Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Phytoplasma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phytoplasmas are obligate bacterial parasites of plant phloem tissue and of the insect vectors that are involved in their plant-to-plant transmission. Phytoplasmas were discovered in 1967 by Japanese scientists who termed them mycoplasma-like organisms. Since their discovery, phytoplasmas have resisted all attempts at in vitro culture in any cell-free medium; routine cultivation in an artificial medium thus remains a major challenge. Although phytoplasmas have recently been reported to be grown in a specific artificial medium, experimental repetition has yet to be reported. Phytoplasmas are characterized by the lack of a cell wall, a pleiomorphic or filamentous shape, a diameter normally less than 1 μm, and a very small genome.
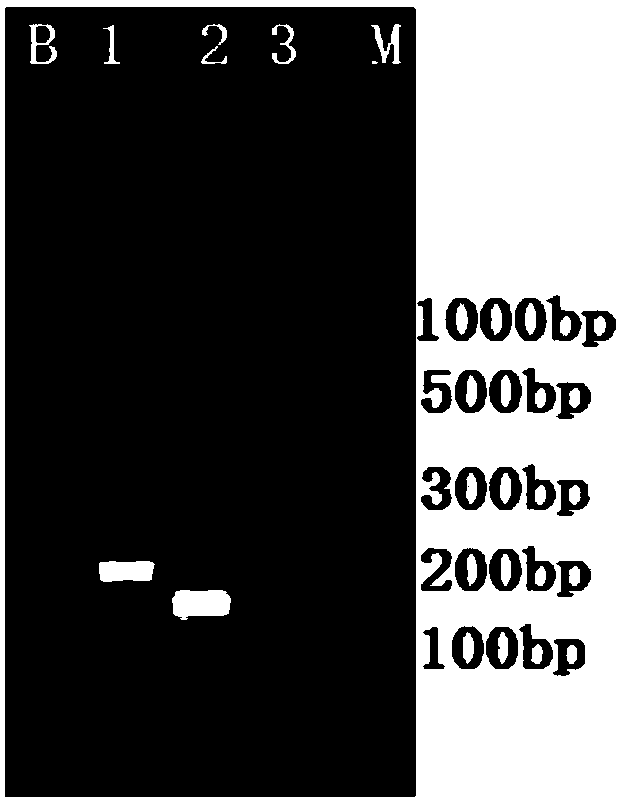
LAMP primer group for detecting phytoplasma as well as kit of LAMP primer group and application of kit
InactiveCN106399490ASimple and fast operationStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyPaulownia
The invention discloses an LAMP primer group for detecting phytoplasma as well as a kit of the LAMP primer group and an application of the kit. The LAMP primer group, which is strong in specificity and is constituted by nucleotide sequences shown as SEQ ID No.2, SEQ ID No.3, SEQ ID No.4 and SEQ ID No.5, is finally obtained by designing six groups of primers for six regions of the conserved sequence of a 16S gene of 16SrI group phytoplasma and designing two groups of primers for six regions of the conserved sequence of a tuf gene of the 16SrI group phytoplasma. The invention further discloses the kit of paulownia witch phytoplasma, Chinaberry witch phytoplasma, mulberry dwarf phytoplasma, lettuce yellow phytoplasma and catharanthus roseus green phytoplasma prepared by virtue of the primer group and the invention also establishes a detection method; the detection method has the advantages of being good in stability, strong in specificity, high in sensitivity and the like; and the method is applicable to the detection of the paulownia witch phytoplasma, the Chinaberry witch phytoplasma, the mulberry dwarf phytoplasma, the lettuce yellow phytoplasma and the catharanthus roseus green phytoplasma.
Owner:INST OF FOREST ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT & PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Phytoplasma probe, gene chip and method for detecting phytoplasma
InactiveCN101805783AStrong specificityQuick checkNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNAGene
The invention relates to a phytoplasma probe, and comprises a gene chip of the probe and a method for detecting phytoplasma with the gene chip. The phytoplasma probe is a specific probe for 11 types of phytoplasma, which is point sampled and manufactured into the gene chip, and the method for detecting the phytoplasma comprises the following steps that: a plant DNA sample is extracted; a sample specific fragment is amplified through a universal primer and a product is marked; hybridization; the sample to be detected and to be marked is added into hybrid buffer fluid, and mixed uniformly into hybrid mixture; the mixture is dripped into a hybrid area of the gene chip, and put into a hybrid box for hybridization; and the hybridized chip is taken out and dried, scanning and data analysis are carried out, and whether phytoplasma exists in the sample is judged. The gene chip manufactured from the probe of the invention can quickly detect 11 types of phytoplasma with high efficiency and highflux.
Owner:SHENZHEN POLYTECHNIC
LAMP primer set for detecting jujube witches disease, locust tree witches broom disease and cherry leaching yellowing phytoplasma
PendingCN106167831AEliminate instrument inputStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseTest sample
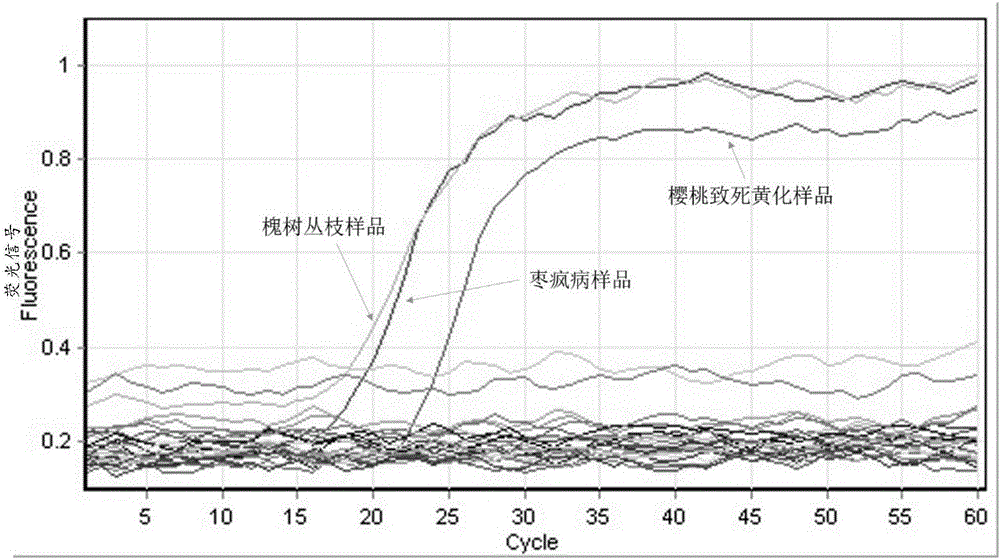
The present invention discloses a LAMP primer set for detecting jujube witches disease, locust tree witches broom disease and cherry lethal yellowing phytoplasma, and its detection kit and application. The LAMP primer set is designed for detecting jujube witches disease, locust tree wilt disease and cherry lethal yellowing phytoplasma for 16SrV-B group phytoplasma tuf gene conservative sequence. The invention also discloses a LAMP detection kit for jujube witches disease, locus tree witches broom disease and cherry lethal yellowing phytoplasma. The LAMP primer set is used to establish the LAMP detection method for jujube witches disease, locust tree witches broom disease and cherry lethal yellow phytoplasma, and carries out ring-mediated isothermal amplification on the sample DNA to be tested, and determines whether the tested sample is infected with phytoplasma according to the amplification result samples. The detection method established in the invention can be used for detection of jujube witches disease, locust tree witches broom and cherry lethal yellow phytoplasma, and can better distinguish phytoplasma between different groups and inside groups, and has the advantages of good stability, specificity and high sensitivity.
