Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Free machining steel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Free machining steel is steel that forms small chips when machined. This increases the machinability of the material by breaking the chips into small pieces, thus avoiding entanglement in the machinery. This enables automatic equipment to run without human interaction. Free machining steel with lead also allow for higher machining rates. Free machining steel costs 15 to 20% more than standard steel, but this higher cost is offset by increased machining speeds, larger cuts, and longer tool life.
High strength non-quenched and tempered free machining steel for automobile connecting bar and technological process thereof
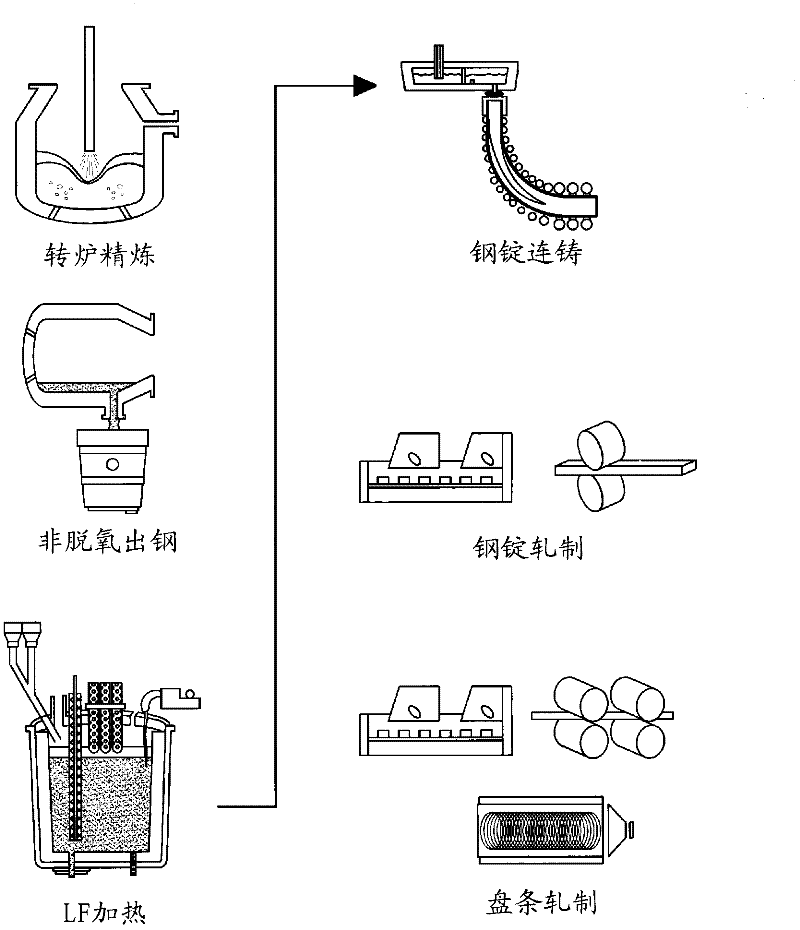
The invention discloses a high-intensity non-quenching and tempering easy-cutting steel used for a vehicle connection rod and a technical method thereof. The invention starts from the principle of improving the intensity of the non-quenching and tempering easy-cutting steel and leads the anti-tension intensity of the non-quenching and tempering easy-cutting steel containing 0.30 to 0.40 percent of carbon to be 1000MPa and the yield strength to be 750MPa by adjusting the components. The technical scheme of the invention is: the high-intensity non-quenching and tempering easy-cutting steel used for a vehicle connection rod consists of the elements of C, Si, Mn, Al, P, S, Cr, V, N and Fe; the weight percentages of the component elements are: 0.30 to 0.4 percent of C, 0. 50 to 0.70 percent of Si, 0.80 to 1.20 percent of Mn, equal to or less than 0.040 percent of P, 0.030 to 0.060 percent of S, 0.010 to 0.040 percent of Al, 0.10 to 0.40 percent of Cr, 0.10 to 0.30 percent of V, 010 to 0.015 percent of N and the rest is Fe and unavoidable impurities. The heating temperature of a continuous casting blank is 1200 DEG C; the heating time is 160min; the start rolling temperature is 1100 DEG C; the final rolling temperature is 900 DEG C; the pressing volume is 16; the cooling speed after rolling is 40 DEG C / min; after bundling, the components are thrown in a pit and slowly cooled.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Free machining steel for machine structural use having improved chip disposability
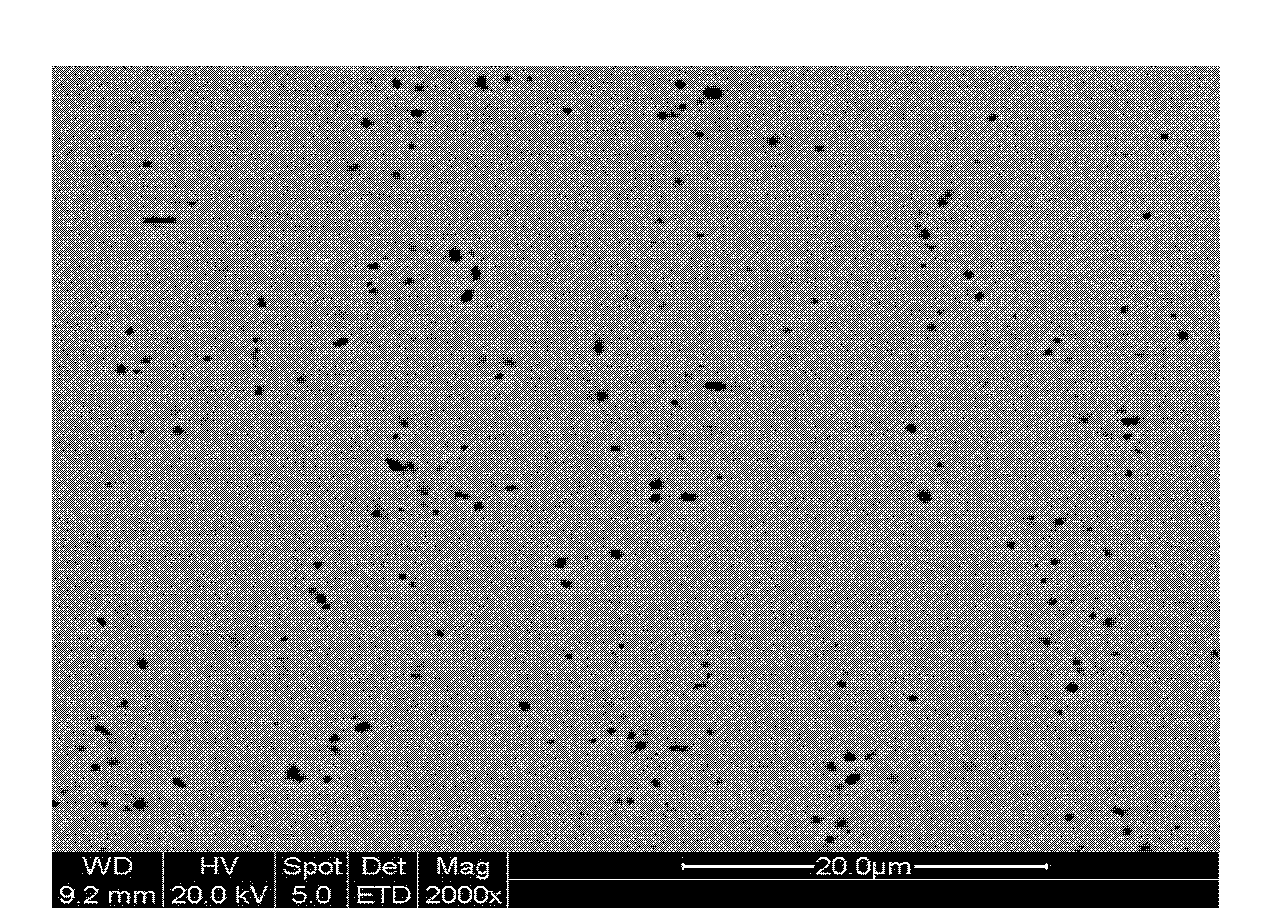
Disclosed is a free machining steel for machine structural use, which can realize very good chip disposability without incorporation of any harmful material such as lead (Pb). This free machining steel is a hot rolled or hot forged free machining steel having improved chip disposability. The free machining steel comprises, by mass, carbon (C): 0.01 to 0.70%, silicon (Si): 0.05 to 2.00%, manganese (Mn): 0.20 to 3.50%, calcium (Ca): 0.0003 to 0.01%, sulfur (S): 0.020 to 0.300%, aluminum (Al): 0.002 to 0.300%, nitrogen (N): 0.003 to 0.035%, and oxygen (O): 0.0010 to 0.0080% with the balance consisting of iron (Fe) and unavoidable impurities. The steel comprises sulfides having the major axis of from 0.5 mum to 20 mum, exclusive, and comprising MnS as the main component, in a number of not less than 30% of the total number of sulfides. The steel also comprises oxide inclusions having the major axis of from 0.5 mum to 50 mum, exclusive, and being present either together with sulfides or singly, in a number of not less than 10 per mm<2>of the inspection area.
