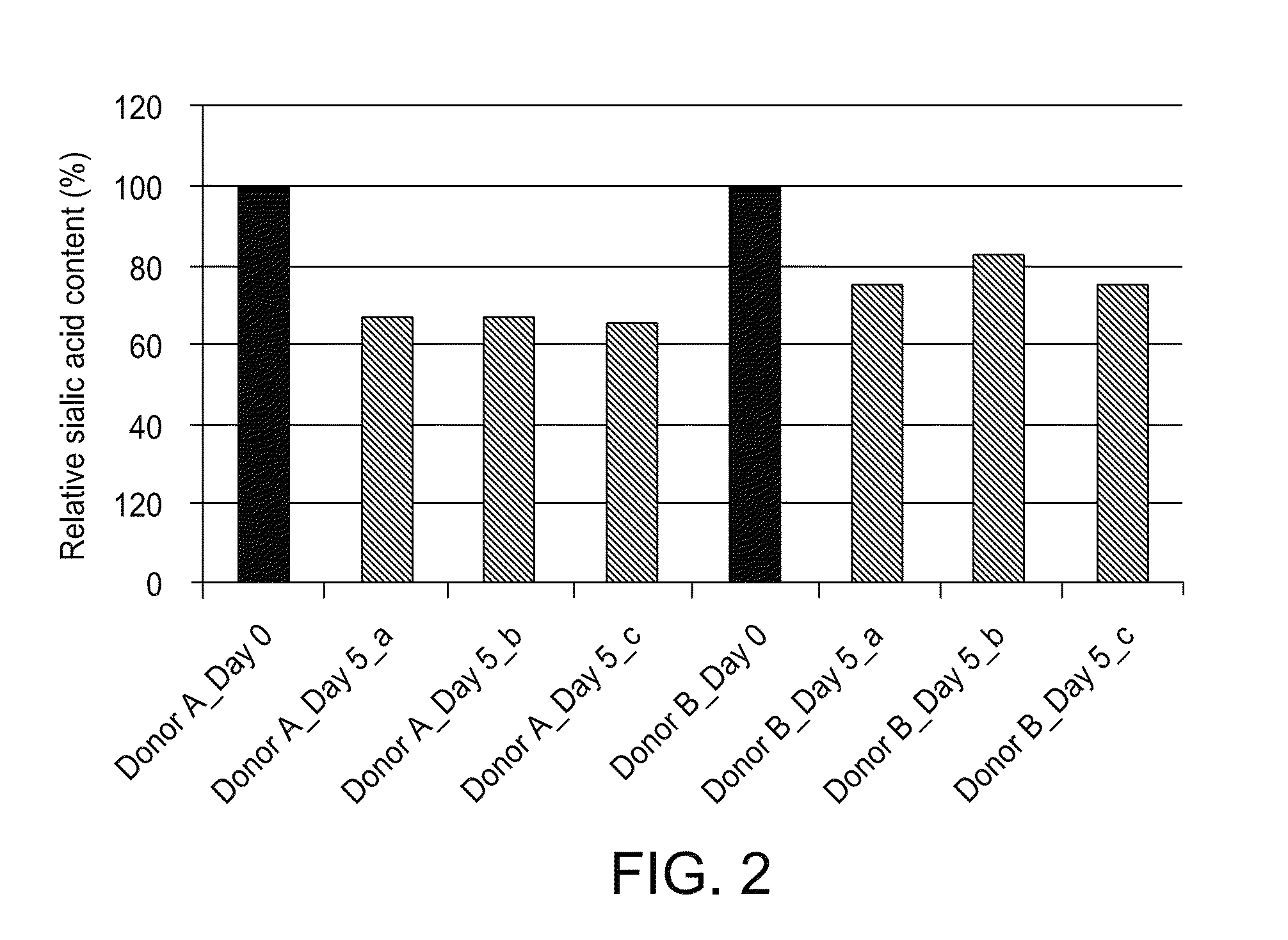
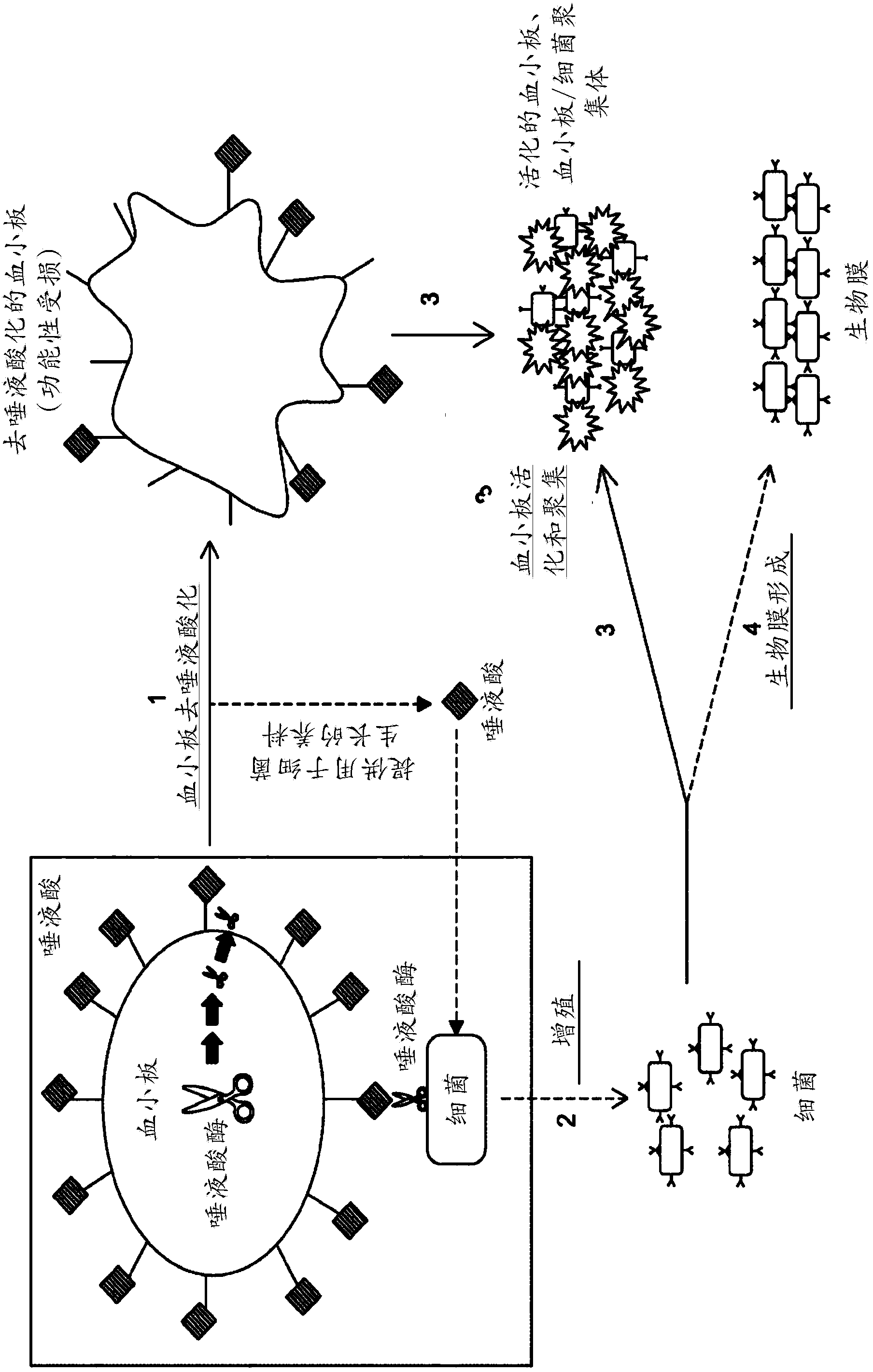
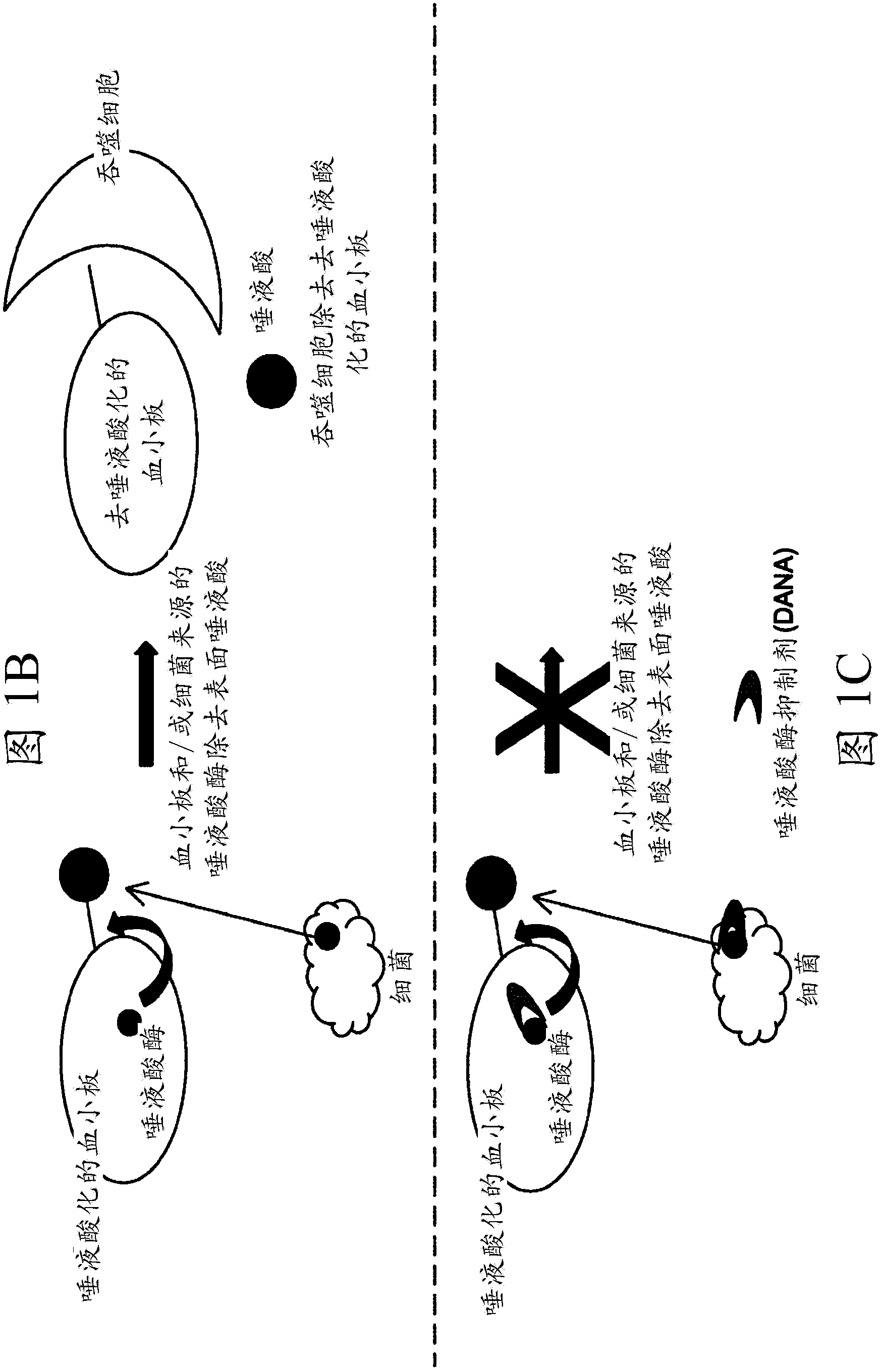
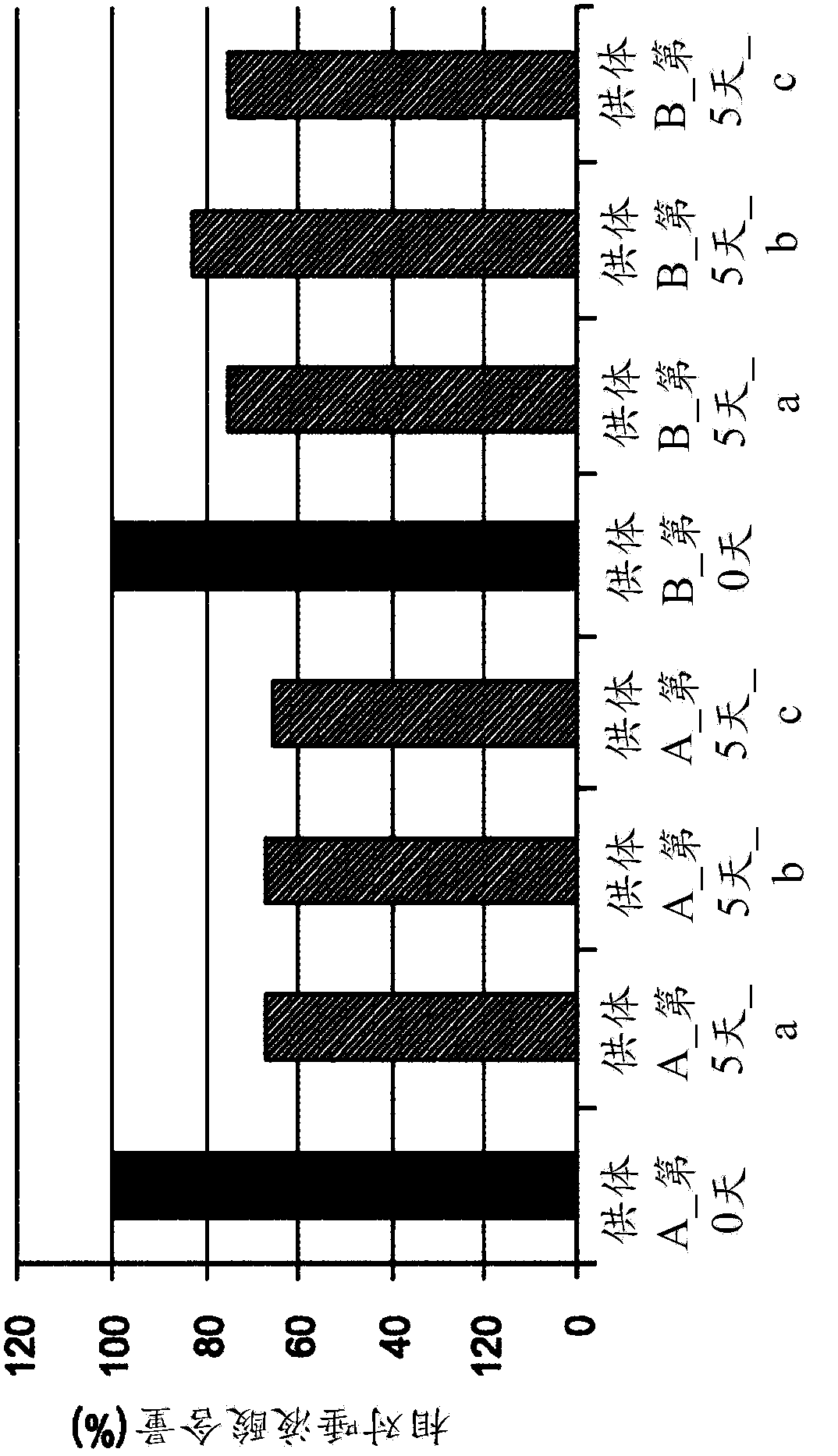
Platelet Storage and Reduced Bacterial Proliferation In Platelet Products Using A Sialidase Inhibitor
InactiveUS20120321722A1Reducing sialidase activityExcess proliferationAntibacterial agentsMammal material medical ingredientsPlatelet productPlatelet storage
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for reducing sialidase activity and inhibiting bacterial proliferation of one or more bacteria in a platelet product preparation from one or more donors. In general, the method includes contacting the platelet product preparation with an amount of a sialidase inhibitor, to thereby obtain a sialidase inhibitor-treated platelet product preparation. Sialidase activity is reduced and the proliferation of one or more bacteria is inhibited, as compared to a platelet product preparation not subjected to the sialidase inhibitor treatment.
Owner:VELICO MEDICAL +1
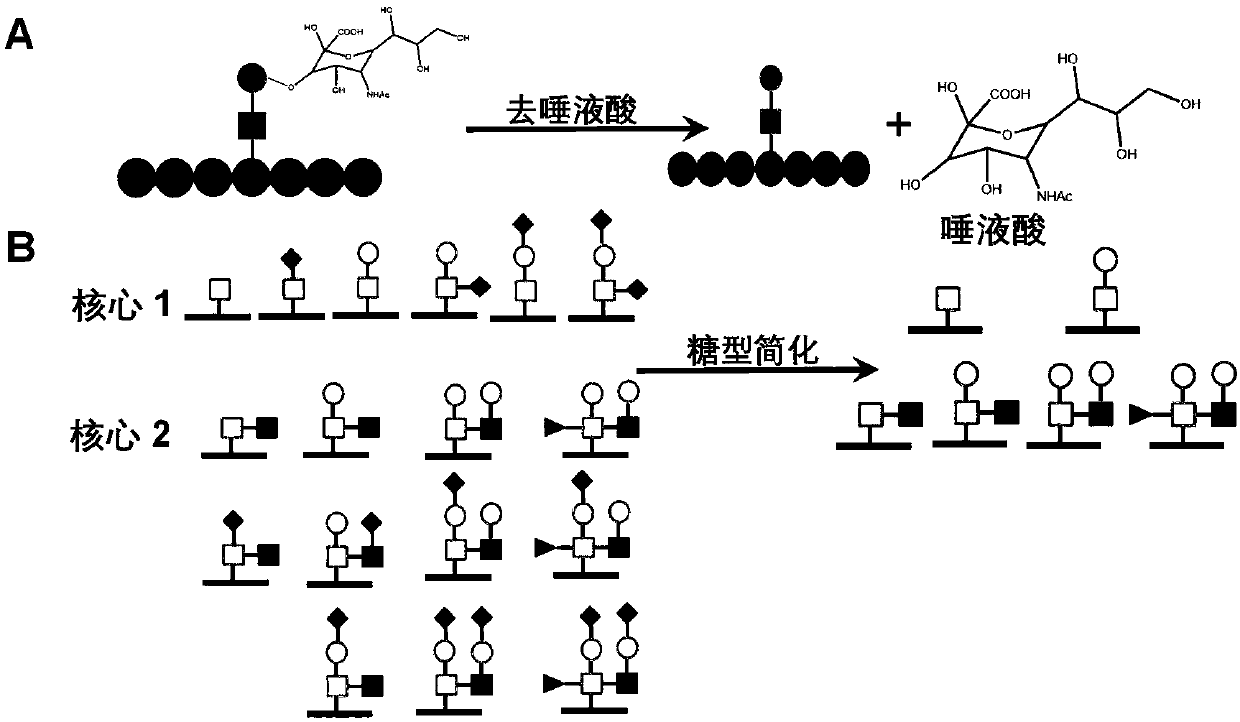
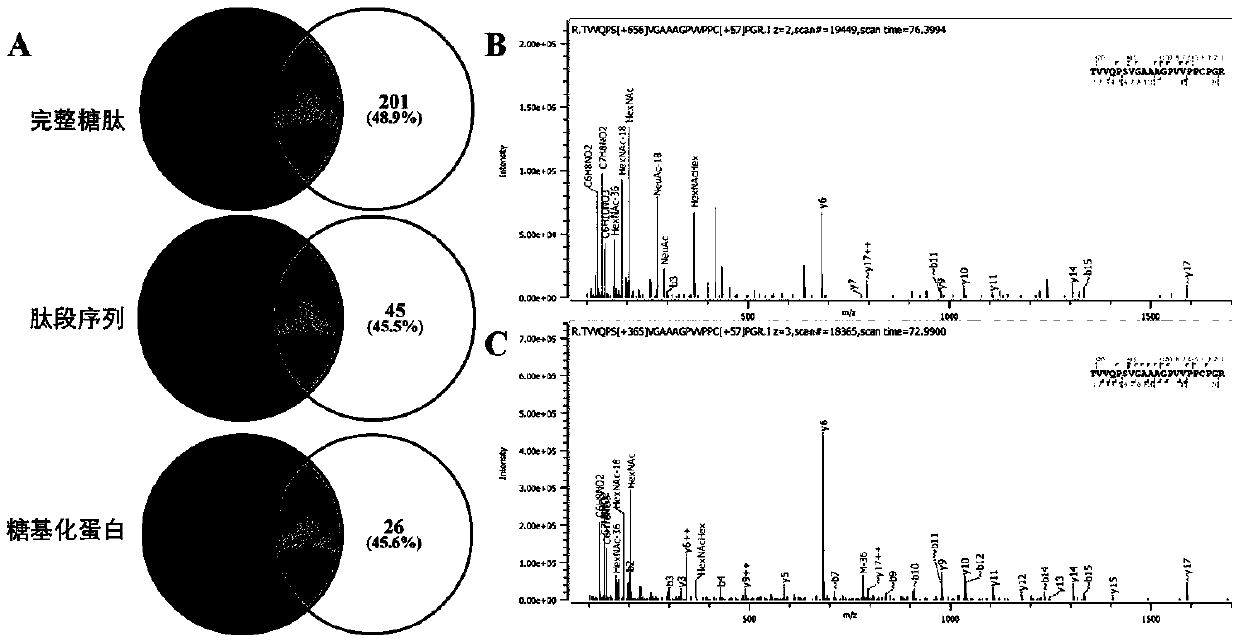
Method for identifying simplified O-GalNAc glycosylation peptide fragment based on chemical reaction
InactiveCN110749736AEasy to operateShort reaction timeComponent separationBiological testingOrganic acidChemical reaction
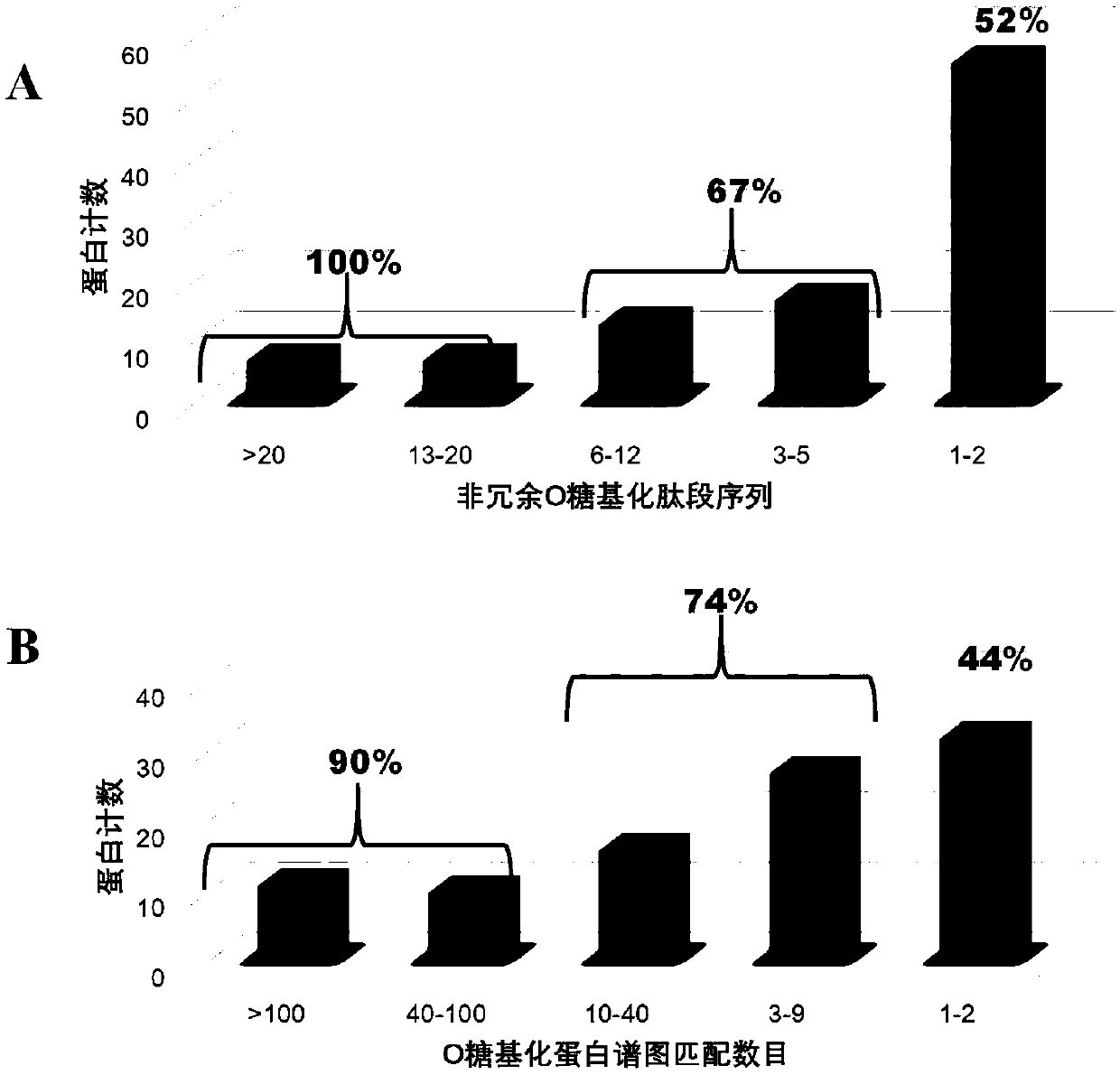
