Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
236 results about "Relaxation (NMR)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
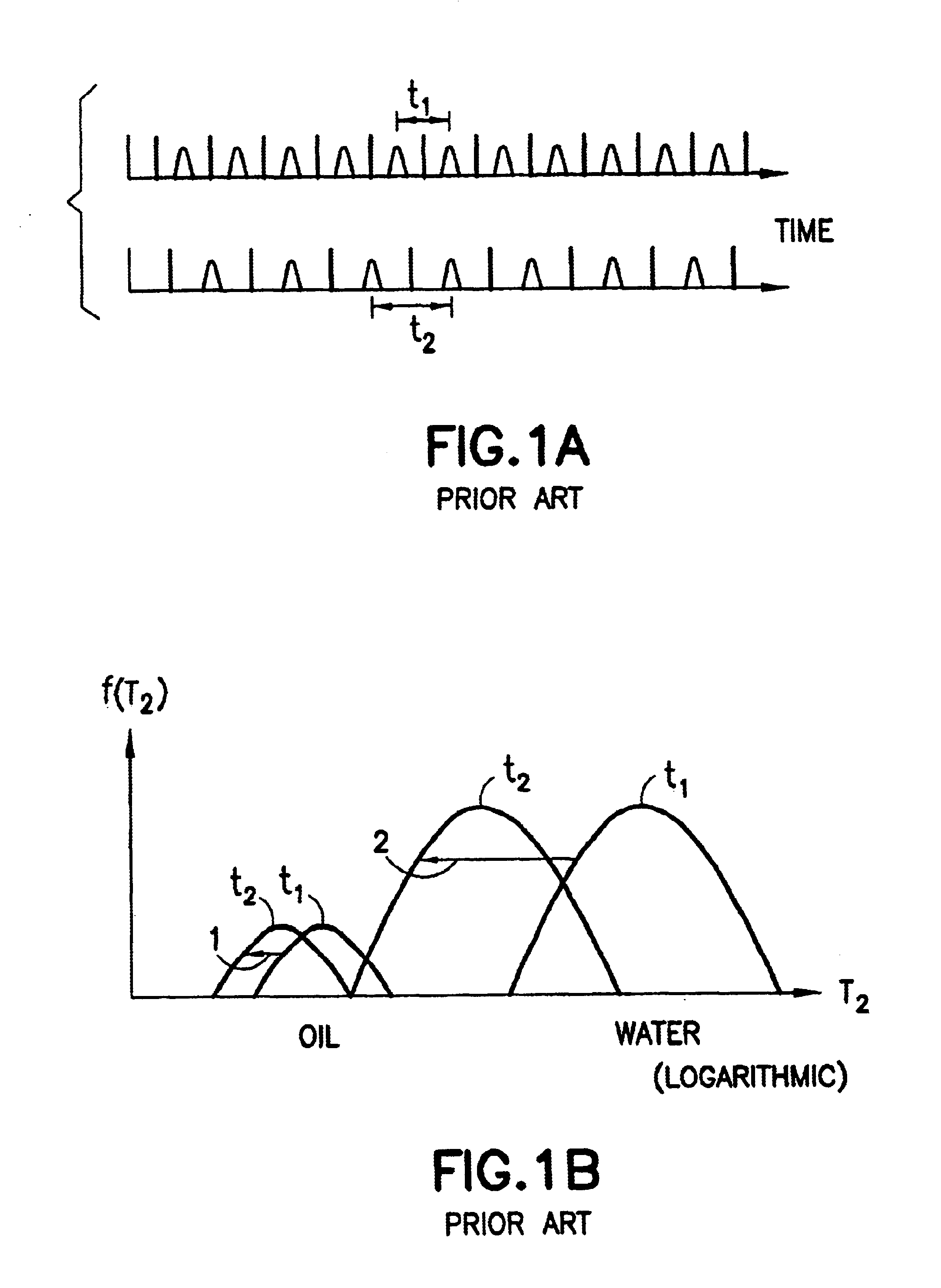
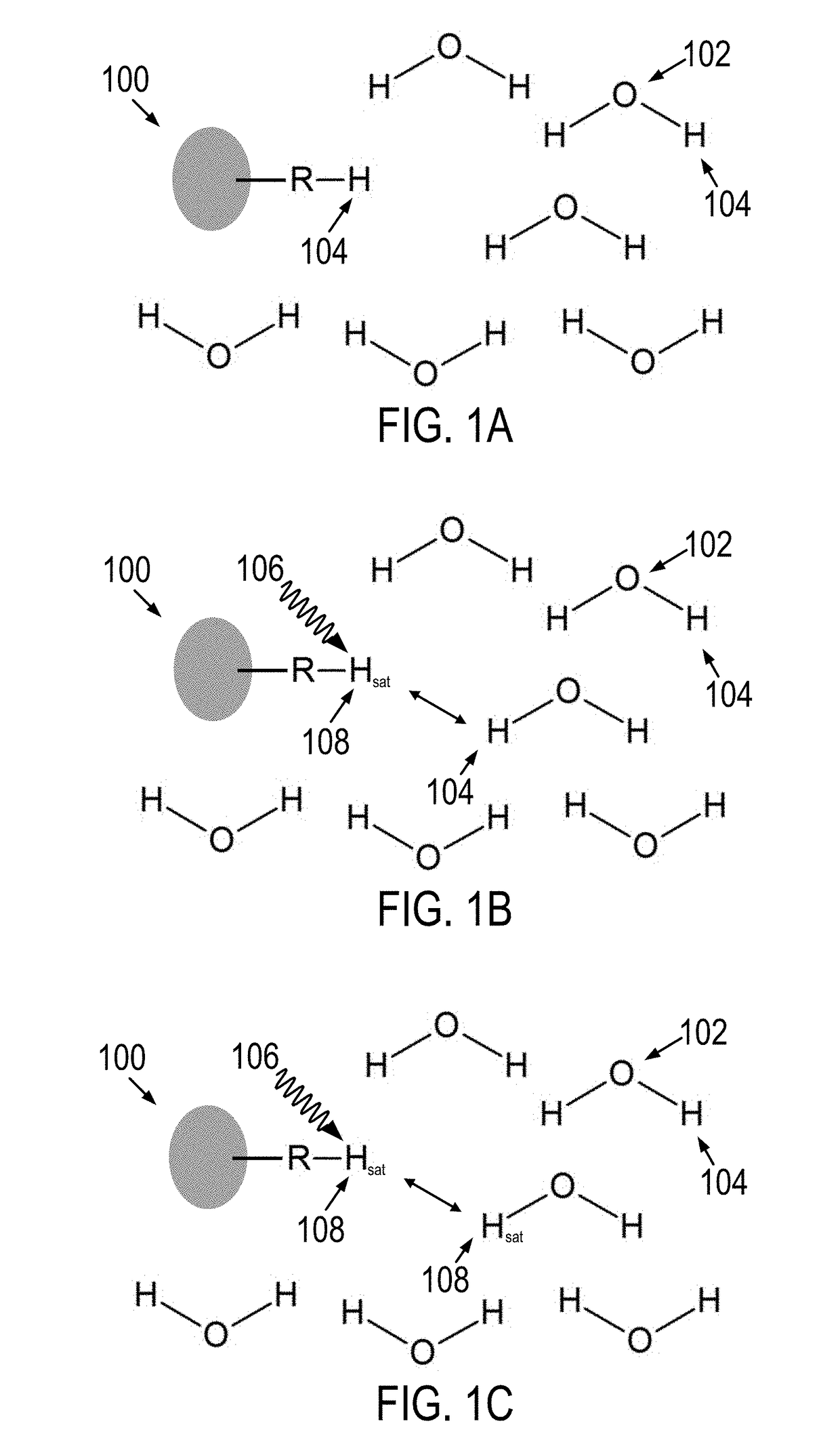
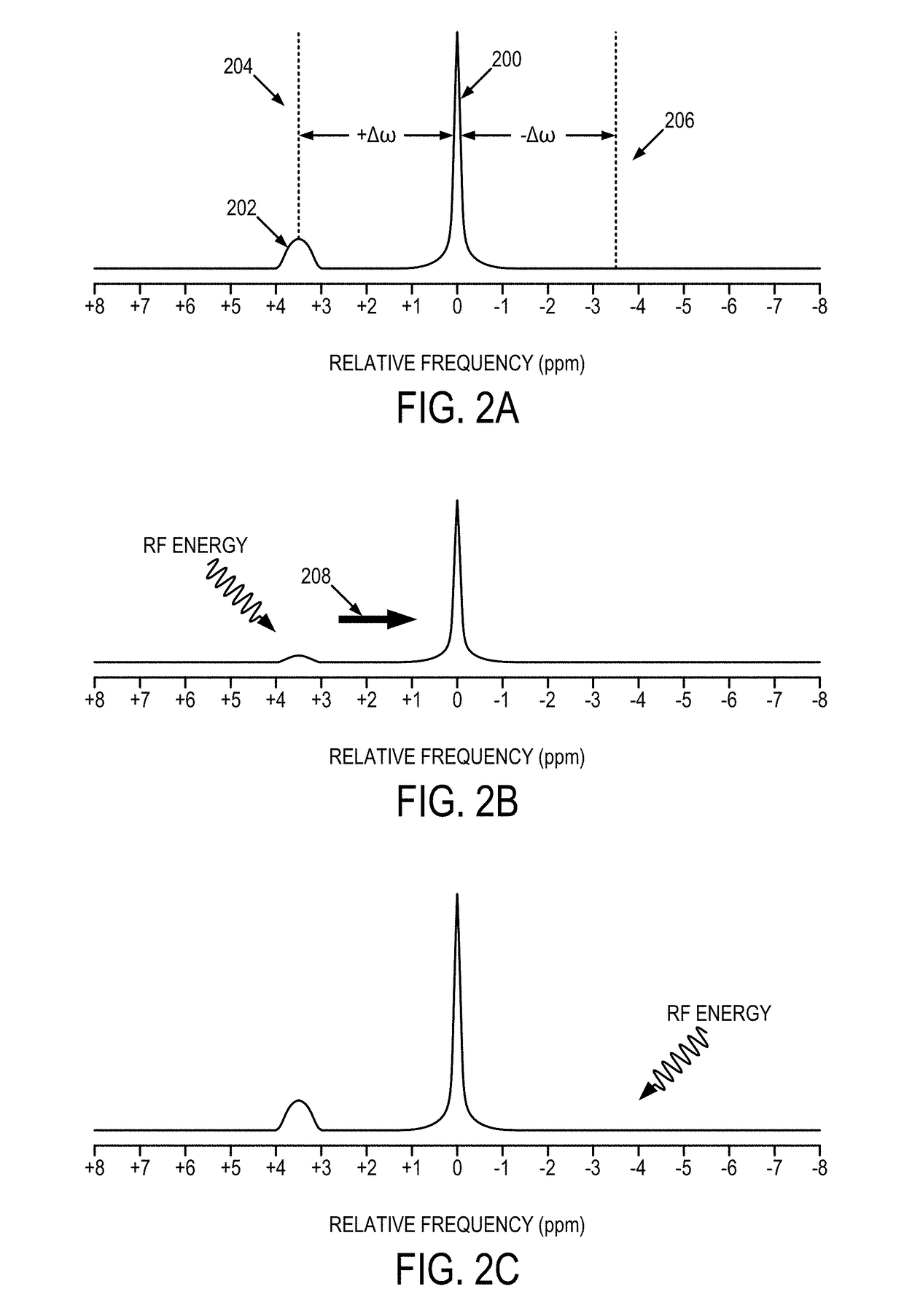
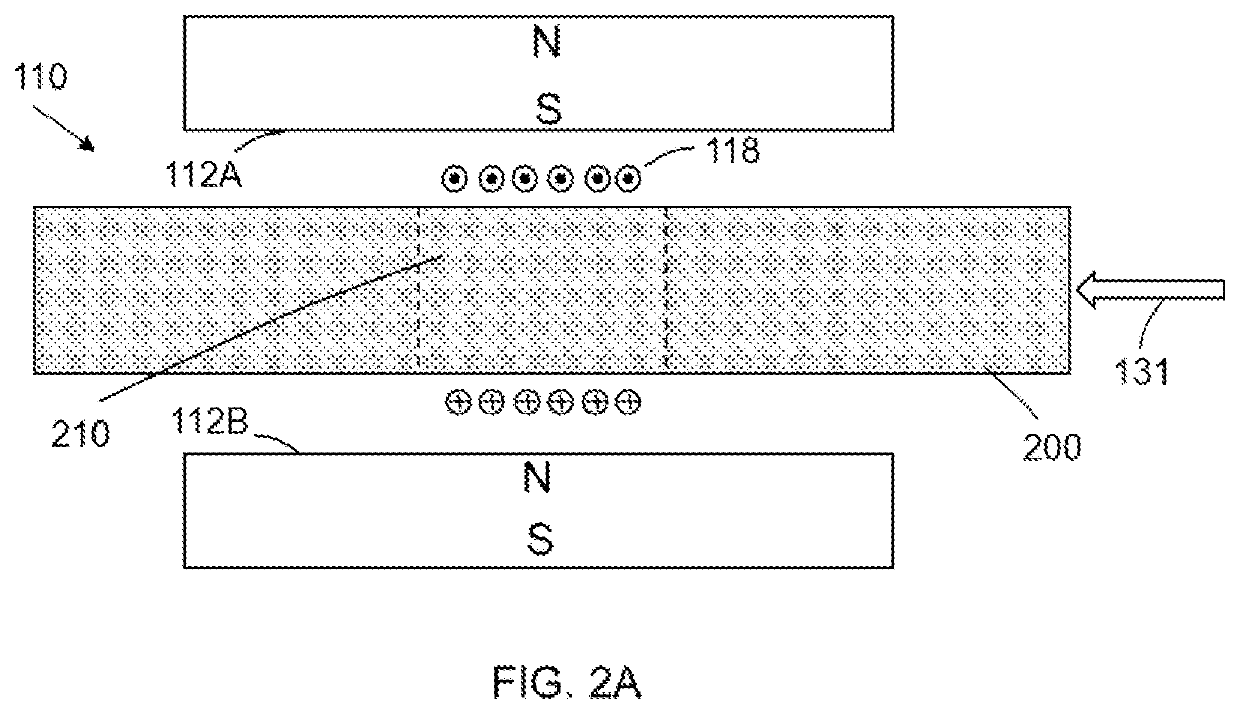
In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR spectroscopy), the term relaxation describes how signals change with time. In general signals deteriorate with time, becoming weaker and broader. The deterioration reflects the fact that the NMR signal, which results from nuclear magnetization, arises from the over-population of an excited state. Relaxation is the conversion of this non-equilibrium population to a normal population. In other words, relaxation describes how quickly spins "forget" the direction in which they are oriented. The rates of this spin relaxation can be measured in both spectroscopy and imaging applications.
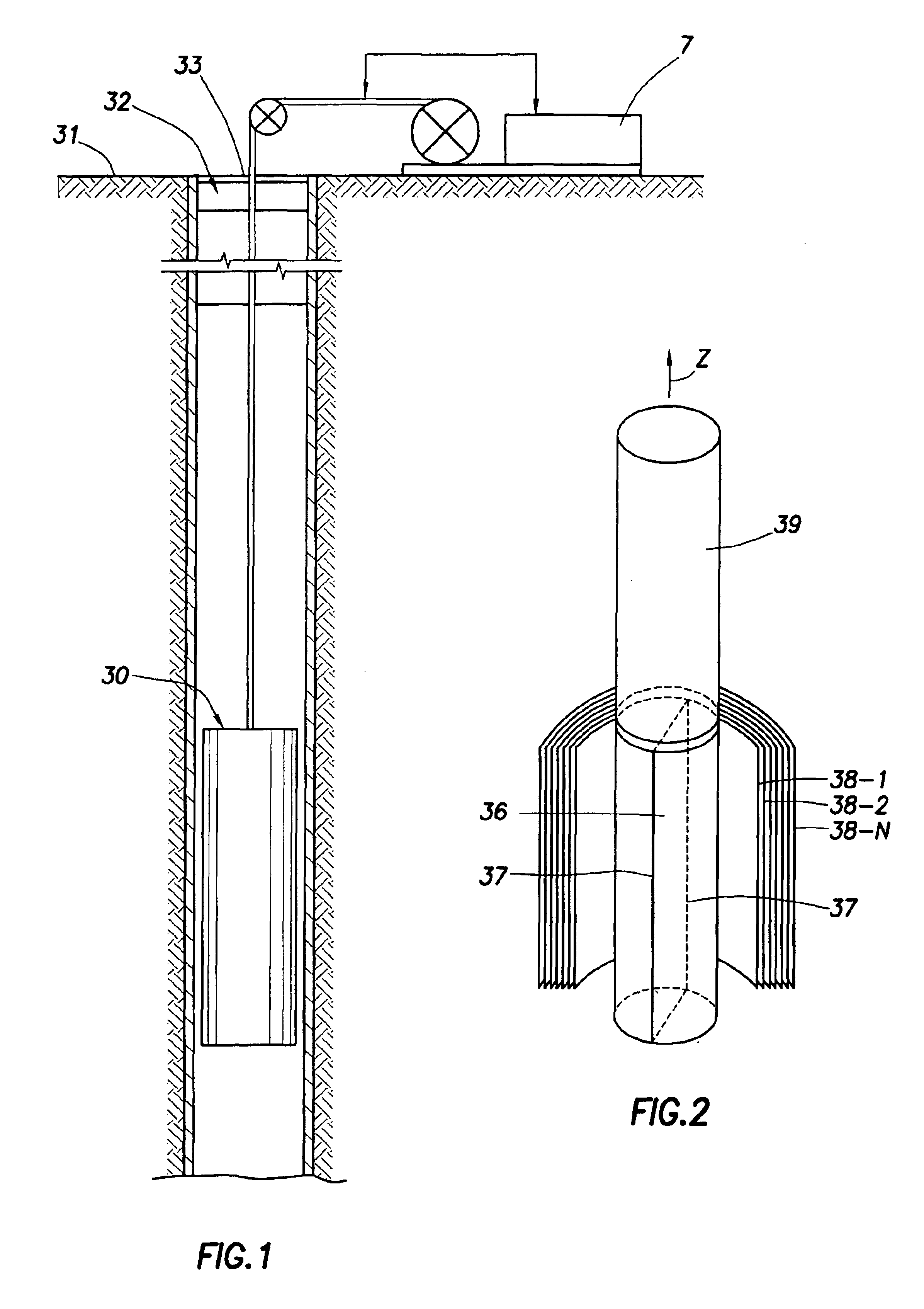
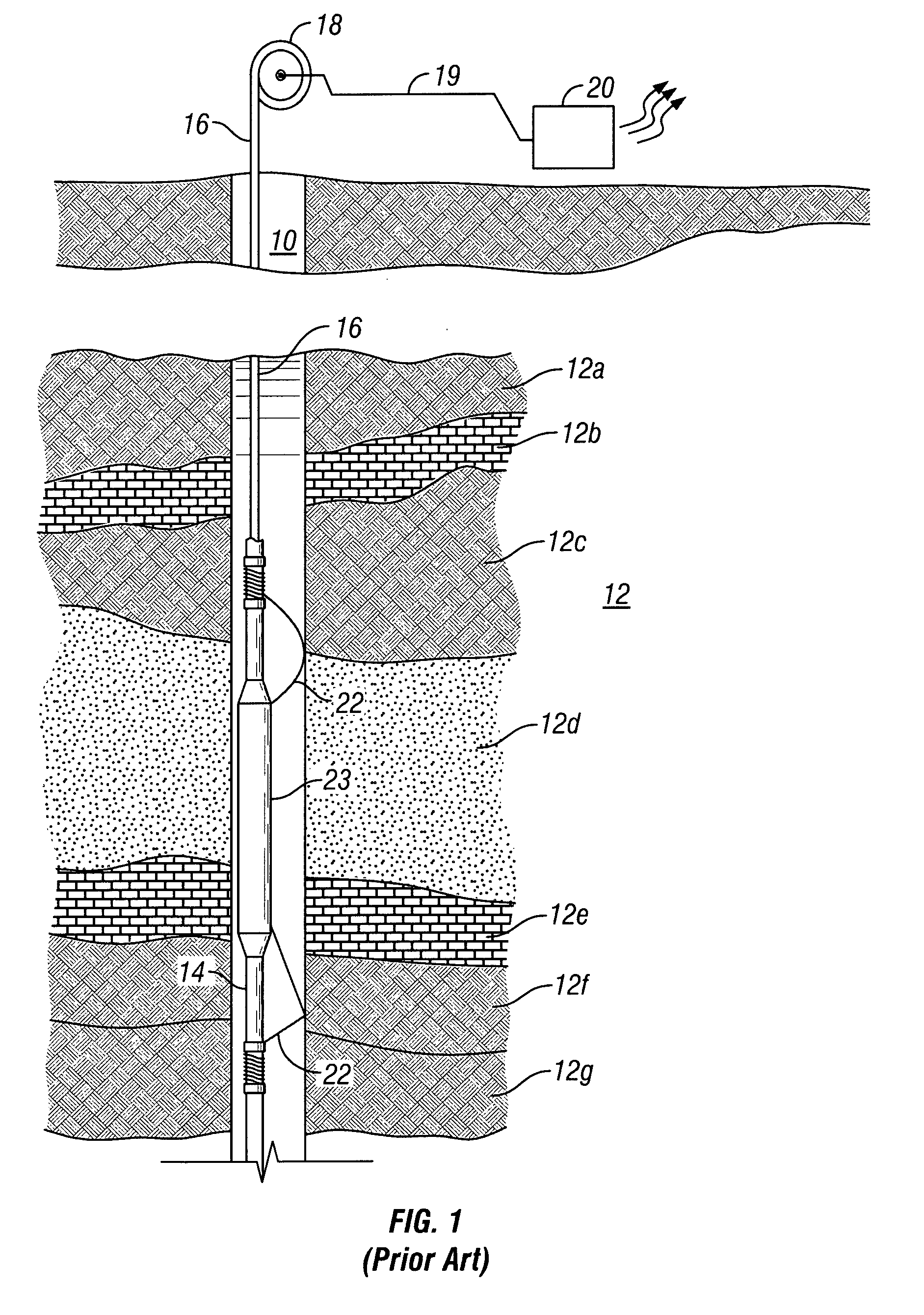
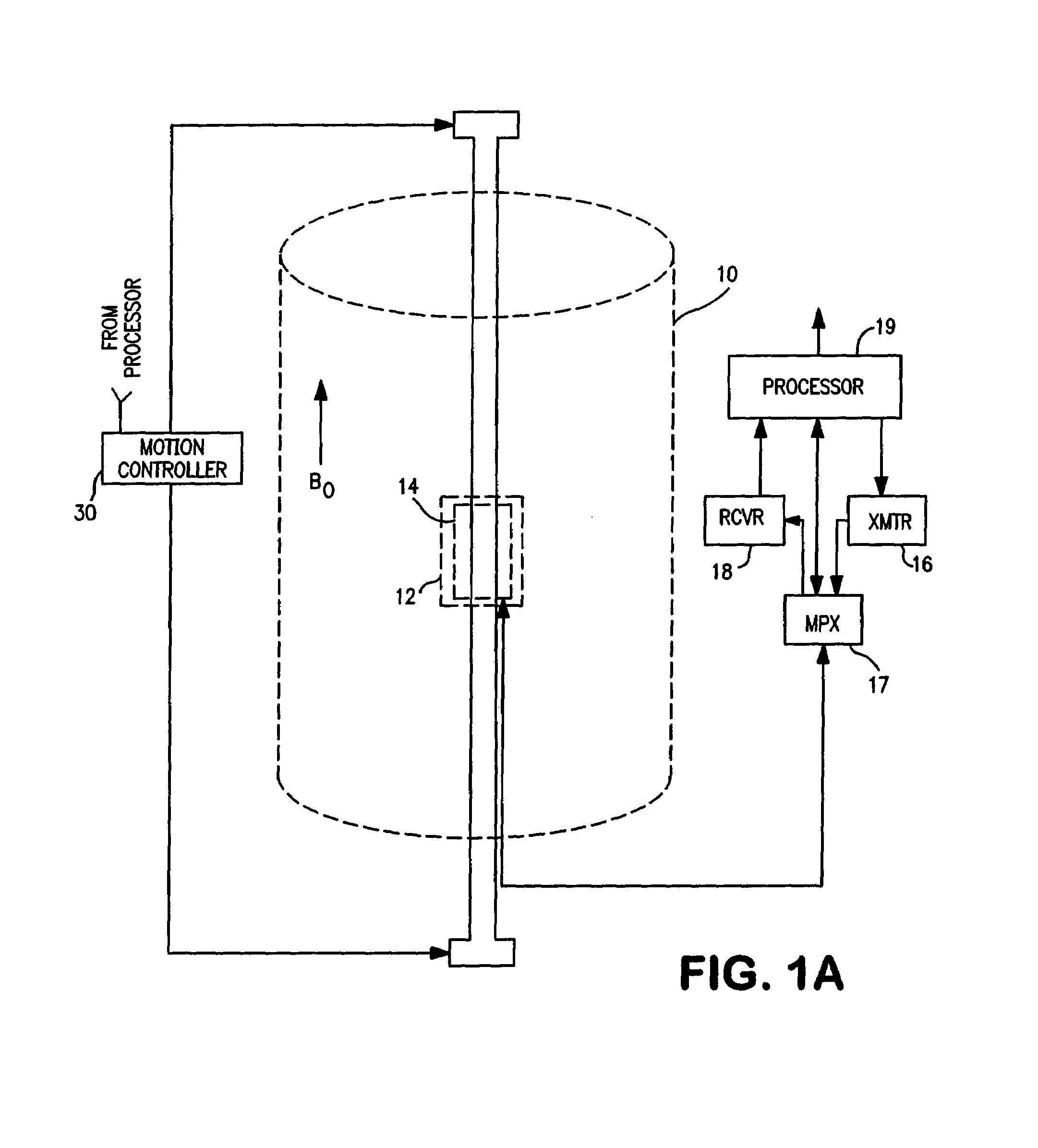
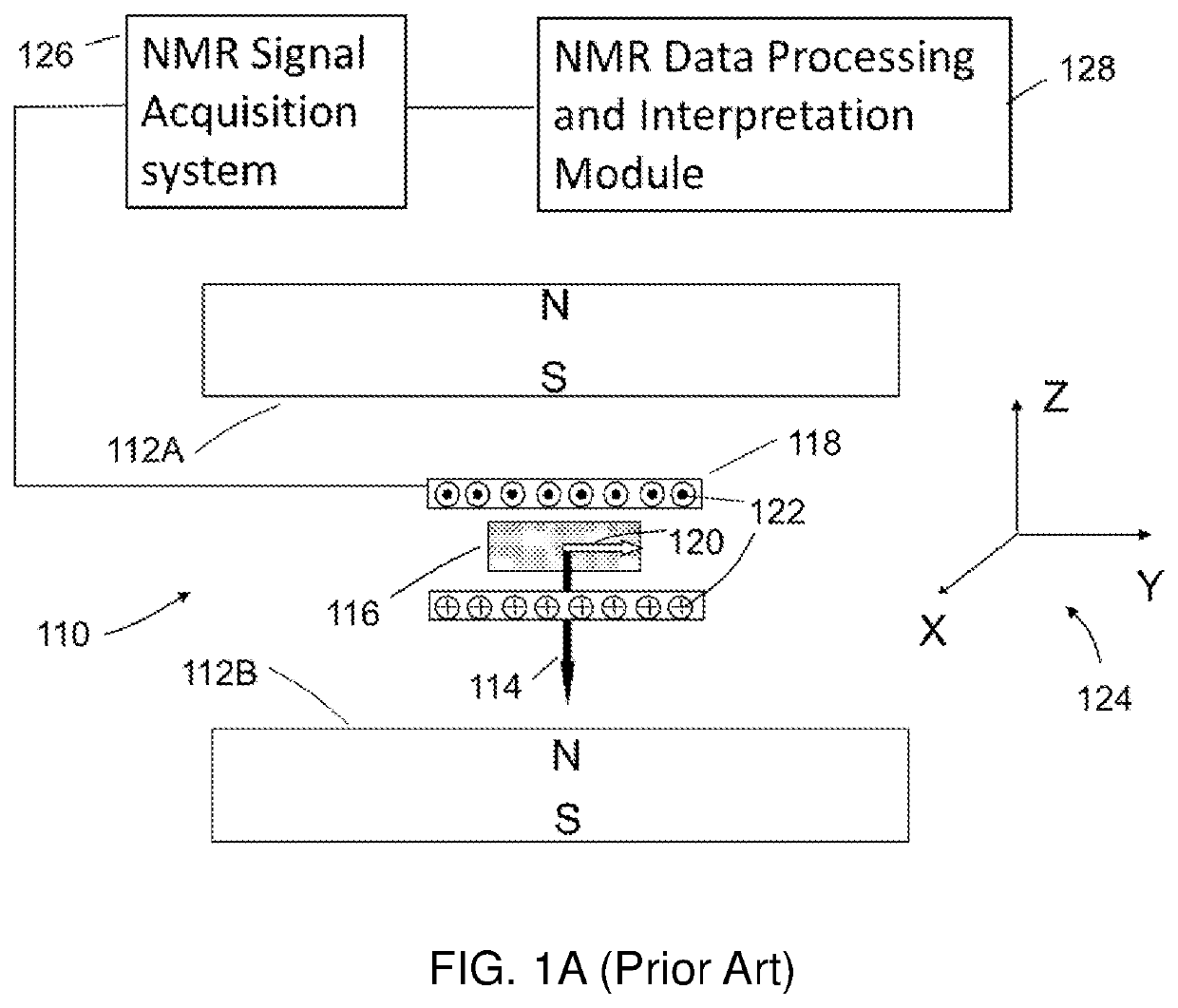
Nuclear magnetic resonance method and logging apparatus for fluid analysis
InactiveUS6891369B2Different sensitivityReadily apparentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
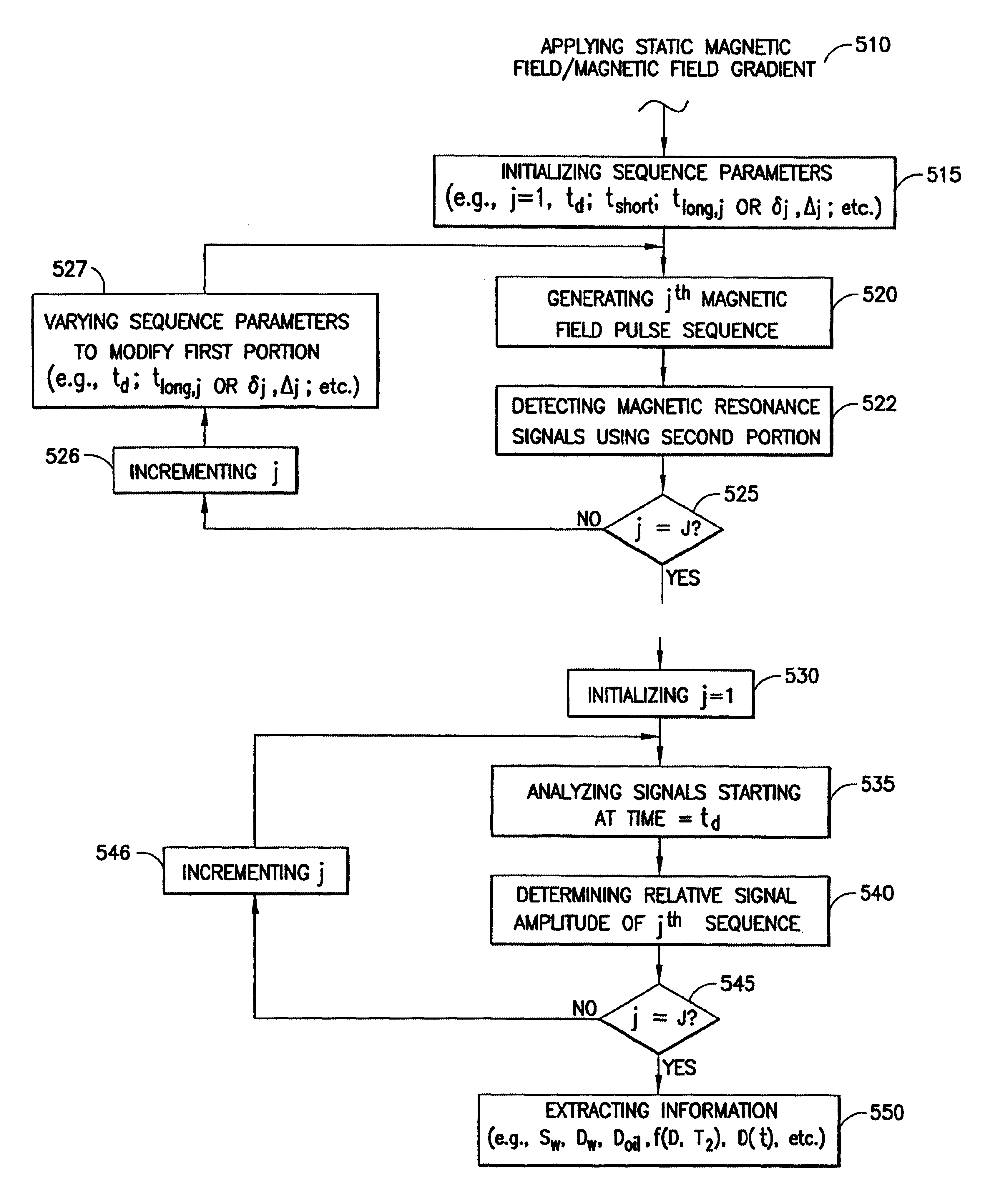
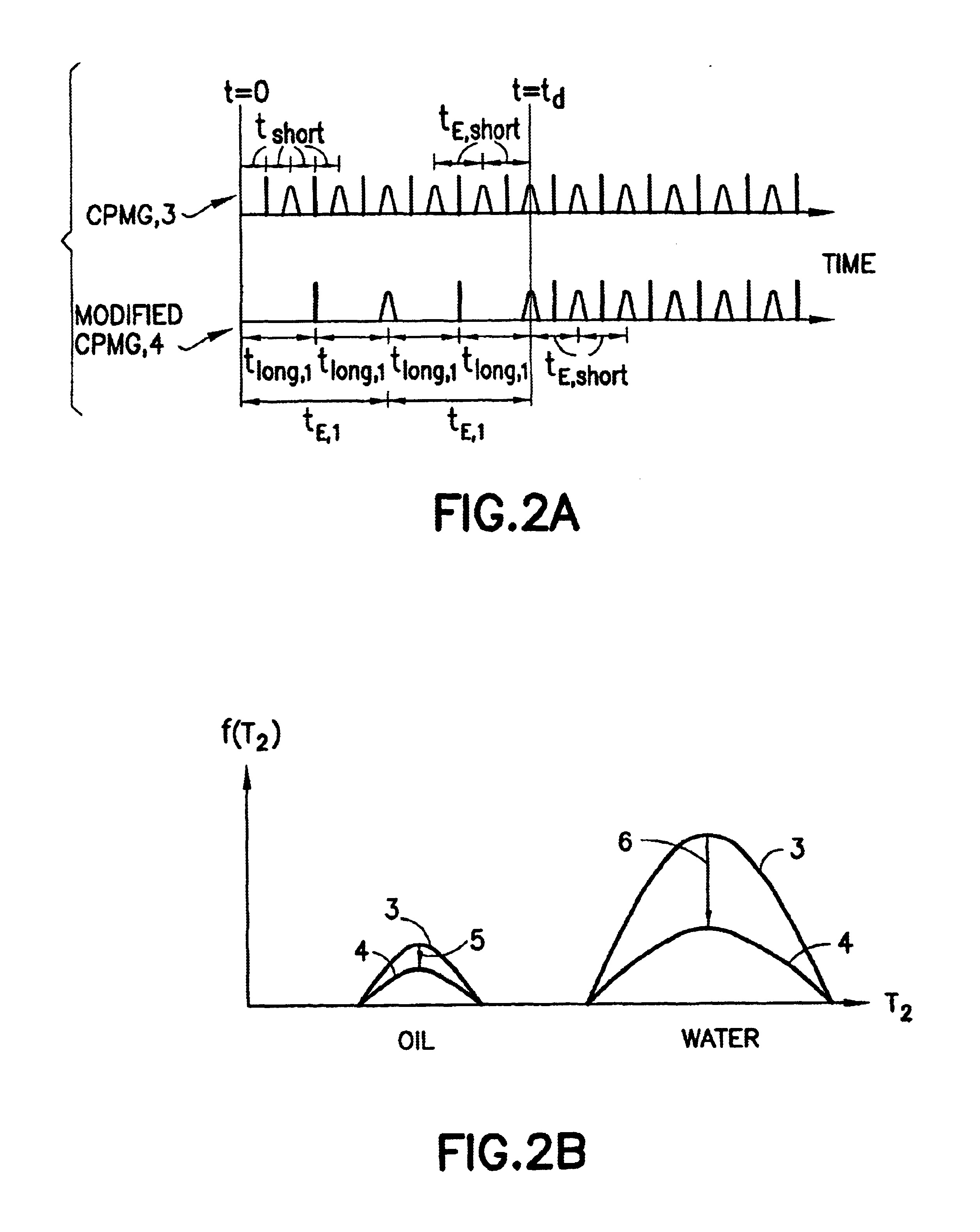
The present invention discloses a diffusion edited pulse technique that allows information about a fluid to be extracted, comprising: a) obtaining a fluid sample; b) generating a sequence of magnetic field pulses in the fluid, the sequence comprising an initial magnetic field pulse, a first portion that follows the initial magnetic field pulse, and a second portion that follows the first portion; c) detecting magnetic resonance signals using the second portion of the sequence; d) modifying the first portion of the sequence, and repeating steps (b) and (c); and e) extracting information about the fluid by determining relaxation and diffusion characteristics and their correlation based on the signals detected in steps (c) and (d). Also disclosed is a logging tool equipped with a processor to implement the diffusion edited pulse technique.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for magnetic resonance fluid characterization