Owner:SANYO SPECIAL STEEL COMPANY
Production method of graphitized free-machining steel
The invention relates to a method for producing graphitized free-machining steel from intermediate-carbon manganese-silicon steel, intermediate-carbon manganese-silicon-aluminum steel and the like. The method comprises the following steps: heating casting blanks; maintaining the temperature; cooling to 1050-1150 DEG C; roughly rolling: controlling the reduction percentage of each gate to be 20-40%; cooling to 850-1000 DEG C; carrying out precision rolling according to 4-6 gates; cooling in air; quickly cooling in water to room temperature; heating the precision rolling plate and maintaining the temperature; and cooling in air or cooling in a furnace to room temperature. By controlling the state of C atoms in steel and C content of austenite before tempering based on a process route of low-temperature rolling, relaxation and phase change, quenching and graphitization tempering, the invention converts all C atoms in the steel into graphite in a short time (5h). In the graphitized free-machining steel produced by the method, graphite grains in the organization are small in size and are uniform in distribution.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Low carbon sulfur free-machining steel
The low carbon sulfur free-machining steel comprises C: 0.05 to less than 0.20%, Si < 0.02%, Mn: 0.7 to 2.2%, P: 0.005 to 0.25%, S: more than 0.40 to 0.60%, Al < 0.003%, O: 0.0090 to 0.0280%, and N: 0.0030 to 0.0250% with the balance consisting of Fe and impurities. The steel optionally comprises one or more of Te, Sn and Se and / or one or more of Cu, Ni, Cr and Mo. The impurities comprise Ca < 0.001%, Mg < 0.001%, Ti < 0.002%, Zr <0.002%, and REM < 0.001% and satisfies Mn O > 0.018 and 2.5 < Mn / (S + O) < 3.5.This invention provides a low carbon sulfur free-machining steel that has machinability favorably comparable with Pb free-machining steels and Pb-added composite free-machining steels in relatively low-speed cutting using HSS tools, has excellent carburizing properties and continuous casting properties, and is suitable as materials for soft small components such as automobile brake components, components for peripheral devices in personal computers and components for electrical machineries and apparatuses.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Environmentally-friendly, Pb-free free-machining steel, and manufacturing method for same
InactiveCN102165085AEasy to manufactureImprove hot rolling performanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesWire rodSulfur
The present invention relates to a PB-free free-machining steel containing, by weight %, C: 0.03 - 0.13%, Si: 0.1% or lower, Mn: 0.7 - 2.0%, P: 0.05 - 0.15%, S: 0.2 - 0.5%, B: 0.001 - 0.01%, Cr: 0.1 - 0.5%, Ti: 0.05 - 0.4%, N: 0.005 - 0.015%, O: 0.03% or lower, the remainder being Fe and other inevitable impurities. The PB-free free-machining steel may contain MnS inclusions with a particle size of 5[mu]m2 or larger, existing in the numbers of 300 to 1000 per material mm2 at the cross-section of the rolling direction of a wire rod. Further, the present invention relates to a method for manufacturing environmentally-friendly, PB-free free-machining steel by properly controlling the total amount of oxygen in the process of manufacturing a steel material.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Fluid bearing device
InactiveUS20050169561A1Change in the viscosity of the lubricant dependingEasy to wearShaftsBearing componentsAusteniteDynamic pressure
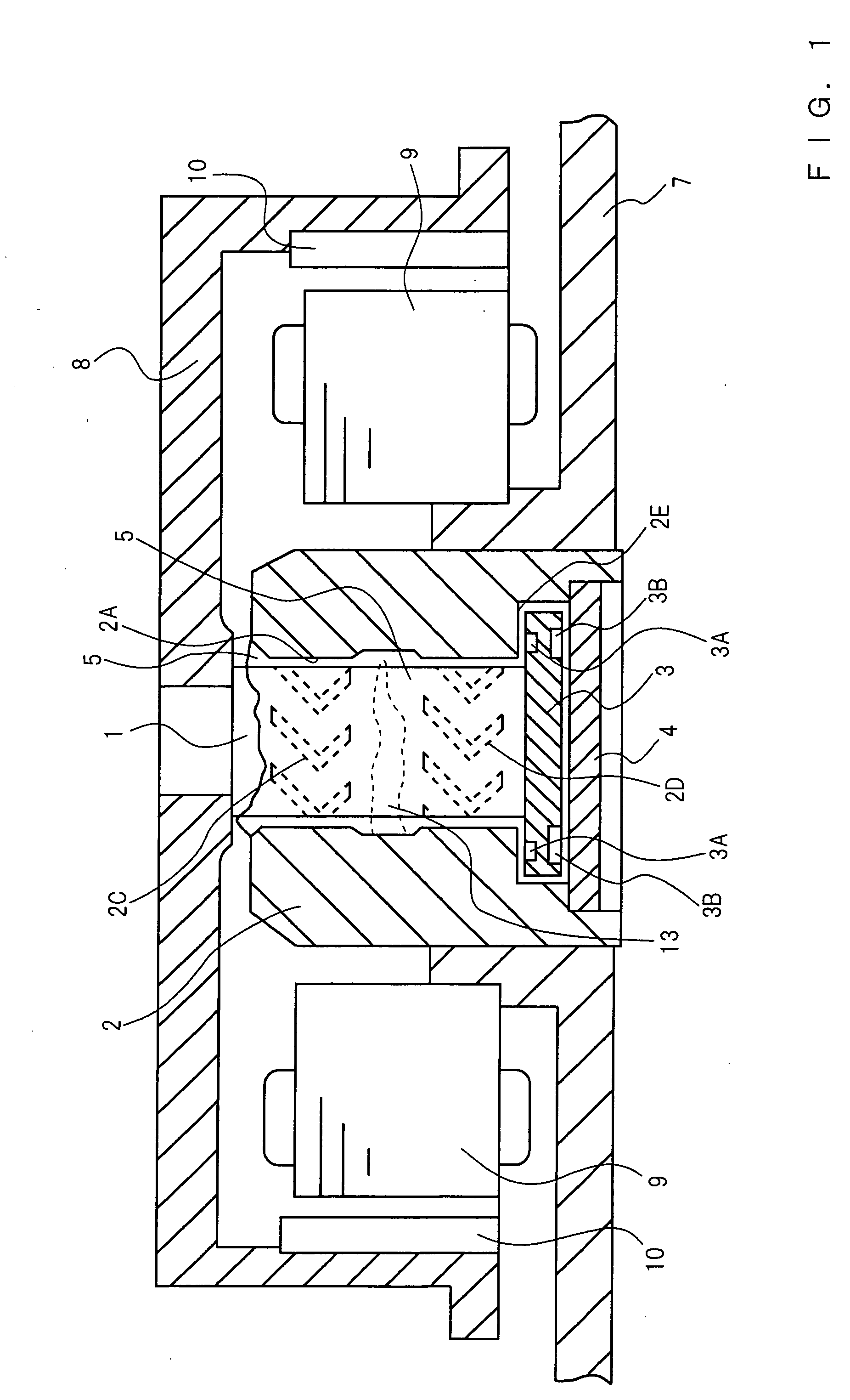
In order to suppress the increase of torque loss at low temperature and the increase of shaft swinging at high temperature and to improve the workability of the sleeve, high manganese chromium steel or austenitic stainless steel is used as the material of the shaft, sulfur free-machining steel is used as the material of the sleeve, and the surface thereof is coated with plating primarily containing nickel and phosphorus. Hence, it is possible to obtain a hydrodynamic bearing wherein the changes in the characteristics of the bearing owing to the change in the viscosity of a lubricant depending on temperature change can be prevented, in addition, the workability of the sleeve and the dynamic pressure generation grooves and the wear resistance of the bearing can be made best.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Homogeneous free machining steel and production process thereof
The invention discloses a homogeneous easy-cutting steel and a method for producing the same. The homogeneous easy-cutting steel comprises the following compositions (in percentage by weight): less than or equal to 0.12 percent of C, less than or equal to 0.07 percent of Si, 0.803 to 1.31 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.07 percent of P, 0.23 to 0.37 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.001 percent of Al and the balance being Fe and residual elements. The homogeneous easy-cutting steel has the advantages of heat processing, good cutting performance, etc. In the homogeneous easy-cutting steel produced by adopting the method, elements are uniformly distributed; sulfide impurities are uniformly distributed in a cambiform or an elongated cambiform, thereby removing adverse influence of the heat processing of FeS impurities and obviously improving the heat processing and easy-cutting performances of the produced homogeneous easy-cutting steel; and the part surface after being cut has better smoothness.
