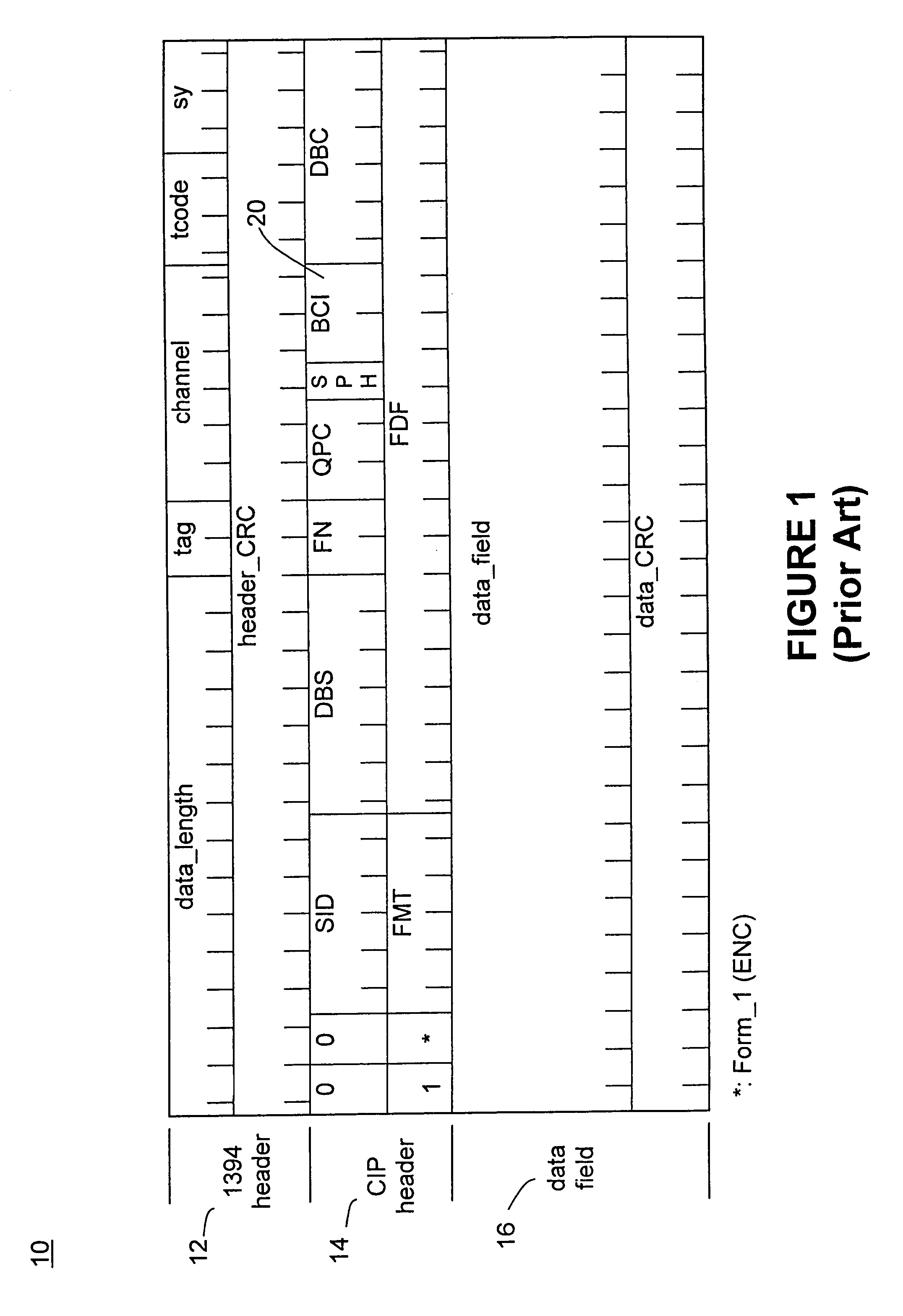
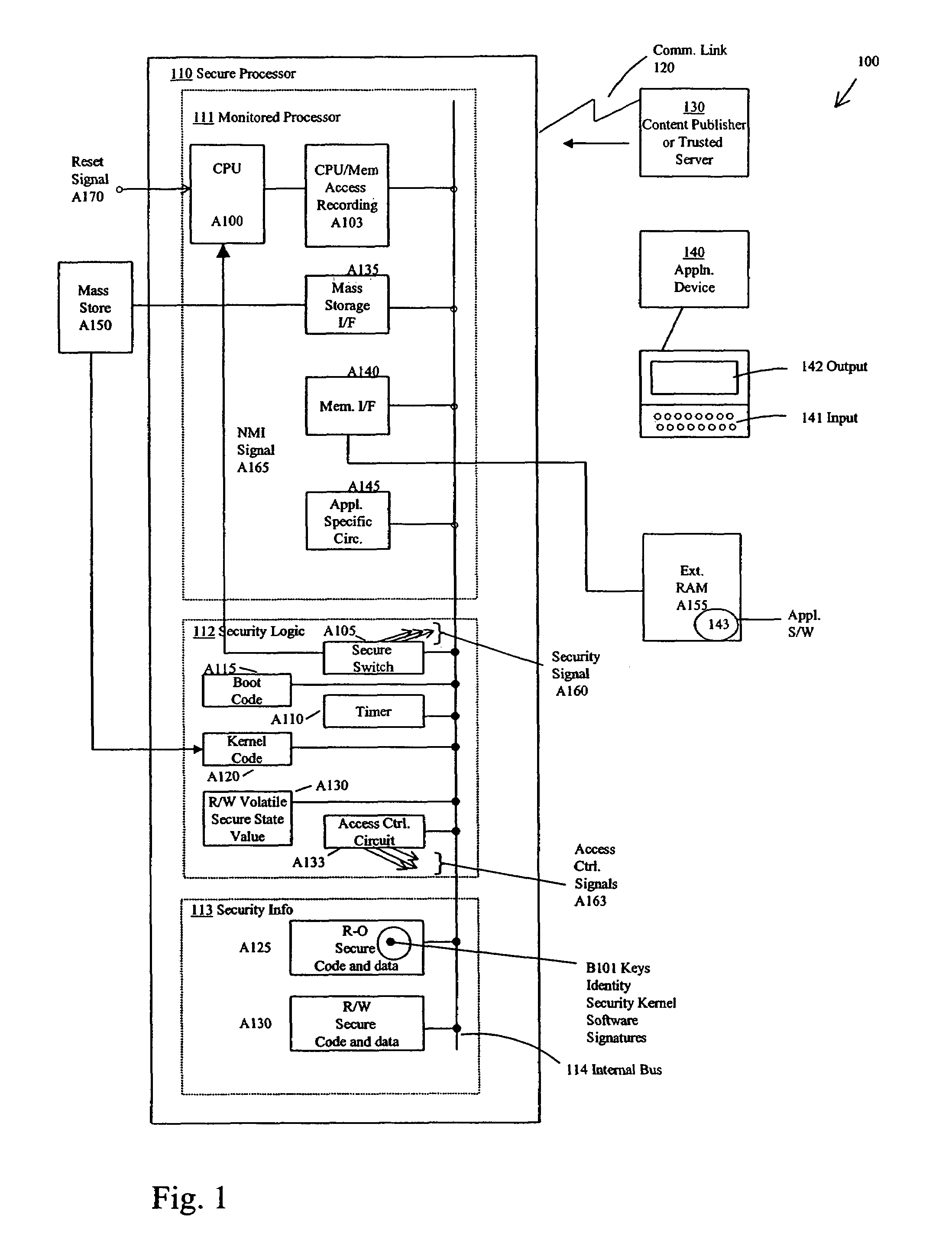
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
540 results about "Security pattern" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Security patterns can be applied to achieve goals in the area of security. All of the classical design patterns have different instantiations to fulfill some information security goal: such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Additionally, one can create a new design pattern to specifically achieve some security goal.
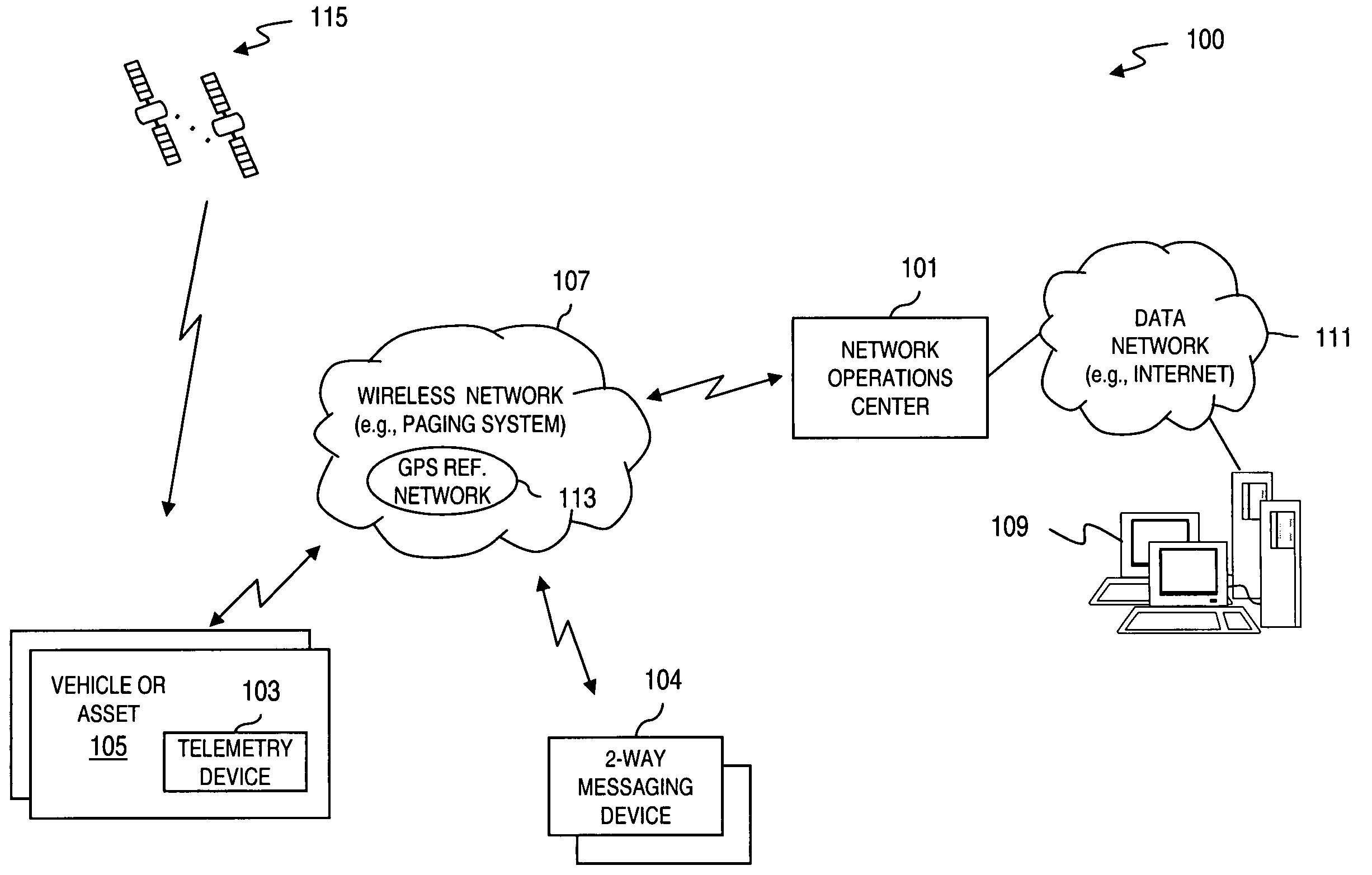
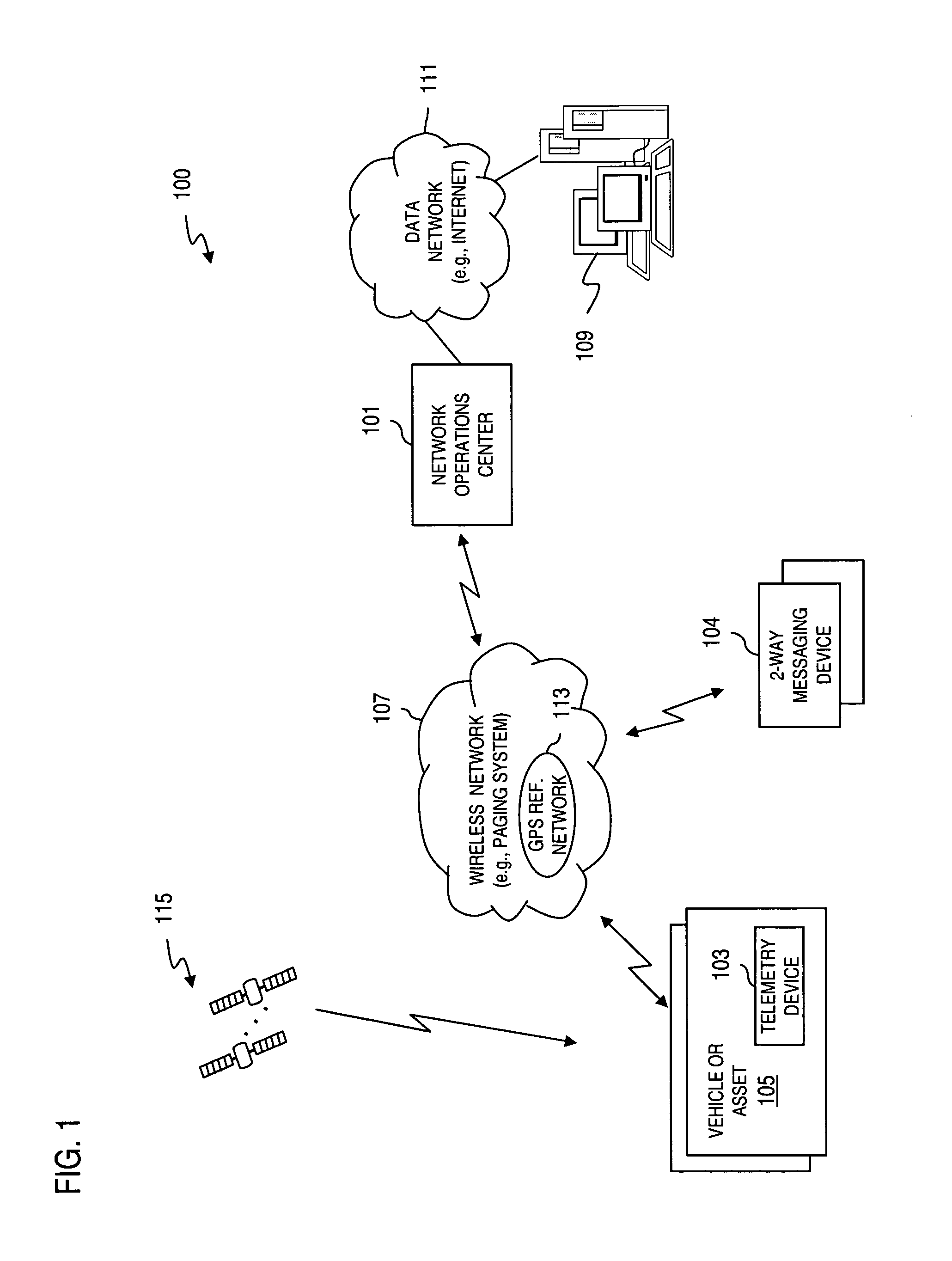
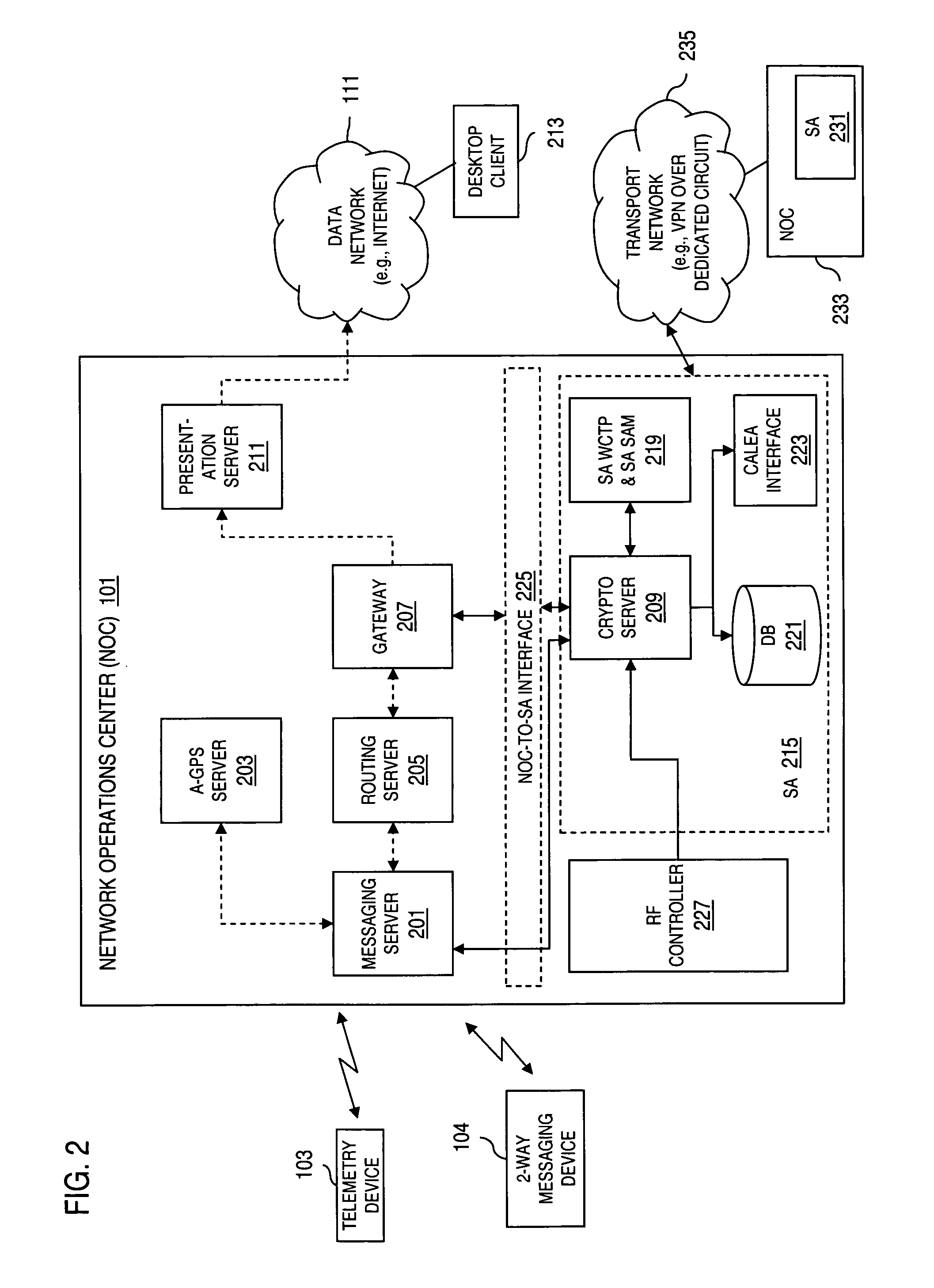
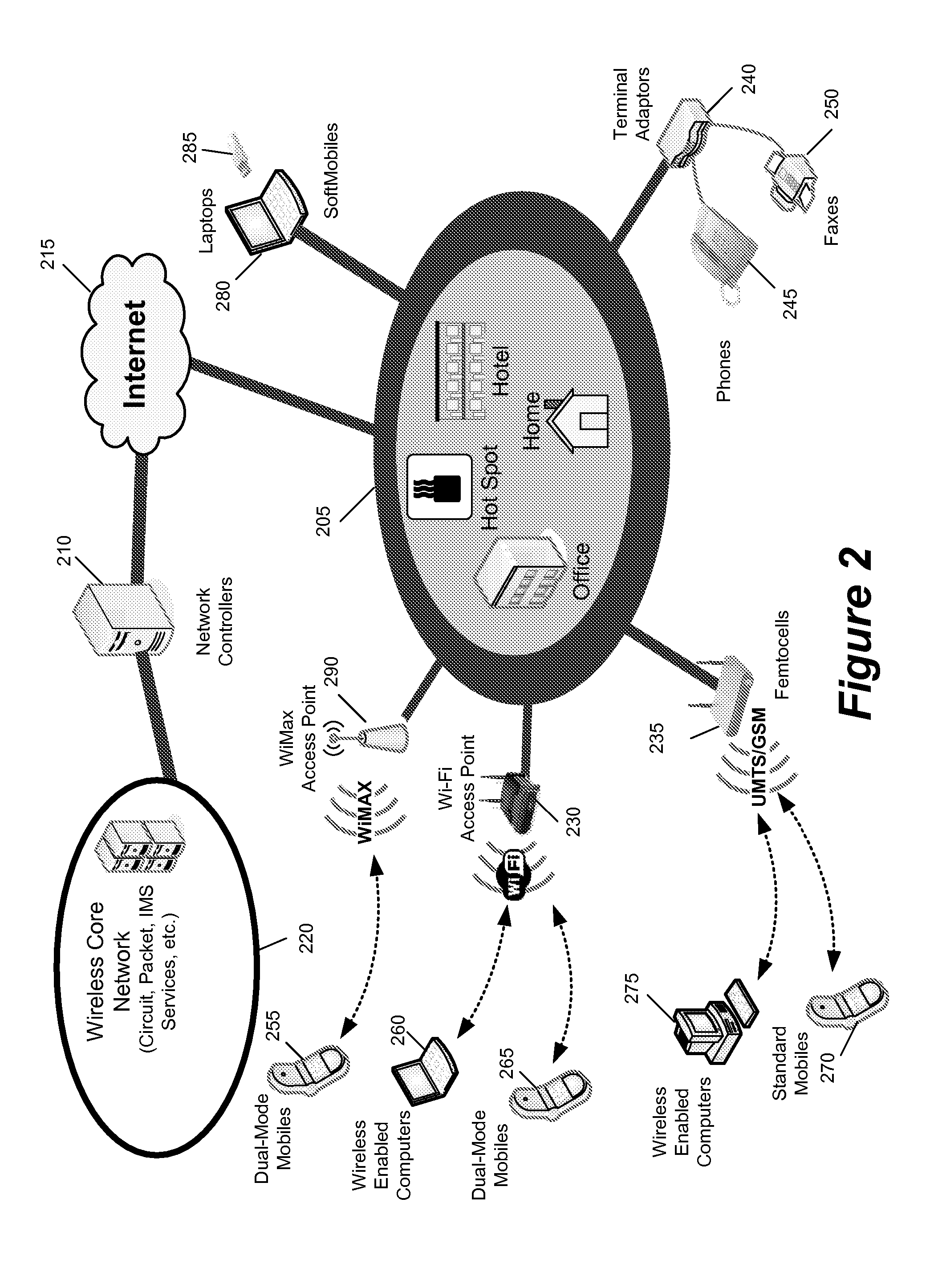
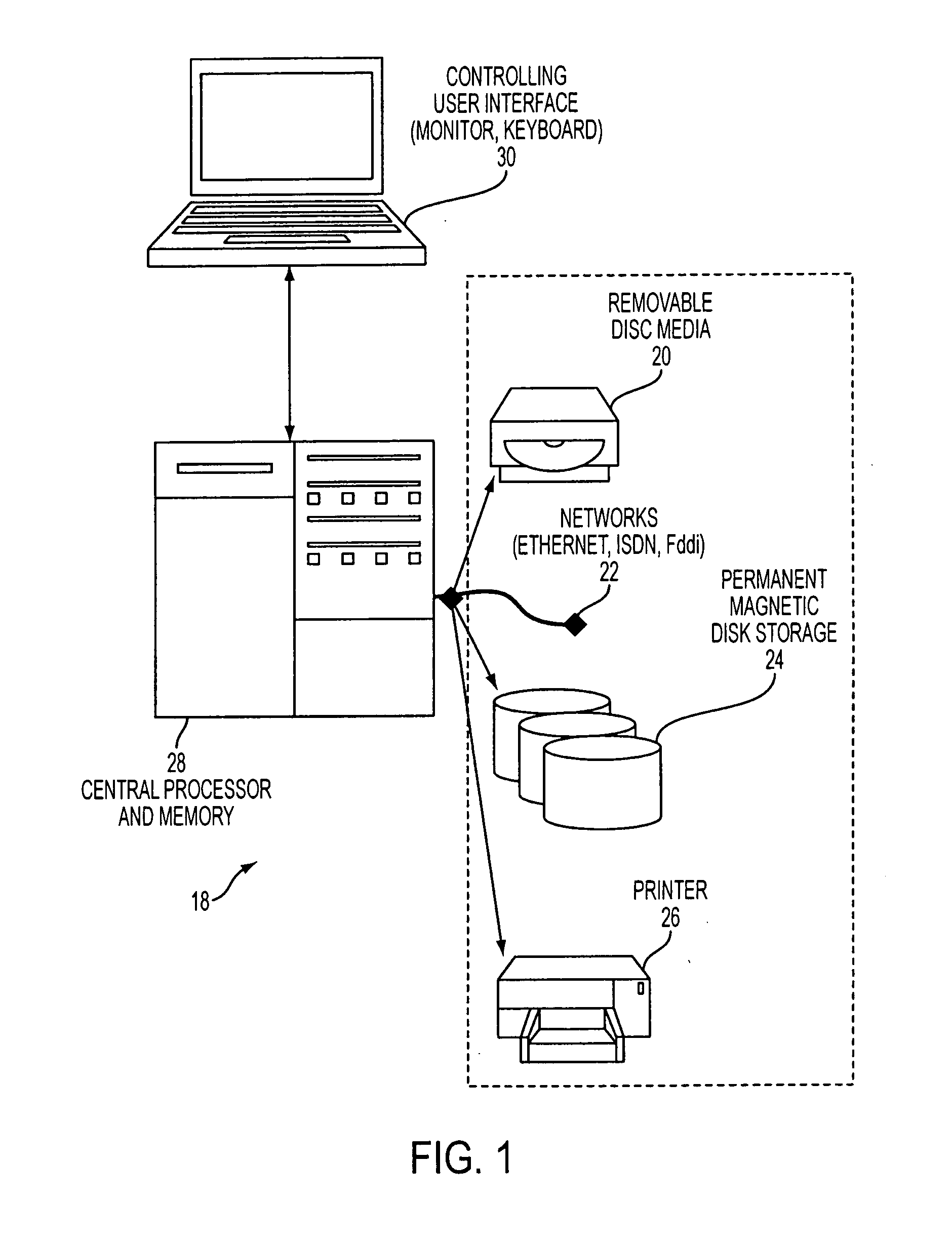
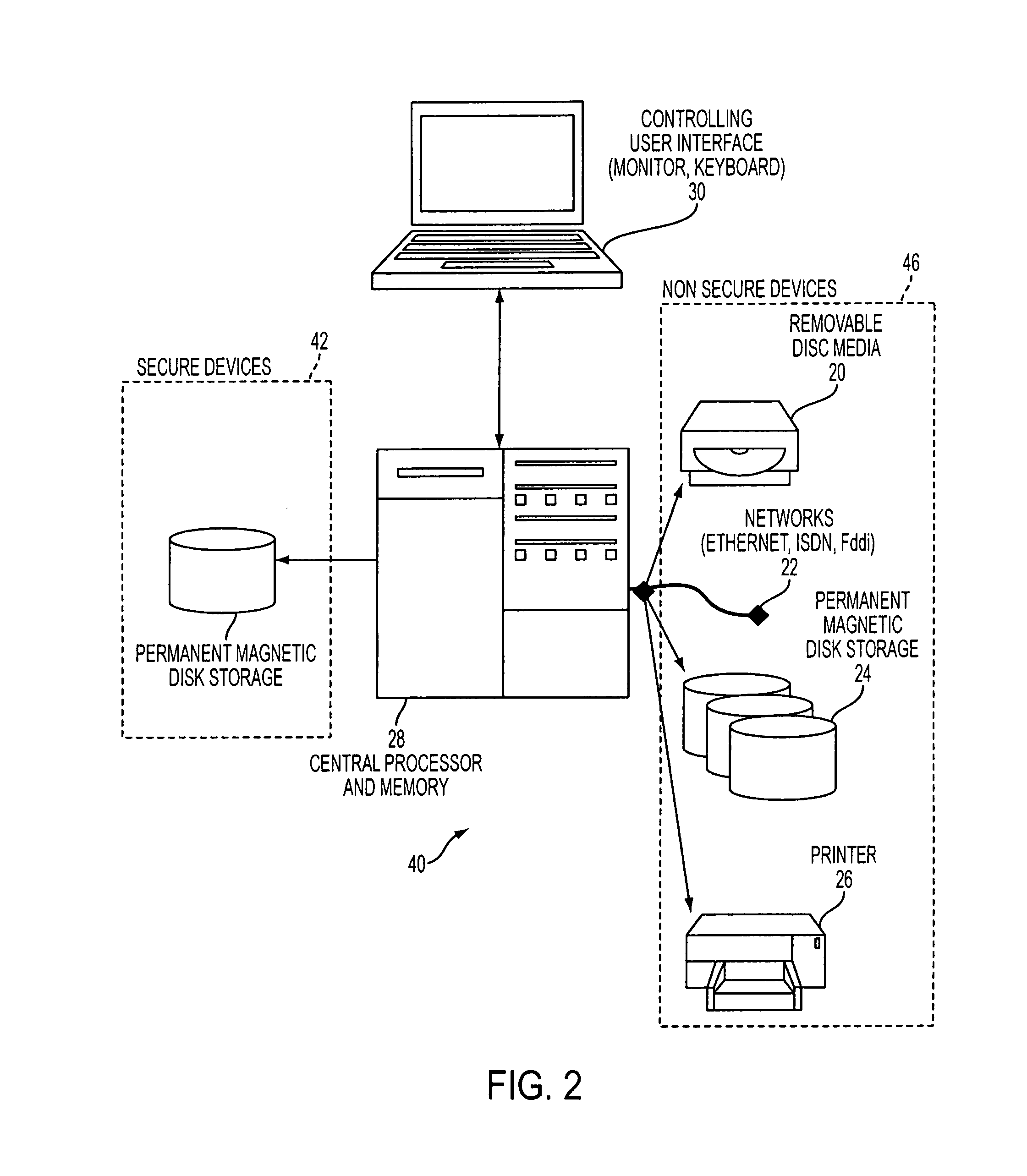
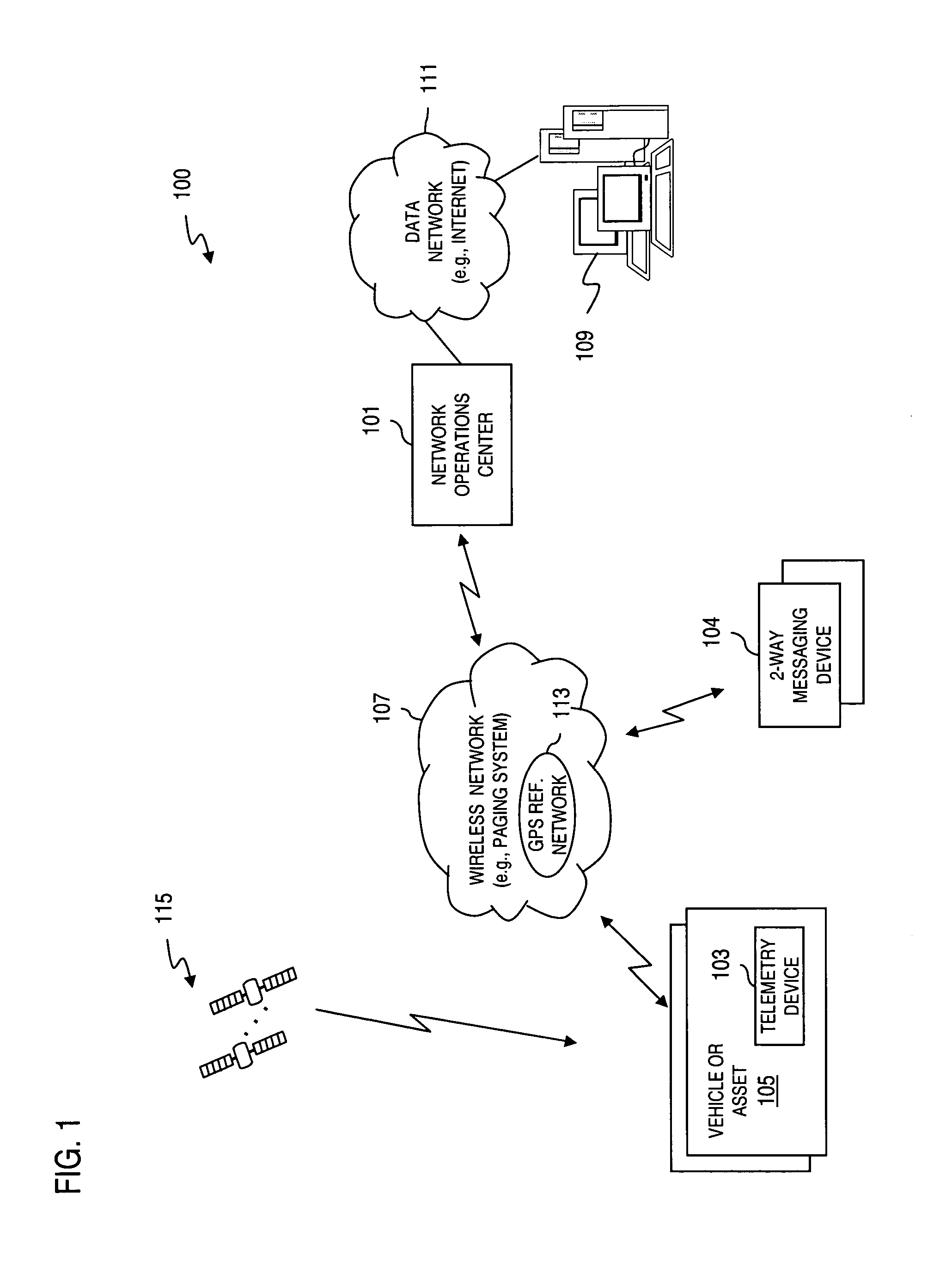
Method and apparatus for providing secure wireless communication
InactiveUS7496347B2Key distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSecure communicationComputer network
An approach is provided for securely communicating in a wireless network. A cryptographic server generates a command to enable a secure mode of operation for a wireless device, wherein the wireless device can operate in a secure mode and an unsecure mode in support of two-way messaging. The cryptographic server sends the command to the wireless device to activate the secure mode of operation. The secure mode of operation provides transmission of an encrypted message by the wireless device over the wireless network.
