Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
198results about How to "Reduce noise signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
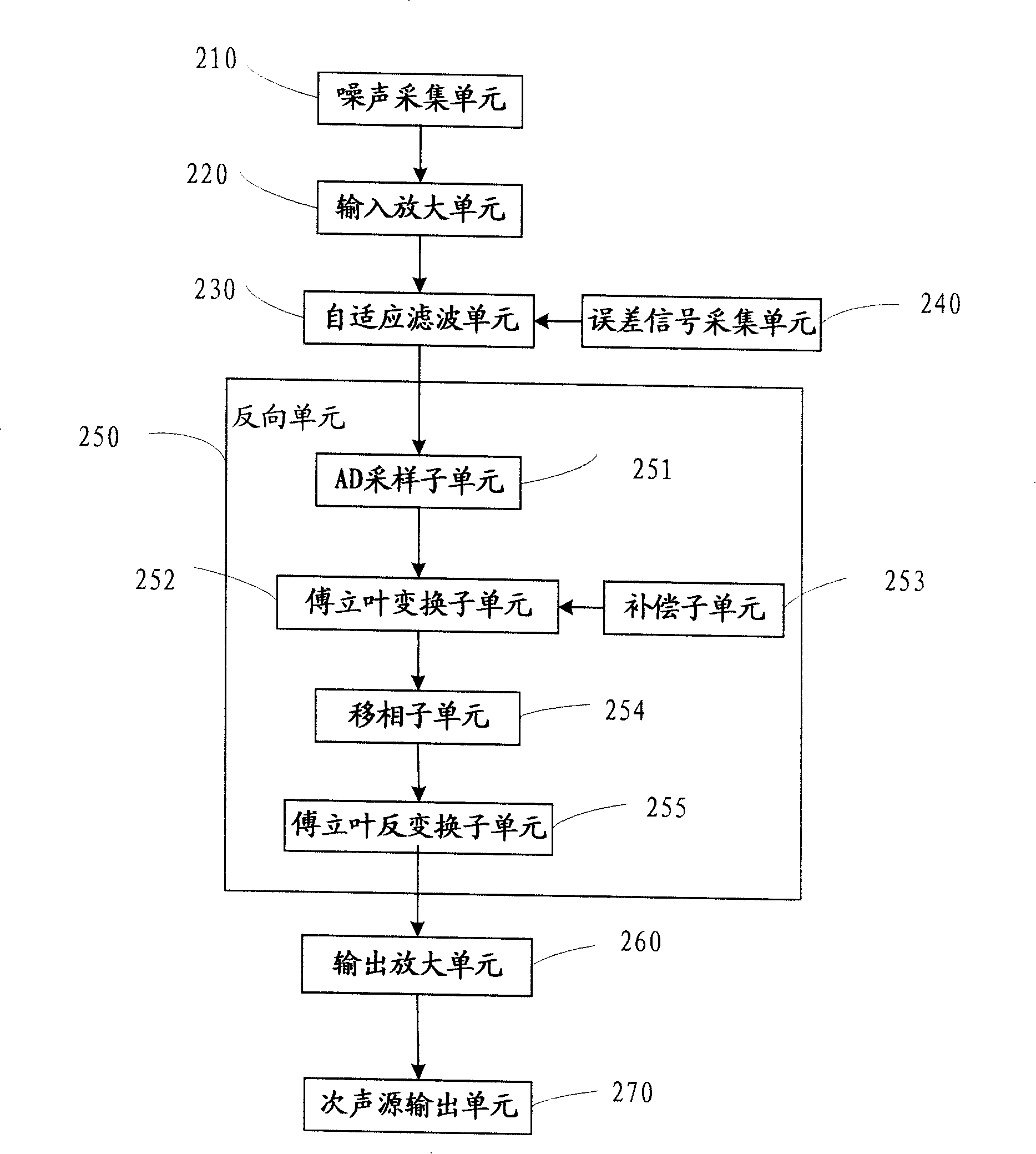
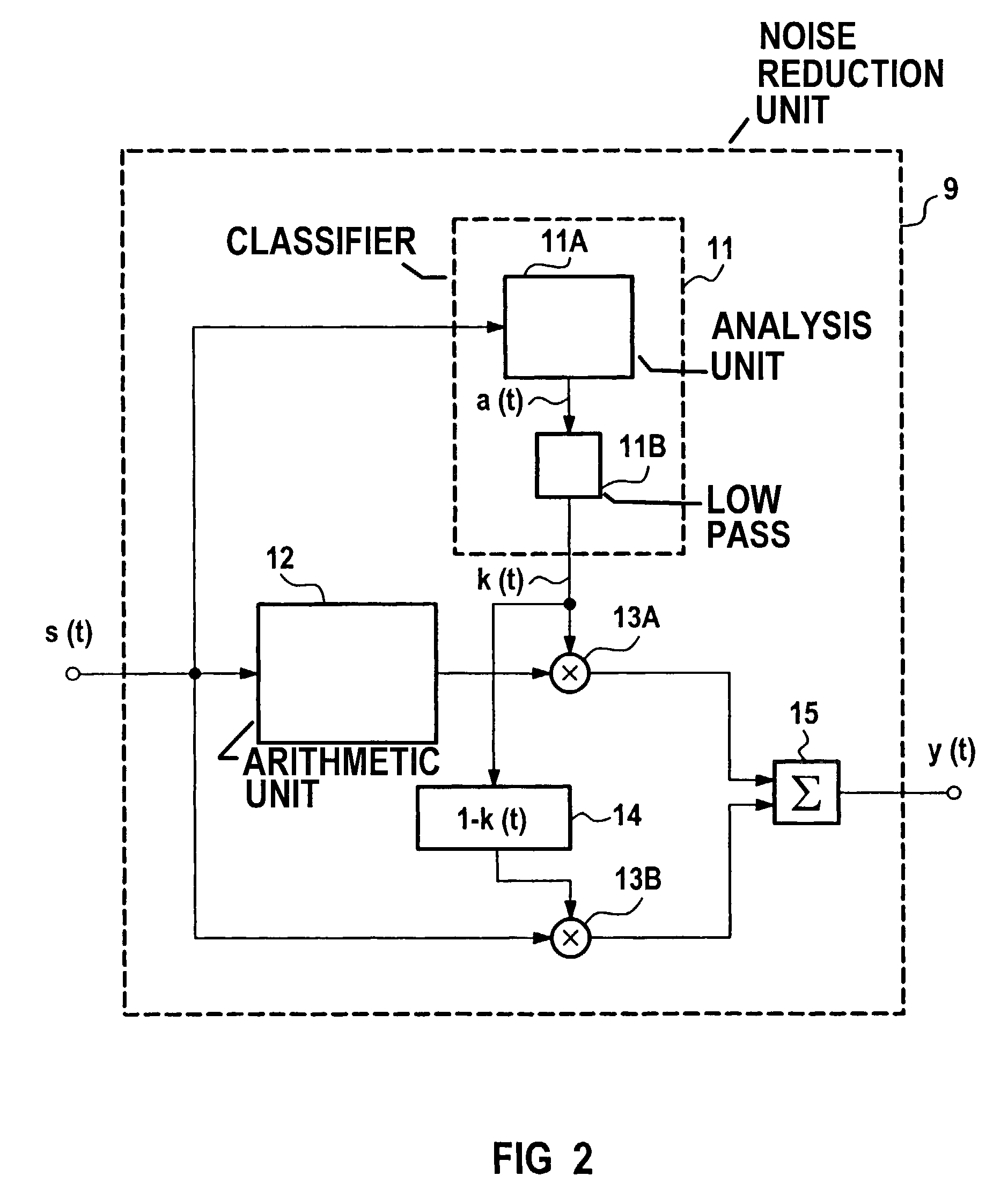
Active noise control system
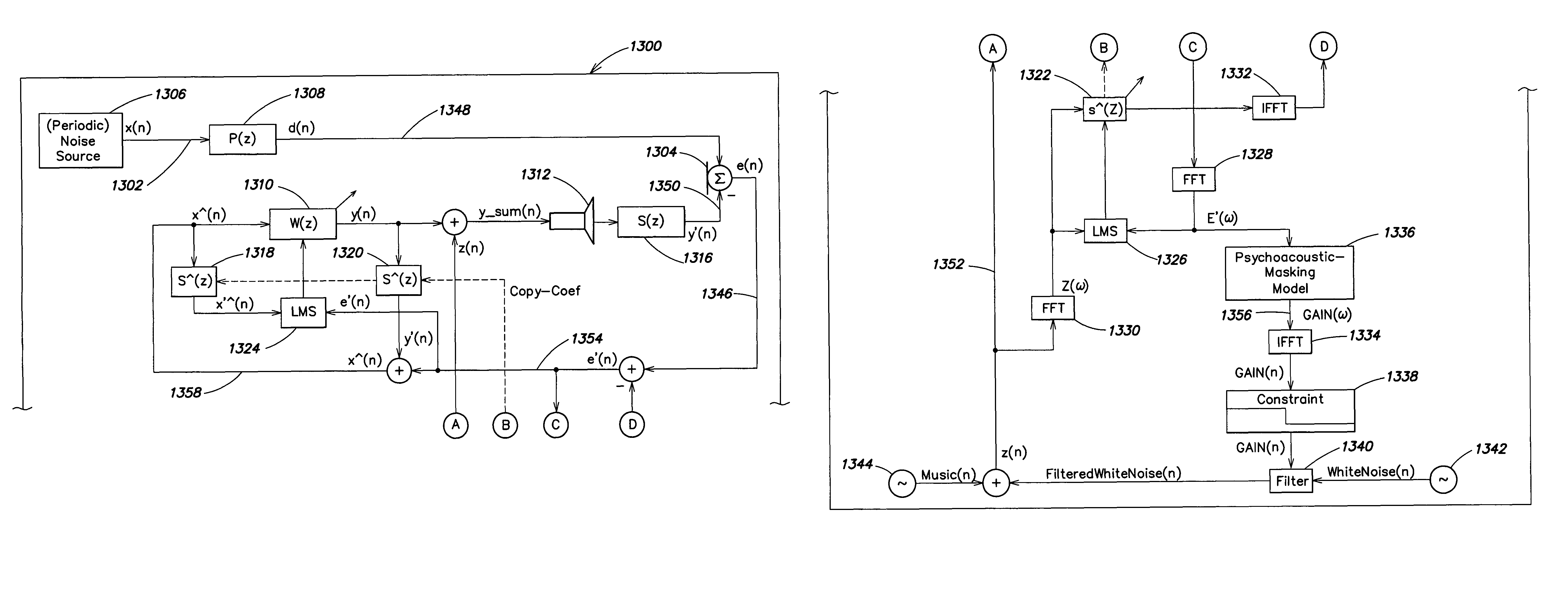
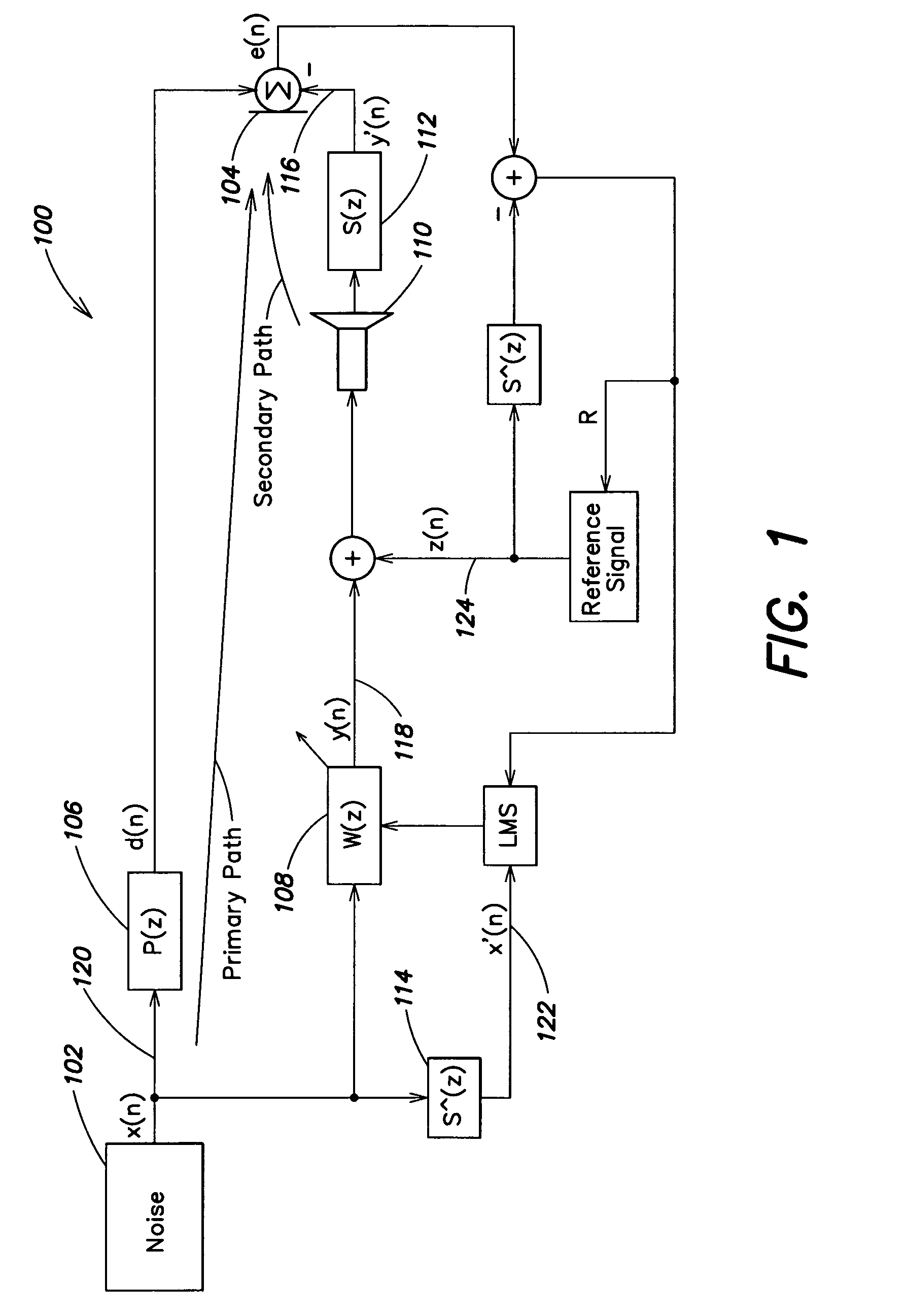
ActiveUS20080181422A1Reduce and cancel unwanted noise signalLower Level RequirementsEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlEngineering
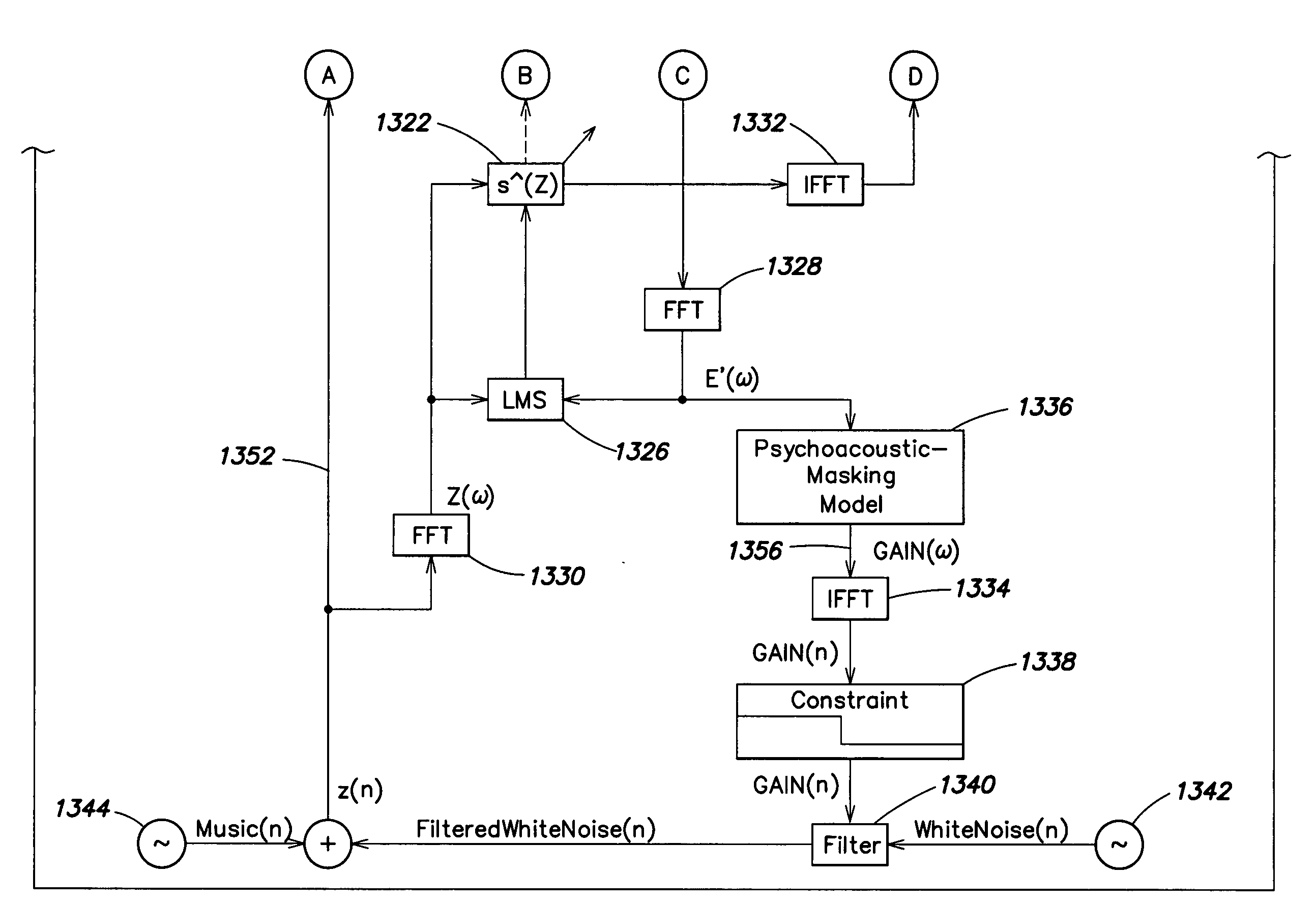
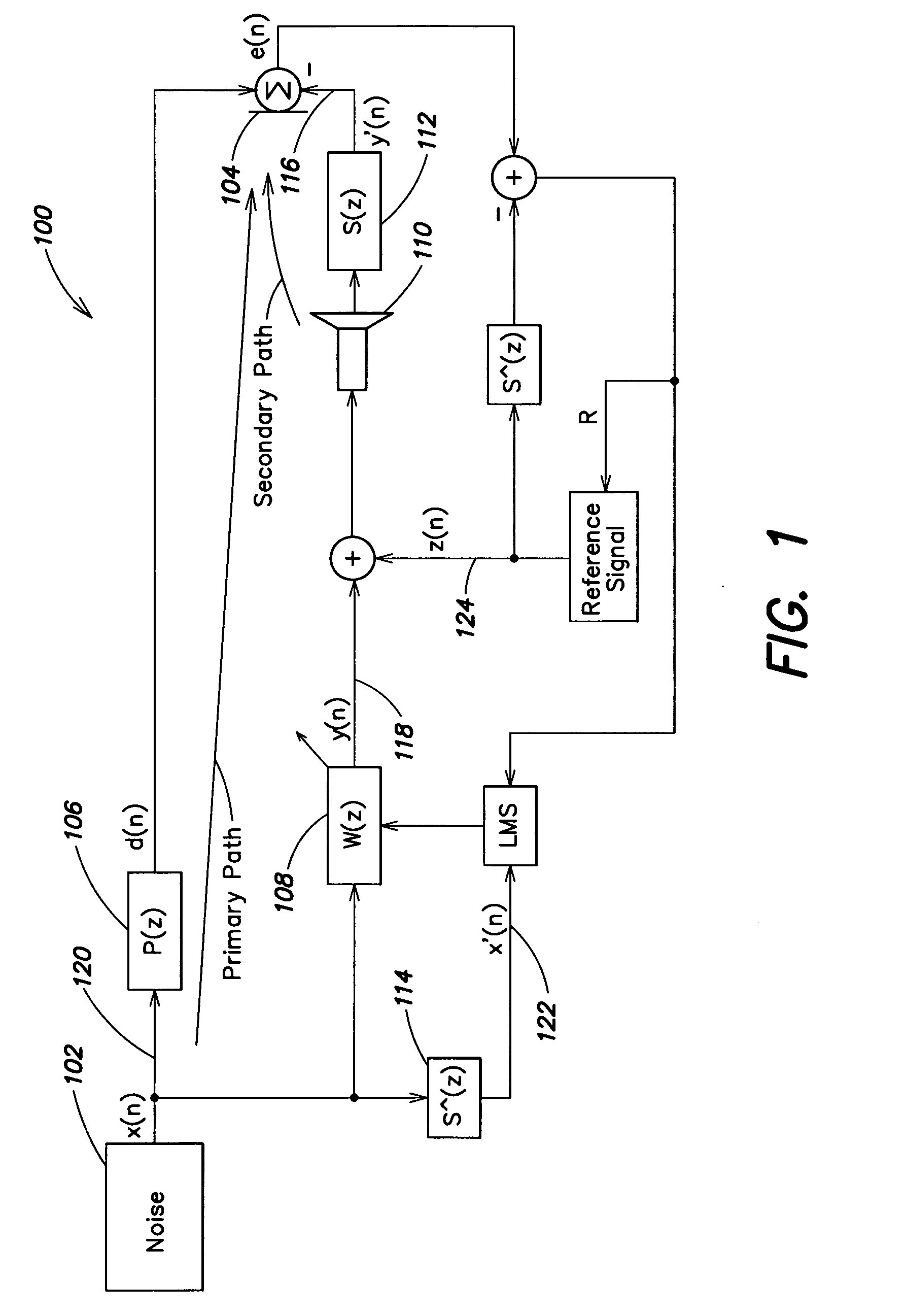
An active control of an unwanted noise signal at a listening site radiated by a noise source uses a reference signal that has an amplitude and / or frequency such that it is masked for a human listener at the listening site by the unwanted noise signal and / or a wanted signal present at the listening site in order to adapt for the time-varying secondary path in a real time manner such that a user doesn't fell disturbed by an additional artificial noise source.