InactiveUS6859033B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic measurements
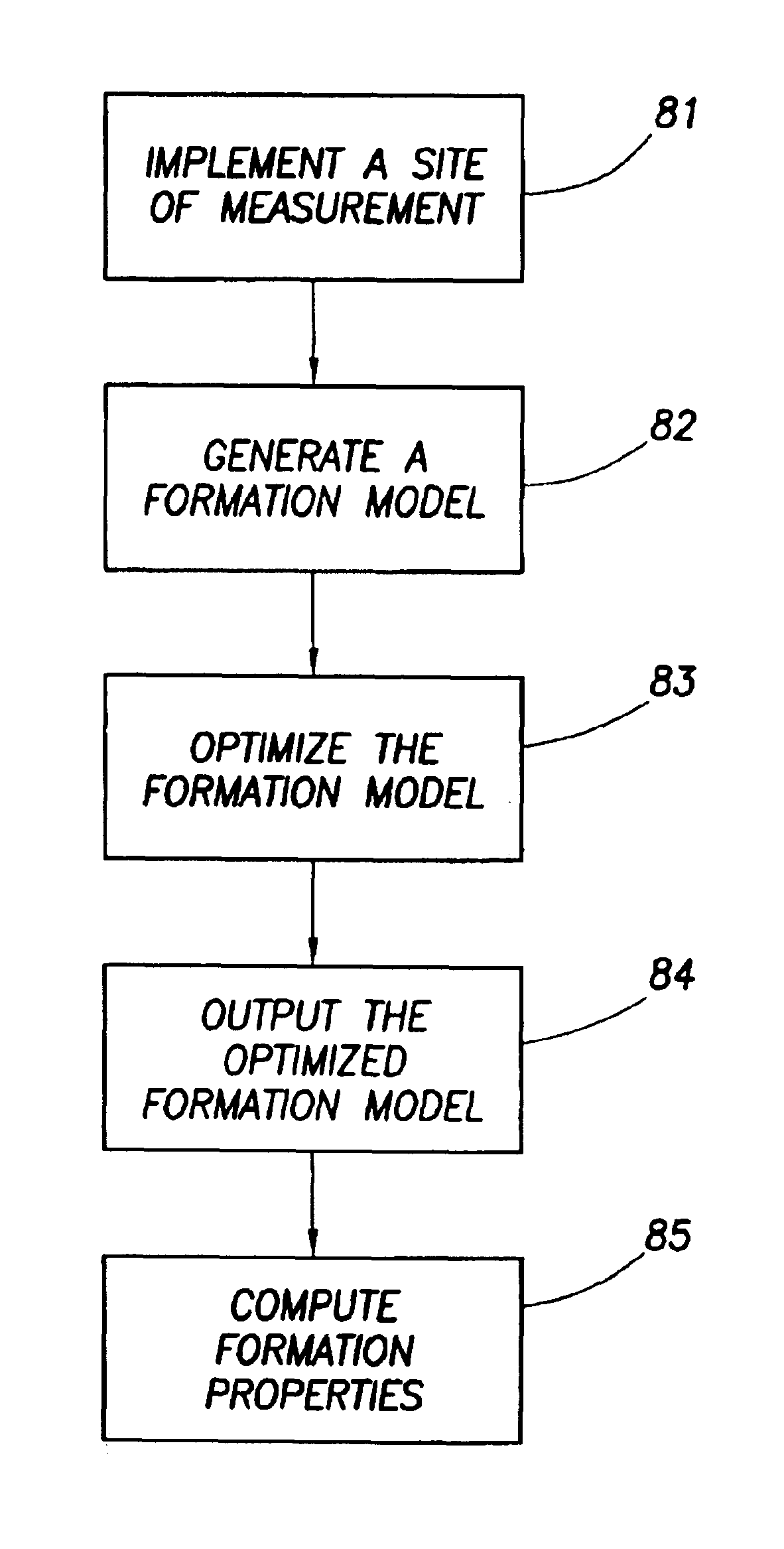
A method for determining properties of a mixture of fluids includes: (a) acquiring a plurality of nuclear magnetic resonance measurements from the mixture of fluids, each of the plurality of nuclear magnetic resonance measurements having a different value in an acquisition parameter for which at least one relaxation selected from the group consisting of longitudinal relaxation and transverse relaxation affects magnitudes of the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements; (b) generating a model of the mixture of fluids; (c) calculating a synthesized nuclear magnetic data set based on the model; (d) comparing the synthesized nuclear magnetic data set with the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements; and (e) adjusting the model and repeating (c) and (d), if difference between the synthesized nuclear magnetic data set and the nuclear magnetic measurements is greater than a minimum.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
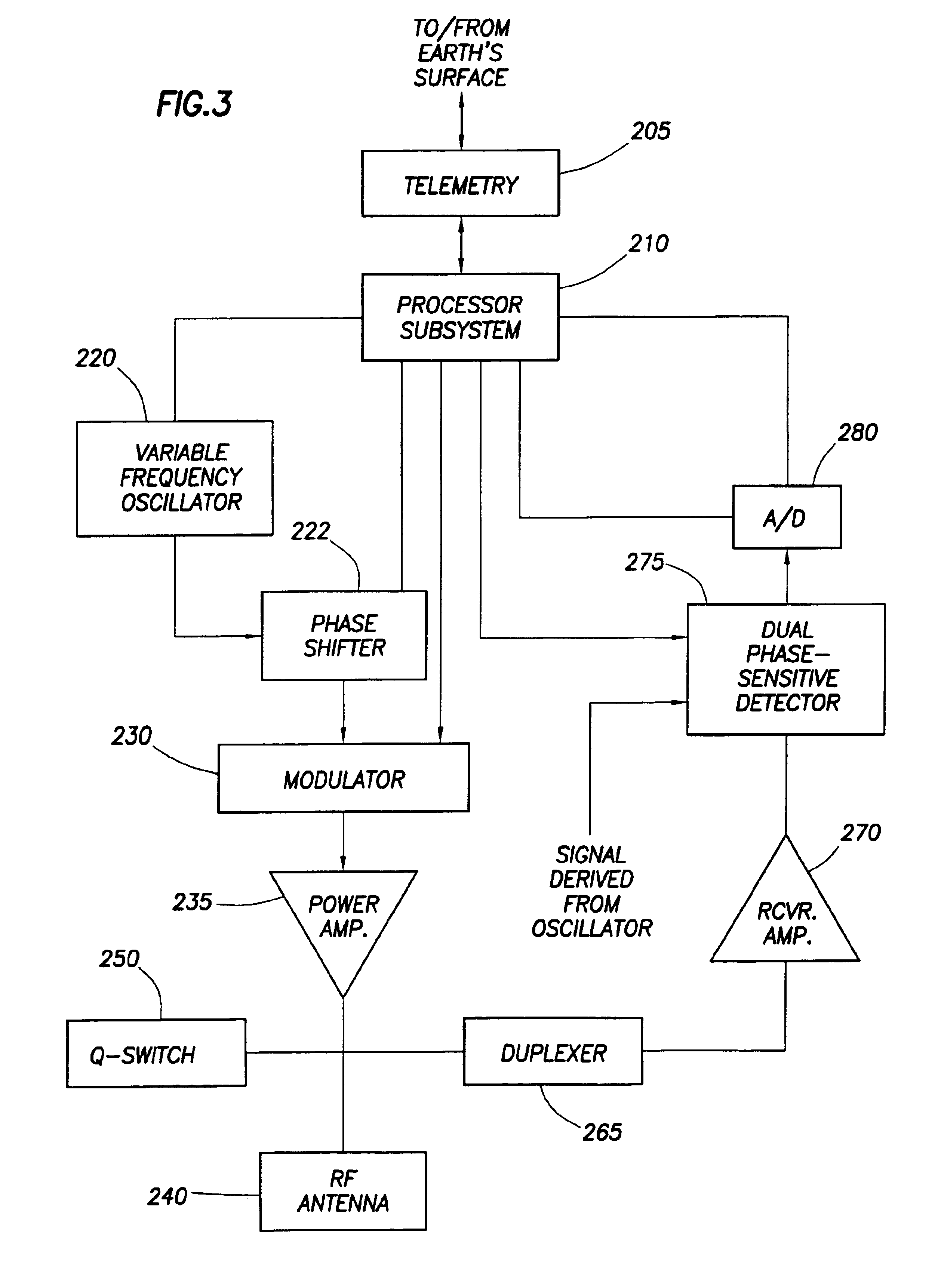
Methods and systems for fast field zeroing for magnetoencephalography (MEG)
PendingUS20210063510A1Easy to operateMagnetic field offset compensationAnalysis using optical pumpingLight beamParticle physics
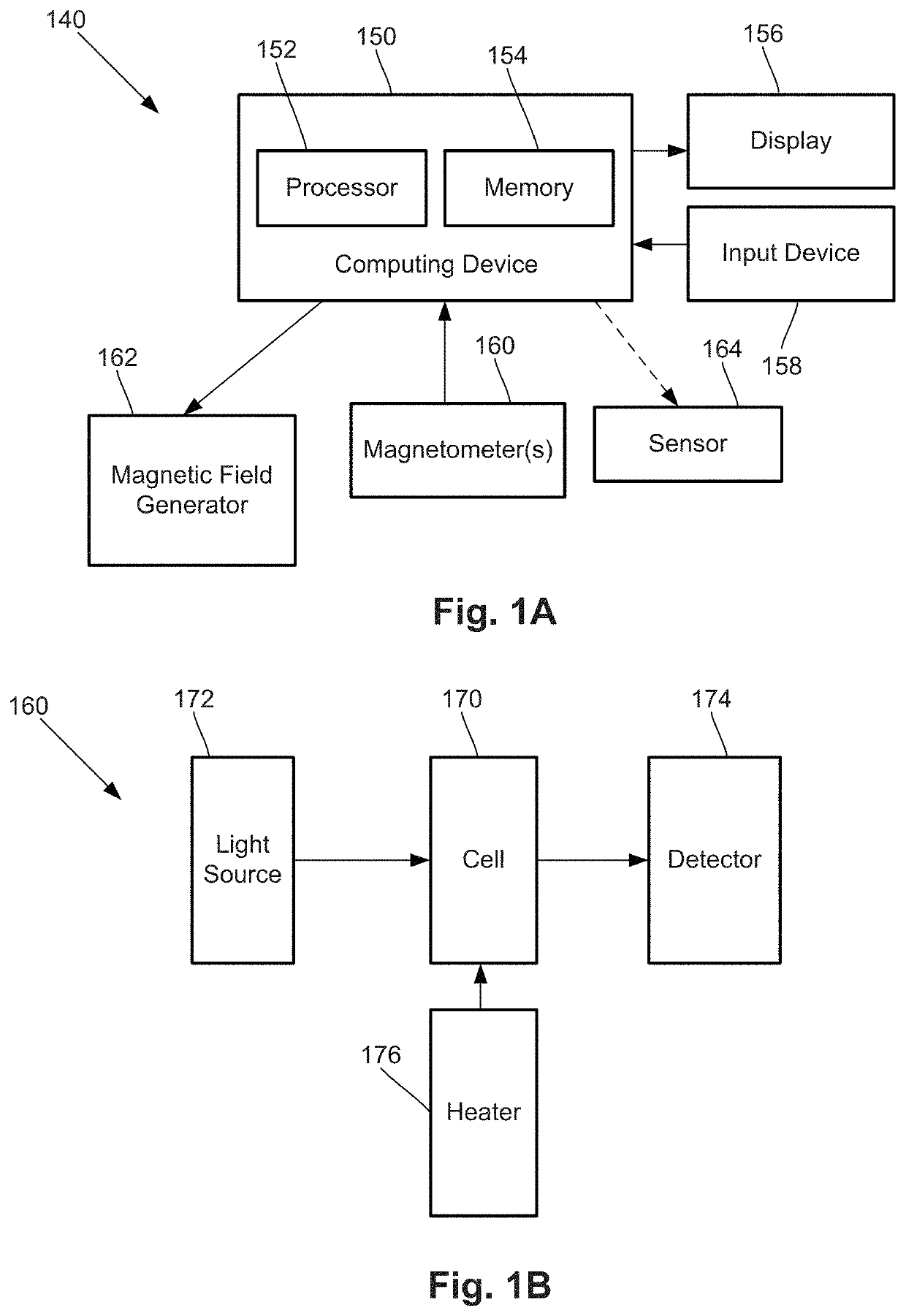
A method of operating an optically pumped magnetometer (OPM) includes directing a light beam through a vapor cell of the OPM including a vapor of atoms; applying RF excitation to cause spins of the atoms to precess; measuring a frequency of the precession; for each of a plurality of different axes relative to the vapor cell, directing a light beam through the vapor cell, applying a magnetic field through the vapor cell along the axis, applying RF excitation to cause spins of the atoms to precess, and measuring a frequency of the precession in the applied magnetic field; determining magnitude and components of an ambient background magnetic field along the axes using the measured frequencies; and applying a magnetic field based on the components around the vapor cell to counteract the ambient background magnetic field to facilitate operation of the OPM in a spin exchange relaxation free (SERF) mode.
