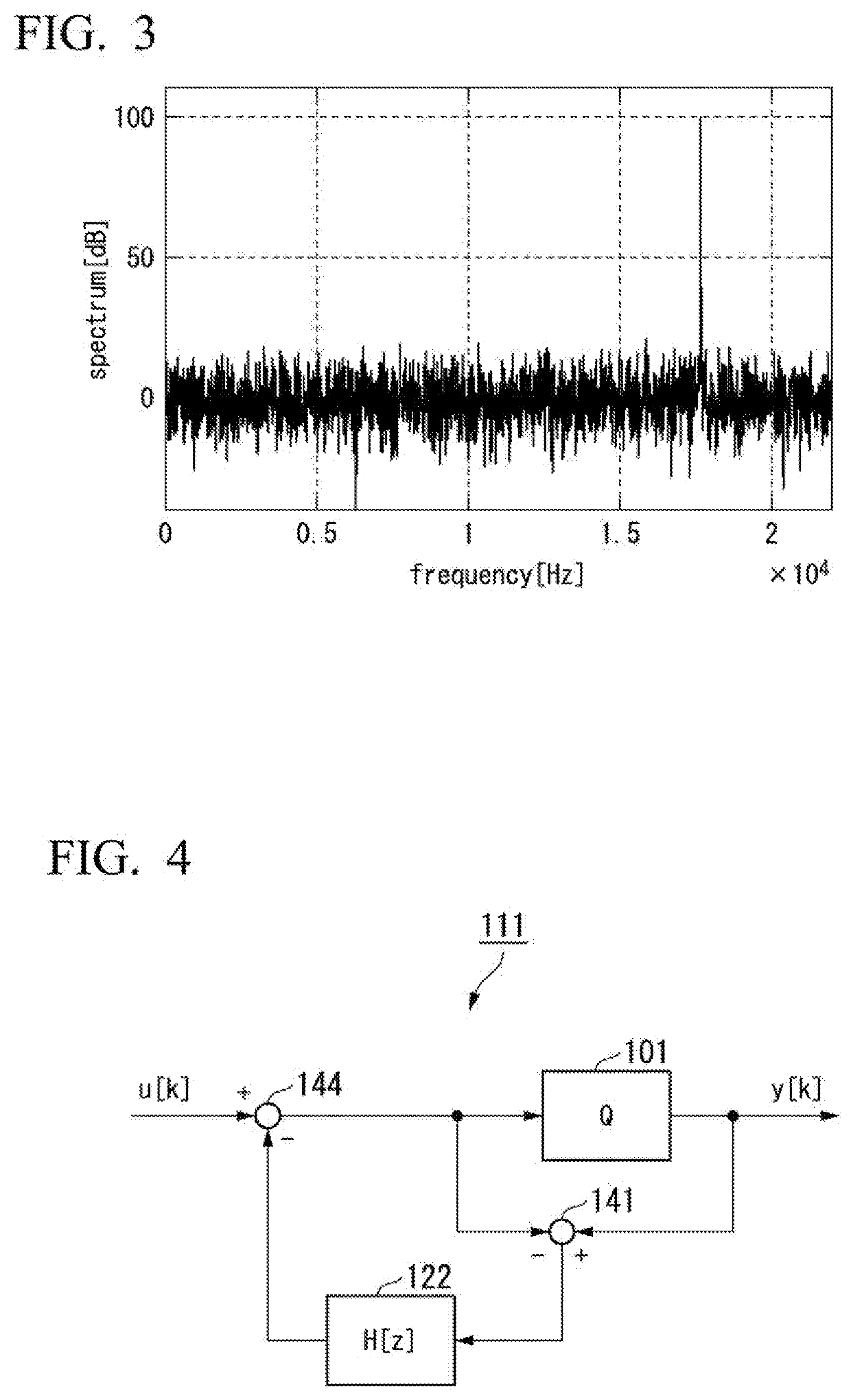
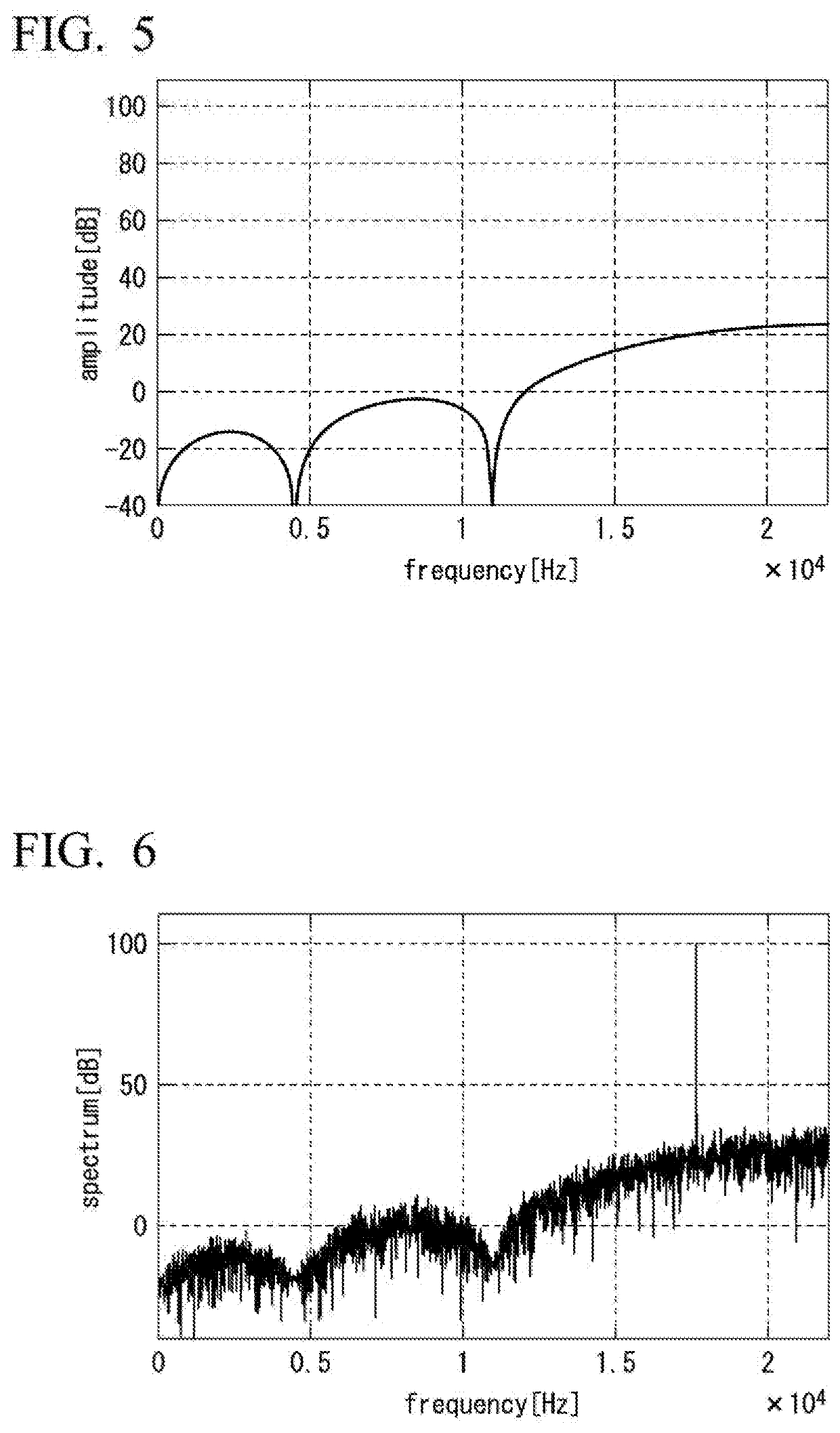
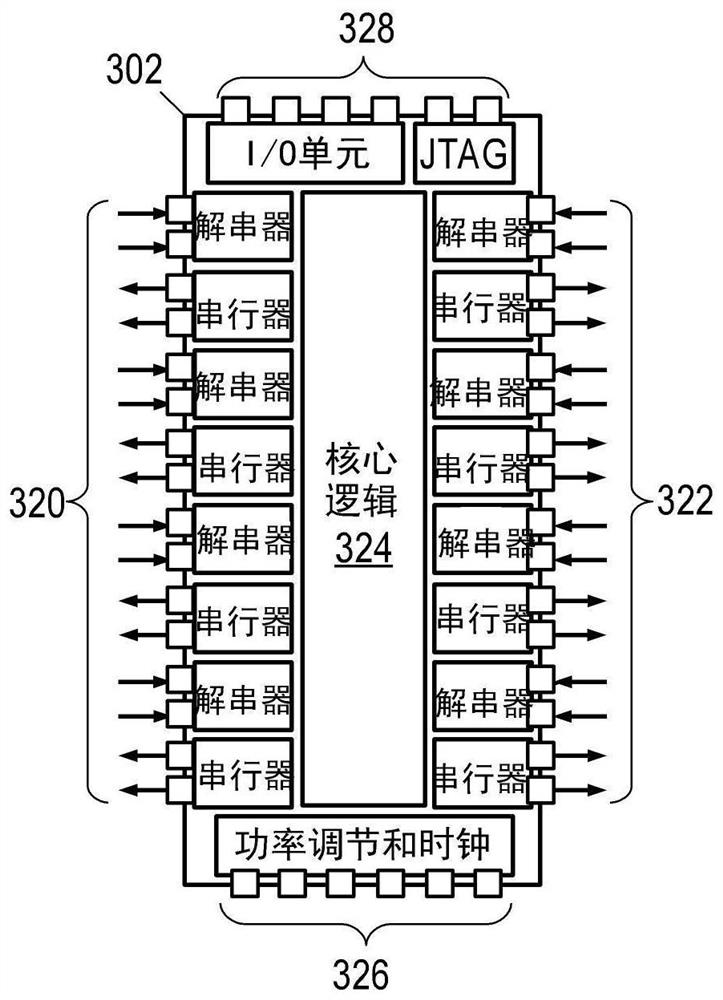
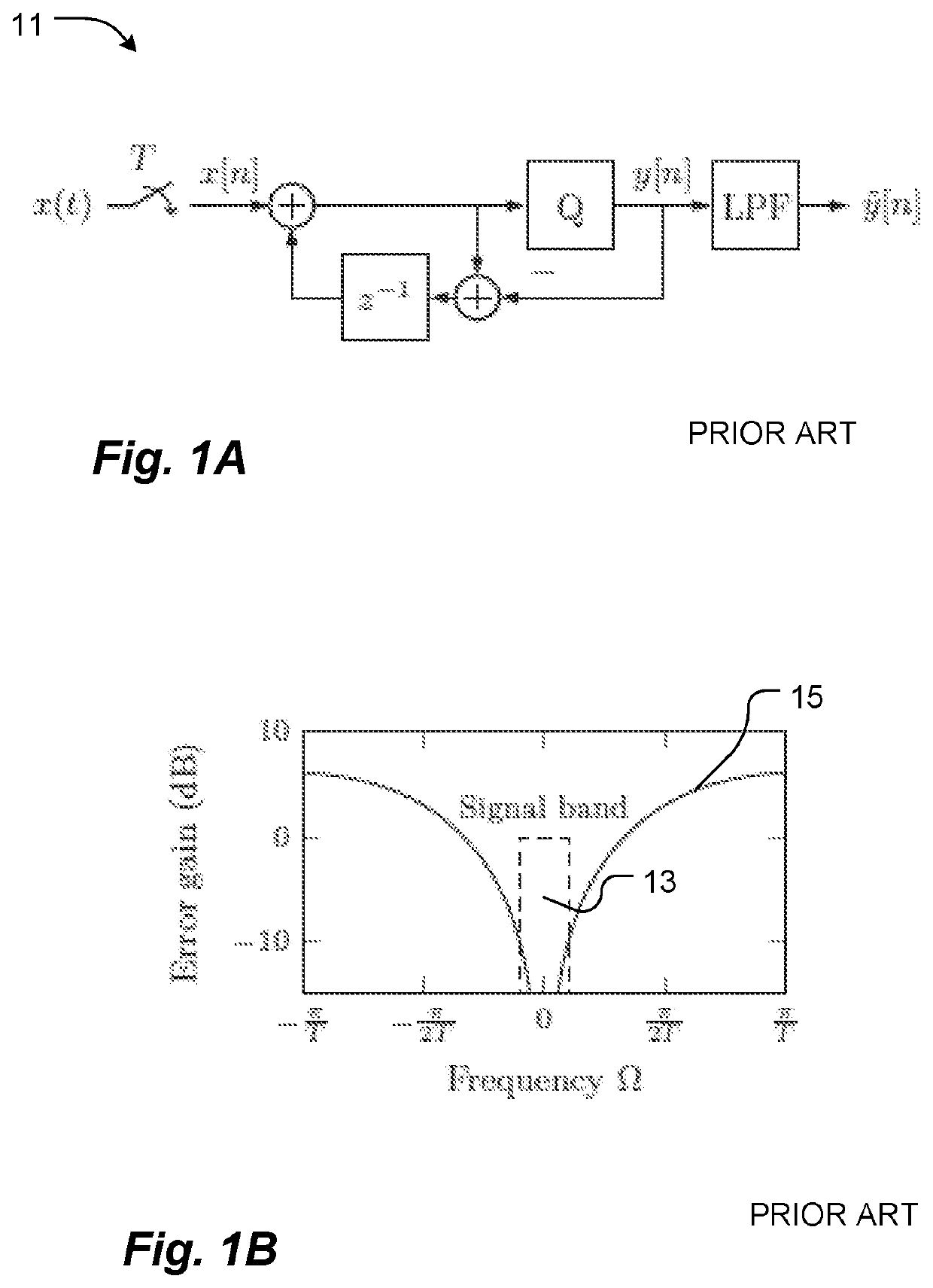
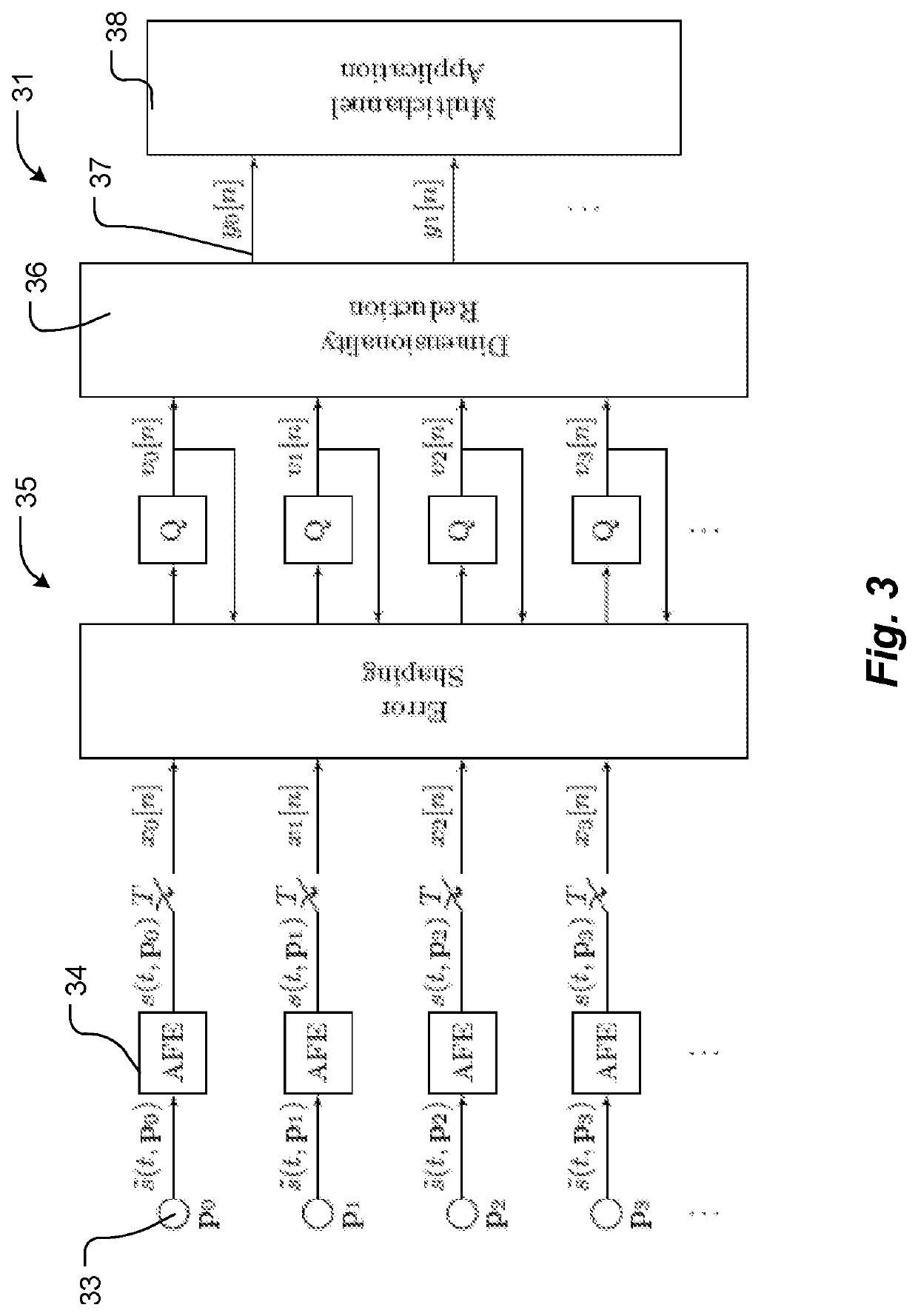
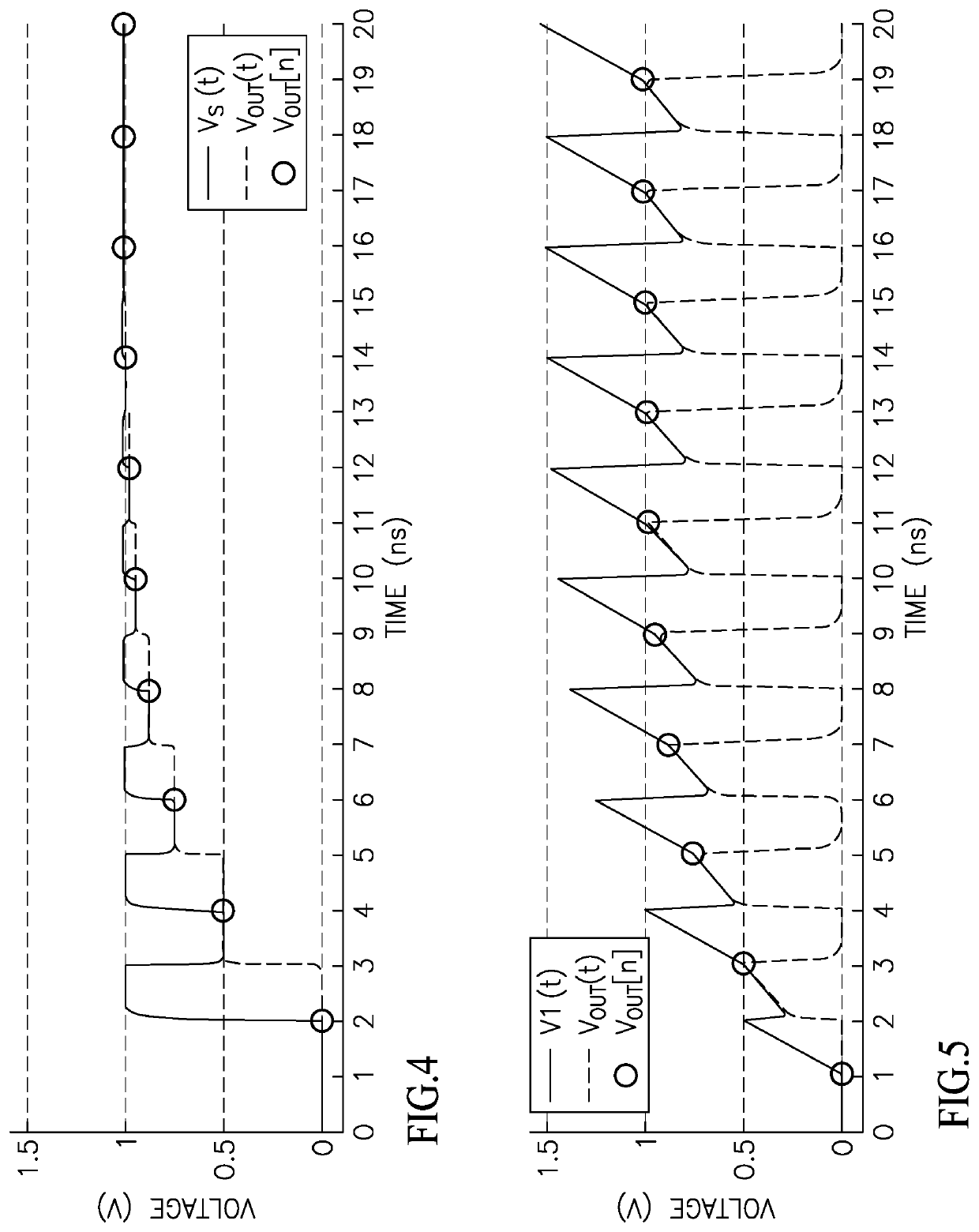
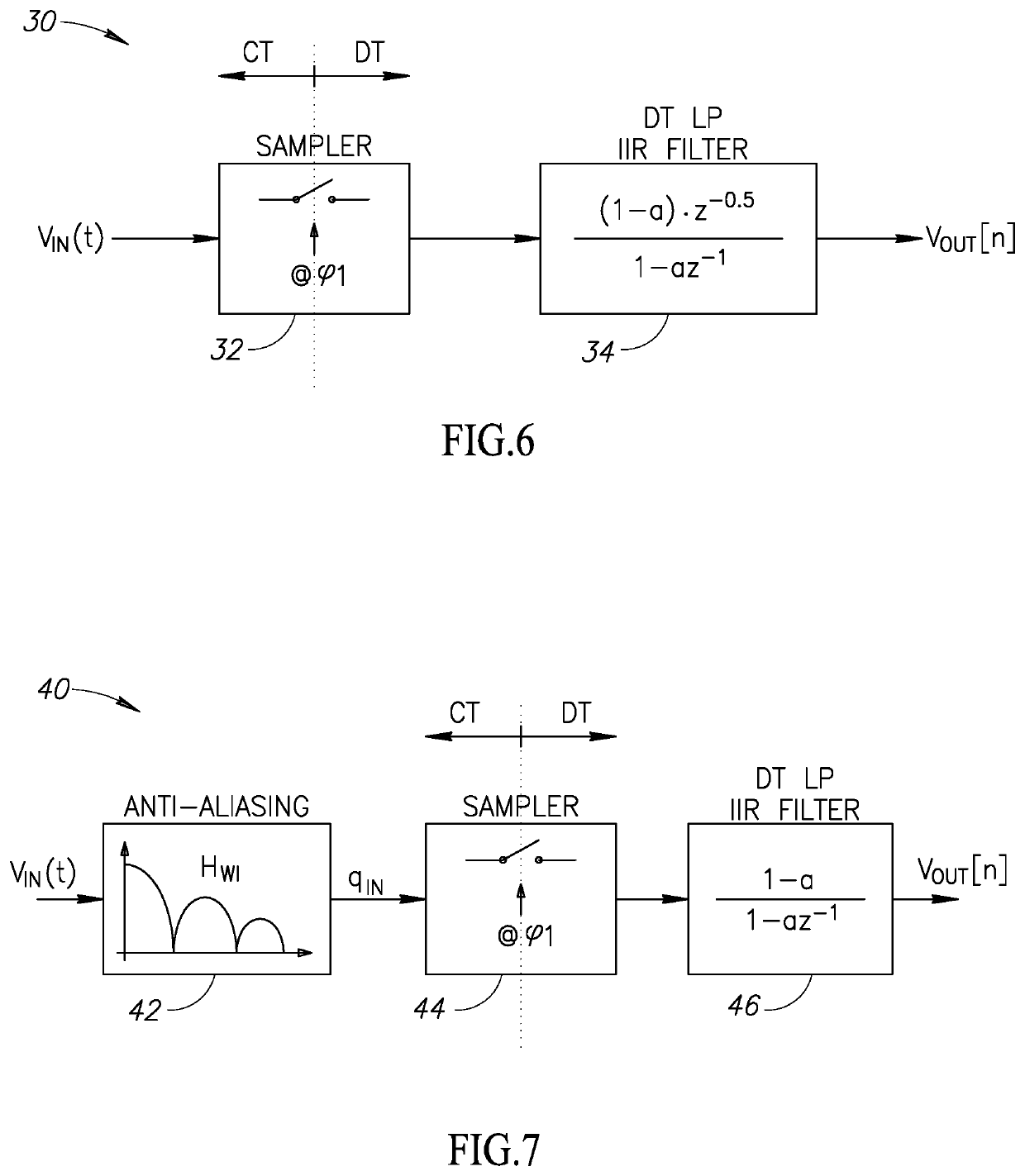
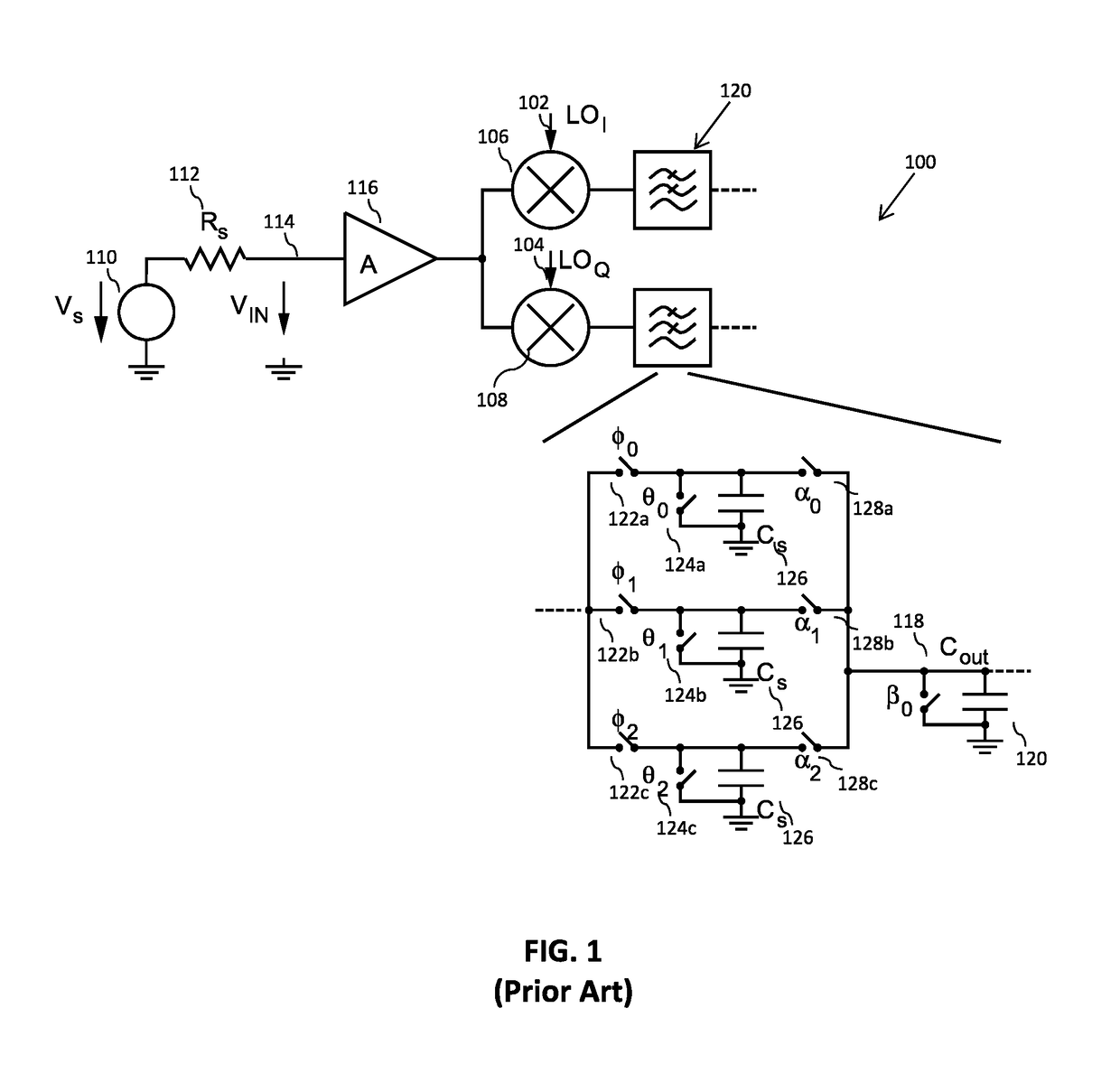
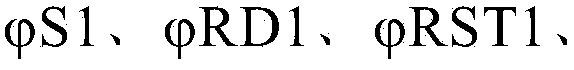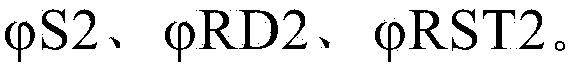Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Discrete time filtering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
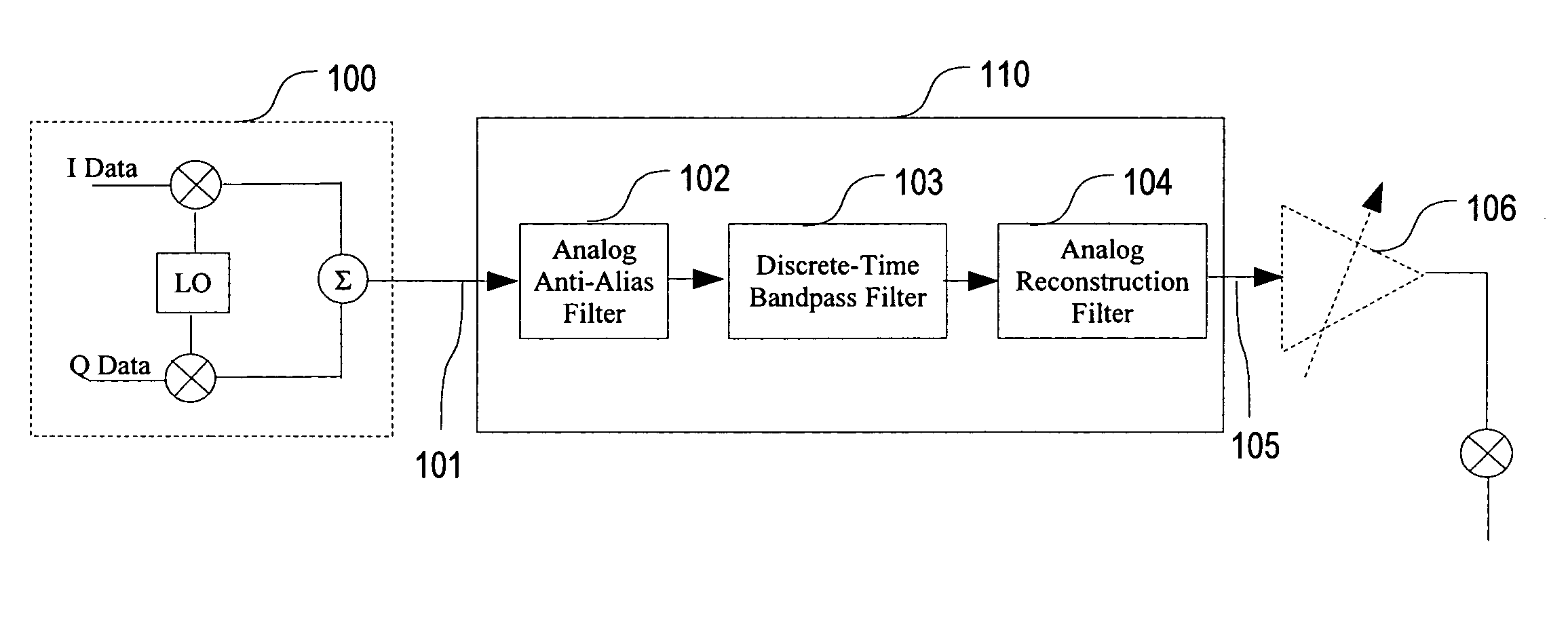
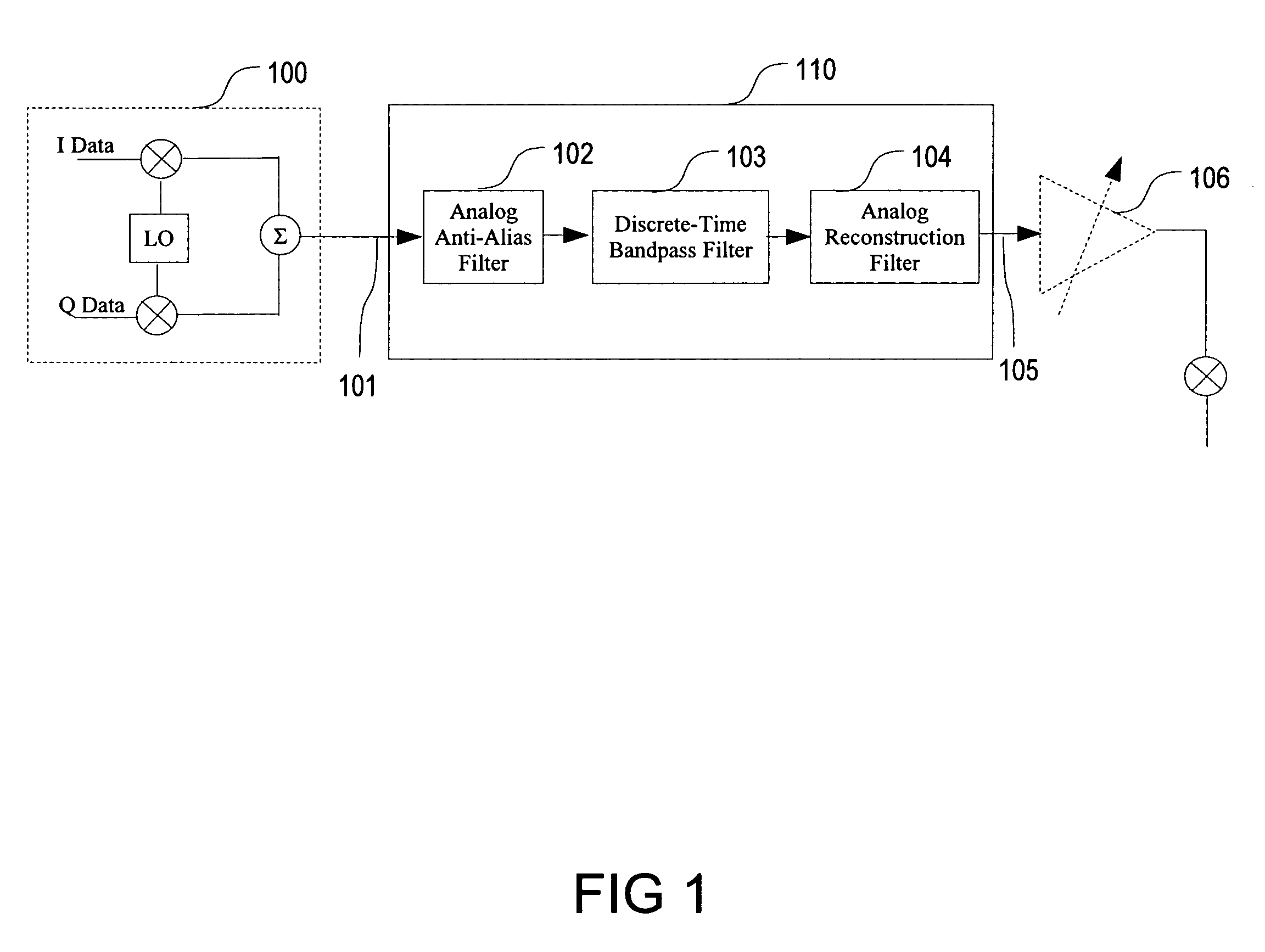
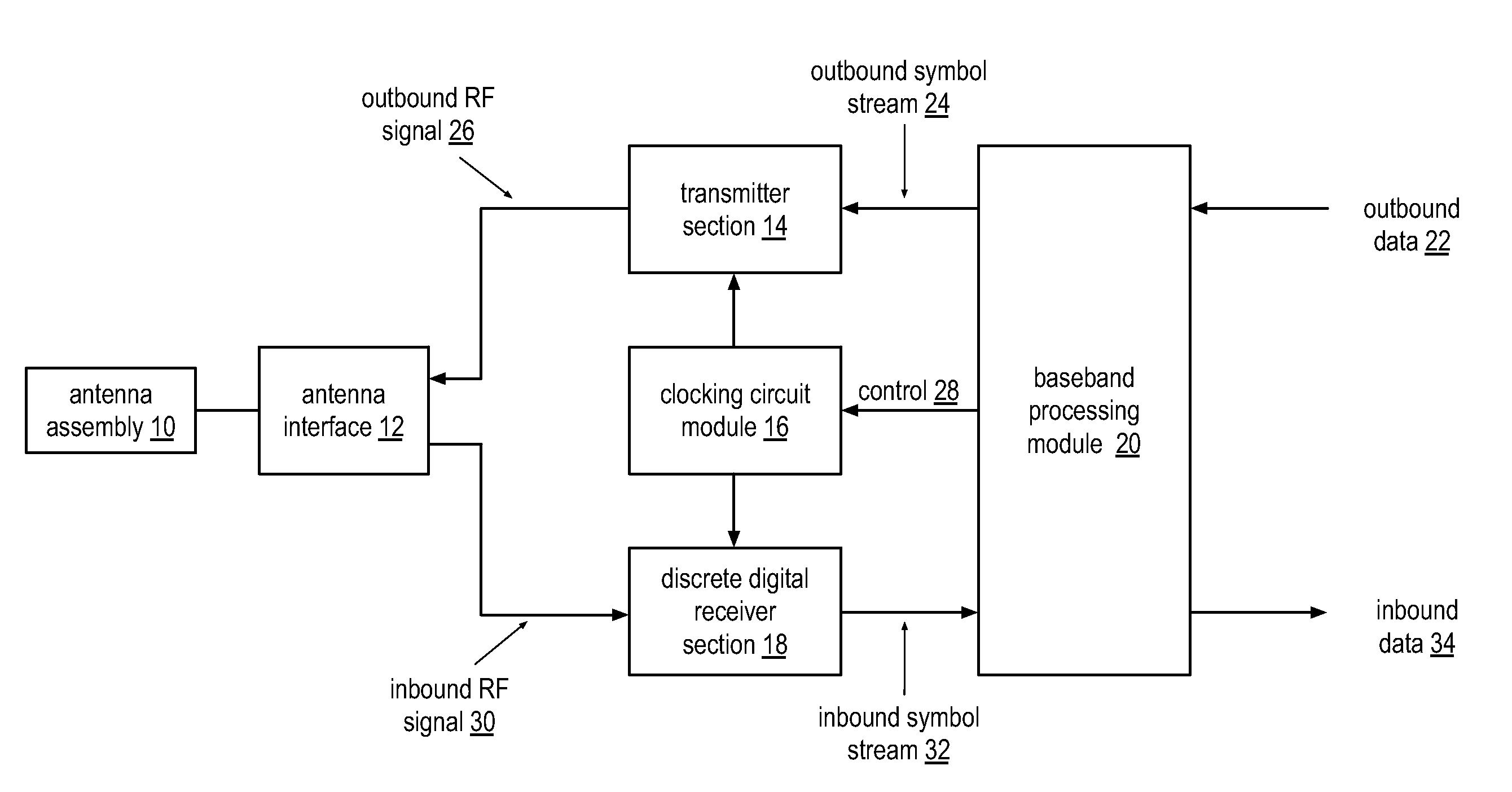
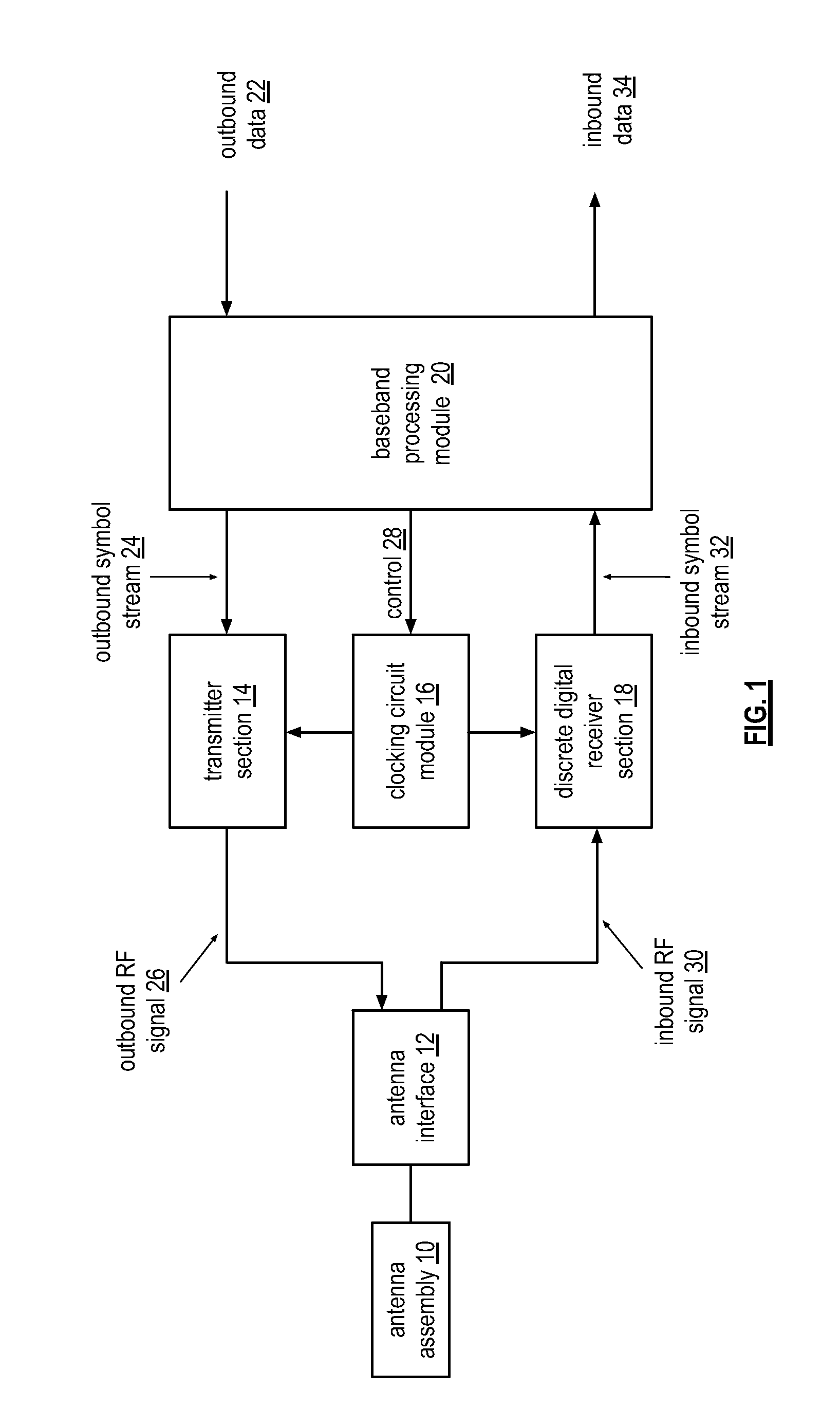
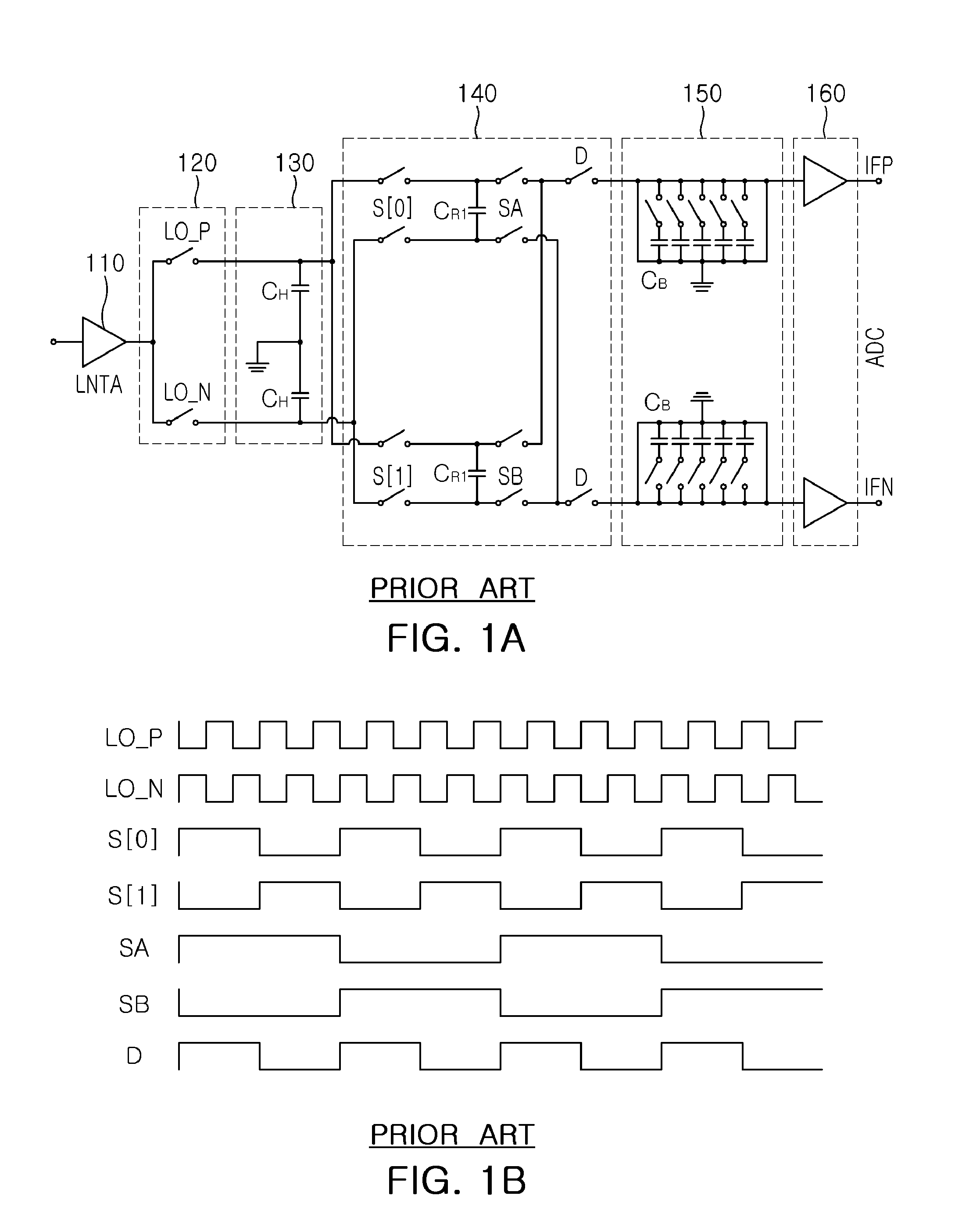
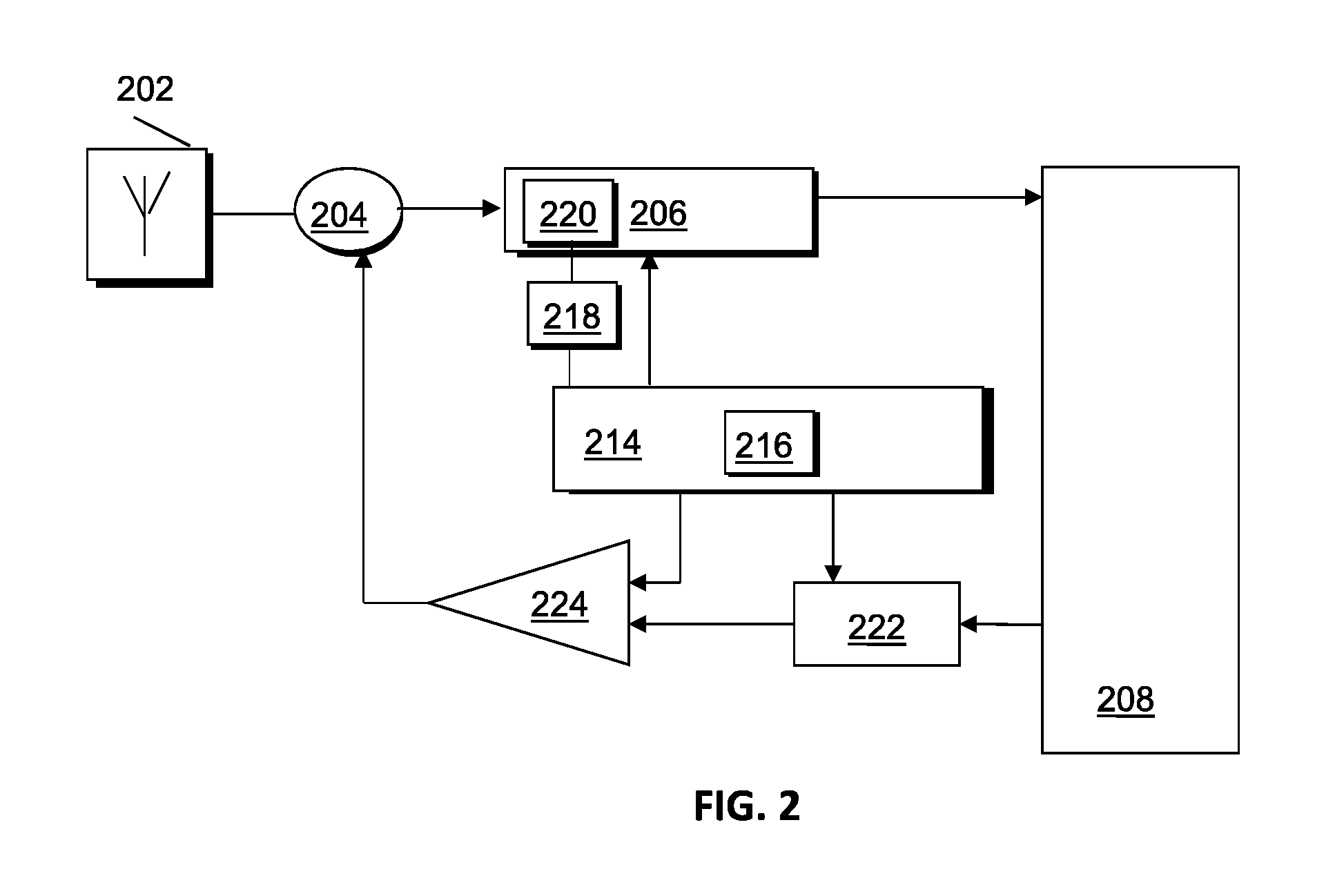
Physical layer repeater with discrete time filter for all-digital detection and delay generation
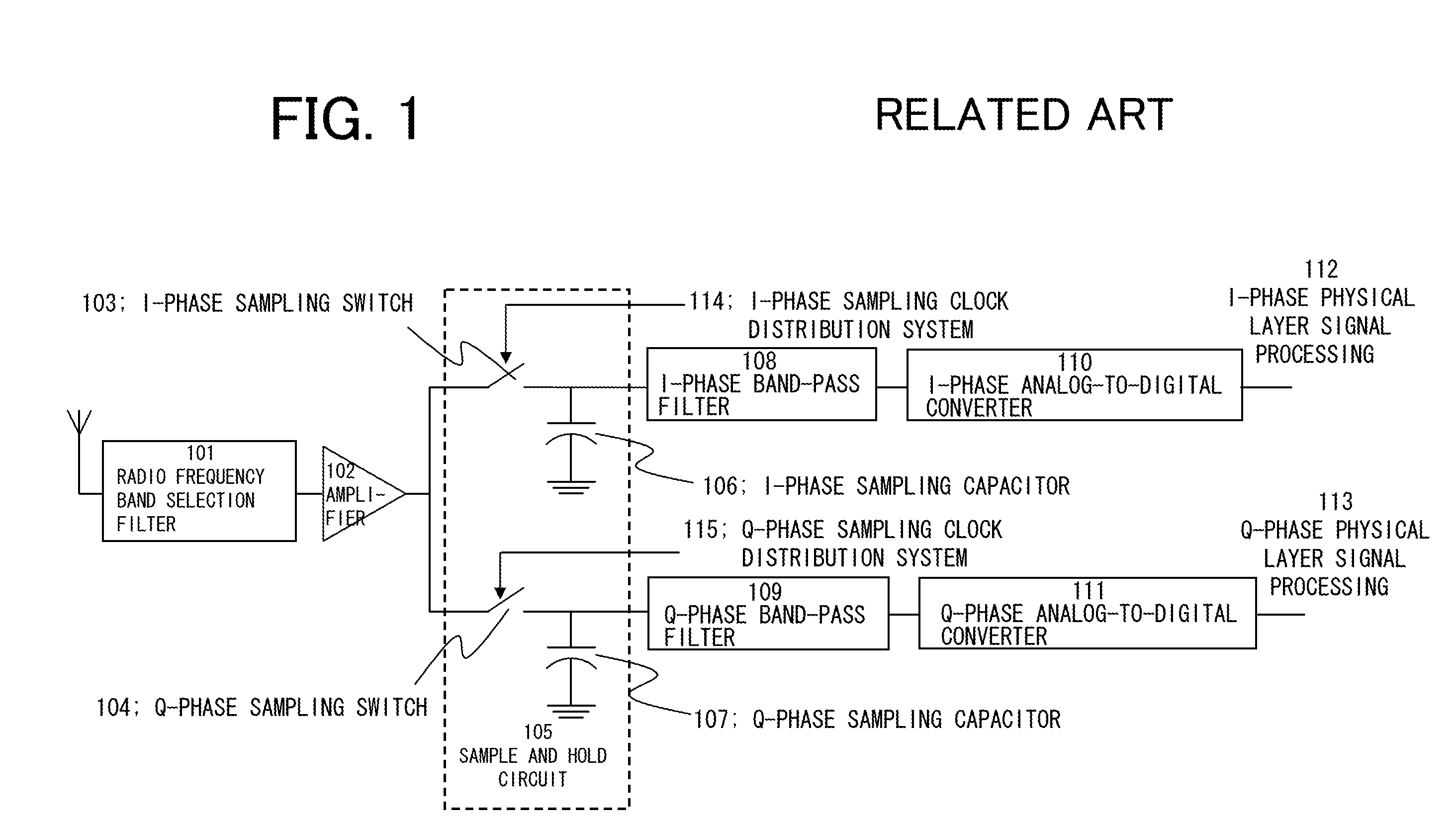
InactiveUS8078100B2Improve performanceQuick checkTransversal filtersDigital technique networkBandpass filteringCommunications system
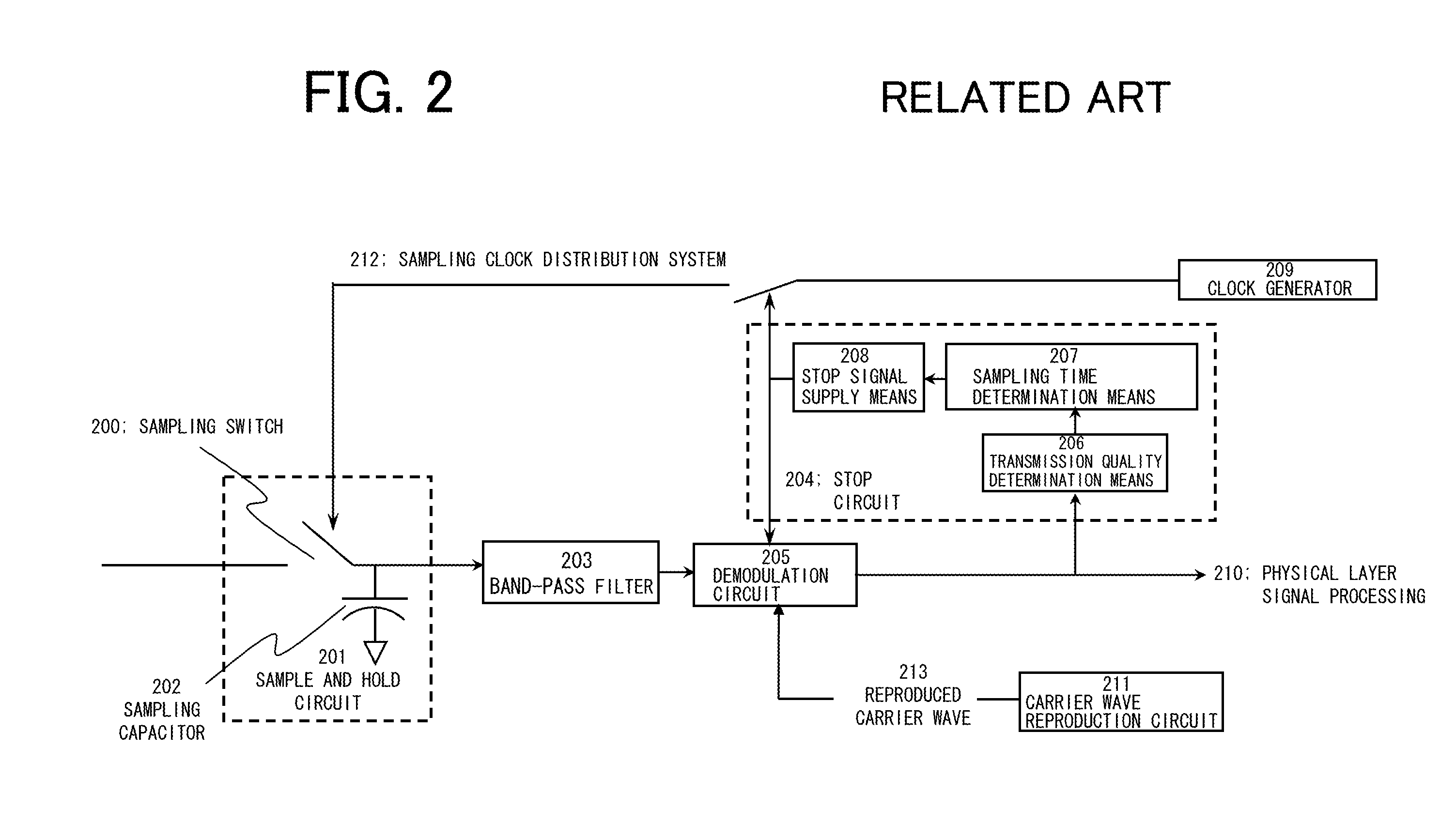
A discrete time bandpass filter element (103) having multiple stages (201, 202, 203, 204, 205) for use in a time division duplex radio protocol communications system including an automatic gain control. Discrete time bandpass filter is used to generate delay and can replace SAW filters in a wireless frequency translating repeater.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
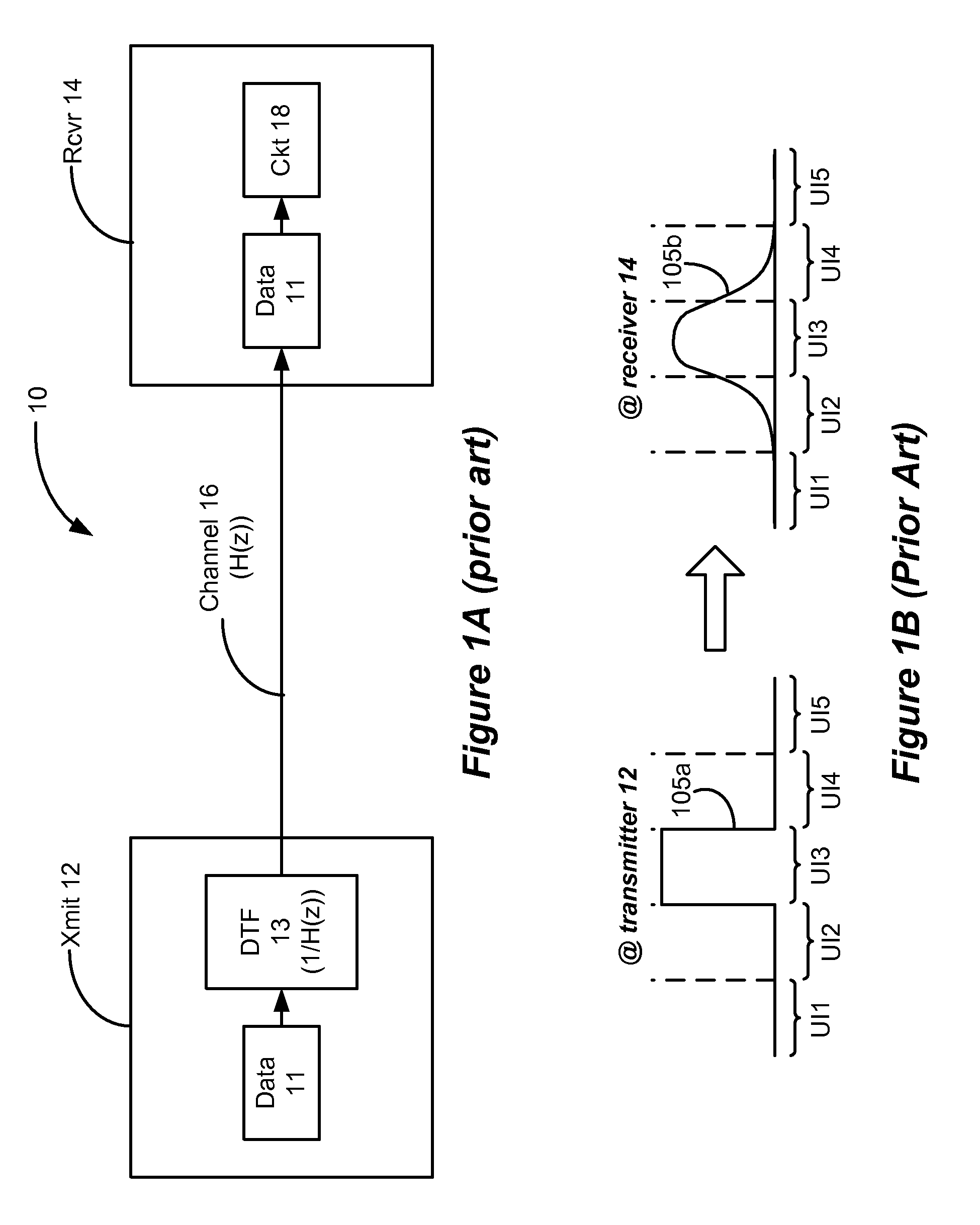
Jittery signal generation with discrete-time filtering
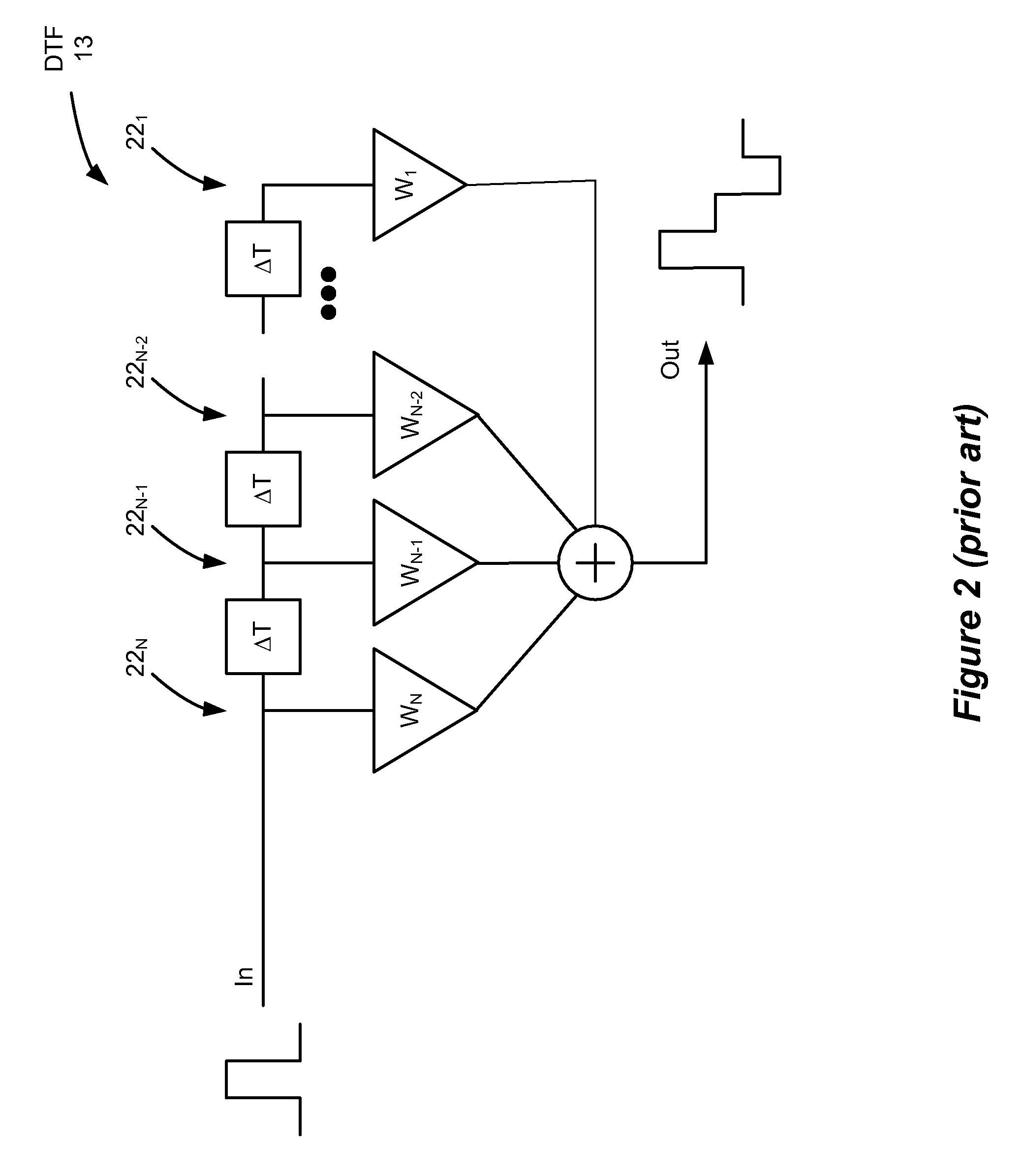
ActiveUS7953579B2Error preventionAnalogue computers for electric apparatusMulti unitDiscrete time filtering
The computer-implementable method allows for the fast creation of a multi-unit interval data signal suitable for simulation. The created signal represents the output of an otherwise ideal Discrete Time Filter (DTF) circuit, and the quick creation of the signal merely requires a designer to input the number of taps and their weights without the need of laying out or considering the circuitry of the DTF. A matrix is created based on a given data stream, and the number of taps and weights, which matrix is processed to create the multi-unit-interval data signal. Noise and jitter can be added to the created signal such that it now realistically reflects non-idealities common to actual systems. The signal can then be simulated using standard computer-based simulation techniques.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Discrete time receiver
InactiveUS20110150142A1High resolutionModulated-carrier systemsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionDiscrete time filteringControl signal
