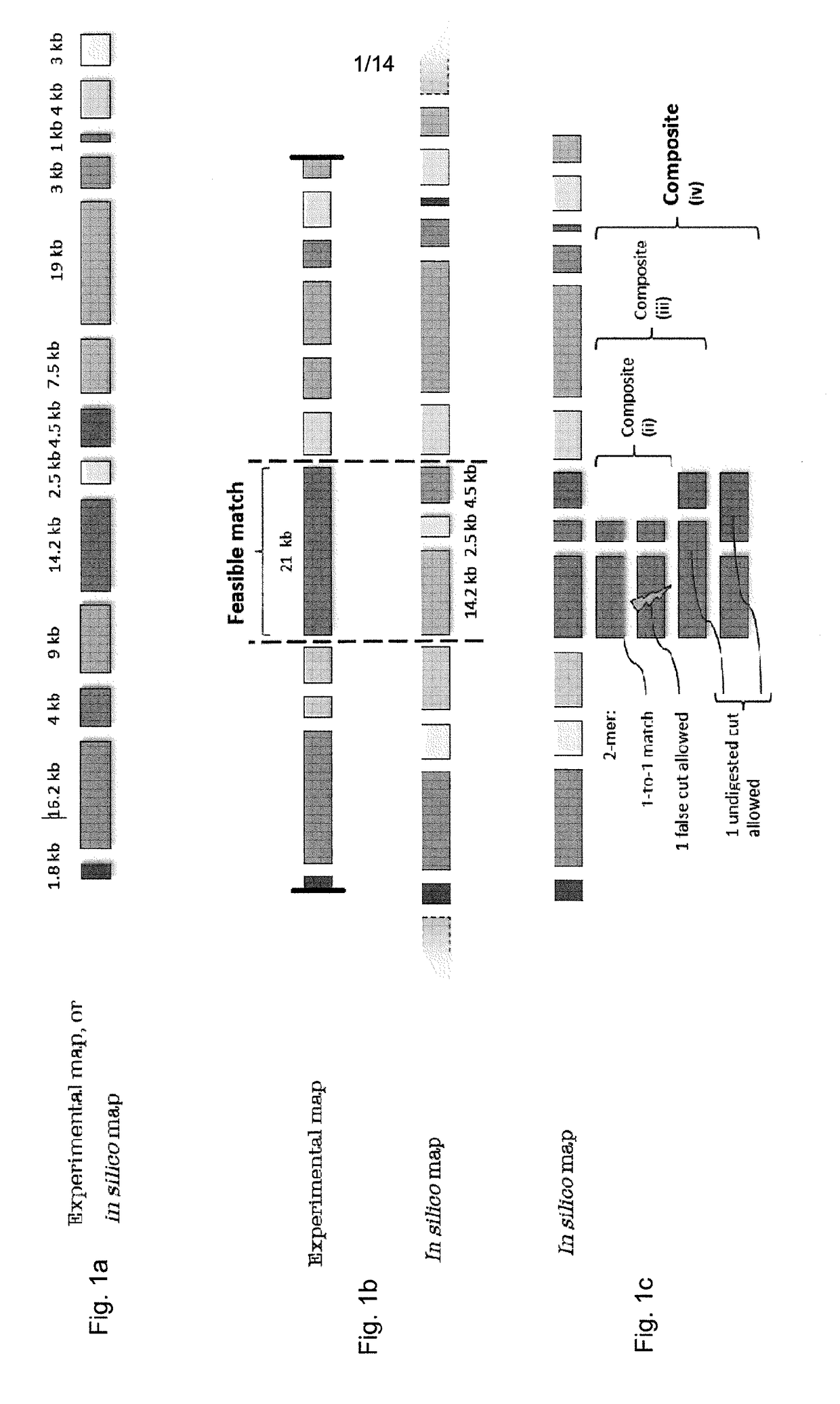
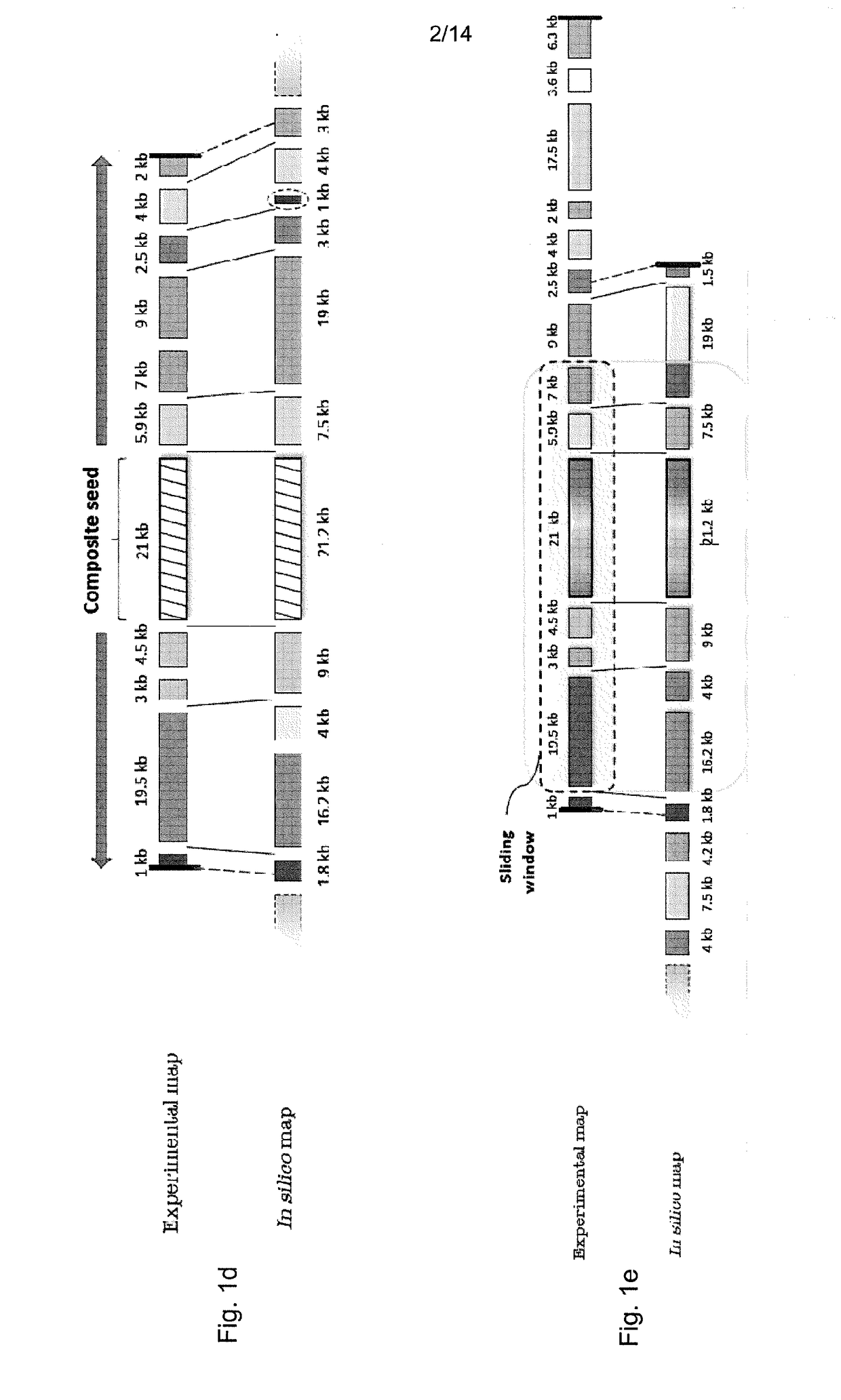
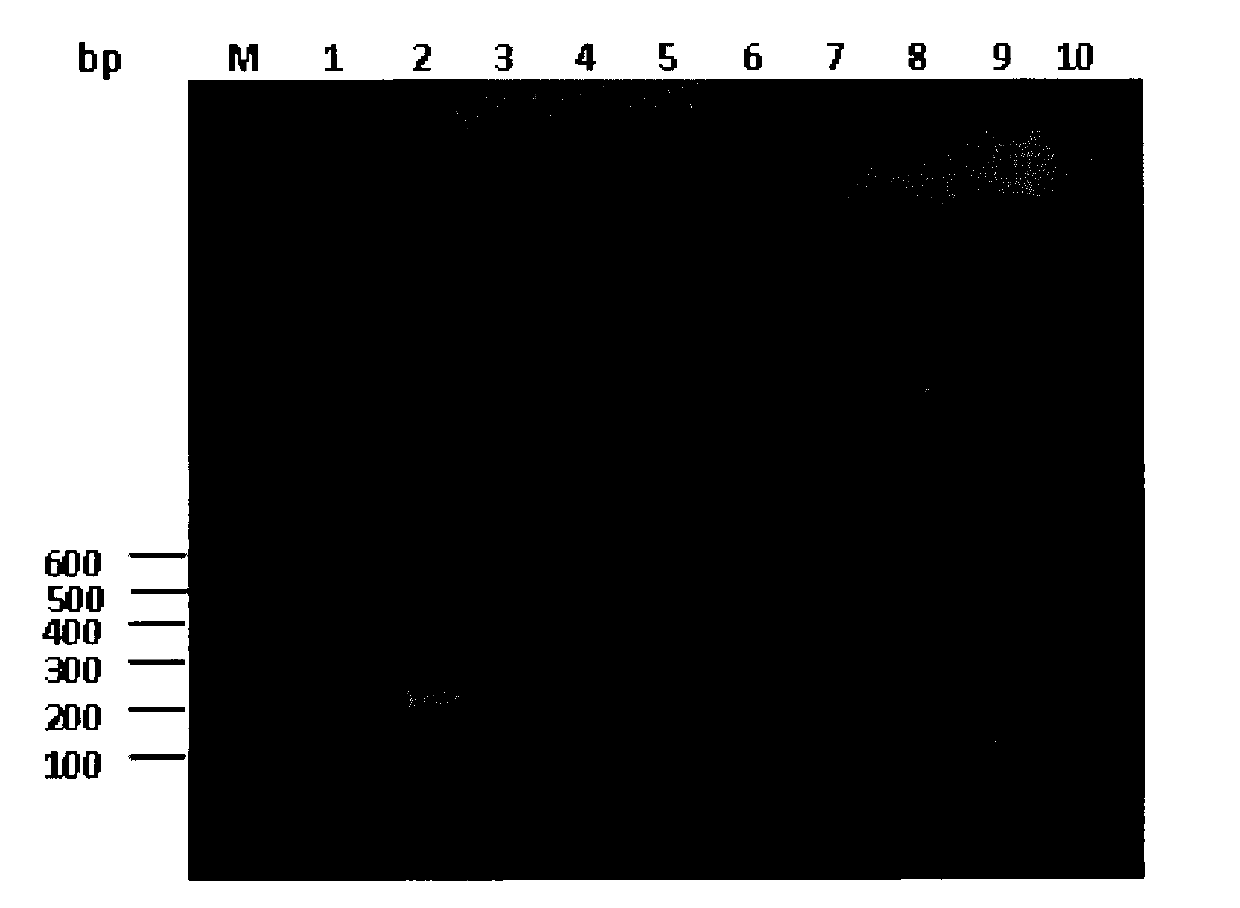
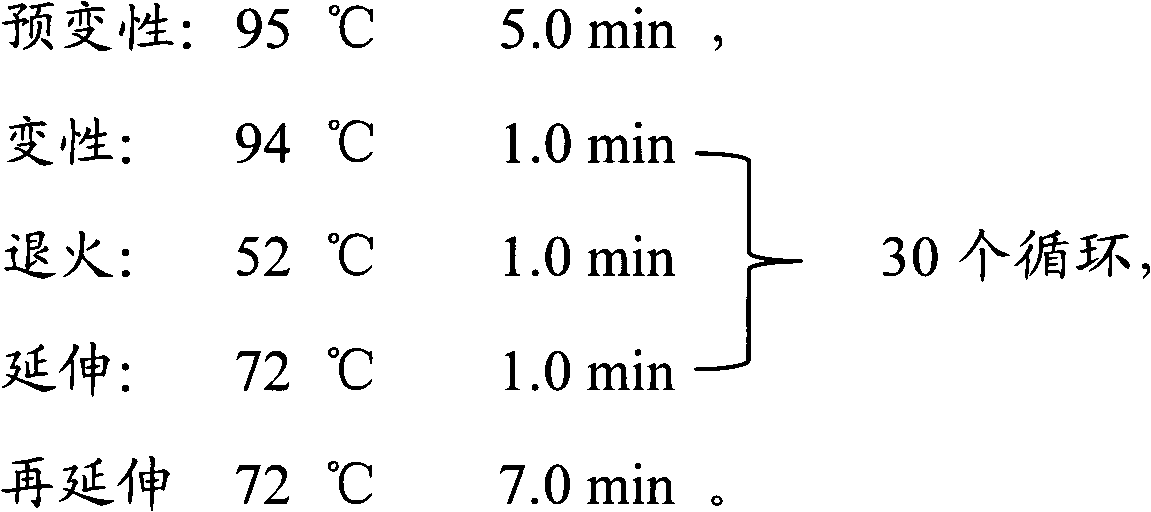
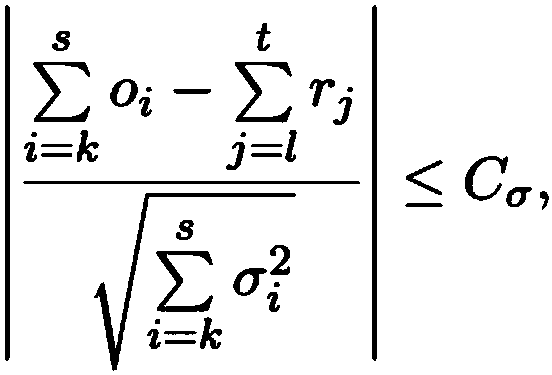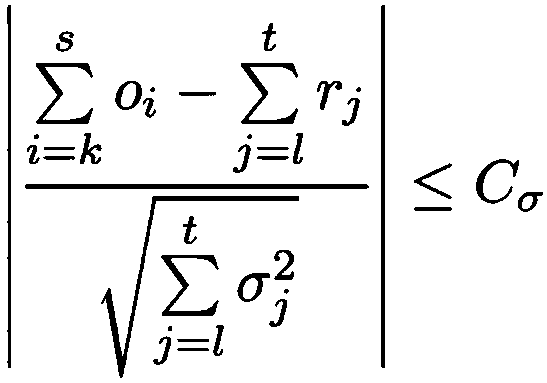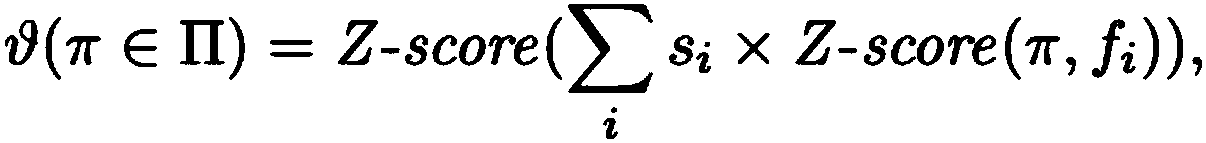Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Restriction map" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
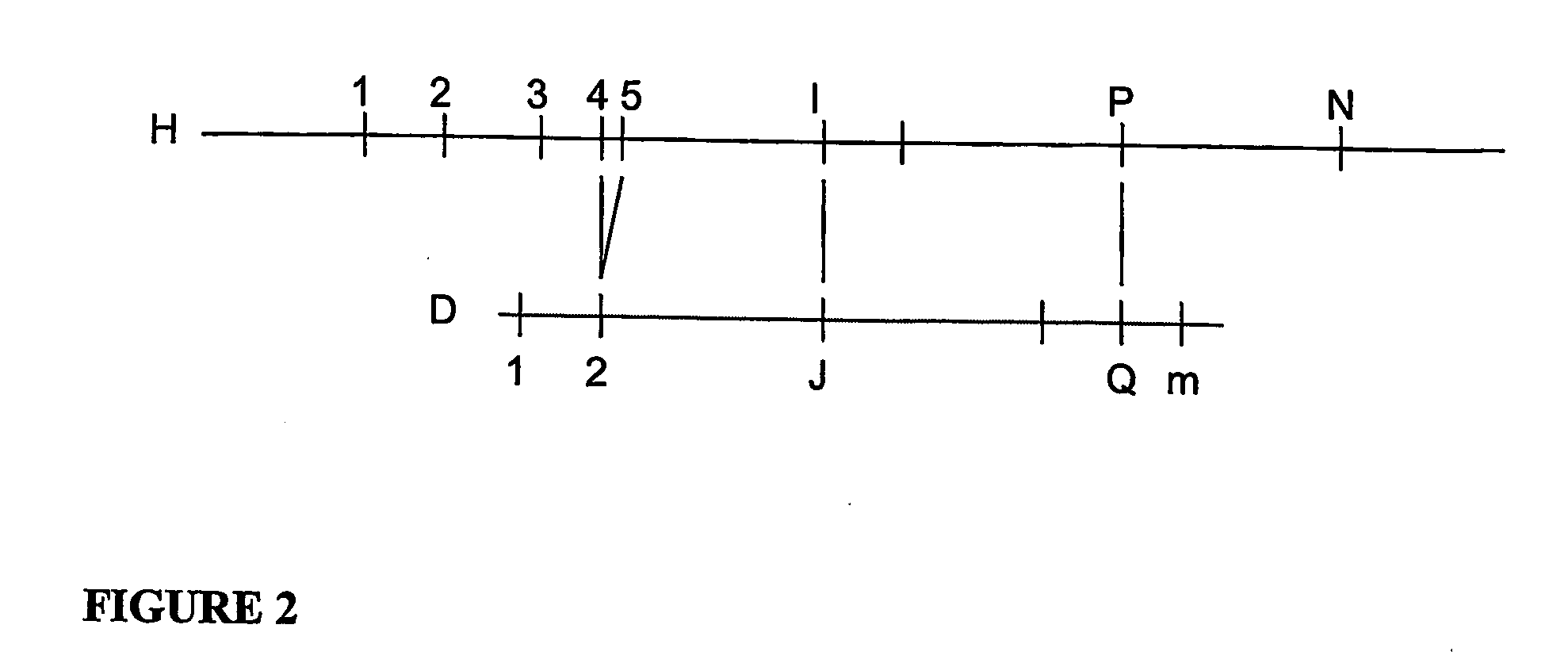
A restriction map is a map of known restriction sites within a sequence of DNA. Restriction mapping requires the use of restriction enzymes. In molecular biology, restriction maps are used as a reference to engineer plasmids or other relatively short pieces of DNA, and sometimes for longer genomic DNA. There are other ways of mapping features on DNA for longer length DNA molecules, such as mapping by transduction.