Owner:LIAONING KAIRUI SPECIAL STEEL
Free-machining steel material
InactiveCN102330040ASolve distributionSolve technical problems such as shape controlFree machining steelMechanical property
The invention relates to a free-machining steel material. The free-machining steel material comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.09 to 0.20 percent of C, 0.70 to 1.55 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.17 percent of Si, less than or equal to 0.19 percent of P, 0.20 to 0.38 percent of S, 0.01 to 0.35 percent of Sb, 0.02 to 0.41 percent of Zr, 0.009 to 0.023 percent of O, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of Al, less than or equal to 0.008 percent of N and the balance of Fe. In the invention, the free-machining steel material is prepared in an economic superior mode; and the machinability of the free-machining steel material is improved on the premise of ensuring the mechanical property of the material.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
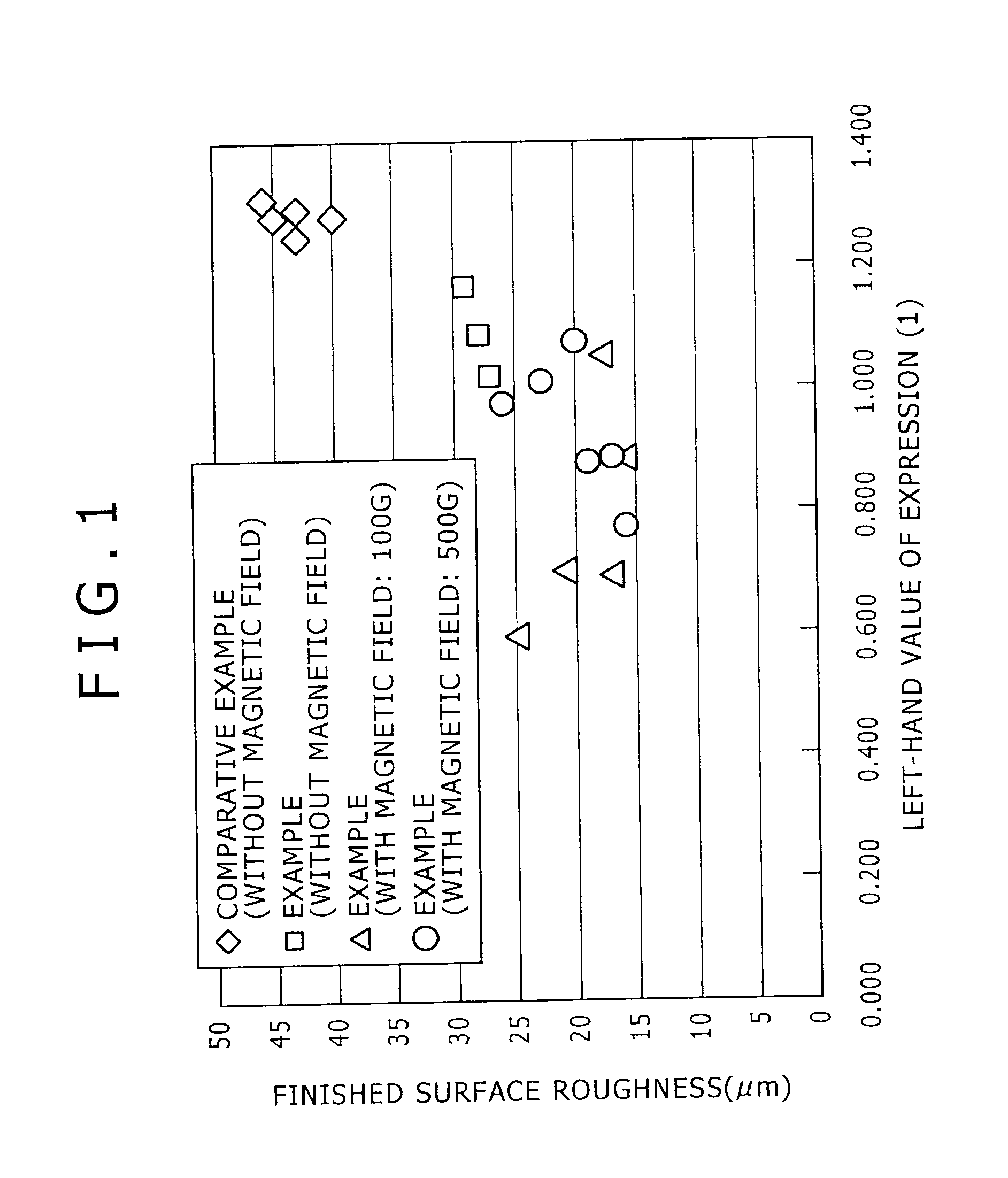
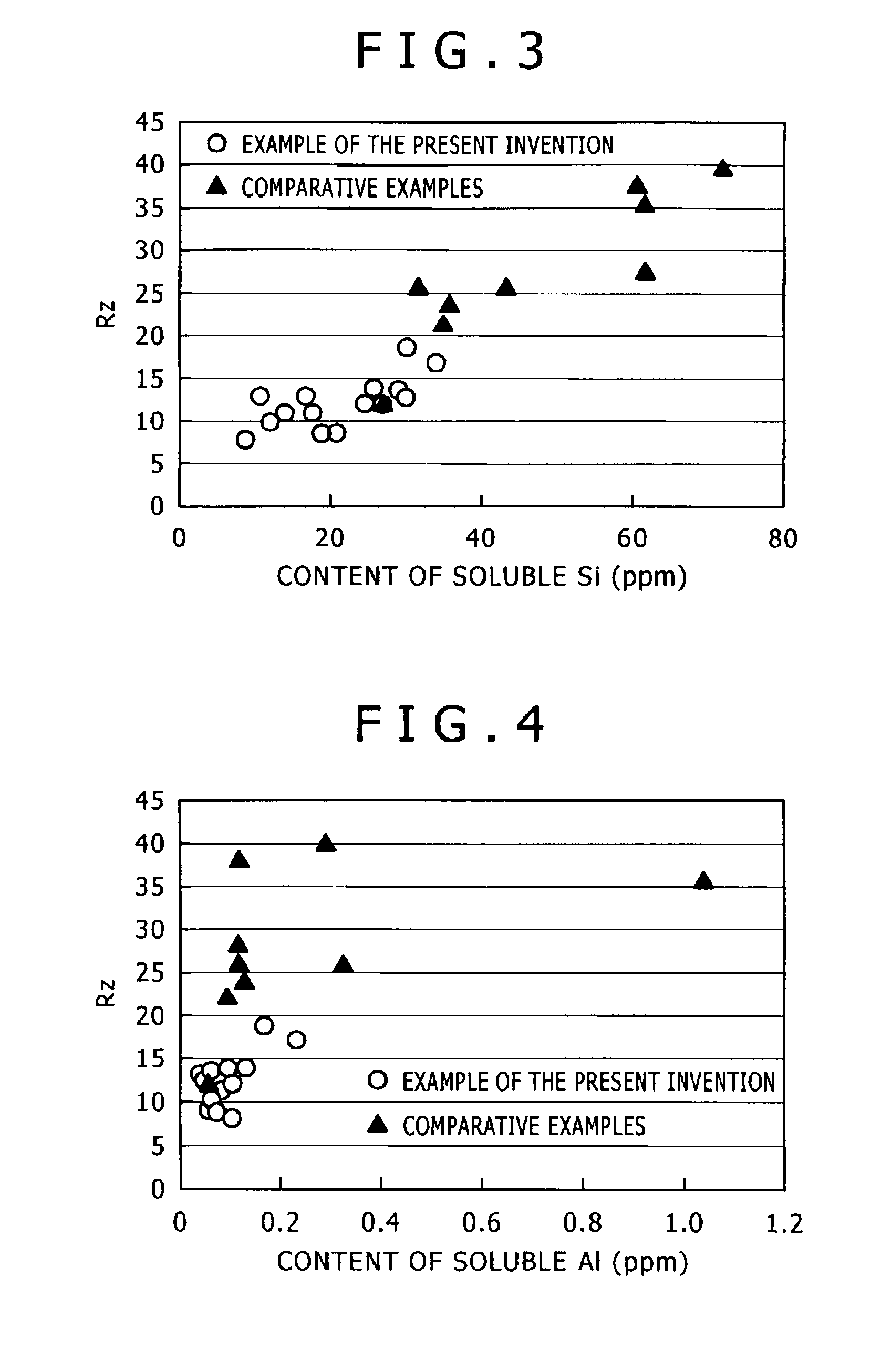
Low carbon composite free-cutting steel product excellent in roughness of finished surface and method for production thereof
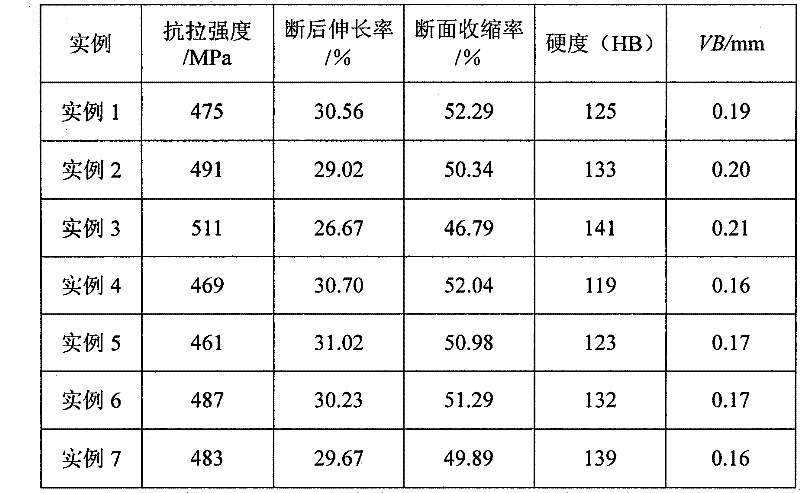
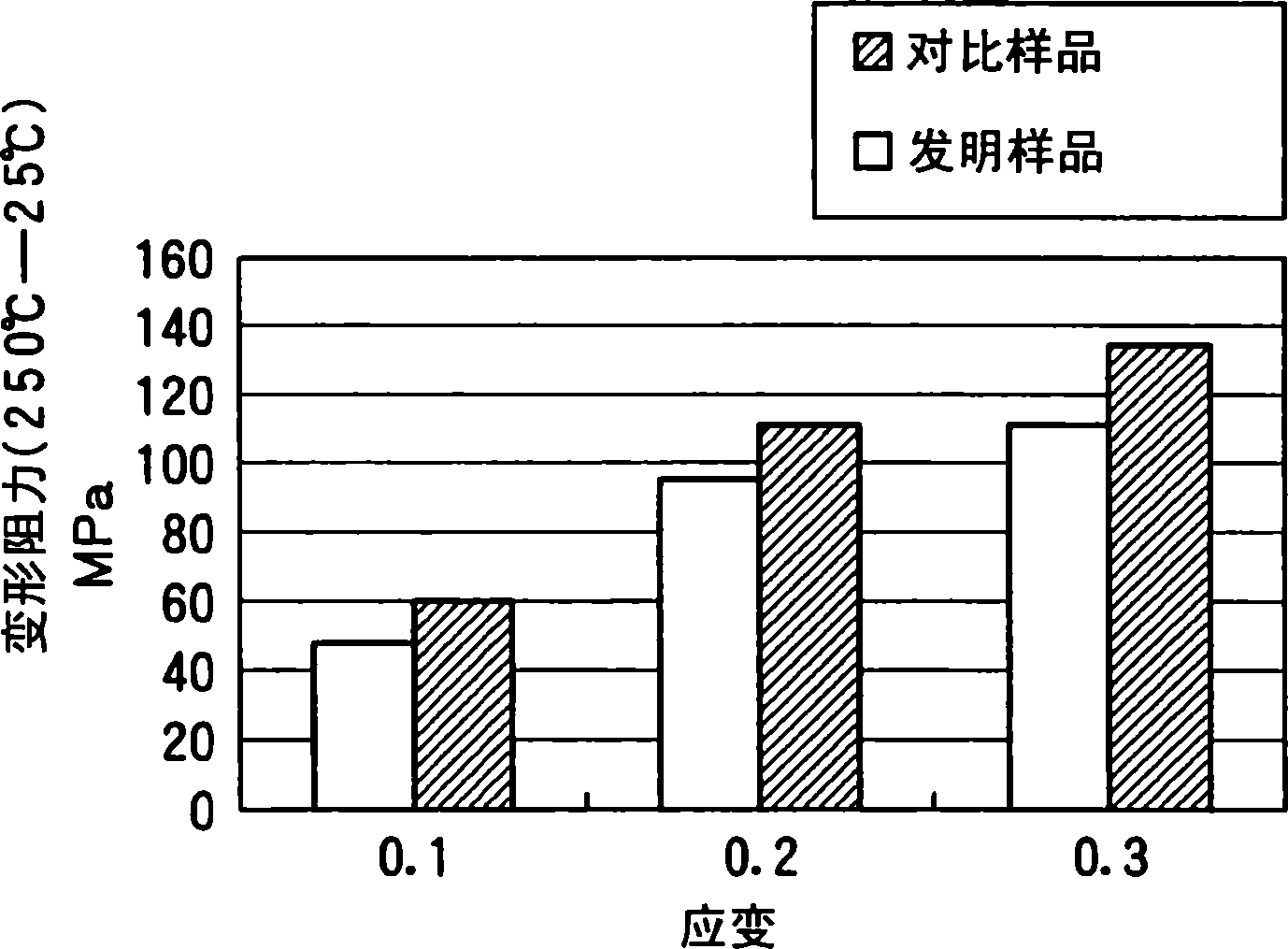
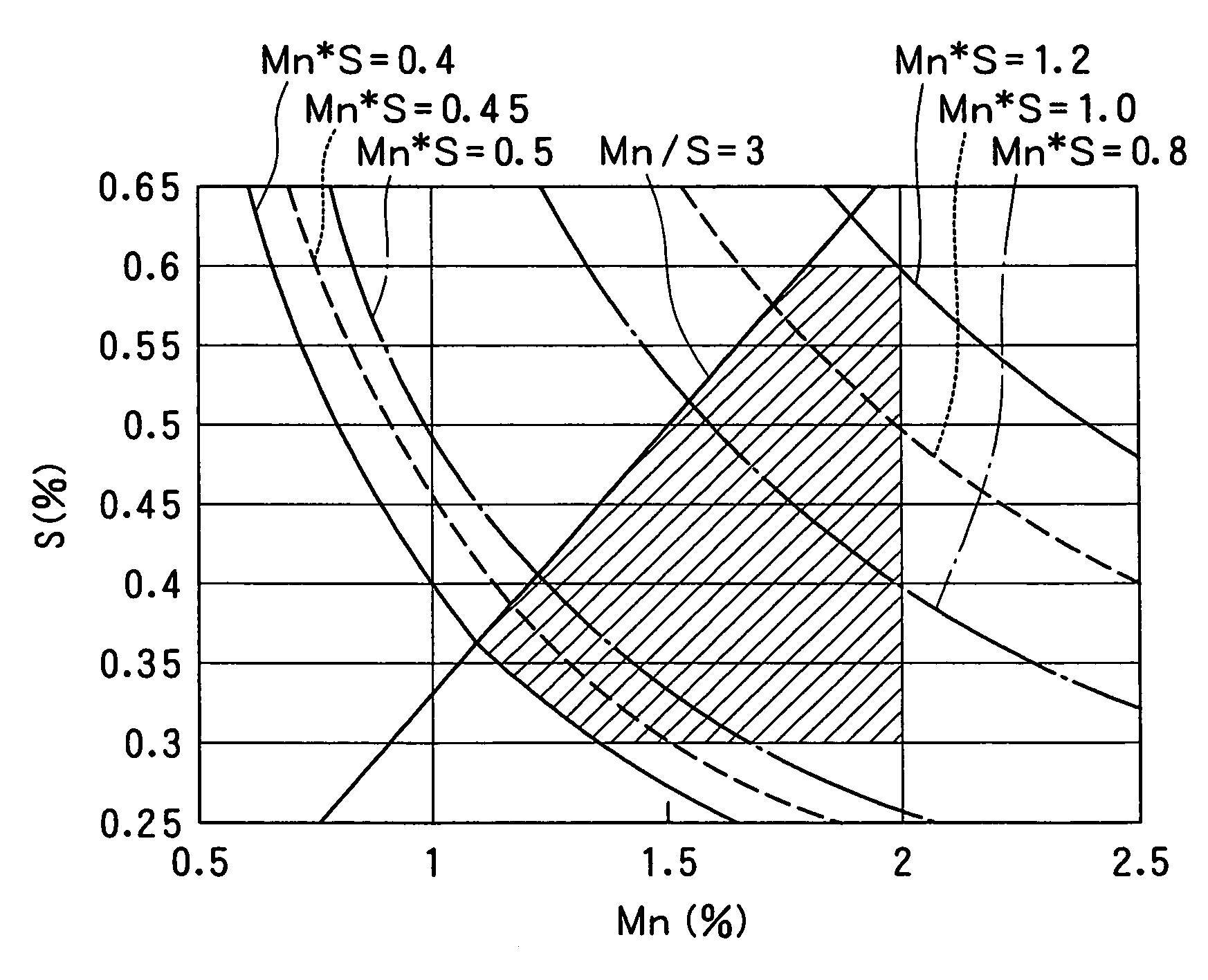
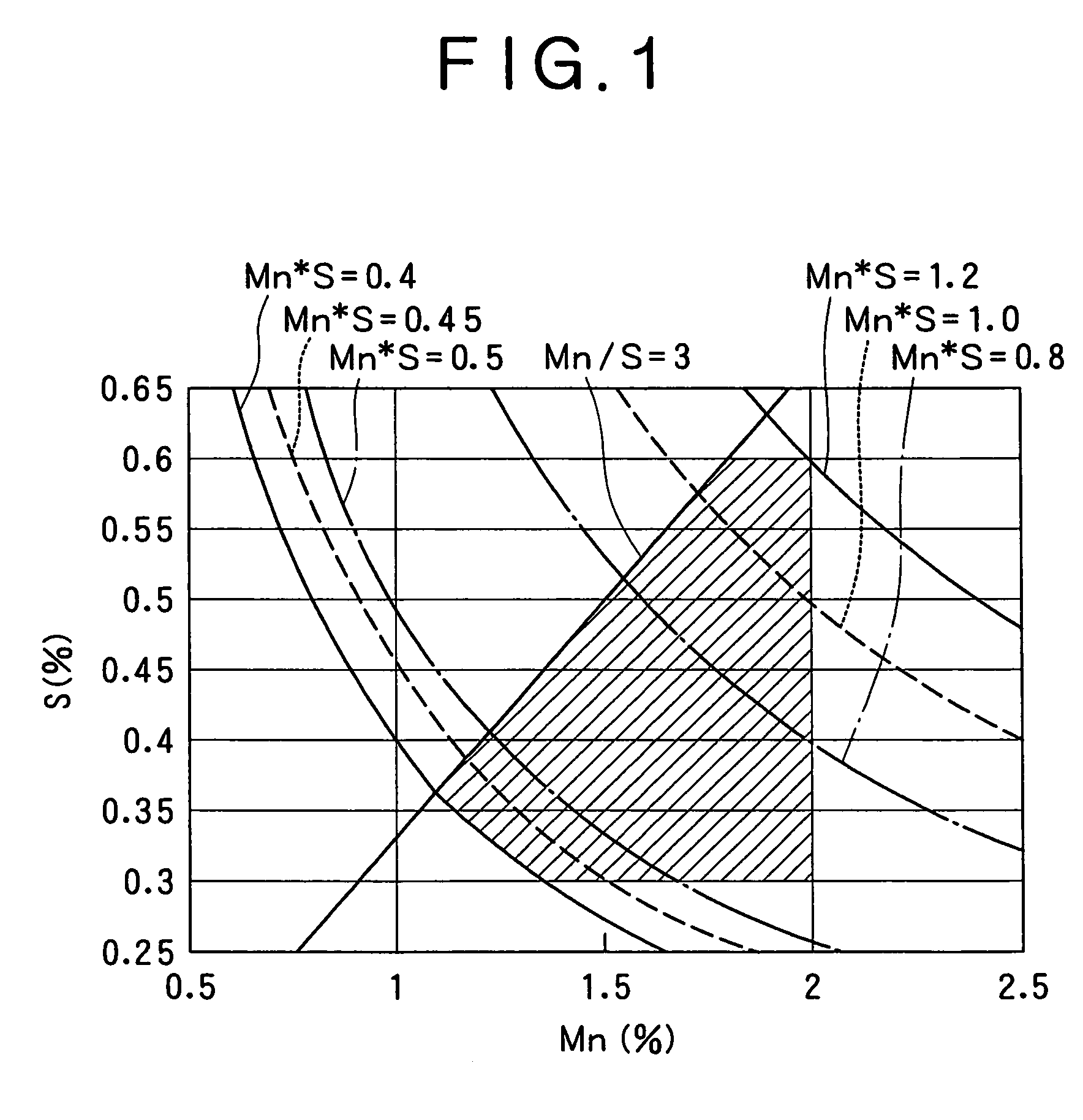
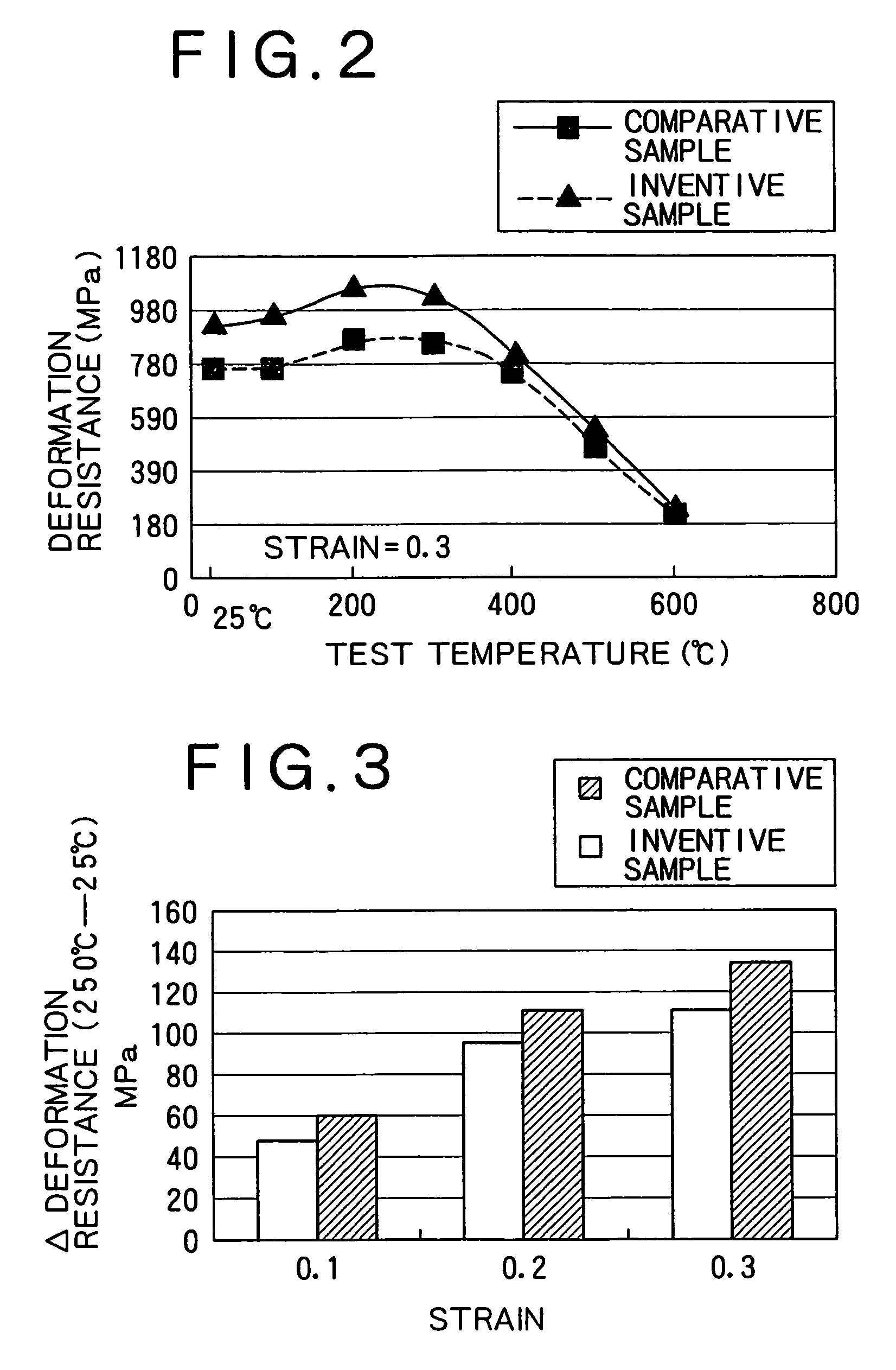
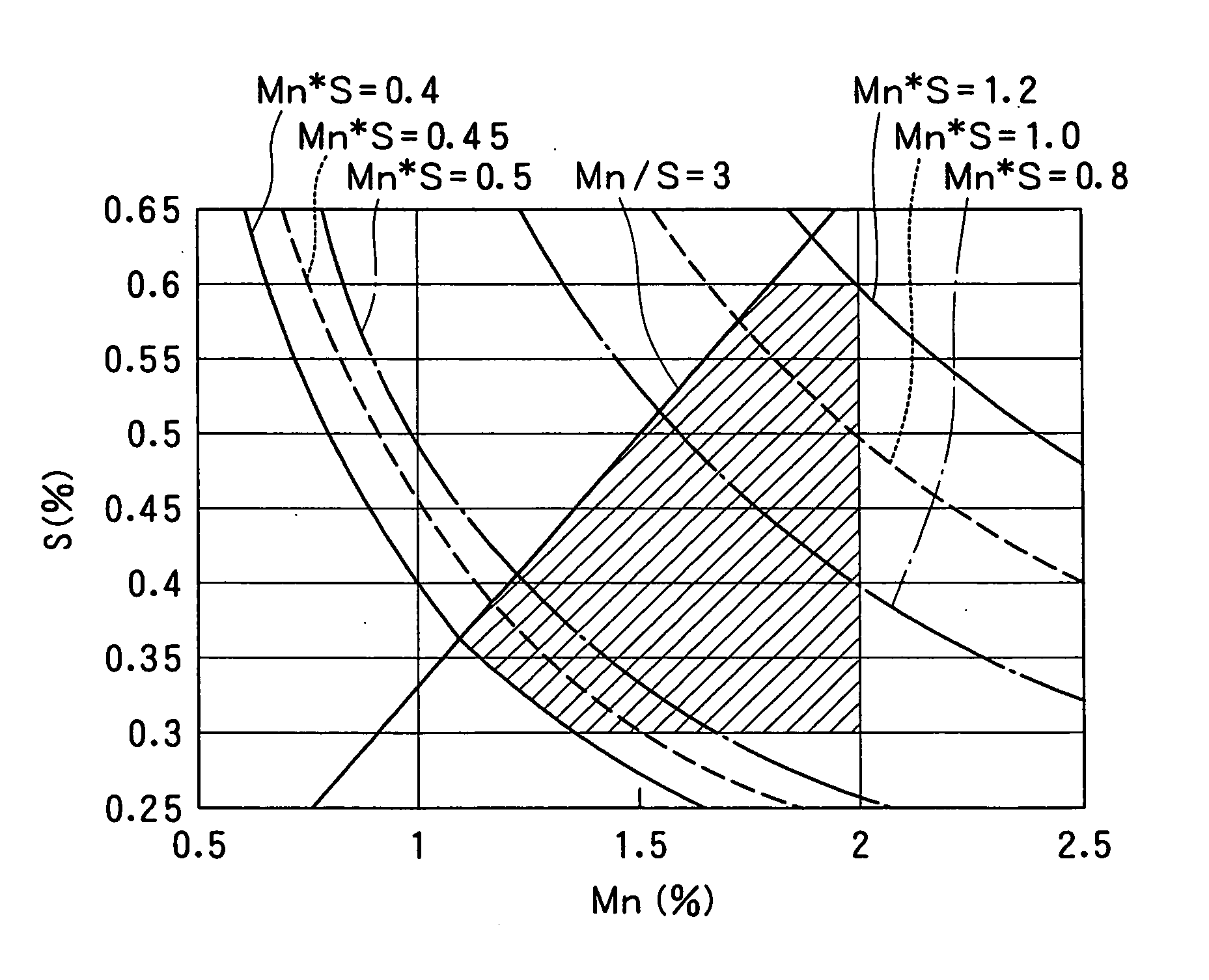
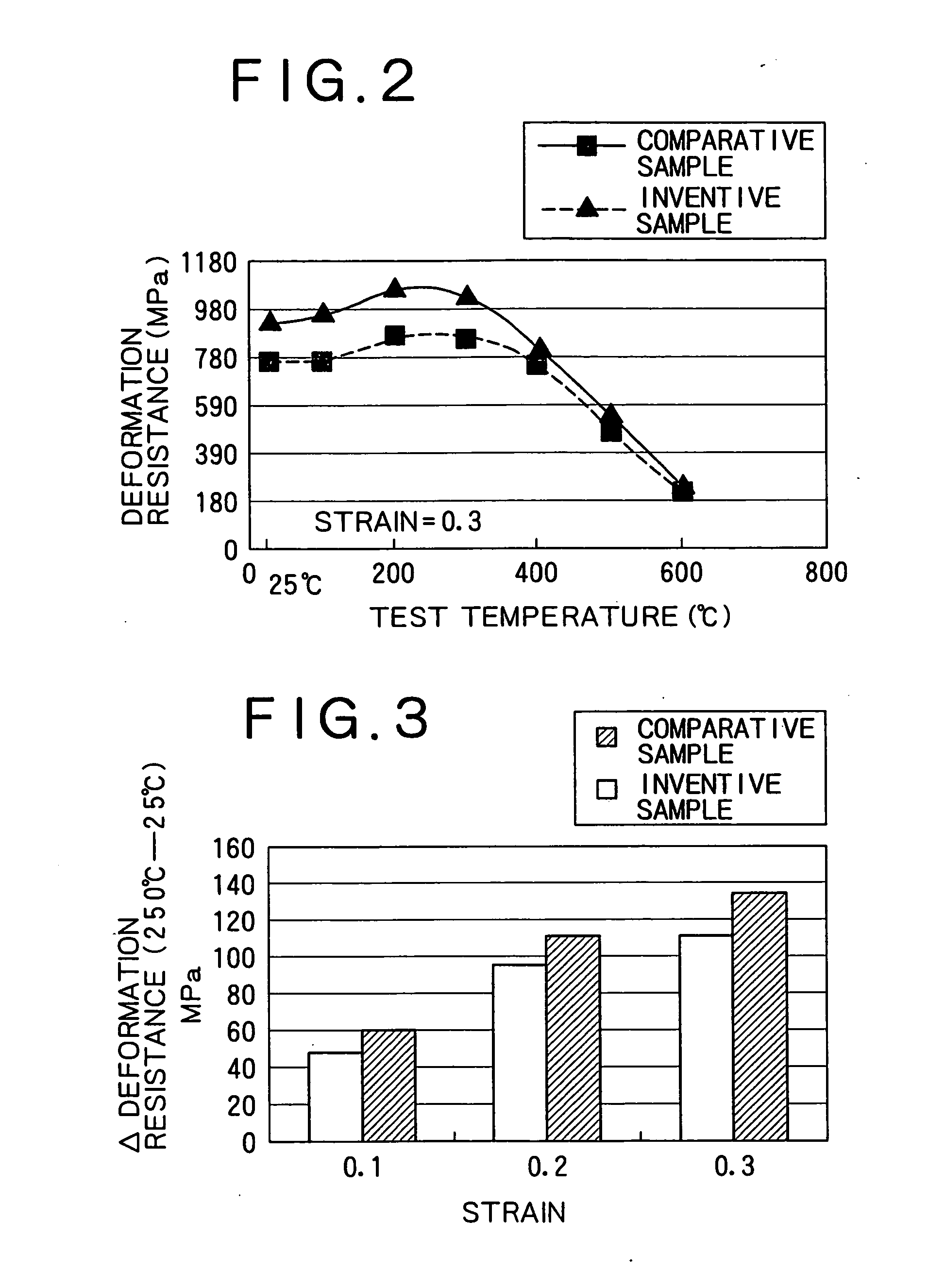
The present invention provides a low-carbon resulfurized free machining steel product excellent in machinability typified by finished surface roughness even though toxic Pb or special elements such as Bi or Te are not added, and a suitable production method thereof. A steel product has a specific composition, has contents of Mn and S satisfying the following conditions: 0.40 Mn*S 1.2 and Mn / S 3.0, and contains a ferrite-pearlite structure as the metallographic structure, in which the average width ( m) of sulfide inclusions in the steel product is 2.8* (log d) or more, wherein