A discrete-time receiver includes: a sampling mixer sampling an input signal according to a sampling clock; a discrete-time filter adjusting a decimation rate by using a control signal and filtering the sampled signal by using a filter clock; and a clock generator generating a sampling clock to be supplied to the sampling mixer, and generating the control signal and the filter clock by comparing the frequency of the sampling clock with a pre-set output frequency. Over a broadband input signal, a dynamic range of an output signal can be improved.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Discrete-time filter
InactiveCN103636125AModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesTransversal filtersDiscrete time filteringEngineering
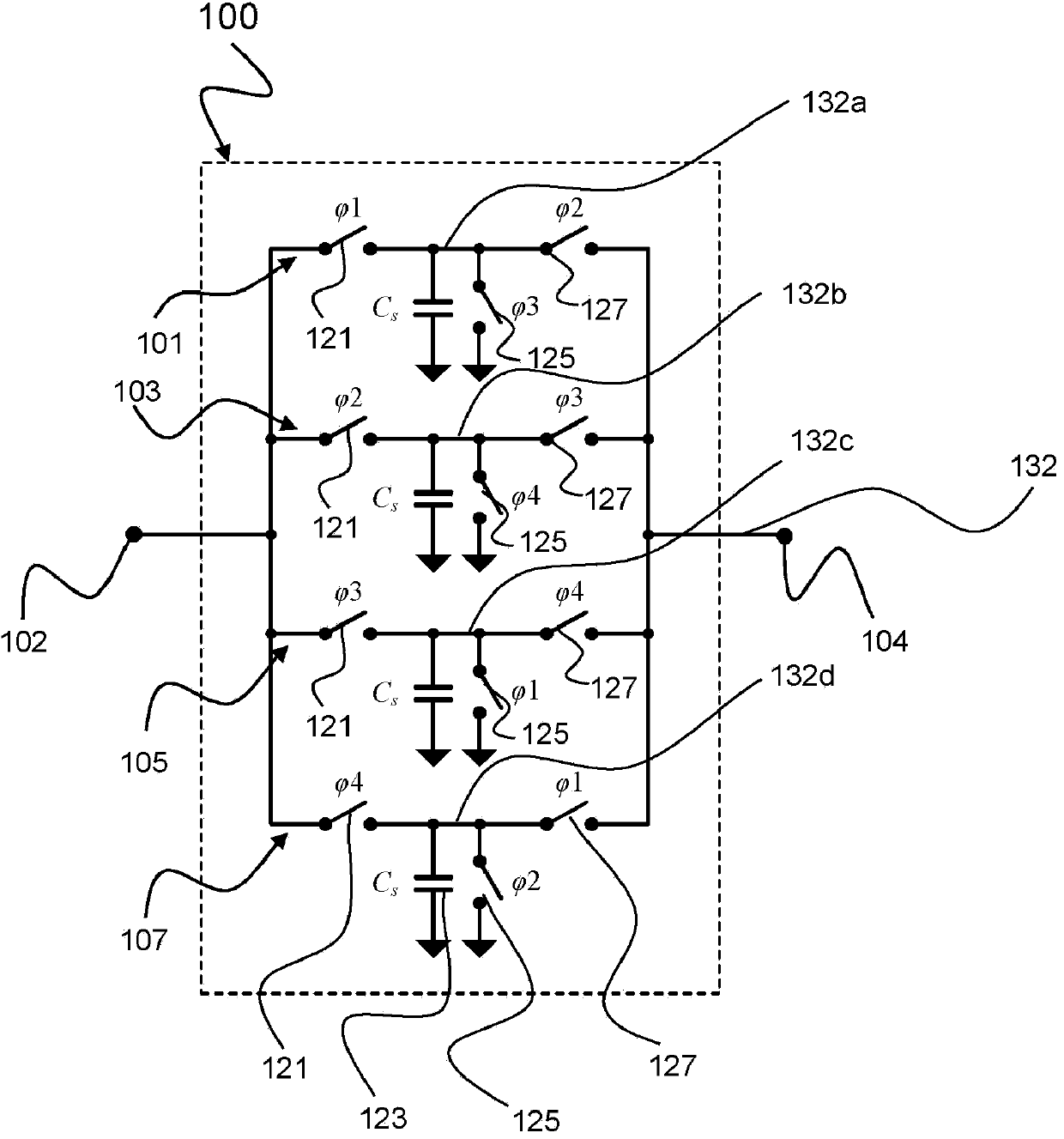
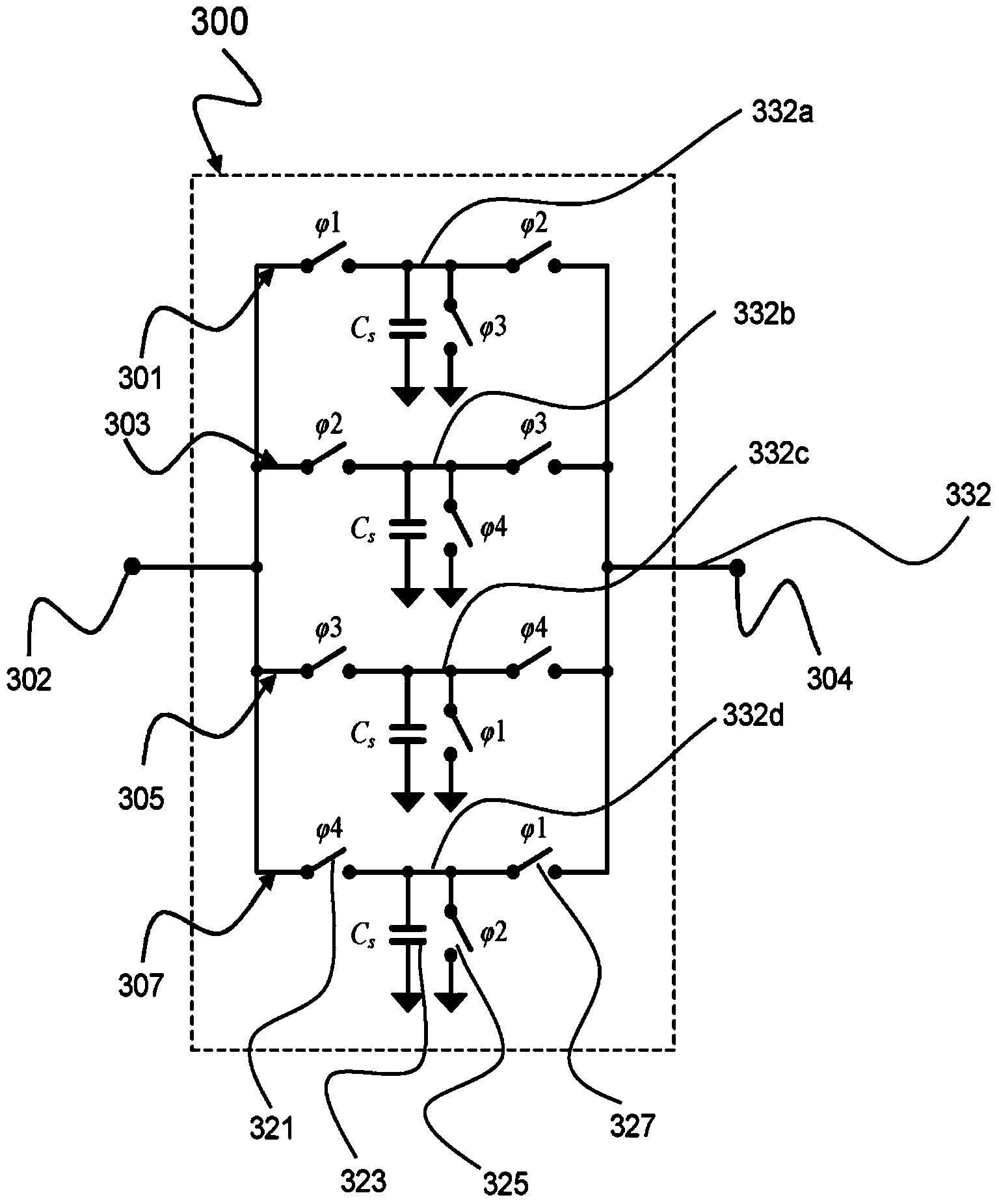
The invention relates to a discrete-time filter for filtering an input signal, the discrete-time filter comprising a switched capacitor network, the switched capacitor network comprising an input (102) and an output (104), a number of switched capacitor paths (101, 103, 105, 107) arranged in parallel between the input (102) and the output (104), each switched capacitor path (101, 103, 105, 107) comprising a capacitor, and a switch circuitry (121, 125, 127) for switching each capacitor at a different time instant for outputting a filtered input signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
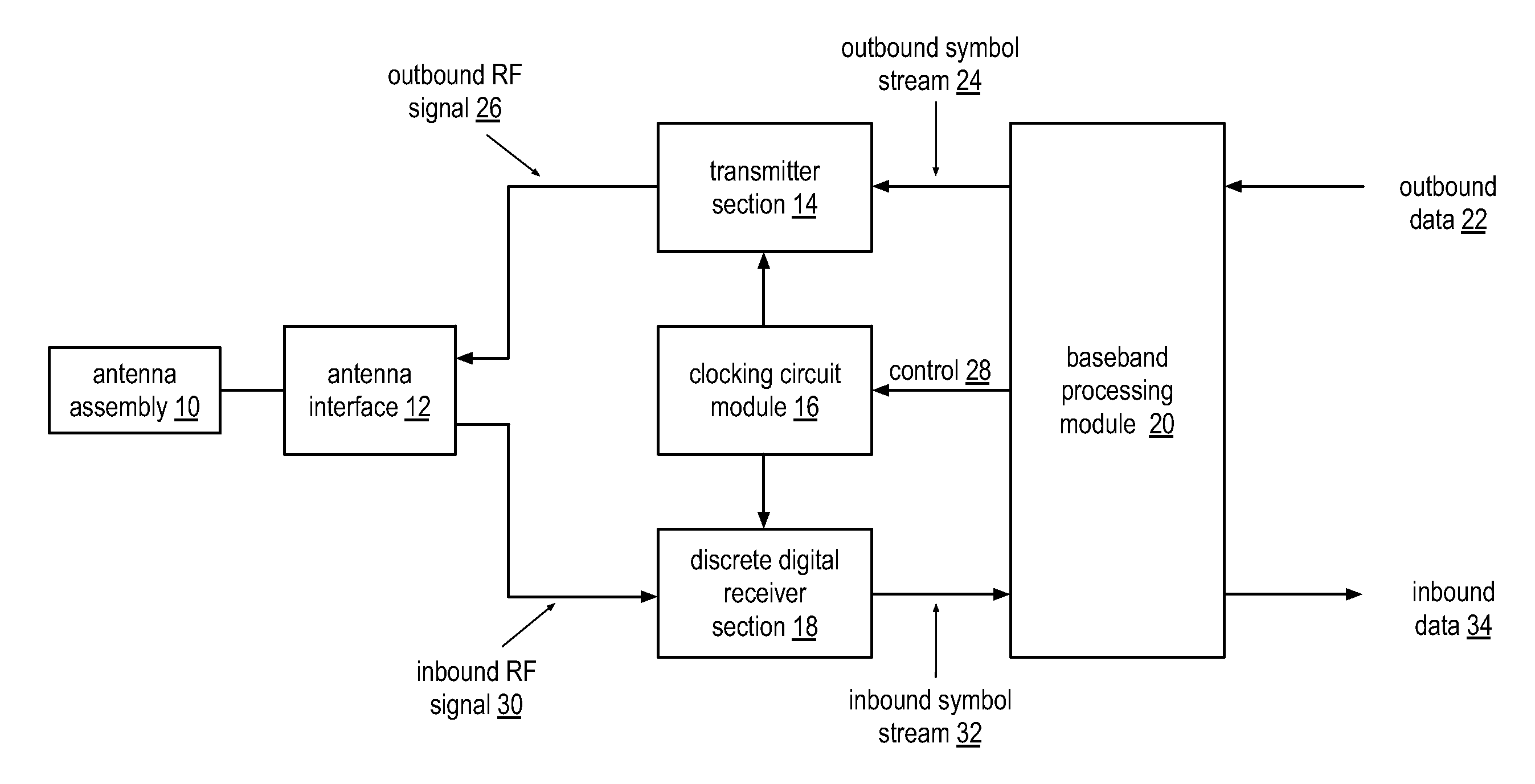
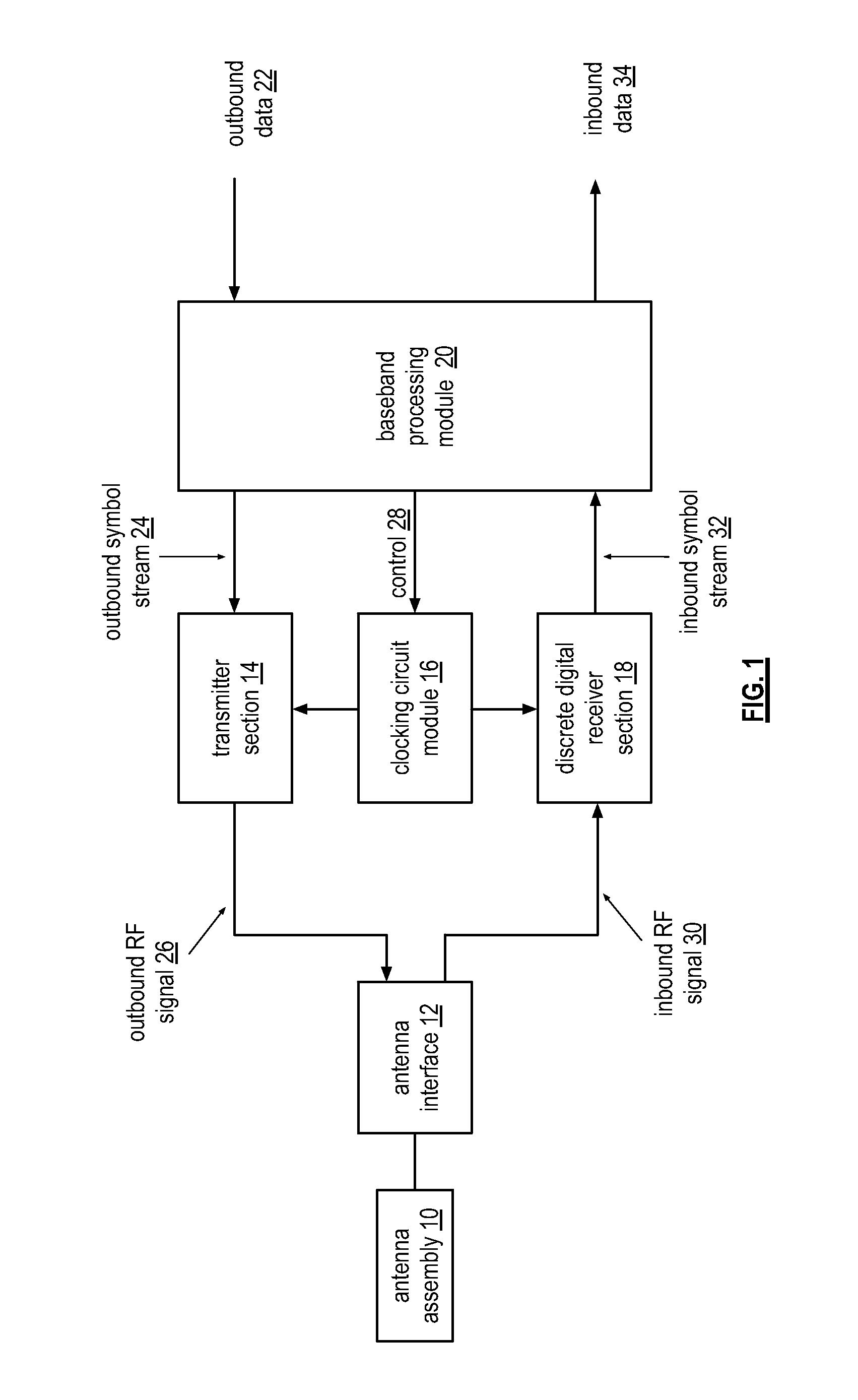
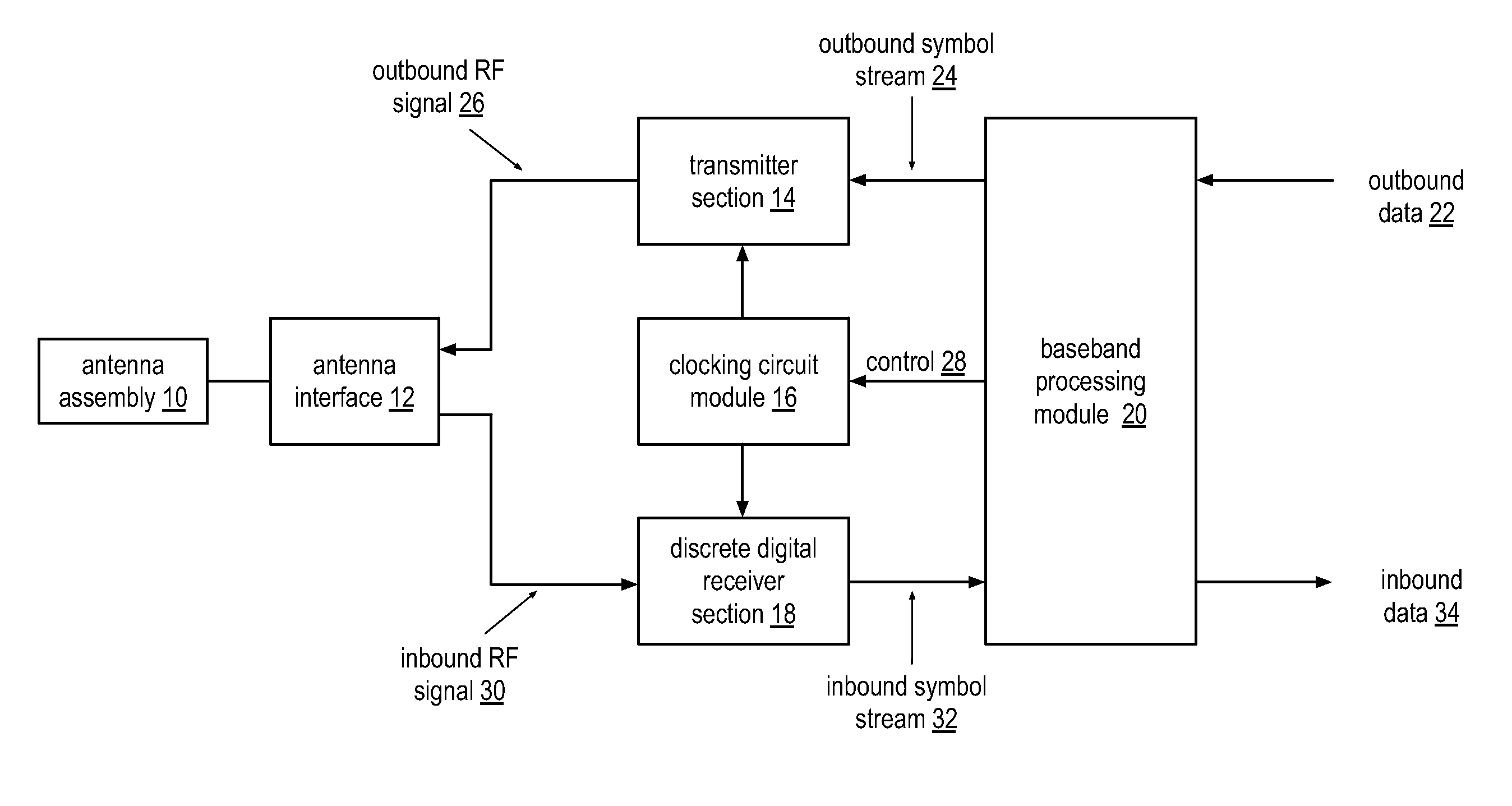
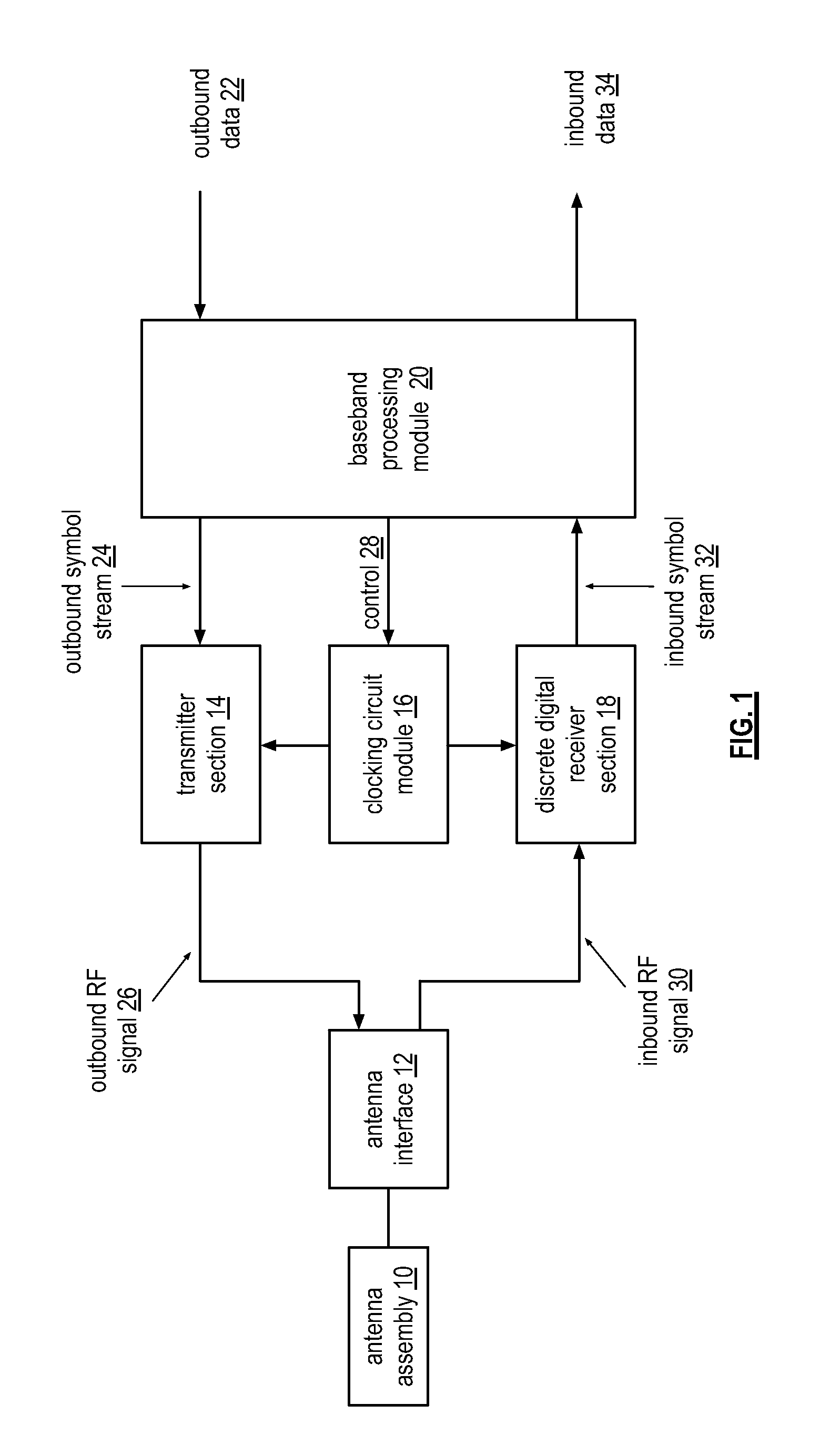
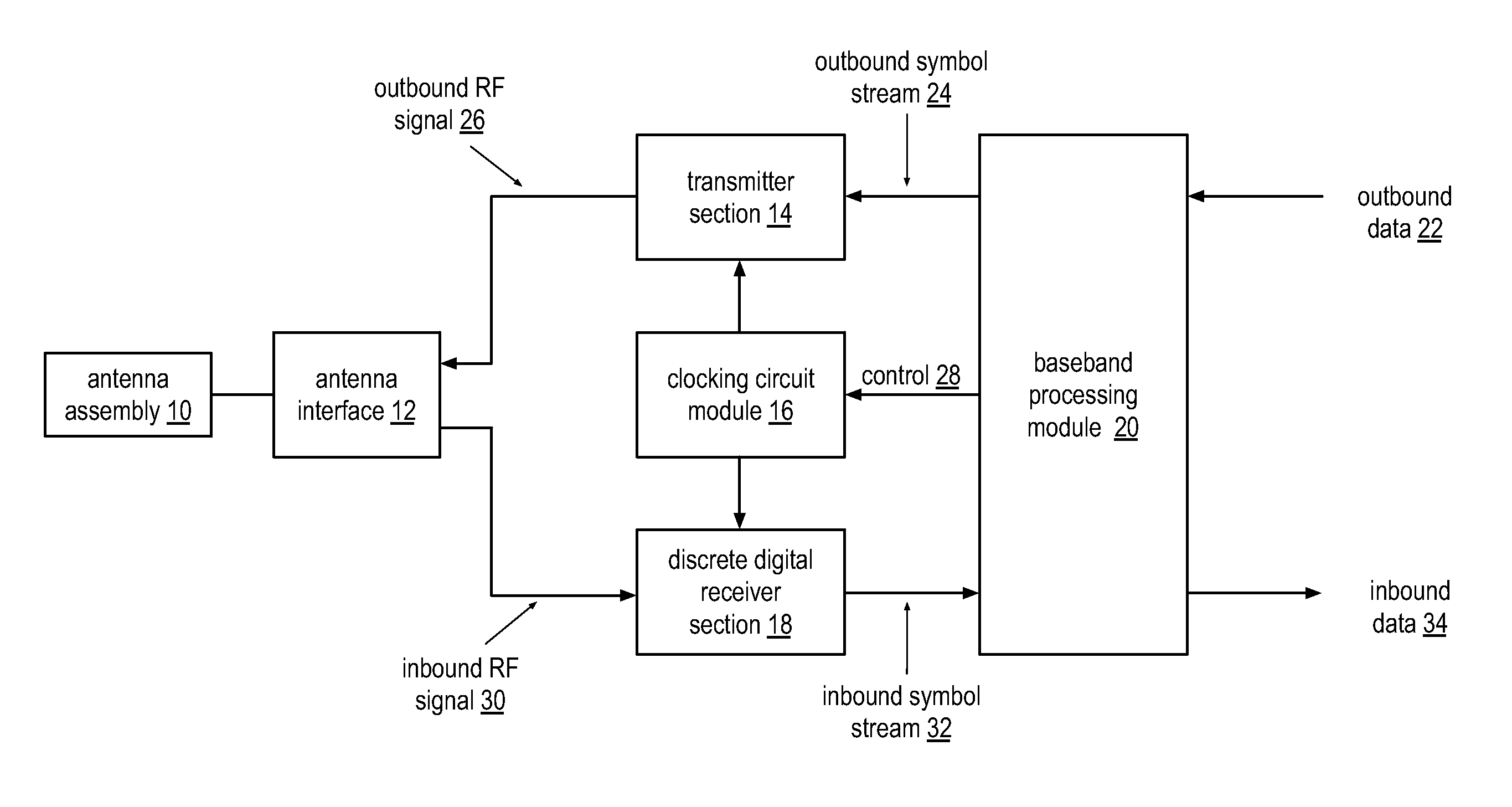
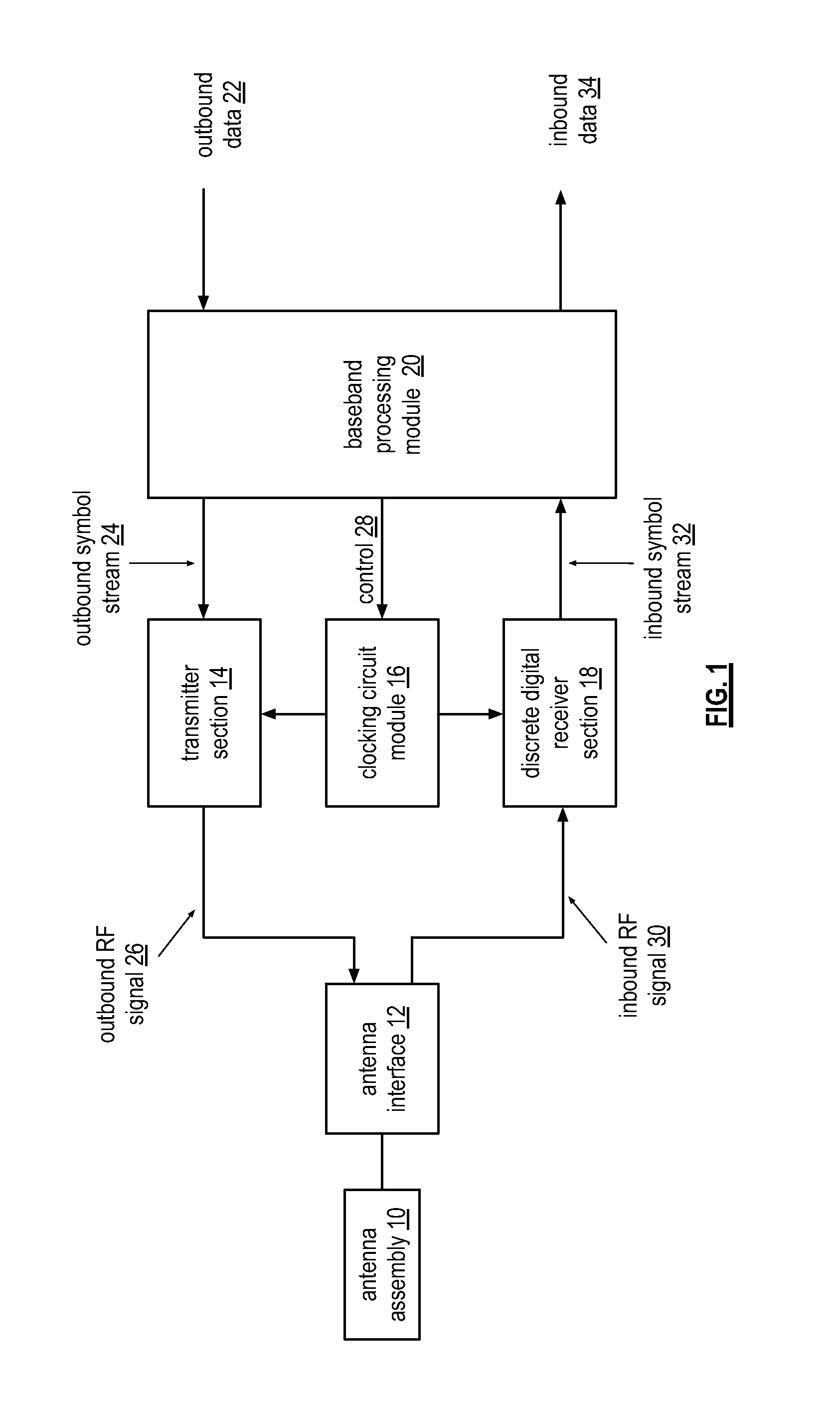
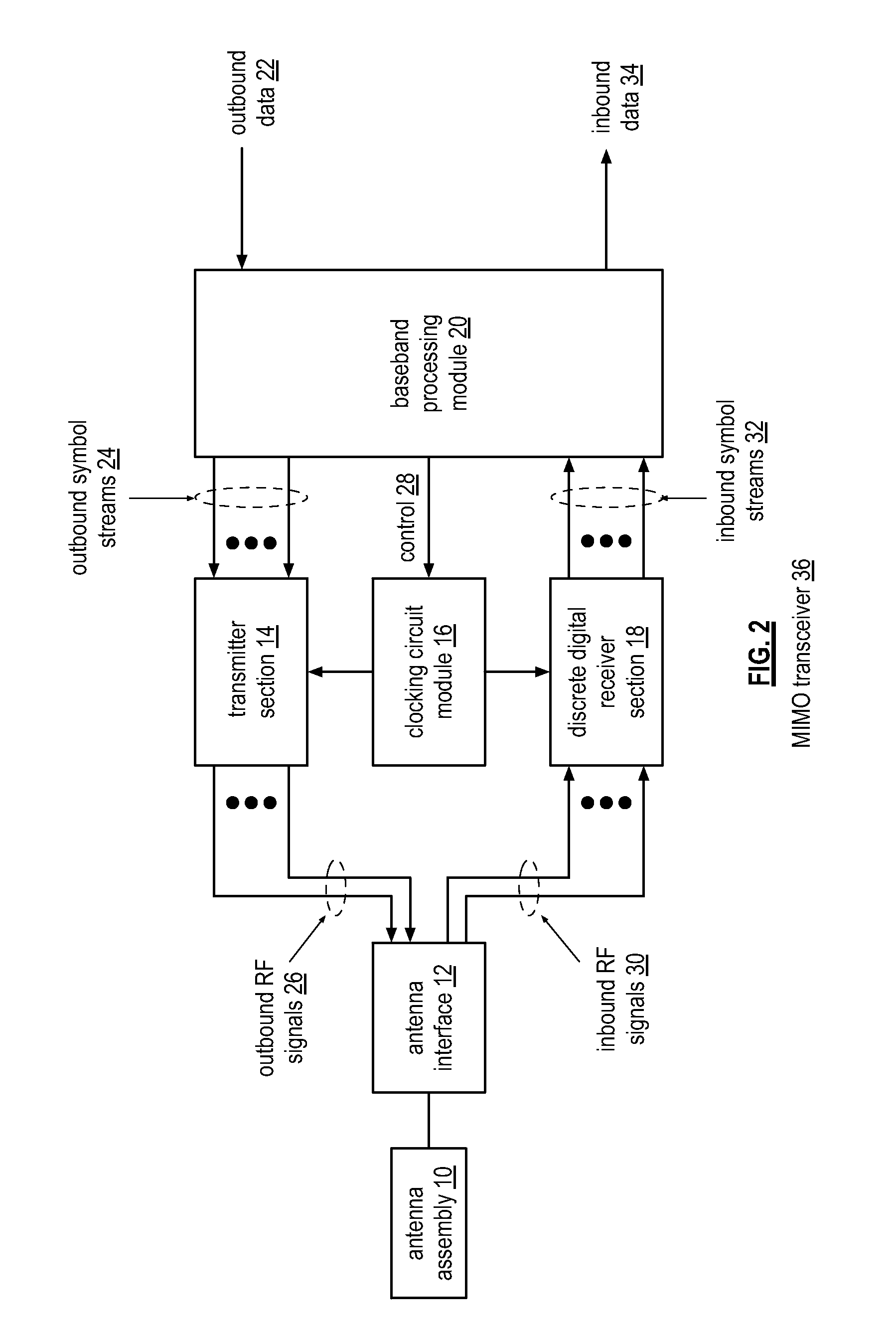
Wide bandwidth discrete digital receiver
A receiver includes a sample and hold module, a discrete time filter module, and a wireless frequency to baseband conversion module. The sample and hold module is operable to sample and hold an inbound wireless signal at a rate corresponding to a multiple of a carrier frequency of the inbound wireless signal to produce a frequency domain sample pulse train. The discrete time filter module is operable to filter the frequency domain sample pulse train to produce a wireless frequency pulse. The wireless frequency to baseband conversion module is operable to convert the wireless frequency pulse to a baseband digital signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
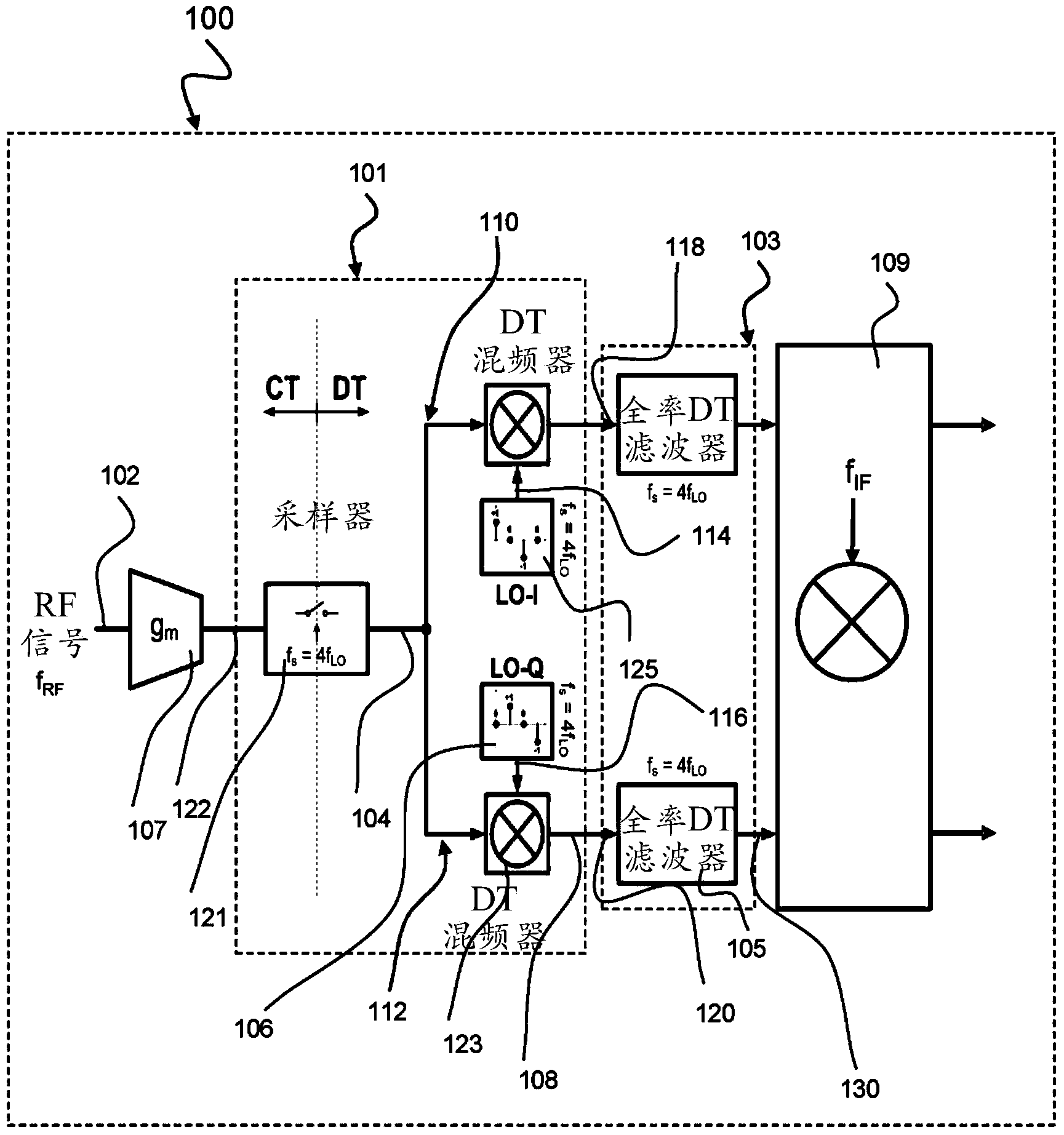
Superheterodyne receiver
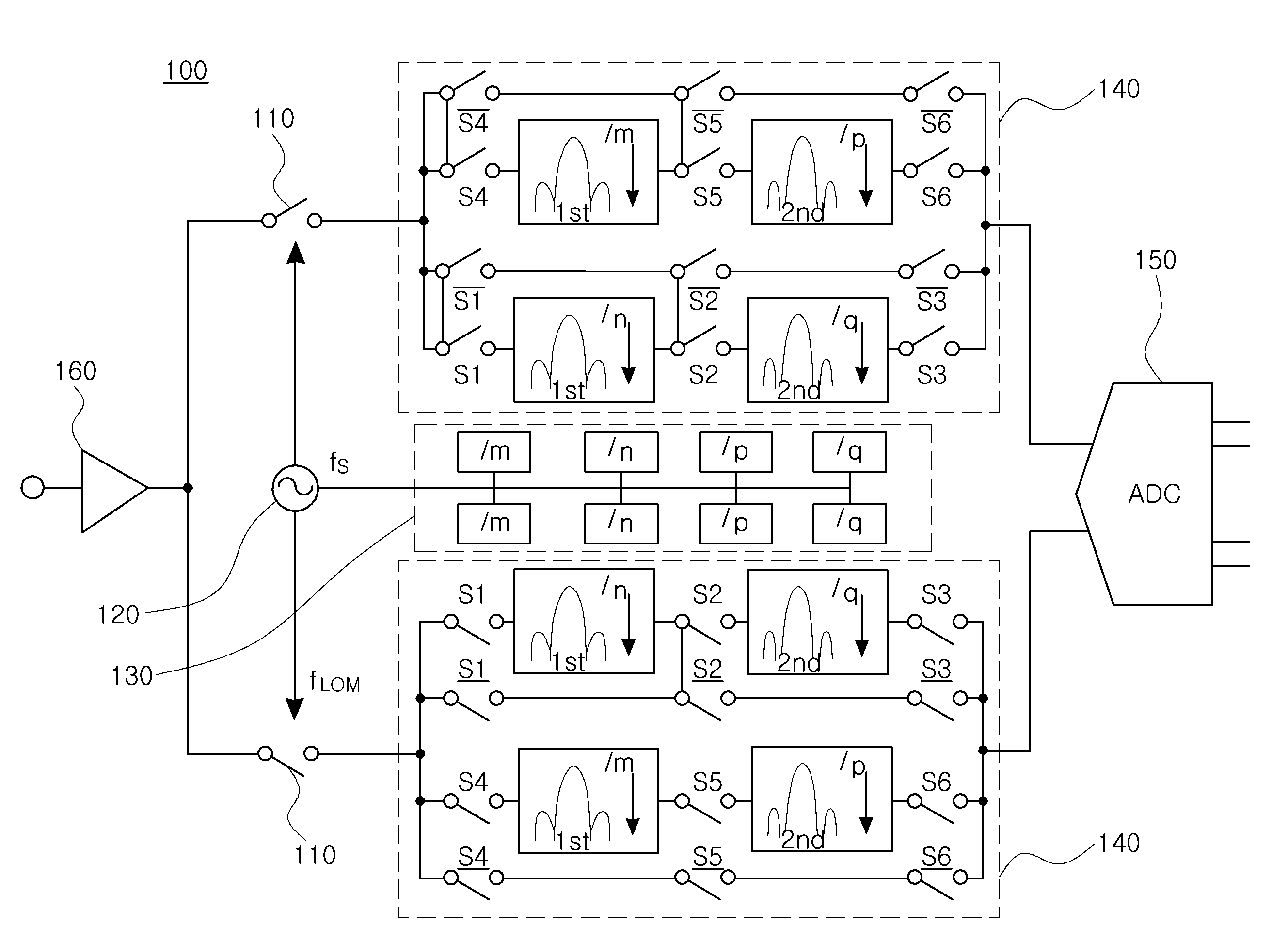
ActiveCN103828244AReduce sensitivitySolving the time-varying DC offset problemTransmissionDiscrete time filteringIntermediate frequency
The invention relates to a superheterodyne receiver (100), comprising: a sampling mixer (101) being configured to sample an analogue radio frequency signal (102) using a predetermined sampling rate (fs) to obtain a discrete-time sampled signal (104), and to shift the discrete-time sampled signal (104) towards a first intermediate frequency (|fRF-fLO|) to obtain an intermediate discrete-time signal (108) sampled at the predetermined sampling rate (fs); a discrete-time filter (103) being configured to filter the intermediate discrete-time signal (108) at the predetermined sampling rate (fs) to obtain a filtered signal (130); and a discrete-time mixer (109) being configured to shift the filtered signal (130) towards a second intermediate frequency (fIF).