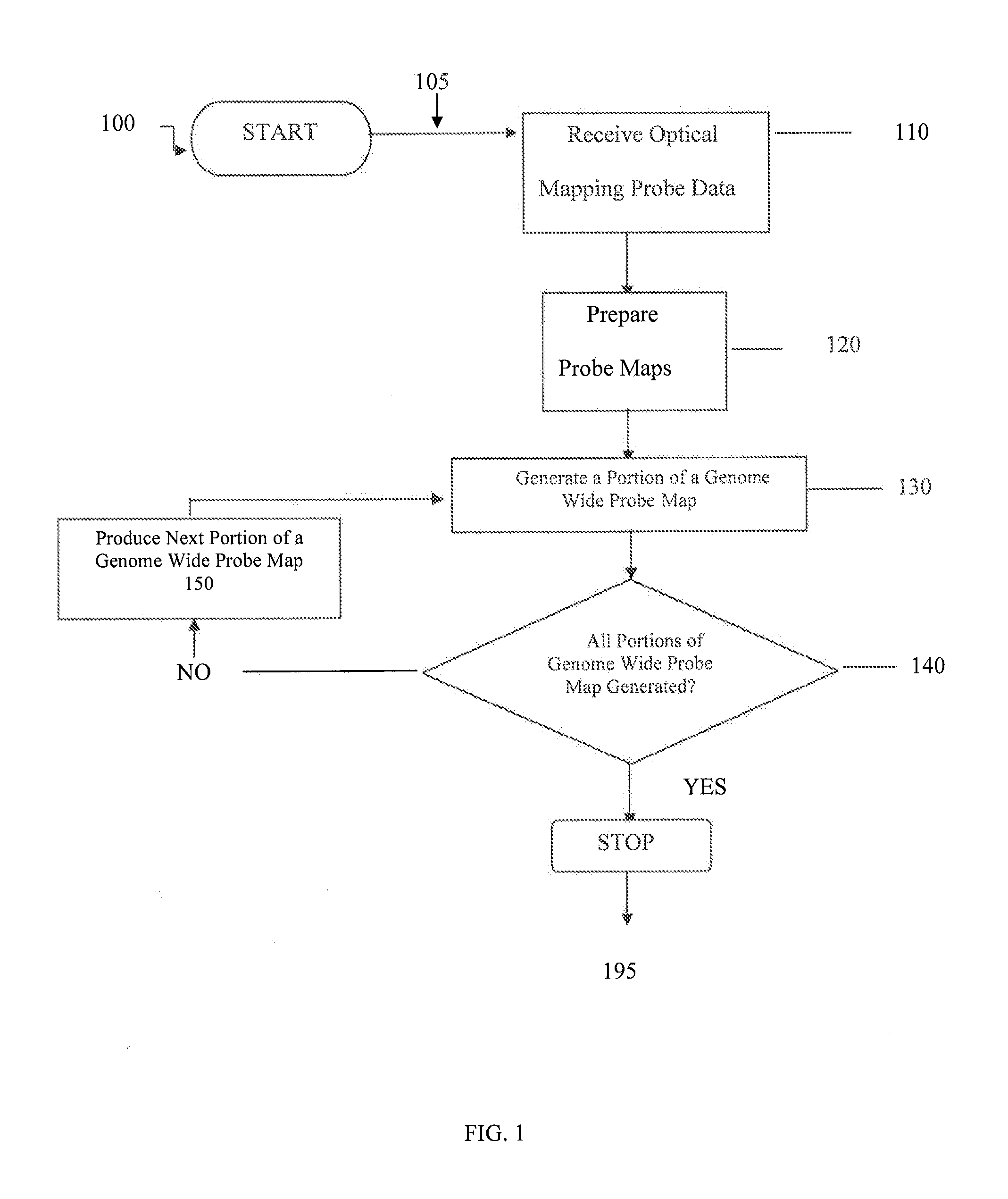
System and process for validating, aligning and reordering one or more genetic sequence maps using at least one ordered restriction map
ActiveUS7831392B2Maximize likelihoodMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDNA restrictionGenome
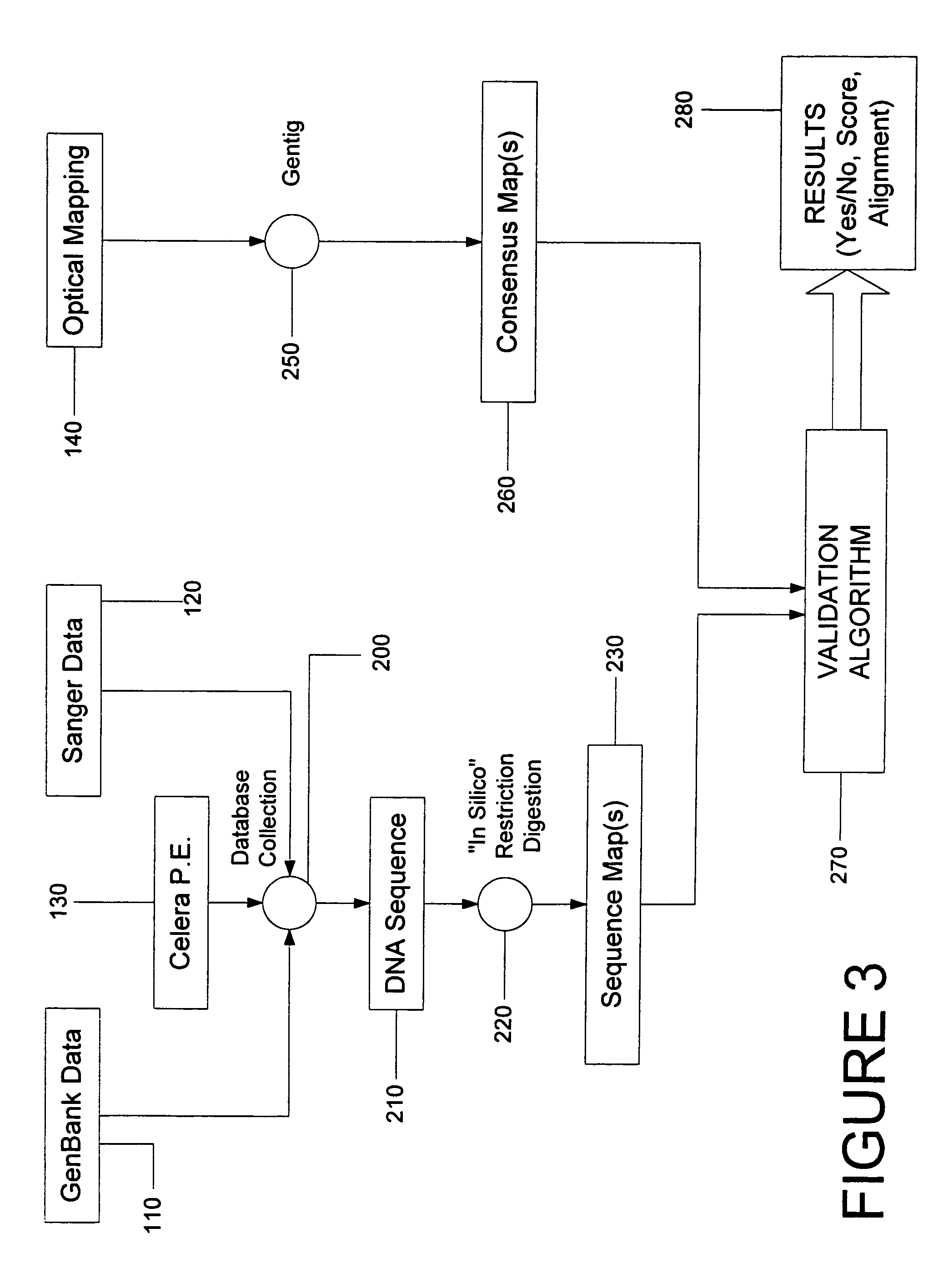
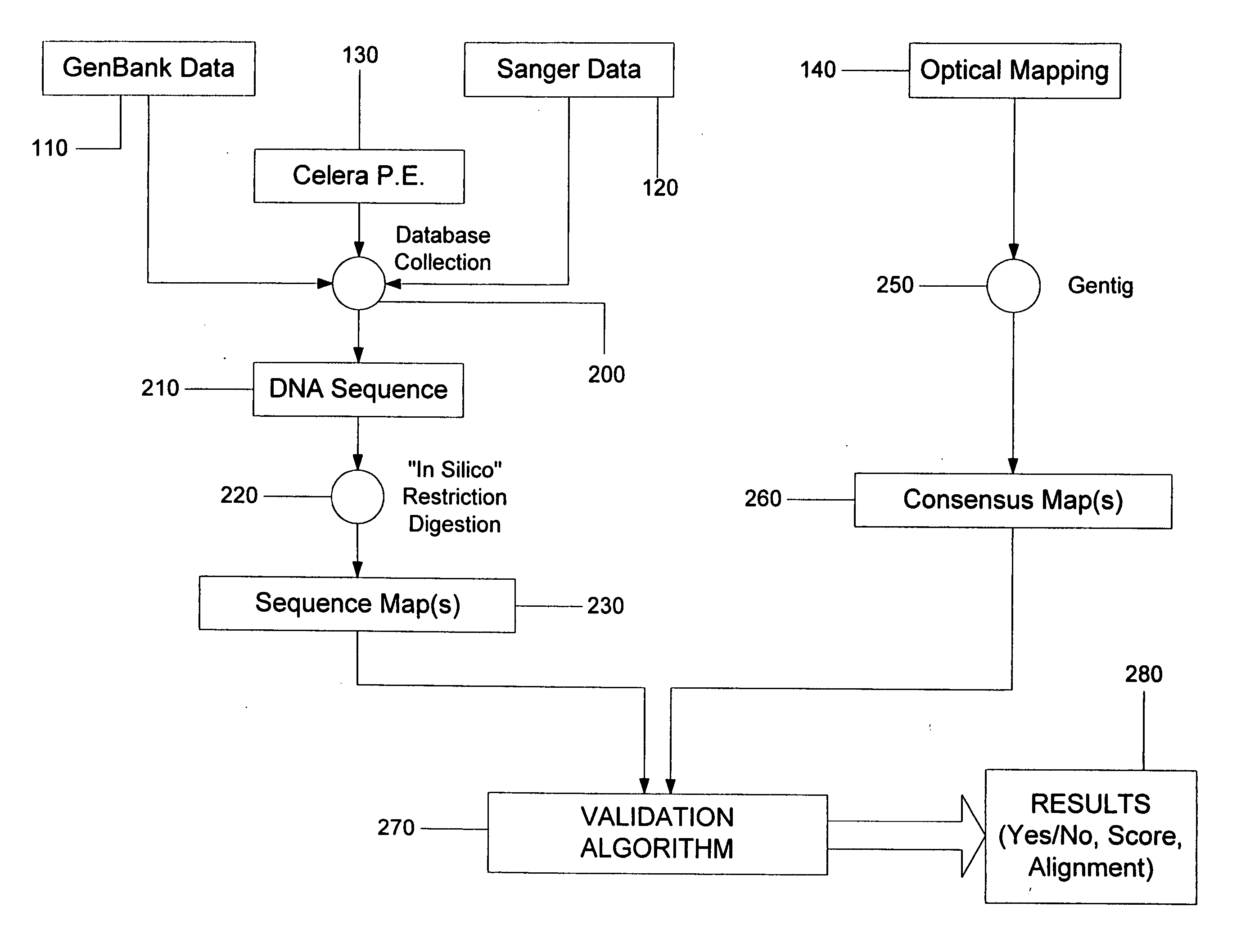
A method and system are provided for comparing ordered segments of a first DNA restriction map with ordered segments of a second DNA restriction map to determine a level of accuracy the first DNA map and / or the second DNA map. In particular, the first and second DNA maps can be received (the first DNA map corresponding to a sequence DNA map, and the second DNA map corresponding to a genomic consensus DNA map as provided in an optical DNA map). Then, the accuracy of the first DNA map and / or the second DNA map is validated based on information associated with the first and second DNA maps. In addition, a method and system are provided for aligning a plurality of DNA sequences with a ordered DNA restriction map. The DNA sequences and the DNA map are received (the DNA sequences being fragments of a genome and the DNA map corresponding to a genomic consensus DNA map which relates to an optical ordered DNA map). Then, a level of accuracy of the DNA sequences and the DNA map is obtained based on information associated with the DNA sequences and the DNA map by means of the method and system described above. The locations of the DNA map at which the DNA sequences are capable of being associated with particular segments of the DNA map are located. Furthermore, it is possible to obtain locations of the DNA map (without the validation) by locating an optimal one of the locations for each of the DNA sequences for each of the locations.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
System and process for validating, aligning and reordering one or more genetic sequence maps using at least one ordered restriction map
A method and system are provided for comparing ordered segments of a first DNA restriction map with ordered segments of a second DNA restriction map to determine a level of accuracy the first DNA map and / or the second DNA map. In particular, the first and second DNA maps can be received (the first DNA map corresponding to a sequence DNA map, and the second DNA map corresponding to a genomic consensus DNA map as provided in an optical DNA map). Then, the accuracy of the first DNA map and / or the second DNA map is validated based on information associated with the first and second DNA maps. In addition, a method and system are provided for aligning a plurality of DNA sequences with a ordered DNA restriction map. The DNA sequences and the DNA map are received (the DNA sequences being fragments of a genome and the DNA map corresponding to a genomic consensus DNA map which relates to an optical ordered DNA map). Then, a level of accuracy of the DNA sequences and the DNA map is obtained based on information associated with the DNA sequences and the DNA map by means of the method and system described above. The locations of the DNA map at which the DNA sequences are capable of being associated with particular segments of the DNA map are located. Furthermore, it is possible to obtain locations of the DNA map (without the validation) by locating an optimal one of the locations for each of the DNA sequences for each of the locations.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods of determining antibiotic resistance
InactiveUS20090317804A1Fast and accurate and detailed informationMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisAntibiotic resistanceBioinformatics
This disclosure relates to methods of determining an antibiotic resistance profile of a bacterium, and methods of treating a patient with a therapeutically effective antibiotic. The methods include comparing the restriction map of the nucleic acid with a restriction map database, and determining antibiotic resistance of the bacterium by matching regions of the nucleic acid to corresponding regions in the database.