Owner:VELOCITA WIRELESS
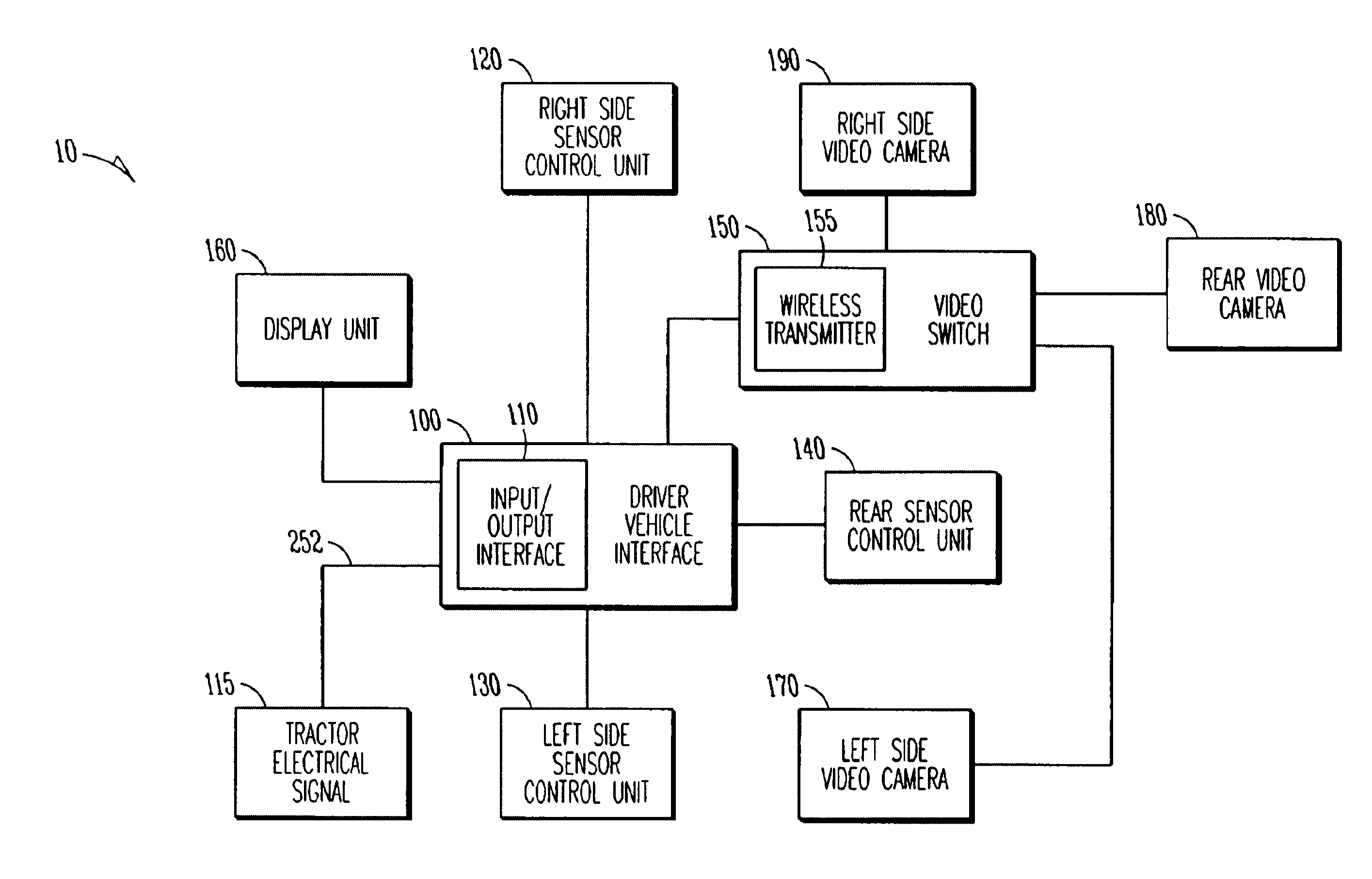
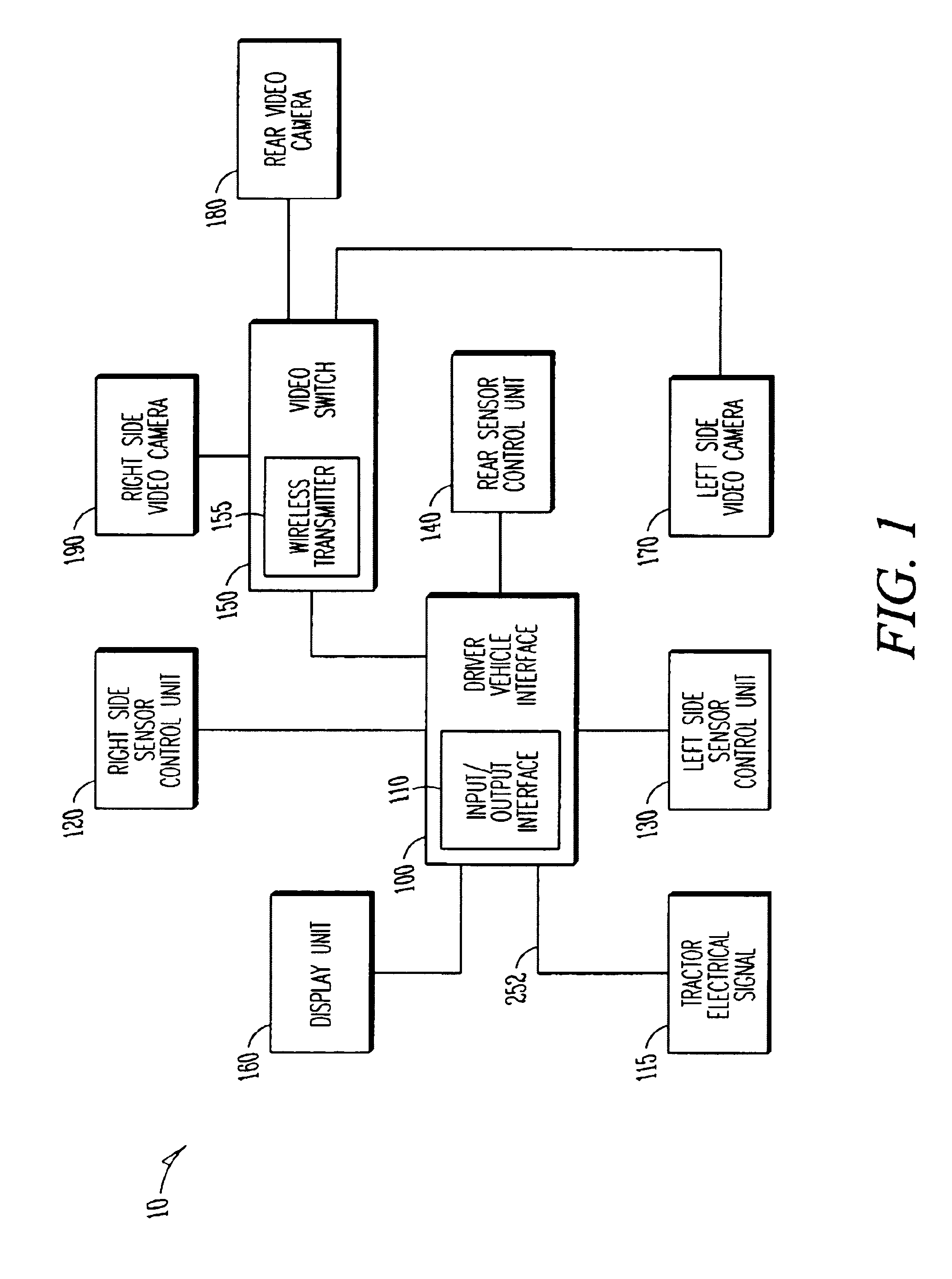
Trailer based collision warning system and method
InactiveUS6933837B2Low costReduced portabilityAnti-collision systemsColor television detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
A trailer based collision warning system includes one or more side object detection sensors, one or more backup assist sensors, a driver vehicle interface, and trailer-mounted display units operating essentially independent of the tractor with all detection and warning system equipment mounted on the trailer. The trailer based collision warning system is coupled to industry-standard tractor to trailer wiring to provide the trailer with power and signals such as left turn indication and right turn indication. The side and rear sensors detect the presence and location of objects and transfer this information to a driver vehicle interface device located on the trailer. The system can also be equipped with video cameras with a means of automatically activating the camera in the area where a hazard condition has been detected. The driver vehicle interface determines the nature of the information and / or warning needed by the driver and provides this information in the form of signals sent to displays that can to assist the driver in safely maneuvering the trailer. The collision warning system can also operate in a security mode.
Owner:ALTRA TECH
Method and apparatus for securing a wireless air interface
InactiveUS20080076392A1Prevent theftUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsCommunications systemAir interface
Some embodiments are implemented in a communication system that includes a first wireless communication system and a second wireless communication system that includes a Femtocell access point (FAP) and a network controller that can communicatively couple the FAP to the first wireless communication system. In some embodiments, the network controller can communicatively couple to the first wireless communication system through a UTRAN Iu interface. Some embodiments provide a method of securing a wireless air interface. The method receives a security mode command that includes a set of security keys and a set of security algorithms at the FAP from the network controller. The method determines the integrity of a set of messages that are exchanged between the FAP and a user equipment that is communicatively coupled to the FAP through an air interface.
Owner:KINETO WIRELESS
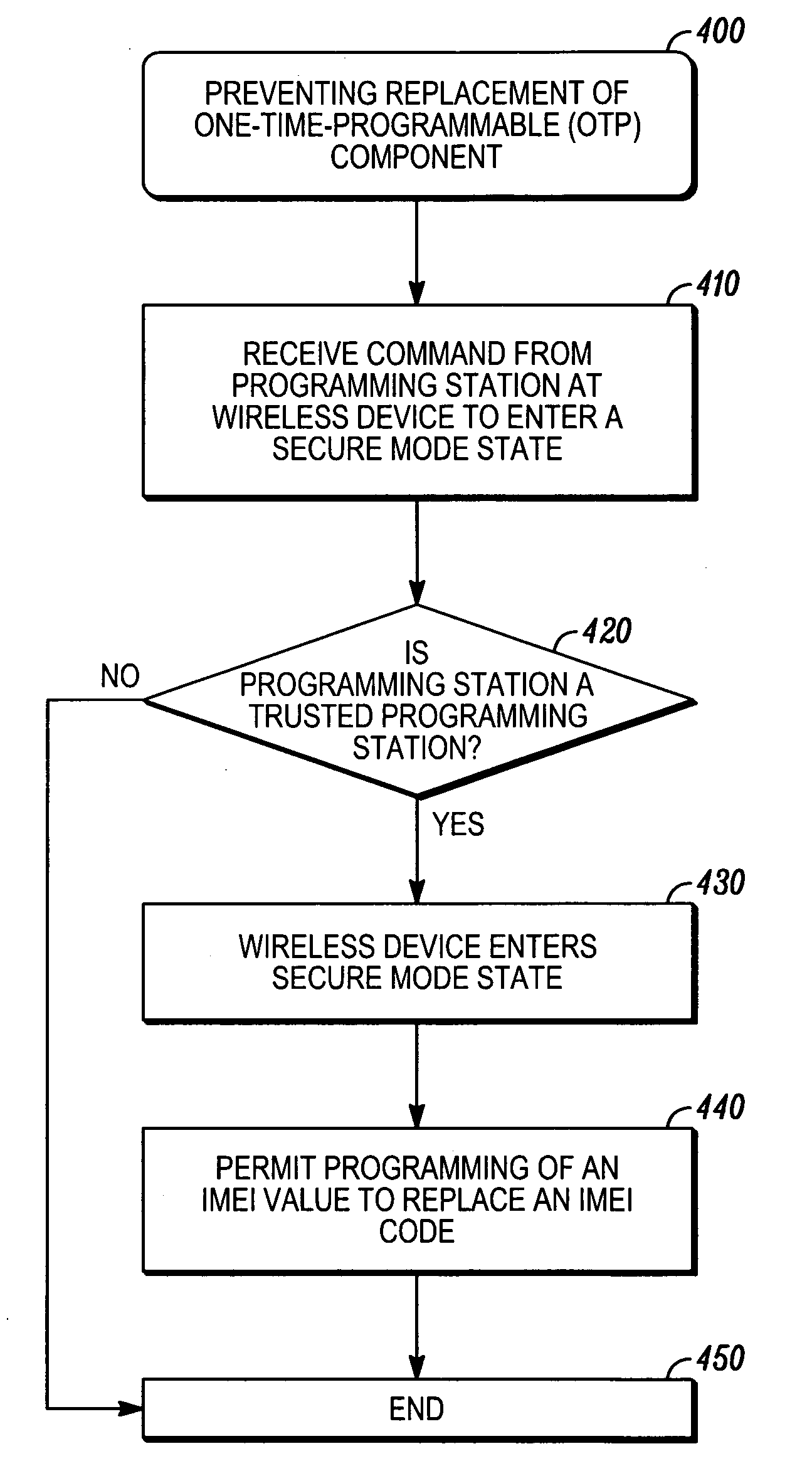
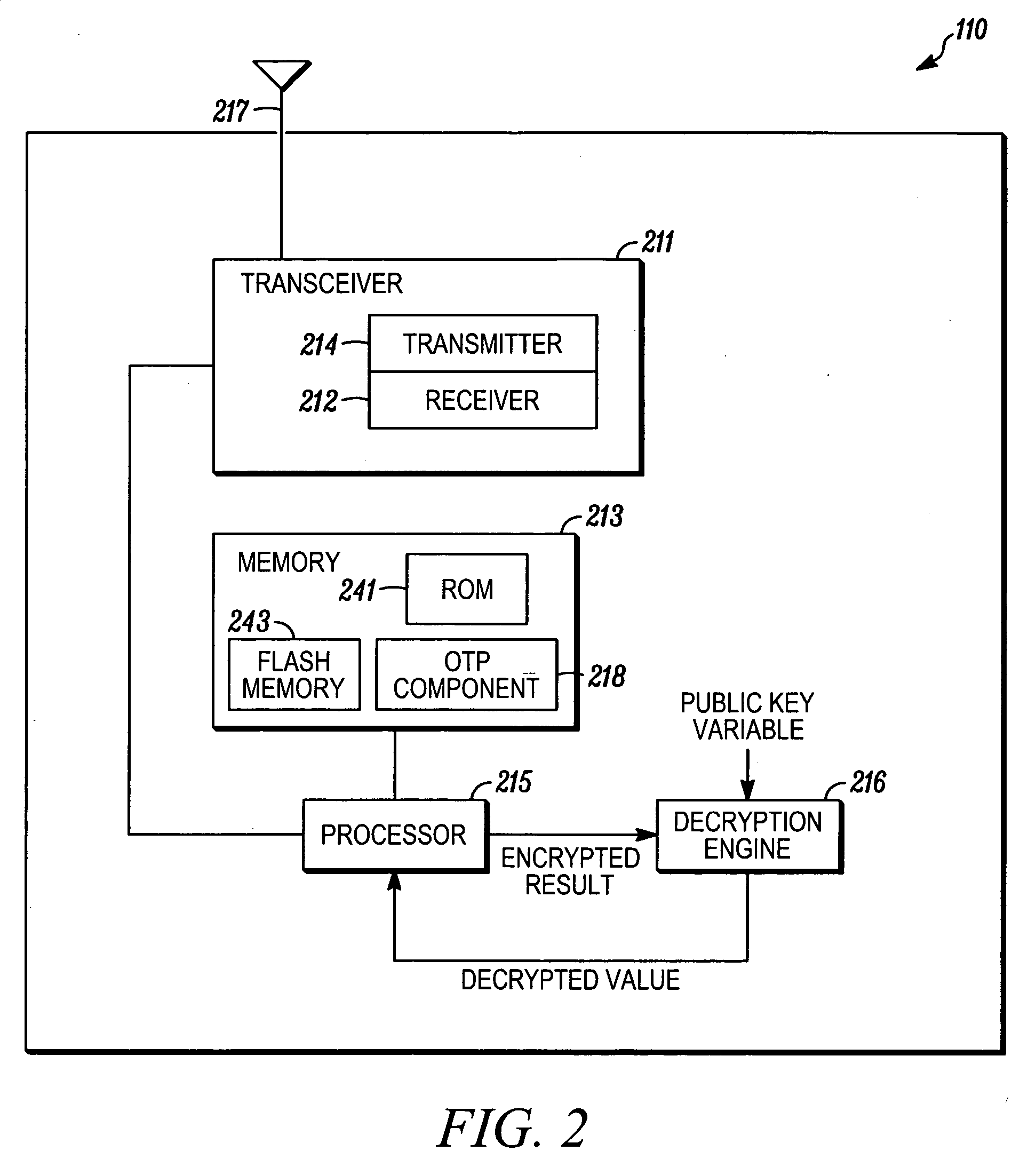
Method, system and apparatus for prevention of flash IC replacement hacking attack
InactiveUS20070050622A1User identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsChallenge responseOne time programmable
Techniques are provided for preventing replacement of a one-time-programmable (OTP) component. The OTP component can be part of a wireless device. The wireless device is configured such that programming of a new IMEI code into the OTP component is permitted only when the wireless device is in a secure-mode state. A challenge-response protocol is used to place the wireless device in this secure-mode state.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Method and apparatus for device detection and multi-mode security in a control network
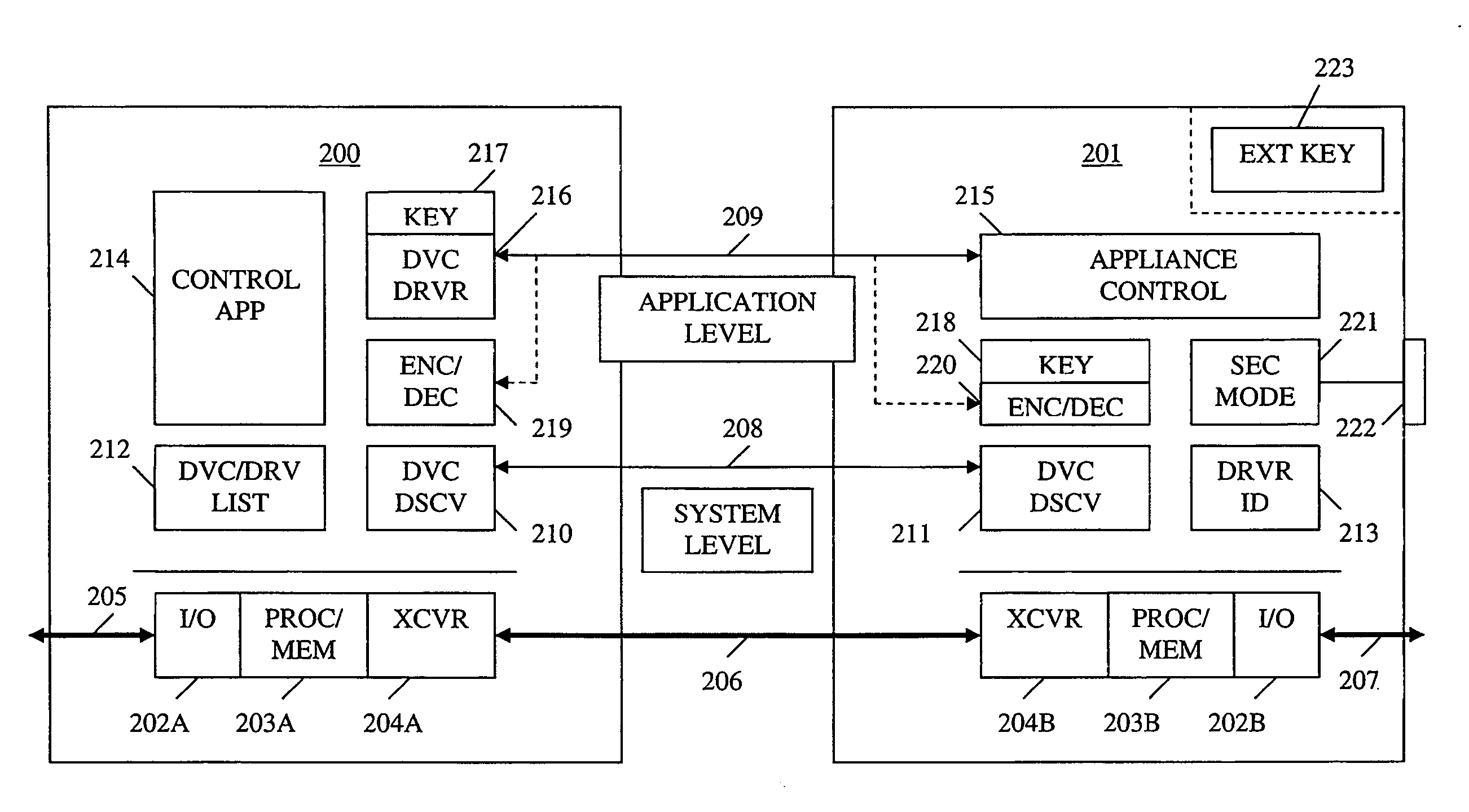
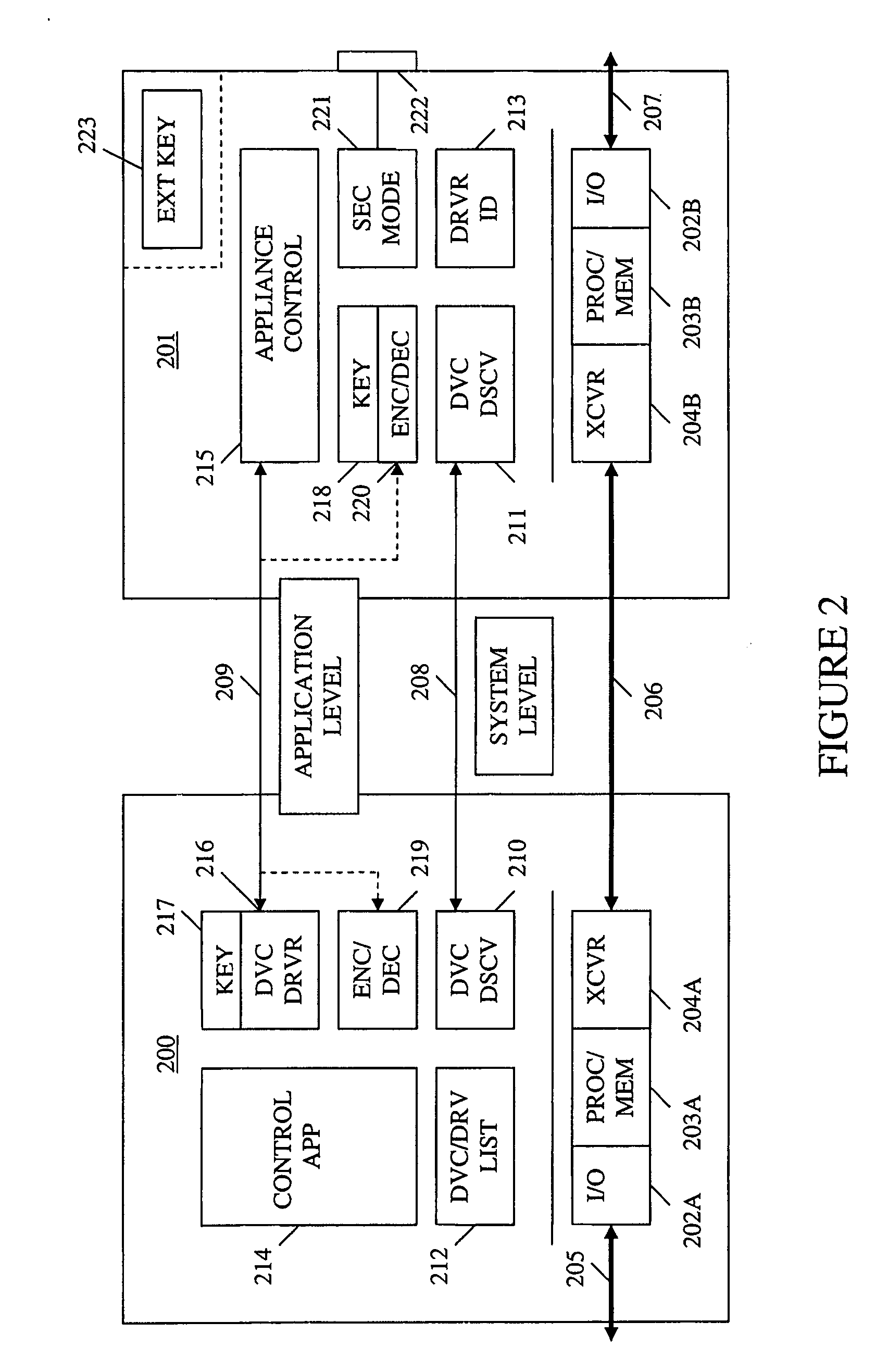
ActiveUS20060174102A1Facilitate key exchangeAvoid reconfigurationSecurity arrangementSecuring communicationWireless controlUser management
A method and apparatus for device discovery and multi-mode security in a wired and / or wireless control network are described. A controlled device is configured with discovery-level instructions and application-level control instructions. The controlled device includes a user-configurable parameter for selecting between multiple security modes. In one or more security modes, the controlled device may ignore application-level messages until encrypted communications are established with a controller. In one mode, the encrypted communication is established with an encryption key exchange using a predetermined security key. In another mode, a specific key is manually entered into the controller by the user / administrator to facilitate the encryption key exchange. Additionally, for control applications where security is not important, an unencrypted security mode may be implemented. A driver ID provided by the controlled device facilitates loading of a preferred device driver by the controller.
