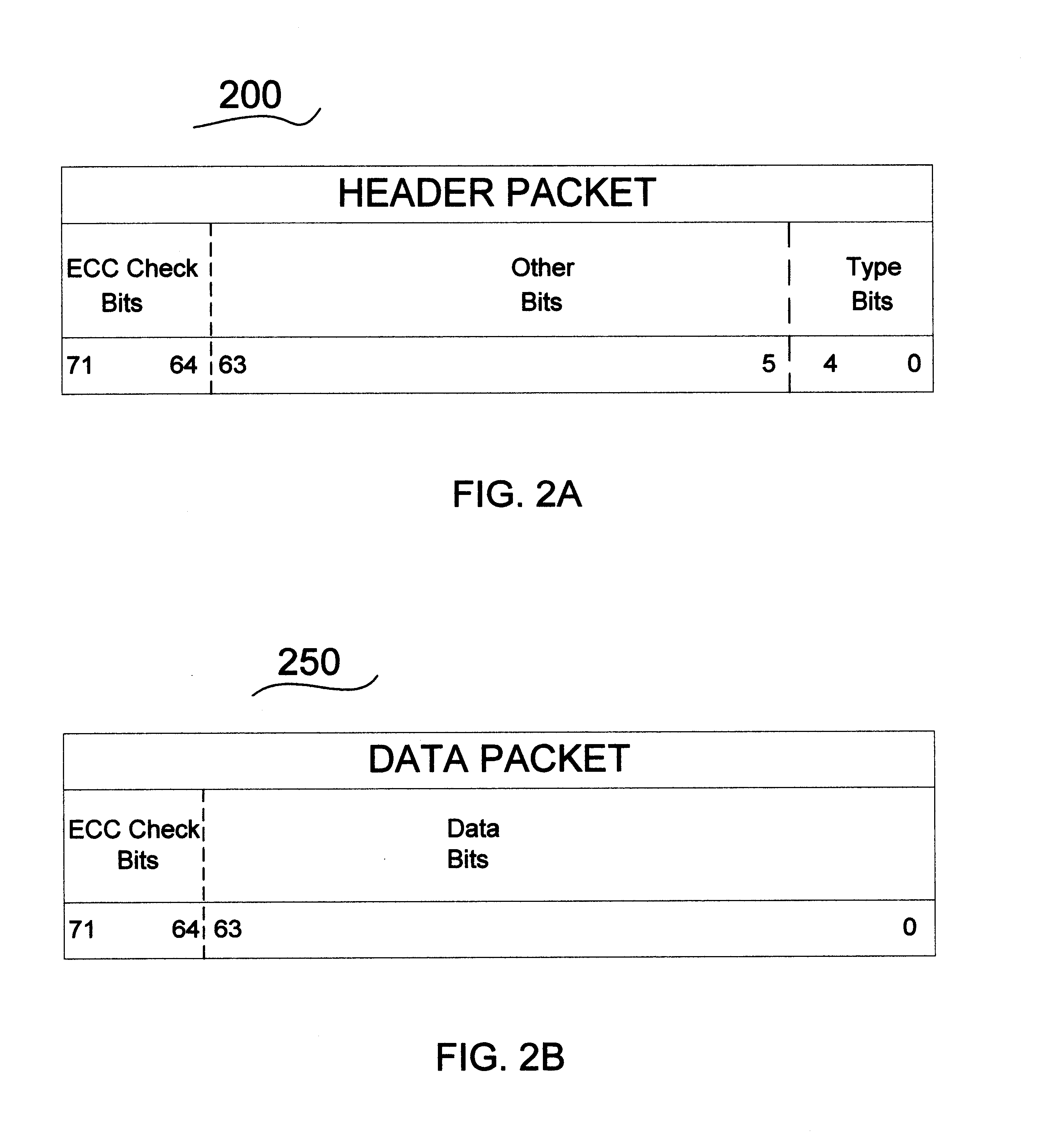
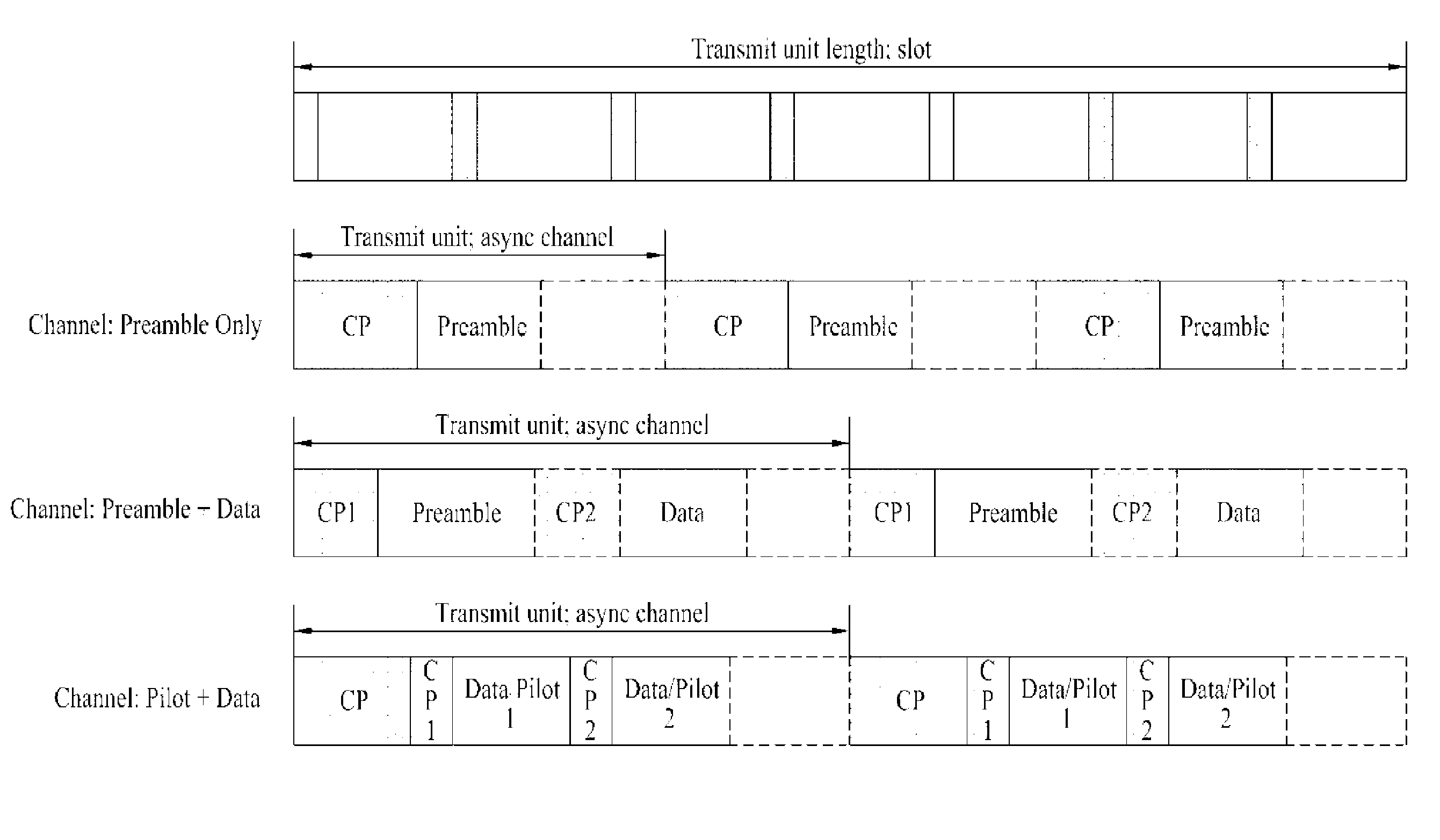
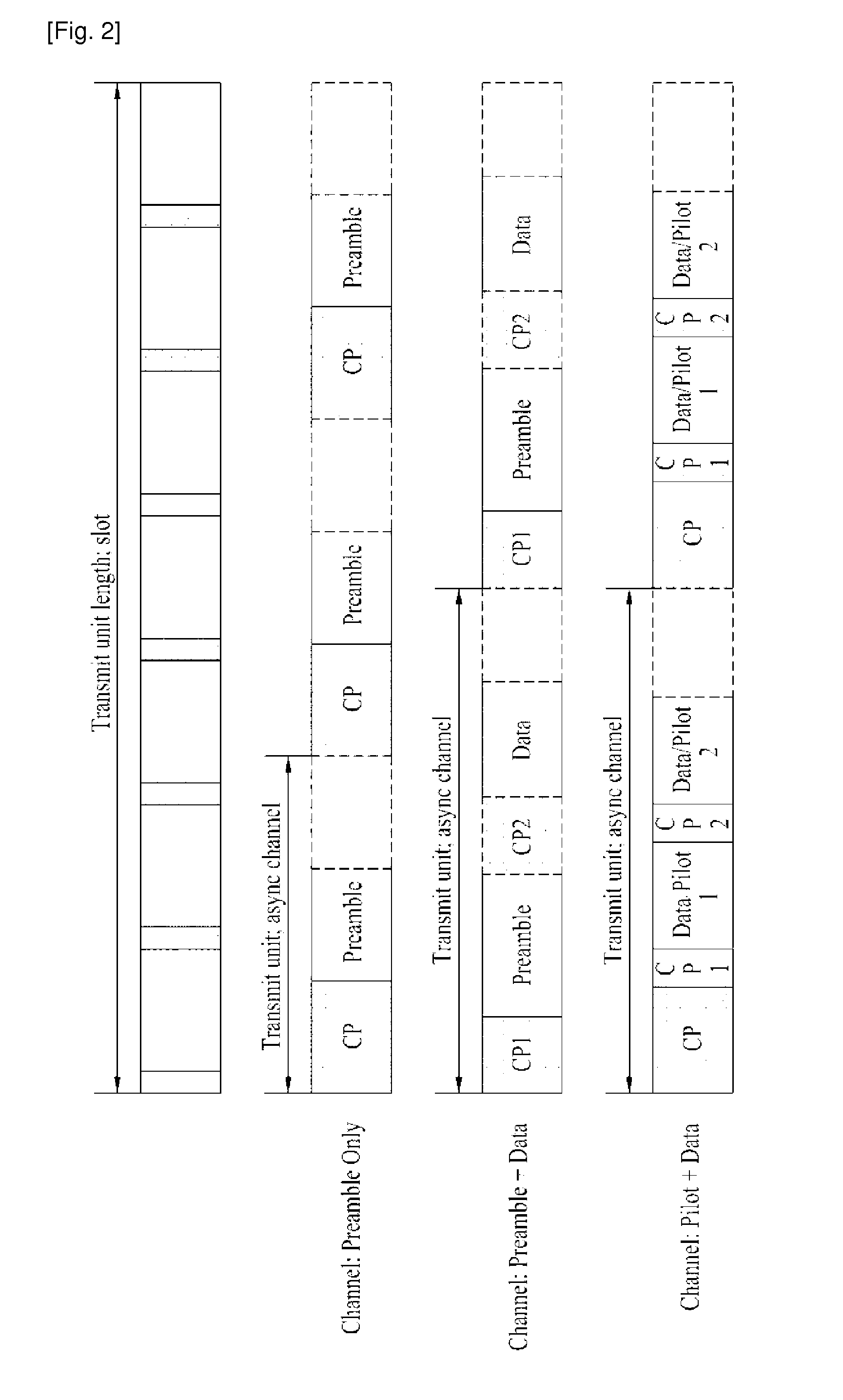
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Asynchronous channels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
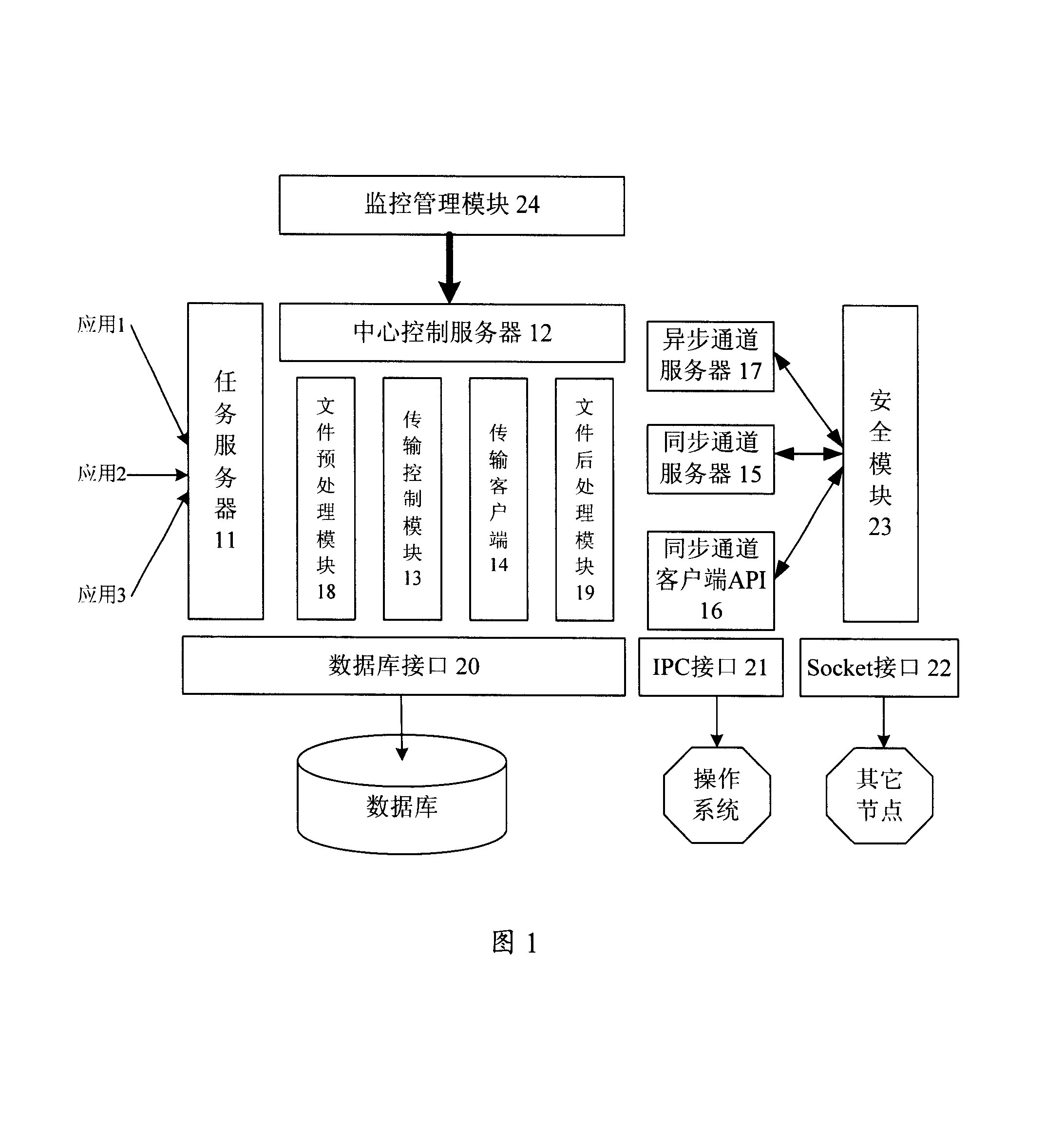
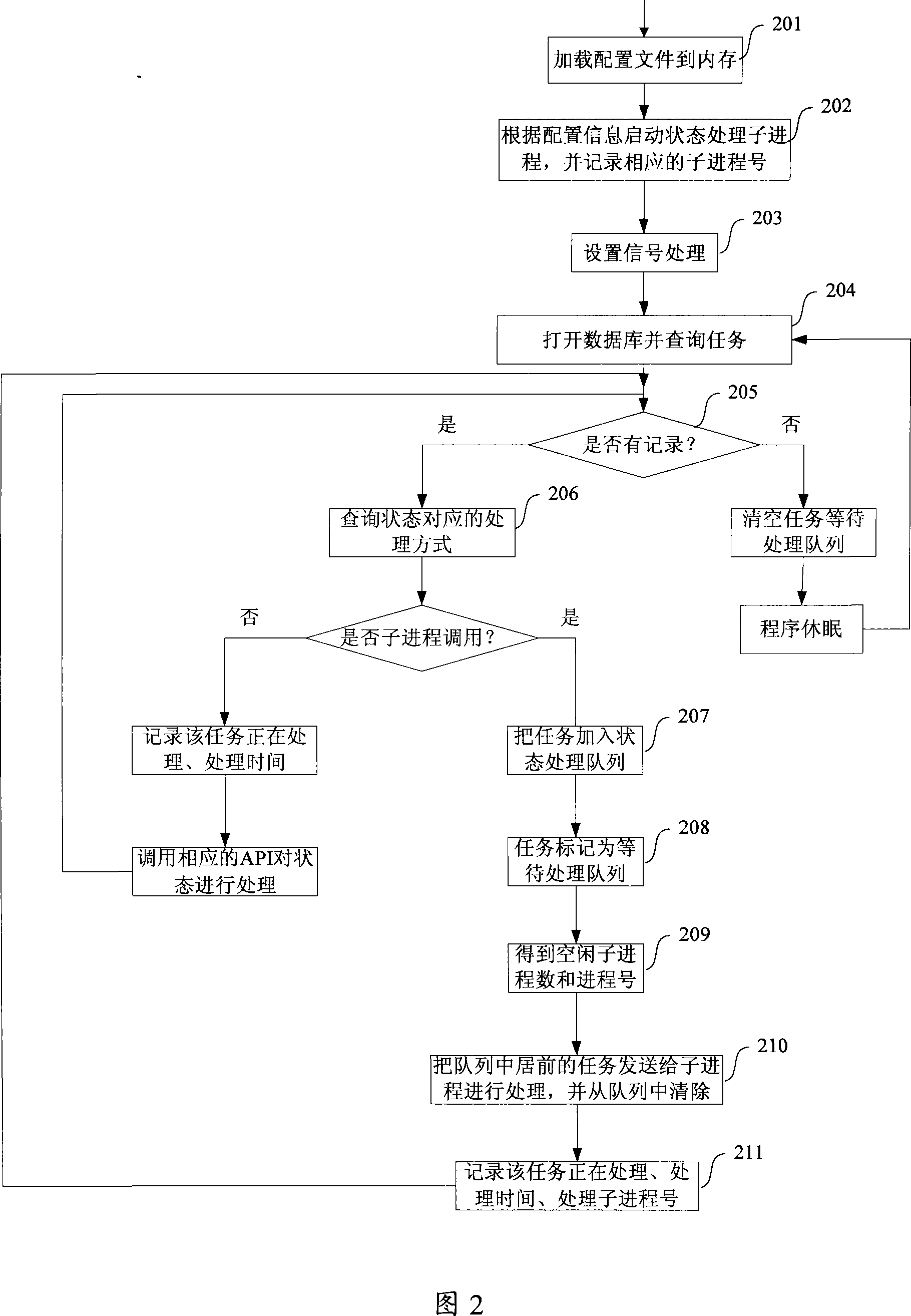
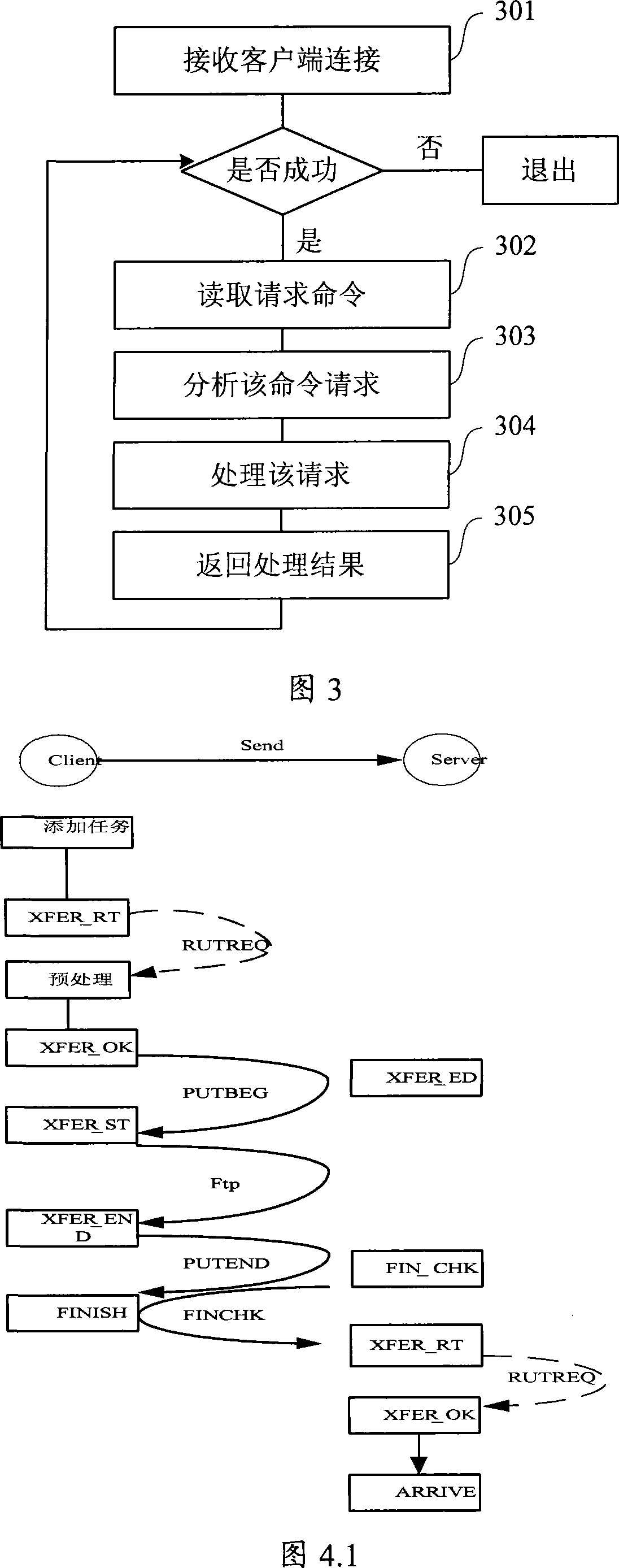
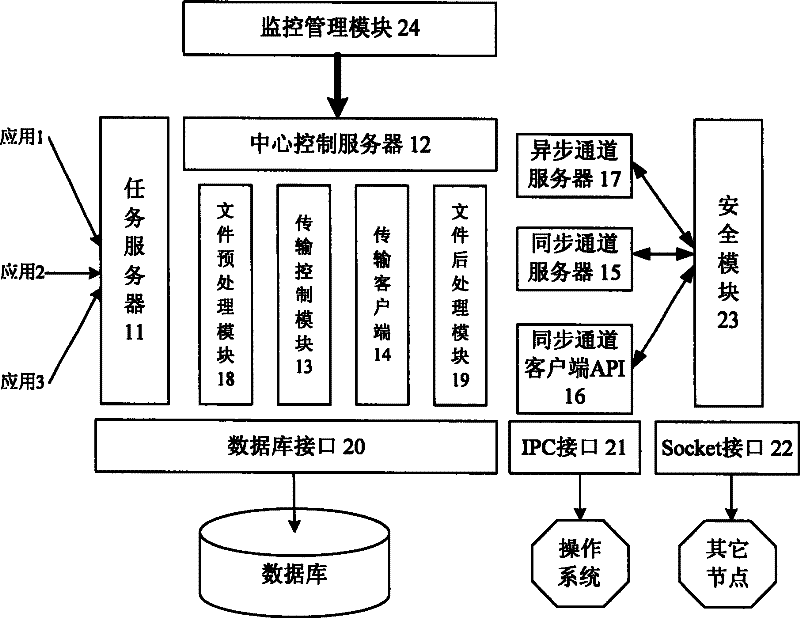
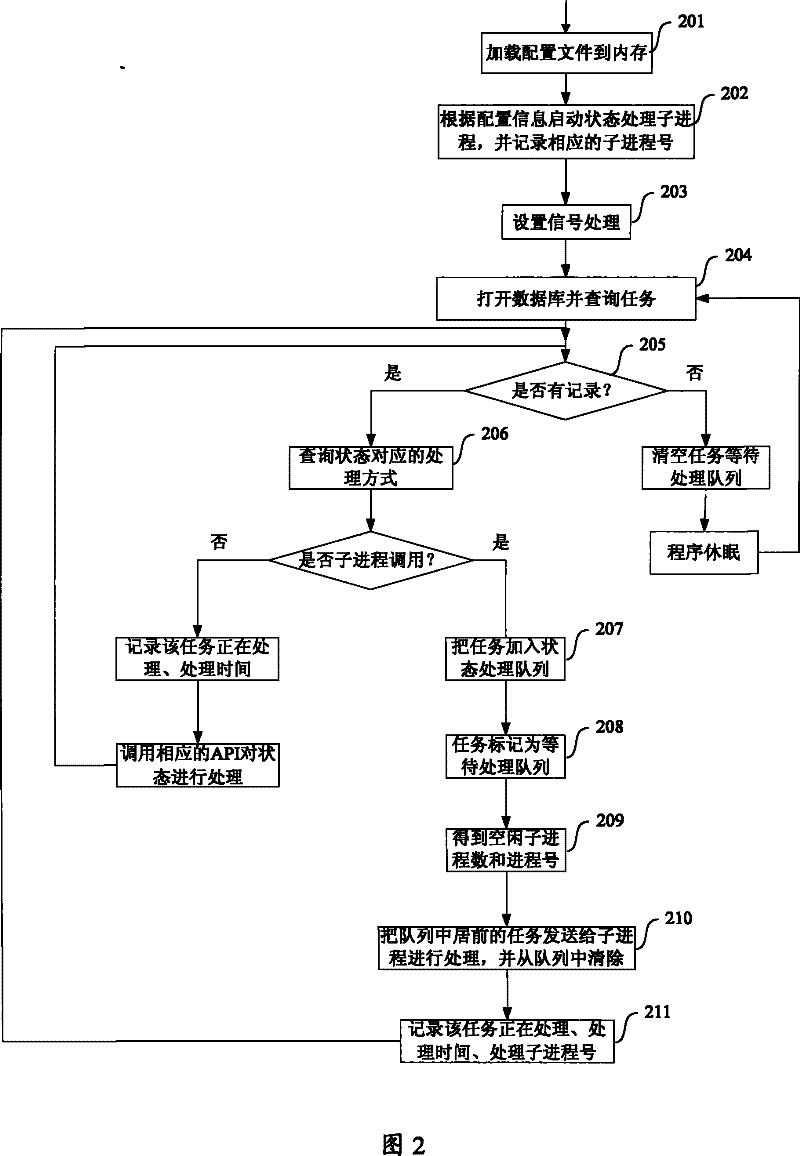
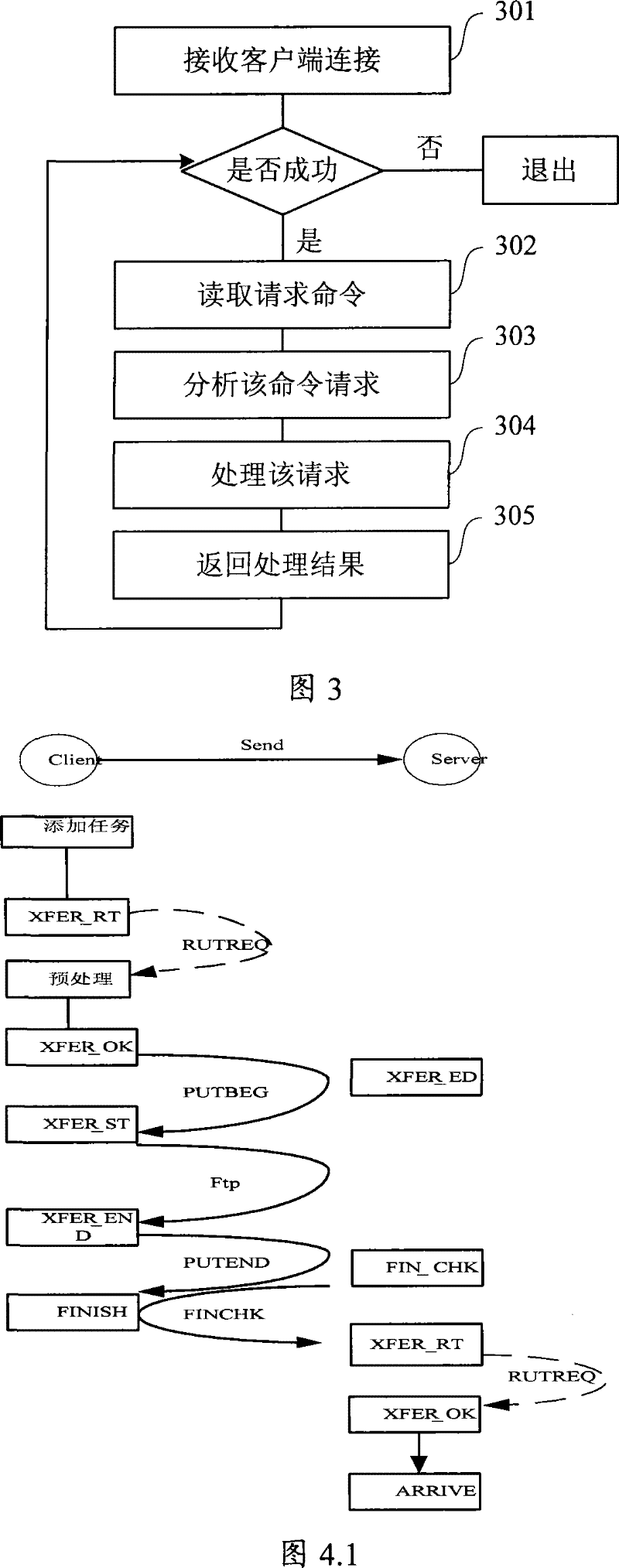
Data transmission system
ActiveCN101252506AReduce correlationImplement direct transfer functionSpecial service provision for substationStore and forwardTransmission channel
The invention discloses a data transmitting system, which solves the problem of the prior data transmitting method that only direct transmission between nodes in an upper and a lower grades and cross-grade storage and forwarding instead of point-to-point transmission can be realized. The system comprises a mission server in charge of monitoring and obtaining requests of source nodes; a central control server in charge of managing and adjusting the working progress which is composed of a transmission controlling module and a transmission client side; the transmission controlling module in charge of communicating with target nodes through a synchronous transmission channel and performing adjustment and control to the mission; the transmission client side is in charge of data transmission, and transmits the data transmission to the target nodes through an asynchronous transmission channel; the synchronous transmission channel is realized by a synchronous channel server and a synchronous channel client side API, and the asynchronous transmission channel is realized by an asynchronous channel server and a transmission client side. The system can realize the direct point-to-point transmission, and is provided with a mission priority managing and flow rate controlling mechanism as well as assemblage and load balancing of application layers.
