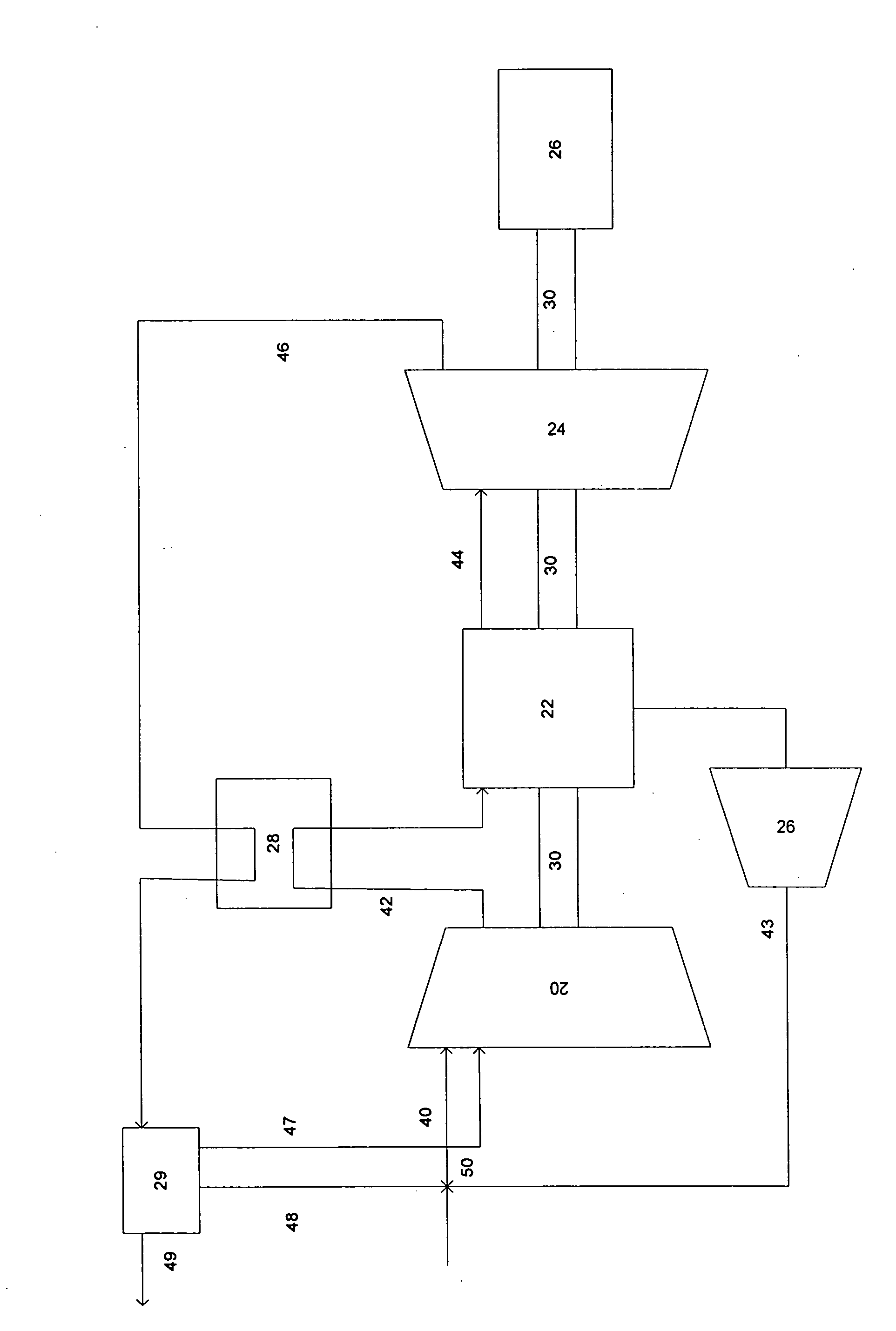Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63 results about "Parasitic load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
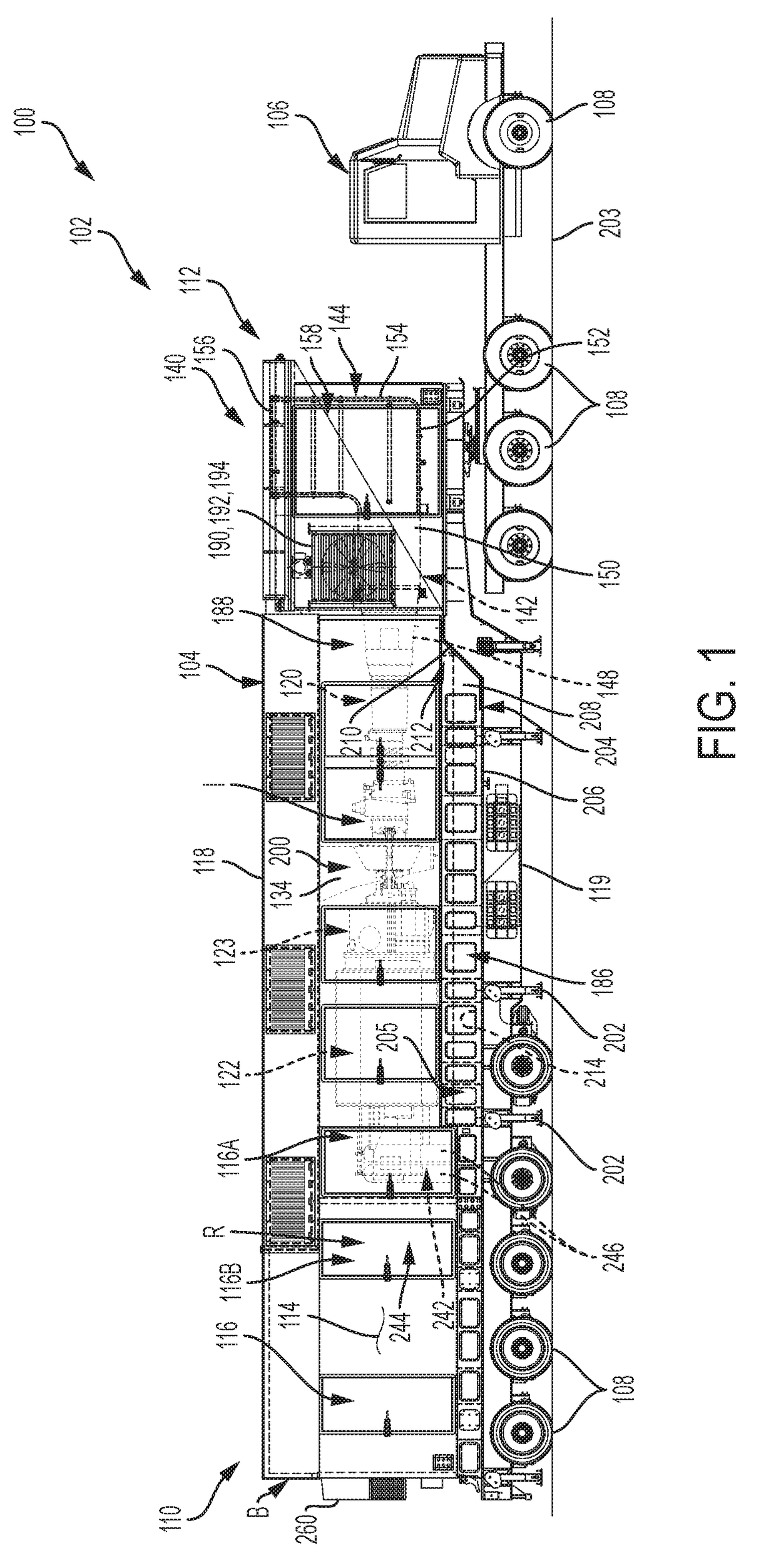
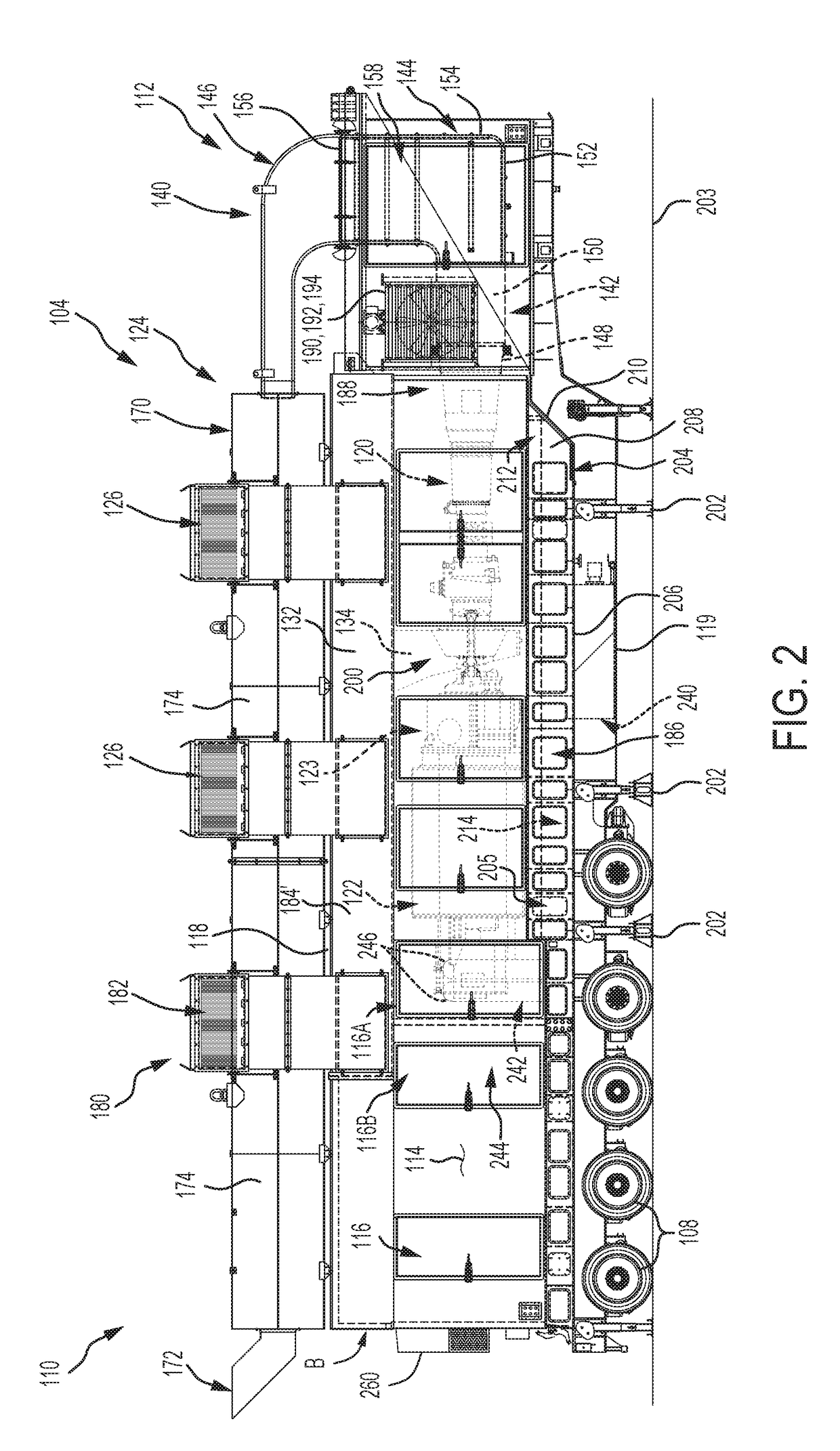
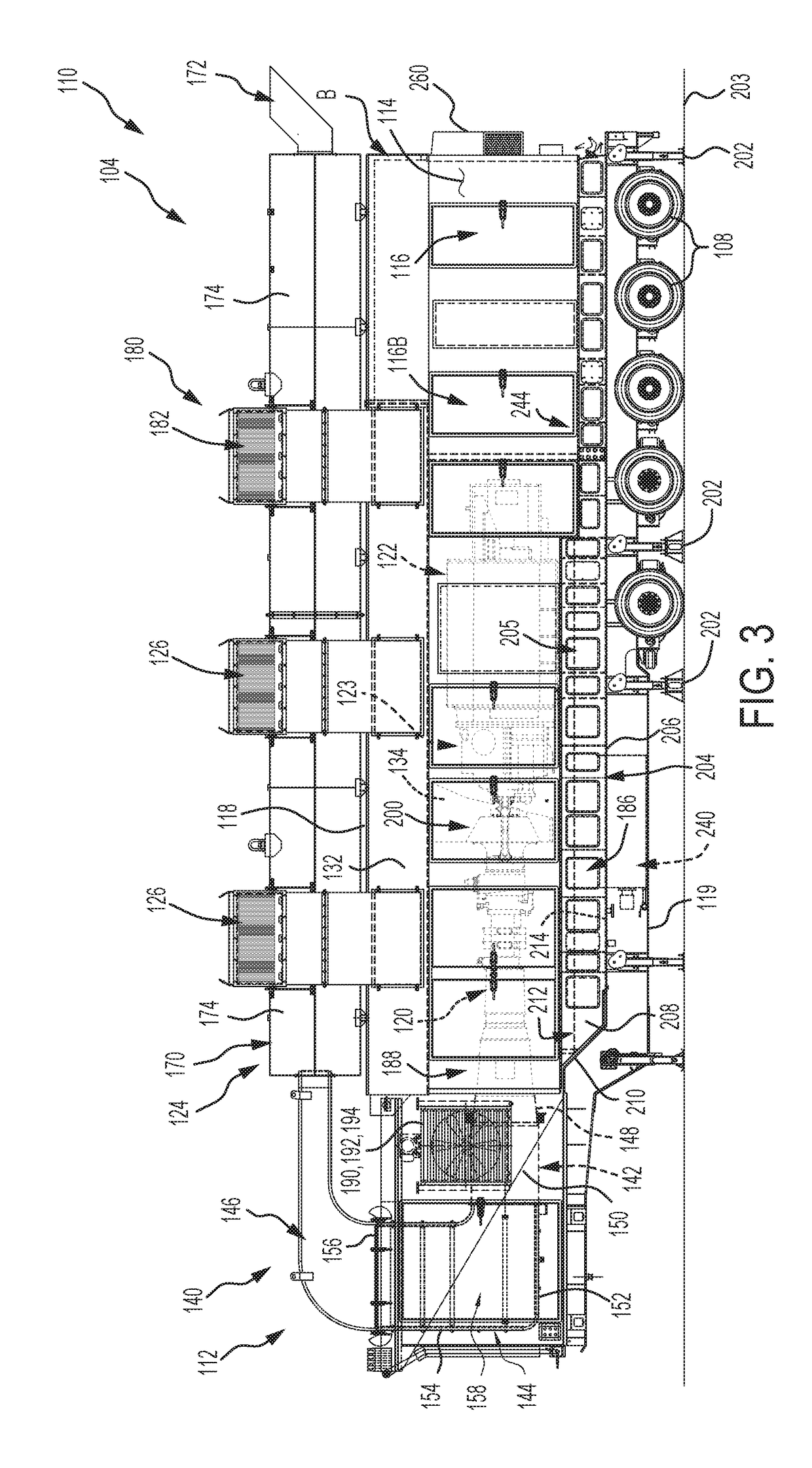
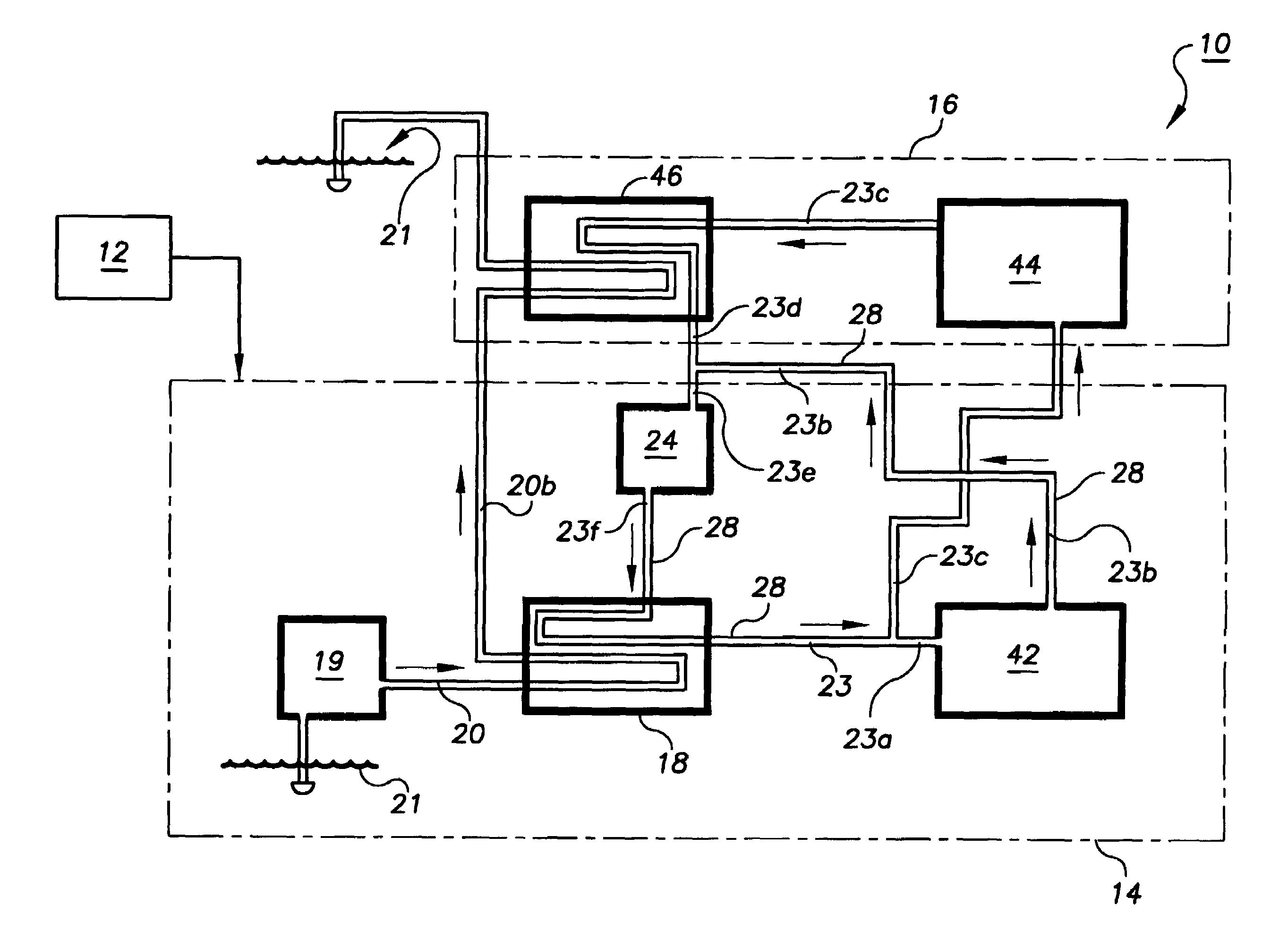
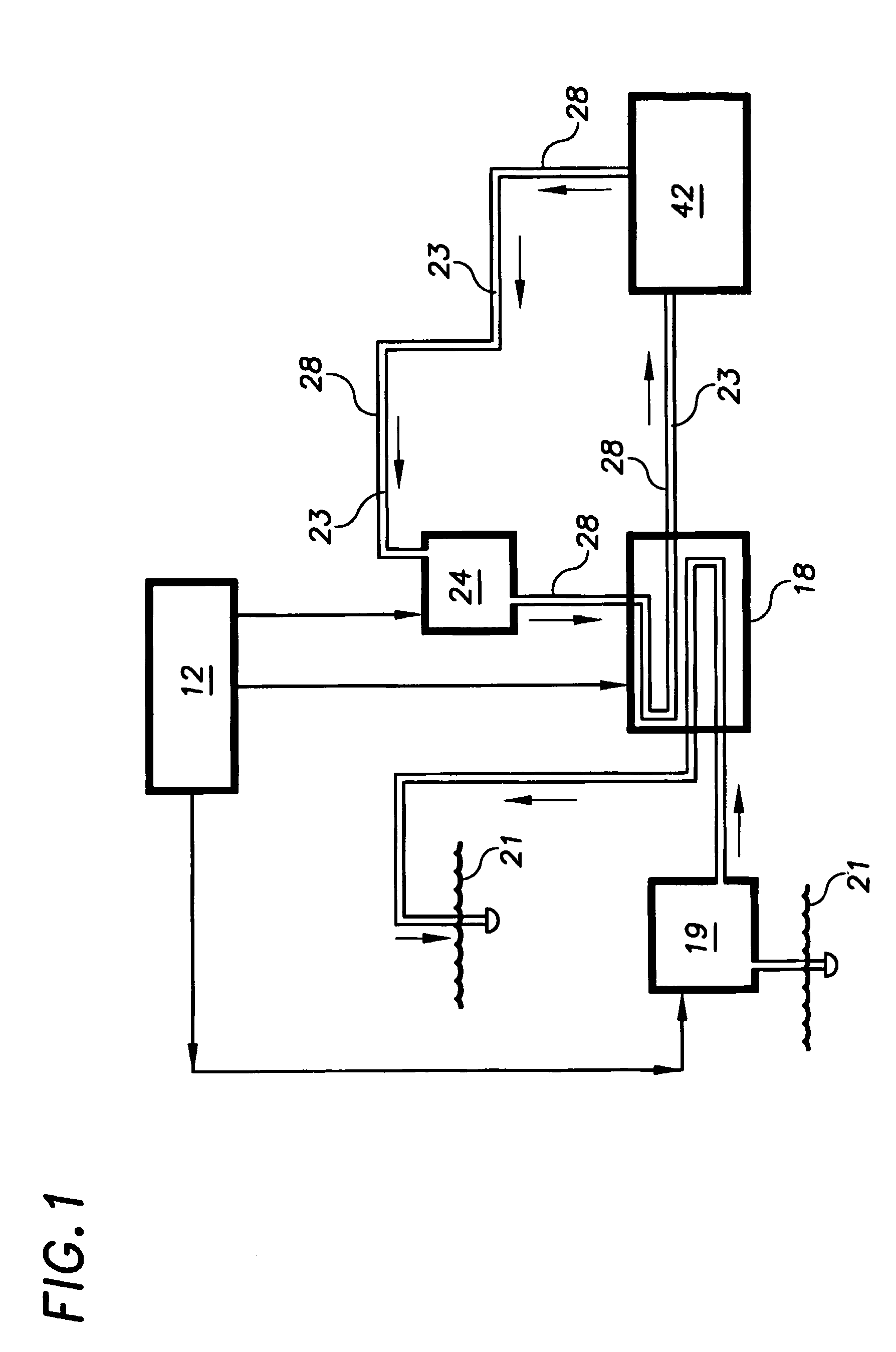
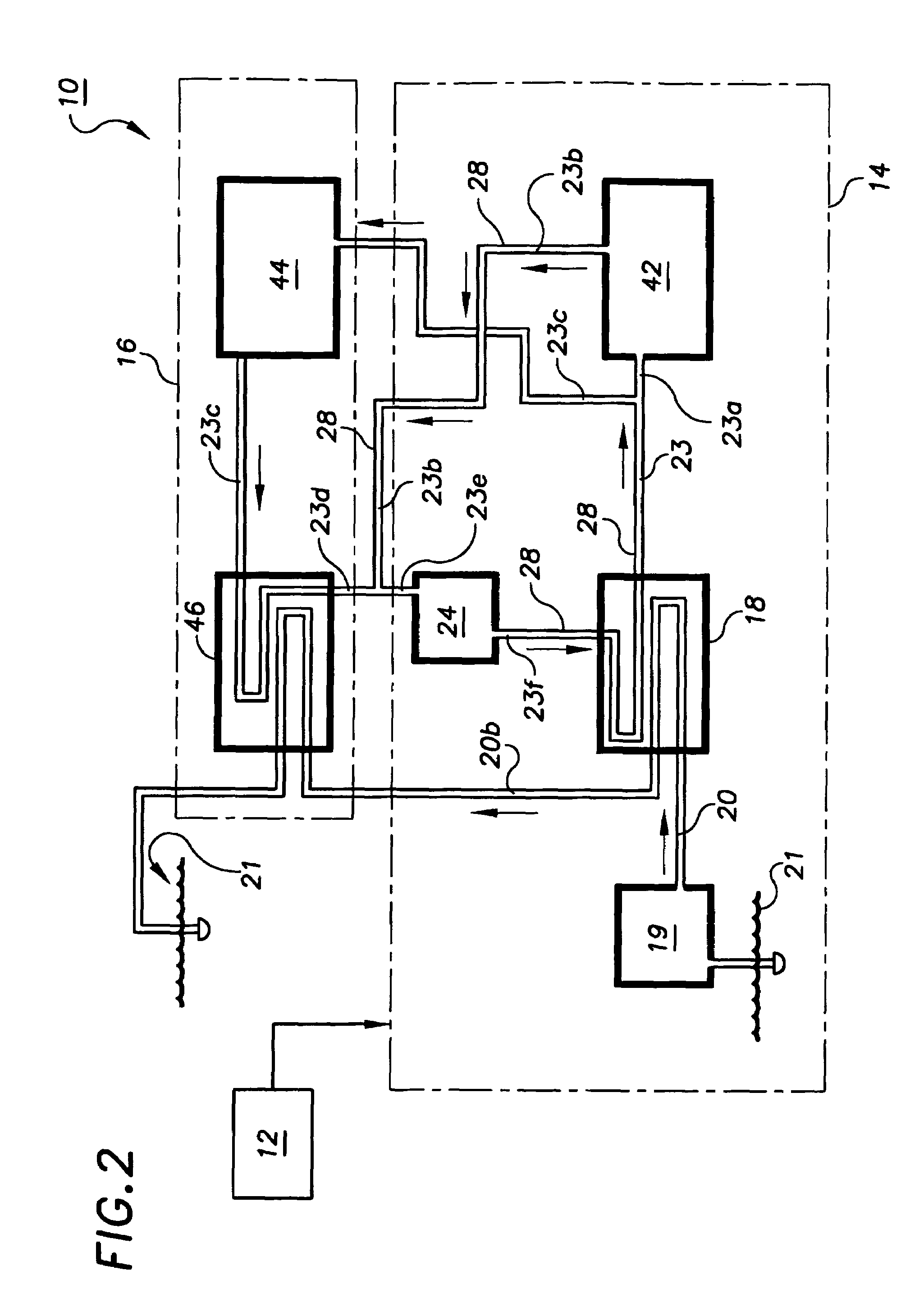
Parasitic load is a term used with regard to electrical appliances and railway locomotives. With regard to electrical appliances, it represents the power consumed even when the appliance is shut off, that is standby power. With regard to railway locomotives, it is any of the loads or devices powered by the prime mover not contributing to tractive effort, such as an air compressor, traction motor blower, or radiator fans.
