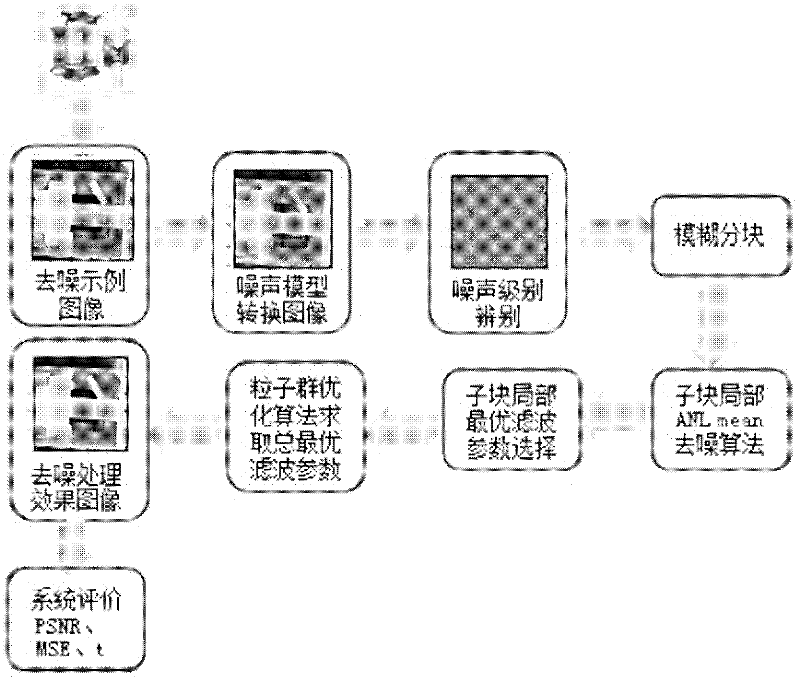
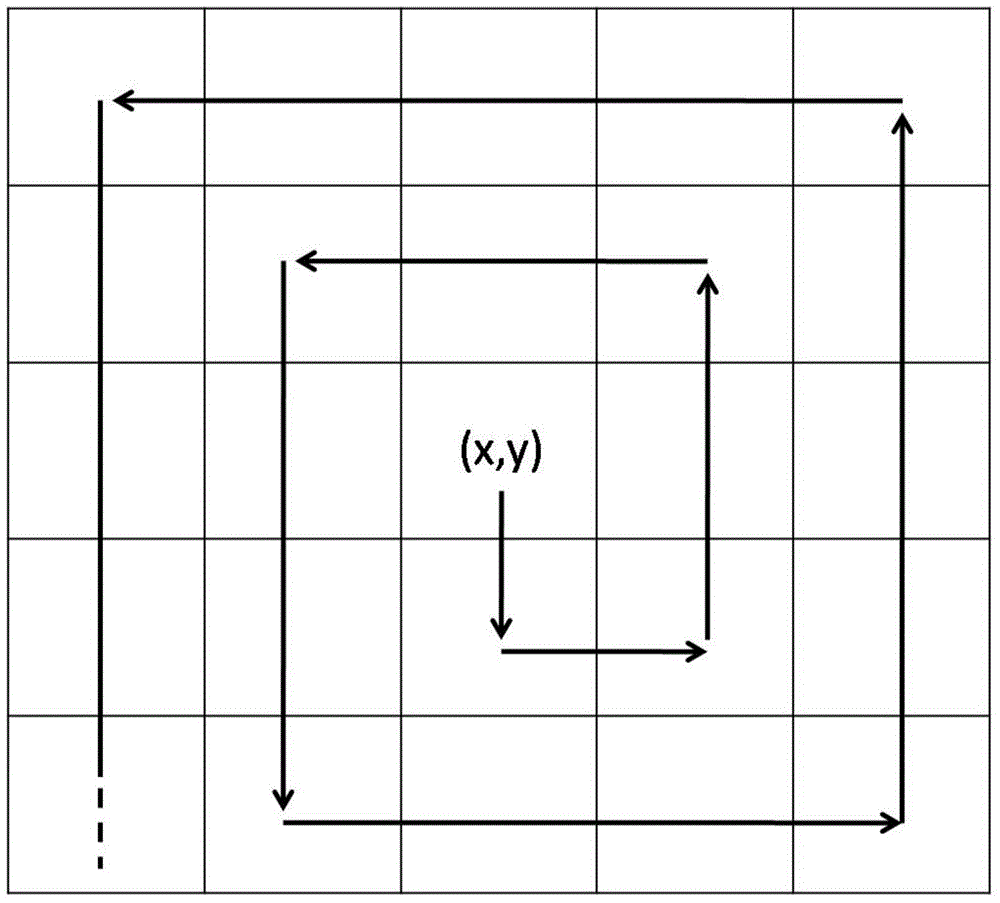
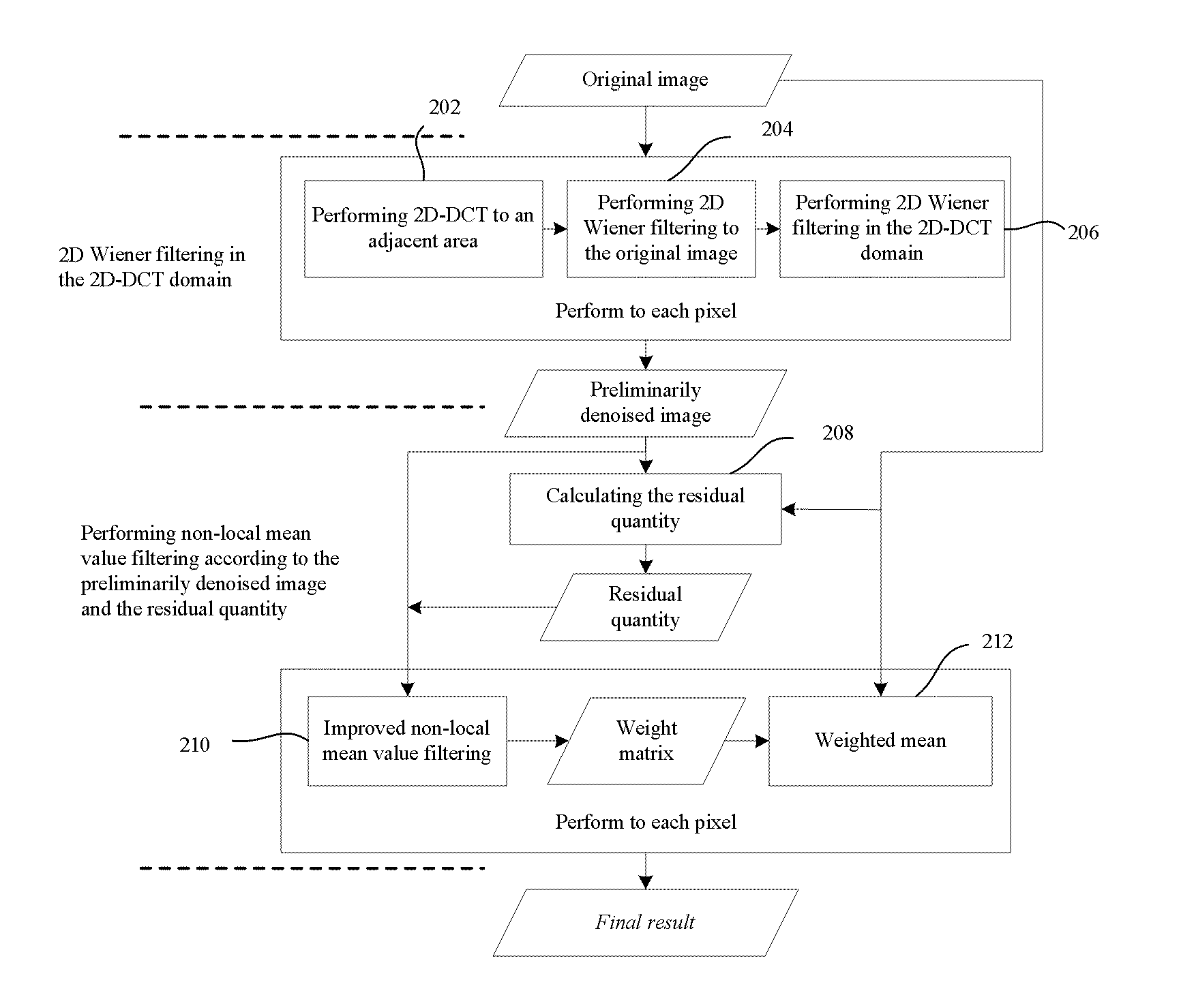
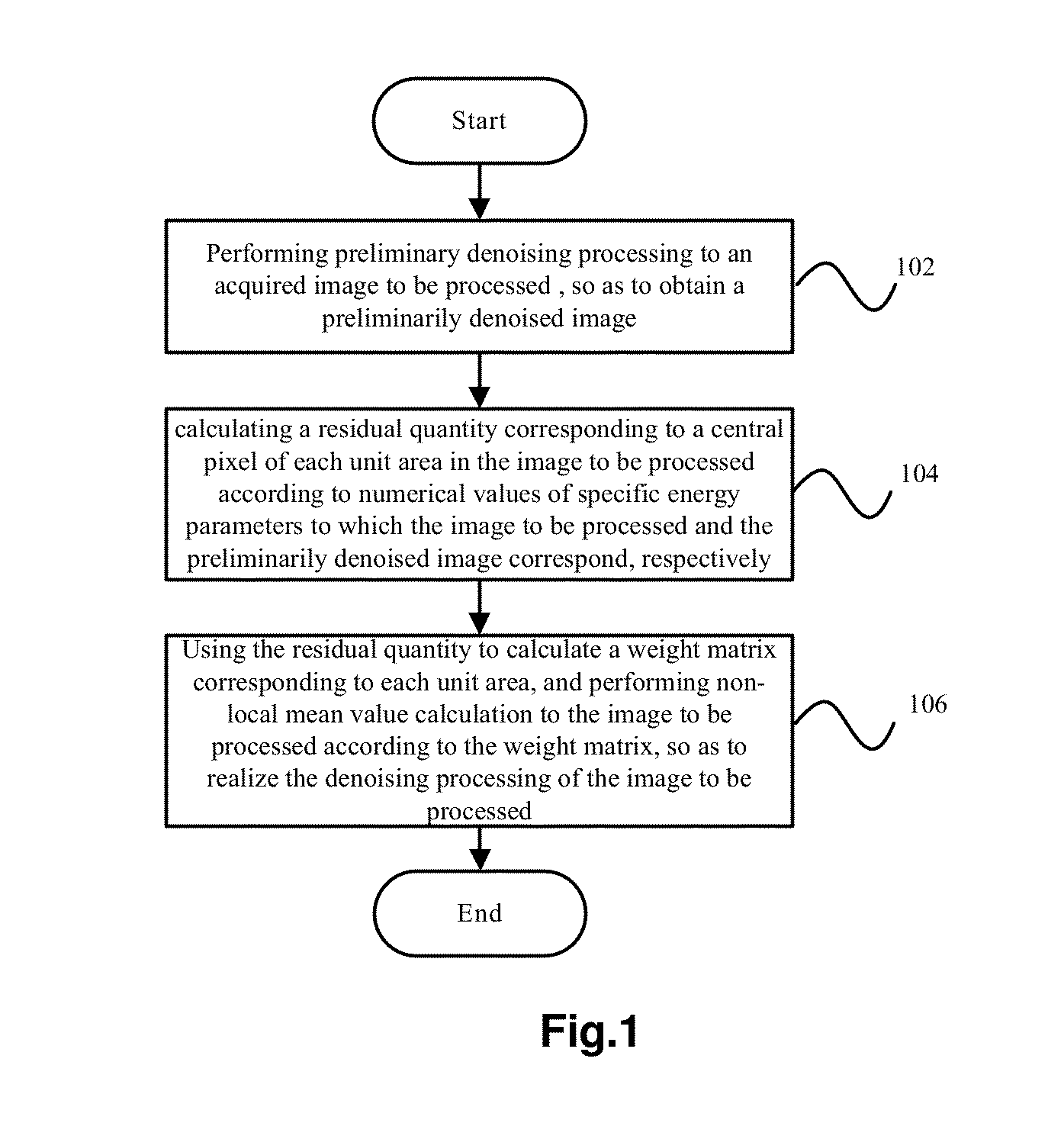
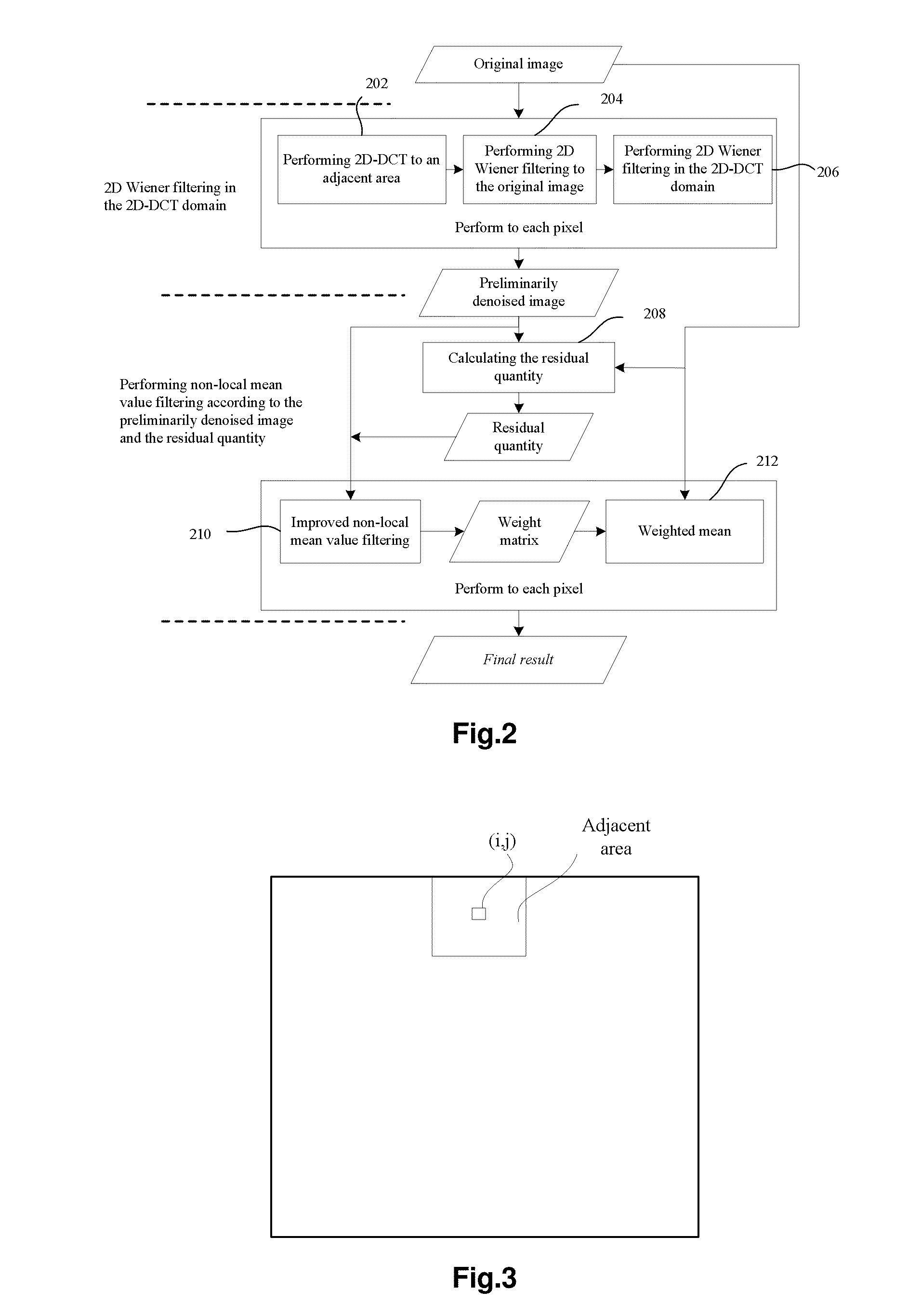
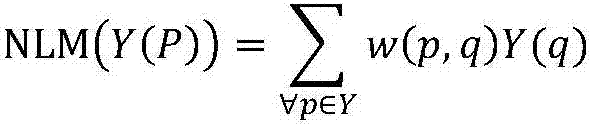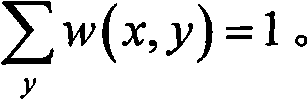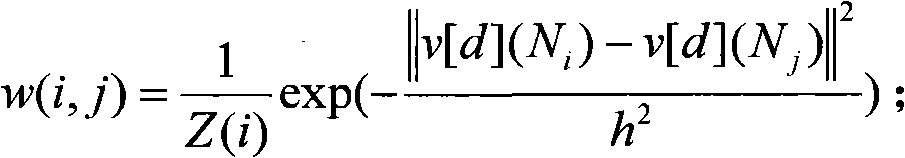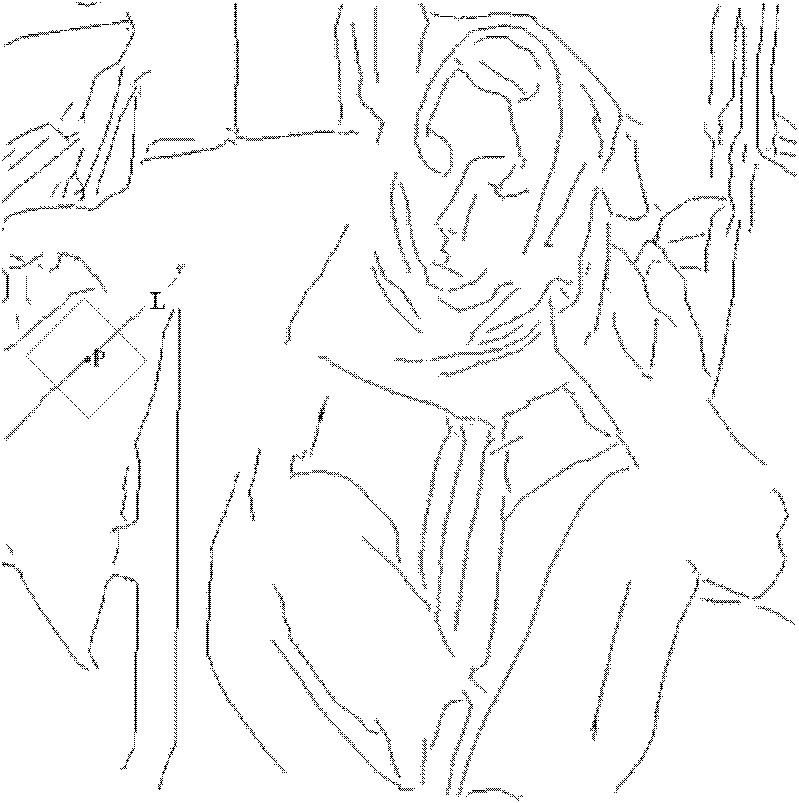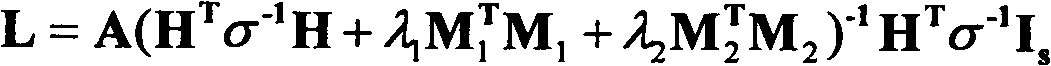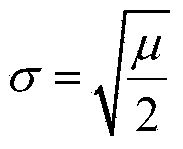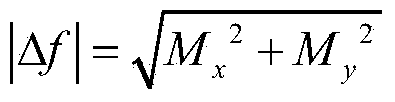Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
316 results about "Non-local means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
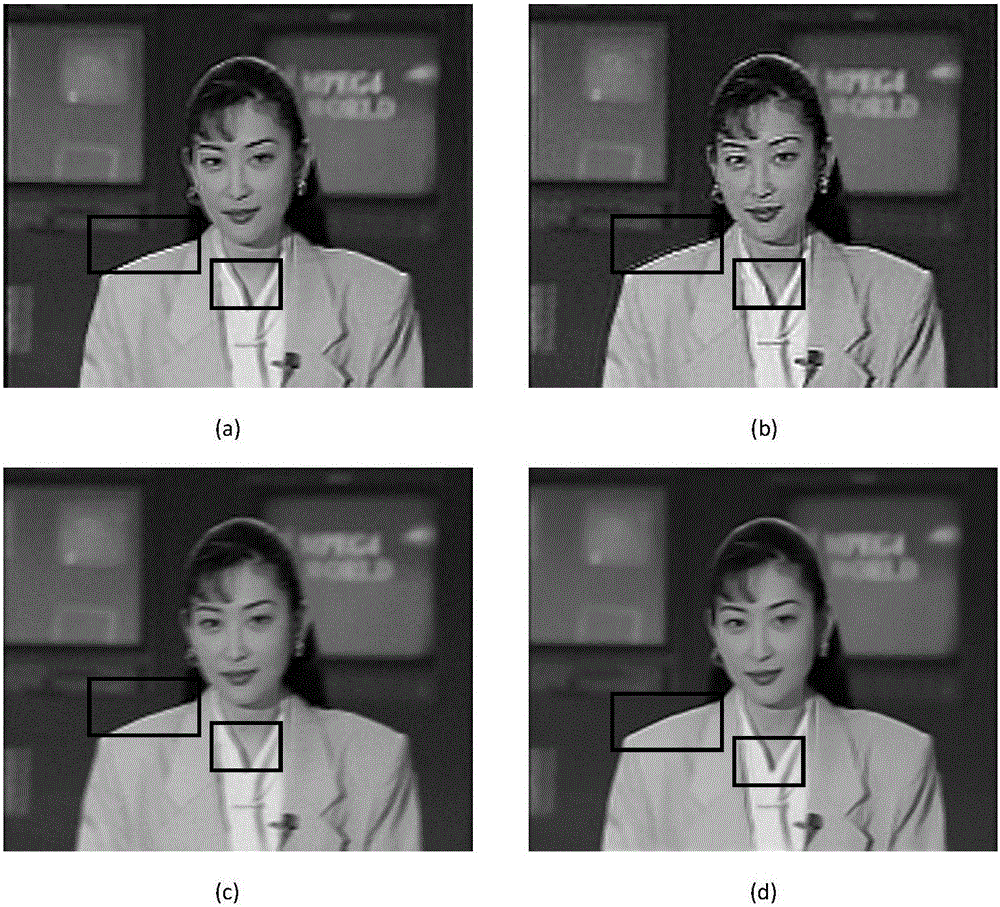
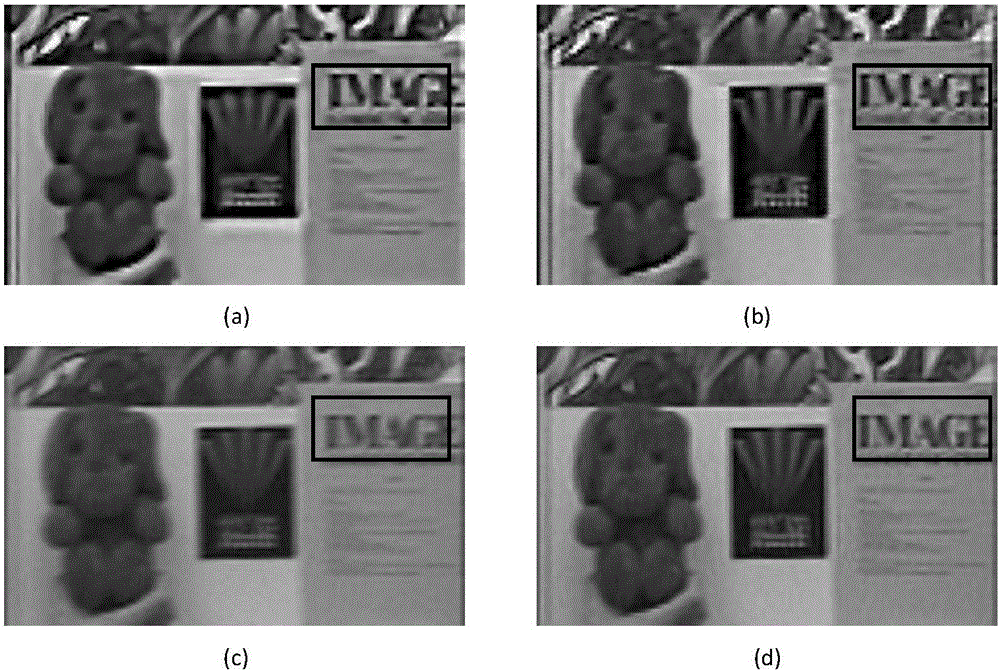
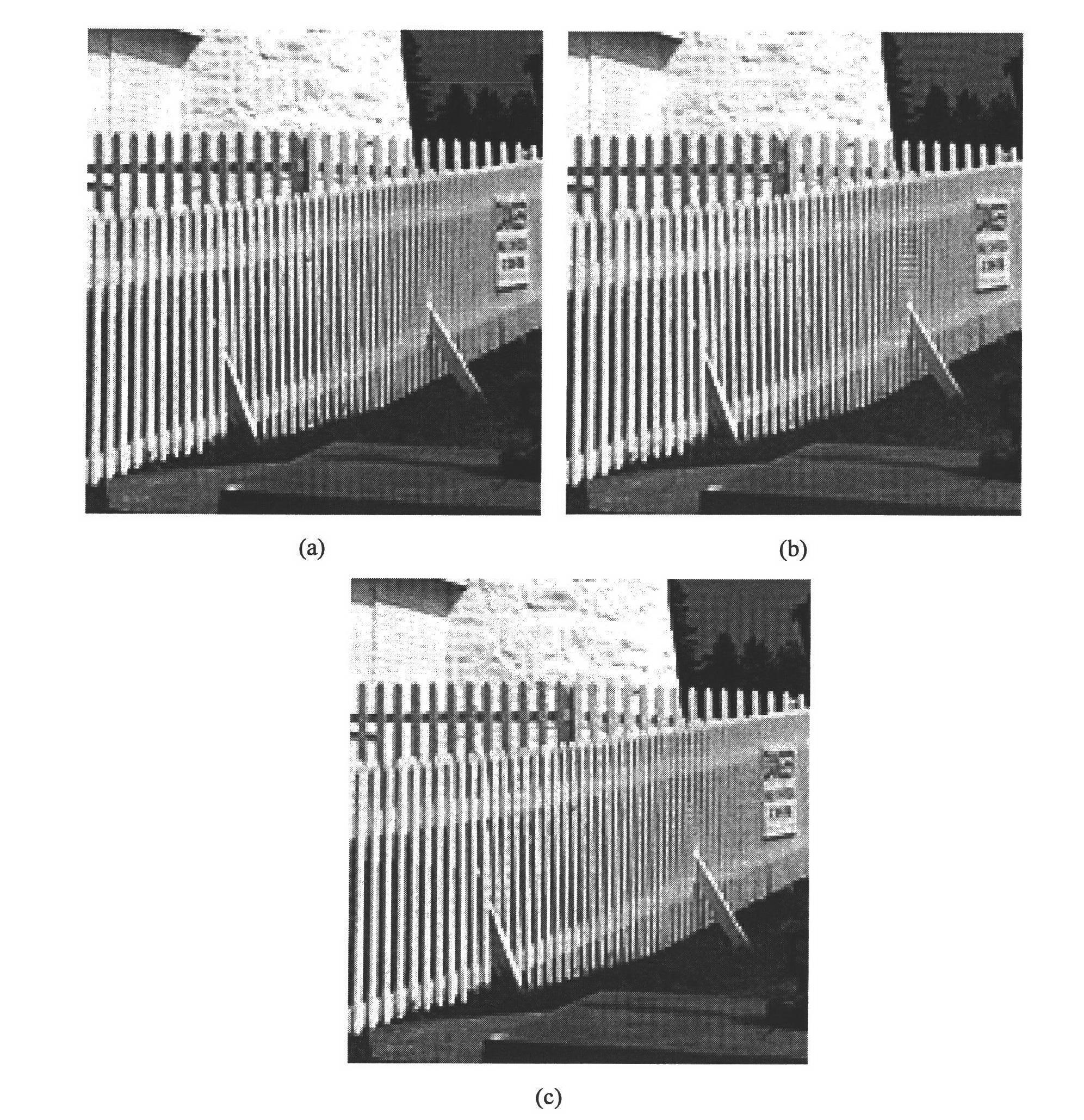
Non-local means is an algorithm in image processing for image denoising. Unlike "local mean" filters, which take the mean value of a group of pixels surrounding a target pixel to smooth the image, non-local means filtering takes a mean of all pixels in the image, weighted by how similar these pixels are to the target pixel. This results in much greater post-filtering clarity, and less loss of detail in the image compared with local mean algorithms.
Three-dimensional MRI image-based breast tumor automatic segmentation method
ActiveCN107464250AReduce workloadShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationAccurate segmentation
The invention provides a three-dimensional MRI image-based breast tumor automatic segmentation method. The method comprises the following steps of performing image preprocessing: providing an initial MRI image and performing preprocessing on the initial MRI image by adopting a non local mean filter; performing breast tumor locating: building a multilayer processing model for a training set, performing hierarchical abstraction on characteristics of a training object by adopting a convolutional