The invention relates to a method for simplifying an O-GalNAc glycosylation structure based on chemical reaction. The sialic acid at the tail end of O-GalNAc glycosylation greatly increases the structural complexity of glycosylation, the characteristic that sialic acid residues at the tail end of the glycosylation peptide fragment are prone to hydrolysis under acidic and heating conditions is utilized, and a certain proportion of organic acid is adopted as an acidic matrix, so that rapid hydrolysis of the sialic acid residues is achieved, the removal efficiency of the sialic acid residues reaches 95% or above, and the structural complexity of glycosylation is remarkably reduced. Moreover, the mass spectrum fragmentation efficiency and the detection sensitivity of the simplified O-GalNAc glycopeptide are more efficient, and the effect of the O-GalNAc glycopeptide is remarkably superior to that of currently commercialized sialidase activity when the O-GalNAc glycopeptide is used for large-scale analysis of O-linked glycosylation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Platelet Storage and Reduced Bacterial Proliferation in Platelet Products Using a Sialidase Inhibitor
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for reducing sialidase activity and inhibiting bacterial proliferation of one or more bacteria in a platelet product preparation from one or more donors. In general, the method includes contacting the platelet product preparation with an amount of a sialidase inhibitor, to thereby obtain a sialidase inhibitor-treated platelet product preparation. Sialidase activity is reduced and the proliferation of one or more bacteria is inhibited, as compared to a platelet product preparation not subjected to the sialidase inhibitor treatment.
Owner:VELICO MEDICAL +1
Reporter gene