Owner:CHINA CONSTRUCTION BANK
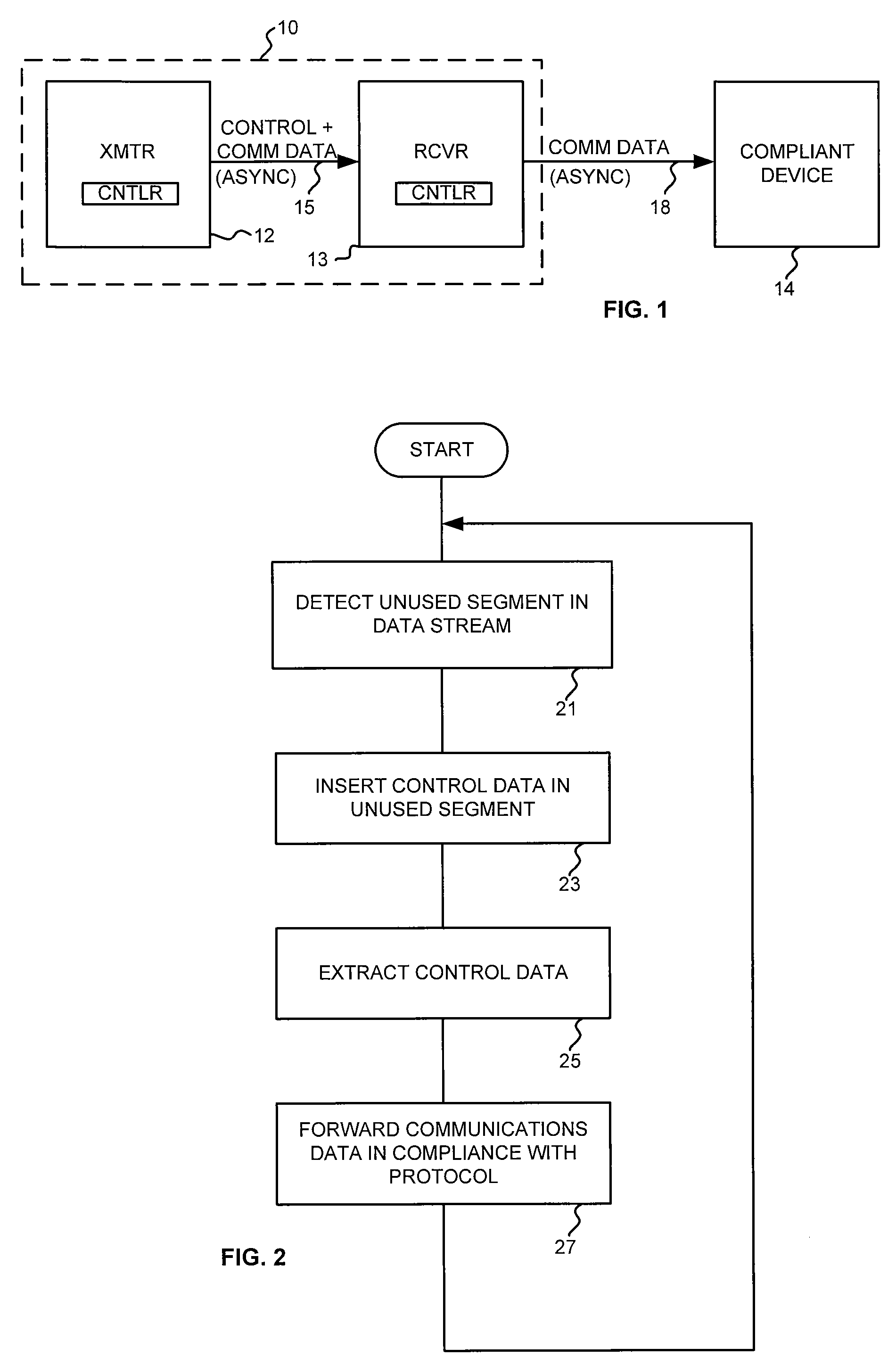
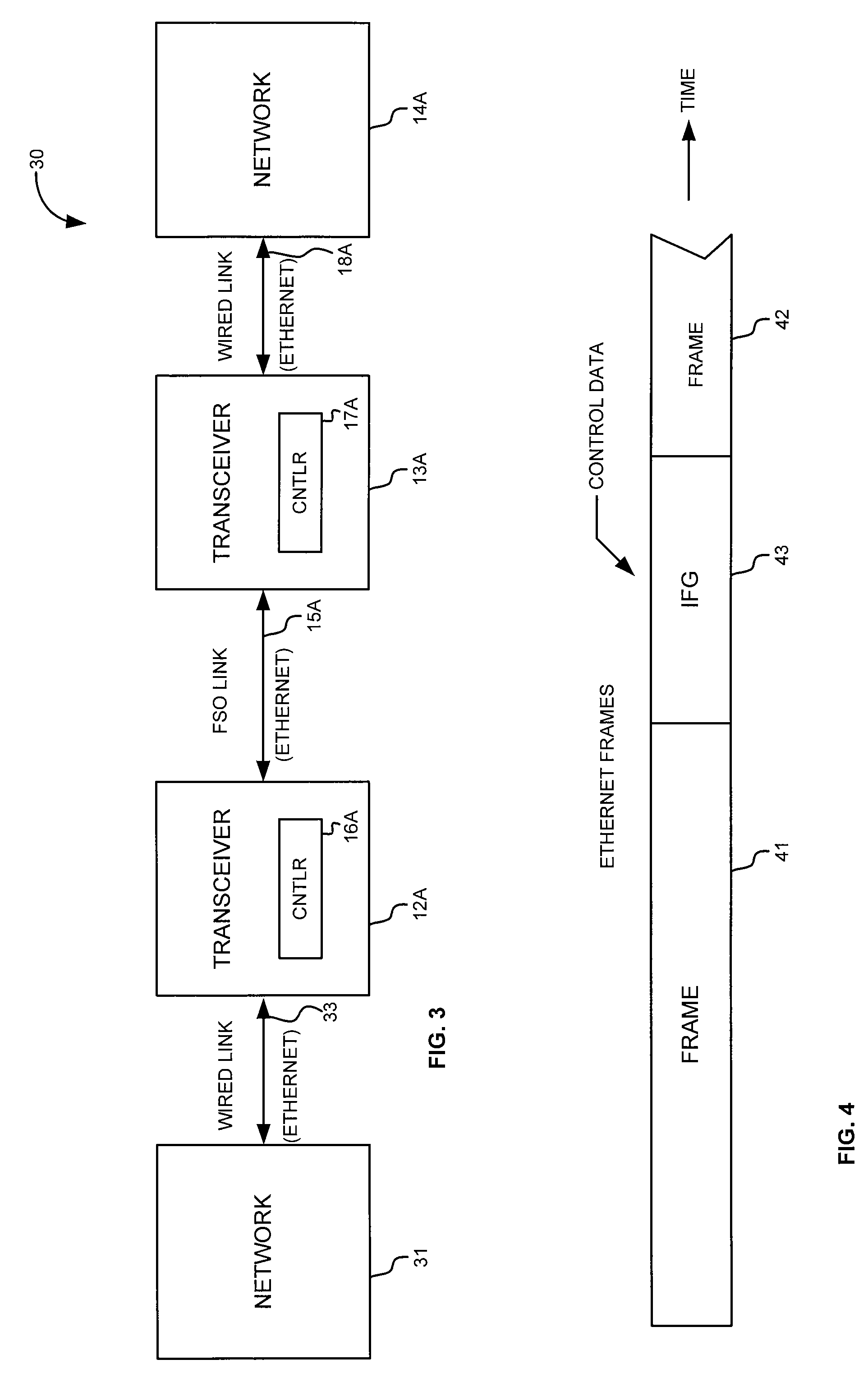
Method and apparatus for communicating control data in an asynchronous communications channel
A communication system communicates control data in unused segments in the data stream of an asynchronous channel. The communication system includes a transmitting unit and a receiving unit. The transmitting unit transmits communications data to the receiving unit via the asynchronous channel, in compliance with the channel's asynchronous protocol. However, the transmitting unit transmits control data to the receiving unit in unused segments of the data stream.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for preventing underflow and overflow across an asynchronous channel
InactiveUS6813275B1Reduces solution complexityElimination of controlData switching by path configurationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlNetwork packetControl circuit
An apparatus and method for an improved asynchronous communication channel between a transmitter and a receiver having separate clocks. The invention provides a simple implementation that solves both the overflow and the underflow problem using the same mechanism, and reduces complexity by elimination of the control split between the two clock domains. A first embodiment of the invention is a method for preventing packet underflow and packet overflow for packets sent across an asynchronous link between a transmitter and a receiver, including a buffer that can store a number of packets greater than an ideal number of packets. The method includes sending a predetermined number of drop-me warning packets and sending one or more drop-me packets from the transmitter to the receiver, receiving the predetermined number of drop-me warning packets and the one or more drop-me packets in the buffer, compensating for packet overflow when the number of packets is greater than the ideal number of packets in the buffer by skipping at least one drop-me packet, and compensating for packet underflow in the buffer when the number of packets is less than the ideal number of packets by stalling access to the buffer for one or more clock cycles. A second embodiment of the invention is an asynchronous link for packets sent between a transmitter having a first clock and a receiver having a second clock, including a buffer to receive the first clock from the transmitter and receive from the transmitter a number of packets equal to or different to a predetermined ideal number of packets, a write pointer, and a read pointer, and a read pointer control circuit to change the read pointer, wherein the buffer can receive drop-me packets, and the read pointer can skip a drop-me packet in the buffer.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Method of Transmitting Signal in a Wireless System
InactiveUS20110305287A1Efficient receptionGuaranteed normal transmissionSynchronisation arrangementSignal allocationCommunications systemControl signal
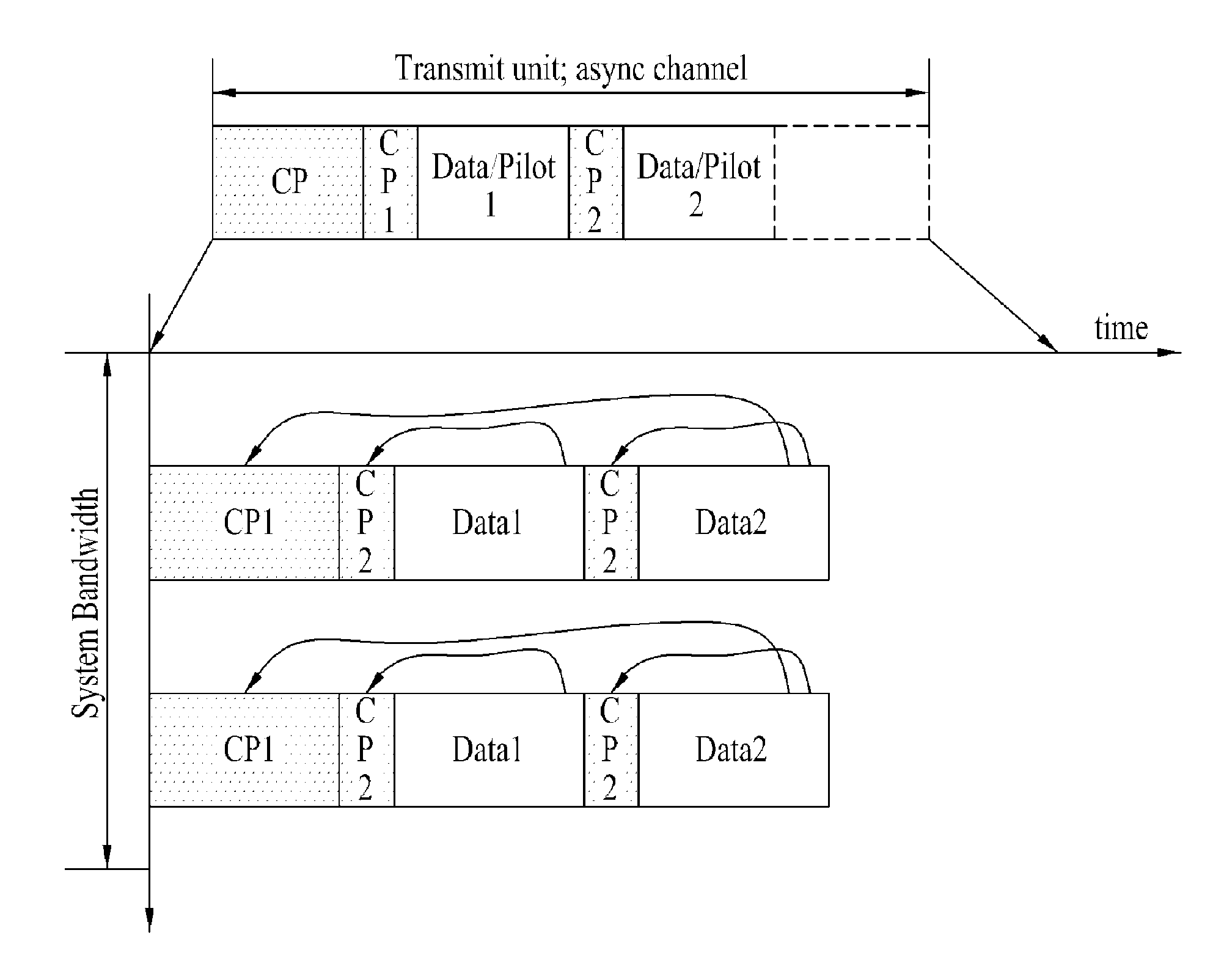
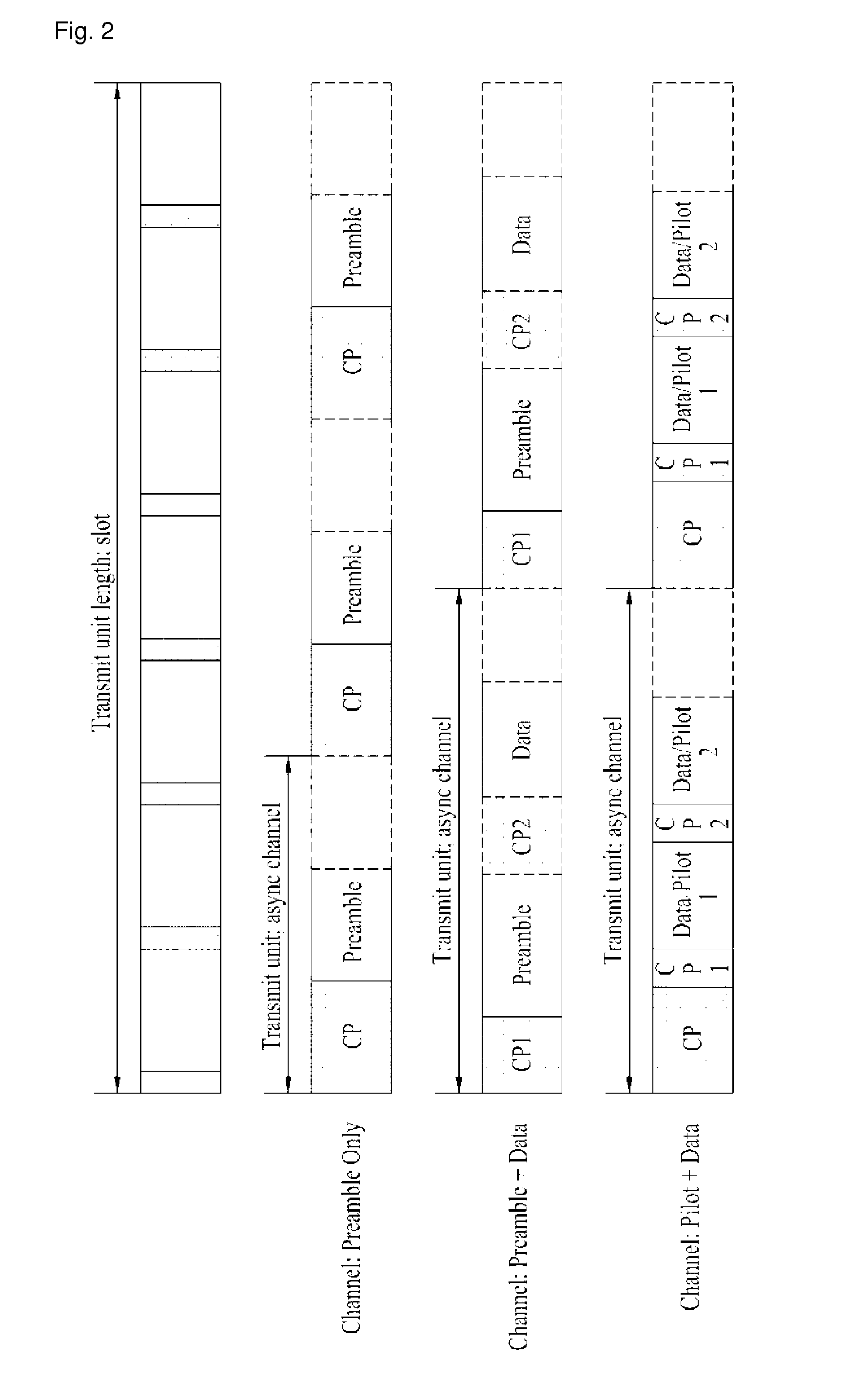
A method of transmitting a signal of a mobile station that performs communication with a plurality of cells in a wireless communication system comprises transmitting a control signal or a data signal through an asynchronous channel to a neighboring cell which is not synchronized with the mobile station, the asynchronous channel including cyclic prefix and guard time.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
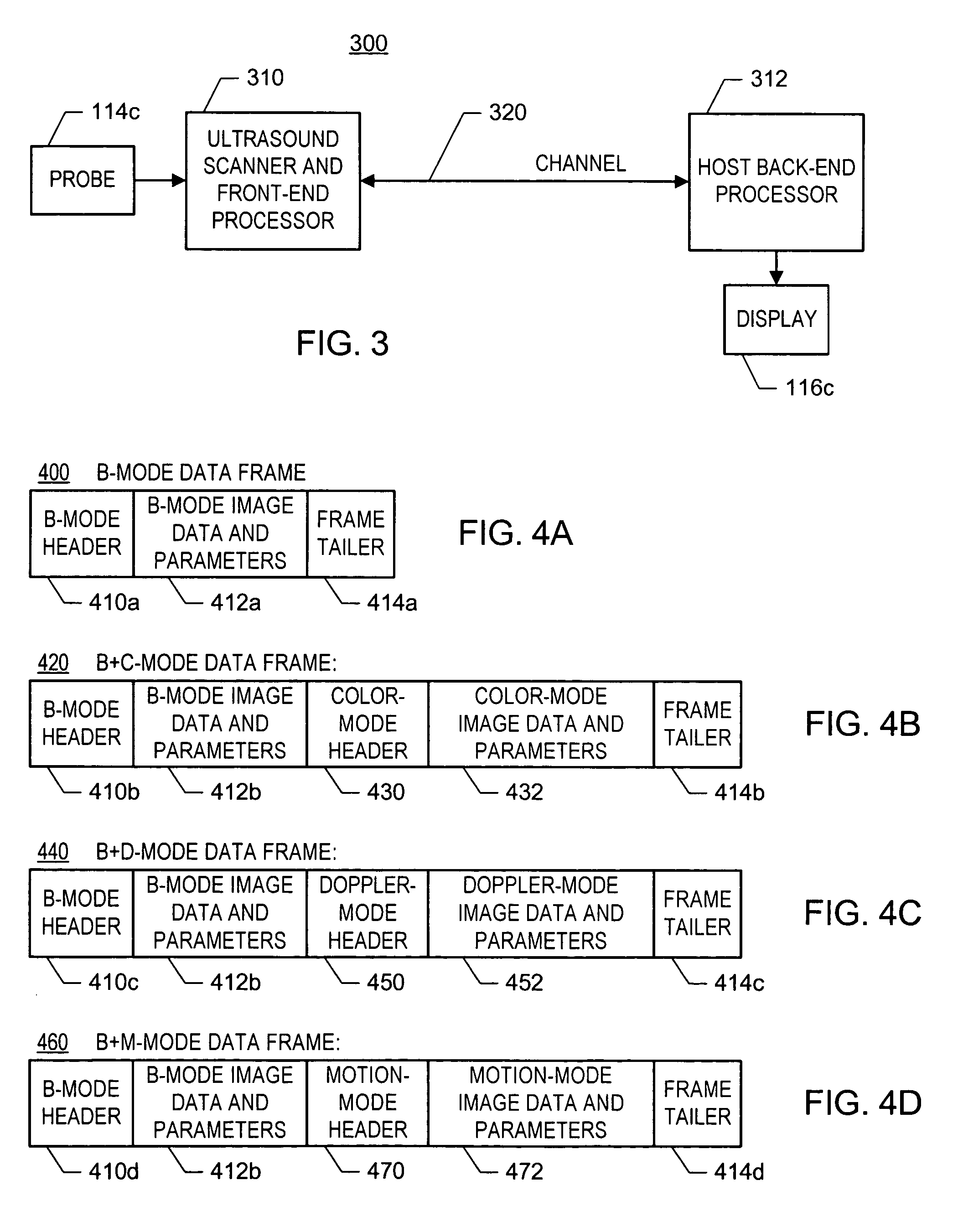
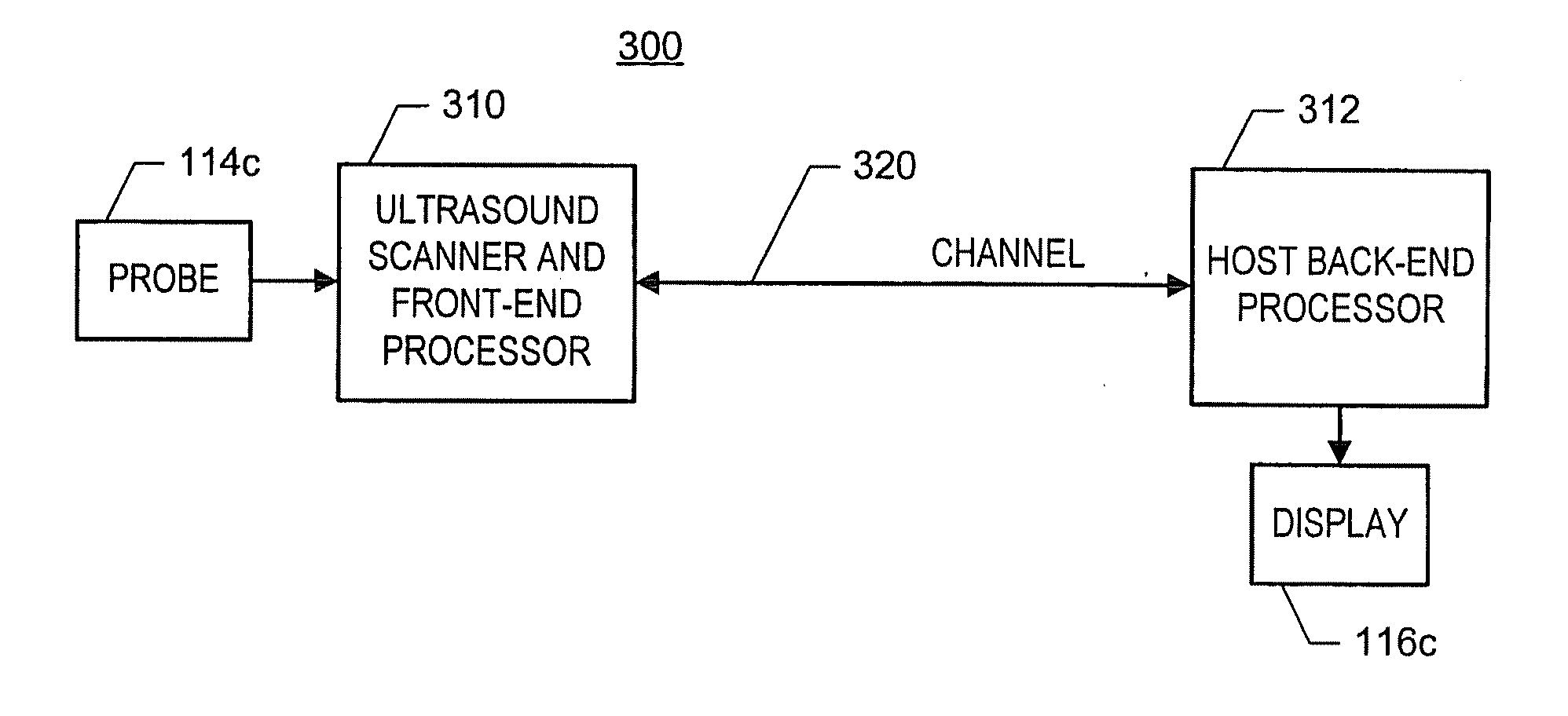
System and method for medical imaging with robust mode switching via serial channel
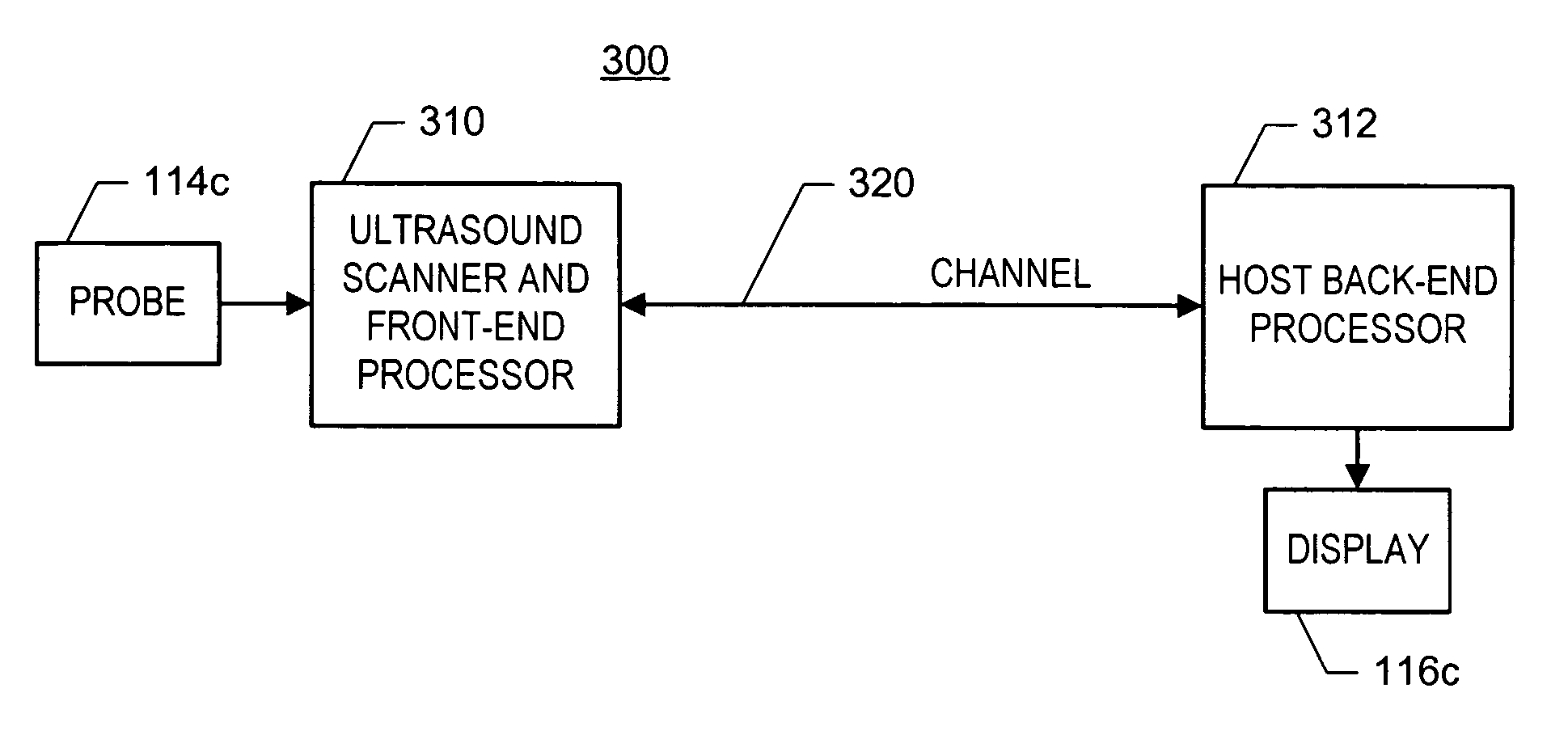
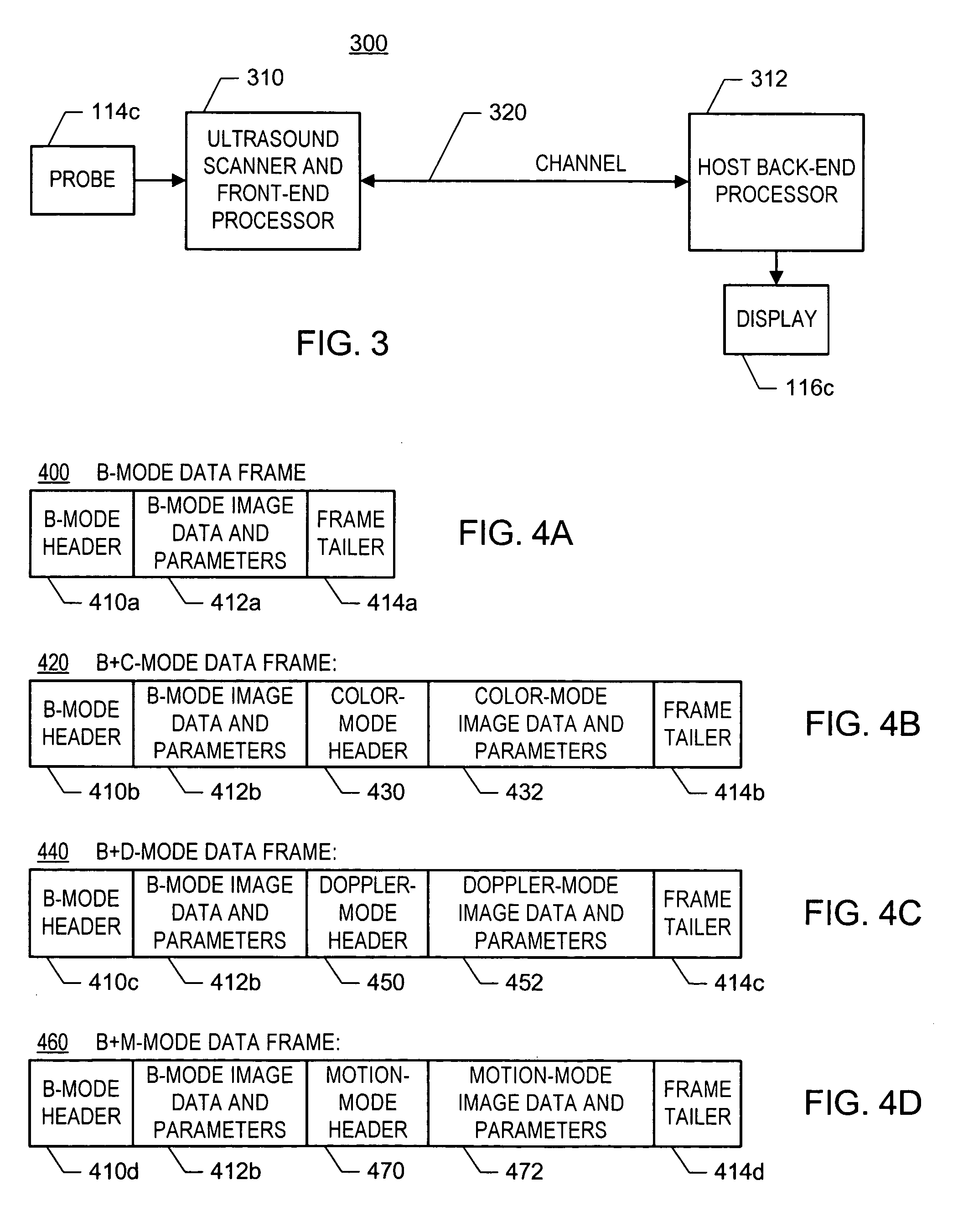
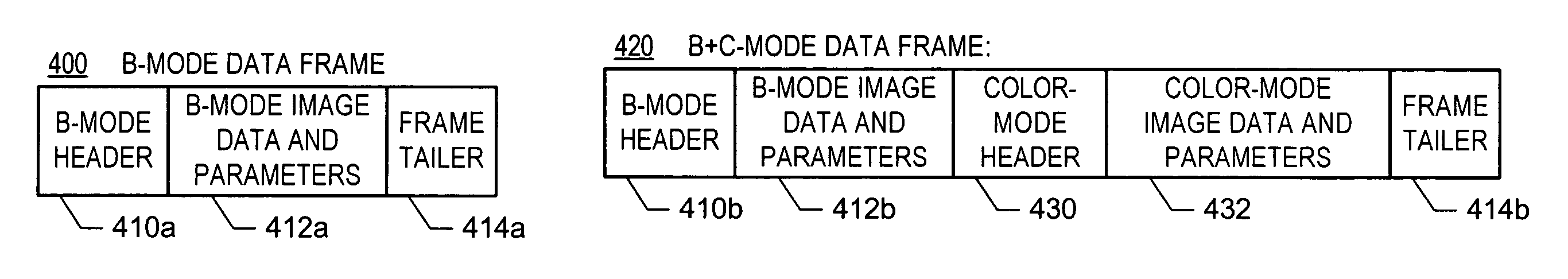
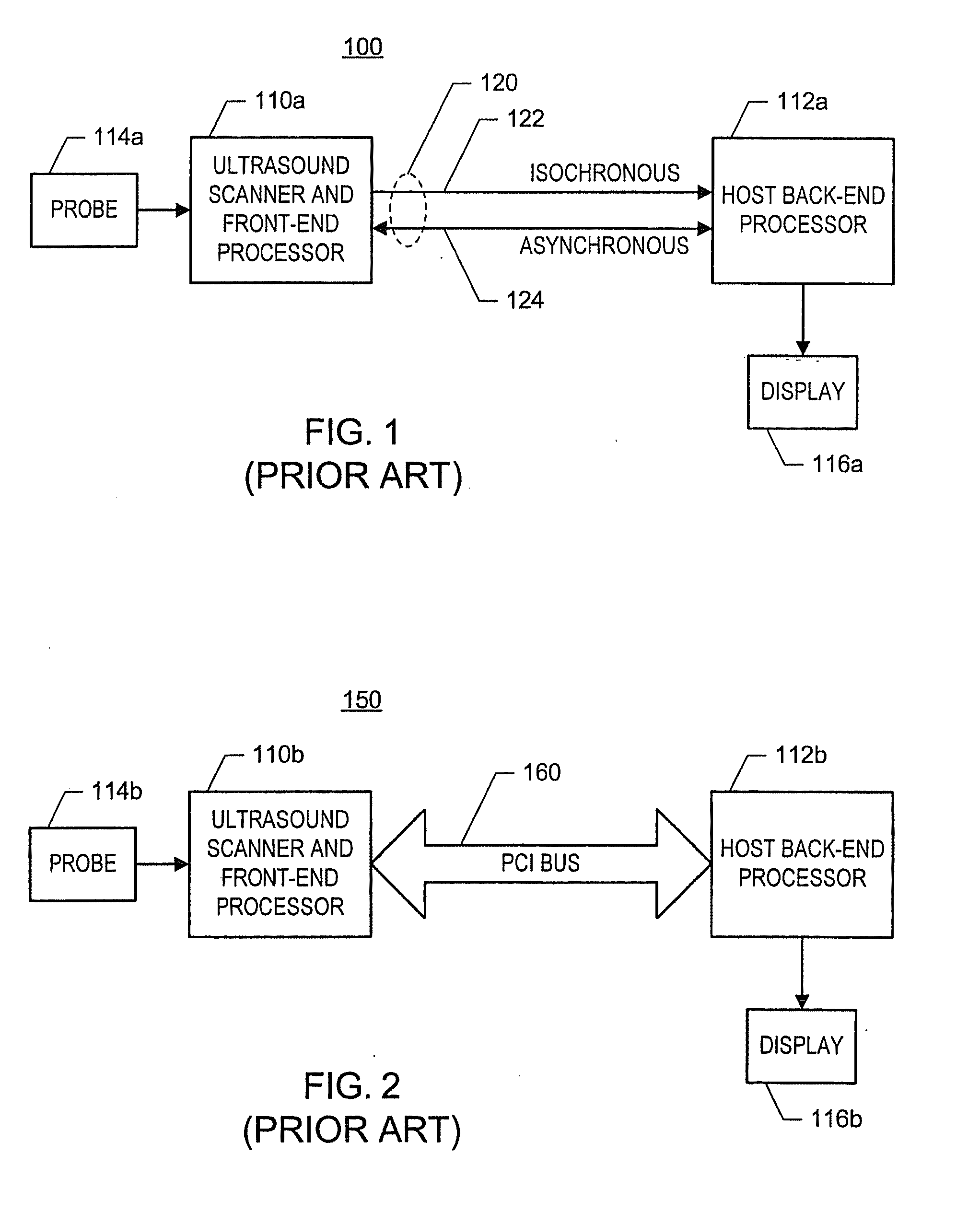
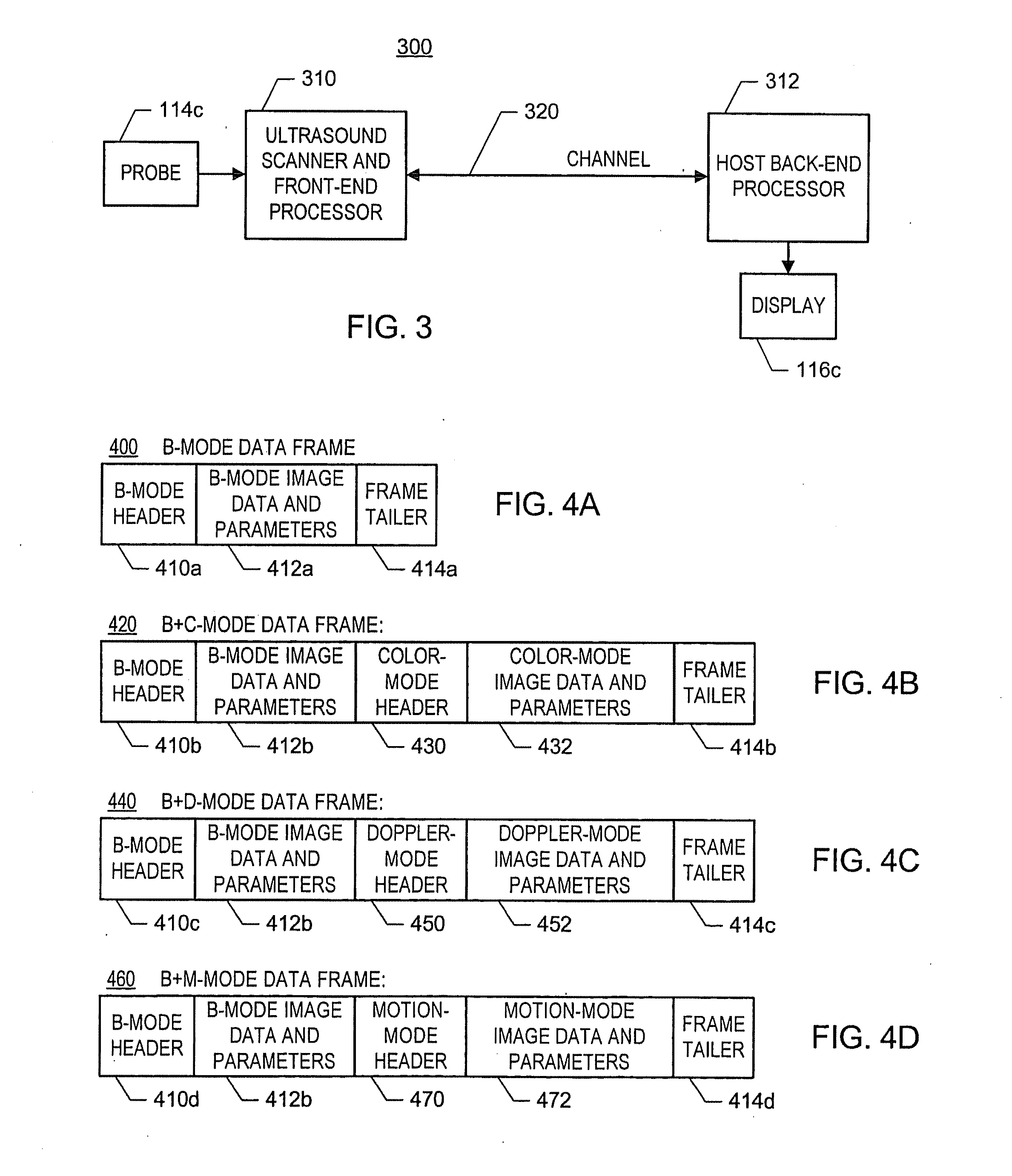
