Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Earth's orbit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi), and one complete orbit takes 365.256 days (1 sidereal year), during which time Earth has traveled 940 million km (584 million mi). Earth's orbit has an eccentricity of 0.0167. Since the Sun constitutes 99.8% of the mass of the solar system, the center of the orbit is extremely close to the center of the Sun.
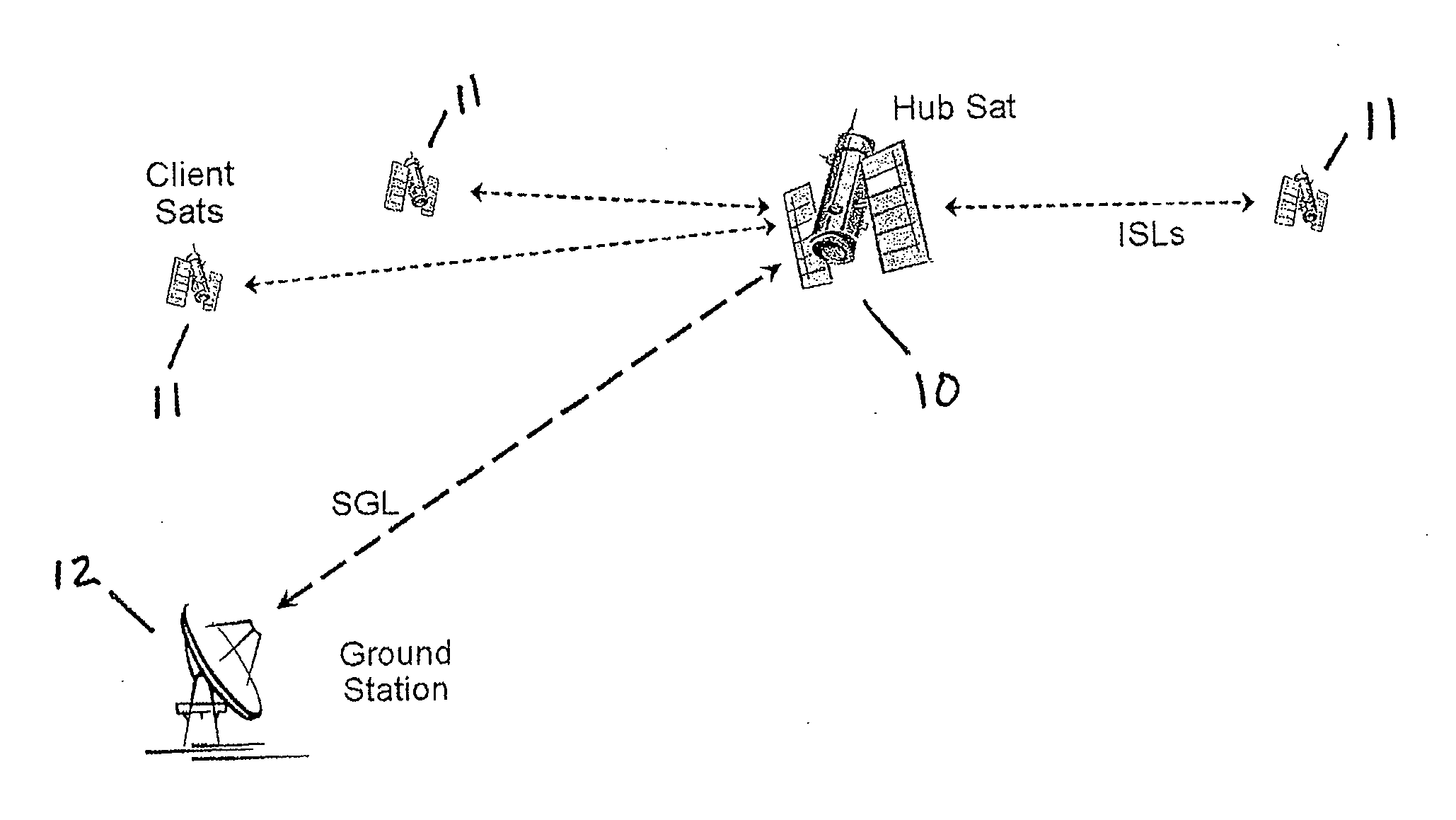
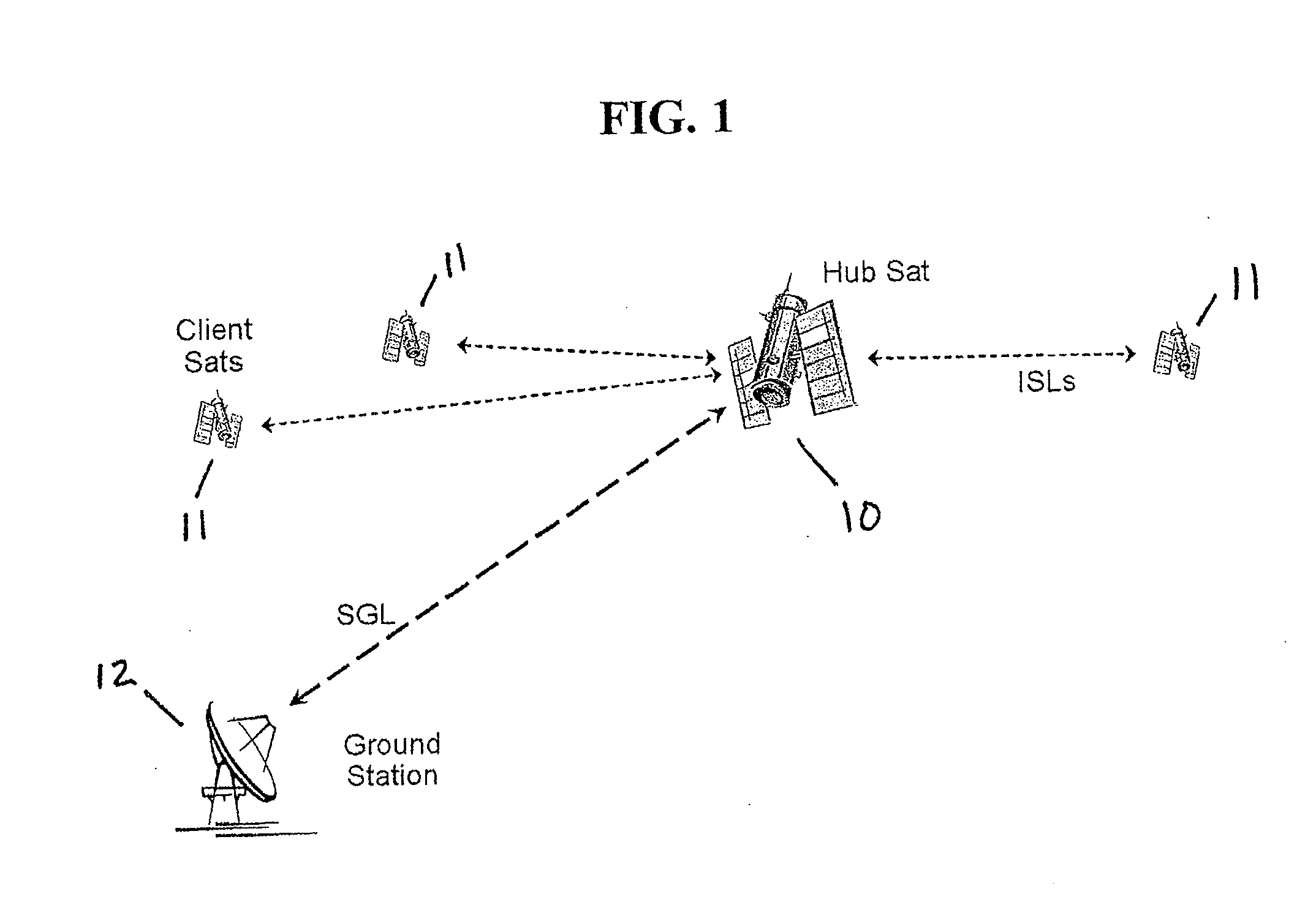
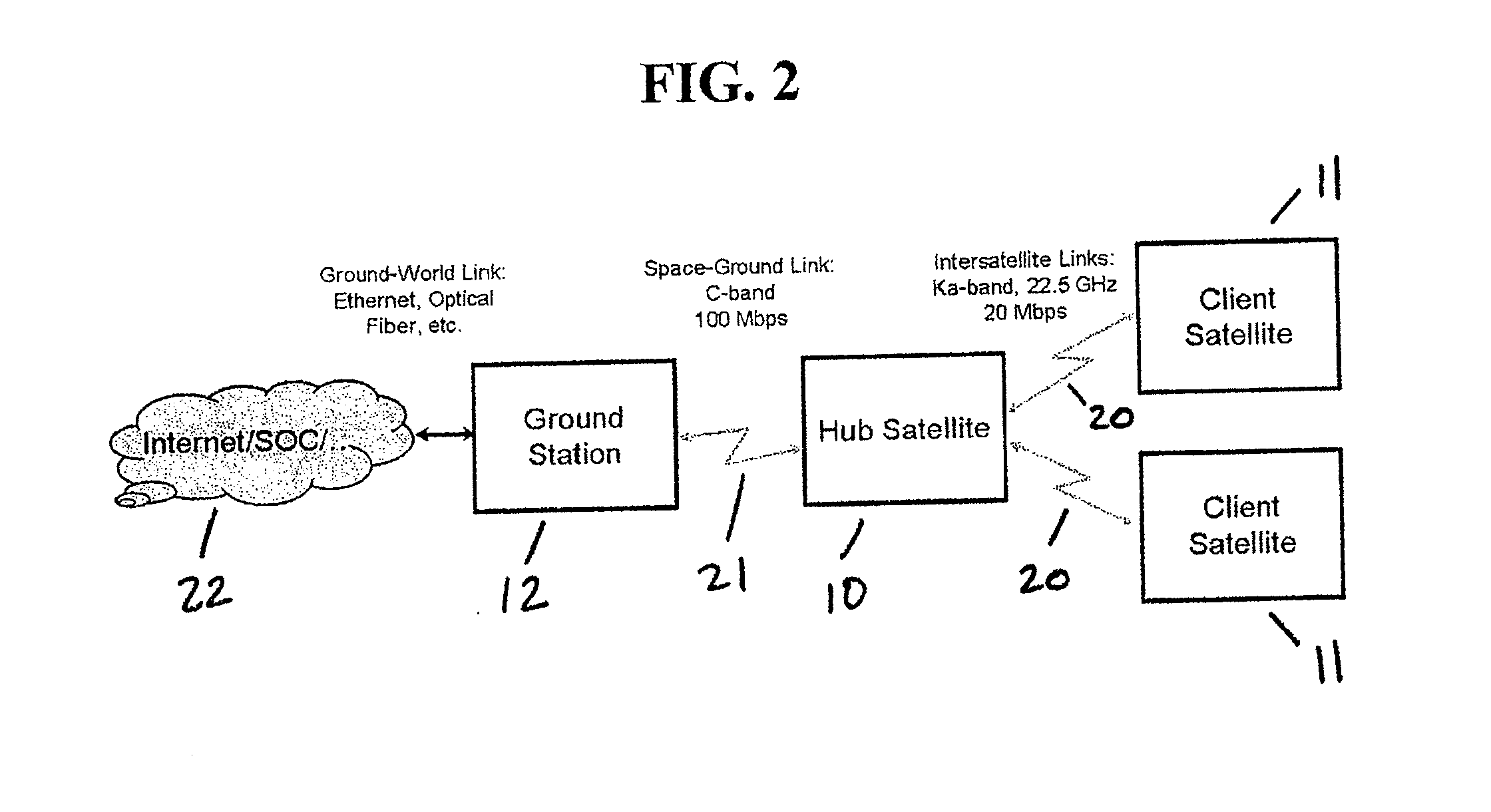
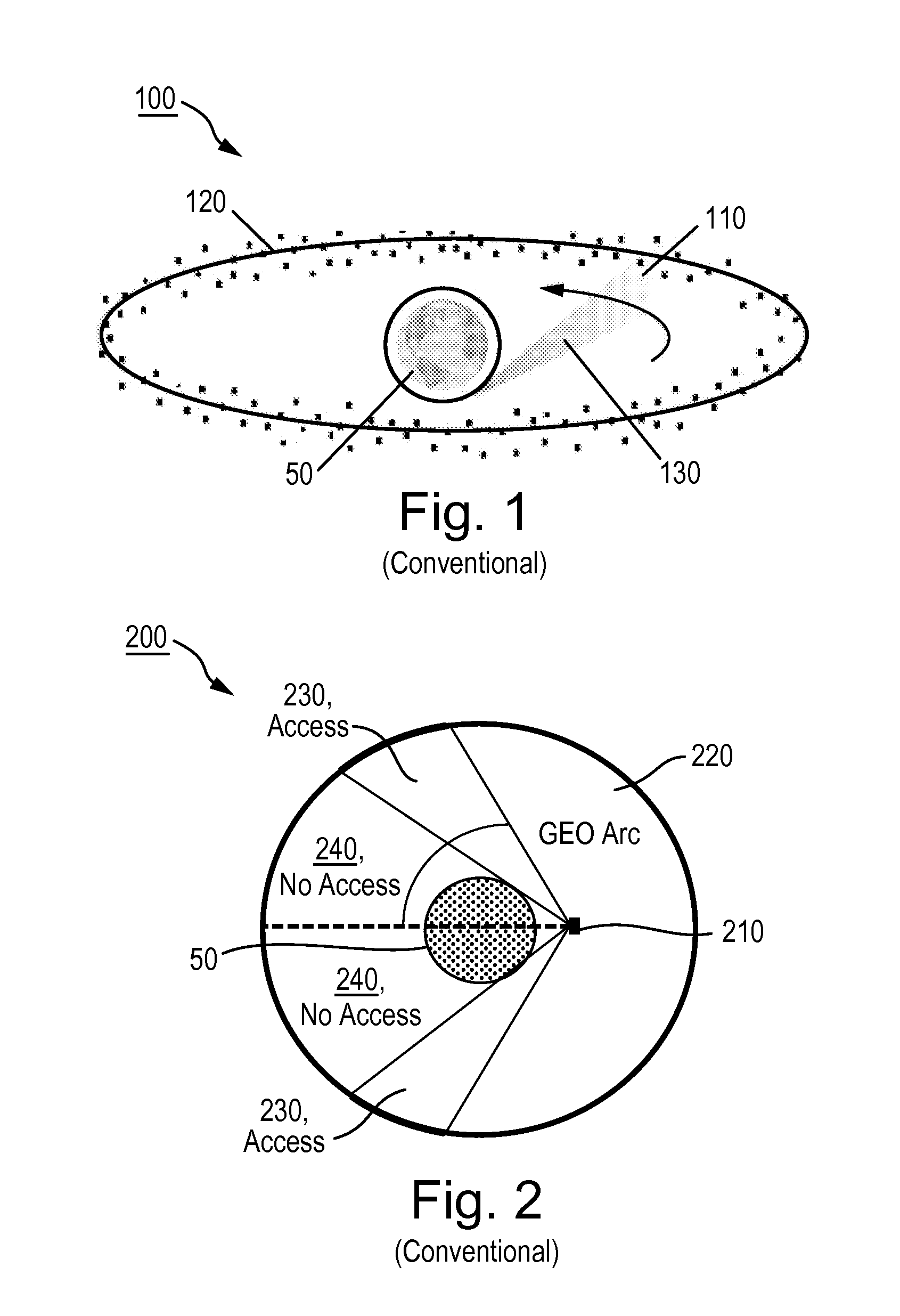
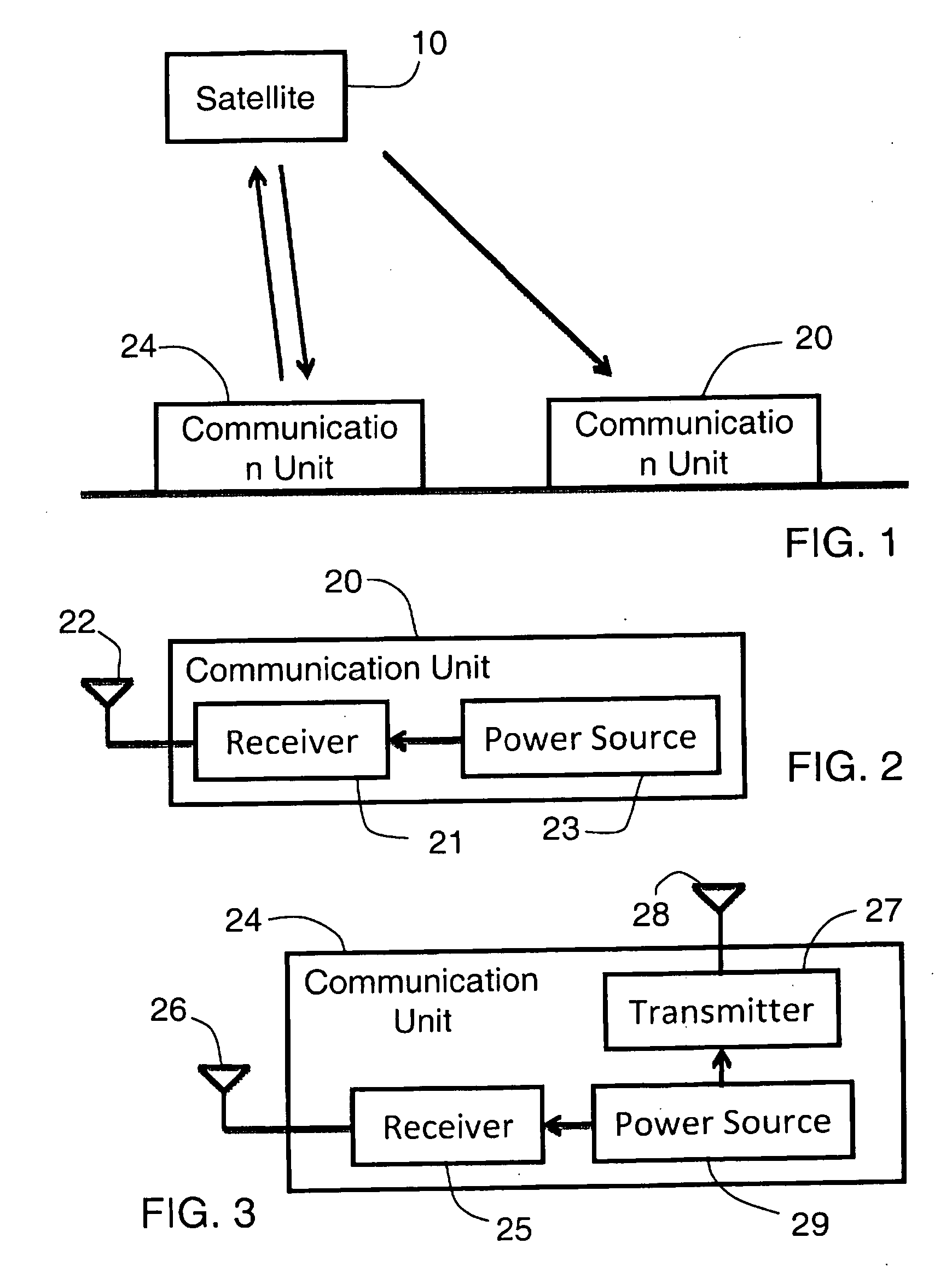
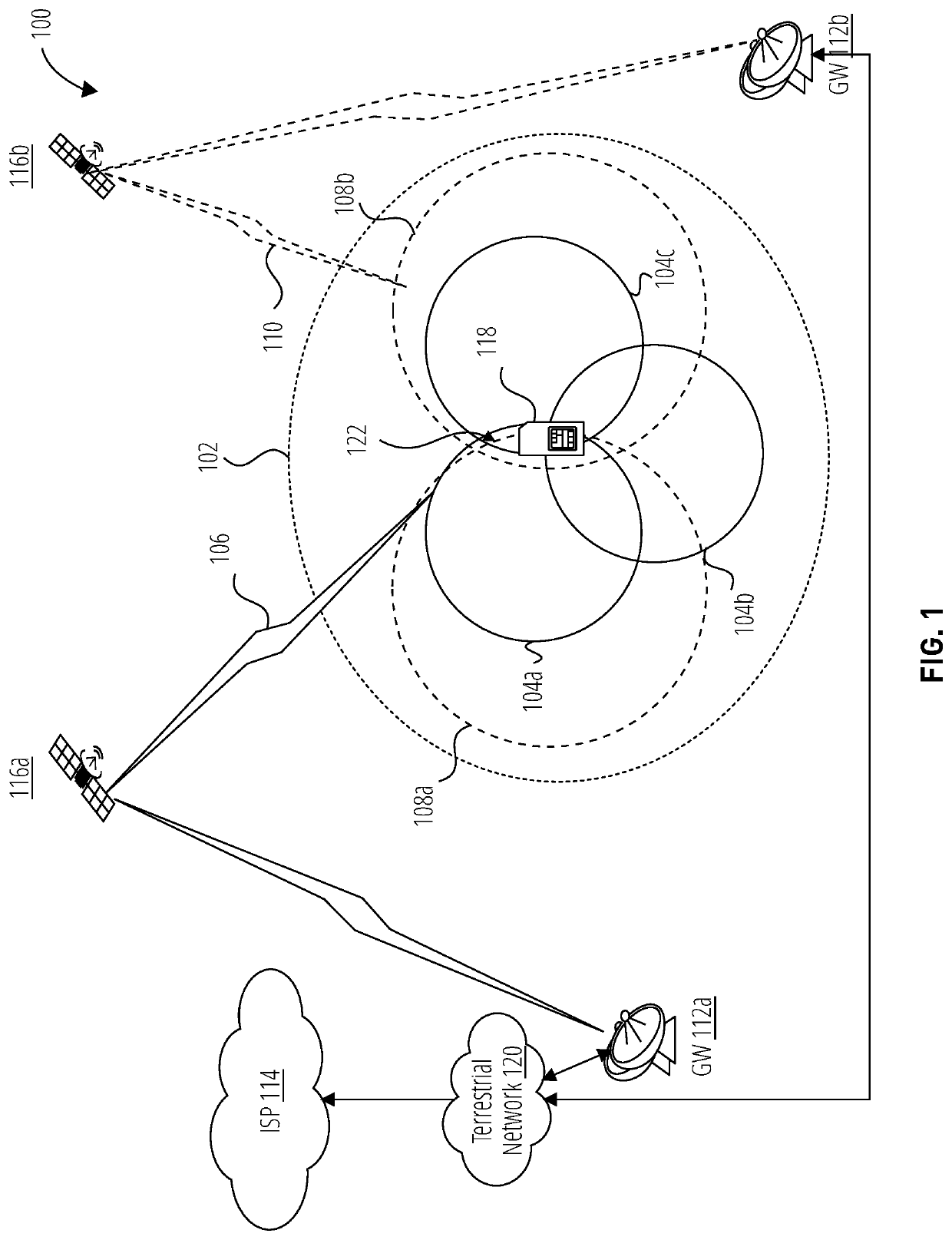
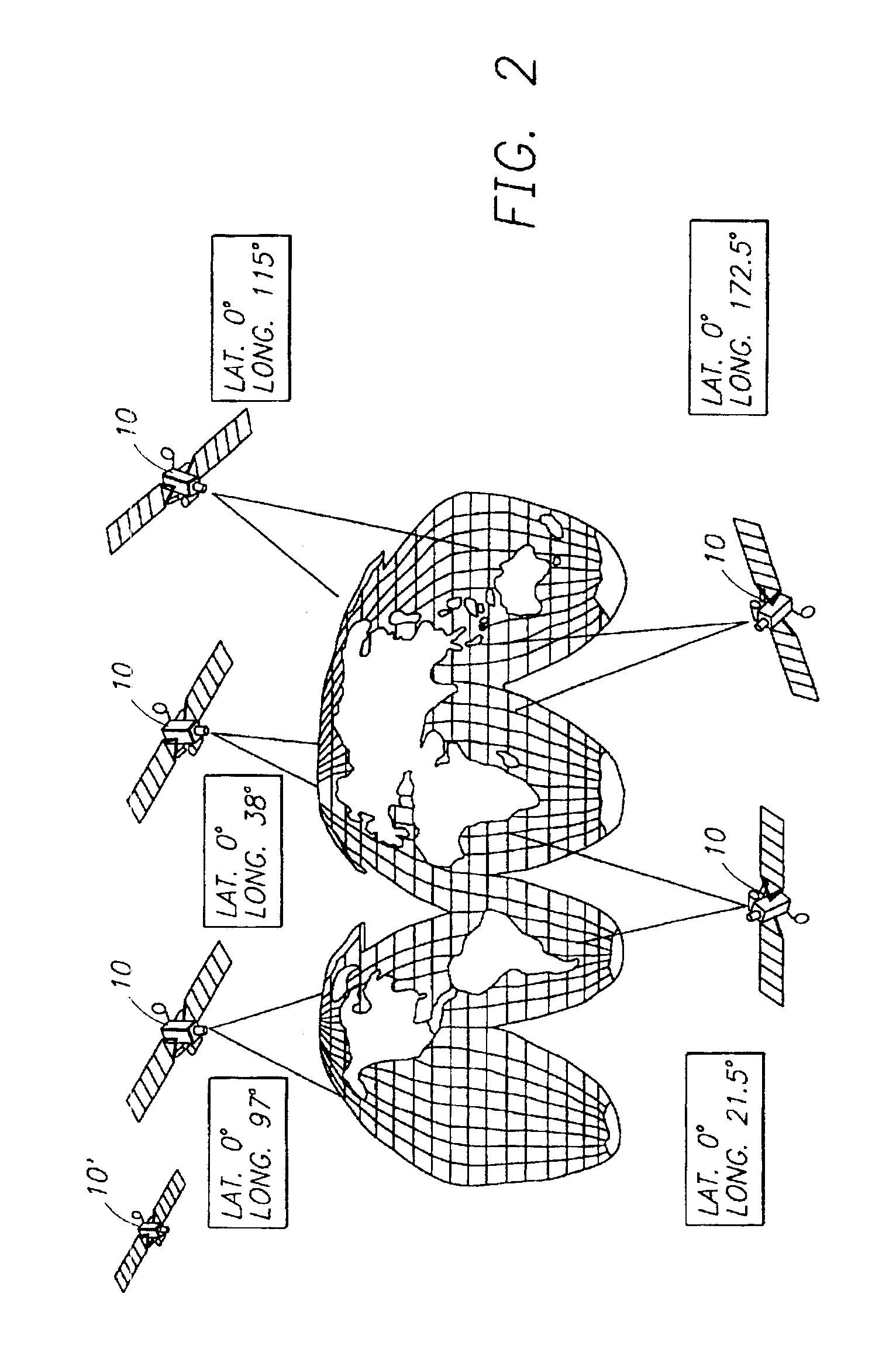
Space based local area network (SBLAN)
A spaced based local area network system for providing dynamically allocated downlink services for spacecraft in Geosynchronous Earth Orbit. The system includes at least two client satellites which host an inter-satellite communications payload; a hub satellite which hosts an inter-satellite communications payload, a downlink communications payload, and an aggregator payload; and a ground station which transmits data to and receives data from the hub satellite. The hub satellite, using the aggregator payload, aggregates at least two data flows received from the at least two client satellites over an inter-satellite link, by the inter-satellite communications payload, into a data stream that is downlinked to the ground station, using the downlink communications payload, over a space-to-ground link.
