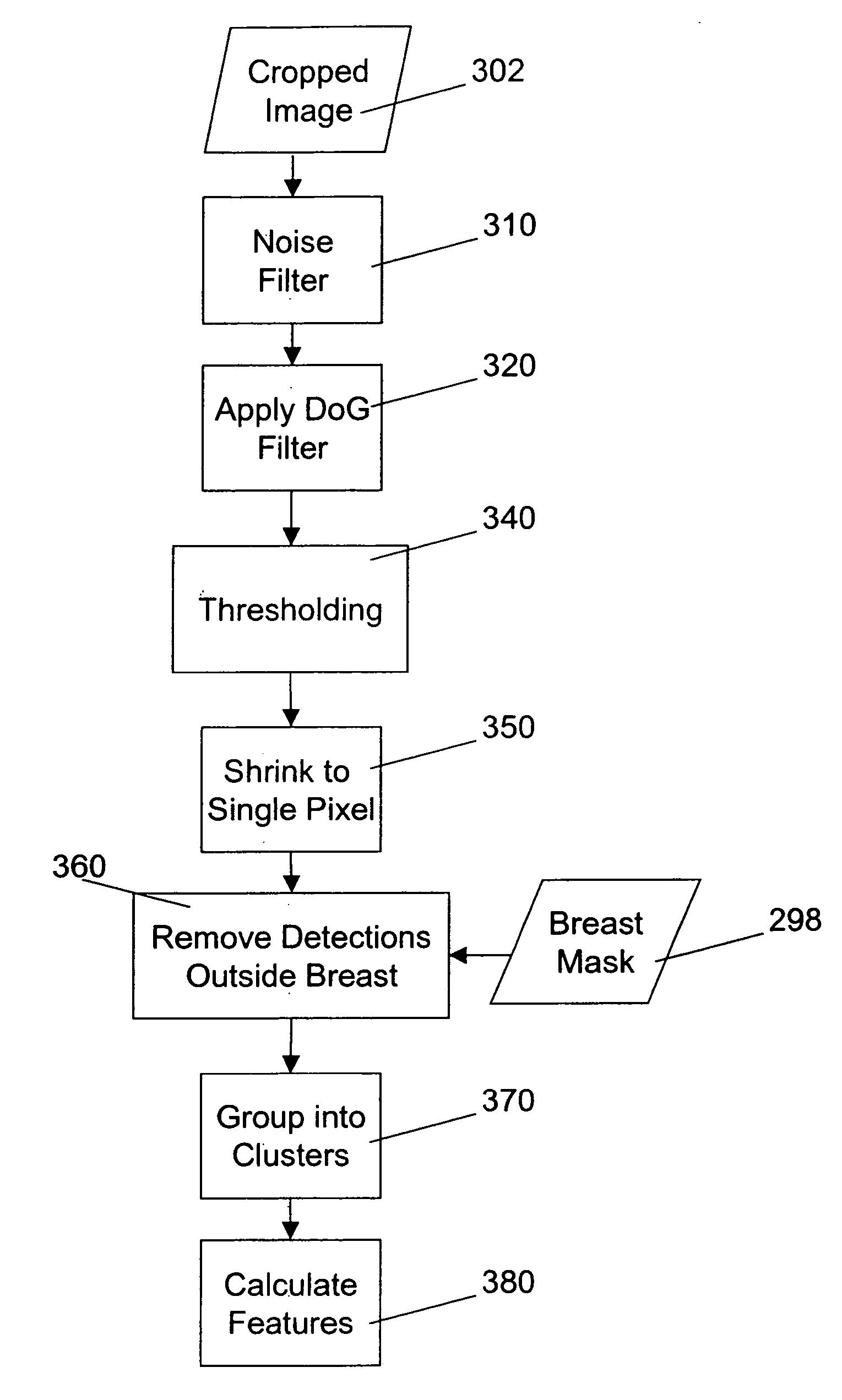
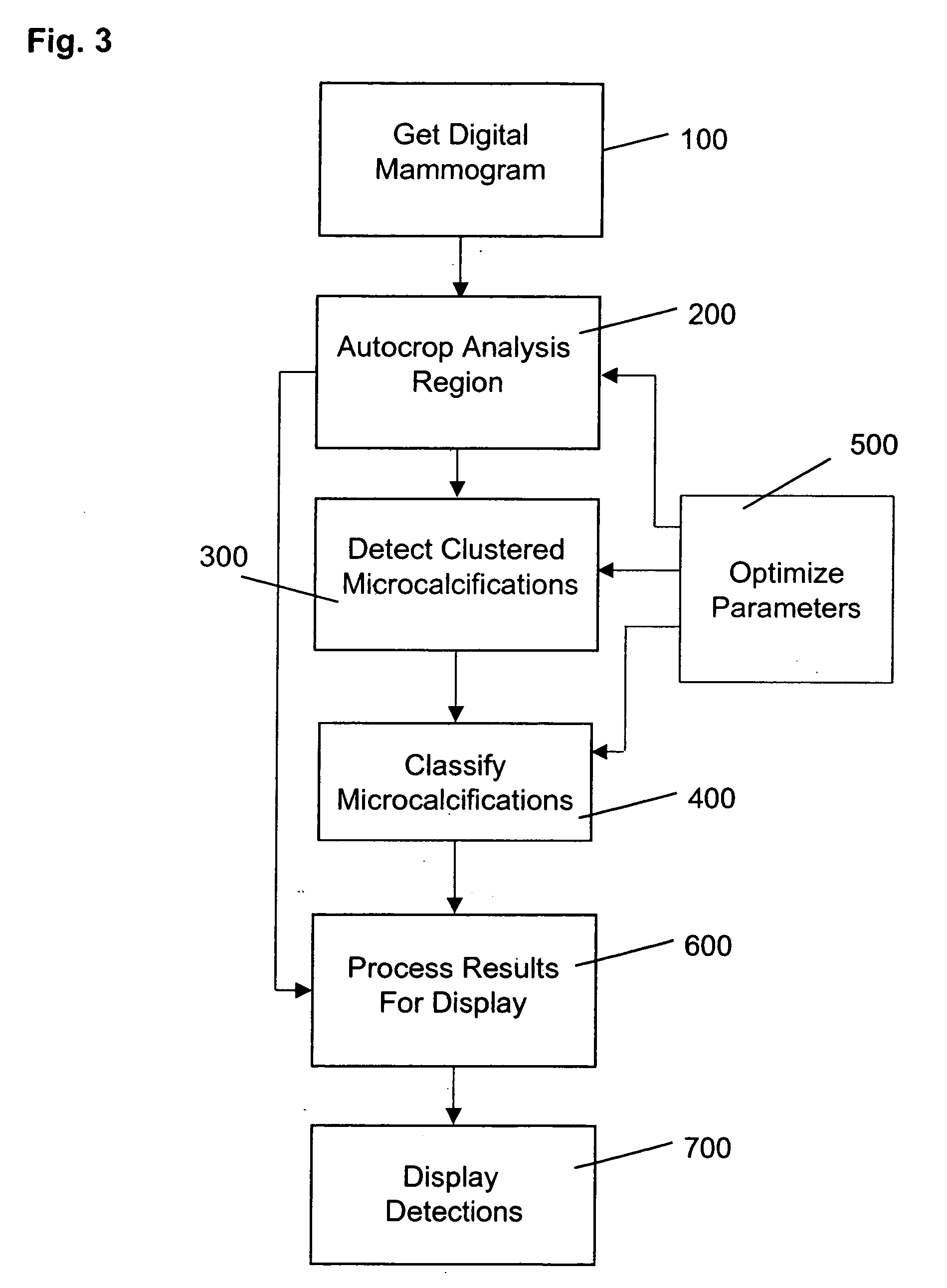
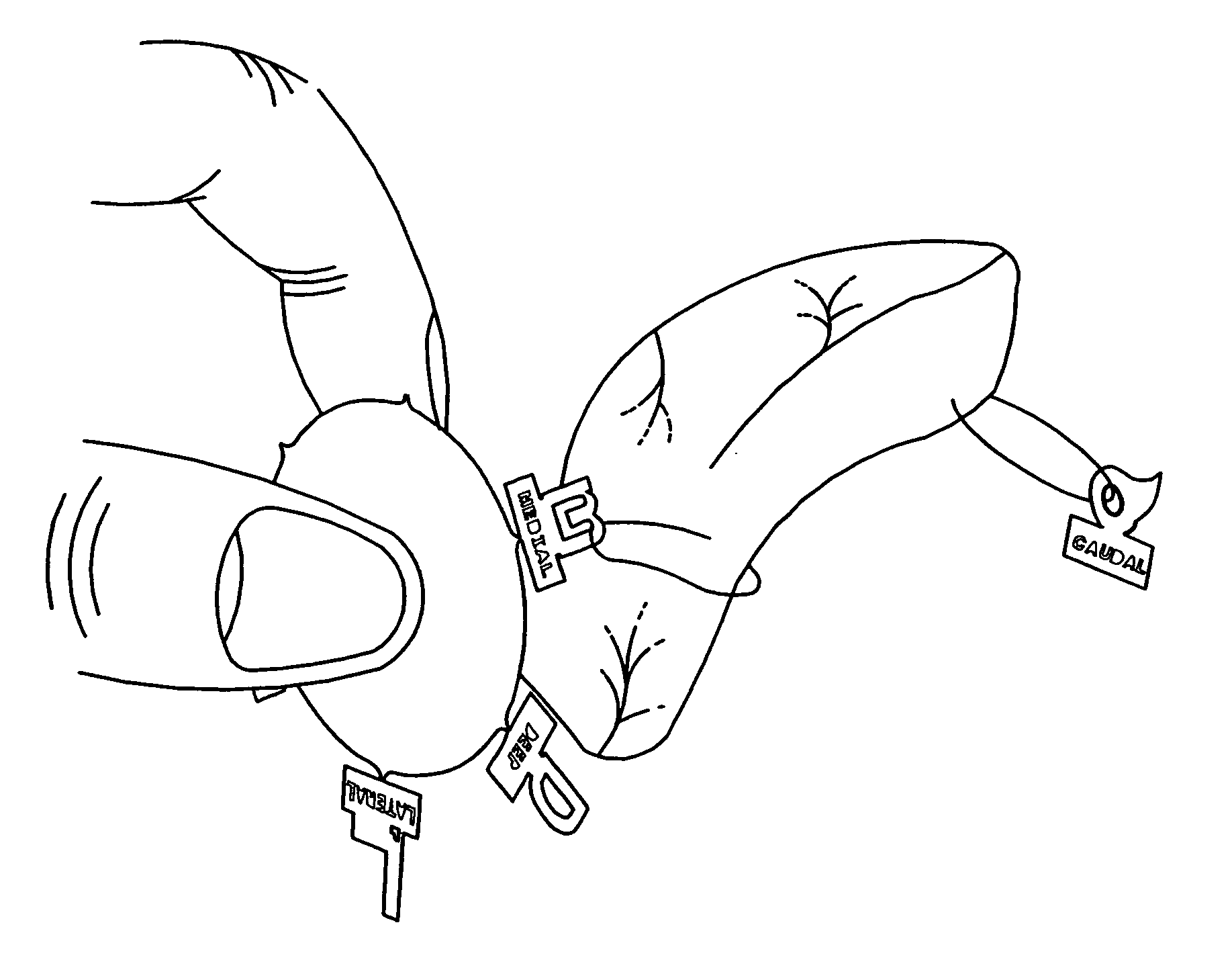Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Reviewing Radiologist" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A radiologist that formally inspects and verifies diagnoses, clinical data, treatment plans, and grant or scientific proposals.