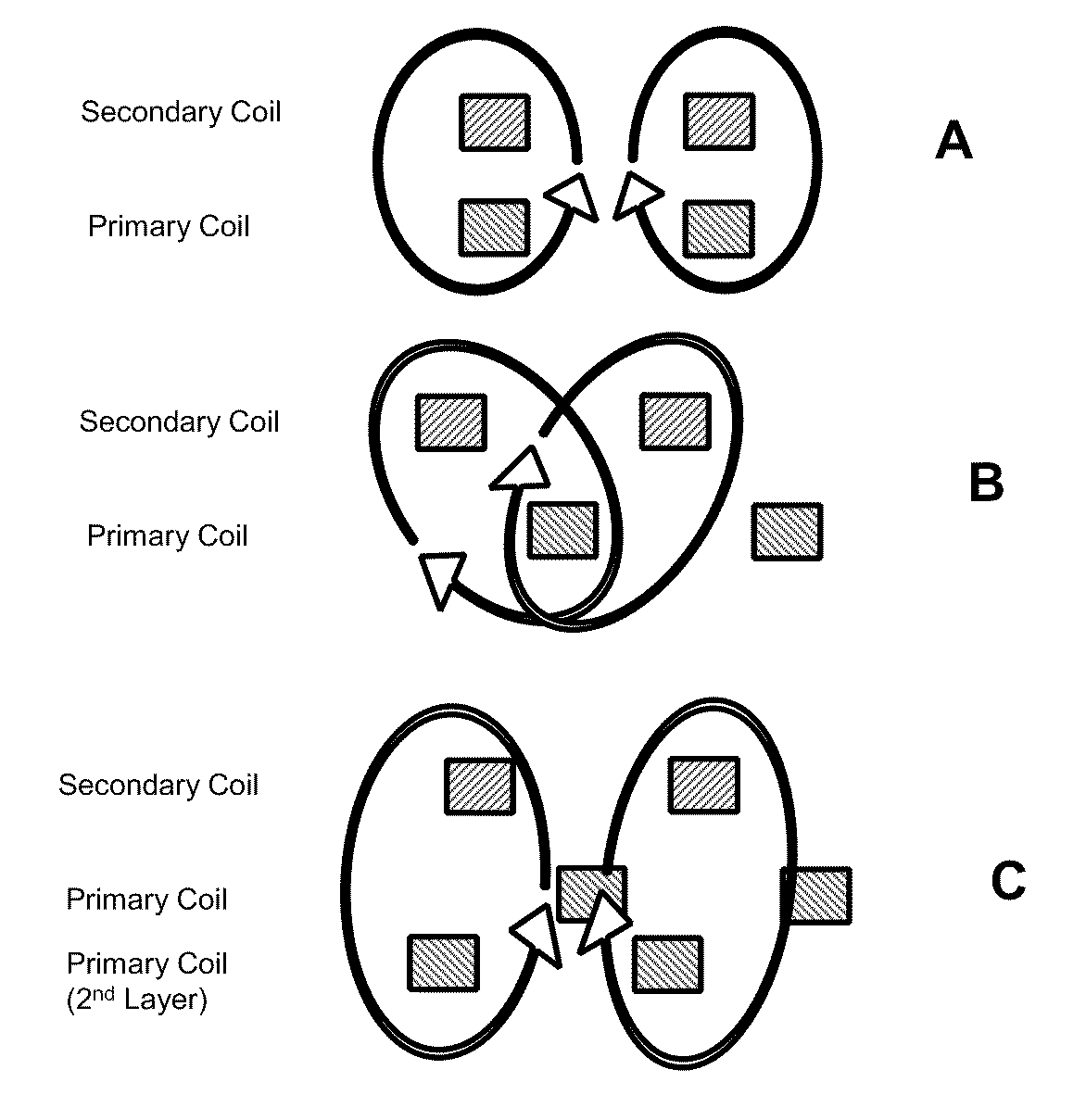
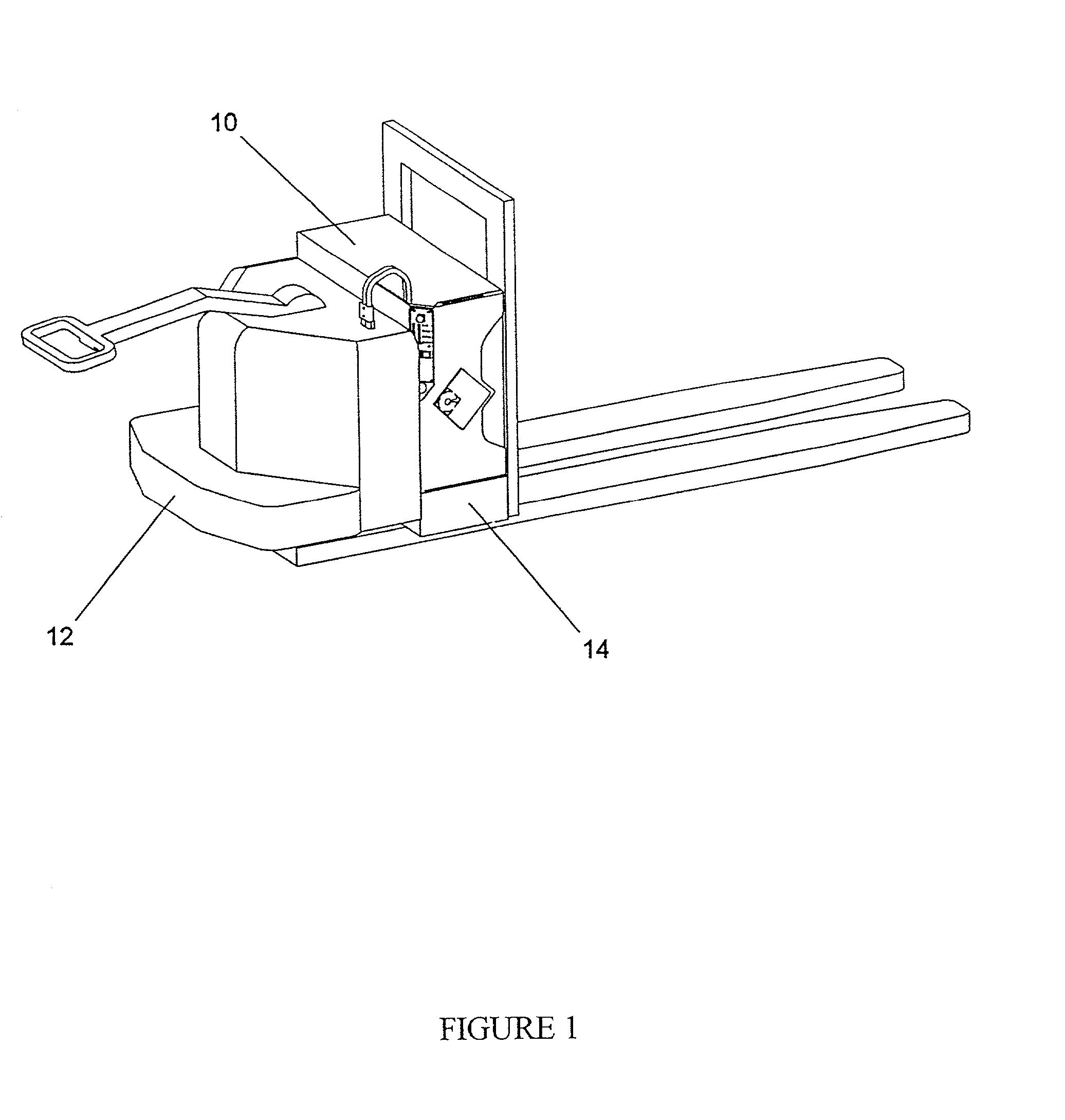
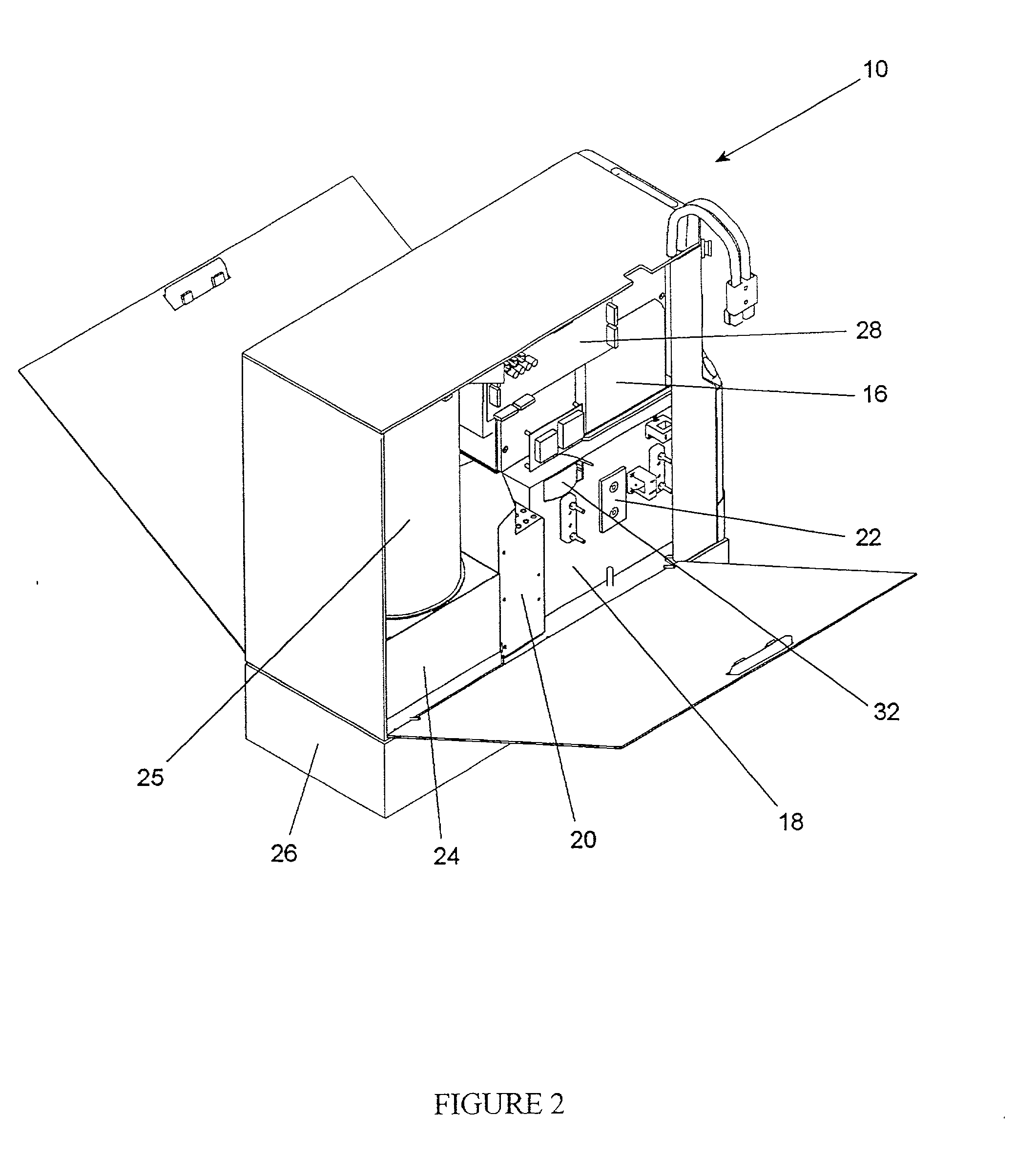
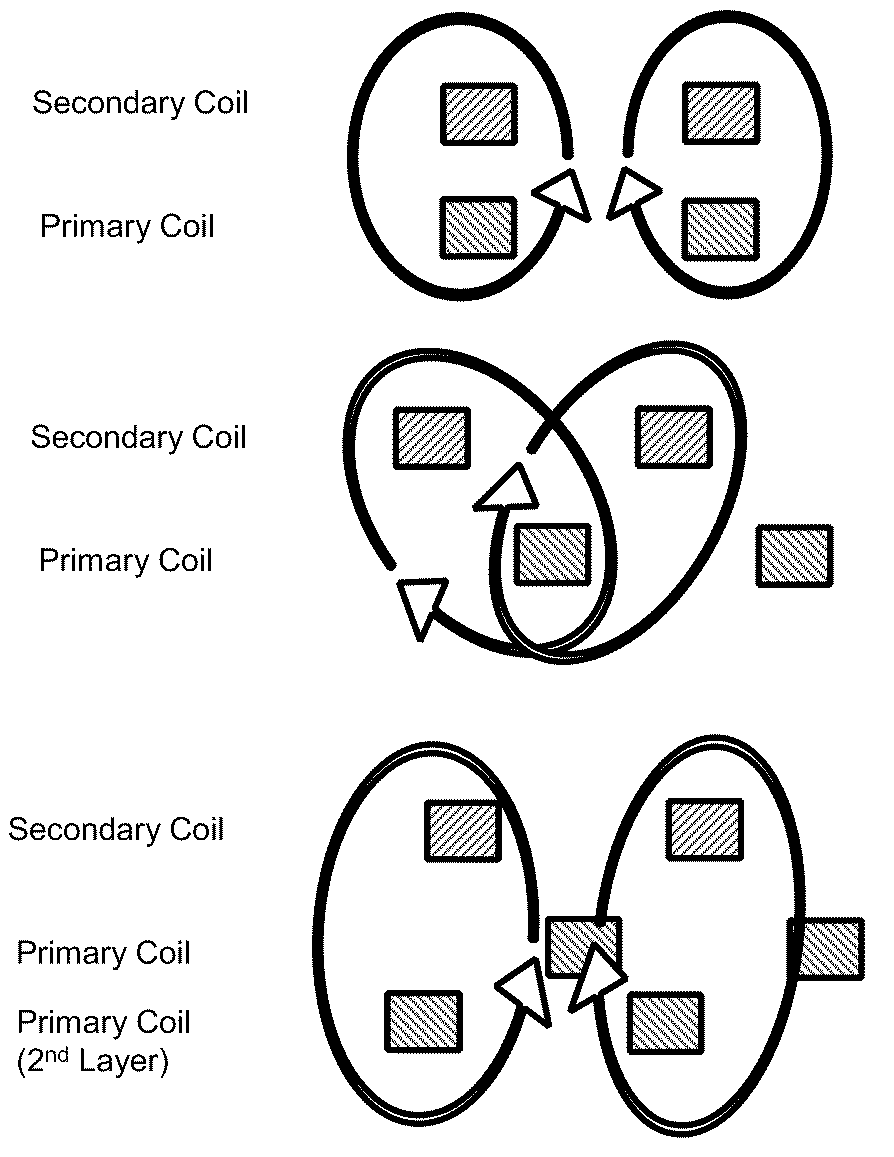
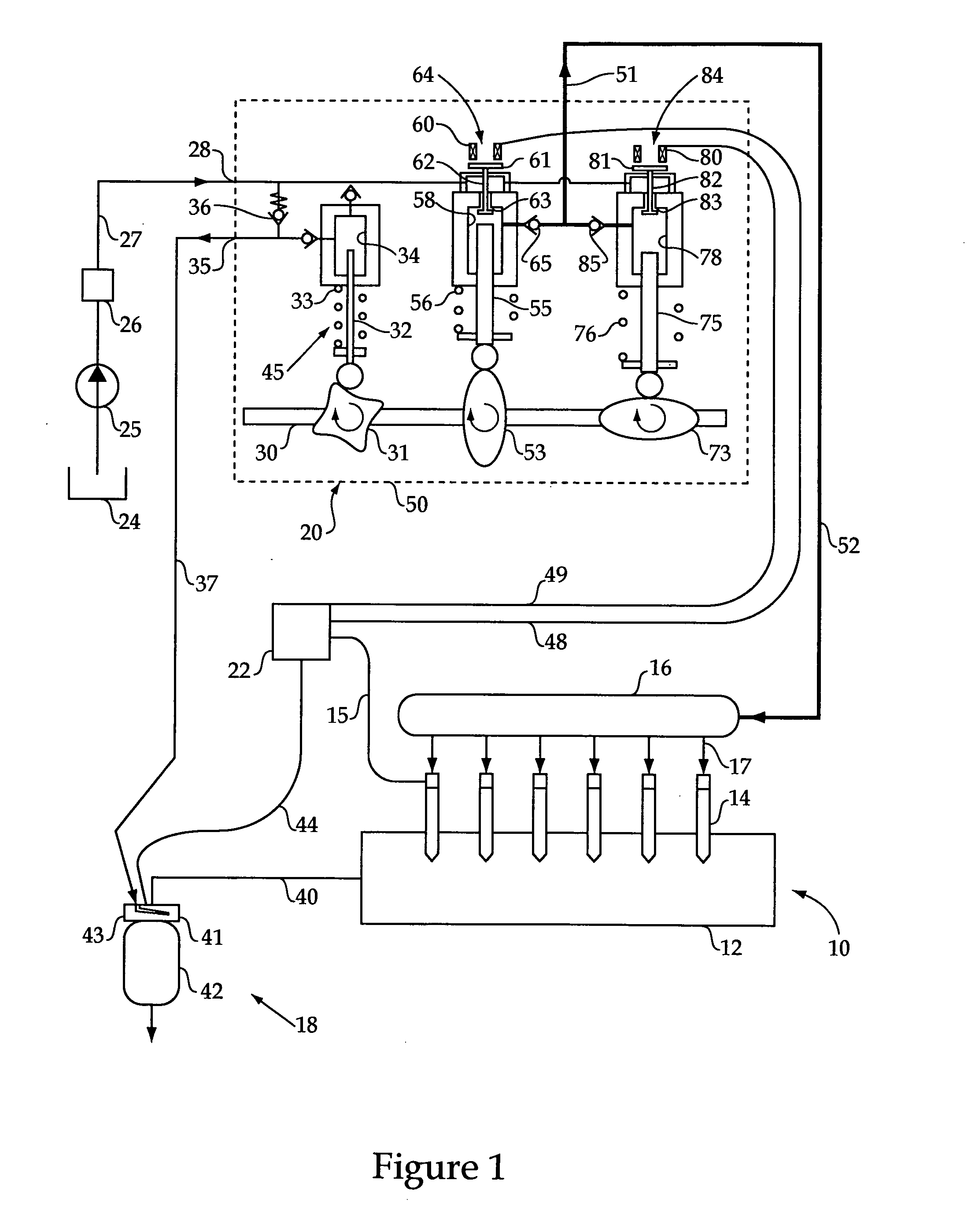
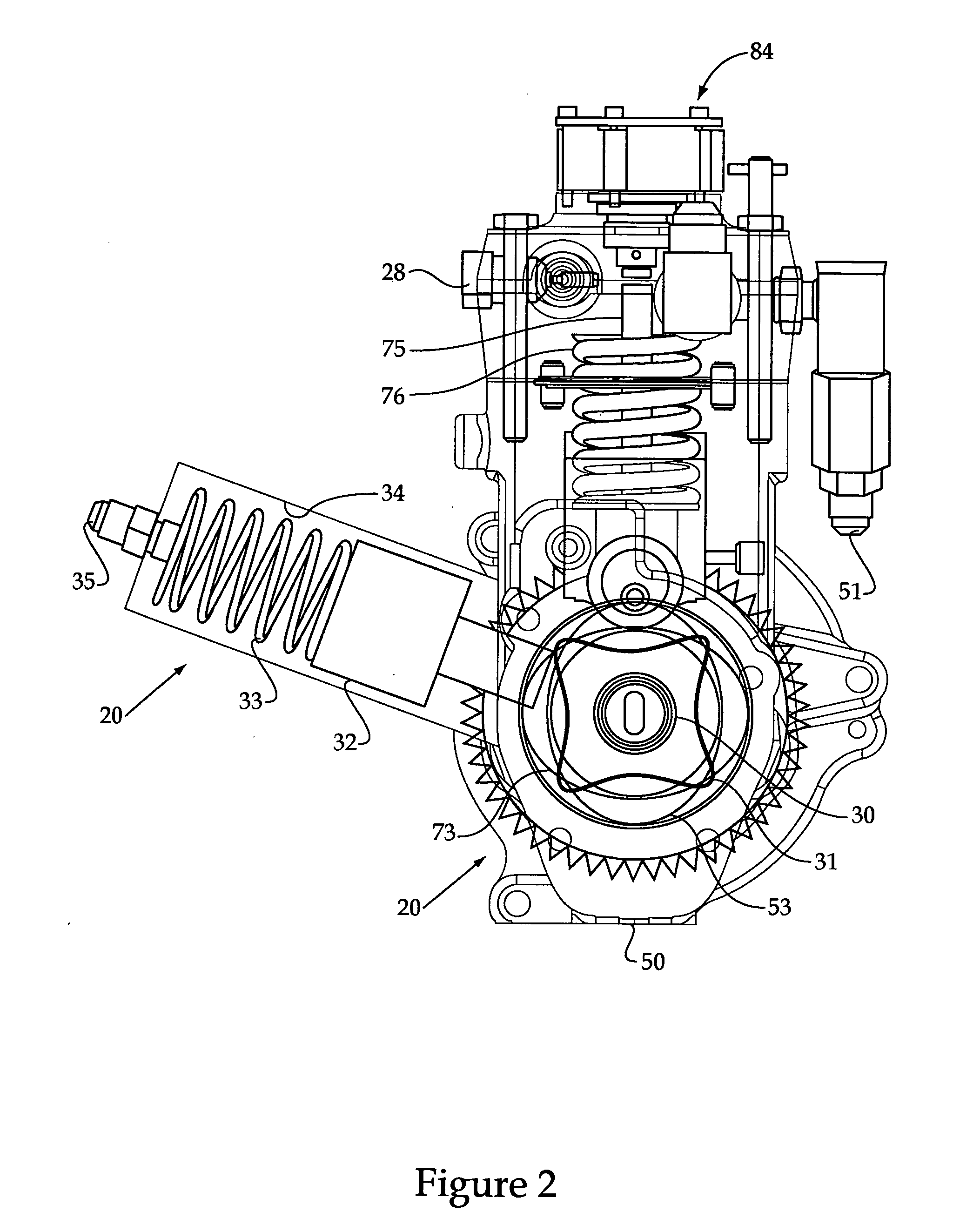
Selectable coil array
ActiveUS20100259217A1Reduce lossesImprove efficiencyImpedence networksMobile unit charging stationsCoil arrayElectric power system
An inductive wireless power system using an array of coils with the ability to dynamically select which coils are energized. The coil array can determine the position of and provide power to one or more portable electronic devices positioned on the charging surface. The coils in the array may be connected with series resonant capacitors so that regardless of the number of coils selected, the resonance point is generally maintained. The coil array can provide spatial freedom, decrease power delivered to parasitic loads, and increase power transfer efficiency to the portable electronic devices.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
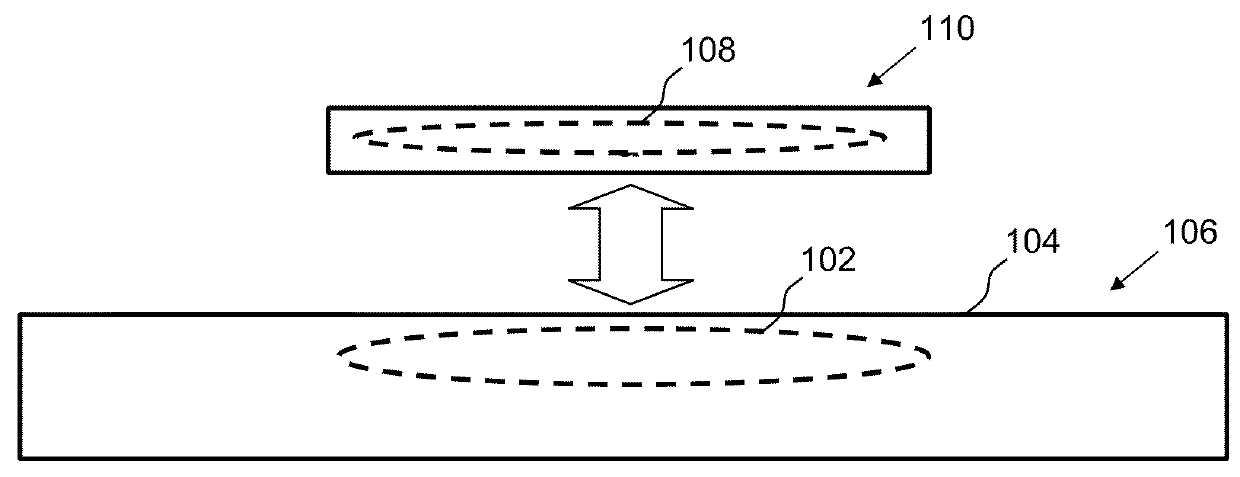
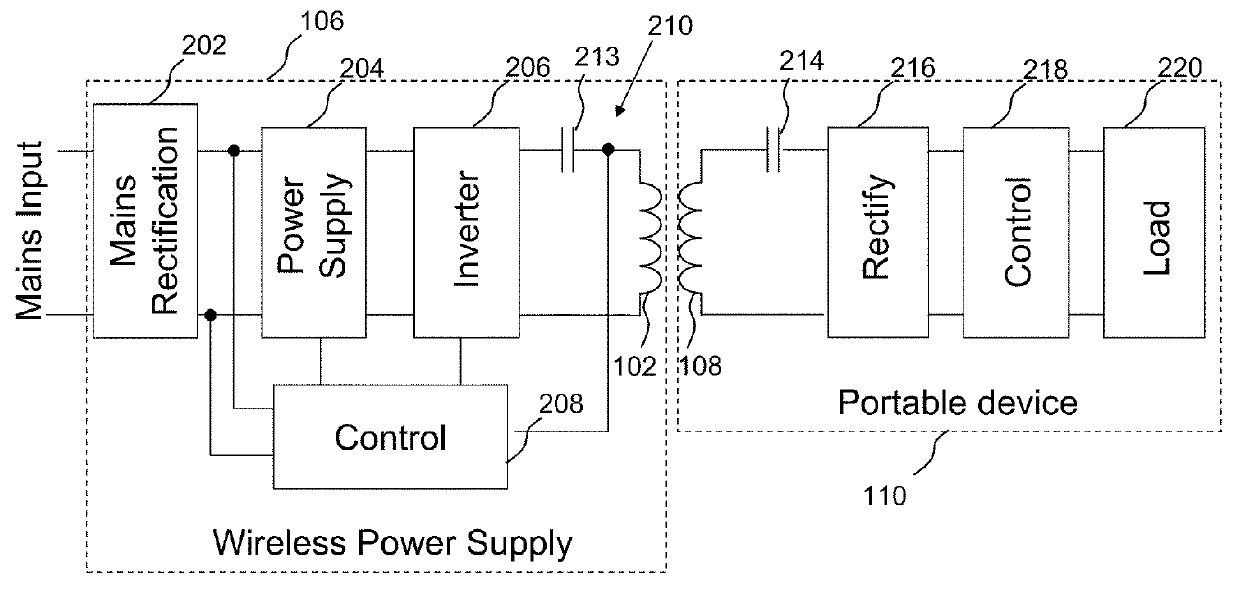
Controlling inductive power transfer systems
ActiveUS7605496B2Enhanced couplingBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemTransfer systemEngineering
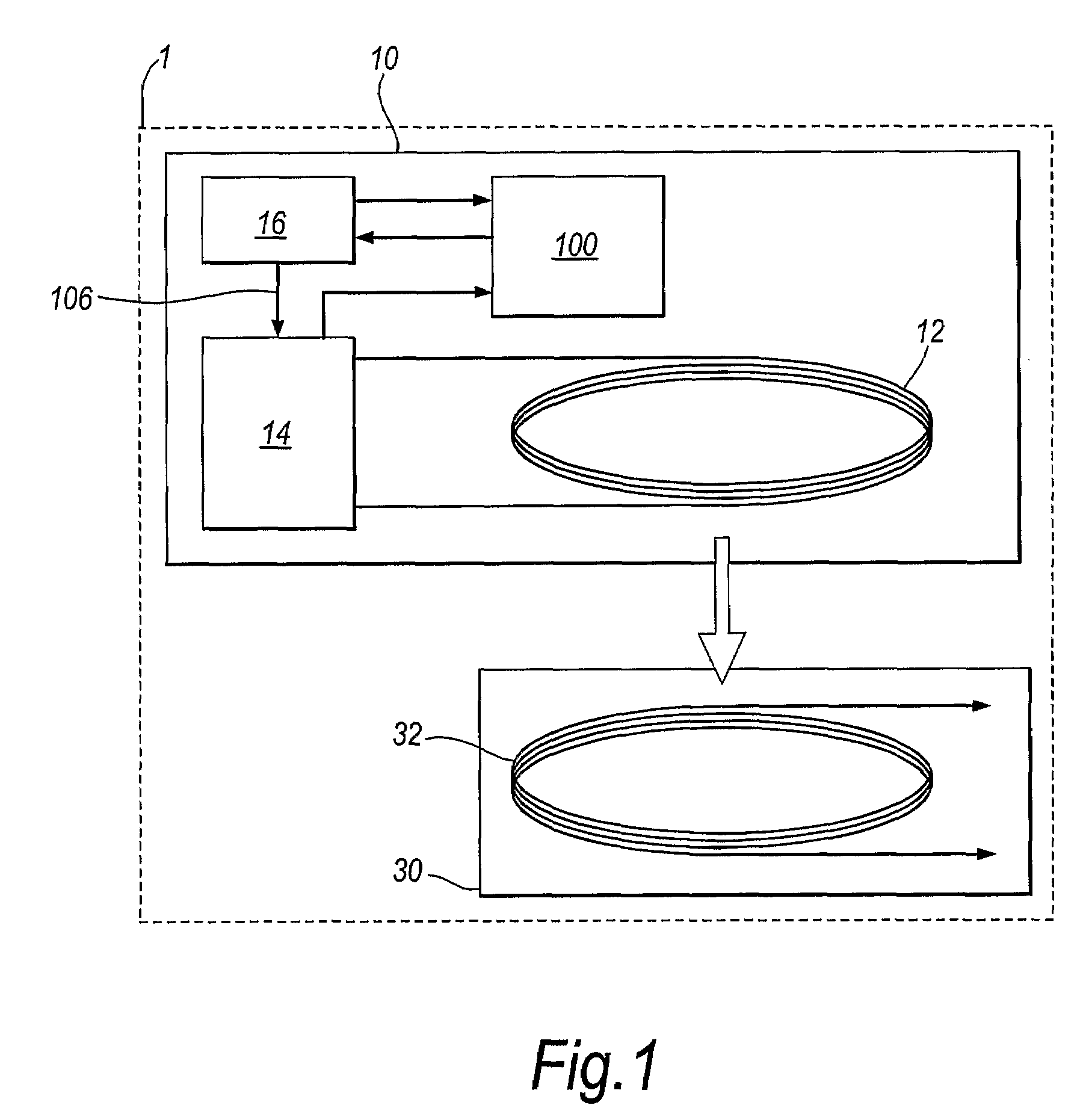
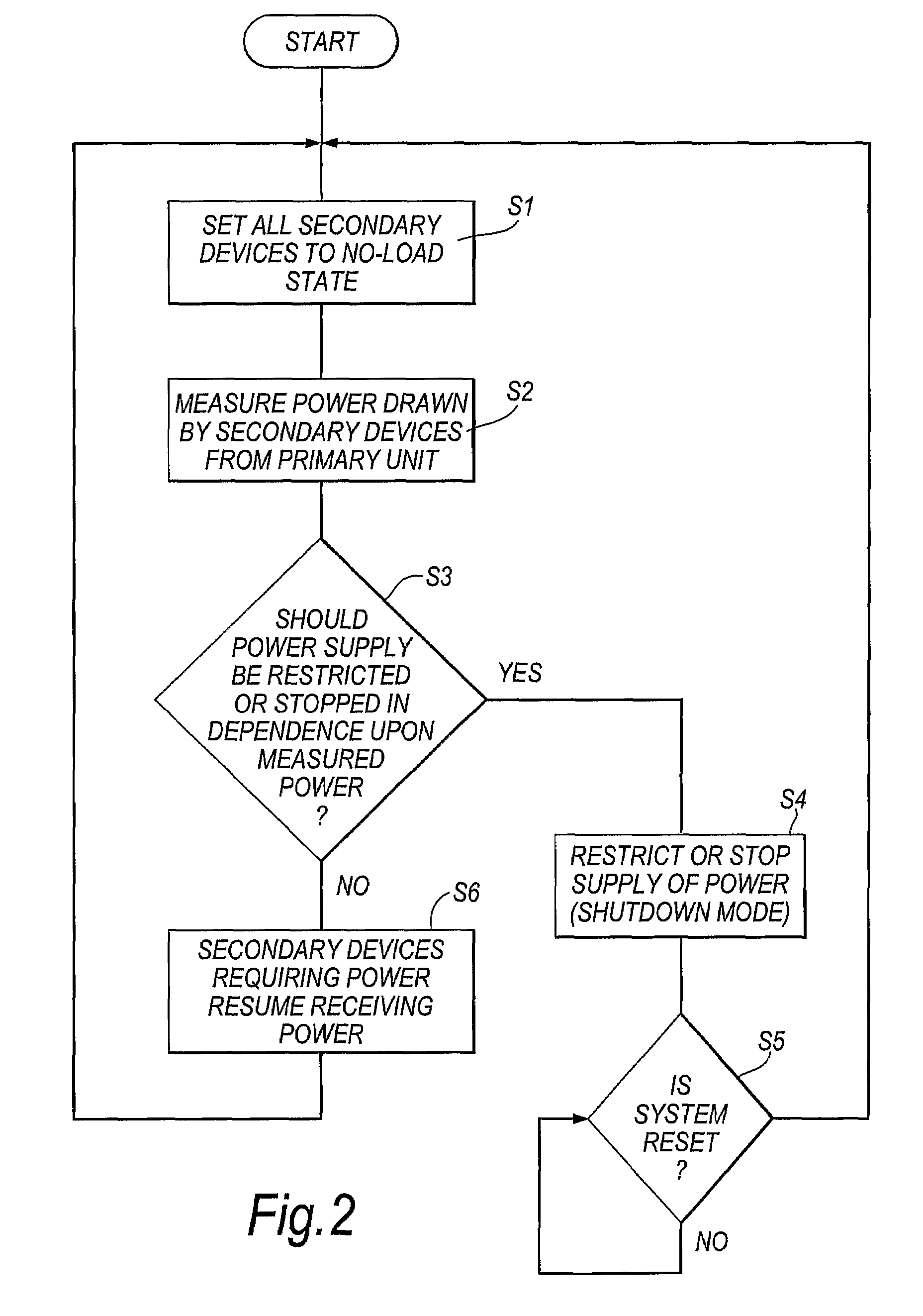
An inductive power transfer system (1) comprises a primary unit (10) operable to generate an electromagnetic field and at least one secondary device (30), separable from the primary unit, and adapted to couple with the field when the secondary device is in proximity to the primary unit so that power can be received inductively by the secondary device from the primary unit without direct electrical conductive contacts therebetween. The system detects if there is a substantial difference between, on the one hand, a power drawn from the primary unit and, on the other hand, a power required by the secondary device or, if there is more than one secondary device, a combined power required by the secondary devices. Following such detection, the system restricts or stops the inductive power supply from the primary unit. Such a system can detect the presence of unwanted parasitic loads in the vicinity of the primary unit reliably.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
Supplementary Thermal Energy Transfer in Thermal Energy Recovery Systems
ActiveUS20090320477A1Maximize power generationIncrease energy contentSteam engine plantsMechanical energyEngineering
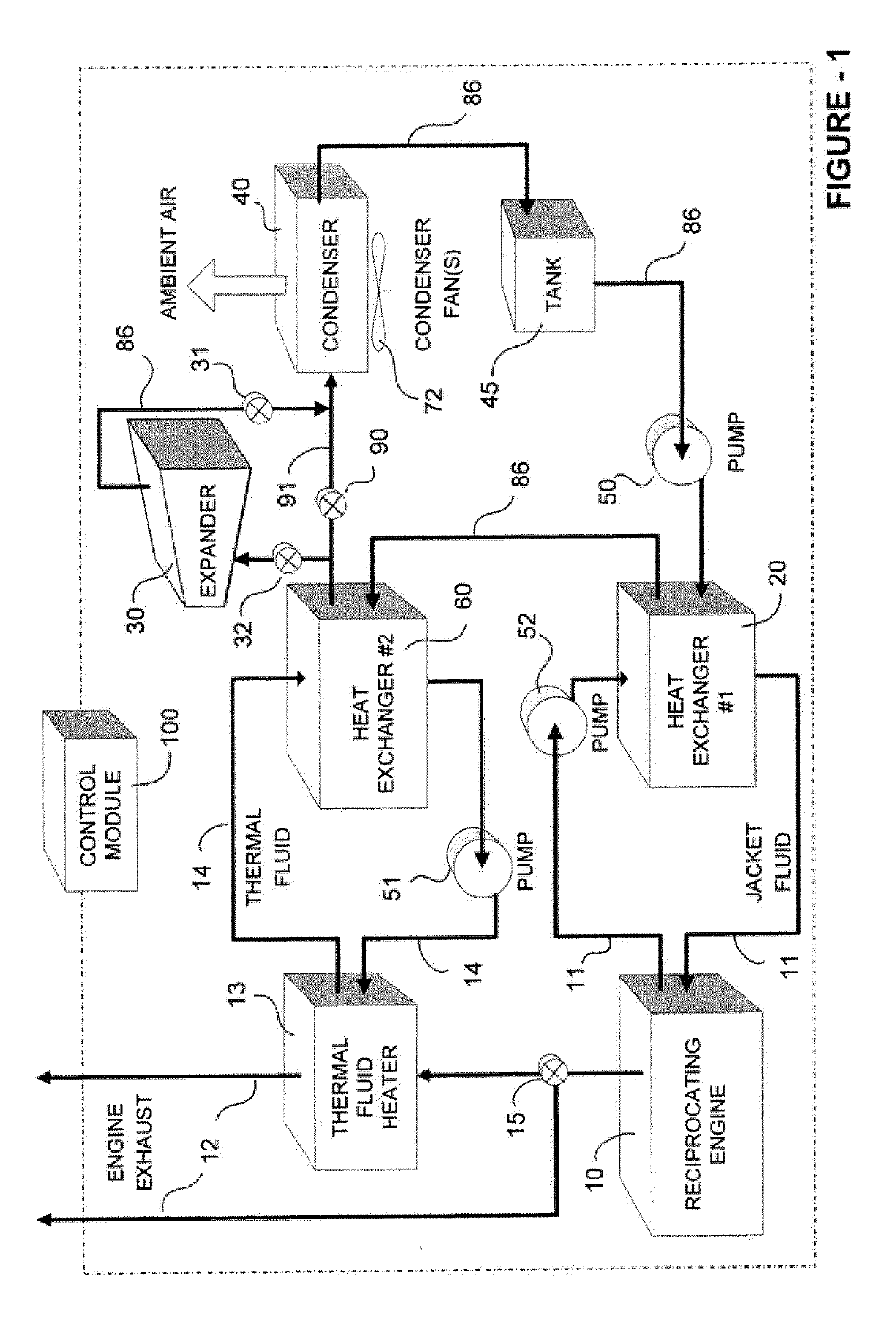
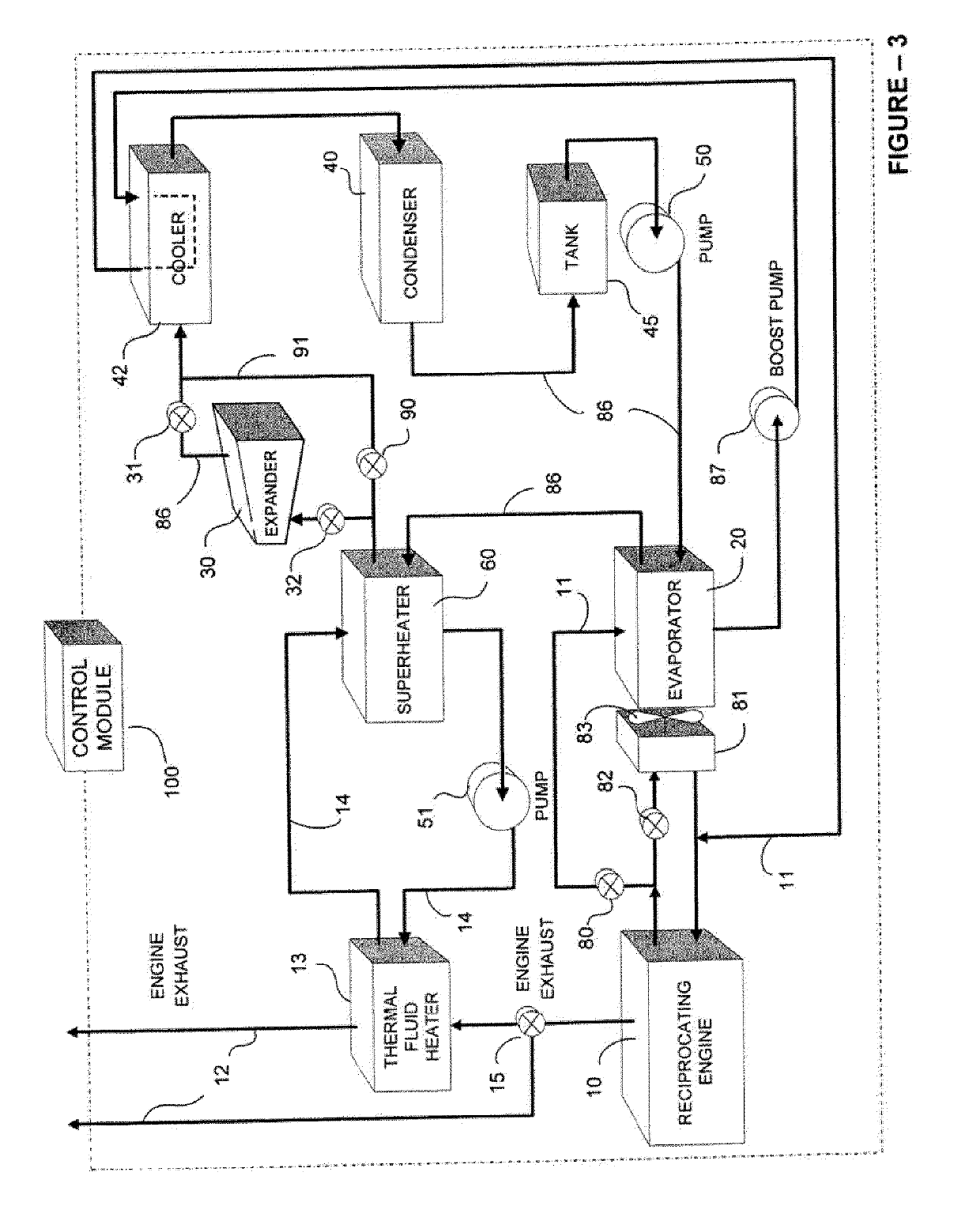
A system for controlled recovery of thermal energy and conversion to mechanical energy. The system collects thermal energy from a reciprocating engine (for example, from engine jacket fluid) and may also collect further thermal energy from a natural gas compressor (for example, from compressor lubricating fluid). The collected thermal energy is used to generate secondary power by evaporating an organic propellant and using the gaseous propellant to drive an expander in production of mechanical energy. Secondary power is used to power parasitic loads, improving energy efficiency of the system. A supplementary cooler may provide additional cooling capacity without compromising system energy efficiency.
Owner:JUCHYMENKO VICTOR
Mobile power generation system including dual voltage generator
InactiveUS20190067991A1Reduce system weightEliminate needSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsMechanical energy handlingElectricityVoltage generator
Mobile power generation system and methods for dual-voltage generation include providing a trailer including a rear end, a front end, a bottom end, and a top end, a gas turbine housed inside the trailer, and an electrical generator coupled to the gas turbine to generate electricity and housed inside the trailer. The electrical generator is at least a dual-voltage generator configured to provide an auxiliary power to generator parasitic loads and a main primary load output power and comprising one or more taps configured to provide the auxiliary power to generator parasitic loads. The electrical generator is at least a dual-voltage generator comprising three-phase circuitry including three lines and one or more taps configured to provide auxiliary power to generator parasitic loads, ends of the three lines configure to provide a main primary load output power.