Owner:INST OF FOREST ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT & PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Method for detecting areca-nut yellow leaf disease phytoplasma pathogen and special reagent kit therefor
ActiveCN101475995AEliminates the chance of false positive contaminationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceFluorescence
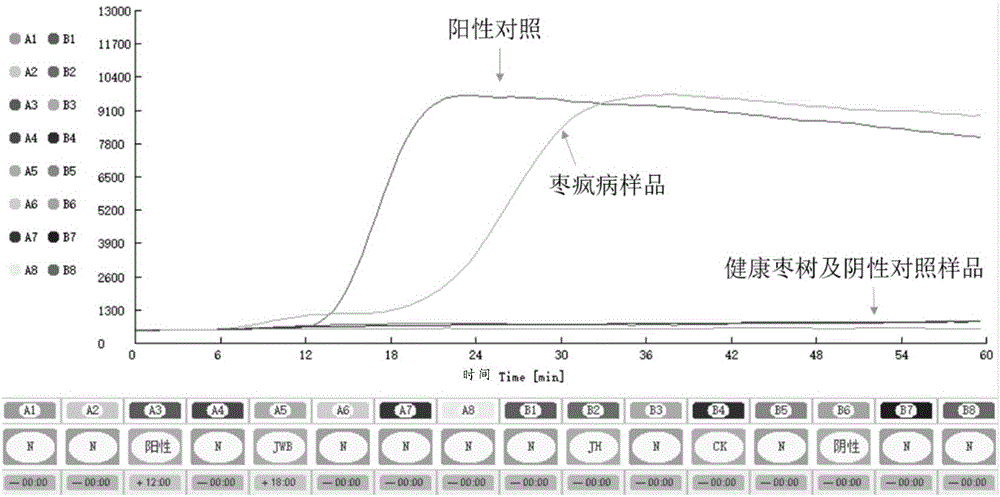
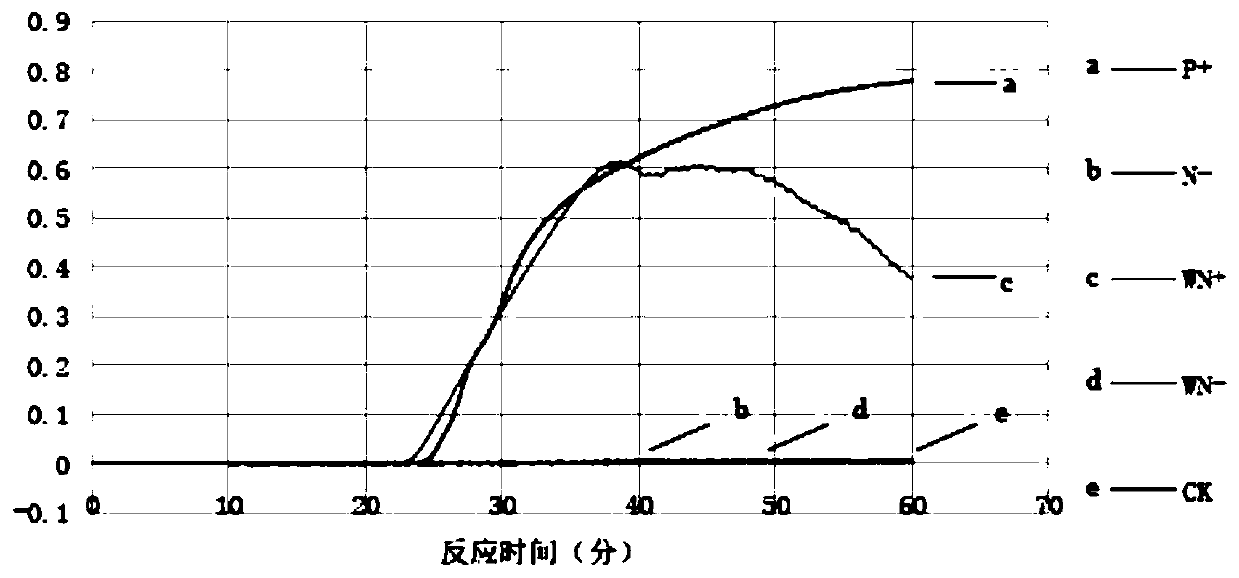
The present invention discloses a method for detecting betelnut yellow phytoplasma pathogen and its special kit. The kit includes a probe whose nucleotide sequence is the sequence 1 of the sequence table, and a primer pair composed of an DNA fragment whose nucleotide sequence is the sequence 2 of the sequence table and an DNA fragment whose nucleotide sequence is the sequence 3 of the sequence table. The method includes: extracting the DNA of the betelnut to be tested as a template, using the above kit to perform real-time fluorescence PCR, if the fluorescence signal is enhanced in the PCR process, the plant infects phytoplasma. Proved by experiment, the sensitivity of the inventive method detecting the betelnut phytoplasma infection is same with that of the traditional nested PCR electrophoresis detection, while the invention has simple operation and closed tube operation, processes automation control in the entire testing, eliminates the PCR false-positive contamination opportunities, does not need post-PCR handling, is suitable for bulk samples, and has simple, rapid, and accurate features.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
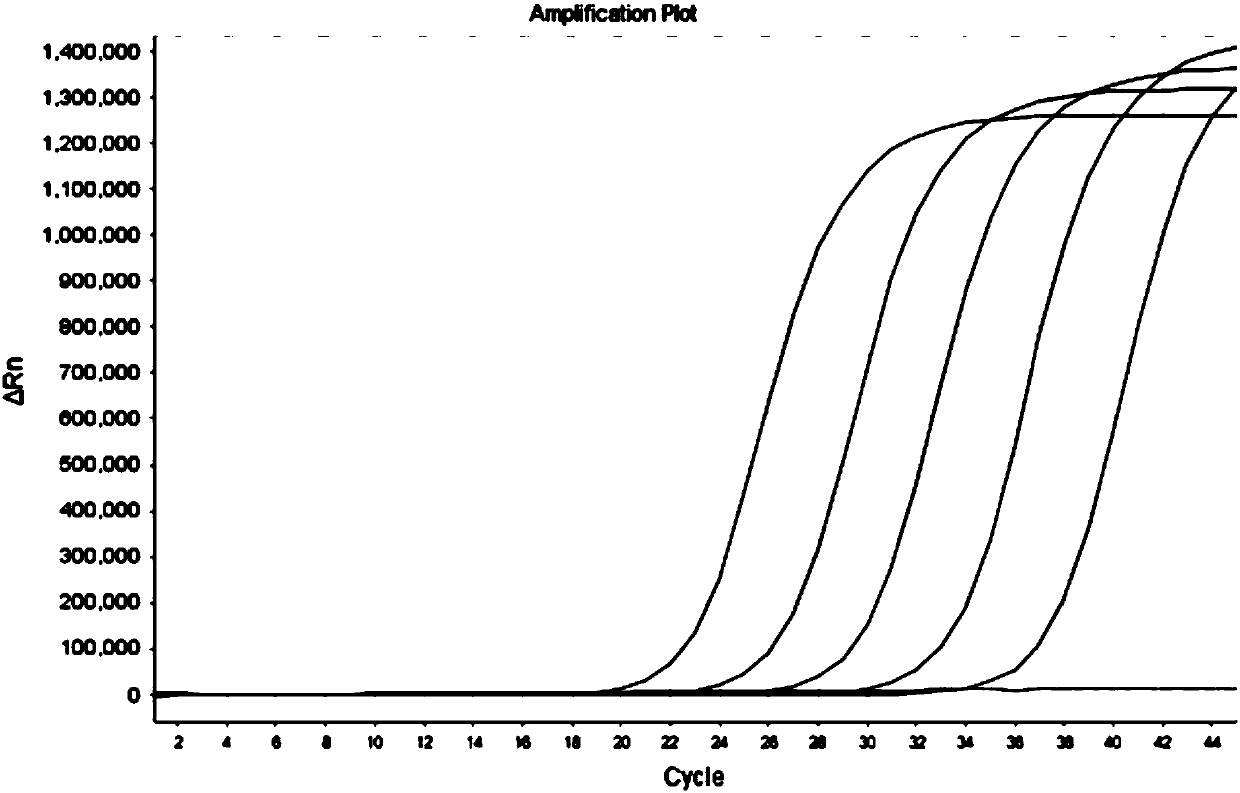
Primer, probe and method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting witches' broom phytoplasma
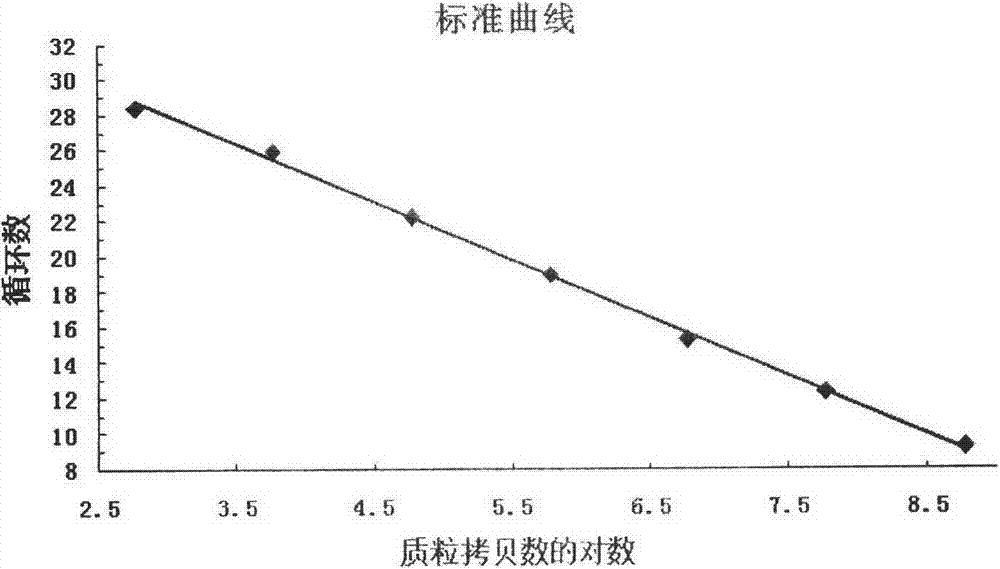
InactiveCN103525923AHigh sensitivityAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPhytoplasmaStandard curve
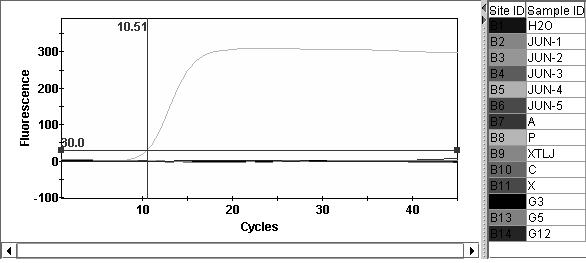
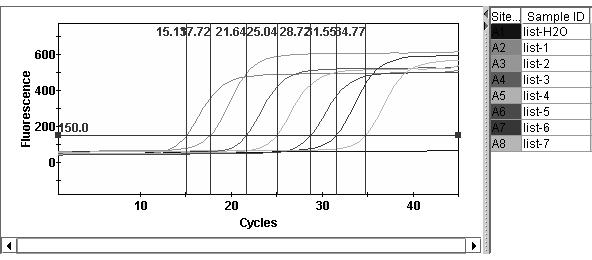
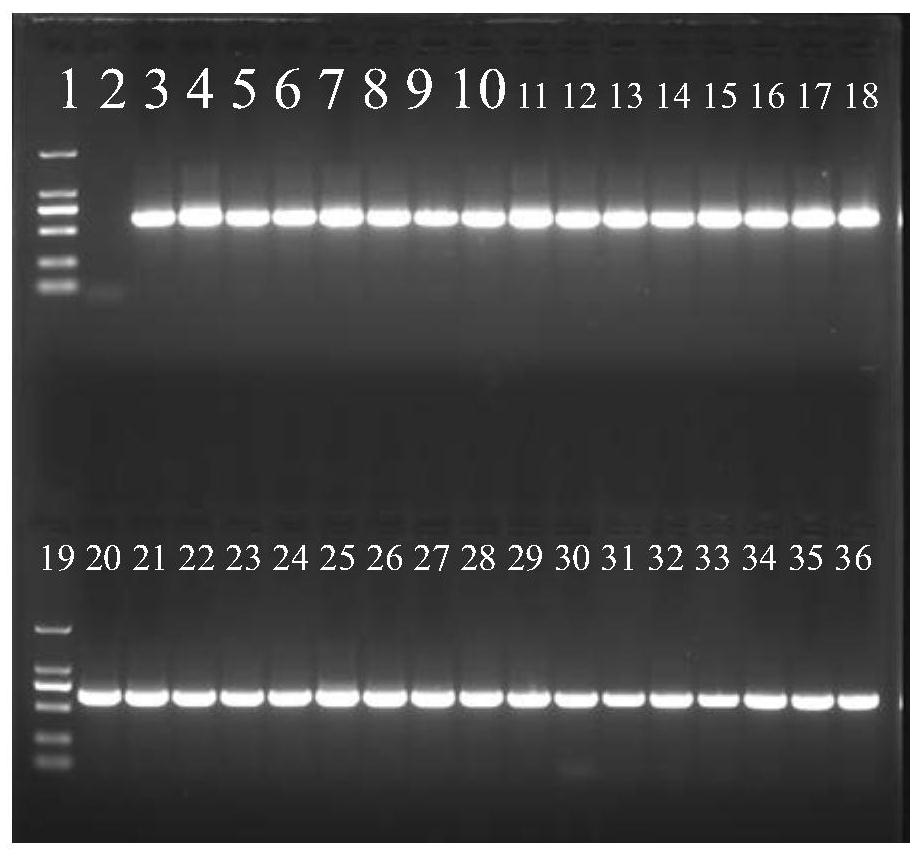
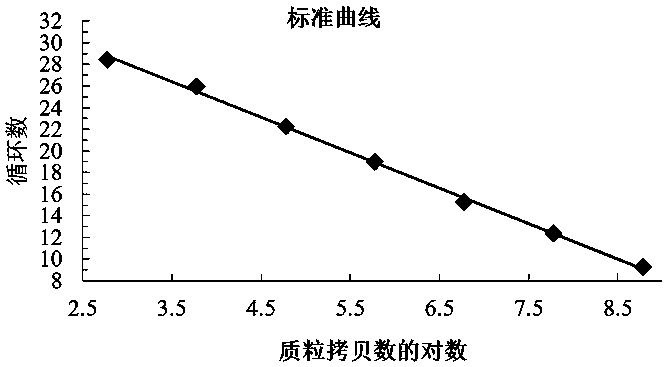
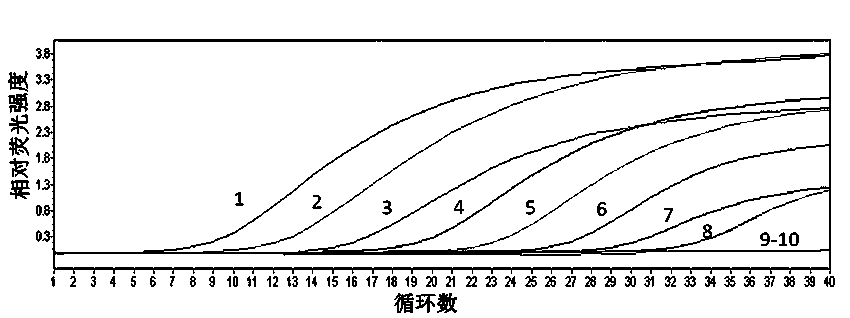
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant quarantine, and relates to a primer, a probe and a method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting witches' broom phytoplasmas. The method comprises the following steps: according to difference between 16S rDNA gene sequences of the witches' broom phytoplasmas and other phytoplasmas, designing a primer pair JWB Primer-F: 5'-TGGTGAGGTAAAGGCTTA-3' / JWB Primer-R: 5'-CTCCCGTAGGAGTTT GG-3' and a TapMan probe JWB-Probe: 5'-FAM-AATGTGGCTGTTCAACCTCTCA-TAMRA-3' for specifically detecting the witches' broom phytoplasmas; measuring a Ct value by an established real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method of the witches' broom phytoplasmas; according to a positive decision criteria of a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection result, qualitatively detecting the witches' broom phytoplasmas; calculating the copy concentration of a 16S rDNA gene segment of the witches' broom phytoplasmas in a sample y a fluorescent quantitative PCR standard curve equation established in advance; and obtaining the number of the witches' broom phytoplasmas in the sample so as to achieve quantitative detection. The primer, the probe and the method have the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity, good repeatability, high throughput and the like, and can be widely used in plant quarantine, plant protection, scientific research and other fields.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Method for enriching jujube witches' broom phytoplasma by using catharanthus roseus
InactiveCN110946050AProlong survival timeEfficient transfection spreadFlowers cultivationBacteriaRootstockPlantlet
