Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
176 results about "Heart rate rhythm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Normal Sinus Rhythm. A normal heart rhythm is called normal sinus rhythm (NSR for short). An NSR will have a heart rate (this is the same as the pulse) between 50 and 100 beats per minute and a normal impulse formation from the SA node (P wave).
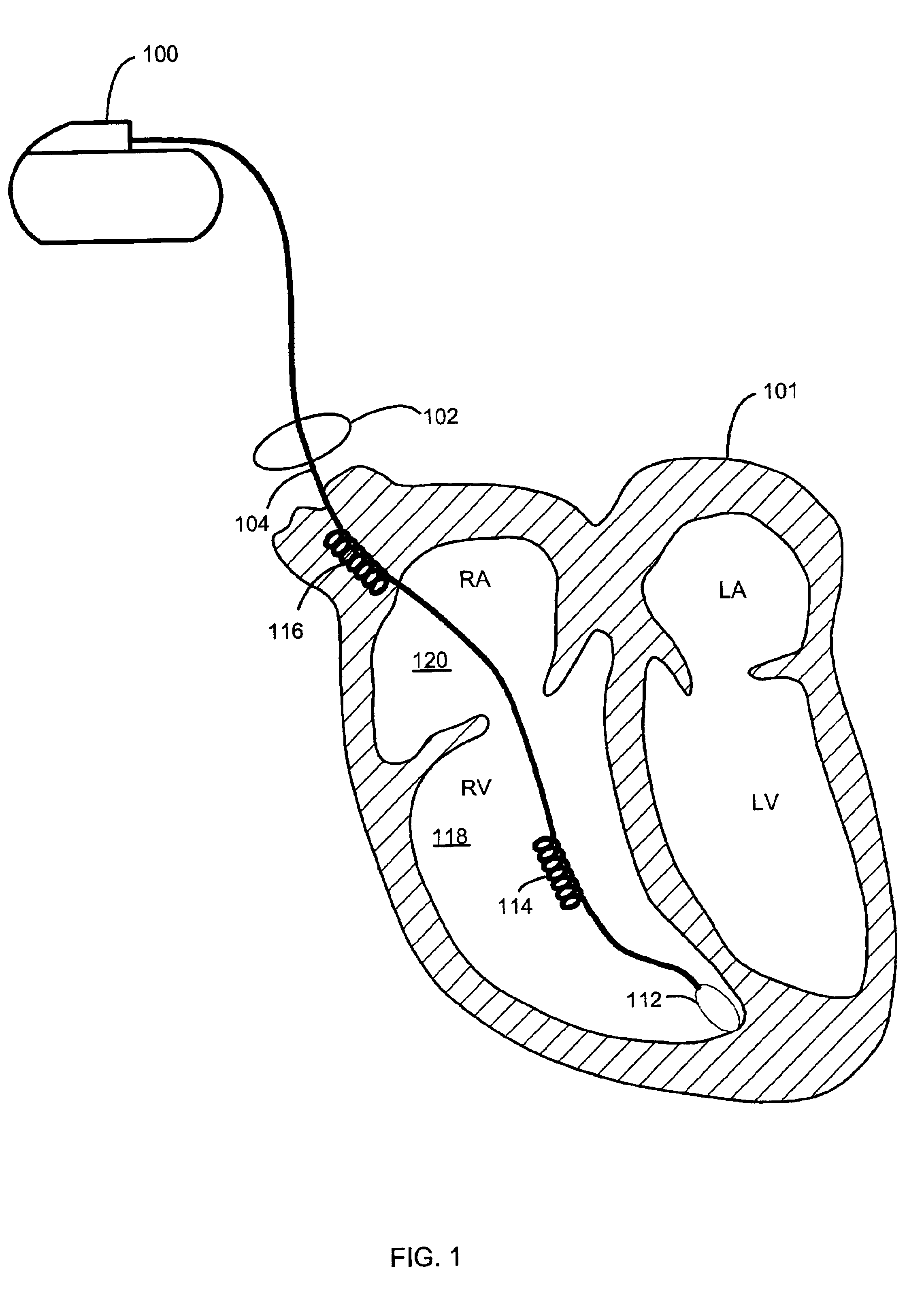
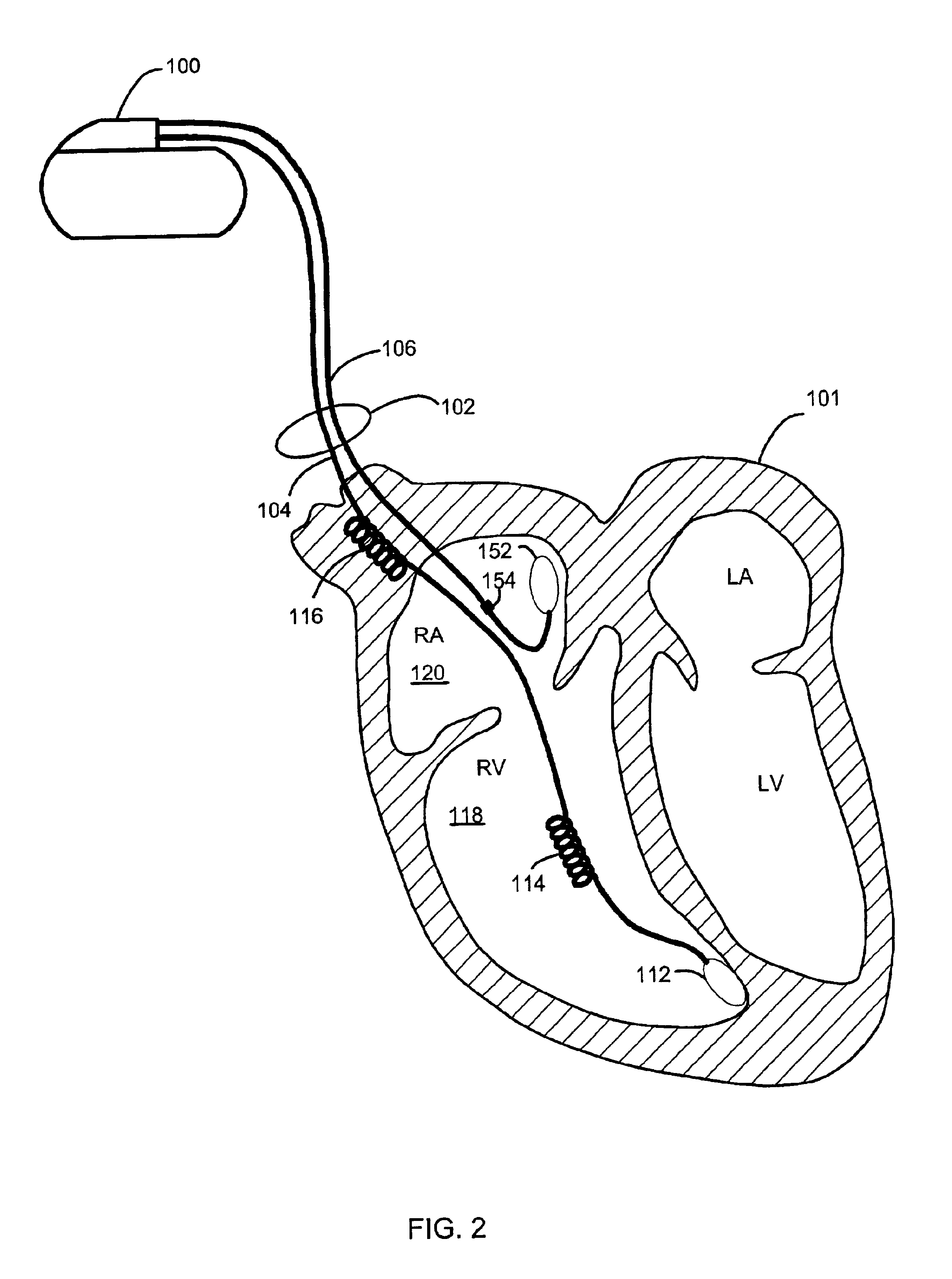
System for cardiac resuscitation
ActiveUS7277752B2Short response timeDegree of communication redundancyPhysical therapies and activitiesMedical communicationCardiac resuscitationEmergency medicine
A system and method for monitoring and controlling the therapy of a cardiac rhythm abnormality victim at a remote site by proving immediate access to a medical professional at a central station. The method comprises the steps of: (1) providing a plurality of electrodes for receiving cardiac signals generated by the victim and for the application of electrical pulses to the victim at a remote site; (2) transmitting the signals from the remote site to a central station; (3) receiving the signals at the central station and displaying them for the medical professional; (4) selecting whether to delivery defibrillation or pacing therapy to the victim based on the medical professional's analysis of the signals (5) transmitting the selection results to the remote site; and (6) receiving the selection results at the remote site and applying the selected therapy to the victim.
Owner:MATOS JEFFREY A
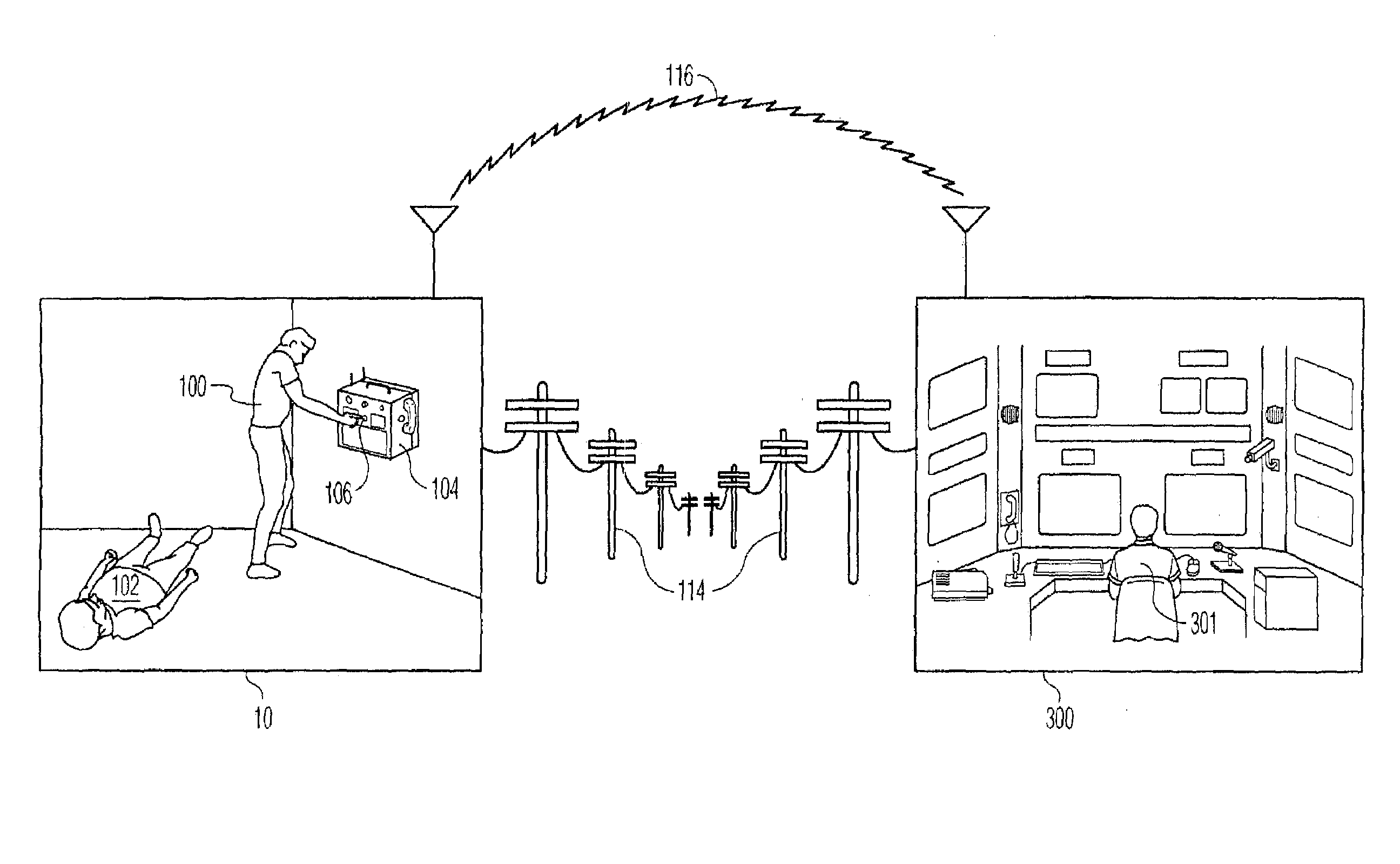
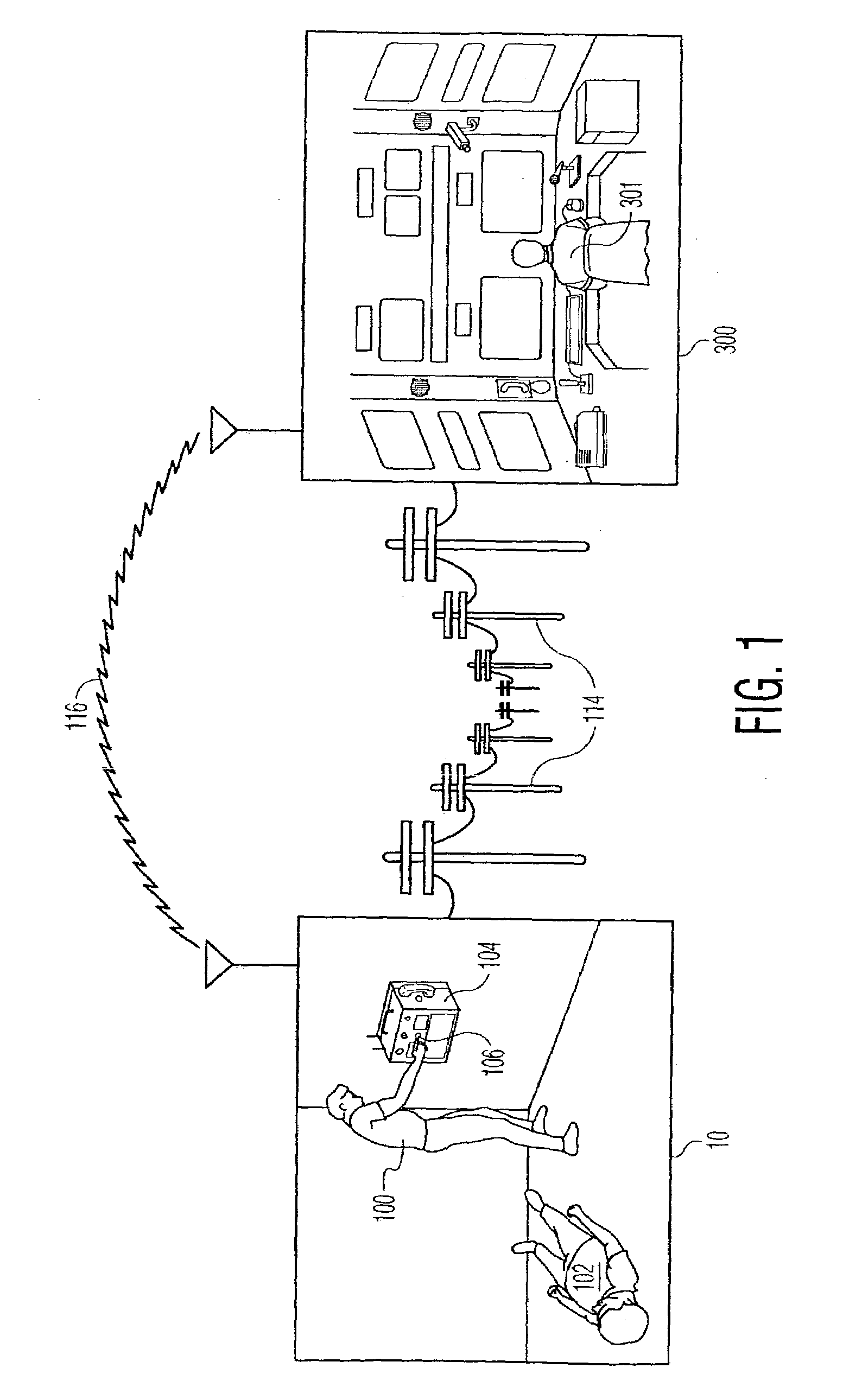
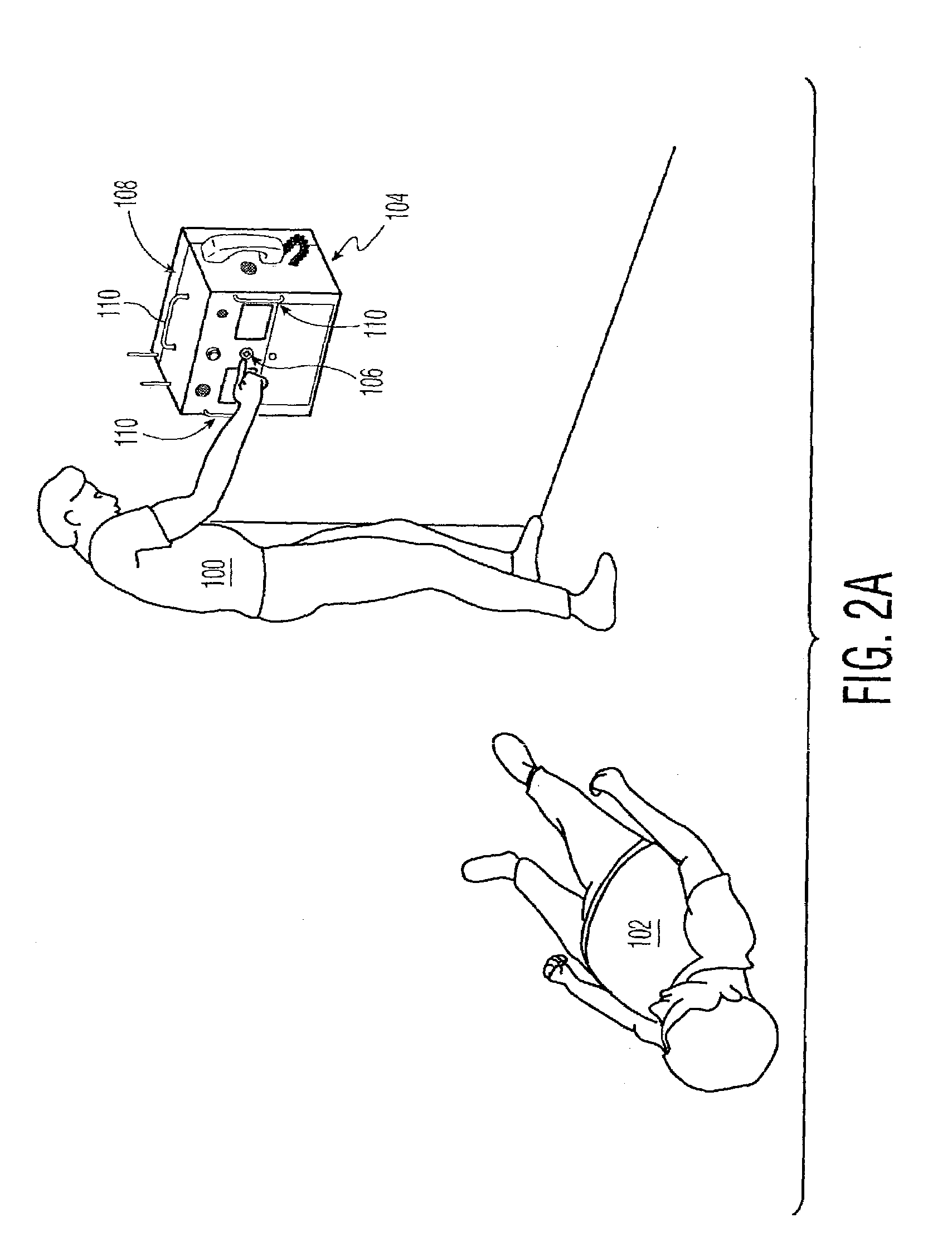
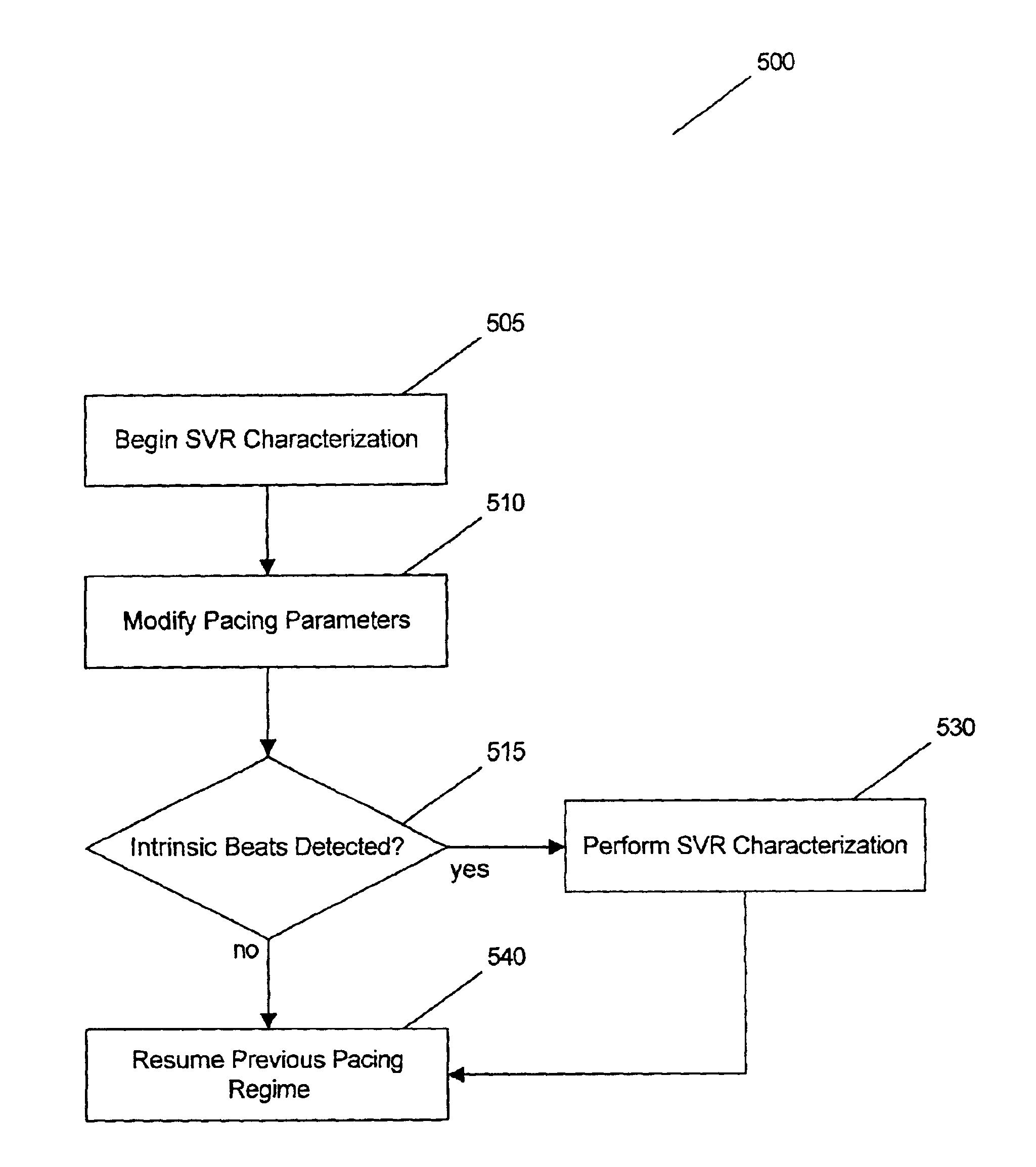
Method and system for characterizing supraventricular rhythm during cardiac pacing
A method and system for generating a characterization of one beat of a patient's supraventricular rhythm (SVR) involves performing such characterization while the heart is being paced. During SVR characterization, various pacing parameters are modified and the patient's supraventricular rhythm is characterized while the pacing parameters are modified. The SVR characterization process is effective in single and multiple chamber pacing modes.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC +1
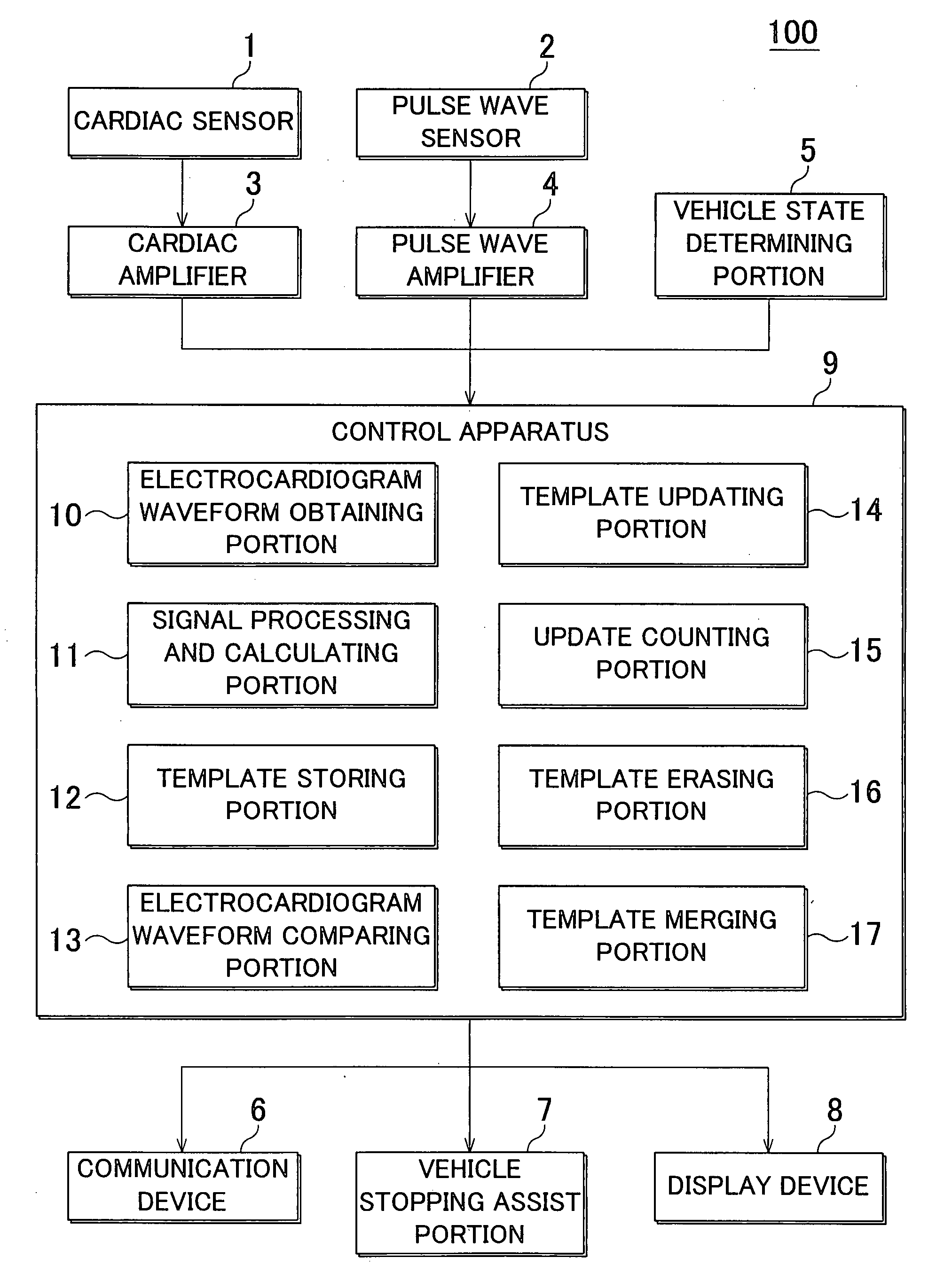
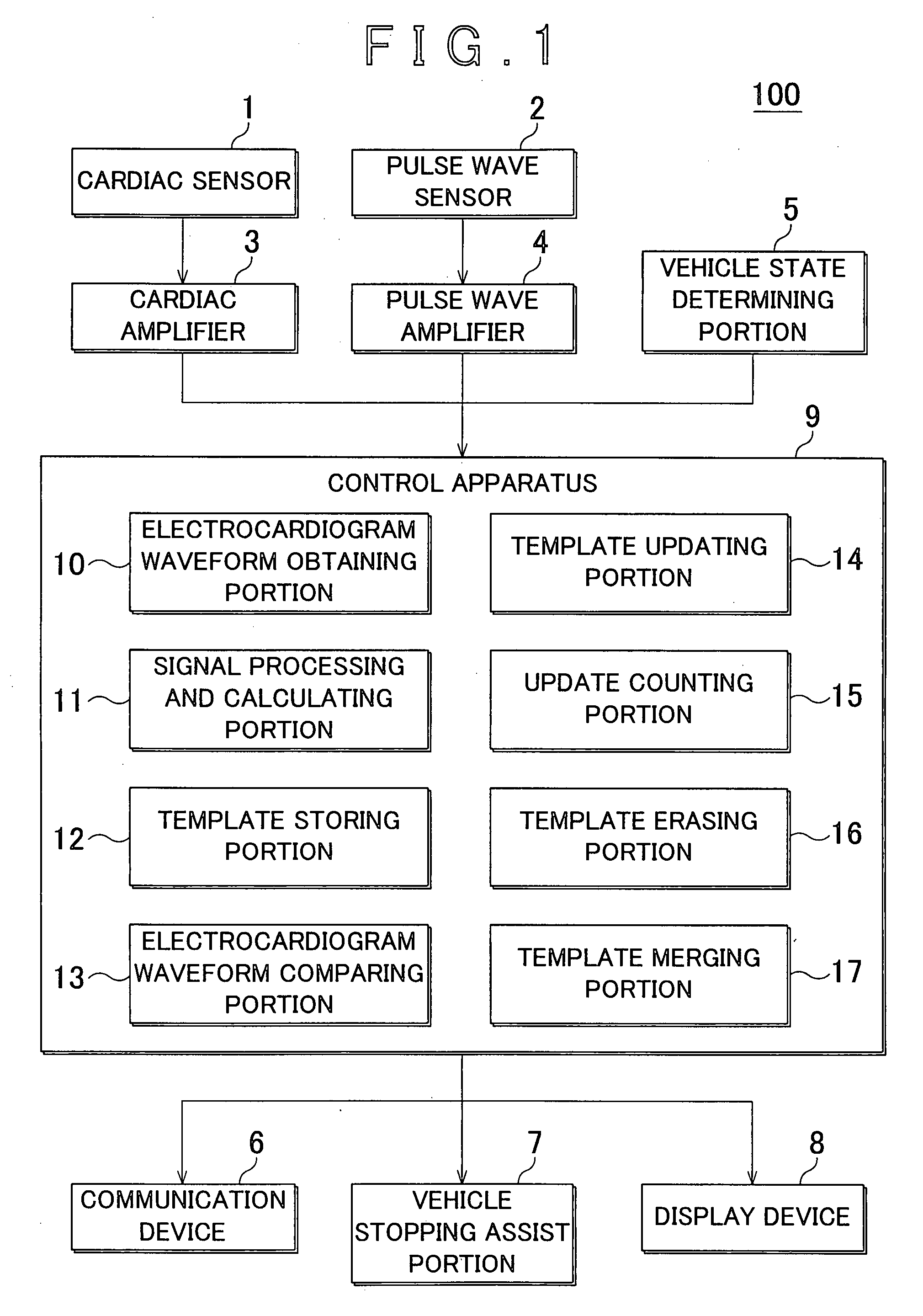
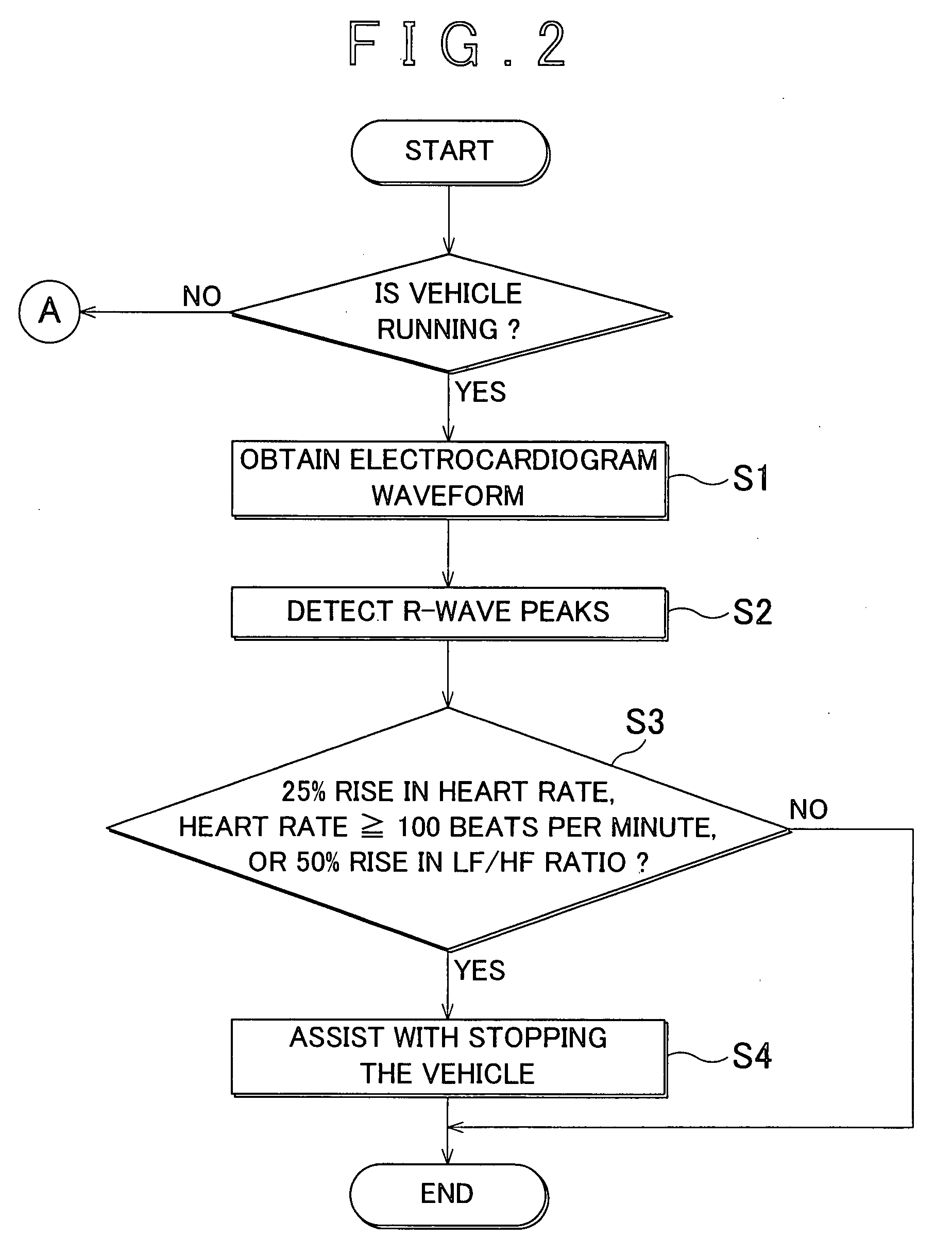
