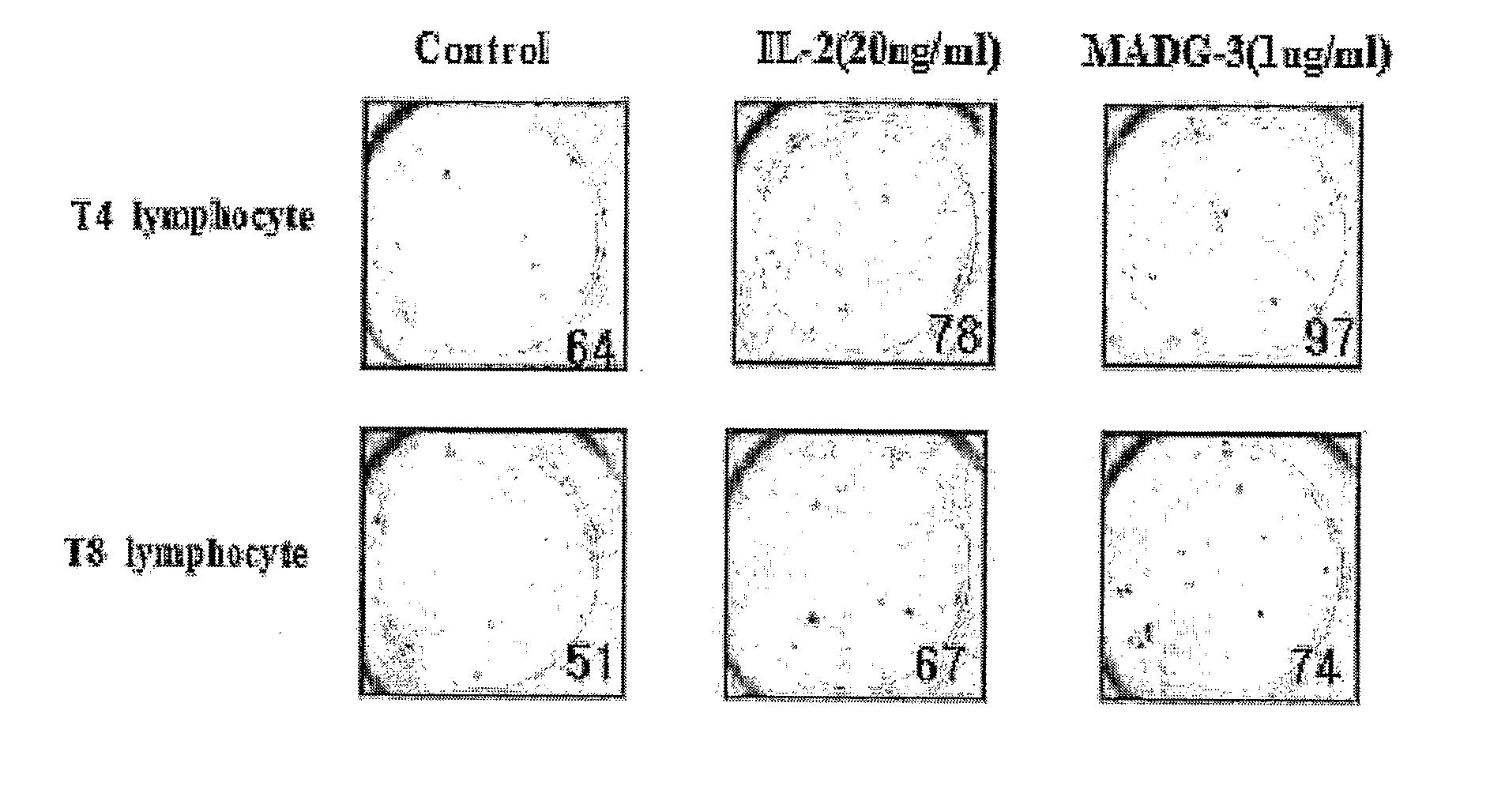
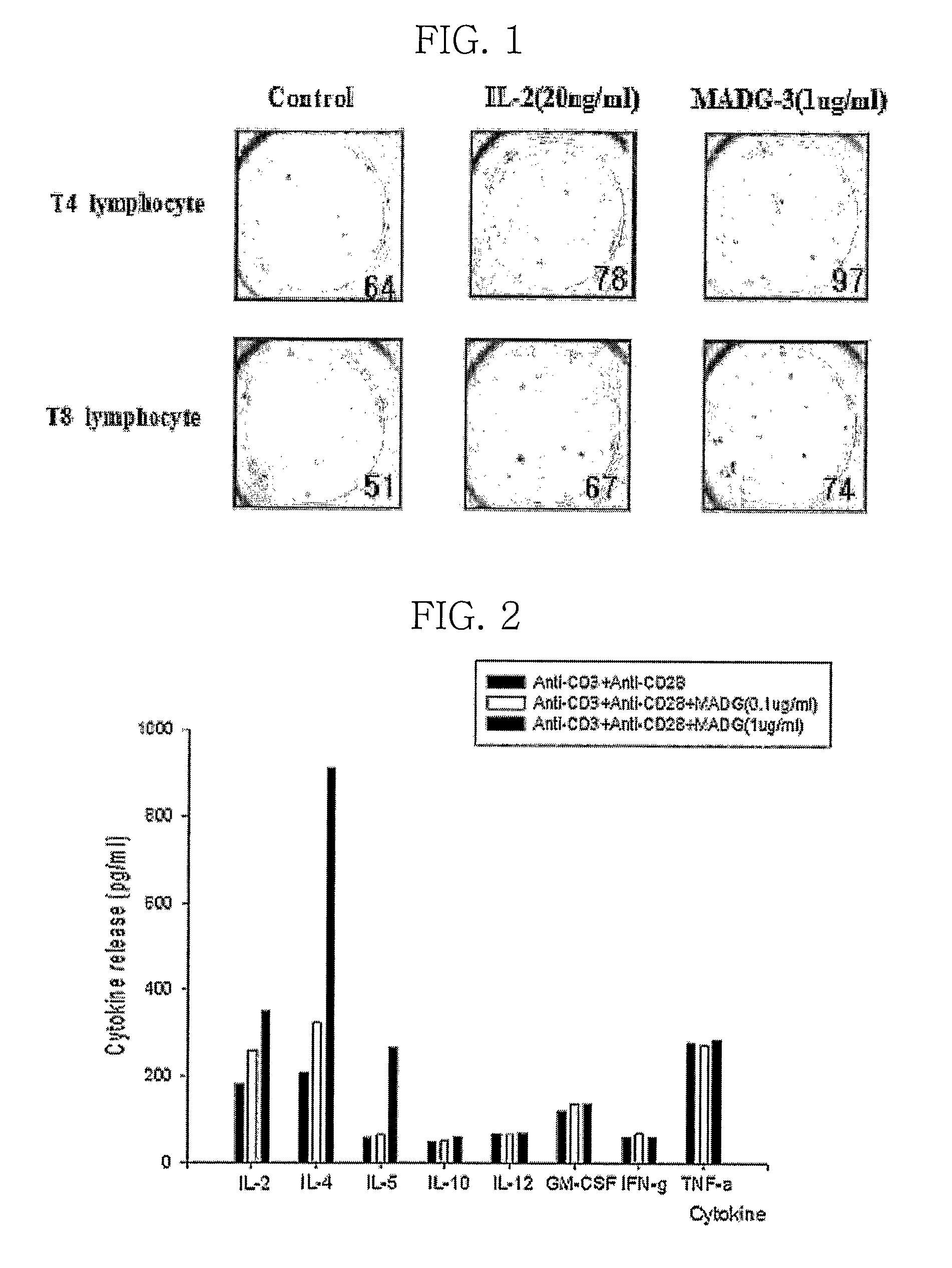
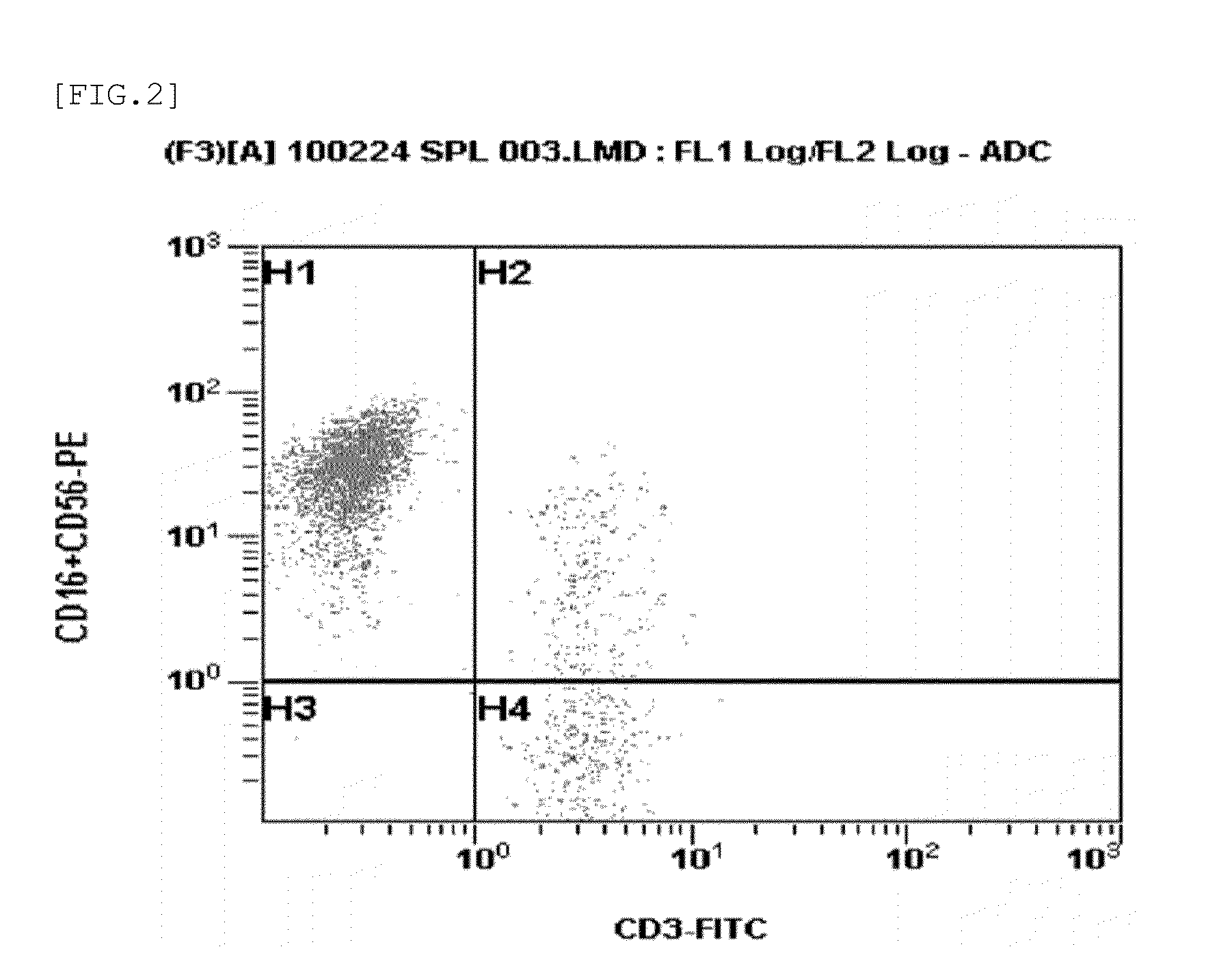
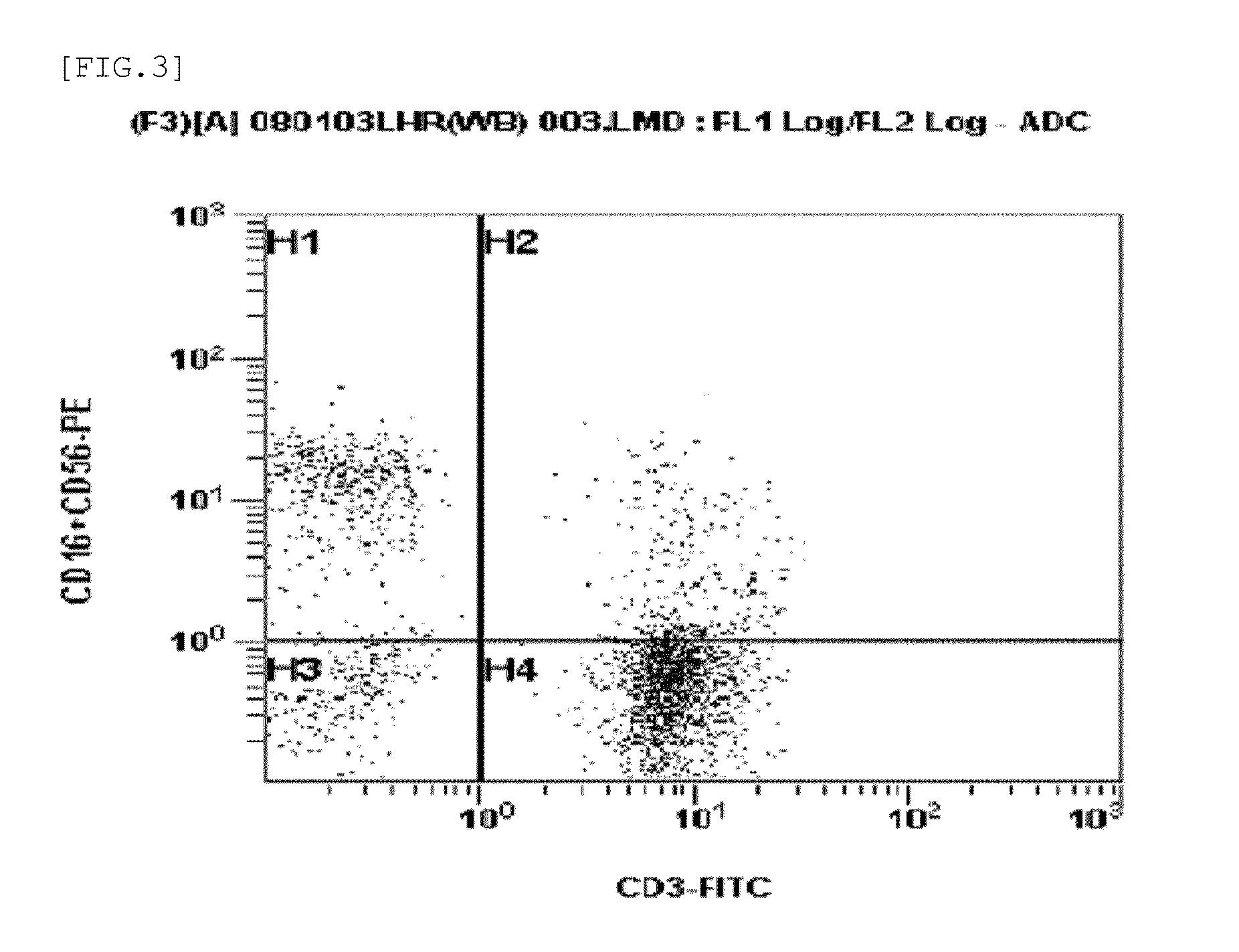
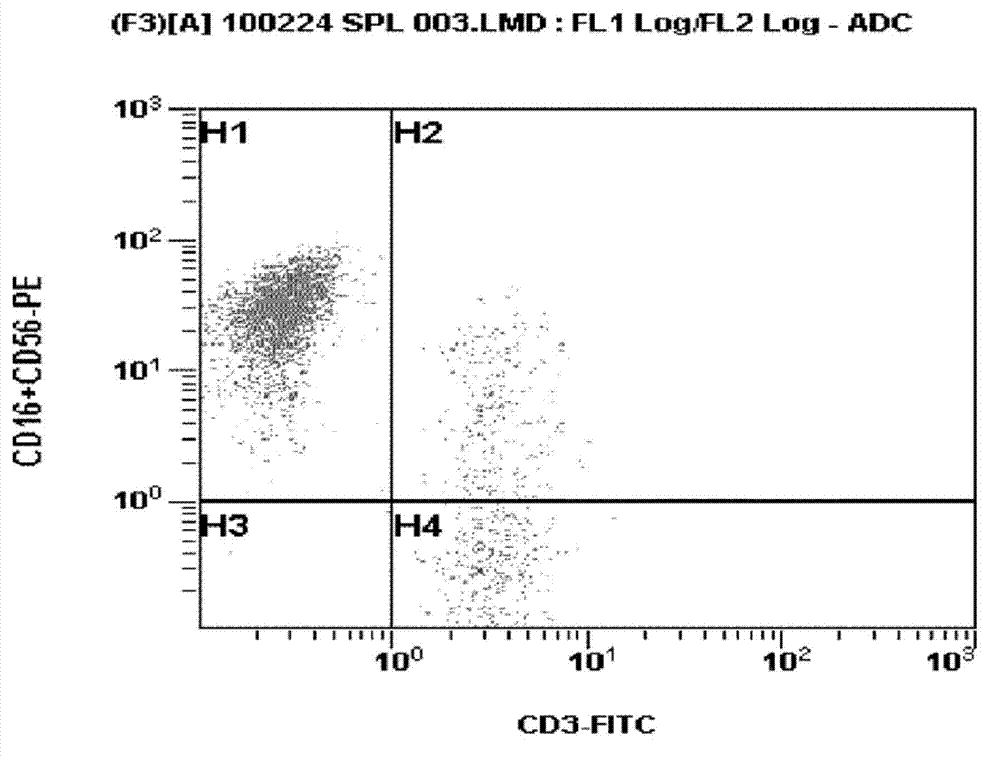
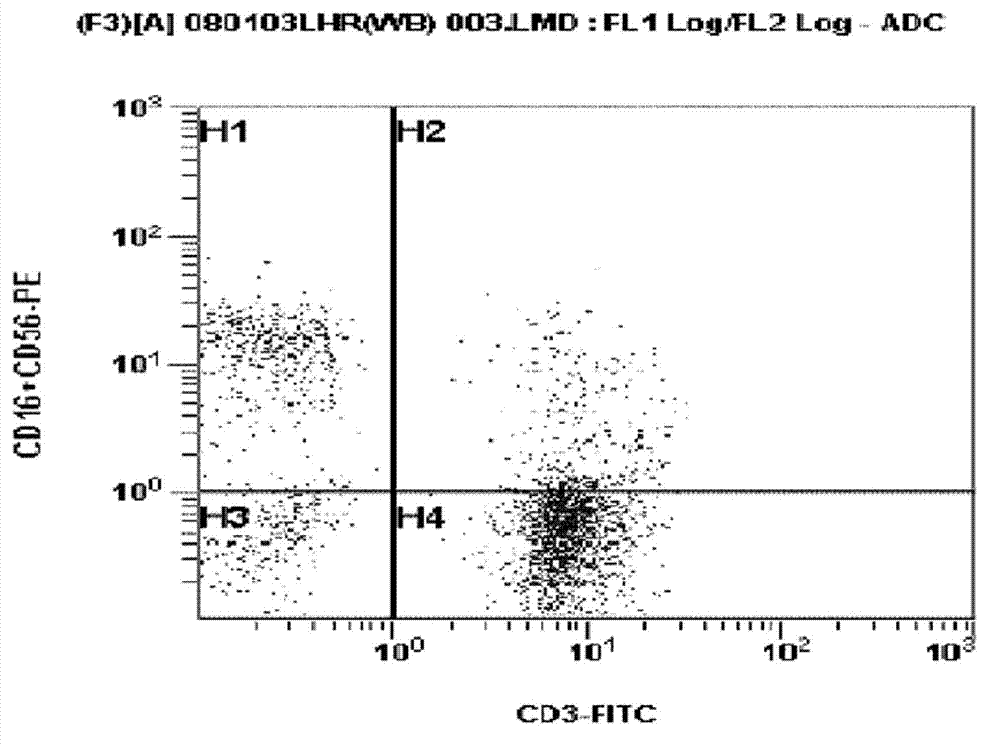
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
76 results about "Activated Lymphocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A white blood cell that, after being in contact with an antigen, rearranges its DNA to defend against that one specific type of antigen. After activation, it can then proliferate and differentiate into memory cells, antibody-secreting cells or plasma cells.
