Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Correlative imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
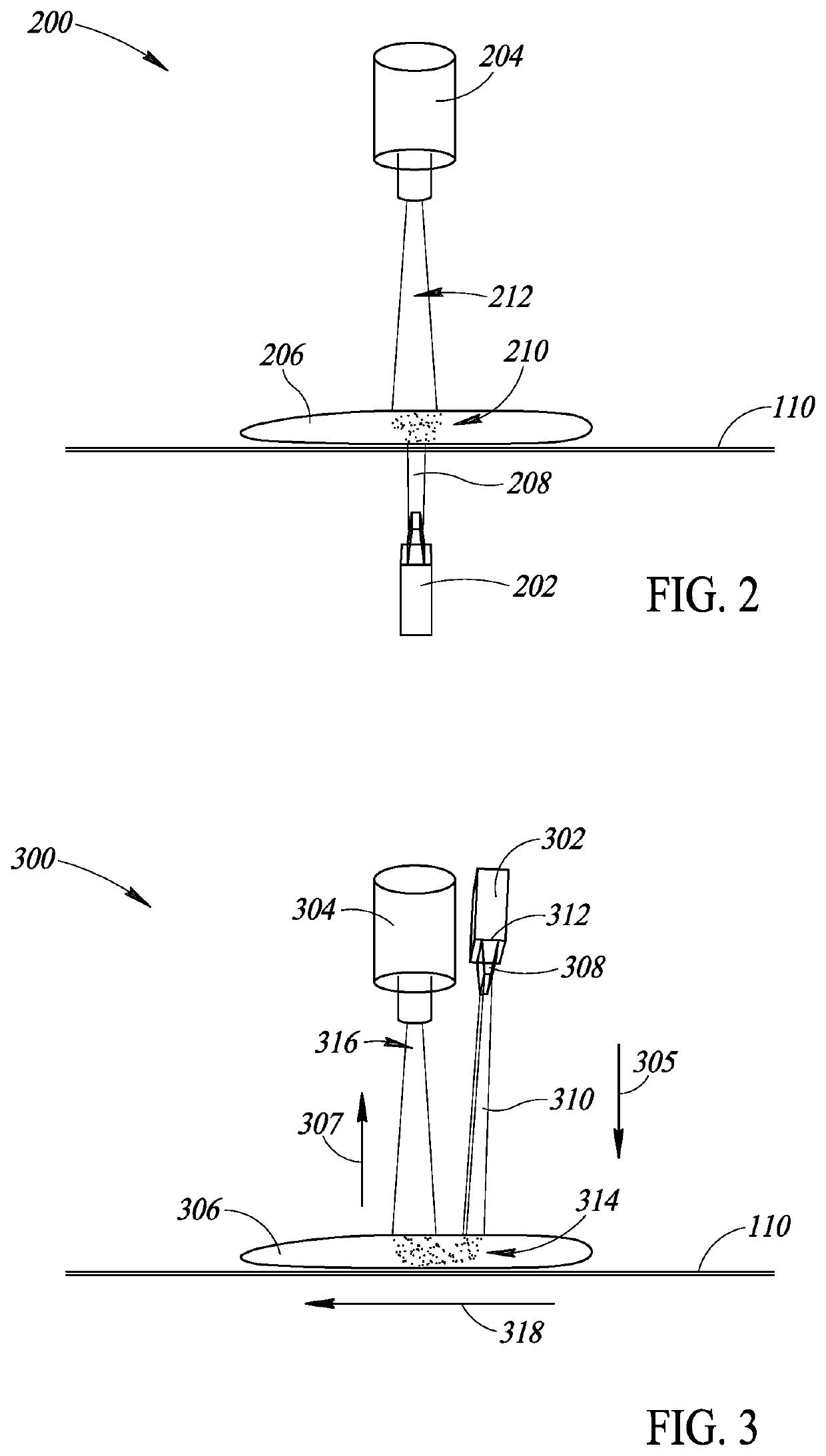
Portable radiometry and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6849849B1Protection elementEasy to installRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesParticulatesEngineering
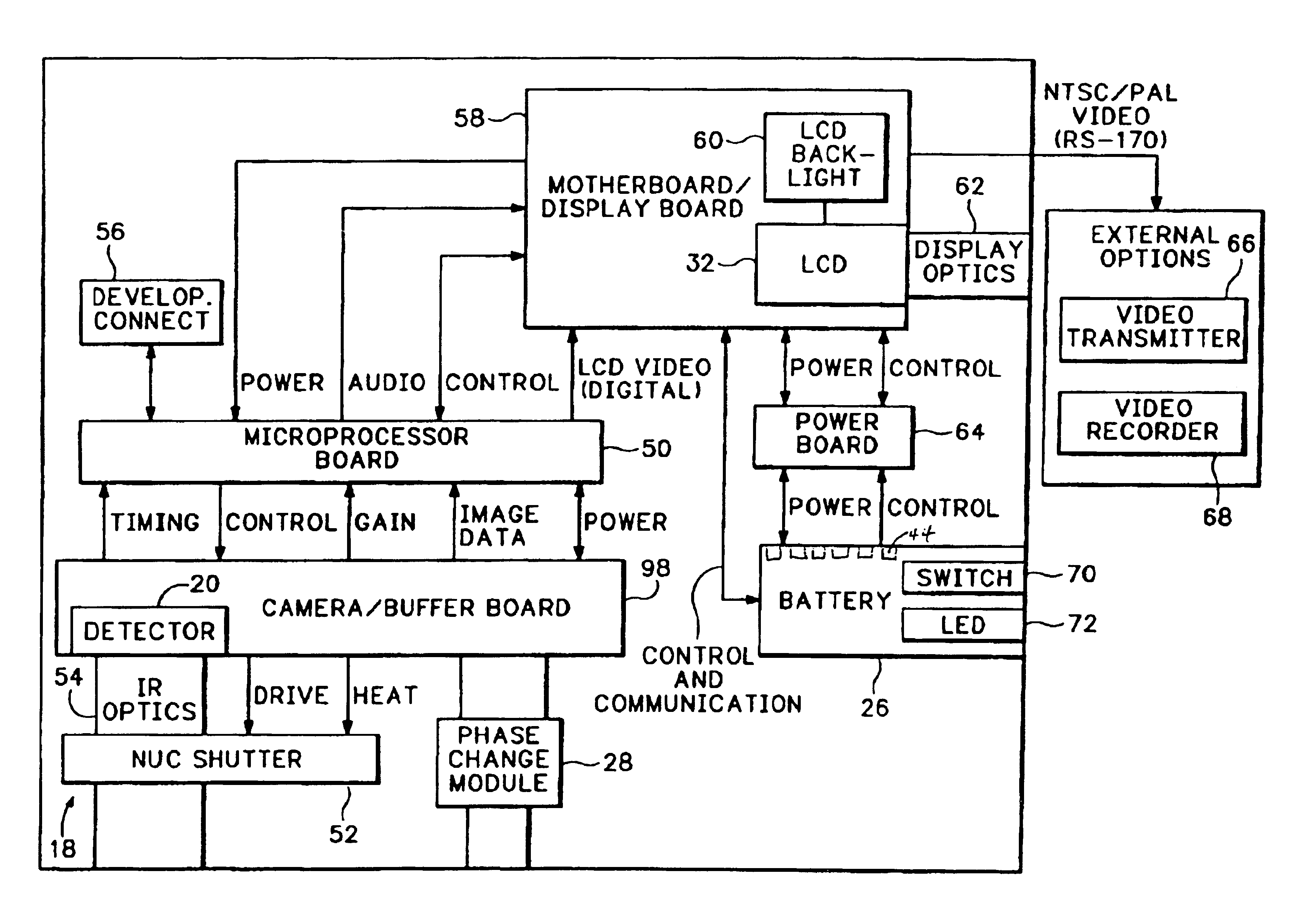
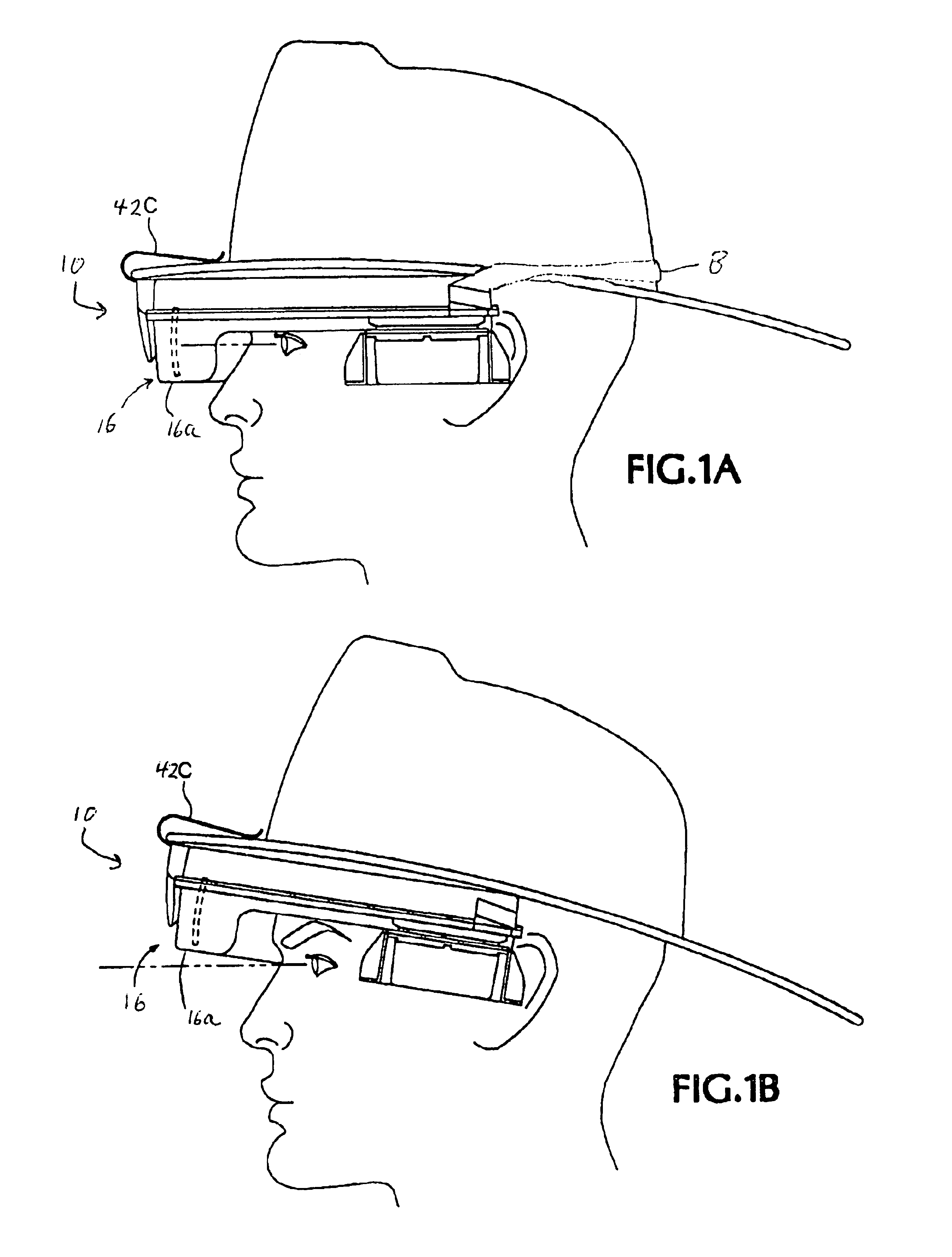
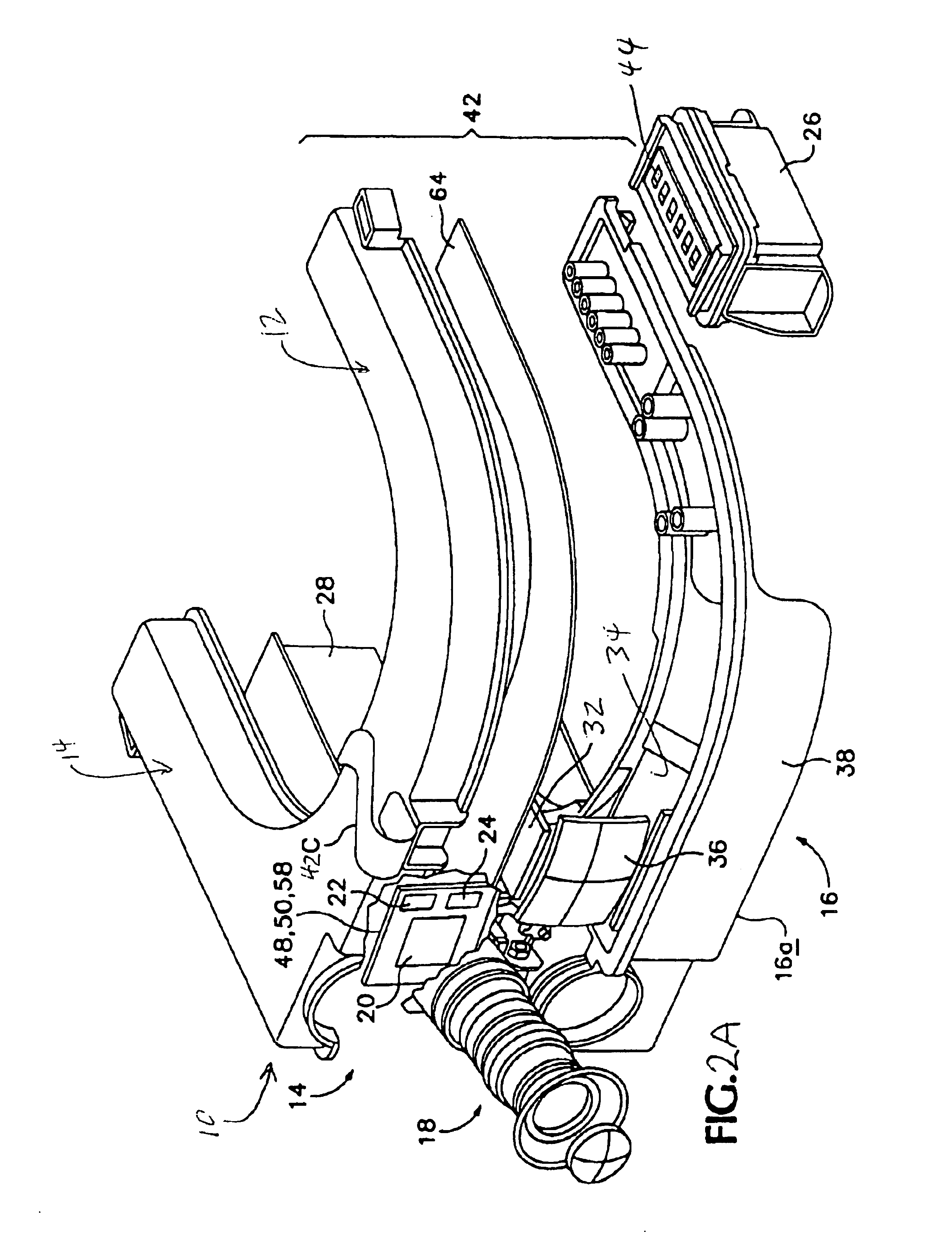
An infrared (IR) camera and associated electronics including power are integrated into portable, self-contained, vision-enhancement apparatus useful in environments of dense air-borne particulate and thermal extremes such as encountered in fire fighting situations, in accordance with the invention. The IR camera is integral with a self-contained power supply so that the system is portable and requires no umbilical cord or other external connections. The camera includes an imager that is preferably an un-cooled focal plane array, and associated imaging, storing, processing and displaying electronics that are cooled in the extreme thermal environment using an integral plural phase heatsink.
Owner:TELEDYNE FLIR LLC
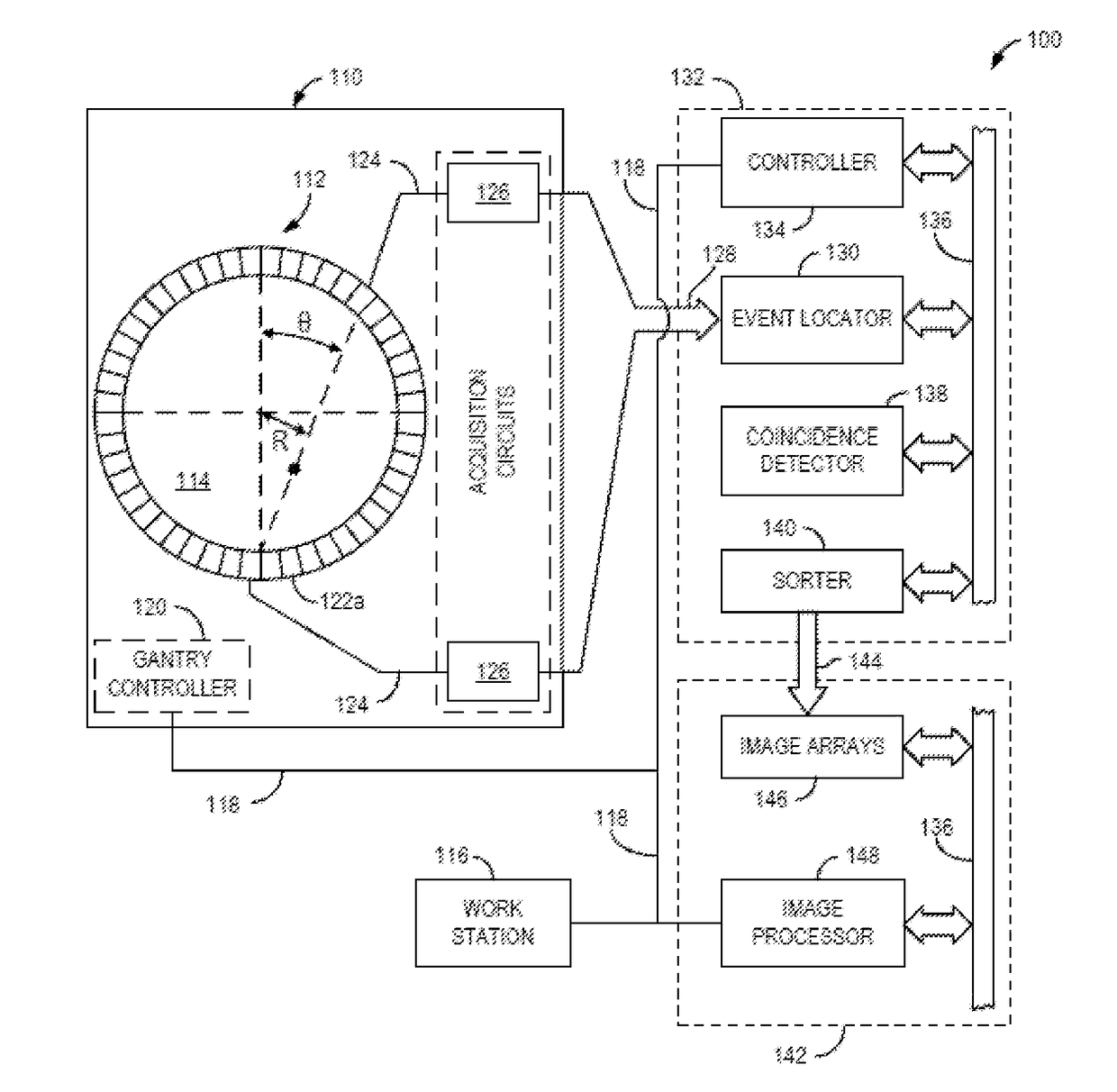
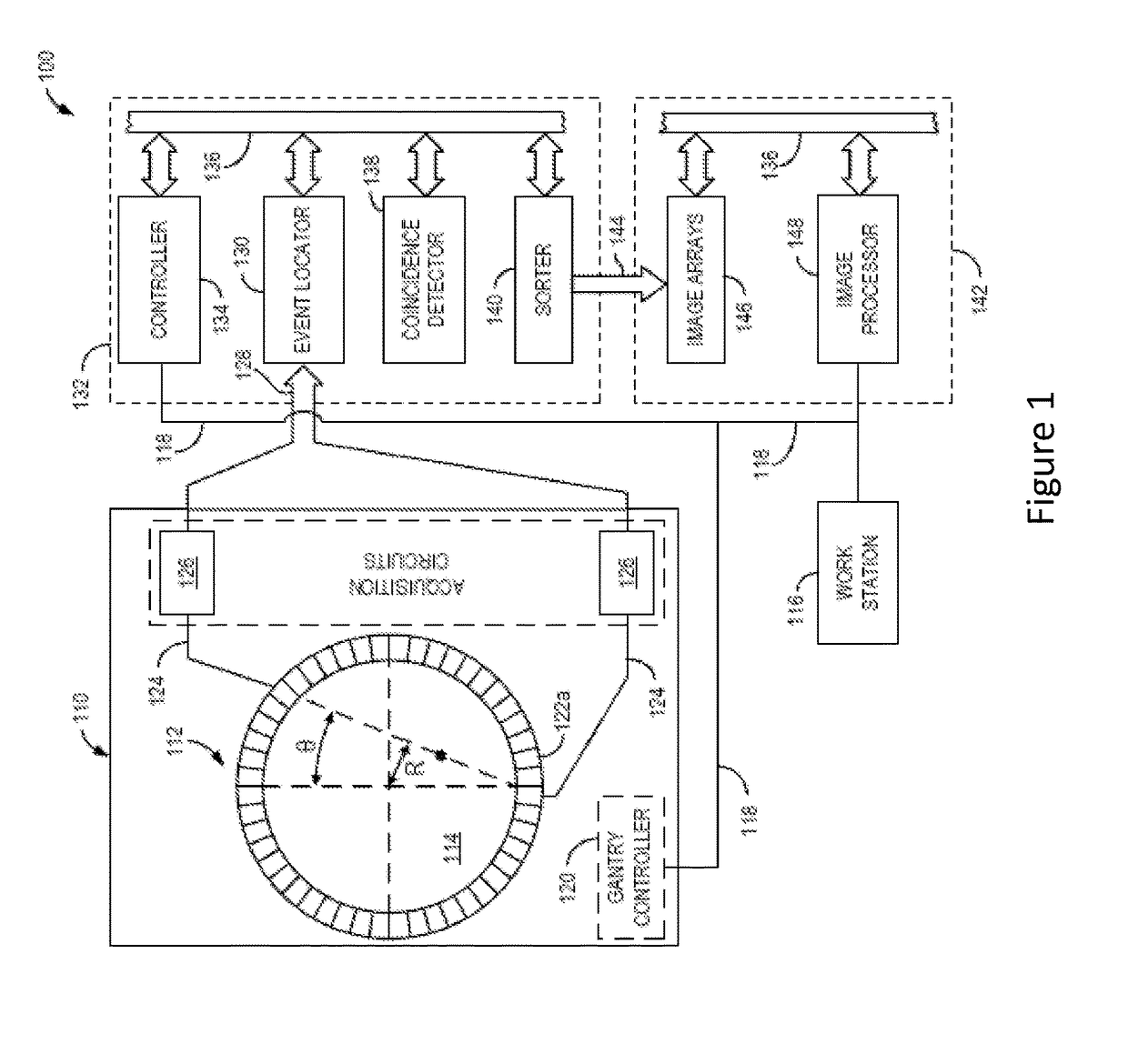
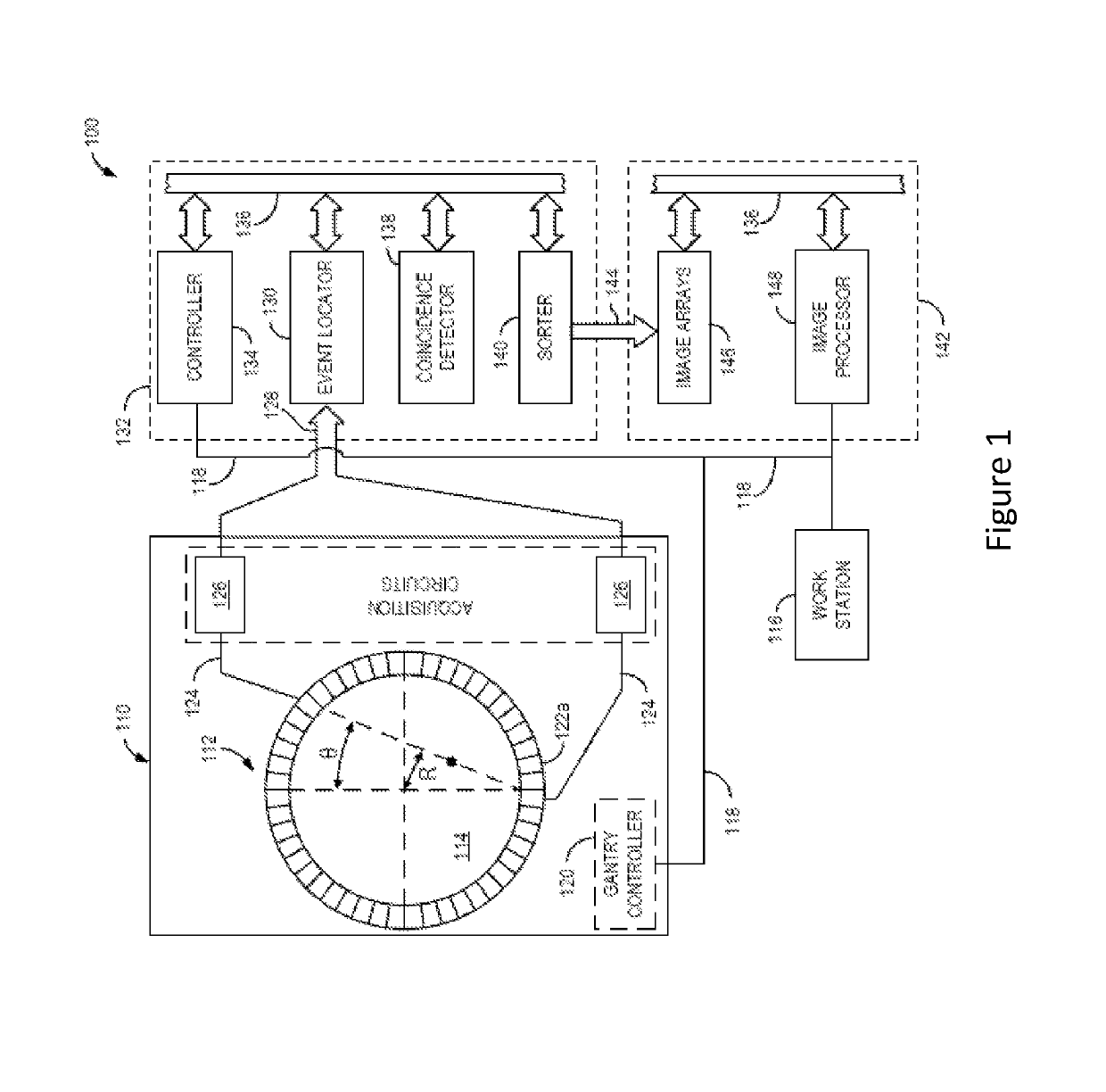
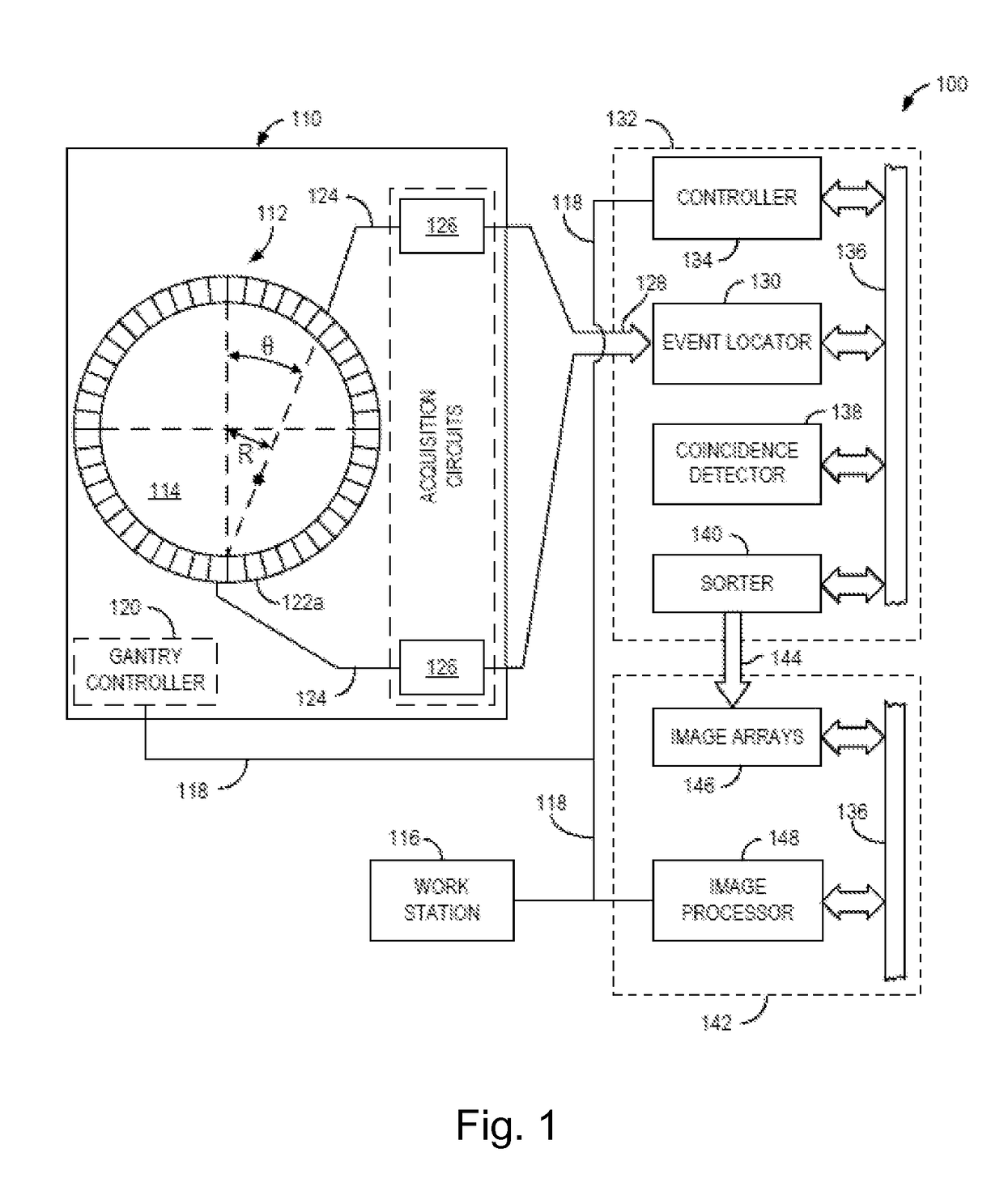
Device and system for enhanced SPECT, PET, and Compton scatter imaging in nuclear medicine
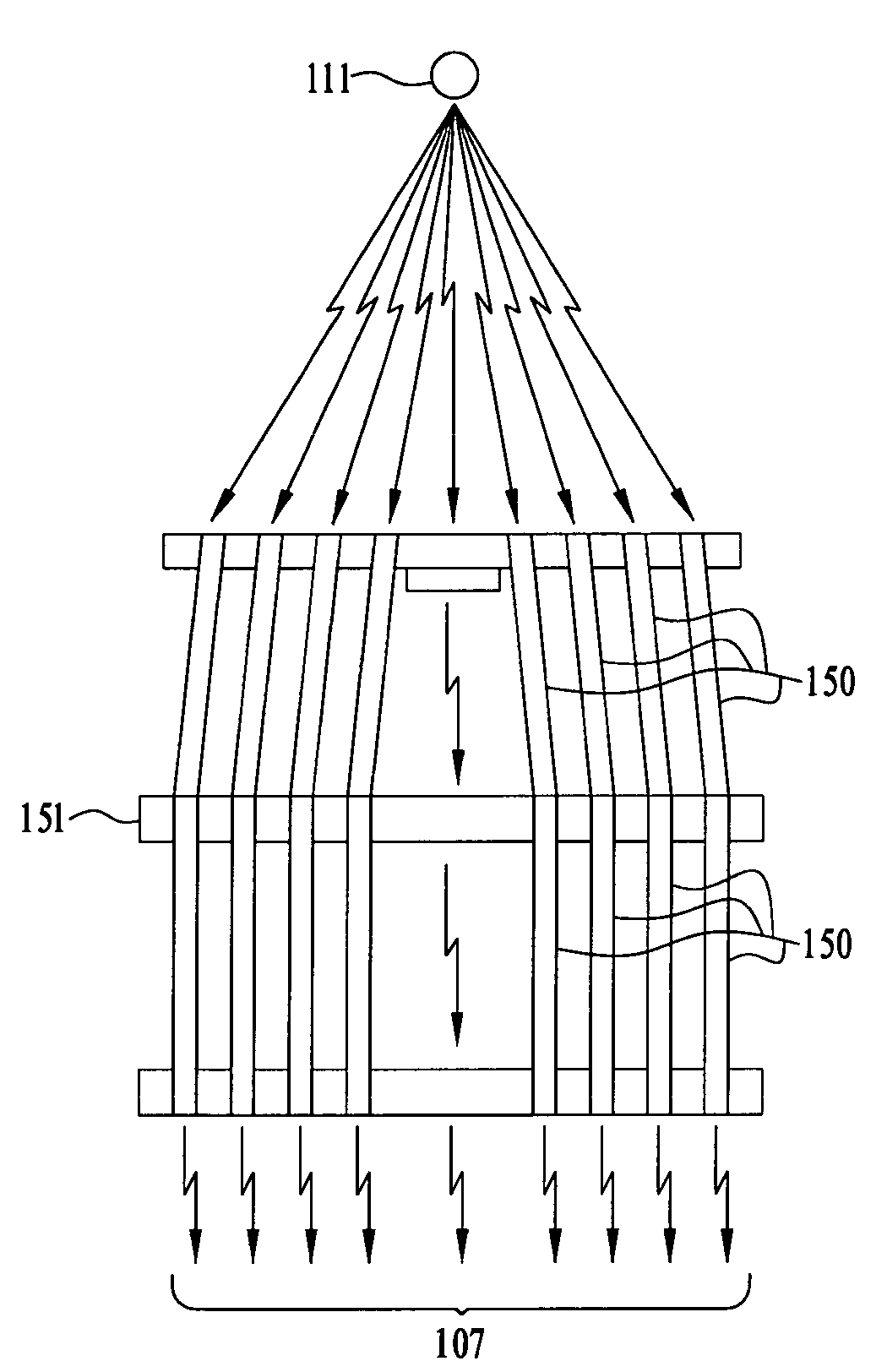
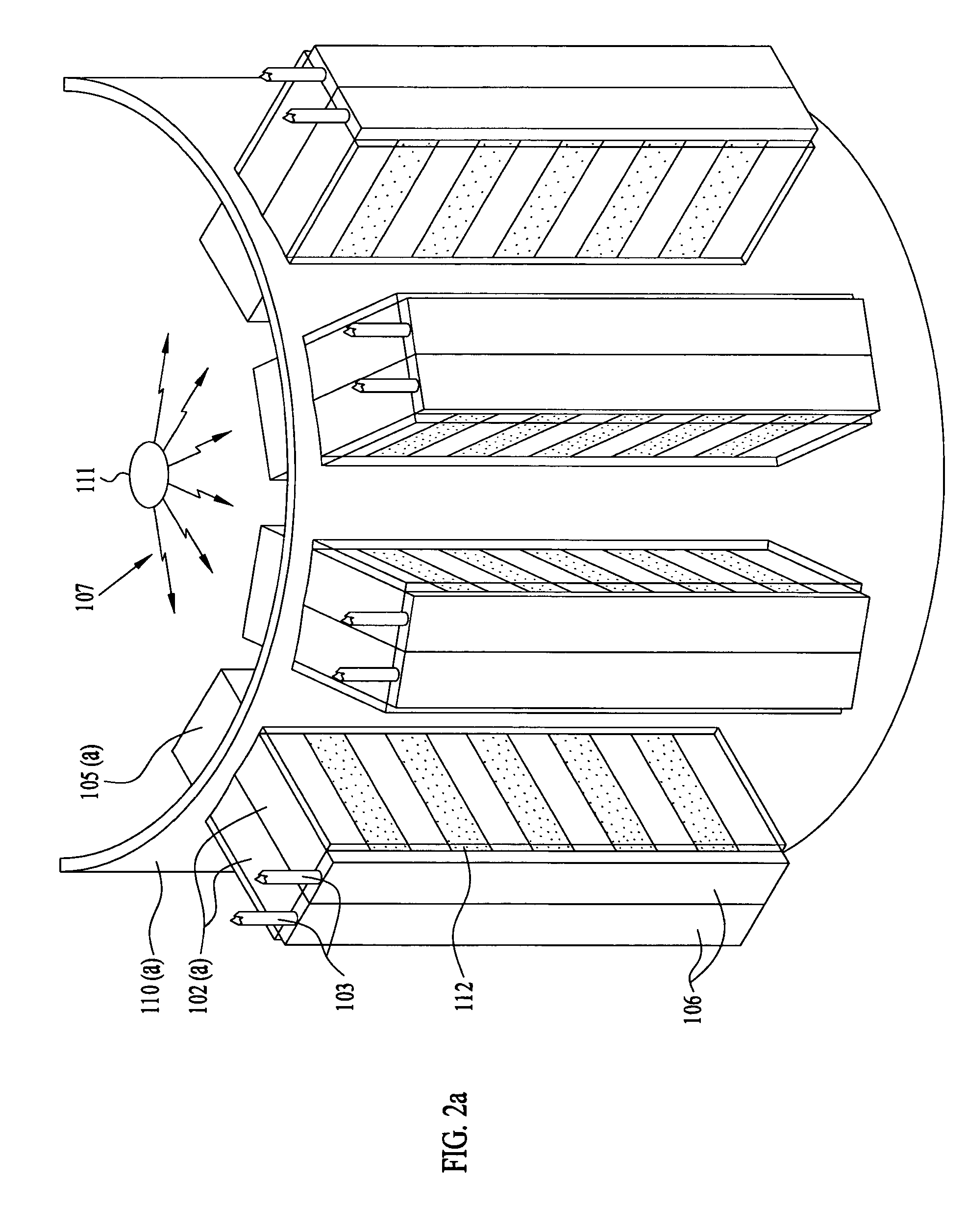
ActiveUS7291841B2Easy to optimizeEnhance analysis capabilitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCorrelative imagingPhysics
A method and apparatus for detecting radiation including x-ray, gamma ray, and particle radiation for radiographic imaging, and nuclear medicine and x-ray mammography in particular, and material composition analysis are described. A detection system employs fixed or configurable arrays of one or more detector modules comprising detector arrays that may be electronically manipulated through a computer system. The detection system, by providing the ability for electronic manipulation, permits adaptive imaging. Detector array configurations include familiar geometries, including slit, slot, plane, open box, and ring configurations, and customized configurations, including wearable detector arrays, that are customized to the shape of the patient. Conventional, such as attenuating, rigid geometry, and unconventional collimators, such as x-ray optic, configurable, Compton scatter modules, can be selectively employed with detector modules and radiation sources. Novel Compton gamma camera designs can be implemented. Edge-on detector resolution may be enhanced by measuring the interaction location along the height of the aperture. Edge-on detectors may be irradiated from the side. The components of the imaging chain can be calibrated or corrected using processes of the invention. X-ray mammography and scintimammography are enhanced by utilizing sectional compression and related imaging techniques.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Stochastic radiation radar coincidence imaging method
ActiveCN108828593AGuaranteed OrthogonalityEnhance non-correlationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar imagingArray aperture