Owner:ON POWER INC
Fuel cell thermal management system and method
InactiveUS20020168556A1Sufficient cooling capacityFuel cell heat exchangeElectric devicesFuel cellsEngineering
This application relates to a system and method for regulating the temperature of a self-contained fuel cell apparatus preferably comprising a fuel reformer. The invention maintains the various components of the fuel cell apparatus within preferred operating temperature ranges while ensuring that exhaust gases and external surfaces of the apparatus do not exceed safe temperature levels. The invention is particularly suited for self-contained hybrid power supply applications, for example for non-road electric vehicles. The various components of the apparatus are strategically configured relative to air flow paths to fully utilize the cooling capacity of the process stream and minimize parasitic loads. In some embodiments the inlet air is pre-heated to enable operation of the apparatus in low temperature environments, such as industrial freezers.
Owner:CELLEX POWER PRODS
Selectable coil array
ActiveUS9231411B2Reduce lossesImprove efficiencyTransformersImpedence networksCoil arrayElectric power system
An inductive wireless power system using an array of coils with the ability to dynamically select which coils are energized. The coil array can determine the position of and provide power to one or more portable electronic devices positioned on the charging surface. The coils in the array may be connected with series resonant capacitors so that regardless of the number of coils selected, the resonance point is generally maintained. The coil array can provide spatial freedom, decrease power delivered to parasitic loads, and increase power transfer efficiency to the portable electronic devices.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
Toroidal intersecting vane gas management system
InactiveUS20060260308A1Improve matchReduced Power RequirementsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineManagement system
The invention relates to the discovery that employing a toroidal intersecting vane machine (TIVM) within the internal combustion engine provides substantial improvements in controlling pressure, air pressure and air flow into an engine, while maintaining a simplified mechanical system and providing a compressor with little or no parasitic load on the engine. This invention covers the use of the TIVM for the purpose of providing this control.
Owner:MECHANOLOGY INC
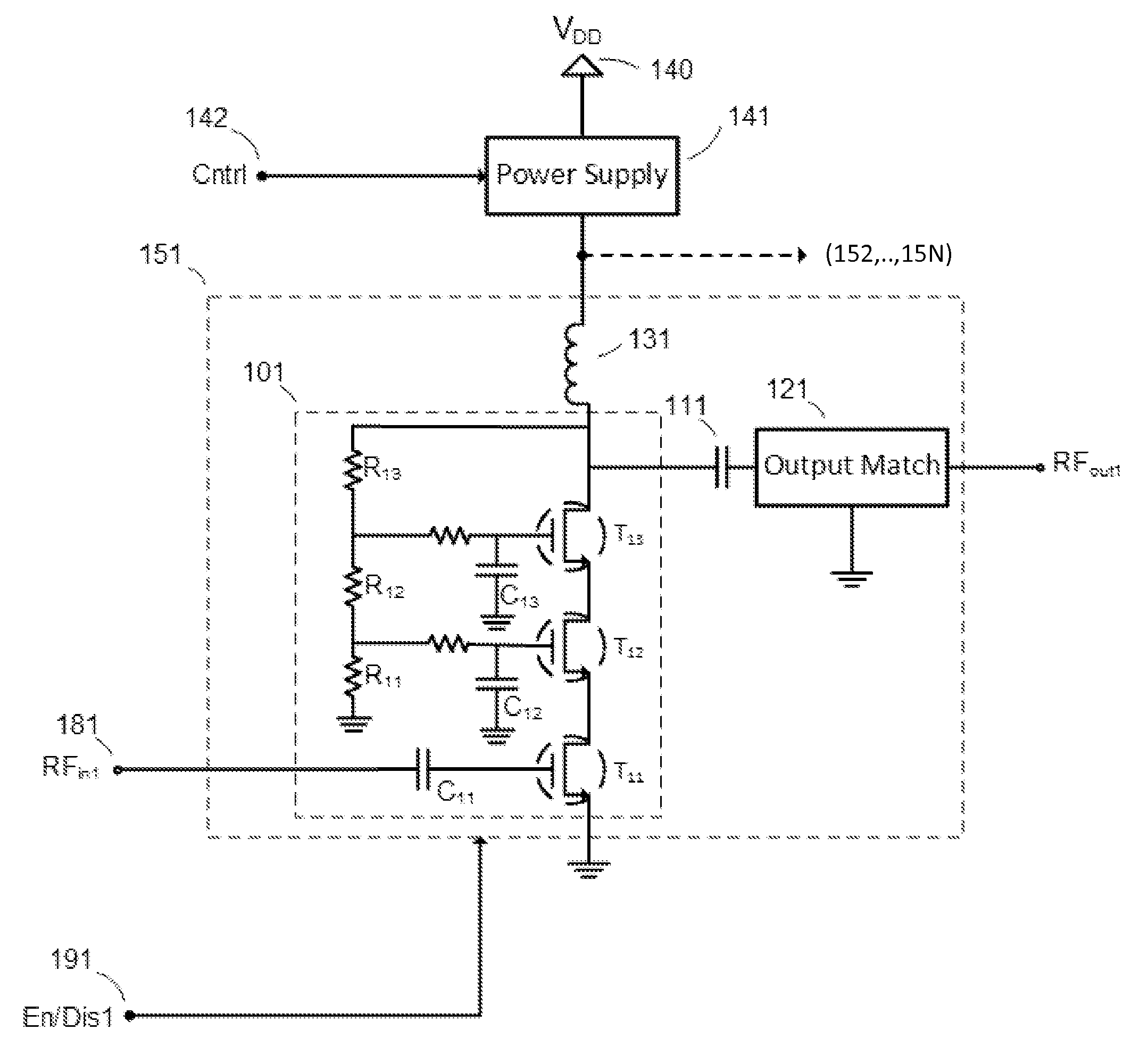
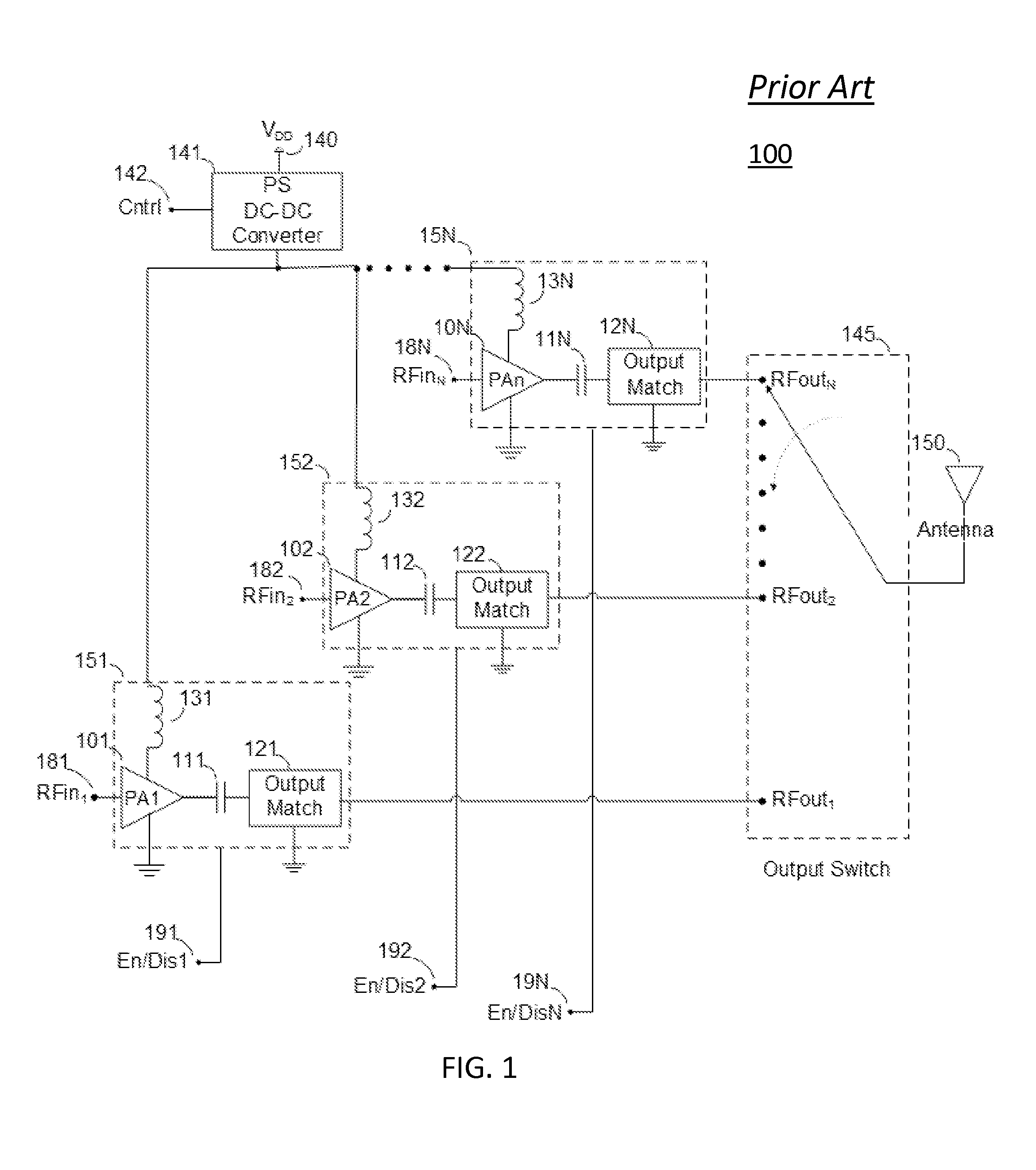
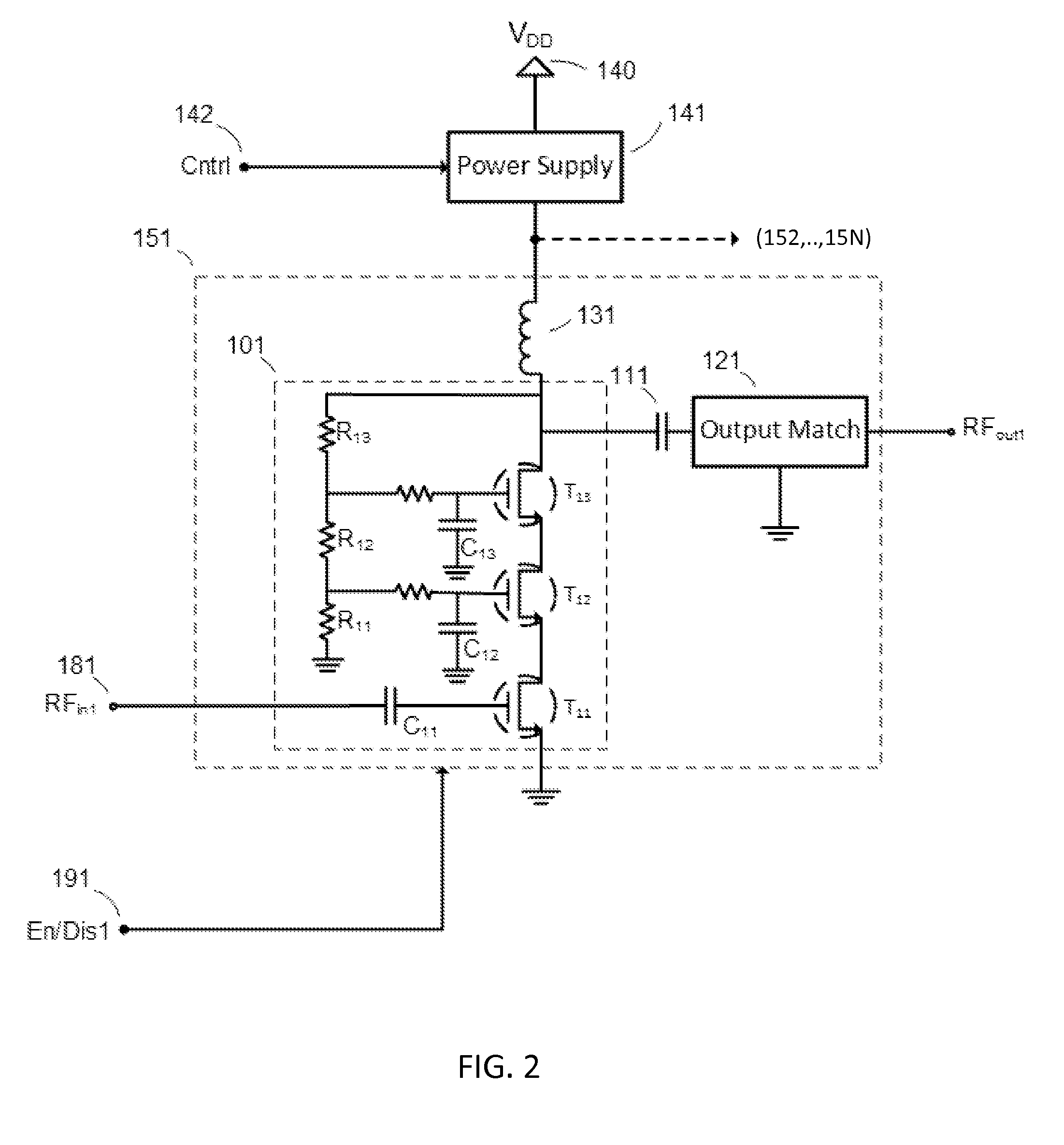
Load compensation in RF amplifiers
ActiveUS9160292B2Reduce power supplyReduce load effectHigh frequency amplifiersPower amplifiersRF power amplifierParasitic load
Methods and systems for reducing parasitic loading on a power supply output in RF amplifier arrangements used in multiband and / or multitude RF circuits are presented. Such RF circuits can comprise a plurality of RF amplifiers of which only one is activated for a given desired transmission mode and / or band.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Ground source heat pump well field design and control strategy for large tonnage
InactiveUS7647773B1Optimal Control StrategyEasy to operateCollector components/accessoriesLighting and heating apparatusModularityGood practice
The present invention features geothermal systems that use of a well field open loop scheme by interconnecting the well field through a system of mains and controlled branches, the latter composed of multiple (2-5) wells. The proposed design lends itself to the use of modular well field kits that minimize installation cost, insures equal return water distribution to the active wells, creates standardization and insures best practices. The benefits of individual branch control include the ability to serve the building load in staged delivery, thereby minimizing well field parasitic load, and maximizing the time available for well field thermal relaxation and availability.