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
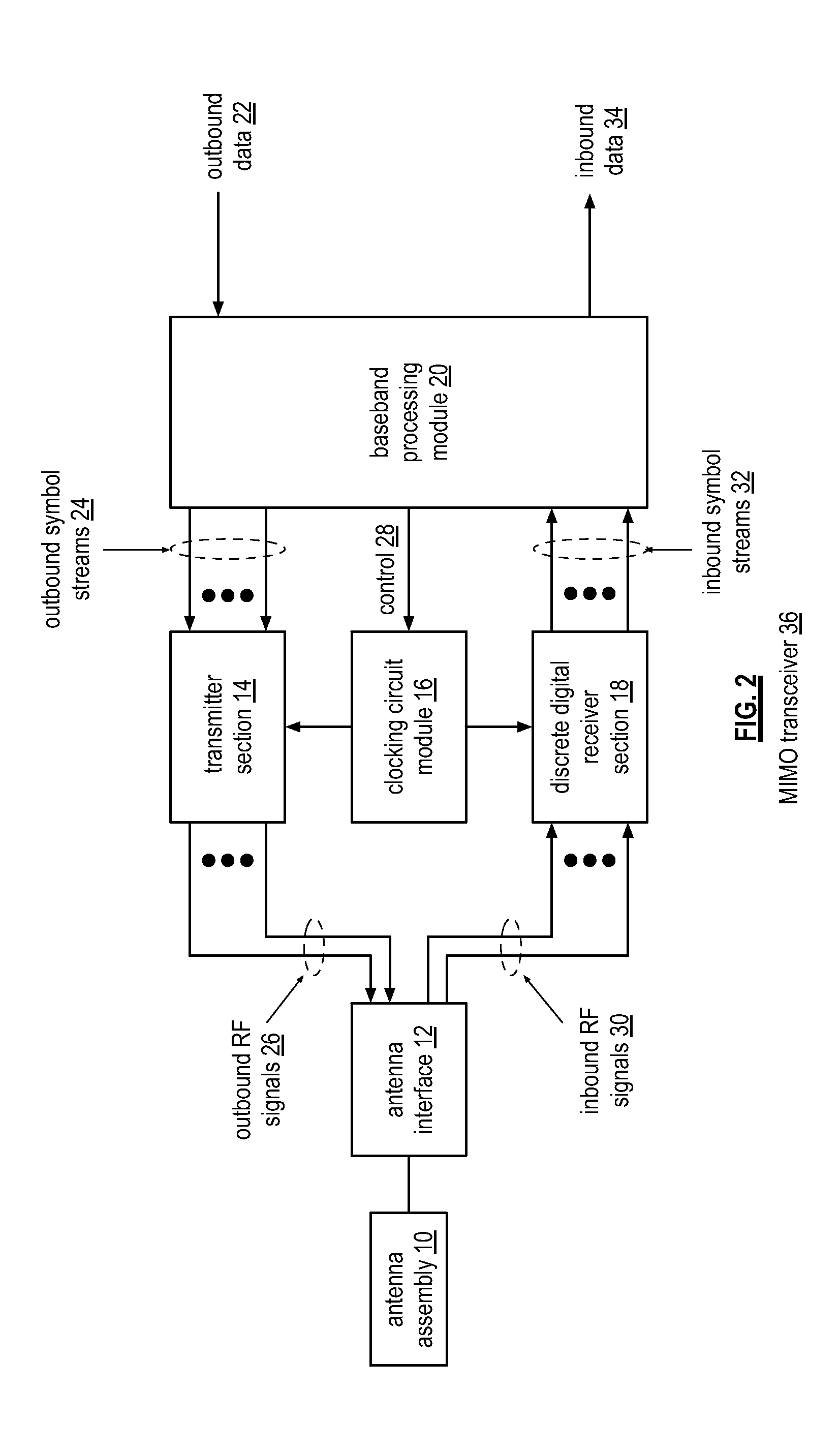
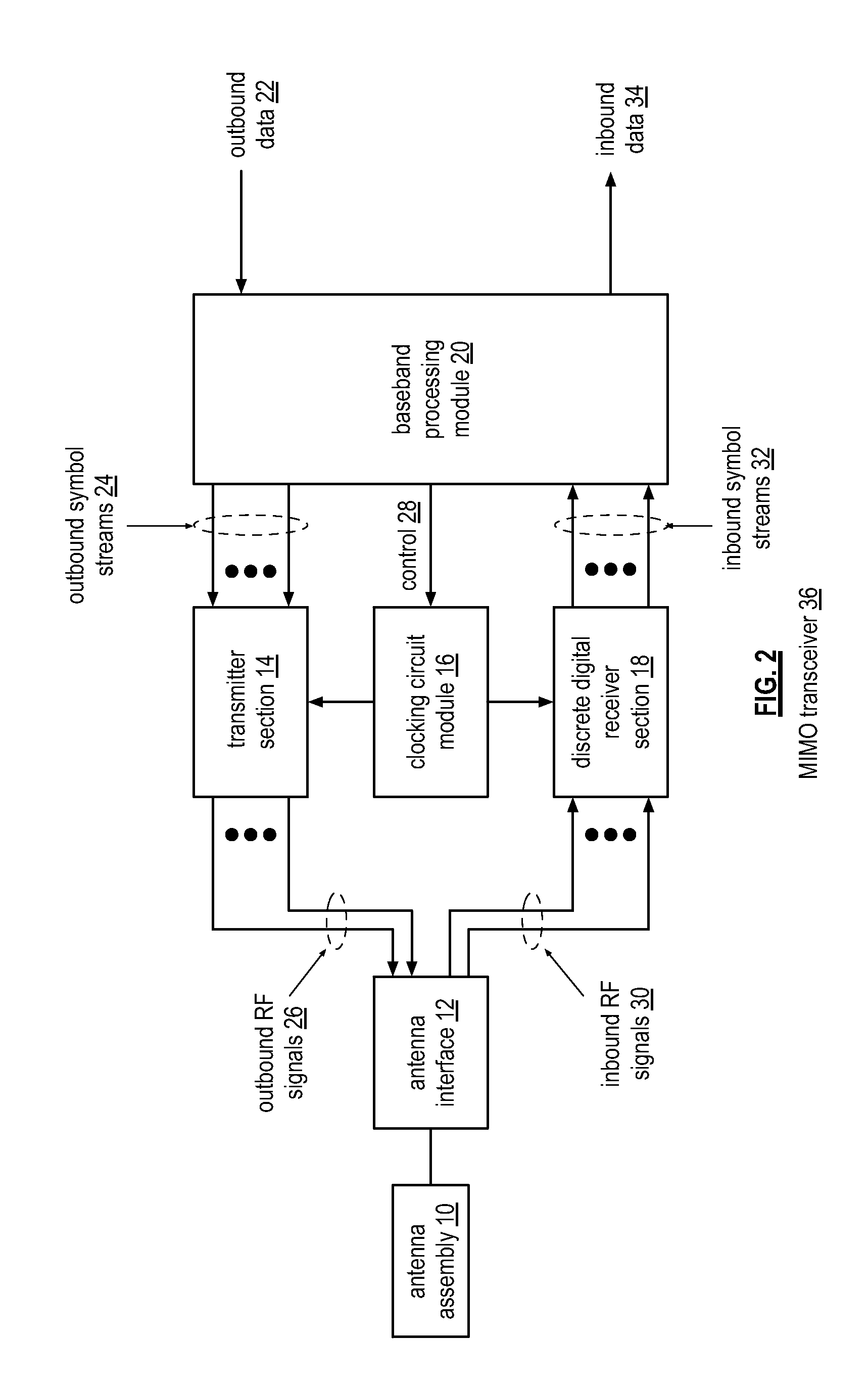
Multiple path discrete digital receiver
ActiveUS20130028362A1Multiple-port networksTransversal filtersBandpass filteringDiscrete time filtering
A receiver includes a bandpass filter module, a sample and hold module, first and second discrete time filter modules, and first and second conversion modules. The bandpass filter module is operable to filter an inbound wireless signal. The sample and hold module is operable to sample and hold the filtered inbound wireless signal to produce a frequency domain sample pulse train. The first discrete time filter module is operable to filter the frequency domain sample pulse train to produce a first filtered sample pulse. The second discrete time filter module is operable to filter the frequency domain sample pulse train to produce a second filtered sample pulse. The first conversion module is operable to convert the first filtered sample pulse into a first inbound baseband signal. The second conversion module is operable to convert the second filtered sample pulse into a second inbound baseband signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
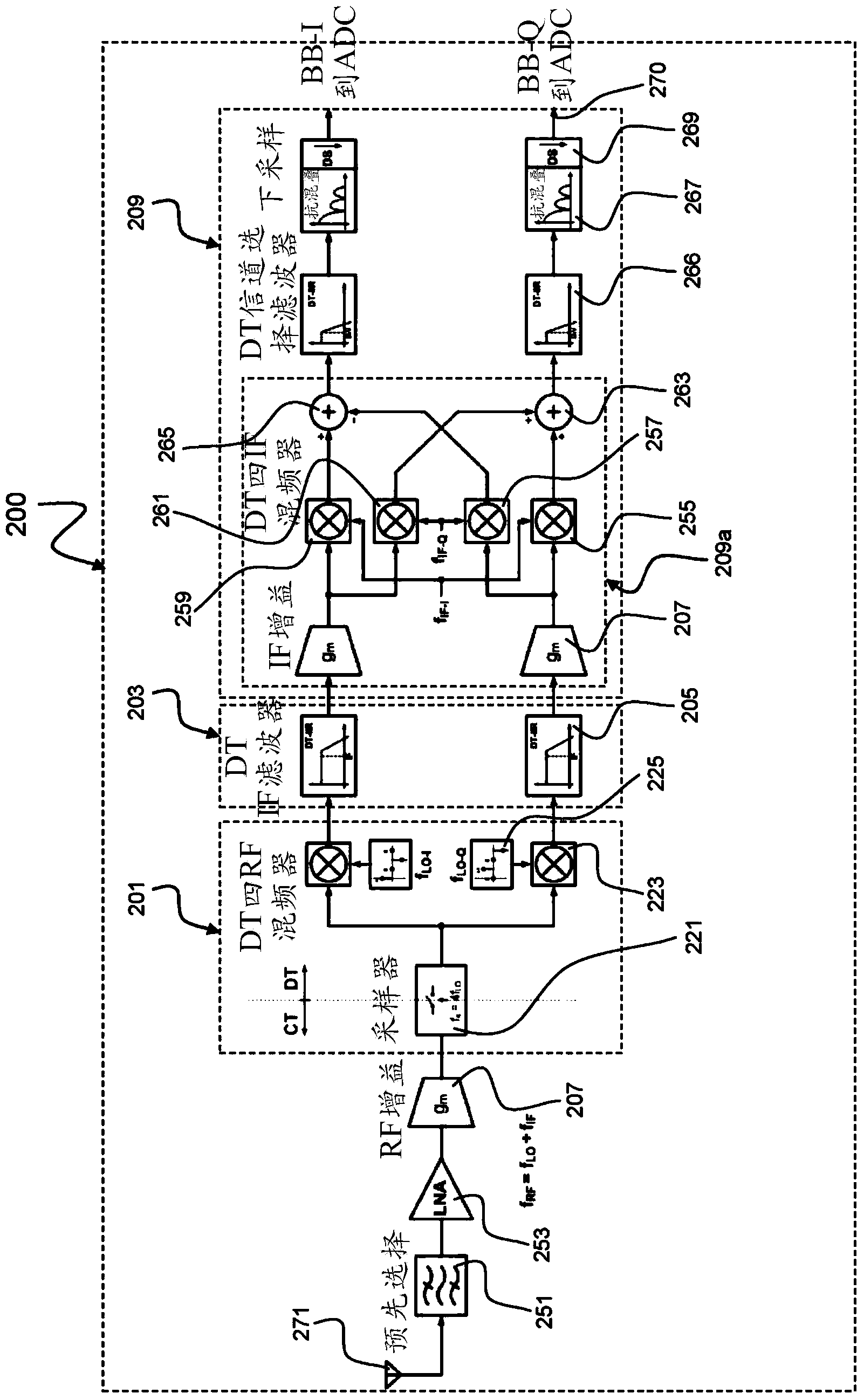
Receiver apparatus and reception method
ActiveUS20100246557A1Area consumption be reducedReduce chip areaFrequency-division multiplexLine-faulsts/interference reductionDiscrete time filteringCarrier signal
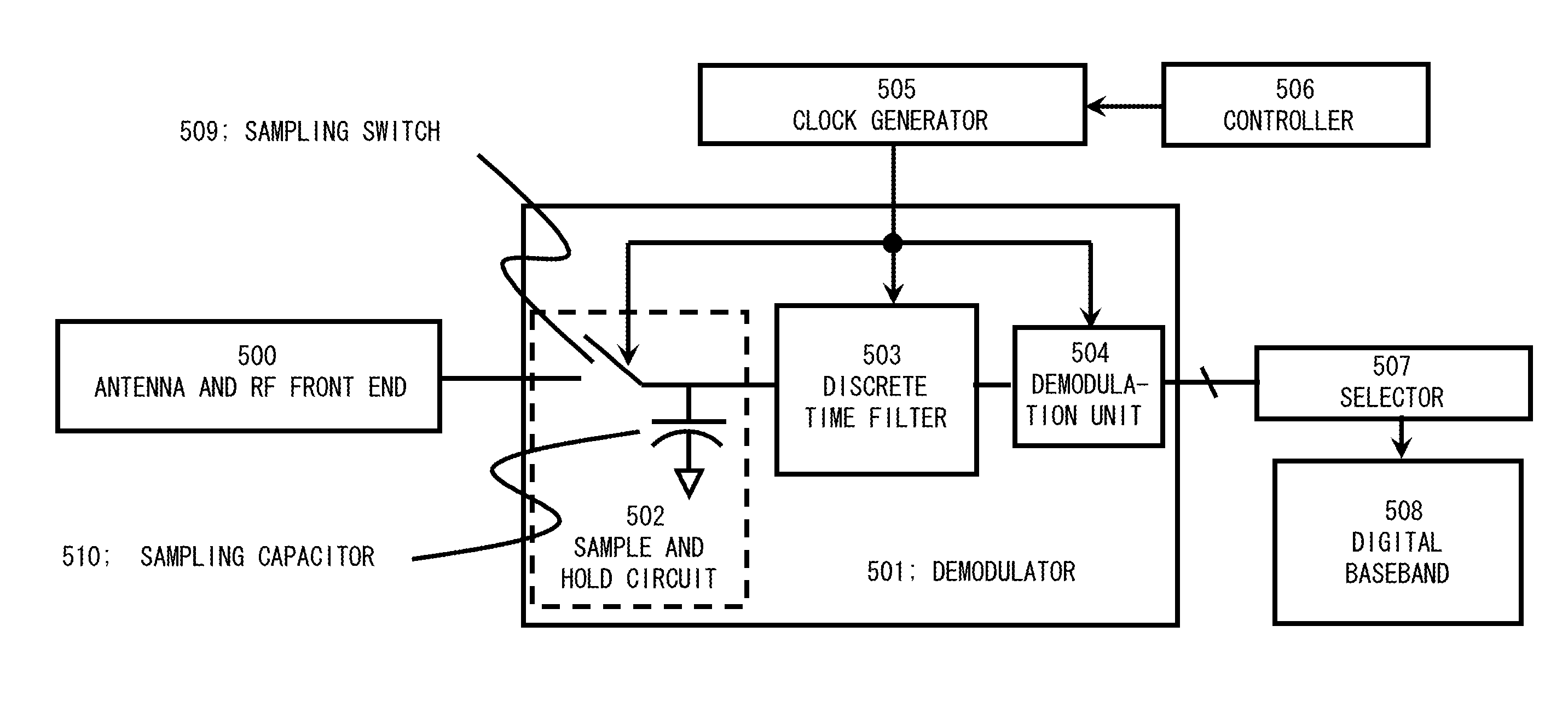
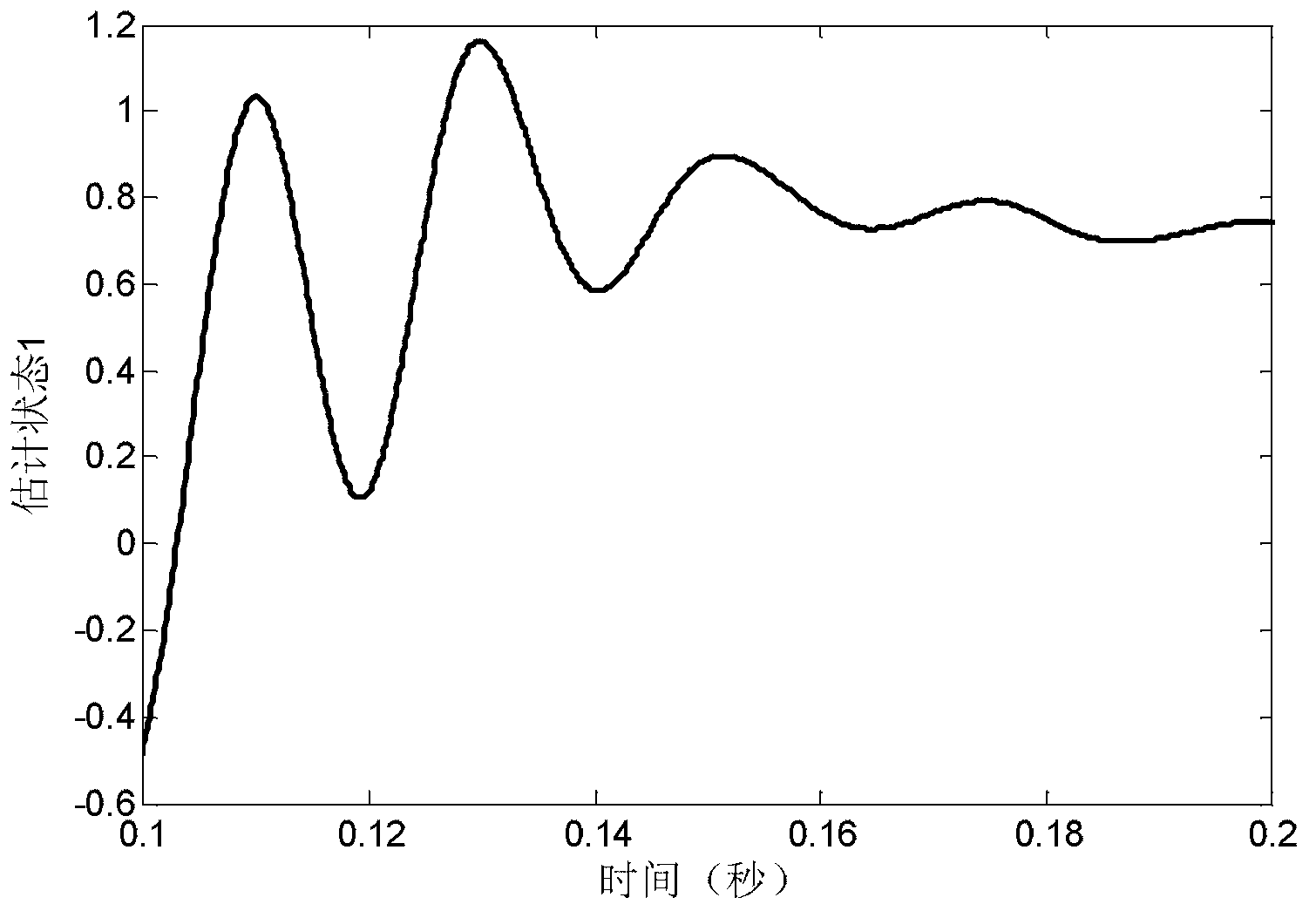
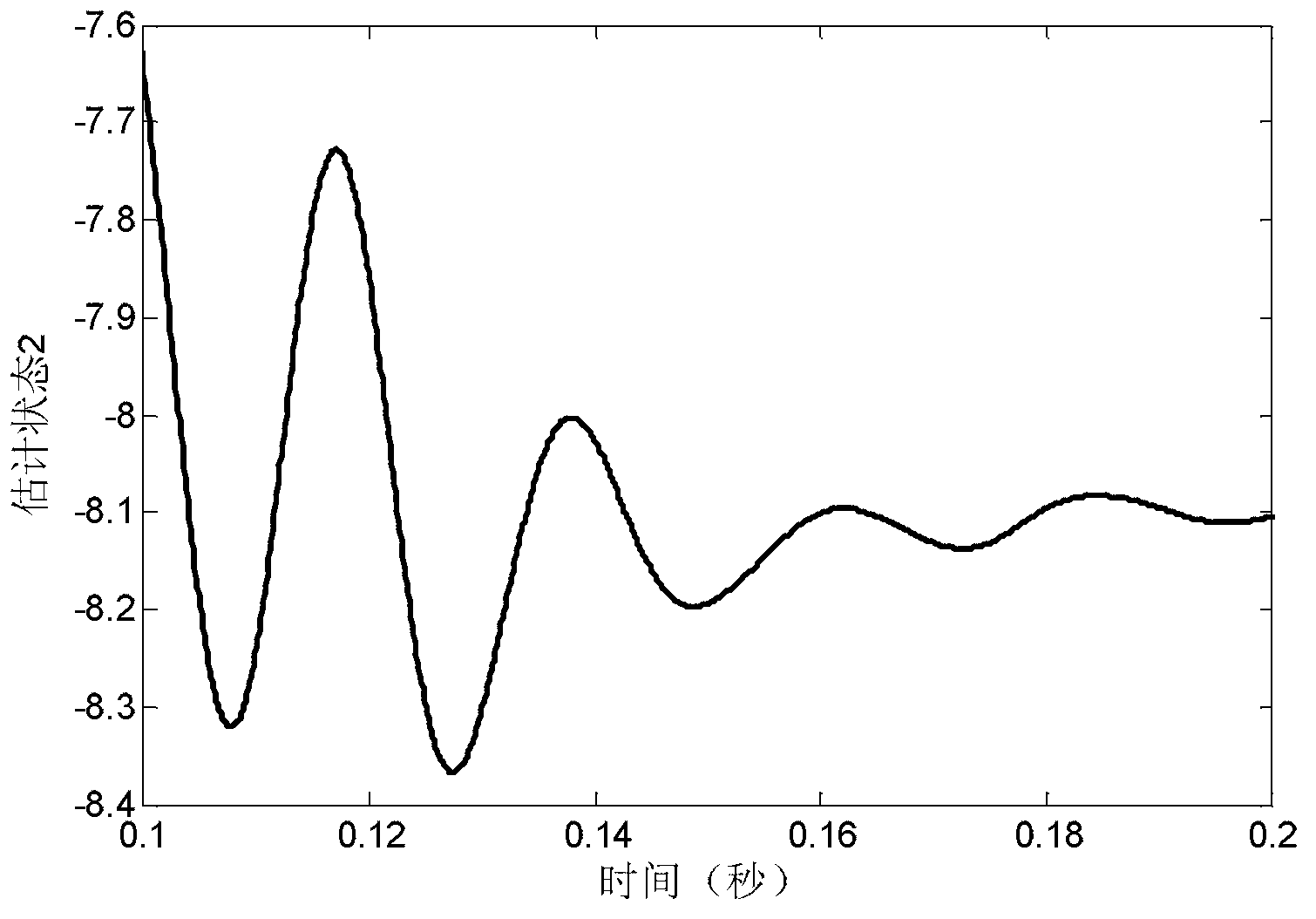
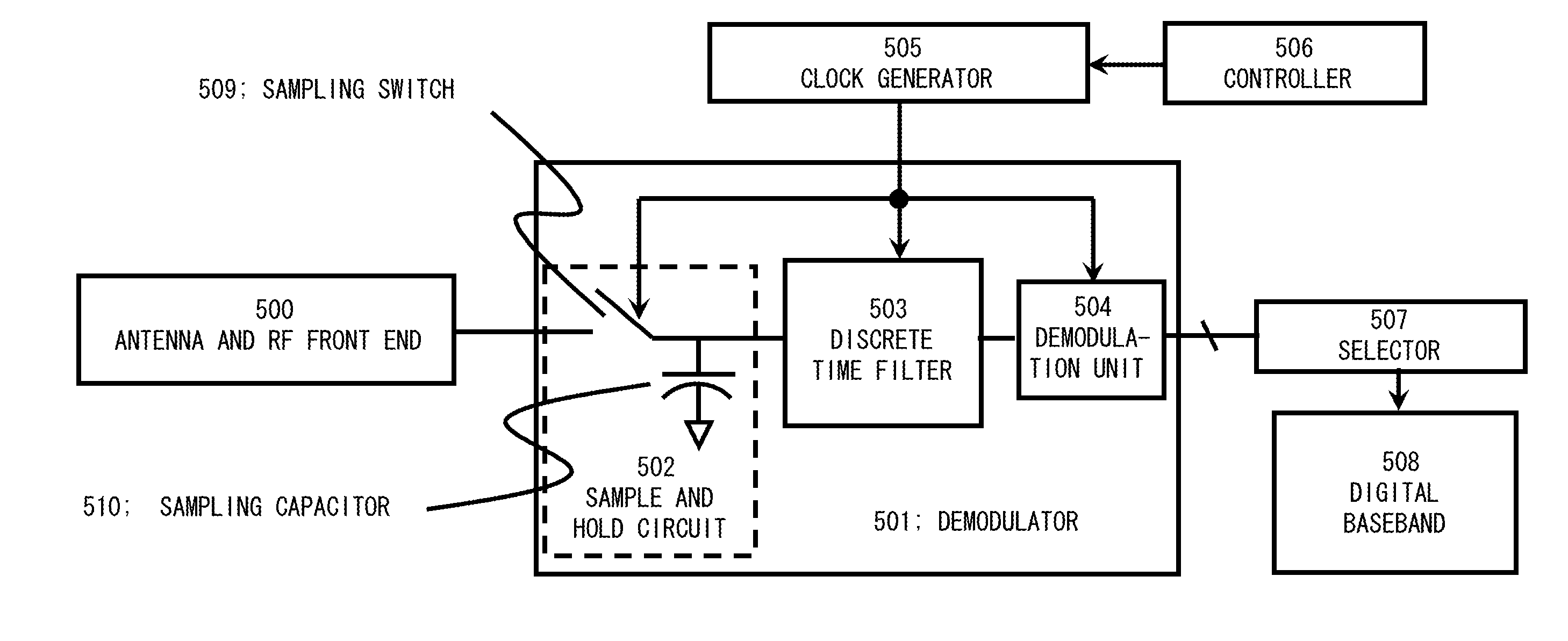
A receiver includes a sample and hold circuit that receives a signal (continuous time signal) that has been subject to frequency division multiplexing modulation, converts the signal to a discrete time signal, and outputs the discrete time signal, a discrete time filter that receives the signal output from the sample and hold circuit and attenuates a frequency component of a subcarrier different from a specified subcarrier, and a demodulation unit that extracts a digital baseband from a signal that has passed through the discrete time filter to complete a demodulation operation within one data symbol reception period.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multiple input discrete digital receiver
InactiveUS20130028363A1Multiple-port networksTransversal filtersDiscrete time filteringComputer module