Owner:APPLE INC
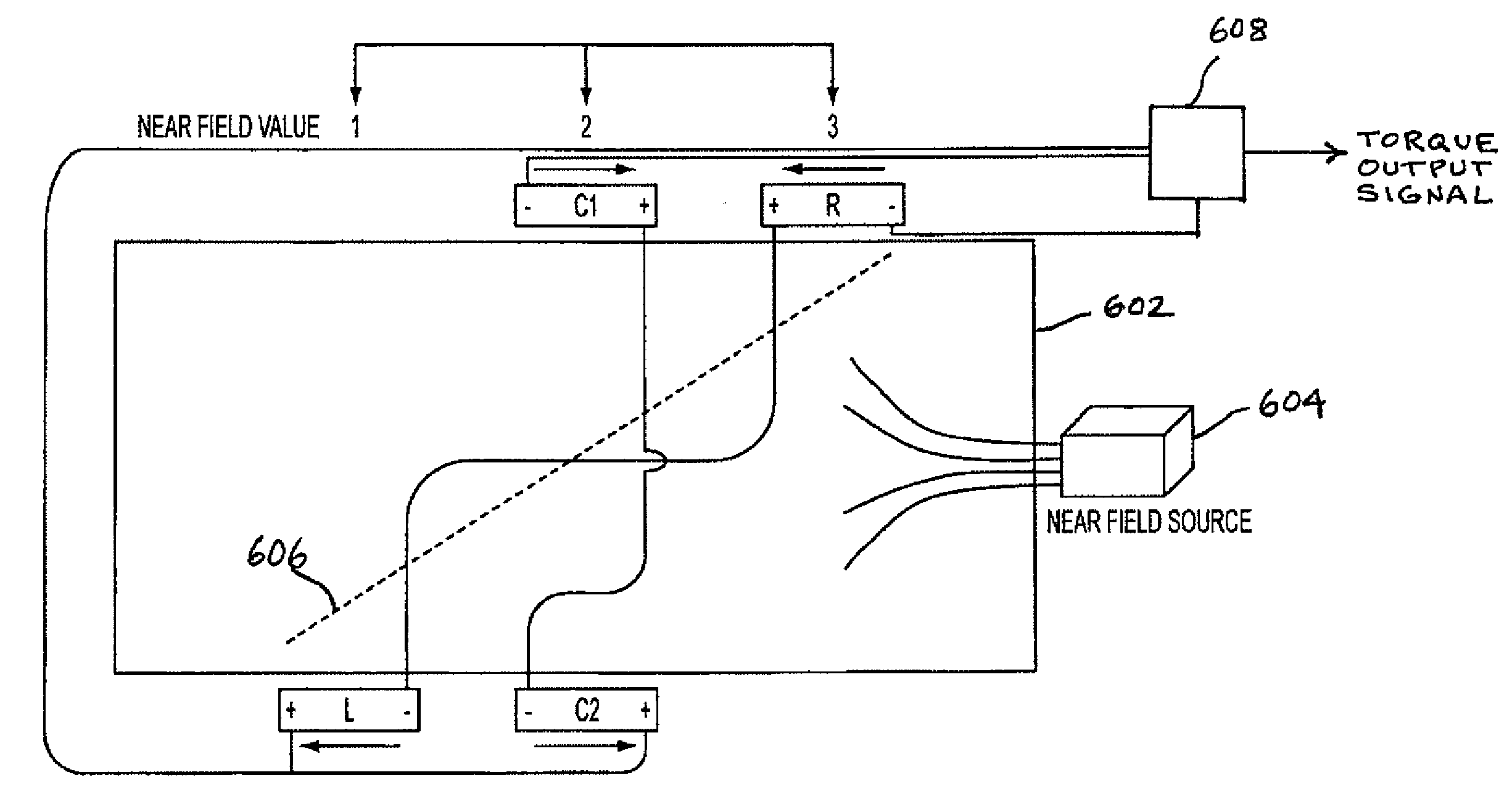
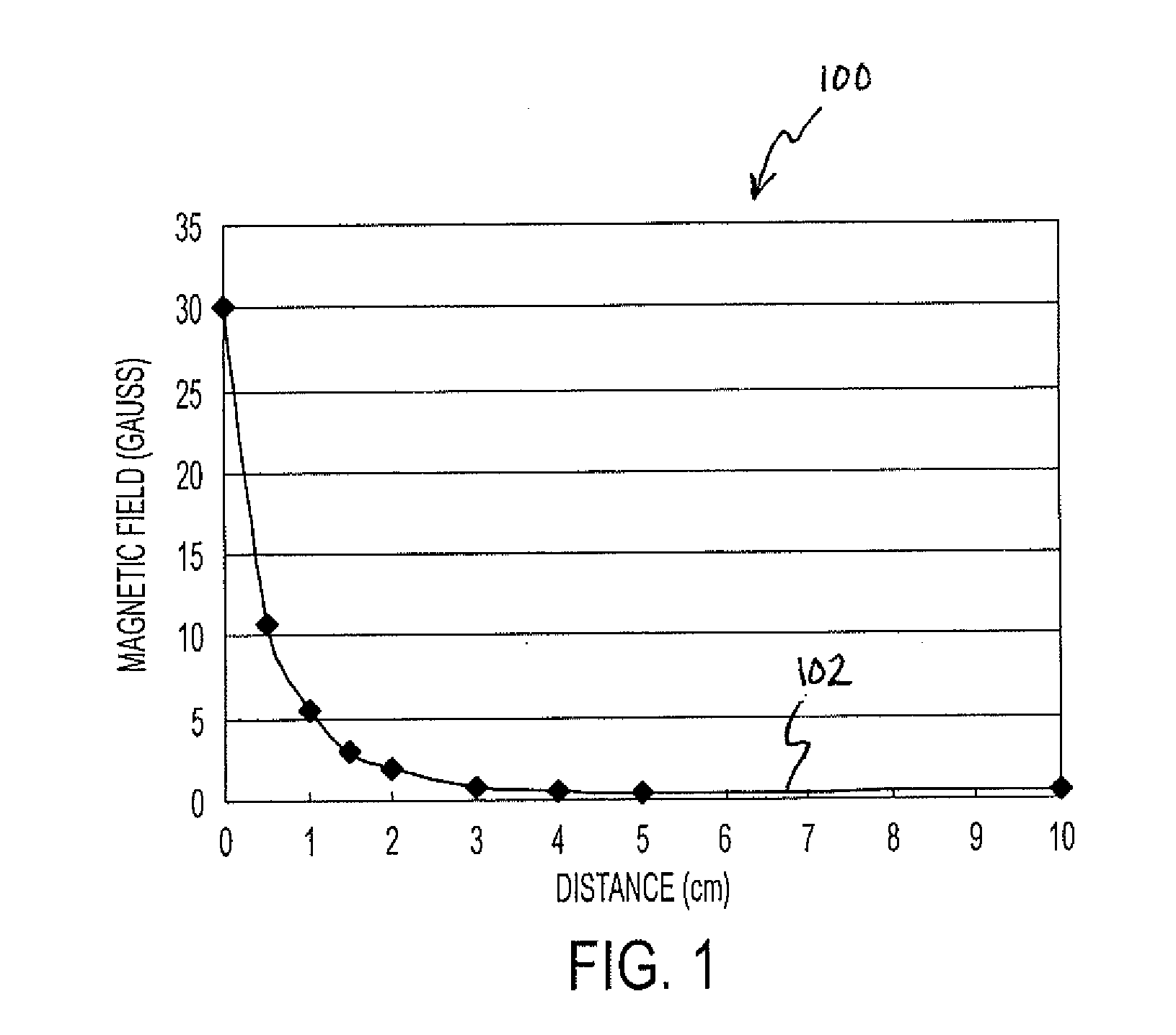
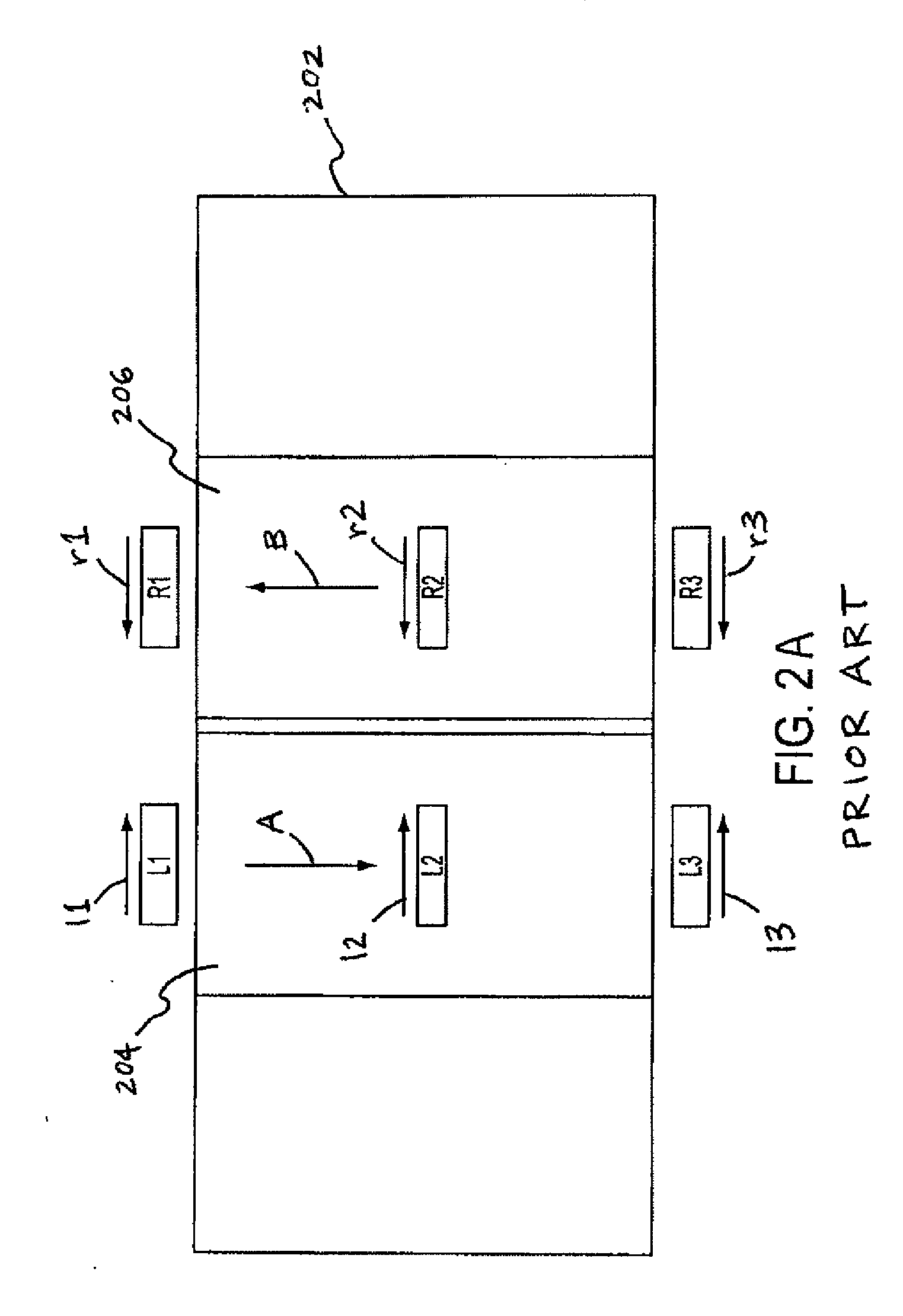
Magnetoelastic torque sensor with ambient field rejection
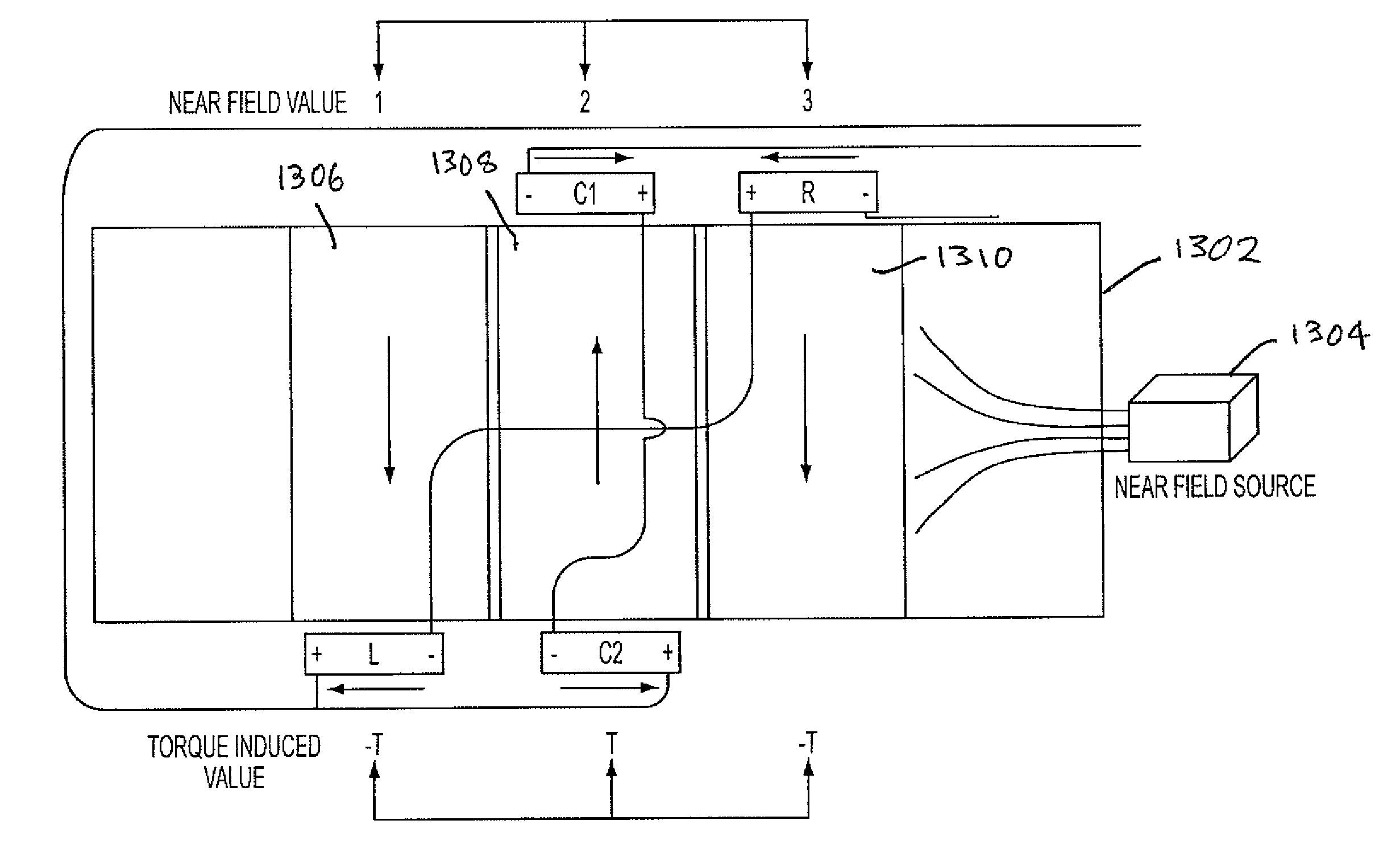
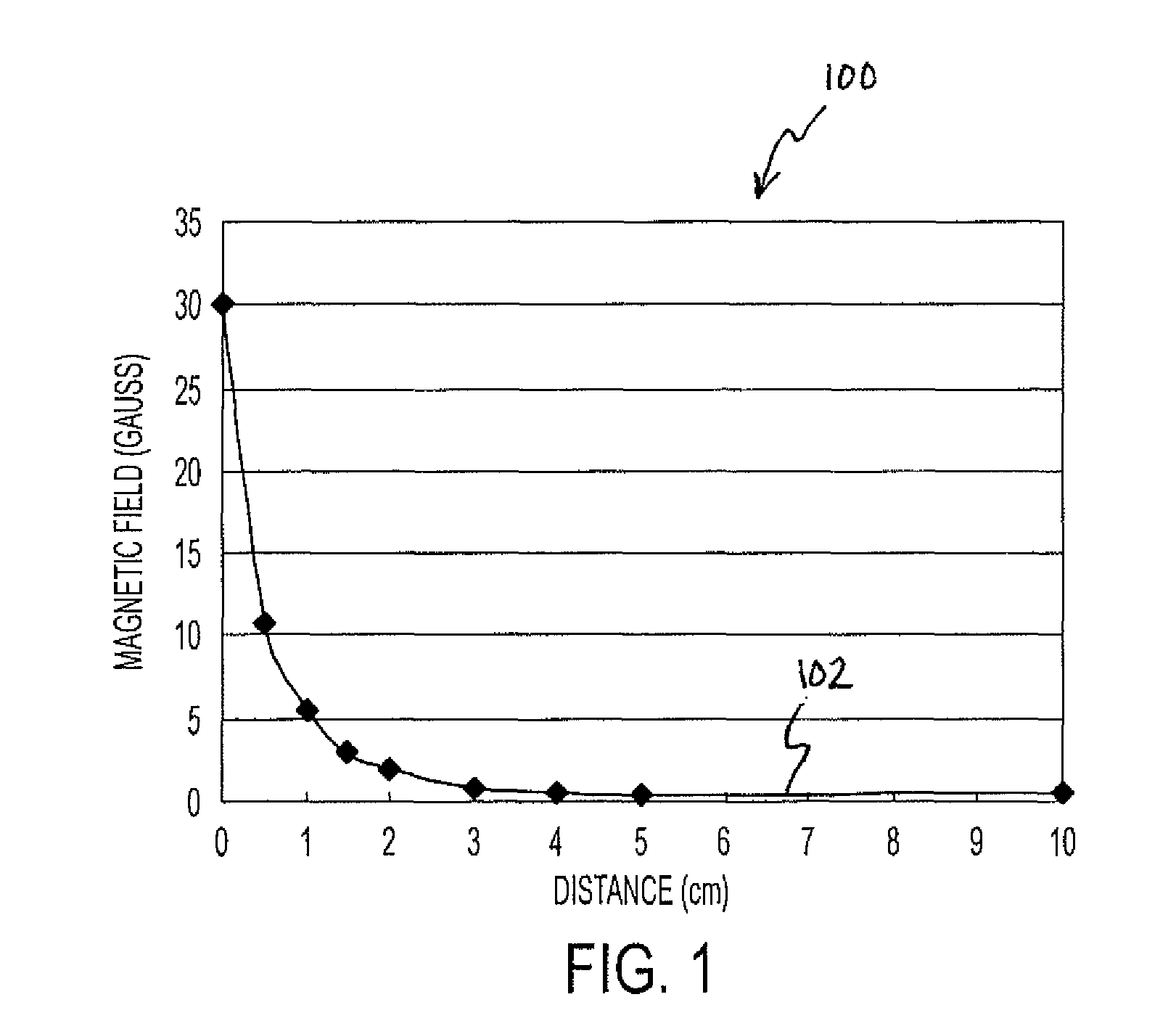
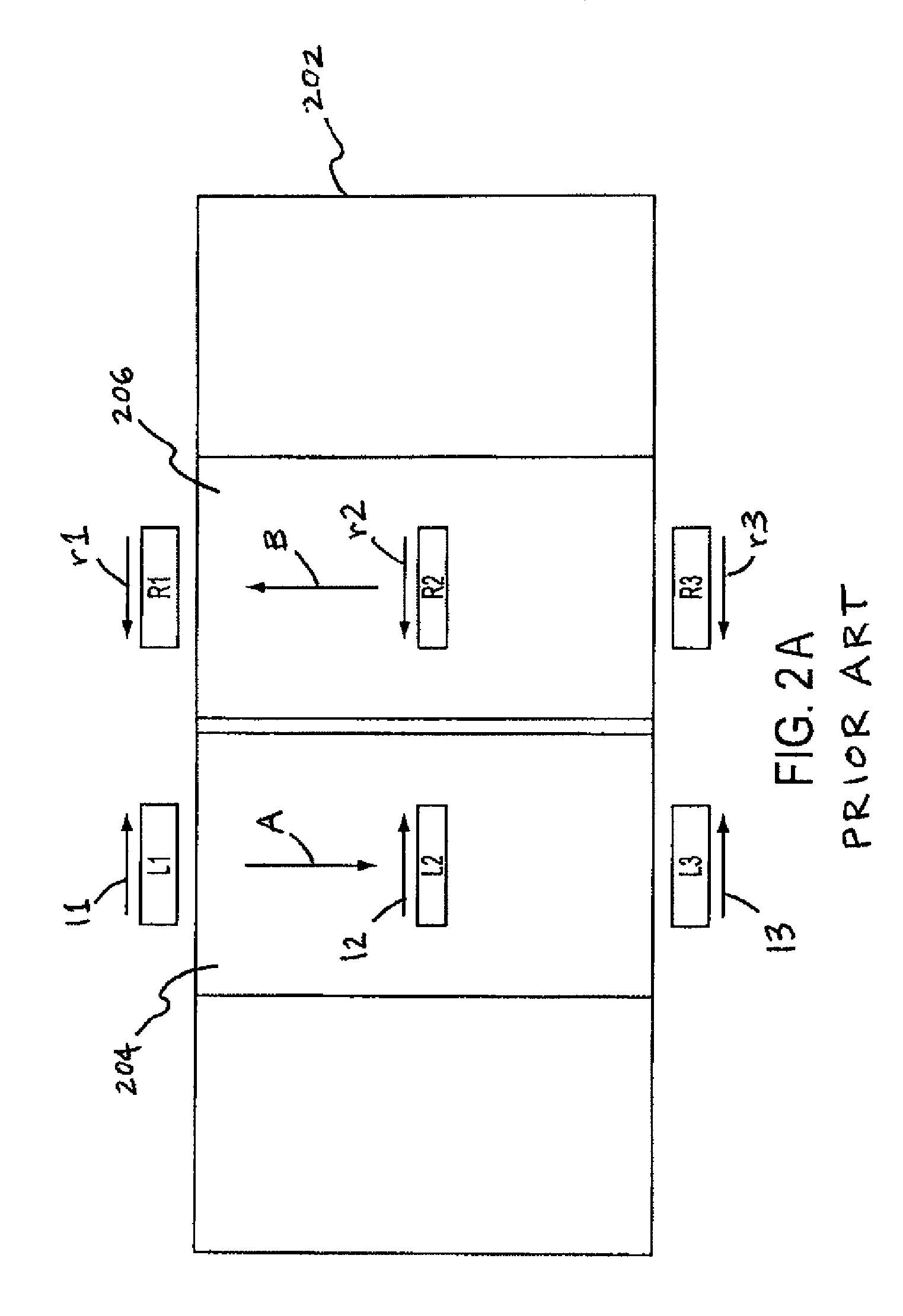
ActiveUS8087304B2Cancellation effectEliminate the effects ofSolid-state devicesWork measurementCondensed matter physicsTorque sensor
Owner:METHODE ELETRONICS INC
Active noise reduction method and device
The invention relates to an active noise reducing method and an active noise reducing device, in particular to active noise reduction for noise generated by importing and exporting wind gate of electrical equipments. The characteristics of amplitude, frequency and phase of noise of noise source are detected through sampling the noise signal. A signal with the same amplitude and reverse phase is generated through filtering and anti-phase processing and output through a speaker to counteract the noise signal so as to achieve the object of noise reduction, wherein the filtered signal is modified adaptively during filtering process so that the filtered signal is closer to the noise source signal while filtering the noise, thus the effect of noise reduction is more ideal.
Owner:HAIER GRP CORP +1
Magnetoelastic torque sensor with ambient field rejection
ActiveUS20090230953A1Cancellation effectEliminate the effects ofSolid-state devicesWork measurementCondensed matter physicsTorque sensor
The present invention involves a method and apparatus for canceling the effects of magnetic field noise in a torque sensor by placing three sets of magnetic field sensors around a shaft, the first set of field sensors being placed in the central region of the shaft and the second and third sets of field sensors being placed on the right side and left side of the field sensors placed at the central region, respectively. A torque-induced magnetic field is not cancelled with this arrangement of field sensors but a magnetic near field from a near field source is cancelled.
Owner:METHODE ELETRONICS INC
Heat barrier coatings damage and its failure procedure acoustic emission real-time detection method
ActiveCN101285796AEasy to moveReduce noise signalAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalAcoustic emissionCorrelation analysis
The invention discloses a real-time acoustic emission detection method for thermal barrier coating damage and a failure process thereof, which comprises the following steps that: a thermal barrier coating sample and an acoustic emission sensor are connected and coupled; a load is imposed on the thermal barrier coating sample, the acoustic emission sensor receives an acoustic wave signal emitted from the sample; the received acoustic wave signal is carried out through wavelet transform to obtain a wavelet energy spectrum coefficient distribution map, the damage pattern of the signal is determined according to the wavelet energy spectrum coefficient distribution map; the quantitative analysis of the damage is performed according to a relationship curve that the number of acoustic emission signal incidents of each damage pattern changes with the imposed load; a signal component under the scale where the maximum value of the wavelet energy spectrum coefficient is located is extracted, the time difference that the signal component reaches each sensor is calculated by a correlation analysis method, and the position of a damage source is determined by a time difference position method. The method can simply and quickly make a real-time detection to the damage of the thermal barrier coating material and also contributes to the accurate forecast to the life of the thermal barrier coating at the same time.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Adhesive-Mountable Head-Wearable EEG Apparatus
InactiveUS20150374255A1Good conditionHigh degree of miniaturizationElectroencephalographySensorsEngineeringWearable eeg
An adhesive-mountable head-wearable EEG apparatus is disclosed. The apparatus includes an EEG sensor for acquiring an EEG signal of a wearer, a central processing unit for receiving the EEG signal, a small circuit board including the EEG sensor and the central processing unit, and a compact enclosing shell for enclosing the small circuit board, the EEG sensor, and the central processing unit. An adhesive electrode assembly attaches to the compact enclosing shell, or to the small circuit board within the enclosing shell, via snaps or magnets. The adhesive electrode assembly includes two or more gel electrodes for acquiring an EEG signal, and for adhering to the forehead so as to wearably support the EEG apparatus on the forehead. The compact enclosing shell includes chamfered edges, and is sized so as to reduce lateral forces on the compact shell that would tend to detach the EEG apparatus from the wearer's forehead.
Owner:VASAPOLLO CURZIO
Doubly-differential interferometer and method for evanescent wave surface detection
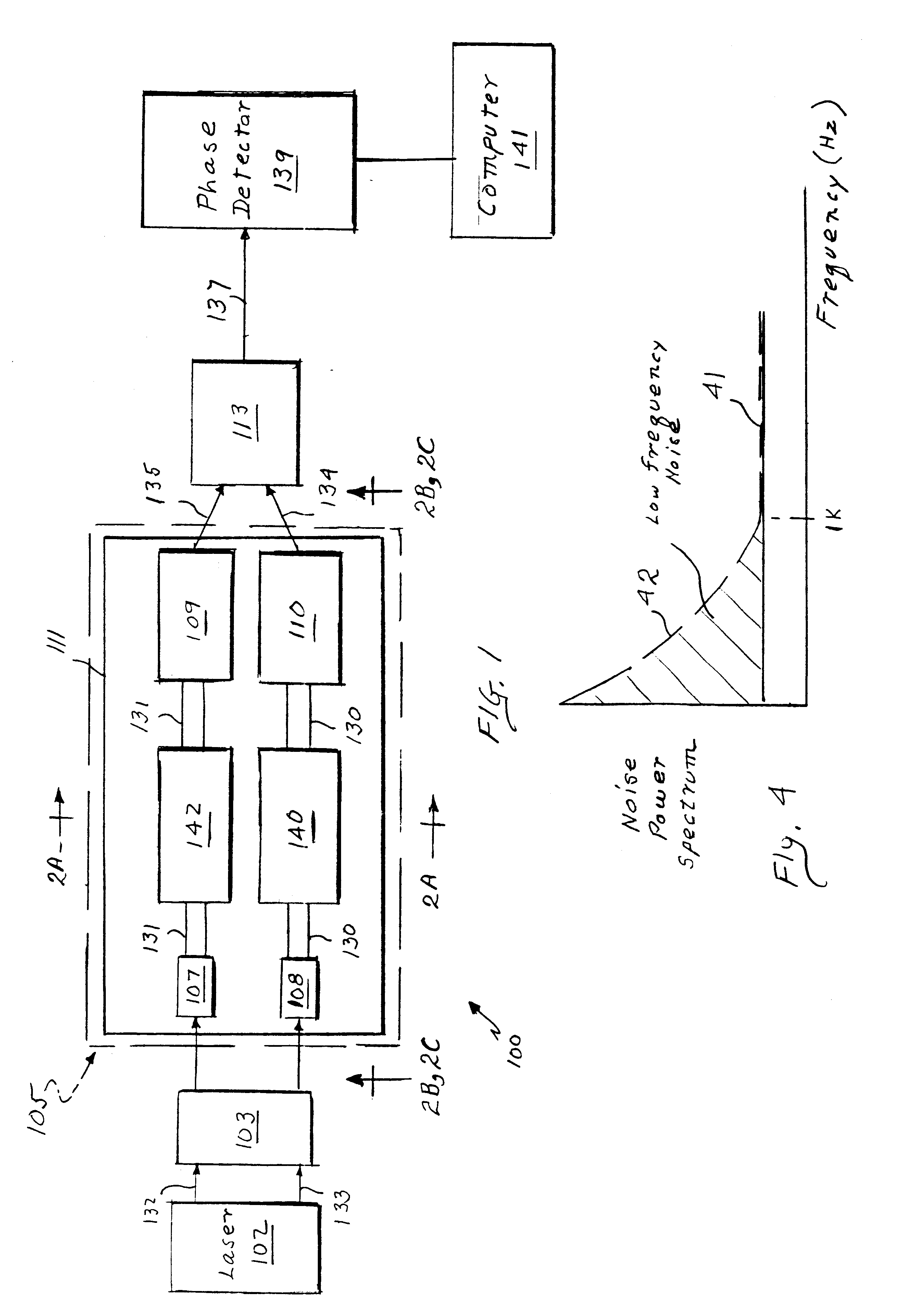
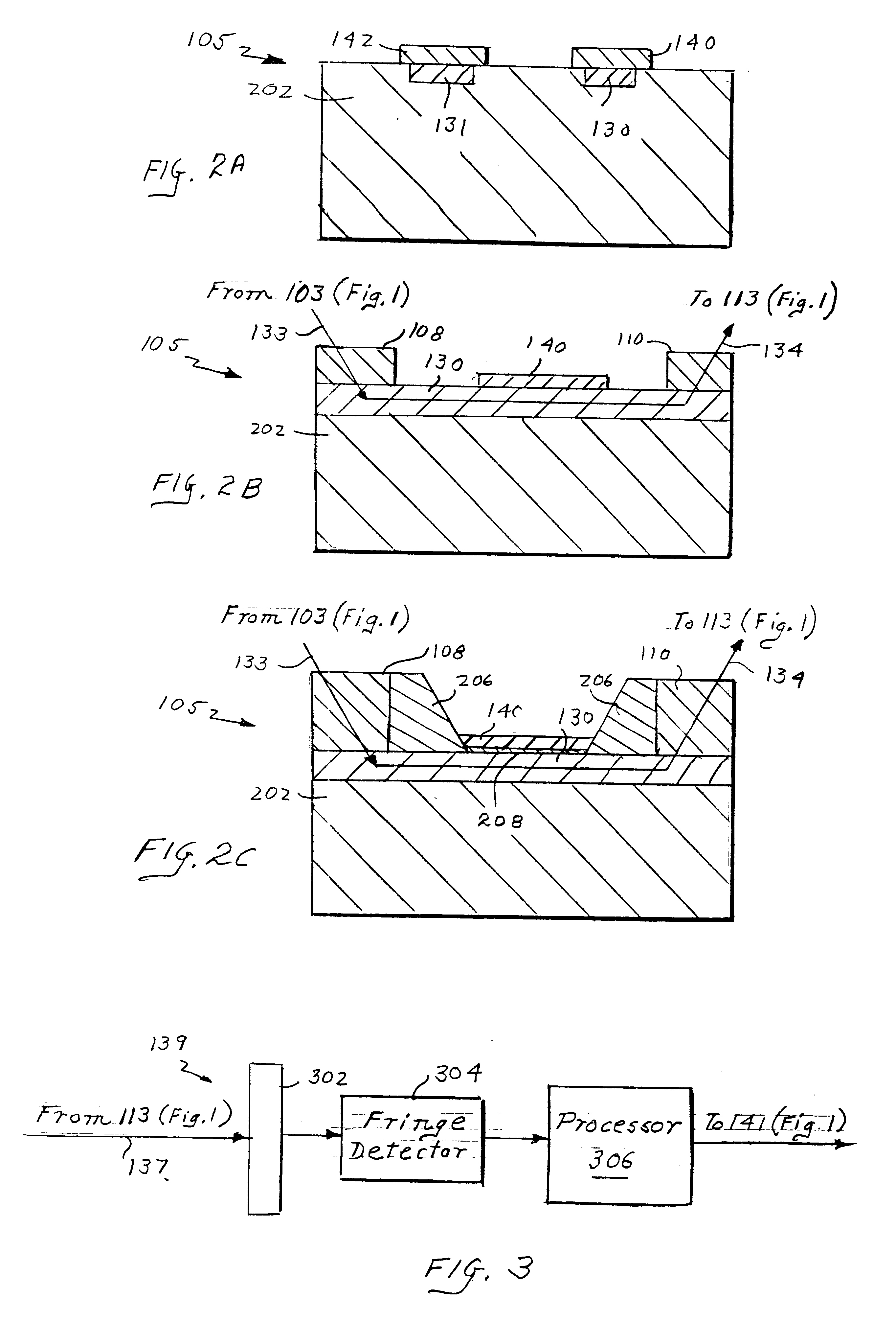
InactiveUS6330064B1Reduce noise signalMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhase-affecting property measurementsReference sampleBio molecules
A high speed, highly sensitive optical sensing platform and a method for detecting and / or measuring characteristics of a substance in a measurement sample are disclosed. The platform includes at least one pair of optical paths formed in a waveguide, a light source for injecting optical beams along the optical paths, a light modulator for enabling the excitement of a transverse electric and a transverse magnetic guide modes, and a phase detector for detecting phase differences between the beams propagating along the optical paths. One of the optical paths has a target analyte of unknown concentration with a measurement sample bound to its upper surface, while the second optical path has a reference sample containing a known concentration of the target analyte bound to its upper surface. A guided mode modulator causes an optical beam to propagate through the waveguide sequentially as two polarized modes. The highly sensitive platform is especially useful for directly detecting and / or measuring very small numbers of small molecules, bio-molecules, microorganisms in a liquid or gaseous test sample.
