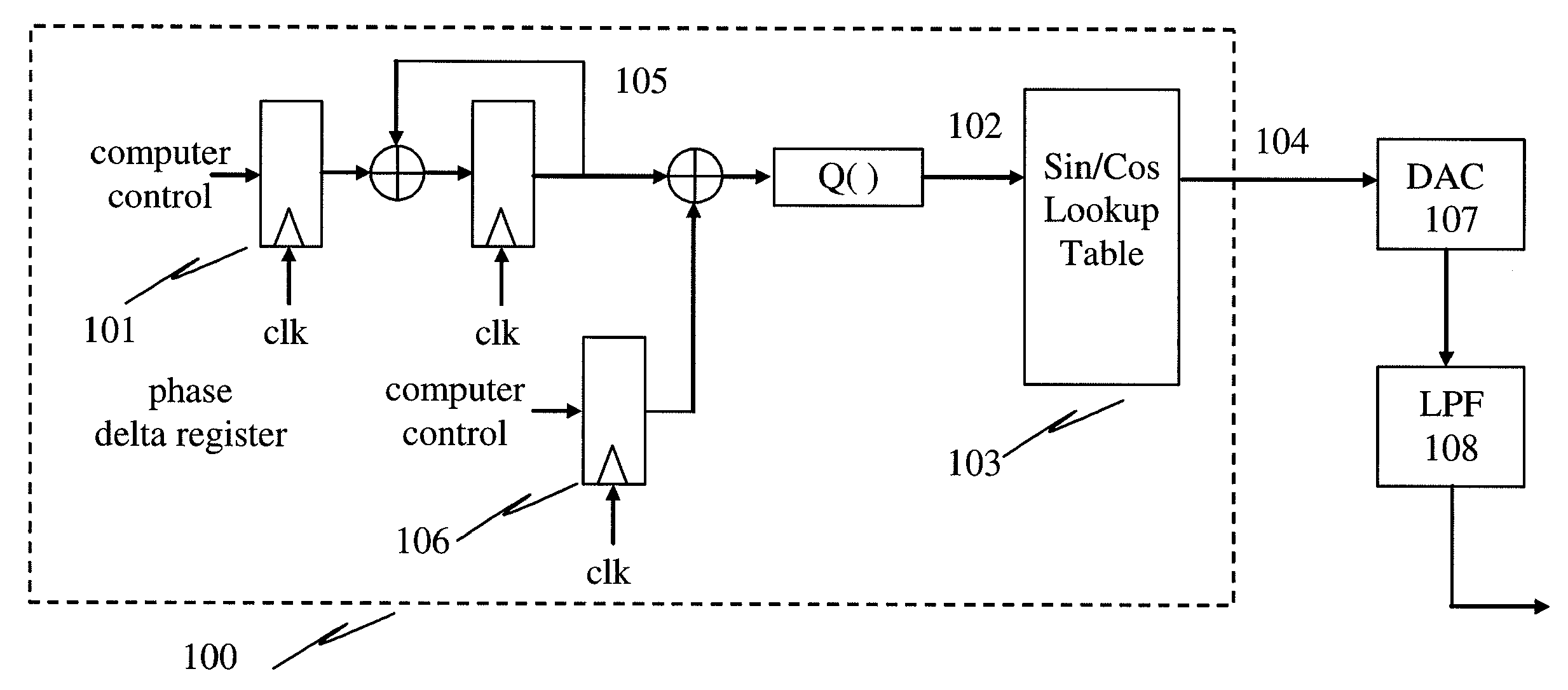
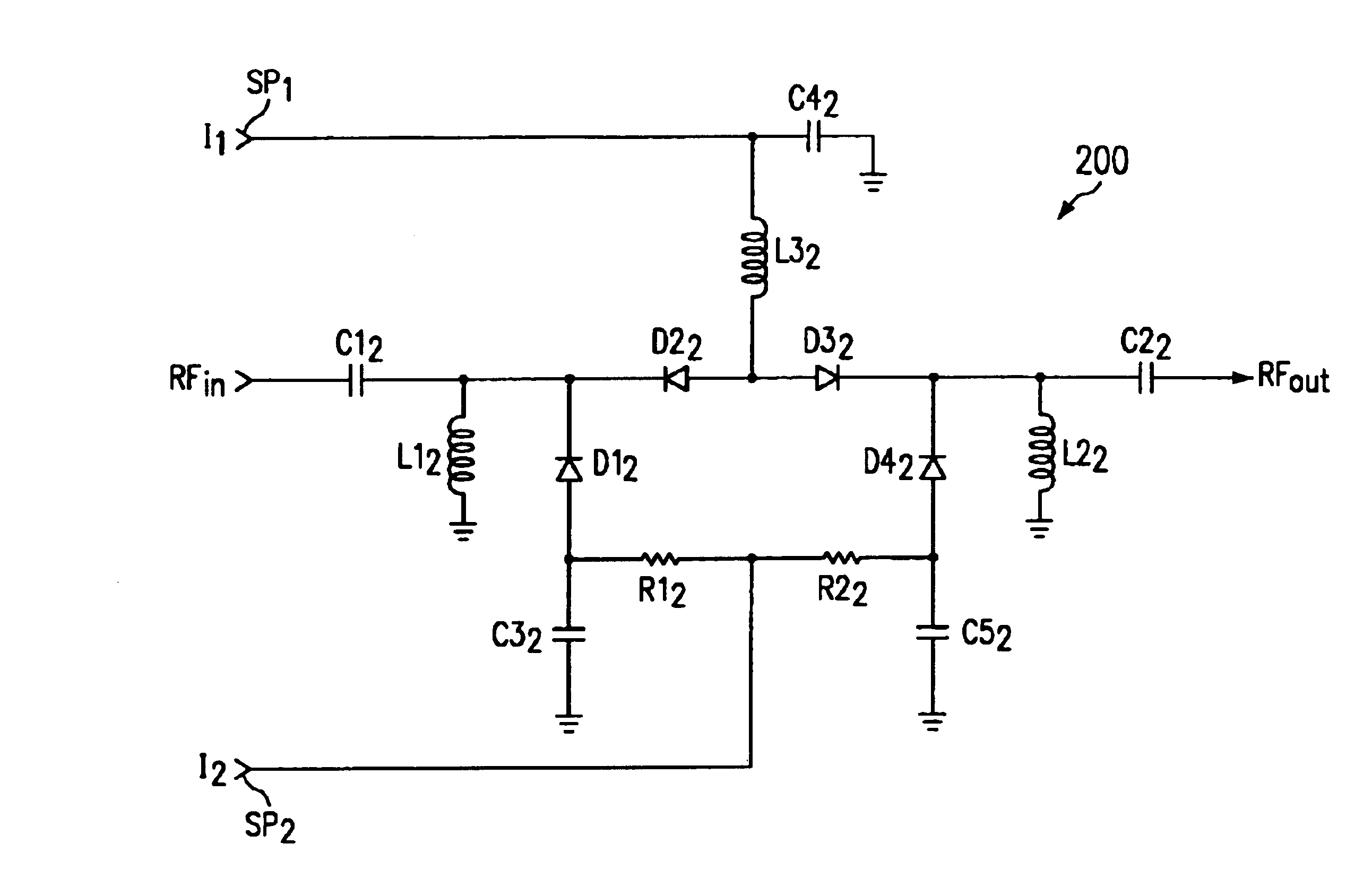
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Insertion loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cascading optical multiplexing device
InactiveUS6167171AReduce complexityLow costLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberMultiplexing
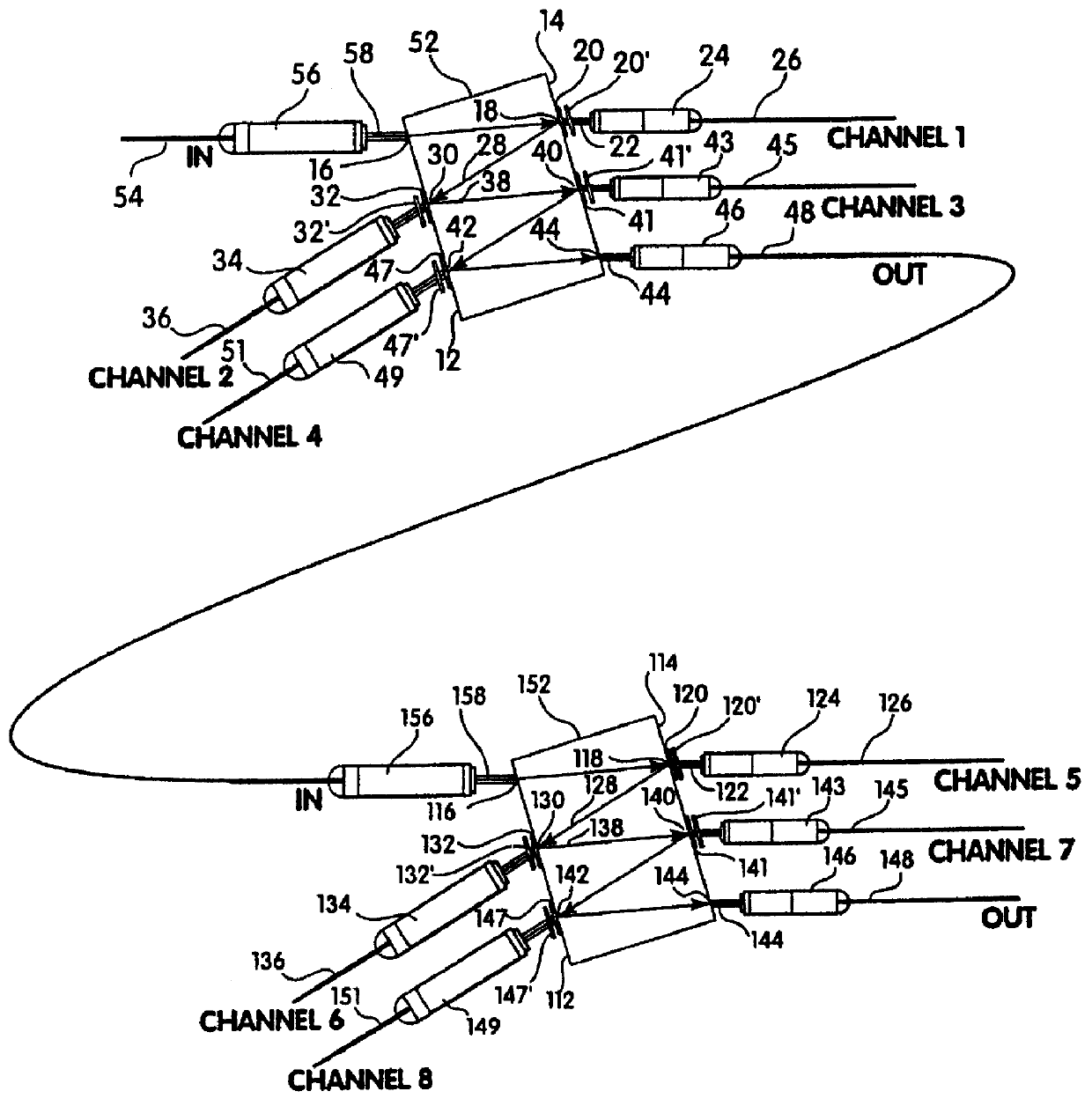
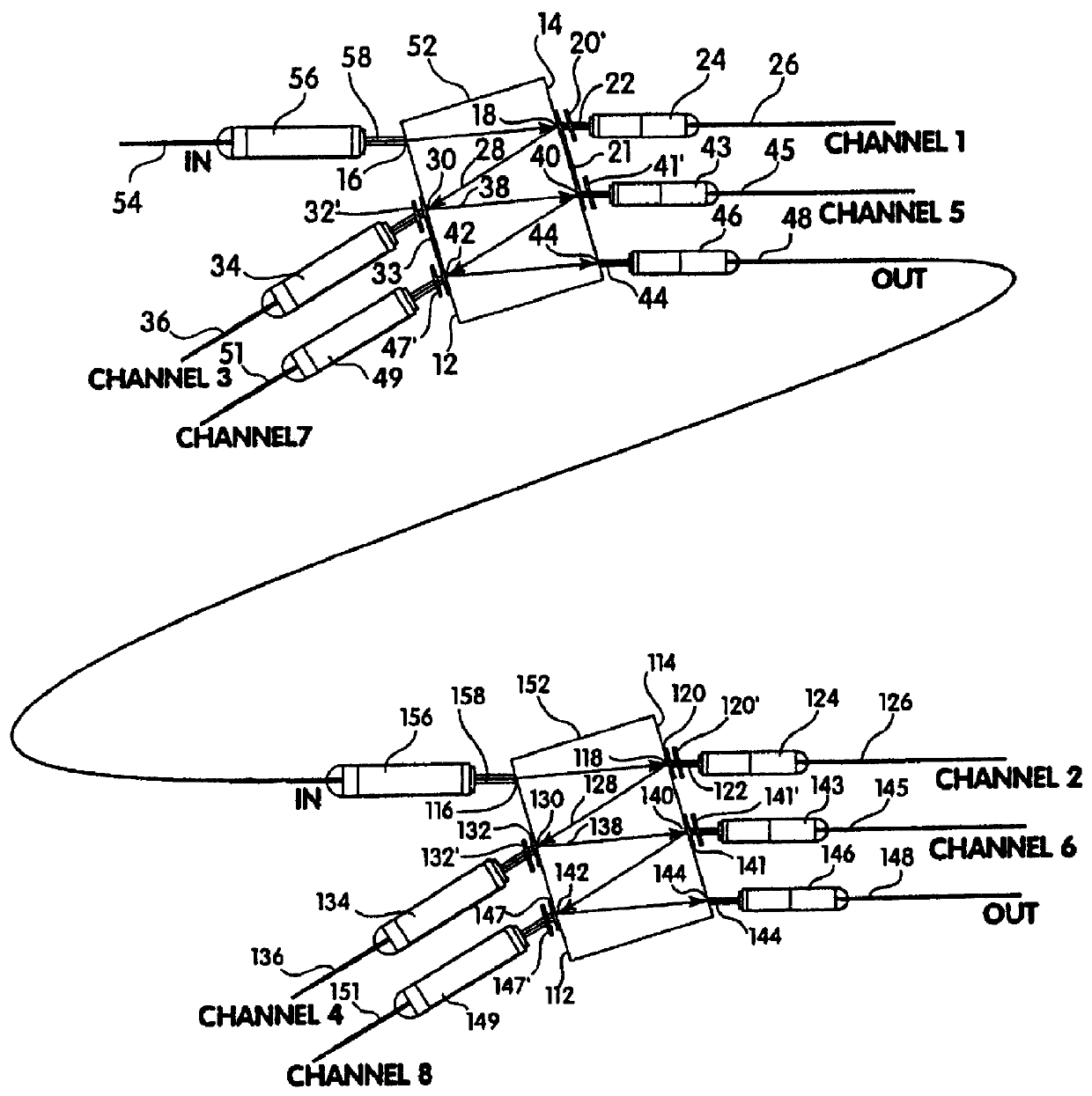
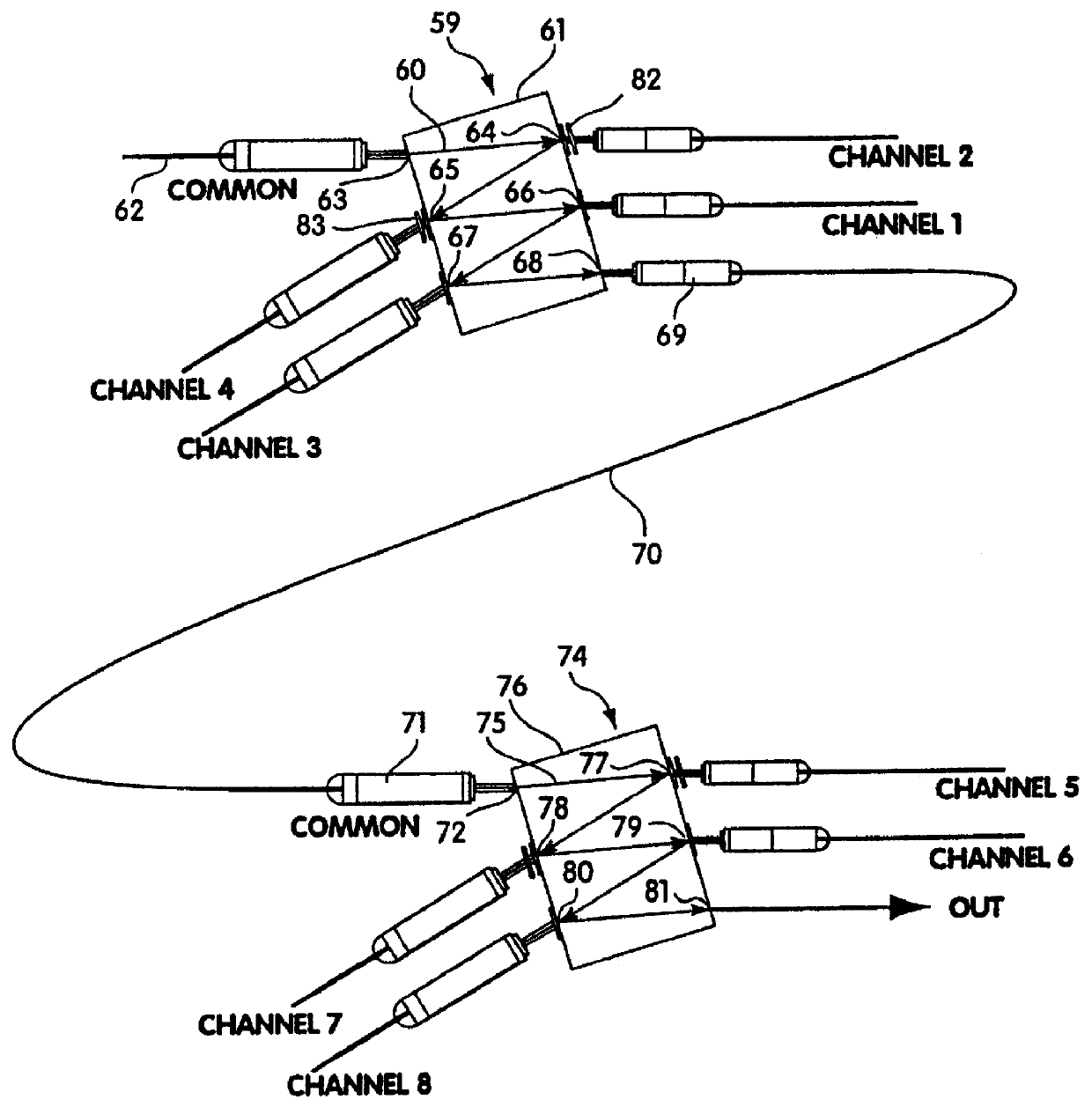
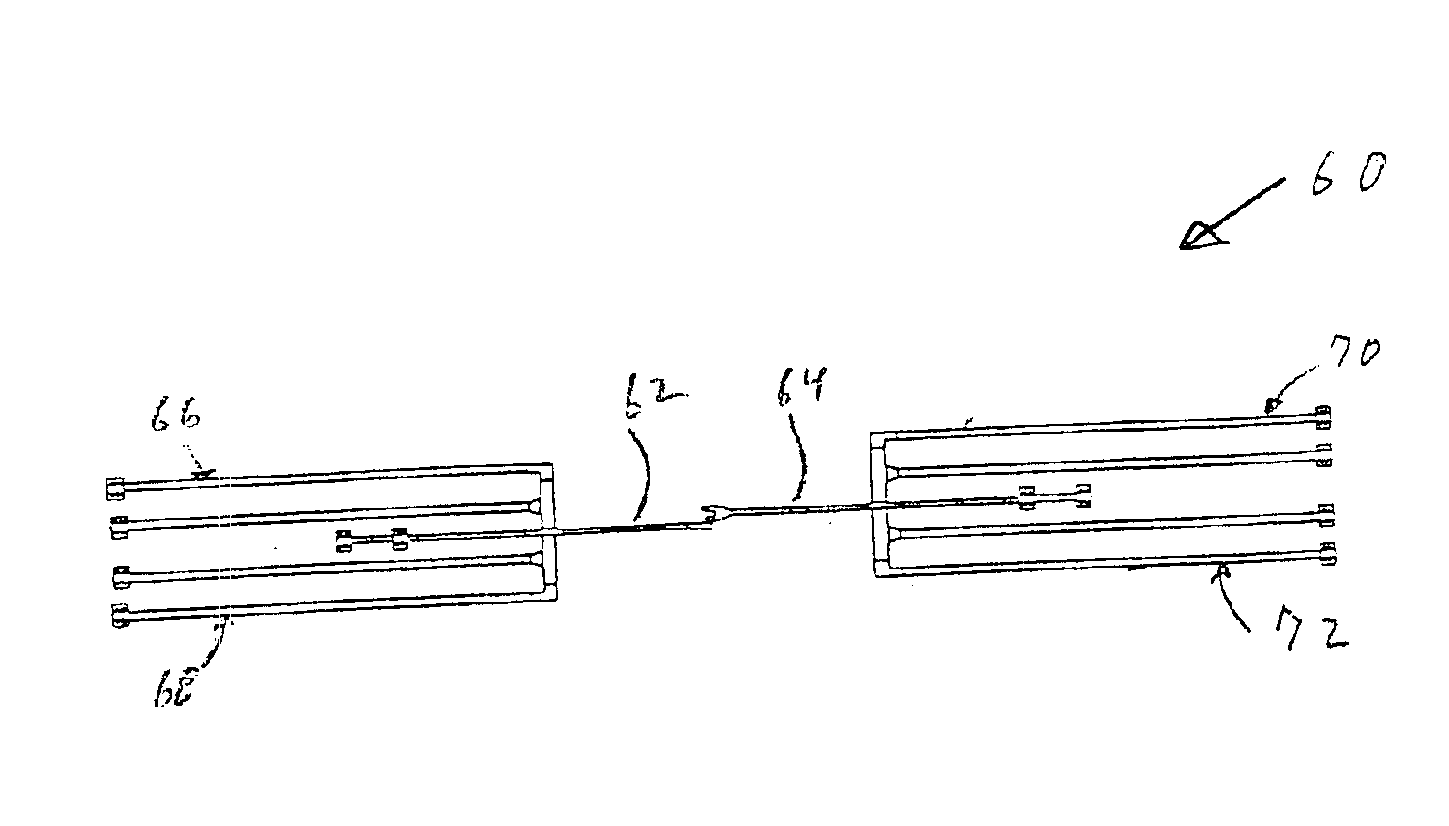
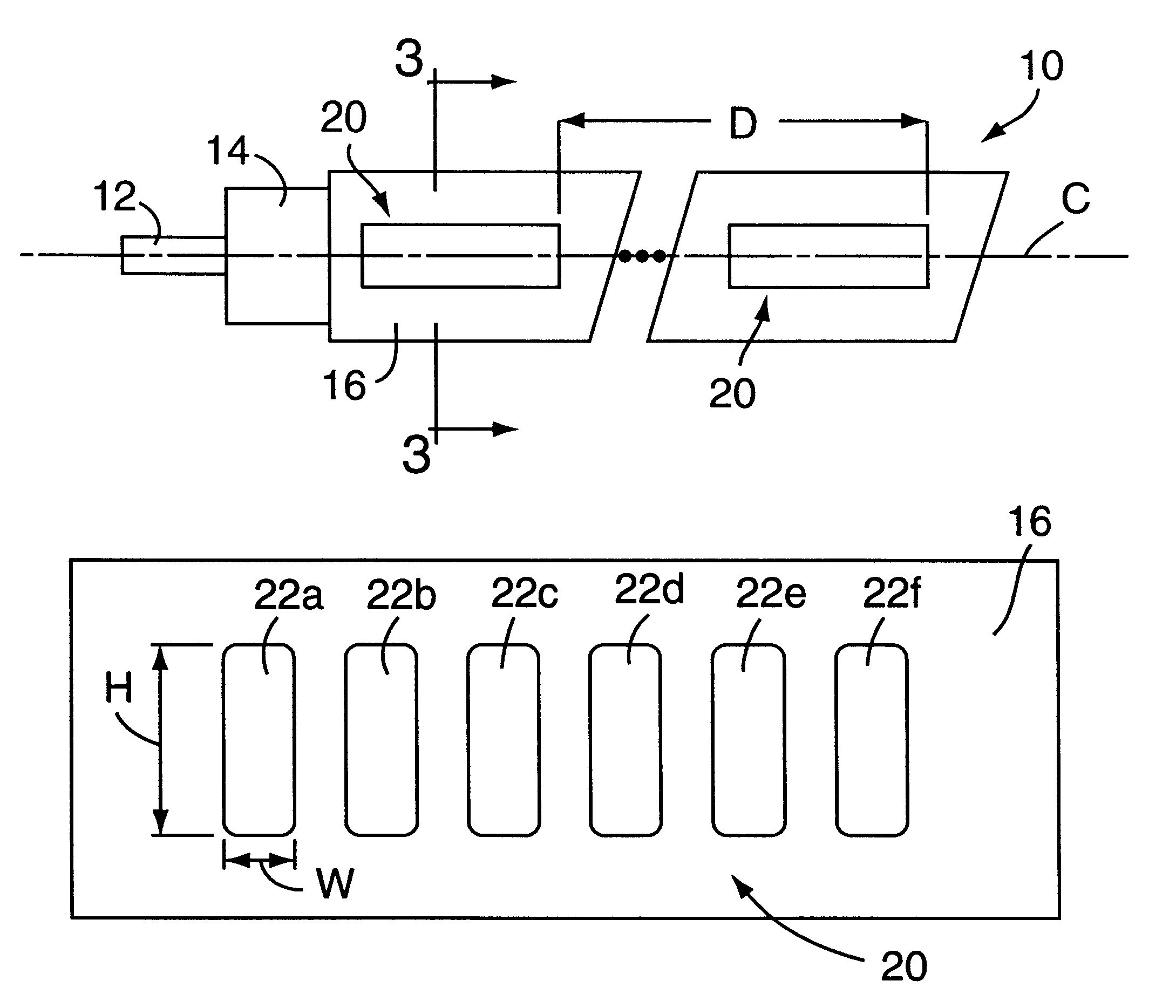
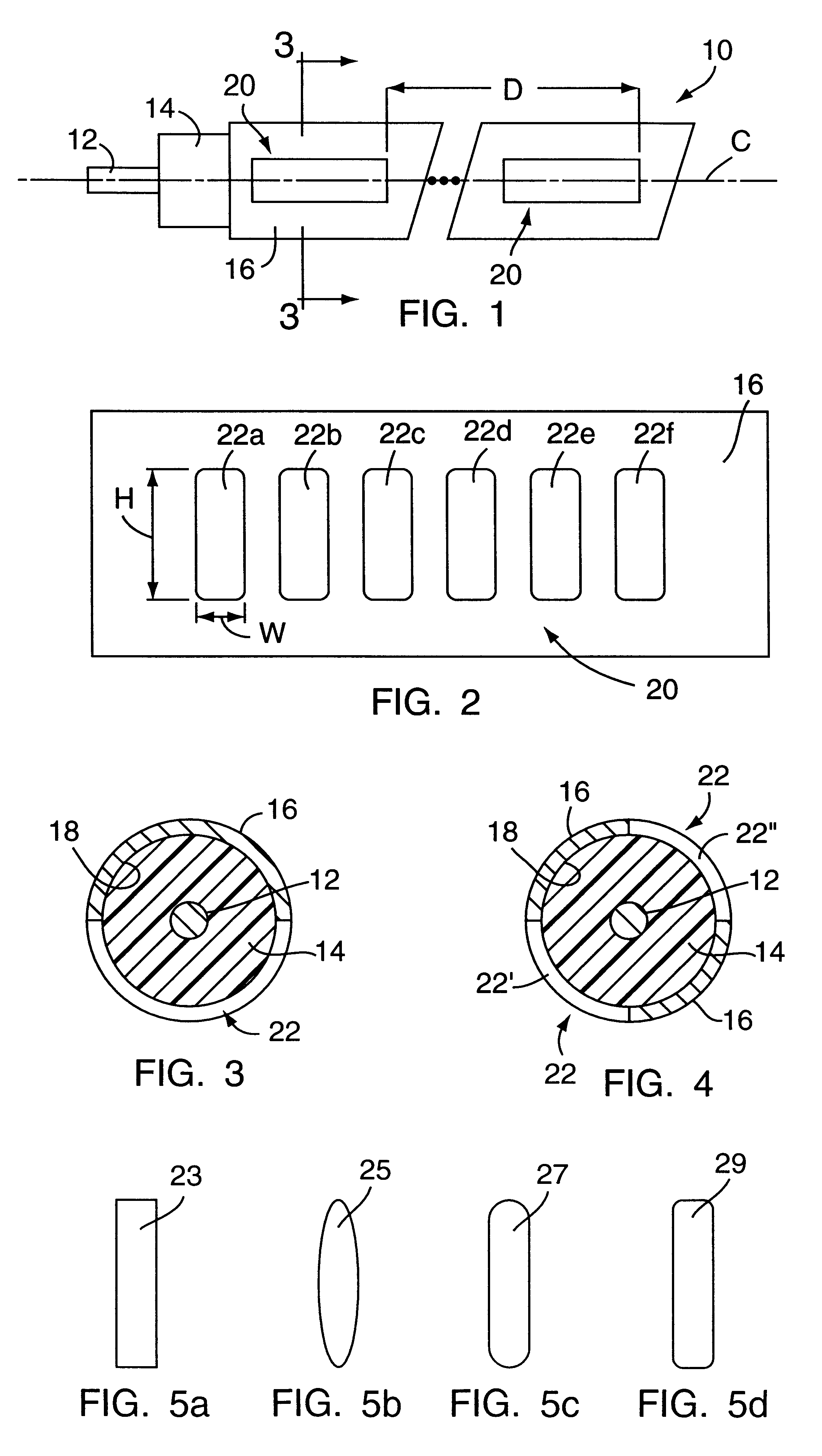
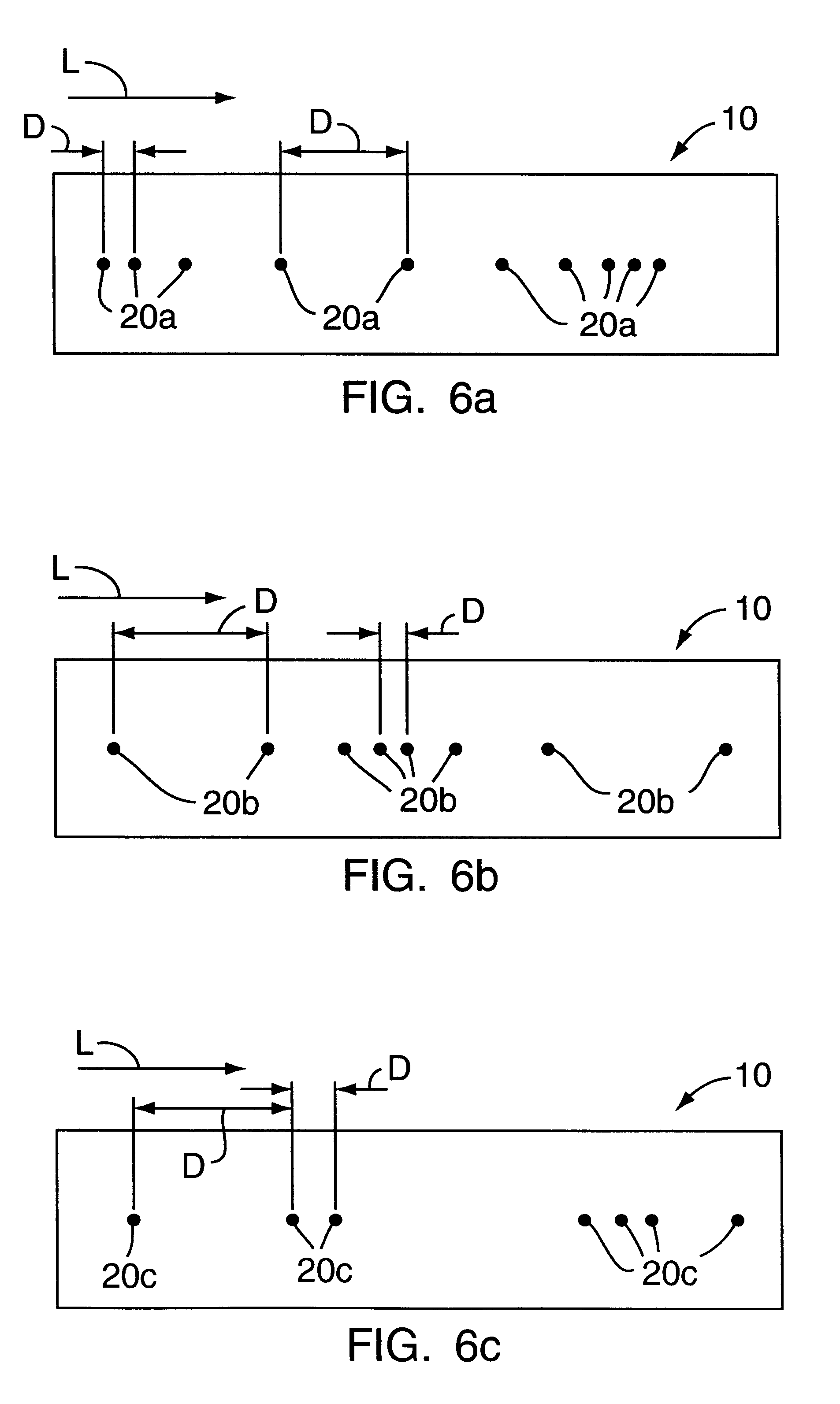
An optical multiplexing device is provided comprising multiple wavelength division multiplexers cascaded together. A first one of the wavelength division multiplexers has a common port and multiple optical ports which are optically coupled to the common port. The common port may be optically coupled to a trunk line of a system employing wavelength division multiplexing, for example, a fiber-optic telecommunication system employing 4, 8, 16 or other number of multiplexed channels. The optical ports include multiple channel ports, each of which is transparent to a corresponding wavelength sub-range and reflective of other wavelengths. The second wavelength division multiplexer has a common port optically coupled to one of the optical ports of the first wavelength division multiplexer. The second wavelength division multiplexer also has multiple optical ports which are optically coupled to its common port and include multiple wavelength-selective channel ports. A waveguide, such as a fiber-optic line, can optically connect the common port of the second wavelength division multiplexer to an optical port of the first wavelength division multiplexer. The cascaded WDMs each may be optically coupled