The invention discloses a method for enriching jujube witches' broom phytoplasma by using catharanthus roseus. The method uses catharanthus roseus as a rootstock, and a jujube witches' broom branch asa scion for grafting, then a grafted plant is moved into an artificial climate control room for cultivation, first dark culture is performed for 1 d under conditions of 23 DEG C and 85% relative humidity, and then culture is performed until the onset of illness under conditions of 16 h photoperiod, 23 DEG C and 65% relative humidity. The method relatively well achieves the enrichment of jujube witches' broom phytoplasma, so that problems such as low content of phytoplasma in an original host, separation difficulty and cumbersome operation in the existing jujube witches' broom phytoplasma separation research are relatively well solved, and thereby the foundation for the in-depth research of jujube witches' broom phytoplasma, and how to prevent and treat jujube witches' broom is laid.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for purifying mulberry phytoplasma genome
InactiveCN105734055AHigh puritySolve the problem of low phytoplasma content and difficult purification by pulse electrophoresisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDNA methylationWoody plant
The invention discloses a method for purifying mulberry phytoplasma genome. By using the characteristic that a phytoplasma has a cell membrane and the genome of the phytoplasma is semi-autonomously copied, and adopting a DNA methylation conjugated protein, the mulberry genome is removed from purified mulberry whole genomes infected by phytoplasma, and semi-quantitative and quantitative PCRs (polymerase chain reactions) prove that the obtained DNA is relatively high in purity and is a mulberry phytoplasma genome DNA relatively high in concentration, so that the problems of low phytoplasma content and difficult pulse electrophoresis purification of woody plants are solved, the effect of the method disclosed by the invention is tested by using quantitative PCR, and the obtained phytoplasma genome is relatively high in concentration and proportion and can be used for PCR experiments and high-throughput sequencing.
Owner:ANKANG UNIV
Method utilizing sprout inhibition agent to control phytoplasma jujube withes broom disease and phytoplasma paulownia withes broom disease of plants
Disclosed is a method utilizing sprout inhibitor to control the phytoplasma jujube withes broom disease and the phytoplasma paulownia withes broom disease of plants. The method includes: selecting the sprout inhibitor in a plant inhibitor or adding one or more organic acids which can induce the plants to develop a resistance to the sprout inhibitor to prepare an agent and injecting the agent into the plants. When the total weight of the sprout inhibitor and the organic acid is counted as 100, in the prepared agent, the weight percentage of the sprout inhibitor is 0-100% but not equal to 0 and the weight percentage of the organic acid is 0-100% but not equal to 100%. The method utilizing sprout inhibitor to control the phytoplasma jujube withes broom disease and the phytoplasma paulownia withes broom disease of the plants expands the application range of the sprout inhibitor in the plant growth inhibitor, provides a new control method for controlling plant phytoplasma diseases, is obvious in effects in the controlling of the jujube withes broom disease and the paulownia withes broom disease, and can be used for controlling other phytoplasma diseases. The method utilizing sprout inhibitor to control the phytoplasma jujube withes broom disease and the phytoplasma paulownia withes broom disease of plants is wide in agent source, low in price, simple in preparation, convenient to use, harmless to people and livestock and capable of being widely used and popularized.