Owner:HI LLC
Imaging method for obtaining spatial distribution of nanoparticles in the body
InactiveUS20100066363A1Accurate and high-spatially resolved imageAccurate focusDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelHigh spatial resolution
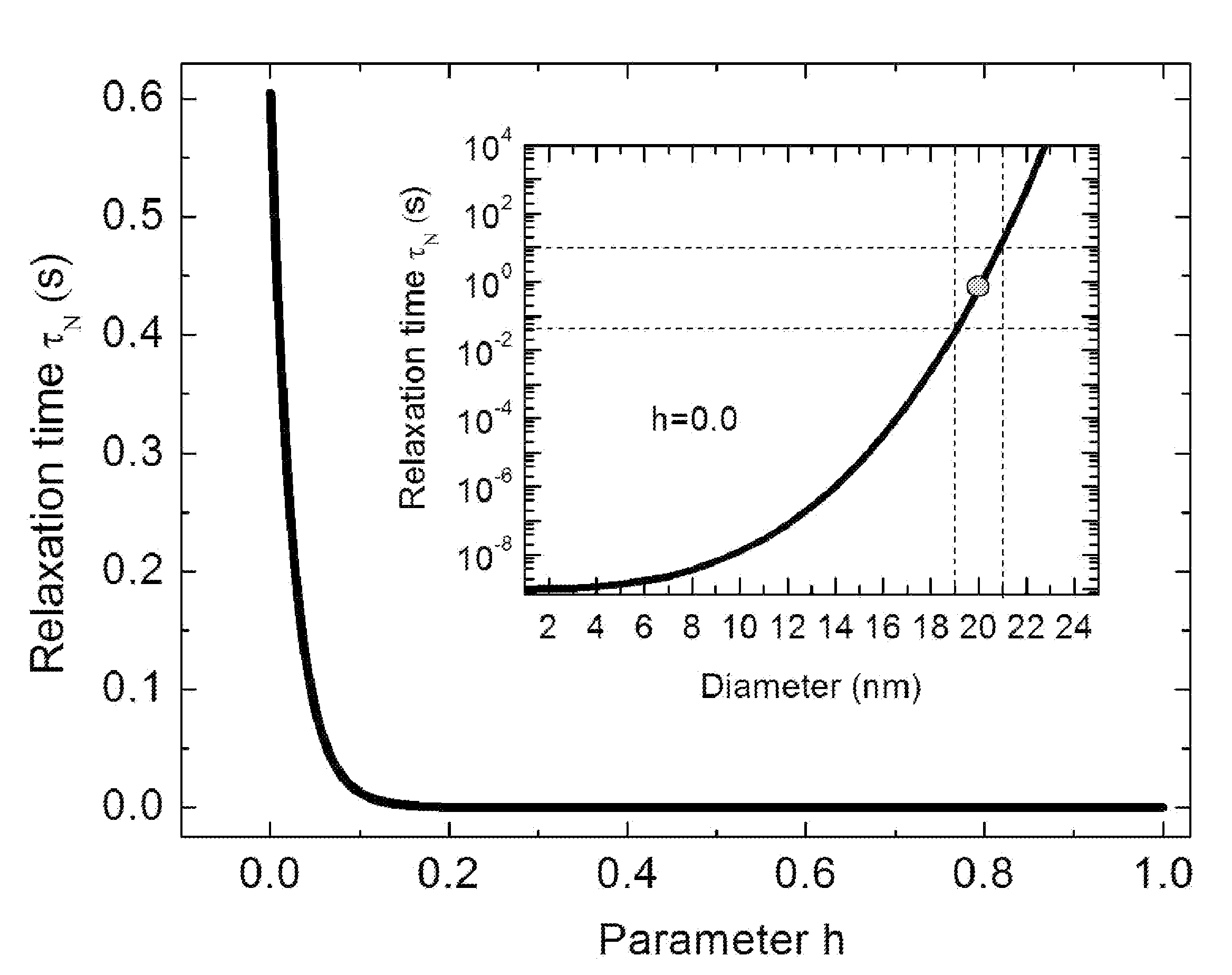
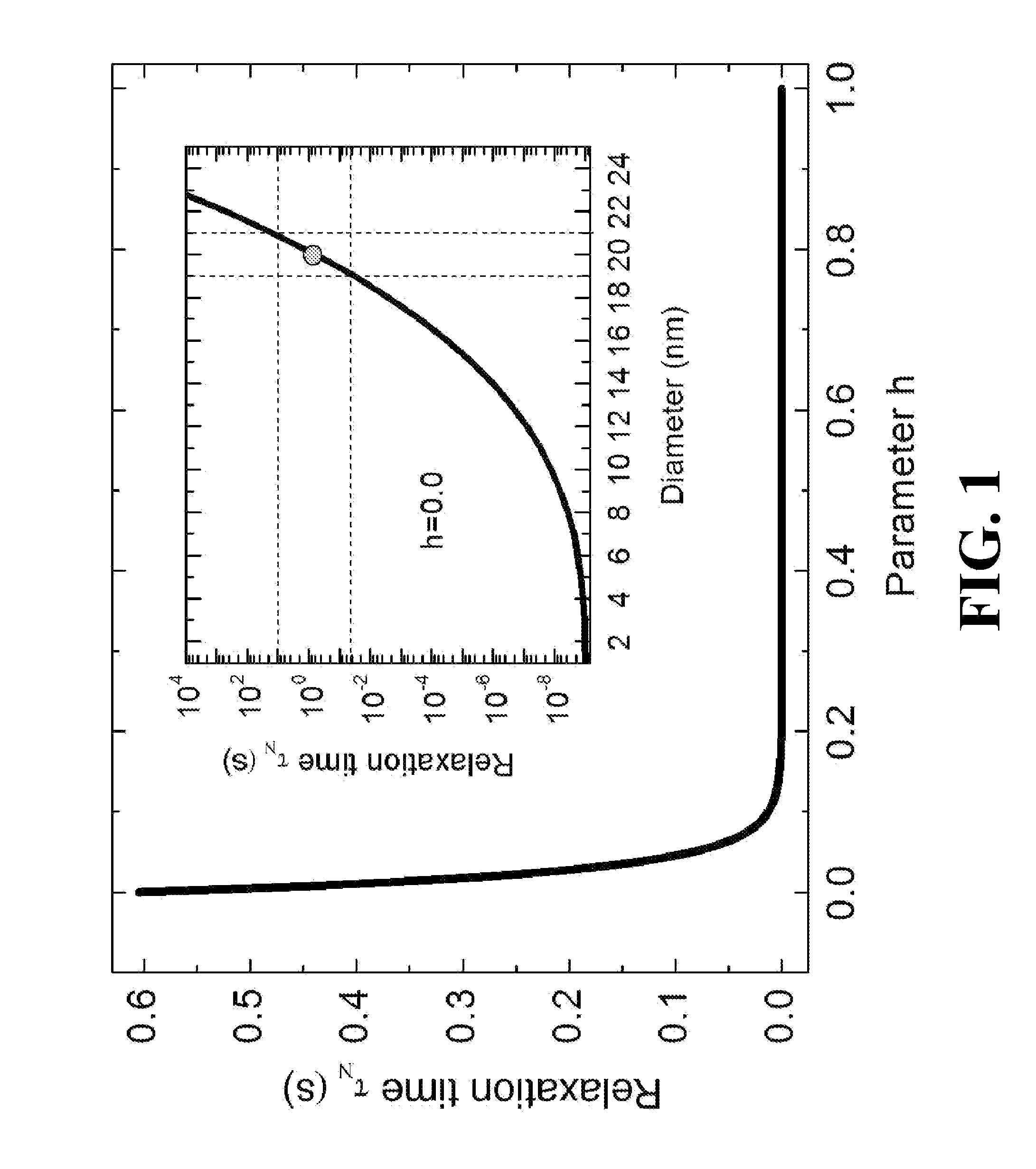
A well-posed magnetic imaging method is disclosed that exploits the non-linear behavior of the characteristic time scale of the Neel relaxation for obtaining accurate high-spatial resolution images of magnetic tracers. The method includes placing an object in a selection field (static field) generated by three pairs of orthogonally arranged coil (drive coils), supplying prudently choice currents to the drive coils, a zero field voxel (ZFV) is formed that can be positioned anywhere in the local region of interest (ROI), switching the magnetizing field off, and collecting an image.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Method and apparatus for multi-frequency NMR diffusion measurements in the presence of internal magnetic field gradients
ActiveUS20050162162A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Pulse sequences are applied to a fluid in an earth formation in a static magnetic field having internal gradients. From the received signals, relaxation and diffusion characteristics of the fluid are determined. The determination takes into account the internal field gradients.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Systems and methods including multi-mode operation of optically pumped magnetometer(s)
ActiveUS10627460B2Magnetic field offset compensationDiagnostic recording/measuringVector modeMaterials science
Owner:HI LLC
Method and apparatus for multi-frequency NMR diffusion measurements in the presence of internal magnetic field gradients
ActiveUS7049815B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
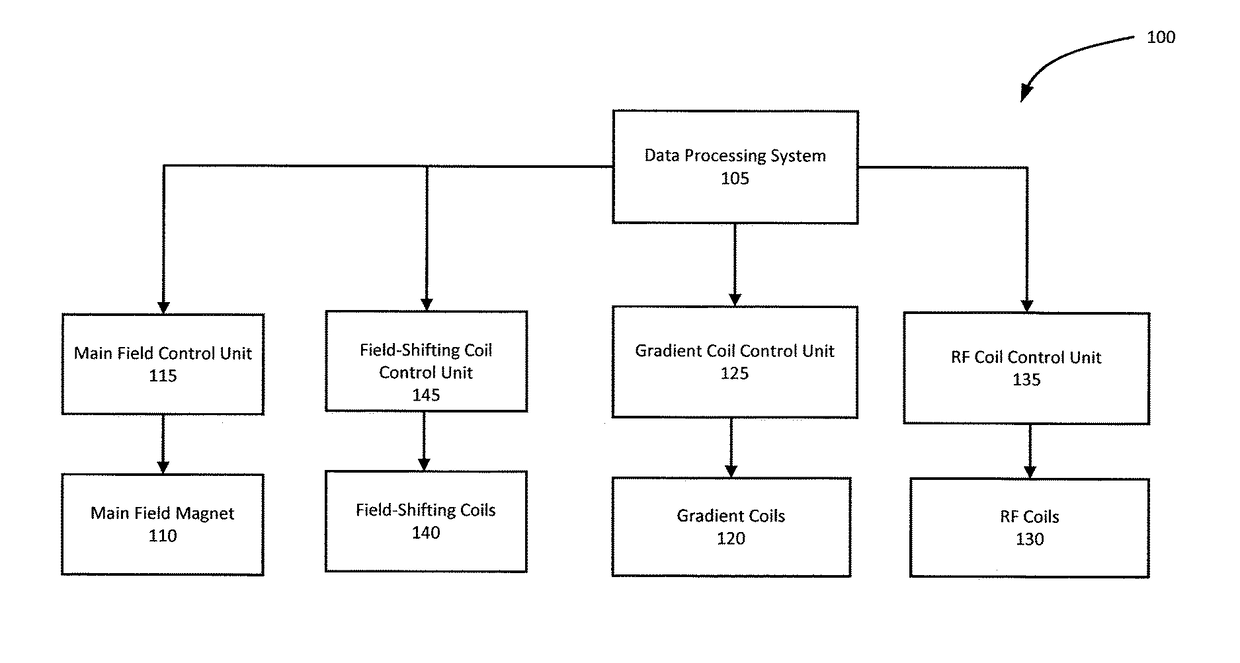
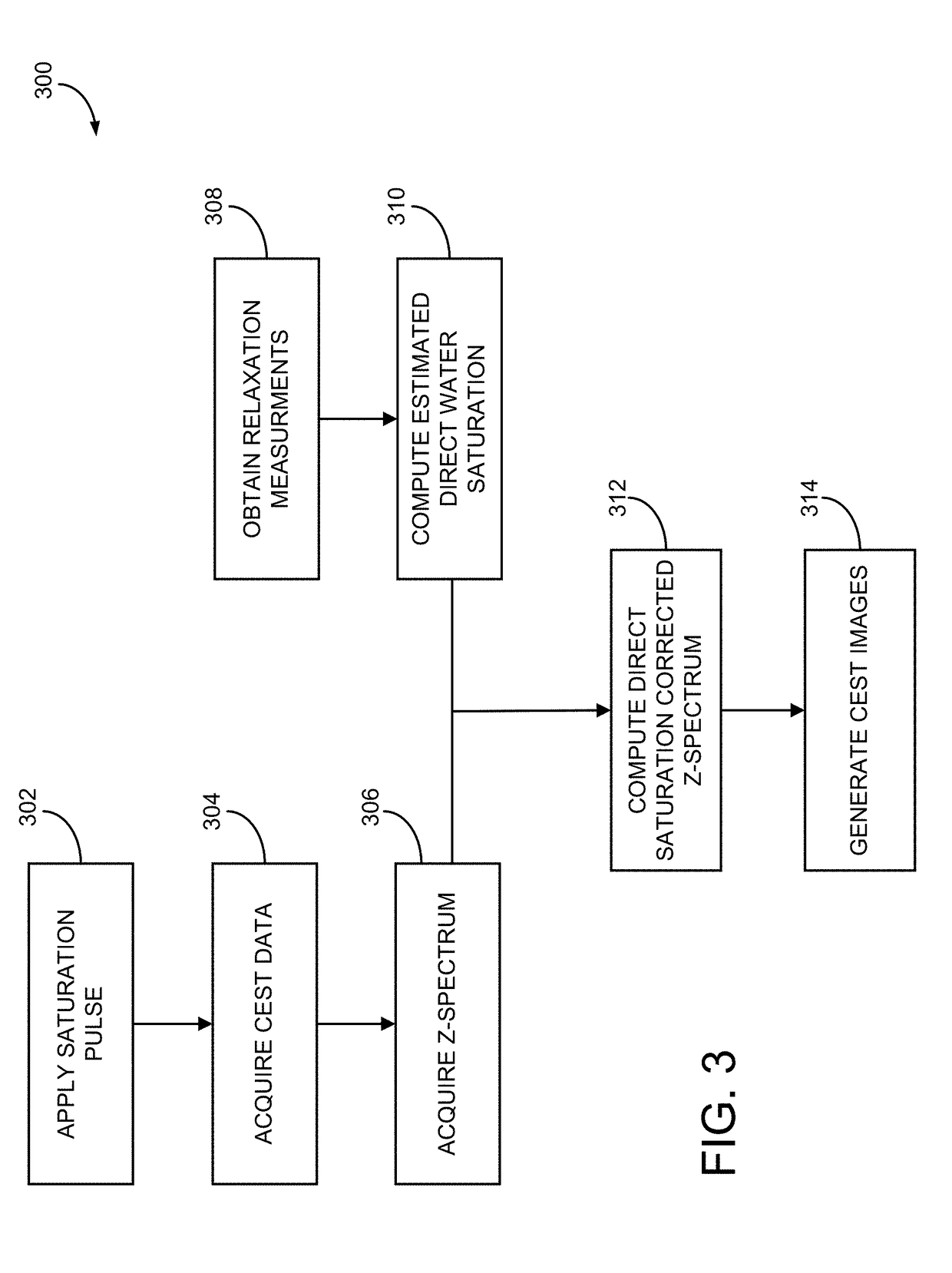
System and method for delta relaxation enhanced magnetic resonance imaging
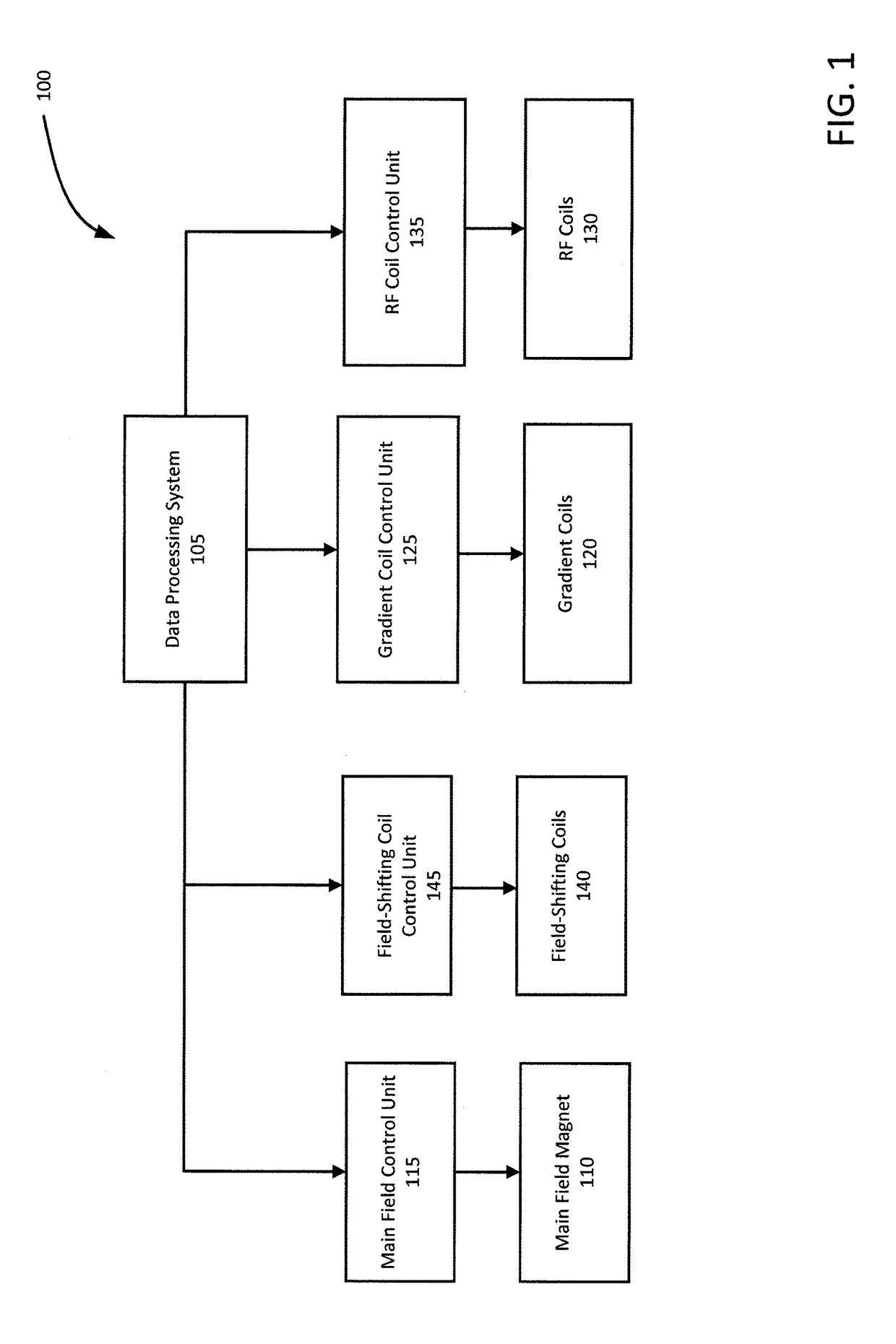
A delta-relaxation magnetic resonance imaging (DREMR) system is provided. The system includes a main field magnet and field shifting coils. A main magnetic field with a strength B0 can be generated using the main filed magnet and the strength B0 of the main magnetic field can be varied through the use of the field-shifting coils. The DREMR system can be used to perform signal acquisition based on a pulse sequence for acquiring at least one of T2*-weighted signals imaging; MR spectroscopy signals; saturation imaging signals and MR signals for fingerprinting. The MR signal acquisition can be augmented by varying the strength B0 of the main magnetic field for at least a portion of the pulse sequence used to acquire the MR signal.
Owner:SYNAPTIVE MEDICAL INC
System and method for direct saturation-corrected chemical exchange saturation transfer (disc-cest)
ActiveUS20190011516A1High contrastReduce data acquisition timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsWater saturationSaturation transfer
A system and method is provided that includes acquiring chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) data with the MRI system and generating an acquired Z-spectrum (Z) from the CEST data. The system and method also includes computing an estimated direct water saturation (Z′) based using at least one of relaxation measurements derived from the CEST data or imaging parameters used to acquire the CEST data with the MRI system, computing a direct saturation corrected Z-spectrum (ΔZ) using the acquired Z-spectrum (Z) and the estimated direct water saturation (Z′), and generating a CEST image of the subject using the direct saturation corrected Z-spectrum (ΔZ).