Owner:OPGEN INC
Bioinformatics data processing systems
InactiveUS20180247012A1Saving in computational timeSave spaceSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemFragment size
Disclosed is a computer-implemented method of determining at least one optimal alignment of at least part of a first map to at least part of a second map or a plurality of second maps, wherein the maps are physical genome maps and / or restriction maps. The method comprises: receiving first map data indicative of a first ordered list of distances between features of the first map, receiving second map data indicative of a second ordered list of distances between features of the second map or second maps; generating, from the second map data, seed data indicative of a plurality of seeds, each seed comprising at least one of the distances in the second ordered list, wherein the features are restriction sites and distances are fragment sizes. The said method further comprises generating a plurality of candidate alignments from the seed data by searching at least part of the first ordered list to find at least approximate matches for respective seeds, and extending the approximate matches by dynamic programming; determining respective alignment scores for respective candidate alignments; and selecting one or more of the candidate alignments as an optimal alignment or optimal alignments, based on the alignment scores.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for identifying sashimi of thunnus obesus, thunnus alalunga and thunnus thynnus
InactiveCN102732630AAccurate identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionElectrophoresis
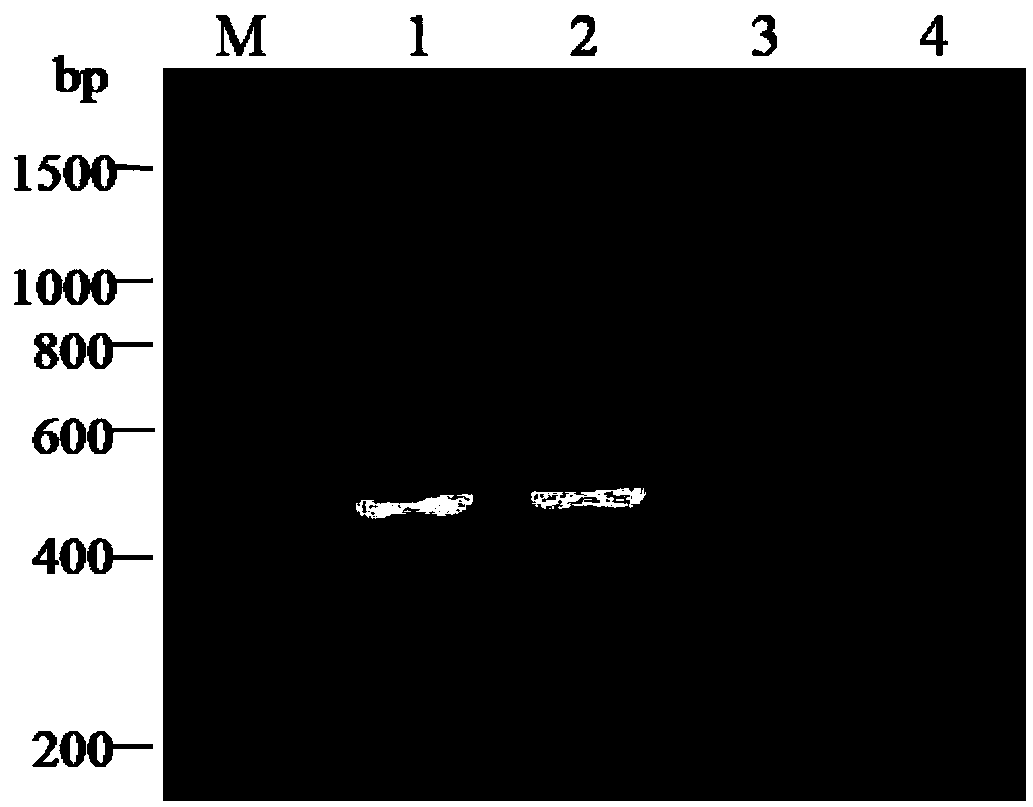
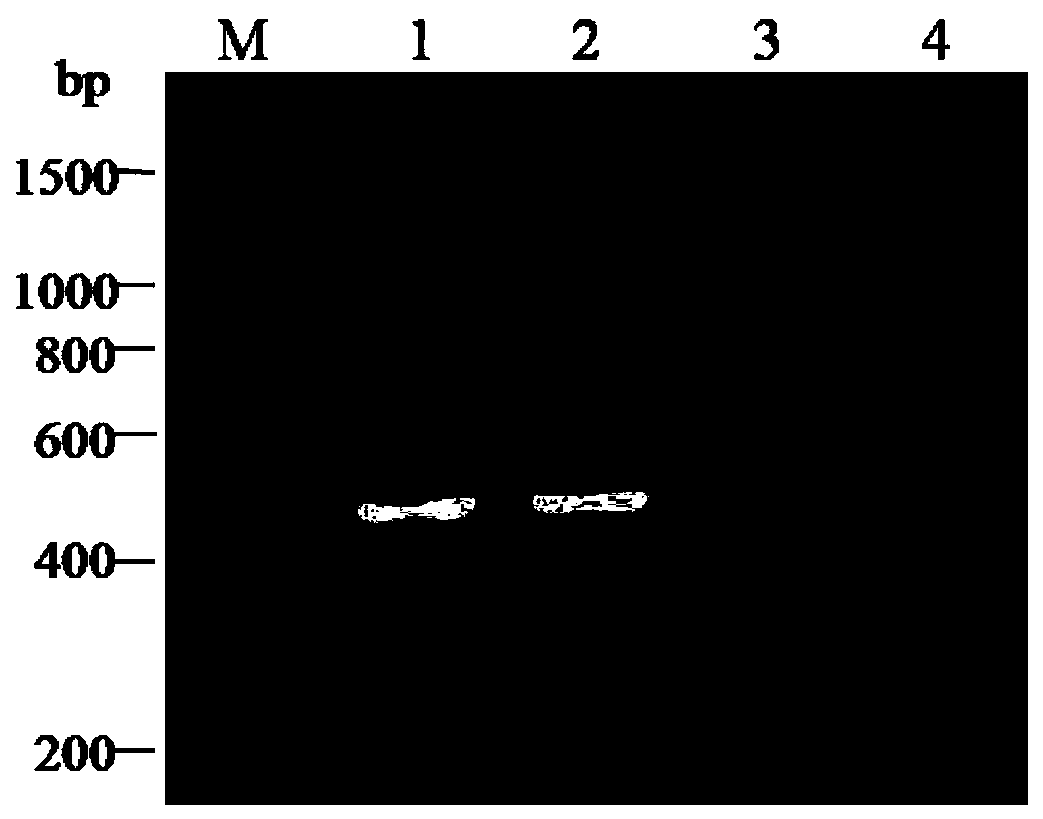
The invention provides a method for identifying sashimi of thunnus obesus, thunnus alalunga and thunnus thynnus, belonging to the technical field of food detection. The method comprises the following steps: extracting thunnus sashimi DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acid), taking the extracted DNAs as templates and F1 / F2 as a primer, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on cytb (cytochrome) gene fragments, carrying out electrophoresis detection on the amplified fragments, carrying out enzyme digestion on the purified PCR products with restriction enzymes Fok I and Stu I, and analyzing a restriction map through agarose gel electrophoresis to identify authenticity of raw fish of the three kinds of thunnus sashimi. By adopting the method, the source fish varieties of thunnus sashimi are identified on a molecular level and the sources of thunnus sashimi can be accurately differentiated. Thus, the method has great significance in standardizing the thunnus sashimi markets.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Methods, computer-accessible medium, and systems for generating a genome wide haplotype sequence