Owner:INTELSAT GLOBAL SERVICE
Optimal space situational awareness system
A satellite system for observing space objects includes two or more satellites positioned in an Earth orbit and configured to observe objects in various orbits including those viewed (i) against the Earth's background; (ii) against a sunlit Earth background; and (iii) against a space background. An electromagnetic sensor may be provided on at least one of the satellites that is responsive to electromagnetic radiation having a wavelength that discriminates against substantial reflection of electromagnetic radiation from the Earth's atmosphere to observe the space object. A method of observing a space object using a satellite system is also disclosed.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Virtual Polar Satellite Ground Station for Low Orbit Earth Observation Satellites Based on a Geostationary Satellite Pointing an Antenna Over an Earth Pole
ActiveUS20120184208A1Attractive solutionShort response timeRadio transmissionEarth observationGeosynchronous satellite
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
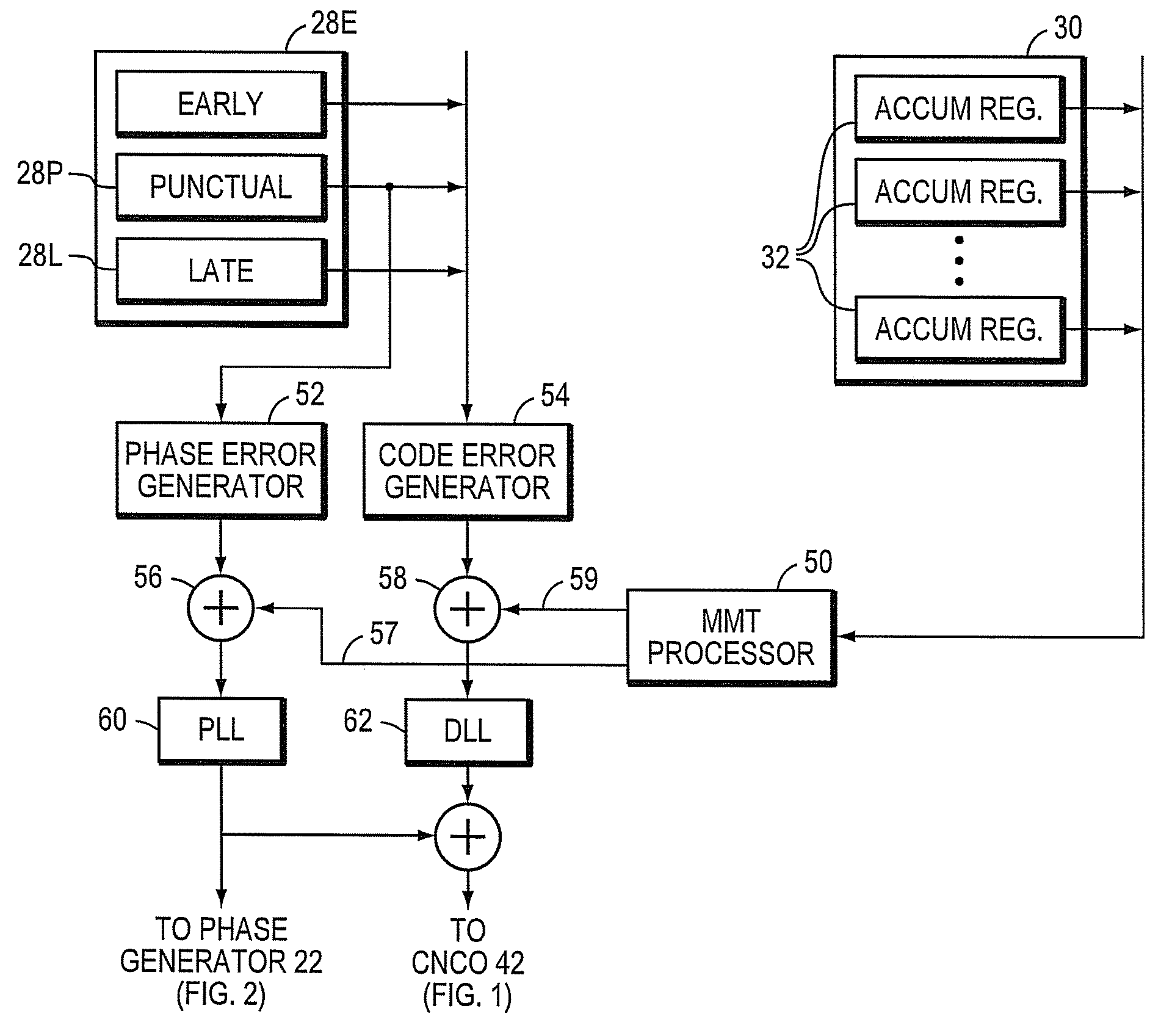
Apparatus for and method of correlating to rising chip edges
ActiveUS7668228B2Suppress noiseAccurate measurementSatellite radio beaconingTransmissionPulse heightDirect path
A receiver for position-determining ranging signals transmitted by earth-orbiting satellites uses a set of accumulators, each of which accumulates signal samples corresponding with a position along the rising edges of incoming PRN pulses. An MMT processor calculates the rising edges of the direct path component of the received signal, selects the accumulator whose content correspond to a reference value related to the pulse height of the direct path component and compares the timing of the samples in that accumulator with the timing of the reference value on a reference pulse.
Owner:NOVATEL INC
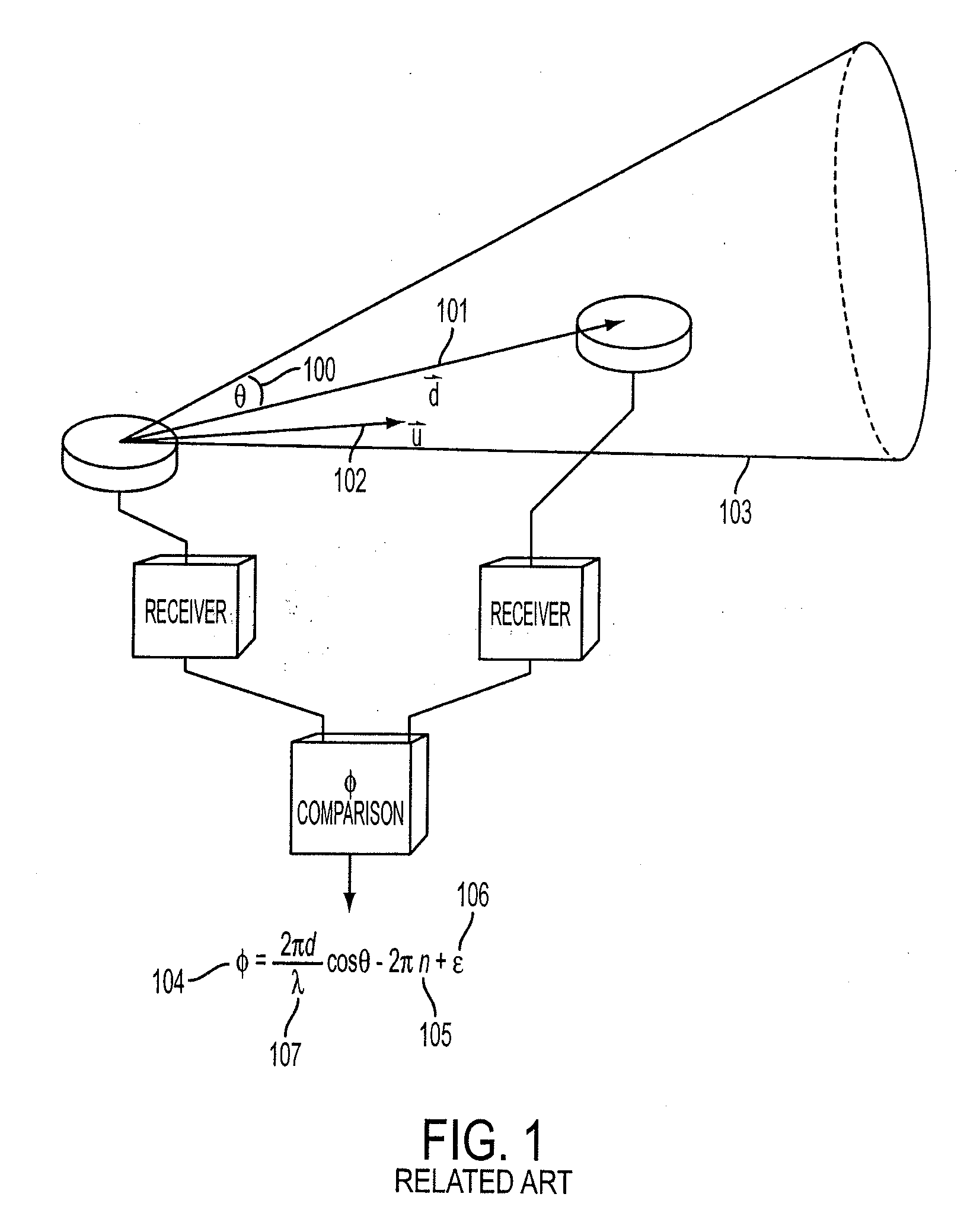
Method for single satellite geolocation of emitters using an ambiguous interferometer array
A method of locating a terrestrial emitter of electromagnetic radiation in the midst of a plurality of emitters in a satellite in orbit about the earth which utilizes a location estimation and location probability determination process with respect to each possible emitter site and its corresponding error region and then using both feedback and feed forward interaction between location and phase ambiguity resolution processes to generate resolved phase from emitter location, update emitter location or some or all of the emitters, and subsequently utilizing the probabilities thus determined to produce a single estimate of the desired emitter's location.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
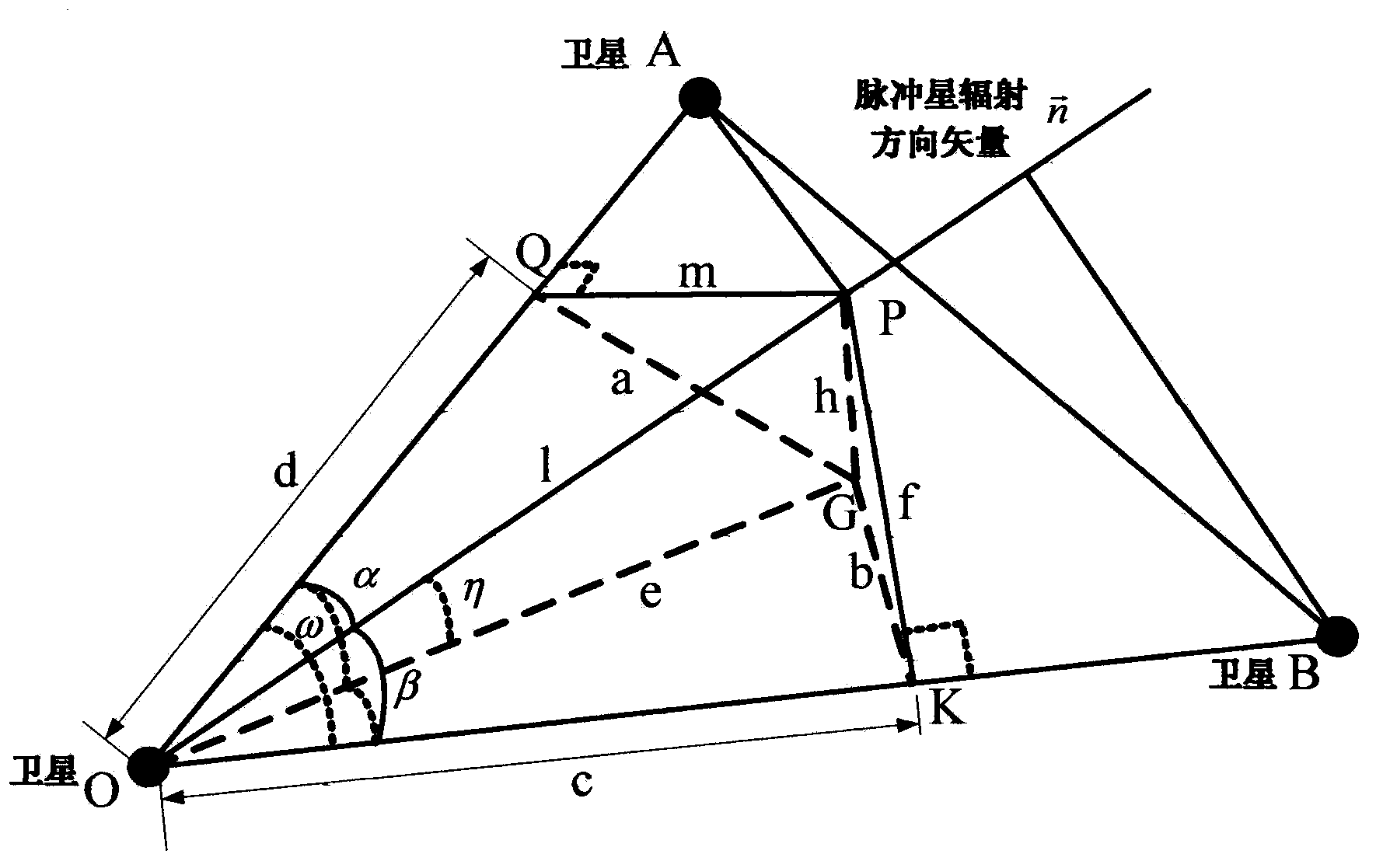
Constellation orientated simulating system and method based on X-ray pulsar
The invention discloses a constellation orientated simulating system and method based on an X-ray pulsar. The constellation orientated simulating method is characterized by comprising the steps of measuring a relative distance between stars by using an equation of light spread by an inter-star link or X-ray pulsar signal between satellites, obtaining an included angle between satellite base lines in a constellation, meanwhile, extracting a pulsar radiation direction vector by a satellite borne X-ray detector and a collimator which are matched, calculating an included angle between the vector and the satellite base lines, further calculating an included angle between the vector and the plane of the constellation, measuring integral rotation and drift of earth orbiting satellites or constellation and correcting. The constellation orientated simulating system based on the X-ray pulsar comprises a signal simulating unit, a time maintaining unit, a modulation unit, a controllable light time delay unit, an optical sending unit, an optical receiving unit, a photon detecting unit and an oriented simulating unit. The constellation orientated simulating system is capable of performing analogue simulation on realization of signal generation, transmission, acquisition, processing and oriented algorithm in the process of orienting the X-ray pulsar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
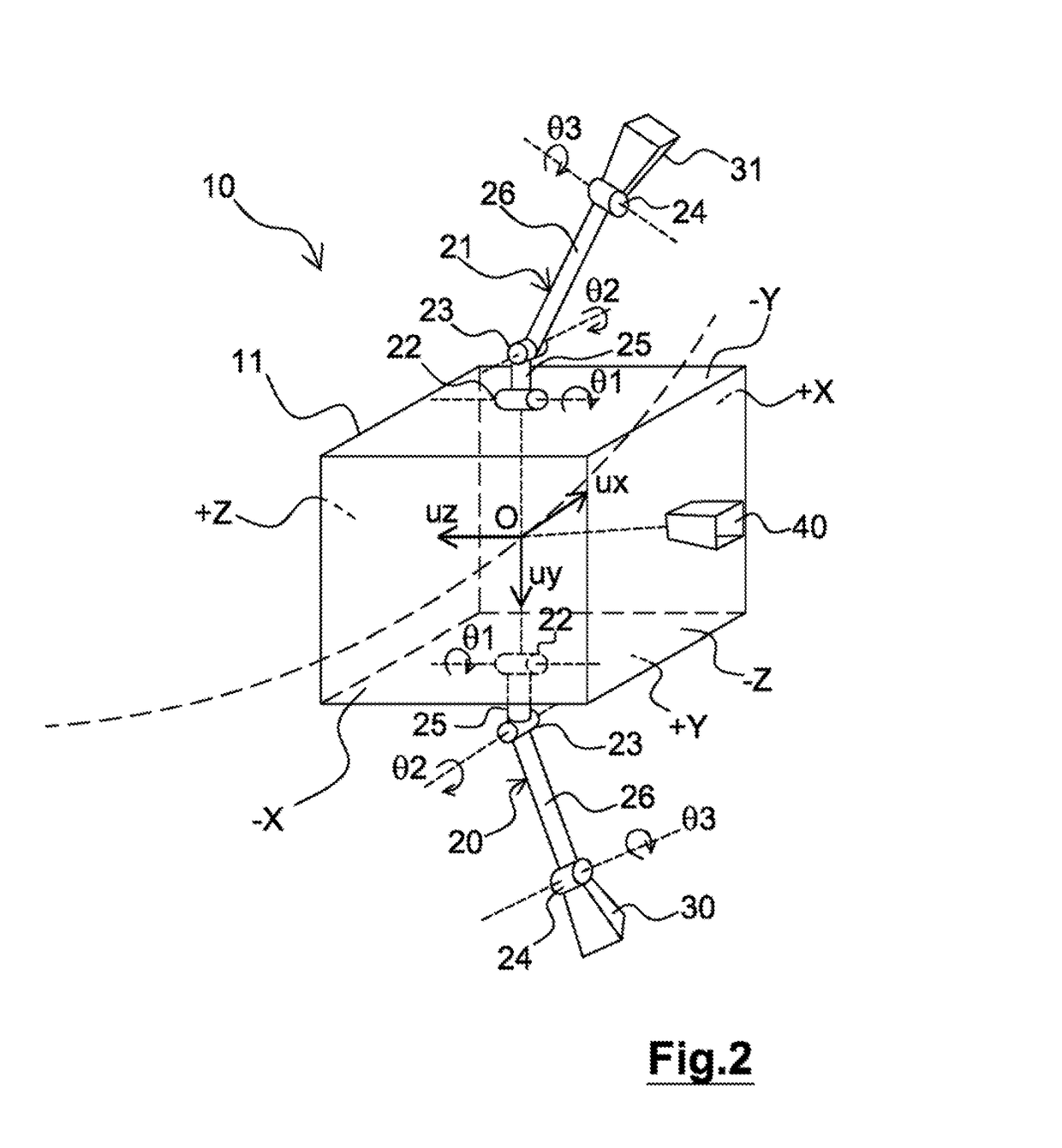
Method for controlling the orbit of a satellite in earth orbit, satellite and system for controlling the orbit of such a satellite
