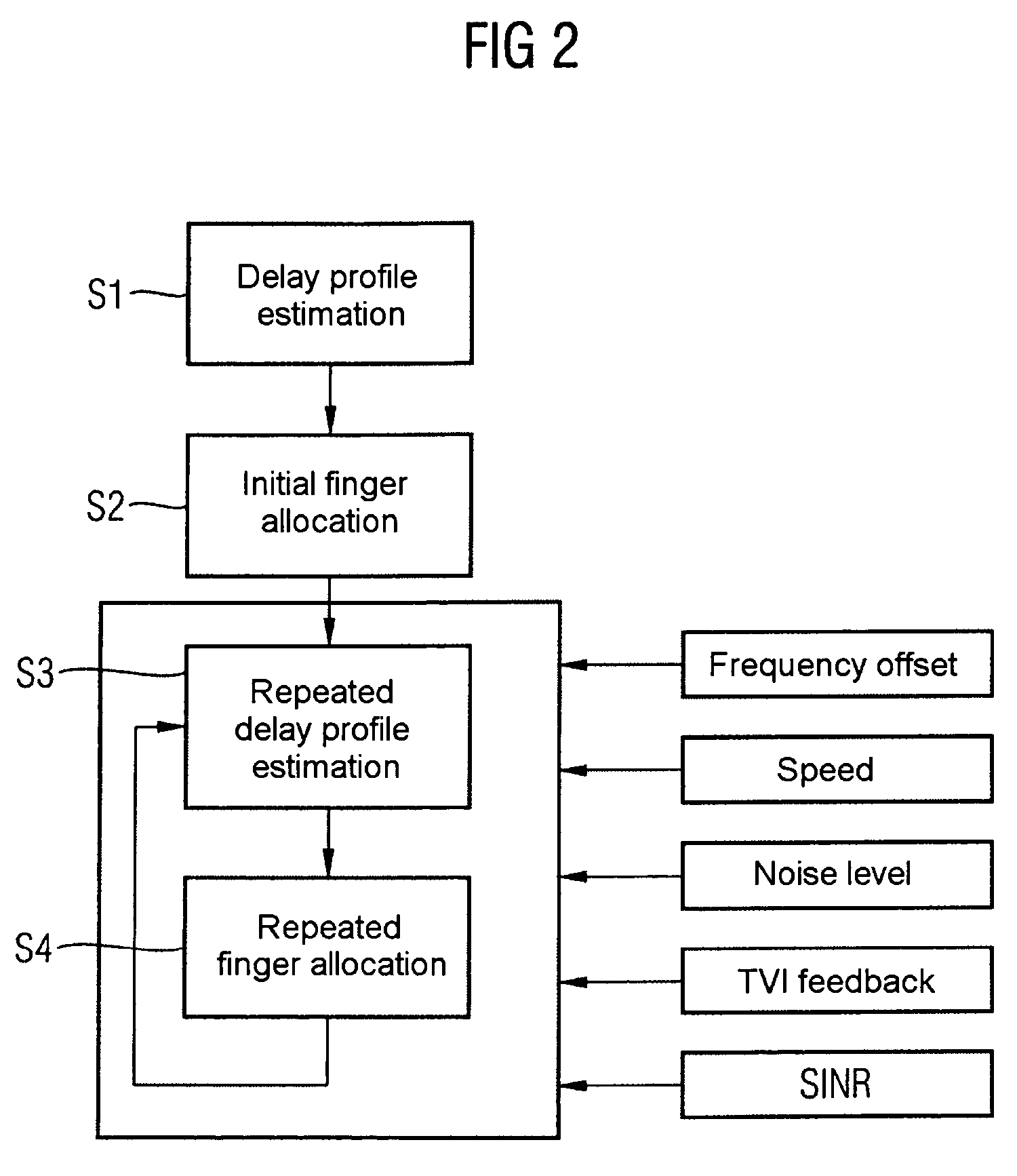
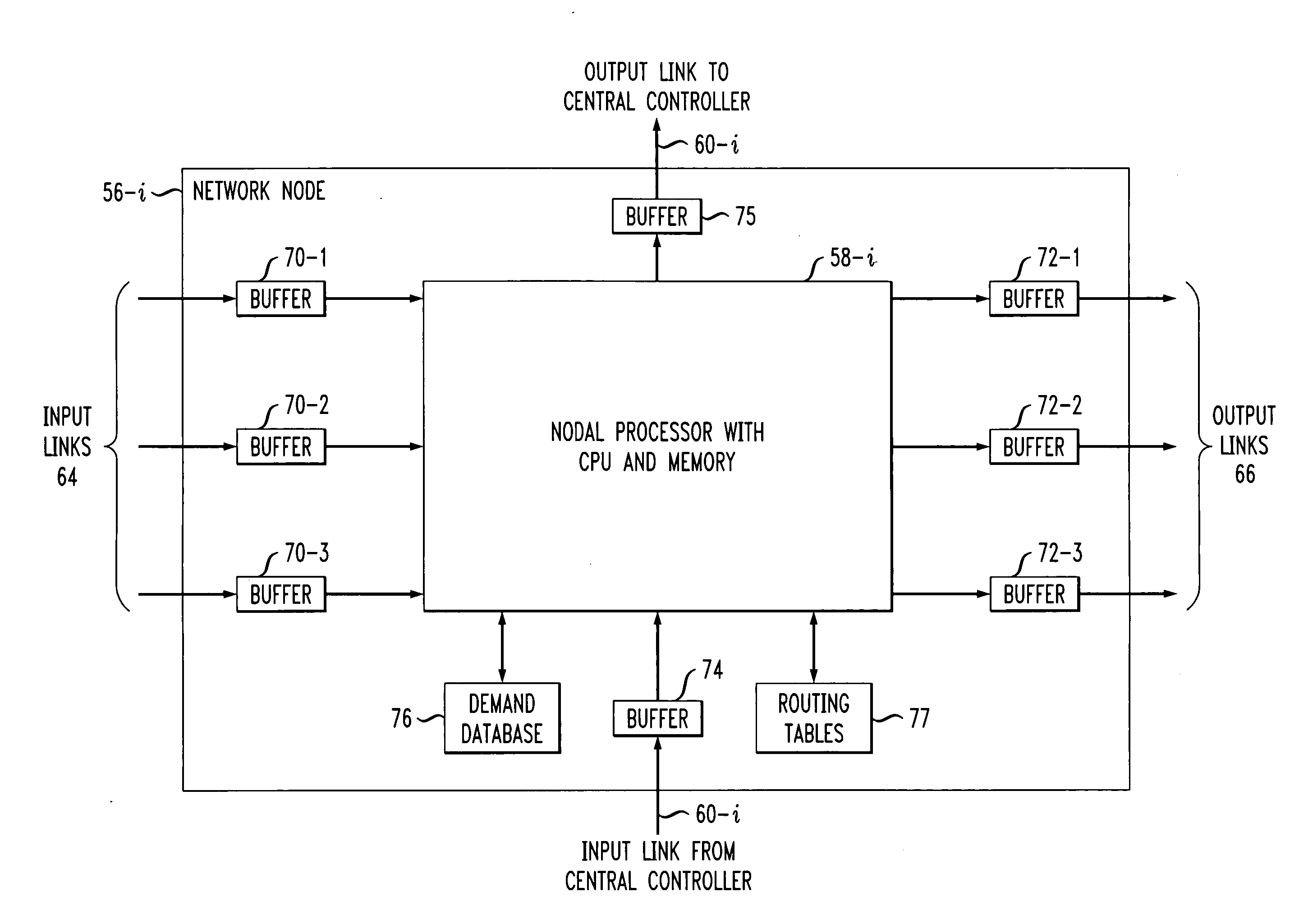
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110 results about "Latency distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
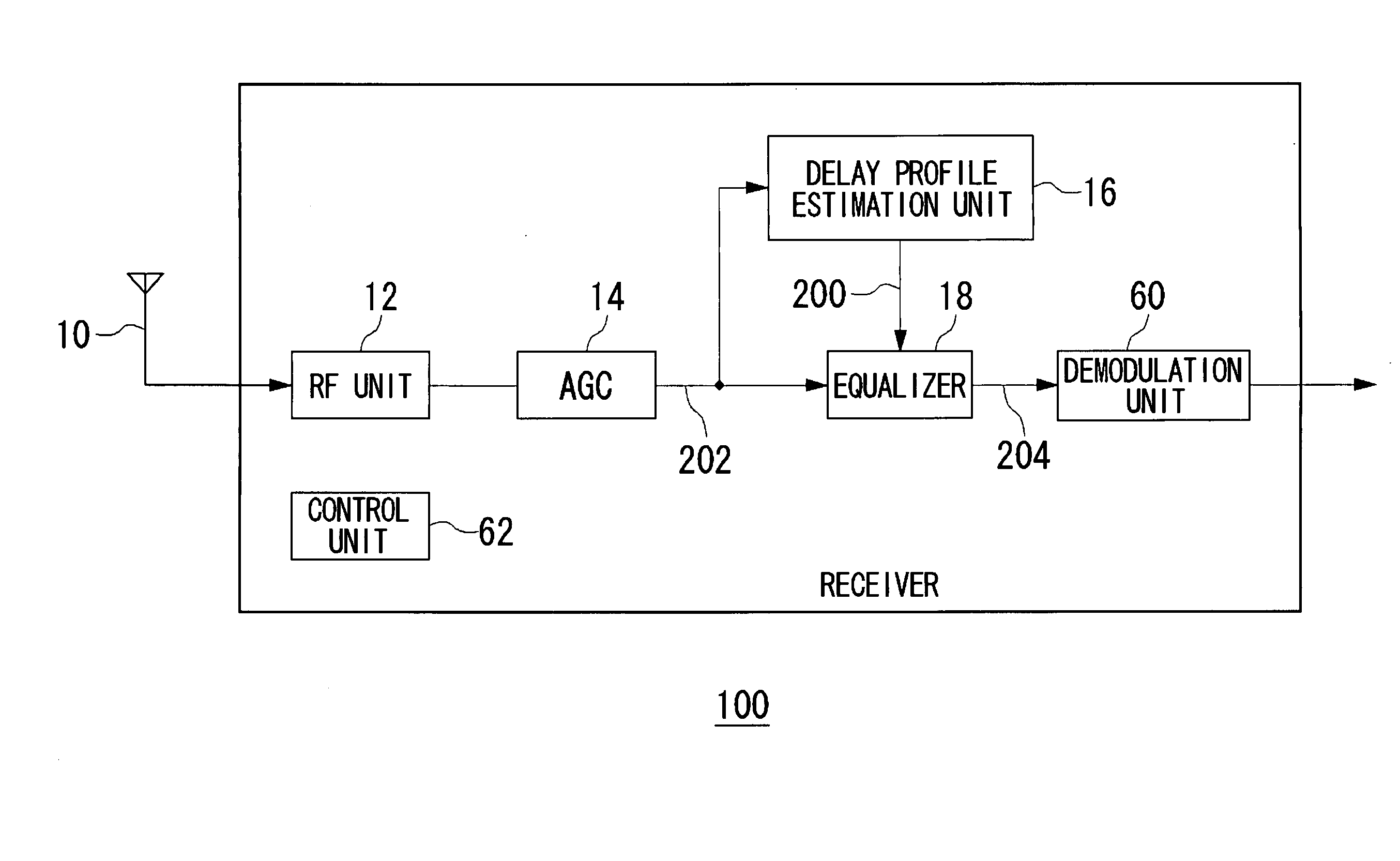
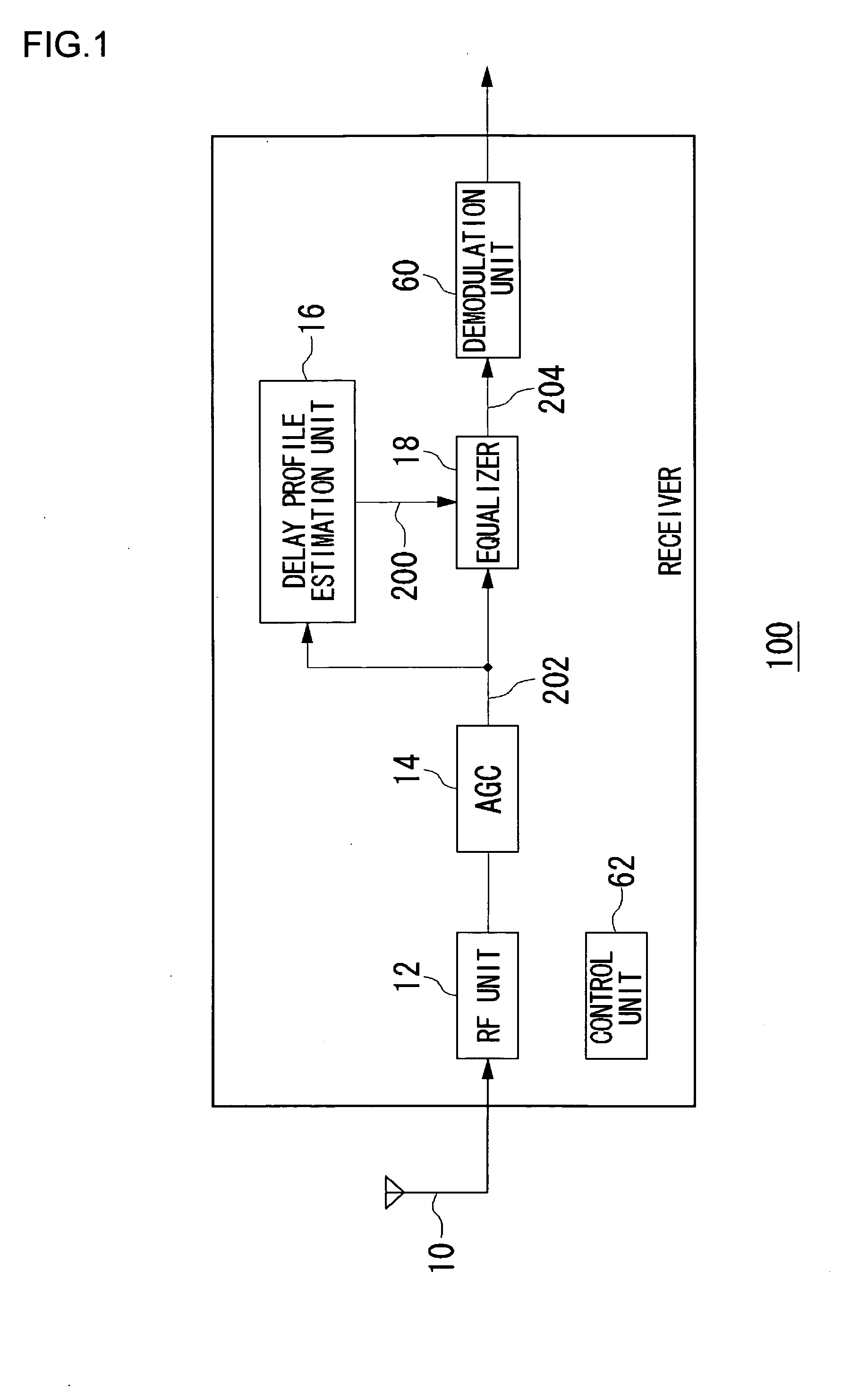
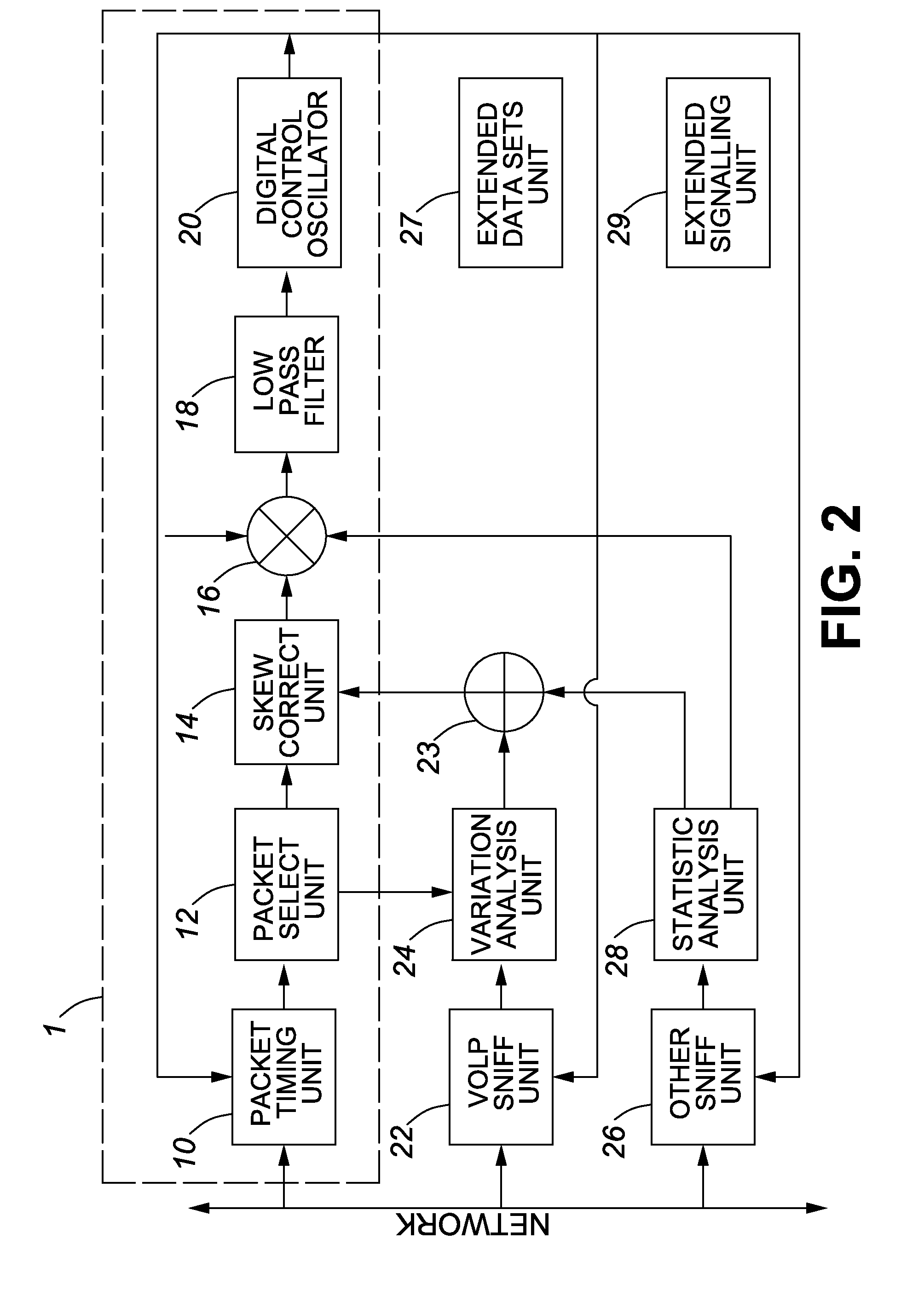
The Distribution Latency (Seconds) alert tracks the amount of time, in seconds, that a replication transaction is at the Publisher waiting for a Distributor to receive it, and has exceeded the warning threshold. The most common cause of high distribution latency is when a transaction has a large amount of commands.
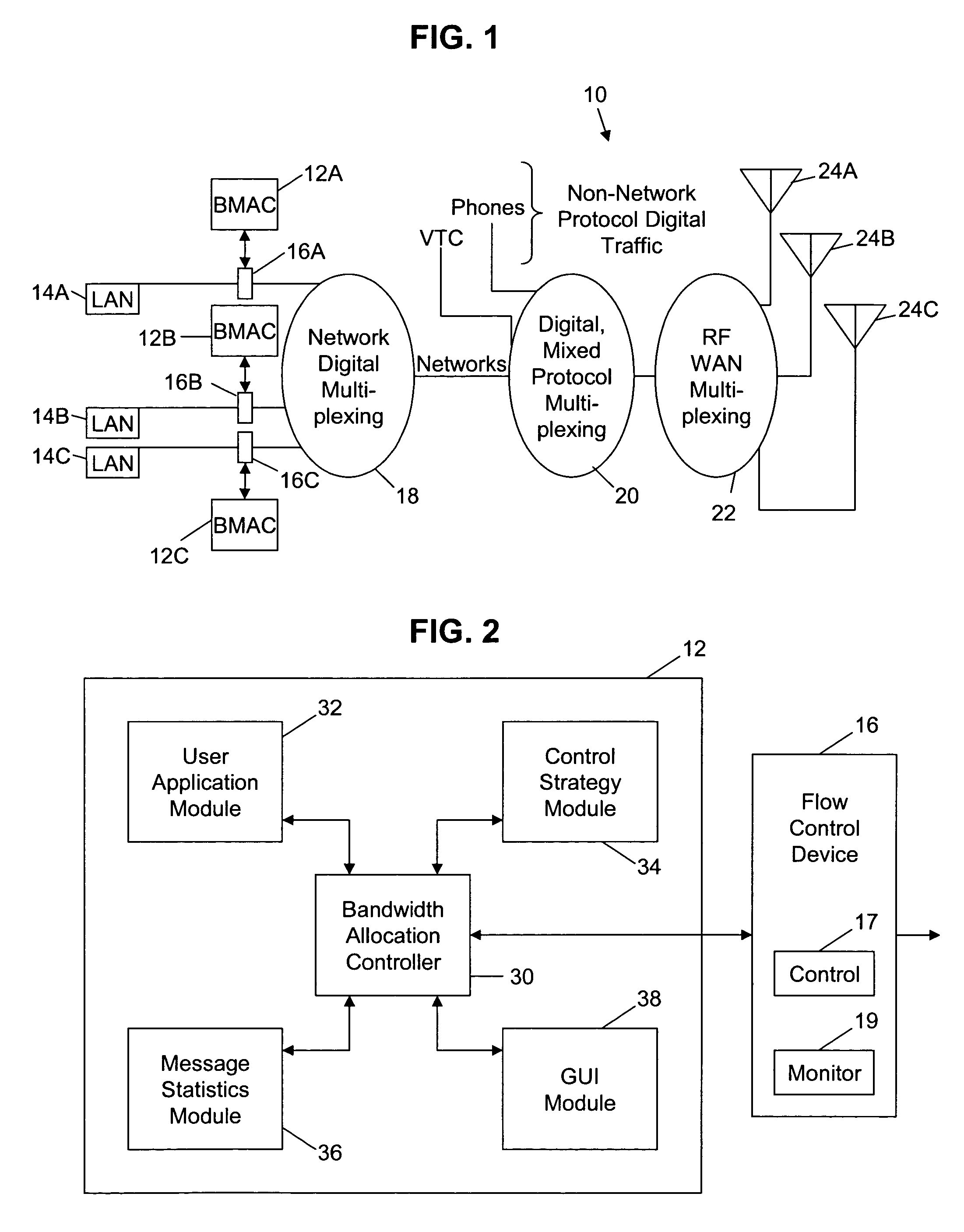
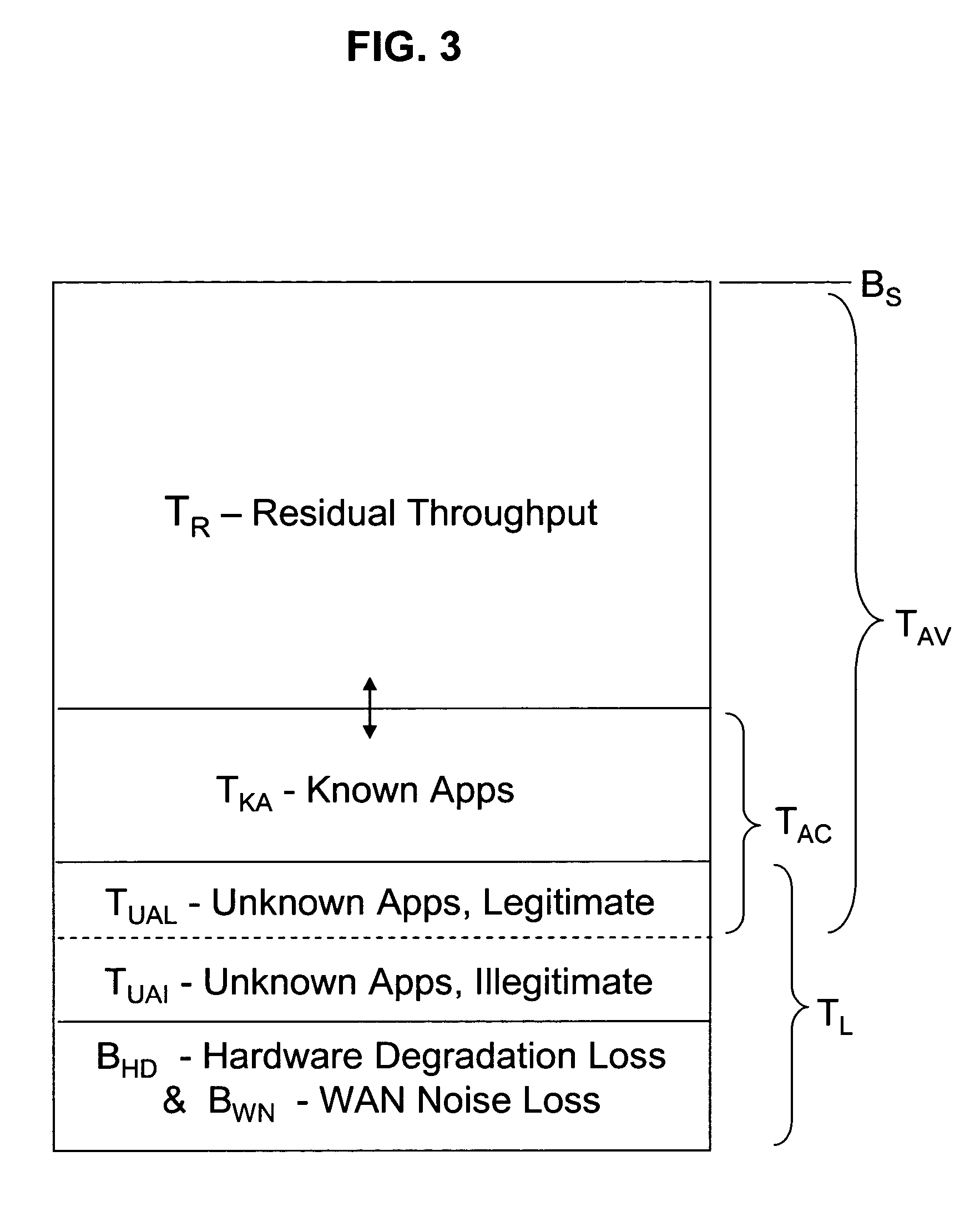
Method and apparatus for controlling the allocation of bandwidth of a network access point to an application having a message transmitted on the network
InactiveUS7493407B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksGraphicsGraphical user interface
An automated bandwidth monitoring and control method and system provides for real time, dynamic control of the allocation of bandwidth to selected applications in a communications network based on the selected operational context and the fixed bandwidth available at a network access point. A graphical user interface, using operational terms common to the overall enterprise in which and for which the network is implemented and understandable by an operator, displays the bandwidth allocation strategy, and in substantially real time displays statistics representative of actual bandwidth use at the access point, input functions for modifying the bandwidth allocation strategy in substantially real time and estimated message delay distributions for the applications of the strategy determined based on the actual bandwidth use statistics.
