An Asynchronous Channel Sensing Method with Unknown Timing
A channel-aware and asynchronous technology, applied in the field of communications, can solve the problems of time difference between transmitter and cognitive user receiver perception, and the inability of authorized users and cognitive users to cooperate in timing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
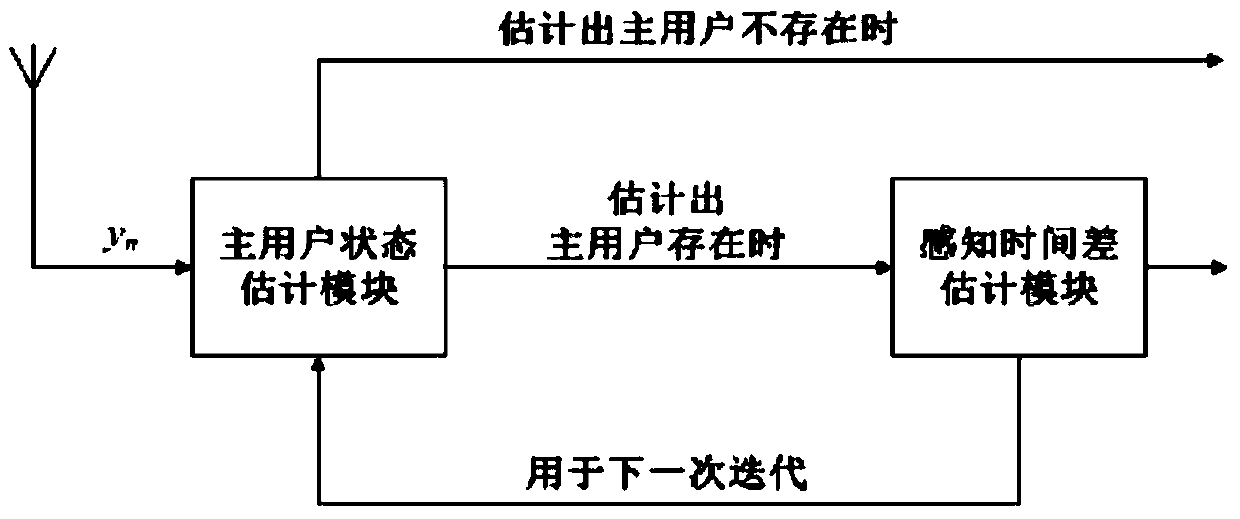
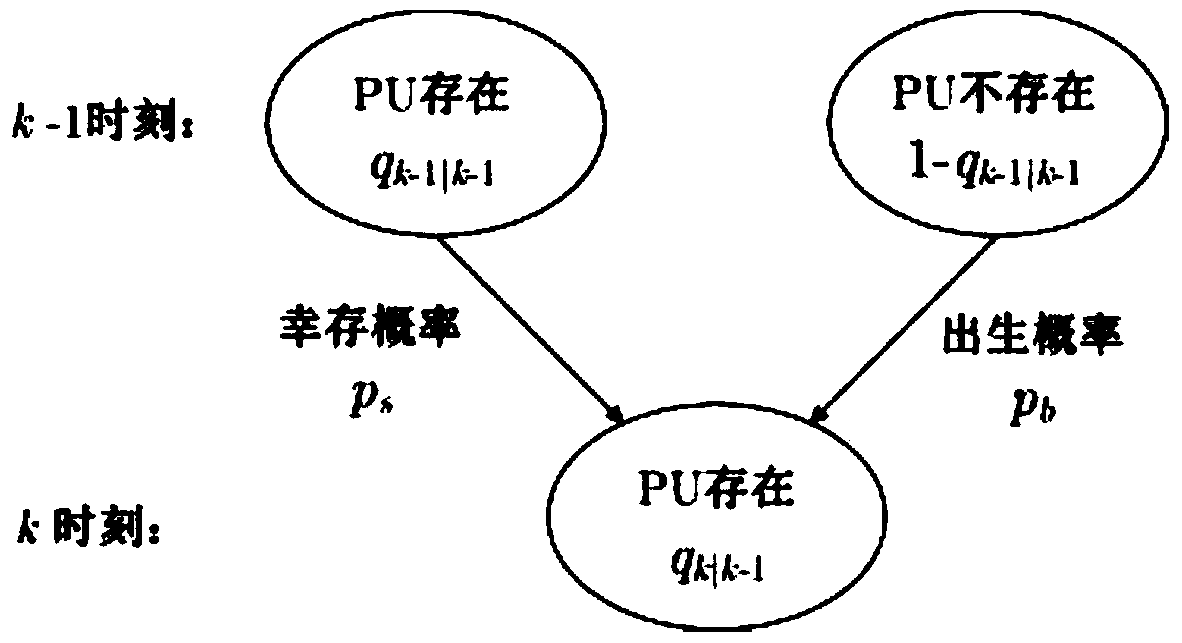
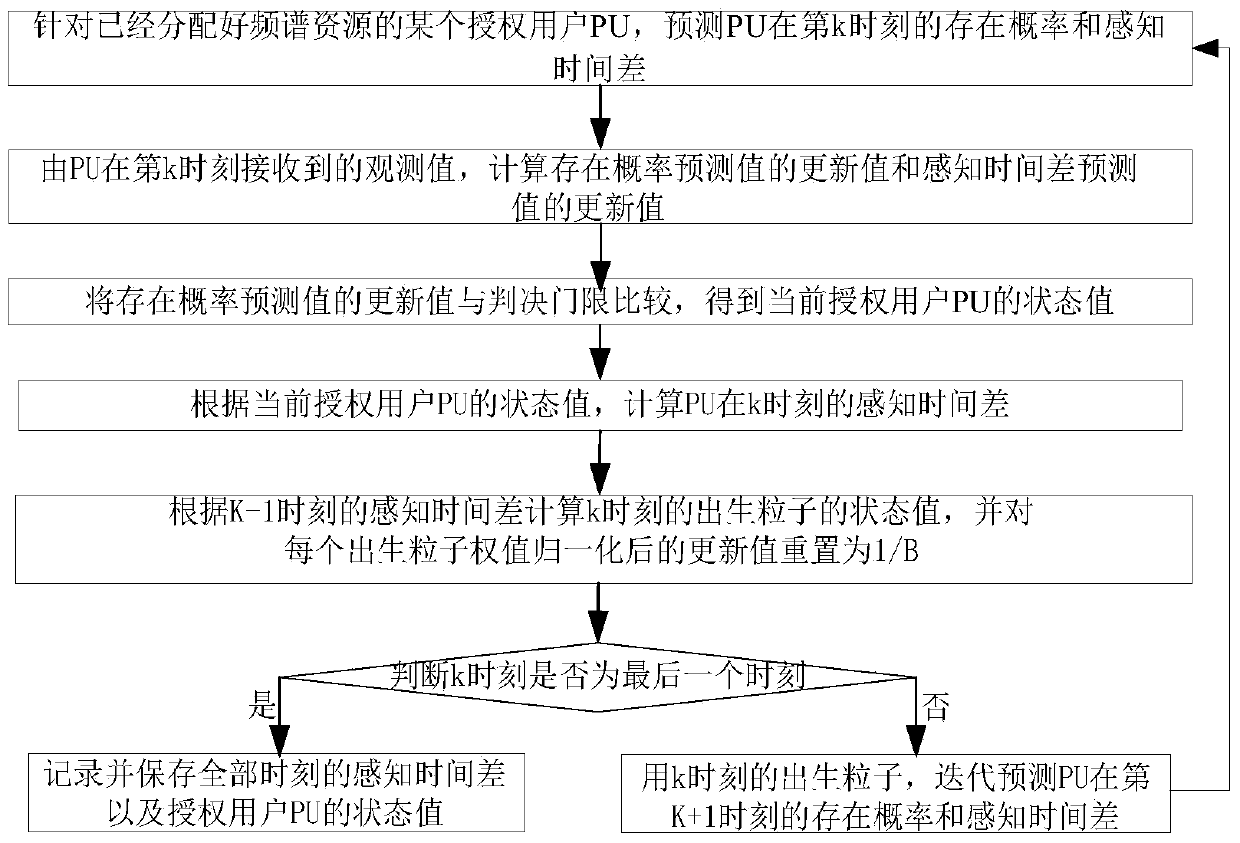
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0165] Simulate the asynchronous channel sensing method of the present invention, and set the birth probability p of the authorized user b = 0.2, the probability of survival is p s =0.8, the number of sampling points M=100, and the total time is set to 4000. m t Indicates the range of the perceived time difference, that is, the perceived time difference t k ∈[0,M t ], take M respectively t are 20, 60, and 100; the simulation results of spectrum sensing performance are as follows Figure 5 as shown, Figure 5 is the total correct detection probability simulation diagram under the three perception time difference ranges, the abscissa is the actual signal-to-noise ratio snr, and the ordinate is the overall correct detection probability P D . It can be seen from the simulation results that in the case of fixed sampling points M=100, the unknown perception time difference M t The larger the dynamic range of , the worse the spectrum sensing performance; at the same time, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com