Method and device for monitoring heart rhythm in a vehicle
ActiveUS20070265540A1Reliably determineReliably determinedElectrocardiographySensorsDriver/operatorCardiac rhythm monitoring
An heart rhythm monitoring device for a vehicle, which determines whether a driver has an arrhythmia includes a vehicle state determining portion that determines whether the vehicle is stopped; an electrode arranged on a steering wheel in a position where the driver grips the steering wheel; an electrocardiogram waveform obtaining portion that obtains a first electrocardiogram waveform from the electrode; and a signal processing and calculating portion that determines whether the heart rhythm of the driver is erratic based on the first electrocardiogram waveform. When the vehicle is in motion, the signal processing and calculating portion determines whether the heart rhythm of the driver is erratic based on the waveform component that is strong with respect to noise in the first electrocardiogram waveform.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +2
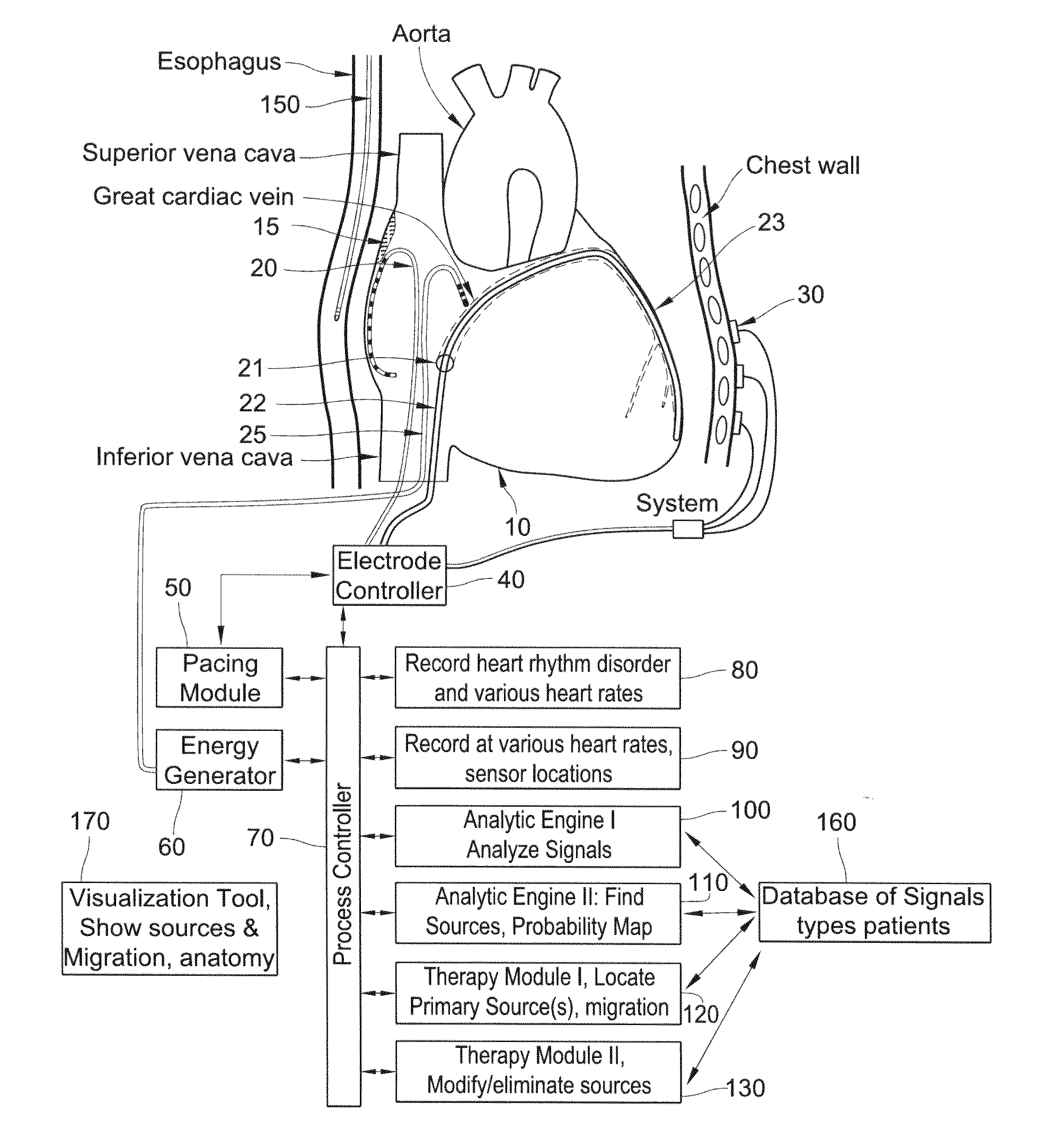
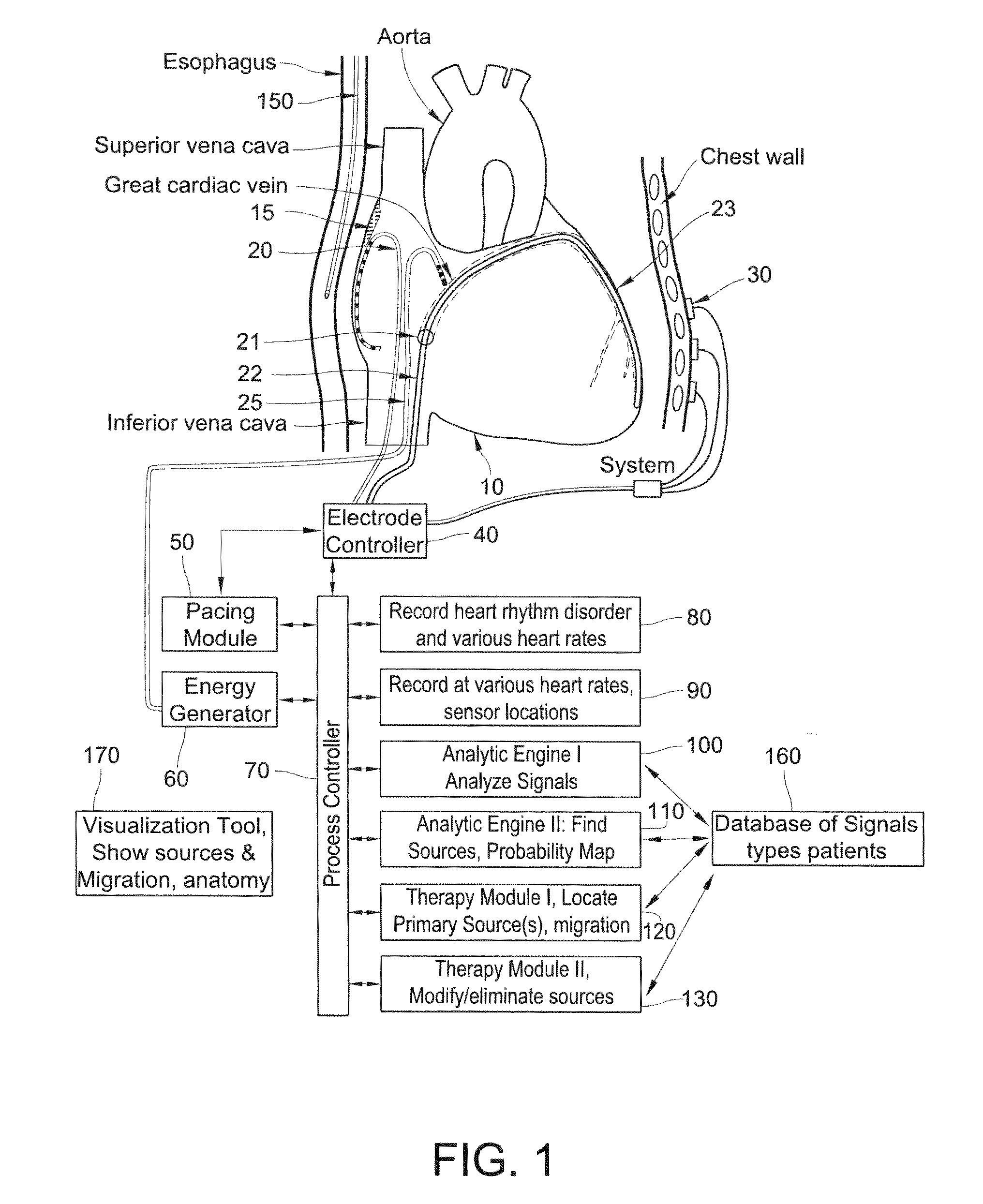
Methods, system and appartus for the detection, diagnosis and treatment of biological rhythm disorders
ActiveUS20100094274A1Improve abilitiesRemove obstaclesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyRhythmCardiac dysrhythmias
Method, system and apparatus to detect, diagnose and treat biological rhythm disorders. In preferred particularly desirable embodiment relating to the real-time detection of heart rhythm disorders, this invention identifies localized sources for complex rhythms including atrial fibrillation to guide the localized application of energy to modify the source and treat the rhythm disorder.
Owner:THE US REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS OFFICE OF THE GENERAL COUNSEL 024 +1
Optical depolarization of cardiac tissue
ActiveUS20090054954A1No painIncrease photosensitivitySurgical instrument detailsViruses/bacteriophagesManagement systemDepolarization
The invention provides a cardiac rhythm management system for stimulating a heart having photosensitive tissue, vectors useful to photosensitize cells expressing the vectors, and methods for light induced depolarization of cells.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System for cardiac resuscitation
