Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Endosymbiosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
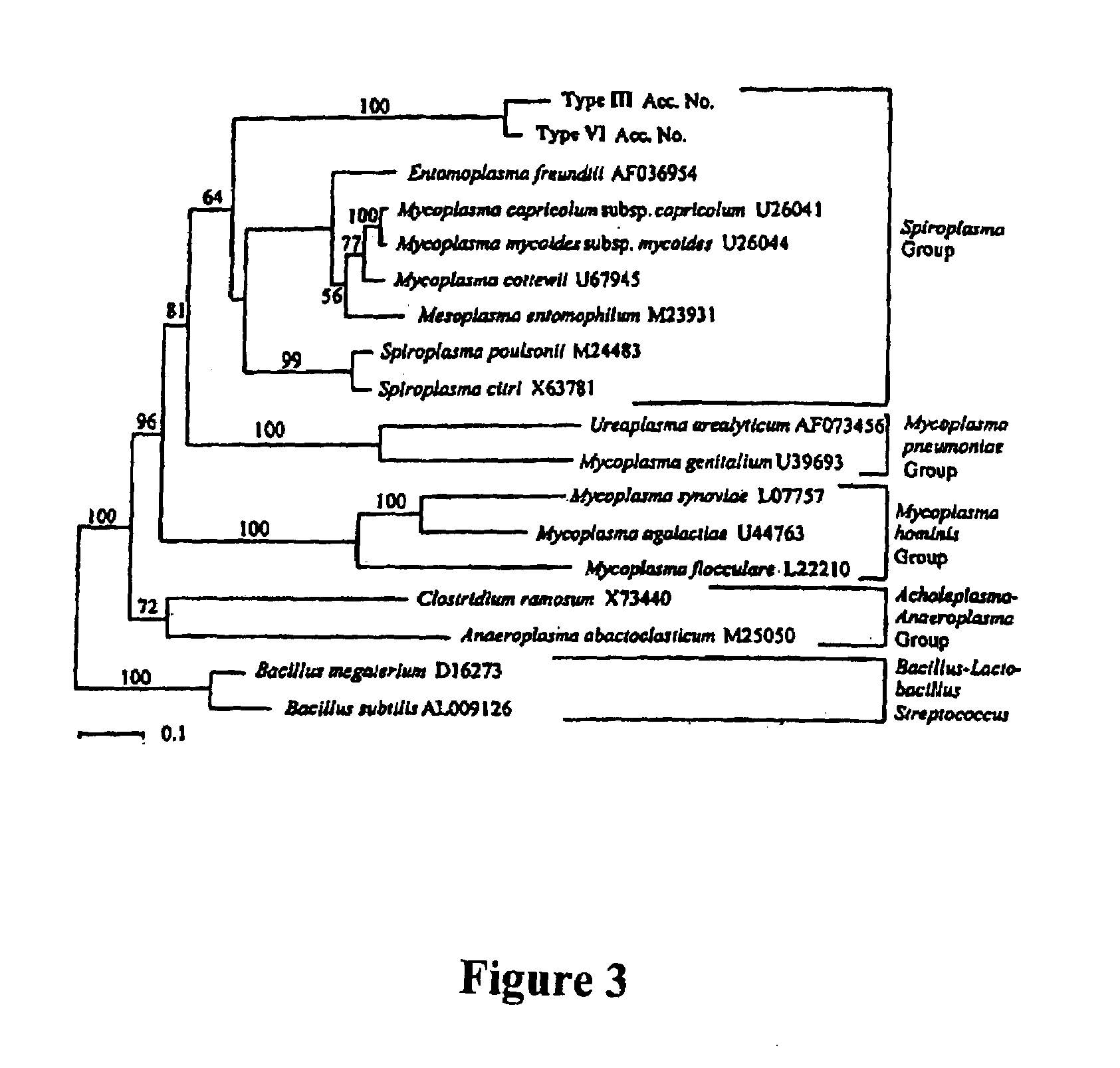
An endosymbiont or endobiont is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship. The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον endon "within", σύν syn "together" and βίωσις biosis "living"). Examples are nitrogen-fixing bacteria (called rhizobia), which live in root nodules on legume roots, single-cell algae inside reef-building corals, and bacterial endosymbionts that provide essential nutrients to about 10–15% of insects.
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
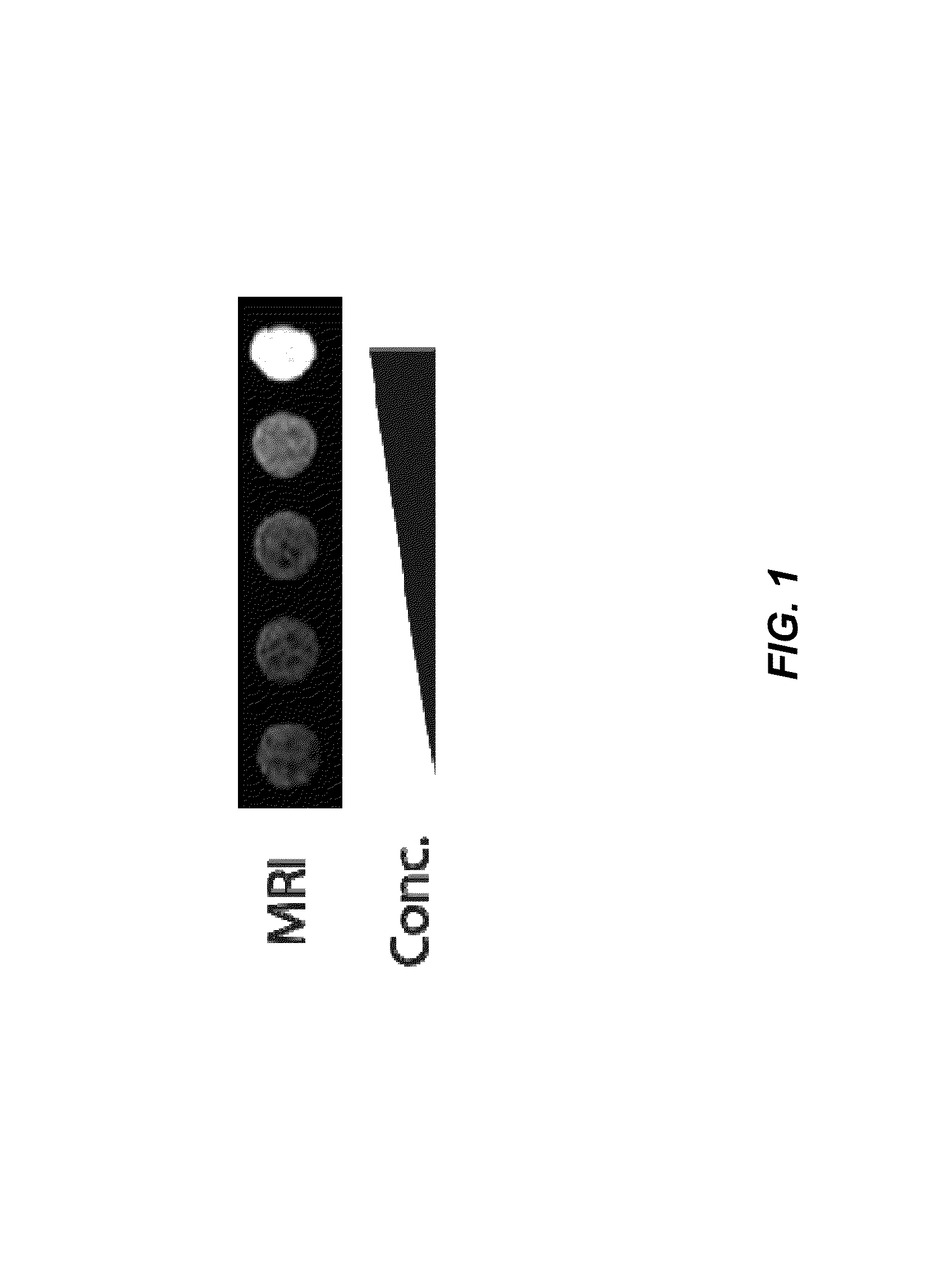
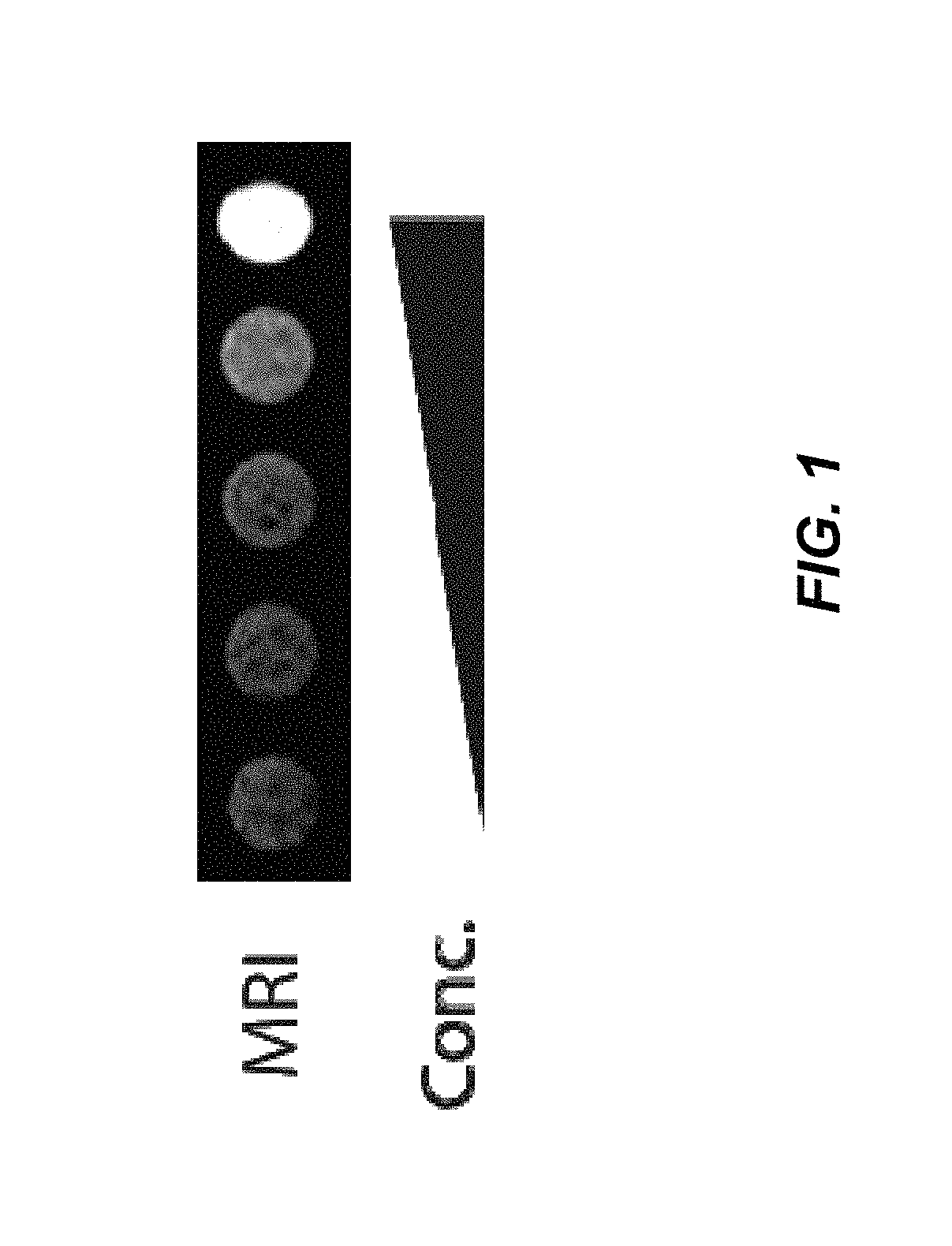
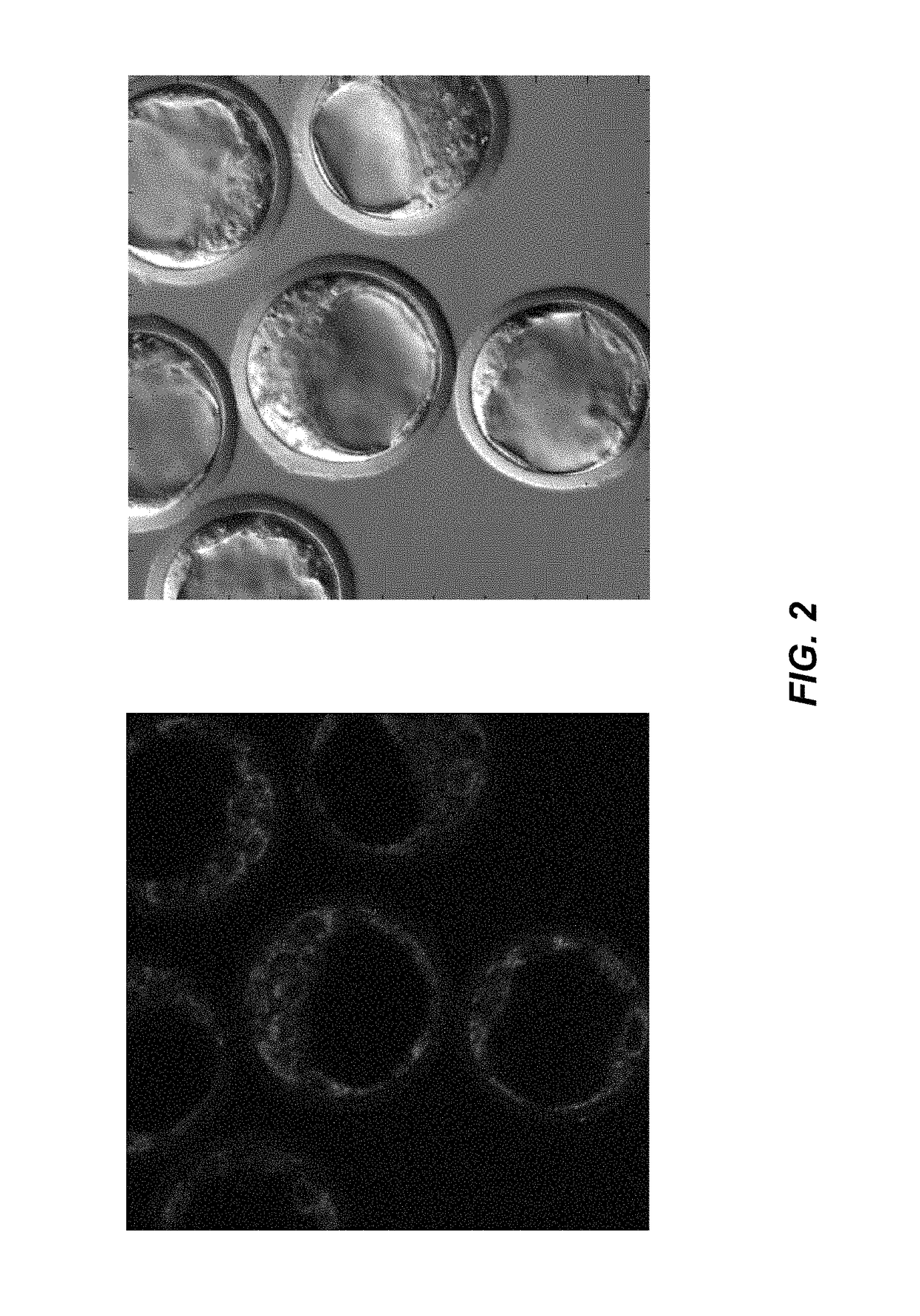
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell through at least five cell divisions, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides methods of using such eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Sequences from an endosymbiont and their uses
rDNA corresponding to an endosymbiotic bacteria associated with Ecteinascidia turbinata has been identified. The bacterium appears to be responsible for the biosynthesis of ecteinascidin compounds. The 16S rDNA sequence corresponding to Candidatus Endoecteinascidia frumentensis SEQ ID NO: 1 has been deposited in GeneBank with the accession number AY054370.
Owner:PHARMA MAR U
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic host cells comprising artificial endosymbionts and methods of introducing artificial endosymbionts into eukaryotic host cells. The invention provides artificial endosymbionts that introduce a phenotype to host cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic host cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Eukaryotic Cells with Artificial Endosymbionts for Multimodal Detection
InactiveUS20150010937A1Good informationBacteriaUnicellular algaeSingle-Celled OrganismBio engineering
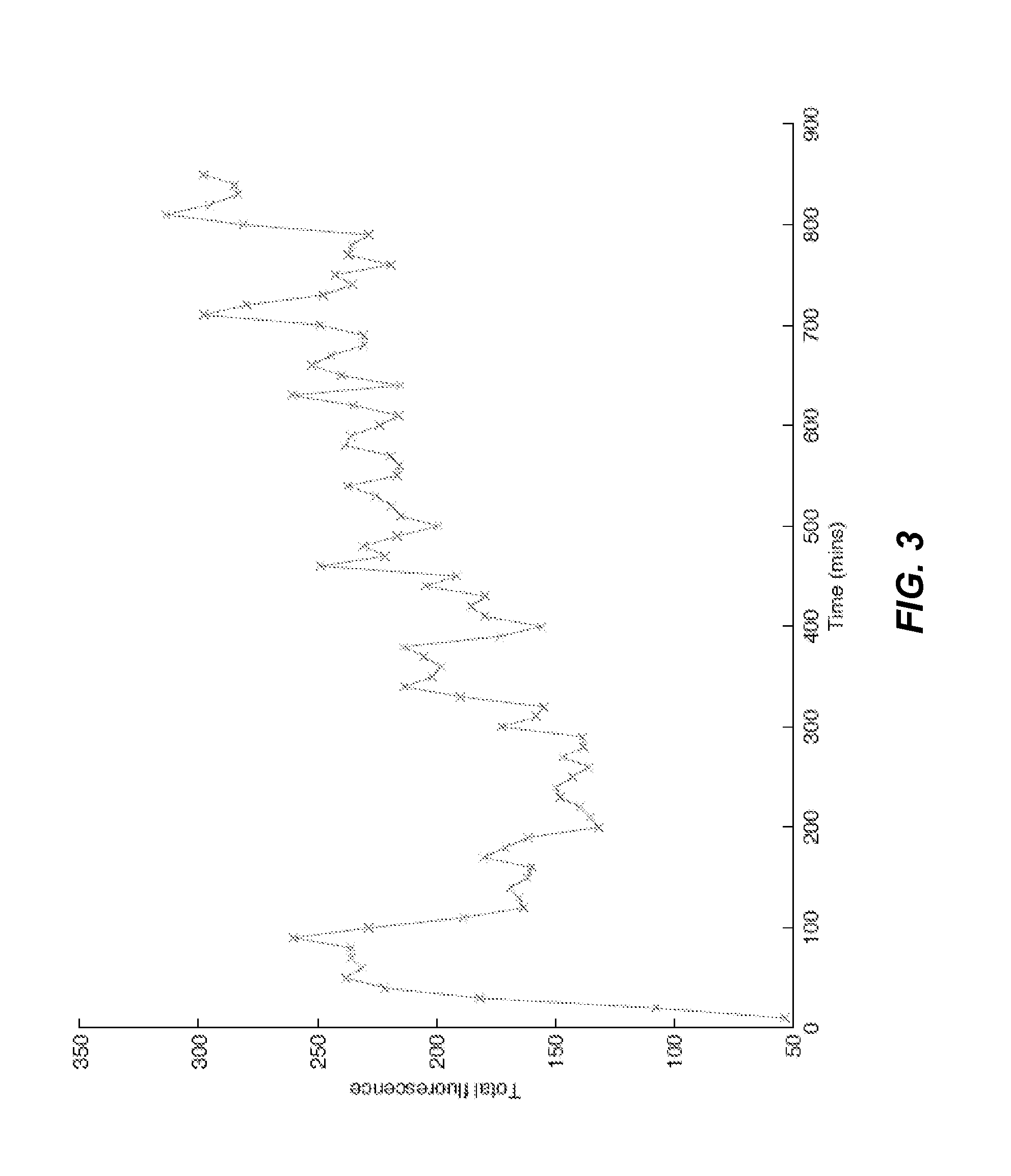
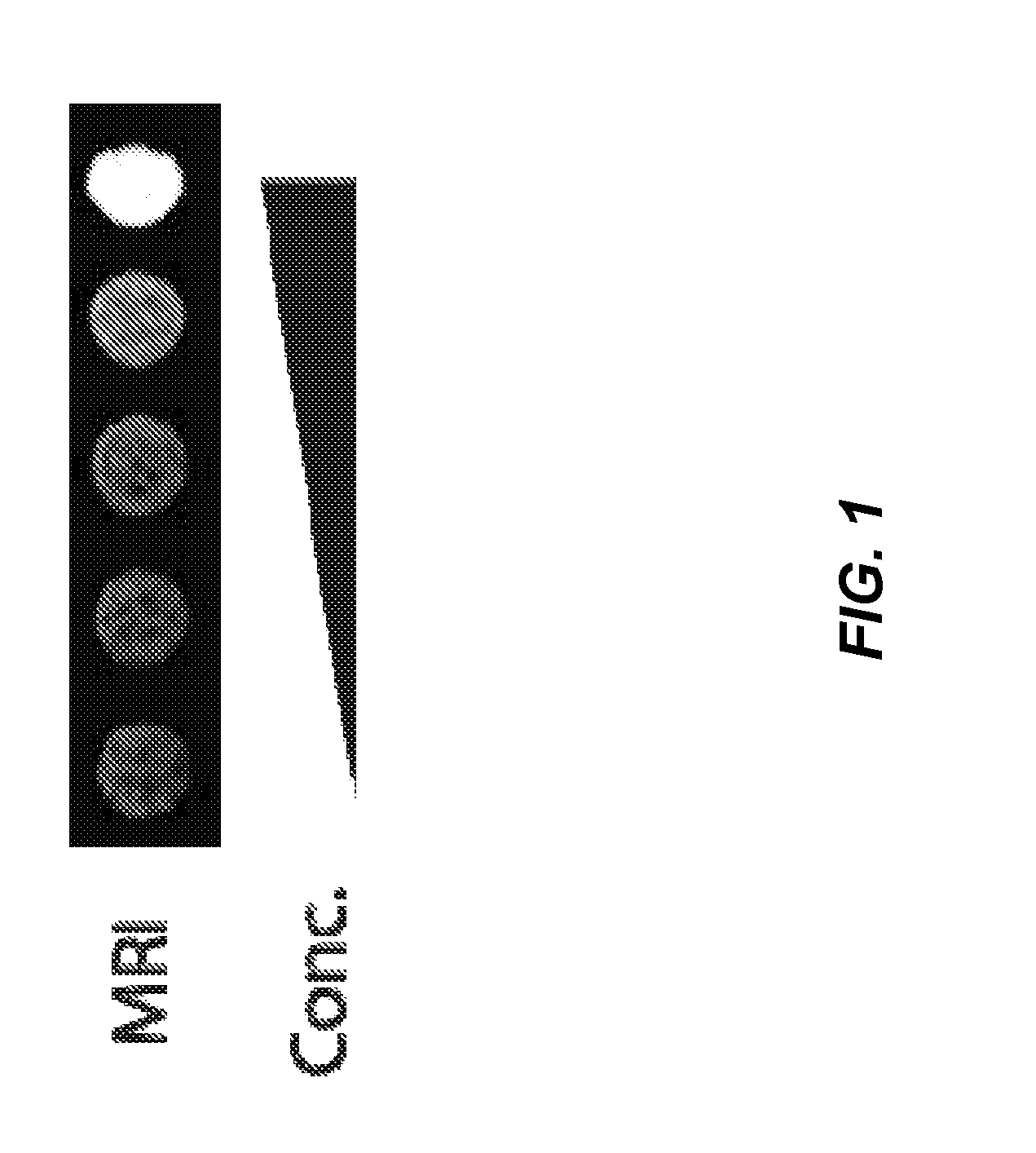
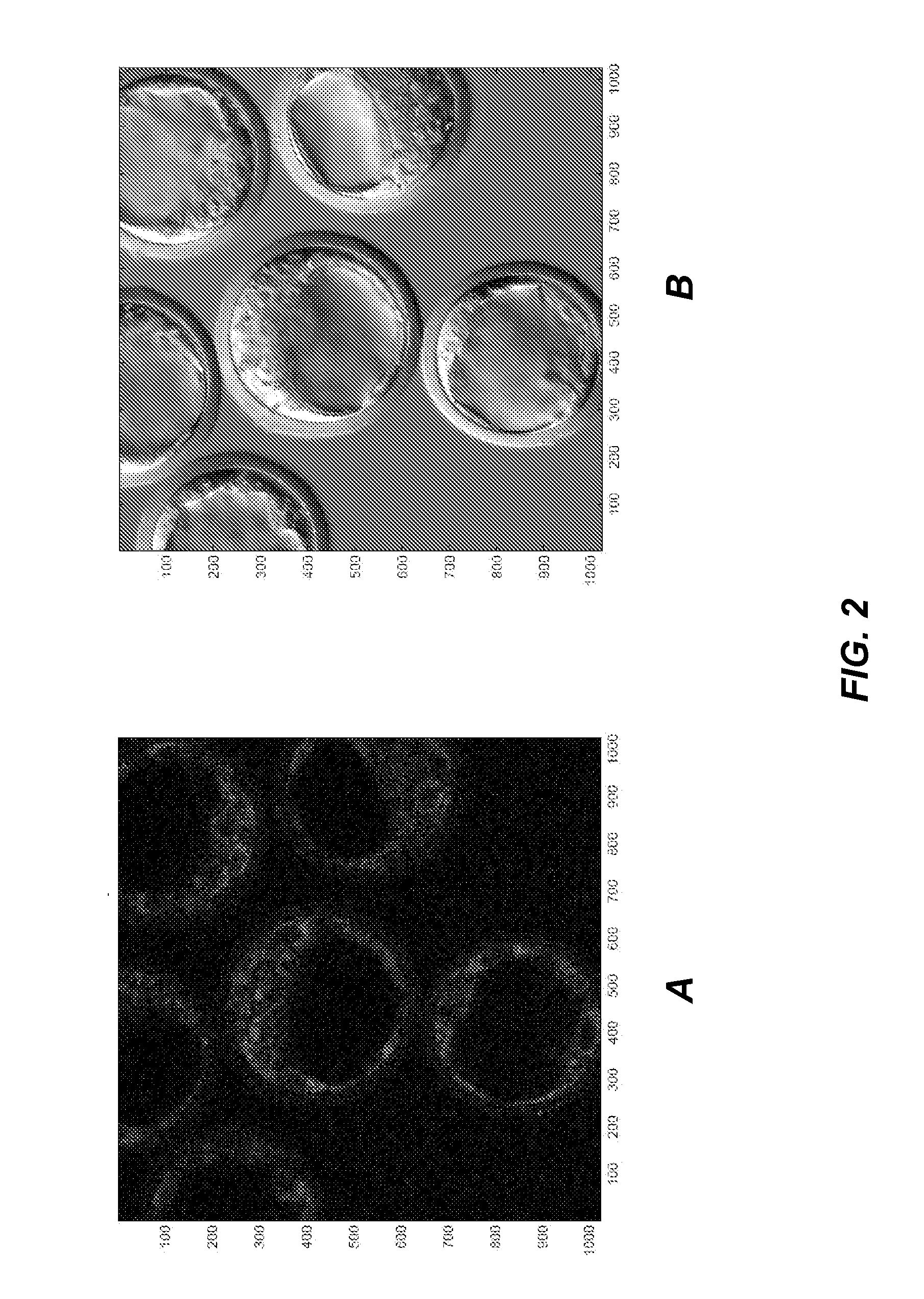
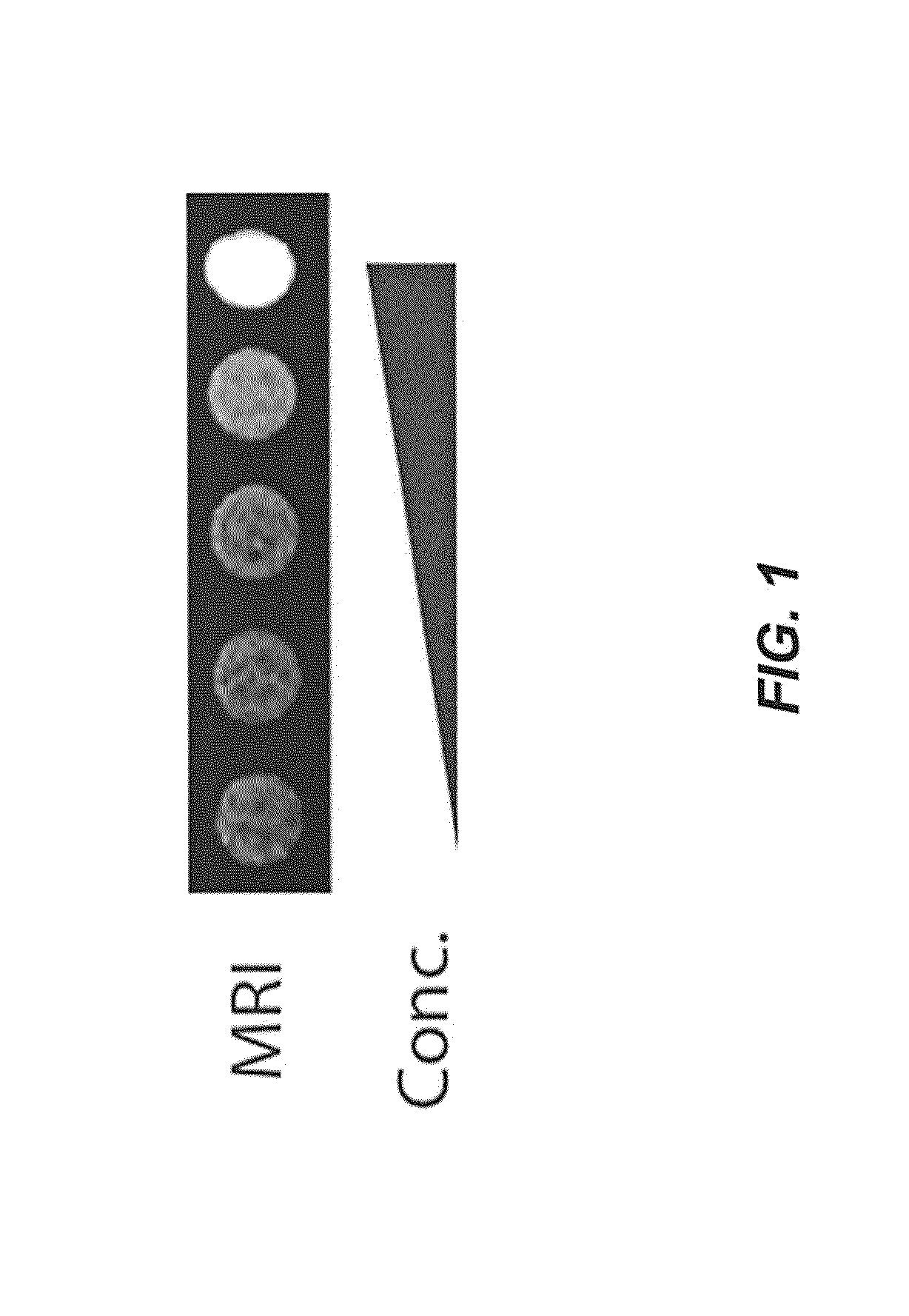
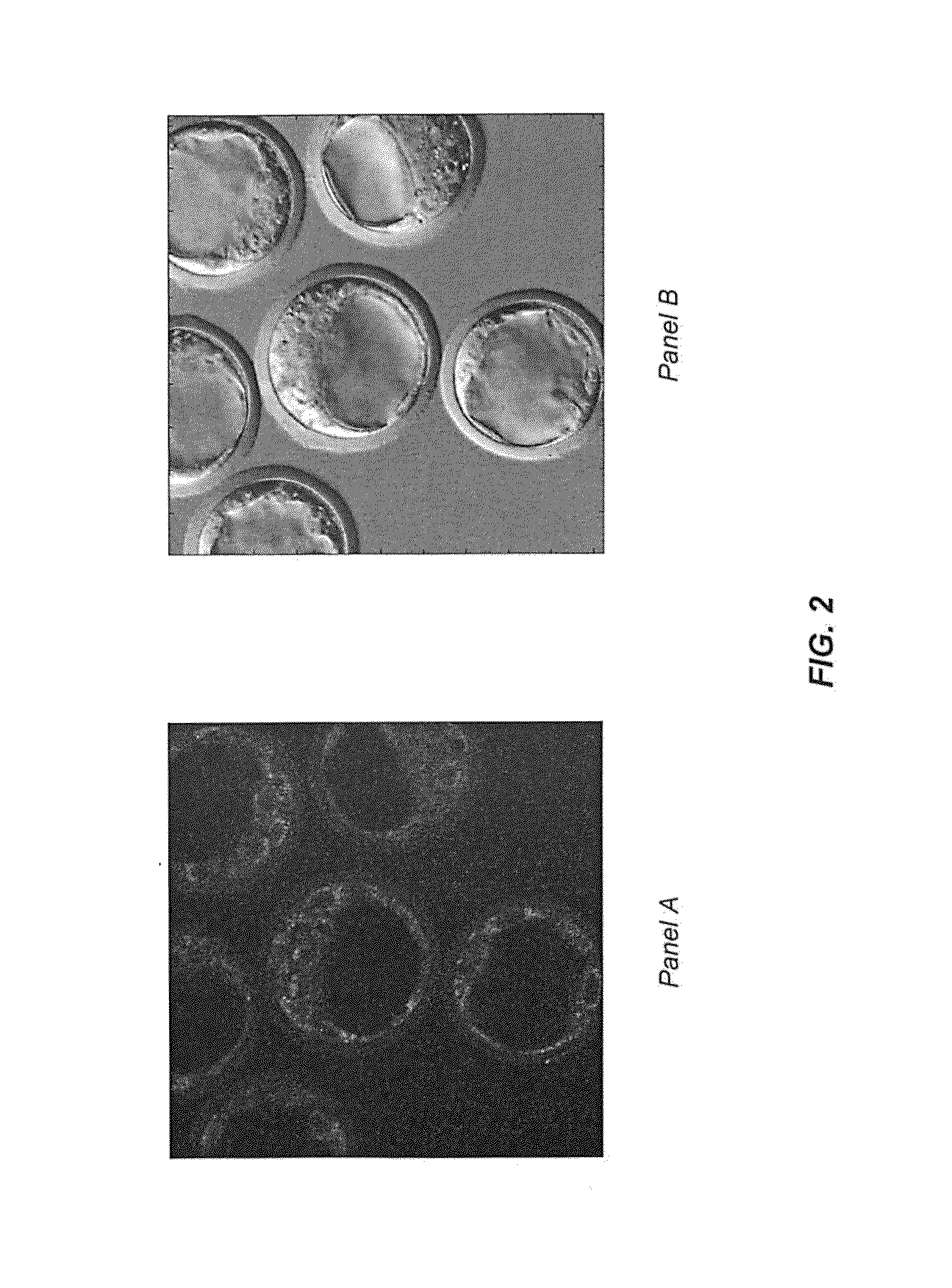
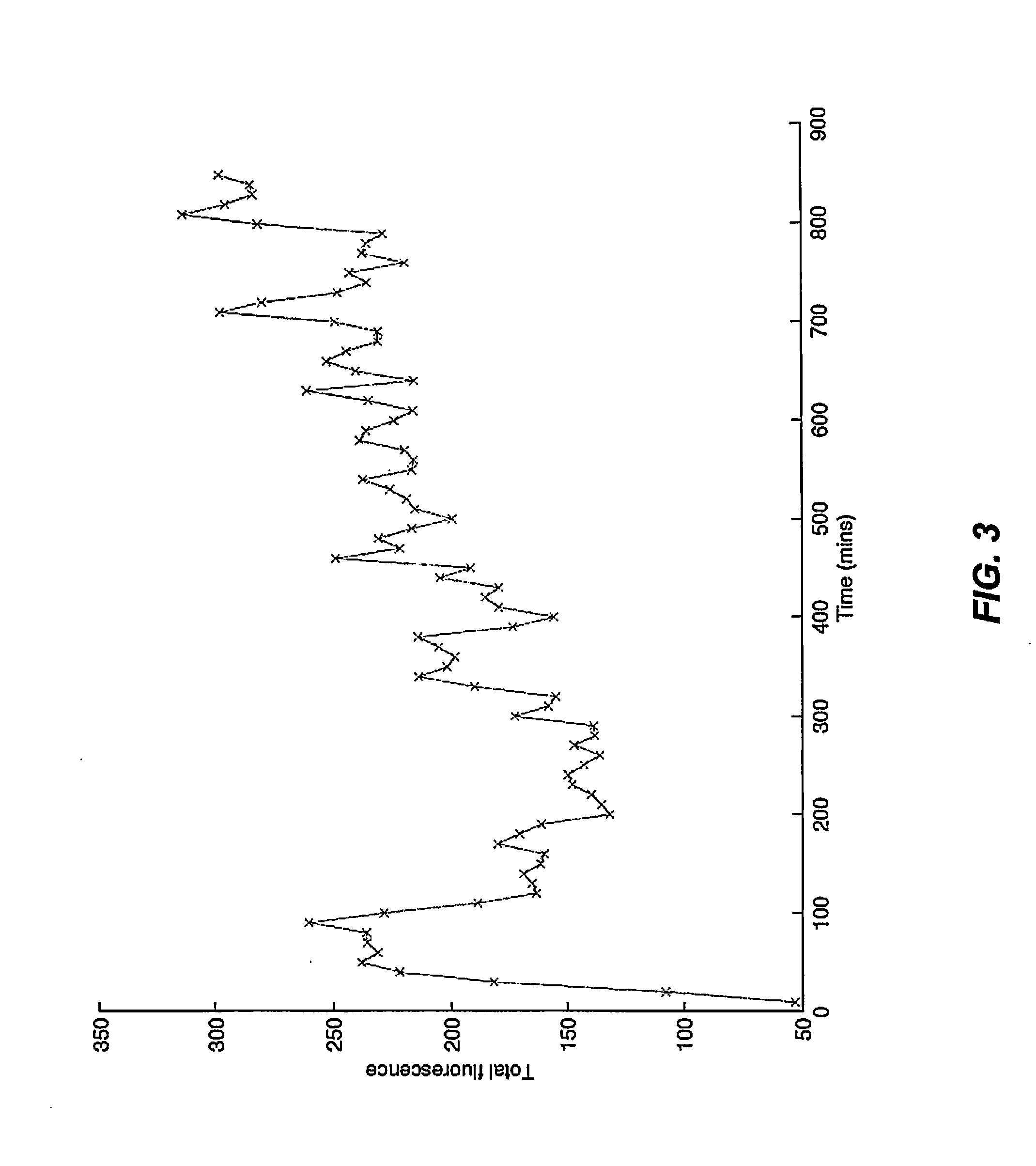
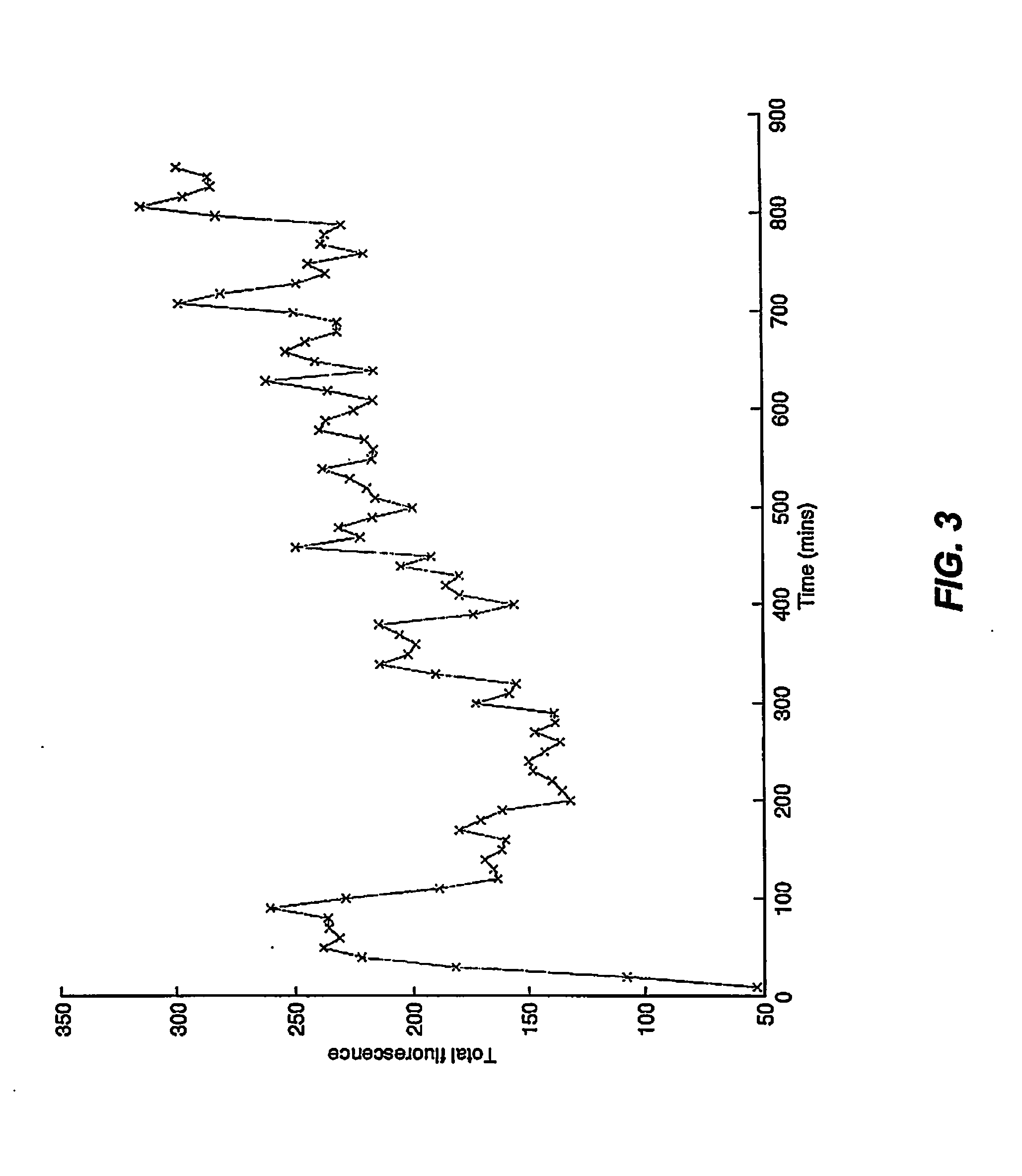
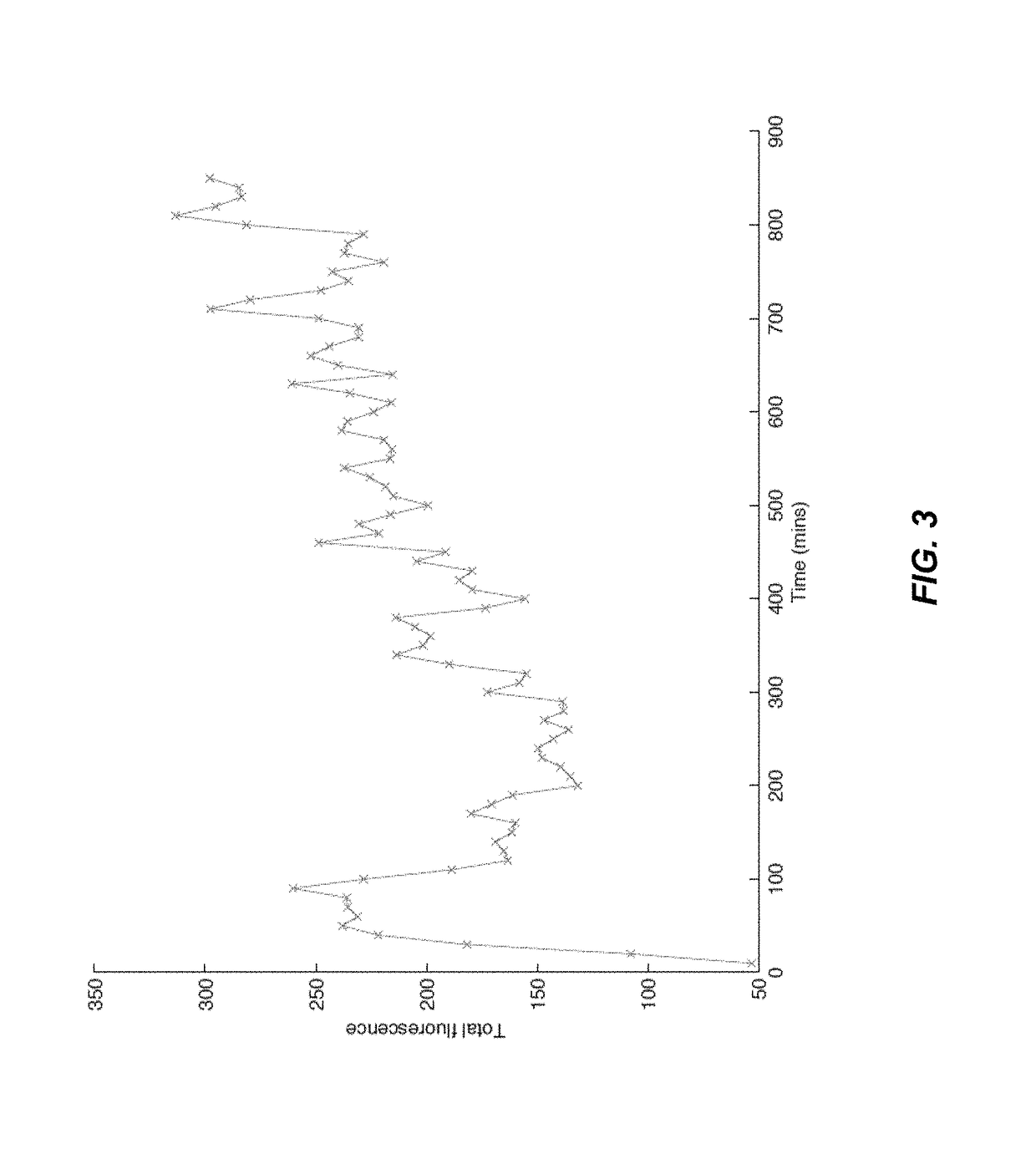
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetic bacteria. The invention further provides eukaryotic cells engineered with single-celled organisms to allow for multimodal observation of the eukaryotic cells. Each imaging method (or modality) allows the visualization of different aspects of anatomy and physiology, and combining these allows the imager to learn more about the subject being imaged.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Host Cells with Artificial Endosymbionts