Owner:SNAP ONE LLC
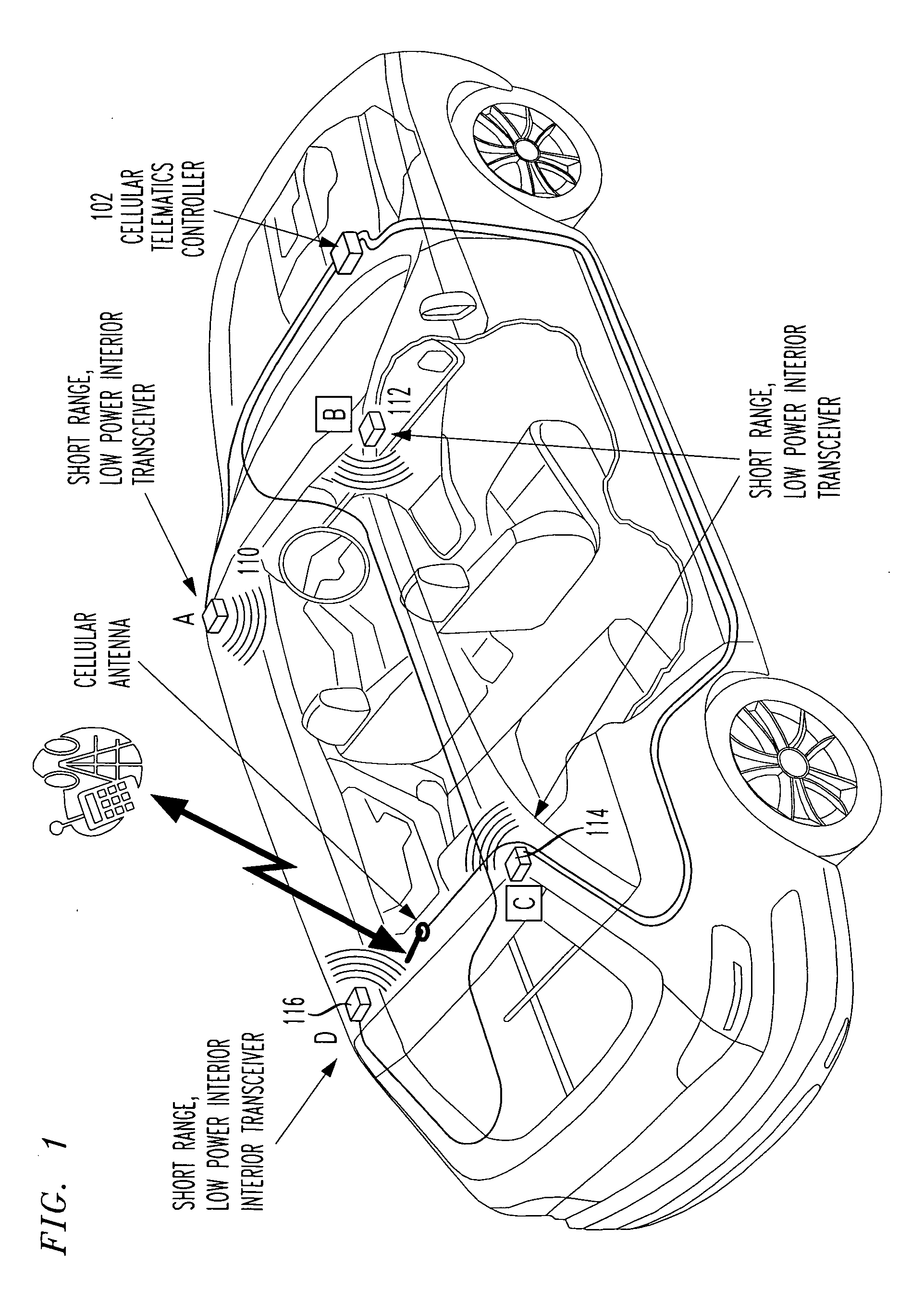
Telematics enhanced mobile device safety interlock
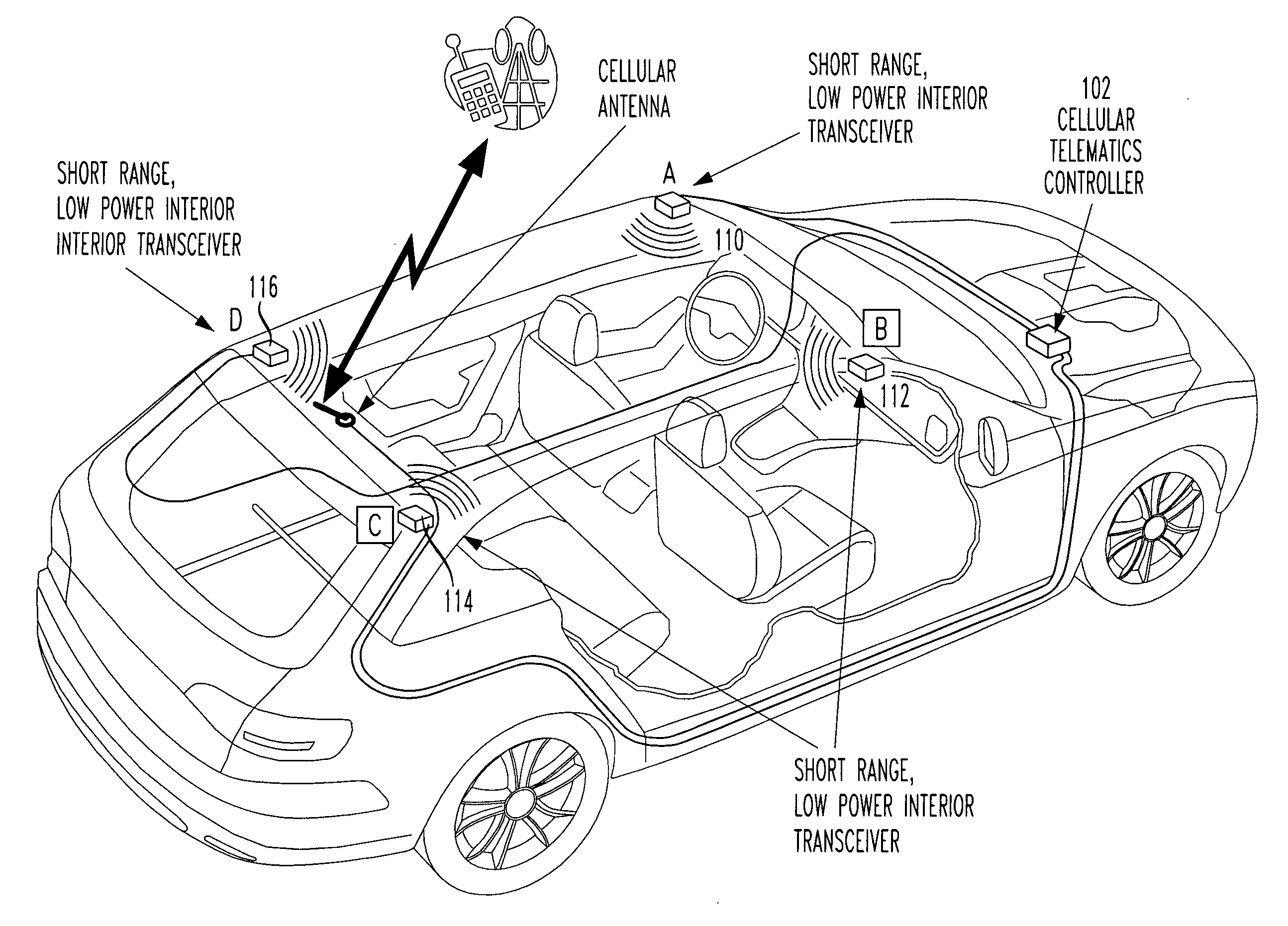
InactiveUS20120006610A1Electric devicesUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDriver/operatorTransceiver
A vehicle includes a telematics controller and at least three short range, low power interior transceivers, one of which is focused on a vehicle's driver's seat only. At least two additional individual short range, low power interior transceivers are focused on a front passenger seat, and a rear seat. A fourth or more short range, low power interior transceiver may be included in a larger vehicle. Synergistic interaction is provided between a vehicle's telematics controller and wireless devices (e.g. cell phones, smart phones, PDAs, wireless laptops, etc.) to parametrically control at least one wireless service or other operation of a wireless device presumed operated by the driver of the vehicle. Example wireless services blocked or forced into a safe mode (such as hands-free operation) include SMS, Email, and Voice services.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Apparatus and method for managing access to a memory
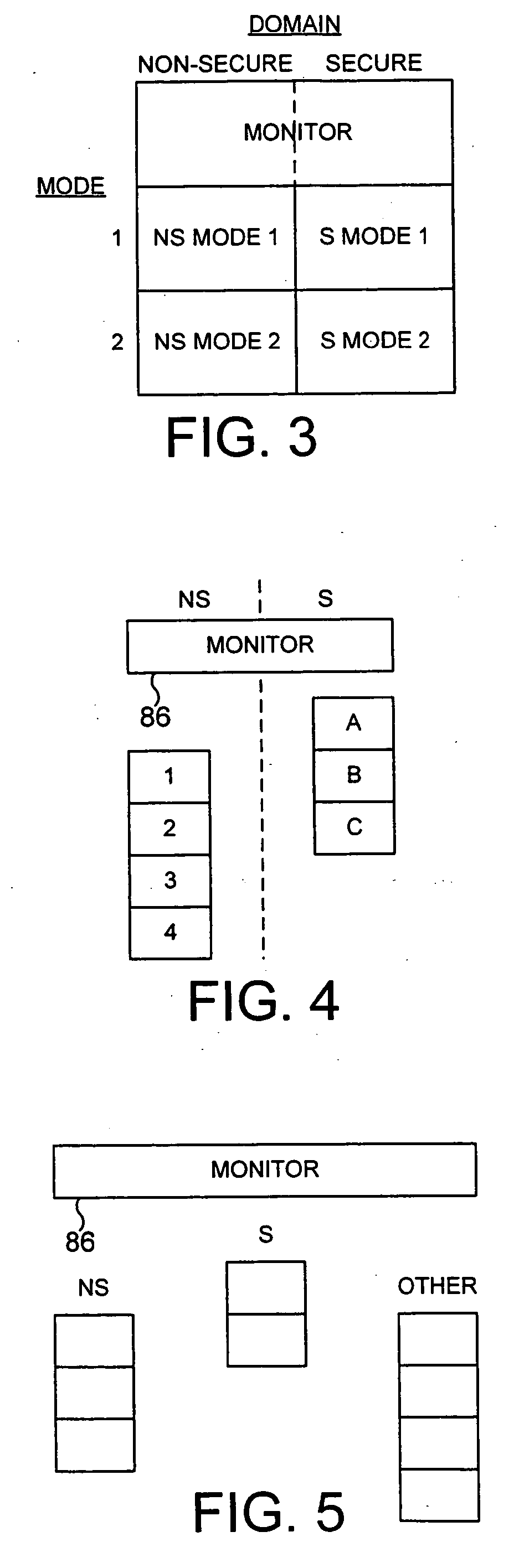
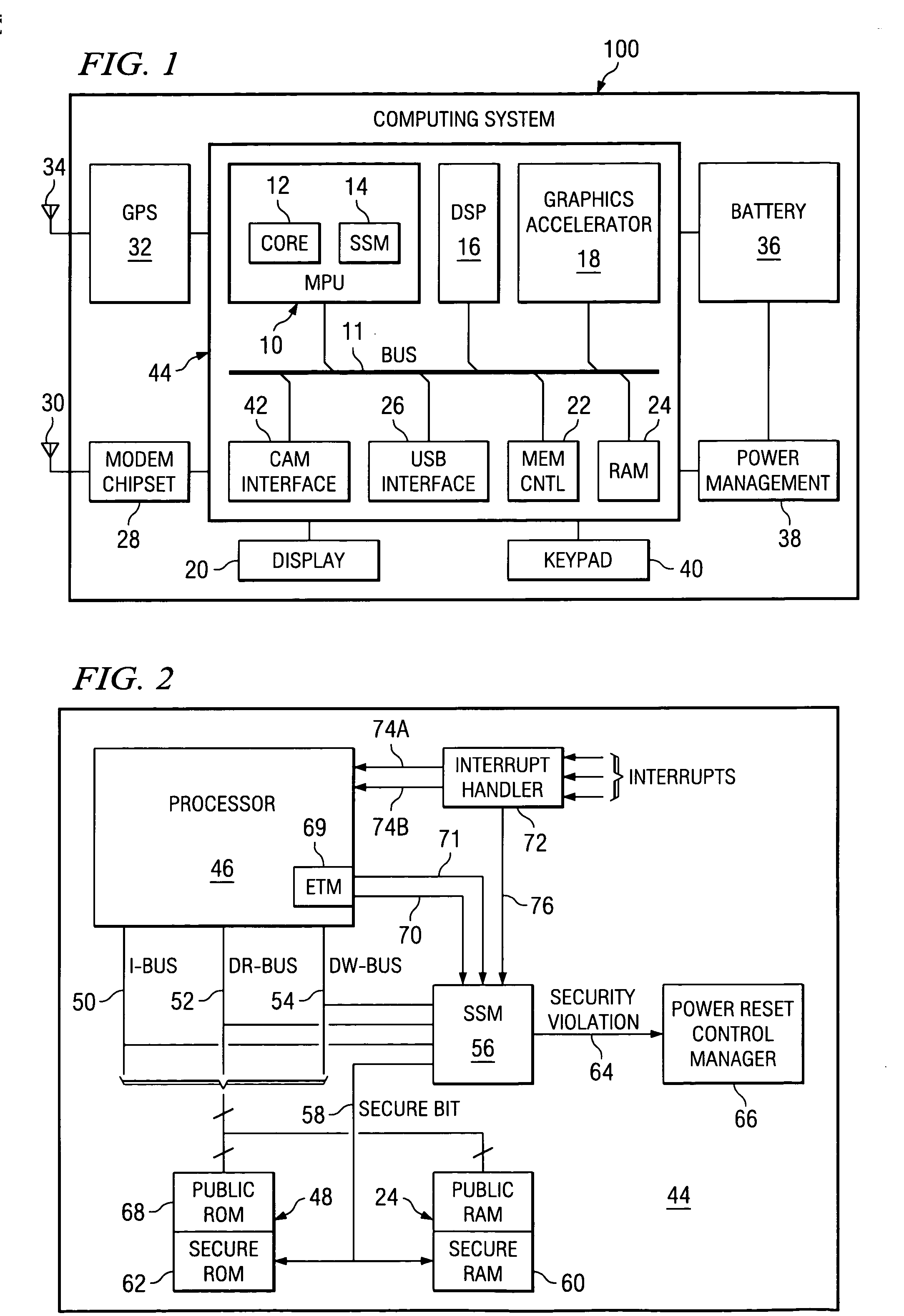
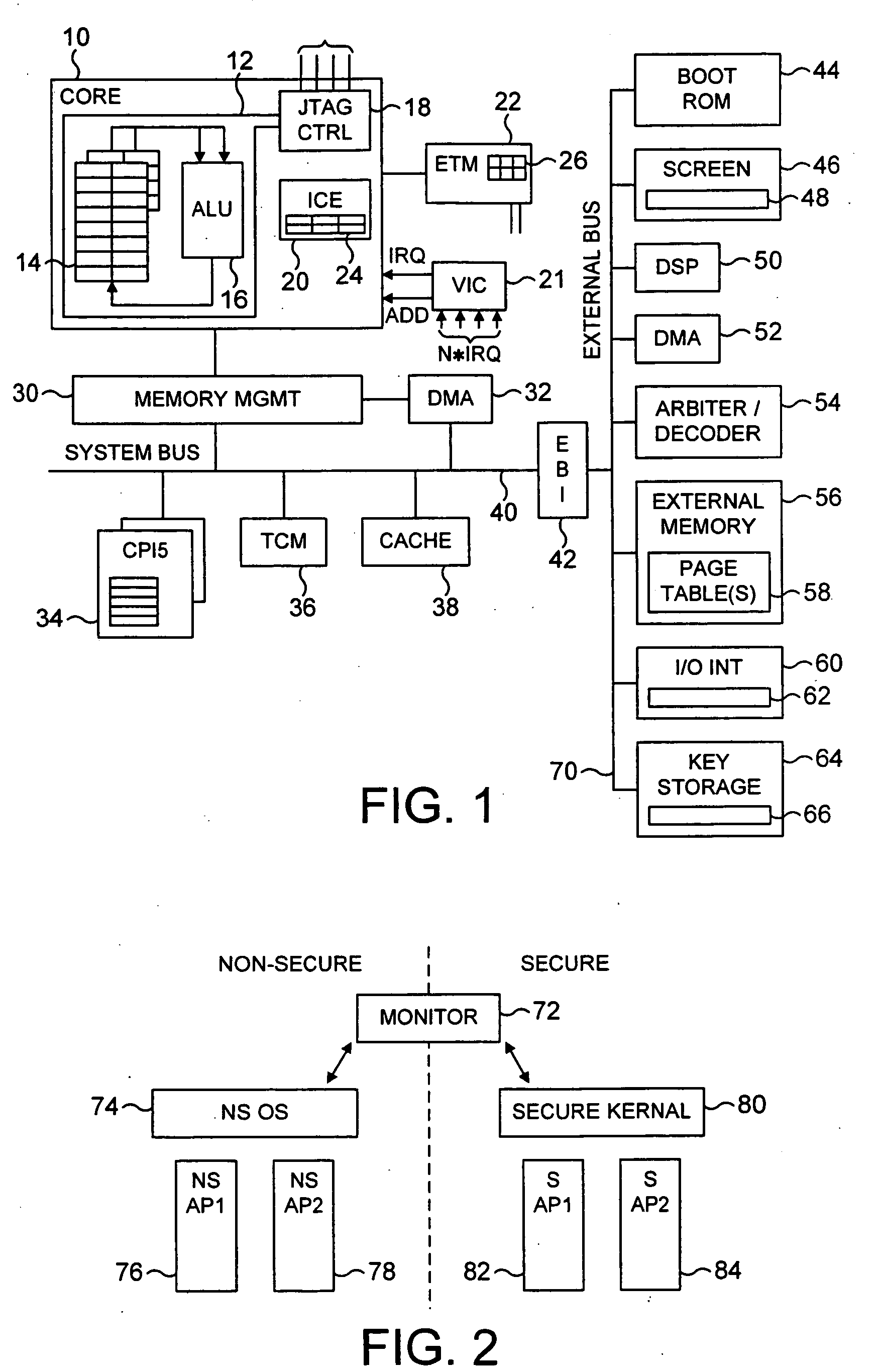
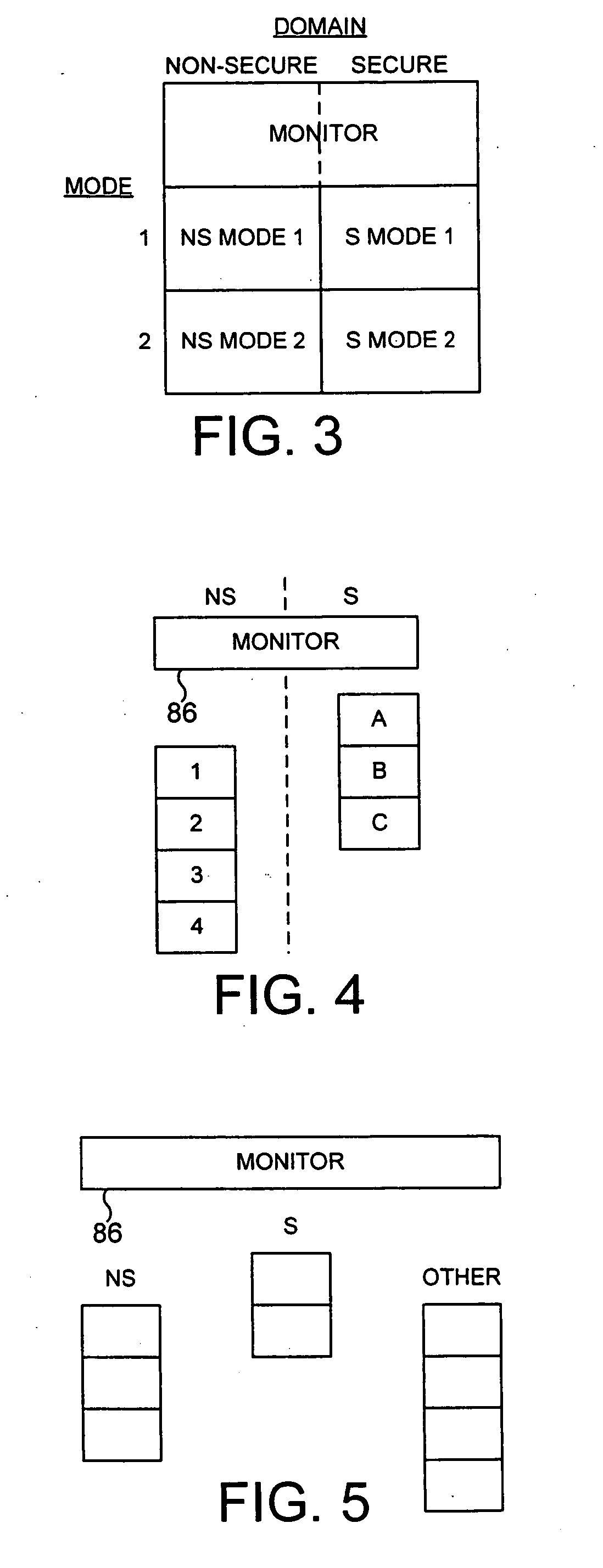
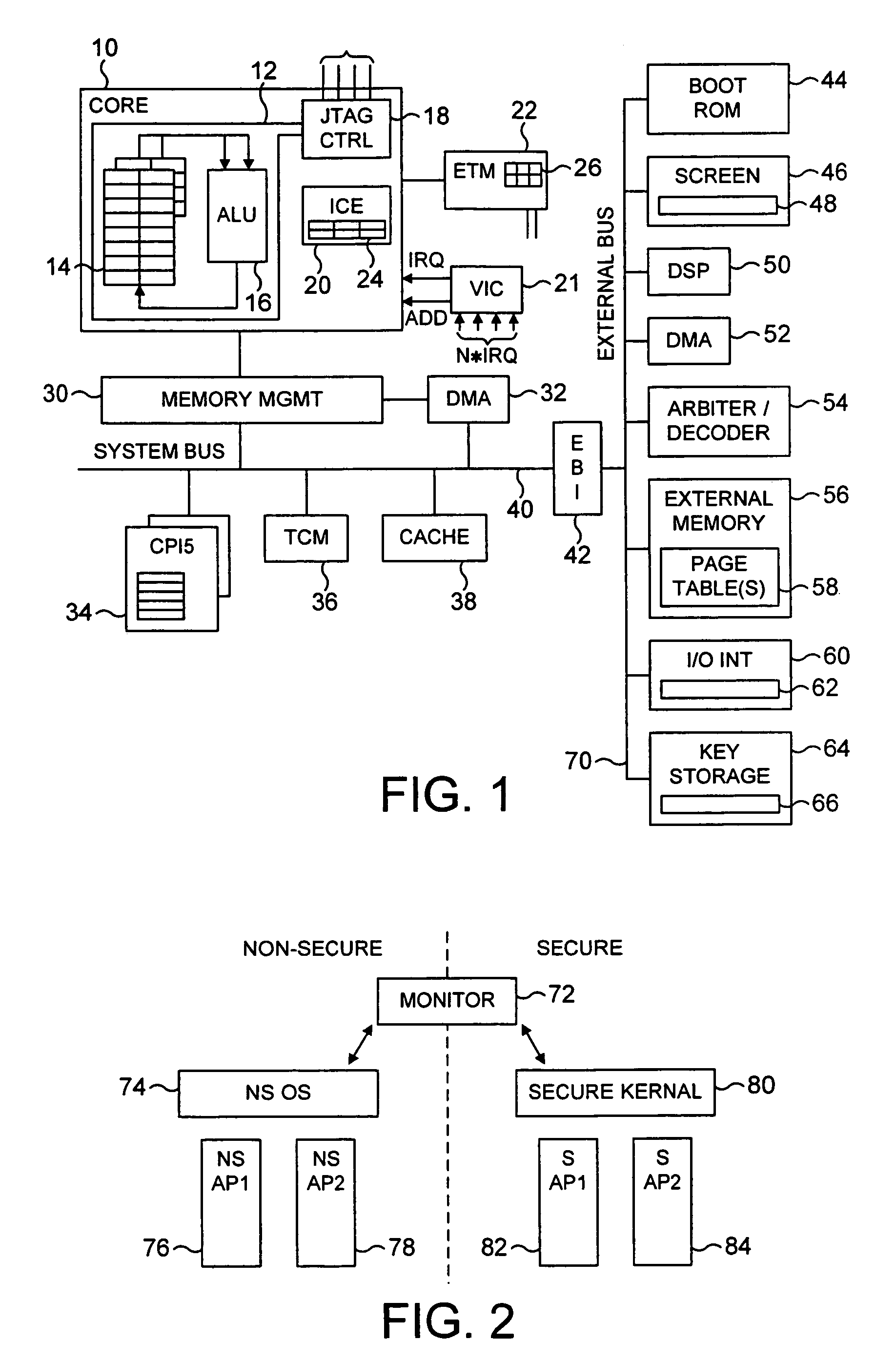
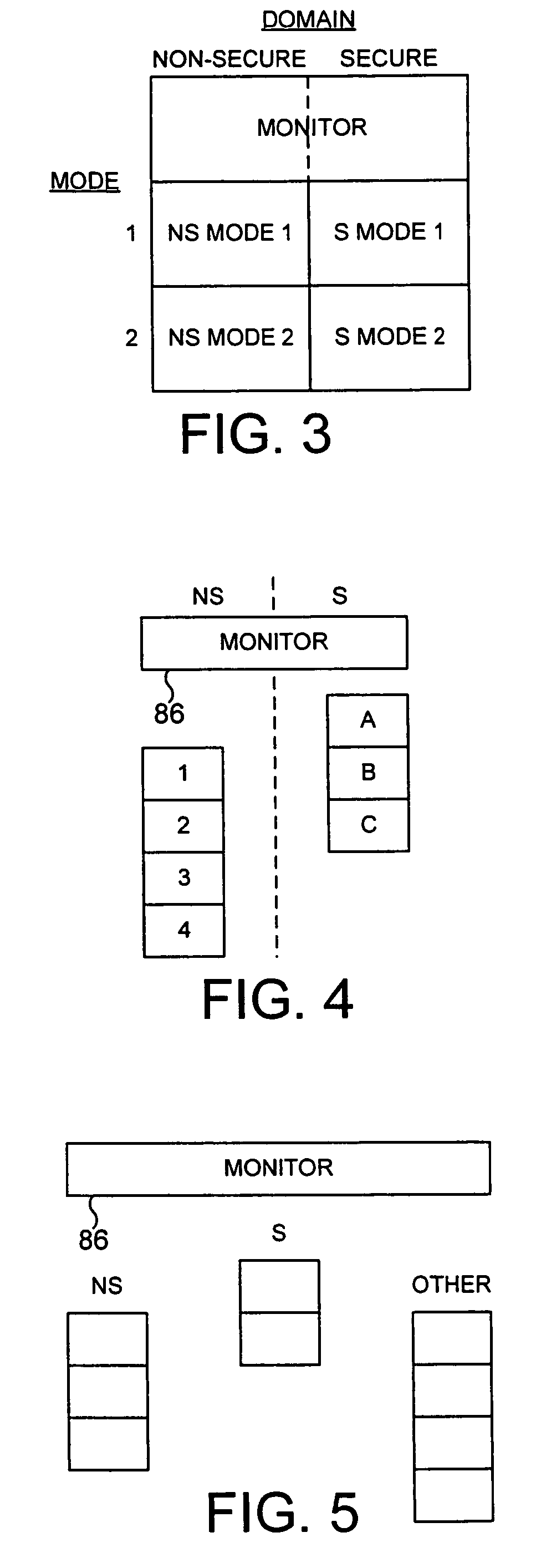
ActiveUS20040177269A1Performance is not affectedEasy to operateMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsManagement unitMultiple modes
The present invention provides a data processing apparatus and method for managing access to a memory within the data processing apparatus. The data processing apparatus comprises a processor operable in a plurality of modes and a plurality of domains, said plurality of domains comprising a secure domain and a non-secure domain, said plurality of modes including at least one non-secure mode being a mode in the non-secure domain and at least one secure mode being a mode in the secure domain, said processor being operable such that when executing a program in a secure mode said program has access to secure data which is not accessible when said processor is operating in a non-secure mode. Further, a memory is provided for storing data required by the processor, and consists of secure memory for storing secure data and non-secure memory for storing non-secure data. The memory further contains a non-secure table and a secure table, the non-secure table being within the non-secure memory and arranged to contain for each of a number of first memory regions an associated descriptor, and the secure table being within the secure memory and arranged to contain for each of a number of second memory regions an associated descriptor. When access to an item of data in the memory is required by the processor, the processor issues a memory access request, and a memory management unit is provided to perform one or more predetermined access control functions to control issuance of the memory access request to the memory. The memory management unit comprises an internal storage unit operable to store descriptors retrieved by the memory management unit from either the non-secure table or the secure table, and in accordance with the present invention the internal storage unit comprises a flag associated with each descriptor stored within the internal storage unit to identify whether that descriptor is from the non-secure table or the secure table. By this approach, when the processor is operating in a non-secure mode, the memory management unit is operable to perform the predetermined access control functions for the memory access request with reference to access control information derived from the descriptors in the internal storage unit retrieved from the non-secure table. In contrast, when the processor is operating in a secure mode, the memory management unit is operable to perform the predetermined access control functions for the memory access request with reference to access control information derived from the descriptors in the internal storage unit retrieved from the secure table. This approach enables different descriptors to be used for the control of accesses to memory in either the secure domain or the non-secure domain, whilst enabling such different descriptors to co-exist within the memory management unit's internal storage unit, thereby avoiding the requirement to flush the contents of such an internal storage unit when the operation of the processor changes from the secure domain to the non-secure domain, or vice versa.
