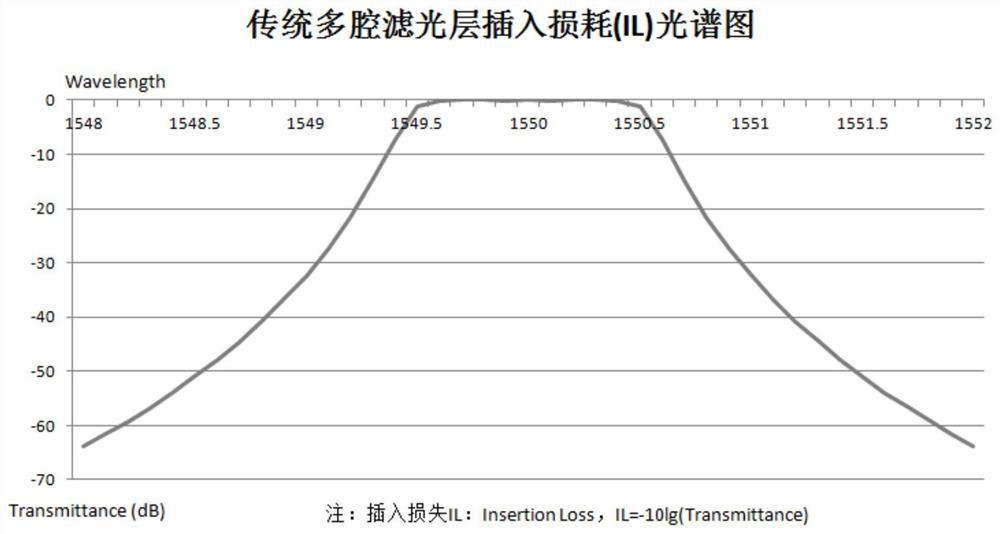
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30results about How to "Suppress light loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
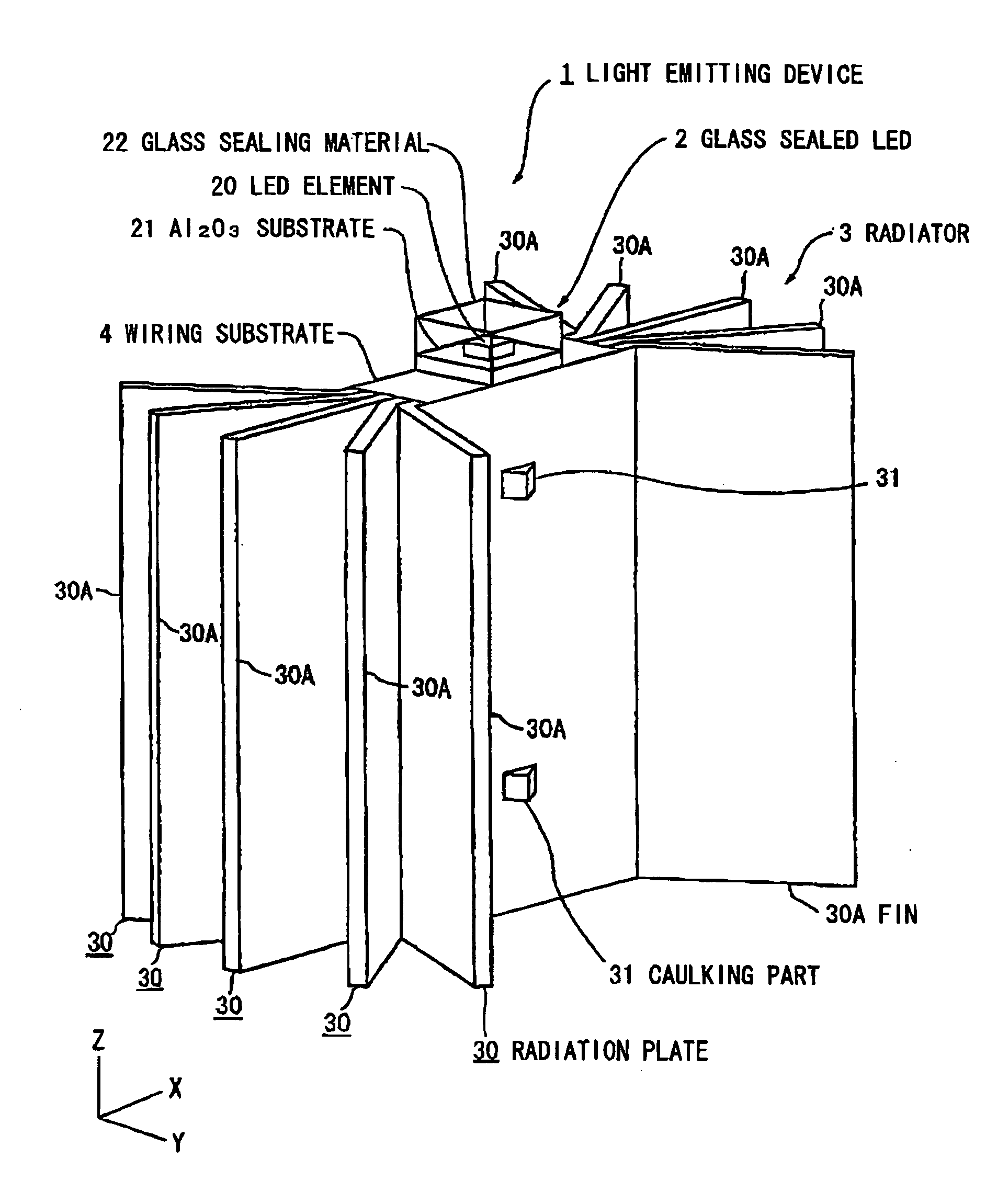
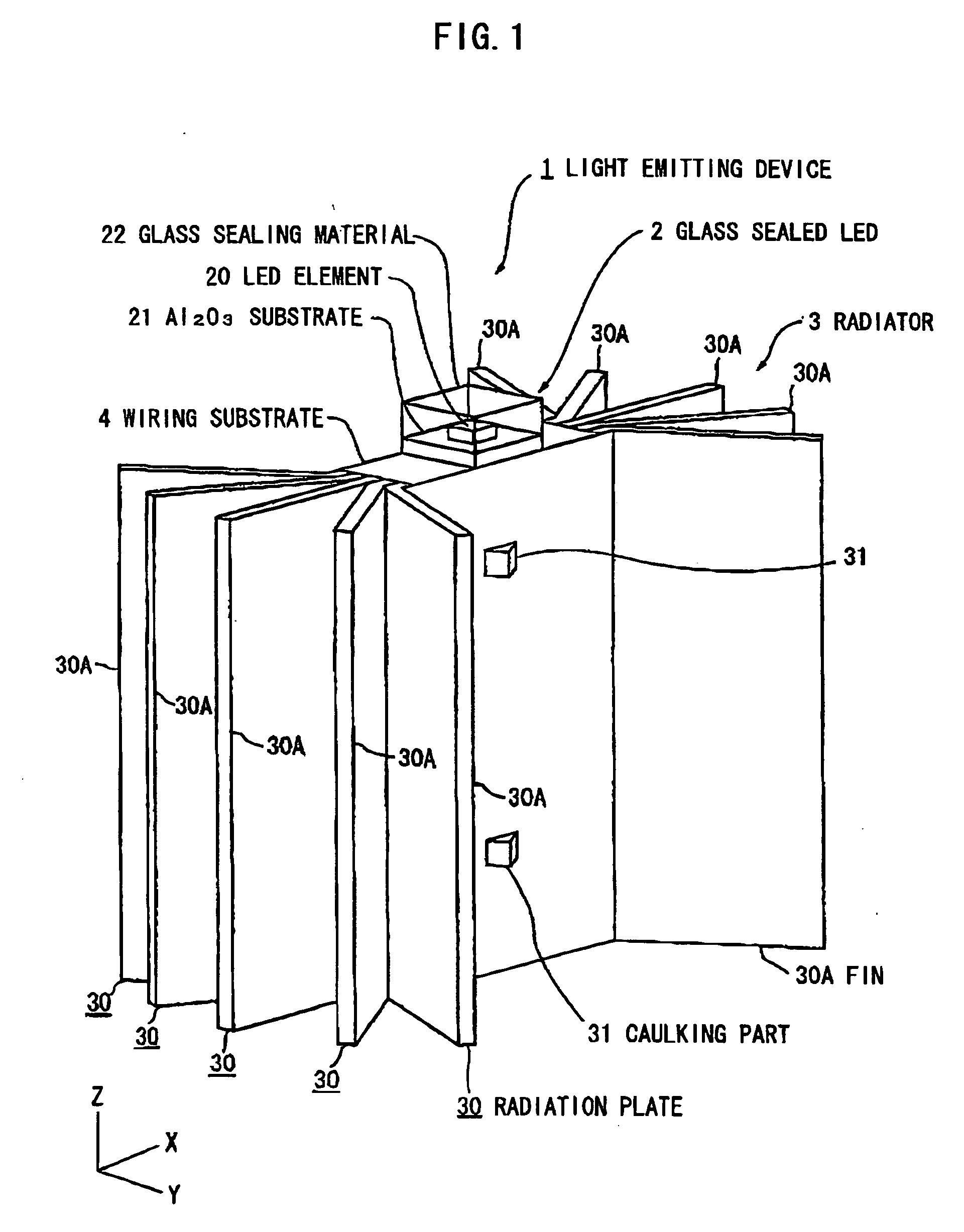
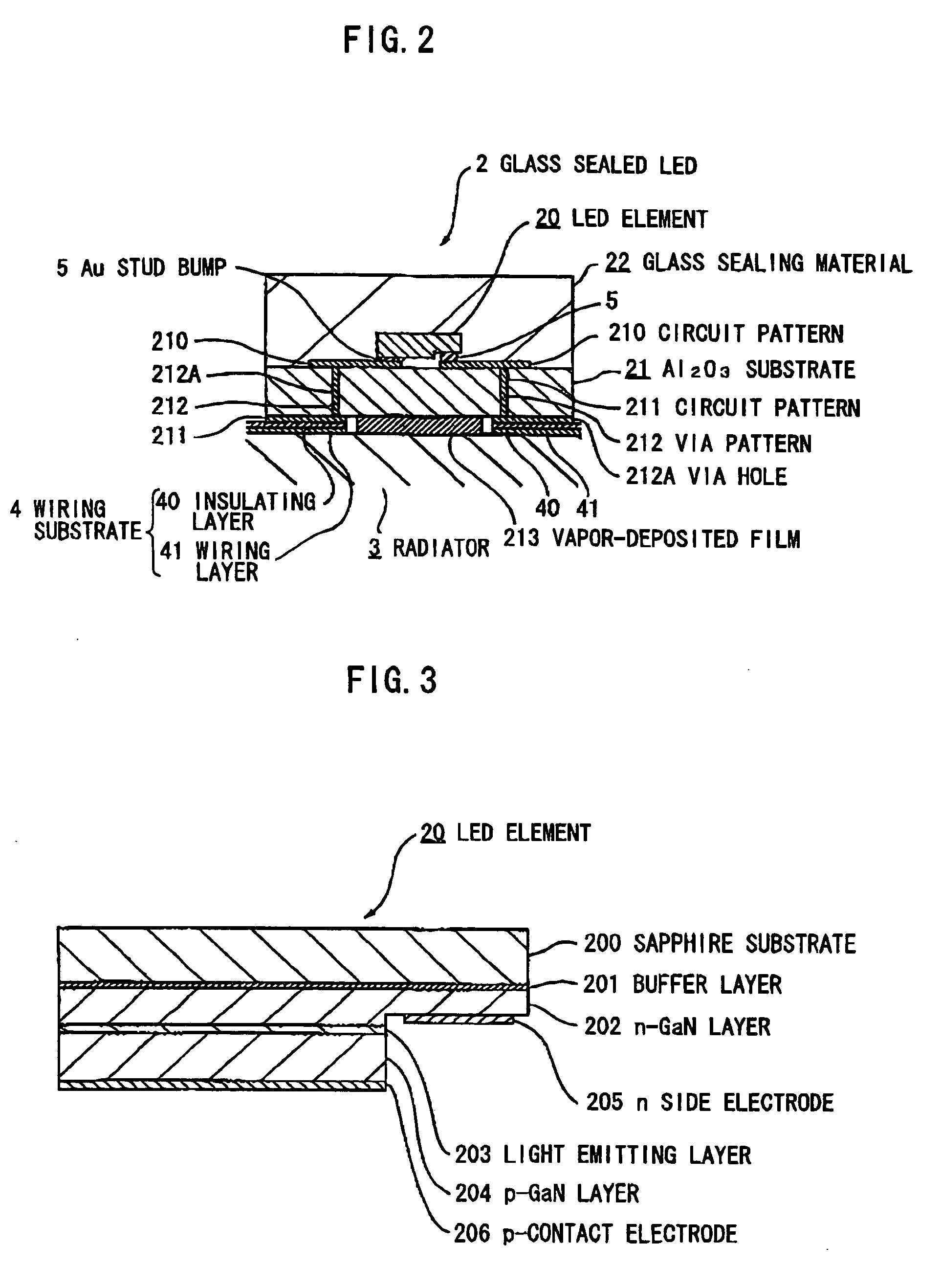
Light emitting device
InactiveUS20070097692A1Easy to assembleEasy downsizedLighting heating/cooling arrangementsOptical signallingConductive materialsLight emitting device
A light emitting device has a light source having a light emitting element; and a radiator having plural plate members formed of a thermally-conductive material. The plural plate members are stacked on each other while allowing formation of a space between each other at an end portion thereof. The light source is mounted on a side surface of the plural stacked plate members.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
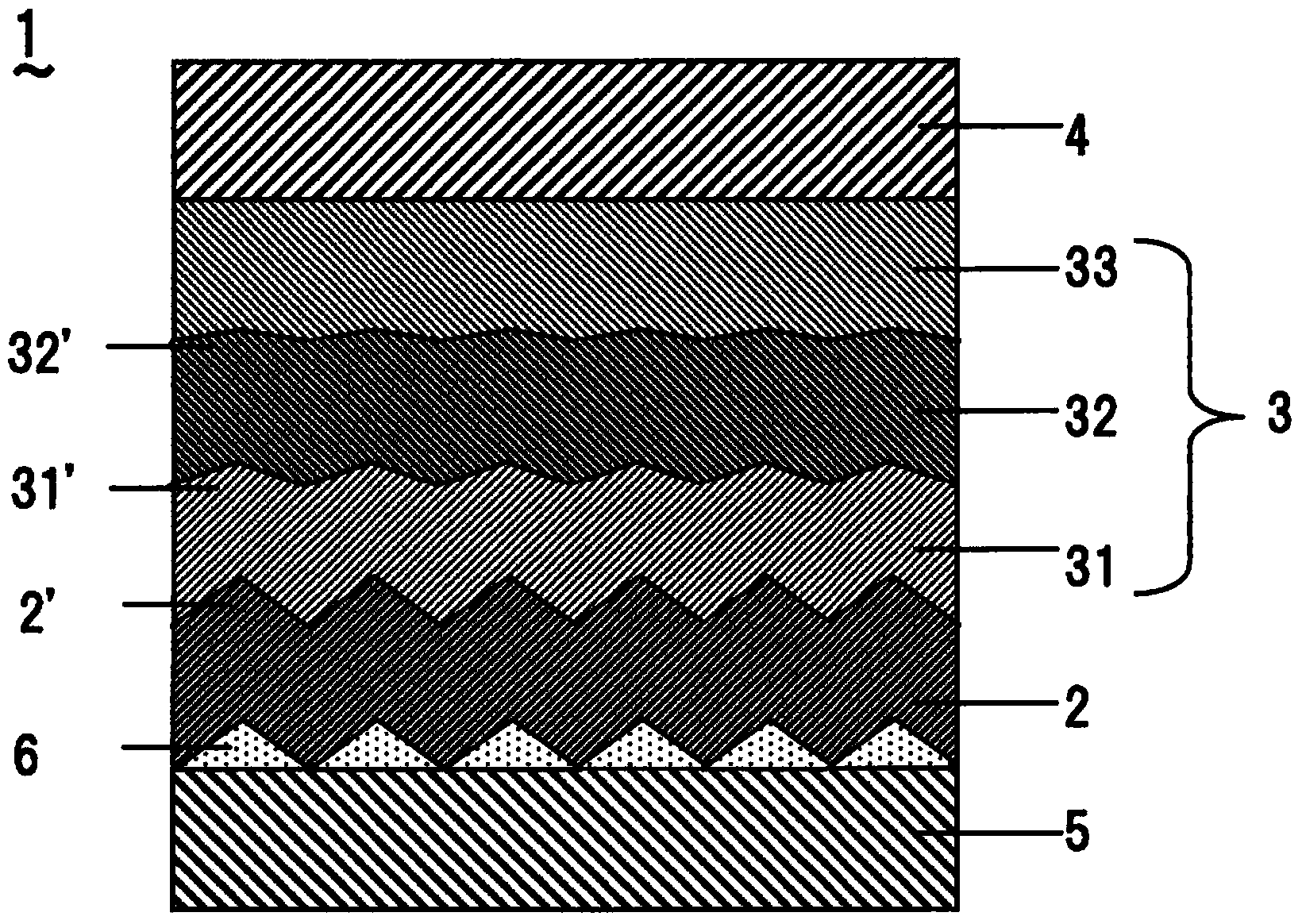
Organic electroluminescence device
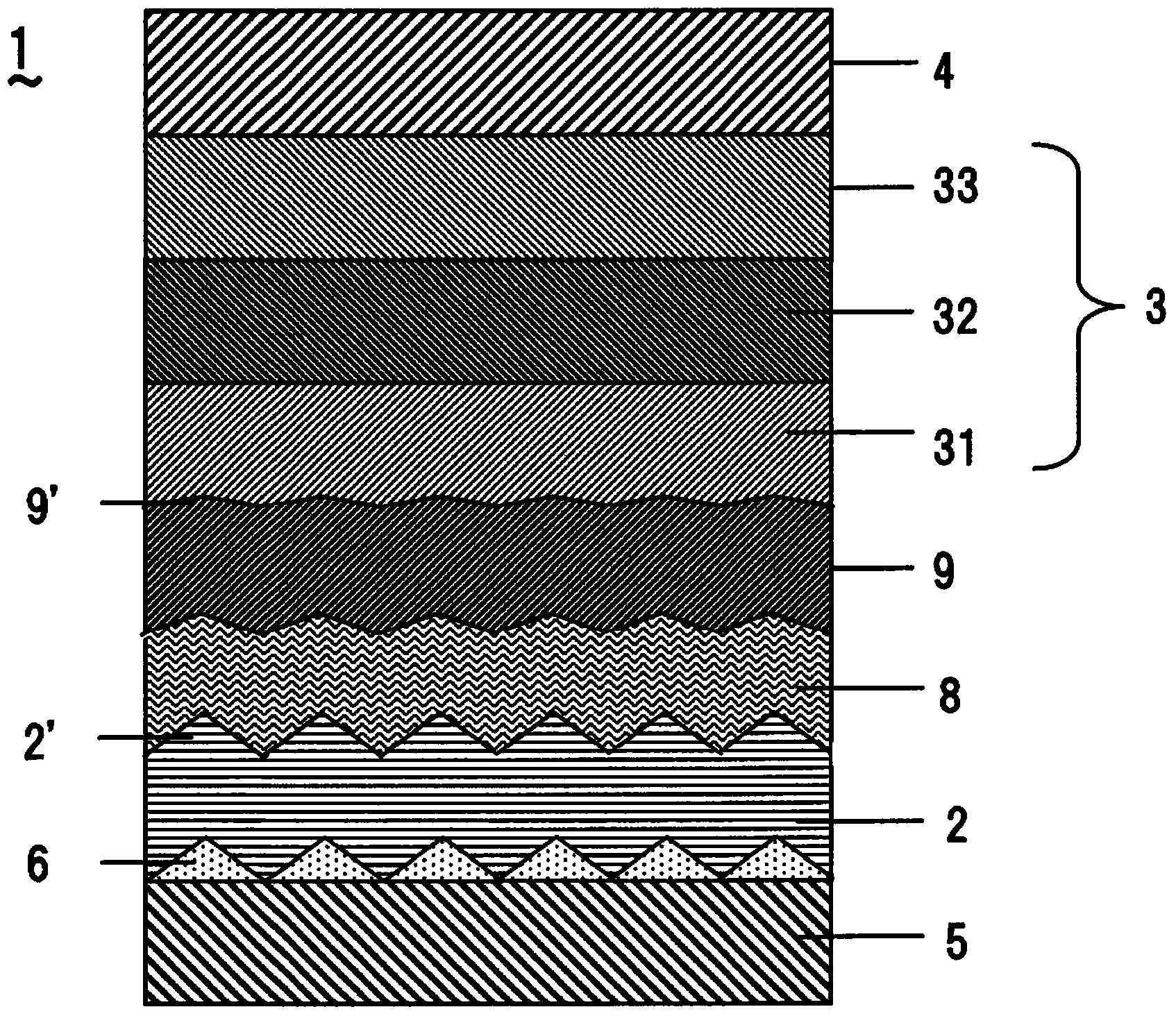
ActiveCN103444262ASuppress light lossSuppress short circuitElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesOrganic electroluminescenceSurface plasmon polariton