Owner:周学尚
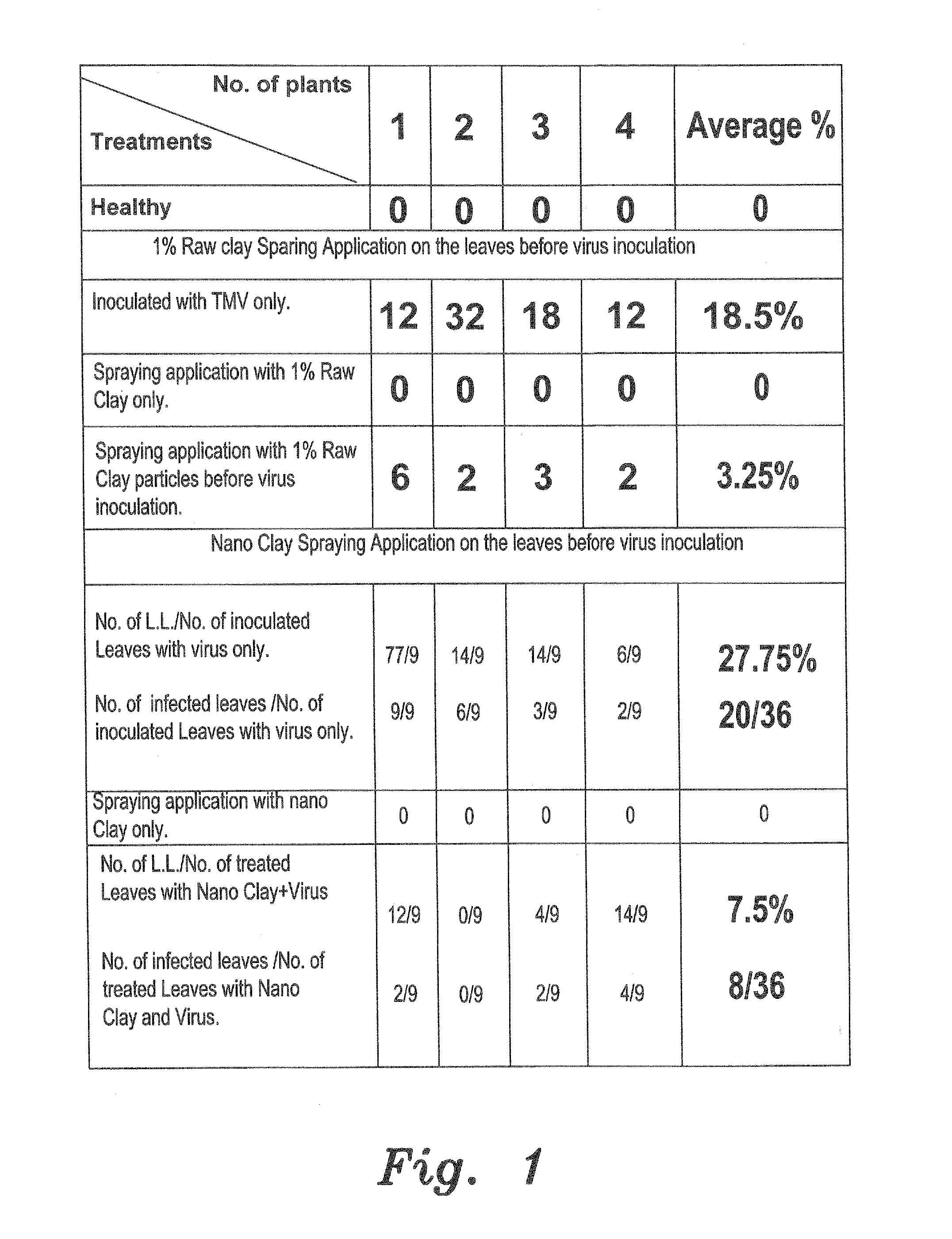
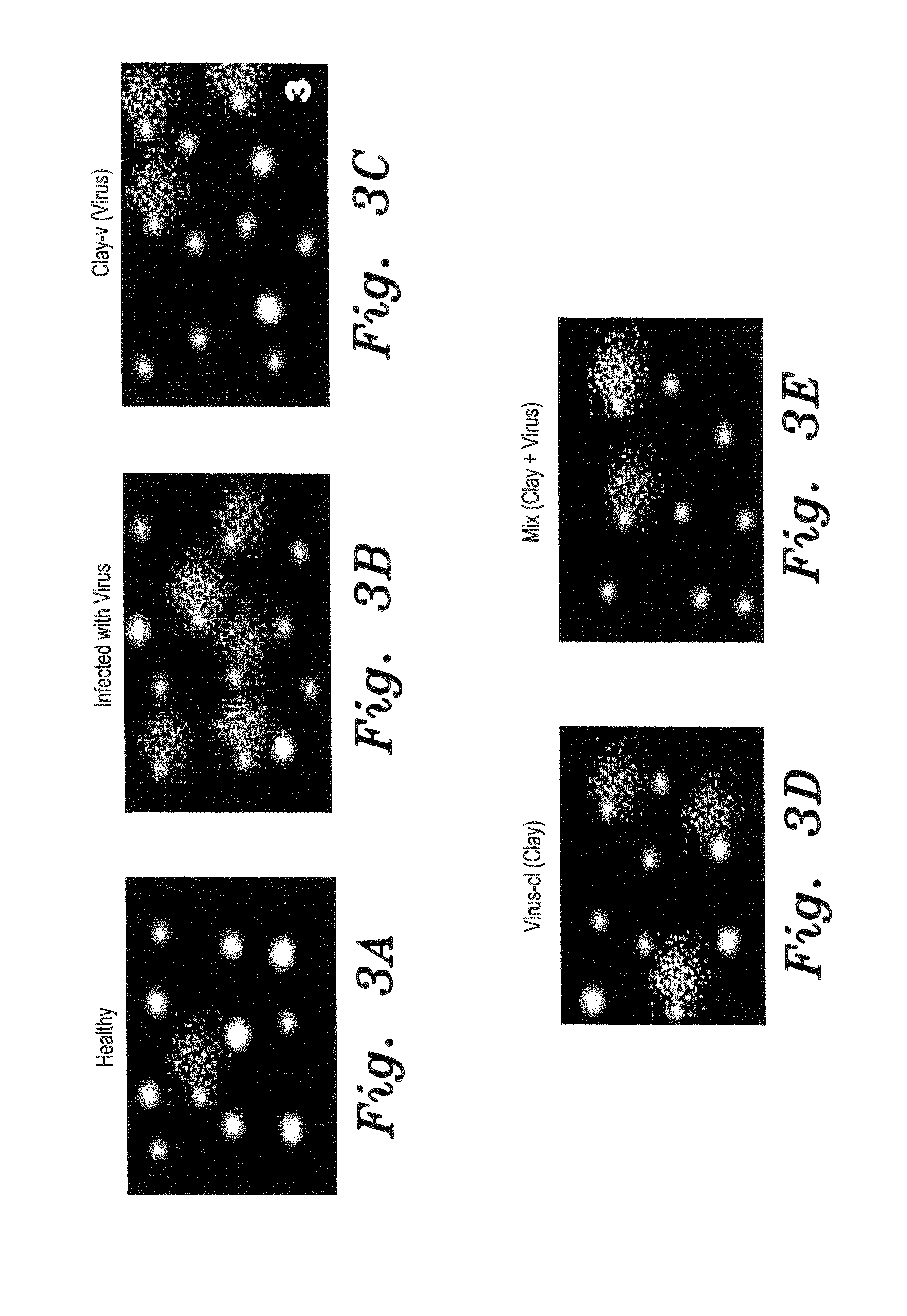
Method of using a clay suspension to prevent viral and phytoplasma diseases in plants
InactiveUS20160360755A1Easy to usePrevent viral and phytoplasma diseaseBiocideAnimal repellantsDiseaseShoot
The method of using a clay suspension to prevent viral and phytoplasma diseases in plants includes administering a clay suspension to the plant, such as through spraying the plant's leaves or soaking the plant's nursery shoots with the clay suspension. The clay suspension is applied to the plant to prevent the viral or phytoplasma disease prior to planting the plant in its nursery shoot stage. The clay suspension is preferably formed from natural clay suspended in water (1% w / v). The clay may be in either its natural form, or may be in the form of clay nanoparticles suspended in water. For a suspension formed from clay nanoparticles, the clay nanoparticles may be separated by sedimentation in distilled water.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
Chip for screening 16SrI group phytoplasmas and application thereof
InactiveCN102492773AImprove compatibilityLess quantityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementQuarantineMicrobiology
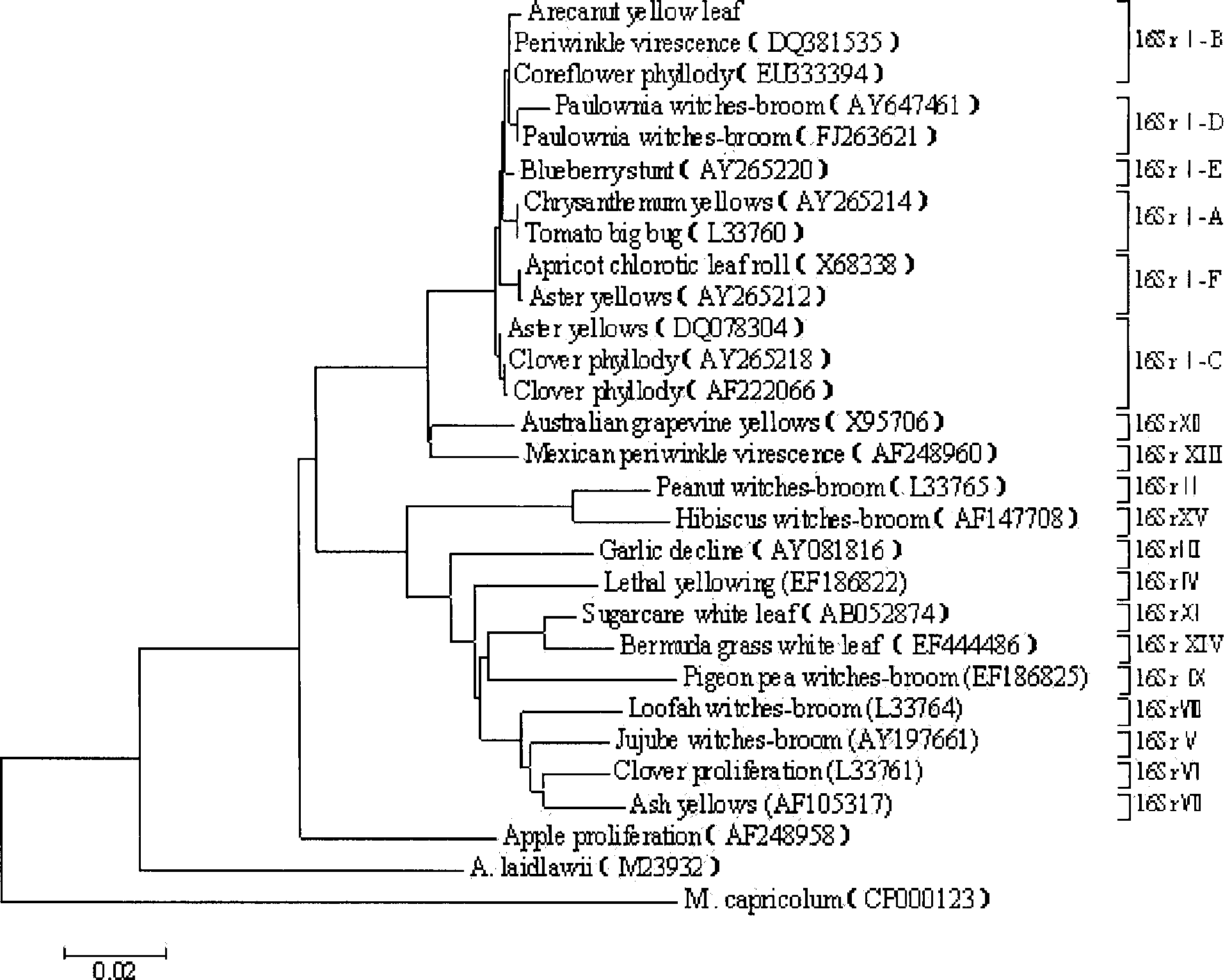
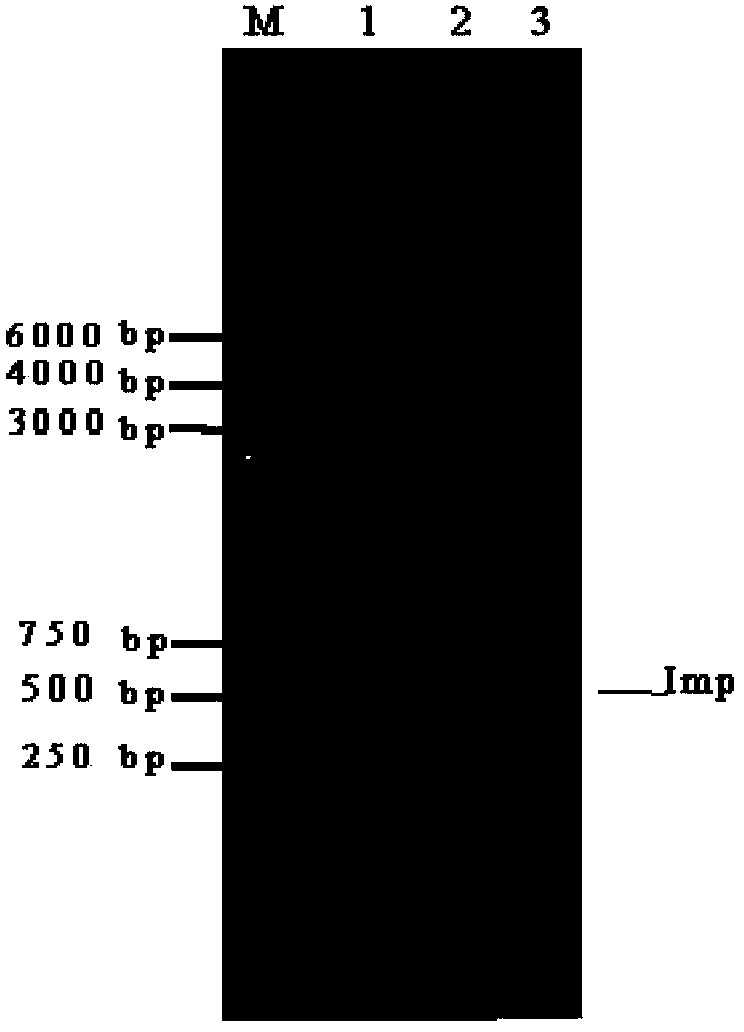
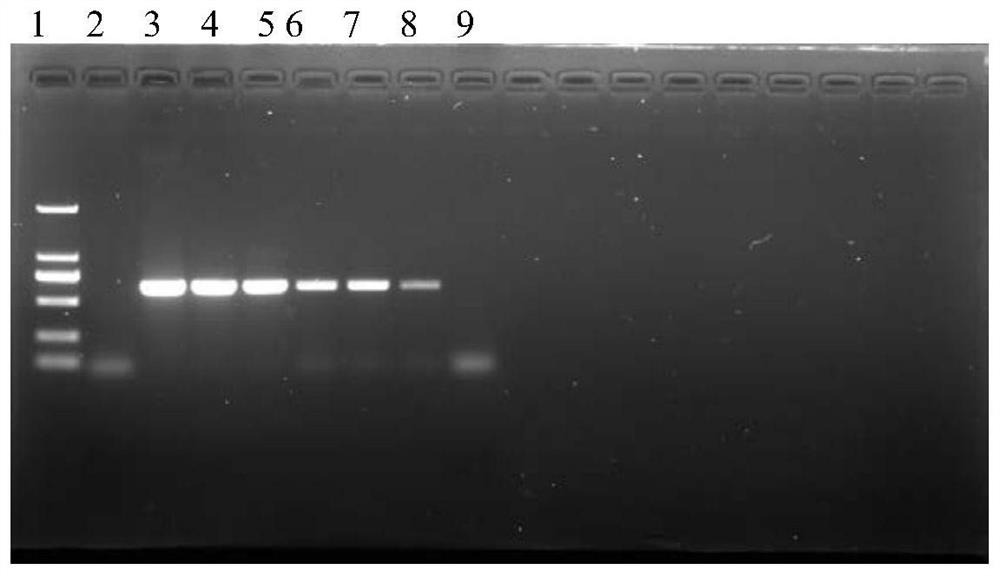
The invention discloses a chip for screening 16SrI group phytoplasmas and application thereof. The nucleotide sequences of five probes for screening 16SrI group phytoplasmas are sequence 1 to sequence 5 in order in a sequence table. The invention also provides a gene chip for screening 16SrI group phytoplasmas, and the probes are fixed on the surface of the chip, so that the gene chip is formed. An experiment proves that the invention adopts a bioinformatic method to analyze the 16S rDNA, 16S-23S rDNA spacer, imp and tuf nucleotide sequences of 16SrI group phytoplasmas and designs the compatible probe for the group, and a standard phytoplasma sample test result proves that the effect of the probe is good. The chip for screening 16SrI group phytoplasmas can be used in the quarantine and identification of 16SrI group phytoplasmas.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Primer, probe and method for real-time fluorescence polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection of pear decline phytoplasma
InactiveCN101948913AAccurate detectionMeet the needs of daily testing workMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiochemistryDiagnosis laboratory
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant quarantine and relates to a primer and a probe for a real-time fluorescence polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection of pear decline phytoplasma. The primer and the probe for the real-time fluorescence PCR detection of the pear decline phytoplasma contain a specific cycling probe and a pair of primers: (1) probe LSTProbe: 5'-(FAM) ATTCTGACTGTA (Eclipse)-3'; and (2) primer LSTPrimer-F:5'-ACTCTGACCGAGCAACGCC-3'; LSTPrimer-R:5'-GATAACGCTTGCCCCCTATG-3', wherein a ribonucleic acid (RNA) alkali base exists in a square frame. Through sequence comparison of a large number of phytoplasmas and bacteria ITS, a set of real-time fluorescence PCR cycling probe and primer is designed, wherein the sensitivity is up to 0.5pgl-1; and the pear decline phytoplasma can be rapidly and correctly detected from a sample. The method has the advantages of simple operation, easy grasping and wide application to daily detection work of laboratories.
Owner:王有福 +3
Primer, probe and method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting witches' broom phytoplasma
InactiveCN103525923BAccurate detectionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRepeatabilityBiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant quarantine, and relates to a primer, a probe and a method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting witches' broom phytoplasmas. The method comprises the following steps: according to difference between 16S rDNA gene sequences of the witches' broom phytoplasmas and other phytoplasmas, designing a primer pair JWB Primer-F: 5'-TGGTGAGGTAAAGGCTTA-3' / JWB Primer-R: 5'-CTCCCGTAGGAGTTT GG-3' and a TapMan probe JWB-Probe: 5'-FAM-AATGTGGCTGTTCAACCTCTCA-TAMRA-3' for specifically detecting the witches' broom phytoplasmas; measuring a Ct value by an established real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method of the witches' broom phytoplasmas; according to a positive decision criteria of a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection result, qualitatively detecting the witches' broom phytoplasmas; calculating the copy concentration of a 16S rDNA gene segment of the witches' broom phytoplasmas in a sample y a fluorescent quantitative PCR standard curve equation established in advance; and obtaining the number of the witches' broom phytoplasmas in the sample so as to achieve quantitative detection. The primer, the probe and the method have the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity, good repeatability, high throughput and the like, and can be widely used in plant quarantine, plant protection, scientific research and other fields.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
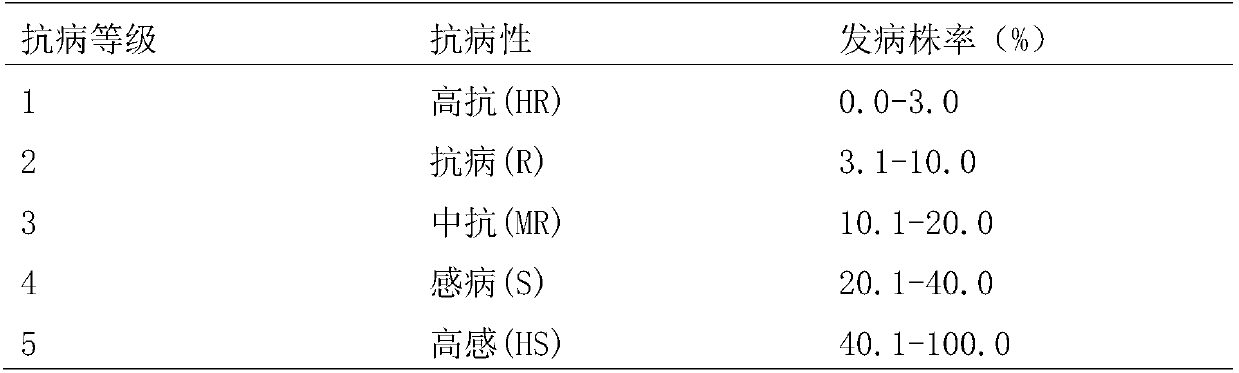
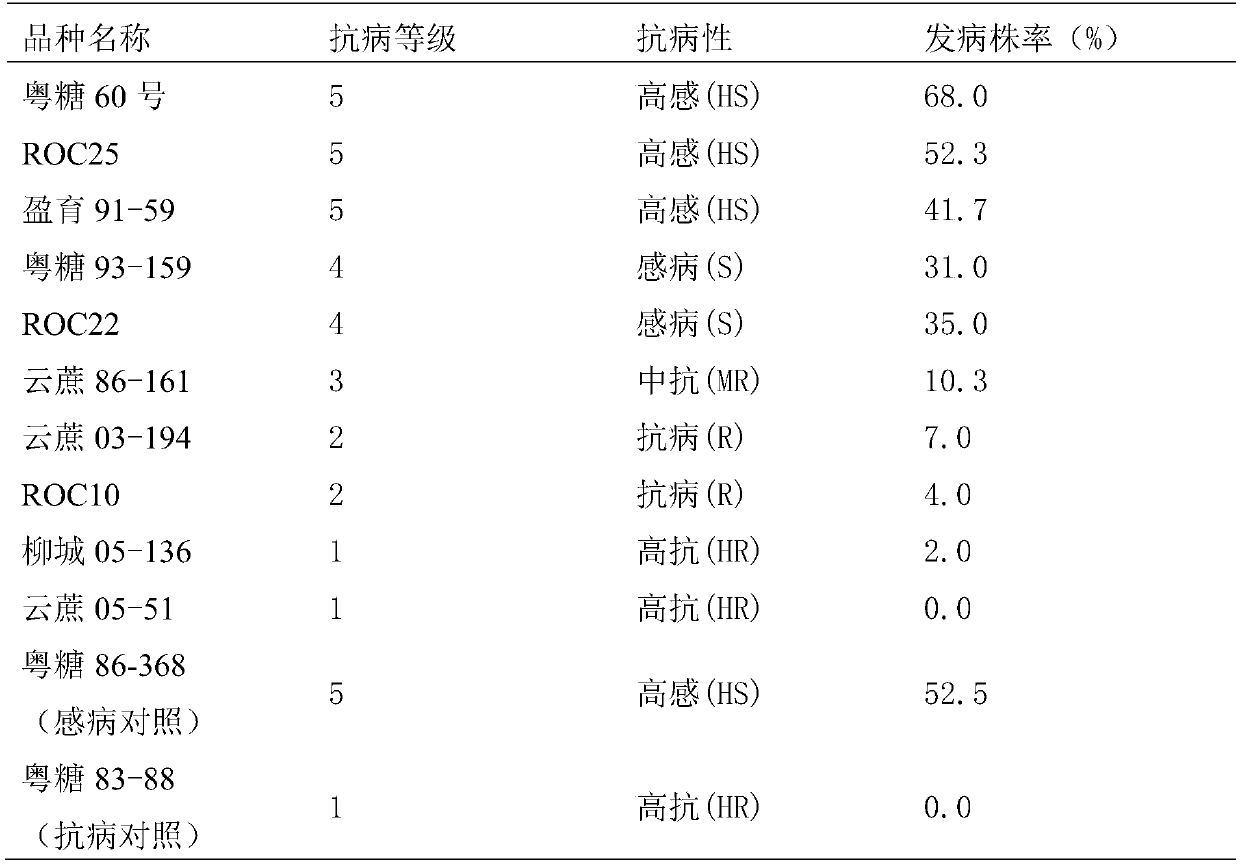
Method for accurately identifying disease resistance of newly-planted sugarcane white leaf
ActiveCN109609588AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseOperability
The invention provides a method for accurately identifying disease resistance of newly-planted sugarcane white leaf. The method comprises: cutting sugarcane stalks infected with sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma, performing juicing, adding 10 times amount of sterile water to prepare an inoculating liquid; cutting the sugarcane stalks which are a sugarcane material to be tested into stalk sections with buds, soaking the sections in running tap water for 48h, performing hot water treatment at 50 DEG C for 2h, and performing soaking with an insecticidal and sterilizing agent for 10min; performingcoating inoculation with a plastic film, and performing moisture preservation at 25 DEG C for 24h; planting an inoculating material in a plastic barrel, and placing the barrel in a 20-30 DEG C insecticidal greenhouse for culture; and investigating infected plant rate, and performing disease resistance evaluation according to 1-5 grade standards. The method of the invention firstly establishes a set of accurate and efficient method for identifying disease resistance of newly-planted sugarcane white leaf, and provides technical support for sugarcane white leaf resistance breeding. The pathogen inoculating liquid is sprayed onto the sugarcane seed and the coating inoculation with a plastic film is performed, so that a disease habitat condition is provided, and the result is objective, true and reliable. The inoculation is quick and simple, the operability is strong, and the work efficiency is high. After the inoculation, the sugarcane white leaf has obvious incidence, high sensitivity andgood reproducibility.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST OF YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for sequencing plant phytoplasma genome
ActiveCN109207617AVerify reliabilityFull disclosureMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNATranscriptome Sequencing
The invention discloses a method for sequencing plant phytoplasma genome, which comprises the following steps: obtaining Paulownia tomentosa tissue culture seedling stem rich in phytoplasma; Isolationand Extraction of Genomic DNA Mixture from Paulownia Alba and Phytoplasma; DNA Sequencing of Paulownia Alba and Phytoplasma Gene Mixture; Phytoplasma genome sequencing data processing, statistics andassembly and Paulownia tomentosa and phytoplasma transcriptome sequencing to verify the reliability of the genome. The invention obtains the genome of Paulownia arbuscular phytoplasma for the first time, and analyzes the information of interaction between Paulownia arbuscular pathogen and host through the genome. The invention is helpful to increase the information of basic metabolic pathway of phytoplasma, and lays a foundation for revealing the genome information of plant phytoplasma comprehensively.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
LAMP primer group and kit for detecting 16SrI-group phytoplasma leading to betel nut yellow leaf diseases in China, and application thereof
InactiveCN111088391AImprove featuresImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBetel nuts
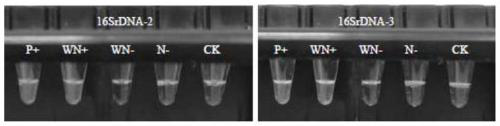
The invention discloses a LAMP primer group and kit for detecting 16SrI-group phytoplasma leading to betel nut yellow leaf diseases in China, and application thereof. The LAMP primer group is a primergroup 16SrDNA-2 or a primer group 16SrDNA-3. The LAMP primer group disclosed by the invention has very good specificity and stability, high detection sensitivity and the lowest detection limit of 200ag / [mu] L. Phytoplasma are detected in betel nut yellow leaf disease samples from Baoting, Tunchang, Wanning and the like in Hainan Province in China by using the two sets of LAMP primers, i.e., 16SrDNA-2 and 16SrDNA-3; and no phytoplasma is detected in negative control. The LAMP primer group and kit provided by the invention are rapid and efficient in detection, simple and convenient to operateand visual in result, play a great role in methods for early detection and field diagnosis of the betel nut yellow leaf diseases, bacteria-carrying detection of betel nut seedlings, breeding of resistant betel nut varieties and the like, and provide technical support and reference basis for pathogen detection, disease prevalence, scientific prevention and control and the like of the betel nut yellow leaf diseases.
Owner:COCONUT RES INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Cow phytoplasma substrate
ActiveCN106399207ALong storage timeReduce dosageAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPenicillinSolvent
The invention discloses a cow phytoplasma substrate and preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of veterinary biology. The cow phytoplasma substrate constitutes a basic substrate and an assistant substrate, wherein, the substrate is constituted from PPLO broth, sodium pyruvate, glucose, fresh yeast extract, L-glutamine, L-cysteine, water solvent milk protein, horse serum, penicillin, phenol red, and deionized water. The substrate can reduce the use level of serum, and increase evidently the active bacterium titer of cow phytoplasma, thus establishing a foundation for studying quality cow phytoplasma vaccine.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Real-time fluorescent quantitative LAMP primer group for detecting purple leaf curl disease phytoplasma of sisal hemp and application thereof
ActiveCN112210614AStrong specificityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyFluorescence
The invention discloses a real-time fluorescent quantitative LAMP primer group for detecting purple leaf curl disease phytoplasma of sisal hemp and application thereof. The LAMP primer group for the purple leaf curl disease phytoplasma consists of nucleotide shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table, nucleotide shown as a sequence 2 in the sequence table, nucleotide shown as a sequence 3 in the sequence table and nucleotide shown as a sequence 4 in the sequence table. An LAMP molecular detection method has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, easiness in operation and reliable result.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
PCR-RFLP identification method for different subgroups of sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma
ActiveCN109652503AEasy to identifyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA EndonucleaseB subgroup
The invention relates to a PCR-RFLP identification method for different subgroups of sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma. A sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma tuf gene is taken as an objectto design a specific primer, a tuf gene fragment is obtained through PCR amplification, then restriction endonuclease Msp I is adopted for digesting the tuf gene fragment obtained through amplification, and the different subgroups of the sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma are distinguished through a differentiated RFLP restriction map. The PCR-RFLP identification method for the different subgroups of the sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma has the advantages that a sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma 16SrXI-B subgroup and a sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma 16SrXI-D subgroup can be quickly, accurately and efficiently identified without sequencing, and is important for the pathogen identification and prevention of sugarcane white leaf diseases.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST OF YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Nucleic acid, kit and method for simultaneous detection of yellow phytoplasma, canker pathogenic bacteria and leaf spot pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN107586863AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseasePathogenic bacteria
The invention relates to a nucleic acid, kit and method for simultaneous detection of three pathogens, namely yellow phytoplasma, canker pathogenic bacteria and leaf spot pathogenic bacteria. The nucleic acid for simultaneous detection of the three pathogens by multiplex PCR comprises upstream and downstream primers of the three pathogens, namely yellow phytoplasma, canker pathogenic bacteria andleaf spot pathogenic bacteria. The nucleic acid for simultaneous detection of the three pathogens by fluorescent quantitative PCR further comprises probes corresponding to the pathogens respectively.The efficient and sensitive method for simultaneous detection of the three pathogens, namely yellow phytoplasma, canker pathogenic bacteria and leaf spot pathogenic bacteria is also established. The method can effectively improve detection sensitivity and avoid the occurrence of false negative results, and provides a technical method for effectively preventing the yellow disease, canker and the leaf spot disease.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method for detecting transmission medium of Sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma
ActiveCN111183812AClear mediaPossess and satisfy the infection pathogenesisMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySugar cane
The invention relates to a method for detecting a transmission medium of Sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma. The method includes the steps that a piece of field in a sugarcane white leaf occurrence areaand with crop rotation for more than 1 year is selected; susceptible varieties are used for screening out phytoplasma infected with white leaf disease and phytoplasma not infected with the white leafdisease to be sugarcane species carried with virus and sugarcane species not carried with virus; the piece of field is divided into three field ditches, one of the field ditches is equipped with a transmission medium measurement field device in which the sugarcane species not carried with virus are planted, the sugarcane species carried with virus and the sugarcane species not carried with virusare planted in the other two field ditches separately, and morbidity situation is investigated; after newly planted sugarcane detection is completed, and biennial roots are cut and harvested; and according to the disease condition of the sugarcane species carried with virus, the sugarcane species not carried with virus, and newly planted and biennial root sugarcane inside and outside the device, asystematic analyzes to determine the transmission medium of Sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma. According to the method, a set of simple, convenient and systematic effective methods for determination of the transmission medium of Sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma is firstly established, theoretical guidance and scientific basis are provided for the effective prevention and control of Sugarcane whiteleaf, and the measurement results are objective, true and reliable.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST OF YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
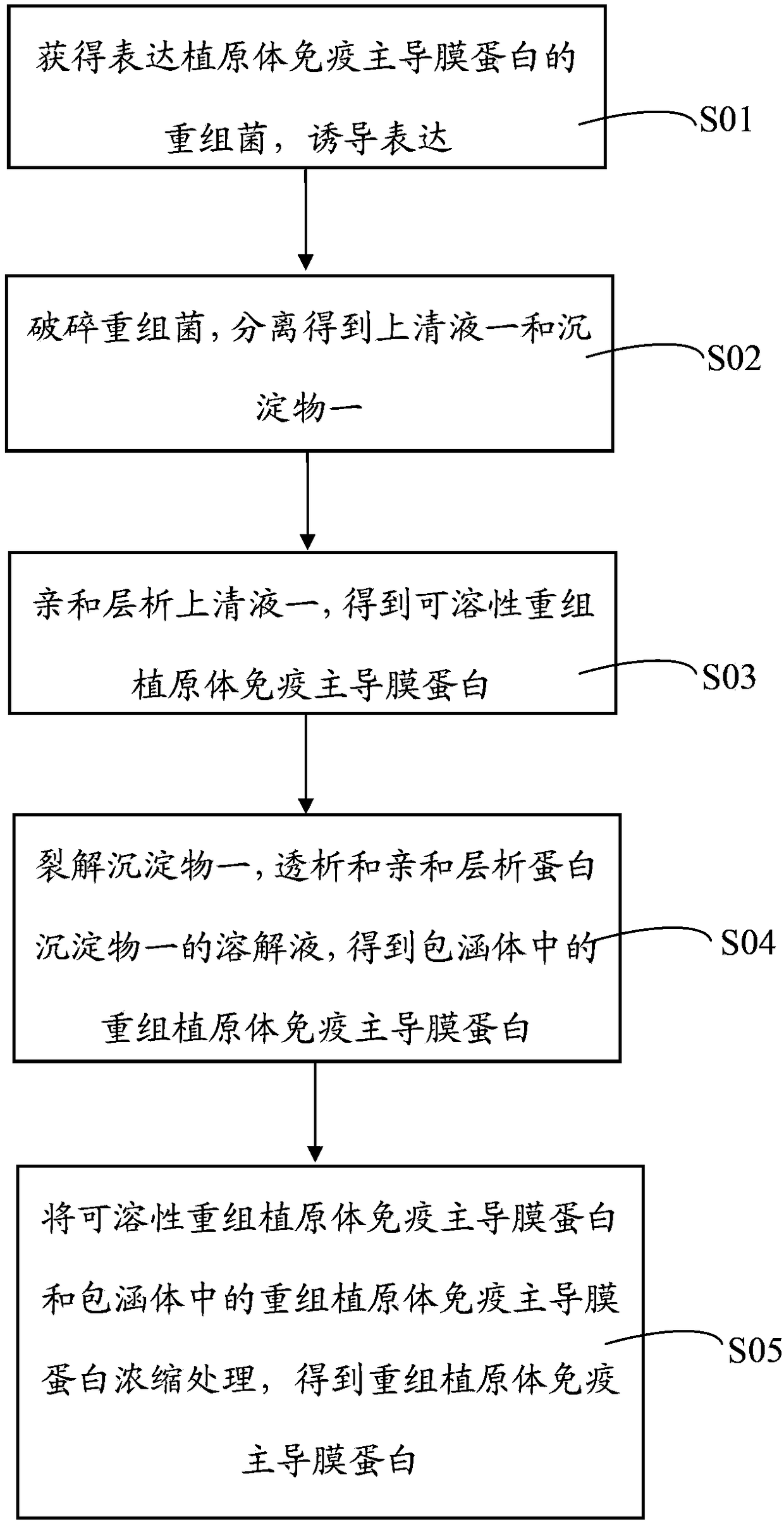
Purification method of immunodominant membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma and application thereof
InactiveCN104232710AImprove the purification effectHigh outputMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsPurification methodsInclusion bodies
The invention provides a purification method of an immunodominant membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma and an application thereof. According to the purification method of the immune leading membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma provided by the invention, the soluble immunodominant membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma expressed by recombinant bacteria is purified by using affinity chromatography, particularly an inclusion body is split, insoluble immunodominant membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma in the inclusion body is purified by a dialysis method and affinity chromatography, and the purification conditions and process parameters are optimized, so that the purification effect of the immunodominant membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma is greatly improved. The purification degree can reach 95% while the purification degree in the conventional method is 60%. The method is simple in process, easy to operate and high in yield, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:深圳市兰科植物保护研究中心