ActiveUS20060094959A1Easy to displayUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsUltrasound imagingSonification
In one embodiment of the invention, there is an ultrasound processing system that communicates images over a single asynchronous serial channel according to a scheme that does not require an isochronous serial channel and that switches among ultrasound imaging modes robustly. For example, the system is configured to packetize ultrasound image data of at least one ultrasound imaging mode into a stream of data frames and to convey the stream of data frames via the asynchronous channel. Each data frame includes indication of the ultrasound imaging mode and includes ultrasound-imaging-mode-specific imaging parameters. Other embodiments exist.
Owner:SONOWISE
Autosynchronous multichannel parallel storage DDS (direct digital synthesis) signal generator
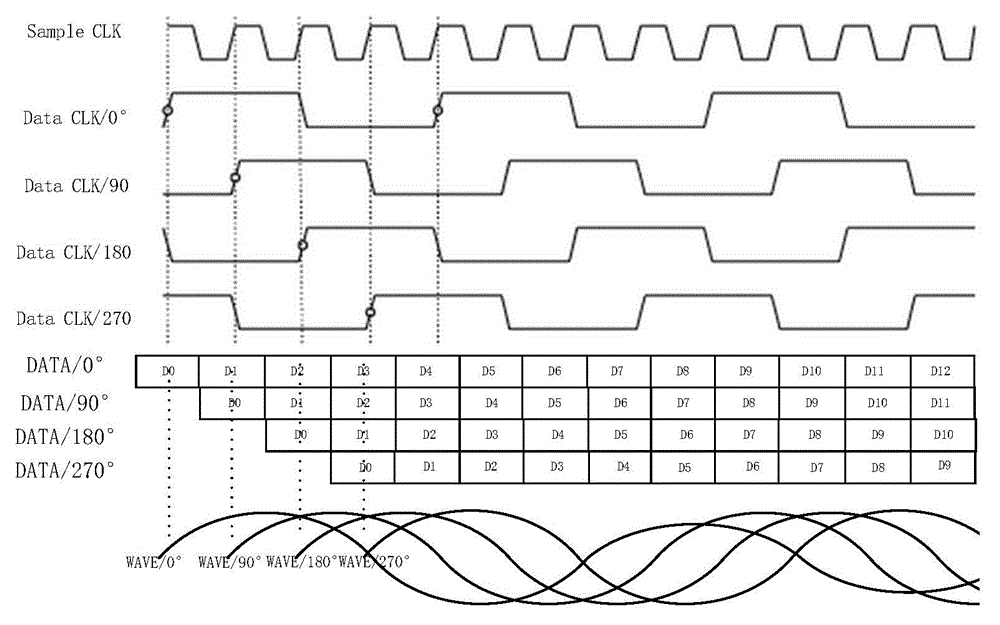
InactiveCN104158515ARealize automatic synchronizationElectric pulse generator circuitsVideo-signal generatorComputer module
The invention discloses an autosynchronous multichannel parallel storage DDS (direct digital synthesis) signal generator. A data clock phase judgment module is added and used for synchronous detection on a data clock obtained after a sampling clock is subjected to m frequency division by each channel DAC, namely, the DAC internal frequency divider of the k path; if certain path (channel) is asynchronous with a reference data clock, the DAC internal frequency divider of the path (channel) is reconfigured and redetected until all channels are synchronous. According to the invention, the data clock phase judgment module is used for synchronous detection of data pulse of all channels and reconfiguring the DAC internal frequency dividers of the asynchronous channels until the channels are synchronous, so that auto synchronization of wave signals output by all channels is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
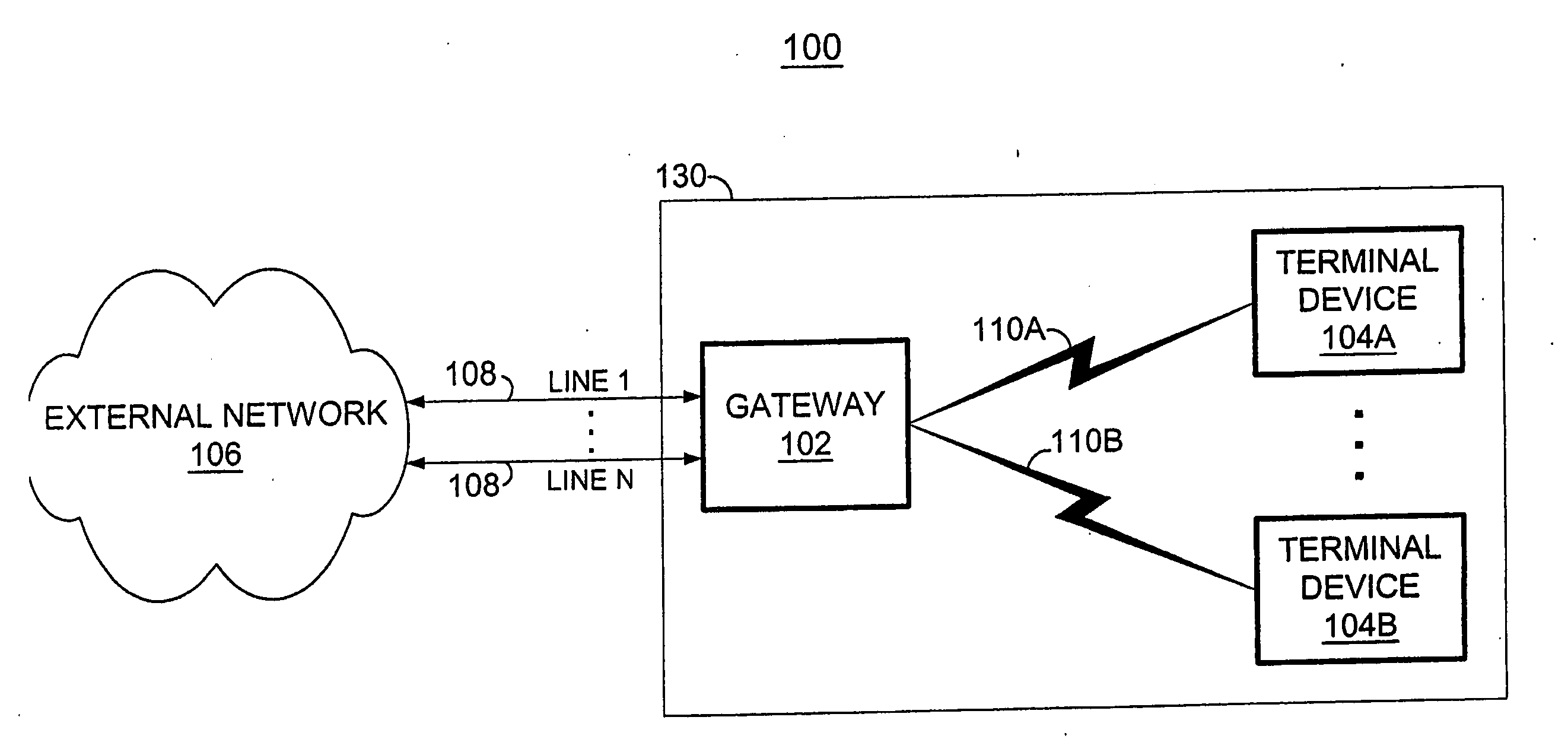
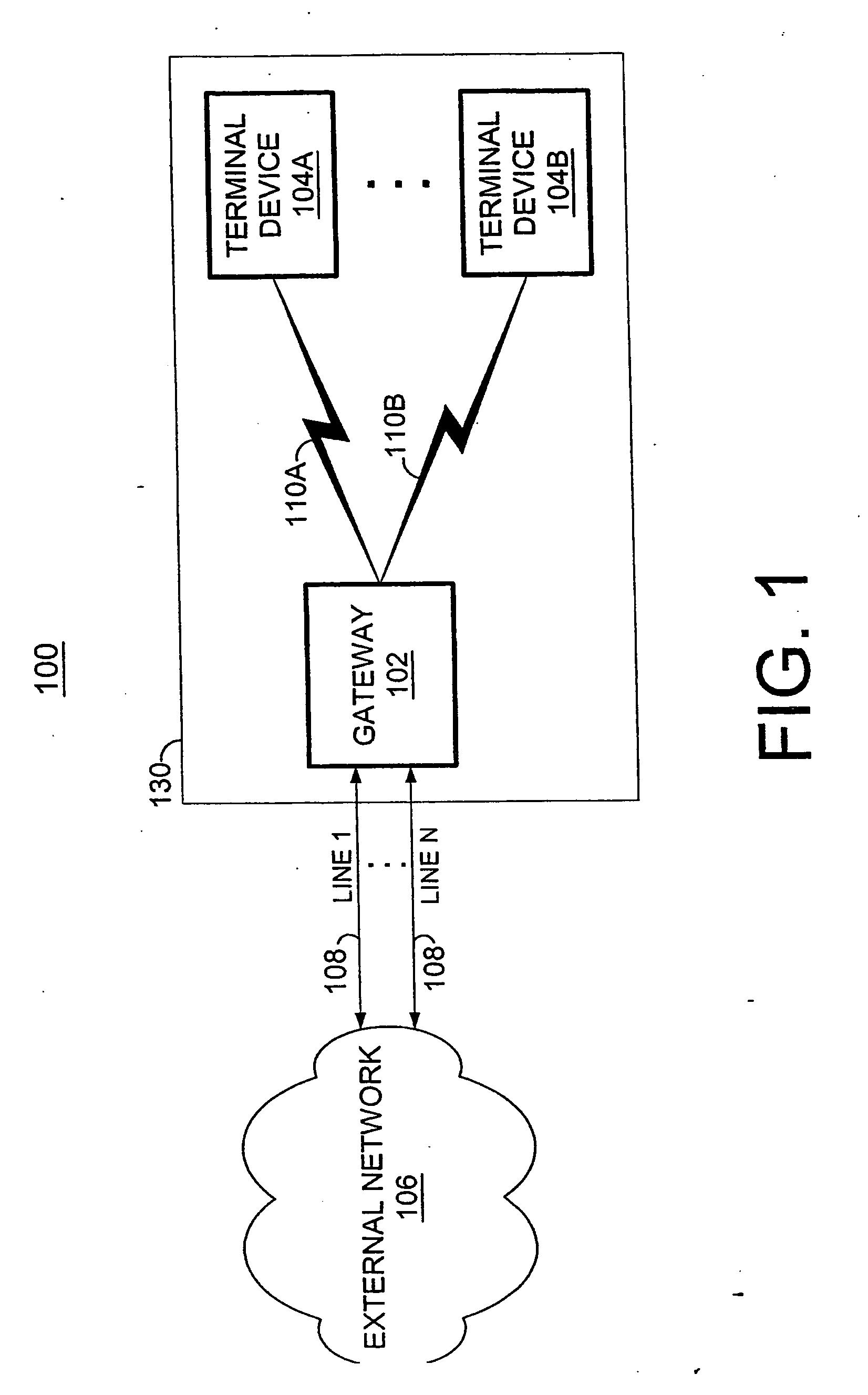
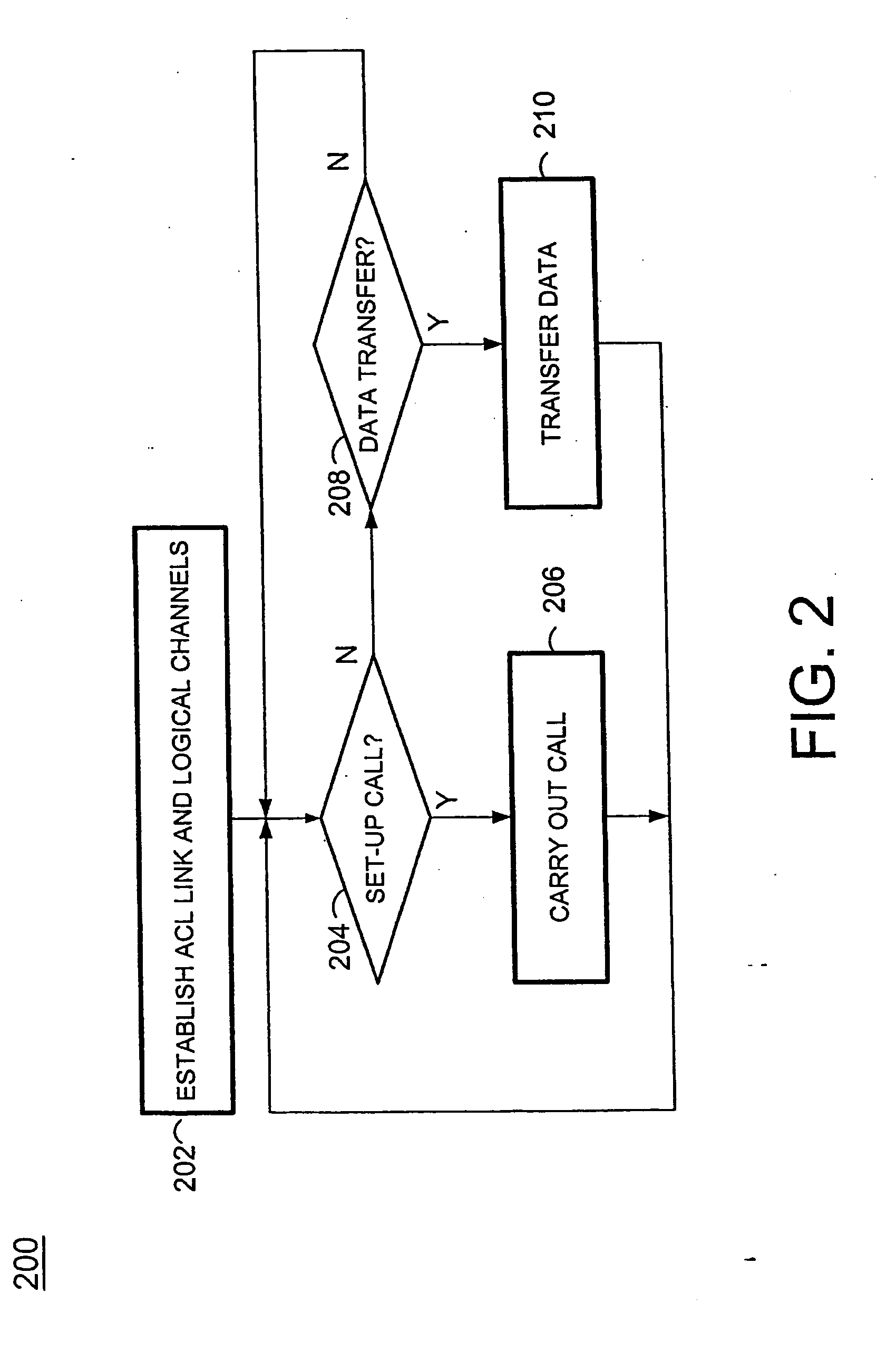
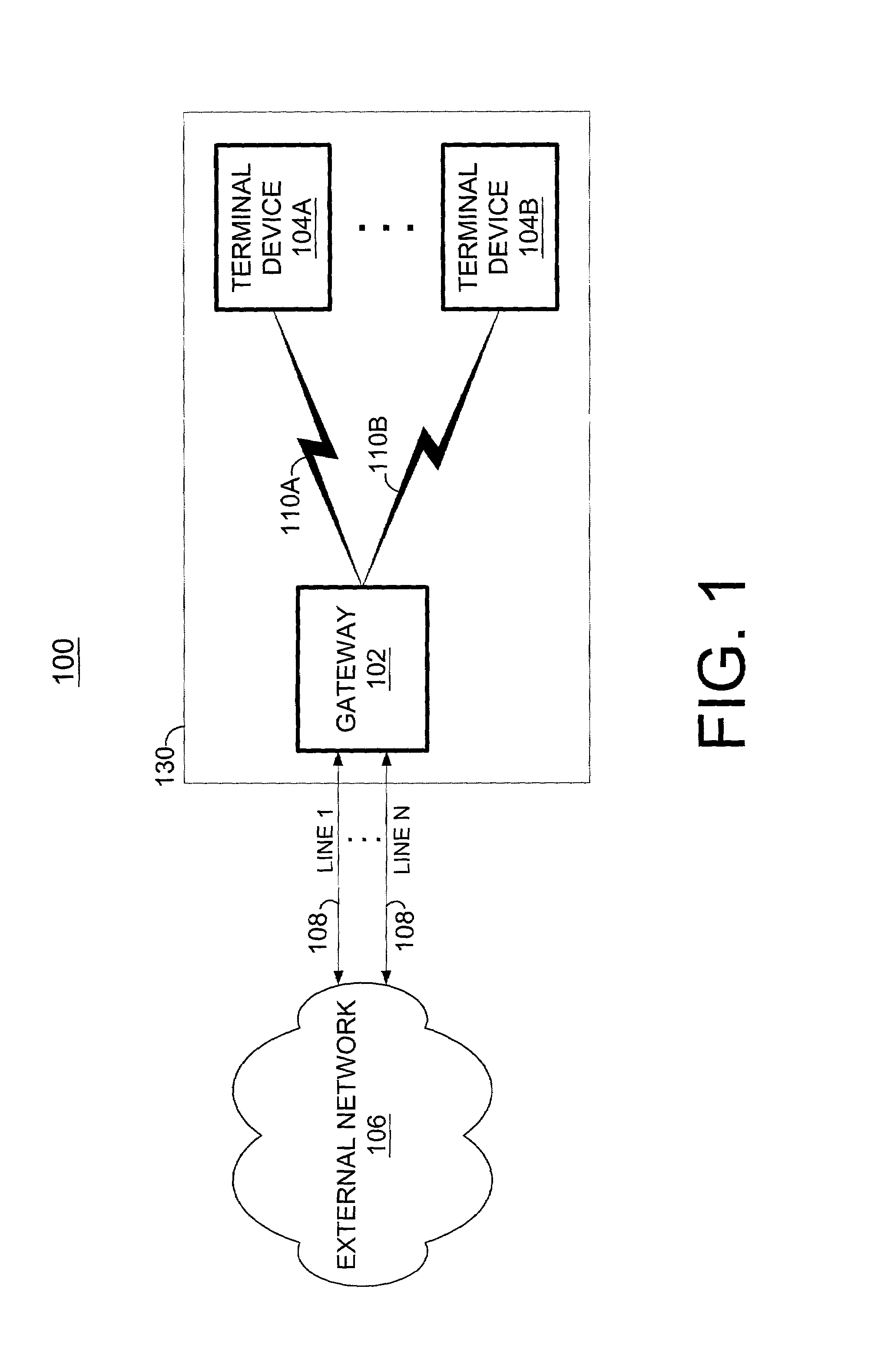
System and method for accessing a multi-line gateway using cordless telephony terminals
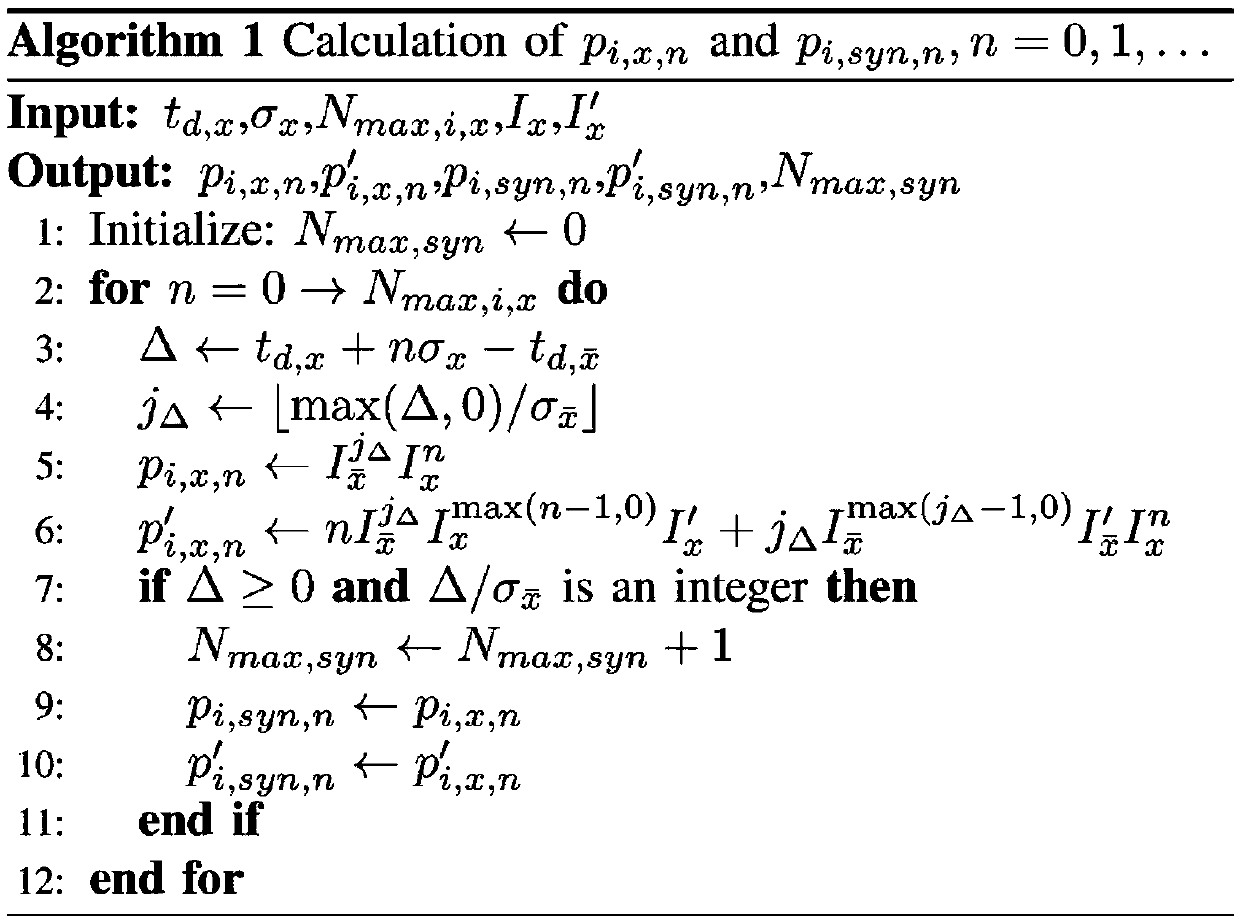
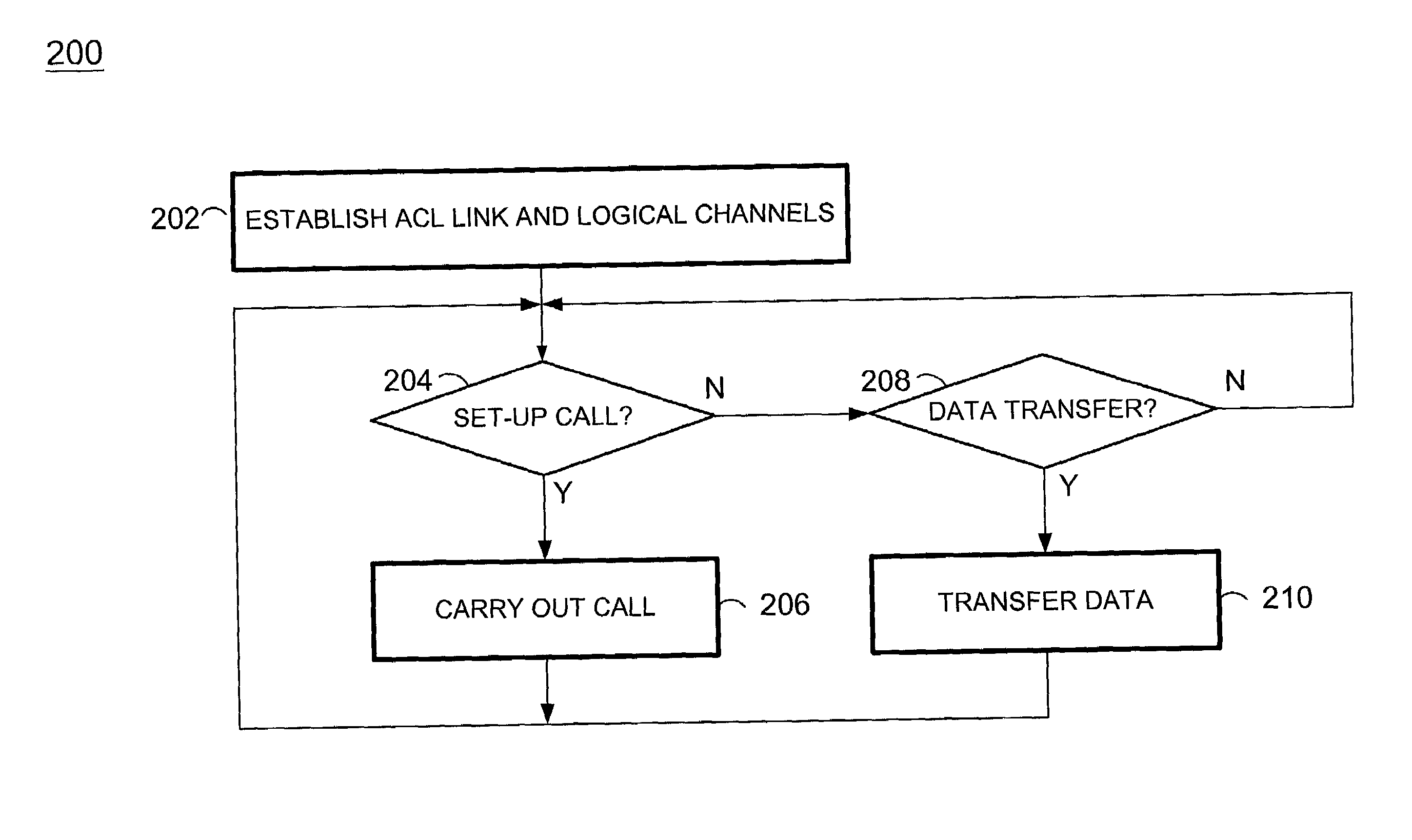
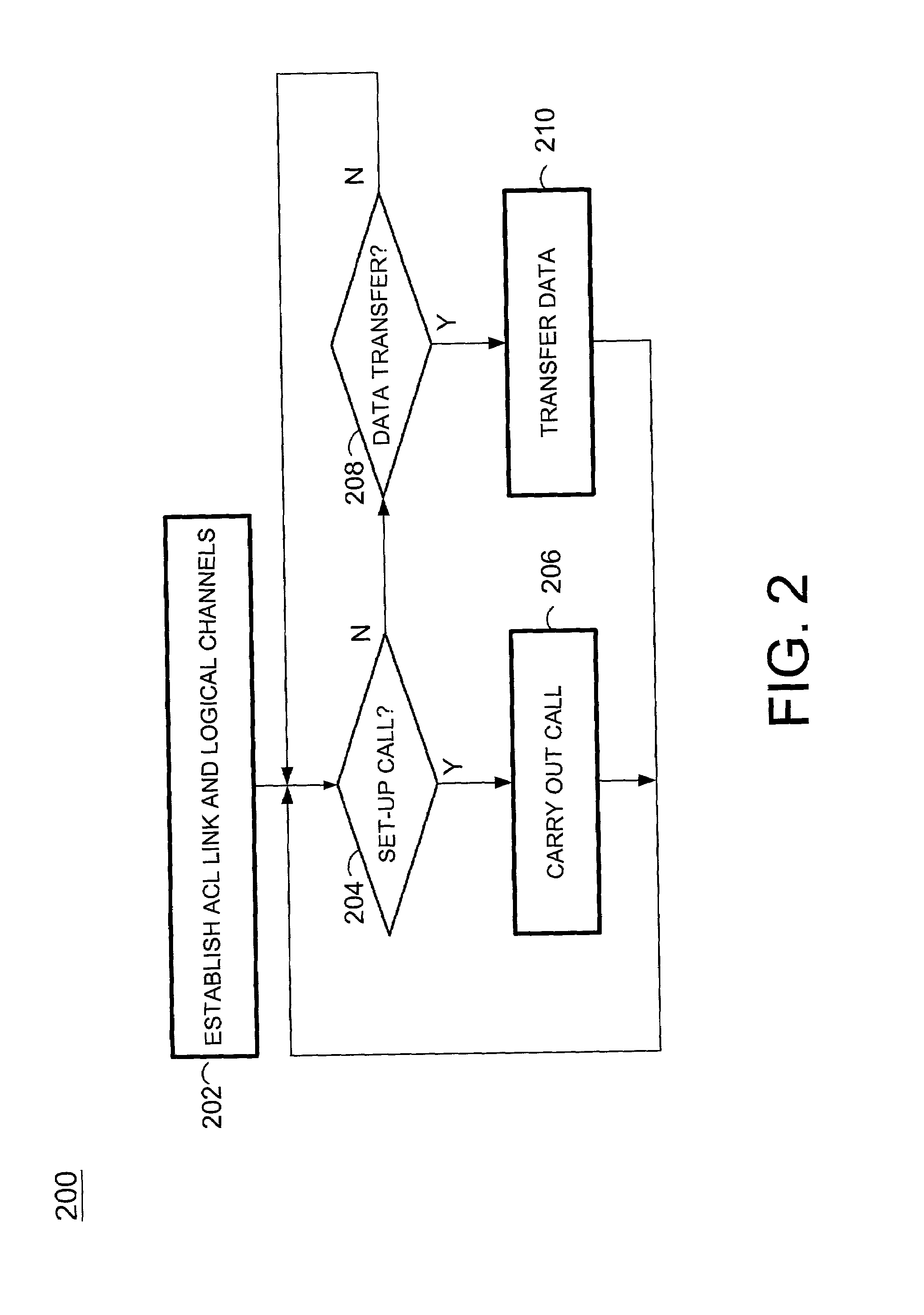
According to the present invention, simultaneous call-handling and data transfer is achieved between a terminal and a multi-line gateway in a cordless telephony environment. Multiple logical channels are established and used as signaling resources for calls on the multiple lines, and also for data transfers between the gateway and terminal. As a result, terminals can handle multiple calls on different lines and at the same time access data stored at the gateway. According to a first aspect of the present invention, two or more logical channels are established over an asynchronous channel between a terminal and a gateway. These logical channels are assigned to calls that are set-up between the terminal and gateway. When used as a signaling resource, the logical channels allow the terminal to distinguish between signaling information for multiple simultaneous calls. The calls are associated with another speech or data channel that will bear the voice signal, referred to herein as a bearer channel. According to a second aspect of the present invention, a logical channel is also established over an asynchronous channel to handle data transfers between the gateway and terminal. Using this logical channel, the terminal can access data stored at the gateway without disrupting any ongoing calls.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
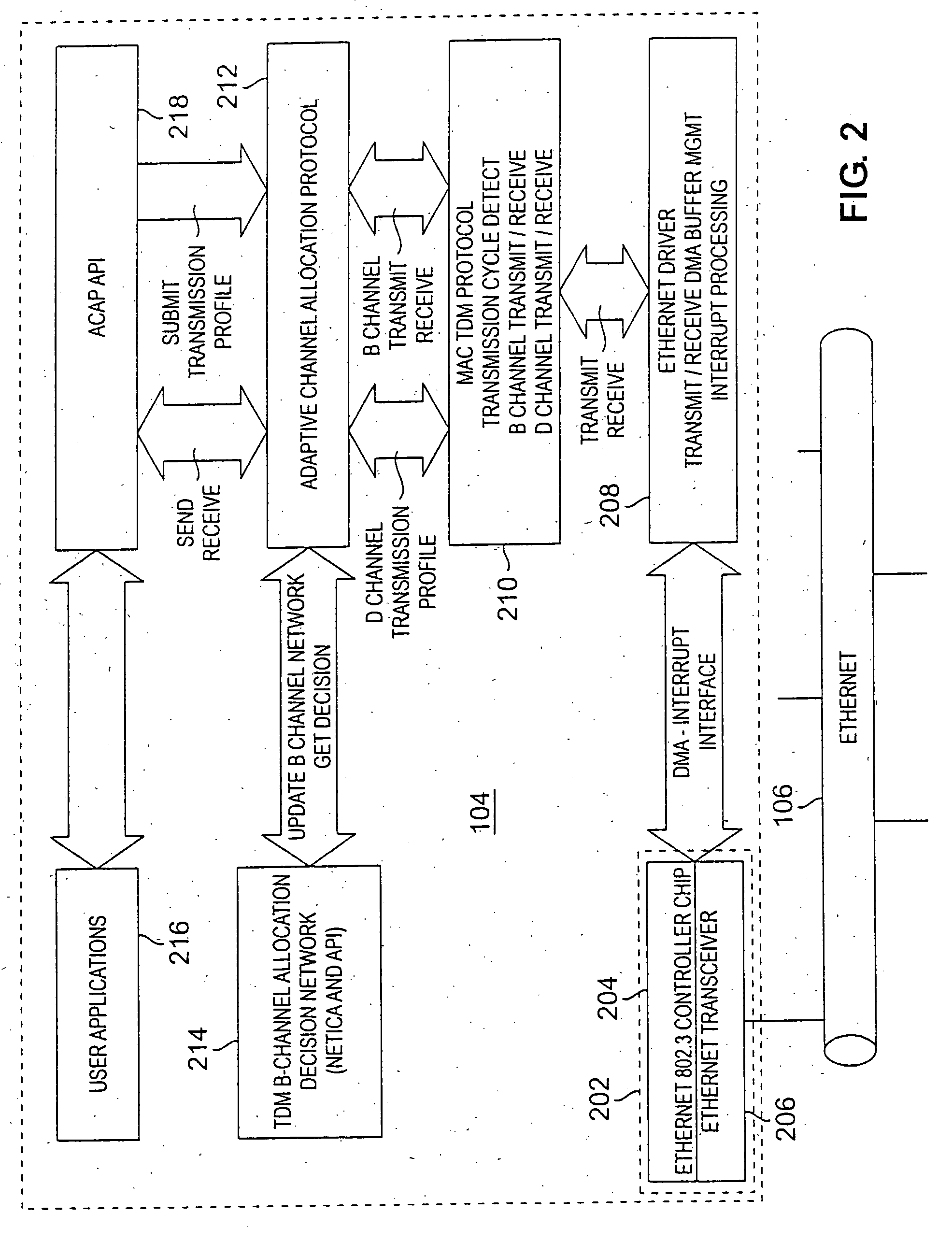
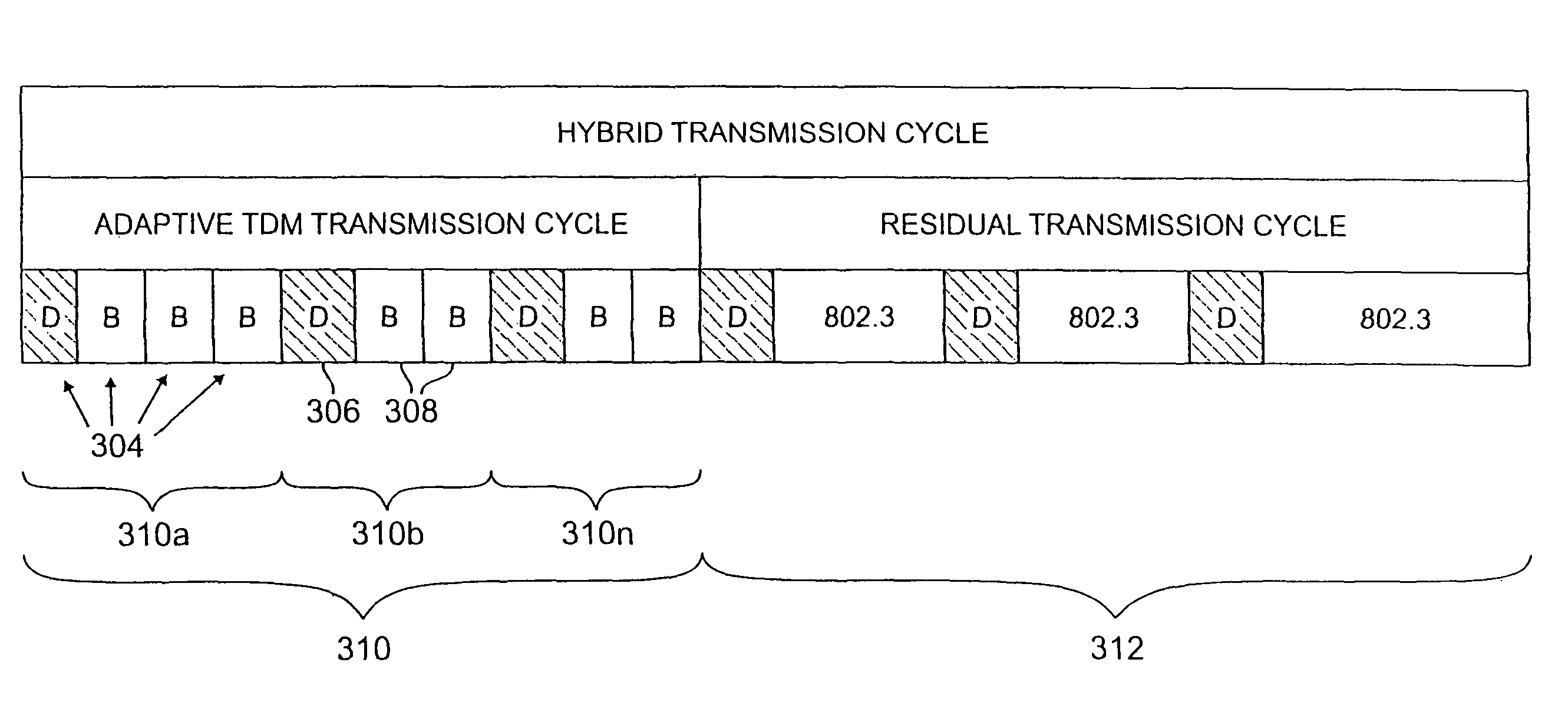
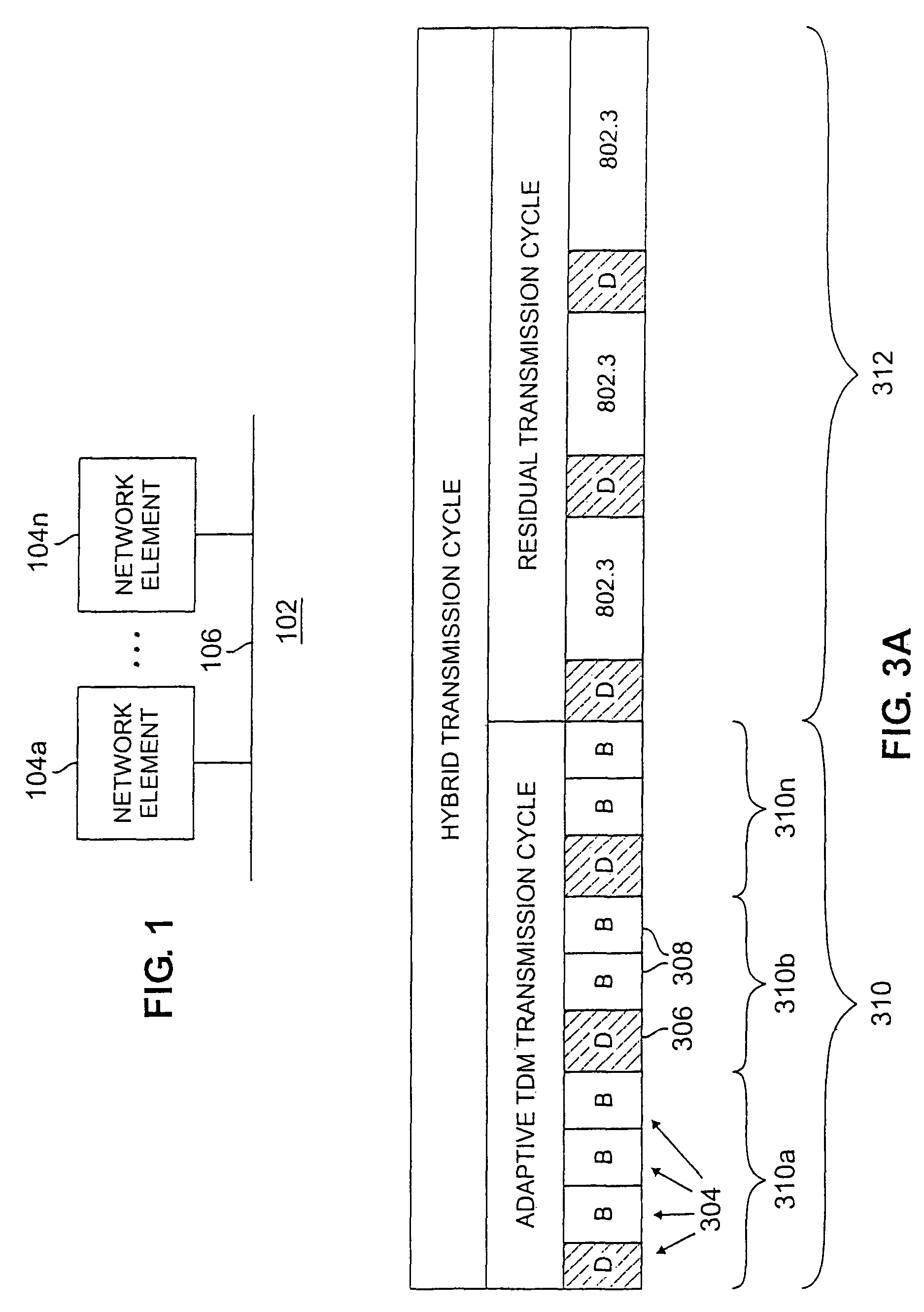
Adaptive transmission in multi-access asynchronous channels
ActiveUS20050111477A1Prevent unacceptable latencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDecision networksTime-division multiplexing