Owner:AMERICAN REFINING GRP
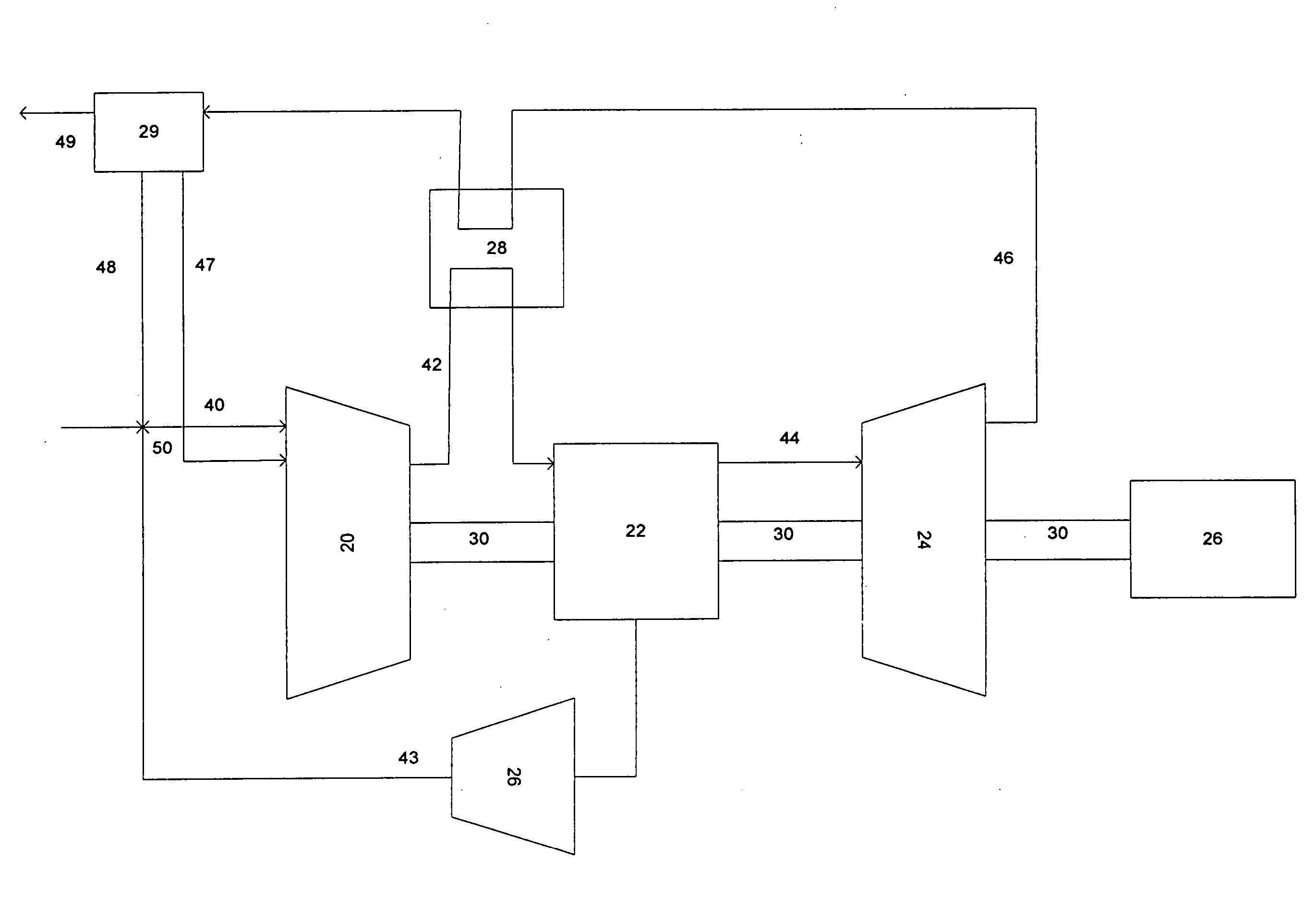
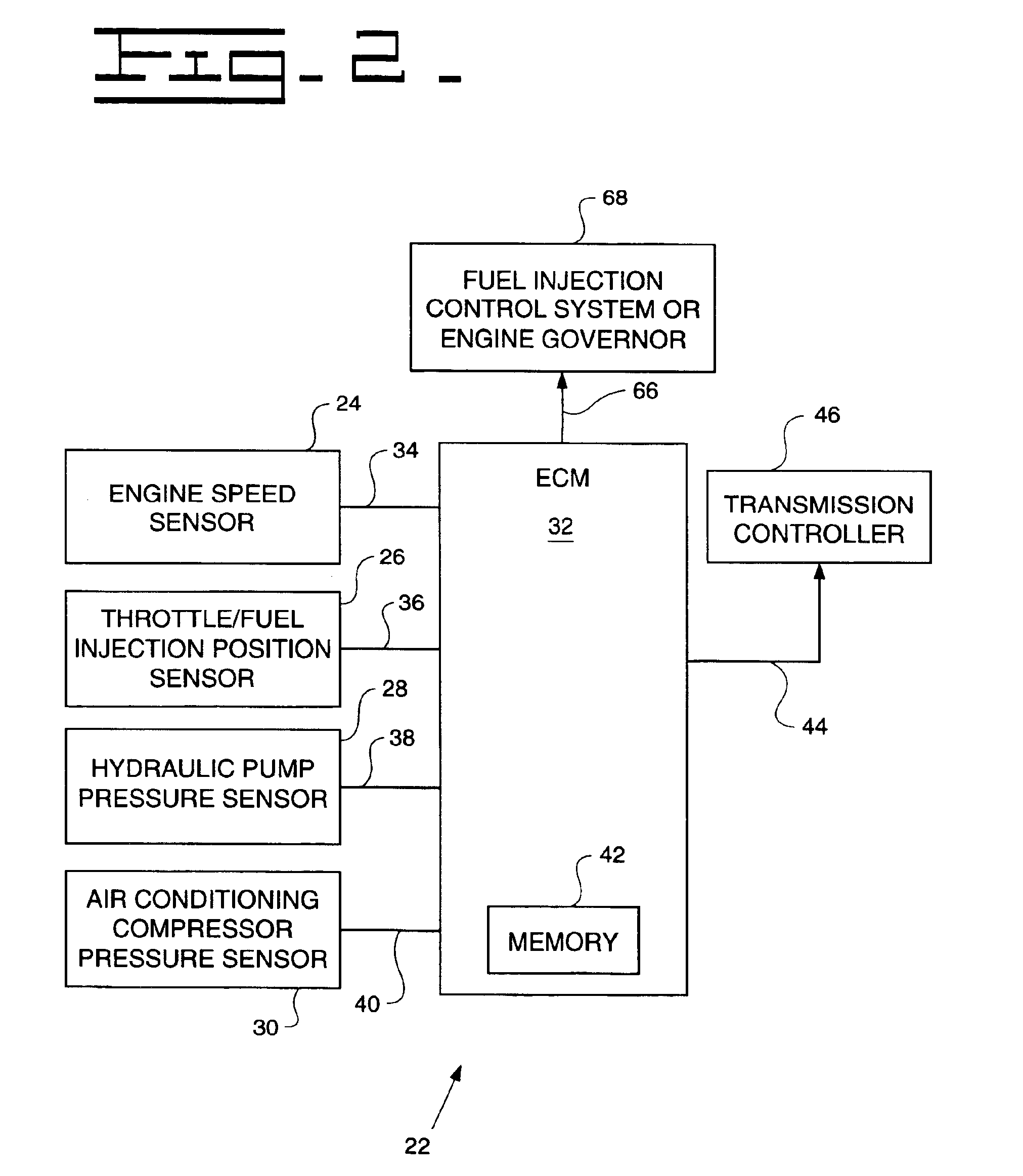
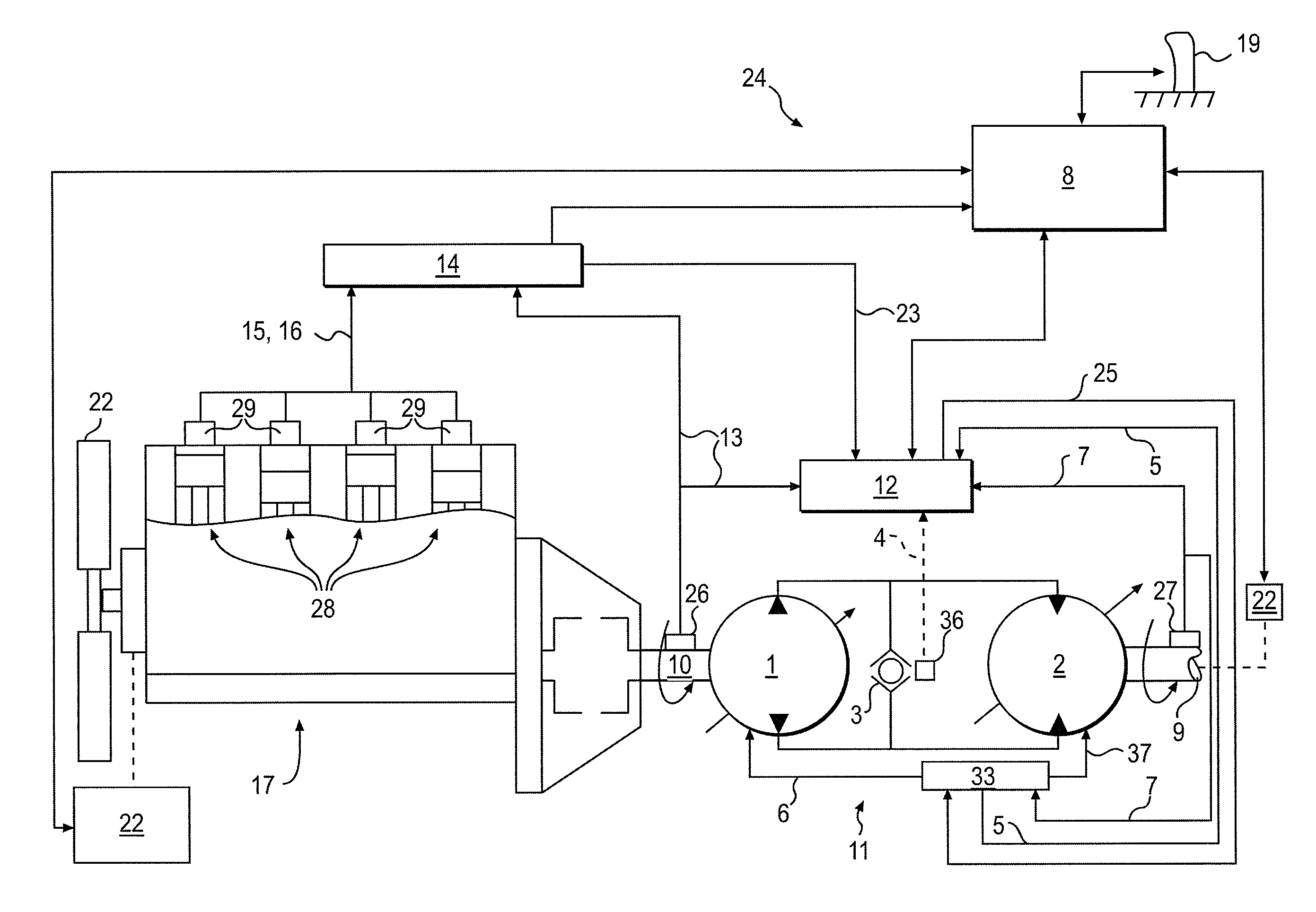
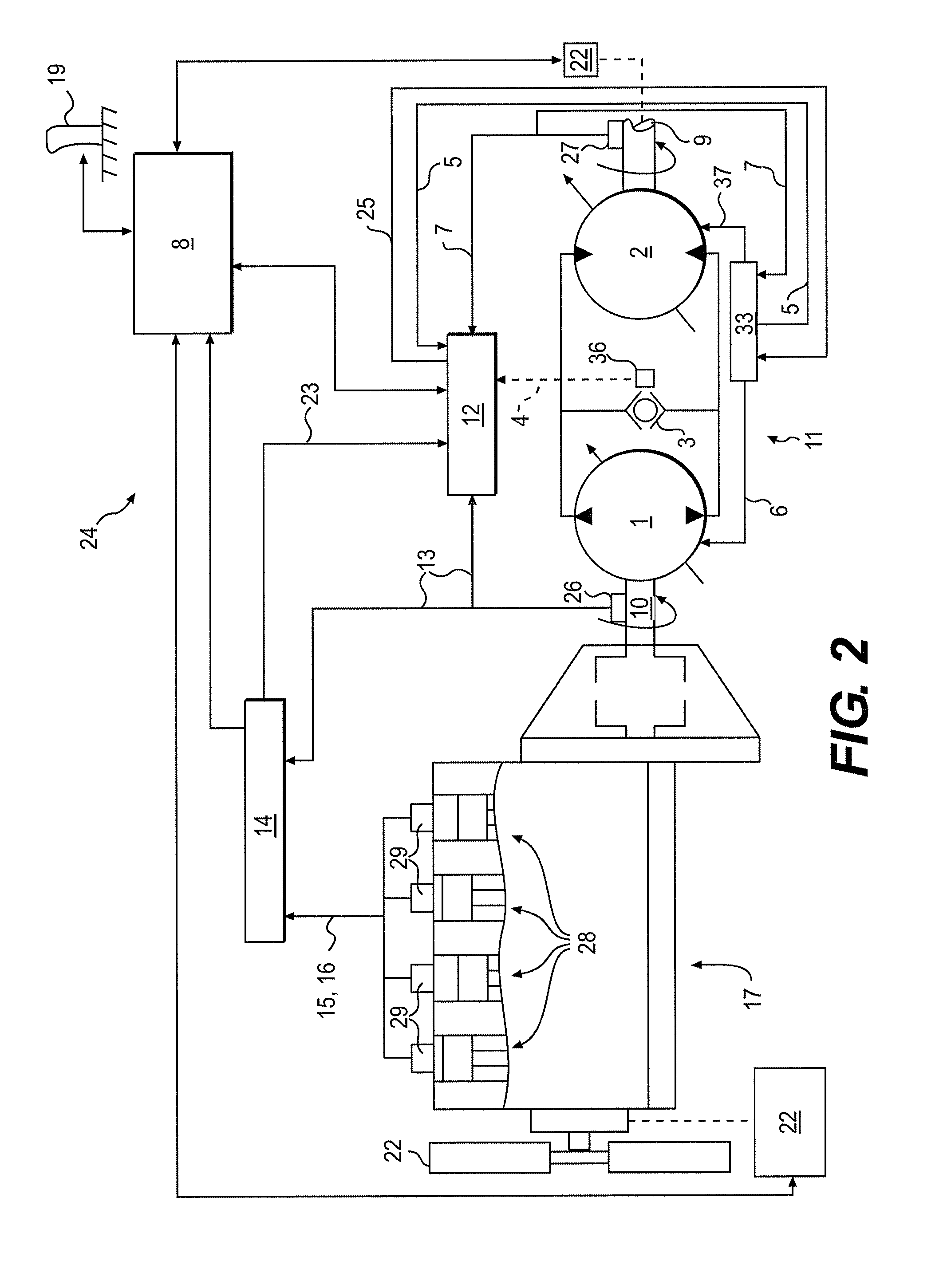
System for dynamically controlling power provided by an engine
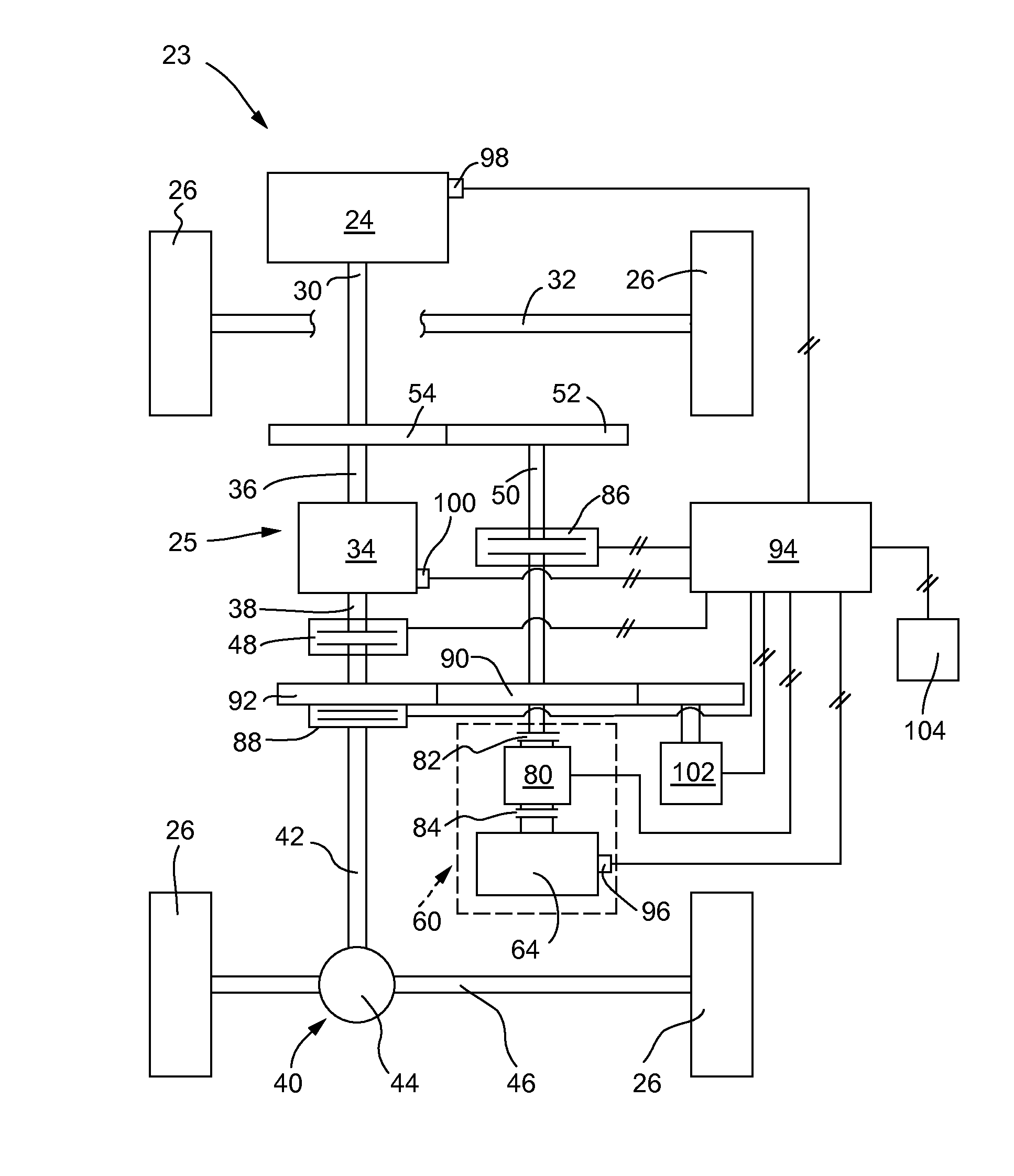
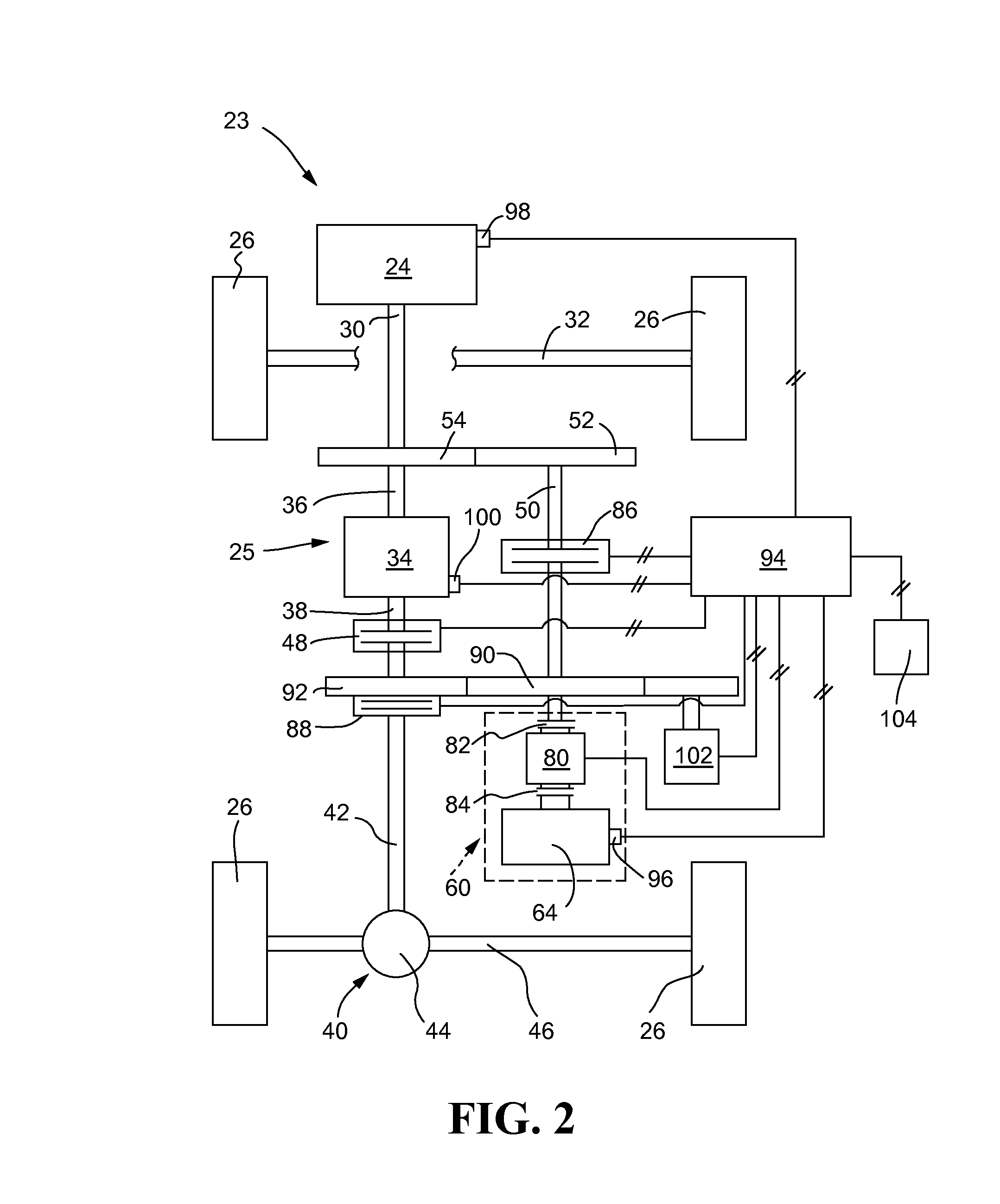
A method and system may be provided to perform a process for controlling power provided by an engine in a machine. In an embodiment of the present invention, a process for controlling power provided by an engine operating in a machine is provided. The process may include determining a first power value reflecting a predetermined first power to be provided by the engine to a component operating in the machine and determining, during machine operations, at least one of a parasitic load power value and an intermittent power load value. A second power value may then be determined that reflects a second power provided by the engine based on the parasitic power value, the intermittent power value, and the net power value. The second power value is adjusted such that the engine substantially provides the predetermined net power to the component.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Method and apparatus for parasitic load compensation
InactiveUS6920387B2Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlElectronic controllerControl system
A control system for determining the net power output of an engine associated with a work machine or other vehicle wherein parasitic loads encountered during engine operation are taken into account, the control system including an electronic controller coupled to the engine, at least one sensor coupled to the controller for inputting at least one signal representative of certain operating parameters associated with the engine, and at least one other sensor coupled to the controller for inputting at least one signal representative of the operation of any parasitic load encountered during engine operation, the controller being operable to determine the total output power of the engine and the power requirements associated with any parasitic load based upon the sensor signals. The controller is also operable to output a signal representative of the difference between the total output power of the engine and the power requirements associated with any parasitic loads encountered during engine operation, the outputted signal being used for controlling the operation of the engine or other peripheral equipment or systems associated with the work machine or other vehicle.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Passive electrode blanketing in a fuel cell