Owner:PERFECT GALAXY INT
Reduced Bend Sensitivity and Catastrophic Bend Loss In Single Mode Optical Fibers and Method of Making Same
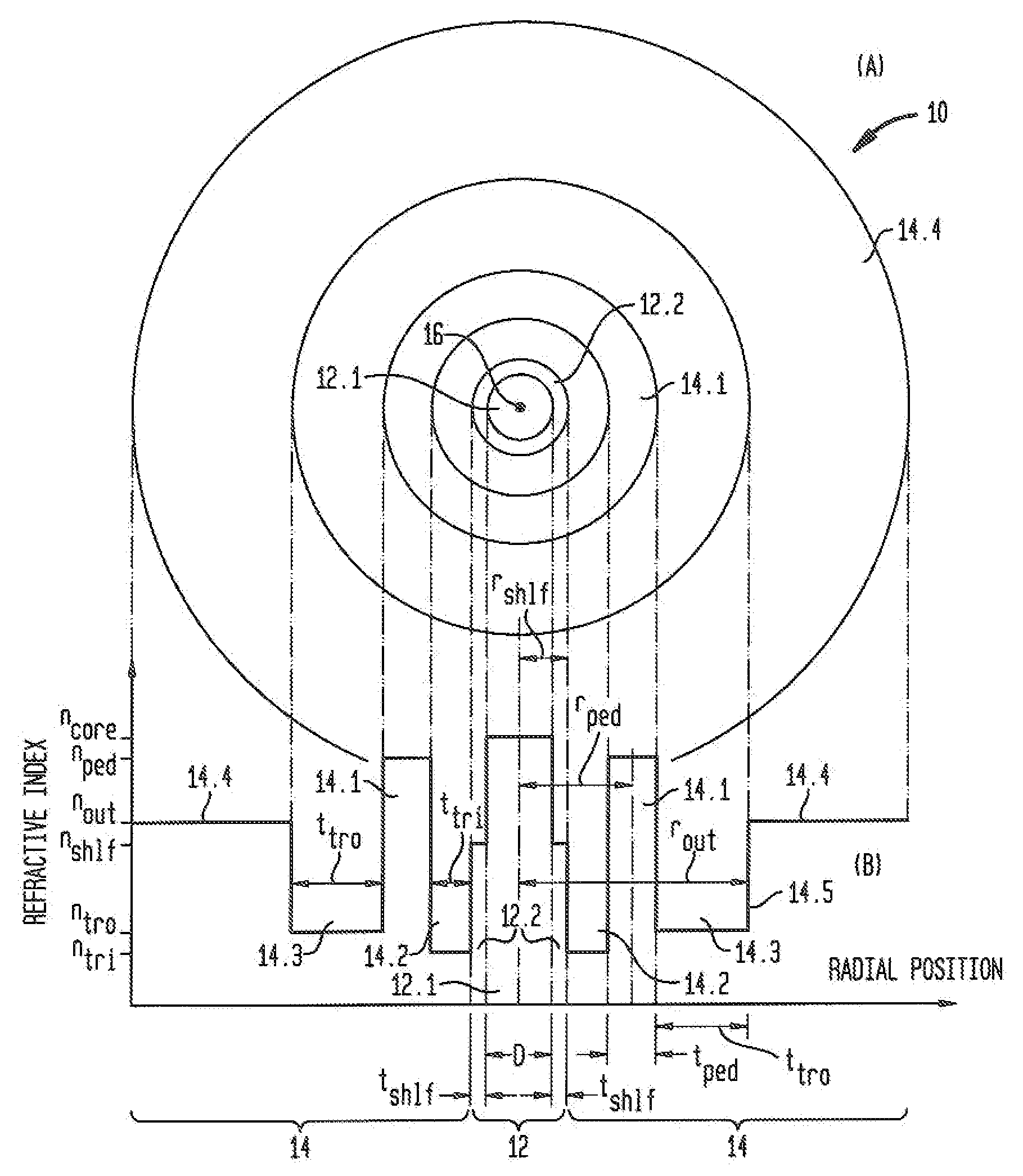
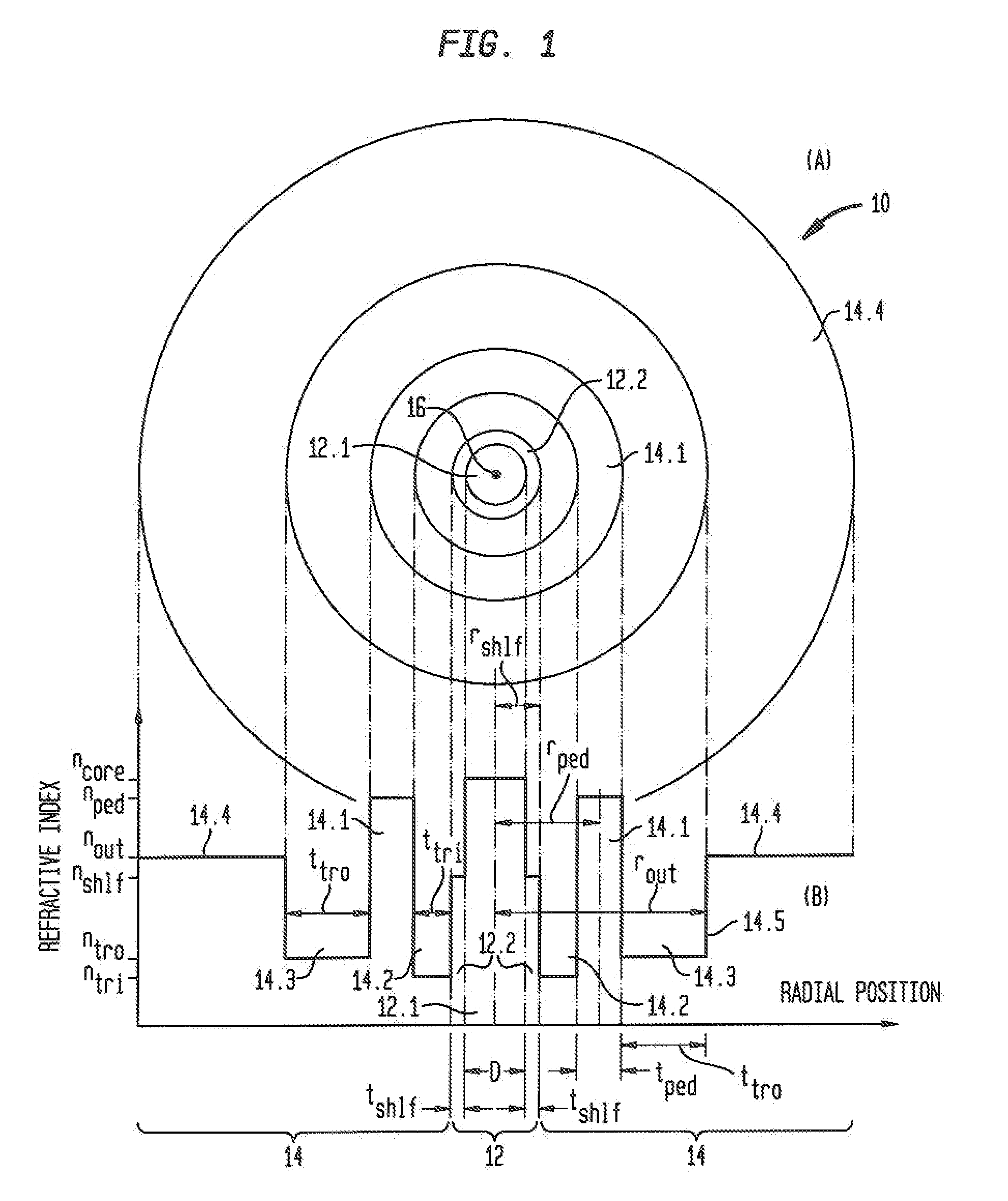
ActiveUS20090290841A1Improve system performanceReduced insertion lossGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingManufacturing technologyTransverse mode
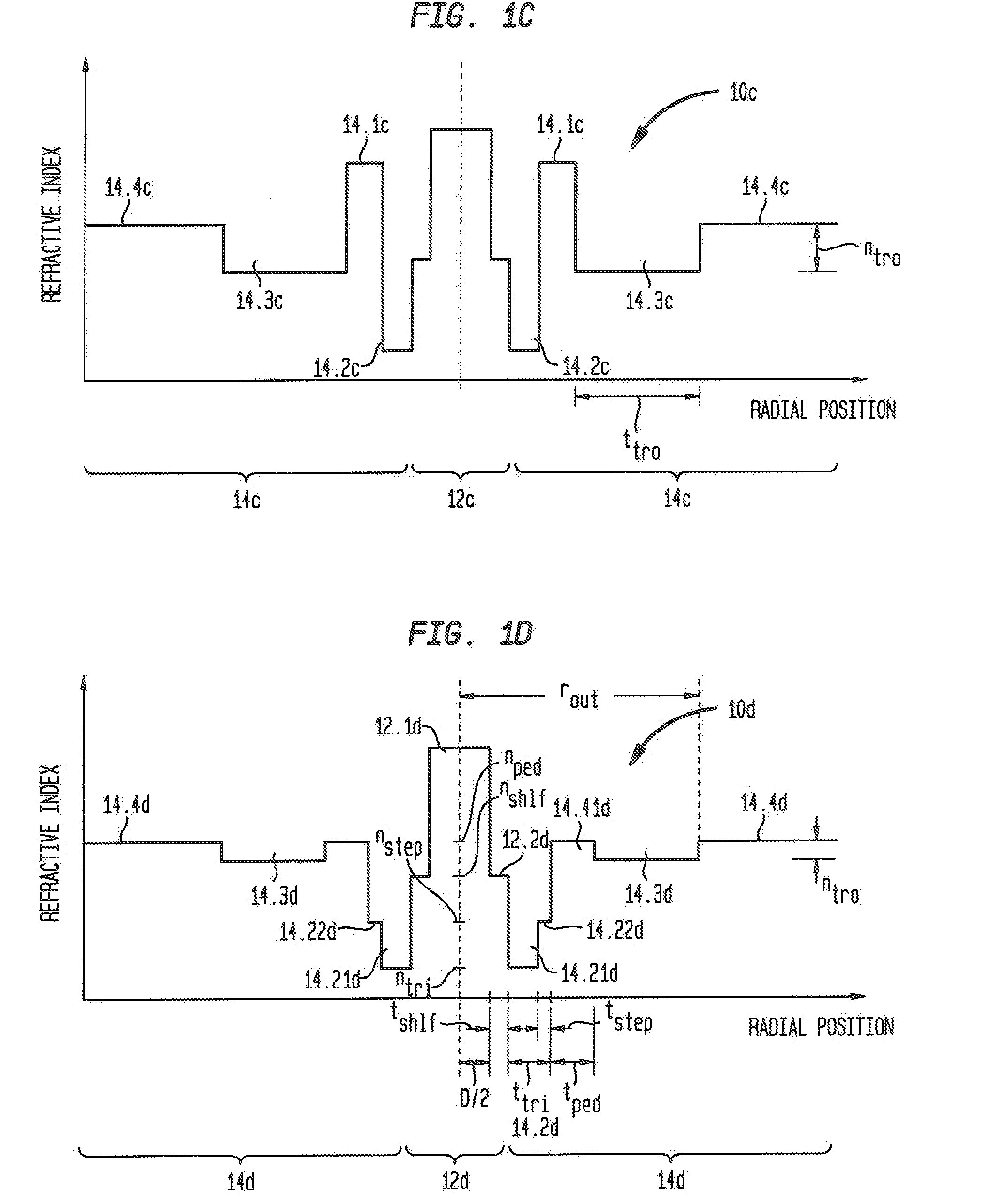
An optical fiber that is relatively insensitive to bend loss and alleviates the problem of catastrophic bend loss comprises a core region and a cladding region configured to support and guide the propagation of light in a fundamental transverse mode. The cladding region includes (i) an outer cladding region, (ii) an annular pedestal (or ring) region, (iii) an annular inner trench region, and (iv) an annular outer trench region. The pedestal region and the outer cladding region each have a refractive index relatively close to that of the outer cladding region. In order to suppress HOMs the pedestal region is configured to resonantly couple at least one (unwanted) transverse mode of the core region (other than the fundamental mode) to at least one transverse mode of the pedestal region. In a preferred embodiment, the fiber is configured so that, at a signal wavelength of approximately 1550 nm, its bend loss is no more than about 0.1 dB / turn at bend radius of 5 mm and is no more than about 0.02 dB / turn at a bend radius of 10 mm. In addition, in one embodiment, the core region also includes an inner core region and an annular outer core (or shelf) region surrounding the inner core region. The outer core region extends radially a distance of less than 9 μm from the fiber axis. In another embodiment, the inner trench region includes an annular inner portion and an annular outer (or step) portion surrounding said inner portion. The refractive index of the step portion is greater than that of the inner portion. In a preferred embodiment, both of the foregoing features of the core region and the inner trench region are incorporated in the fiber. Also described are multi-tube fabrication techniques for making such fibers.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Magnetoelastic torque sensor with ambient field rejection
ActiveUS20120074933A1Cancellation effectEliminate the effects ofWork measurementMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesCondensed matter physicsTorque sensor
The present invention involves a method and apparatus for canceling the effects of magnetic field noise in a torque sensor by placing three sets of magnetic field sensors around a shaft, the first set of field sensors being placed in the central region of the shaft and the second and third sets of field sensors being placed on the right side and left side of the field sensors placed at the central region, respectively. A torque-induced magnetic field is not cancelled with this arrangement of field sensors but a magnetic near field from a near field source is cancelled.
Owner:METHODE ELETRONICS INC
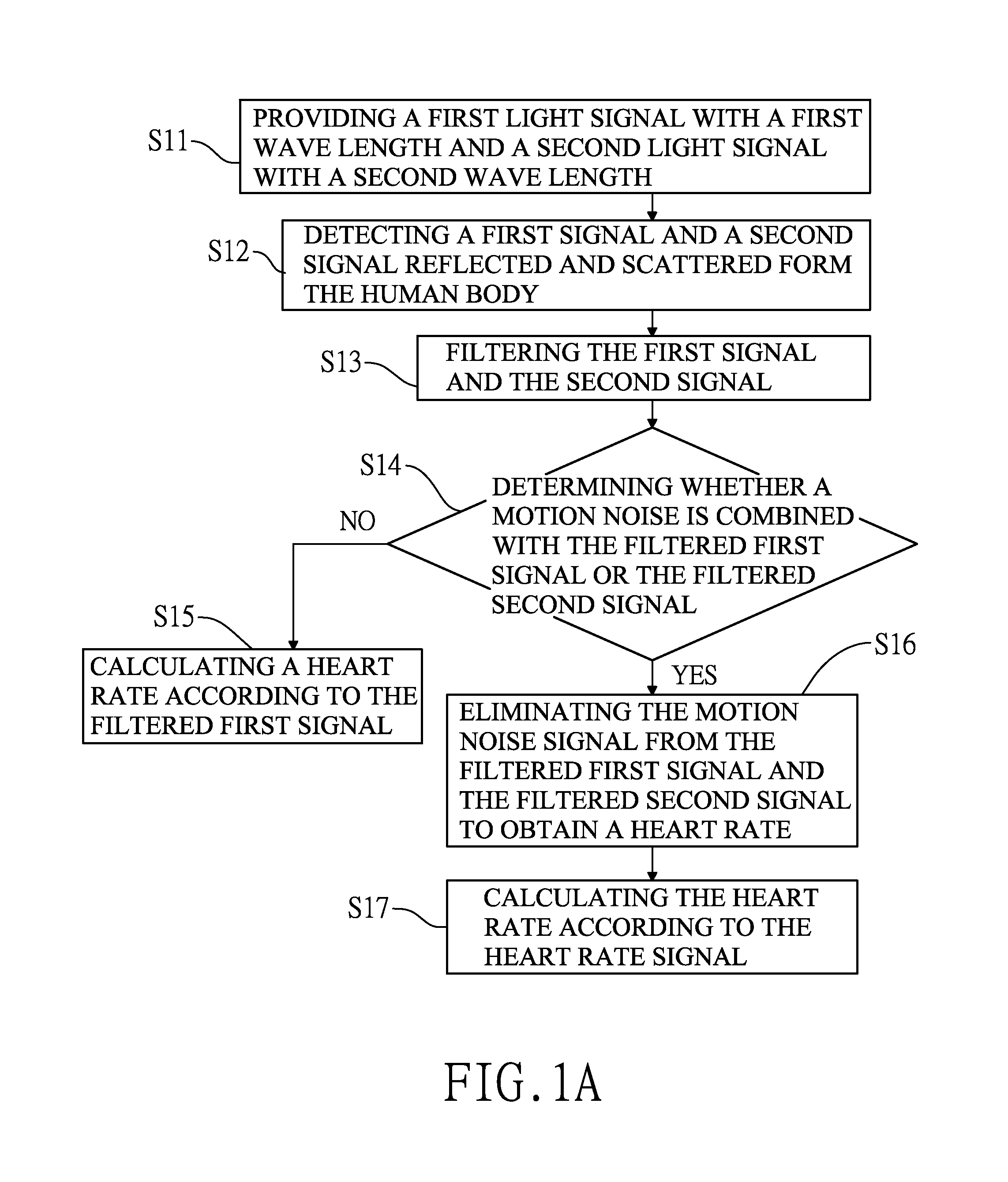
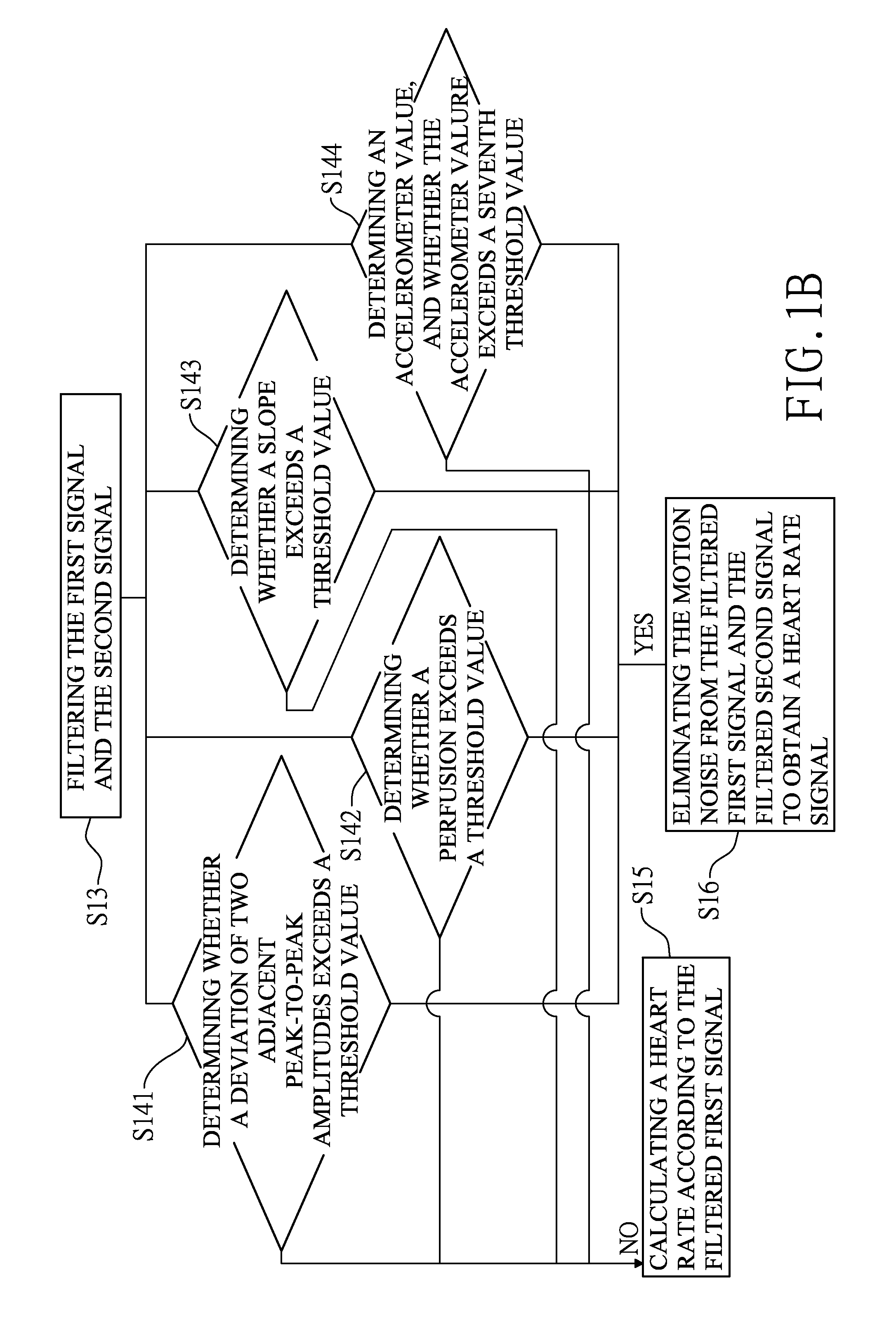
Heart rate monitoring method and devcie with motion noise signal reduction
InactiveUS20150313549A1Accurate heart rateRemove noise signalInertial sensorsCatheterTime domainPhotodetector
A heart rate monitoring method and device to analyze signals in time or frequency domain with motion noise signal reduction comprises at least two LEDs for providing two different light signals for incidenting into a portion of a human, a photodetector for detecting two reflected and scattered signals reflected and scattered form the human, and a processor for eliminating motion noise signal cause by any motion of the human. The processor may compare the two reflected and scattered signals and execute an independent component analysis to obtain a correct heart rate signal in time domain, and then the processor can calculate the correct heart rate. The processor may transform the two reflected and scattered signals form time domain to frequency domain and compare the two reflected and scattered signals in frequency domain to obtain a heart rate signal in frequency domain, and then the processor can calculate the heart rate.
Owner:DIGIO2 INT
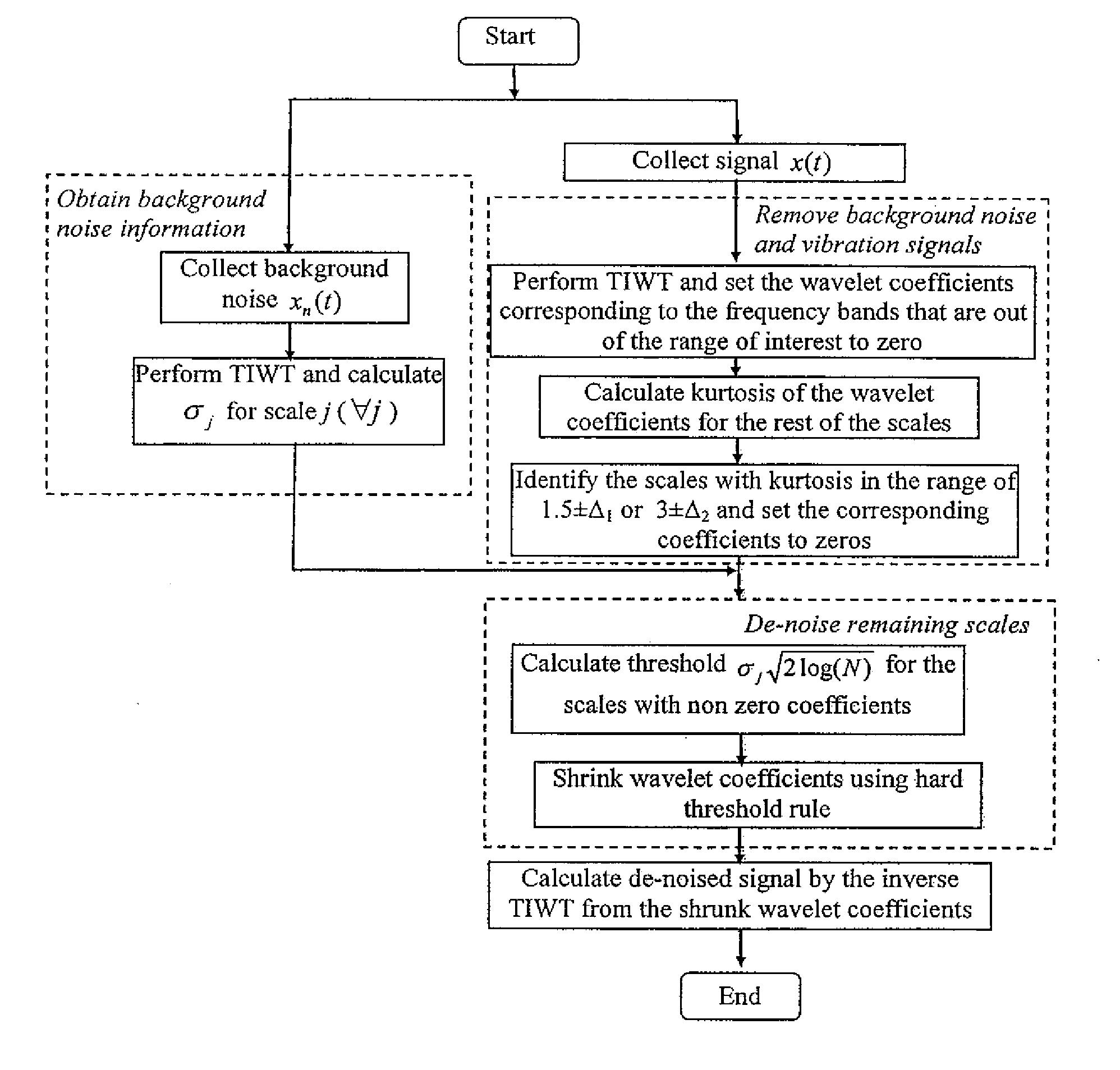
Method to extract target signals of a known type from raw data containing an unknown number of target signals, intereference, and noise
InactiveUS20100076693A1Improve abilitiesReduce noise signalAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePattern recognitionData set
A signal analysis method extracts transient target signals of known type from a raw data source signal that contains an unknown number of target signals. The method can enhance the analysis of data obtained from in-line oil-debris sensors. The method comprises steps of: defining signatures of the known target signal, and of at least one of the intrinsic noise and interfering signals; performing a mathematical transform that decomposes the raw data into distinct data sets; using the signal signatures to identify and nullify the data sets containing noise and interfering signal signatures; using the target signal signatures to identify the data sets containing target signal components, or may further use a thresholding rule to remove intrinsic noise from said data sets, and finally applying the inverse transform to the processed data sets in order to reconstruct an enhanced output signal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Method and device for analyzing a periodic or semi-periodic signal
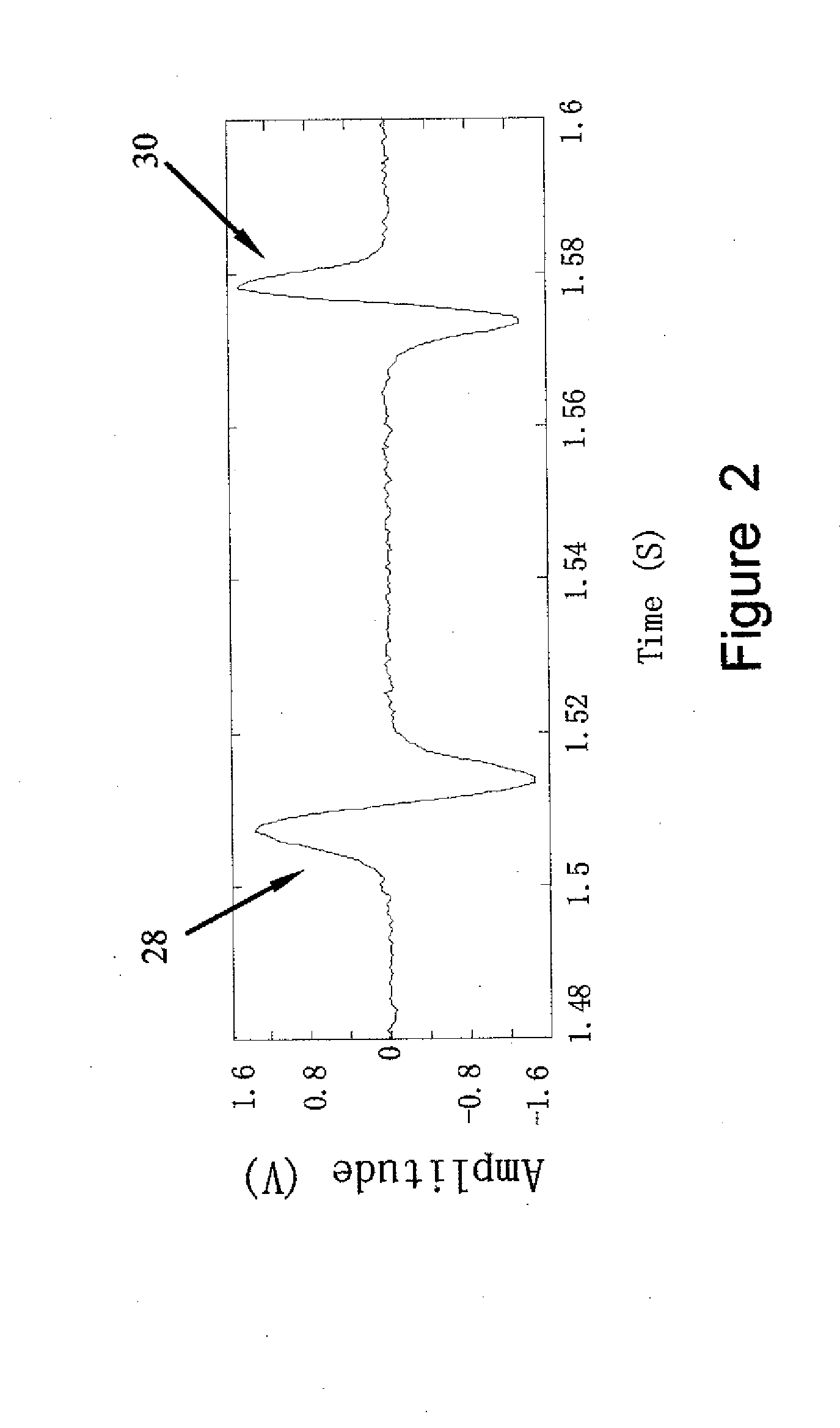
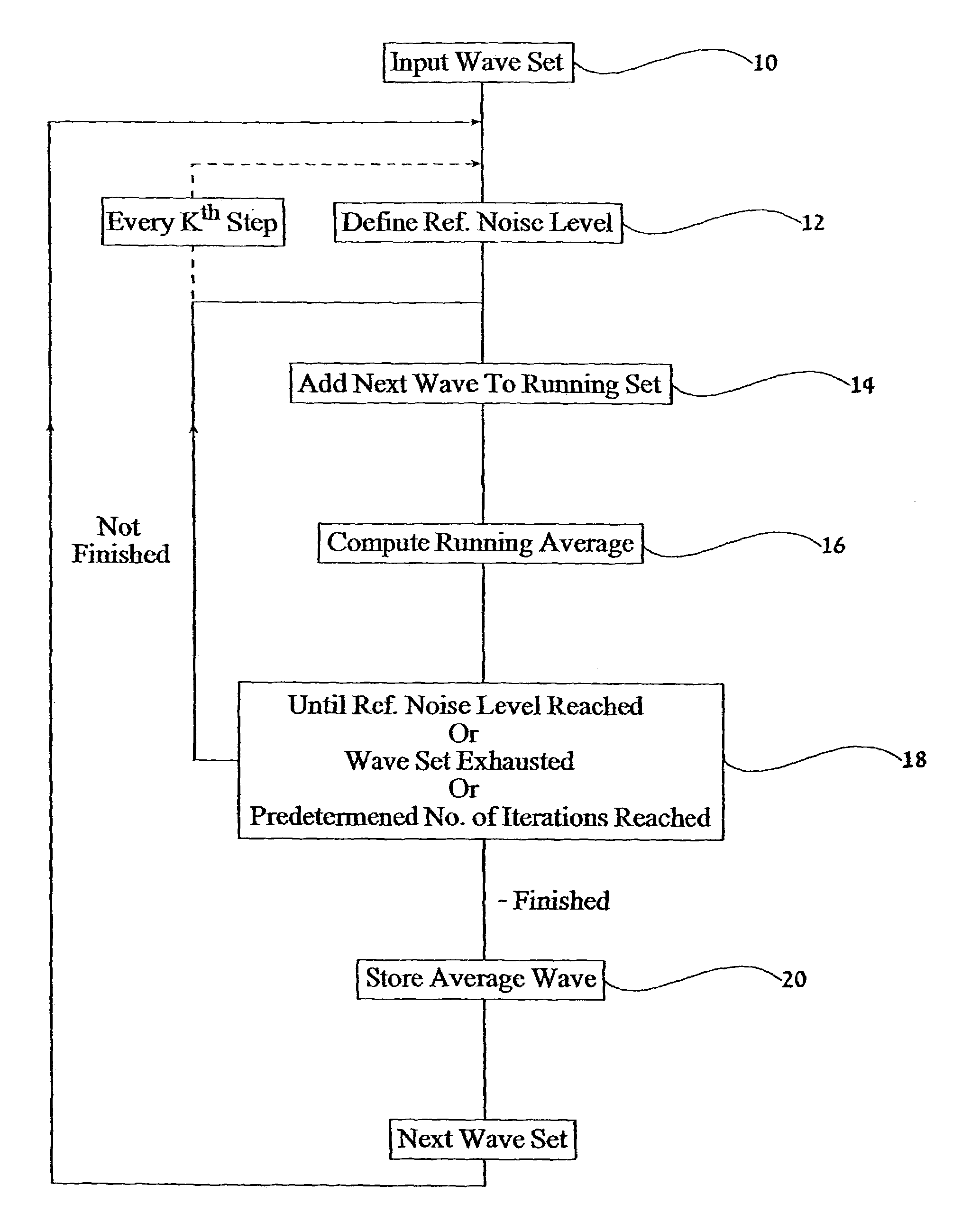
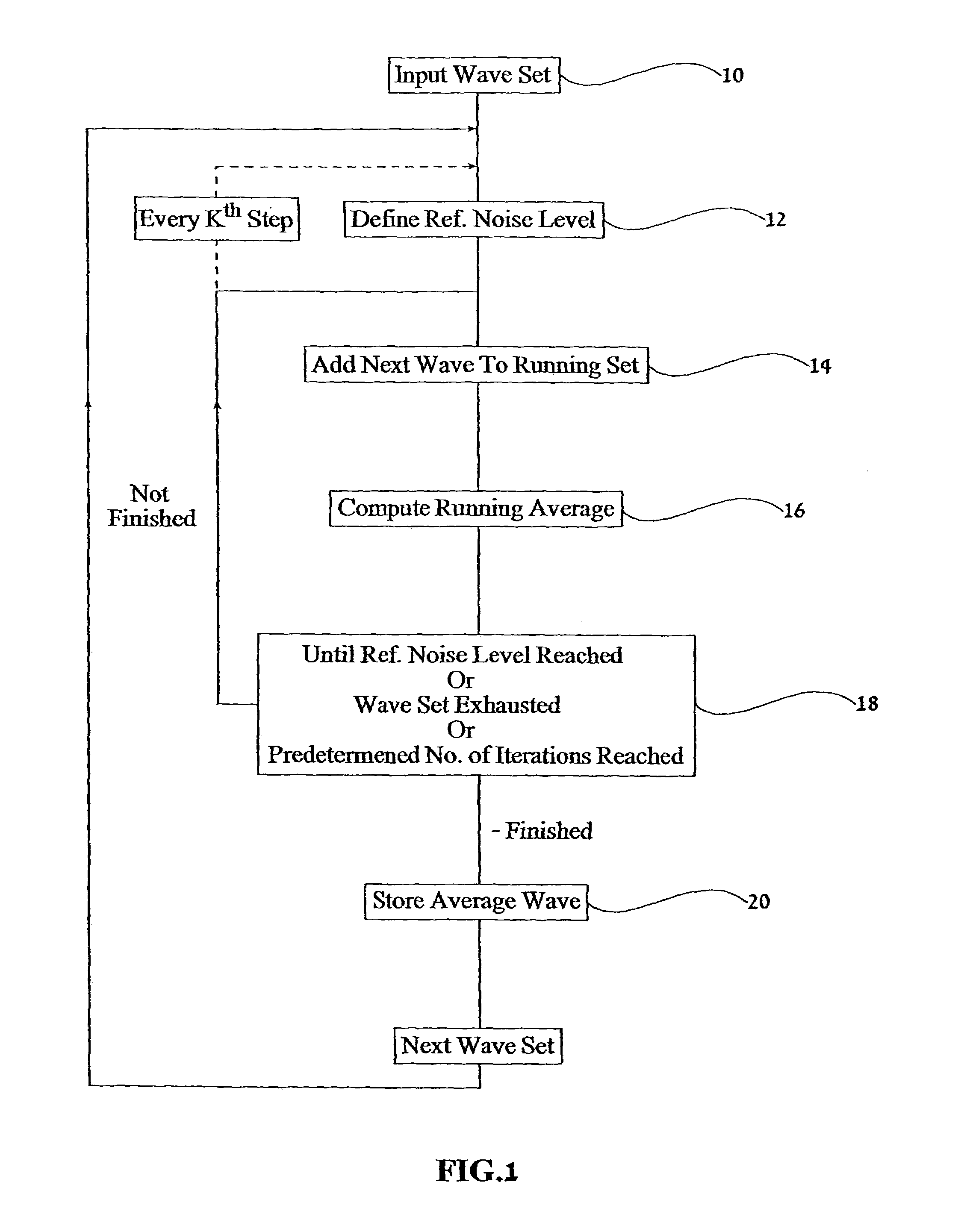
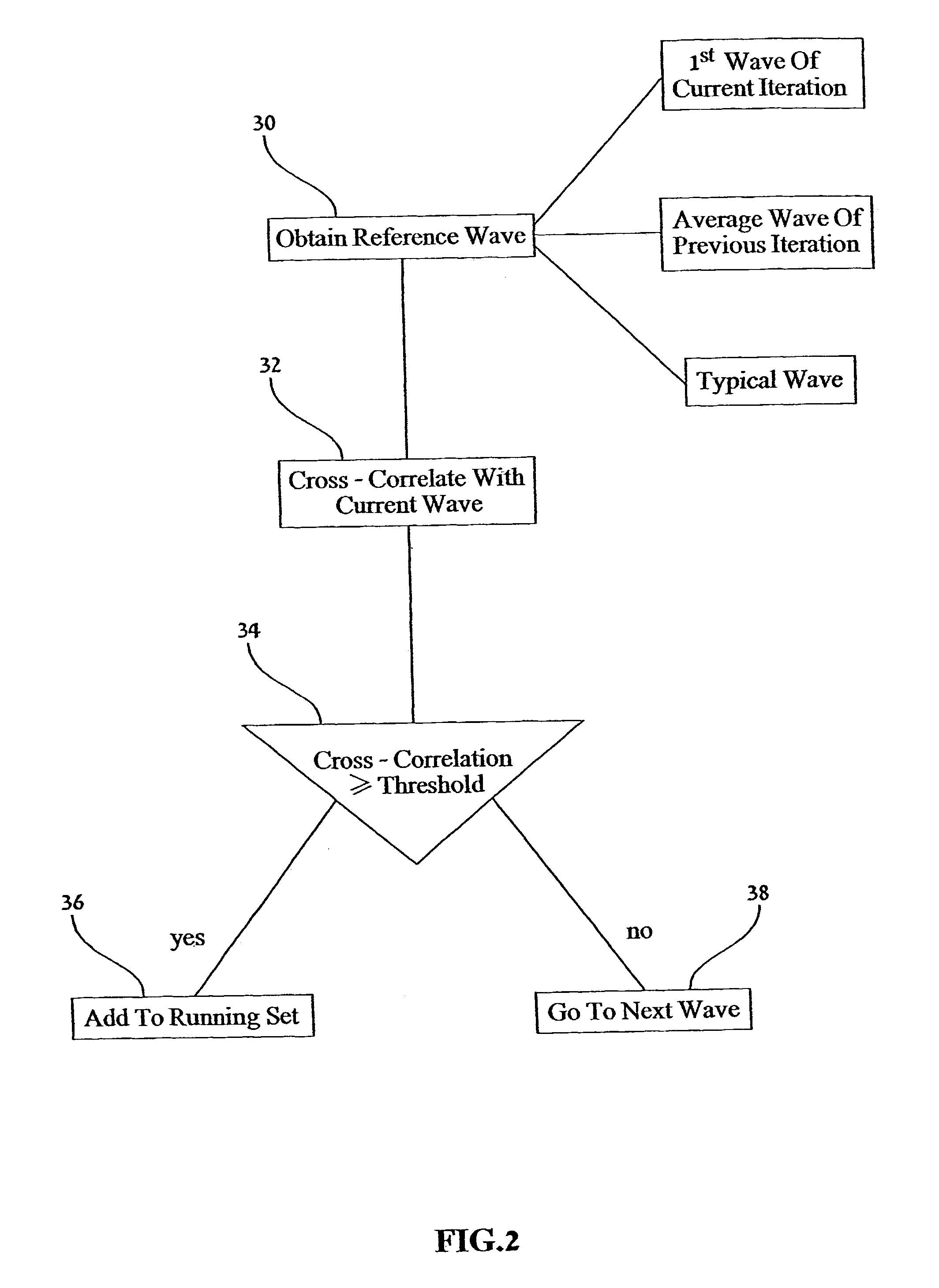
A device for reducing noise in signals having successive substantially repetitive portions, comprising: an iterative averager operative to superimpose and average said substantially repetitive portions to produce a running average thereof, and an iteration ender comprising a noise analyzer for determining a noise level in said running average and ending operation of said iterative averager when said noise level reaches a predetermined level. Also, a method of obtaining an indication of ischemia in a patient using an ECG signal therefrom, the method comprising: extracting an ECG signal over a duration, extracting from said ECG signal a series of QRS complexes over said duration, extracting high frequency components of said QRS complexes, analyzing said high frequency components over said duration for at least one of a predetermined quality, and inferring from said predetermined quality an indication of ischemia.
