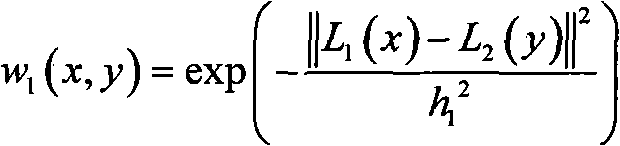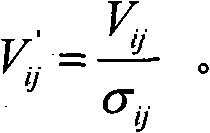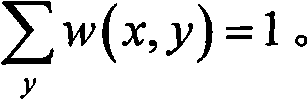Non-local mean de-noising method for natural image
A non-local mean, natural image technology, applied in the field of denoising, can solve the problems of limited directional information, poor coefficient sparsity in high dimensions, blurred image edges and details, etc., to achieve the effect of accurate calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] Refer to attached figure 1 , the present invention provides a natural image non-local mean denoising method, comprising the following steps:
[0031] Step 1. Do wavelet transform on the input noisy natural image, and decompose it into low-frequency image and high-frequency image.
[0032] Due to the limitations of imaging equipment and imaging conditions, digital images are inevitably polluted by noise. Many actual noises can be considered as Gaussian additive white noise. The natural image model with noise is:
[0033] v=u+n
[0034] Among them, v is the gray value of the noisy image, u is the gray value of the clean image, n is Gaussian additive white noise, it mainly uses the redundant information in the natural image to achieve the purpose of denoising, due to the stationary wavelet decomposition The output image is equal to the original image, which keeps the redundancy of image information. In the experiment, the present invention selects a stationary wavelet to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com