ActiveUS20170129627A1Reduce in quantityCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCosmonautic power supply systemsEarth's orbitInertia
A method for controlling the orbit of a satellite in earth orbit. The orbit of the satellite is controlled by commanding, according to a maneuver plan, a propulsion system having at least one thruster and a transporter to move the propulsion system. The maneuver plan includes at least two orbit-control maneuvers. The thrust powers of the propulsion system during the two orbit control maneuvers have respective thrust directions that are not parallel in an inertial frame of reference. Each thrust power is determined to simultaneously control the inclination and the position of the orbit of the satellite as well as to form a momentum that is suitable for unloading a device for storing angular momentum of the satellite in a plane orthogonal to the direction of thrust of the thrust power.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Phased multi-rate self-adaptive measurement and control system of mars exploration deep space spacecraft
ActiveCN102717902AHigh sensitivityCosmonautic vehicle trackingRadio transmissionHigher PowerExploration of Mars
The invention provides a phased multi-rate self-adaptive measurement and control system of a mars exploration deep space spacecraft, which is characterized by comprising an X-frequency range deep space responder, a high stable frequency source, an X-frequency range solid state power amplifier, an X-frequency range high-power traveling wave tube, an output multiplexer, an input low noise amplification receiving unit, a wide-beam low-gain receiving antenna, a wide-beam low-gain transmitting antenna, an intermediate-gain transmitting antenna, a two-dimensional driven high-gain measurement and control antenna and a waveguide switch. According to the invention, the problems of communication with the ground and measurement and control of the deep space explosion spacecraft are solved in the whole process that the deep space explosion spacecraft is launched from the earth, flies from the earth to the mars cruising segment and flies around the mars. The phased multi-rate self-adaptive measurement and control system has an excellent effect for the mars exploration deep space spacecraft to complete the measurement communication control from the earth orbit flight to the mars orbit flight. The phased multi-rate self-adaptive measurement and control system can solve the key difficult points of measurement and control of the mars deep space spacecraft and has a certain effect on the aspect of improving the reliability of the deep space spacecraft.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
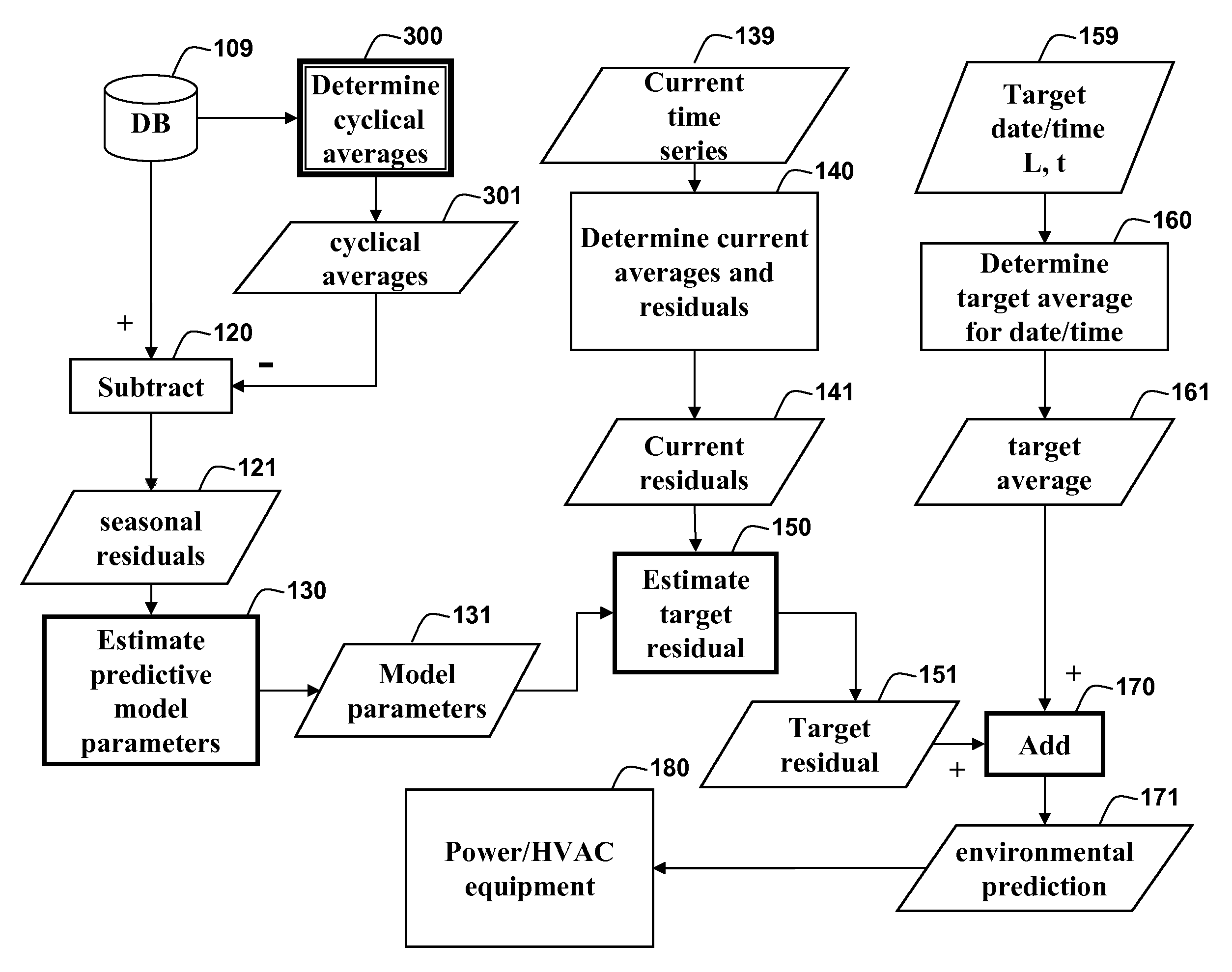
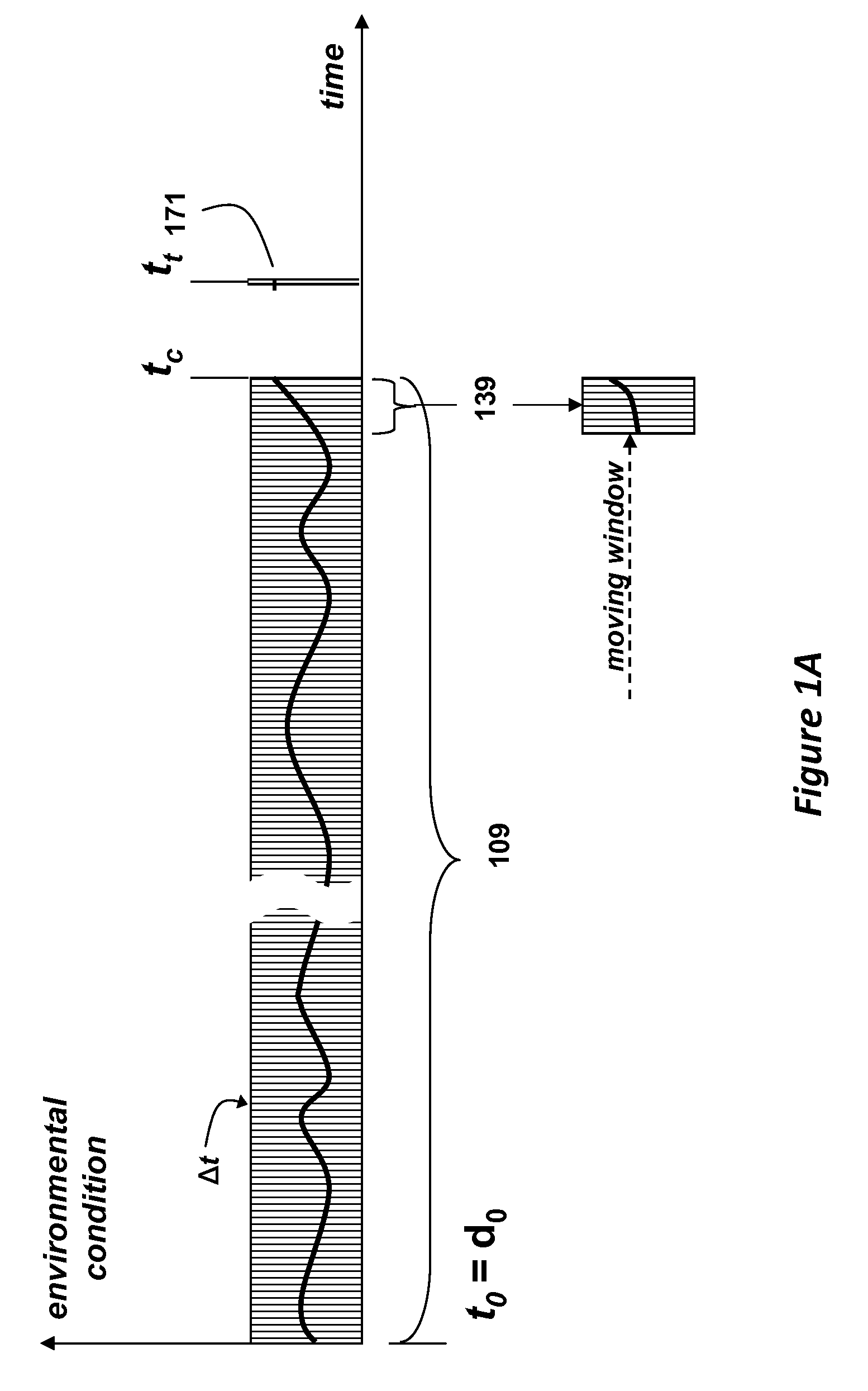
Method for Predicting Future Environmental Conditions
ActiveUS20110016070A1Improve forecast accuracySampled-variable control systemsComputer controlAtmospheric sciencesOrbit
An average environmental condition for a specified target date and time is determined by indexing a database of time series data to retrieve the environment condition for each day and time where an orbital position of the earth with respect to the sun is nearest to the orbital position of the earth on the target date and time. The average environmental condition is then determined from the retrieved environmental conditions.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
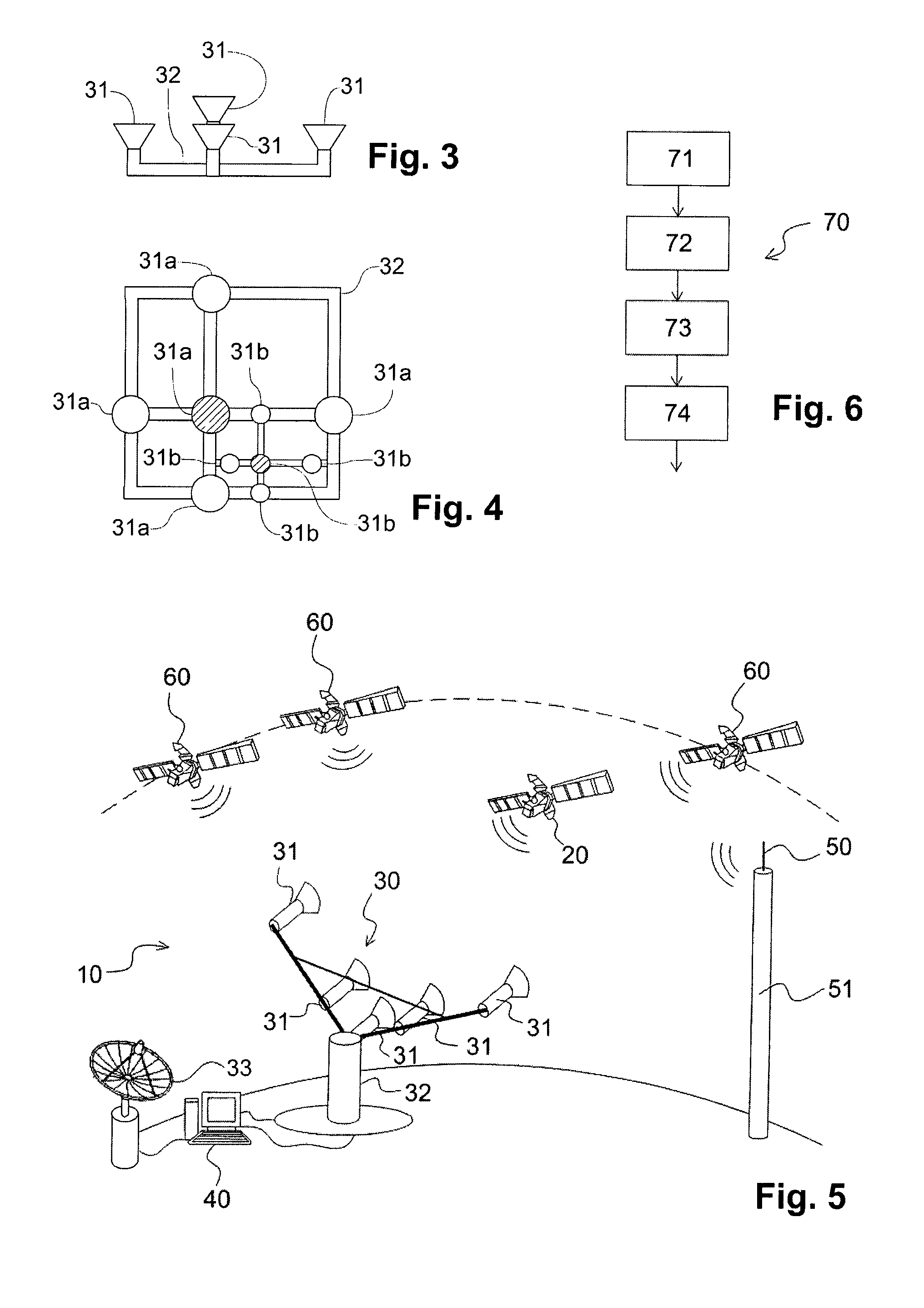
Method and system for monitoring a phase for transferring a satellite from an intial orbit to a mission orbit
ActiveUS20160131737A1Low costWithout risk of losingLaunch systemsCosmonautic partsTarget signalMonitoring methods
Disclosed is a method (70) for monitoring a phase for transferring a satellite (20) from one earth orbit, called “initial orbit”, to another earth orbit, called “mission orbit”, in particular a transfer using electric propulsion unit. The monitoring method includes a step for estimating the direction of the satellite during the transfer phase by way of an earth array antenna (30) including a plurality of elementary antennas (31), each elementary antenna having a primary radiation lobe with a width greater than or equal to 20°, the elementary antennas (31) being oriented such that their respective fields of vision overlap, the direction of the satellite being estimated based on at least one useful phase difference measurement between signals corresponding to a target signal, transmitted by the satellite and received on a pair of elementary antennas (31).