d (mm) is the diameter of the steel product, and pro-eutectoid ferrite in the metallographic structure has a hardness HV of 133 to 150 or a difference in deformation resistance at a strain of 0.3 between 200 DEG C and 25 DEG C is 110 MPa or more and 200 MPa or less, the deformation resistances being determined in a compression test at a deformation rate of 0.3 mm / min.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Rolling technique of lead treated steel
InactiveCN101386031AAvoid stacking steel accidentsHigh yieldTemperature control deviceWork treatment devicesFree machining steelRolling mill
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy and relates to rolling process of lead-containing free-machining steel. A rolling mill is used for rolling, in the rough rolling process, the rolling temperature is controlled at 1030-1060 DEG C, the former three-pass material form is reduced 1-3mm based on the standard material form; in the intermediate rolling process, the roll material form is the standard material form, and the rolling temperature is controlled at 980-1030 DEG C; in the pre-finish rolling process, the roll material form is the standard material form, the rolling temperature is controlled at 1060-1030 DEG C, and the temperature of the rolled piece reaches 1005-1040 DEG C after the pre-finish rolling process; in the finish rolling process, the temperature of the rolled piece in a finishing mill is less than 980 DEG C, the roll material form is the standard material form, and the rolling temperature is controlled at 1020-1050 DEG C. The rolling process can prevent steel heaping caused by the cleavage crack of the cold, hot and frailty susceptible head of the rolled piece, prevent sliding accident caused by the high temperature of the steel, steadily increase the yield of the lead-containing free-machining steel, obviously reduce the waste, and greatly reduce the 100t steel fault time.
Owner:NANJING NANGANG IND DEV CO LTD
Free machining steel for use in machine structure of excellent mechanical characteristics