ActiveUS7769465B2Short response timeEliminate needHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalEmergency medicine
System and method for monitoring and controlling, defibrillation and pacing which allows a victim of a cardiac rhythm abnormality immediate access to a medical professional at a central station, who will remotely monitor, diagnose and treat the victim at one of a plurality of remote sites in accordance with the following steps:(1) providing a plurality of contact electrodes for a victim at a remote site for the receipt of ECG signals and for the application of electrical pulses to the victim;(2) transmitting the signals from the remote site to a central station and displaying them for review by the medical professional;(3) the medical professional selecting from a menu of defibrillation and pacing pulses, if the application thereof is appropriate;(4) transmitting the selection results to the remote site; and(5) receiving the selection results at the remote site and applying the selected pulses to the victim.
Owner:MATOS JEFFREY A
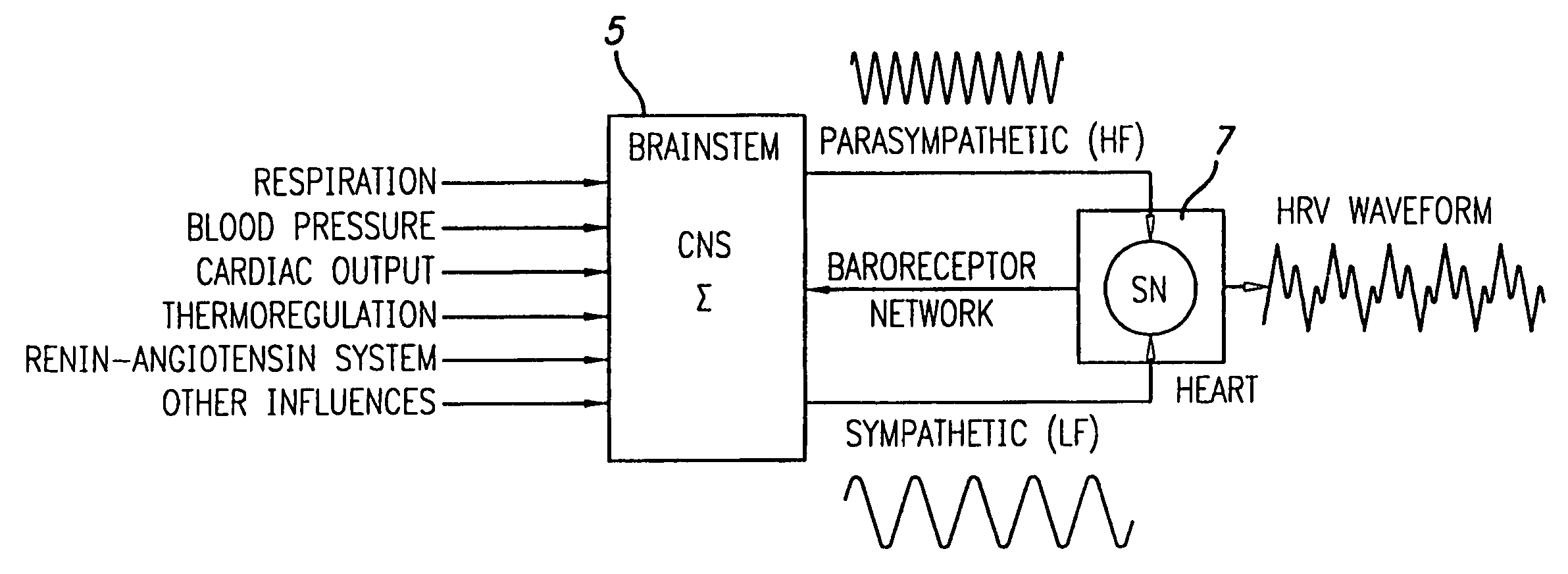
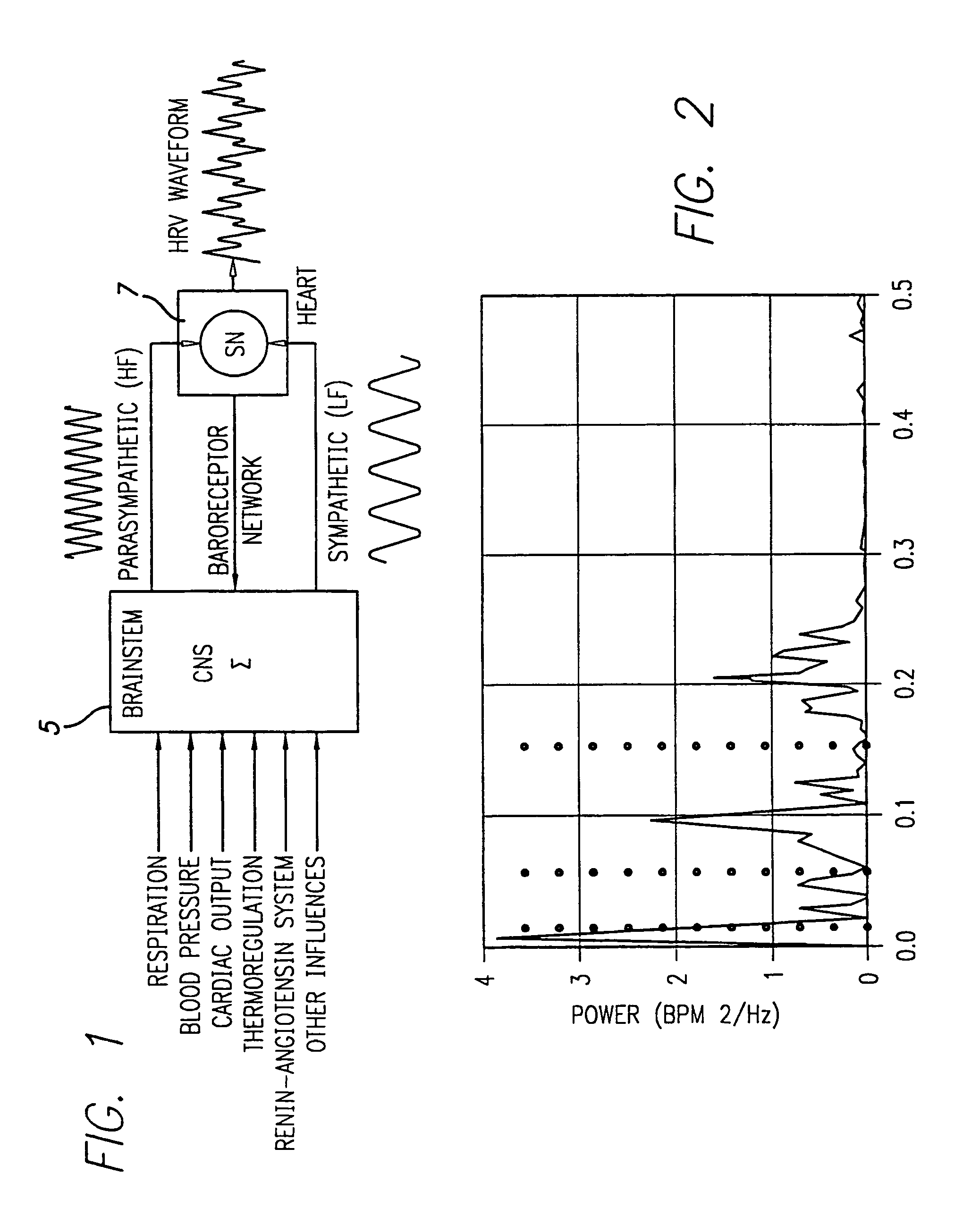
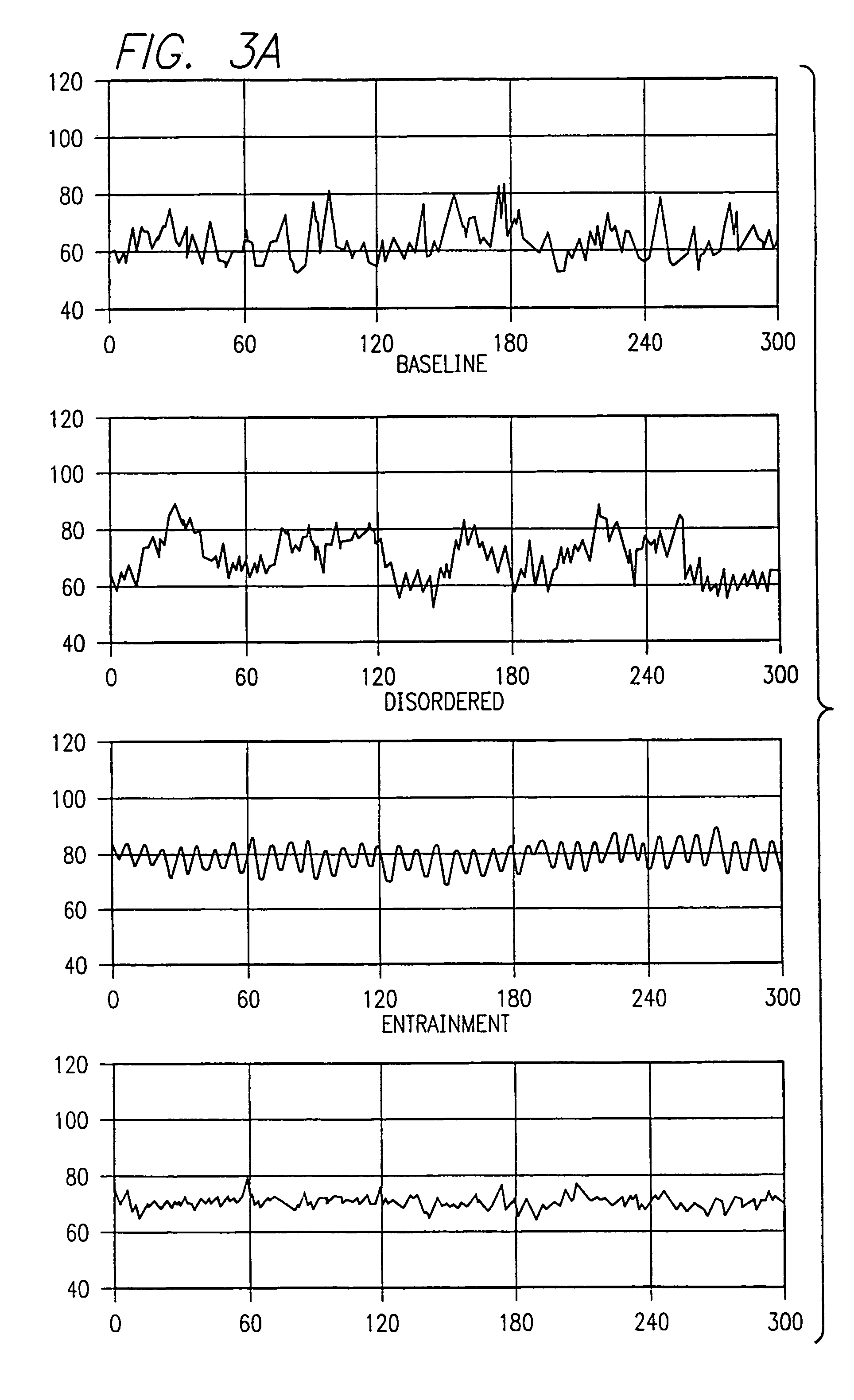
Method and apparatus for facilitating physiological coherence and autonomic balance
Method and apparatus for determining the state of entrainment between biological systems which exhibit oscillatory behavior such as heart rhythms, respiration, blood pressure waves and low frequency brain waves based on a determination of heart rate variability (HRV) and an evaluation of the power spectrum thereof. Entrainment reflects a harmonious balance between the two branches of the autonomic nervous system within the body. This internal state of heightened physiological efficiency enhances health and promotes optimal performance. According to one embodiment a method is used to determine the entrainment level based on an entrainment parameter related to HRV. The method first determines the power distribution spectrum (PSD) and then calculates an entrainment parameter (EP), which is a measure of the power distribution in the HRV spectrum. High EP values occur when this power is concentrated within a relatively narrow range of frequencies, and lower values when the power is distributed over a broader range of frequencies. In one embodiment, an apparatus is provided for monitoring the heart beat and presenting this information via a personal computer, handheld device, or other processing means.