Owner:DRS TECHN SERVICES
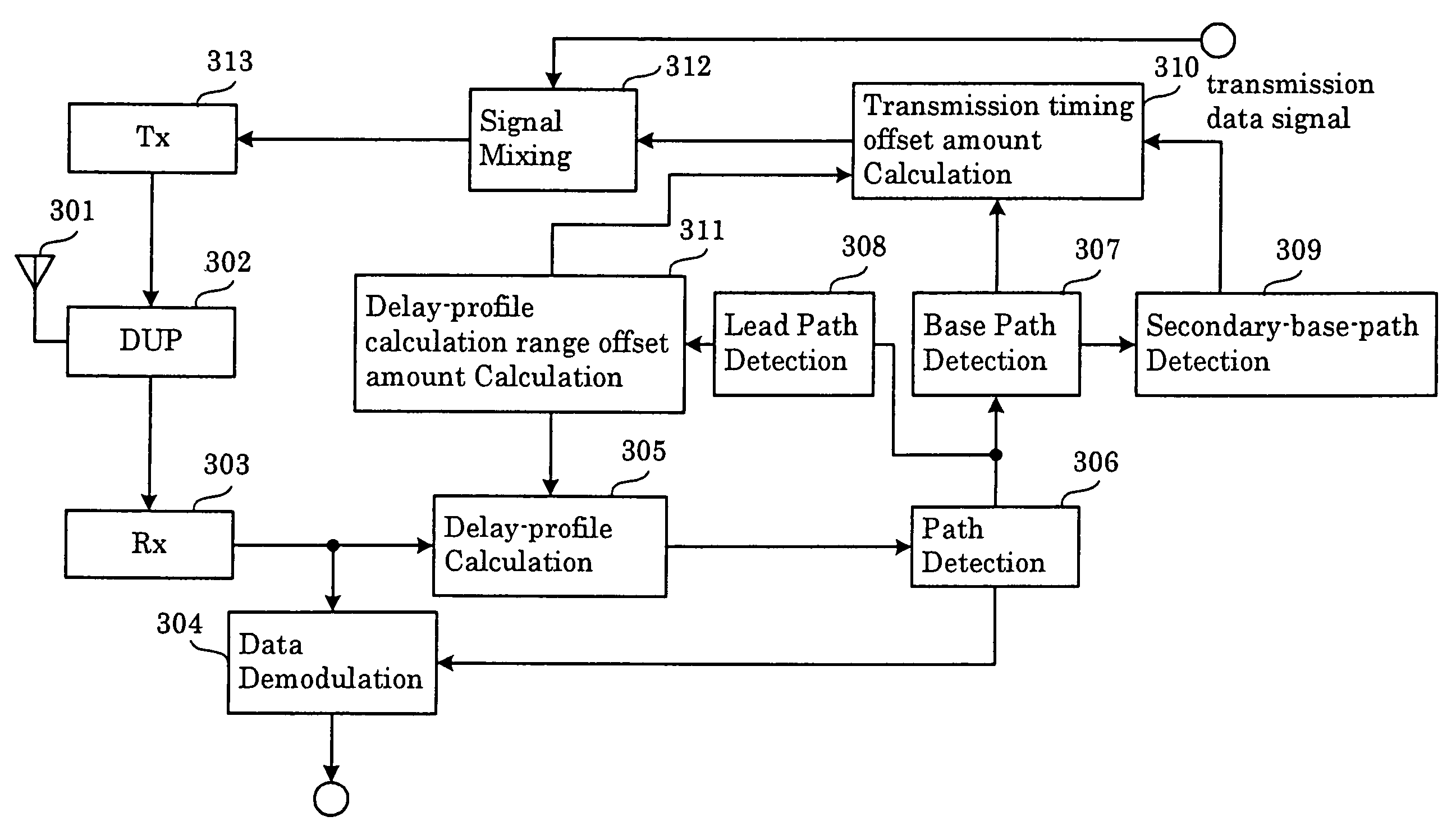
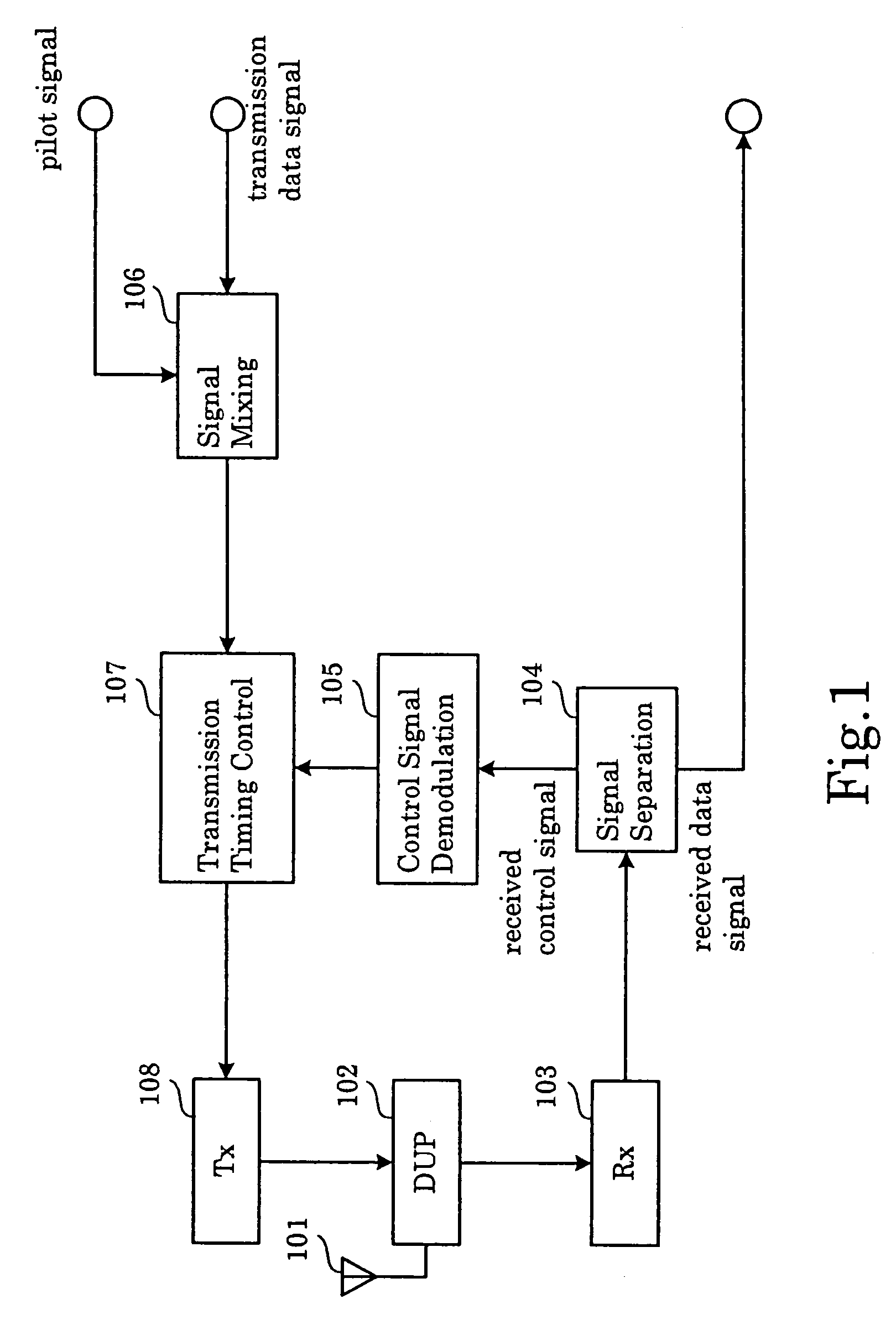
Adaptive transmission timing control method, wireless communication system and wireless communication device
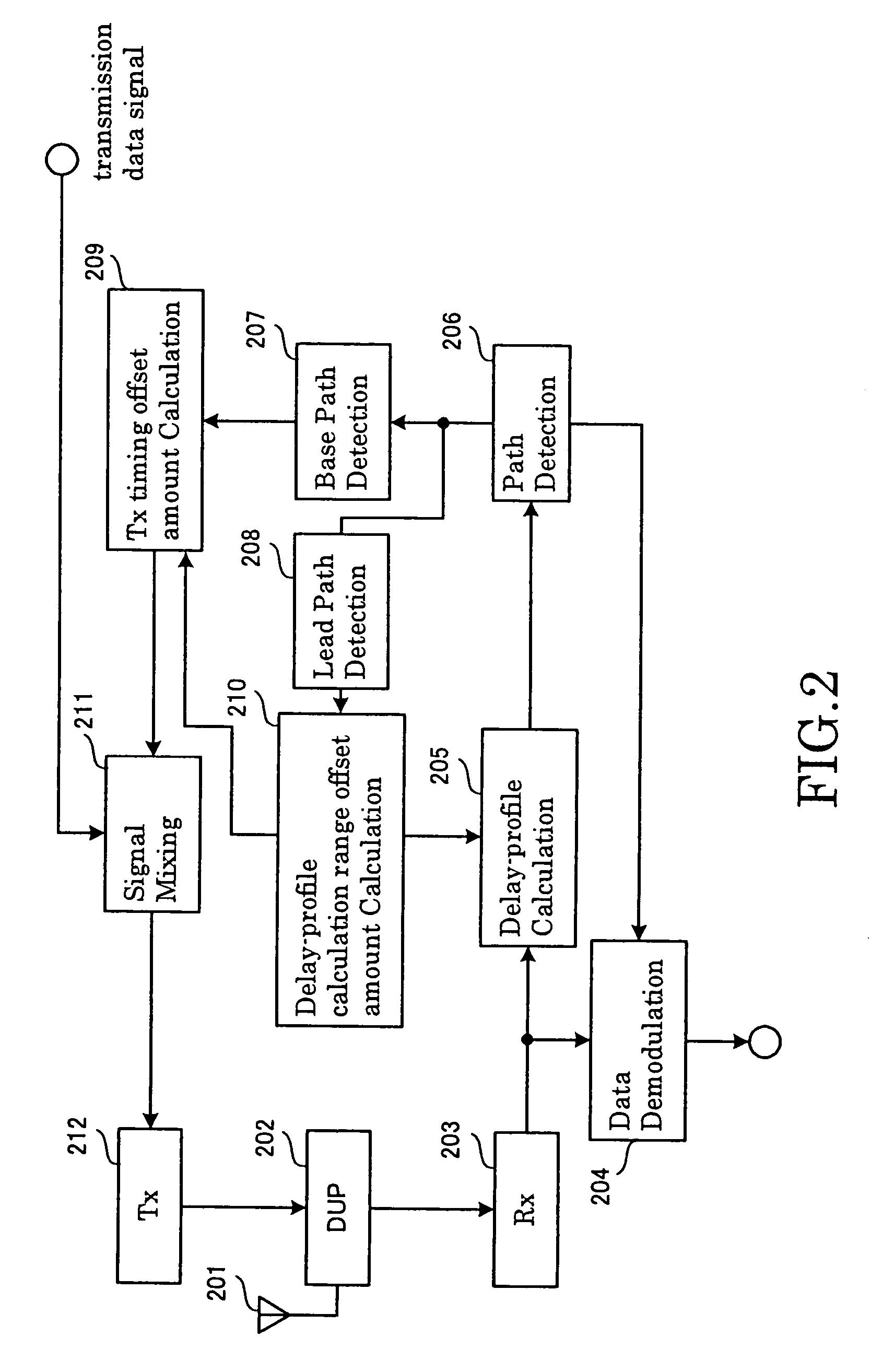
InactiveUS7577167B2Preventing overlookingSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTime rangeCommunications system
In a method for adaptive transmission timing control, the overlooking of a base path at the side of the base station that occurs when the transmission timing offset amount changes to the extent of falling outside the current delay-profile calculation range, and the side of the mobile station fails to demodulate the control information that contains the transmission timing offset amount, is prevented. A limit is put on the transmission timing offset amount applied in a single transmission timing control iteration. Together with setting the transmission timing offset value such that the main component of the delay profile calculated from the pilot signal transmitted with offset transmission timing falls within the time range of when the current delay profile was calculated, the time range for calculating the next delay profile is shifted such that a delay profile calculated from the pilot signal transmitted with offset transmission timing falls within the shifted range, starting at the earliest component.
Owner:NEC CORP
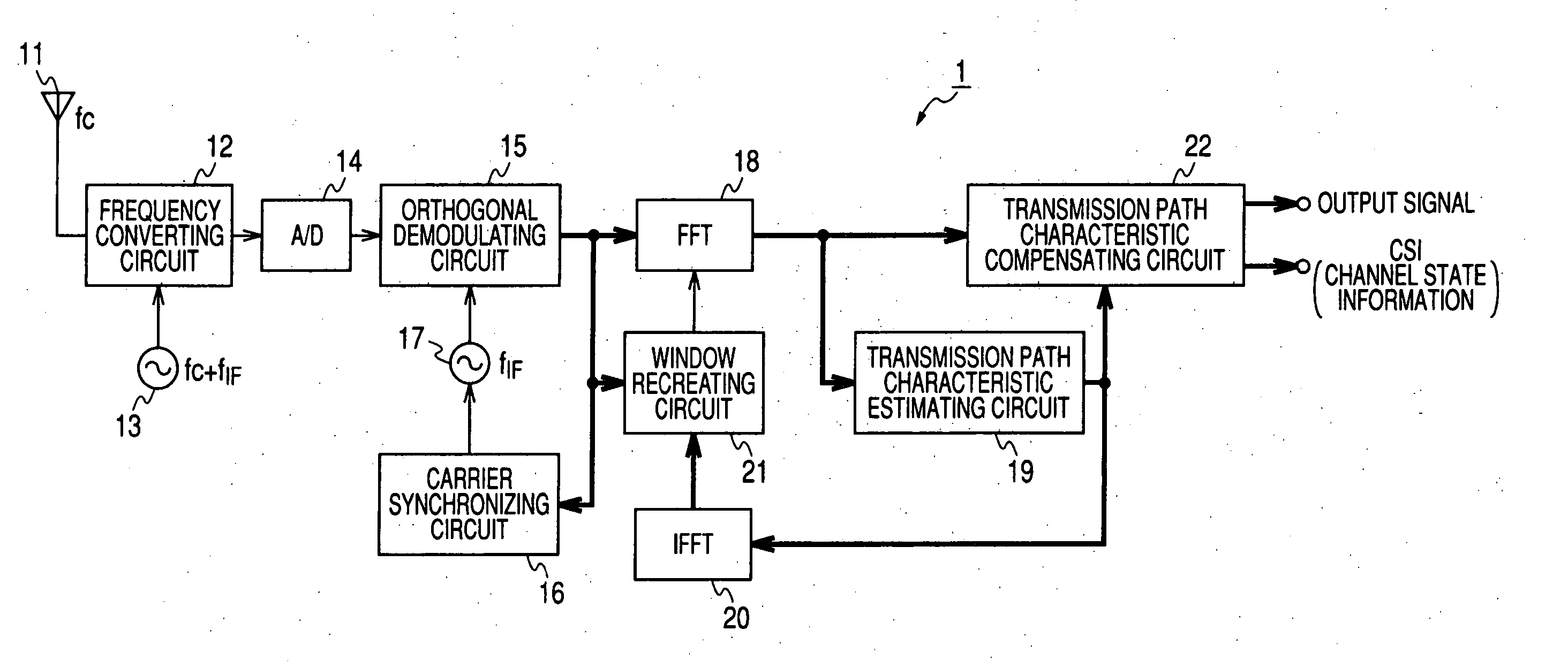
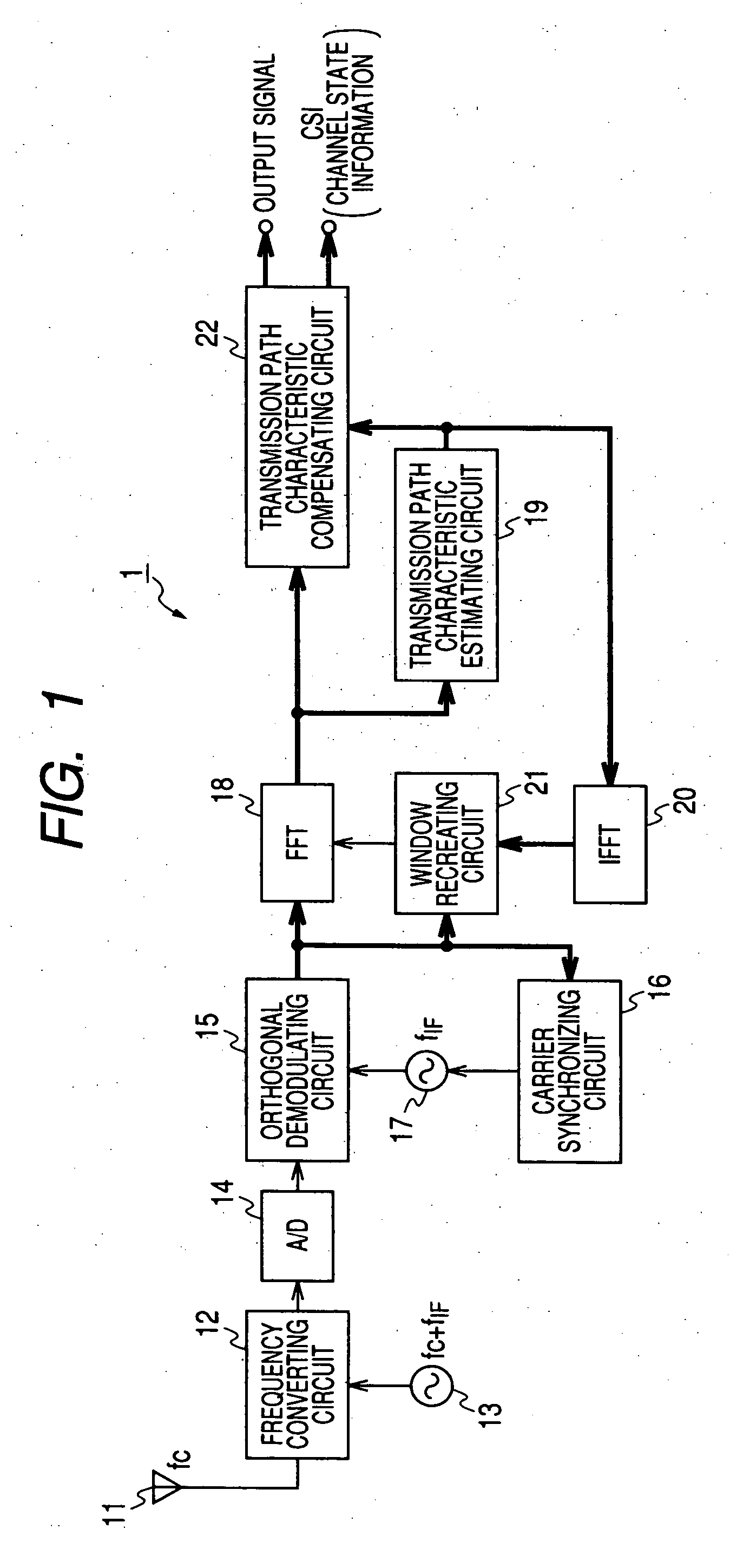
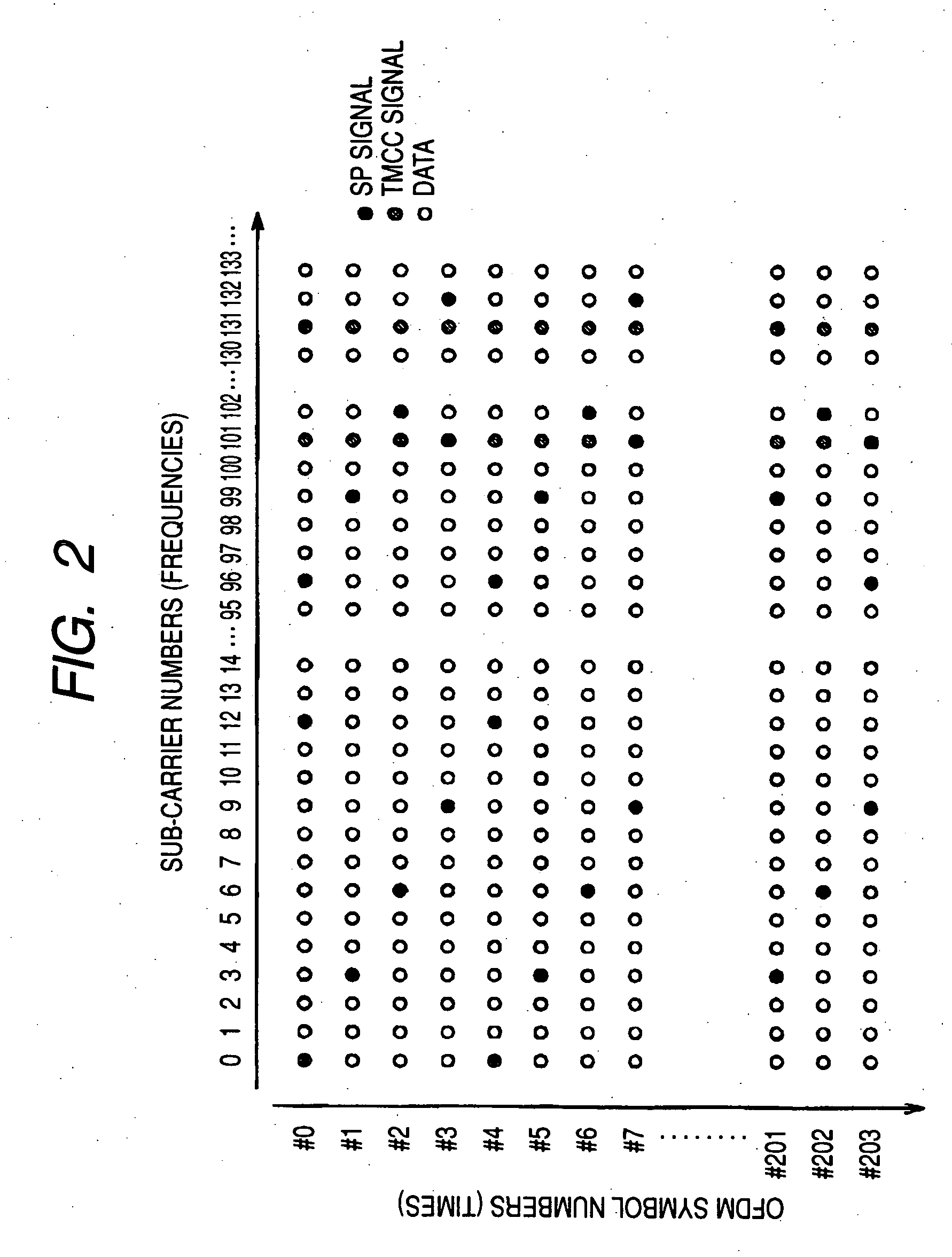
OFDM demodulating apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070070882A1Secret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFourier transform on finite groupsEngineering
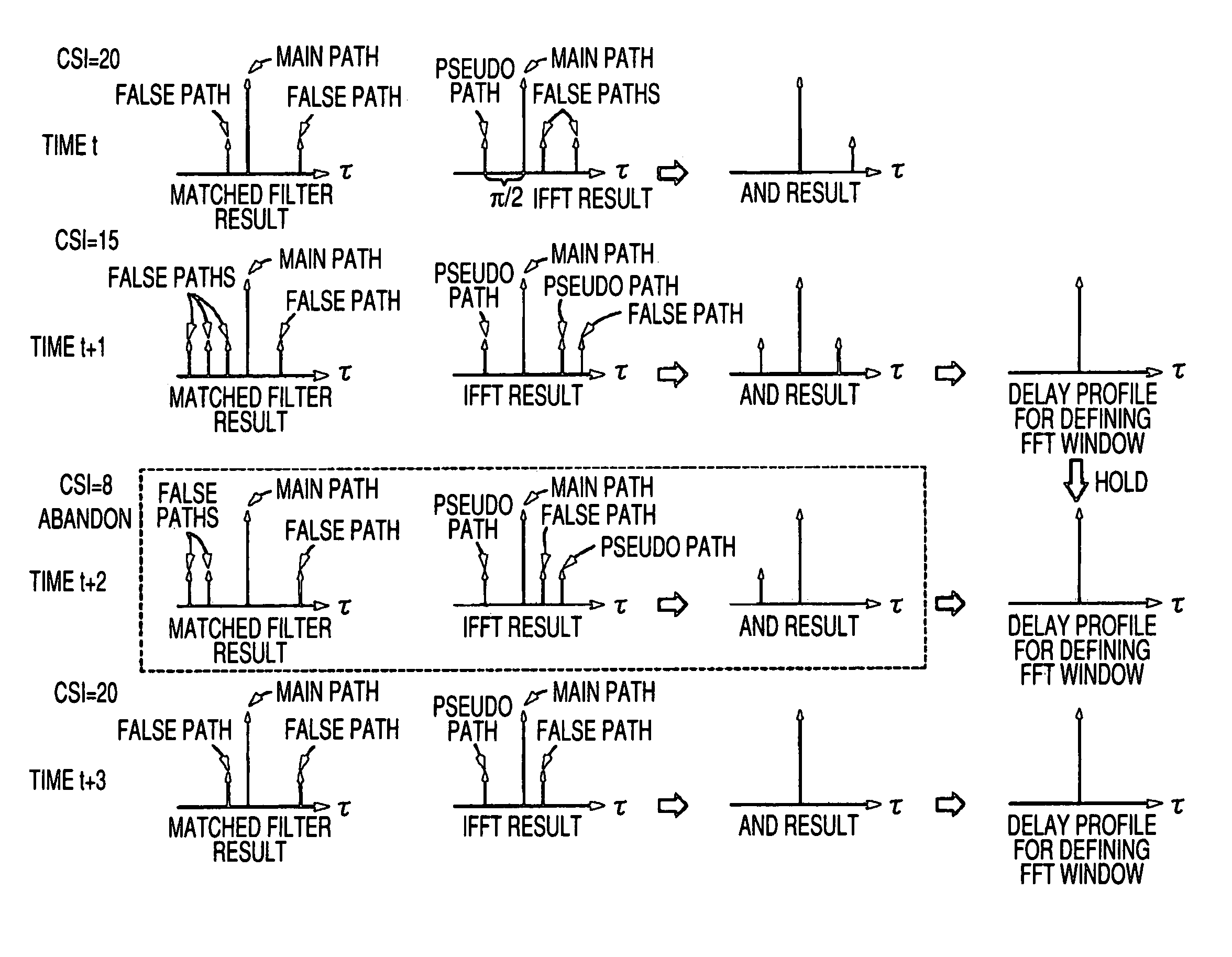
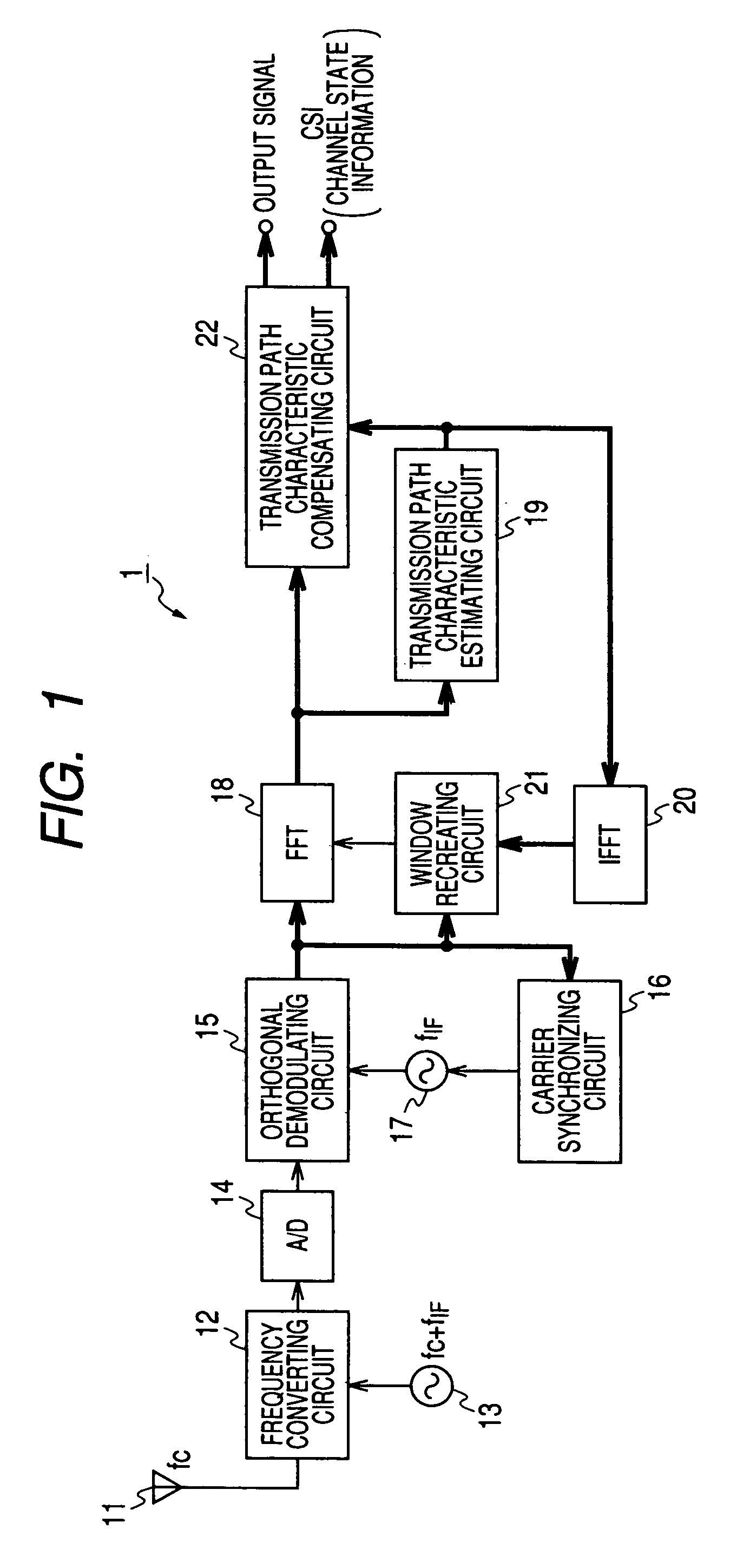
An orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) demodulating apparatus includes a delay profile creating section, a Fourier converting section, a pilot signal extracting section, a transmission path characteristic estimating section, an inverse Fourier converting section, and a window control section. In this case, the window control section creates a delay profile for defining a calculation range by leaving a path which exists at a same position in both the delay profiles created by the delay profile creating section and the inverse Fourier converting section and the number of times of detection which is equal to or higher than a threshold value and defines a higher threshold value for the path at a predetermined position from the position of the main path within the delay profile created by the inverse Fourier converting section than for the paths at the other positions.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for scheduling cell search in CDMA mobile receivers
ActiveUS7089004B2Efficiently monitoring (searching)Save battery powerEnergy efficient ICTPower managementSignal qualityCell search
Search scheduling circuitry for use with a wireless communication device, such as a mobile telephone, includes a search time calculator, a search period calculator, a queue circuit, and a search time circuit. The search scheduler generates a prioritized list of cells to be adaptively searched in response to the network requirements and the capability of the search hardware. If there are very few “handoff” possibilities the search hardware may be turned off and then back on in time to meet the search rate requirements. However, if there is an excessive number of possibilities, the searcher list is prioritized and pared to assure the most likely candidates are searched. This search scheduling minimizes battery power consumption while meeting the search rate requirement and maximizes use of the search hardware for measuring signal quality from multiple neighboring cells and estimating the delay profile of active cells.