The invention discloses a stochastic radiation radar coincidence imaging method applied to the field of radar imaging technology. The invention aims to solve a problem of comparatively high matrix relevance of a radiation field under an array aperture with limited bandwidth since that the radiation field formed by a prior stochastic radiation field construction method has comparatively large redundant information. According to the invention, a space stochastic field is obtained through stochastic signals of a transmission space of a transmission antenna array and the radiation field changes stochastically over time on the basis of configured transmission signal parameters; distribution of a space-time two-dimensional stochastic radiation field is obtained according to the configuration ofan antenna array, parameters of transmission signals and target distance history and echo signals are obtained according to the distribution of the stochastic radiation field by a receiving antenna; and finally, a coincidence imaging result of a target scene is obtained according to the relation between the distribution of the stochastic radiation field and the echo signals. The method provided bythe invention ensures the orthogonality of stochastic amplitude and phase of transmission signals and enhances incoherence of an echo stochastic scattered field.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
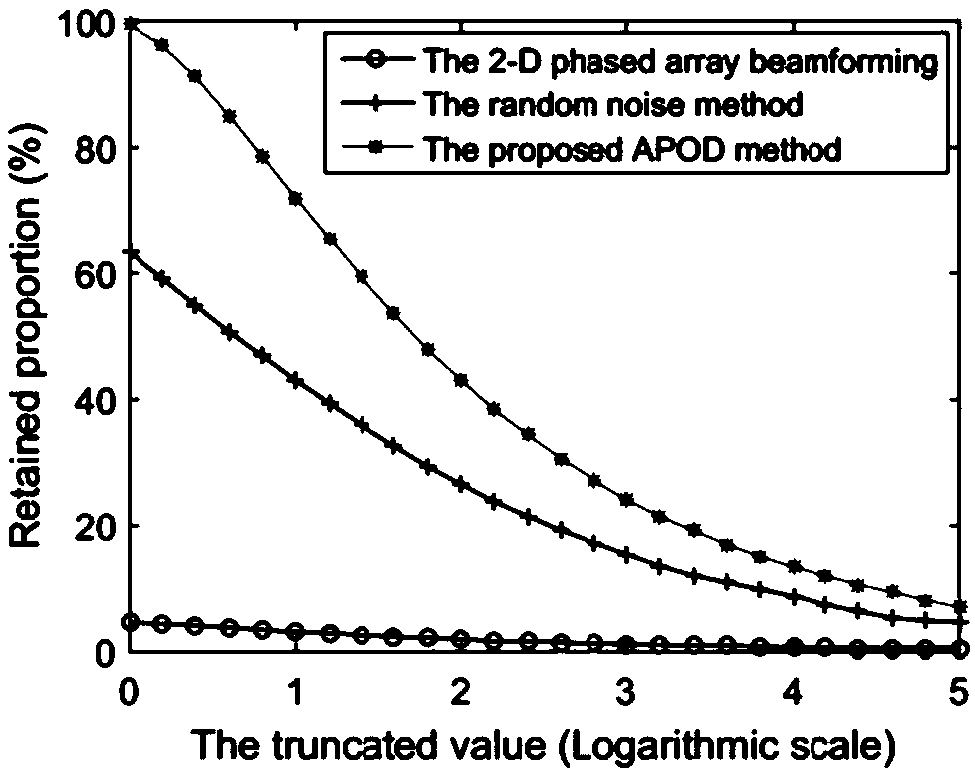
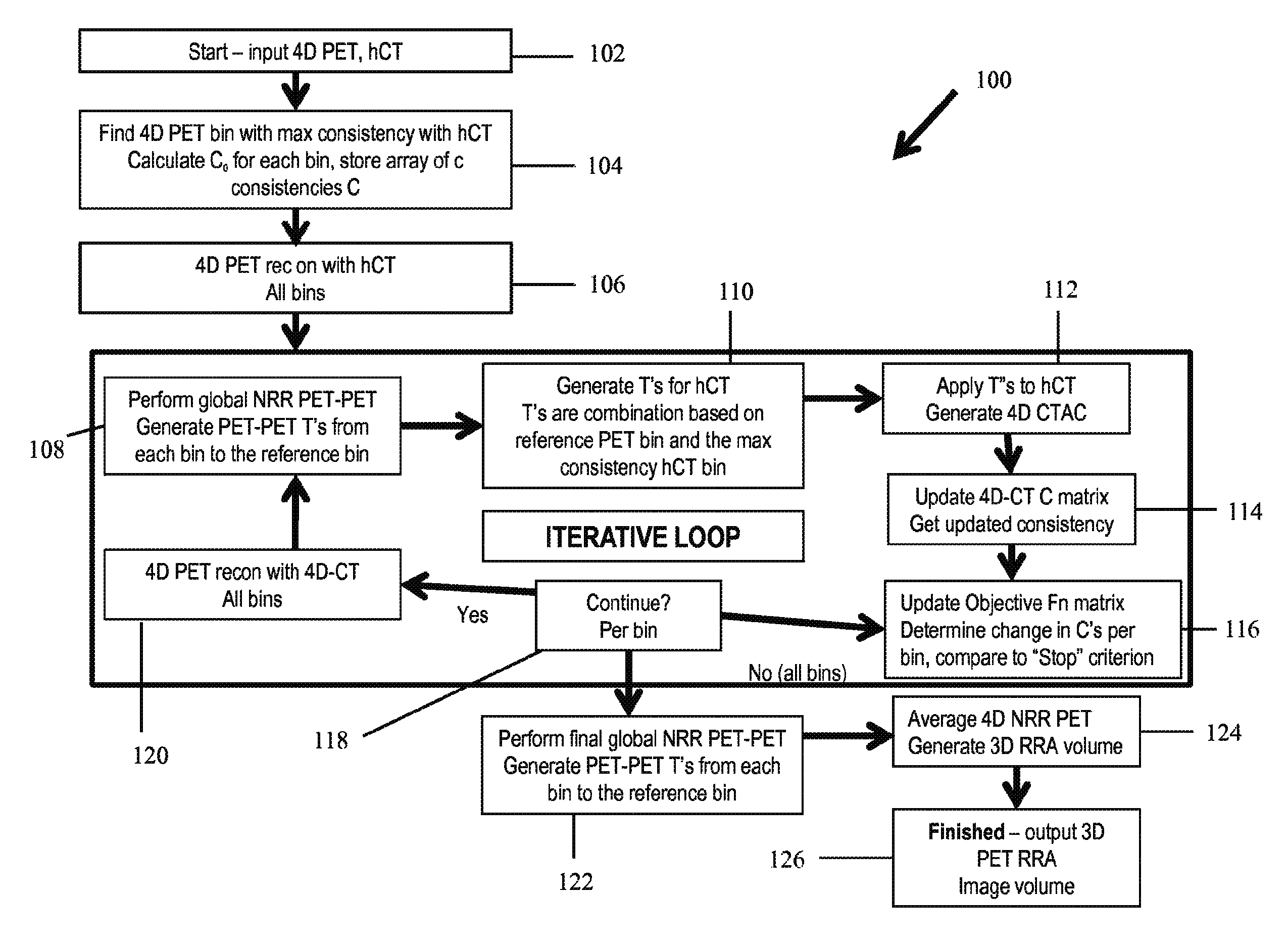
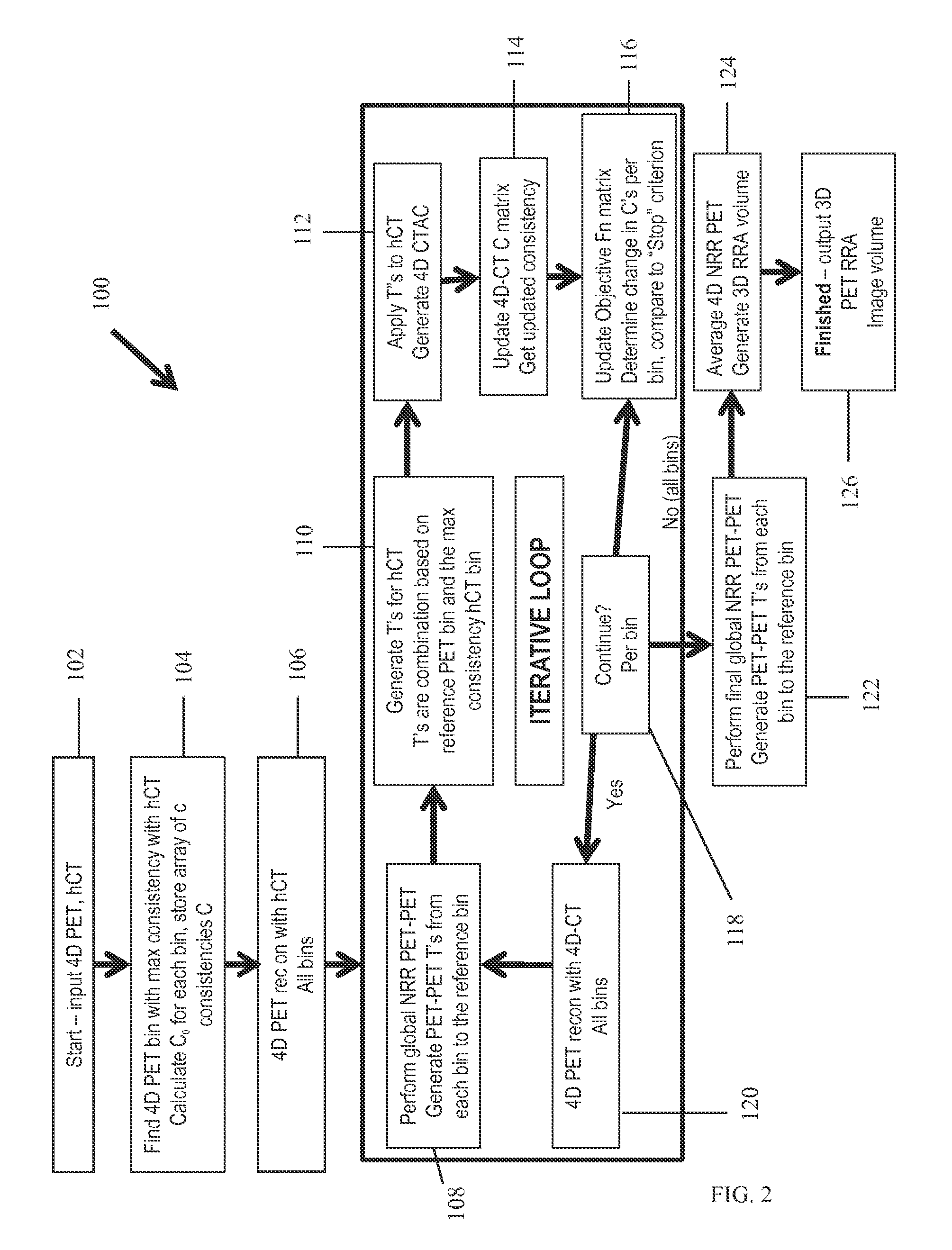
Method and apparatus for reducing motion related imaging artifacts using consistency values
A method for reducing, in an image, motion related imaging artifacts. The method includes obtaining a single image of a subject using a computed tomography (CT) imaging system, obtaining a plurality of images of the subject using a positron emission tomography (PET) imaging system, generating a plurality of consistency values, and utilizing the plurality of consistency values to register the CT image and the plurality of PET images.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
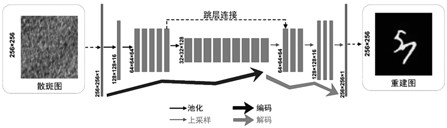
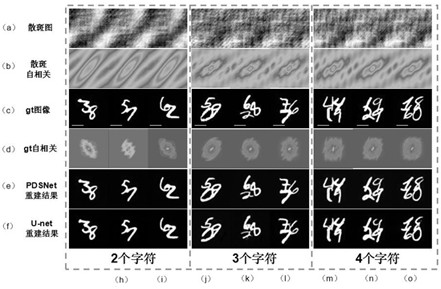
Method for imaging object passing behind scattering medium based on convolutional neural network
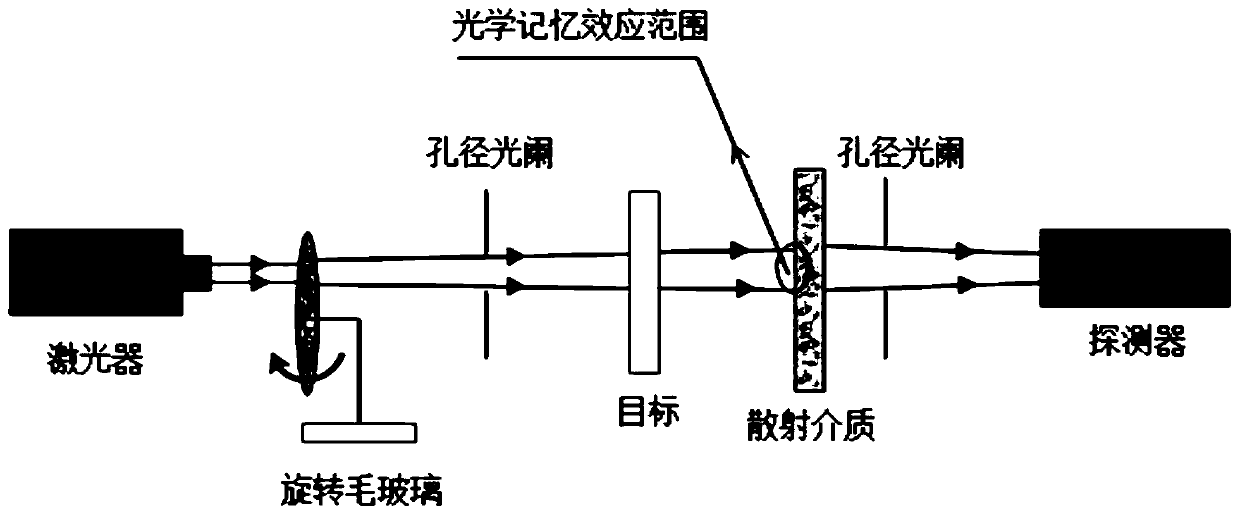
InactiveCN111739117ASuccessfully rebuiltOptical memory effect range extensionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmSpeckle correlation
The invention discloses a method for imaging an object behind a scattering medium based on a convolutional neural network PDSNet. According to the method, the traditional speckle correlation imaging algorithm principles are combined, the design and optimization of the network are guided, and the limitation of the optical memory effect OME on the imaging field angle FOV is eliminated in a data driving mode. The convolutional neural network PDSNet is a neural network structure suitable for a random scale and a complex target. The hidden object recovery capability of the convolutional neural network PDSNet is experimentally tested, and at least 40 times of optical memory effect range expansion is realized on the premise that the average PSNR is kept above 24dB. And meanwhile, under an untrained scale, the average PSNR of the recovered image is more than 22dB, and complex targets such as a human face are successfully reconstructed. Experimental results given in the invention verify the accuracy and effectiveness of the method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ore prospecting method utilizing ground high-precision gravity measurement
ActiveCN110888176APromote resultsObvious channel sedimentary featuresGravitational wave measurementField separationComputational physics