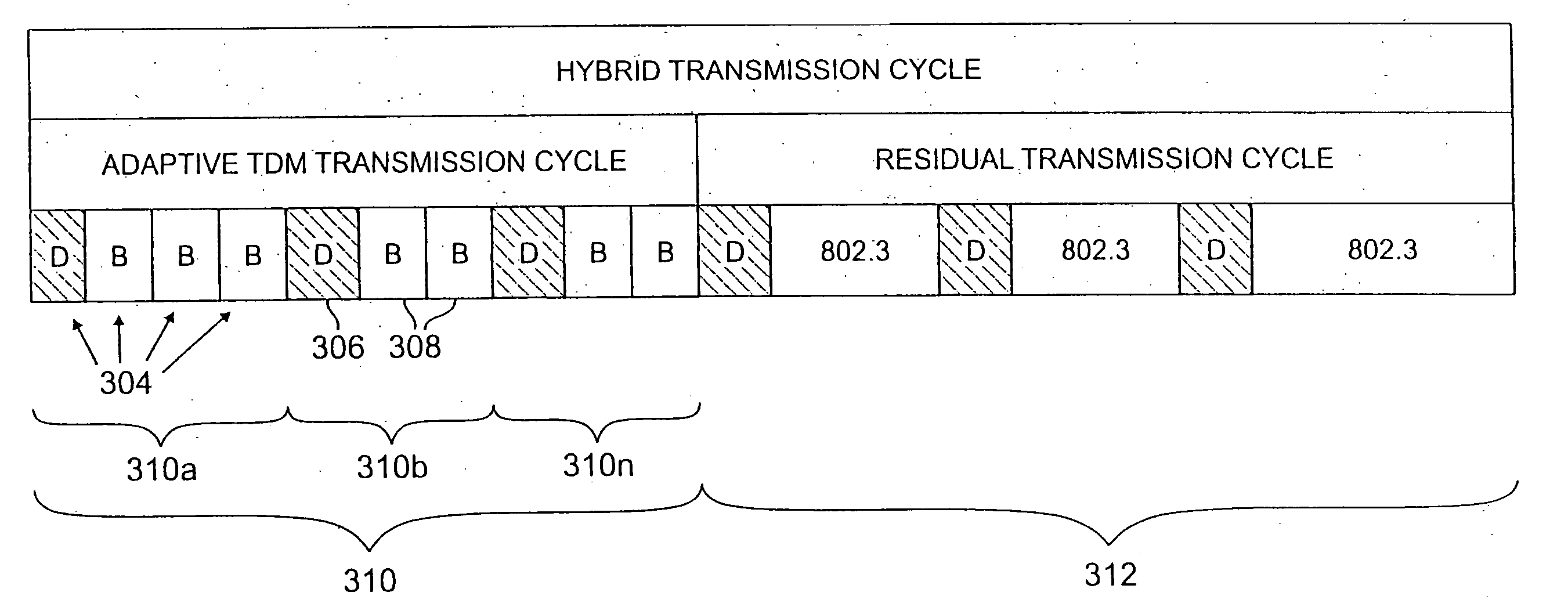
A hybrid transmission cycle (HTC) unit of bandwidth on a shared transmission medium is defined to include an adaptive, time division multiplexing transmission cycle (ATTC), which is allocated in portions sequentially among all participating network entities, and a residual transmission cycle (RTC), which is allocated in portions, as available, to the first network entity requesting access to the shared medium during each particular portion. The ratio of logical link virtual channels, or D-Channels, to data payload virtual channels, or B-Channels, within the ATTC is adaptive depending on loading conditions. Based on transmission profiles transmitted on the D-Channels during the ATTC, each network entity determines how many B-Channels it will utilize within the current HTC. This calculation may be based on any decision network, such as a decision network modelling the transmission medium as a marketplace and employing microeconomic principles to determine utilization. The ratio of the duration of the ATTC segment to the duration of the RTC segment is also adaptive depending on loading conditions, to prevent unacceptable latency for legacy network entities employing the shared transmission medium. During the RTC, utilization of the shared medium preferably reverts to IEEE 802.3 compliant CSMA / CD transmission, including transmissions by HTC-compliant network entities.
Owner:GLOBAL COMM INVESTMENT LLC
System and method for medical imaging with robust mode switching via serial channel
ActiveUS7771355B2Easy to displayUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsUltrasound imagingSonification
In one embodiment of the invention, there is an ultrasound processing system that communicates images over a single asynchronous serial channel according to a scheme that does not require an isochronous serial channel and that switches among ultrasound imaging modes robustly. For example, the system is configured to packetize ultrasound image data of at least one ultrasound imaging mode into a stream of data frames and to convey the stream of data frames via the asynchronous channel. Each data frame includes indication of the ultrasound imaging mode and includes ultrasound-imaging-mode-specific imaging parameters. Other embodiments exist.
Owner:SONOWISE
Adaptive transmission in multi-access asynchronous channels
InactiveUS7719981B2Prevent unacceptable latencyError preventionTransmission systemsDecision networksTime-division multiplexing
A hybrid transmission cycle (HTC) unit of bandwidth on a shared transmission medium is defined to include an adaptive, time division multiplexing transmission cycle (ATTC), which is allocated in portions sequentially among all participating network entities, and a residual transmission cycle (RTC), which is allocated in portions, as available, to the first network entity requesting access to the shared medium during each particular portion. The ratio of logical link virtual channels, or D-Channels, to data payload virtual channels, or B-Channels, within the ATTC is adaptive depending on loading conditions. Based on transmission profiles transmitted on the D-Channels during the ATTC, each network entity determines how many B-Channels it will utilize within the current HTC. This calculation may be based on any decision network, such as a decision network modelling the transmission medium as a marketplace and employing microeconomic principles to determine utilization. The ratio of the duration of the ATTC segment to the duration of the RTC segment is also adaptive depending on loading conditions, to prevent unacceptable latency for legacy network entities employing the shared transmission medium. During the RTC, utilization of the shared medium preferably reverts to IEEE 802.3 compliant CSMA / CD transmission, including transmissions by HTC-compliant network entities.