Owner:BREAKWATERS INNOVATIONS +1
Determination and selection of transmission paths as a function of the operating situation for setting up rake fingers for rake receiver units in mobile communication terminals
ActiveUS20050111526A1MoreMore objective accuracySpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsNoise levelEngineering
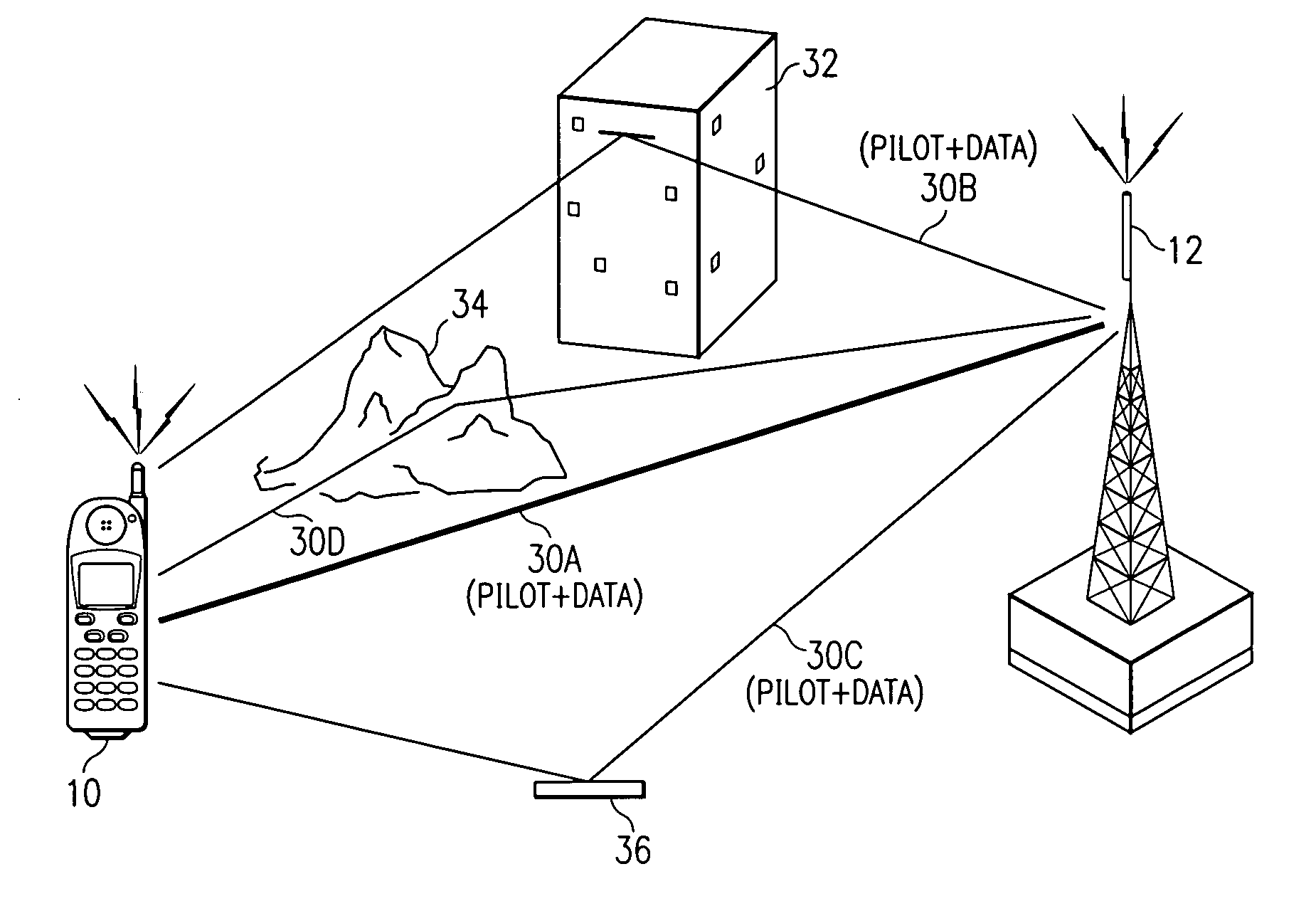
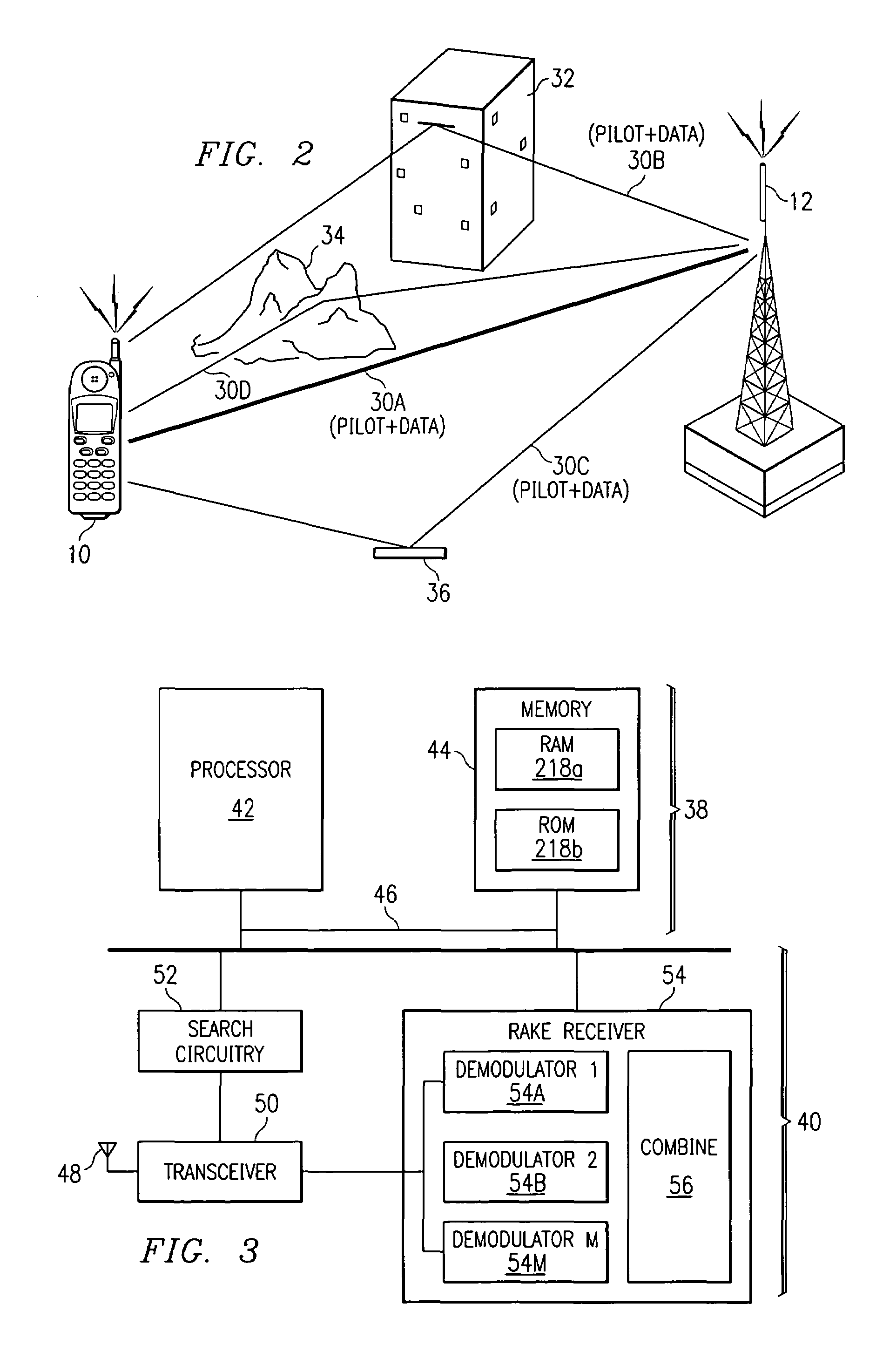
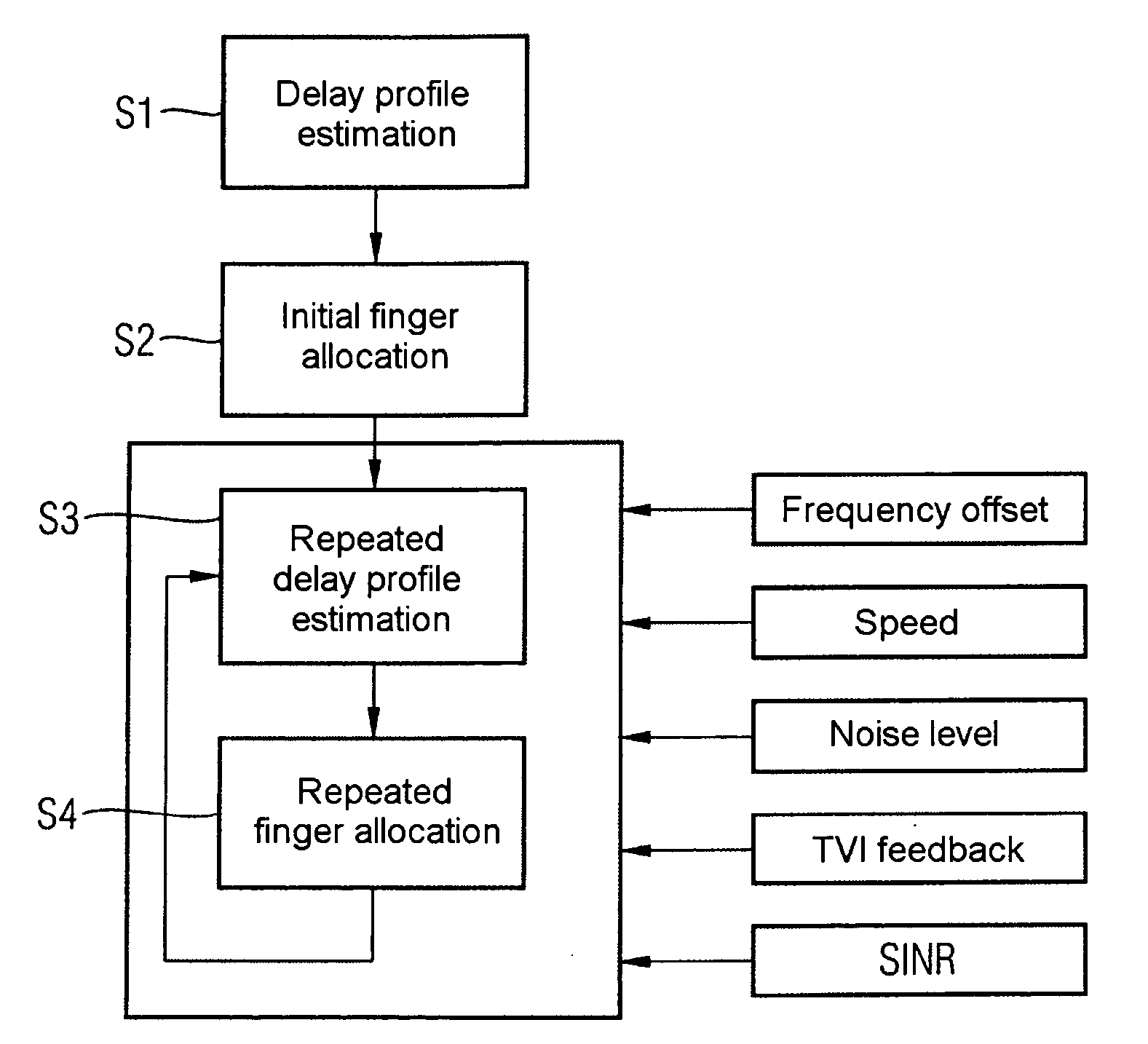
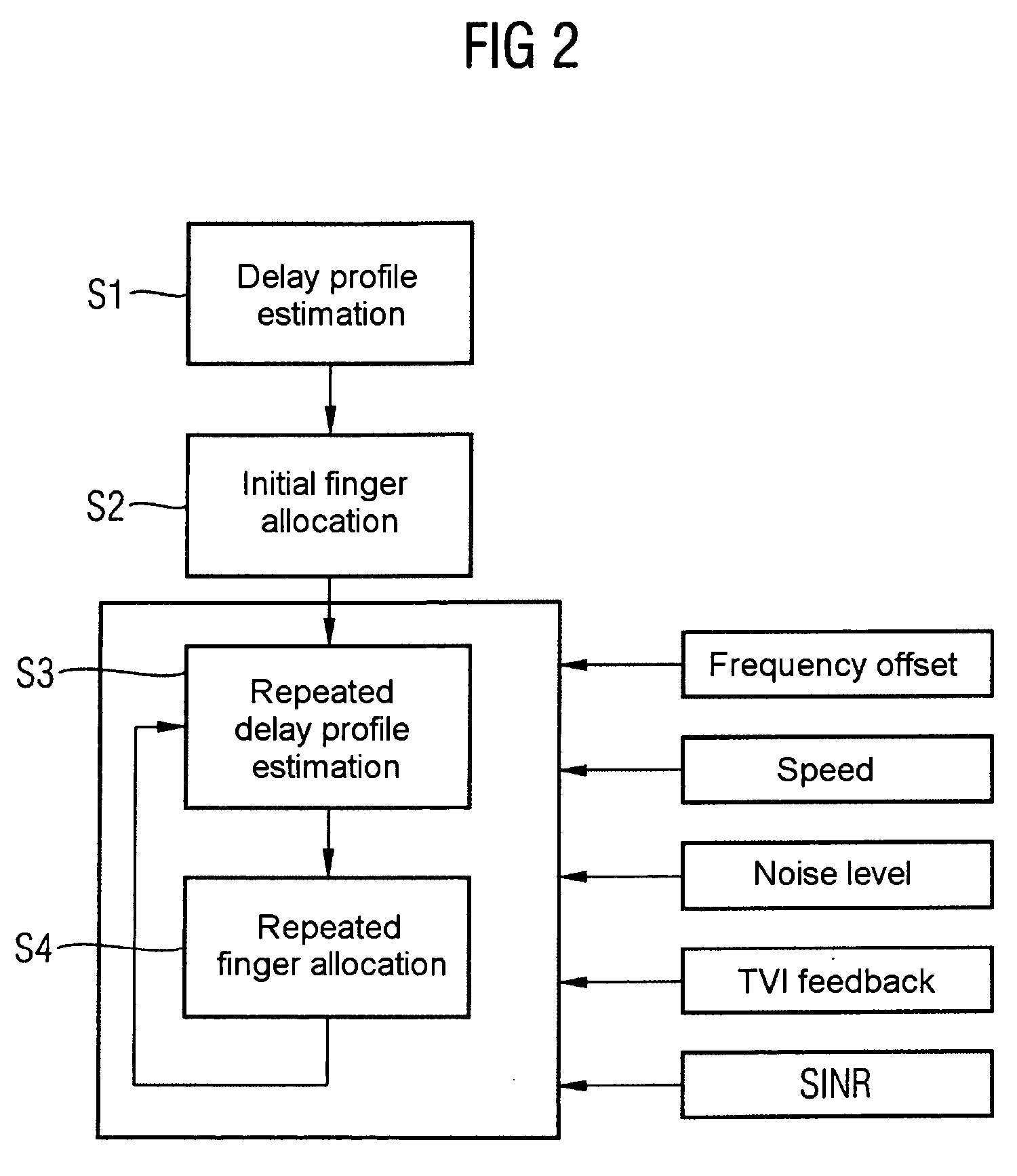
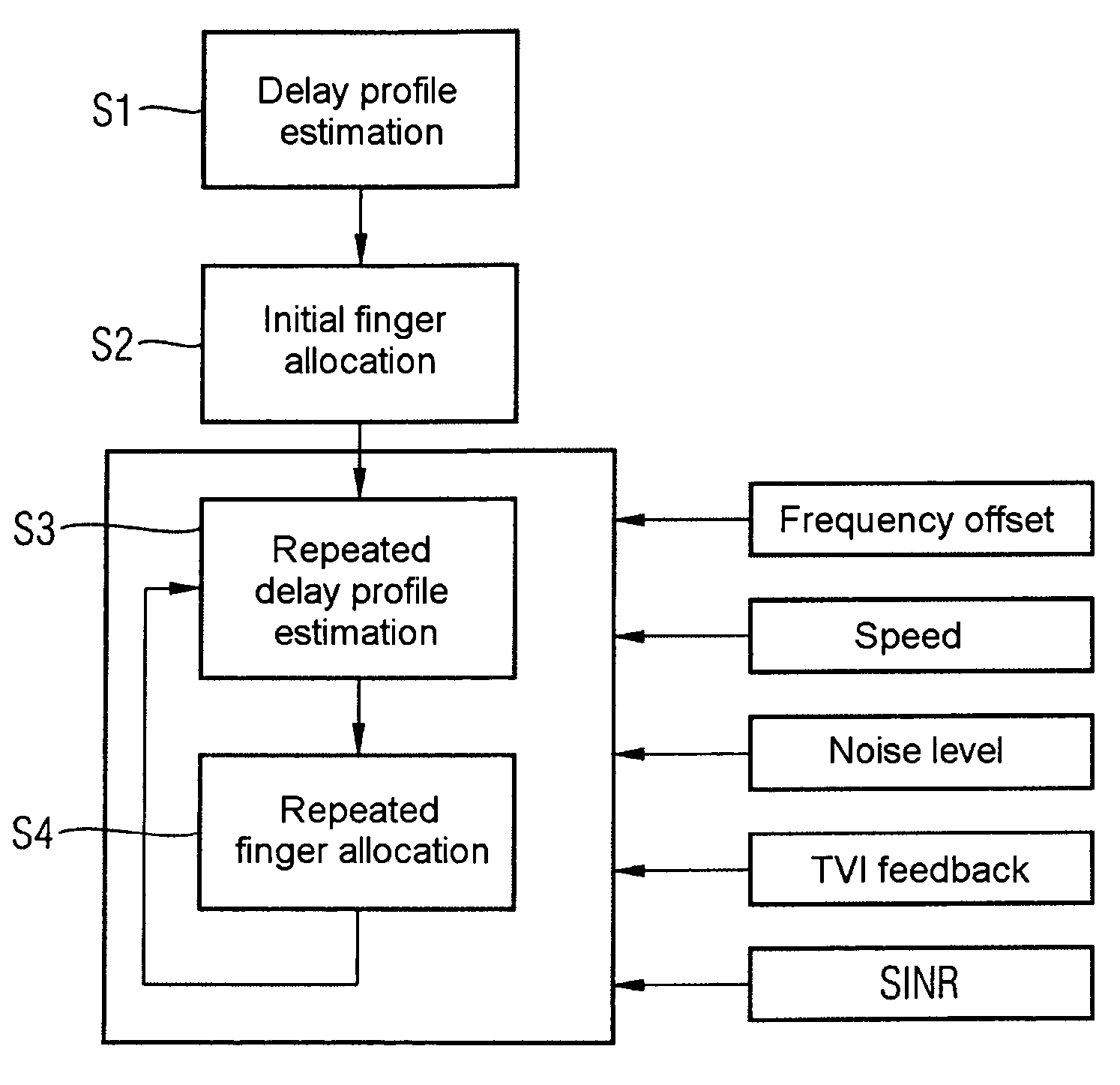
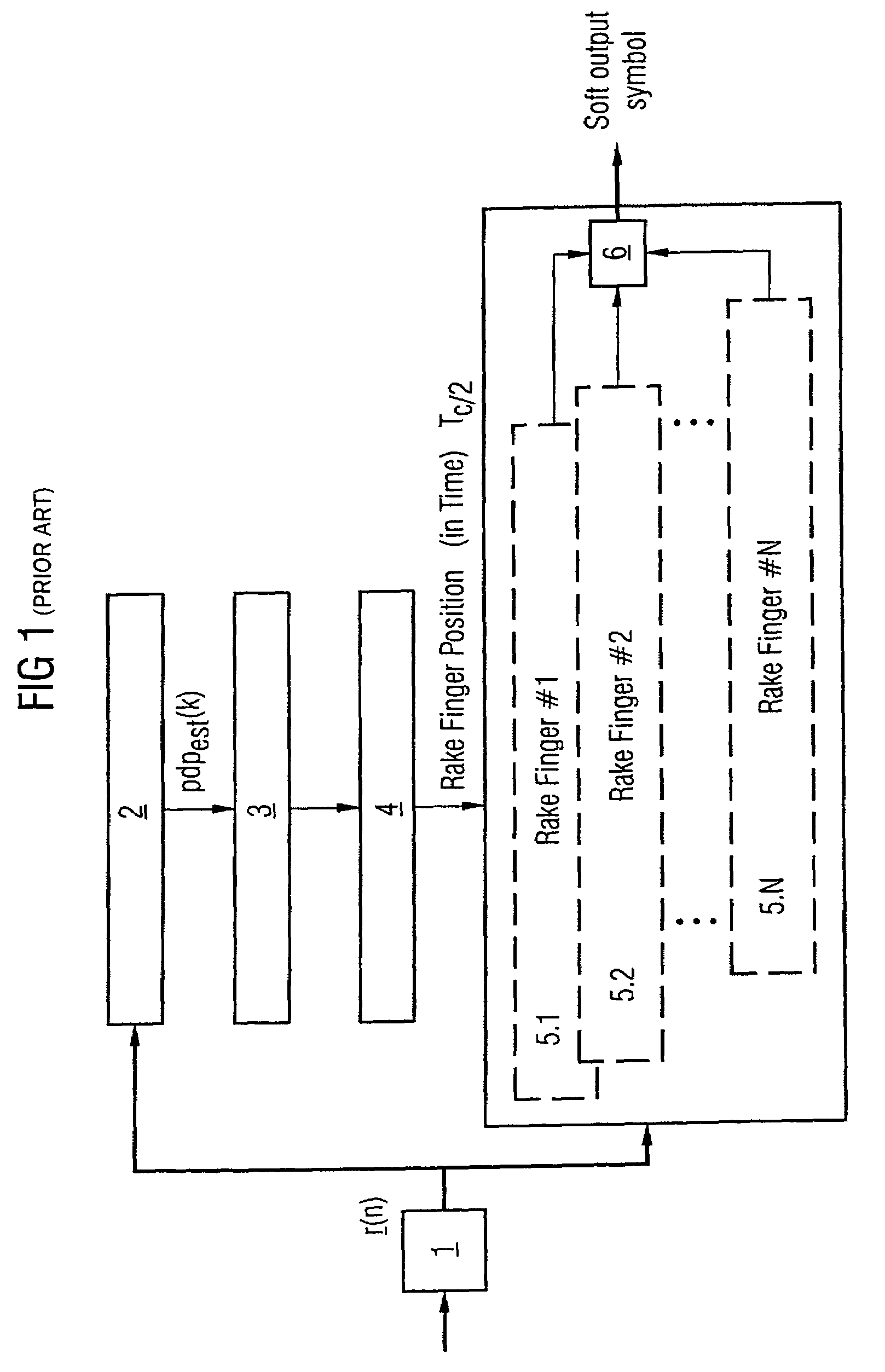
Correlations between the received signal to which pilot symbols have been applied at the transmitter end, and a correlation signal which contains the pilot symbols are carried out in the receiver in order to determine a path delay profile. Averaging processes are carried out over two or more delay profiles obtained in this way. Evaluations are carried out in one or more threshold value selection units (22.1, 22.2) on two or more averaged delay profiles with the aim of path selection. The parameters which govern the correlations and / or the averaging processes and / or the evaluations, and / or the repetition interval of these calculations are set as a function of the relative speed between the transmitter and the receiver, the frequency error between the carrier frequency of the received signal and the reference frequency that is set at the receiving end, and the noise level of the received signal. In the case of reception from two or more base stations, a final path selection is made in a finger allocation unit (40).
Owner:APPLE INC
Mobile terminal, a base station, and a synchronization control method
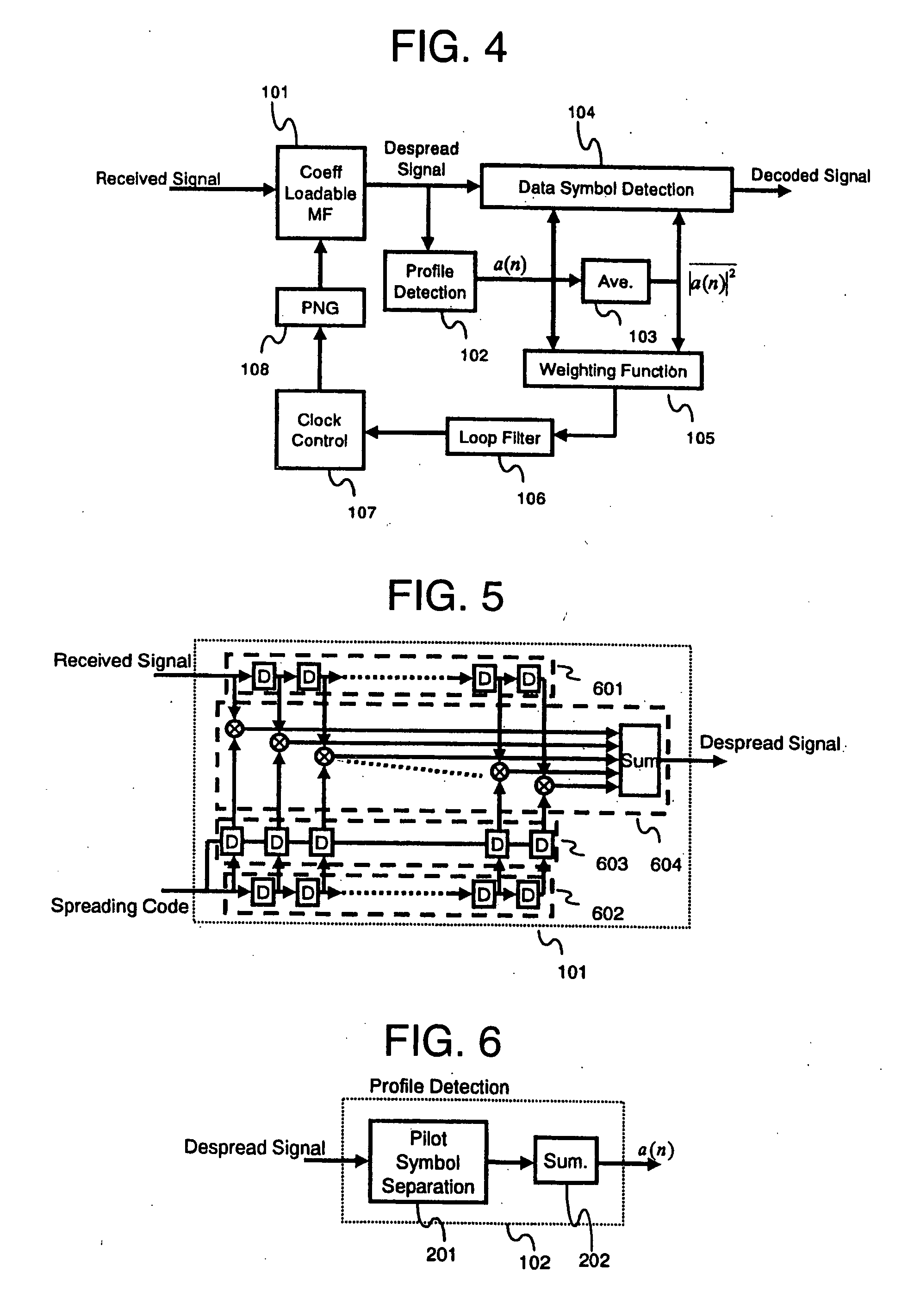
In a mobile communication system, the tracking of synchronization is conducted in a stable state even in a multipath environment. A delay profile detector calculates a delay profile a(n) using a despread signal for each processing unit n. A delay profile averaging unit averages a(n) to produce Ave(|a(n)|<2>). A data symbol detector conducts rake combining of the despread signal using a(n) and Ave(|a(n)|<2>). According to a(n) and Ave(|a(n)|<2>, a weighting function unit calculates a representative value representing delay waves. A loop filter generates a control signal in response to the representative value. A clock controller controls a spread code generator according to the control signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Receiver which demodulates OFDM symbol
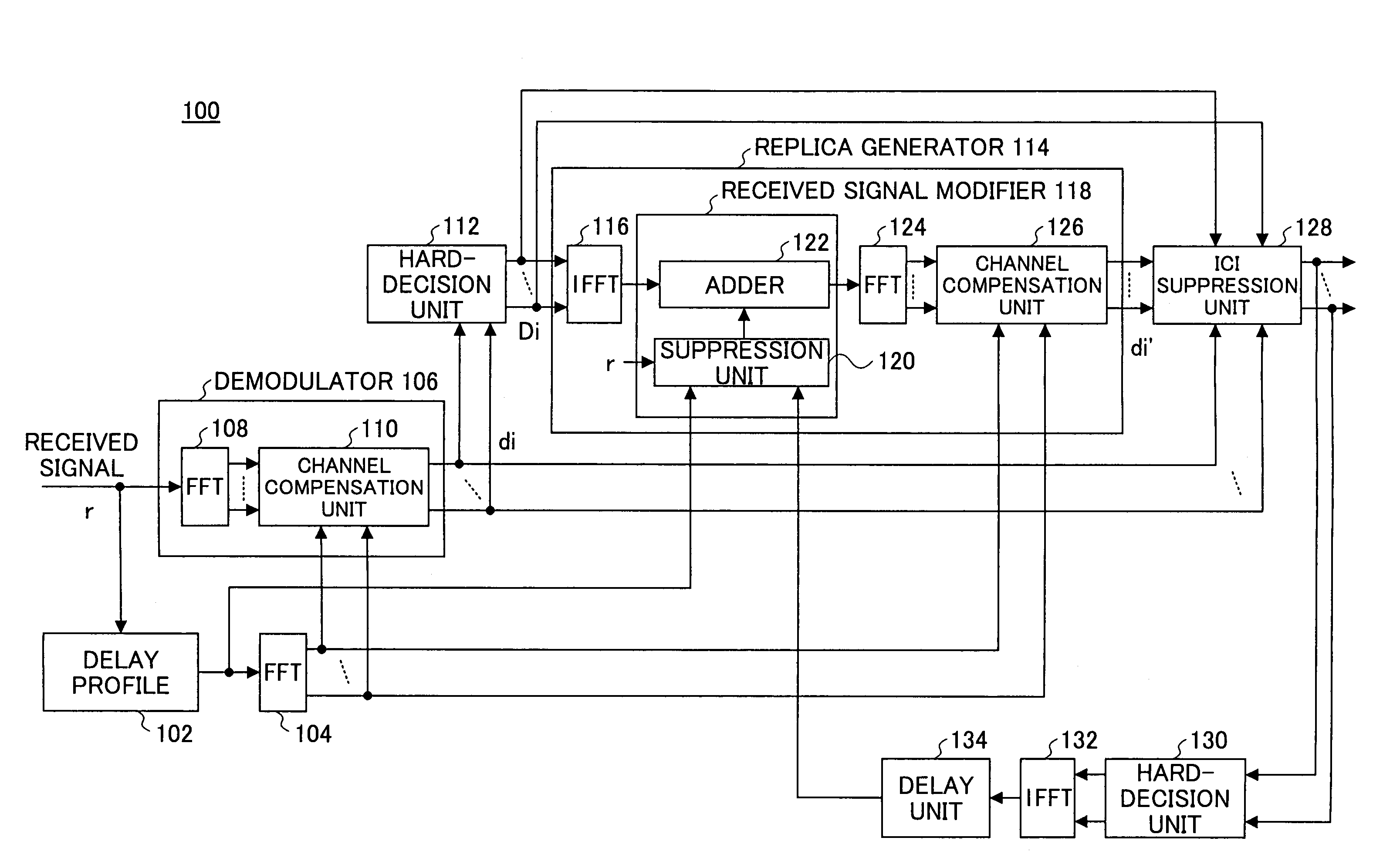
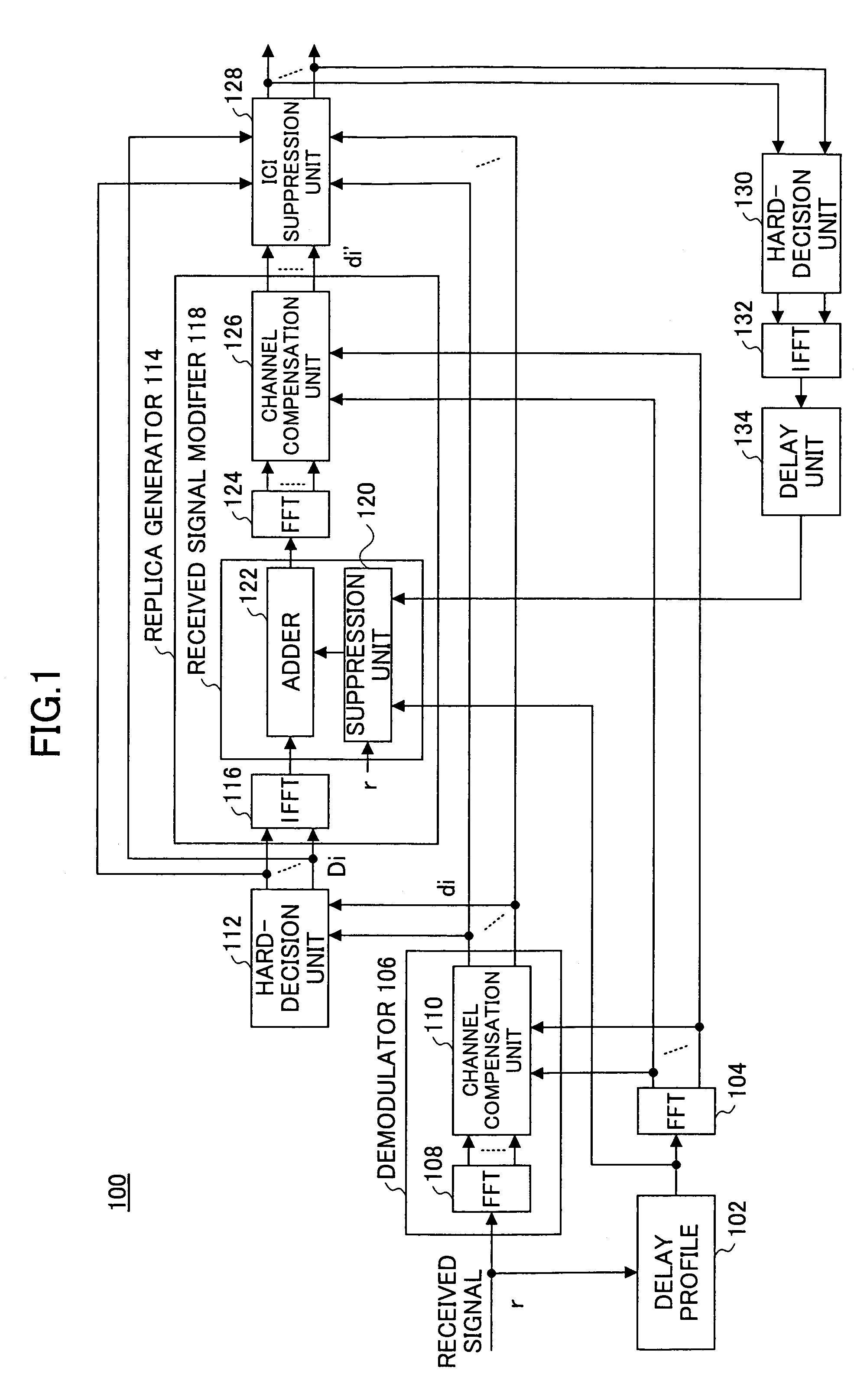
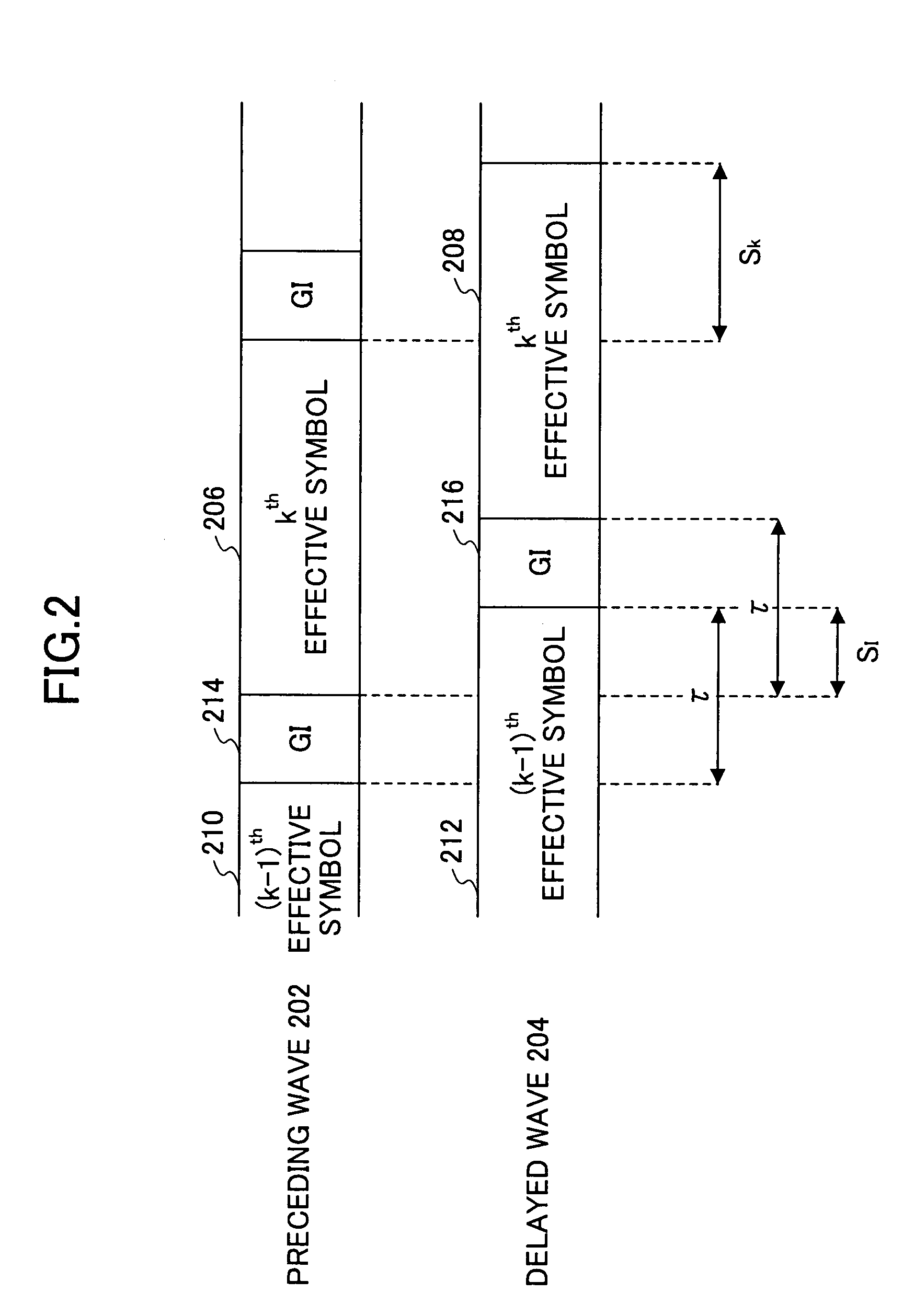
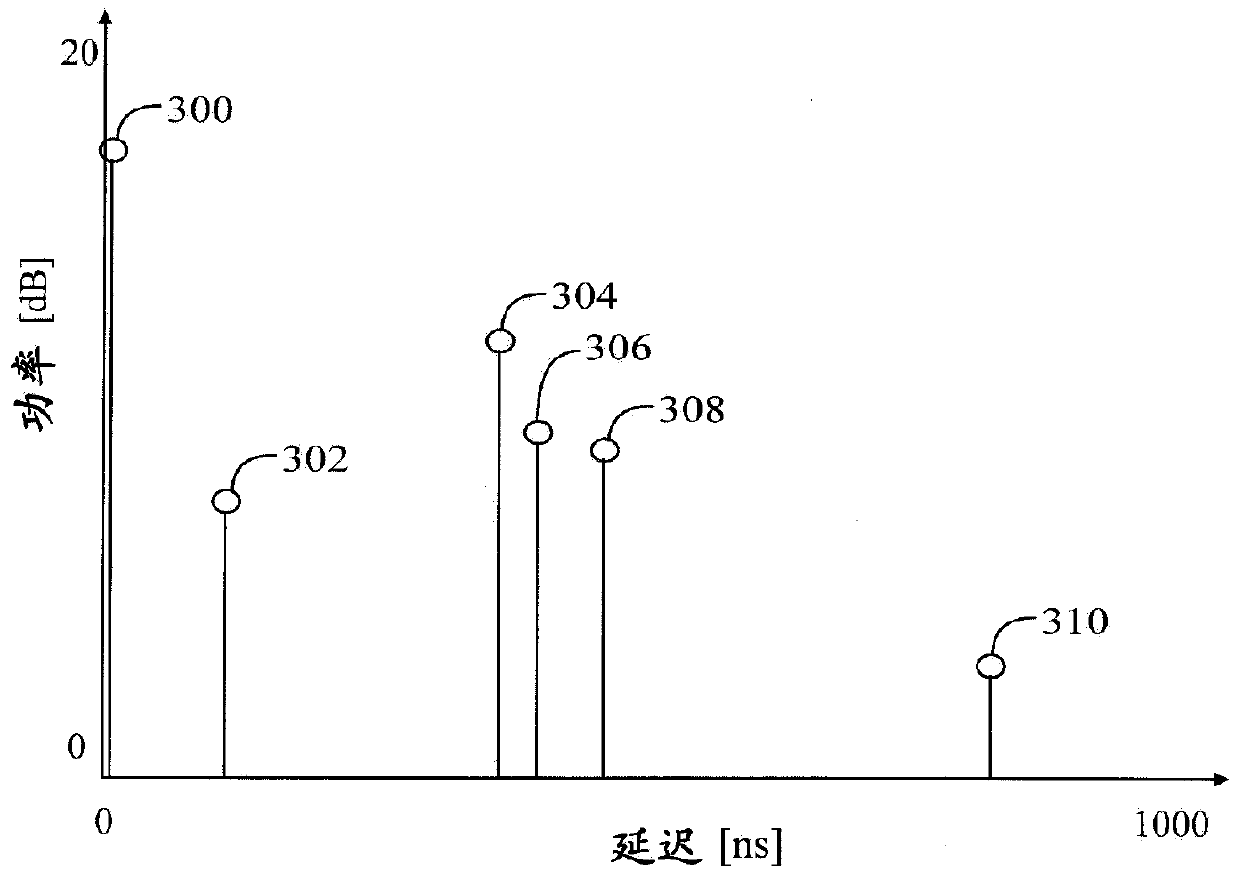
InactiveUS7313189B2Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCarrier signalLatency distribution
A receiver is disclosed that demodulates an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbol transmitted by an OFDM method. The receiver includes a delay profile generation unit that generates a delay profile regarding a preceding wave and a delayed wave included in a received signal, a demodulation unit that demodulates the received signal so as to output a demodulated signal per sub-carrier, a hard-decision unit that makes a hard decision per sub-carrier on a signal point based on the demodulated signal so as to output a hard-decision signal, a replica generation unit that uses the hard-decision signal to generate a replica signal per sub-carrier, and an inter-carrier interference suppression unit that adds a difference between the hard-decision signal and the replica signal to the demodulated signal so as to suppress an inter-carrier interference.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Equalization method and apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20050111539A1Undertaken easily and accuratelyMultiple-port networksAdaptive networkPropagation delayLinear filter
