Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Non-aqueous phase liquid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
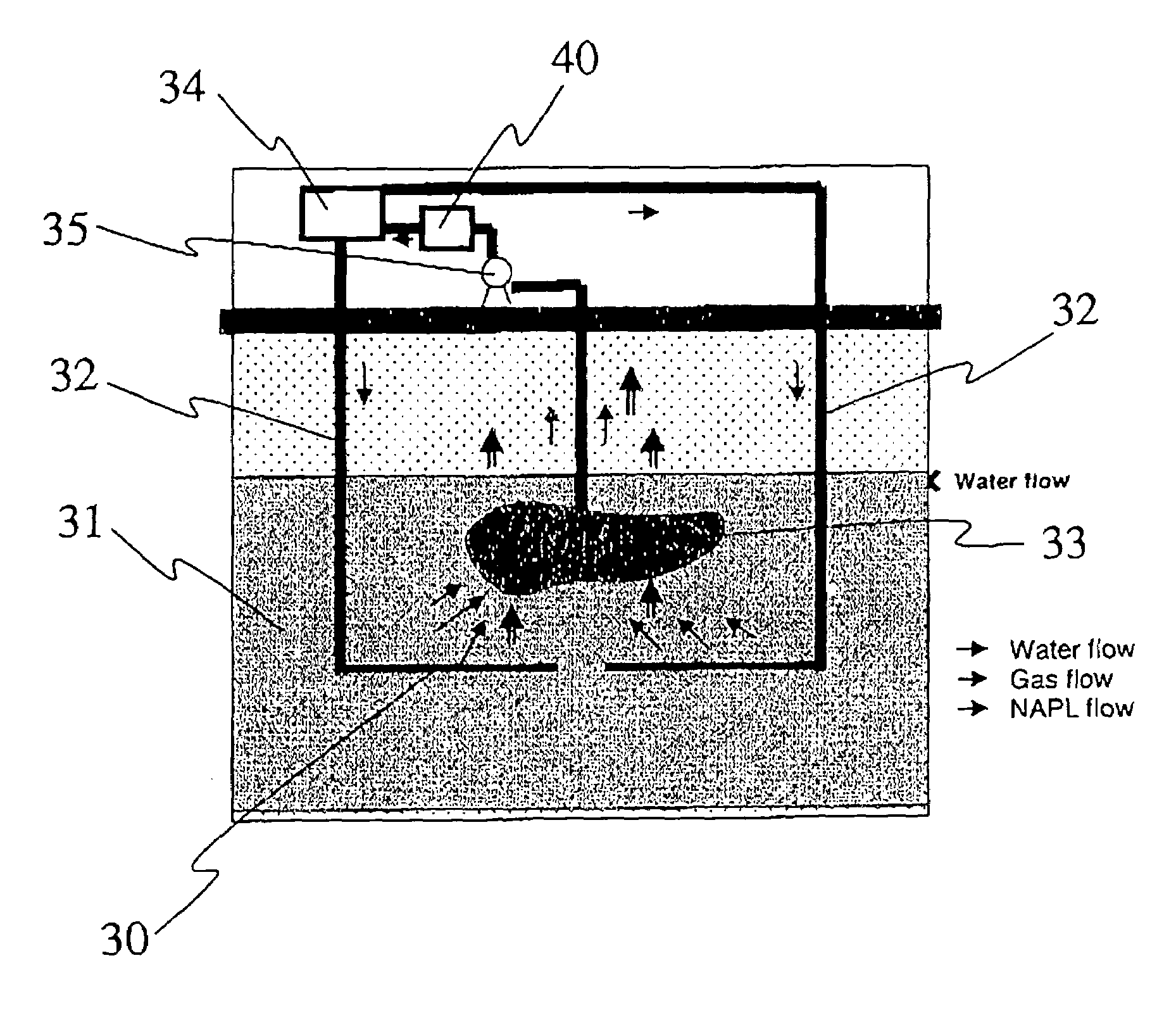
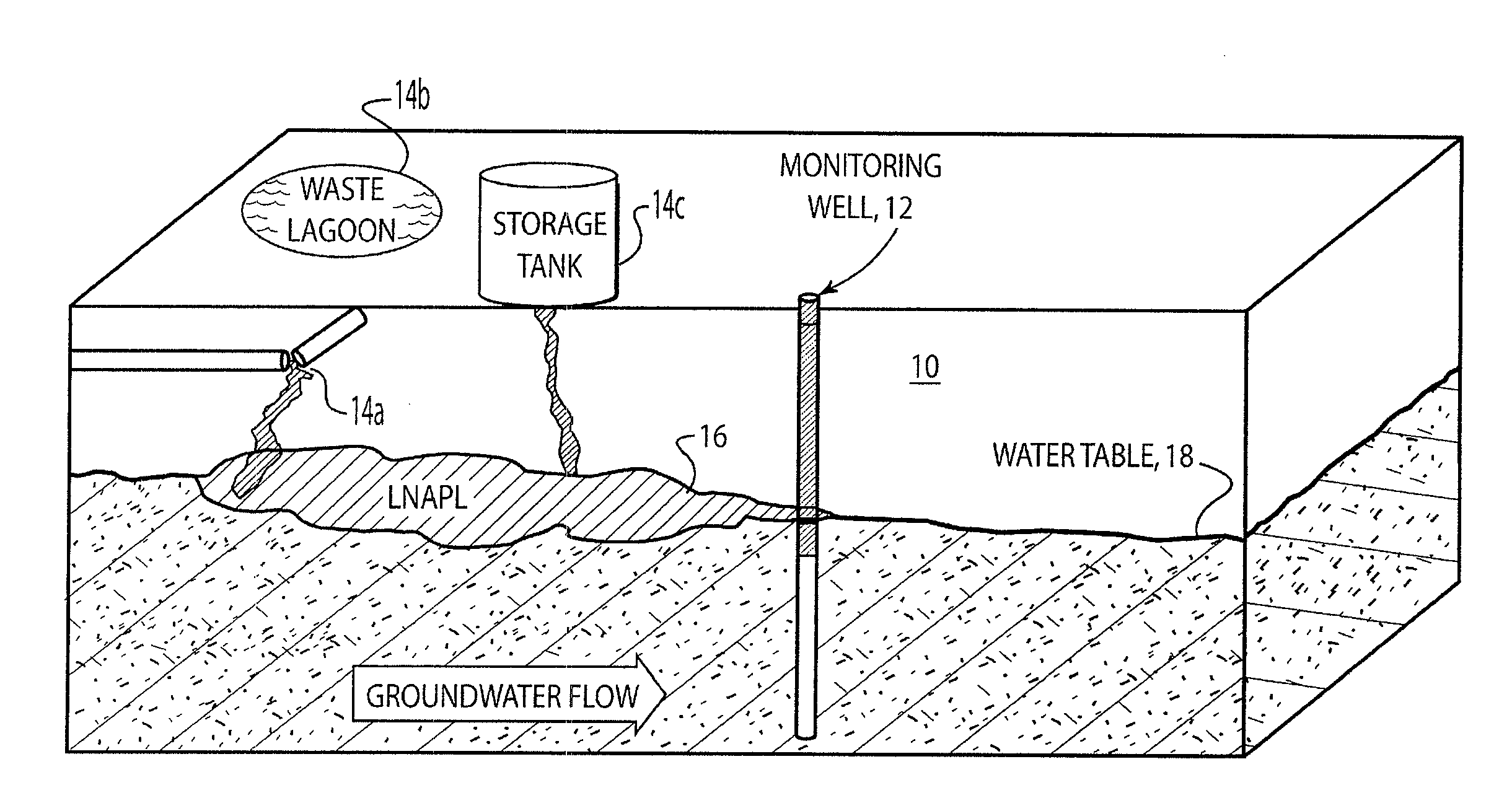
Non-aqueous phase liquids or NAPLs are liquid solution contaminants that do not dissolve in or easily mix with water (hydrophobic), like oil, gasoline and petroleum products. NAPLs tend to contaminate soil and groundwaters. Many common groundwater contaminants such as chlorinated solvents and many petroleum products enter the subsurface in nonaqueous-phase solutions. They do not mix readily with water and therefore flow separately from ground water.