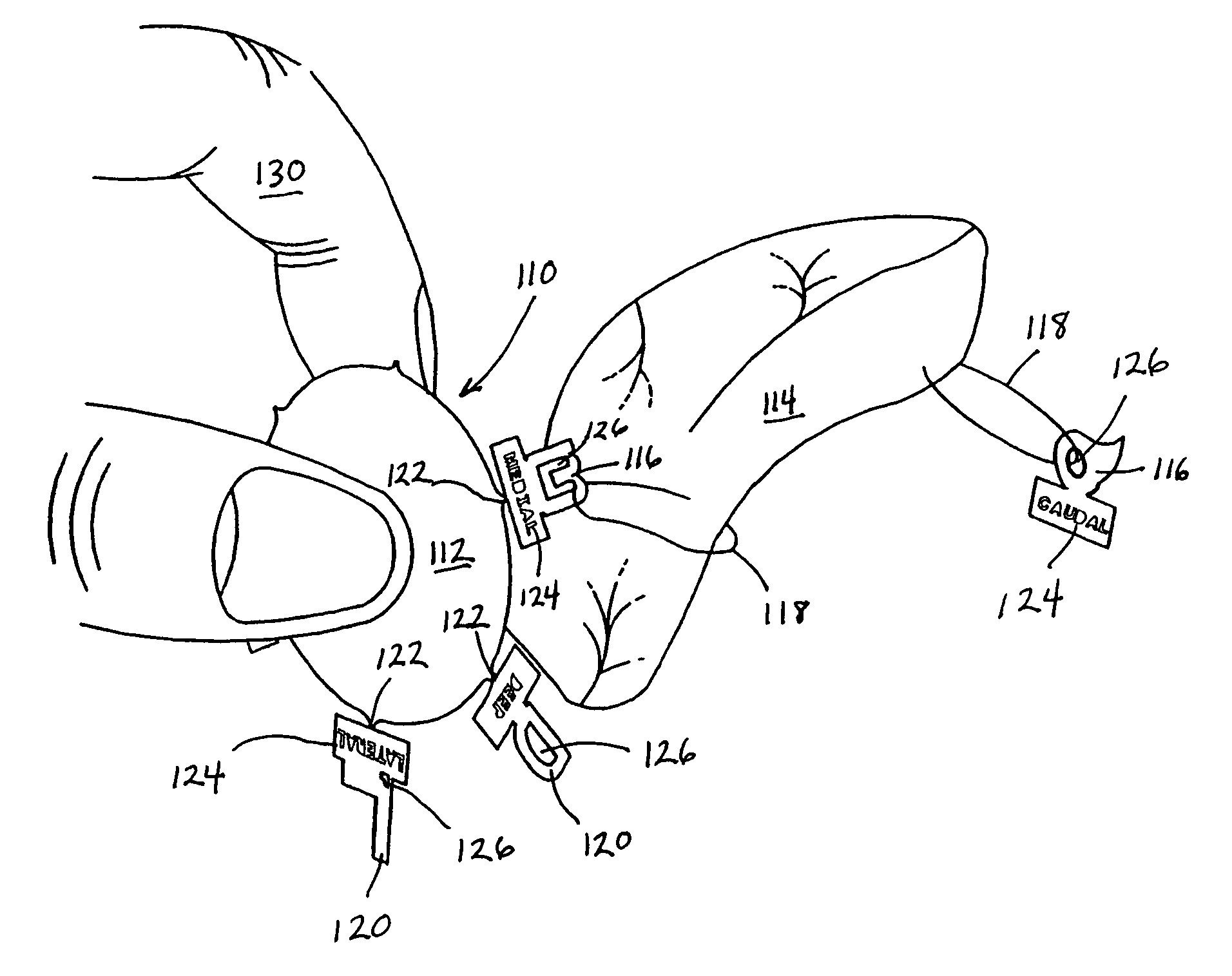
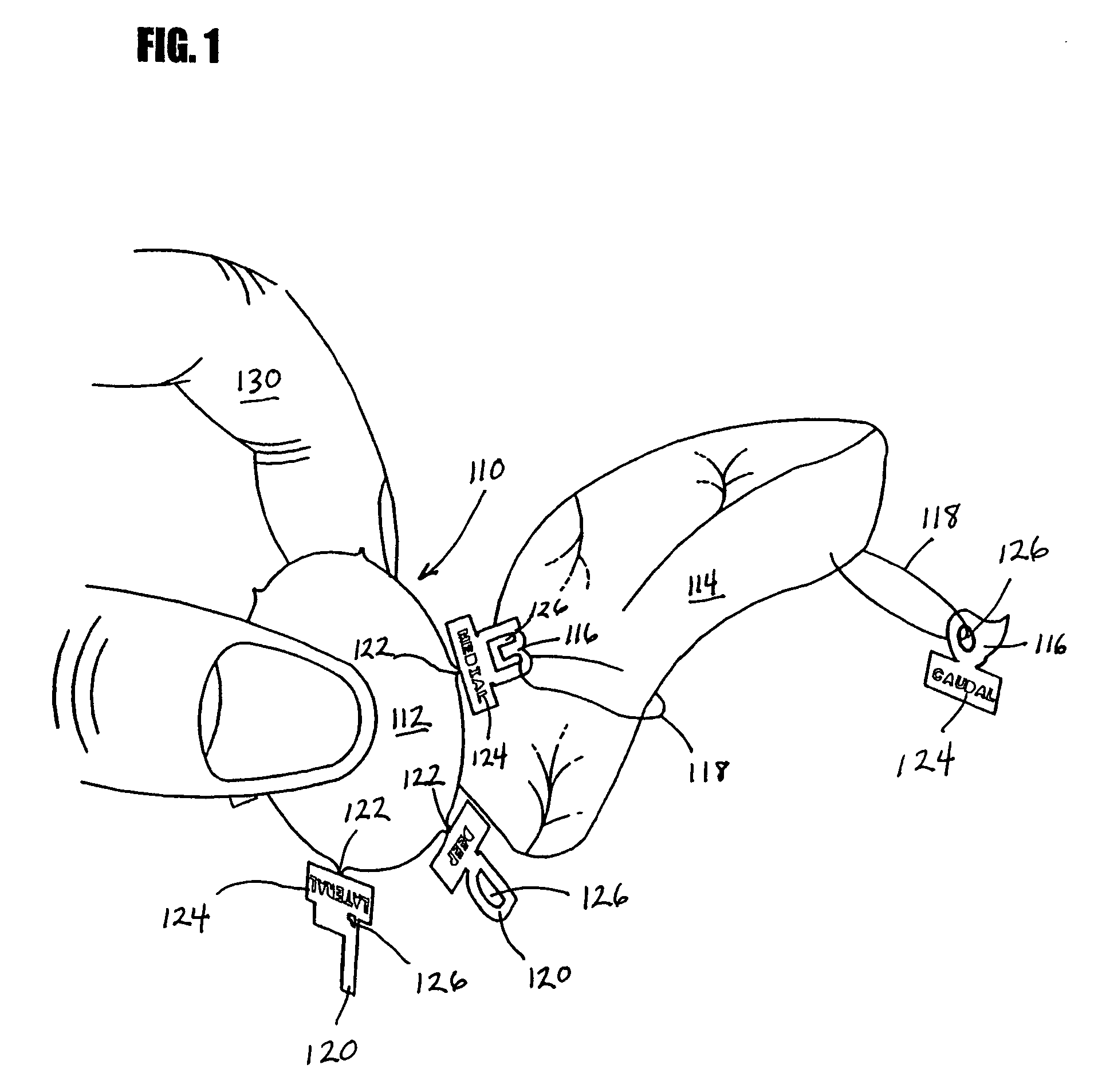
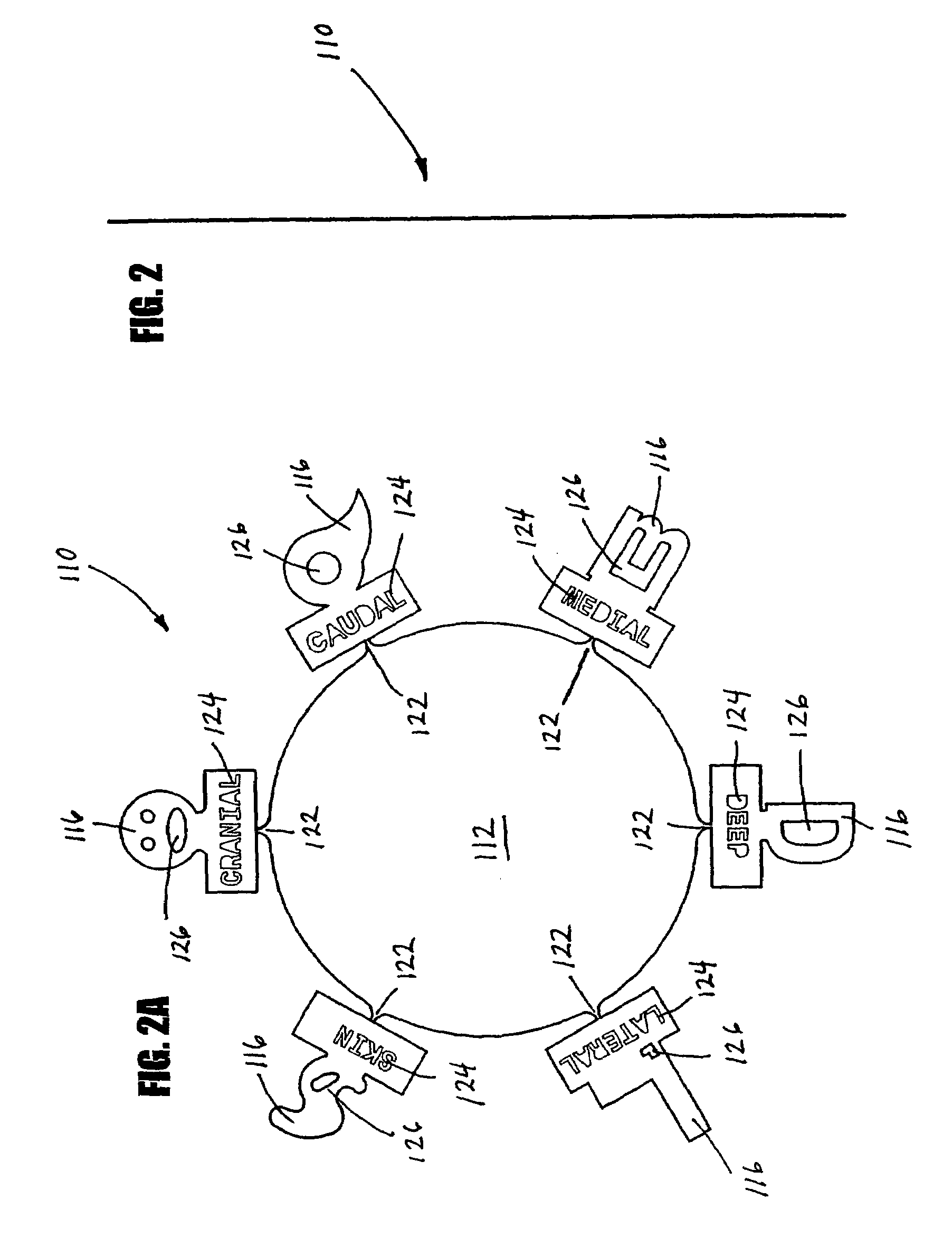
Device and method for margin marking tissue to be radiographed
InactiveUS7127040B2Eliminate confusionEasy to holdSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsPathology diagnosisRadiography
Owner:BEEKLEY A CT
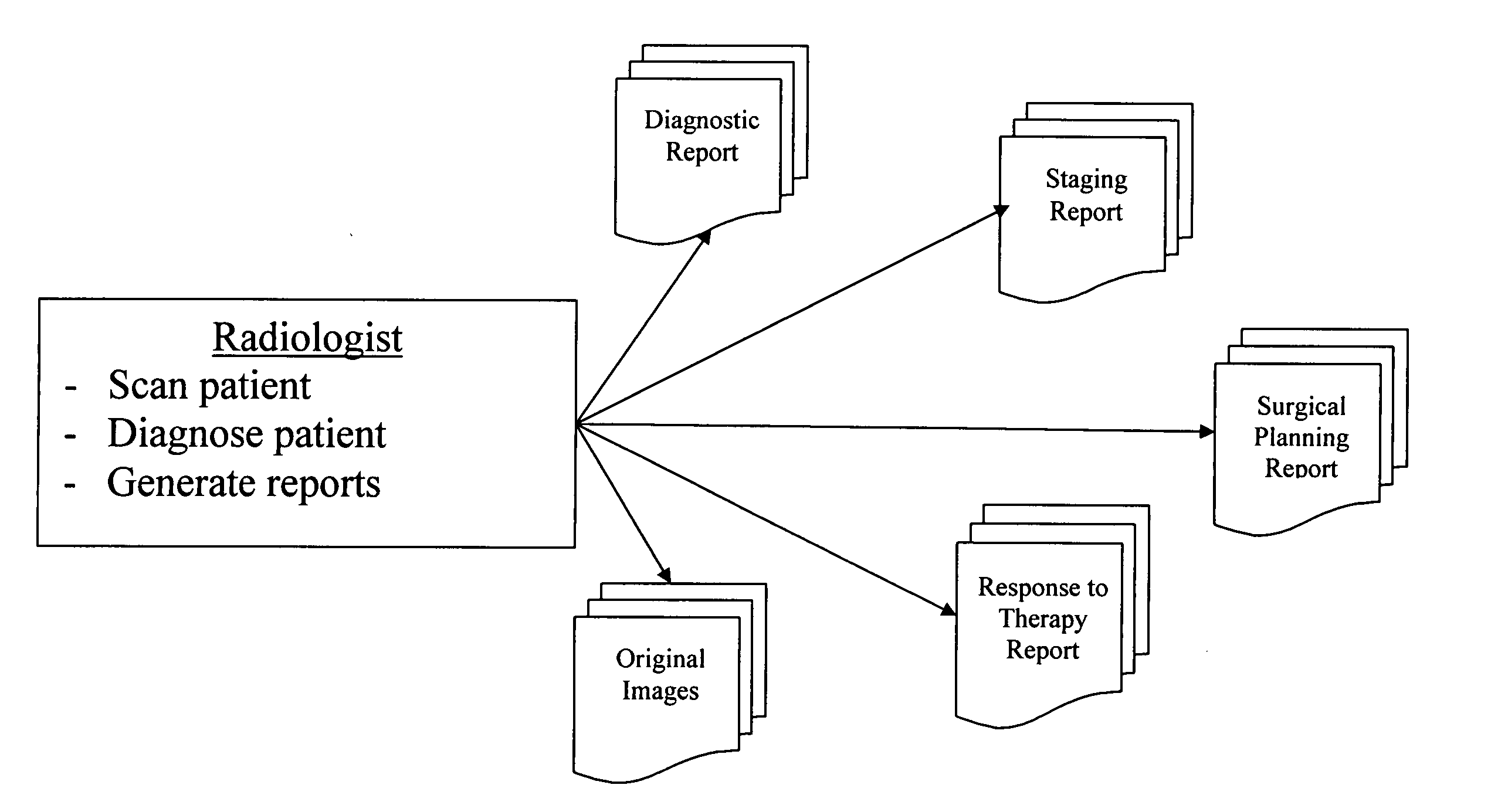
Apparatus and method for customized report viewer
InactiveUS20050096530A1Character and pattern recognitionMedical report generationAbnormal tissue growthBI-RADS
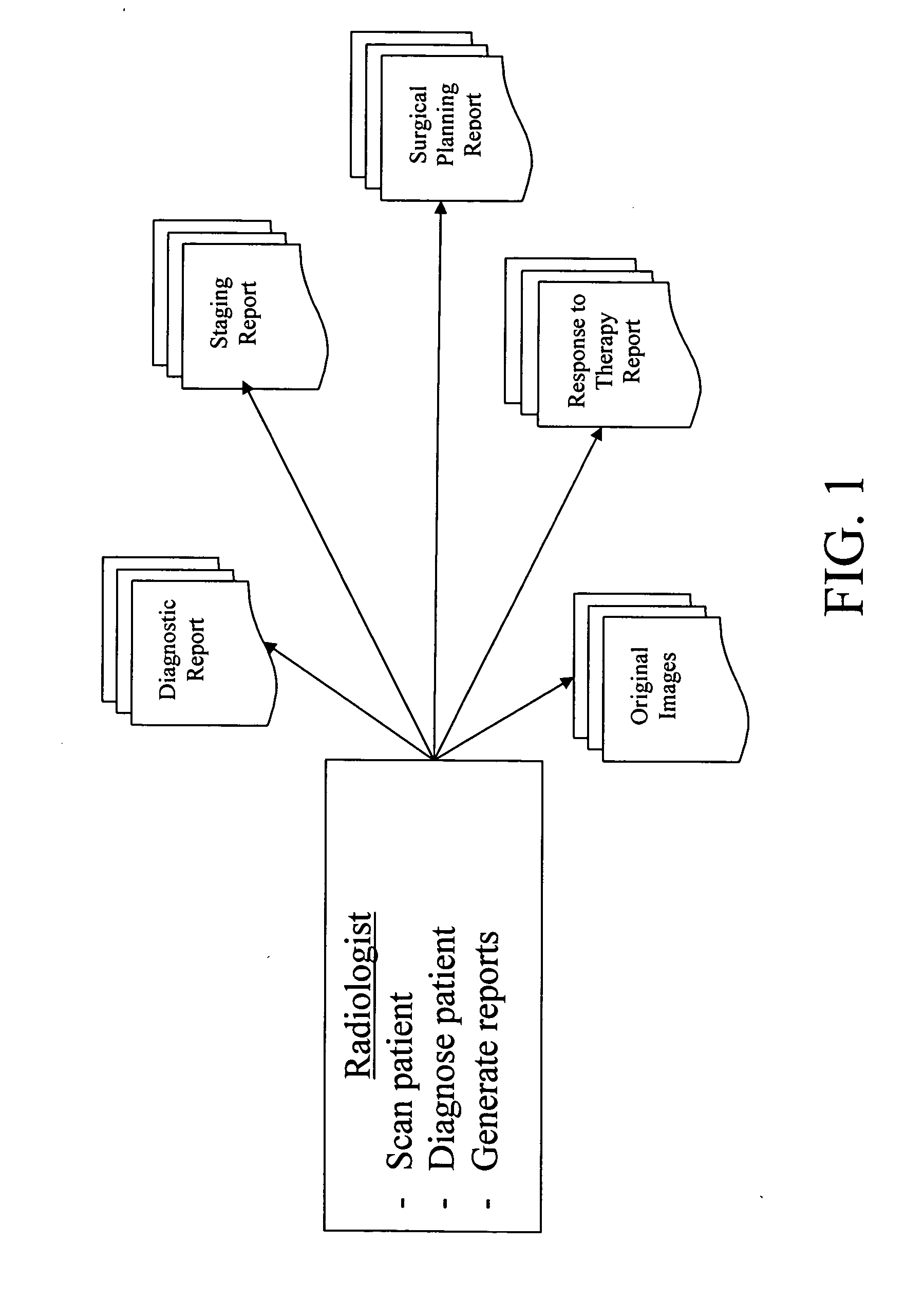
A system for the automatic generation of custom report viewing utilizes imaging data and computer-aided detection technology to identify cancerous tumors. A typical collection of data from a patent's scan may include hundreds of images and associated data. The custom report viewer allows one physician, such as a radiologist, to analyze the data and prepare a report. The generated report may contain images, computed measurements, classifications based on a standard (such as the ACR BI-RADS for Breast MR), and locations relative to landmarks. Different physicians, such as an oncologist or a surgeon, may have need of differing images and supporting data for their own purposes. Each physician may select, in advance, custom selection criteria that are stored in association with that physician. A report generator module uses the stored selection criteria and report filtering to extract the images and supporting data specified by the particular physician. The system allows a surgeon to alter the selection criteria and obtain further images if necessary and permits the generation of multiple selection criteria by one physician for different purposes, such as surgical planning, therapy reporting, and the like.