Free machining steel for use in machine structures capable of stably and reliably providing excellent machinability (chip disposability and tool life) and mechanical characteristics (transverse direction toughness) comparable, in a Pb free state, with existent Pb-added steels the machining steel being manufactured so as to contain 0.0005 to 0.02 mass % of Mg and provide a distribution index F1 for the sulfide particles defined by the following equation (1) of 0.4 to 0.65 or a distribution index for the sulfide particles defined by the following equation (2) of 1 to 2.5:as described in the specification.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Low carbon composite free-cutting steel product excellent in roughness of finished surface and method for production thereof
The present invention provides a low-carbon resulfurized free machining steel product excellent in machinability typified by finished surface roughness even though toxic Pb or special elements such as Bi or Te are not added, and a suitable production method thereof. A steel product has a specific composition, has contents of Mn and S satisfying the following conditions: 0.40≦Mn*S≦1.2 and Mn / S≧3.0, and contains a ferrite-pearlite structure as the metallographic structure, in which the average width (μm) of sulfide inclusions in the steel product is 2.8*(log d) or more, wherein d (mm) is the diameter of the steel product, and pro-eutectoid ferrite in the metallographic structure has a hardness HV of 133 to 150 or a difference in deformation resistance at a strain of 0.3 between 200° C. and 25° C. is 110 MPa or more and 200 MPa or less, the deformation resistances being determined in a compression test at a deformation rate of 0.3 mm / min.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Low carbon composite free-cutting steel product excellent in roughness of finished surface and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20070044867A1Surface roughness is deterioratedProlong lifeCarbon compositesSurface roughness