InactiveUS20050221335A1Easy to measureRevolutionised analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesNucleotideBacillus perfringens
Use of a gene which codes for a sialidase activity as a reporter gene is described. The gene may be used as a reporter gene in eukaryotic organisms or cells. A modified gene encoding a protein having sialidase enzymatic activity is also described. The nucleotide sequence encodes a prokaryotic or eukaryotic sialidase enzymatic activity preferably the nucleotide sequence encodes a Clostridium perfringens sialidase activity.
Owner:TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN
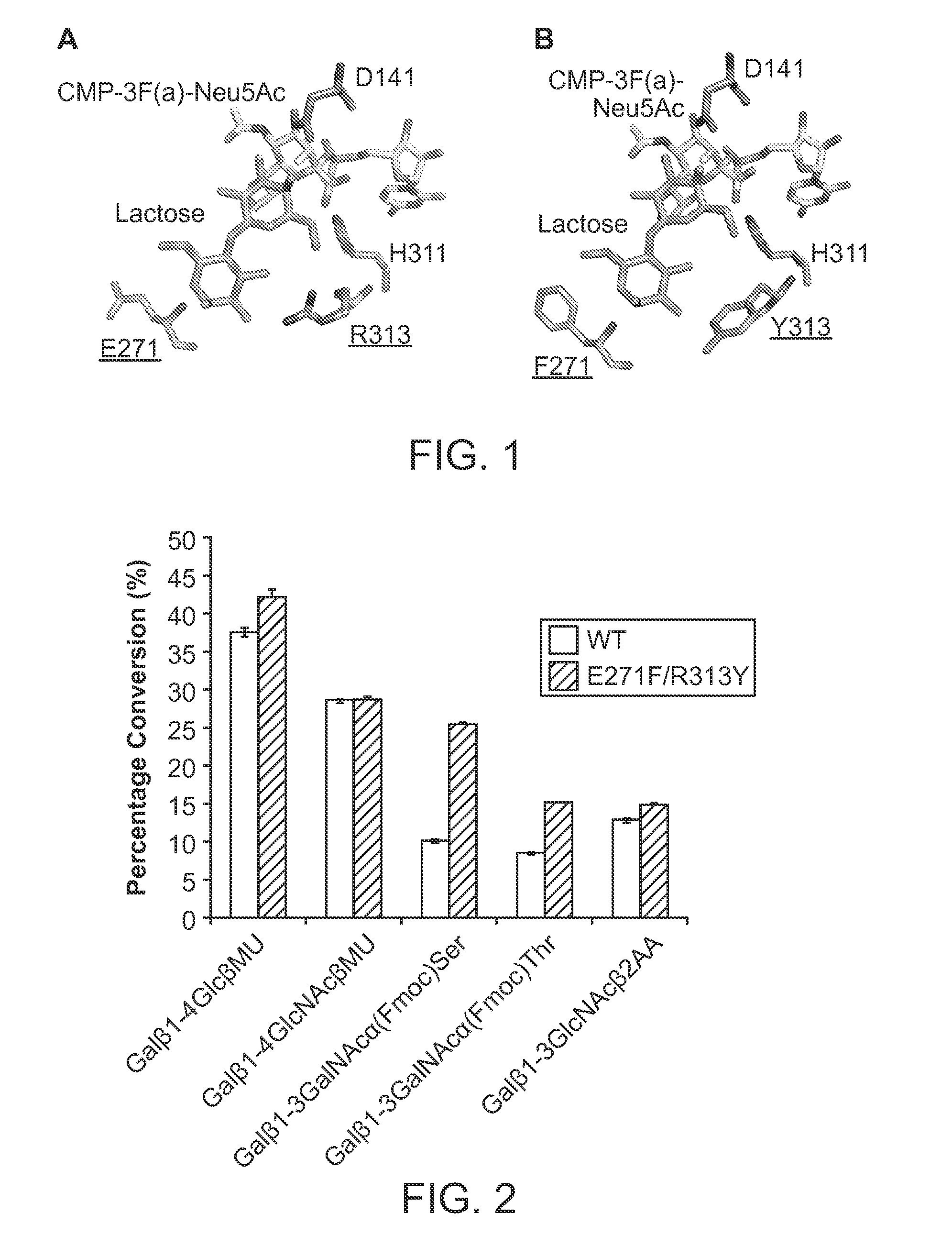
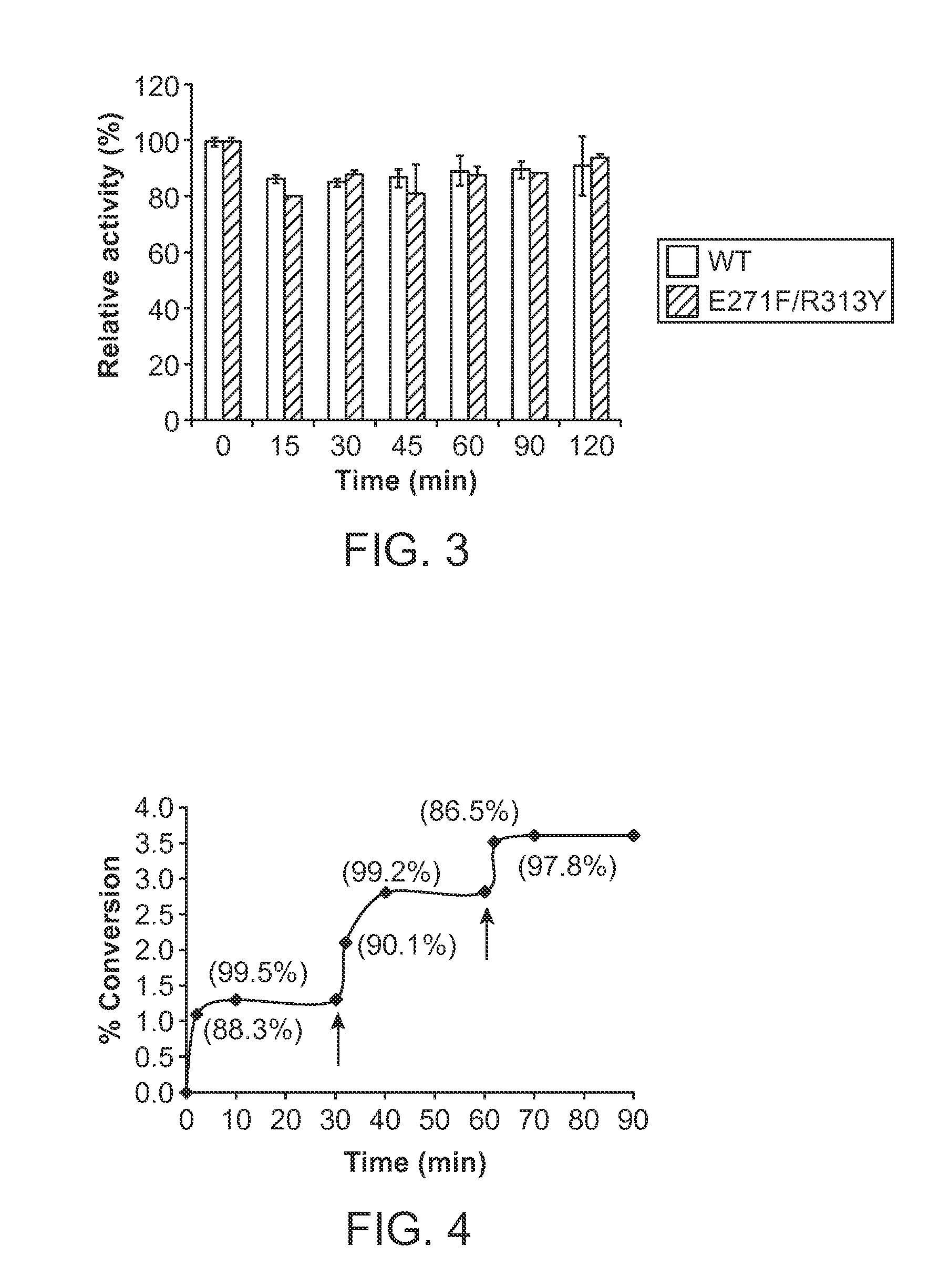
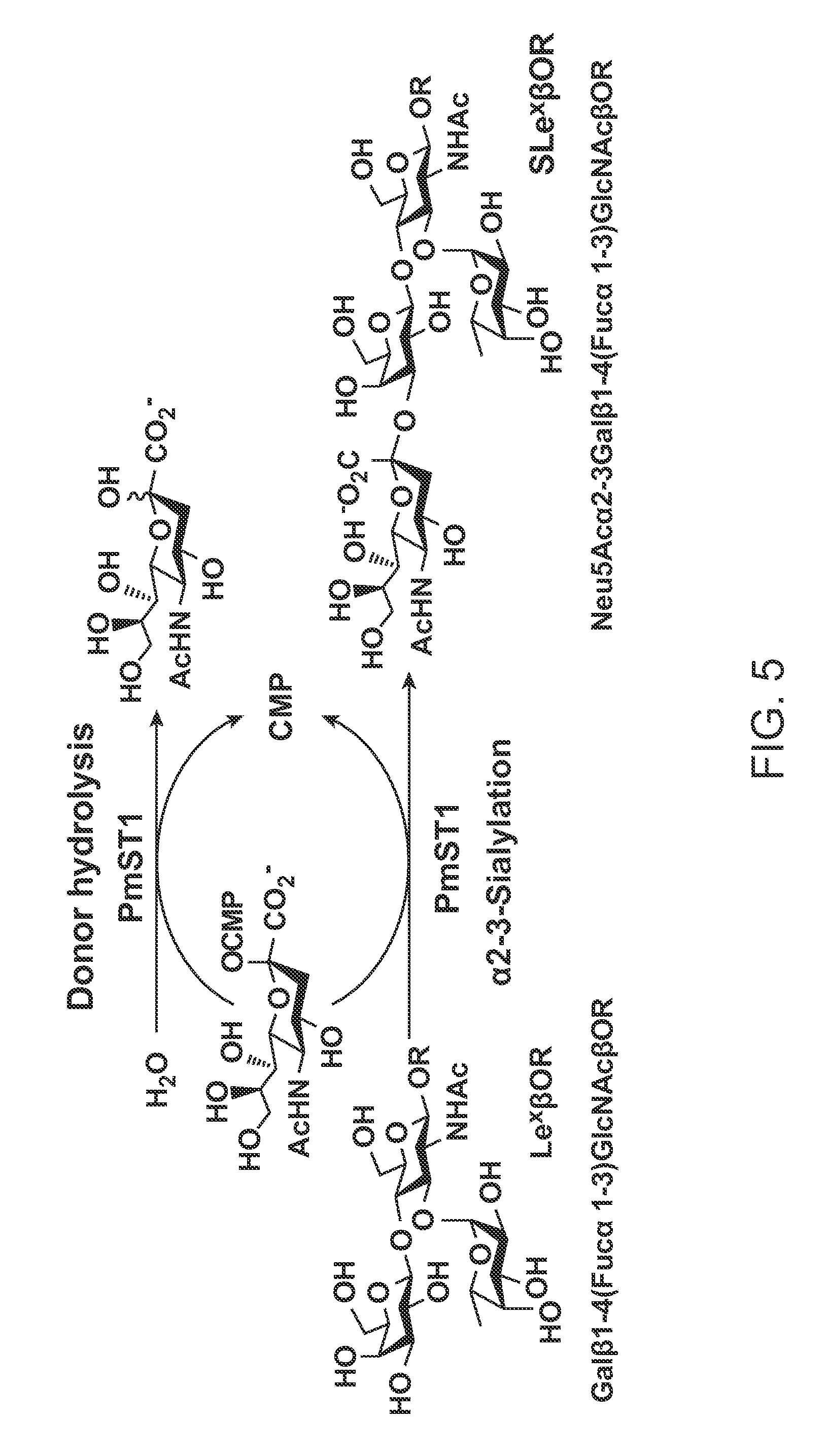
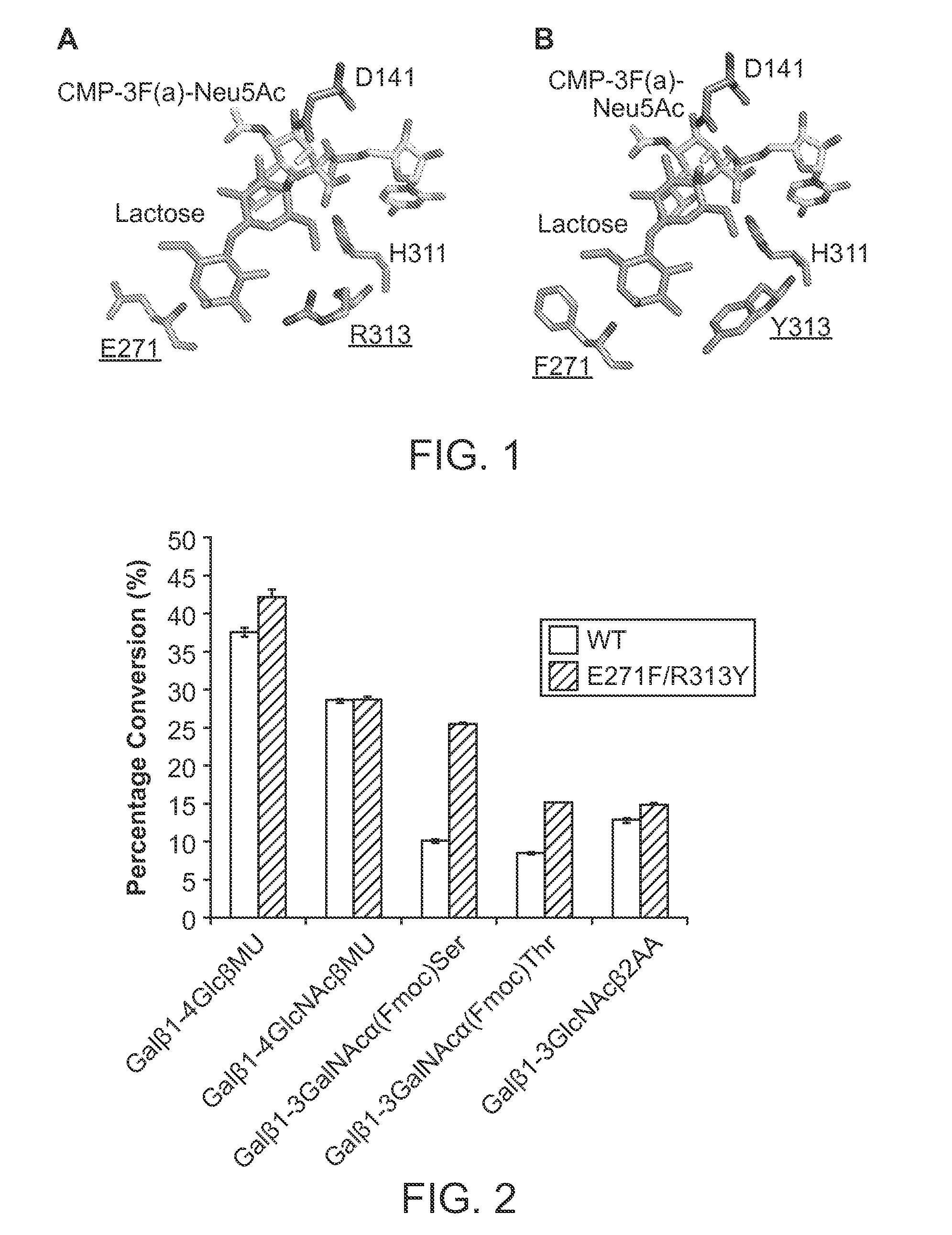
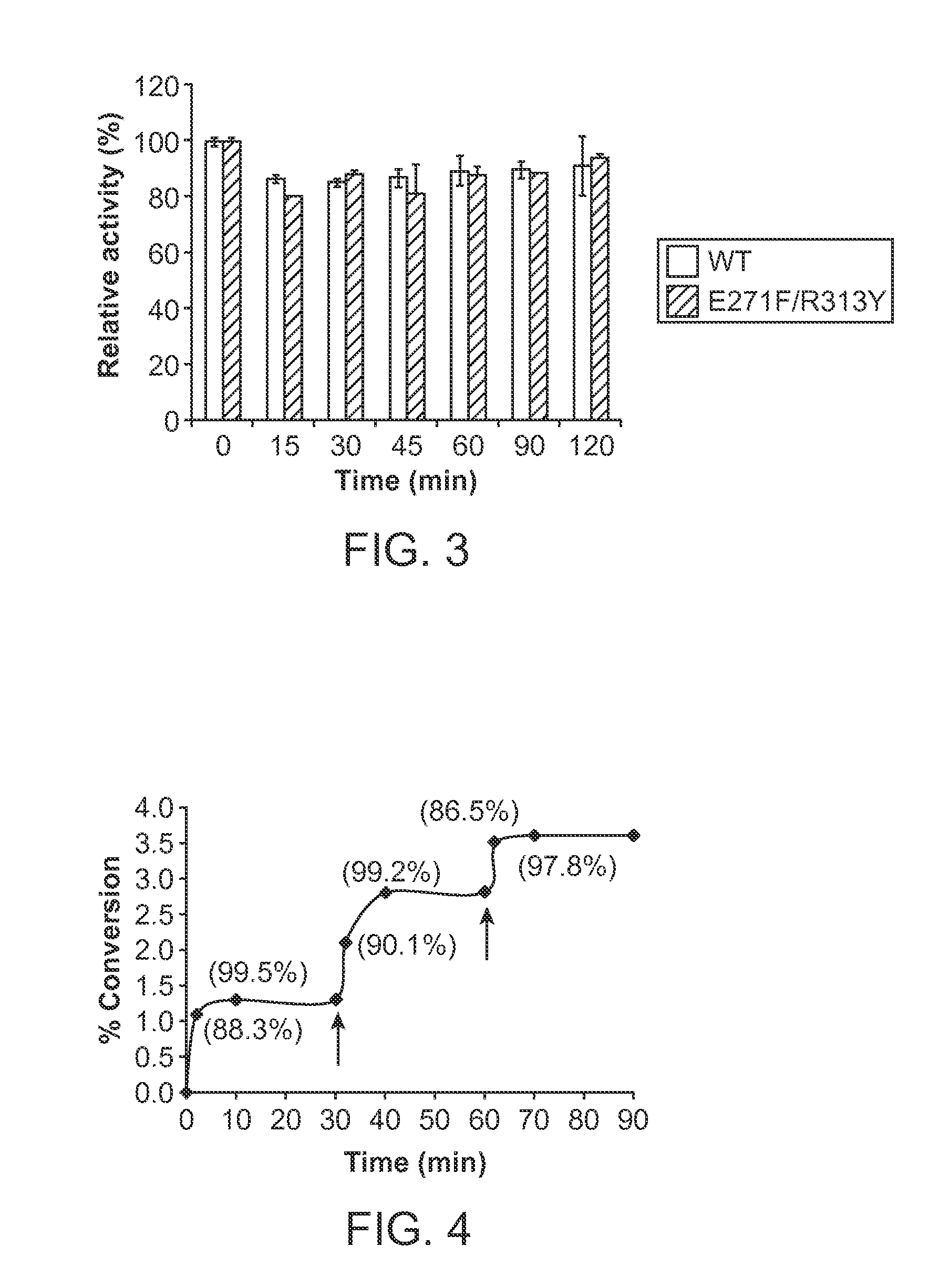
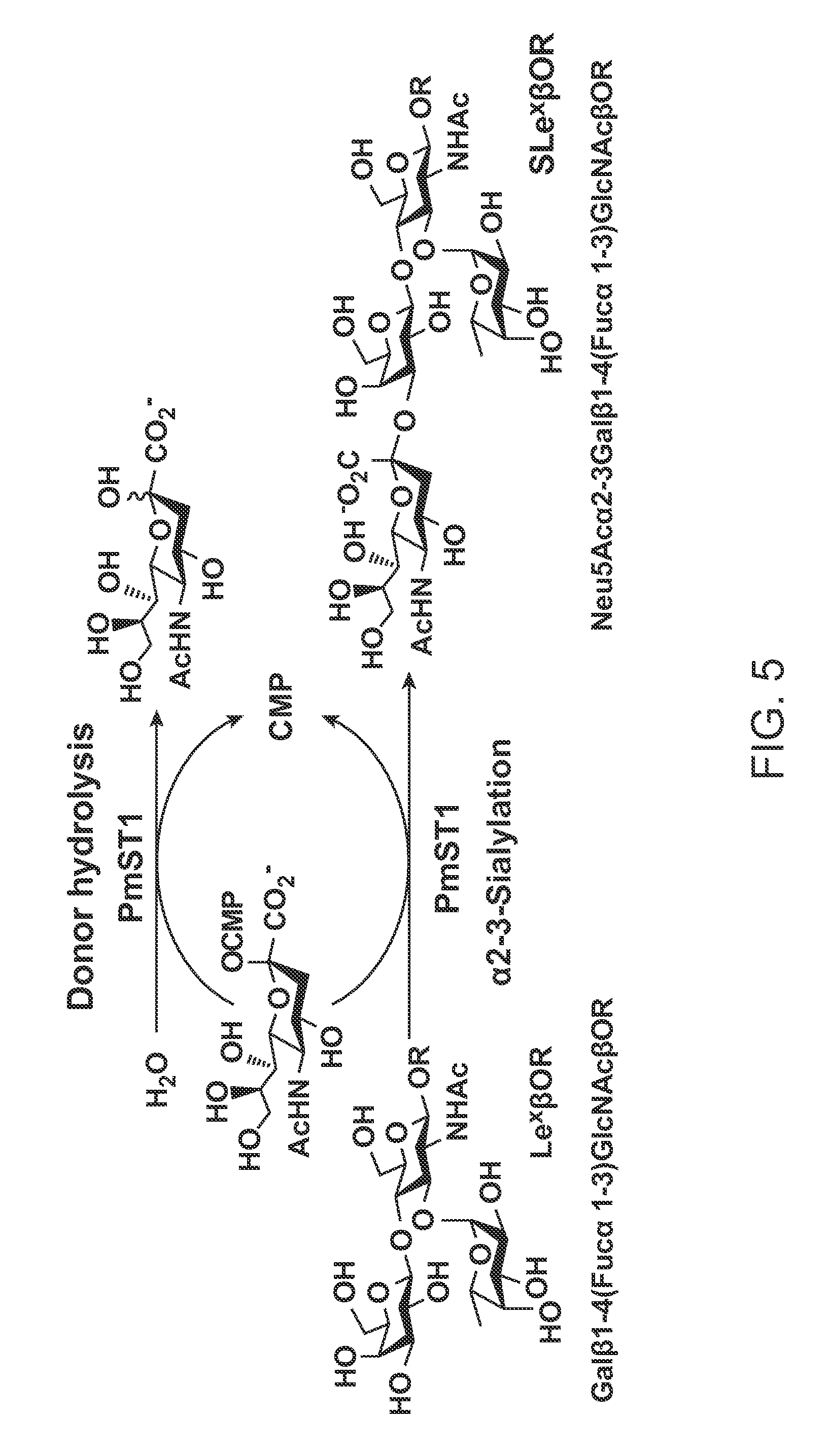
Pmst1 mutants for chemoenzymatic synthesis of sialyl lewis x compounds
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Improved platelet storage using a sialidase inhibitor
InactiveCN103702556ADead animal preservationMammal material medical ingredientsIn vivoPlatelet preservation
The present invention relates to a platelet additive solution (PAS) having an amount of one or more sialidase inhibitors and optionally one or more glycan-modifying agents; and one or more of PAS components that includes a salt, a citrate source, a carbon source, and any combination thereof. The present invention also relates to methods, compositions and kits for increasing the in vivo circulation time of isolated platelets by storing the