A linear filter unit is provided with a plurality of taps and subjects an equalizer input signal to an equalization process so as to output a filter output signal. A DFE unit is provided with a plurality of taps and subjects the filter output signal to an equalization process according to decision feedback so as to output an equalizer output signal. An LMS algorithm unit computes tap coefficients of the linear filter unit and the DFE unit. A determination unit compares a plurality of received power levels corresponding to a plurality of propagation delays in input delay profile data with a threshold level, selects received power levels equal to or higher than the threshold levels and determines a maximum time corresponding to one of the selected power levels.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
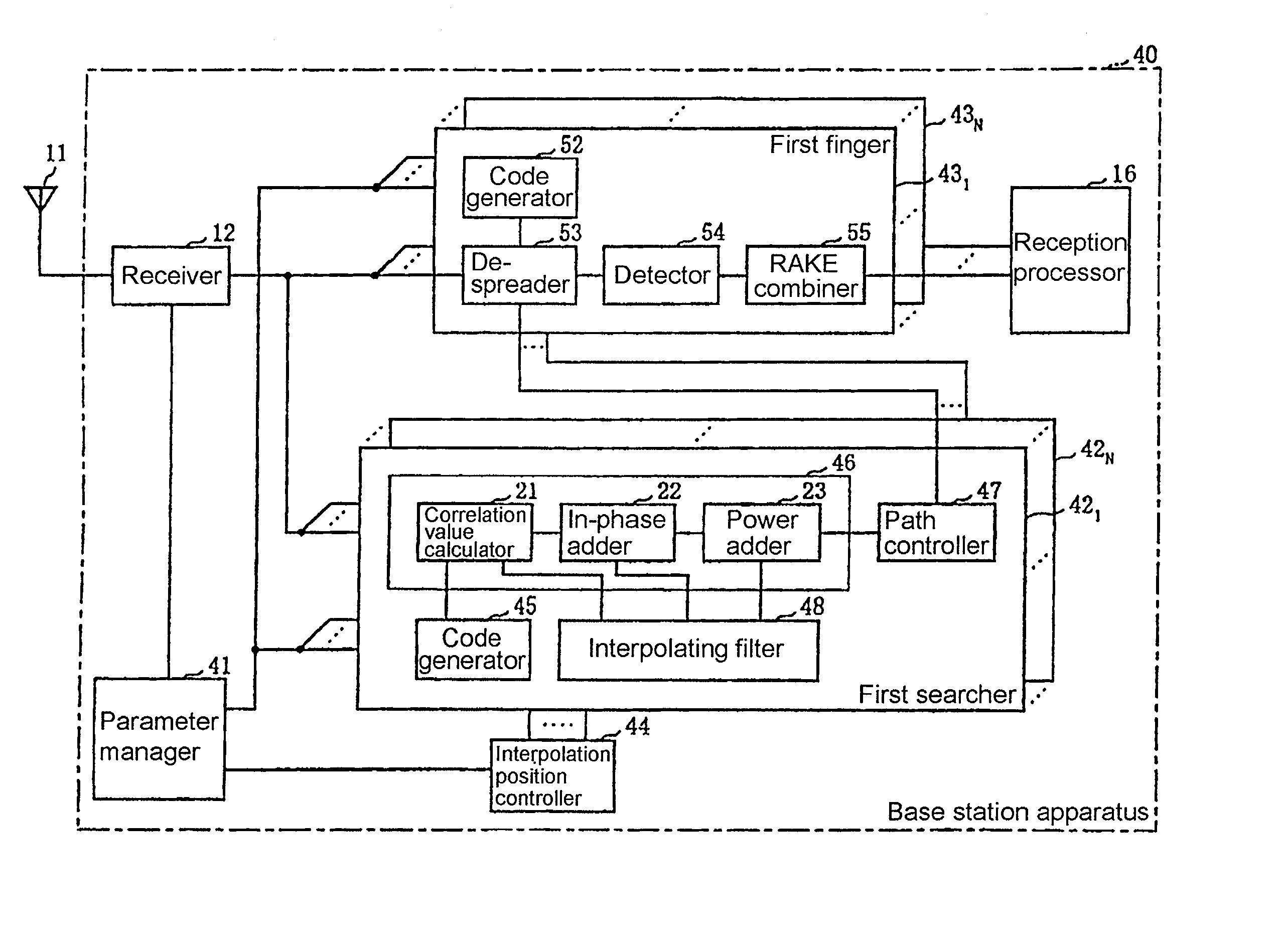
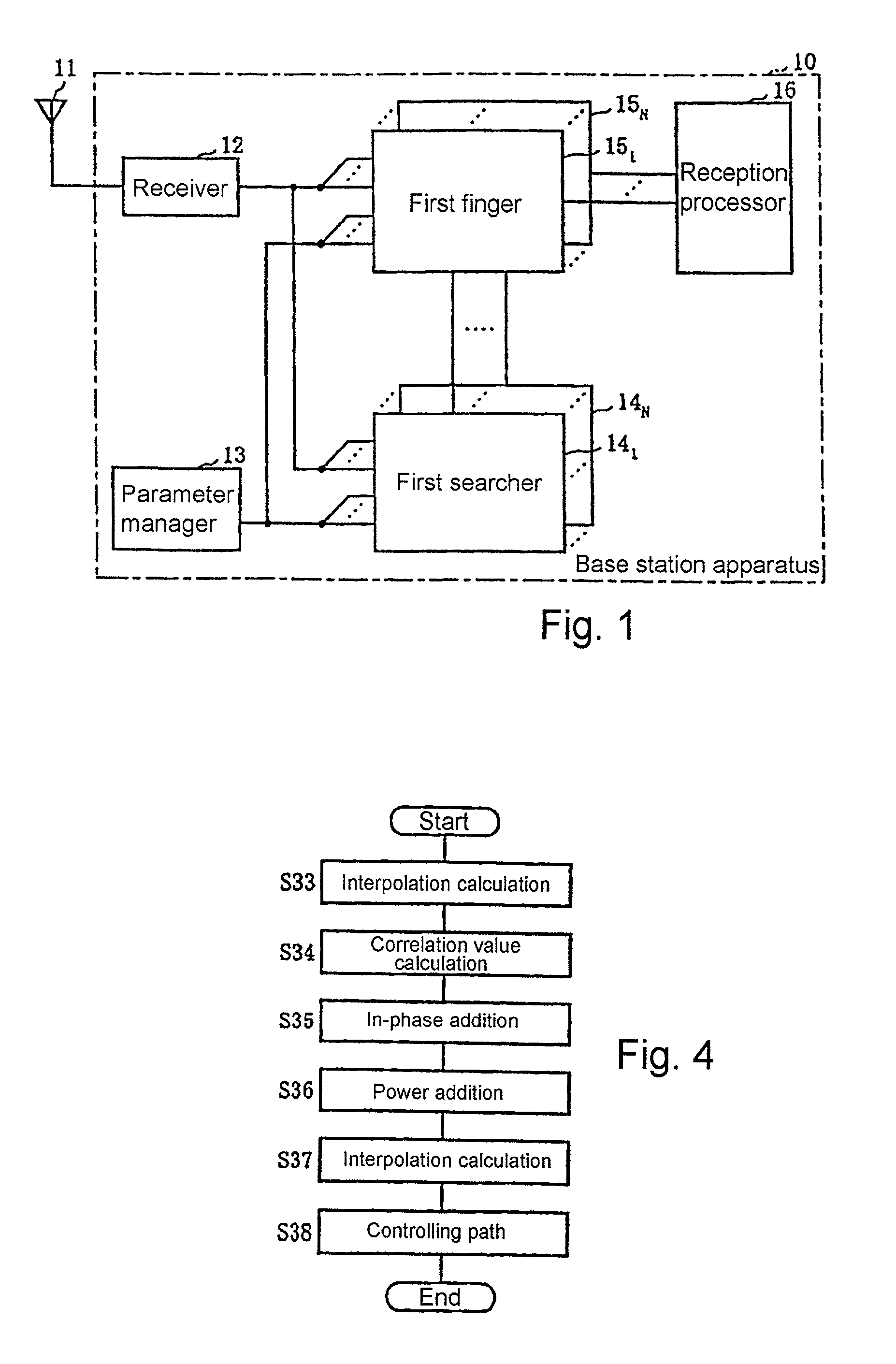
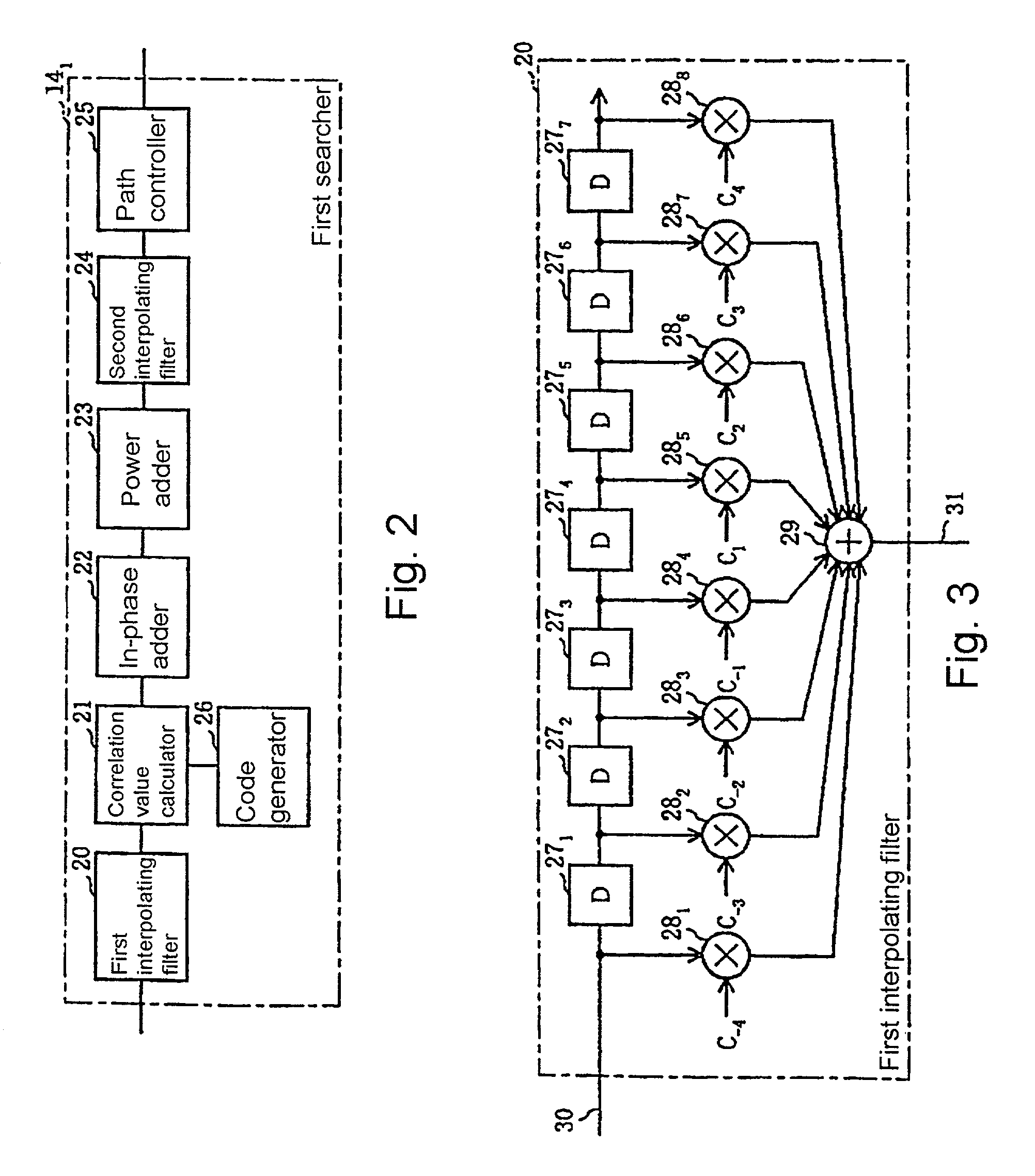
Path searching method and device
InactiveUS7042862B1Improve accuracyDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCode division multiplexCode division multiple accessLatency distribution
A path searching apparatus which is used in a base station apparatus according to the CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) systems for increasing the accuracy for path detection depending on the number of communication channels to be processed. The path searching apparatus has a path searcher for generating a delay profile through to a path searching process composed of a plurality of processing units, an interpolation information storage for storing interpolation information indicative of whether an interpolation process for reducing a chip interval is to be performed or not before and after each of the processing units, an interpolation position processing control for enabling the path searcher to perform an interpolation process before and after each of the processing units based on the interpolation information stored in the interpolation information storage according to the number of the communication channels to be processed, and a path detector for detecting a reception path based on the delay profile generated by the path searcher.
Owner:NEC CORP
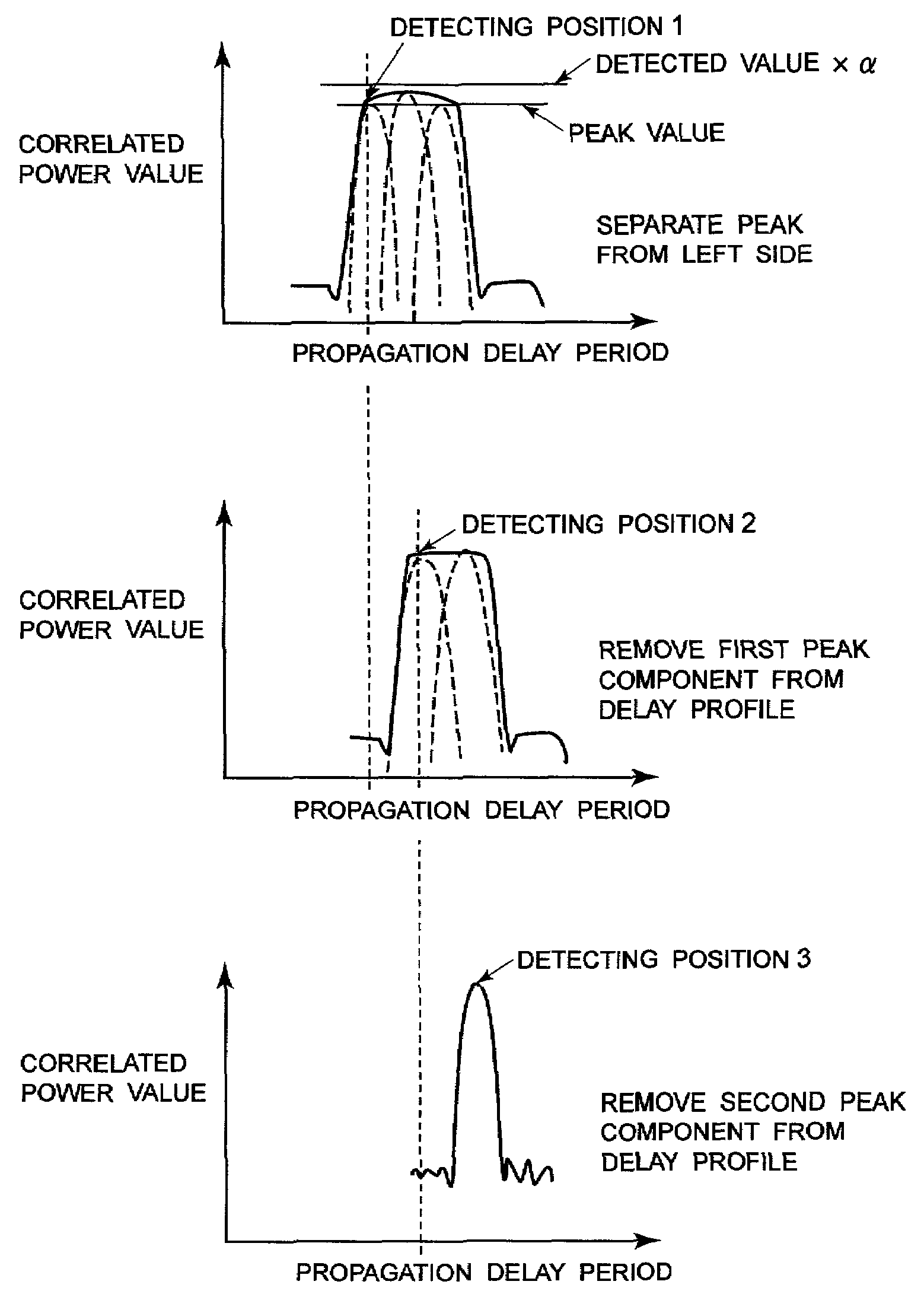
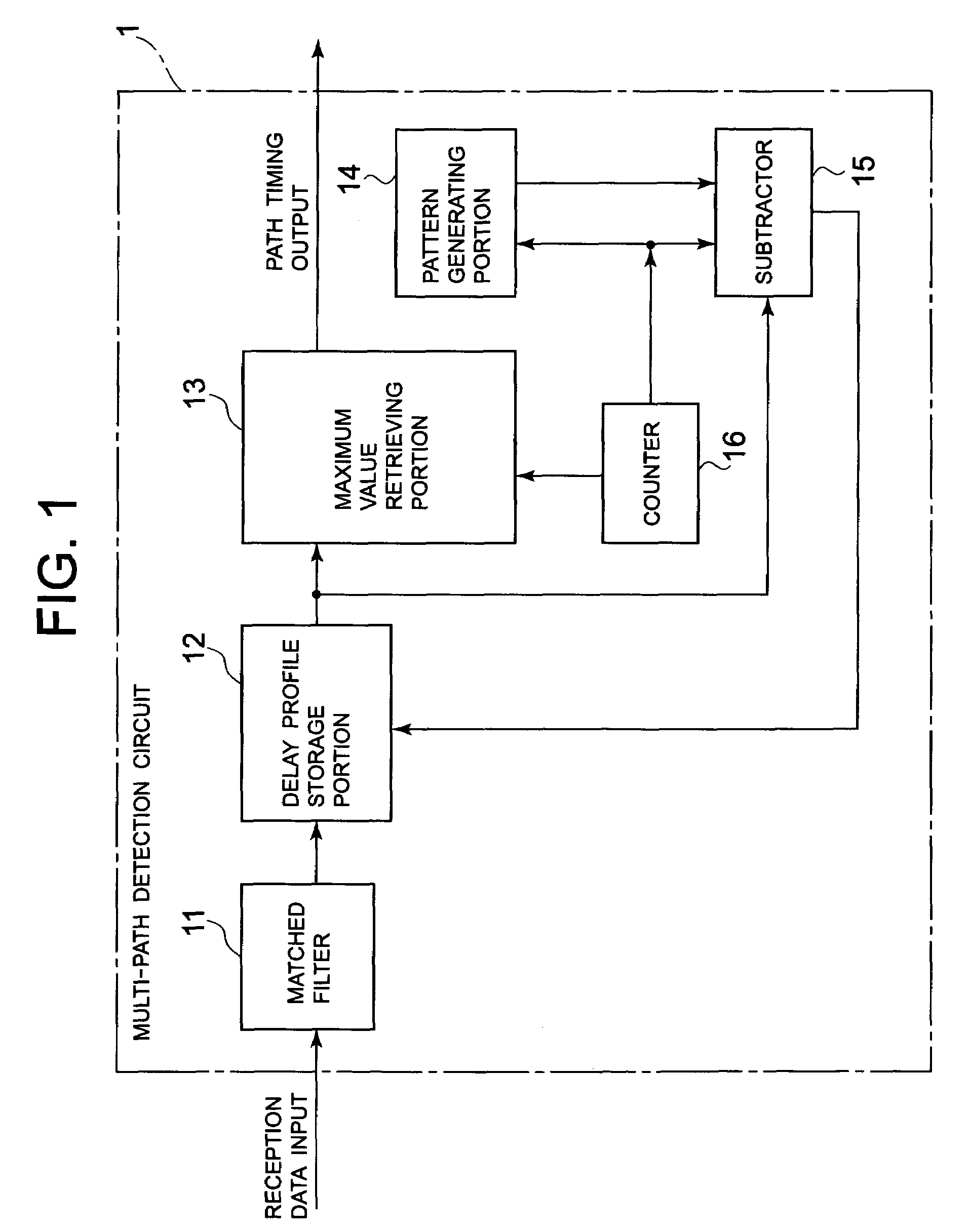
Pattern generation circuit, multi-path detection circuit employing the same and multi-path detection method
InactiveUS6996157B2Improve reception performanceHigh precisionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsPattern generationEngineering
A multi-path detection circuit can improve path detection accuracy in the environment where the path is located close in the extent of one chip in the multi-path detection circuit of CDMA type receiver unit. The multi-path detection circuit has generating means for generating a logic pattern of a correlated peak in the delay profile, and removing means for removing a power component of the detected correlated peak from the delay profile using the logical pattern of the correlated peak generated by the generating means.