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Nmr sensor and methods for rapid, non-invasive determination of hydration state or vascular volume of a subject
ActiveUS20160120438A1CatheterMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceHydrogen
The invention features methods for detecting the hydration state or vascular volume of a subject using a device capable of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurement. The methods involve exposing a portion of a tissue of the subject in vivo to a magnetic field and RF pulse from the device to excite hydrogen nuclei of water within the tissue portion, and measuring a relaxation parameter of the hydrogen nuclei in the tissue portion, the relaxation parameter being a quantitative measure of the hydration state or vascular volume of the subject as a whole. The invention also features devices and computer-readable storage media for per forming the methods of the invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for removing noise from nuclear magnetic resonance signals and images
InactiveUS7253627B1Readily apparentMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceThresholding
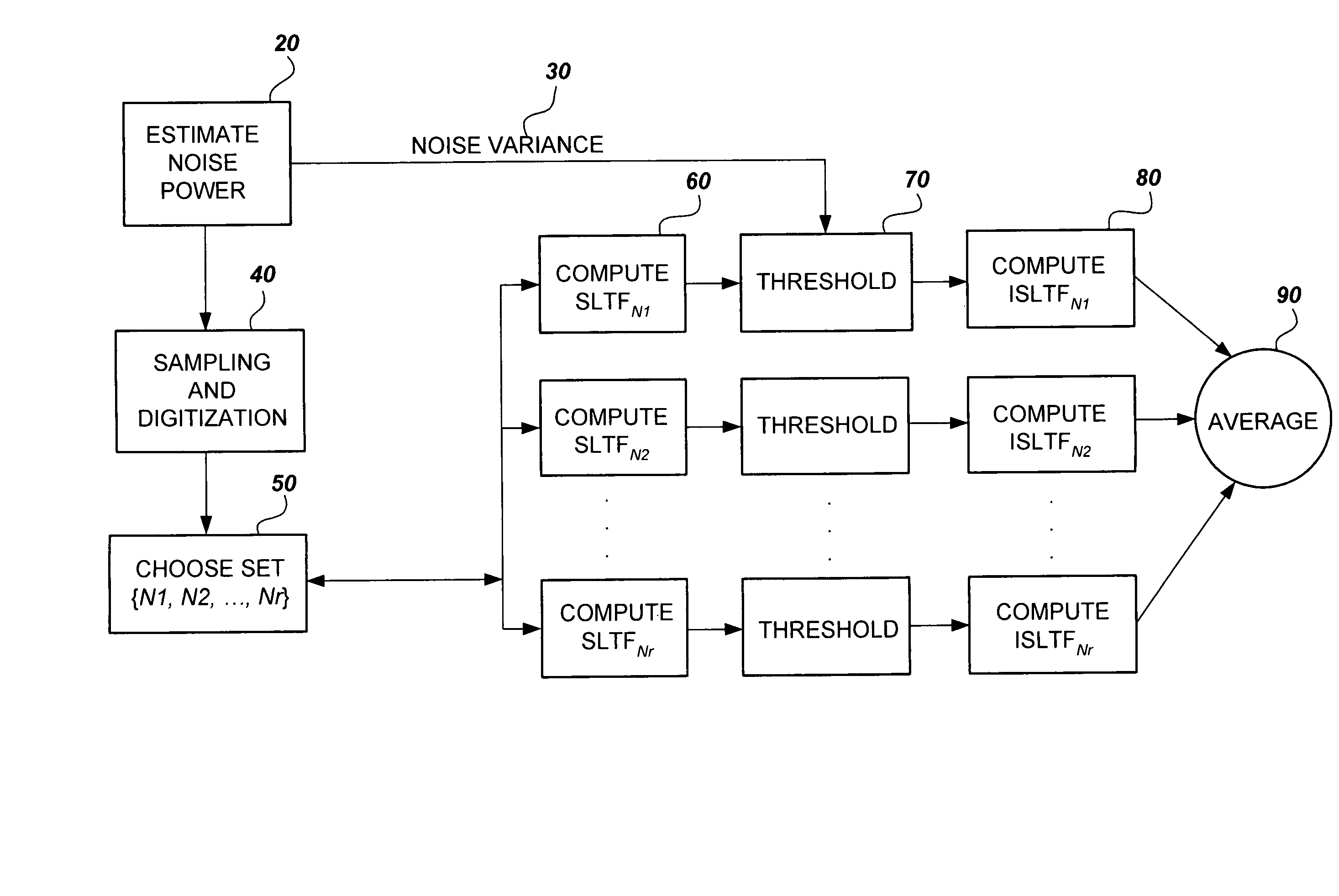
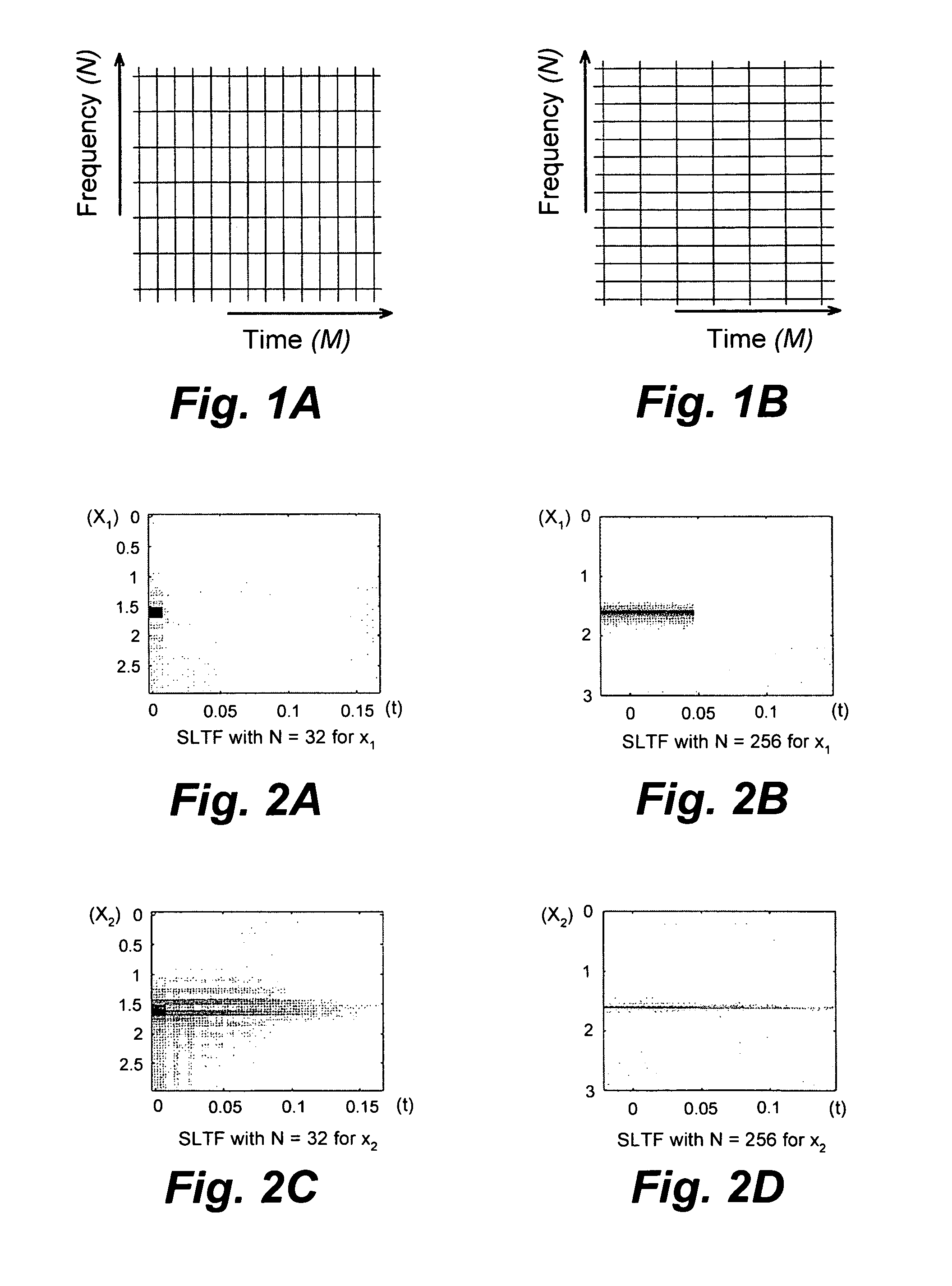
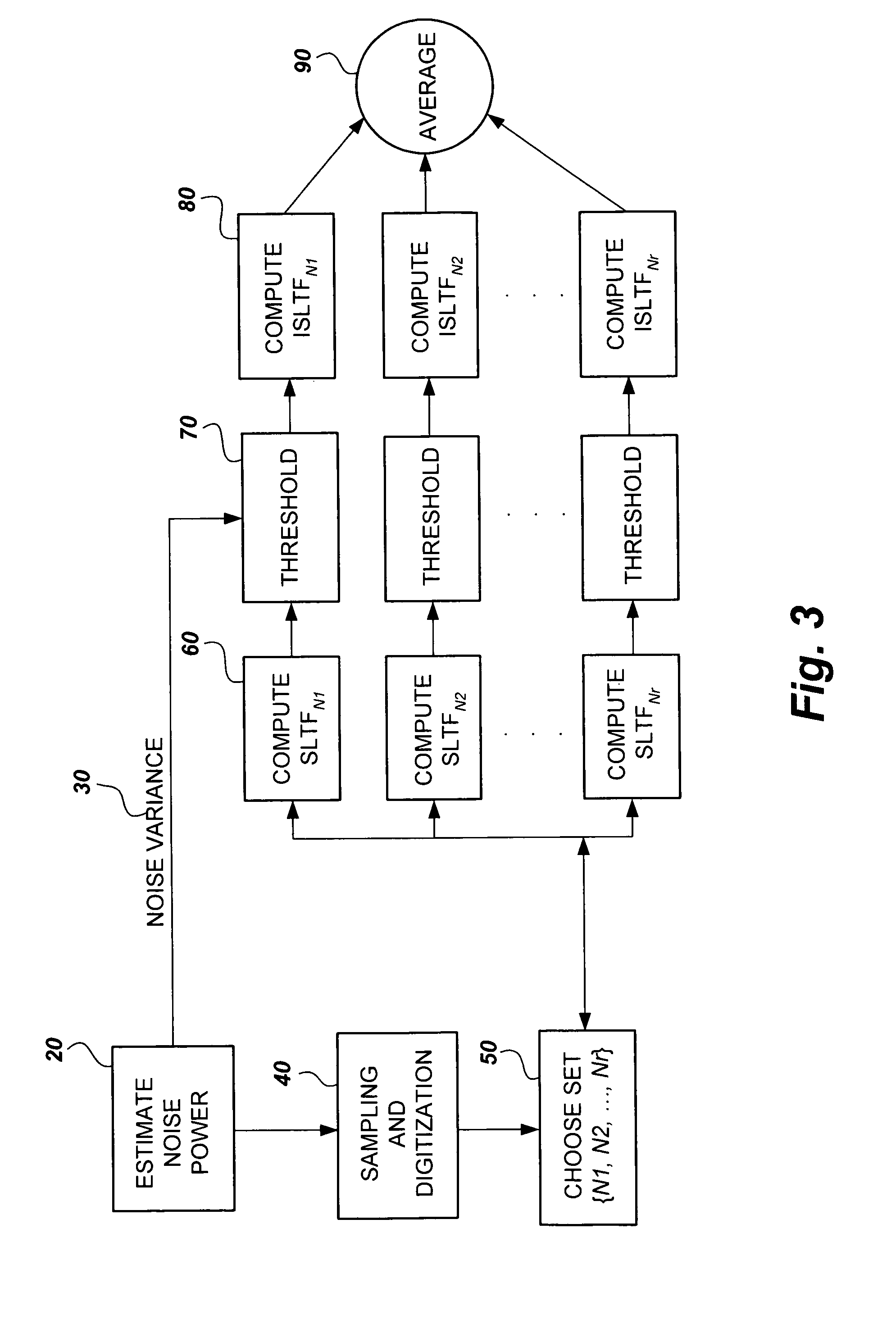
The method for removing noise from nuclear magnetic resonance signals and images involves removing noise from NMR signals through the application of stable linear time-frequency (SLTF) transforms. According to the method, a noise variance for a particular NMR signal is calculated and the NMR signal is sampled and digitized. A set of analysis samples that vary in the number of samples in frequency is selected so that each member of the set has a compact signal / image representation for at least one component according to the differing component relaxation times of the signal / image. Each member of the set is then processed by the SLTF to determine the transform coefficients, the coefficients are subjected to threshold value criteria to denoise the coefficients, and the inverse SLTF transform is computed for each member of the set to obtain the denoised signal. The member signals are then averaged to obtain the denoised NMR signal.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
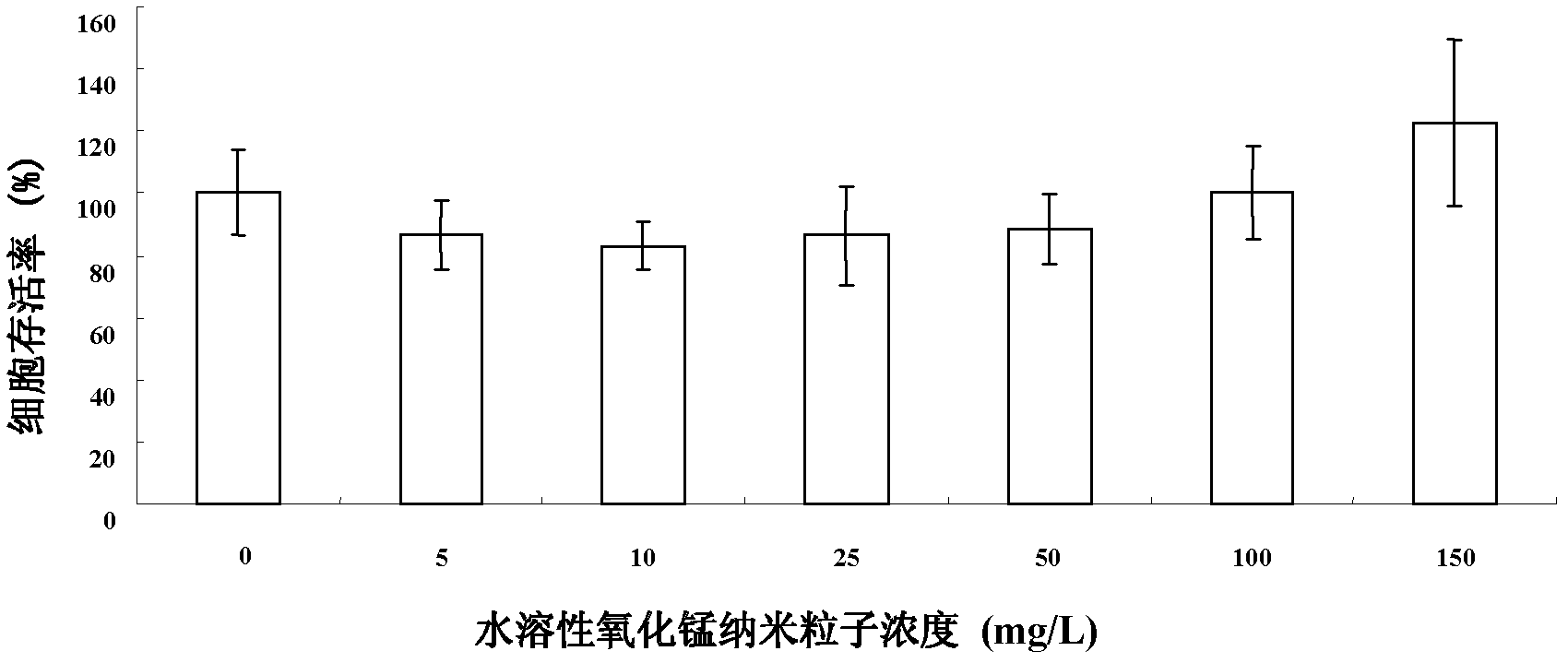
Method for preparing water-soluble manganese oxide magnetic resonance contrast agent and application thereof
InactiveCN102614533AImprove imaging effectGood relaxation efficiencyEmulsion deliveryCancer cellSuperparamagnetism
The invention discloses a method for preparing a water-soluble manganese oxide magnetic resonance contrast agent and application thereof, which is a superparamagnetic water-soluble manganese oxide magnetic resonance contrast agent. Firstly, manganese oleate and octadecene are mixed evenly to prepare superparamagnetic oily manganese oxide nano particles through a high temperature thermal decomposition mothod, then oil-soluble manganese oxide is converted into water-soluble manganese oxide through oil-water phase inversion, and finally the water-soluble manganese oxide is wrapped by a surface polymer to prepare water-soluble manganese oxide nano particles. The water-soluble manganese oxide nano particles serving as a novel nuclear magnetic resonance contrast agent are transfected to K652 cancer cells cultured in vitro, thereby showing the enhancement of magnatic resonance imaging (MRI) effect. By means of intravenous injection to a mouse tail, the MRI effect is analyzed, and good MRI enhancing effect is shown. The water-soluble manganese oxide nano particles have good relaxation efficiency, and can obviously shorten the T1 relaxation time of tissues and improve contrast ratio of imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
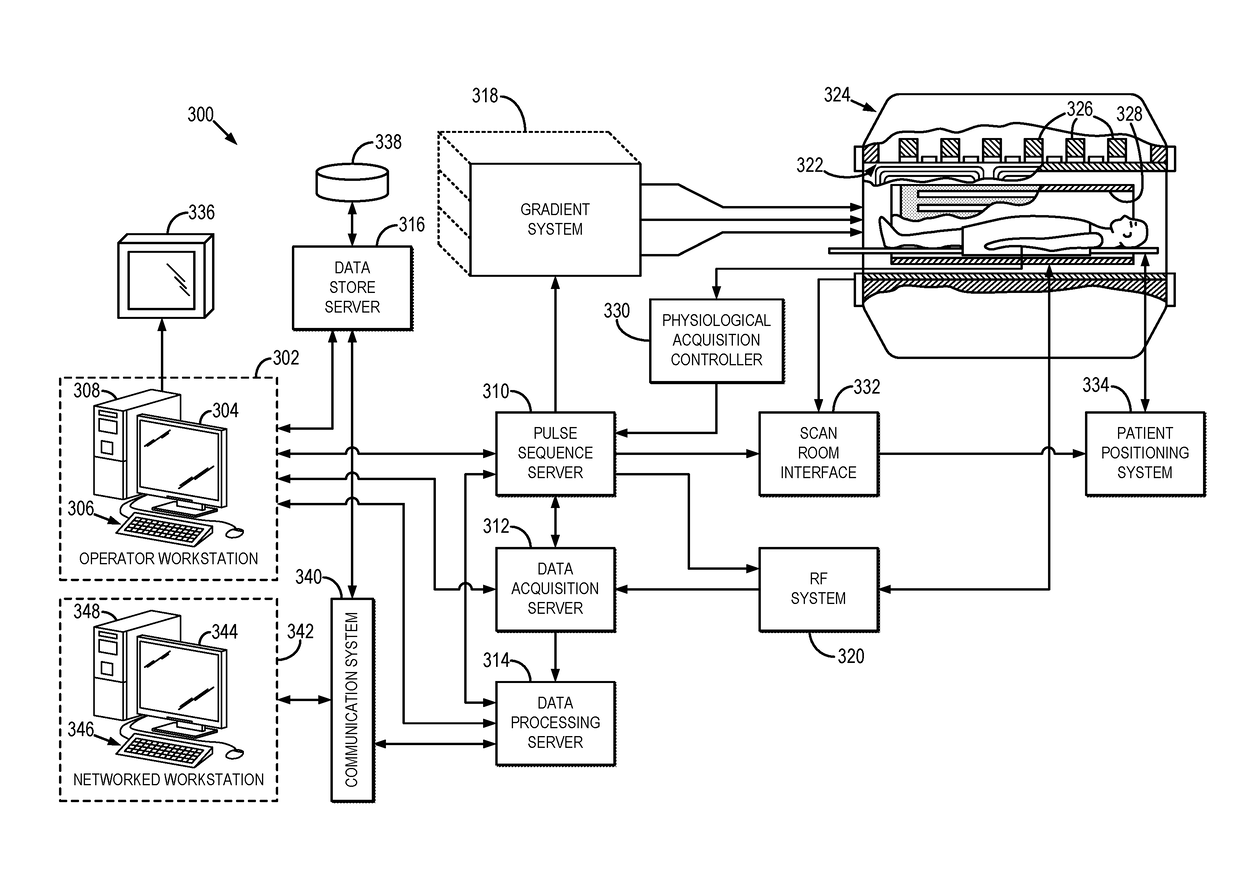
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus with application of the truefisp sequence and sequential acquisition of the MR images of multiple slices of a measurement subject
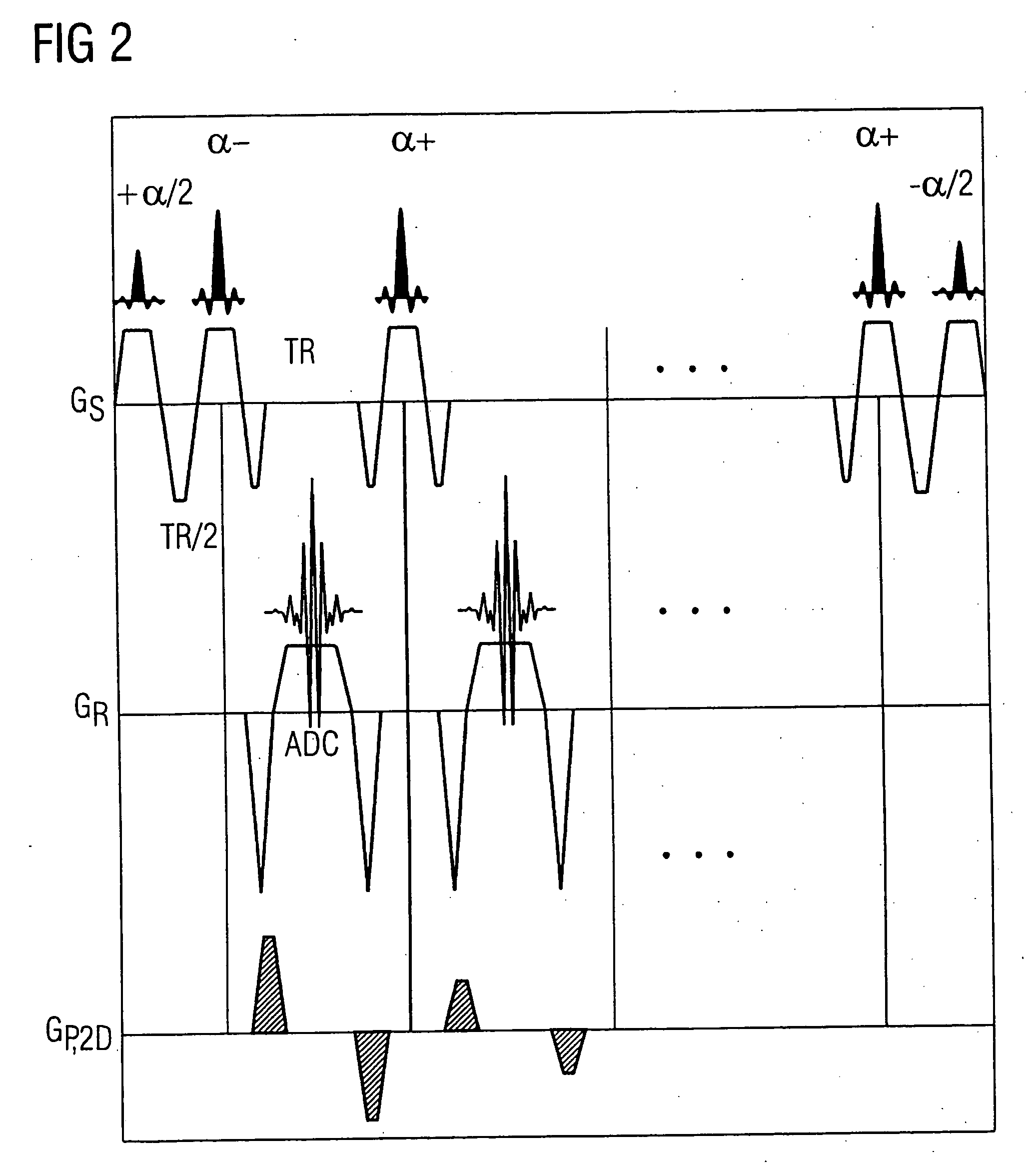
InactiveUS20070035299A1Eliminate fluctuationsReduce Image ArtifactsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetizationPhase Code
In a method and apparatus for generation of magnetic resonance (MR) images based on the TrueFISP sequence with simultaneous acquisition of the MR images of a number of parallel slices of a measurement subject the number of the slices N to be acquired in the measurement subject is established whereby N is at least, the number of the phase coding lines MA per raw data matrix and slice N are established, with the requirement that the quotient of MA and N is a natural number, the repetition time TR, the radio-frequency pulse duration RF and the flip angle α are established, of each raw data matrix is sub-divided into S separate segments to be measured, whereby S is equal to N or a whole-number multiple of N, with the requirement that the quotient Q of MA and S that corresponds to the number of the phase coding lines per segment is a natural number, data are acquired for all segments S of all slices N, whereby the time duration, in msec, TSeg for the acquisition of the data of each segment is TSeg=TR+RF+MAS·TR,and the measurement of all segments S of all slices N is implemented such that the time duration TRelax is TRelax=(N−1)·TSeg [msec] for the relaxation of the magnetization MZ with the relaxation constant T1 in a slice N that corresponds to the time span from the end of the measurement of a first segment up to the beginning of the measurement of a second segment of the same slice.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
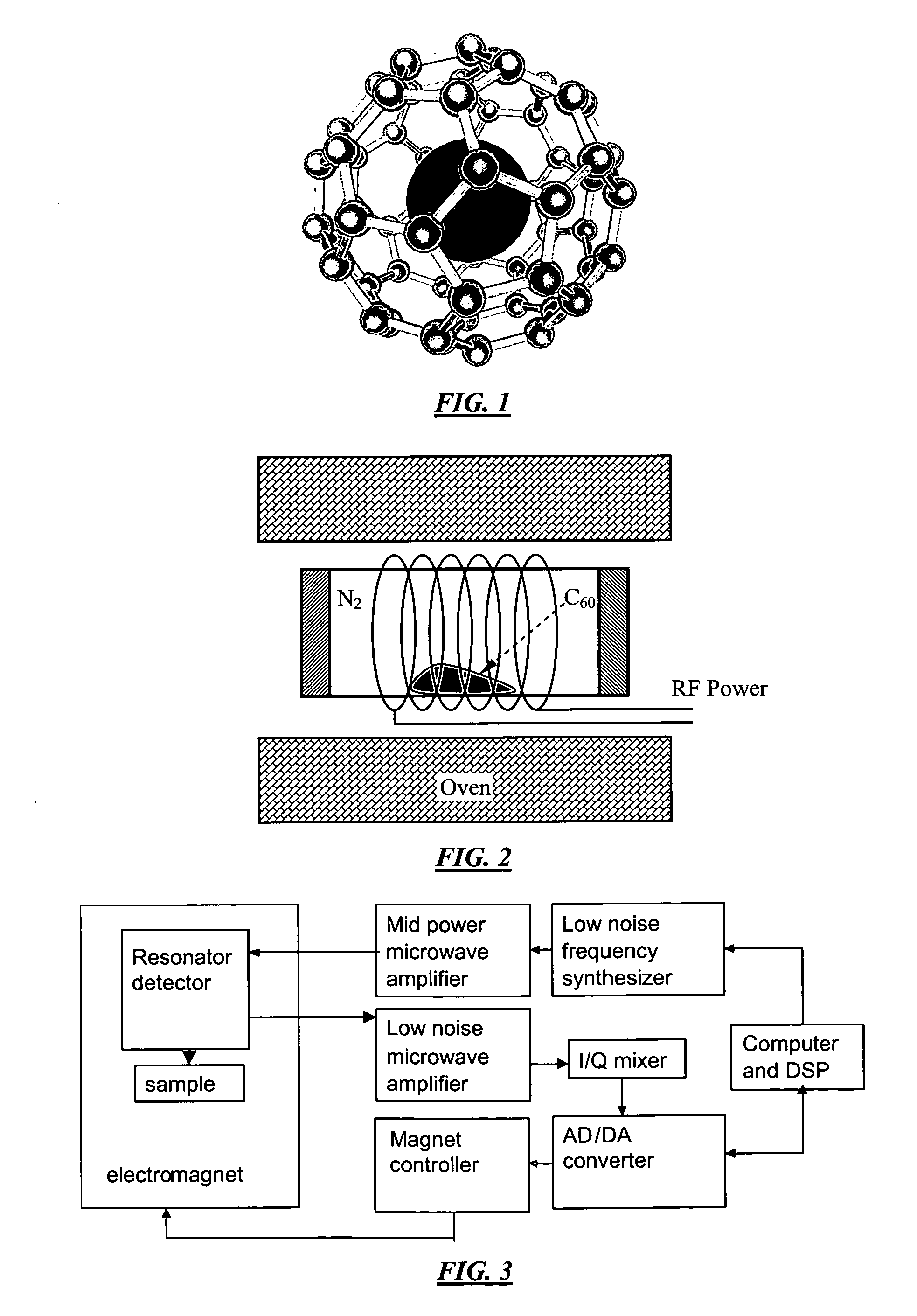
New MRI technique based on electron spin resonance and nitrogen endohedral C60 contrast agent
InactiveUS20060280689A1Short relaxation timeOvercomes drawbackEnergy modified materialsNanomedicineParamagnetismContrast medium
Methods and systems for electron spin MRI (eMRI) and novel methods for fabricating N@C60 fullerenes using the discovery that certain endohedral fullerenes can be used as functional paramagnetic materials exhibiting increased relaxation times. These endohedral fullerenes provide improved labels for use in electron spin resonance (ESR) detection systems.