Owner:ARM LTD
Computerized method and system for managing the exchange and distribution of confidential documents
A method and system for sending, receiving and managing the exchange of messages between an intranet and multiple external users using a secure server as an intermediary interface for Internet communications. In one form, the secure server operates in a replication mode with a Lotus Domino server wherein secure transmissions are designated by an @secure URL. In another form, secure transmissions are implemented by establishing a secure connection to the secure server using a browser addressing the server URL. The server operating system interfaces with the intranet so that the intranet user can use standard groupware, such as Lotus Notes, to create, send and receive secure documents. External users are notified by normal e-mail of the presence of secure documents at the server and must connect to the server in a secure mode to retrieve documents. Responses to documents are automatically returned to the sender's e-mail server using secure transmission.
Owner:FLEET NAT BANK
Secure documents with hidden signals, and related methods and systems
InactiveUS7555139B2Character and pattern recognitionSecret communicationPattern recognitionLine width
A security document comprising artwork including a security pattern, characterized in that the security pattern has the form of a line structure in which lines width or line spacing is adjusted to carry predefined data. The artwork is generated by the modifying at least one color of at least a part of the artwork to embed the security pattern in the artwork. Methods for detecting the security pattern include use of a frequency domain structure to detect the security pattern despite rotation and scaling of the document, use of signal tiling to improve signal detection, and use of statistical analyses to verify detection of the security pattern.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
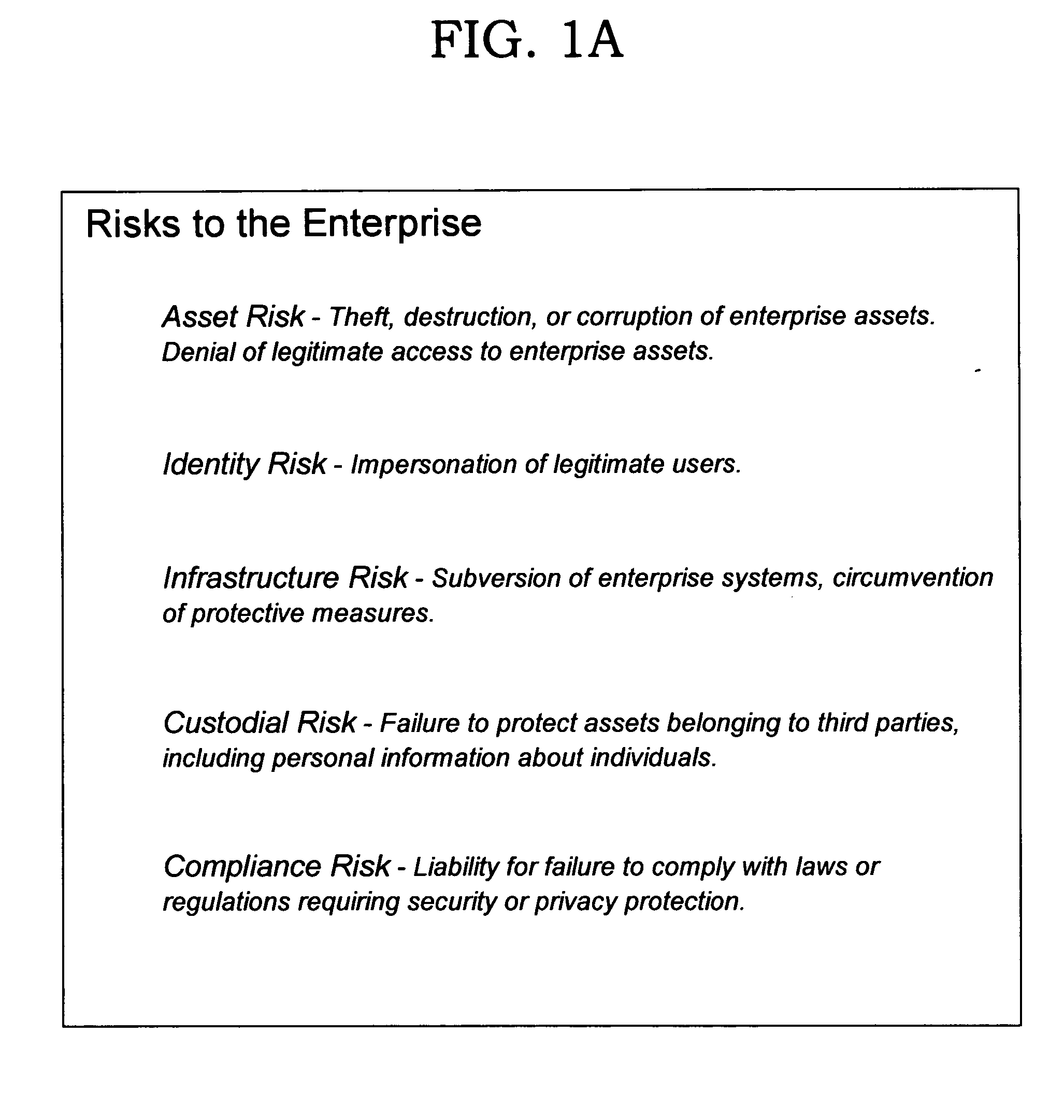
Deriving security and privacy solutions to mitigate risk
InactiveUS20050080720A1Reduce security risksFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsSecurity solutionDecision maker
Techniques are disclosed for systematically assessing an enterprise's security risks in view of a set of security patterns. Each pattern that is applicable to the enterprise's operation is then considered against the backdrop of a set of common attributes that are used, in turn, to further distinguish each pattern from a risk and security solution perspective. Using the disclosed techniques, specific security risks can be identified and appropriate security products can be selected to address those risks in a systematic manner, thereby assisting information technology decision makers across a wide variety of enterprises in deriving security solutions. These security solutions will typically be more effective and efficient from a functional perspective, as well as being more cost-effective, than security solutions created using prior art ad hoc approaches. The disclosed techniques may also be leveraged to create a requirements list for function to be included in a security product.
Owner:IBM CORP
Secure and backward-compatible processor and secure software execution thereon
ActiveUS7322042B2Substantial in resourcesSubstantial in speedDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionExternal storageApplication software
A secure processor assuring application software is executed securely, and assuring only authorized software is executed, monitored modes and secure modes of operation. The former executes application software transparently to that software. The latter verifies execution of the application software is authorized, performs any extraordinary services required by the application software, and verifies the processor has obtained rights to execute the content. The secure processor (1) appears hardware-identical to an ordinary processor, with the effect that application software written for ordinary processors can be executed on the secure processor without substantial change, (2) needs only a minimal degree of additional hardware over and above those portions appearing hardware-identical to an ordinary processor. The secure processor operates without substantial reduction in speed or other resources available to the application software. Functions operating in secure mode might reside in an on-chip non-volatile memory, or might be loaded from external storage with authentication.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
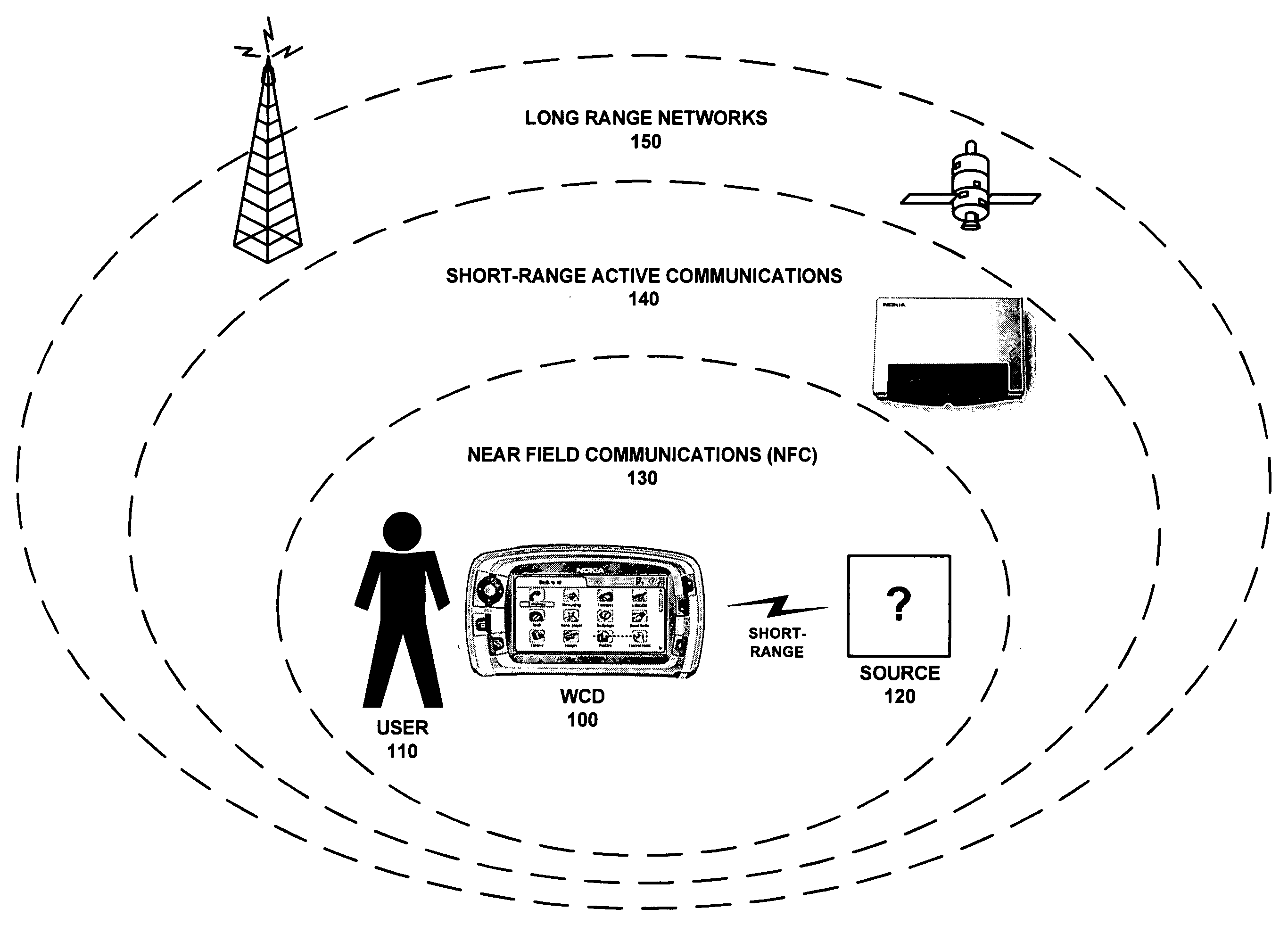
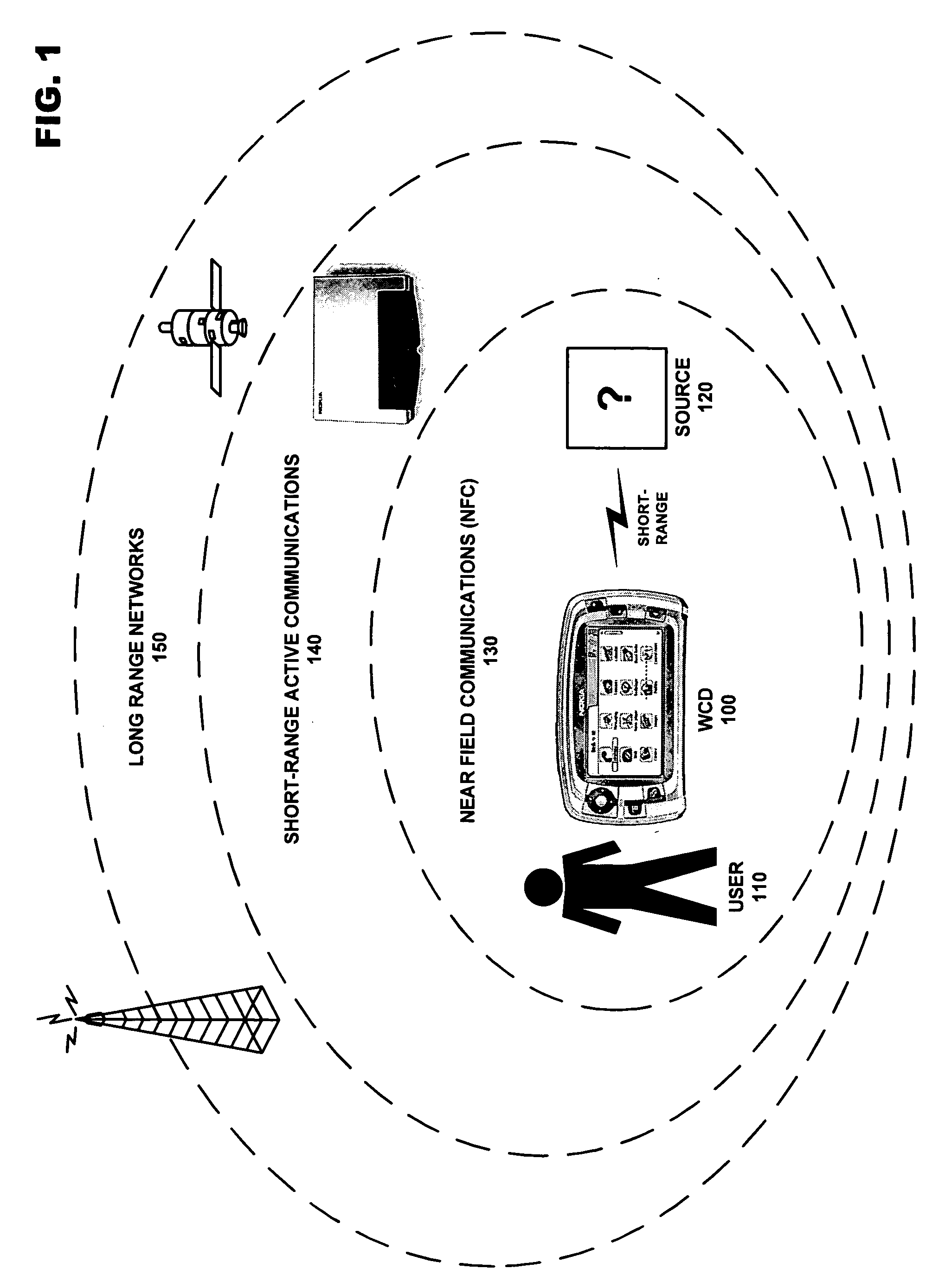
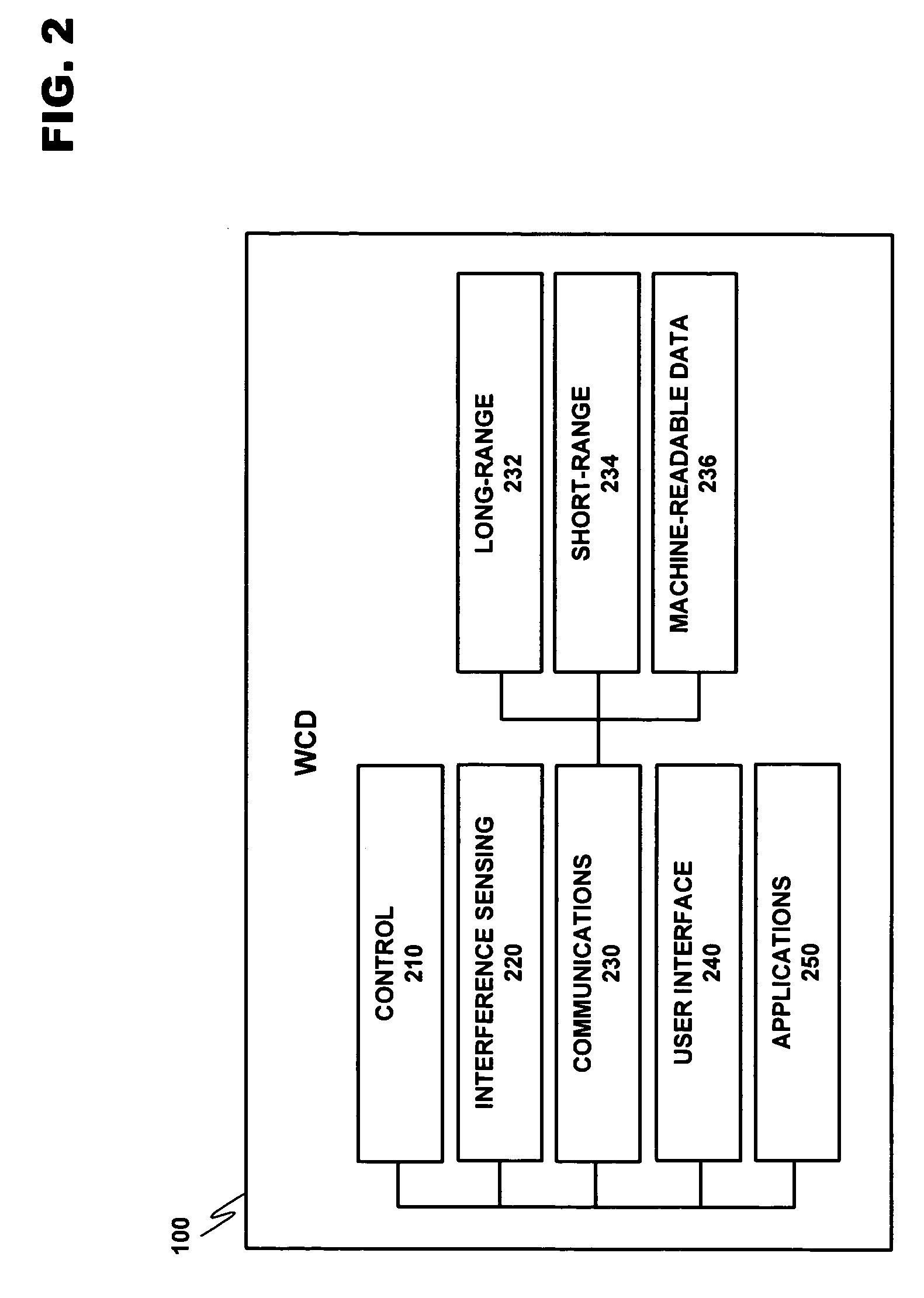
Conditional utilization of private short-range wireless networks for service provision and mobility
ActiveUS20080008140A1Without depletionWithout securityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsService provision
A system for managing the integration of a private short-range wireless network into a service / mobility domain. The private short-range wireless network may be converted into a semi-private short range wireless network by managing access to the network in accordance with rules defined by a home user. These rules allow a home user to define how visitors will be granted access to the semi-private short-range network when the user is at home or away. Restricted access may be enforced when the home user is present, and security measures may force the semi-private short-range wireless network to enter a safe mode when a condition is met.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Secure execution architecture
ActiveUS20050033969A1Mode is changingExecuted easy and fastDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionOperation modeSchema for Object-Oriented XML