to the output of a passive coupler and a housing may be provided defining an enclosed space in which the optical multiplexing device is mounted. Optionally, additional WDMs may be cascaded with the first two WDMs in a parallel or branched formation, an in-line formation or some combination. Preferably, the channels are interleaved, such that they are removed from the multiplexed signal in certain non-sequential order. The optical multiplexing device also may employ compound interleaving wherein adjacent channels are multiplexed by different ones of the cascaded WDMs. The optical multiplexing devices can operate to add signals, remove signals or a combination of both.
Owner:CORNING OCA CORPORATION
Thin film shape memory alloy actuated microrelay
InactiveUS7084726B2Average power consumptionHigh currentContact mechanismsElectrothermal relaysDevice formAlloy
A microrelay device formed on a silicon substrate wafer for use in opening and closing a current path in a circuit. A pair of electrically conducting latching beams are attached at their proximal ends to terminals on the substrate. Proximal ends of the beams have complementary shapes which releasably fit together to latch the beams and close the circuit. A pair of shape memory alloy actuators are selectively operated to change shapes which bend one of the beams in a direction which latches the distal ends, or bend the other beam to release the distal ends and open the circuit. The microrelay is bistable in its two positions, and power to the actuators is applied only for switching it open or closed.
Owner:TINI ALLOY
Electrical connector
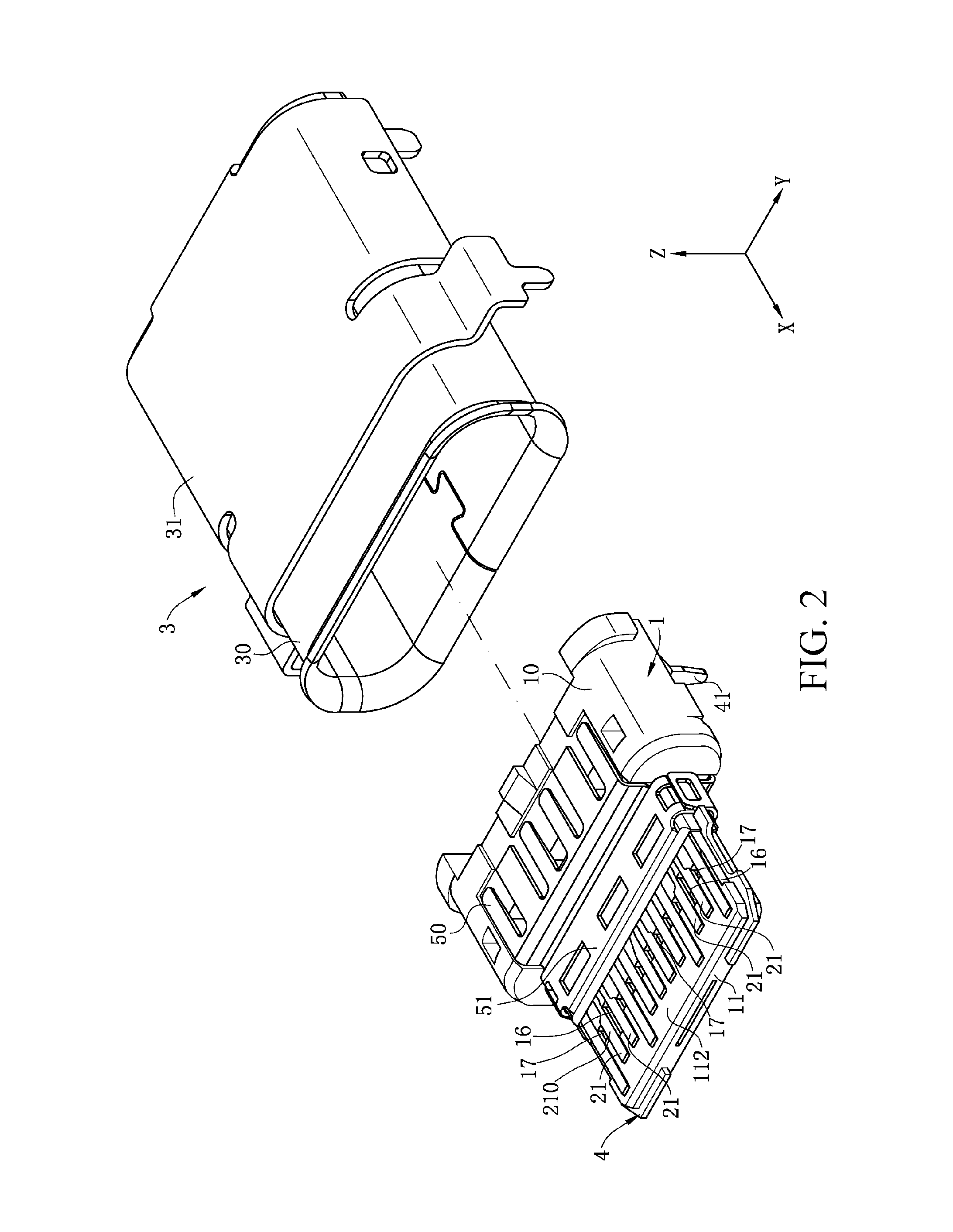
ActiveUS20160020560A1Improve high frequency performanceReduce decreaseContact member cases/bases manufactureTwo-part coupling devicesElectrical connectorElectrical and Electronics engineering