Owner:INTEMATIX
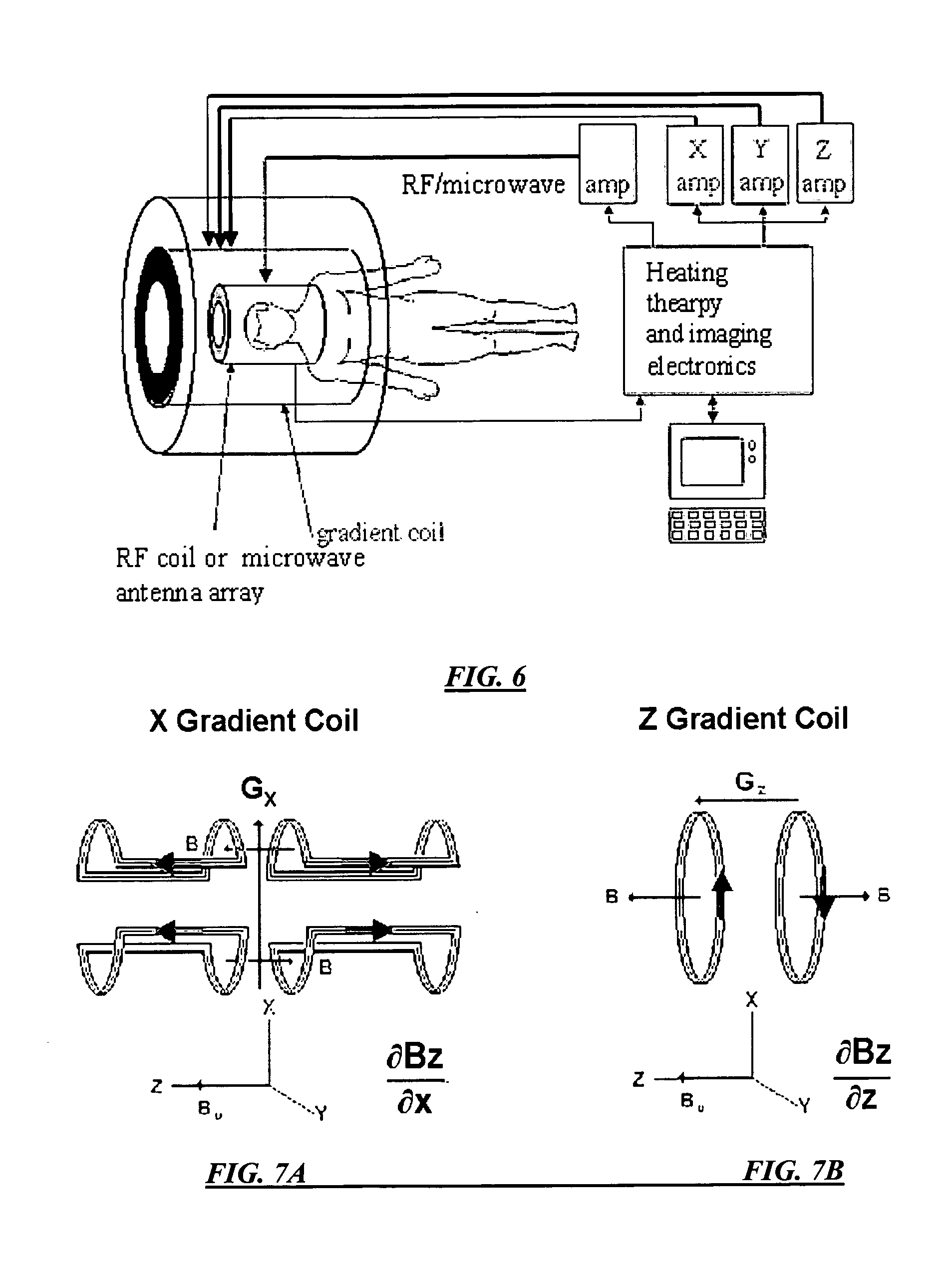
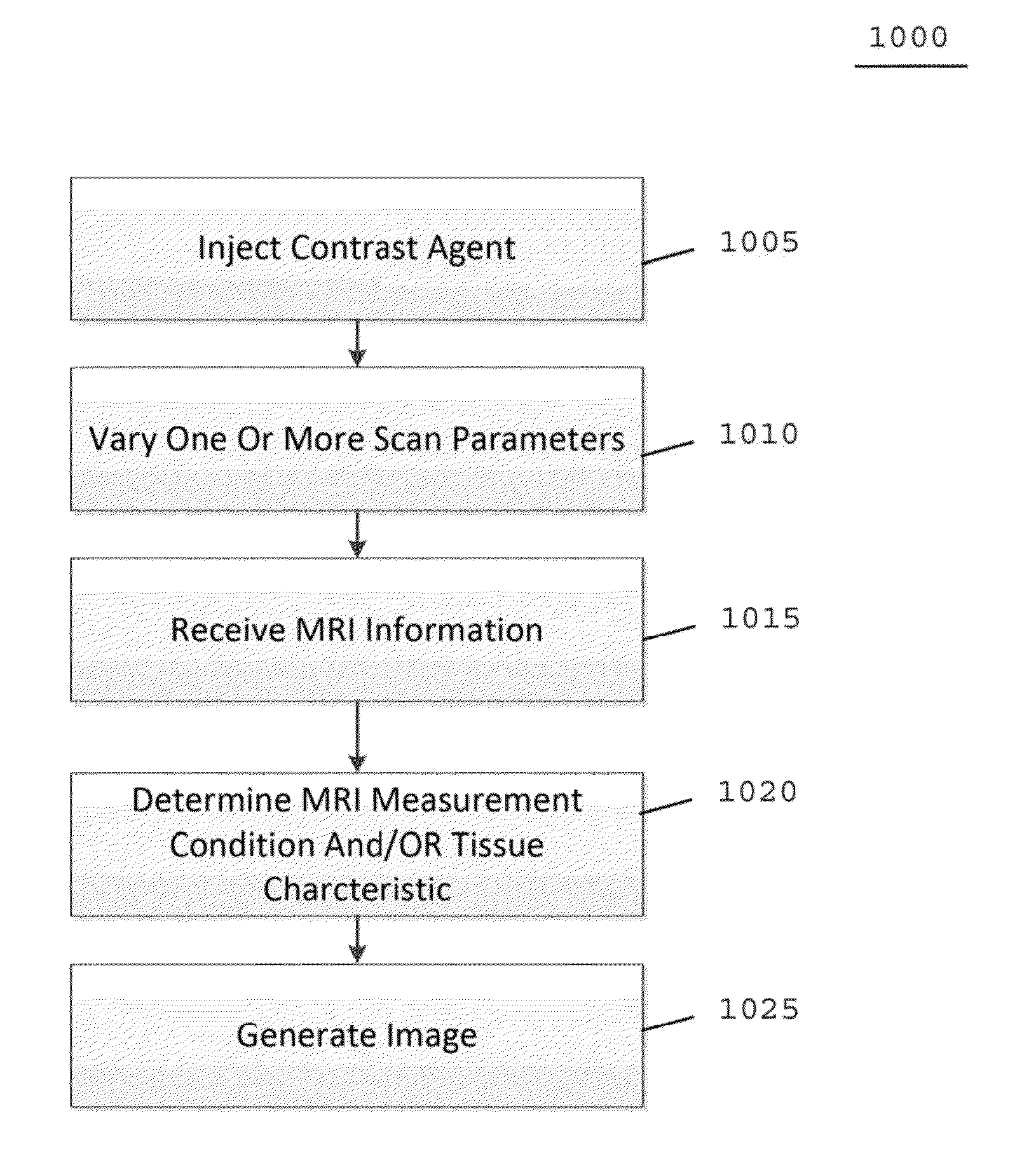
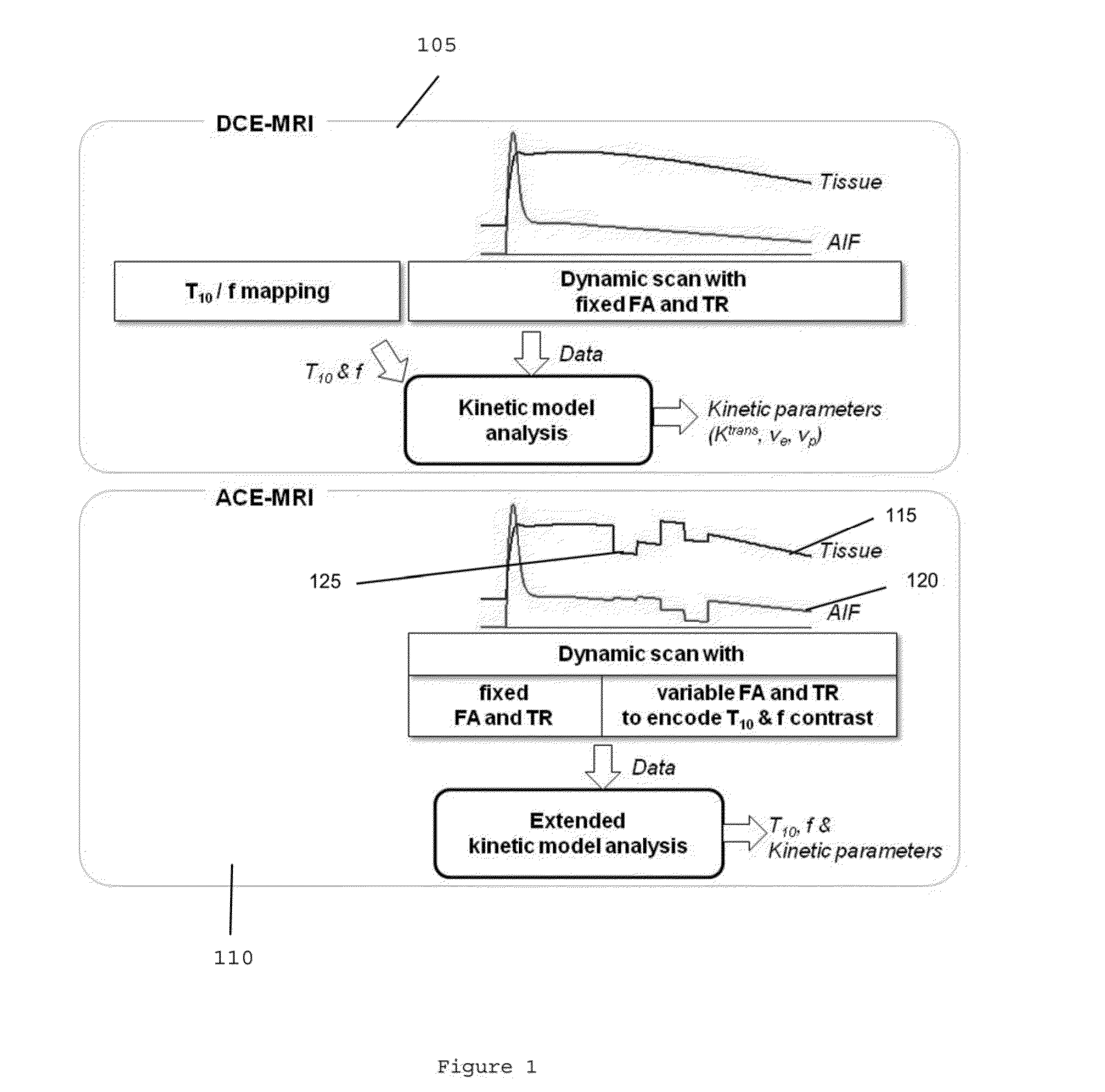
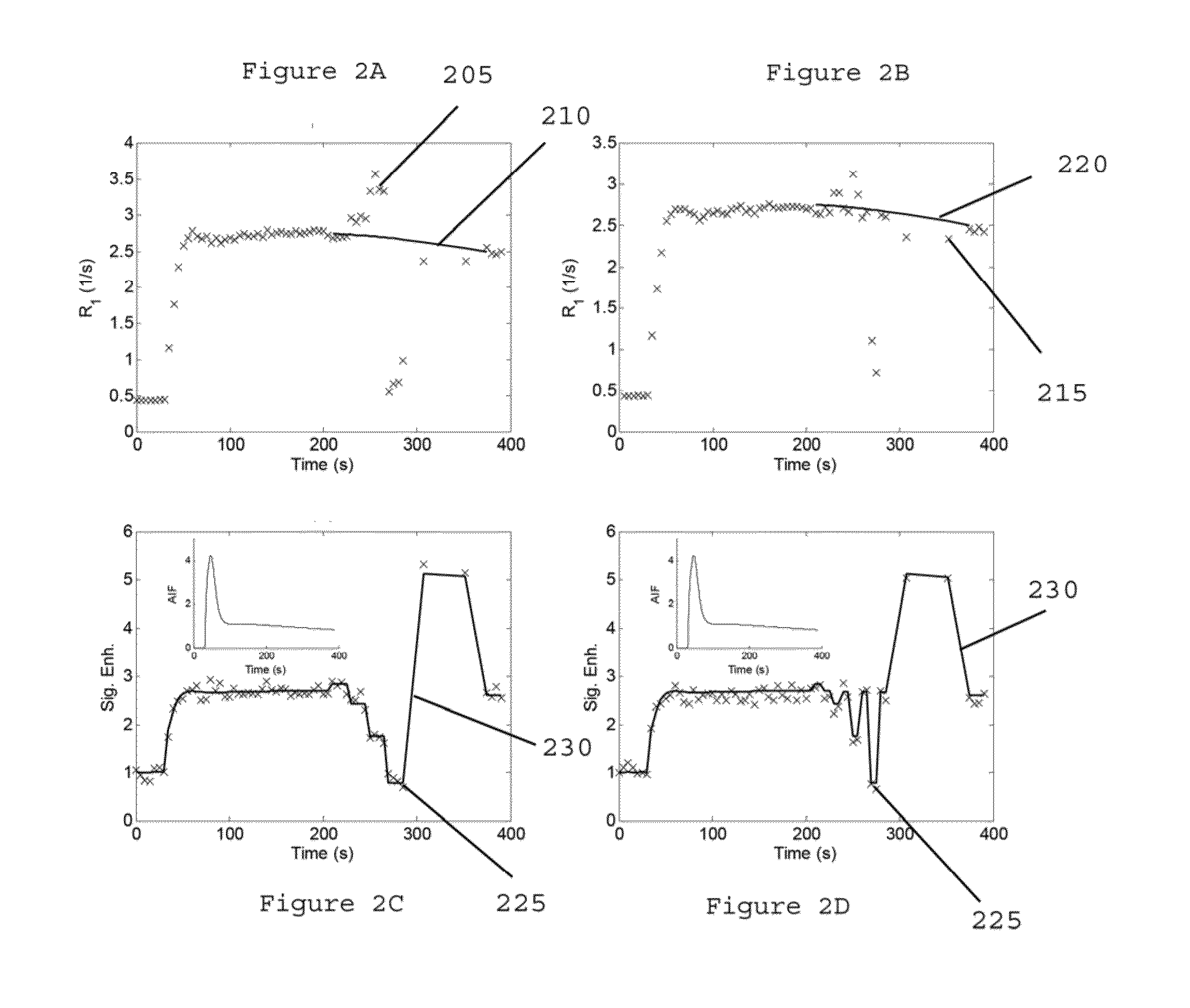
System, method, and computer-accessible medium for determining at least one characteristic of at least one tissue or at least one MRI measurement condition of the at least one tissue using active contrast encoding magnetic resonance imaging procedure(s)
ActiveUS20150309141A1Magnetic Resonance ImagingMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceData acquisition
In another exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure is an exemplary system, method and computer-accessible for determining a characteristic(s) of a tissue(s), that can include, for example, receiving magnetic resonance imaging information regarding the tissue(s) including a time-intensity curve(s) of the tissue(s) based on a contrast agent(s) concentration, actively encoding a part of the time-intensity curve(s) with a magnetic resonance relaxation property(s) of the tissue(s) by varying a magnetic resonance imaging scan parameter(s) to generate encoded data during magnetic resonance data acquisition, and determining the tissue characteristic(s) based on the encoded data.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
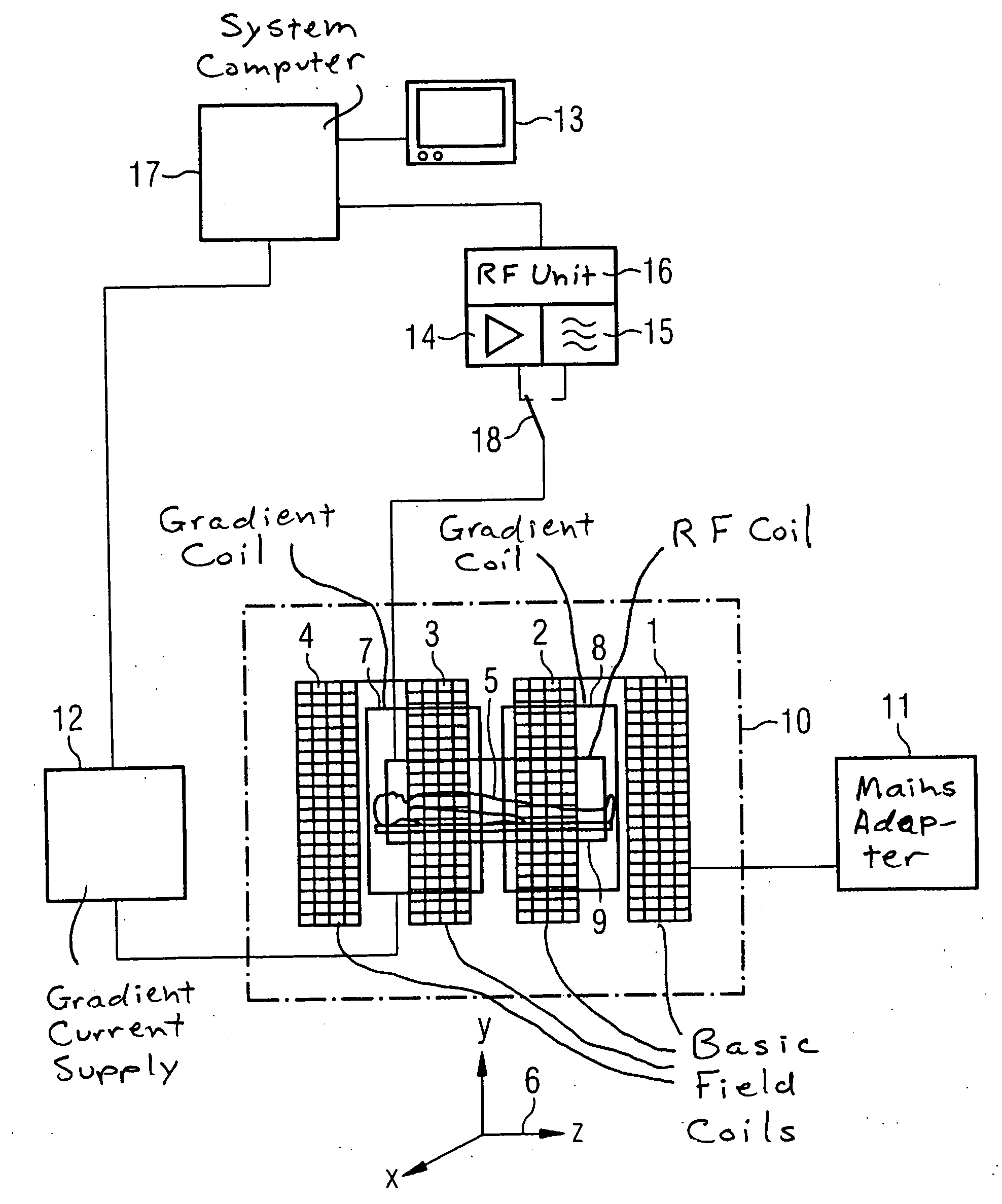
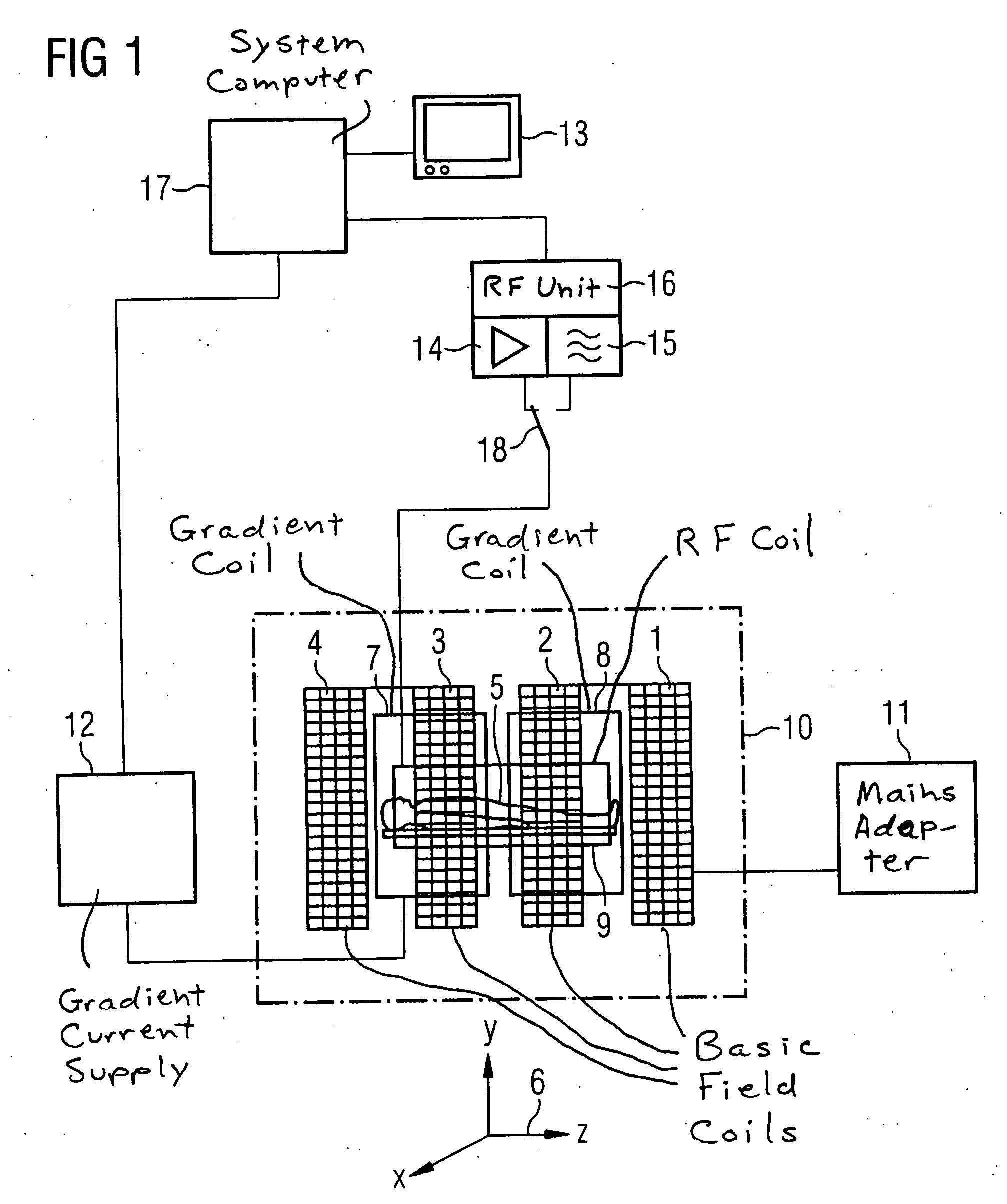
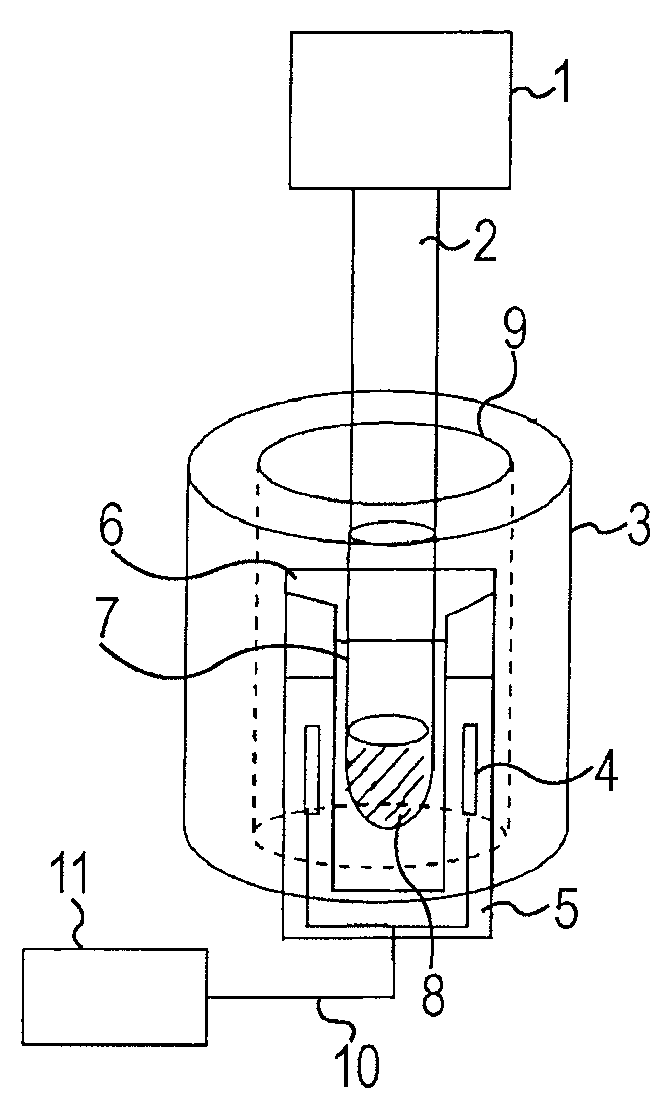
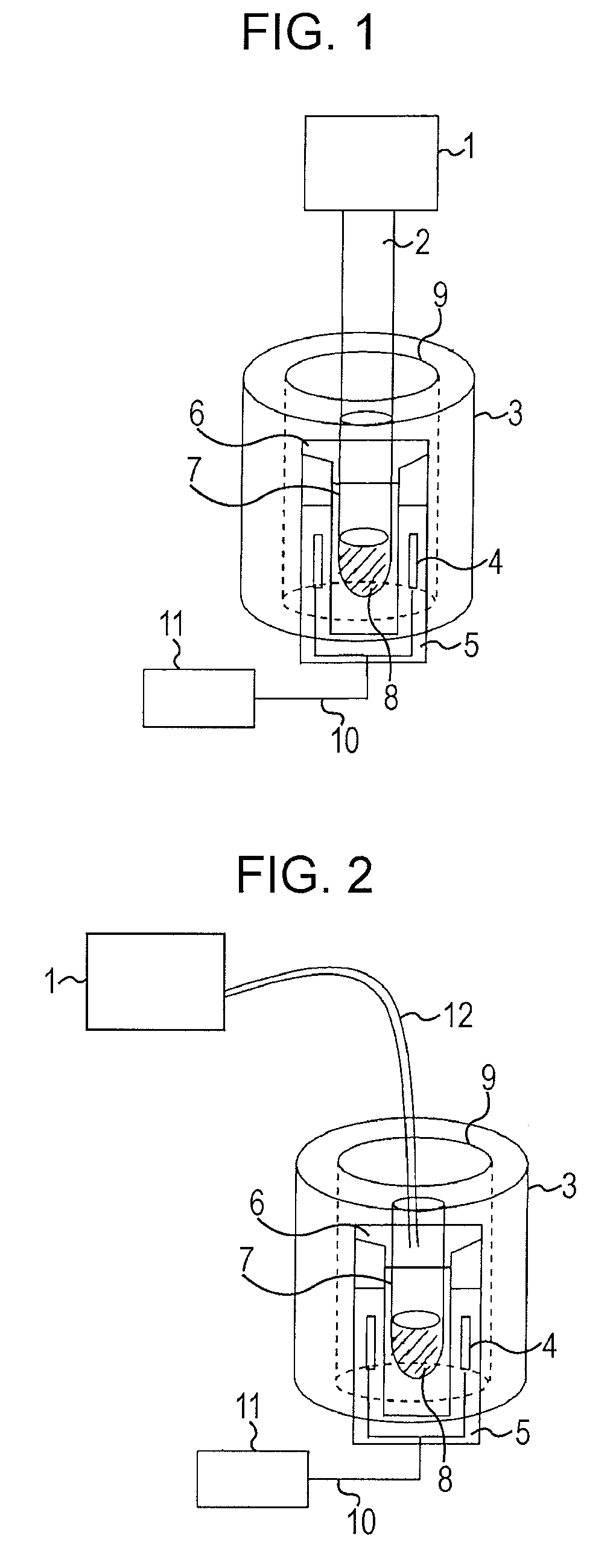
Configuration for nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with an MRI phantom
ActiveUS7368912B2Suppresses disturbances in the main chamberSimple disposalMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSpatial OrientationsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
An MRI configuration comprising an MRI phantom positioned in a volume under investigation, wherein the MRI phantom has a chamber disposed in a housing and filled with a liquid, in which a gas bubble forms, the liquid nuclei which have an NMR relaxation time T1 of between 100 ms and 20 s, is characterized in that the chamber the MRI phantom a main chamber and a partial chamber, the main chamber being delimited from the partial chamber such that the gas bubble can completely enter the partial chamber due to its buoyancy by changing the spatial orientation of the MRI phantom in the gravitation field, and remains in the partial chamber in a measurement orientation of the MRI phantom due to its buoyancy. This eliminates imaging artefacts despite the presence of a gas bubble.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
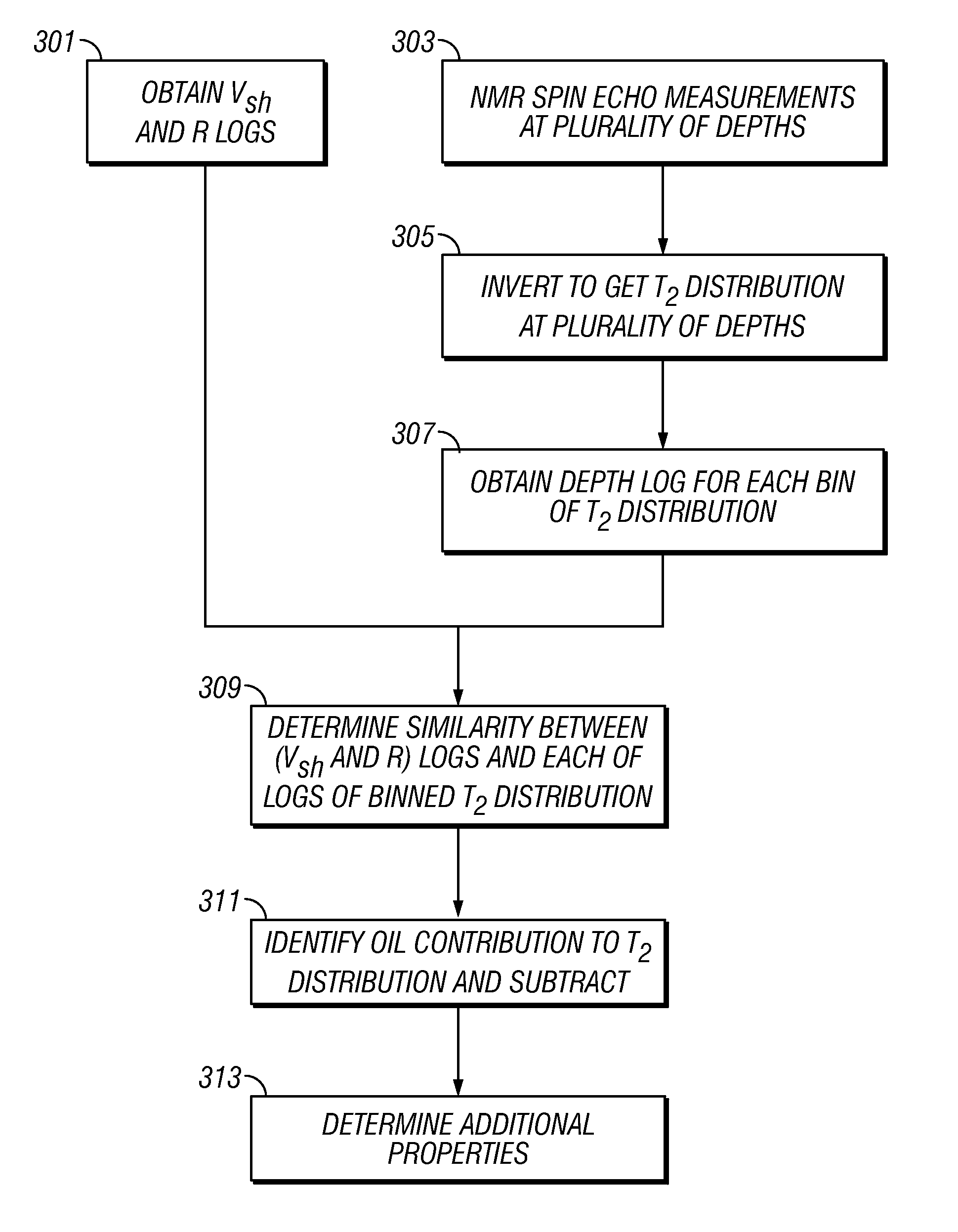
Methodology for interpretation and analysis of NMR distributions
ActiveUS7804297B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDiffusionSubject matter
Pulse sequences are applied to a fluid in an earth formation in a static magnetic field and NMR spin echo signals are obtained. The signals are inverted to give T2 distributions at a plurality of depths. Similarities between logs of the T2 bins with resistivity and / or gamma ray logs are used to identify and subtract contributions to the NMR signal from oil. having internal gradients. From the received signals, relaxation and diffusion characteristics of the fluid are determined. The determination takes into account the internal field gradients. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Rapid sample multiplexing
InactiveUS7088102B1Improved signal-to-noise ratio performanceElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMultiplexingData acquisition
A time multiplex arrangement for presenting multiple samples to a single channel of NMR excitation / data acquisition includes means for rapid exchange of physical position between plural samples or sample portions from the measurement volume of the NMR instrument while said samples remain in a substantially the same homogeneous magnetic field. While a delay is imposed upon time evolution or relaxation of an NMR excited sample outside the sensitive volume of an RF resonator, another sample is actively excited within said RF resonator whereby the steps of NMR measurement are overlapped between at least two samples.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Magnetic Relaxometry using Brownian Randomization, Neel Relaxation, or Combinations Thereof