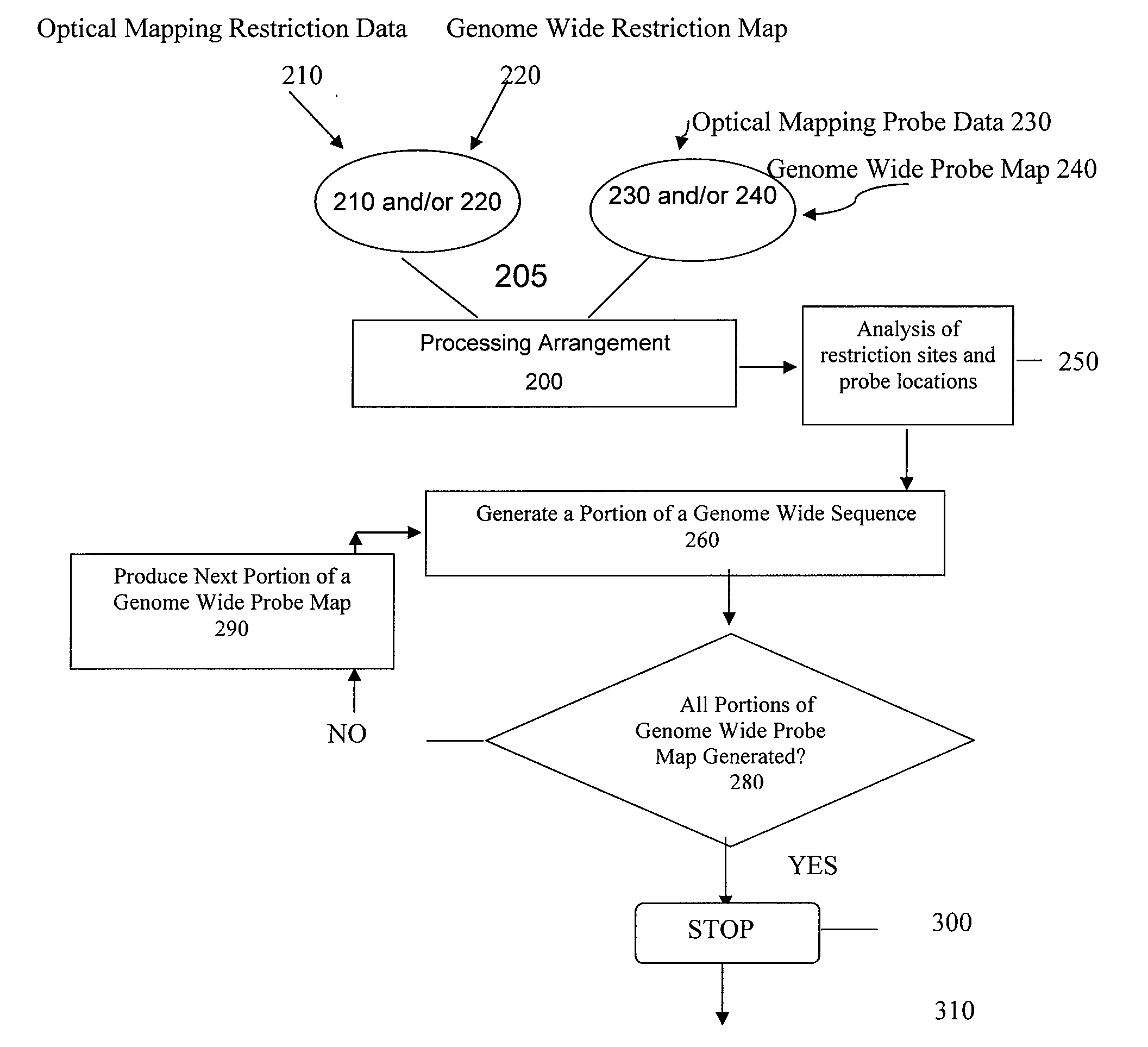
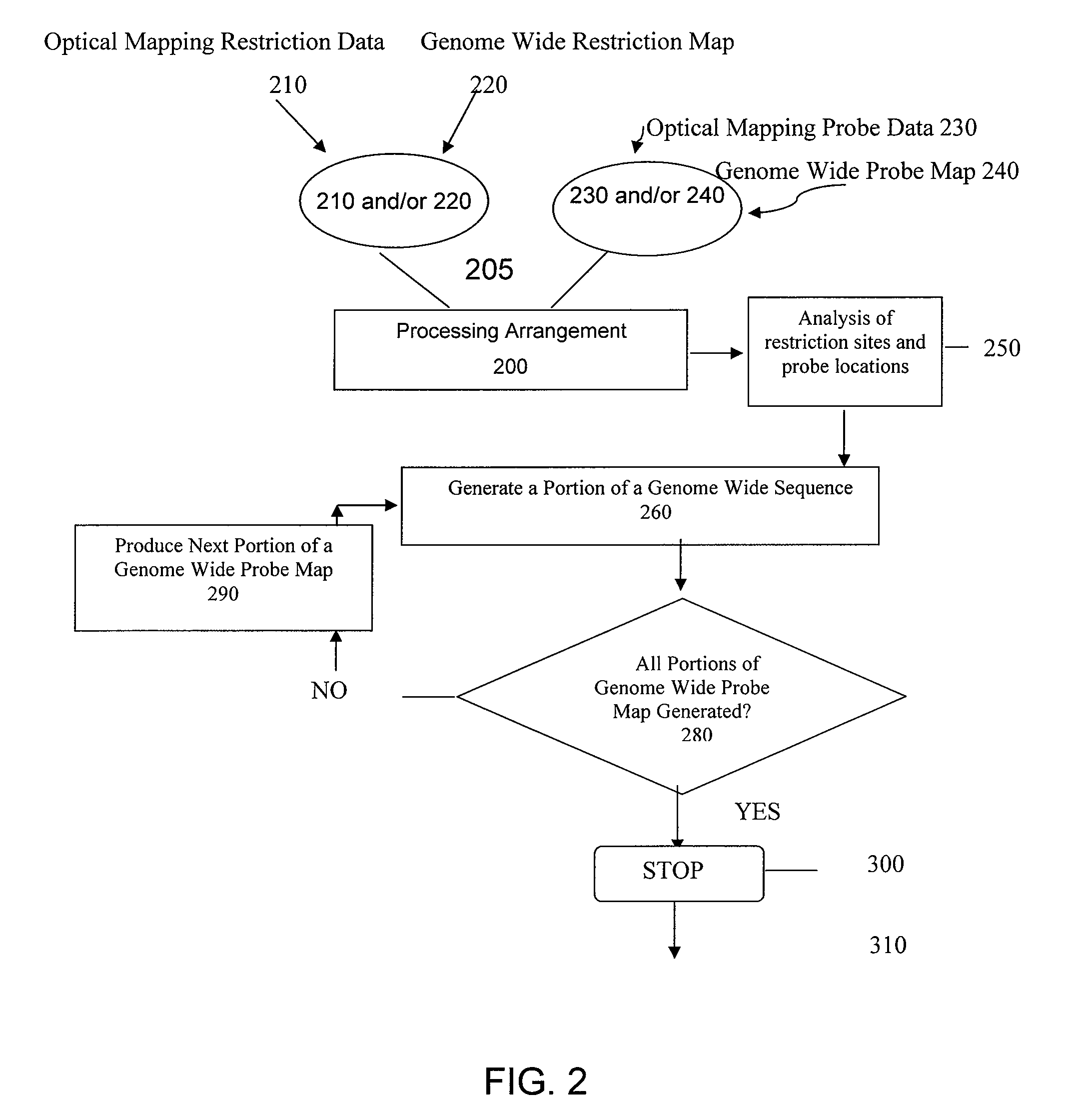
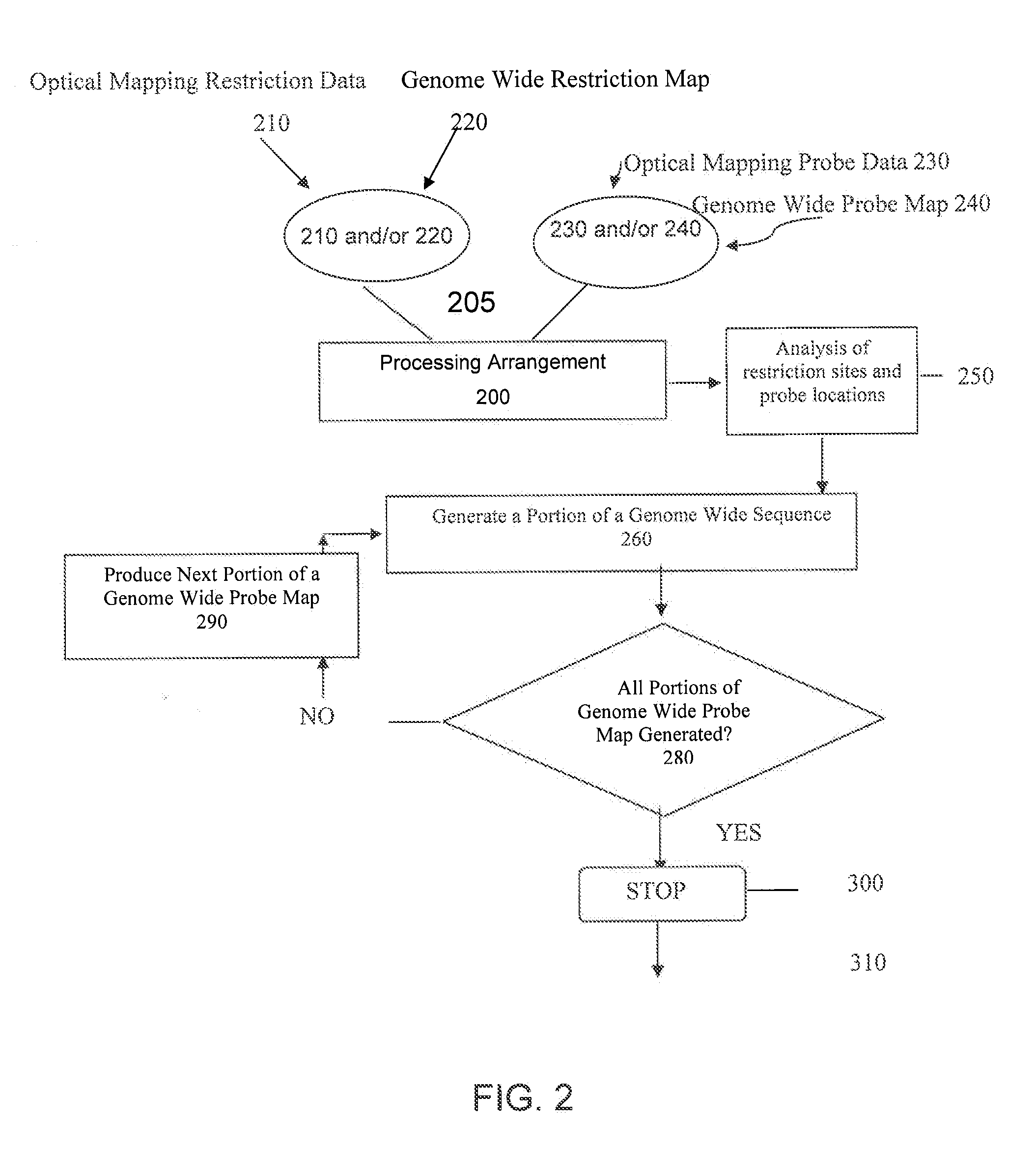
ActiveUS20080228457A1Analogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsConsensus mapRestriction site
Methods, computer-accessible medium, and systems for generating a genome wide probe map and / or a genome wide haplotype sequence are provided. In particular, a genome wide probe map can be generated by obtaining a plurality of detectable oligonucleotide probes hybridized to at least one double stranded nucleic acid molecule cleaved with at least one restriction enzyme, and detecting the location of the detectable oligonucleotide probes. For example, genome wide haplotype sequence can be generated by analyzing at least one genome wide restriction map in conjunction with at least one genome wide probe map to determine distances between restriction sites of the at least one genome wide restriction map and locations of detectable oligonucleotide probes of the at least one genome wide probe map and defining a consensus map indicating restriction sites based on each of the at least one genome wide restriction map and locations of detectable oligonucleotide probes based on each of the at least one genome wide probe map.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Gene detection or gene typing composition and method thereof
PendingCN106555011ASolving Design ChallengesQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTypingCurrent technology
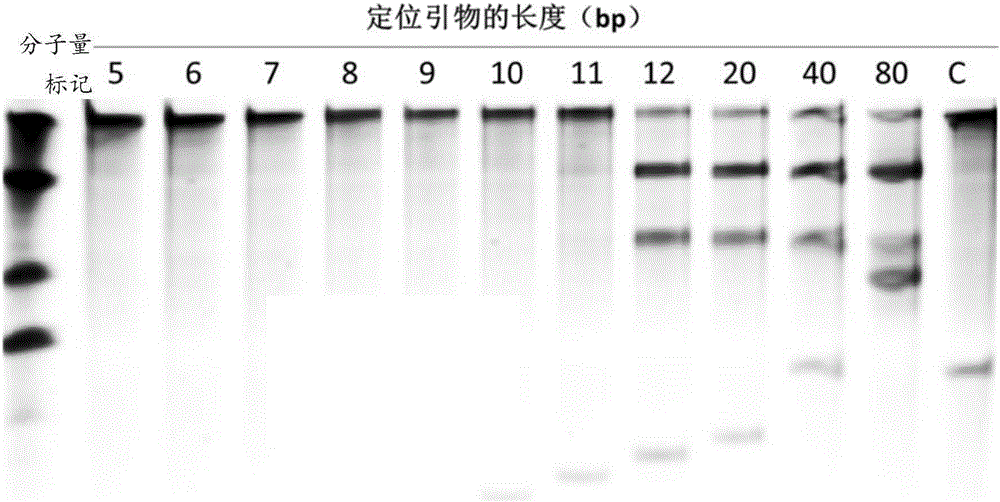
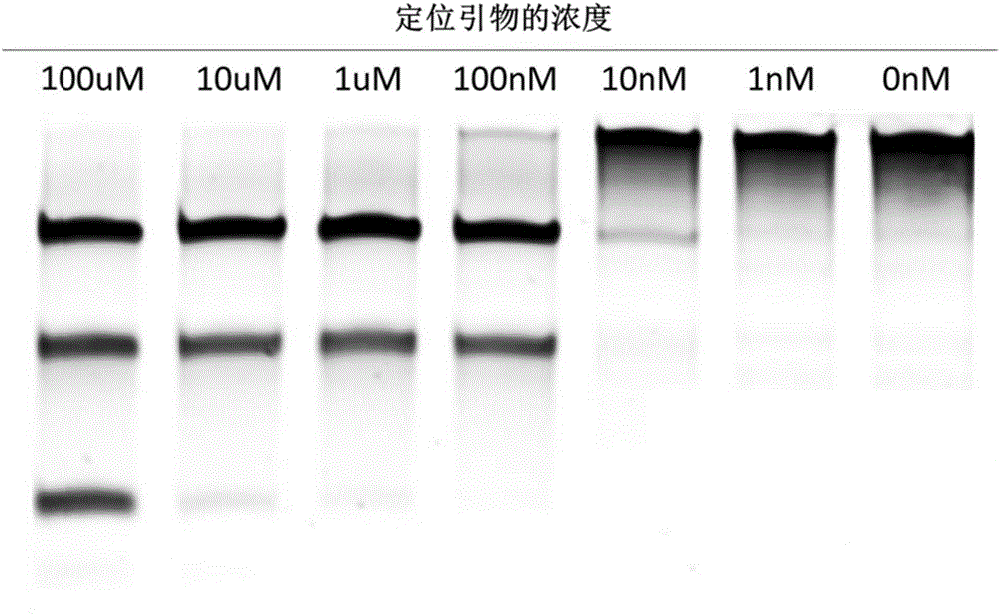
The invention relates to a gene detection and / or gene typing composition and a method thereof. Concretely speaking, the invention relates to the gene detection and / or gene typing composition, and the method for detecting and / or typing gene by using the composition, and more specifically relates to the composition by using Argonaute enzyme and a positioning primer for gene detection or gene typing and the method for gene detection or gene typing by using the composition. The composition and the method overcome the technical defect of the current technologies of multiple PCR and restriction map, and can rapidly and easily perform gene detection or gene typing.