InactiveUS20130253303A1ElectrotherapyMaterial analysis by optical meansCell divisionMagnetotactic bacteria
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell through at least five cell divisions, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides methods of using such eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Host Cells with Artificial Endosymbionts
InactiveUS20140273203A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCell divisionMagnetotactic bacteria
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell through at least five cell divisions, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides methods of using such eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Eukaryotic cells with artificial endosymbionts for multimodal detection
InactiveUS9023612B2Good informationHybrid cell preparationNanomedicineEucaryotic cellBio engineering
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Method for horizontal transfection of exogenesis endosymbiosis bacterium to bemisia tabaci gennadius
InactiveCN101220377AOvercoming the problem of easy slidingOvercome the disadvantage of sticking to adultsMicroinjection basedInfection rateEndosymbiotic bacteria
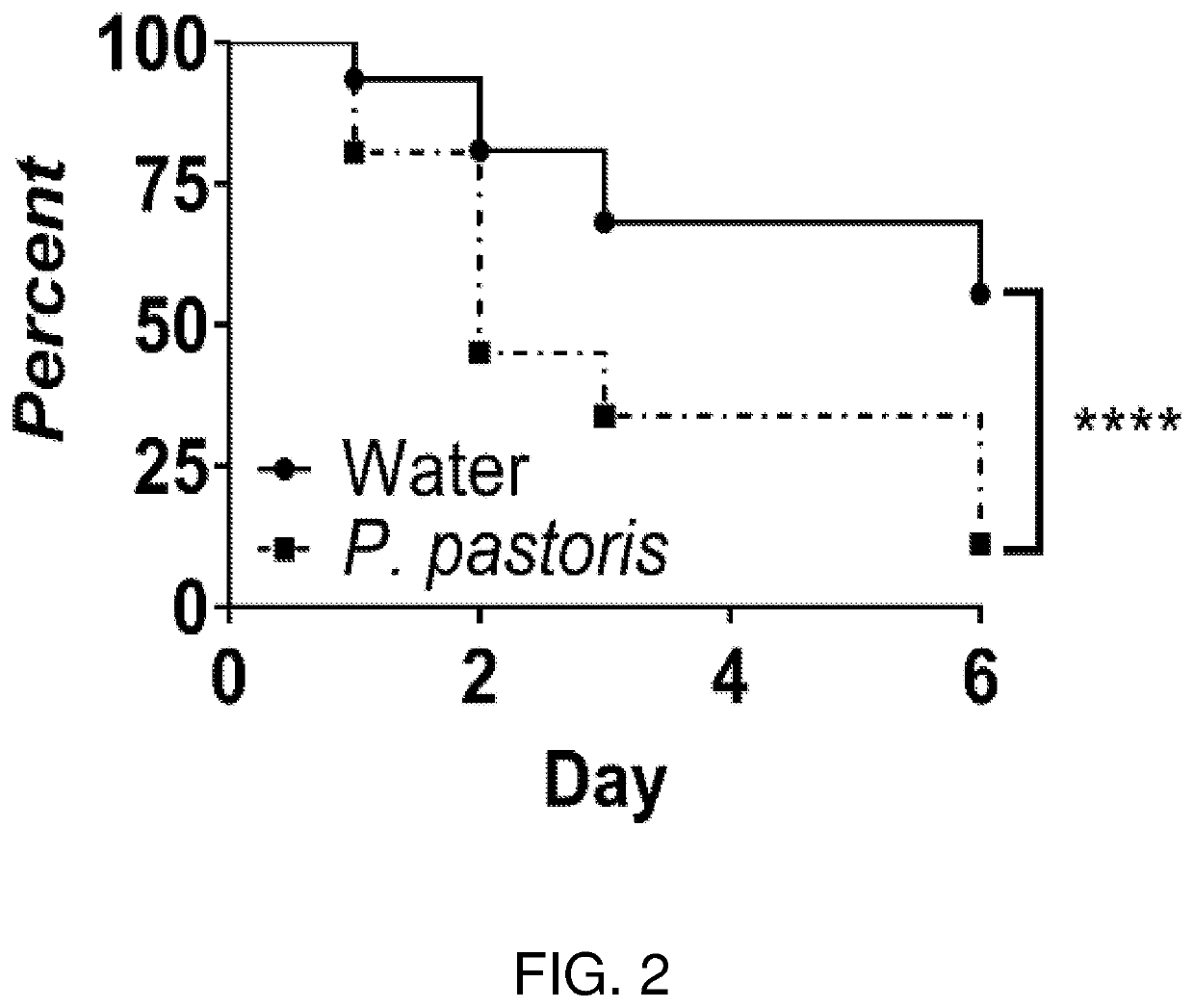
The invention relates to a method for the horizontal transfection of bemisia tabaci of the exogenous endosymbiotic bacteria, which pertains to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The preparation method includes: the purification of the exogenous endosymbiotic bacteria Wolbachia, the collection and fixation of a bemisia tabaci receptor, the horizontal transfection of the exogenous endosymbiotic bacteria Wolbachia to the bemisia tabaci receptor, the collection and fixation of an injection individual and the detection of the endosymbiotic bacteria. The invention is simple and quick, which can successfully transfect the exogenous endosymbiotic bacteria to a bemisia tabaci individual, and a bemisia tabaci offspring has higher infection rate.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Extraction method of Tobacco whitefly endosymbiont mycetocytes