Owner:NEC CORP
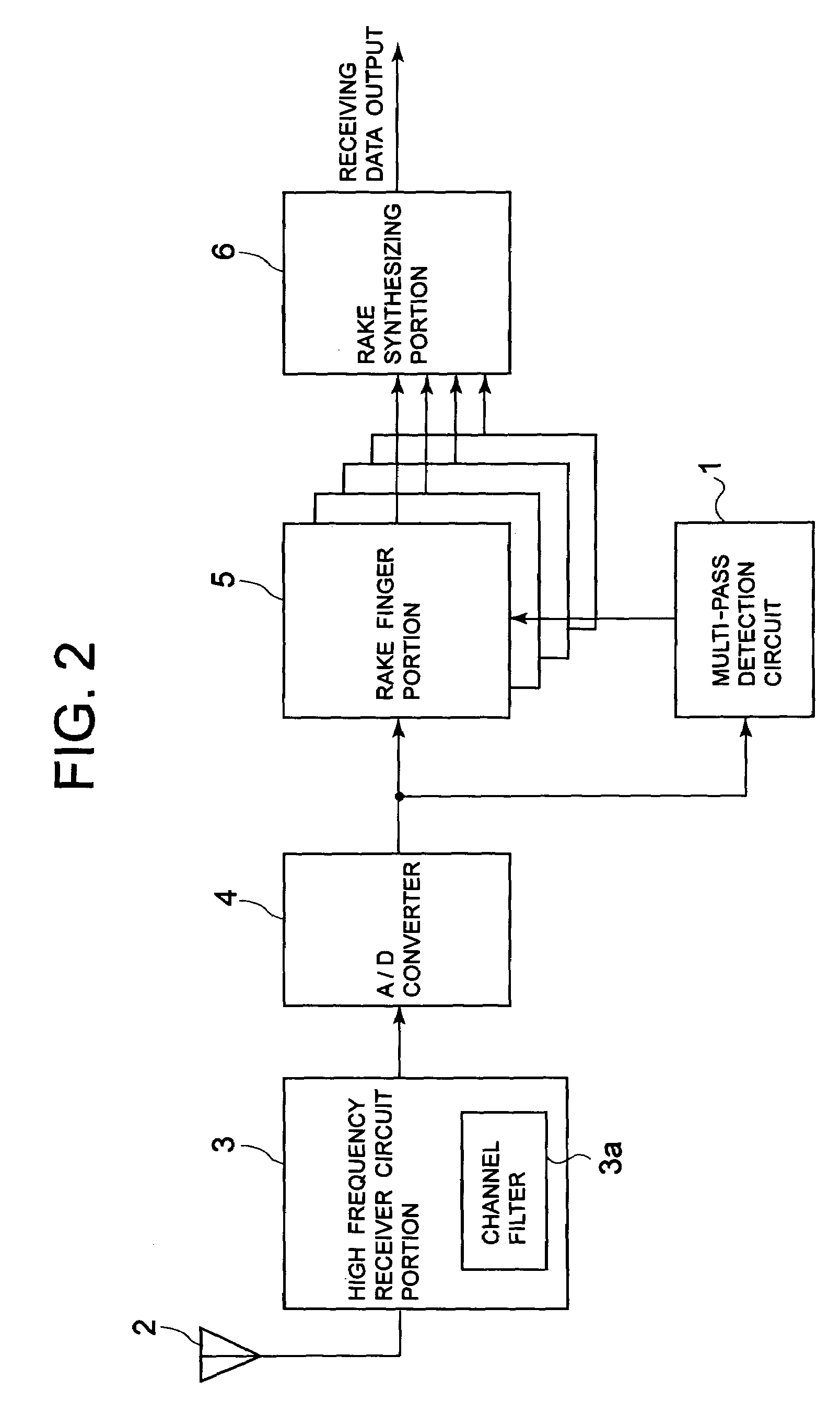
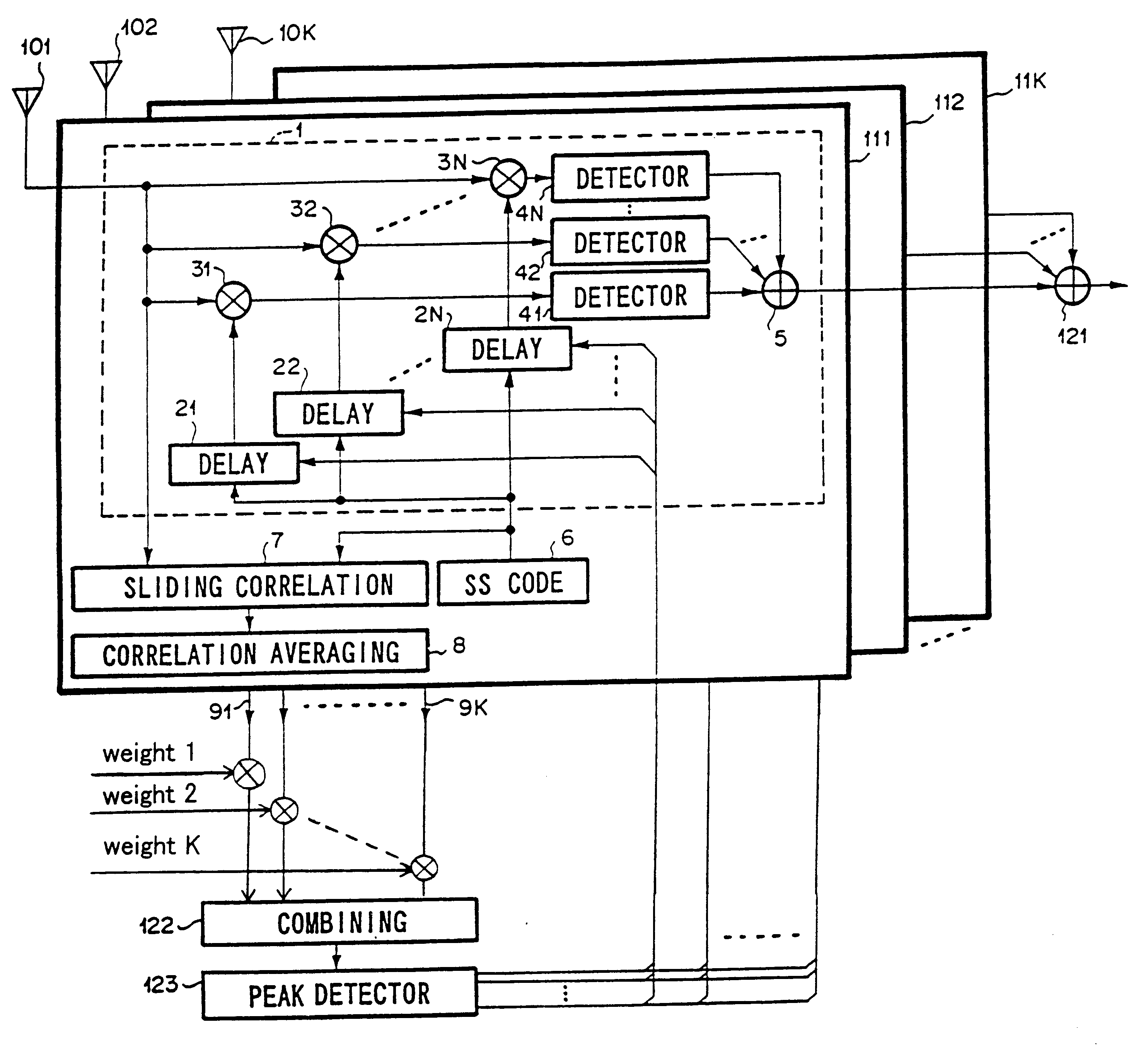
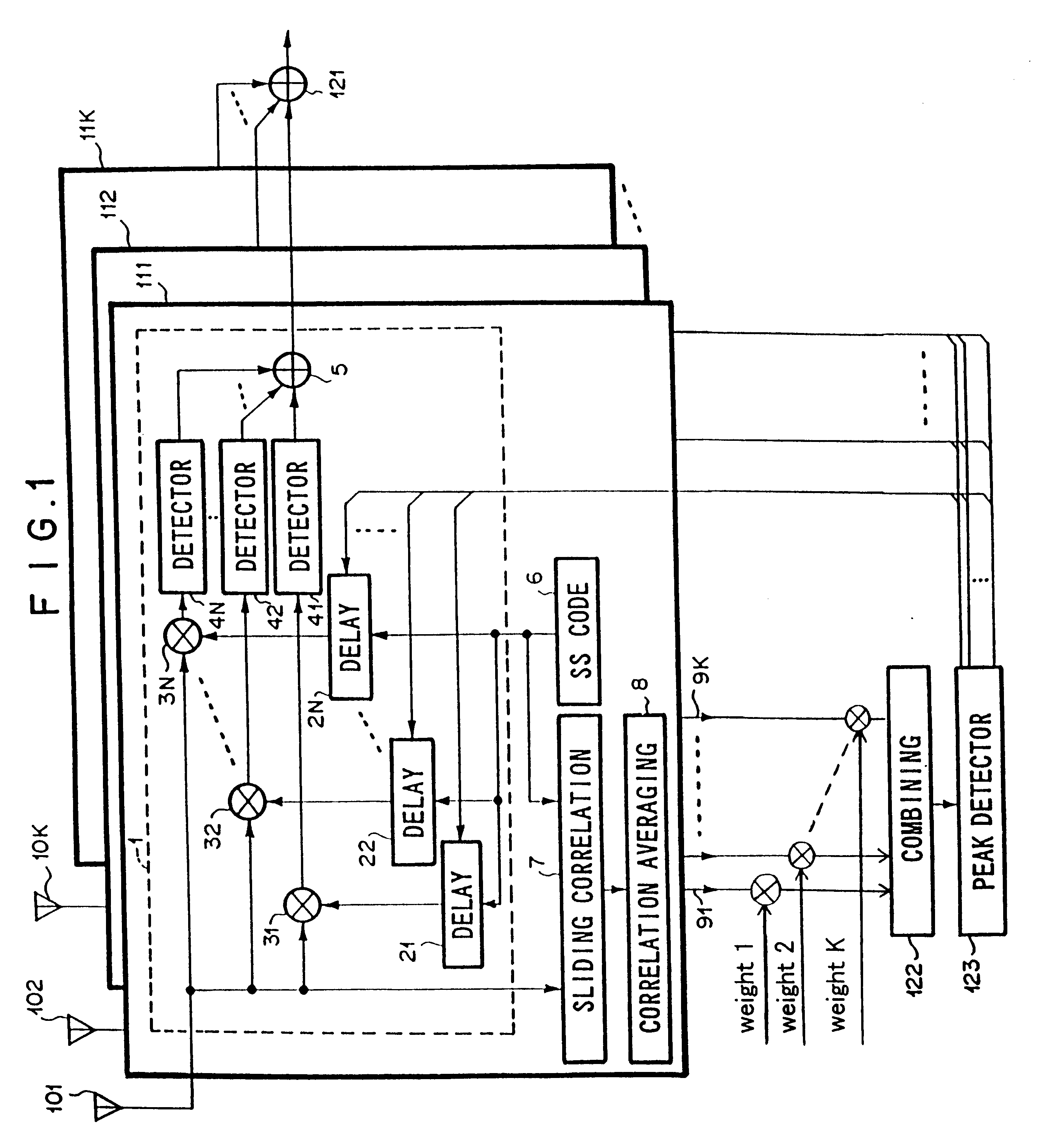
Path search circuit, radio receiver and radio transmitter, utilizing a directional beam
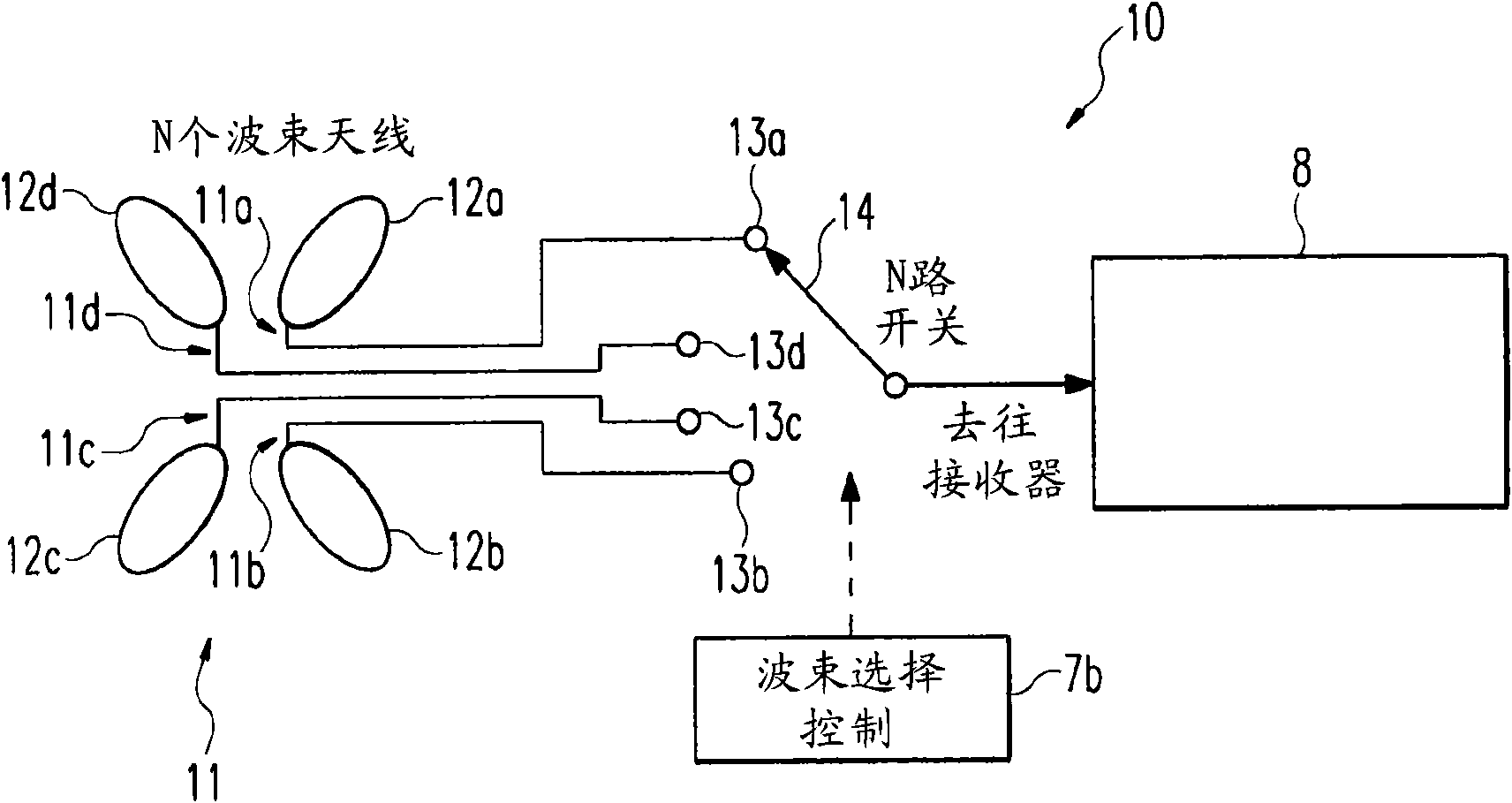
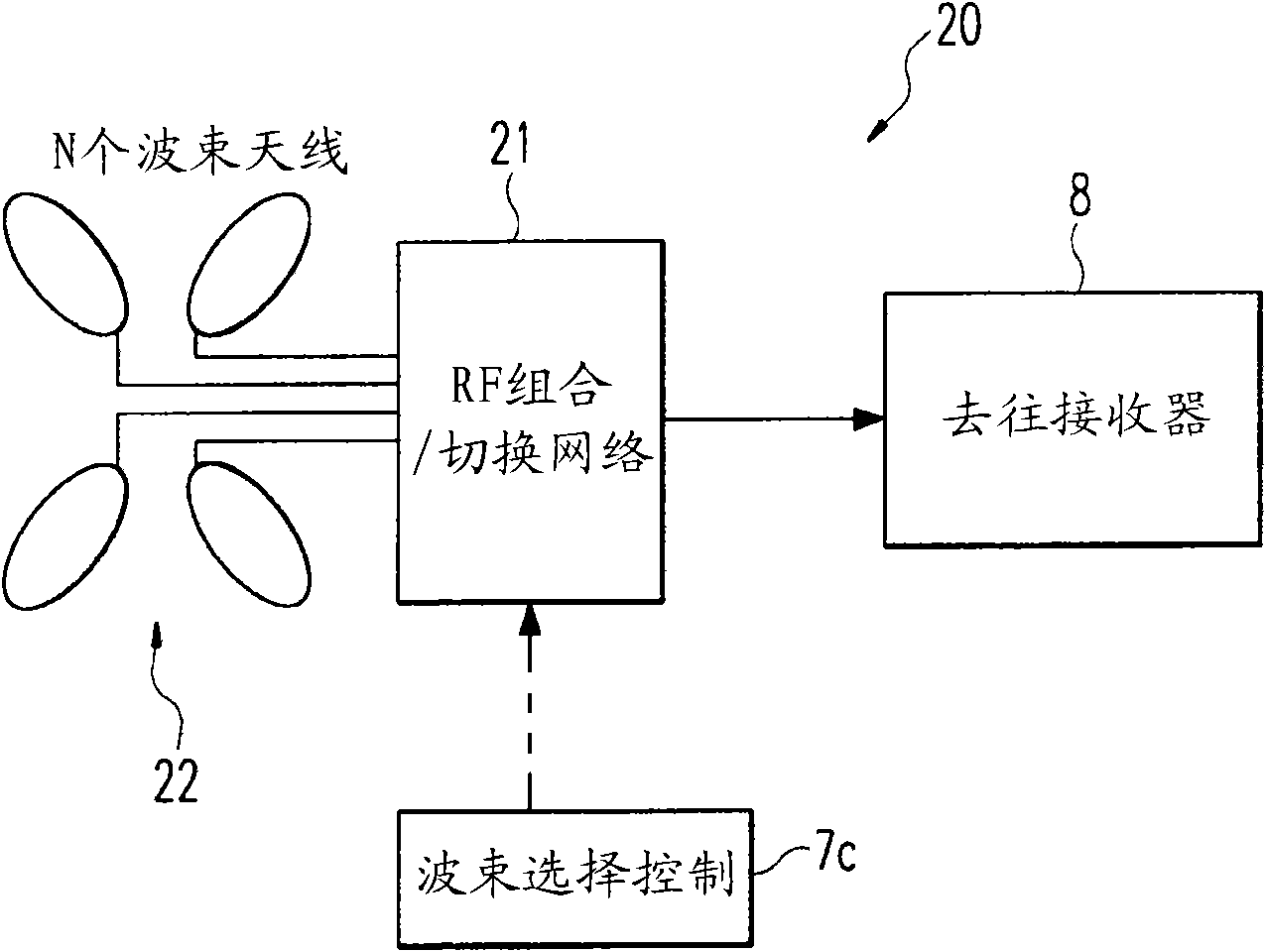
ActiveUS7088956B2Reduce direct dependenceRule out the possibilitySpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityRadio receptionRadio receiver
A path search circuit according to the present invention has an orthogonal multi-beam forming section 4 for directional reception with a plurality of orthogonal multi-beams orthogonal one to another, correlation-operating sections 61–6M for correlation-operating outputs of the orthogonal multi-beam forming section 4 with a known signal, weight multiplying sections 81–8Nb for multiplying the output of the correlation-operating section 61–6M by a weight converted into a beam space, delay profile generating sections 91–9Nb for generating delay profiles from the output signals of the weight multiplying sections 81–8Nb, and a path detecting section 10 for detecting a reception timing and arrival direction of arrival path from the delay profile. This path search circuit can enhance the accuracy of path direction detection by the use of a directional reception signal, and further reduce the direction dependence of path timing detection accuracy.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
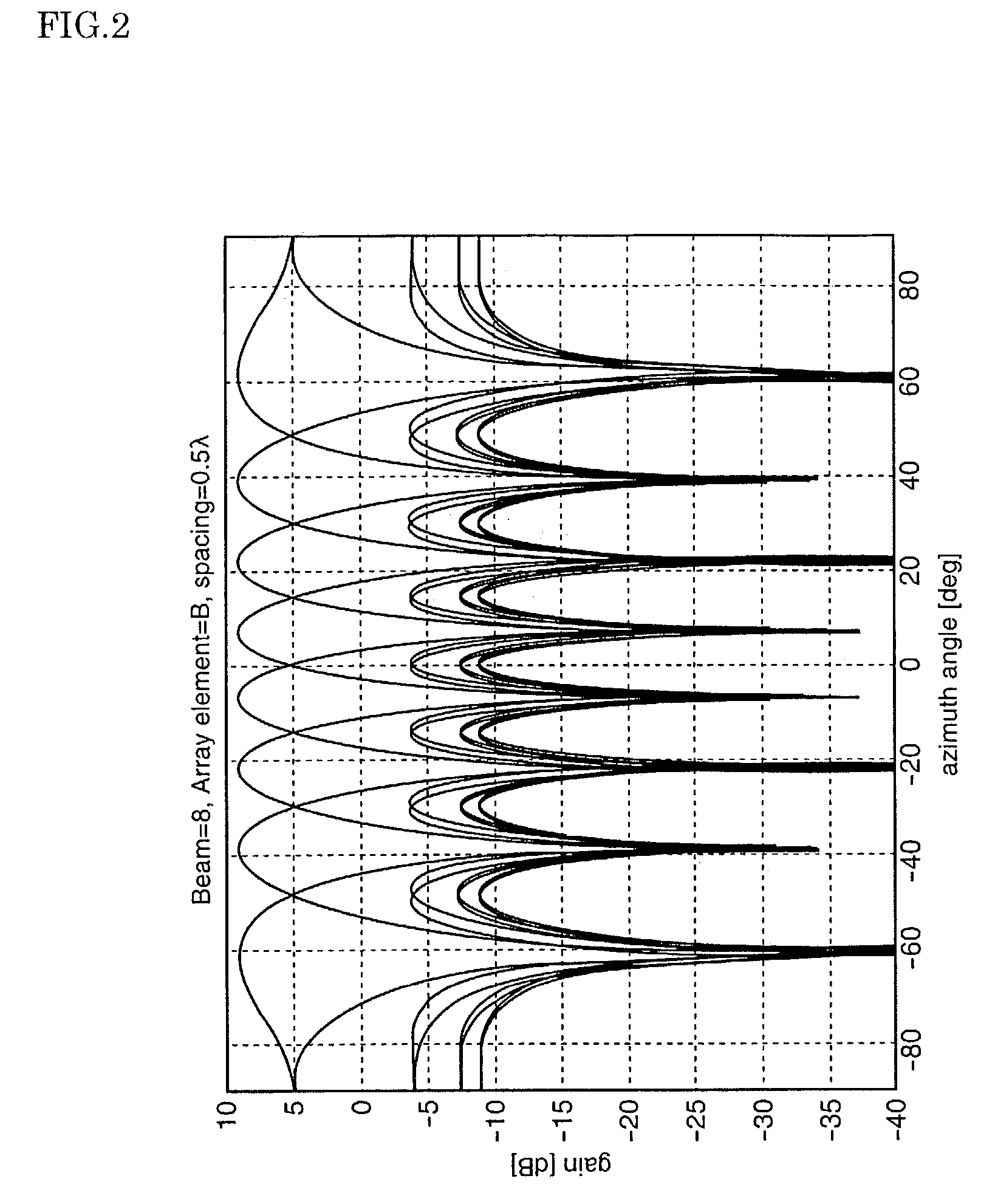
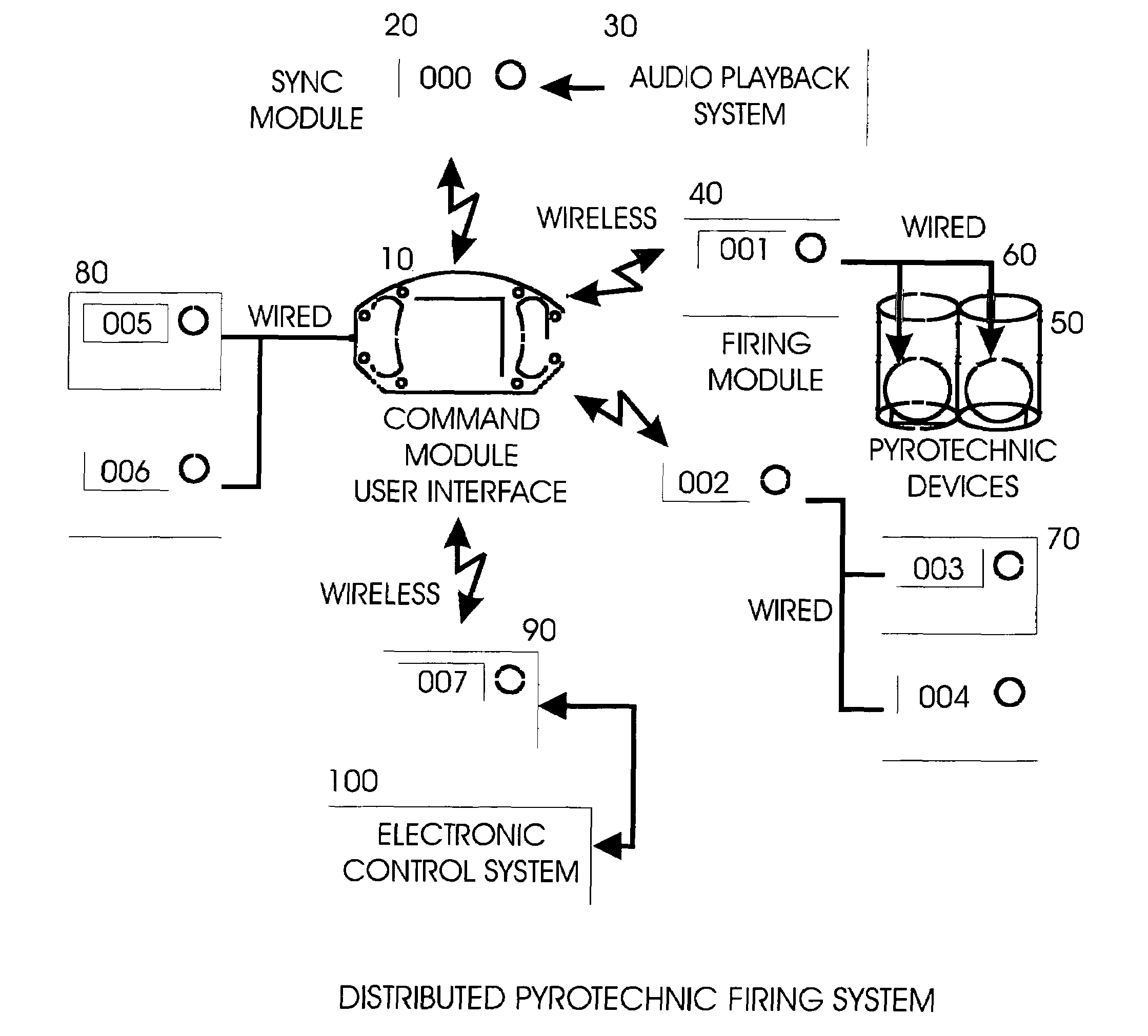
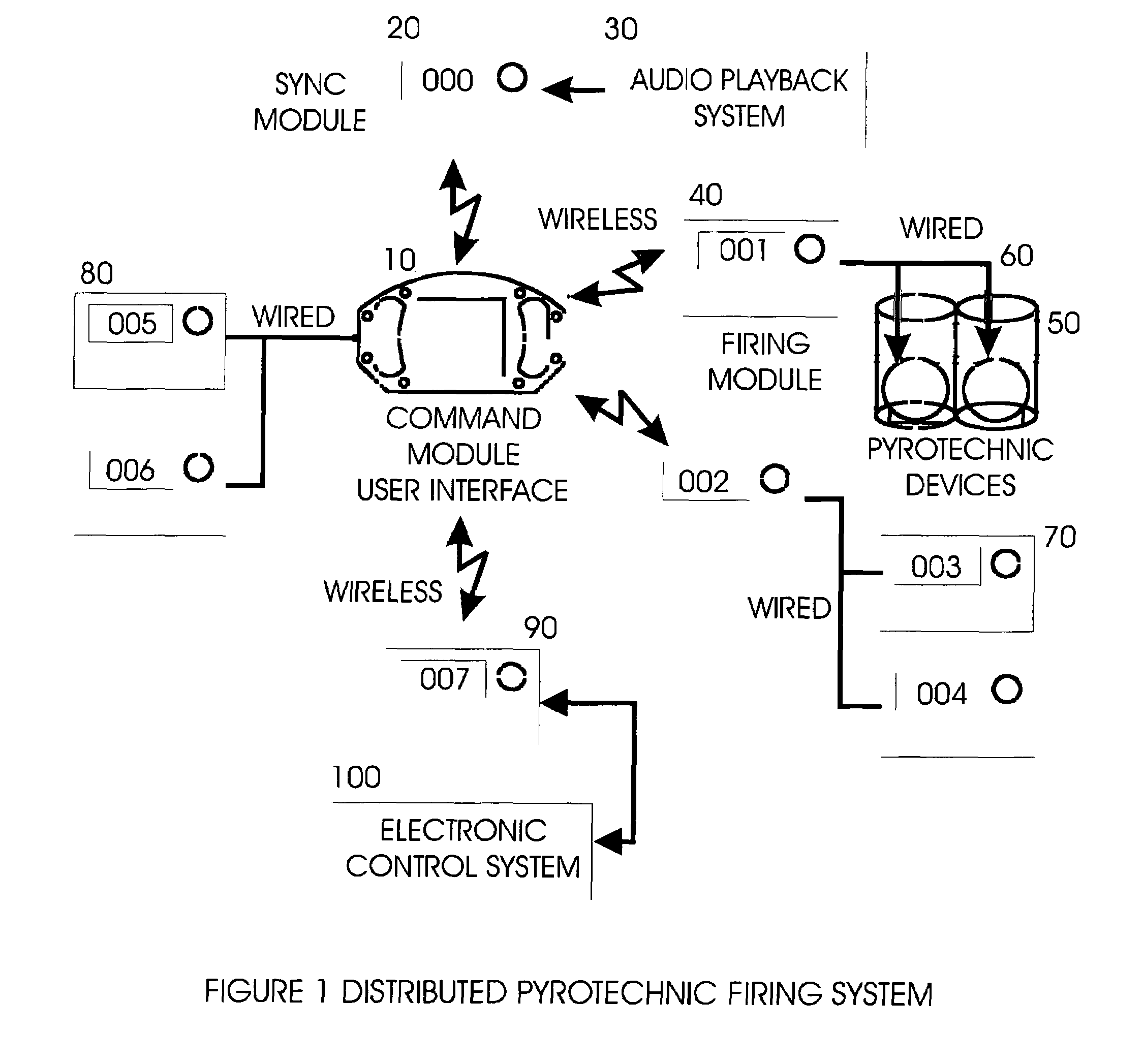
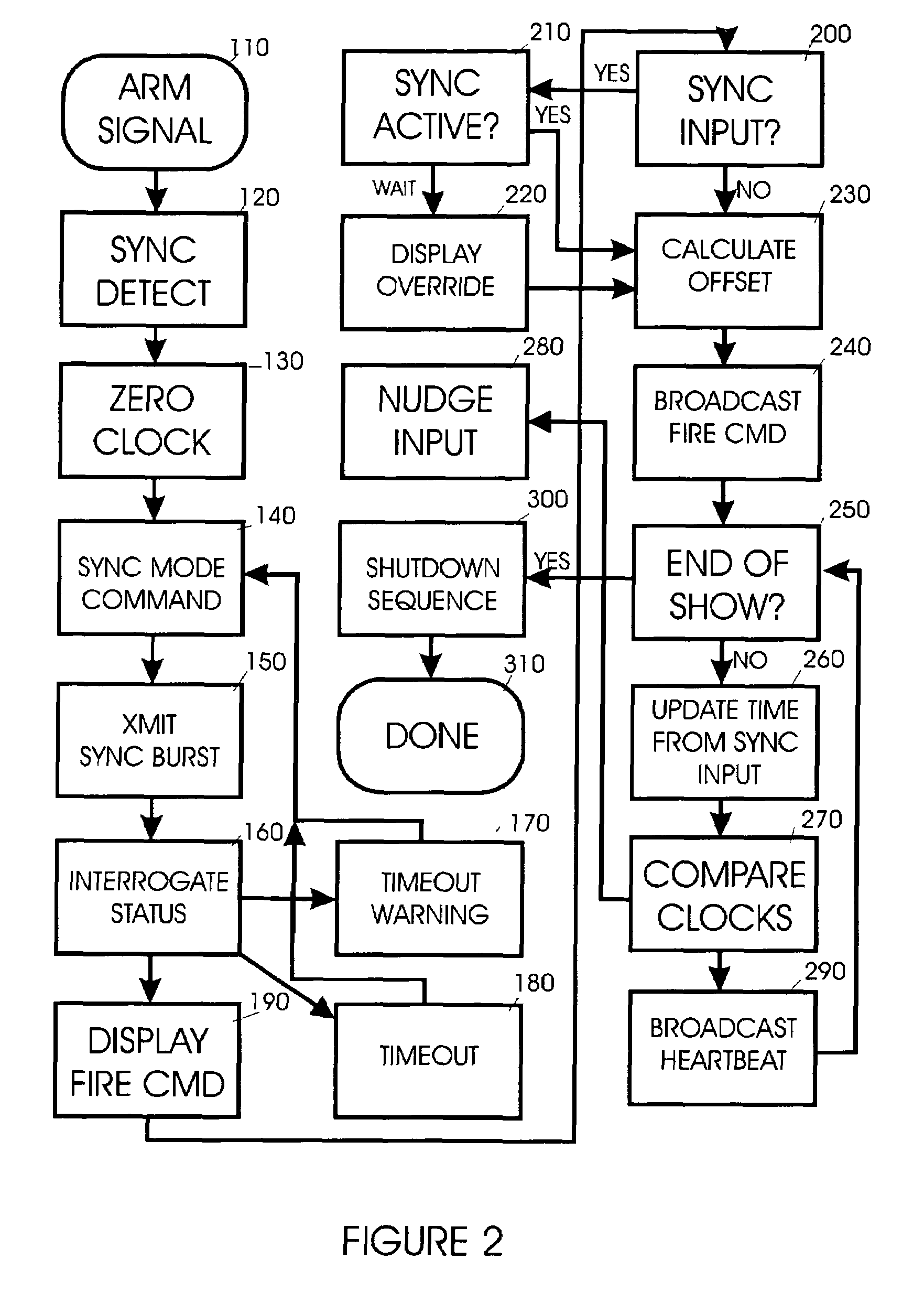
System and method for zero latency distributed processing of timed pyrotechnic events
ActiveUS7493859B2Energy optimizationZero delayAmmunition projectilesIncandescent ignitionMaster controllerLatency distribution
A method for achieving zero, or near zero, latency timed pyrotechnic events by utilizing distributed processing is presented. A list of timed events may be used to synchronize a pyrotechnic firing sequence with music or other external events. This list is distributed over a series of embedded microprocessors. Each microprocessor is then synchronized to a master controller clock, and enabled such that each processor may then fire independently as required by the master list. This distributed process removes the split-second timing requirement from the main controller enabling the achievement of zero latency and providing significantly more timing events to be processed simultaneously while alleviating problems such as wireless radio interference delays. Each module is capable of forwarding information to other modules, which may be a position that prevents wireless communication directly with the master controller.