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Solar power collection with near infrared wideband reflector coating
InactiveUS20050103374A1Lower operating temperatureImprove conversion efficiencyPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationSolar angleLow earth orbit
A near infrared (NIR) wideband reflector coating designed to start reflecting solar energy wavelengths from at least 1.2 microns in a typical geosynchronous earth orbit or medium earth orbit satellite and from at least 1.3 microns in a typical low earth orbit satellite. Also, the (NIR) wideband reflector coating reflects solar energy wavelengths below 0.35 microns in all three applications. This invention works on triple junction (TJ) solar cells. The performance of at least 1.2-microns is on solar panels with near-normal incident solar angle, typical of Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO) and Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites. The performance of at least 1.3-microns is on solar panels with wide range of incident solar angles, a design requirement for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
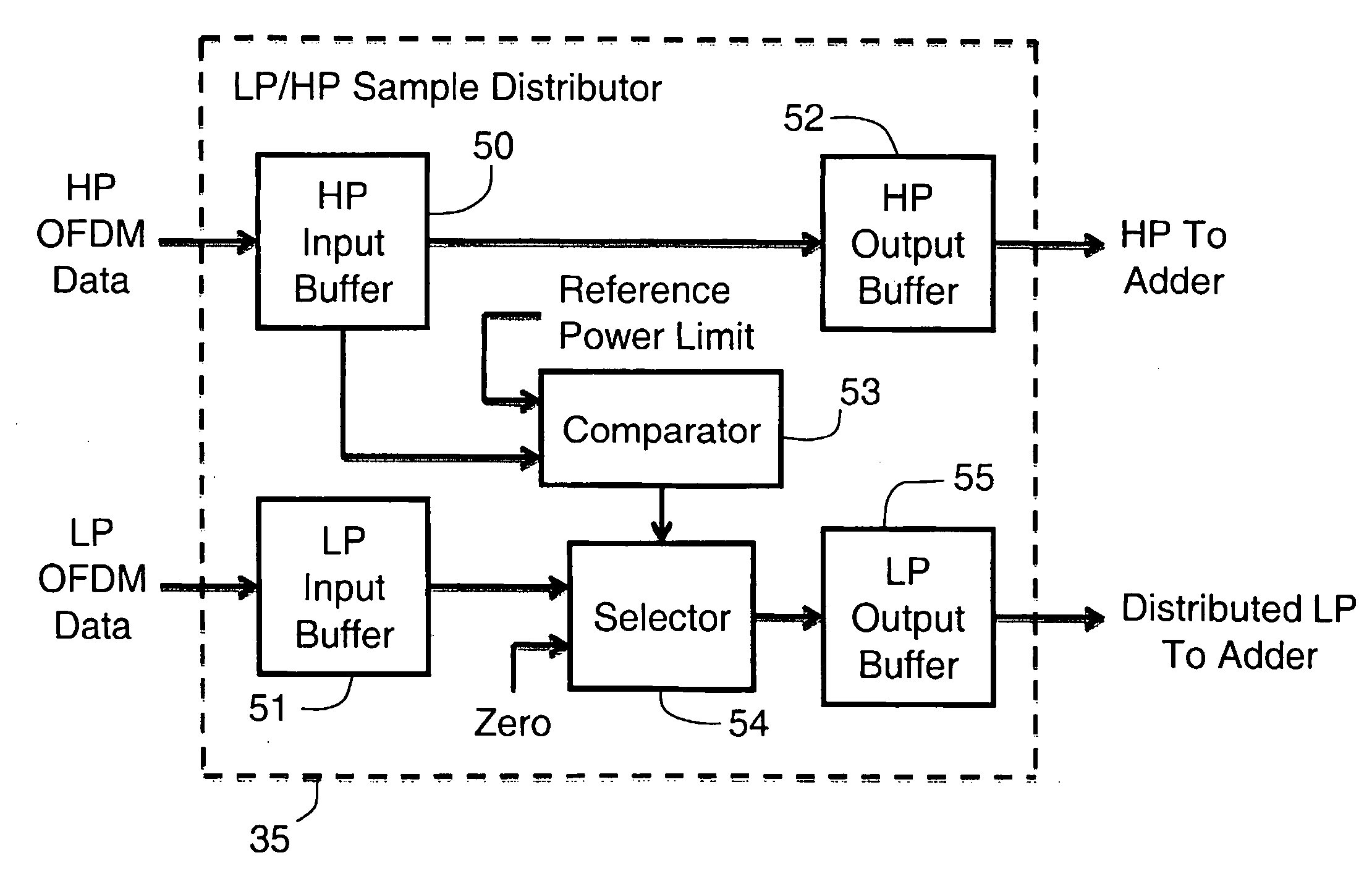
Hierarchically modulated OFDM communication from a satellite-based transmitter with reduced secondary data loss from clipping
ActiveUS20100195482A1Improve the immunityReduce clippingError preventionModulated-carrier systemsDigital dataData loss
High priority data and low priority digital data are transmitted as primary and secondary data in hierarchically modulated, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) from an earth-orbiting satellite. To enable the transmitter amplifier to be operated with less back-off from saturation without clipping, the low priority OFDM symbols have fewer samples than the high priority OFDM symbols, and the high priority samples on which the low priority samples are superimposed are selected according to a first deterministic rule using sample power comparisons of the high priority samples to concentrate the low priority samples on those high priority samples having lower (optimally, the lowest) sample power. The low priority samples are distributed on the selected high priority samples according to a second deterministic rule relating the original low priority sample order to the original high priority sample order.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
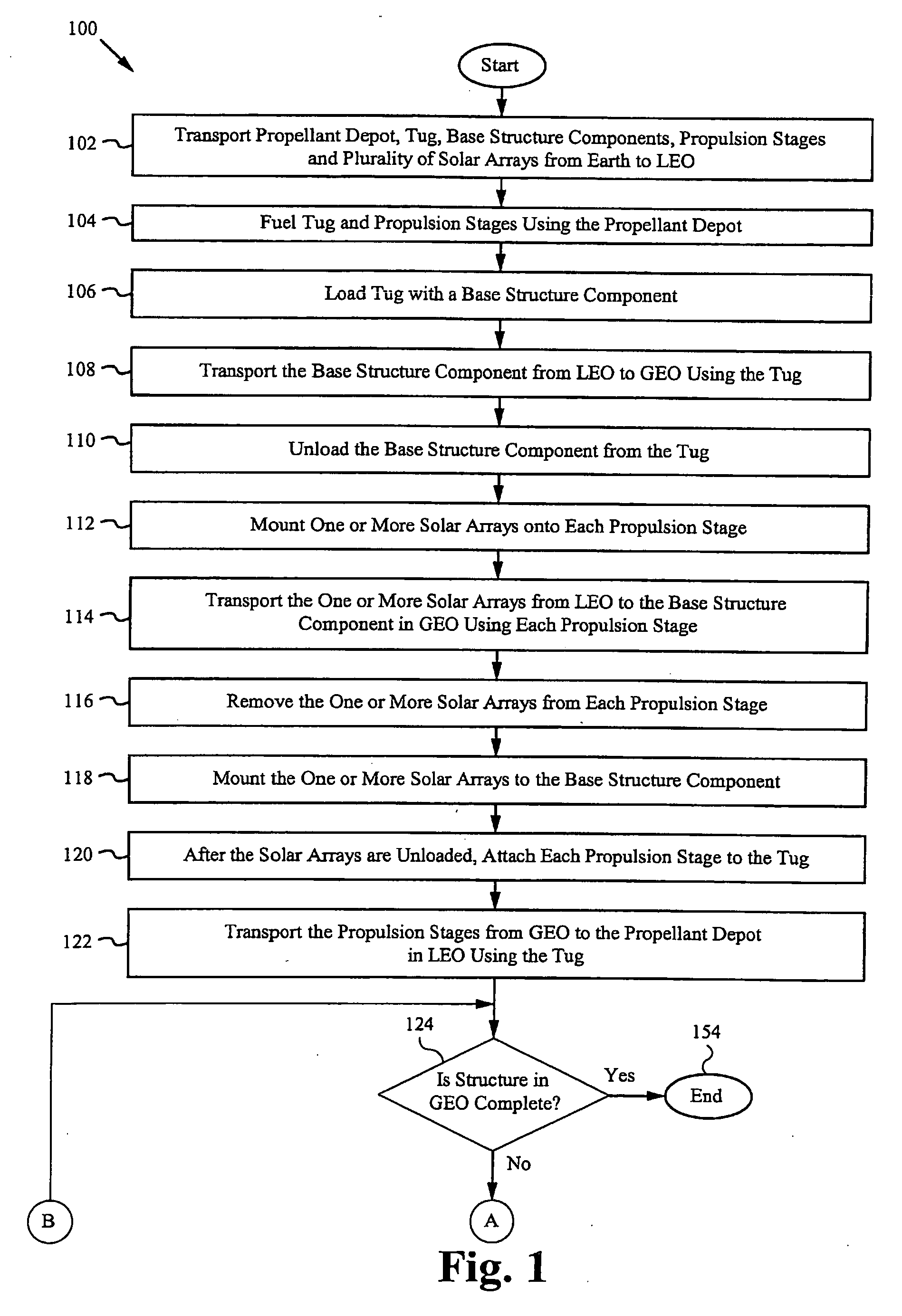
Architecture and method of constructing a Geosynchronous Earth Orbit platform using solar electric propulsion
InactiveUS20090101757A1Launch systemsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusPropellant depotHigh Earth orbit
A space construction method and system transports construction materials, a propellant depot, solar electric propulsion (SEP) vehicles, and robotic equipment from Earth into a lower-Earth orbit. The SEP vehicles are used to transport payload between the lower-Earth orbit and a construction area in higher-Earth orbit, such as GEO. The robotic equipment transfers materials between various vehicles and assembles the transported construction materials in the higher-Earth orbit. A tug SEP vehicle transports heavier construction materials from the propellant depot in lower-Earth orbit to the construction area in higher-Earth orbit. A propulsion stage SEP vehicles transport lighter construction materials from the propellant depot to the construction area. The tug is also transports the fuel-depleted propulsion stages from higher-Earth orbit back to the propellant depot in lower-Earth orbit, where both the tug and the propellant stages are refueled and reloaded for another trip to the construction area in higher-Earth orbit. As additional supplies they are transported from Earth to the propellant depot in lower-Earth orbit.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
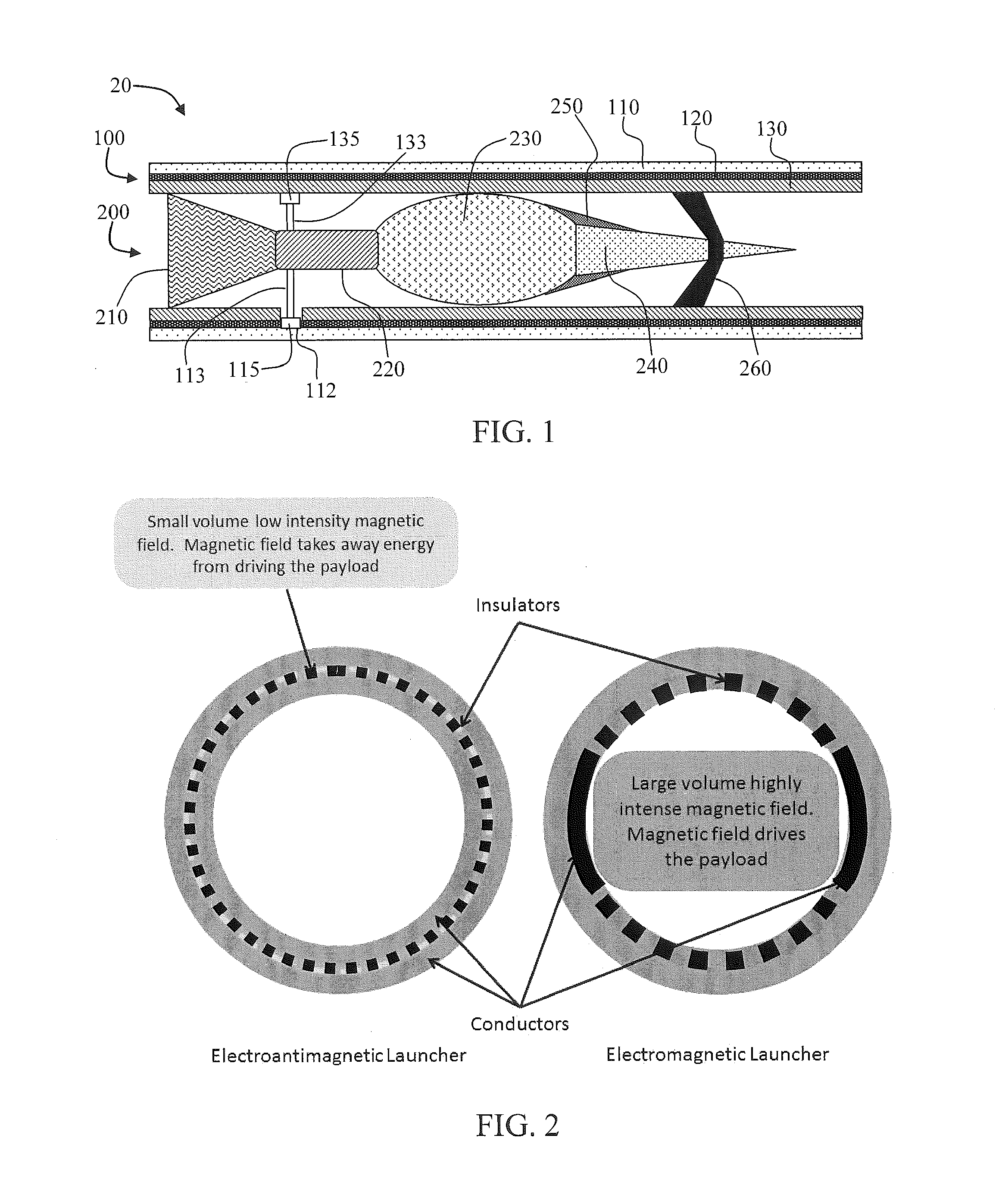
Launch vehicle and system and method for economically efficient launch thereof
ActiveUS20140306064A1Long orbital lifetimeLow costAmmunition projectilesElectromagnetic launchersElectrical connectionInductor
The present disclosure relates to a launch system, a launch vehicle for use with the launch system, and methods of launching a payload utilizing the launch vehicle and / or the launch system. The disclosure can provide for delivery of the payload at a terrestrial location, an Earth orbital location, or an extraorbital location. The launch vehicle can comprise a payload, a propellant tank, an electrical heater wherein propellant, such as a light gas (e.g., hydrogen) is electrically heated to significantly high temperatures, an exhaust nozzle from which the heated propellant expands to provide an exhaust velocity of, for example, 7-16 km / sec, and sliding electrical contacts in electrical connection with the electrical heater. The launch vehicle can be utilized with the launch system, which can further comprise a launch tube formed of concentric electrically conductive tubes, as well as an electrical energy source, such as a battery bank and associated inductor.