The present invention relates to circuitry and a method for providing data security, which circuitry contains at least one processor and at least one storage circuit. The invention is based on the idea that circuitry is provided in which a processor is operable in at least two different modes, one first secure operating mode and one second unsecure operating mode. In the secure mode, the processor has access to security related data located in various memories located within the circuitry. The access to these security data and the processing of them need to be restricted, since an intruder with access to security data could manipulate the circuitry. When testing and / or debugging the circuitry, access to security information is not allowed. For this reason, the processor is placed in the unsecure operating mode, in which mode it is no longer given access to the protected data.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Computer system with dual operating modes
ActiveUS20060212945A1Safely and securely co-existDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsOperation modeCurrent mode
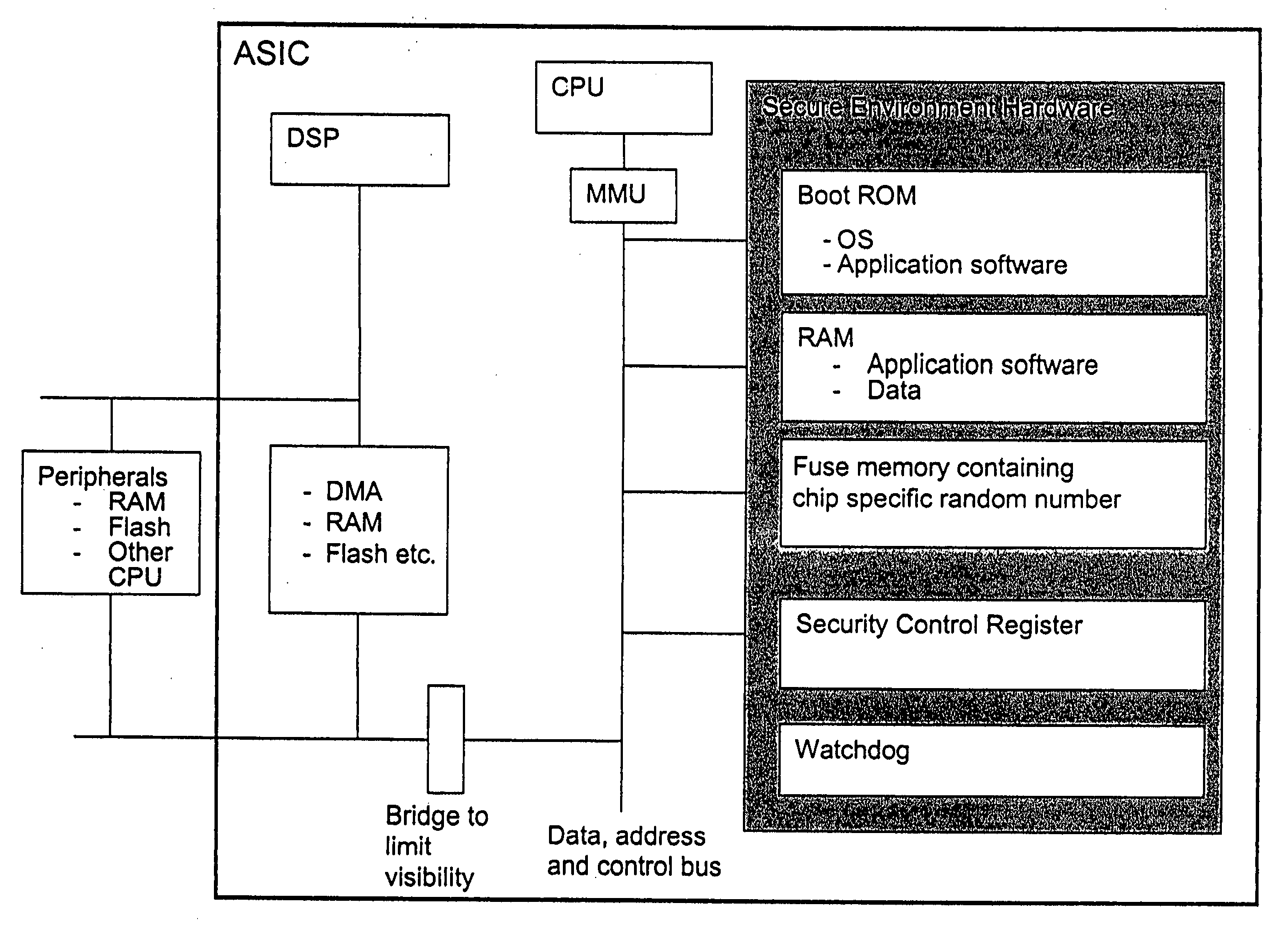
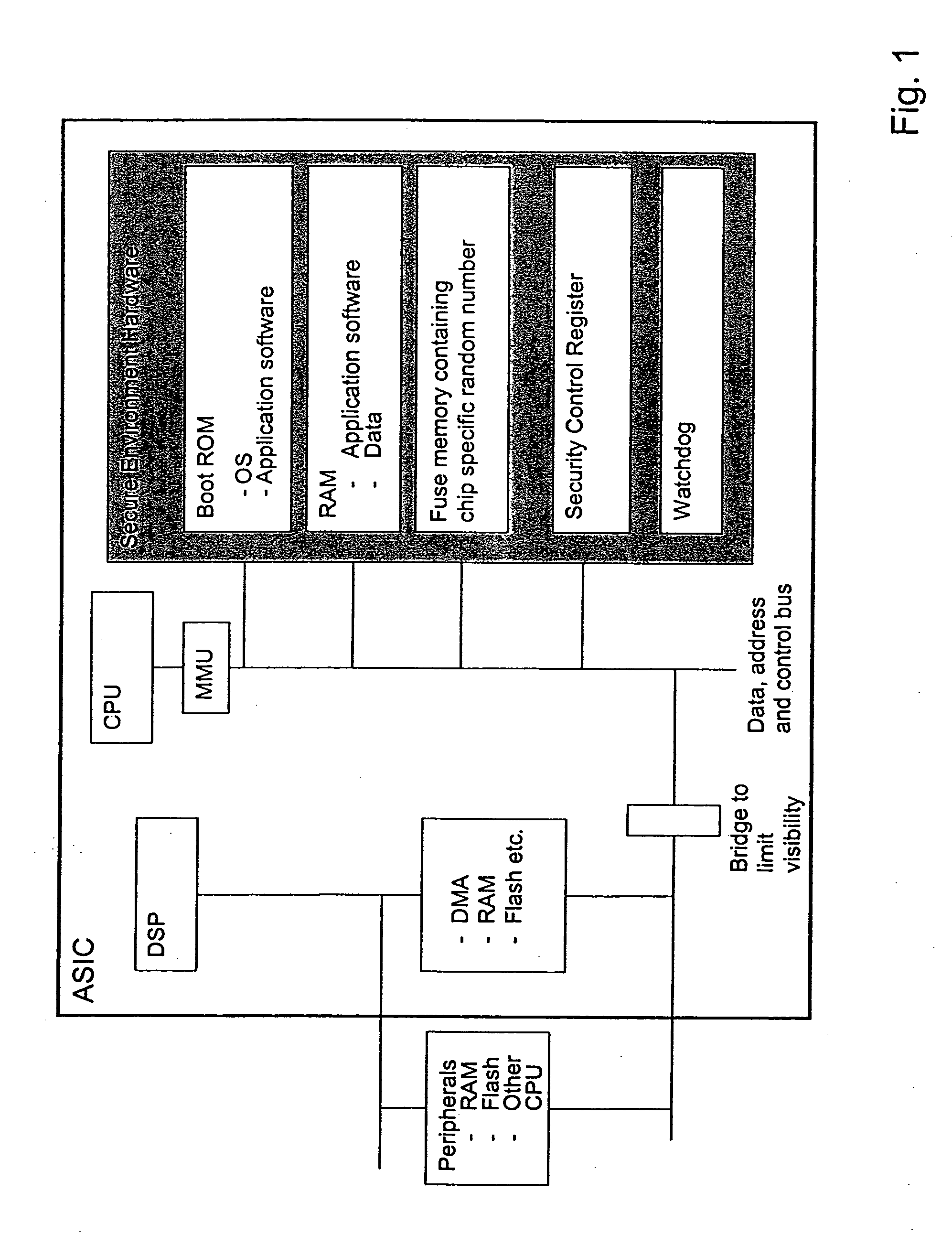
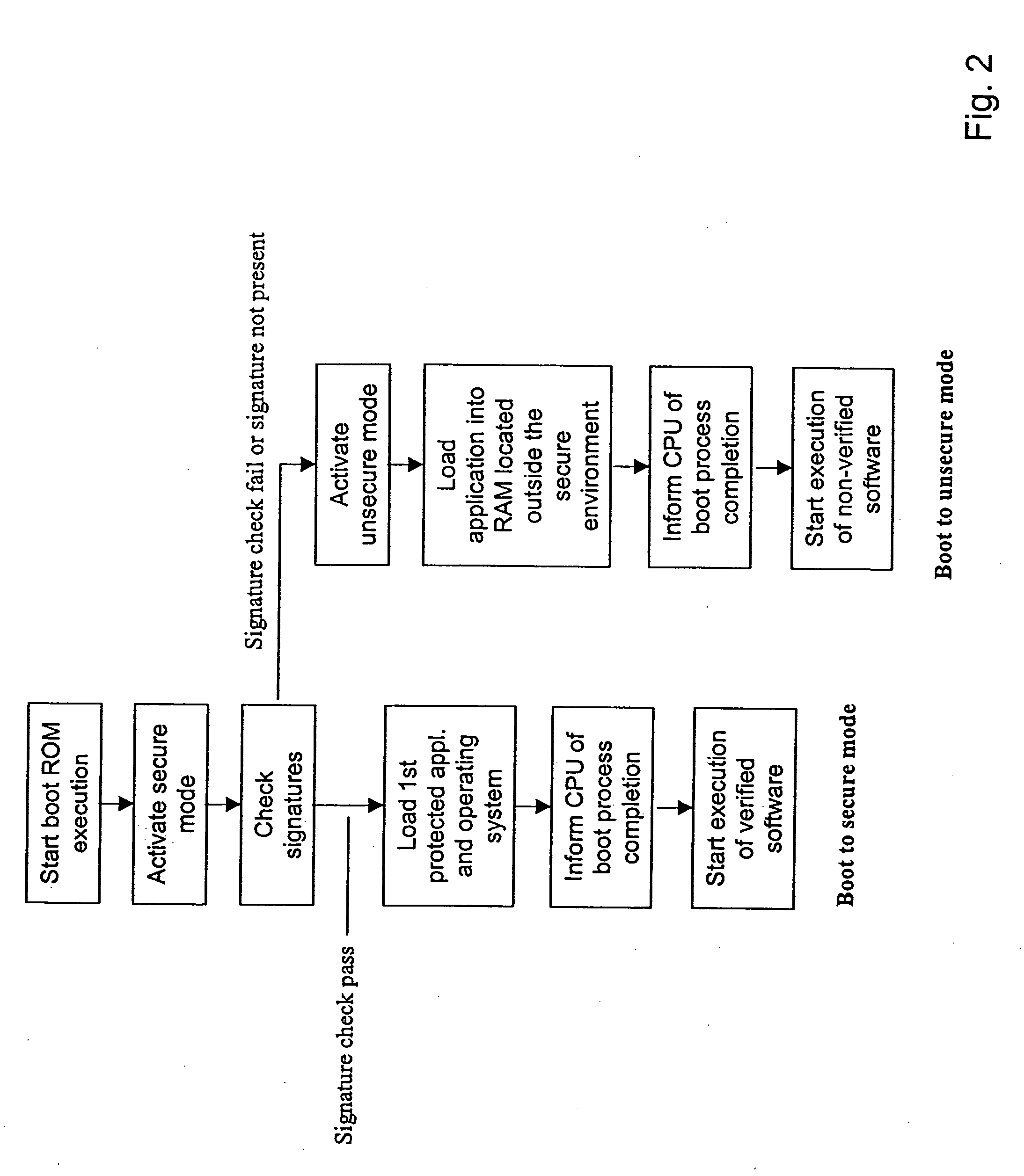
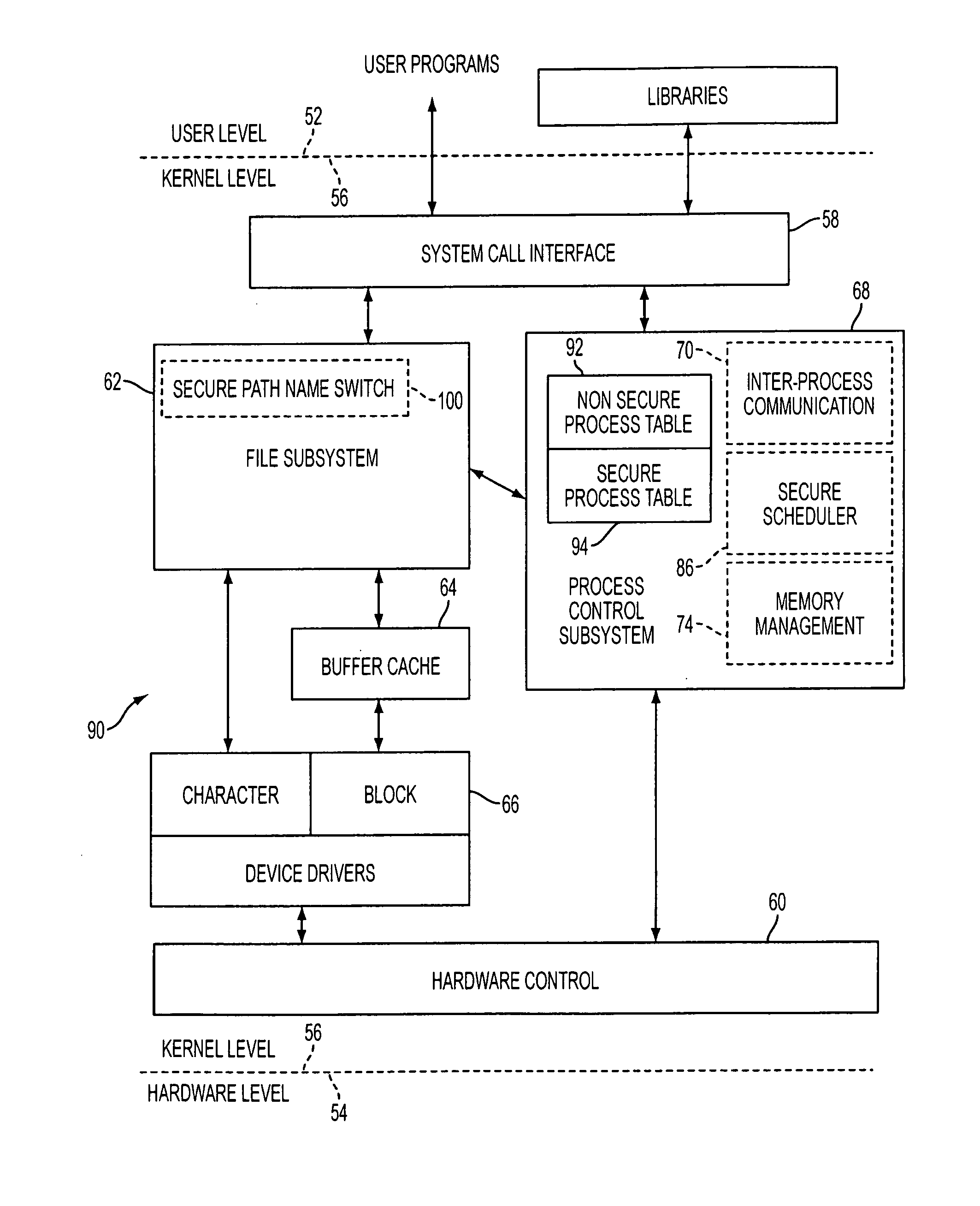
The present invention is a system that switches between non-secure and secure modes by making processes, applications and data for the non-active mode unavailable to the active mode. That is, non-secure processes, applications and data are not accessible when in the secure mode and visa versa. This is accomplished by creating dual hash tables where one table is used for secure processes and one for non-secure processes. A hash table pointer is changed to point to the table corresponding to the mode. The path-name look-up function that traverses the path name tree to obtain a device or file pointer is also restricted to allow traversal to only secure devices and file pointers when in the secure mode and only to non-secure devices and files in the non-secure mode. The process thread run queue is modified to include a state flag for each process that indicates whether the process is a secure or non-secure process. A process scheduler traverses the queue and only allocates time to processes that have a state flag that matches the current mode. Running processes are marked to be idled and are flagged as unrunnable, depending on the security mode, when the process reaches an intercept point. The switch operation validates the switch process and pauses the system for a period of time to allow all running processes to reach an intercept point and be marked as unrunnable. After all the processes are idled, the hash table pointer is changed, the look-up control is changed to allow traversal of the corresponding security mode branch of the file name path tree, and the scheduler is switched to allow only threads that have a flag that corresponds to the security mode to run. The switch process is then put to sleep and a master process, either secure or non-secure, depending on the mode, is then awakened.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
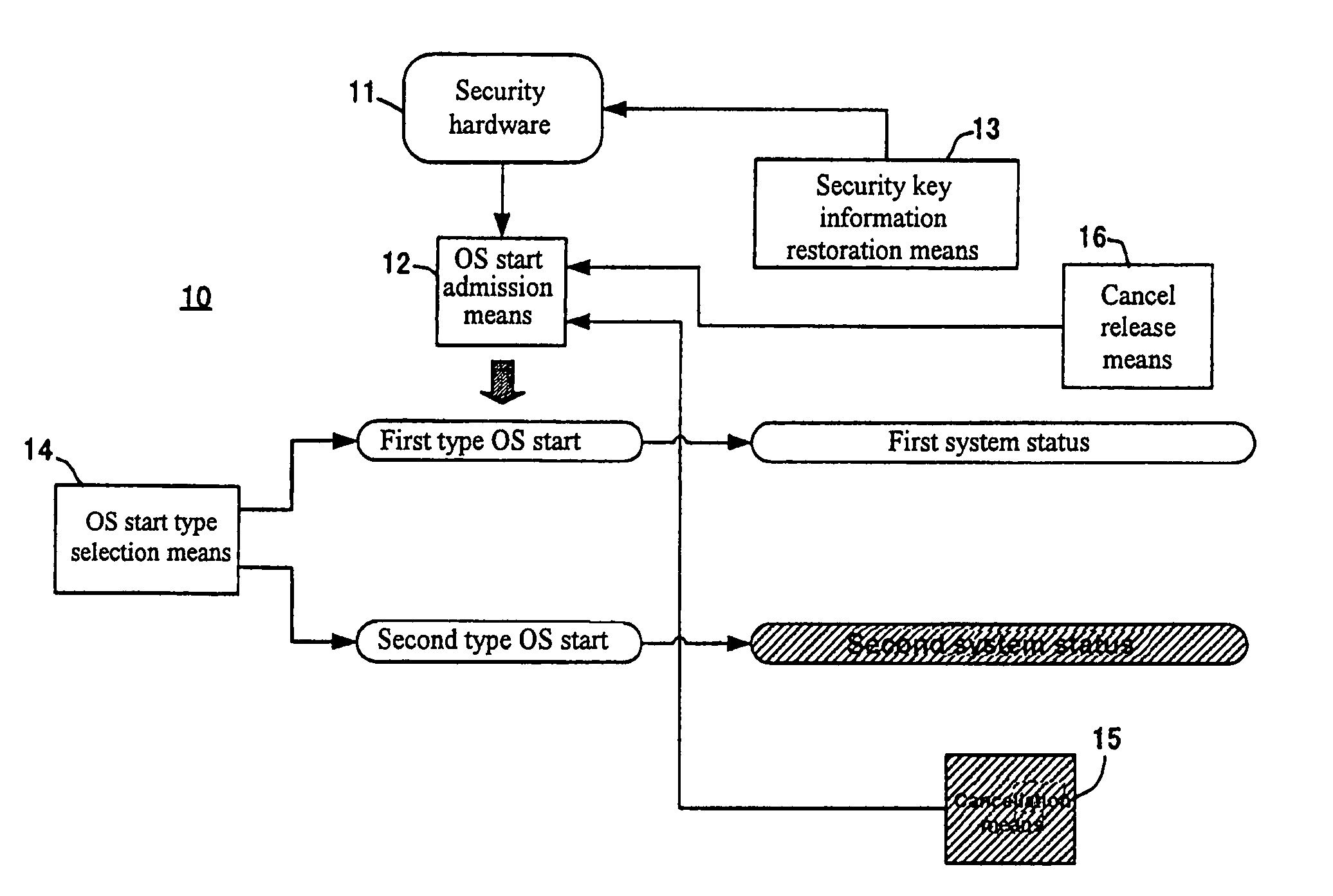
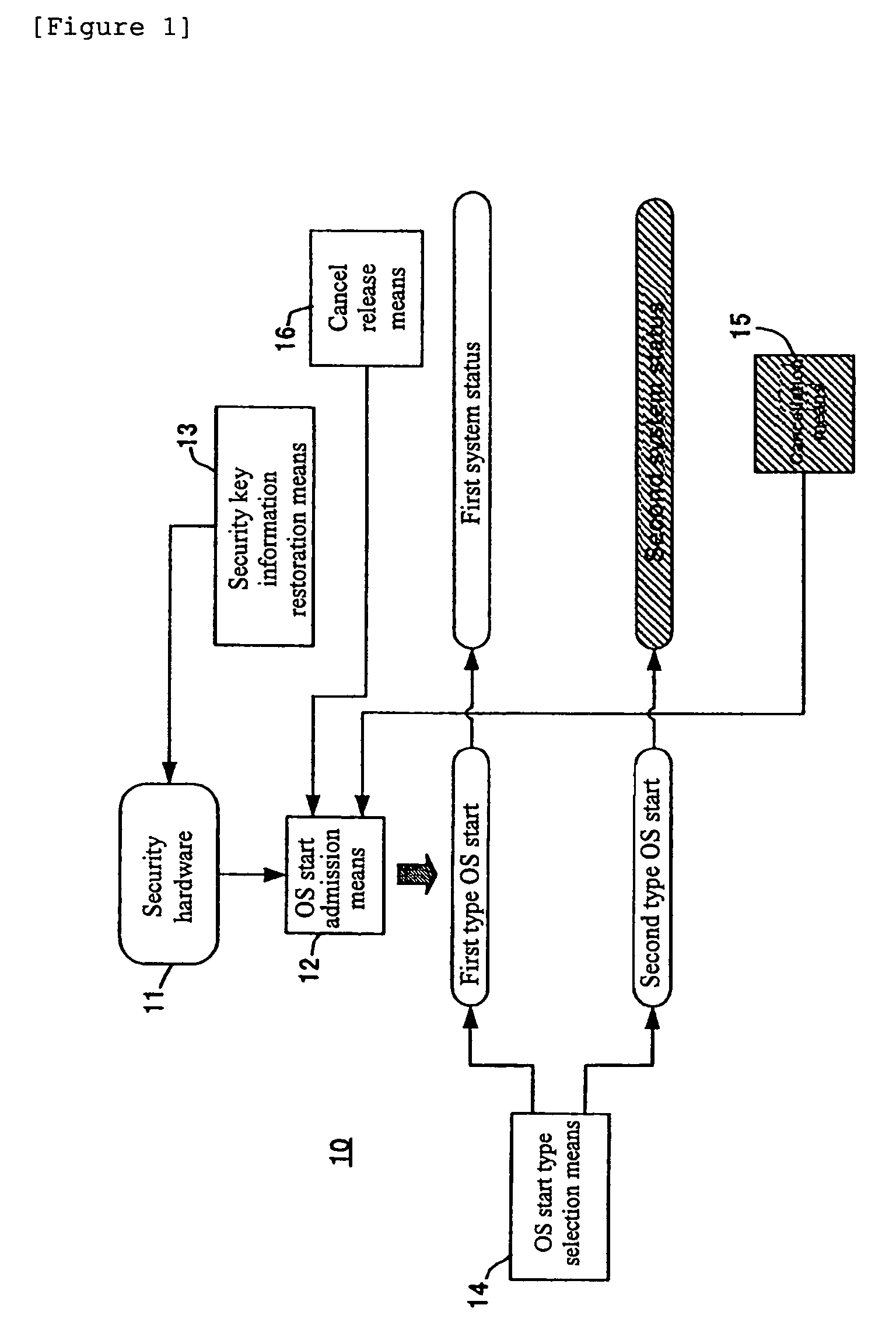
Information processing apparatus for secure information recovery
ActiveUS7290276B2Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsInformation processingInformation recovery
In an information processing apparatus for performing user certification when an OS starts based on security key information of security hardware, a need has arisen to restore the security key information before replacement of the security hardware replaced for troubleshooting. A cancellation means is generated in a second system status generated by a functionally restricted second type OS start such as a safe mode. Although the user certification based on the security key information of the security hardware is usually performed in a first type OS start, the cancellation means cancels it. Thus, it is possible to put the information processing apparatus in a first system status without undergoing the user certification so as to restore the security key information. A cancel release means releases cancellation of the user certification so that the user certification on the first type OS start is restored after the restoration of the security key information.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Location-based security for a portable computer
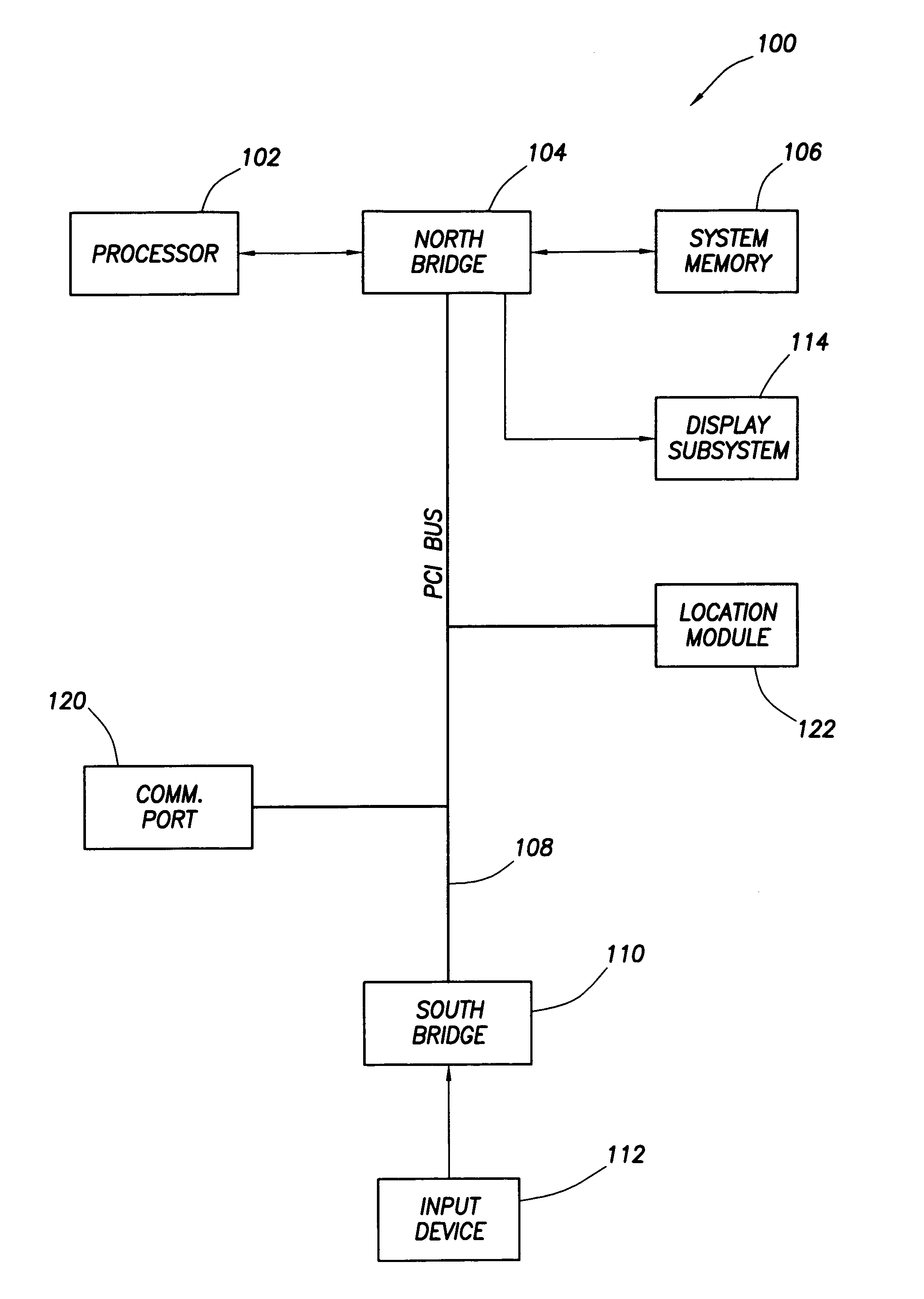
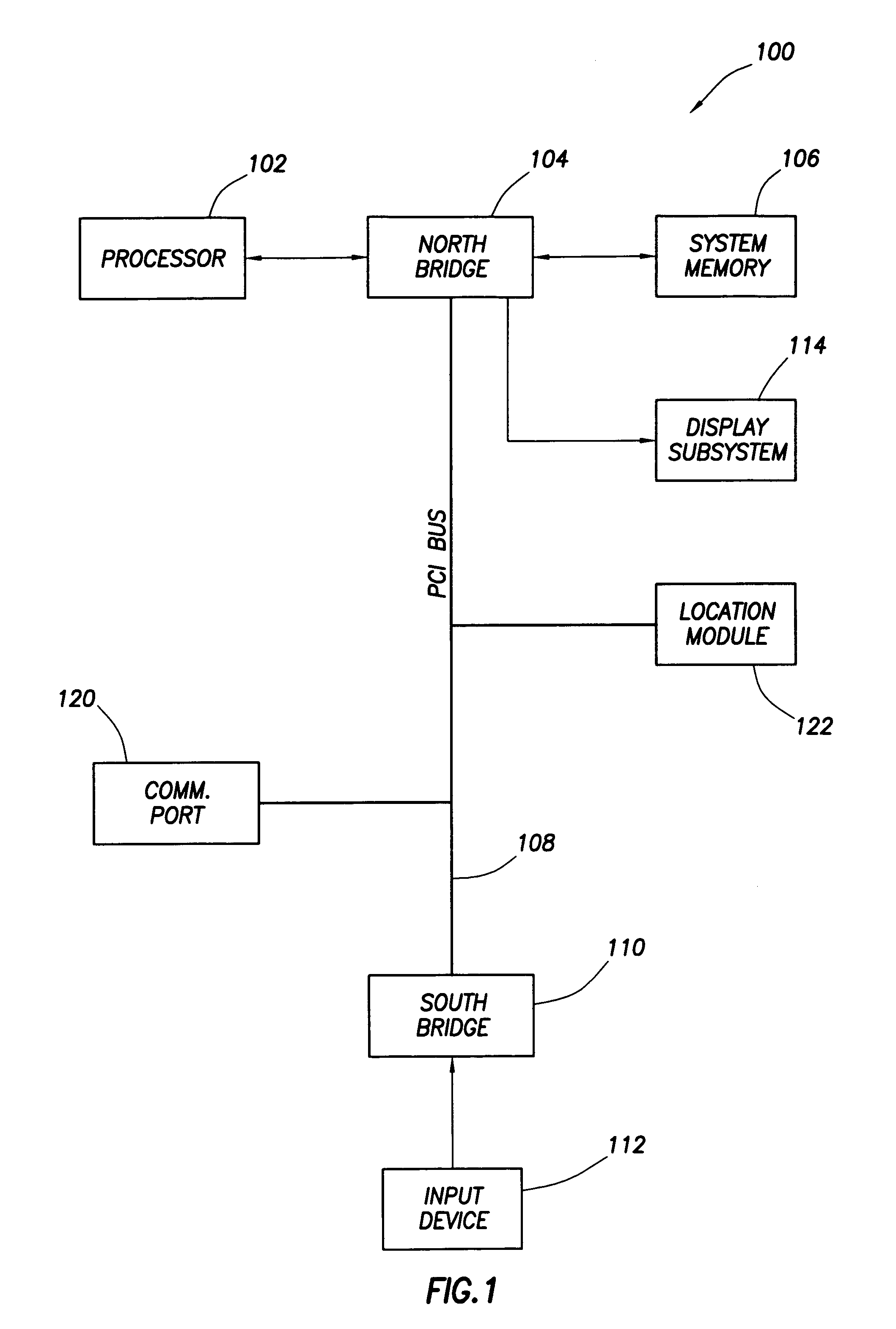
ActiveUS7051196B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsElectronic systemsEngineering
An electronic system embodies a security system which provides varying levels of security based on the location of the system. As such, the system includes a location module, such as a geosynchronous positioning system (“GPS”) receiver that permits the system to determine its location relative to a plurality of preset location areas. Such location areas might be programmed to include the user's office, home, predetermined location for a business trip and the like. Based on the location area in which the system is located, the system invokes a security mode associated with that particular location area. Different location areas may have different security modes.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method and apparatus for providing secure wireless communication
InactiveUS20060105740A1Key distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSecure communicationComputer network
An approach is provided for securely communicating in a wireless network. A cryptographic server generates a command to enable a secure mode of operation for a wireless device, wherein the wireless device can operate in a secure mode and an unsecure mode in support of two-way messaging. The cryptographic server sends the command to the wireless device to activate the secure mode of operation. The secure mode of operation provides transmission of an encrypted message by the wireless device over the wireless network.
