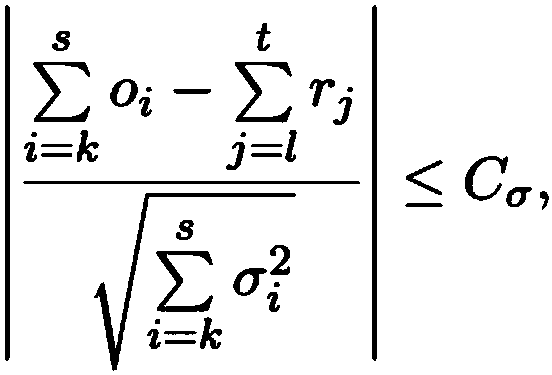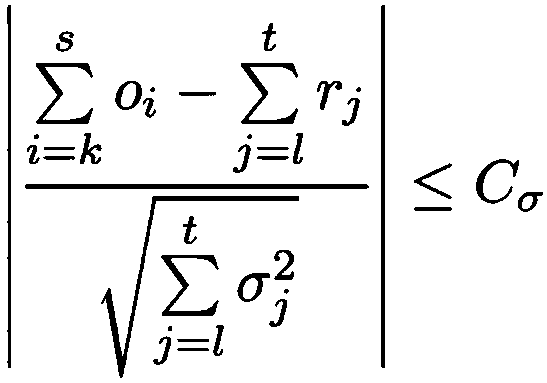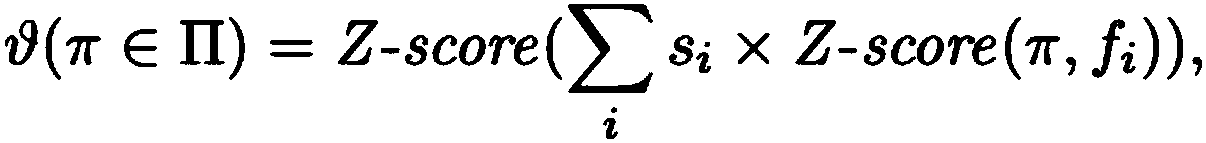Bioinformatics data processing systems
A data and physical technology, applied in the field of map comparison, can solve the problems of unclear map and sequence aligner, expansion is not straightforward, simple, different, etc., to achieve the effect of improving sensitivity and runtime, and reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0074] Detailed description of the preferred embodiment
[0075] Describes a novel seeded and extended global-local (glocal, short for global-local) alignment method, OPTIMA (and a sliding window extension for overlapping alignments, OPTIMA-Overlap), which allows for continuous-valued Mapping data is indexed, taking into account mapping errors. Also presented is a novel statistical model for conservatively assessing the significance of alignments without relying on expensive permutation-based tests, which is agnostic with respect to technique-dependent error rates.
[0076] As will be shown, OPTIMA and OPTIMA-Overlap are advantageous over prior art approaches because OPTIMA and OPTIMA-Overlap are more sensitive (1.6–2 times sensitive), more efficient (170–200%), and in terms of their alignment More precise (almost 99% accurate). These advantages are independent of the quality of the data, showing that the indexing approach and statistical evaluation of the present invention ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com