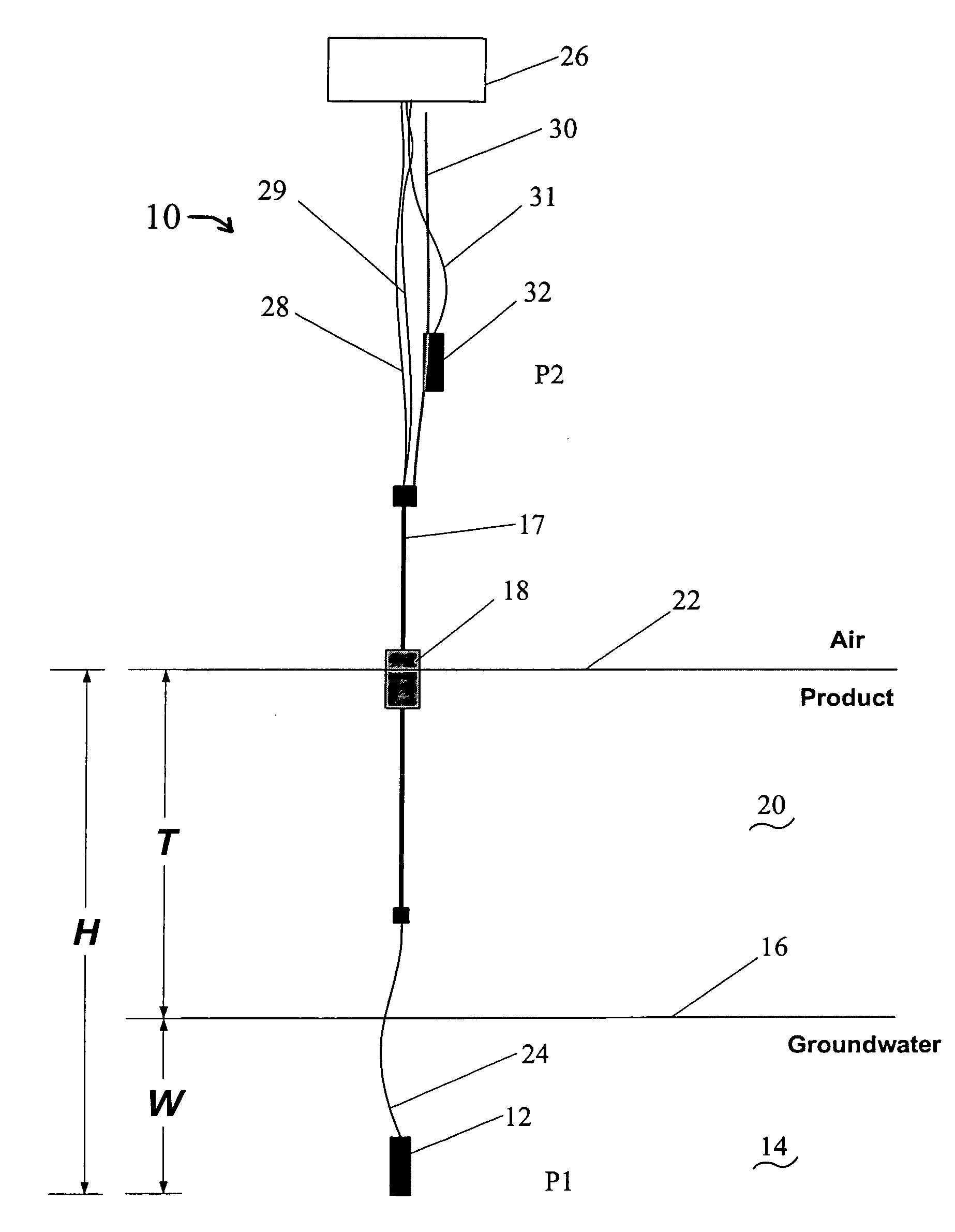
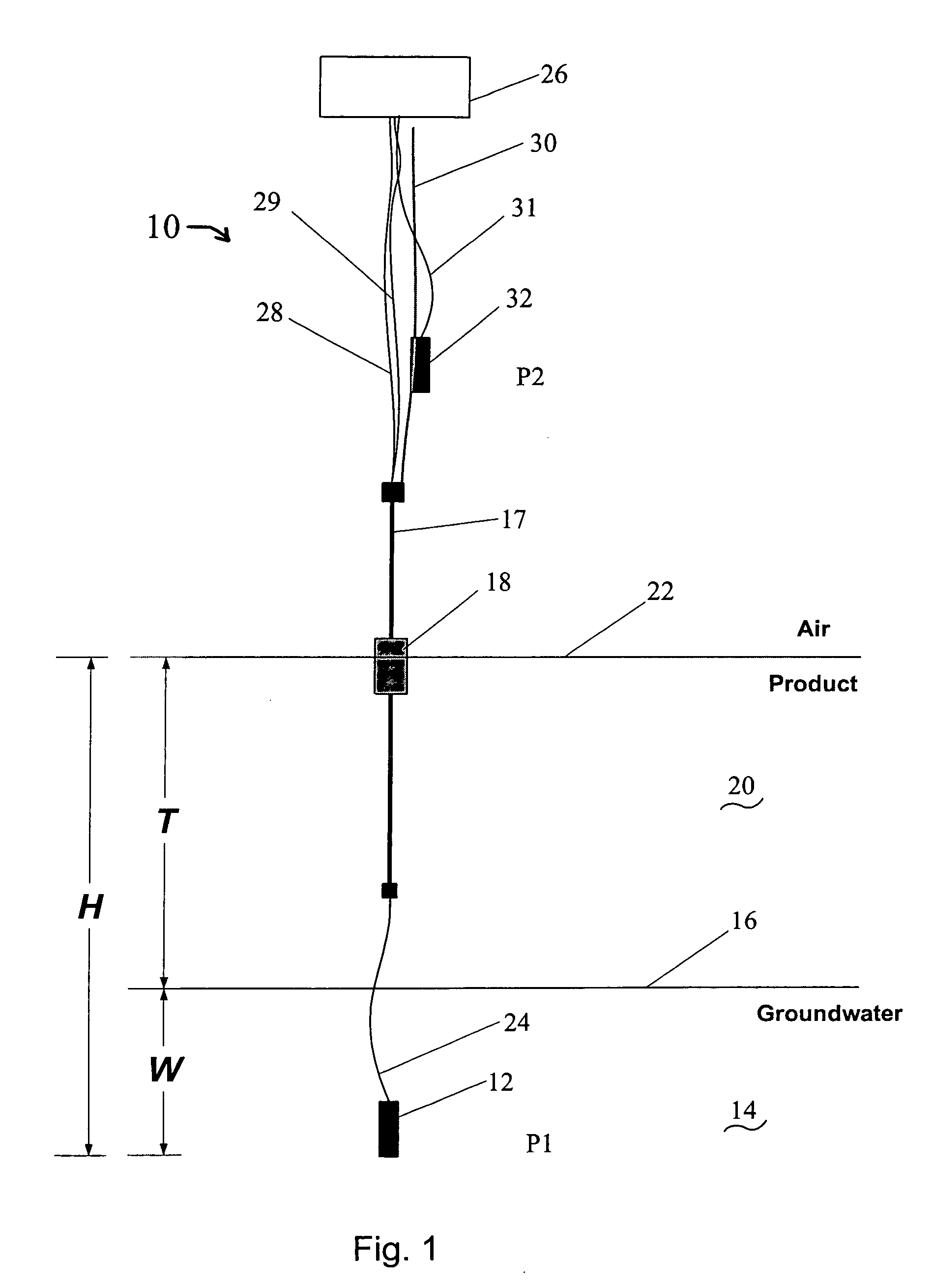
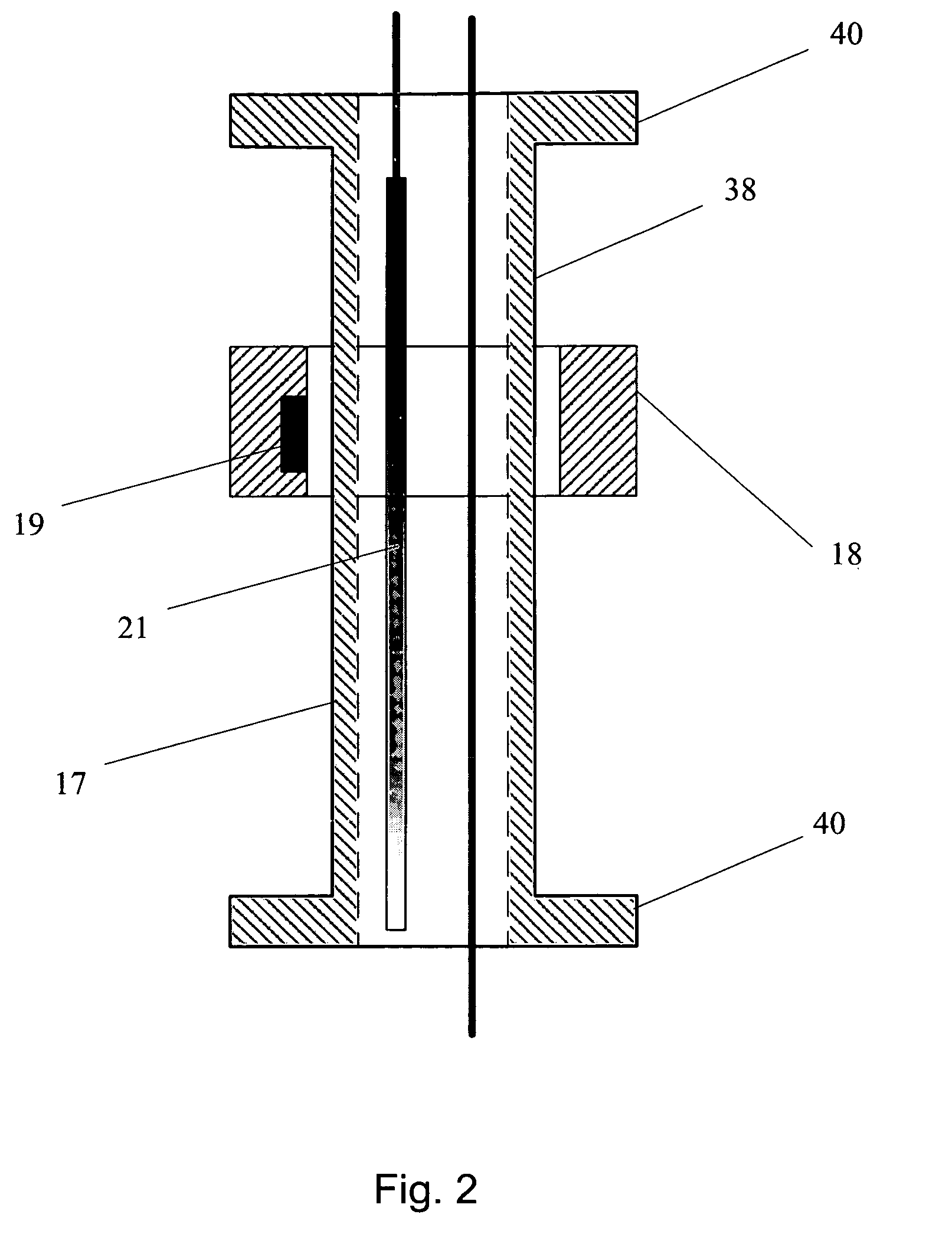
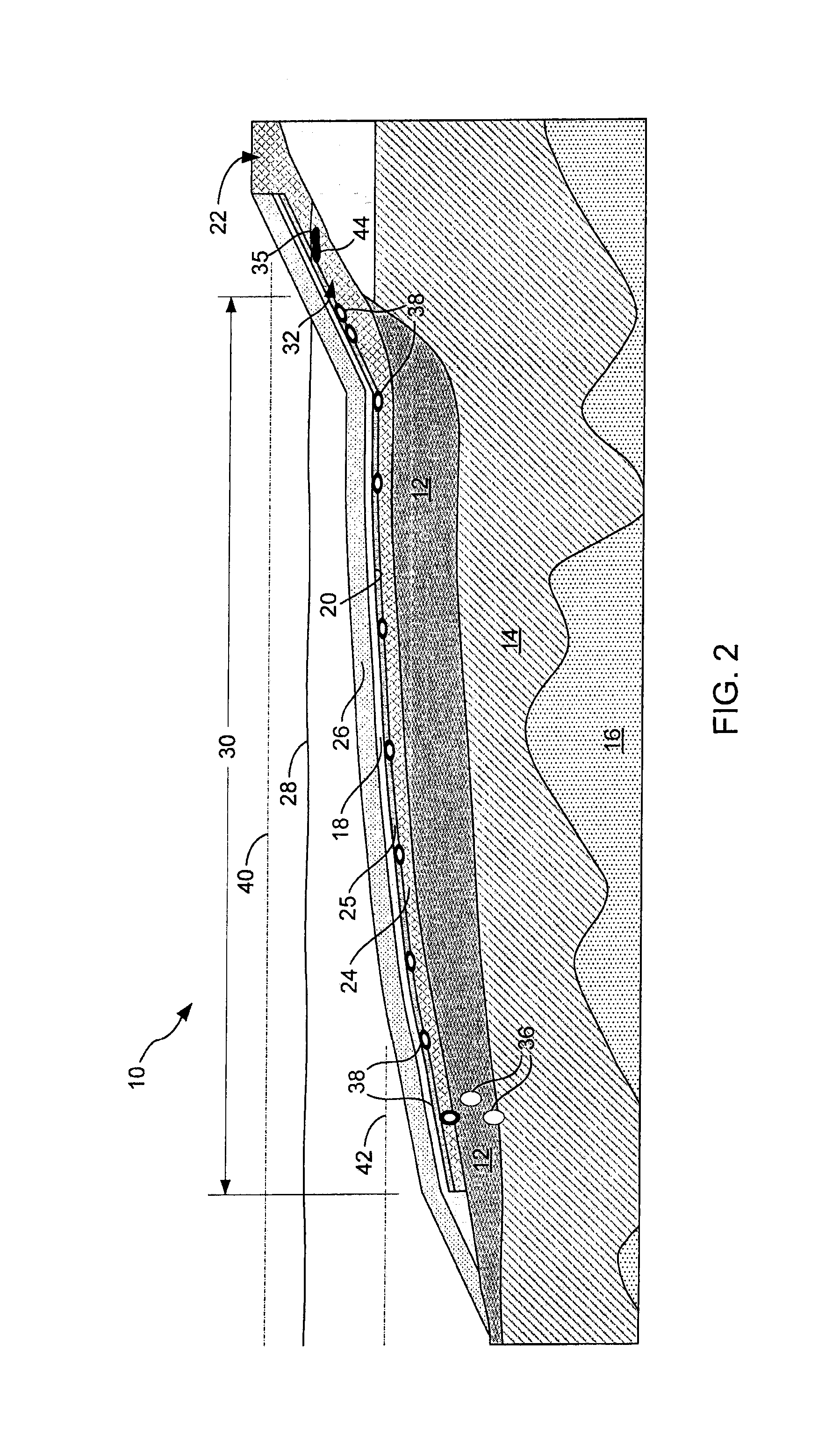
Method of monitoring dual-phase liquid and interface levels
InactiveUS6928862B1Removal from serviceSmall diameterSpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesSurface/boundary effectSpecific gravityContinuous signal
A dual-phase level monitoring (DPLM) instrument that provides continuous signals that enables determination of the location of the top surface of the lighter of two immiscible fluids (the product) and the hydrostatic pressure below the total fluid column of both immiscible fluids. By knowing the fluid specific gravities, the output signals are processed to yield the location of the air / product and liquid / liquid interfaces, and the depth of the lighter phase. The instrument is intended for use in groundwater monitoring wells with a light non-aqueous phase liquid (product) and tanks or vessels with dual-phase liquids and level monitoring and / or control issues. The DPLM instrument includes a first pressure transducer situated beneath the surface of the liquid with a greater specific gravity, which will typically be ground water. A level element with a float selected so as to be buoyant and float on the surface of the lighter fluid is positioned above the first pressure transducer. A signal from the level element is proportional to the position of the float or the total distance the float is positioned above the bottom of the level element and therefore the total distance above the first pressure transducer, the pressure transducer located in the heaver liquid phase. A second pressure transducer can be deployed above the surface of the liquid if greater accuracy of measurement (as compared to assuming ambient pressure) is desired.
Owner:ROBBINS BRYCE V