An organic EL device (1) is provided with a metal layer (2) whereon projections and recessions (2') on a nano order of magnitude are provided on one face, and a plurality of organic layers (3) that include a light emission layer (31) provided on one side of the metal layer (2). The height of the projections and recessions at each boundary face of the organic layers (3) is configured to be smaller than the projections and recessions (2') disposed on the metal layer (2). This configuration enables, due to the projections and recessions (2') of one of the faces of the metal layer (2), a reduction of the light loss that occurs in the conversion of surface plasmon to propagation light; and by making the projections and recessions of each boundary face of each organic layer (3) smaller than the projections and recessions on the face of the metal layer (2), shorts within the device can be suppressed.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
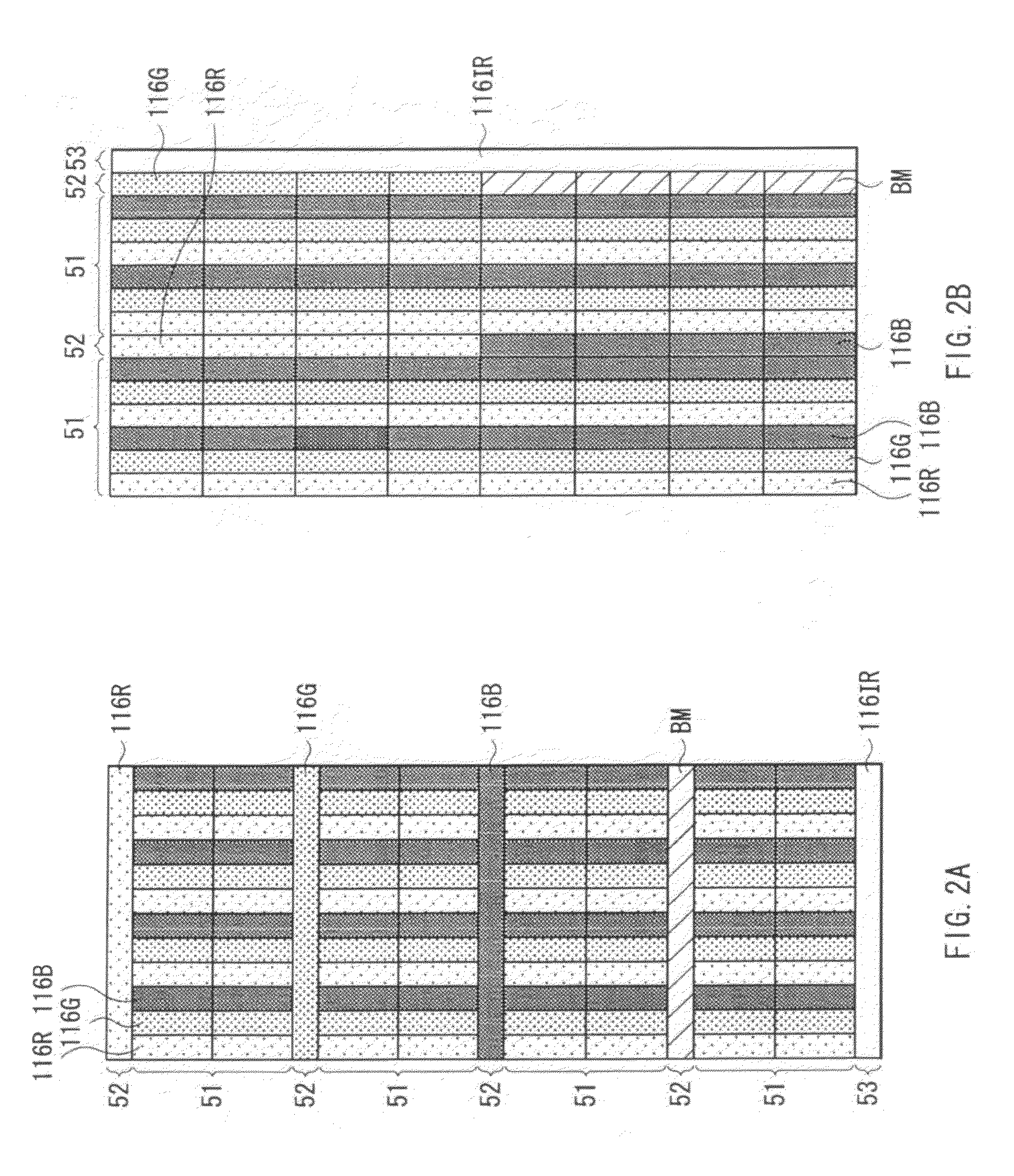
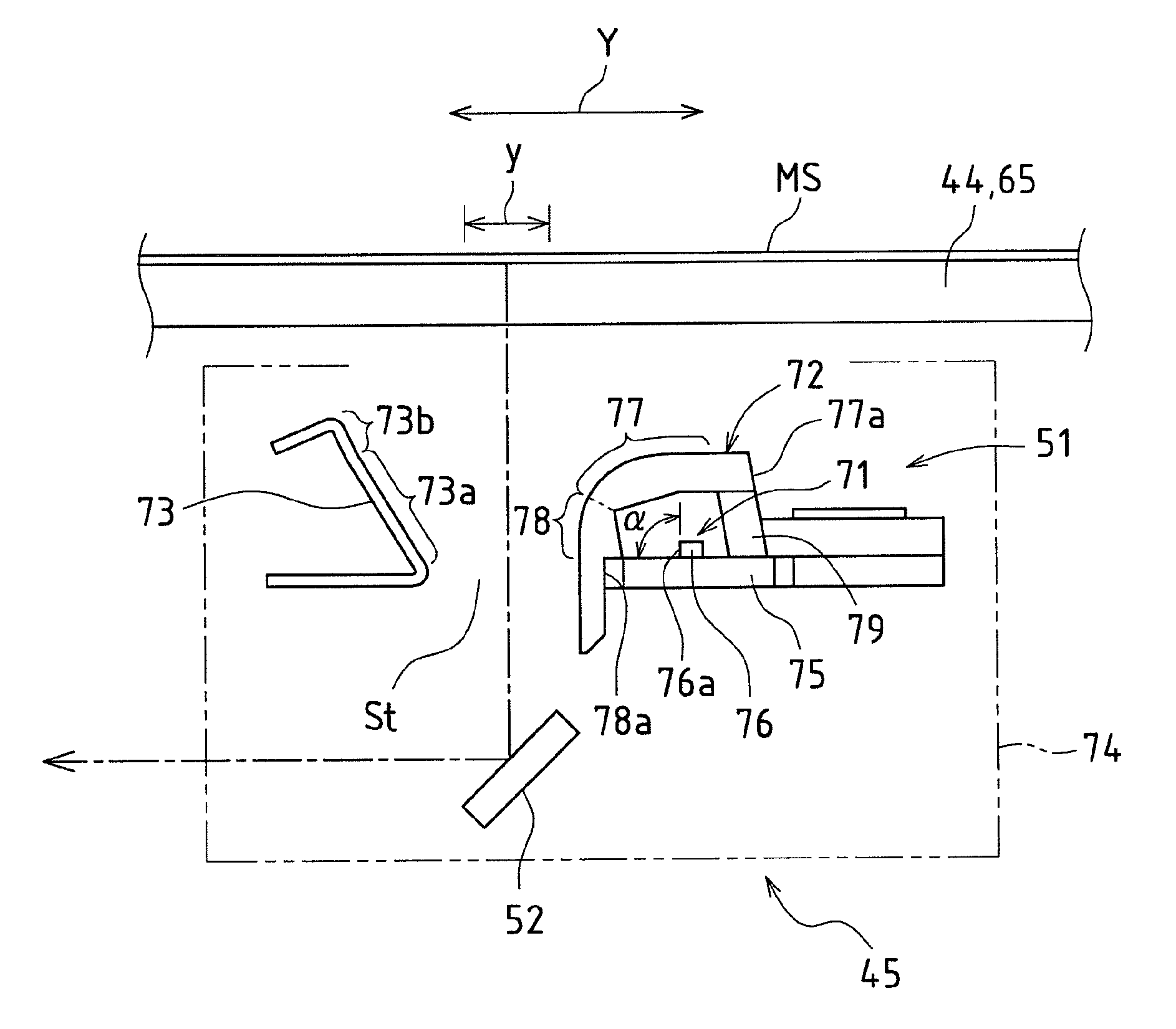
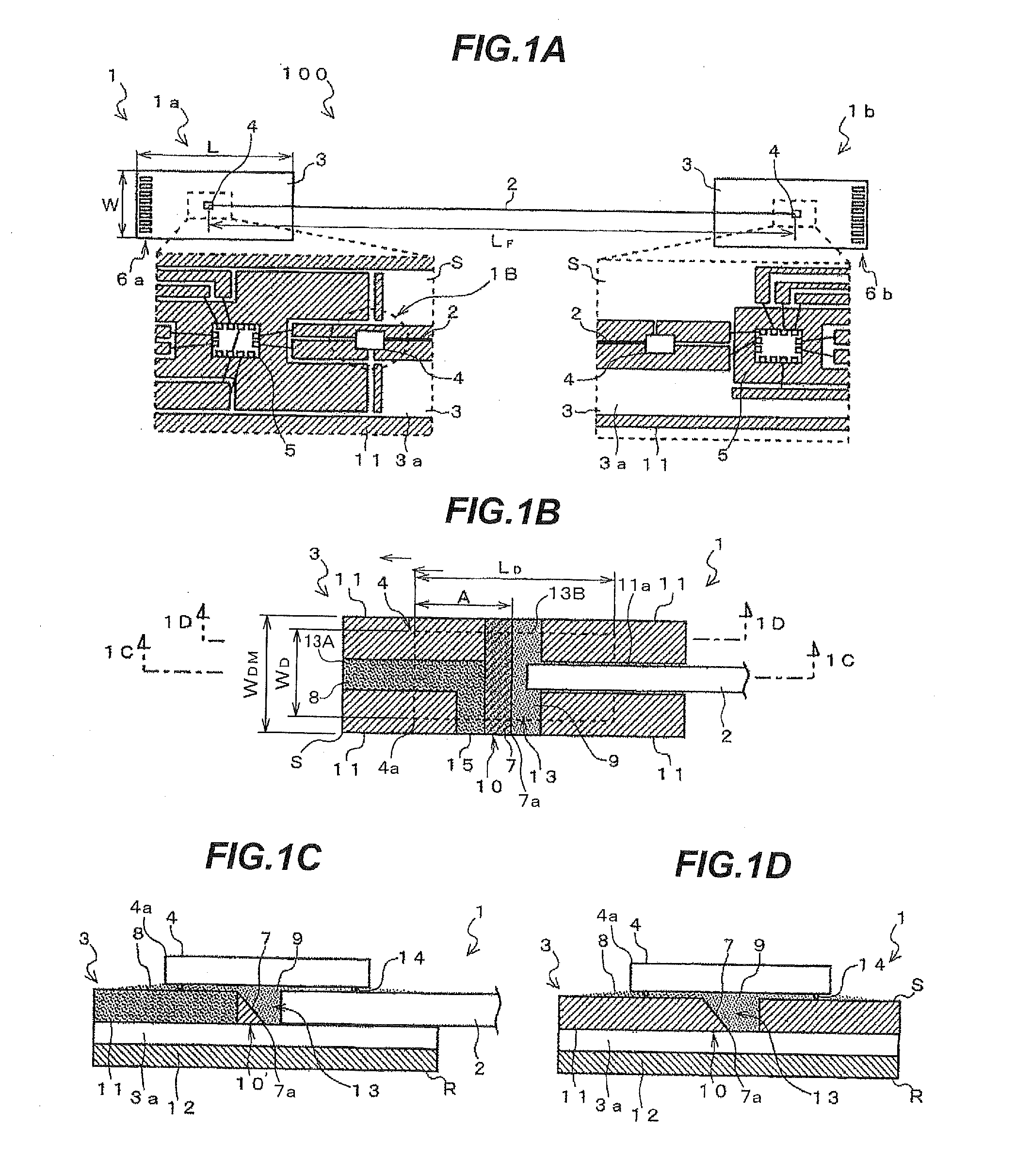
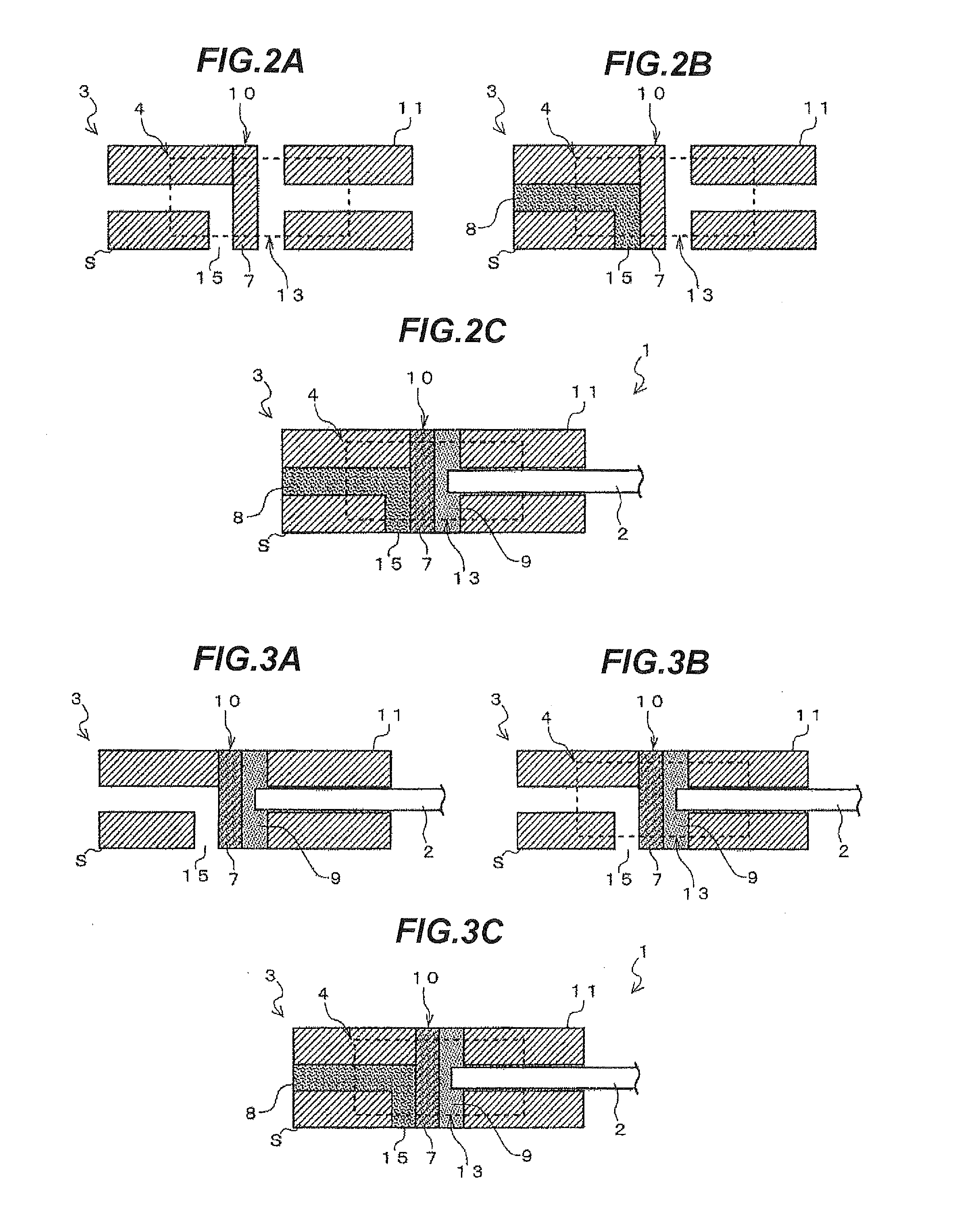
Illuminating device, image reading apparatus including the illuinating device, and image forming apparatus including the image reading apparatus