neural network, automatically extracting segmentation characteristics, and outputting a probability distribution graph of a tumor position; performing breast tumor boundary segmentation: providing a breast three-dimensional MRI image, determining a seed point based on the probability distribution graph of the tumor position, and finishing segmentation initialization to obtain an initial region C0 of a tumor; and performing accurate segmentation on the tumor by using a region growth algorithm.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for X-ray image
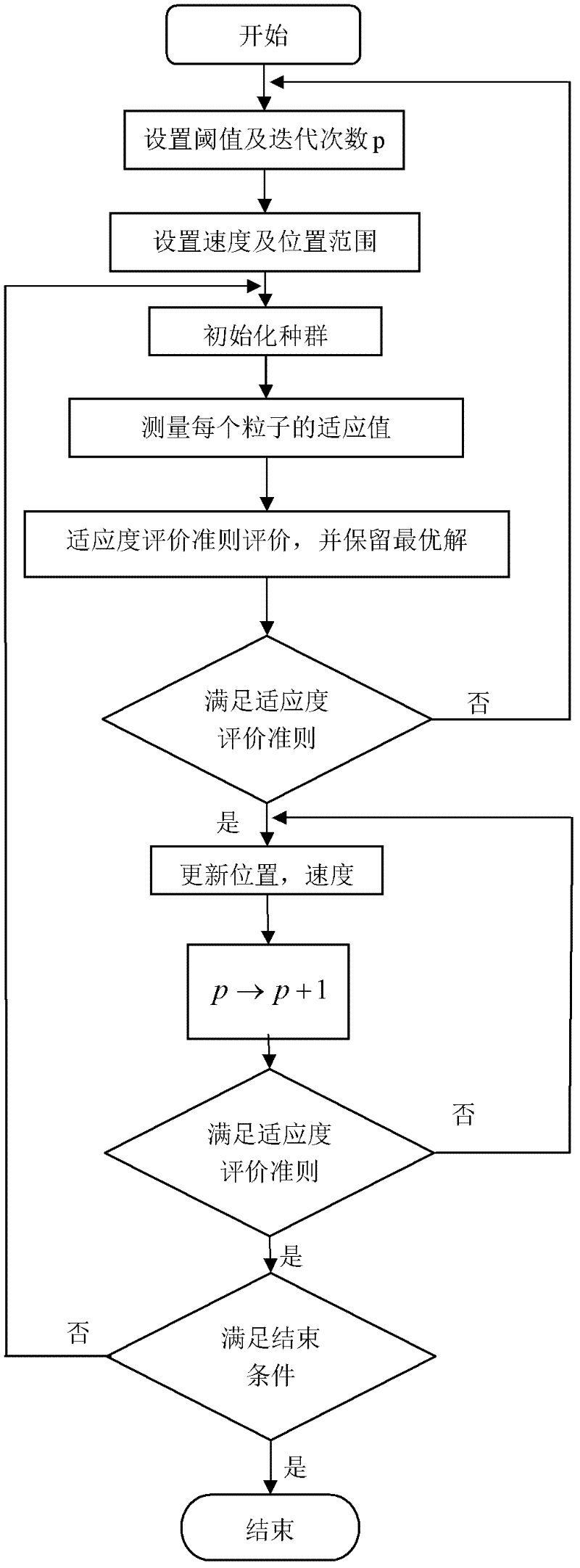
The invention provides a bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for an X-ray image. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) a selecting method of a fuzzy de-noising window; and 2) a bivariate fuzzy adaptive nonlocal average filtering algorithm. The method has the beneficial effects that in order to preferably remove the influence caused by the unknown quantum noise existing in an industrial X-ray scan image, the invention provides the bivariate nonlocal fuzzy adaptive non-linear average filtering de-noising method for the X-ray image, in the method, a quantum noise model which is hard to process is converted into a common white gaussian noise model, the size of a window of a filter is selected by virtue of fuzzy computation, and a relevant weight matrix enabling an error function to be minimum is searched. A particle swarm optimization filtering parameter is introduced in the method, so that the weight matrix can be locally rebuilt, the influence of the local relevancy on the sample data can be reduced, the algorithm convergence rate can be improved, and the de-noising speed and precision for the industrial X-ray scan image can be improved, so that the method is suitable for processing the X-ray scan image with an uncertain noise model.