Novel multifunctional materials for in-situ environmental remediation of chlorinated hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20130058724A1Low costEasy to removeMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesSorbentMicrosphere
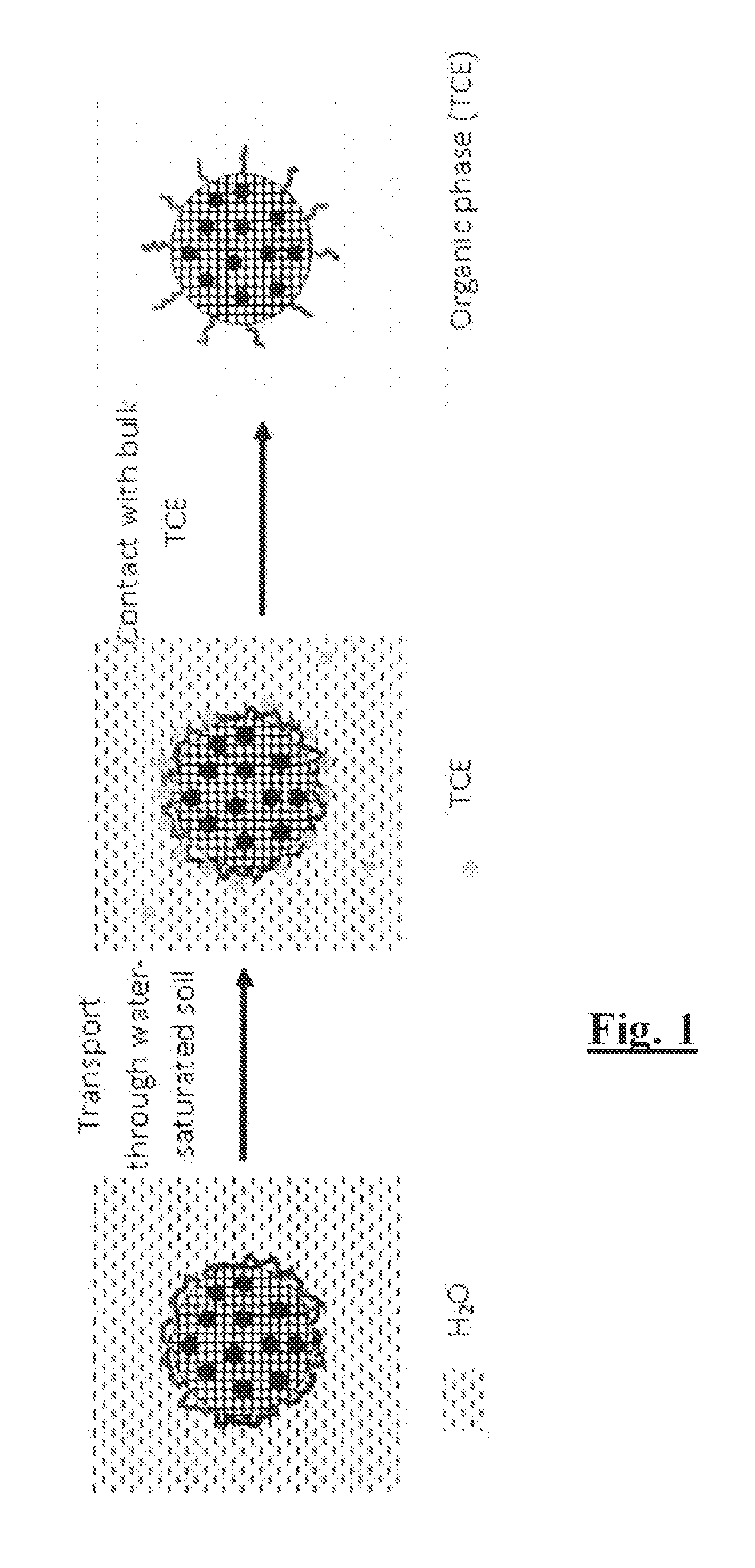
Effective in-situ injection technology for the remediation of dense nonaqueous phase liquids (DNAPLs) such as trichloroethylene (TCE) benefits from the use of decontamination agents that effectively migrate through the soil media, and react efficiently with both dissolved TCE and bulk TCE. A novel decontamination system contains highly uniform carbon microspheres preferably in the optimal size range for transport through the soil. The microspheres are preferably enveloped in a polyelectrolyte (such as carboxymethyl cellulose, CMC) to which preferably a bimetallic nanoparticle system of zerovalent iron and Pd is attached. The carbon serves as a strong adsorbent to TCE, while the bimetallic nanoparticles system provides the reactivity. The polyelectrolyte serves to stabilize the carbon microspheres in aqueous solution. The overall system resembles a colloidal micelle with a hydrophilic shell (the polyelectrolyte coating) and a hard hydrophobic core (carbon). In contact with bulk TCE, there is a sharp partitioning of the system to the TCE side of the interface due to the hydrophobicity of the core. These multifunctional systems appear to satisfy criteria related to remediation and are relatively inexpensive and made with potentially environmentally benign materials. An aerosol process is preferably used to produce zerovalent iron particles supported on carbon. A method of lubricating includes creating carbon microspheres produced from a monosaccharide or polysaccharide, the carbon microspheres having a diameter of 50 nm to 6 microns, coating the microspheres with a surface coating and using the carbon microspheres as a lubricant.