Owner:QUANTUM INTECH INC
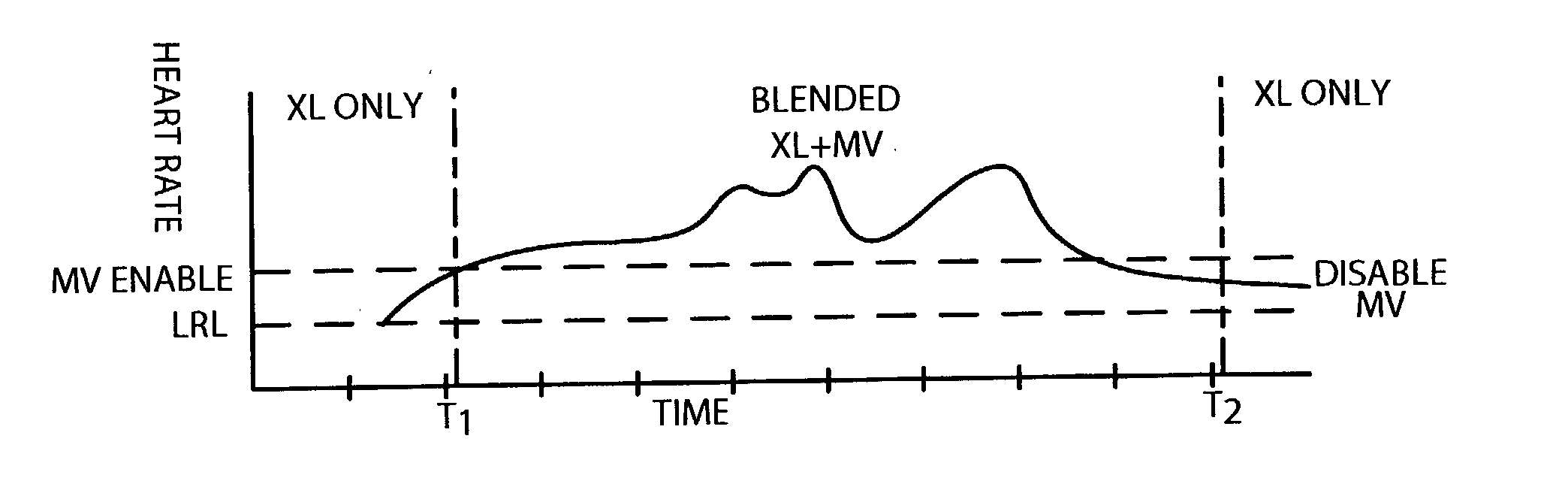
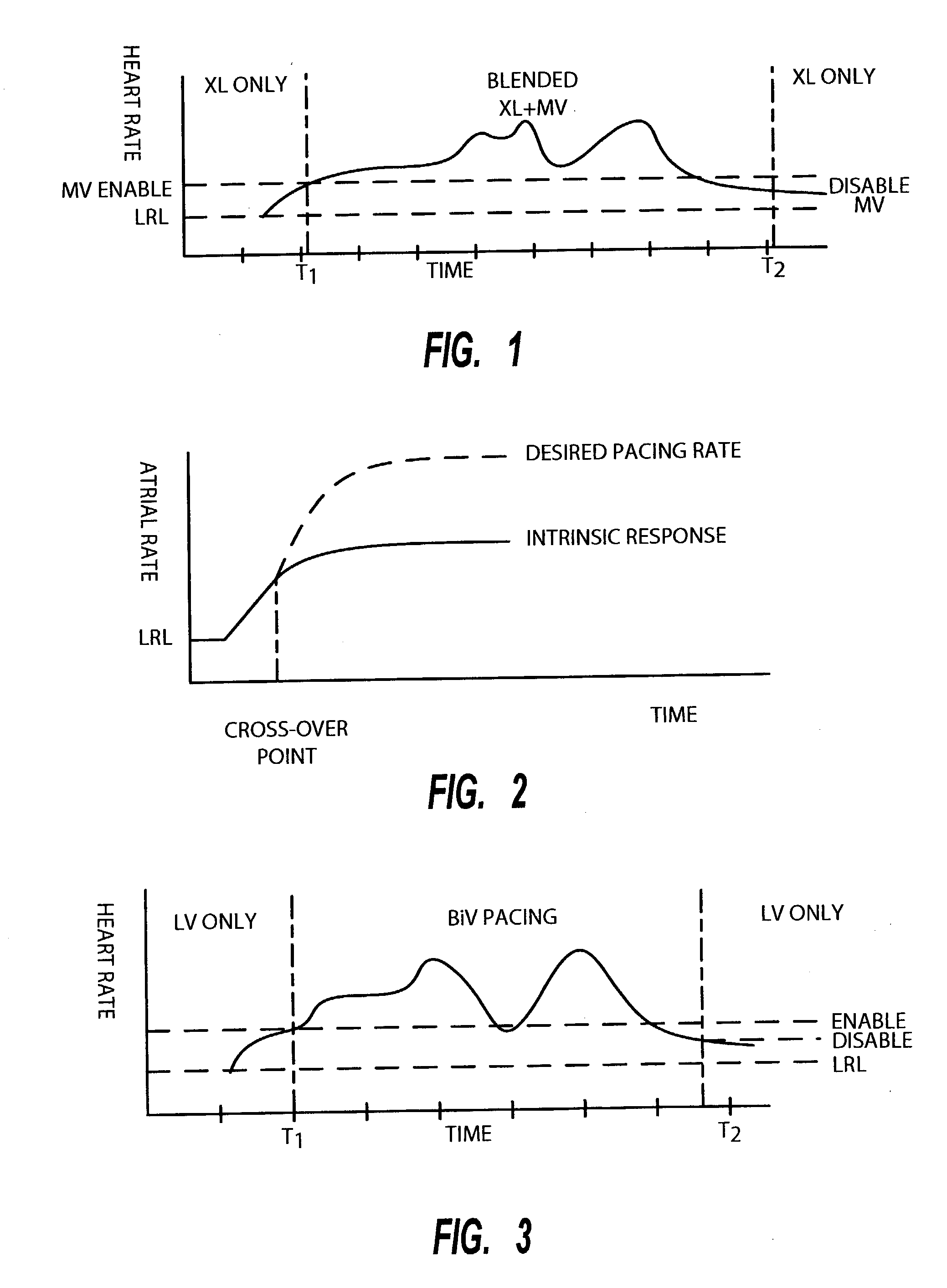
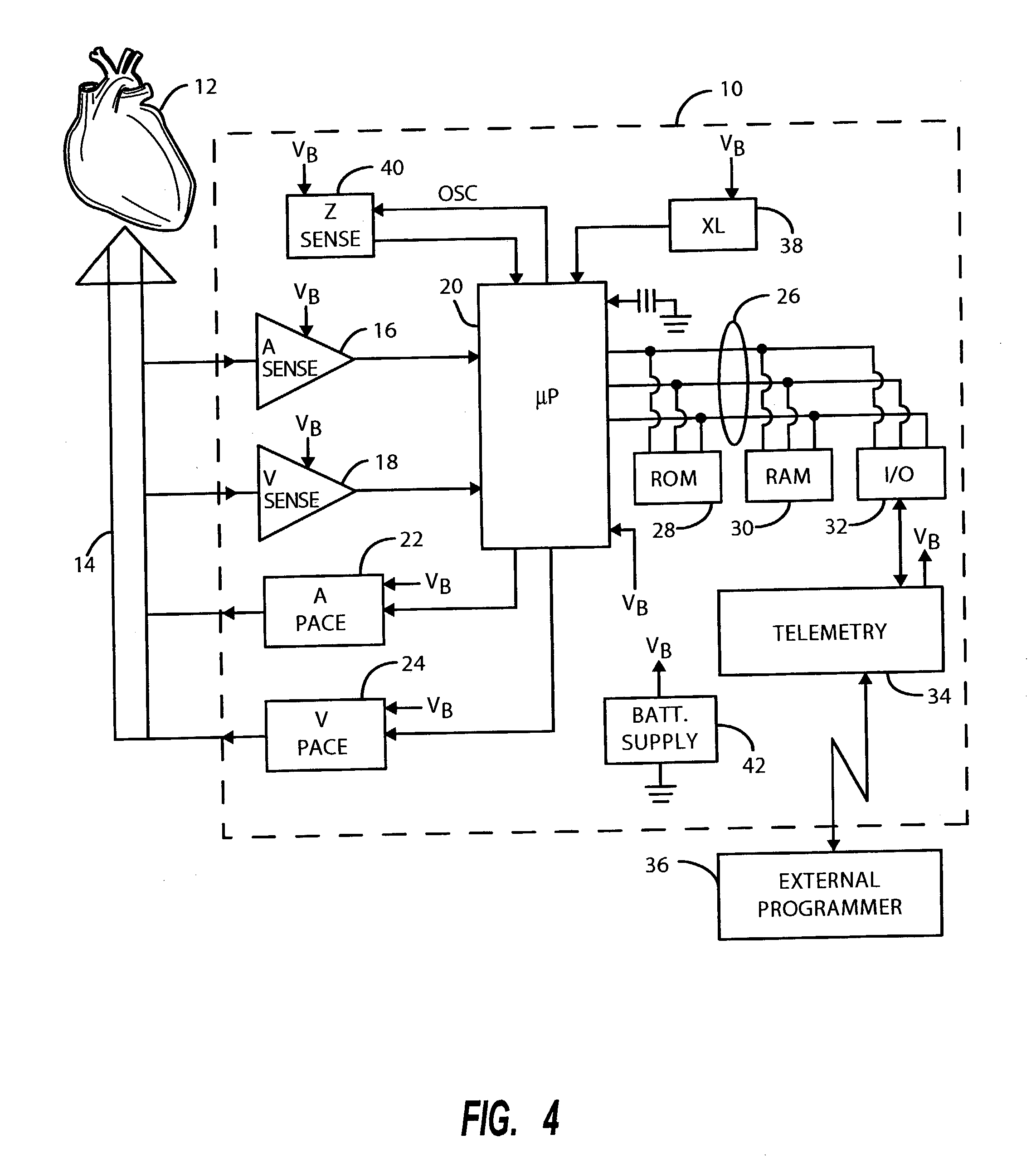
Method of operating implantable medical devices to prolong battery life
ActiveUS20040098060A1Alters Cardiac FunctionHigh incidenceHeart stimulatorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationElectrical battery
A method of conserving power and extending the life of a battery in an implantable rate-responsive cardiac rhythm management device. In accordance with the preferred embodiment, a first physiologic sensor is used to enable a power consuming feature only when the first sensor produces an output falling within a predetermined range and subsequently disables the power consuming feature when the output of the first sensor falls back outside the predetermined range. The first sensor may measure heart rate, physical movement, posture or other parameters and the power consuming feature may comprise further physiologic sensors, a different mode of pacing or a combination thereof
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System for detection of different types of cardiac events
A system for the detection of cardiac events occurring in a human patient is provided. At least two electrodes are included in the system for obtaining an electrical signal from a patient's heart. An electrical signal processor is electrically coupled to the electrodes for processing the electrical signal and a patient alarm means is further provided and electrically coupled to the electrical signal processor. The electrical signal is acquired in the form of electrogram segments, which are categorized according to heart rate, ST segment shift and type heart rhythm (normal or abnormal). Baseline electrogram segments are tracked over time.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
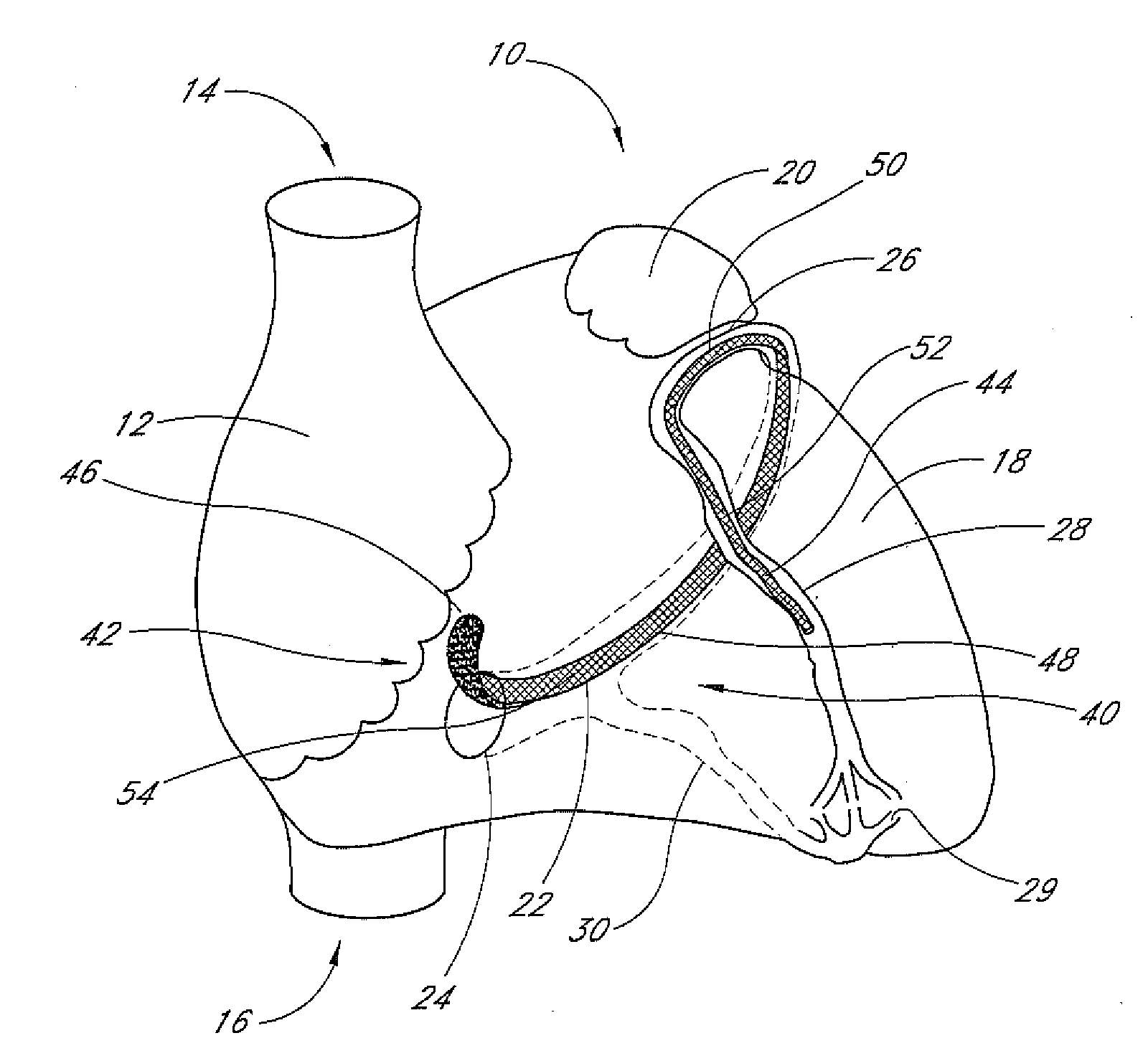
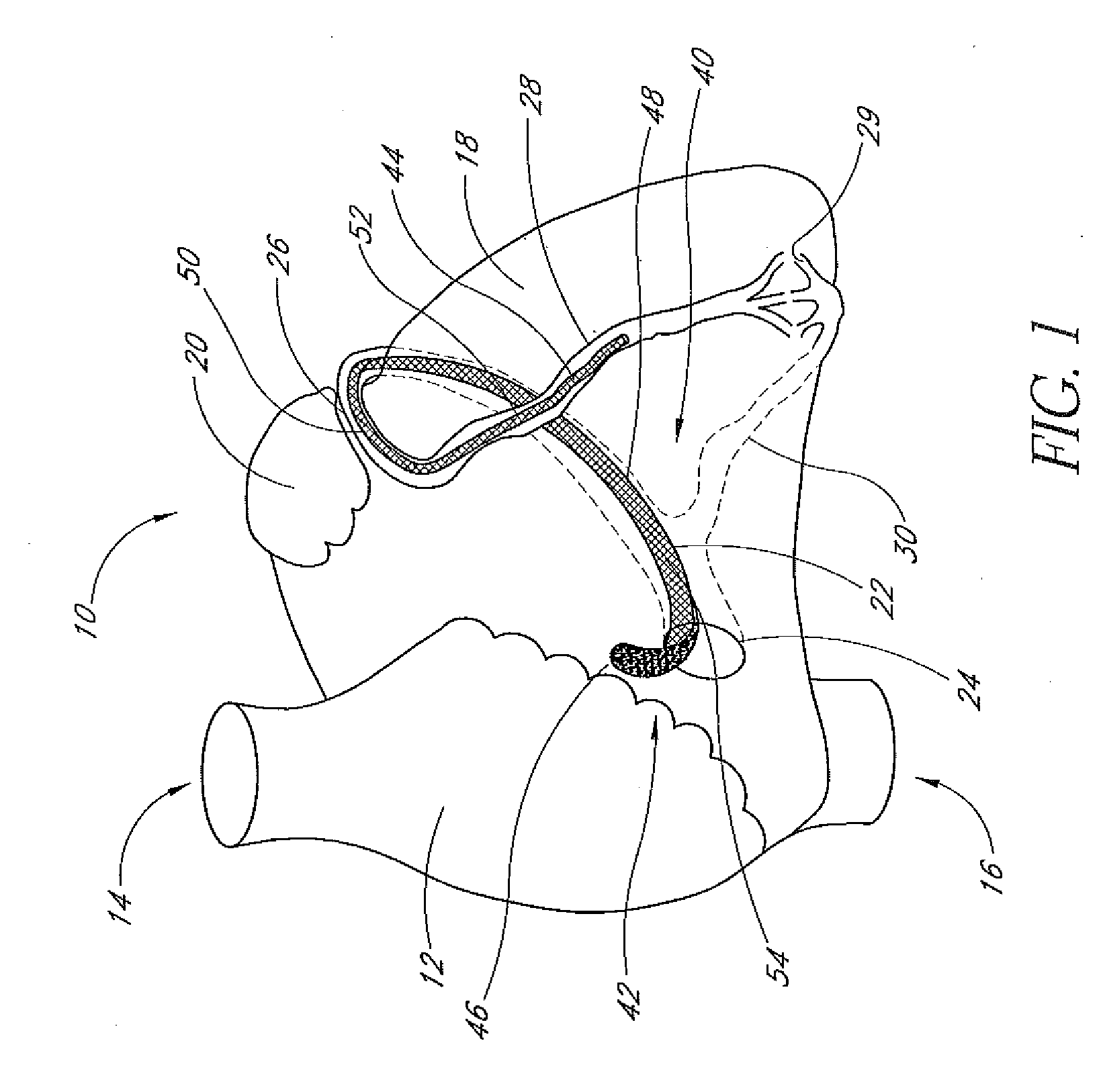
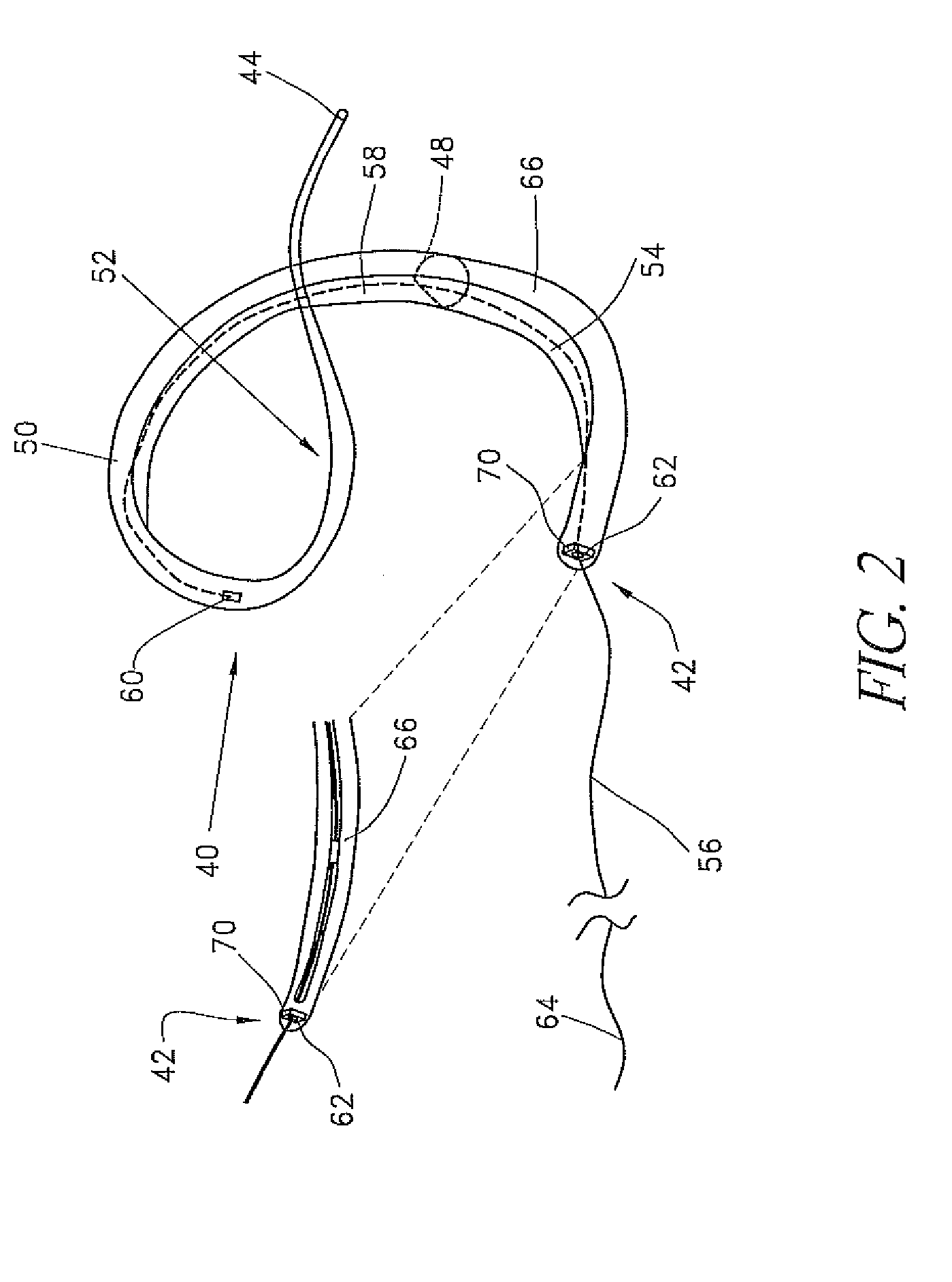
Percutaneous mitral annulplasty with cardiac rhythm management
InactiveUS20110009957A1Increase frictionTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart valvesCoronary sinusHemodynamics
A minimally invasive method of performing mitral annuloplasty is disclosed. An implantable device is positioned within the coronary sinus and tightened around the mitral annulus. Mitral valve regurgitation is monitored before, during, and / or after the tightening step. An on-going drug therapy may be determined, taking into account post-implantation hemodynamic function.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Cardiac harness and method of delivery by minimally invasive access
InactiveUS20050171589A1Limit cardiac functionFunction increaseEpicardial electrodesHeart valvesGuide wiresCable harness
A system for treating the heart includes a cardiac harness associated with a cardiac rhythm management device which includes at least one electrode and a conductor lead that is connected to a power source. The electrodes include lumens for the removable insertion of a stylet or guide wire, which will provide the electrodes and the cardiac harness with the necessary columnar strength to push the cardiac harness over the heart. The stylet or guide wire also can be used to steer or lead the cardiac harness into position around at least a portion of the heart.