The invention relates to an extraction method of insect endosymbiont mycetocytes, and concretely relates to an extraction method of Tobacco whitefly endosymbiont mycetocytes. The method mainly comprises the steps of dissecting, filtration and discontinuous density gradient centrifugation, and the interferences of exogenous microbes can be fully removed layer by layer through the steps to obtain pure and adequate mycetocytes, so the influences of hosts and in-vivo exogenous microbes thereof are eliminated in the subsequent researches of the functions of endosymbionts, thereby the Tobacco whitefly endosymbiont mycetocytes can be used in the subsequent tests of the sequencing and active substance separation of the whole genome of the endosymbionts to comprehensively and deeply understand the functions of the Tobacco whitefly endosymbionts.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell through at least five cell divisions, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides methods of using such eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Multiple PCR detection method for detecting symbiotic bacteria in tetranychus truncatus ehara body
InactiveCN101603081AShorten the timeSave preciousMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSymbiotic bacteriaMultiplex pcrs
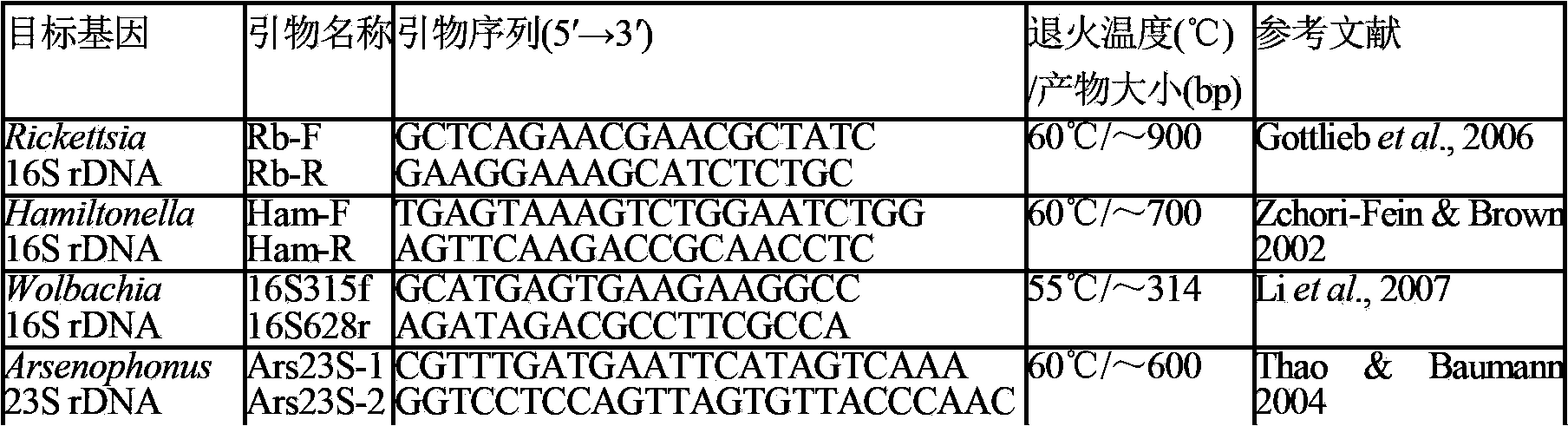
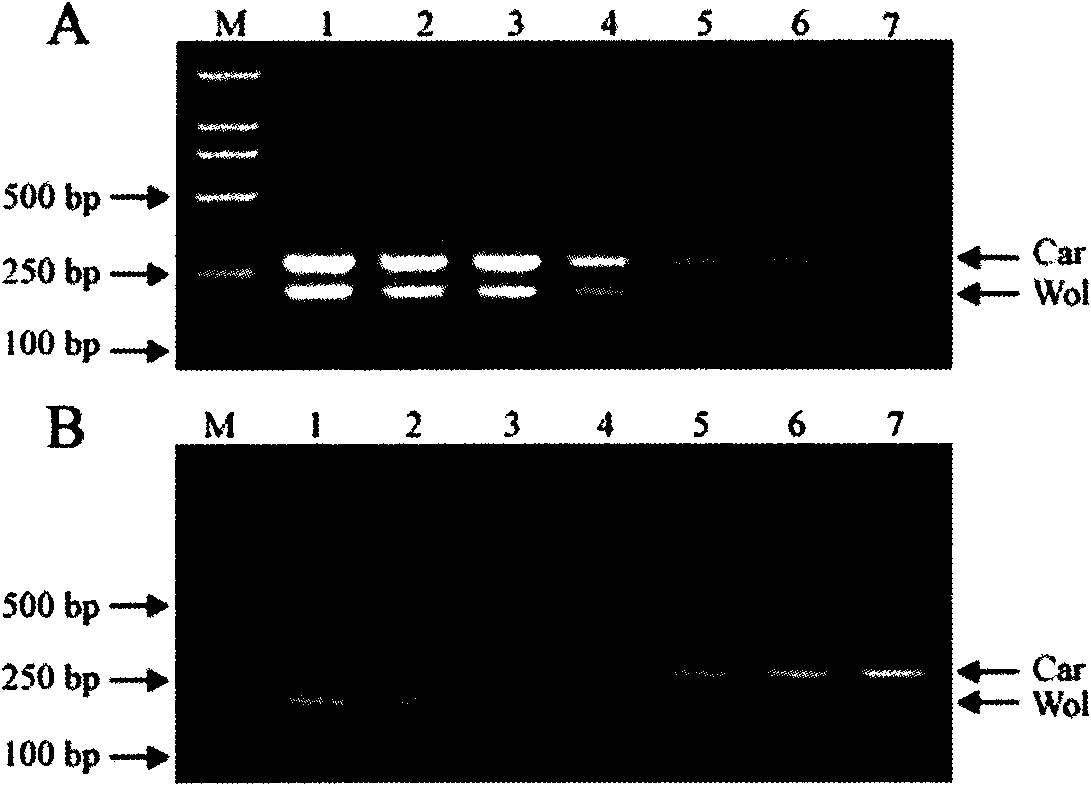
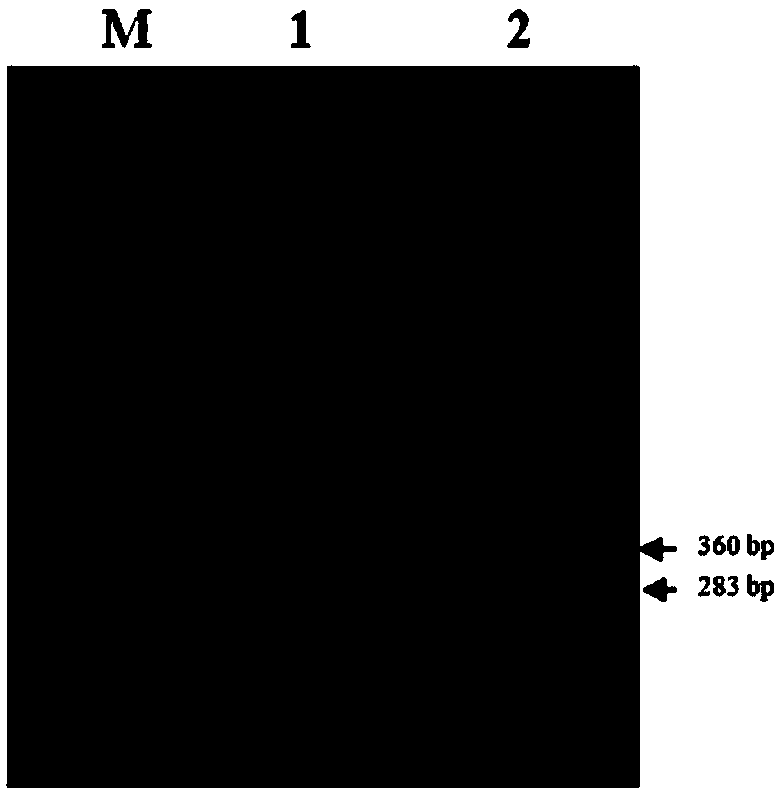
The invention relates to a multiple PCR detection method for detecting Wolbachia and Cardnium symbiotic bacterias in tetranychus truncatus ehara body at the same time, belonging to the field of agricultural biotechnologies; the multiple PCR is an improved PCR technology on the basis of a common PCR, a plurality of pairs of auele specific primers are added in a PCR reaction system, aiming at different areas of a plurality of DNA templates or the same template, a plurality of purpose fragments are amplified. According to Wolbachia wsp gene sequence and Cardnium 16S rDNA gene sequence, two pairs of new auele specific primers are designed, and two purpose fragments - 211bp and 279bp which has different size, are amplified. The multiple PCR detection method has high specificity, sensibility, feasibility and effectiveness, namely, the detecting cost is saved and the template is saved. The multiple PCR detection technology for detecting the Wolbachia and Cardnium symbiotic bacterias at the same time can be widely applied to the detection of the two symbiotic bacterias in tetranychus truncatus ehara.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of melatonin to influence on rhizosphere soil microorganism diversity of medicinal plants