Owner:BIRKET IP HLDG INC
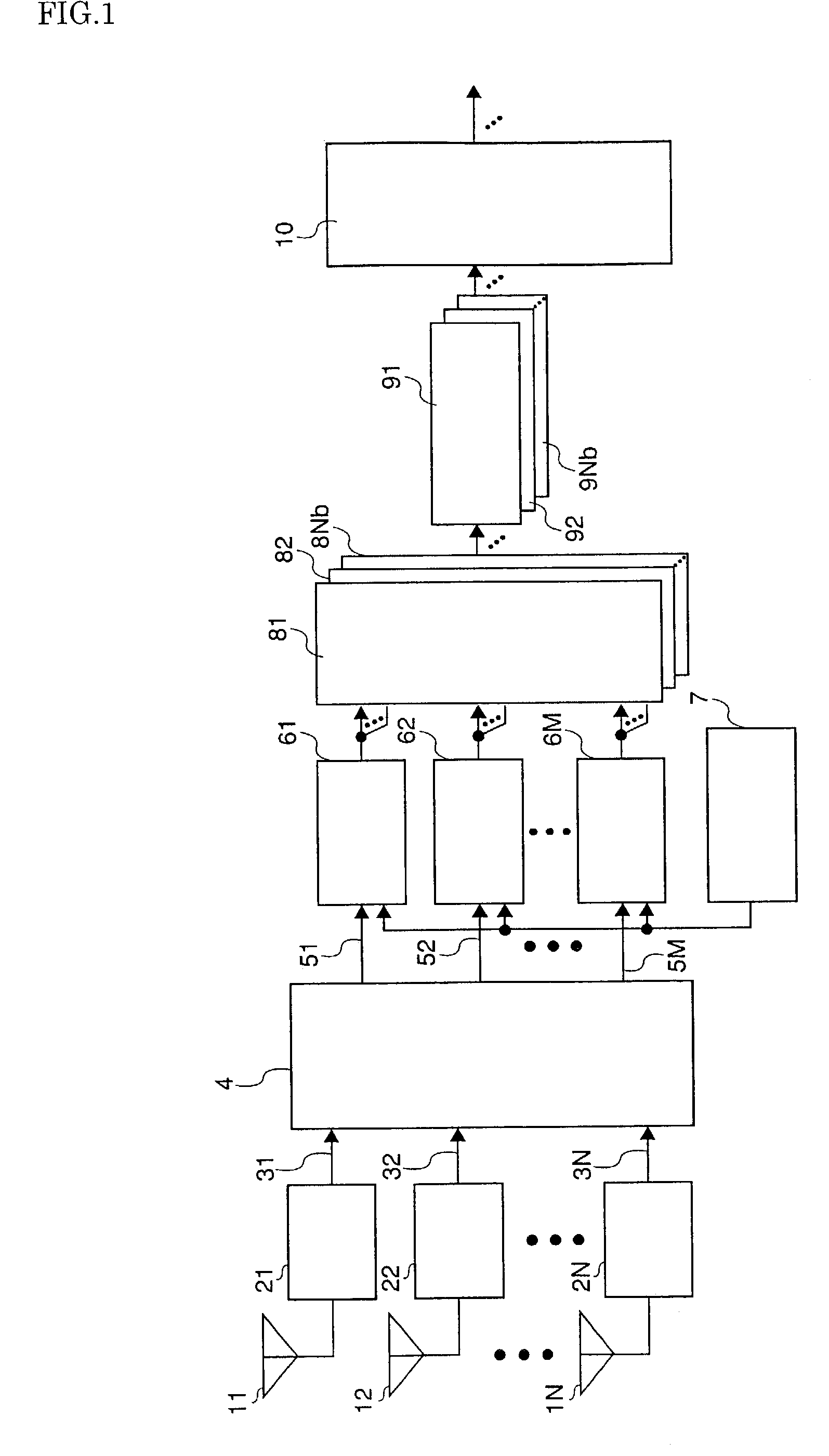
Radio Channel Data and the Use Thereof
ActiveUS20130210474A1Effective wayTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionWireless transmissionEngineering
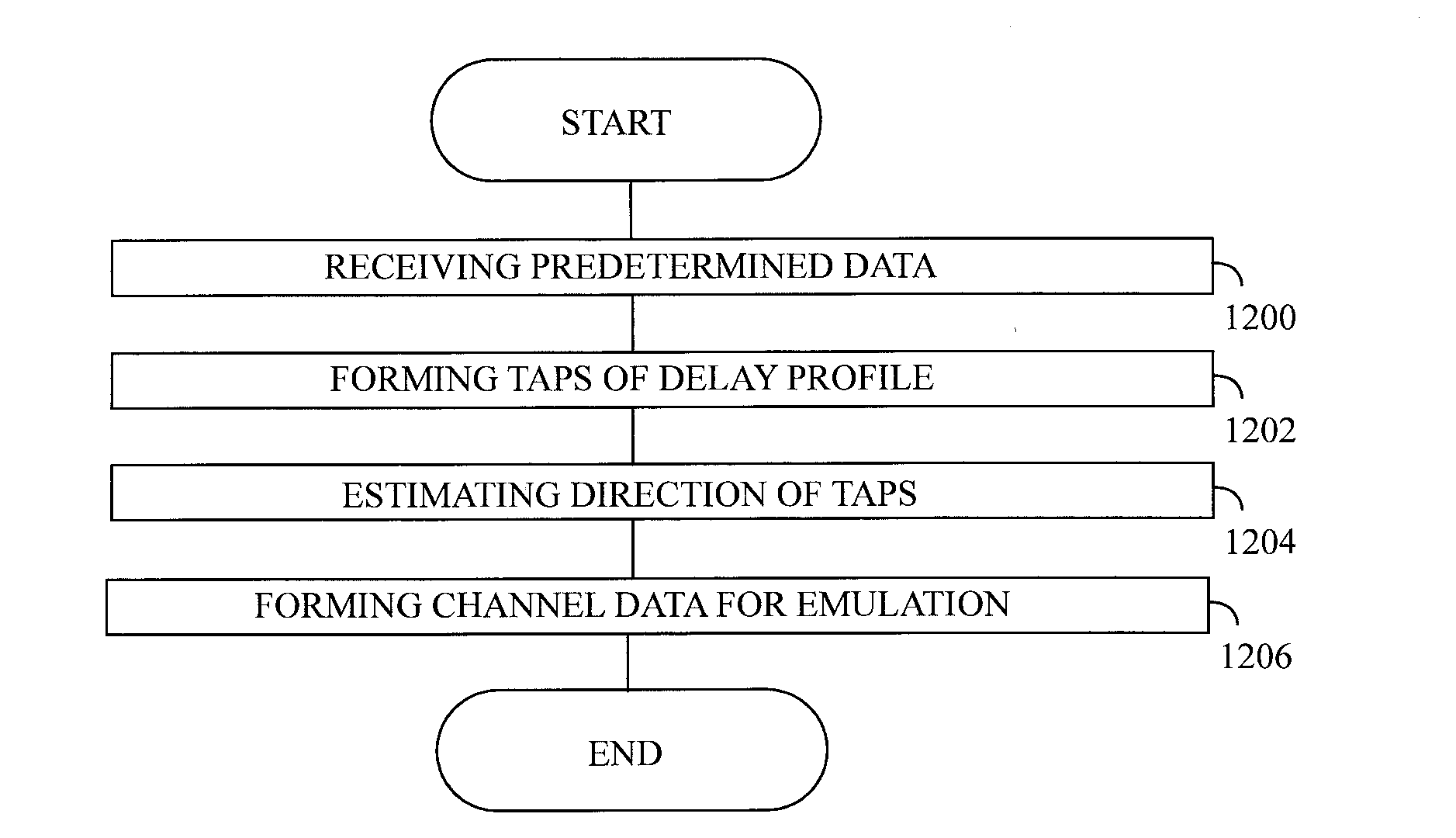
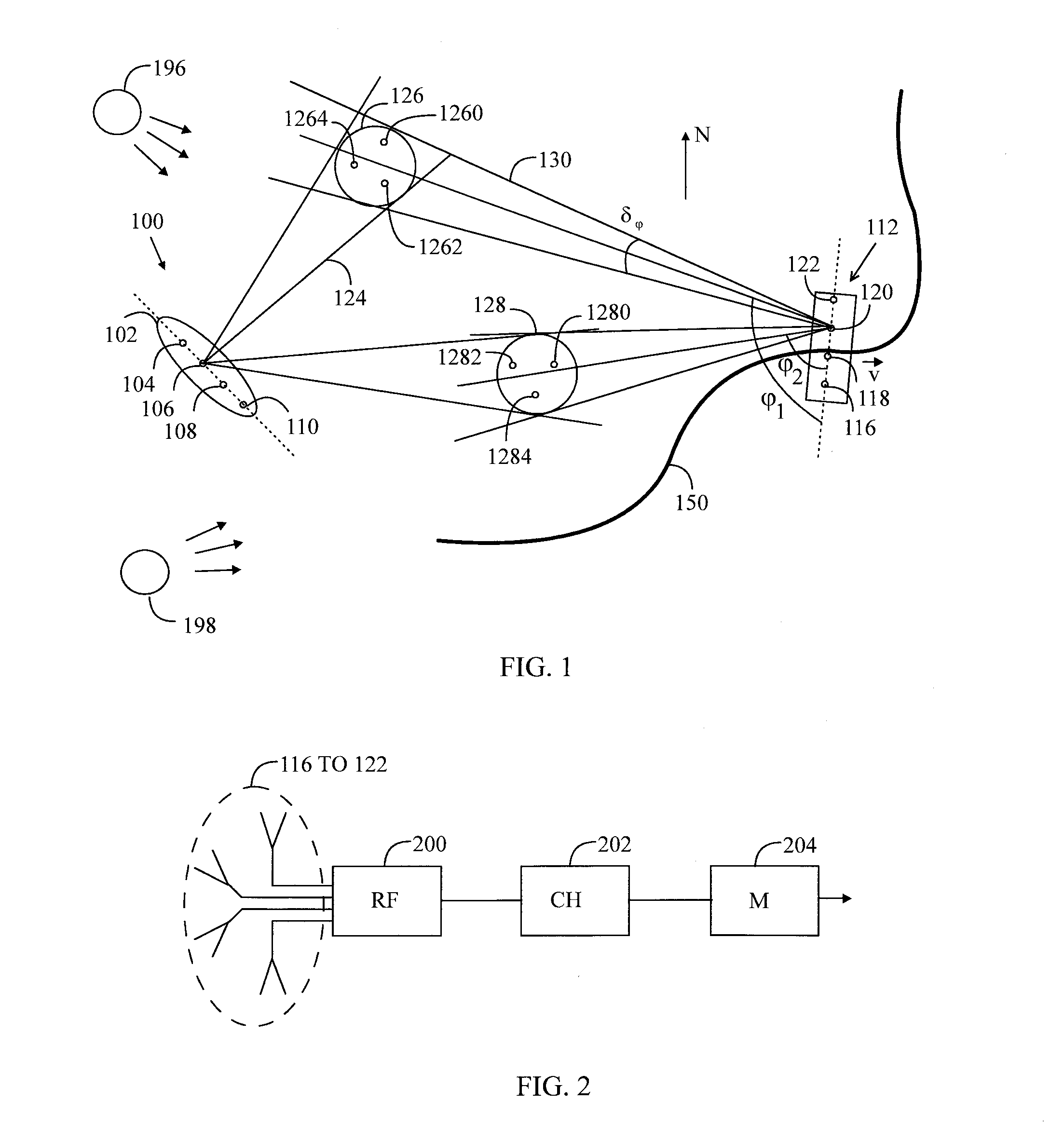
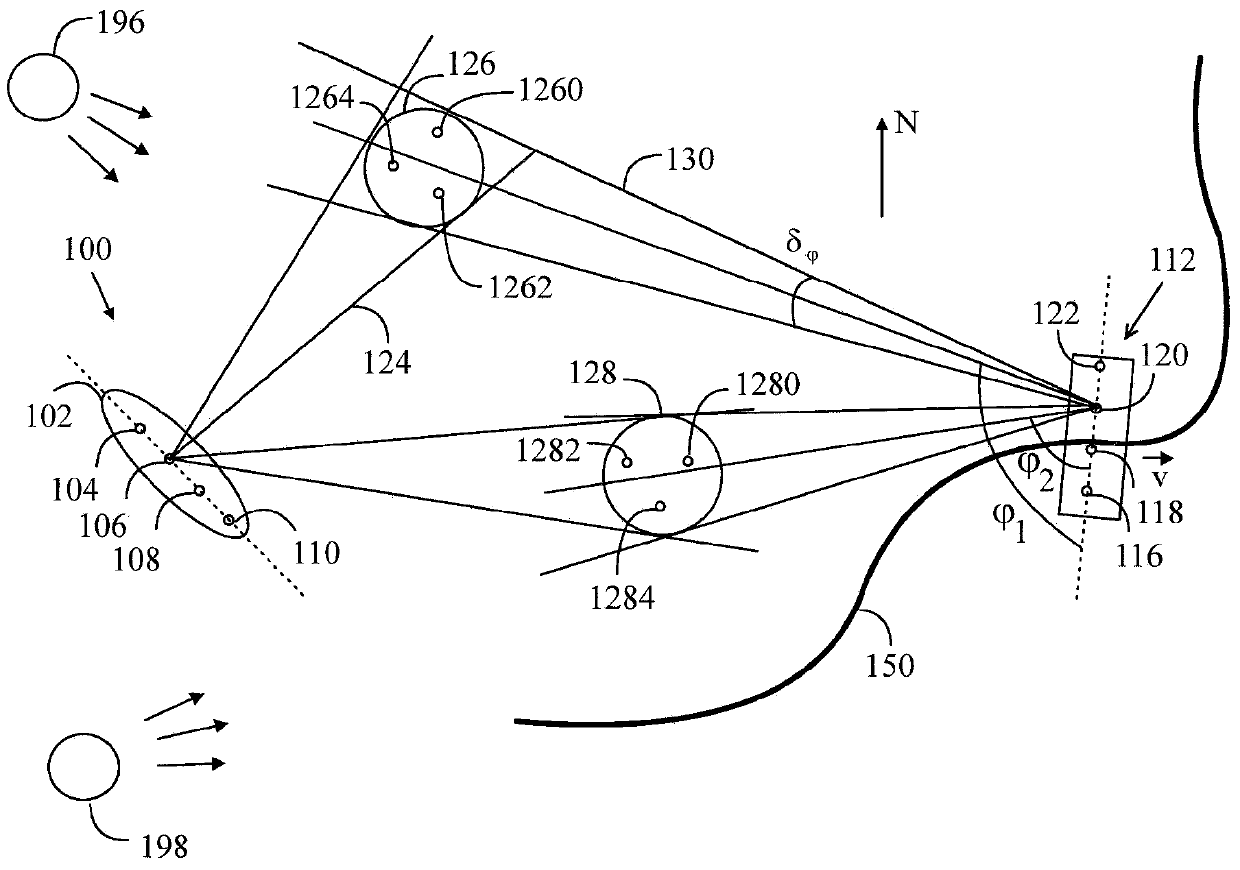
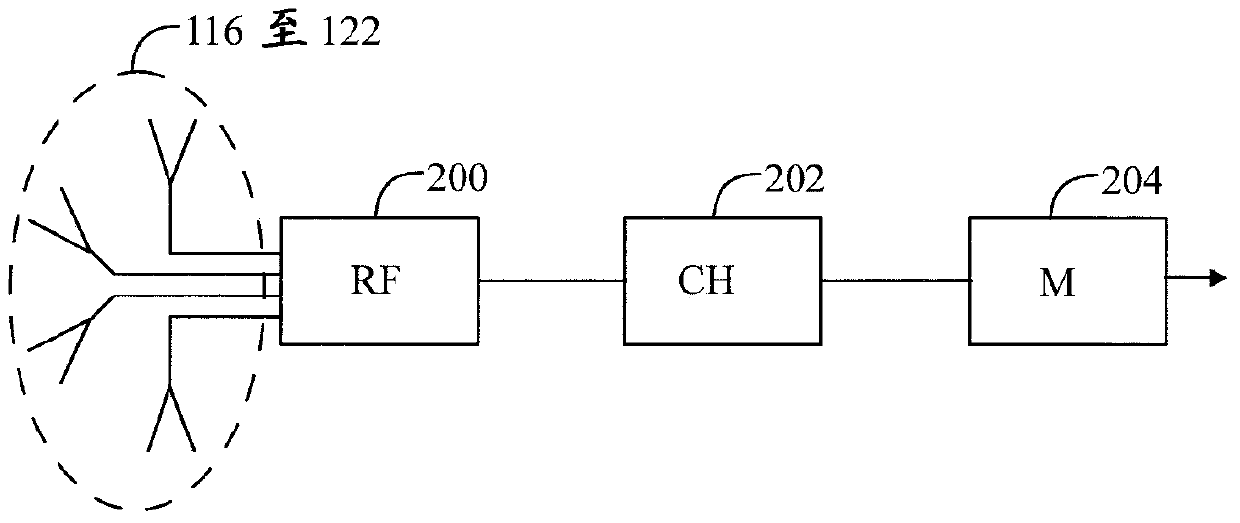
An apparatus comprises a receiver receiving wireless transmission of a real radio system from at least one base station of a radio system as a function of reception direction. The transmission comprises predetermined data. The apparatus comprises also a processing unit that forms taps of a delay profile on the basis of comparison between the data that is received and corresponding predetermined data. The processing unit estimates direction for the taps of the delay profile on the basis of a reception direction of the transmission, and forms radio channel data by associating the taps of the delay profile with the estimated direction. The radio channel data is for a radio channel model of a MIMO emulation in an OTA chamber having a plurality of antennas around a test zone where a device-under-test may be placed.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH SINGAPORE (SALES) PTE LTD
Scheme for realizing path selection using optimum path selection threshold in radio communication
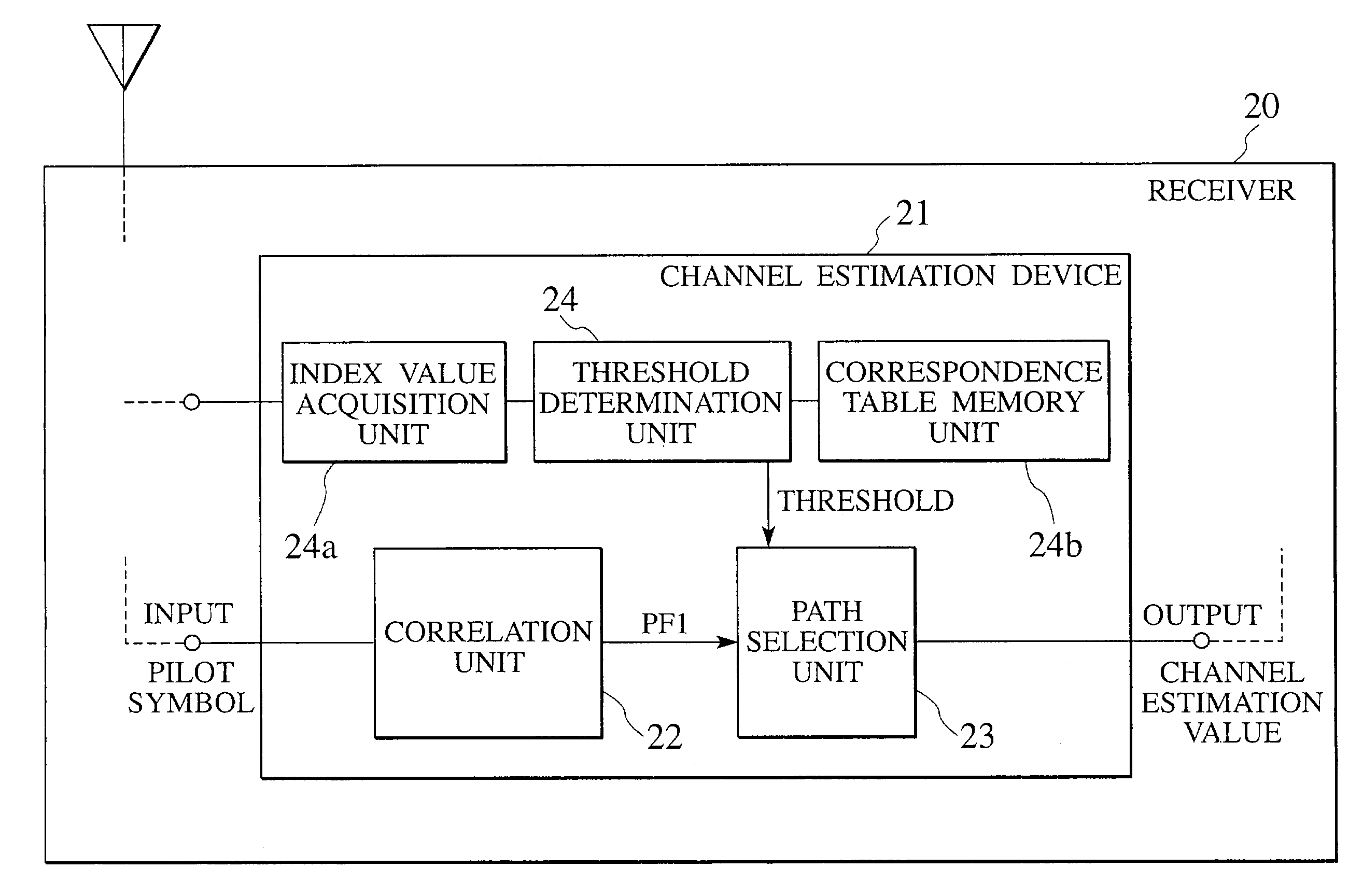
InactiveUS7151948B2Reduce error rateBaseband system detailsTransmission control/equalisingEngineeringMobile station
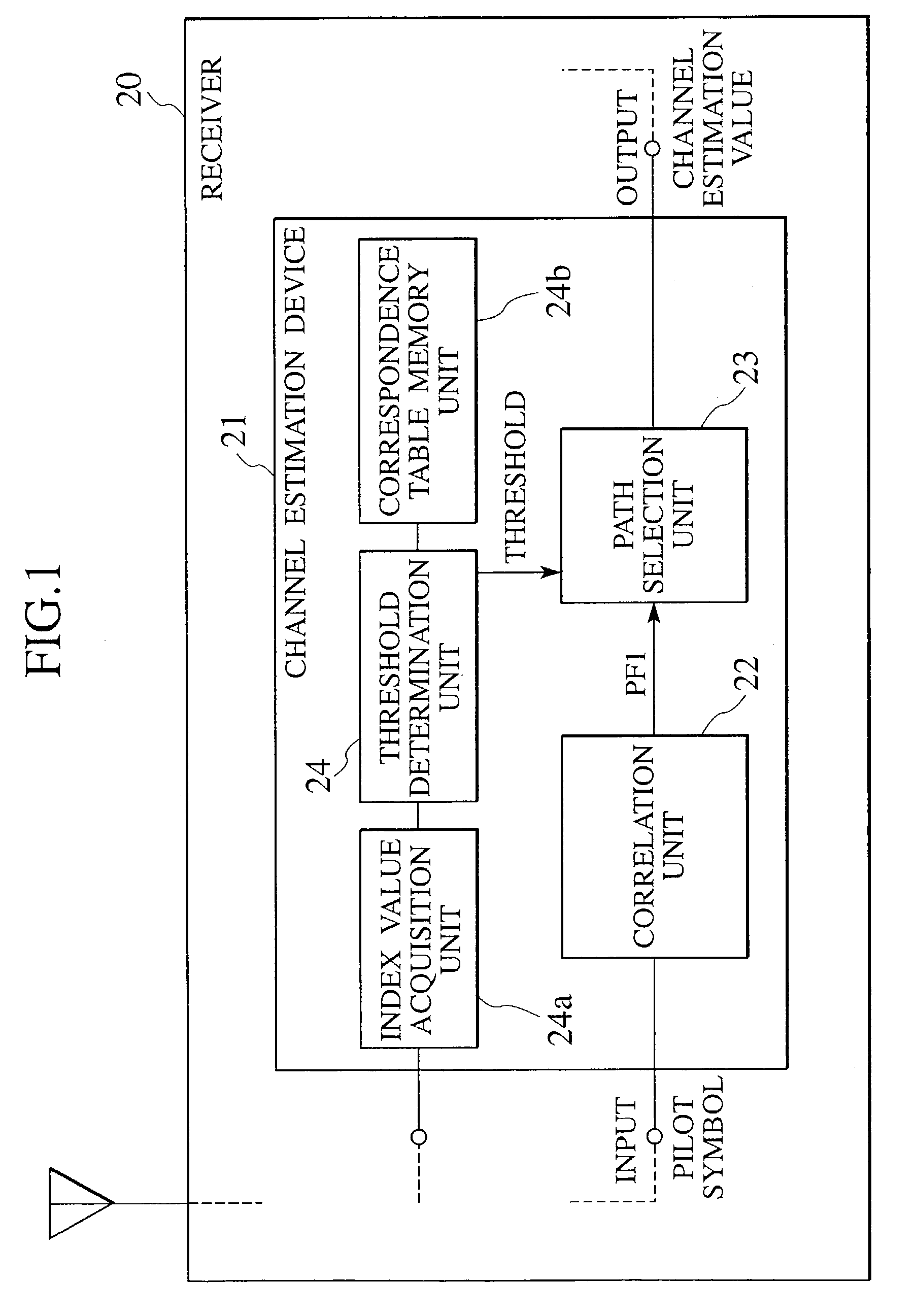
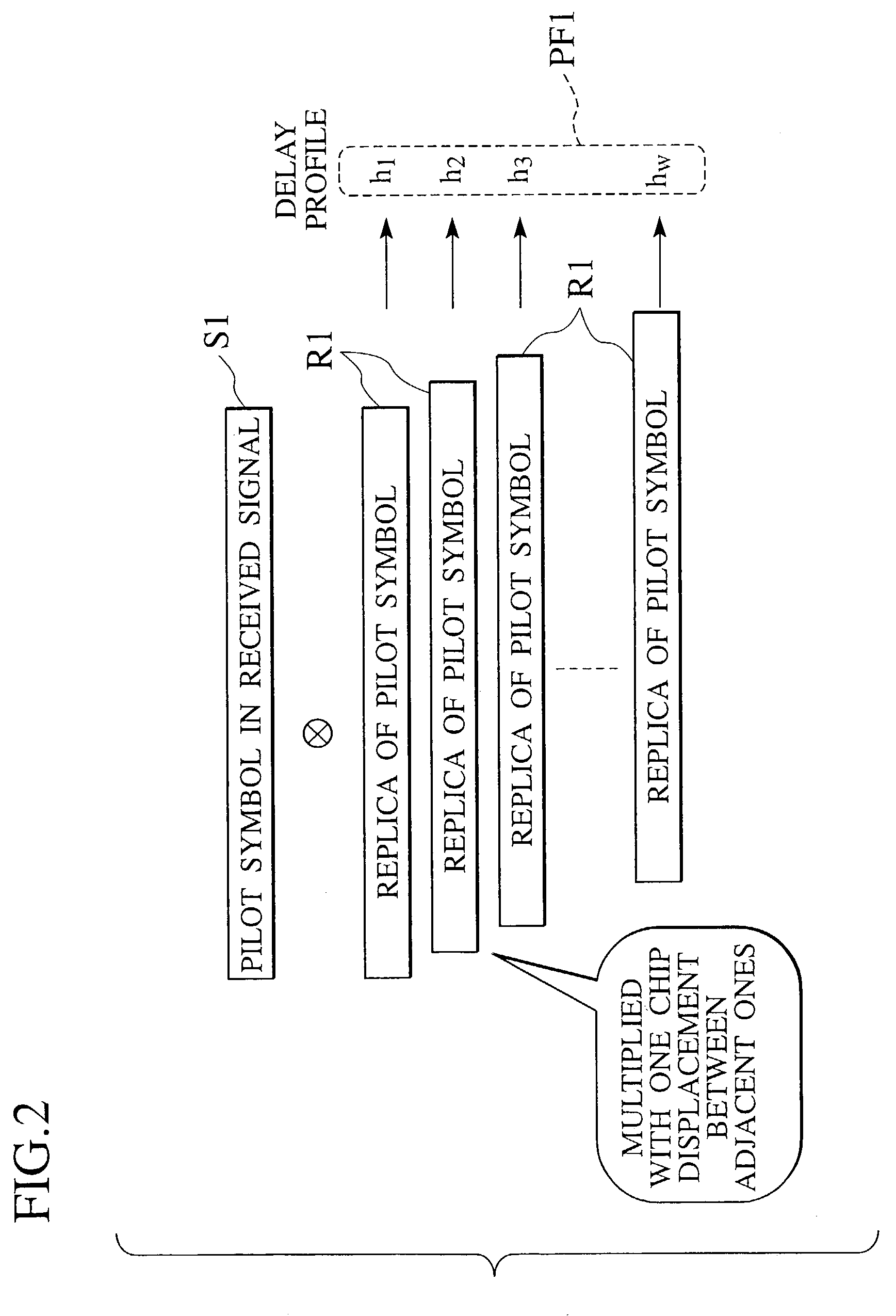
A receiver of a mobile station or a base station in radio communications is formed by a correlation unit for generating a delay profile for specifying paths by taking correlations by using replica signals for a received pilot signal, and a path selection unit for comparing a power level of each path in the delay profile with a threshold determined according to an index value regarding a communication state, selecting paths for which a comparison result satisfies a prescribed condition as valid paths, and outputting a selected delay profile formed by the valid paths as a channel estimation value.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
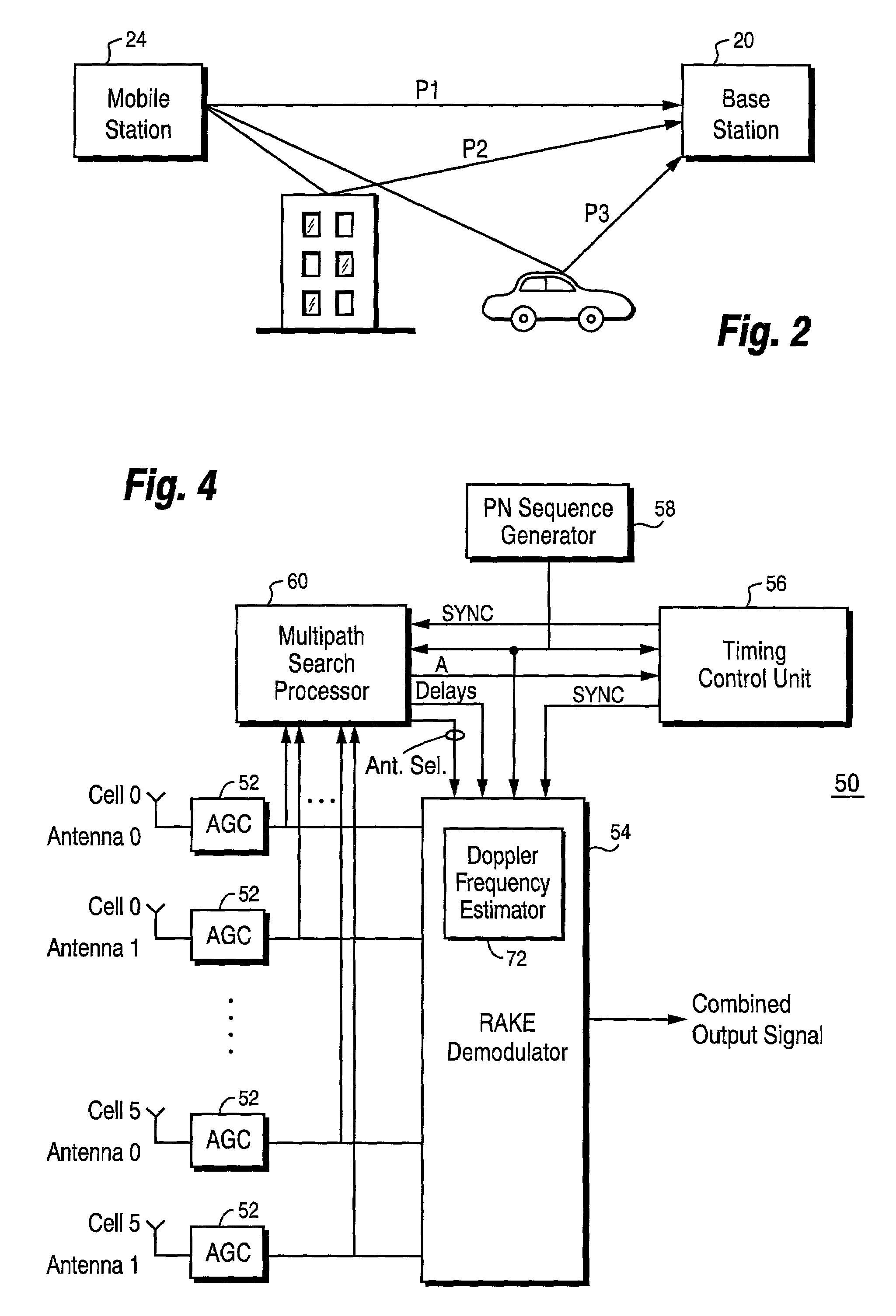
Search window delay tracking in code division multiple access communication systems
InactiveUS7058399B2Suppress interferenceSpreads” the bandwidth of the information data streamRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionChannel impulse responseCommunications system
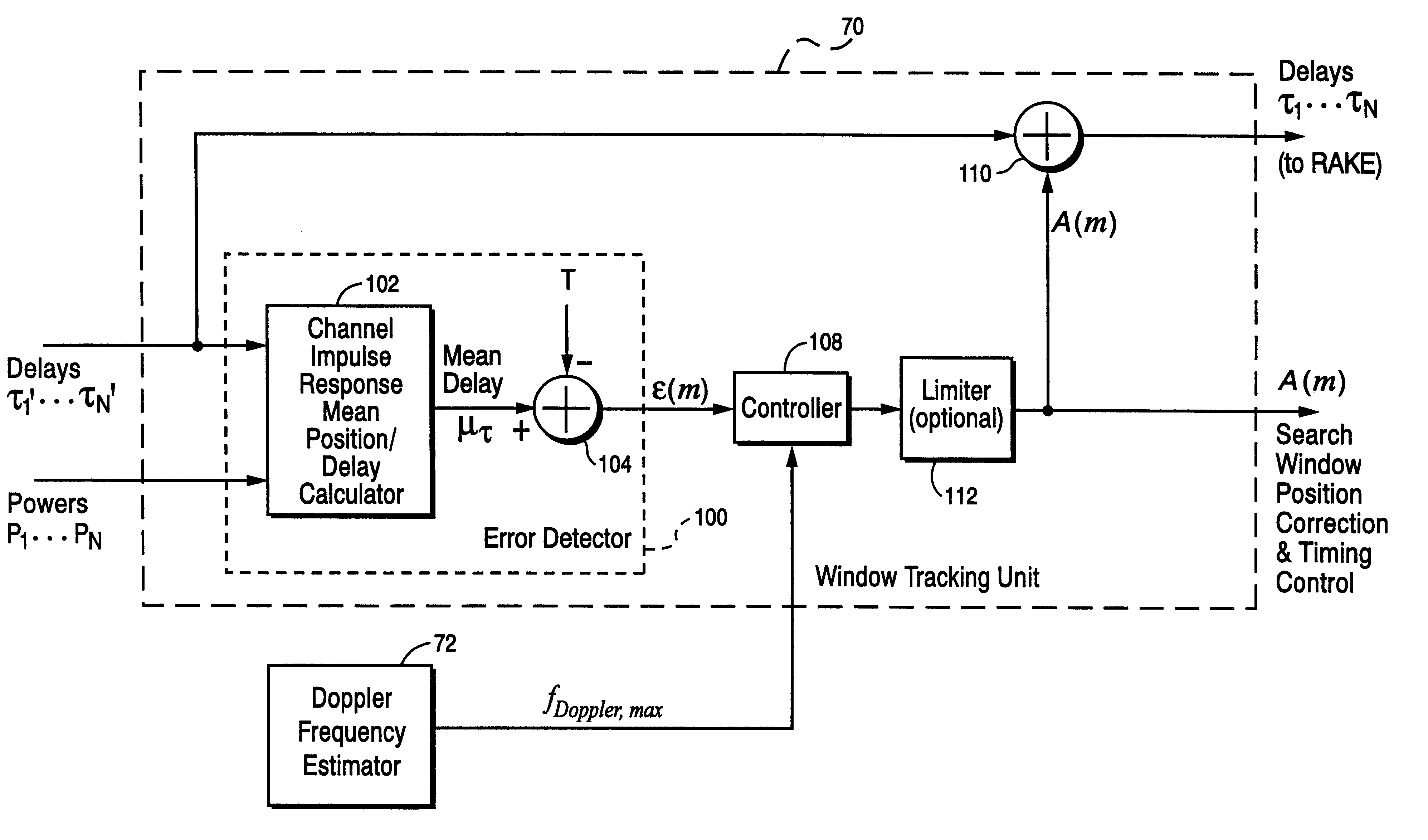
The present invention provides a search window delay tracking procedure for use in a multipath search processor of a CDMA radio receiver. A channel impulse response is estimated for a received signal containing plural paths, each path having a corresponding path delay. A search window defines a delay profile that contains the plural paths of the received signal. A mean or average delay is calculated for the estimated channel impulse response (CIR), and an error is determined between the mean CIR delay and a desired or target delay position of the Cir. search window. An adjustment is made to reduce that error to align the targeted position of the search window and the mean CIR delay. A Doppler frequency is estimated for each path. The adjustment is made taking into account a Doppler effect caused by relative movement between the transmitter and receiver.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and apparatus for receiving spread spectrum signal
To synchronize spread spectrum (SS) signal with PN sequence, even when a Doppler frequency of fading is low. Delay profile combining means outputs a combined delay profile from delay profiles which are outputted from receiving units. Further, the synch chip timing which is obtained from the combined delay profile is fed commonly to receiving units for path diversity combining.