Owner:YUN NAN ELECTRIC TEST & RES INST GRP CO LTD ELECTRIC INST +1
Non-local mean de-noising method for natural image
InactiveCN101950414AAccurate calculationPreserve and restore edgesImage enhancementImaging processingNon-local means
The invention discloses a non-local mean de-noising method for a natural image, which belongs to the technical field of image processing and mainly solves the problem of inaccurate similarity calculation in the non-local mean de-noising of the conventional natural image. The method comprises the following processes of: (1) performing wavelet transformation on the input noise-containing natural image; (2) performing variance normalization on high-frequency information; (3) calculating the similarities of a pixel point x and a pixel point y in a search area to obtain weights of all pixel points in the search area; (4) performing weighted average on all the pixel points in the search area to obtain gray values of the corrected pixel points according to the calculated weights of all the pixel points in the search area; and (5) substituting the gray values of the corrected pixel points for the gray values of the pixel points in the input noise-containing natural image to obtain a de-noised image. The method is superior to other de-noising methods on overall performance, can keep the details of the natural image such as edges, textures and the like at the same time of better smoothing the noise, and can be used for de-noising the natural image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Image denoising method based on non-local means and multi-level directional images
ActiveCN101847257AQuality improvementAccurate targetImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisDecomposition
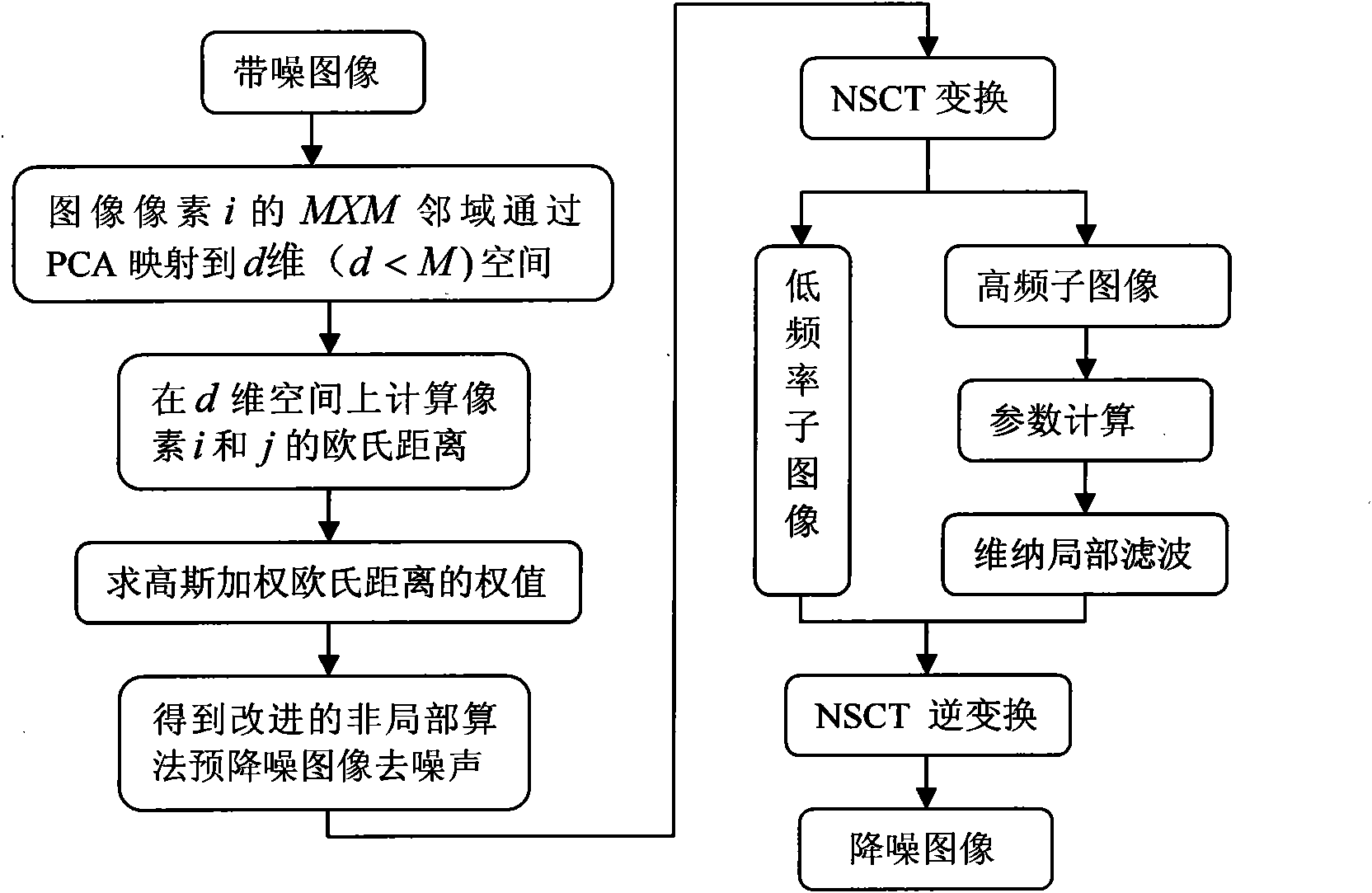
The invention relates to an image denoising method based on non-local means and multi-level directional images, comprising the steps of: firstly, carrying out preprocessing on an image with noise in an empty space by utilizing a non-local mean arithmetic of a small window and the similarity of the local structure of the image, and mapping the local window to a low-dimensional space to improve the speed of the arithmetic by utilizing principal component analysis (PCA); then carrying out multi-scale multi-direction sparse decomposition on the preprocessed image through NSCT (Non-subsampled Contourlet); eliminating low-frequency noise by adopting Wiener filtering in an NSCT transform domain by utilizing the neighborhood statistical property of the coefficient; and obtaining the denoised image through NSCT inverse transformation. The method improves the quality of the denoised image, provides more comprehensive and accurate targets and background information, and achieves relatively ideal denoising effect. The invention has wide application prospect in systems in the military field and the non-military field such as optical imaging, target detection, safety monitoring, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER +1
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and storage medium
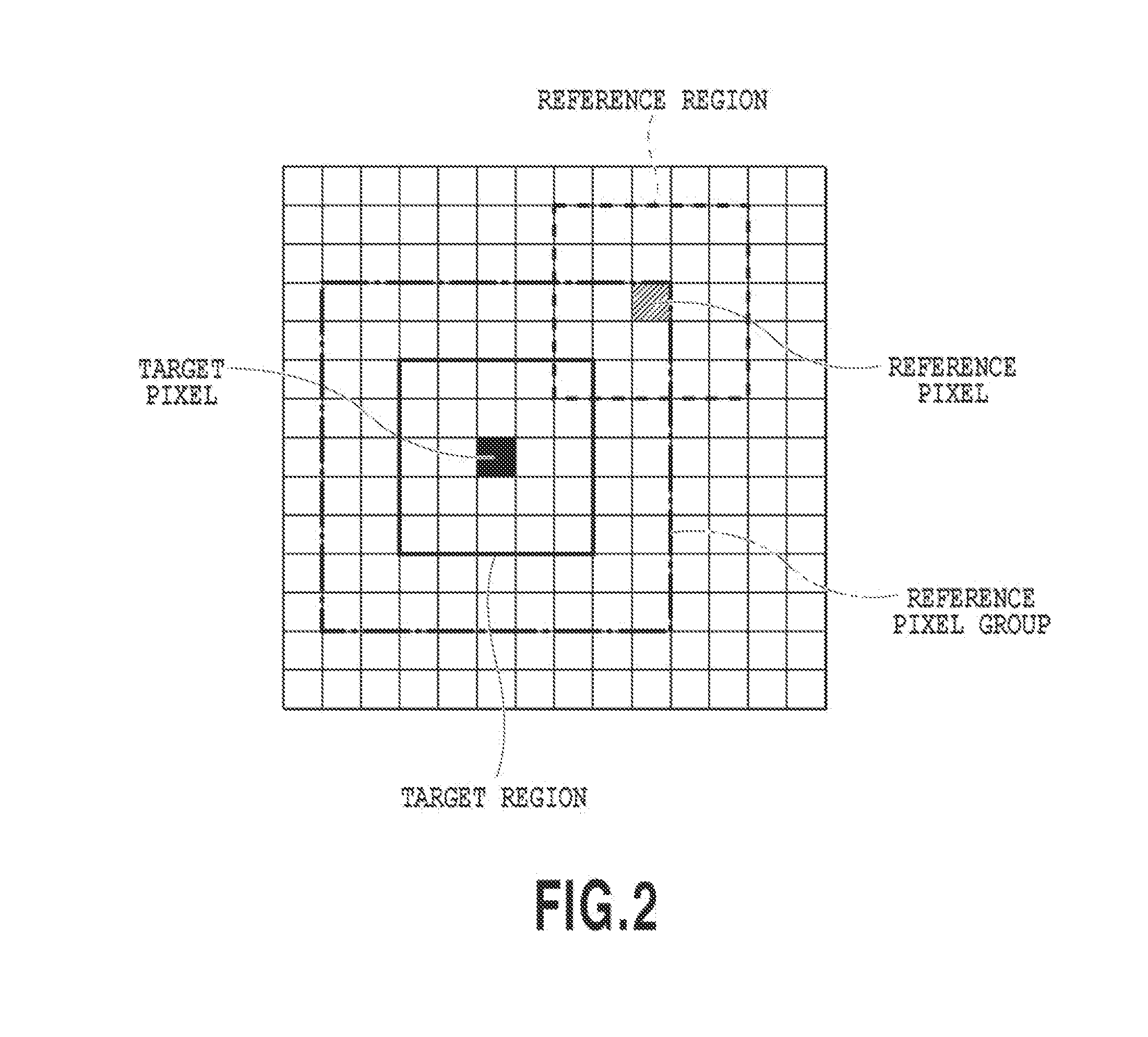
A non-local means method is insufficient in its noise reduction effect or edge retainability due to a perfect match between blocks in a case where a reference pixel matches a target pixel. Therefore, information on a target region and plural reference regions is obtained for the target pixel. Whether the target region matches any one of the reference regions is determined from the obtained information. Switching between weight derivation methods based on similarity between the target region and the reference region is performed according to a determined result.
Owner:CANON KK
Realization method based on bayesian non-local mean filter
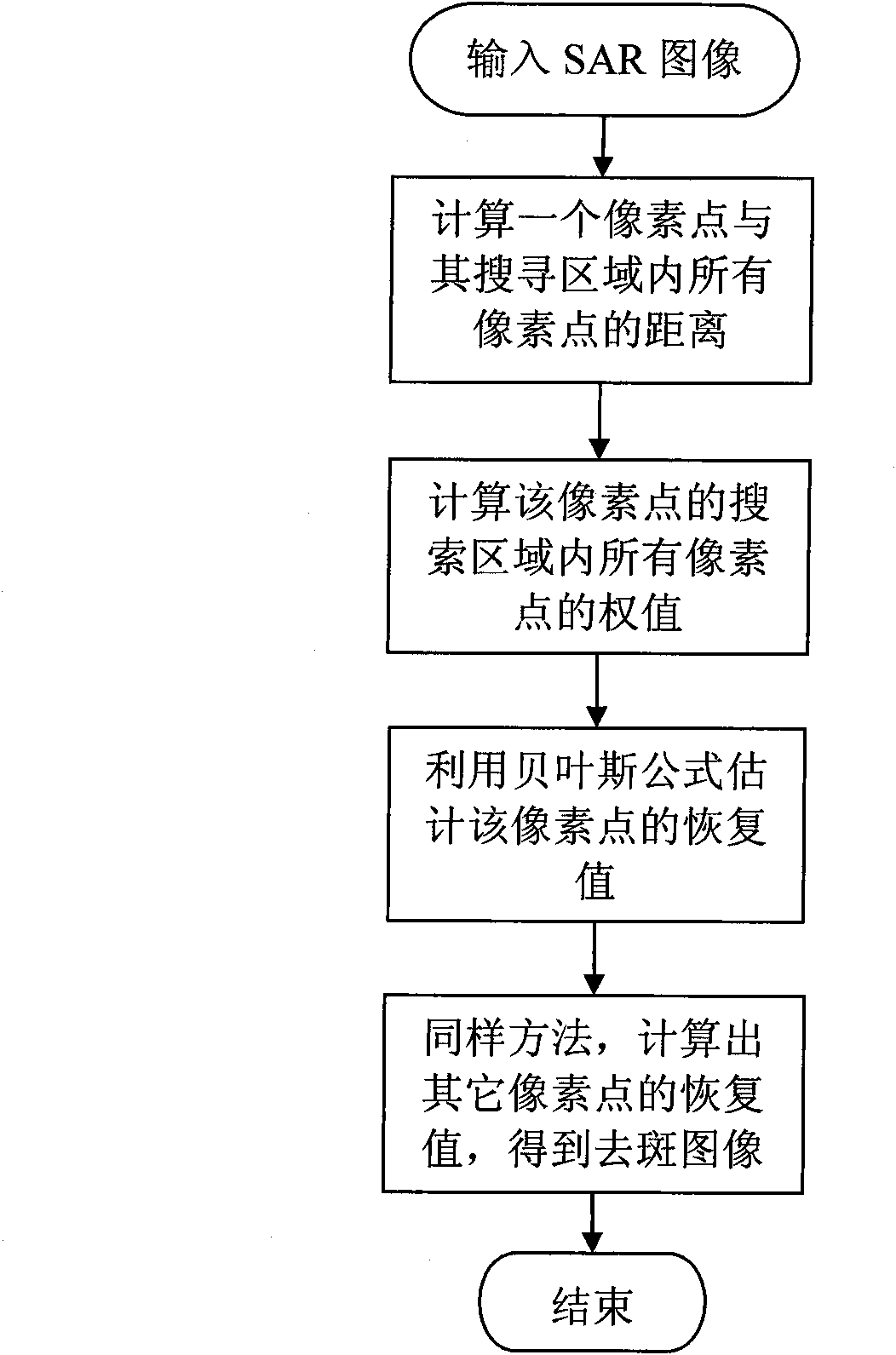
InactiveCN101661611AThe implementation process is simpleAccurate calculationImage enhancementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging processingNon-local means
The invention discloses a realization method based on a bayesian non-local mean filter, belonging to the field of image processing technology and mainly overcoming the contradiction problem of detailmaintenance and smooth degree in the prior spot removing result of SAR images. The realization process comprises the following steps: (1) calculating the distance between a pixel and all of the pixelsin a search area according to a distance formula for the pixel of the input SAR image; (2) calculating the weight of all of the pixels in the search area by using a weight calculating formula according to the calculated distance of all of the pixels; (3) carrying out weighted average on all of the pixels in the search area to obtain a recovery value of the pixel according to the calculated weightof all of the pixels in the search area; and (4) calculating the recovery value of each pixel according to the steps to obtain a spot removing image. Compared with other classical sport removing methods, the invention can better smooth spots and noise, maintain edge and texture details of the SAR image, and can be used for spot removing processing of the SAR images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
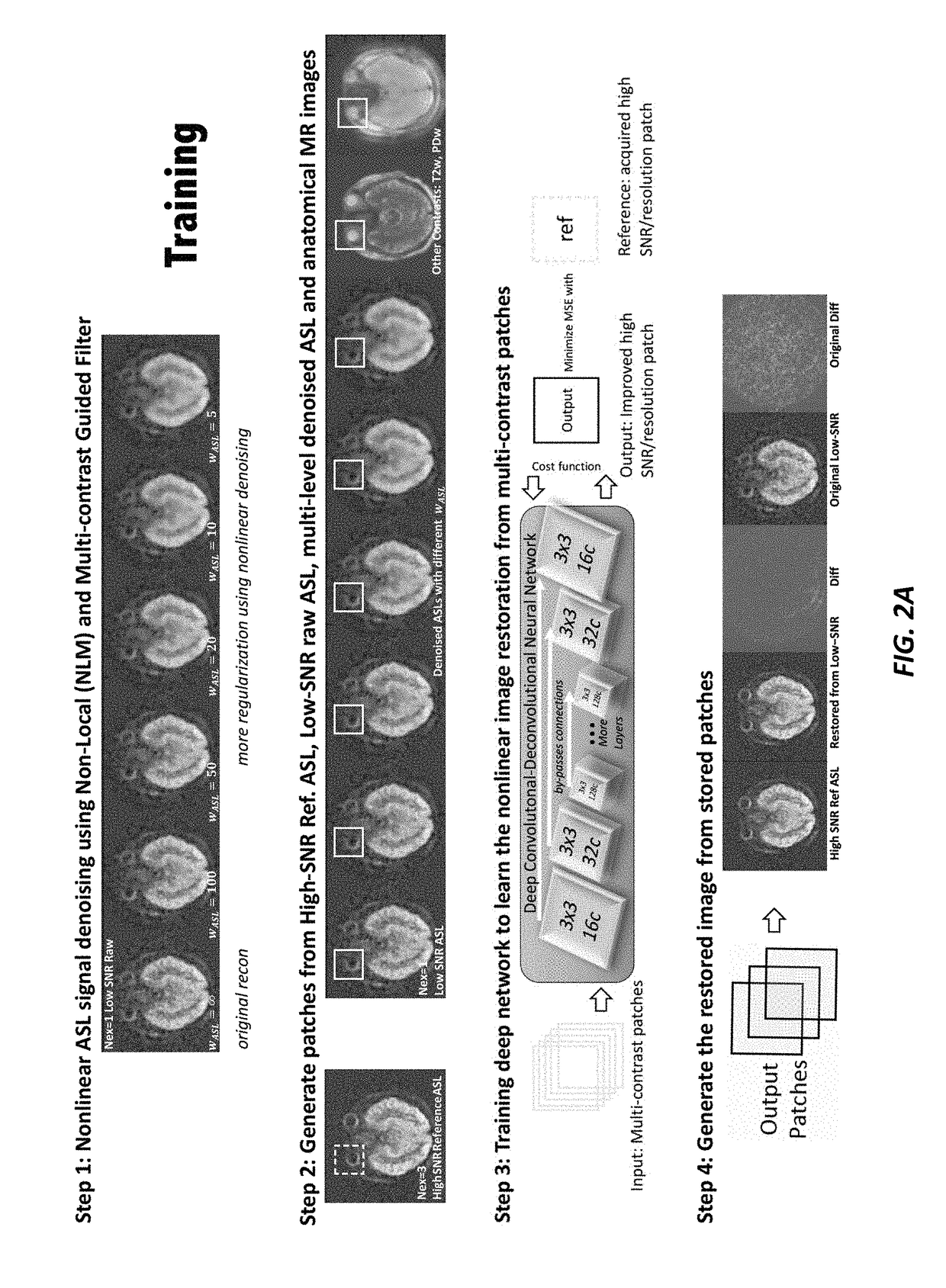
Quality of Medical Images Using Multi-Contrast and Deep Learning
ActiveUS20180286037A1Reduced imaging timeImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisNetwork modelModel parameters
