Method and apparatus for transferring data at an asynchronous channel between domains with different clock speeds
A technology for transmitting data and data, which is applied in the direction of synchronization devices, transmission systems, measuring devices, etc., and can solve problems such as insufficient differential error standards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
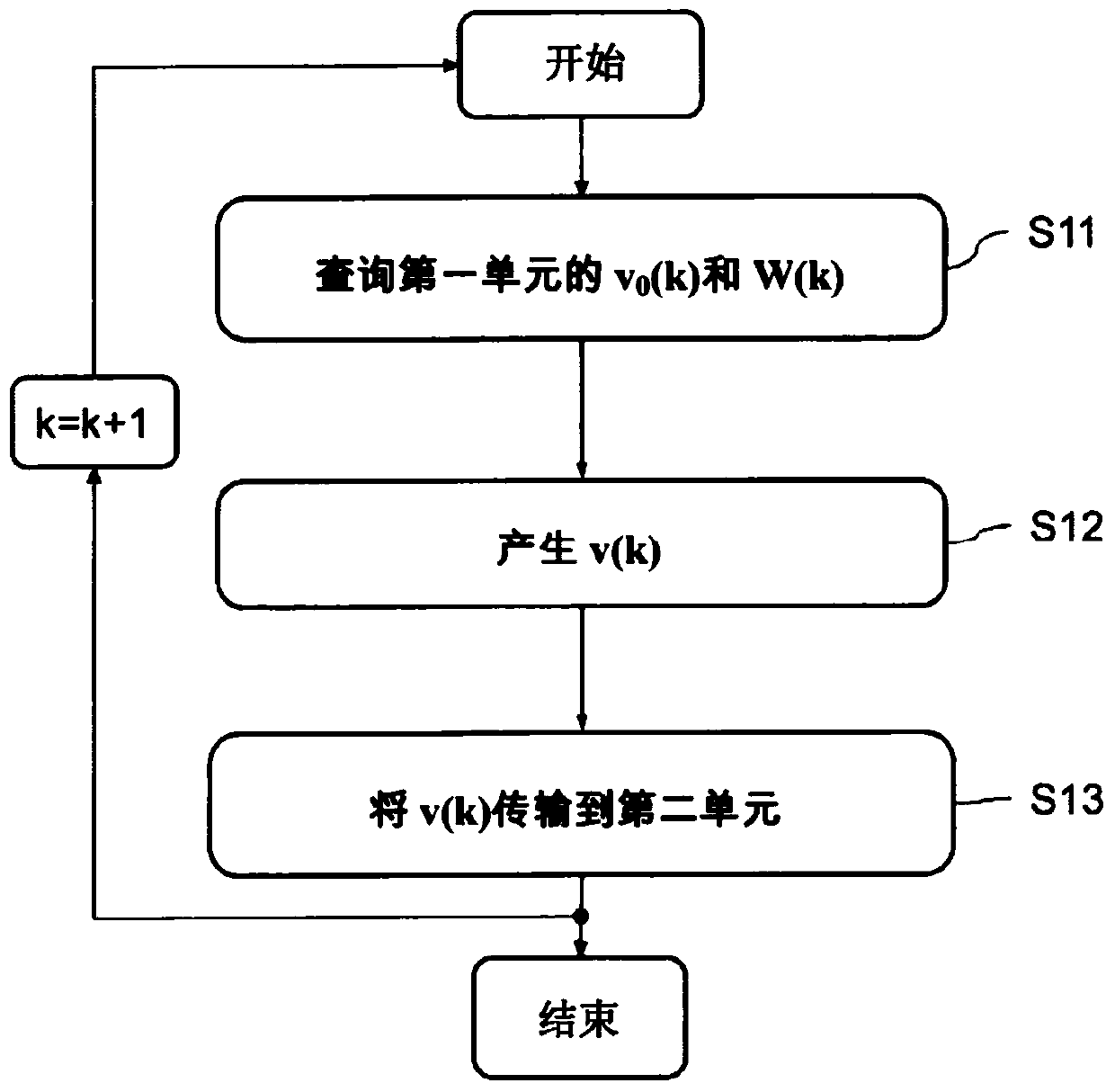
Embodiment Construction
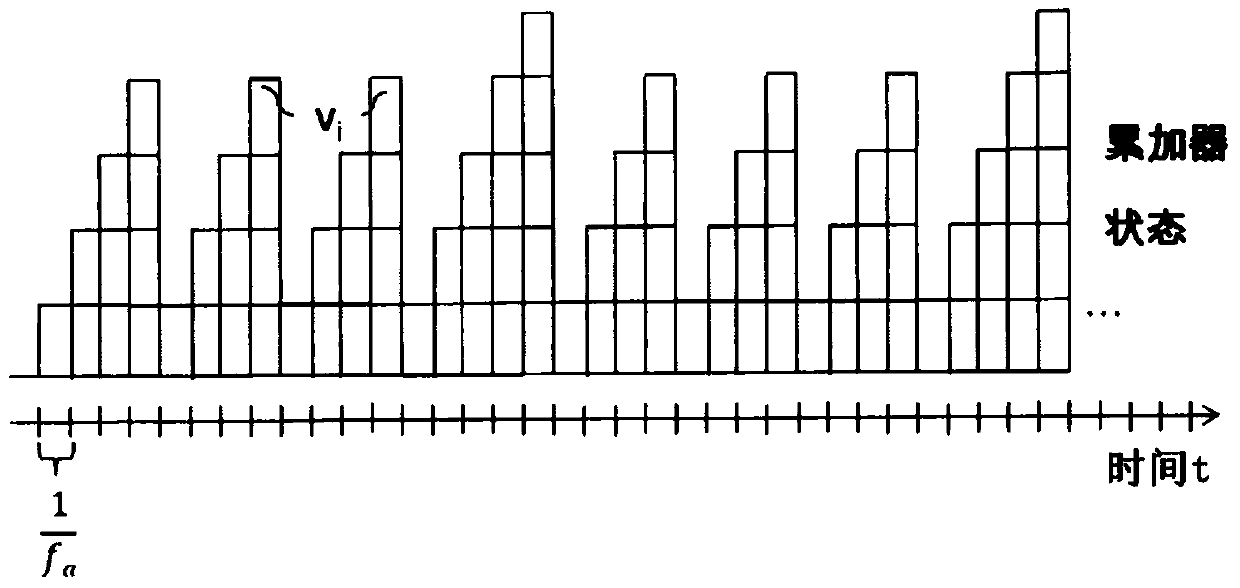
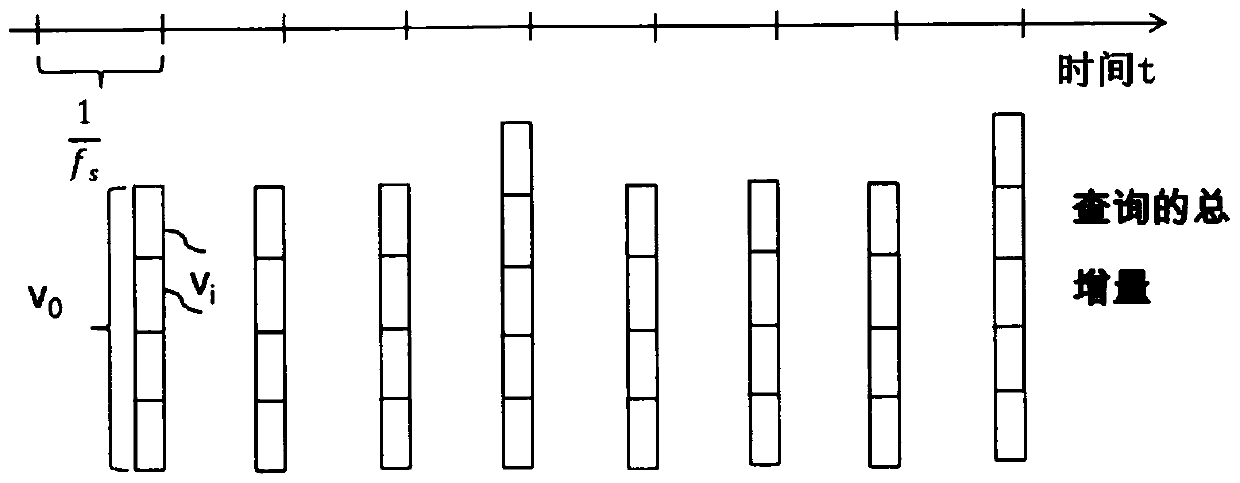
[0017] Figure 1A and Figure 1B Used to illustrate the problem on which the invention is based. exist Figure 1A is shown with the first frequency f a The time course of the data line ticks of the and the accumulator status matched to each data line tick, that is, the partial increment v accumulated in the accumulator i the number of Figure 1B is shown with a second frequency f s The time course of the query tick and the total increment v queried or read out in the corresponding query tick 0 . For example, the first frequency f a Take 3.4kHz, the second frequency f s Take 800Hz. so from One query beat is formed in one data line beat.
[0018] Since the accumulation can only take place over an integer number of data line cycles, in order to transmit all data completely, the accumulation is performed three times over four data line cycles and once over five data line cycles. That is, included in a total increment v 0 The partial increment v in i The number of chan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com