InactiveUS20130289383A1Saving considerable later discomfortDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineNanoparticle
The present invention can provide a method of determining the communication of substances between a first region and a second region of a patient's body. An example method according to the present invention can comprise: (a) introducing into the first region a plurality of superparamagnetic nanoparticles, having properties such that they undergo Brownian motion that randomizes the orientation of the nanoparticles according to a predetermined characteristic time; (b) after a time sufficient to allow transport of nanoparticles from the first region to the second region, subjecting the second region to an applied magnetic field of sufficient strength to induce magnetization of individual nanoparticles, and having a substantially uniform direction throughout the second region; (c) measuring the magnetic field of the second region at a plurality of times after ceasing application of the magnetic field; (d) analyzing the measured magnetic field to detect signals that correspond to decay of the magnetic field due to randomization of the nanoparticles' orientation by Brownian motion; (e) determining the presence of nanoparticles in the second region from the signals detected in step (d).
Owner:IMAGION BIOSYST INC
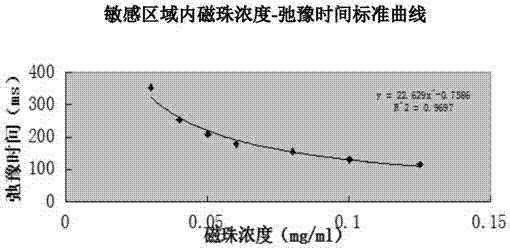
Low field NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance)-based magnetic bead concentration detection method and application thereof
InactiveCN104122284AEfficiently assess capture efficiencyImprove sorting conditionsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a low field NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance)-based magnetic bead concentration detection method and application thereof, the method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a series of concentrations of magnetic bead suspensions, using measured NMR relaxation time T as y-coordinates, using the magnetic bead suspension concentrations as x-coordinates to draw a magnetic bead concentration-relaxation time curve to obtain a magnetic bead concentration change sensitive area; (2) preparing a series of magnetic bead suspension standard samples with the concentrations in the sensitive area, using measured relaxation time Tsample as y-coordinates, using the magnetic bead suspension standard sample concentrations as x-coordinates to draw a sensitive area magnetic bead concentration-relaxation time standard curve; (3) preparing a magnetic bead suspension sample to be tested, diluting to the concentration change sensitive area, detecting the relaxation time Ttest, and obtaining the concentration of the magnetic bead suspension sample to be tested from the sensitive area magnetic bead concentration-relaxation time standard curve. The method can rapidly detect the magnetic bead concentration, provides effective and accurate quality control information to experimenters, and has important significance for the effective use and sorting and efficiency evaluation of magnetic beads.
Owner:张祥林
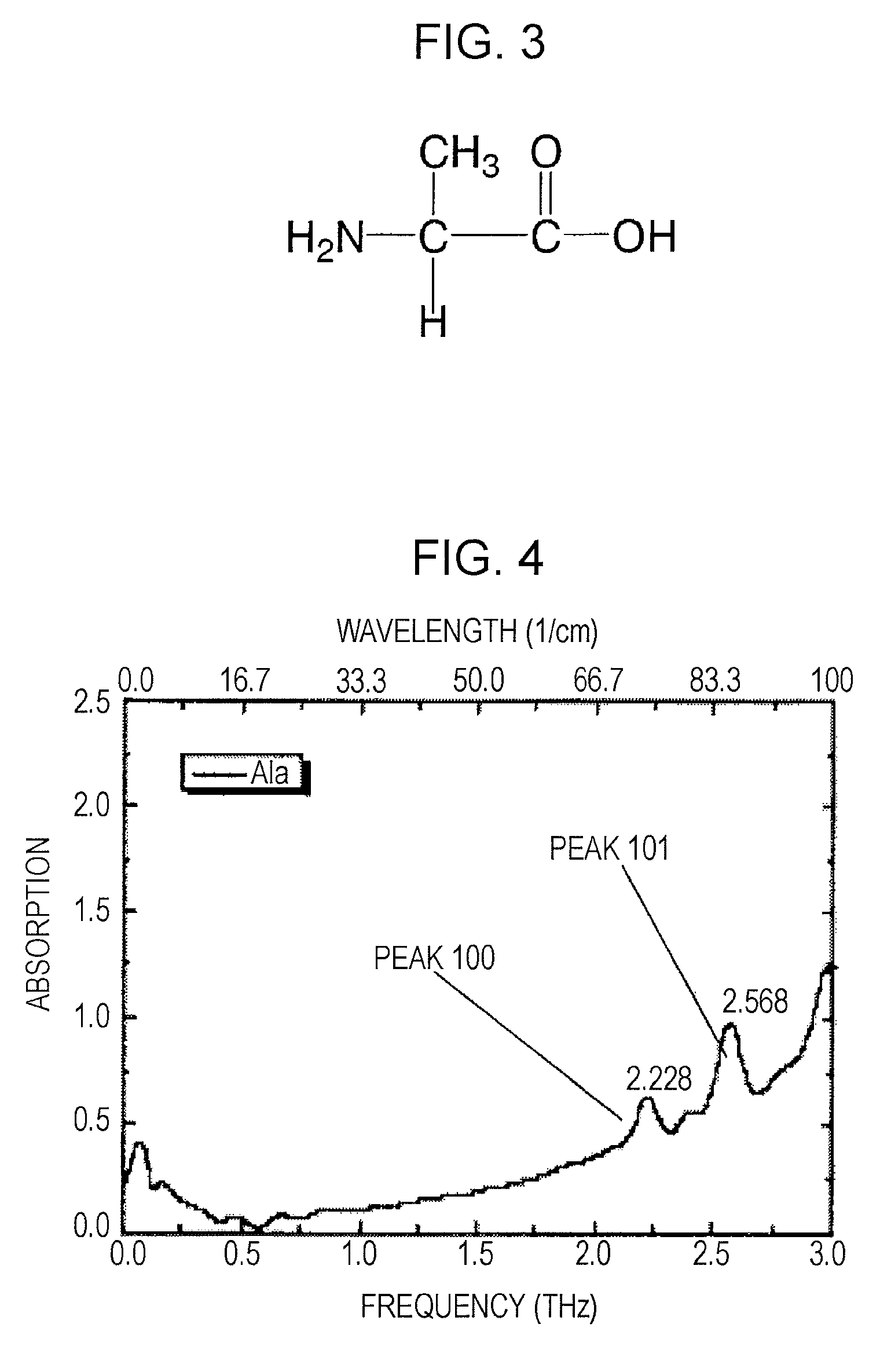
Method and apparatus for analyzing sample utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance under terahertz-wave irradiation
InactiveUS20070252596A1Material analysis using microwave meansMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMR - Magnetic resonance
The nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of a sample, which is a target material analyzed, and changes in relaxation times of nuclear magnetic resonance signals are measured while the sample is irradiated with terahertz waves containing frequency components corresponding to peak portions of absorption or reflectance spectrum of the sample. On the basis of the changes in relaxation times, the relationship between peak portions and information about a three-dimensional structure, conformational alteration, molecular relaxation, and the like is observed, the peak portions being in the absorption or reflectance spectrum in the terahertz range of the sample.
