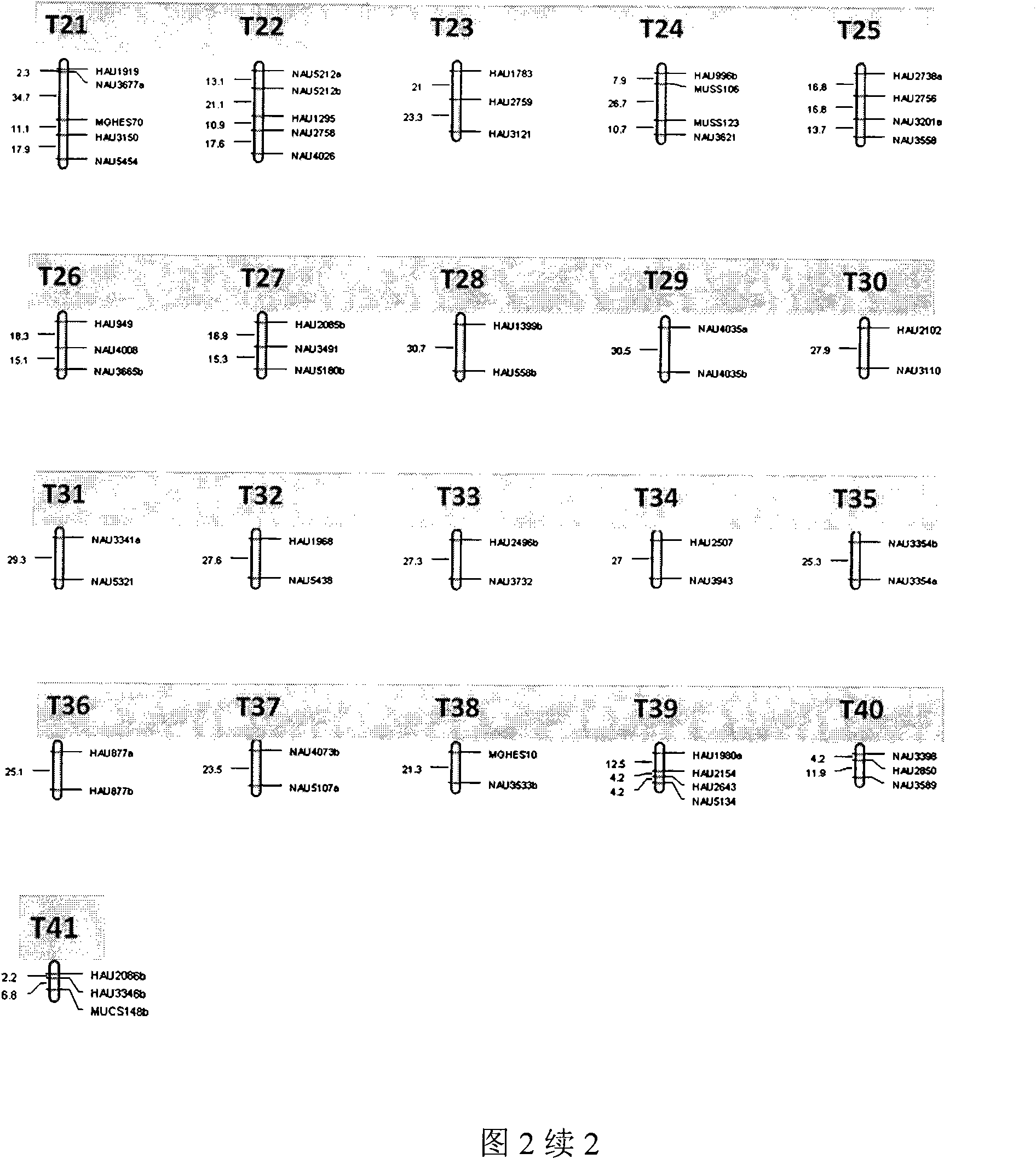Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Gossypium barbadense" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gossypium barbadense, also known as extra-long staple (ELS) cotton, is a species of cotton plant that has been cultivated to have ELS fibres – fibres longer than 34 millimetres (1 3 ⁄ 8 in) – which are associated with high quality cotton cloth.. The species is a tropical, frost-sensitive perennial that produces yellow flowers and has black seeds. It grows as a small, bushy tree and ...
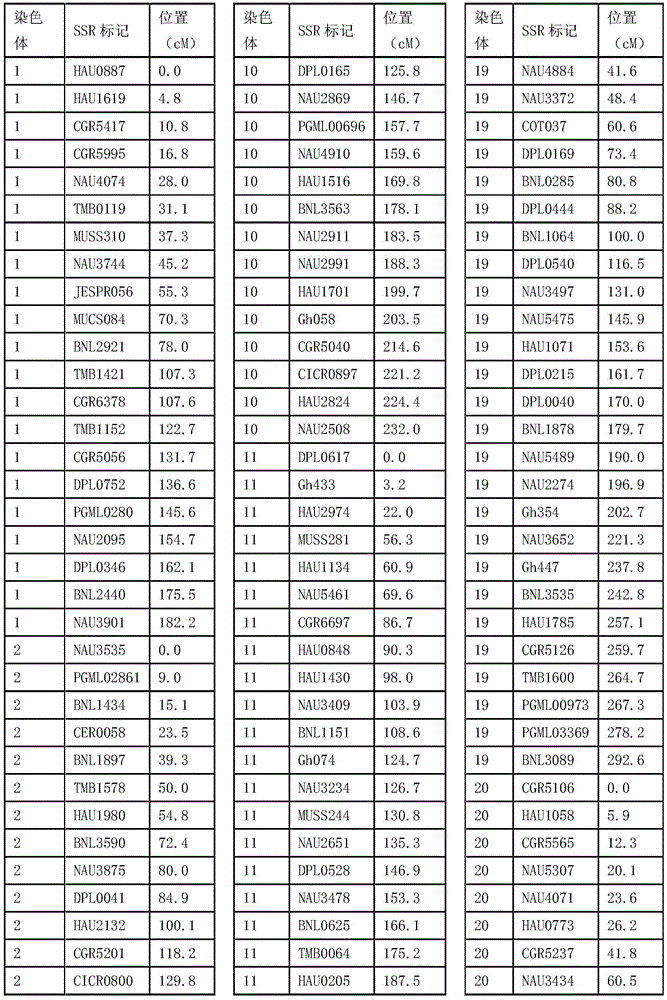
Molecular breeding method capable of improving length of cotton fibers by using gossypium barbadense chromosome segment introgression line
InactiveCN102229979ABreed fastEfficient cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationFiberAgricultural science
The invention discloses a molecular breeding method capable of improving length of cotton fibers by using gossypium barbadense chromosome segment introgression line, which is particularly used for crop (cotton) economical character oriented improvement and new variety bredding. An introgression line IL040-A4-1 of which the fiber length is increased obviously is screened out by cotton fiber detection of the gossypium barbadense chromosome segment introgression line. In the method, introgression line is used as a nonrecurrent parent, Xinluzao No.26, which is a variety promoted in cotton area in north of Xinjiang, is used as a recurrent parent are hybridized, hybridizing, two generations of back crossing and three generations of selfing are performed, molecular markers are also used to help to select cotton new lines with high fiber length. A high-quality and high-yield cotton new line named 'Nannong Haidao No.1' was bred by using the method.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
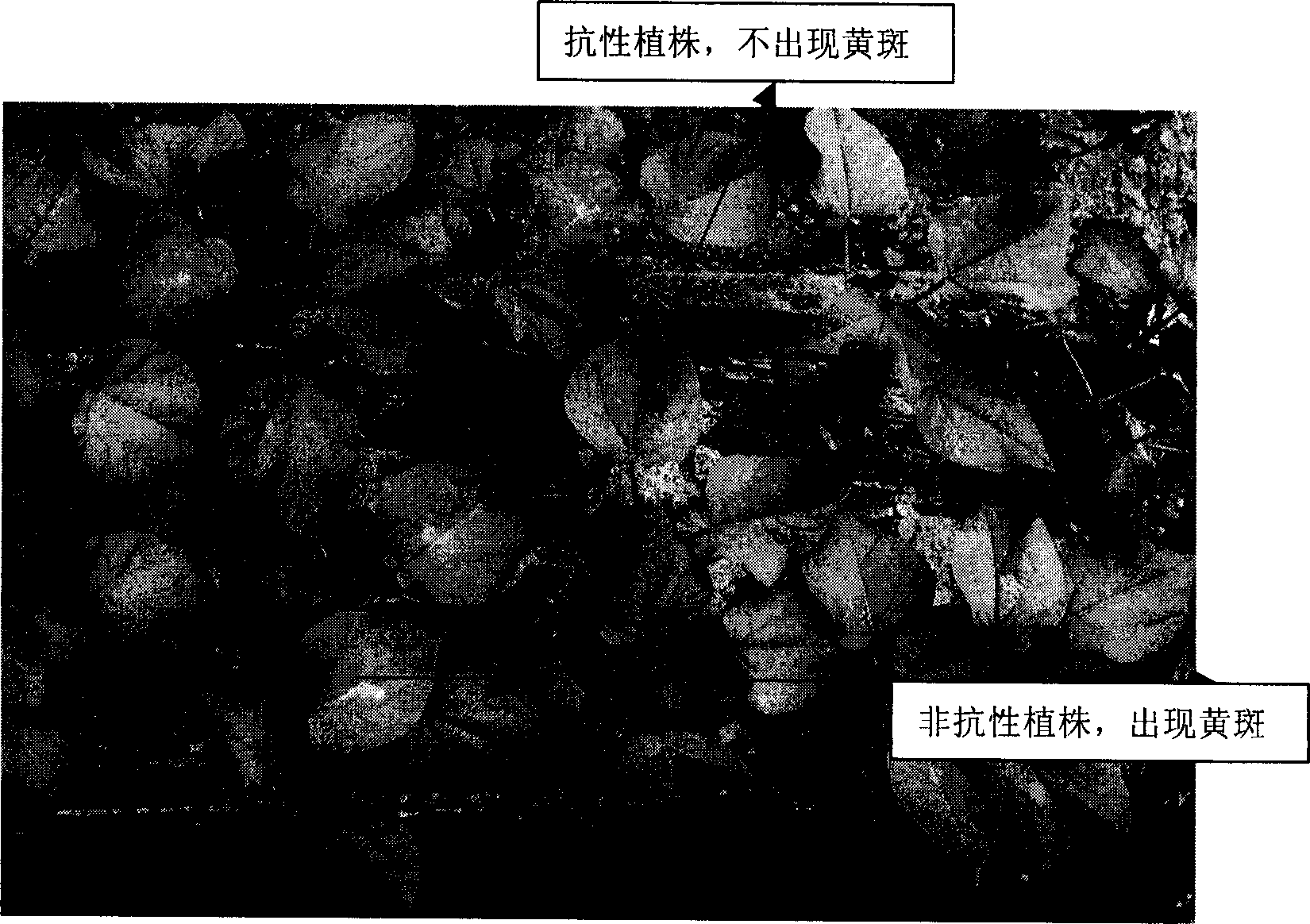
Cotton GbVe gene, protein coded thereby and use thereof in vegetable verticillium wilt resistance
InactiveCN101928338AVerticillium wilt resistance increasedHelps reveal molecular mechanismsFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention relates to cotton GbVe gene and a protein coded thereby. In the invention, a Ve gene associated with verticillium wilt resistance is obtained by cloning in a gossypium barbadense variety having high verticillium wilt resistance; a 5'-terminal GbVe gene fragment and a 3'-terminal GbVe gene fragment, which are obtained by amplification, are spliced; a primer capable of amplifying the full-length GbVe gene is designed and synthesized according to a gene sequence; the sequence of the full-length GbVe gene is obtained by the conventional colony sequencing method according to an RT-PCR technique; and the nucleotide sequence of the full-length GbVe gene is represented by SEQ ID No.1. In the invention; a new and important candidate gen is provided for vegetable verticillium wilt resistant gene project; and the obtained full-length GbVe gene and a vegetable expression vector constructed by the full-length GbVe gene lay a foundation for further transforming important crops for improving the verticillium wilt resistance of transgenic crops and have great economic benefits and application values.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Gossypium barbadense chromosome segment capable of improving verticillium wilt resistance of gossypium hirsutum and molecular markers