Owner:HYDROGENICS CORP
Apparatus for mounting electronic module assembly in sensor
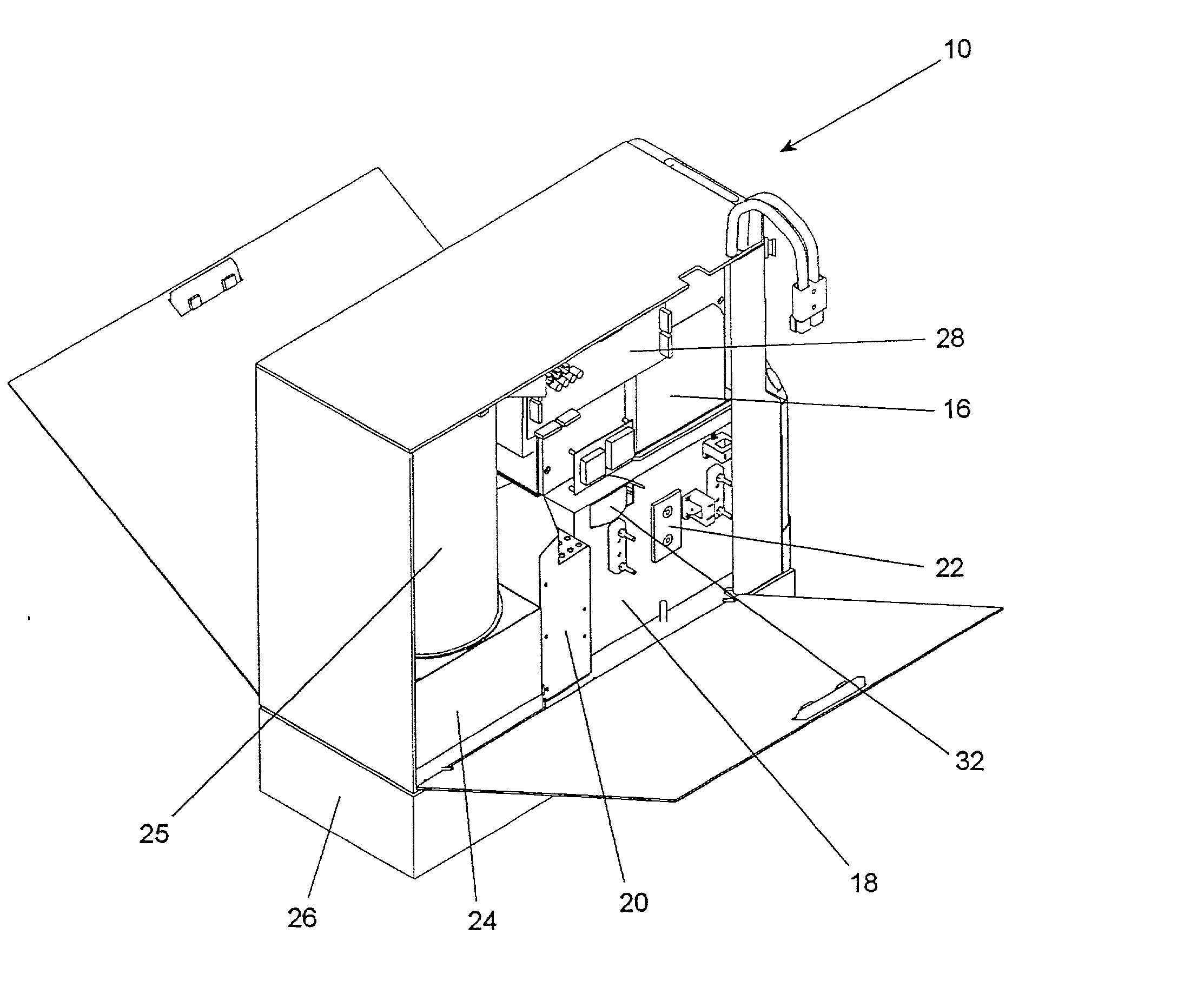
ActiveUS20050284238A1High sensitivityImprove stabilityPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementForce measurementComputer moduleElectrical connector
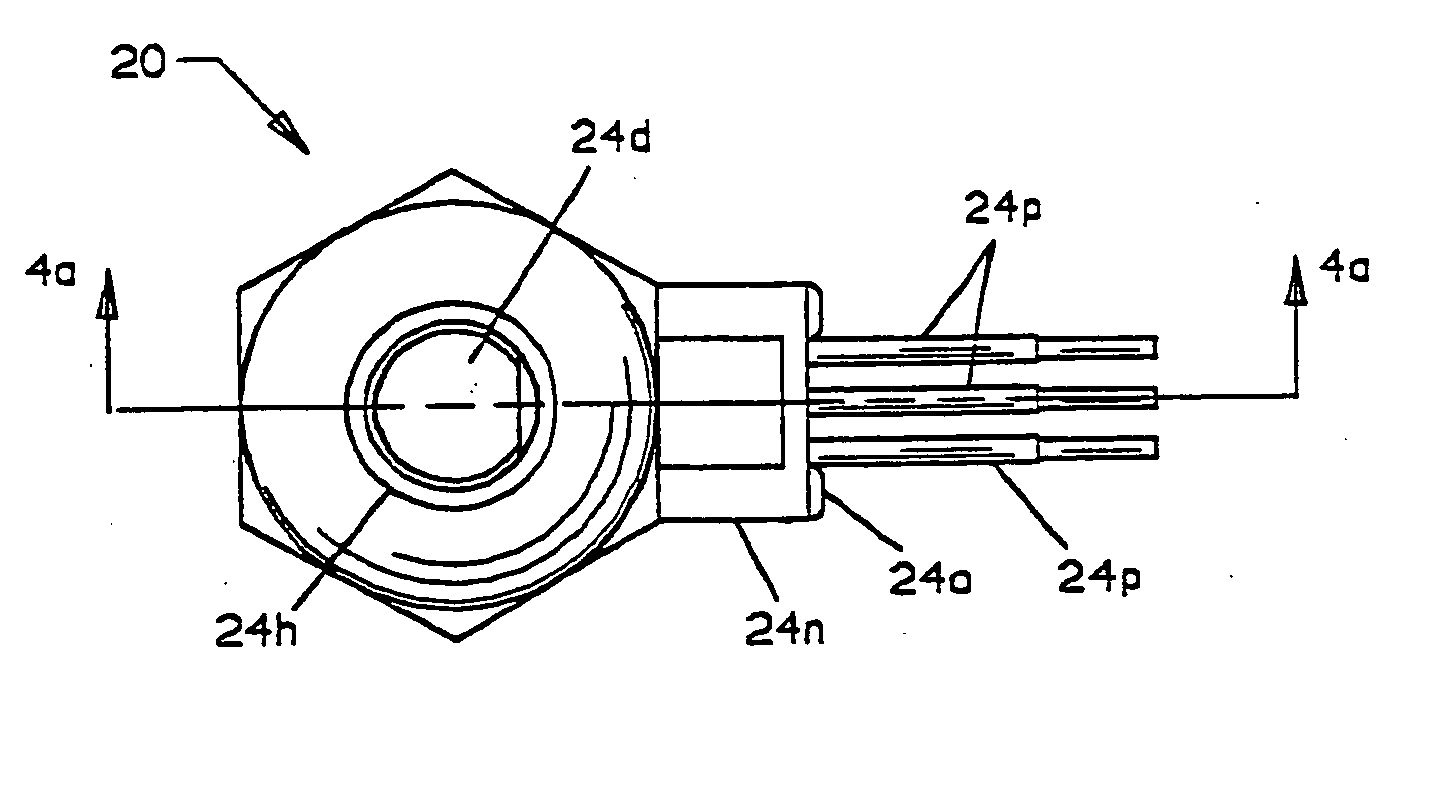
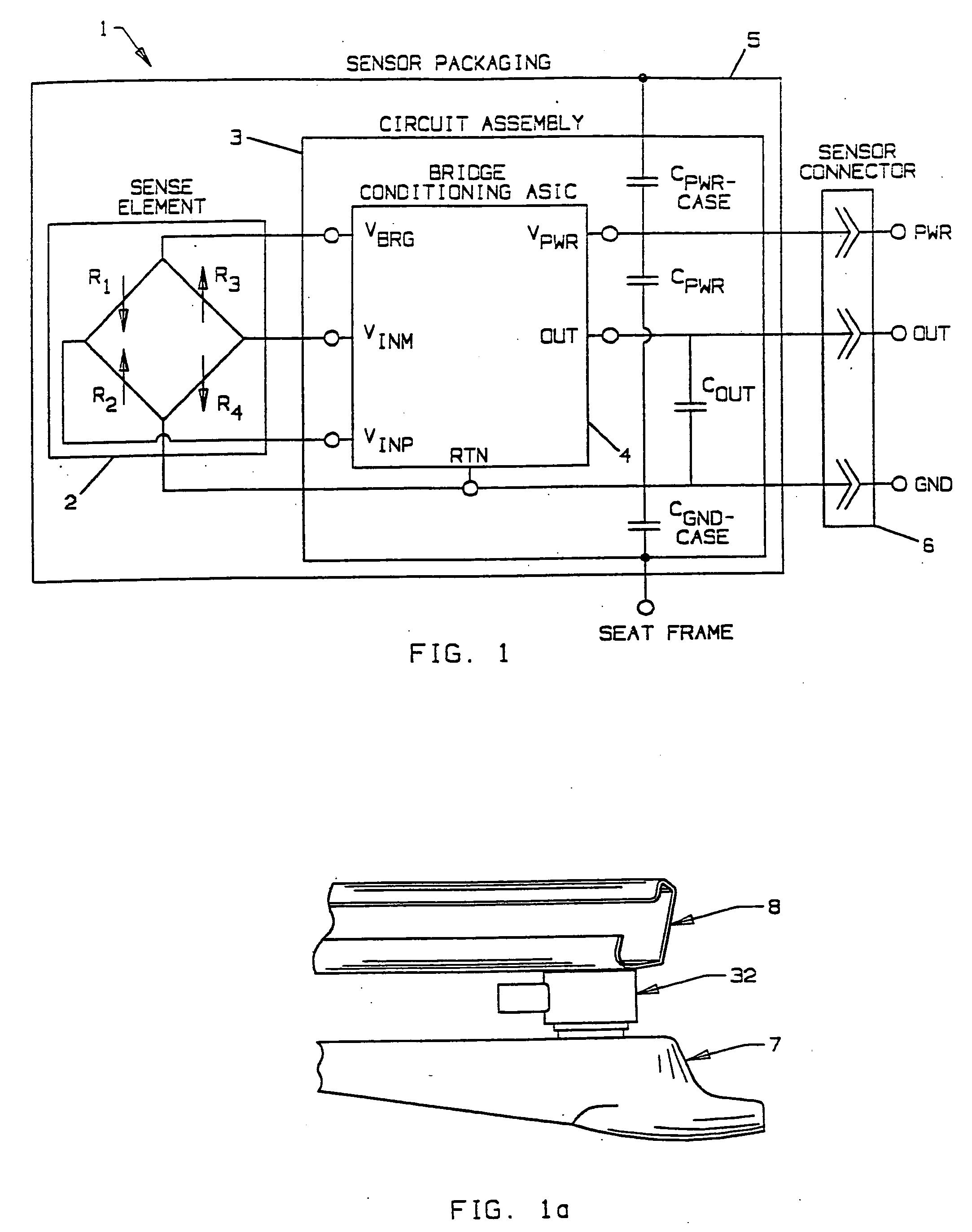
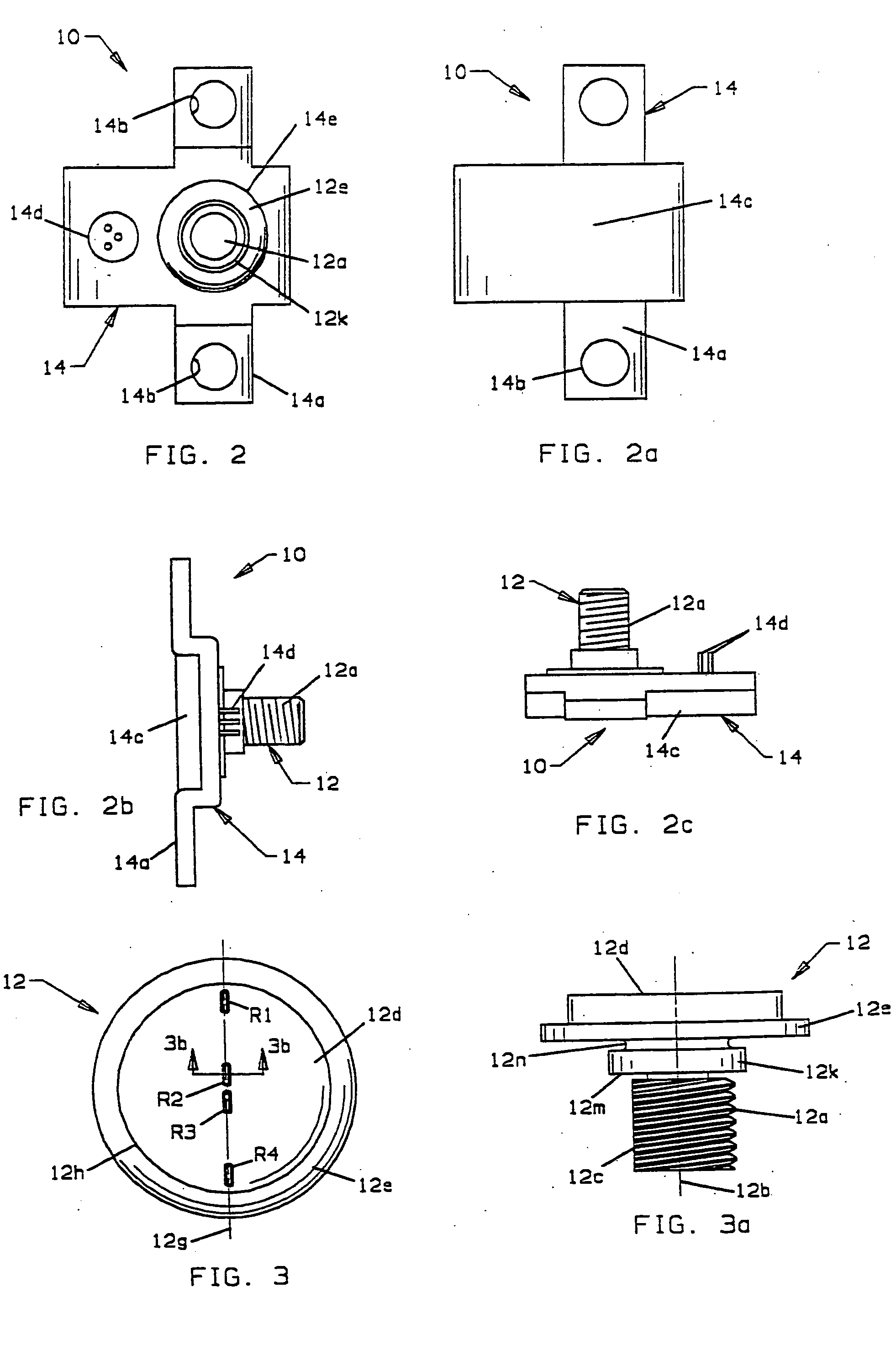
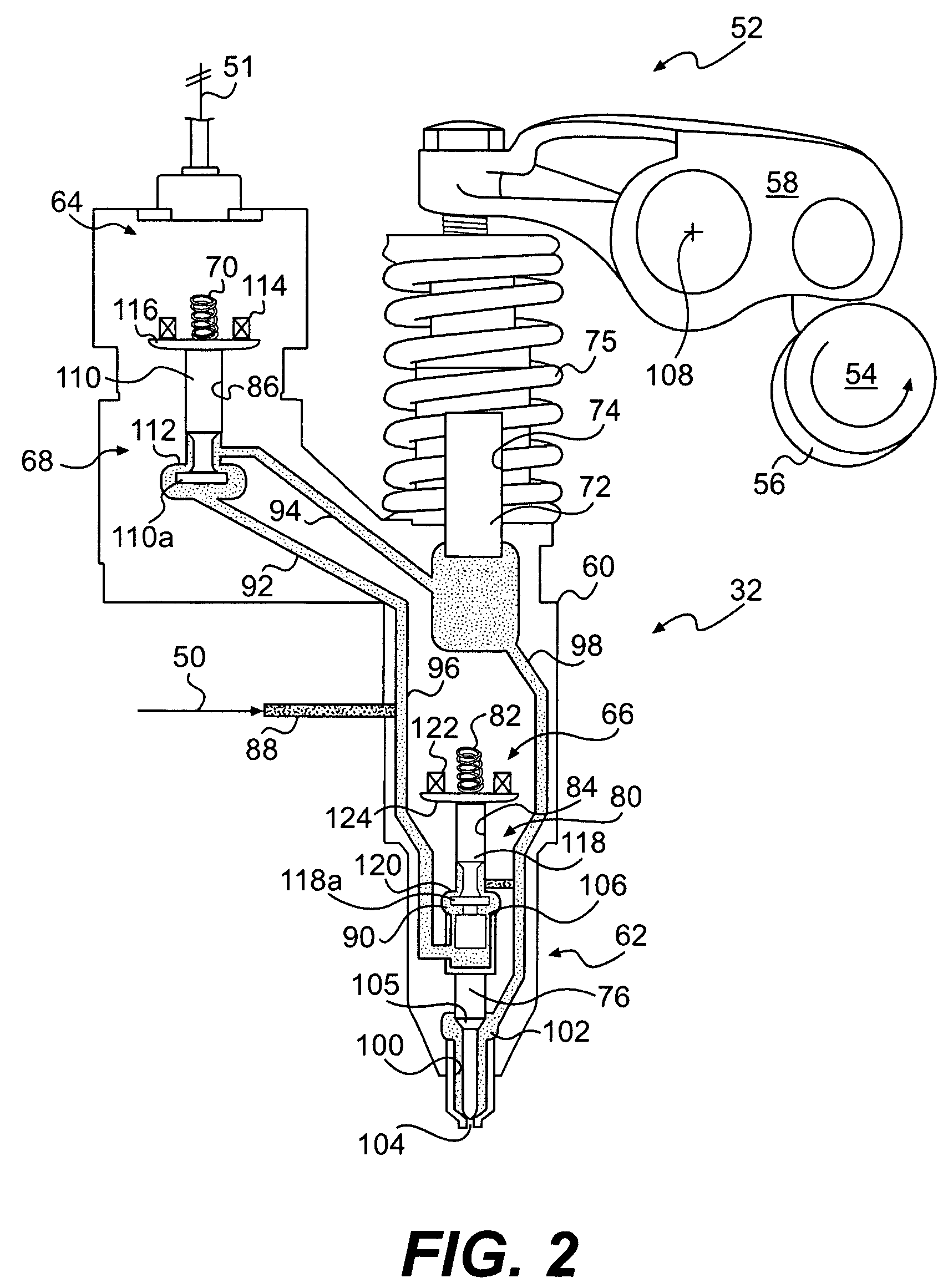
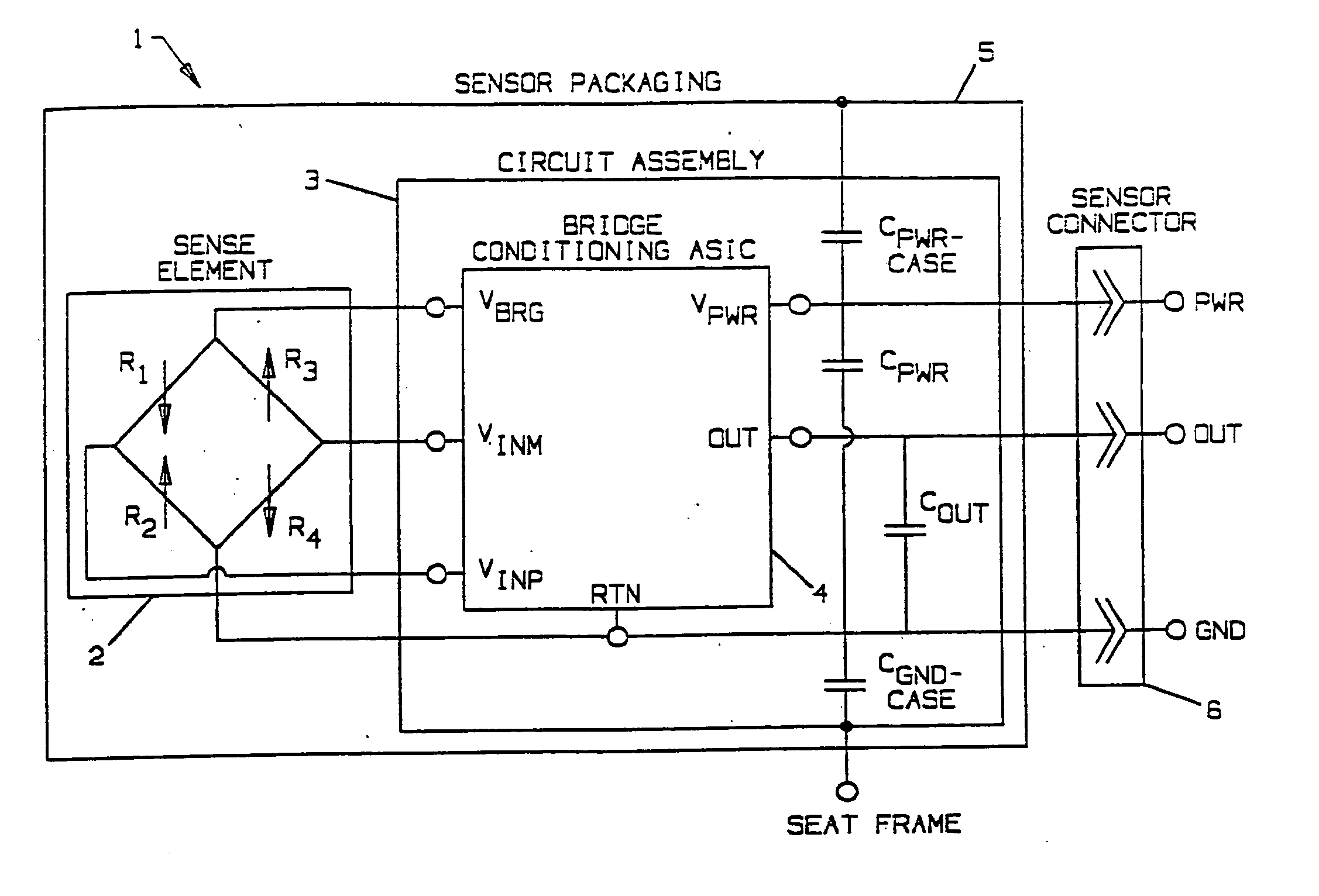
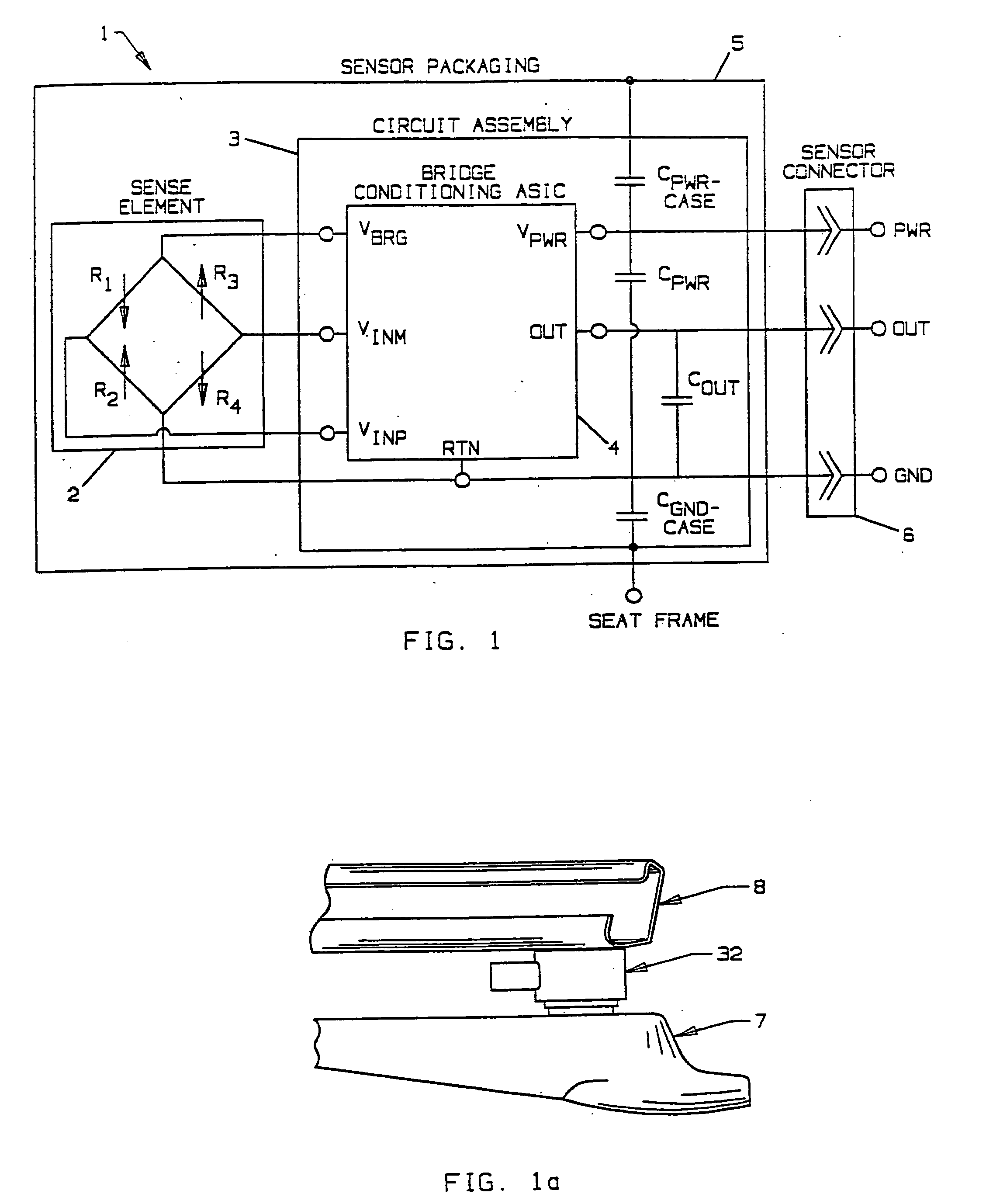
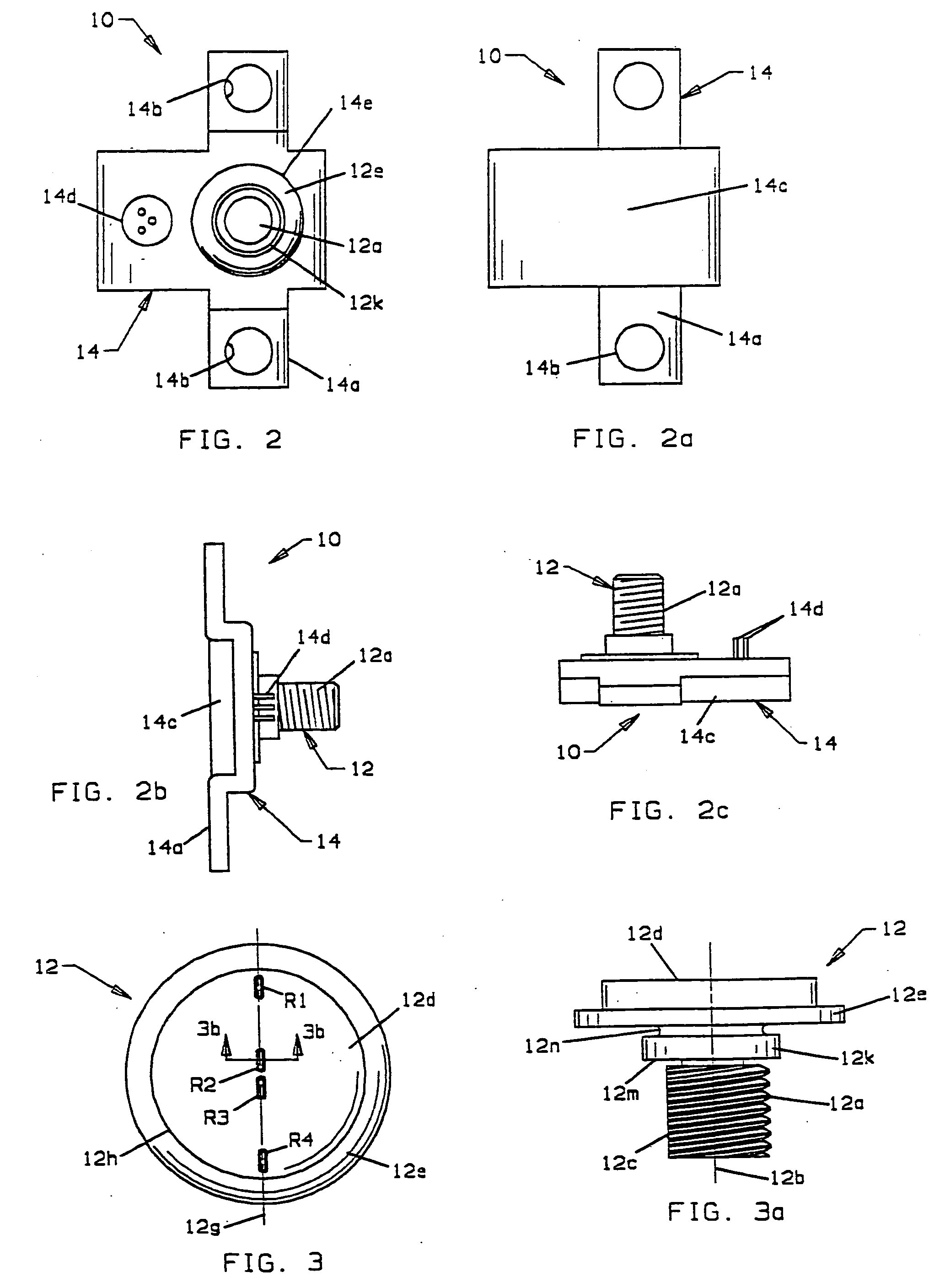
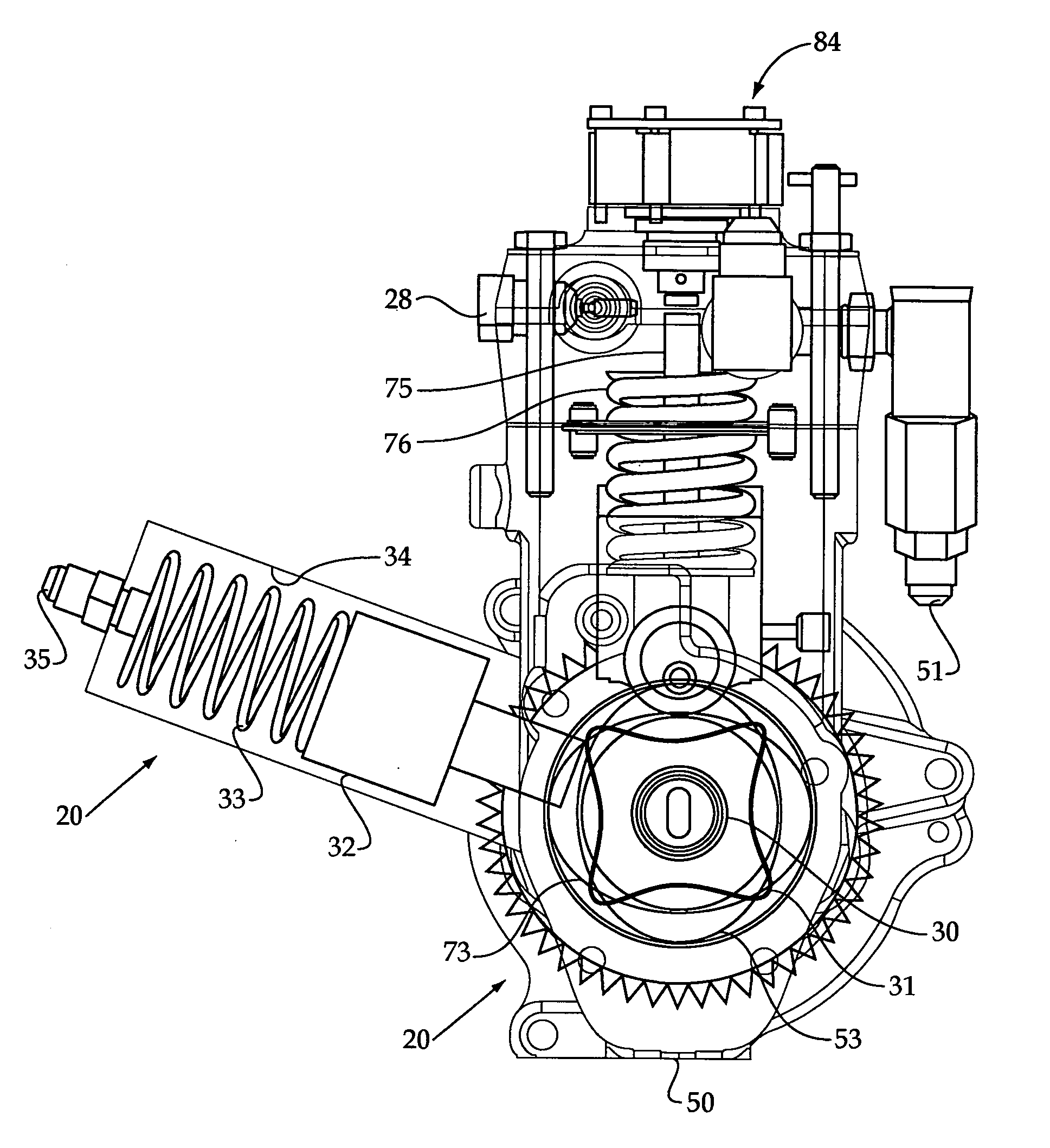
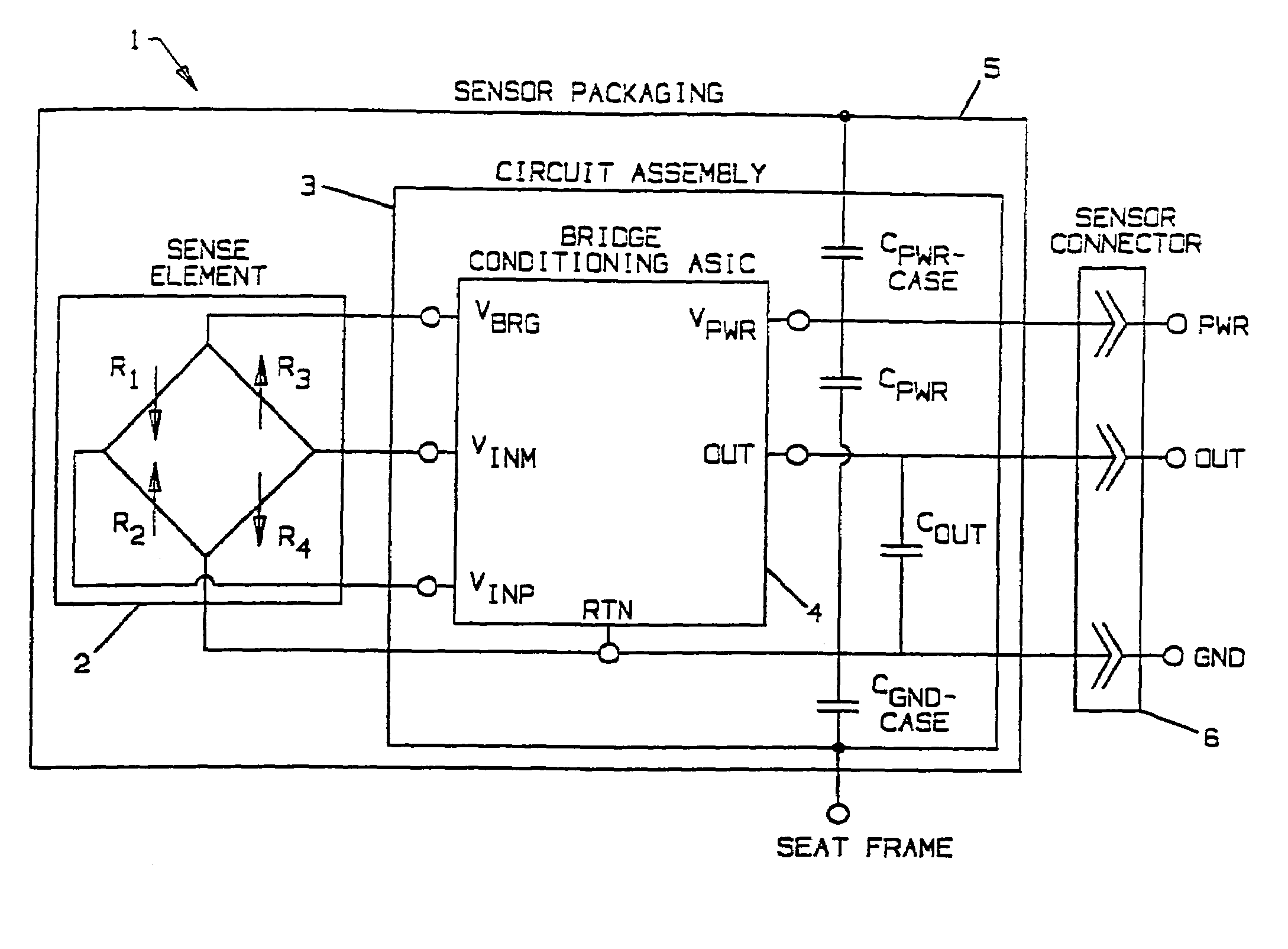
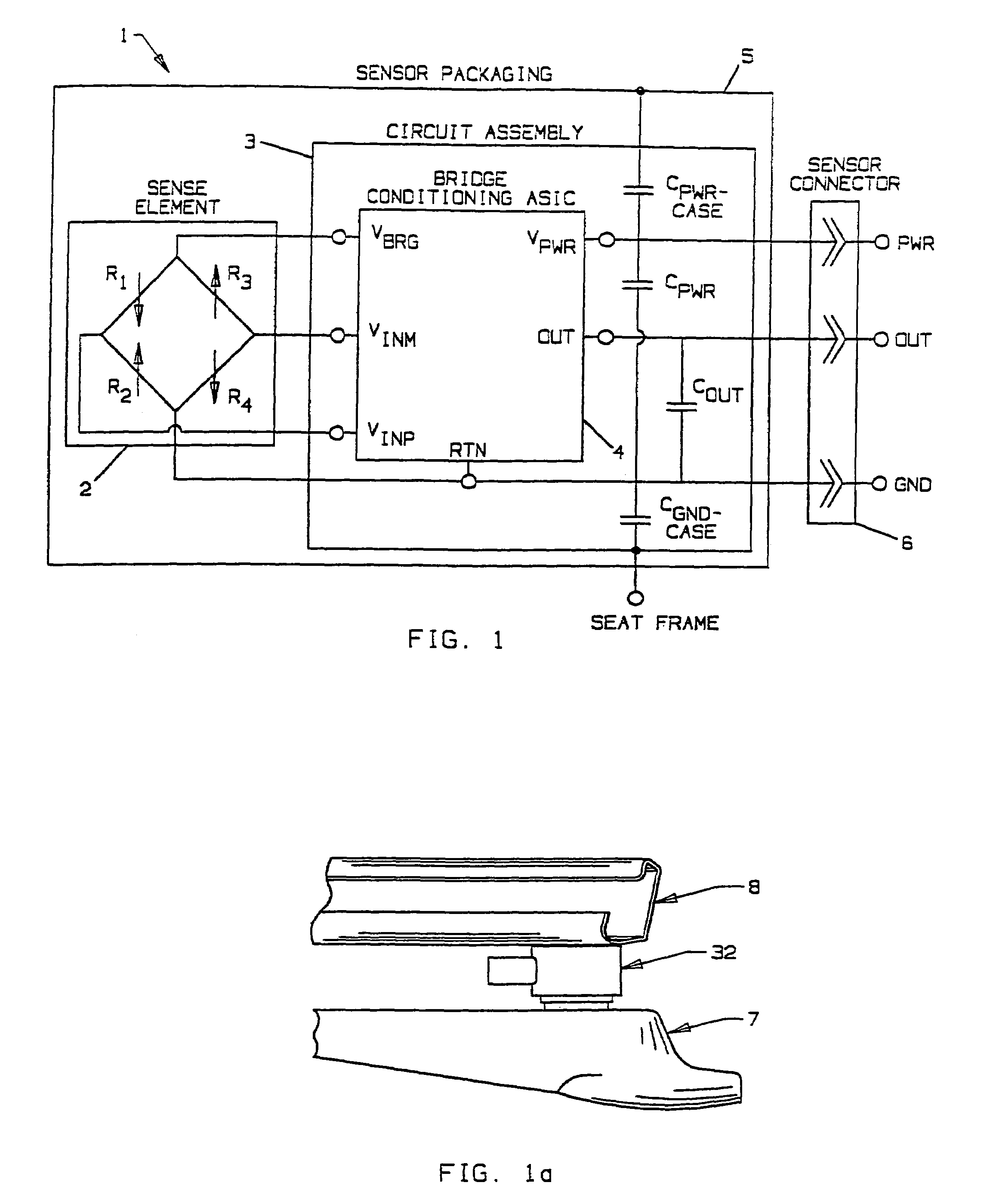
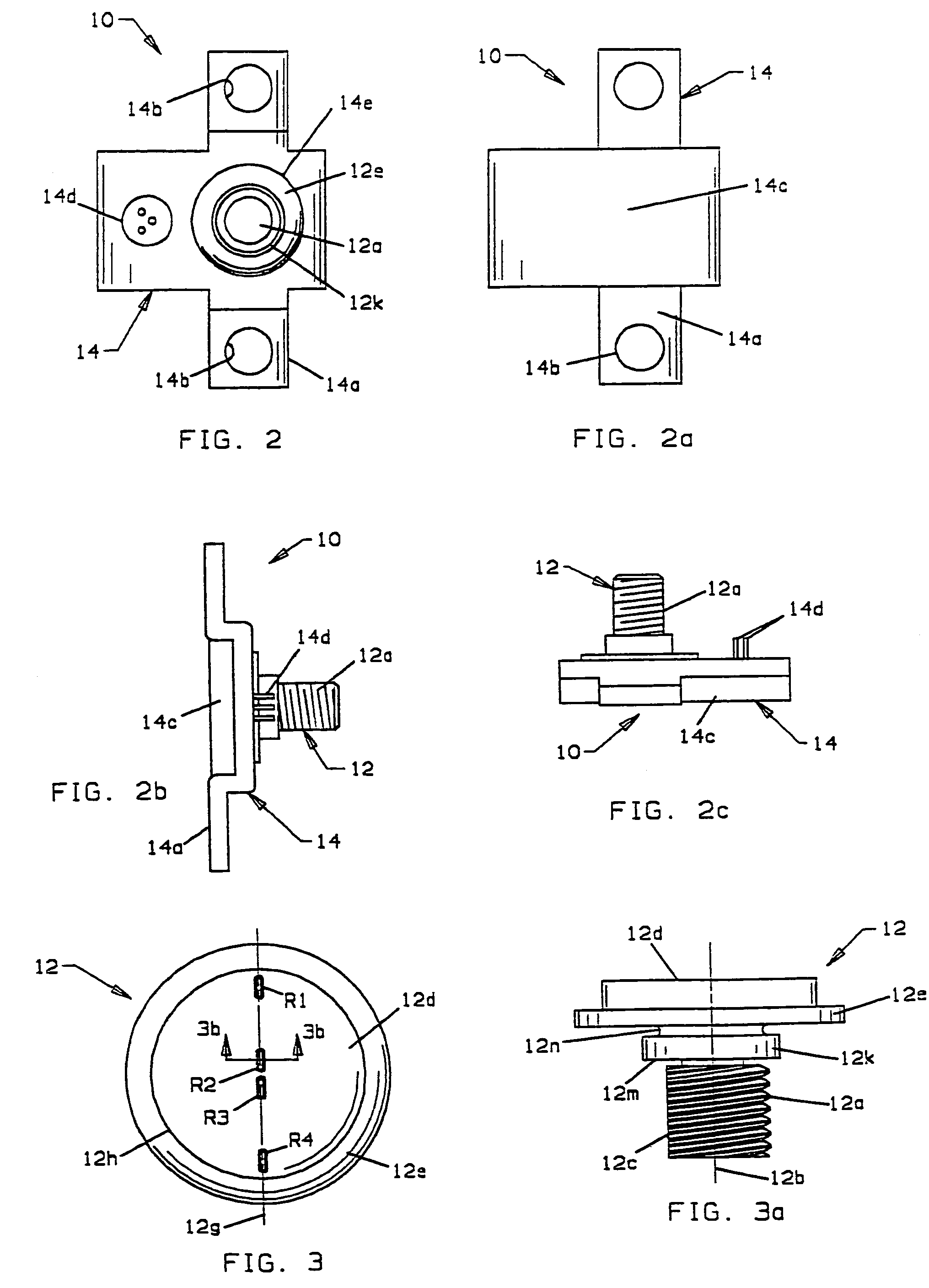
An occupant weight sensor (1) for placement between a frame (7) fixed to the chassis of a vehicle and a second frame (8) supporting a vehicle seat has a sense element having a first body (12, 22, 28, 34, 50, 62, 64, 68, 84) formed with a planar sense surface on which are mounted piezoresistors electrically connected in a Wheatstone bridge configuration. A post (12a, 22c, 28c, 34e, 50b, 62a, 64a, 68b, 84g) extends outwardly from the first body for attachment to the first frame. A second body is formed with a force transfer portion (14a, 24g, 30d, 36b, 52a, 70a, 94a) permanently attached to the first body along an outer periphery circumscribing the sense surface. The piezoresistors are electrically connected to conditioning electronics received in a chamber formed between the two bodies. The effects of parasitic loads on the sense element are minimized by selected placement of the piezoresistors on the sense surface. In one embodiment, attachment stresses of an electronic module assembly (88) are isolated from the sense surface by attaching the assembly to a support ring end wall (86a) welded to a portion of the first body removed from the sense surface and providing a control gap between the support ring and the sense surface. Several variations are disclosed for attaching the sensor to the first and second frames and both longitudinally and laterally extending electrical connectors are shown.