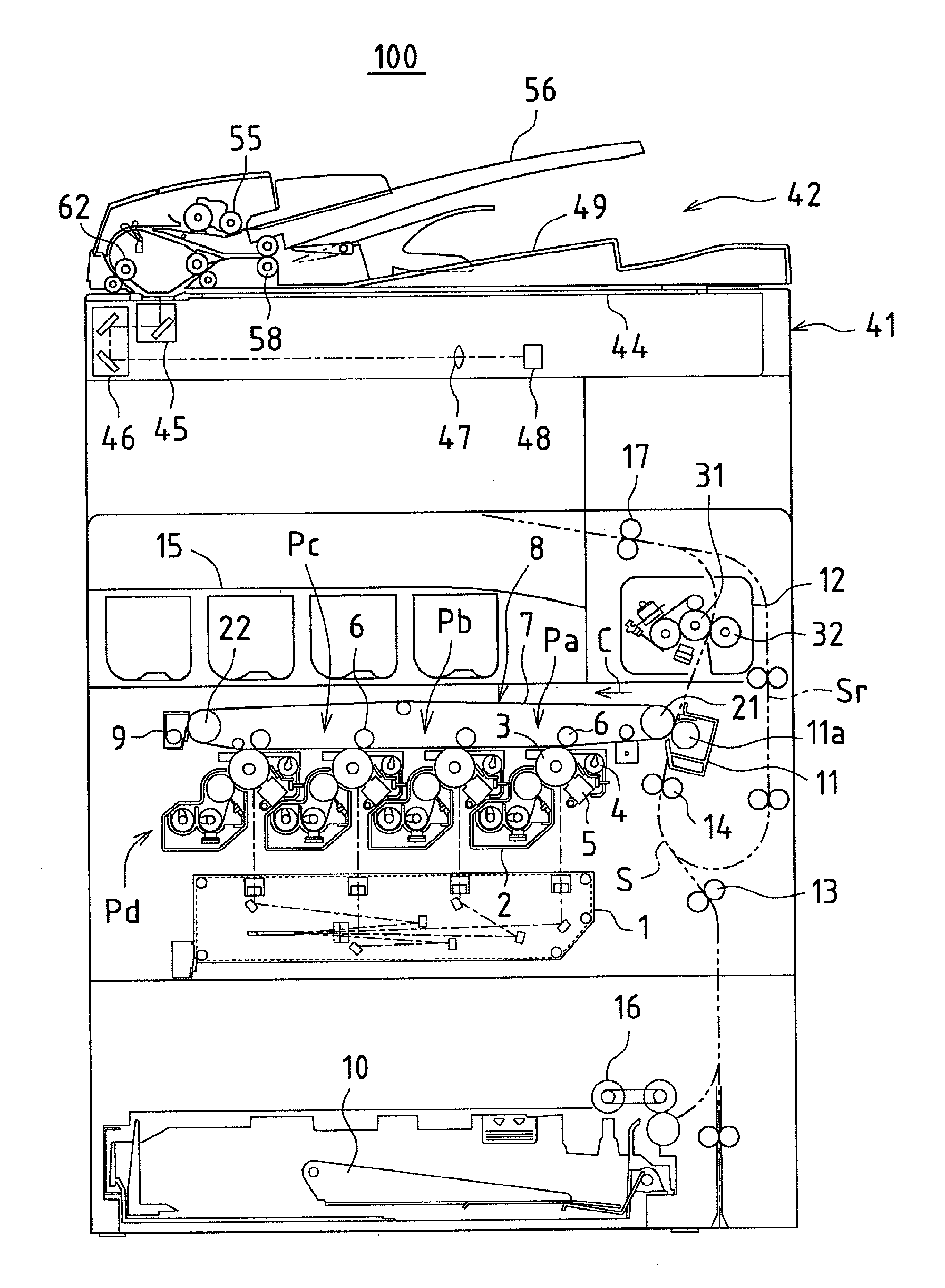
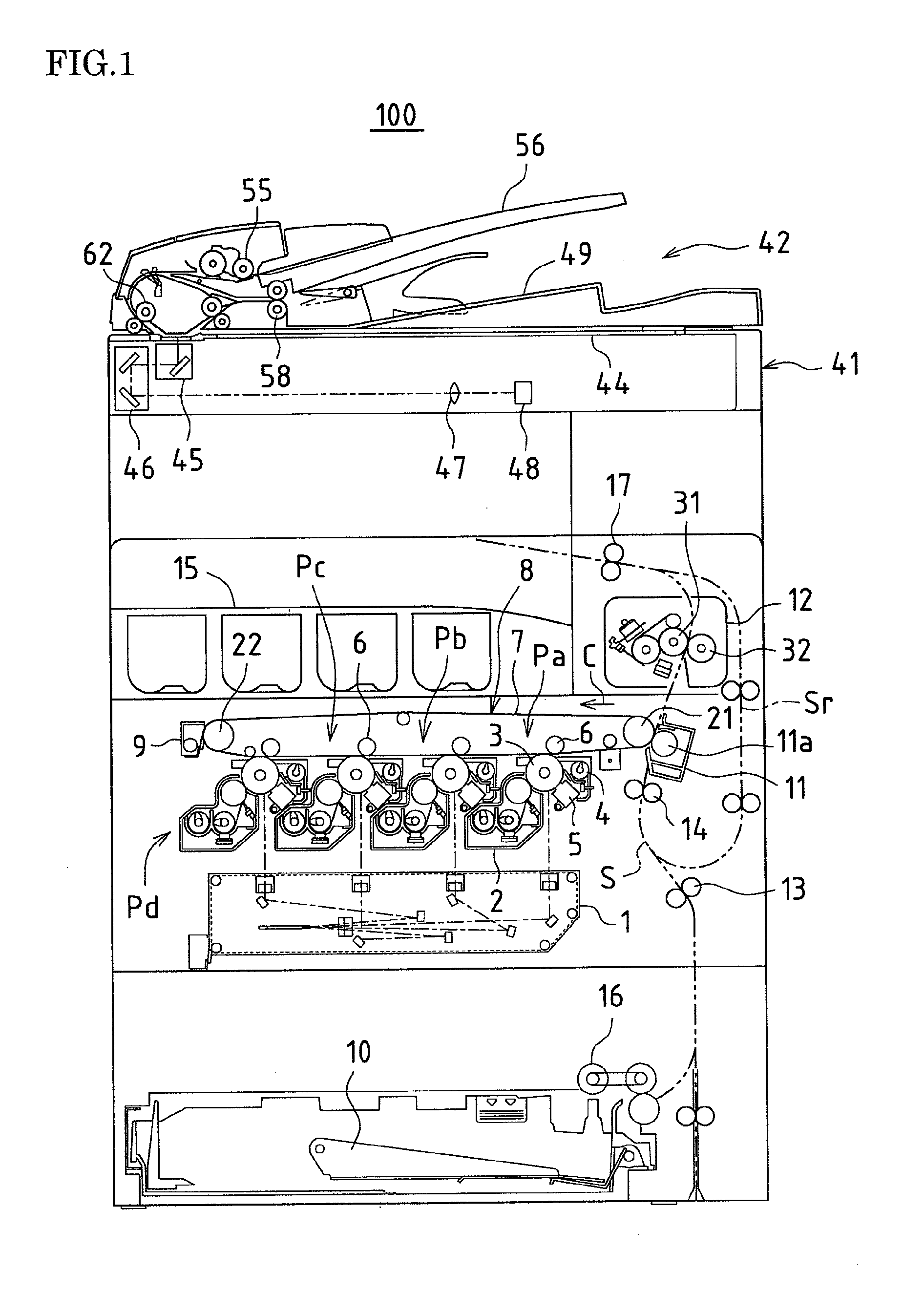
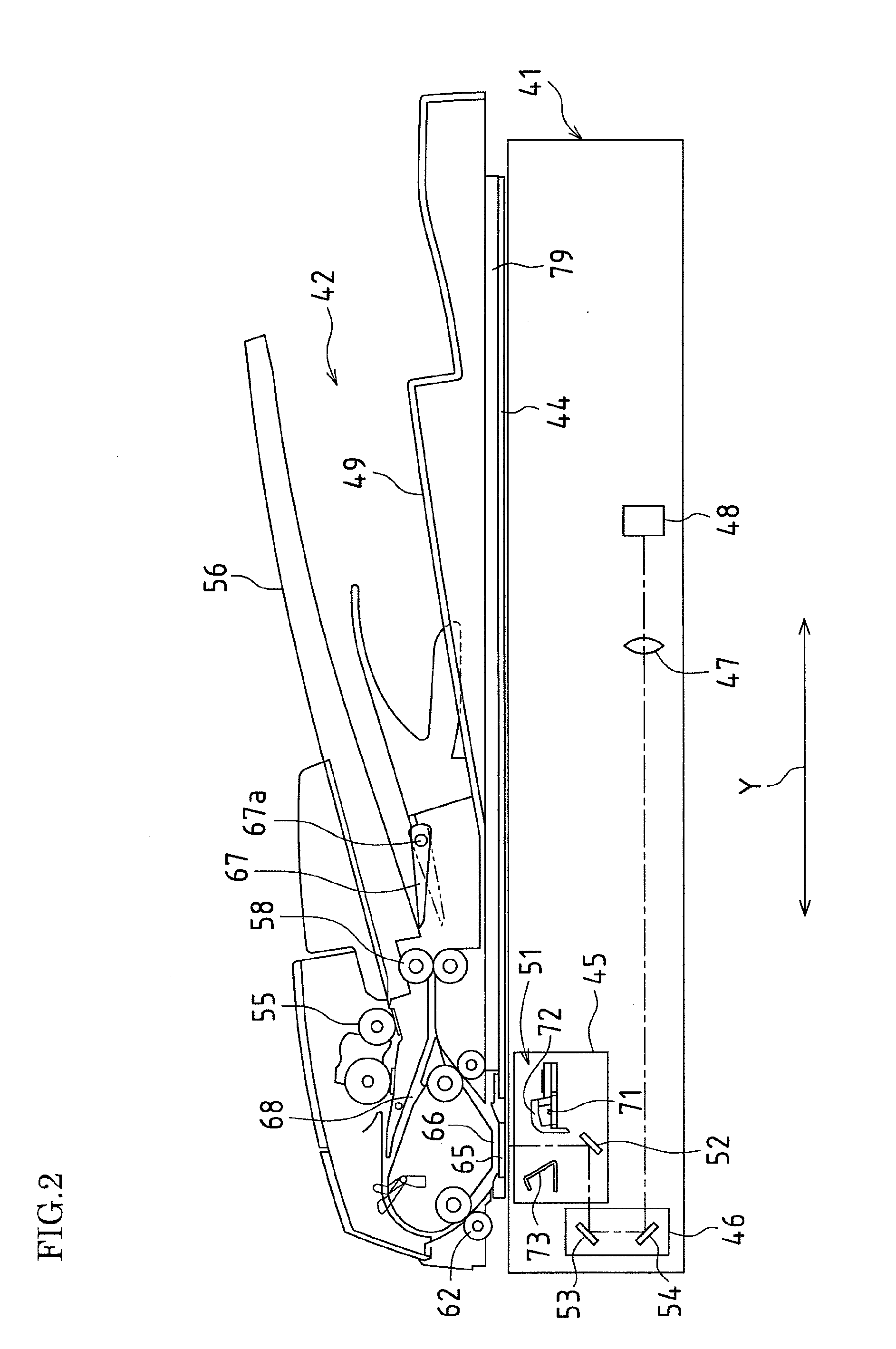
ActiveUS20120206779A1Suppress light lossReadily illuminated unevenlyElectrographic process apparatusPhotographic printingLight guideImage formation
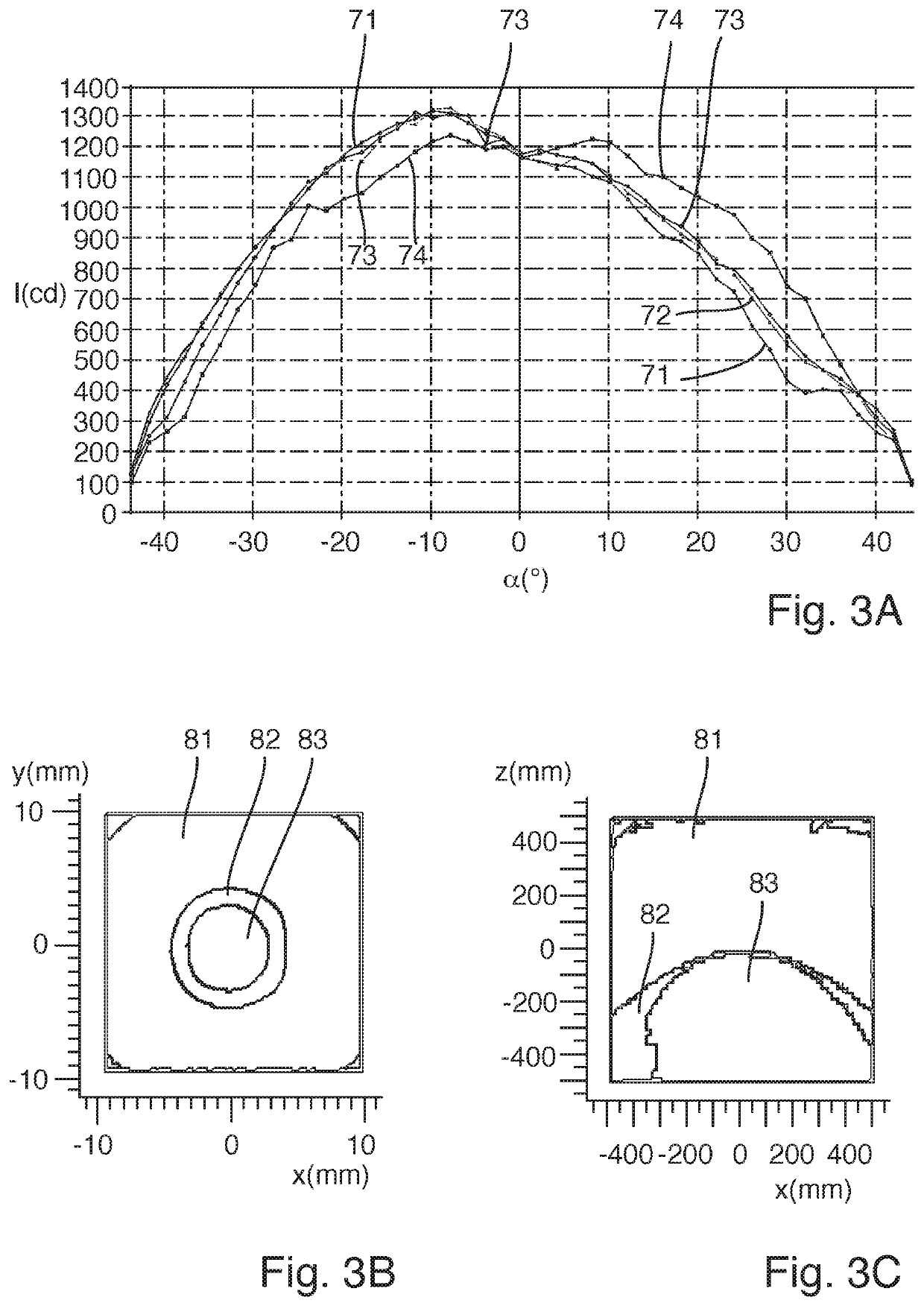
An illuminating device capable of stably illuminating an irradiated object such as a document while suppressing light loss with a simply structure is provided.An LED array (71) and a reflective plate (73) are disposed sandwiching a slit (St) through which light reflected by a document MS passes and a light-guiding member (72) is disposed on the side of the LED array (71). The light-guiding member (72) includes a direct emission unit (77) disposed between an illumination range y centered on a document reading position and the LED array (71) and an indirect emission unit (78) disposed between the reflective plate (73) and the LED array (71), a light incidence face of the direct emission unit (77) and a light incidence face of the indirect emission unit (78) are disposed at mutually different position around the LED array (71), and the LED array (71) is disposed on a side of an interior angle formed by the light incidence faces.