Owner:MERGE CAD
Device and method for margin marking of radiography specimens
InactiveUS20050152841A1Eliminate confusionEasy to holdSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsEngineeringVisual perception
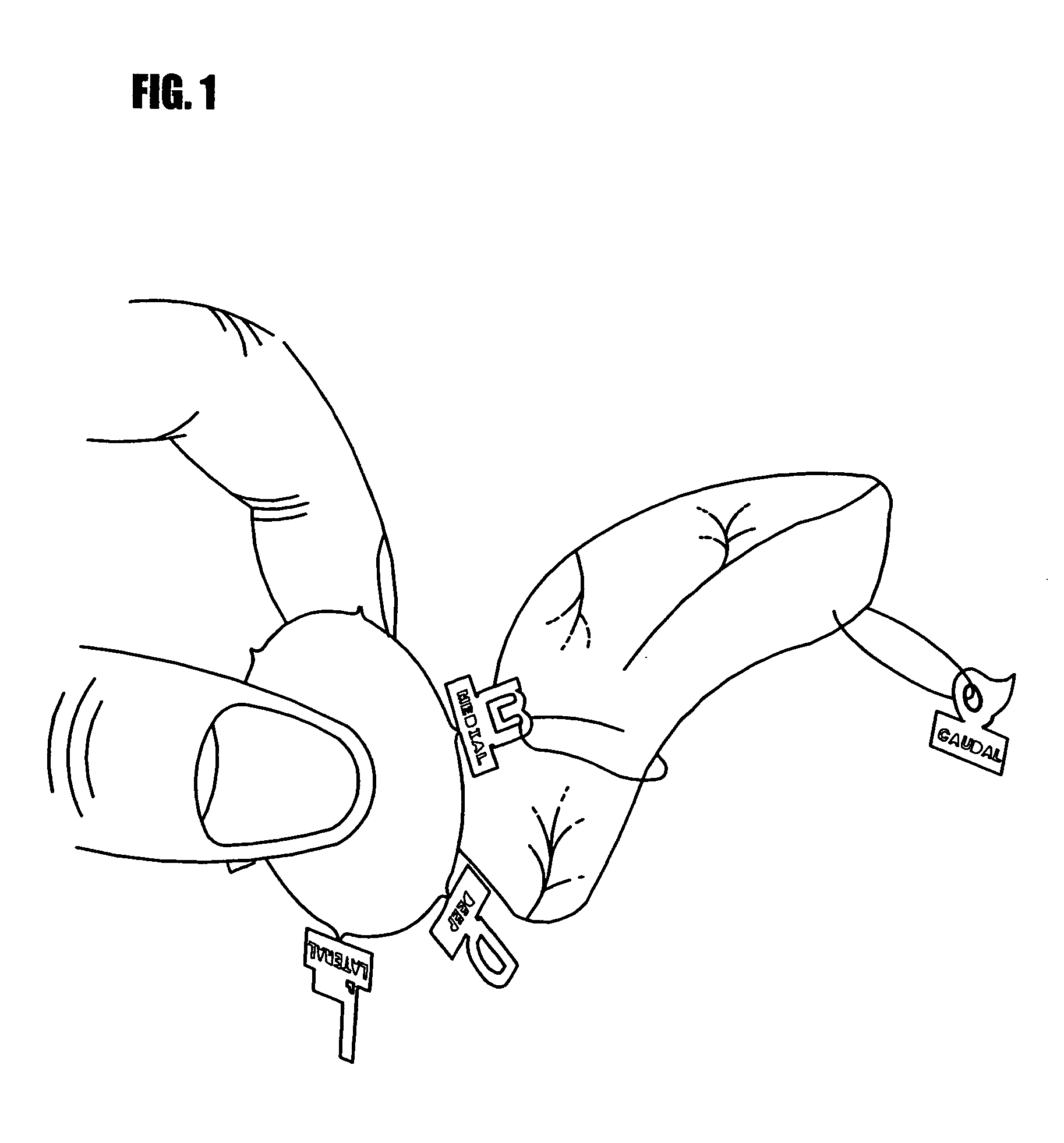
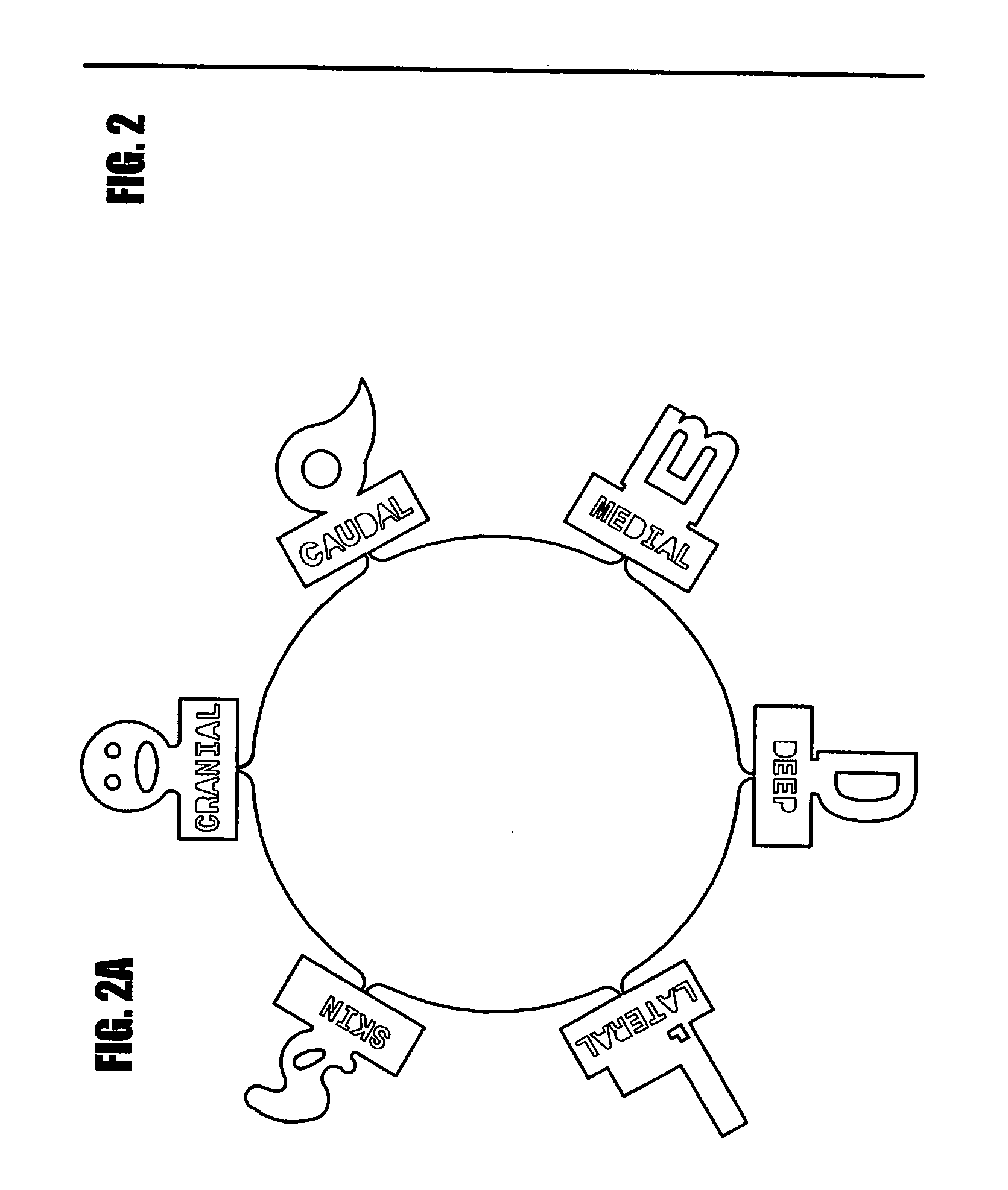
A marking device for defining the margins and orientation of radiography specimens includes a plurality of visually distinctive markers joined by a base that holds the markers until the markers are secured to a specimen. The base serves as a holder for the individual markers as the markers are secured to a specimen with sutures or staples, at which time the markers are disconnected from the base. One or more markers may be secured to a specimen as needed to define the orientation of the specimen. By securing markers to specific locations on a specimen, a surgeon can indicate to radiologists and pathologists the specimen's orientation in the body before removal, thus aiding in future study of the specimen. Since the markers are made either wholly or partially from radiopaque material, the markers are visible when radiographed.
Owner:BEEKLEY A CT
Use of computer-aided detection system outputs in clinical practice
InactiveUS20060171573A1Efficient and precise positioningAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineMinutiae
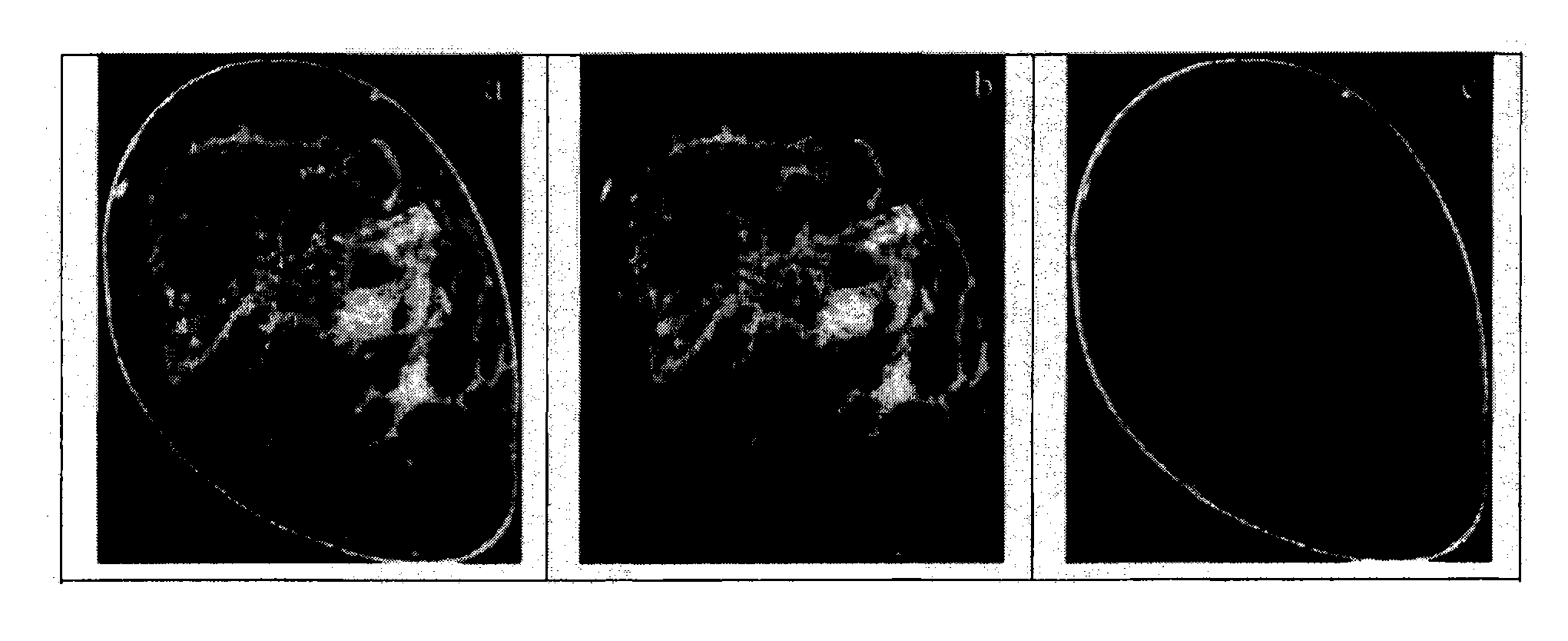
The present invention provides for the use of computer-aided detection (CAD) system output displays for providing accurate representations of areas for subsequent exams. Since the CAD output, unlike the original medical imagery, is not used during the initial reading, the radiologist does not mark it until a final determination is reached regarding subsequent procedures. Additionally, since the CAD output contains versions of the original imagery, the regions indicated by the radiologist are shown in the context of the particular anatomical detail for a given patient. This detail assists the technologist, other physicians and patients in more efficiently and accurately locating the exact area for subsequent exams.