The invention discloses an ore prospecting method utilizing ground high-precision gravity measurement. The ore prospecting method mainly comprises six methods, namely a wave number domain iteration method of a potential field high-order derivative, a potential field separation method based on an iterative filtering method, a TASD method for identifying a boundary of a geologic body, an Euler deconvolution method for potential field data processing, a potential field abnormal cross-correlation imaging technical method and a gravity man-machine interaction profile forward modeling method. The ore prospecting method utilizing ground high-precision gravity measurement has the advantages of processing and explaining data of a plurality of gravity profiles, adopting the explaining methods covering the wave number domain derivative iteration method, the iterative filtering method of field separation and the cross-correlation imaging technology based on residual anomalies to be applied to gravity data, and achieves a good processing result.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
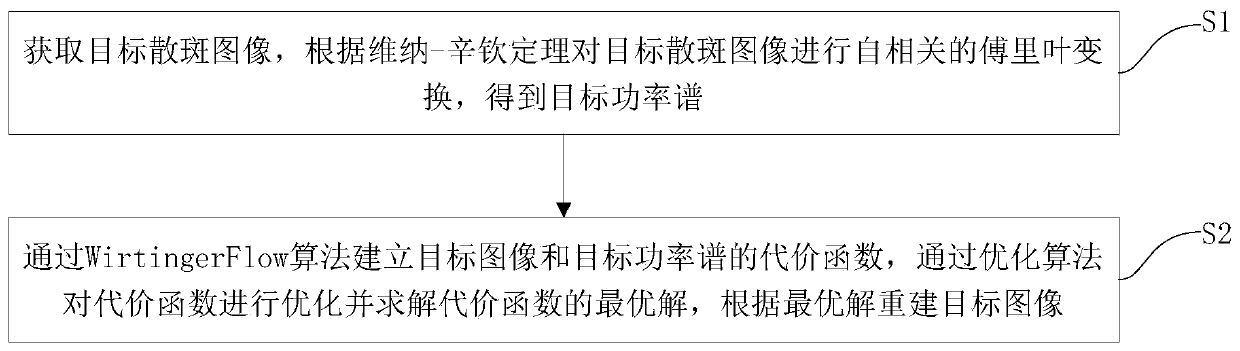
Speckle correlation imaging method and speckle correlation imaging device based on Wirtinger Flow algorithm
ActiveCN110807822AImprove robustnessQuality improvementImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionAlgorithmSpeckle correlation
The invention discloses a speckle correlation imaging method and device based on a Wirtinger Flow algorithm, and the method comprises the steps: S1, obtaining a target speckle image, and carrying outthe autocorrelation Fourier transform of the target speckle image according to the Wiener-Khinchin theorem, and obtaining a target power spectrum; and S2, establishing a cost function of the target image and the target power spectrum through a Wirtinger Flow algorithm, optimizing the cost function through an optimization algorithm, solving an optimal solution of the cost function, and reconstructing the target image according to the optimal solution. According to the method, the robustness of the target reconstruction process to measurement noise and system distortion can be improved, any prior information of the target is not needed, and the quality of the reconstructed target is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
An Imaging Study Completion Processing System
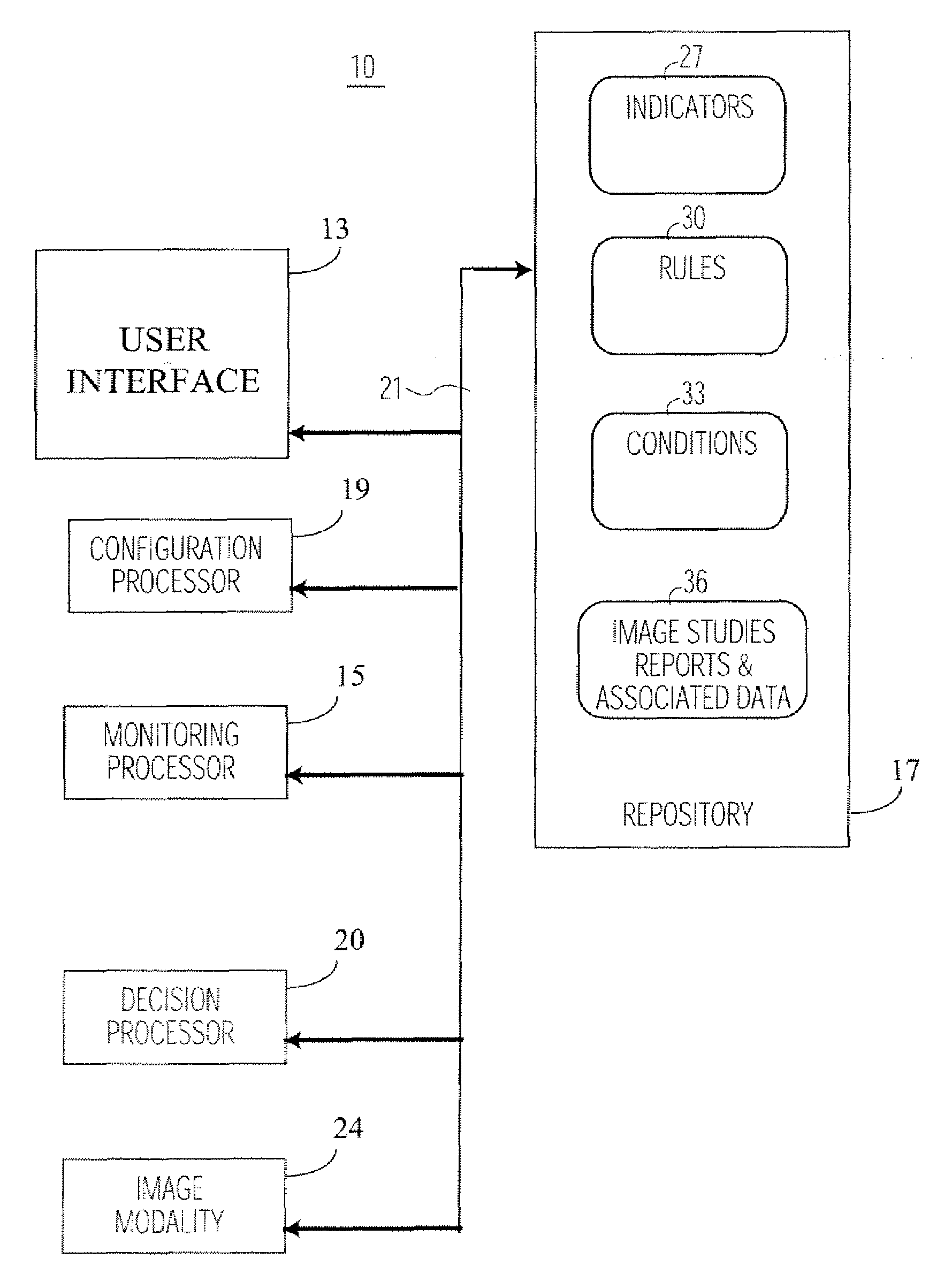
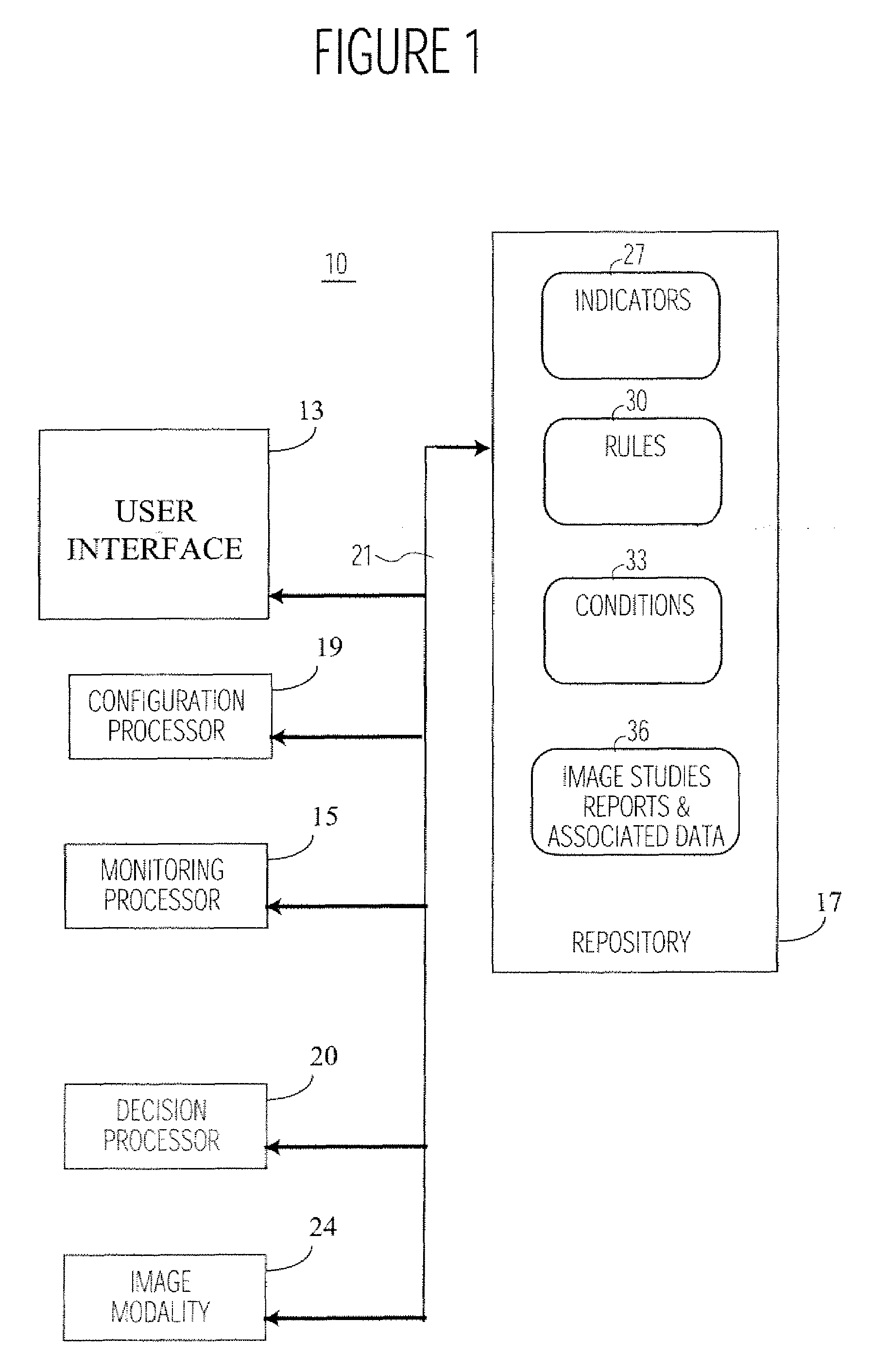
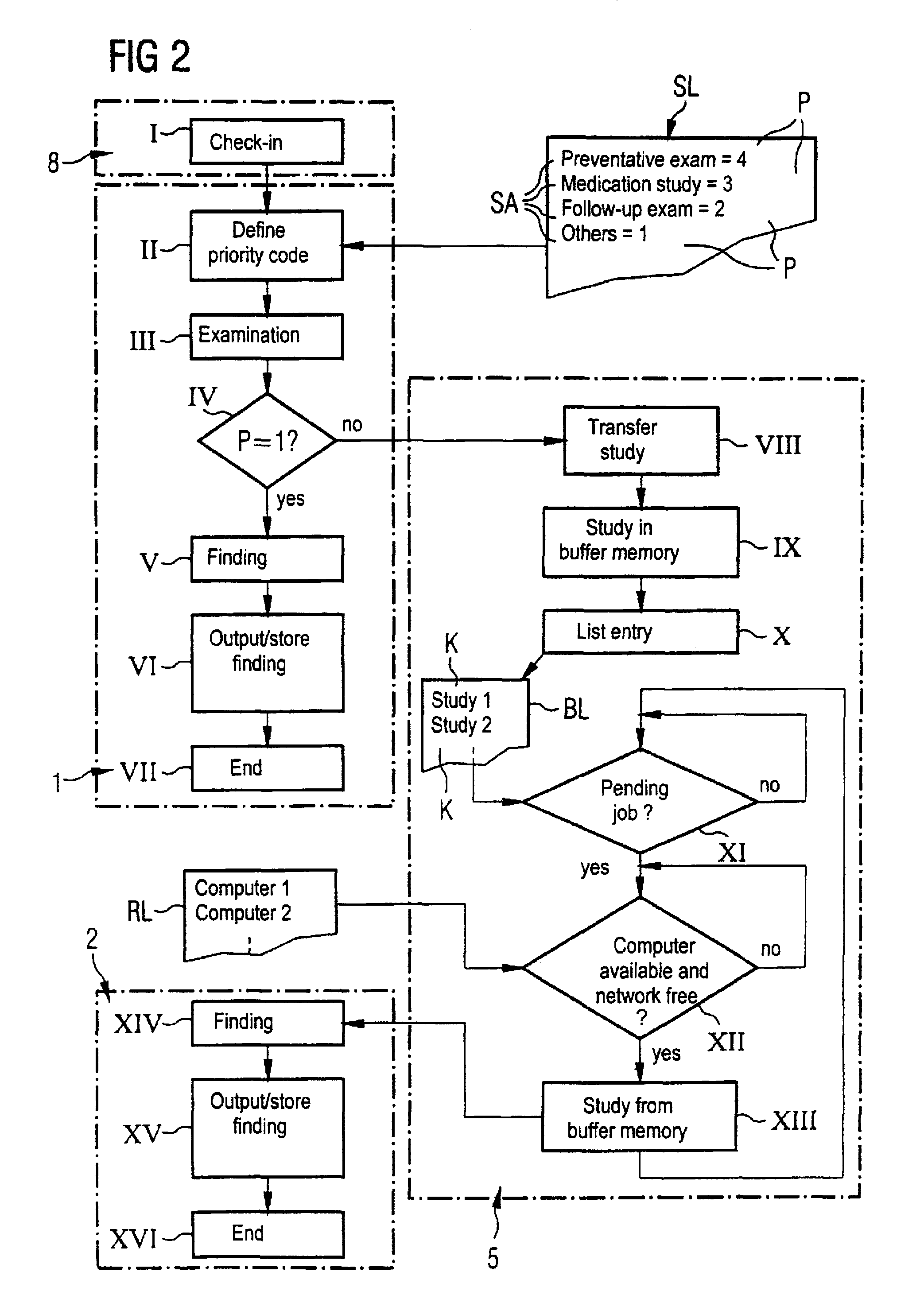
ActiveUS20080123917A1Optimize workflowImage analysisInput/output to record carriersDiagnostic dataCompletion Status
A system enables a user to signify completion of an imaging study comprising a collection of reports, worksheets and diagnostic data, based upon rules configured by a user saving user time and increasing reliability of image study processing. An automated system manages completion of a medical imaging study having one or more different reports associated with one or more different personnel and being produced during a patient imaging examination. A user interface provides multiple display images. A configuration processor enables a user, using a display image, to assign a predetermined completion status to a report. The predetermined completion status is used to indicate a report is complete as required for an associated imaging study to be designated complete. A monitoring processor monitors stored indicators indicating current status of corresponding reports associated with the imaging study. A decision processor, in response to the monitoring of the stored indicators, automatically determines whether a current status of a report matches a corresponding predetermined completion status of a report for individual reports associated with the imaging study and in response to a match for the individual reports, initiates generation of a message indicating the imaging study is complete.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