Owner:SHARP KK
Light emitting diode package and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20160372642A1Suppress light lossUniform brightnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) package includes a light-emitting structure, a transmissive material layer on the light-emitting structure, and a support structure covering at least a portion of a side surface of the transmissive material layer, a side surface of the light-emitting structure, and at least a portion of a bottom surface of the light-emitting structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Backlight and displaying/imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20100246212A1Suppress lossReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesOptical light guidesImaging equipmentLight guide
The present invention provides a backlight capable of suppressing loss of light from an invisible light source and a displaying / imaging apparatus using the same. The backlight includes: a light guide plate having a light emitting face and a rear face opposed to the light emitting face; a visible light source disposed on a side face of the light guide plate; an invisible light source disposed on a side face of the light guide plate; a first reflection film disposed on the rear face side of the light guide plate, reflecting light from the visible light source, and transmitting light from the invisible light source; and a second reflection film disposed on the rear face side of the light guide plate and reflecting light from at least the invisible light source out of the visible light source and the invisible light source.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Illuminating device, image reading apparatus including the illuinating device, and image forming apparatus including the image reading apparatus
ActiveUS8755095B2Readily illuminated unevenlyStably illuminateElectrographic process apparatusPhotographic printingIndirect emissionsLed array
An illuminating device capable of stably illuminating an irradiated object such as a document while suppressing light loss with a simply structure is provided.An LED array (71) and a reflective plate (73) are disposed sandwiching a slit (St) through which light reflected by a document MS passes and a light-guiding member (72) is disposed on the side of the LED array (71). The light-guiding member (72) includes a direct emission unit (77) disposed between an illumination range y centered on a document reading position and the LED array (71) and an indirect emission unit (78) disposed between the reflective plate (73) and the LED array (71), a light incidence face of the direct emission unit (77) and a light incidence face of the indirect emission unit (78) are disposed at mutually different position around the LED array (71), and the LED array (71) is disposed on a side of an interior angle formed by the light incidence faces.
Owner:SHARP KK
Cantilever for near field optical microscopes, plasmon enhanced fluorescence microscope employing the cantilever, and fluorescence detecting method
InactiveUS20090101815A1Fluorescence enhancementEasy to detectMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotometryFluorescence microscopeCantilever
A cantilever for near field optical microscopes is equipped with a probe in the vicinity of a free end thereof. The probe includes a thin film portion constituted by at least one layer of thin film that serves as the surface of the probe, and an inner bulk portion which is covered by the thin film portion. The outermost layer of the thin film portion is a thin dielectric film, and a metal portion is provided toward the interior of the probe from the thin dielectric film.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Light fixture and lens for a light fixture
ActiveUS10480725B2Improve optical efficiencyAvoid damageCondensersSemiconductor devices for light sourcesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
A light fixture has a housing having a depression in which at least one light-emitting diode is received. The light-emitting diode is mounted on a mounting surface and in operation of the light fixture emits light with an initial emission angle of more than 80°. A lens is arranged downstream of the light-emitting diode, having a central focus area and an outer area radially surrounding the focus area. The central focus area is configured and / or arranged in such a way that a part of the light propagating through the focus area is focused in such a way that a final emission angle of the light propagated through the focus area is at least 50° and at most 80°. The outer area of the lens is spaced at least 2 mm from the mounting surface in a vertical direction.
Owner:LEDVANCE GMBH
Processing method
InactiveUS20110193268A1Suppress light lossWidely availableLaser beam welding apparatusLaser lightPhysics
In a processing method using laser light, light energy is effectively used and a time necessary for processing is shortened. The processing method includes a basic shape formation step of forming a recess pattern smaller in depth than a recess shape on a surface of a workpiece; and a shape growth step of irradiating the recess pattern with laser light which has a fluence such that the etching rate at a recess bottom surface of the recess pattern is larger than the etching rate on the workpiece surface and has a beam diameter larger than a width of the recess pattern so as to process the recess shape.
Owner:CANON KK
Backlight and displaying/imaging apparatus
ActiveUS8287169B2Suppress light lossStatic indicating devicesOptical light guidesLight guideLight-emitting diode