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
Characterization of organic contaminants and assessment of remediation performance in subsurface formations
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Zero-valent metal emulsion for reductive dehalogenation of DNAPLs
InactiveUS7037946B1Easy to degradeNon toxicOther chemical processesMixing methodsEmulsionDense non-aqueous phase liquid
A zero-valent metal emulsion is used to dehalogenate solvents, such as pooled dense non-aqueous phase liquids (DNAPLs), including trichloroethylene (TCE). The zero-valent metal emulsion contains zero-valent metal particles, a surfactant, oil and water. The preferred zero-valent metal particles are nanoscale and microscale zero-valent iron particles.
Owner:NASA
Organic-polluted soil restoration method
InactiveCN104759463APromote decompositionGood for volatilizationContaminated soil reclamationPollution soilGreenhouse
The invention relates to an organic-polluted soil restoration method. Excavated polluted soil is divided into two types of soil, the first type of the soil contains non-aqueous phase liquid and the second type of the soil does not contain non-aqueous phase liquid. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out crushing and screening on the polluted soil containing non-aqueous phase liquid by a crushing-screening combined device, simultaneously, carrying out flushing pre-treatment by a surfactant, uniformly spreading and stacking all the polluted soil subjected to crushing and screening in an enclosed greenhouse, heating the polluted soil to a temperature of 80-100 DEG C by a geothermal system at the lower part of the polluted soil, keeping the temperature of the heated polluted soil in a range of 80-100 DEG C for 2-4h, then spraying a first oxidizing agent to the polluted soil by a spraying system in the enclosed greenhouse, then carrying out heating treatment on the polluted soil to a temperature of 60-80 DEG C and keeping the temperature for 6-10h.
Owner:NANJING SREMOL ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Method for remediation of soil polluted by high-concentration organic matters
ActiveCN106269823AEasy to handleHigh removal rateContaminated soil reclamationHigh concentrationSolubility
The invention relates to a method for remediation of soil containing high-concentration organic pollutants. According to the method, the solubility of the organic pollutants in a groundwater environment is improved by adding a solubilizing agent, or organic matters in the soil are consumed by adding a non-selective oxidizing agent, so that the adsorption capacity of the soil is lowered, the permeability of the soil is improved, the deabsorption of 'non-aqueous phase liquid' in a high-concentration pollution source area and adsorbed-state organic pollutants in the soil is promoted, and the 'non-aqueous phase liquid' and the adsorbed-state organic pollutants are dissolved into a water phase or the effects of deabsorption and solubilizing are improved by using both the non-selective oxidizing agent and the solubilizing agent; and a chemical oxidizing / reducing agent is added on the basis of deabsorption and solubilizing to further degrade dissolved-state organic pollutants, so that the purpose of remediation is achieved. According to the method, non-aqueous phase-state pollutants, soil absorbed-state pollutants and organic pollutants in groundwater can be treated effectively and quickly, the sources of the agents are wide, the treatment method is simple, the remediation effect is good, and the removal rate of organic pollutants is high.
Owner:中节能大地(杭州)环境修复有限公司
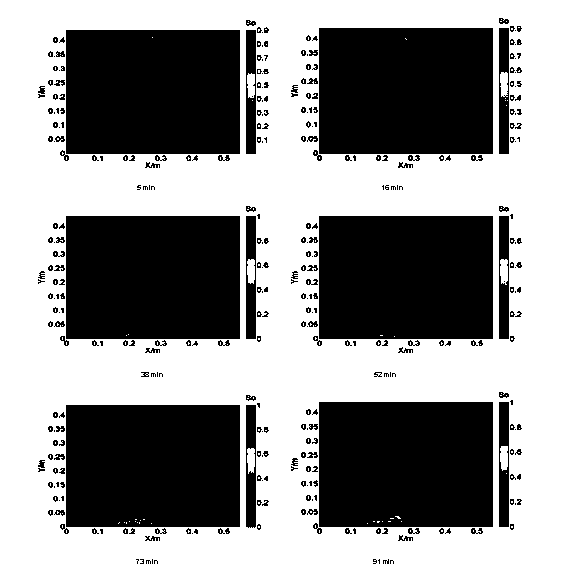
Method for quantitatively monitoring DNAPL (Dense Nonaqueous Phase Liquid) migration process and saturation degree
ActiveCN103852425ARealize quantitative measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansMaterial resistanceElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively monitoring a DNAPL (Dense Nonaqueous Phase Liquid) migration process and the saturation degree. According to the method, an infiltration test of DNAPL is carried out in a two-dimensional sand box and a light transmission method and a high-density resistivity method are used for dynamically monitoring; a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera and an LCR (Inductance, Capacitance and Resistance) digital electric bridge are respectively used for acquiring data. A calculation formula of the DNAPL saturation degree in water-DNAPL two phases is used for processing the data of the light transmission method. The data processing of the high-density resistivity method is to convert resistance value data into a resistivity value and utilize an Archie formula to obtain saturation degree space distribution of heavy non-aqueous phase liquid. In the Archie formula, a parameter beta value is obtained by a novel method combined with the light transmission method and the total amount of the DNAPL injected into the sand box can be evaluated by the saturation degree space distribution of different moments; then the total amount is compared with an actually-measured infiltration capacity. A result shows that an infiltration process of the DNAPL in a saturated pore medium can be quantitatively monitored and the estimated DNAPL infiltration capacity is matched with an actually-measured value very well.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Geophysical method for quantification of dense non-aqueous phase liquids in the subsurface
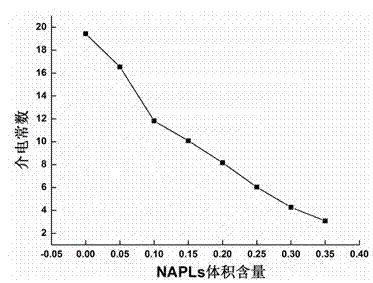
The present invention is a method of calculating non-aqueous phase liquid saturation in a soil sample including the steps of measuring the bulk dielectric constant of the sample, measuring the bulk density of the sample, estimating the bulk porosity of the sample from the measured bulk density and calculating the non-aqueous phase liquid saturation from the measured bulk dielectric constant and the estimated bulk porosity.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Electric power control and repairing system and method of nonaqueous phase liquid pollutant in soil
ActiveCN104307857AEffective controlEfficient repairContaminated soil reclamationPower control systemEngineering
The invention discloses an electric power control and repairing system and an electric power control and repairing method of nonaqueous phase liquid pollutants in soil. The electric power control and repairing system consists of an electrode well, a conductive electrode, an insulating electrode, a power supply control system as well as an injected liquid mixing device, an injection pump, an injection well and a sucking well. Aiming at nonaqueous phase liquid pollution of soil, a non-uniform fragrance variable electric field is applied, together with the solubilization of a surfactant, electroosmosis, electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis effects as migration driving power of pollutants are applied to nonaqueous phase liquid pollutants, and the migration direction of the nonaqueous phase liquid pollutants in soil can be changed and controlled, so that the purposes of solubilization, migration control and final enrichment and removal of the nonaqueous phase liquid pollutants in soil and underground water are achieved. In addition, the electric power control and repairing system and the electric power control and repairing method can be also used for controlling the pollution range of nonaqueous phase liquids to be within or outside a specific spatial area.