ActiveCN105713976AImprove disease resistanceIncrease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyDisease
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Cotton GbSTK gene, encoding protein thereof and application for resisting verticillium wilt of plants
InactiveCN101942426AHas anti-Verticillium wilt effectFungiBacteriaRapid amplification of cDNA endsThreonine
The invention relates to a cotton GbSTK gene and encoding protein thereof. Sea island cotton Pima90-53 is taken as a material, a cDNA-AFLP technology is used for screening to obtain differential fragments related to verticillium wilt resistance, and then, a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and a RACE (rapid-amplification of cDNA ends) technology are used for amplifying to obtain a resistance gene of cotton verticillium wilt, namely a serine / threonine protein kinase (GbSTK) gene. The functional studies of the gene and the encoding protein thereof show that the GbSTK gene has certain effect on resisting verticillium wilt.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Method for building cotton fiber transcription genetic linkage map by EST-SSR sign
InactiveCN101880714AThe method is simple and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementFiberAgricultural science
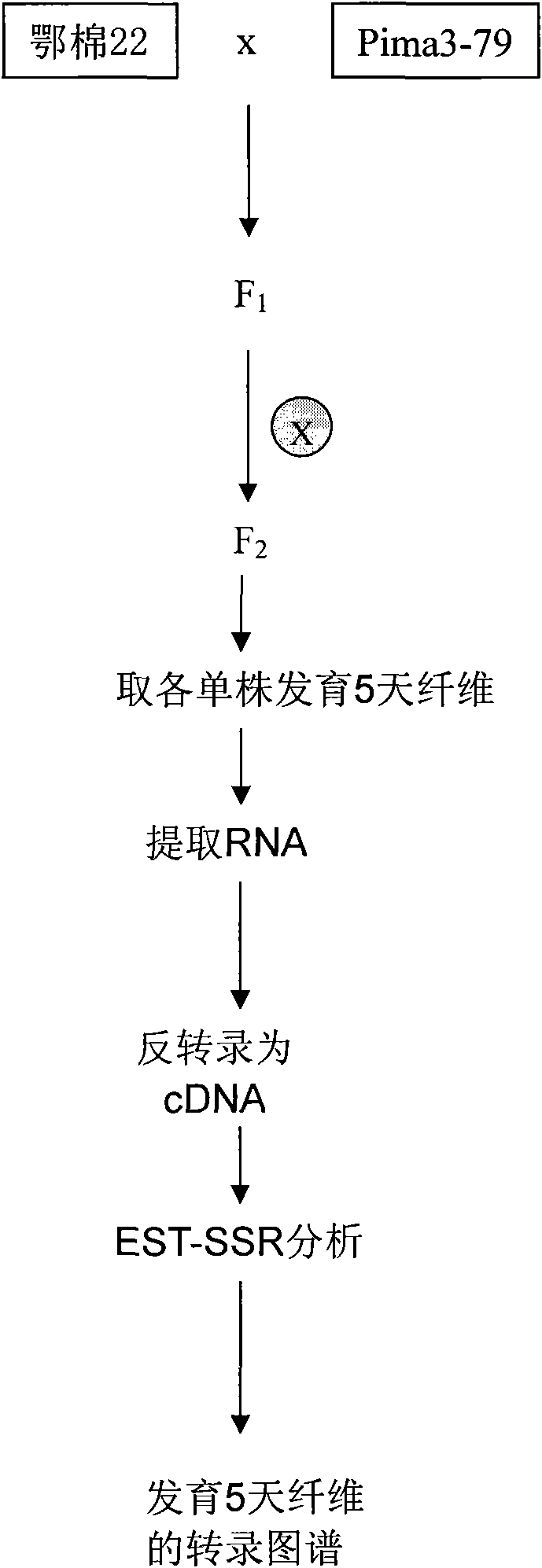
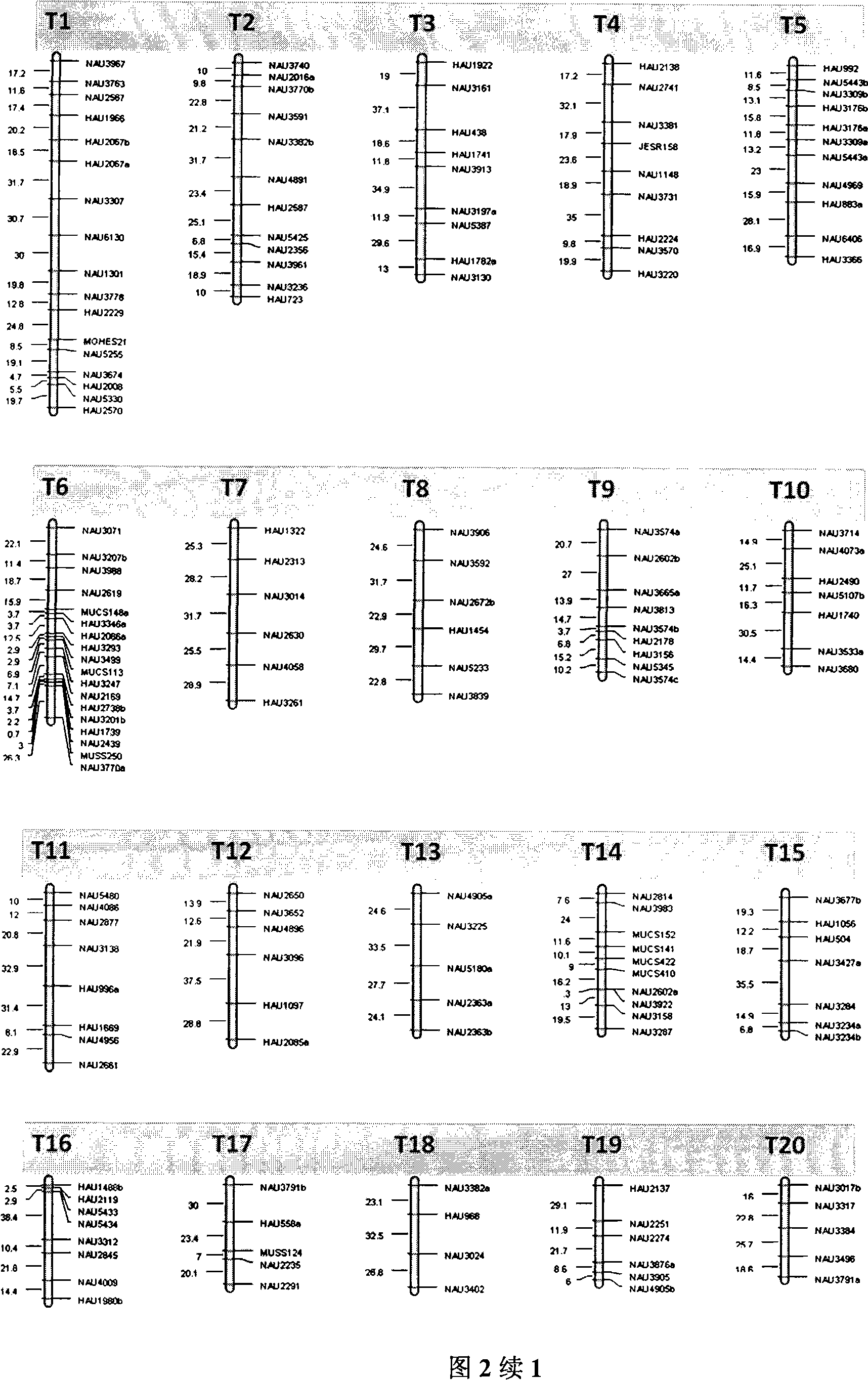
The invention belongs to the technical field of cotton molecule breeding, particularly relating to a method for building a cotton fiber transcription genetic linkage map by EST-SSR signs. The method comprises the following steps: taking gossypium barbadense Pima 3-79 as a male parent and Gossypium hirsutum Emian 22 as a female parent, and hybridizing to obtain F1; planting F1, and causing F1 to be inbreeded to obtain F2; taking the F2 single plant as a starting material for the fiber transcription map to be plotted; extracting the RNA of the fiber of the field F2 single plant in 5 days after the single plant blooms, and carrying out reverse transcription of the RNA into cDNA to be served as a plotting group of the transcription map; utilizing the reported EST-SSR primer and the primer shown by a self-designed sequence table SEQ ID NO:1-90 to carry out the plotting group analysis to the F2 single plant by a denatured polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis; and finally, analyzing data by MAPMAKER / EXP.3.0 mapping software, and manufacturing and obtaining the transcription map. Compared with the existing method, the method of the invention is simple and practical, has accurate QTL positioning and is convenient for cloning genes relevant to cotton fiber development.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
