Equalizer with perturbation effect based adaptation
An equalizer and adaptive technology, applied in baseband systems, baseband system components, shaping networks in transmitters/receivers, etc., and can solve problems such as frequent use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] Note that the specific embodiments given in the drawings and the following description do not limit the present disclosure. On the contrary, they provide a basis for those skilled in the art to discern alternatives, equivalents and modifications included within the scope of the claims.
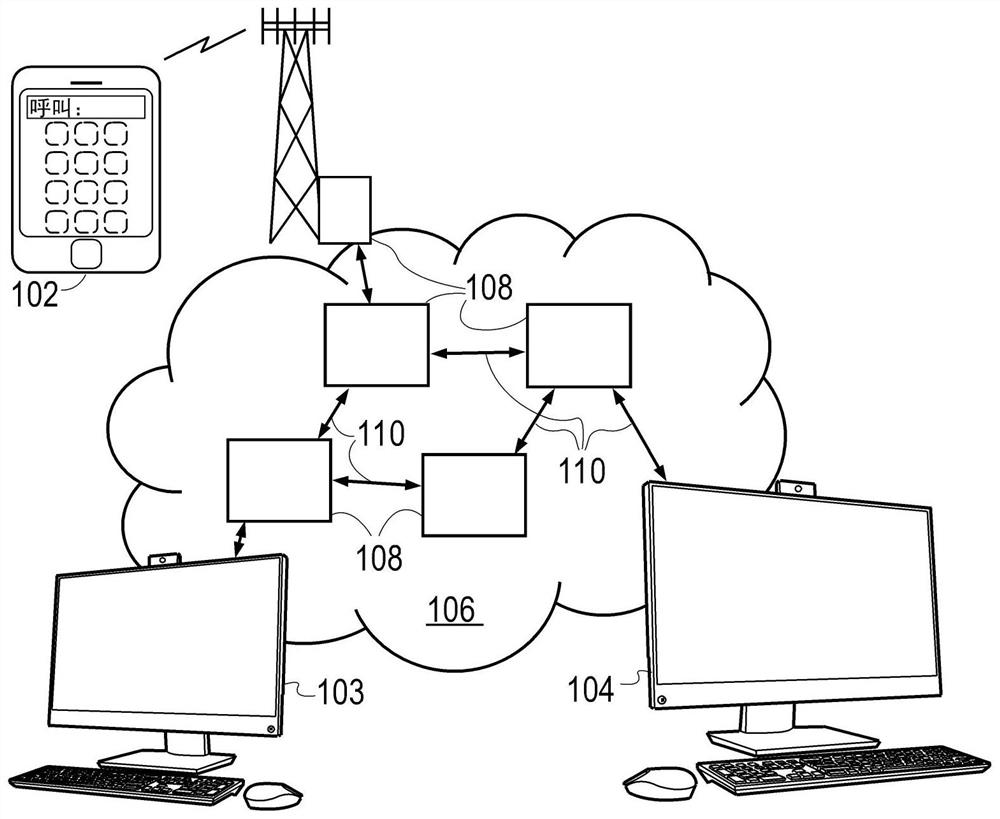
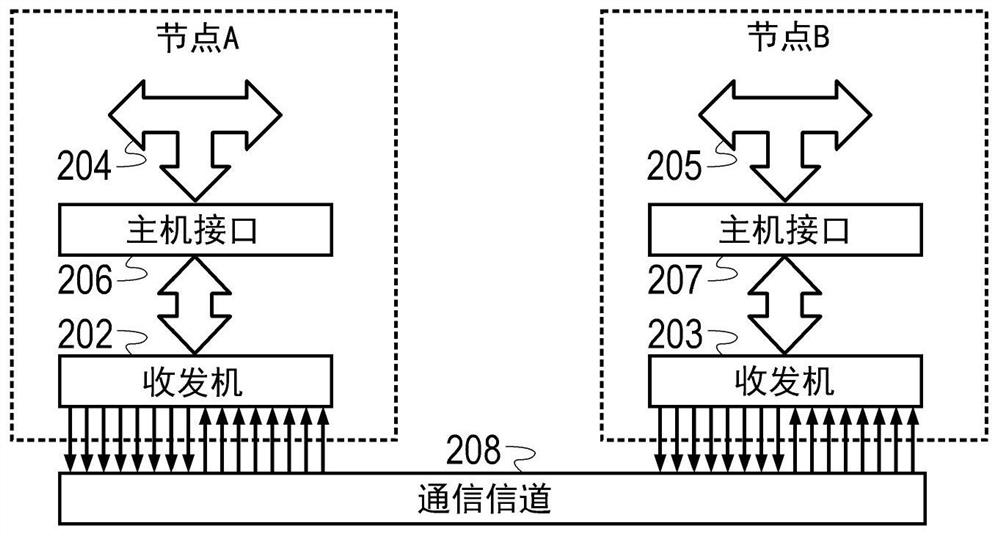
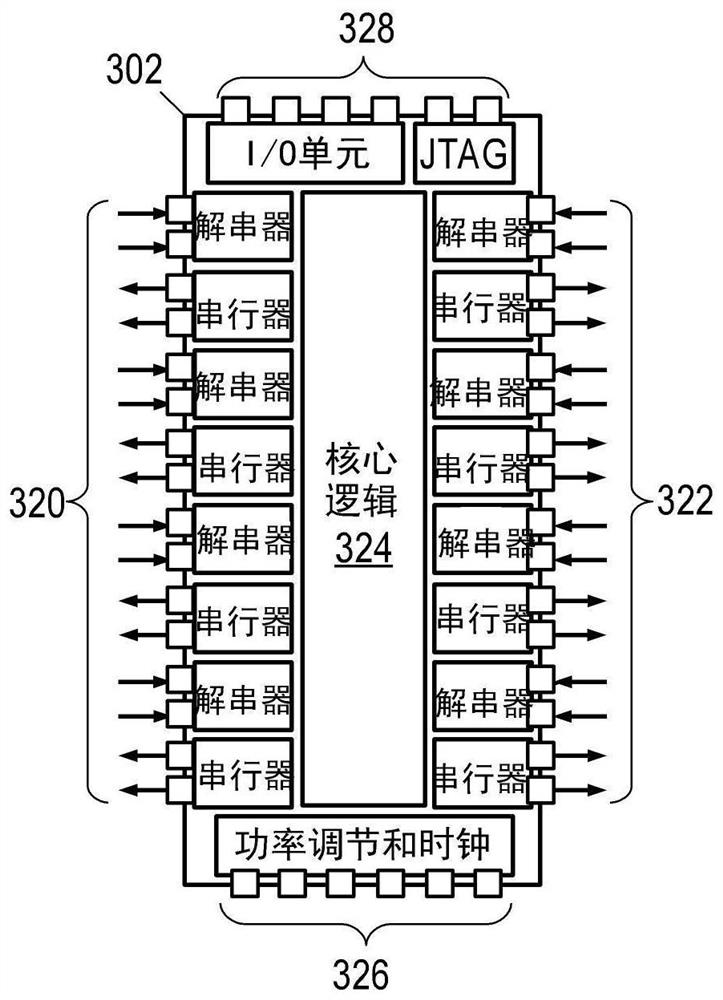
[0018] The disclosed equalizers and equalization methods are best understood in the context of the larger environment in which they operate. Correspondingly, figure 1 An illustrative communications network is shown that includes mobile device 102 and computer systems 103-104 coupled via packet-switched routing network 106. Routing network 106 may be or include, for example, the Internet, a wide area network, or a local area network. exist figure 1 , routing network 106 includes a network of equipment items 108 such as hubs, switches, routers, bridges, and the like. Items of equipment 108 are connected to each other and to computer systems 103-104 via point-to-point communication lin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com