Owner:厦门科林尔环保科技有限公司
Method and compositions for treatment of subsurface contaminants
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
3D printed water-permeable pavement scale simulation device and method under action of runoff
The invention discloses a 3D printed water-permeable pavement scale simulation device under the action of runoff. The device comprises a model box provided with an opening in the top, wherein a lower base course, an upper base course and a 3D printed water-permeable pavement are sequentially inside the model box from bottom to top, and the water-permeable pavement is transparent or translucent; and a section is obtained by scanning the concrete water-permeable pavement, and is reconstructed in a 3D printer to obtain the 3D printed water-permeable pavement, and a seepage port is formed in the bottom of the model box and is communicated with a collector. The interaction among rainwater runoff, sediment particles and the water-permeable pavement is studied comprehensively through a non-aqueous phase liquid migration law test and a non-aqueous liquid-wrapped sand transport law test to give the variation trend of movement speeds of the non-aqueous liquid and particles in a pore channel in each direction at different seepage flow velocities, and the experimental effect has good guiding significance.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Apparatus for rapidly measuring liquid levels and volume of groundwater within wells that eliminates cross contamination between wells
InactiveUS7021137B1Avoid accumulationFlat surfaceSurveyConstructionsResistive circuitsElectrical resistance and conductance
A dedicated liquid level detection method having a sensor positioned into the casing of a groundwater well. The detector is in the form of an elongated thin film sensor tape that extends along the full length of the well casing which detects the level, thickness and volume of both groundwater and any light or dense non-aqueous phase liquid that may be present.This is accomplished through the use of a conductive and hydrostatic resistive circuit measuring the level of liquids in a groundwater well at one hundredths of foot resolution or greater. Once the elongated sensor is installed, liquid levels can be gauged from the surface. The data is stored using a battery operated hand held digital display temporarily connected at the top well section casing. Since a sensor probe is not lowered into the well, cross contamination between wells is eliminated.
Owner:MILONE CHRISTOPHER J
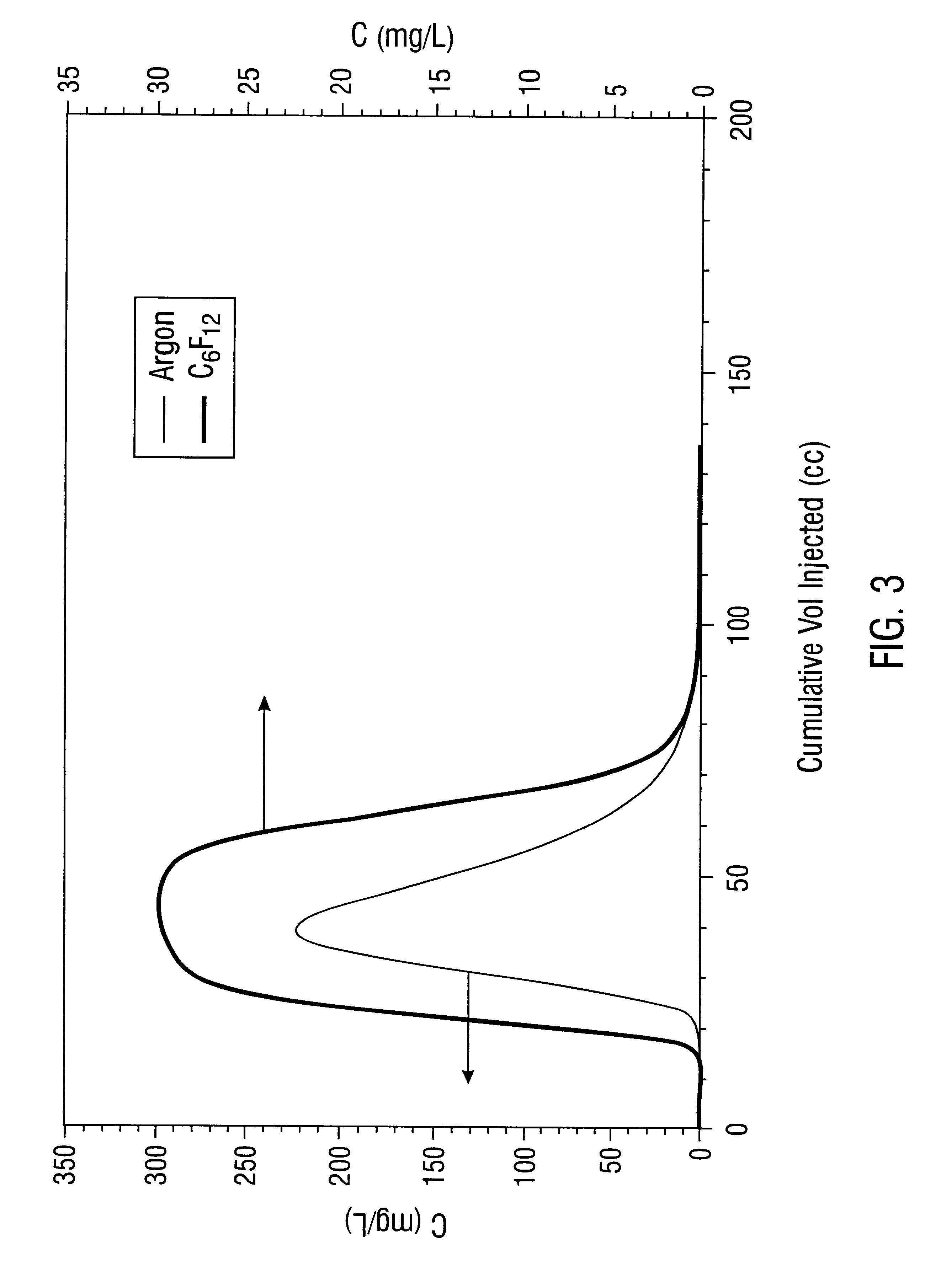
Measurement of non-aqueous phase liquid flow in porous media by tracer dilution
A method and apparatus for measuring in situ flow of non-aqueous phase liquids (NAPLs) through a porous medium is described. A tracer is introduced into a well or boring located in the medium and the tracer concentration in the well kept uniform by mixing. The rate at which the tracer is depleted from the well has been determined to be proportional to the flow rate of the NAPL through the well or boring and surrounding formation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC +1
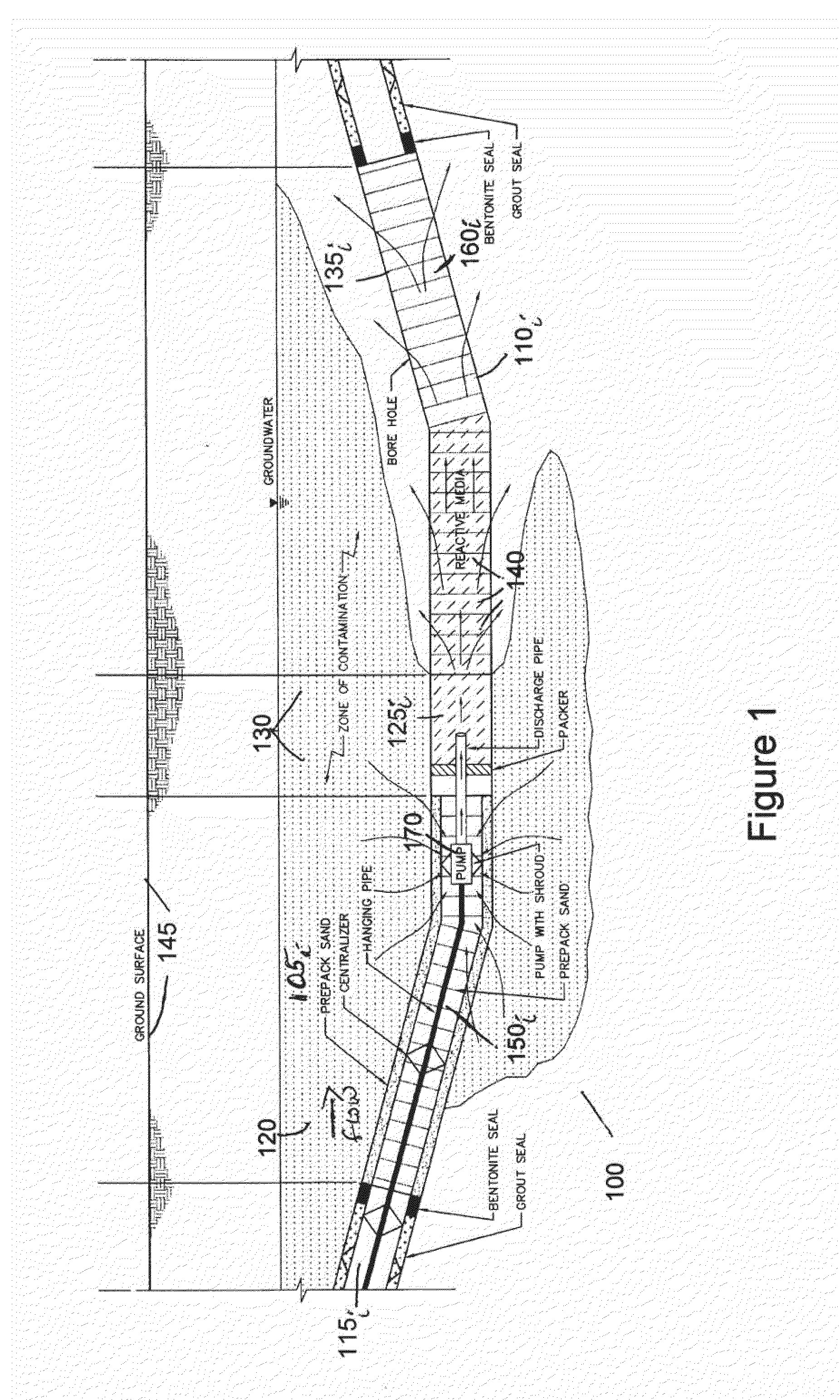
Horizontal In-Well Treatment System and Source Area Bypass System and Method For Groundwater Remediation
ActiveUS20120261125A1Improve performanceReduce in quantityContaminated soil reclamationFluid removalHigh concentrationGroundwater remediation
The application relates to a sustainable and green remedial approach for in situ remediation. The system and method use directionally drilled horizontal wells filled with granular reactive media generally installed in the direction of groundwater flow for groundwater remediation. “Flow-focusing” behavior is leveraged to capture and passively treat proportionally large volumes of groundwater in situ. The system and method perform well in low hydraulic conductivity environments where the success of other in situ remediation methods is controlled by aquifer injectability. Reactive media are selected according to the contaminants to be treated and site characteristics. Energy conservation and other considerations result in considerable cost savings compared to current in situ remediation systems. Also disclosed is a source area bypass system comprising one or more horizontal wells, constructed in a manner to allow unimpacted or cleaner groundwater to bypass a nonaqueous phase liquid zone or high-concentration source area of contamination and discharge downgradient. Reactive media may or may not be used in a source area bypass system. In some configurations, groundwater pumps may be installed to enhance performance. Core elements of green remediation according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency are achieved.