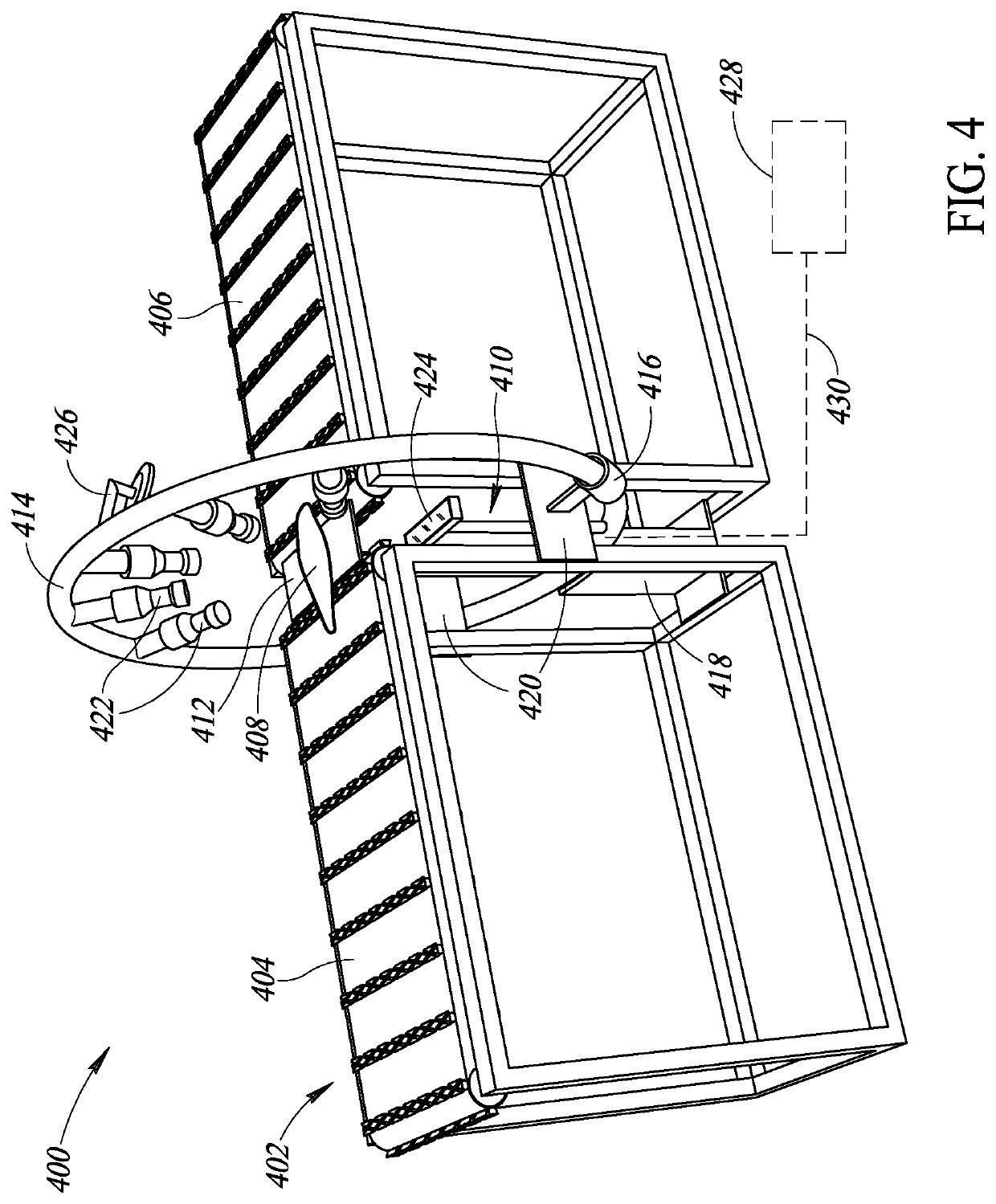
Multi-view imaging system and methods for non-invasive inspection in food processing
ActiveUS11120540B2Television system detailsDetails involving processing stepsEngineeringFood material
Owner:THAI UNION GRP PUBLIC CO LTD
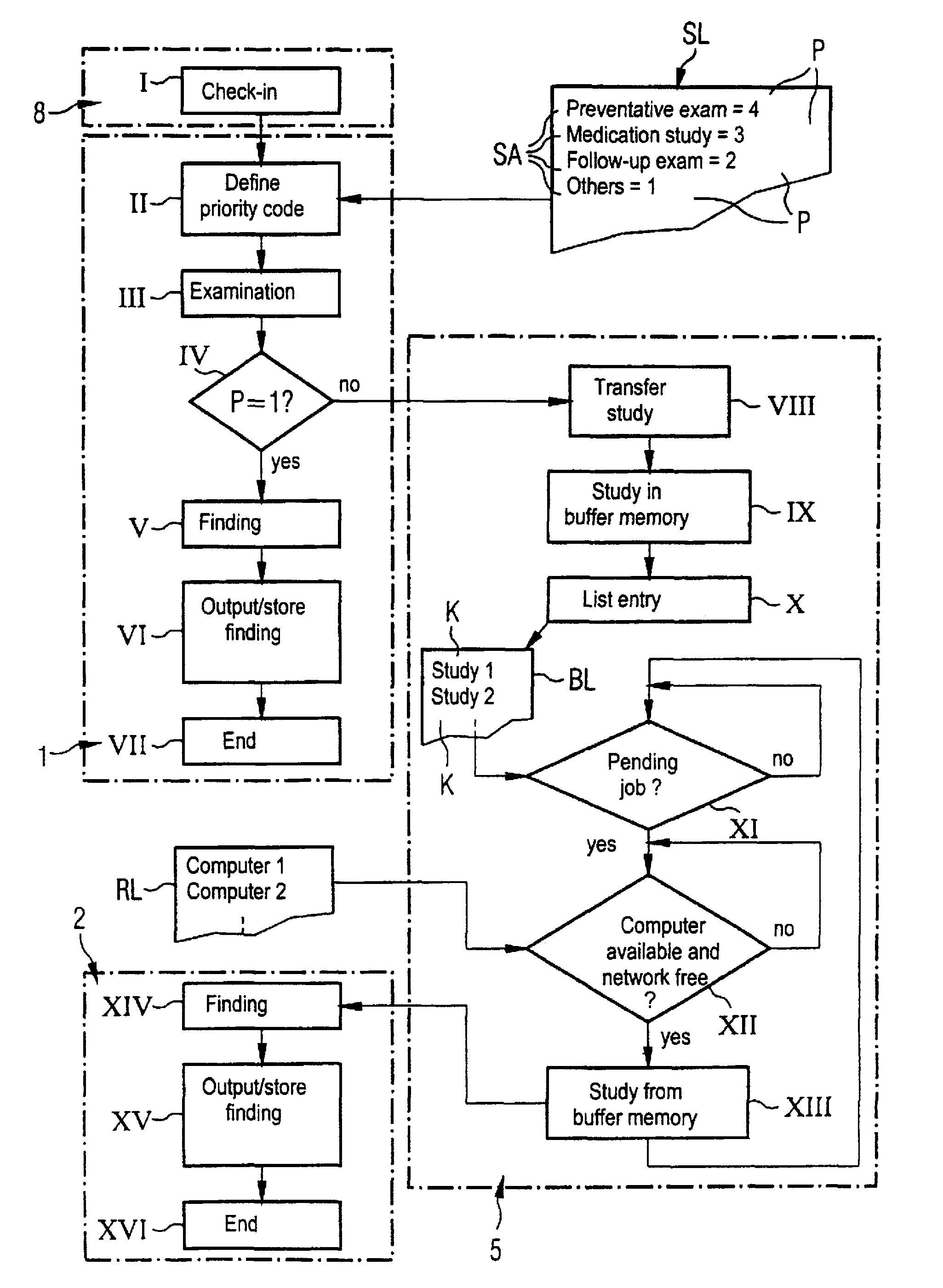
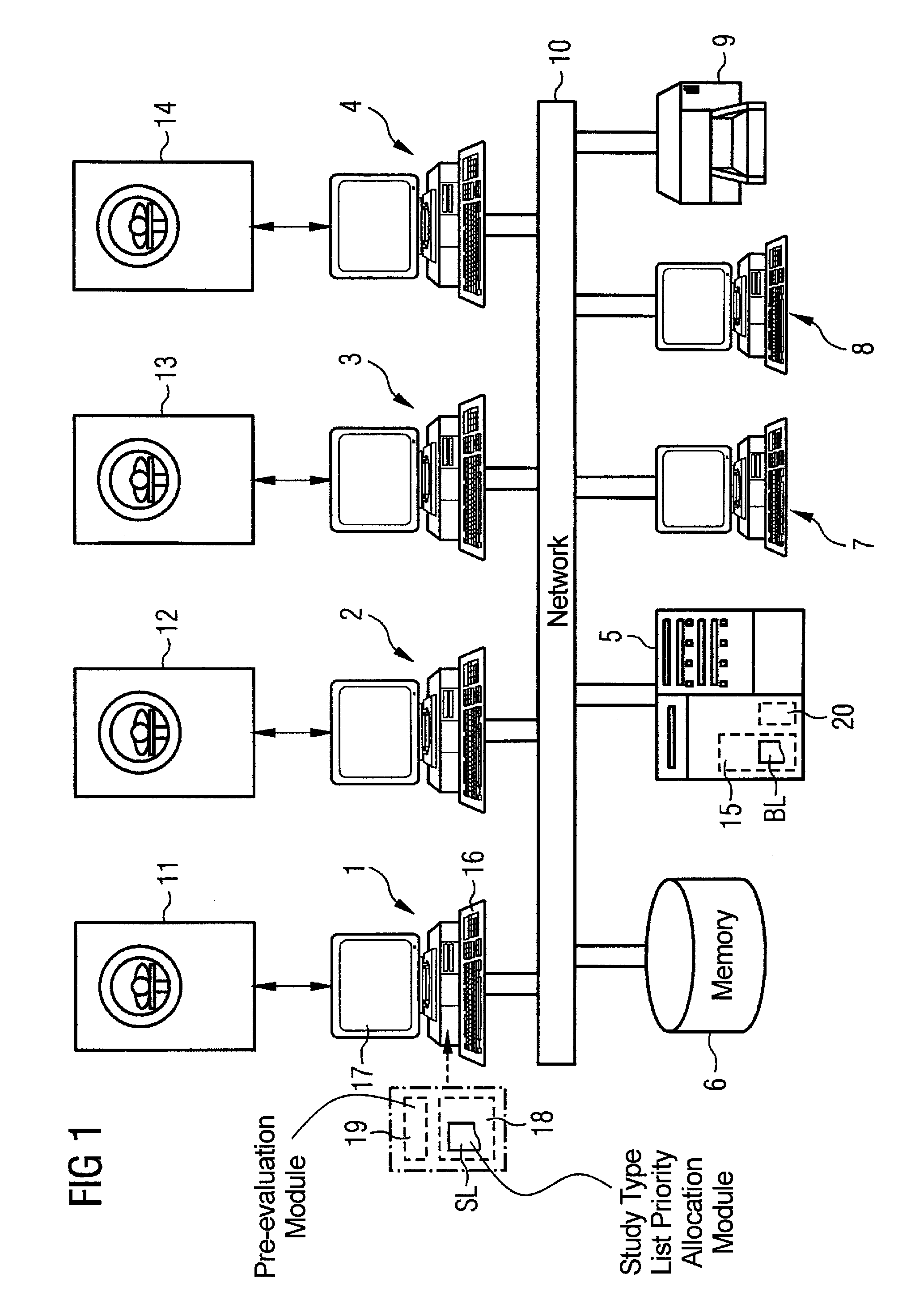
Method and computerized system for automatically processing studies acquired by an imaging examination system
InactiveUS7444008B2Data processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionSequence processingComputerized system
In a method and system for automatically processing studies of imaging examination systems, each of the studies is given a priority code. Dependent on its priority code, the study is either processed immediately on a first computer allocated to the appertaining imaging examination system or the study is first intermediately stored in a memory device for a later processing, and an identifier allocated to the study is stored in a processing job list. At later points in time, the studies whose identifiers are stored in the processing job list are processed according to a predefined sequence. The first computer has further computers allocated to it for this purpose. The availability of the allocated, further computers is then checked and, insofar as one of the allocated computers is available for a processing of the study, an intermediately stored study is communicated to the appertaining, allocated computer for processing.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
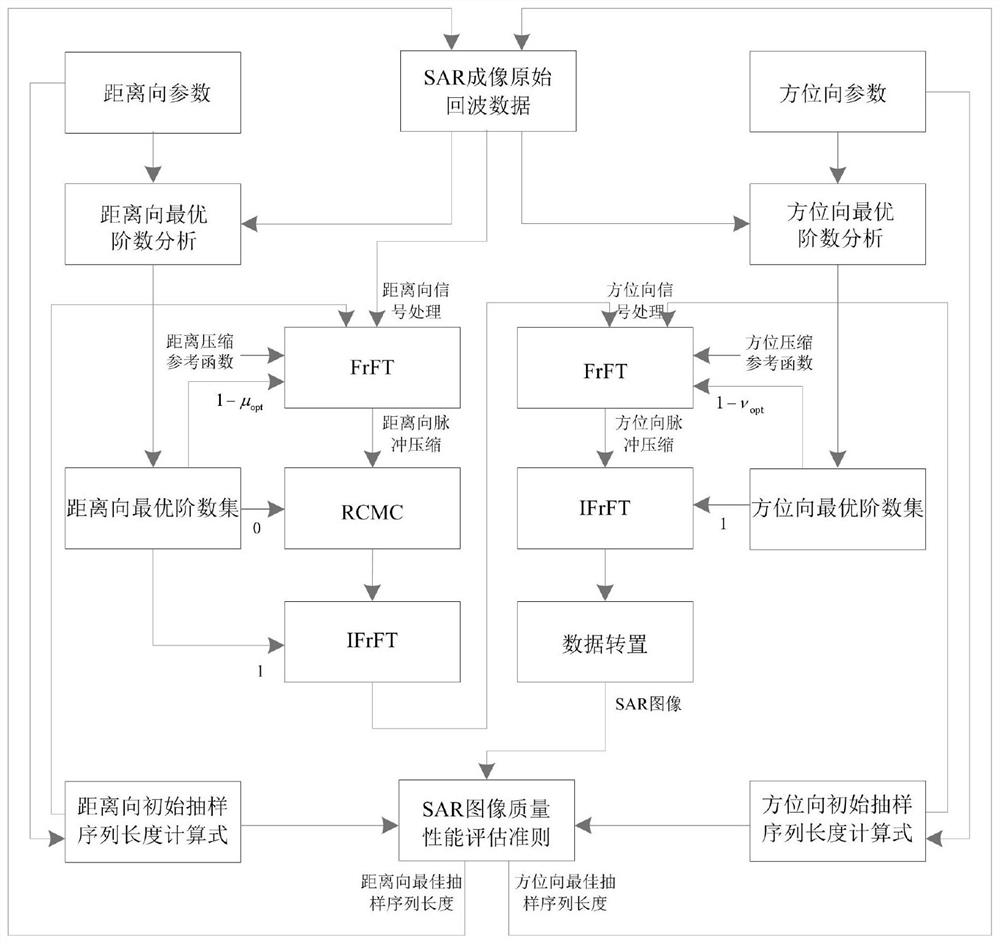
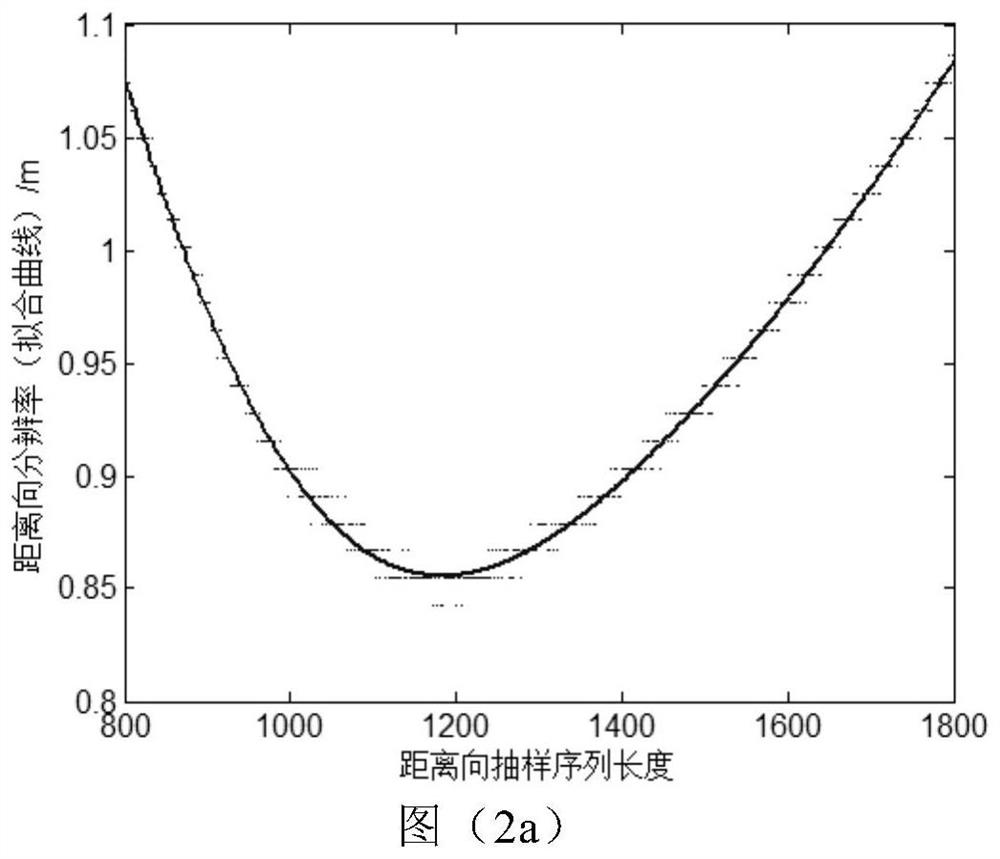
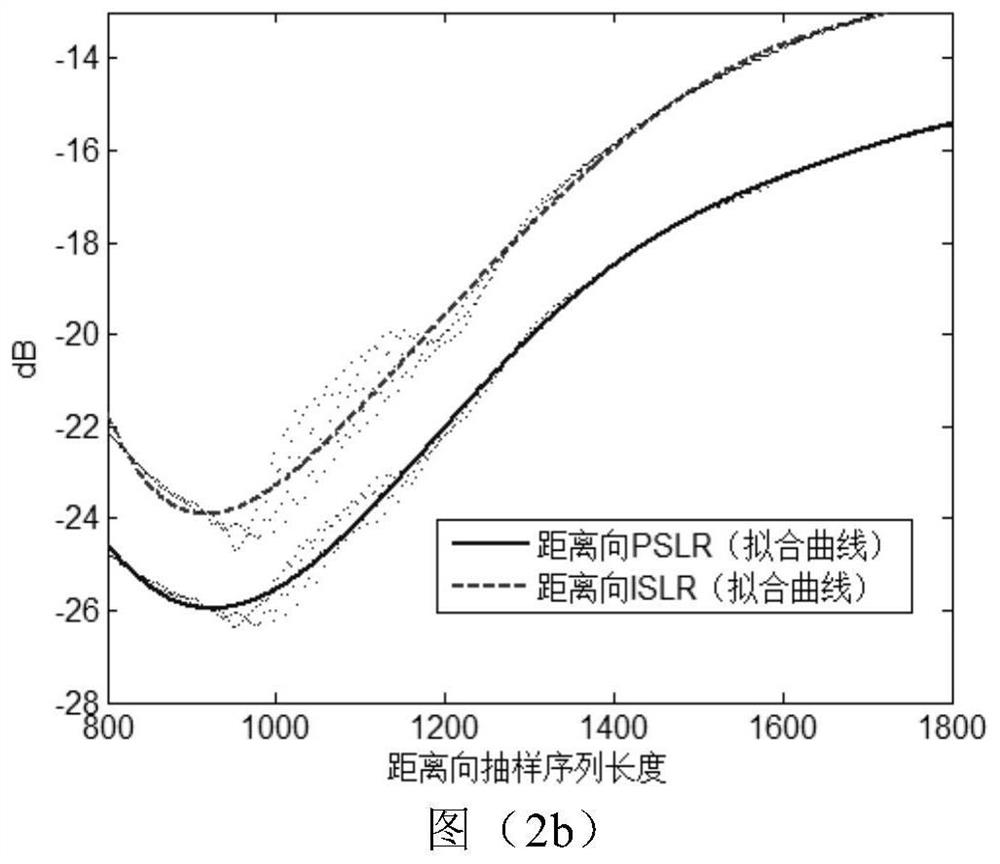
SAR imaging method based on sampling sequence length constraint condition
PendingCN112305541AFocusOvercoming the problem of low image qualityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging qualityImage resolution
The invention discloses an SAR imaging method based on an optimal sampling sequence length constraint condition, and the method comprises the steps: a calculation formula of an initial sampling sequence length is designed according to related imaging parameters in an SAR distance direction and an azimuth direction; the obtained initial sampling sequence length and the corresponding criterion of SAR image quality performance evaluation are utilized, the optimal sampling sequence length in the distance direction and the optimal sampling sequence length in the azimuth direction are determined within the reasonable interval change range in combination with curve extreme values, the optimal sampling data length support is provided for global optimal imaging, and a high-resolution SAR imaging method is constructed on the basis of the optimal sampling data length support; the SAR imaging method comprises the steps of order calculation of fractional Fourier transform applied to SAR echo signals, setting of sampling sequence length constraint conditions and construction of the high-resolution SAR imaging method. According to the method, the problem of low imaging quality of a traditional distance Doppler method is solved in synthetic aperture radar imaging, and the range resolution and the azimuth resolution of the SAR image are remarkably improved.