Owner:PARACOR MEDICAL INC
Symptom recording patient interface system for a portable heart monitor
A patient interface device contemporaneously records patient symptoms with an automated recording of heart rhythm data from a portable heart monitor. The patient interface device includes the portable heart monitor and a computer with a user input means to enter symptoms and store them in computer memory. Code means operable on the computer enables entry and recording of the symptoms. Where the portable heart monitor is activated automatically, a signaling means alerts the patient that it has begun recording and that symptoms experienced by the patient should be entered and recorded. Preferably, the electronic record of patient symptoms and the recording of the patient's abnormal heart rhythm event are linked such that they are accessed and used together.
Owner:LEVINE GLENN N
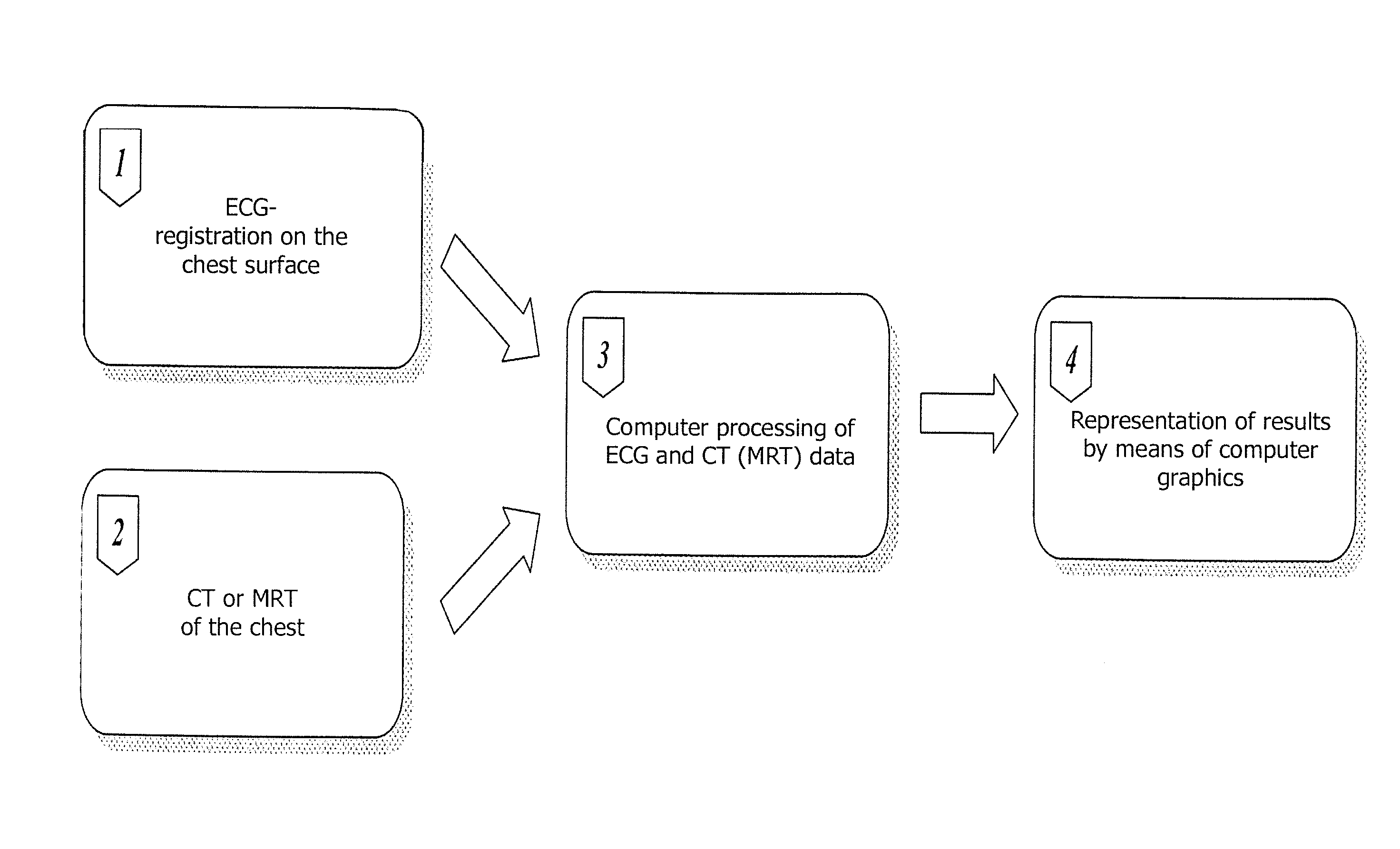
Method of noninvasive electrophysiological study of the heart
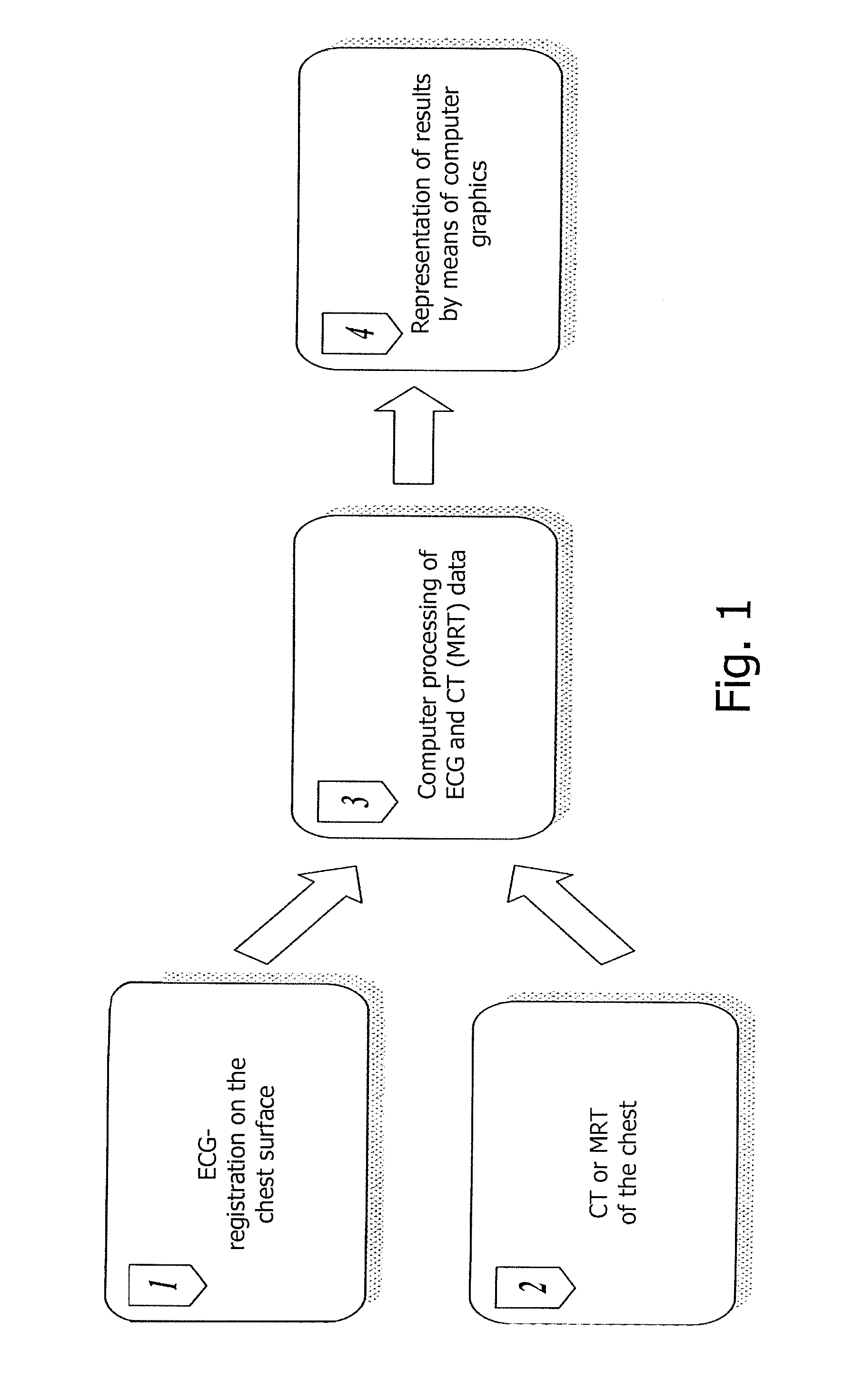
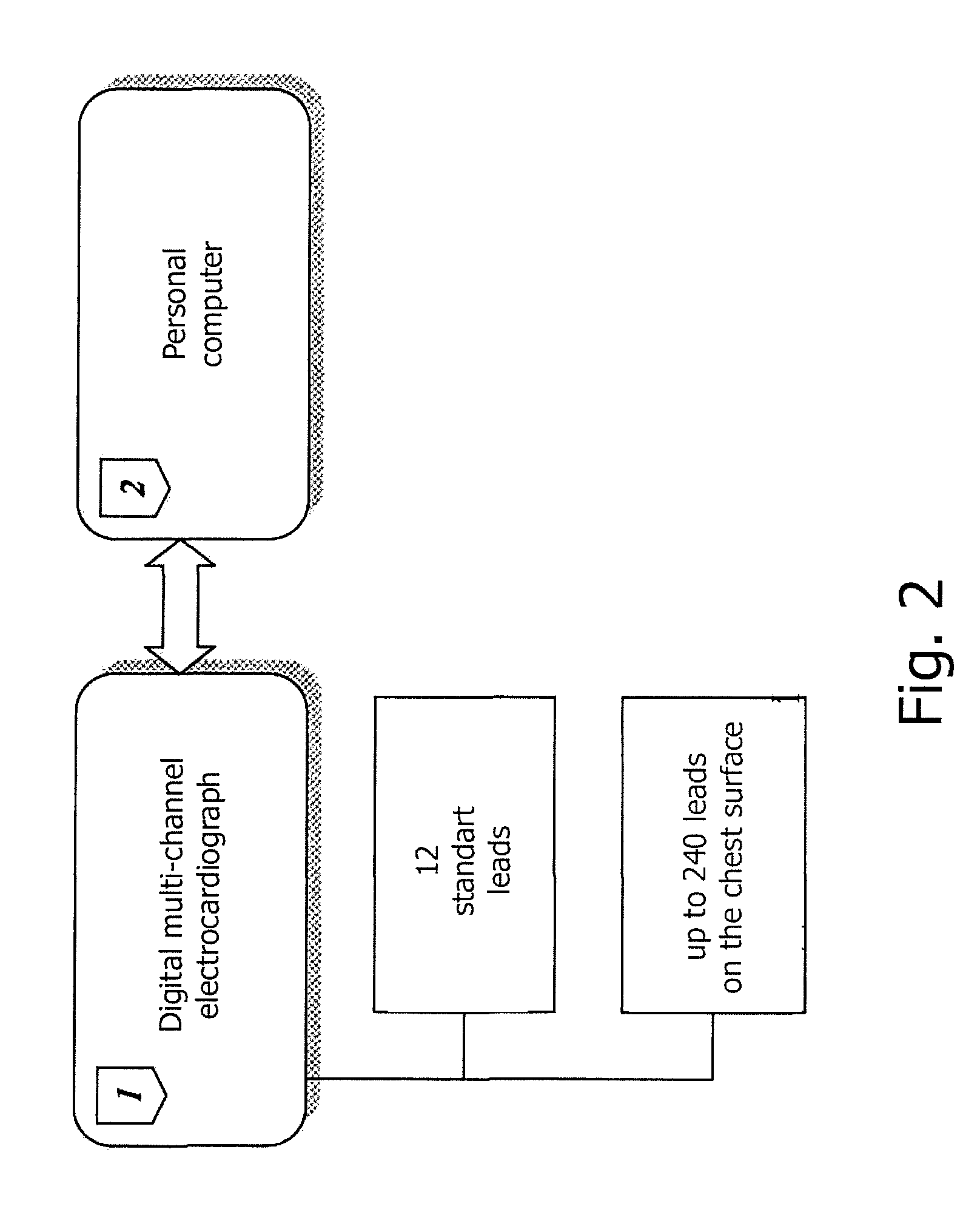
The invention relates to medicine, namely to cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, functional diagnosis and clinical electrophysiology of the heart. The invention consists in reconstructing electrograms, whose experimental registration requires an invasive access, by computational way on unipolar ECGs recorded at 80 and more points of the chest surface. Based on reconstructed electrograms, isopotential, isochronous maps on realistic models of the heart are constructed, the dynamics of the myocardium excitation is reconstructed and electrophysiological processes in the cardiac muscle are diagnosed. Application of the method allows one to improve the accuracy of non-invasive diagnosis of cardiac rhythm disturbances and other cardio-vascular diseases.
Owner:EP SOLUTIONS SA
Cardiac harness having electrodes and epicardial leads
InactiveUS20050137673A1Limit cardiac functionFunction increaseEpicardial electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesVeinSystole
A system for treating the heart includes a cardiac harness associated with a cardiac rhythm management device which includes at least one electrode associated with the cardiac harness, epicardial leads attached directly to the heart, and a power source connected to the leads. The system may also include transvenous leads that are located within a chamber of the heart and attached to the power source. The cardiac harness applies a compressive force on the heart during diastole and systole, and the electrodes will deliver an electrical shock to the heart for defibrillation and / or can be used for pacing / sensing. The cardiac harness and electrodes are delivered and implanted on the heart by minimally invasive access.