Owner:ARCADIS U S
Portable self-powered recovery system for contaminated fluids
InactiveUS20060239777A1Economical and simpleContaminated soil reclamationEnvironmental SettingCombined use
The invention is a portable, fully independent, pump-based remediation device and methods for the collection of non-aqueous phase liquids and other fluid contaminants in environmental settings. The device is comprised of a compact, weather-resistant housing equipped with: electric pump; independent power supply; programmable timer and / or sensor; and control and monitoring systems. The device is used in combination with a variety of suitable fluid storage containers. A method for removing fluid contaminants from environmental installations such as groundwater monitoring wells, piezometers, product recovery wells and trenches by transporting said device to the treatment location, installing the fluid storage container, installing the device pump tube systems, connecting safety systems, and programming the timer and / or sensor. Primary advantages over other existing systems include the device's compact, portable size, integrated components, independent power supply, and flexibility in application and installation.
Owner:MARTIN DOUGLAS ADAMS
Sampling well system for investigation and long-term monitoring of organic contaminated site, and well building method thereof
PendingCN110095308AImprove work efficiencyWithdrawing sample devicesBorehole/well accessoriesSoil scienceThree stage
The invention relates to a sampling well system for investigation and long-term monitoring of an organic contaminated site, and a well building method thereof. The sampling well system can be used forsampling a soil gas, a light non-aqueous phase liquid (LNAPLs) layer, a dense non-aqueous phase liquid (DNAPLs) layer and underground water of the stratum at different depths respectively in three stages of site investigation, treatment and restoration, and subsequent monitoring. For the organic contaminated site, the sampling well system has the function of sampling various kinds of contamination media in different stages by means of one monitoring well, reduces the building and maintenance costs of the sampling well, and improves the efficiency.
Owner:MCC ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION +1
Method for degrading heavy non-aqueous phase liquid component composite hydrochloric ether pollutants in underground water
InactiveCN105399193ANon-toxicLow costWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentIndustrial waste waterSodium sulfate
Provided is a method for degrading heavy non-aqueous phase liquid component composite hydrochloric ether pollutants in underground water. The steps are as follows: a mixture of sodium persulfate and sodium hydroxide is added into water containing composite hydrochloric ether pollutants, and degradation and restoration are carried out. The cost is low, and operation is simple, safe and practicable. The restoration reagent has stable chemical properties, the reaction conditions are mild, and the restoration reagent has universality in most of underground environments. Various hydrochloric ether kinds can be degraded, and have a representativeness of pollution of underground water by composite hydrochloric ether. The method has characteristics of high degradation efficiency, rapid degradation rate, nontoxic products and the like. The method is suitable for in-situ restoration of underground water composite hydrochloric ether pollutants, can be extended for restoration composite hydrochloric ether in soil or industrial waste water, and is widely applied.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
In-situ continuous penetrating probe used in non-aqueous phase liquids (NAPLs) polluted sandy soil field investigation
ActiveCN103116189AQuick screeningQuick in situDetection using electromagnetic wavesTime domainElectricity
The invention discloses an in-situ continuous penetrating probe used in non-aqueous phase liquids (NAPLs) polluted sandy soil field investigation. A time-domain reflective penetrating probe is mounted between a feeler lever and a friction barrel of a traditional static penetrometer. The structure of the time-domain reflective penetrating probe is that six symmetrical stainless steel needles are embedded in an outer surface of a hollow Derlin pole and are fixed on the Derlin pole through bolts, two coaxial cable inner conductors are respectively welded with a pair of bolts which are positioned on the top of the Derlin pole and penetrates through the diameter of the Derlin pole, and two adjacent bolts on two sides of the pair of bolts are form a group and are welded with coaxial cable outer conductors respectively. The penetrating probe is capable of acquiring dielectric constants, conductivities, tie resistances and side frictions of soil layers of different depth quickly, continuously and accurately. According to the electricity parameters and the mechanical parameters, polluted area and pollution degree of the NAPLs polluted sandy soil field are identified. The in-situ continuous penetrating probe provides a powerful tool in fast screening NAPLs polluted field.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Pretreatment of produced water to facilitate improved metal extraction
ActiveUS20190010068A1Efficient and cost-effectiveWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsWater usePh control
A water treatment system that removes calcium and magnesium using coagulants and pH controls, aqueous phase organic materials from water using a biological removal system that includes microorganisms and a physical separation system that includes sparging equipment for sparging the water to remove non-aqueous phase liquid organic materials, volatile phase organic materials. An apparatus, system and method for pretreating oilfield produced water to completely remove or significantly reduce concentrations of substances that are known to interfere with downstream recovery of metals including lithium. This technology facilitates a more efficient and cost-effective extraction method from alternate sources to meet the increasing global demand.
Owner:KATZ WATER TECH LLC
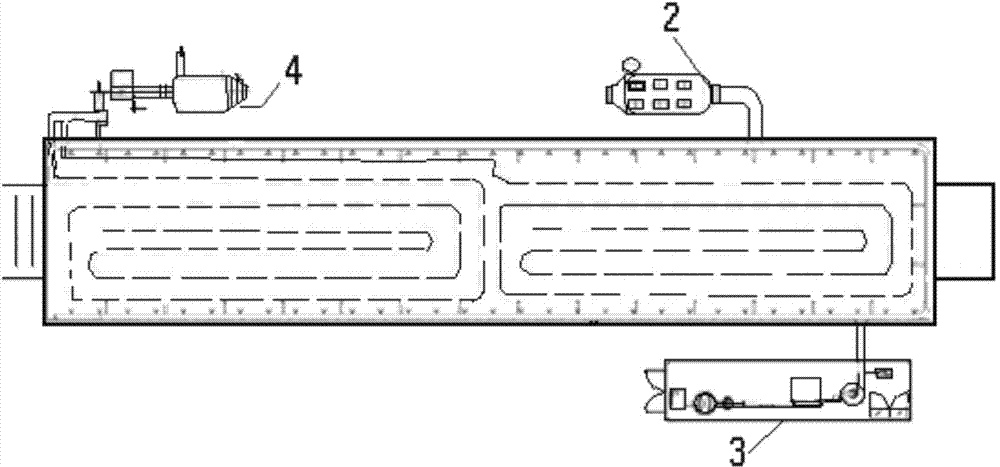
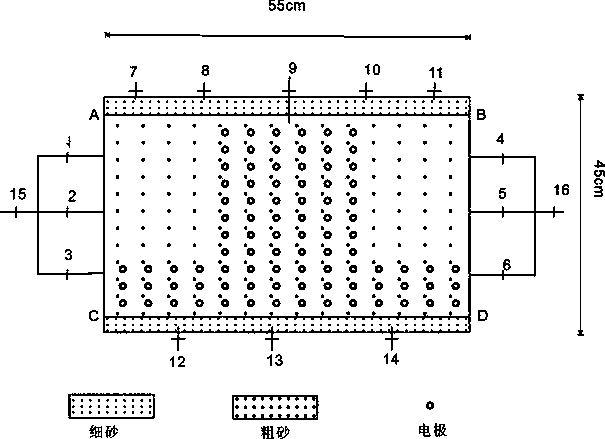
System and method for testing migration and obstruction of non-aqueous phase liquid pollutants in underground water
ActiveCN111157406AResearch migrationResearch RedistributionSurface/boundary effectPermeability/surface area analysisSewageGroundwater
The invention provides a system for testing migration and obstruction of non-aqueous phase liquid pollutants in underground water. The system comprises a test soil sample chamber, a uniform variable speed sewage supply module, a water supply module and a solution collection module, wherein the test soil sample chamber at least comprises a first sand tank, a second sand tank and an engineering barrier isolation tank which are arranged in sequence and provided with a water permeable structure therebetween; and the uniform variable speed sewage supply module is communicated with the first sand tank, the water supply module is communicated with the bottom end of the first sand tank, and the solution collection module is arranged at the bottom ends of the engineering barrier isolation tank andthe second sand tank. According to the scheme, the migration and diffusion of non-aqueous phase liquid pollutants in the stratum can be simulated according to different geological conditions and different working conditions on site; the migration and distribution characteristics of the non-aqueous phase pollutants in porous media with different particle sizes are studied; and meanwhile, the isolation, resistance and control effects of an engineering barrier isolation wall on pollution plumes generated after migration and diffusion of the non-aqueous phase liquid pollutants in an underground environment can be systematically studied.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Device and method for trapping non-aqueous-phase liquids prior to a permeable reactive barrier for the treatment of contaminated groundwater
ActiveUS9884771B1Fatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater contaminantsMedicineContaminated water
A groundwater treatment system for collecting a non-aqueous-phase liquid (NAPL) in a flow path of contaminated water in a body of water, the contaminated water moving toward a permeable reactive barrier (PRB) including a treatment agent for treating the contaminated groundwater. The groundwater treatment system including a collection layer positioned up-gradient of the PRB and permeable to the NAPL and the contaminated water. The collection layer including a NAPL collecting element to inhibit the NAPL from flowing to the PRB.