The present invention provides a low-carbon resulfurized free machining steel product excellent in machinability typified by finished surface roughness even though toxic Pb or special elements such as Bi or Te are not added, and a suitable production method thereof. A steel product has a specific composition, has contents of Mn and S satisfying the following conditions: 0.40≦Mn*S≦1.2 and Mn / S≧3.0, and contains a ferrite-pearlite structure as the metallographic structure, in which the average width (μm) of sulfide inclusions in the steel product is 2.8*(log d) or more, wherein d (mm) is the diameter of the steel product, and pro-eutectoid ferrite in the metallographic structure has a hardness HV of 133 to 150 or a difference in deformation resistance at a strain of 0.3 between 200° C. and 25° C. is 110 MPa or more and 200 MPa or less, the deformation resistances being determined in a compression test at a deformation rate of 0.3 mm / min.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Free machining steel for machine structural use having improved chip disposability
Disclosed is a free machining steel for machine structural use, which can realize very good chip disposability without incorporation of any harmful material such as lead (Pb). This free machining steel is a hot rolled or hot forged free machining steel having improved chip disposability. The free machining steel comprises, by mass, carbon (C): 0.01 to 0.70%, silicon (Si): 0.05 to 2.00%, manganese (Mn): 0.20 to 3.50%, calcium (Ca): 0.0003 to 0.01%, sulfur (S): 0.020 to 0.300%, aluminum (Al): 0.002 to 0.300%, nitrogen (N): 0.003 to 0.035%, and oxygen (O): 0.0010 to 0.0080% with the balance consisting of iron (Fe) and unavoidable impurities. The steel comprises sulfides having the major axis of from 0.5 mum to 20 mum, exclusive, and comprising MnS as the main component, in a number of not less than 30% of the total number of sulfides. The steel also comprises oxide inclusions having the major axis of from 0.5 mum to 50 mum, exclusive, and being present either together with sulfides or singly, in a number of not less than 10 per mm<2>of the inspection area.