Treatment of immunological disorders using anti-dc30 antibodies
InactiveUS20050123536A1Enhancing cytotoxicEnhancing cytostatic effectOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseAntibody conjugate
The present invention relates to methods for the treatment of immunological disorders other than cancer, comprising administering proteins characterized by their ability to bind to CD30 and exert a cytostatic or cytotoxic effect on an activated lymphocyte. Such proteins include monoclonal antibodies AC10 and IleFi1. AC10 and HeFi-1 derivatives, and antibodies that compete with AC10 and HeFi-1 for binding to CD30. Other such proteins include multivalent anti-CD30 antibodies and anti-CD30 antibodies conjugated to cytotoxic agents. Treatment modalities with antibodies of the invention are also provided.
Owner:SEATTLE GENETICS INC
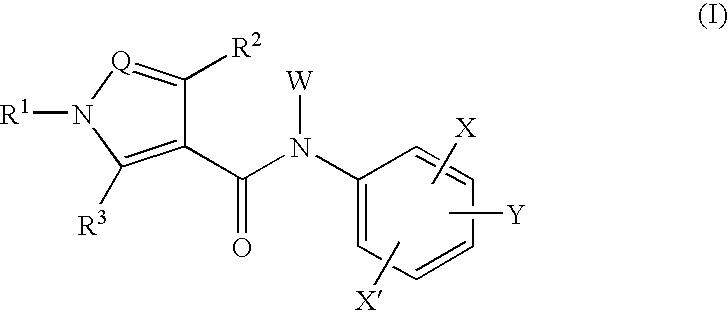
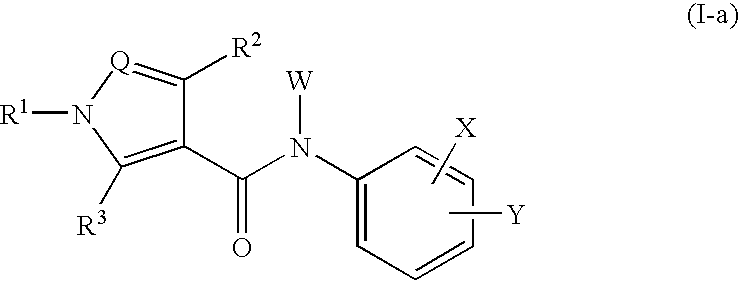
Amide compounds and medicinal use thereof
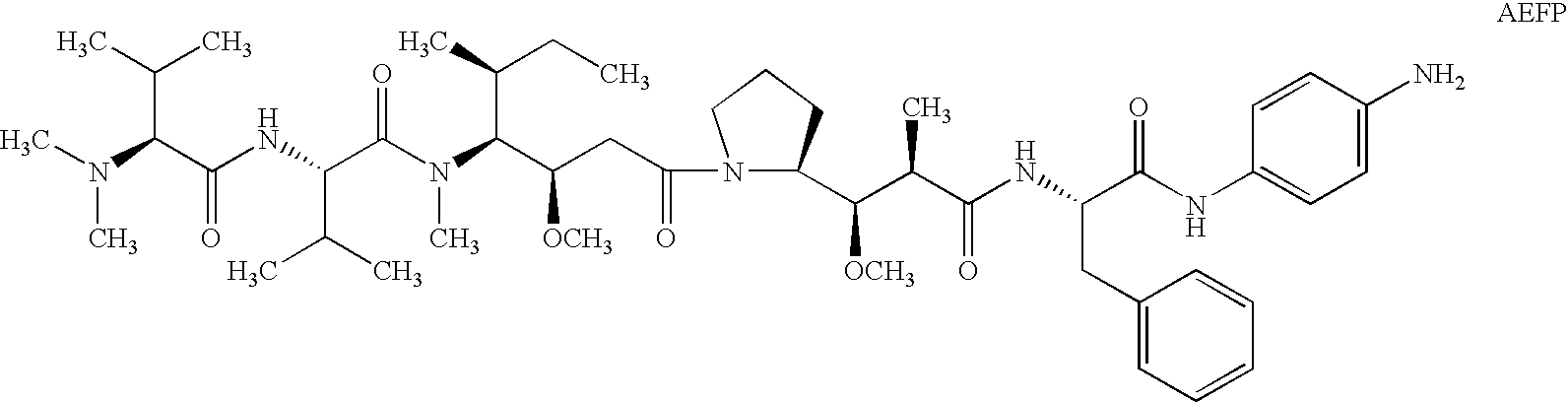
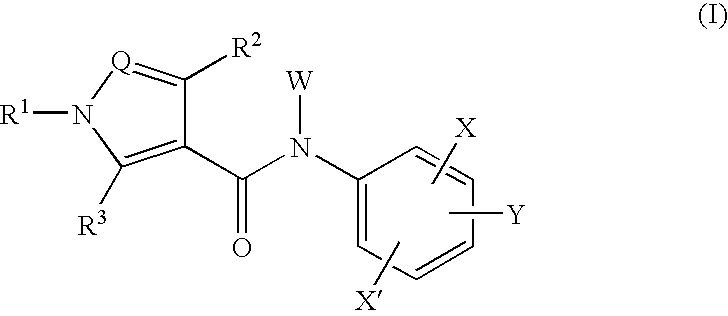
The present invention relates to a compound of the formula wherein R1 is substituted aryl, heteroaryl and the like, R2 and R3 are hydrogen, alkyl, halogen, hydroxyl group and the like, Q is N, CH and the like, W is hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxycarbonylalkyl and the like, X is halogen, cyano, nitro, amino and the like, X′ is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro, and Y is alkyl, hydroxyl group, alkoxy, mercapto and the like and a salt thereof, and a medicine containing the said compound. The compound of the present invention shows a superior inhibitory effect on activated lymphocytes proliferation and is useful as an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of various autoimmune diseases.
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
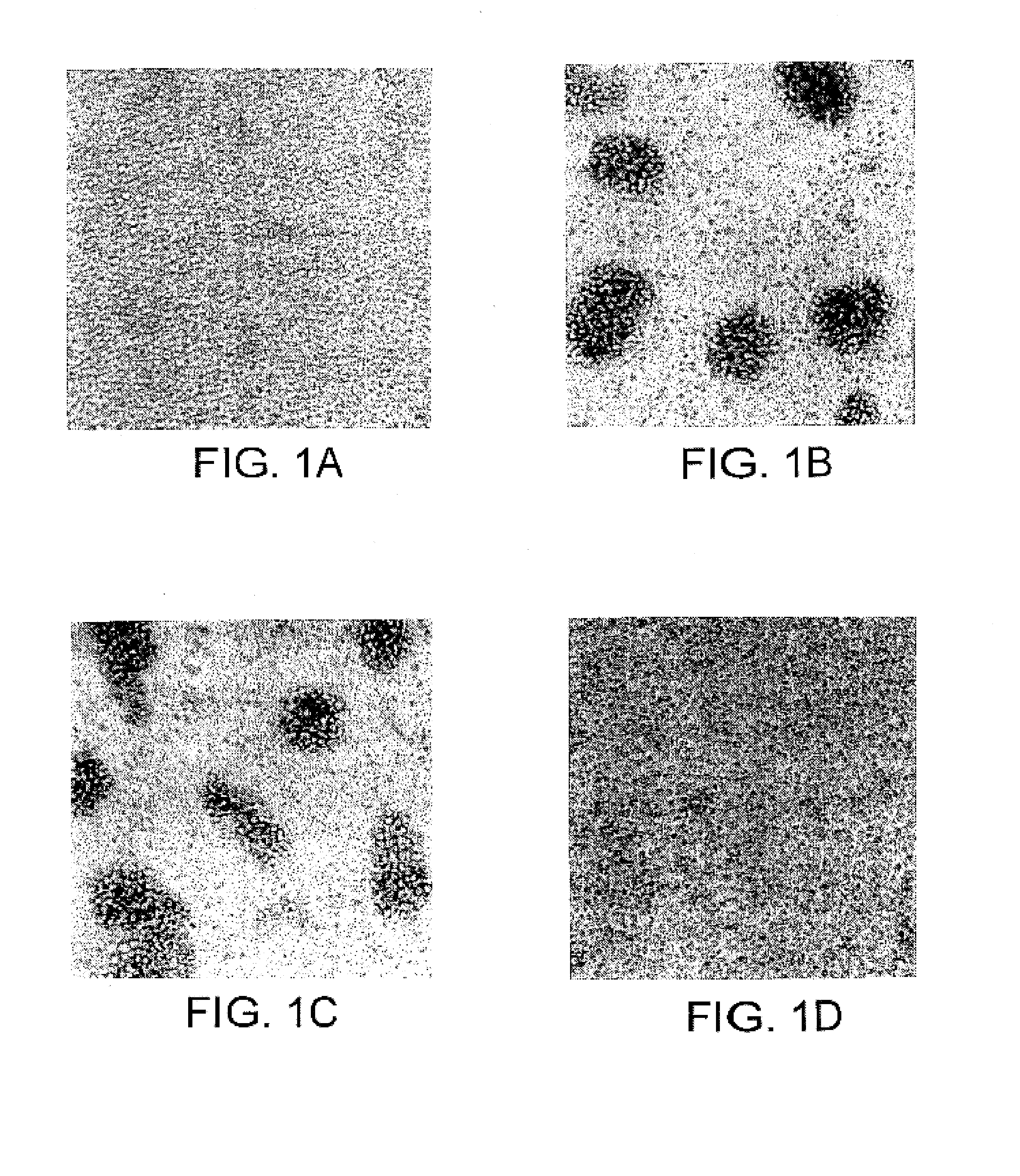
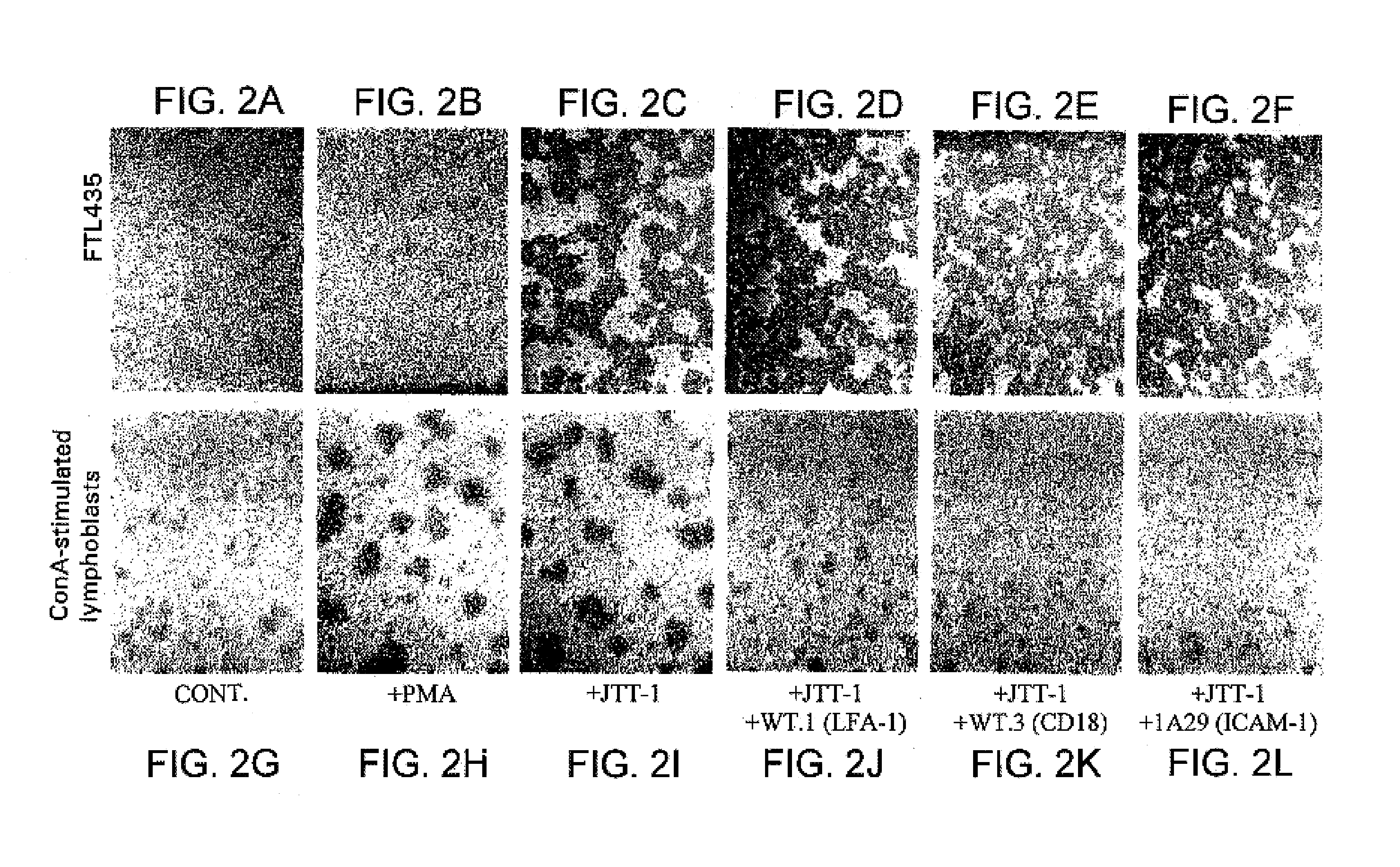
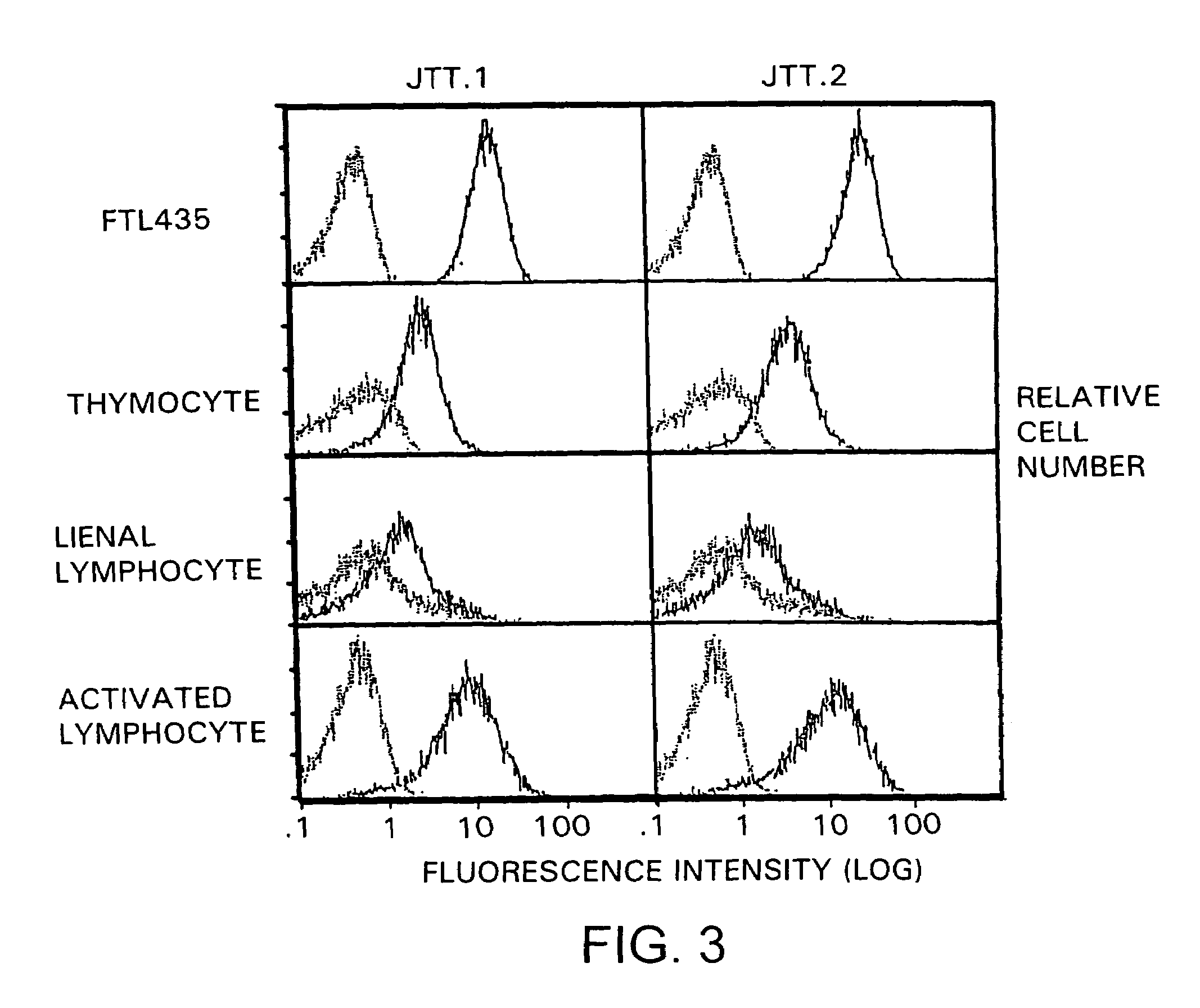
JTT-1 protein and methods of inhibiting lymphocyte activation
InactiveUS7112655B1Increased proliferationImprove purification effectCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological activationPeripheral blood lymphocyte
A cell surface molecule that is expressed specifically in thymocytes, lymphocytes activated by ConA-stimulation, and peripheral blood lymphocytes. This molecule is involved in signal transmission of the secondary signal (costimulatory signal) essential for the activation of lymphocytes such as T cells and regulates functions of activated lymphocytes such as activated T cells. Disclosed are a polypeptide of the cell surface molecule; a polypeptide fragment thereof; a fusion polypeptide comprising the fragment; a pharmaceutical composition comprising any one of the above; and methods of using the compositions.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Compositions for down-regulation of CCR5 expression and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060154857A1Reduces receptor sitesSuppressing transcriptionBiocideAntiviralsG1/S checkpointHIV receptor
The present invention relates to the downregulation of surface receptor CCR5 expression through manipulation of the cell cycle in activated lymphocytes by administering a composition that arrests the G1 phase of the cell cycle, thereby reducing receptor sites for entry of HIV into T cells, and thus, the effects of HIV. Further, compositions are disclosed that include at least one G1 phase arresting agent and at least one antiviral agent, wherein the combination of agents synergistically enhances the activity of the antiviral agent.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