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to application of melatonin serving as an effective component of a foliar spraying agent to influence on rhizosphere soil microorganism diversity of medicinal plants. The content of the melatonin in the foliar spraying agent is 100-300 mg / L, and an inducer further contains 0.05 g / L of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose. The melatonin can reduce the content of endogenous salicylic acid and hydrogen peroxide of plants, increase the content of jasmonic acid, promote proliferation and endosymbiosis of rhizosphere probiotic fungi and change the rhizosphere soil microorganism diversity of the paris polyphylla. In conclusion, when the melatonin is sprayed on the leaf surfaces, the composition of rhizosphere microorganisms can be adjusted by changing the endogenous hormone level, so that the effects of resisting diseases and promoting growth of the paris polyphylla are achieved. The foliar spraying agent taking the melatonin as the effective component is used for cultivating paris polyphylla var chinensis and has the effects of resisting diseases and promoting growth, the preparation and use methods are simple, the cost is low, and popularization and application can be realized.
Owner:GANSU ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY
Preparing and applying method of cutting propagation growth promoting agent of tea tree endogenous herbaspirillum seropedicae
InactiveCN104585241AImprove disease resistanceRealize comprehensive utilizationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant hormoneMetabolite
The invention provides a preparing and applying method of a cutting propagation growth promoting agent of tea tree endogenous herbaspirillum seropedicae. By using biological characteristics of the tea tree endogenous herbaspirillum seropedicae, a tea tree endogenous herbaspirillum seropedicae culturing solution is prepared by virtue of fermentation of the tea tree endogenous herbaspirillum seropedicae, and is diluted according to a certain ratio and then used for performing soaking treatment on a tea tree cutting wood. Plant hormones secreted by bacteria in the growth promoting agent are used for inducing the cutting wood to form adventitious roots; the bacteria in the growth promoting agent enter the cutting wood to perform endosymbiosis and continuously secret metabolites, so that quick growth of tea seedlings is promoted. The treated and cut cutting wood is developed in root system and high in planting percent, and tea seedlings are darkly green in leaves, and grow vigorously. The technical method provided by the invention is low in cost and simple to operate, is green and safe, and has multiple effects and durable action. The growth promoting agent can be used for cutting propagation of tea trees as commercial crops and can also be used for cutting propagation of other camellia plants.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Establishing method for indoor symbiotic relationship of amanita flavipes and cyclobalanopsis glaucoides as symbiotic plant