Owner:JIANGSU POLICE INST
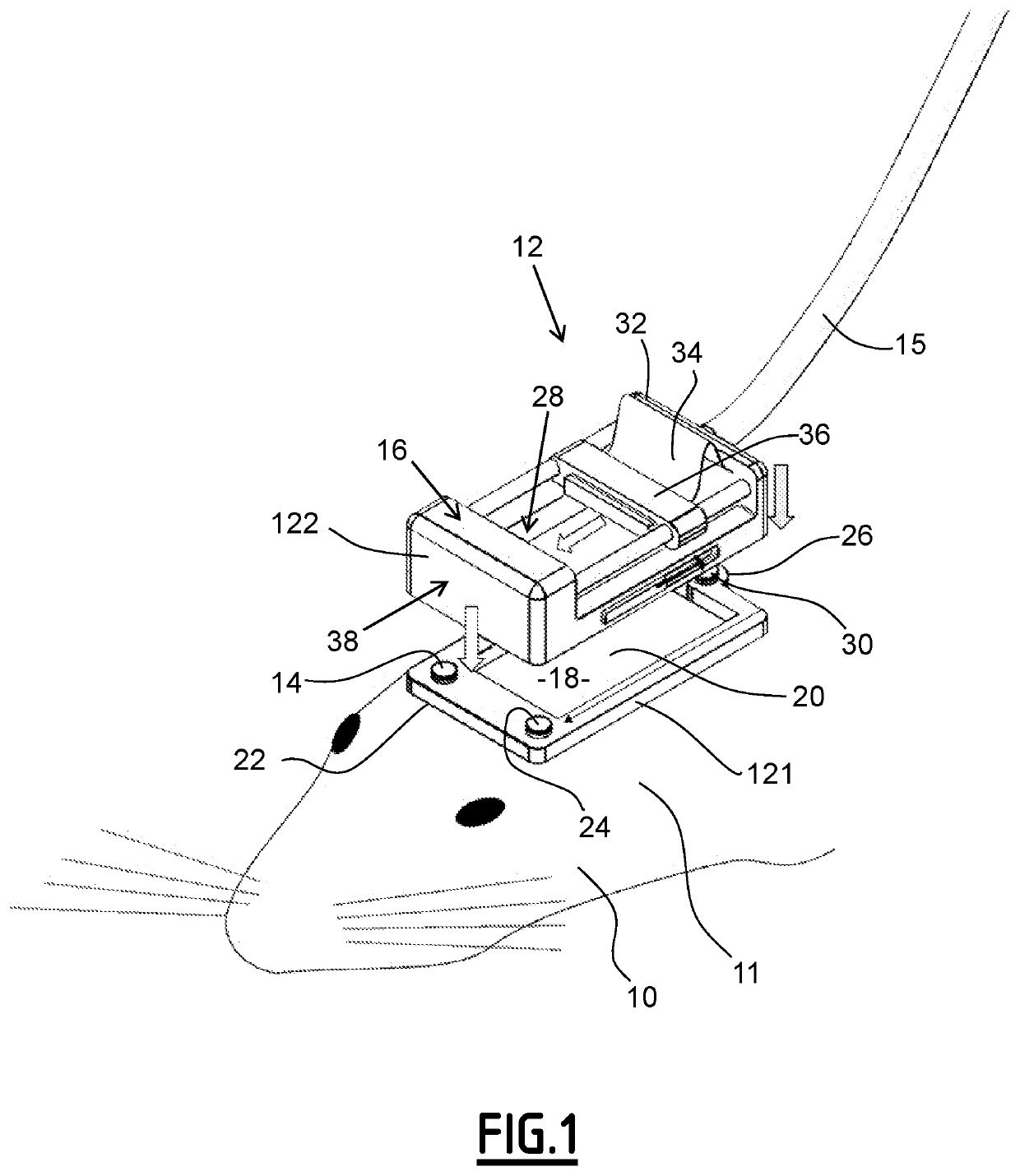
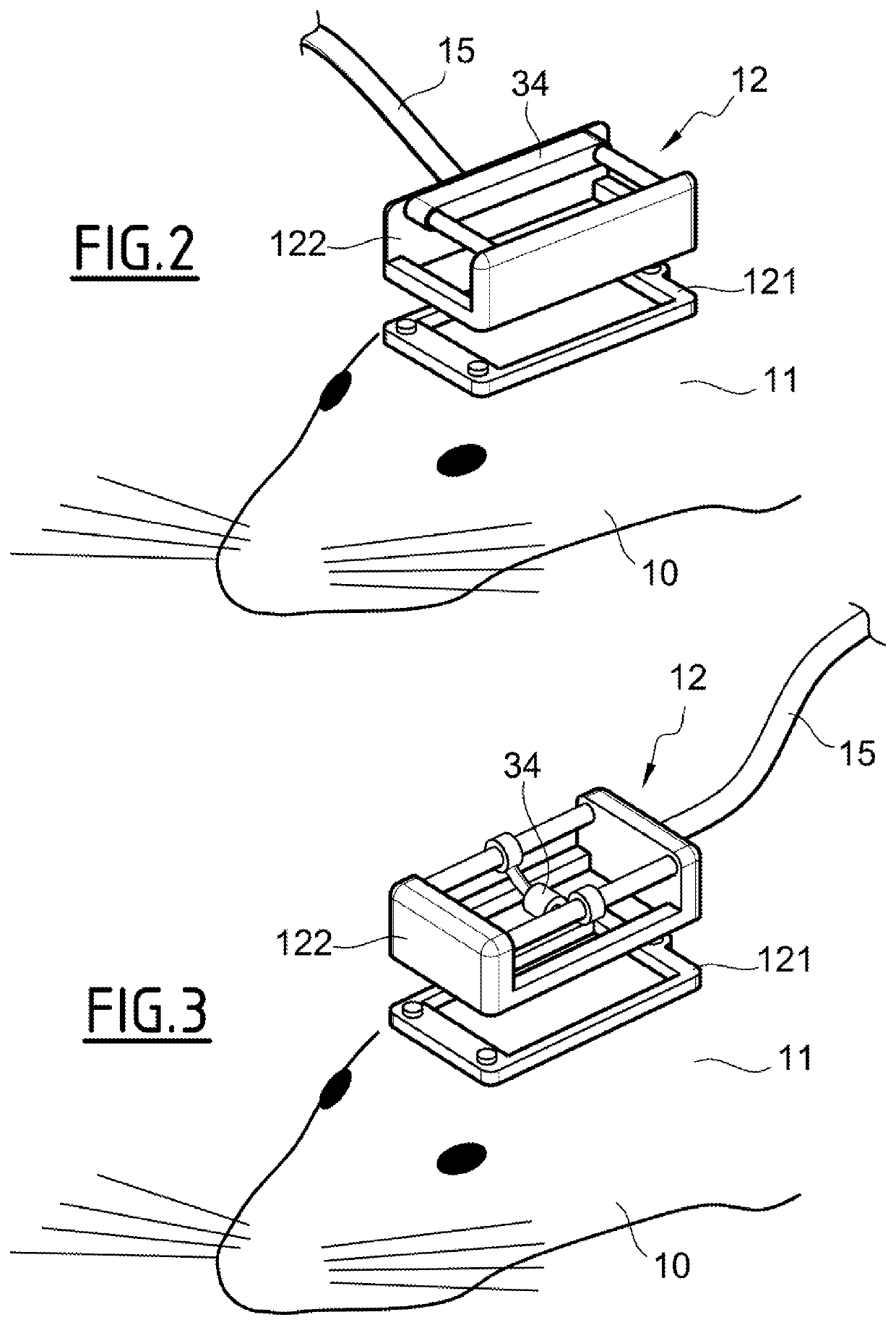
Detecting apparatus and associated imaging method
The invention concerns a detecting apparatus (12) for imaging at least two areas of a brain of a subject (10), the detecting apparatus (12) comprising: —a holder comprising: —a frame (14) devoted to be cemented on the skull of the subject (10), the frame (14) delimitating an inner portion (18) which is transparent to ultrasound waves, —a removable imaging device comprising: —a platform (16) delimitating an inner space (28), the inner space (28) facing the inner portion (18), —a fixing element (30) adapted to temporary fix and lock the platform (16) to the holder, —an ultrasound probe (32), and —a moving stage (34) holding the ultrasound probe (32) and being adapted to move the ultrasound probe (32) within the inner space (28).
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +3
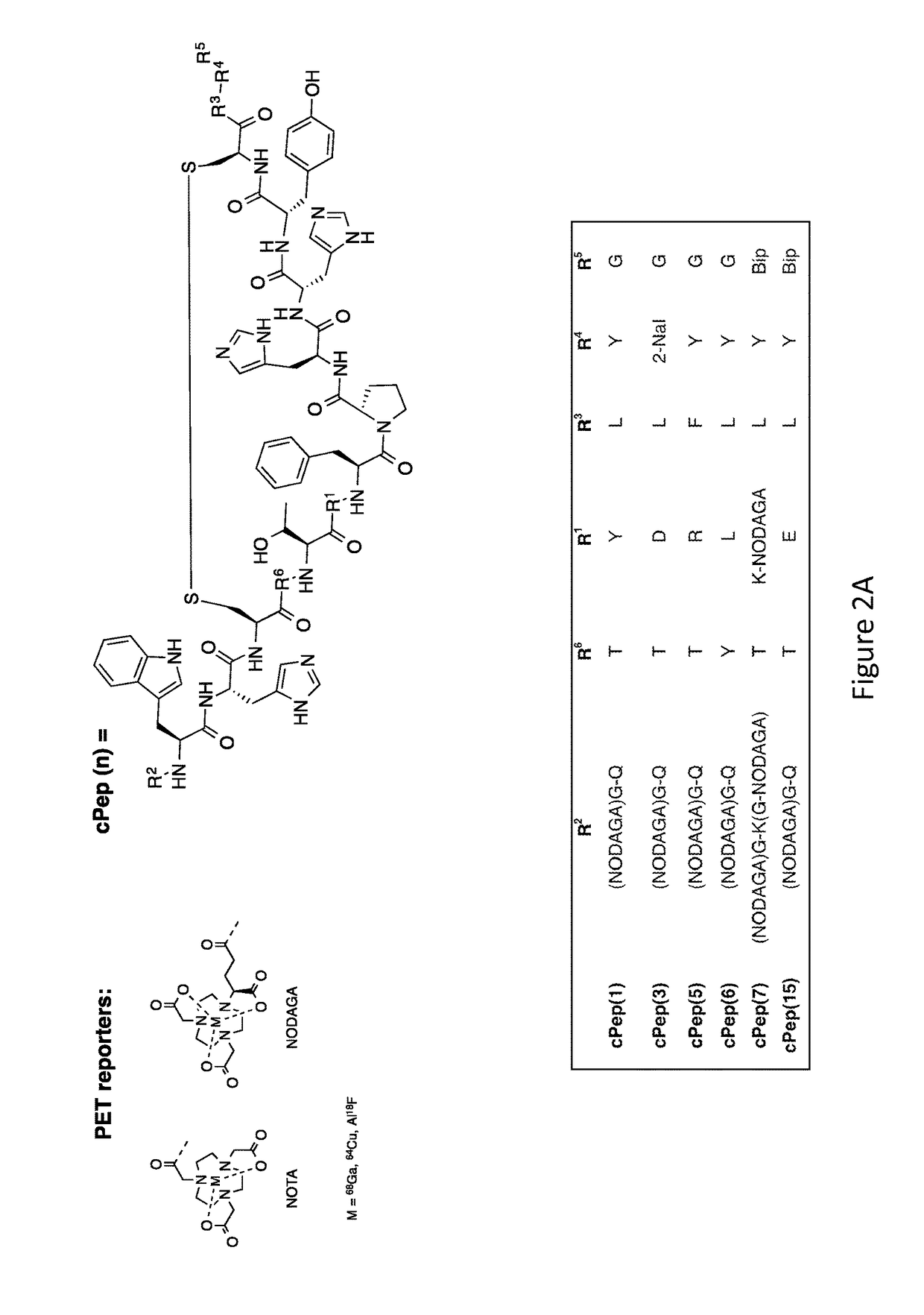
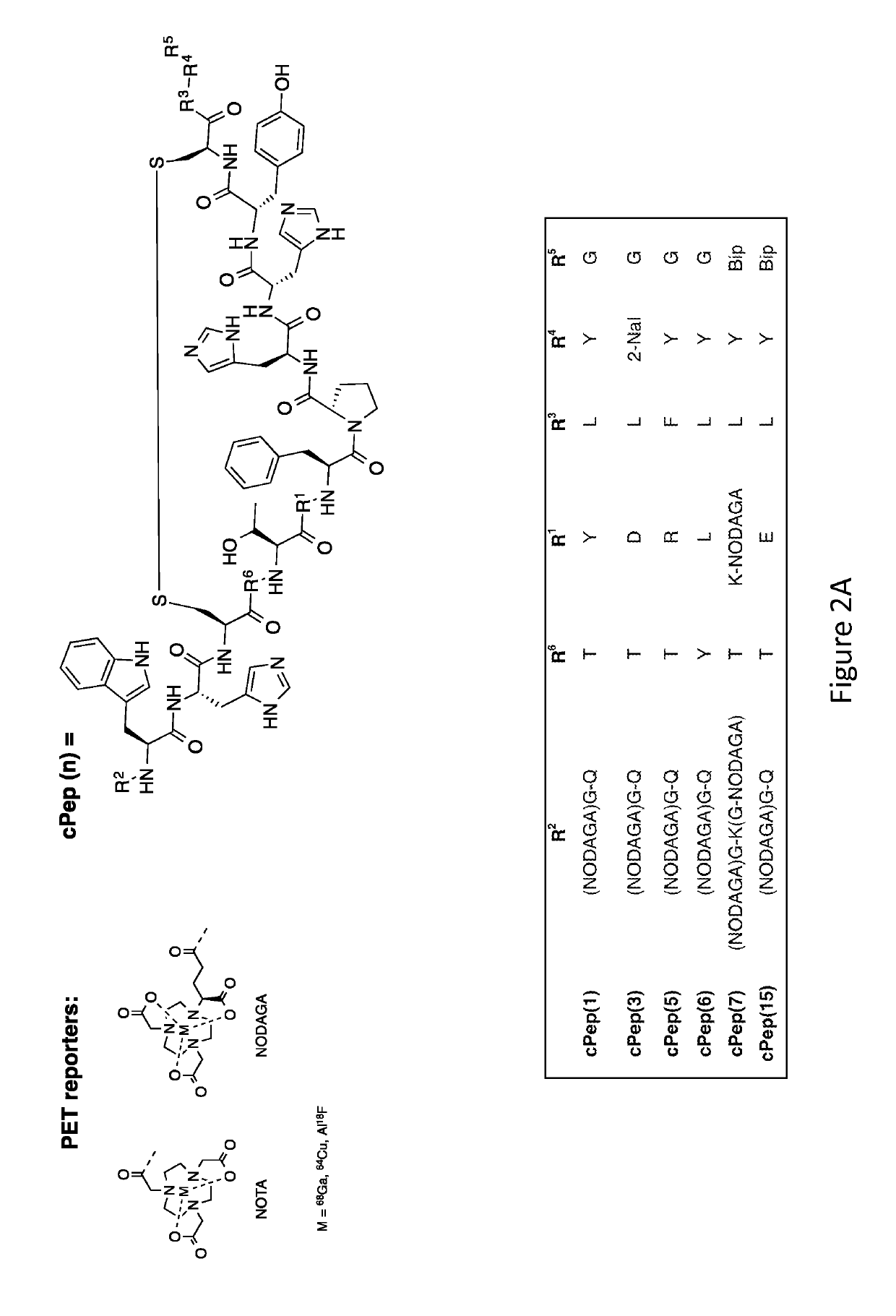
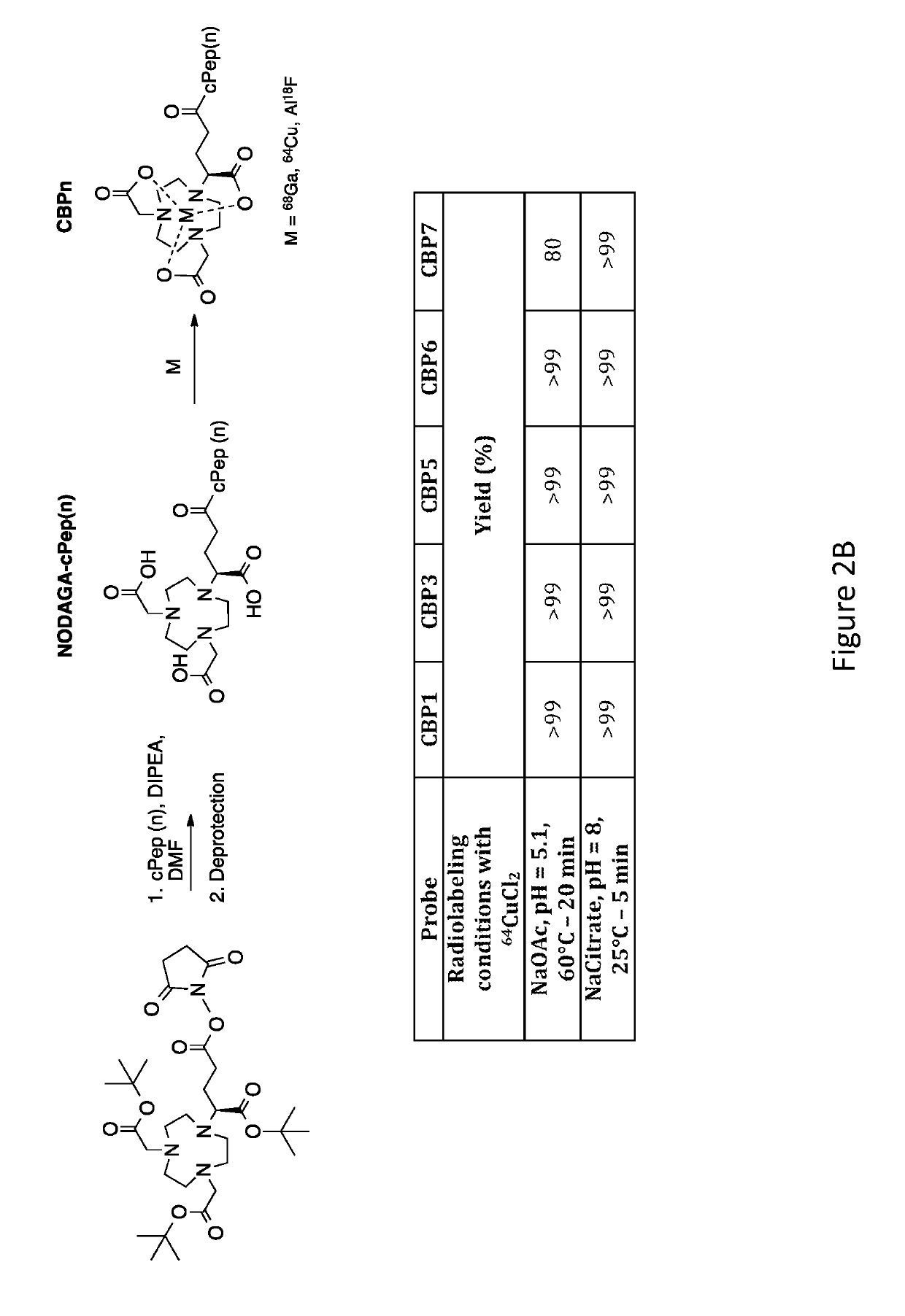
Collagen Targeted Imaging Probes
ActiveUS20170360967A1Promote absorptionPeptide/protein ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersImaging agentCollagen VI
Disclosed herein are collagen-targeted imaging agents for positron emission tomography and related imaging methods using the collagen-targeted imaging agents. The collagen-targeted imaging agent is a cyclic polypeptide comprising a cyclic main body, wherein the cyclic main body comprises at least one S—S bond; at least two branches, wherein each of the at least two branches comprises at least three amino acids; and a linker, wherein the linker is capable of linking an imaging reporter.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Collagen targeted imaging probes
ActiveUS10471162B2Promote absorptionPeptide/protein ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersImaging agentCollagen VI
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
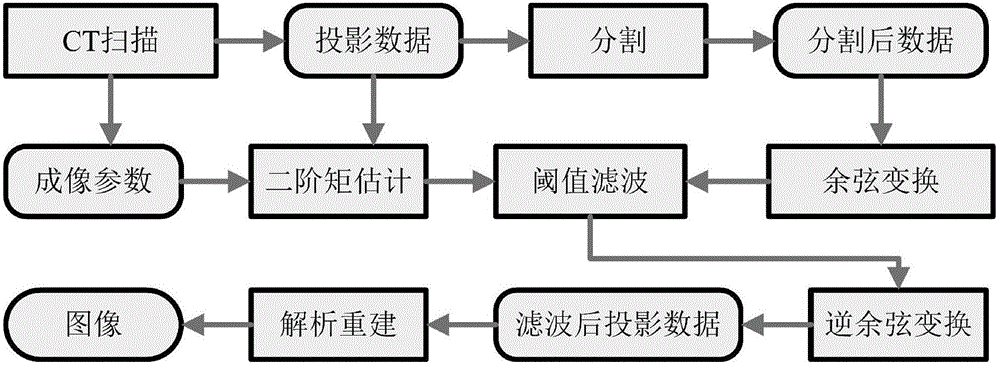
Cosine transform-based method for adaptive threshold filtering reconstruction of projection data of X-ray computed tomography (CT) medical image
InactiveCN102750676AQuality rebuildKeep image edgesImage enhancementReconstruction methodDiscrete cosine transform
The invention discloses a cosine transform-based method for adaptive threshold filtering reconstruction of projection data of an X-ray computed tomography (CT) medical image. The method comprises the steps of (1) using a CT device to collect the projection data on the condition of a low tube current scanning protocol, and obtaining relevant imaging parameters; (2) estimating secondary moment statistical characteristics of the projection data; (3) conducting gray-scale feature-based adaptive segmentation on the collected projection data; (4) conducting discrete cosine transform on the projection data subjected to segmentation in Step (3); (5) conducting data threshold filtering modeling on the projection data subjected to discrete cosine transform in Step (4) by using projection data variances calculated in Step (2); (6) conducting inverse discrete cosine transform on filtered data obtained in Step (5), and obtaining the filtered projection data before reconstruction; and (7) for the filtered projection data obtained in Step (6), using an analytic reconstruction method to achieve reconstruction of the CT image. By the aid of the method, high-quality reconstruction of the CT image can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Two-way wave pre-stack depth migration method based on matrix multiplication
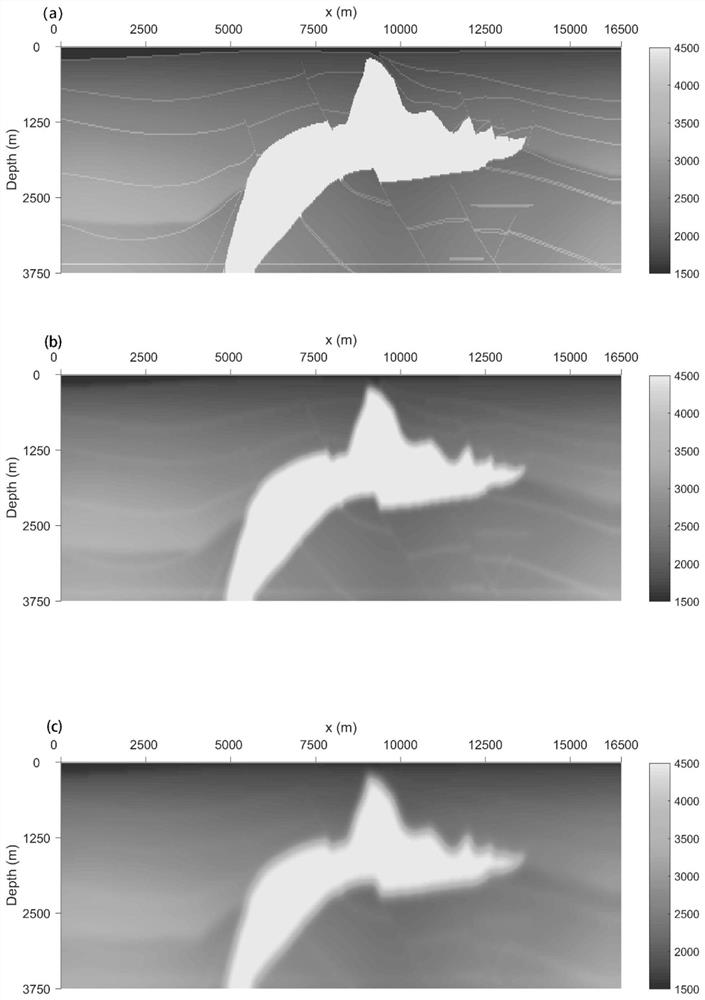
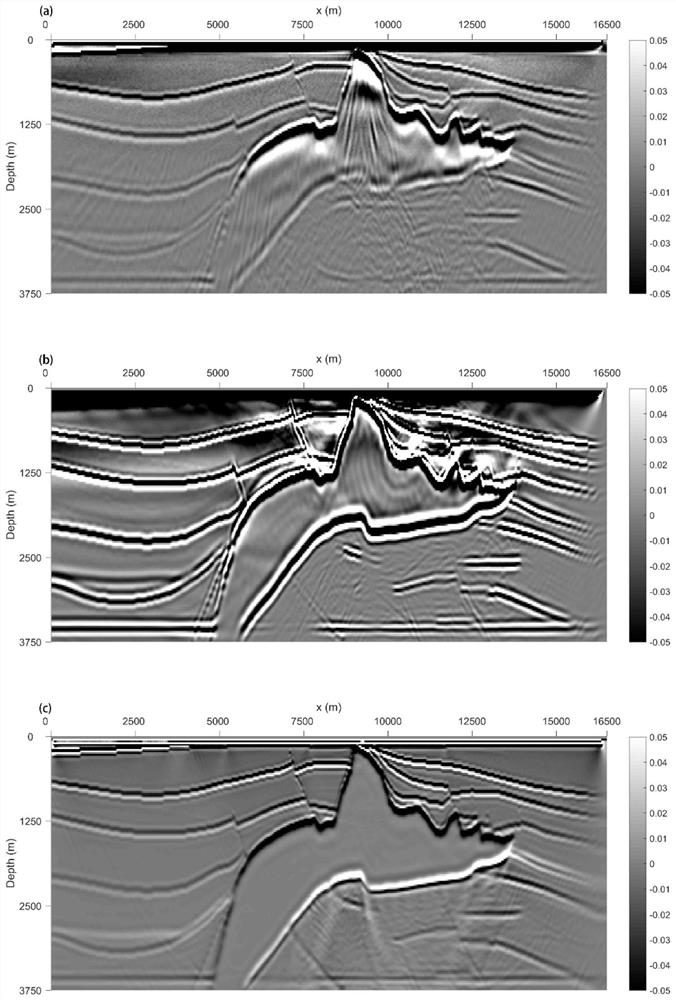
ActiveCN111077567ASolve problemsImprove imaging effectSeismic signal processingZ eigenvalueWave field
The invention discloses a two-way wave pre-stack depth migration method based on matrix multiplication. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a first-order equation system about adepth variable; S2, performing calculation to obtain eigenvalue decomposition or spectral decomposition of a matrix H; S3, performing calculation to obtain a recursive two-way wave field depth continuation equation from z to z+delta z; S4, calculating a vertical wave number and a trigonometric function of the vertical wave number according to matrix multiplication; S5, bringing the vertical wavenumber and the trigonometric function thereof back to the S3, and calculating a recursive two-way wave field depth continuation equation in a general form; S6, after calculation a continuation wave field of the next depth, calculating an offset result by utilizing a cross-correlation imaging principle; S7, judging whether the offset program is calculated to the maximum model depth or not, and if so, ending the algorithm; otherwise, repeating the steps from S3 to S6; and S8, verifying the stability and accuracy of structure imaging under the salt mounds in the steps from S1 to S7 based on the salt mound model.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
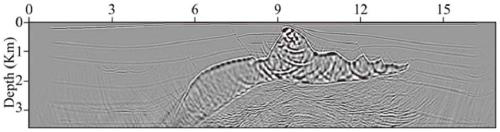
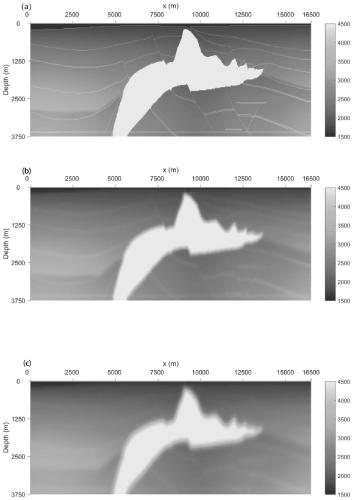
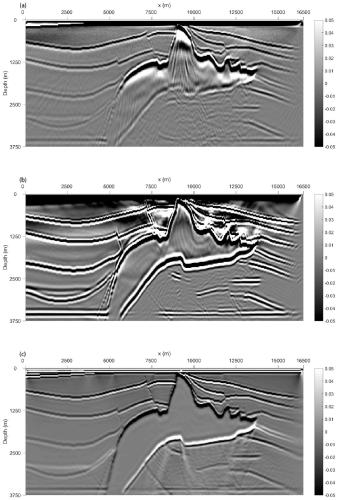
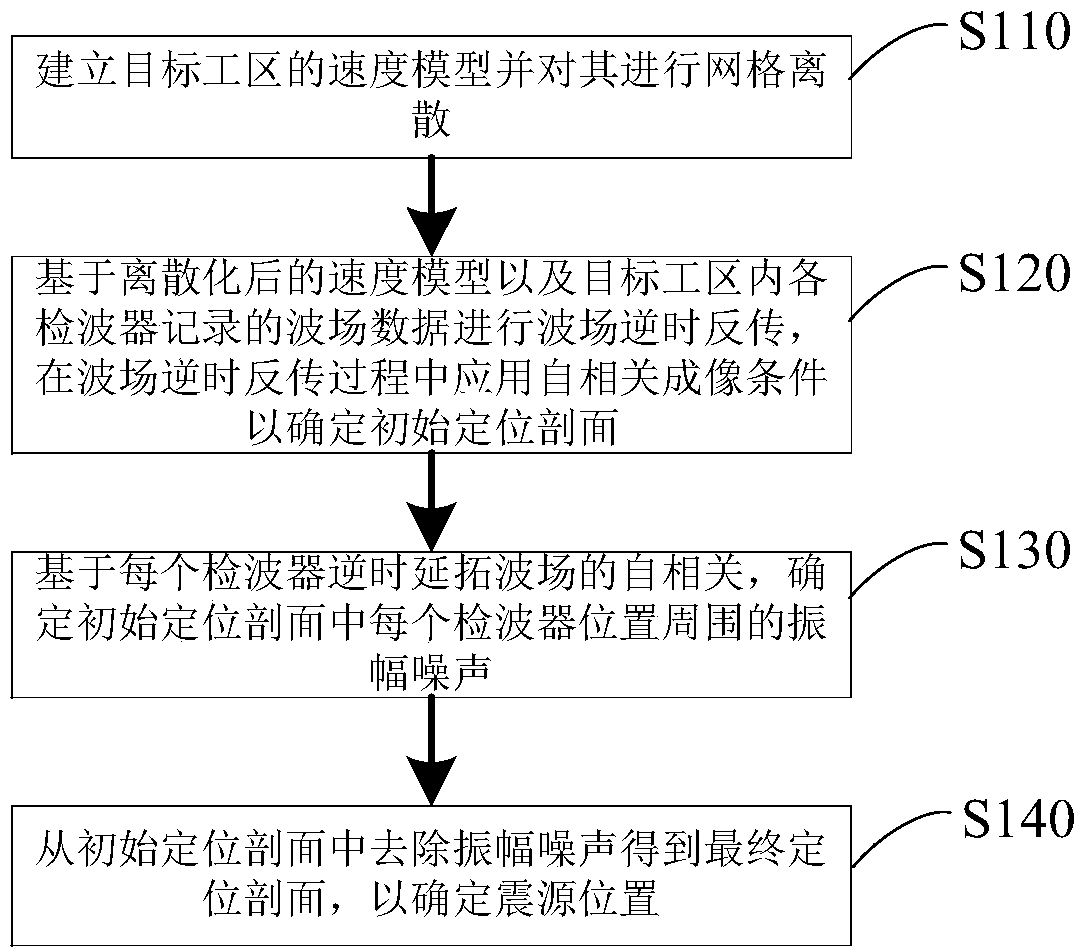
Improved seismic source reverse time positioning method and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN110967733AHigh positioning accuracyEliminate strong amplitude noiseSeismic signal recordingGeophoneImaging condition
The invention discloses an improved seismic source reverse time positioning method and a computer readable storage medium, and the positioning method comprises the steps: building a speed model of a target work area, and carrying out the grid discretization of the speed model; performing wave field reverse time back propagation based on the discretized speed model and wave field data recorded by each detector in the target work area, and applying an autocorrelation imaging condition in the wave field reverse time back propagation process to determine an initial positioning profile; determiningamplitude noise around each detector position in the initial positioning profile based on the autocorrelation of the reverse time continuation wave field of each detector; and removing amplitude noise from the initial positioning profile to obtain a final positioning profile so as to determine the position of the seismic source. The positioning method can improve the seismic source positioning precision and reduce the positioning artifacts, and is especially suitable for the application scene of detector sparse distribution.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Correlative Imaging Spectral Camera and Its Imaging Method Based on Non-Rayleigh Speckle Field