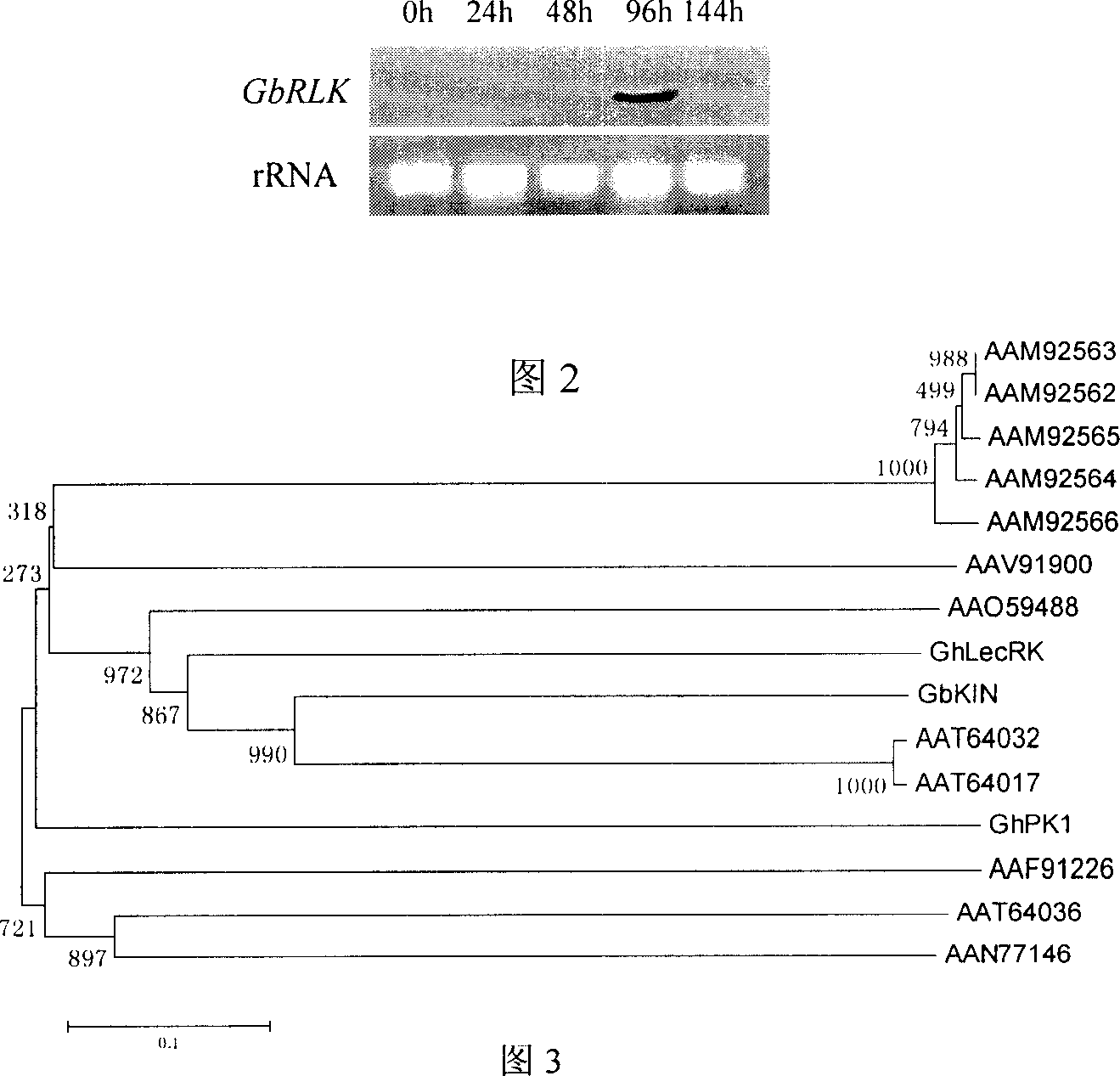
Sea island cotton receptor analogous protein kinase gene and its application
InactiveCN1974772AIncrease Verticillium Wilt ResistanceReduce lossesTransferasesFermentationFull length cdnaPcr method
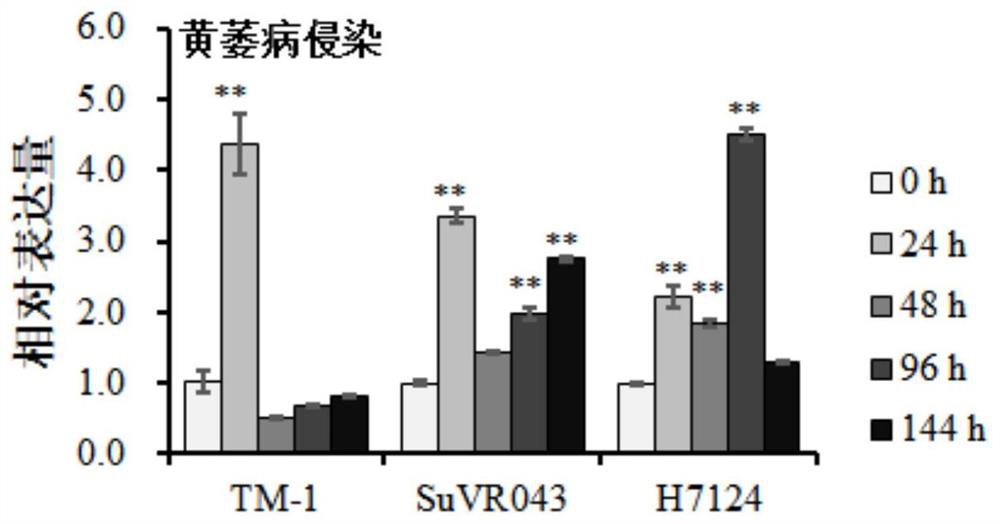
The present invention relates to the cloning of sea island cotton receptor analogous protein kinase gene, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The present invention clones the full length cDNA sequence of sea island cotton receptor analogous protein kinase gene, designs one pair of specific primers for sea island cotton receptor analogous protein kinase, detects the expression of the gene in resistant sea island cotton breed Hai-7124 with inoculated verticillum wilt in the RT-PCR method, and verifies the result by means of Northern hybridization. It is shown that the gene is expressed only in 96 hr after verticillum wilt treatment, so that the gene is relate directly with verticillum wilt. The gene may be used as the target gene in culturing verticillum wilt resisting cotton breed.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
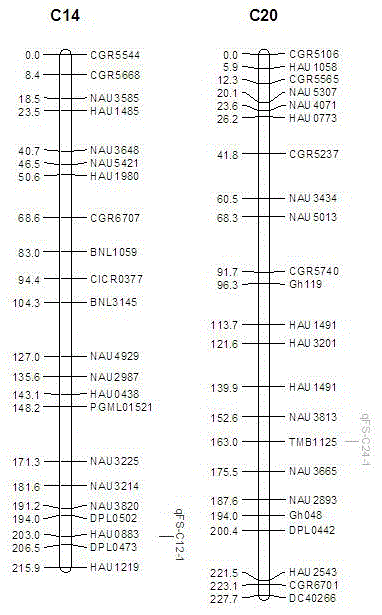
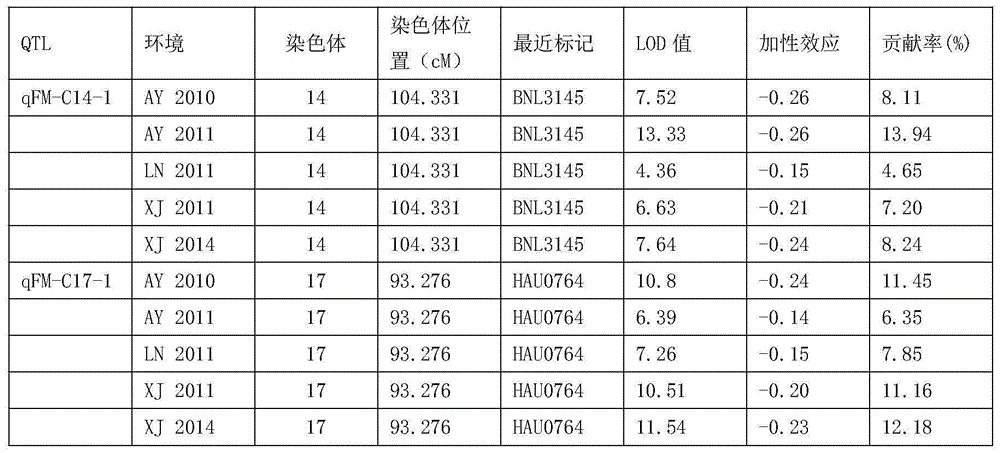
Fiber strength related molecular mark from gossypium barbadense and application thereof
ActiveCN105483248AHigh strengthEnhanced strength traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention relates to the field of molecular breeding, and particularly relates to a fiber strength related molecular mark from gossypium barbadense and application thereof. The molecular mark is HAU0883125 and TMB1125220, wherein the HAU0883125 is closely linked with the site qFS-C14-1 of cotton fiber strength QTL, and the TMB1125220 is closely linked with the site qFS-C20-1 of cotton fiber strength QTL; and the qFS-C14-1 is located on chromosome C14, and the qFS-C20-1 is located on chromosome C20. The molecular mark can be used for improving the selection efficiency of fiber strength, overcoming the defect in existing breeding technology for fiber quality identification and accelerating the culturing progress of high-quality new varieties.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
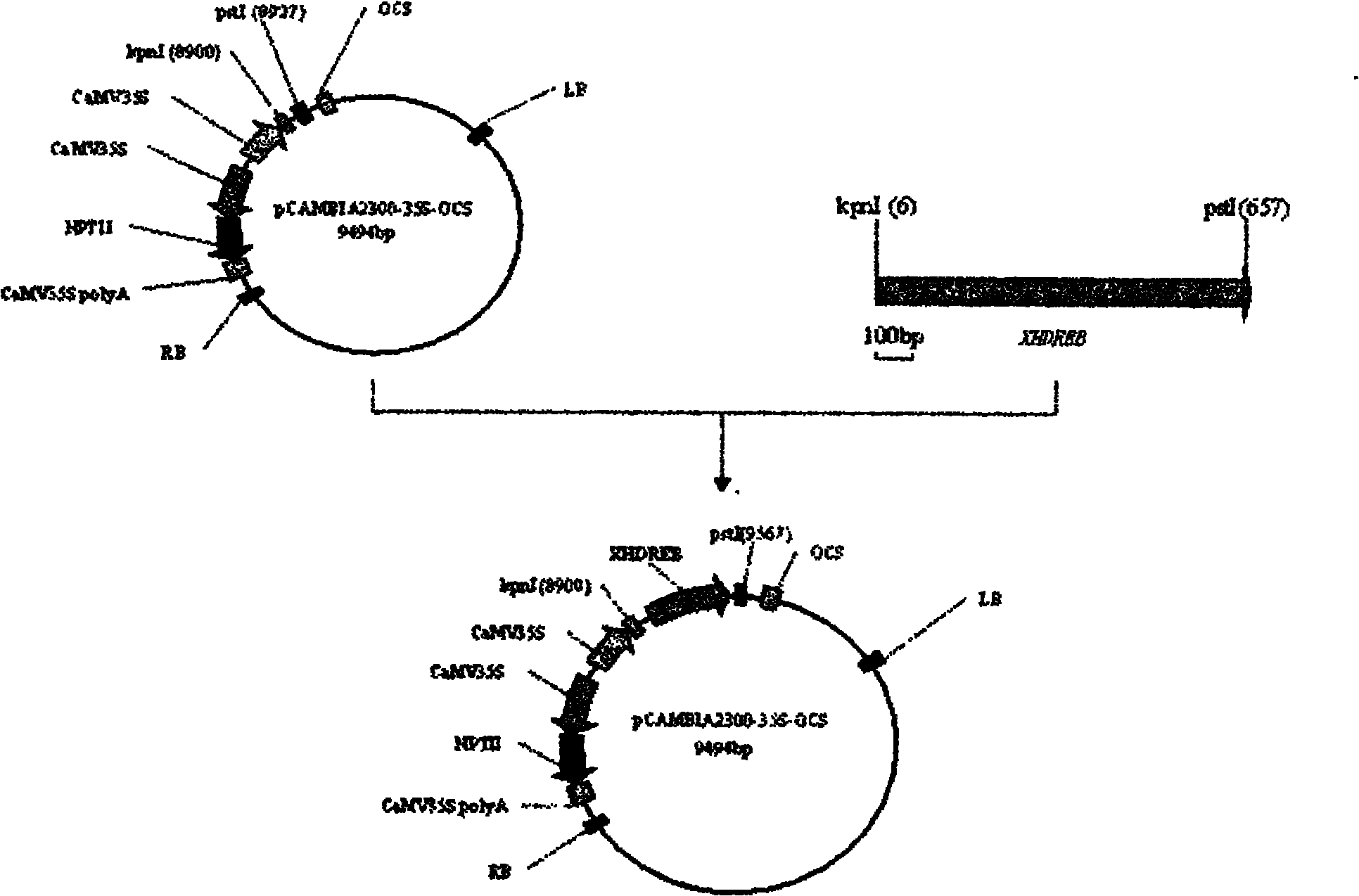
Gossypium barbadense DREB transcription factor gene and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering, and provides a gossypium barbadense DREB transcription factor gene which has the nucleotide sequence shown as the SEQ ID NO:1. The gossypium barbadense DREB transcription factor gene is constructed by the steps of constructing a pC-XHDREB plant expression vector, transforming the tobacco by the agrobactrium tumefaciens to obtain the XHDREB gene transformed tobacco, and verifying the XHDREB gene transformed tobacco by the drought simulation experiment. The tobacco has the capacities of drought resistance, saline resistance and cold resistance due to the over-expression of the XHDREB.