Owner:8 RIVERS CAPTTAL LLC
Method for controlling the orbit of a satellite in earth orbit, satellite and system for controlling the orbit of such a satellite
ActiveCN106660641ACosmonautic vehiclesRocket engine plantsInertial frame of referenceOrbital control
The present invention relates to a method (50) for controlling the orbit of a satellite (10) in earth orbit, the orbit of the satellite (10) being controlled by commanding, according to a plane of operation, the propulsion means (30, 31), including at least one thruster, and means for moving (20, 21) said propulsion means. According to the invention, said plane of operation includes at least two orbit-control operations, thrust powers of the propulsion means (30, 31) during said two orbit-control operations having respective thrust directions that are not parallel in an inertial frame of reference, each one of said thrust powers being determined so as to simultaneously control the inclination and the position of the orbit of the satellite as well as to form a momentum that is suitable for unloading a device for storing angular momentum of said satellite in a plane orthogonal to the direction of thrust of said thrust power.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE SAS
Method and system for controlling the orbit of a satellite in earth orbit
ActiveUS10232959B2Reduce in quantityCosmonautic vehiclesRocket engine plantsMomentumHigh Earth orbit
A method for controlling the orbit of a satellite in earth orbit. The orbit of the satellite is controlled by commanding, according to a maneuver plan, a propulsion system having at least one thruster and a transporter to move the propulsion system. The maneuver plan includes at least two orbit-control maneuvers. The thrust powers of the propulsion system during the two orbit control maneuvers have respective thrust directions that are not parallel in an inertial frame of reference. Each thrust power is determined to simultaneously control the inclination and the position of the orbit of the satellite as well as to form a momentum that is suitable for unloading a device for storing angular momentum of the satellite in a plane orthogonal to the direction of thrust of the thrust power.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Pulsed detonation engines for reaction control systems
InactiveUS7278611B2Improve performanceEffective controlCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusControl systemMissile defense
Owner:LEIDOS
Method and apparatus for utilizing a lifeboat for a space station in earth orbit to serve as a lunar spacecraft
InactiveUS7392964B1Low costVast supplyLaunch systemsCosmonautic thermal protectionFlight vehicleEngineering
Methods and an apparatus for a lifeboat of a space station in orbit to be docked with and used in combination with a separately launched logistics module having an upper stage propulsion capability as a space craft for human pilots and passengers to be flown to orbits and trajectories in deep space beyond low Earth orbit including the Moon, at the lowest practical cost.
Owner:ANDERMAN DAVID
Method of traveling to earth's orbit using lighter than air vehicles
InactiveUS20070029448A1Improve the forceImprove securityAircraft componentsConvertible aircraftsFlight vehicleEngineering
A method for transporting people and cargo from the surface of the Earth to orbit around the Earth is disclosed. The present invention uses a series of lighter-than-air vehicles to allow for a far safer and less strenuous trip to orbit than using current rocket-based technology. The high altitude atmospheric airship is flown from the ground to the upper atmosphere, where it docks with the buoyant transfer station, and from there, the people and cargo transfer to an orbital airship for the remainder of the trip to orbit. The orbital airship returns to the station for another transfer back to the atmospheric airship for the return back to the surface of Earth.
Owner:POWELL JOHN MARCHEL
Atomic Oxygen-Resistant, Low Drag Coatings and Materials
ActiveUS20190210325A1Increasing atomic oxygen resistanceReduce resistanceArtificial satellitesChemical vapor deposition coatingOrbitAtomic oxygen
Coatings and materials that are atomic oxygen resistant and have an atomically smooth surface that can reduce drag are disclosed. The coatings and materials can be used on at least a portion of a spacecraft intended to operate in harsh environments, such as stable Earth orbits at about 100 km to about 350 km.
Owner:SKEYEON INC
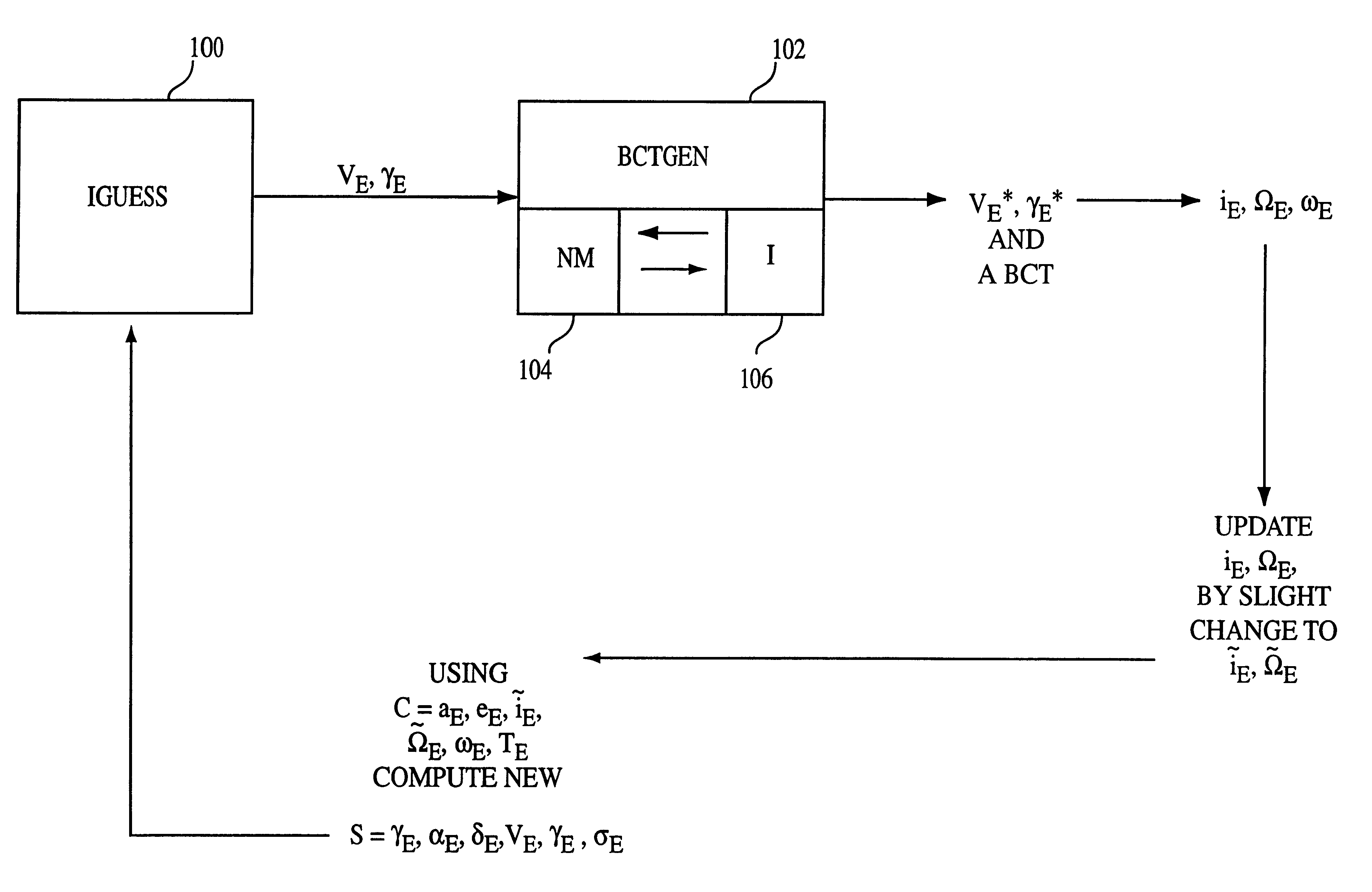
Procedure for generating operational ballistic capture transfer using computer implemented process
InactiveUS6278946B1Low propellant requirementEfficient methodLaunch systemsInstruments for comonautical navigationEngineeringLunar orbit
A method generates an operational ballistic capture transfer for an object emanating substantially at earth or earth orbit to arrive at the moon or moon orbit using a computer implemented process. The method includes the steps of entering parameters including velocity magnitude VE, flight path angle gammaE, and implementing a forward targeting process by varying the velocity magnitude VE, and the flight path angle gammaE for convergence of target variables at the moon. The target variables include radial distance, rM, and inclination iM. The method also includes the step of iterating the forward targeting process until sufficient convergence to obtain the operational ballistic capture transfer from the earth or the earth orbit to the moon or the moon orbit.