ActiveCN109520619BSimple structureQuality improvementSpectrum investigationBandpass filteringBeam splitter
A correlative imaging spectral camera based on non-Rayleigh speckle field and its imaging method, the device includes a front imaging mirror, a beam splitter, a bandpass filter, a monitoring detector, a polarizer, a beam splitter, a spatial light modulation detectors, area detectors and computers. The invention utilizes the reversible characteristics of the optical path to generate non-Rayleigh speckle fields without lenses, and applies it to a correlated imaging spectral camera based on compressed sensing, wherein imaging using hyper-Rayleigh speckle fields can be performed in Improve the quality and resolution of reconstructed images under low signal-to-noise ratio conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
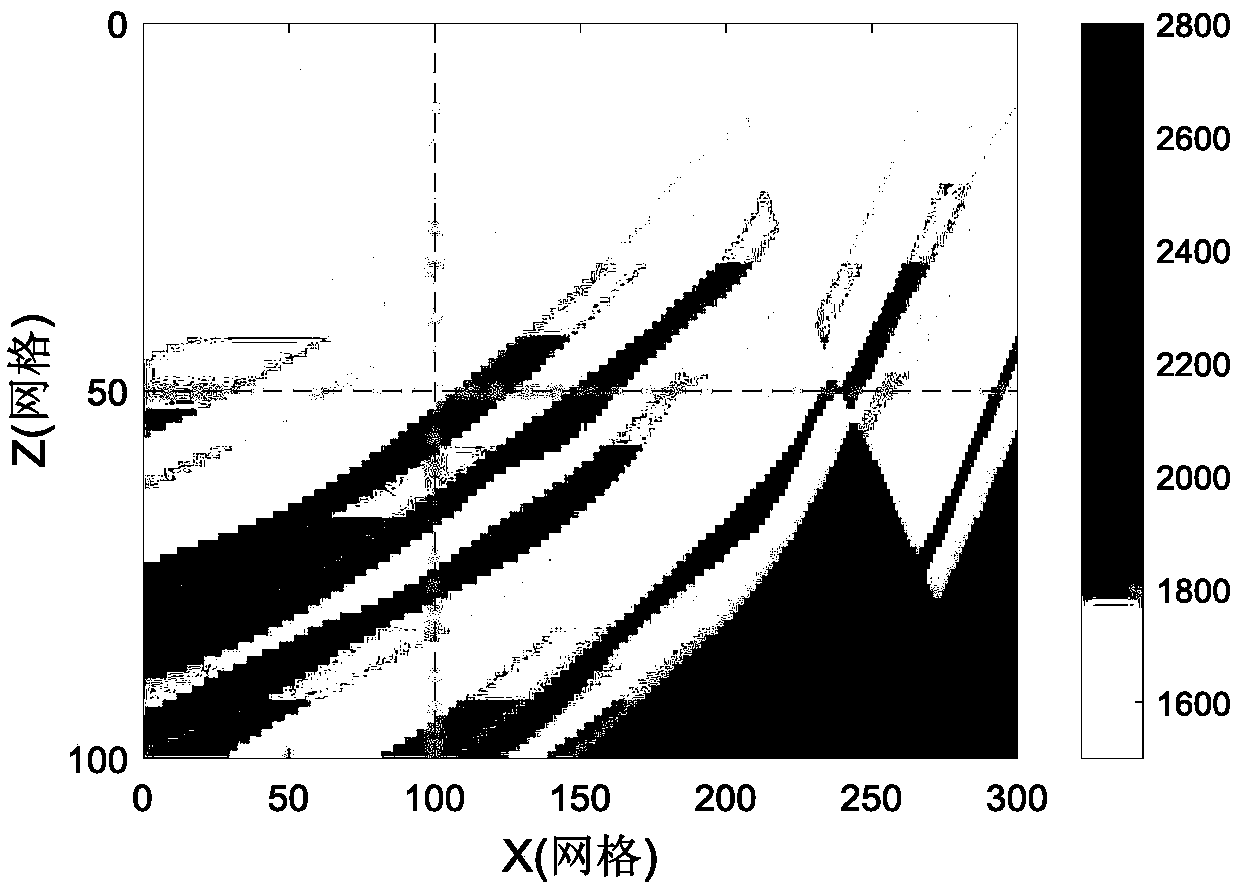
A Correlation Imaging Method Based on Multicomponent Gradient Data Union and Depth Weighting
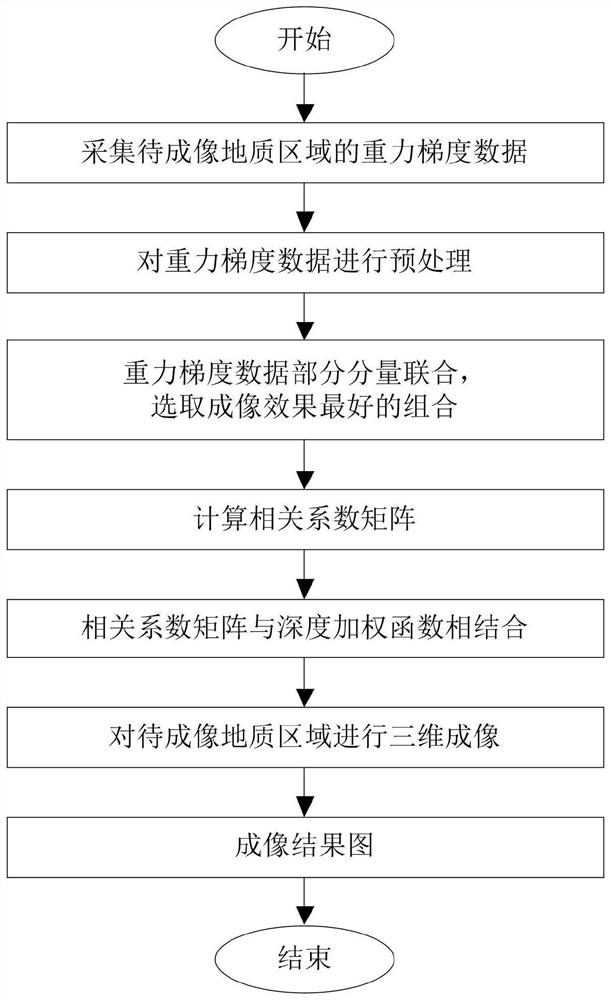
ActiveCN110501751BHigh-resolutionDetermine the upper and lower boundariesGravitational wave measurementData interpretationData combination
The invention relates to the technical field of geophysical data interpretation and provides a correlation imaging method based on multi-component gradient data combination and depth weighting. First, use a gravimeter to collect gravity gradient data of the geological area to be imaged; then, preprocess the gravity gradient data; then, combine some components of the preprocessed gravity gradient data to select the multi-component gradient with the best imaging effect The data is combined to calculate the correlation coefficient matrix; then based on the prior geological data of the geological area to be imaged, the top surface burial depth and bottom surface burial depth of the geological area to be imaged are obtained, the underground space of the geological area to be imaged is divided into blocks, and a depth weighting function is introduced , calculate the weighted correlation coefficient matrix; finally, use the weighted correlation coefficient matrix to perform three-dimensional imaging of the geological area to be imaged. The invention can improve the resolution of imaging results in the depth direction, more accurately determine the upper and lower boundaries of the geological body, and has high calculation efficiency.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
An ore prospecting method using high-precision ground gravity measurement
ActiveCN110888176BPromote resultsObvious channel sedimentary featuresGravitational wave measurementBit fieldField separation
A prospecting method using high-precision gravity measurement on the ground, which mainly includes six methods, namely, the wavenumber domain iteration method of the high-order derivative of the potential field, the separation method of the potential field based on the iterative filtering method, the TASD method of identifying the boundaries of geological bodies, Euler deconvolution method for potential field data processing, potential field anomaly cross-correlation imaging technology method, and gravity human-computer interaction profile forward modeling method. The advantages of the present invention are: using the ore prospecting method of high-precision gravity measurement on the ground, data processing and interpretation of multiple gravity profiles, the interpretation method covers wave number domain derivative iteration method, field separation iterative filtering method, and interactive analysis based on residual anomalies. Correlation imaging technology has been applied to gravity data and achieved good processing results.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A Parameter Estimation Method of Moving Target Based on Correlation Function
ActiveCN104898119BRealize detectionHigh speed detection accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainAlgorithm
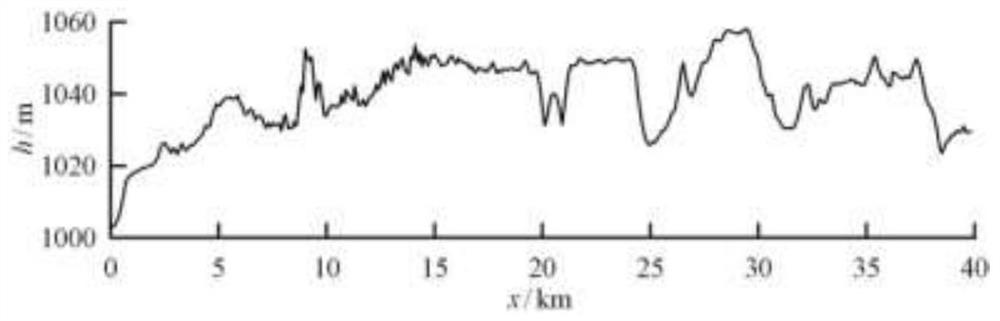
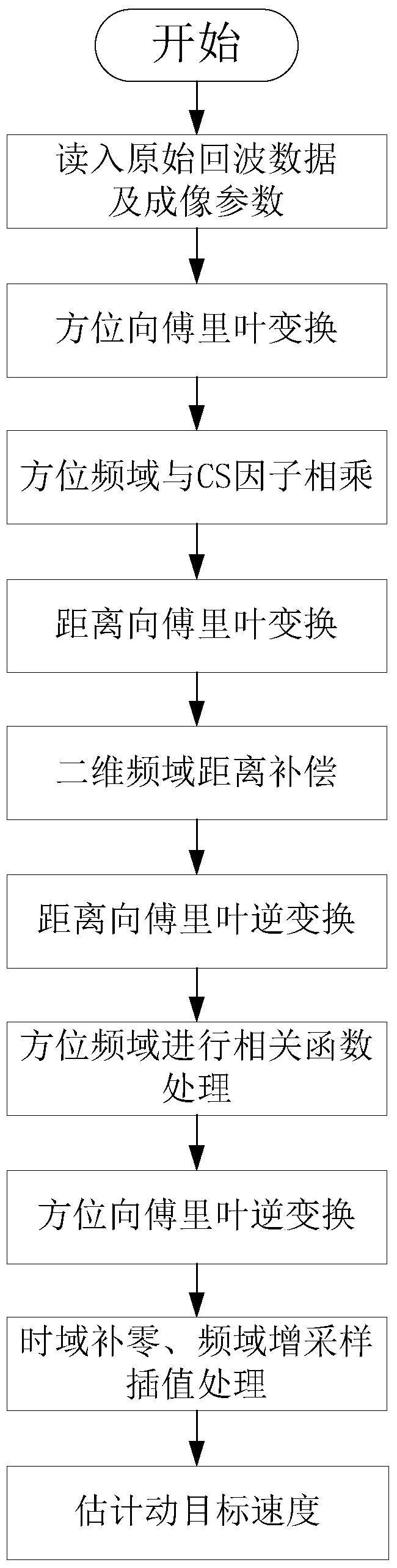
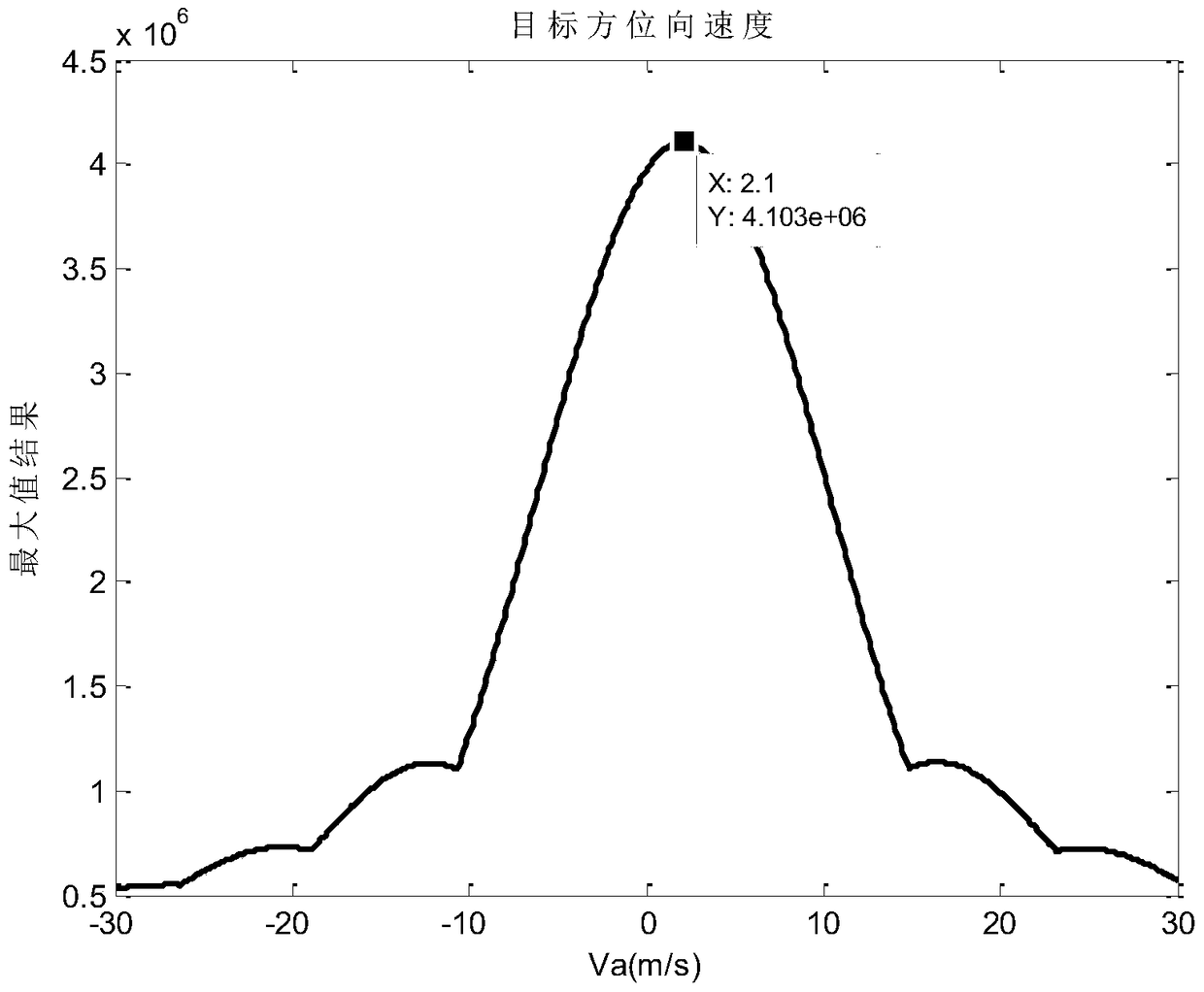
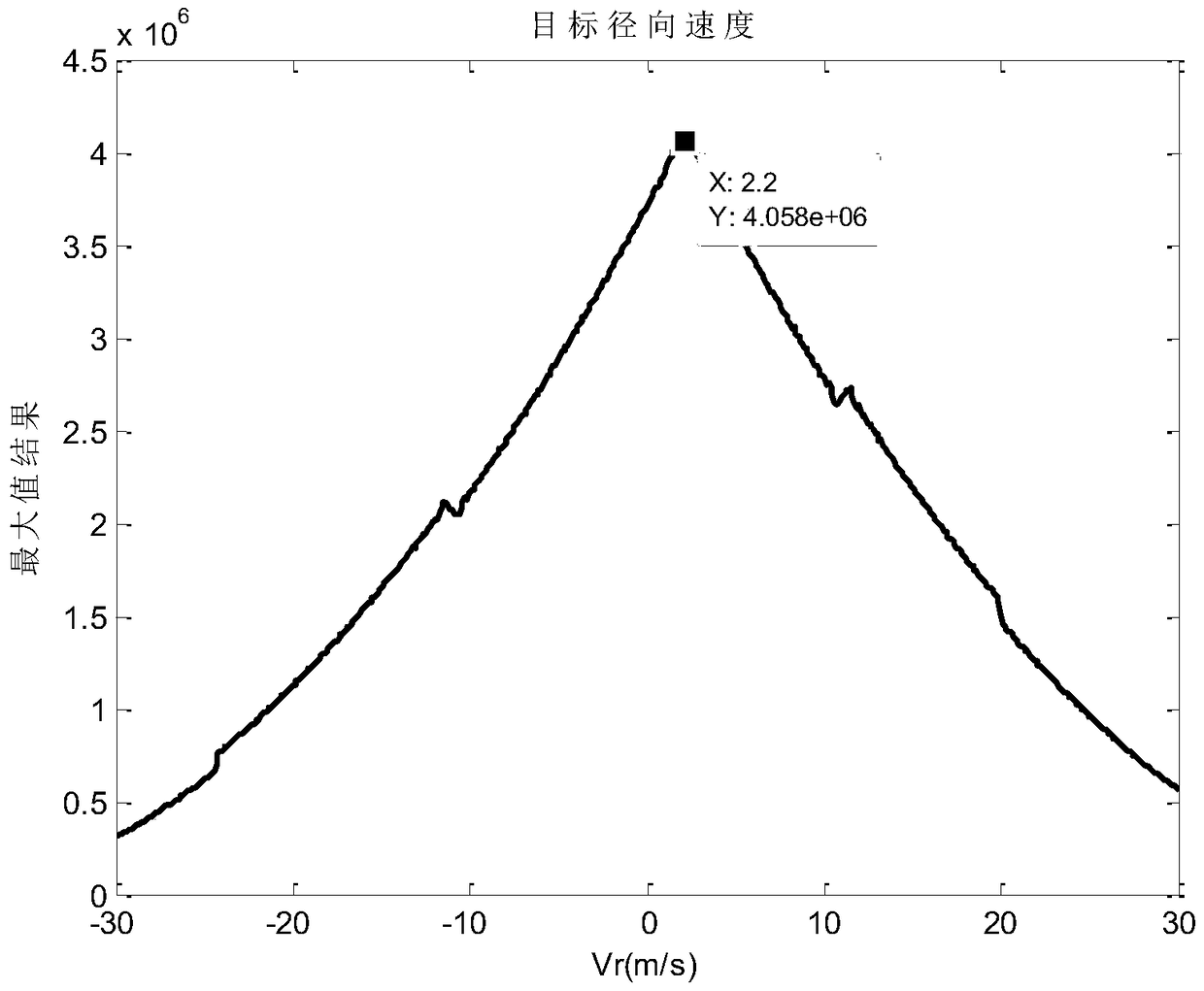
The invention discloses a method for estimating parameters of a moving target based on a correlation function, which comprises the following steps: Step 1: reading in the original moving target echo data and related imaging parameters; Step 2: processing the azimuth Fourier transform; Three: Compensation by multiplying the azimuth with the CS factor; Step four: Fourier transform processing of the distance direction; Step five: Multiplying the distance direction with the distance compensation factor for distance compression processing; Step six: Inverse Fourier transform of the distance direction Processing; Step 7: Correlation function processing in the range-Doppler domain; Step 8: Inverse Fourier transform processing in the azimuth direction; Step 9: Filling zero in the frequency domain, and upsampling in the time domain to perform interpolation processing on the correlation processing results to obtain maximum value; Step ten: Estimate the target speed from the correlation processing maximum value. The invention proposes a method for estimating parameters of a moving target based on a correlation function, realizes estimating the target azimuth and radial velocity at the same time, improves the accuracy of current spaceborne SAR in estimating the moving target velocity, and proposes a new detection method.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A pet-ct scanning imaging method and related imaging method