Owner:曲延英 +1
Molecular breeding method for breeding new anti-verticillium cotton seed
ActiveCN102517396AChoose poor reliabilityLong breeding cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationMolecular breedingAgricultural science
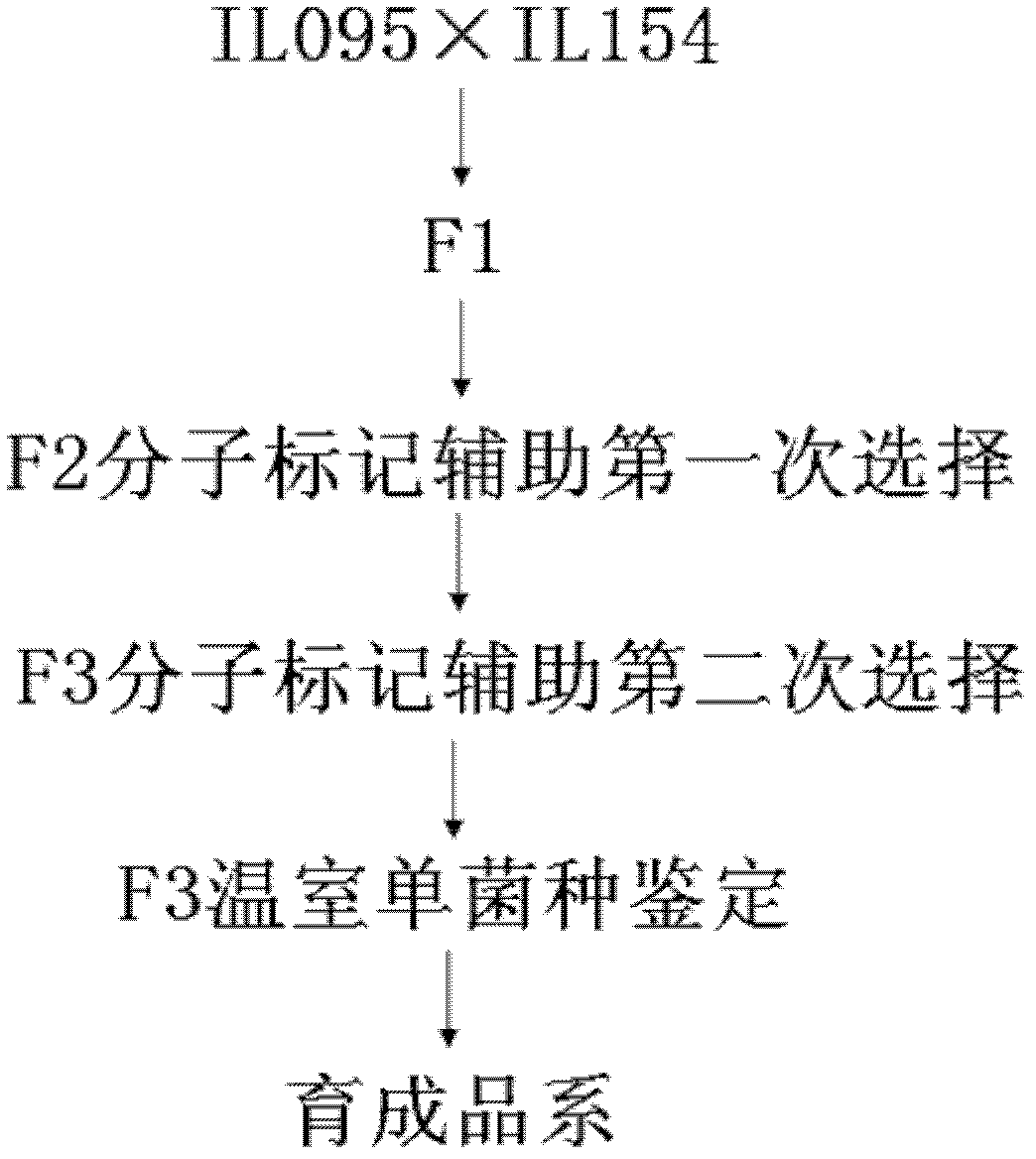
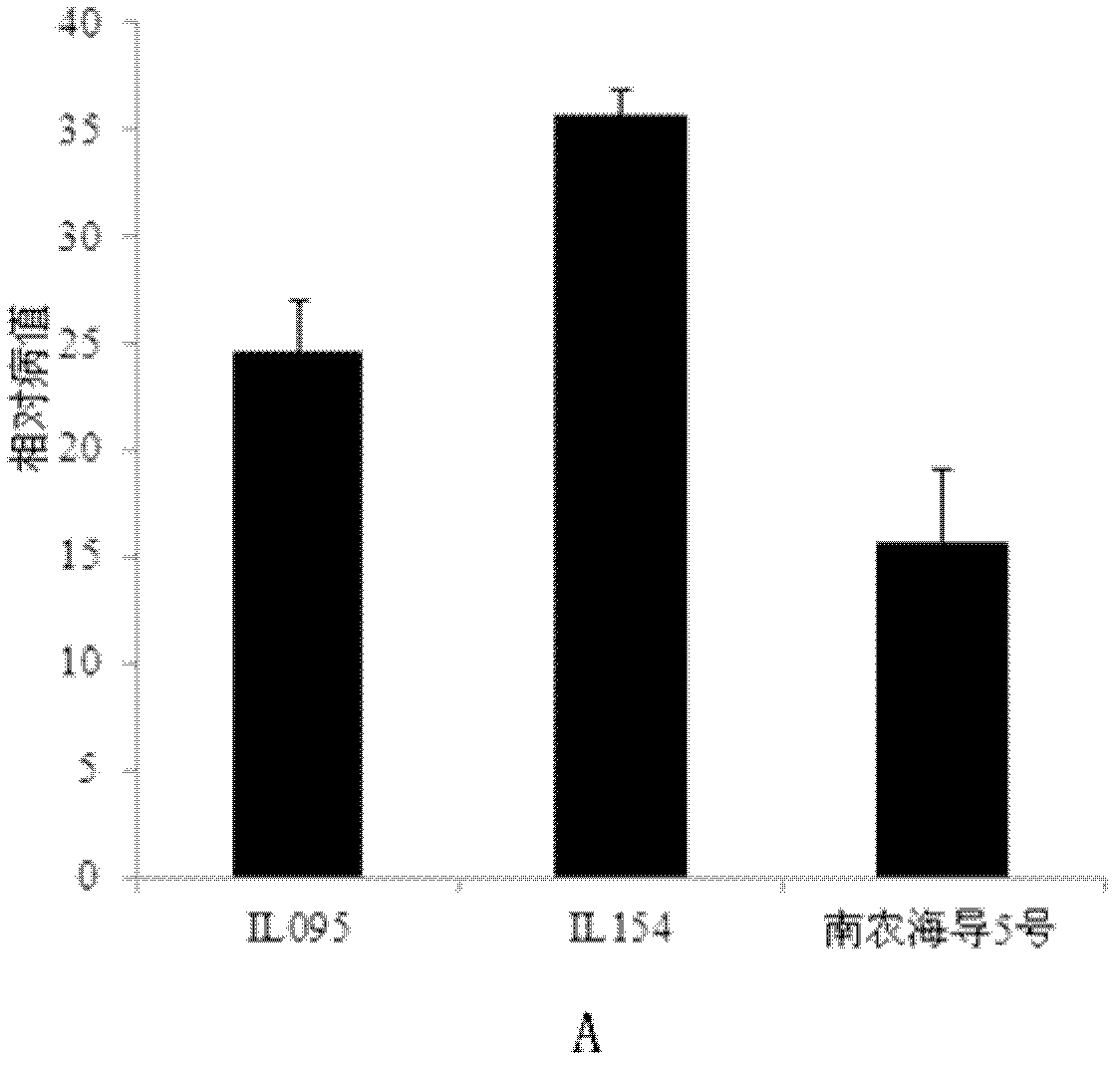
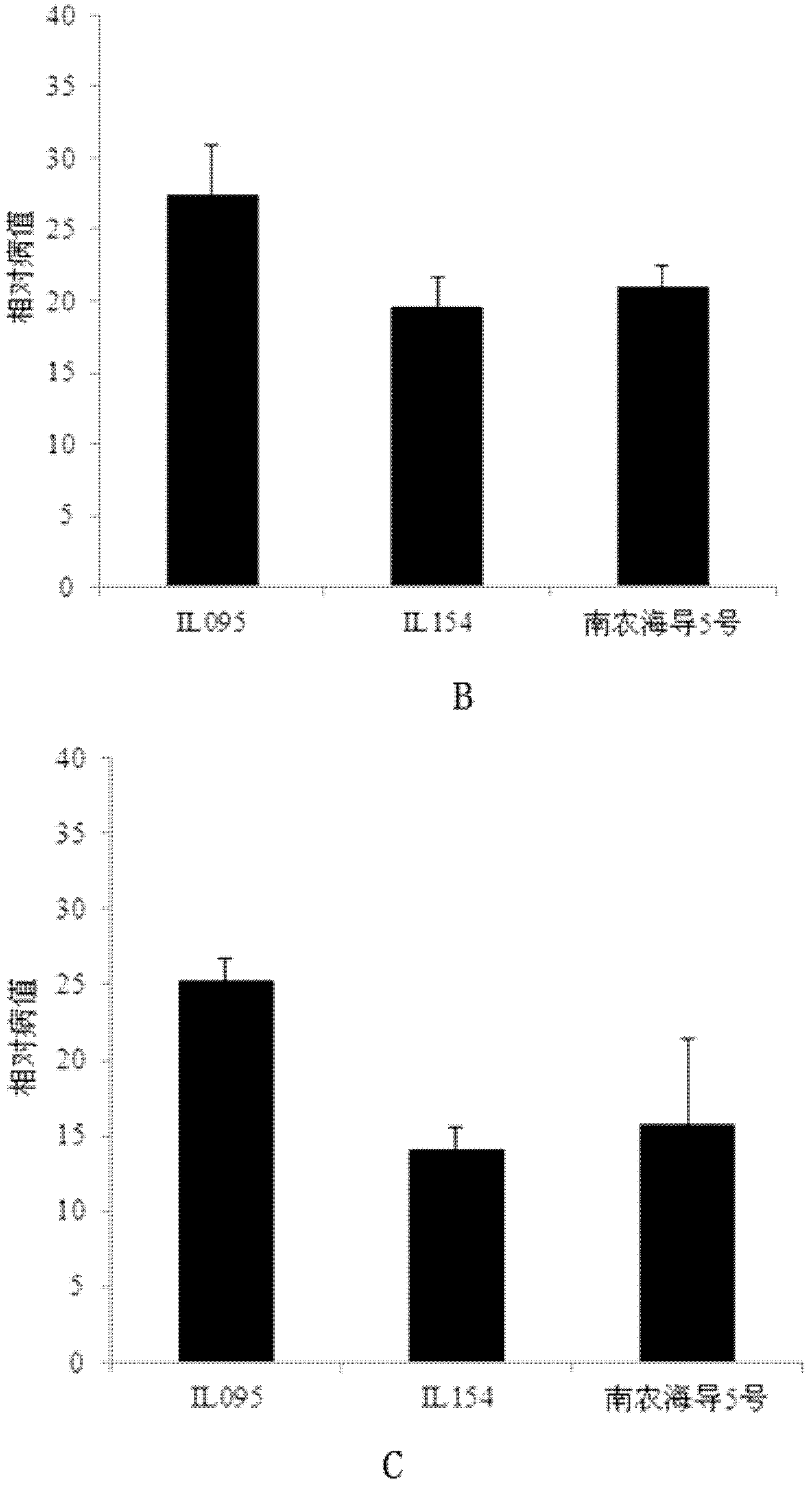
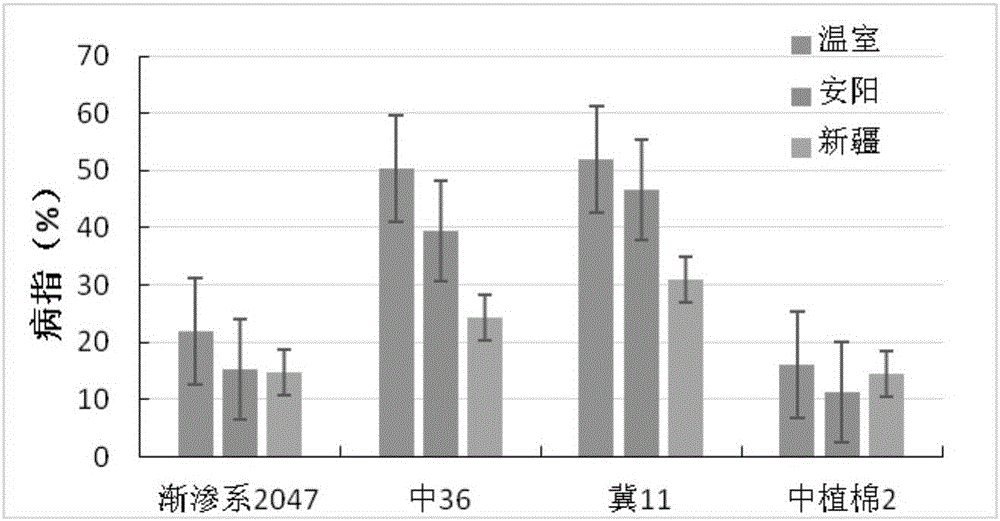
The invention belongs to the field of molecular breeding, and relates to a molecular breeding method for breeding a new anti-verticillium cotton seed. The method comprises the following steps: taking a chromosome segment introgression line 1L095 of sea-island cotton of which the collection number is CGMCC No.5574 as a female parent and a chromosome segment introgression line 1L154 of sea-island cotton of which the collection number is CGMCC No.5575 as a male parent to crossbreed a generation I seed, and obtaining F2 from the crossbred generation I seed, wherein each generation is collected bya single strain; and selecting by taking a molecular marker for assistance to obtain a novel multi-strain prevention cotton strain. Through the adoption of the method, the novel multi-strain prevention cotton strain-Nannong haidao V is bred. As the molecular marker is taken for assistance to select a target trait, the novel multi-strain prevention cotton strain can be bred in 2 to 3 years fast and effectively. The corresponding disease index of Nannong haidao V is 15.51 to 20.97 percent.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular breeding method for improving cotton fiber length, fiber strength, and micronaire value
InactiveCN102229982AImproved fiber lengthHigh fiber strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceCotton fibre
The invention relates to a molecular breeding method for improving cotton fiber lengths, fiber strengths, and micronaire values. The method is applied in oriented improving of crop (cotton) agronomic properties, and in selective breeding of novel breeds. According to the invention, cotton fiber quality detection is carried out upon gossypium barbadense chromosome segment introgression lines (CSIL), and an introgression line IL080-D6-1 with substantially increased fiber length and fiber strength, and substantially reduced micronaire value is selected. The introgression line is regarded as a non-backcross parent, and Xinluzao No.38, which is a breed from Xinjiang cotton region, is regarded as a backcross parent. Crossing is carried out between the two. The resulting breeds are backcrossed for 2 generations and self for 3 generations. With molecular marker auxiliary selection, a novel cotton line with good fiber length, fiber strength, and micronaire value is obtained. With the method, a novel high-quality and high-yield cotton line, which is Nannong gossypium barbadense No.2, is obtained.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular breeding method for improving cotton fiber length, fiber strength, and micronaire value
InactiveCN102229982BImproved fiber lengthHigh fiber strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention relates to a molecular breeding method for improving cotton fiber lengths, fiber strengths, and micronaire values. The method is applied in oriented improving of crop (cotton) agronomic properties, and in selective breeding of novel breeds. According to the invention, cotton fiber quality detection is carried out upon gossypium barbadense chromosome segment introgression lines (CSIL), and an introgression line IL080-D6-1 