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
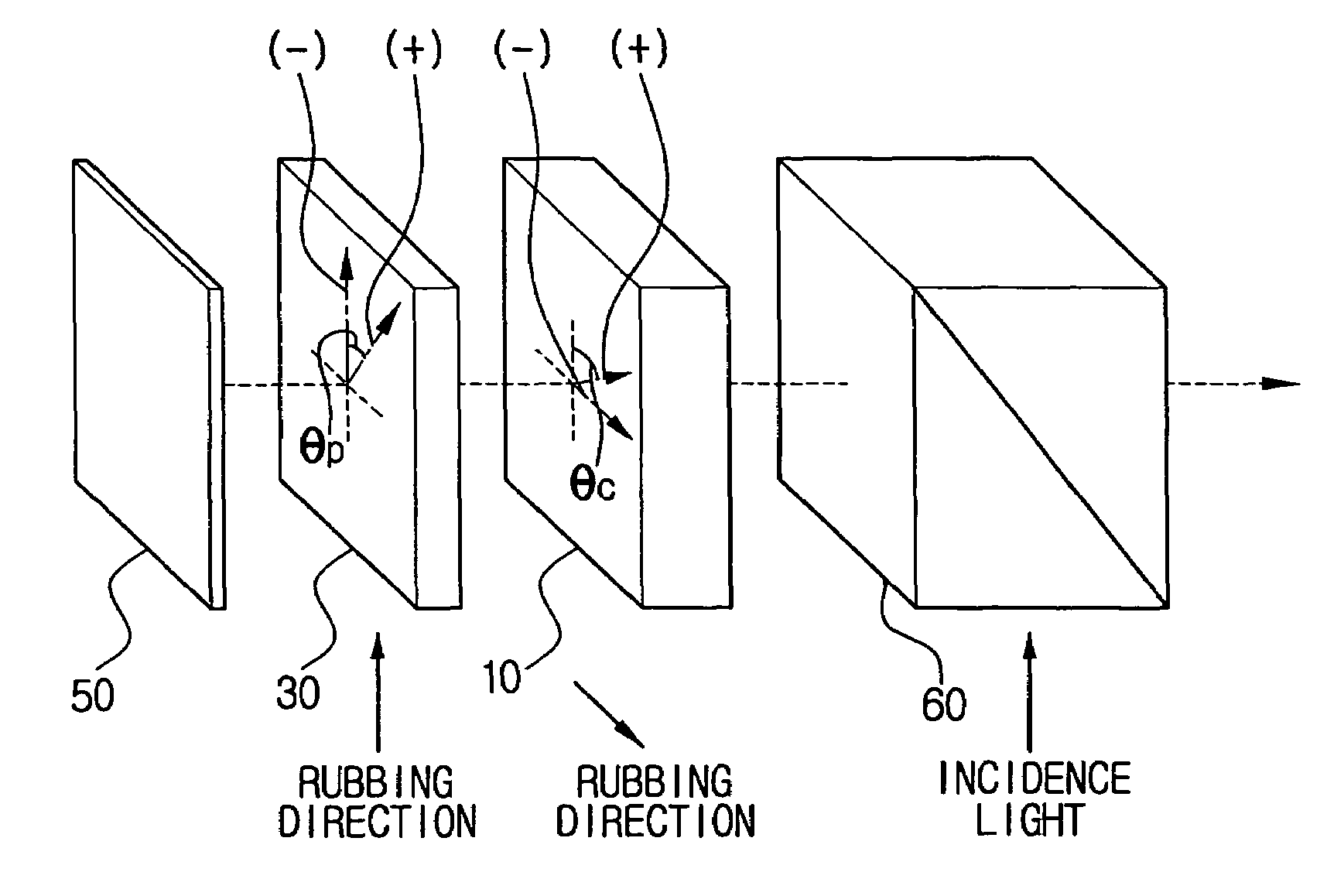
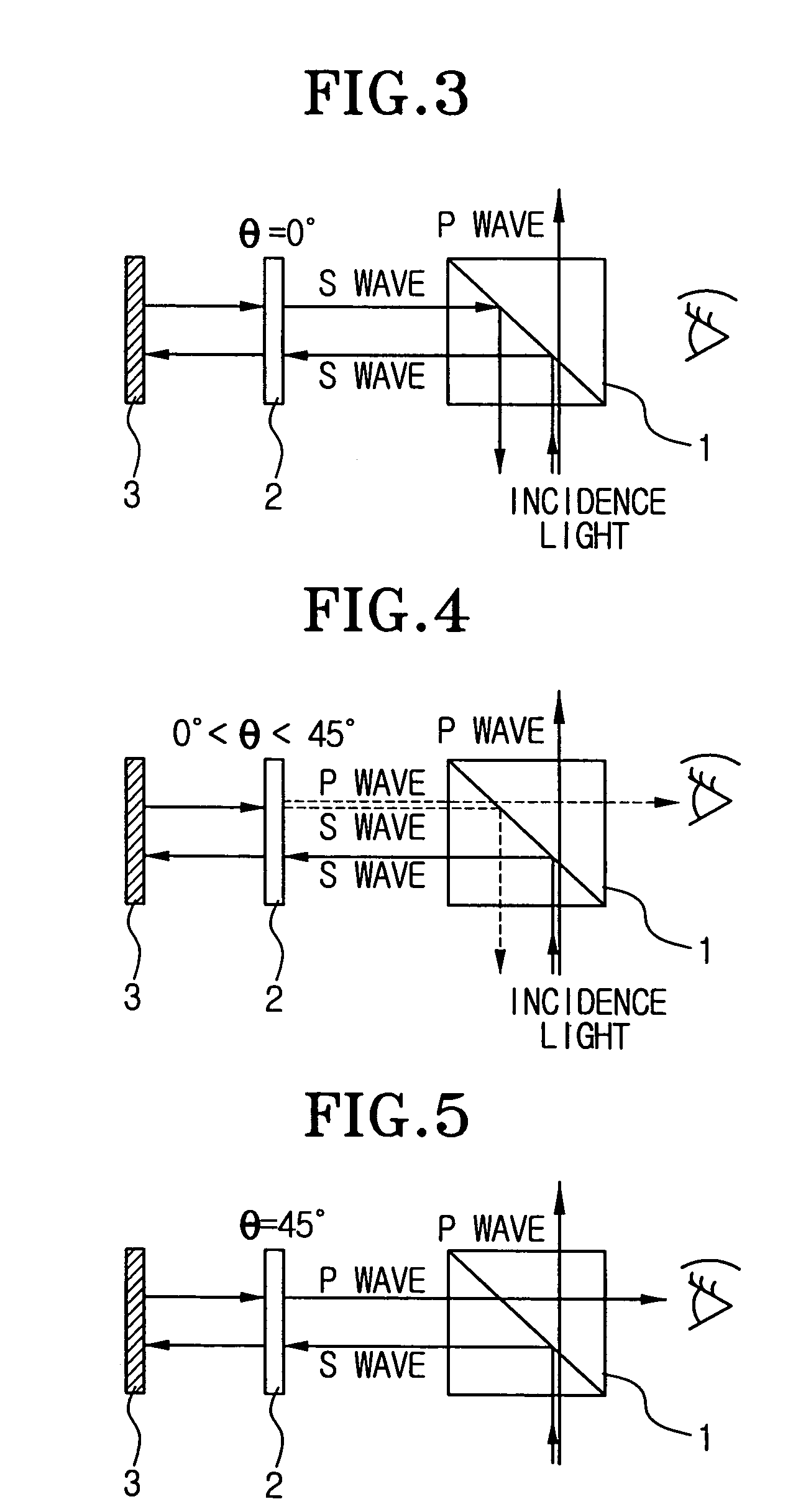
Reflective type ferroelectric liquid crystal display and driving method thereof
InactiveUS7110055B2Suppress light lossAccurate displayLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayFerroelectric liquid crystal display
The present invention discloses a reflective type ferroelectric liquid crystal display and a driving method thereof. The reflective type ferroelectric liquid crystal display comprises a display panel which is disposed between a polarization beam splitter and a mirror to satisfy a quarter plate condition, and in which a liquid crystal layer formed between electrode layers is filled with half-V type ferroelectric liquid crystal having a bookshelf structure, the electrode layers being disposed between substrates to be orthogonal and opposite to each other; and a compensation panel which is disposed between the display panel and the polarization beam splitter to satisfy a half plate condition, and in which a liquid crystal layer formed between electrode layers is filled with half-V type ferroelectric liquid crystal having a bookshelf structure, the electrode layers being disposed between substrates to be opposite to each other. Therefore, the light loss can be reduced, and thus the gray scale display can be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
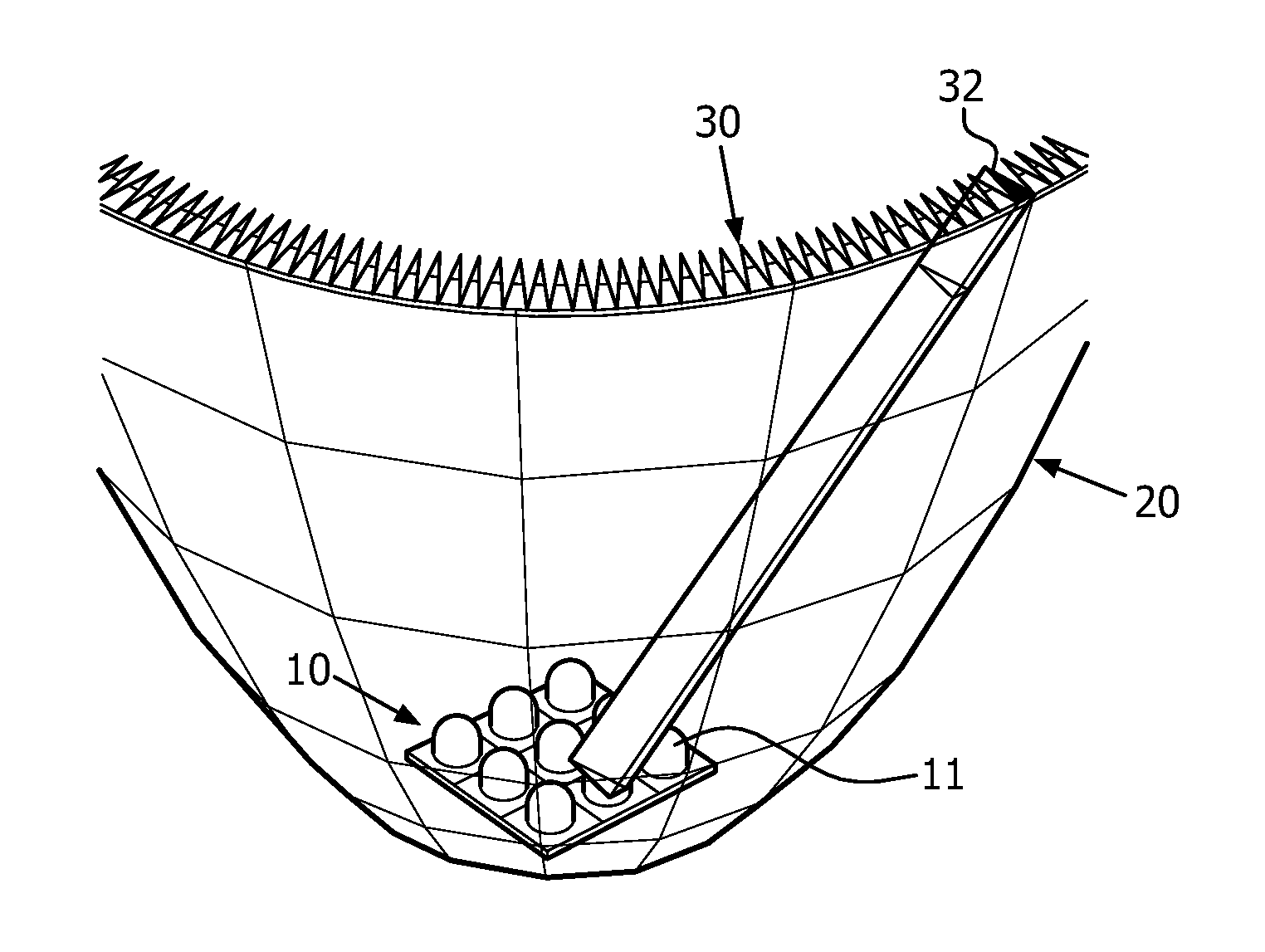
Beam transforming element, illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and exposure method
InactiveCN101369054ASuppress light lossEfficient preparationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLight fluxLight beam
A lighting optical device capable of forming a bracelet-form lighting pupil distribution in a peripherally-polarized state with a light quantity loss satisfactorily controlled, the device comprising a light flux conversion element (50) for forming a bracelet-form light intensity distribution on a specified surface based on an incident light flux. The light flux conversion element comprises a first basic element (50A) formed of an optically-rotating optical material, for forming a first arcuate area distribution based on an incident light flux out of bracelet-form light intensity distribution, a second basic element (50B) for forming a second arcuate area distribution, a third basic element (50C) for forming a third arcuate area distribution, and fourth basic element (50D) for forming a fourth arcuate area distribution. Respective basic elements have mutually different thicknesses along the light transmitting direction.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Optical device
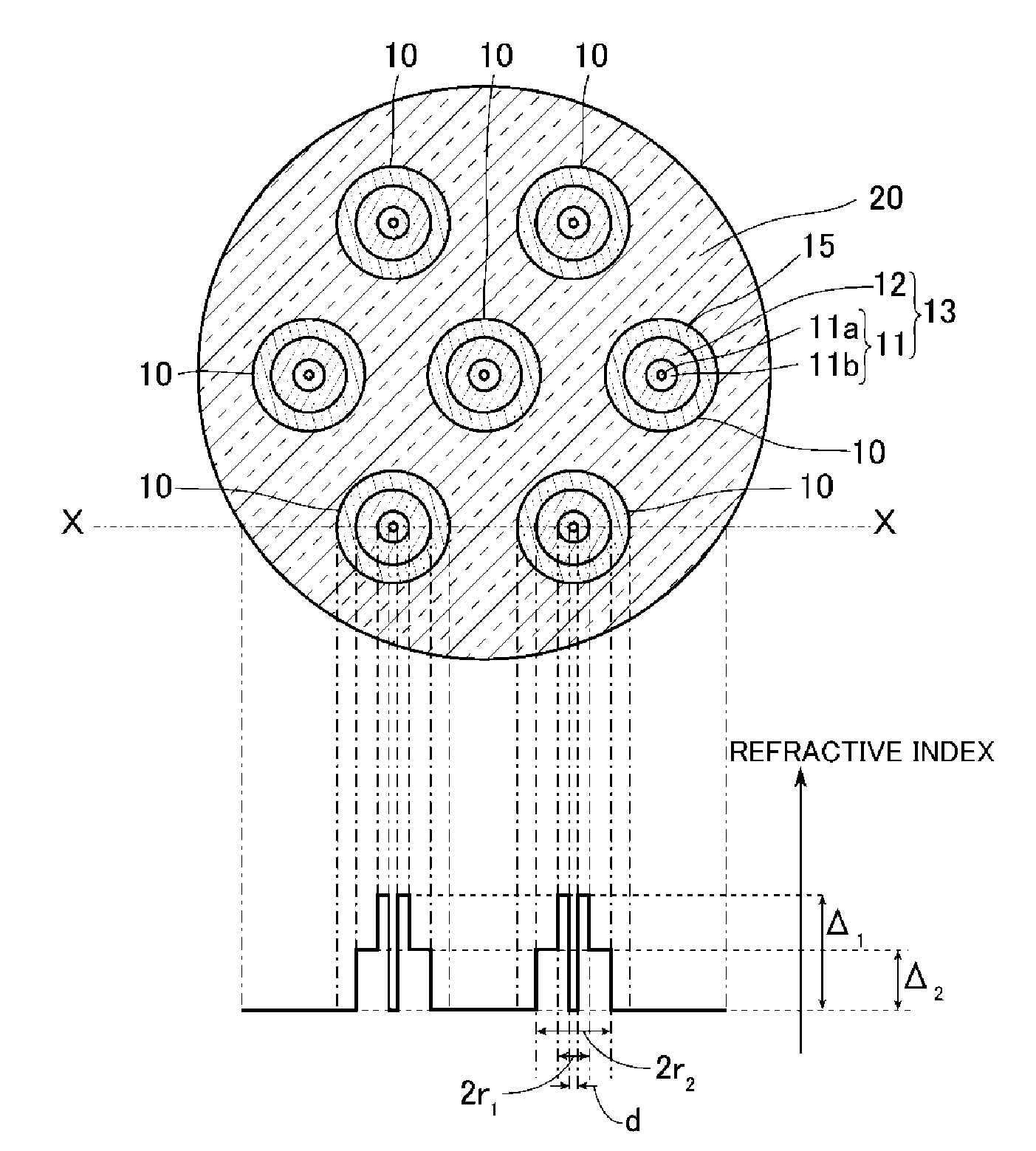
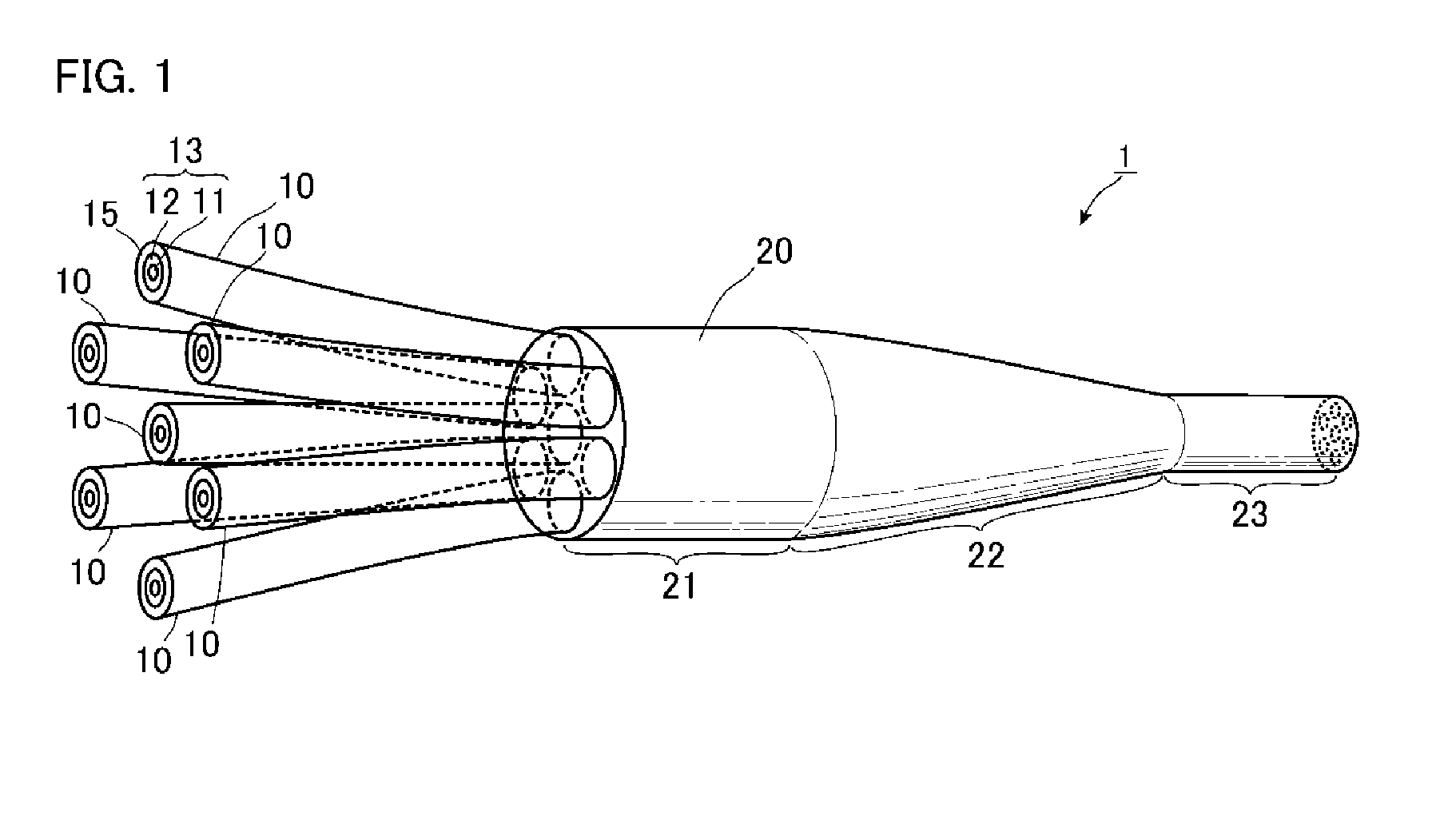
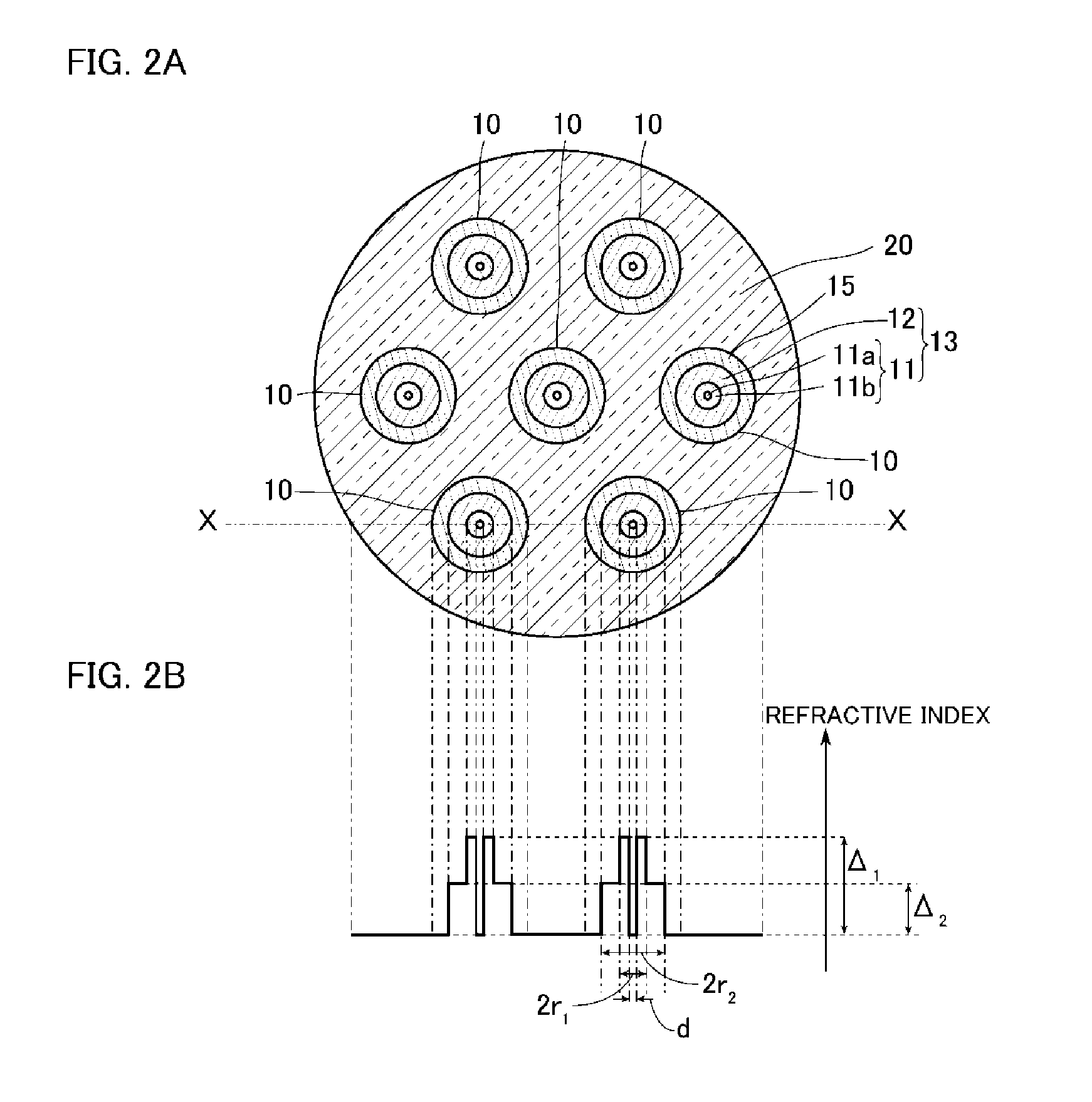
ActiveUS9477035B2Suppress light lossEasy to switchOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexEngineering
An optical device includes: multiple cores each including an inner core and an outer core surrounding an outer circumferential surface of the inner core without any gap therebetween; and cladding surrounding an outer circumferential surface of the cores without any gap therebetween and having a refractive index lower than that of the outer core, wherein each of the cores has a tapered portion that is tapered from one side toward the other side thereof in a longitudinal direction, each of the inner cores includes a low-refractive-index portion, and a high-refractive-index portion surrounding an outer circumferential surface of the low-refractive-index portion without any gap therebetween and having a refractive index higher than that of the low-refractive-index portion, and the outer core has a refractive index lower than that of the high-refractive-index portion.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD +1
Lighting device having a smooth cut-off
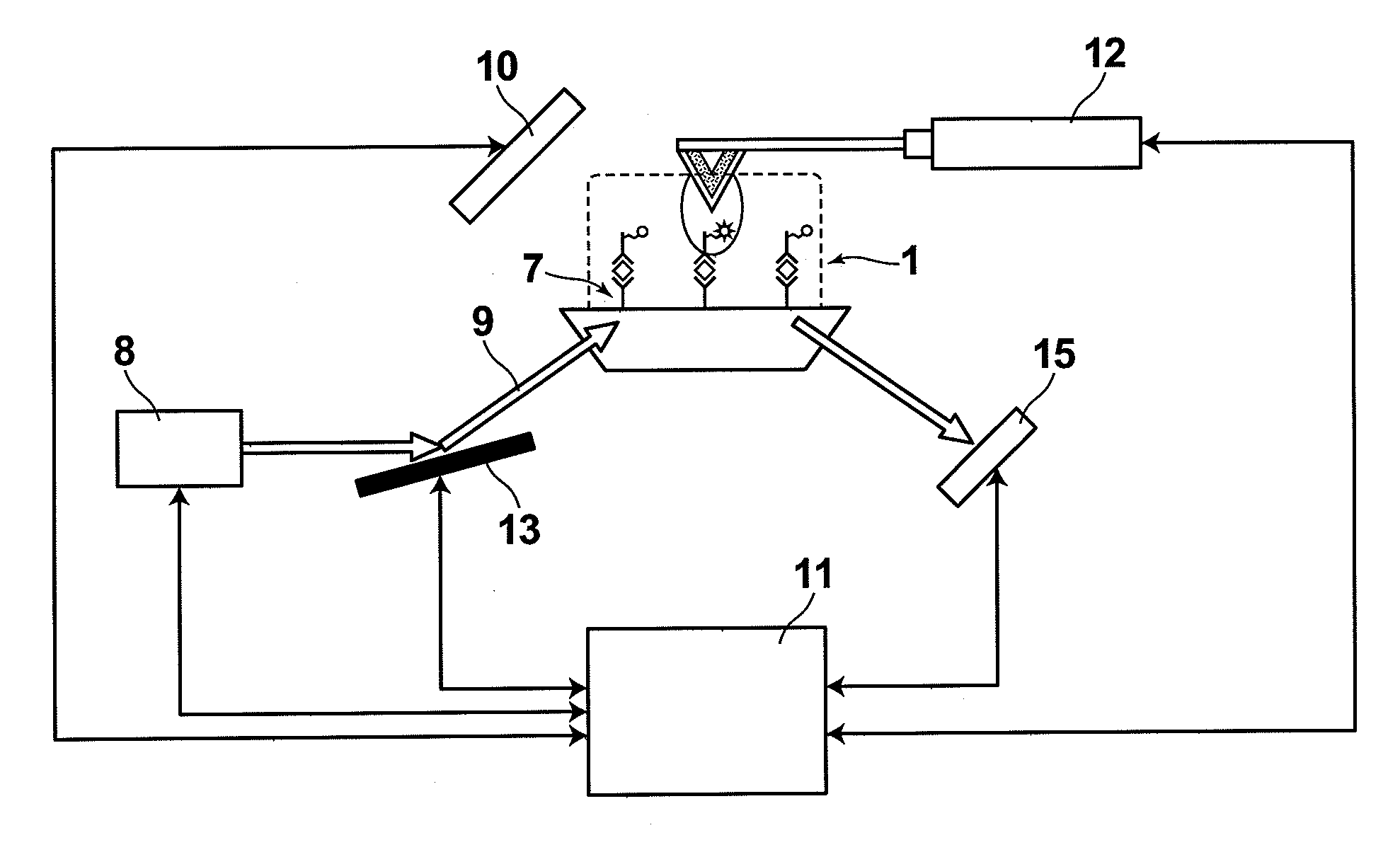
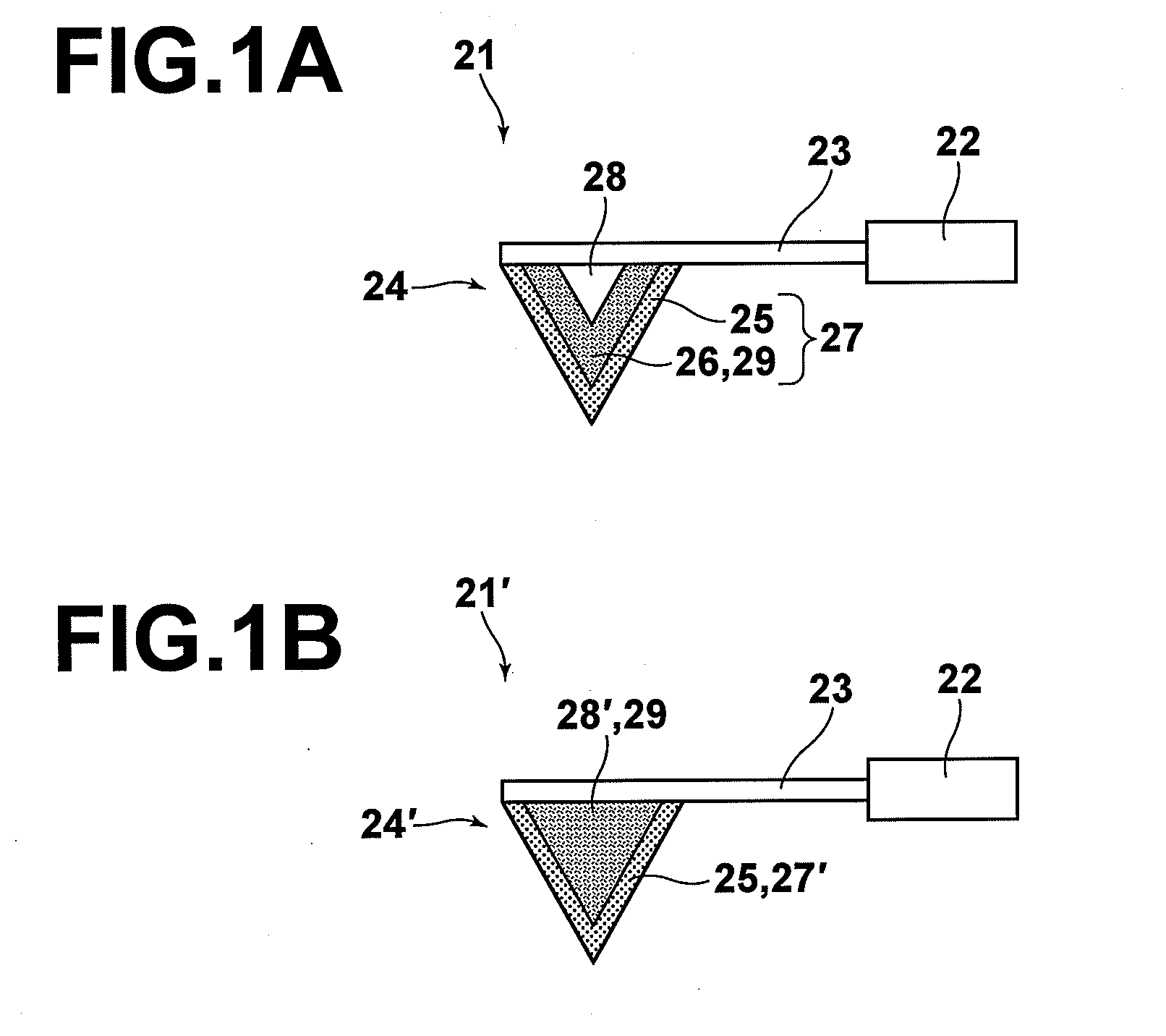
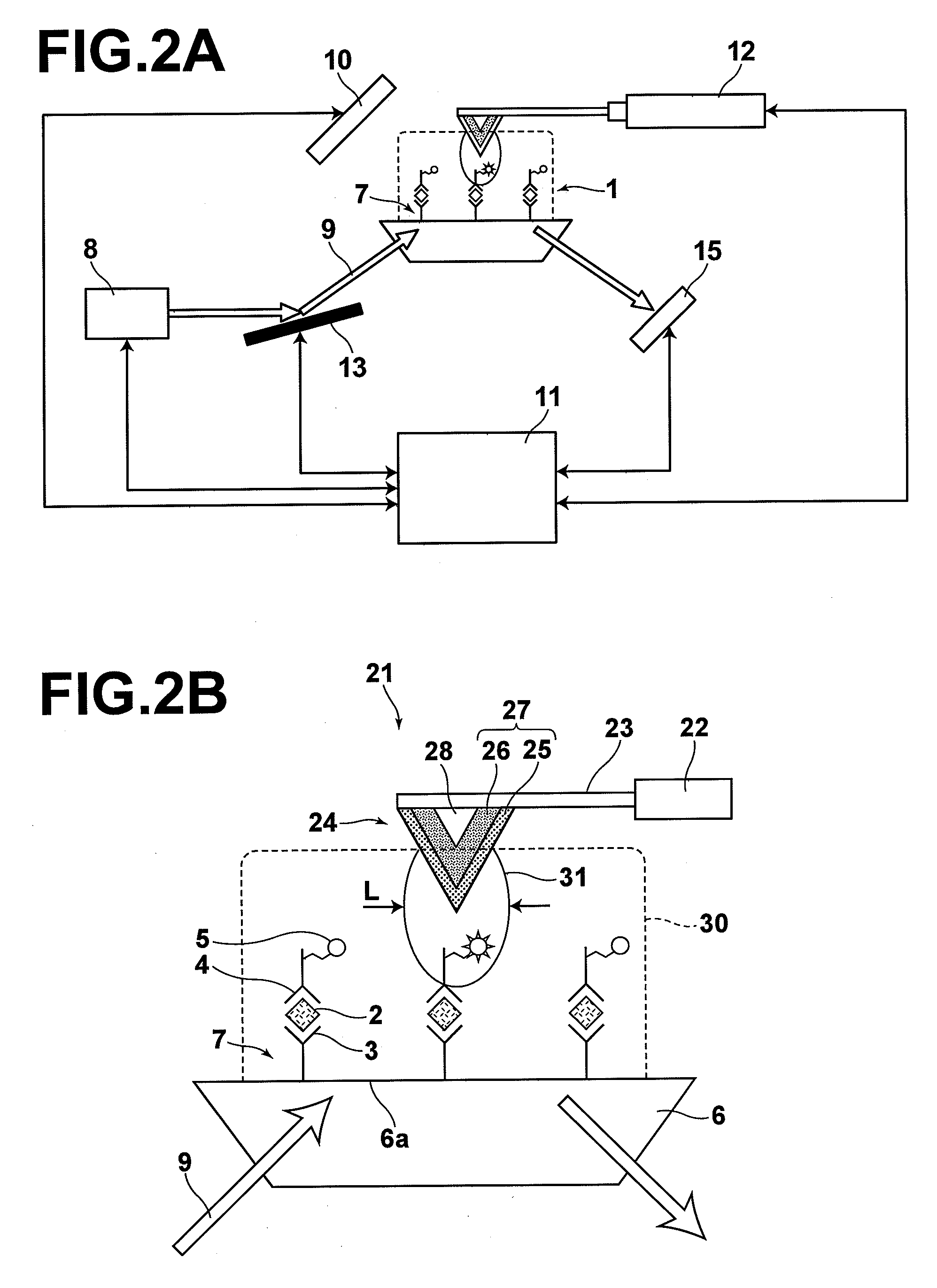
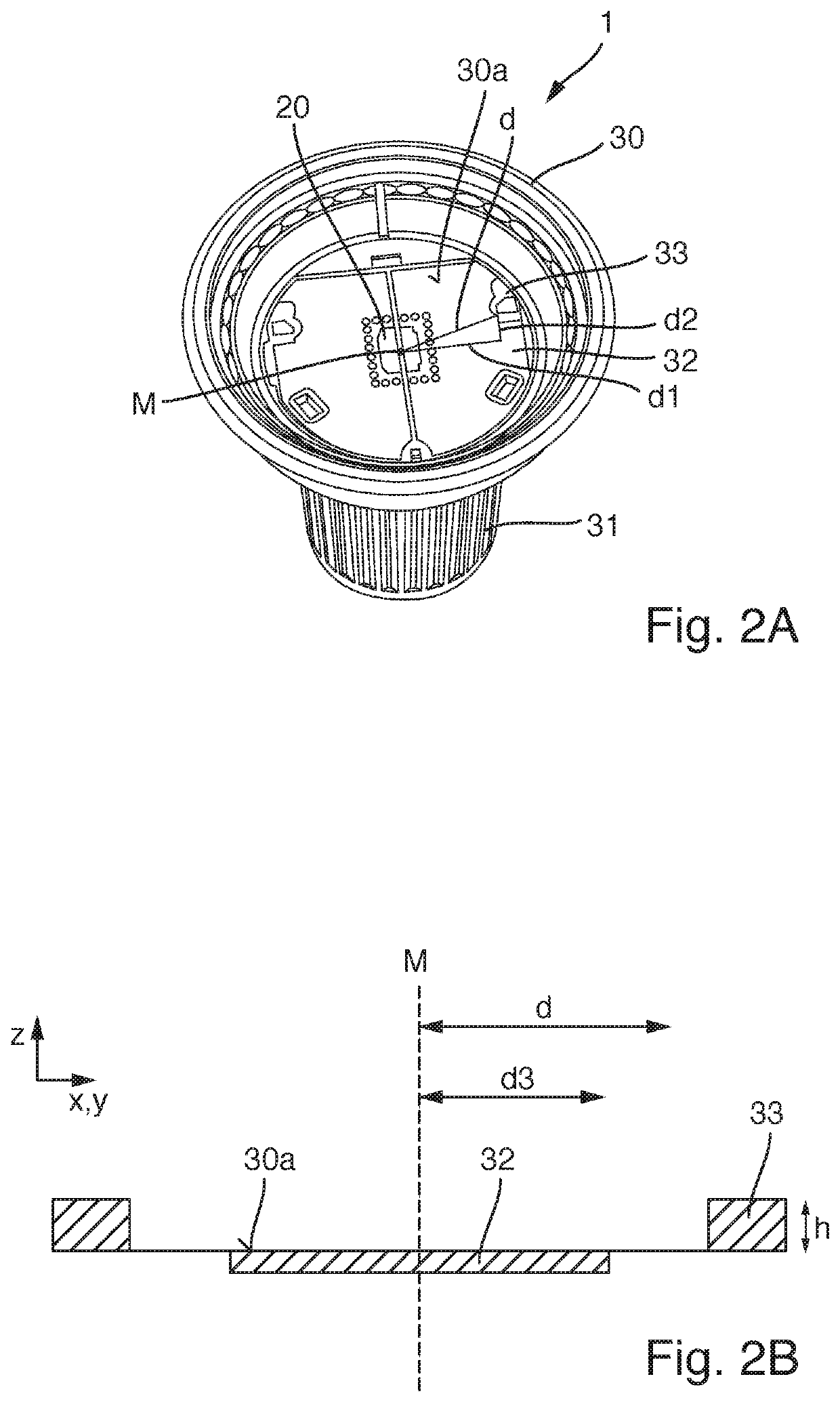
ActiveUS9151469B2Easy to controlSuppress light lossPlanar light sourcesNon-electric lightingEffect lightLight source
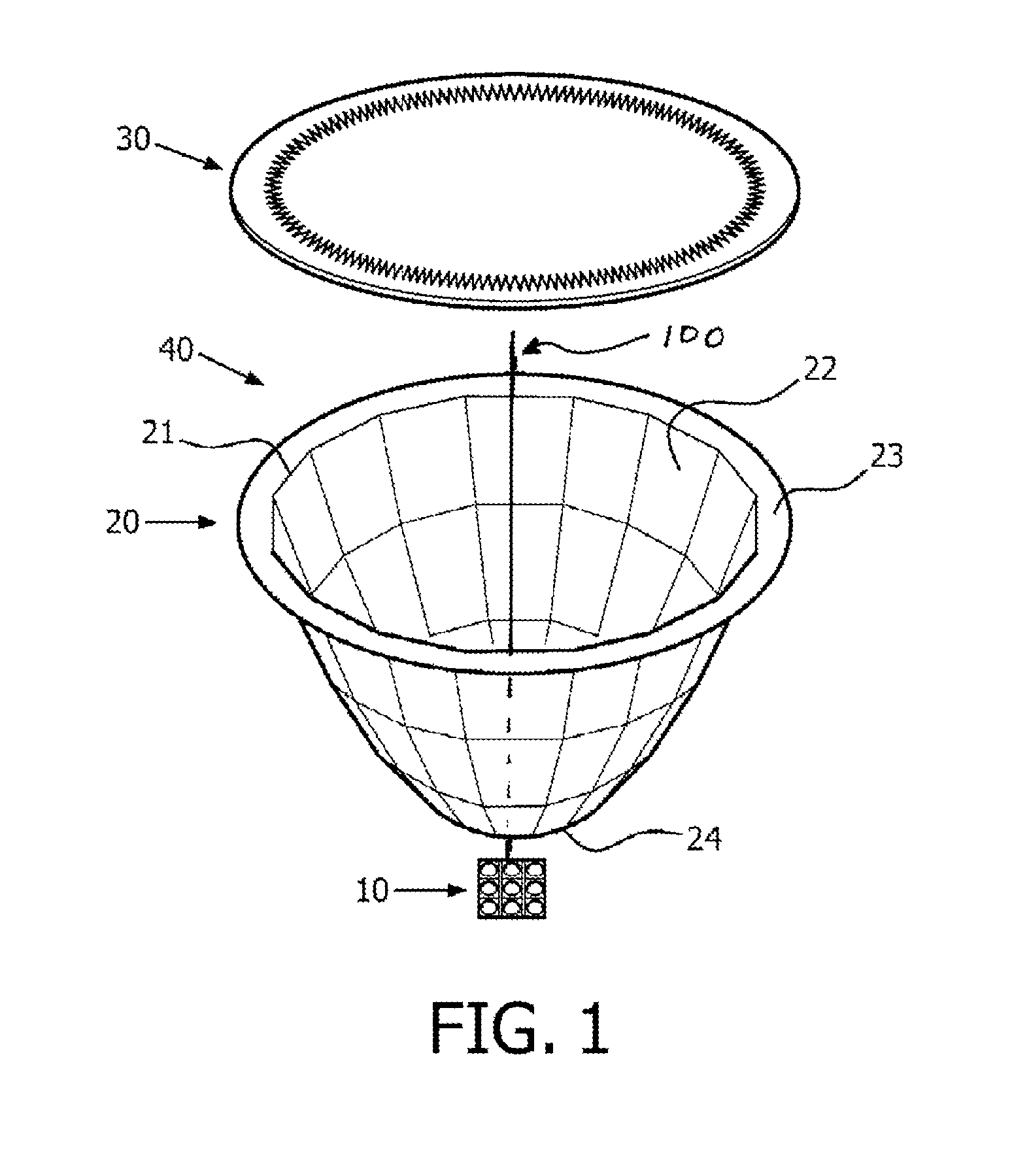
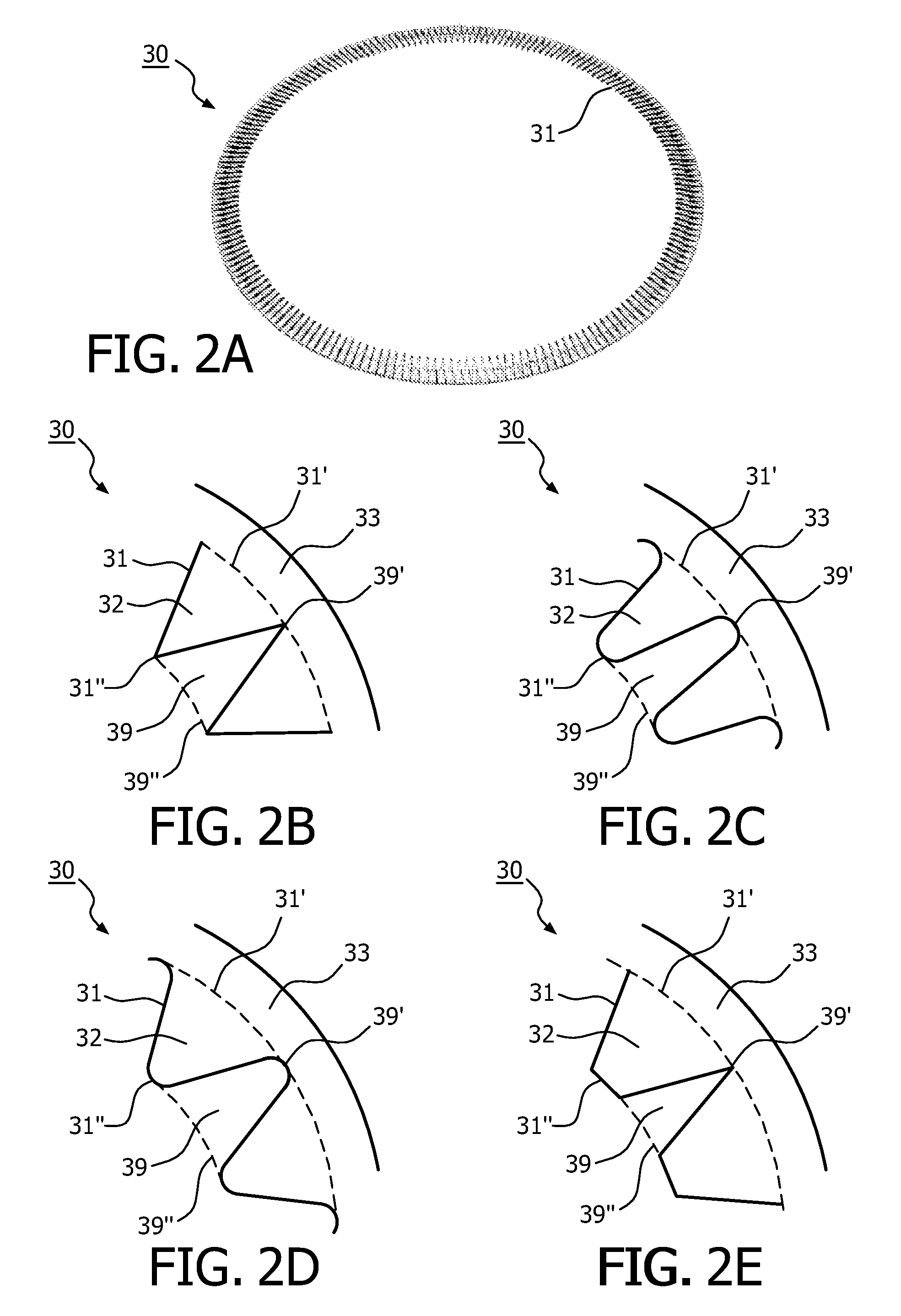
The invention relates to a lighting device comprising: —at least one light source (11); —a reflective member (20) comprising a reflective surface (22) and an edge (21) (“first edge”) forming a light cut-off of light rays passing in a region adjacent to this first edge (21); —a light-modifying member (30) adapted to modify lighting feature(s) of light rays and having an edge (“second edge”). The light-modifying member (30) extends from the reflective member (20) to this second edge (31) over a surface area defined to receive a part of the light rays passing in said region. The second edge is designed such that, among said part of light rays, the light-modifying member (30) modifies proportionally more light rays passing proximate the first edge than light rays passing less proximate the first edge (21). The invention relates also to said light-modifying member (30) per se.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Planar light-emitting device and display apparatus having the same
InactiveUS7926999B2Suppress light lossWithout reducing light emission efficiencyOptical light guidesIlluminated signsEdge surfaceLight guide
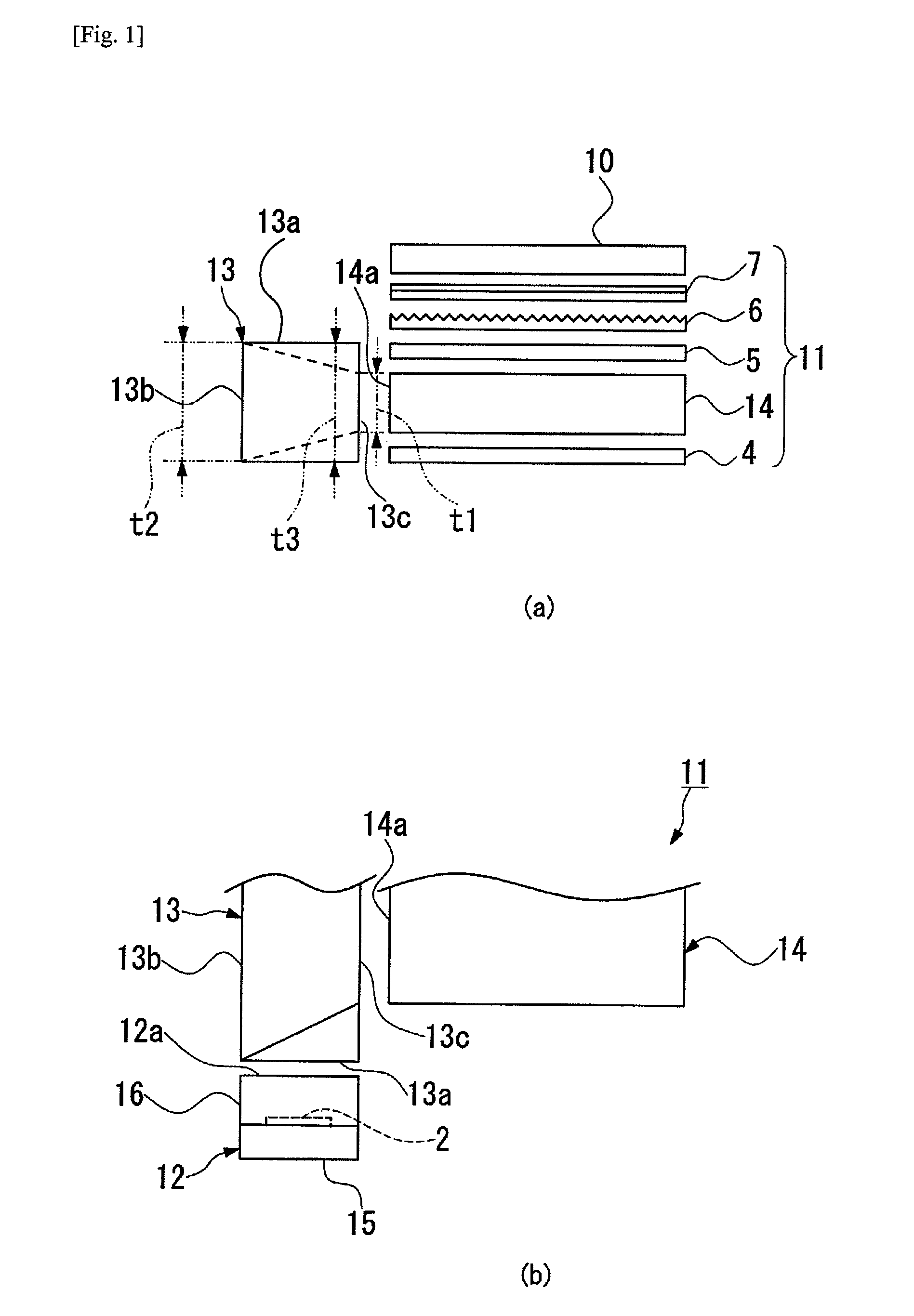
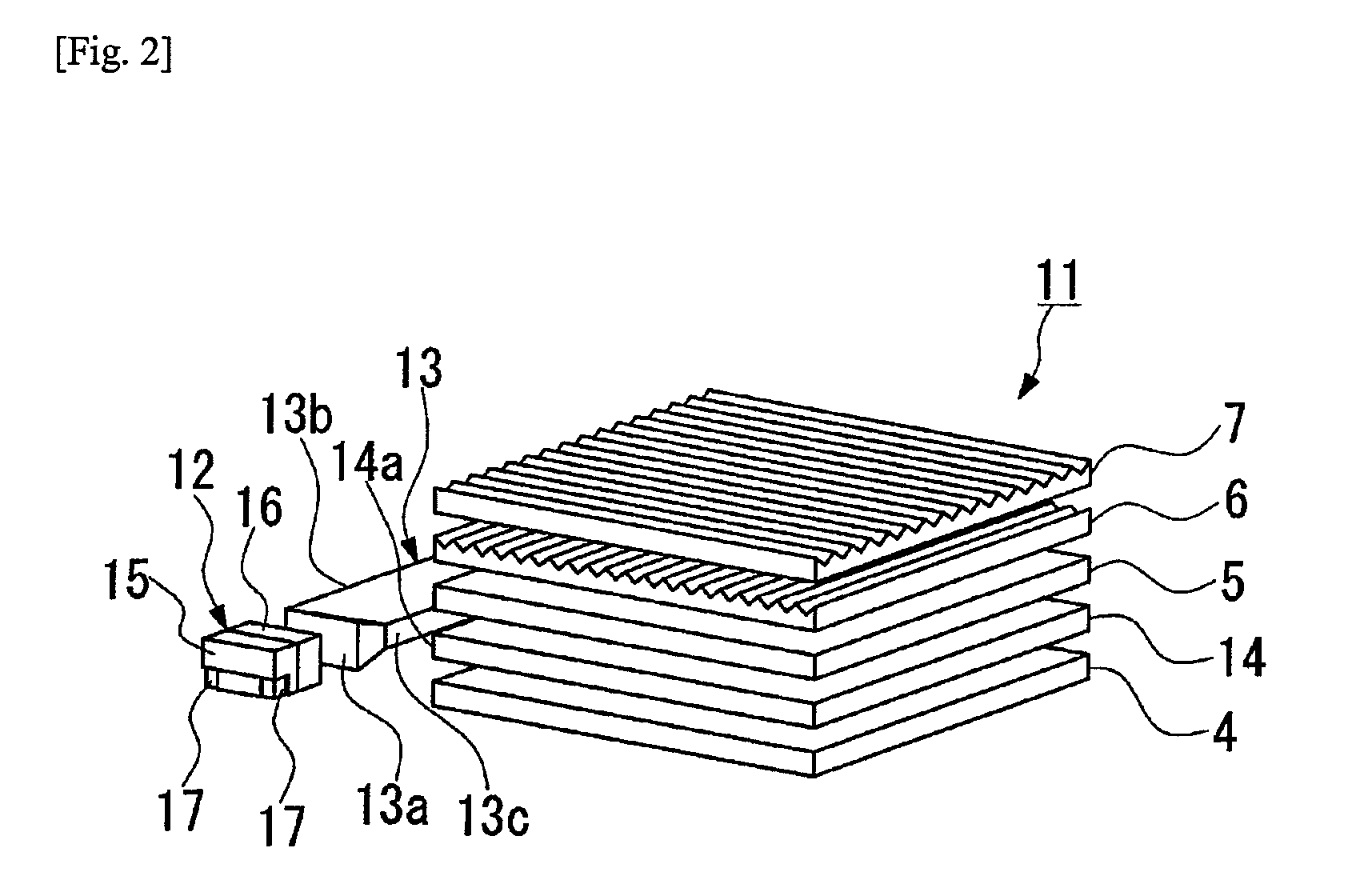