Owner:GLOBAL COMM INVESTMENT LLC
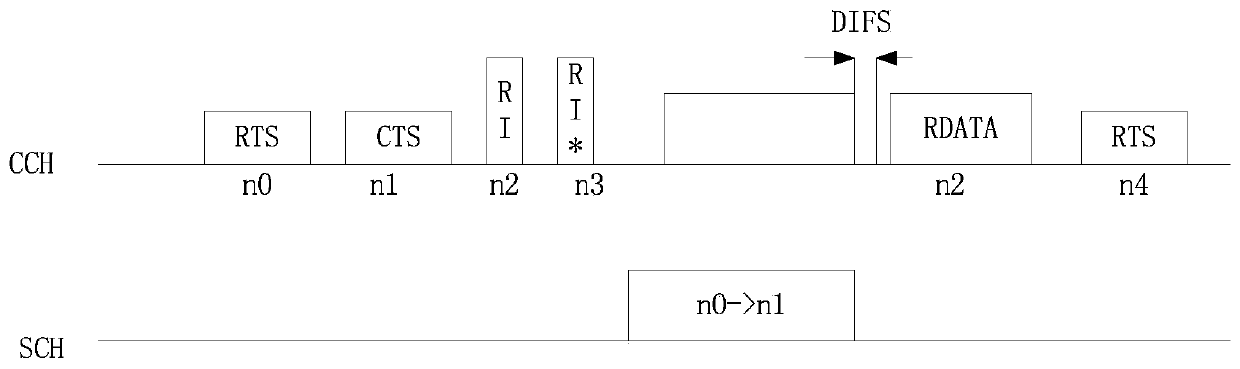
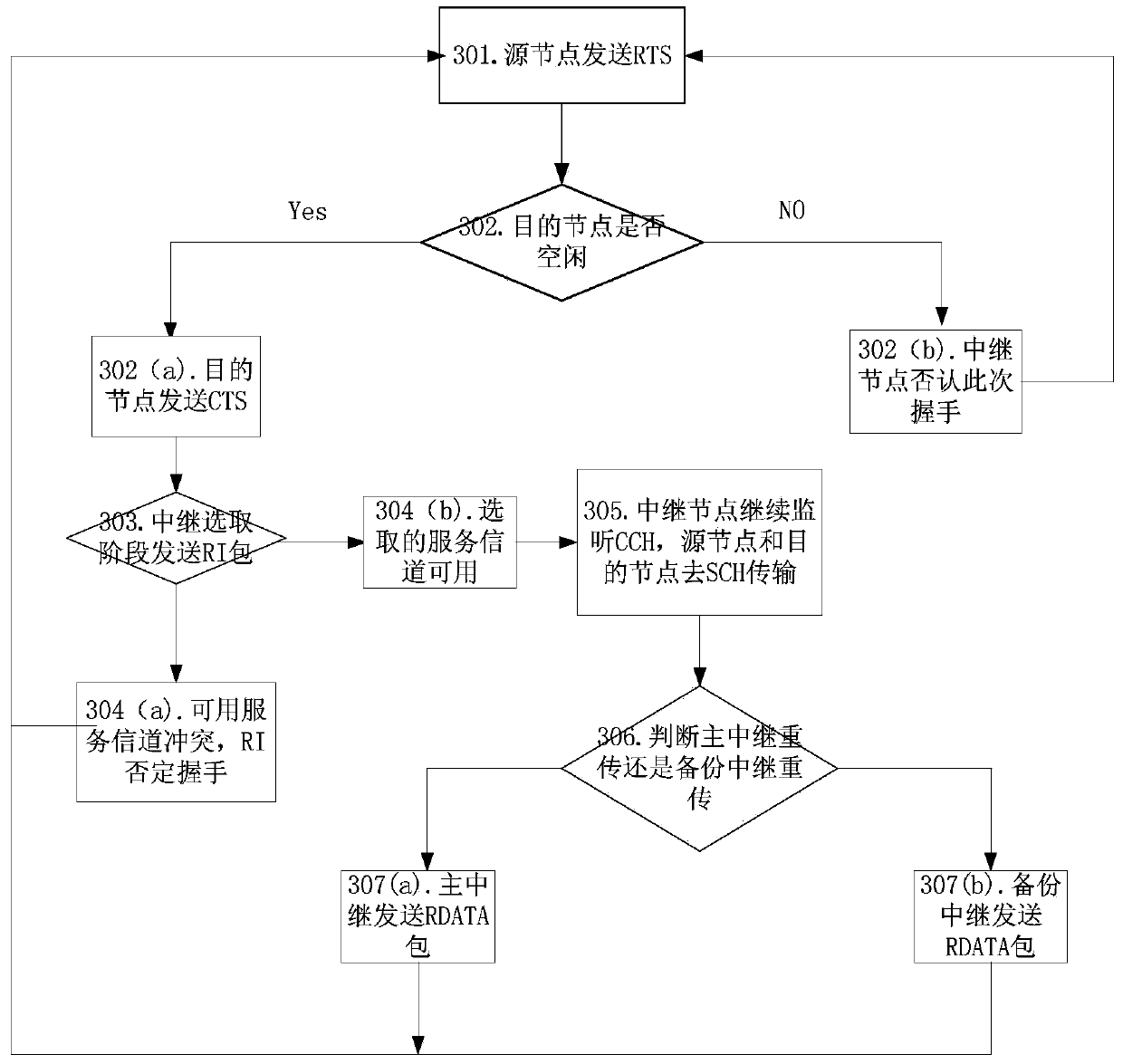
Cooperative MAC protocol implementation method on basis of multiple asynchronous channels in vehicular vdhoc networks
ActiveCN103763076AImprove real-time performanceImprove effectivenessError prevention/detection by using return channelWireless communicationReliable transmissionEngineering
The invention discloses a cooperative MAC protocol implementation method on the basis of multiple asynchronous channels in vehicular vdhoc networks, and belongs to the technical field of vehicle-mounted wireless communication. The cooperative MAC protocol implementation method on the basis of the multiple asynchronous channels in the vehicular vdhoc networks comprises a method for selecting cooperative relay nodes, a multi-channel selection and coordination strategy and a retransmission mechanism of emergency messages and handshake messages. According to the cooperative MAC protocol implementation method on the basis of the multiple asynchronous channels in the vehicular vdhoc networks, mutual cooperation between the nodes is carried out, channel state information and other node state information can be obtained, and the problem that hidden terminals of the multiple channels exist in the transmission process is well solved; due to the retransmission mechanism of the cooperative relay nodes, nodes working in other service channels can also receive lost information of a control channel, reliable transmission of data in the highly-mobile environment is achieved, and communication reliability and the network throughput are improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
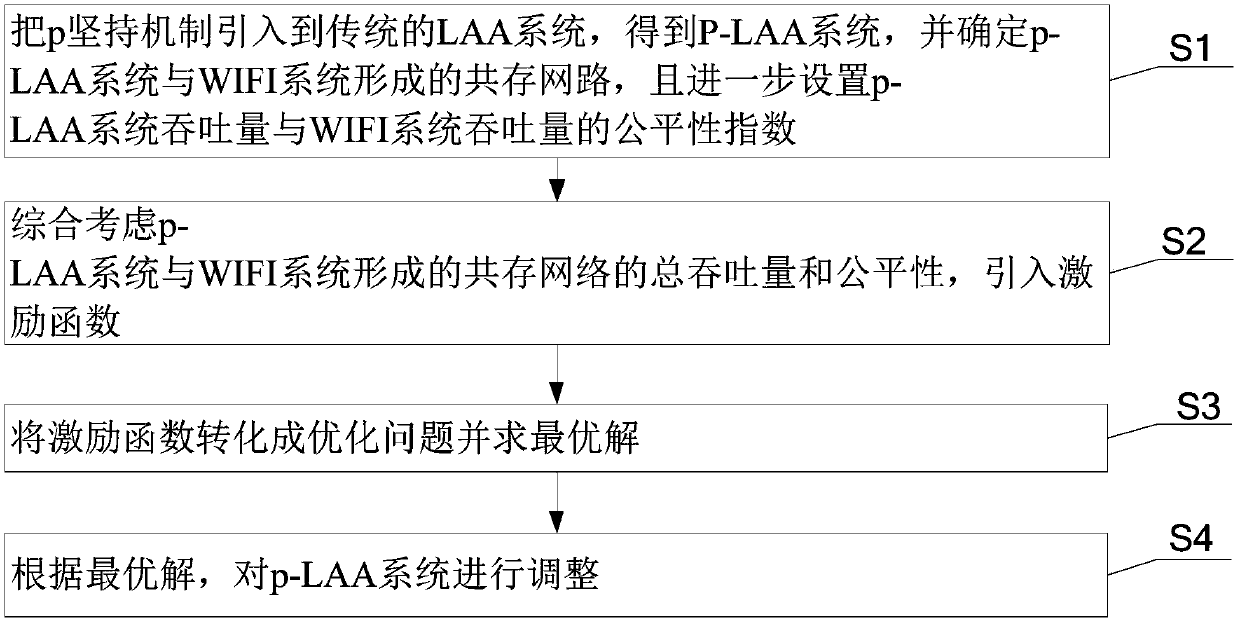
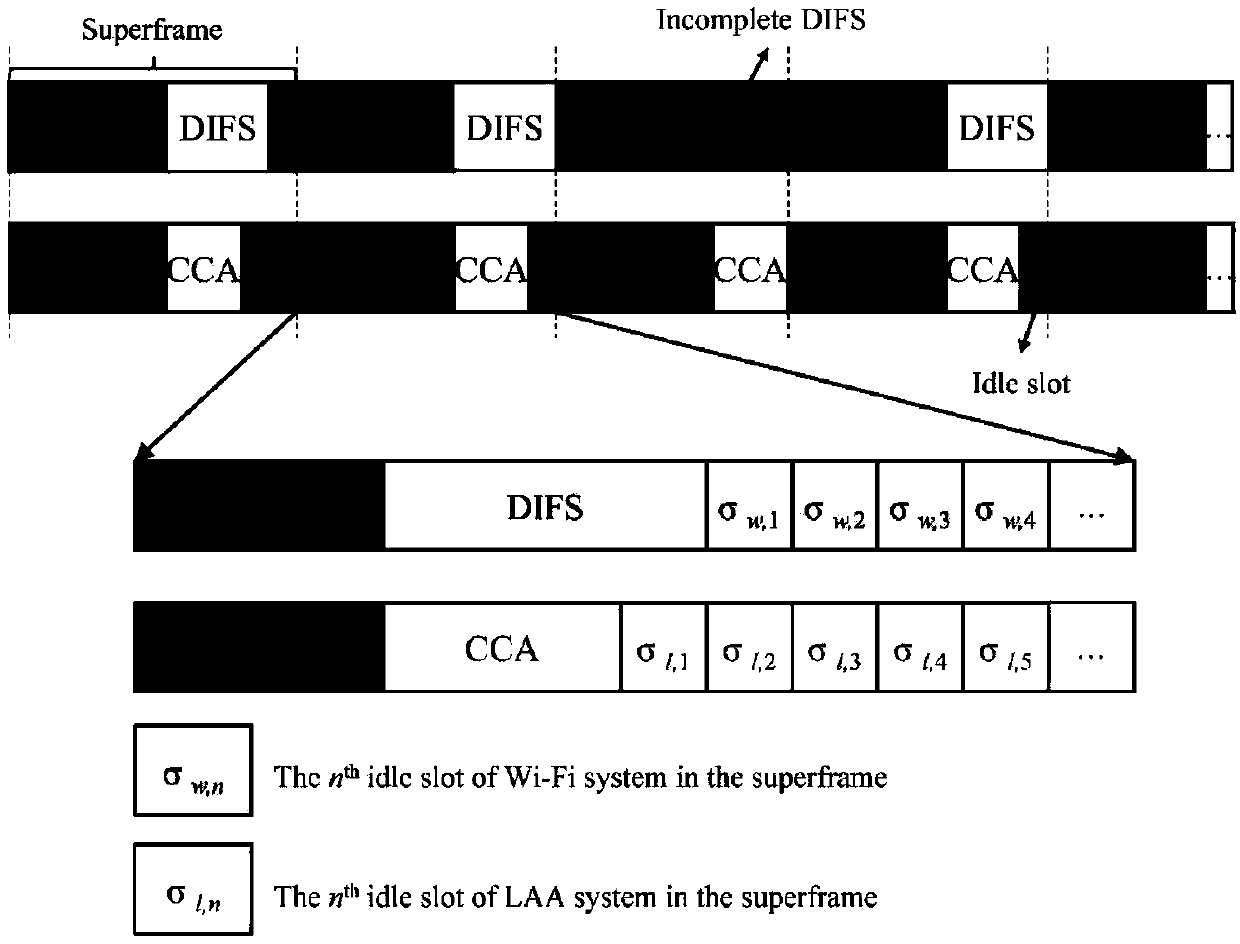
A method for optimizing the performance based on LAA and WIFI coexistence network
ActiveCN109041068AMinor changesVisit SatisfactionNetwork planningHigh level techniquesAdaptive optimizationSelf adaptive
Owner:温州大学苍南研究院
System and method for accessing a multi-line gateway using cordless telephony terminals
According to the present invention, simultaneous call-handling and data transfer is achieved between a terminal and a multi-line gateway in a cordless telephony environment. Multiple logical channels are established and used as signaling resources for calls on the multiple lines, and also for data transfers between the gateway and terminal. As a result, terminals can handle multiple calls on different lines and at the same time access data stored at the gateway. According to a first aspect of the present invention, two or more logical channels are established over an asynchronous channel between a terminal and a gateway. These logical channels are assigned to calls that are set-up between the terminal and gateway. When used as a signaling resource, the logical channels allow the terminal to distinguish between signaling information for multiple simultaneous calls. The calls are associated with another speech or data channel that will bear the voice signal, referred to herein as a bearer channel. According to a second aspect of the present invention, a logical channel is also established over an asynchronous channel to handle data transfers between the gateway and terminal. Using this logical channel, the terminal can access data stored at the gateway without disrupting any ongoing calls.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
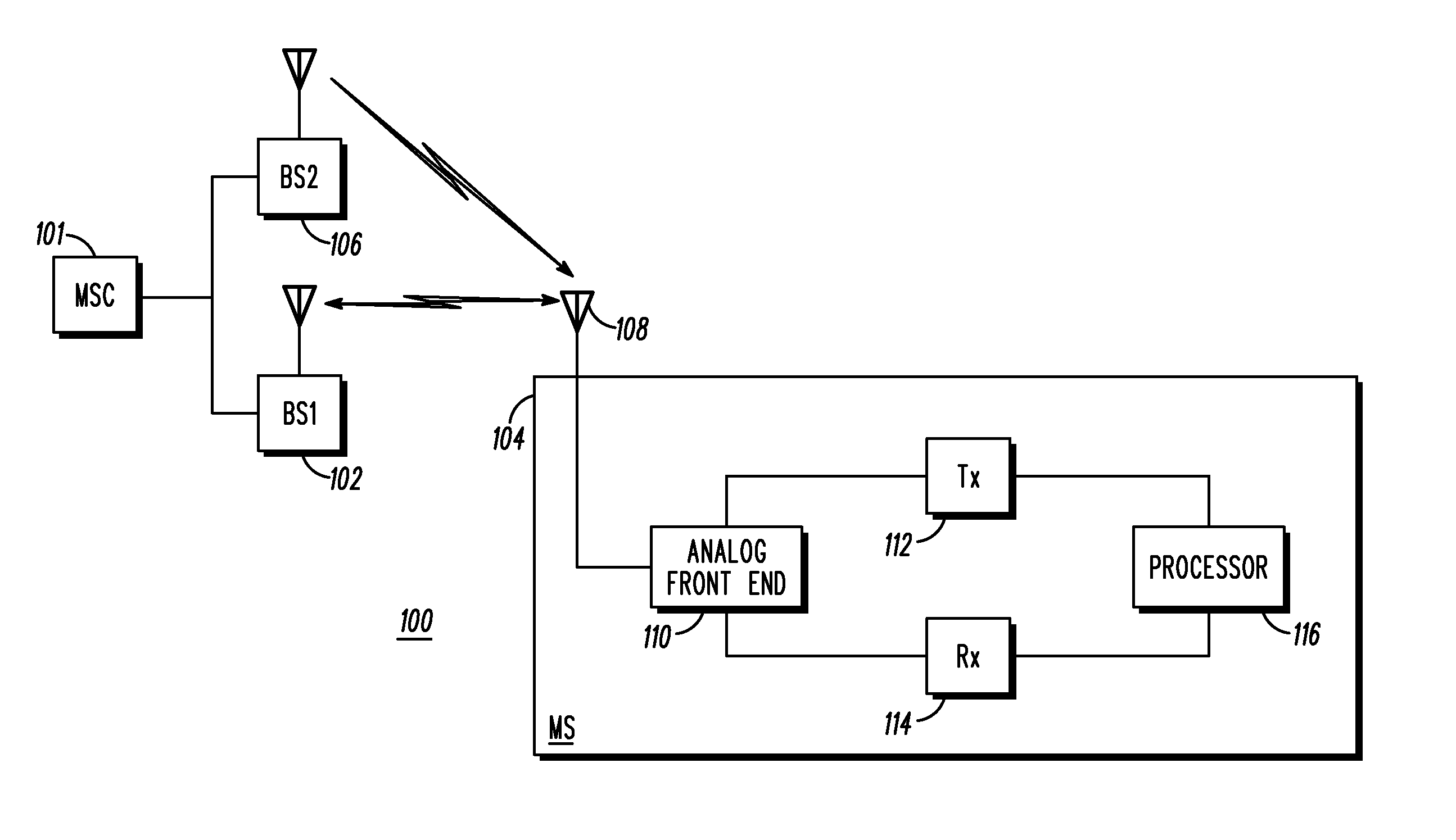
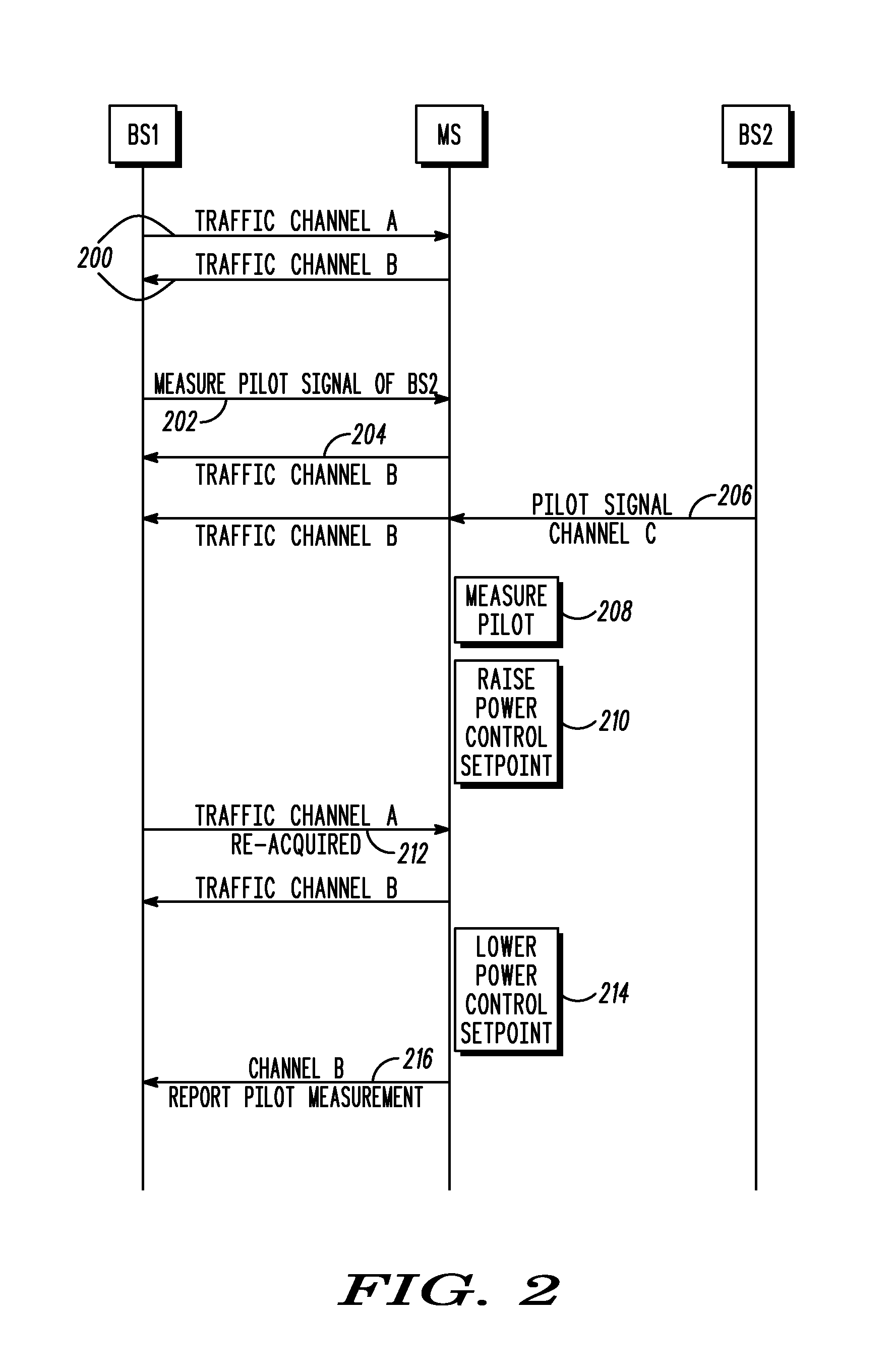
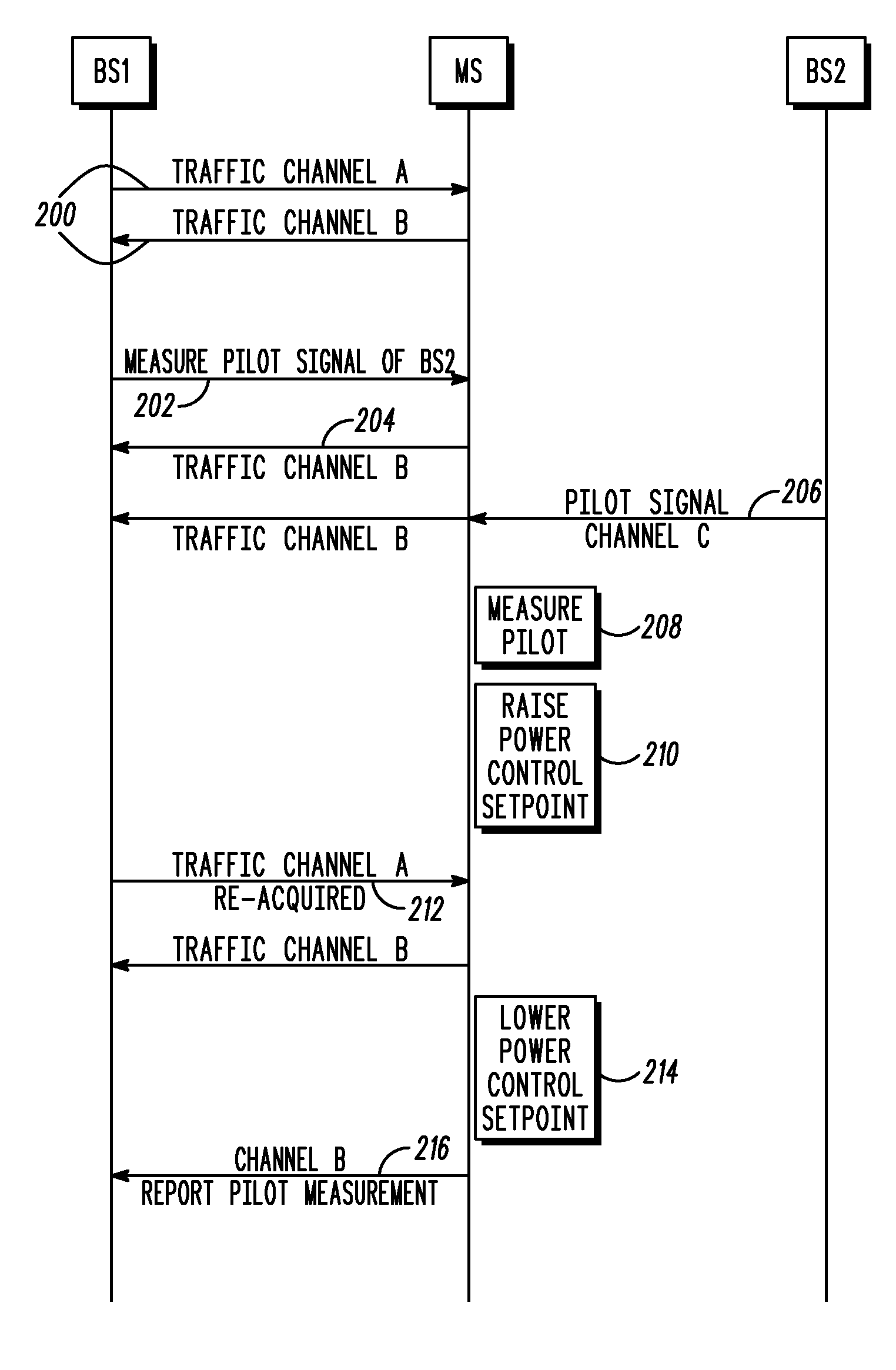
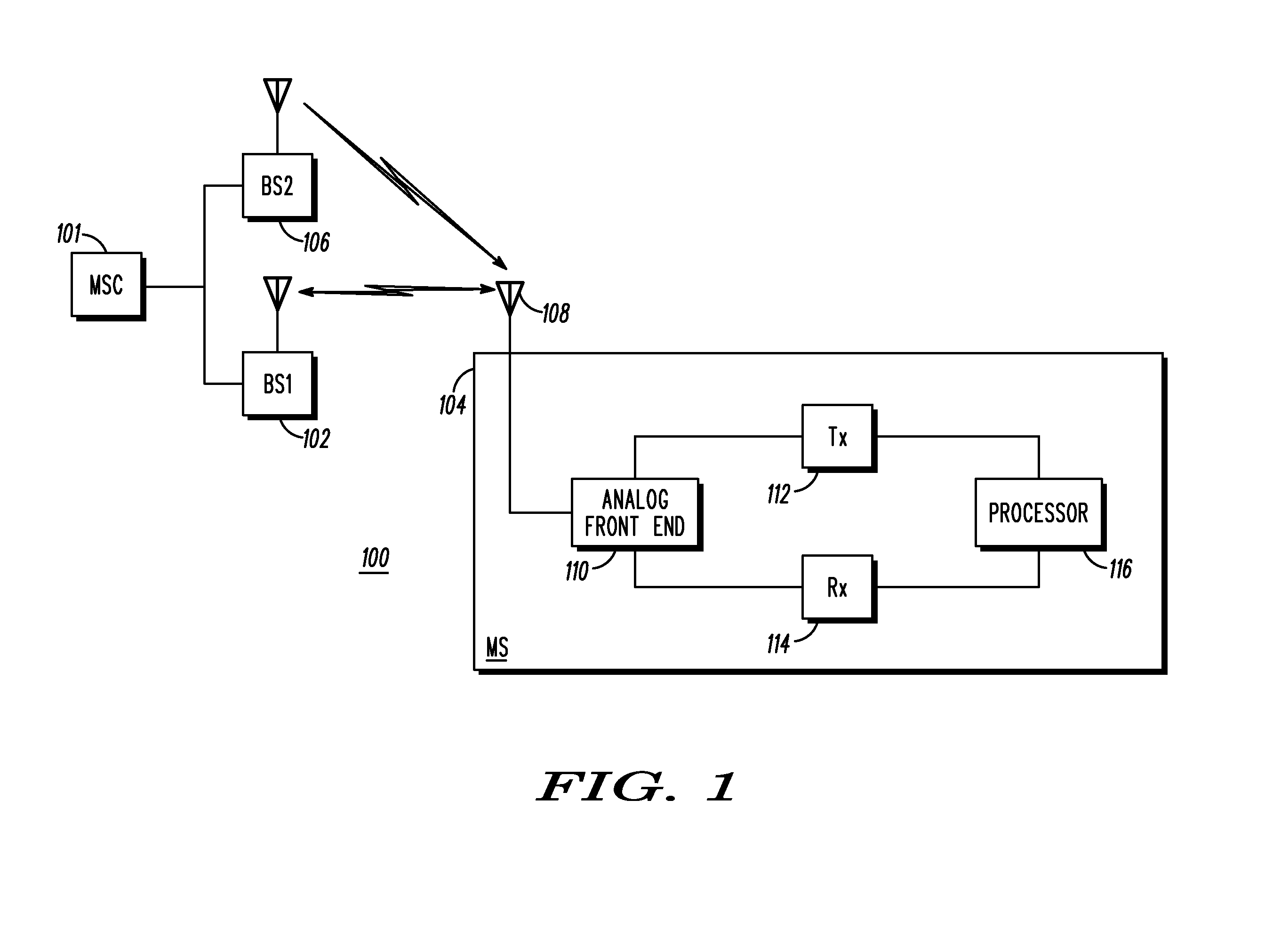
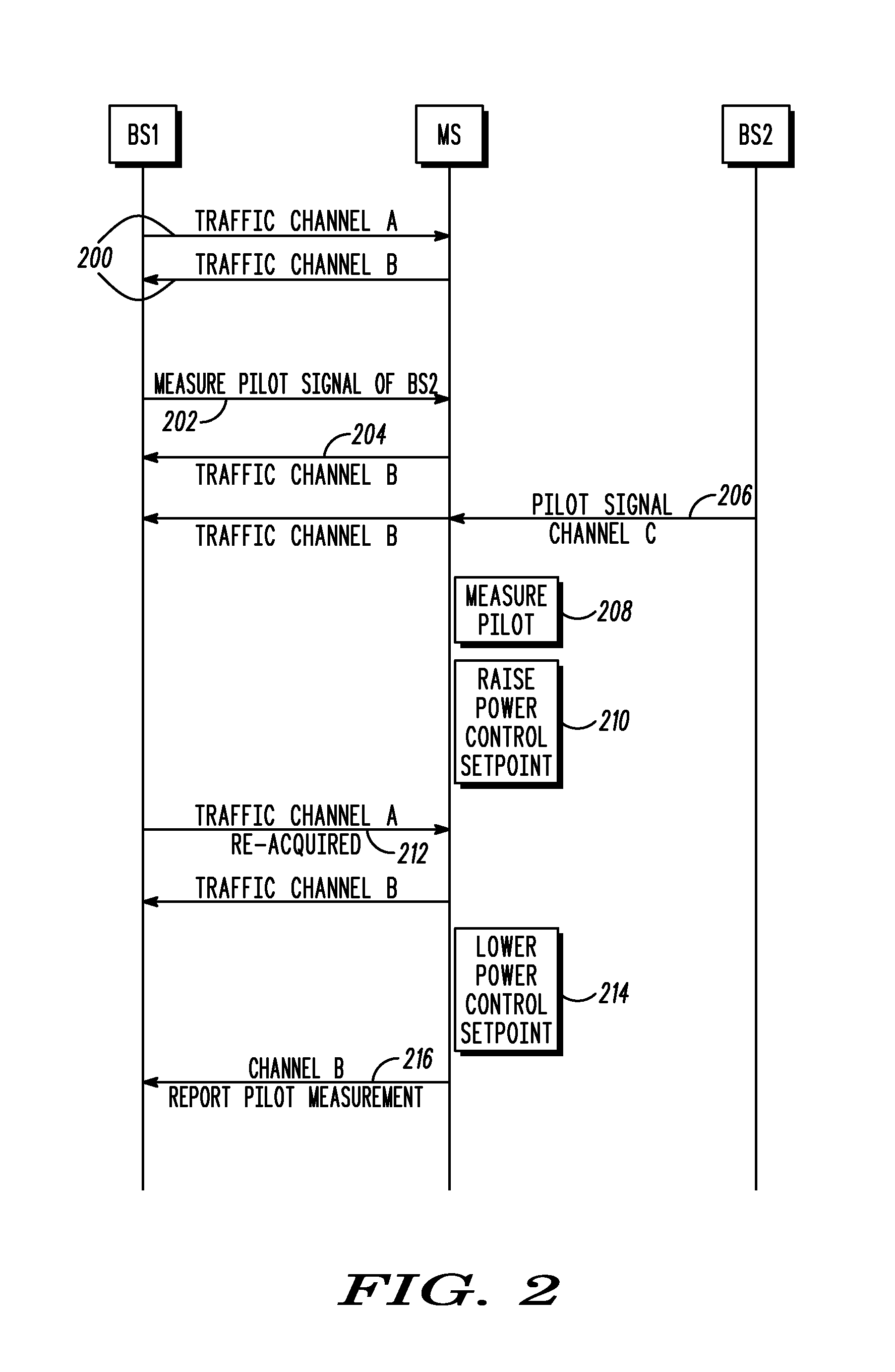
Mobile handoff functionality using asynchronous channel in a communication system
ActiveUS20070281698A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemReal-time computing
A apparatus and method for using an asynchronous channel for mobile handoff in a communication system includes a first step of operating a mobile unit on a forward link channel and a reverse link channel, wherein the forward and reverse link channels are different. A next step includes dropping the forward link while maintaining a connection to the reverse link channel. A next step includes acquiring a pilot signal of a new forward link channel targeted for handoff while maintaining the previous reverse link channel. A next step includes measuring a pilot signal power level of the targeted channel. A next step includes re-acquiring the previous forward link. A next step includes reporting the pilot signal power level of the targeted channel on the re-acquired forward link.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
System and method for medical imaging with robust mode switching via serial channel
ActiveUS20100280377A1Easy to displayUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsUltrasound imagingSonification
In one embodiment of the invention, there is an ultrasound processing system that communicates images over a single asynchronous serial channel according to a scheme that does not require an isochronous serial channel and that switches among ultrasound imaging modes robustly. For example, the system is configured to packetize ultrasound image data of at least one ultrasound imaging mode into a stream of data frames and to convey the stream of data frames via the asynchronous channel. Each data frame includes indication of the ultrasound imaging mode and includes ultrasound-imaging-mode-specific imaging parameters. Other embodiments exist.