An electrical connector includes a body having a tongue, a pair of first differential signal terminals and a pair of second differential signal terminals fixed to the body, and a middle shielding sheet fixed to the tongue, and located between the first and second differential signal terminals. The tongue includes an upper surface having two depressed first receiving slots and a lower surface having two depressed second receiving slots. A first groove is depressed from each first receiving slot. A second groove is upward depressed from each second receiving slot. Each first differential signal terminal has a first contact portion fixed to and exposed from the upper surface of the tongue. Each second differential signal terminal has a second contact portion fixed to and exposed from the lower surface of the tongue. The first and second contact portions are partially accommodated in the first and second receiving slot respectively.
Owner:LOTES
Radiating coaxial cable having groups of spaced apertures for generating a surface wave at a low frequencies and a combination of surface and radiated waves at higher frequencies
InactiveUS6292072B1Reduce coupling lossMinimize the numberWaveguidesSlot antennasElectrical conductorCoaxial cable
A radiating coaxial cable includes an inner conductor, an electrical insulator located about a periphery of the inner conductor, and an outer conductor located about a periphery of the electrical insulator. The outer conductor defines groups of apertures spaced from each other a predetermined distance in the range of from about twice the longest operational wavelength of the cable to less than ten meters. The aperture groups are designed in such a way to excite a surface wave at low operating frequencies and a combination of surface and radiating waves at high operational frequencies.