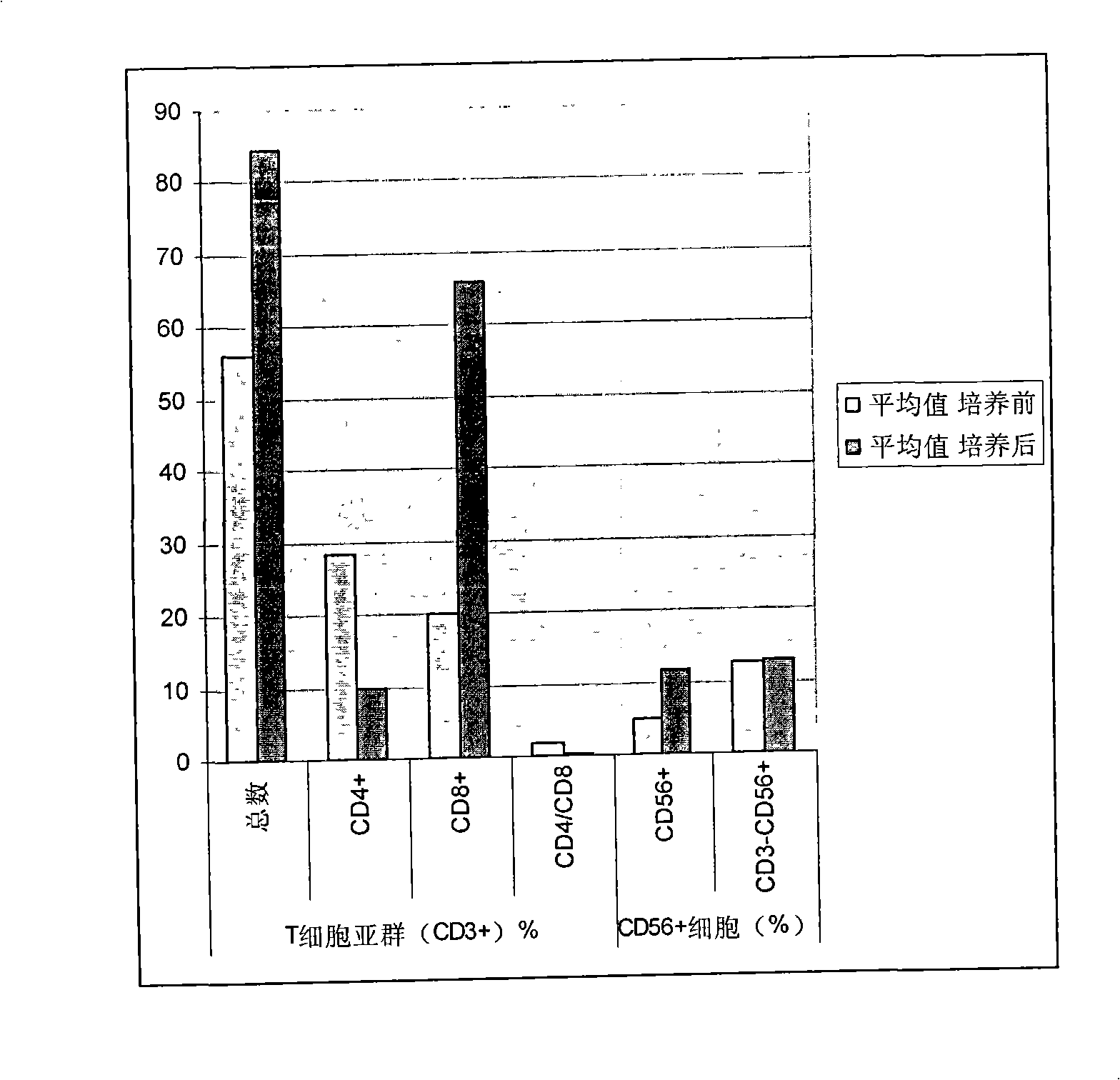
Amplifying, freezing and storing and recovering method of activated lymphocyte with CD3+CD8+as major
InactiveCN102839153ASolve the problem of multiple blood collectionHigh purityDead animal preservationBlood/immune system cellsPatient needT lymphocyte
The invention discloses culturing, freezing and recovering methods of an activated lymphocyte with CD3+CD8+as major, which can solve problems that a patient needs carrying out blood sampling for many times caused by continuously utilizing the activated lymphocyte with CD3+CD8+as major. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) contacting the extracted lymphocyte of the peripheral blood with IL-2, IL-15, an anti-CD3 antibody and an anti-CD28 antibody, so as to amplify the activated lymphocyte with CD3+CD8+as major; (2) freezing and storing the activated lymphocyte; and (3) recovering the activated lymphocyte. The activated lymphocyte cultured via the method disclosed by the invention has clear components, and comprises few CD4+CD25+Treg cells and more CD8+T lymphocyte; feedback time and frequency of the activated lymphocyte can be adjusted according to other treatments for a patient, such as a radiotherapy or a chemotherapy, so that diseases, such as tumor, infectious diseases and immunodeficiency can be treated well.
Owner:JINAN TAISHENG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Immunomodulating Agent, Anti-Cancer Agent and Health Food Containing Monoacetyldiacylglycerol Derivatives
The uses of mono acetyl diacyl glycerol derivatives extracted from deer antler for immunomodulating agent disclosed. Medical supplies and health foods containing the same as an effective ingredient also disclosed. Mono acetyl diacyl glycerol derivatives shows significantly effect for immuno modulation including immune enhancing. In the case of inducing cancer in a hamster by injecting cancer cell line, cancer development was delayed by activating lymphocytes, monocytes, and dendritic cells that are important factors to promote immunity and apoptosis of cancer cell was induced by promoting cytotoxicity of immune cell against cancer cell. Also in the case of mouse induced septic shock, it shows 100% survival rate even after lapse of 120 hours by control of immune function and suppression effect apoptosis. Therefore, mono acetyl diacyl glycerol derivatives according to the present invention can be effectively used for an immunomodulating agent, a sepsis treatment, a cancer treatment, and a health food for an immune modulation or the prevention of cancer.
Owner:ENZYCHEM LIFESCI CORP
Monoacetyldiacylglycerol derivative for the treatment of sepsis
The uses of mono acetyl diacyl glycerol derivatives extracted from deer antler for immunomodulating agent disclosed. Medical supplies and health foods containing the same as an effective ingredient also disclosed. Mono acetyl diacyl glycerol derivatives shows significantly effect for immuno modulation including immune enhancing. In the case of inducing cancer in a hamster by injecting cancer cell line, cancer development was delayed by activating lymphocytes, monocytes, and dendritic cells that are important factors to promote immunity and apoptosis of cancer cell was induced by promoting cytotoxicity of immune cell against cancer cell. Also in the case of mouse induced septic shock, it shows 100% survival rate even after lapse of 120 hours by control of immune function and suppression effect apoptosis. Therefore, mono acetyl diacyl glycerol derivatives according to the present invention can be effectively used for an immunomodulating agent, a sepsis treatment, a cancer treatment, and a health food for an immune modulation or the prevention of cancer.