A receiver includes a sample and hold module, a discrete time filter module, and a conversion module. The sample and hold module is operable to sample and hold a first inbound wireless signal and a second inbound wireless signal to produce a frequency domain sample pulse train. The discrete time filter module is operable to filter the frequency domain sample pulse train to produce a first filtered sample pulse corresponding to the first inbound wireless signal and to produce a second filtered sample pulse corresponding to the second inbound wireless signal. The conversion module is operable to convert the first filtered sample pulse into a first inbound baseband signal and to convert the second filtered sample pulse into a second inbound baseband signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Device and method for receiving RF signals based on heterodyne architecture using complex IF subsampling
InactiveUS8705675B2Reduce power consumptionReduce usageModulated-carrier systemsTransmission monitoringBandpass filteringDiscrete time filtering
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
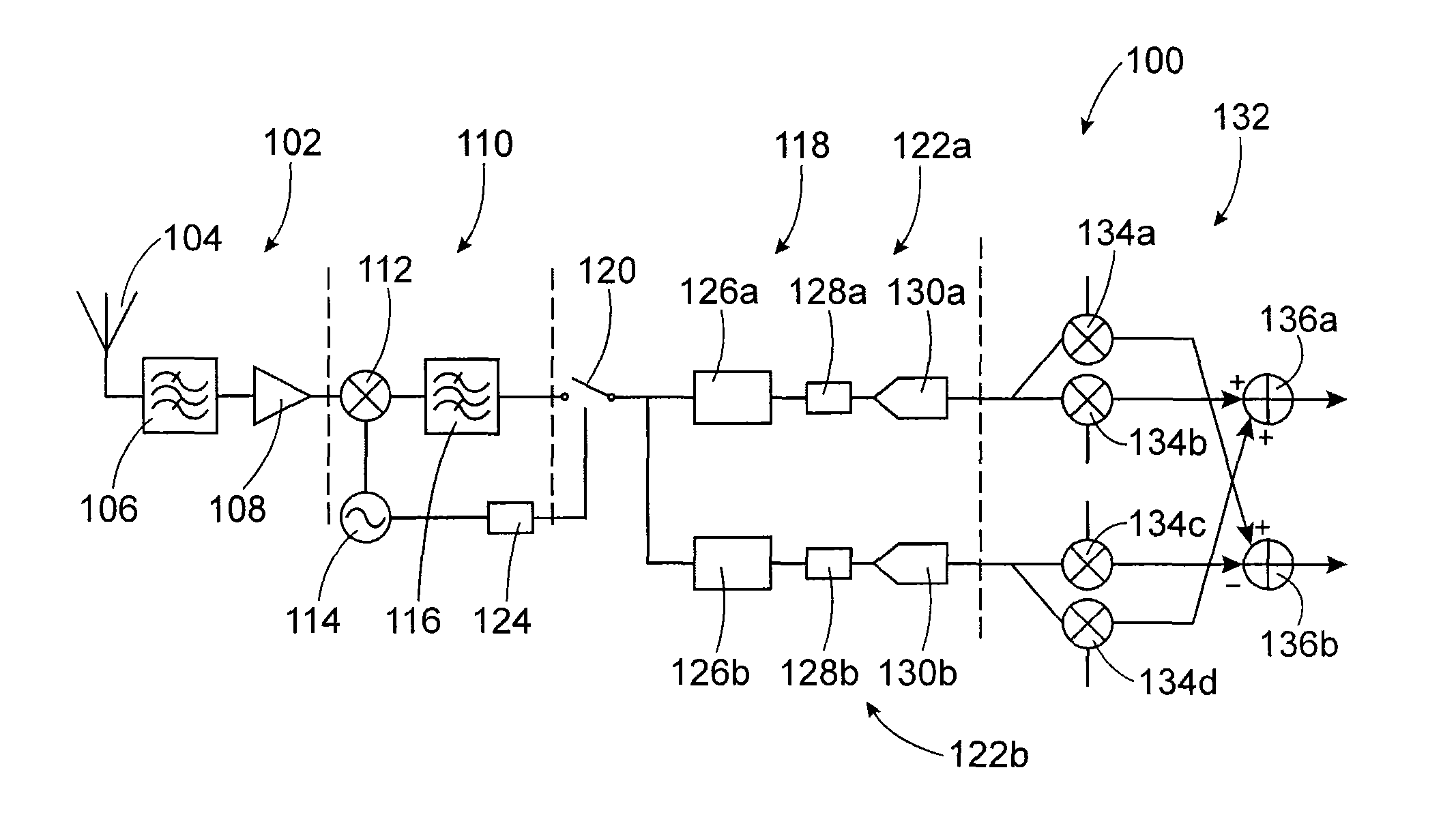
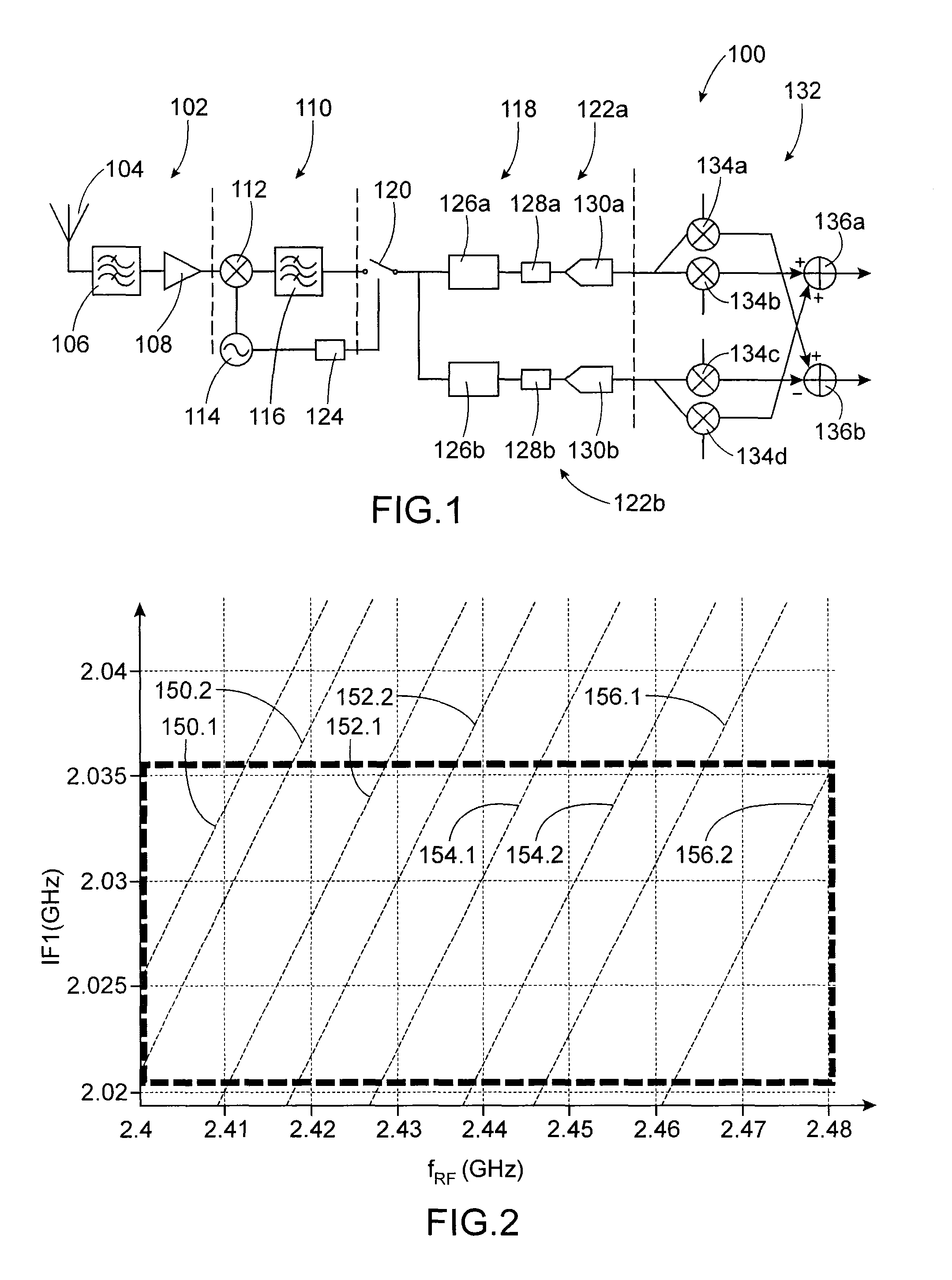
Device and method for receiving RF signals based on heterodyne architecture using complex if subsampling
InactiveUS20120250810A1Reduce usageReduce frequencyAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsBandpass filteringDiscrete time filtering
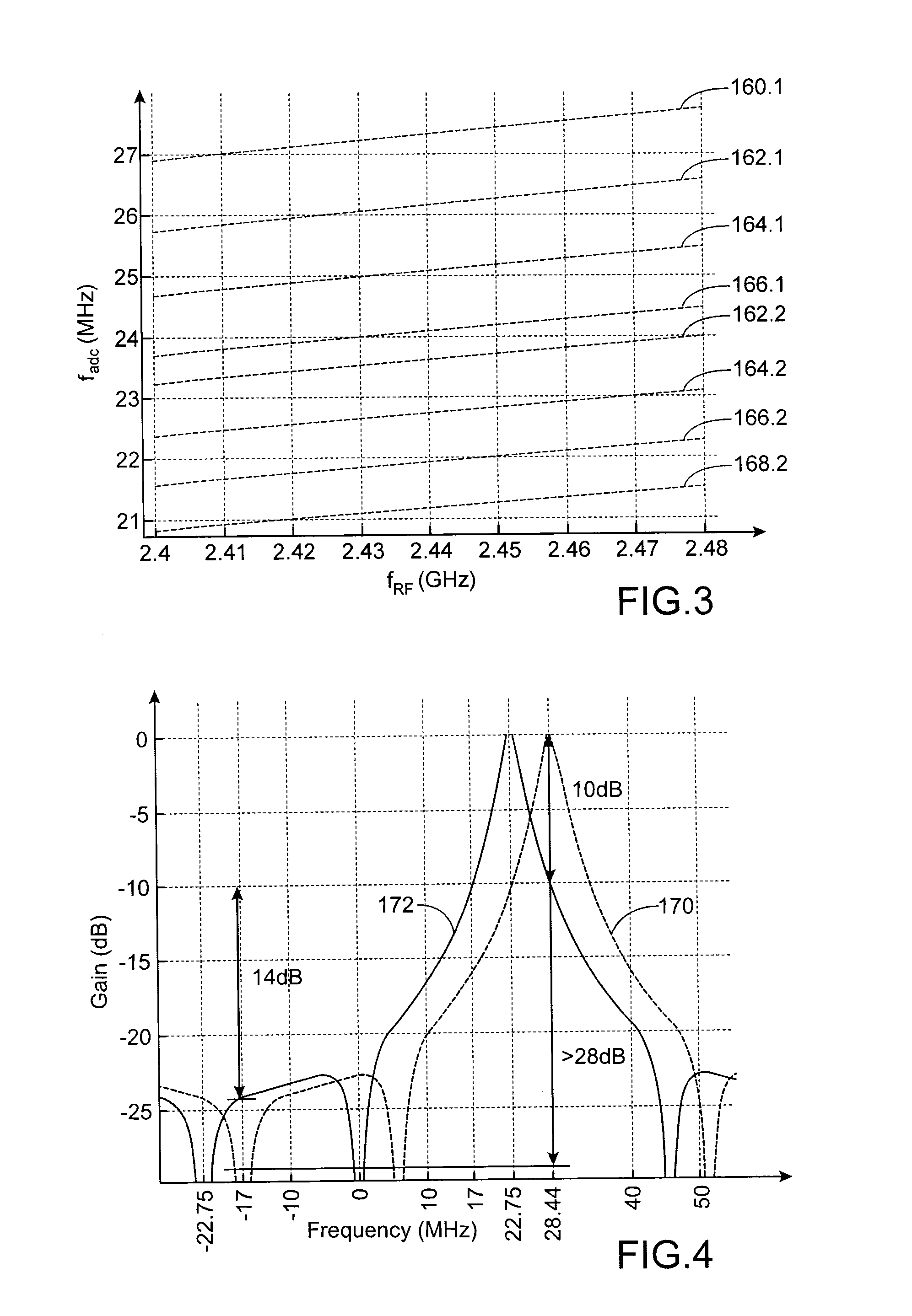
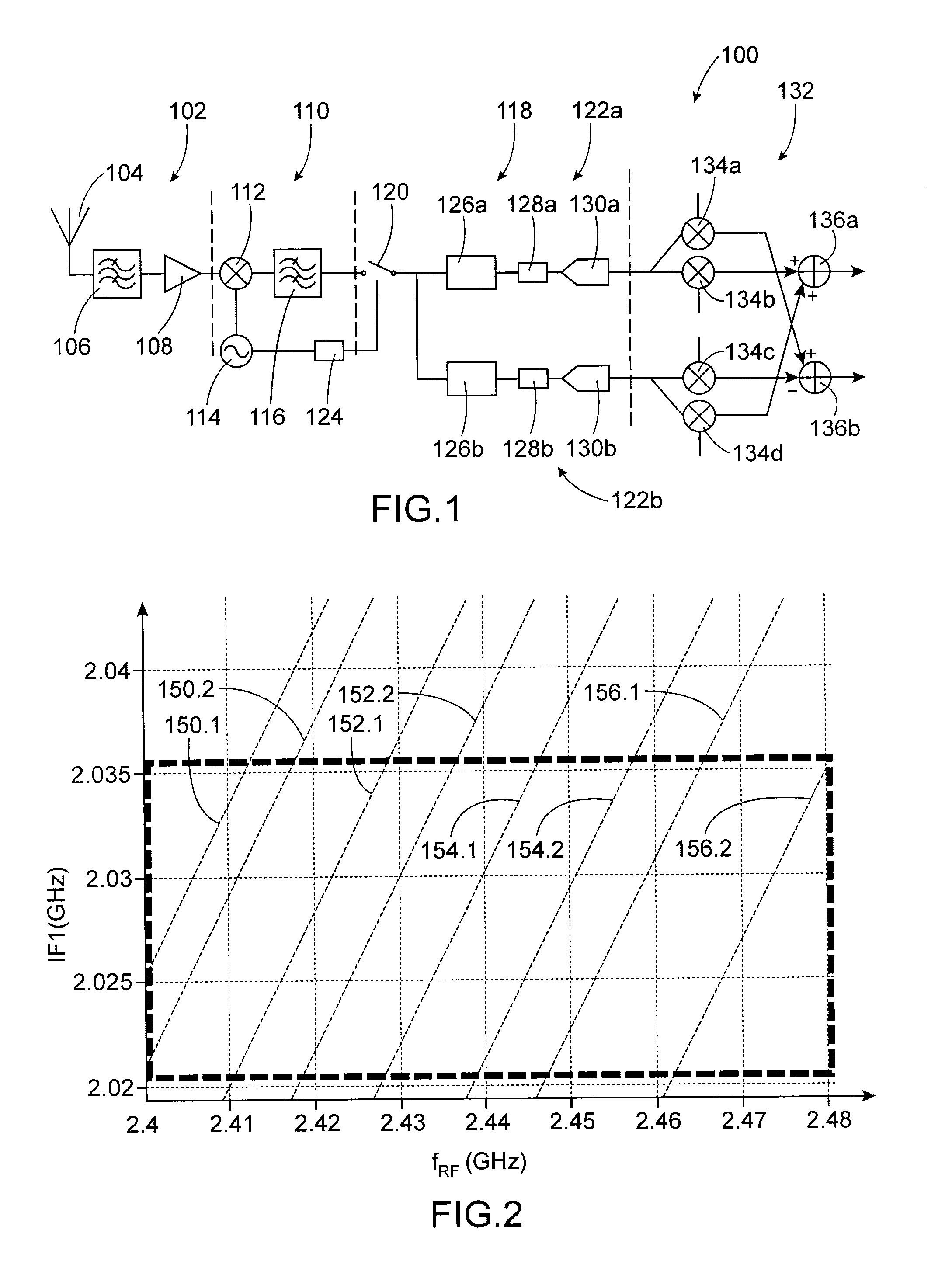
An RF signal reception device including: a transposition device of signals of frequency fRF to a first intermediate frequency IF1<fRF; a first bandpass filter centered on IF1; a sampler at a frequency fs<IF1; a second discrete-time filter centered on a second intermediate frequency IF2=α·fs / M+fs / (M·n); a decimation device of a factor M; an analog-digital convertor to operate at a frequency fs / M; where α, n and M are strictly positive real numbers chosen such that: α<fs / (2·BWch·M), and BWch / 2<fs / M·n), with BWch: bandwidth of a channel of the received RF signals.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
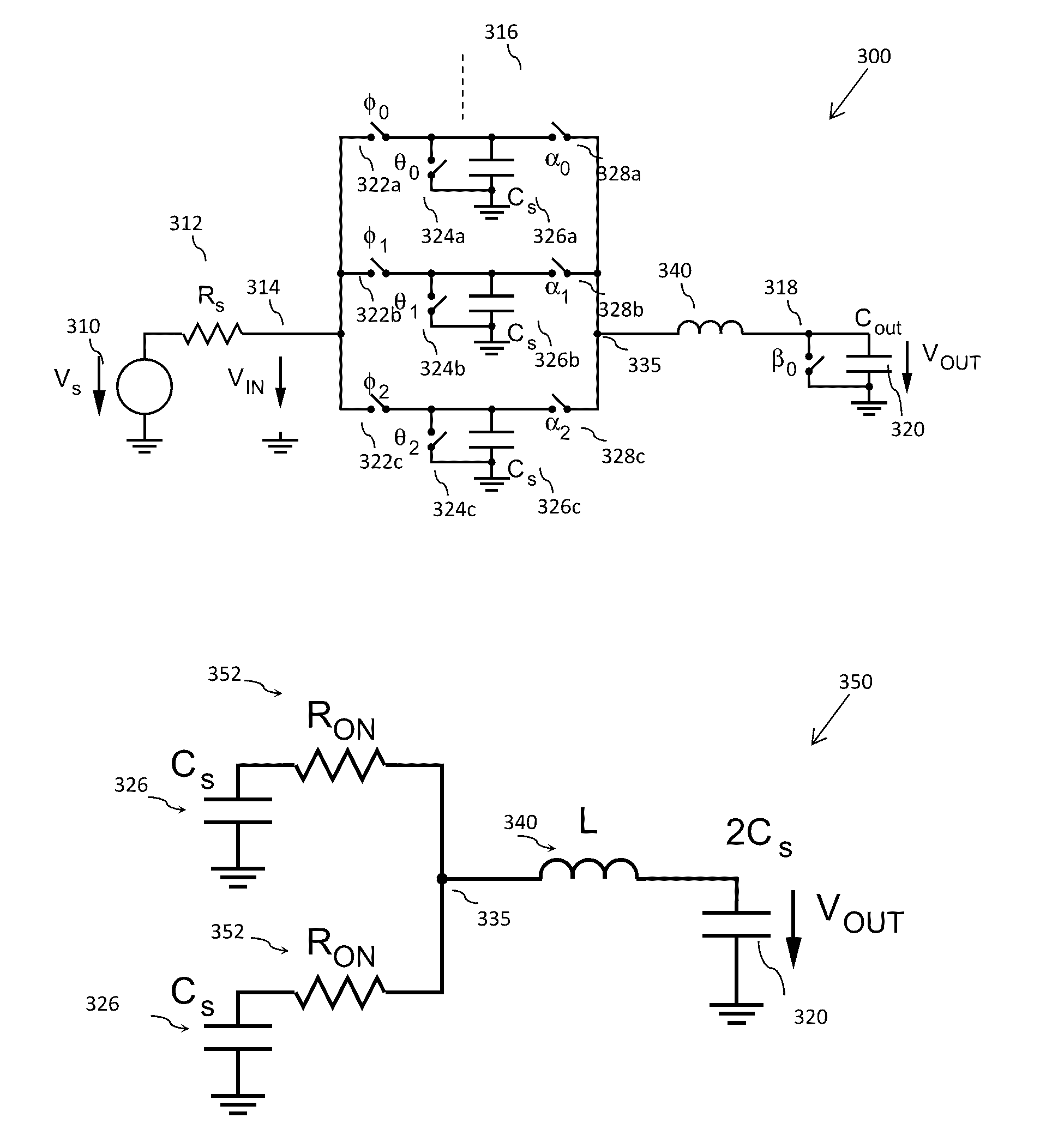
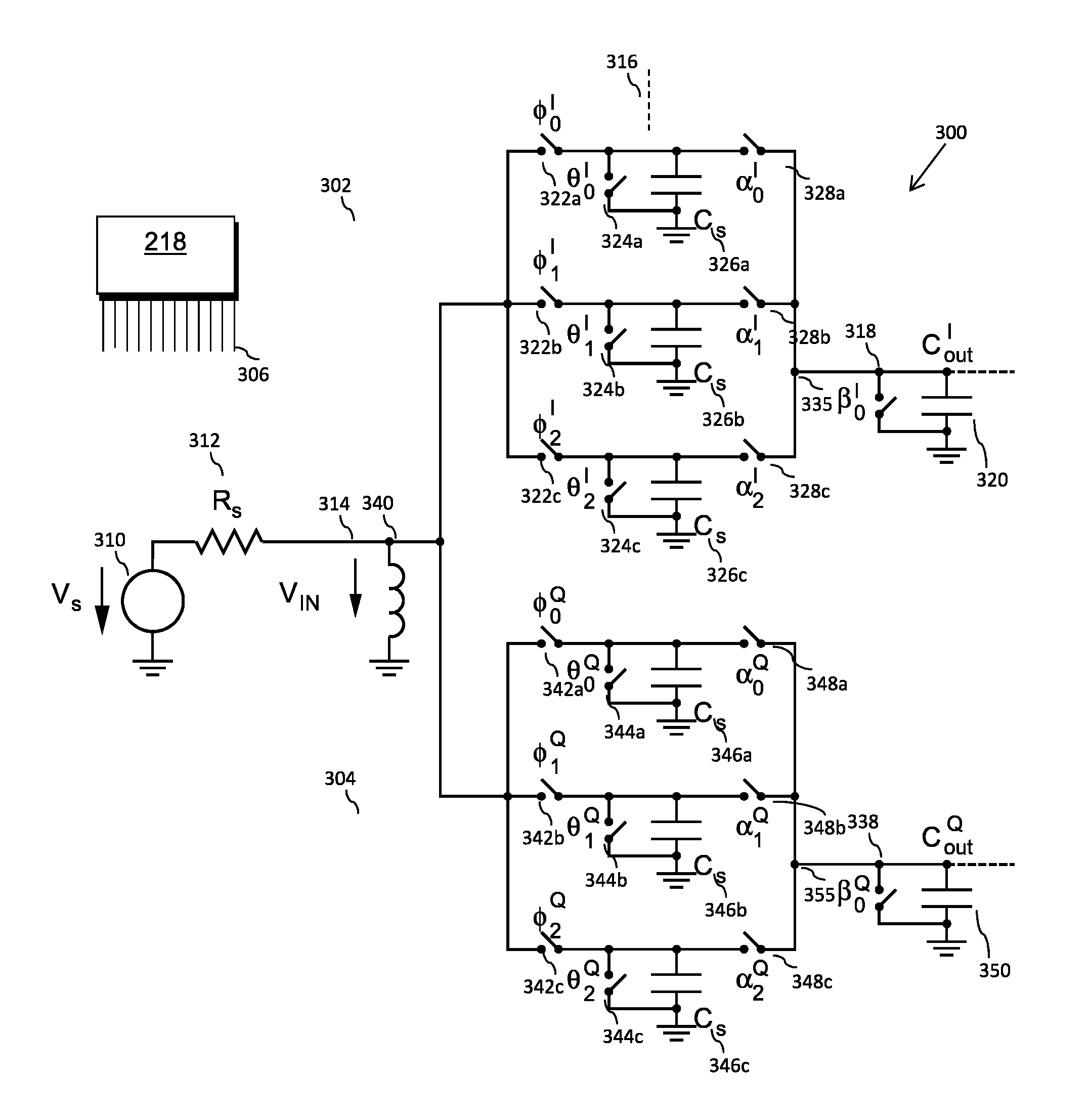
Discrete time filter, communication unit, and method for resonant charge transfer
ActiveUS20170012607A1Reduced band widthTransversal filtersAdaptive networkCapacitanceCommunication unit
A discrete time filter, DTF, is described that comprises a summing node; N parallel branches, each branch having a set of input unit sampling capacitances where each unit sampling capacitance is independently selectively coupleable to the summing node; and an output capacitance connected to the summing node. The output capacitance has a value equal to a sum of the sampling capacitances that are to be selectively connected to the summing node; and the discrete time filter further comprises an inductance connected between the summing node and the output capacitance.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
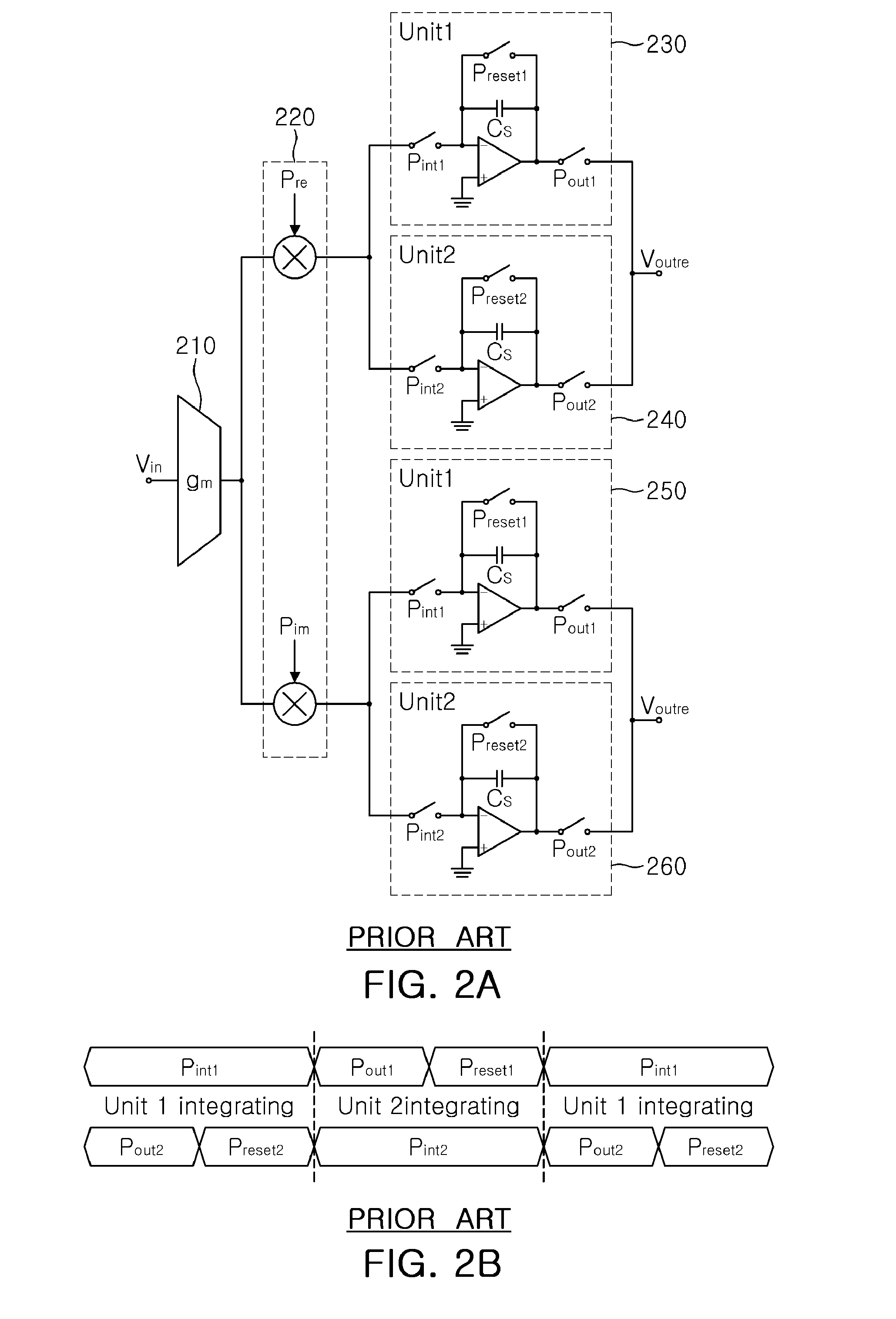
Discrete-time filter apparatus and discrete-time receiver system having the same