platelets with one or more sialidase inhibitors. Additionally, the present invention relates to methods and compositions for reducing sialidase activity and inhibiting bacterial proliferation of one or more bacteria in a platelet product preparation from one or more donors.
Owner:VELICO MEDICAL +1
PMST1 mutants for chemoenzymatic synthesis of sialyl lewis x compounds
The present invention provides mutants of PmST1 for the preparation of sialyl-Lewisx oligosaccharides, and other sialosides with decreased sialidase activity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
CMP-dependent sialidase activity
The present disclosure is directed to the properties of certain glycosyltransferase variants having N-terminal truncation deletions or internal deletions. Any of the mutants disclosed in here exhibit alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase enzymatic activity in the presence of CMP-activated sialic acid as co-substrate, and in the presence of a suitable acceptor site. A fundamental finding documented in the present disclosure is that such enzyme are not only capable of catalyzing transfer of a sialidyl moiety but they are also capable of catalyzing hydrolytic cleavage of terminally bound sialic acid from a glycan. Particularly it was found that in the presence of cytidine 5'-monophosphate (CMP) glycosyltransferase activity is inhibited, and sialidase activity is stimulated. Sialidase activity was found to be dependent on the presence of a particular stretch of amino acids (position 90 to 108) in the polypeptide sequence of the reference (wild type) hST6Gal-I