Owner:ENZYCHEM LIFESCI CORP
Compositions and methods for protecting organs, tissue and cells from immune system-mediated damage
InactiveUS20080241194A1Organic active ingredientsFungiVascular endotheliumNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
This invention concerns novel compositions and methods for for the protection of organs and cells from damage caused by activated lymphocytes, NK-cells and NK-like cells, more particularly compositions and methods for the protection of vascular endothelial cells from immune system-mediated damage.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods For Detecting Th1 Cells
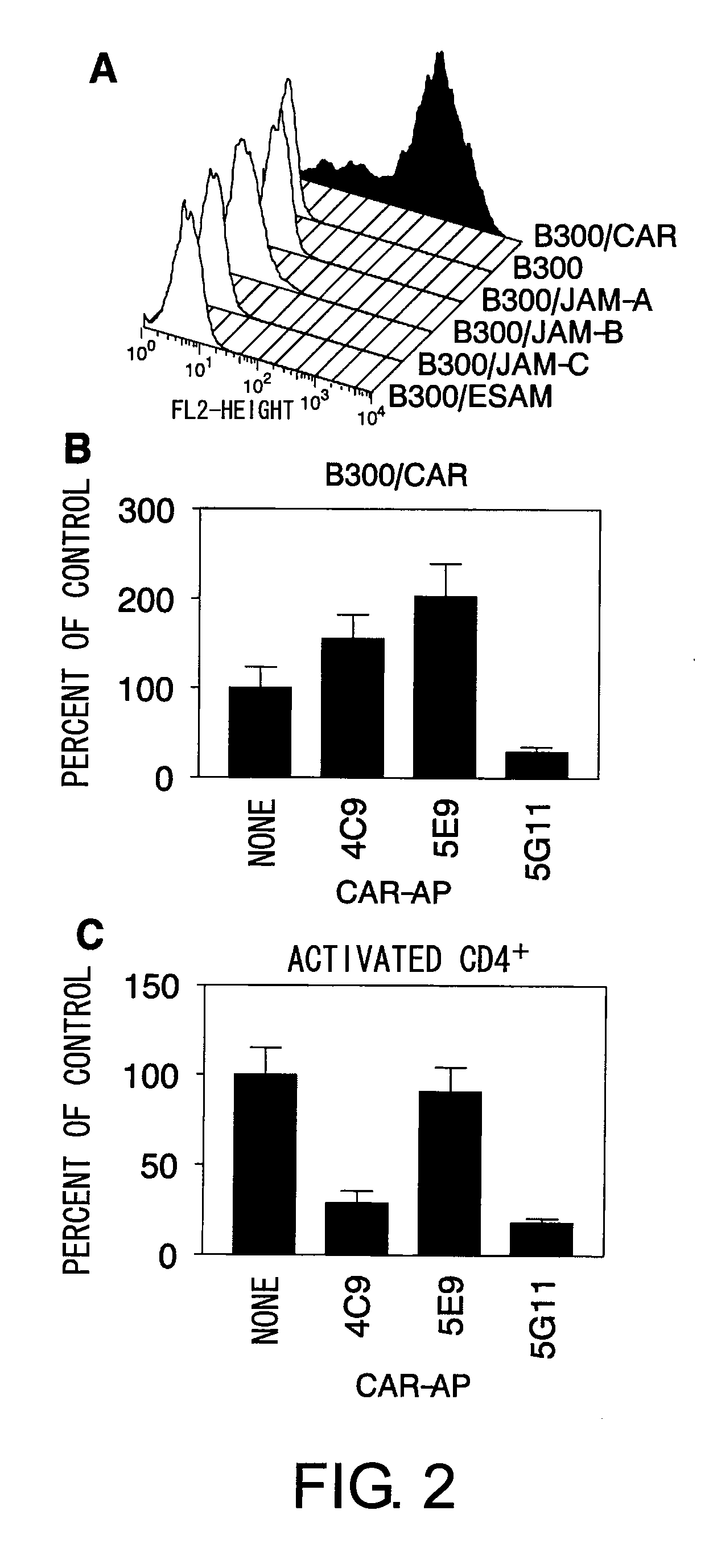
InactiveUS20080248502A1Suppress immune responseDisease controlMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisActivated LymphocyteCell biology
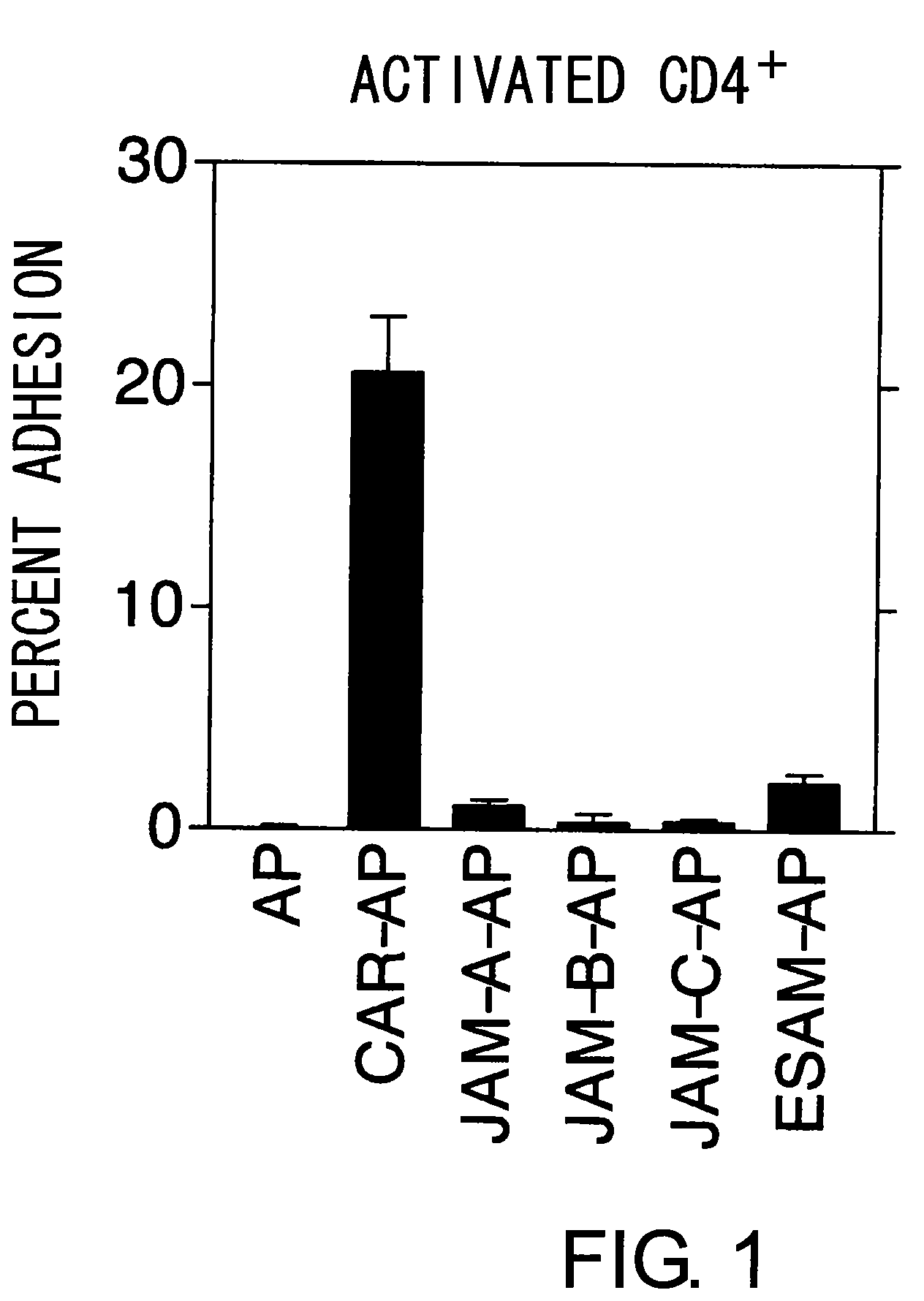
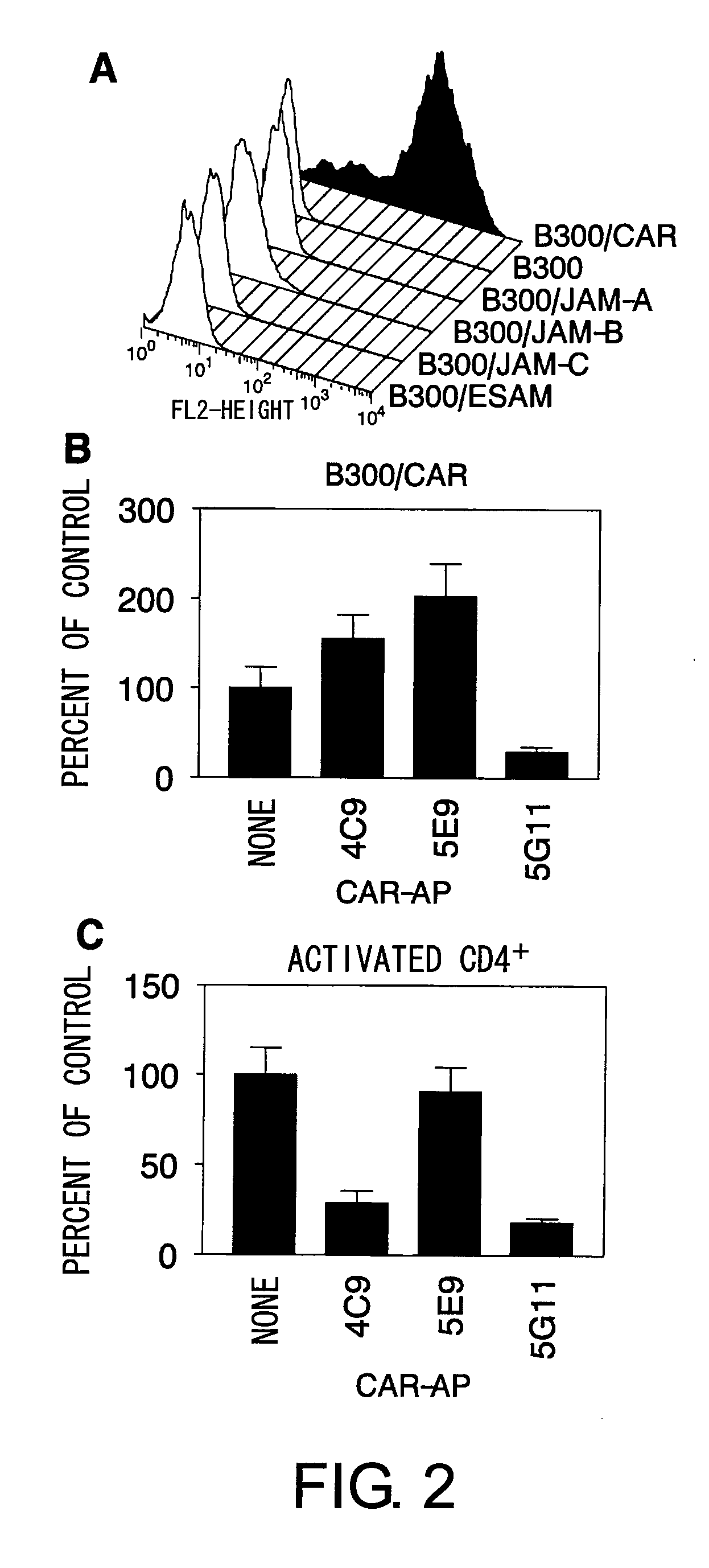
The inventors discovered that the adhesion molecule CAR, known to be localized in intracellular adhesion sites, functioned as an adhesion molecule for activated lymphocytes. Further, the inventors identified CARL, a novel CAR ligand expressed in lymphocytes, and clarified that the ligand was expressed selectively in Th1 cells. In addition, they found that anti-CAR antibodies could inhibit the adhesion of activated lymphocytes to CAR molecules. Thus, the present invention provides methods for detecting Th1 cells using CAR or anti-CARL antibodies, and methods of screening for inhibitors suppressing the adhesion of Th1 cells using the binding between CAR and CARL as an index. Furthermore, the present invention relates to methods of screening for inhibitors of the binding between CAR and CARL, antibodies that inhibit the binding between CAR and CARL, and therapeutic compositions comprising these antibodies. These are expected to be useful in diagnosing diseases, such as inflammation, in which infiltration of Th1 cells is involved, and in providing pharmaceutical agents for alleviating such diseases.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Highly effective method for amplifying activated lymphocyte and cultivation system
ActiveCN101302491AAvoid damageLow costMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsAbnormal tissue growthAcquired immunodeficiency
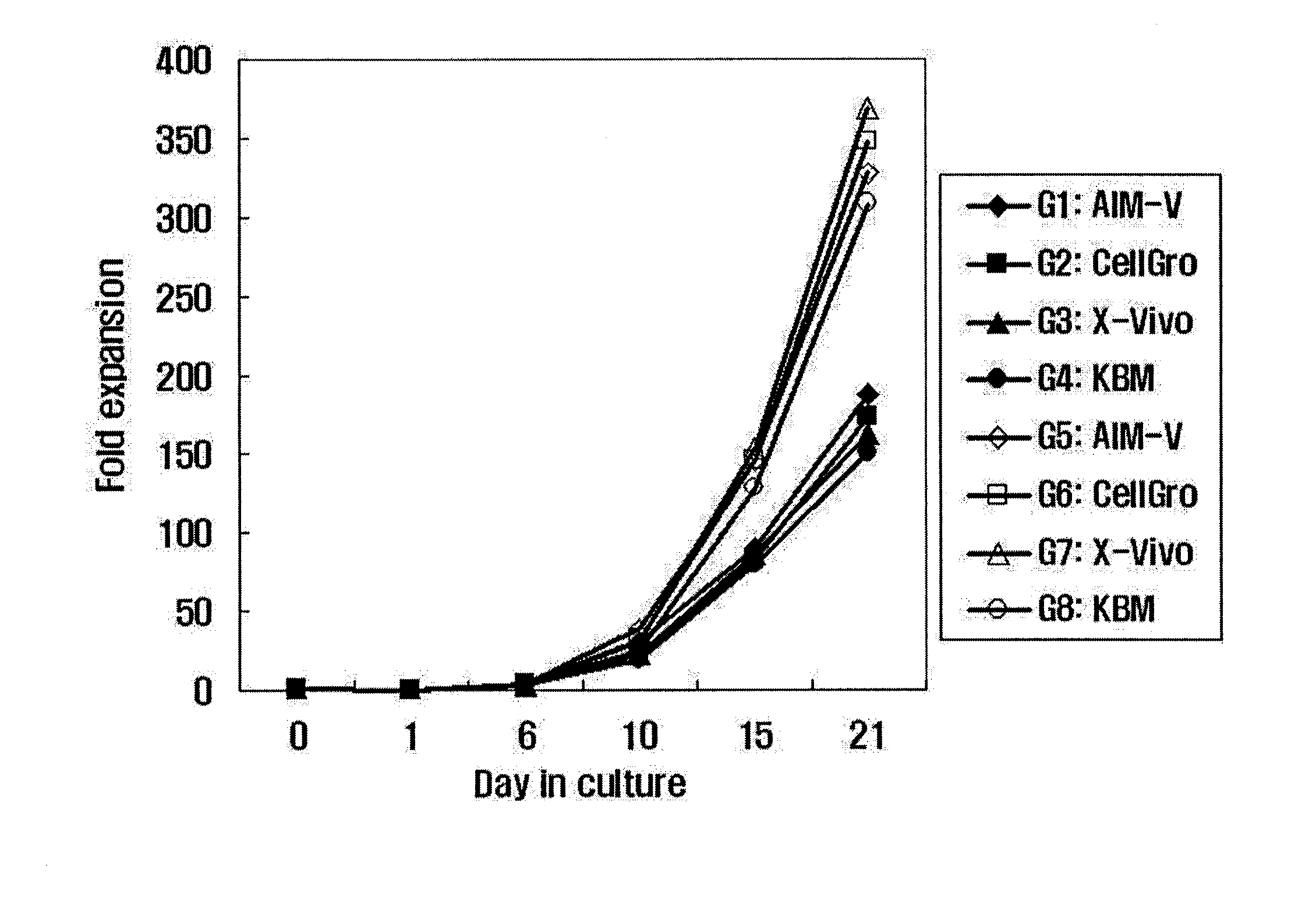
The invention relates to a method for expanding activated lymphocyte, comprising the steps of allowing biologic sample containing lymphocytes to contact immobilized anti-CD 3 antibodies, then cultivating activated lymphocytes with culture mediums in different IL-2 concentrations to expand the activated lymphocytes. The invention also relates to a cultivation system used for expanding activated lymphocytes. The expanded activated lymphocytes can be applied in the immunotherapy of tumor, infectious diseases, and congenital or acquired immunodeficiency diseases.
Owner:BEIJING YONGTAI IMMUNITY APPL TECH
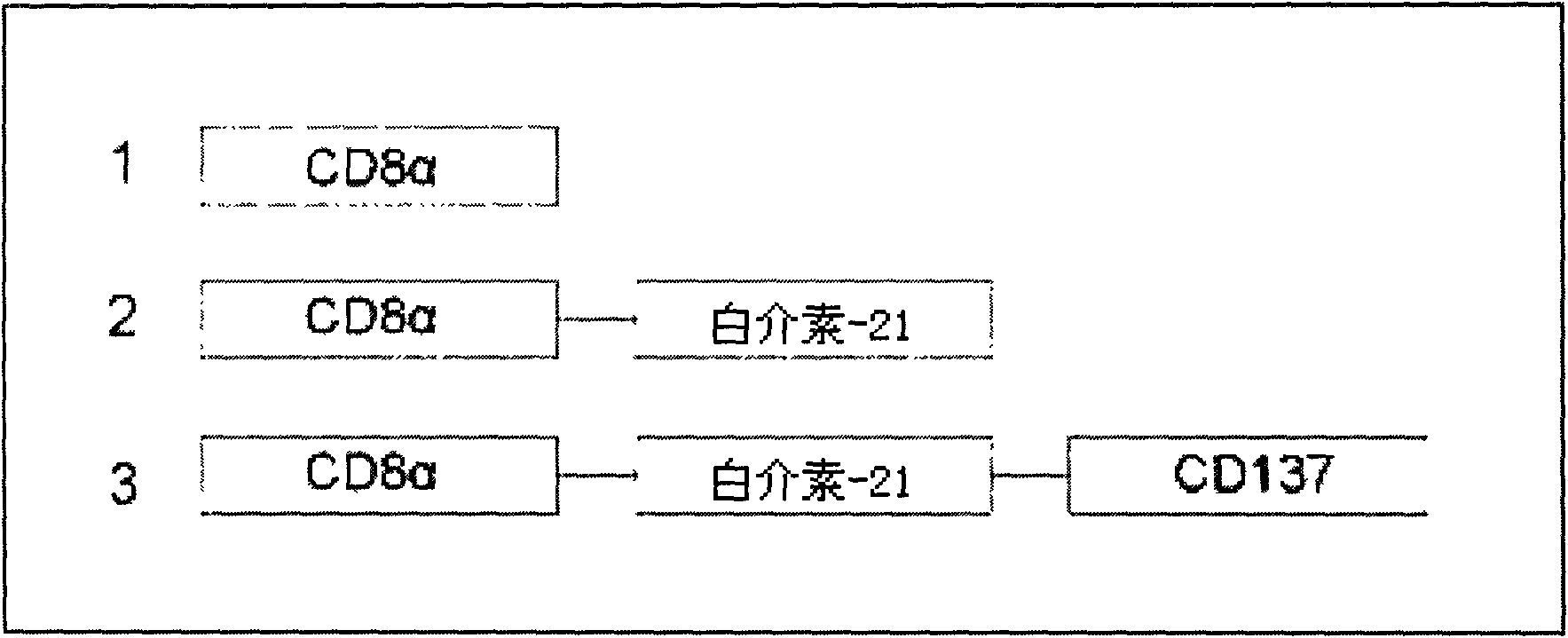