with substantially increased fiber length and fiber strength, and substantially reduced micronaire value is selected. The introgression line is regarded as a non-backcross parent, and Xinluzao No.38, which is a breed from Xinjiang cotton region, is regarded as a backcross parent. Crossing is carried out between the two. The resulting breeds are backcrossed for 2 generations and self for 3 generations. With molecular marker auxiliary selection, a novel cotton line with good fiber length, fiber strength, and micronaire value is obtained. With the method, anovel high-quality and high-yield cotton line, which is Nannong gossypium barbadense No.2, is obtained.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
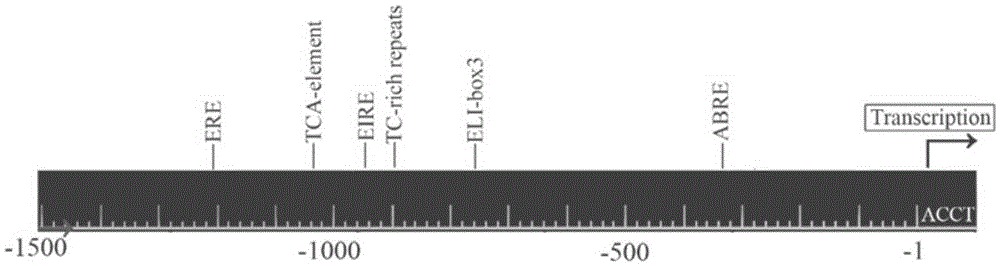
Gossypium barbadense GbHyPRP1 gene promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN105238789AVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsHormones regulationNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to a gene promoter, and particularly discloses a gossypium barbadense GbHyPRP1 gene promoter. A nucleotide sequence of the gene promoter is as shown in SEQ ID No.1 or is a nucleotide sequence formed by deriving from the sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 encoding the same functional amino acid sequence and substituting, deleting and / or adding one or more nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID No.1. Elements associated to the control of hormones and effectors in the promoter are verified by virtue of experiments; and the gene promoter has capacity for promoting the expression of GUS genes and promotes the genes on roots and tips.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Evaluation method of Gossypium hirsutum-Gossypium barbadense introgression lines
ActiveCN106048033AGood for physical locationAssisted selection breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural sciencePhysical Maps
The invention relates to an evaluation method of Gossypium hirsutum-Gossypium barbadense introgression lines. The invention discloses a comprehensive evaluation method of Gossypium hirsutum-Gossypium barbadense introgression lines. The method comprises the following steps: (1) identifying verticillium wilt resistance; (2) carrying out molecular marker analysis on Gossypium hirsutum-Gossypium barbadense introgression lines; (3) determining the physical location of the molecular marker in the cotton genome; and (4) according to the physical location of the molecular marker, carrying out physical location on the introduced disease-resistant chromosome segment, and drawing a physical map of the Gossypium hirsutum-Gossypium barbadense introgression lines. By combining the verticillium wilt resistance identification and molecular marker analysis, the molecular marker sequence is compared with the tetraploid Gossypium hirsutum genome, and the disease-resistant gene carried in the Gossypium hirsutum-Gossypium barbadense introgression lines is located, thereby laying the foundation for disease-resistant gene cloning and disease-resistant variety improvement.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cotton GbSTK gene, encoding protein thereof and application for resisting verticillium wilt of plants