A planar light-emitting device includes an elongate first lightguide plate (13) having a light entrance end surface (13a) disposed facing an exit surface (12a) of a light-emitting package (12), a reflecting side surface (13b) extending substantially at right angles to the light entrance end surface to reflect light entering through the light entrance end surface, and a light exit side surface (13c) facing the reflecting side surface, and a flat plate-shaped second lightguide plate (14) having a light entrance side edge surface (14a) facing the light exit side surface (13c). The first lightguide plate is configured to satisfy the condition of t1<t2≦t3, where: t1, t2 and t3 are the respective heights of the light exit side surface (13c), the reflecting side surface (13b) and the light entrance end surface (13a). The surfaces of the first lightguide plate other than the light entrance end surface (13a) and the light exit side surface (13c) are reflecting surfaces.
Owner:CITIZEN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Lighting device having a smooth cut-off
ActiveUS20130044479A1Easy to controlSuppress light lossPlanar light sourcesNon-electric lightingEffect lightLight source
The invention relates to a lighting device comprising:—at least one light source (11);—a reflective member (20) comprising a reflective surface (22) and an edge (21) (“first edge”) forming a light cut-off of light rays passing in a region adjacent to this first edge (21);—a light-modifying member (30) adapted to modify lighting feature(s) of light rays and having an edge (“second edge”). The light-modifying member (30) extends from the reflective member (20) to this second edge (31) over a surface area defined to receive a part of the light rays passing in said region. The second edge is designed such that, among said part of light rays, the light-modifying member (30) modifies proportionally more light rays passing proximate the first edge than light rays passing less proximate the first edge (21). The invention relates also to said light-modifying member (30) per se.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Optical module and method for producing the same
InactiveUS9103971B2Suppress light lossImprove connection strengthMetal rolling stand detailsCoupling light guidesOptical ModuleEngineering
An optical module includes a substrate, an optical device including a surface-emitting or -receiving element mounted on a surface of the substrate with a light-emitting or -receiving portion, an optical fiber disposed parallel to the surface of the substrate and in a longitudinal direction of the substrate, a damming member provided between the optical device and the substrate to extend in a width direction of the substrate and dividing a gap between the optical device and the substrate in the longitudinal direction of the substrate into a first portion and a second portion, and a mirror provided at one side surface of the damming member a tip of the optical fiber. The first portion provided on an opposite side to the optical fiber is filled with an underfill resin, and the second portion provided on a side close to the optical fiber is filled with an optical fiber fixing resin.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Light emitting diode package and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS10971662B2Suppress light lossUniform brightnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) package includes a light-emitting structure, a transmissive material layer on the light-emitting structure, and a support structure covering at least a portion of a side surface of the transmissive material layer, a side surface of the light-emitting structure, and at least a portion of a bottom surface of the light-emitting structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Agricultural daylighting member and agricultural box
PendingUS20220322615A1Suppress light lossEfficient introductionAgricultural articlesClimate change adaptationGreenhouseRefractive index
A greenhouse has a daylighting member supported by a frame. The daylighting member partitions a growing space for agricultural products from an outside world, and emits light, which has entered from a light incident surface on one side, from a light emitting surface on the other side. The daylighting member has a transparent substrate layer and a transparent light emitting layer provided closer to a light emitting surface side than the substrate layer. The light emitting layer has a refractive index of 1.54 or less, water absorbability, and an equilibrium moisture content of 10% or greater at 25° C. and a relative humidity of 80%.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical module and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20130188907A1Easy to installEasy to produceMetal rolling stand detailsOptical waveguide light guideOptical ModuleComputer module
An optical module includes a substrate, an optical device including a surface-emitting or -receiving element mounted on a surface of the substrate with a light-emitting or -receiving portion, an optical fiber disposed parallel to the surface of the substrate and in a longitudinal direction of the substrate, a damming member provided between the optical device and the substrate to extend in a width direction of the substrate and dividing a gap between the optical device and the substrate in the longitudinal direction of the substrate into a first portion and a second portion, and a mirror provided at one side surface of the damming member a tip of the optical fiber. The first portion provided on an opposite side to the optical fiber is filled with an underfill resin, and the second portion provided on a side close to the optical fiber is filled with an optical fiber fixing resin.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Optical module