Owner:BSP BIOLOGICAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
Active noise control system
ActiveUS8199923B2Reduce noise signalLower Level RequirementsEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlEngineering
An active control of an unwanted noise signal at a listening site radiated by a noise source uses a reference signal that has an amplitude and / or frequency such that it is masked for a human listener at the listening site by the unwanted noise signal and / or a wanted signal present at the listening site in order to adapt for the time-varying secondary path in a real time manner such that a user doesn't feel disturbed by an additional artificial noise source.
Owner:APPLE INC
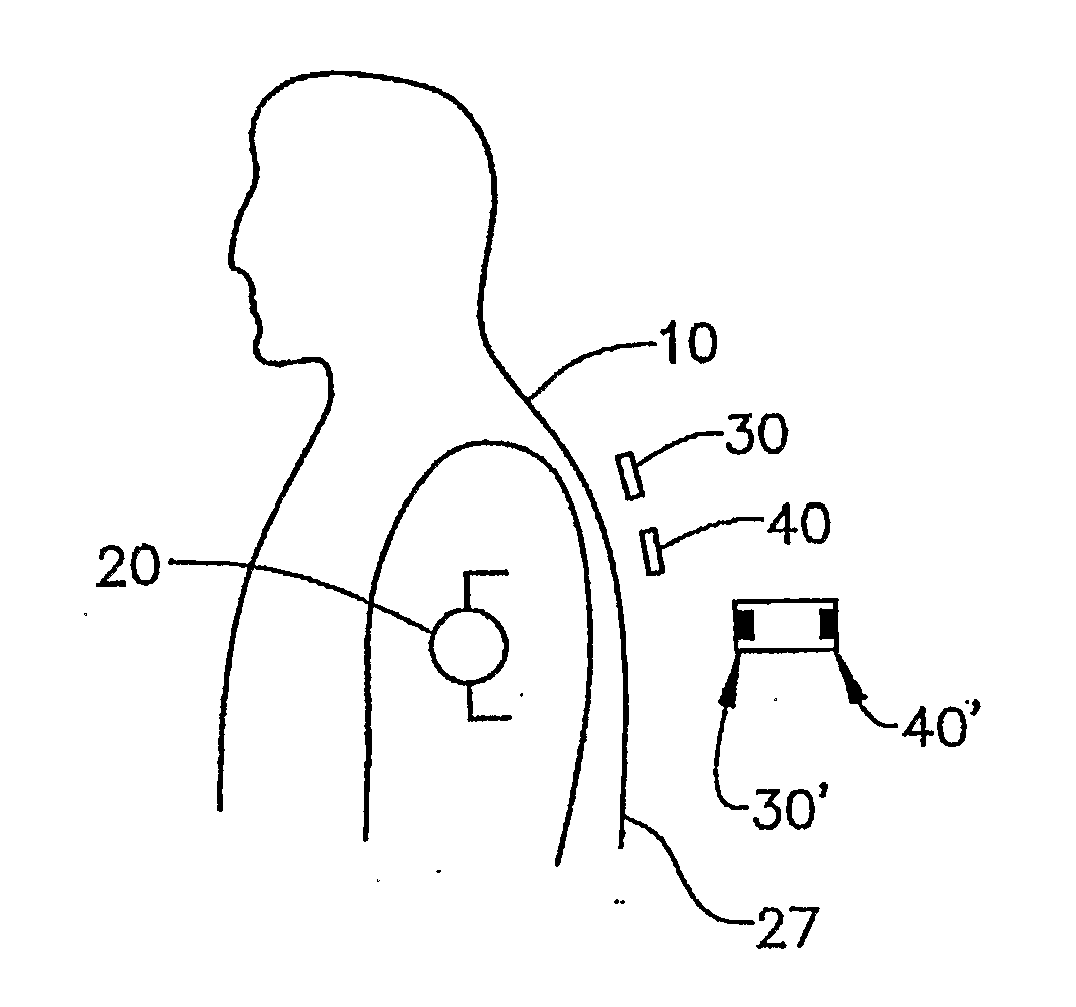
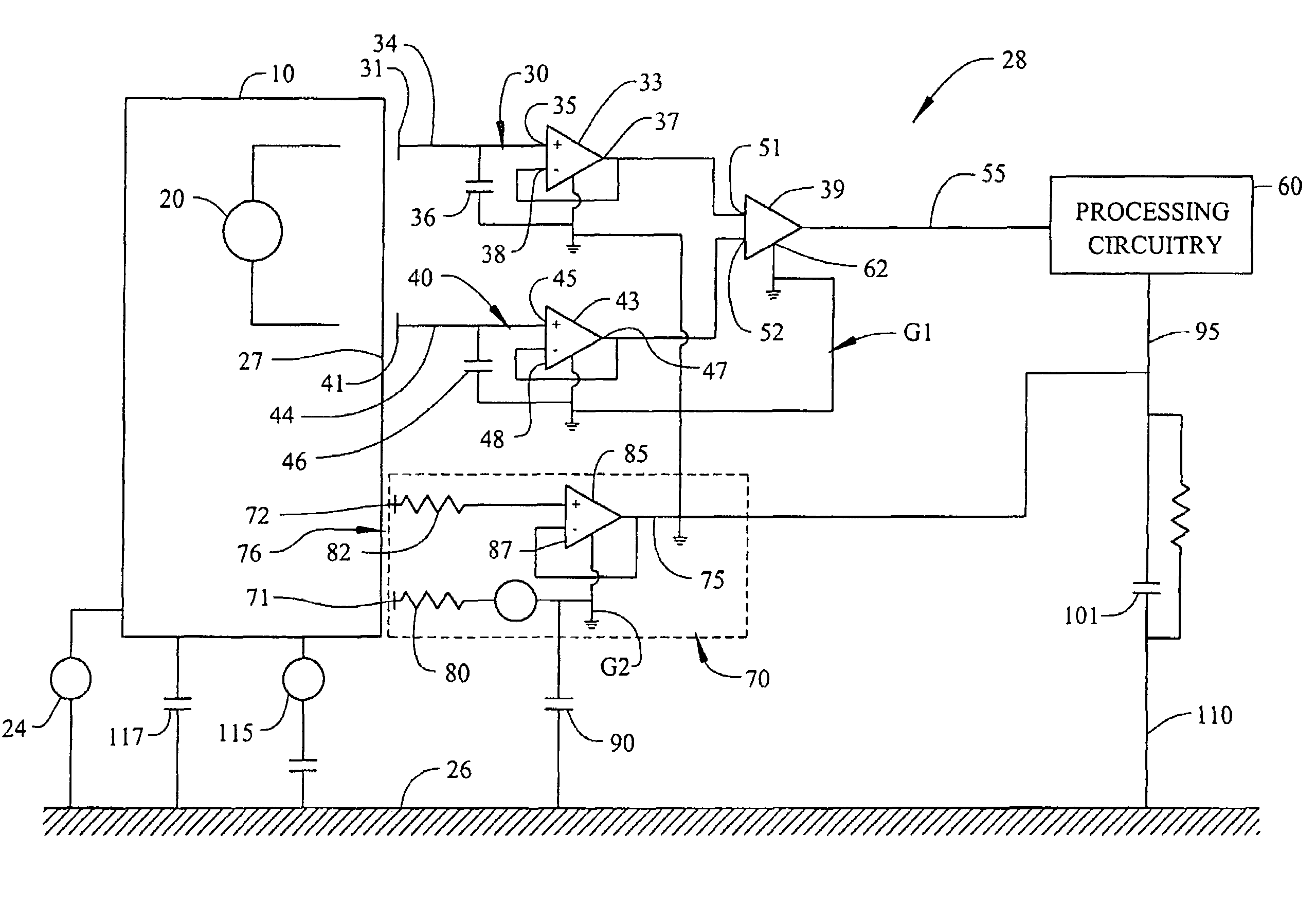
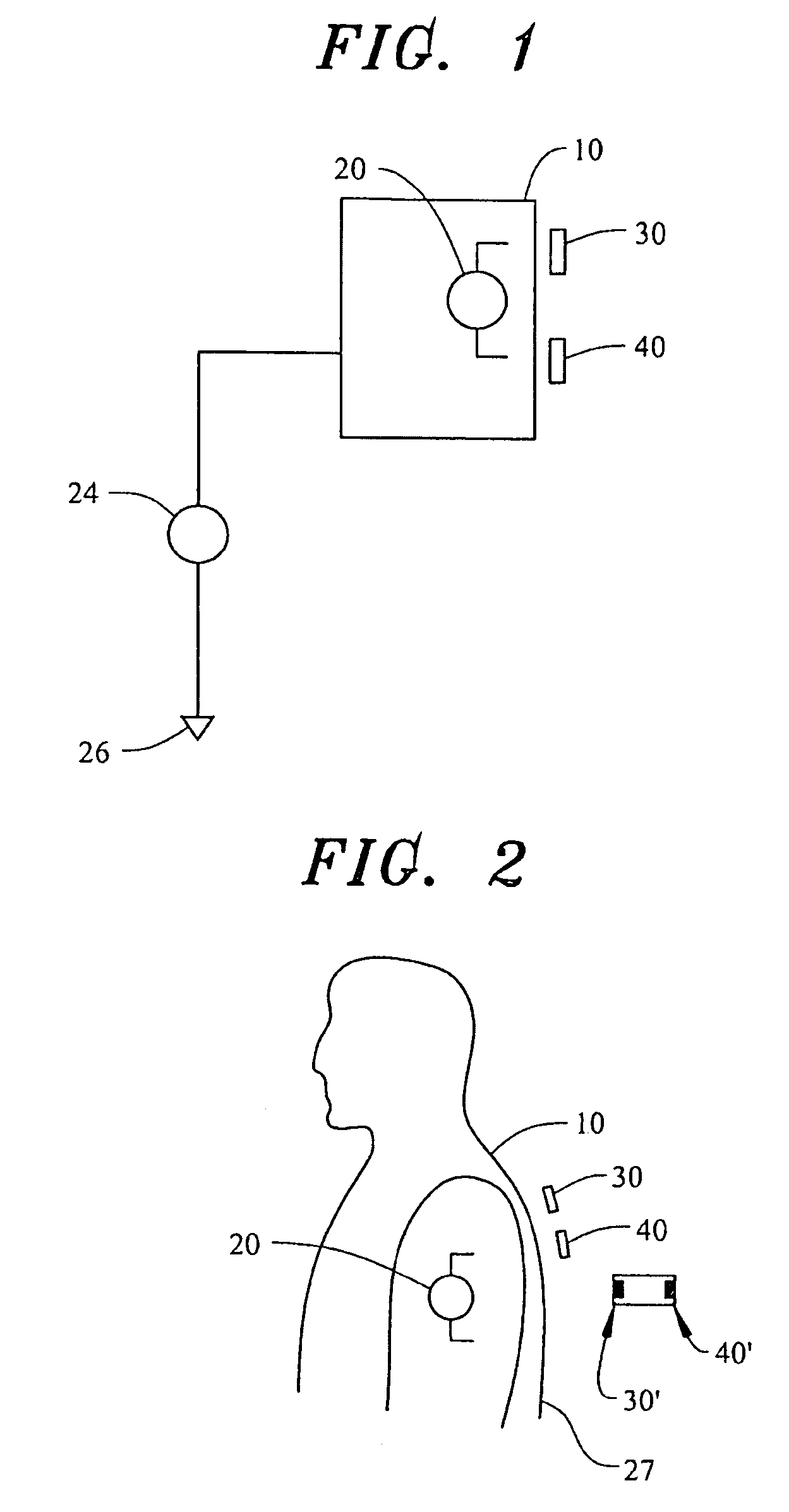
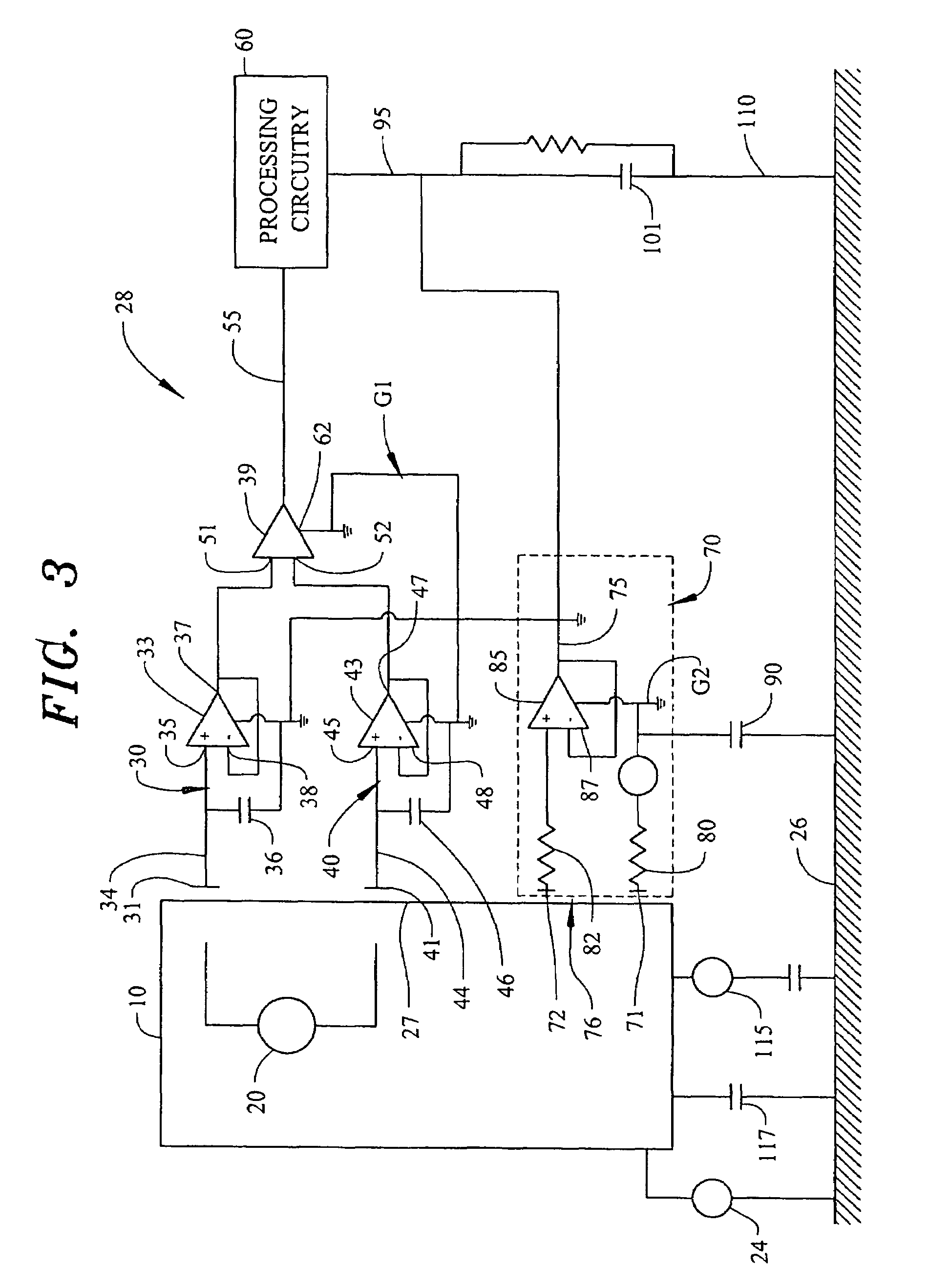
Sensor system for measuring an electric potential signal of an object
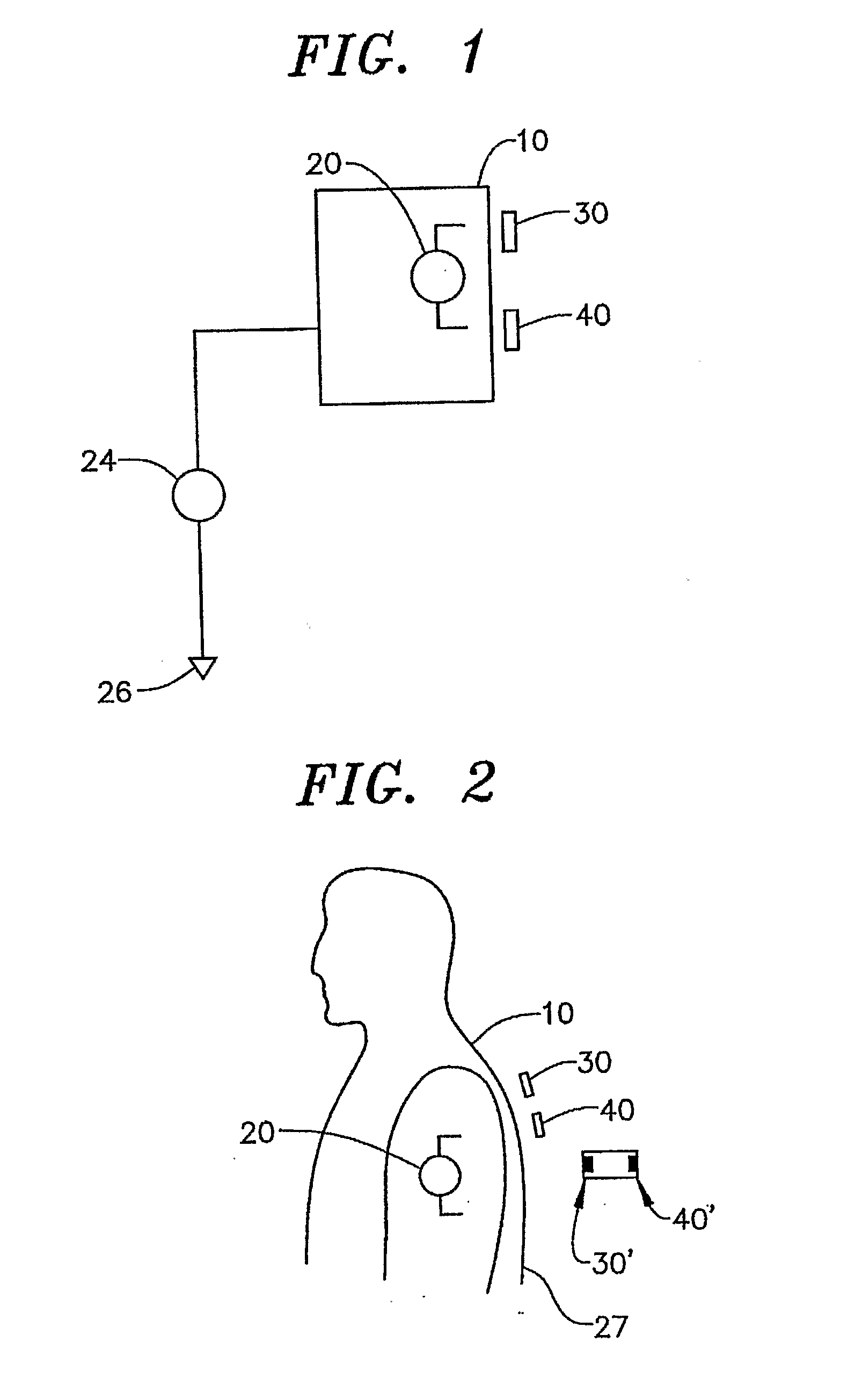
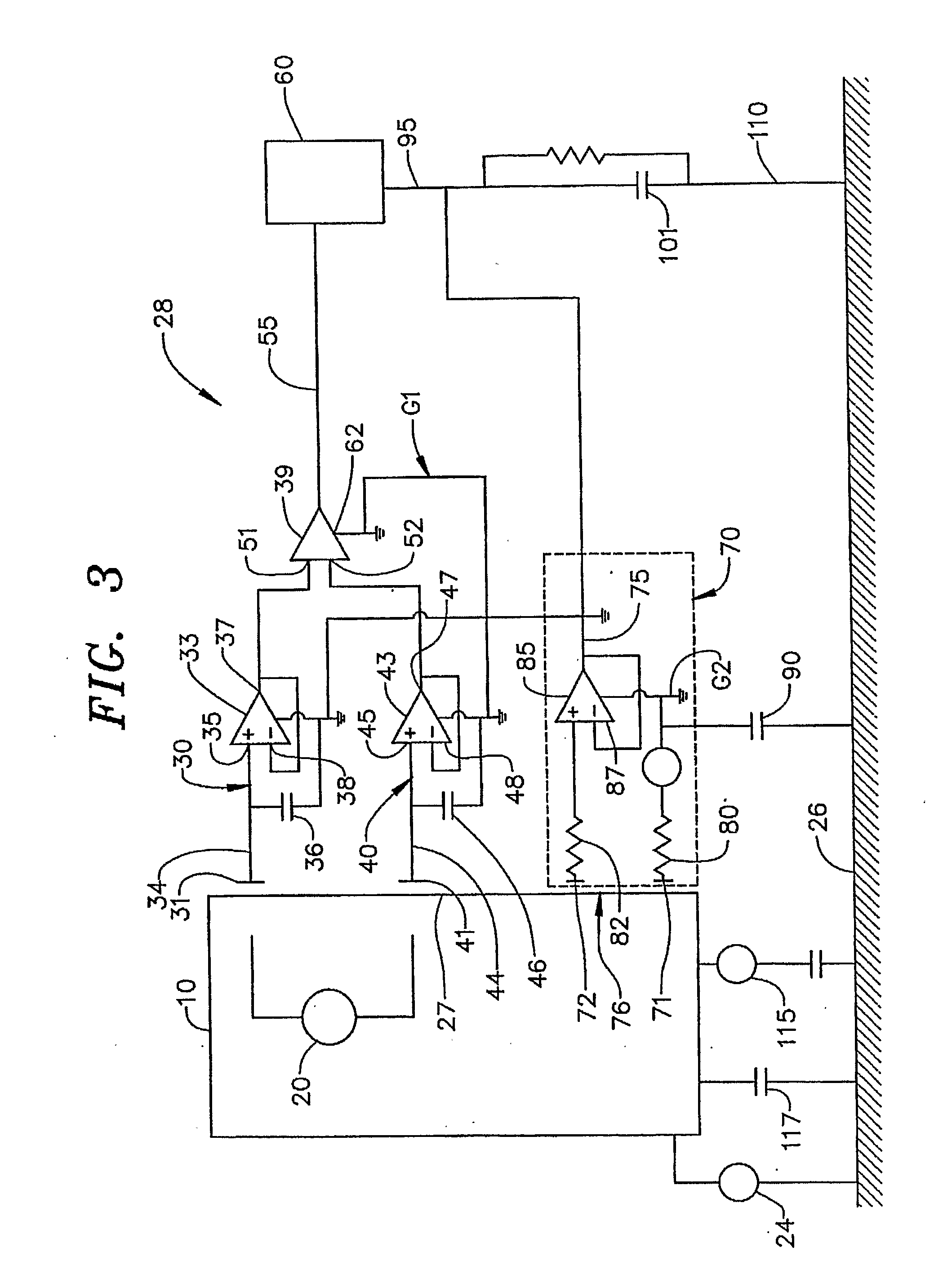
ActiveUS20070135701A1Reduce noise in signalReduce signalElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyElectric fieldNon invasive
The invention generally pertains to reducing artifact noise signals present when non-invasive capacitive-type signal measurements are taken of static electric fields produced by an object (10) of interest. According to a first preferred embodiment of the invention, a given static artifact signal is reduced by minimizing the potential difference between a ground point (G1) of sensor circuitry and the potential of the object (10). According to a second preferred embodiment of the invention, the change in signal due to motion of the sensor (30, 40; 30′, 40′; 230; 330; 430; 530; 630) in the field produced by the object (10) is minimized by reducing the impact of changes in coupling to the signal source.
