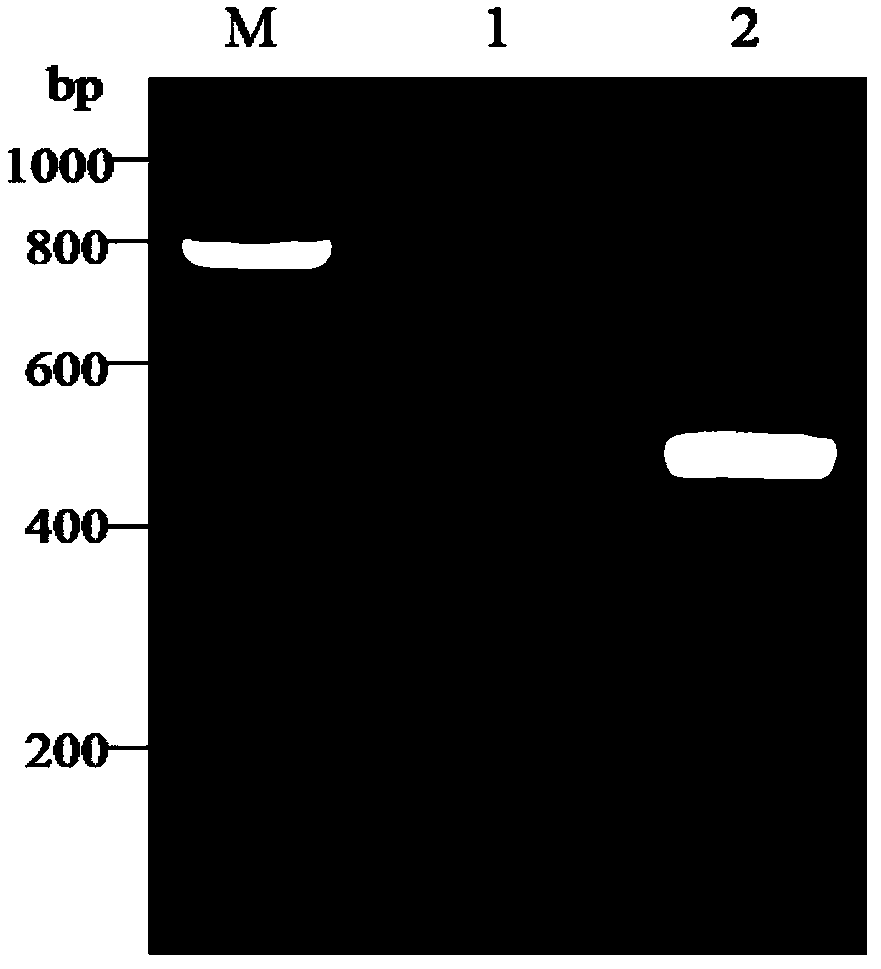
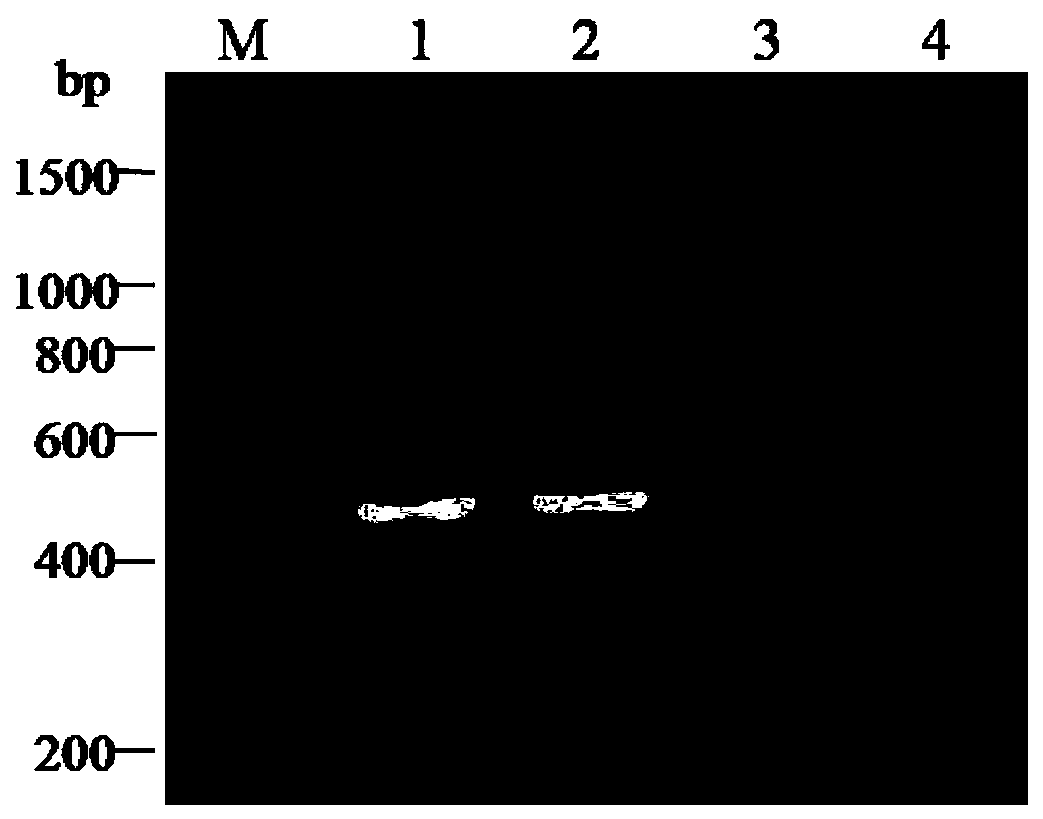
A pcr-rflp identification method for different subgroups of sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma
A phytoplasma and sugarcane technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of unestablished identification methods, time-consuming and labor-intensive, accuracy impact, etc., to save time, The effect of reducing costs and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the examples, and those without special instructions in the examples are conventional methods.
[0024] 1. Total DNA Extraction
[0025] According to the literature "Zhang R Y, Li W F, Huang Y K, et al.Group 16SrXI phytoplasmastrains, including subgroup 16SrXI-B and a new subgroup, 16SrXI-D, are associated with sugar cane white leaf. International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology, 2016,6 (1):487-491." method detected the sugarcane leaves infected with the 16SrXI-B subgroup and 16SrXI-D subgroup of the sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma, and the 16SrXI-B subgroup infected with the sugarcane white leaf disease phytoplasma and 0.2 g of sugarcane leaves of the 16SrXI-D subgroup respectively, using the plant genomic DNA extraction kit (taking the Easy Pure plant Genomic DNAKit plant DNA extraction kit from Beijing Quanshijin Biotechnology Company as an example) to extract the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com