The discrete-time receiver system includes: a voltage current conversion device low-noise-amplifying an input voltage signal, and converting the amplified signal into a current signal; a first filter performing IIR filtering on the current signal output from the voltage current conversion device; a discrete-time filter performing FIR filtering on a signal output from the first filter; and a second filter performing IIR filtering on a signal output from the discrete-time filter, wherein the discrete-time filter includes a plurality of current supply units generating a current having a size obtained by multiplying an input current by a determined gain, respectively, an adding unit adding currents supplied from the plurality of current supply units, and a plurality of controllers connecting the plurality of current supply units and the adding unit and controlling the flow of current supplied from the current supply units to the adding unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
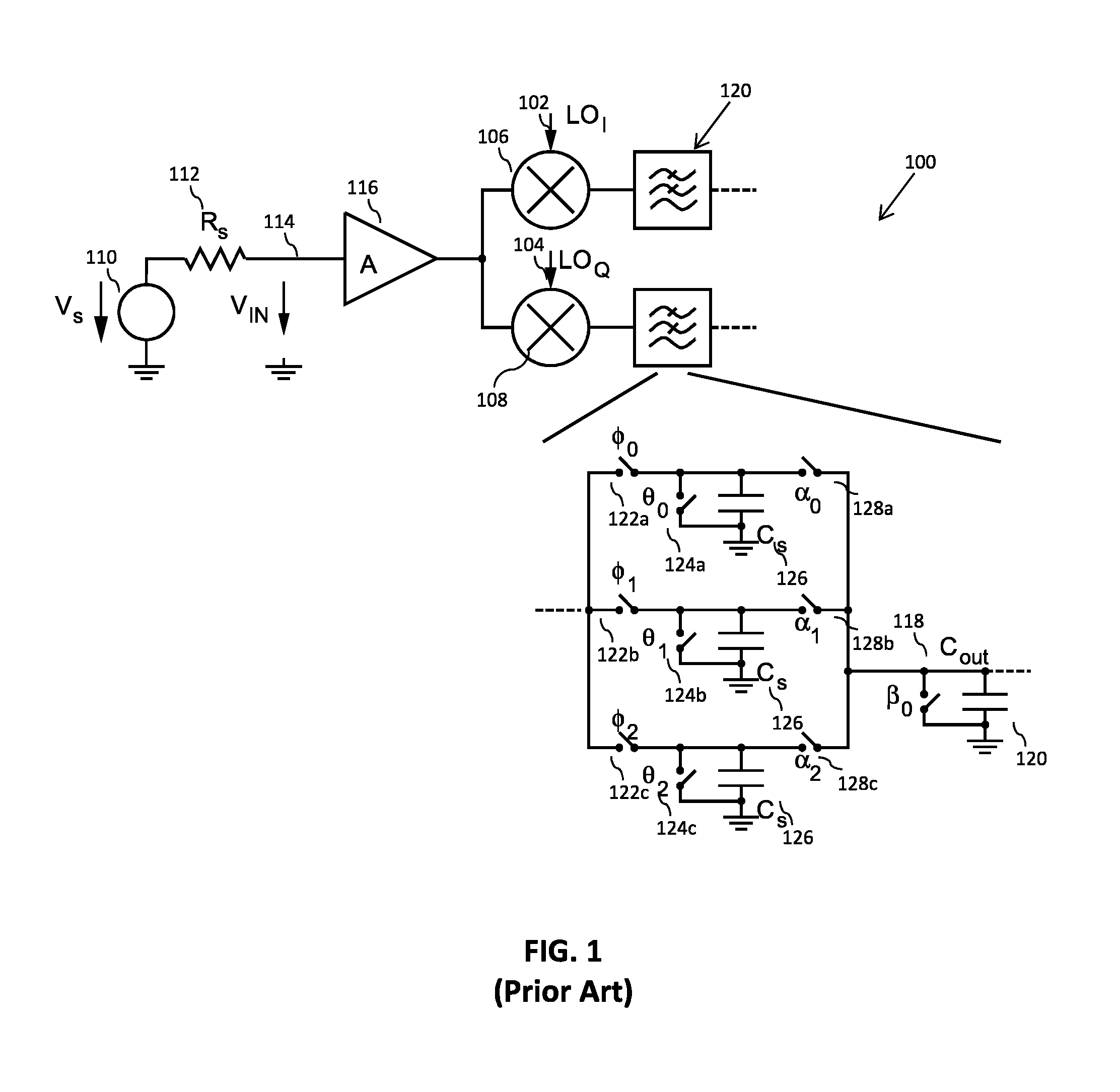
Receiver, communication unit, and method for down-converting a radio frequency signal
ActiveUS20170012655A1Increase capacitance densityReduce areaTransversal filtersAdaptive networkFinite impulse responseCapacitance
There is provided a communication receiver comprising: an input for receiving a radio frequency, RF, input signal; and at least one finite impulse response, FIR, discrete time filter, DTF. The at least one FIR DTF comprises: an input circuit comprising an input port for sampling the RF input signal at a sampling frequency that is comparable to the input RF input signal; and N parallel branches, each branch having a set of input unit sampling capacitances, where each unit sampling capacitance is independently selectively coupleable to an output summing node. The input circuit is configured to convert an equivalent input impedance of the at least one FIR DTF around the sampling frequency to a real impedance.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
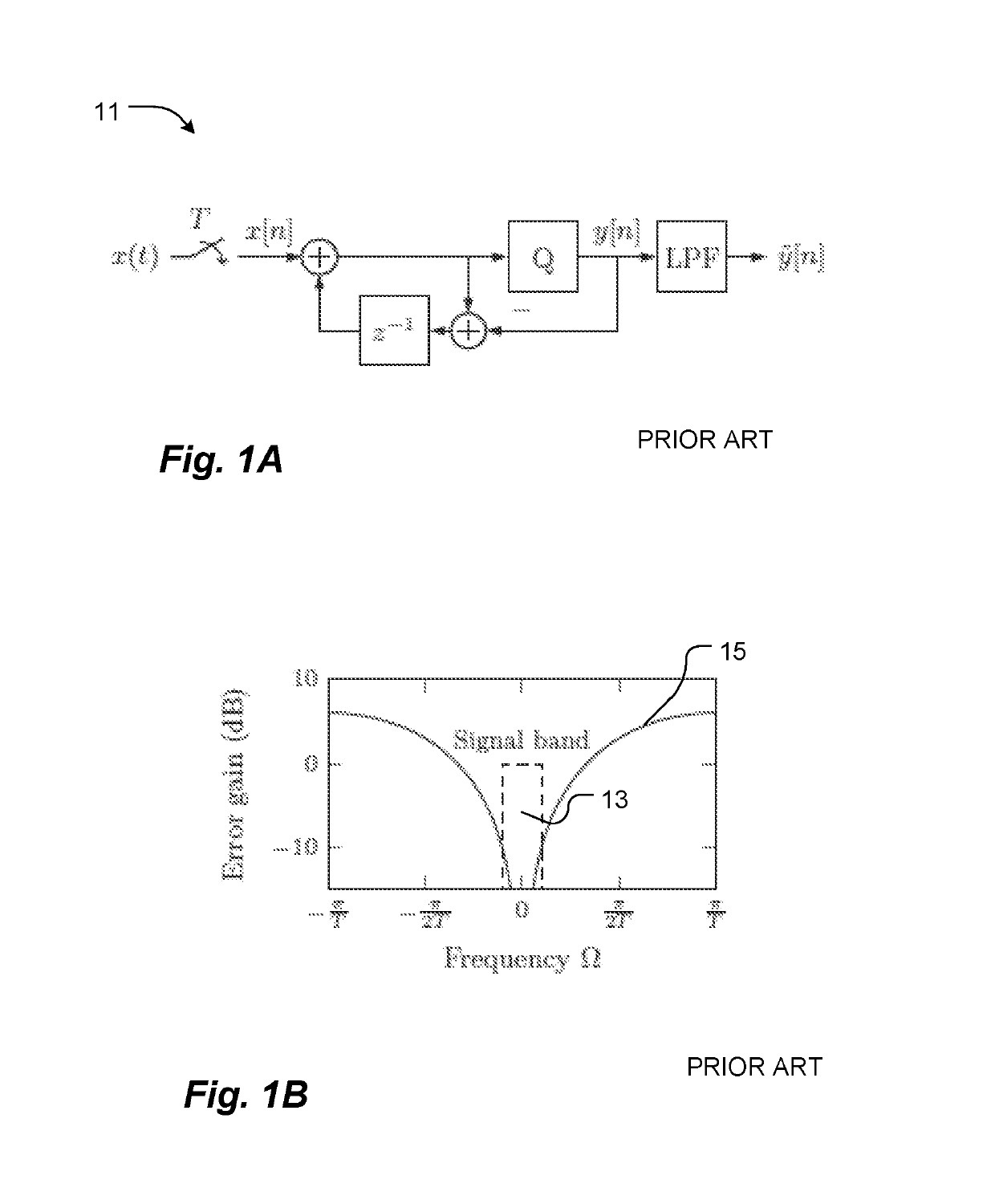
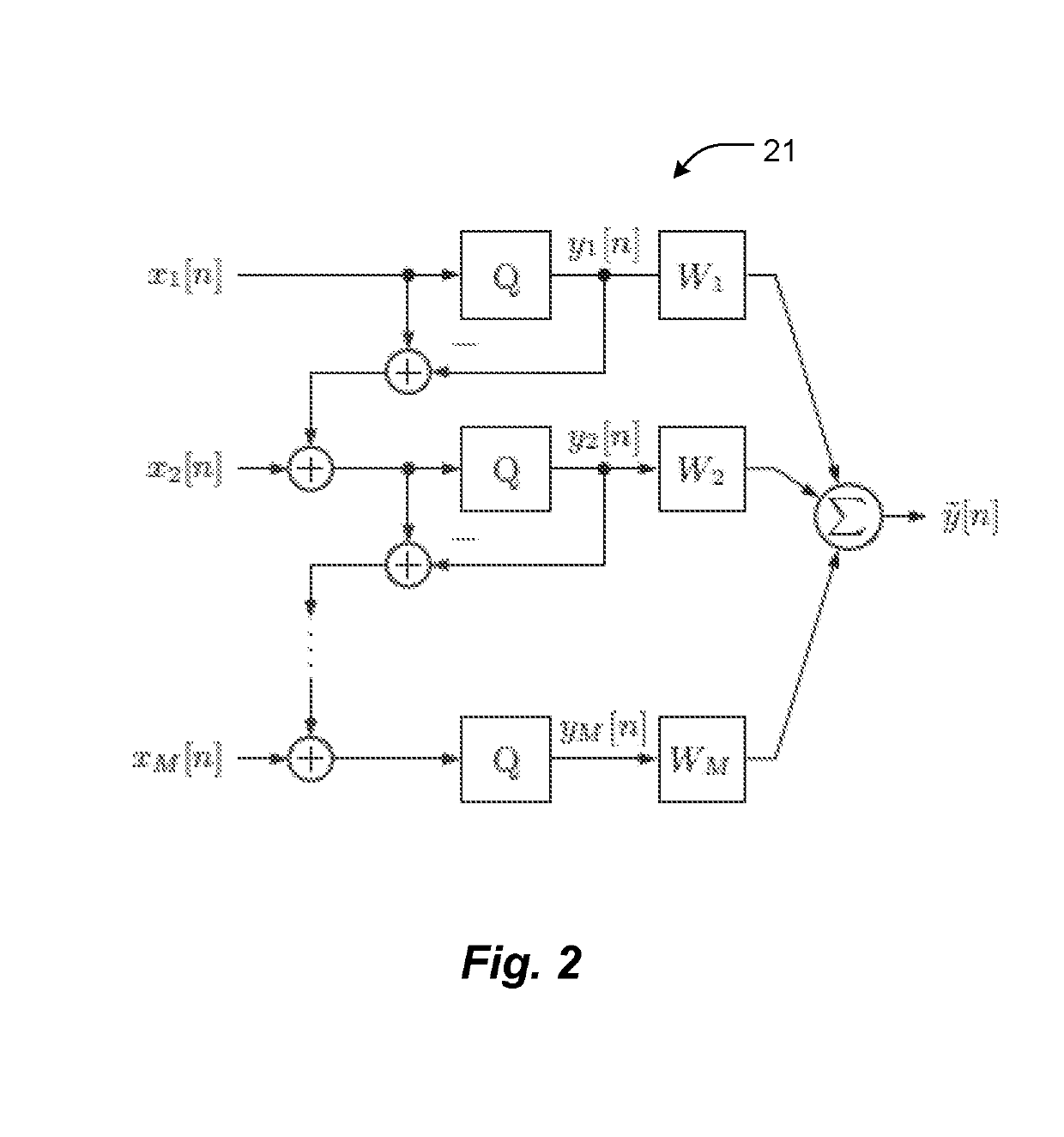
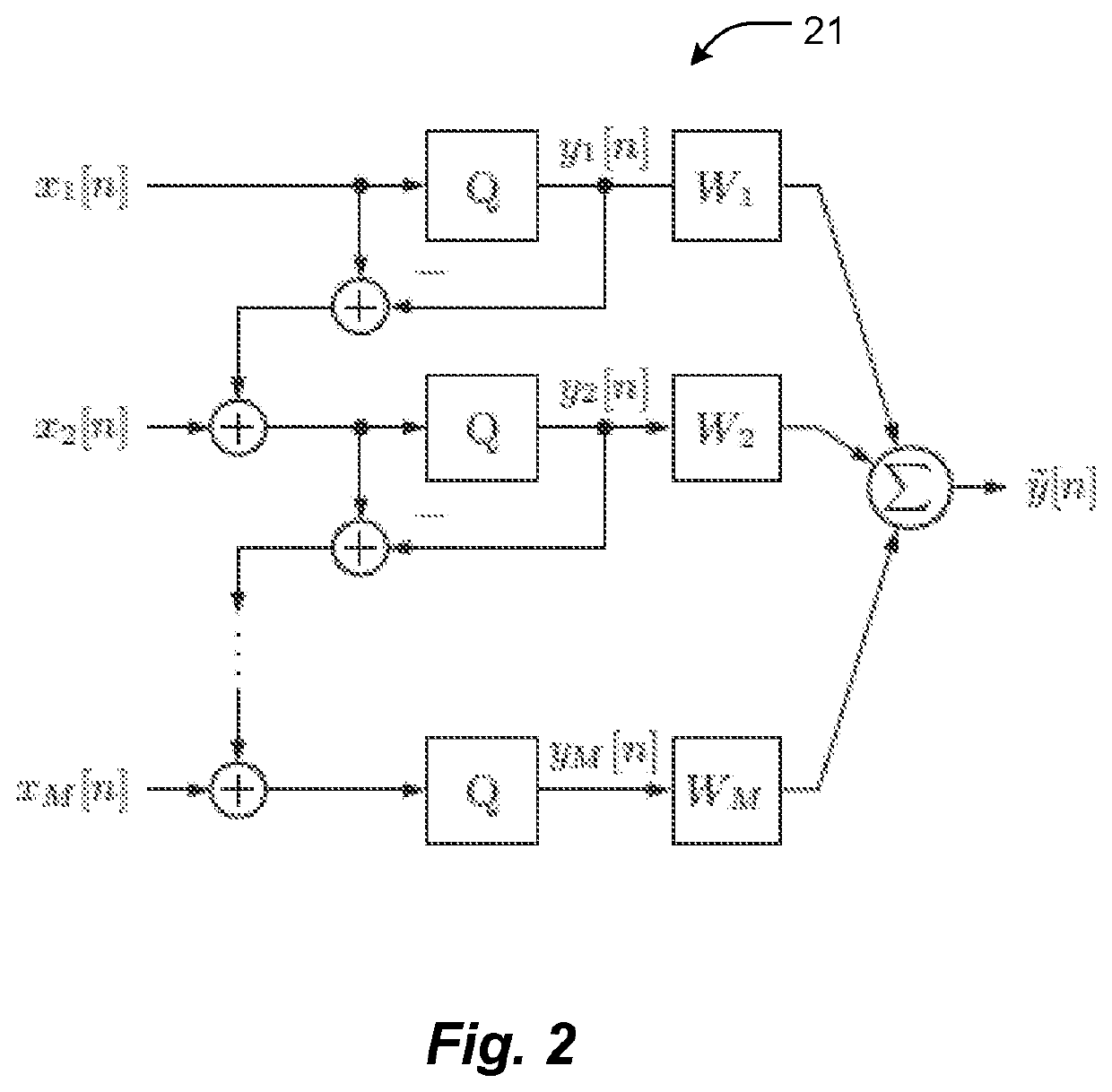
Space-time oversampling and error shaping for coarsely quantized arrays
ActiveUS20190238373A1Reduce dimensionalityAnalogue conversionSource coding adaptationSensor arrayMulti input
Methods and apparatus for shaping and filtering quantization errors conjointly in space and time to produce a higher-precision output in a spatially and temporally oversampled array. A space-time error-shaping array system has an array of sensors, each sensor producing a temporal signal comprising quantized waveforms. A multi-input multiple-output (MIMO) discrete-time filter structure with multiple inputs, each coupled to a sensor of the array of sensors, shapes quantization errors of the array of sensors on the basis of temporal aspects of the quantized waveforms conjointly with spatial aspects of the quantized waveforms.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Programmable discrete digital receiver components