Owner:ICAD INC
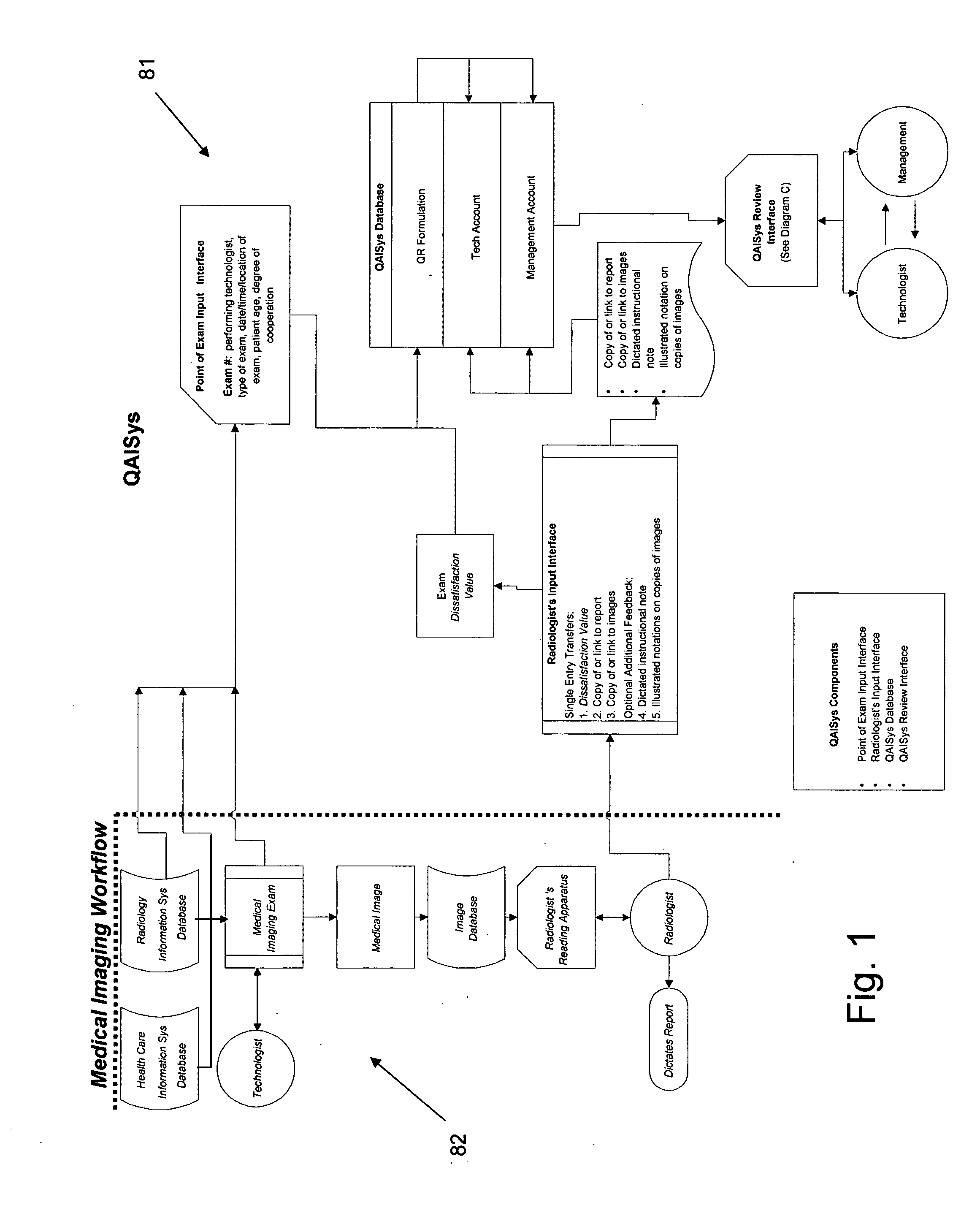
Medical imaging-quality assessment and improvement system (QAISys)
InactiveUS20050256743A1Facilitate efficient communicationFacilitate communicationData processing applicationsSurgeryReviewing RadiologistMedical imaging
The business method known as QAISys (Quality Assessment and Improvement System) is a process that rates comprehensively and continually the quality of medical images as determined by the interpreting radiologist. The output of this system conveys feedback from the radiologist to the performing technologist and his / her supervisor. This feedback enables medical radiologists, technologists, and managers to bridge any communication gaps between themselves in respect to the quality and effectiveness of medical images. It permits management to assess and track image quality for an entire medical imaging department by modality, location, and / or shift, and for each individual technologist. The QAISys method reveals the nature of recurrent quality failures and highlights which exam types need to be improved. QAISys then indicates practical, cost-effective means of assessing and improving the overall medical images for future patients.
Owner:DALE RICHARD B
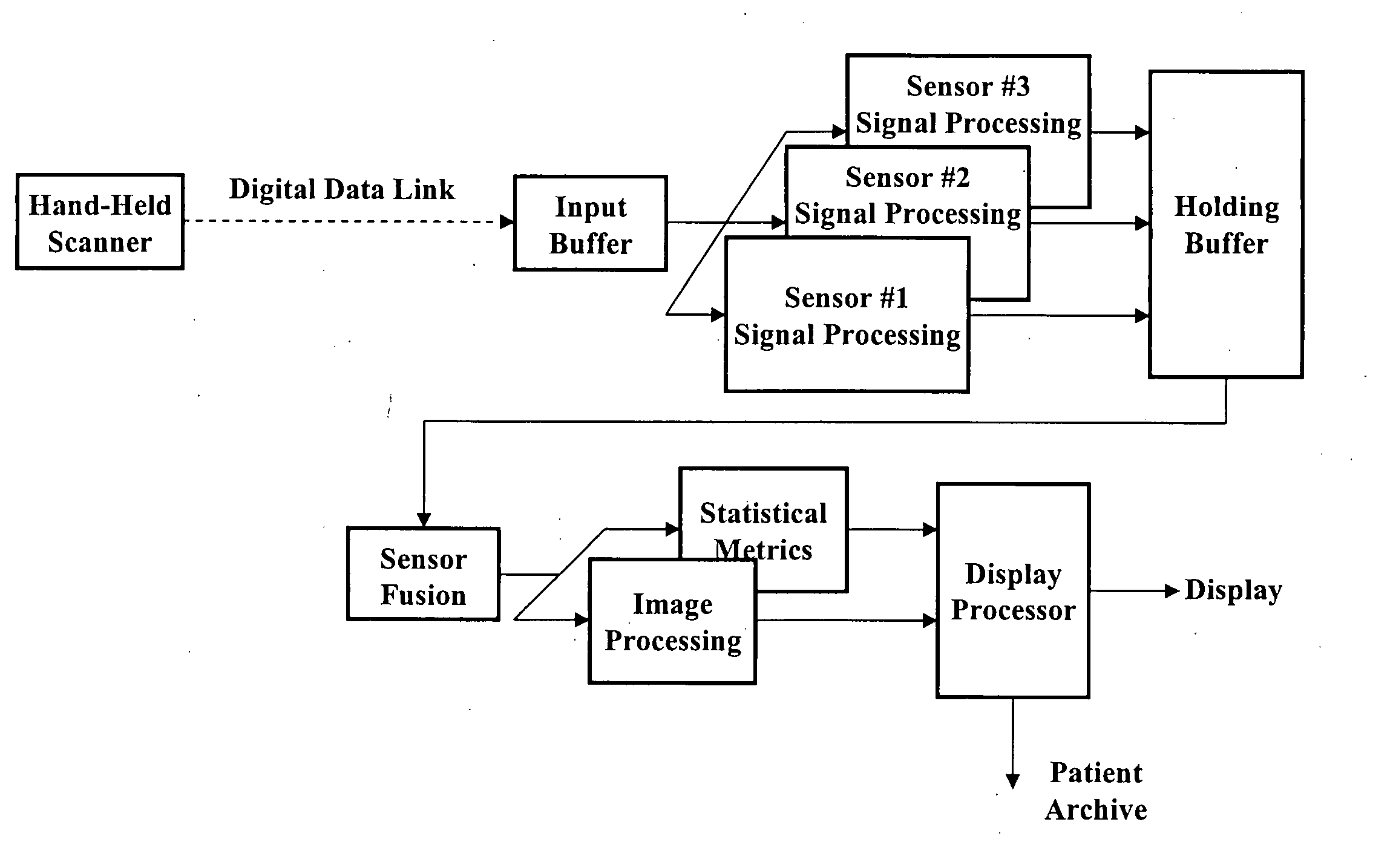
Multi-sensor breast tumor detection
InactiveUS20040220465A1Strong specificityIncrease cost/complexityOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringGeneral practionerBreast cancer screening
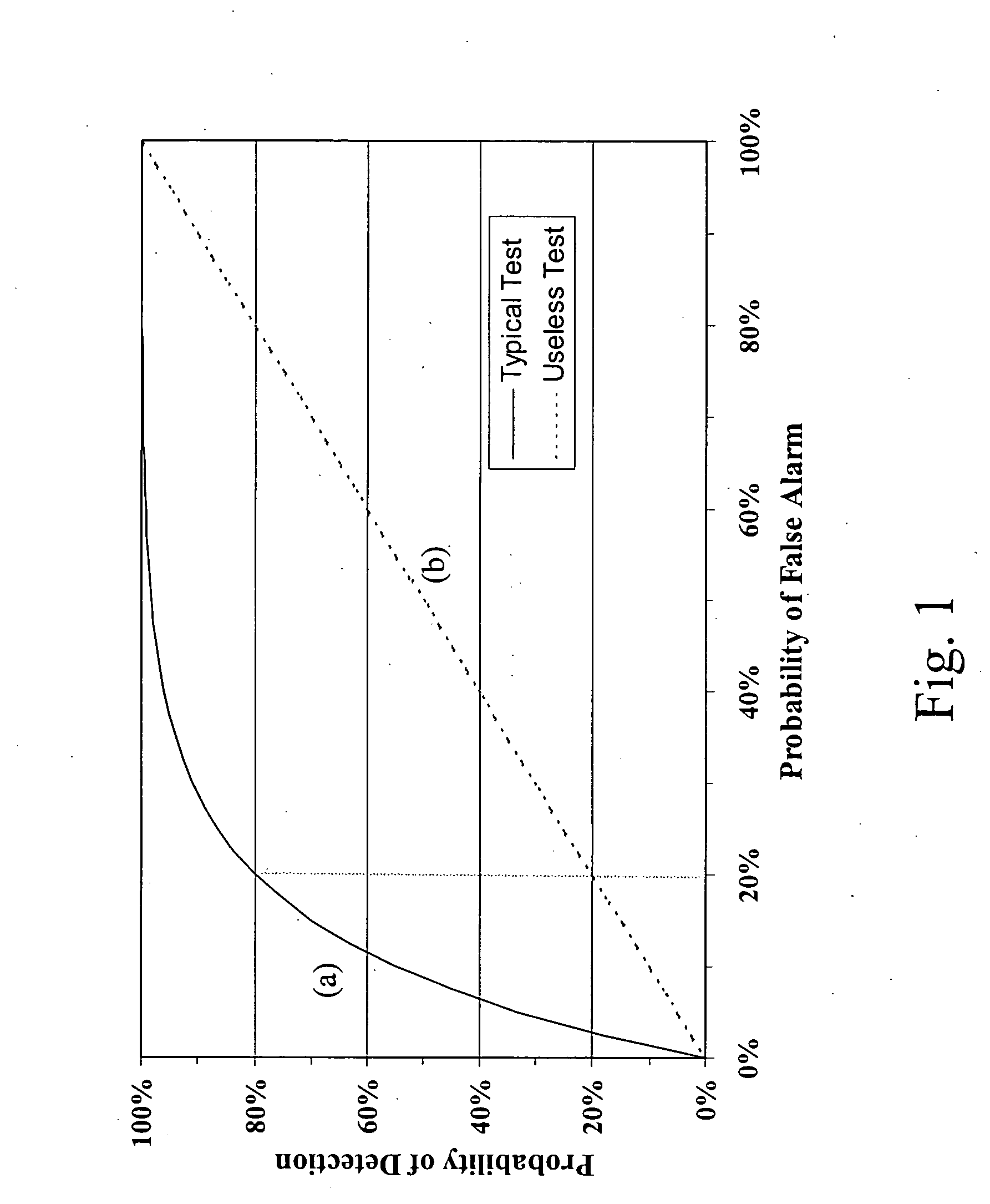
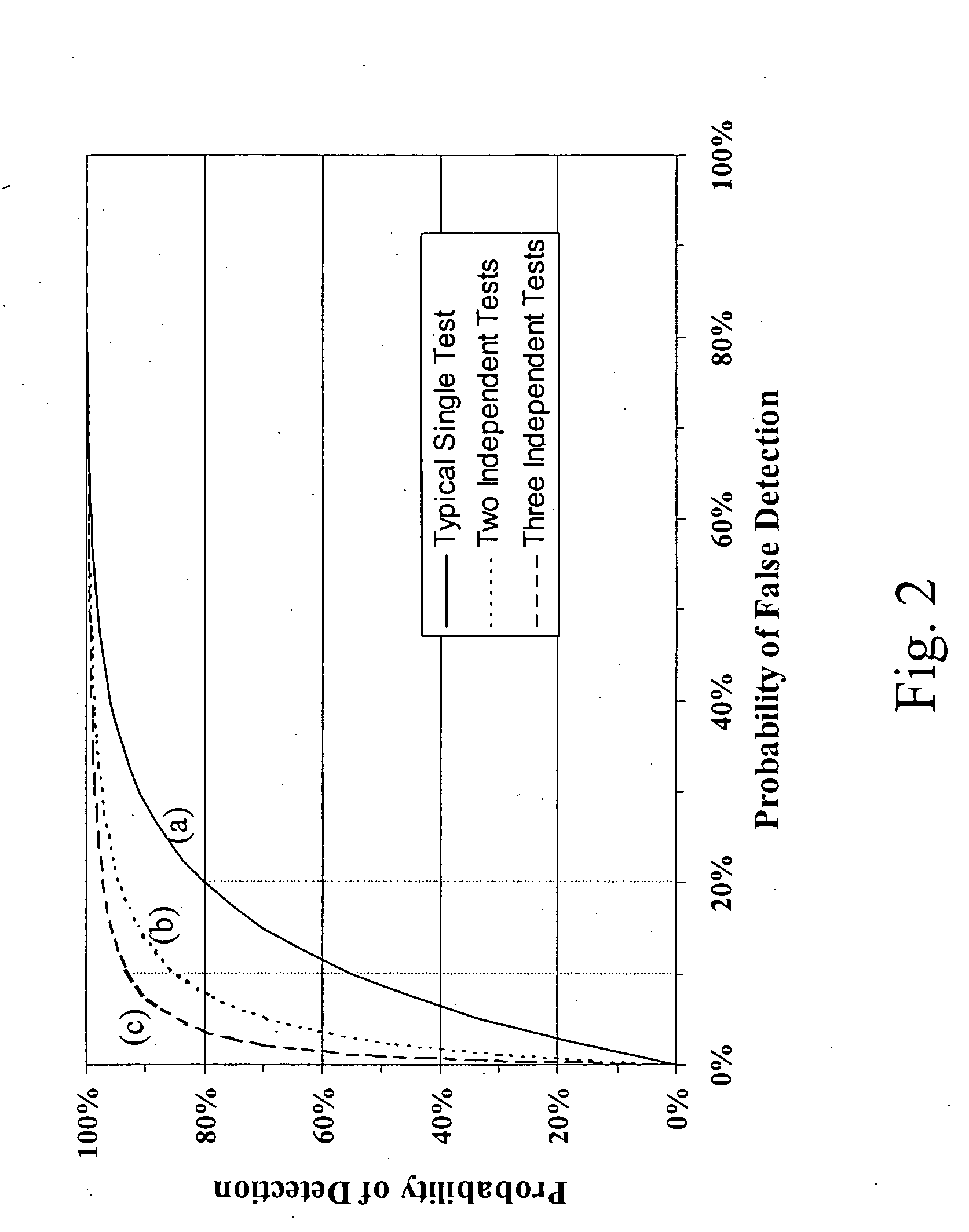
X-ray mammography has been the standard for breast cancer screening for three decades, but offers poor statistical reliability; it also requires a radiologist for interpretation, employs ionizing radiation, and is expensive. The combination of multiple independent tests, performed effectively at the same time and co-registered, can produce substantially more reliable detection performance than that of the individual tests. The multi-sensor approach offers greatly improved reliability for detection of early breast tumors, with few false positives, and also can be designed to support machine decision, thus enabling screening by general practitioners and clinicians; it avoids ionizing radiation, and can ultimately be relatively inexpensive.