The invention relates to a cotton GbSTK gene and encoding protein thereof. Sea island cotton Pima90-53 is taken as a material, a cDNA-AFLP technology is used for screening to obtain differential fragments related to verticillium wilt resistance, and then, a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and a RACE (rapid-amplification of cDNA ends) technology are used for amplifying to obtain a resistance gene of cotton verticillium wilt, namely a serine / threonine protein kinase (GbSTK) gene. The functional studies of the gene and the encoding protein thereof show that the GbSTK gene has certain effect on resisting verticillium wilt.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
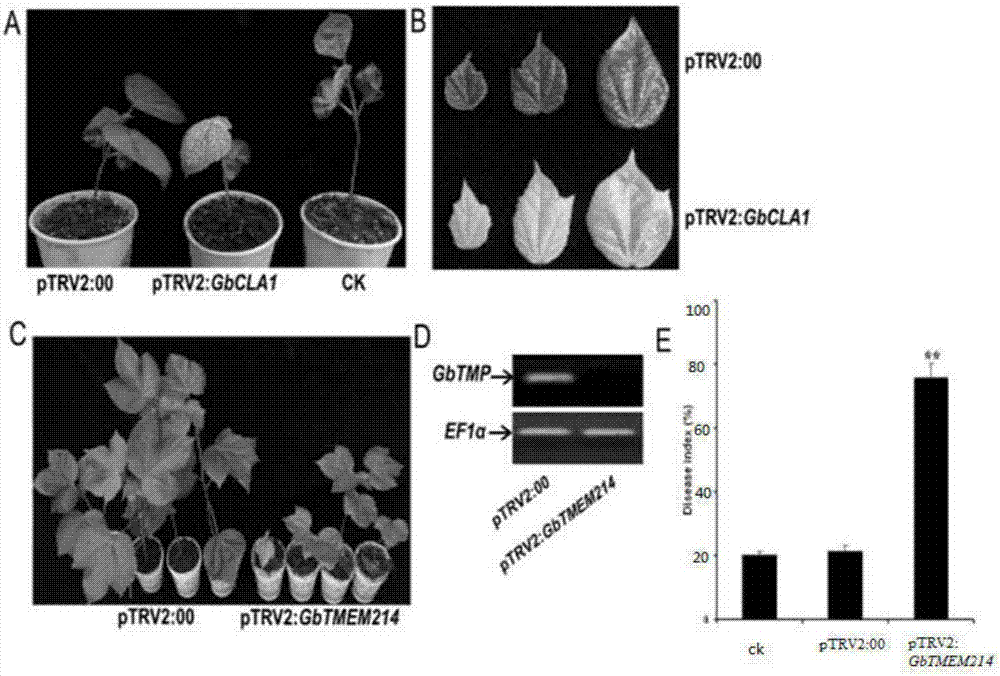
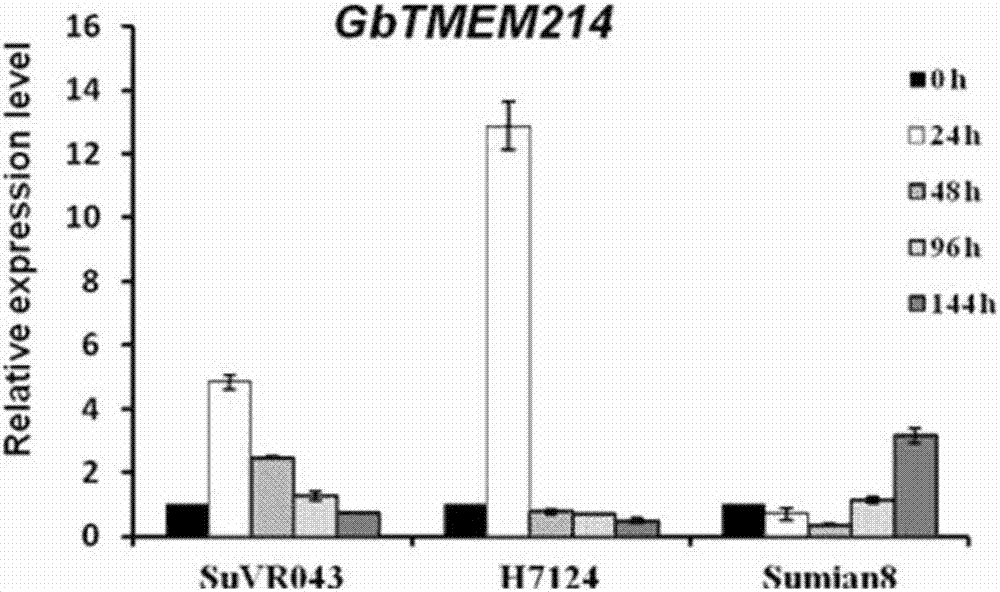
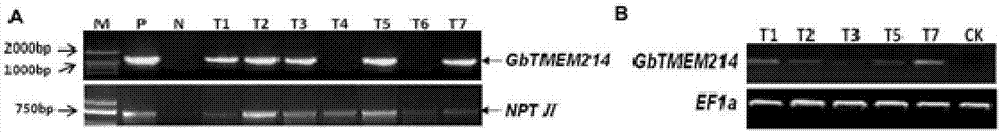
Gossypium barbadense transmembrane protein gene, primers, and application of Gossypium barbadense transmembrane protein gene
ActiveCN107254474ALower resistanceIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationDiseaseVerticillium wilt
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Molecular breeding method capable of improving length of cotton fibers by using gossypium barbadense chromosome segment introgression line
InactiveCN102229979BBreed fastEfficient cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationFiberAgricultural science
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Verticillium wilt resistant associated protein GbVIP1, coding gene and application thereof
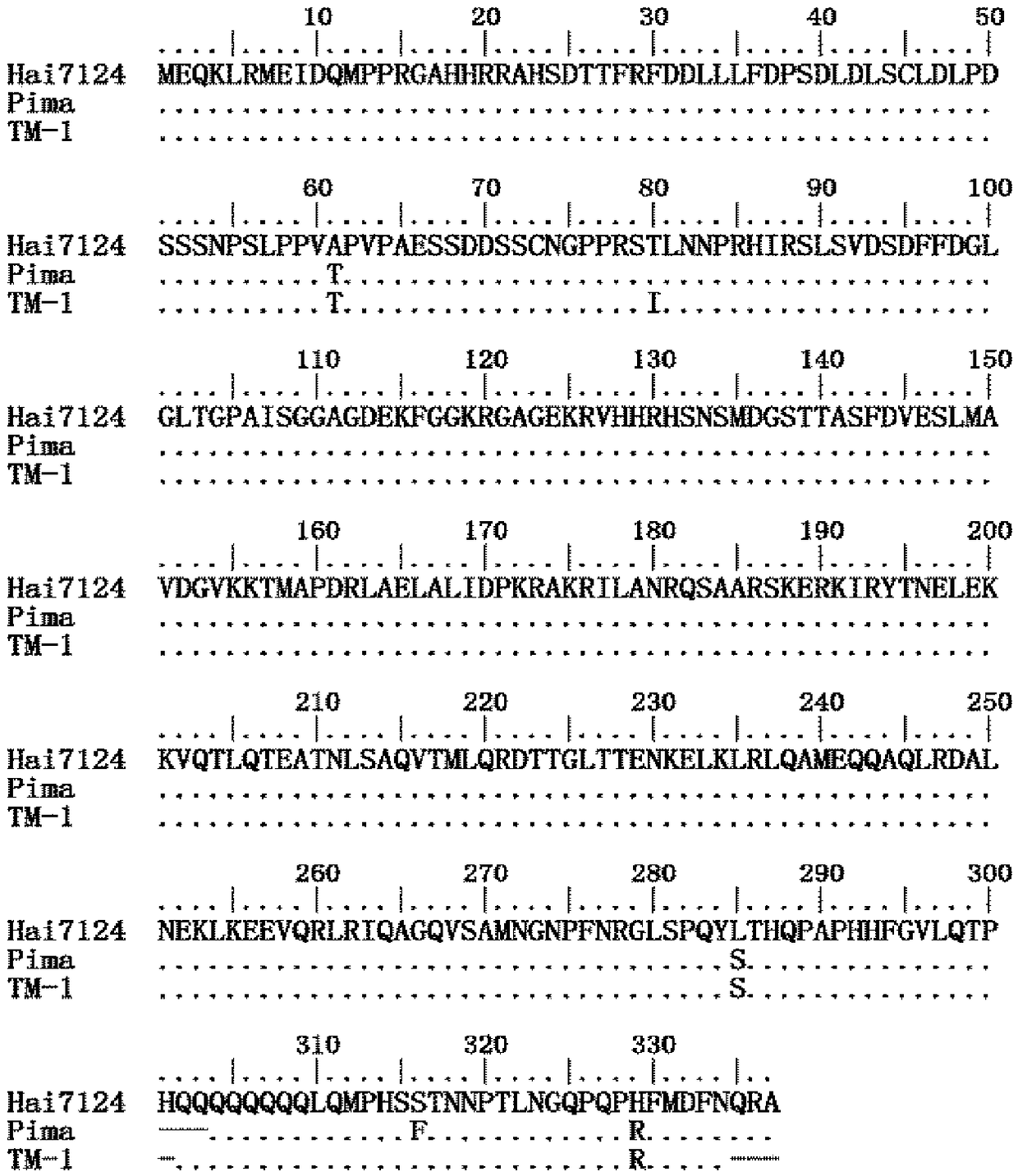
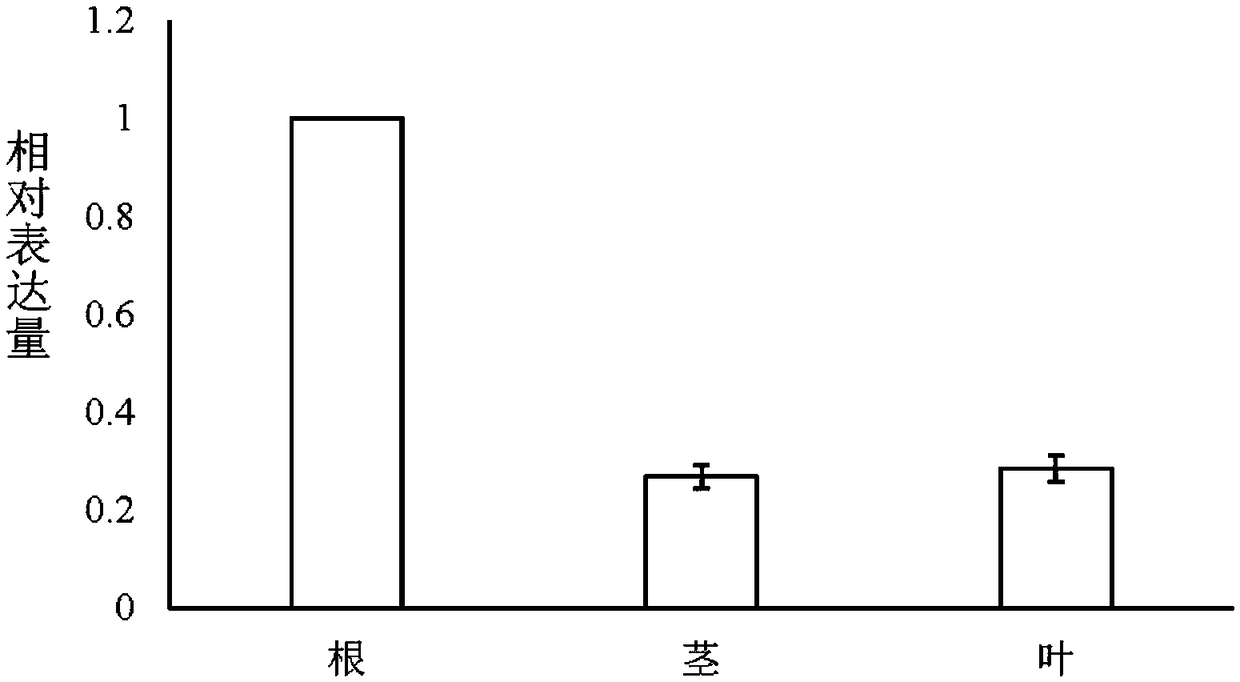
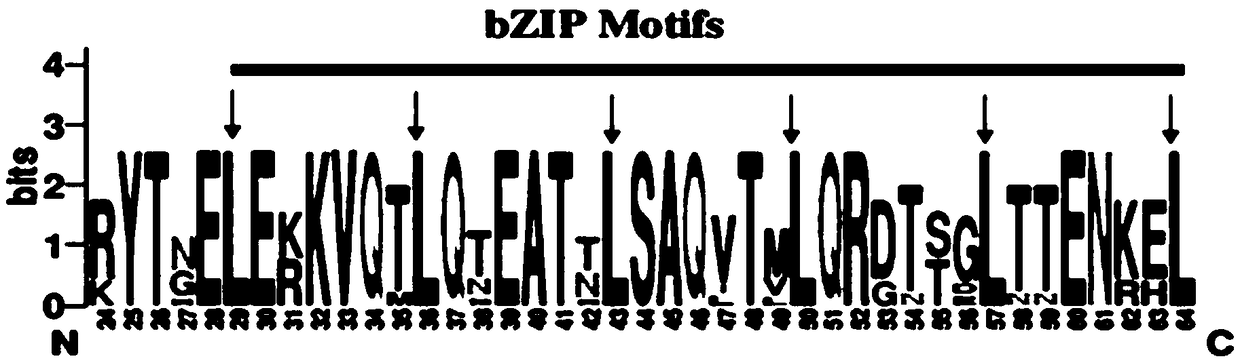
The invention discloses a verticillium wilt resistant associated protein GbVIP1, a coding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the protein is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The protein GbVIP1 provided by the invention comes from the verticillium wilt resistant gossypium barbadense variety Hai7124, belongs to the subfamily I of bZIP transcription factor family, and has a conservative bZIP structural domain. The study of the invention finds that the GbVIP1 gene has up-regulated expression under a verticillium dahlia infection condition, and silencing of the GbVIP1 gene lowers the resistance of gossypium barbadense to verticillium dahlia, therefore the GbVIP1 protein has important significance for verticillium wilt resistant breeding of cotton.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Temperature-controlled grafting method for regenerated plants of transgenic cotton
The invention discloses a temperature-controlled grafting method for regenerated plants of transgenic cotton. The method comprises the following specific operation steps: 1, preparation of stock seedlings, wherein gossypium barbadense seeds which are good in disease resistance and long in growing period are selected and sowed in a small basin, the height of the small basin is 10-12 cm, the diameter of an upper opening is 10-12 cm, the diameter of a lower opening is 9 cm, and when 1-4 main leaves emerge, the seedlings are reserved for standby application; 2, grafting and temperature control. By means of the method, the phenomenon that the total plants die due to the fact that at the high temperature time in summer, stock roots or the upper portions of the regenerated plants of the transgenic cotton are prone to being rotten can be effectively reduced, when the atmosphere temperature is equal to or greater than 35 DEG C in summer, after the grafted seedlings are grafted and 1-7 days later, and when the wrapped space temperature is less than or equal to 28 DEG C, the survival rate of the grafted seedlings can reach over 95%, and the survival rate of the regenerated plants of the transgenic cotton can be raised by over 15% in a high temperature season.