Owner:QUANTUM APPLIED SCI & RES
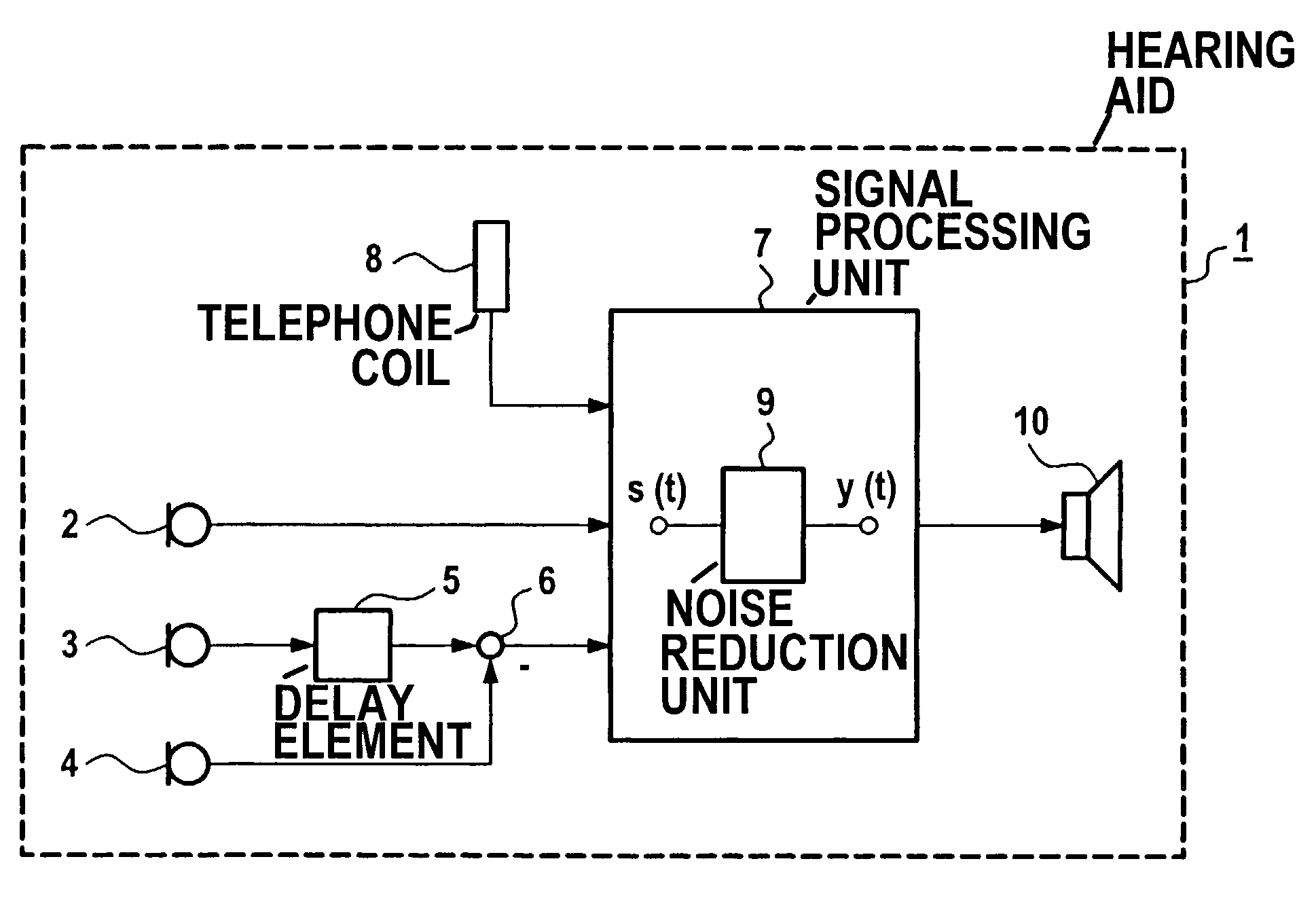
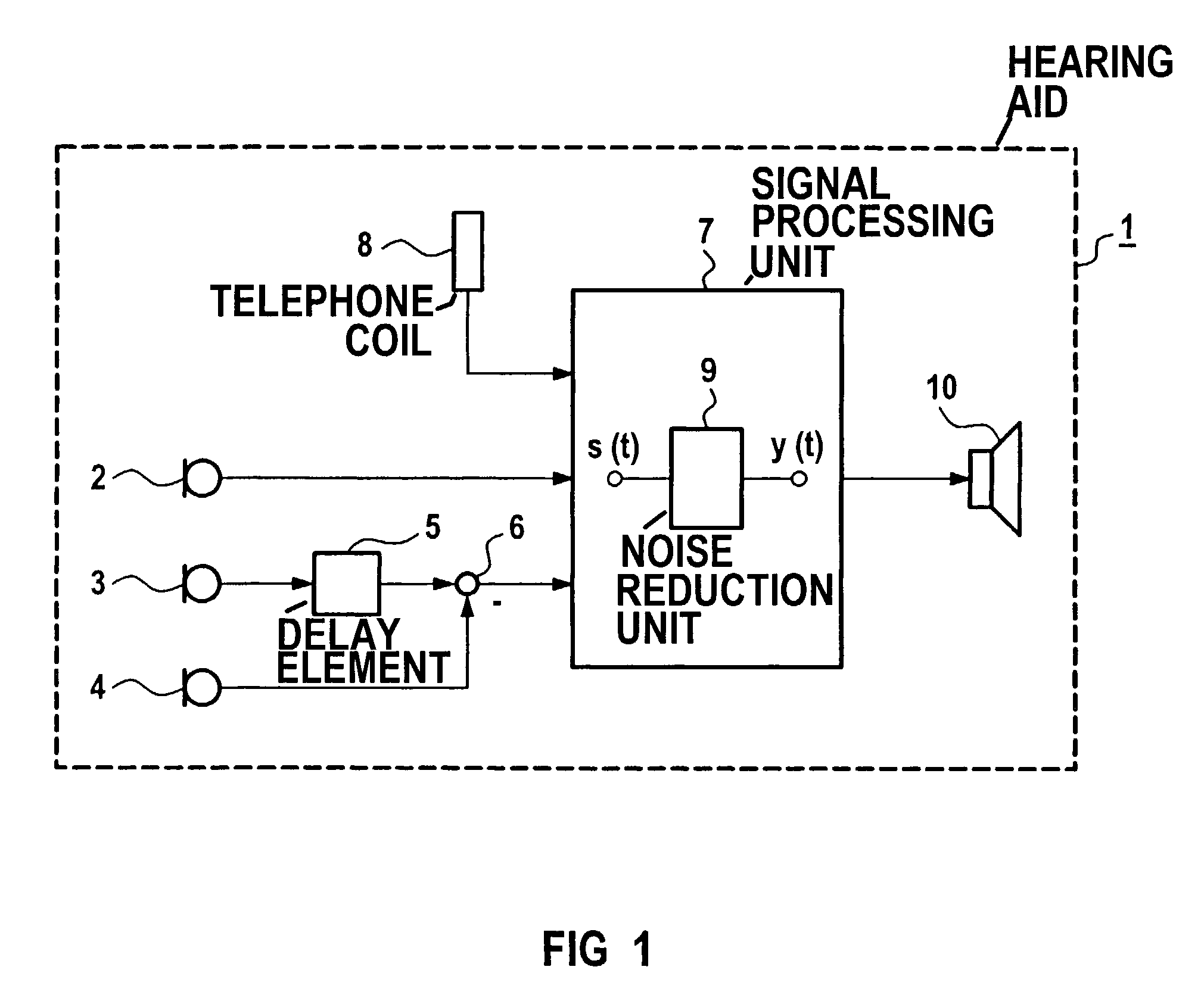
Method for the operation of a hearing aid as well as a hearing aid
ActiveUS7181033B2Avoid disturbing acoustic effectReduce noise signalElectronic input selection/mixingEngineeringAcoustic effect
A hearing aid is provided that avoids disturbing acoustic effects caused by on, off, or switchover events. The signal processing in the hearing aid is switched in sliding fashion from a first operating condition into a second operating condition. According to the invention, both operating conditions are simultaneously present in the hearing aid during the switching event. The sliding transition ensues by a parallel signal processing in at least two signal paths of the hearing aid, whereby a signal that results from the first operating condition and a signal that results from the second operating condition are added in changing weighting.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
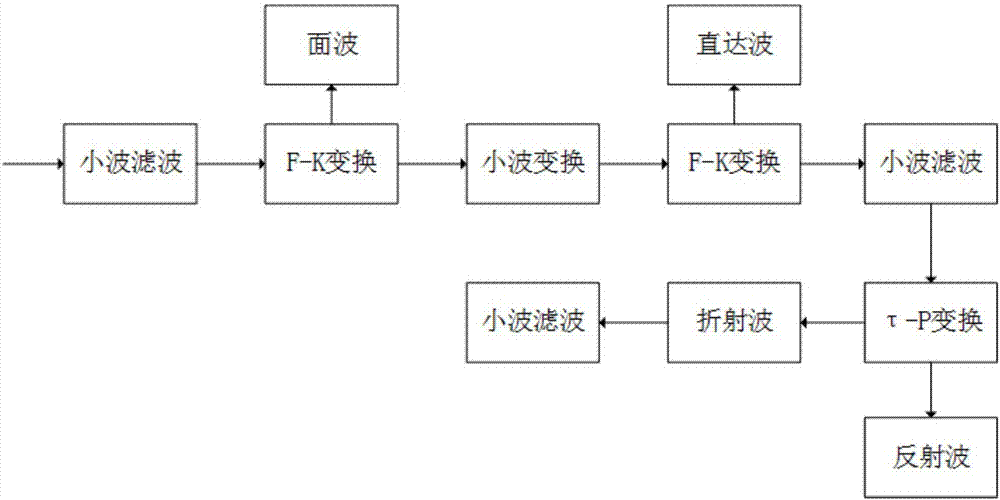
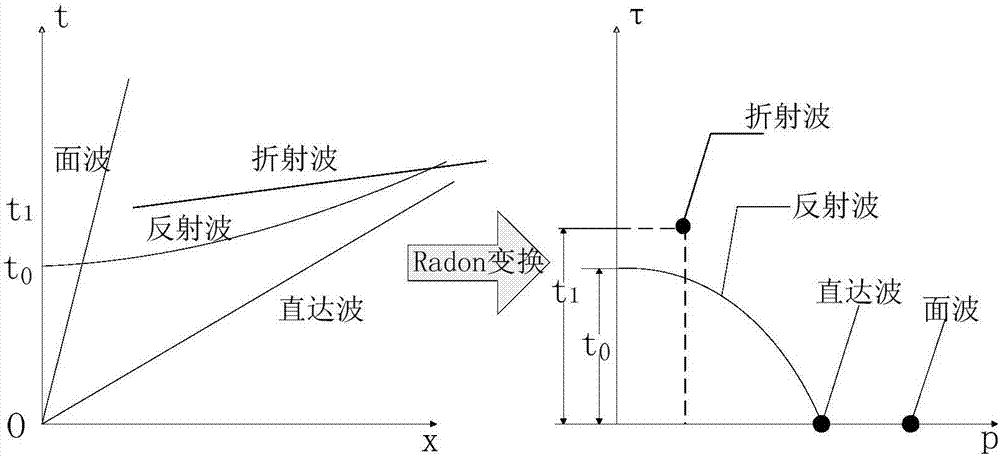
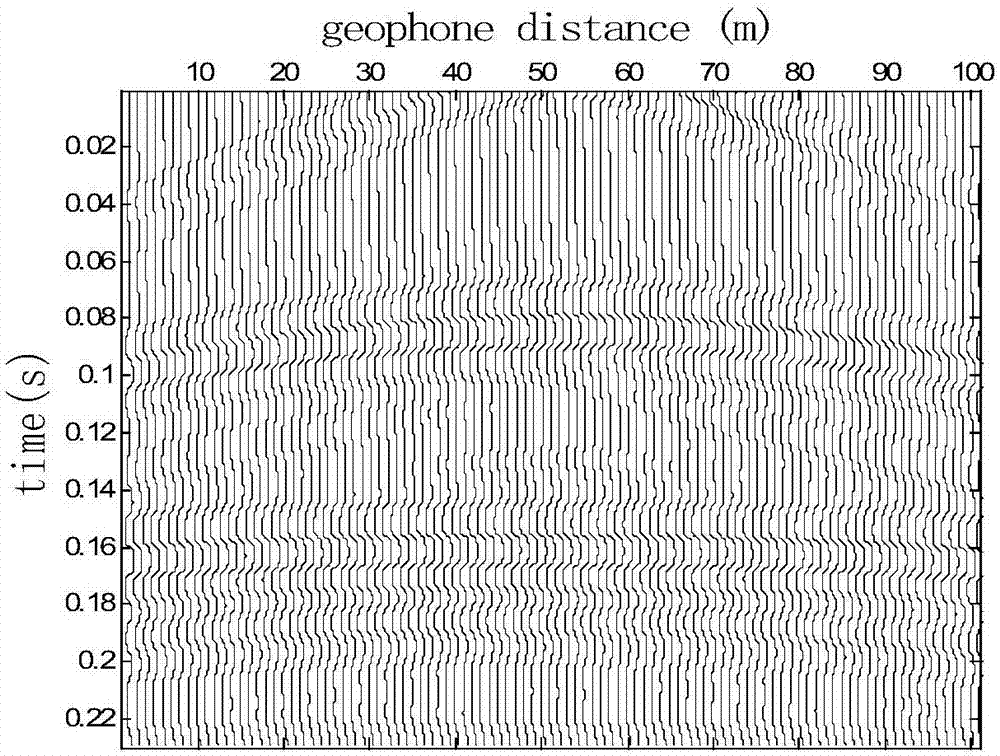
Seismic wave field separation method
ActiveCN107144880AReduce noise signalComprehensive responseSeismic signal processingWave fieldNoise reduction
The invention relates to a seismic wave field separation method. A demodulator, a wavelet filter and engineering seismograph data preprocessing software are utilized for acquiring and analyzing a seismic wave. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring an initial seismic wave signal by means of a demodulator, and performing noise reduction on the initial seismic wave signal through the wavelet filter; performing F-K frequency domain conversion, reverse-F-K frequency domain conversion, linear Radon conversion and reverse Radon conversion on the seismic wave signal after noise reduction, thereby separating out a direct wave, a reflected wave, a refracted wave and a surface wave signal in the seismic wave signal. The seismic wave field separation method effectively improves precision and reliability in wave field separation.
Owner:CHINA MERCHANTS CHONGQING COMM RES & DESIGN INST
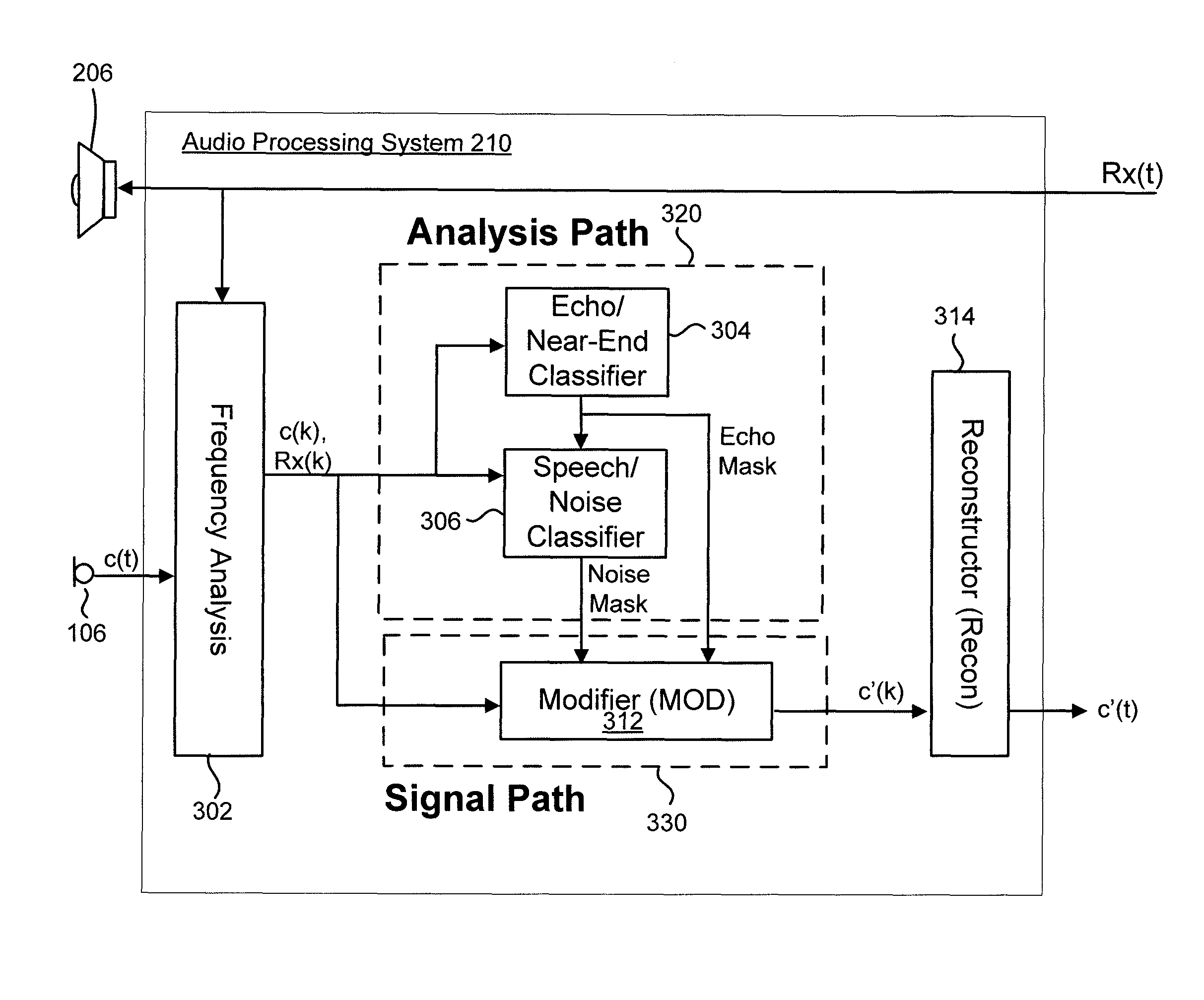
Robust noise suppression system in adverse echo conditions
ActiveUS9343073B1Reduce echoReduce near-end noise signalInterconnection arrangementsSpeech analysisNoise suppressionSelf adaptive
The present technology provides adaptive noise and echo reduction of an acoustic signal which can overcome or substantially alleviate problems associated with mistaken adaptation of speech and noise models to acoustic echo. The present technology carries out a multi-faceted analysis to identify echo within the near-end acoustic signal to derive an echo model. Echo classification information regarding the derived echo model is then utilized to build near-end speech and noise models. These echo, speech, and noise models are then used to generate one or more signal modifications applied to the acoustic signal to preserve the desired near-end speech signal and reduce the echo and near-end noise signals. By building near-end speech and noise models utilizing echo classification information, the present technology can prevent adaptation of the speech and noise model to the acoustic echo.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
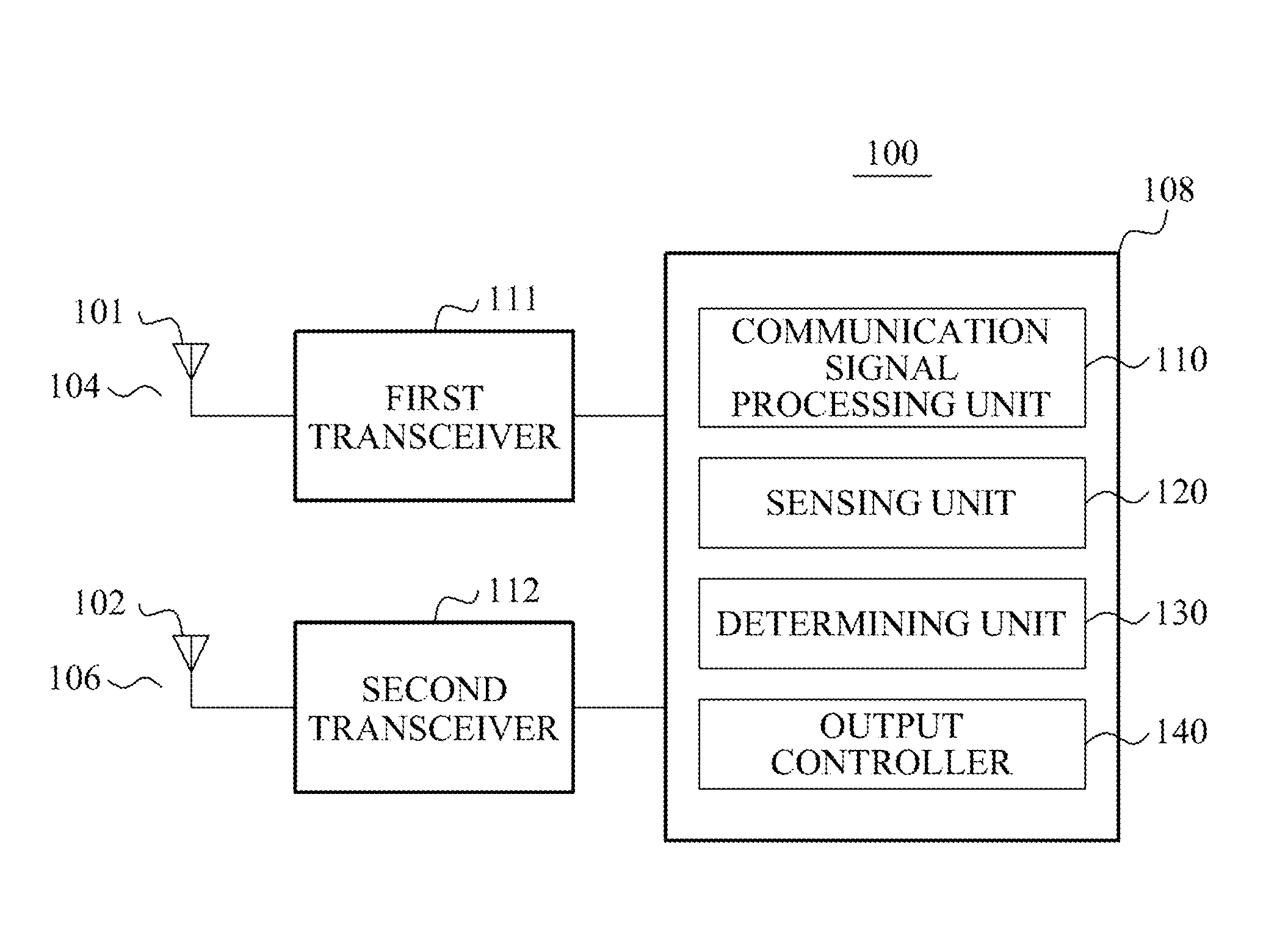
Method for reducing intermodulation noise signal and communication terminal
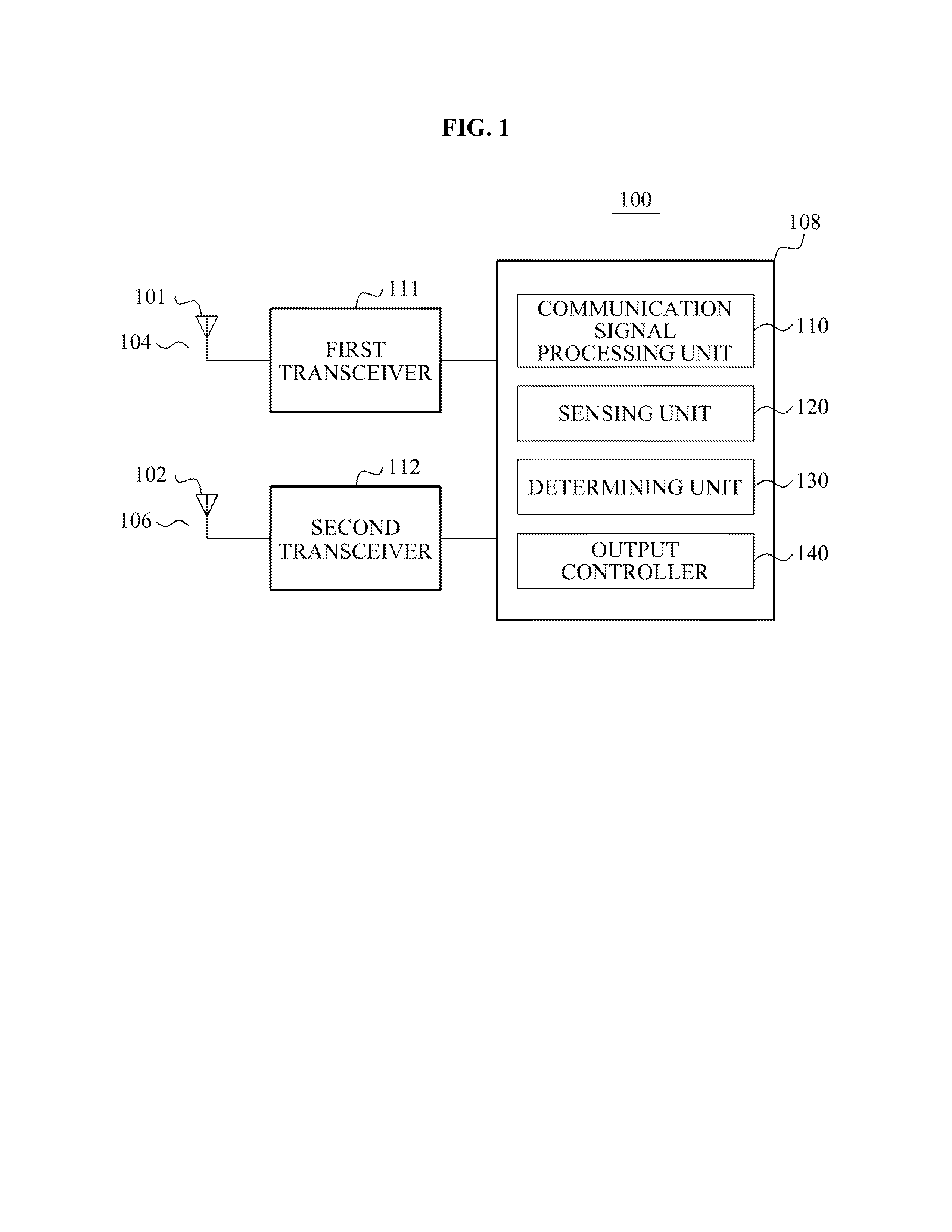
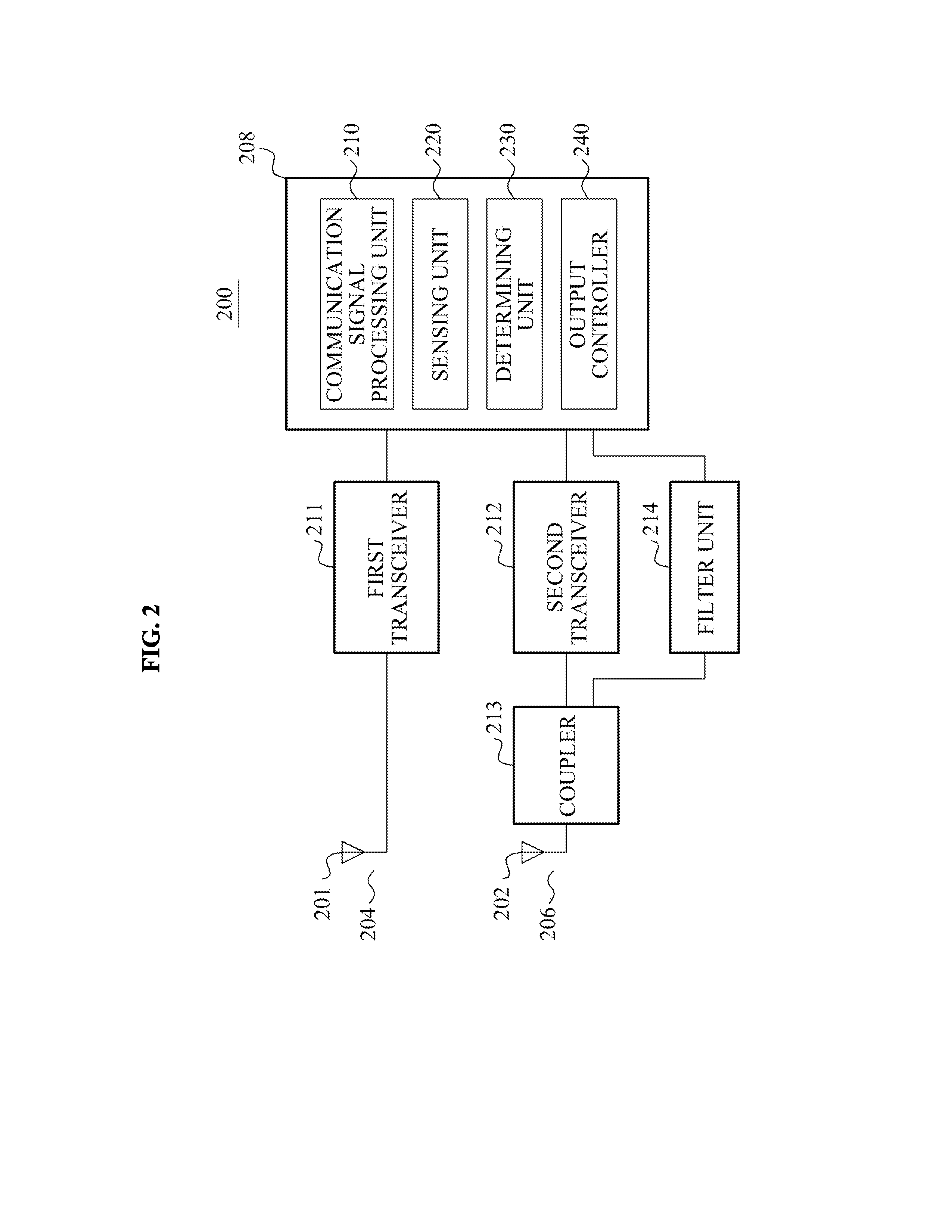
InactiveUS20130225095A1Reduce noise signalReduce noisePower managementEcho effect reductionTerminal equipmentEngineering
A communication terminal apparatus to reduce an intermodulation noise between channels may perform wireless communication at different frequencies using a first channel and a second channel. The communication terminal apparatus may include a sensing unit to measure a signal to noise ratio (SNR) in a communication associated with the second channel, a determining unit to determine whether the measured SNR is less than a first threshold, and an output controller to decrease a strength of an output signal in the communication associated with the first channel if the measured SNR is less than the first threshold, and to increase the strength of the output signal in the communication associated with the first channel until the SNR is substantially similar to the first threshold if the determining unit determines that the measured SNR is greater than the first threshold.