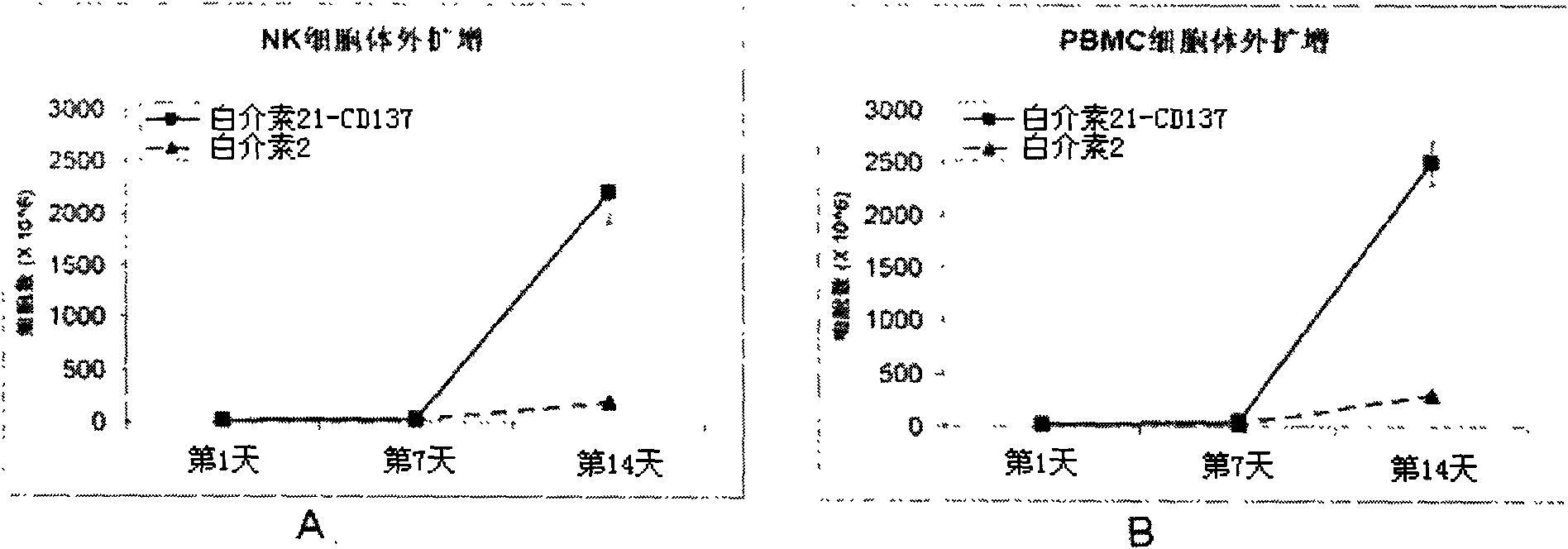
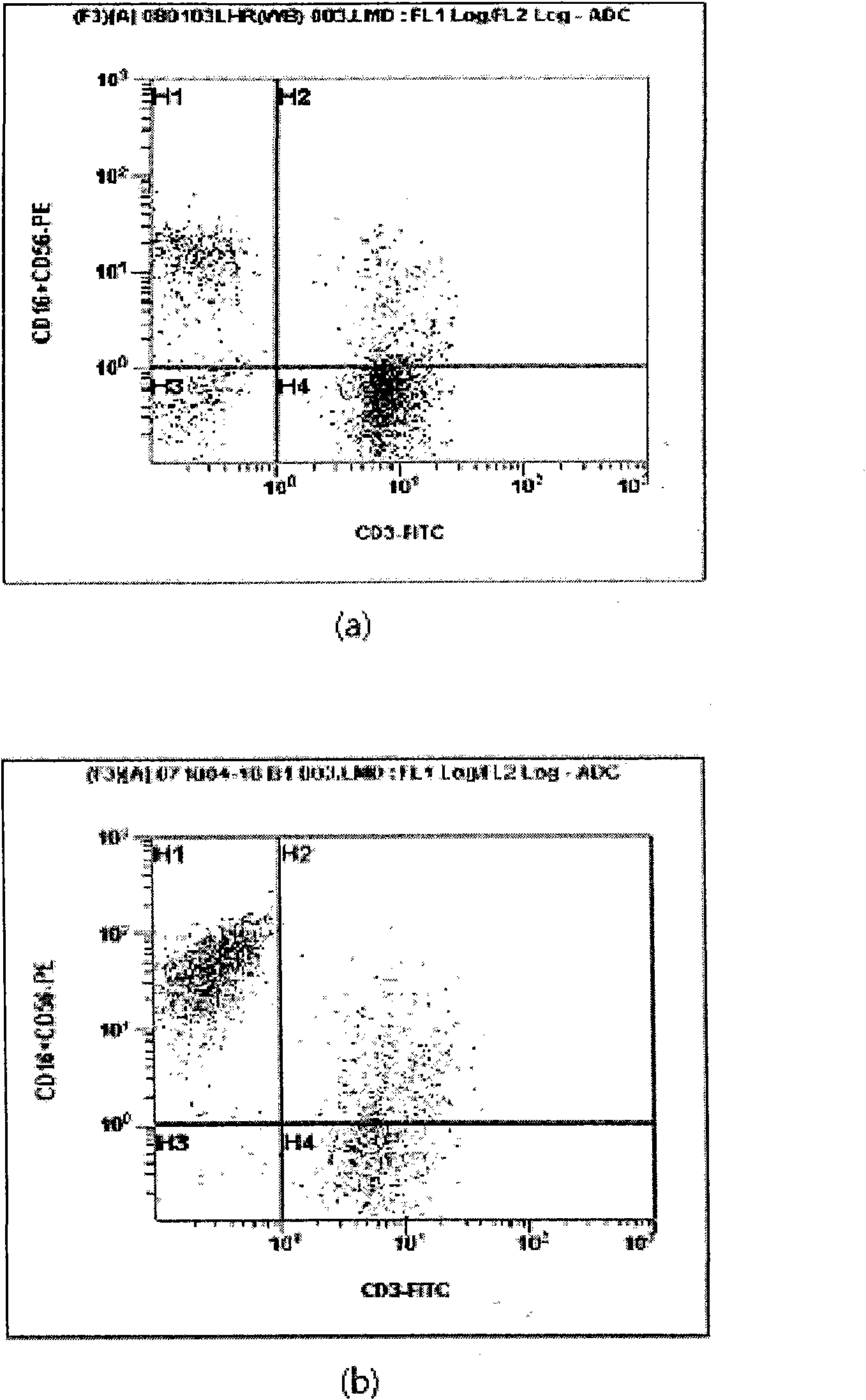
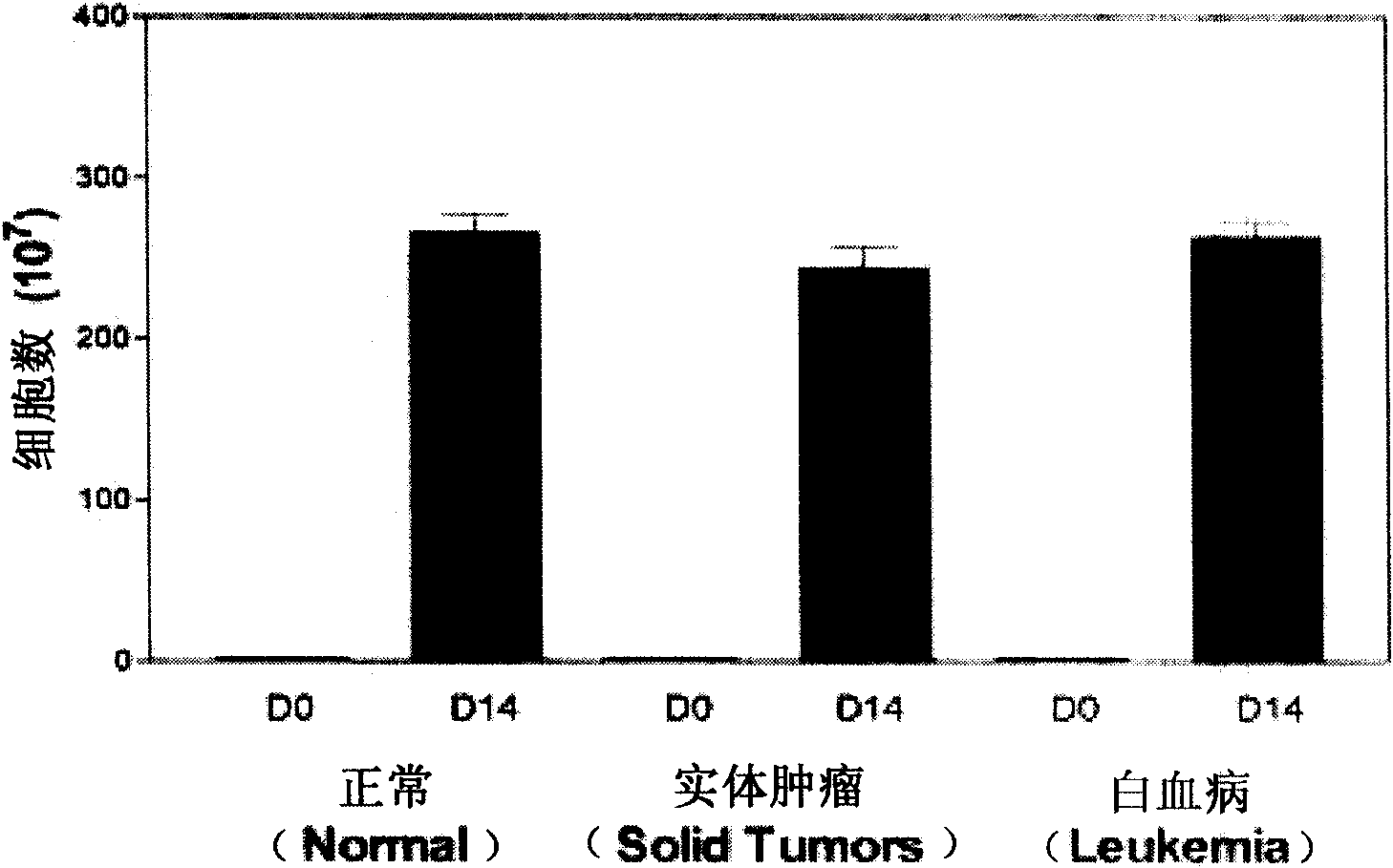
Method for amplifying and activating lymphocyte by using CD8 alpha-interleukin 21-CD137 compound
The invention relates to the field of immunology, in particular to a method for amplifying and activating a natural killer (NK) cell into a lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell by using a CD8 alpha-interleukin 21-CD137 compound. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: forming the CD8 alpha-interleukin 21-CD137 compound by using CD8 alpha, interleukin 21 and a CD137 functional polypeptide, making an exogenous expression vector enter a host K562 cell, then activating a promoter and culturing a cell to obtain a cell for expressing a transmembrane interleukin 21-CD137 compound; and purifying the compound in the conventional way, and amplifying and activating a lymphocyte by using the purified compound to generate the LAK cell. The method has the advantage that: the LAK cell cultured and amplified by using the transmembrane interleukin 21-CD137 compound and a small dose of interleukin 2 is used for enhancing the immunity of a patient to help the patient resist tumors, viruses and bacteria. The method has a wide clinical using prospect.
Owner:杭州中赢生物医疗科技有限公司
A method for cultivating self activated lymphocyte
InactiveCN101603029ALittle side effectsImproved prognosisCancer antigen ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsCancer cellCD16
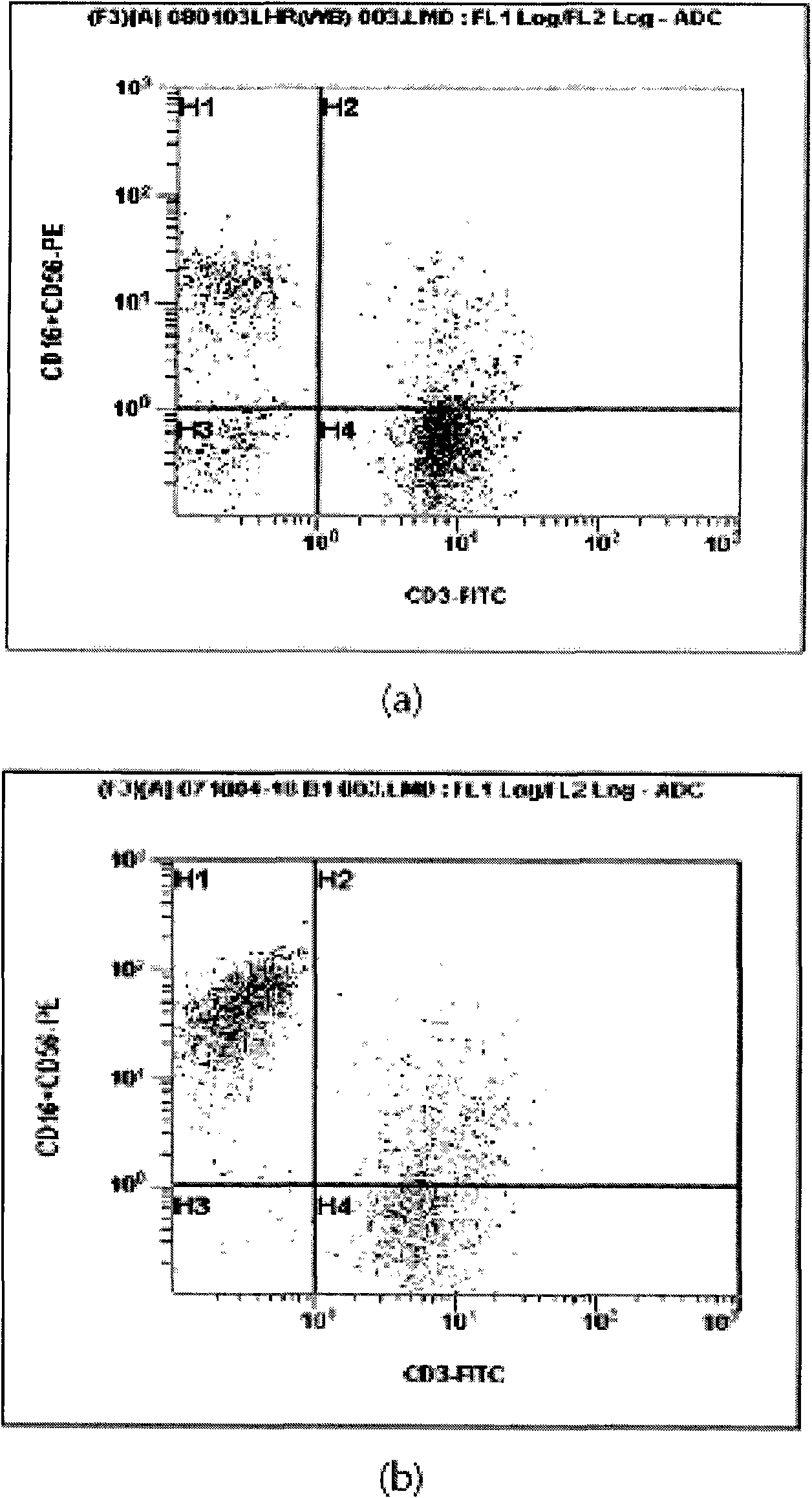
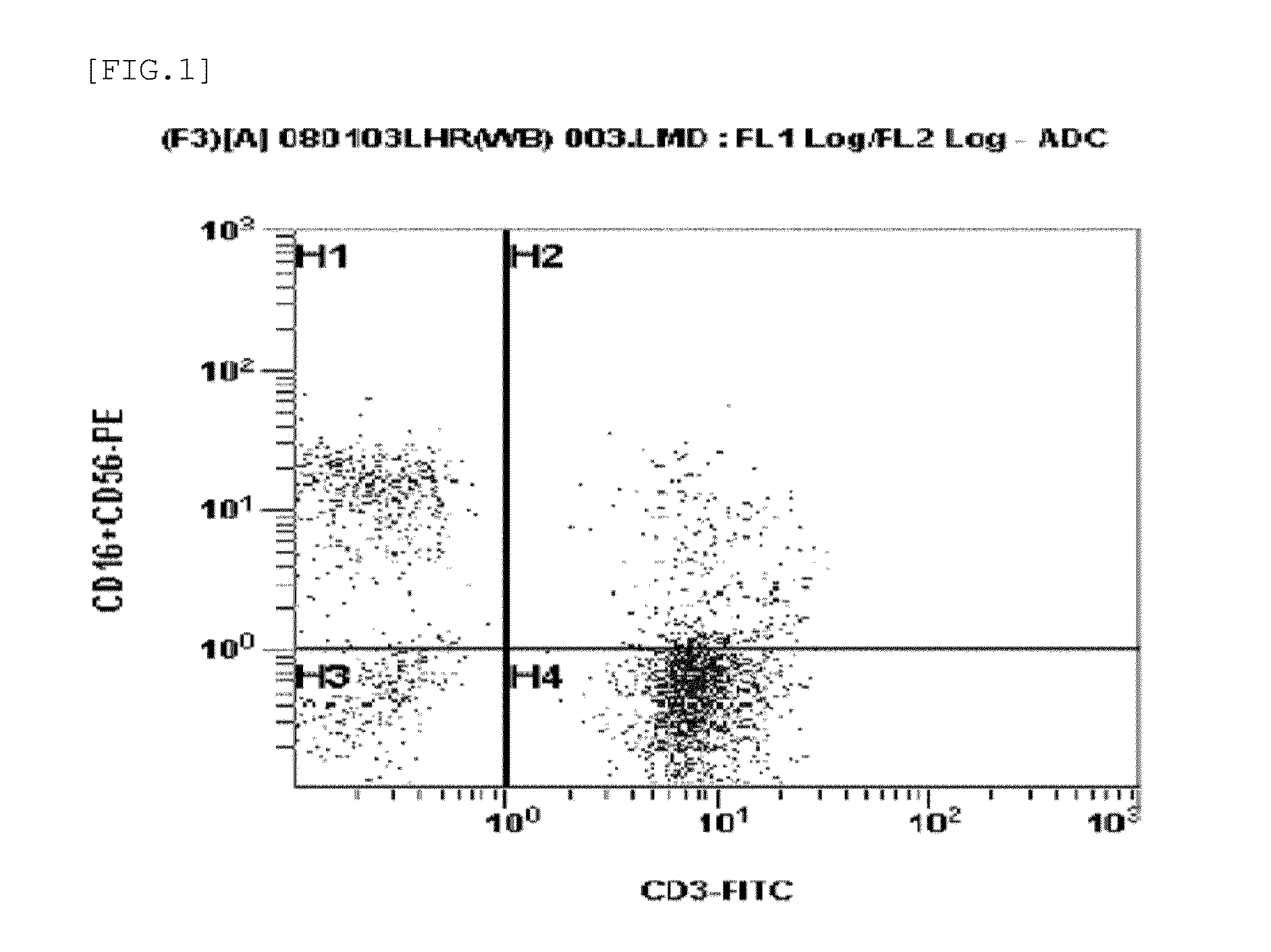
Provided is a method of culturing self-activated lymphocytes applicable to the treatment of malignant tumors. The method raises the percentage's of natural killer (NK) cells of the lymphocytes and evenly activate the NK cells, T cells and natural killer T (NKT) cells, and thus can be used to effectively eliminate various kinds of cancer cells. The method of culturing self- activated lymphocytes involves: extracting lymphocytes from human peripheral blood; performing a first culturing step of culturing the extracted lymphocytes in a culture fluid to which IL-2, L-glutamine and autochthonous plasma are added, in the presence of anti-CD3, anti- CD 16, and anti-CD56 antibodies; and performing a second culturing step of culturing the mixed culture fluid resulting from the first culturing step in the presence of anti-CD3, anti-CD16, and anti-CD56 antibodies after being admixed with a culture fluid to which IL-2, L-glutamine and autochthonous plasma are added.
Owner:NKBIO
A medium composition for cultivating self activated lymphocyte
InactiveCN101603028AEnhance killing activityLittle side effectsCancer antigen ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsCD16Cell culture media
Provided is a medium composition for culturing self- activated lymphocytes applicable to the treatment of malignant tumors, to which anti-CD3, anti-CD16 and anti-CD56 antibodies are added along with interleukin2 (IL-2) to evenly activate natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and natural killer T (NKT) cells, and thus the medium composition can be used to culture im- munocytes that can effectively treat various kinds of malignant tumors. The medium composition includes a cell culture medium and additives added to the cell culture medium, wherein the additives include interleukin2 (IL-2), anti-CD3 antibodies, anti-CD16 antibodies, and anti-CD56 antibodies.