A method of improving diagnostic and functional imaging is provided by obtaining at least two input images of a subject, using a medical imager, where each input image includes a different contrast, generating a plurality of copies of the input images using non-local mean (NLM) filtering, using an appropriately programmed computer, where each input image copy of the subject includes different spatial characteristics, obtaining at least one reference image of the subject, using the medical imager, where the reference image includes imaging characteristics that are different form the input images of the subject, training a deep network model, using data augmentation on the appropriately programmed computer, to adaptively tune model parameters to approximate the reference image from an initial set of the input and reference images, with the goal of outputting an improved quality image of other sets of low SNR low resolution images, for analysis by a physician.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
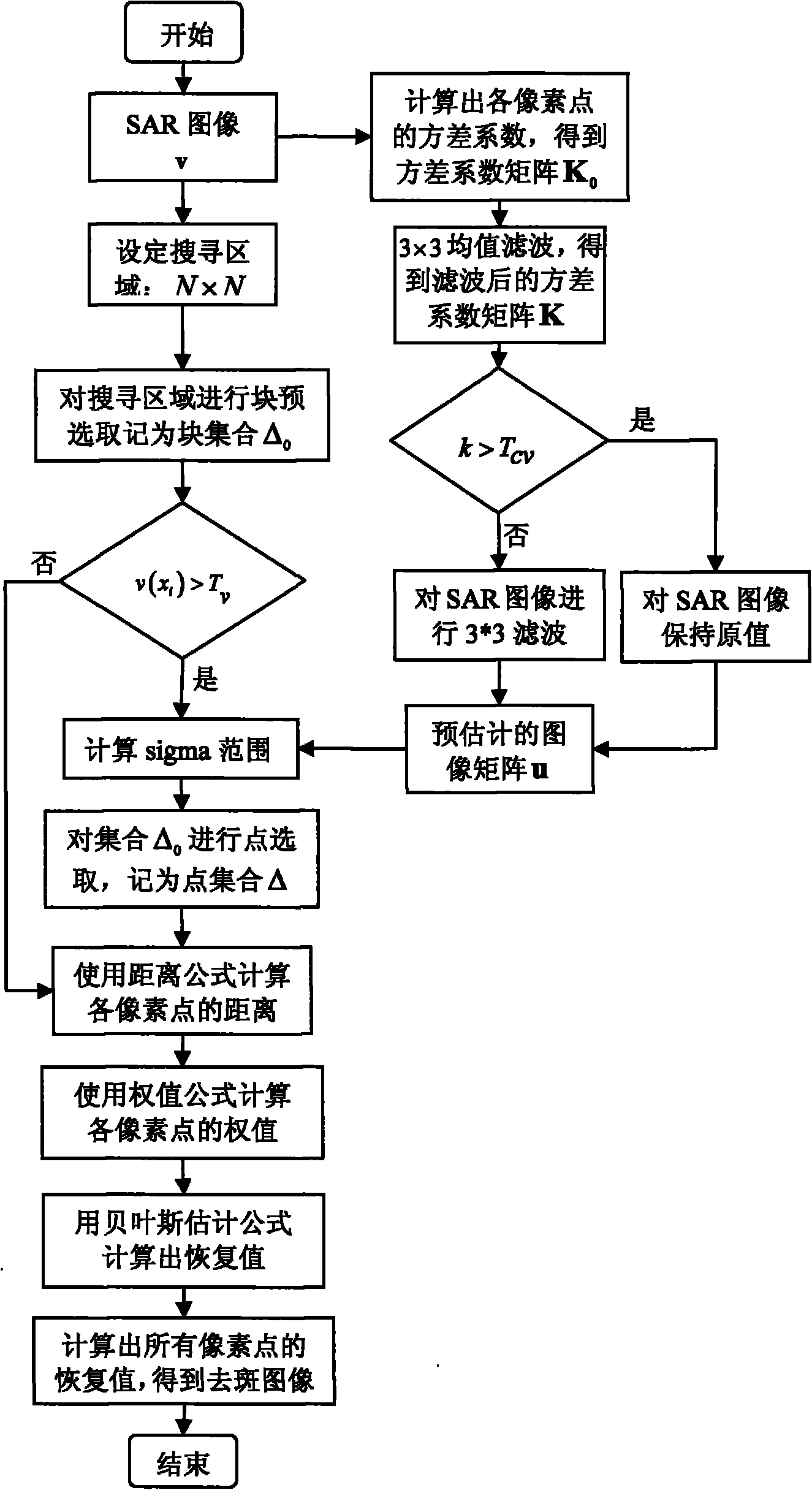
SAR image de-speckling method based on improved Bayes non-local mean filter
InactiveCN101833753APrevent blurProtect strong reflective point targetsImage enhancementImaging processingBrightness perception
The invention discloses an improved Bayes non-local mean filter used in a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image de-speckling method, which belongs to the technical field of image processing and mainly overcomes the problems of compressed brightness of strong reflection targets such as points, edges and the like and unsatisfied mean maintenance and the like in a de-speckling result of the original Bayes non-local mean filter. The method is implemented by the following steps: (1) performing mean pre-evaluation on an input SAR image v to obtain a pre-evaluated mean matrix u; (2) pre-selecting blocks in a search area at the xi position of a pixel point in the input SAR image, and marking the result as a block set delta 0; (3) pre-selecting points on elements in the block set delta 0, and marking the result as a point set delta; and (4) adopting the Bayes non-local mean filter on each pixel point in the input SAR image to obtain de-speckling image by using the mean matrix u and the point set delta. The method can realize mean and texture maintenance, better keep the brightness of strong reflection targets such as points, edges and the like and is favorable to point target and edge detection.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
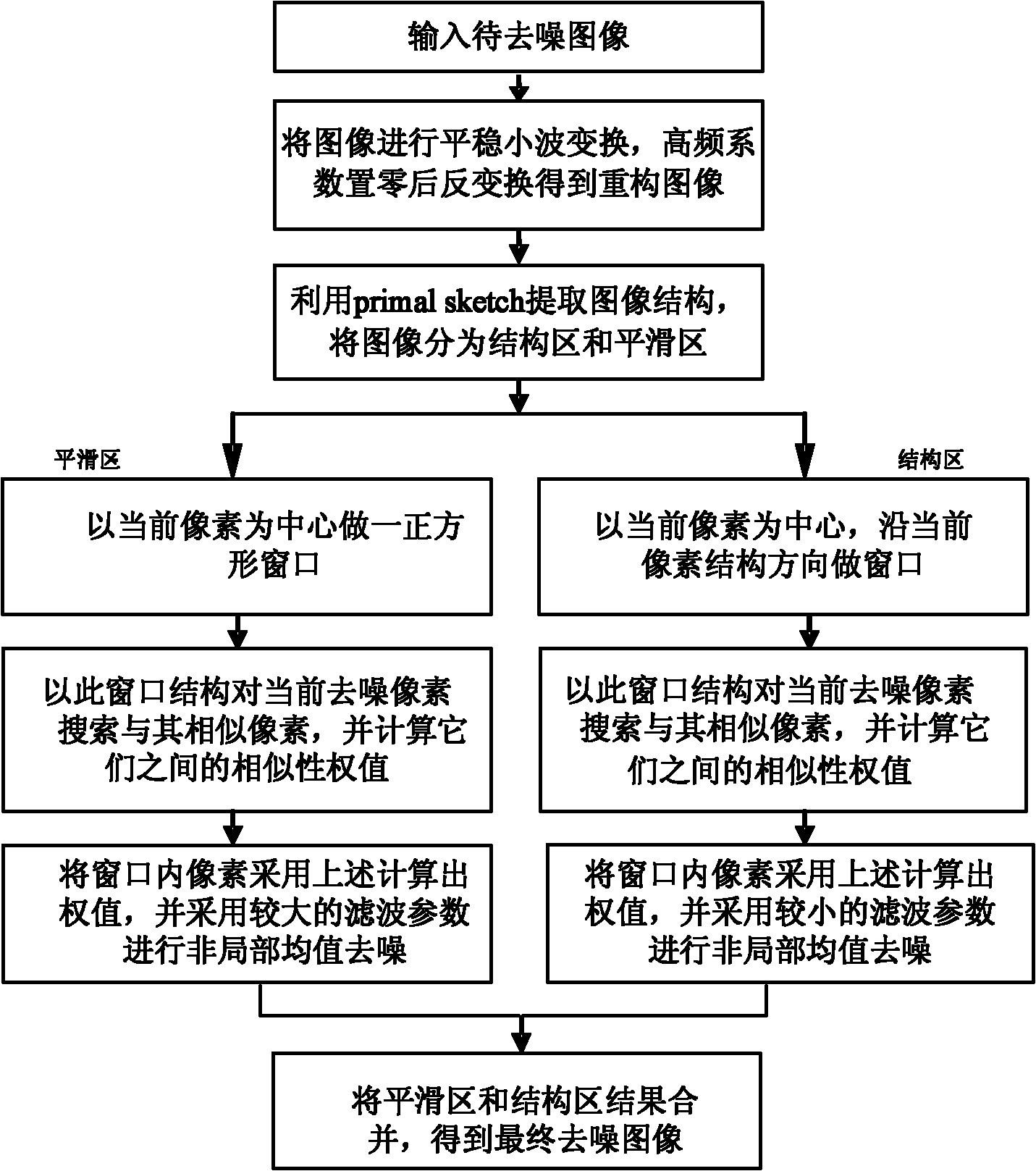
Non-local mean image denoising method combined with structure information
ActiveCN102117482AEliminate false texturesClear edgesImage enhancementImage denoisingWavelet transform
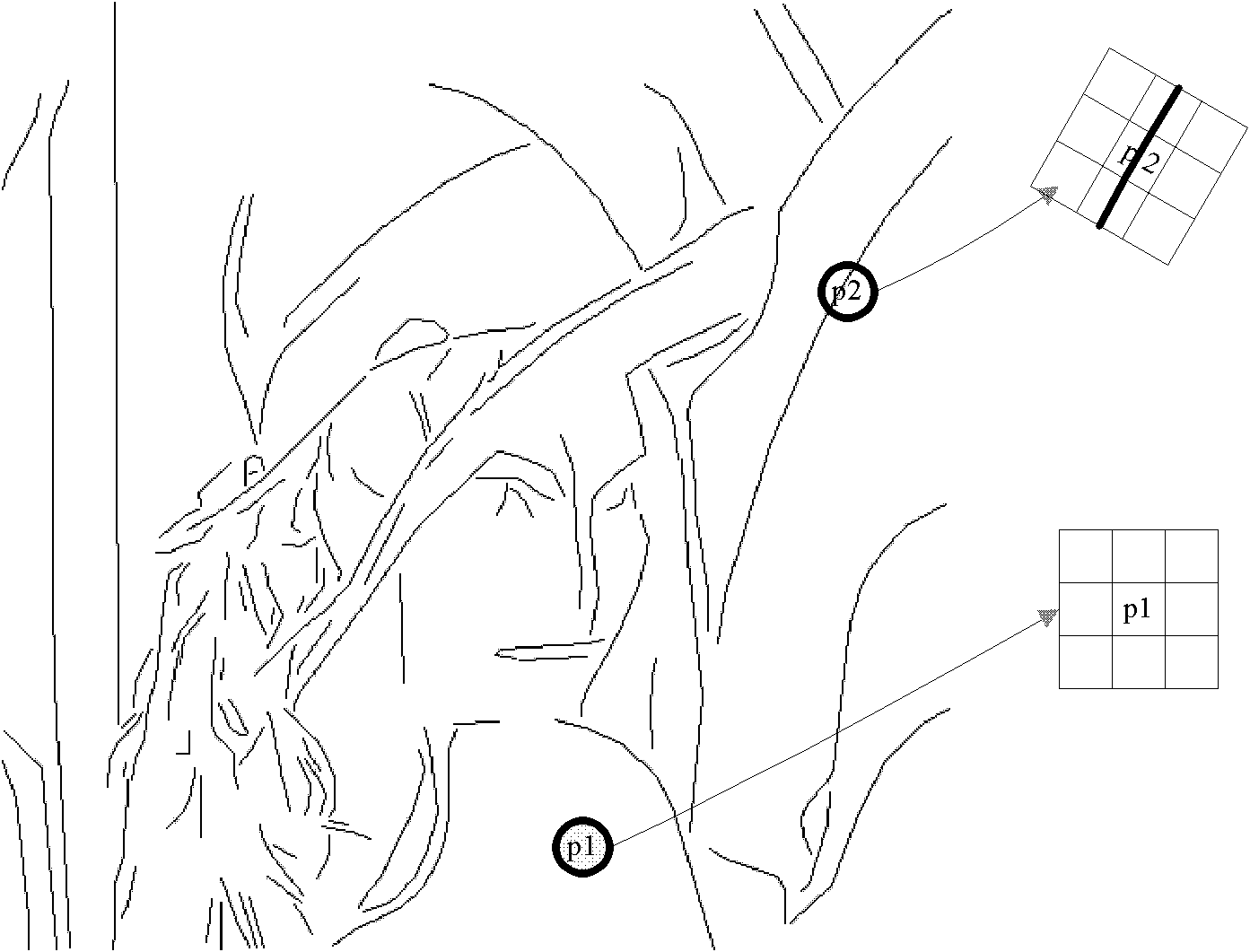
The invention discloses a non-local mean image denoising method combined with structure information, and the method provided by the invention is mainly used for solving the problem of pseudo image traces generated after the non-local means deonising. The non-local mean image denoising method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting an image to be denoised; (2) carrying out two-dimensional stationary wavelet transformation and inverse transformation on the image to obtain a reconstructed image; (3) extracting the structure information of the image by means of primal sketch to obtain a sideridge sketch of the image, and dividing the reconstructed image into a smooth region and a structure region; (4) forming a square window with a pixel as the center in the smooth region so as to search similar pixels, and calculating the similarity weights to re-estimate all of the pixels in the window; (5) forming a window with a pixel as a center along the structure direction of the structure region to search the similar pixels, and calculating the similarity weights to re-estimate all of the pixels in the window; and (6) combining the re-estimation results of the pixels in the smooth regionand the structure region to obtain a final denoised image. The method can be used for natural image denoising.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Natural image denoising method based on regional division
ActiveCN102663702AGood removal effectImprove smoothnessImage enhancementDenoising algorithmBlock match
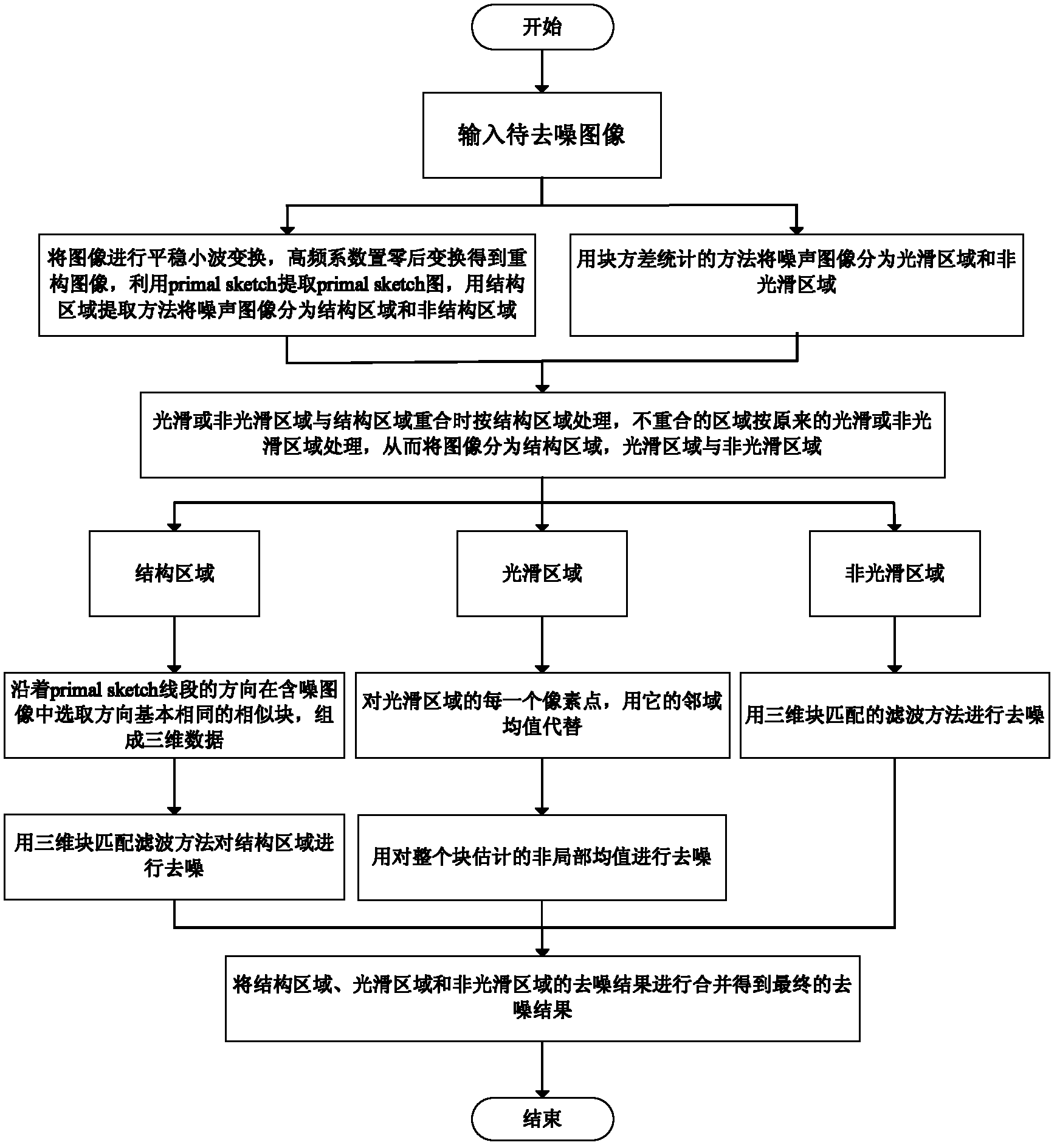
The invention discloses a natural image denoising method based on the regional division, which mainly solves the problem that patches exist in an image after an image is donoised through the existing three-dimensional block matching denoising algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing two-dimensional stationary wavelet transform on an input image to be denoised, and performing inverse transform on a high frequency coefficient subjected to zero setting, so as to obtain a reconstructed image; secondly, exacting the structural information of the reconstructed image, so as to obtain an image structure sketch; thirdly, dividing the noisy original image into a structure region, a smooth region and a non-smooth region through statistic features of an image block and the image structure sketch; fourthly, performing denoising on the smooth region with an improved non-local mean method, performing denoising on the non-smooth region with a BM3D (Block matching 3D) method, and performing denoising on the structure region with a directional feature-based BM3D method; and fifthly, combining estimated results of the structure region, the smooth region and the non-smooth region, so as to obtain the final denoised image. The method can be used for preprocessing natural images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Image denoising method based on Treelet and non-local means
InactiveCN102063708AReduce computational complexityReduce the effect of denoisingImage enhancementFeature vectorImage denoising
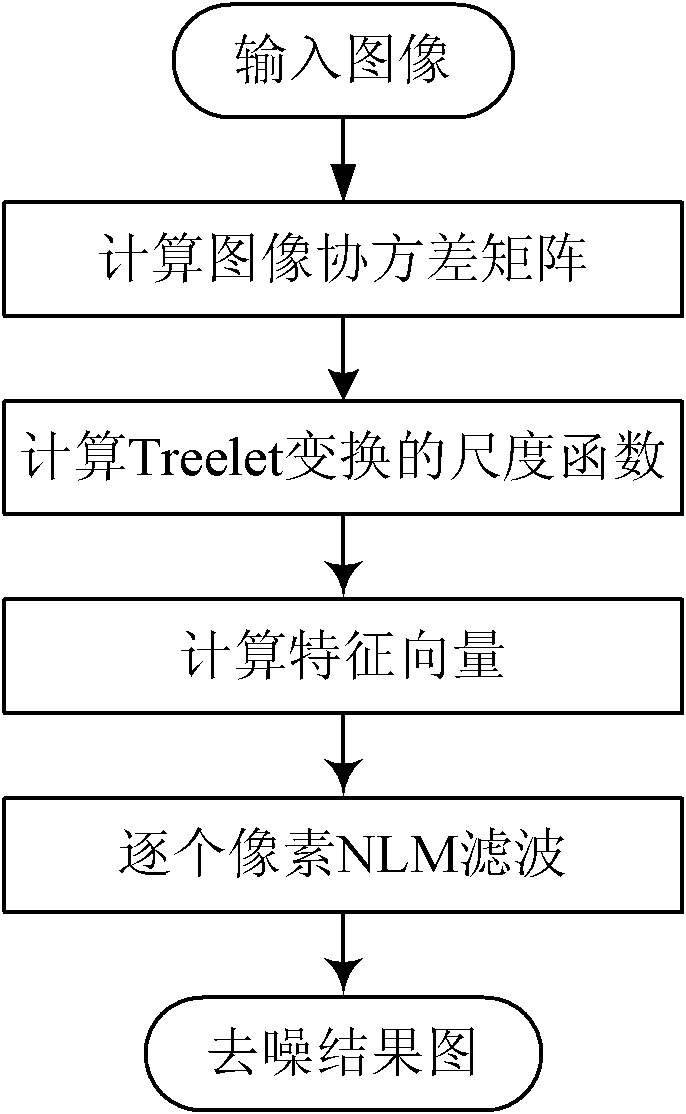