ActiveCN105078495BIncrease scan timeIncreased CT radiation doseComputerised tomographsTomographyRadiation DosagesCorrelative imaging
The invention discloses a PET-CT scanning imaging method and a related imaging method. The PET-CT scanning imaging method includes: positioning and scanning the area to be imaged, obtaining and displaying a positioning image of the area to be imaged, and the displayed positioning image It is used for the user to determine the scan area; receive the scan area information input by the user, and determine the PET total scan area according to the scan area information; generate multiple PET sub-scan areas from the PET total scan area, and each PET sub-scan area Corresponding to a PET scanning bed, each PET sub-scanning area is superimposed to completely cover the total PET scanning area; performing multi-bed PET scanning; performing CT scanning; reconstructing a PET-CT image from scanning data. The technical scheme of the present invention eliminates irrelevant scanning areas in PET-CT scanning imaging, reduces the scanning time of PET-CT, and reduces the CT radiation dose received by patients in PET-CT scanning.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
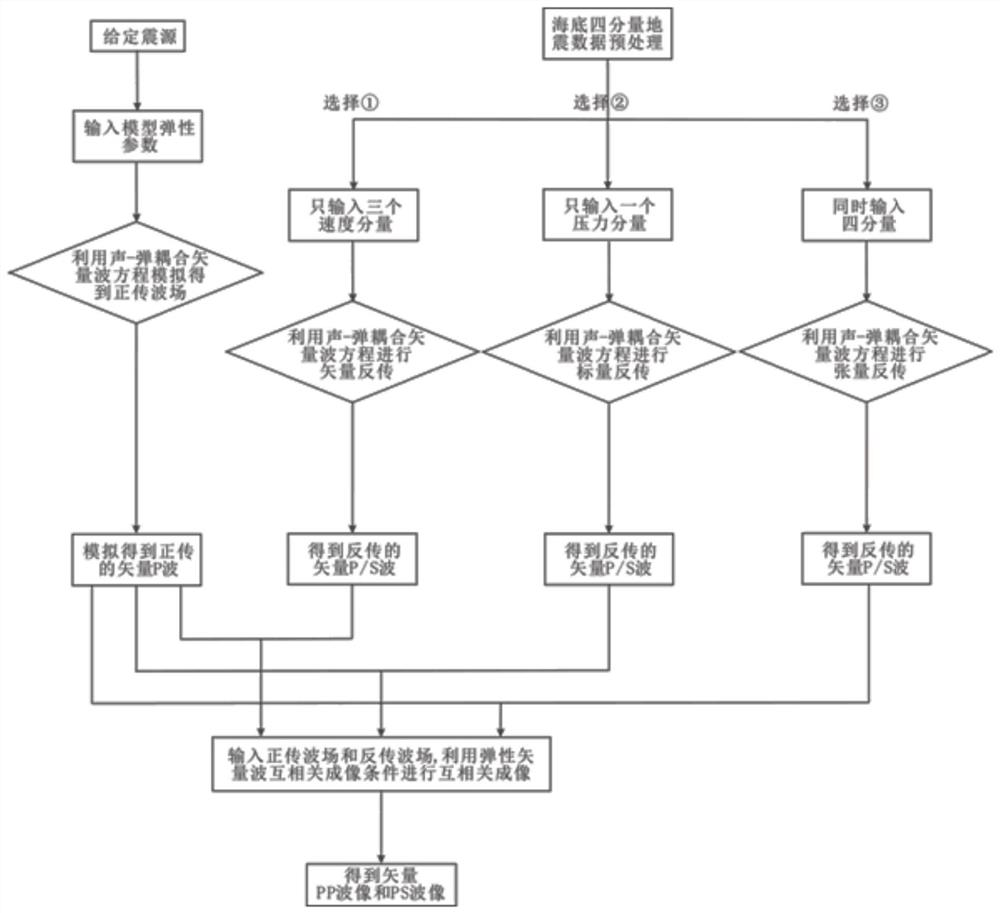
Method for carrying out elastic vector wave imaging by using seabed multi-component seismic records
The invention discloses a method for carrying out elastic vector wave imaging by using seabed multi-component seismic records, which belongs to the technical field of seismic imaging. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) preprocessing acquired seabed multi-component seismic data, including repositioning, interpolation, denoising, ghost wave suppression, multiple waves and the like, so that the acquired seabed multi-component seismic data can be used for elastic wave imaging; 2) inputting an elastic parameter of a model, and simulating by using an acoustic-elastic coupling equation to obtain a forward vector P wave; 3) reversely transmitting seismic records by using a sound-elastic coupling equation to obtain a P wave and an S wave of a vector; and 4) obtaining a vector PP wave image and a PS wave image by using a vector cross-correlation imaging condition. According to the method, different seabed multi-component seismic data can be selectively utilized to carry out elasticwave imaging of a seabed complex structure, especially, seabed four-component seismic data can be simultaneously utilized to carry out tensor continuation of a receiving end, non-physical artifacts existing in conventional elastic wave imaging can be suppressed, and the imaging quality is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
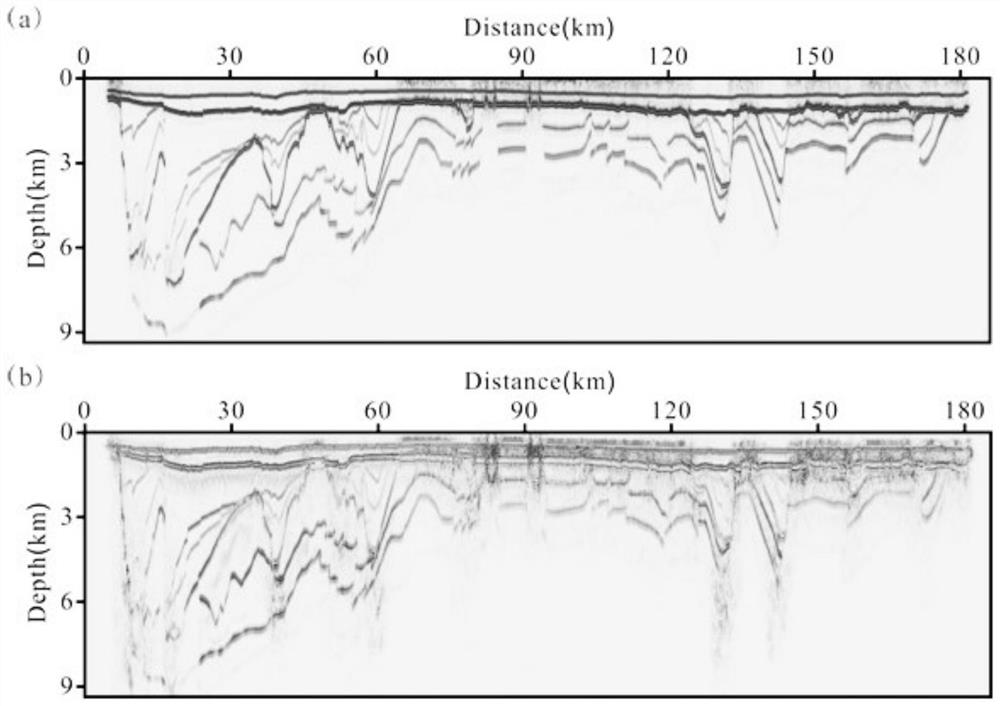
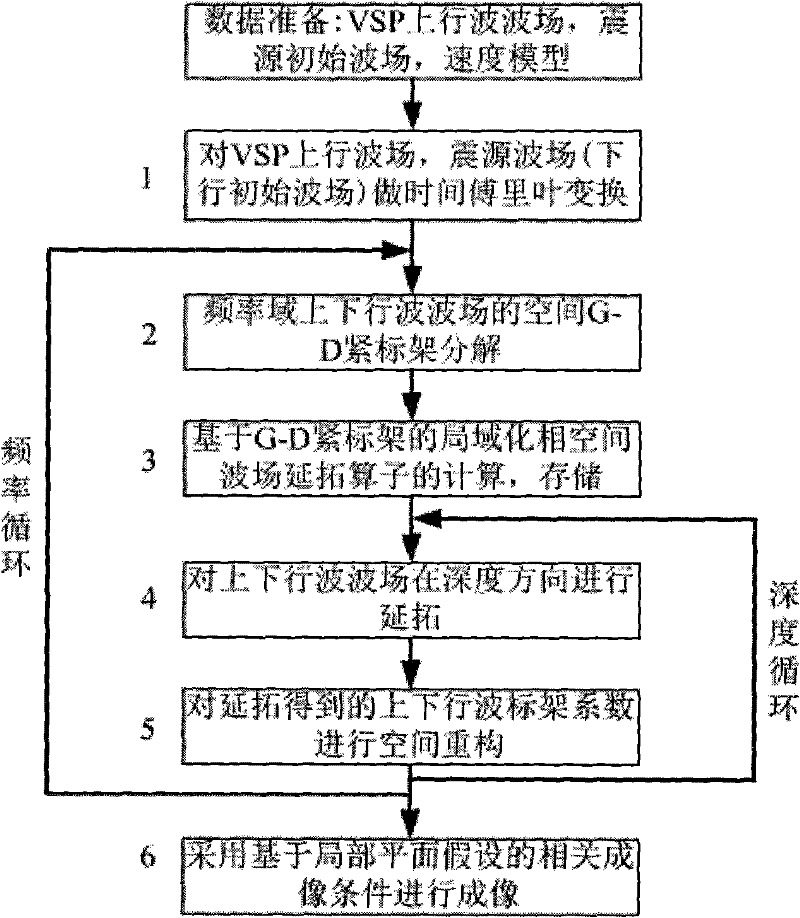
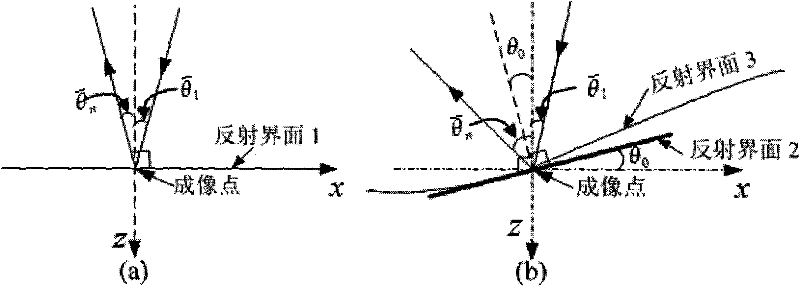
Localized phase space method of multi-offset VSP imaging
InactiveCN101706583BHigh precisionImprove computing efficiencySeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsImaging conditionDecomposition
The invention discloses a localized phase space method of multi-offset VSP imaging. The localized phase space method comprises the following steps: adopting localized phase space one-way wave continuation operator based on wave field decomposition of a Gauss-Daubechies tight frame (G-D tight frame) to carry out continuation to the wave field of upgoing wave of the VSP and the wave field of downgoing wave of the seismic source, and improving computational efficiency by means of an asymptotic expansion analytic expression of the continuation operator; in order to effectively weaken offset falseimage on an imaging section, adopting imaging conditions based on the local planar assumption; combining the information of wave number (corresponding to direction of propagation) of the continuationwave field, determining a main reflecting angle corresponding to a main incident angle based on a mirror reflection at an imaging point, executing relevant imaging to the localized planar wave and carrying out superposition. The method considers the asymptotic expansion form of the continuation operator of the localized phase space, has higher computational efficiency, adopts the imaging conditions based on the local planar assumption, also can effectively weaken the offset false image and interference noise while the calculated quantity is not increased. The imaging method is beneficial to improving the effectiveness and reliability of seismic processing and explanation, can be used for seismic signal processing in oil and gas exploration, carry out exquisite imaging to underground structure form beside a well, eliminate false anomaly and improve the precision of exploration and development in oil and gas fields.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
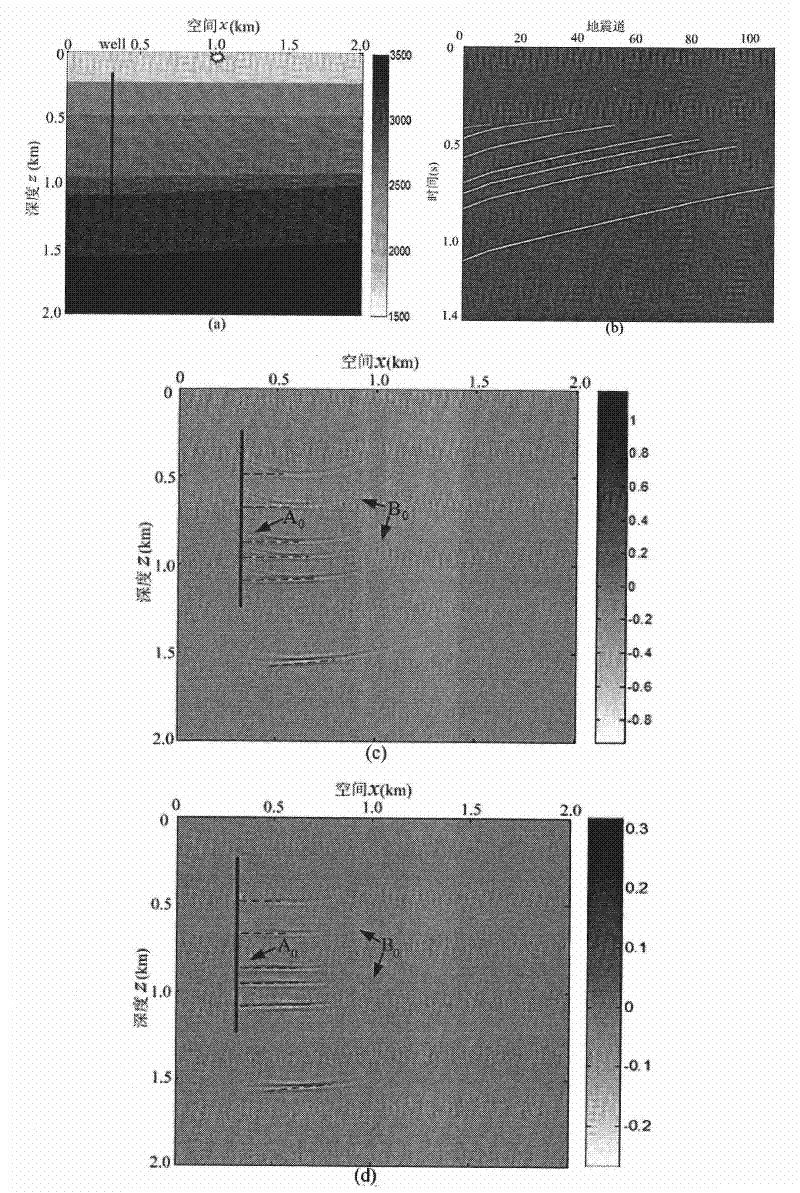
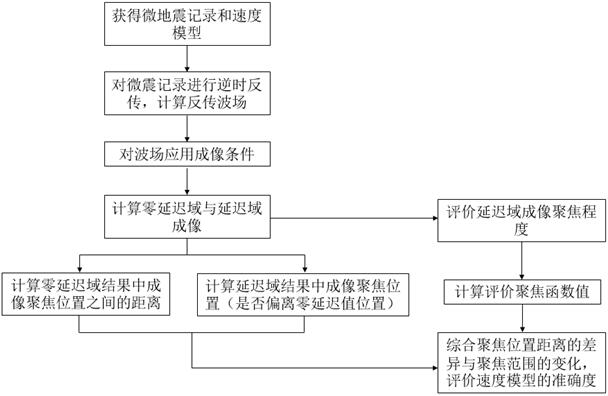
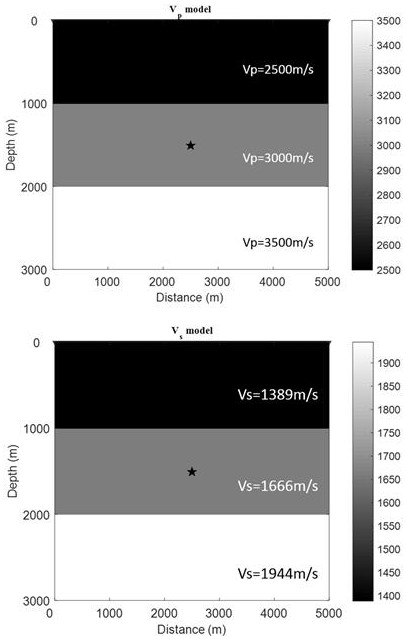
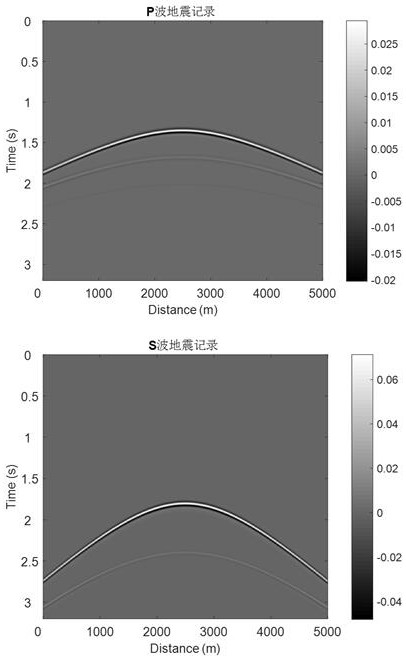
Velocity Model Evaluation Method Based on Microseismic Imaging Features
ActiveCN111060963BAccuracy understandingLearn about validitySeismic signal processingMicroscopic observationLongitudinal wave
The invention relates to a speed evaluation method based on microseismic reverse time imaging focus position and focus characteristics, and belongs to the technical field of microseismic monitoring. The invention comprises the following steps: obtaining micro-seismic observation records; using the given longitudinal wave and shear wave velocity models, adopting finite difference to carry out reverse time propagation on the seismic records, and obtaining the longitudinal wave autocorrelation, shear wave autocorrelation, longitudinal and transverse wave mutual Correlation and space-time delay domain and two-dimensional spatial delay domain P-S wave cross-correlation time-reverse imaging results; according to the difference in focus position of these zero-delay domain autocorrelation and cross-correlation imaging, and space-time delay domain and two-dimensional space The change of the imaging position and focusing degree of the longitudinal and transverse wave cross-correlation in the delay domain evaluates the accuracy of the velocity model used in the reverse time imaging to solve the evaluation problem of the velocity model used in the microseismic monitoring source location.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