Owner:SANYO SPECIAL STEEL COMPANY
Lead-containing free-machining steel
ActiveCN104995324AImprove cutting performanceMetal rolling arrangementsMetallurgyFree machining steel
Provided is a lead-containing free-machining steel having excellent machinability. This lead-containing free-machining steel contains, in terms of mass%, 0.005-0.2% C, 0.3-2.0% Mn, 0.005-0.2% P, 0.01-0.7% S, 0.03-0.5% Pb, 0.004-0.02% N, and 0.003-0.03% O, with the remainder comprising Fe and impurities. The steel contains Pb inclusions (40) having a diameter of 0.01-0.5 μm in terms of equivalent-circle diameter, the number of the inclusions being 10,000 per mm2 or larger.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
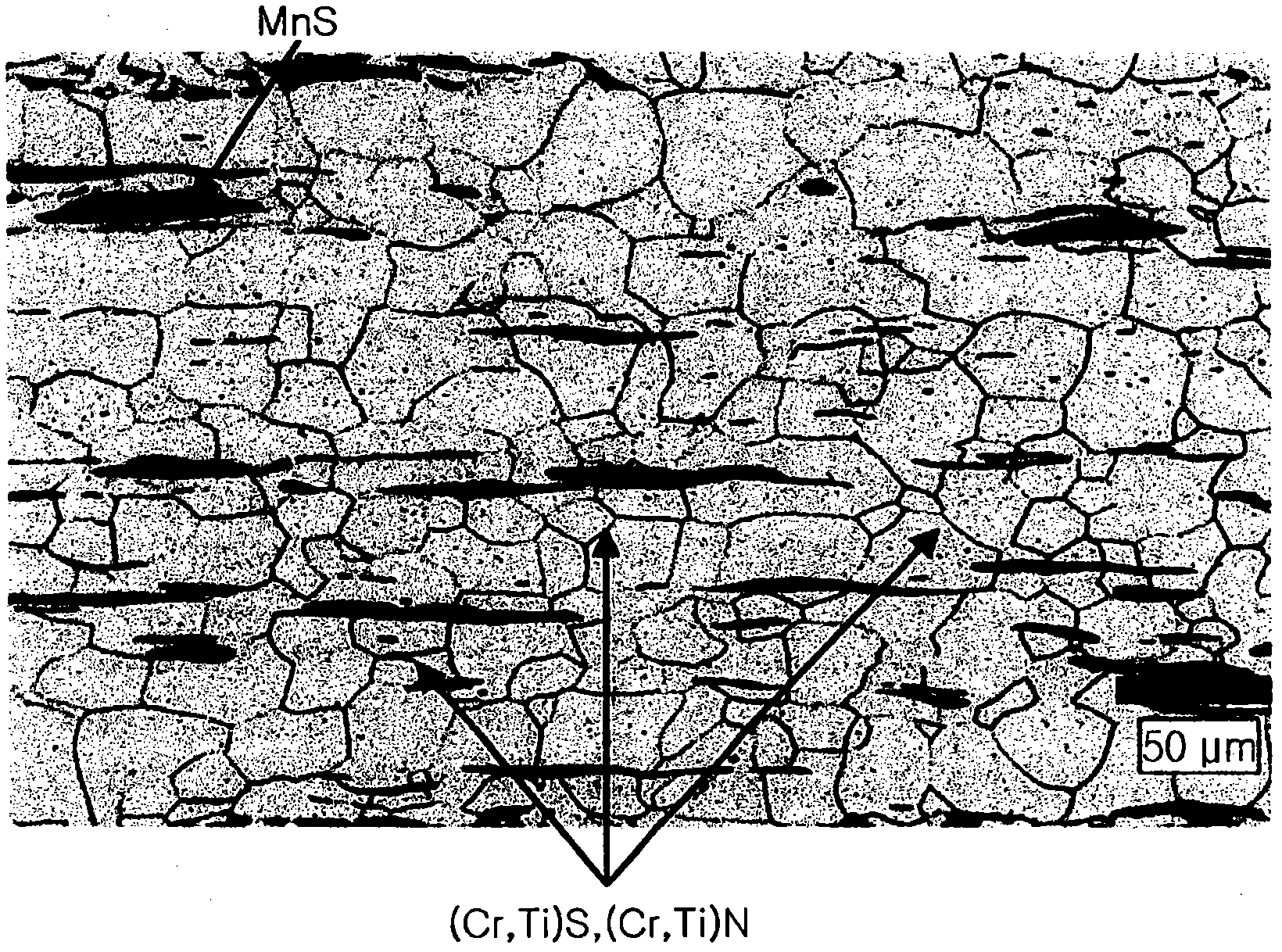
Method for developing austenite grain boundary of sulfur free-machining steel through electrolytic corrosion
InactiveCN107860634ADoes not damage the original shapeThe implementation process is smooth and safePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrolysisAustenite grain
The invention belongs to the technical fields of metallographic preparation and nonmetal inclusion control, and especially relates to a method for developing the austenite grain boundary of sulfur free-machining steel through electrolytic corrosion. The method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a sample; S2, preparing an electrolyte; S3, performing the electrolytic corrosion; S4, treating a steel sample; and S5, carrying out metallographic observation. The method for developing the austenite grain boundary of sulfur free-machining steel through electrolytic corrosion allows the austenite grain boundary of the sulfur free-machining steel to be clearly displayed, the sulfur free-machining steel also contains manganese sulfide, the method does not damages the original morphology ofthe manganese sulfide in the electrolytic corrosion process, and the enforcement process of the method is stable and safe, is simple to operate, and can be easily controlled.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Tin calcium titanium series free-cutting steel
The invention relates to a tin-calcium ¿Ctitanium free machining steel that belongs to metallic material field, especially to manufacture high strength bolt, crankshaft, connecting bar, etc. that is the important part of automobile or mechanism. The Y15SnCaTi free machining steel contains carbon content 0.12-0.18% has the following mechanical properties: tensile strength reaches 400MPa, specific elongation is 22.0%, contraction of area is 37%, hardness of HB is less than 170 that has reached the standard of the corresponding steel of Y15Pb in GB8731-88 that can be used to manufacture high strength bolt. The Y45SnCaTi free machining steel has the following mechanical properties: tensile strength reaches 800MPa, specific elongation is 17.7%, contraction of area is 47%, and the hardness of HB is less than 240 that have reached the standard of the corresponding steel of Y45Ca in GB8731-88 that can be used to manufacture crankshaft and connecting bar.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Rolling technique of lead treated steel
InactiveCN101386031BAvoid stacking steel accidentsHigh yieldTemperature control deviceWork treatment devicesFree machining steelRolling mill
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy and relates to rolling process of lead-containing free-machining steel. A rolling mill is used for rolling, in the rough rolling process, the rolling temperature is controlled at 1030-1060 DEG C, the former three-pass material form is reduced 1-3mm based on the standard material form; in the intermediate rolling process, the roll material form is the standard material form, and the rolling temperature is controlled at 980-1030 DEG C; in the pre-finish rolling process, the roll material form is the standard material form, the rolling temperatureis controlled at 1060-1030 DEG C, and the temperature of the rolled piece reaches 1005-1040 DEG C after the pre-finish rolling process; in the finish rolling process, the temperature of the rolled piece in a finishing mill is less than 980 DEG C, the roll material form is the standard material form, and the rolling temperature is controlled at 1020-1050 DEG C. The rolling process can prevent steel heaping caused by the cleavage crack of the cold, hot and frailty susceptible head of the rolled piece, prevent sliding accident caused by the high temperature of the steel, steadily increase the yield of the lead-containing free-machining steel, obviously reduce the waste, and greatly reduce the 100t steel fault time.