Owner:PANTECH CO LTD
Automatic wind noise reduction circuit and automatic wind noise reduction method
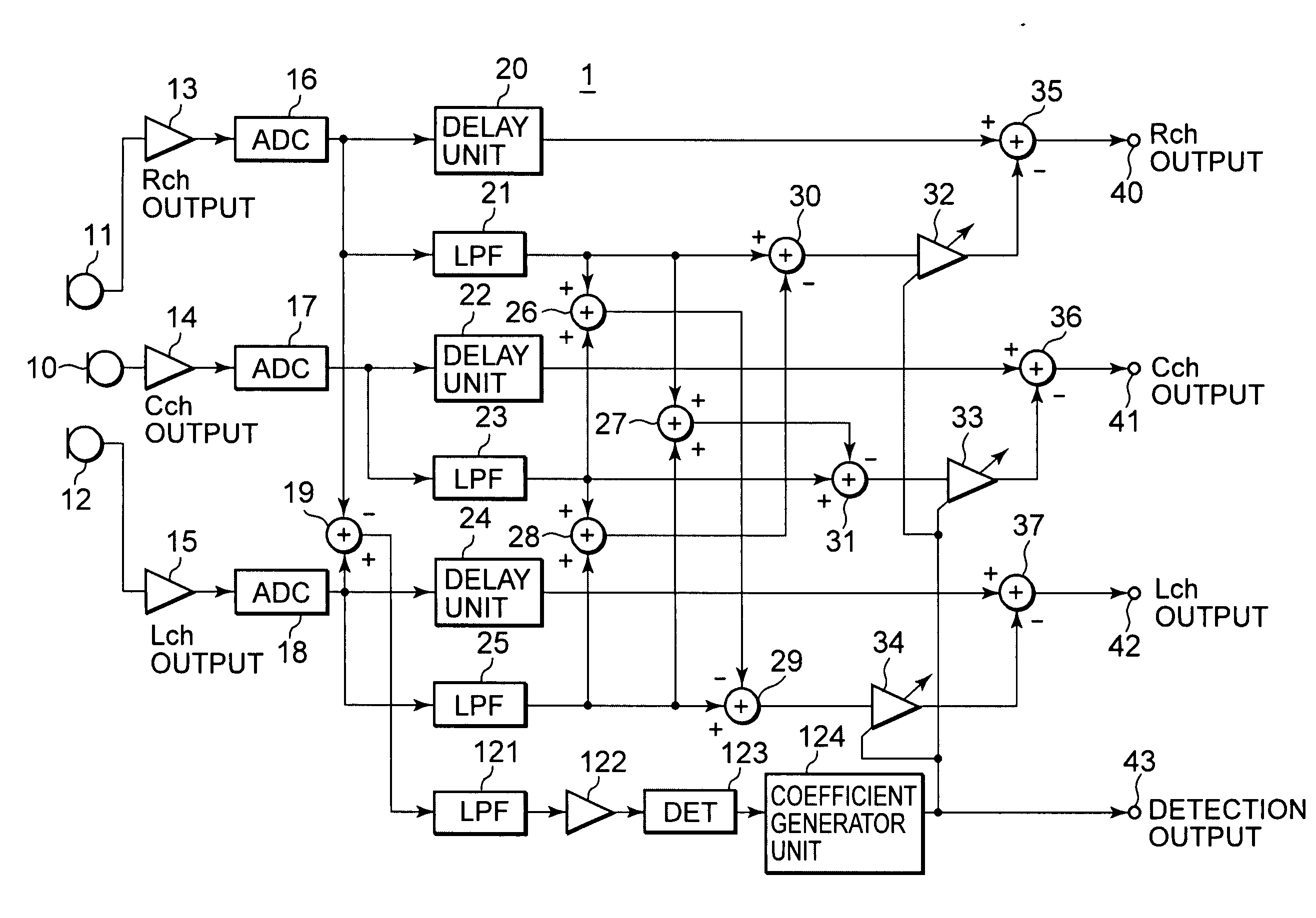
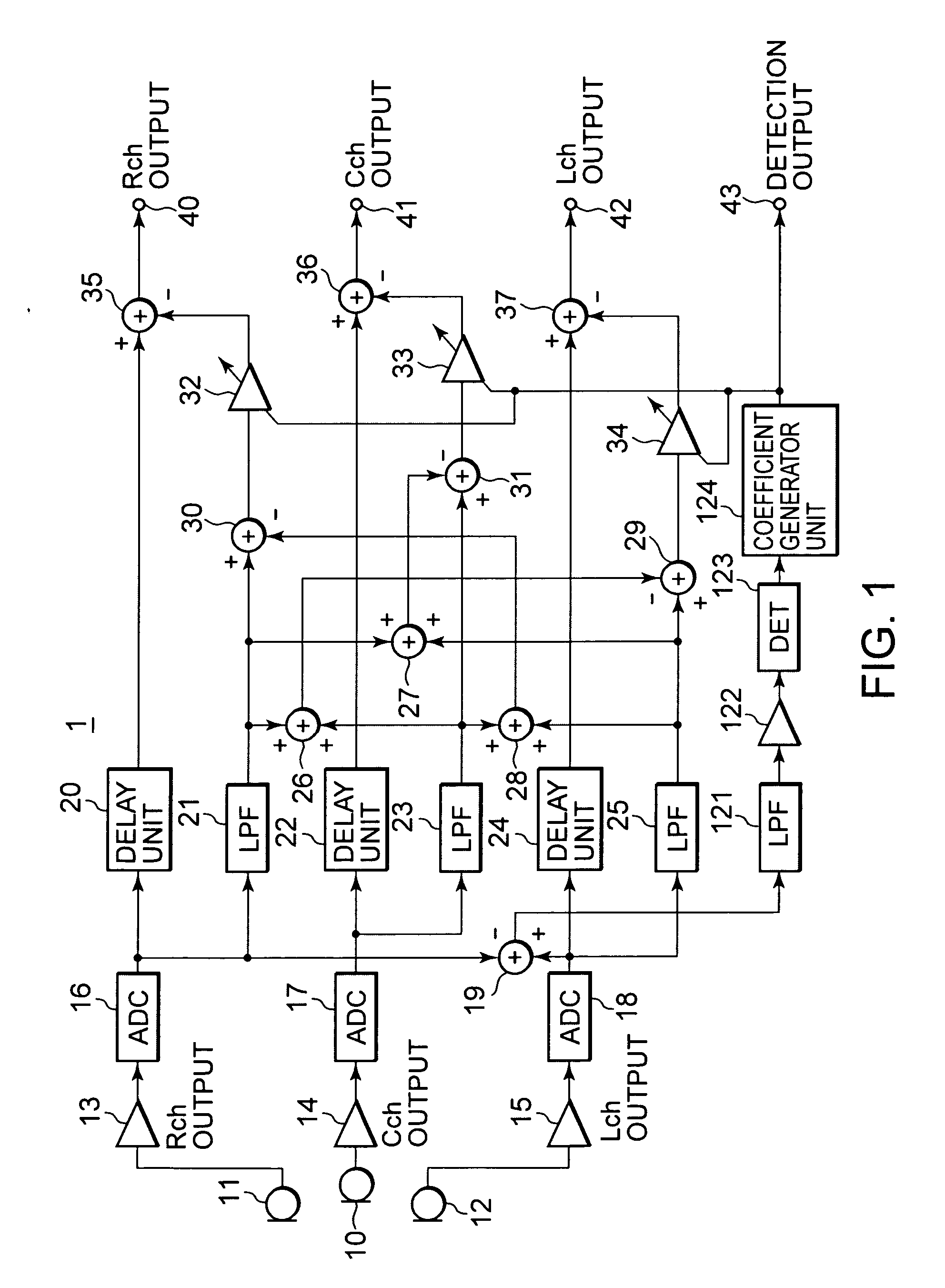
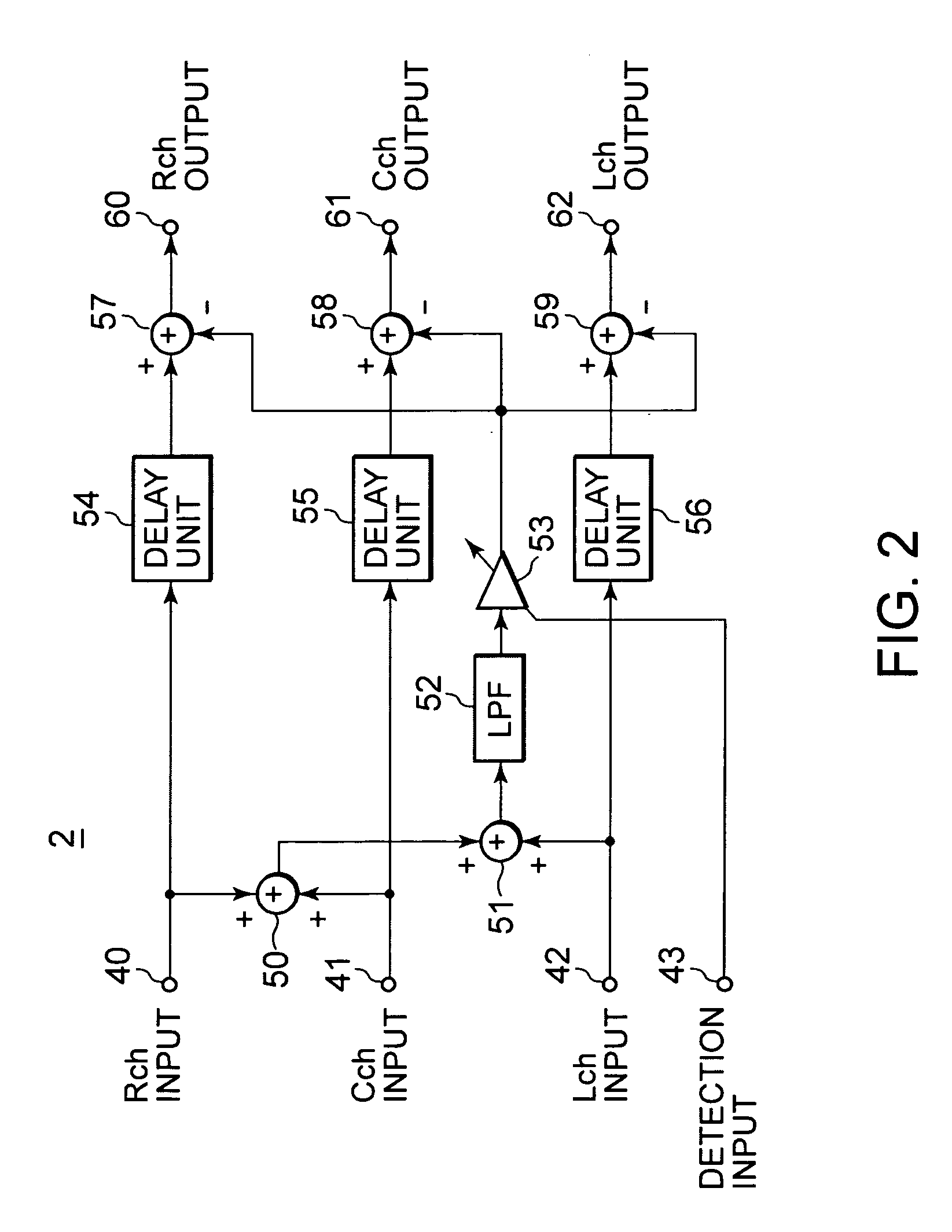
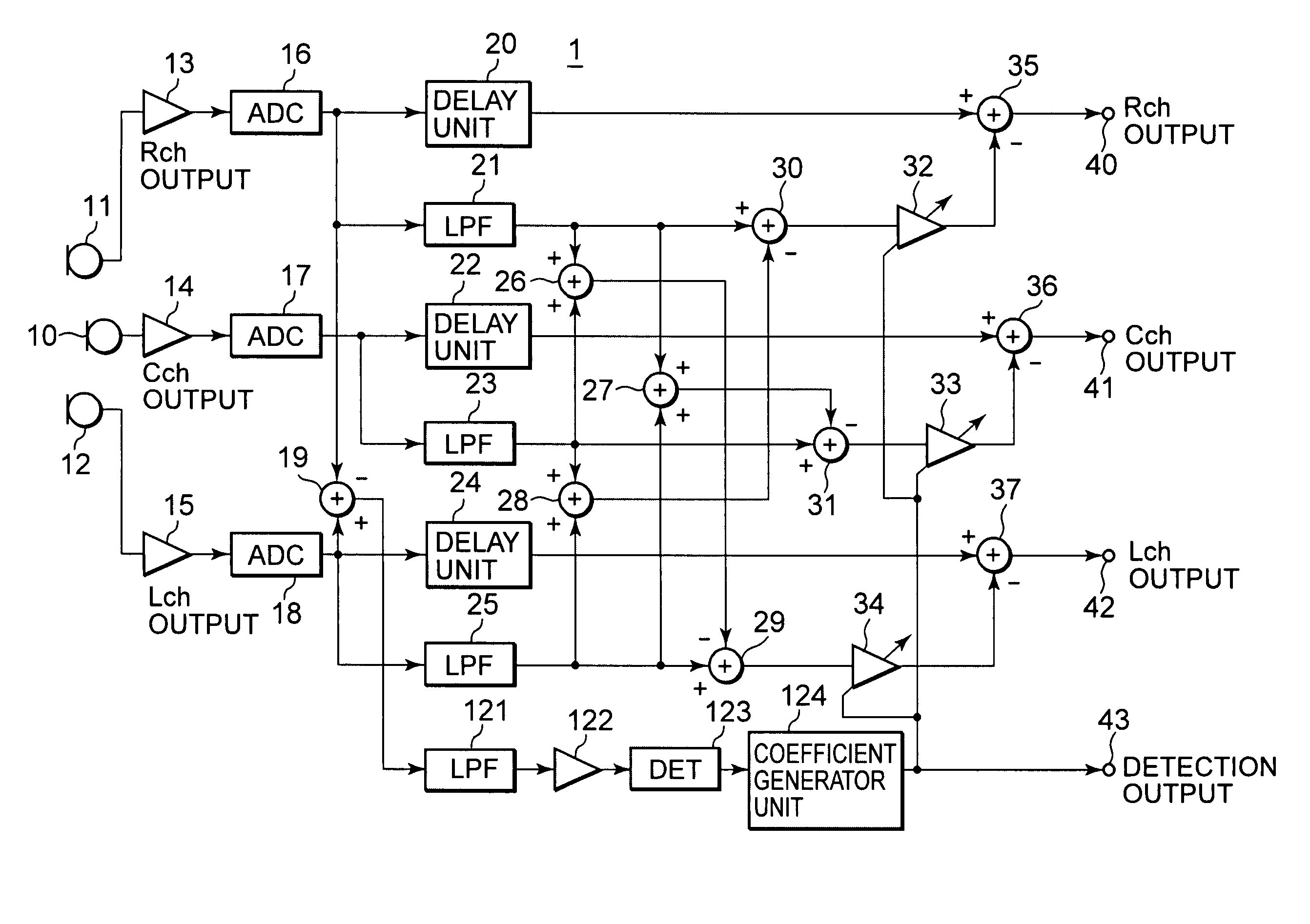
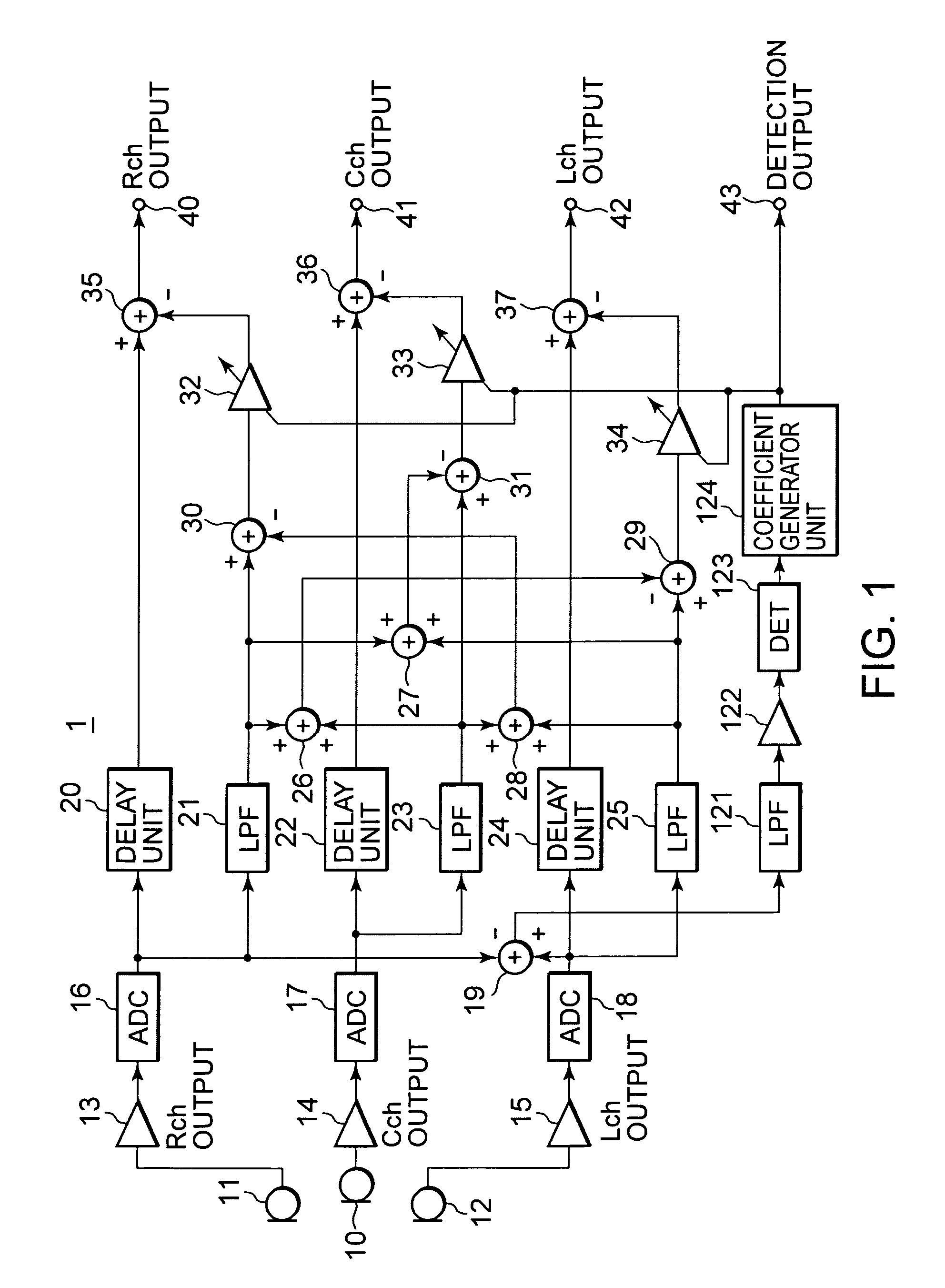
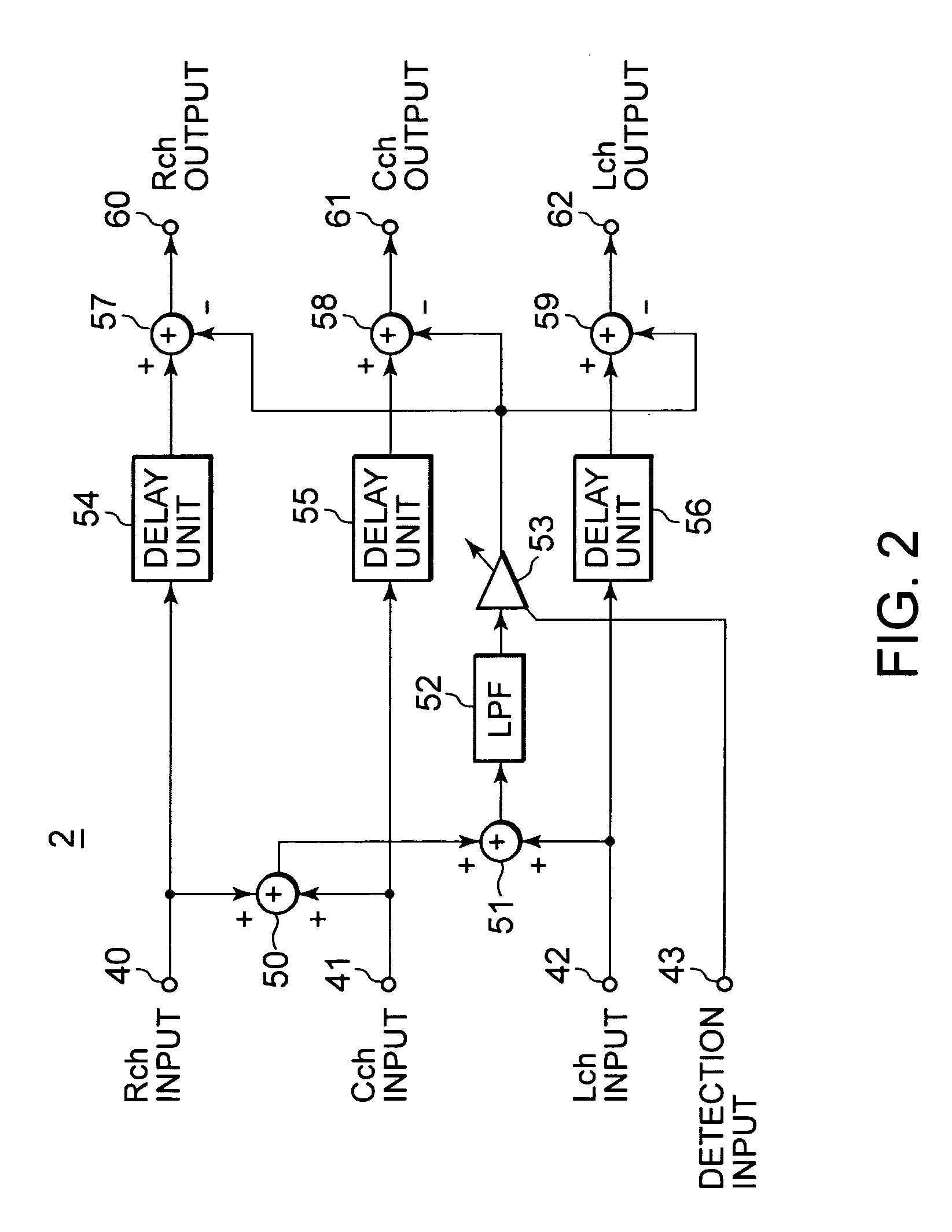
InactiveUS20050238183A1Eliminate effectiveReduce noise signalMicrophonesSpeech analysisSystems designEngineering
An object is to provide an automatic wind noise reducing circuit and an automatic wind noise reducing method, which are capable of coping with a multichanneling trend of audio signals, and improving performance as well as the degree of freedom in system design. Arithmetic units (26, 27, 28) obtain added signals of audio signals of audio channels excluding respective selected audio channels, which are selected so as to be different from each other. Arithmetic units (29, 30, 31) subtract respective added signals of the arithmetic units (26, 27, 28) from corresponding audio signals of the selected audio channels. The subtraction signals from the arithmetic units (29, 30, 31) are subjected to a band limit control and limited to a frequency band of a wind noise signal by LPFs (21, 23, 25). After level-controlling of the subtraction signals from the arithmetic units (29, 30, 31) which are limited to the wind noise signal band by variable level amplifiers (32, 33, 34), the subtraction signals are subtracted from respective audio signals of corresponding audio channels.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image Capturing Apparatus
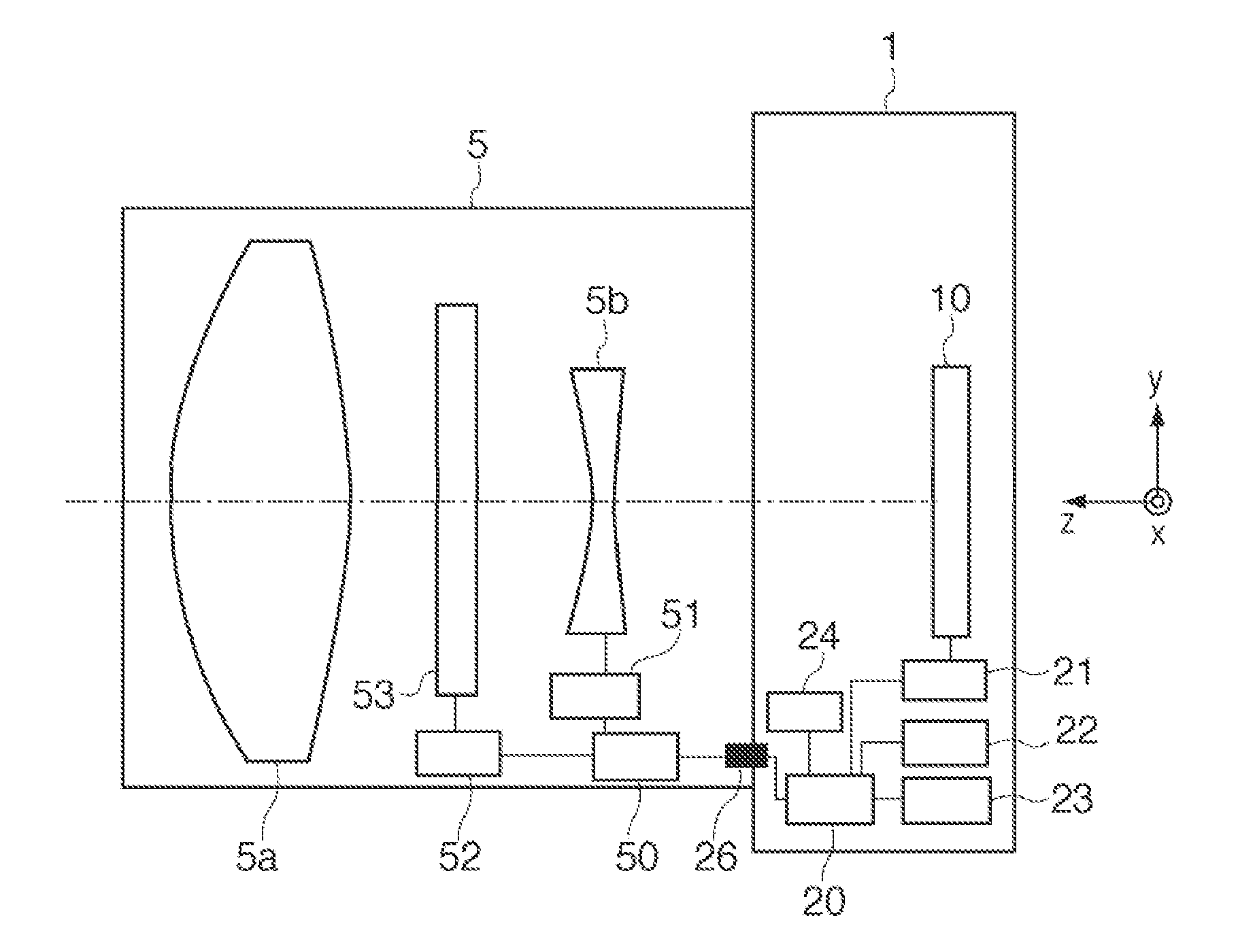
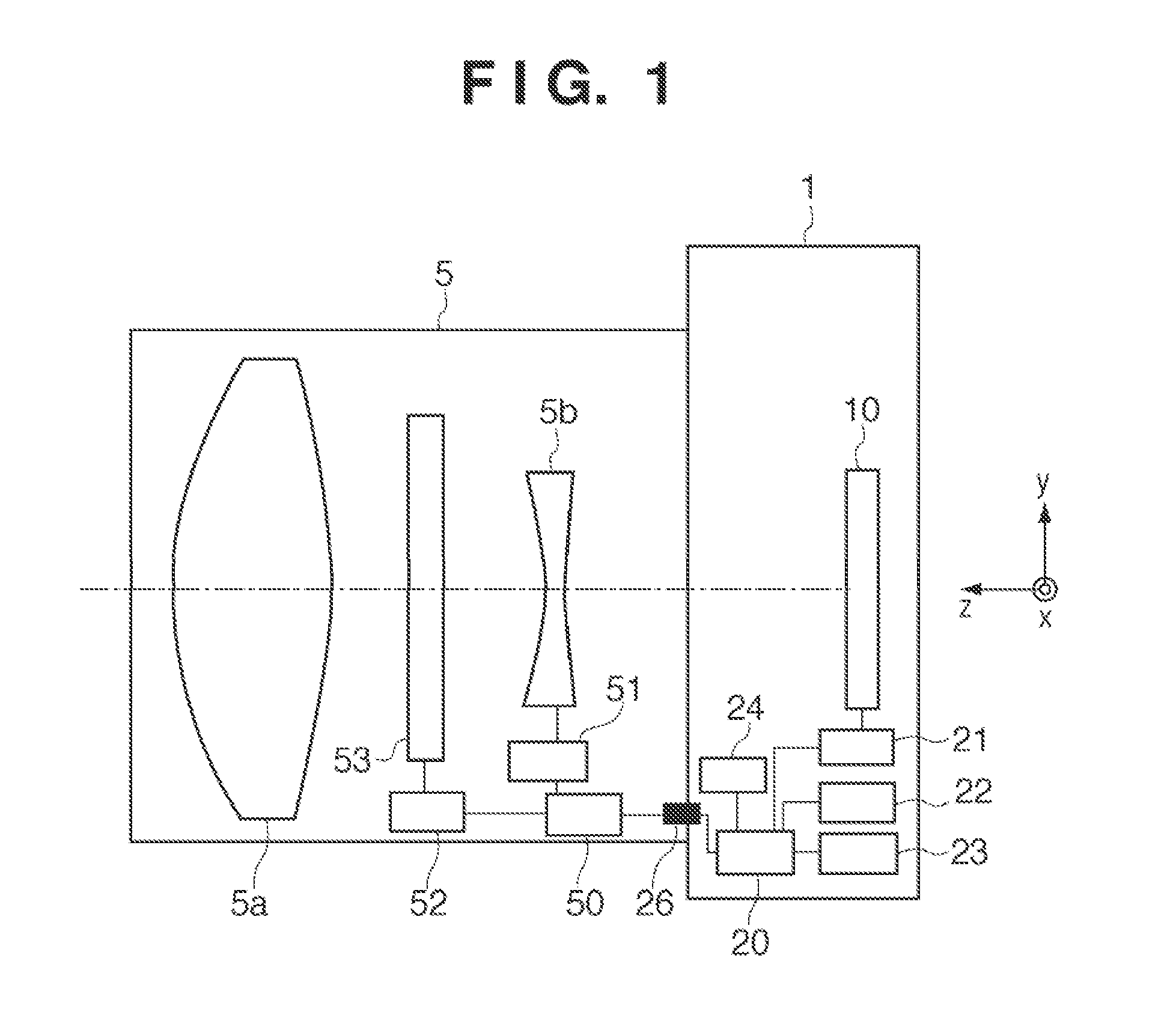
InactiveUS20120229696A1Reduce noiseImprove focus detection accuracyTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensObject based
An image capturing apparatus comprises: an image sensor having image forming pixels for receiving light that has passed through an entire pupil area of an imaging lens which forms an object image, and focus detection pixels, which are arranged discretely among the image forming pixels, for receiving light that has passed through part of the pupil area of the imaging lens; a detection unit configured to detect an edge direction of an object based on an image signal acquired by the image sensor; an averaging unit configured to average image signals, while shifting a phase of the image signals, which are acquired respectively from each of the focus detection pixels, based on the edge direction detected by the detection unit; and a calculation unit configured to calculate a defocus amount of the imaging lens using the image signal averaged by the averaging unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Automatic wind noise reduction circuit and automatic wind noise reduction method
InactiveUS7174023B2Reduce noise signalReduce componentsMicrophonesSpeech analysisSystems designEngineering
An object is to provide an automatic wind noise reducing circuit and an automatic wind noise reducing method, which are capable of coping with a multichanneling trend of audio signals, and improving performance as well as the degree of freedom in system design. Arithmetic units (26, 27, 28) obtain added signals of audio signals of audio channels excluding respective selected audio channels, which are selected so as to be different from each other. Arithmetic units (29, 30, 31) subtract respective added signals of the arithmetic units (26, 27, 28) from corresponding audio signals of the selected audio channels. The subtraction signals from the arithmetic units (29, 30, 31) are subjected to a band limit control and limited to a frequency band of a wind noise signal by LPFs (21, 23, 25). After level-controlling of the subtraction signals from the arithmetic units (29, 30, 31) which are limited to the wind noise signal band by variable level amplifiers (32, 33, 34), the subtraction signals are subtracted from respective audio signals of corresponding audio channels.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetic detection device and equipment
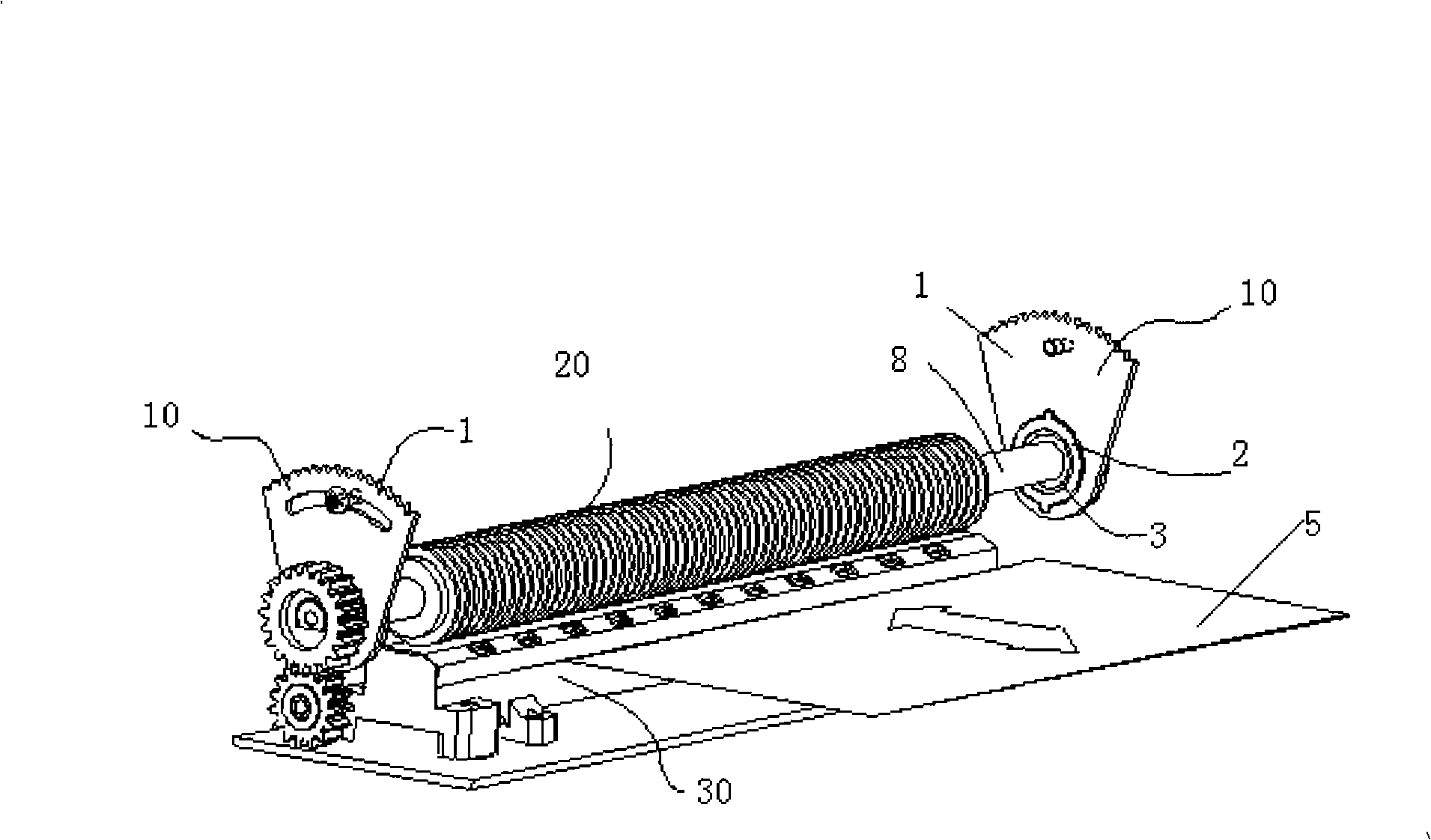
InactiveCN101527057AReduce noise signalImprove the ability to identify anti-counterfeitingPaper-money testing devicesMagnetic property measurementsTesting equipmentEngineering
The embodiment of the invention discloses a magnetic detection equipment and a magnetic detection device, comprising a magnetic sensor and a press wheel component; magnetic detection is carried out by transmitting magnetic objects through a transmission channel between the magnetic sensor and the press wheel component; the press wheel component comprises a driving roller and an elastic cylindrical press wheel which is sleeved on the driving roller; and the surface of the elastic cylindrical press wheel is a threaded flexible deformed narrow strip. By implementing the embodiment of the invention, the anti-counterfeit capability and the stability of bank note discrimination are improved.