Owner:TIMES MICROWAVE SYST DIV OF SMITHS AEROSPACE
Dynamic eas detection system and method
InactiveUS20080303673A1Insertion lossImprove signal-to-noise ratioLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreResonant long antennasMonitoring systemEngineering
This invention relates to dynamically controlled, electronic article surveillance (EAS) systems whereby an array of antenna elements is digitally phased and actively driven for concurrent transmission, and digitally phased and combined in the receiver unit to improve security tag detection. In particular, the individual frequency and phase of the plurality of the transmit / receive signals are rapidly varied to allow for automated manipulation (steering) of the transmit field pattern and receive field sensitivity. It is the object of this invention to achieve the following features via means of digital phasing and dynamic computer control: sufficient far-field cancellation, null-free detection and uncompromised detection performance regardless of tag's orientation.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
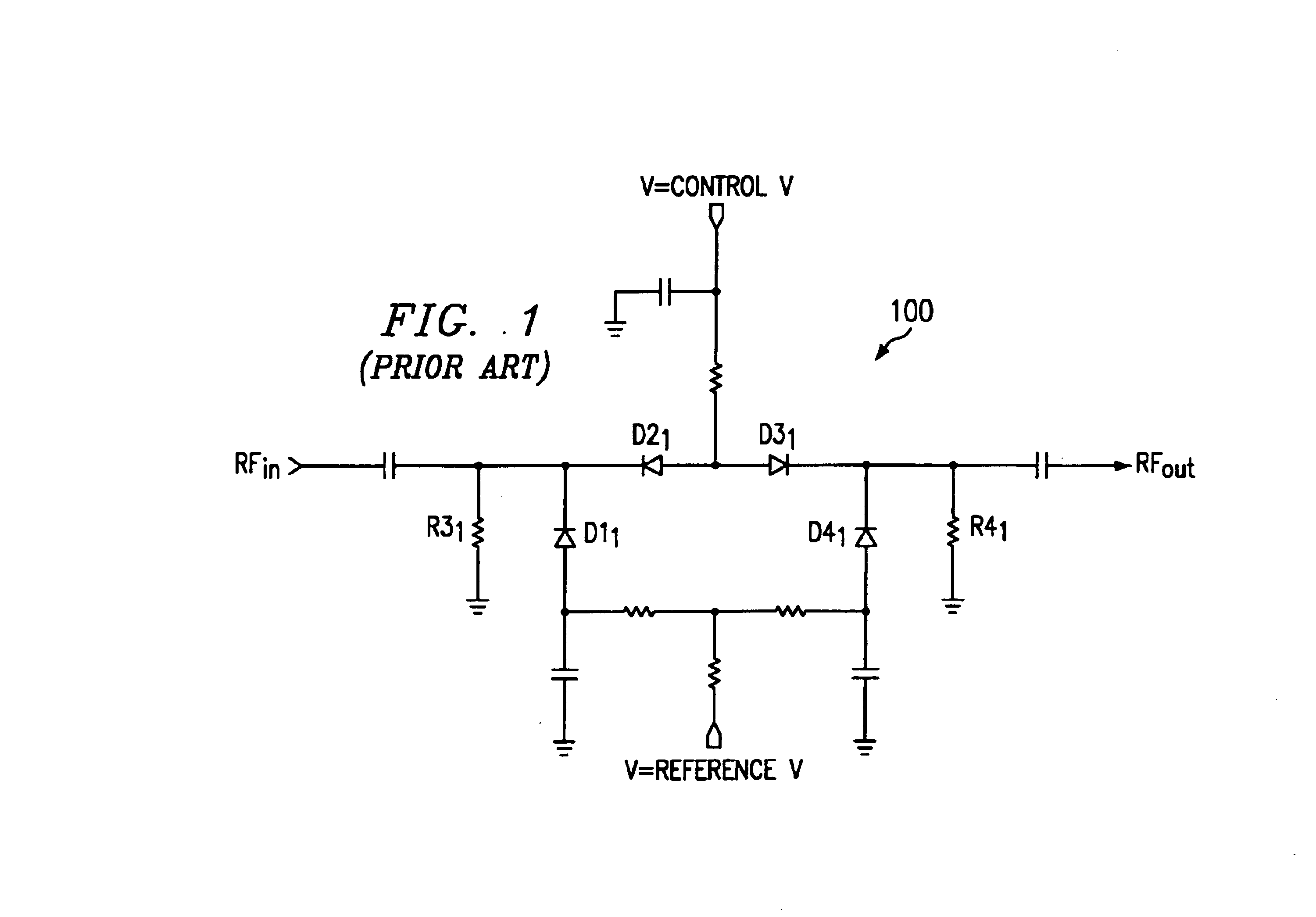
Broadband PIN diode attenuator bias network
InactiveUS6919774B2Additional control circuitLarge dynamic rangeMultiple-port networksPulse automatic controlUltrasound attenuationControl signal
Diode network configurations are disclosed in which cathode bias voltage is held substantially constant to provide an attenuator circuit in which return loss is optimized throughout a broad dynamic attenuation range. Preferred embodiments include PIN diodes arranged in a π network having two attenuation control signals provided thereto. Alternative embodiments include PIN diodes arranged in a T network having two attenuation control signals provided thereto.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