Owner:PARACOR MEDICAL INC
Chaos-based detection of atrial fibrillation using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS20110152957A1Mitigating detection problemReduce decreaseElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsCardiac monitoringEctopic beat
Techniques are provided for detecting atrial fibrillation (AF) based on variations in ventricular intervals detected by a pacemaker, implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) or implantable cardiac monitor (ICM). In one example, ventricular beats are detected and intervals between the ventricular beats are measured, such as RR intervals. Irregular ventricular beats are identified, including ectopic beats, bigeminal beats, and the like. The degree of variability within the ventricular intervals is then determined while excluding any intervals associated with irregular beats. AF is then detected based on the degree of variability. That is, AF is detected based on variability occurring within ventricular intervals after ectopic beats and other irregular beats have been eliminated, thus mitigating detection problems that might arise if the variability were instead calculated based on all ventricular beat intervals. Techniques are also described herein for distinguishing AF from sinus tachycardia, which can also cause a high degree of variability in RR intervals.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
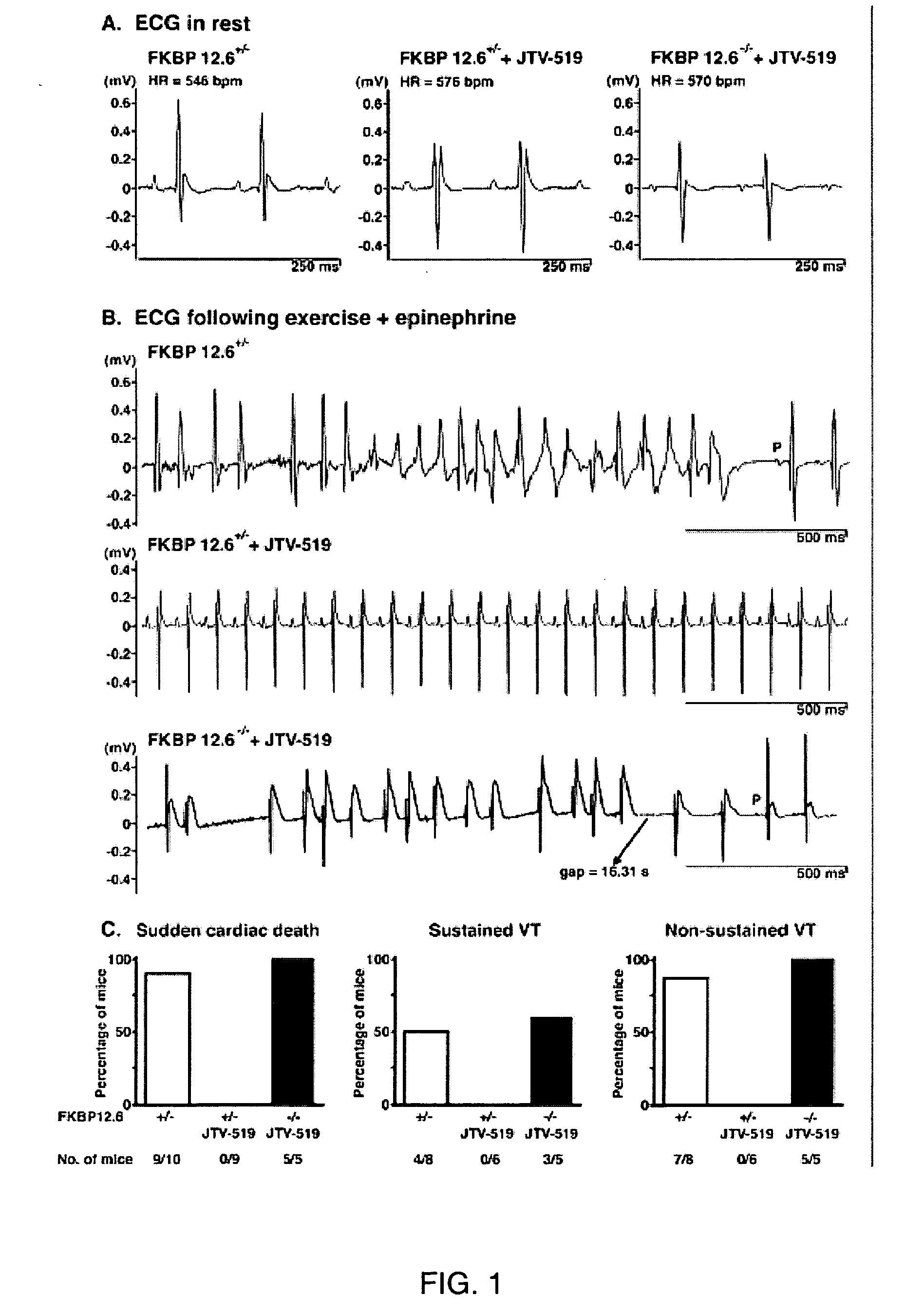
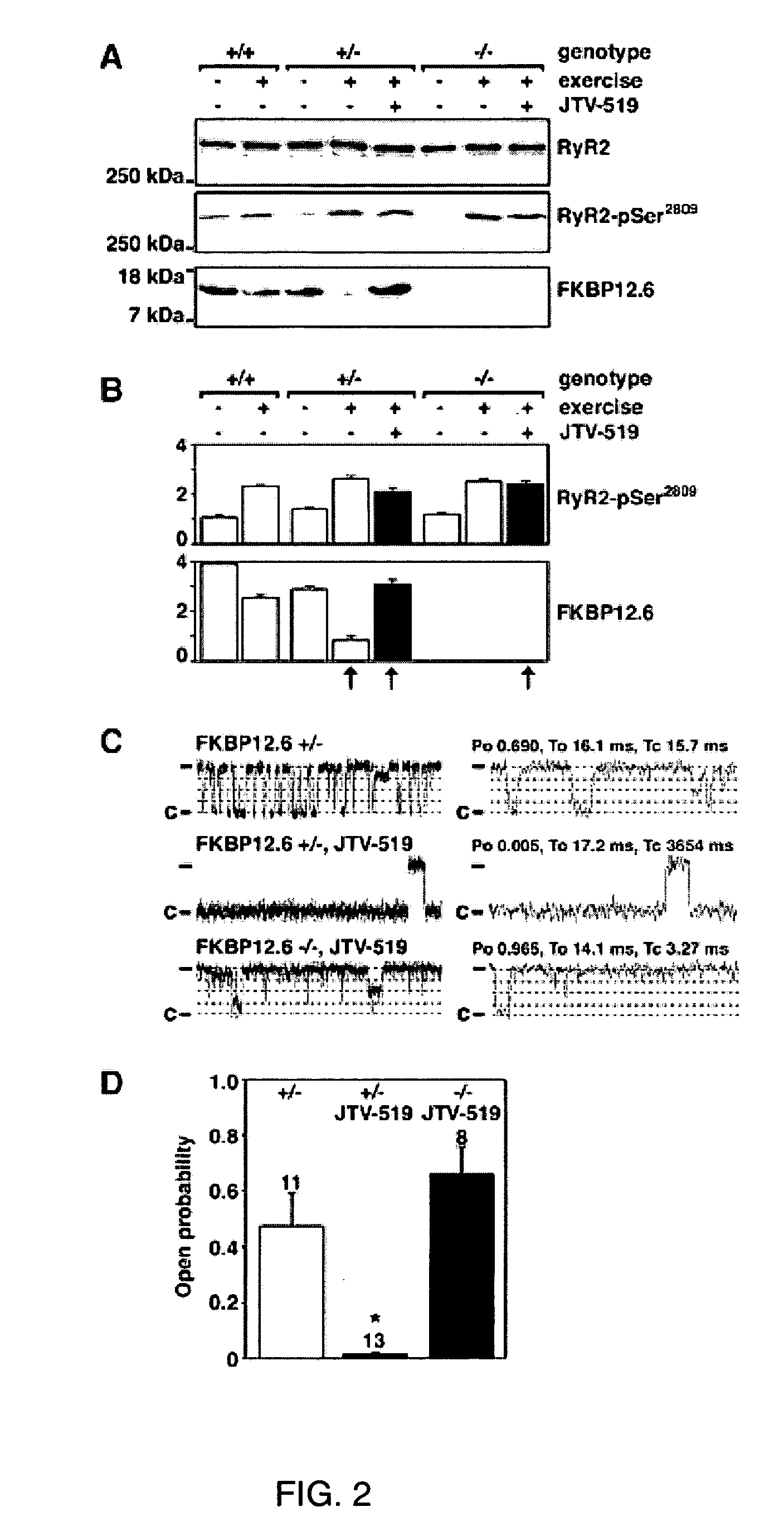
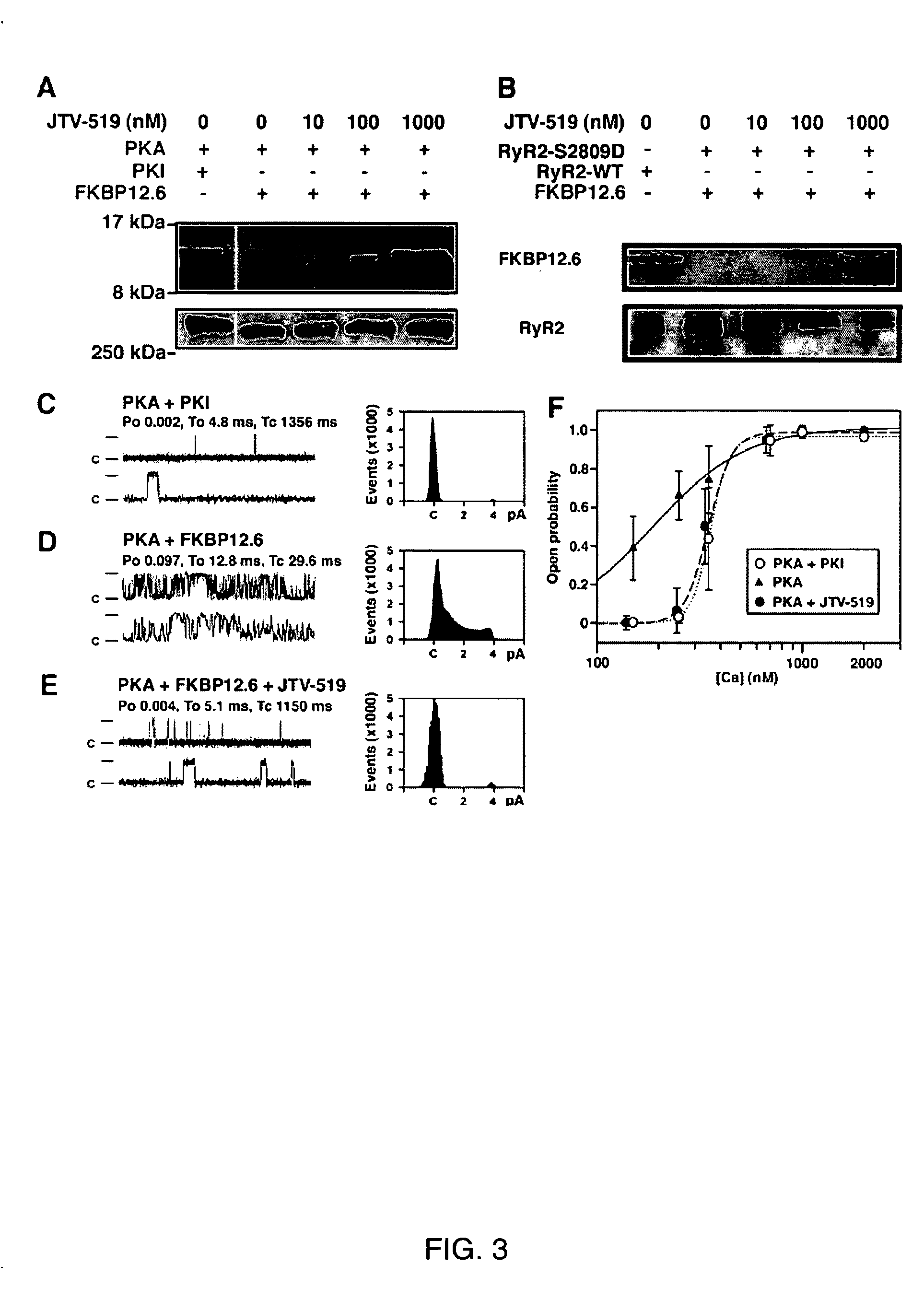
Novel anti-arrhythmic and heart failure drugs that target the leak in the ryanodine receptor (RyR2) and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050215540A1Inhibition of fibrillationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsVentricular dysrhythmiaRyanodine receptor
The present invention provides methods for limiting or preventing a decrease in the level of RyR2-bound FKBP12.6 in a subject. The present invention further provides methods for treating and preventing atrial and ventricular cardiac arrhythmias, heart failure, and exercise-induced sudden cardiac death in a subject. Additionally, the present invention provides use of JTV-519 in a method for limiting or preventing a decrease in the level of RyR2-bound FKBP12.6 in a subject who has, or is a candidate for, atrial fibrillation. Also provided are uses of 1,4-benzothiazepine derivatives in methods for treating and preventing atrial and ventricular cardiac arrhythmias and heart failure in a subject, and for preventing exercise-induced sudden cardiac death. The present invention also provides methods for identifying agents for use in treating and preventing atrial fibrillation and heart failure, and agents identified by these methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
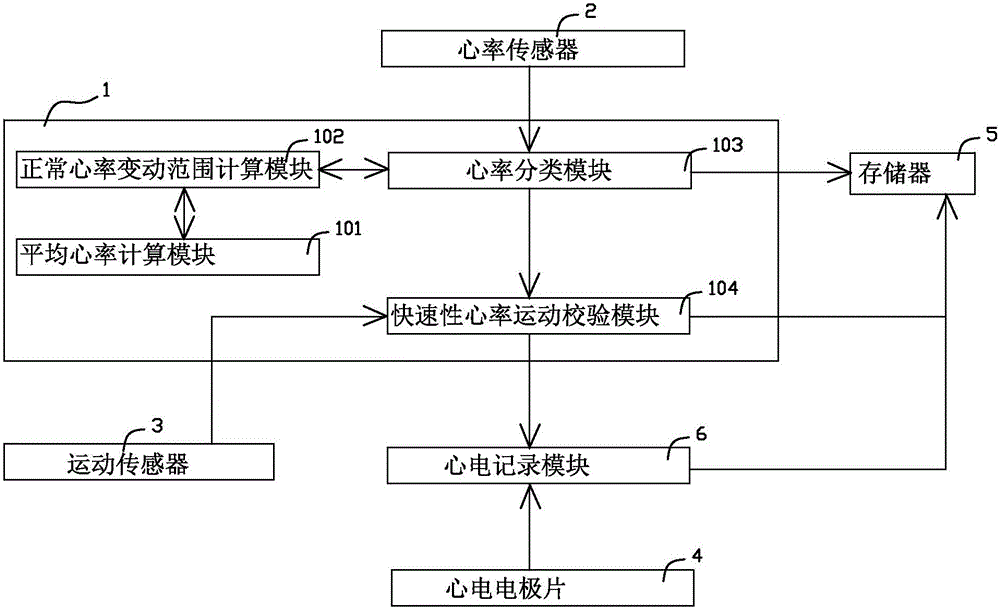
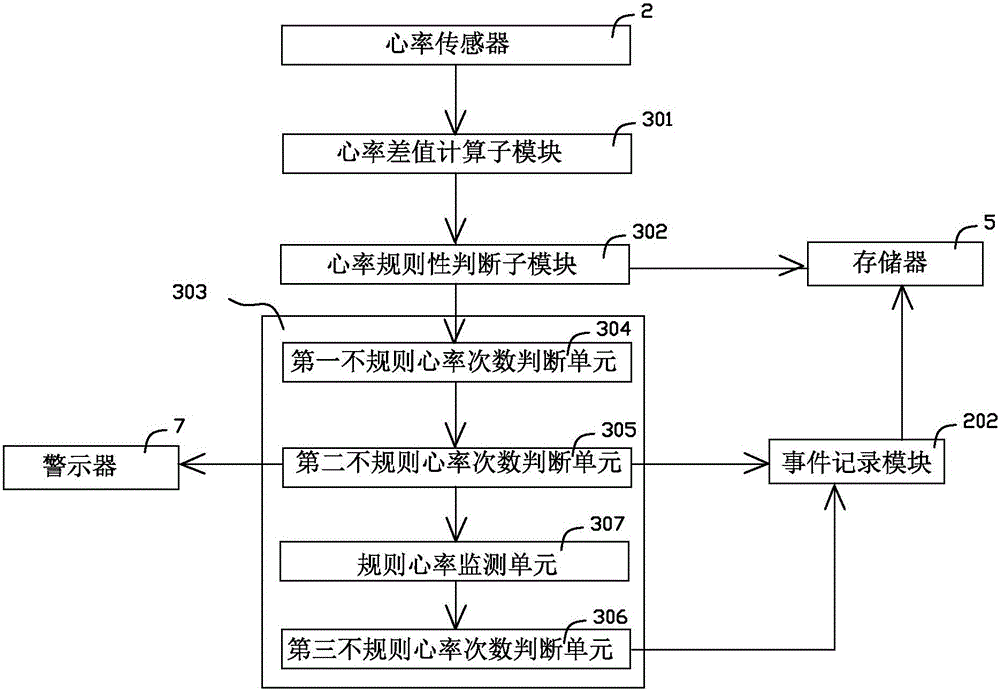
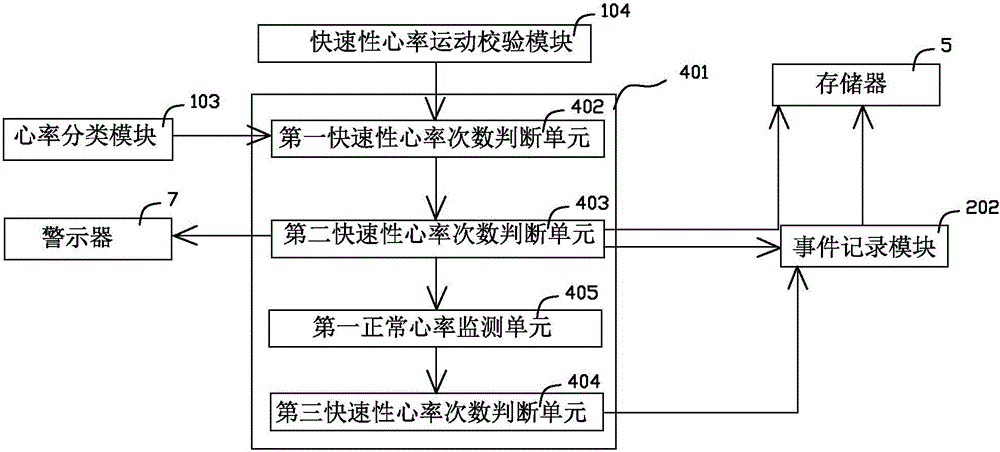
Wearable heart rhythm monitoring device and heart rhythm monitoring system
ActiveCN105943021ALong-term wearDoes not affect daily lifeSensorsBlood characterising devicesCardiac rhythm monitoringData information
The invention relates to a wearable heart rhythm monitoring device. The wearable heart rhythm monitoring device comprises a processor, as well as a heart rate sensor, a motion sensor, at least two electrocardioelectrodes, a storage and an electrocardiogram recording module which communicate with the processor, wherein the processor comprises an average heart rate computation module, a normal heart rate variation range computation module, a heart rate classification module and a rapid heart rate motion check module; the storage is used for receiving and storing data information. The wearable heart rhythm monitoring device can be worn by a user for a long time, and the daily life of the user is not influenced; meanwhile, the monitoring device carries out monitoring from the point of view of medical science, can collect all key data including the heart rate, the motion, the electrocardiogram and the oxygen saturation relevant to the arrhythmia, and can automatically monitor and record the arrhythmia incident found in the heart rate monitoring process; the monitoring device automatically analyzes each heartbeat from many dimensions, and accurately classifies the heartbeats, and thus various potential arrhythmia problems are found.
Owner:赵伟
Method and apparatus for detecting and discriminating arrhythmias
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
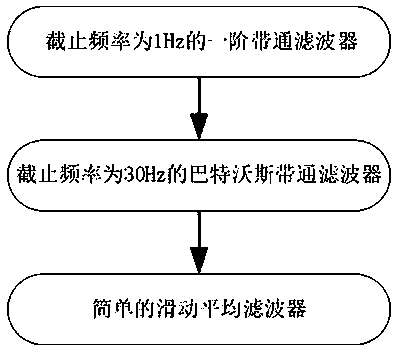
Automatic shockable rhythm identification and classification method combined with electrocardio time-frequency domain feature analysis
ActiveCN104382590AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalBand-pass filter
The invention provides an automatic shockable rhythm identification and classification method combined with electrocardio time-frequency domain feature analysis. The method comprises specific steps as follows: S1, pretreating electrocardio signals; S2, automatically identifying cardiac arrest rhythms, and if discrimination conditions are not met, implementing S3; S3, on the basis of an integral coefficient band-pass filter, calculating the maximum amplitude proportion value (Pa), the average amplitude proportion value (Pb) and the average deviation proportion value (Pc) of output signals; S4, S5, S6 and S7, discriminating shockable rhythms and non-shockable rhythms according to frequency domain feature values such as the Pa, the Pb, the Pc and the like, and implementing S8 in case of failure; S8, calculating an electrocardio standard grid bar projection standard deviation; S9, discriminating the shockable rhythms and the non-shockable rhythms according to the standard deviation. The method can be applied to instruments and equipment which automatically identify and classify the shockable rhythms according to body surface electrocardiograms, the shockable rhythm identification sensitivity and the non-shockable rhythm specificity are improved, and the algorithm operating efficiency is improved.