ActiveUS8774241B2Suppress light lossEasy alignmentLaser cooling arrangementsSolid state laser constructional detailsSolid-state laser deviceOptical Module
To constitute an optical module comprising a mount and a board that supports the mount, wherein a solid-state laser device that oscillates fundamental laser light, a pump light source that pumps the solid-state laser device, and a wavelength converting device that converts a wavelength of the fundamental laser light oscillated by the solid-state laser device are mounted on the mount, the mount is divided into three blocks, that is, a first block on which a laser medium is mounted, a second block on which the pump light source is mounted, and a third block on which the wavelength converting device is mounted. A side surface or a bottom surface of only the second block is fixed to the board, the first block is fixed to the other side surface of the second block, and the third block is fixed to a side surface of the first block.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Optical member and display device
ActiveCN101788132BSuppress light lossReduce brightnessPoint-like light sourceOptical light guidesFluorescencePhosphor
An optical member realizing suppressed occurrence of a light loss between a phosphor layer performing color conversion and itself, and a display device using the same is provided. The optical member includes a base member having two opposed surfaces, and a phosphor layer provided integrally with one surface of the base member and containing a phosphor that converts a color light to another color light.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Beam transforming element, illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and exposure method
InactiveCN101369056ASuppress light lossEfficient preparationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsLight fluxLight beam
A lighting optical device capable of forming a bracelet-form lighting pupil distribution in a peripherally-polarized state with a light quantity loss satisfactorily controlled, the device comprising a light flux conversion element (50) for forming a bracelet-form light intensity distribution on a specified surface based on an incident light flux. The light flux conversion element comprises a first basic element (50A) formed of an optically-rotating optical material, for forming a first arcuate area distribution based on an incident light flux out of bracelet-form light intensity distribution, a second basic element (50B) for forming a second arcuate area distribution, a third basic element (50C) for forming a third arcuate area distribution, and fourth basic element (50D) for forming a fourth arcuate area distribution. Respective basic elements have mutually different thicknesses along the light transmitting direction.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Laser module
The invention discloses a laser module. When forming the laser module which comprises a substrate and a base plate, the substrate is divided into three blocks, wherein the substrate is used for carrying a solid laser element, an excitation laser source and a wave length converting element. The solid laser element is used for emitting fundamental wave lasers through oscillation, the excitation laser source is used for exciting the solid laser element, and the wave length converting element is used for converting the wave length of the fundamental wave lasers emitted by the solid laser element through oscillation. The base plate is used for supporting the substrate. The three blocks comprise the first block carrying a laser medium, the second block carrying the excitation laser source and the third block carrying the wave length converting element. The side face or the bottom face of only the second block is fixed to the base plate, the first block is fixed to the other side face of the second block, and the third block is fixed to the side face of the first block.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Objective lens for optical pickup device, optical pickup device, and optical information recording/reproduction device
InactiveCN103262168AImprove light utilization efficiencyGood temperature characteristicsOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical pickupRefractive index
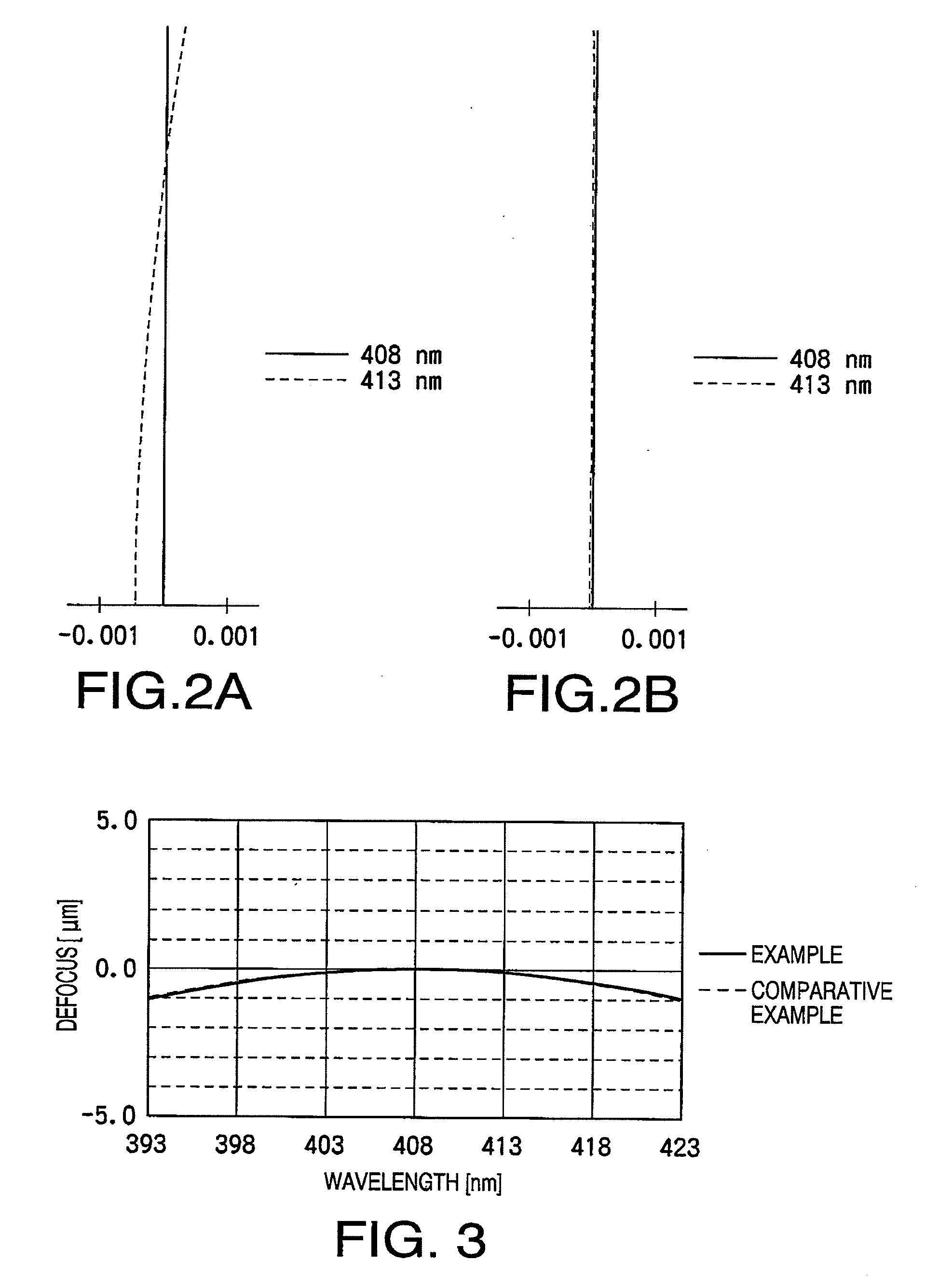
Provided are: an optical pickup device and optical information recording / reproduction device provided with an objective lens capable of improving temperature characteristics and wavelength characteristics while making it possible to support three types of optical disc, namely Blu-ray Discs, DVDs, and CDs, with a shared objective lens; and an objective lens suitable therefor. A first optical-path-difference creation structure, in which at least a first basic structure and second basic structure are superimposed, reduces a step difference in the optical-axis direction, thereby keeping the diffraction efficiency from decreasing upon wavelength changes. Furthermore, when the wavelength of incident light increases, spherical aberration from the aforementioned first basic structure and second basic structure changes in the direction in which more correction is needed; thus, when the index of refraction of the objective lens changes as a result of an increase in the temperature of the optical pickup device, the fact that the wavelength of the light source also increases as a result of the increase in ambient temperature is utilized to correct spherical-aberration degradation due to the change in the index of refraction of the objective lens.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Intensive optical wave multiplexing optical filter