Owner:GRG BAKING EQUIP CO LTD
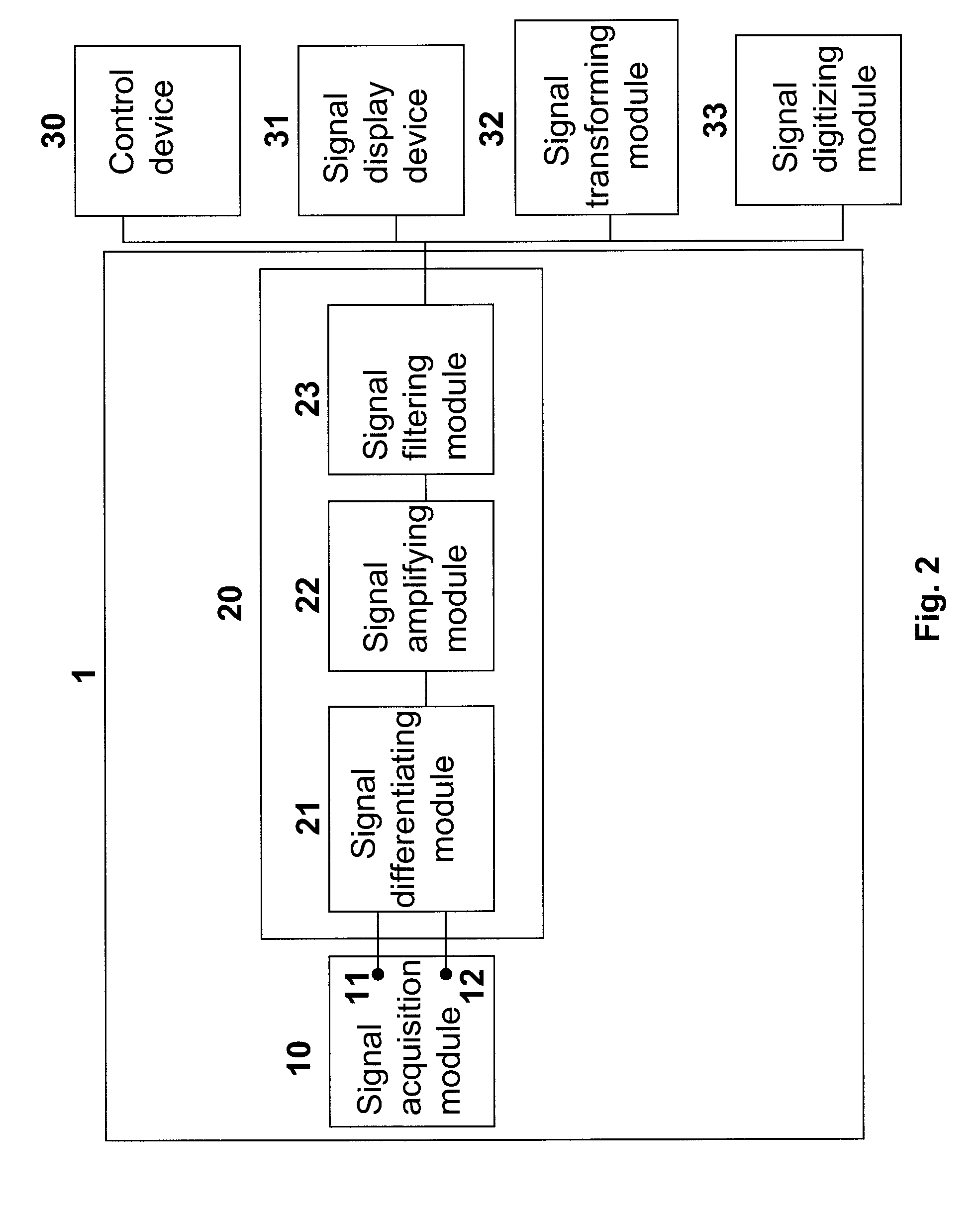
Sensor Device for Detecting LEEG Signals and Detecting Method Thereof
InactiveUS20070073184A1Reduce noise signalElectroencephalographySensorsSignal processingSignal acquisition
A sensor device that detects Laplacian electroencephalogram (LEEG) signals includes a signal acquisition module placed on a scalp of a subject to acquire brain signals. A signal processor is coupled or connected to the signal acquisition module to perform a Laplacian operation on the signals acquired by the signal acquisition module such that the noise signal is reduced to yield an analog LEEG signal with a high signal-to-noise (S / N) ratio.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Sensor system for measuring an electric potential signal of an object
ActiveUS7466148B2Reduce signalingReduce impactElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyPotential differenceNon invasive
The invention generally pertains to reducing artifact noise signals present when non-invasive capacitive-type signal measurements are taken of static electric fields produced by an object of interest. According to a first preferred embodiment of the invention, a given static artifact signal is reduced by minimizing the potential difference between a ground point of sensor circuitry and the potential of the object. According to a second preferred embodiment of the invention, the change in signal due to motion of the sensor in the field produced by the object is minimized by reducing the impact of changes in coupling to the signal source.
Owner:QUANTUM APPLIED SCI & RES
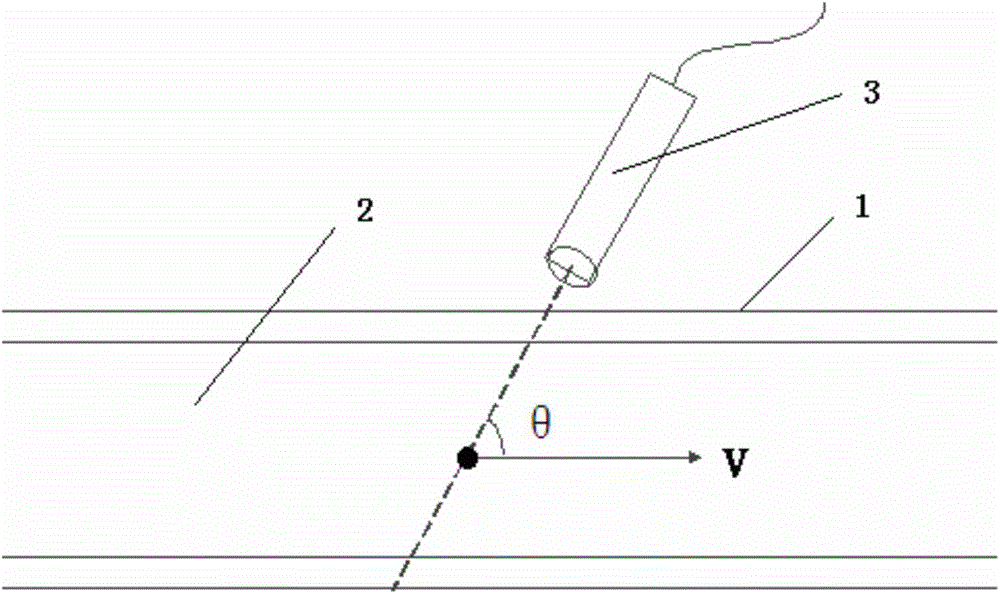
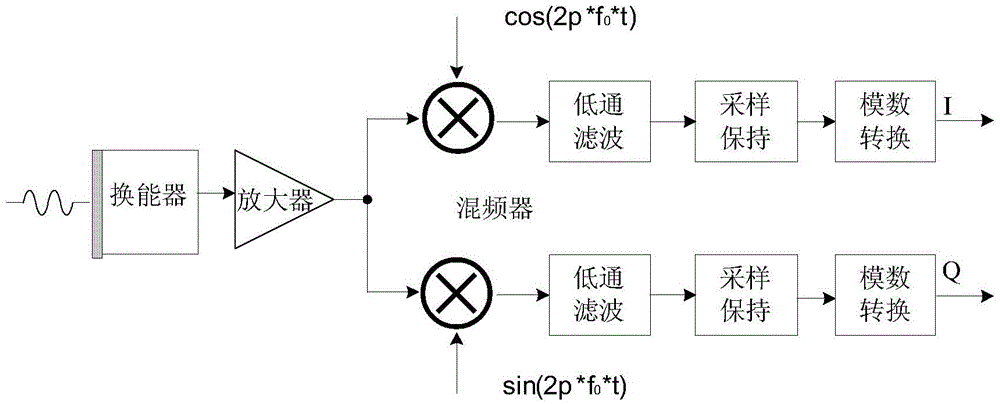
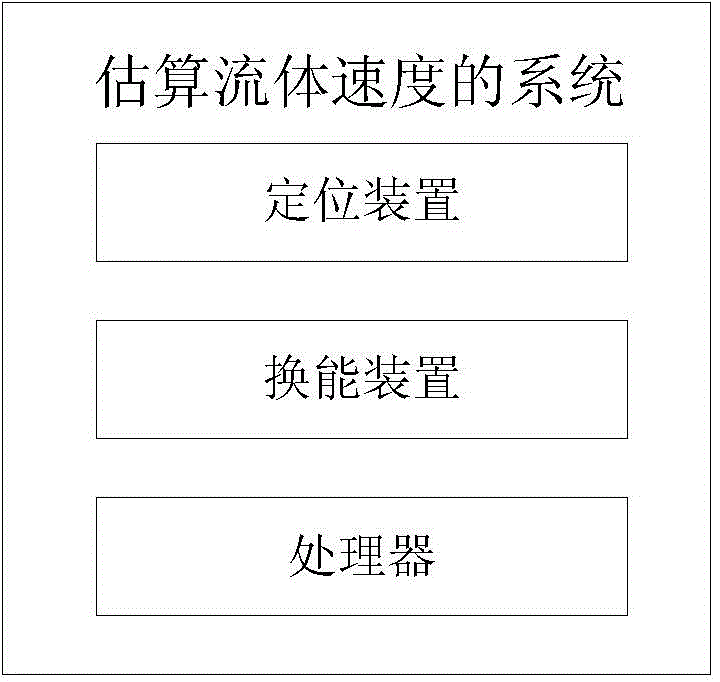
Estimating system and method for fluid velocity
InactiveCN104146731AReal-time reflection of abnormal blood flowImprove real-time performanceBlood flow measurement devicesSonificationCurve fitting
The invention discloses an estimating system and method for fluid velocity. The estimating system comprises a positioning device, a transducer and a processor. The positioning device is used for determining position of to-be-detected fluid through ultrasonic imagining and selecting a plurality of signal sampling sites on a determined section of to-be-detected velocity. The transducer is used for, under the control of the processor, sending ultrasonic to the fluid and receiving pulse echo signals. The processor is used for processing the pulse echo signals, calculating the fluid velocities of the signal sampling sites and performing curve fitting to fluid velocity values of the signal sampling sites to acquire a section curve of the fluid velocity. With the processor, such as FPGA (field-programmable gate array), blood flow velocities with different depth in blood vessels are simultaneously sampled and measured so as to achieve the blood flow velocities. In this way, abnormal blood flow is timely reflected, and signal processing timeliness and calculation accuracy are higher, so that diagnostic basis is provided for diagnosis of vascular diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
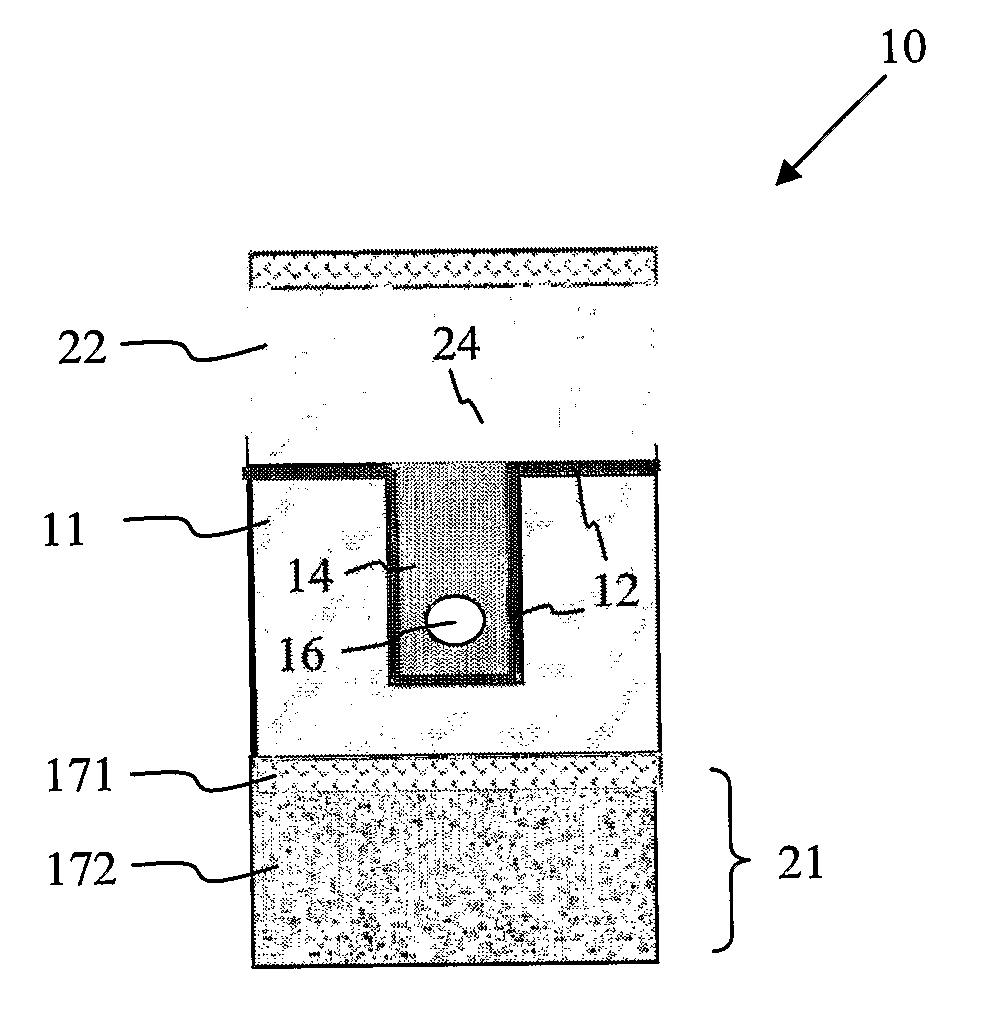
Transparent microfluidic device
InactiveUS20100055673A1Easy to analyzeReduce noise signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringBiological entity
A device for analysing the status of a biological entity. The device (10) comprises a substantially transparent base substrate (11) having a recess defined therein by at least two opposing lateral walls and a base wall, a substantially transparent filler member (14) having at least a portion thereof occupying the recess, a substantially transparent separation layer (12) disposed between the filler member and the base substrate, and a channel (16) defined in the filler member, wherein the channel comprises an inlet and an outlet, the inlet being arranged on a first lateral wall of the filler member, and the outlet being arranged on a second lateral wall of the filler member, said first lateral wall of the filler member being arranged in opposing relationship with the second lateral wall of the filler member, and at least a portion of the first and the second lateral walls of the filler member being at least substantially perpendicular to the opposing lateral walls defining the recess.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method and system for denoising noise image
ActiveCN101719267ABreak down meticulously and thoroughlyReduce noise signalImage enhancementImage denoisingContourlet