Owner:SONOWISE
Mobile handoff functionality using asynchronous channel in a communication system
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
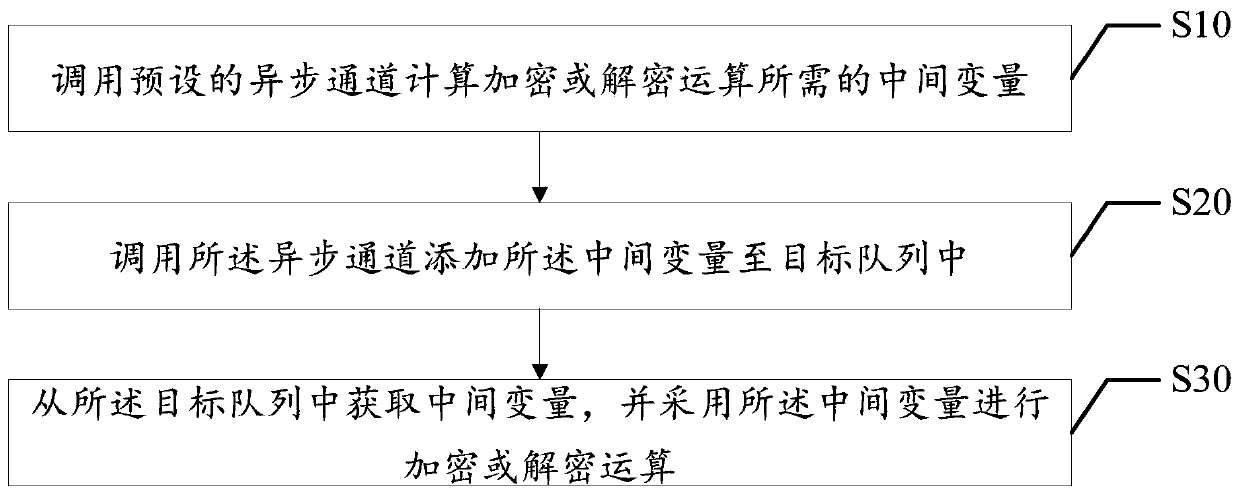
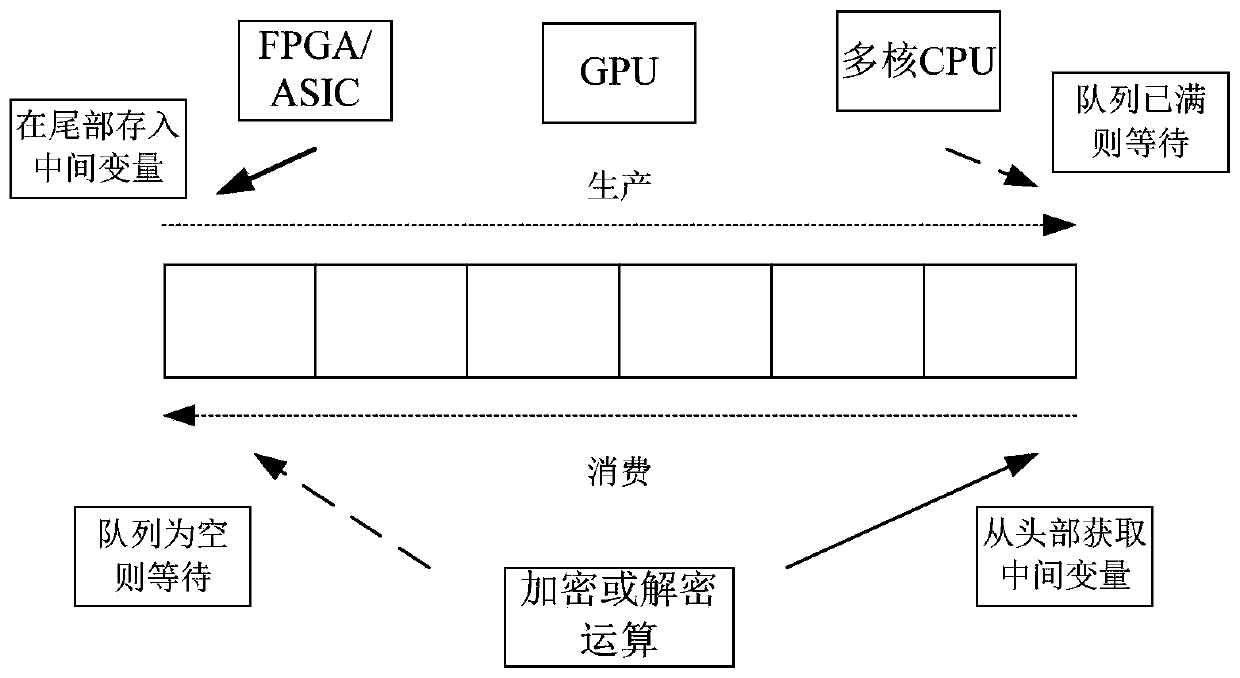
Asynchronous encryption implementation method and device, apparatus and readable storage medium
PendingCN110674526AShorten the timeImprove computing efficiencyDigital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionComputer hardwareEmbedded system
The invention discloses an asynchronous encryption implementation method and device, an apparatus and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps of calling a preset asynchronous channelto calculate an intermediate variable required by an encryption or decryption operation; calling the asynchronous channel to add the intermediate variable into a target queue; and obtaining the intermediate variable from the target queue, and performing the encryption or decryption operation by adopting the intermediate variable. According to the present invention, the time-consuming intermediatevariable does not need to be calculated during the encryption or decryption process, so that the encryption or encryption operation efficiency is improved, and the encryption or decryption operationperformance is also improved.
Owner:WEBANK (CHINA)
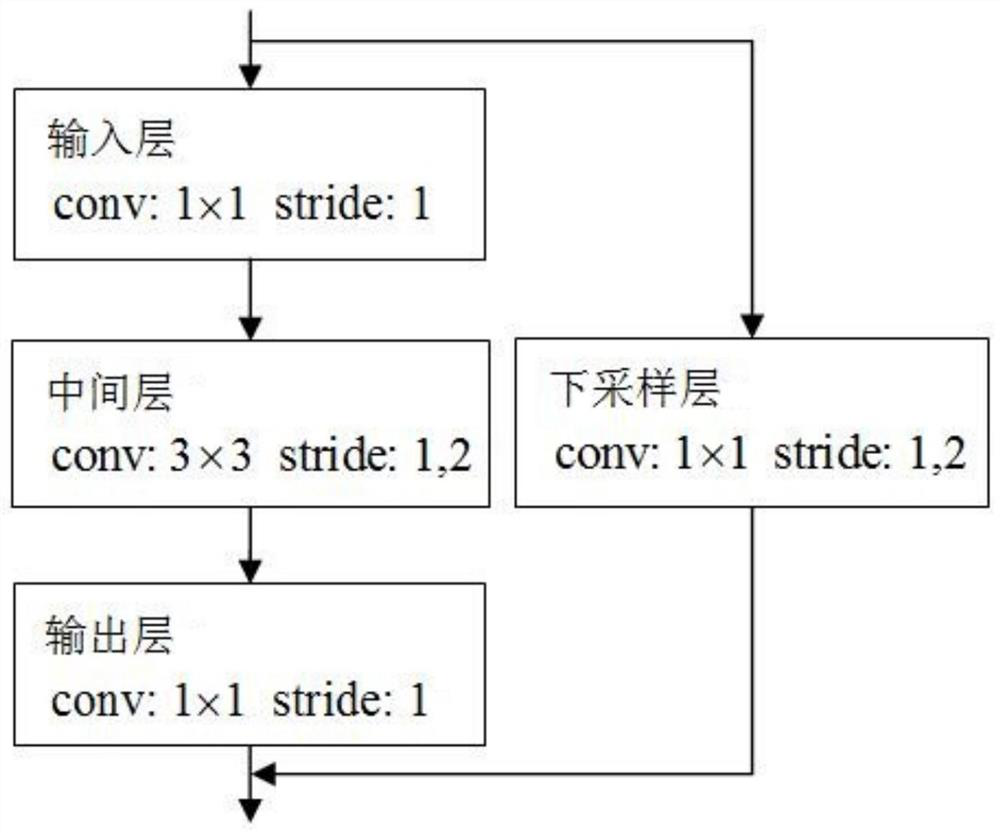
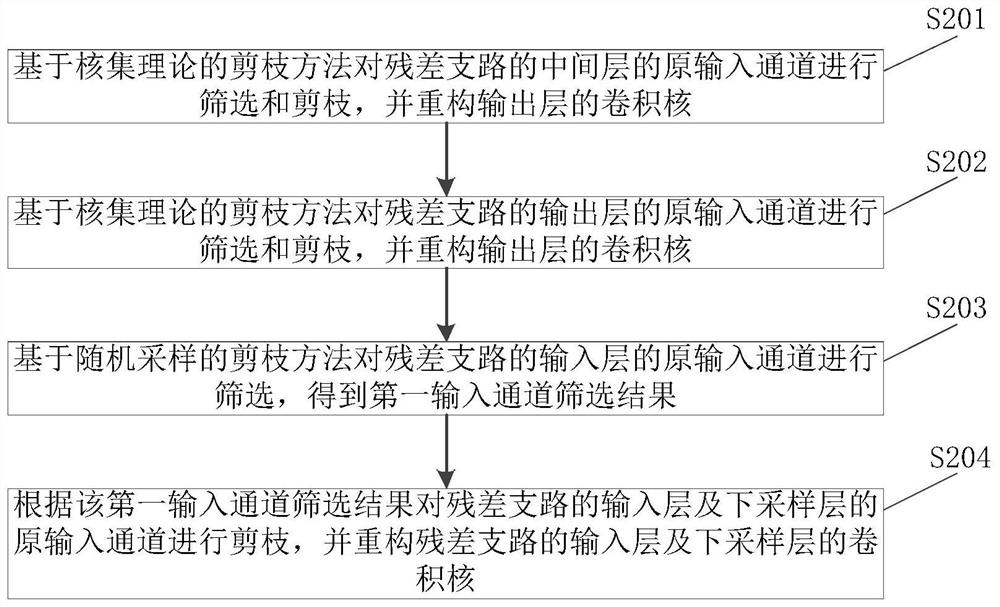
Neural network pruning method and device, equipment and storage medium
PendingCN113705775AIncrease the compression ratioImprove task processing speedNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsAlgorithmNetwork model
The invention discloses a neural network pruning method and device, equipment and a storage medium. When the neural network is pruned, a network layer to be pruned can be used as a target network layer for channel pruning and convolution kernel reconstruction. Therefore, when the multi-branch structure is compressed by the scheme, the compression is not limited to an intermediate layer; network layers such as an input layer, an output layer, a down-sampling layer and the like can be compressed, so that the compression ratio of the neural network is greatly improved, the calculation amount required by a neural network model to execute tasks is reduced, and the task processing speed of the neural network is increased; moreover, the scheme is a data-independent asynchronous channel pruning method, which is beneficial to keeping the robustness of the compressed neural network, and can also realize pruning of different sparse granularities in different network layers of the neural network, thereby improving the compression flexibility.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
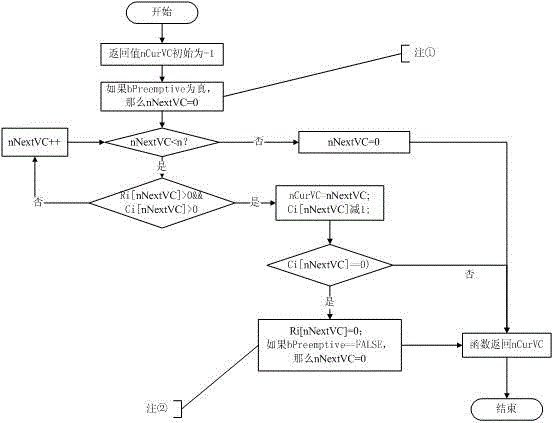
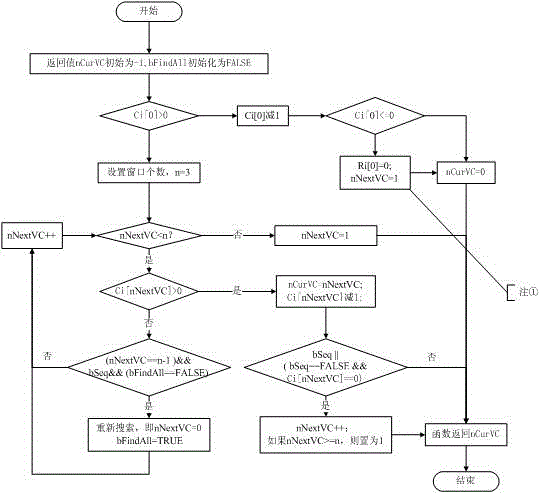
Virtual channel general scheduling algorithm based on dynamic windows
ActiveCN105933083AMeet Simulation NeedsImplement sequential scheduling/exclusive scheduling strategiesRelay systems monitoringHybrid SchedulingChannel scheduling
The invention relates to a virtual channel general scheduling algorithm based on dynamic windows. The algorithm realizes full-synchronous scheduling, full-asynchronous scheduling, synchronous / asynchronous mixed scheduling, and mixed scheduling considering the emergency channel, and can stimulate the virtual channel scheduling of various types of satellites. The algorithm divides the channel scheduling into an emergency window, a synchronization window, and an asynchronization window, and realizes the sequential and monopolized scheduling strategies of window scheduling, the sequential and monopolized scheduling strategies of synchronous channel scheduling, and the preemptive and non-preemptive scheduling strategies of asynchronous channel scheduling, and the switching of the eight scheduling strategies is realized through the parameter setting.
Owner:中国卫星海上测控部
Method of transmitting signal in a wireless system
InactiveUS8861624B2Efficient receptionGuaranteed normal transmissionSynchronisation arrangementSignal allocationCommunications systemControl signal
A method of transmitting a signal of a mobile station that performs communication with a plurality of cells in a wireless communication system comprises transmitting a control signal or a data signal through an asynchronous channel to a neighboring cell which is not synchronized with the mobile station, the asynchronous channel including cyclic prefix and guard time.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and system for correcting asynchronous sampling time sequences between channels
ActiveCN113422658ABroaden the range of versatilityQuick correctionTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringIntermediate frequencyRadio frequency signal
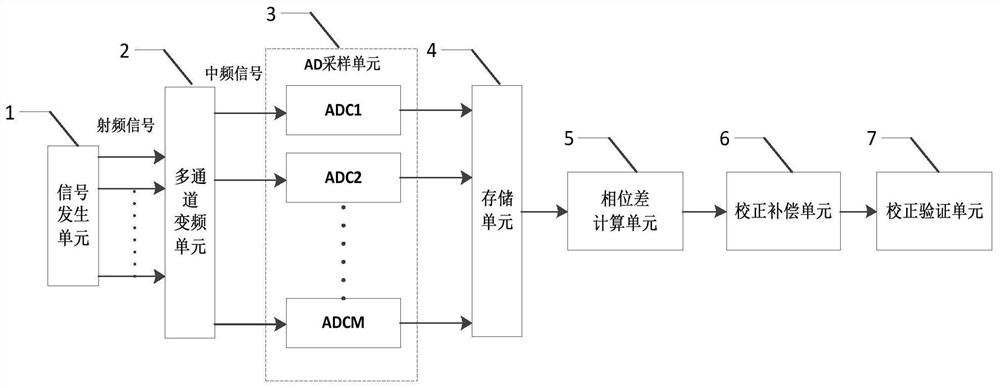
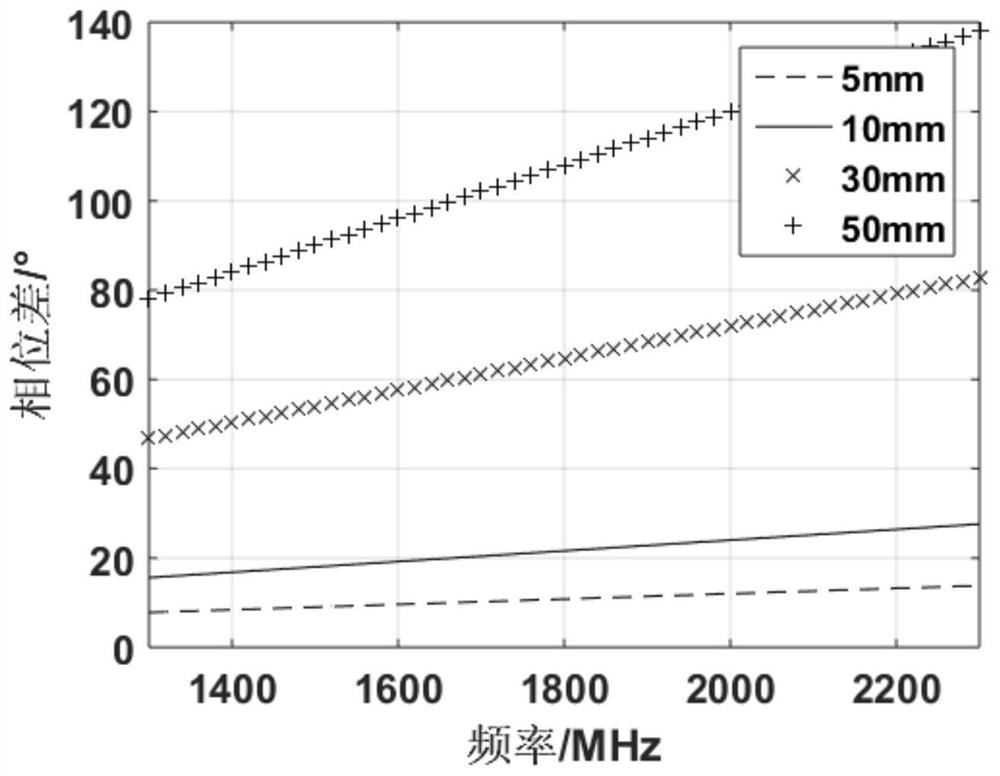
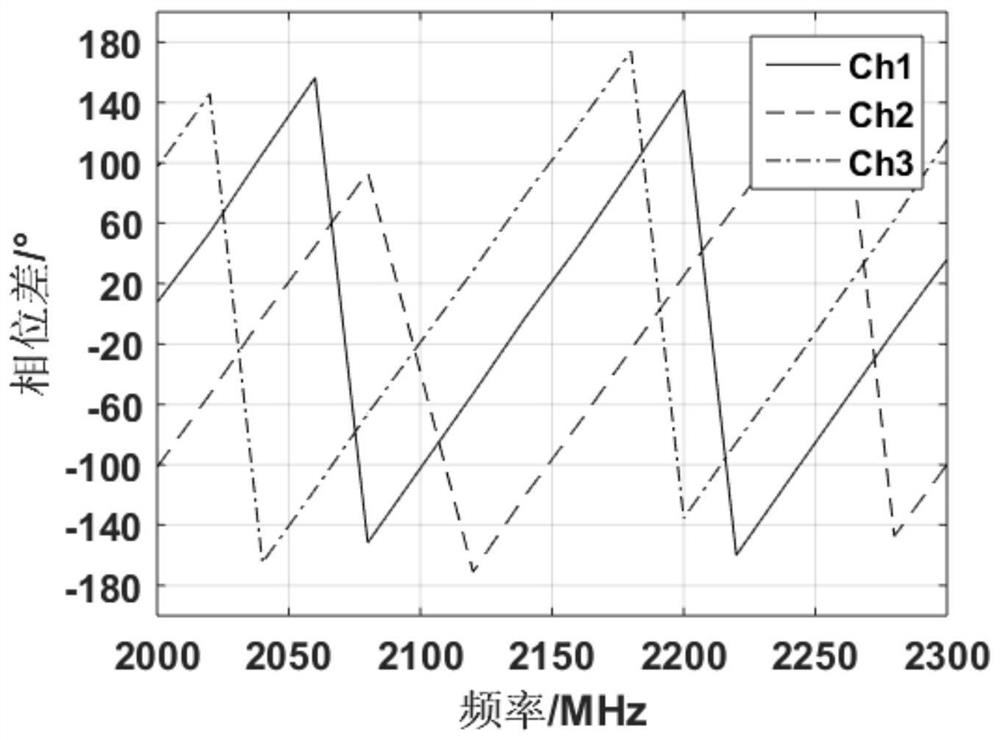
The invention provides a method for correcting asynchronous sampling time sequences between channels, which comprises the following steps of: S1, setting a radio frequency signal with a specified frequency, outputting M radio frequency signals and converting the M radio frequency signals into intermediate frequency signals; S2, acquiring and storing the M intermediate frequency signals through an AD sampling unit, repeating the S1 to S2 to sample and store the AD data of the intermediate frequency signals of multiple frequencies; S3, calculating the phase difference between the collected and stored AD data of other channels and that in the reference channel under all frequencies, drawing a phase difference curve that the phase difference changes along with the frequency, and drawing a real phase difference change trend curve at the same time; S4, determining channels with asynchronous sampling according to the phase difference curve, and performing corresponding correction on the asynchronous channels; and S5, verifying the corrected channels. The invention aims to quickly correct the delay inequality of asynchronous sampling time sequences of cross-signal periods among multiple channels without introducing calculation errors, hardware required by a correction system is simple, the synchronous debugging efficiency is greatly improved, and the universality range of the correction method is expanded.
Owner:SOUTHWEST CHINA RES INST OF ELECTRONICS EQUIP
Data transmission system
ActiveCN101252506BReduce correlationImplement direct transfer functionSpecial service provision for substationStore and forwardTransmission channel
The invention discloses a data transmitting system, which solves the problem of the prior data transmitting method that only direct transmission between nodes in an upper and a lower grades and cross-grade storage and forwarding instead of point-to-point transmission can be realized. The system comprises a mission server in charge of monitoring and obtaining requests of source nodes; a central control server in charge of managing and adjusting the working progress which is composed of a transmission controlling module and a transmission client side; the transmission controlling module in charge of communicating with target nodes through a synchronous transmission channel and performing adjustment and control to the mission; the transmission client side is in charge of data transmission, and transmits the data transmission to the target nodes through an asynchronous transmission channel; the synchronous transmission channel is realized by a synchronous channel server and a synchronous channel client side API, and the asynchronous transmission channel is realized by an asynchronous channel server and a transmission client side. The system can realize the direct point-to-point transmission, and is provided with a mission priority managing and flow rate controlling mechanism as well as assemblage and load balancing of application layers.
Owner:CHINA CONSTRUCTION BANK
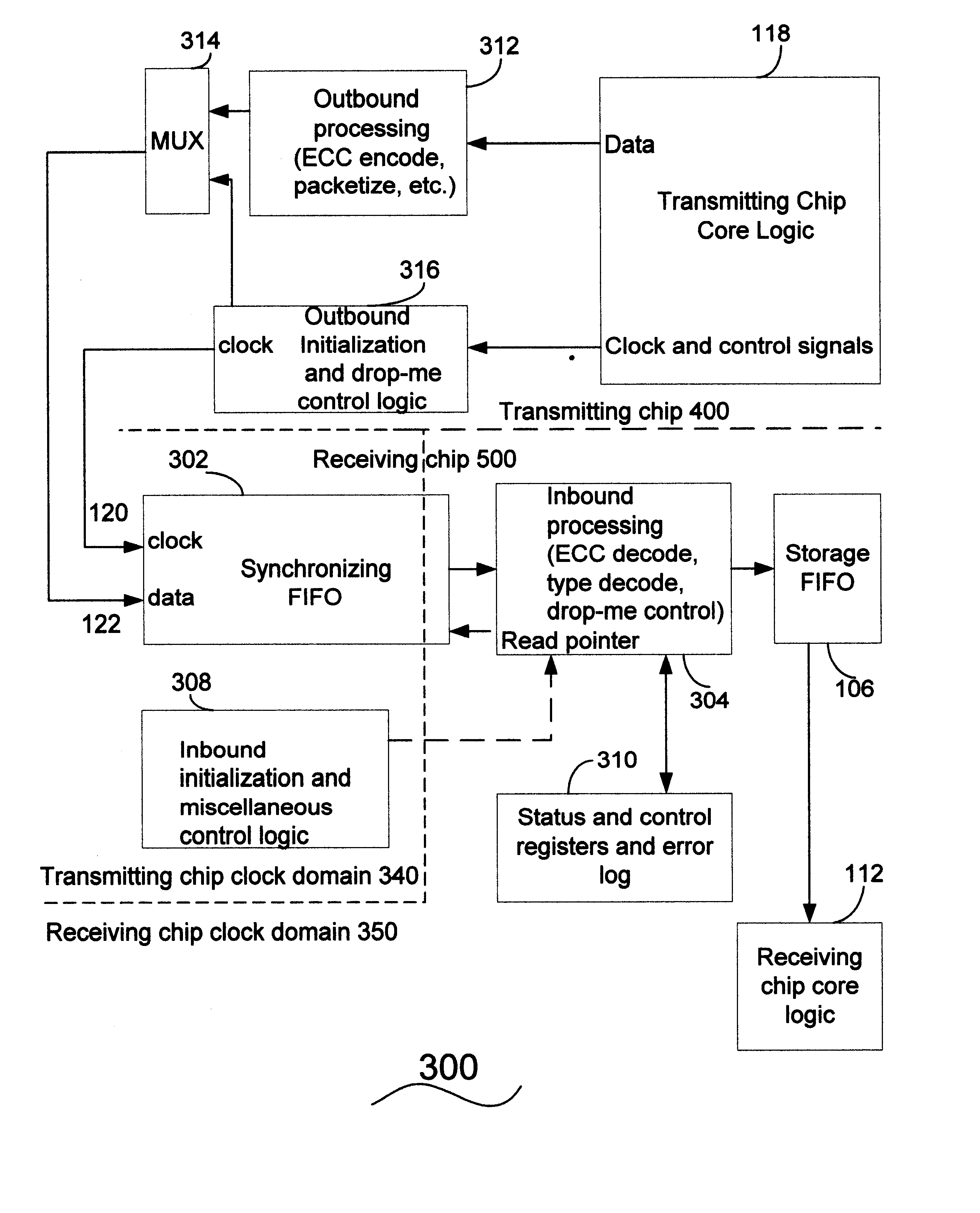
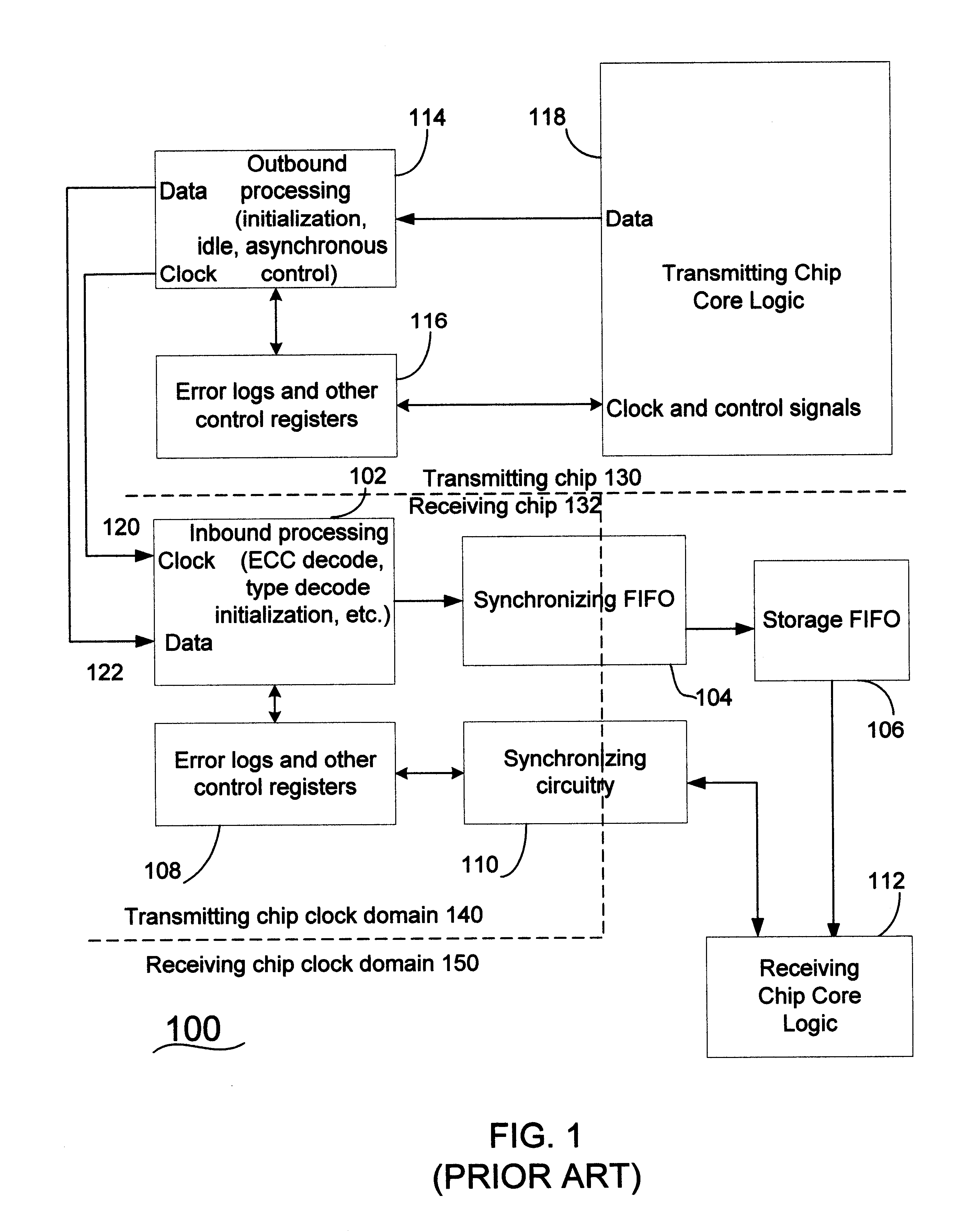
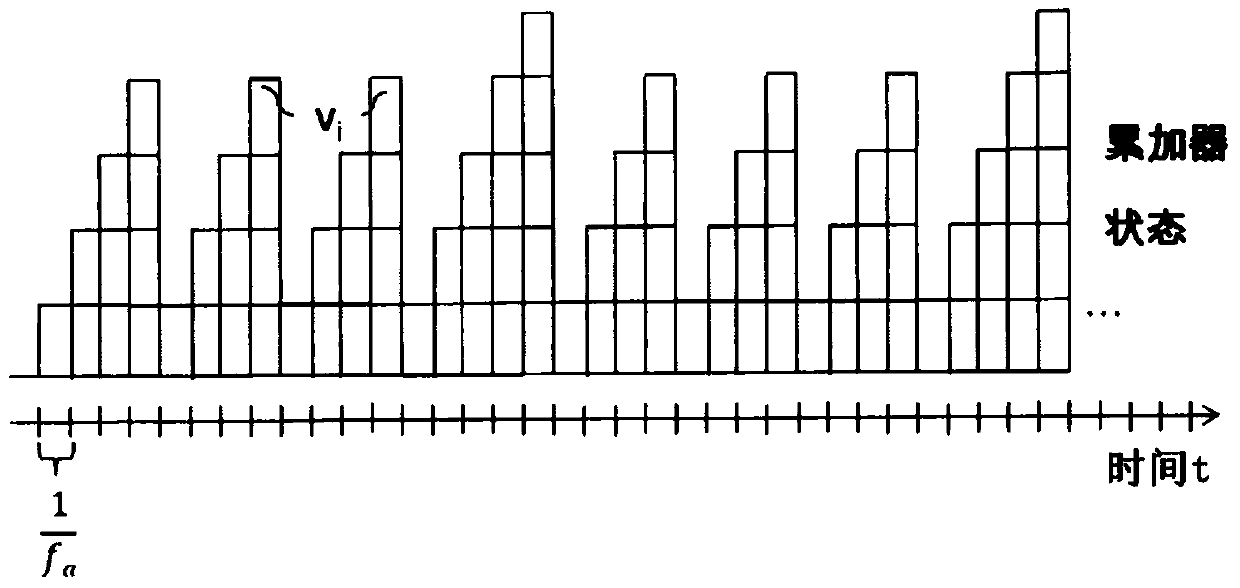
Method and apparatus for transferring data at an asynchronous channel between domains with different clock speeds
ActiveCN105794143BElectric/magnetic signal storageMeasurement arrangements for variableData contentComputer science
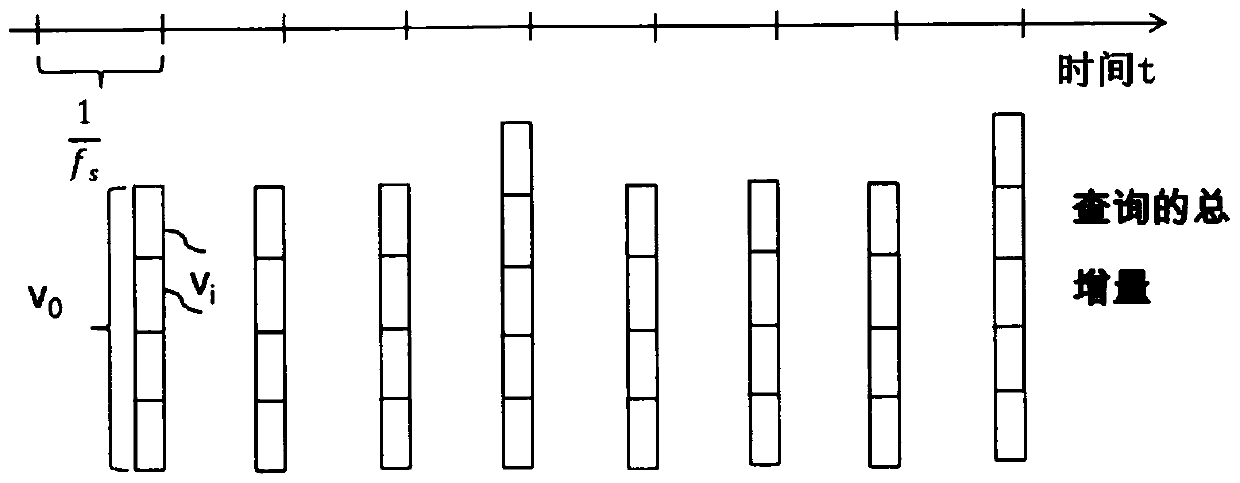
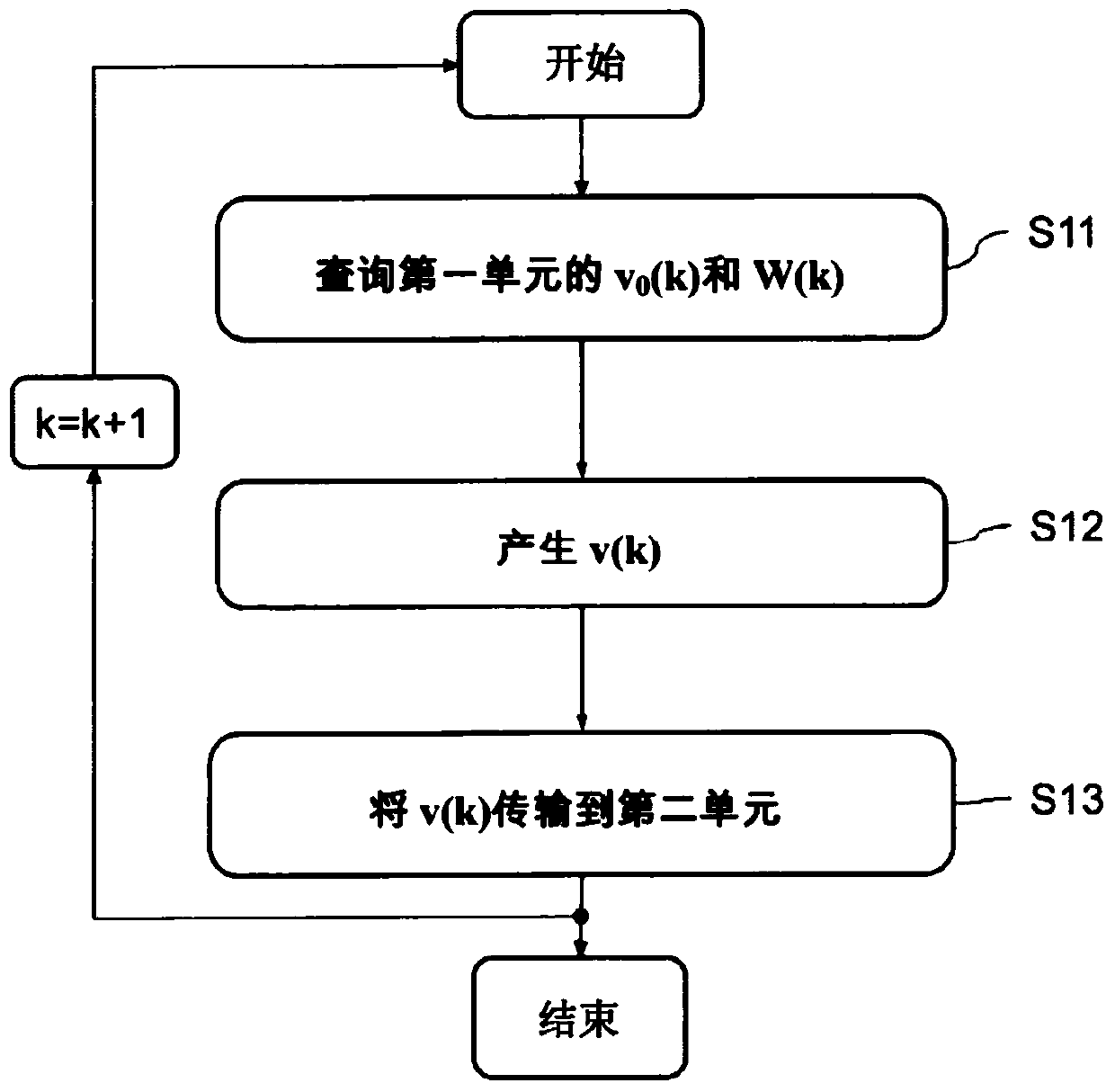
A method for transferring data between a first unit and a second unit, wherein the first unit accumulates data produced at a first frequency and the second unit queries the accumulated data at a second frequency, comprising querying the first unit's first total delta and a first value representing a time delta matching the first total delta, where the first total delta is the data content of the accumulated data blocks present in the first unit at the time of the query, determined by the first The total delta is generated by using the first value to generate a second total delta, wherein the second total delta is the data content of a data block adapted to a nominal time increment of the second frequency, and transmitting the second total delta to Second unit.