polypeptide. Deletion of this sequence portion in an N-terminal truncation variant was found to abolish sialidase activity, notably both in the presence and in the absence of CMP. Thus, disclosed are compositions, uses and methods employing the CMP-mediated feed-back regulation documented herein.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Bacterial vaginosis diagnostic
PendingCN112513288AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisBacterial vaginosisSialic acid
The invention provides a sialidase enzyme activity detection kit or device comprising: (i) an indicator molecule comprising a sialylated peptide and a capture site; (ii) a capture zone comprising capture molecules; and (iii) binding molecules capable of binding to the de-sialylated derivative of the indicator molecule. Also provided are methods of using the kits or devices, as well as specific indicator molecules and specific binding molecules.
Owner:MOLOGIC LTD
Sialyl transferase variants having neosialidase activity
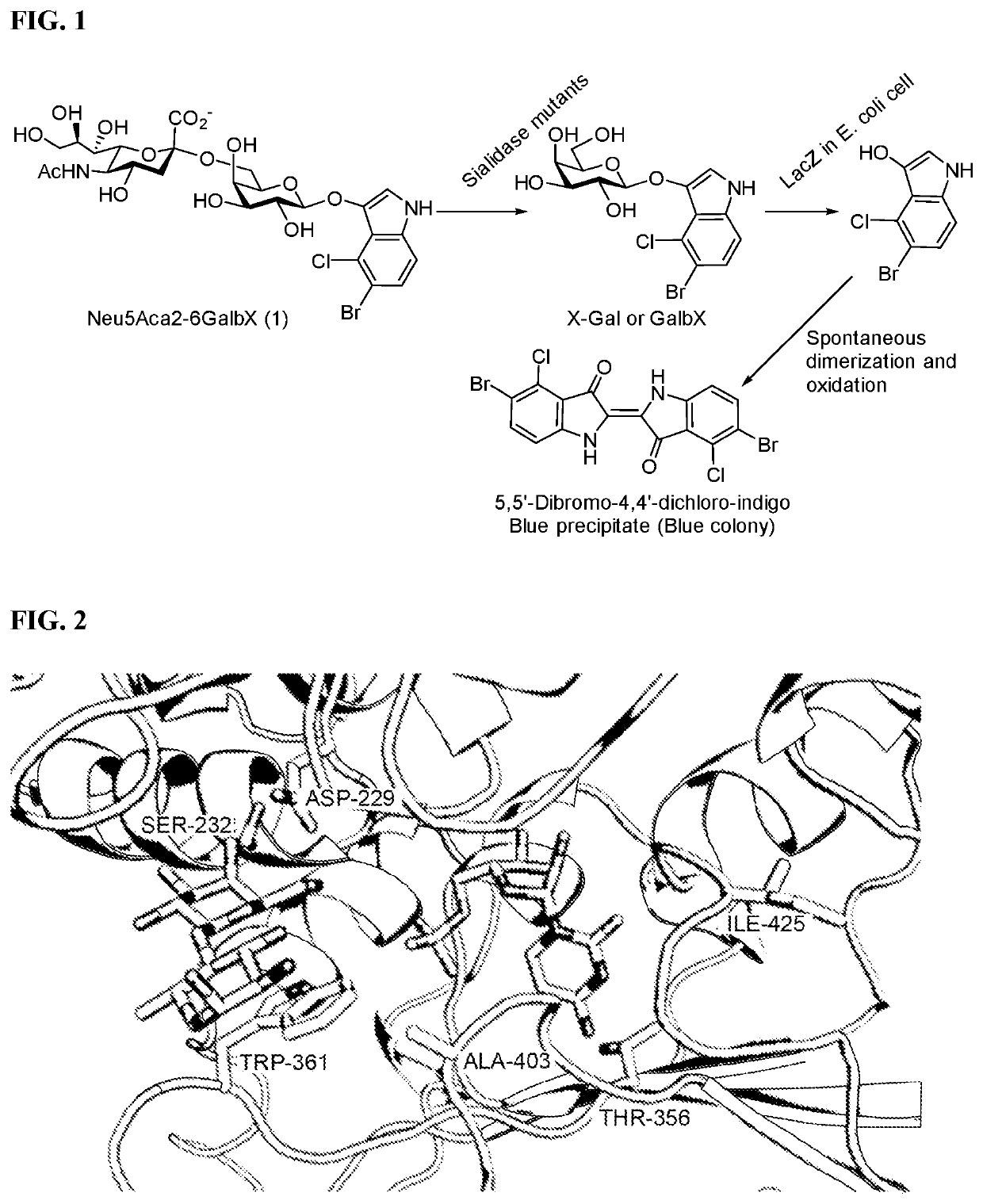
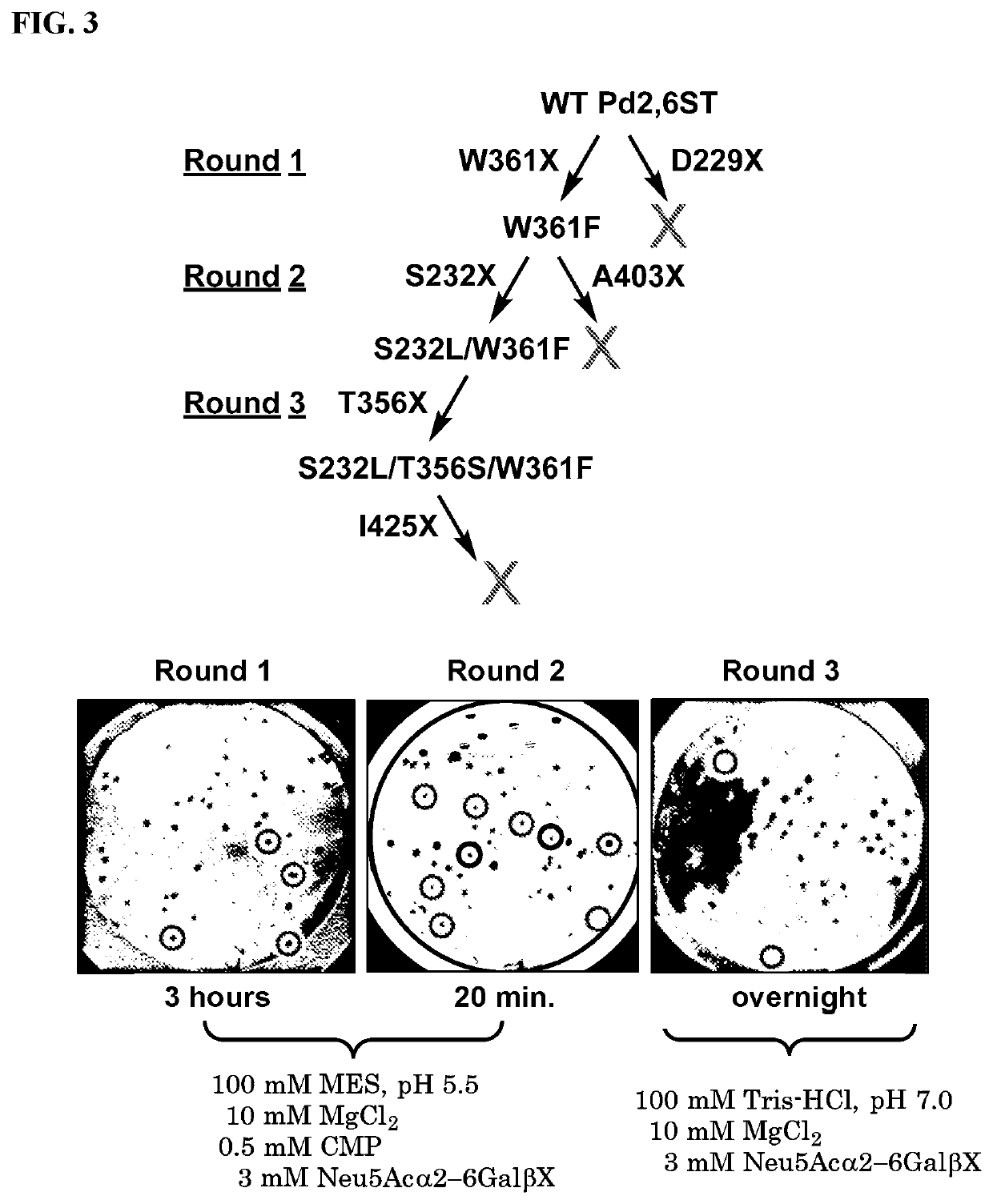
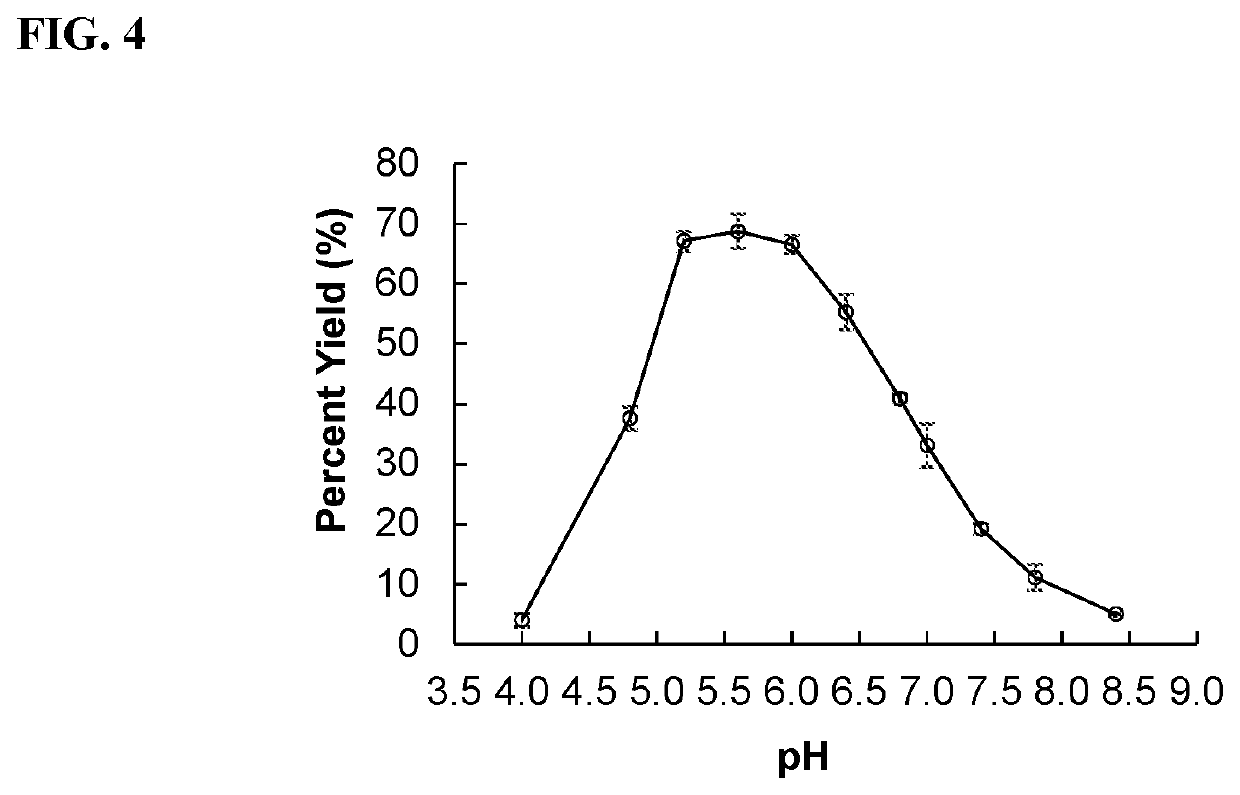
α2-6-Sialyltransferase (2,6ST) variants having improved α2-6-specific sialidase activity as compared to the native 2,6ST enzymes are described. The variants include GT80 sialyltransferases such as P. damselae Pd2,6ST. Methods for making de-sialylated products and screening sialidase activity are also described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
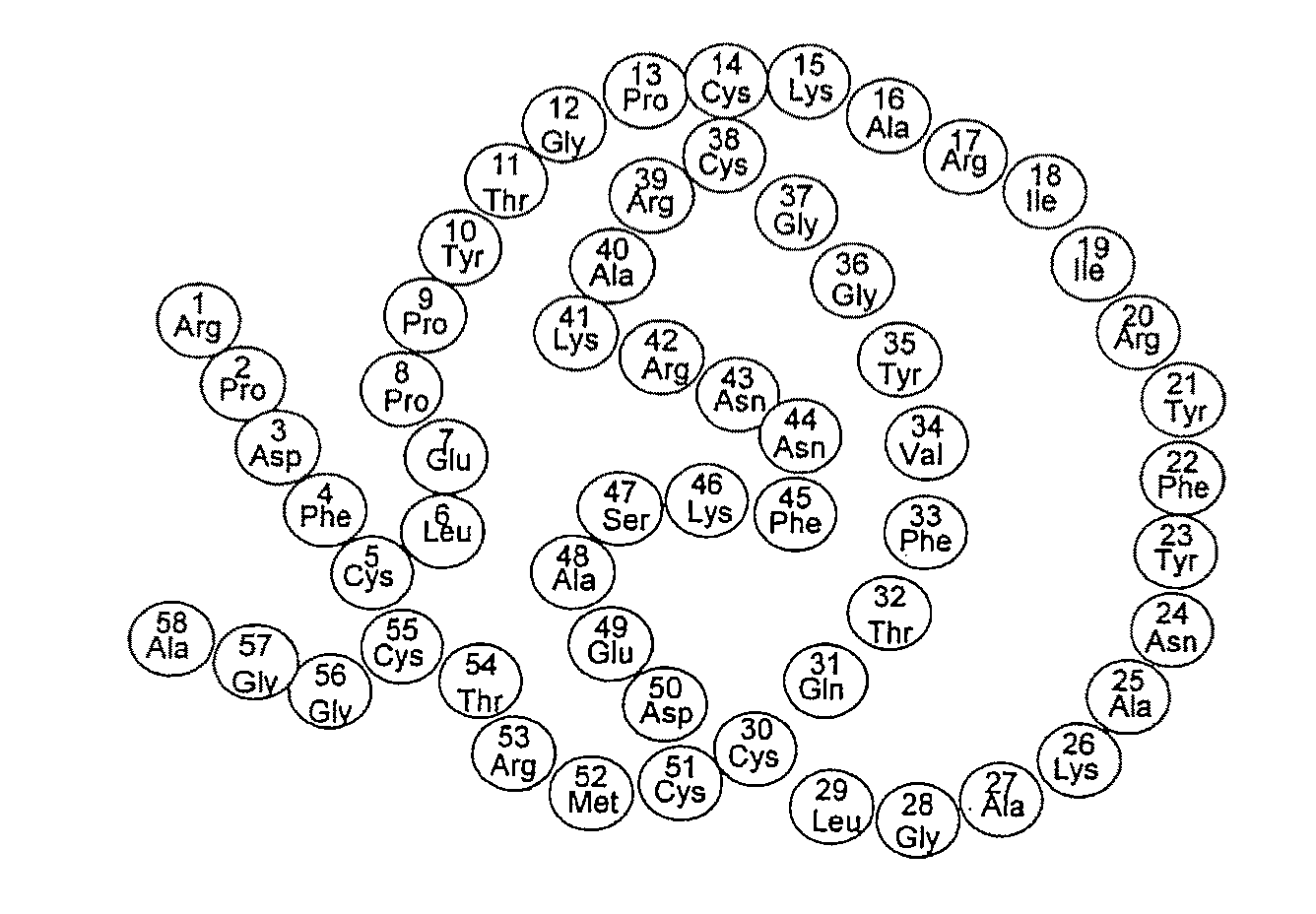
Novel sialidases