ActiveUS20130028359A1Multiple-port networksTransversal filtersDiscrete time filteringComputer module
A receiver includes a sample and hold module, a discrete time filter module, and a conversion module. The sample and hold module includes a sample switching module, an impedance module, and a hold switching module. The sample switching module outputs samples of an inbound wireless signal in accordance with a sampling clock signal. The impedance module temporarily stores the samples. The hold switching module outputs a filtered representation of the samples in accordance with a hold clock signal to produce a frequency domain sample pulse train, wherein a filter response of the sample and hold module is in accordance with a ratio between the sampling clock signal and the hold clock signal. The discrete time filter module, which may be programmable, filters the frequency domain sample pulse train. The conversion module, which may be programmable, converts the filtered sample pulse into an inbound baseband signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
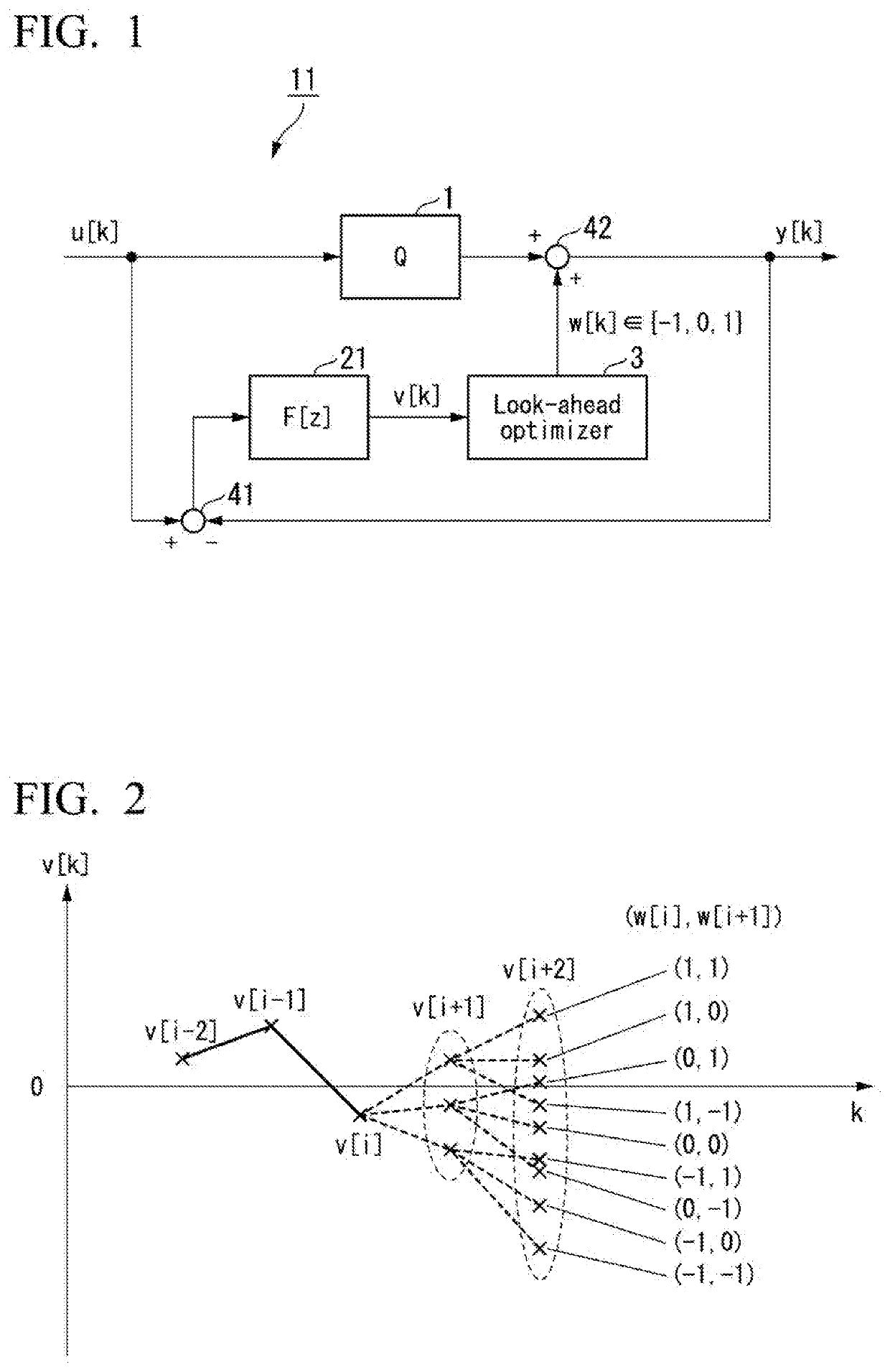
Re-Quantization Device Having Noise Shaping Function, Signal Compression Device Having Noise Shaping Function, and Signal Transmission Device Having Noise Shaping Function
ActiveUS20200266828A1Suppressing increase in quantization noiseSuppress of ratioAnalogue conversionDiscrete time filteringNoise shaping
What is provided is a subtractor, as a re-quantization device, which is configured to detect re-quantization noise, a discrete time filter which is configured to perform frequency weighting on the detected re-quantization noise, an adder which is configured to add an additional signal to quantization noise, and an additional signal selector which is configured to select a value at the present time of a column of an additional signal for minimizing the magnitude of quantization noise having been subjected to frequency weighting evaluated one sampling or more later.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
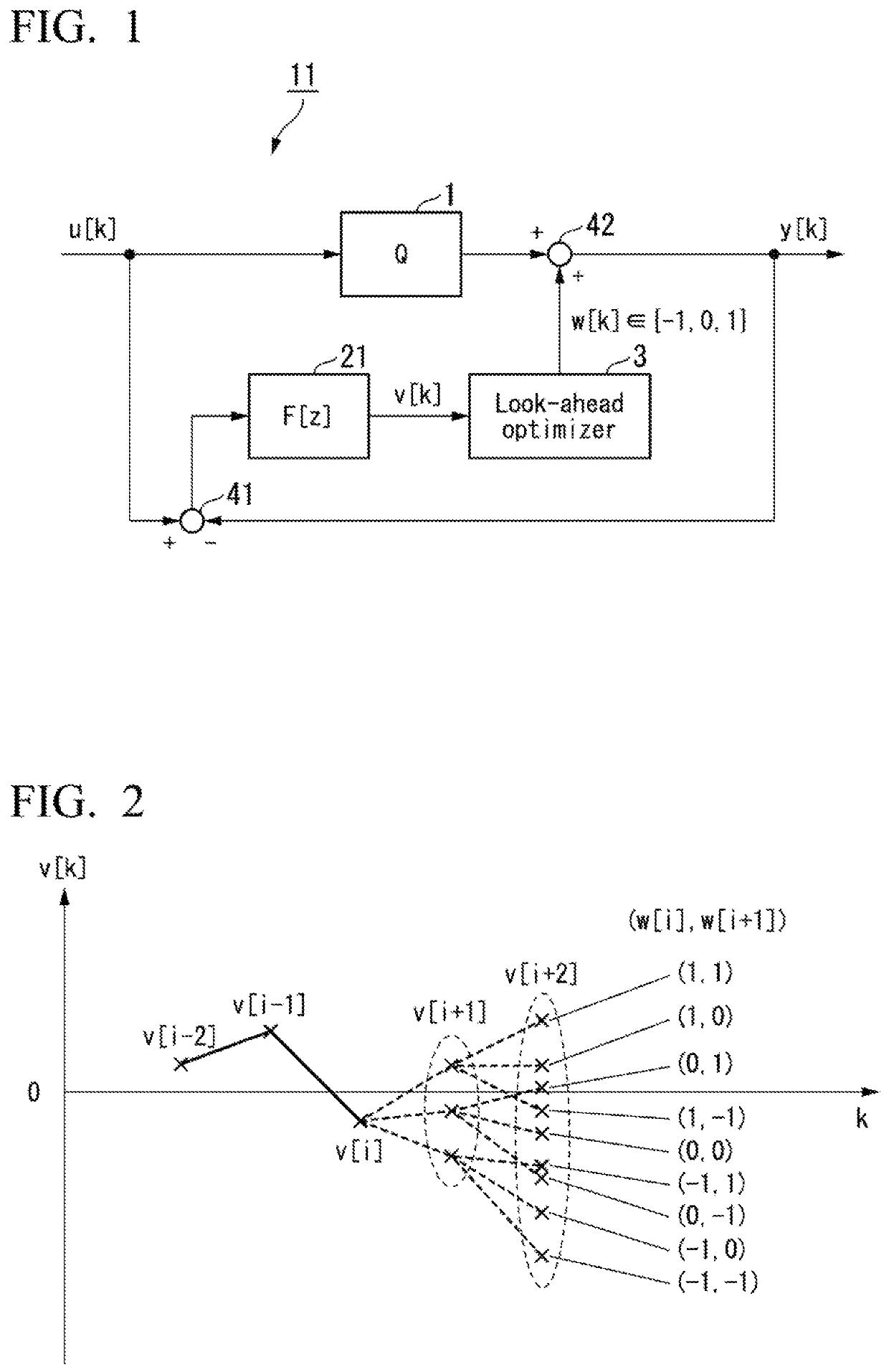
Equalizer with perturbation effect based adaptation
Equalization methods and equalizers employing discrete-time filters are provided with dynamic perturbation effect based adaptation. Tap coefficient values may be individually perturbed during the equalization process and the effects on residual ISI monitored to estimate gradient components or rows of a difference matrix. The gradient or difference matrix components may be assembled and filtered to obtain components suitable for calculating tap coefficient updates with reduced adaptation noise. The dynamic perturbation effect based updates may be interpolated with pre-calculated perturbation effect based updates to enable faster convergence with better accommodation of analog component performance changes attributable to variations in process, supply voltage, and temperature.