Owner:CANON KK
System and method for dynamic multiple contrast enhanced, magnetic resonance fingerprinting (dmce-mrf)
The present disclosure provides a method of DDCE-MRF. The method can include: a) introducing two or more contrast agents to a region of interest (ROI) of a subject, the two or more contrast agents having different relaxivities; b) measuring a T1 relaxation time and a T2 relaxation time for locations within the ROI using magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF); c) determining, using equations that relate the different relaxivities, the T1 relaxation time, the T2 relaxation time, and concentrations of the two or more contrast agents, the concentrations of the two or more contrast agents for each of the locations within the ROI; and d) producing an image depicting the ROI based, at least in part, on the concentrations of the two or more contrast agents.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
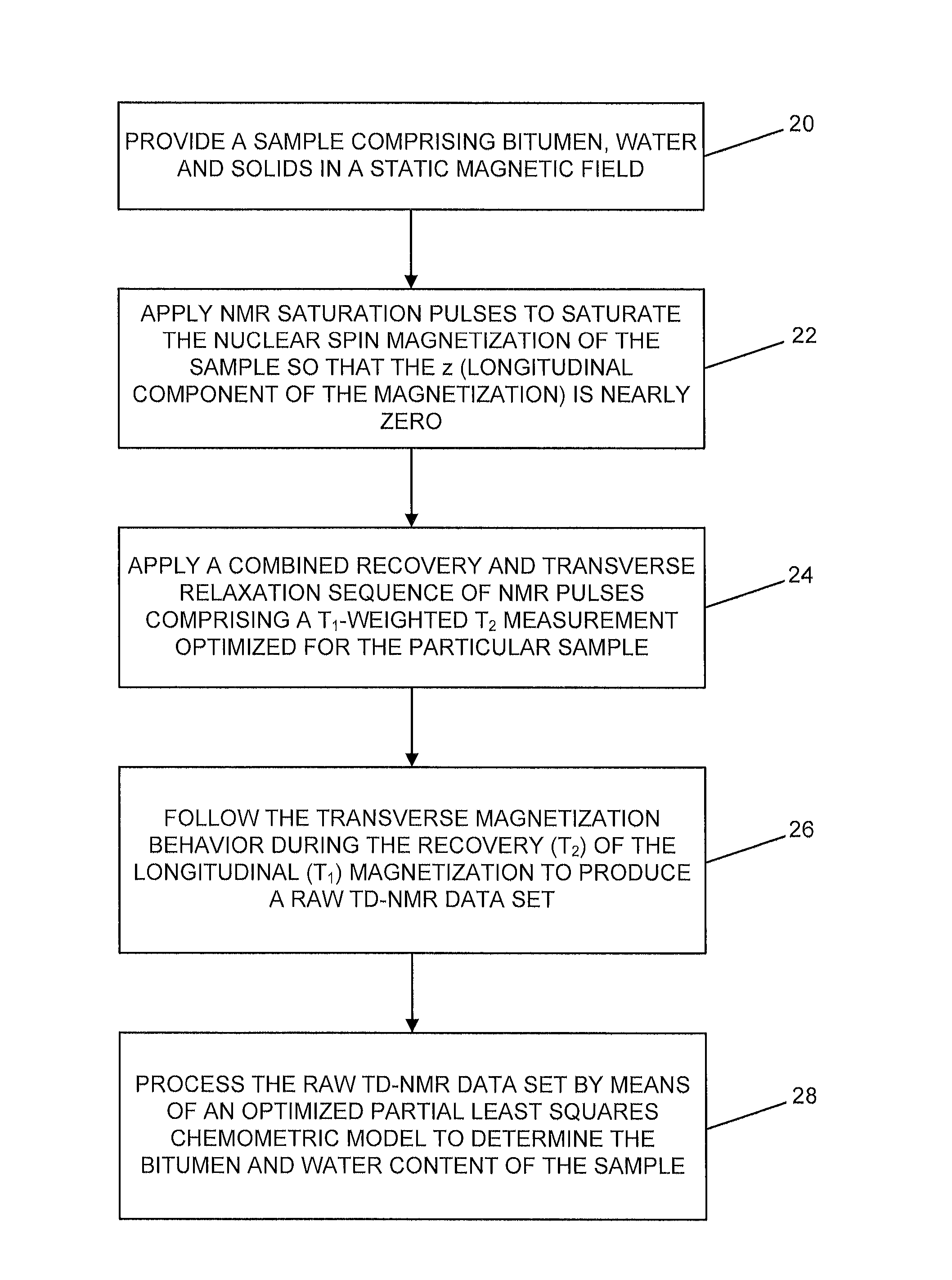
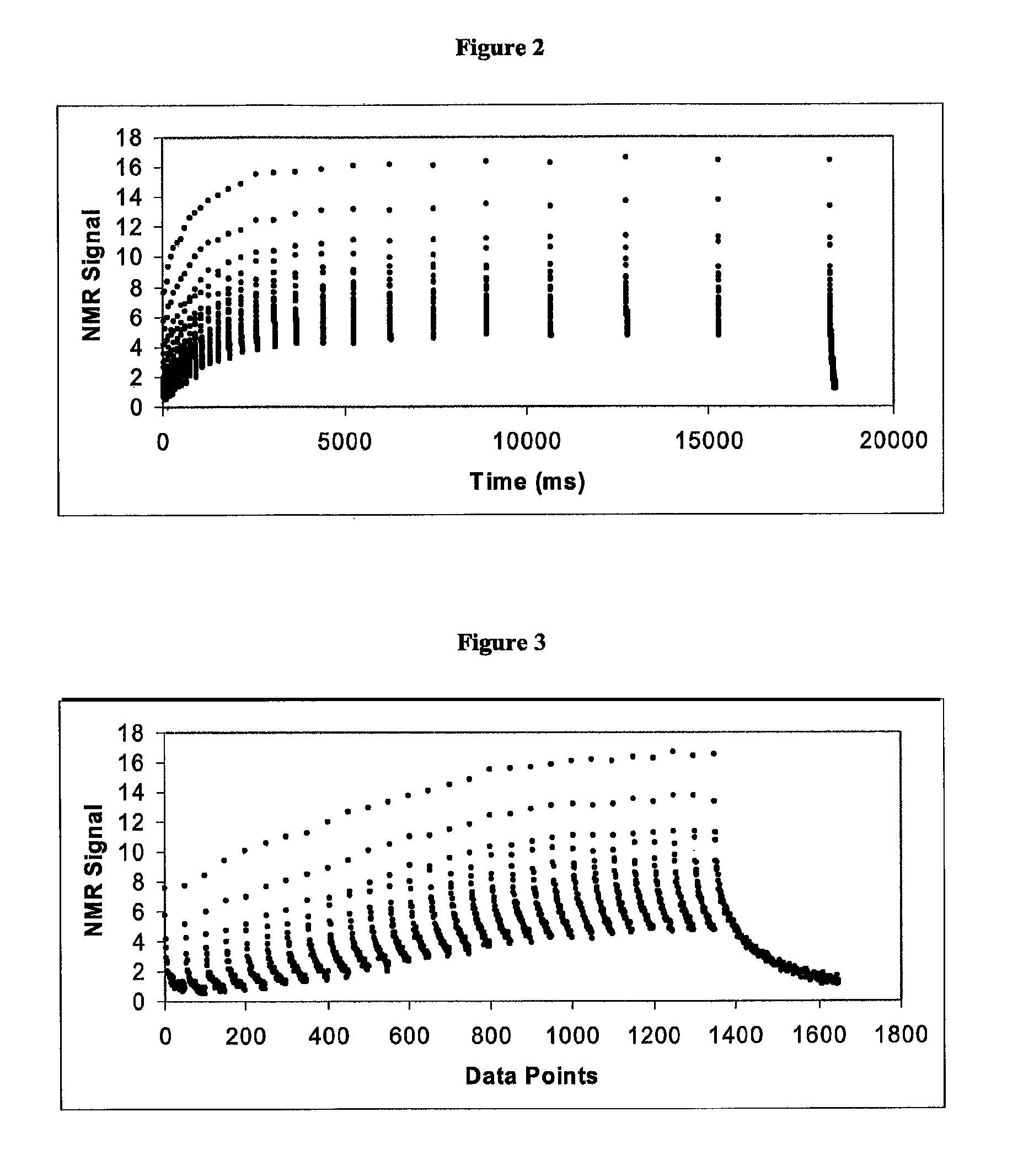
Simultaneous determination of bitumen and water content in oil sand and oil sand extraction process samples using low-field time-domain NMR
ActiveUS8547096B2Rapid simultaneous quantificationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMaterial analysis by using resonanceData setMagnetization
A method for quantifying bitumen and / or water in a sample comprising bitumen, water and solids using a time-domain nuclear magnetic resonance pulse spectrometer is provided comprising the steps of: initially saturating the magnetization of the sample so that essentially no magnetization remains in the +Z axis; subjecting the sample to a sequence of radio-frequency pulses optimized for the measurement of bitumen and water in the sample; allowing the recording of the transverse relaxation (T2) echo trains after incremental longitudinal relaxation to produce a raw TD-NMR data set for the sample; and determining the amount of bitumen and water by means of a partial least squares optimization based chemometric model relating TD-NMR data sets obtained from a training set of samples comprising bitumen, water and solids to the training samples' corresponding reference values obtained from a standard analysis method for determining bitumen and water.
Owner:BRUKER +2
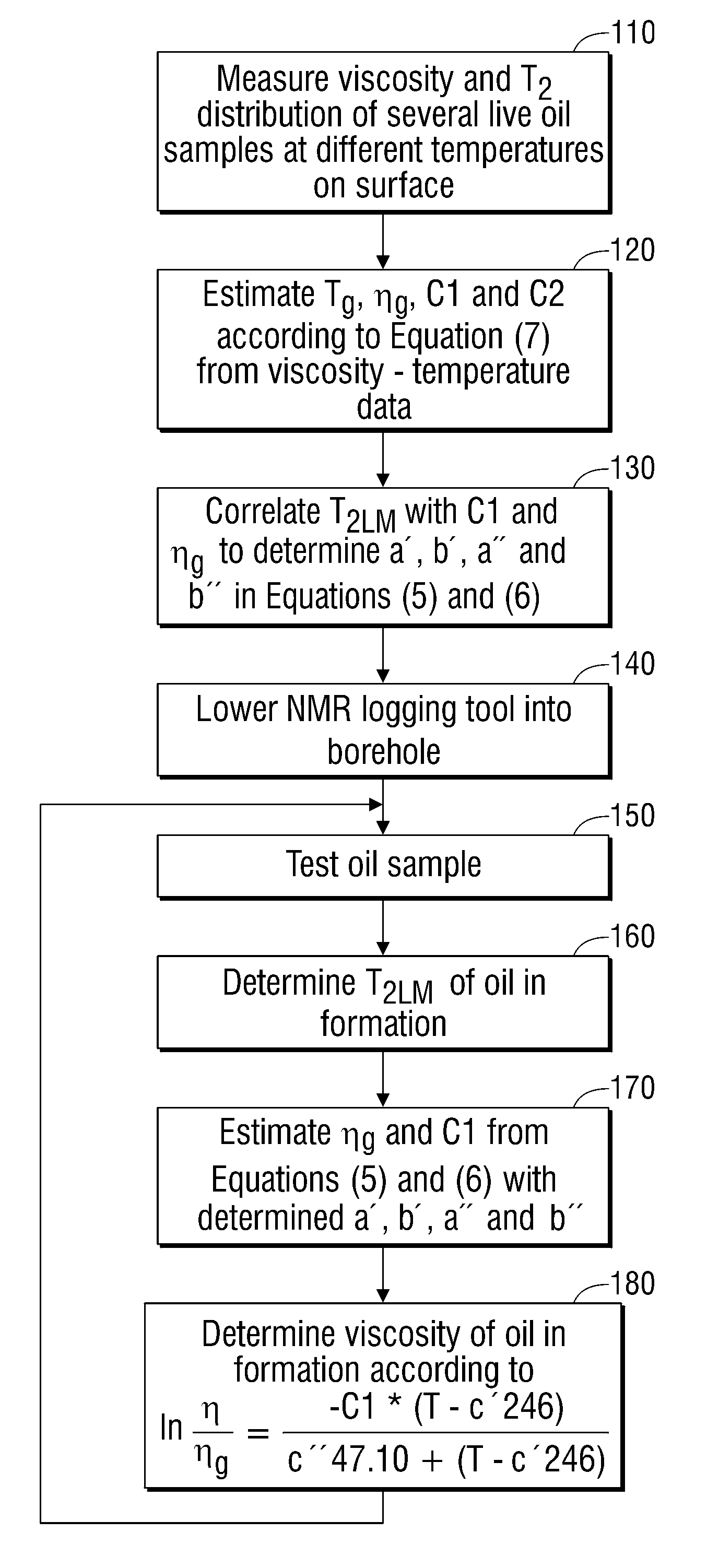
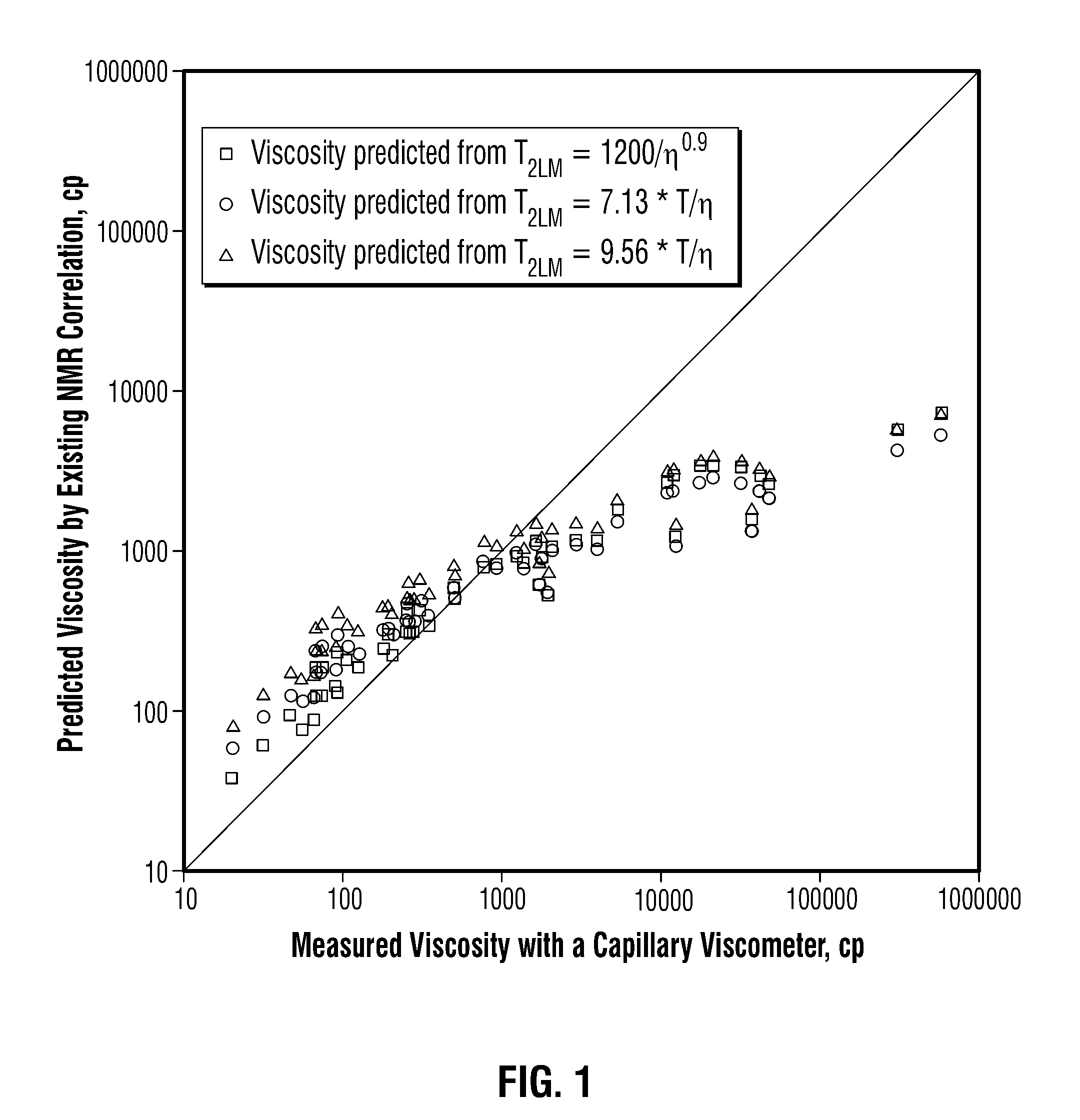
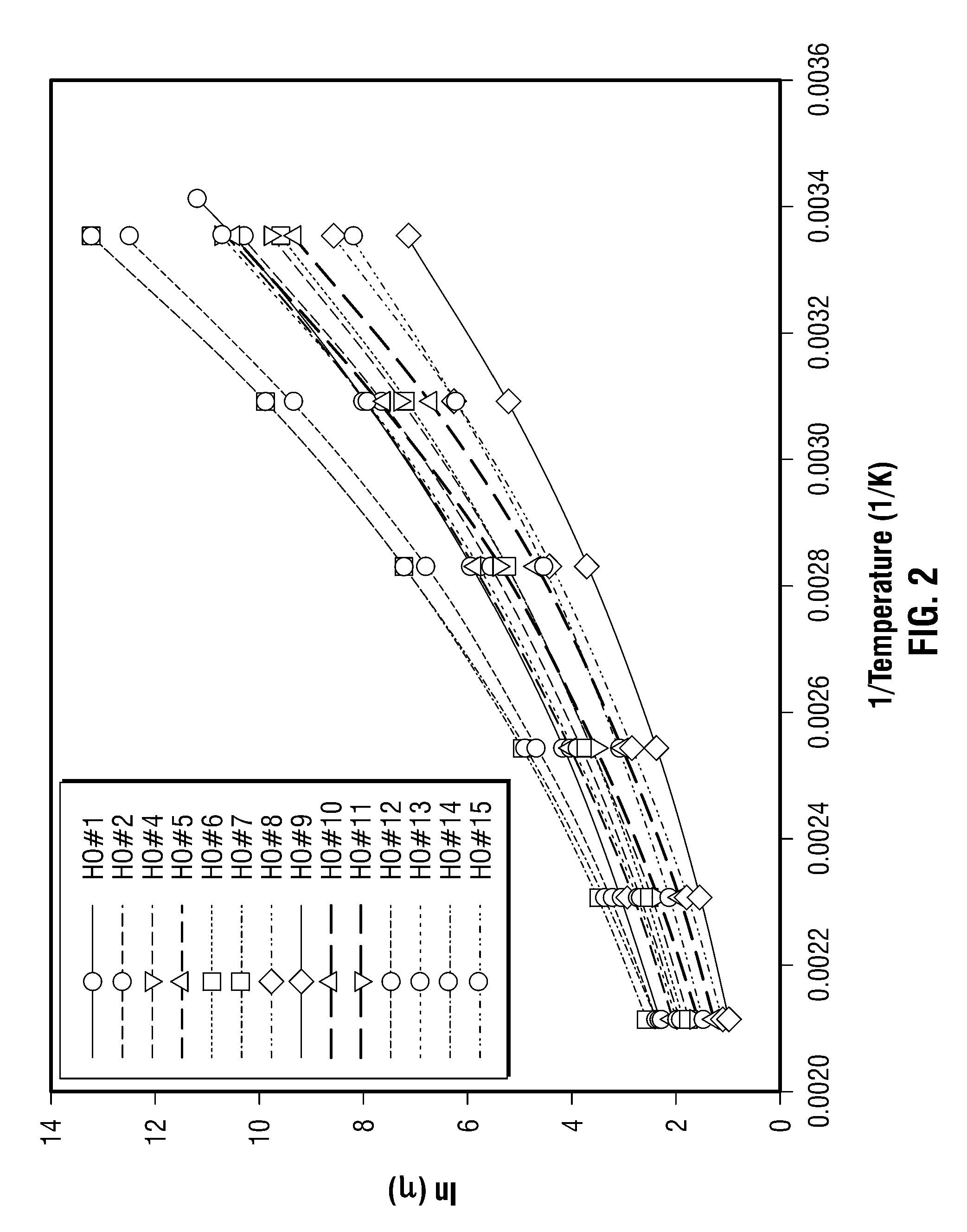
Methods for determining in situ the viscosity of heavy oil using nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time measurements
ActiveUS8013601B2Solid dispersion analysisElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceGlass transition
The viscosity η (in centipoise) of a heavy oil sample is determined according to an equation of the form lnηηg=-C1*(T-c′246)c″47.10+(T-c′246),where T is the temperature of the heavy oil, T2LM is the logarithmic mean of the T2 distribution of the sample obtainable from nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements, c′=1.0±0.05, c″=1.0±0.04, ηg is the glass transition temperature viscosity of the heavy oil and a function of T2LM, and C1 is a variable which is a constant for the heavy oil and is a function of T2LM. Both C1 and ηg are considered functions of certain NMR values associated with the heavy oil sample, with ηg and C1 preferably estimated by empirically fitting data to the equations ln T2LM=a′+b′ ln ηg and ln T2LM=a″+b″C1, where a′, b′, a″ and b″ are constants.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for nuclear magnetic resonance measurements on borehole materials
ActiveUS20190346385A1Increase measurement throughputImprove throughputAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceDrill cuttings
A method (and apparatus) for NMR relaxation measurements on borehole materials (e.g., drill cuttings, sidewall cores and whole cores) is based on combining an FID signal and spin-echo signals to obtain relaxation properties of a sample having fast relaxation components. The method comprises acquiring NMR signals from the sample, acquiring calibration NMR signals and acquiring a background signal (e.g., ringing after an excitation pulse). The background signal may be acquired using an additional static magnetic field to substantially spoil the NMR excitation volume in the sample. The acquired signals are processed to obtain a nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation property of the sample with at least one (first point) on the relaxation data produced from the FID and with the background data eliminated from the relaxation data.