Owner:德诺杰亿(北京)生物科技有限公司
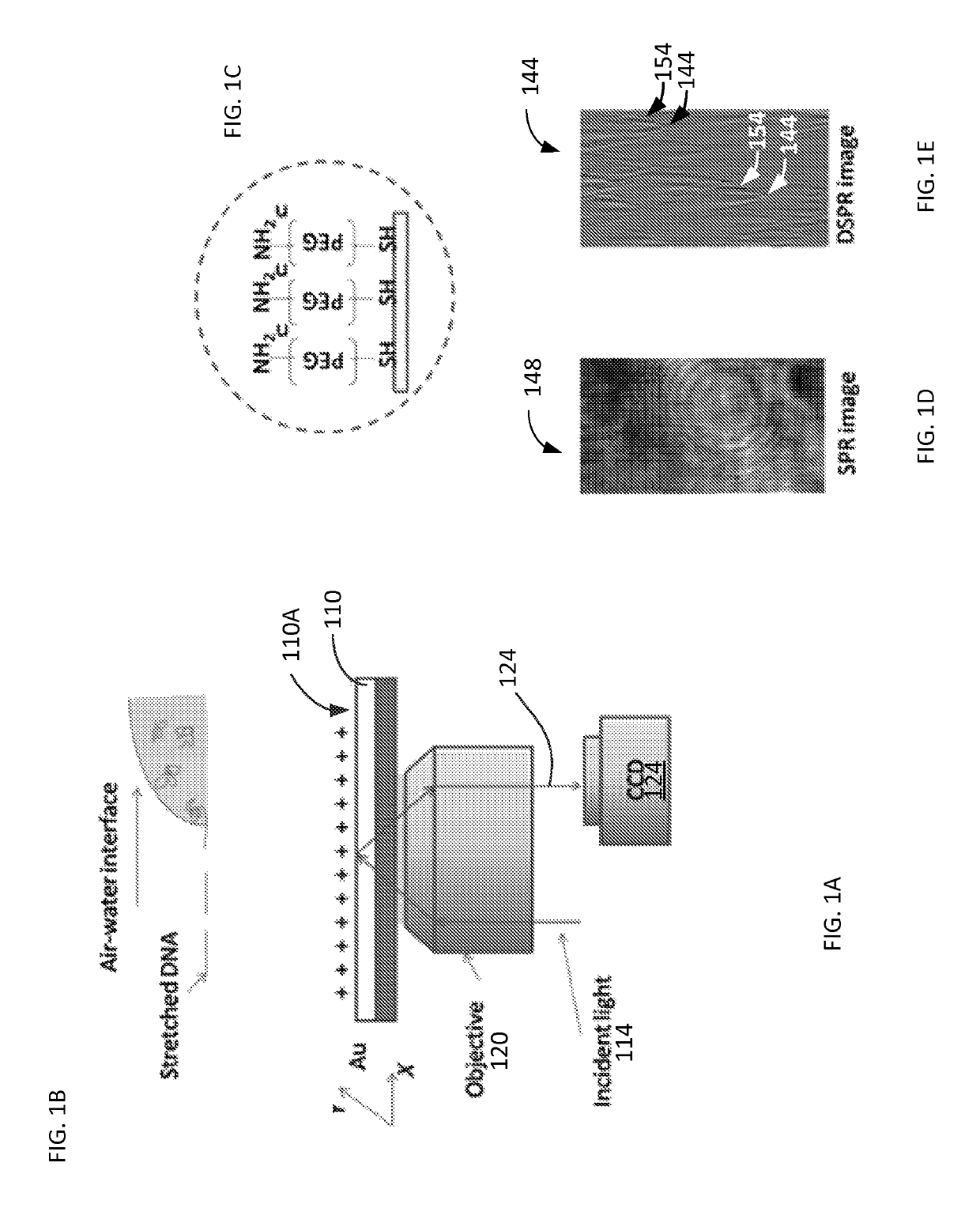
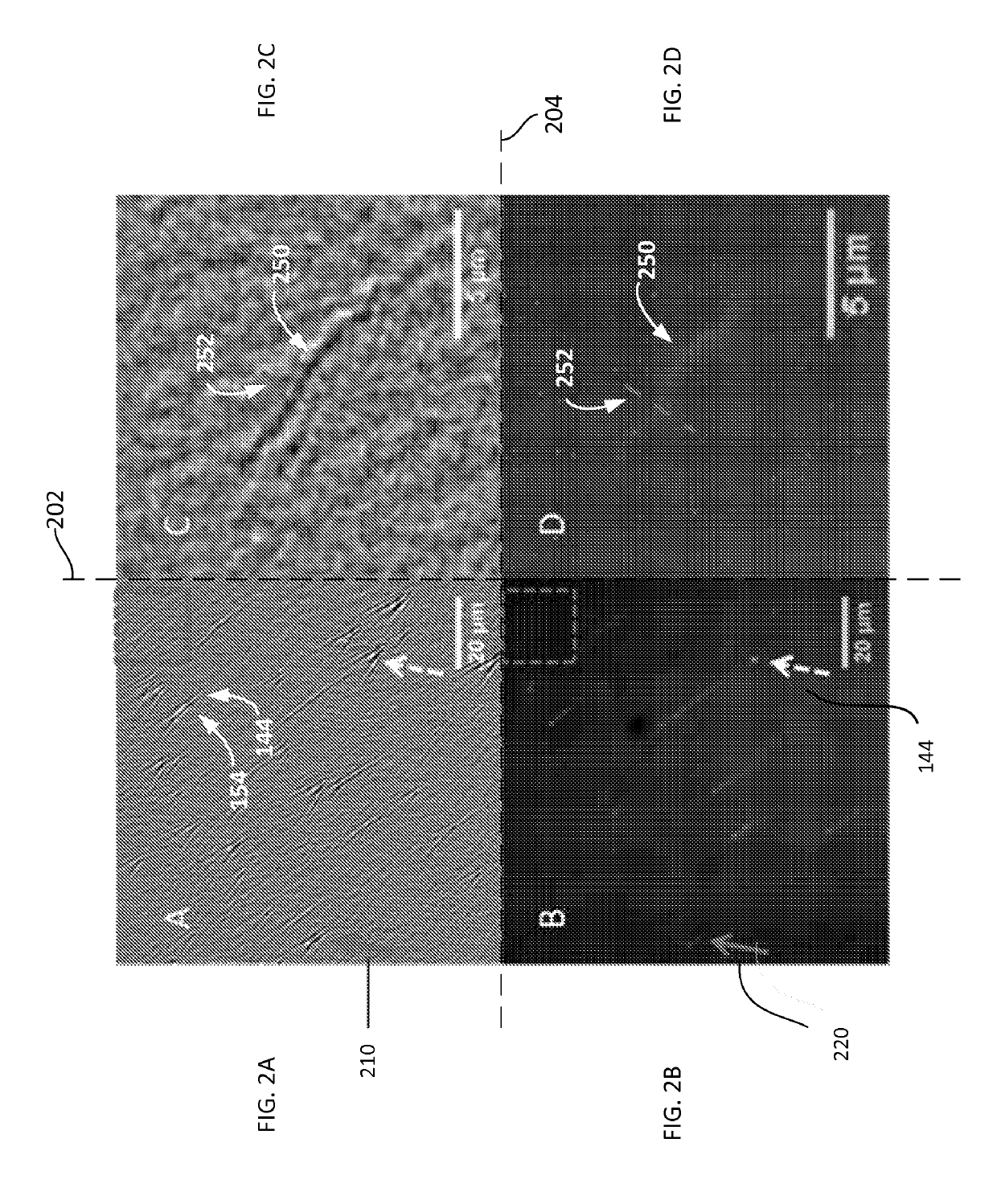
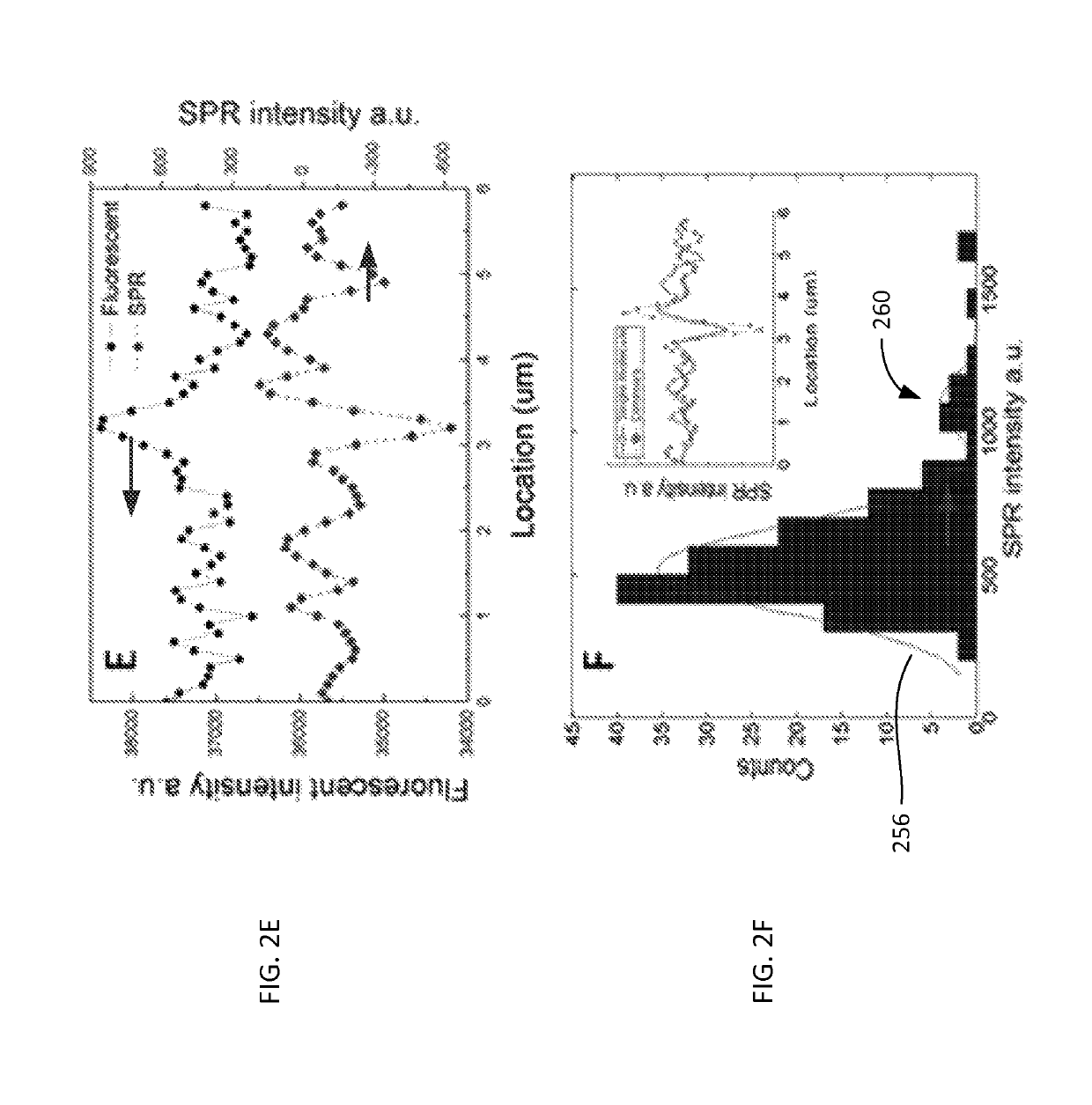
Plasmonic imaging and detection of single DNA molecules
ActiveUS10408757B2Improve image contrastBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImaging qualitySurface plasmon resonance imaging
Method and system to remove background noise with a differential approach in optical imaging is disclosed. The differential approach moves the sample position laterally over a small distance, and a differential image is generated from the images recorded before and after the lateral translation. This approach can significantly improve the image quality of objects, including single DNA molecules, for label-free optical imaging techniques, such as surface plasmon resonance imaging. Disclosed imaging technique provides high-resolution genome-wide restriction maps of single DNA molecules.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for rapid identification of liriomya huidobresis blanchard similar species by using PCR-RFLP technology
InactiveCN101200764ARapid identificationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementRapid identificationQuarantine
The invention discloses a method which can rapidly identify liriomyza approximate species by PCR-RFLP technology, which belongs to the insect species identification technical field. The method includes: (1) the DNA extraction of liriomyza trifolii, Americanliriomyza and South American liriomyza samples; (2) obtaining DNA sequence of 805bp by the PCR reaction of COII gene according to insect COII gene universal primers; (3) obtaining the COII sequence respectively through the clone, the transformation and the sequencing; (4) the selection of restriction endonuclease DraI; (5) the distinction of three approximate liriomyzas through a restriction map. The invention has the characteristics of accuracy, stability, fastness, cheapness, etc. And the invention can be applied in related departments of quarantine inspection, forecast, prevention, etc. to realize the rapid detection on the three approximate liriomyzas.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Identification method of PCR-restriction map for fritillary bulb and similar medicine material
InactiveCN1487091ALow toxicityCultivation is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationIsoschizomerBiology
The present invention belongs to the field of Chinese medicine material quality identifying technology, and aims at providing one kind of PCR-RFLP method for identifying fritillary bulb and similar medicine material accurately. PCR amplification adopts the primer series including P1:5'-CGT AAC AAG GTT TCC GTA GGTGAA-3' and P2: 5' -GCT ACG TTC TTC ATC GAT-3'; the characteristic base sequence of fritillary bulb is 5'-TGCCCGCCCTGCCCGGGACCTCGC-3'; and the restriction endonuclease Sma I and its isoschizomer can identify and incise the sequence. The identification process includes: extracting medicine DNA, PCR amplification with the primers P1 and P2, digesting the PCR product with restriction endonuclease Sma I, agarose gel electrophoresis to obtain the analysis result, compared with fritillary bulb PCR-RFLP characteristic result to judge whether the sample is fritillary bulb.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
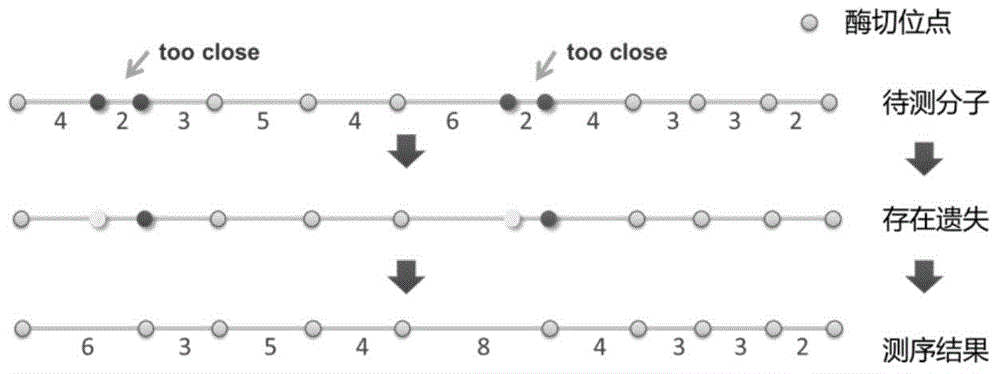
Genome restriction map splicing method and system
InactiveCN104951673AOvercome the defect of not being able to express the loss of enzyme cutting sitesQuick buildSpecial data processing applicationsRoute searchLine segment
The invention relates to the field of genomic sequence splicing in the field of molecular biology, and provides a genome restriction map splicing method and system. The method includes the steps of preprocessing gene sequence molecules in the genome restriction map, obtaining new gene sequence molecules, and cutting the new gene sequence molecules into FLES segments, wherein the FLES segments are gene segments which have the fixed total segment lengths and do not need to have the same restriction locus number; clustering the FLES segments to form a representative FLES set, and conducting error correction on the gene sequence molecules according to the representative FLES set; establishing an FLES map according to the FLES set and the gene sequence molecules where error correction is conducted, conducting route search on the FLES map, obtaining the Hamilton route of the FLES map to serve as the restriction locus sequence of a genome, and completing splicing of the genome restriction map. By means of the method and the system, the restriction locus map of the genome can be rapidly and accurately established.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting gene cassette array in bacterium integron by using EcoRII enzyme digestion restriction map library
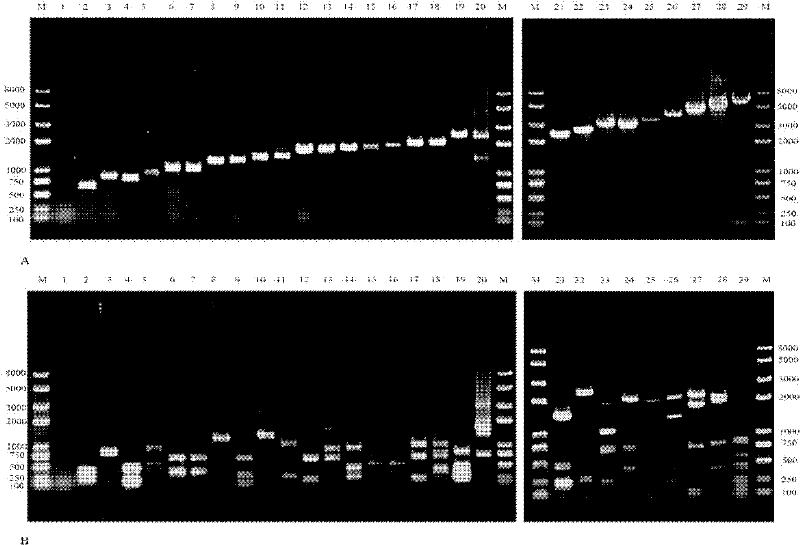
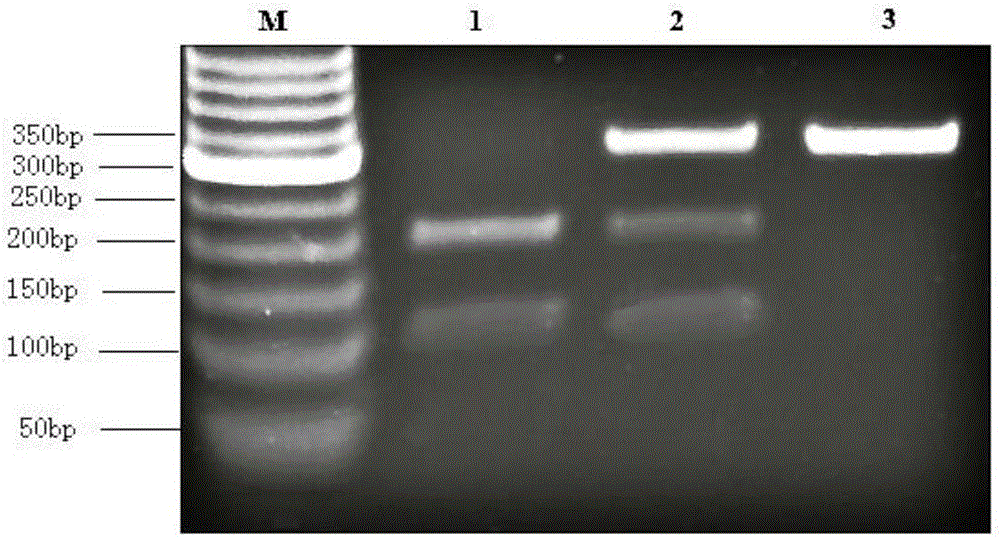
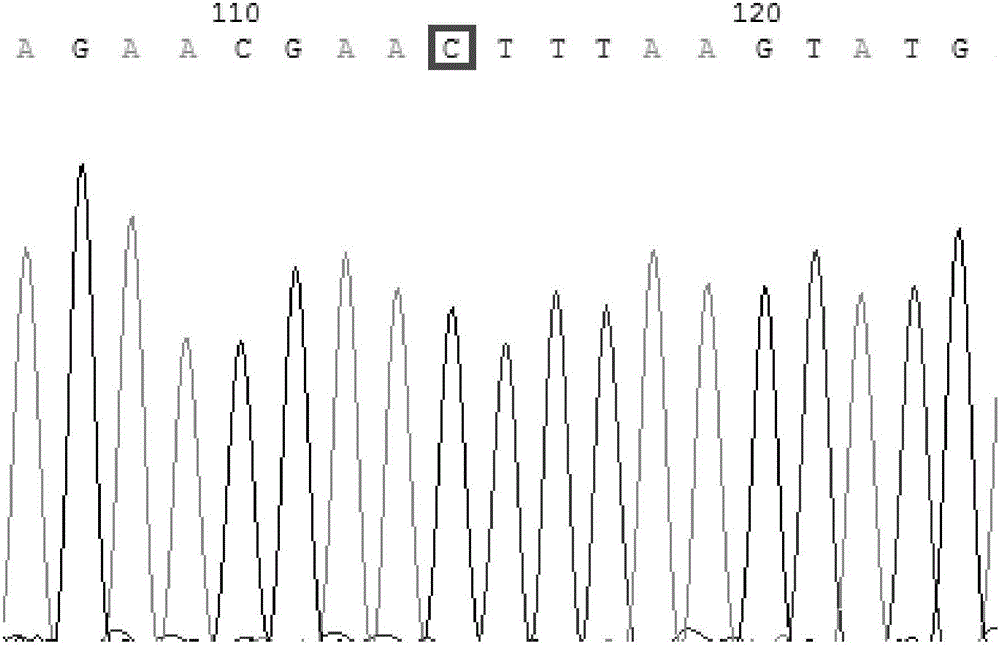
InactiveCN102191322ADirect sequencing avoidsWay accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionQuarantine
The invention discloses a method for detecting a gene cassette array in a bacterium integron by using an EcoRII enzyme digestion map library, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out enzyme digestion on the gene cassette array by adopting the restriction enzyme EcoRII when a new screened gene cassette array is determined; comparing the gene cassette array with the constructed EcoRII enzyme digestion map library so as to determine the novelty of the gene cassette array; and selecting connection, transformation and sequencing analysis so as to realize purposeful sequencing if maps in the library are not matched with the gene cassette array. The method is accurate, rapid and economic and is convenient for information sharing. The method is more suitable for relevant departments such as hospitals, quarantine inspection, forecast, preventive treatment and the like to realize the effective monitoring and prevent the outbreak prevalent of drug-resistant bacteria caused by the horizontal transferring and spreading of the drug-resistant bacteria containing the integron under the condition that antibiotic misuse is not well restrained.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method and kit for detecting rs1801131 polymorphic site genotype in MTHFR (5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) gene