InactiveCN102715089ABuild a symbiotic systemConvenient researchHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySporocarp (fungi)
The invention relates to an establishing method for indoor symbiotic relationship of amanita flavipes and cyclobalanopsis glaucoides which is a symbiotic plant, and belongs to the field of biotechnology (plant tissues and Fungus cultivation). An overwhelming majority of amanita belongs to ectomycorrhizal fungi, can not be yet subjected to artificial cultivation at present, and can be hardly developped and utilized; and growth and development of sporocarps of the amanita has a close relationship with cyclobalanopsis glaucoids which is a symbiotic plant. The establishing method is characterizedin that myceliums are induced through the sporocarps of amanita flavipes for reproduction; aseptic seedlings and potted seedlings are successfully obtained by using seeds of cyclobalanopsis glaucoides, collected in the field; reproduced myceliums are inoculated to the roots of the aseptic seedlings and the potted seedlings respectively; the result shows that inoculated seedlings are more exuberant than the non-inoculated seedlings and have more leaves, the leaves of inoculated seedlings are dark green, disease resistance of inoculated seedlings are reinforced; and therefore, the indoor symbiotic relationship of amanita flavipes and cyclobalanopsis glaucoides is innovatively established, and a technological reserve is provided for future researches on symbiotic mechanism and mechanism generated in the sporocarps of amanita.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for naturally propagating seeds of wild centranthera grandiflora
InactiveCN106900316AImprove seedling rateImprove natural reproductive capacityPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsDiseaseLoment
The invention relates to a method for naturally propagating seeds of wild centranthera grandiflora. The method includes the following steps that 1, capsule pods are selected; 2, after-ripening treatment is carried out on the seeds; 3, seeds of endosymbiosis herbages in centranthera grandiflora groups are selected; 4, land is selected; 5, a natural propagation seedling bed is prepared; 6, the seeds are treated with an inducer; 7, sowing and sterilizing are carried out; 8, a seedling-growing shed is set up; 9, the germination conditions