InactiveCN112099124AReduce the number of coating layersAvoid damageOptical light guidesEngineeringLight filter
The invention discloses an intensive optical wave multiplexing optical filter, which comprises a substrate, and an optical filter layer and an anti-radiation layer which respectively cover two opposite surfaces of the substrate, and is characterized in that the surface, opposite to the substrate, of the optical filter layer is also provided with an anti-scraping layer, so that the optical filter layer can be prevented from being damaged due to friction when polishing operation is required subsequently, and the yield of the optical filter is ensured; meanwhile, the first dielectric sub-layer forming the filter layer is made of silicon hydride, so that the total layer number of the filter layer is reduced to be not more than 84, and the layer thickness is not more than 20 [mu] m. Compared with the prior art, the thickness of the filter layer is greatly reduced, and light loss, light path disruption and stress accumulation caused by over-thickness of the filter layer are effectively inhibited; and the overall manufacturing cost is reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU JIAHE PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Objective lens and optical pickup device
InactiveCN104335277APrevent effectHigh diffraction efficiencyRecord information storageSystems characterised by carrier structureOptical pickupSingle element
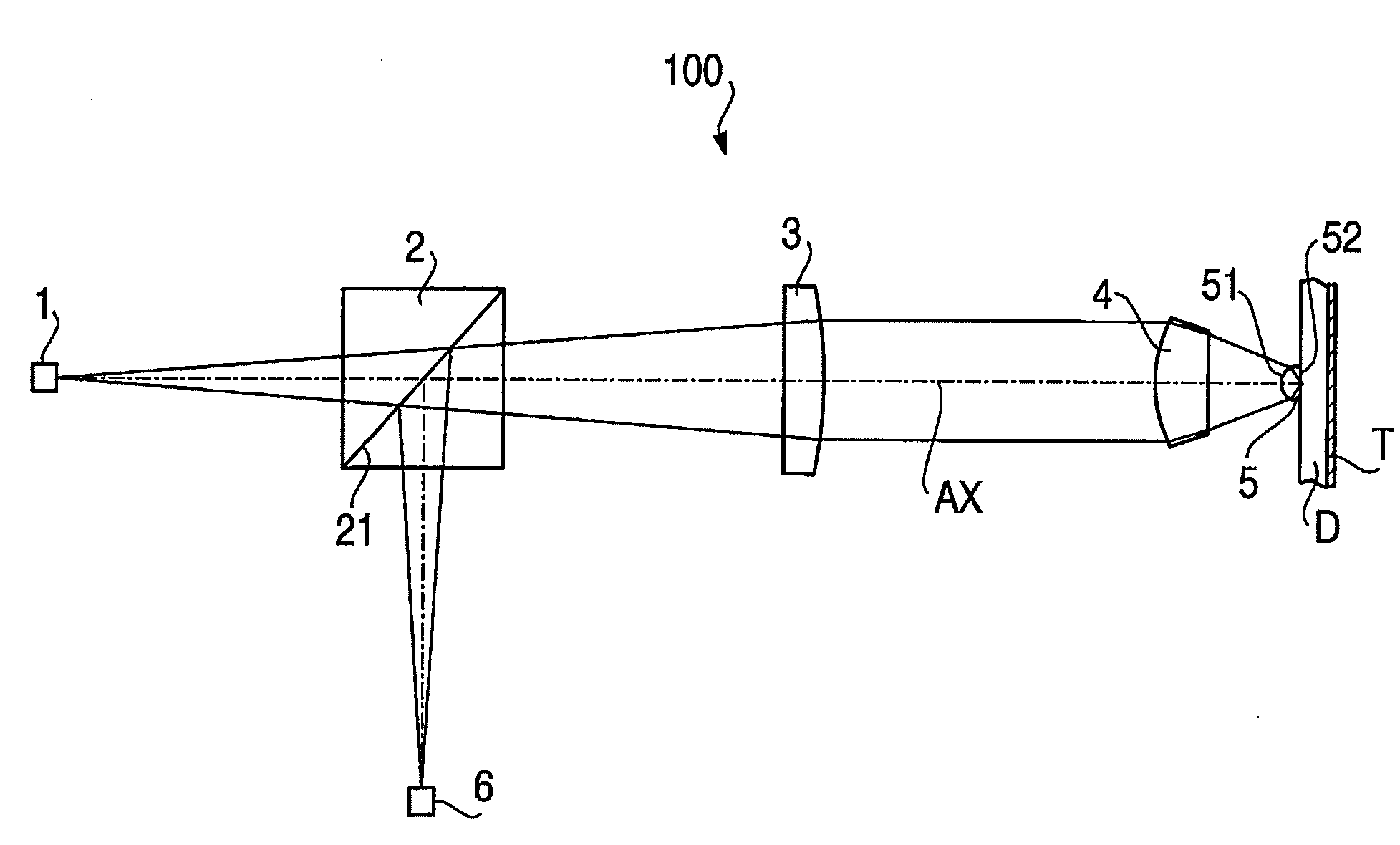
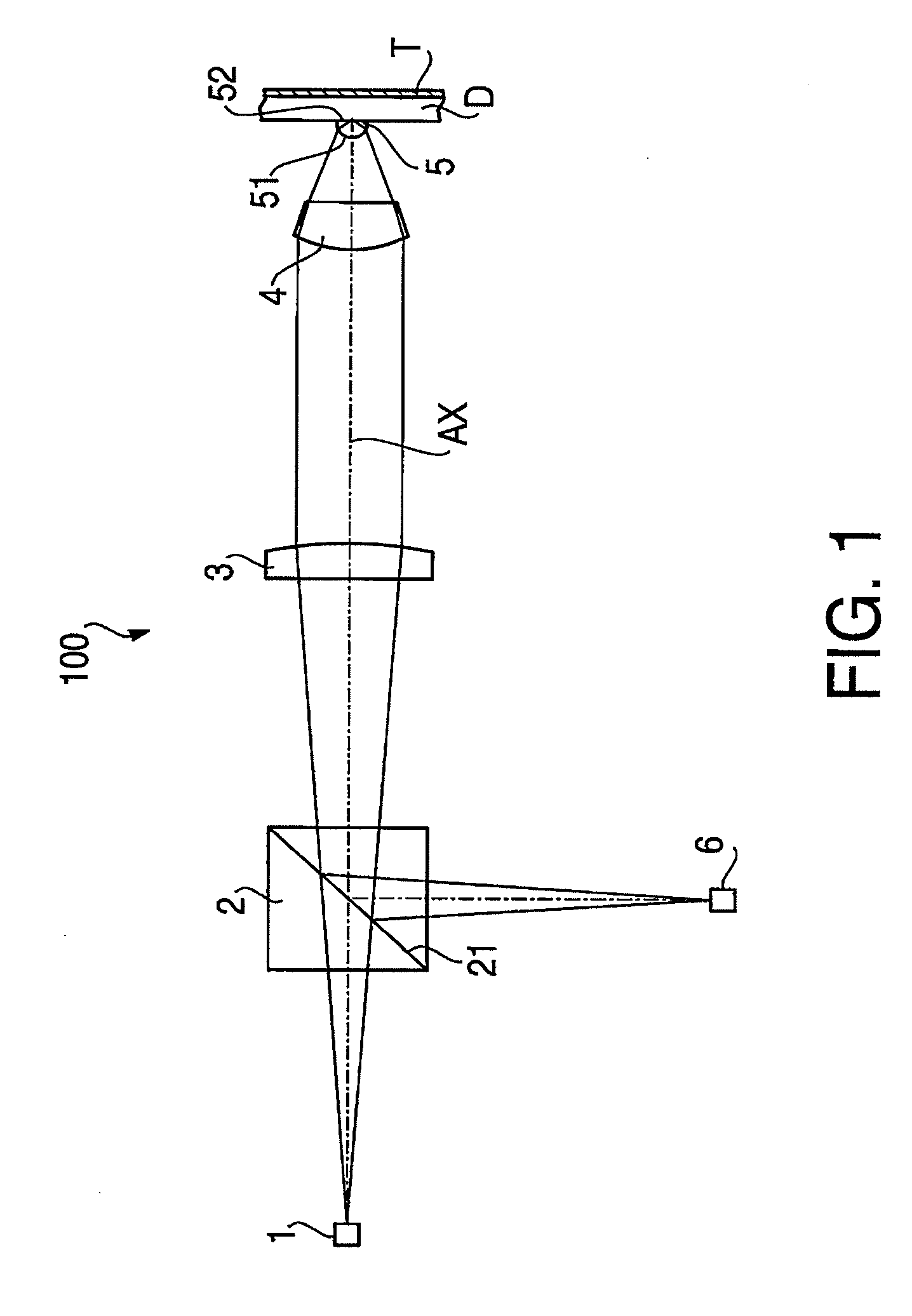
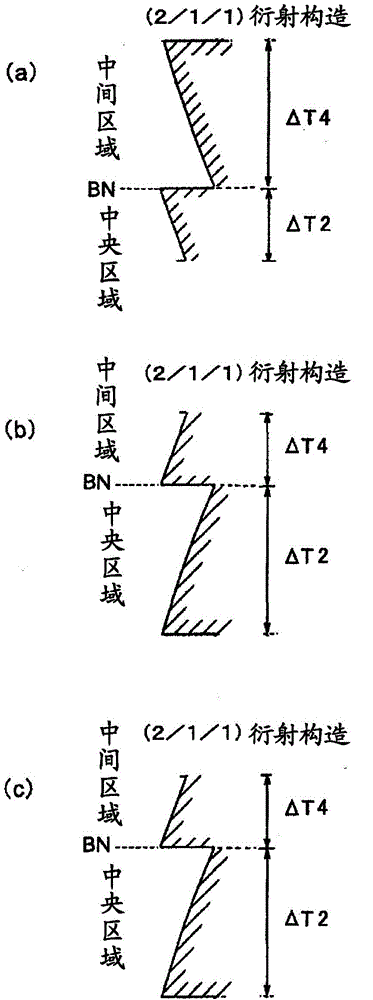
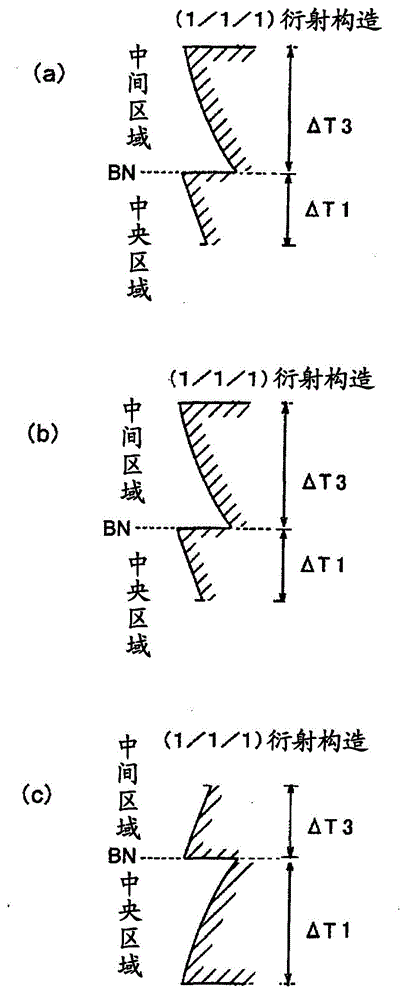
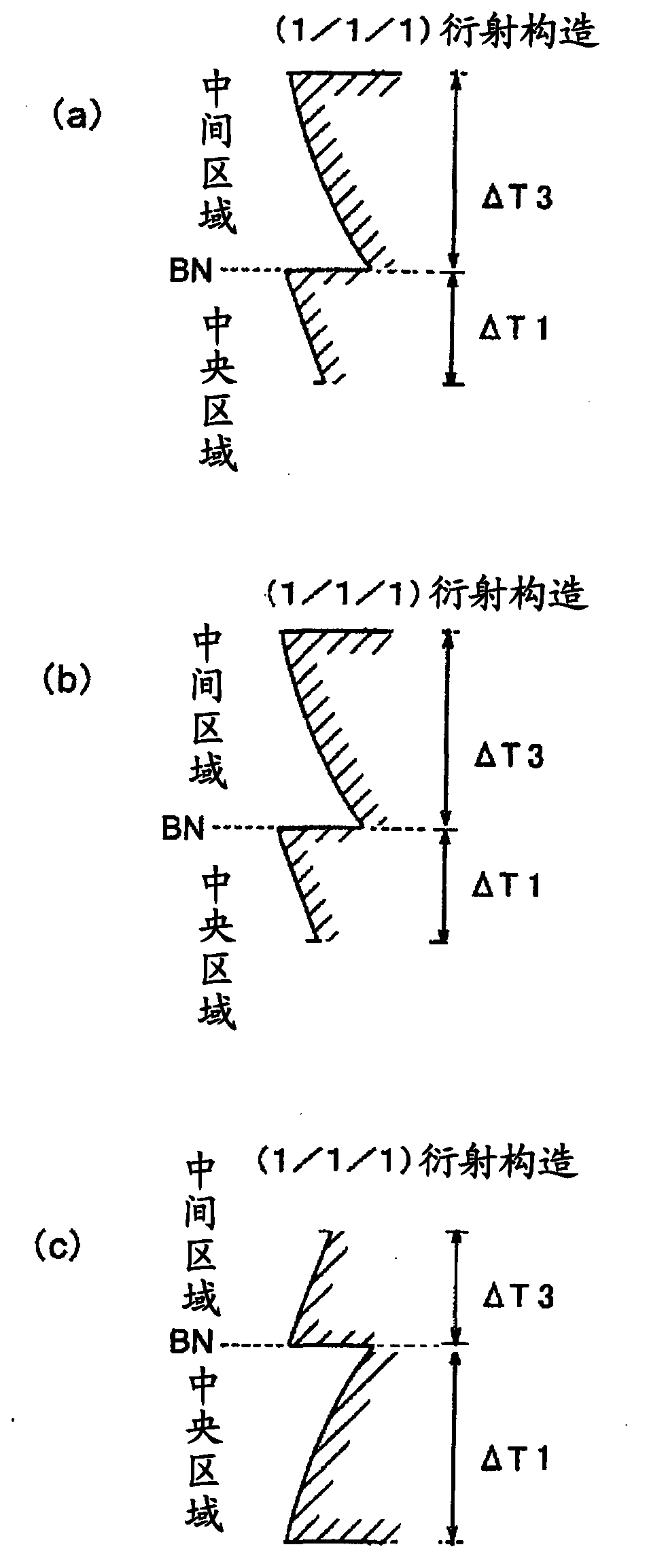
Provided are a single-element objective lens compatible with optical disks of the three formats BD / DVD / CD, the objective lens being adaptable to compact size while having good moldability, and being capable of stable recording and playback of information due formation of an appropriate spot diameter, even during use with a BD, making the lens suitable for a compact optical pickup device; and an optical pickup device equipped with this objective lens. A first optical path difference-imparting structure in the center region of the objective lens is structured to have a (2 / 1 / 1) first fundamental structure and a (1 / 1 / 1) second fundamental structure. A second optical path difference-imparting structure in an intermediate region is structured to have a (1 / 1 / 1) fourth fundamental structure and a (7 / 4) or (5 / 3) third fundamental structure. A third optical path difference-imparting structure in a peripheral region is structured to have a fifth fundamental structure whereby the quantity of second-order or fourth order refracted light of a first light beam is greater than the quantity of refracted light of any other order.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Optical element and objective optical system
InactiveUS20090201786A1High recording densitySuppress longitudinal chromatic aberrationRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansComputational physicsOptical path
There is provided an optical element for an objective optical system of an optical information recording / reproducing device. The objective optical system is configured to satisfy conditions: λ<500; NA≧0.7; and f≦1.0, and at least one of surfaces of the optical element includes a diffraction structure defined by an optical path difference function φ(h):φ(h)=(P2h2+P4h4+P6h6+P8h8+P10h10+P12h12)mλwhere P2, P4, P6 . . . denote coefficients of 2nd order, 4th order, 6th order . . . , respectively, h denotes a height from an optical axis of the optical element, and m denotes a diffraction order at which diffraction efficiency for the laser beam is maximized. The diffraction structure satisfies conditions:P2<0 (4);P2×P4<−100 (5); and−60<P2 / P4<0 (6).
Owner:HOYA CORP
Objective lens for optical pickup device and optical pickup device
InactiveCN103210446BImprove light utilization efficiencyEnsure working distanceTelevision system detailsRecord information storageOptical pickupFlare
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Ojbective lens for optical pickup device and optical pickup device
InactiveCN103210446AImprove light utilization efficiencyEnsure working distanceTelevision system detailsRecord information storageOptical pickupFlare
Provided is an objective lens with which three types of optical disks, BB / DVD / DC, are interchangeable using a typical objective lens, and with which high-order aberrations can be suppressed and formability can be increased; also provided is an optical pickup device using said objective lens. The objective lens has a central region wherein second basic structures having a blazed structure are superposed, and an intermediate region wherein fourth basic structures having a blazed structure are superposed. On either side of the boundary between the central region and the intermediate region, the pitch P2 at the position of the second basic structures of the central region nearest to the boundary, and the pitch P4 at the position of the fourth basic structures of the intermediate region nearest to the boundary, fulfill the relationship P4 - P2 > 0 when the codes corresponding to the orientation of the steps is considered. Thus, the power in the intermediate region is greater than the power in the central region, and consequently a negative spherical aberration of the base aspherical surface remains in the intermediate region, and it is possible to emit flares when a CD is used.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com