The present invention relates to an isolated polypeptide which has sialidase activity, selected from the group consisting of: (a) a polypeptide which has an amino acid sequence which has at least 60% amino acid sequence identity with amino acids 1 to 407 of SEQ ID NO: 3; (b) a polypeptide which is encoded by a polynucleotide which hybridizes under low stringency conditions with (i) the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 or 2 which is at least 80% or 90% identical over 60, preferably over 100 nucleotides, more preferably at least 90% identical over 200 nucleotides, or (ii) a nucleic acid sequence complementary to the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 or 2.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Fluorescent probe for detecting activation of sialidase
PendingUS20220186286A1Good biocompatibilityImprove compound stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluoProbesAryl
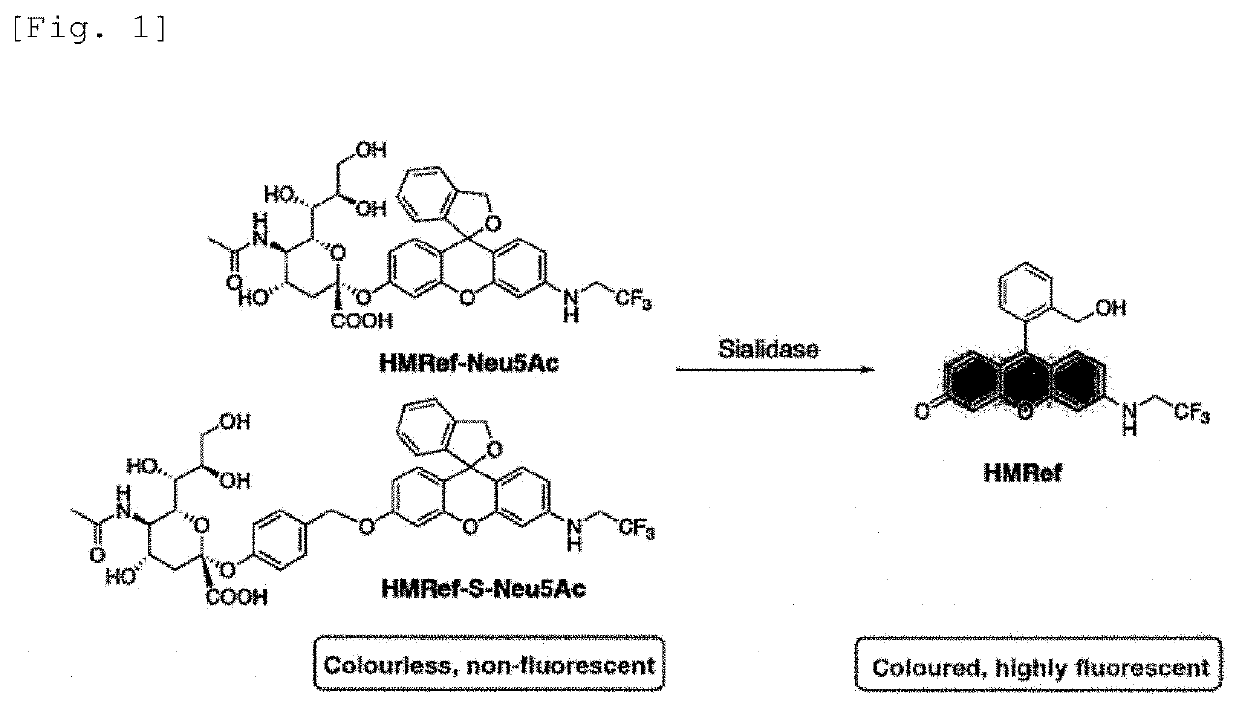
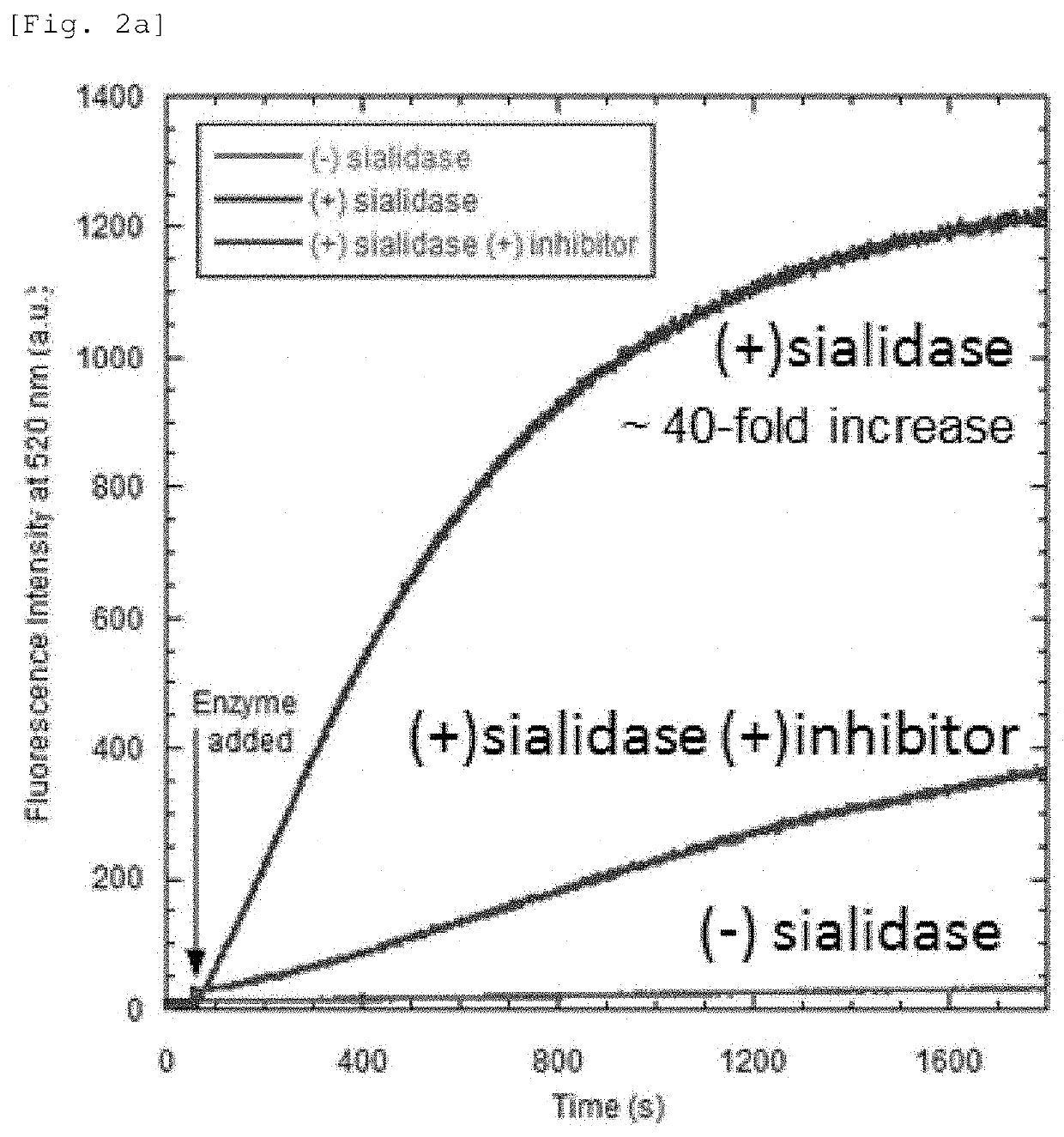
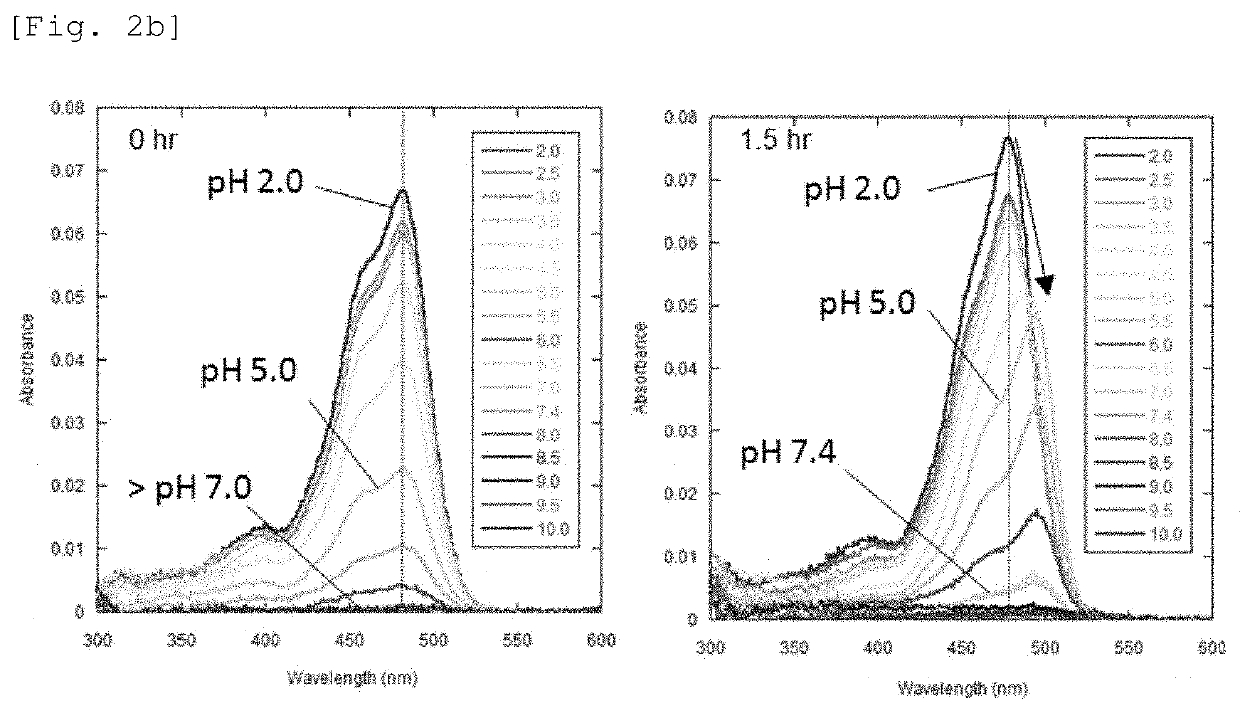
A fluorescent probe for sialidase activity detection, is a compound represented by the following general formula or a salt thereof.R1, if present, represents the same or different monovalent substituent present on a benzene ring. R2 and R3 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, or a halogen atom. R4 and R5 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, or a halogen atom. R6 represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms, or a fluorinated alkyl group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms. R6′ represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, and R6′ may form, together with R3 or R5 a five to seven-membered heterocyclyl or heteroaryl containing a nitrogen atom to which R6′ is bonded.