Owner:CREDO TECH GRP LTD
Space-time oversampling and error shaping for coarsely quantized arrays
Methods and apparatus for shaping and filtering quantization errors conjointly in space and time to produce a higher-precision output in a spatially and temporally oversampled array. A space-time error-shaping array system has an array of sensors, each sensor producing a temporal signal comprising quantized waveforms. A multi-input multiple-output (MIMO) discrete-time filter structure with multiple inputs, each coupled to a sensor of the array of sensors, shapes quantization errors of the array of sensors on the basis of temporal aspects of the quantized waveforms conjointly with spatial aspects of the quantized waveforms.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
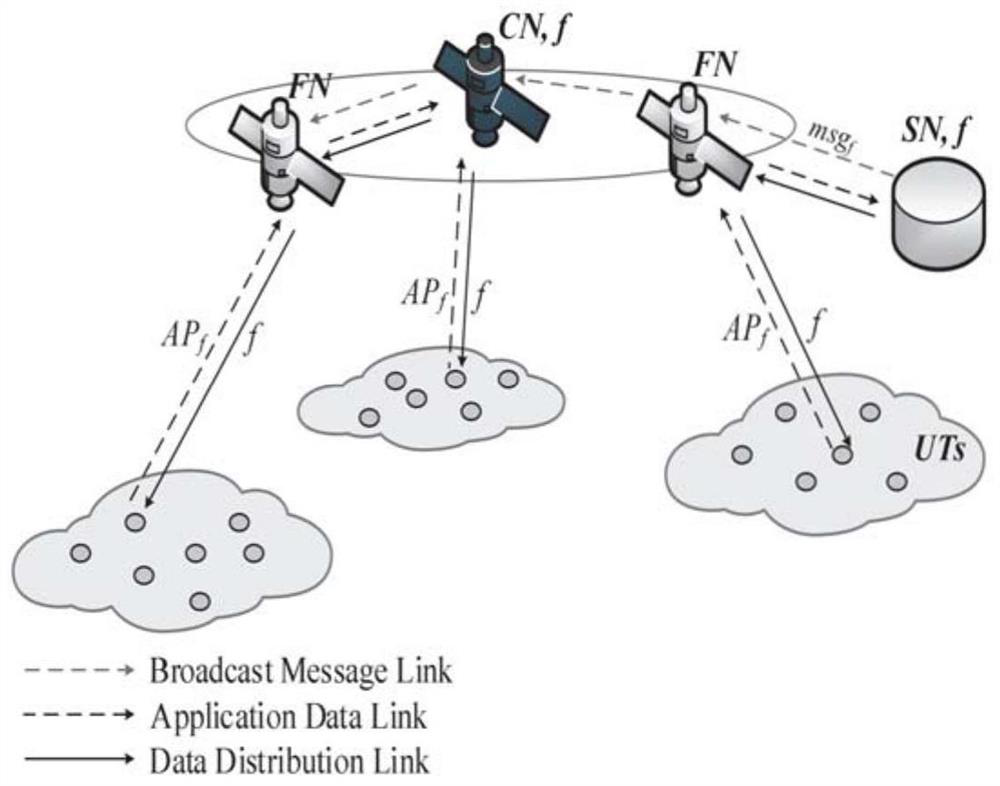
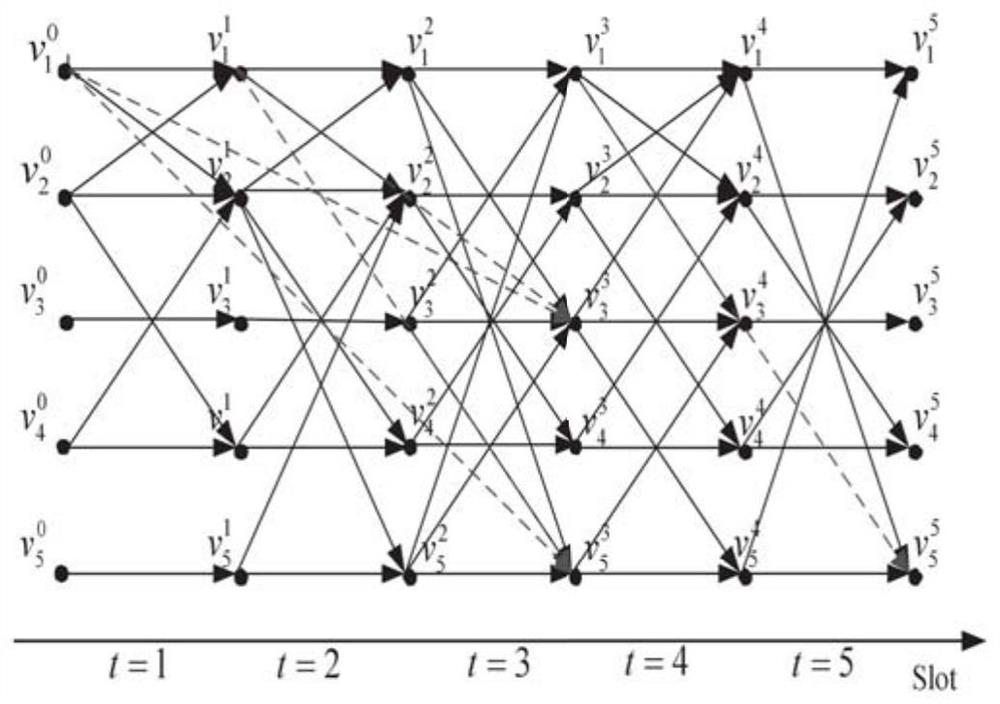
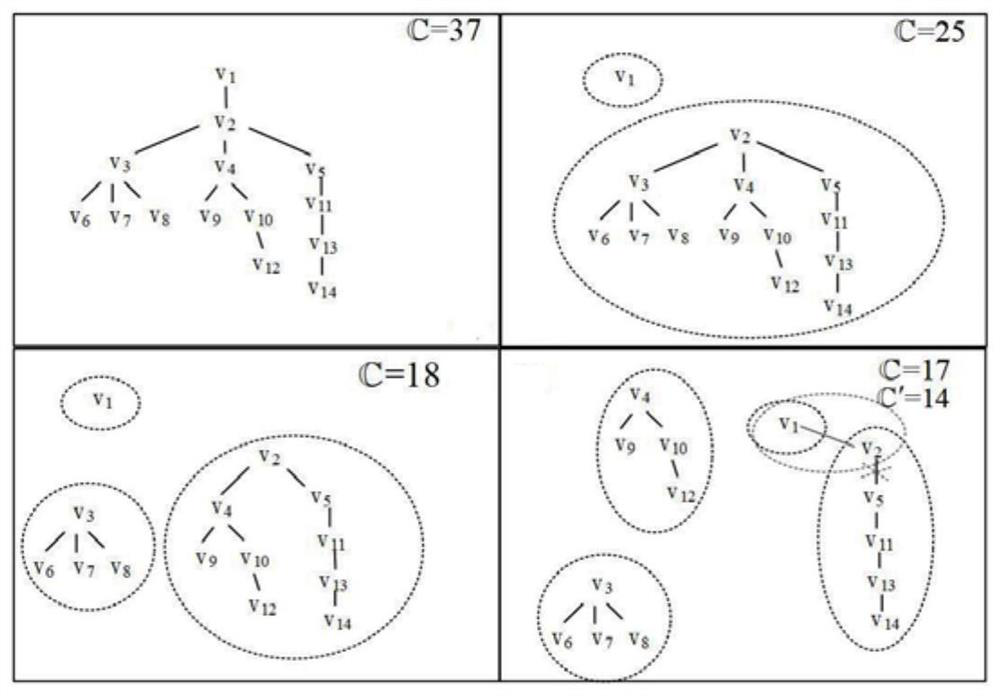
Data distribution method based on on-path cache in star-earth hybrid network
ActiveCN109412950BImprove distribution performanceReduce transmission delayData switching networksMix networkDiscrete time filtering
The present invention provides a data distribution method based on on-path cache in a satellite-ground hybrid network. After the satellite network scene is set, the dynamic satellite network is divided into a series of equal-length discrete time slices according to the satellite topology control strategy. And establish a cross-slot connection relationship graph, based on which to improve the data distribution routing algorithm; according to the characteristics of the satellite network, use the proposed node selection algorithm to select some nodes as cache nodes, thereby reducing the transmission delay of data distribution and data transmission. storage overhead.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
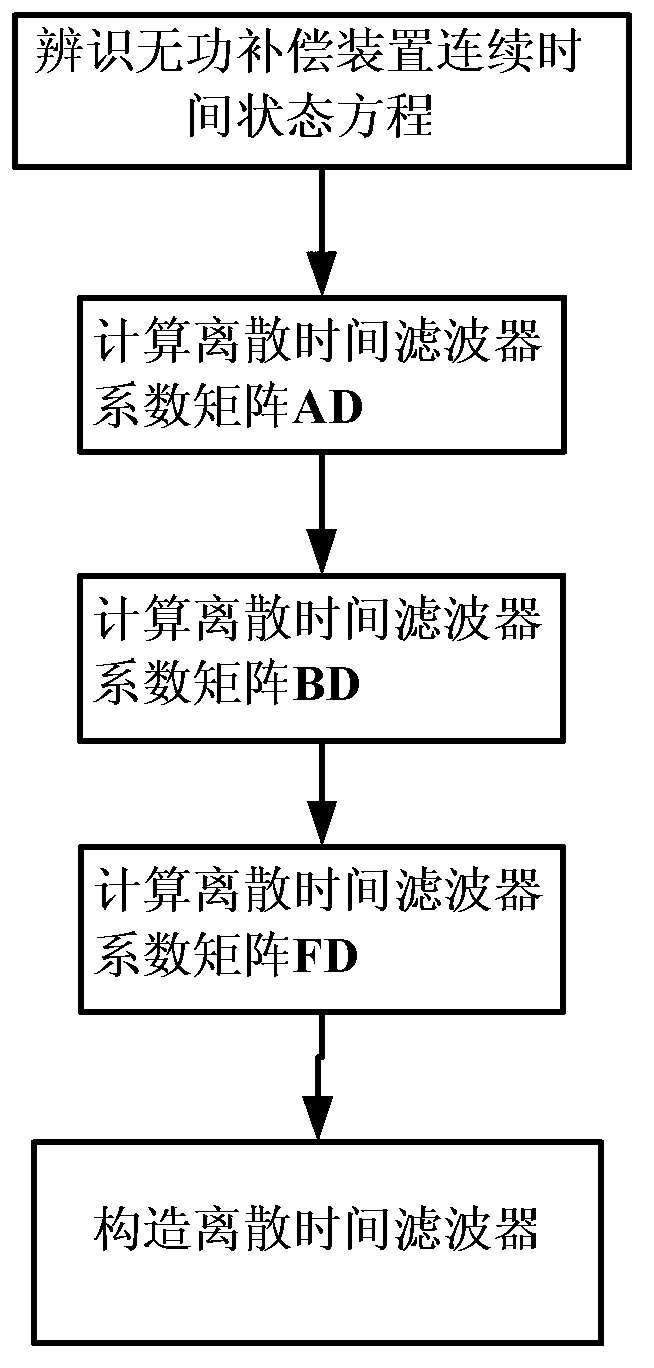
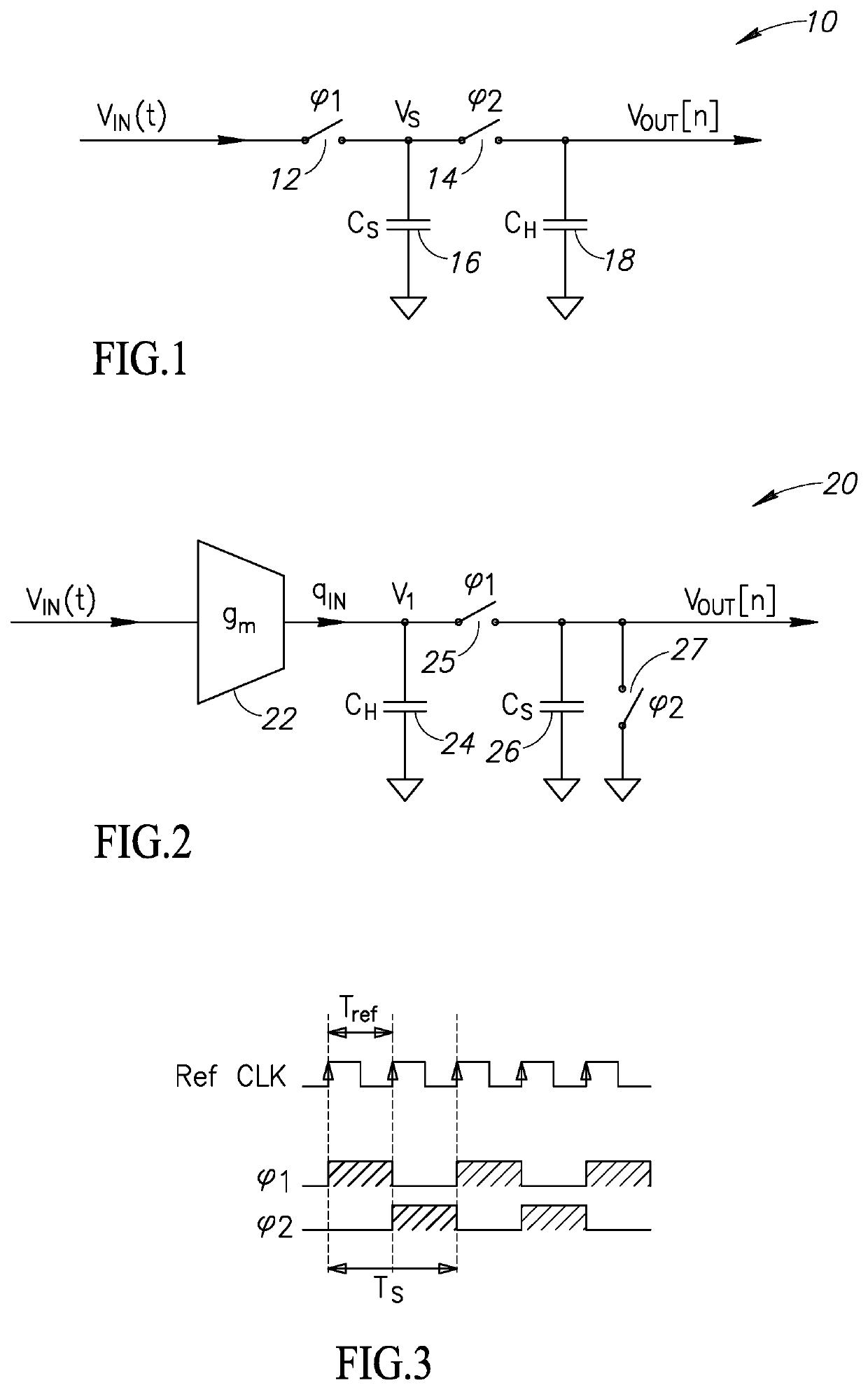
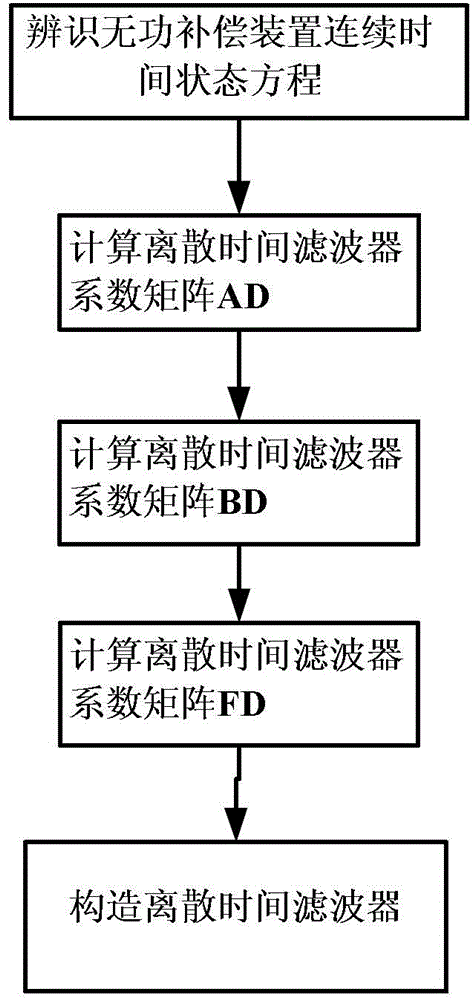
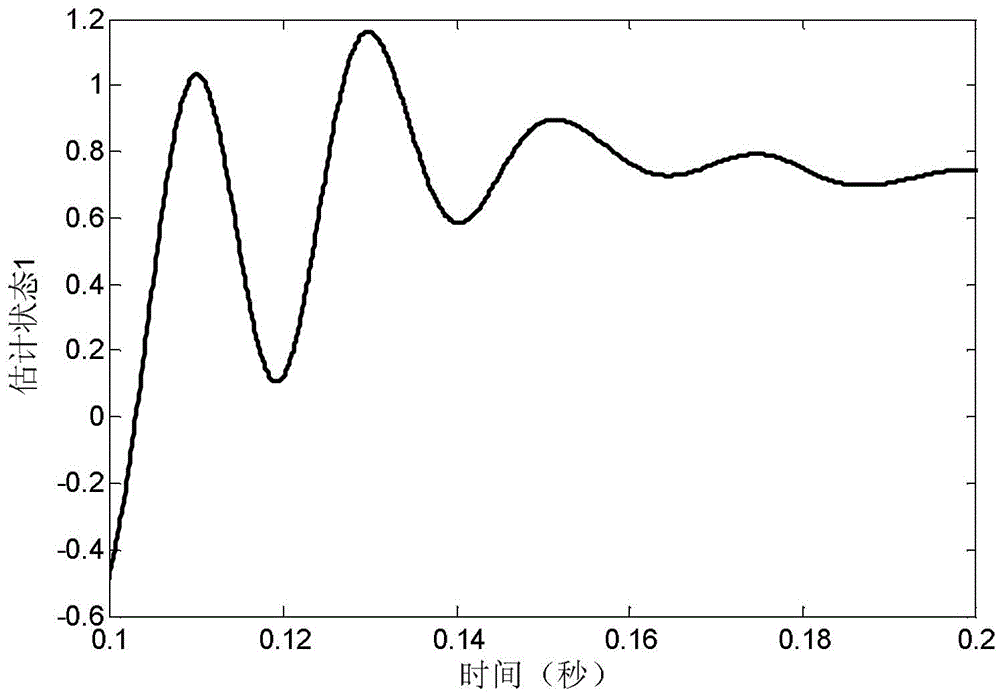
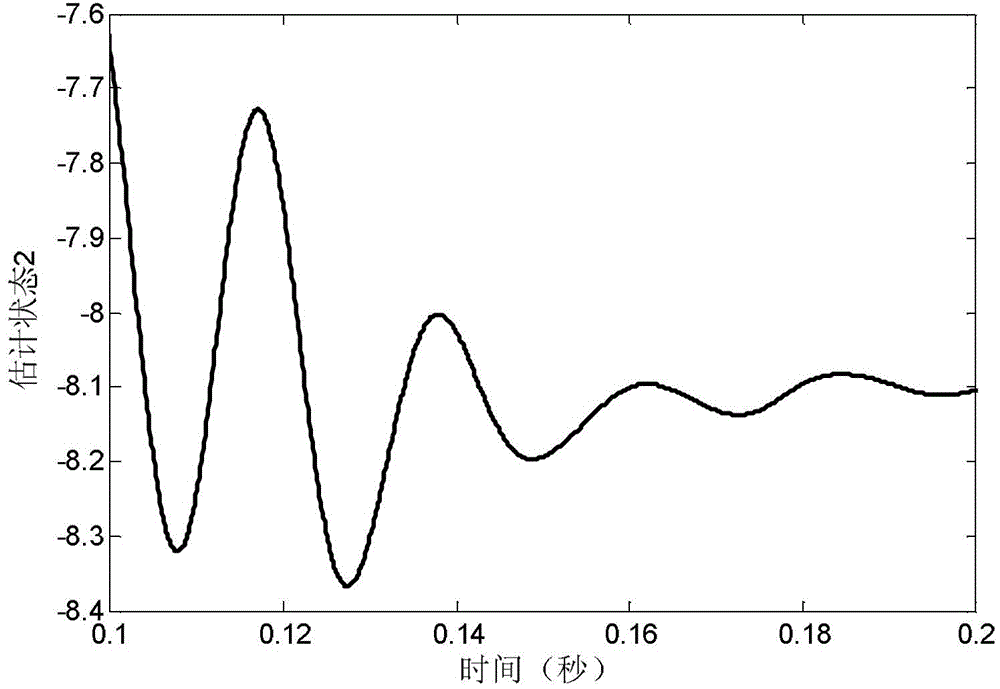
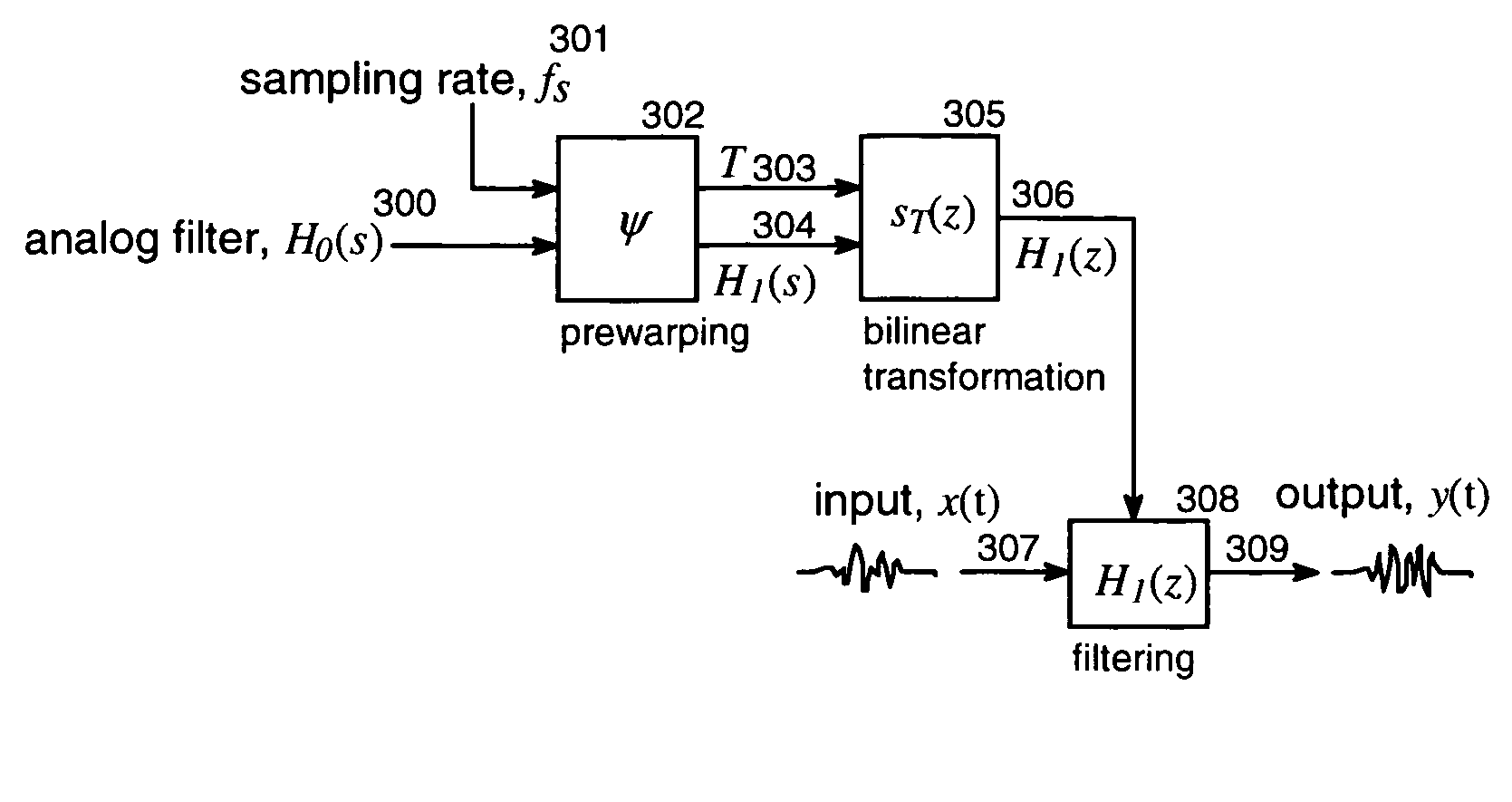
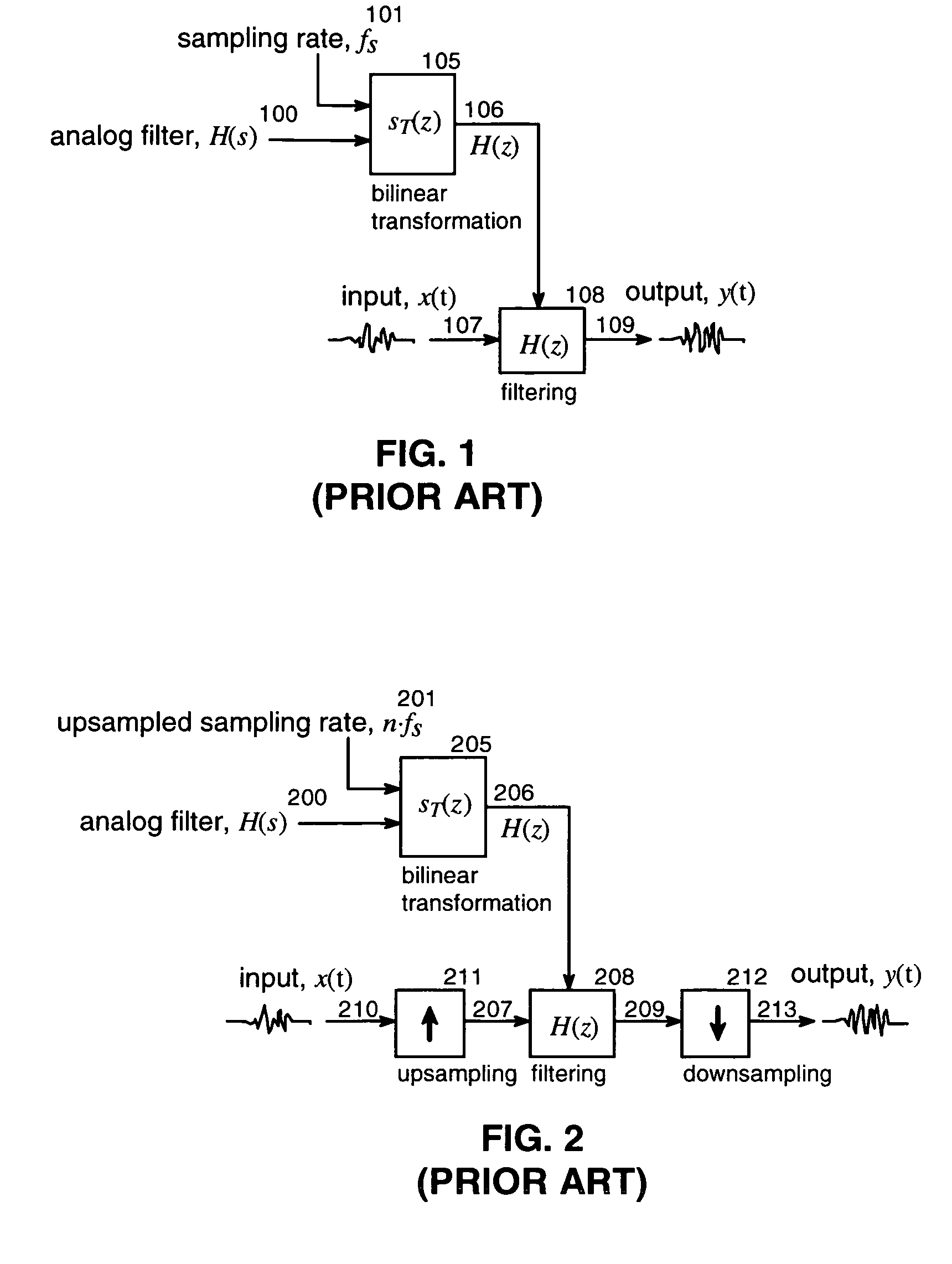
Method for transforming continuous-time filter to discrete-time filter
ActiveCN103176406AImprove performanceSuitable for engineering practical applicationAdaptive controlSystems designPartial differential equation
The invention provides a method for transforming a continuous-time filter to a discrete-time filter. The method includes: sampling input quantity and output quantity of a controlled system, and utilizing an identification algorithm for obtaining a continuous-time model of the system; constructing the continuous-time filter according to the continuous-time model; adopting a partial differential equation method to compute a coefficient matrix of the discrete-time filter according to coefficients in a continuous-time filter equation and adopted time of a discrete system; and constructing a discrete-time filter structure. The discrete-time filter is obtained by performing discrete transformation to the designed continuous-time filter. Compared with an existing discrete-time filter design method, the method has the advantages that discretization processes of a controlled object and filter designing processes based on the discrete system are decreased, and by utilizing advantages of a filter design theory based on a continuous-time system, the filter excellent in performances can be designed, system design and development time can be saved, and the method is particularly suitable for practical engineering application of digital control systems.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Receiver apparatus and reception method
ActiveUS8345800B2Reduce power consumptionLow costFrequency-division multiplexLine-faulsts/interference reductionDiscrete time filteringDiscrete-time signal
A receiver includes a sample and hold circuit that receives a signal (continuous time signal) that has been subject to frequency division multiplexing modulation, converts the signal to a discrete time signal, and outputs the discrete time signal, a discrete time filter that receives the signal output from the sample and hold circuit and attenuates a frequency component of a subcarrier different from a specified subcarrier, and a demodulation unit that extracts a digital baseband from a signal that has passed through the discrete time filter to complete a demodulation operation within one data symbol reception period.