Use of hydroxyapatite as a carrier of bioactive substances for treating vascular diseases in plants
InactiveUS20180139958A1Degree of crystallinity of will decreaseImprove solubilityBiocideAnimal repellantsDiseaseXanthomonas axonopodis
The subject matter of the invention is a hydroxyapatite carrier, corresponding to the formula: Ca(10-x)Mx(PO4)(6-y)(CO3)y(OH)2 in which: M is chosen from Cu, Mg, Zn, Pb, Cd, Ba, K, Mn, Mo, Fe, Ag, B, Se or a combination of at least two of such elements; —x is comprised between 0 and 2, preferably between 0 and 1, more preferably between 0 and 0.8, even more preferably between 0.02 and 0.05; —y is comprised between 0 and 2, preferably between 0 and 1, more preferably between 0.002 and 0.030, The hydroxyapatite is a carrier of a bioactive substance chosen among a metal ion selected from Cu, Zn, S, Mn, Mg, K, Fe, B, Mo, Se and / or an extract of vegetal origin. The bioactive substances are active in the treatment of vascular diseases of plants, in particular: grapevine yellows (caused by grapevine phytoplasma), bacterial canker in kiwifruit (caused by Pseudomonas syringae), olive quick decline syndrome (caused by Xylella fastidiosa) and Citrus bacterial canker disease (caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis).
Owner:NDG NATURAL DEVEMENT GRP SRL
Nested PCR primer group, kit and detection method for specifically detecting sisal hemp purple leaf curl phytoplasma
ActiveCN112176080AShorten the timeIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention discloses a nested PCR primer group, a kit and a detection method for specifically detecting sisal hemp purple leaf curl phytoplasma. The nested PCR primer group consists of nucleotide shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table, nucleotide shown in a sequence 2 in the sequence table, nucleotide shown in a sequence 3 in the sequence table and nucleotide shown in a sequence 4 in the sequence table. The detection method is a nested molecular detection method for the sisal hemp purple leaf curl phytoplasma, which is high in specificity, high in sensitivity, easy to operate and reliable in result.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
PCR detection method of sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma
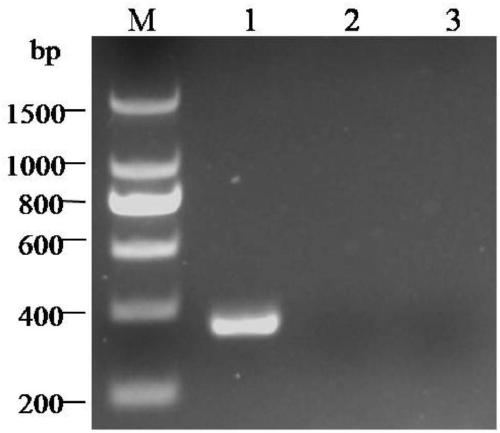
InactiveCN109371172AStrong specificityClear bandMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesElectrophoresisSequence determination
The invention discloses a PCR detection method of sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma. The PCR detection method of sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma is established by designing a specificprimer SecA-F / SecA-R according to the SecA gene sequence of the sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma and optimizing the reaction system and program. By adopting the specific primer and method disclosed by the invention, PCR amplification is needed only once, whether the detected sample is infected by the sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma can be determined according to whether the electrophoresis result has a specific band, and the amplification product does not need sequencing determination; therefore, the detection specificity and accuracy are improved, the detection time is saved,and the detection cost is lowered.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST OF YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
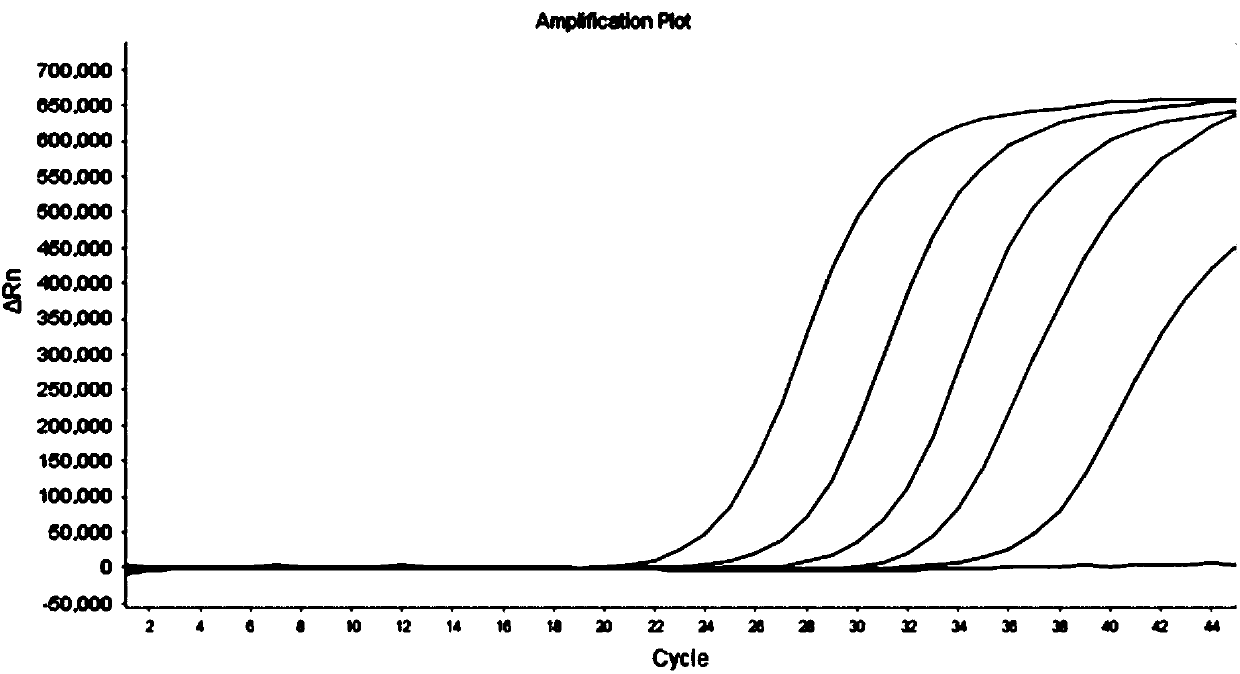
Qualitative and quantitative detection method for Xinjiang isolates of apricot chlorotic leaf roll (ACLR) phytoplasma
ActiveCN110894536AHigh sensitivityAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologySpecific detection
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant quarantine, and relates to a qualitative and quantitative detection method for Xinjiang isolates of apricot chlorotic leaf roll (ACLR) phytoplasma. According to the qualitative and quantitative detection method, according to the difference of the ACLR phytoplasma and other phytoplasma in sequence of a 16S rDNA gene, a primer pair ACLR-F1 / ACLR-R1 and a probe ACLR-Probe which are used for specific detection of the ACLR phytoplasma are designed, a cycle threshold (Ct) is determined through an established real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection method for the ACLR phytoplasma, and qualitative detection of the ACLR phytoplasma can be realized according to the positive judgment standard of a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection result; then, the segment copy concentration of the 16S rDNA genes of the ACLR phytoplasma in detected samples is worked out by a pre-established fluorescent quantitative PCR standard curve equation, and thus, the number of the ACLR phytoplasma in the samples is obtained, and thereby, quantitative detection is realized. The qualitative and quantitative detectionmethod has the advantages of high sensitivity, high specificity, high repeatability, high throughput, and the like, and can be widely applied to the fields of plant quarantine, plant protection, scientific research, and the like.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Free branching poinsettia
ActiveUS9193975B2Vector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsPoinsettiaGenetics
Free branching poinsettia plants are provided which comprise a heritable lateral branching trait. In certain aspects, poinsettia plants comprising a lateral branching trait are not pinched, are not grafted and / or are free of phytoplasma infection. Methods for growth and breeding such free branching poinsettias are also provided.