Owner:SENSATA TECHNOLOGIES INC
System and methods for efficient provision of arc welding power source
ActiveUS20100320182A1Efficient implementationAc-dc conversionArc welding apparatusEngineeringTransistor
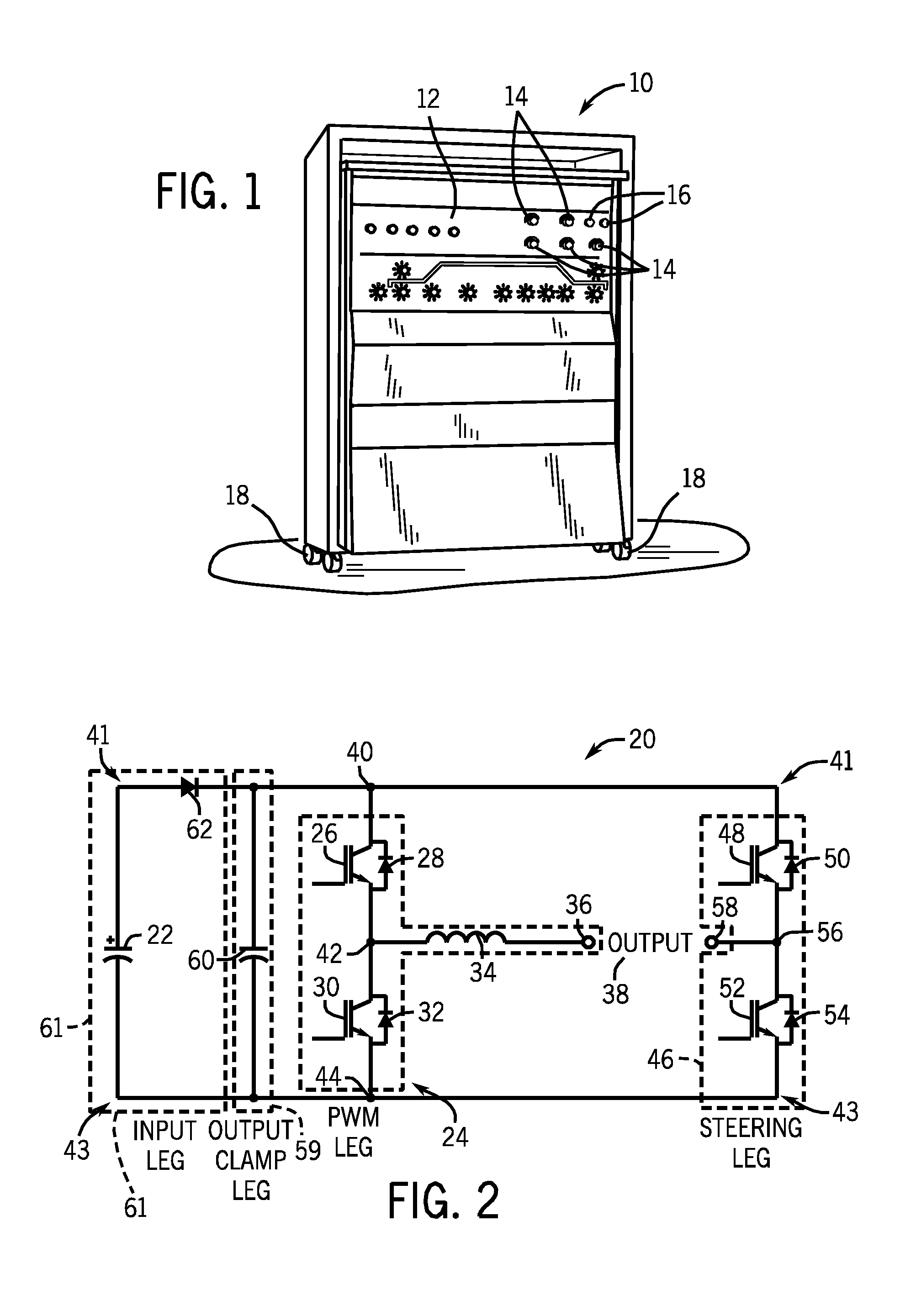
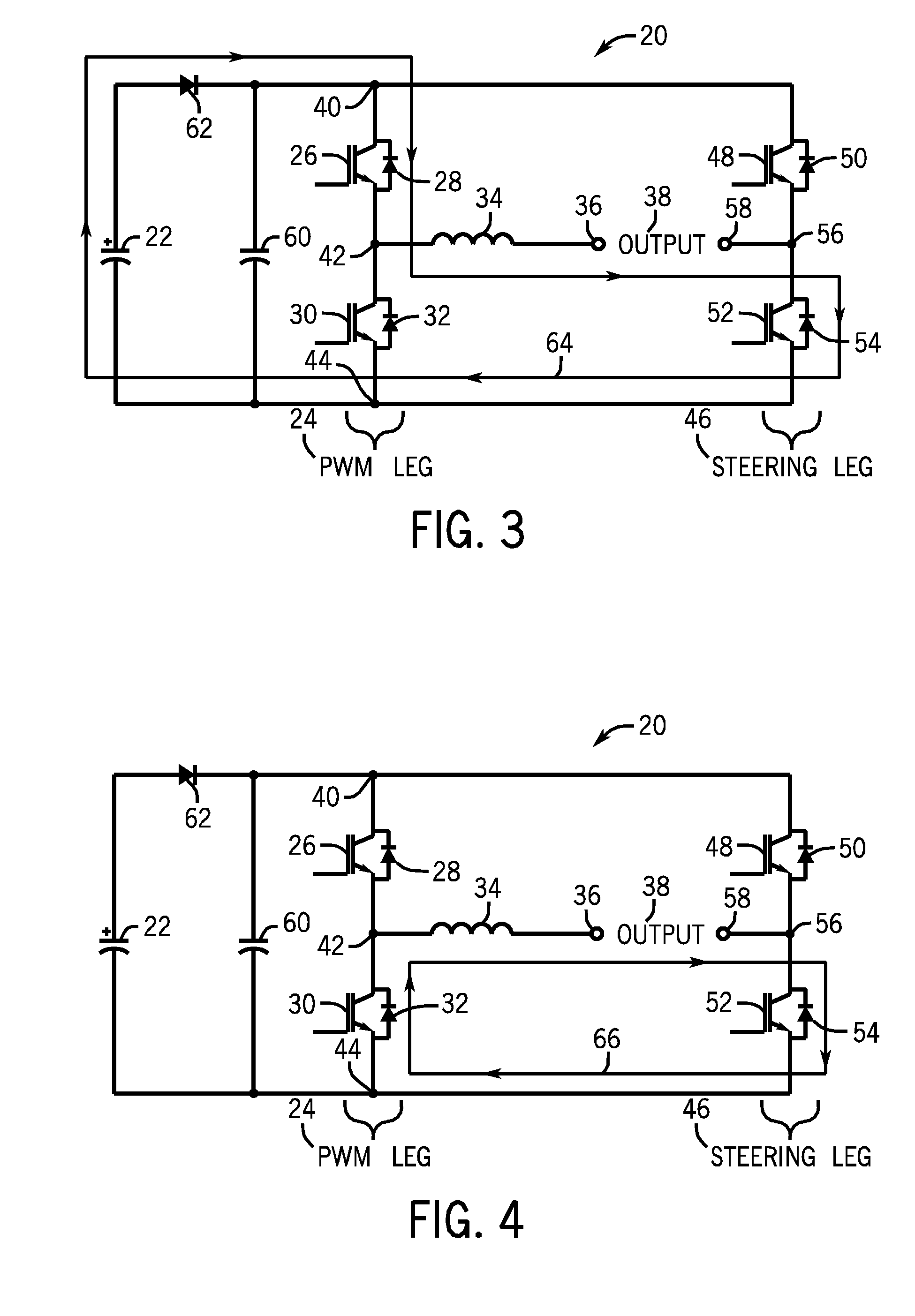
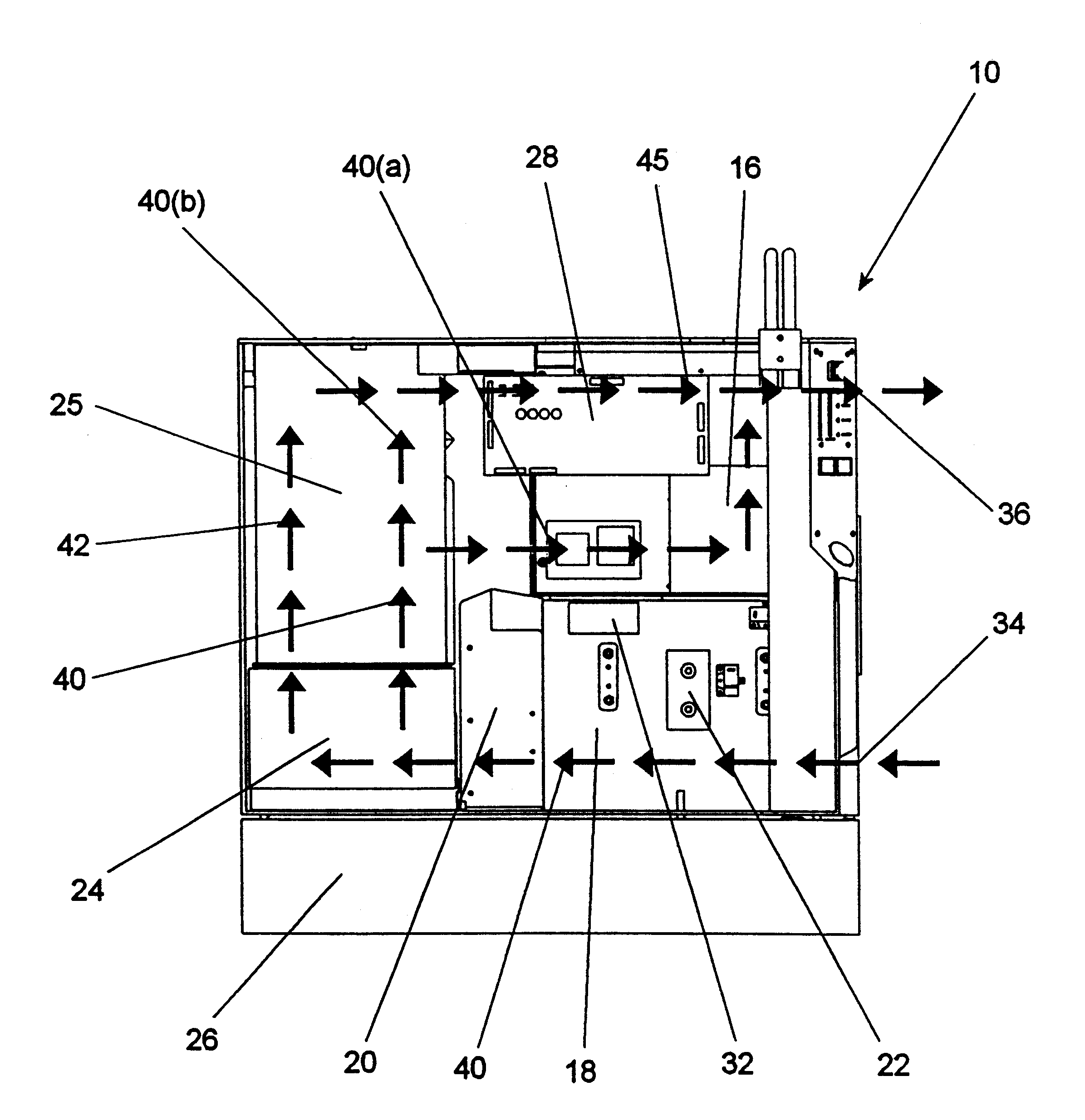
Methods and systems for creating and controlling an AC output for welding, plasma cutting or heating are provided. One embodiment of the present disclosure achieves a desired square wave AC output and reduces the number of circuit components needed by combining components of a buck converter and a full bridge inverter. Current flow paths through a power control circuit that are generated via switching of transistors in the circuit on and off are provided. In one embodiment, a pulse width modulation leg, which controls the level of current flow through an inductor, is provided. Certain embodiments include a bidirectional buck converter that converts an unregulated DC flow to a regulated DC flow through an inductor. In one embodiment, a steering leg is provided, which controls a direction of current flow through the inductor. Additionally, an output clamp circuit, which suppresses the parasitic load inductance during polarity reversal is provided.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Load bank
Owner:NORTHERN LIGHT
System and Method for Efficiently Operating Multiple Flywheels
A flywheel assembly may include first and second flywheels having respective first and second flywheel parasitic load profiles. Operating speeds of the first and second flywheels may be selected based at least in part on the first and second flywheel parasitic loads. The operating speeds may be determined such that an aggregate of the first and second flywheel parasitic loads is minimized, thereby increasing the efficiency of the flywheel assembly.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Fuel cell thermal management system and method
This application relates to a system and method for regulating the temperature of a self-contained fuel cell apparatus preferably comprising a fuel reformer. The invention maintains the various components of the fuel cell apparatus within preferred operating temperature ranges while ensuring that exhaust gases and external surfaces of the apparatus do not exceed safe temperature levels. The invention is particularly suited for self-contained hybrid power supply applications, for example for non-road electric vehicles. The various components of the apparatus are strategically configured relative to air flow paths to fully utilize the cooling capacity of the process stream and minimize parasitic loads. In some embodiments the inlet air is pre-heated to enable operation of the apparatus in low temperature environments, such as industrial freezers.
Owner:CELLEX POWER PRODS
Parasitic load control system for exhaust temperature control
ActiveUS7523606B2Increase loadIncrease exhaust temperatureElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTemperature controlCombustion chamber
A parasitic load control system is provided. The system may include an exhaust producing engine and a fuel pumping mechanism configured to pressurize fuel in a pressure chamber. The system may also include an injection valve configured to cause fuel pressure to build within the pressure chamber when in a first position and allow injection of fuel from the pressure chamber into one or more combustion chambers of the engine when in a second position. The system may further include a controller configured to independently regulate the pressure in the pressure chamber and the injection of fuel into the one or more combustion chambers, to increase a load on the fuel pumping mechanism, increasing parasitic load on the engine, thereby increasing a temperature of the exhaust produced by the engine.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Load bank
Owner:NORTHERN LIGHT
Occupant weight sensor for vehiclular seats, method for making and system therefor
InactiveUS20050023065A1Strong signal to noise ratioImprove the level ofWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersElectric devicesEngineeringElectrical connector
An occupant weight sensor (1) for placement between a frame (7) fixed to the chassis of a vehicle and a second frame (8) supporting a vehicle seat has a sense element having a first body (12, 22, 28, 34, 50, 62, 64, 68) formed with a planar sense surface on which are mounted piezoresistors electrically connected in a Wheatstone bridge configuration. A post (12a, 22c, 28c, 34e, 50b, 62a, 64a, 68b) extends outwardly from the first body for attachment to the first frame. A second body is formed with a force transfer portion (14a, 24g, 30d, 36b, 52a, 70a) permanently attached to the first body along an outer periphery circumscribing the sense surface. The piezoresistors are electrically connected to conditioning electronics received in a chamber formed between the two bodies. The effects of parasitic loads on the sense element are minimized by selected placement of the piezoresistors on the sense surface. Several variations are disclosed for attaching the sensor to the first and second frames and both longitudinally and laterally extending electrical connectors are shown.