Owner:TRC ENVIRONMENTAL CORP
Recovery of non-aqueous phase liquids from ground sources
InactiveUS7300227B2Increase relative volatilityEfficient injectionSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationAbove groundGas phase
The invention disclosed relates to a method and apparatus for recovering non-aqueous phase liquids (NAPL) from regions below ground where NAPL spills are sources of aquifer contamination. The apparatus includes a system to supply gas-supersaturated liquid, a system of ground wells in fluid communication with the contaminated ground water region (source of contamination) and with an above-ground NAPL recovery system, said system of wells including an injection well in fluid communication with the system to supply gas-supersaturated liquid and with the contaminated region below ground, an extraction well in fluid communication with the contaminated region below ground and with the NAPL recovery system, wherein the NAPL is in the gaseous phase or gas-mobilized non-volatile liquid phase or both, and a pump for delivering the gas-supersaturated liquid to the vicinity of the contaminated region below ground.
Owner:LI TOMMY M W +2
Measurement of non-aqueous phase liquid flow in porous media by tracer dilution
A method and apparatus for measuring in situ flow of non-aqueous phase liquids (NAPLs) through a porous medium is described. A tracer is introduced into a well or boring located in the medium and the tracer concentration in the well kept uniform by mixing. The rate at which the tracer is depleted from the well has been determined to be proportional to the flow rate of the NAPL through the well or boring and surrounding formation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC +1
Water treatment systems and methods for concurrent removal of various types of organic materials
InactiveUS20160214876A1Fatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesTreatment using aerobic processesMicroorganismWater treatment system
A water treatment method that concurrently subjects water to: (1) a biological water treatment process that removes a first set of organic materials from the water and (2) a physical water treatment process that removes a second set of organic materials from the water. A water treatment system that concurrently removes aqueous phase organic materials from water using a biological removal system that includes microorganisms and a physical separation system that includes sparging equipment for sparging the water to remove non-aqueous phase liquid organic materials, volatile phase organic materials.
Owner:AUSTIN ELEMENTS INC
Devices and methods for directing migration of non-aqueous phase liquids from sediment
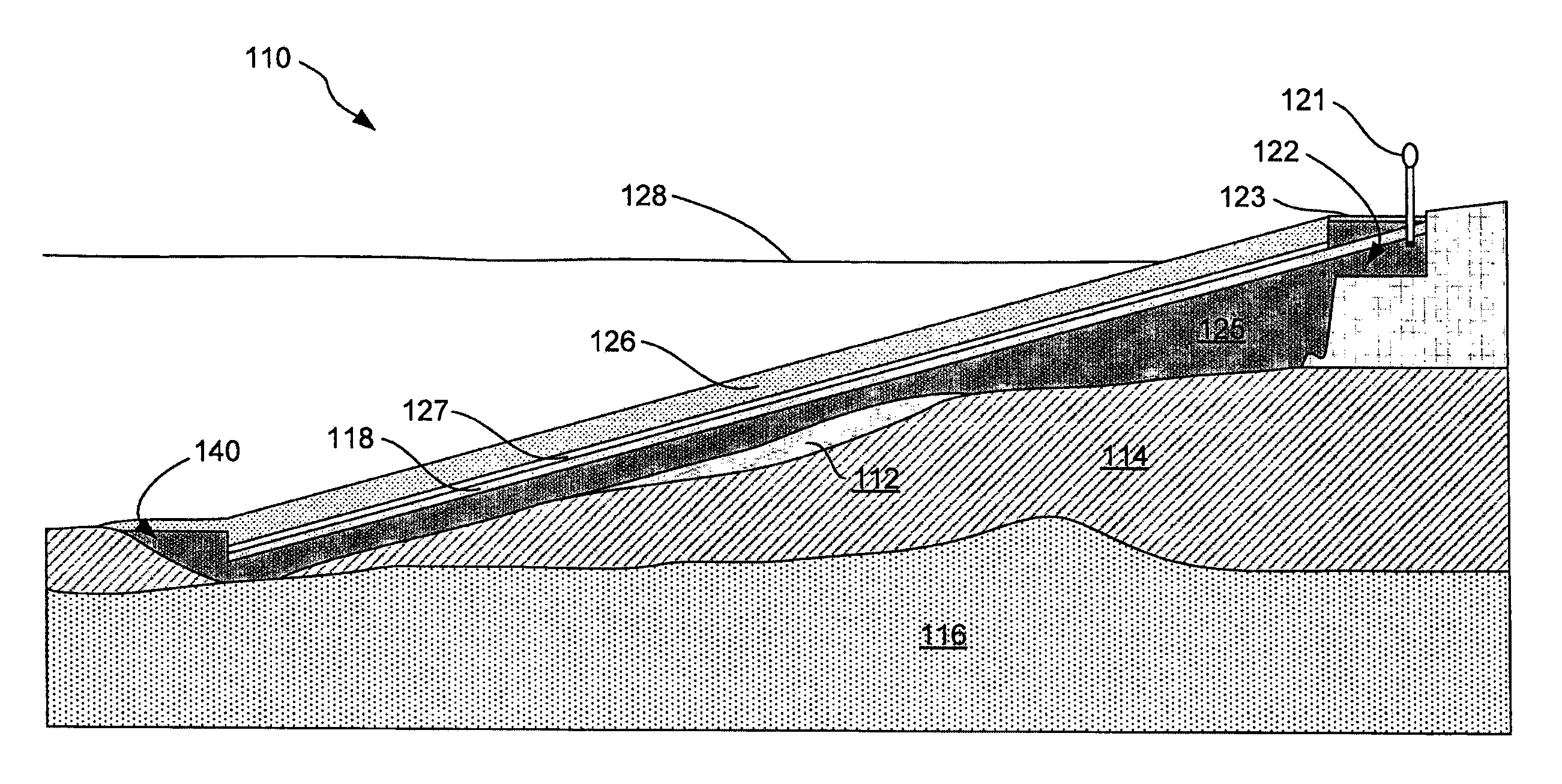
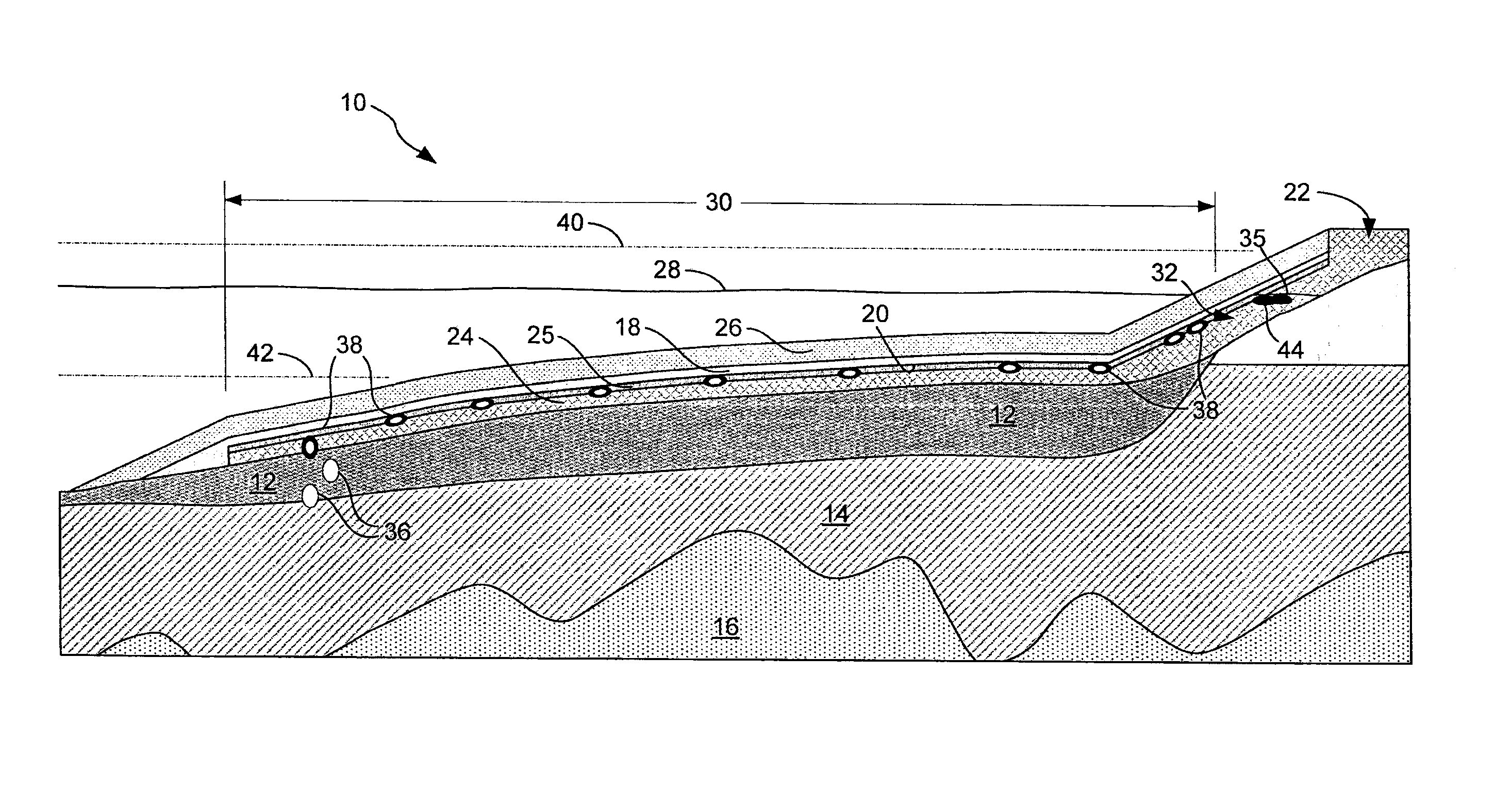
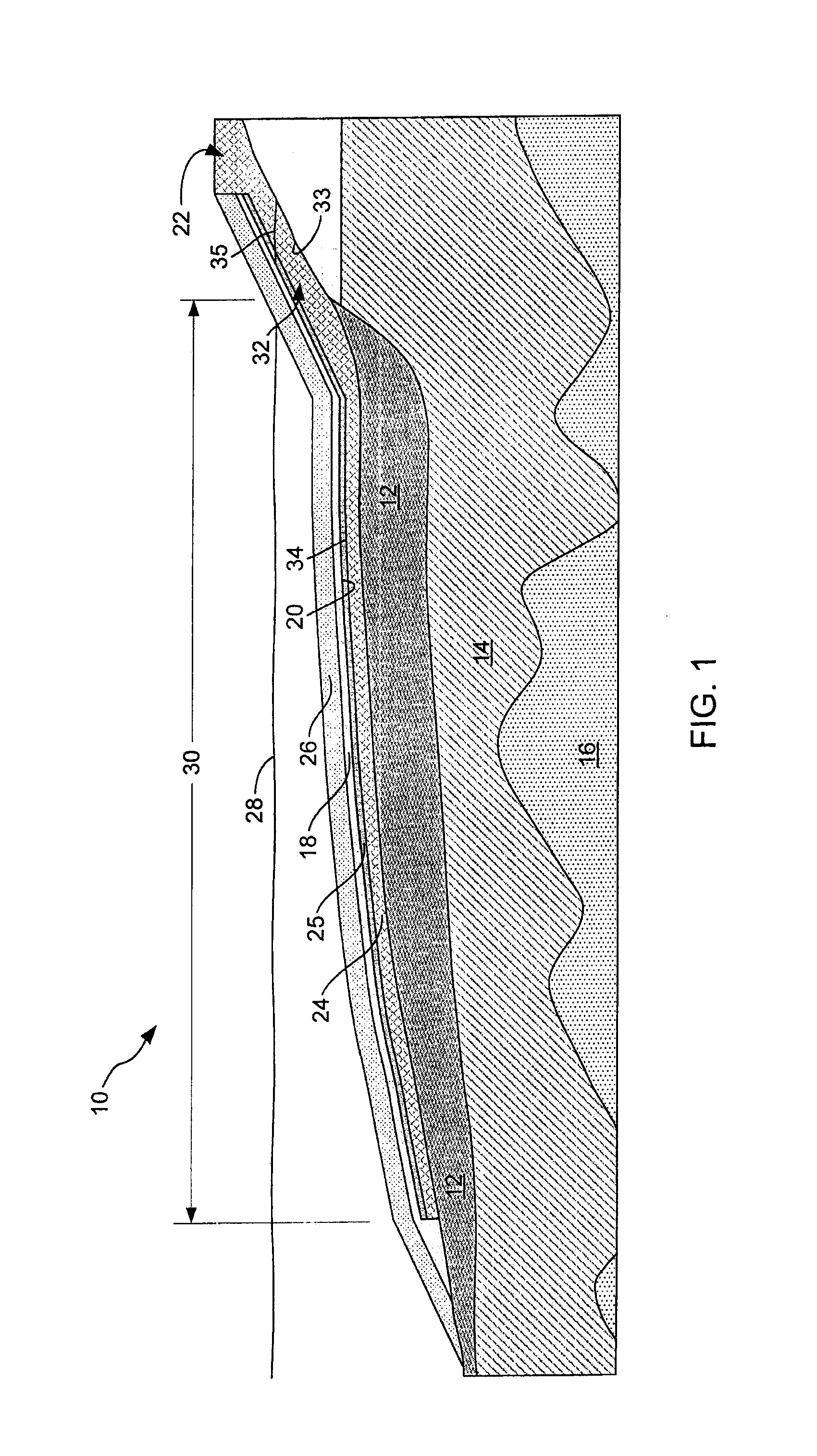
ActiveUS8419314B1Avoid percolationReduce penetrationSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationAccumulation zoneTrapping
Devices and methods for directing a non-aqueous phase liquid (NAPL) that migrate entrained in a fluid (e.g., a gas) from sediments in bodies of water by using trapping caps having an upwardly sloped surface toward an accumulation zone that contains a water table, in which migration of the gas carries the NAPL toward the accumulation zone.
Owner:TRC ENVIRONMENTAL CORP
Recovery of non-aqueous phase liquids from ground sources
InactiveUS20070014633A1Increase relative volatilityEfficient injectionSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationAbove groundGas phase
The invention disclosed relates to a method and apparatus for recovering non-aqueous phase liquids (NAPL) from regions below ground where NAPL spills are sources of aquifer contamination. The apparatus includes a system to supply gas-supersaturated liquid, a system of ground wells in fluid communication with the contaminated ground water region (source of contamination) and with an above-ground NAPL recovery system, said system of wells including an injection well in fluid communication with the system to supply gas-supersaturated liquid and with the contaminated region below ground, an extraction well in fluid communication with the contaminated region below ground and with the NAPL recovery system, wherein the NAPL is in the gaseous phase or gas-mobilized non-volatile liquid phase or both, and a pump for delivering the gas-supersaturated liquid to the vicinity of the contaminated region below ground.
Owner:LI TOMMY M W +2
Measurement of liquid flow in porous media by tracer dilution without continuous mixing