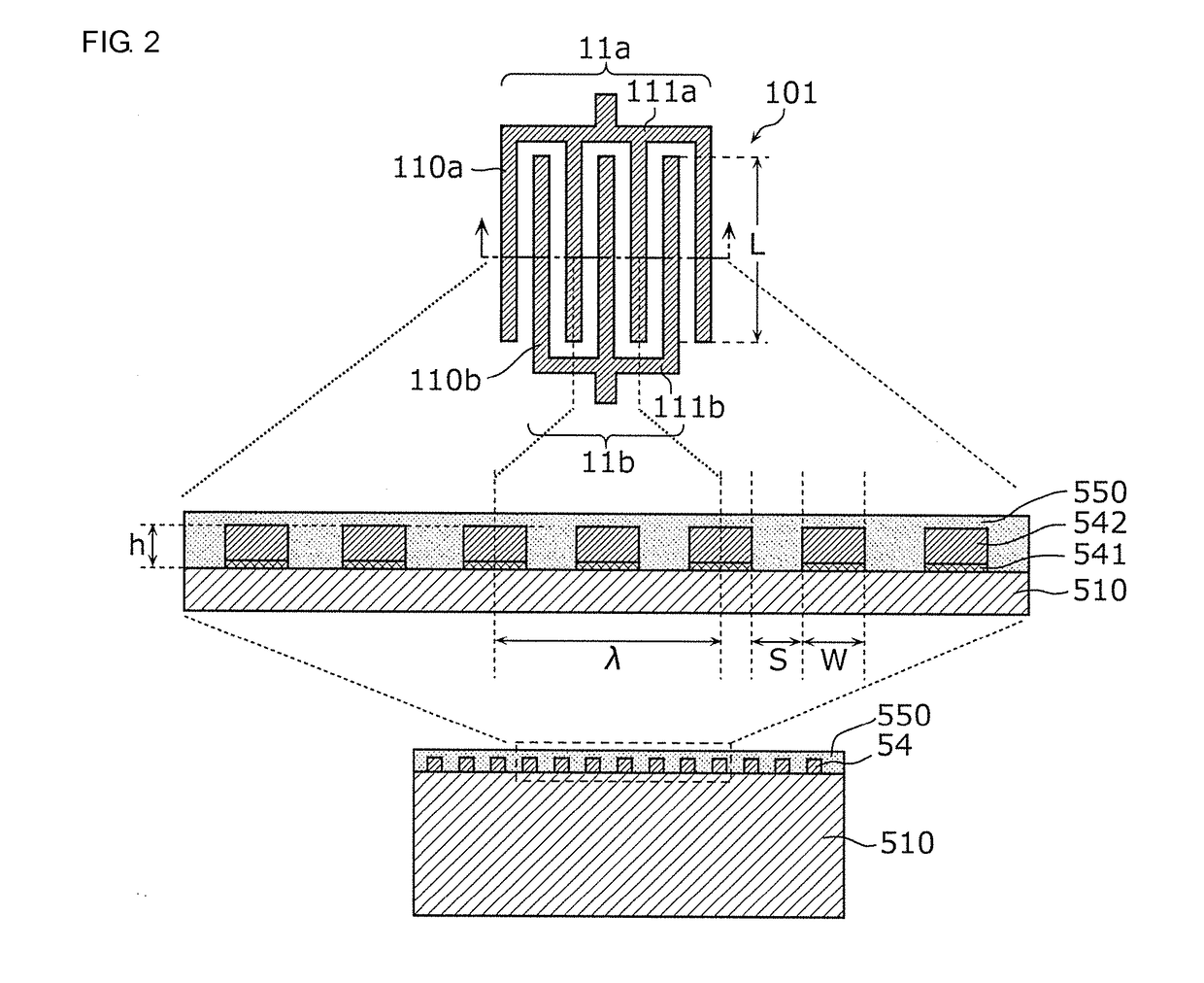
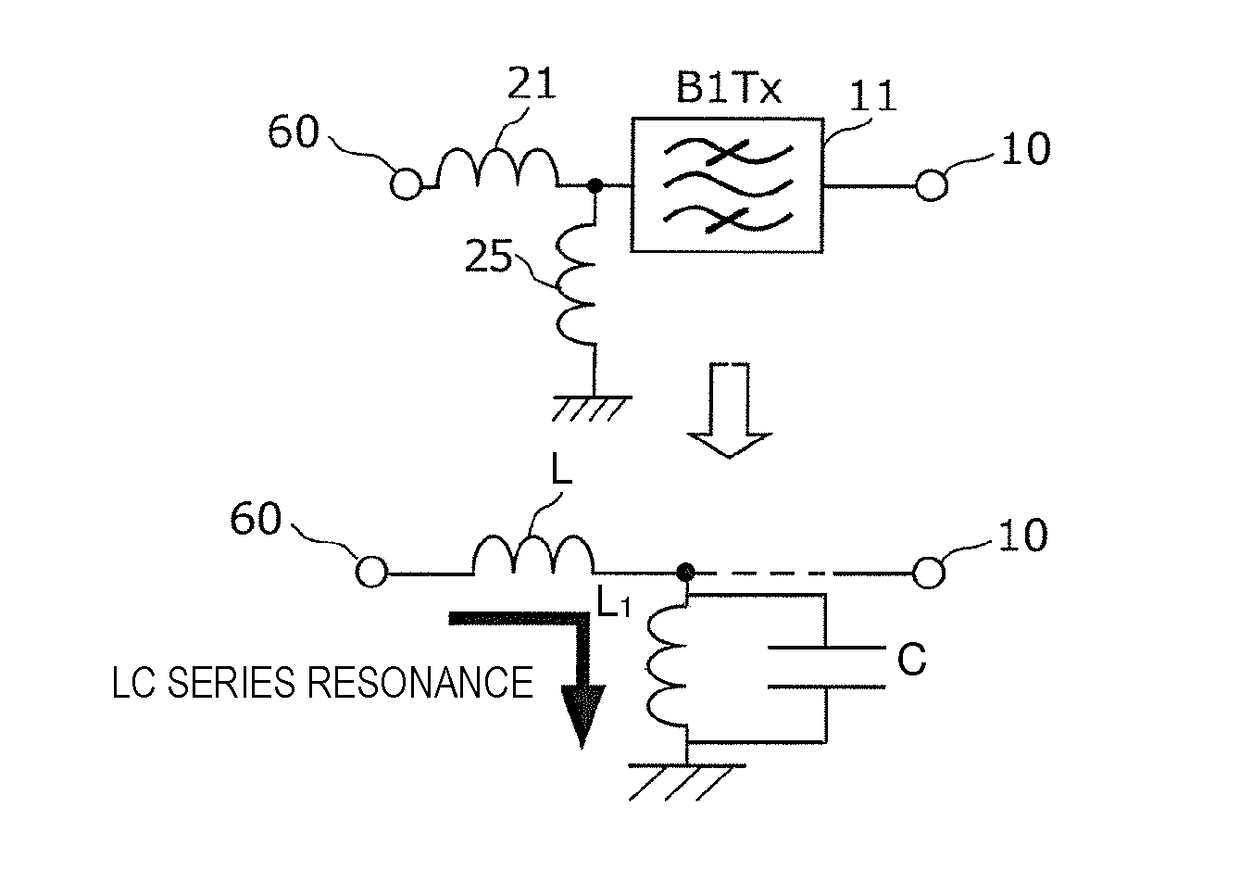
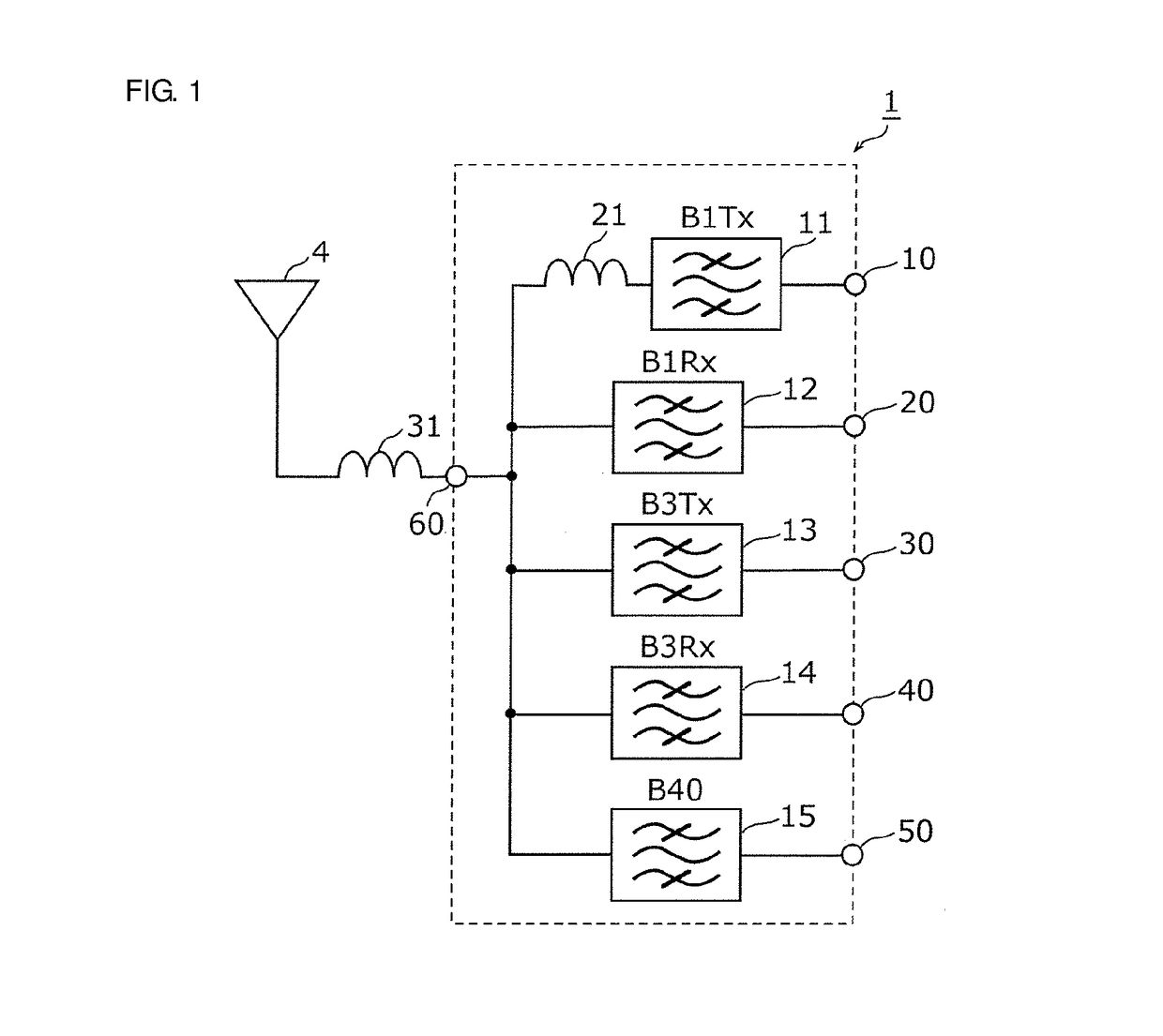
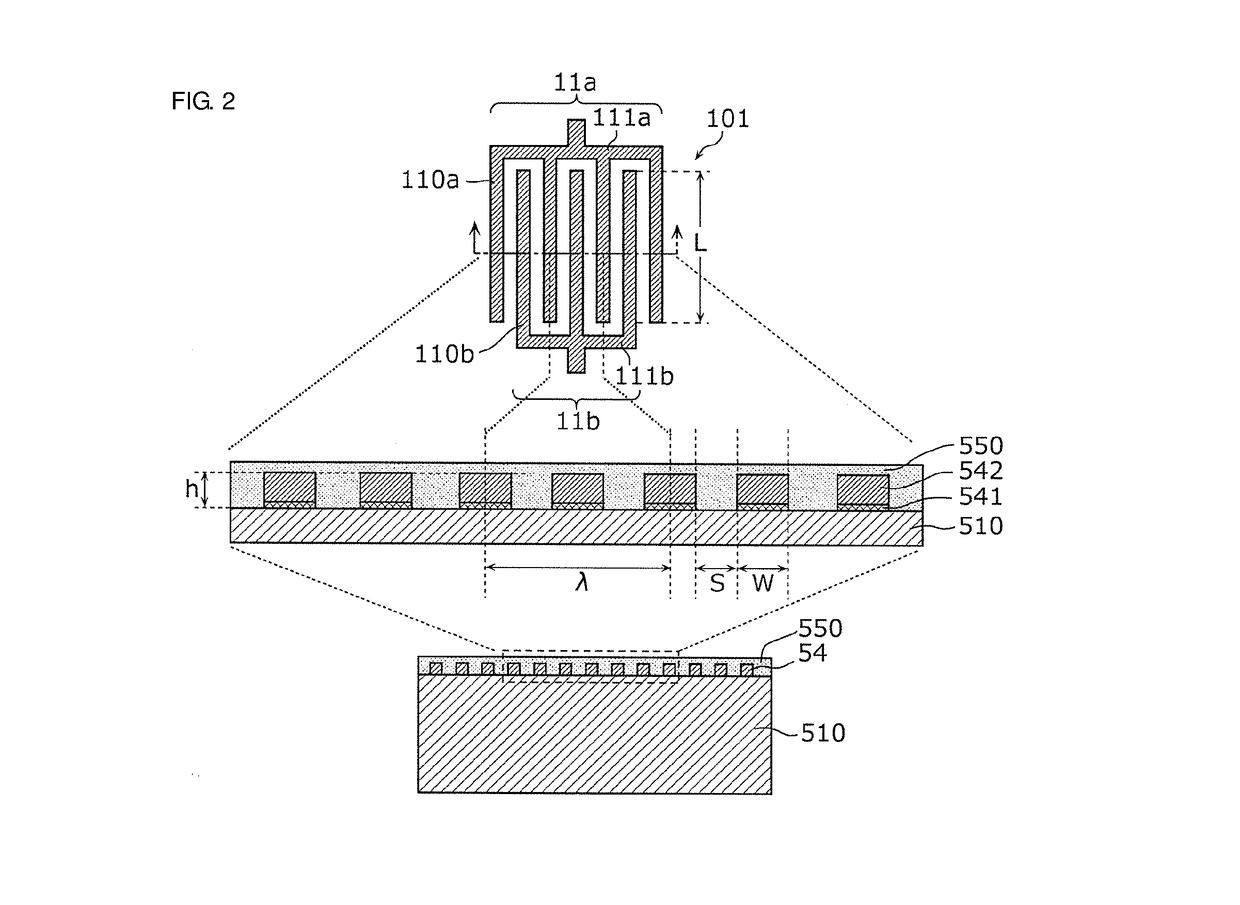
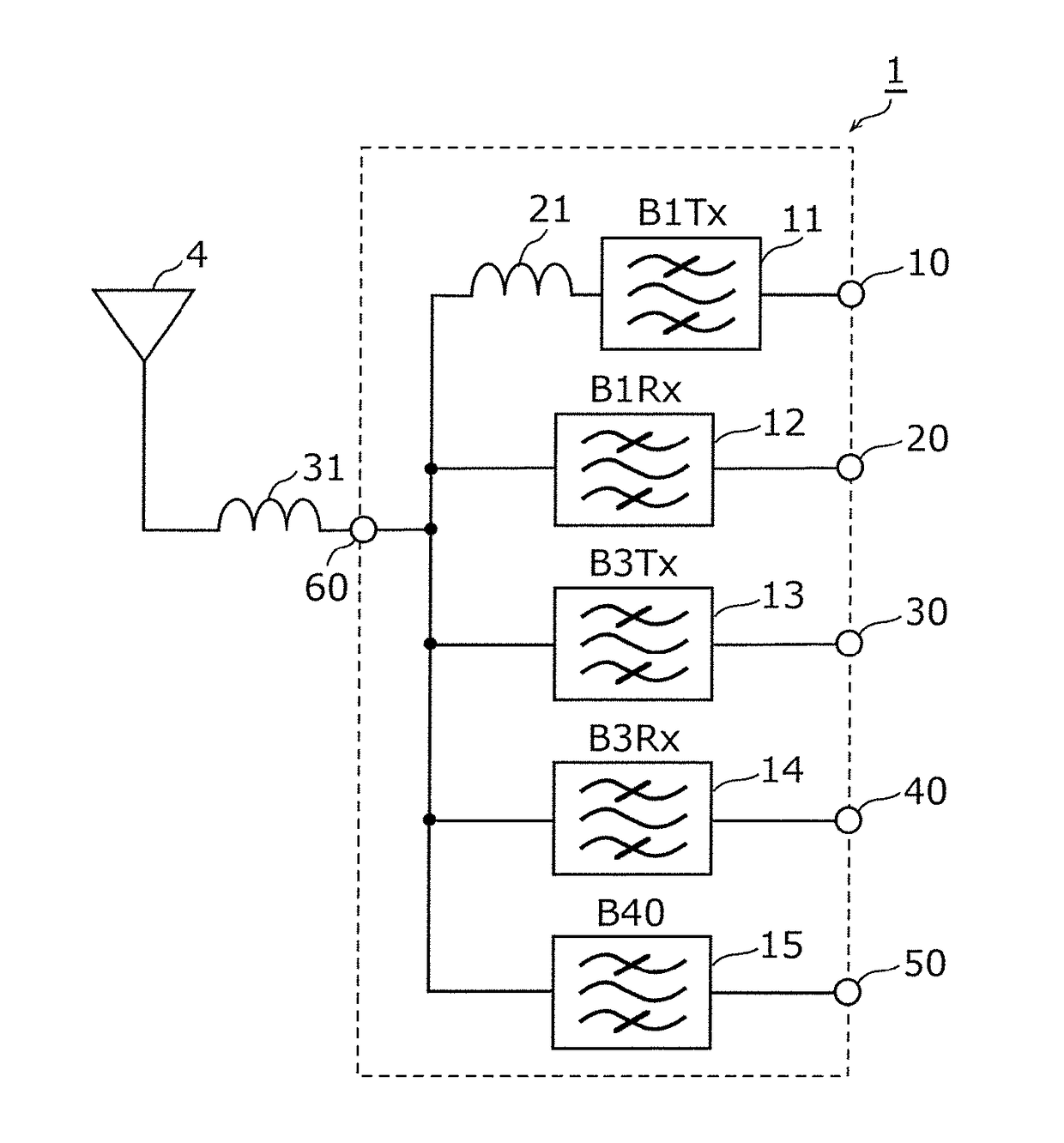
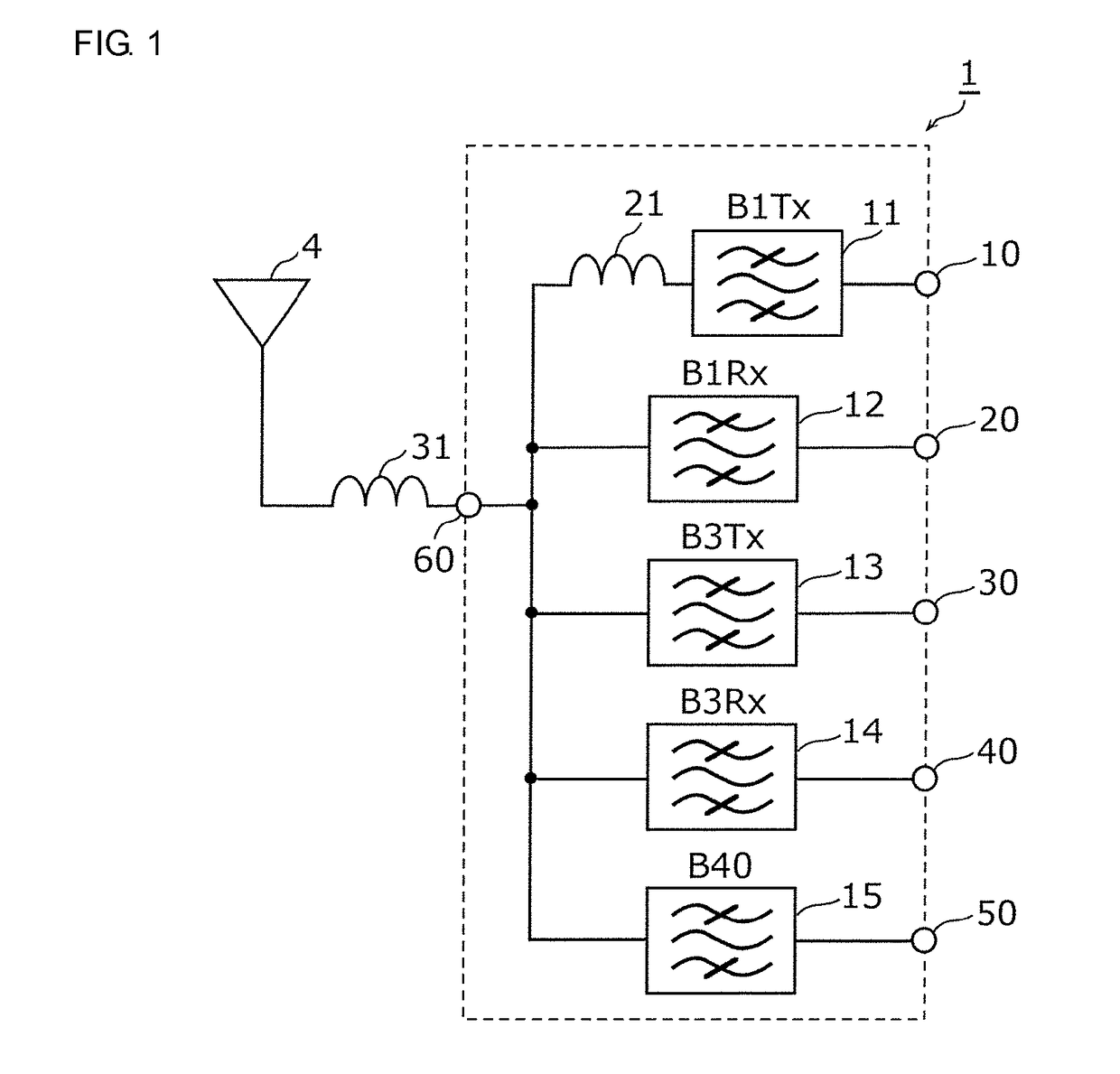
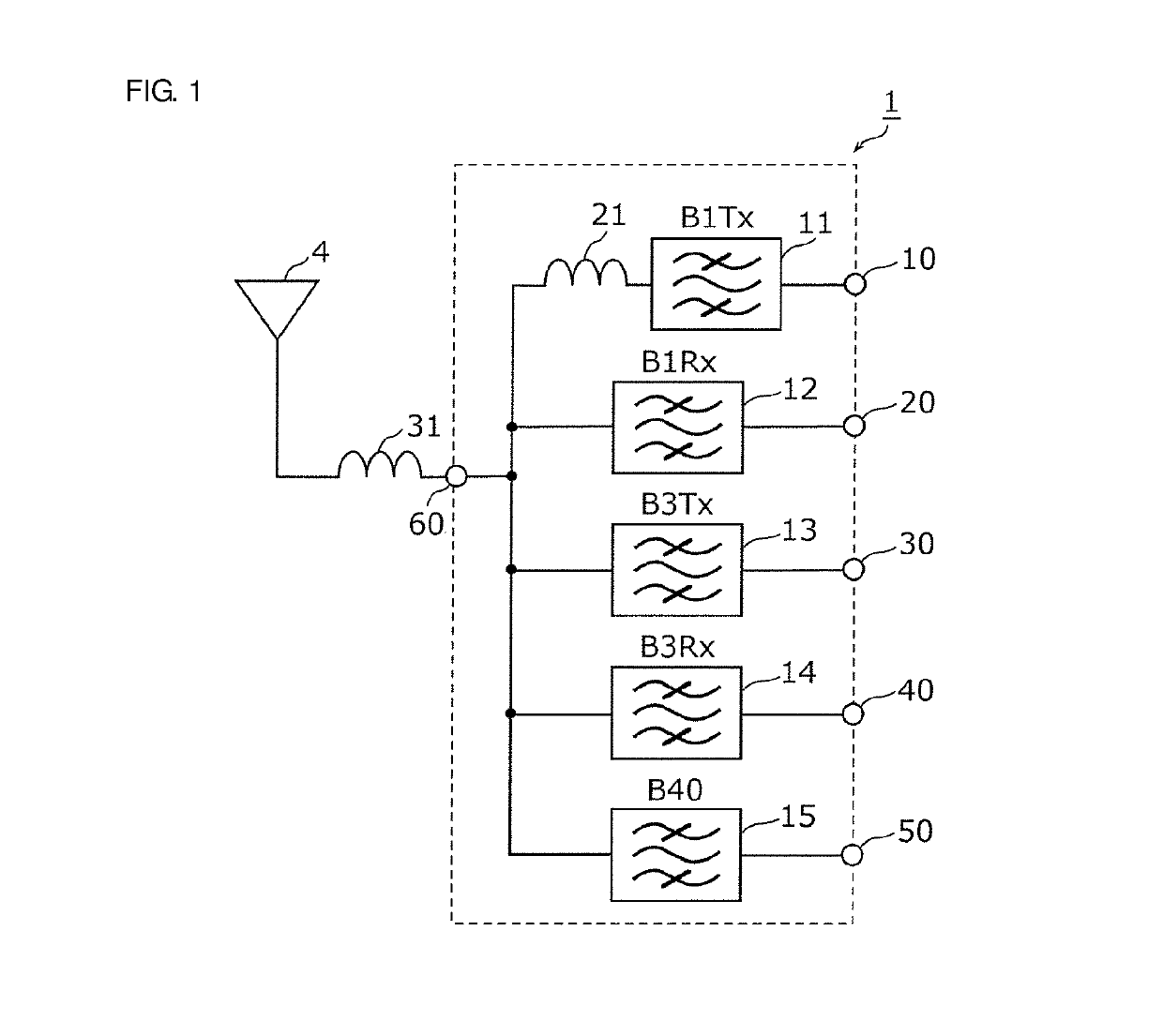
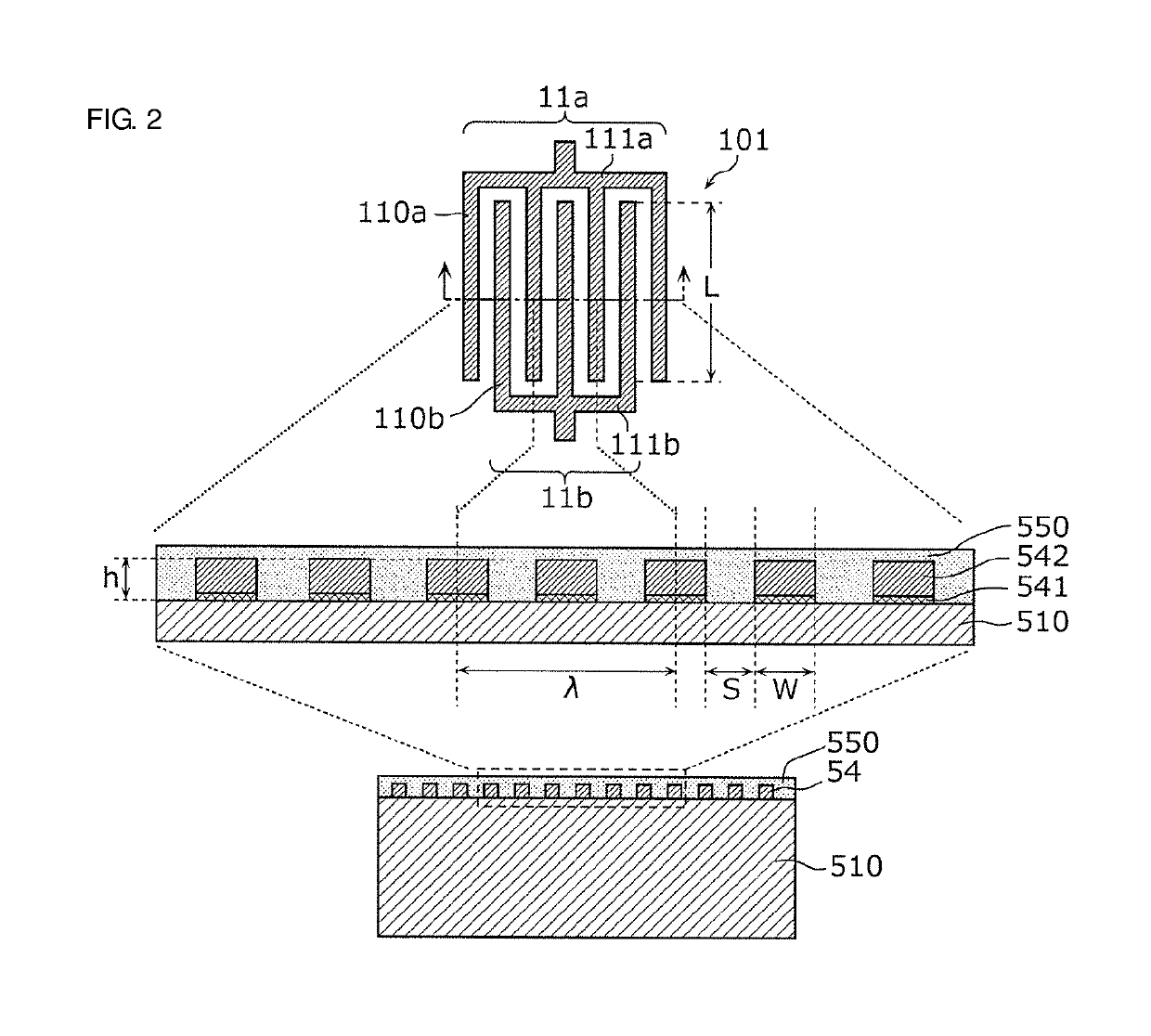
Multiplexer, transmission apparatus, and reception apparatus
ActiveUS20170244431A1Insertion lossMultiple-port networksFrequency-division multiplex detailsCapacitanceMultiplexer
A multiplexer includes a common terminal connected to an inductance element at a connection path with an antenna element, filter elements including different pass bands and connected to the antenna element with the common terminal therebetween, and an inductance element arranged in series between a transmission filter with a largest capacitance when viewed from the antenna side among the filter elements and the