The invention discloses an image denoising method based on Treelet and non-local means, mainly used for solving the problems that the traditional non-local means method has poor denoising effect on high-noise corrupted natural images. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) calculating the covariance matrix of an input image; (2) calculating the scaling vector of image Treelet transform on the covariance matrix; (3) picking out a sliding window from the image pixel by pixel to be multiplexed with the scaling vector to obtain a characteristic vector function; and (4) filtering the image by the characteristic vector function pixel by pixel to obtain a denoised image. The invention has the advantage of good denoising effect on the high-noise corrupted natural images, can recover the original characteristics of the images, and can be used for preprocessing the images during variation detection and target identification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
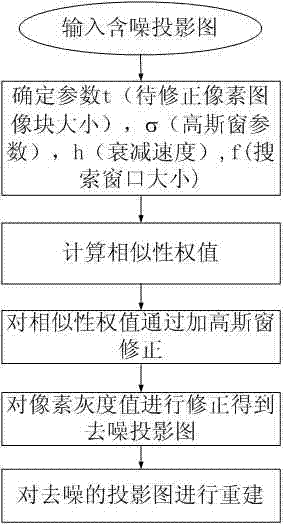
Neighborhood windowing based non-local mean value CT (Computed Tomography) imaging de-noising method
The invention discloses a neighborhood windowing based non-local mean value CT (Computed Tomography) imaging de-noising method for mainly improving original CT projected image data by adopting a search region and weight calculation in a non-local mean value technology. The main implementation process of the neighborhood windowing based non-local mean value CT imaging de-noising method comprises: (1) setting a mean square error of a Gaussian window for a collected original CT projected image; (2) finding all the similar blocks in the search region; (3) calculating a Gaussian Euclidean distance between the similar blocks and a block where a current spot locates; (4) calculating a similarity weight by utilizing a negative index function, wherein the level of similarity increases along with the increase of the weight; (5) obtaining a product of the similarity weight and a distance weight to obtain a mixed weight; (6) performing weighted average on all the pixel point values in the search region by using the mixed weight to obtain a corrected pixel point value; and (7) reconstructing de-noised projection image data to form a final chromatographic X-ray image. By the adoption of the neighborhood windowing based non-local mean value CT imaging de-noising method disclosed by the invention, the purpose of restoring the original image better and improving the de-noising performances for the image can be realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Natural image denoising method based on non-local mean value of shearlet region
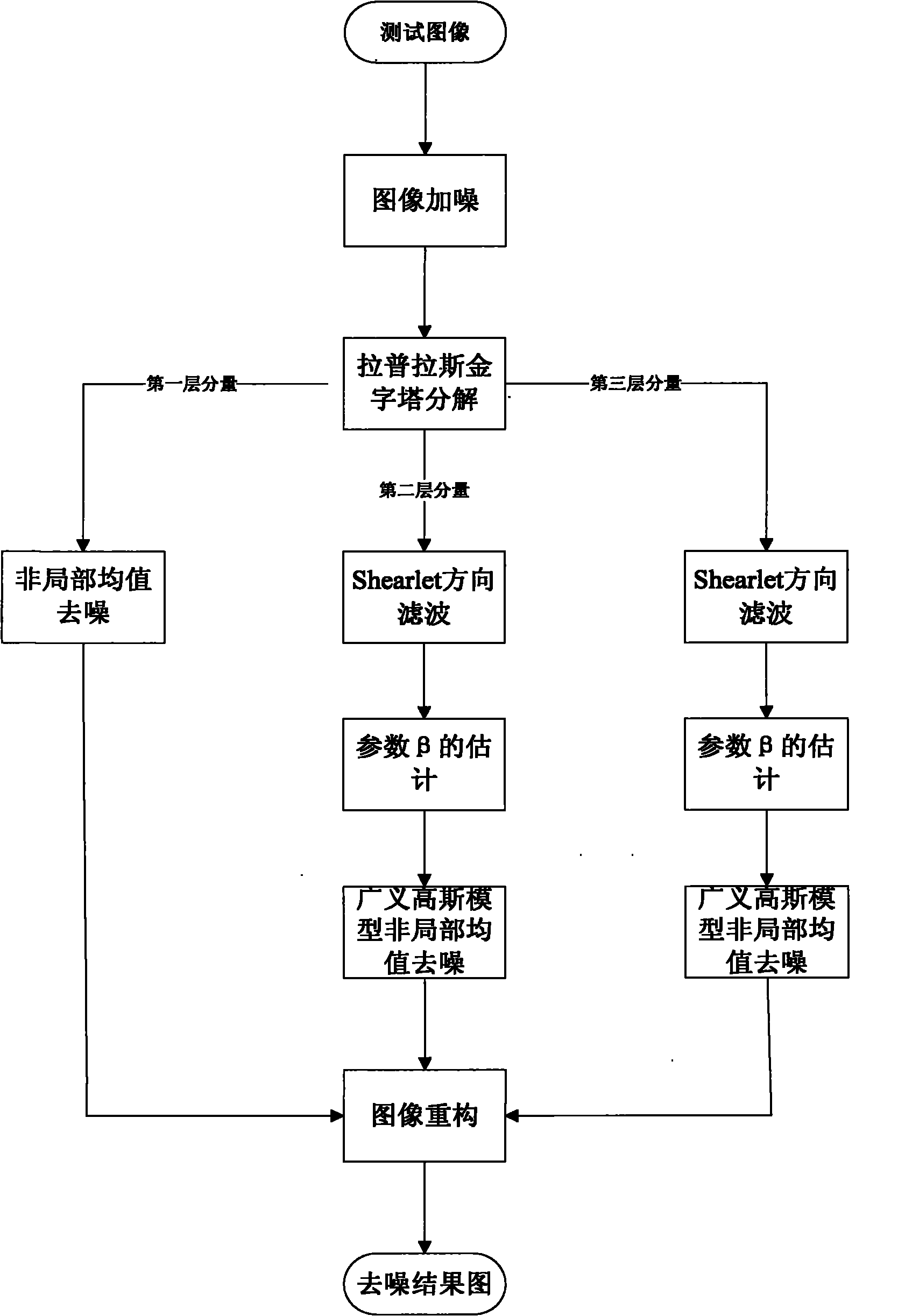
ActiveCN101930598AOvercome the shortcomings that cannot be applied to the transform domainOvercome the problem of low solution efficiencyImage enhancementImage denoisingPattern recognition
The invention discloses a natural image denoising method based on a non-local mean value of a shearlet region, which mainly solves the problem that the traditional non-local mean value method has poor denoising effect of a natural image corroded by high noise. The method comprises the following implementation steps of: inputting a test image, and adding gaussian white noise with the noise standard deviation of 50; decomposing the image into three layers by utilizing a Laplacian pyramid method, wherein denoising treatment is carried out on the first layer by using a non-local mean value method, the second layer and the third layer are respectively decomposed into four groups of shearlet coefficients by using a shearlet directional filter group firstly, then estimation of a beta value is carried out on each group of shearlet coefficients, and then the denoising treatment of the non-local mean value method under a general Gauss model is carried out on each group of shearlet coefficients; and reconstructing a denoising result to obtain a final denoising result. The invention has the advantages of favorable denoising effect for the natural image corroded by high noise, can restore the original characteristics of the image and be used for variation detection and pretreatment of the image when an object is identified.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
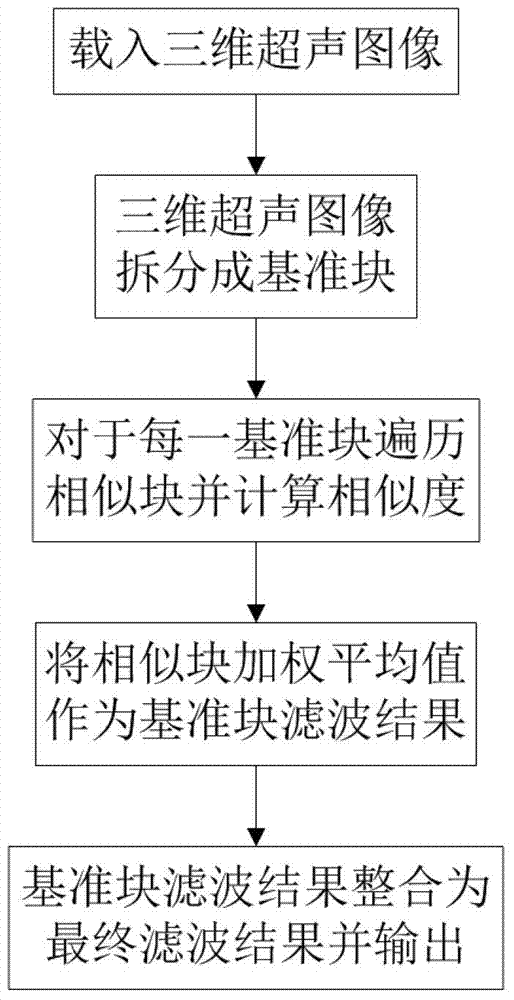
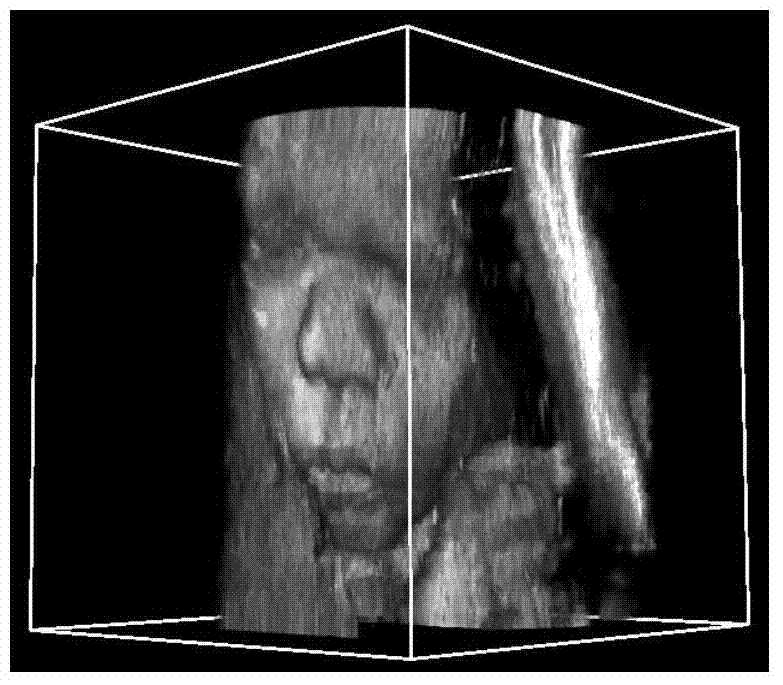
Non-local mean filter method for three-dimensional ultrasonic images
ActiveCN103544682AAvoid distortionAvoid serious problems with loss of detailsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention discloses a filter method for three-dimensional ultrasonic images, and belongs to the field of three-dimensional image processing. The filter method includes loading a to-be-filtered three-dimensional ultrasonic image, splitting the to-be-filtered target three-dimensional ultrasonic image into reference blocks, and specifying a search area for each reference block; using all image blocks with the sizes identical to the size of each reference block in the corresponding search area as similar blocks and computing a similarity degree of each similar block and the corresponding reference block; using a weighted mean value of the corresponding similar blocks as a filter result of each reference block and a weight of the corresponding weighted mean value as a similarity degree of each reference block; integrating the filter results of the reference blocks to obtain a final filter result of the three-dimensional ultrasonic image. Compared with the prior art, the filter method has the advantages that the three-dimensional image can be directly filtered without being split into two-dimensional image frames to be filtered, and gray information among frames can be utilized, so that a filter effect can be obviously improved, and detail information of the image can be effectively preserved; the filter method is applicable to accelerating a GPU (graphics processing unit), so that the filter time can be greatly shortened.