of the seeds are controlled; 10, seedlings are trained and managed; 11, fertilizer application and seed removal are carried out on the seedlings; 12, diseases and insect pests of the seedlings are prevented and treated; transplanting is carried out. By the utilization of the method, the natural propagation capacity of the seeds of the wild centranthera grandiflora is greatly improved, the qualified seedling percentage of natural germination is increased to 8% or more from 0.2% or less, namely, the qualified seedling percentage is increased 40 or more times, and the problems that at the present, resources are lack, and are not protected can be effectively solved. The method achieves natural propagation of the seeds of the wild centranthera grandiflora for the first time, and is simple, low in cost, convenient to operate and suitable for actual production and application.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Fluorescence in-situ hybridization method for endosymbiotic bacteria in insect ovary
InactiveCN108179202AAvoid freezingAvoid the tedious process of slicingMicrobiological testing/measurementStainingFluorescence
The invention relates to a fluorescence in-situ hybridization method for endosymbiotic bacteria in an insect ovary. The method comprises following steps: the insect ovary is dissected under a microscope, the dissected insect ovary is transferred to a glass slide, an insect tissue stationary liquid is added for fixation, and a destaining solution is added for destaining; pre-hybridization and hybridization staining are performed on a specimen, and an eluant is added for elution after hybridization is completed; finally, a sample is sealed with glycerin, and observation and photographing are performed under a confocal microscope. By means of the method, a good cell staining effect can be kept, the operation can be simplified, time can be shortened, reagents can be saved and the cost can be reduced. Several endosymbiotic bacteria in the ovary can be subjected to multiple staining simultaneously, a good staining effect is obtained, and the method is simple, convenient, rapid and economical.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DsRNA of gene of symbiotic bacterium of aphids and application thereof to inhibition of growth of aphids