Owner:NEC CORP
Discrete time charge sharing IIR bandpass filter incorporating clock phase reuse
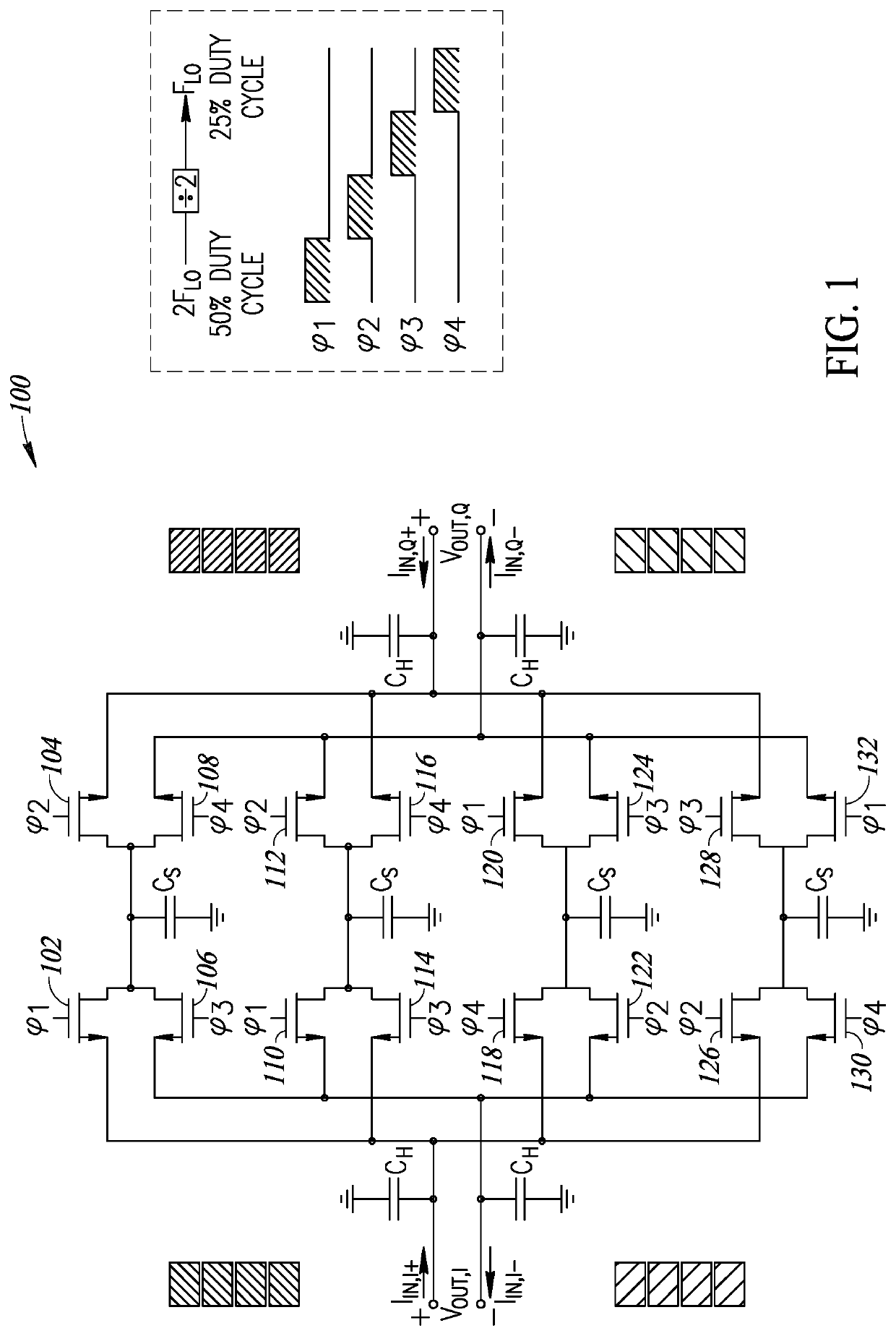
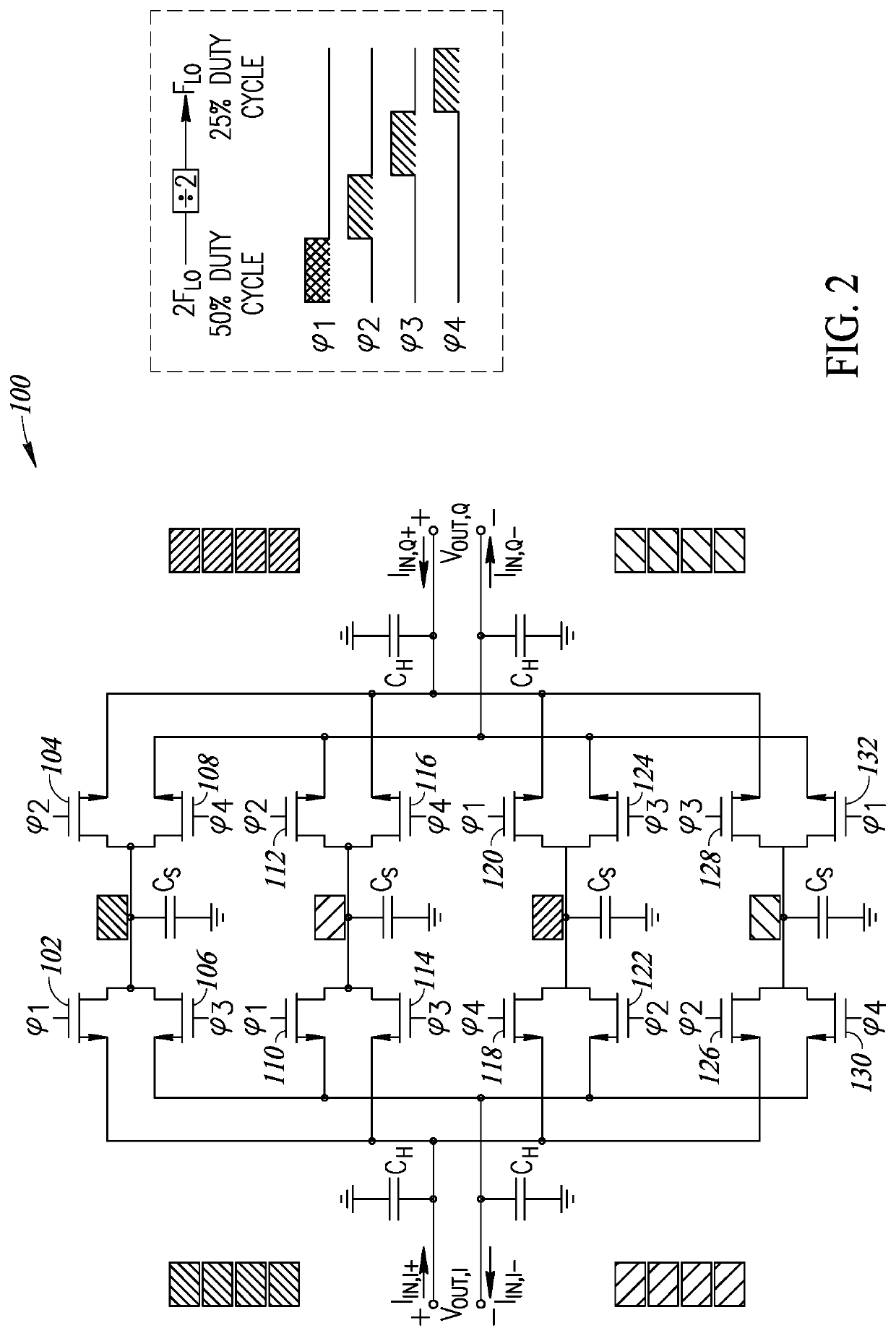
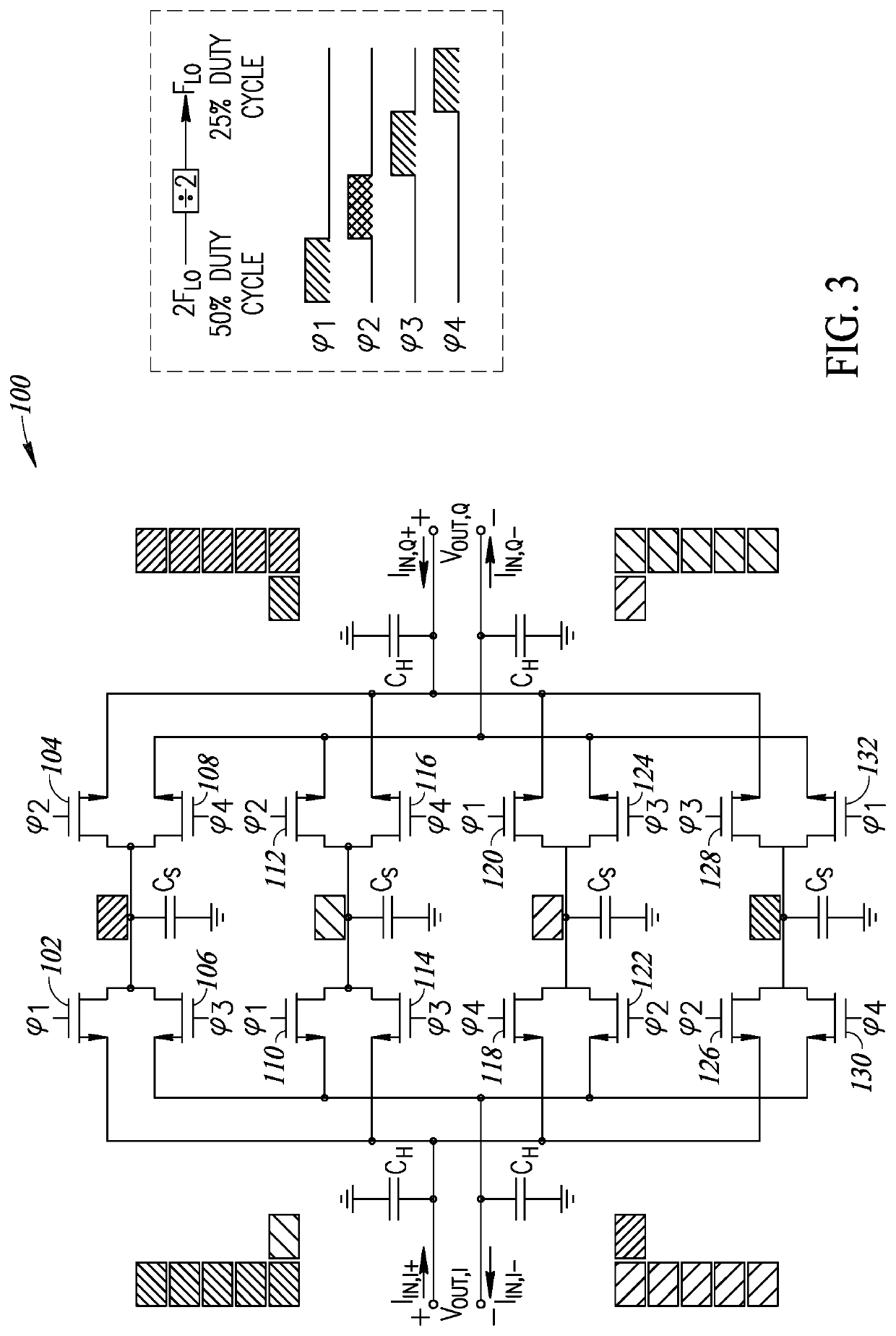
ActiveUS11190167B2Improve filtering effectImprove orderTransversal filtersDigital technique networkBandpass filteringSoftware engineering
A novel and useful discrete time IIR bandpass filter is disclosed that takes advantage of clock phase reuse thereby leading to significant improvements in filtering, especially stop band rejection in comparison to prior art filters. The bandpass filter of the present invention achieves improved filtering performance without adding any additional clock phases to the circuit. In particular, reuse of the already existing clock phases increases the order and performance of the filter. The invention exploits reuse of the clock phases to provide higher order filtering along with a discrete time IIR filter design which is capable of operating at high frequency. Consequently, much better filtering is achieved and the quality factor of the filter is improved leading to sharper transition bands especially for close-in band blockers in modern 4G / 5G receivers.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE DUBLIN NAT UNIV OF IRELAND DUBLIN
Discrete time IIR filter with high stop band rejection
ActiveUS10840890B2High stop band rejectionStop band rejection improvesDigital technique networkTime-varying networkIir filteringDiscrete time filtering
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE DUBLIN NAT UNIV OF IRELAND DUBLIN
Receiver, communication unit, and method for down-converting a radio frequency signal
ActiveUS10200014B2Increase capacitance densityReduce areaTransversal filtersAdaptive networkFinite impulse responseCapacitance
There is provided a communication receiver comprising: an input for receiving a radio frequency, RF, input signal; and at least one finite impulse response, FIR, discrete time filter, DTF. The at least one FIR DTF comprises: an input circuit comprising an input port for sampling the RF input signal at a sampling frequency that is comparable to the input RF input signal; and N parallel branches, each branch having a set of input unit sampling capacitances, where each unit sampling capacitance is independently selectively coupleable to an output summing node. The input circuit is configured to convert an equivalent input impedance of the at least one FIR DTF around the sampling frequency to a real impedance.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
Superheterodyne receiver and receiving method
ActiveCN103828244BReduce sensitivitySolving the time-varying DC offset problemTransmissionDiscrete time filteringIntermediate frequency
The invention relates to a superheterodyne receiver (100) comprising: a sampling mixer (101) for sampling an analog radio frequency signal using a predetermined sampling rate (fs) (102) Sampling to obtain a discrete-time sampled signal (104) for shifting said discrete-time sampled signal (104) towards a first intermediate frequency (|fRF-fLO|), thereby obtaining said predetermined sampling rate ( fs) the sampled intermediate discrete-time signal (108); a discrete-time filter (103) for filtering said intermediate discrete-time signal (108) at said predetermined sampling rate (fs) to obtain filtered signal (130); and a discrete time mixer (109) for shifting said filtered signal (130) towards a second intermediate frequency (fIF).
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
A Method of Converting Continuous Time Filters to Discrete Time Filters
ActiveCN103176406BImprove performanceSuitable for engineering practical applicationAdaptive controlSystems designPartial differential equation
The invention provides a method for transforming a continuous-time filter to a discrete-time filter. The method includes: sampling input quantity and output quantity of a controlled system, and utilizing an identification algorithm for obtaining a continuous-time model of the system; constructing the continuous-time filter according to the continuous-time model; adopting a partial differential equation method to compute a coefficient matrix of the discrete-time filter according to coefficients in a continuous-time filter equation and adopted time of a discrete system; and constructing a discrete-time filter structure. The discrete-time filter is obtained by performing discrete transformation to the designed continuous-time filter. Compared with an existing discrete-time filter design method, the method has the advantages that discretization processes of a controlled object and filter designing processes based on the discrete system are decreased, and by utilizing advantages of a filter design theory based on a continuous-time system, the filter excellent in performances can be designed, system design and development time can be saved, and the method is particularly suitable for practical engineering application of digital control systems.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Re-quantization device having noise shaping function, signal compression device having noise shaping function, and signal transmission device having noise shaping function
ActiveUS10892774B2Suppressing increase in quantization noiseSuppress deterioration of signal-to-noiseAnalogue conversionDiscrete time filteringNoise shaping
What is provided is a subtractor, as a re-quantization device, which is configured to detect re-quantization noise, a discrete time filter which is configured to perform frequency weighting on the detected re-quantization noise, an adder which is configured to add an additional signal to quantization noise, and an additional signal selector which is configured to select a value at the present time of a column of an additional signal for minimizing the magnitude of quantization noise having been subjected to frequency weighting evaluated one sampling or more later.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
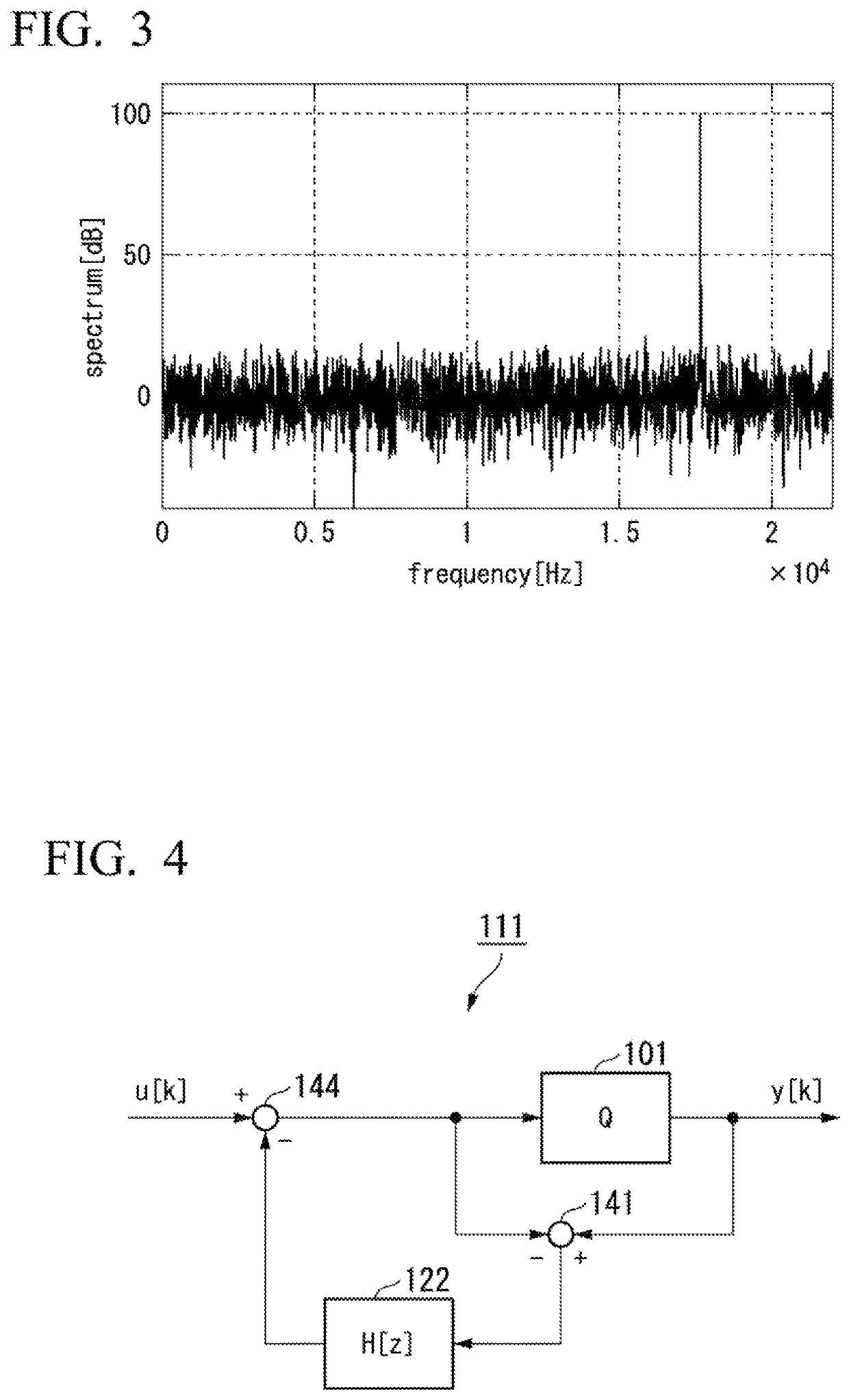
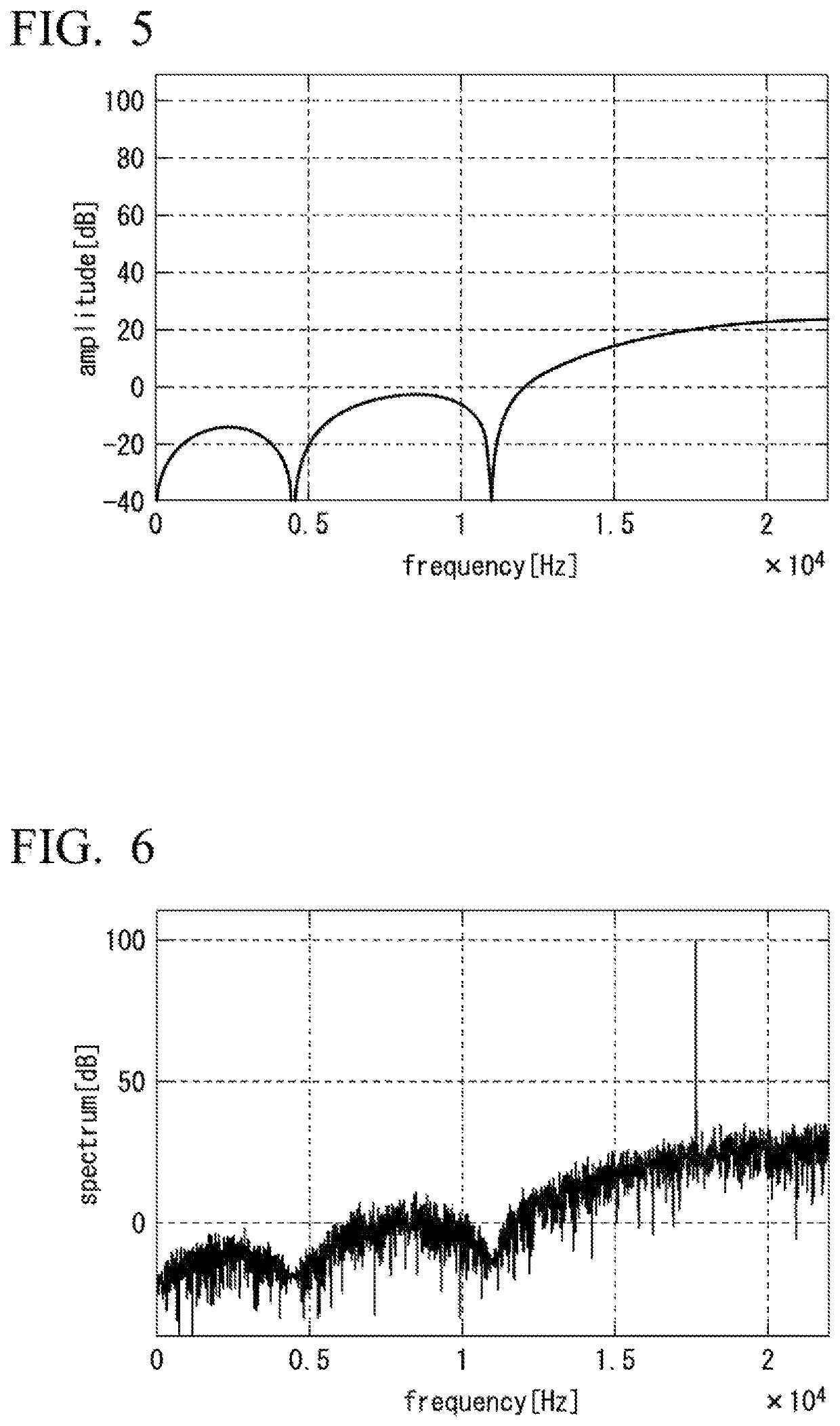
Digital resonant shelf filter
InactiveUS7831645B1Digital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsBilinear transformDiscrete time filtering
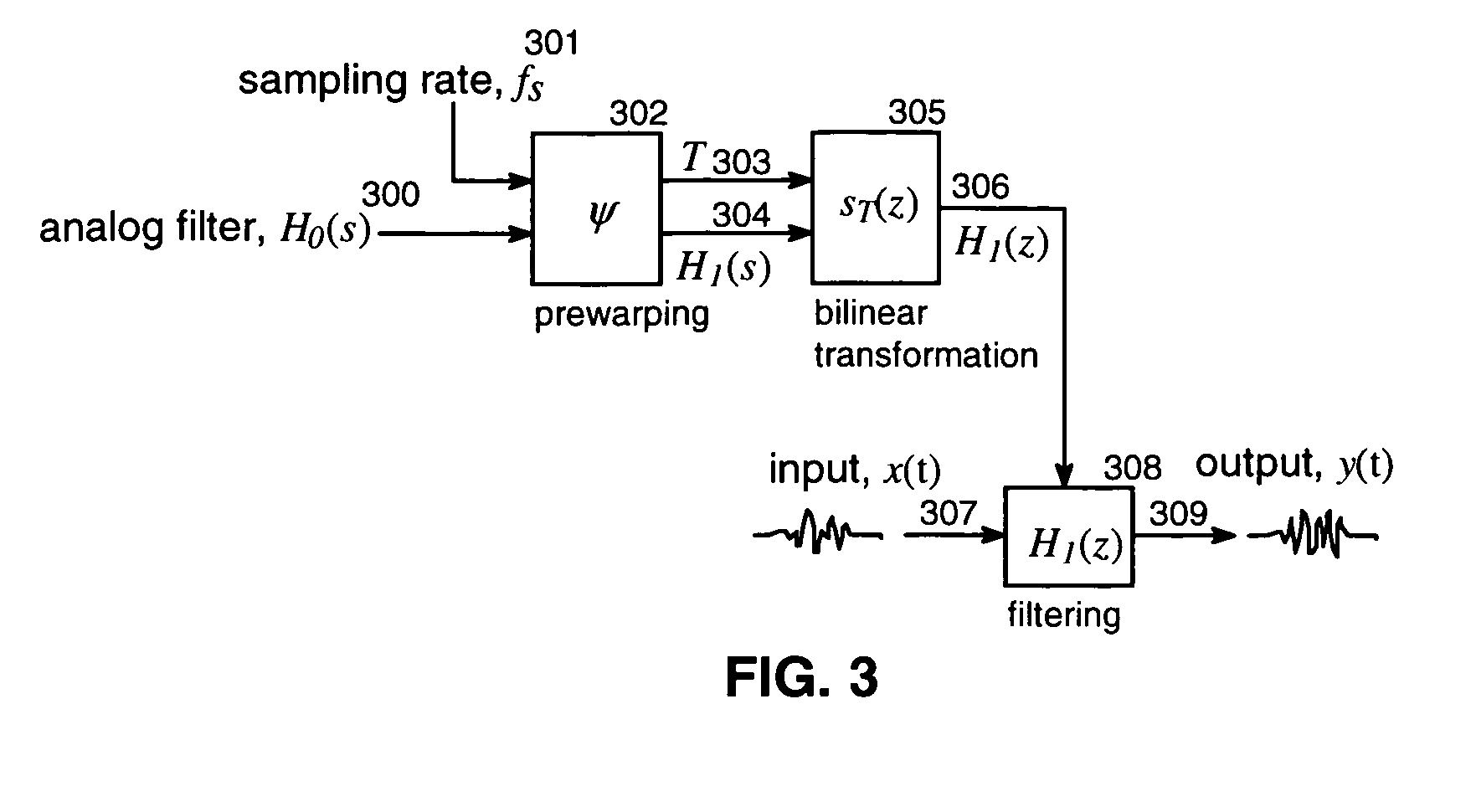
A method and system for designing a discrete-time filter having a transfer function which approximates that of an analog shelf filter is disclosed. Prior art methods include applying the bilinear transform to the analog filter, which has the drawback of warping high-frequency features of the desired transfer function. In an embodiment of the present invention, an analog filter is designed which anticipates the warping imposed by the bilinear transform. For filters whose features approach the Nyquist limit, the inventive method provides a closer approximation to the analog response than direct application of the bilinear transform.
Owner:KIND OF LOUD TECH
Discrete Time IIR Filter With High Stop Band Rejection
ActiveUS20190207587A1High stop band rejectionStop band rejection improvesDigital technique networkTime-varying networkLow-pass filterMoore's law
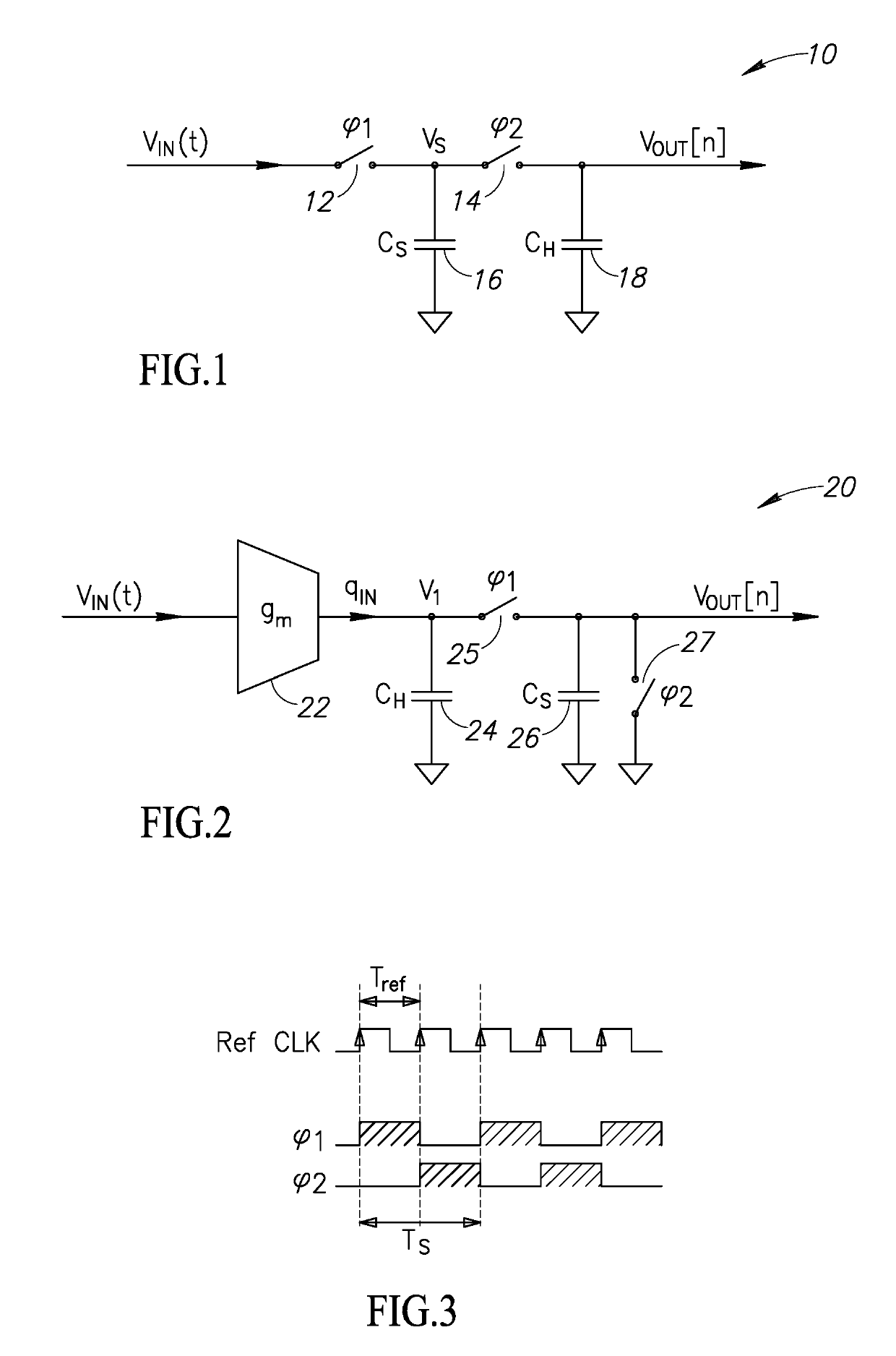
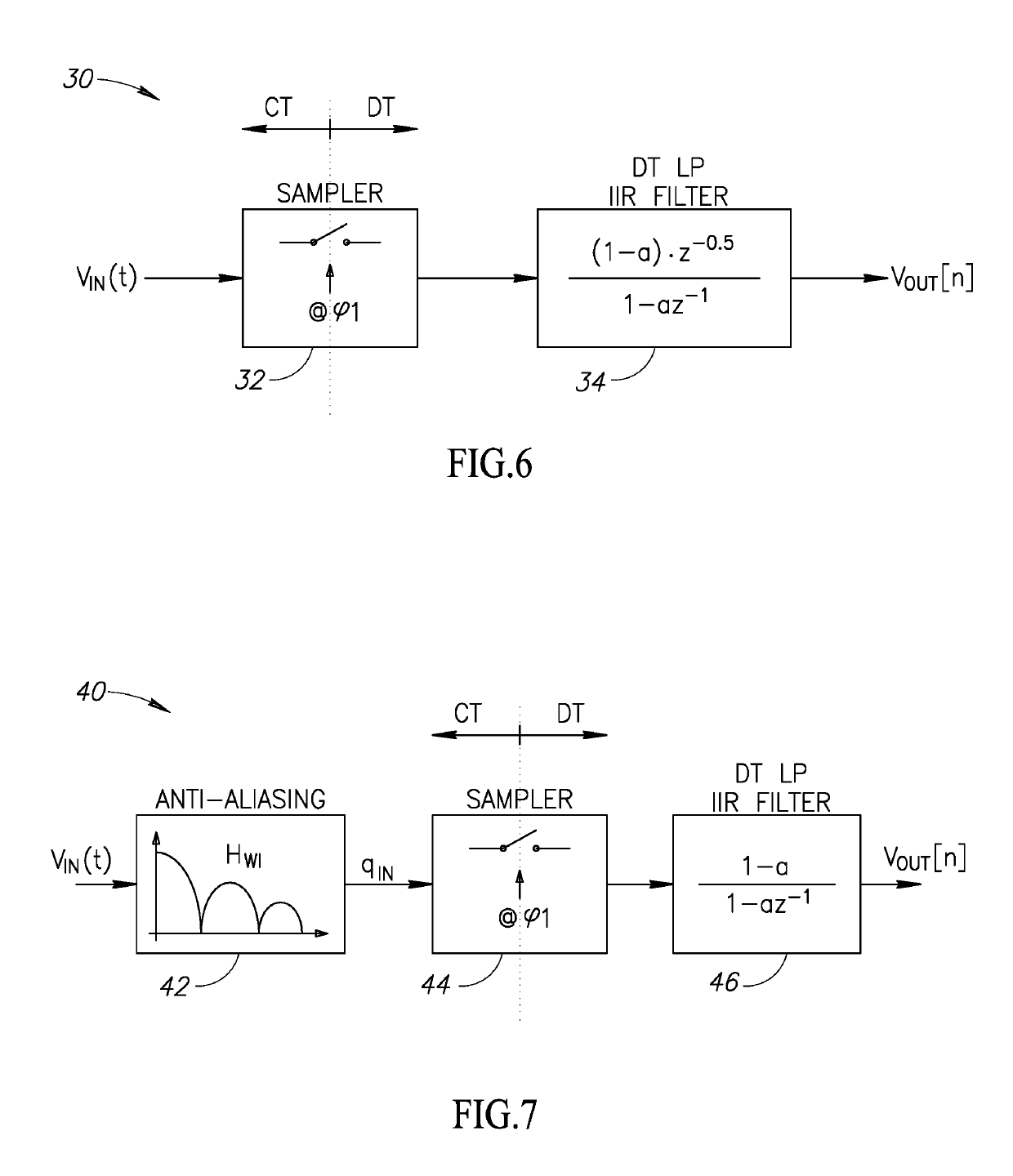
A novel and useful high-order discrete-time charge rotating (CR) infinite impulse response (IIR) low pass filter is presented. The filter utilizes history capacitor arrays incorporating banks of capacitors. A linear interpolation technique is used in the IIR filter with second order antialiasing filtering, whose transfer function is sinc(x)2 per stage. It also uses a gm cell, rather than operational amplifiers, and is thus compatible with digital nanoscale technology. A 7th-order charge-sampling discrete time filter is disclosed. The order of the filter is easily extendable to higher orders. The charge rotating filter is process scalable with Moore's law and amenable to digital nanoscale CMOS technology. Bandwidth of the filter is precise and robust to PVT variation. The filter exhibits very low power consumption per filter pole, low input-referred noise, wide tuning range, excellent linearity and low area per minimum bandwidth and filter pole.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE DUBLIN NAT UNIV OF IRELAND DUBLIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com