Owner:SENSATA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Pump with torque reversal avoidance feature and engine system using same
InactiveUS20080115770A1Positive torqueWear reducing fuel injectionPump parameterAfter treatmentCommon rail
A high pressure pump for a common rail fuel system avoids torque reversals in its cam shaft by applying a cyclic parasitic load. As the high pressure pump pistons transition from a pumping stroke to a retraction stroke, the cyclic parasitic loading device is loaded to avoid torque reversals in the cam shaft. The cyclic parasitic load device may include a medium pressure pump, such as for supplying medium pressure fuel to a particle trap regeneration device associated with the exhaust after treatment system.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
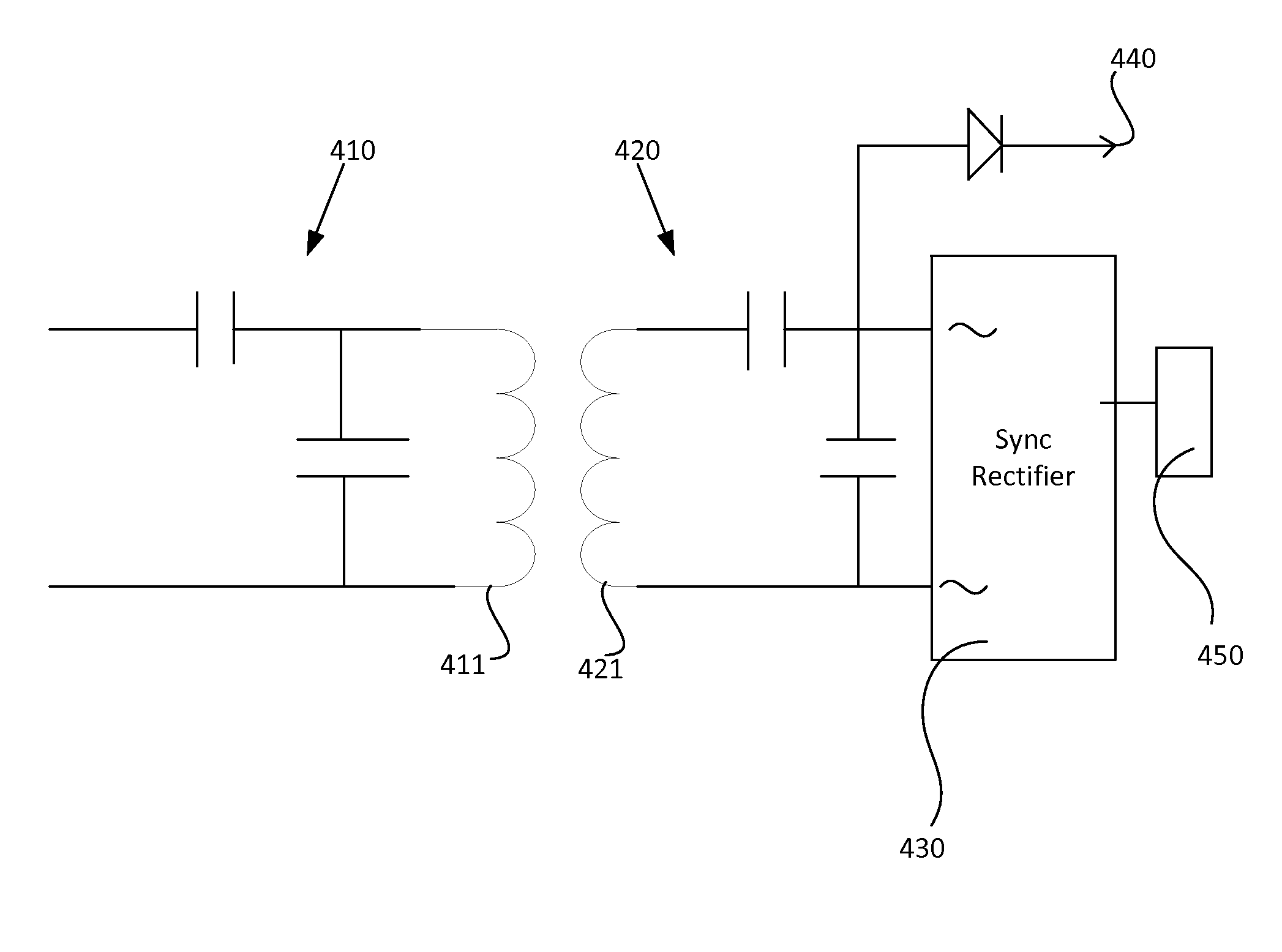
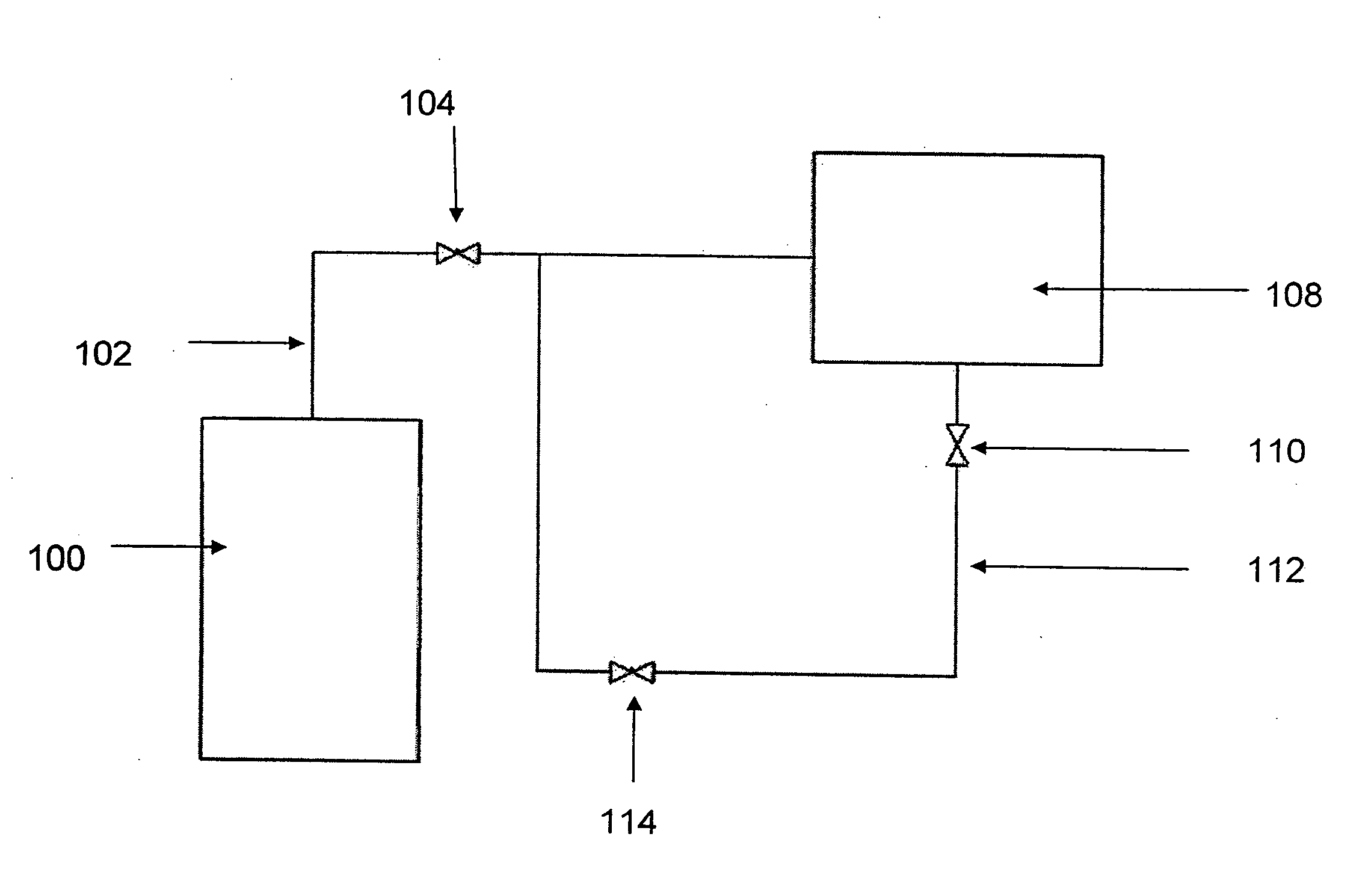
Foreign Object Detection Method for Wireless Charging Systems
ActiveUS20150318708A1TransformersTransformers/inductances circuitsForeign matterForeign object detection
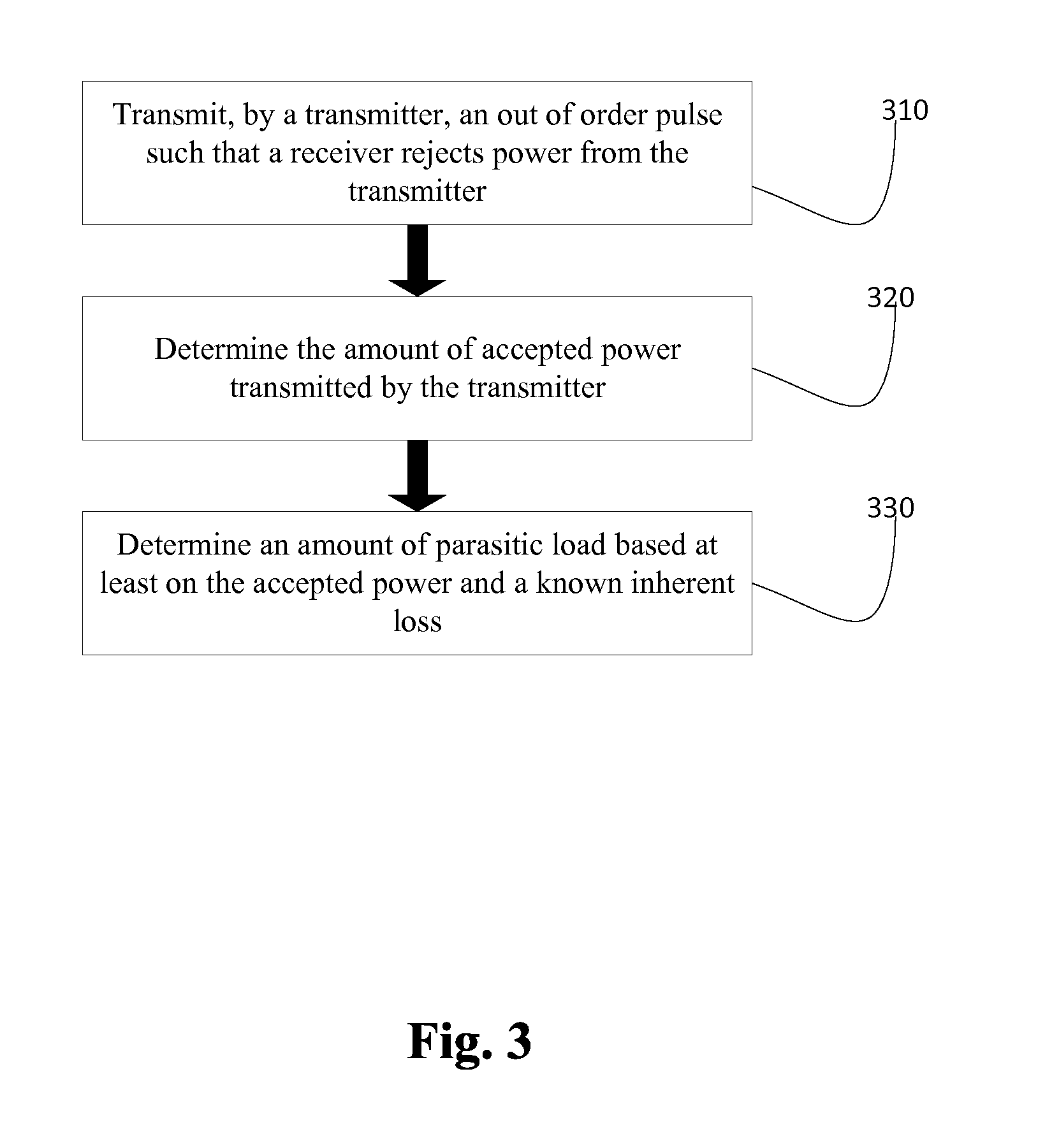
Systems, device and techniques are disclosed for measuring a parasitic load in an environment. A transmitter may transmit an out of order pulse such that a receiver with synchronous rectification circuitry rejects induced power from the transmitter based on the out of order pulse. The parasitic load is determined by measuring the amount of power induced by the transmitter while the intended receiver rejects the power subtracted by known inherent loss.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Methods and systems for powering auxiliary devices in photovol taic system
InactiveUS20120176076A1Reduced field maintenance requirementEliminate biasBatteries circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic monitoringElectricityElectrical battery
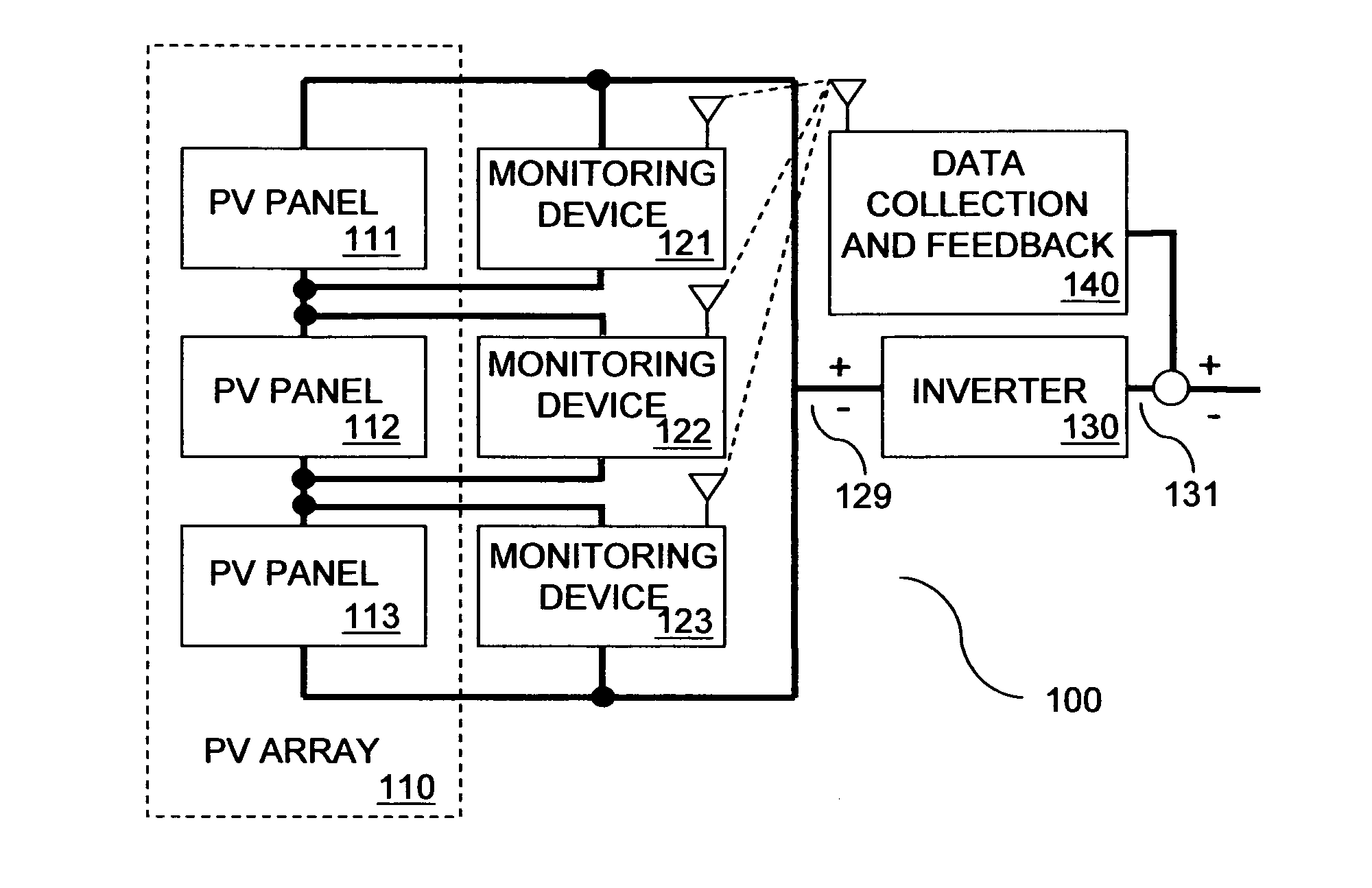
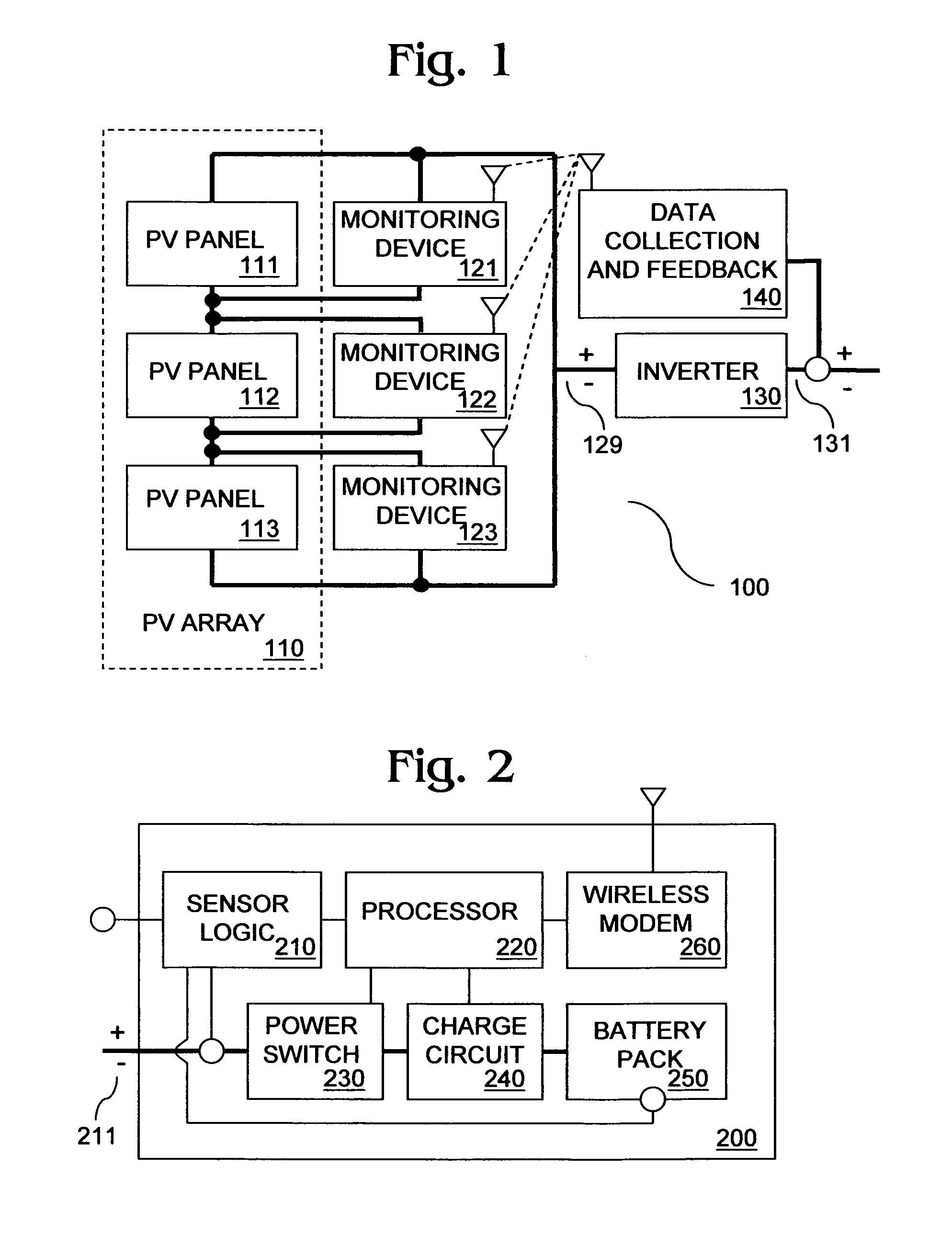
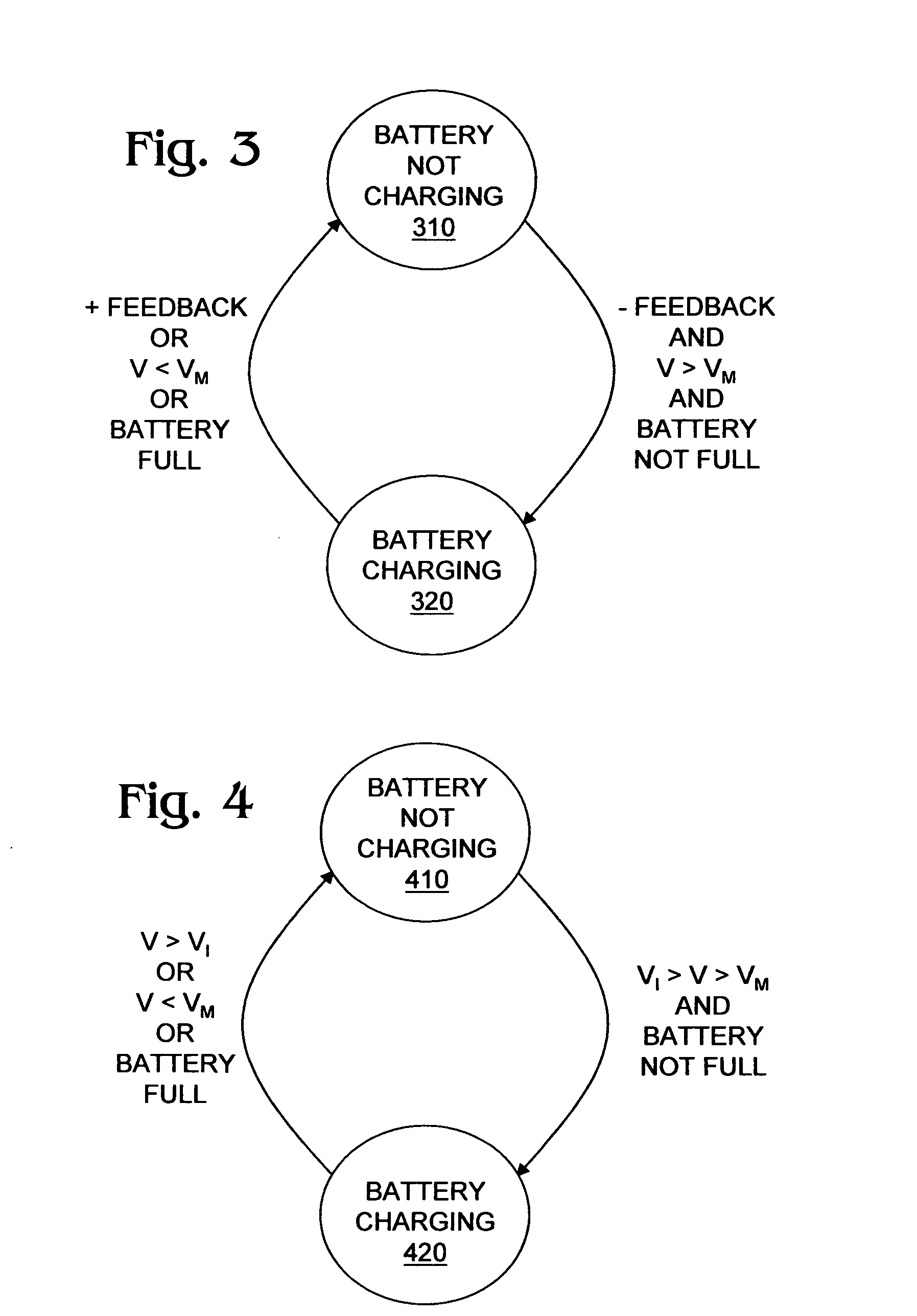
Methods and systems for powering auxiliary devices in photovoltaic (PV) systems address shortcomings of conventional PV systems by harvesting unused electricity generated by the PV system to power the auxiliary devices. The methods and systems use PV panel power that is below the PV system inverter's harvesting threshold to charge rechargeable batteries in the auxiliary devices. The invention offers significant advantages over conventional PV systems, including full-time operability of auxiliary devices by virtue of rechargeable batteries that are charged using below threshold PV panel power, reduced field maintenance requirements for auxiliary devices (e.g., battery pack replacement), and elimination of bias in PV system performance data caused by parasitic load of auxiliary devices.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
Torque control system
A method of controlling a machine includes receiving a torque demand associated with at least one of a first parasitic load and a second parasitic load. At least the first parasitic load receives power from a power source of the machine via a transmission coupled to the power source. The method also includes providing torque from the power source to the at least one of the first and second parasitic loads in response to receiving the torque demand. In such a method wherein torque is provided to the at least one of the first and second parasitic loads based on a torque priority value associated with the at least one of the first and second parasitic loads. In addition, the torque priority value is adjustable by an operator of the machine during operation of the machine.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
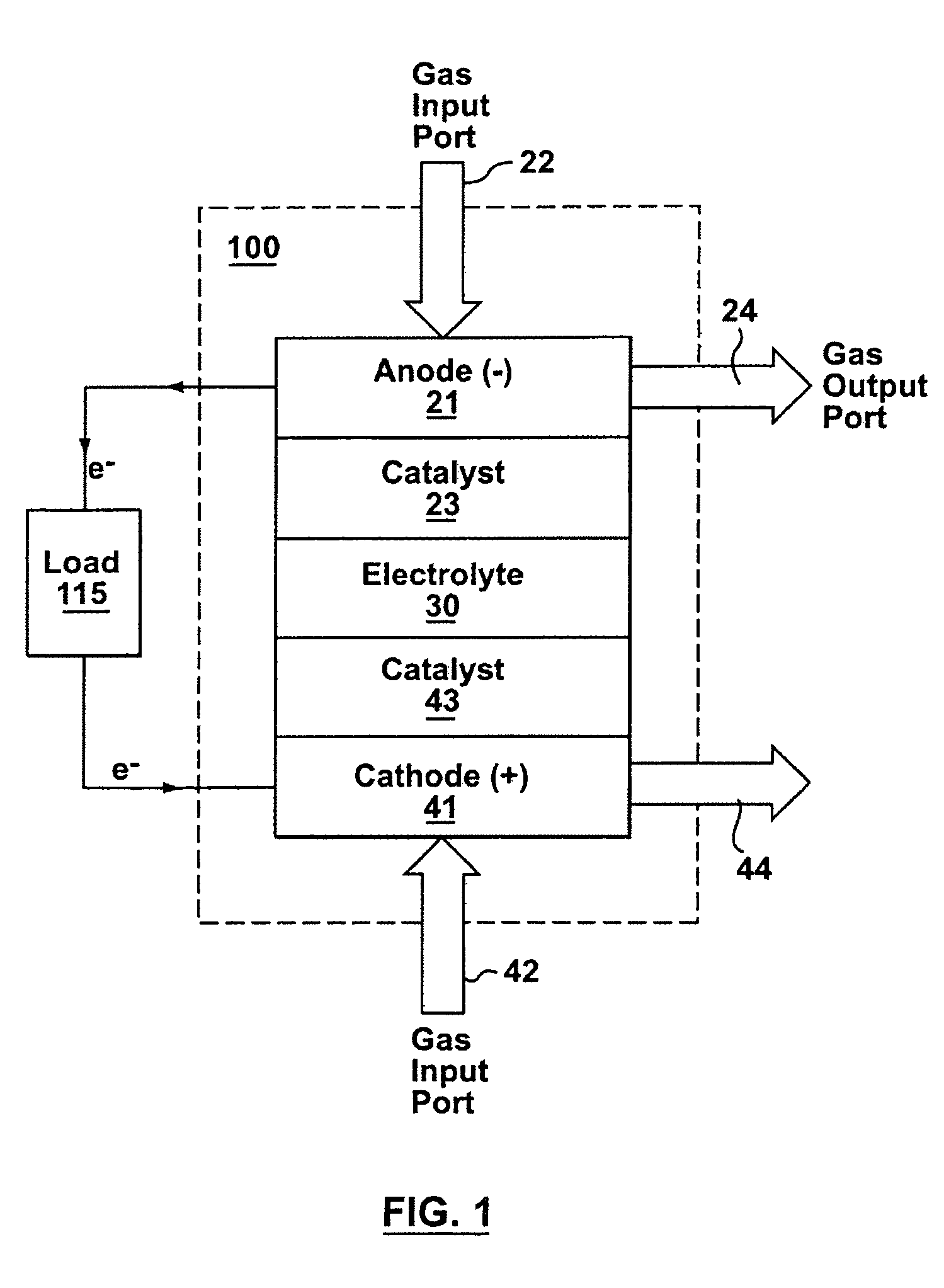
Fuel cell purge cycle apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080160360A1Improve battery efficiencyMinimal parasitic loadFuel cell auxillariesAqueous electrolyte fuel cellsHydrogenFuel cells
Systems and methods are provided in which a fuel cell purge cycle recaptures fluid material such as water and hydrogen from an electrode of a fuel cell and can recycle the hydrogen to the anode, leading to improved fuel cell efficiency with minimal parasitic load. Pressure fluctuations of a hydrogen generation system may be integrated with the fuel cell purge cycle to recycle hydrogen to the fuel cell and water to the hydrogen generation system.
Owner:MILLENNIUM CELL +1
System for heating a fuel
An embodiment of the present invention takes the form of a system that uses exhaust from the combustion turbine engine to heat the fuel gas consumed by a combustion turbine engine. The benefits of the present invention include reducing the need to use a parasitic load to heat the fuel gas.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Starter durability test verification method and system
ActiveCN108072525AExplicit observation of durabilityClear observation characteristicsInternal-combustion engine testingCyclic testTest sample
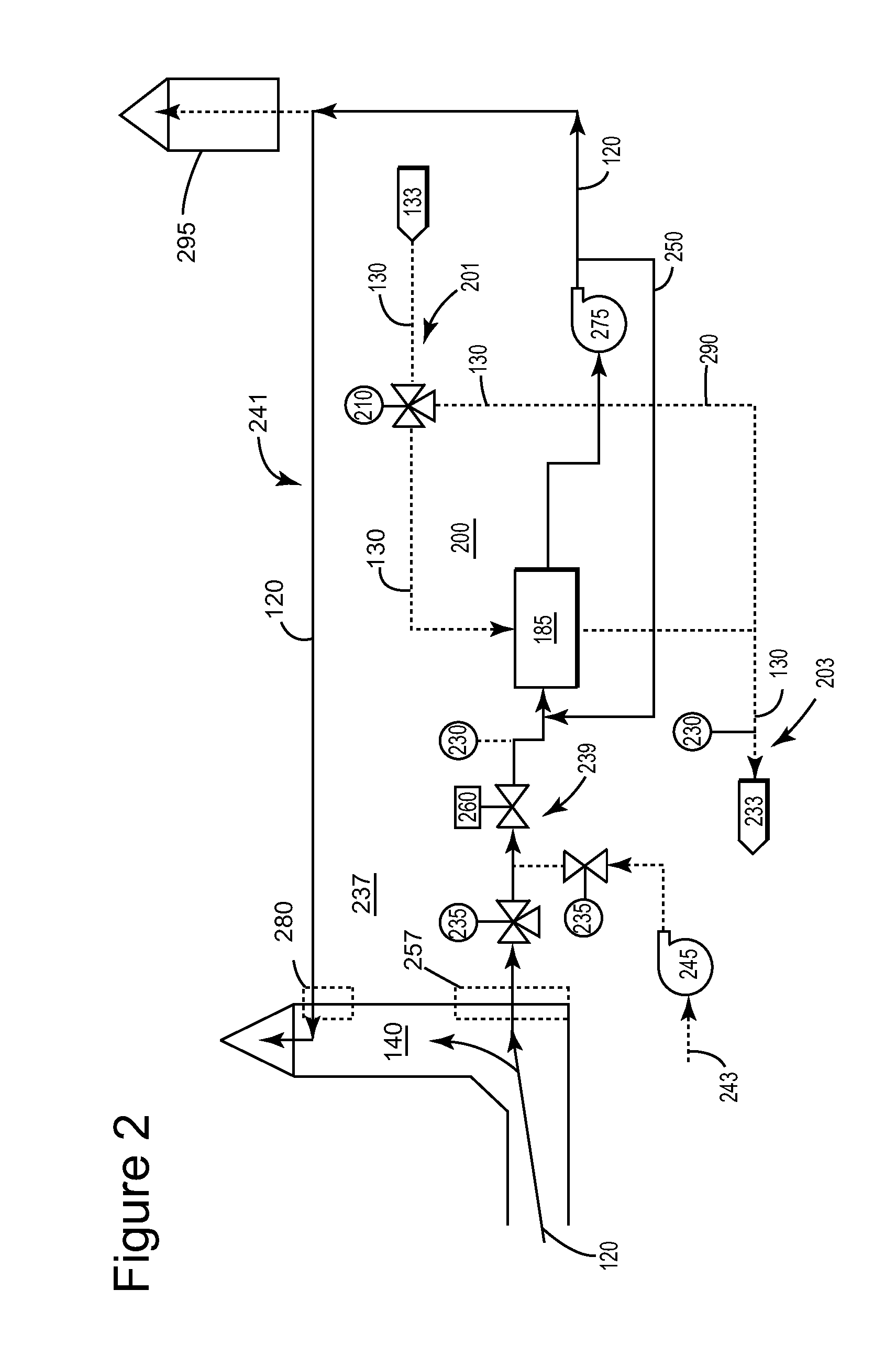
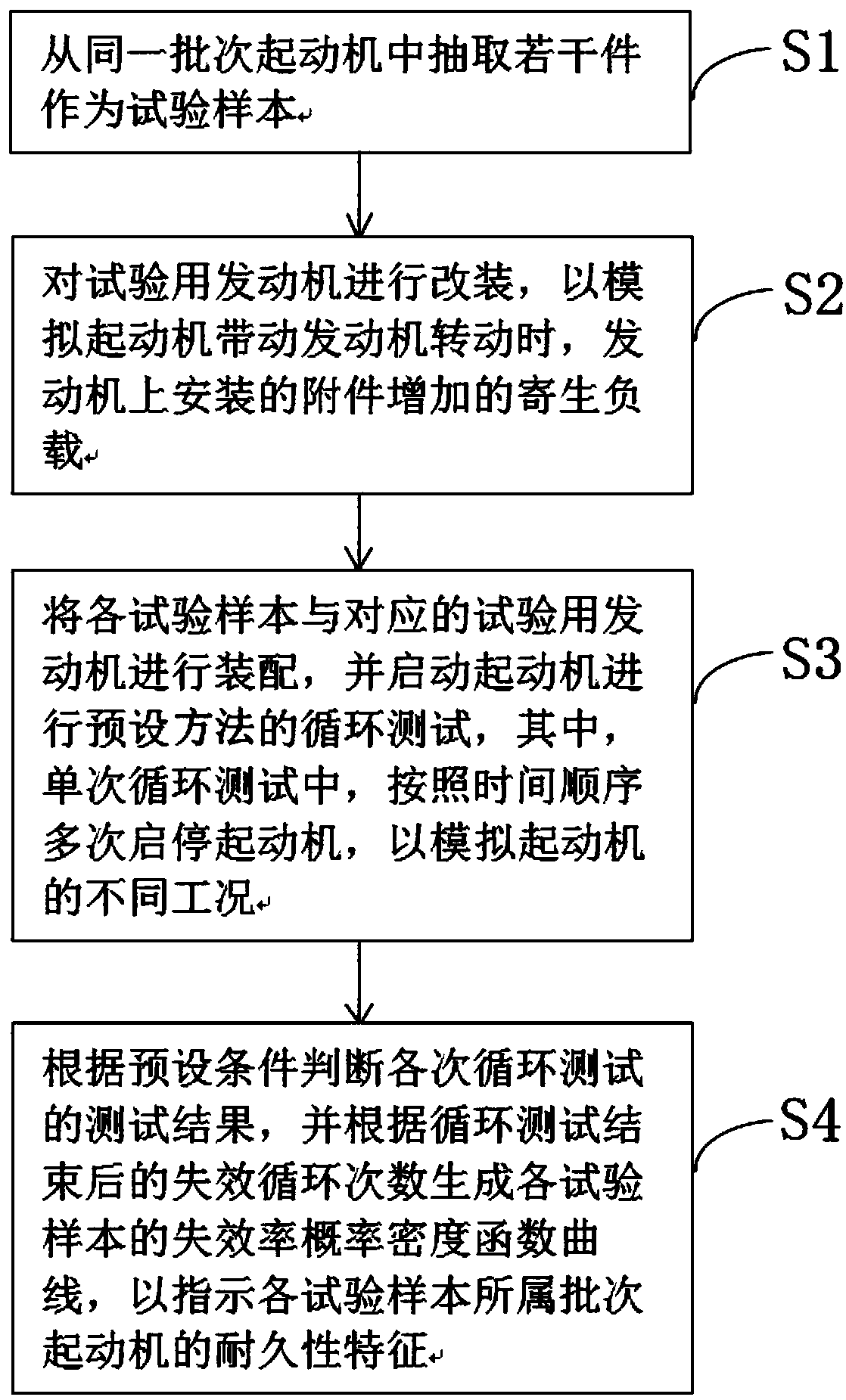
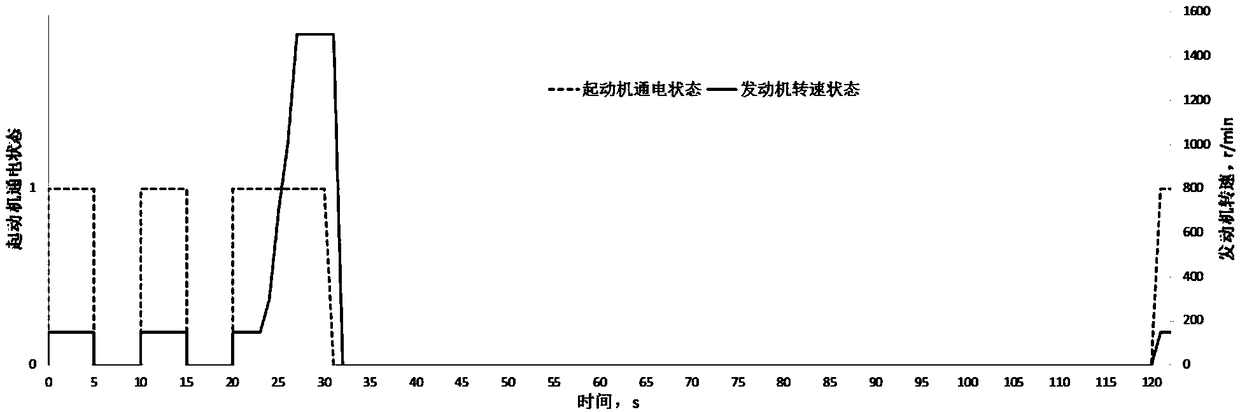
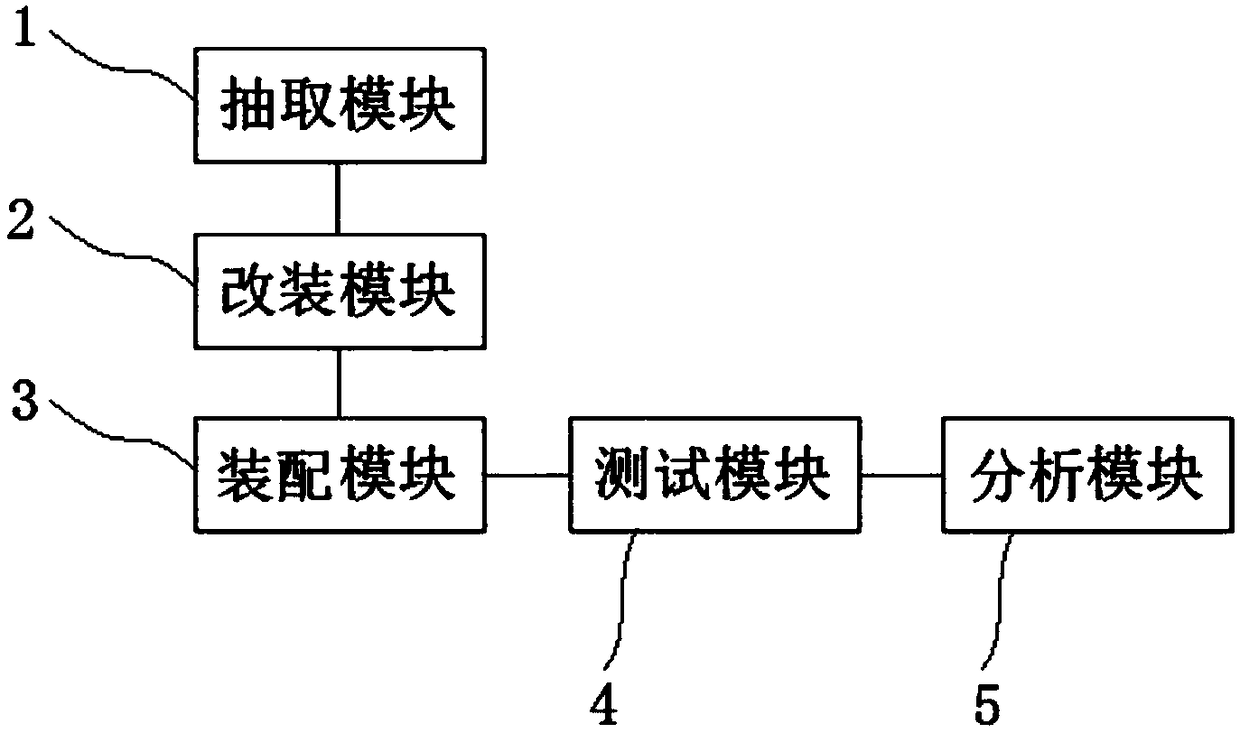
The invention discloses a starter durability test verification method, which comprises the following steps: taking a plurality of samples from the same batch of starters as test samples; carrying outrefitting on a test engine to simulate increased parasitic load of an accessory mounted on the engine when the starter drives the engine to rotate; assembling each test sample with the corresponding test engine, and starting the starter to carry out loop test based on a preset method, wherein in the single cycle test, starting and stopping the starter for many times according to the time sequenceto simulate different starting conditions of the starter; and judging test result of each cycle test according to preset conditions, and generating a failure probability density function curve of a test sample group according to failure cycle number obtained after ending of the cycle test to indicate durability characteristics of the batch of starters of the test samples. The method can effectively improve starter test result reliability, improve starter durability test result accuracy, improve assessment mechanism and reduce test time.