The invention discloses dsRNA of a gene of a symbiotic bacterium of aphids and an application thereof to inhibition of growth of aphids. DsRNA provided by the invention is double-stranded RNA formed by a nucleotide shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table and a nucleotide shown in an inverse complementary sequence of the sequence 2. Experiments prove that the gene of the endotrophic symbiotic bacterium hamiltonella defensa 28469 of wheat aphids is obtained; the gene of the endotrophic symbiotic bacterium hamiltonella defensa 28469 of wheat aphids can be inhibited or silenced, impaired growth and development of the wheat aphids can be caused and lethal effects can be generated by adopting the method of feeding dsRNA in vitro.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
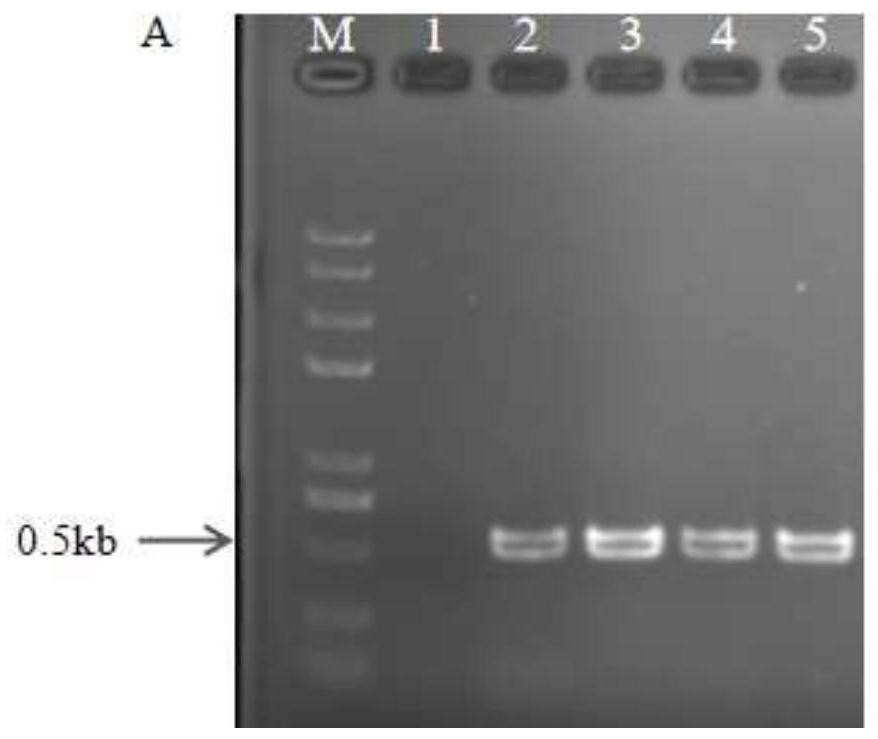
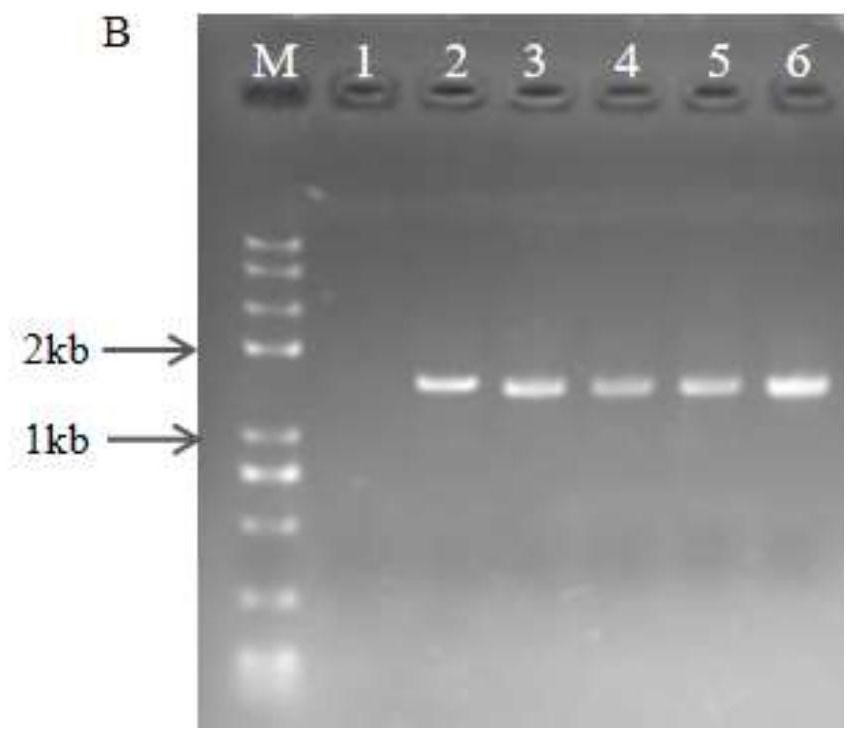
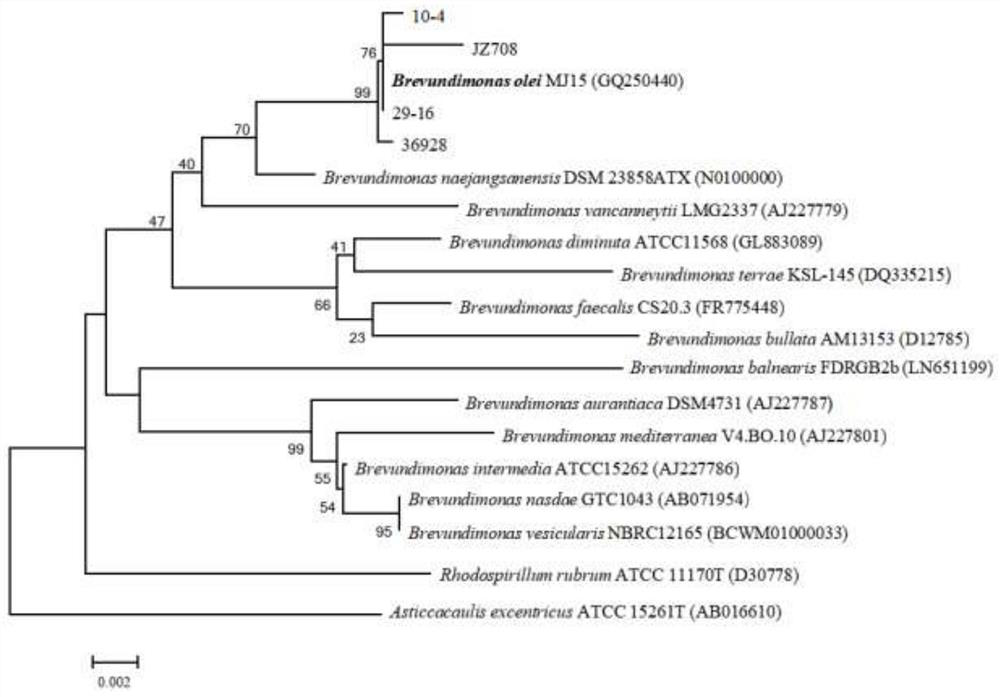
Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei and application thereof
ActiveCN112175887AHigh antibacterial rateProduce inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyXenorhabdus sp.
The invention discloses Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei and application thereof. The Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei is named as Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei, and the preservation number of the Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei is CCTCC NO: M 2020392. The strain is determined to be Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei through morphological identification and diversity sequencing analysis, and the influence of B.olei fermentation liquor on growth of the Brevundimonas oleei and microsclerosis is explored through a co-culture experiment. Through scanning electron microscope observation, as the culture time and the concentration of the fermentation liquor increase, formation of conidia of the Brevundimonas oleei is reduced, the hypha morphology is expanded, broken and deformed, the microsclerosisis gradually reduced and disappears, and it is proved through the research that the symbiotic B.olei has good bacteriostatic activity on the Brevundimonas olei.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell through at least five cell divisions, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides methods of using such eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Sequences from an endosymbiont and their uses
InactiveUS20060167228A1Sugar derivativesBacteriaBacteroidesCandidatus Endoecteinascidia frumentensis
rDNA corresponding to an endosymbiotic bacteria associated with Ecteinascidia turbinata has been identified. The bacterium appears to be responsible for the biosynthesis of ecteinascidin compounds. The 16S rDNA sequence corresponding to Candidatus Endoecteinascidia frumentensis SEQ ID NO: 1 has been deposited in GeneBank with the accession number AY054370.