Owner:CAFARELLA JOHN H
Deep residual network-based semantic mammary gland molybdenum target image lump segmentation method
ActiveCN107886514ALess parameters to learnImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionData set
The invention discloses a deep residual network-based semantic mammary gland molybdenum target image lump segmentation method. The method comprises the following steps of: labelling pixel categories of lumps and normal tissues corresponding to a collected mammary gland molybdenum target image so as to generate label images, and dividing the mammary gland molybdenum target image and the corresponding label images into training samples and test samples; preprocessing the training samples to form a training data set; constructing a deep residual network, and training the network by utilizing thetraining data set, so as to obtain a deep residual network training model; after a to-be-segmented mammary gland molybdenum target image lump is preprocessed, carrying out binary classification and post-processing on a pixel of the to-be-segmented mammary gland molybdenum target image by utilizing the deep residual network training model, and outputting lump segmentation image to realize semanticsegmentation of the mammary gland molybdenum target image lump. The method is capable of effectively improving the automatic and intelligent levels of mammary gland molybdenum target image lump segmentation, and can be applied to the technical field of assisting radiologists to carry out medical diagnosis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
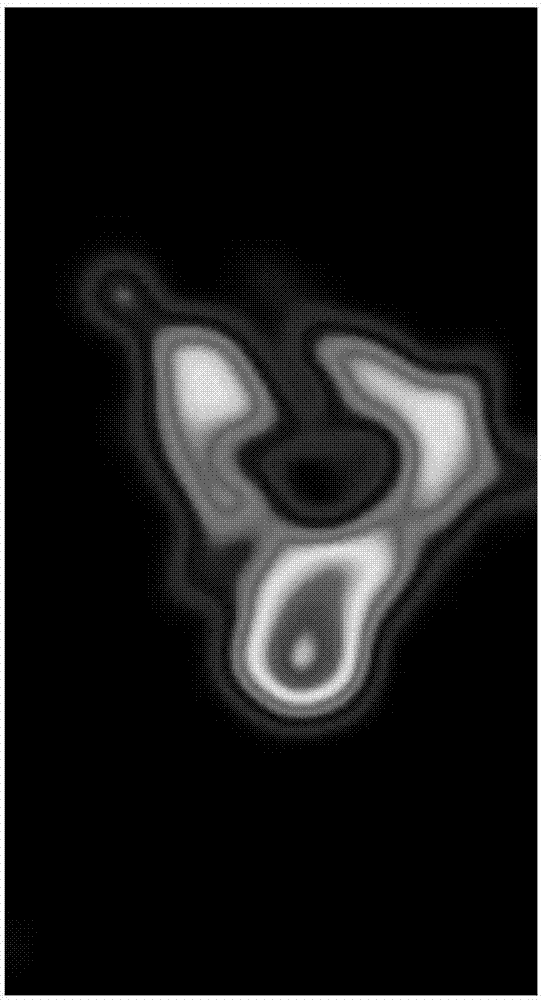
Breast lump image feature extraction method based on edge neighborhood weighing
InactiveCN103425986AImprove classification accuracyOvercome the disadvantage of not including the local features of the tumor edgeCharacter and pattern recognitionScale-invariant feature transformImaging Feature
The invention discloses a breast lump image feature extraction method based on edge neighborhood weighing. The breast lump image feature extraction method mainly solves the problem that in the prior art, extracted features do not contain the edge neighborhood local features of a breast lump. The breast lump image feature extraction method comprises the steps of (1) inputting an image, (2) adjusting the size of the breast lump image which is input, (3) extracting a lump edge, (4) determining the number of inner indentation pixel points and the number of outer extension pixel points, (5) determining the inner region of a lump which undergoes inner indentation, (6) determining the inner region of the lump which undergoes outer extension, (7) obtaining an edge neighborhood image of the breast lump, (8) obtaining weighing values, (9) extracting scale invariant features, (10) extracting word bag features and (11) obtaining features of the breast lump image which undergoes edge neighborhood weighing. By means of the breast lump image feature extraction method, expression of the features of the breast lump image are more robust, the image features are expressed more effectively, the benign and malignant classification accuracy of lumps is improved, and therefore doctors in the radiology department can be assisted in conducting medical diagnosis.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for detection and diagnosis of lung and pancreatic cancers from imaging scans
ActiveUS20200160997A1Improve performanceLarge gainImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleParanasal Sinus Carcinoma
A method of detecting and diagnosing cancers characterized by the presence of at least one nodule / neoplasm from an imaging scan is presented. To detect nodules in an imaging scan, a 3D CNN using a single feed forward pass of a single network is used. After detection, risk stratification is performed using a supervised or an unsupervised deep learning method to assist in characterizing the detected nodule / neoplasm as benign or malignant. The supervised learning method relies on a 3D CNN used with transfer learning and a graph regularized sparse MTL to determine malignancy. The unsupervised learning method uses clustering to generate labels after which label proportions are used with a novel algorithm to classify malignancy. The method assists radiologists in improving detection rates of lung nodules to facilitate early detection and minimizing errors in diagnosis.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
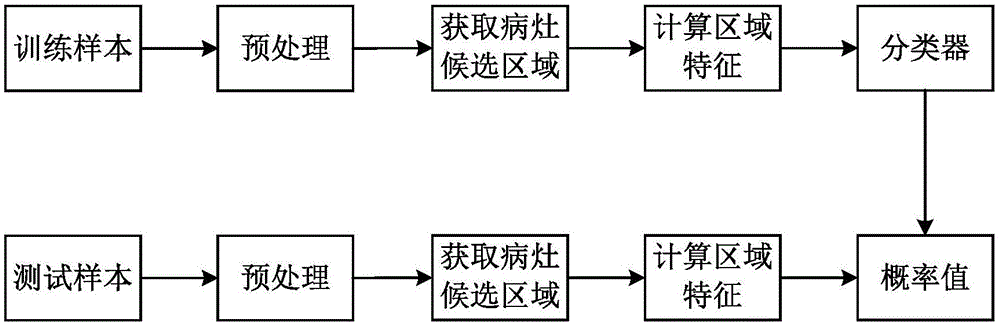
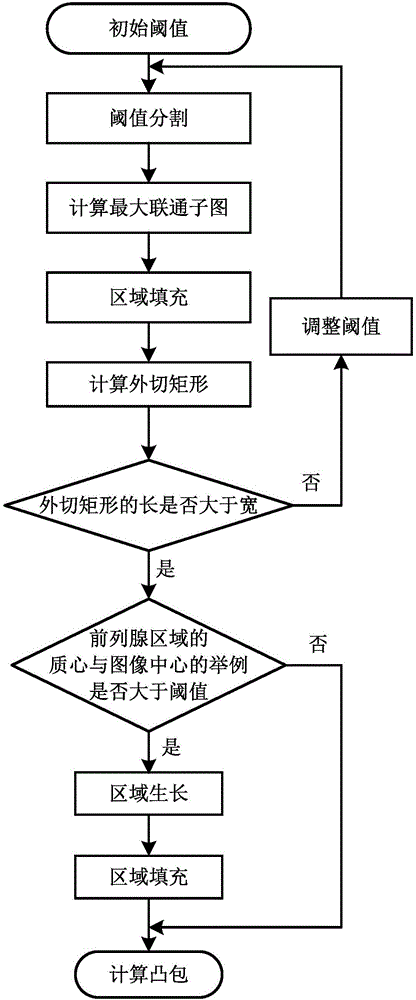
Prostatic cancer computer-assisted detection method and system based on multi-parameter MRI