Owner:NKBIO
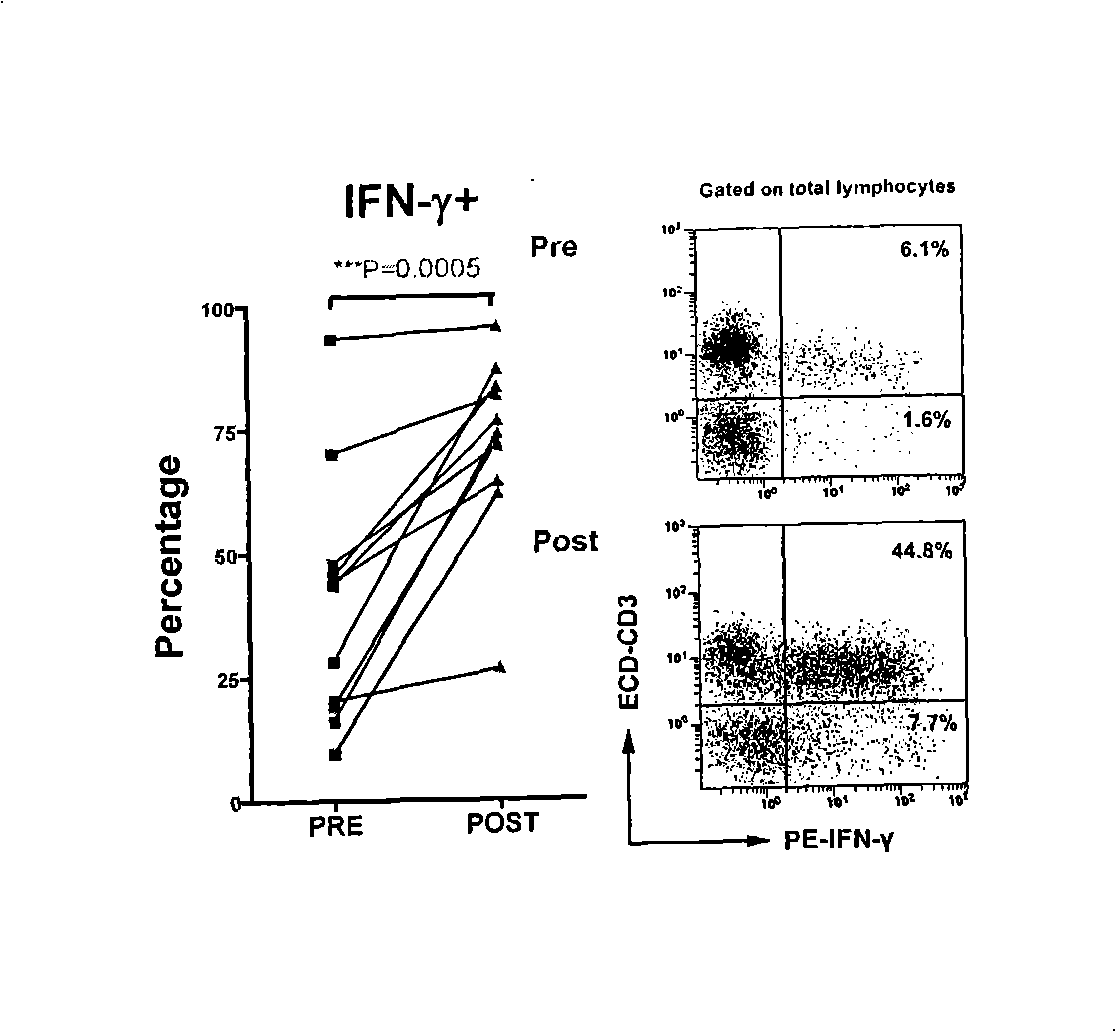
Manufacturing Method of Activated Lymphocytes for Immunotherapy
InactiveUS20100233192A1Easy to killGood killing effectSnake antigen ingredientsAntiviralsNatural killer cellImmunotherapy
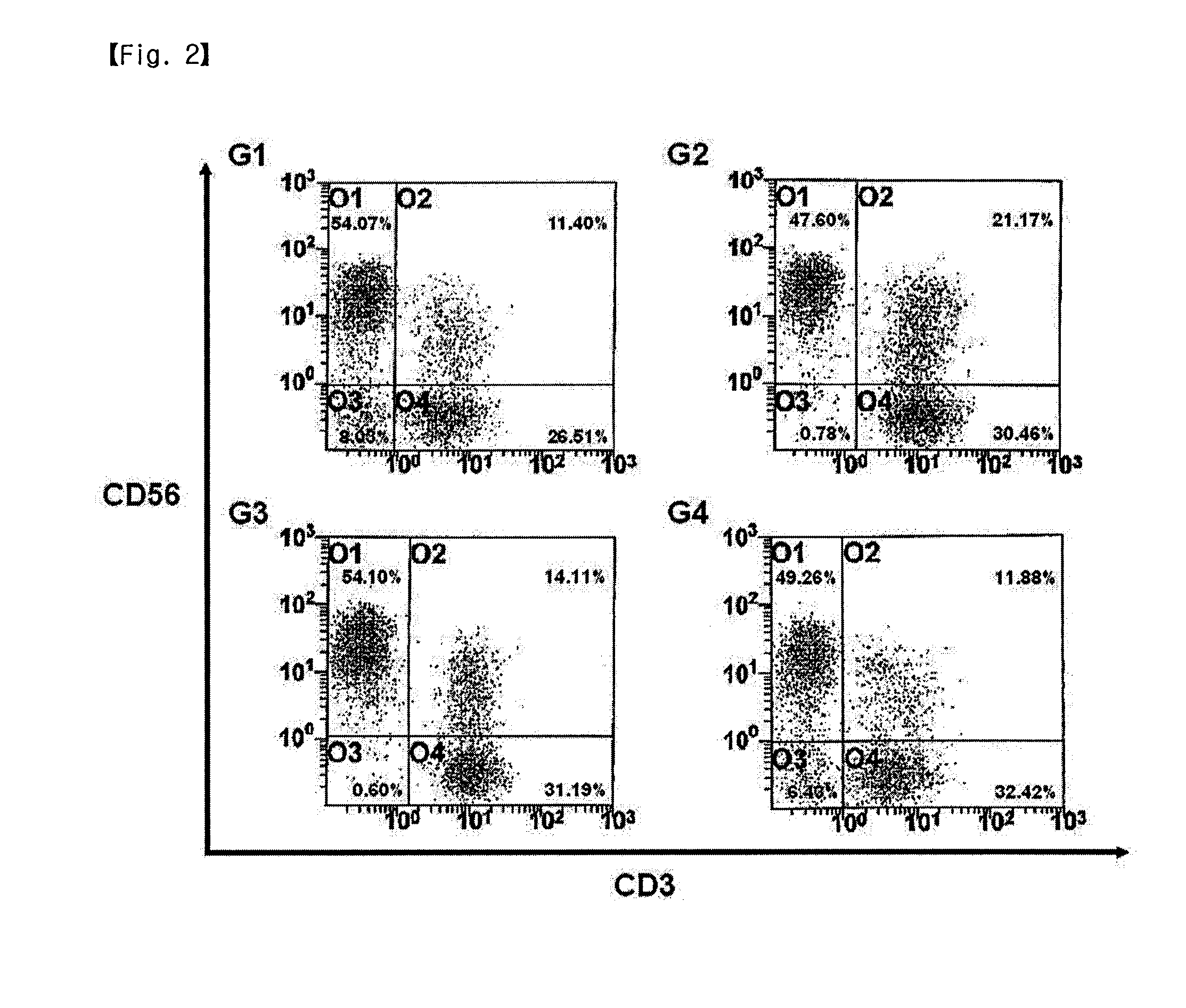
Disclosed is a method for preparing activated lymphocytes, which comprises isolating lymphocytes from peripheral blood and proliferating and activating the isolated lymphocytes in vitro. According to the disclosed method, highly effective toxic cells can be prepared in large amounts by culturing human peripheral lymphocytes in the presence of an anti-CD3 antibody, IFN-γ and IL-2. The activated lymphocytes proliferated according to the disclosed preparation method comprise both CD3-CD56+ (natural killer cell marker) cells that are the main components of LAK cells, and CD3+CD56+ cells that are the main components of CIK cells, and can be cultured in large amounts. Thus, the lymphocyte cells can show a significantly higher anticancer effect compared to when the LAK cells and the CIK cells are used alone.
Owner:BINEX CO LTD
Medium composition for culturing self-activated lymphocytes and method for culturing self-activated lymphocytes using same
InactiveUS20130157364A1Raise the ratioLess side effectsCancer antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulinsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsCD16
Disclosed is a medium composition for culturing self-activated lymphocytes, which contains anti-CD3 antibody and anti-CD16 antibody in addition to interleukin 2 (IL-2), interleukin 12 (IL-12) and interleukin 18 (IL-18) in a medium, and thus can efficiently proliferate and activate NK cells, T cells and NKT cells and, at the same time, can significantly increase the ratio of NK cells in lymphocytes so as to provide immunocytes having excellent effects on the treatment of various kinds of malignant tumors, and a method for culturing self-activated lymphocytes using the medium composition.
Owner:CELLTECH LTD
Medium composition for culturing self-activated lymphocytes and method for culturing self-activated lymphocytes using same
InactiveCN103080302ARaise the ratioLittle side effectsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCancer antigen ingredientsCD16Interleukin II
Disclosed is a medium composition for culturing self-activated lymphocytes, which contains anti-CD3 antibody and anti-CD16 antibody in addition to interleukin 2 (IL-2), interleukin 12 (IL-12) and interleukin 18 (IL-18) in a medium, and thus can efficiently proliferate and activate NK cells, T cells and NKT cells and, at the same time, can significantly increase the ratio of NK cells in lymphocytes so as to provide immunocytes having excellent effects on the treatment of various kinds of malignant tumors, and a method for culturing self-activated lymphocytes using the medium composition.
Owner:CELLS SCI CORP
Manufacturing method of activated lymphocytes for immunotherapy
Disclosed is a method for preparing activated lymphocytes, which comprises isolating lymphocytes from peripheral blood and proliferating and activating the isolated lymphocytes in vitro. According to the disclosed method, highly effective toxic cells can be prepared in large amounts by culturing human peripheral lymphocytes in the presence of an anti-CD3 antibody, IFN-gamma and IL-2. The activated lymphocytes proliferated according to the disclosed preparation method comprise both CD3-CD56+ (natural killer cell marker) cells that are the main components of LAK cells, and CD3+CD56+ cells that are the main components of CIK cells, and can be cultured in large amounts. Thus, the lymphocyte cells can show a significantly higher anticancer effect compared to when the LAK cells and the CIK cells are used alone.
Owner:BINEX CO LTD
Method for treating tumors, infectious diseases, and autoimmune diseases with an activated HLA matching donor-originating lymphocyte
InactiveUS20080014174A1Effective treatmentHigh antineoplastic effect and antiviral effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthAutoimmune condition
According to the present invention, HLA matching donor-originating activated lymphocytes highly effective in the treatment of patients with tumors, viral infections and autoimmune diseases are prepared by collecting cells contained in peripheral blood originating from an HLA matching donor or peripheral blood originating from an HLA matching donor achieving micro-chimerism and by stimulating and propagating the cells thus collected with, for instance, interleukin 2 and anti-CD3 antibodies or the like. The HLA matching donor-originating activated lymphocytes thus prepared can be administered to an HLA matching patient with a tumor, a viral infection or an autoimmune disease for therapeutic or preventive purposes.
Owner:LYMPHOTEC
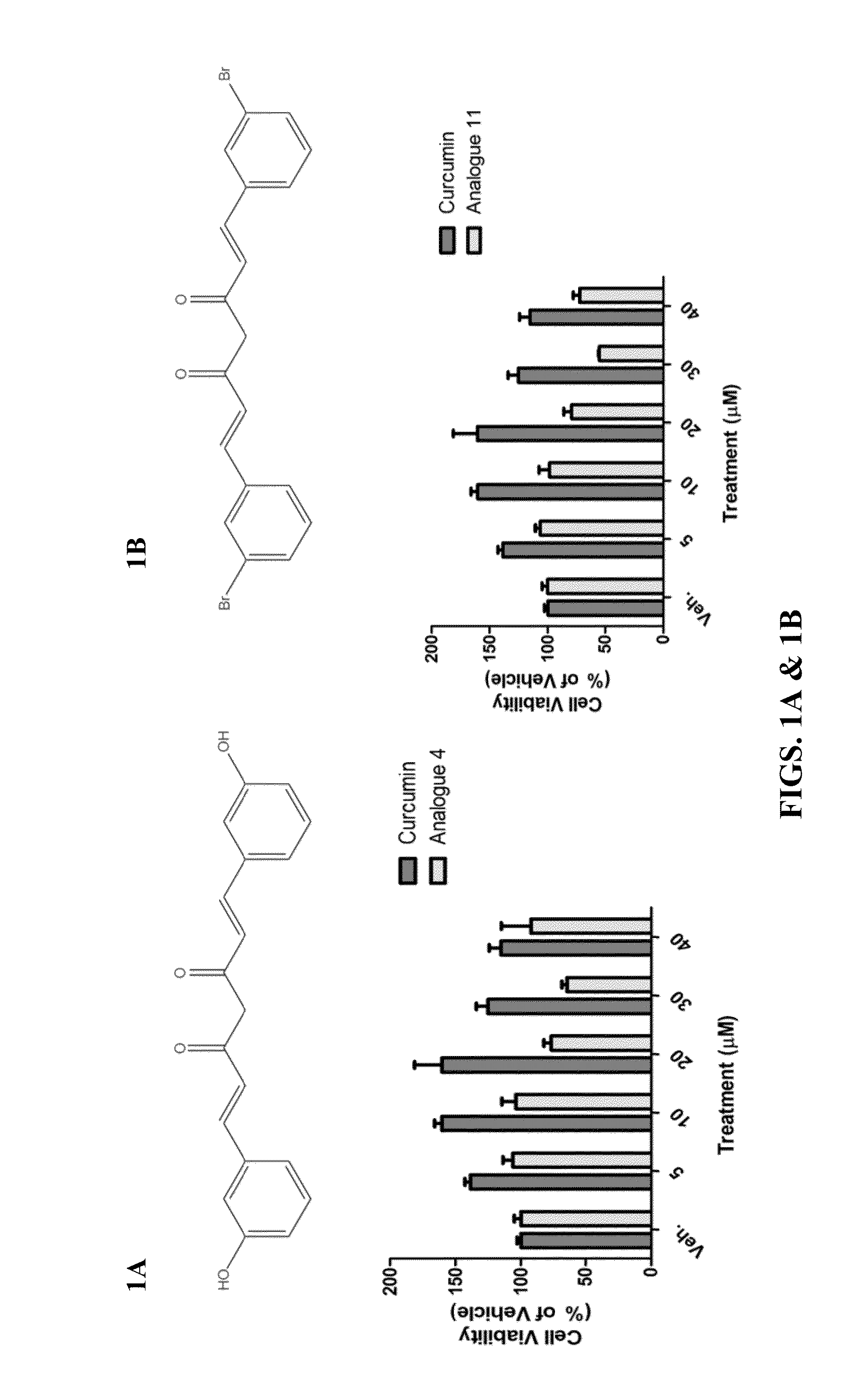
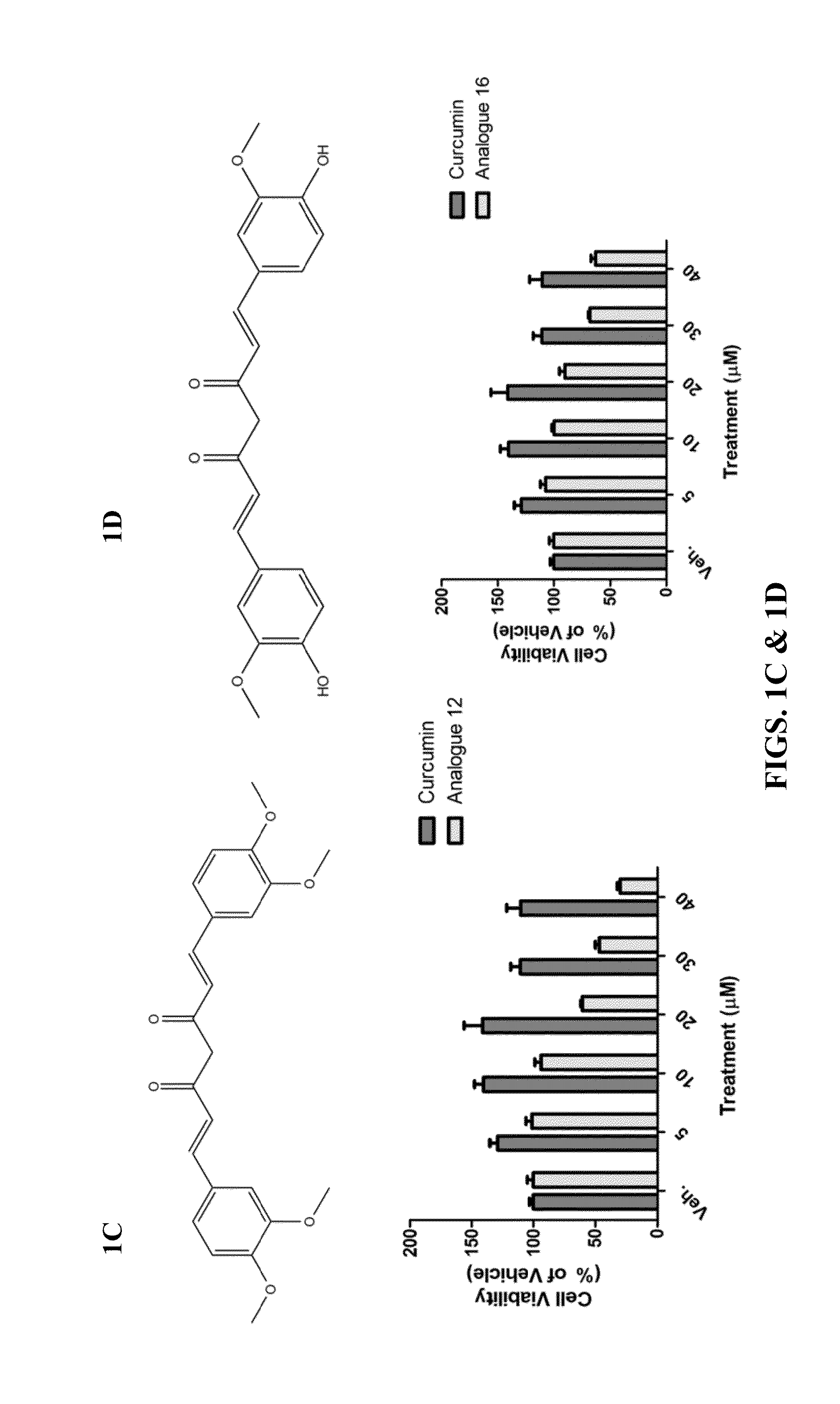
Protective Effects of Curcumin Against Hemorrhagic Stroke Injury
ActiveUS20150087705A1Reduce disruptionIncrease neurological outcome scoreBiocideOrganic chemistryMedicineActivated Lymphocyte
Disclosed herein are compounds, compositions and methods for preventing and treating diseases such as intracerebral hemorrhage, cancer, or conditions associated with damaged cells, activated lymphocytes, or microbial products. The disclosed compounds are curcumin analogs. The curcumin analogs possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which in part, reduce AP-1 and NF-κB activity.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
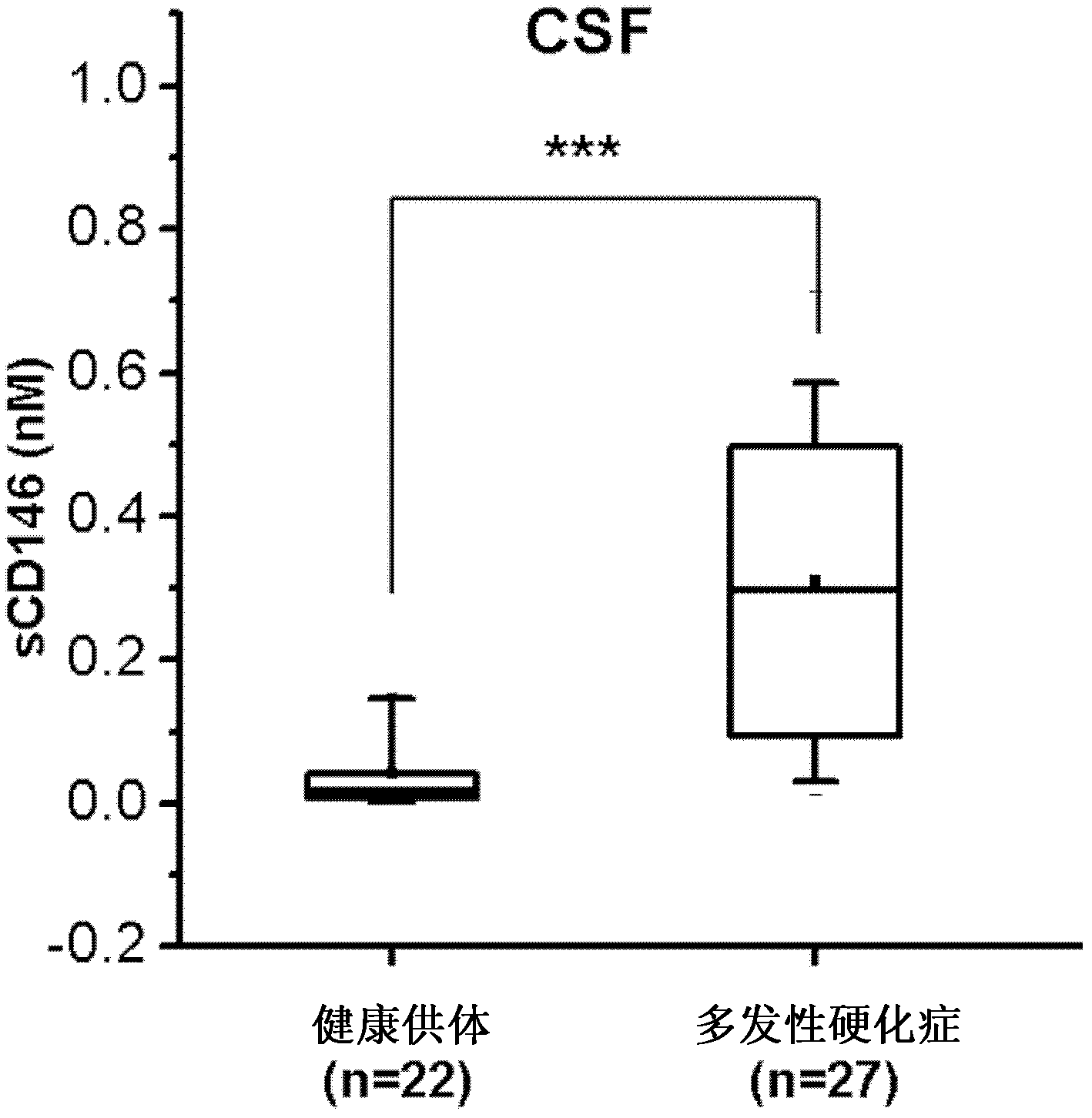
CD (cluster differentiation) 146 and application thereof to antibody diagnosis and treatment for inflammable diseases such as autoimmunity diseases
ActiveCN102861331ALittle side effectsNo damageNervous disorderAntipyreticSide effectAutoimmune responses