Owner:维视医学影像有限公司
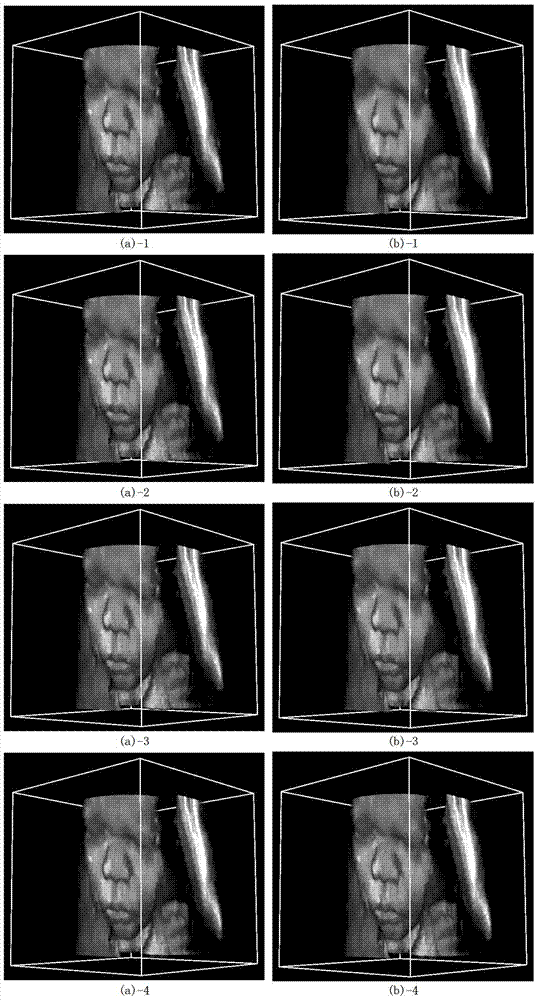
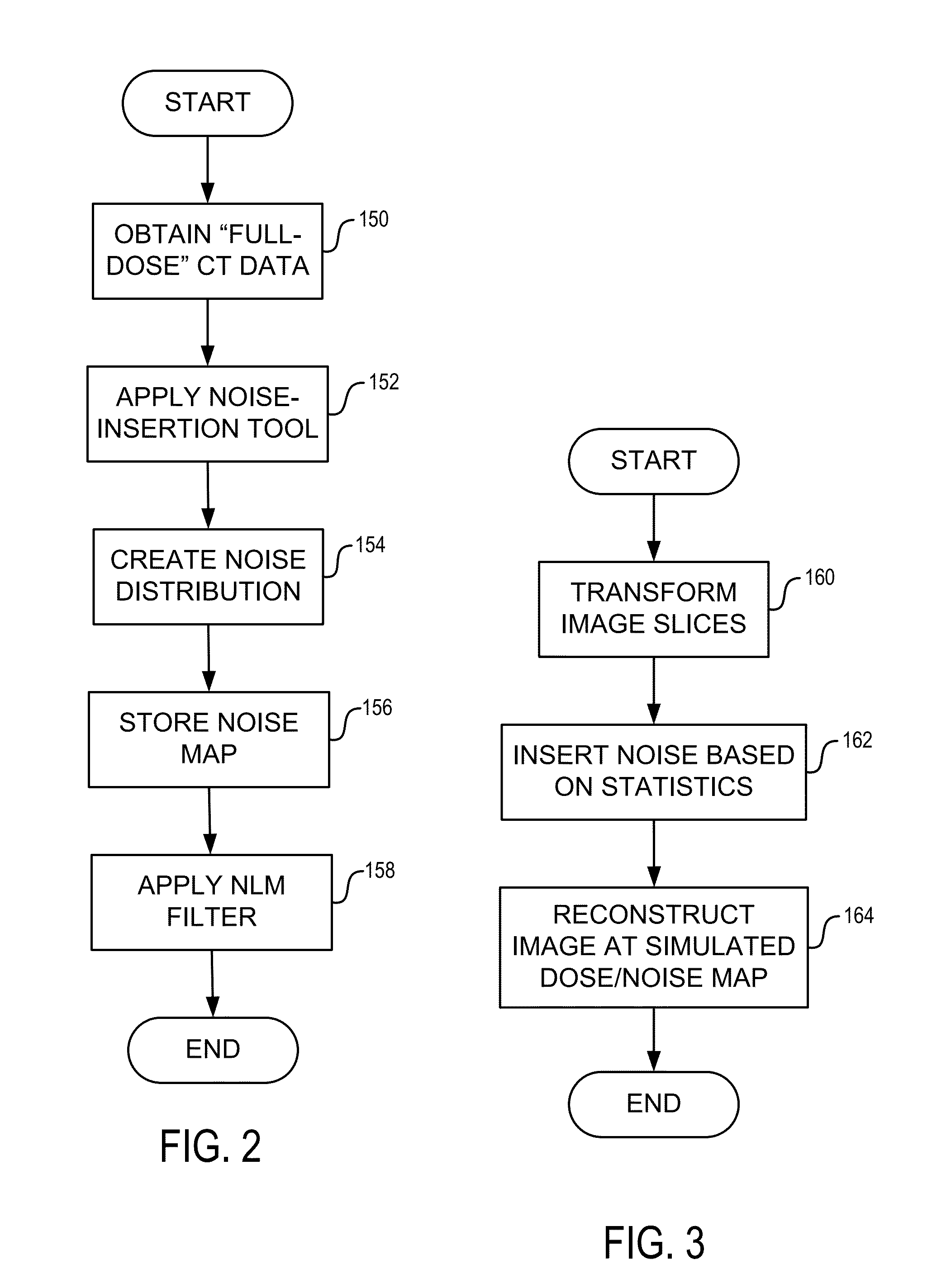
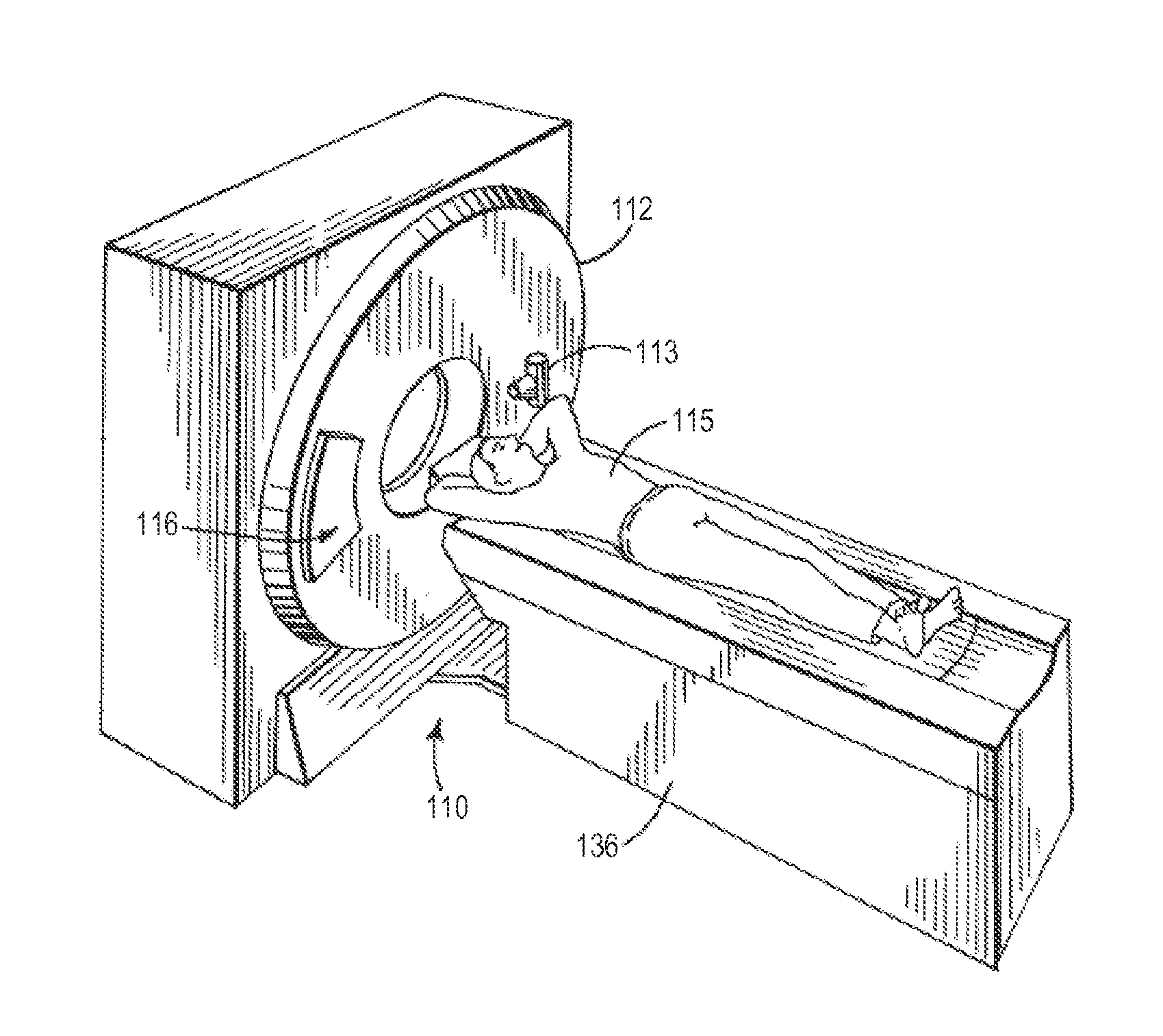
System and Method for Controlling Radiation Dose for Radiological Applications
InactiveUS20130202079A1Reduce doseReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDose ReducedMedical imaging data
A system and method for reconstructing an image acquired by delivering an irradiating dose of radiation to a subject includes acquiring imaging data using a dose of irradiating radiation and selecting at least one of a plurality of mechanisms for reducing the dose that could be delivered to the subject to acquire additional imaging data. Noise is inserted into the imaging data to simulate the at least one of the plurality of mechanisms for reducing the dose that could be applied to acquire the additional imaging data to thereby generate simulated imaging data at a reduced dose of irradiating radiation. A simulated reduced dose image is reconstructed from the simulated imaging data. A method is provided for utilizing a non-local means filter adapted using a map of local noise to produce denoised medical imaging data reflecting reduced local nose levels from those in originally-acquired medical imaging data.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
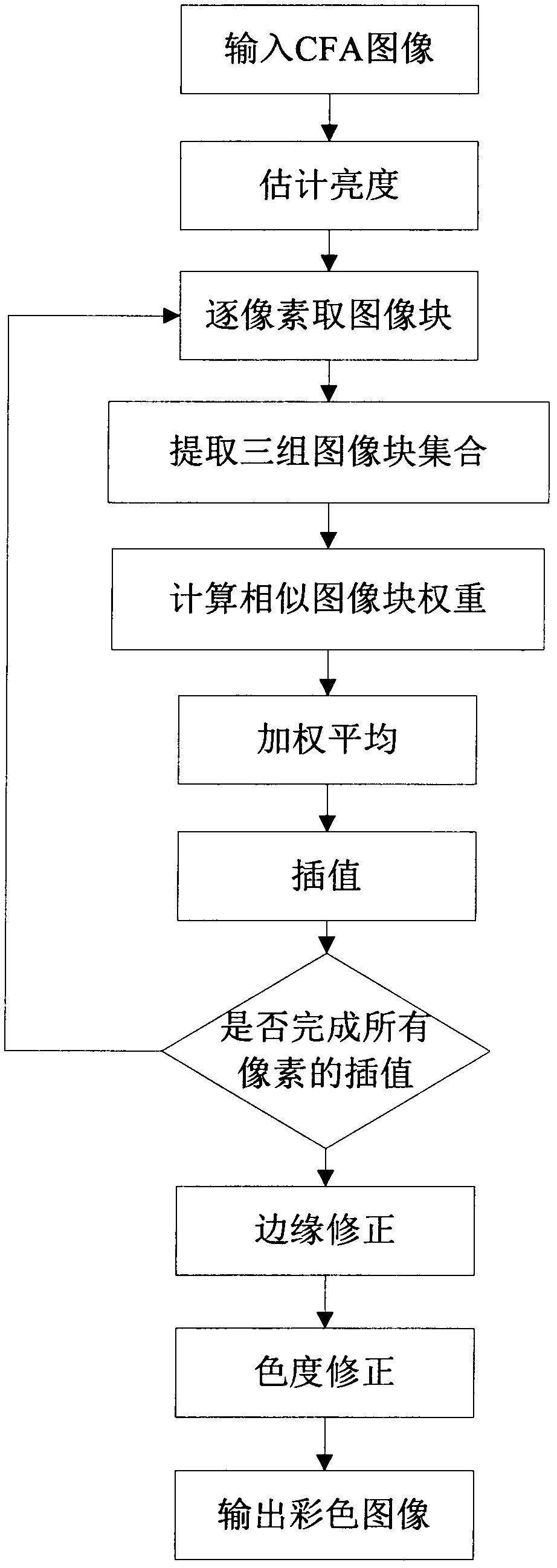
Bayer-pattern CFA image demosaicking method based on non-local mean
InactiveCN102663719AImprove interpolationSuppress false color effectsImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageFalse color
The invention discloses a bayer-pattern CFA image demosaicking method based on a non-local mean, mainly solving the problem of poor effect of interpolation on a small fringe part of an image in the prior art, comprising the following steps:(1) inputting a Bayer-pattern CFA image; (2) estimating brightness; (3) adopting an image block pixel by pixel as a current to-be-demosaicked image block; (4) extracting three image block sets; (5) calculating weights of the image blocks; (6) performing weighted average on the similar image blocks; (7) performing interpolation on the current to-be-demosaicked image block; (8) determining whether interpolation on all pixels is completed, if yes, executing step (9), if not shifting to step (3); (9) correcting an edge; (10) correcting a color; and (11) outputting a color image. By adopting the method provided in the invention small fringe area information of an image can well restored, and false color effects can be effectively inhibited; and the method is especially suitable for a CFA image with more textures.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
System and Method for Denoising Medical Images Adaptive to Local Noise
ActiveUS20130202080A1Effective estimateReduce image noiseReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPattern recognitionNoise level
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
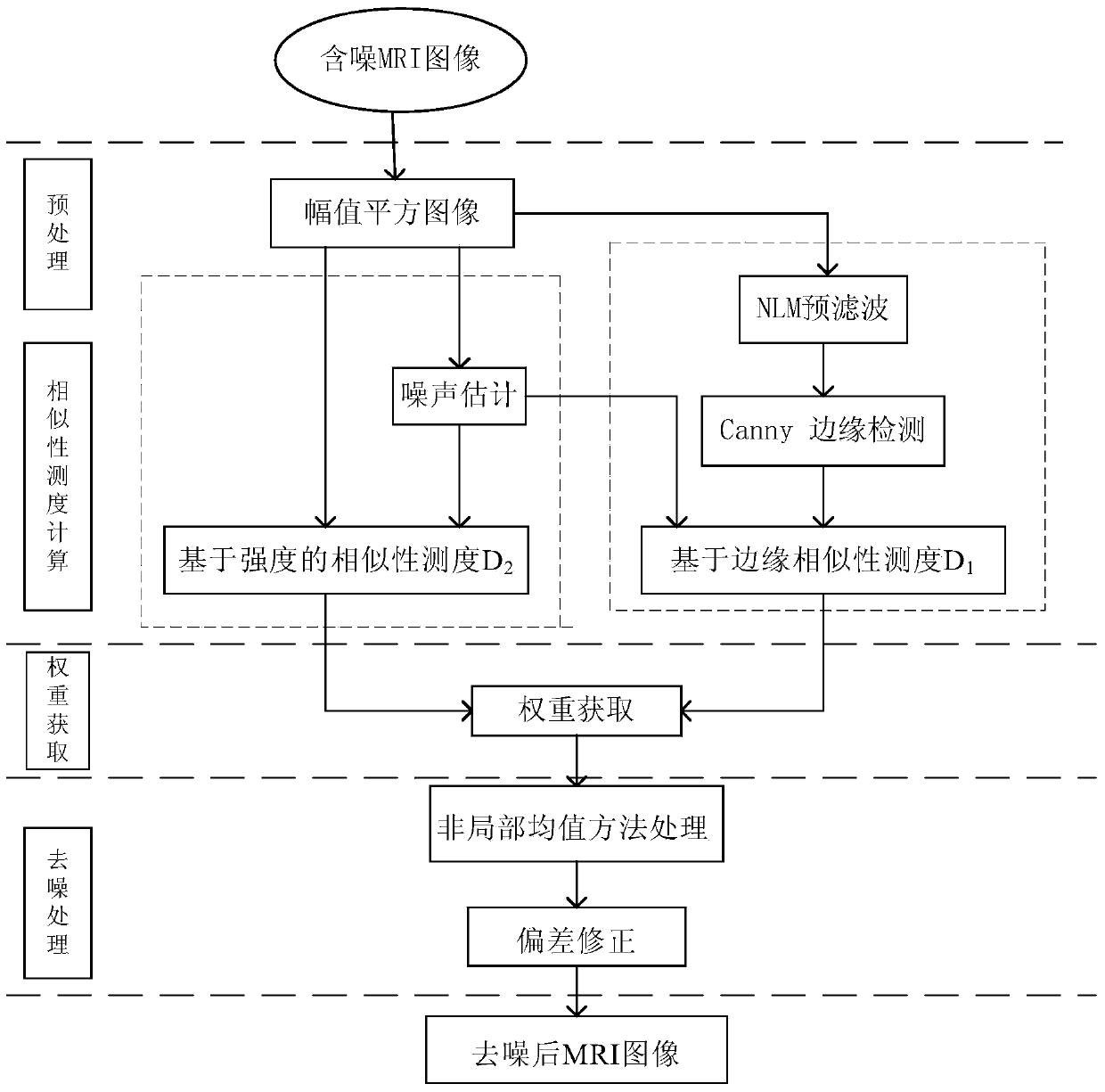
Improved canny edge detection based non-local means MRI (magnetic resonance image) denoising method
ActiveCN104200442AImprove denoising effectSimilarity measurement is accurateImage enhancementImage denoisingResonance
The invention discloses an improved canny edge detection based non-local means MRI (magnetic resonance image) denoising method. The method includes: (1) subjecting an MRI to amplitude square processing to obtain an amplitude square image; (2) performing noise estimation; (3) adopting a canny operator to extract edges of the amplitude square image; (4) computing edge / intensity similarity measure between the edges of two similar blocks; (5) computing weight parameters; (6) processing via a non-local means method; (7) correcting deviation. The method has the advantages that due to the fact that edge similarities between the similar blocks are taken into consideration at the same time, the improved canny edge detection technology is adopted, drawbacks caused by the fact that the distance between the similar blocks is subjected to weight parameter computation by only relaying on single parameter of pixel intensity in a traditional NLM method are overcome, similarity measure is more accurate, and further effect of image denoising is improved; non-local means filter replaces Gaussian filter, the edges are well kept, part of noise is removed, and edge detection is more accurate.