Owner:PHARMA MAR U
Eukaryotic cells with artificial endosymbionts for monitoring the duration and persistence of the eukaryotic cell
InactiveUS20170239375A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsEmulsion deliverySingle-Celled OrganismMagnetotactic bacteria
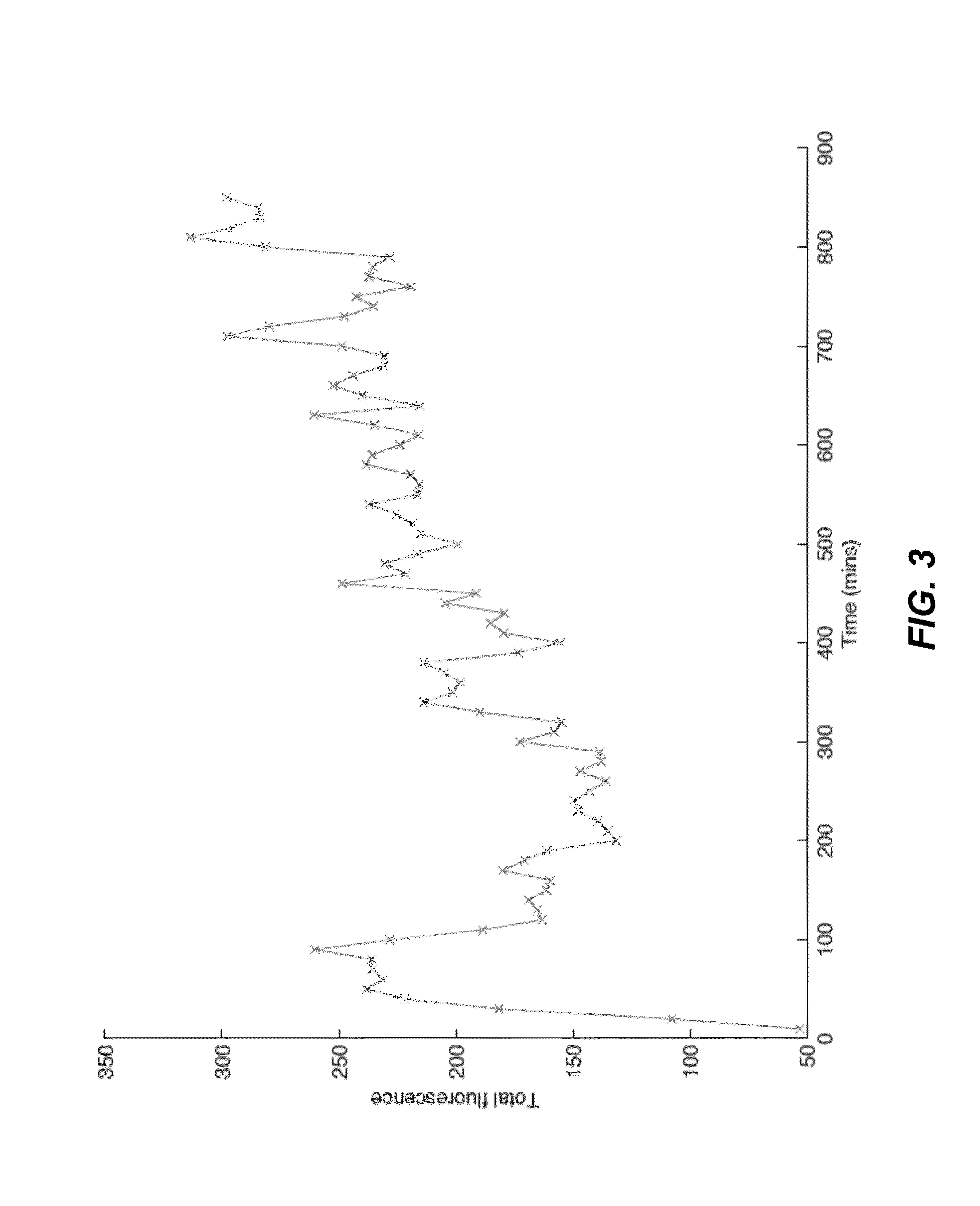
The present invention relates generally to the field of endosymbiosis, eukaryotic cells engineered with artificial endosymbionts, and magnetotactic bacteria. In particular, the invention provides single-celled organisms such as artificial endosymbionts, including magnetotactic bacteria, eukaryotic cells to host those single-celled organisms, and methods of using eukaryotic cells containing single-celled organisms. The invention also provides eukaryotic cells engineered with intracellular single-celled organisms which eukaryotic cells can be tracked in an animal and monitored for viability. The invention also provides for multimodal detection of a eukaryotic cell in an animal to monitor the location and viability of the eukaryotic cell.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Method for regulating and controlling pest populations by using symbiotic bacteria in parasitic wasps
InactiveCN108496901AIncreased parasitic abilityImprove damage control effectPlant protectionAnimal husbandrySymbiotic bacteriaInfection rate
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Cellulase gene gk2691 for encoding cellulase family GH30, and application thereof
InactiveCN111394374AImprove degradation efficiencyEfficient use ofFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a novel cellulase gene gk2691 for encoding a cellulase family GH30. The gene is cloned from a symbiotic microorganism meta-gene in corals, and has a nucleotide sequence shown bya sequence table SEQ ID NO.1. The invention also provides an amino acid sequence of the cellulase gene gk2691 for encoding the cellulase family GH30, wherein the sequence is shown by SEQ ID NO.2. Inaddition, the invention also provides an expression vector containing the gene as well as a host cell transformed by the expression vector. Cellulase encoded with the cellulase gene gk2691 has wide usages in degradation of cellulose.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
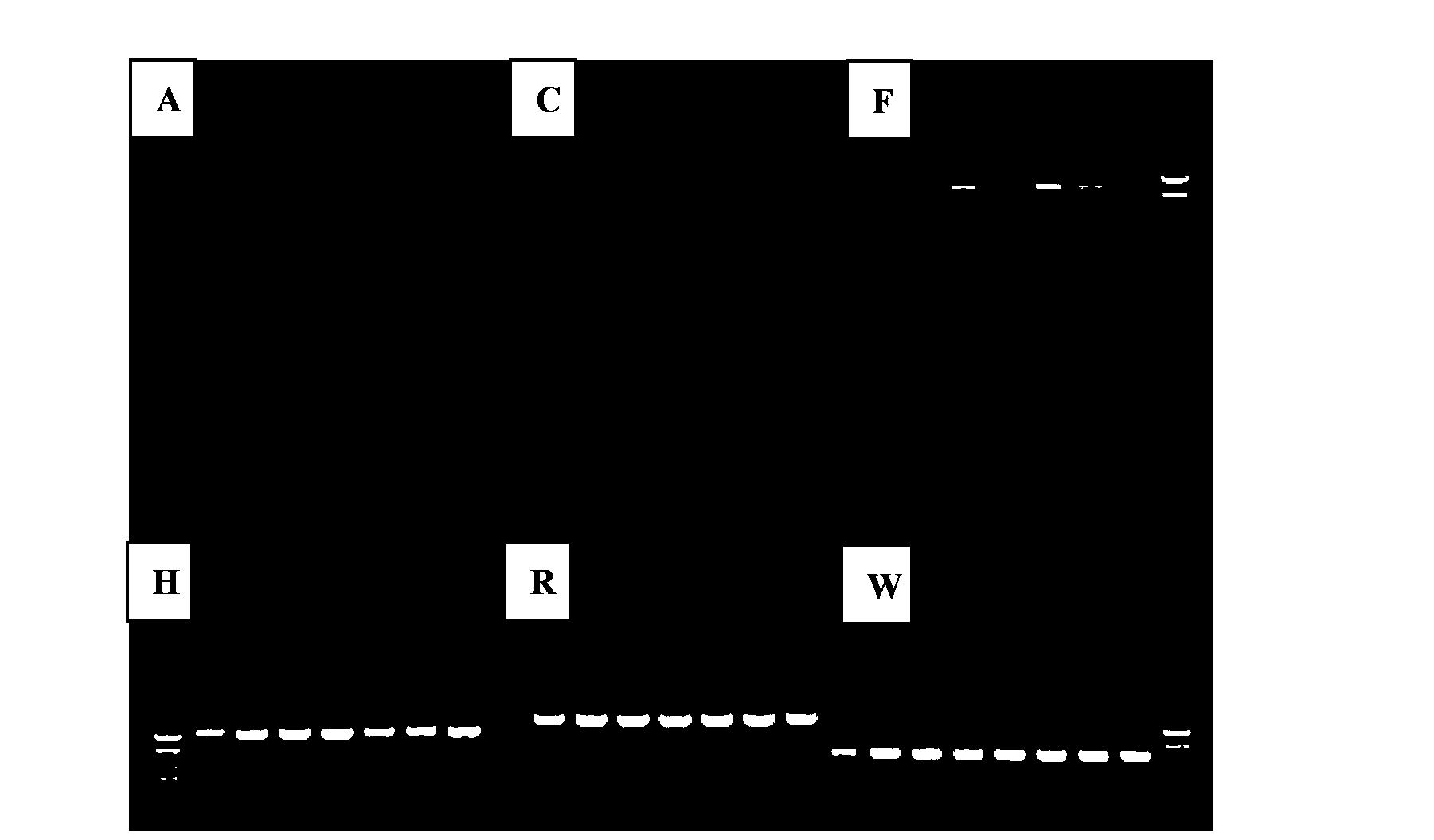
Method for building bemisia tabaci populations which contain rickettisa bacteria and do not contain rickettisa bacteria
The invention relates to building of insect infection endosymbiosis bacteria populations, in particular to a method for building bemisia tabaci populations which contain rickettisa bacteria and do not contain rickettisa bacteria. The method includes the following steps that the bemisia tabaci populations are collected and cultured in a laboratory; a plurality of bemisia tabaci are selected and observed under a microscope so that male and female bemisia tabaci can be determined; one male bemisia tabaci and one famele bemisia tabaci are selected by sucking and inoculated to the back of a muskmelon leaf; culturing is performed; deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of single bemisia tabaci is extracted, then the DNA of the bemisia tabaci is subjected to molecular identification by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method, and purification is performed to obtain stable populations. According to the technical scheme, living conditions of the bemisia tabaci under natural survival conditions are simulated to build the populations, change of biological characteristics of the bemisia tabaci is absent, and influence of the rickettisa bacteria on the bemisia tabaci can be correctly known.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Chroococcidiorella tianjinensis as well as culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN111925943AClear genetic backgroundClassification is clear and stableUnicellular algaeClimate change adaptationBiodieselNutrition
The invention discloses a first green alga TDX16-DE with a known origin as well as a culture method and application of the green alga TDX16-DE, and belongs to the technical field of microalgae biology. The TDX16-DE is formed by transforming endosymbiotic blue algae (cyanobacteria)-chromonas paramamosain TDX16 after obtaining DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of host green algae-haematococcus pluvialis of the endosymbiotic blue algae (cyanobacteria)-chromonas paramamosain TDX16; the TDX16-DE is classified and named as Chroococcidiorella tianjinensis, is preserved in the China Center for Type CultureCollection on August 6, 2020, and has a preservation number of CCTCC AF 2020007 T. The Chroococcidiorella tianjinensis has strong adaptability to the environment; a large amount of carotenoid, such asprotein, polysaccharide, lipid and astaxanthin as well as active substances, bacteriostatic substances and antioxidant substances for promoting cell proliferation and growth can grow and be synthesized rapidly under autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixed nutritional conditions; and thus theChroococcidiorella tianjinensis can be used for producing foods, medicines, health care products, cosmetics, carotenoids, animal feeds, baits, biodiesel and biological fertilizers, and treating waste gas and wastewater.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Host cell modification with artificial endosymbionts
The present invention is directed generally to host cells with artificial endosymbionts, wherein the artificial endosymbiont and the host cell communicate with each other to alter a phenotype of the host cell. In some embodiments, the communication comprises the secretion of a polypeptide from the artificial endosymbiont into the host cell. The secreted polypeptide can be a selectable marker, a reporter protein, a transcription factor, a signal pathway protein, a receptor, a growth factor, a cytokine, an effector molecule or other factors that can produce a phenotype in the host cell.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Quality-improving microbial agent and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111849824AGuarantee the stability of active ingredientsComposition is stableFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a quality-improving microbial agent. The formula of the quality-improving microbial agent comprises the following components by weight component: chitosan, glucose, polysaccharide crude extract dry powder, corn steep liquor dry powder, composite endosymbiotic bacillus, saccharomycetes, lactic acid bacteria, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, potassium bacteria, phosphate solubilizing bacteria, polyacrylamide, saccharomycetes fermentation liquor and lactic acid bacteria fermentation liquor. The pH value of the soil is regulated and controlled so that the problems of soil pH value, soil hardening and subsequent fertilizer utilization rate reduction are reduced; the invention also provides a preparation method of the quality-improving microbial agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing a basic solution, adding a bacterial carbon source, adding anaerobic bacteria, adding facultative bacteria, checking the activity of strains, mixing and blending themicrobial inoculants at a proper temperature according to the mass components of the formula, and ensuring the effective components of the microbial inoculants by regulating and controlling the temperature and the rotating speed.
Owner:河南浩创农业科技集团有限公司
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
InactiveUS10076579B2Genetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell divisionMagnetotactic bacteria
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Compositions and related methods for modulating endosymbionts
PendingUS20190367943A1Reduce diversityReduce functionBiocideElcosanoid active ingredientsNematodeBiology
Provided herein are methods and compositions for modulating the fitness of a host invertebrate (e.g., insect, mollusk, or nematode) by altering interactions between the host and one or more micoorganisms resident in the host. The invention features a composition including a modulating agent (e.g., a polypeptide, nucleic acid, small molecule, or combinations thereof) that can induce changes in the host's microbiota in a manner that modulates (e.g., increases or decreases) host fitness. The modulating agent described herein may modulate the fitness of a variety of invertebrates that are important for agriculture, commerce, and / or public health.
Owner:FLAGSHIP PIONEERING INNOVATIONS V INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com