ActiveCN106778005AAuxiliary diagnosisImprove performanceImage enhancementImage analysisMalignancyTest phase
The invention discloses a prostatic cancer computer-assisted detection method and system based on multi-parameter MRI and relates to the field of medical image processing. The method includes the following steps that at a training stage, firstly, a clinical case sample is preprocessed, then a prostate region and a focus candidate region are automatically extracted, and then features of the focus candidate region are calculated and used for training a classifier; at a testing stage, the trained classier is used for classifying the features of the focus candidate region automatically extracted from the tested clinical case sample, and a corresponding diagnosis result is obtained and serves as reference comments to be provided for doctors. A series of quantitative indexes and corresponding malignancy probability values are provided for radiologists, and the doctors can be effectively assisted in diagnosing the prostatic cancer through an MRI image.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Method and system for automatic identification and orientation of medical images
ActiveUS20070076938A1Reduce errorsShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammogramDisplay device
A method and system for computer-aided detection of abnormal lesions in digital mammograms is described, wherein digital films are processed using an automated and computerized method of detecting the order and orientation of a set of films. In one embodiment, anatomic features are used to detect the order, orientation and identification of a film series. In another embodiment of the invention, a technologist feeds films into the system in any order and orientation. After processing, the system provides an output on a display device to a radiologist that is in an order and orientation preferred by the radiologist. In yet another embodiment of the invention, films from one case are distinguished from films of another case. In this manner and through the use of a bulk loader, a large number of films can be stacked together and fed into the system at one time.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
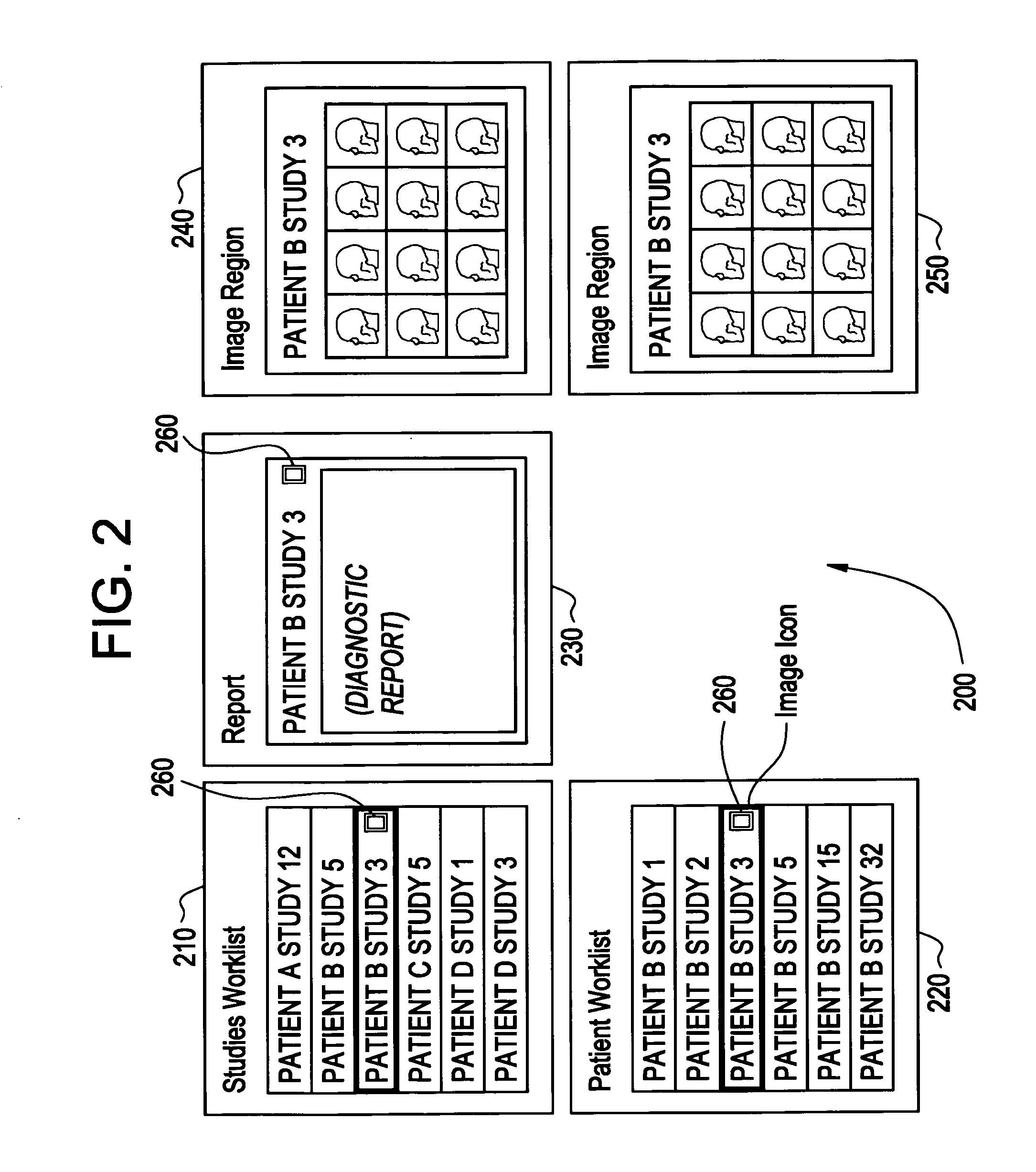
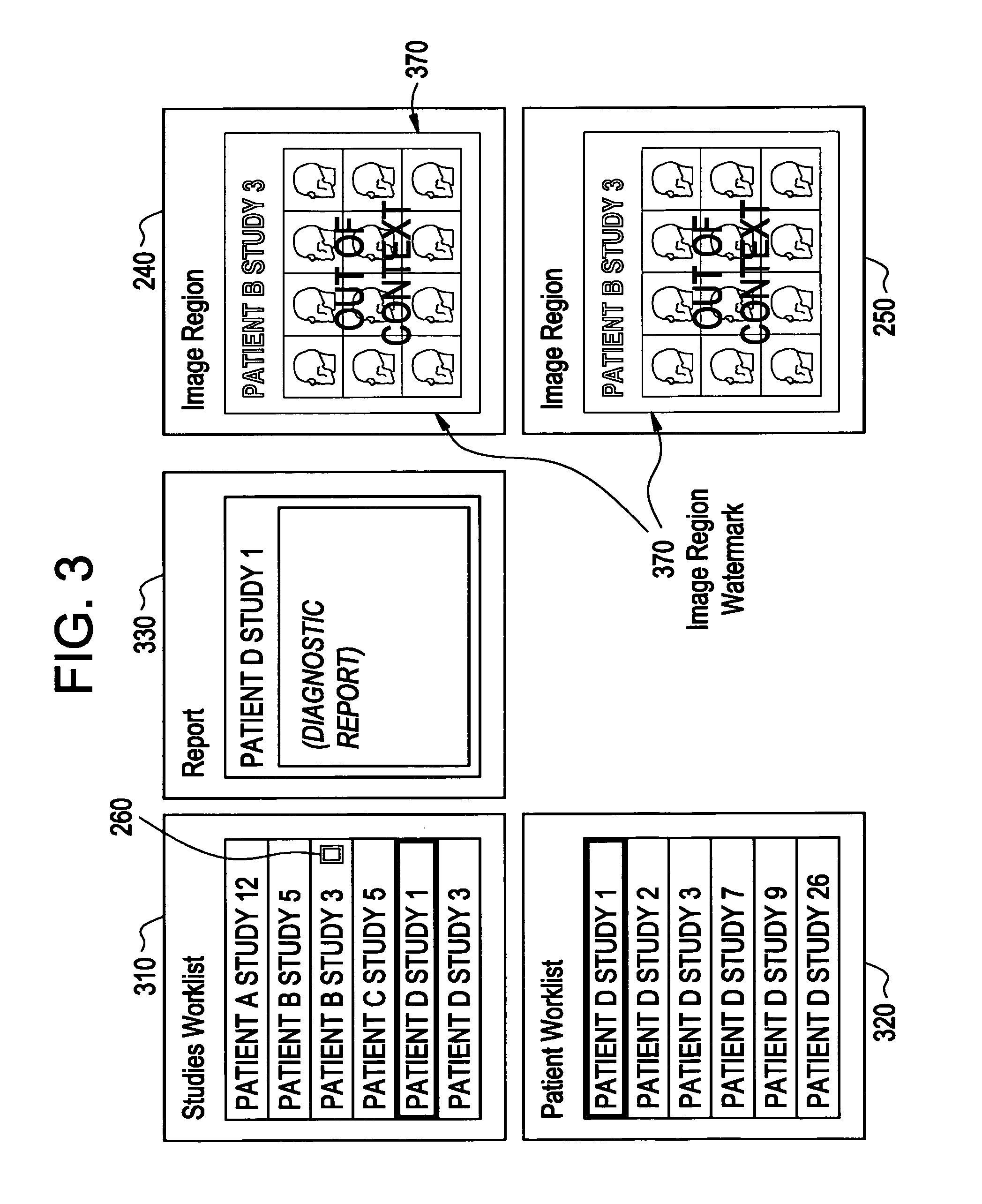
Method and apparatus for managing multi-patient contexts on a picture archiving and communication system
A system and method to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of a radiologist. A context manager for managing the display of multi-patient contexts. In an embodiment computer software operates as a context manager and correlates the context of at least one information container with at least one image container. A graphical container displaying information about a patient, as opposed to an image, may be an information container. A graphical container displaying images of a patient, as opposed to information, may be an image container. In order to minimize occurrences of a user viewing information about a first patient and images of a second patient, and mistakenly believing the information and images belong to the same patient, a visual indicator may be displayed over images that are out-of-context with the information displayed. The visual indicator may be a watermark to alert a user of a difference in context.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
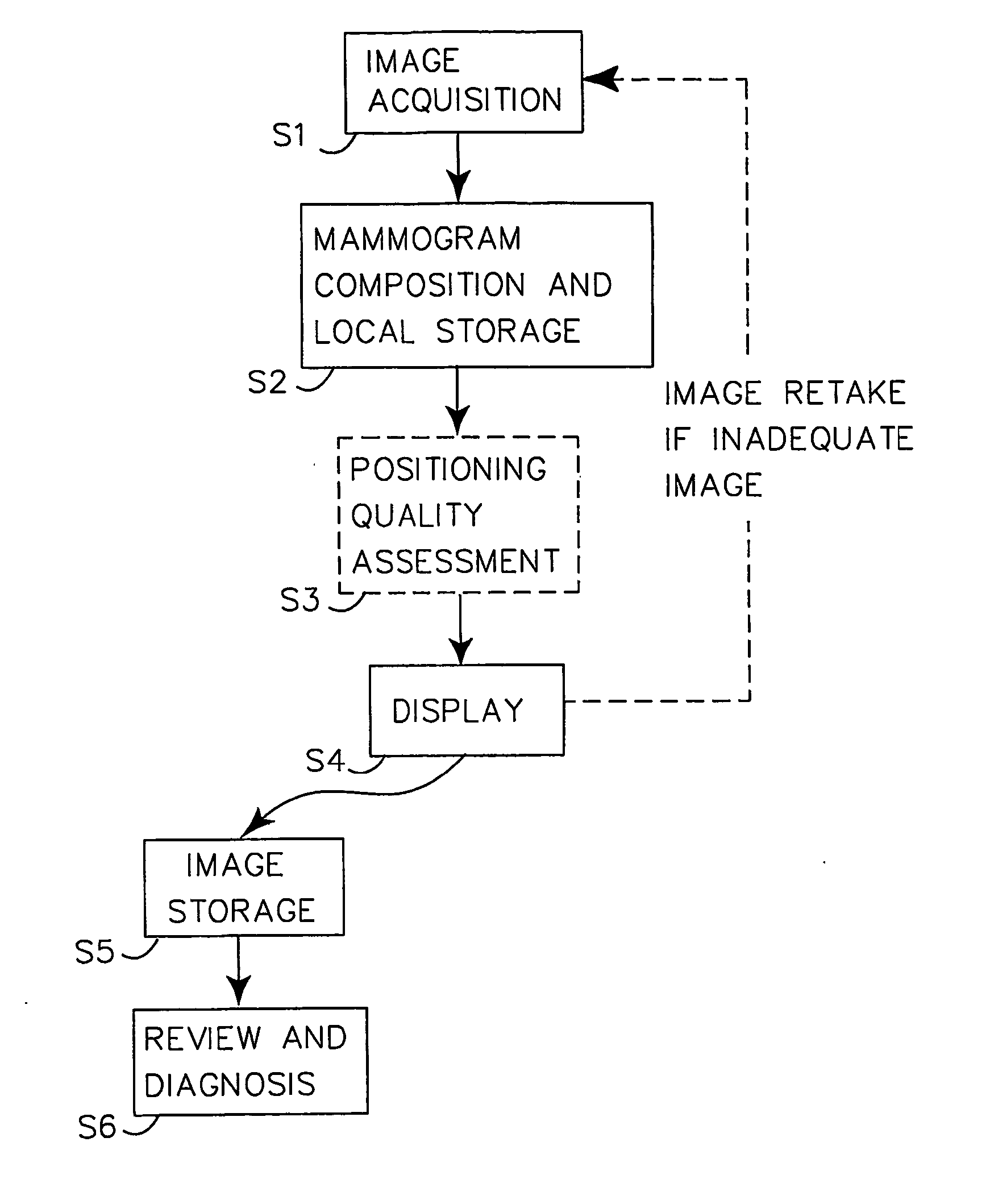
Automatic Positioning Quality Assessment for Digital Mammography
InactiveUS20070248210A1Improve overall mammography processReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammographyQuality assessment
The invention presents a way to automatically assess the quality of acquired (S1, S2) digital mammographic images with respect to the image positioning of a patient's breast. The automated digital quality assessment (S3) is executed in real time and preferably notifies (S4) the technologist instantly if the image positioning quality of a mammographic image is inadequate. This makes it possible to retake the image while the patient is still present at the examination facility. The quality assessment notification includes information to the technologist, preferably both visually and statistically of land-mark positioning measurements. Alternatively, the digital quality assessment is accompanied by a computerized decision of whether the mammogram needs to be retaken, requiring a minimum of involvement, if at all, from the technologist. The invention hence provides a set of quality-assured mammographic images that can be stored (S5) and later accessed by a radiologist for review and diagnosis (S6).