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Method for using the kit for detecting sialidase in sperm
ActiveCN105671126BReduce typesReduce experiment costMicrobiological testing/measurementMale infertilityDecomposition
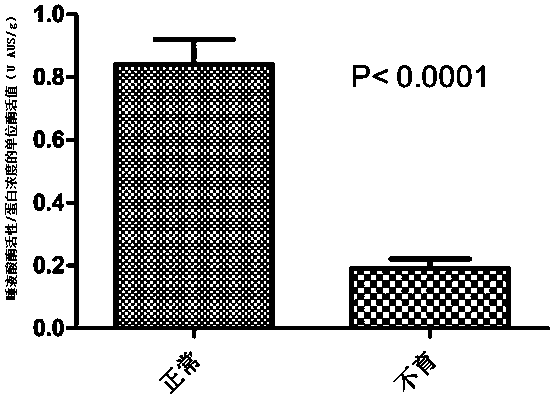
The invention provides a method for evaluating semen quality. The method comprises the following specific steps: 1, collecting a fresh liquefied seminal fluid sample, washing semen with a phosphate buffer solution or a BWW culture solution, removing residual seminal plasma constituents completely, and then conducting centrifugal separation on the semen; 2, adding cell lysis buffer and a protease inhibiting agent cocktail to the semen obtained through separation in step 1, mixing the mixture to be uniform, and after no obvious cell sedimentation is found, in other words, complete splitting decomposition is achieved, conducting high speed centrifugation at the temperature of 4 DEG C, wherein supernatant is protein extract; 3, measuring the protein concentration of the protein extract; 4, measuring sialidase activity of the semen, and finally obtaining the sialidase activity value / protein concentration value, so that the process is ended. According to the method, through detection of activity of sialidase in the semen, the diagnosis basis and clinical reference are provided for a patient suffering from male infertility with the clinical reasons unclear.