Owner:CHONGQING CUMMINS ENGINE
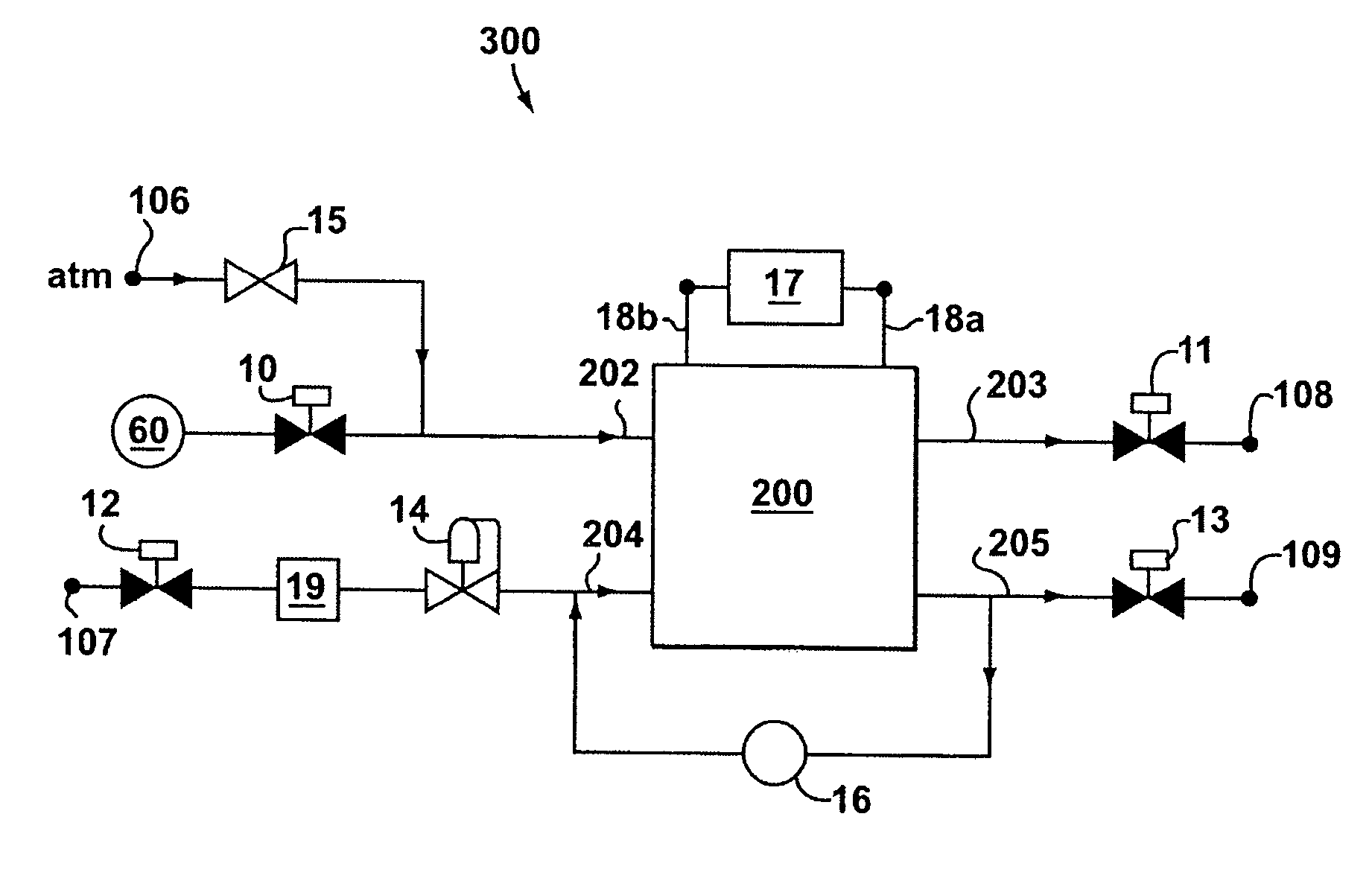
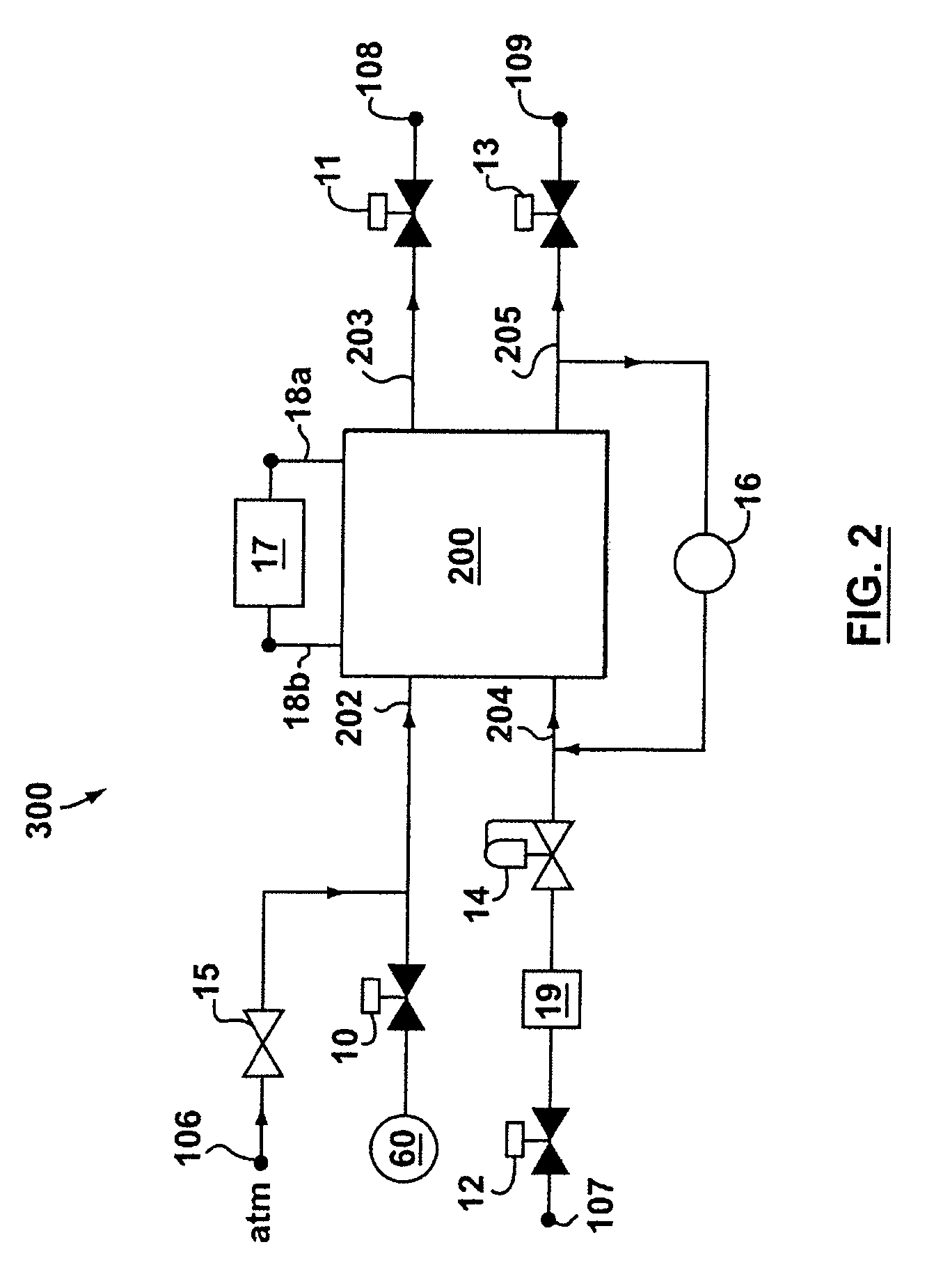
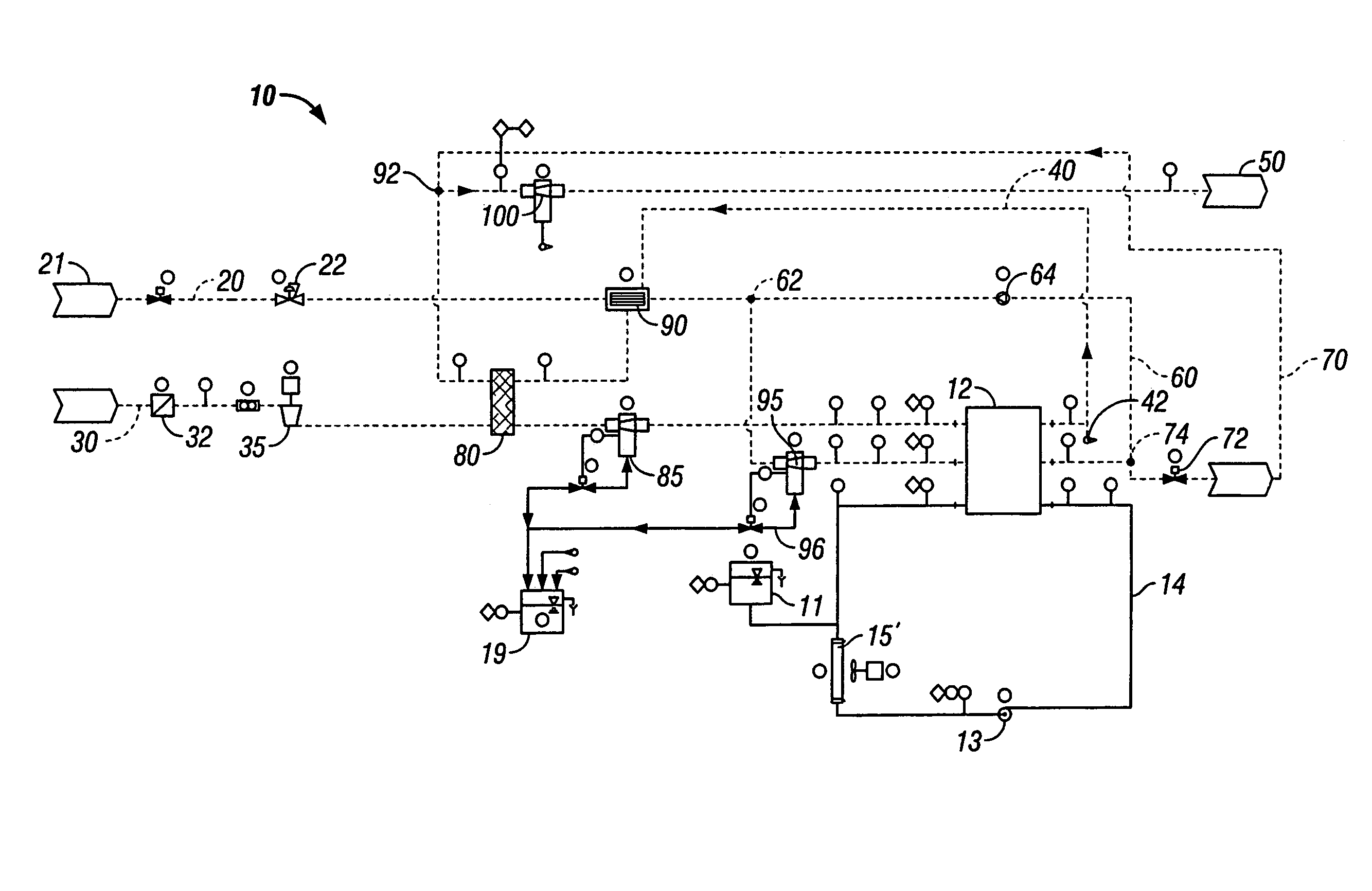
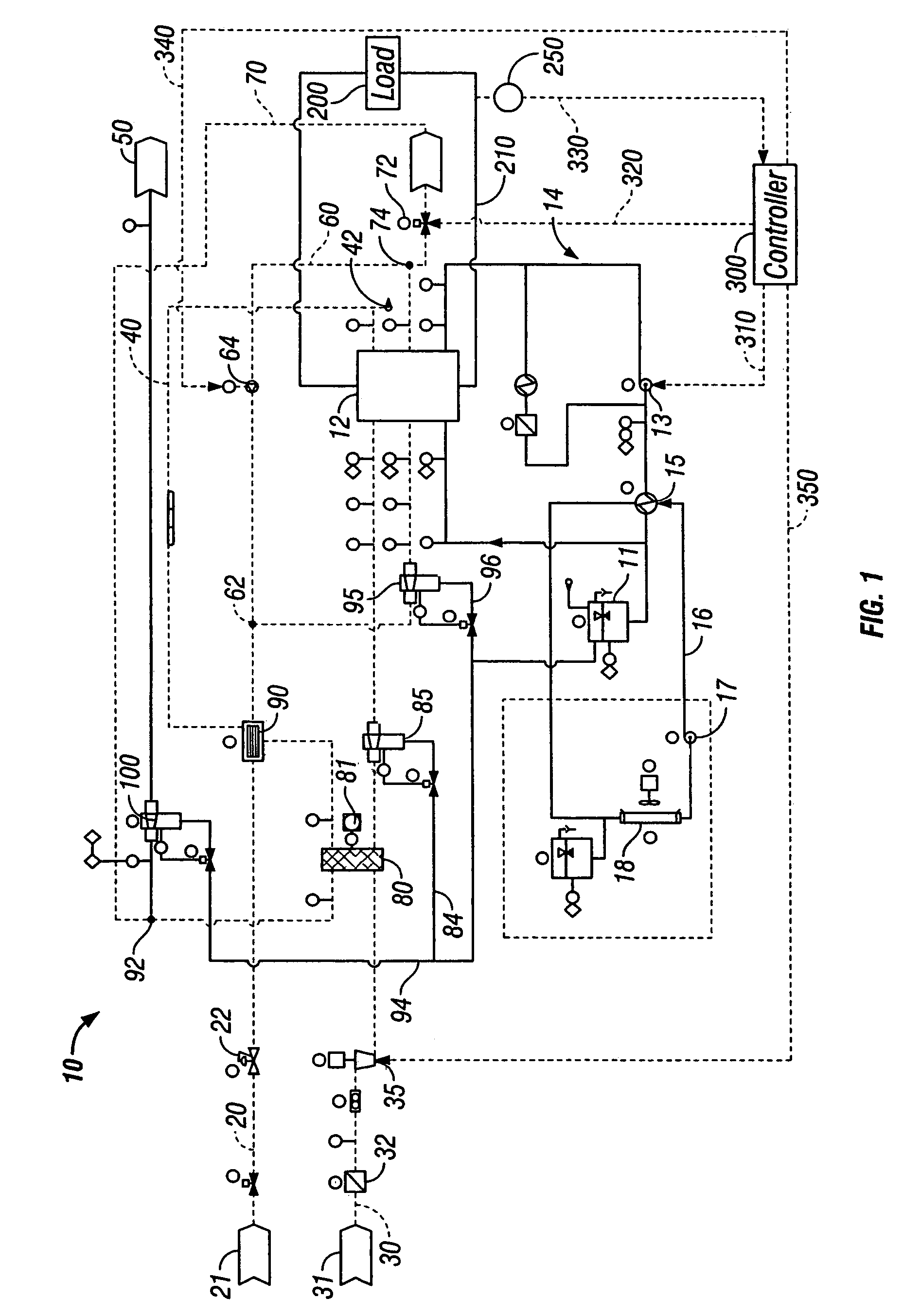
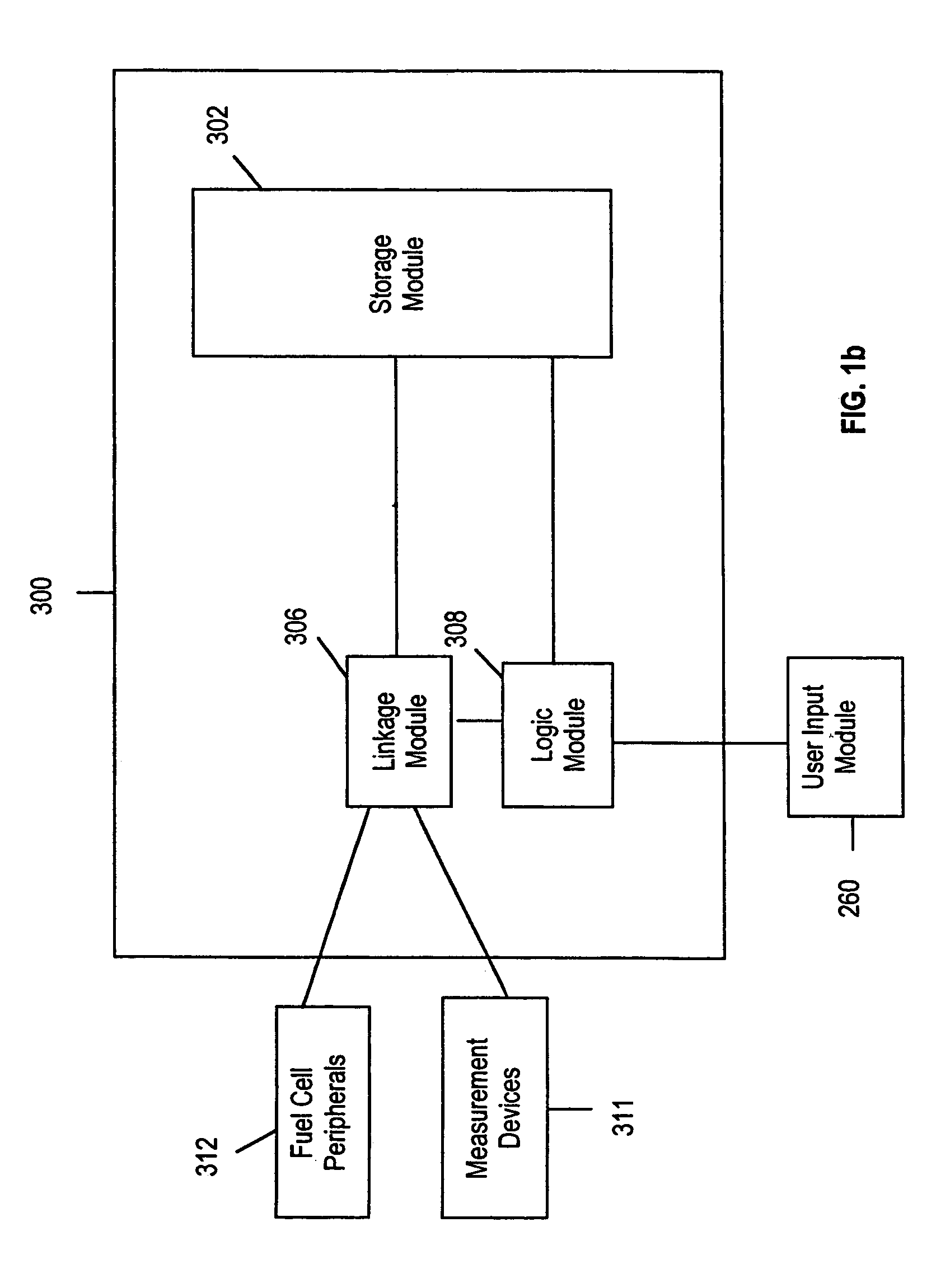
Fuel cell system and method of operation to reduce parasitic load of fuel cell peripherals
A fuel cell system and a method of operating same are provided. The fuel cell system includes a fuel cell for driving a load, at least one fuel cell peripheral, a device for measuring at least one fuel cell operation characteristic, and at least one controller for controlling the operation of at least one fuel cell peripheral based on the at least one fuel cell operation characteristic. The fuel cell operation characteristic is divided into at least two ranges, and operation of at least one fuel cell is controlled to provide it with a respective operational characteristic for each range of operation of the fuel cell system.
Owner:HYDROGENICS CORP
Occupant weight sensor for vehicular seats, method for making and system therefor
InactiveUS7255015B2High sensitivityImprove stabilityWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersElectric devicesEngineeringElectrical connector
An occupant weight sensor (1) for placement between a frame (7) fixed to the chassis of a vehicle and a second frame (8) supporting a vehicle seat has a sense element having a first body (12, 22, 28, 34, 50, 62, 64, 68) formed with a planar sense surface on which are mounted piezoresistors electrically connected in a Wheatstone bridge configuration. A post (12a, 22c, 28c, 34e, 50b, 62a, 64a, 68b) extends outwardly from the first body for attachment to the first frame. A second body is formed with a force transfer portion (14a, 24g, 30d, 36b, 52a, 70a) permanently attached to the first body along an outer periphery circumscribing the sense surface. The piezoresistors are electrically connected to conditioning electronics received in a chamber formed between the two bodies. The effects of parasitic loads on the sense element are minimized by selected placement of the piezoresistors on the sense surface. Several variations are disclosed for attaching the sensor to the first and second frames and both longitudinally and laterally extending electrical connectors are shown.
Owner:SENSATA TECHNOLOGIES INC
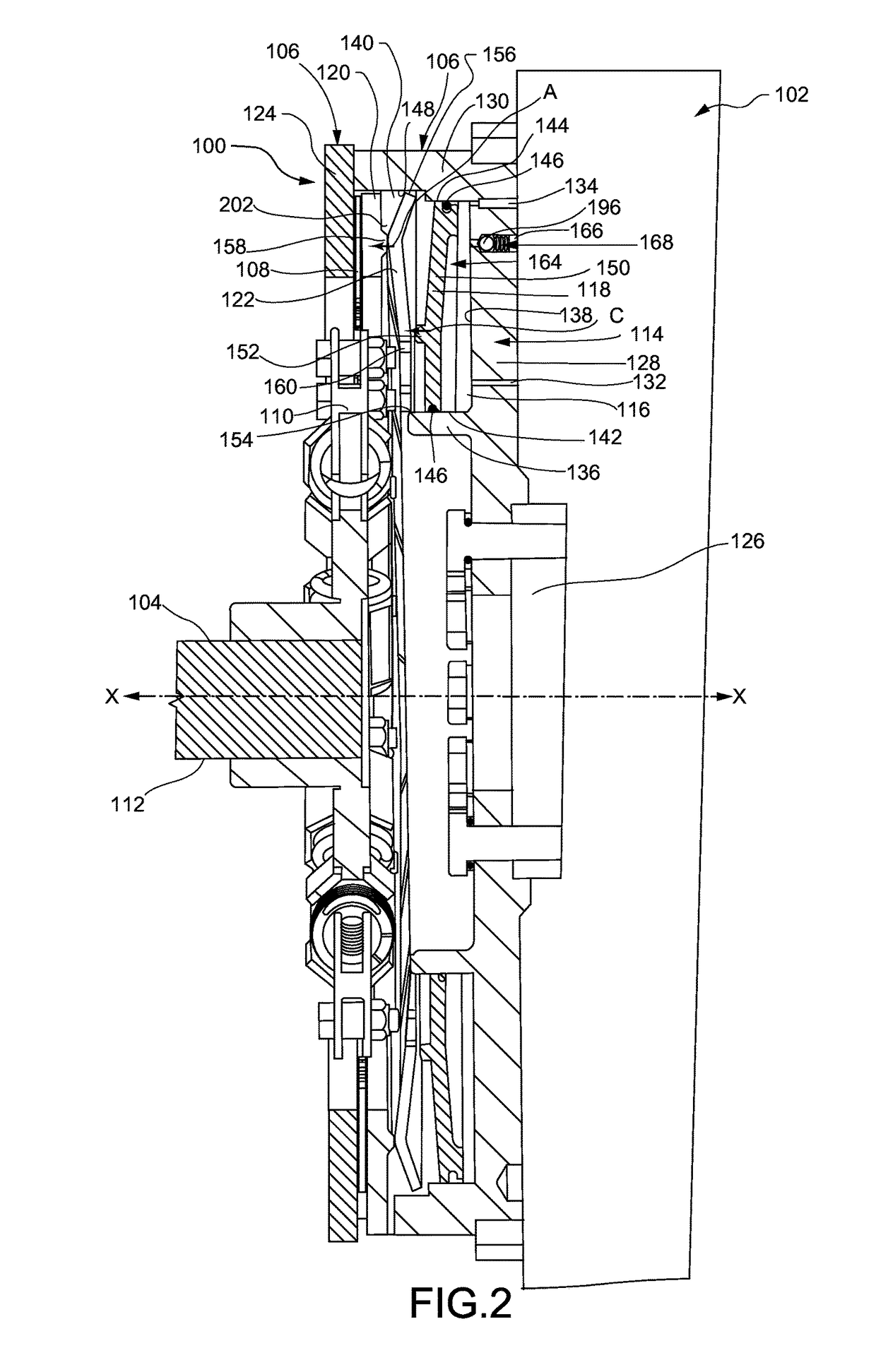
Disconnect clutch
A disconnect clutch and method of controlling the connection of a parasitic load to an engine disposed on a machine is disclosed. The disconnect clutch may comprise a flywheel assembly, a friction plate and a coupling. The flywheel assembly may include a flywheel having a cavity, a chamber, a piston moveable between a contracted position and an expanded position, a pressure plate, a lever, and a coupling operably connected to the friction plate. The flywheel may include an end plate. The chamber may be defined by the flywheel and the piston. The lever may apply an activation force to the pressure plate when the piston is in the expanded position. The friction plate may be attached to and rotatable with the flywheel assembly when the piston is in the expanded position and generally stationary when the piston is in the contracted position.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com