Owner:SECTRA IMTEC
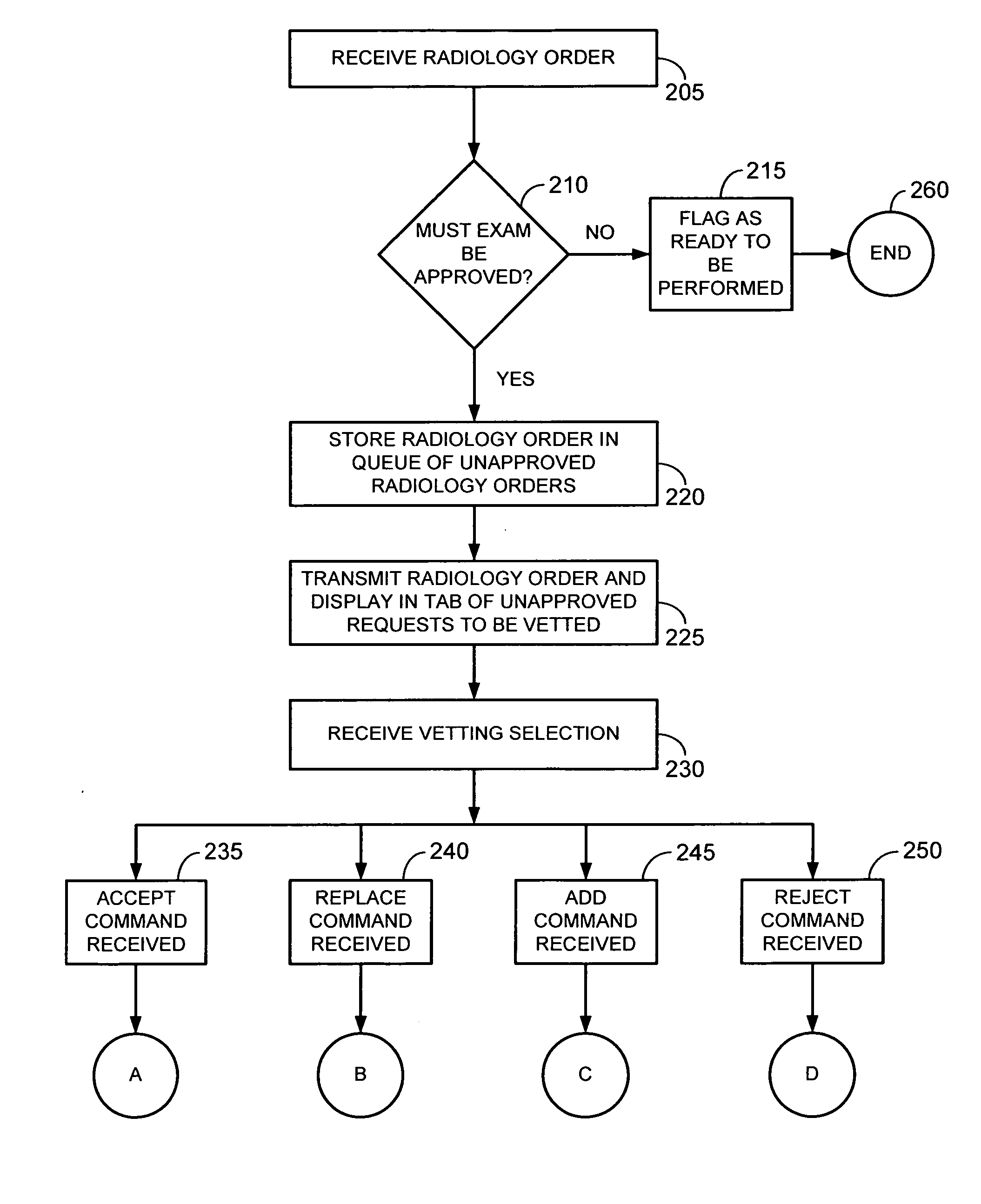
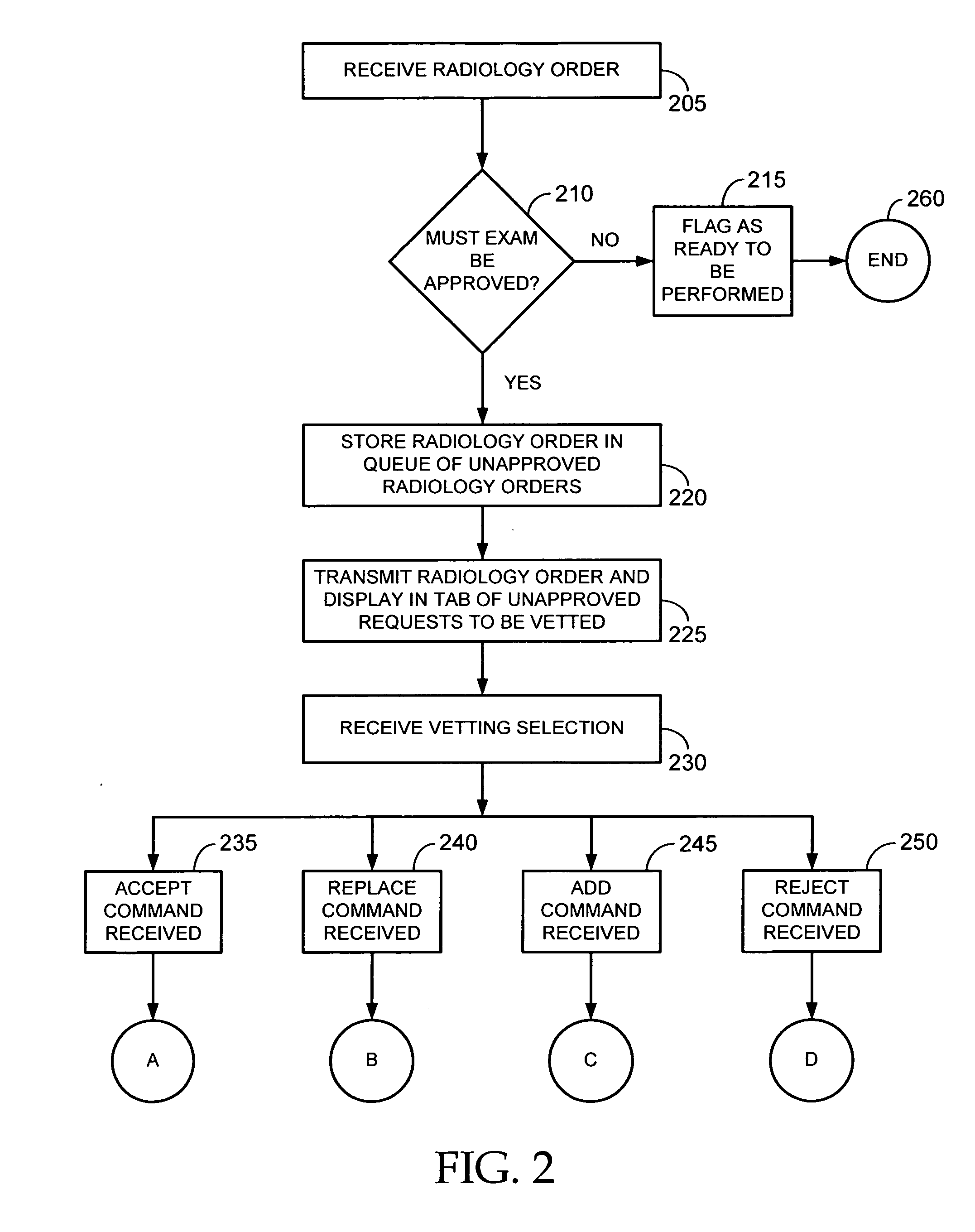
Handling radiology orders in a computerized environment
InactiveUS20070143136A1Data processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisPatient acceptanceOrdering Physician
Computerized methods, systems, and user interfaces for handling one or more radiology orders are provided. Such methods, systems, and user interfaces allow a radiologist, radiological technician, or other healthcare professional to efficiently review and approve, modify, or reject electronic requests from ordering physicians to have patients undergo radiological examination. Such methods, systems, and user interfaces also allow regulators to audit the radiology vetting process to ensure that proper review of radiological examination requests is being conducted. Computerized methods, systems, and user interfaces for automatic electronic notification of ordering physicians of modified or cancelled radiological examination requests are also provided.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
Mammographic system and apparatus
InactiveUS20050213702A1Guaranteed to workImprove efficiencyPatient positioning for diagnosticsStereoscopic photographyComputer scienceRadiography
A mammographic apparatus comprises an identification information reader and the identification information reader transmits the cassette identification information read by the identification information reader together with the radiography execution information to the control apparatus, in the control apparatus, it becomes possible to automatically correlate the radiographic order information and the radiography execution information based on the cassette ID (identification information). Accordingly, since the radiologist can eliminate the selection work to select of the radiographic order information for correlating the radiography execution information prior to the radiography, the efficiency of radiographic work can be improved. In the case of mammography which conducts a plurality of radiographs with different radiographic body parts with different radiographic directions, since the selection operation can be eliminated, the radiologist does not need to move the control apparatus for a selection operation and especially, the efficiency of radiographic work can be improved.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
Method and apparatus for volume rendering display protocol
A system and method to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of a radiologist. A display protocol for medical imaging equipment may allow a plurality of three-dimensional medical images to be concurrently displayed and navigated. The three-dimensional medical images may be linked so a user can manipulate the viewing angle and pointer in the linked images. The display protocol can be configured to display a three-dimensional image from a current exam and a three-dimensional comparison image. Moreover, a display protocol for medical imaging equipment may allow at least one three-dimensional medical image to be concurrently displayed with at least one two-dimensional medical image. The three-dimensional medical image may be linked with the two-dimensional medical image so a user can manipulate the viewing angle and pointer in the linked images. The display protocol can be configured to display a three-dimensional image with axial, sagital, coronal, or non-standard oblique views.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Mammary gland molybdenum target X-ray image block feature extraction method based on tower-shaped principal component analysis (PCA)
ActiveCN104182755AA lot of grayscale informationReasonable grayscale informationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisX-ray
The invention discloses a mammary gland molybdenum target X-ray image block feature extraction method based on tower-shaped principal component analysis (PCA). The mammary gland molybdenum target X-ray image block feature extraction method based on tower-shaped PCA mainly overcomes the defect that features extracted in the prior art do not contain the feature that the density of the middle of a lump is large while the density of the edge of the lump is small. The method comprises the following steps of (1) carrying out pretreatment, (2) constituting a tower-shaped structure, (3) obtaining a gray feature vector of each image layer, (4) training a feature space of the gray feature of each image layer, (5) obtaining principal component features of each image layer, and (6) obtaining mammary gland molybdenum target X-ray image block features based on tower-shaped PCA. According to the method, the mammary gland molybdenum target X-ray image block features can be represented more robustly, image features can be represented more effectively, the accurate rate of detection of a lump region in a mammary gland molybdenum target X-ray photography image is increased, and therefore radiologists are assisted to carry out clinical diagnosis.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for cone beam breast CT image-based computer-aided detection and diagnosis
ActiveUS9392986B2Ensure high efficiency and accuracyAccurate assessmentImage enhancementImage analysisBreast densityMalignancy
Cone Beam Breast CT (CBBCT) is a three-dimensional breast imaging modality with high soft tissue contrast, high spatial resolution and no tissue overlap. CBBCT-based computer aided diagnosis (CBBCT-CAD) technology is a clinically useful tool for breast cancer detection and diagnosis that will help radiologists to make more efficient and accurate decisions. The CBBCT-CAD is able to: 1) use 3D algorithms for image artifact correction, mass and calcification detection and characterization, duct imaging and segmentation, vessel imaging and segmentation, and breast density measurement, 2) present composite information of the breast including mass and calcifications, duct structure, vascular structure and breast density to the radiologists to aid them in determining the probability of malignancy of a breast lesion.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +1
Radiology order entry and reporting system
InactiveUS20050114181A1Easy to useHighly accurate flowData processing applicationsMedical equipmentSystem usageMobile device
A physician in an emergency room inputs a radiology order into a first mobile device. A radiologist receives the order over a second mobile device and inputs a report into the device. The devices provide prompts to input the information according to American College of Radiology guidelines. Information summaries for billing are produced. Physicians who frequently input inappropriate orders can be identified. A learning system uses patient clinical outcomes and pathology results to assess the usefulness of the examinations being performed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Multi-parameter MRI prostate cancer CAD method and system based on two kinds of classifiers
ActiveCN107133638AImprove performanceSpecial data processing applicationsRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsHuman bodyImaging processing
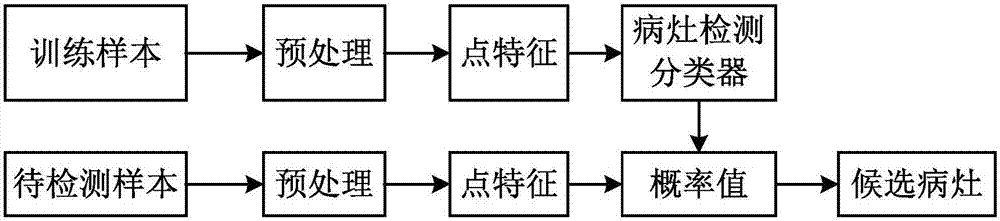
The invention discloses to a multi-parameter MRI prostate cancer CAD method and system based on two kinds of classifiers, relating to the medical image processing field. The multi-parameter MRI prostate cancer CAD method comprises candidate focus automatic detection and candidate focus computer aided diagnosis. The candidate focus automatic detection comprises steps of respectively performing pre-processing on three MRI sequences of each case: T2WI, DWI, ADC to make resolution ratios and sizes of the T2WI, the DWI, the ADC identical, wherein pixels of a same position basically correspond to a same part of a human body, and respectively extracting point characteristics on three kinds of MRI sequences of each case, and inputting the point characteristics into a focus detection classifier to obtain a candidate focus. The candidate focus computer aided diagnosis comprises steps of calculating regional characteristics of the candidate focus in three kinds MRI sequences of each case and inputting the regional characteristics into a focus diagnosis classifier to obtain a corresponding diagnosis result. The multi-parameter MRI prostate cancer CAD method and system based on two kinds of classifiers can provide a series of quantized indexes and a malignant probability value.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Cloud storage and medical image seamless joint system
The invention discloses a cloud storage and medical image seamless joint system. The system comprises a medical image information acquisition device, a radiology department server, an imaging center server, a front server, a storage gateway, a cloud storage, a radiologist workstation, a clinician workstation, and a tape backup device, wherein the medical image information acquisition device is used for sending acquired information to the radiology department server and the information is copied through the tape backup device, the radiology department server is connected with the imaging center server and used for sending data to an imaging center, the imaging center server is connected with the front server and used for sending the data to the front server; the front server is used for sending the data to the storage gateway, and then the data is stored in the cloud storage through the storage gateway.