Owner:NEC CORP
OFDM receiver
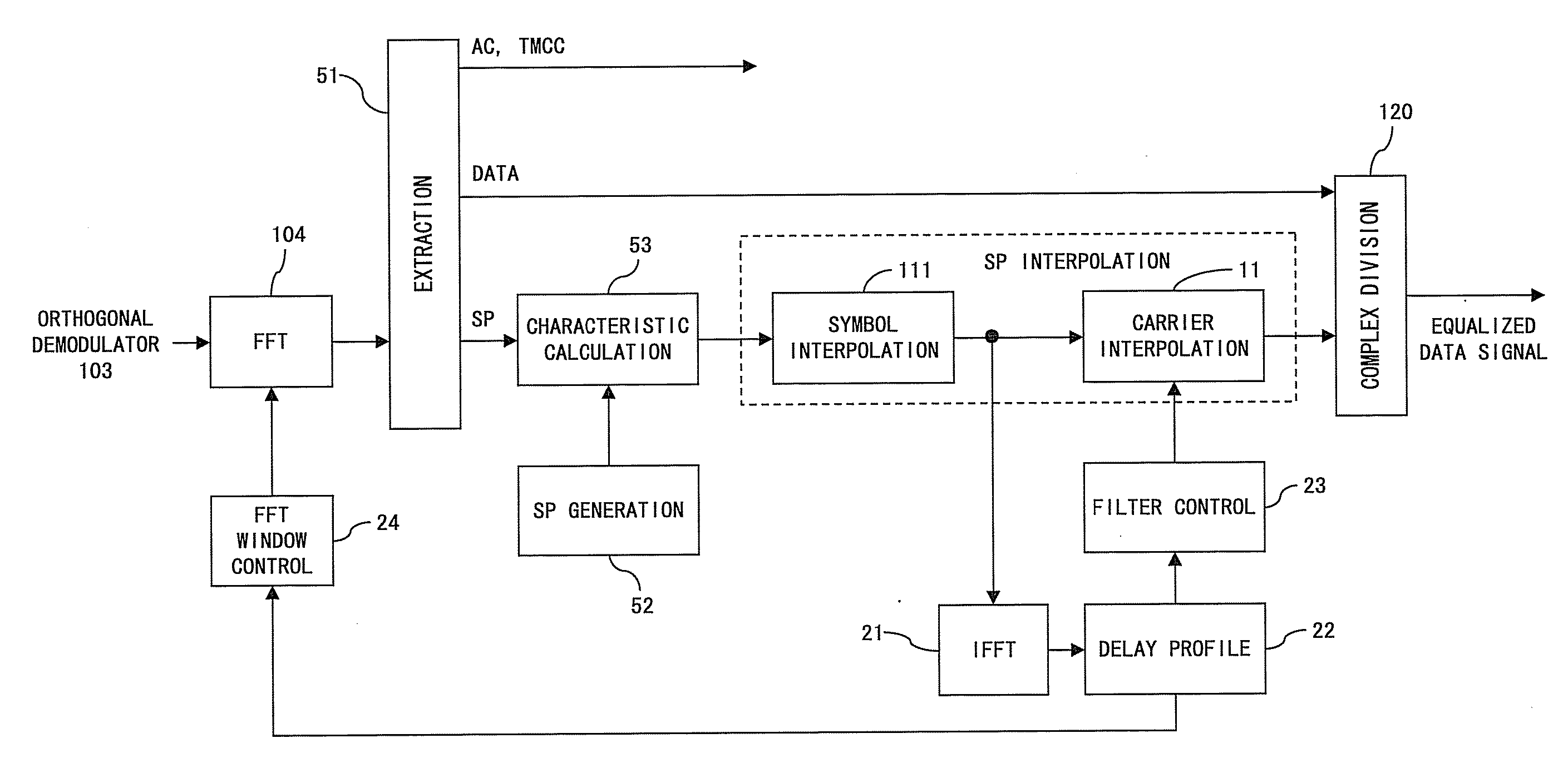
InactiveUS20070274406A1Large delay timeImprove reception qualityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationTime domainDelayed time
A carrier interpolation unit (a digital filter) performs interpolation processing of SP signal in the frequency domain. An IFFT circuit converts a frequency-domain signal into a time-domain signal. A delay profile generation unit generates a delay profile based on an output of the IFFT circuit. The filter control unit controls a pass band of the digital filter in accordance with the delay profile. An FFT window control unit controls a position of a window to extract a calculation range of FFT in accordance with the delay profile. When delay time of multipath is larger than the guard interval, and when the reception power of the interference wave is larger than a threshold, the pass band of the digital filter is minimized.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Positioning of a path searcher window in a CDMA receiver
InactiveUS7715464B2Avoid detectionReduce complexityTime-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDigital radioPower delay profile
Multipath components of signals transmitted through time-varying digital radio channels are received with individual delays, and signals through a given channel comprise a code identifying that channel. A delay profile indicating a magnitude (Y) for delay values in a search window is calculated repetitively for known channels; the delays of multipath components for known channels estimated; a signal strength indicator calculated; and a search for new multipath components not already estimated performed at regular time intervals. When a new multipath component is found, its identification code is compared to the codes of the known channels. If the code of the new component is identical to the code of a known channel, a delay profile and a signal strength indicator is calculated for a window transposed to include the new multipath component. In this way as many multipath components as possible are included in the search window for a new cell.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Beam selection method
Owner:SONY CORP
Radio channel data and the use thereof
ActiveCN104137448ADirection finders using radio wavesTransmission monitoringWireless transmissionRadio channel
Apparatus comprises a receiver receiving wireless transmission of a real radio system from at least one base station of a radio system as a function of reception direction. The transmission comprises predetermined data. The apparatus comprises also a processing unit that forms taps of a delay profile on the basis of comparison between the data that is received and corresponding predetermined data. The processing unit estimates direction for the taps of the delay profile on the basis of a reception direction of the transmission, and forms radio channel data by associating the taps of the delay profile with the estimated direction. The radio channel data is for a radio channel model of a MIMO emulation in an OTA chamber having a plurality of antennas around a test zone where a device-under-test may be placed.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH SINGAPORE (SALES) PTE LTD
OFDM demodulating apparatus and method
InactiveUS7701841B2Secret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFourier transform on finite groupsLatency distribution
An orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) demodulating apparatus includes a delay profile creating section, a Fourier converting section, a pilot signal extracting section, a transmission path characteristic estimating section, an inverse Fourier converting section, and a window control section. In this case, the window control section creates a delay profile for defining a calculation range by leaving a path which exists at a same position in both the delay profiles created by the delay profile creating section and the inverse Fourier converting section and the number of times of detection which is equal to or higher than a threshold value and defines a higher threshold value for the path at a predetermined position from the position of the main path within the delay profile created by the inverse Fourier converting section than for the paths at the other positions.
Owner:SONY CORP
Mobile terminal, a base station, and a synchronization control method
In a mobile communication system, the tracking of synchronization is conducted in a stable state even in a multipath environment. A delay profile detector calculates a delay profile a(n) using a despread signal for each processing unit n. A delay profile averaging unit averages a(n) to produce Ave(|a(n)|<2>). A data symbol detector conducts rake combining of the despread signal using a(n) and Ave(|a(n)|<2>). According to a(n) and Ave(|a(n)|<2>, a weighting function unit calculates a representative value representing delay waves. A loop filter generates a control signal in response to the representative value. A clock controller controls a spread code generator according to the control signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Multi-path detection circuit and method for a CDMA receiver
ActiveUS7075974B2Increase speedHigh speed machiningTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpatial transmit diversityPeak valueLatency distribution
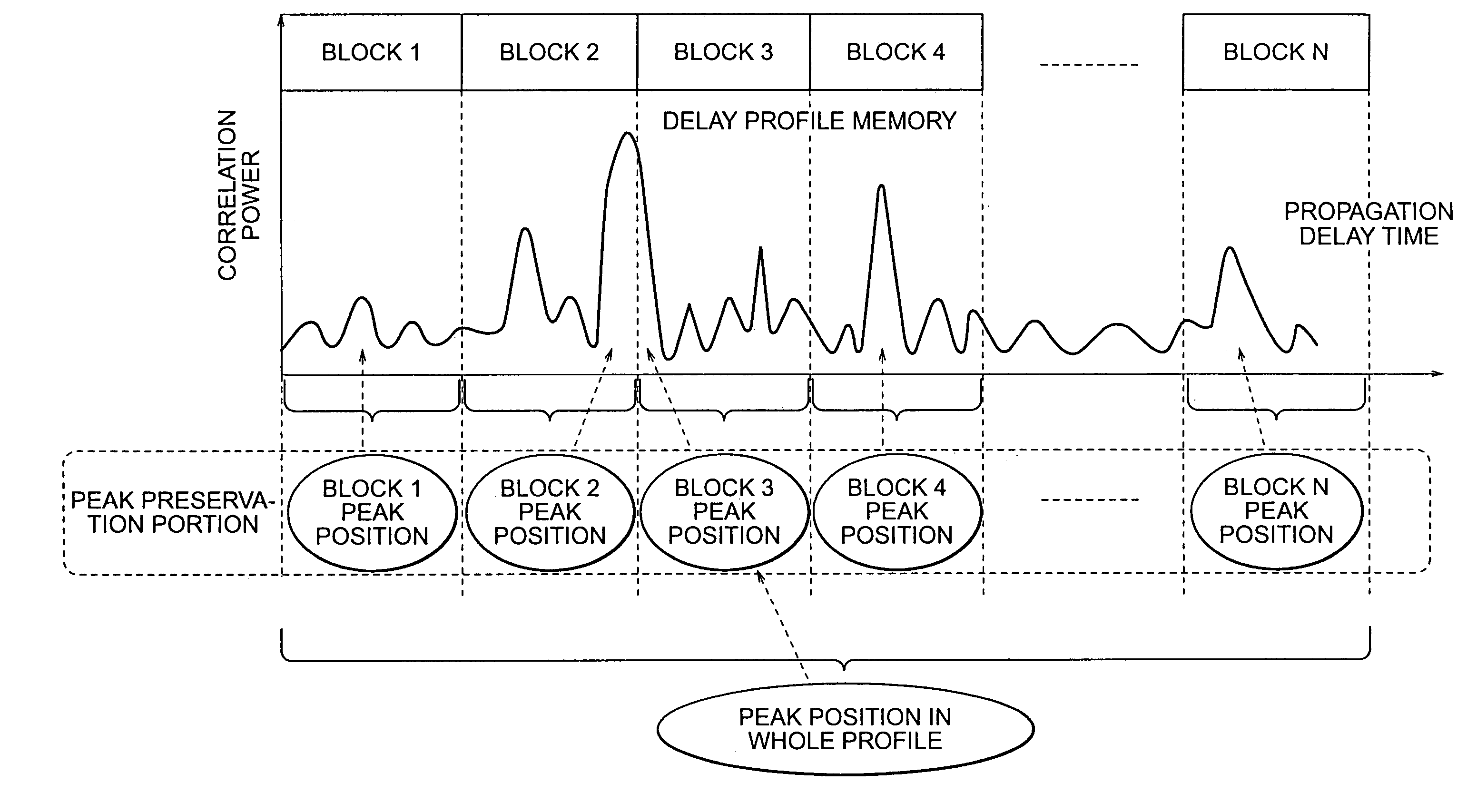
In a multi-path detection circuit for use in a CDMA communication system, a first peak is detected by searching a maximum value over a whole of data blocks composed of delay profile data. A second and the following peaks are detected by carrying out maximum value searching operation again only about a data block that is renewed in the delay profile data. As the remaining data blocks, a maximum value searched a previous time is preserved and used a next time and, therefore, reduction is possible in connection with the number of detection cycles necessary for detecting the second and the following peaks.
Owner:NEC CORP
Digital broadcasting receiving apparatus with channel estimation function
InactiveUS7817738B2Improve the channel estimation levelImprove reception performanceError preventionTransmission path divisionMobile vehicleDecision circuit
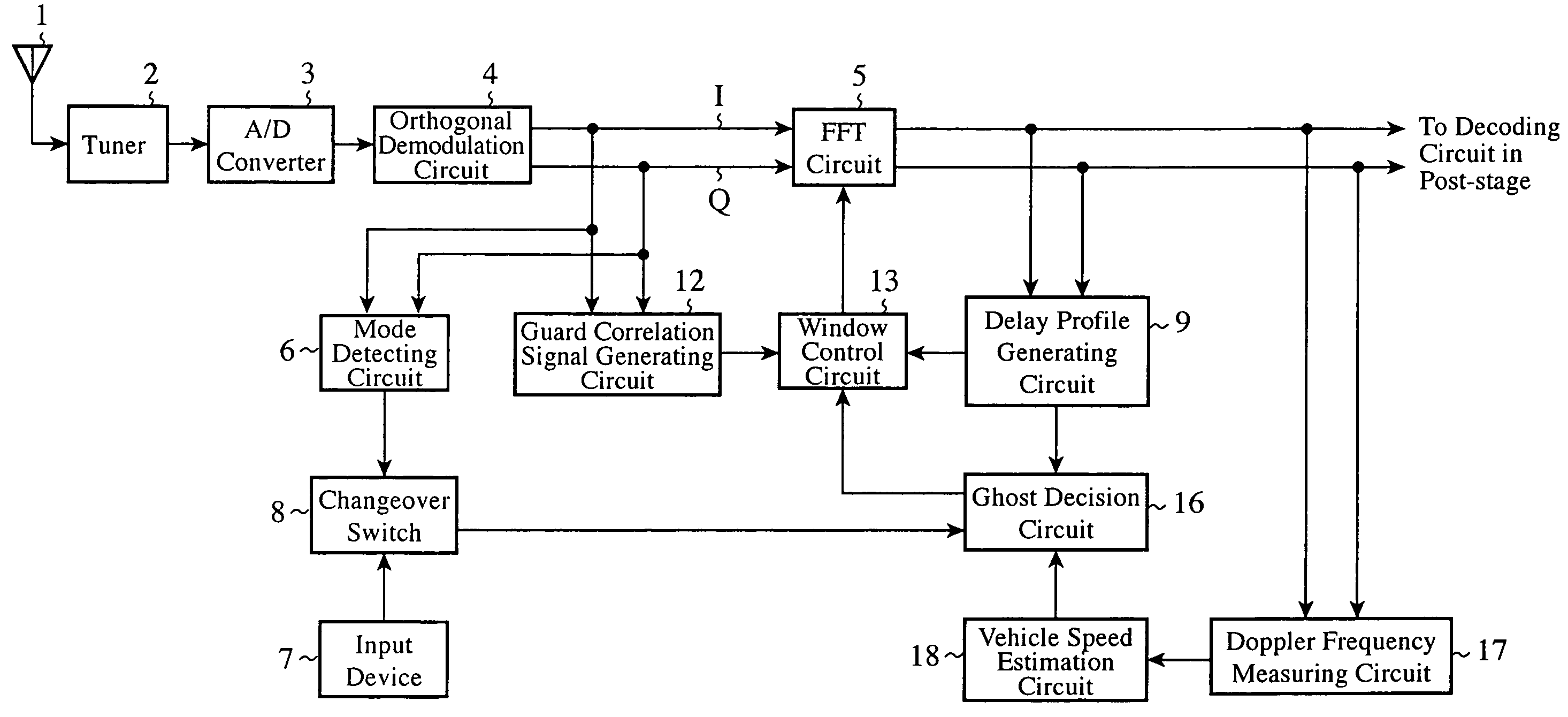
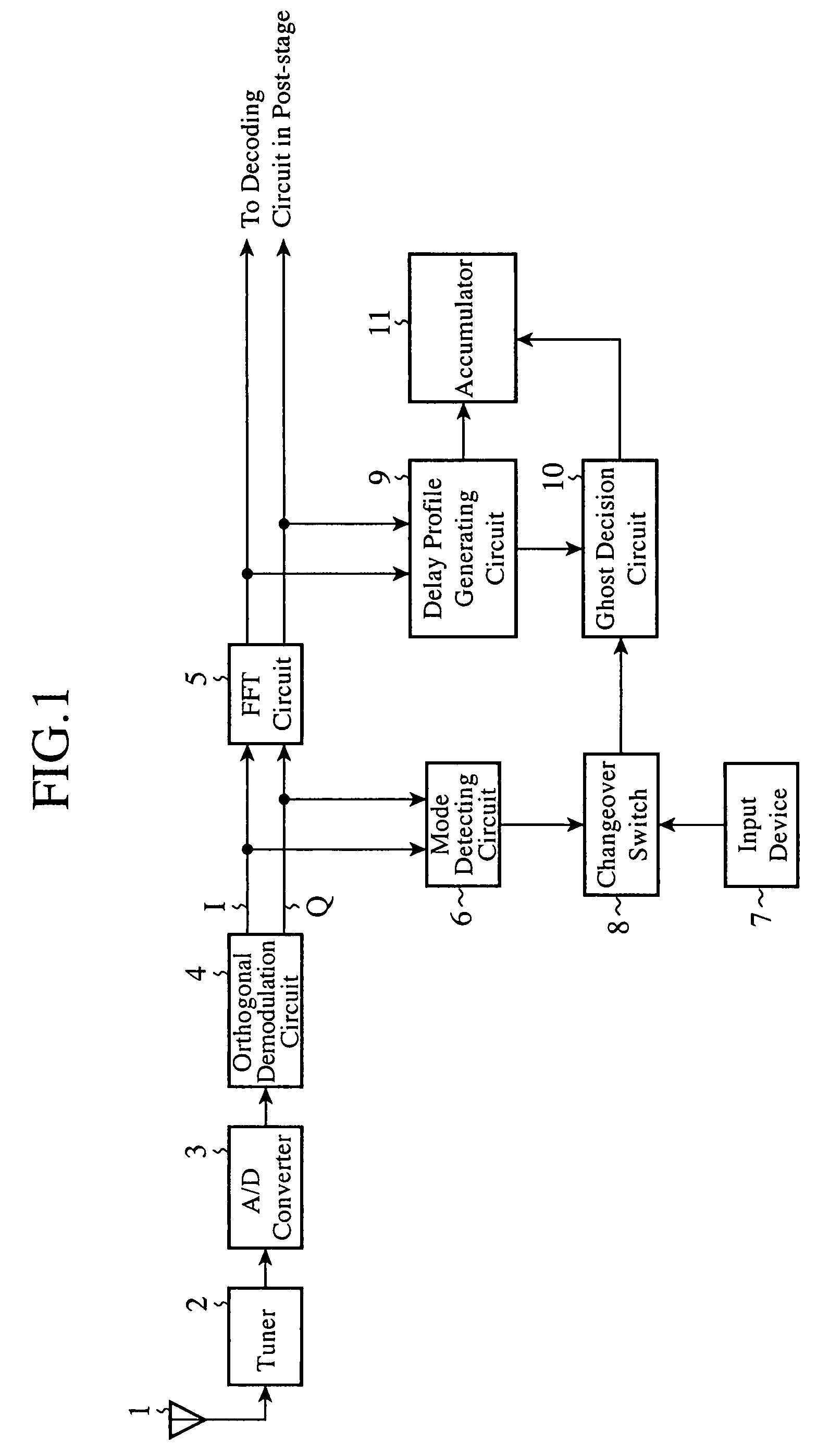
A delay profile generating circuit 9 generates a delay profile signal. Concerning the delay profile signal, a ghost decision circuit 10 makes a decision as to the presence or absence of ghosts that will appear during traveling of a mobile vehicle in response to a transmission mode signal fed from a changeover switch 8. The delay profile signal and the decision signal about the presence / absence of the ghosts are delivered to a window control circuit 13 via an accumulator 11. The window control circuit 13 sets and controls the FFT window position of an FFT circuit 5 in response to a guard correlation signal fed from a guard correlation signal generating circuit 12 and a signal fed from the accumulator 11.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Determination and selection of transmission paths as a function of the operating situation for setting up rake fingers for rake receiver units in mobile communication terminals
ActiveUS7508862B2MoreMore objective accuracySpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsNoise levelRake receiver
Correlations between the received signal to which pilot symbols have been applied at the transmitter end, and a correlation signal which contains the pilot symbols are carried out in the receiver in order to determine a path delay profile. Averaging processes are carried out over two or more delay profiles obtained in this way. Evaluations are carried out in one or more threshold value selection units (22.1, 22.2) on two or more averaged delay profiles with the aim of path selection. The parameters which govern the correlations and / or the averaging processes and / or the evaluations, and / or the repetition interval of these calculations are set as a function of the relative speed between the transmitter and the receiver, the frequency error between the carrier frequency of the received signal and the reference frequency that is set at the receiving end, and the noise level of the received signal. In the case of reception from two or more base stations, a final path selection is made in a finger allocation unit (40).