common terminal. An inductive component of the inductance element and a capacitive component of the transmission filter element define an LC series resonant circuit, and a resonant frequency of the LC series resonant circuit is lower than any of pass bands of the filter elements.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
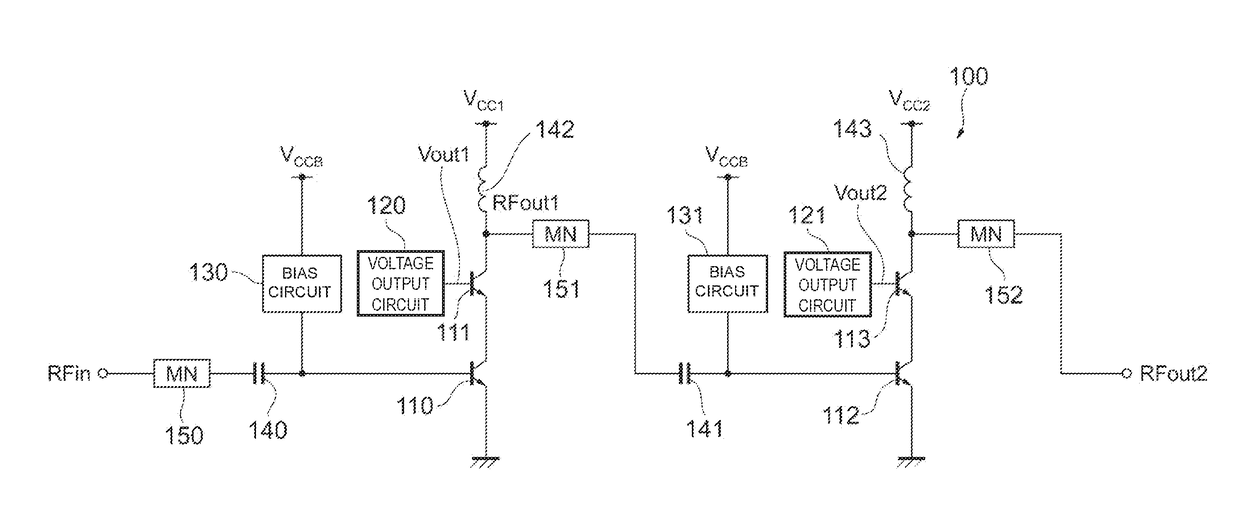
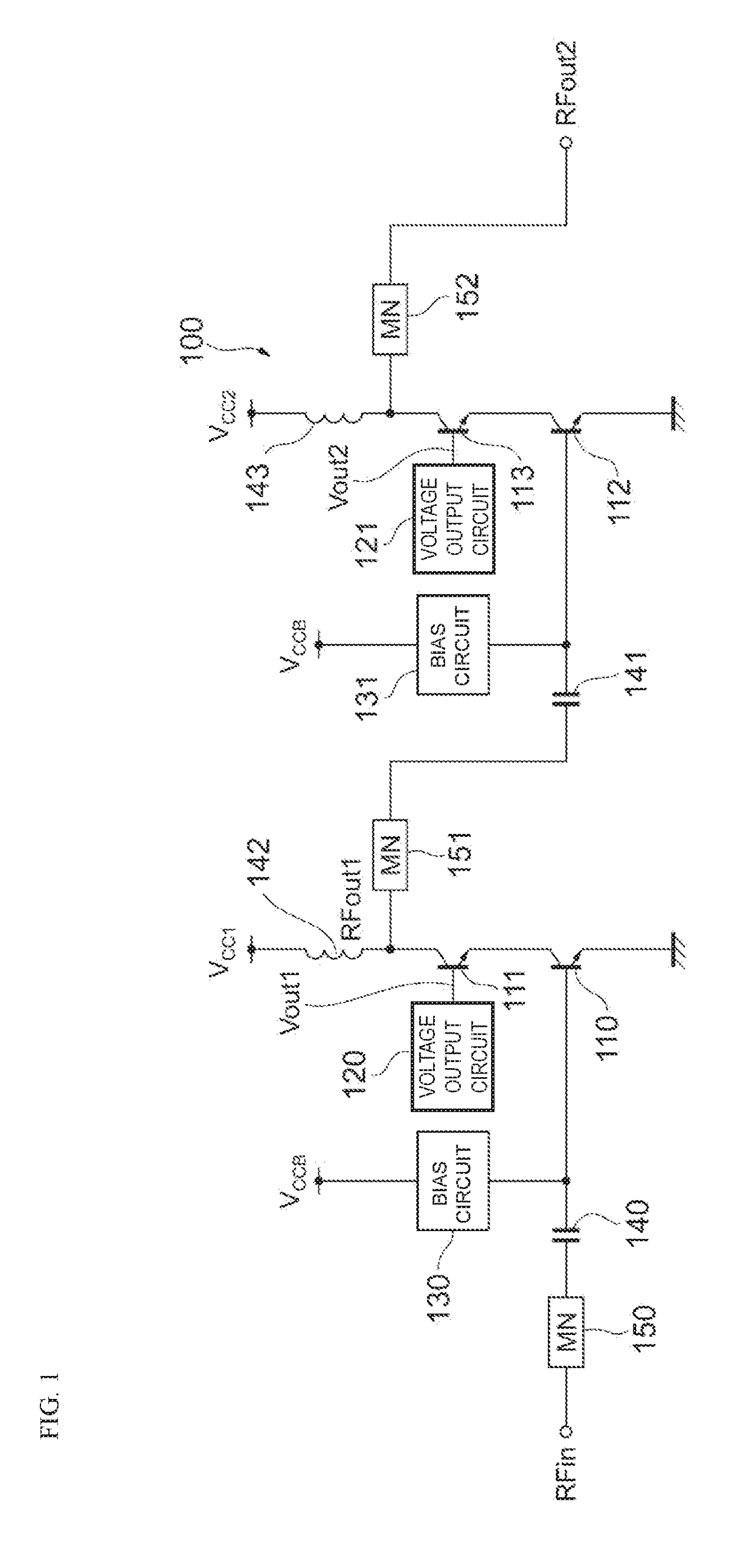
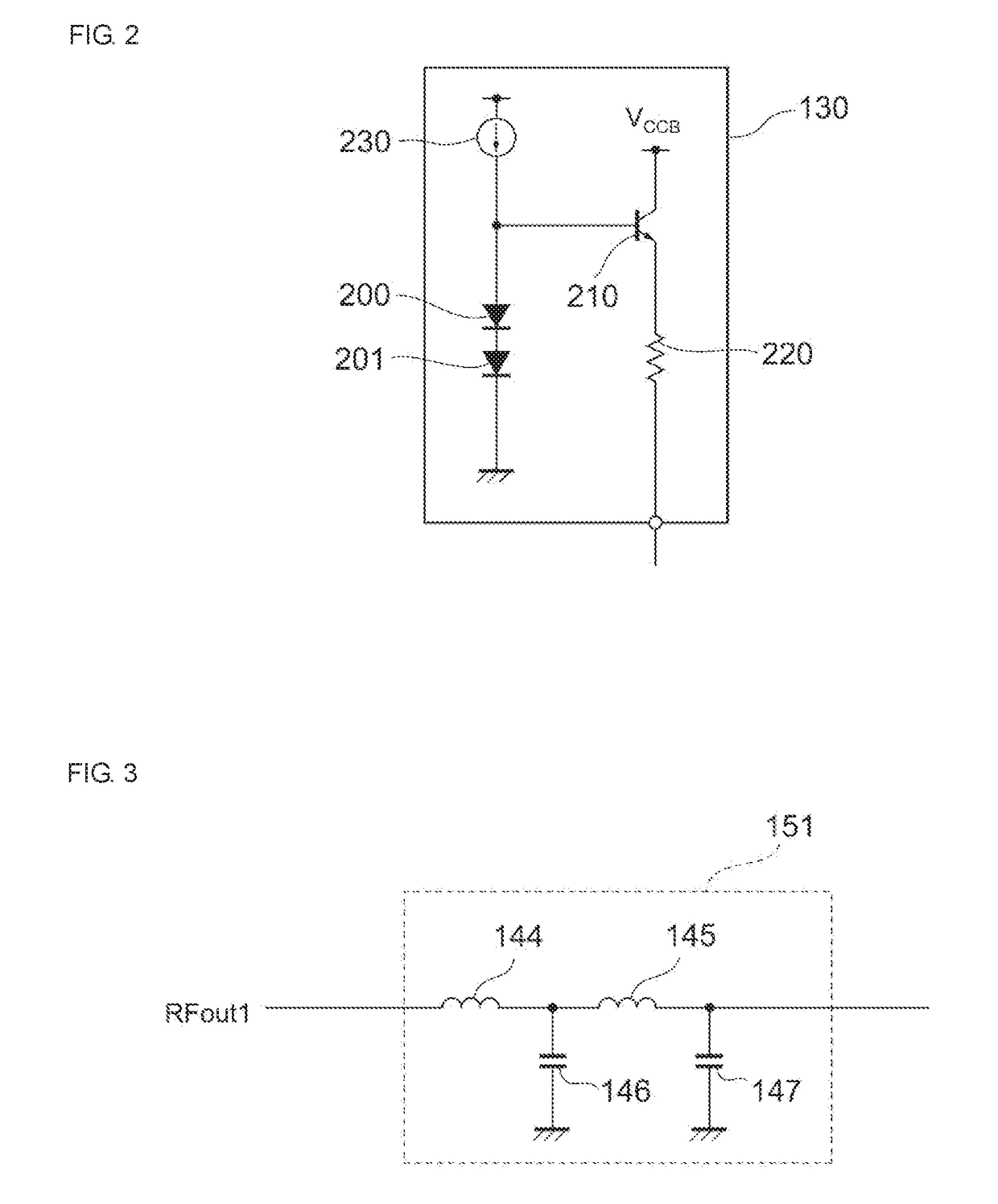
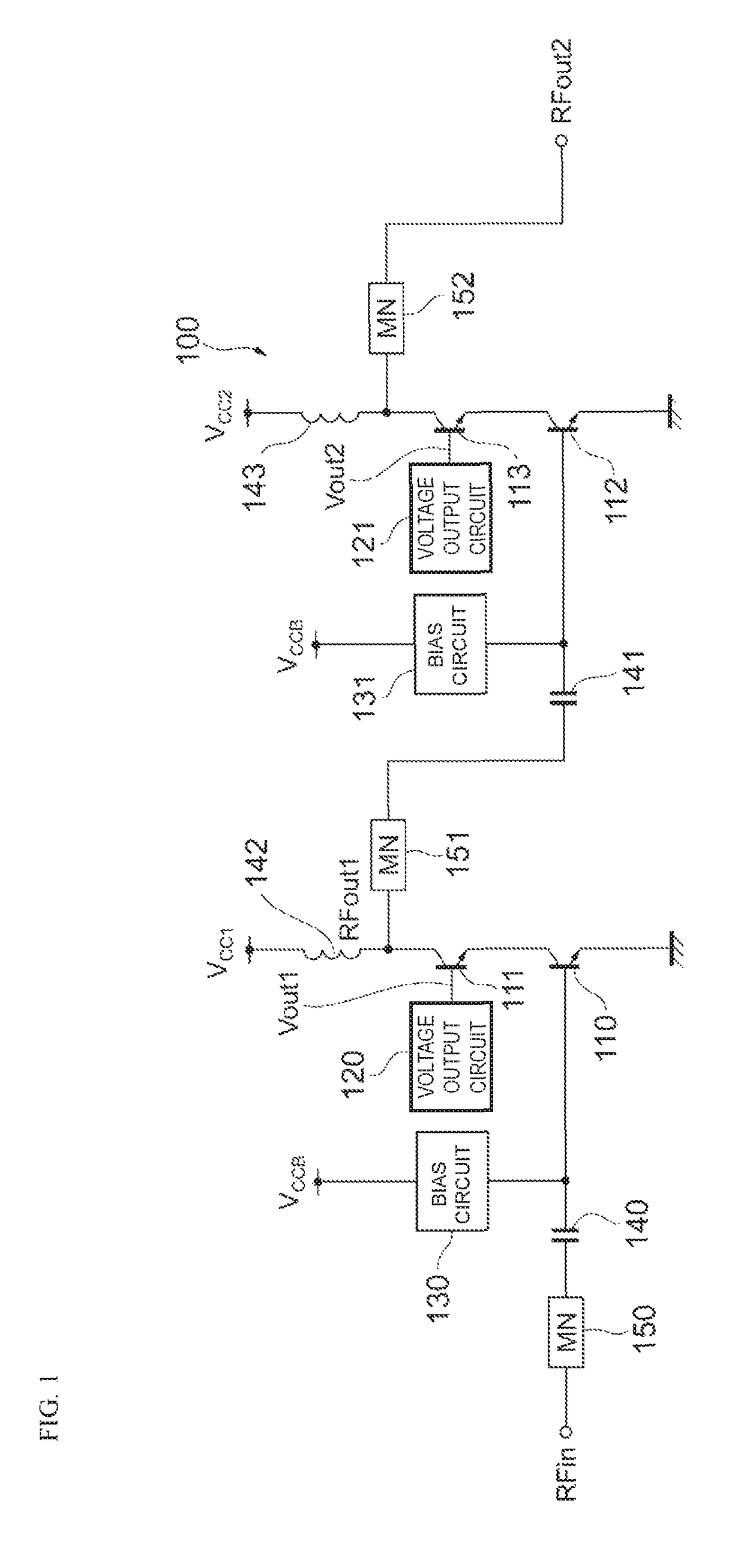
Power amplifier circuit
ActiveUS20170359038A1Reduce lossesIncrease load impedanceTransmission path divisionPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierRadio frequency signal
A power amplifier circuit includes first and second transistors and a first voltage output circuit. A radio frequency signal is input into a base of the first transistor. The first voltage output circuit outputs a first voltage in