Owner:成都瑞迪康医疗科技有限公司
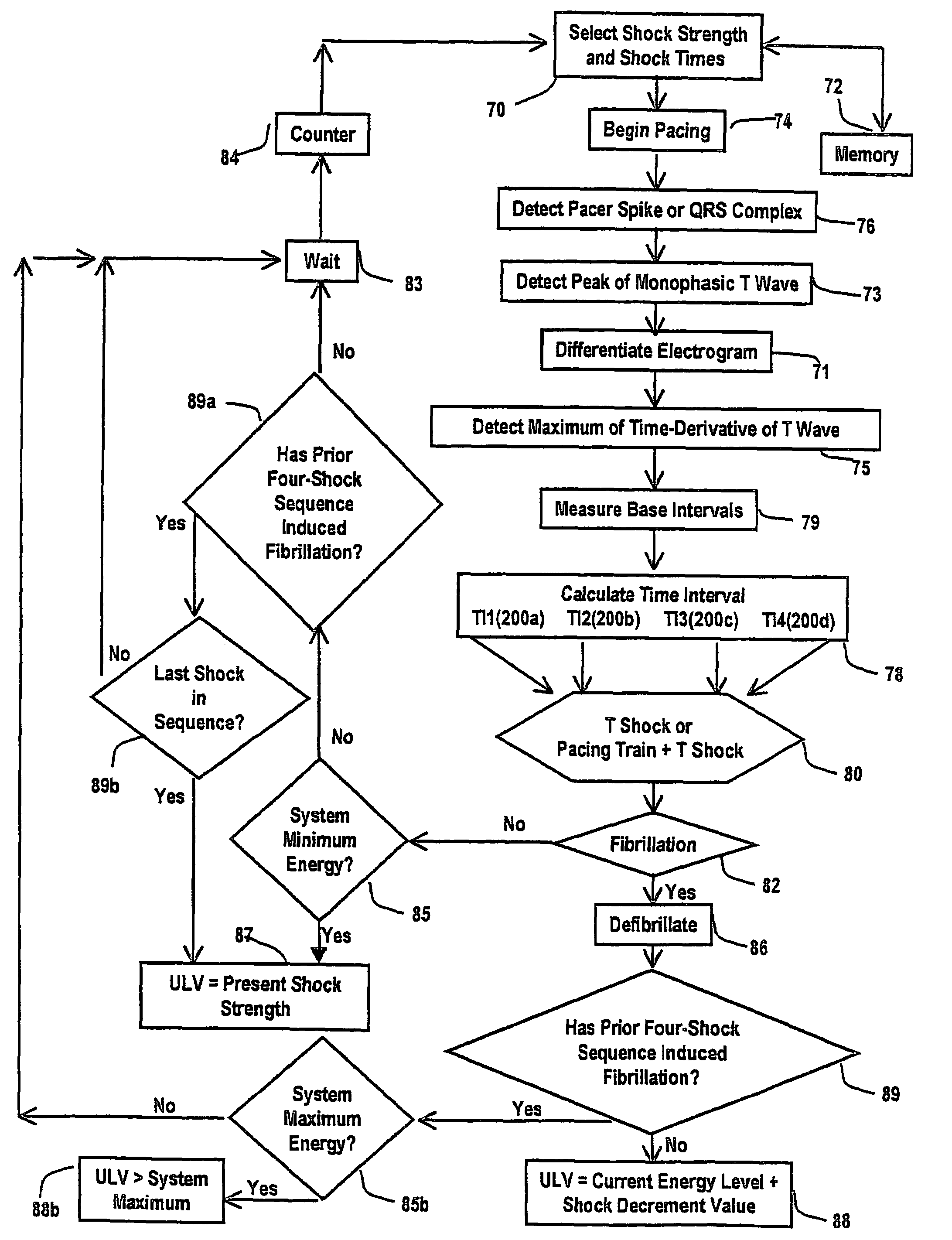
Defibrillation shock strength determination technology
ActiveUS7257441B2Sure easyQuickly and accurately determinesHeart defibrillatorsSpecific testMedicine
A method for determining a cardiac shock strength, for example the programmed first-therapeutic shock strength of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), including the steps of sensing a change in a T-wave of an electrogram with respect to time such as the maximum of the first derivative of a T-wave of an electrogram; delivering a test shock by (i) delivering a test shock at a test-shock strength and at a test-shock time relating to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave with respect to time; and (ii) sensing for cardiac fibrillation. If fibrillation is not sensed, test-shock delivery is repeated at the same test-shock strength and at specific, different test-shock times relating to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave. If fibrillation is still not sensed, the shock strength is decreased and test shocks are repeated at the same specific test shock times relative to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave. And if fibrillation is sensed, the programmed therapeutic shock strength of the ICD is set as a function of the incrementally greater test-shock strength. Also disclosed is an apparatus for selecting a programmed first-shock strength of an ICD, including a shock subsystem for delivering therapeutic shocks and test shocks to the heart, and a ULV subsystem connected to the shock subsystem, to provide test shocks of test-shock strengths and at test-shock times relating to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave with respect to time, and to determine the therapeutic shock strength of the ICD as a function of the test-shock strengths.
Owner:SWERDLOW CHARLES D +1
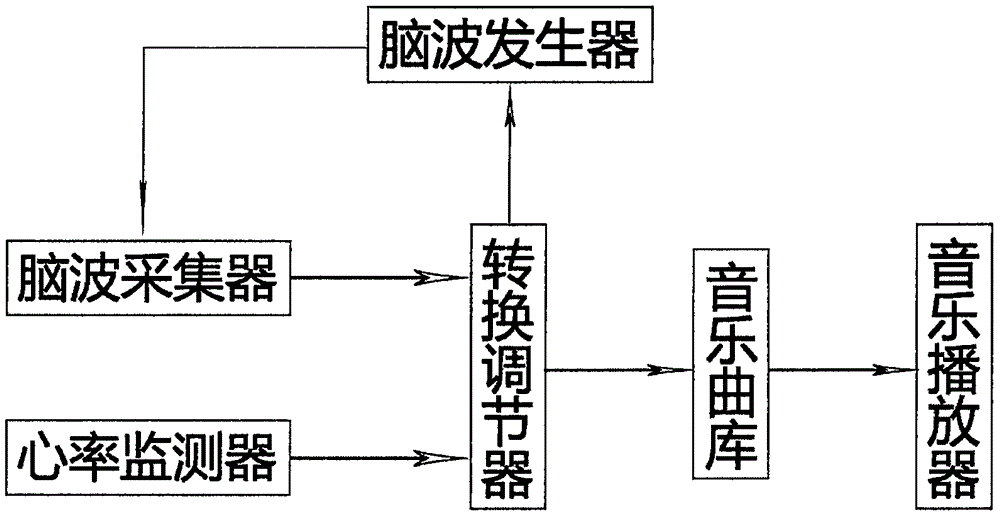
Resonance psychological training device
InactiveCN106806973ACoordinate and improve physiological comprehensive technical indicatorsImprove moodSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateHuman bodyNervous system
The invention provides a resonance psychological training device. Based on brain science and musical treatment principles, the device comprises a brain wave collector, a brain wave generator, a heart rate monitor, a music library, a conversion regulator and music playing equipment, wherein the brain wave collector is responsible for collecting the frequency and the relaxation degree of an individual brain wave; the brain wave generator is responsible for generating a wave of corresponding frequency to be guided into a human body; the conversion regulator is responsible for corresponding to selected music in the music library according to the values of the heart rate rhythm and the relaxation degree of the individual under different function modules; the music playing equipment is responsible for playing the selected music; the playing modes comprise a power amplifier playing mode and an earphone playing mode; and a corresponding earphone is configured. The device is divided into three functional modules: an auxiliary mindfulness training module, an auxiliary sleeping module and an auxiliary emotion promotion module. The training device can balance an autonomic nerves system, the results of physiological synthesis technique indexes are coordinated and promoted, and the functions of assisting the individual to carry out mindfulness training, sleeping and emotion promotion are achieved.
Owner:天使智心(北京)科技有限公司
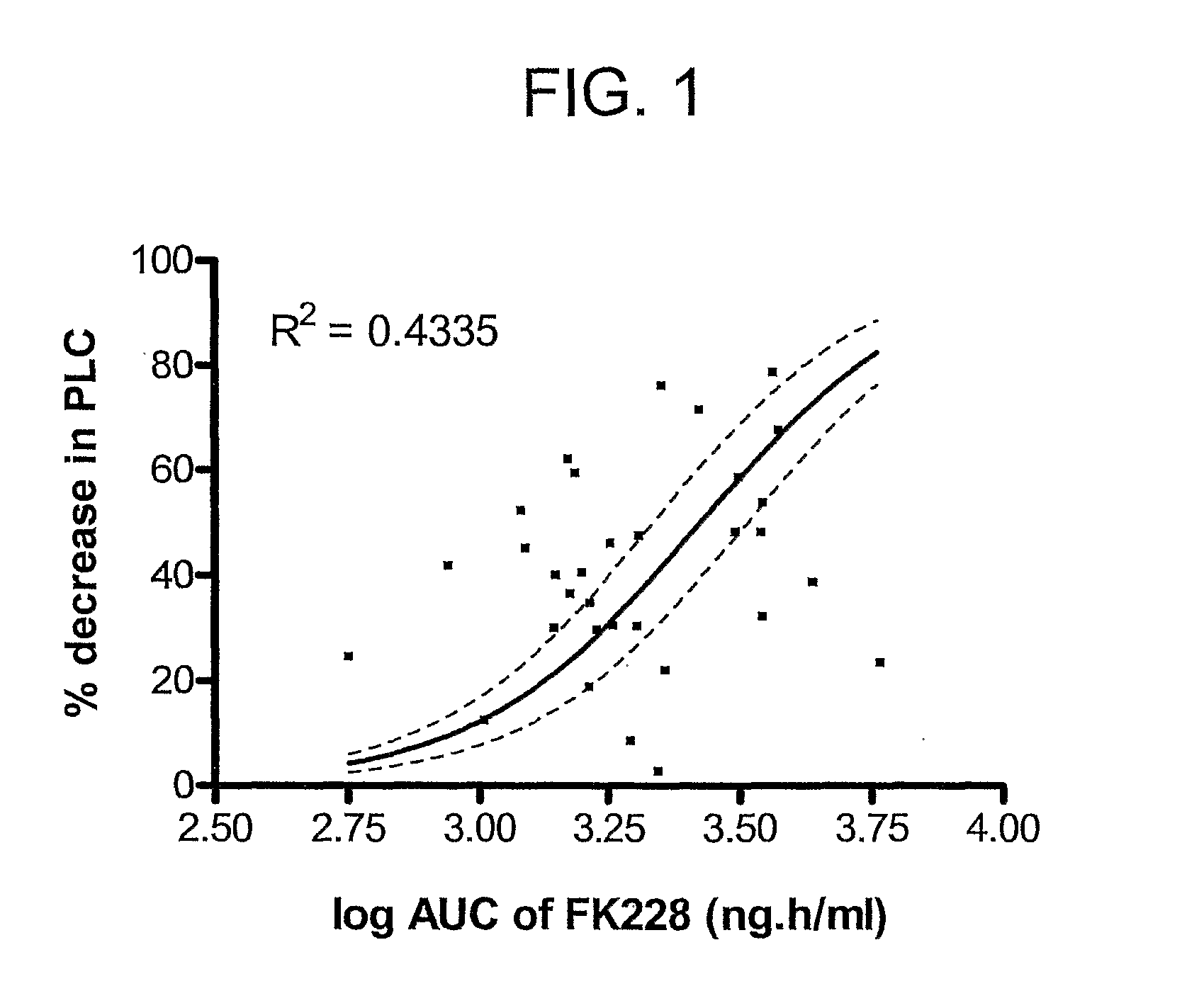
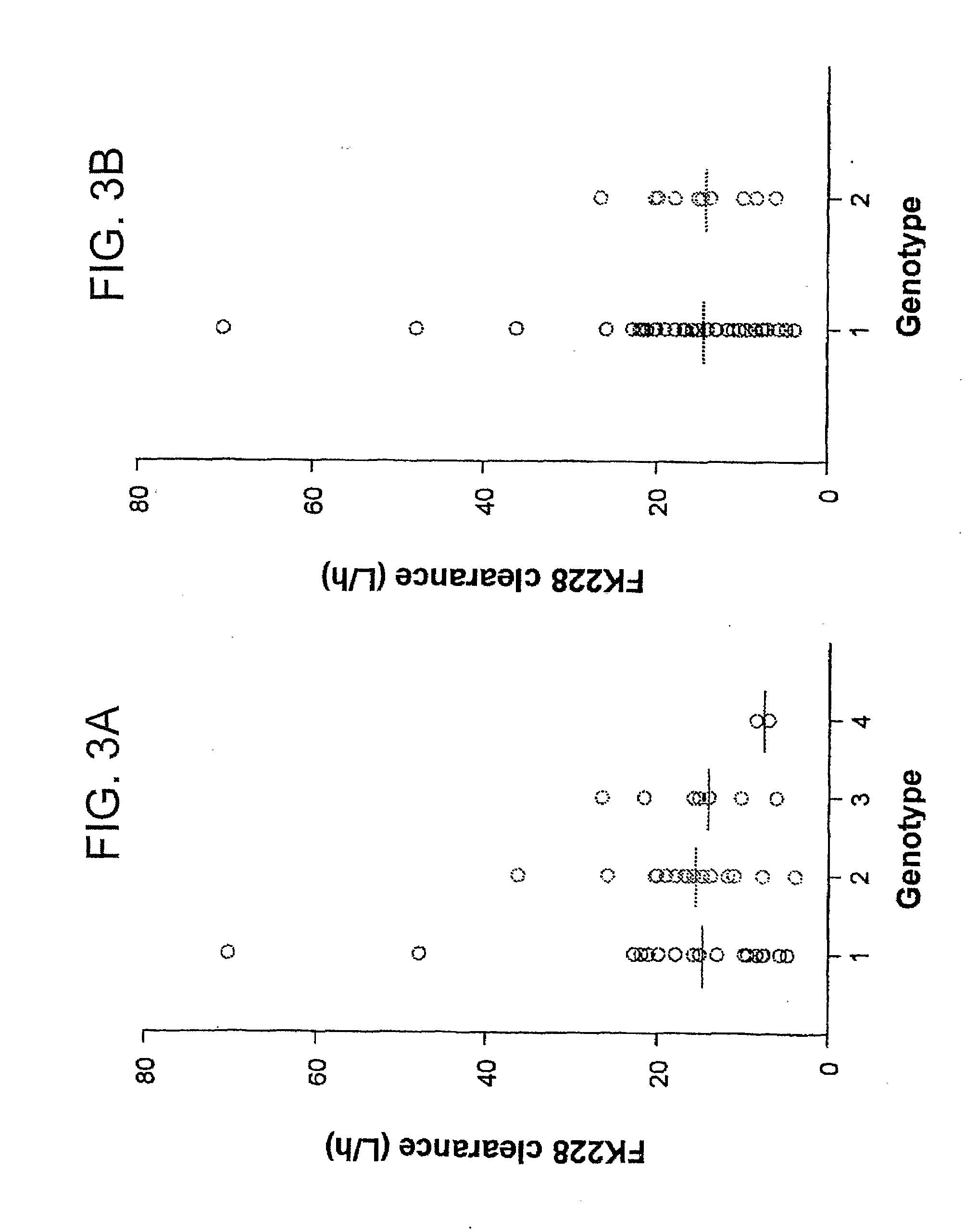
Materials and methods for abcb1 polymorphic variant screening, diagnosis, and treatment
The invention provides methods and materials for screening for polymorphic variants in ABCB1 and diagnosing altered susceptibilities for drug-induced heart rhythm irregularities based on the same. These methods allow better treatment regimens for using drugs that bind a protein encoded by the ABCB1 and / or induce heart rhythm irregularities such as the anti-cancer drug FK228.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
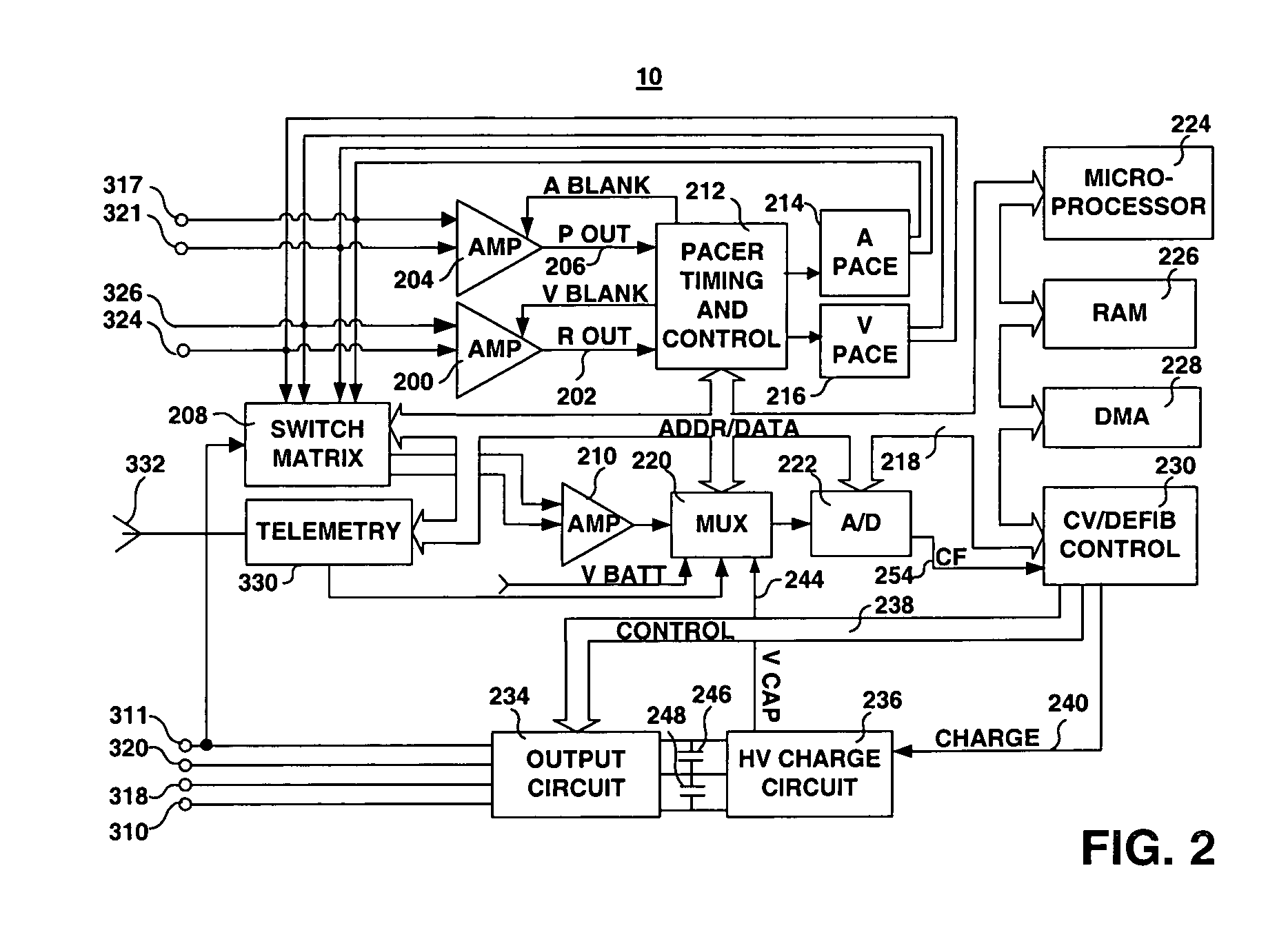
CRM-device ventricular-pacing blanking control
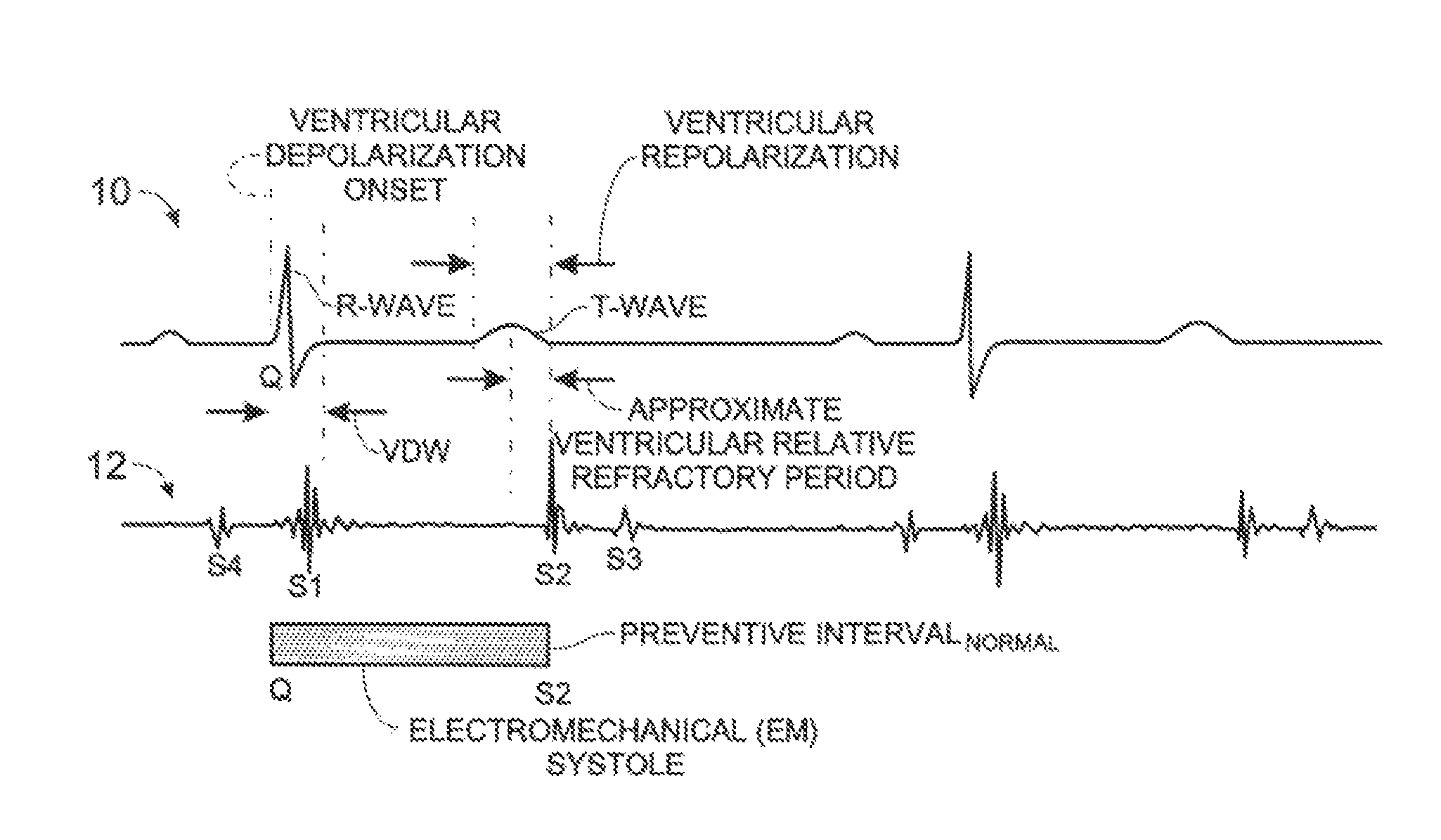
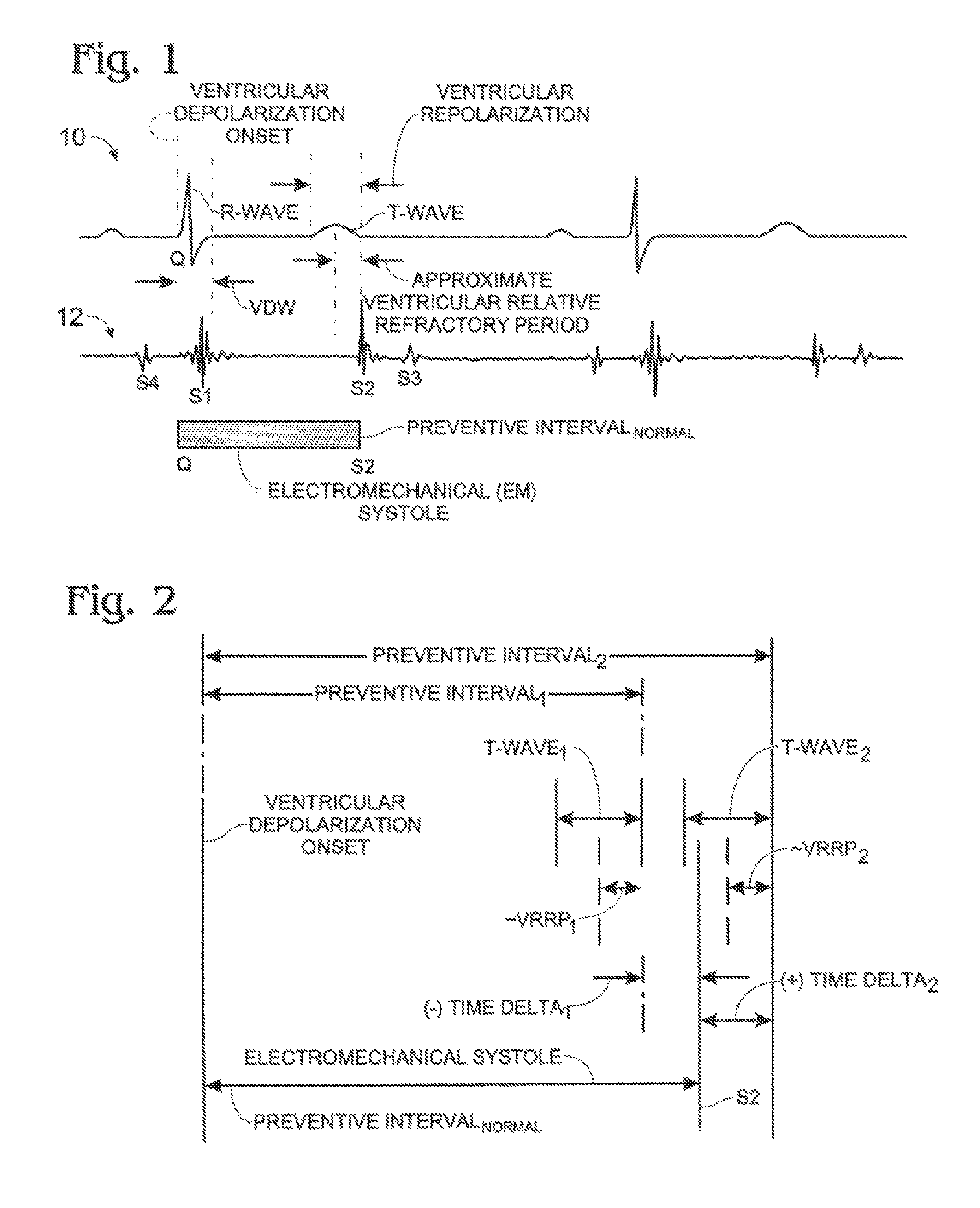
A system, operatively connectable both to a cardiac-rhythm-management (CRM) subject, and to a CRM device associated with that subject, and an associated method, operable, in relation to received-and-processed, real-time, CRM-subject-specific, simultaneous ECG and heart-sound information, and other information including measurement time markers where available, for blocking, under all circumstances during the ventricular relative refractory period lying within each of successive CRM-subject cardiac cycles occupying a span of such cycles, the ventricular pacing activity of the subject-associated CRM device—the beginning and ending of such blocking in each cardiac cycle being system-defined to lie preferably, and respectively, (a) within the real-time, ventricular depolarization window in the cycle, and (b) at the time of the real-time, S2 heart-sound, plus or minus any user-defined time-delta.
Owner:INOVISE MEDICAL
Heart rhythm classification system based on machine learning
PendingCN111297349AImprove classification performanceOvercome the problem of not being able to handle long-distance dependencies wellMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringCoding decodingEngineering
The invention discloses a heart rhythm classification system based on machine learning. The heart rhythm classification system comprises a data collection module, a data preprocessing module and a classification algorithm module; the data collection module collects an electrocardiosignal of a subject; and the data preprocessing module performs noise analysis and filtration, collects 45% of samplesin a left interval and correspondingly collects 55% of samples in a right interval to complete segmentation of a heart beat, and performs normalization processing at last. On the basis, the classification algorithm module for a convolutional neural network (CNN) model and an encoding-decoding model is established, and a classification model is established by using a good characteristic extractionability of the CNN and a time sequence characteristic extraction ability of long short-term memory (LSTM), so the problem that the RNN cannot process a far-distance reliance independently is overcome; and according to the heart rhythm classification system provided by the invention, the average sensitivity and the average accuracy are greatly improved, the complex characteristic extraction is avoided, the influence on a classification result due to manual extraction of a characteristic value is reduced, and the heart rhythm classification effect is improved.