Owner:VELOCITA WIRELESS
Method and system of ensuring integrity of a secure mode entry sequence
InactiveUS20060004964A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsSafe operationOperating system
A method and system of ensuring integrity of a secure mode entry sequence. At least some of the exemplary embodiments may be a method comprising transferring a plurality of instructions to a microprocessor, wherein the instructions prepare the processor for entry into a secure mode of operation. The instructions comprise flushing the processor pipelines and removing contents of at least some processor caches and buffers.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
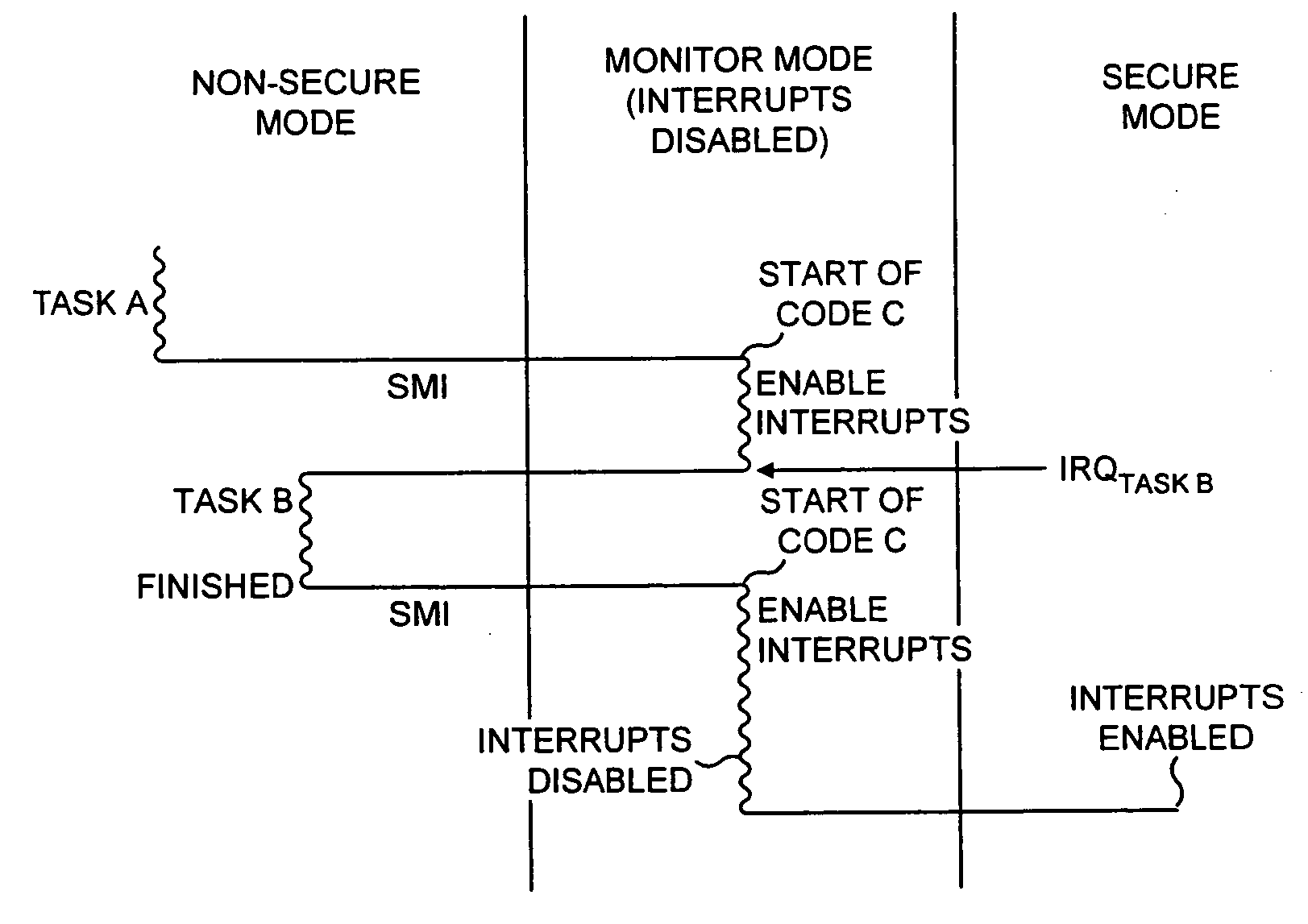
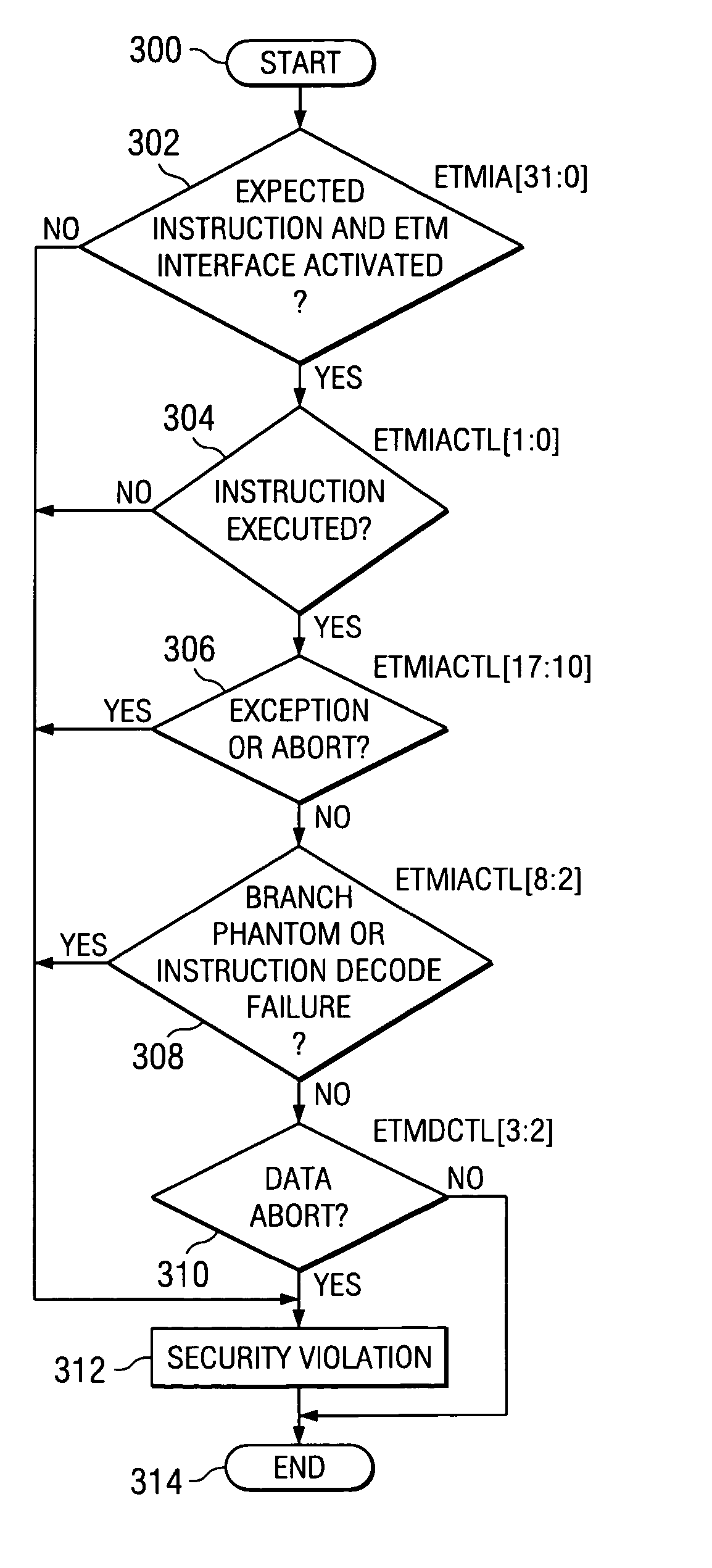
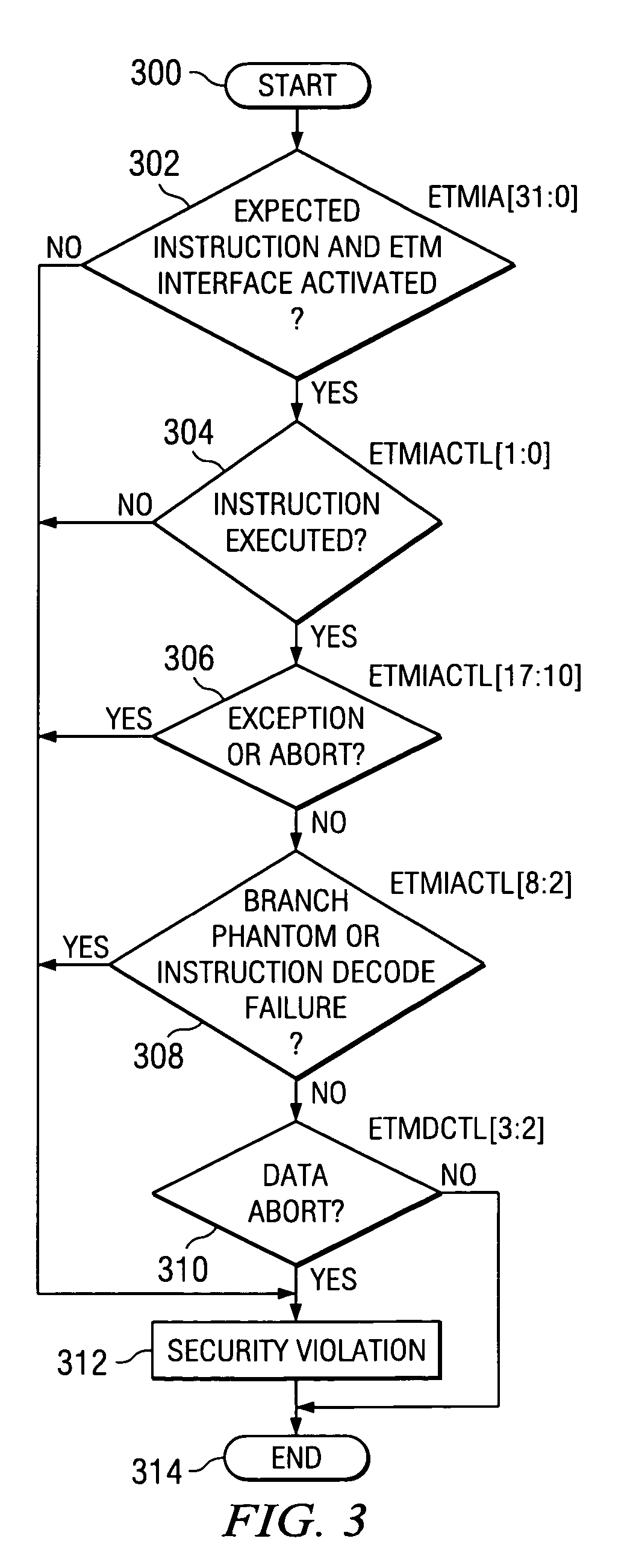
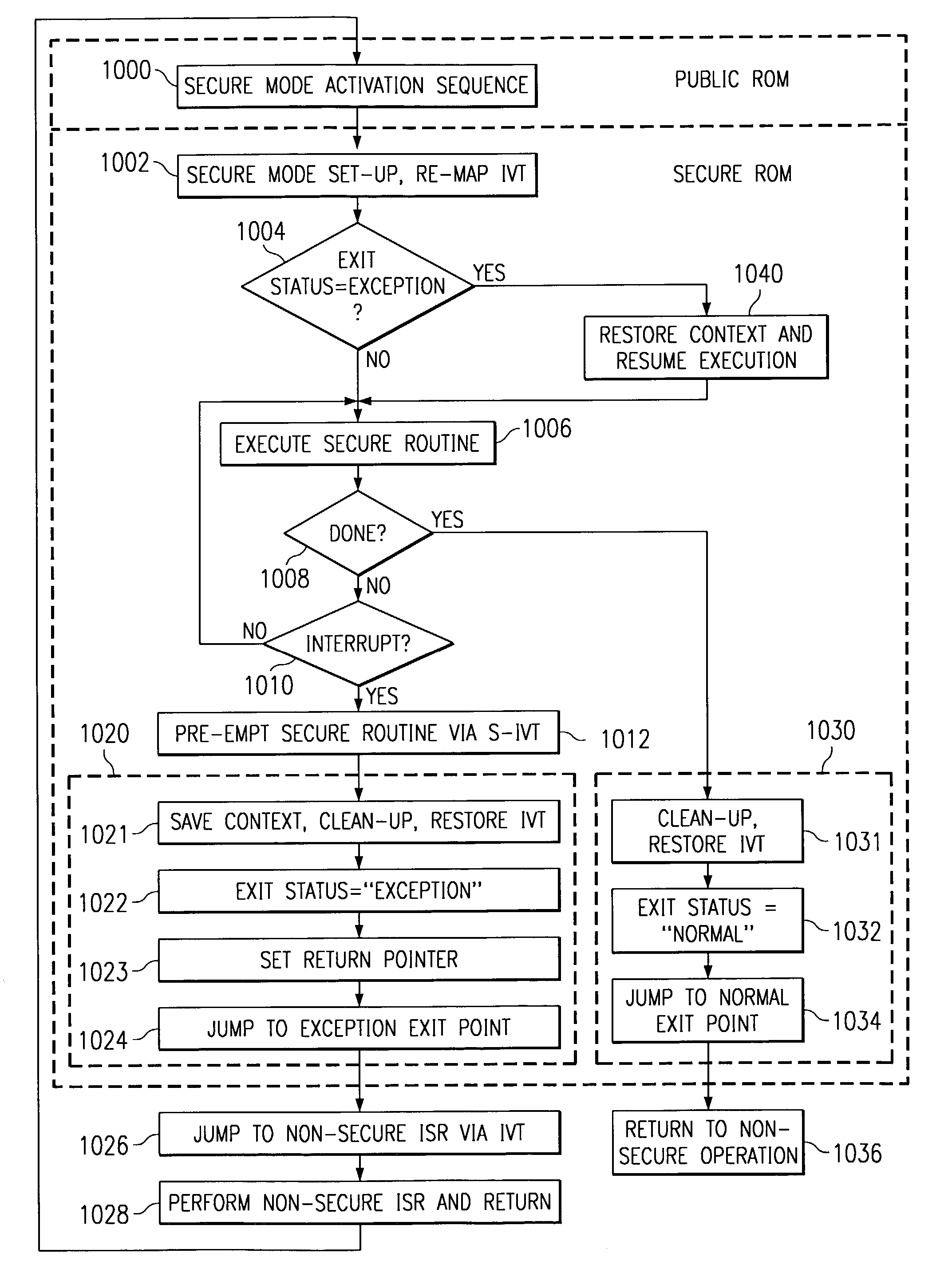
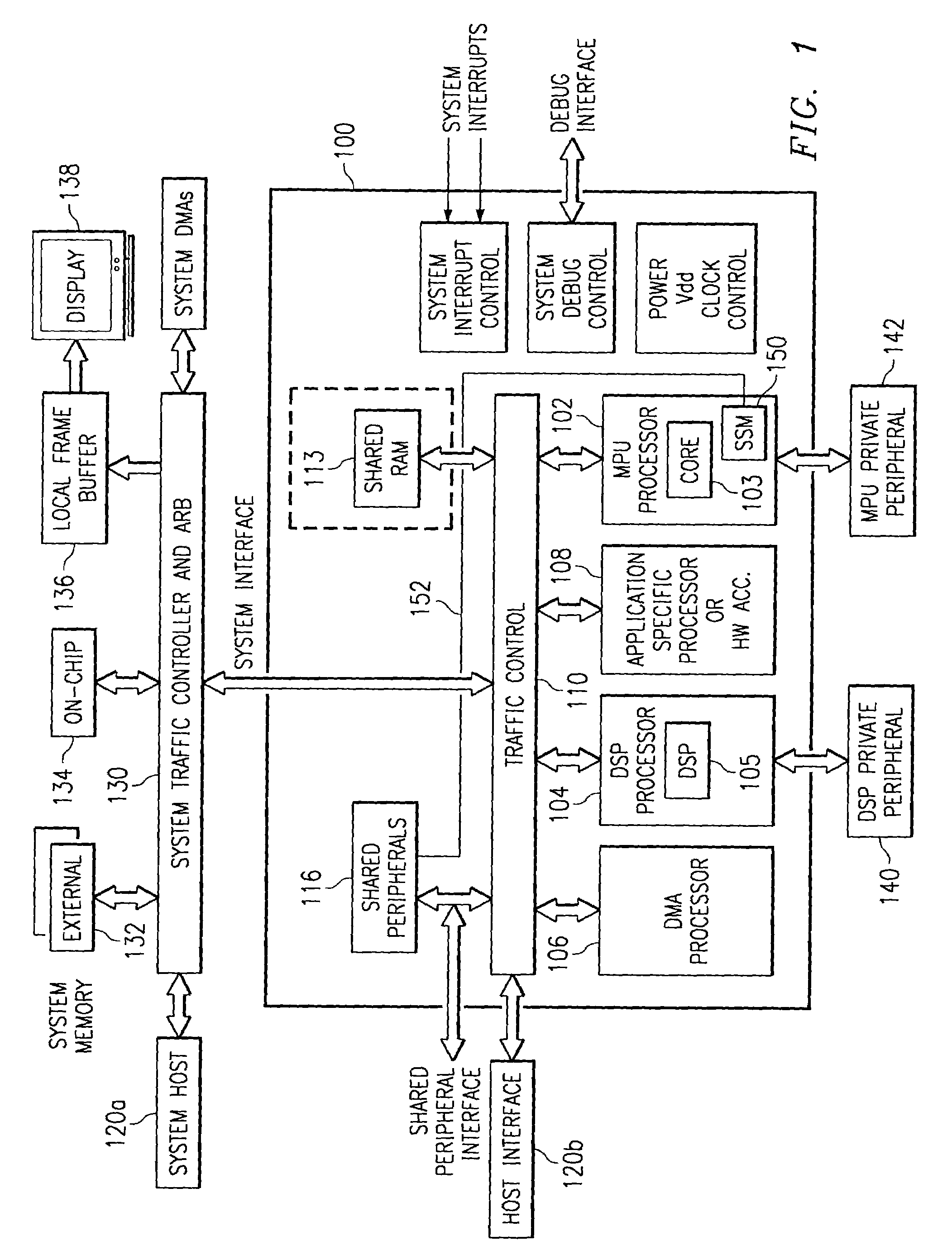
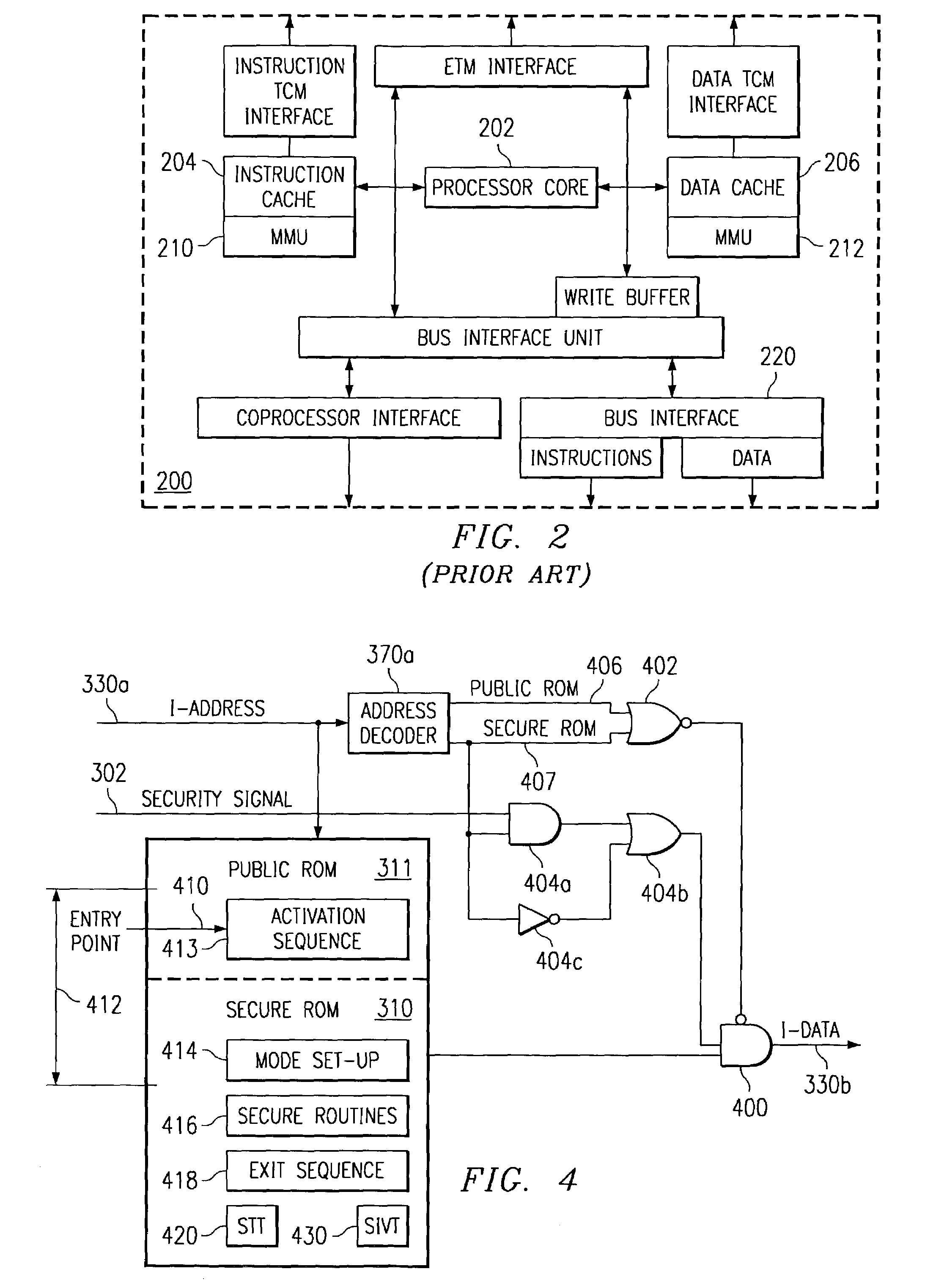
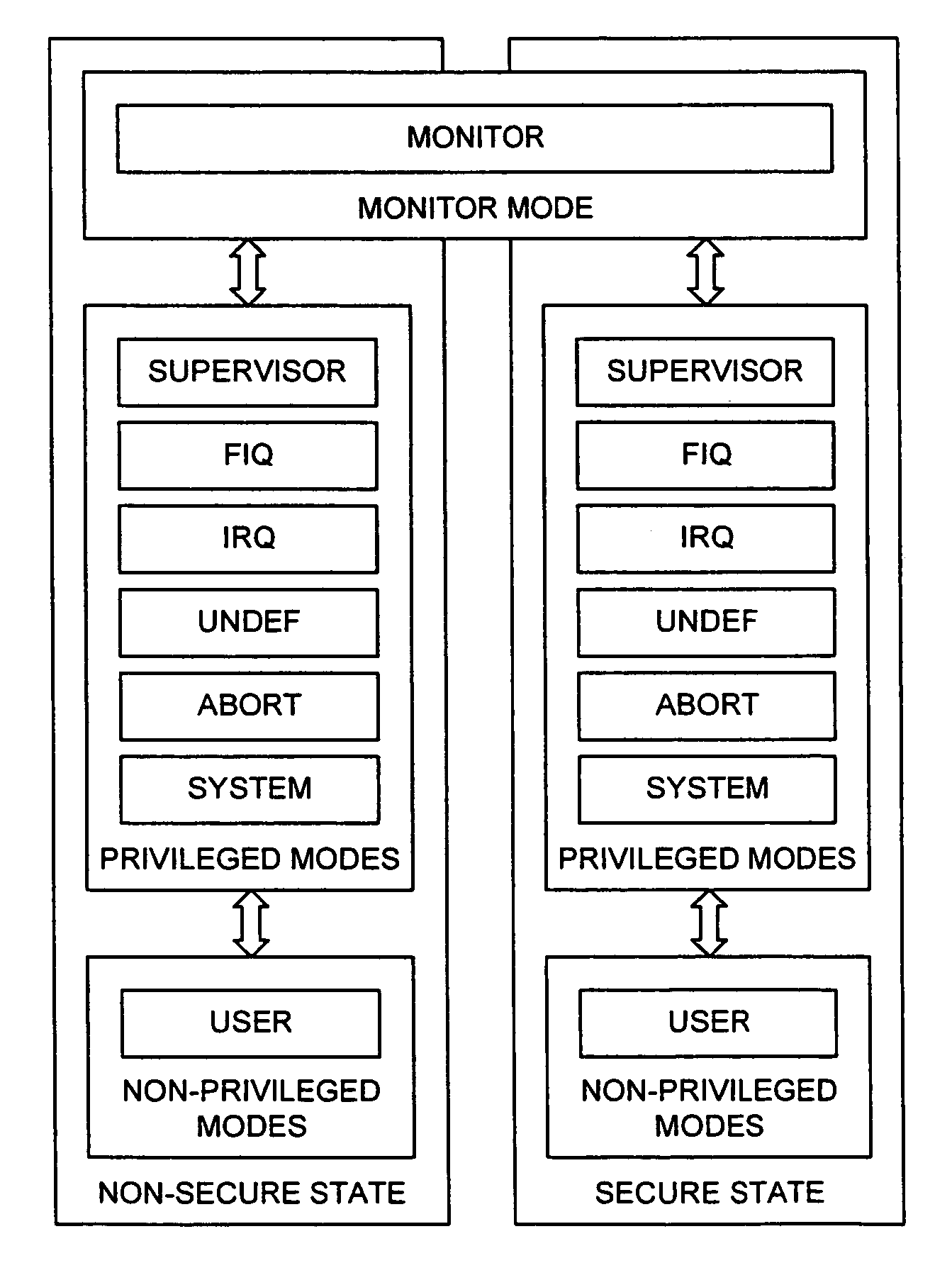
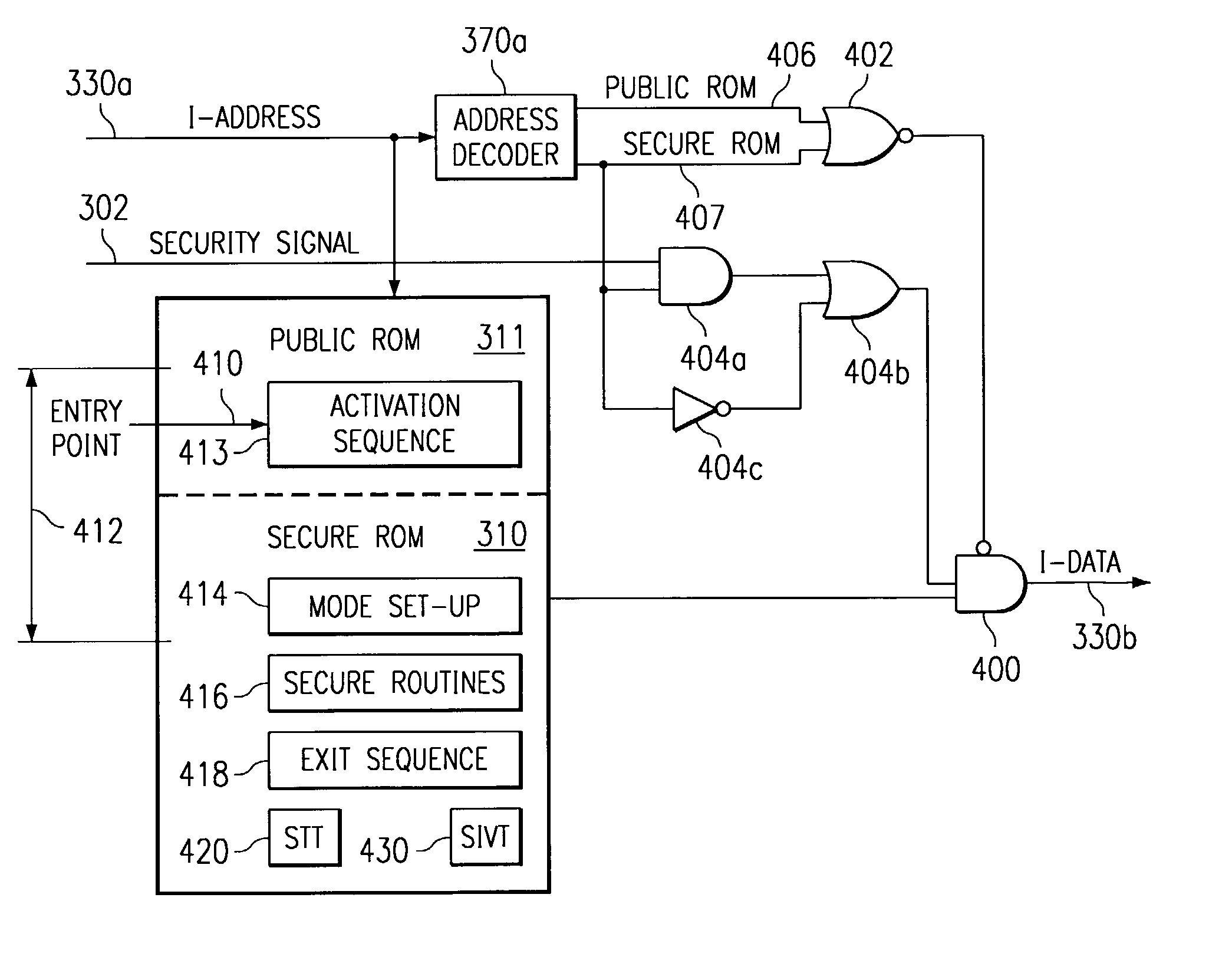
Secure mode for processors supporting interrupts
ActiveUS7237081B2Specific access rightsDigital data processing detailsOperational systemManagement unit
A digital system is provided with a secure mode (3rd level of privilege) built in a non-invasive way on a processor system that includes a processor core, instruction and data caches, a write buffer and a memory management unit. A secure execution mode is thus provided on a platform where the only trusted software is the code stored in ROM. In particular the OS is not trusted, all native applications are not trusted. A secure execution mode is provided that allows virtual addressing when a memory management unit (MMU) is enabled. The secure execution mode allows instruction and data cache to be enabled. A secure execution mode is provided that allows all the system interruptions to be unmasked. The secure mode is entered through a unique entry point. The secure execution mode can be dynamically entered and exited with full hardware assessment of the entry / exit conditions. A specific set of entry conditions is monitored that account for caches, write buffer and MMU being enabled. The structure of the activation sequence code accounts for caches, write buffer and MMU being enabled. The structure of the exit sequences code accounts for caches, write buffer and MMU being enabled. A specific way is provided to manage a safe exit of secure mode under generic interruptions and allows return from interruption through entry point and activation sequence and a proper resuming of the secure execution. A specific way is provided to manage the MMU in secure mode and provide data exchange between secure and non-secure environment.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
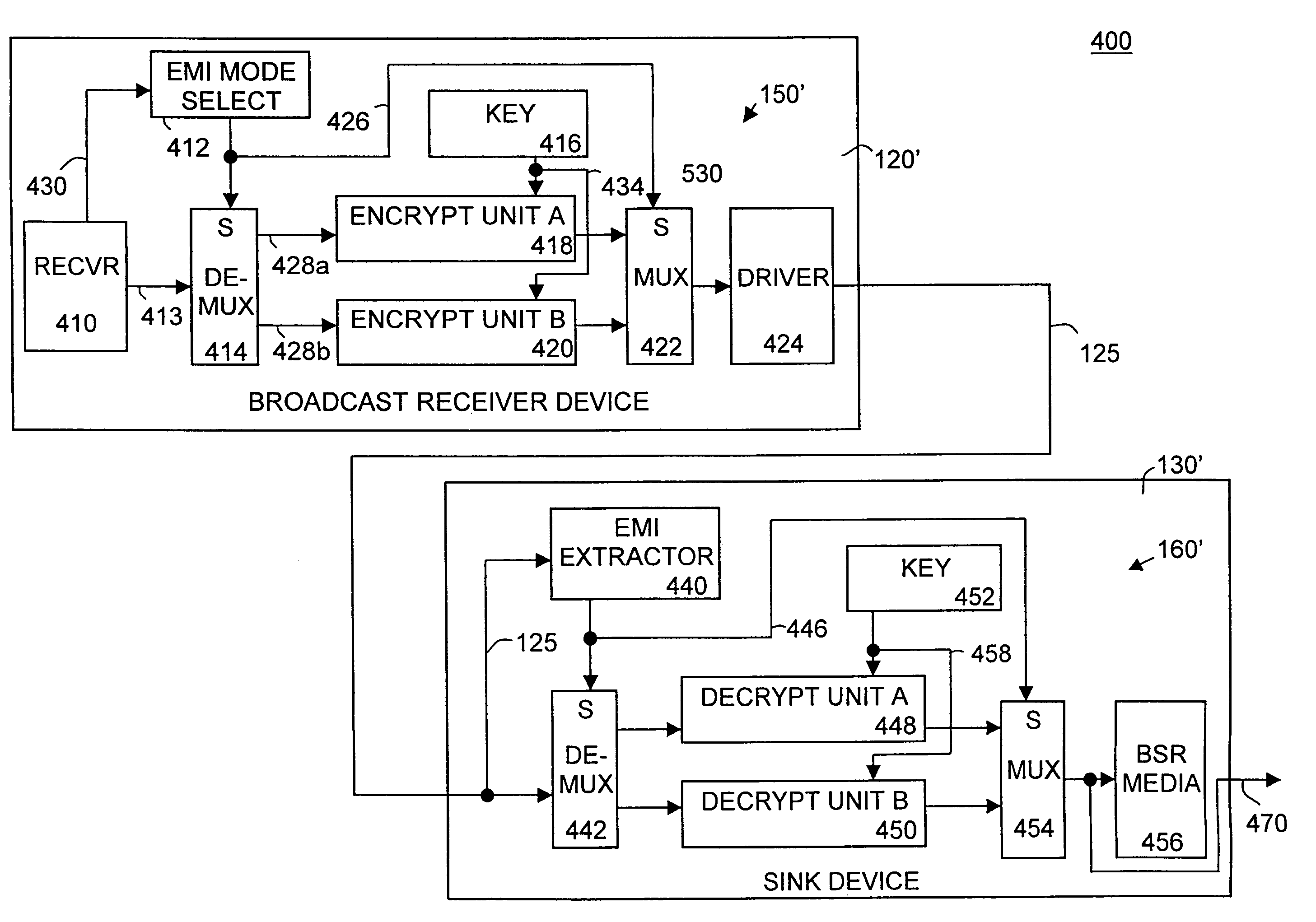
Method and system for transferring information using an encryption mode indicator
A method and system for transferring information using an encryption mode indicator (EMI). The present invention provides several secure information communication modes in which data (e.g., representing an audio / visual work) can be transmitted from a source device to a sink device (receiving station) in a number of secure modes. In one secure mode, EMI mode A, the information of the transmission is not allowed to be copied as a whole work; this is the highest level of copy protection. In second secure mode, EMI mode B, the information of the transmission is allowed to be copied once and once only by the sink device. In a third transmission mode, no encryption is used and free copying is available.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Secure and backward-compatible processor and secure software execution thereon
InactiveUS7380275B2Substantial in resourcesSubstantial in speedDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionExternal storageApplication software
A secure processor assuring application software is executed securely, and assuring only authorized software is executed, monitored modes and secure modes of operation. The former executes application software transparently to that software. The latter verifies execution of the application software is authorized, performs any extraordinary services required by the application software, and verifies the processor has obtained rights to execute the content. The secure processor (1) appears hardware-identical to an ordinary processor, with the effect that application software written for ordinary processors can be executed on the secure processor without substantial change, (2) needs only a minimal degree of additional hardware over and above those portions appearing hardware-identical to an ordinary processor. The secure processor operates without substantial reduction in speed or other resources available to the application software. Functions operating in secure mode might reside in an on-chip non-volatile memory, or might be loaded from external storage with authentication.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
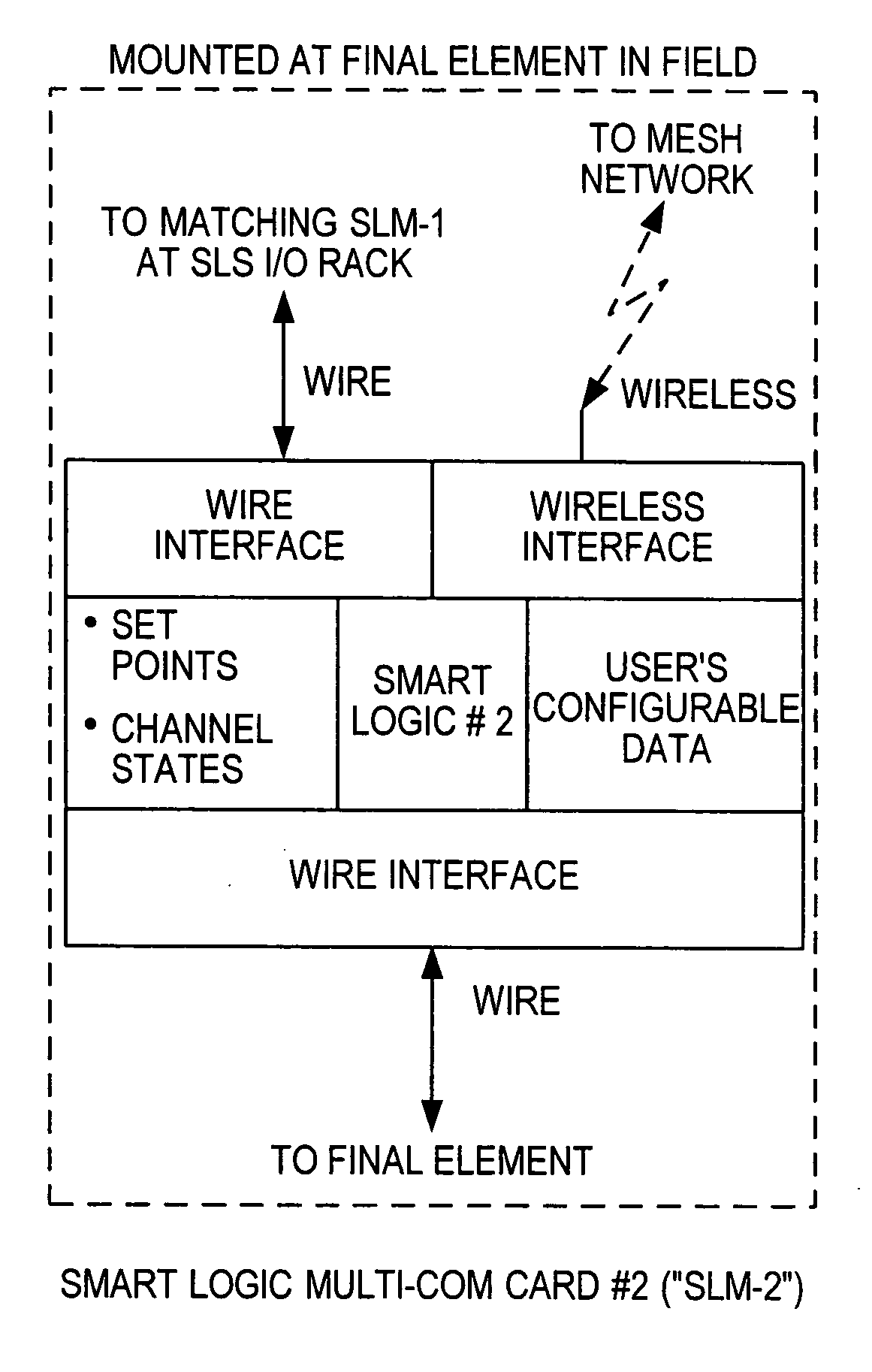
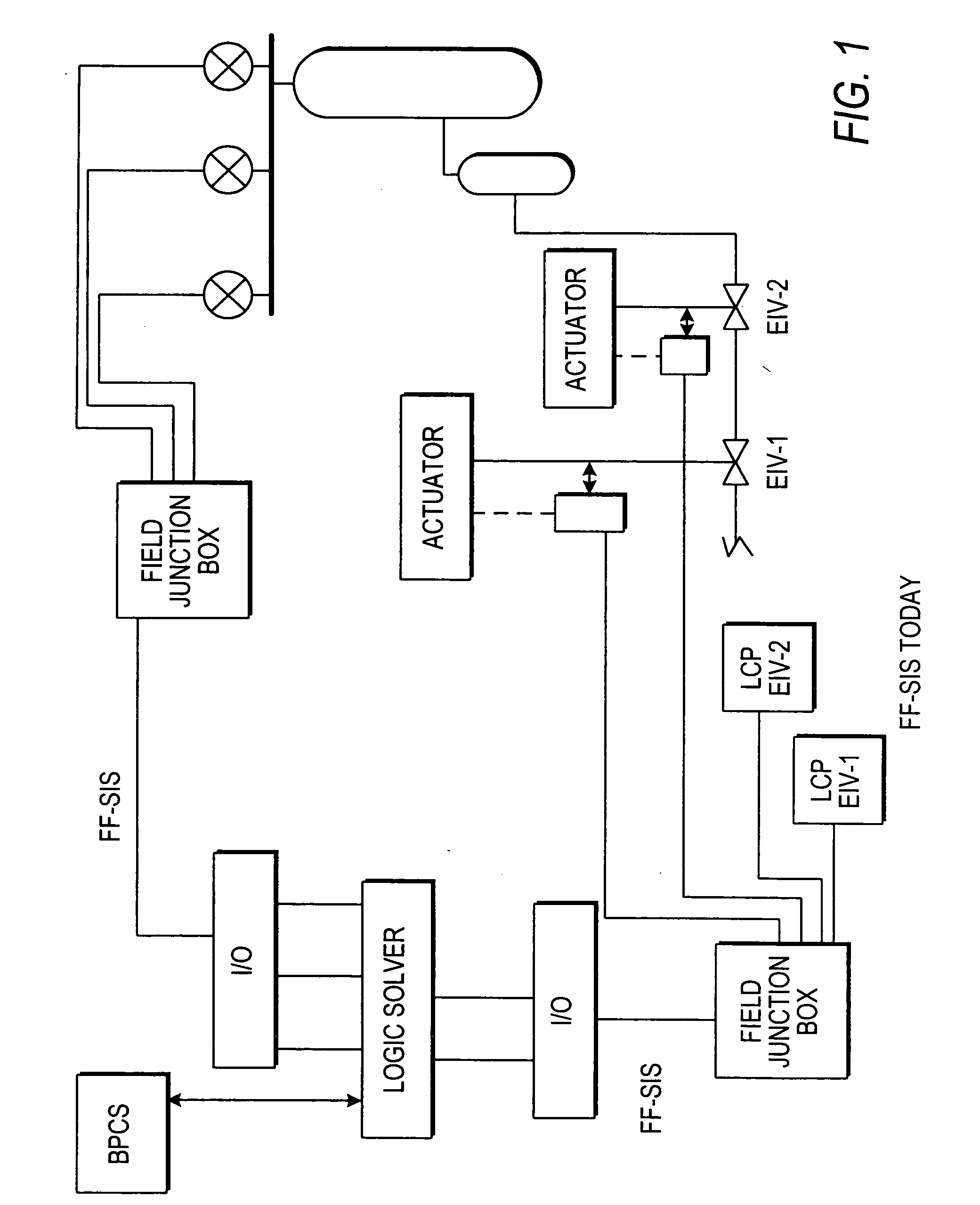
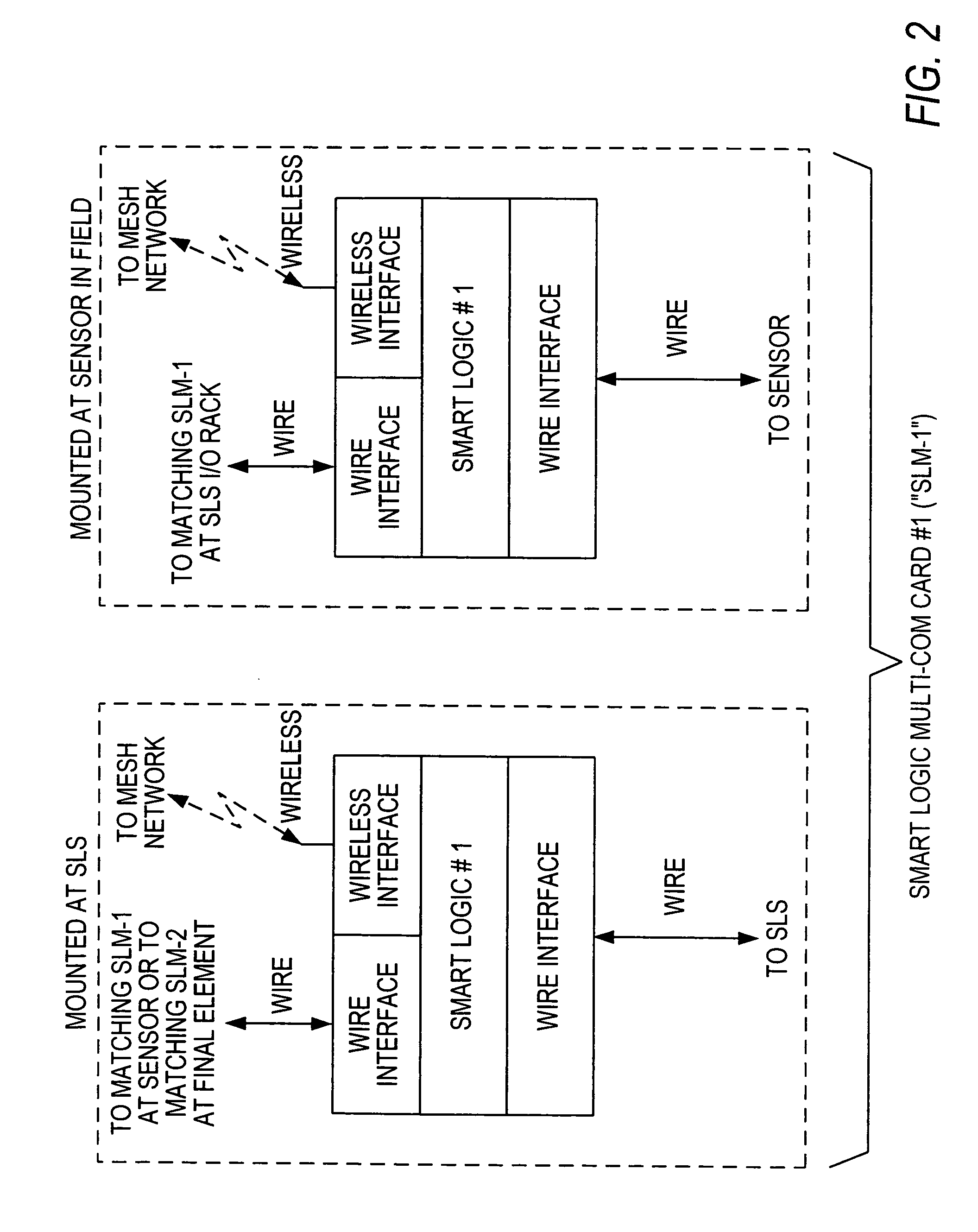
Distributed and adaptive smart logic with multi-communication apparatus for reliable safety system shutdown