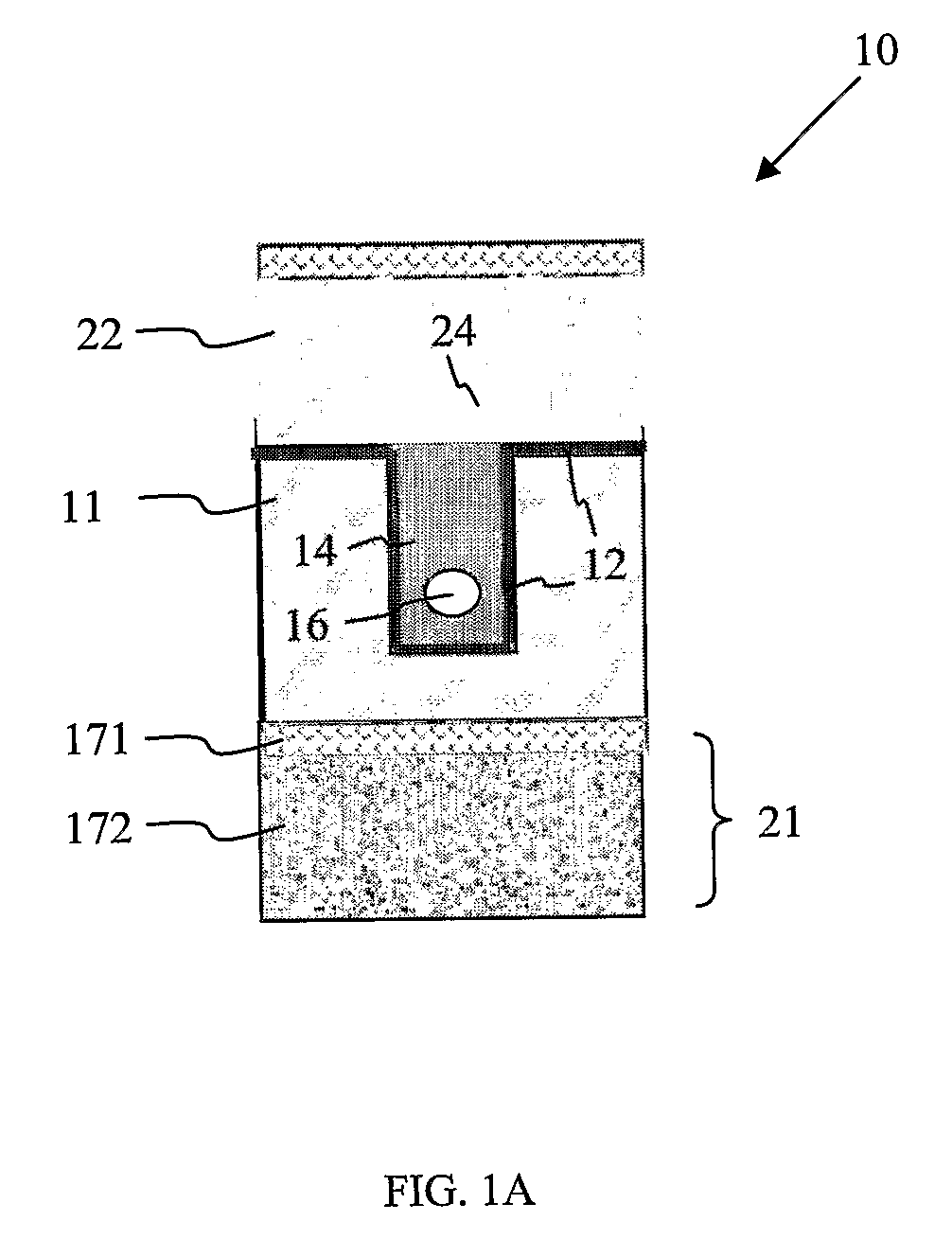
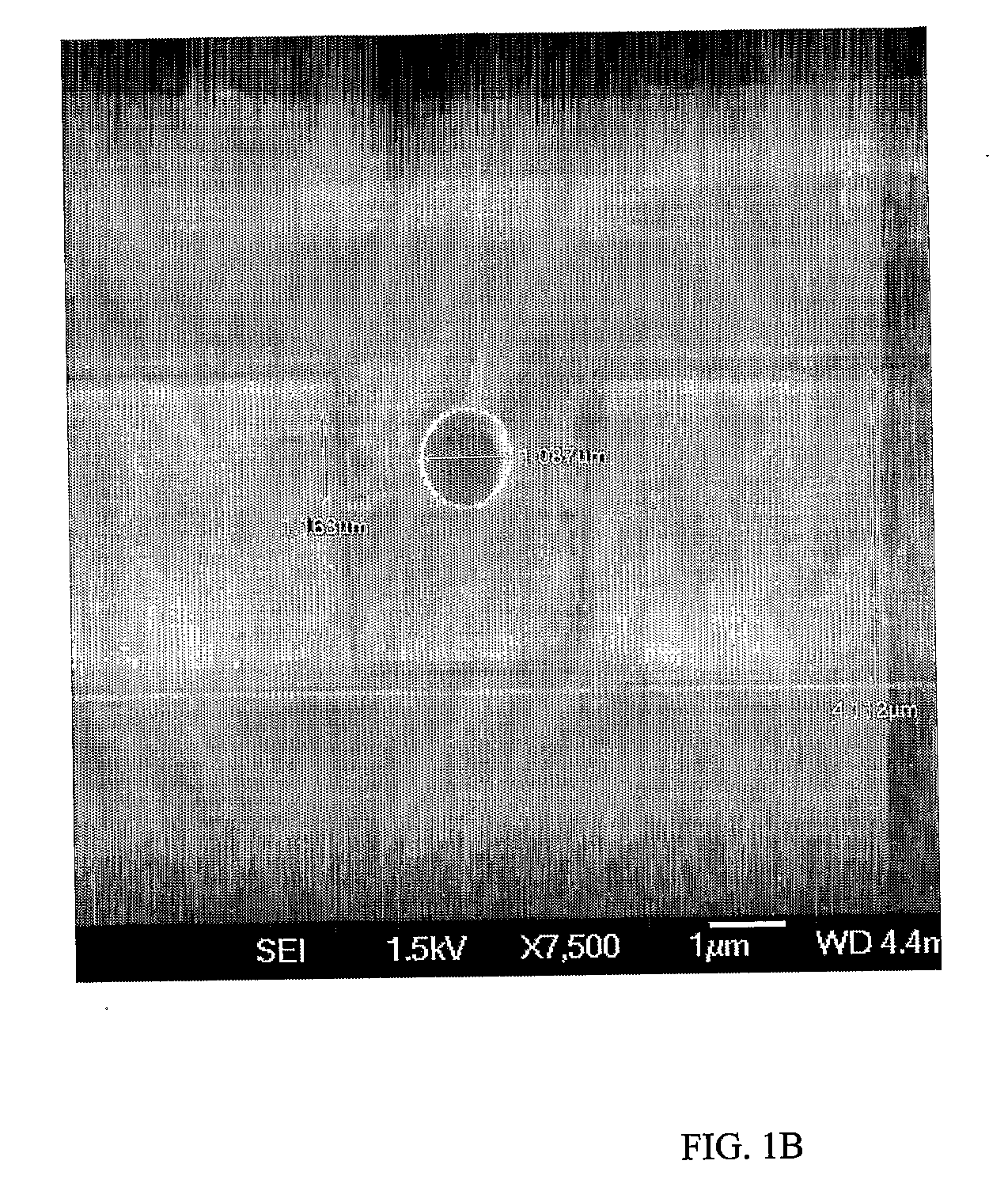
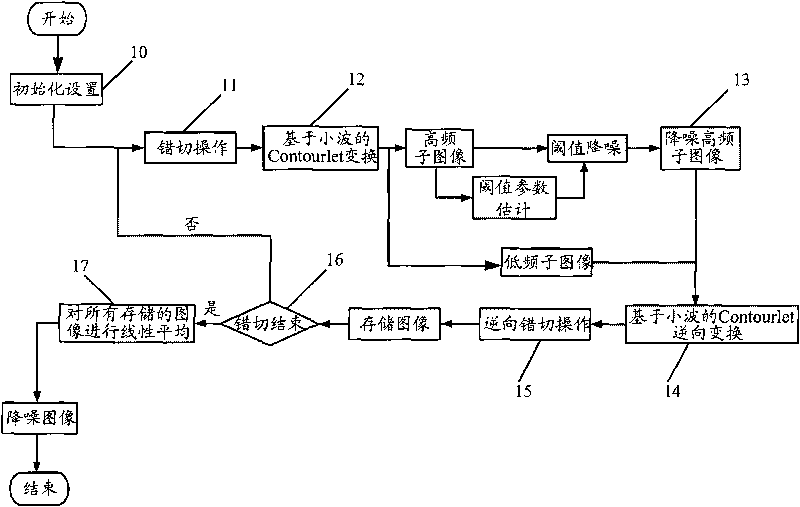
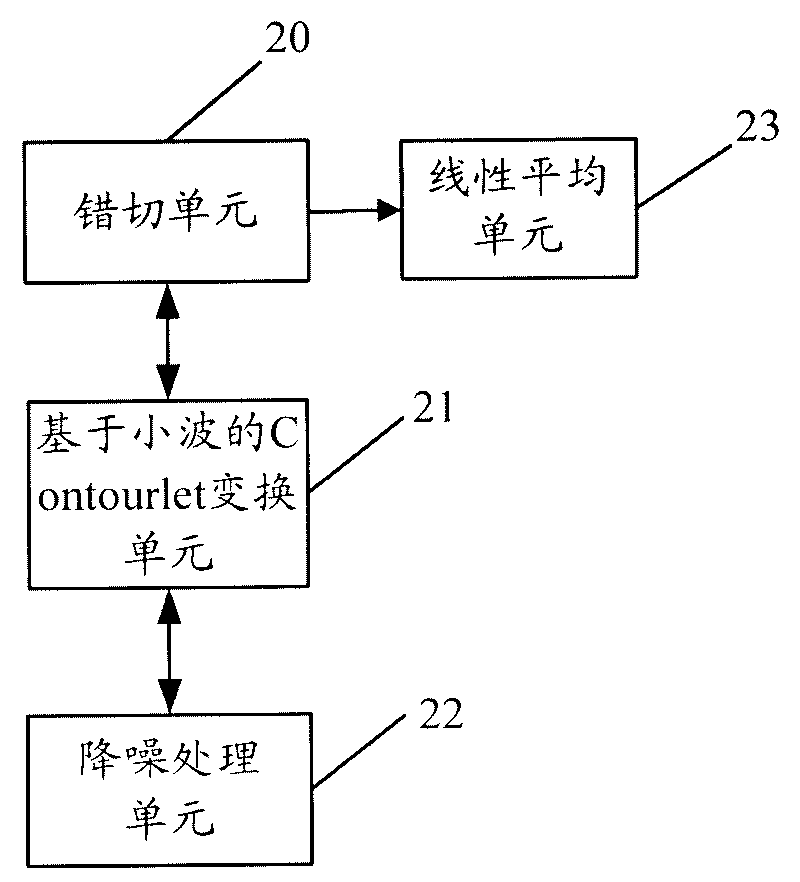
The invention discloses a method for denoising a noise image, which comprises the following steps: shearing the input noise image to acquire a sheared image; sparsely decomposing the sheared image by a wavelet-based Contourlet conversion to acquire low-frequency sub-images and high-frequency sub-images, and denoising each high-frequency sub-image to acquire a denoised high-frequency sub-image; and performing a wavelet-based Contourlet reverse conversion on the low-frequency sub-images and the denoised high-frequency sub-images, and performing reverse shearing operation with the same shearing amplitude on the low-frequency sub-images and the denoised high-frequency sub-images. The invention also discloses a system for denoising the noise image. The method and the system of the invention effectively decrease noise signals in the image, effectively keep detail information of the image, greatly improve image denoising effect and improve the quality of the image.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGXING SOFTWARE
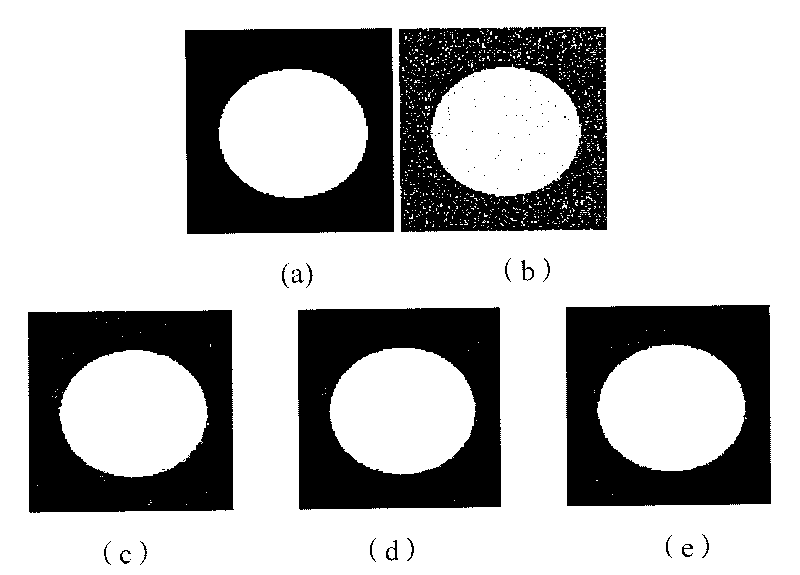
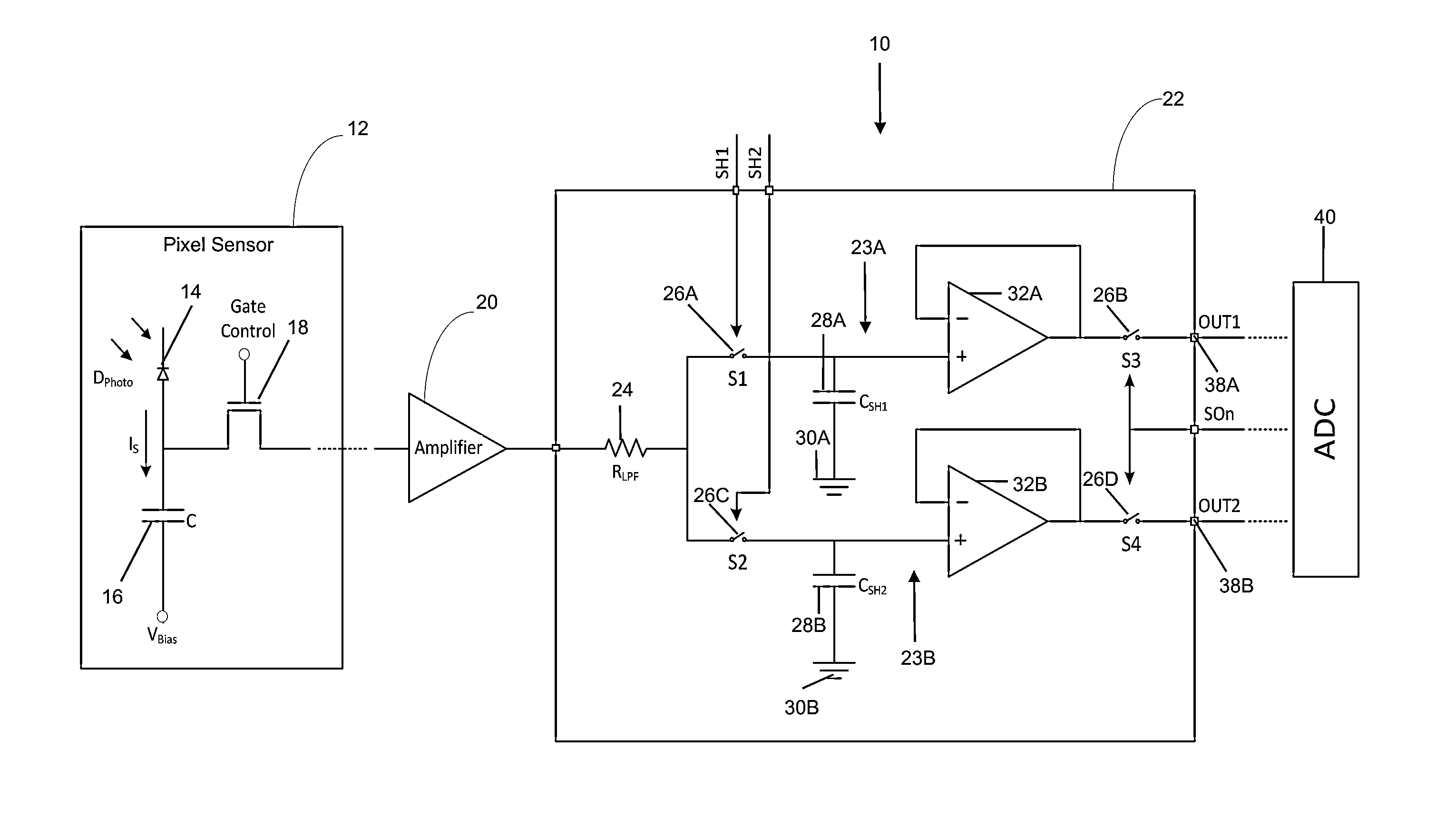
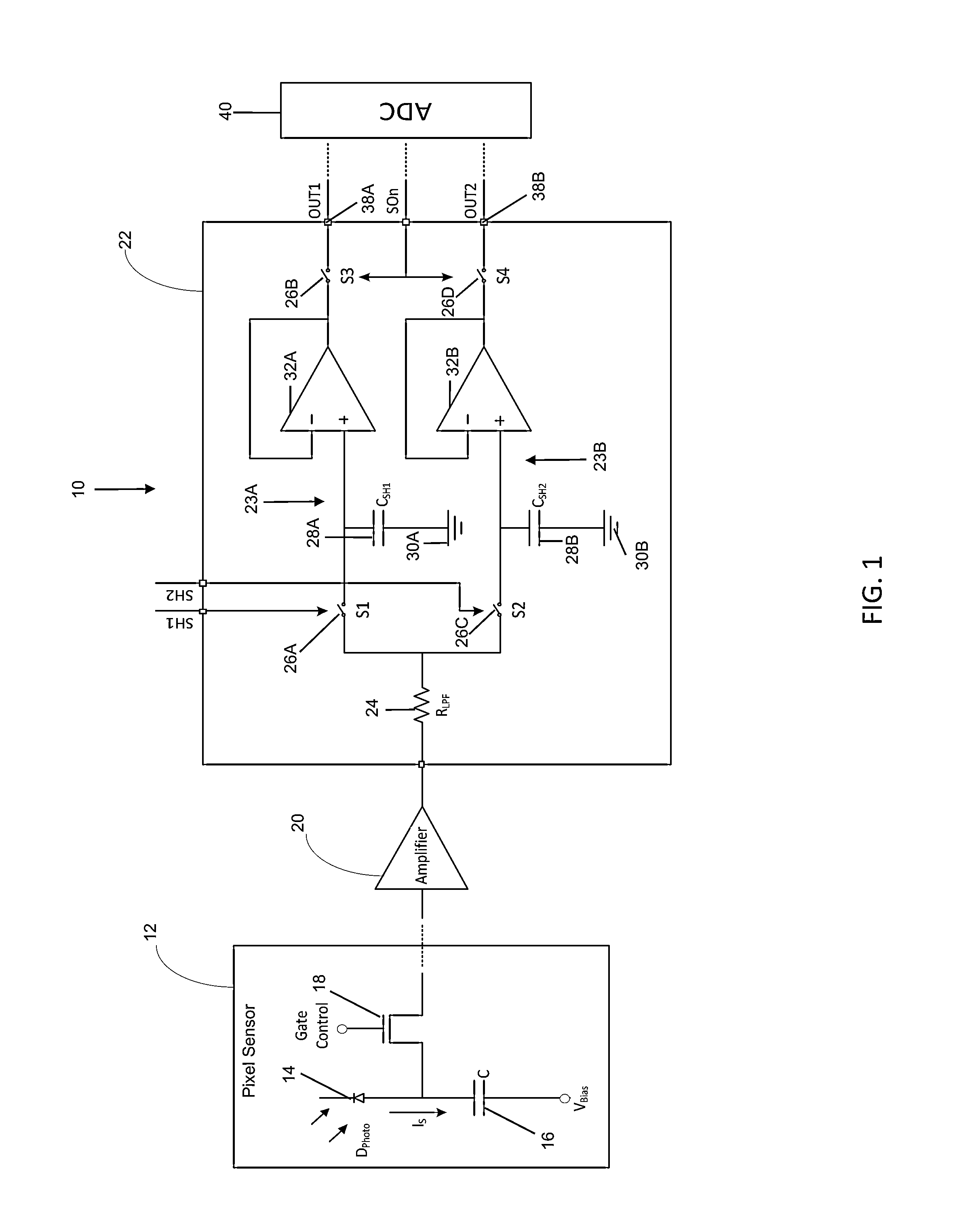
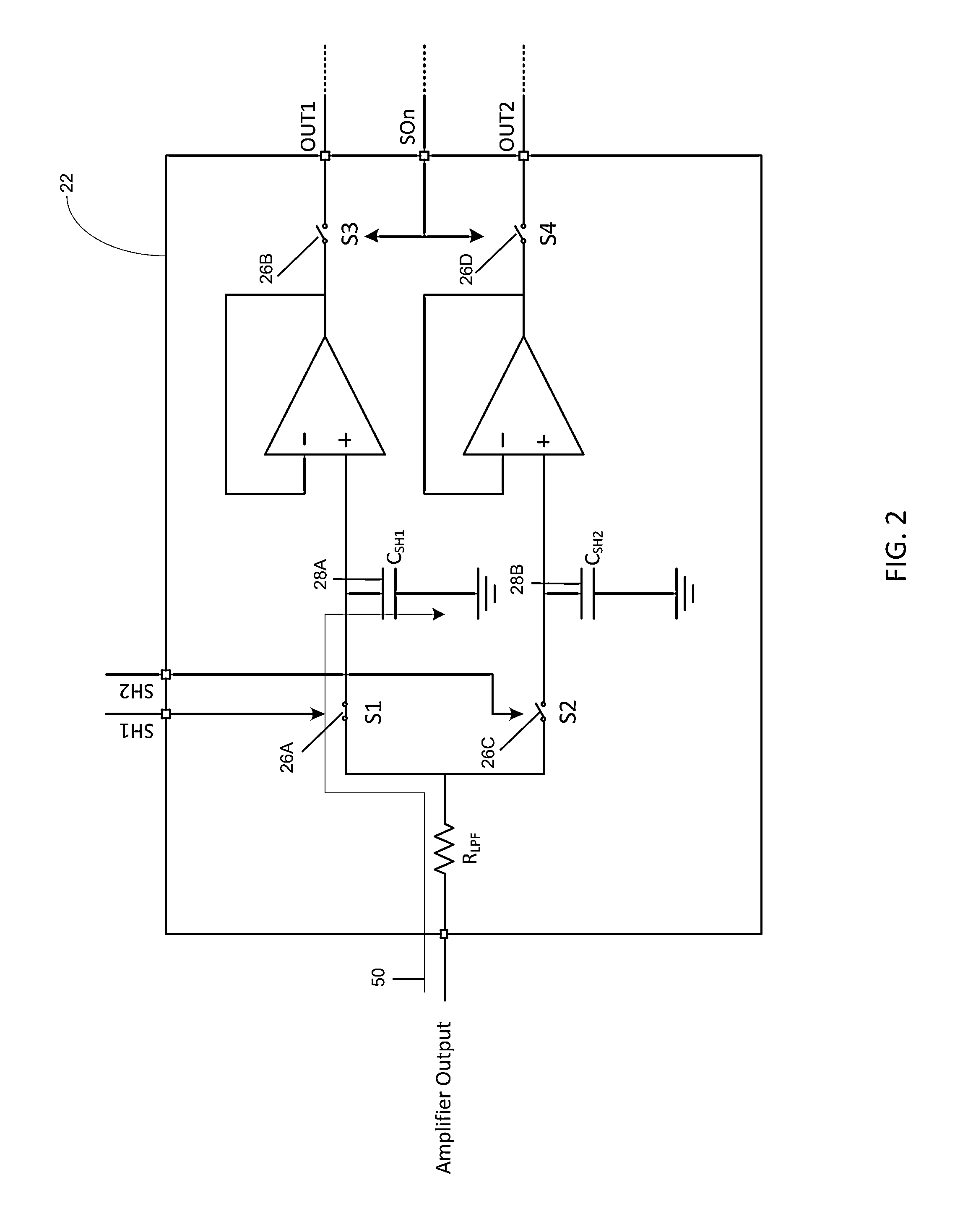
Noise-resistant sampling circuit and image sensor
InactiveUS20140049291A1Reduce noise levelReduce noise signalElectric analogue storesElectronic switchingCapacitanceLow-pass filter
An approach for a sampling circuit to reduce noise in signals (e.g., as received from photo diodes or the like) is provided. In one embodiment of the present invention, there is a sampling circuit comprising: an amplifier, which amplifies charge signals generated at photo diodes and converts them to voltage signals; the first sample and hold circuit, which samples the voltage signal and charges the first capacitor according to the first switching signal, and outputs the stored charge as a reset signal based on a readout signal; the second sample and hold circuit, which samples the signals and charges the second capacitor according to the second switching signal that is non-overlapping to the first switching signal, and outputs the stored charge as a reset signal based on the readout signal; a resistor that acts as a low-pass filter placed in between the first and the second capacitors' common nodes.
Owner:LUXEN TECH +1
Chip with measuring reliability and a method thereof
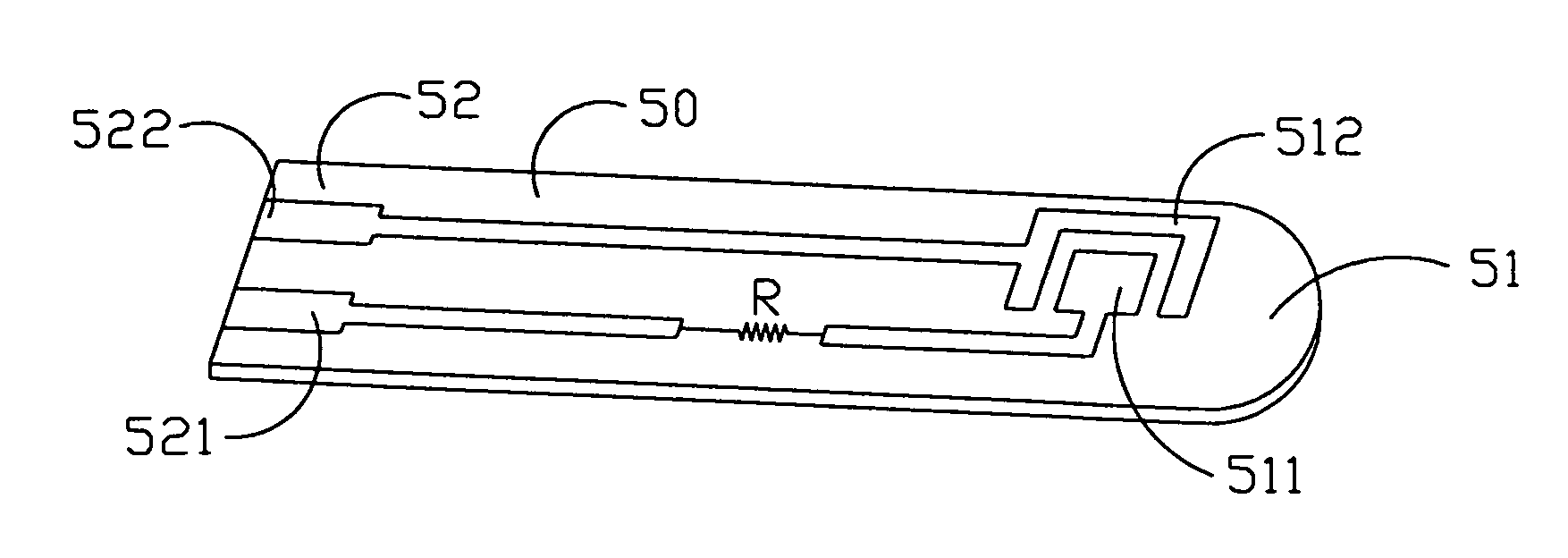
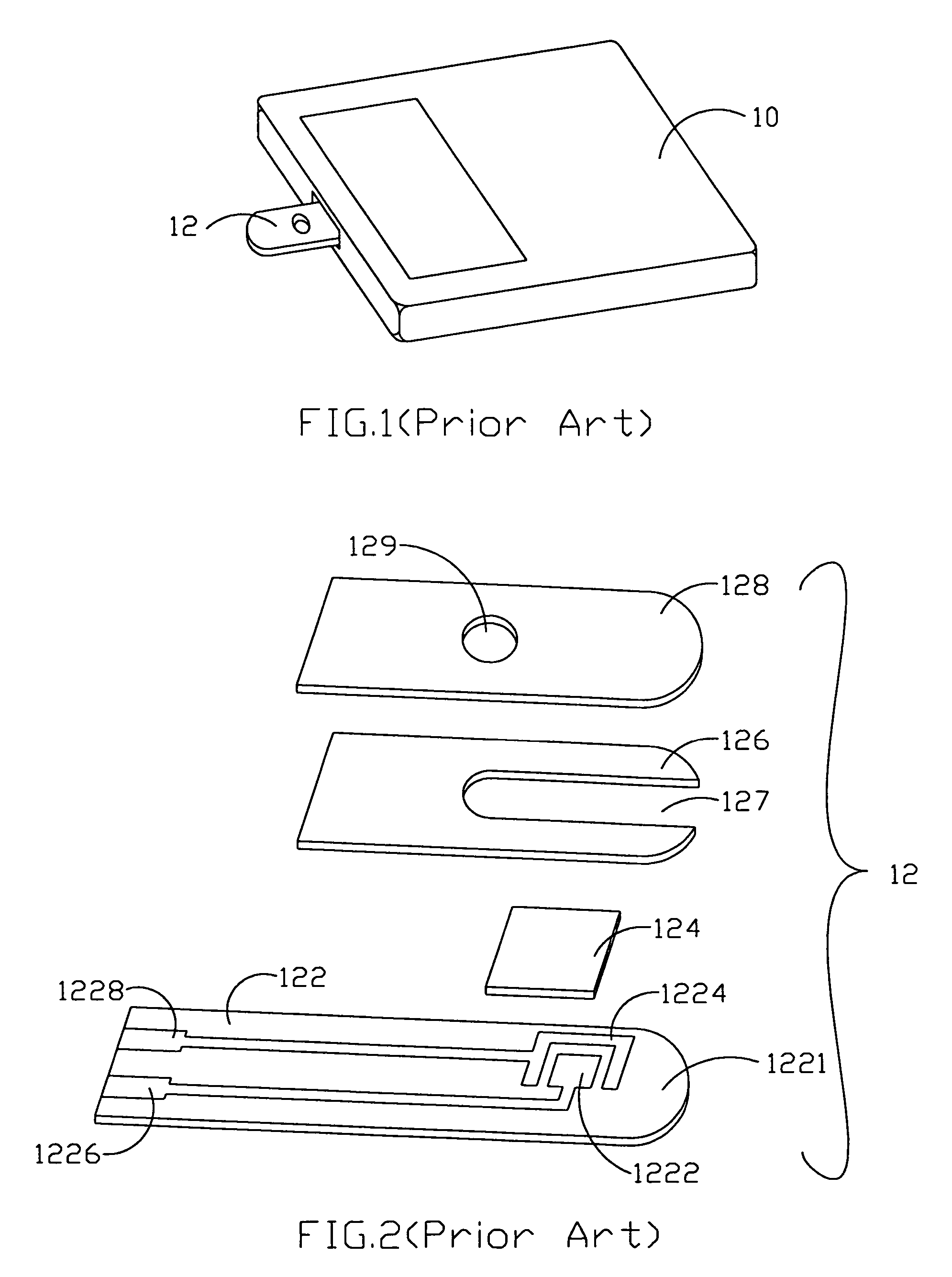
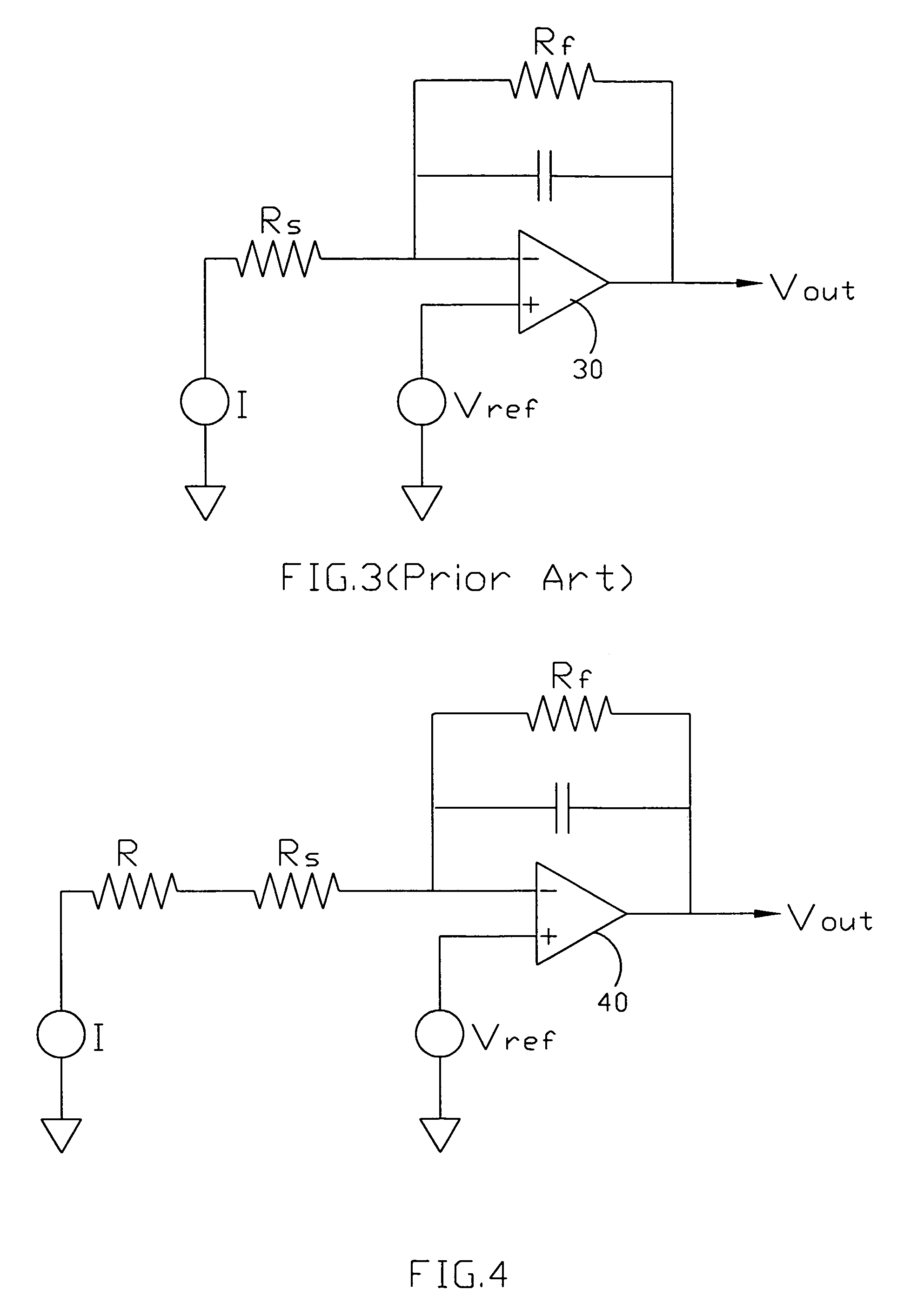
ActiveUS7374721B2Improve chip reliabilityImprove measurement reliabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical resistance and conductanceResistor
A chip with measuring reliability and a method thereof are provided. The present invention serially connects a resistor having a resistance equal to or a little more than a maximum resistance of the chip itself to the resistor Rs of the chip so as to compensate the resistance differences among chips. A noise to signal (N / S) ratio of the chip is decreased, and a measuring reliability of the chip is improved.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Pressure sensing method and system
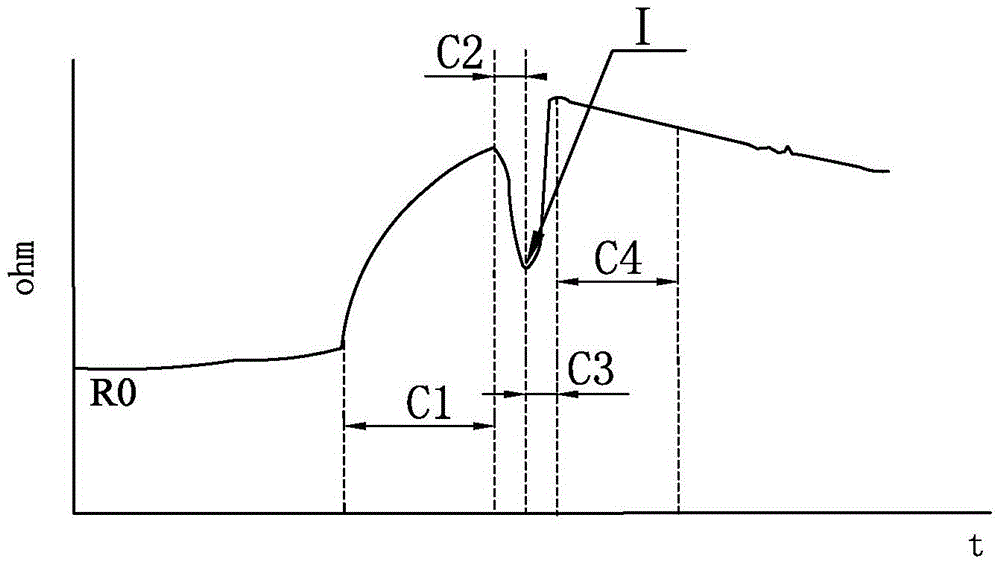
ActiveCN105630235AIn line with thinning trendAccurate detectionForce measurementInput/output processes for data processingElectrical resistance and conductancePressure sense
The invention provides a pressure sensing method and system. The pressure sensing method comprises the steps of reading stored resistance values Rn and calculating difference values delta Rn of resistance values at previous and next moments to obtain at least one delta Rn / Rn-1; and according to at least one delta Rn / Rn-1 or the sum of multiple delta Rn / Rn-1, performing matching with at least one preset value database to obtain pressure values Fn corresponding to at least one delta Rn / Rn-1 or the sum of the multiple delta Rn / Rn-1. Therefore, the maximum of a deformation resistance value can be accurately obtained, variable factors and noise signals generated by adopting an existing value-taking and operation method are effectively reduced, and a pressure sensing signal can be effectively and accurately detected and processed without the need for specially limiting the material or structure of a pressure sensing electrode.
Owner:TPK TOUCH SOLUTIONS (XIAMEN) INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com