Owner:NANJING NANGANG IND DEV CO LTD
Bismuth-titanium alloy and application thereof
The invention discloses a bismuth-titanium alloy, and belongs to the technical field of the preparation of free-machining alloy steel. The bismuth-titanium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 15 to 75 weight percent of bismuth, less than or equal to 0.8 weight percent of inevitable impurities, and the balance of titanium. The invention has the characteristics that the alloying treatment is feasible, the yield of the bismuth is high and the like; and the bismuth-titanium alloy is applicable to additives of alloying treatment of free-machining steel.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
Low-carbon sulfur-containing free-cutting steel with excellent cuttability
A low-carbon resulfurized free-machining steel is excellent in machinability and contains 0.02% to 0.15% by mass of C; 0.004% by mass or less (exclusive of 0%) of Si; 0.6% to 3% by mass of Mn; 0.02% to 0.2% by mass of P; 0.35% to 1% by mass of S; 0.005% by mass or less (exclusive of 0% by mass) of Al; 0.008% to 0.03% by mass of 0; and 0.007% to 0.03% by mass of N, with the remainder being iron and inevitable impurities, in which the ratio [Mn] / [S] of the manganese content [Mn] to the sulfur content [S] is within the range of 3 to 4, and the carbon content [C], the manganese content [Mn] and the nitrogen content [N] satisfy the following Expression (1): 10[C]×[Mn]−0.94+1226[N]2≦1.2, wherein [C], [Mn] and [N] represent the contents on the percent by mass basis of carbon, manganese, and nitrogen, respectively.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Low carbon composite free-cutting steel product excellent in roughness of finished surface and method for production thereof
The present invention provides a low-carbon resulfurized free machining steel product excellent in machinability typified by finished surface roughness even though toxic Pb or special elements such as Bi or Te are not added, and a suitable production method thereof. A steel product has a specific composition, has contents of Mn and S satisfying the following conditions: 0.40 Mn*S 1.2 and Mn / S 3.0, and contains a ferrite-pearlite structure as the metallographic structure, in which the average width ( m) of sulfide inclusions in the steel product is 2.8* (log d) or more, wherein d (mm) is the diameter of the steel product, and pro-eutectoid ferrite in the metallographic structure has a hardness HV of 133 to 150 or a difference in deformation resistance at a strain of 0.3 between 200 DEG C and 25 DEG C is 110 MPa or more and 200 MPa or less, the deformation resistances being determined in a compression test at a deformation rate of 0.3 mm / min.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Bismuth-titanium alloy and application thereof
The invention discloses a bismuth-titanium alloy, and belongs to the technical field of the preparation of free-machining alloy steel. The bismuth-titanium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 15 to 75 weight percent of bismuth, less than or equal to 0.8 weight percent of inevitable impurities, and the balance of titanium. The invention has the characteristics that the alloying treatment is feasible, the yield of the bismuth is high and the like; and the bismuth-titanium alloy is applicable to additives of alloying treatment of free-machining steel.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
Leaded Free Cutting Steel
Provided is a lead-containing free-machining steel having excellent machinability. This lead-containing free-machining steel contains, in terms of mass%, 0.005-0.2% C, 0.3-2.0% Mn, 0.005-0.2% P, 0.01-0.7% S, 0.03-0.5% Pb, 0.004-0.02% N, and 0.003-0.03% O, with the remainder comprising Fe and impurities. The steel contains Pb inclusions (40) having a diameter of 0.01-0.5 μm in terms of equivalent-circle diameter, the number of the inclusions being 10,000 per mm2 or larger.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Production method of graphitized free-machining steel
The invention relates to a method for producing graphitized free-machining steel from intermediate-carbon manganese-silicon steel, intermediate-carbon manganese-silicon-aluminum steel and the like. The method comprises the following steps: heating casting blanks; maintaining the temperature; cooling to 1050-1150 DEG C; roughly rolling: controlling the reduction percentage of each gate to be 20-40%; cooling to 850-1000 DEG C; carrying out precision rolling according to 4-6 gates; cooling in air; quickly cooling in water to room temperature; heating the precision rolling plate and maintaining the temperature; and cooling in air or cooling in a furnace to room temperature. By controlling the state of C atoms in steel and C content of austenite before tempering based on a process route of low-temperature rolling, relaxation and phase change, quenching and graphitization tempering, the invention converts all C atoms in the steel into graphite in a short time (5h). In the graphitized free-machining steel produced by the method, graphite grains in the organization are small in size and are uniform in distribution.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Homogeneous free machining steel and production process thereof
The invention discloses a homogeneous easy-cutting steel and a method for producing the same. The homogeneous easy-cutting steel comprises the following compositions (in percentage by weight): less than or equal to 0.12 percent of C, less than or equal to 0.07 percent of Si, 0.803 to 1.31 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.07 percent of P, 0.23 to 0.37 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.001percent of Al and the balance being Fe and residual elements. The homogeneous easy-cutting steel has the advantages of heat processing, good cutting performance, etc. In the homogeneous easy-cuttingsteel produced by adopting the method, elements are uniformly distributed; sulfide impurities are uniformly distributed in a cambiform or an elongated cambiform, thereby removing adverse influence oftheheat processing of FeS impurities and obviously improving the heat processing and easy-cutting performances of the produced homogeneous easy-cutting steel; and the part surface after being cut hasbet ter smoothness.
Owner:LIAONING KAIRUI SPECIAL STEEL
Environmentally-friendly, Pb-free free-machining steel, and manufacturing method for same
InactiveCN102165085BEasy to manufactureImprove hot rolling performanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSteelmakingManganese
A lead-free free-cutting steel includes, by wt%, about 0.03-0.13% of carbon (C), about 0.1% or less of silicon (Si), about 0.7-2.0% of manganese (Mn), about 0.05-0.15% of phosphorous (P), about 0.2-0.5% of sulfur (S) of, about 0.001-0.01% of boron (B), about 0.1-0.5% of chromium (Cr), about 0.003-0.2% of titanium (Ti), about 0.005-0.015% of nitrogen (N), about 0.03% or less of oxygen (O), residual iron (Fe), and other unavoidable impurities. In the lead-free free-cutting steel, the number of manganese sulfide (MnS) inclusions having a particle size of about 5 µm 2 or more may include in the range of about 300-1000 per mm 2 of a material in a section of a wire rod rolling direction. The present invention is also related to a method of manufacturing an eco-friendly lead-free free-cutting steel by properly controlling a total oxygen content by step in steelmaking steps.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High strength non-quenched and tempered free machining steel for automobile connecting bar and technological process thereof
The invention discloses a high-intensity non-quenching and tempering easy-cutting steel used for a vehicle connection rod and a technical method thereof. The invention starts from the principle of improving the intensity of the non-quenching and tempering easy-cutting steel and leads the anti-tension intensity of the non-quenching and tempering easy-cutting steel containing 0.30 to 0.40 percent of carbon to be 1000MPa and the yield strength to be 750MPa by adjusting the components. The technical scheme of the invention is: the high-intensity non-quenching and tempering easy-cutting steel used for a vehicle connection rod consists of the elements of C, Si, Mn, Al, P, S, Cr, V, N and Fe; the weight percentages of the component elements are: 0.30 to 0.4 percent of C, 0. 50 to 0.70 percent of Si, 0.80 to 1.20 percent of Mn, equal to or less than 0.040 percent of P, 0.030 to 0.060 percent of S, 0.010 to 0.040 percent of Al, 0.10 to 0.40 percent of Cr, 0.10 to 0.30 percent of V, 010 to 0.015 percent of N and the rest is Fe and unavoidable impurities. The heating temperature of a continuous casting blank is 1200 DEG C; the heating time is 160min; the start rolling temperature is 1100 DEGC; the final rolling temperature is 900 DEG C; the pressing volume is 16; the cooling speed after rolling is 40 DEG C / min; after bundling, the components are thrown in a pit and slowly cooled.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Low-carbon resulfurized free-machining steel excellent in machinability
A low-carbon resulfurized free-machining steel is excellent in machinability and contains 0.02% to 0.15% by mass of C; 0.004% by mass or less (exclusive of 0%) of Si; 0.6% to 3% by mass of Mn; 0.02% to 0.2% by mass of P; 0.35% to 1% by mass of S; 0.005% by mass or less (exclusive of 0% by mass) of Al; 0.008% to 0.03% by mass of 0; and 0.007% to 0.03% by mass of N, with the remainder being iron and inevitable impurities, in which the ratio [Mn] / [S] of the manganese content [Mn] to the sulfur content [S] is within the range of 3 to 4, and the carbon content [C], the manganese content [Mn] and the nitrogen content [N] satisfy the following Expression (1): 10[C]×[Mn]−0.94+1226 [N]2≦1.2, wherein [C], [Mn] and [N] represent the contents on the percent by mass basis of carbon, manganese, and nitrogen, respectively.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Tin containing free-cutting steel
The present invention relates to a tin-contained free machining steel. Said steel can be used for making important standard parts of high-strength Bolts, etc. of automobile and machinery, and is characterized by that in said steel 0.03-0.05% of Sn is contained. Said invention adopts the several measures of neutral covering slag molten steel, diffusing deoxygenation and solid electrolyte oxygen concentration difference cell to quickly define oxygen to develop out the leadless free machining steel (Y20Sn) with excellent mechanical propery and free-cutting machinability. The tests show that the tensile strength of its sample is up to 460MPa, percentage elongation is 25%-30% and reduction of cross-sectional area is 55%-60%.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Low carbon resulfurized free-machining steel having high machinability
A low carbon resulfurized free-machining steel having a high machinability is provided. This steel comprises 0.02 to 0.15% by mass of C, up to 0.004% by mass (more than 0% by mass) of Si, 0.6 to 3% by mass of Mn, 0.02 to 0.2% by mass of P, 0.2 to 1% by mass of S, up to 0.005% by mass (more than 0%) of Al, 0.008 to 0.04% by mass of O, and 0.002 to 0.03% by mass of N; and the average oxygen concentration in the MnS in the steel is at least 0.4% by mass.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com