Owner:GALAXY DEVMENT
Mobile satellite modem for combined geostationary, medium and low earth orbit satellite operation
ActiveUS11233562B1Readily apparentRadio transmission for post communicationModem deviceSatellite modem
The present teachings include a method and computing apparatus for triggering synchronization of a satellite modem to a carrier frequency of a beam of a satellite, retrieving ephemeris information for the satellite and beam configuration information for the beam, calculating a velocity of the satellite per the ephemeris information, and adjusting the carrier frequency of the satellite modem when communicating via the beam to compensate for a doppler offset induced in the carrier frequency by the velocity. In the method, the satellite has a satellite type selected from a Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) or Low Earth Orbit (LEO) type of satellite, and the satellite type is different than a satellite type of an immediately preceding synchronization.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
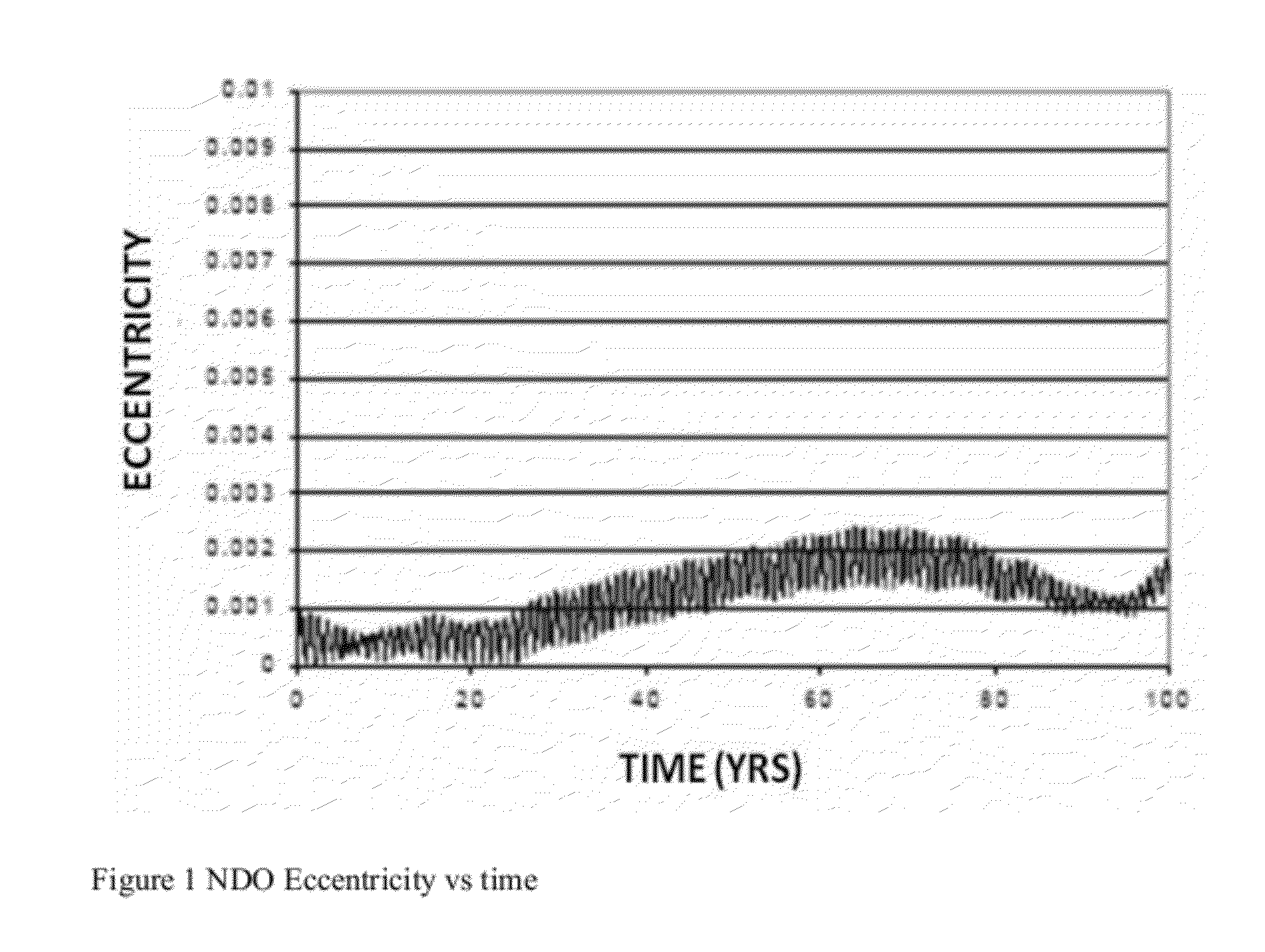
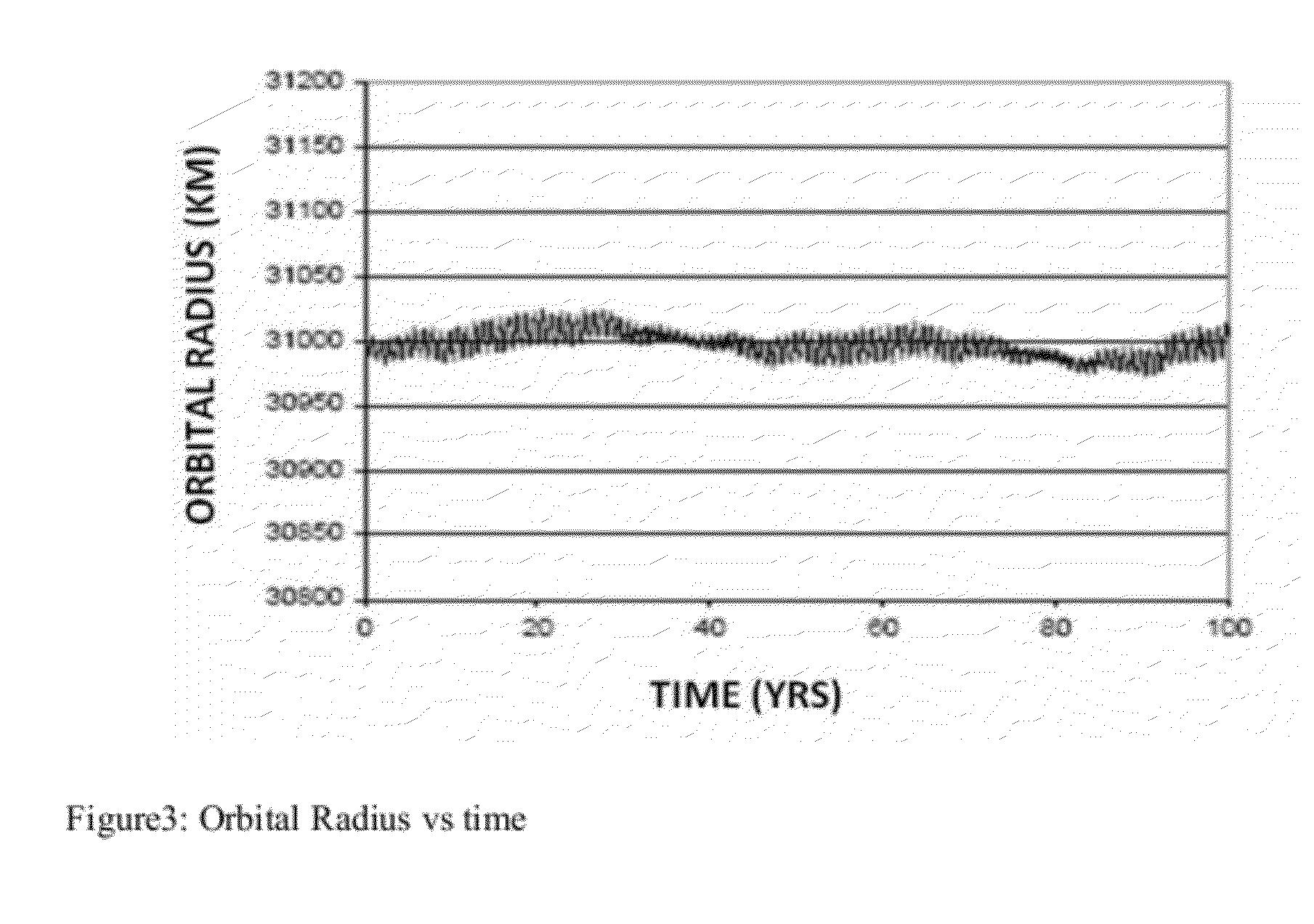
Deorbiting a Spacecraft from a Highly Inclined Elliptical Orbit
Deorbiting of an earth-orbiting satellite is accomplished by executing an orbit transfer maneuver, the orbit transfer maneuver resulting in transference of the satellite from an operational orbit to a disposal orbit, where the disposal orbit is substantially circular and has a nominal radius of approximately, 31,000 kilometers. The operational orbit may be substantially geosynchronous and have at least one of (i) an inclination of greater than 10 degrees and (ii) a nominal eccentricity greater than 0.1. Alternatively, the operational orbit may be a medium earth orbit.
Owner:SPACE SYST LORAL INC
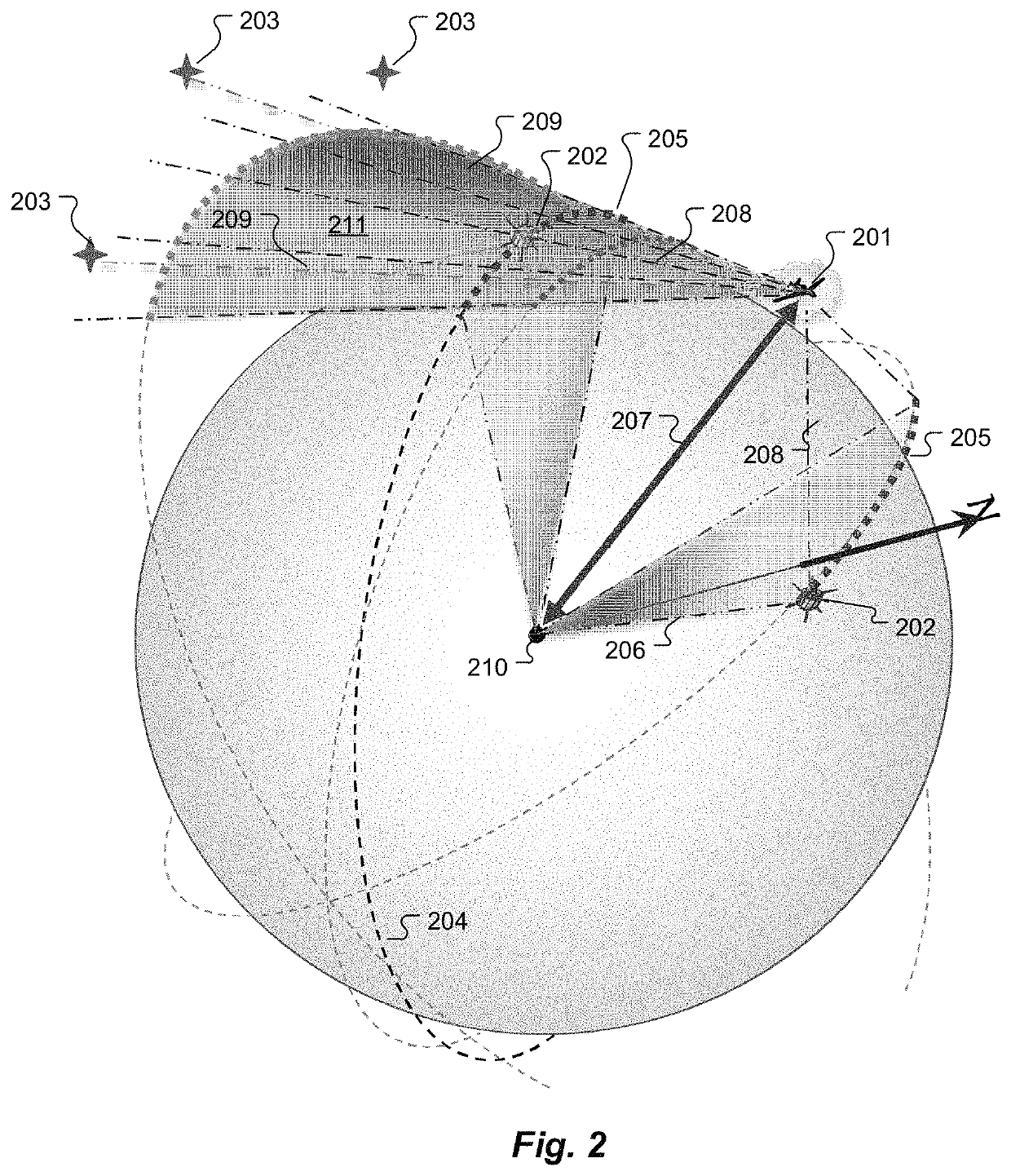
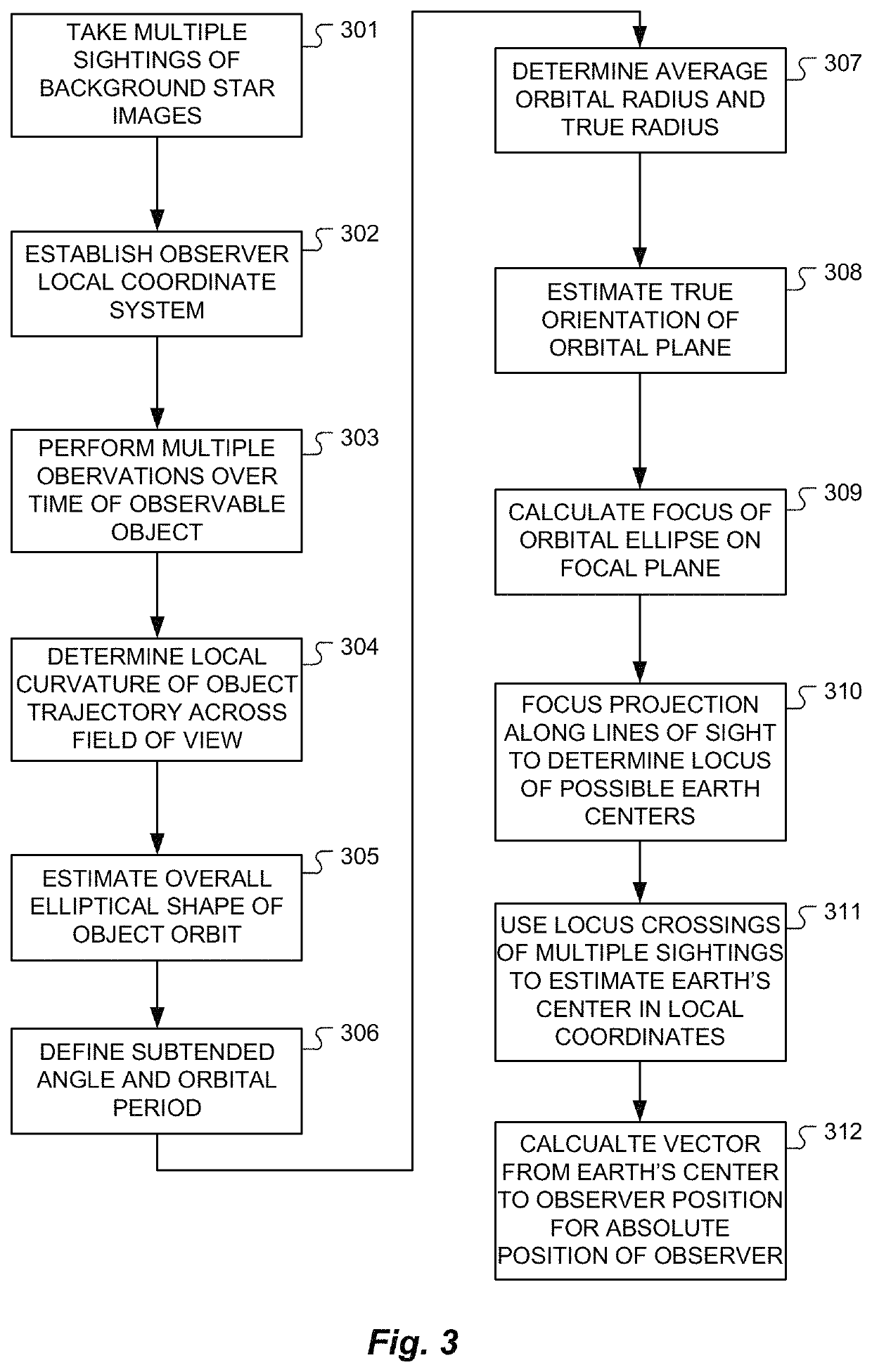
Ephemerides-free celestial navigation
Methods for use in celestial navigation system use multiple star observations from an unknown observer location using an observer camera with an observational field of view along a boresight axis and a focal plane perpendicular to the boresight axis. An observer local ECI coordinate system is determined from the star observations. Then for each of multiple observable objects in orbit around the Earth, multiple optical angular measurements relative to stars are performed over time to estimate its orbital ellipse, and its focus at the center of the Earth. From the multiple focus estimates, a position of the center of the Earth is estimated in the observer local coordinate system without use of object ephemeris data. From the estimated position of the center of the Earth, a radius vector to the observer is determined that represents the estimated observer location in Earth centered Earth fixed coordinates.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
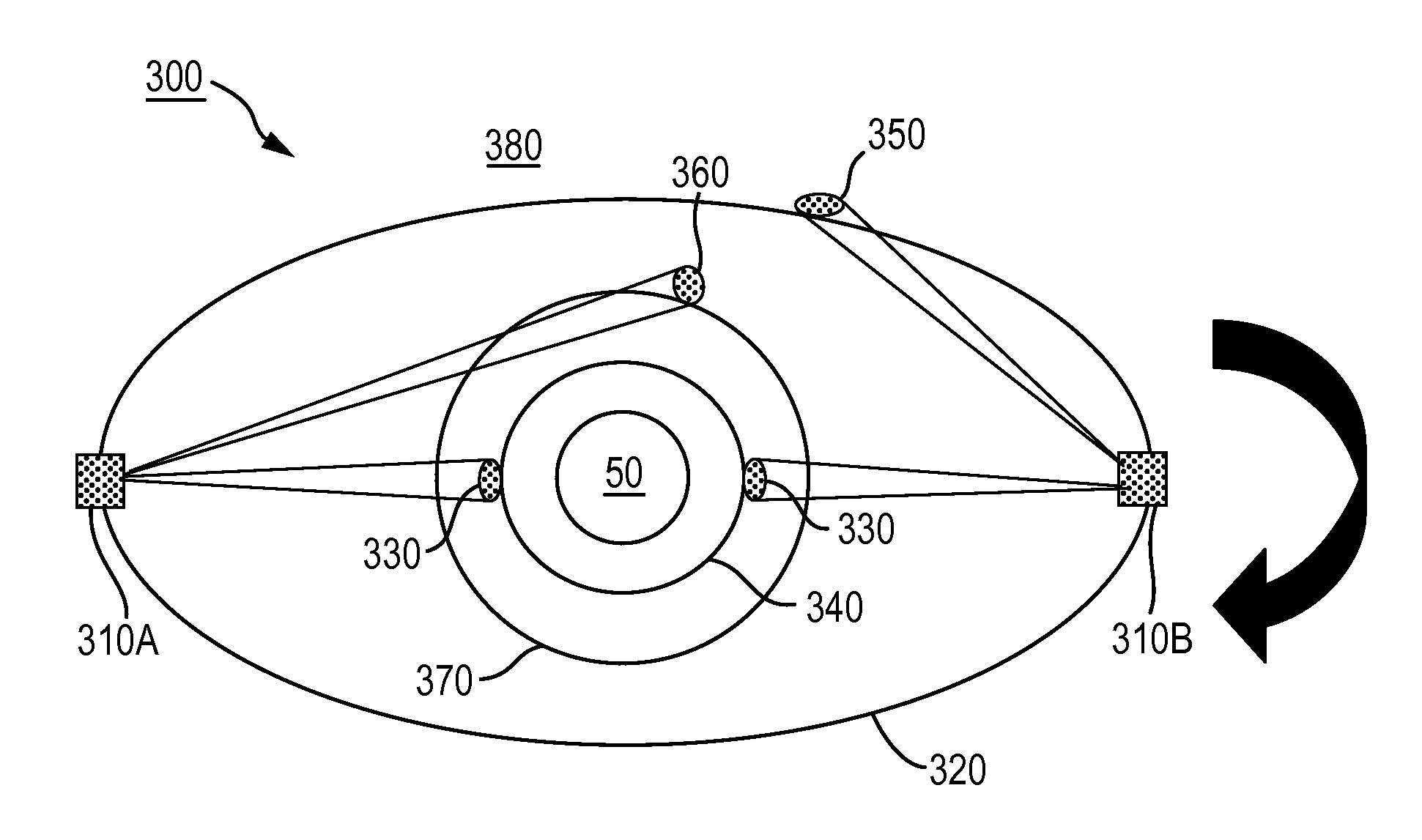
Design method of multifunctional space gravitational wave detector based on TRIZ
InactiveCN103675935AThe principle is simpleEasy to operateGravitational wave measurementIsoetes triquetraDifferentiator
The invention discloses a design method of a multifunctional space gravitational wave detector based on the TRIZ. Seven inventive principles recommended by the TRIZ serve as technological evolution paths, a ground laser interference gravitational wave detector can be evolved into a multifunctional space gravitational wave detector. The multifunctional space gravitational wave detector comprises devices such as spacecrafts. As shown in the figure, the multifunctional space gravitational wave detector is characterized in that the three spacecrafts form an equilateral triangle constellation with the 103-109km side length, the center of the equilateral triangle constellation moves on the earth orbit, an optical table on each spacecraft and an optical table on the adjacent spacecraft can have interference through coherent light beams generated by lasers, if gravitational waves scan the spacecrafts, the strength of light passing through photodiodes of photodetectors changes, a differentiator and a correlator are used for calculating the relation between the strength of the light and the phase position, and the value of the gravitational waves to be measured is obtained. The multifunctional space gravitational wave detector is characterized in that the low and medium frequency gravitational waves are detected, and a double-star system, large-mass black holes and random background gravitational waves are surveyed.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
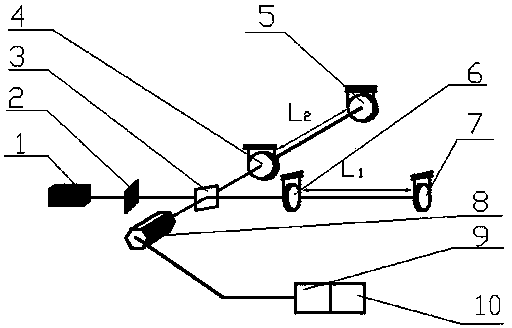
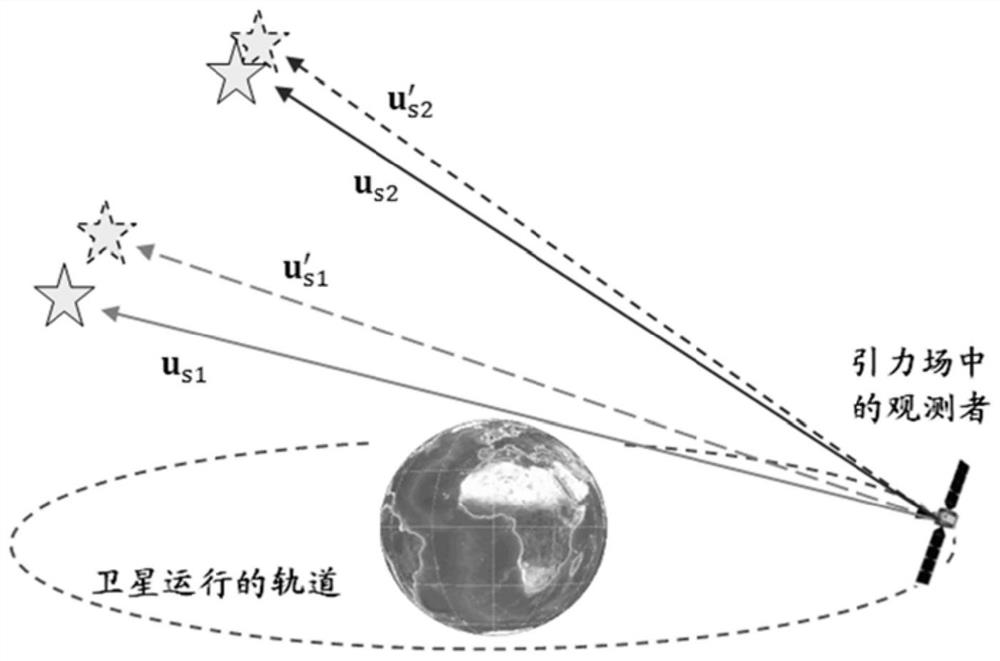
Spacecraft autonomous navigation method based on fixed star sight relativistic effect
PendingCN113091731AMeet the technical requirements of high-precision autonomous navigationNavigation by astronomical meansSatellite radio beaconingFixed starsAngular distance
The invention relates to a spacecraft autonomous navigation method based on a fixed star sight relativistic effect, which is characterized in that a fixed star angular distance is measured by using a space optical interferometer on a spacecraft, and the value of the fixed star angular distance reflects fixed star aberration caused by the movement of the spacecraft and the light gravity deflection effect caused by a celestial body gravitational field. The fixed star aberration reflects the movement speed of the spacecraft perpendicular to the fixed star sight line direction, the light gravity deflection effect reflects the relative position relation between the spacecraft and a gravitational body, and the fixed star aberration and the light gravity deflection effect both comprise information needed by autonomous navigation of the spacecraft. Furthermore, in combination with a spacecraft orbit kinetic equation, a fixed star angular distance observed quantity on a time sequence is processed through a navigation filtering algorithm, and estimated values of a spacecraft position vector and a speed vector are obtained. The method does not depend on ground measurement and control and inter-satellite links, is not prone to electromagnetic interference, can easily achieve high positioning precision through the technical level of a measurement sensor at the present stage, can be used for earth orbit spacecrafts and can also be used for autonomous navigation of deep space probes.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