Owner:DUMMEN GRP BV
Purification method and application of recombinant phytoplasma immune dominant membrane protein
InactiveCN104232710BImprove the purification effectHigh outputMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsPurification methodsInclusion bodies
The invention provides a purification method of an immunodominant membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma and an application thereof. According to the purification method of the immune leading membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma provided by the invention, the soluble immunodominant membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma expressed by recombinant bacteria is purified by using affinity chromatography, particularly an inclusion body is split, insoluble immunodominant membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma in the inclusion body is purified by a dialysis method and affinity chromatography, and the purification conditions and process parameters are optimized, so that the purification effect of the immunodominant membrane protein of recombinant phytoplasma is greatly improved. The purification degree can reach 95% while the purification degree in the conventional method is 60%. The method is simple in process, easy to operate and high in yield, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:深圳市兰科植物保护研究中心
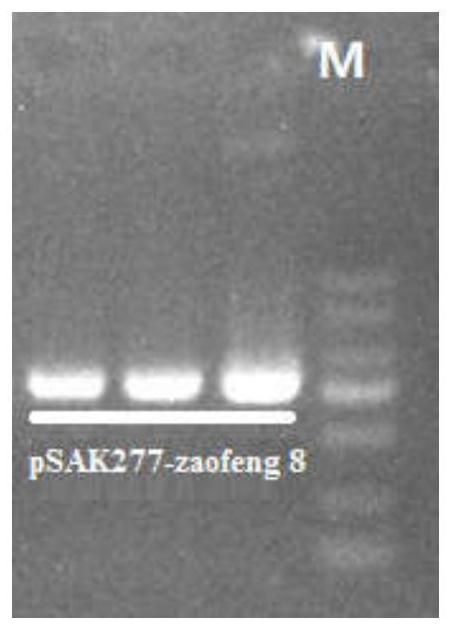
Jujube witches broom phytoplasma effector gene Zaofeng8 and application thereof
The invention discloses a jujube witches broom phytoplasma effector gene Zaofeng8 and application. The nucleotide sequence of the jujube witches broom phytoplasma effector gene Zaofeng8 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, the gene has the functions of dwarfing plants, enabling the plants to form arbuscular phenotypes and enabling the plants to generate leaflet symptoms, and the Zaofeng8 is obtained through PCR technology cloning. The gene is transferred into Columbia type arabidopsis thaliana for functional verification by using an agrobacterium-mediated method, so that the infection mechanism of phytoplasma to hosts in the occurrence process of the jujube witches broom symptom can be clarified from a molecular mechanism, and the gene has a positive guiding effect on further prevention and treatmentof the jujube witches broom.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
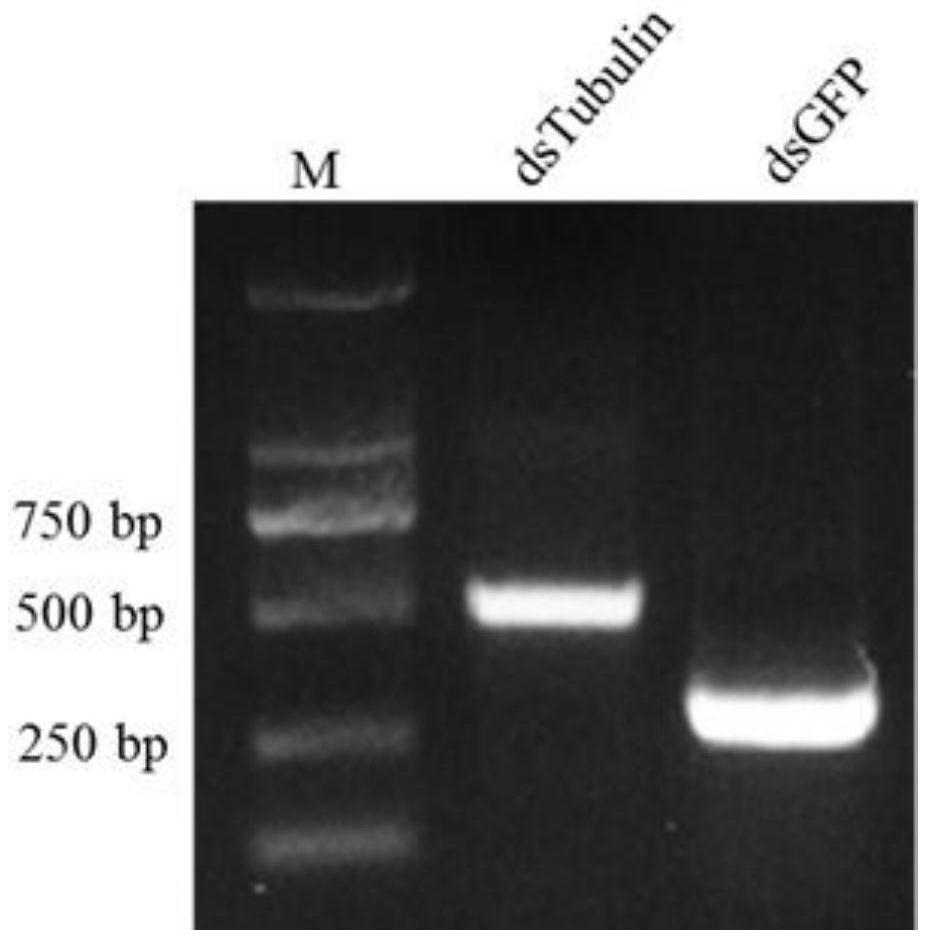
Method for establishing influence of interacting protein on phytoplasma propagation through RNAi (Ribonucleic Acid Interference)
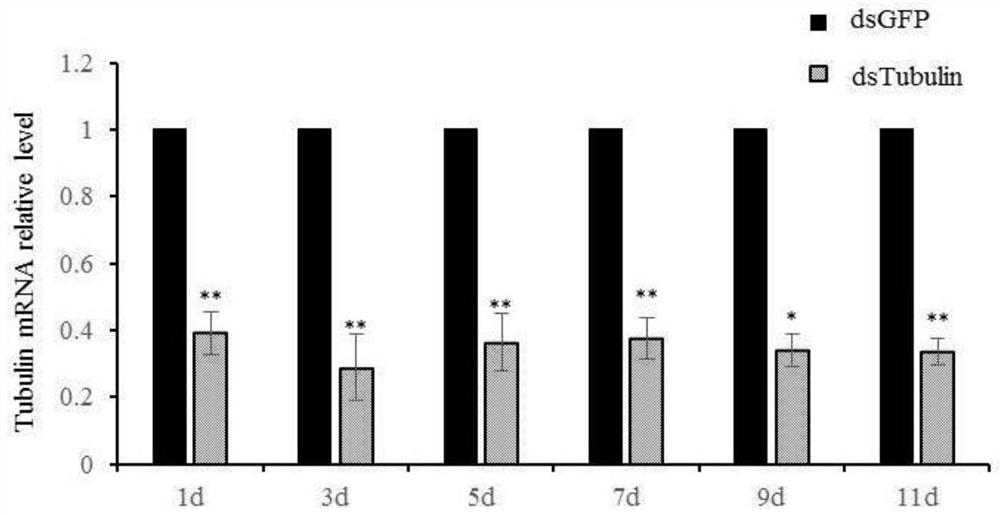
PendingCN114350764AReduce the efficiency of virus transmissionMicrobiological testing/measurementAccessory food factorsGeneticsMicrotubule Proteins
The invention discloses a method for establishing influence of interacting protein on phytoplasma propagation through RNAi (Ribonucleic Acid Interference). The phytoplasma is wheat blue dwarf phytoplasma, the mediator is heterosachalina fulica, and the interaction protein is heterosachalina fulica microtubulin; the method comprises the following steps: synthesizing interaction protein genes dsRNA and dsGFP, respectively feeding a mediator with the interaction protein genes dsRNA and dsGFP, detecting the gene expression of the wheat blue dwarf phytoplasma by using qRT-PCR, infecting healthy wheat with the contaminated mediator to determine the virus transmission efficiency, and determining the influence of the interaction protein on phytoplasma transmission. According to the invention, the propagation influence of the heterosacharide microtubulin on the wheat blue dwarf phytoplasma is proved, and a foundation is laid for subsequent research on interaction of the phytoplasma and a mediator.
Owner:黑龙江省农业科学院水稻研究所 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com