Owner:APPLE INC
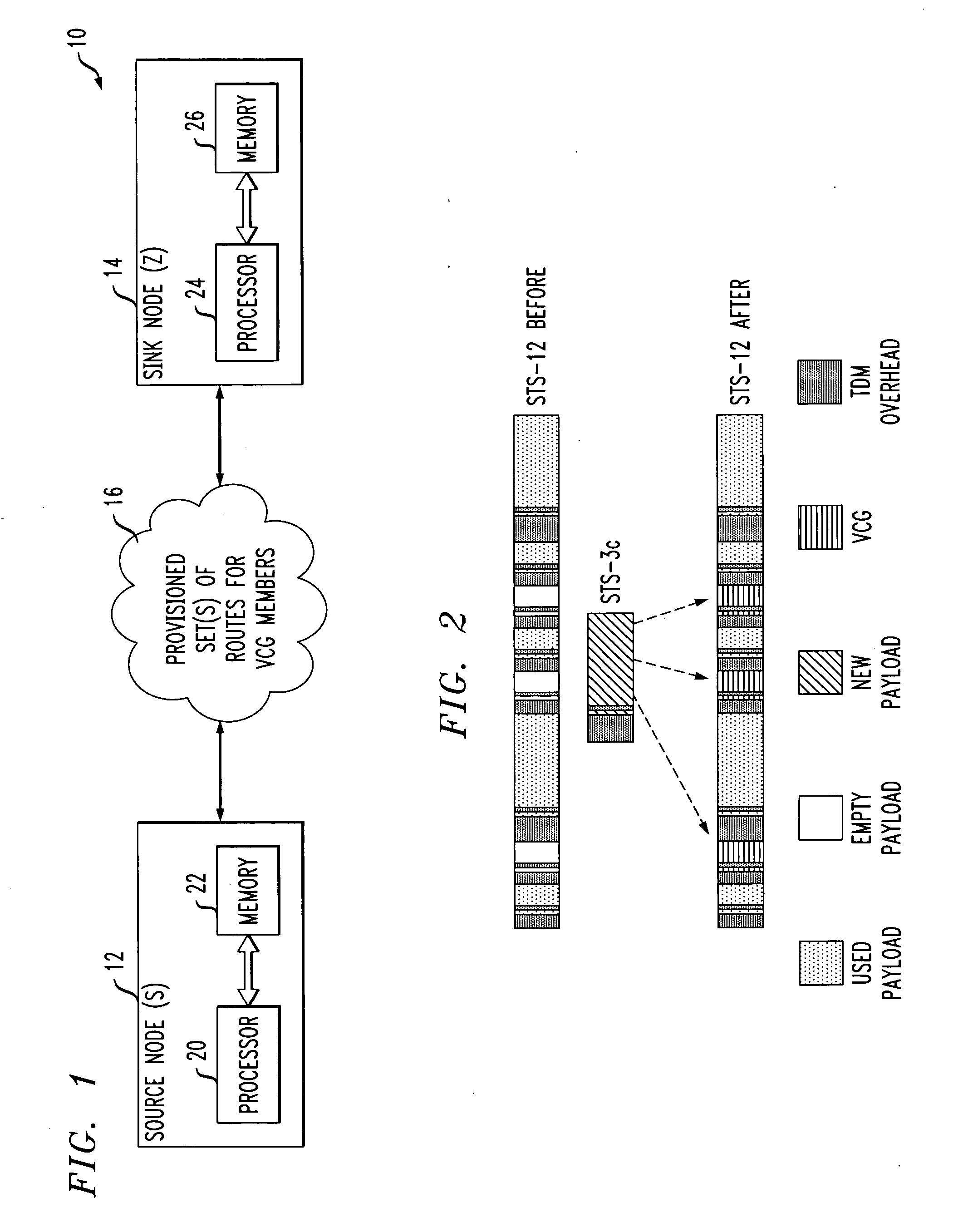
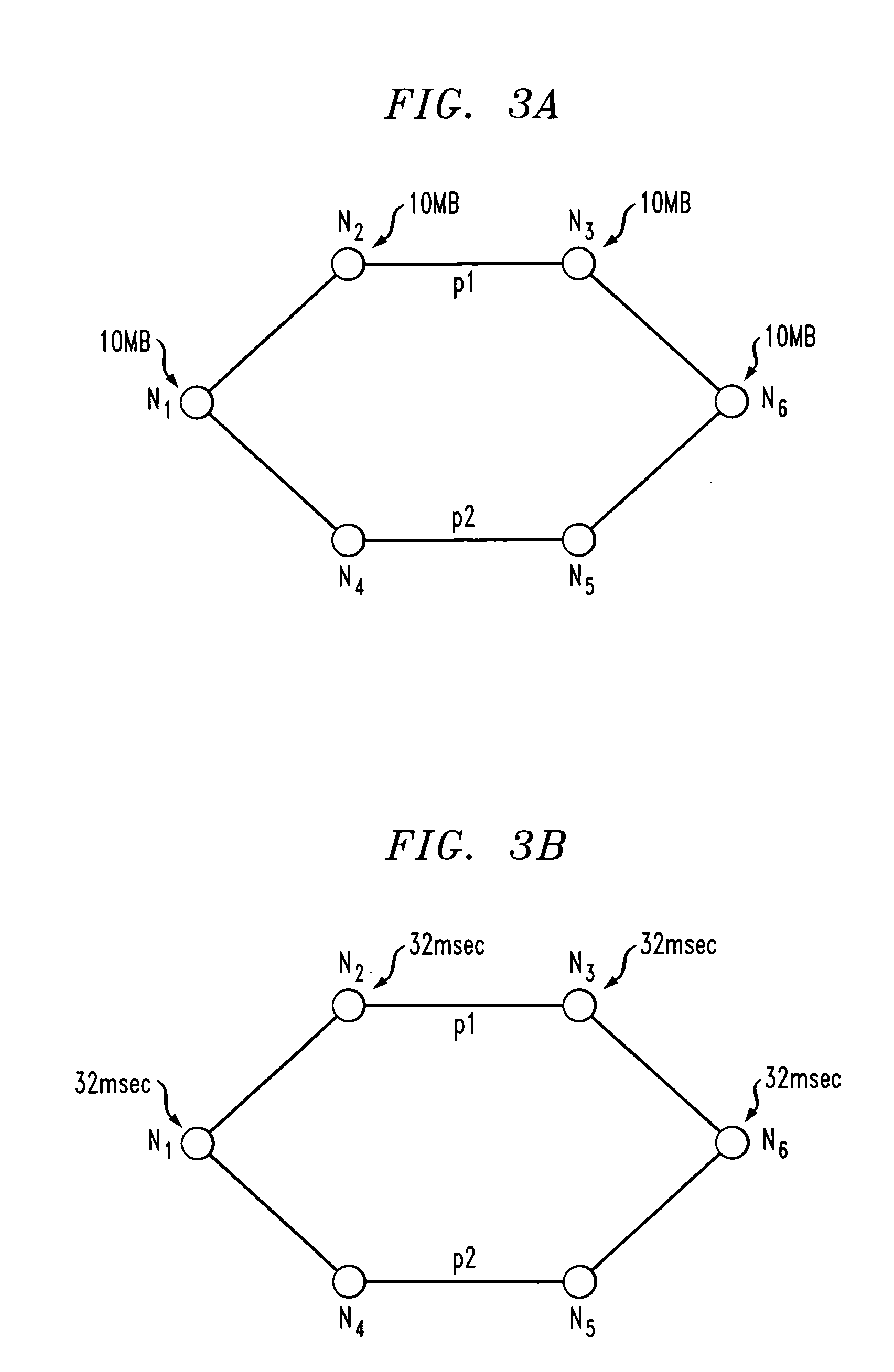
Delay distributed virtually-concatenated data traffic
ActiveUS20060140116A1Buffer size requiredDestination be minimizedError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityLatency distribution
Network design techniques and techniques for routing virtually-concatenated data traffic in a network in a manner which distributes delay to intermediate nodes of the network are disclosed. For example, in one aspect of the invention, a technique for routing virtually-concatenated data traffic in a network comprising a plurality of nodes comprises, for a given traffic demand to be routed from a source node to a destination node in the network, the following steps / operations. Two or more paths are determined to route the given traffic demand. Each of the two or more paths correspond to a member of a virtually-concatenated group. At least one path of the two or more paths comprises the source node, the destination node and at least one other node coupled between the source node and the destination node. Further, at least a subset of the source node, the destination node and the one other node buffer at least a portion of the given traffic demand such that a delay is distributed over the at least one path. The given traffic demand is routed over the two or more determined paths. The at least one path is preferably the shorter of the two or more determined paths.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method of adjusting a local clock in asynchronous packet networks
ActiveUS20130308660A1Reduce congestionAccurate timingTime-division multiplexTransmissionArrival timeLatency distribution
In a computer-implemented method of adjusting a local clock at a receiver in a packet network, the local clock is generated by a phase locked loop locked to a master clock with the aid of time-stamped timing packets arriving over the network from the master clock with a packet delay distribution about a nominal delay. The timing packets are filtered to adjust for the packet delay distribution. A control input for the phase locked loop is derived from the timing packets. The amount of skew in the packet delay distribution about the nominal delay is determined, and the arrival times of timing packets are then selectively modified to correct for the amount of skew in the packet delay variation distribution prior to filtering the timing packets.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
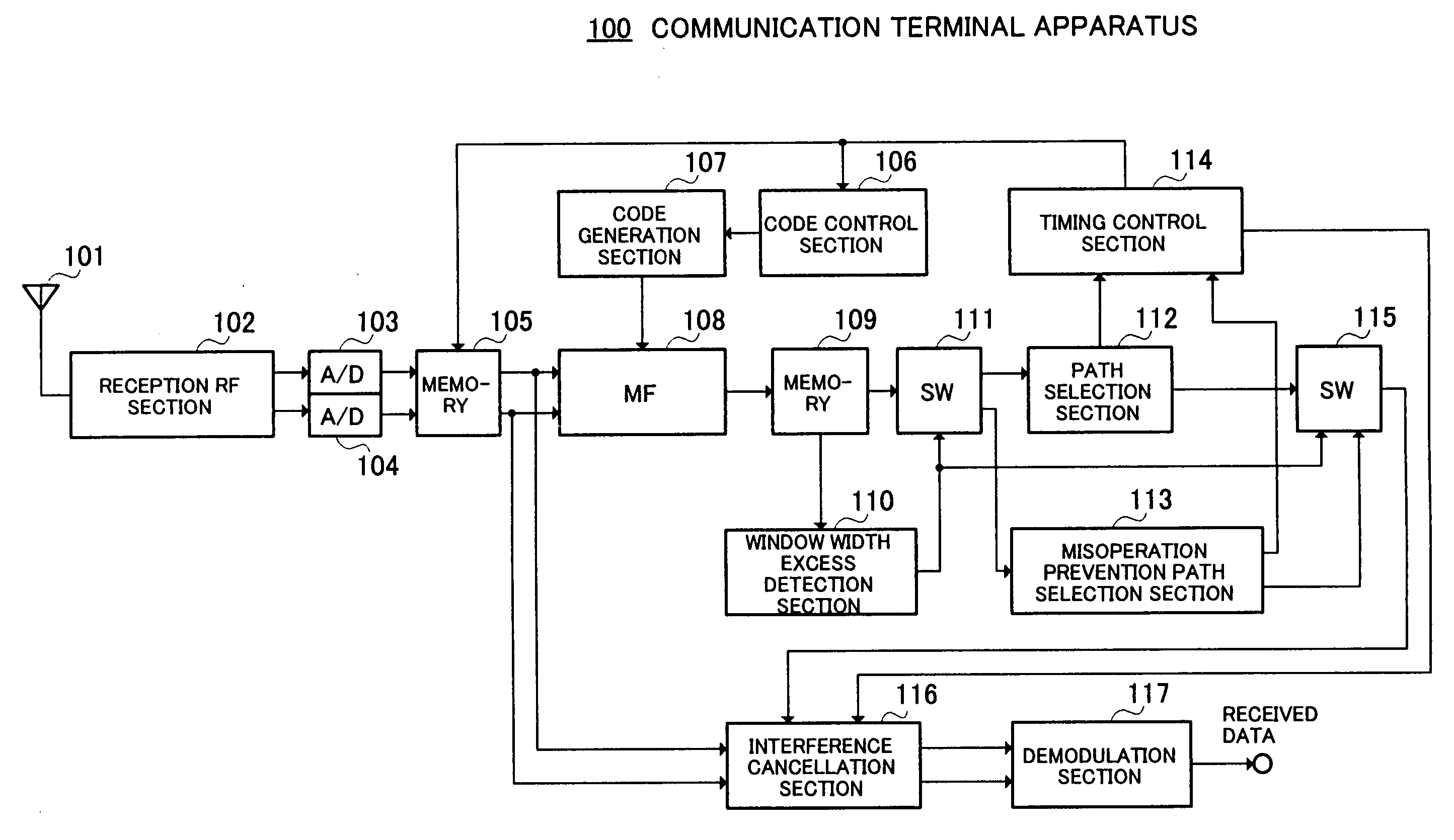
Apparatus and method for reception
The radio reception section 1102 receives a received signal whose band has been restricted using a filter. The delay profile creation section 1104 creates continuous delay profiles for every midamble shift. The distortion component creation section 1106 creates start path distortion components by multiplying the power value of the start sample of each midamble shift by a coefficient of the filter. The removing section 1107 removes the start path distortion components of the following midamble shift from predetermined samples behind the delay profile of each midamble shift. The path selection section 1108 selects samples whose power value is equal to or greater than a threshold as paths from the delay profile with the start path distortion components removed as paths.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of detecting path timings and CDMA receiving apparatus using the same
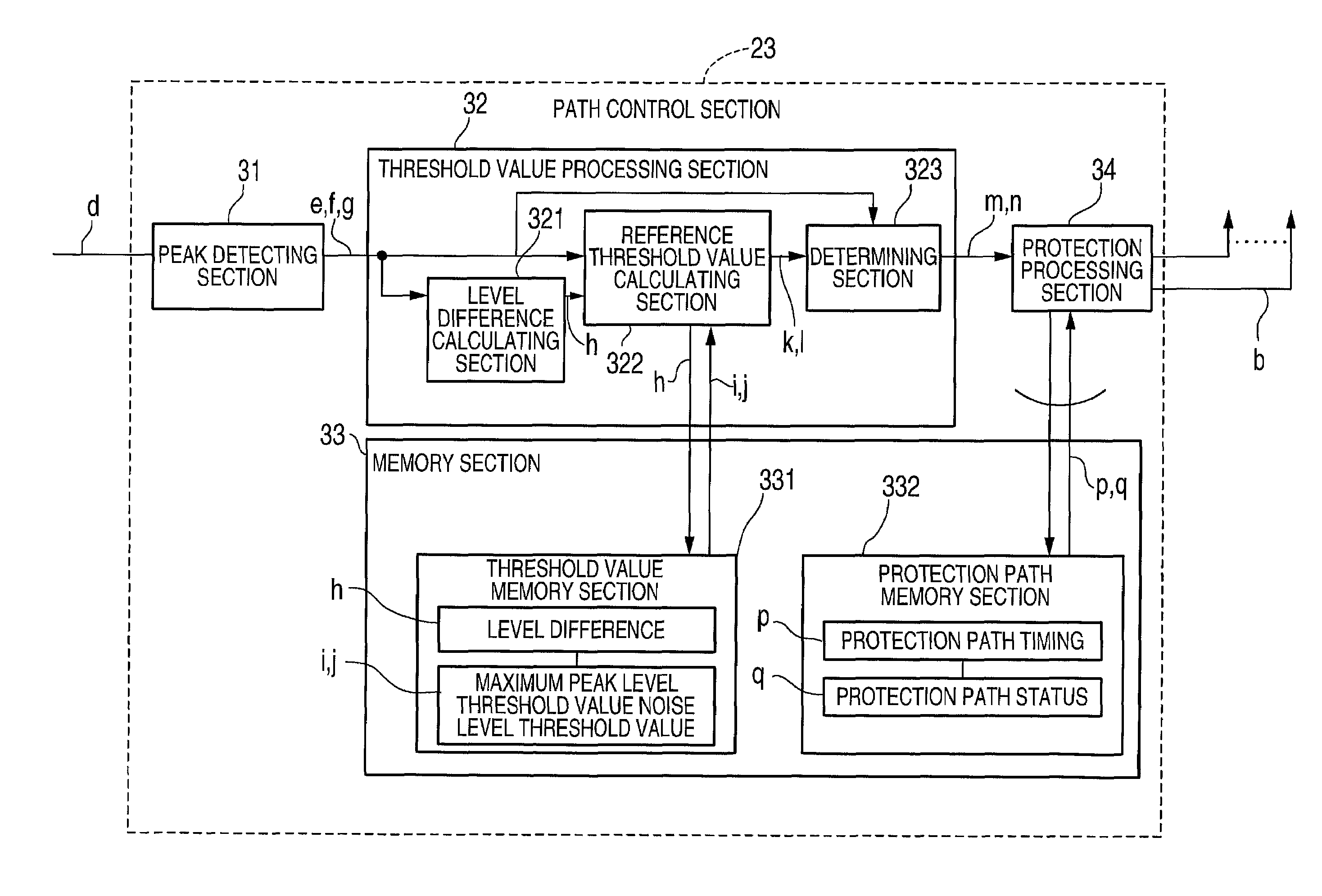
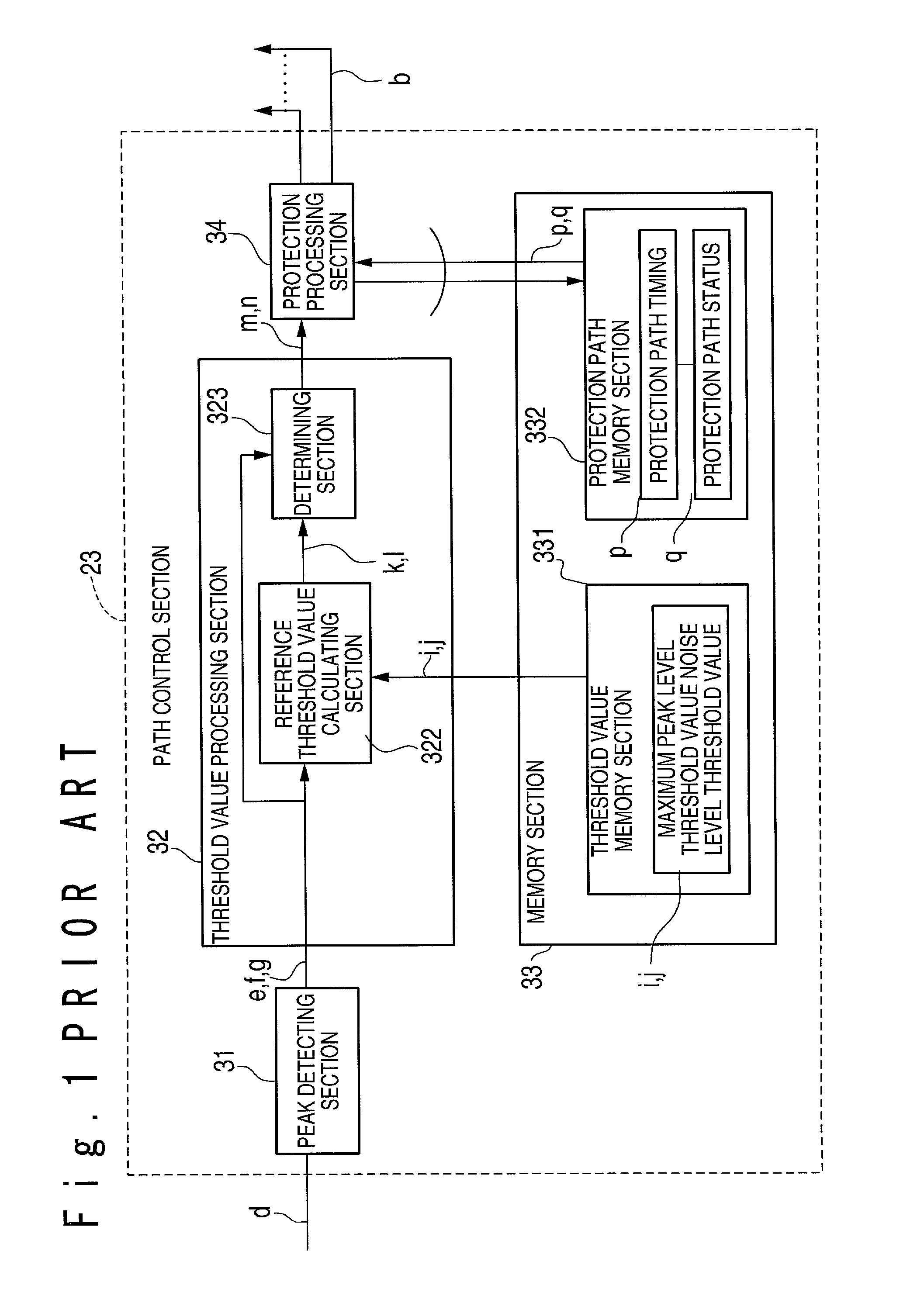
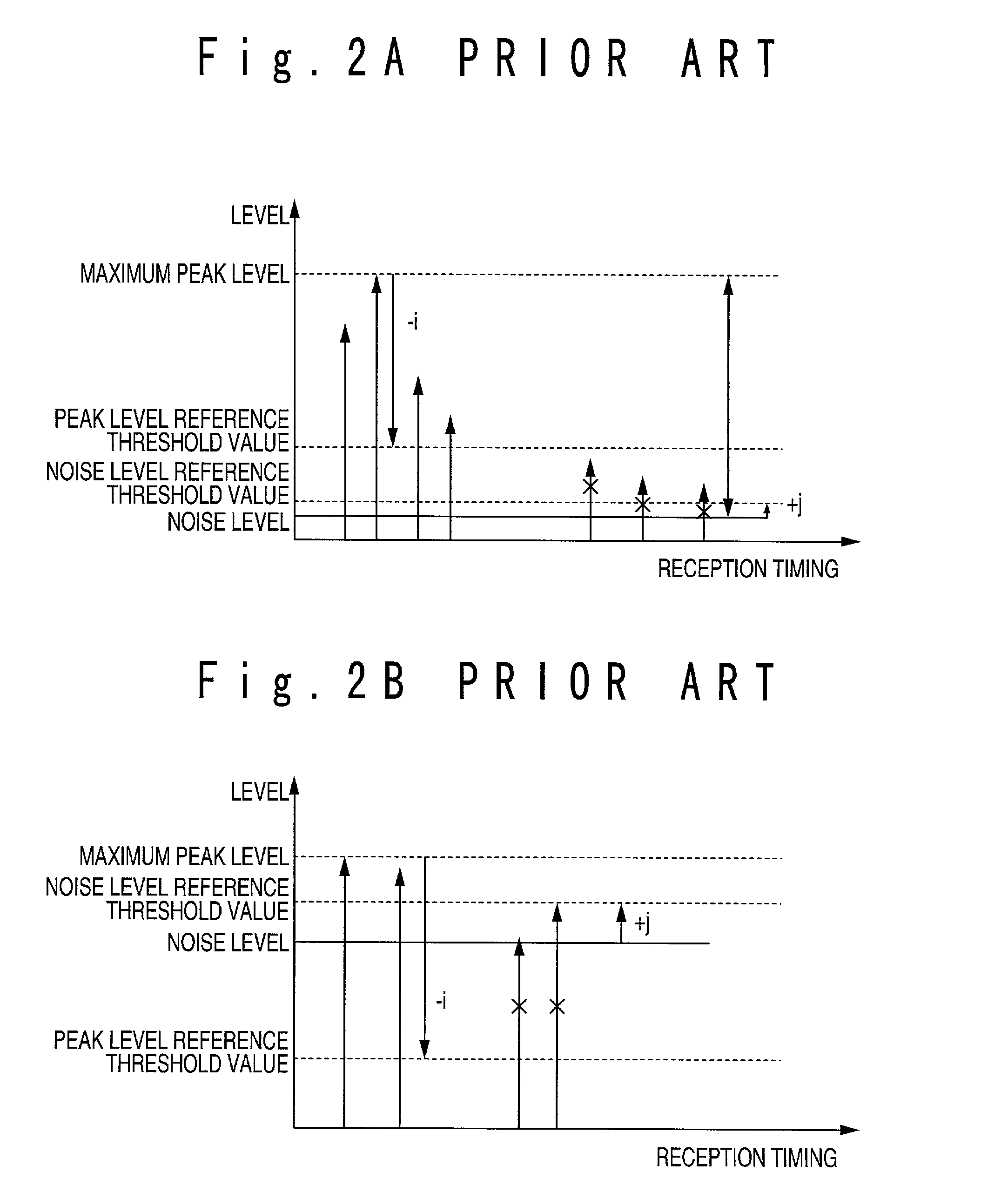
InactiveUS7050484B2Improve reception characteristicsStrong pathDiversity/multi-antenna systemsNoise levelPeak value
A CDMA receiving apparatus includes a searcher section, a finger section, a RAKE synthesizing section and a decoding section. The searcher section has a protection path memory, generates a delay profile from a reception signal, and finds peaks from the delay profile based on a variable peak level reference threshold value and a variable noise level reference threshold value which are determined based on the delay profile. Also, the searcher section reads out protection path data in a previous cycle from the protection path memory, and determines timings of valid paths based on timing of the found peaks and protection path timings of the read out protection path data. The finger section detects a signal from the reception signal for every path in response to the valid path timings. The RAKE synthesizing section carries out RAKE synthesis to the detected signals to produce a RAKE synthesis signal. The decoding section decodes the RAKE synthesis signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Radio terminal
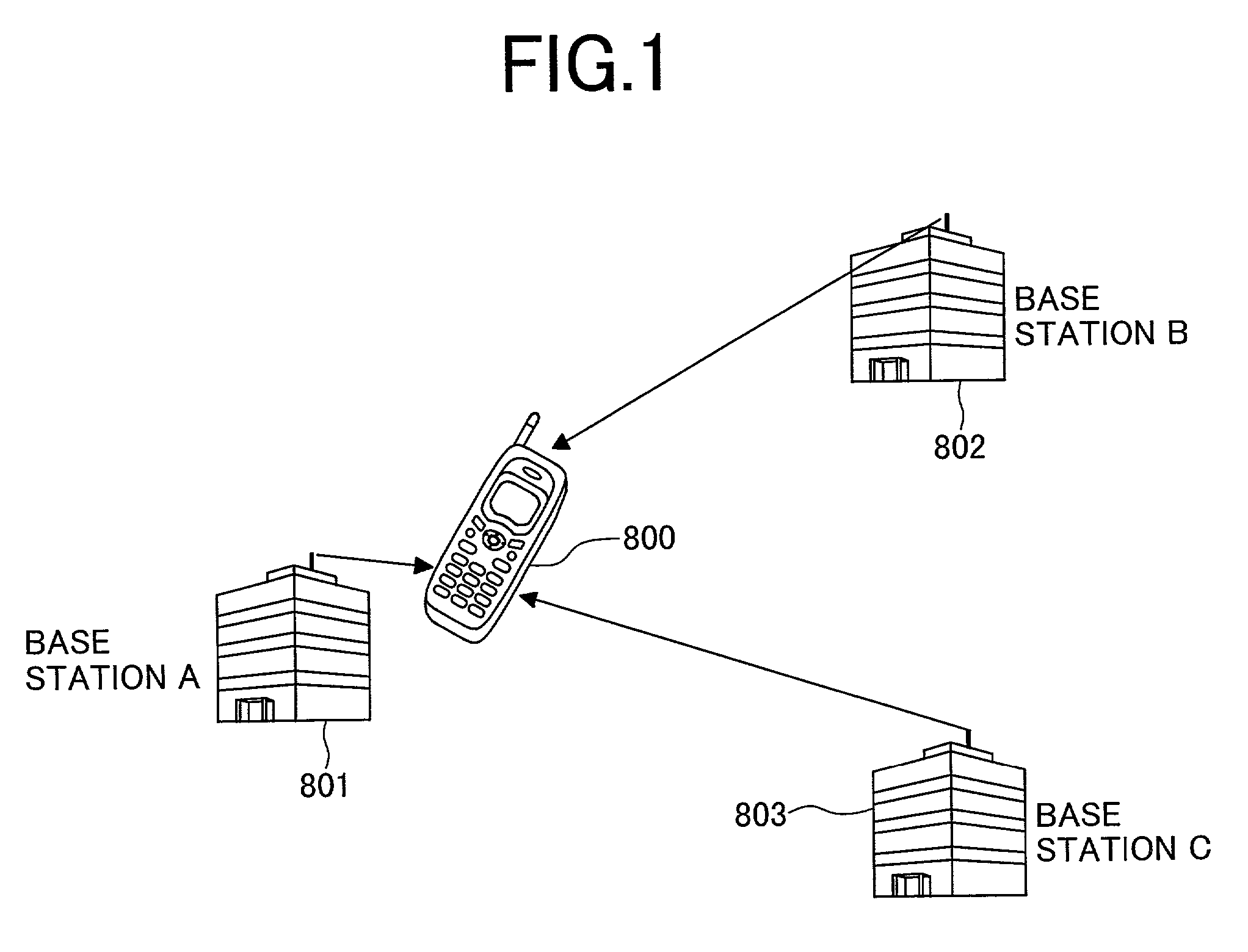
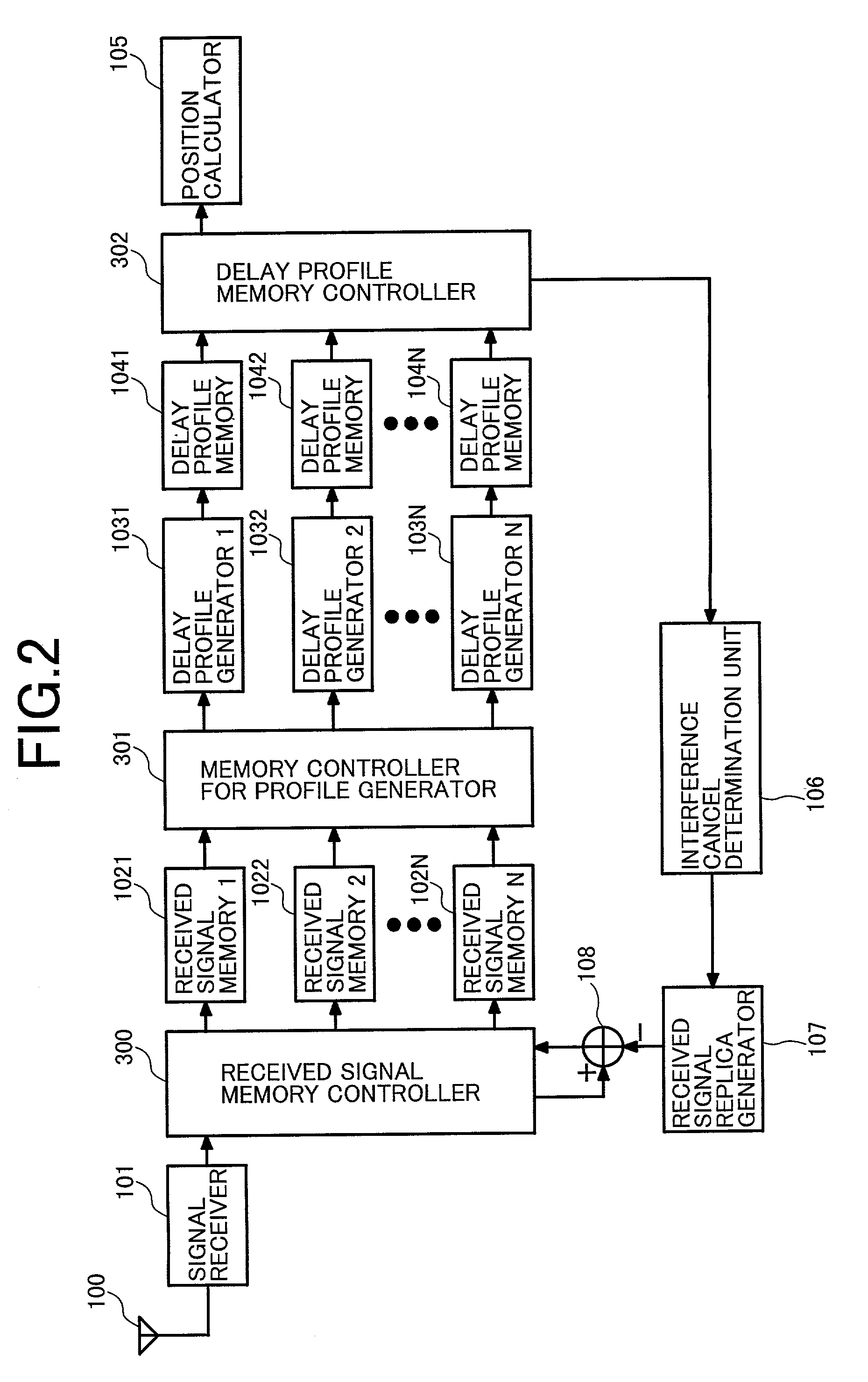
ActiveUS7016653B2Reduce capacitySpeedPosition fixationTransmission monitoringComputer terminalLatency distribution
A radio terminal that receives signals from a plurality of radio stations to calculate its current position has: interference canceling means for canceling each interference signal from the plurality of received signals; a plurality of delay profile generating means for generating delay profiles of the plurality of interference-canceled received signals with use of respective corresponding codes; and position calculating means for calculating its current position, which is a signal receiving point, with use of the plurality of delay profiles, whereby advantageously reducing the capacity of a memory mounted in the mobile terminal while the position calculation is speeded up
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com