Owner:BEIJING BLUE SATELLITE COMM TECH
Quick starting external programmer for implantable medical device
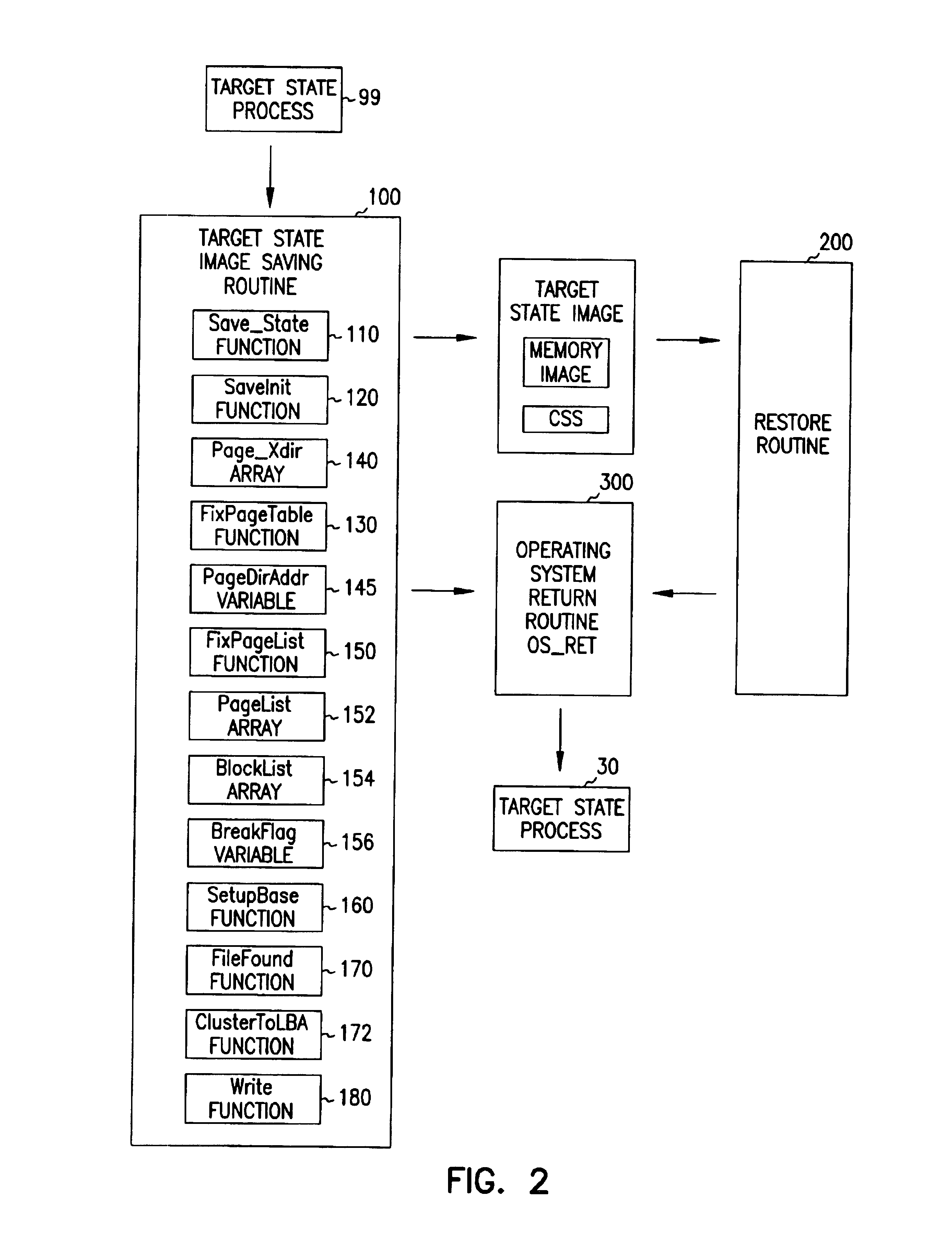
A system and method for restoring a microprocessor-based system to a previously booted target state in which an image of memory and the processor registers in the previously booted state is saved and stored in a storage device. A restore routine executing in ROM retrieves the image from the storage device and restores the system memory and processor registers to the target state. An operating system return routine then returns control of the system to the operating system software. In an exemplary implementation, a system in accordance with the invention is incorporated into a microprocessor-based external programmer for a cardiac rhythm management device in order to allow quick starting of the programmer from a powered down condition without going through a time consuming boot process.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Defibrillation shock strength determination technology
InactiveUS20080051841A1Quickly and accurately determinesPractical and reliable and accurateElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsSpecific testT wave
A method for determining a cardiac shock strength, for example the programmed first-therapeutic shock strength of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), including the steps of sensing a change in a T-wave of an electrogram with respect to time such as the maximum of the first derivative of a T-wave of an electrogram; delivering a test shock by (i) delivering a test shock at a test-shock strength and at a test-shock time relating to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave with respect to time; and (ii) sensing for cardiac fibrillation. If fibrillation is not sensed, test-shock delivery is repeated at the same test-shock strength and at specific, different test-shock times relating to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave. If fibrillation is still not sensed, the shock strength is decreased and test shocks are repeated at the same specific test shock times relative to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave. And if fibrillation is sensed, the programmed therapeutic shock strength of the ICD is set as a function of the incrementally greater test-shock strength. Also disclosed is an apparatus for selecting a programmed first-shock strength of an ICD, including a shock subsystem for delivering therapeutic shocks and test shocks to the heart, and a ULV subsystem connected to the shock subsystem, to provide test shocks of test-shock strengths and at test-shock times relating to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave with respect to time, and to determine the therapeutic shock strength of the ICD as a function of the test-shock strengths.
Owner:IMPERCEPTION
Security inspection device capable of recognizing criminals
Disclosed is a security inspection device capable of recognizing criminals. Acoustic optoelectronic technologies such as radar, laser, microwave, Doppler and ultra-wideband are used to acquire people's mental languages such as electrocardiogram, heart rhythm, blood pressure and breath in a certain distance without contacting human bodies. Cameras are used to acquire people's body languages such as actions, expressions and eye expressions so as to find out criminal suspects. The security inspection device capable of recognizing criminals has the advantages that the security inspection device capable of recognizing criminals is simple and convenient to operate, fast in inspection, criminal suspects can be found out directly, safety of security inspection staff can be guaranteed to the maximum extent, space occupation of the device is low, antipathy of people can be avoided due to the fact that the bodies and privacy of people are not contacted, no high-energy rays harmful to human bodies such as X-ray are needed and the like.
Owner:刘永强
Cinnamic aldehyde series preparation and its preparation process
InactiveCN1634000ALow priceReduce manufacturing costAntibacterial agentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseDrug content
The invention provides a preparation for treating viral myocarditis, wherein the medicinal reactivity of cinnamic aldehyde for antiviral, immunity adjustment, cardiac rhythm stabilization and blood vessel amplificatus, the cinnamic aldehyde can be prepared into cinnamic aldehyde slow release tablet, cinnamic aldehyde slow release capsule and cinnamic aldehyde injection for treating viral myocarditis. The invention has the advantages of stabilized medicinal content, high biological availability, small amount of administration, high curative effect, and low toxicity.
Owner:中国人民解放军第四军医大学药物研究所
Method of noninvasive electrophysiological study of the heart
ActiveUS20110275921A1Improve accuracyIncrease ratingsElectrocardiographySensorsRadiologyVascular surgery
The invention relates to medicine, namely to cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, functional diagnosis and clinical electrophysiology of the heart. The invention consists in reconstructing electrograms, whose experimental registration requires an invasive access, by computational way on unipolar ECGs recorded at 80 and more points of the chest surface. An application of the method allows one to improve the accuracy of non-invasive diagnosis of cardiac rhythm disturbances and other cardio-vascular diseases.
Owner:EP SOLUTIONS SA
Unitary subcutaneous only implantable cardioverter-defibrillator and optional pacer
InactiveUS7289854B2Easy to identifyEliminating a significant impediment to broader scale prophylacetic useHeart defibrillatorsVeinElectrical cardioversion
A unitary subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator has a long thin housing in the shape of a patient's rib. The housing contains a source of electrical energy, a capacitor, and operational circuitry that senses the presence of potentially fatal heart rhythms. Provided on the housing are cardioversion / defibrillation electrodes located to deliver electrical cardioversion-defibrillation energy when the operational circuitry senses a potentially fatal heart rhythm. The unitary subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator does not have a transvenous, intracardiac, epicardial, or subcutaneous electrode.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com