ActiveCN107058478AReduce usageAccurate judgmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRestriction Enzyme Cut SiteGenetics
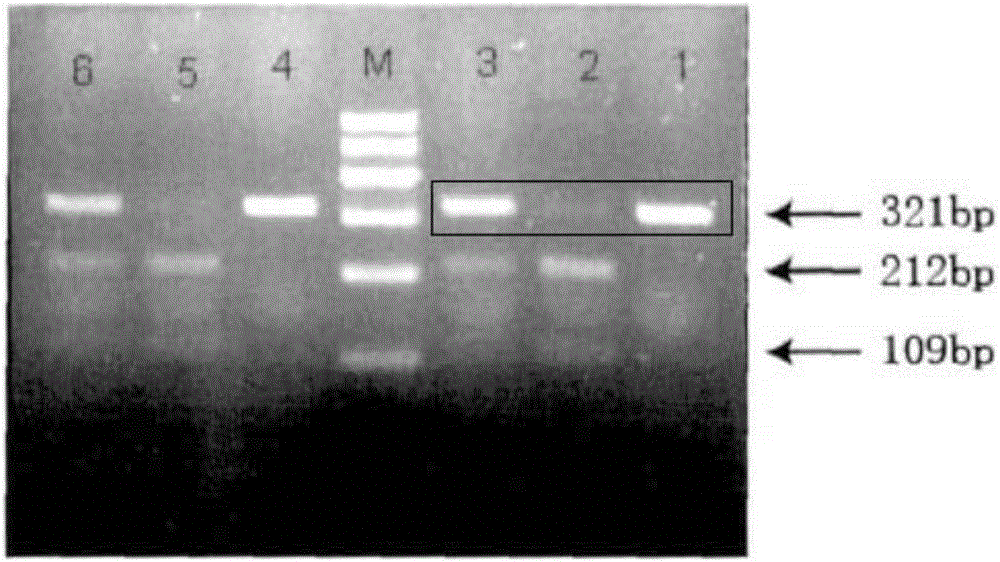
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting rs1801131 polymorphic site genotype in MTHFR (5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) gene. In a process of detecting the rs1801131 polymorphic site genotype in the MTHFR gene on the basis of a PCR-RFLP method, endonuclease, which is low in cost, is adopted; meanwhile, by introducing a specific 'internal quality control' mechanism, namely introducing an internal control restriction enzyme cutting site to a PCR product, the circumstance of incomplete enzyme cutting can be identified in accordance with a restriction map, and interference from residual PCR product or intermediate products of enzyme cutting can be prevented; and the genotype can be accurately judged in accordance with characteristic bands, so that the accuracy of a detection result is greatly enhanced.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Method for detecting polymorphism of human gastric cancer susceptible genes IL17A rs3748067 by aid of ApoI
InactiveCN105695613AReduce disease riskEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestionStomach cancer
The invention discloses a method for detecting the polymorphism of human gastric cancer susceptible genes IL17A rs3748067 by the aid of ApoI. The method includes amplifying target DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments by means of polymerase chain reaction; digesting to-be-detected DNA fragments by the aid of restriction incision enzymes; identifying and cutting specific sequences by the aid of the restriction incision enzymes; carrying out electrophoresis on digested products; analyzing cleavage sites of the sequences of the fragments by the aid of restriction maps; comparing the difference of gene sequences from different sources by the aid of the diversity of the fragments. The method has the advantages that briefly speaking, the corresponding target fragments are amplified by means of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) at first, then digestion reaction is carried out by the aid of the restriction incision enzymes, the restriction maps are observed and compared after electrophoresis is carried out, and accordingly the difference between the sequences can be analyzed; the method is good in repeatability, easy to implement and low in cost, and digestion results are easy to identify; the method and detection reagent kits which are easy to implement, low in cost and wide in application range can be provided for detecting the polymorphism of the human gastric cancer susceptible genes IL17A rs3748067.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Nucleic acid analysis
InactiveUS20050153293A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionNucleic acid sequencing
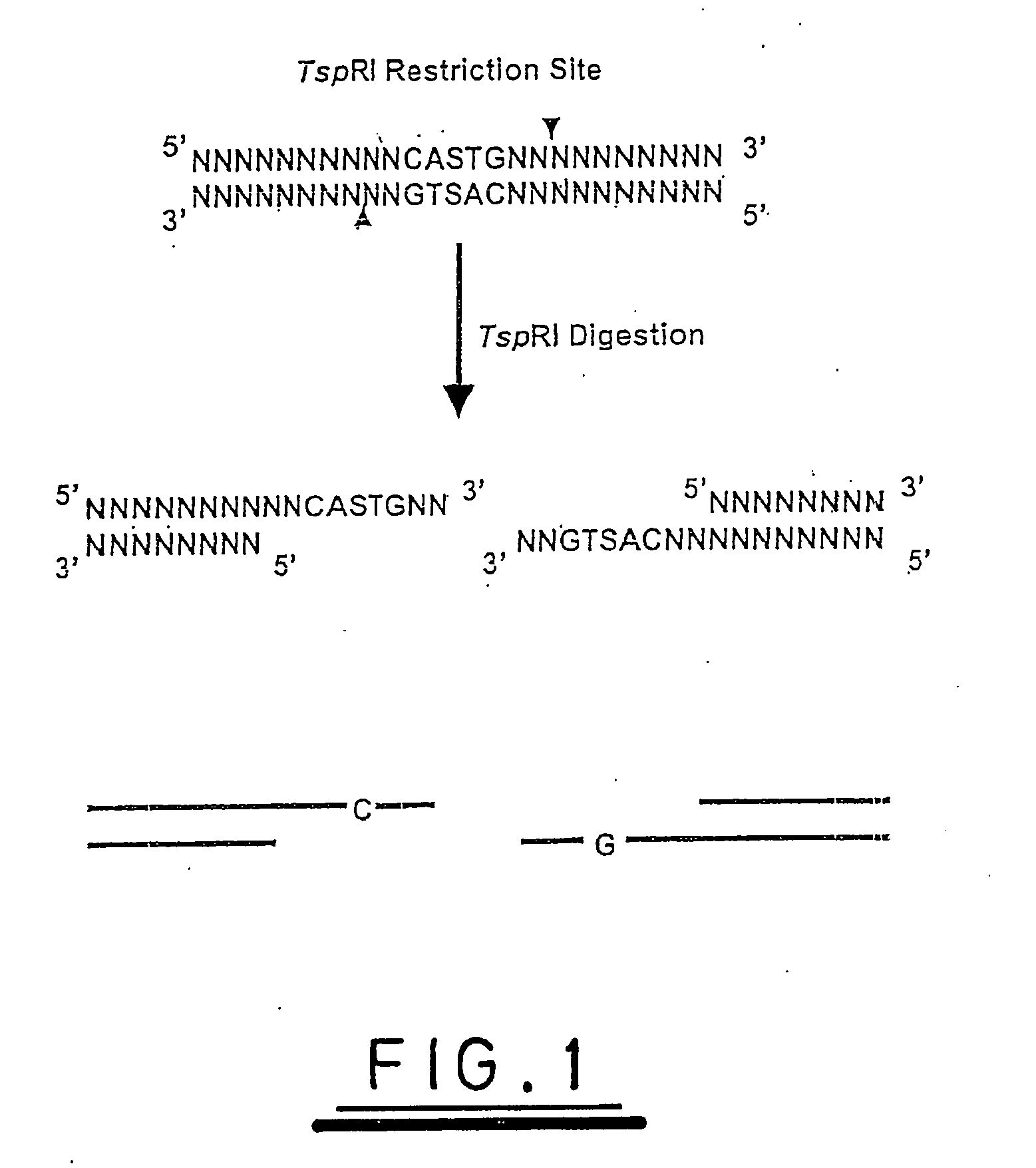
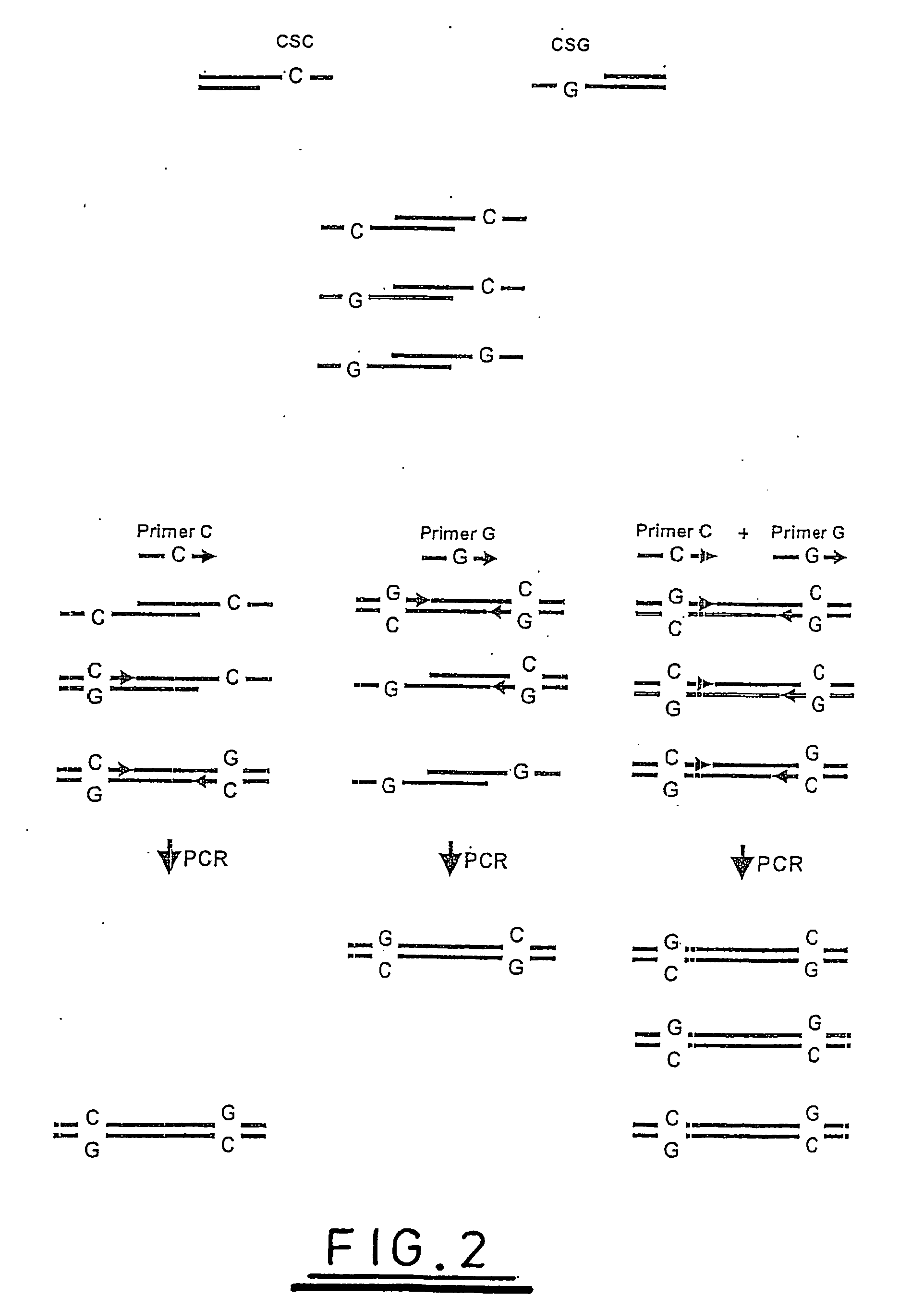
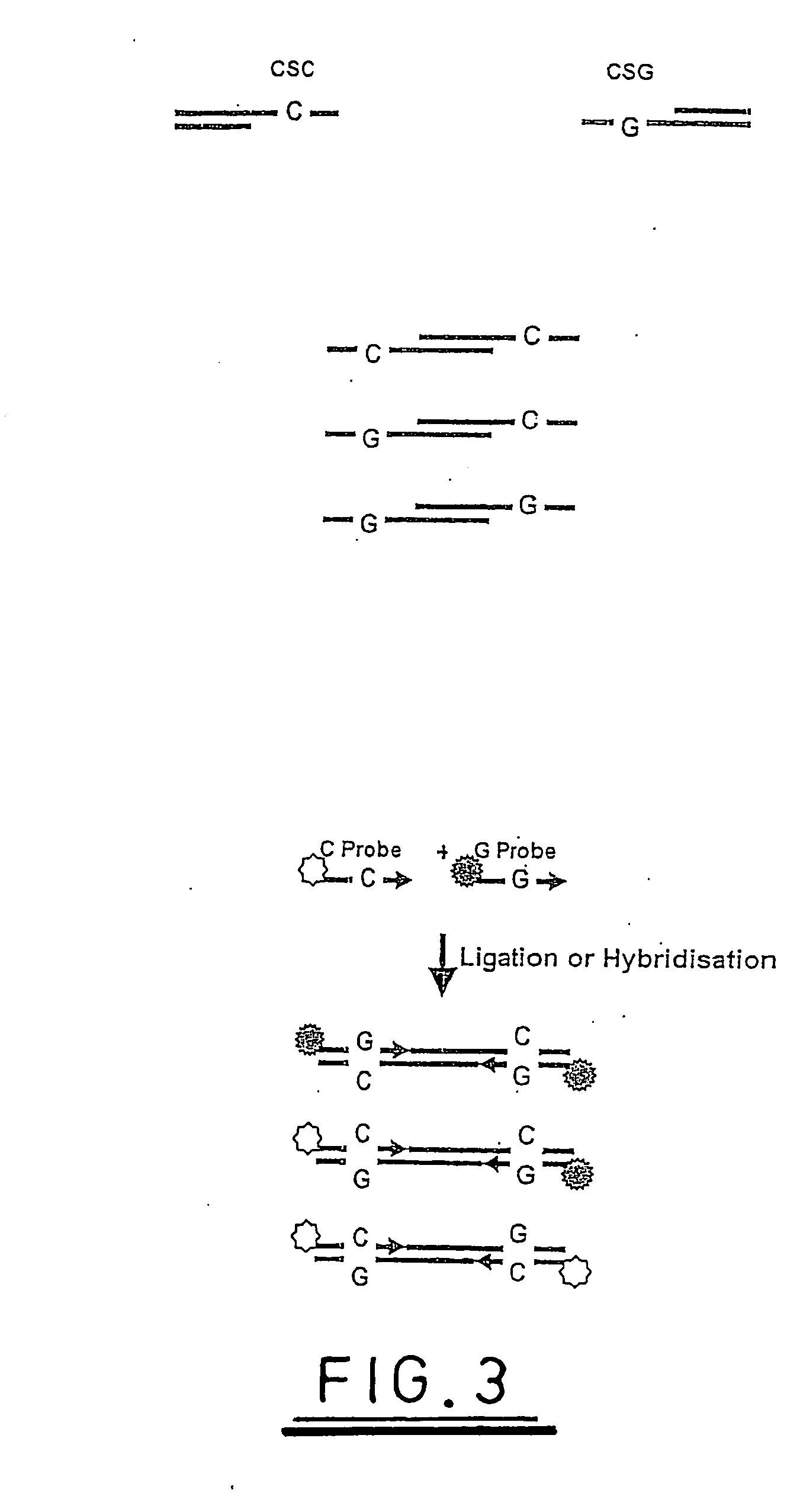
A method of analysing a nucleic acid sequence comprises digesting the sequence with a restriction enzyme which cleaves the nucleic acid to produce fragments with overhangs containing at least one partially random or at least one semi-random base. The fragment mixture may be analysed to determine the relative size of the fragments and the sequences of their ends. Alternatively the fragment mixture may be analysed to determine the identity of at least one of said random or semi-random bases and optionally to determine the relative size of the fragments to obtain sequence data that can be used to order the fragments relative to each other to generate partial or complete restriction maps of said nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:TEPNEL MEDICAL
Method for identifying polymorphism of human breast cancer genes RAD51 rs7180135 by aid of BccI
InactiveCN105695615AEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestionHuman breast
The invention discloses a method for identifying the polymorphism of human breast cancer genes RAD51 rs7180135 by the aid of BccI. The method is implemented by the aid of polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism processes, and includes amplifying target DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments by means of polymerase chain reaction; digesting to-be-detected DNA fragments by the aid of restriction incision enzymes; identifying and cutting specific sequences by the aid of the restriction incision enzymes; carrying out electrophoresis on digested products; analyzing specific cleavage sites of the sequences of the fragments by the aid of restriction maps; comparing the differences of the gene sequences from different sources by the aid of the diversity of the fragments. The method has the advantages that briefly speaking, the corresponding target fragments are amplified by means of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) at first, then digestion reaction is carried out by the aid of the restriction incision enzymes, the restriction maps are observed and compared after electrophoresis is carried out, and accordingly the difference between the sequences can be analyzed; the method is good in repeatability, easy to implement and low in cost, and digestion results are easy to identify; the method and detection reagent kits which are easy to implement, low in cost and wide in application range can be provided for detecting the polymorphism of the human breast cancer susceptible genes RAD51 rs7180135.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
PCR-RFLP identification method for different subgroups of sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma
ActiveCN109652503AEasy to identifyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA EndonucleaseB subgroup
The invention relates to a PCR-RFLP identification method for different subgroups of sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma. A sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma tuf gene is taken as an objectto design a specific primer, a tuf gene fragment is obtained through PCR amplification, then restriction endonuclease Msp I is adopted for digesting the tuf gene fragment obtained through amplification, and the different subgroups of the sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma are distinguished through a differentiated RFLP restriction map. The PCR-RFLP identification method for the different subgroups of the sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma has the advantages that a sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma 16SrXI-B subgroup and a sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma 16SrXI-D subgroup can be quickly, accurately and efficiently identified without sequencing, and is important for the pathogen identification and prevention of sugarcane white leaf diseases.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST OF YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method and kit for detecting CYP2C19*2 polymorphic site genotype
InactiveCN106222275AAccurate judgmentJudgment does not affectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrobiologyEnzyme
The invention discloses a method and kit for detecting the CYP2C19*2 polymorphic site genotype. During the process of detecting CYP2C19*2 polymorphic site genotype, a specific internal quality control mechanism is introduced, namely, an internal control enzyme cutting site is introduced into a PCR product; according to the restriction map, the incomplete enzyme cutting can be identified; moreover, under the situation that the enzyme cutting is incomplete and part of enzyme cutting strips is obscure, the genotype can still be judged accurately, and the accuracy of detection results is greatly improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Molecular genetic marker for slaughter performance of Bian chicken and application thereof
InactiveCN103820550ANot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementMyostatinMarker-assisted selection
The invention relates to the field of poultry breeding, specifically to a molecular genetic marker for slaughter performance of Bian chicken and application thereof. The invention discloses application of a myostatin (MSTN) gene as the molecular genetic marker for slaughter performance of Bian chicken. A method for improving slaughter performance of Bian chicken by using the MSTN gene comprises the following concrete steps: carrying out amplification so as to obtain a target fragment of the MSTN gene (162 bp), subjecting the target fragment to digestion by restriction enzyme BbvI, carrying out gel electrophoresis, then carrying out silver staining for color development so as to obtain a restriction map of DNA and based on the quantity and the sizes of stripes in the restriction map, judging slaughter performance of to-be-tested samples and selecting samples according with breeding purposes, wherein samples with only 162 bp stripes are homozygous samples with high slaughter performance and samples with only 127 bp stripes are homozygous samples with low slaughter performance. The method provided by the invention is simple and fast, is not affected by an external environment and can be used for molecular genetic marking of slaughter performance of Bian chicken and for marker assisted selection.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
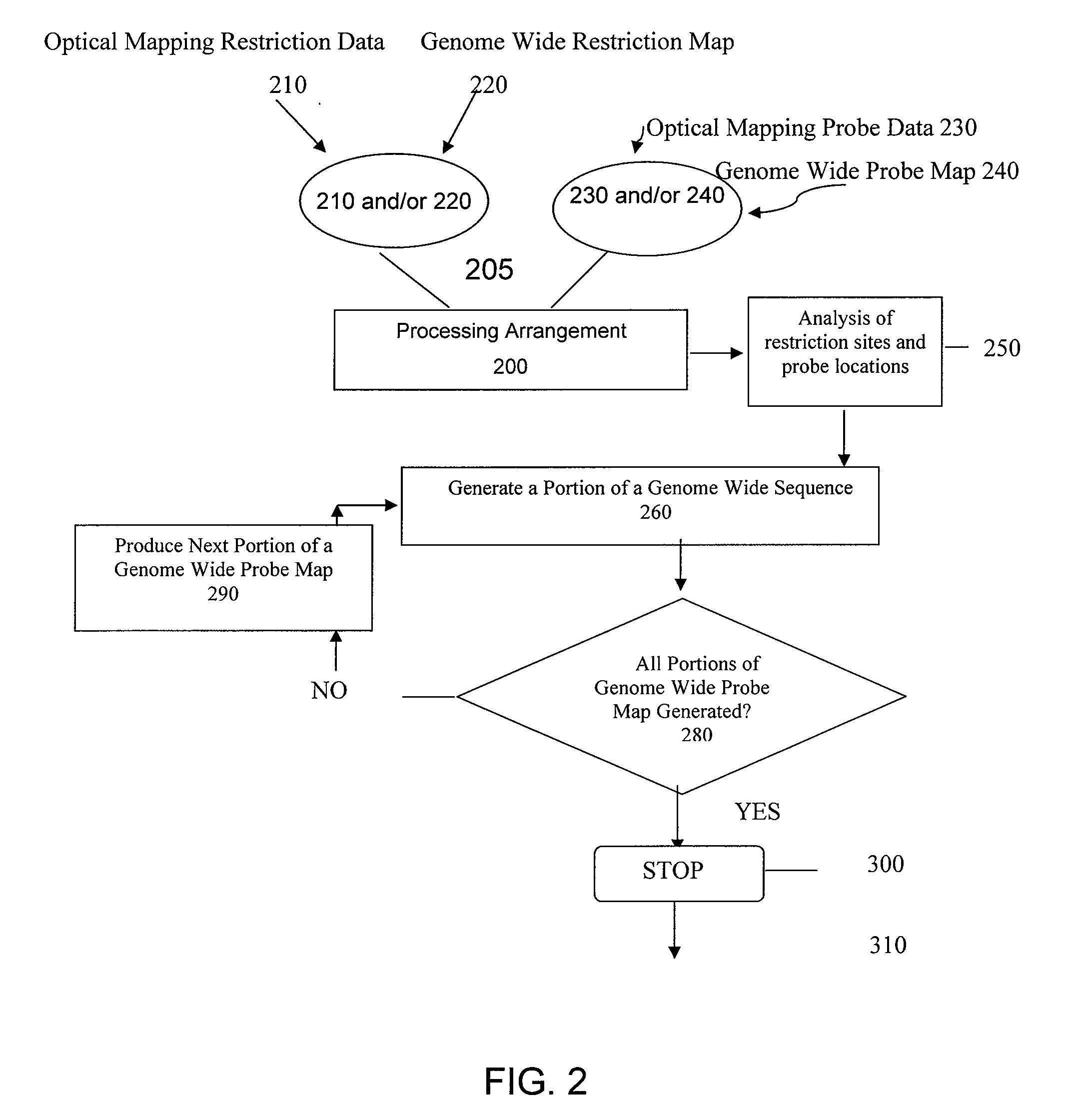
Methods, computer-accessible medium, and systems for generating a genome wide haplotype sequence
ActiveUS8140269B2Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesConsensus mapRestriction site
Methods, computer-accessible medium, and systems for generating a genome wide probe map and / or a genome wide haplotype sequence are provided. In particular, a genome wide probe map can be generated by obtaining a plurality of detectable oligonucleotide probes hybridized to at least one double stranded nucleic acid molecule cleaved with at least one restriction enzyme, and detecting the location of the detectable oligonucleotide probes. For example, genome wide haplotype sequence can be generated by analyzing at least one genome wide restriction map in conjunction with at least one genome wide probe map to determine distances between restriction sites of the at least one genome wide restriction map and locations of detectable oligonucleotide probes of the at least one genome wide probe map and defining a consensus map indicating restriction sites based on each of the at least one genome wide restriction map and locations of detectable oligonucleotide probes based on each of the at least one genome wide probe map.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Methods, computer-accessible medium, and systems for generating a genome wide haplotype sequence
Methods, computer-accessible medium, and systems for generating a genome wide probe map and / or a genome wide haplotype sequence are provided. In particular, a genome wide probe map can be generated by obtaining a plurality of detectable oligonucleotide probes hybridized to at least one double stranded nucleic acid molecule cleaved with at least one restriction enzyme, and detecting the location of the detectable oligonucleotide probes. For example, genome wide haplotype sequence can be generated by analyzing at least one genome wide restriction map in conjunction with at least one genome wide probe map to determine distances between restriction sites of the genome wide restriction map(s) and locations of detectable oligonucleotide probes of the genome wide probe map(s) and defining a consensus map indicating restriction sites based on the genome wide restriction map(s) and / or locations of detectable oligonucleotide probes based on each of the genome wide probe map(s).