Owner:REIDERMAN ARCADY
NMR detection method for food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on Fe3O4 nano-material
InactiveCN103207198AQuick filterEfficient detectionAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceBiotechnologyMagnetic bead
The invention provides a rapid detection method for food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on an NMR nanometer probe of Fe3O4, belonging to the field of rapid detection technology for pathogenic bacteria in food safety. According to the invention, based on an established nuclear magnetic resonance detection method applicable to detection of pathogenic bacteria in a liquid food sample, a Fe3O4 nano-material is used for preparing an immunomagnetic bead for specific enrichment of a target bacterium, and influence of paramagnetic and super-paramagnetic characteristics of Fe3O4 on nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time is used for detecting whether the sample contains a target pathogenic bacterium or not. A different concrete corresponding relationship is that the super-paramagnetic immunomagnetic bead presents linear relation under certain conditions, i.e., the greater the content of the immunomagnetic bead is, the smaller a T2 / T1 value of the sample is, and quantitative detection of the target bacterium can be realized in a certain range. The method provided by the invention is applicable to rapid detection of harmful pathogenic bacteria in a food sample, so the method can be used for rapid screening of large quantities of to-be-detected samples.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
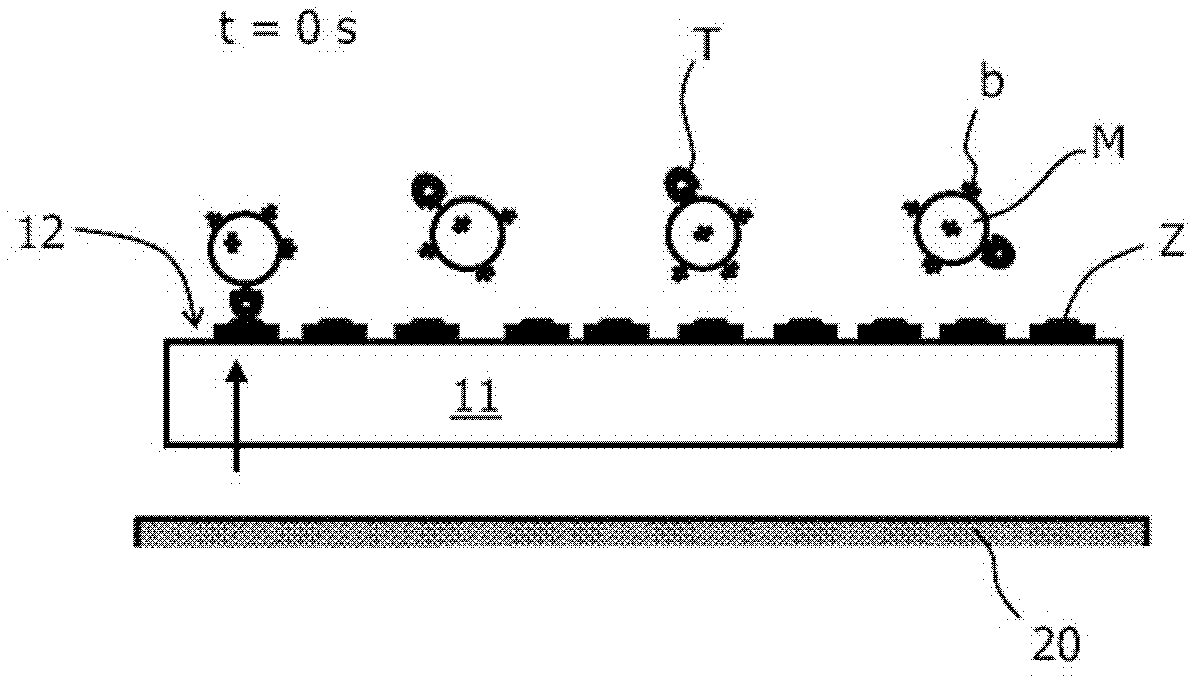
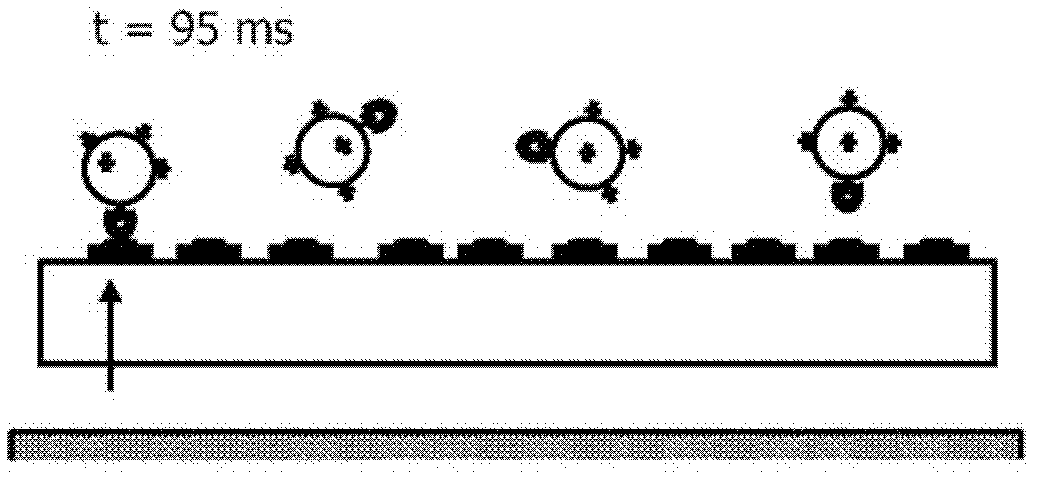
Sensor device for magnetic particles with a high dynamic range
InactiveCN102439448AReduce the probability of bindingImproved transverse relaxationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh dynamic rangeMagnetism
The invention relates to a method and a sensor device (100) for the detection of magnetic particles (M) in a sample. The magnetic particles (M) can bind to binding sites (Z) at a binding surface (12), where they can be detected by a detection unit (13, 14). A controller (15) is provided for controlling magnetic attraction (B) of the magnetic particles (M) towards the binding surface (12) in dependence on the detection signal (S) of the detection unit (14) in such a way that rotational relaxation conditions for the magnetic particles (M) are changed. In particular, this change can be controlled to maximize the binding of magnetic particles (M) to the binding surface (12) within a given measurement time. The change can for example be achieved by repeatedly switching the magnetic attraction off for prolonged periods, giving the magnetic particles (M) better chances to orient properly with respect to the binding surface (12).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
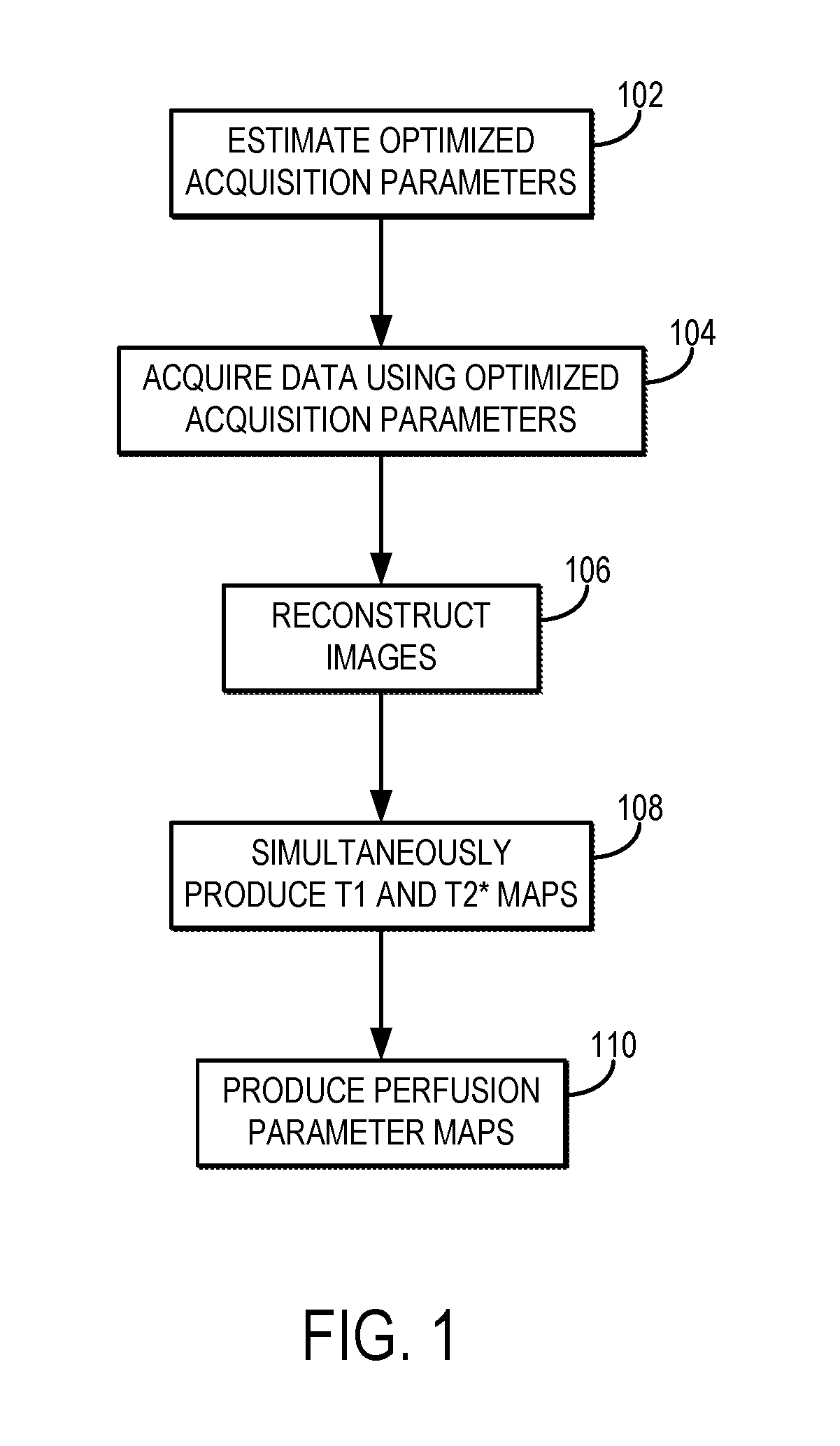
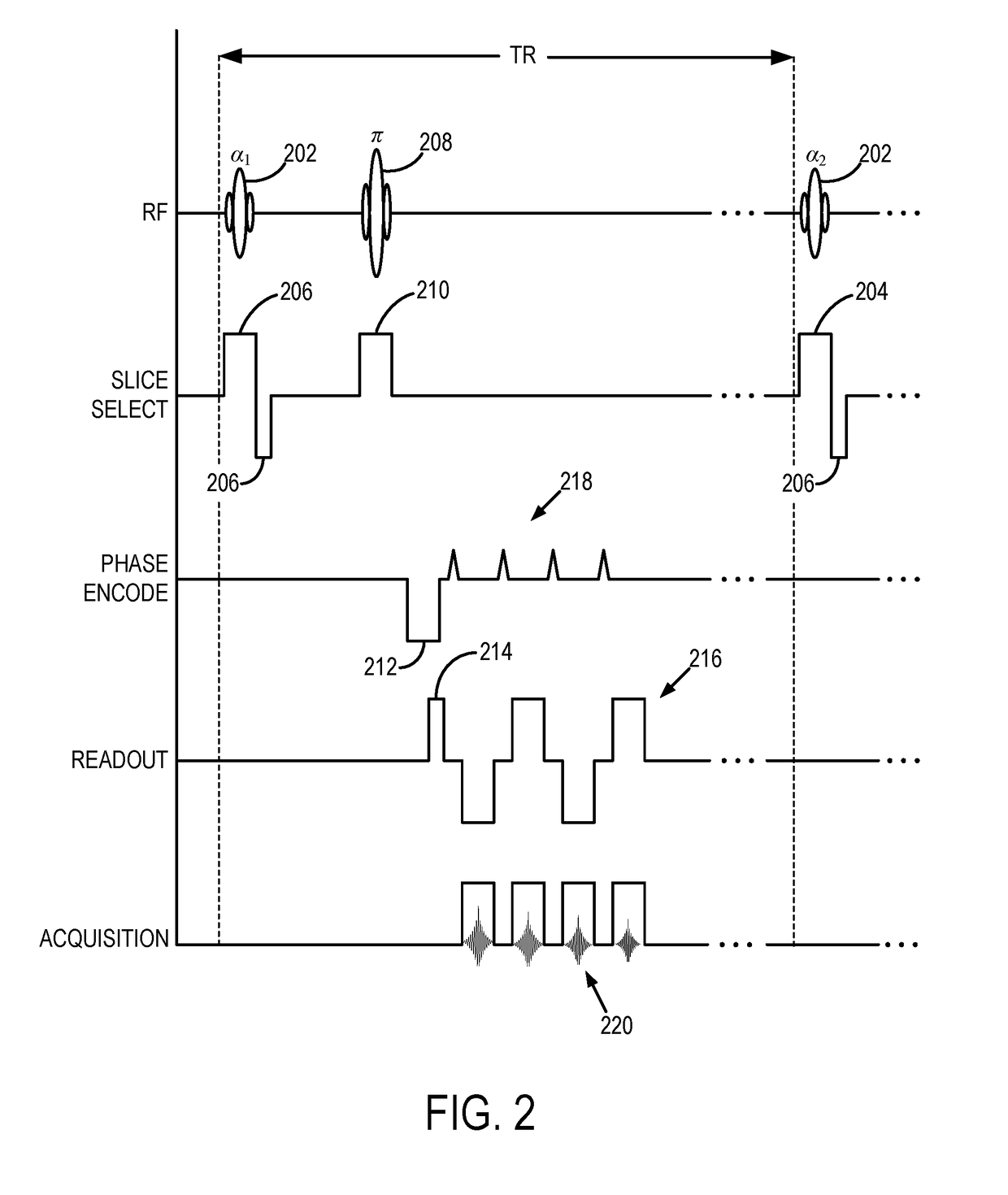
Simultaneous dynamic contrast enhanced and dynamic susceptibility magnetic resonance imaging using magnetic resonance fingerprinting
ActiveUS20170276753A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsDynamic contrastContrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Described here are systems and methods for generating quantitative perfusion parameter maps based on multiple different relaxation parameter maps that are simultaneously produced from images acquired using contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”) techniques.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
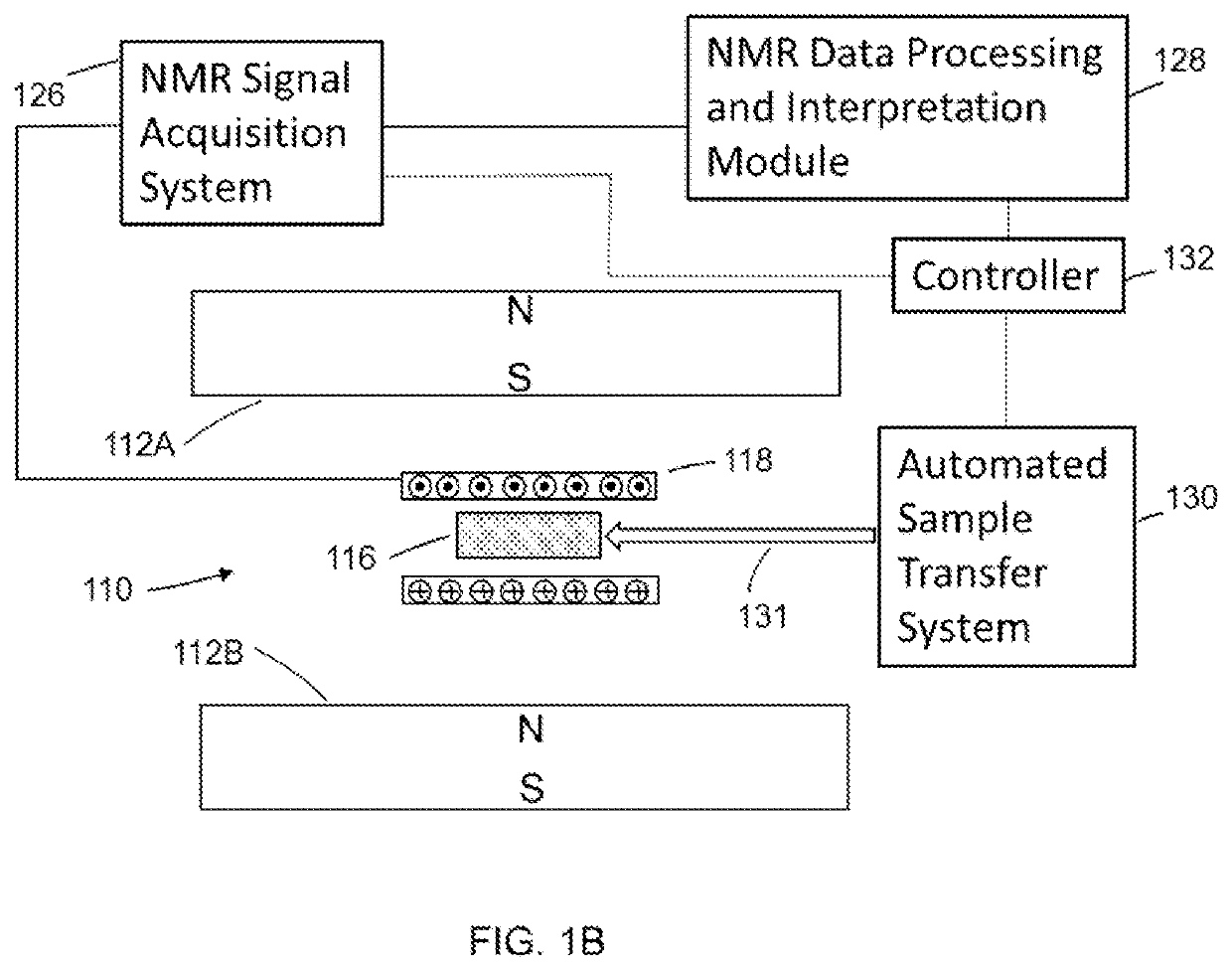
Apparatus and method for nuclear magnetic resonance measurements on borehole materials
ActiveUS20180364184A1Increase measurement throughputImprove throughputMagnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceTransfer system
An apparatus (and method) for automated NMR relaxation measurements on borehole materials (e.g., drill cuttings, sidewall cores and whole cores) includes a sample cassette and a sample transfer system operating synchronized with the NMR experiment. The apparatus implements an automatic calibration, adaptive data stacking and automated measurements of the sample volume for irregular shaped samples. The measurements throughput may be increased by creating more than one excitation / detection volume during a measurement cycle. The NMR surface data may be interpreted together with other bulk sensitive measurement data (e.g. natural gamma ray spectroscopy) or / and downhole data to evaluate earth formations while drilling an oil well.
Owner:REIDERMAN ARCADY
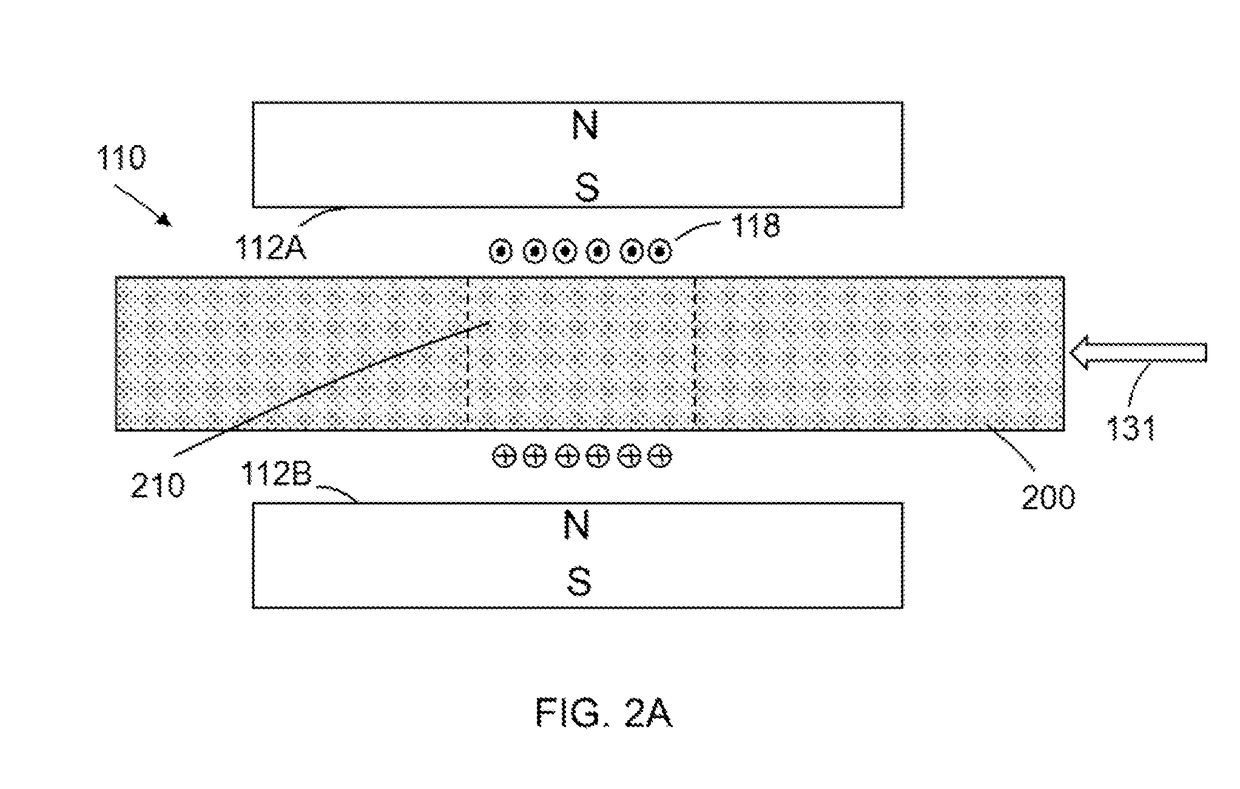
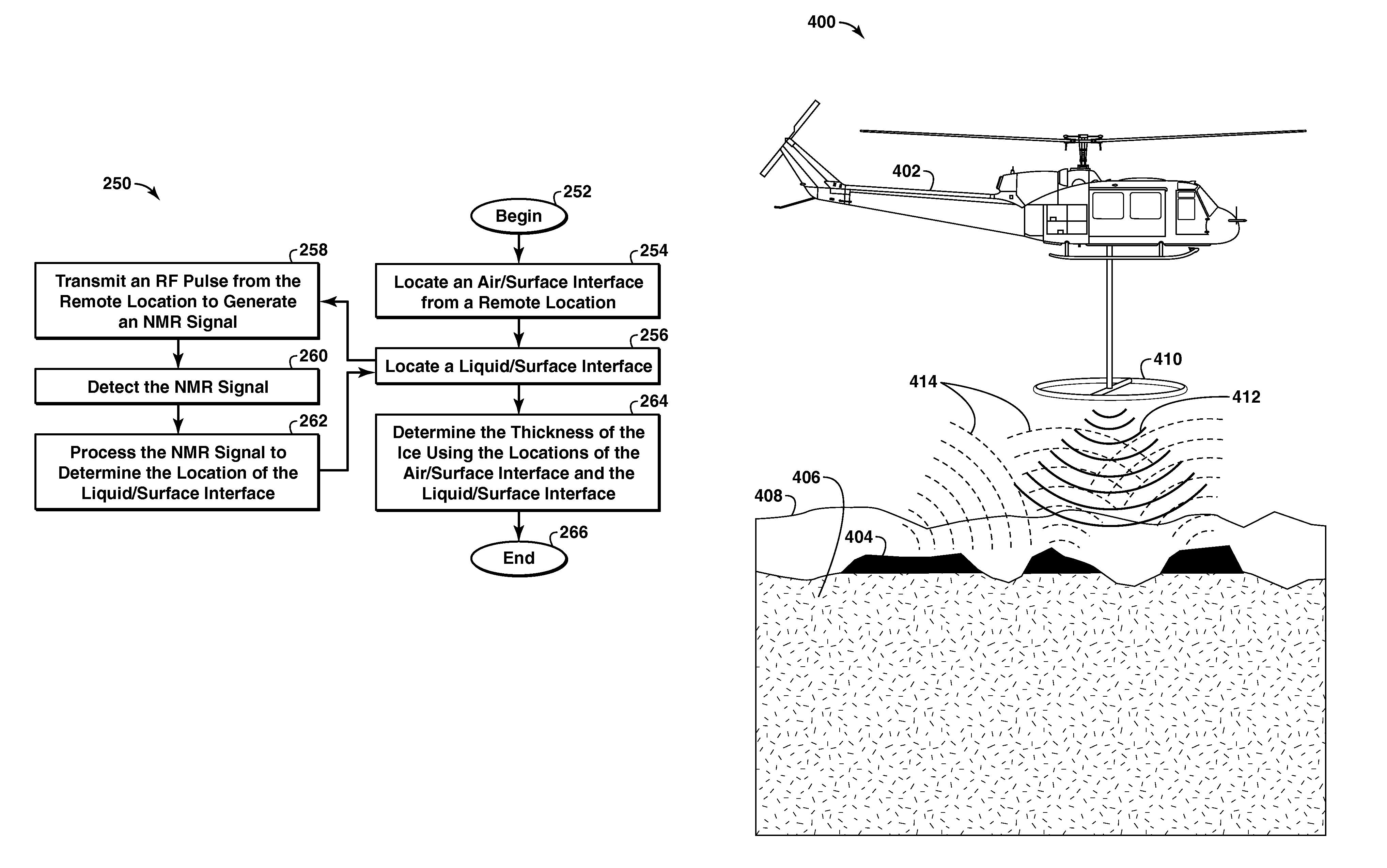
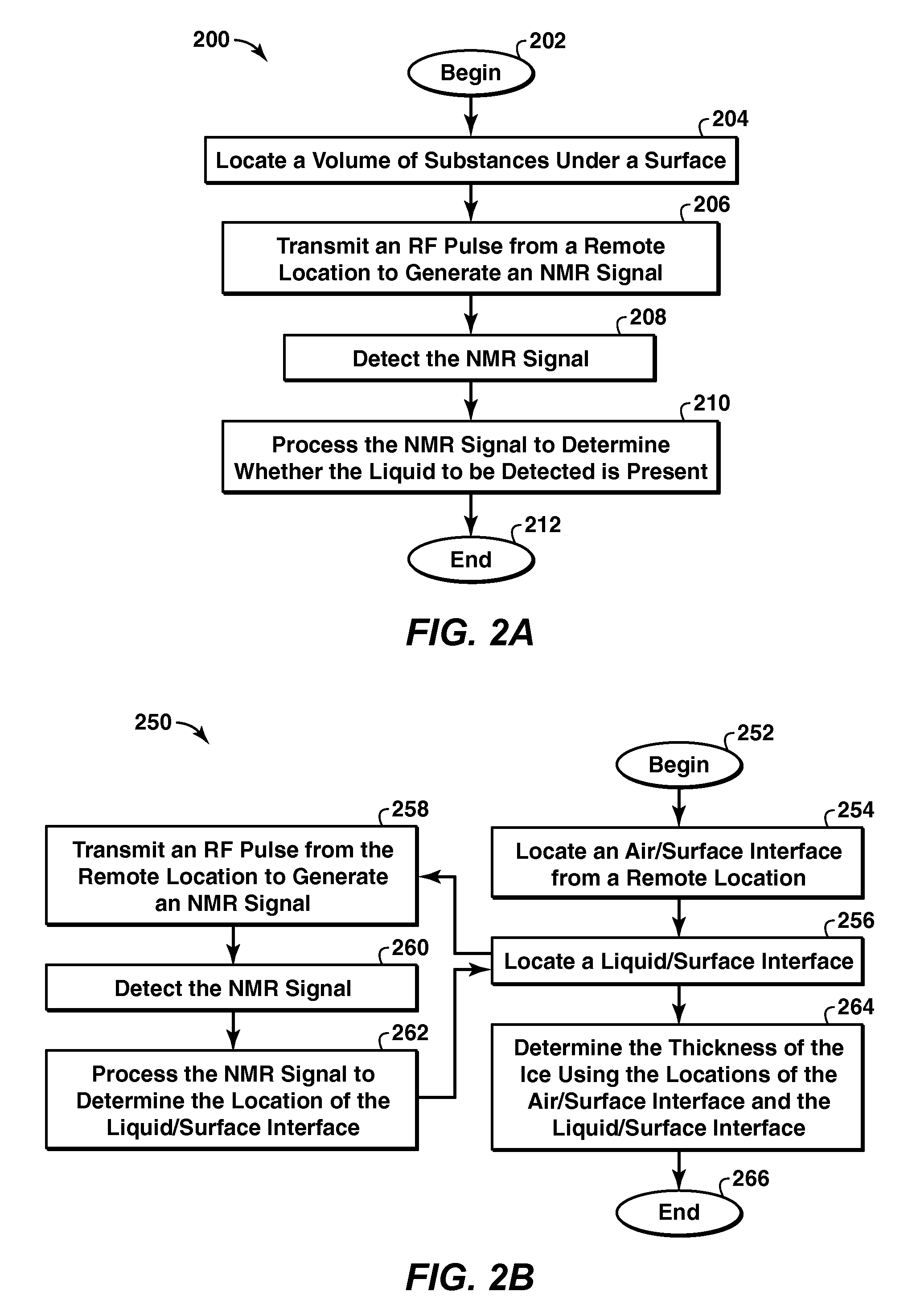
Method and apparatus for detection of a liquid under a surface
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com