The invention relates to a CD (cluster differentiation) 146 and application thereof to antibody diagnosis and treatment for inflammable diseases such as autoimmunity diseases. The CD146 is a novel target for treating the inflammable diseases such as the autoimmunity diseases, and an antibody to the CD146 is a novel targeted drug for treating the diseases. Accordingly, the invention provides the CD146 or the antibody to the CD146 or functions and the form of the antibody in terms of application to preparing drugs for diagnosing and / or for treating the inflammable diseases. The function mechanism of the antibody to the CD146 in terms of treatment of the inflammable diseases (such as multiple sclerosis) mainly includes that inflammatory cells are stopped from penetrating through blood brain barriers and other vascular endothelial cell barriers of a patient, injury to myelin sheaths of the central nervous system and other relevant tissues of the patient caused by activated lymphocytes is further suppressed, accordingly, the progress and recurrence of the multiple sclerosis and injury to the relevant tissues are delayed, and symptoms of the multiple sclerosis and development of relevant inflammable diseases are relieved. Compared with a conventional glucocorticoid drug for treating the autoimmunity diseases, the antibody to the CD146 is low in side effect, and cannot cause injury to immune functions of the whole body of the patient.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Methods for detecting Th1 cells
InactiveUS8017344B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansActivated LymphocyteBinding inhibition
The inventors discovered that the adhesion molecule CAR, known to be localized in intracellular adhesion sites, functioned as an adhesion molecule for activated lymphocytes. Further, the inventors identified CARL, a novel CAR ligand expressed in lymphocytes, and clarified that the ligand was expressed selectively in Th1 cells. In addition, they found that anti-CAR antibodies could inhibit the adhesion of activated lymphocytes to CAR molecules. Thus, the present invention provides methods for detecting Th1 cells using CAR or anti-CARL antibodies, and methods of screening for inhibitors suppressing the adhesion of Th1 cells using the binding between CAR and CARL as an index. Furthermore, the present invention relates to methods of screening for inhibitors of the binding between CAR and CARL, antibodies that inhibit the binding between CAR and CARL, and therapeutic compositions comprising these antibodies. These are expected to be useful in diagnosing diseases, such as inflammation, in which infiltration of Th1 cells is involved, and in providing pharmaceutical agents for alleviating such diseases.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Application of triptolide and triptolide derivative to preparation of medicine for treating and/or preventing lung injury diseases
InactiveCN106994129APrevent proliferationInhibition of replicationOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsDiseaseMethylprednisolone
The invention provides a novel purpose of triptolide and a triptolide derivative. The triptolide can obviously inhibit the GFP fluorescent protein and P24 antigen rise effect in a phorbol ester activated lymphocyte model. When the concentration of the lymphocyte concentration is higher, the GFP positive cell percentage and the P24 antigen concentration are lower; the negative dosage-effect relationship exists. Even when the concentration of the methylprednisolone is as high as 400 uM, the inhibition effect cannot reach the inhibition effect of the triptolide with the concentration being 0.02 uM; the cell apoptosis proportion obviously exceeds the triptolide with the concentration being 0.02 uM. According to the principle, the triptolide inhibits the G0 / G1 period cell proportion rise and S period cell proportion descending due to PMA; the cell period is promoted to be stopped in the unactivated state; the triptolide achieves the effect of inhibiting the lymphocyte cell proliferation and activation through regulating the cell period; meanwhile, the effect of inhibiting the virus replication is also achieved. The triptolide and the triptolide derivative can replace glucocorticoid analogues or can be combined with the glucocorticoid analogues to be used, and are used for treating and / or preventing lung injury diseases.
Owner:王晓辉
Detection, localization and staging of tumors using labeled activated lymphocytes directed to a tumor specific epitope
InactiveUS20060171883A1Bind more effectivelyGood effectDisease diagnosisRadioactive preparation formsAbnormal tissue growthCell specific
A Disclosed are methods for detecting and localizing a cell-specific antigen in a mammal, such as a human subject, comprising exposing peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of the mammal to an immunogenic peptide epitope of the antigen, under conditions for antigen-specific activation of T lymphocytes in the PBMCs, thereby producing antigen-specific T lymphocytes that at least bind to the cell-specific antigen. Labeled antigen-specific T lymphocytes are administered to the mammal, typically with-out IL-2, either intraperitoneally or intravenously. The distribution of these cells in the mammal is determined by imaging, thereby detecting and localizing cell-specific antigen in the mammal. Exposing PBMCs to the immunogenic peptide typically involves a cell-free peptide preparation and interleukin-2 (IL-2), but no additional cells such as antigen presenting cells (APC) separately pulsed with antigen. The antigen-specific T lymphocytes typically are cytolytic for cells expressing the cell-specific antigen and may comprise CD4+, CD8+, and / or CD45RO+ memory T cells.
Owner:PHILLIPS CATHERINE A DR +1
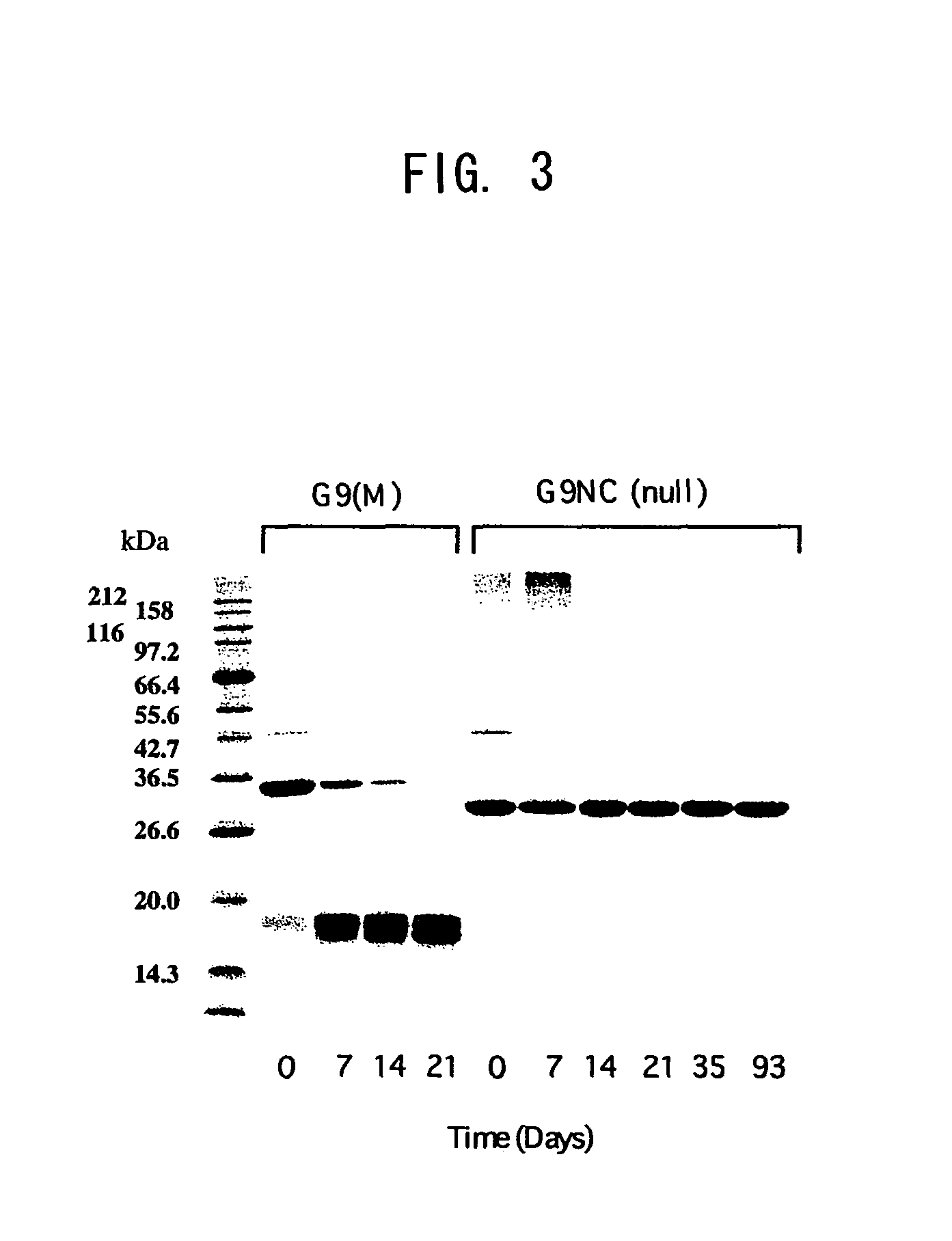
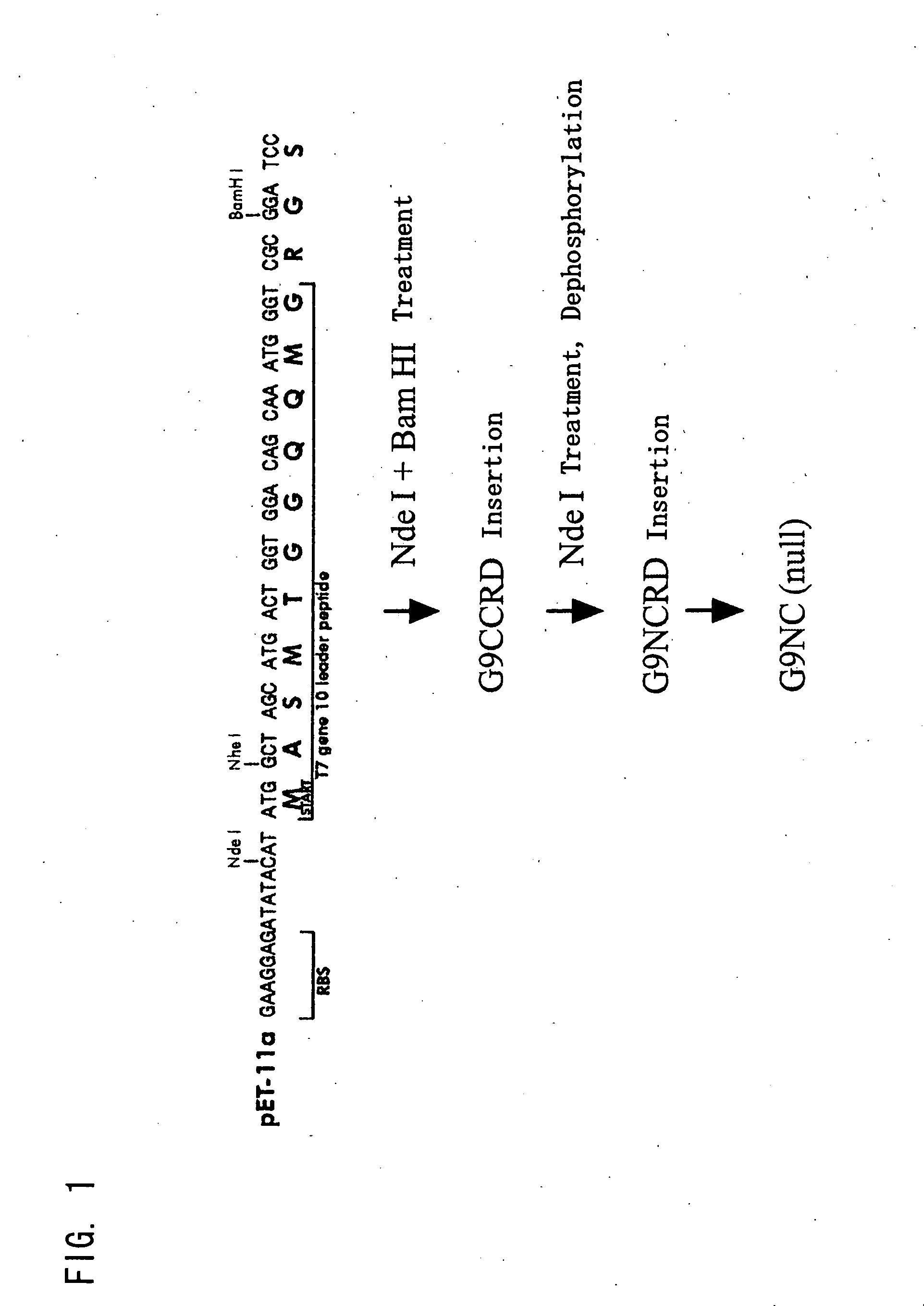
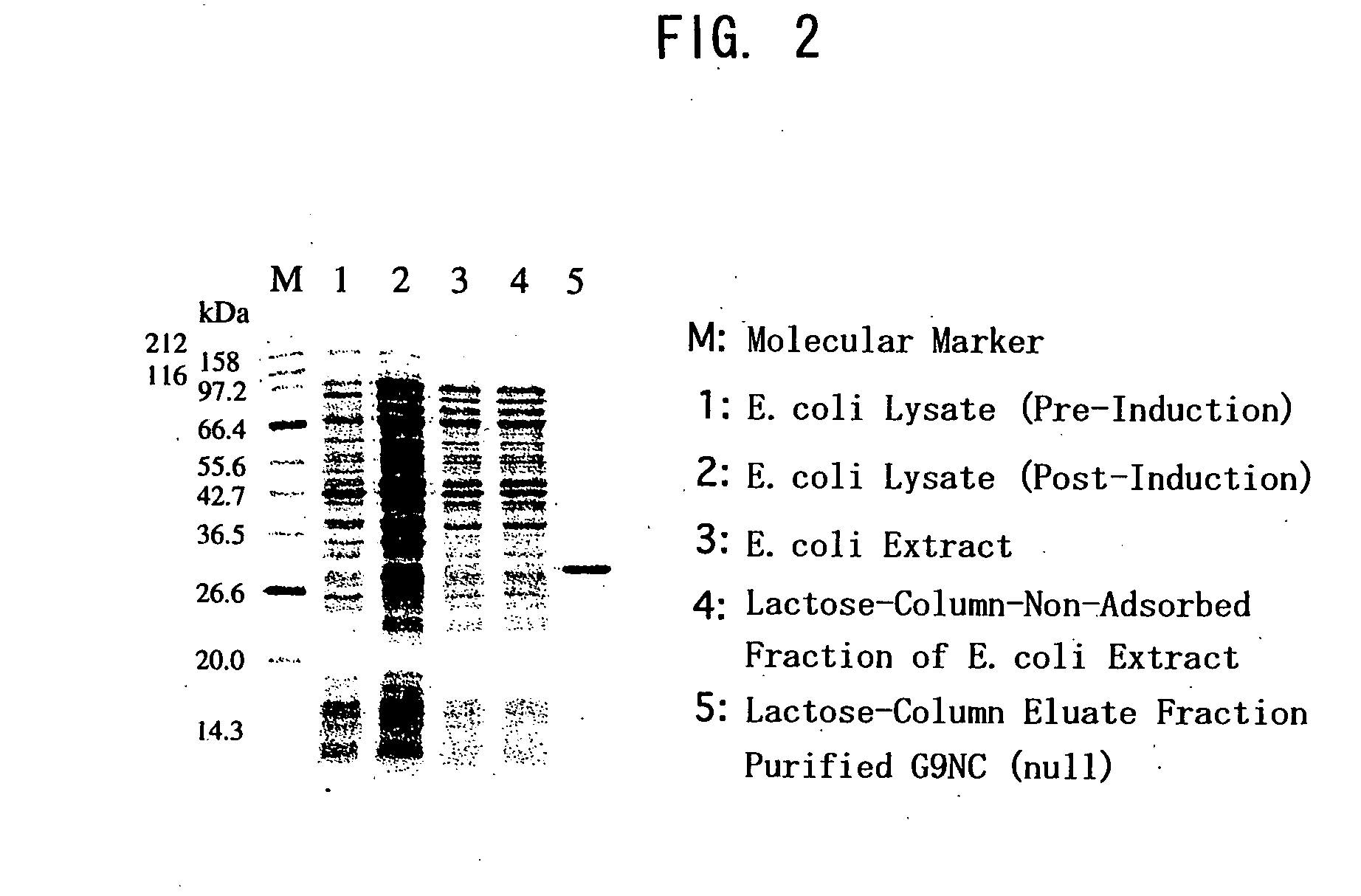
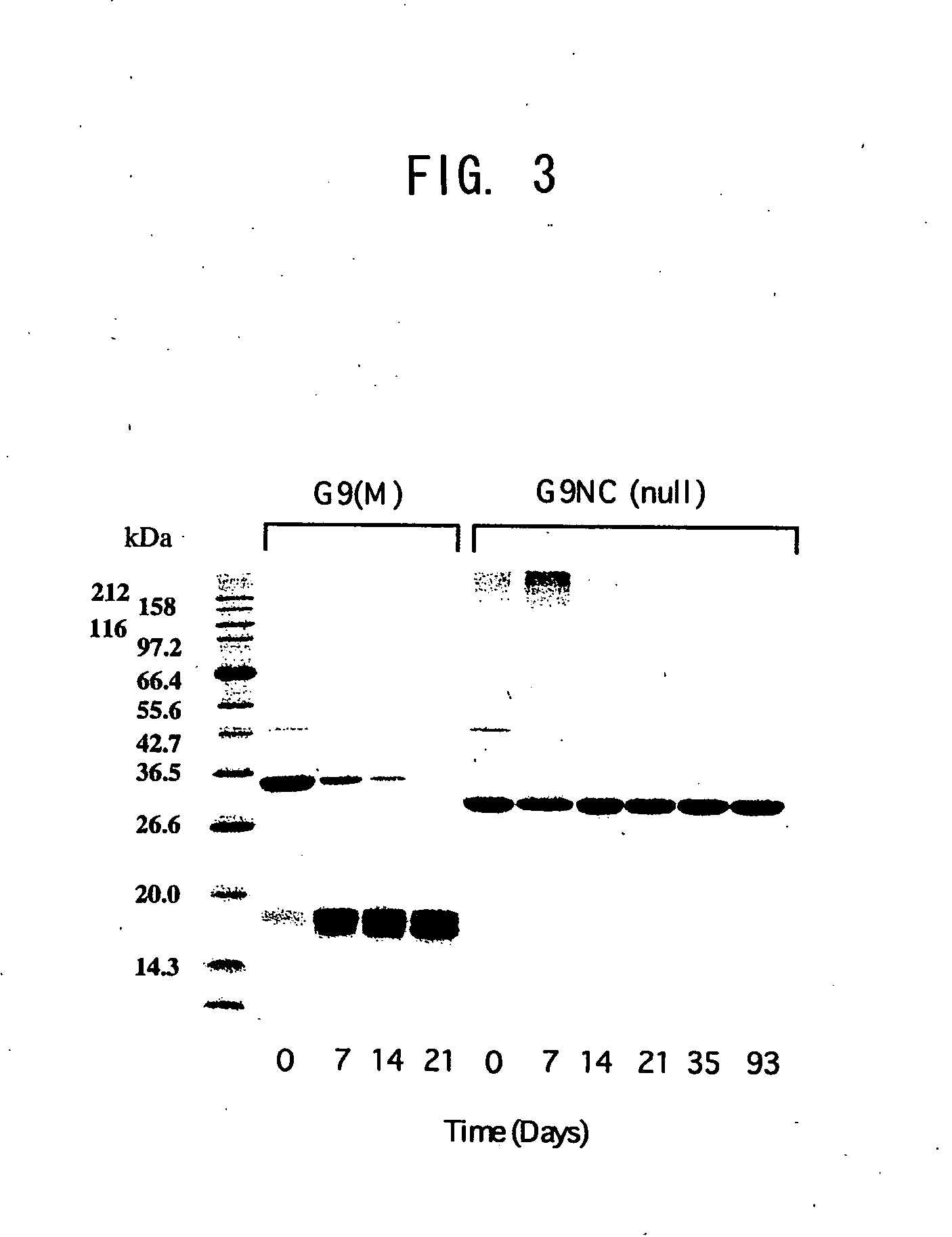
Modified galectin 9 proteins and use thereof
ActiveUS8268324B2More stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliSynovial Cell
It is suggested that recombinant galectin 9 (rGal 9), produced in host Escherichia coli, exhibits an immune system-mediated action and a direct action on tumor cells (i.e., activity of inducing the intercellular adhesion and apoptosis of the tumor cells), thereby potent in inducing the inhibition of cancer metastasis and reduction. Moreover, the rGal 9 exerts no efficacy on non-activated lymphocytes but can induce apoptosis in activated T cells, in particular, CD4-positive T cells causing an excessive immune response. The rGal 9 has a further potent apoptosis-inducing property on synovial cells participating in joint deformation in rheumatism, etc. In the rGal 9, however, a link domain linking two CRDs is highly susceptible to protease and, therefore, is very easily digestible with the enzyme, thereby losing the above activities. Thus, there is a need for a more stabilized molecule in view of further studies. Modification of the link domain linking two CRDs in galectin 9 provides a modified molecule having an elevated activity without any undesirable effects on the above activities.