Owner:西安电子科技大学青岛计算技术研究院
Binocular visual image super-resolution fusion de-noising method
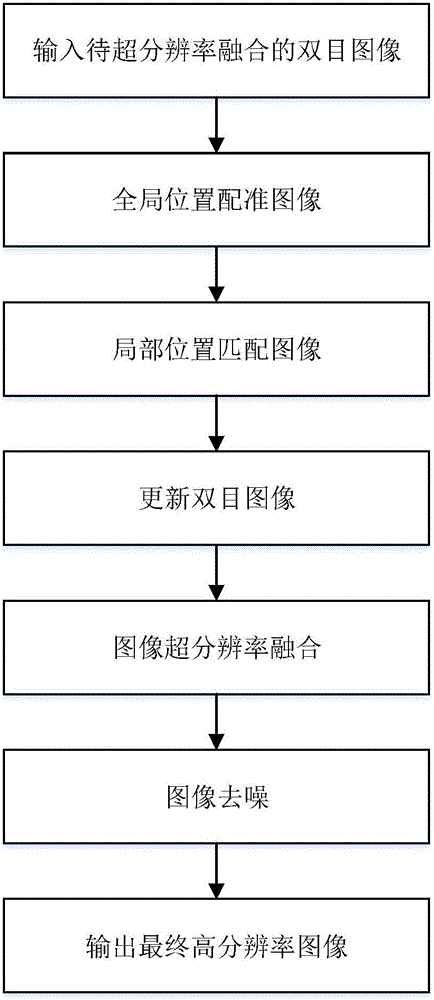
ActiveCN105844630AConducive to super-resolution fusion processingOvercome the local position mismatchImage enhancementImage analysisHigh resolution imageImage matching
The invention discloses a binocular visual image super-resolution fusion de-noising method, comprising steps of (1) inputting a binocular image to be subjected to super-resolution fusion, (2) performing global position image registration, (3) performing local position image matching, (4) updating the binocular image, (5) performing image super-resolution fusion, (6) performing image de-noising, and (7) outputting a final high resolution image. In the image registration process, a local position registration method is added, a Laplace operator is applied to the image super resolution fusion, and a non-local mean value filtering method is employed to perform de-noising on the fusion image. The binocular visual image super-resolution fusion de-noising method overcomes the deficiencies in the prior art that image local positions are not matched, detail enhancement is not enough and the function of noise inhibition is absent. The binocular visual image super-resolution fusion de-noising method obtains a super resolution fusion image which has enhanced image details and reduced noise.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Local and non-local combined self-adaption image denoising method
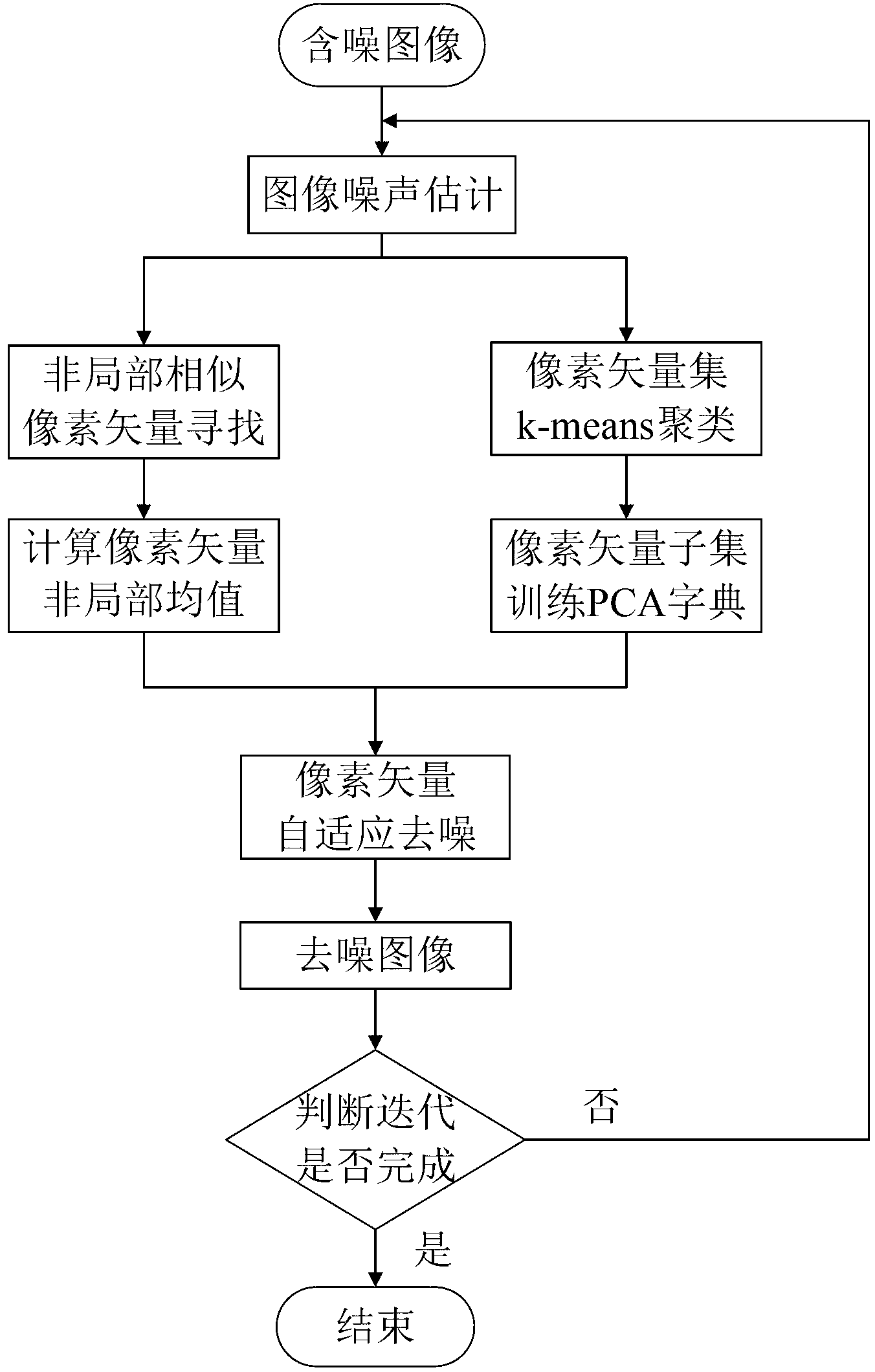
InactiveCN103077506AStrong sparse abilityKeep the edgeImage enhancementPattern recognitionImage denoising
The invention discloses a local and non-local combined self-adaption image denoising method, mainly solving the problem of poor denoising effect of the prior denoising method. The method comprises the steps of: (1) inputting noisy images; (2) estimating the noise standard deviation of the noisy images; (3) extracting pixel vectors by taking any pixel of the noisy images as a center, and calculating a pixel vector non-local mean value; (4) performing the step 3 on all pixels of the noisy images; (5) clustering all of the pixel vectors and training dictionaries on each type of vector subset; (6) respectively performing self-adaption denoising on all of the pixel vectors; (7) pulling all of the denoised pixel vectors into image blocks and clustering to obtain denoised images; (8) judging if the iteration is finished, if so, outputting the denoised images, and if not so, transferring the denoised images as the noisy images into the step 2 for the next iteration. According to the method disclosed by the invention, noise of natural images containing the white Gaussian noise is effectively eliminated, and the method is available for digital image processing in the fields of medical images, video multi-media, and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
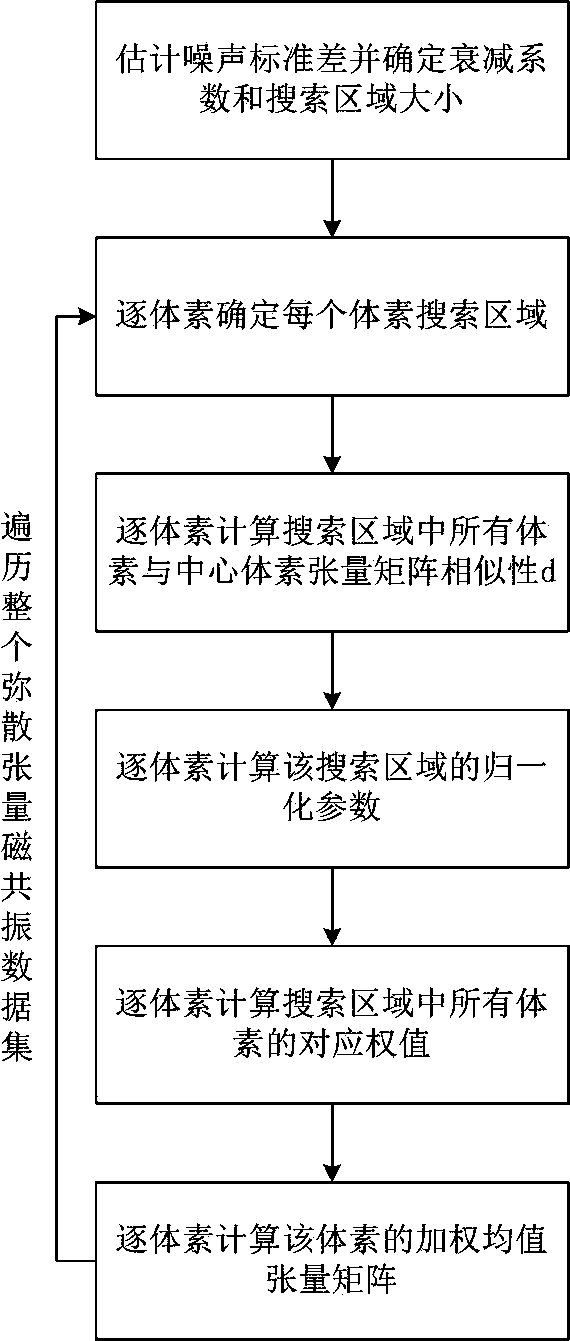
Dispersion tensor magnetic resonance image tensor domain non-local mean denoising method
The invention discloses a dispersion tensor magnetic resonance image tensor domain non-local mean denoising method, and belongs to the technical field of digital image processing and applied mathematics interdisciplines. The problem that a dispersion tensor magnetic resonance image is easily affected by noise is solved. The method comprises the steps of firstly, sequentially conducting traversal on voxels of the dispersion tensor magnetic resonance image, setting a corresponding search region by using each voxel obtained by traversal as the center, then, conducting tensor matrix similarity comparison between all the voxels inside the search region and the center voxel, finally giving different weights to the voxels inside the search region according to the degree of the tensor matrix similarity, calculating a weighted mean tensor matrix, and obtaining the denoising result of the center voxel. The problem that the dispersion tensor magnetic resonance image is easily affected by the noise is solved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Non-local mean value image denoising method based on filter window and parameter adaption
ActiveCN104978715AAvoid Weighted Results InfluenceImprove denoising qualityImage enhancementImage denoisingPattern recognition
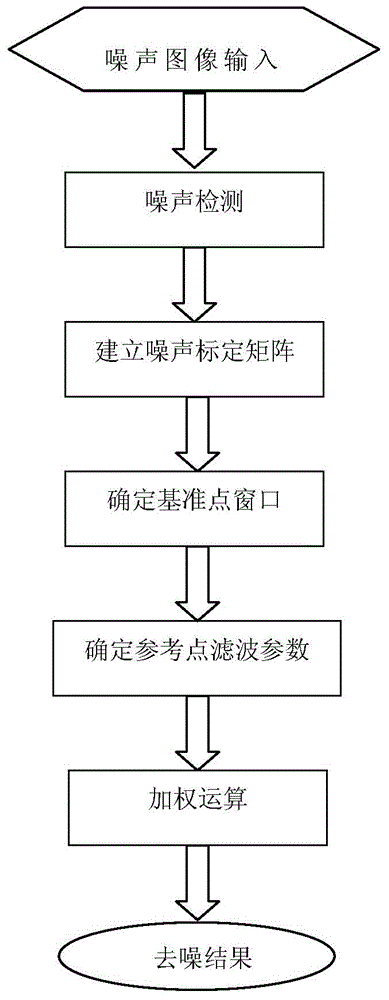
The invention discloses a non-local mean value image denoising method based on a filter window and parameter adaption. According to the invention, firstly, noise is detected, and a noise calibration matrix is established according to a detection result; the size of the noise calibration matrix is consistent with the size of an image, and the matrix value at a corresponding position of each noise point is set to be 1, and the matrix value at a corresponding position of each non-noise point is set to be 0. Then, each pixel of a noise image is successively taken as a reference point, and centric to the point, a predetermined number of non-noise reference points are taken in a counterclockwise direction to be involved in computation. Finally adaptive weighting parameters are determined according to the locations of the reference points, and a weighted result is calculated and a restored pixel value is obtained; the corresponding element in the noise calibration matrix is set to be 0 and the pixel point after denoising can be used as a reference point of other noise points. Compared with traditional image denoising methods, the method provided by the invention is added with the noise detection and noise point screening, thus improving algorithm accuracy, changing a reference point selection window and improving algorithm adaptability.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image denoising method and image denoising apparatus
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
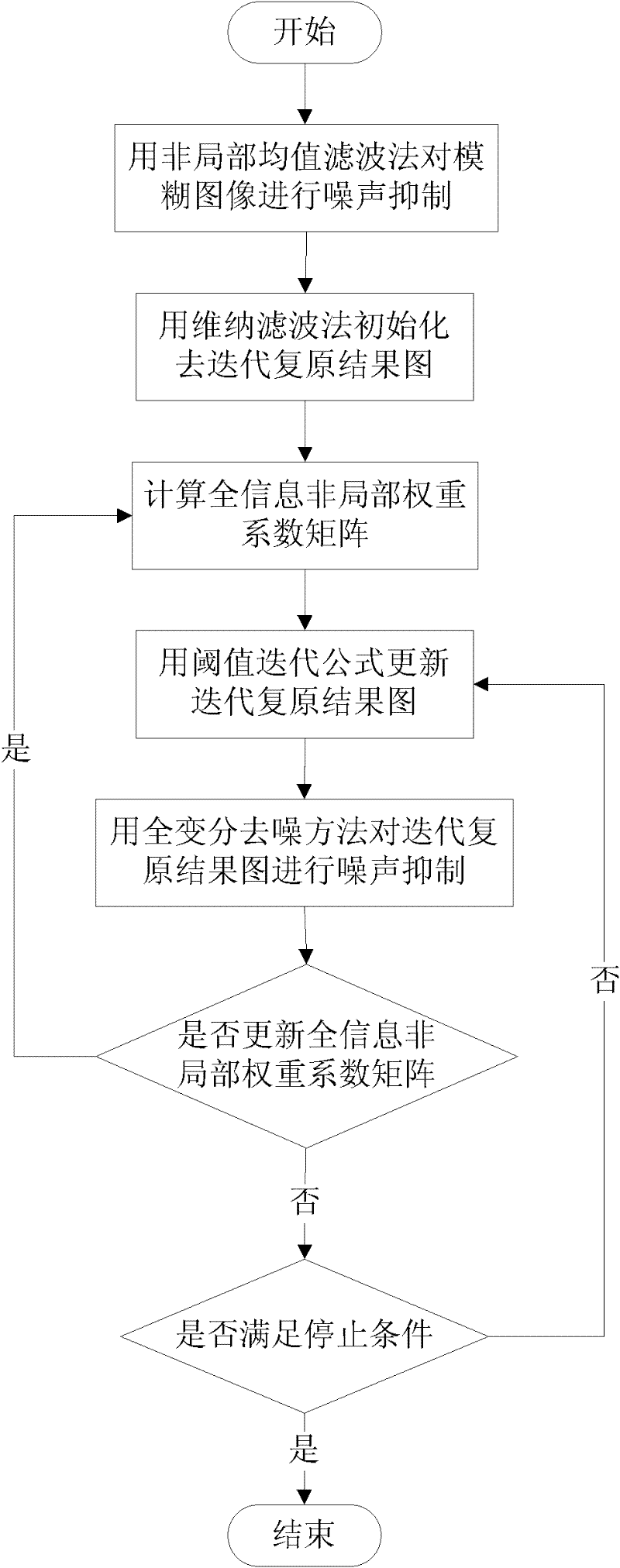
Perfect information non-local constraint total variation method for image recovery
ActiveCN102393955ASolve the problem that is prone to the ladder effectMulti-Frequency DetailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionWeight coefficient
The invention discloses a perfect information non-local constraint total variation method for image recovery. By the method, the problems that edges cannot be sharpened and high-frequency details cannot be recovered during the image recovery in the prior art are solved. The technical scheme is as follows: (1) suppressing noise of an indefinite image by using a non-local mean value filter method; (2) initializing a recovered result by using a wiener filter method; (3) calculating a perfect information non-local weight coefficient matrix; (4) updating the recovered result by using a threshold value iterative formula; (5) suppressing noise of the recovered result by using a total variation denoising method; (6) judging whether to update the perfect information non-local weight coefficient matrix, if so, returning to the step (3), otherwise, executing step (7); and (7) judging whether a stop condition is met, if so, obtaining a final result, otherwise, returning to the step (4) until the stop condition is met. During recovery, the edge of an image can be sharpened and the high-frequency details of the image can be recovered; and the method can be used for recovering the indefinite image in a known indefinite type.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Hyper-spectral image classification method based on non-local similarity and sparse coding
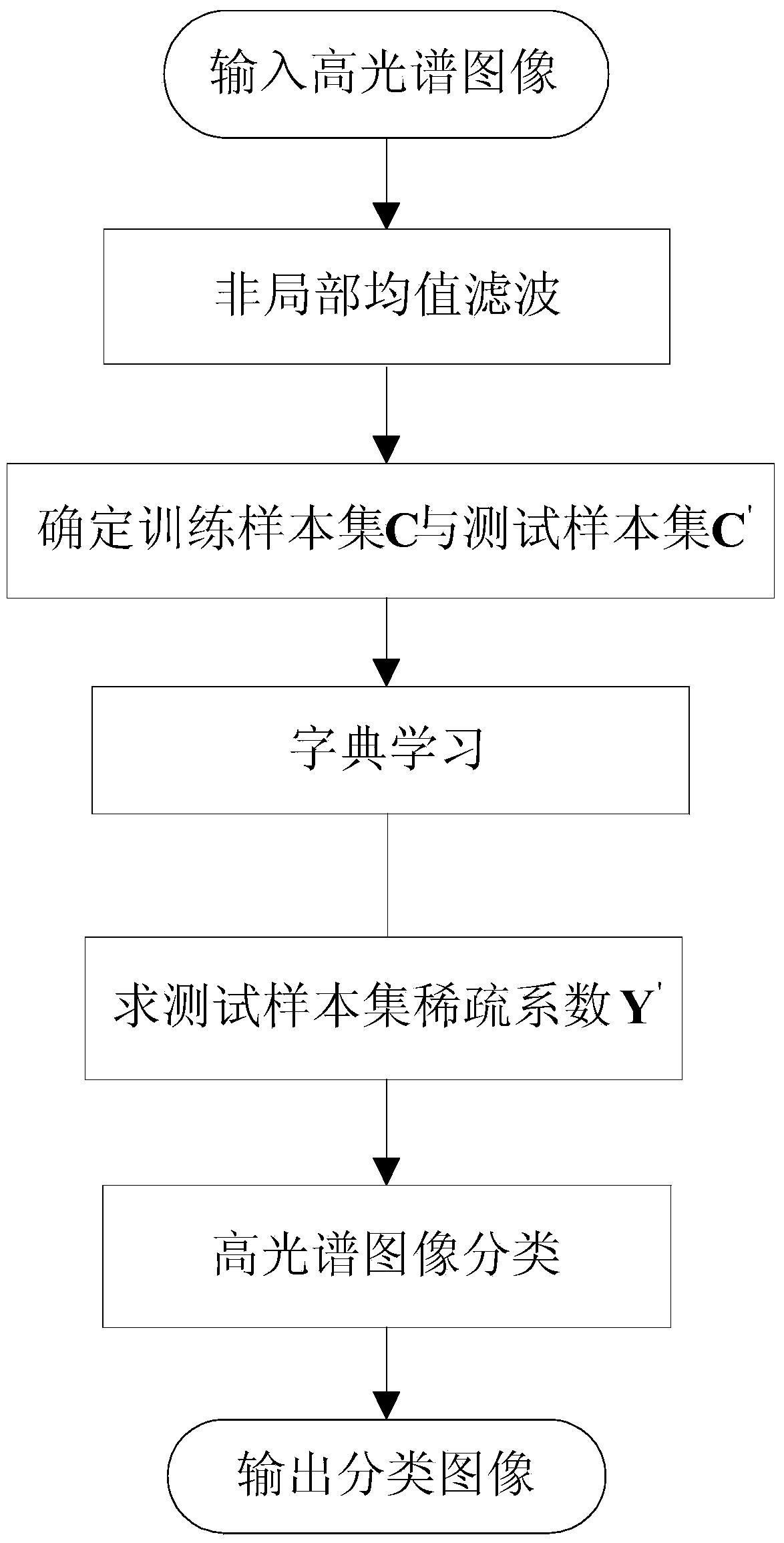
ActiveCN104239902AOvercome the disadvantages of misclassificationAccurate classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningImaging processing
The invention belongs to the technical field image processing and particular relates to a hyper-spectral image classification method based on non-local similarity and sparse coding. The hyper-spectral image classification method based on the non-local similarity and the sparse coding comprises the achieving steps of 1 inputting a hyper-spectral image; 2 filtering a non-local average; 3 determining a training sample set C and a test sample set C'; 4 performing dictionary learning; 5 calculating the sparse coefficient of the test sample set; 6 performing hyper-spectral image classification; 7 outputting classified images. By means of the non-local average filtering method, the defect that in the prior art, only spectral information of the hyper-spectral image is utilized to perform hyper-spectral image classification and accordingly edge portion misclassification is caused is overcome, and the hyper-spectral image classification method can have the advantage that the edge portion misclassification is accurate. In addition, the shortcoming that neighborhood information of the hyper-spectral image cannot be effectively utilized in the prior art is overcome, and the hyper-spectral image classification method can have the advantage that the homogeneous area classification effect is good.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