InactiveUS20100004761A1Increase decision reliabilityGood flexibilityVehicle testingBurglar alarmSafety instrumented systemEngineering
This invention relates to safety instrumented systems (“SIS”) for monitoring and controlling chemical and other industrial process field devices, and that are responsive to signals for the emergency shutdown of the process or system. The patent will significantly improve the reliability of communications within an emergency shutdown system, reduce unwanted trips, and adapt to process conditions by failing to a safe mode in dynamic conditions that are not considered by prior art logic solvers.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Apparatus and method for controlling access to a memory unit
ActiveUS20040143714A1Program initiation/switchingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData storingData store
The present invention provides a data processing apparatus and method for controlling access to a memory unit. The data processing apparatus comprises a processor operable in a plurality of modes and a plurality of domains, said plurality of domains comprising a secure domain and a non-secure domain, said plurality of modes including at least one non-secure mode being a mode in the non-secure domain and at least one secure mode being a mode in the secure domain. The processor is operable such that when executing a program in a secure mode the program has access to secure data which is not accessible when the processor is operating in a non-secure mode. A memory unit is also provided that comprises a plurality of entries and is operable to store data required by the processor. Each entry is operable to store one or more data items consisting of either secure data or non-secure data, and a flag is associated with each entry in the memory unit to store a value indicating whether the one or more data items stored in the associated entry are secure data or non-secure data. When the processor is operating in the at least one non-secure mode, the memory unit is operable, upon receipt of a memory access request issued by the processor when access to an item of data is required, to prevent access to any data item within an entry of the memory unit that the associated flag indicates has secure data stored therein.
Owner:ARM LTD
Information processing apparatus, information processing control system, control method for information processing apparatus, control program for informaion processing apparaus recording meduim on which control program for information processing apparatus is recorded
InactiveUS20070176778A1Avoid misuseElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageInformation processingCommunication unit
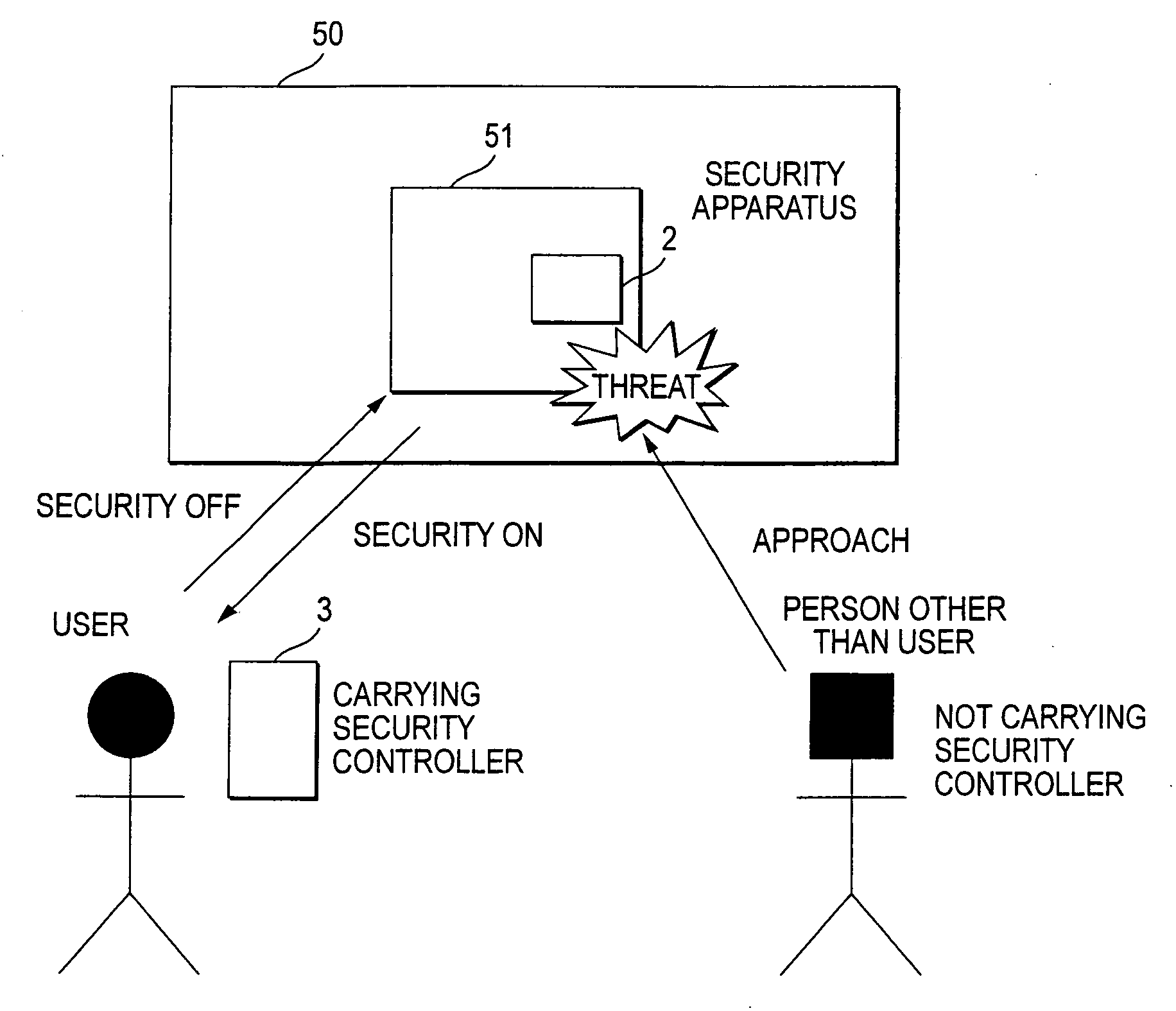
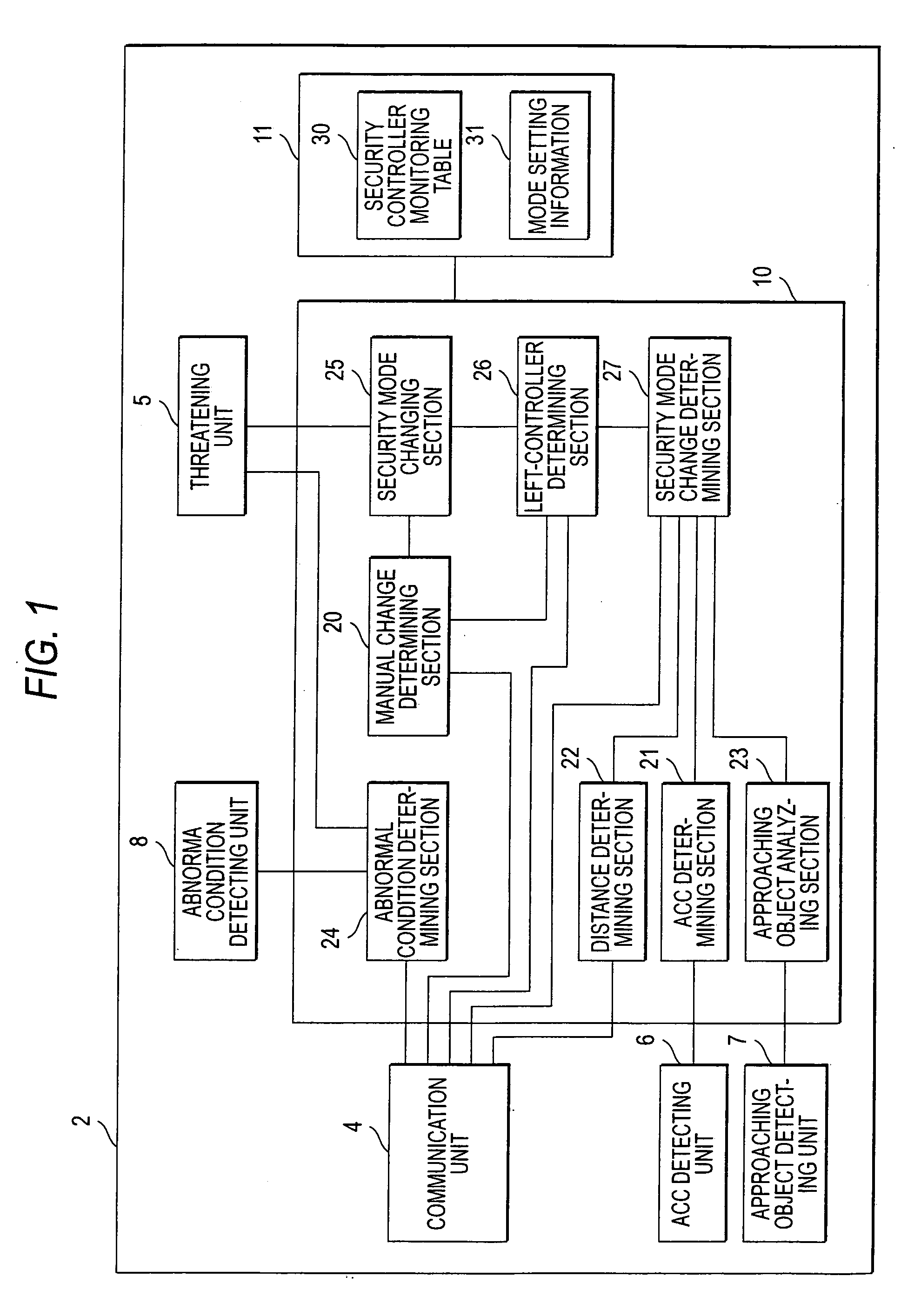
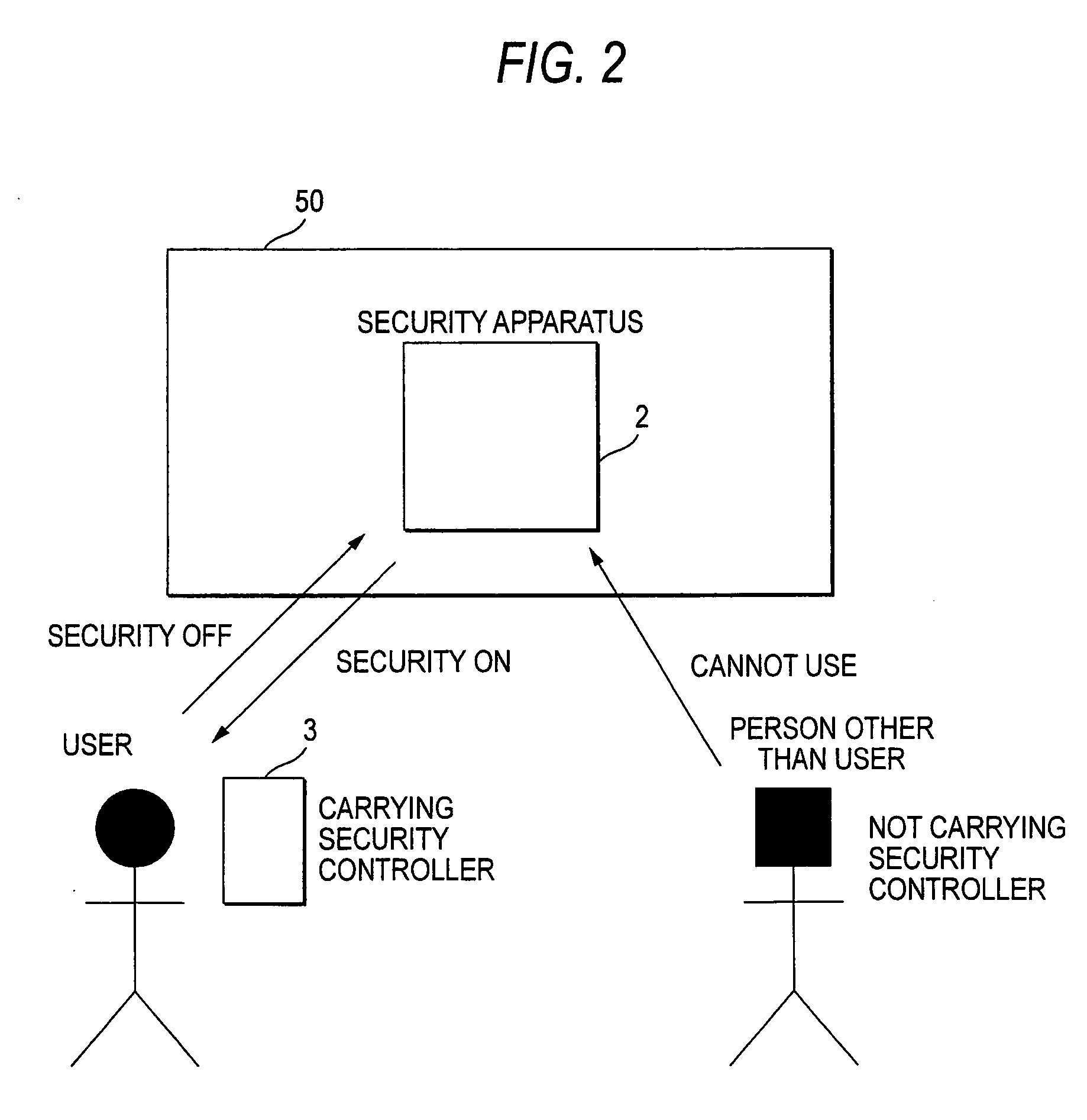
A security apparatus (2) monitors movement of users carrying security controllers (3a) through (3c) into and out of a security area (50), and controls security operations. The security apparatus (2) includes a communication unit (4) for communicating with each of the security controllers (3a) through (3c) and obtaining position information on the respective security controllers (3a) through (3c), a storage unit (11) for storing a security controller monitoring table (30), and a left-controller determining section (26) for judging whether any of the security controllers (3a) through (3c) has been left within the security area (50) and determining whether setting or canceling of the security mode is commanded automatically or based on the input operations by the users.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Apparatus and method for controlling access to a memory unit
ActiveUS7340573B2Program initiation/switchingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData storingData store
The present invention provides a data processing apparatus and method for controlling access to a memory unit. The data processing apparatus comprises a processor operable in a plurality of modes and a plurality of domains, said plurality of domains comprising a secure domain and a non-secure domain, said plurality of modes including at least one non-secure mode being a mode in the non-secure domain and at least one secure mode being a mode in the secure domain. The processor is operable such that when executing a program in a secure mode the program has access to secure data which is not accessible when the processor is operating in a non-secure mode. A memory unit is also provided that comprises a plurality of entries and is operable to store data required by the processor. Each entry is operable to store one or more data items consisting of either secure data or non-secure data, and a flag is associated with each entry in the memory unit to store a value indicating whether the one or more data items stored in the associated entry are secure data or non-secure data. When the processor is operating in the at least one non-secure mode, the memory unit is operable, upon receipt of a memory access request issued by the processor when access to an item of data is required, to prevent access to any data item within an entry of the memory unit that the associated flag indicates has secure data stored therein.