Owner:成都思瑞迪医疗科技有限公司
PmST1 mutants for chemoenzymatic synthesis of sialyl lewis X compounds
The present invention provides mutants of PmST1 for the preparation of sialyl-Lewisx oligosaccharides, and other sialosides with decreased sialidase activity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
cmp-dependent sialidase activity
The present invention relates to the properties of certain glycosyltransferase variants with N-terminal truncating deletions or internal deletions. Any of the mutants disclosed herein exhibit α-2,6-sialyltransferase enzymatic activity in the presence of CMP-activated sialic acid as a co-substrate and in the presence of a suitable acceptor site. A fundamental finding documented in the present invention is that such enzymes are not only able to catalyze the transfer of sialidyl moieties, but they are also able to catalyze the hydrolytic cleavage of terminally bound sialic acids from glycans. Specifically, it was found that in the presence of cytidine-5'-monophosphate (CMP), glycosyltransferase activity is inhibited and sialidase activity is stimulated. Sialidase activity was found to be dependent on the presence of a specific stretch of amino acids (positions 90-108) in the polypeptide sequence of the reference (wild-type) hST6 Gal-I polypeptide. Deletion of part of this sequence in N-terminal truncated variants was found to abolish sialidase activity, especially in the presence and absence of CMP. Thus, compositions, uses and methods employing the CMP-mediated feedback regulation documented herein are disclosed.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Methods and compositions to detect the level of lysosomal exocytosis activity and methods of use
ActiveUS20140377245A9Nervous disorderMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSialic acid aldolaseState dependent
Methods are provided for the prognosis, diagnosis and treatment of various pathological states, including cancer, chemotherapy resistance and dementia associated with Alzheimer's disease. The methods provided herein are based on the discovery that various proteins with a high level of sialylation are shown herein to be associated with disease states, such as, cancer, chemotherapy resistance and dementia associated with Alzheimer's disease. Such methods provide a lysosomal exocytosis activity profile comprising one or more values representing lysosomal exocytosis activity. Also provided herein, is the discovery that low lysosomal sialidase activity is associated with various pathological states. Thus, the methods also provide a lysosomal sialidase activity profile, comprising one or more values representing lysosomal sialidase activity. A lysosomal sialidase activity profile is one example of a lysosomal exocytosis activity profile. As such, the level of lysosomal exocytosis activity and / or lysosomal sialidase activity is predictive of a diagnosis and / or prognosis of cancer, chemotherapy resistance or dementia associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
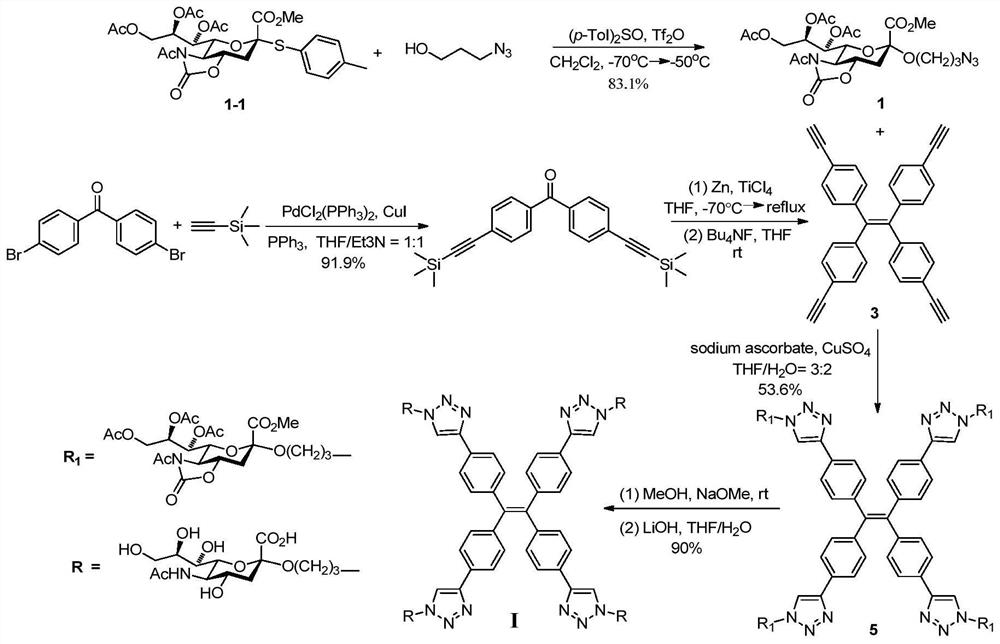
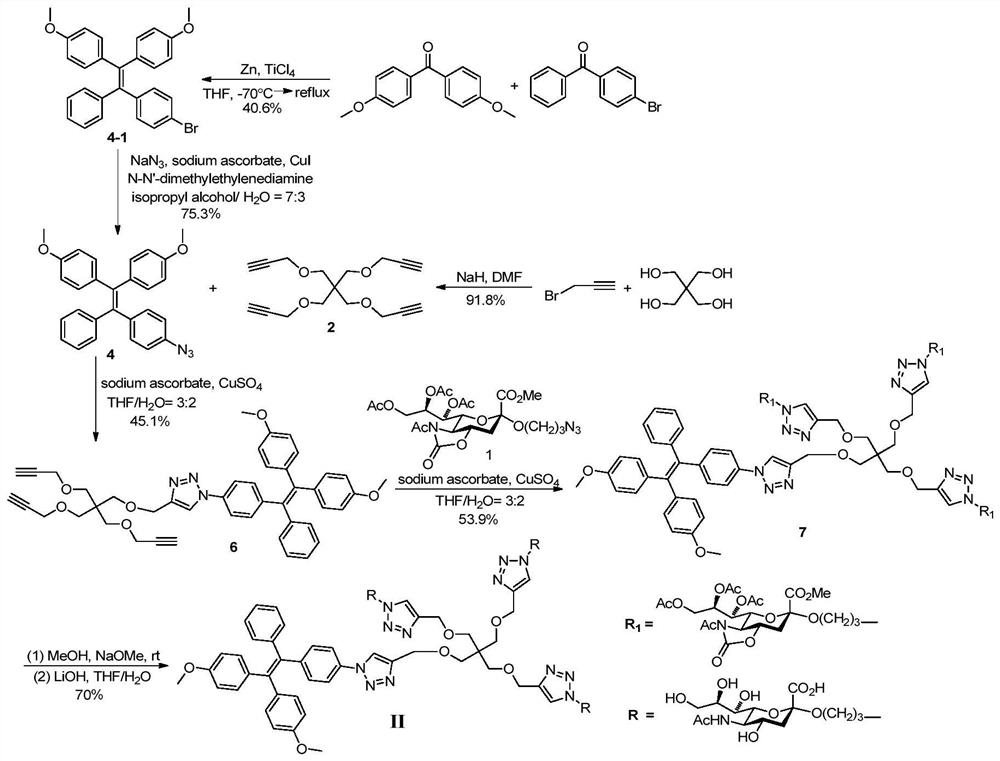
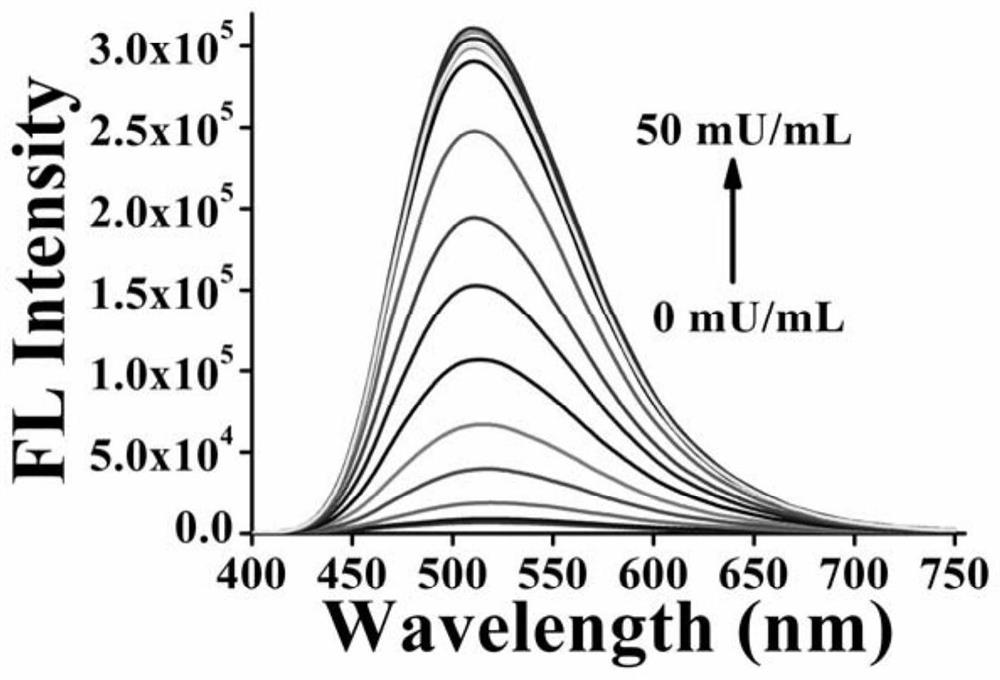
Tetraphenylethylene compound containing sialic acid glycosyl unit, preparation method and application
The invention relates to detection of sialidase activity by an aggregation induced luminescence probe. In particular, the invention relates to two tetrastyrene compounds containing sialic acid glycosyl units, and a preparation method and an application thereof in sialidase detection. The compounds disclosed by the invention have the structures shown in the formulas (I and II). Three or four sialicacid glycosyl units are contained and the sialic acid glycosyl units are connected onto tetrastyrene through triazole and pentaerythritol. The compounds can be applied to detection of sialidase and have application value in the diagnosis of diseases related to sialidase.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com