VSP Slit-hole Diffraction Imaging Method Based on Symmetrical Observation
ActiveCN108375794BDiffraction Imaging ImplementationEffective diffraction imagingSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingImaging conditionWave field
The invention provides a VSP fracture-vug diffraction imaging technical method based on symmetrical observation; the method comprises the following steps: vertically deploying multi-stage detectors atequal intervals in a well; enabling an excitation point wave field to extrapolate downwards from the ground according to a depth sampling interval; enabling a reception point wave field to extrapolate downwards from the most shallow reception point depth according to the depth sampling interval, and adding the reception point wave field into the extrapolating wave field each time certain reception point depth is reached; aiming at each depth sampling point, enabling the reception point extrapolating wave field and excitation point extrapolating wave field to carry out related imaging according to imaging conditions; respectively processing two imaging areas with separated well positions after all depth sampling points finish offset imaging, using the imaging area with no excitation pointas VSP diffraction wave imaging, and using the imaging area with excitation points as VSP reflection wave imaging. The technical method is efficient and stable in operation, flexible and convenient inprocessing, and has a higher identification ability in fracture-vug type reservoir imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI JINDI SOFTWARE DEV
A Method of Two-Way Wave Prestack Depth Migration Based on Matrix Multiplication
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
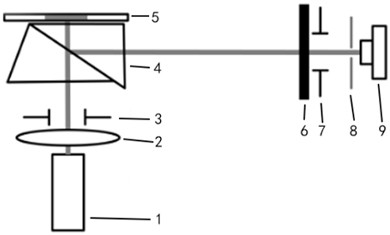
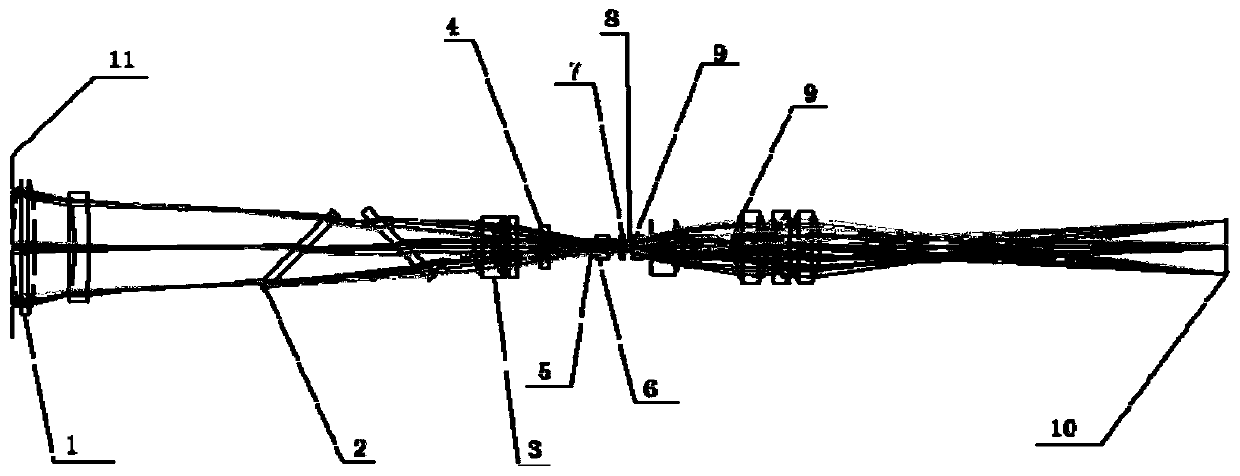
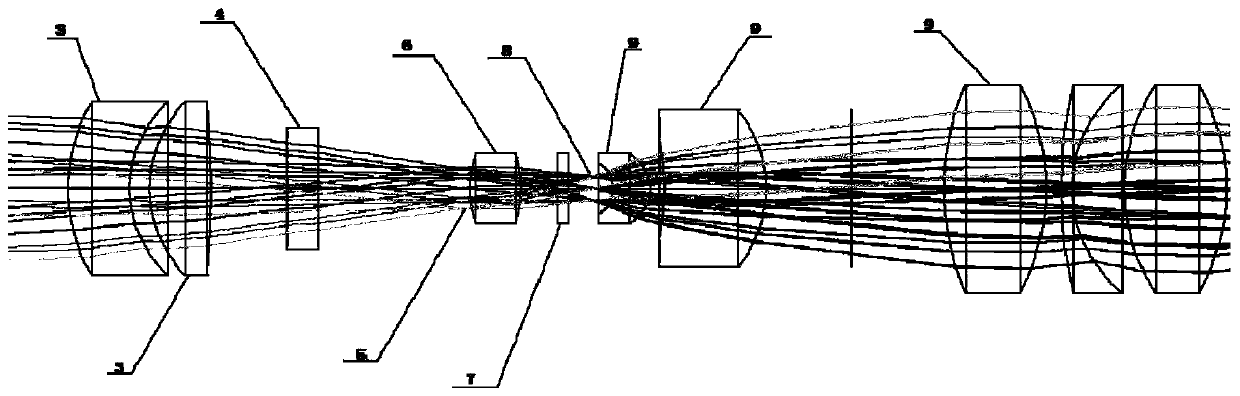
Passive Correlative Imaging Optical System
ActiveCN107390214BMeet spatial resolution requirementsDifferent imaging effectsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOphthalmology3d image
The invention relates to a passive correlated-imaging optical system comprising four parts: a pre imaging lens group, a field lens imaging lens, a phase plate speckle modulator and a relay secondary imaging lens group. Under the circumstance of an object is irradiated by natural light, the pre imaging lens group images the object on a primary real time plane; the field lens imaging lens images an entrance pupil of the pre imaging lens group to an interference speckle field, wherein the interference speckle field is one formed behind a phase plate at a distance of 1.5mm; and then the relay secondary imaging lens group images the interference speckle field to a CCD. According to the invention, spectrum conversion is carried out on information of the spatial object; the interference speckle field is formed at the exit pupil plane, wherein information at each point on the exit pupil plane includes energy information of all object points; and then after the CCD collects the interference speckle information, the speckle field image is calculated based on an association operation and a high-spectrum object image is obtained by inversion. Therefore, a hyperspectral, three-dimensional image is obtained under single exposure.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
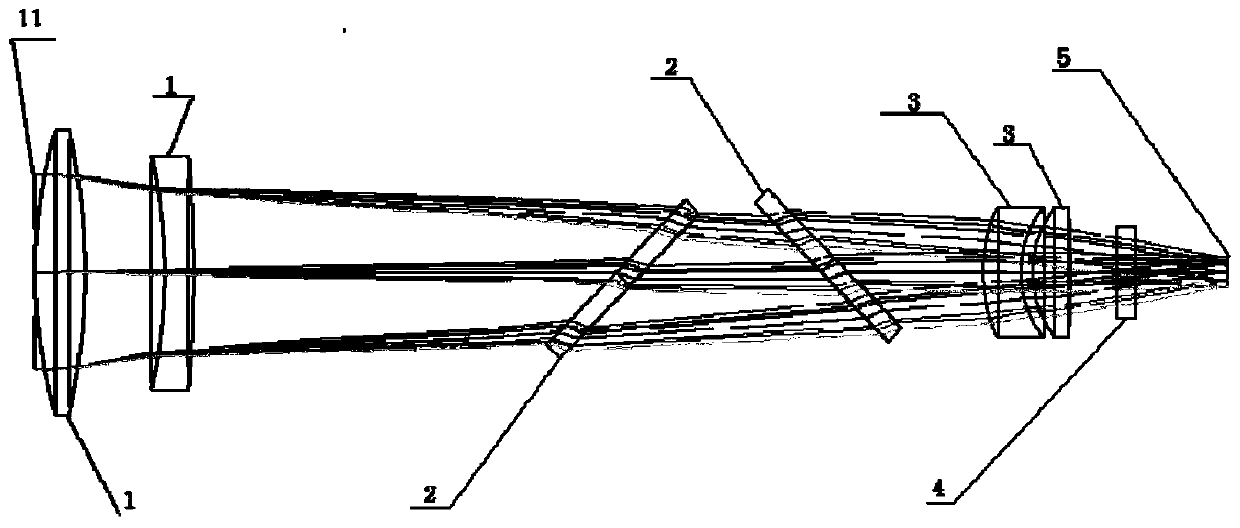
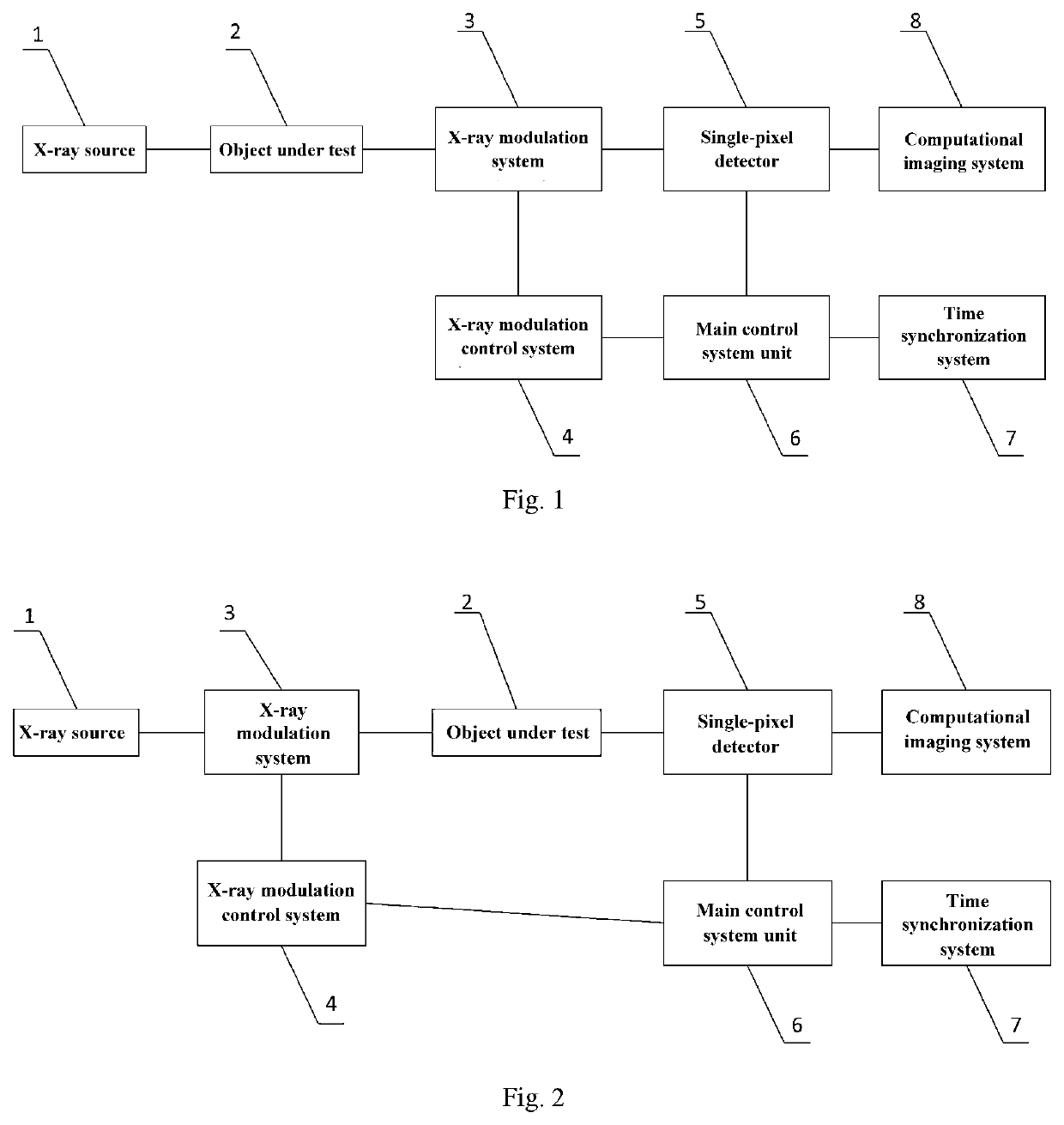
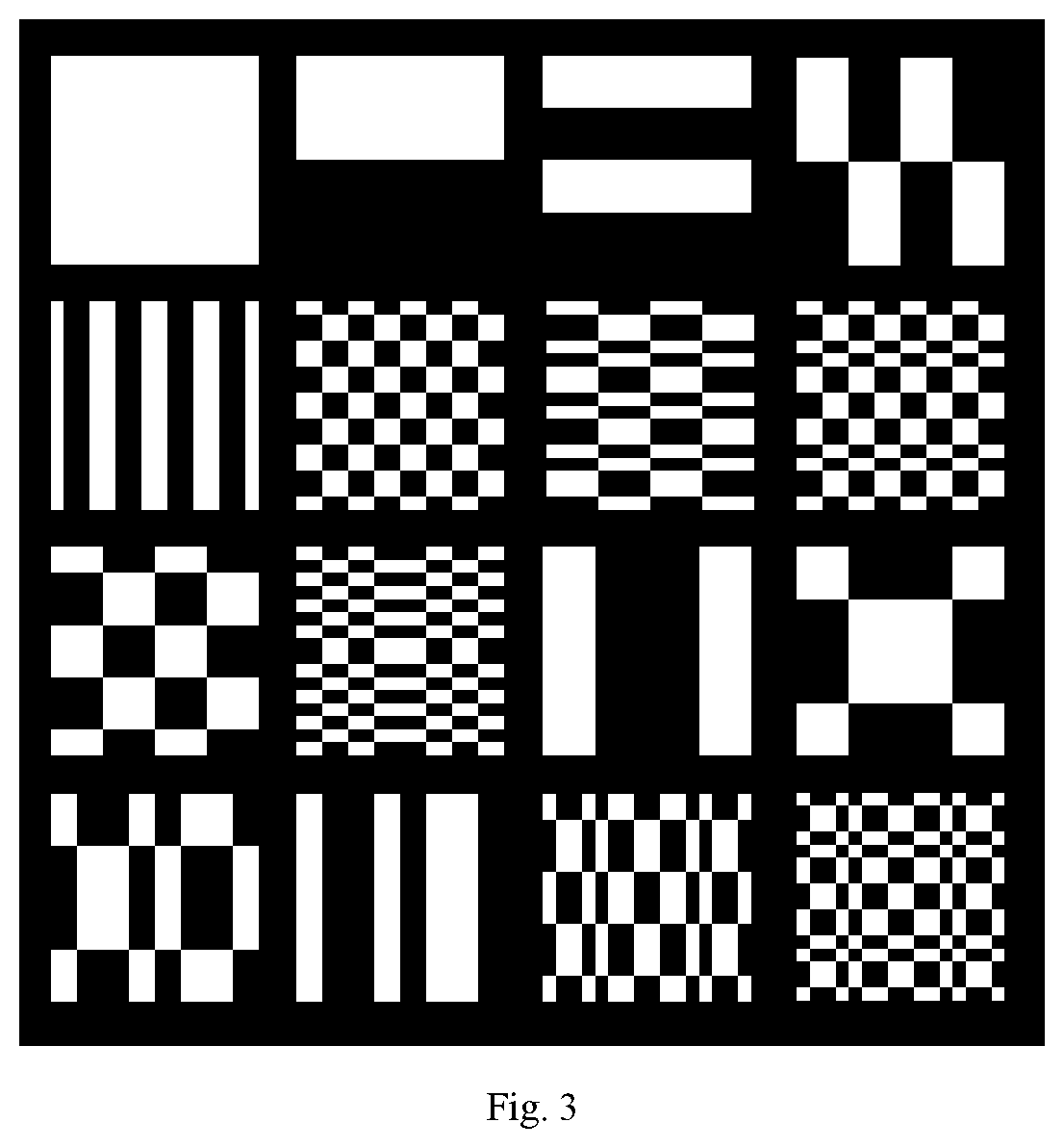
X-ray single-pixel camera based on x-ray computational correlated imaging
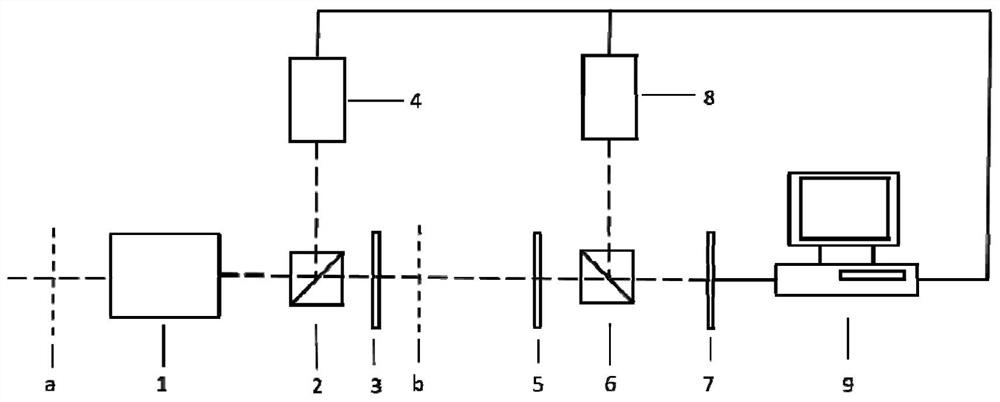
ActiveUS20220042928A1Low costImage degradationUsing optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentImaging qualityDose imaging
An X-ray single-pixel camera based on X-ray computational correlated imaging, which belongs to the technical research fields of X-ray computational correlated imaging and X-ray single-pixel imaging. The X-ray single-pixel camera includes: an X-ray modulation system (3), an X-ray modulation control system (4), an X-ray single-pixel detector (5), a main control system unit (6), a time synchronization system (7) and a computational imaging system (8). The main control system unit (6) controls each module through software; the time synchronization system (7) controls synchronization of each module for automatic collection; and the computational imaging system (8) is configured to perform a second-order correlated computation or a compressed sensing computation or a deep learning computation on the signals collected by the X-ray single-pixel detector (5) and a preset modulation matrix, so as to obtain an image of an object under test. The X-ray single-pixel camera based on X-ray computational correlated imaging, provided by the present invention, realizes single-pixel imaging, greatly reduces the sampling number while ensuring the imaging quality, and reduces the X-ray radiation dose in an imaging process.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Imaging histone deacetylases with a radiotracer using positron emission tomography
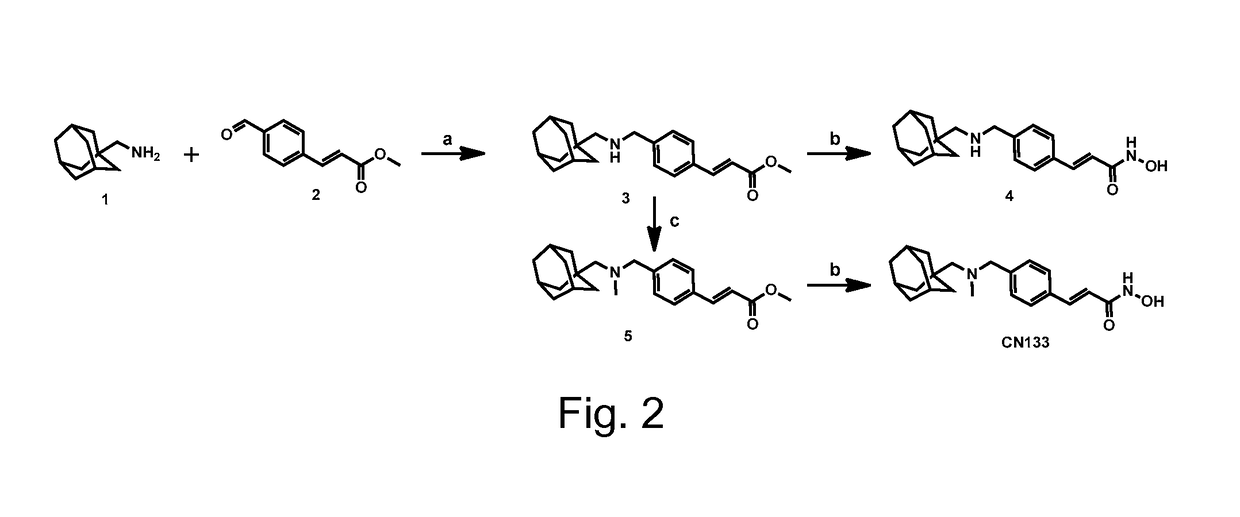
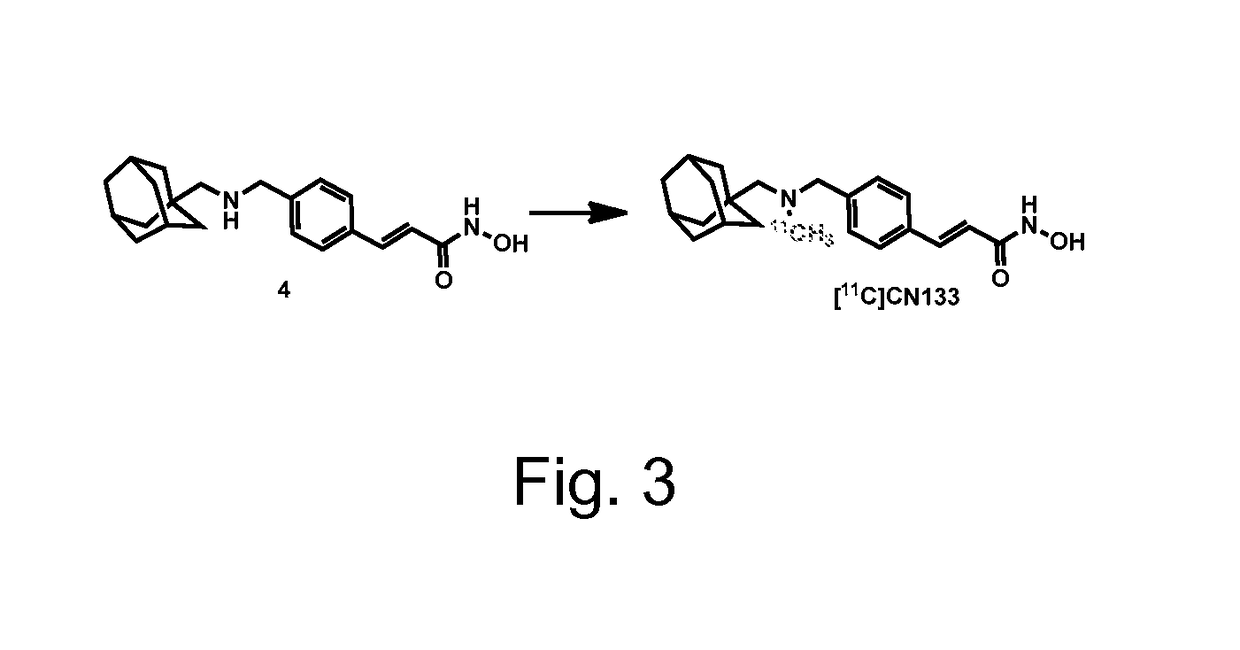
ActiveUS10188756B2Enable non-invasive and repetitive in vivo imagingOrganic chemistry methodsRadioactive preparation carriersArylRadioactive tracer
Disclosed herein are histone deacetylase imaging agents for positron emission tomography and related imaging methods using the histone deacetylase imaging agents. The histone deacetylase imaging agents may be a compound of formula (I): wherein R1 is a moiety including a positron emitter; R2 represents hydrogen, or substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, or substituted or unsubstituted aryl, or substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl; and n is an integer selected from 0 or 1. In one version of the compound of formula (I), R1 is a moiety including an adamantyl group.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com