Owner:ARM LTD
Method and apparatus for operating a computer in a secure mode
InactiveUS7043643B1Quick and convenient encryption protectionFirmly connectedDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCard readerProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A method for activating an encryption control device that is in communication with a computer for providing a secure computing environment for a user is provided. The method initiates with providing a card for insertion into a card reader of the encryption control device. The card is configured to receive and pass data. Next, a biometric identifier is received from the user. The biometric identifier enables validation of the user as the authorized owner of the card. Then, a challenge / response protocol between the encryption control and the inserted card is run. The challenge / response protocol establishes that the card and the encryption control device are compatible. Next, an encryption engine of the encryption control device is activated to create a secure computing environment if the user is validated as the authorized owner of the card and the challenge / response protocol is successfully executed.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Secure mode for processors supporting MMU
A digital system is provided with a secure mode (3rd level of privilege) built in a non-invasive way on a processor system that includes a processor core, instruction and data caches, a write buffer and a memory management unit. A secure execution mode is thus provided on a platform where the only trusted software is the code stored in ROM. In particular the OS is not trusted, all native applications are not trusted. A secure execution mode is provided that allows virtual addressing when a memory management unit (MMU) is enabled. The secure execution mode allows instruction and data cache to be enabled. A secure execution mode is provided that allows all the system interruptions to be unmasked. The secure mode is entered through a unique entry point. The secure execution mode can be dynamically entered and exited with full hardware assessment of the entry / exit conditions. A specific set of entry conditions is monitored that account for caches, write buffer and MMU being enabled. The structure of the activation sequence code accounts for caches, write buffer and MMU being enabled. The structure of the exit sequences code accounts for caches, write buffer and MMU being enabled. A specific way is provided to manage a safe exit of secure mode under generic interruptions and allows return from interruption through entry point and activation sequence and a proper resuming of the secure execution. A specific way is provided to manage the MMU in secure mode and provide data exchange between secure and non-secure environment.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
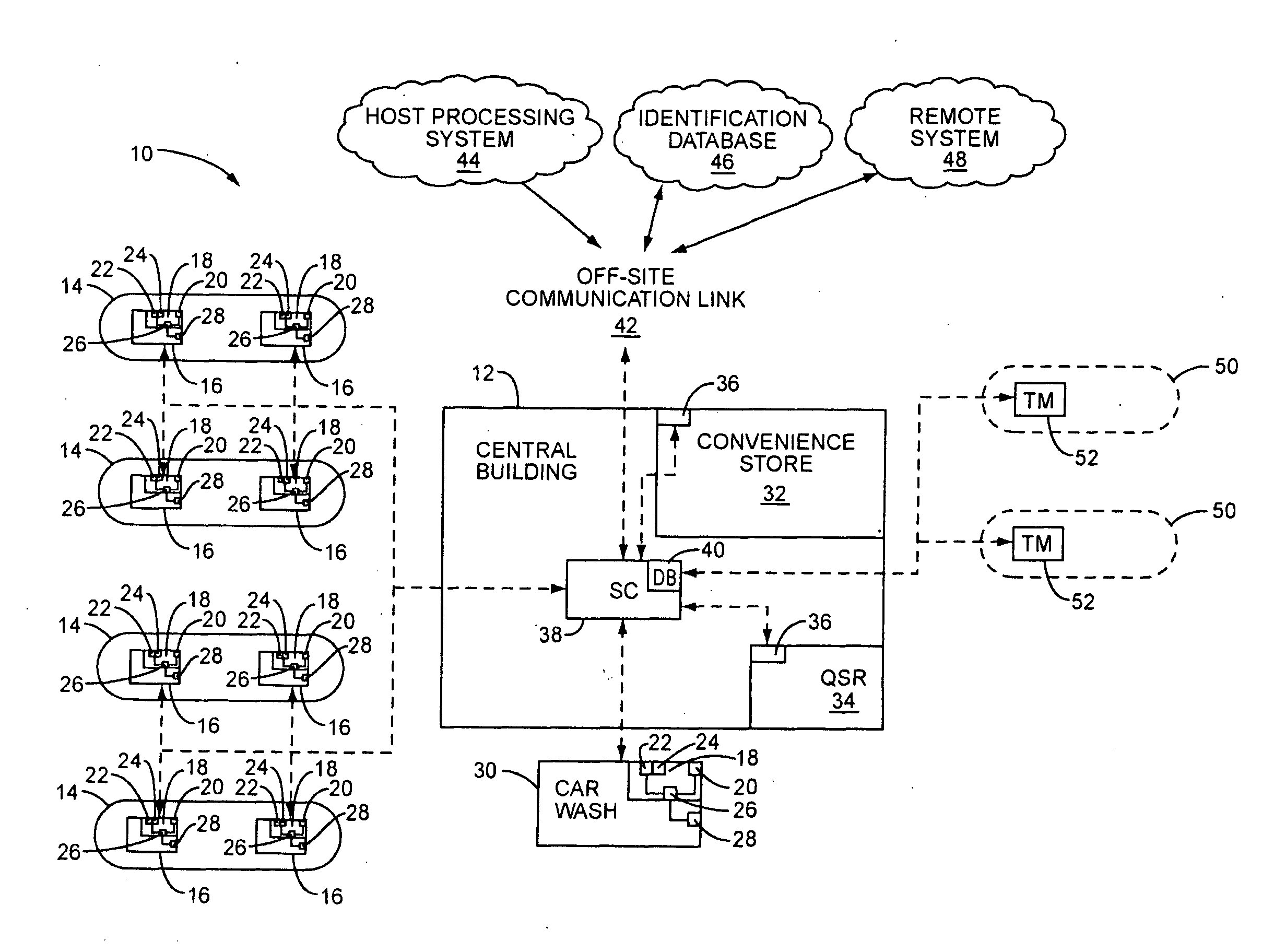
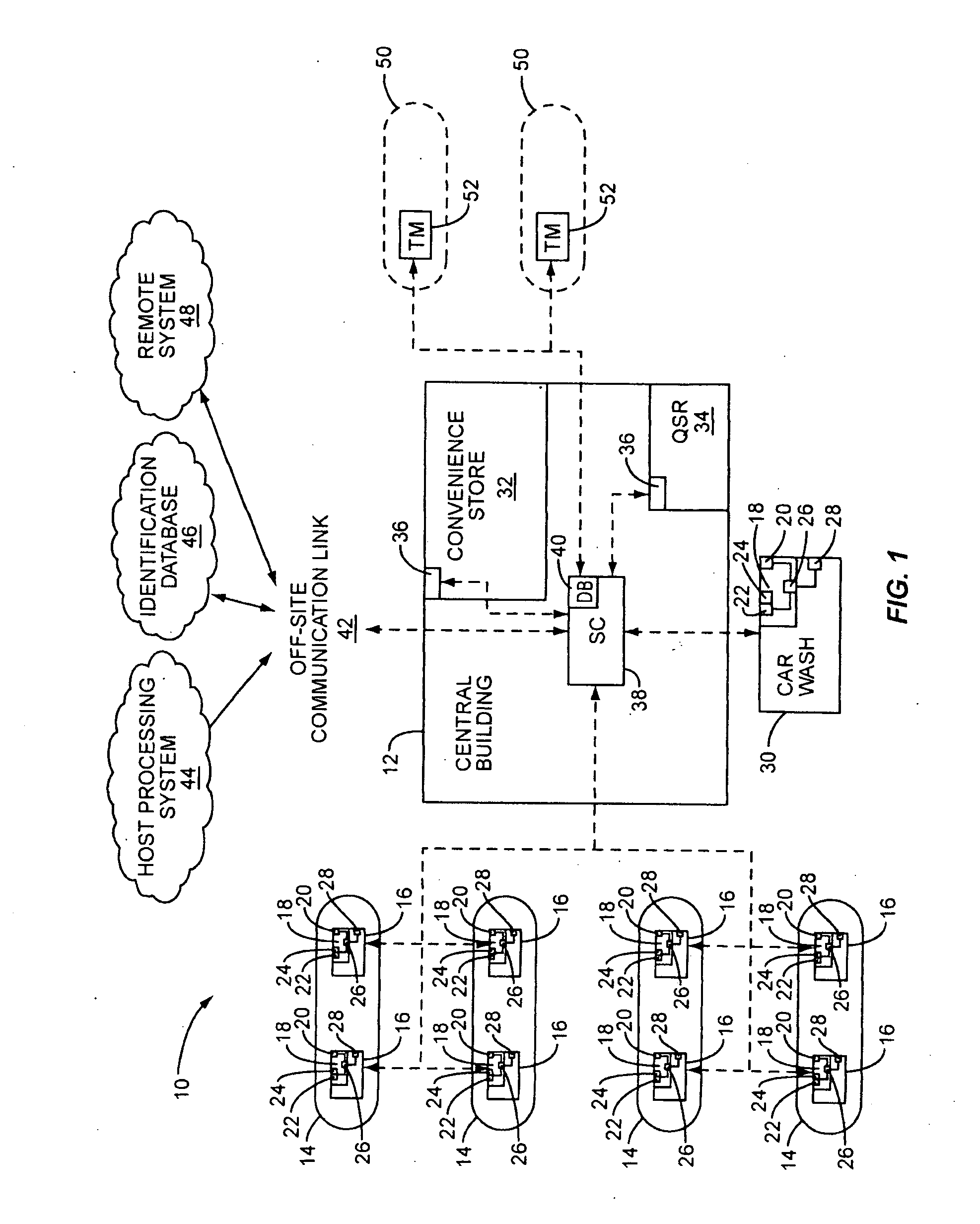
System and method for controlling secure content and non-secure content at a fuel dispenser or other retail device
ActiveUS20090265638A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPaymentUser input
A retail payment, advertising, and content switching system and method are disclosed. According to one embodiment, a secure content source or a non-secure content source is allowed to drive a customer user interface, respectively, without compromising security requirements. The content may be video, audio, prompts, or any other type of content. A secure controller is provided to control one or more user input devices and a user interface access module to control whether a secure source or a non-secure source drives the user interface, depending on the security mode of the system. The secure controller, the user interface access module, and the customer input devices are provided in an anti-tampering module. The secure controller prevents the non-secure source from providing unauthorized prompts on the customer user interface to “fake out” the customer so that sensitive customer information is not passed “in the clear.”
Owner:GILBARCO
Security Document Carrying Machine Readable Pattern
InactiveUS20100163629A1Easy to detectImage data processing detailsOther printing apparatusDocumentationLine structure
The present invention relates generally to security documents (e.g., banknotes, ID documents, certificates, packaging, etc.). One claim recites a security document including a security pattern provided thereon. The security pattern includes a line structure in which lines width or line spacing is adjusted to convey a predefined, machine-readable pattern in a frequency transform domain. Another claim recites a security document including a security pattern provided thereon. The security pattern is provided in the security document through modifications to a color provided on the security document. The security pattern conveys a predefined, machine-readable pattern in a frequency transform domain. Of course, additional combinations and claims are provided as well.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
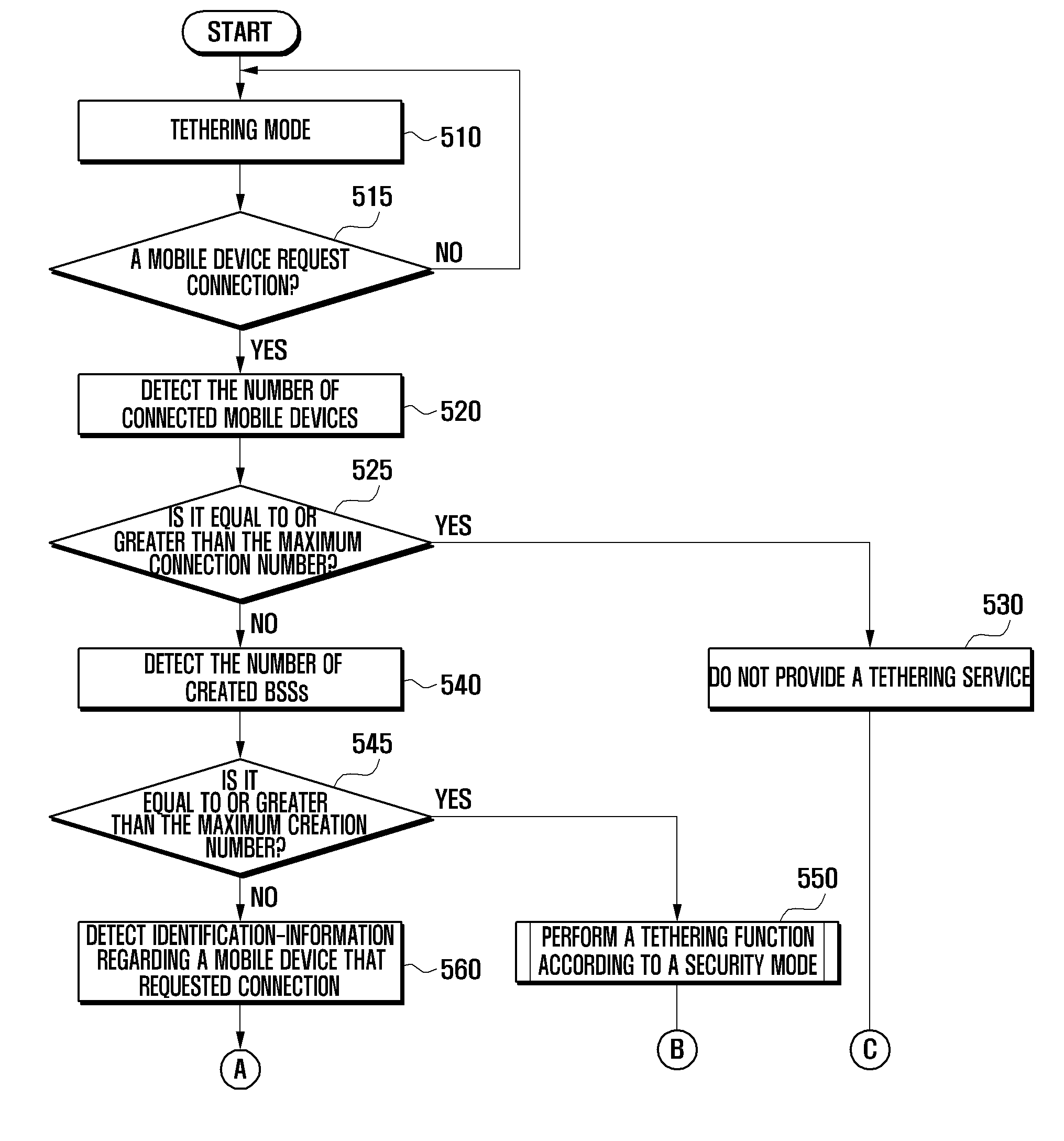
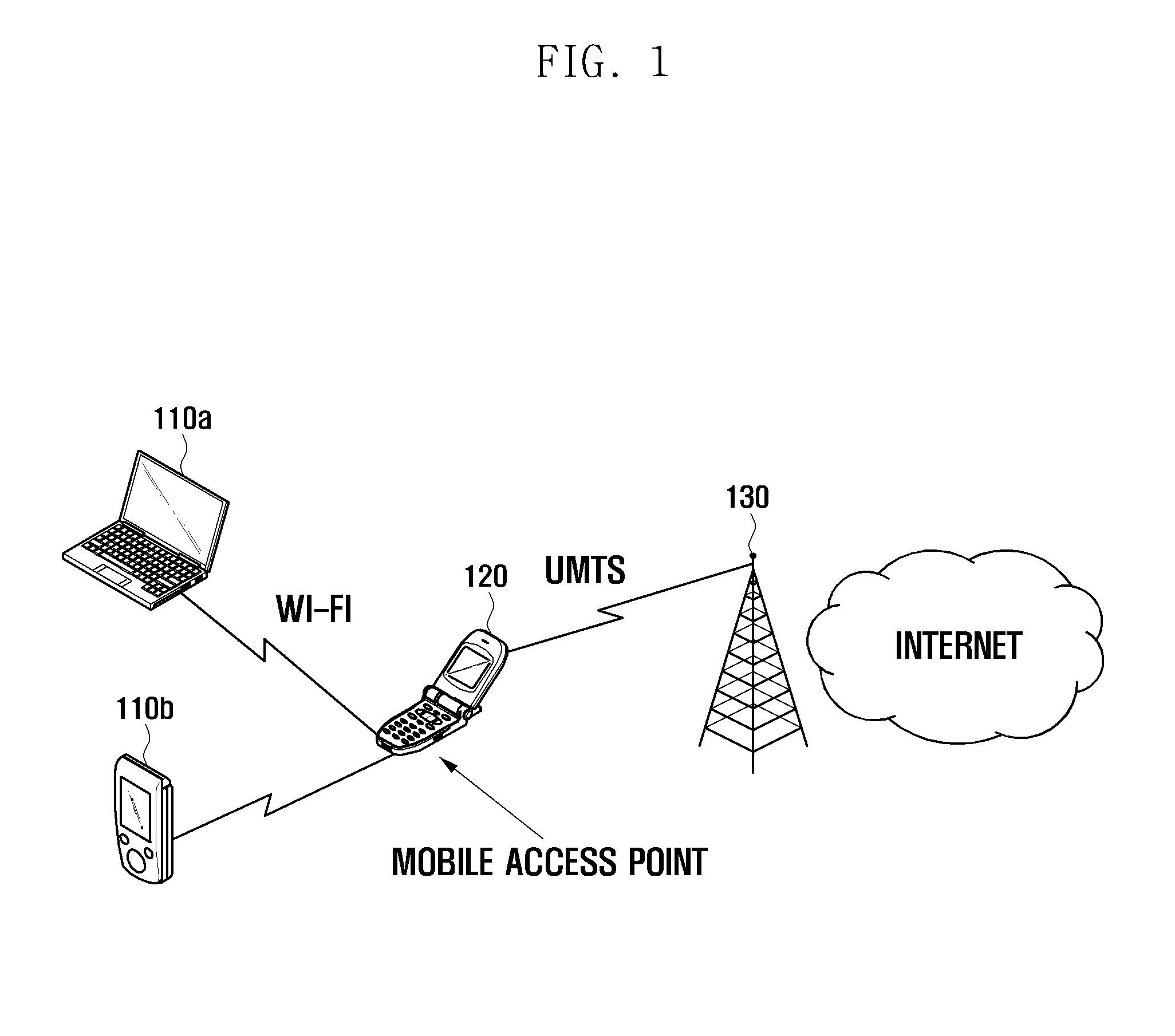
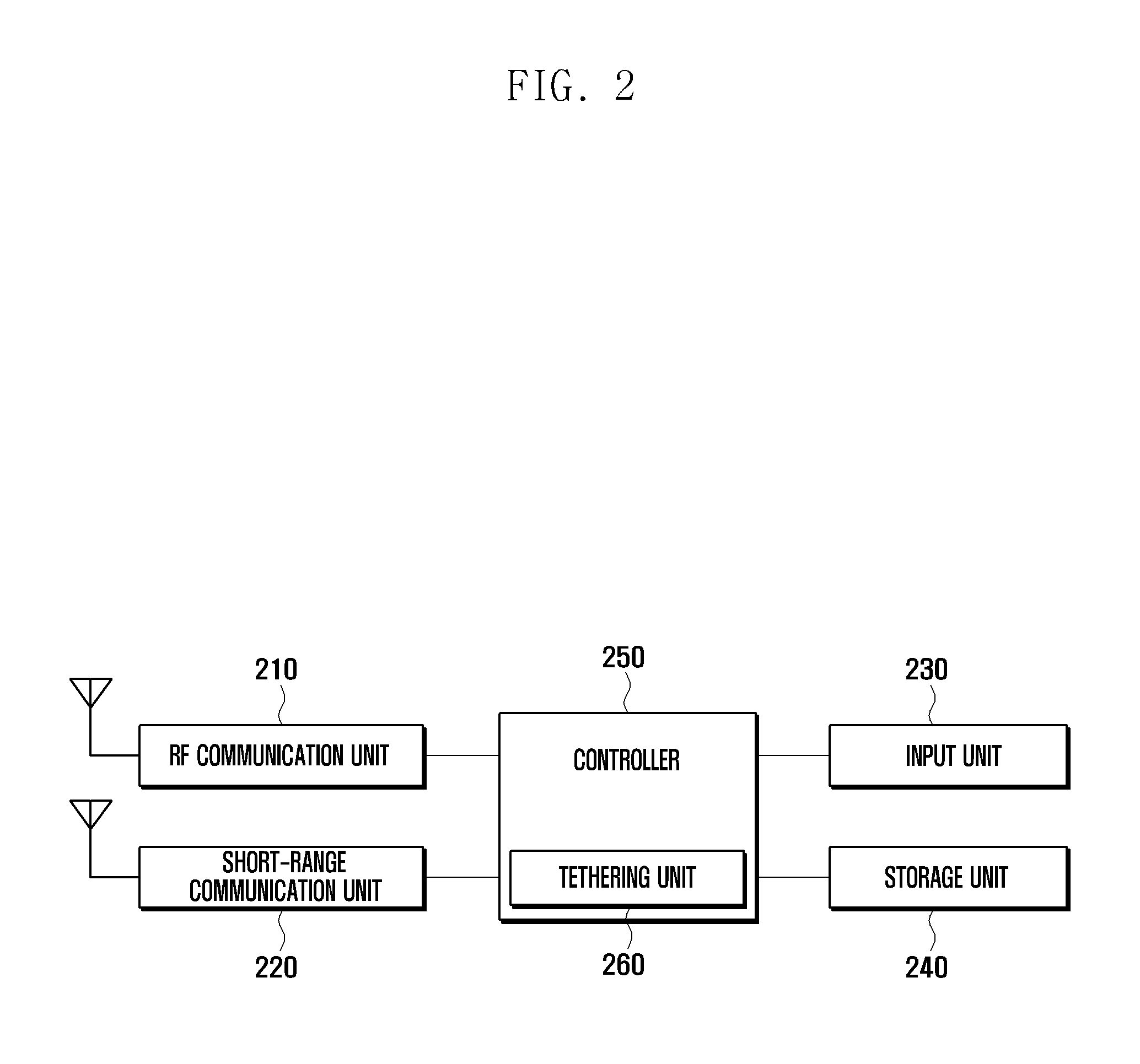
Tethering method and mobile device adapted thereto
ActiveUS20110283001A1Network traffic/resource managementConnection managementBasic serviceConnection number
A mobile device and a method for providing a tethering service via a security mode and a list of preferred mobile devices are provided. The method includes determining, when the mobile device receives a connection request from a client mobile device, a number of client mobile devices that are currently connected to the mobile device, determining, when the number of connected client mobile devices is less than a preset maximum connection number, the number of created Basic Service Sets (BSSs), determining, when the number of BSSs is less than a preset maximum creation number, the identification-information regarding the client mobile device that requested connection, and providing a tethering service to the client mobile device according to the determined identification-information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com