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
A kind of rice breeding method
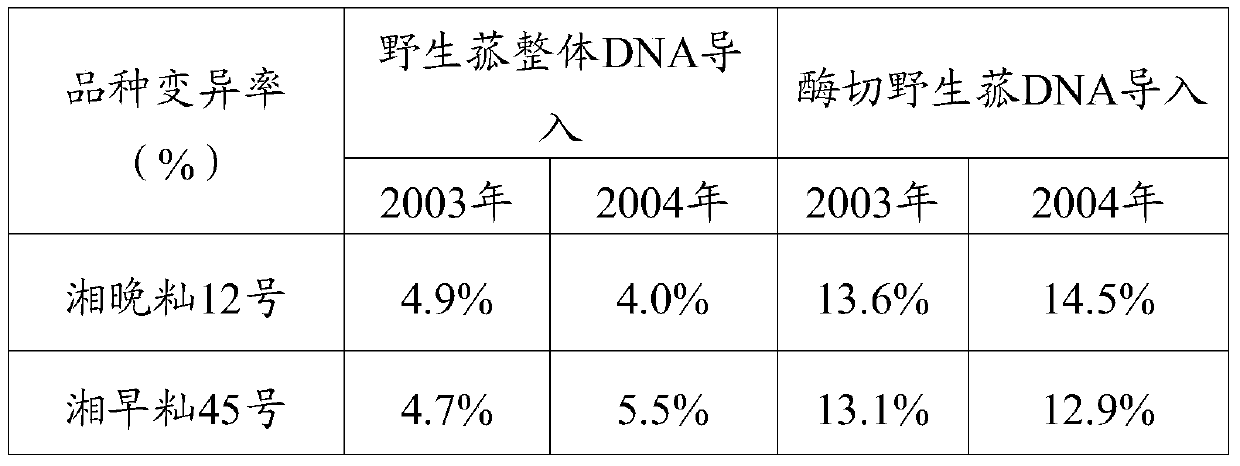
InactiveCN104830909BIncrease mutation rateFast stabilizationOther foreign material introduction processesAngiosperms/flowering plantsDiseaseRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention provides a rice breeding method, comprising the following steps: a) using CTAB method to extract wild wild rice DNA; b) using restriction endonuclease to digest the wild wild rice DNA obtained in step a) to obtain enzyme-cleaved wild wild rice DNA c) using the pollen tube passage method to introduce the enzyme-cut wild wild mushroom DNA obtained in step b) into rice, and select mutant materials for breeding. In the present invention, after restriction endonuclease digestion of wild rice wild rice DNA is introduced into rice, the mutation rate of offspring is significantly higher than that of complete DNA introduction, the stabilization speed is fast, and excellent new strains and varieties of rice are obtained. The experimental results show that the new rice variety introduced by enzymatic cutting of wild wild rice DNA has thick stems, large ears and many grains, and fast filling speed in the later stage, which overcomes the defects of large ears, weak tillering ability, neck wrapping, and low seed setting rate; It is a group of resource materials with great potential to increase production if serious pest damage is found.
Owner:田杰
Bioinformatics data processing systems
InactiveCN107533589ASequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemGenome map
Disclosed is a computer-implemented method of determining at least one optimal alignment of at least part of a first map to at least part of a second map or a plurality of second maps, wherein the maps are physical genome maps and / or restriction maps. The method comprises: receiving first map data indicative of a first ordered list of distances between features of the first map, receiving second map data indicative of a second ordered list of distances between features of the second map or second maps; generating, from the second map data, seed data indicative of a plurality of seeds, each seed comprising at least one of the distances in the second ordered list, wherein the features are restriction sites and distances are fragment sizes. The said method further comprises generating a plurality of candidate alignments from the seed data by searching at least part of the first ordered list to find at least approximate matches for respective seeds, and extending the approximate matches bydynamic programming; determining respective alignment scores for respective candidate alignments; and selecting one or more of the candidate alignments as an optimal alignment or optimal alignments,based on the alignment scores.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for detecting gene cassette array in bacterium integron by using EcoRII enzyme digestion restriction map library
InactiveCN102191322BDirect sequencing avoidsWay accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionQuarantine
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Identification method of PCR-restriction map for fritillary bulb and similar medicine material
InactiveCN1227358CLow toxicityNot easy to cultivateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiologyIsoschizomer
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Pure honeysuckle polymerase chain reaction-restriction map identification method
InactiveCN1238369CSolve the identification problemGuarantee the quality of medicinal materialsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisPolymerase L
The invention provides a polymerase chain reactino-restrictive enzyme-cut chart molecule (PCR-RFLP) method accurately identifying honeysuckle in genuine producing areas (Henan, Shandong) and nongenuine producing areas (other producing areas). The characteristic DNA alkali sequence of honeysuckle in genuine: 5'-GCCCCCCCGC CCCGCCTCCC ACAGGGTCGC G-3'; restrictive inner cut enayme EcoNi and its same cut-enzyme can identify and cut this sequence. The identifying course: extracting DNA of medical materials; using a pair of guide matters to make PCR increase; using restrictive inner cut enayme EcoNI and its same cut enayme to digest PCR product; analyzing the result by using gelation and electrophoresis of gelose; in contrast with the characteristic result of PCR-RFLP of genuine honeysuckle, judging if the tested product is genuine honeysuckle.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
A pcr-rflp identification method for different subgroups of sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma
ActiveCN109652503BEasy to identifyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologySugar cane
Disclosed is a PCR-RFLP identification method for different subgroups of sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma, wherein a tuf gene of a sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma is taken as an object for designing specific primers, a tuf gene fragment is obtained by PCR amplification, and a restriction endonuclease Msp I is then used to digest the tuf gene fragment obtained by amplification, and different subgroups of the sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma are distinguished by a differentiated RFLP restriction map. Therefore, a sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma subgroup 16SrXI-B and a sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma subgroup 16SrXI-D can be identified without sequencing.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST OF YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
PCR primer and method for detecting genotype of SNP locus of MTRR gene
ActiveCN108251541AGuaranteed accuracyOvercoming the disadvantages of relatively low efficiency and easy to cause incomplete enzyme digestionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRestriction Enzyme Cut SiteTyping
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting a genotype of rs1801394 polymorphic locus of an MTRR gene. According to the method, the genotype of the rs1801394 locus of the MTRR gene is detected by a PCR-RFLP method; a PCR product carries an internal control restriction enzyme cutting site of NdeI or an isoschizomer thereof; a rapid restriction endonuclease is used for digestion of thePCR product to obtain a restriction map for genotyping, so that a typing time can be shortened; meanwhile, results can be comprehensively judged according to residual PCR products, residual digestionintermediate products and characteristic strips of each genotype sample after complete digestion so as to avoid genotype misjudgment caused by incomplete digestion of traditional methods.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
System, Process And Software Arrangement For Disease Detection Using Genome Wide Haplotype Maps
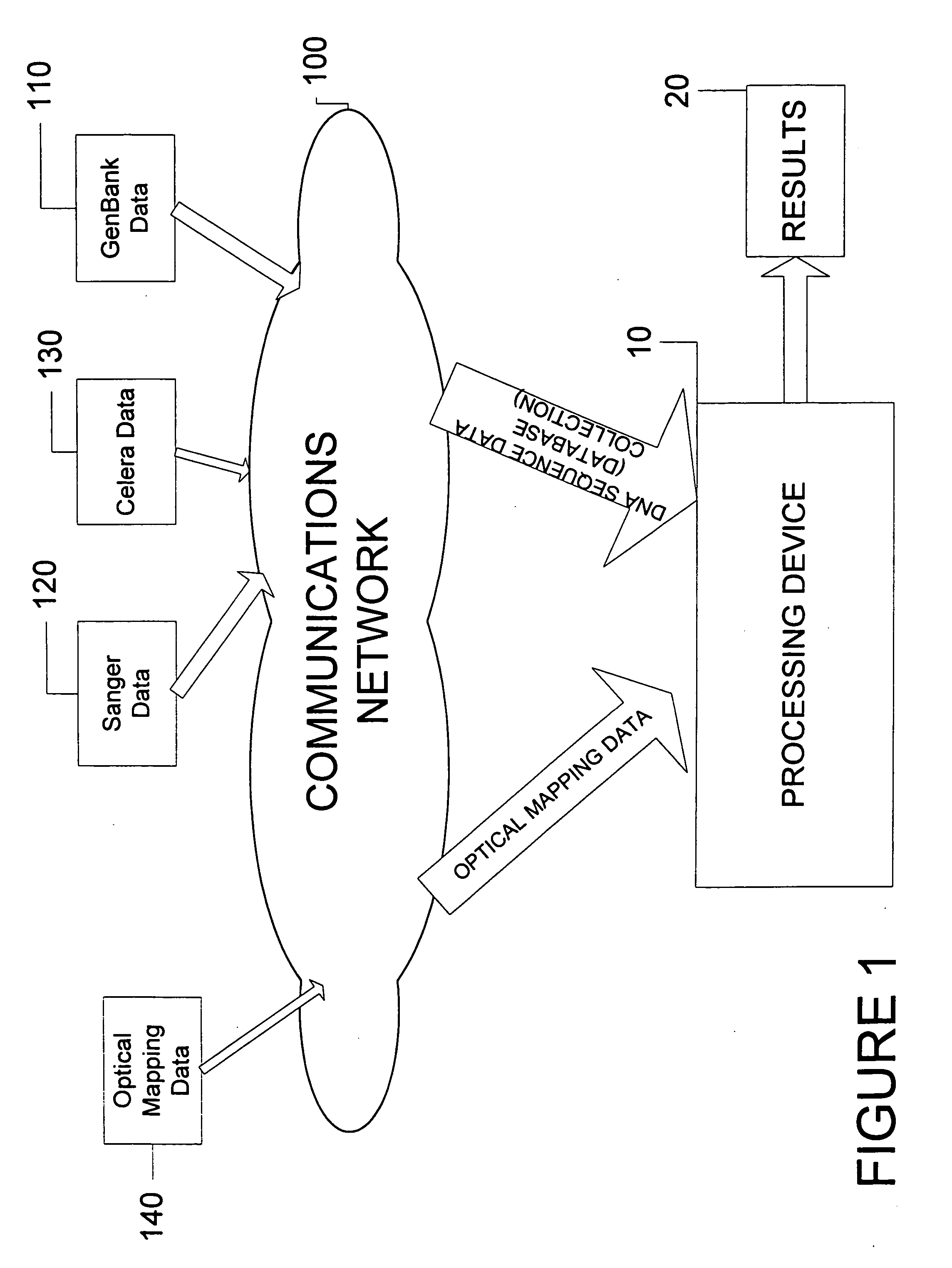
PendingUS20080046191A1Low costImprove throughputData visualisationMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseaseOptical mapping
System, process and software arrangement produces high resolution, high accuracy, ordered, genome wide haplotyped maps from single molecule based approximate ordered maps and the location of genes responsible for genetic diseases are determined by performing an association study using a population of genome wide haplotyped maps. This can also be used with Optical Mapping data to assemble a genome wide haplotyped restriction map based on multiple distinguishable restriction enzymes. This invention can also be used with any other single molecule process that can produce approximate ordered physical map from randomly broken DNA pieces of a particular genome.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
A kind of detection mtrr gene snp site genotyping pcr primer and method
ActiveCN108251541BGuaranteed accuracyOvercome the disadvantages of incomplete enzyme digestionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRestriction Enzyme Cut SiteMedicine
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting a genotype of rs1801394 polymorphic locus of an MTRR gene. According to the method, the genotype of the rs1801394 locus of the MTRR gene is detected by a PCR-RFLP method; a PCR product carries an internal control restriction enzyme cutting site of NdeI or an isoschizomer thereof; a rapid restriction endonuclease is used for digestion of thePCR product to obtain a restriction map for genotyping, so that a typing time can be shortened; meanwhile, results can be comprehensively judged according to residual PCR products, residual digestionintermediate products and characteristic strips of each genotype sample after complete digestion so as to avoid genotype misjudgment caused by incomplete digestion of traditional methods.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com