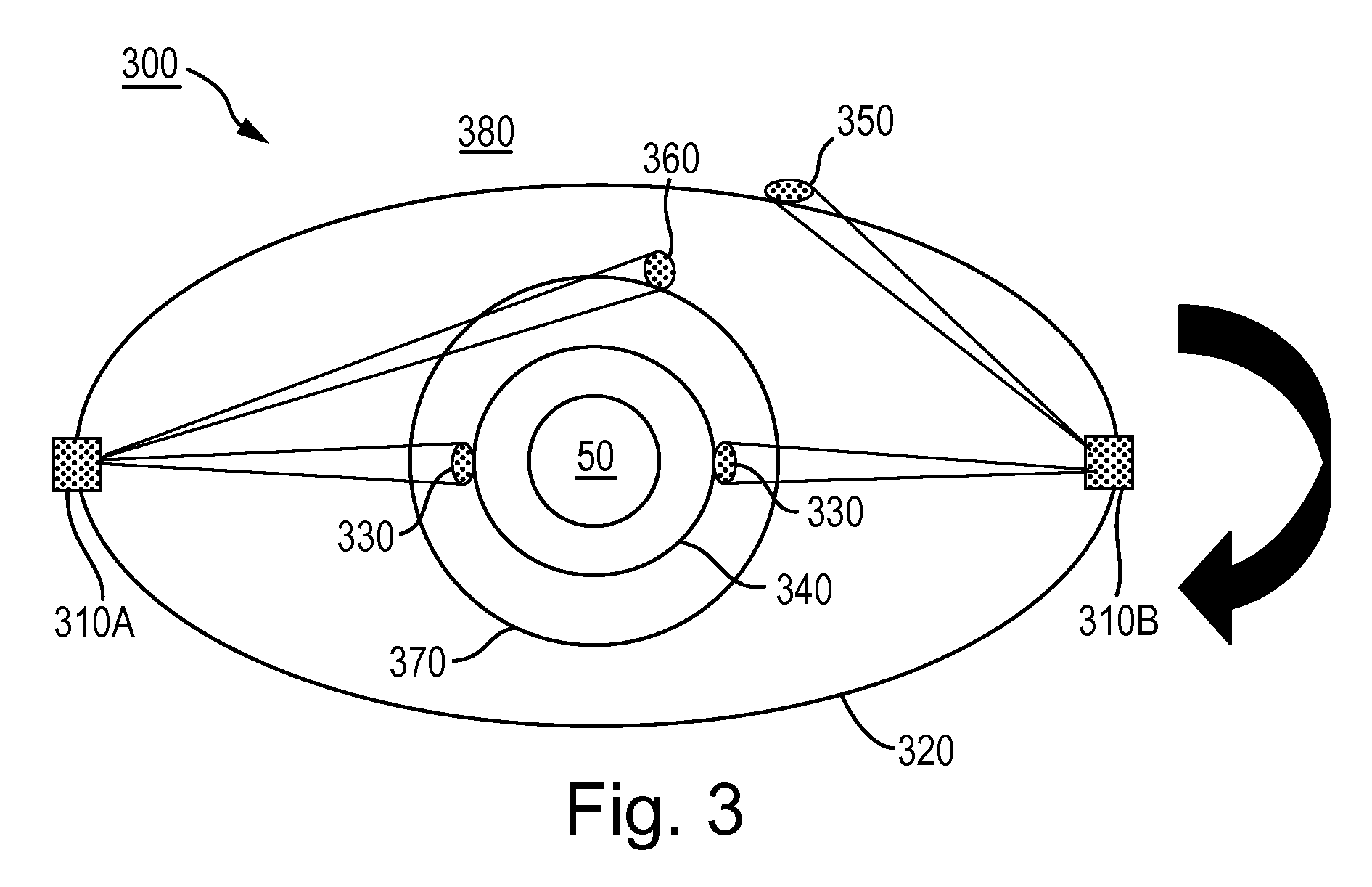
Space-based server network architecture
InactiveUSRE39503E1Guaranteed connectivityReduce needActive radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsControl data
A space-based server network architecture (1) which permits on demand transfer of mission and control data between client satellites (14) in an orbit about earth and an earth station (20, 22, 24, 26) irrespective of the location of the client satellite (14) relative to the earth station (20, 22, 24, 26). The architecture includes a plurality of server satellites (10) located spaced apart in a earth orbit above the orbit of the client satellites (14). The server satellites (10) provide substantially total world-wide communications coverage to and connectivity with designated and authorized earth stations (20, 22, 24, 26) and the plurality of client satellites (14). Each server satellite (10) includes: a communications downlink (18, 18a, 18b) for providing intercommunication with designated and authorized earth stations within its field of view; communications crosslinks (12, 12a, 12b) for providing intercommunications with other server satellites within its field of view; and communications links (16, 16a, 16b) for providing intercommunication with a client satellite within its field of view. Client satellite control data originating from an earth station is passed directly to an accessible server satellite, which then passes the control data either directly to the intended client satellite if within its communications field of view, or forwards the control data to a server satellite having direct communications access to the intended client satellite. Mission data from a client satellite can at any time be transmitted to a designated earth station, irrespective of its location on earth, by transmitting first to a server satellite within its communication field of view, where the mission data is then either downlinked directly to the designated earth station if within its communications field of view, or transmitting to a server satellite having communications downlink access to the designated earth station.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method and system for acquiring images via a constellation of observation satellites
ActiveUS10532831B2Shorten the timeCosmonautic partsNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsGround station
A method for acquiring images using a constellation of satellites in non-geosynchronous terrestrial orbit. The satellites include respective devices for inter-satellite communication. An aggregate of work plans intended for various satellites is formed. A ground station transmits the aggregate intended for one satellite. The satellite receiving the aggregate retransmits the aggregate intended for at least one other satellite from the ground station. Each satellite receiving the aggregate from another satellite re-transmits the aggregate intended for at least one other satellite. Each satellite recovers its work plan from the aggregate received.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Affordable vehicle avionics system
ActiveUS10669045B1Low costEliminate measurement errorsLaunch systemsSpacecraft guiding apparatusControl systemIn vehicle
A system and method of providing an affordable navigation, guidance and control system for arbitrary nano / micro launch vehicles by integrating commercial grade sensors with advanced estimation algorithms in a manner that provides sufficient accuracy of the resulting vehicle state estimates to inject nano / micro satellites into low earth orbits. The system and method uses commercial grade sensors and an advanced sensor-fusion estimator software that estimates and removes the estimated measurement errors and filters noise produced by the commercial grade sensors, resulting in estimated states with suitable accuracy. The filtered data are sent to a guidance and control system where actuator commands are formulated based on the filtered data. A simulated launch and flight of the launch vehicle is performed using the filtered data to validate that the GNC system and launch vehicle are ready for launch.
Owner:US REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTRATOR OF THE NASA
Adaptive augmented reality satellite acquisition
Satellite acquisition, for enabling a user device to engage in satellite communications, may be implemented using augmented reality (AR). An AR display may be presented to a user, and the user may use the AR display to point the user device toward a desired satellite. The process may include offsetting the position of a satellite icon representing the desired satellite in the AR display if acquisition is unsuccessful and thus indicating that the user device should be pointed to the offset position. In the case of a non-geosynchronous earth-orbit (non-GEO) satellite, such as a low-earth-orbit (LEO) satellite, the position of the satellite icon representing such a non-GEO satellite may be compensated for satellite movement during a satellite acquisition attempt.
Owner:HIGHER GROUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com