Owner:COTTON RES INST SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for marking chromosome terminals of cotton A genome and A sub-genome
The invention belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetic, and concretely relates to a method for marking chromosome terminals of cotton A genome and A sub-genome. The method comprises: using BAC coming from gossypium barbadense pima-90BAC library to clone 350B21, performing BAC-FISH on mitosis mid-term chromosomes of different cotton species, and discovering the phenomena that the terminals of all chromosomes of A genome and A sub-genome generate strong hybridization signals, while the hybridization signals of all chromosomes of D genome and D sub-genome are not obvious. By utilizing the BAC-FISH method for BAC cloning, the chromosome terminals of cotton A genome and A sub-genome can be rapidly effectively marked.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
Application of sea island cotton GbNAC1 in verticillium wilt resistance
ActiveCN106282200AReduced Verticillium Wilt ResistanceIncreased resistance against Verticillium wiltPlant peptidesFermentationVerticillium speciesGene silencing
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and particularly relates to application of sea island cotton GbNAC1 gene in verticillium wilt resistance. The GenBank ID of a GbNAC1 gene is KP317496, and the gene is relevant to the verticillium wilt resistance of plants. The inventor finds that when the plants are infected by verticillium dahlia, the expression quantity of the gene is reduced, the verticillium wilt resistance of the plants is reduced after the gene is further silenced, and the verticillium wilt resistance of the plants is improved after the gene overexpression. Based on the characteristics, GbNAC1 overexpression plants can be cultivated or screened, better references can be provided for new varieties of plants having better verticillium wilt resistance, and accordingly the sea island cotton GbNAC1 has a better application value on the aspect of cultivation of new varieties of plants.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Gossypium-barbadense-Hai-1-derived molecular markers related to fiber Micronaire value and application thereof
ActiveCN105177175ADecreased fiber micronaireHelps to filterMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFiberAgricultural science
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular breeding, particularly Gossypium-barbadense-Hai-1-derived molecular markers related to fiber Micronaire value and application thereof. The molecular markers are BNL3145330 and HAU0764220. The molecular markers are beneficial to overcoming the defects in the fiber quality identification in the existing breeding technique, and can enhance the fiber Micronaire value selection efficiency and accelerate the culturing progress of high-quality new species.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Embryo rescue method for overcoming cross-incompatibility of upland cotton-turneri cotton amphidiploid
ActiveCN106305405AAvoid the conundrum of rescue failureImprove survival ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAgricultural scienceRootstock
The invention discloses an embryo rescue method for overcoming cross-incompatibility of upland cotton-turneri cotton amphidiploid, comprising the steps of 1) hybridizing upland cotton with upland cotton-turneri cotton amphidiploid; 2) drip-applying gibberellin: drip-applying gibberellin aqueous solution to bracts on the pollination day; 3) culturing ovules; 4) grating seedlings: grafting the seedlings cultured in step 3) to Gossypium barbadense rootstocks. The method of the invention is efficient in preventing early dropping of bolls and avoiding pre-mortality of embryos, hybrids of upland cotton-turneri cotton amphidiploid with upland cotton are acquired successfully, upland cotton-turneri cotton pentaploid (sesquidiploid) material is acquired, fertility of such material is greatly improved as compared with the amphidiploid, the pentaploid is back-crossed successfully with upland cotton parents to obtain back-crossed offspring groups, and basis is laid for breeding utilization of the cotton species.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Crossbreeding method for pyramiding cotton superior traits
ActiveCN109997682AShorten the improvement periodExpand sourcePlant genotype modificationAgricultural sciencePhenotypic trait
The invention relates to the field of cotton variety breeding, in particular to a crossbreeding method for pyramiding cotton superior traits. The method includes steps: taking a cotton variety authorized in Shandong Province which is a main cotton production region in the Yellow River basin as a female parent, taking two lines with fiber superior traits as male parents, and performing crossbreeding of the female parent with the male parents respectively to obtain a generation F1, wherein at least one of the male parents belongs to chromosome segment substitution lines from gossypium hirsutum and gossypium barbadense or recombinant inbred lines thereof; collecting pollens of stamens of generation F1 plants, mixing, performing pollination backcrossing on the generation F1 plants, and harvesting to obtain a double-cross generation F2; subjecting the generation F2 to continuous selfing for 3-10 times, and screening to obtain cotton superior traits pyramided line. By means of specific multi-parent double-cross pyramiding breeding, the character of high yield of the female parent is kept in the final generation, combining abilities of varieties are explored, pyramiding of superior traitsand certain lines is realized, a superior variety improving term is shortened, and genetic improvement efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Sea island cotton pollen tube passage method transgene technology
ActiveCN1769466AOriginalityPromote conversionMicroinjection basedAngiosperms/flowering plantsTransgenic technologyEcology
This invention relates to an island cotton improving technique, which maily relates to an island cotton pollen channel transfer method, this method is simple and effective, which changes the lower transfrom rate of the present pollen channel technique on inland cotton. Besids, this invention also gets island cotton with transformed outer gene.