Owner:GALPHARMA CO LTD
Novel modified galectin 9 proteins and use thereof
ActiveUS20100203628A1Readily apparentMore stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliSynovial Cell
It is suggested that recombinant galectin 9 (rGal 9), produced in host Escherichia coli, exhibits an immune system-mediated action and a direct action on tumor cells (i.e., activity of inducing the intercellular adhesion and apoptosis of the tumor cells), thereby potent in inducing the inhibition of cancer metastasis and reduction. Moreover, the rGal 9 exerts no efficacy on non-activated lymphocytes but can induce apoptosis in activated T cells, in particular, CD4-positive T cells causing an excessive immune response. The rGal 9 has a further potent apoptosis-inducing property on synovial cells participating in joint deformation in rheumatism, etc. In the rGal 9, however, a link domain linking two CRDs is highly susceptible to protease and, therefore, is very easily digestible with the enzyme, thereby losing the above activities. Thus, there is a need for a more stabilized molecule in view of further studies. Modification of the link domain linking two CRDs in galectin 9 provides a modified molecule having an elevated activity without any undesirable effects on the above activities.
Owner:GALPHARMA CO LTD
Methods of Treating CD166-Expressing Cancer
ActiveUS20180207269A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCancer cellALCAM
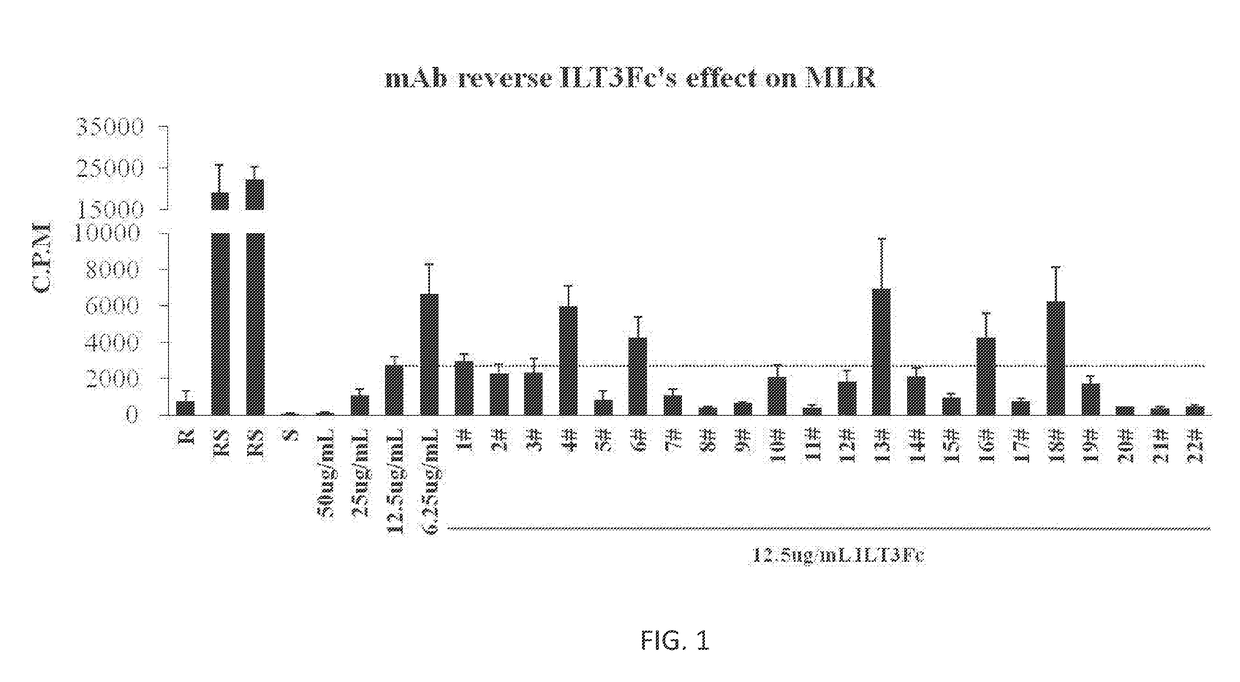
It has now been discovered that activated lymphocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM)-also known as CD166-is the ligand of the innate immune receptor ILT3 that is expressed by DC and monocytes. It has been further discovered that the specific binding of ILT3 to its ligand CD166 on the surface of CD166-expressing cancer cells, arrested cancer cell growth and initiated apoptosis. Therefore, certain embodiments relate to methods and compositions for treating CD166-expressing cancers by administering ILT3Fc, full-length ILT3 or any CD166 ligand-binding fragment thereof.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Activated lymphocyte from umbilical cord blood, preparations containing it as main content and method therefor
InactiveCN1363681AEliminate infectionEliminates the possibility of recurring tumorsAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
Activated lymphocytes derived from cord blood are excellently effective for preventing and treating various types of tumors and various types of infection. With interleukin 2 and / or anti-CD3 antibody, the lymphocytes derived from the cord blood is prepared by segregating lymphocytes from the cord blood and proliferating the segregated lymphocytes directly in vitro or segregating monocytes from cord blood and proliferating the monocytes in vitro. Also, the cord blood-derived activated lymphocytes can be effectively used for preventing recurrence of the diseases and promoting the take of stem cells or other organs.
Owner:HUMANTEC
Compositions for down-regulation of CCR5 expression and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7863242B2Reduces receptor sitesSuppressing transcriptionBiocideAntiviralsG1/S checkpointHIV receptor
The present invention relates to the downregulation of surface receptor CCR5 expression through manipulation of the cell cycle in activated lymphocytes by administering a composition that arrests the G1 phase of the cell cycle, thereby reducing receptor sites for entry of HIV into T cells, and thus, the effects of HIV. Further, compositions are disclosed that include at least one G1 phase arresting agent and at least one antiviral agent, wherein the combination of agents synergistically enhances the activity of the antiviral agent.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Hla matching donor-originating activated lymphocytes
InactiveCN1481901AImprove physical conditionInorganic non-active ingredientsAntiviralsAutoimmune conditionAntiendomysial antibodies
According to the present invention, HLA matching donor-originating activated lymphocytes highly effective in the treatment of patients with tumors, viral infections and autoimmune diseases are prepared by collecting cells contained in peripheral blood originating from an HLA matching donor or peripheral blood originating from an HLA matching donor achieving micro-chimerism and by stimulating and propagating the cells thus collected with, for instance, interleukin 2 and anti-CD3 antibodies or the like. The HLA matching donor-originating activated lymphocytes thus prepared can be administered to an HLA matching patient with a tumor, a viral infection or an autoimmune disease for therapeutic or preventive purposes.
Owner:LYMPHOTEC
Detection, localization and staging of tumors using labeled activated lymphocytes directed to a tumor specific epitope
InactiveCN1711475AEffective combinationDisease diagnosisRadioactive preparation formsAbnormal tissue growthCell specific
This paper discloses methods for detecting and localizing cell-specific antigens in mammals such as humans, including exposing mammalian peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to antigen-specific immunization under conditions of antigen-specific activation of T lymphocytes in PBMCs. antigenic peptide epitopes, thereby generating at least antigen-specific T lymphocytes that bind to the cell-specific antigen. Labeled antigen-specific T lymphocytes are administered intraperitoneally or intravenously to mammals, usually in the absence of IL-2. The distribution of these cells in mammals is determined by imaging, allowing detection and localization of cell-specific epitopes in mammals. Exposure of PBMCs to immunogenic peptides generally involves cell-free peptide preparations and interleukin-2 (IL-2), but not other cells such as antigen-presenting cells (APCs) that are independently activated by antigen. Antigen-specific T lymphocytes can typically lyse cells expressing the cell-specific antigen and may include CD4+, CD8+ and / or CD45RO+ memory T cells.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com