Owner:NORSROP GRUMAN LITEF GMBKH
An Asynchronous Channel Sensing Method with Unknown Timing
ActiveCN105634634BAvoid complicated signaling interactionImprove realizabilityTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumDecision threshold
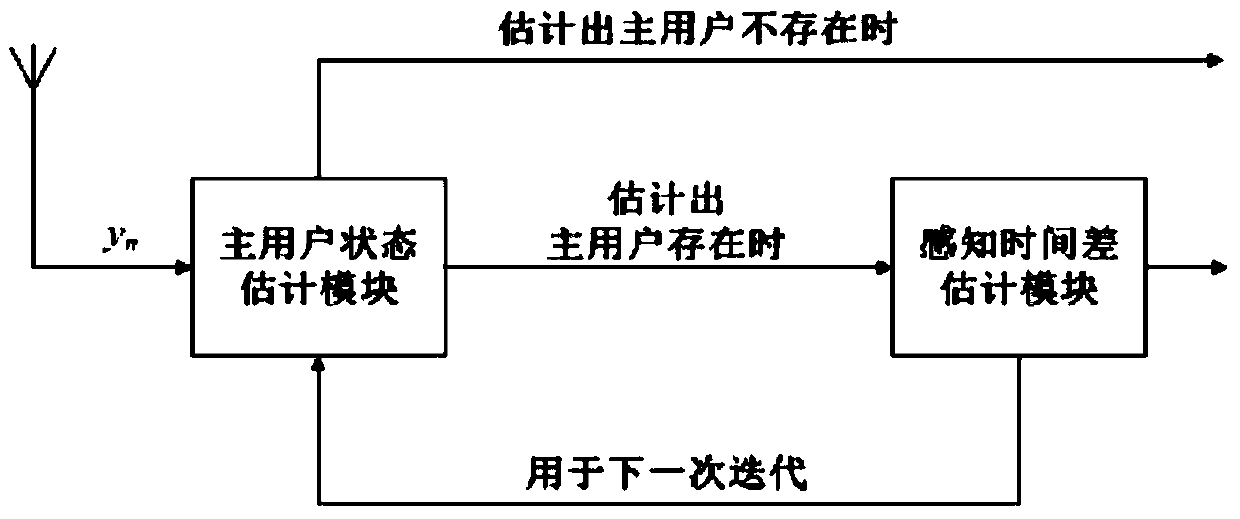
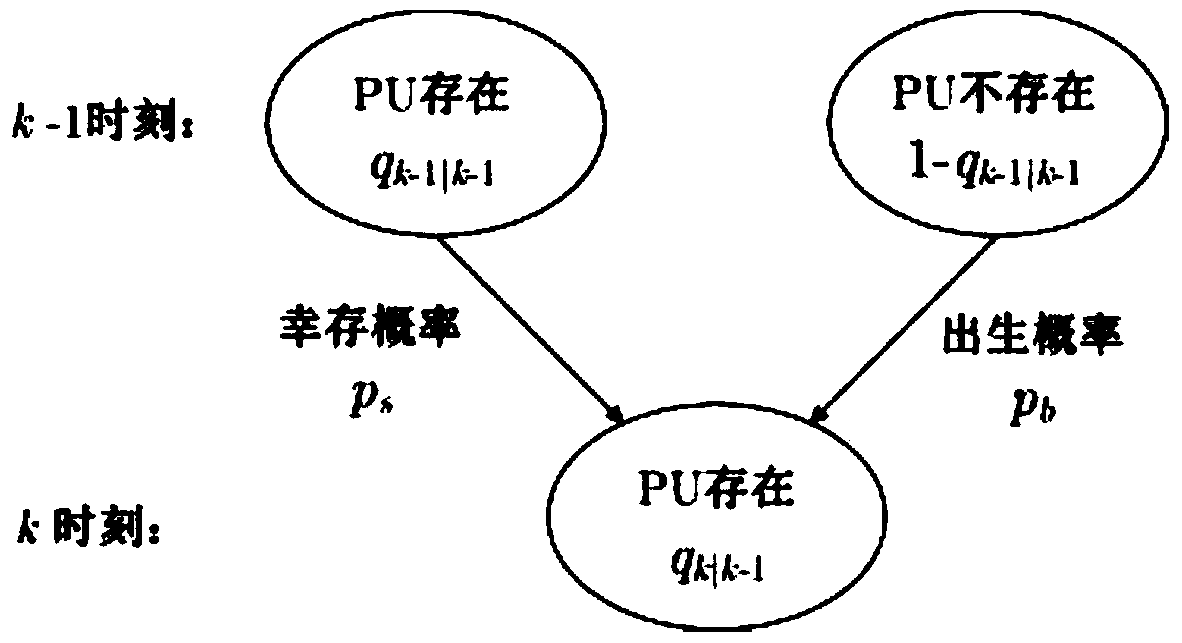
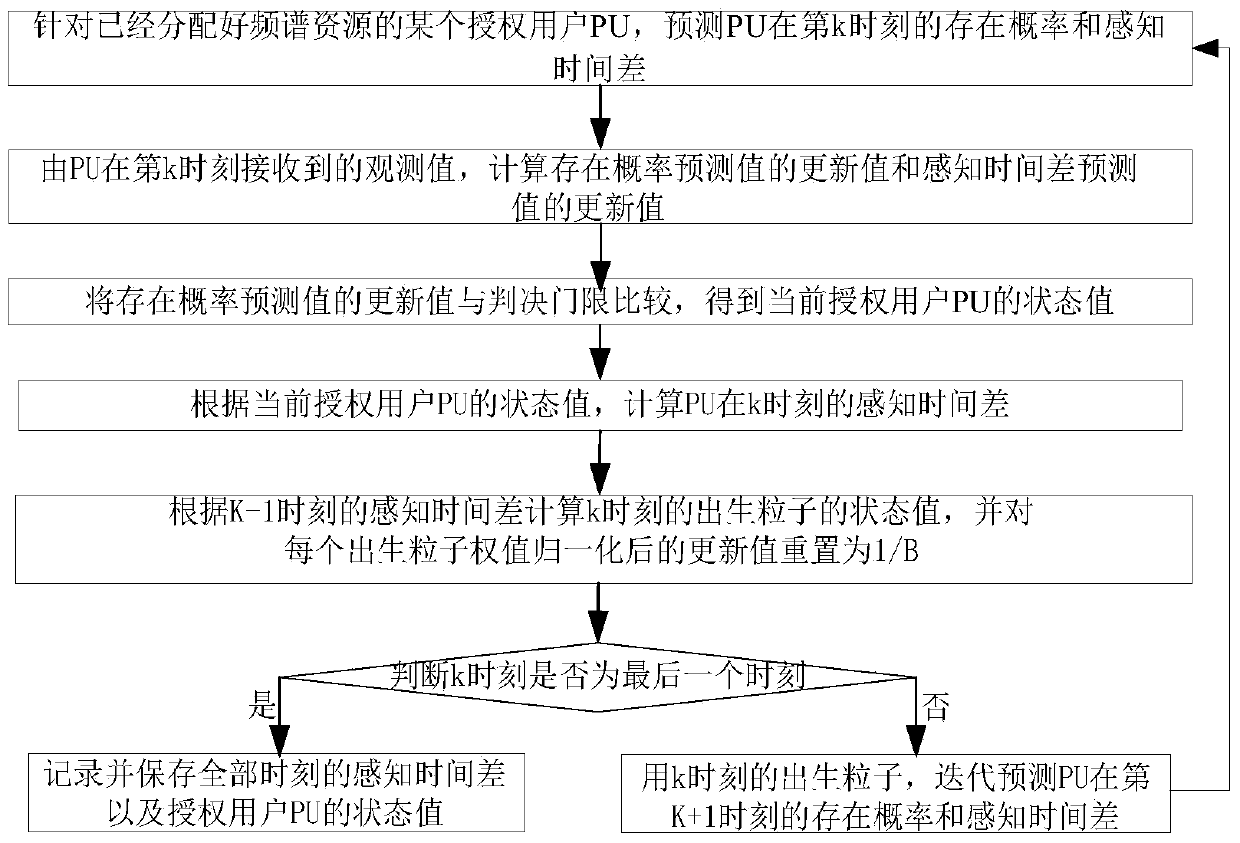
The invention discloses an asynchronous channel perception method with unknown timing. The asynchronous channel sensing method specifically comprises the following steps: a first step, predicating an existence probability and a perception time difference of a certain PU at a k moment; a second step, updating the existence probability predicted value and the perception time difference via an observation value; a third step, comparing the updated existence probability predicted value with a decision threshold to obtain a state value of the PU; a fourth step, calculating the perception time difference of the PU at the k moment according to the state value; a fifth step, calculating a state value and a weight of a born particle at the k moment according to the perception time difference at a k-1 moment; and a sixth step, judging whether the k moment is the last moment, if so, recording and storing the perception time differences and state values of all moments; and otherwise, iteratively predicting the existence probability and the perception time difference of the PU at a k+1 moment through a particle set at the k moment. The asynchronous channel perception method has the advantages of being suitable for the dynamic spectrum sharing of a heterogeneous wireless network, avoiding the frequent signaling interaction between the PU and SU, reducing the configuration complexity of a CR system and saving the time and the energy cost.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
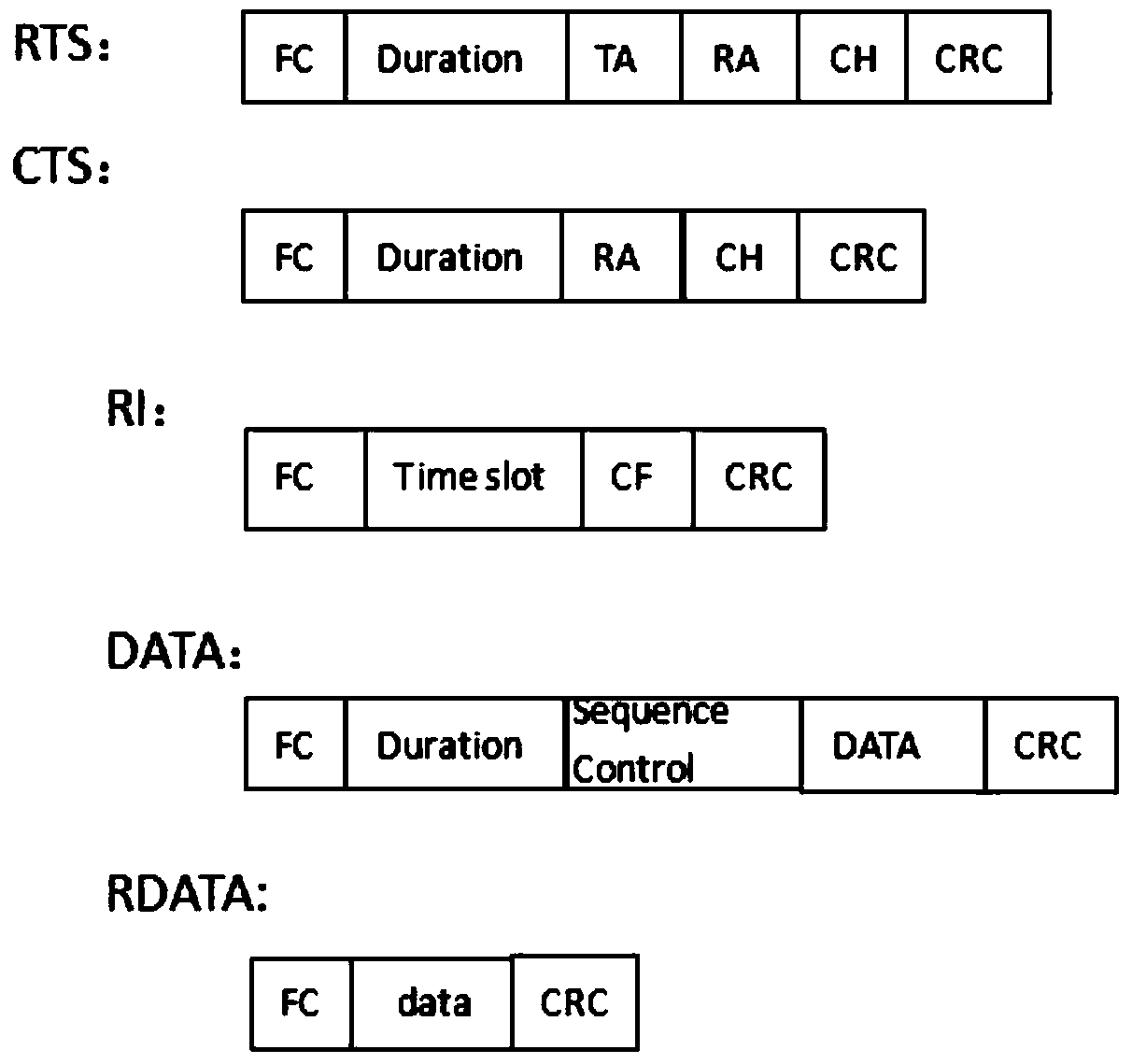
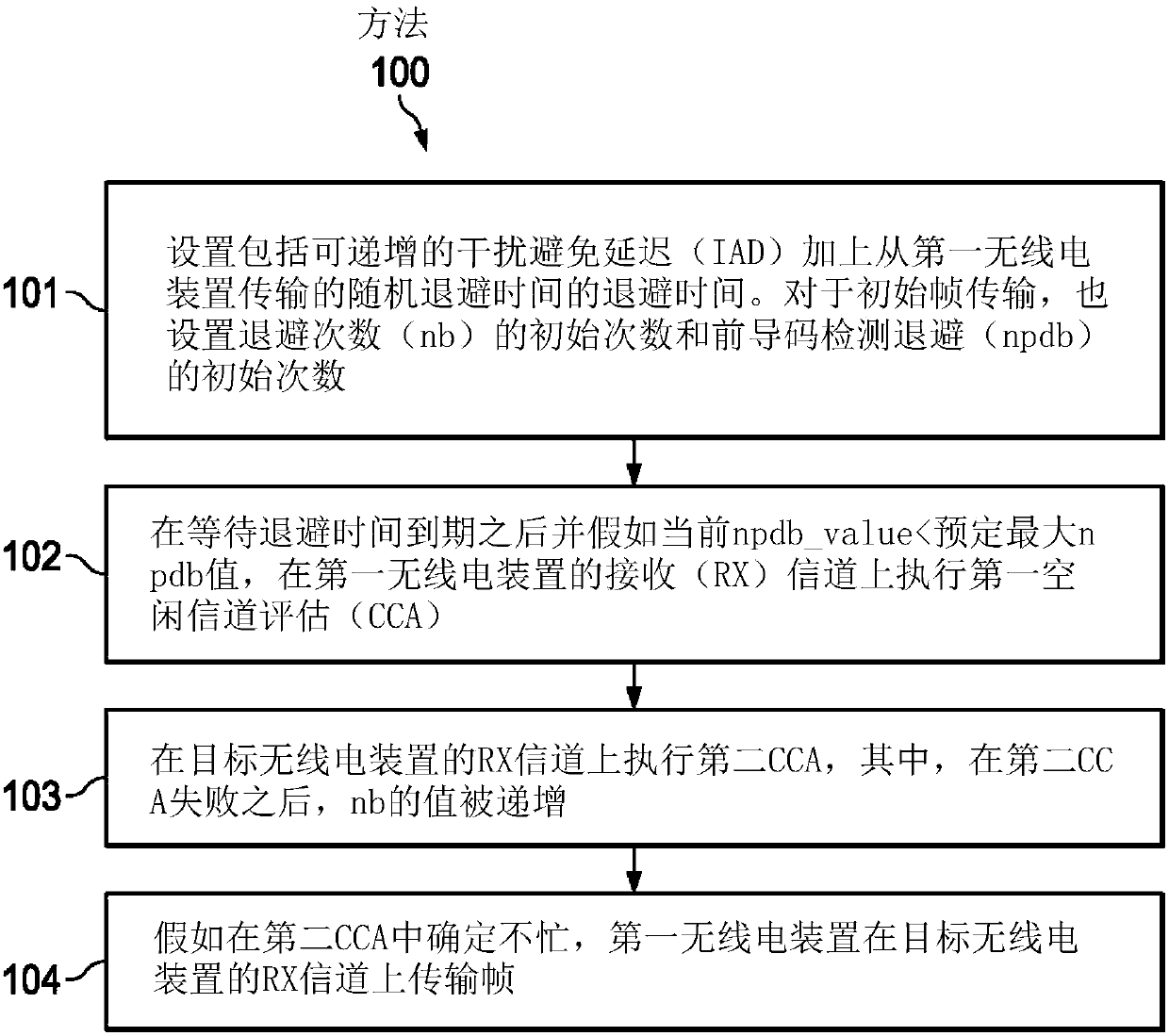
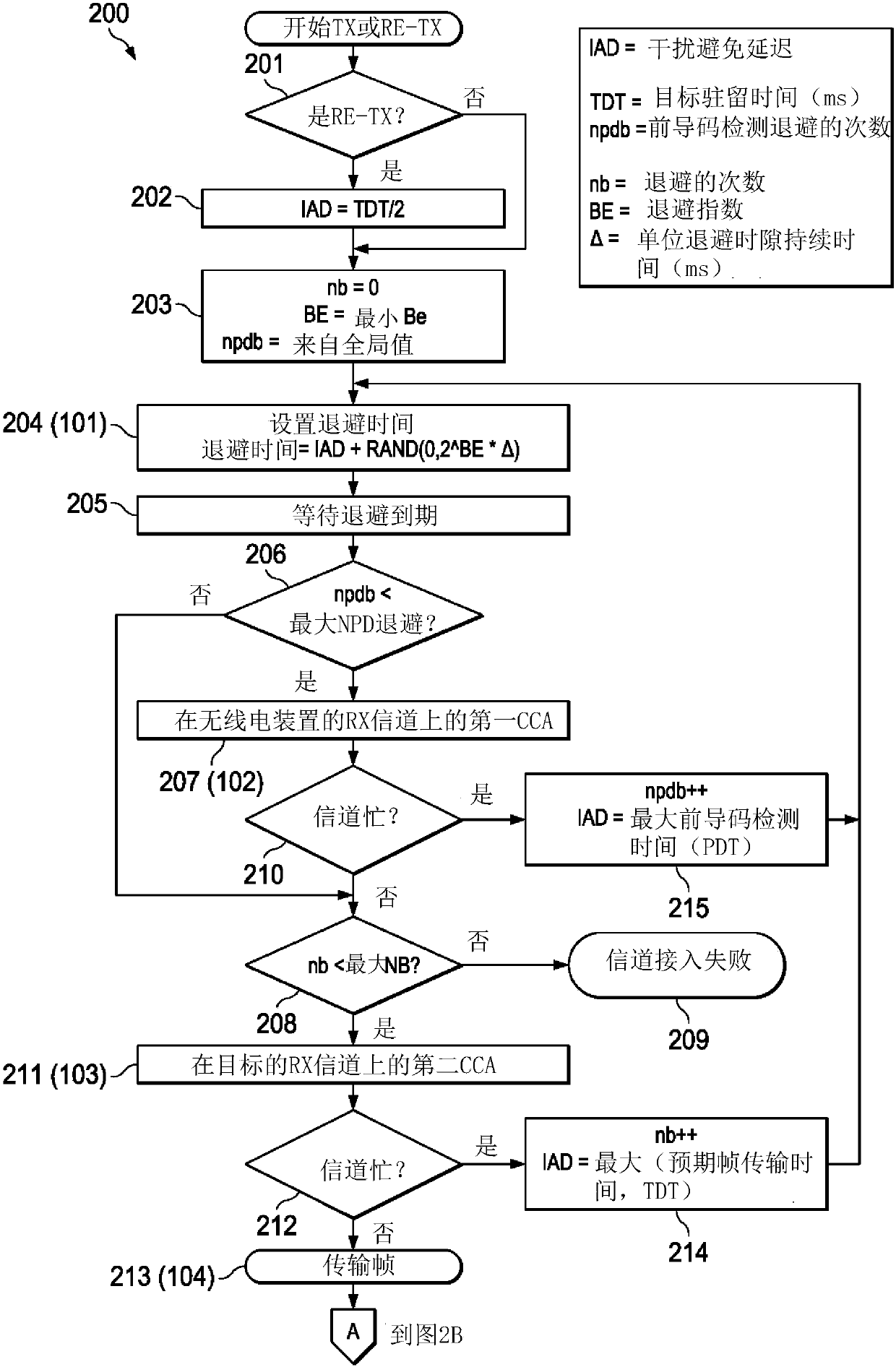
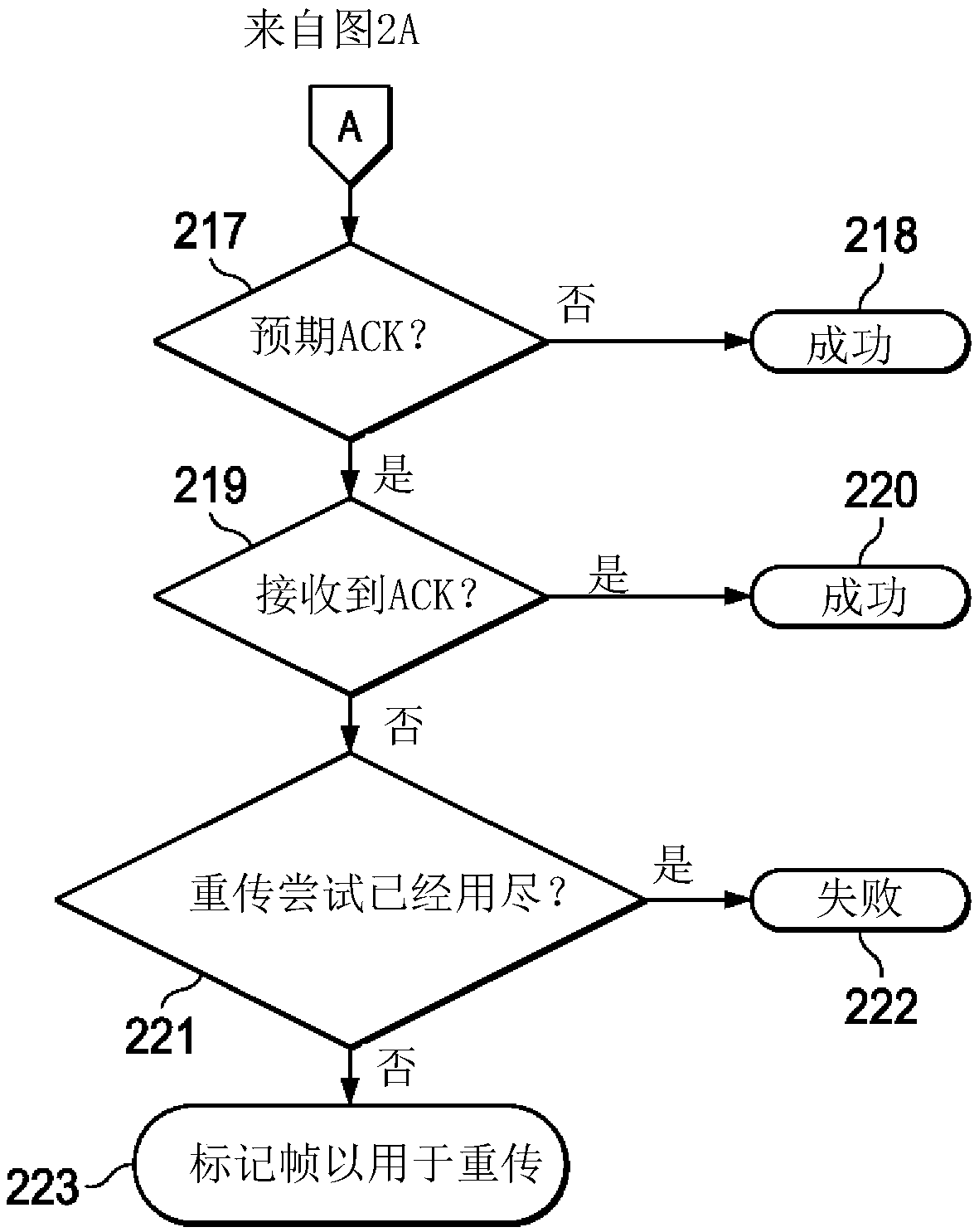
Channel hopping aware channel access and re-transmission
ActiveCN107634820AError prevention/detection by using return channelSignal allocationTelecommunicationsWireless network
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
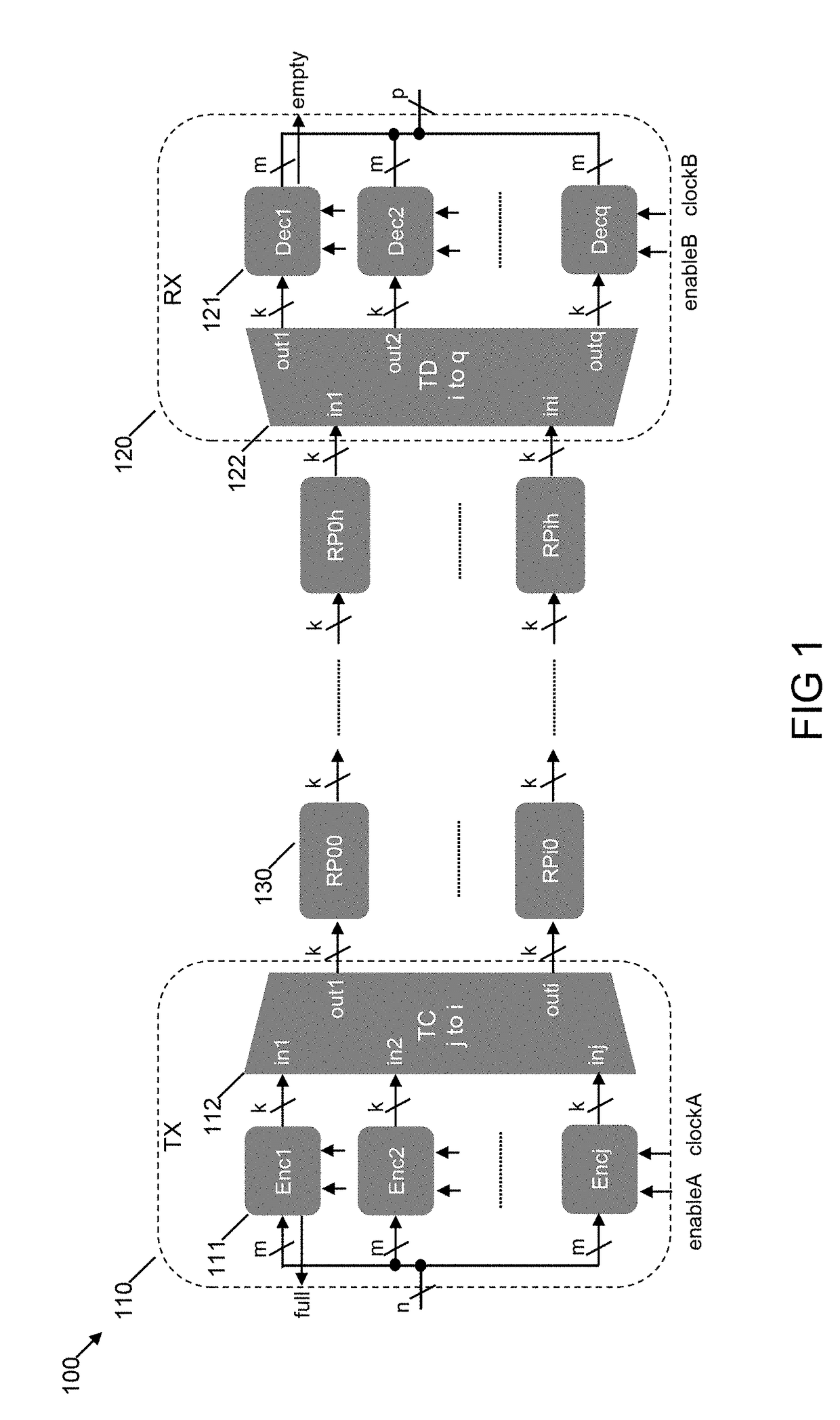
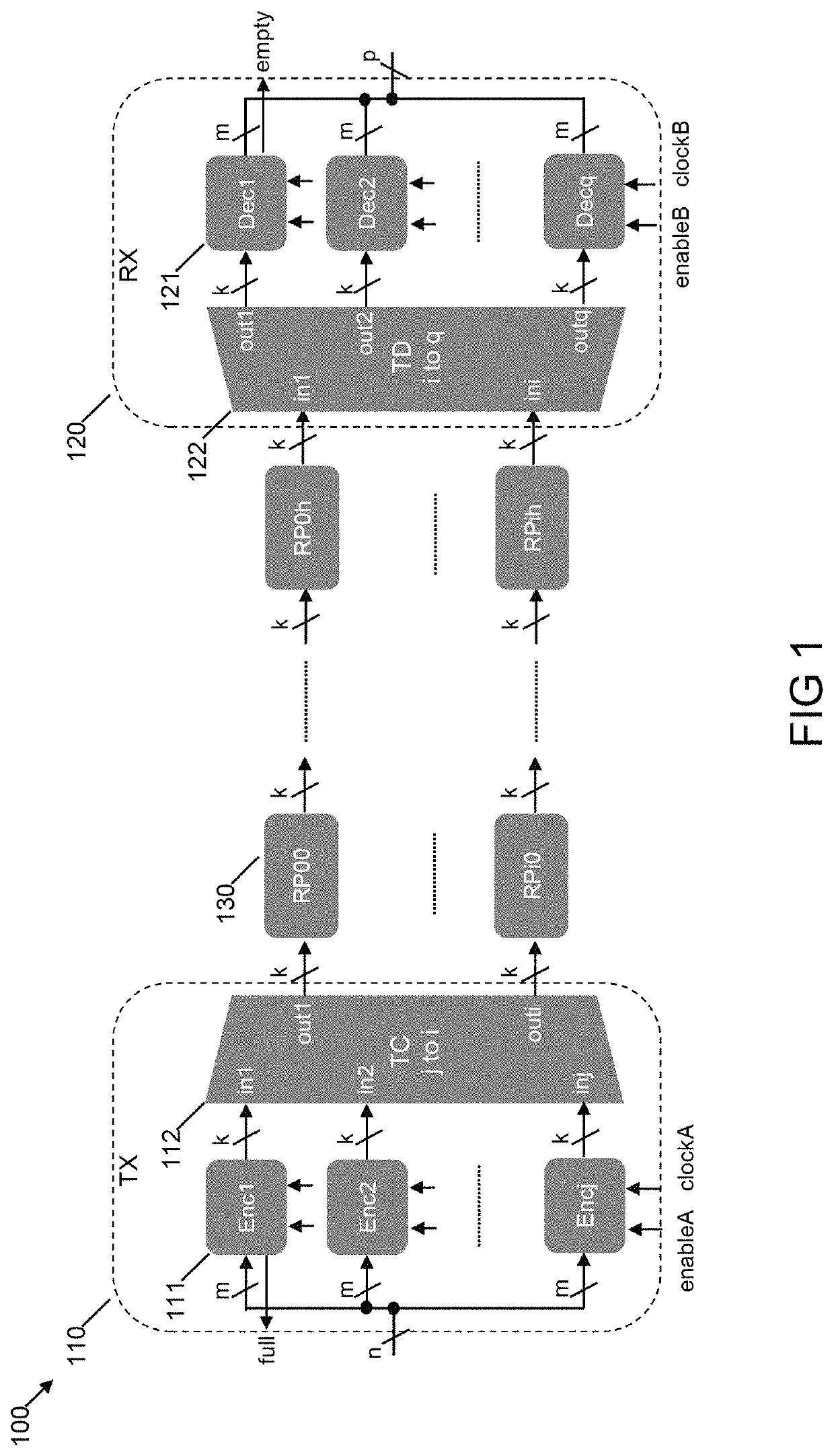
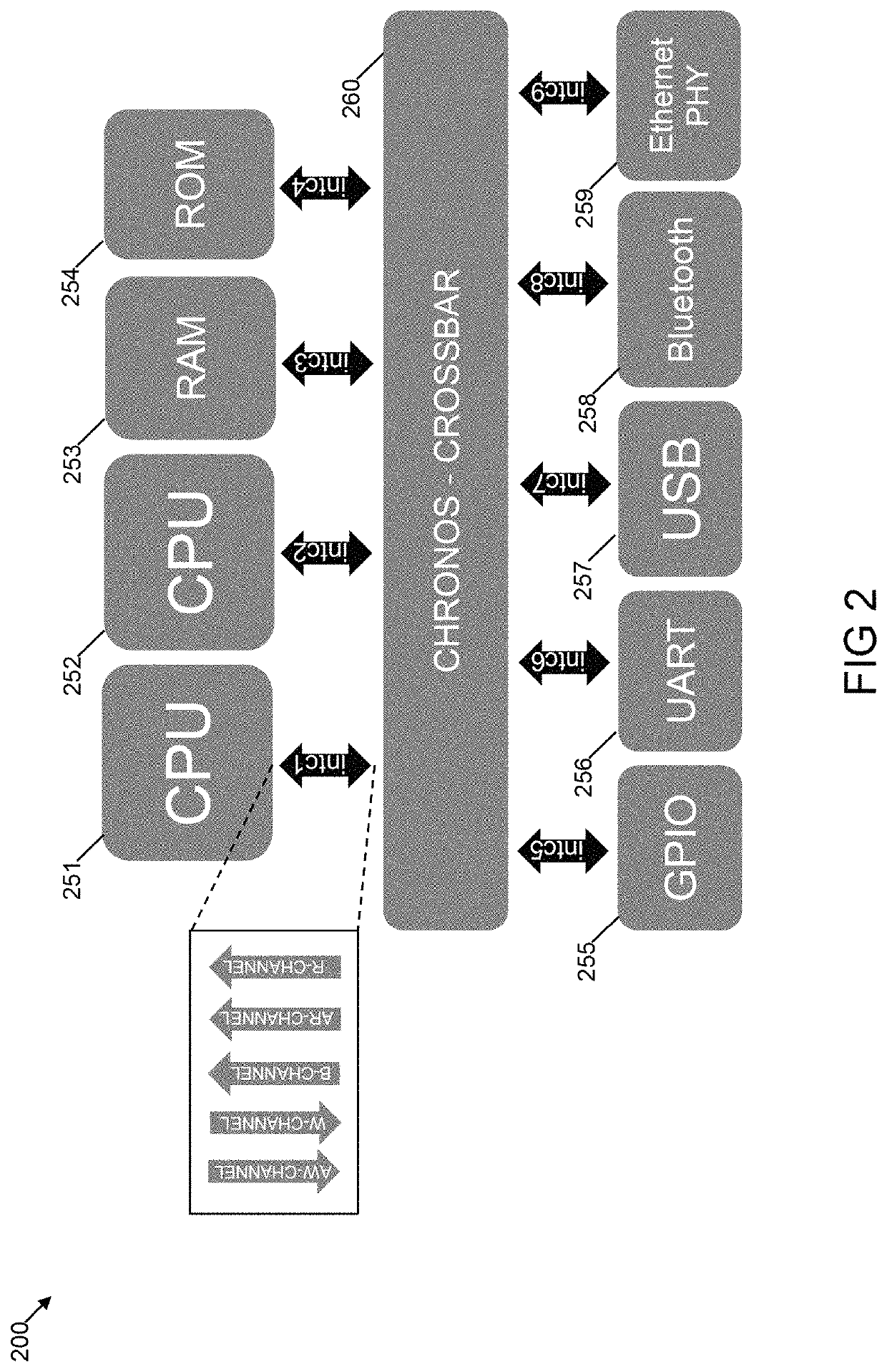
System and methods for measuring performance of an application specific integrated circuit interconnect
ActiveUS20190044625A1Measurement is performedTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringAsynchronous circuitIntegrated circuit interconnect
This application discloses circuits and apparatus configured to measure performance of asynchronous circuits by injecting data in to inputs of asynchronous circuits and consuming data from the outputs without interfering in the functionality of the asynchronous circuits. This application also discloses systems and methods for assessing the performance of asynchronous channels and / or IP blocks by providing an unambiguous performance value which can be used for performance analysis and comparison.
Owner:CHRONOS TECH LLC
System and methods for measuring performance of an application specific integrated circuit interconnect
ActiveUS10637592B2Measurement is performedTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringAsynchronous circuitComputer architecture
This application discloses circuits and apparatus configured to measure performance of asynchronous circuits by injecting data in to inputs of asynchronous circuits and consuming data from the outputs without interfering in the functionality of the asynchronous circuits. This application also discloses systems and methods for assessing the performance of asynchronous channels and / or IP blocks by providing an unambiguous performance value which can be used for performance analysis and comparison.
Owner:CHRONOS TECH LLC
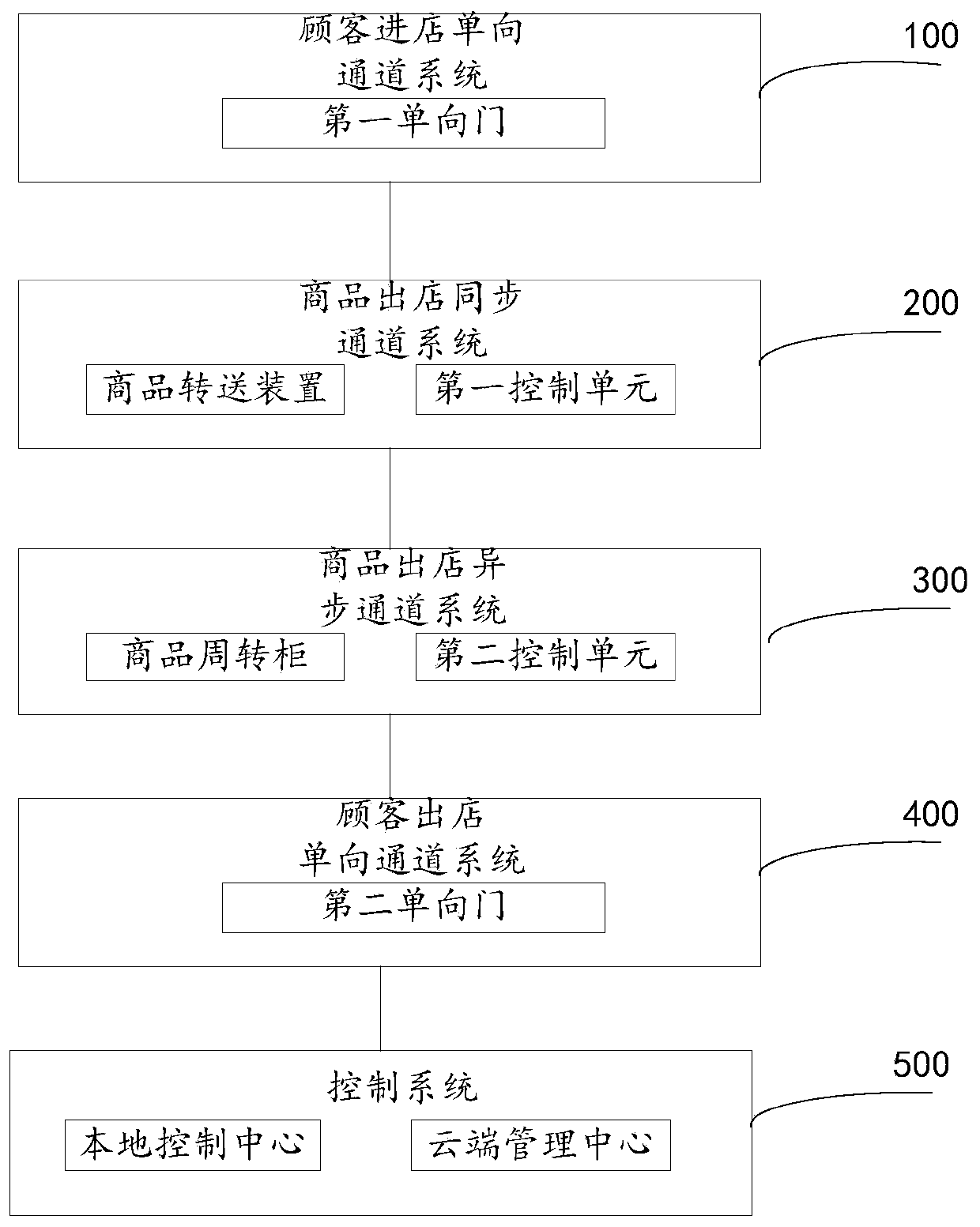
Self-service shopping system and method with separation of people and goods, unattended store