Owner:SINKIANG YIDA AGRI TECH
High-yield cultivation method of crop rotation of sea island cottons with long and short fruit branches
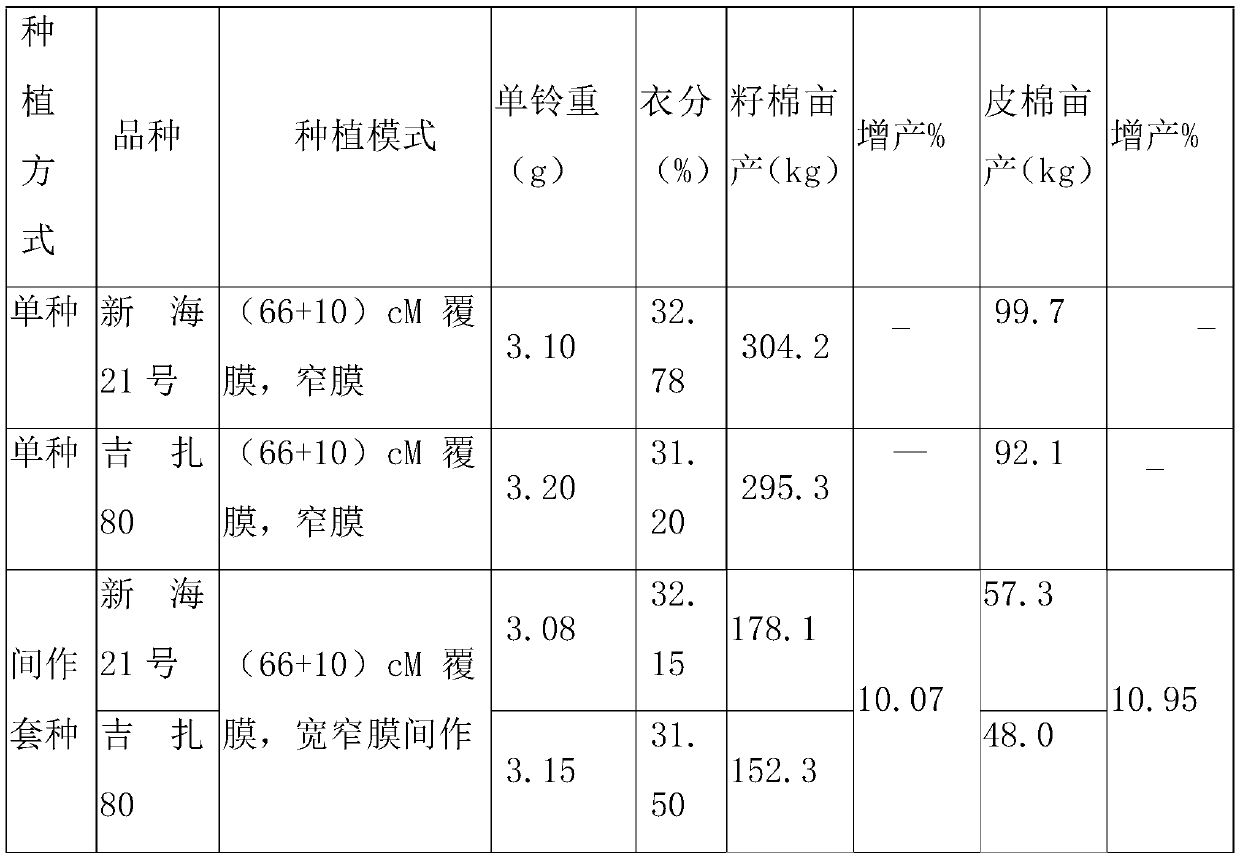
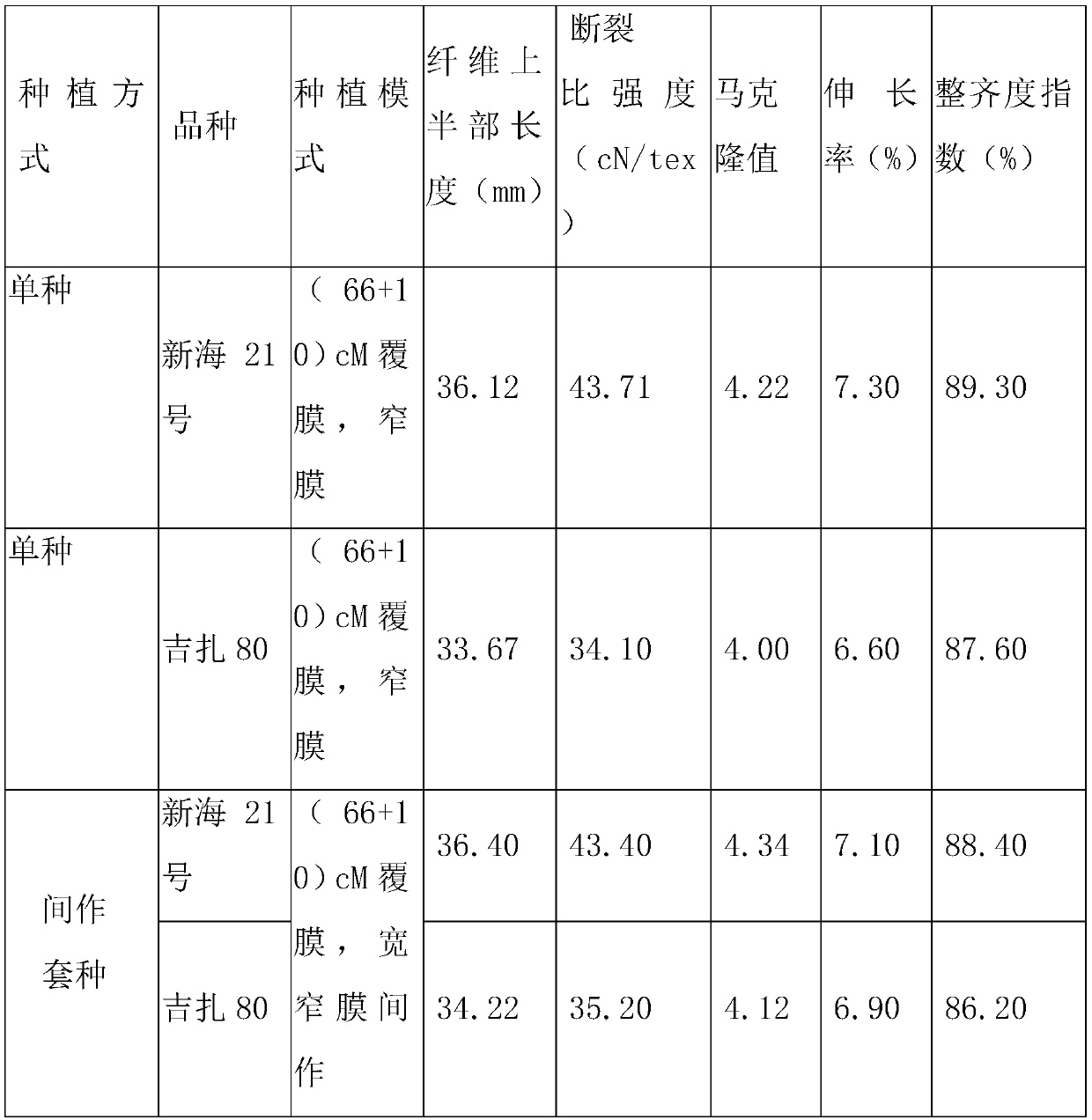
The invention discloses a high-yield cultivation method of crop rotation of sea island cottons with long and short fruit branches, which comprises the following steps of: autumn tillage and winter irrigation, fine land preparation, preparation of suitable varieties, field planting mode, scientific field management and timely harvesting; according to the method, the long fruit branch sea island cotton and the short fruit branch sea island cotton are planted in an intercropping way, so that the marginal effect of the long fruit branch sea island cotton can be increased, the utilization rate of space resources is effectively improved, and the economic benefit is greatly improved; the method mainly adopts the currently commonly used planting mode of machine-picked cotton in Xinjiang, one filmcorresponds four rows, one film of long fruit branch loose plant type sea island cotton is adjacent with two films of short fruit branch compact plant type sea island cotton and one film of long fruitbranch sea island cotton, the arrangement is repeated in this way, the arrangement of crops in the field is optimized, the planting layout of the plant type structure alternate arrangement of loose-compact-loose is integrally formed, no significant difference exists in the quality of the sea island cotton fiber, but the yield of seed cotton and lint cotton can be increased by 10.07% and 10.95% respectively, and the yield and benefit of cotton per unit area can be obviously improved.
Owner:XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & RECLAMATION SCI
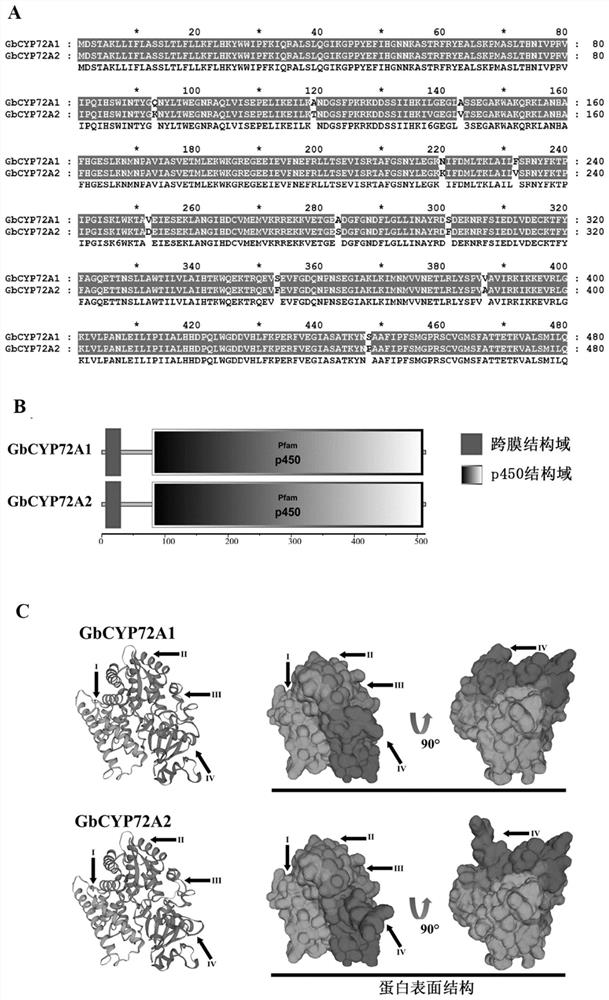
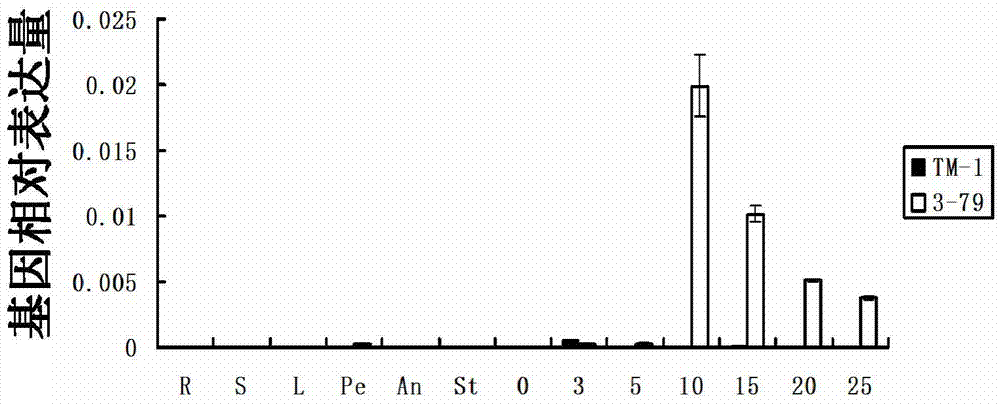
Sea island cotton GbCYP72A2 gene as well as encoding protein and application thereof
PendingCN111635906ALower resistanceIncrease resistanceOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyTranscription initiation site
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Cotton cell wall extensin gene GbEXPATR and application
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and particularly relates to cell wall extensin gene GbEXPATR separated and cloned from cotton and application. The cell wall extensin gene GbEXPATR which is obtained through sea island cotton fiber specific expression in a cDNA library at different sea island cotton fiber development stages and lack of a second structural domain, and a nucleotide sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO:1, wherein 52-306 represents a basic group region which is a coding region and exceptionally and efficiently expressed in a sea island cotton fiber elongation period, a conversion period and a secondary wall synthesis initial stage. An obtained overall-length ORF is established on a plant excessive expression vector Pcambia2301M, sea island cotton is converted into upland cotton by using an agrobacterium-mediated transformation genetic transformation method, the quality of transgenic offspring fiber is analyzed, and the cell wall extensin gene GbEXPATR can effectively promote fiber elongation is proved. A Micron-aire reduced. The fiber quality is improved from the grade C2 to the grade B2. The breakage ratio and the strength are improved. The cotton fiber quality can be effectively improved by utilizing the cell wall extensin gene GbEXPATR.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A Molecular Marker Related to Cotton Fiber Length and Its Application
ActiveCN108559787BIncrease the lengthImprove length traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFiberFishery
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cotton stearyl desaturase gene GbSSI2 and application thereof
InactiveCN103421821BComposite controlReduced gene expressionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionVerticillium speciesBiotechnology
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Cotton tissue culturing method using cotyledon petiole as explant
ActiveCN1311739CImprove conversion efficiencyShort cycleHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureNormal growthBud
The invention relates to a method that utilizing the cotyledon stalk of Gossypium barbadense( G. barbadense L. ) as explant to produce regenerative plants by tissue culture. The seeds of Gossypium barbadense disinfected are laid on the culture medium of seed to germinate, and the cut cotyledon stalks are laid in the inducing culture medium, and grown clump buds are cut to lay in the stretching culture medium for stretching, afterwards transferred into culture medium for growing root, to get regenerative plants. The inventive method can produce tufted buds that clumping and have no limitation of genetic types between every kind, short period of cultivation, normal growth of regenerative plants. The regenerative system of tufted buds of Gossypium barbadense cotyledon stalks established by said inventive method is suitable for every kind of Gossypium barbadense.
Owner:SINKIANG YIDA AGRI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com