Owner:JIAXING NO 1 HOSPITAL
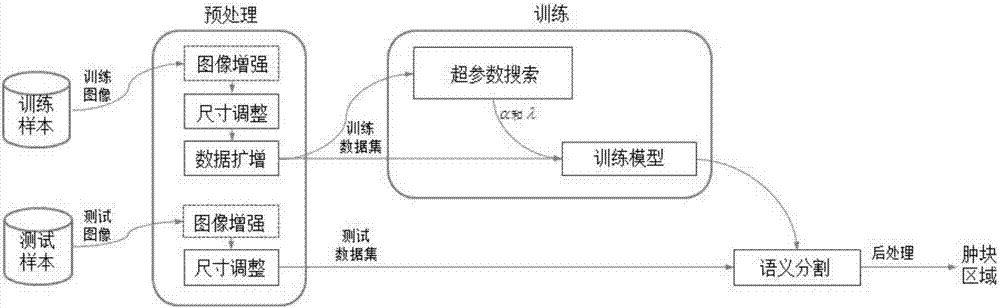
Medical image automatic segmentation method based on deep learning
ActiveCN113516659AOvercome limitationsImprove segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationNuclear medicine
The invention relates to a medical image automatic segmentation method based on deep learning, and provides a solution for challenges such as complex imaging background, lack of shape features, intensity specificity and position priori in a tumor or organ segmentation task, so that automatic positioning and segmentation of a tumor or an organ are realized. Specifically, a segmentation strategy based on a region of interest is designed, a sparse target detection module is used to automatically position and classify tumors or organs, and mask branches are used to finely segment the region of interest. In addition, boundary segmentation is fused into mask segmentation to obtain a finer segmentation result. The invention aims at solving the limitation of a conventional semantic segmentation method in tumor or organ segmentation tasks, and solving the problem of working efficiency of radiologists to a certain extent and reducing manual wrong segmentation caused by personal deviation and clinical experience by realizing full-automatic tumor or organ segmentation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
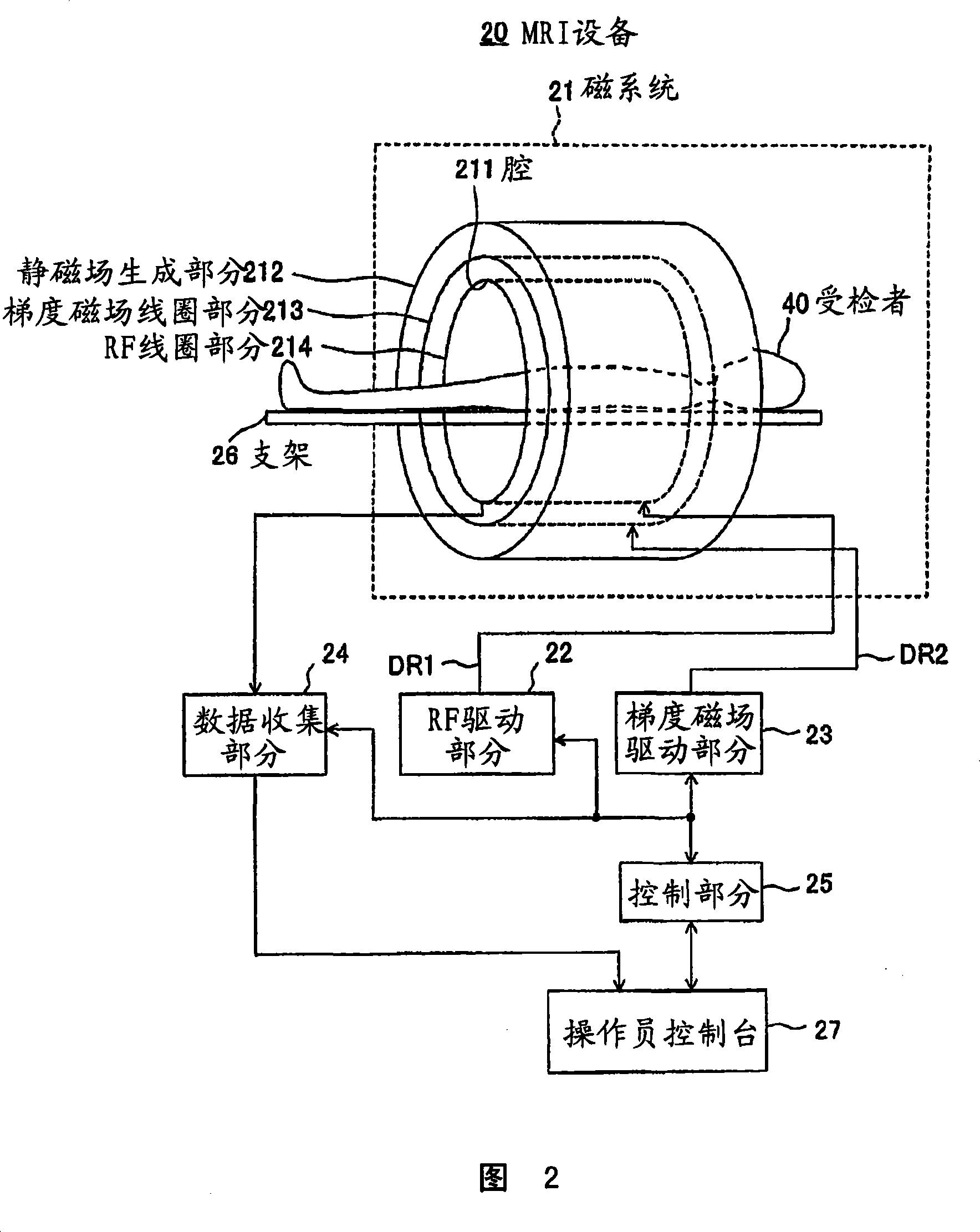
Medical imaging apparatus, workflow notification system, method and program
InactiveCN101165695AOptimize workflowData switching by path configurationDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer terminalMedical imaging
According to the attributes of notification targets such as patients, radiology doctors, and nurses, information owned by medical imaging apparatuses is provided in appropriate timing to improve a workflow of hospitals. A dispatch agent being a software component is executed on a processor of a medical imaging apparatus. Different types of observer terminals (cellular phones, etc.) in which observer agents conforming to the attributes of notification targets operate register information (event) desired for notification in the dispatch agent. The dispatch agent monitors various processing processes being executed in the processor, and on detecting the occurrence of a registered event, notifies the observer terminals of its occurrence. Since the dispatch agent is also a sort of processes executed in the processor, network traffic is not increased by its monitoring of various processing processes.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Management method and platform for an acute cerebral apoplexy first-aid process
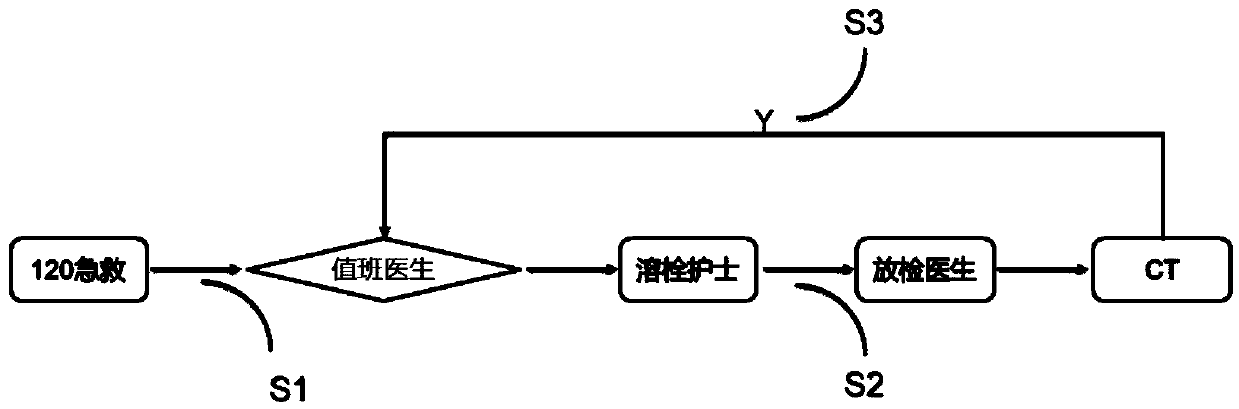
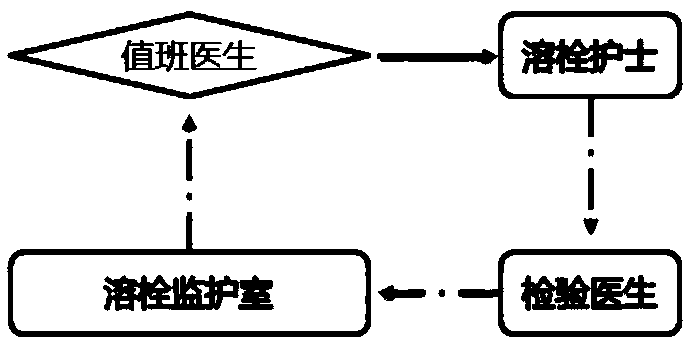
InactiveCN109657972AImprove the level ofHigh speedMedical communicationResourcesClosed loopLaboratory facility
The invention discloses a management method and platform for an acute cerebral apoplexy first-aid process, and belongs to the technical field of medical first-aid. The intelligent bracelet is introduced; First-aid personnel bind the smart bracelet through the App and upload patient information. after receiving the information through the App, the doctors in the hospital carry out first-aid early warning in advance; An on-duty doctor, a thrombolysis nurse, a radiologist, a clinical laboratory doctor and an interventional doctor App mobile terminal carry out high-efficiency dispersion in each link of an in-hospital first-aid process in a task distribution mode, and an intelligent bracelet automatically senses key node time and uploads the key node time through an App to finally complete thewhole process of acute cerebral apoplexy first-aid. According to the invention, resources in necessary fields of the acute cerebral apoplexy first-aid link are more comprehensively integrated, complete closed-loop linkage is realized, an efficient first-aid process is provided, and the medical rescue level can be greatly improved.
Owner:韩玉庆
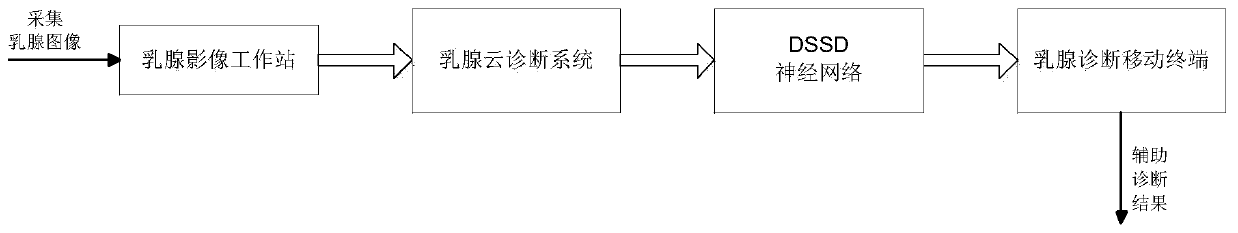
Breast nodules auxiliary diagnosis method based on DSSD and system
PendingCN110379509AEffective diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisSecond opinionImagery technique
The invention relates to the field of medical image technology, and particularly to a breast nodules auxiliary diagnosis method based on DSSD and a system. The system comprises a breast image workstation, a breast cloud diagnosis system and a breast diagnosis mobile terminal. The breast image workstation performs breast image acquisition. The breast cloud diagnosis system comprise training set anda testing set preprocessing, marking and neural network discriminating, wherein the training set and the testing set preprocessing comprises multi-scale image de-noising and enhancing. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a breast graph by the breast image workstation, performing discriminating through mainly using a DSSD neural network, and finally transmitting a result which is obtainedthrough processing of the breast cloud diagnosis system to the breast diagnosis mobile terminal. According to the method and the system, a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system based on deep learningis developed for aiming at the field of the medical image (unnatural image), thereby supplying a second opinion for diagnosis to a radiology department doctor, and more effectively assisting the doctor in performing diagnosis.
Owner:安徽磐众信息科技有限公司
Method to modify imaging protocols in real time through implementation of artificial intelligence
InactiveUS20200124691A1Processing speedLower medical costsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionPatient data
Imaging protocols are modified in real time through implementation of artificial intelligence. Key steps include: inputting of medical images and patient data; performing artificial intelligence analysis; outputting a potentially modified radiological imaging examination protocol; if applicable, an option for the radiologist to review the patient data, images acquired and the AI's potentially modified radiological imaging examination protocol; delivery of the modified radiological imaging examination protocol to the imaging device; and, if applicable, an option for the radiologist to provide feedback and re-train the artificial intelligence algorithm. Further, some of the images that are utilized by the AI system include processed images, such as segmented and filtered volume rendered images.
Owner:DOUGLAS DAVID +2
Medical image efficient classification management method based on big data
InactiveCN110399891AImprove work efficiencyCalculation speedCharacter and pattern recognitionTime complexityHistogram equalization
The invention relates to a medical image efficient classification management method based on big data, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the image standardization of a T2 weighted magnetic resonance image, and obtaining a standardized image; performing gaussian filtering on the standardized image; performing contrast stretching on the denoised image; extracting brightness features of the stretched image; carrying out histogram equalization on the stretched image to obtain an image with enhanced contrast; extracting texture features of the contrast-enhanced image through a gray level co-occurrence matrix; training and verifying the classification model through a support vector machine by adopting a one-leaving method; establishing a graphical user interface for human-computerinteraction. According to the invention, the classification precision of the classifier is improved and the time complexity of the algorithm is reduced through background removal; through two times of image enhancement, the texture of the image is more obvious, so that the classification precision is improved; the working efficiency of radiologists can be improved; different features are extracted for different stages, and image features of different stages are met.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method to determine relevant prior radiology studies using pacs log files
InactiveUS20200051699A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsEasy to operateMedical data miningMedical practises/guidelinesRadiology reportDisplay device
A radiology workstation (10) includes a computer (12) connected to access radiology studies stored in an radiology studies archive (20) with at least one processor (22) programmed to operate the computer to: provide a user interface (24) for performing readings of radiology studies including: displaying images on a display (14) of a current radiology study being read; receiving user inputs via one or more user input devices (16) and operating on the user inputs to manipulate the display of images and to open and view past radiology studies during the reading and to receive a radiology report summarizing the reading and store the radiology report in the radiology studies archive; and recording a activity log of user inputs received via the one or more user input devices during readings of radiology studies. While providing the user interface for performing a reading by a radiologist of a current radiology study of a patient, tire at least one processor is Anther programmed to perform a relevant past radiology study recommendation process including: identifying at least one previously-read radiology study of the patient stored in the radiology studies archive as being relevant to the current radiology study of the patient using a radiologist-specific relevance identification criterion derived from content of the activity log recording the radiologist opening and viewing past radiology studies during readings performed by the radiologist; and displaying an indication of the at least one relevant previously-examined radiology study on the display.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Medical Image Pre-Processing at the Scanner for Facilitating Joint Interpretation by Radiologists and Artificial Intelligence Algorithms
A method and system for medical image pre-processing at the medical image scanner that facilitates joint interpretation of the medical images by radiologists and artificial intelligence algorithms is disclosed. Raw medical image data is acquired by performing a medical image scan of a patient using a medical image scanner. Input data associated with the medical image scan of the patient and available downstream automated image analysis algorithms is acquired. A set of pre-processing algorithms to apply to the raw medical image data is selected based on the input data associated with the medical image scan of the patient and the available downstream automated image analysis algorithms using a trained machine learning based model. One or more medical images are generated from the raw medical image data by applying the selected set of pre-processing algorithms to the raw medical image data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Artificial intelligence engine for directed hypothesis generation and ranking
PendingUS20220261668A1Quality improvementRelational databasesBiological modelsDiseaseSearch analytics
An artificial intelligence engine for directed hypothesis generation and ranking uses multiple heterogeneous knowledge graphs integrating disease-specific multi-omic data specific to a patient or cohort of patients. The engine also uses a knowledge graph representation of ‘what the world knows’ in the relevant bio-medical subspace. The engine applies a hypothesis generation module, a semantic search analysis component to allow fast acquiring and construction of cohorts, as well as aggregating, summarizing, visualizing and returning ranked multi-omic alterations in terms of clinical actionability and degree of surprise for individual samples and cohorts. The engine also applies a moderator module that ranks and filters hypotheses, where the most promising hypothesis can be presented to domain experts (e.g., physicians, oncologists, pathologists, radiologists and researchers) for feedback. The engine also uses a continuous integration module that iteratively refines and updates entities and relationships and their representations to yield higher quality of hypothesis generation over time.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com