InactiveCN109635893BRealize the separation of people and goodsImprove shopping efficiencyCo-operative working arrangementsCash registersComputer networkControl system
The invention provides a people-goods separation type self-service shopping system and method, and an unattended store. The self-service shopping system comprises a self-service shopping system and aself-service shopping system, The invention discloses a customer in-store one-way channel system. The invention discloses a commodity delivery synchronous channel system and / or a commodity delivery asynchronous channel system and a control system. The control system comprises a local control center. When the self-service shopping system comprises a commodity out-of-store asynchronous channel system, the control system further comprises a cloud management center which is used for communicating with the mobile phone APP of the customer, receiving a function request instruction sent by the customer through the mobile phone APP, and pushing related system states and operation prompt information. According to the invention, separation of people and goods during commodity settlement is realized,theft is effectively prevented, the shopping settlement efficiency of customers is improved, and the operation management cost and the labor cost are reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Information transmitting/receiving device by network including synchronous and asynchronous paths
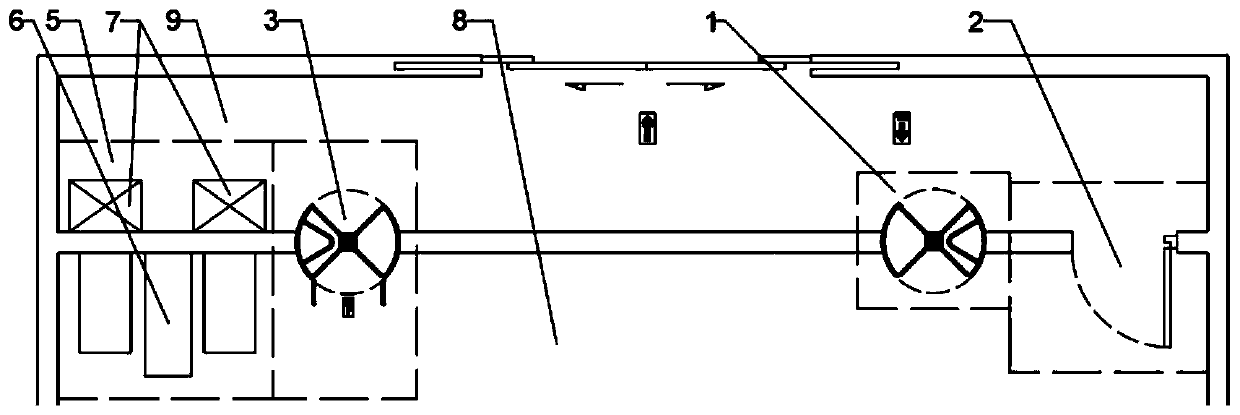
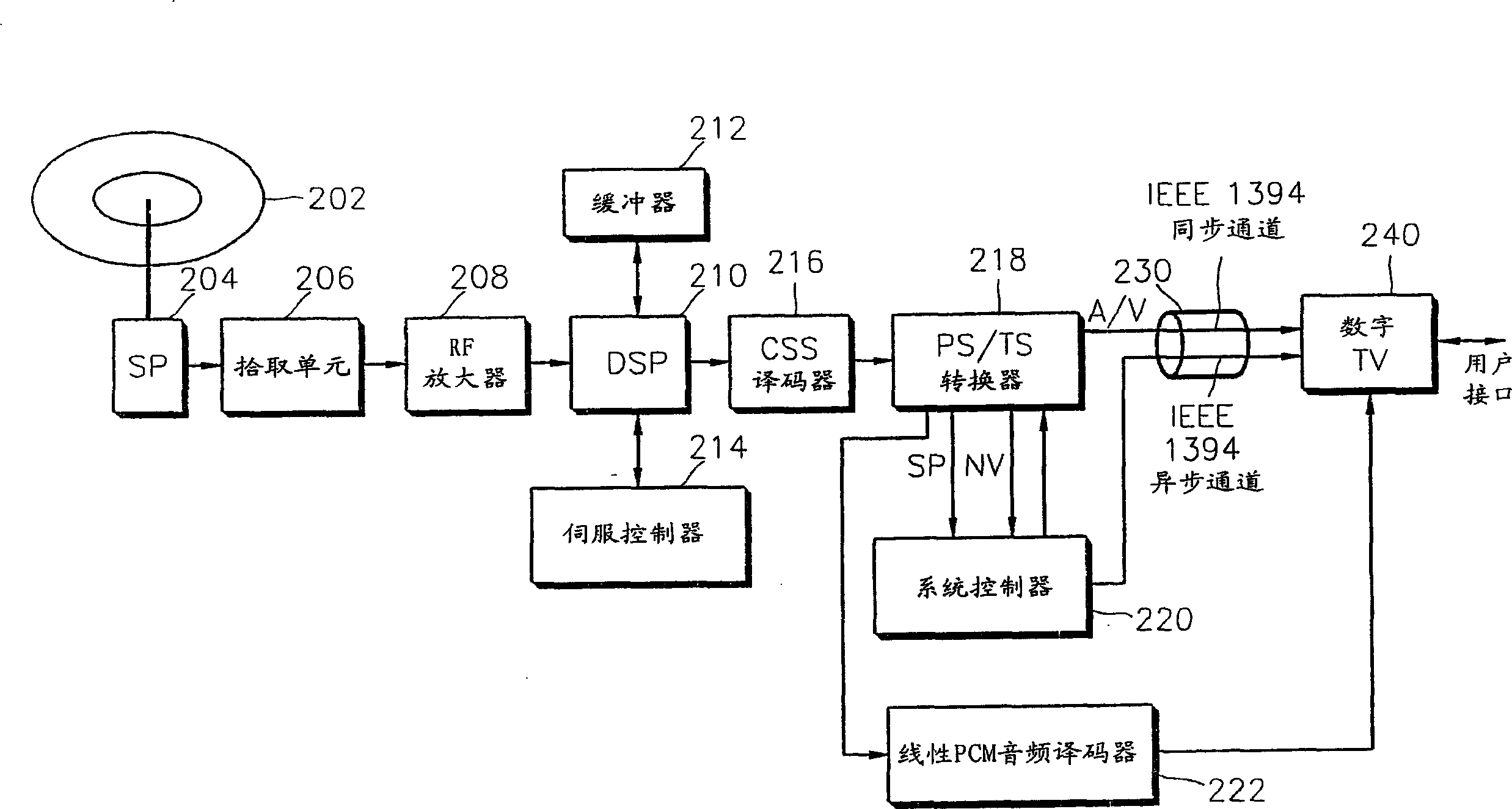
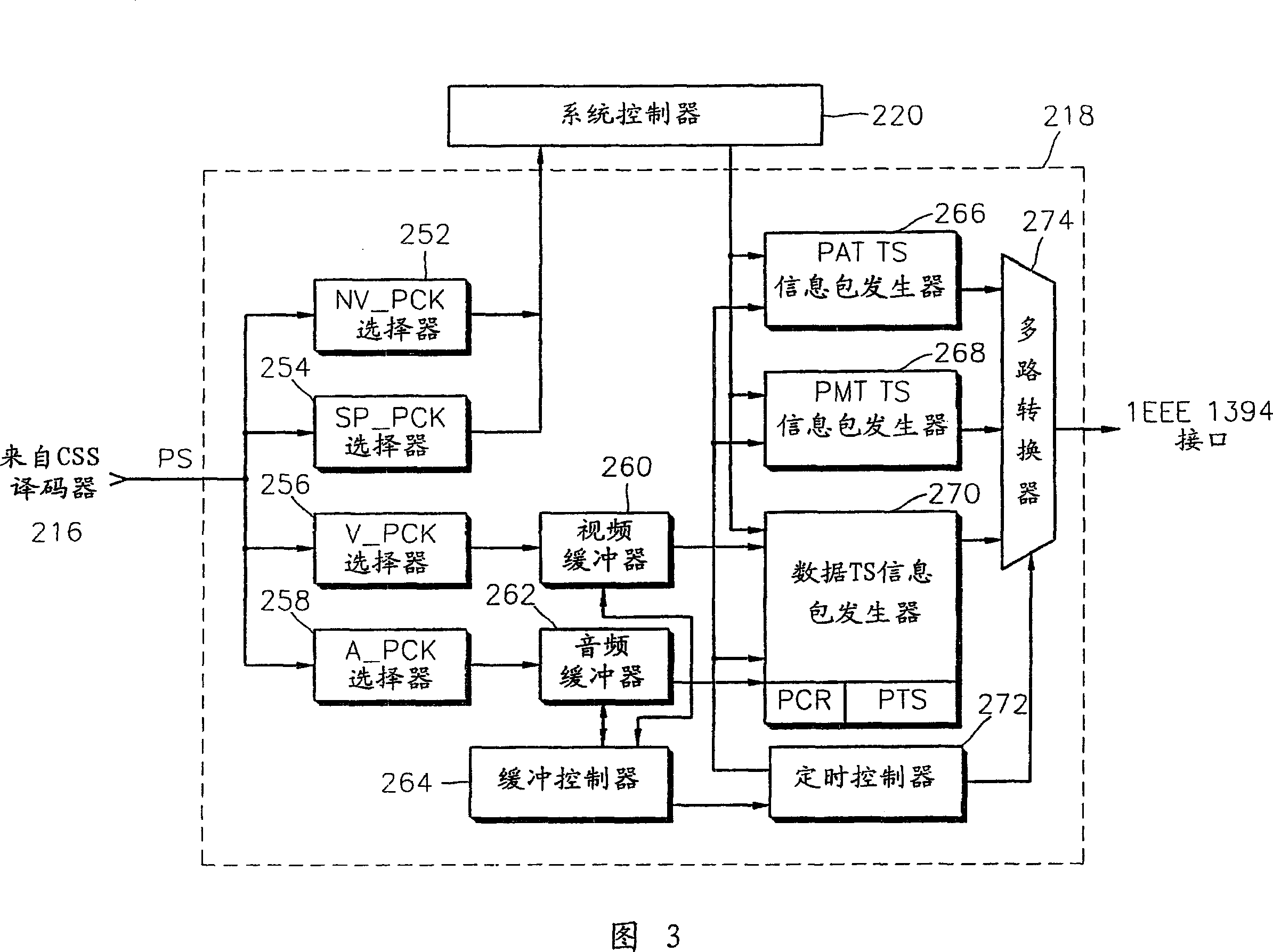
InactiveCN1722812ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsInformation transmissionCommand and control
An apparatus for transmitting information via a network, and a method are provided. The information transmission apparatus includes a first device having a transport format converter for receiving user interface data in put via a user interface, the user interface for commanding and controlling the first device, and for converting information into a transport format for transmission, a second device having a display unit, the display unit for displaying the user interface or commanding and controlling the first device, and a physical layer for linkig the first and second devices for communications. The IEEE 1394 interface is adopted as the physical layer, so that the second device can control the operation of a digital versatile disc player as the first device, and interfacing between devices using the MPEG-2 transport stream becomes easier.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data processing method and device, equipment and storage medium
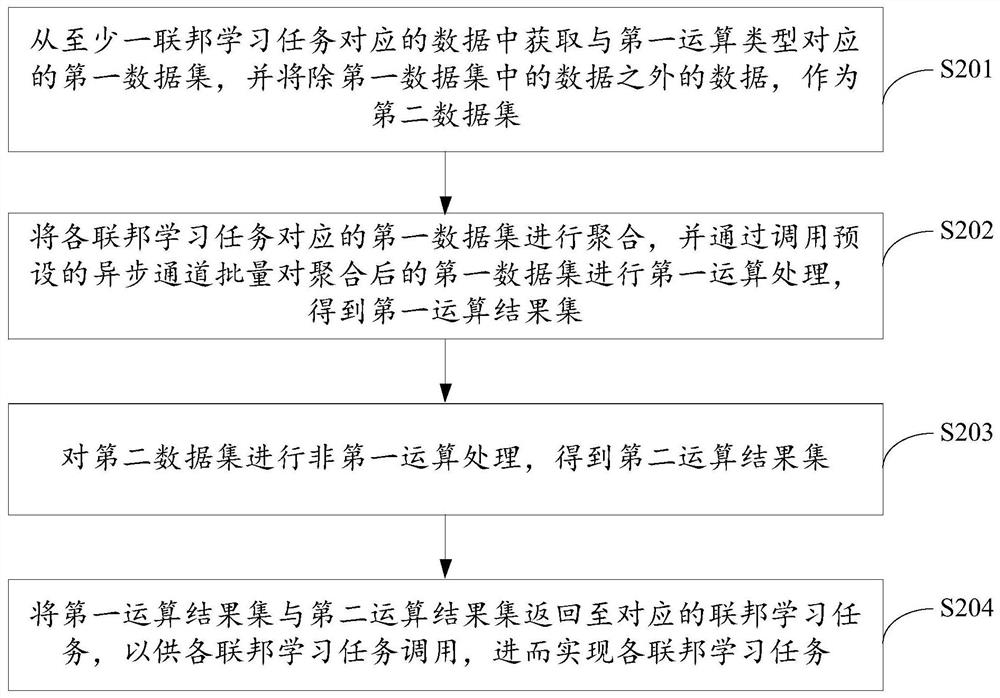
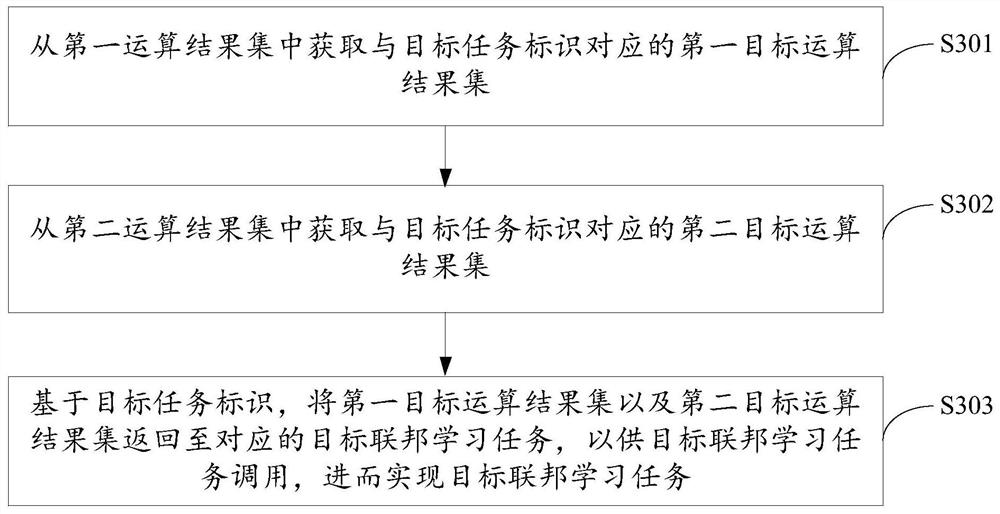
PendingCN114386612AImprove learning progressImprove processing efficiencyMachine learningData setEngineering
The invention discloses a data processing method and device, equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a first data set corresponding to a first operation type from data corresponding to at least one federated learning task, and taking data except the data in the first data set as a second data set, aggregating the first data sets corresponding to the federated learning tasks, performing first operation processing on the aggregated first data sets in batches by calling a preset asynchronous channel to obtain a first operation result set, and performing non-first operation processing on the second data set to obtain a second operation result set, and returning the first operation result set and the second operation result set to the corresponding federated learning tasks to be called by the federated learning tasks so as to realize the federated learning tasks. According to the invention, the processing efficiency of the federal learning task is improved, and the learning progress of federal learning is accelerated.
Owner:WEBANK (CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com