A natural gradient, single well, tracer dilution non-continuous mixing apparatus and method for measuring flow of liquids through porous media are described. The method has been applied to concentrations of Light Nonaqueous Phase Liquid (LNAPL) in monitoring wells to measure the rate of LNAPL flow through the wells and through the adjacent formation. Similar measurements were made for concentrations of water in other formations. A LNAPL-soluble fluorescing tracer was added to LNAPL in the wells, and a water-soluble fluorescing tracer was added to water in the wells. The tracer is initially uniformly-mixed into the LNAPL or water in the well, and the tracer concentration is measured using a fiber optic cable and a spectrometer. The LNAPL or water with dissolved tracer is then allowed to flow from the well without any mixing. At a later time, the LNAPL or water and tracer in the well are mixed to a uniform tracer concentration, and the tracer concentration is remeasured. Using the initial tracer concentration, the subsequently mixed tracer concentration, the elapsed time, and the well diameter, a LNAPL flow rate is calculated.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC +1
Groundwater light non-aqueous phase liquid pollutant cleaning system
PendingCN110627263ARealize resource utilizationImprove extraction efficiencyFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesMultistage water/sewage treatmentGas phaseWater table
The invention belongs to the technical field of polluted groundwater environment restoration engineering, and specifically provides a groundwater light non-aqueous phase liquid pollutant cleaning system. The system comprises a sewage treatment module, a groundwater extraction well containing a groundwater layer and a light non-aqueous phase liquid layer, wherein the light non-aqueous phase liquidlayer floats on the surface of the groundwater layer, and the system also comprises a groundwater level monitoring module, a liquid phase extraction module and a gas phase extraction module, wherein the groundwater level monitoring module is used to monitor a liquid level of the groundwater extraction well in real time, and feedback the liquid level to the liquid phase extraction module and the gas phase extraction module; the liquid phase extraction module is used to extract a light non-aqueous phase liquid located on the surface of groundwater to a sewage treatment module according to the liquid level; and the gas phase extraction module is used to evacuate the upper part of the groundwater extraction well to form a negative pressure to the sewage treatment module according to the liquidlevel. The system can greatly improve the restoration efficiency and restoration effect of the non-aqueous phase liquid, can reduce or eliminate the affection of the "tailing" effect, and avoids expansion of a pollution scope of the non-aqueous phase liquid.
Owner:CHINA CITY ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION ENGINEERING LIMITED COMPANY
Devices and methods for directing migration of non-aqueous phase liquids from sediment
Devices and methods for directing a non-aqueous phase liquid (NAPL) that migrate entrained in a fluid (e.g., a gas) from sediments in bodies of water by using trapping caps having an upwardly sloped surface toward an accumulation zone that contains a water table, in which migration of the gas carries the NAPL toward the accumulation zone.
Owner:TRC ENVIRONMENTAL CORP
Method for evaluating migration characteristic of pollutants in no-filling rough single fracture
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the migration characteristic of pollutants in a no-filling rough single fracture. The method concretely comprises the following steps: determining the kind and the dissolvability of the pollutants; establishing a rough single fracture model by using a fractal theory; establishing a no-filling rough single fracture value model based on a finite element technology; evaluating the migration process of the pollutants in the fracture by using a convection-dispersion equation for soluble pollutants; and evaluating the migration process of the pollutants in the fracture by using a level set technology for non-aqueous phase liquid pollutants. The method has the following advantages: 1, evaluation of the migration characteristic of the soluble pollutants in the fracture is realized; 2, evaluation of the migration characteristic of the non-aqueous phase liquid pollutants in the fracture is realized; and 3, migration parameters of the pollutants in the fracture, obtained in the invention, can be used as underground water pollution repairing base parameters.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com