MCMC sampling and threshold low-rank approximation-based image de-noising method
InactiveCN105260998AEasy to keepPreserve texture detail informationImage enhancementSingular value decompositionHigh dimensional
The invention discloses an MCMC sampling and threshold low-rank approximation-based image de-noising method. According to the method, firstly, during the denoising process, an image block is generated through the MONTE-CARLO sampling process. Secondly, based on a plurality of statistical features in a histogram, a similarity judging function that meets the condition of the Markov chain can be obtained. Thirdly, the singular value decomposition on all kinds of image block clusters is conducted and the self-adaptive threshold estimation for singular values is conducted according to the prior information corresponding to an image. Fourthly, on the basis of a decomposed low-rank structure, the image reconstruction is conducted according to the low-rank approximation algorithm, so that the de-noising purpose is realized. According to the invention, the characteristics of the similar non-local geometric structure information of images and the better treatment of high-dimensional data based on a low-rank matrix are fully utilized. Meanwhile, the defect in the prior art that the conventional non-local mean-value traversing search method is high in block-selecting complexity can be overcome. The block-selecting robustness is therefore improved. moreover, to a certain extent, the algorithm operating period is shortened.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Method for restoring non-local images by combining GMRF priori
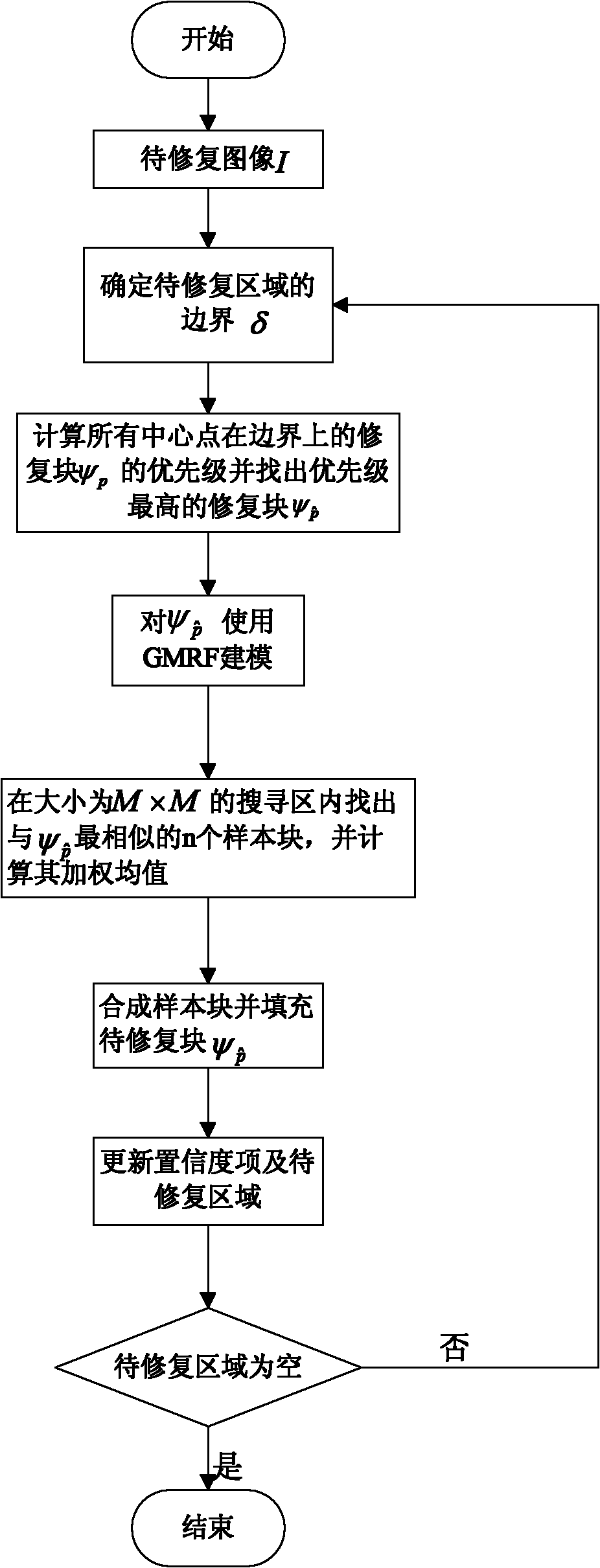
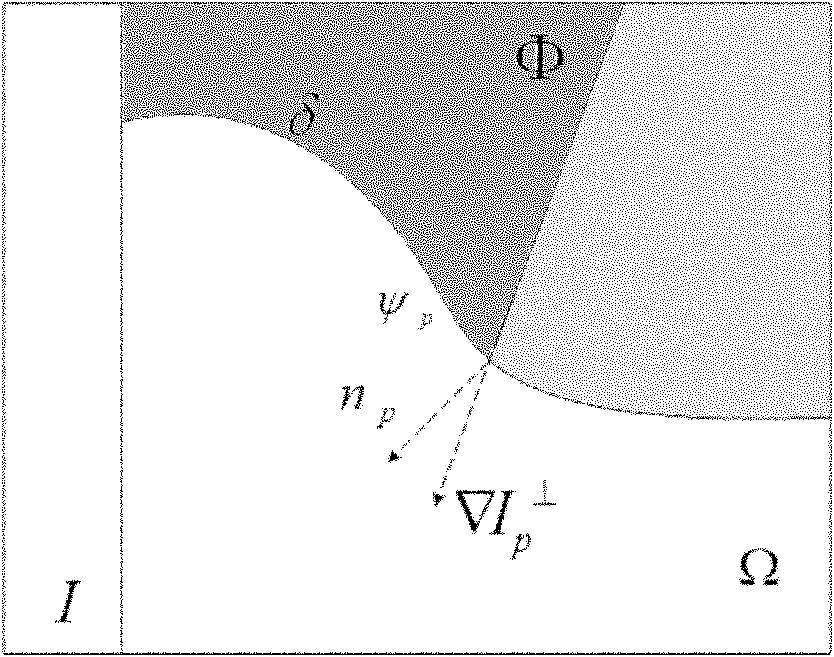
InactiveCN101980285AFine detail textureEfficient use ofImage enhancementPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention discloses a method for restoring non-local images by combining GMRF priori, which belongs to the technical field of image processing, and mainly solves the problem of inaccurate similarity weight calculation in the conventional sample-based method for restoring non-local means. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) determining an area omega to be restored and a boundary delta of the area omega to be restored for an image I to be restored; (2) calculating the priority P(p) of a block to be restored of a central point on the boundary, finding out the restored block withthe highest priority, and modeling the restored block by using GMRF; (3) searching n sample blocks which are most similar to the block to be restored in a search area, and obtaining a filling block psi p' serving as a filling block to be restored by using a GMRF-based non-local mean method; and (4) updating a confidence coefficient item and the area to be restored, and repeating the steps (1)-(4)until all points in the area to be restored are restored. The method can better connect image texture information, can make a restoration result closer to an original image in brightness, and can be used for restoring image damaged areas and removing objects in images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Fuzzy clustering analysis method for detecting synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image changes based on non-local means
InactiveCN102938071AImprove the accuracy of analysisReduce time complexityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFuzzy clustering analysisSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a fuzzy clustering analysis method for detecting SAR image changes based on non-local means. The method is implemented through the processes of inputting a difference chart composed of two SAR images in a same region at different times; correcting pixels of the difference chart according to similarity measure indexes in a fast global fuzzy C-Means clustering (FGFCM) algorithm to obtain a local spatial information pixel matrix; performing non-local mean processing on the difference chart to generate a pixel matrix of non-local filtering waves; weighting and summing up the two matrixes and generating a complete pixel matrix; clustering the complete pixel matrix through the FGFCM algorithm to generate a change detection binary result image and complete the change detection of the two SAR images integrally. According to the fuzzy clustering analysis method for detecting SAR image changes based on non-local means, local spatial information and non-local mean information of images are considered simultaneously and combined organically, so that noise influences are overcome effectively and image details are kept in an image analysis clustering process, and accurate difference chart analysis results are obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
SAR image change detecting method based on non-local mean
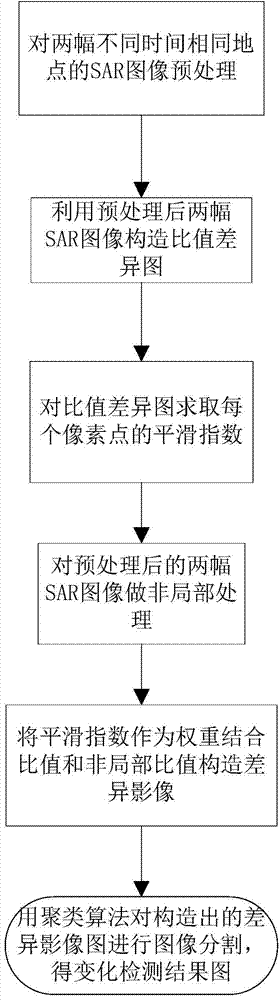
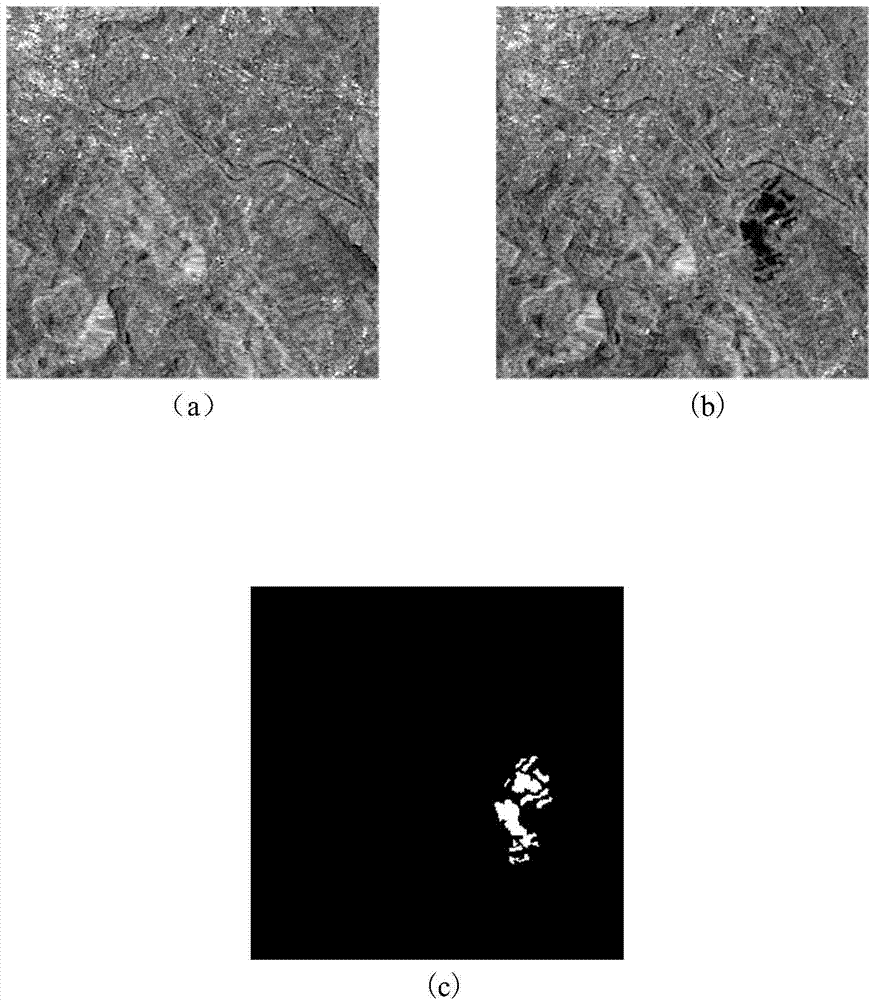
InactiveCN103927737AQuality improvementImprove performanceImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDifference-map algorithm
The invention discloses an SAR image change detecting method based on non-local mean filtering. The SAR image change detecting method comprises the steps that two SAR images which are obtained from the same region at different times are pre-processed; the two pre-processed SAR images are used for constructing a ratio difference shadowgraph; all pixels of the ratio difference shadowgraph are traversed and a smooth index matrix of each pixel point is calculated; after non-local mean filtering is conducted on the two pre-processed SAR images respectively, ratio calculation is conducted, and a non-local mean filtering ratio graph is obtained; the ratio difference shadowgraph and the non-local mean filtering ratio graph are summated with smoothness indexes as weights so as to obtain a final difference shadowgraph; the final difference shadowgraph is divided by using the fuzzy local C mean clustering method to obtain a change detecting result graph. According to the SAR image change detecting method based on non-local mean filtering, difference graph edge information is maintained by using the characteristics of the image smoothness indexes, a non-local mean is used for correcting the pixels in a homogeneous region with a low smoothness index, therefore, noise is effectively restrained, actual change information is better shown and the change detecting result accuracy is improved.
Owner:王浩然
Improved blind super-resolution reconstruction algorithm based on multi-image fuzzy kernel estimation
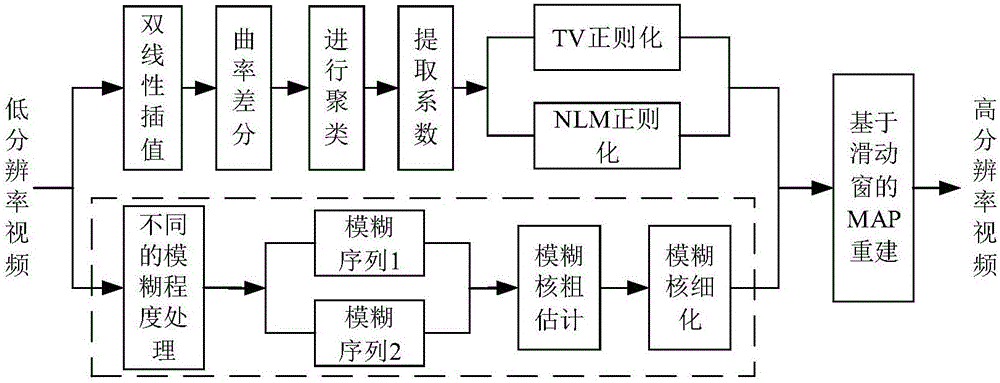
The invention discloses an improved blind super-resolution reconstruction algorithm based on multi-image fuzzy kernel estimation, which mainly comprises the steps of carrying out different degrees of fuzzy processing on a first frame image in inputted low-resolution video frames so as to acquire two images with different fuzzy degrees of the same scene, that is, two images with different fuzzy degrees are acquired; generating a rough fuzzy kernel through adopting a robust deconvolution algorithm by using the two images with different fuzzy degrees of the same scene, carrying out fuzzy processing on all of the video frames by using the fuzzy kernel, and acquiring a processed group of image sequence fk to act as input of subsequent processing; extracting spatial structure information by using a curvature difference operator, then carrying out clustering on the spatial structure information to acquire a regional space adaptive weighting coefficient, wherein the coefficient is used for carrying out adaptive weighting on a total variation and a non-local means regularization item; weighting the regularization item by using the acquired adaptive weighting coefficient so as to determine a reconstruction cost function; and optimizing the reconstruction cost function by using a gradient descent method, carrying out fuzzy kernel estimation again in each time of iteration process, carrying out deblurring, and finally acquiring an outputted high-resolution image sequence.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com