accordance with a power supply voltage. The first voltage is supplied to a base or a gate of the second transistor. An emitter or a source of the second transistor is connected to a collector of the first transistor. A first amplified signal generated by amplifying the radio frequency signal is output from a collector or a drain of the second transistor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
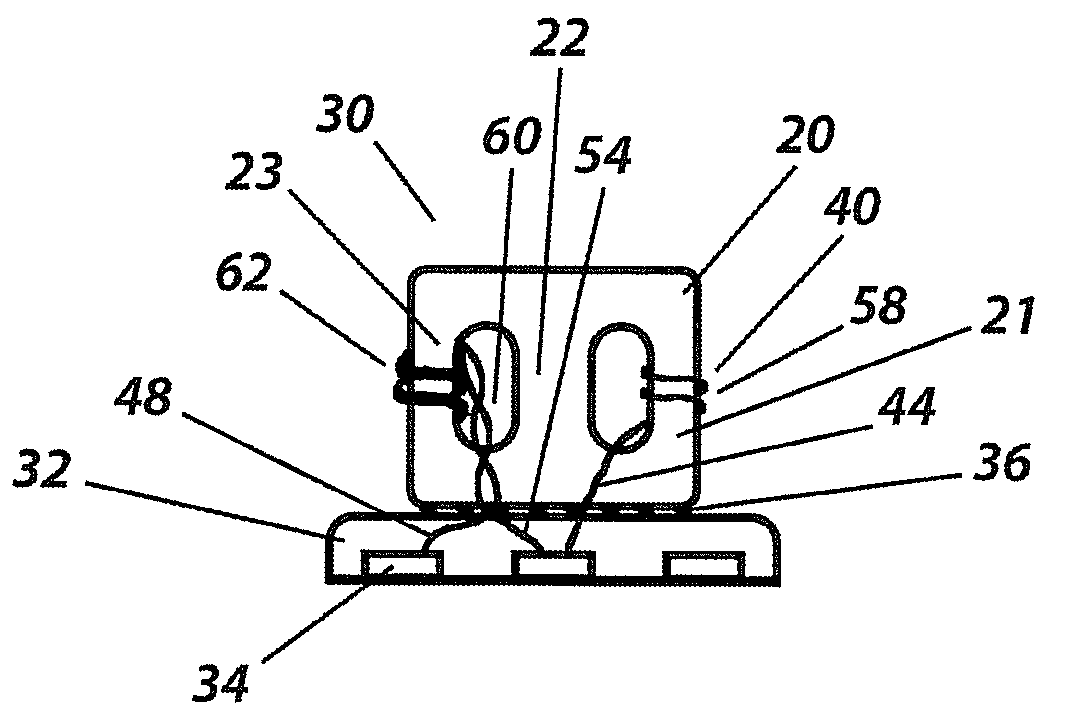
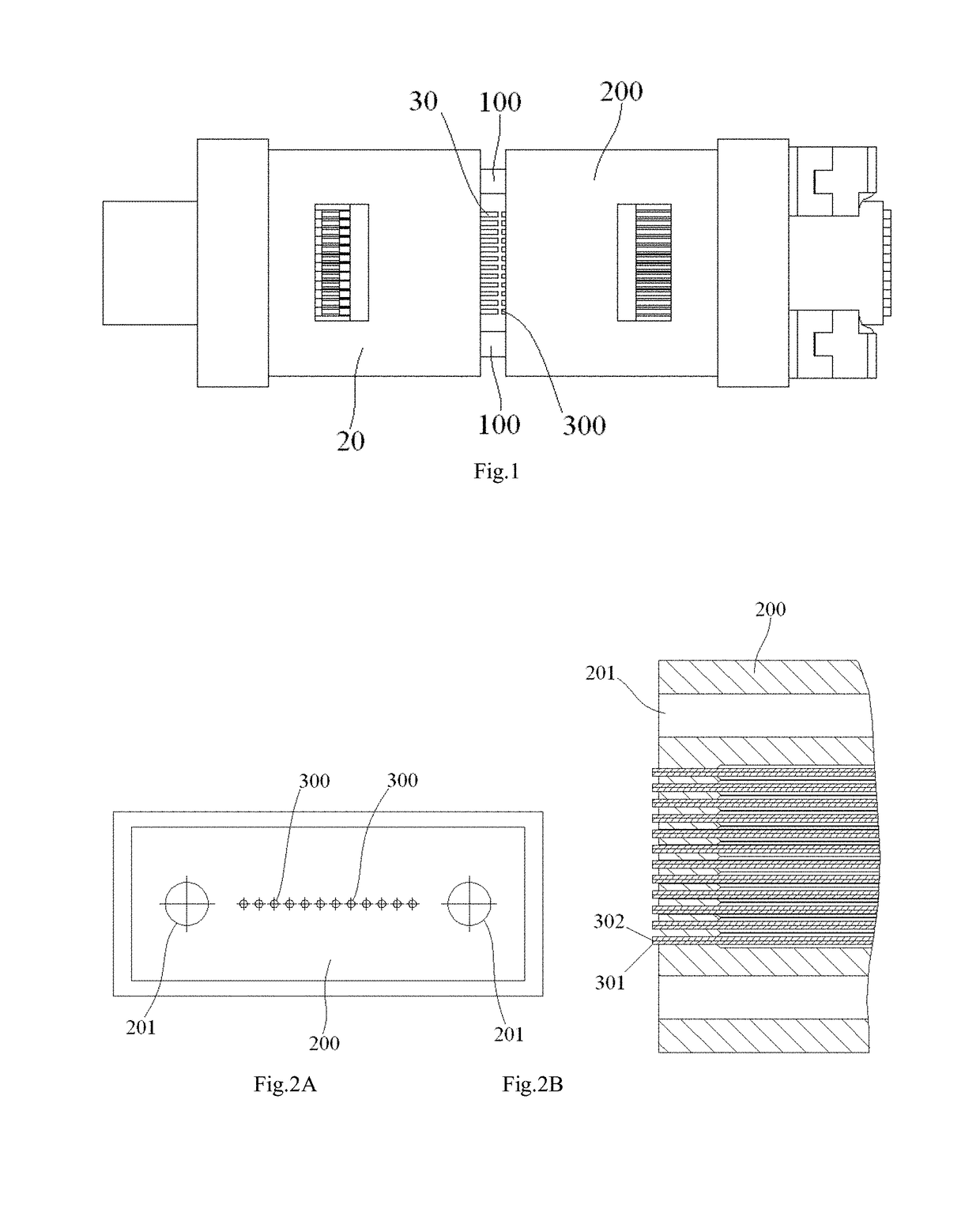
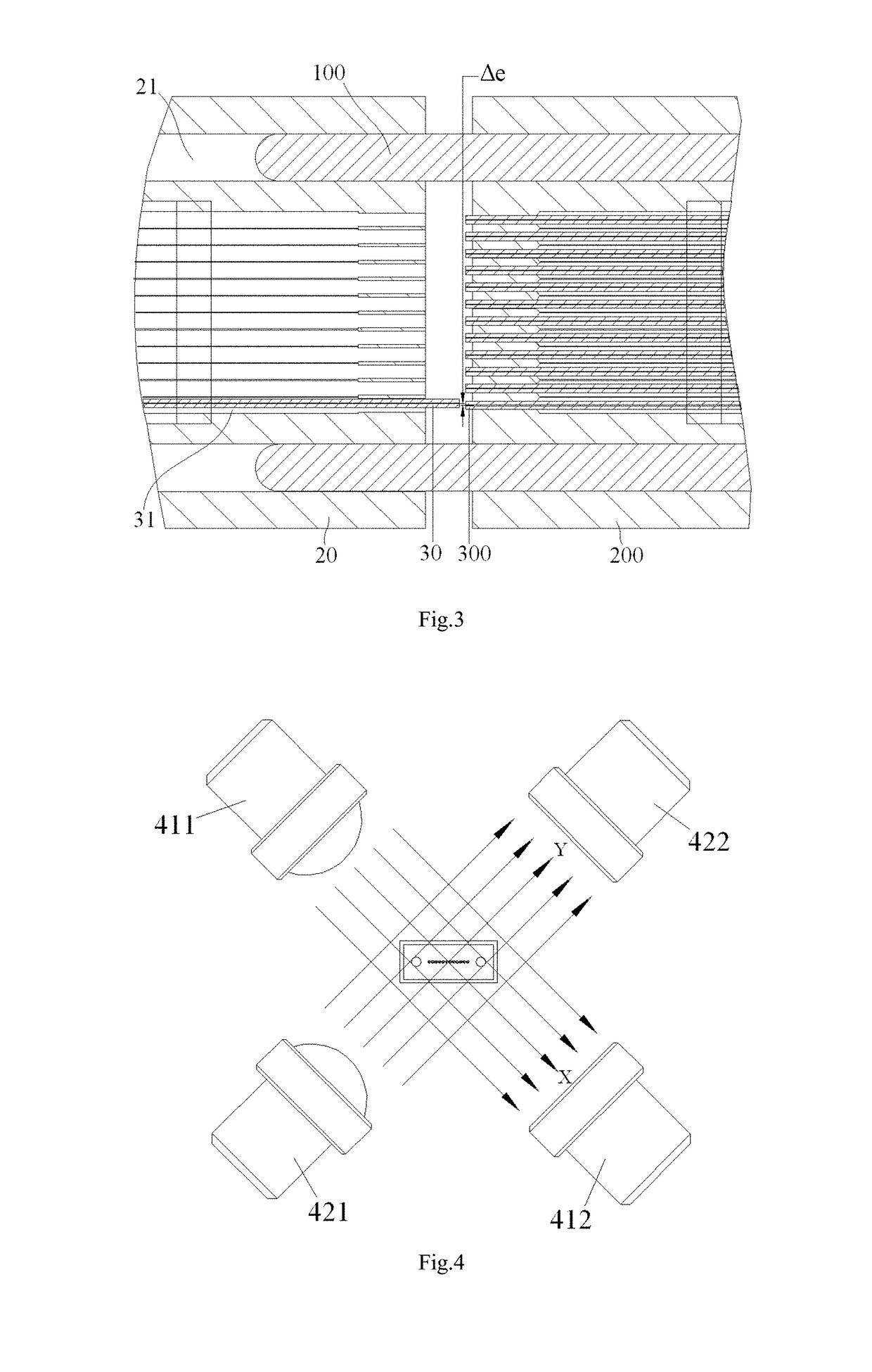
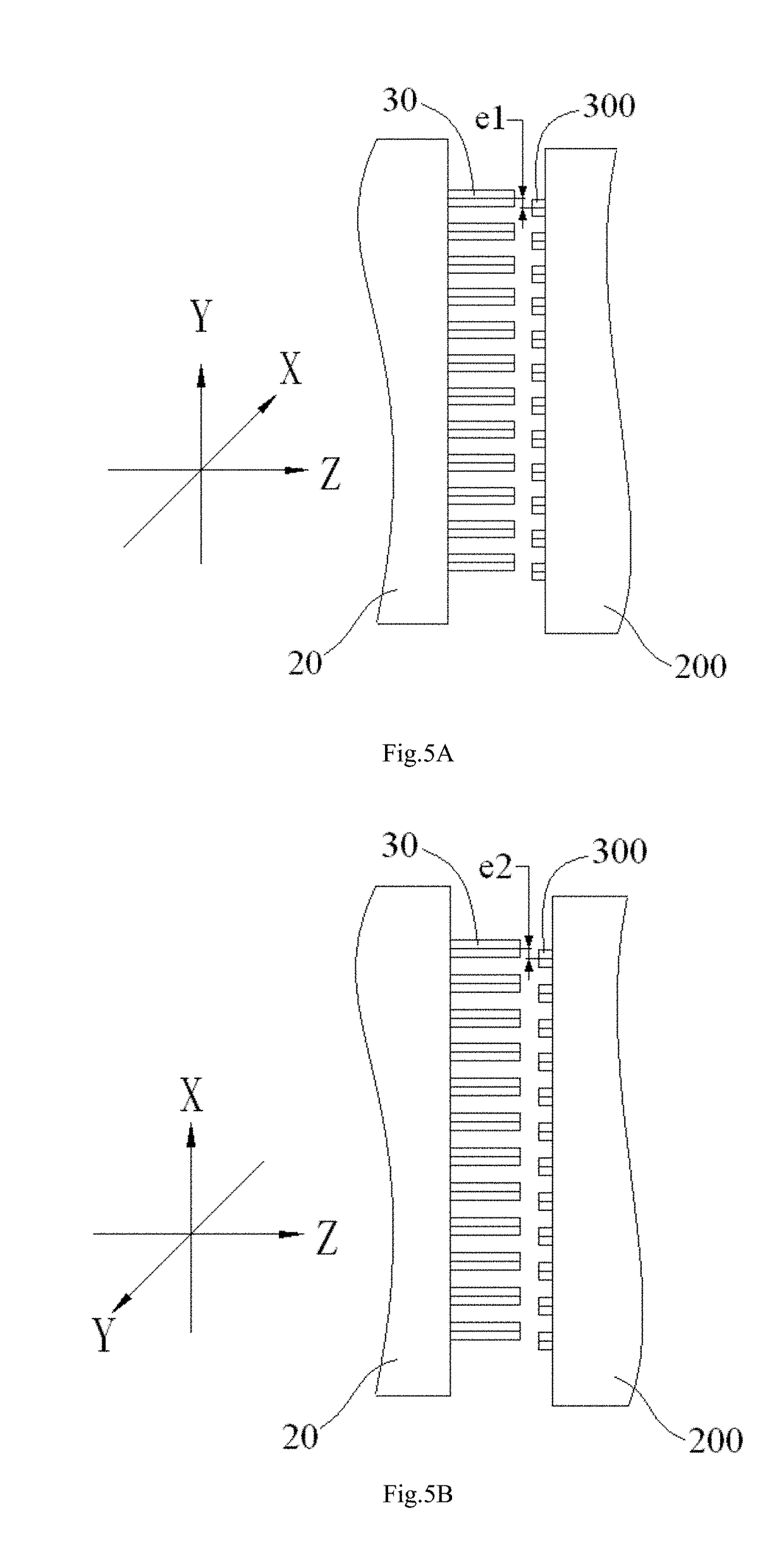
Alignment system and method for calibrating position of optical fiber bore ferrule
ActiveUS20160377818A1Low costImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFiberEngineering
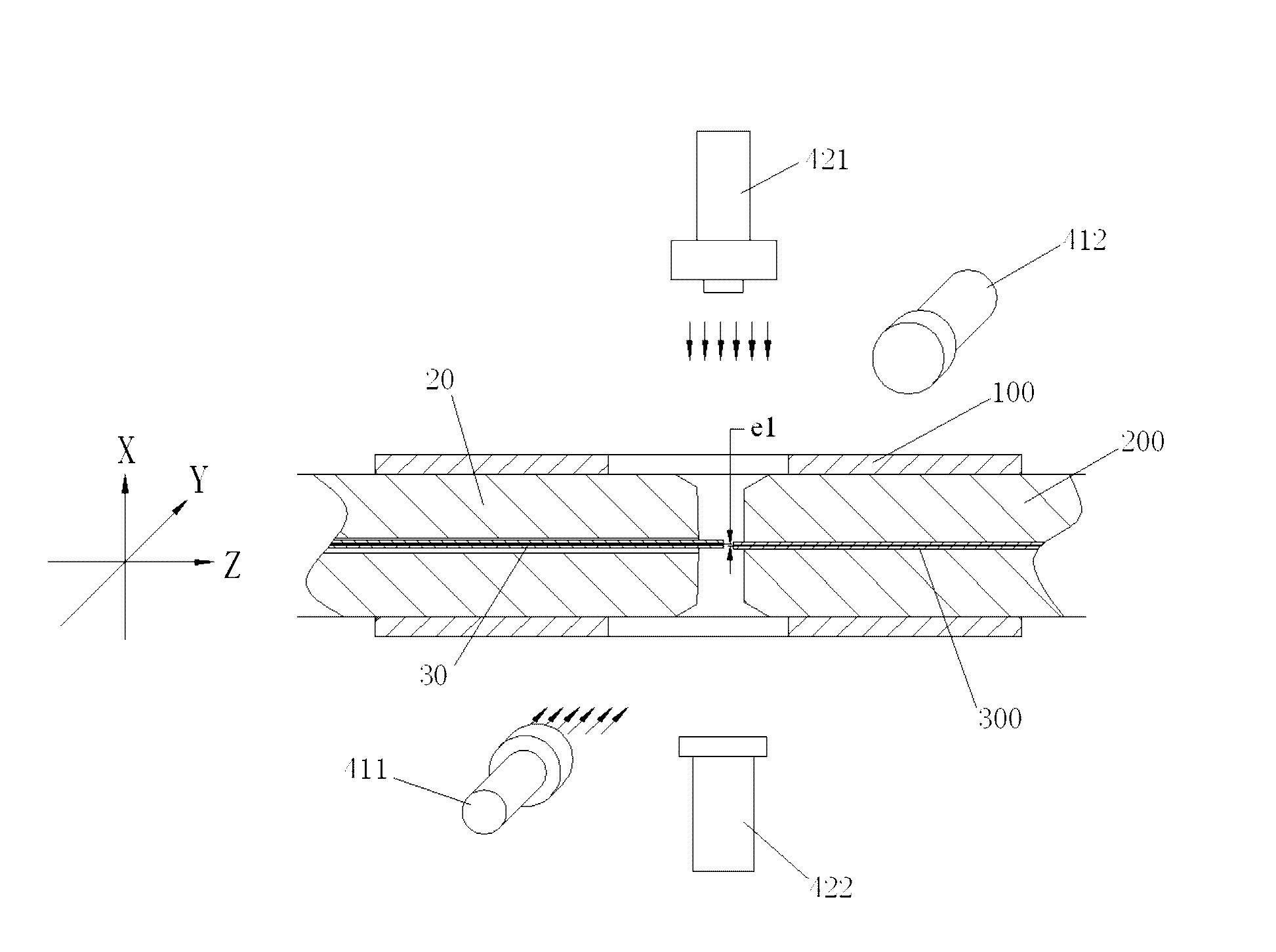
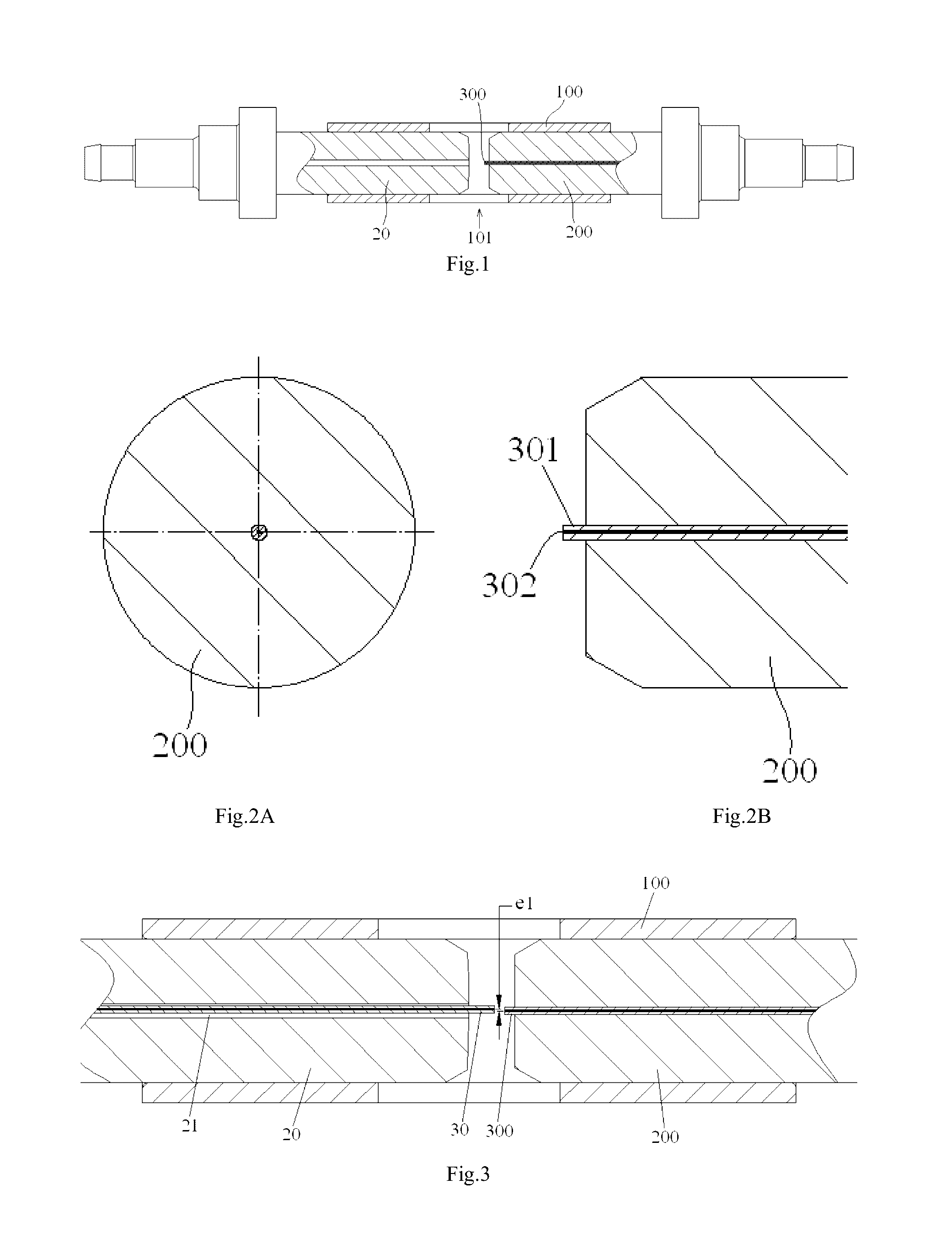
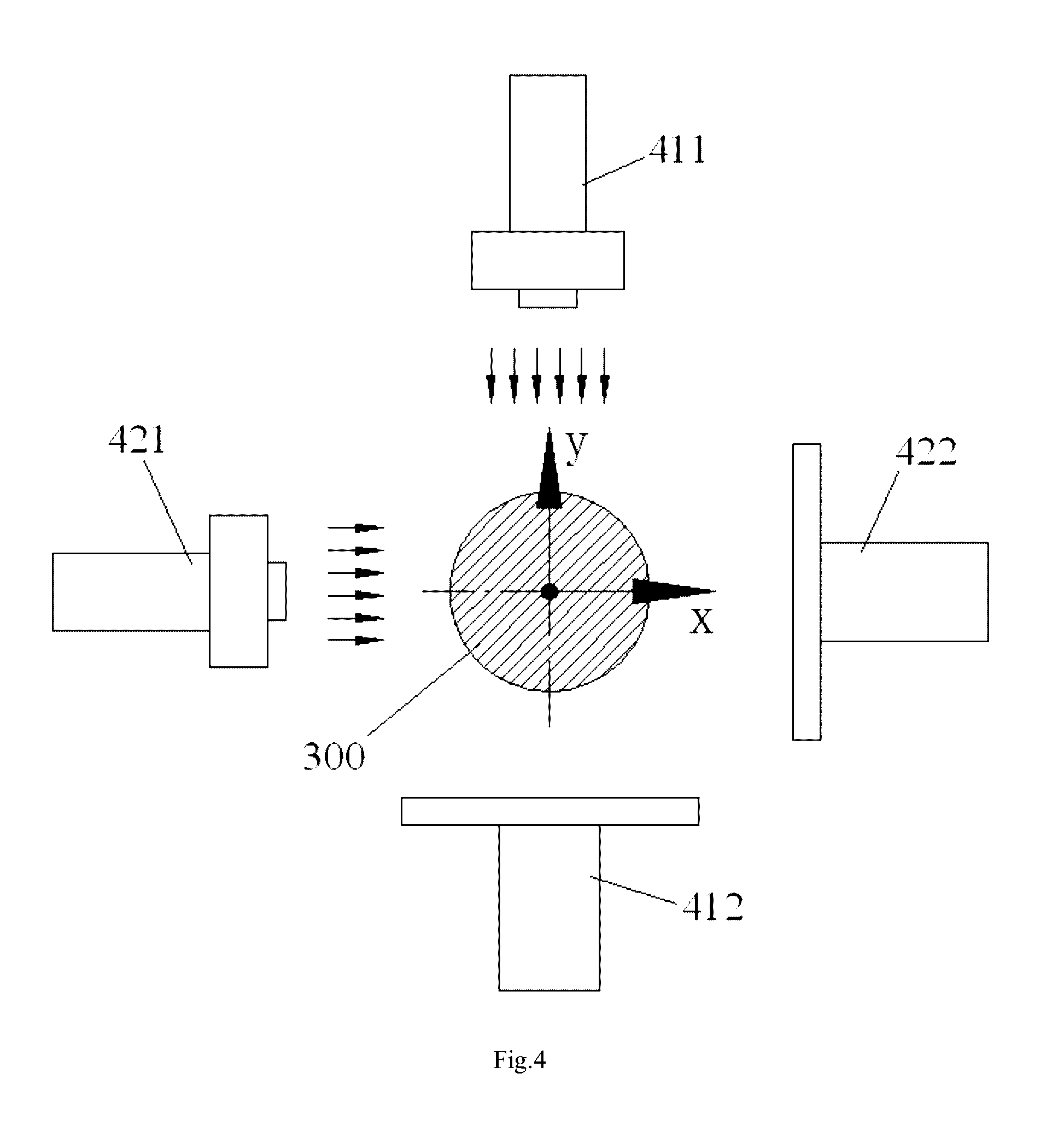
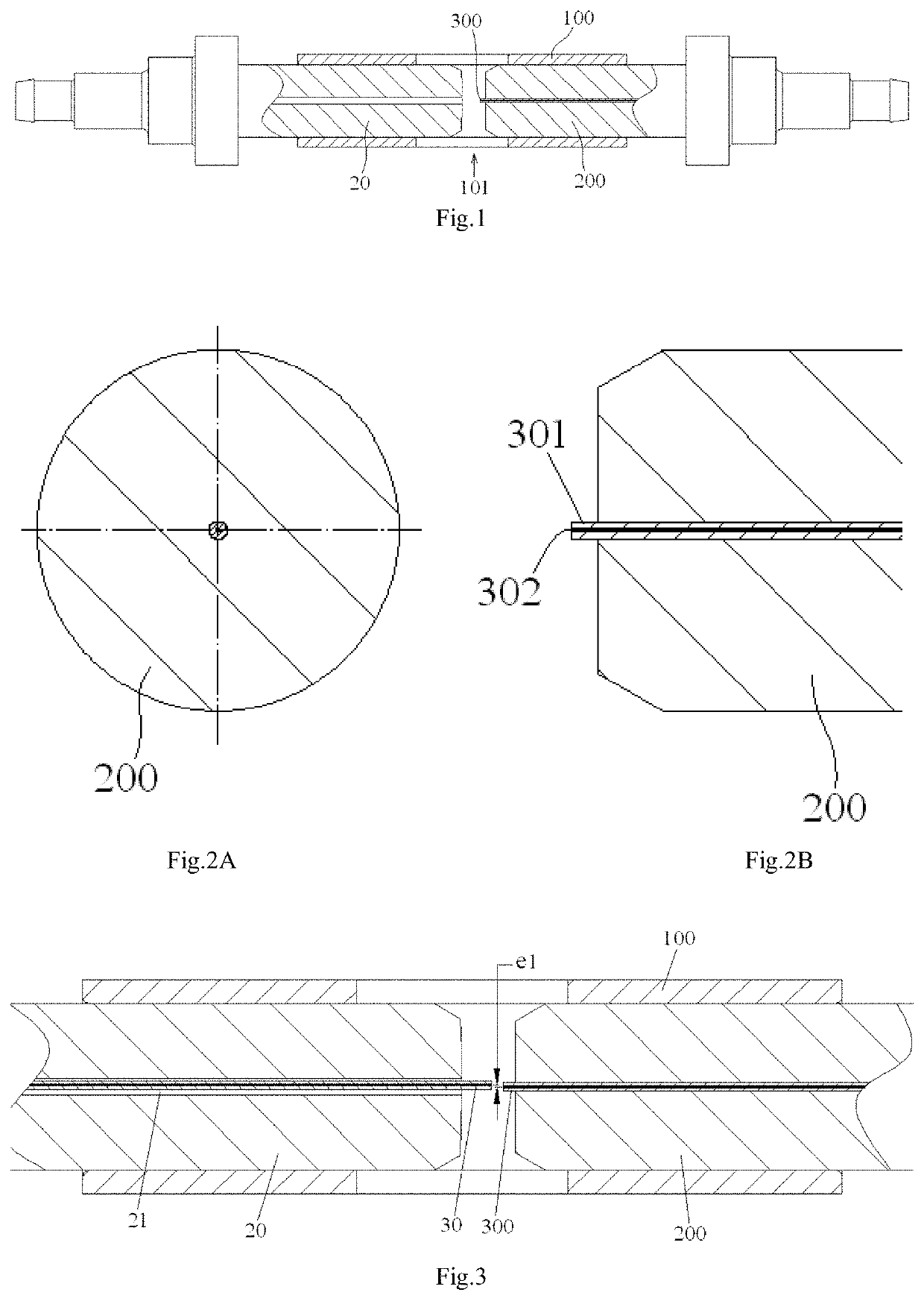
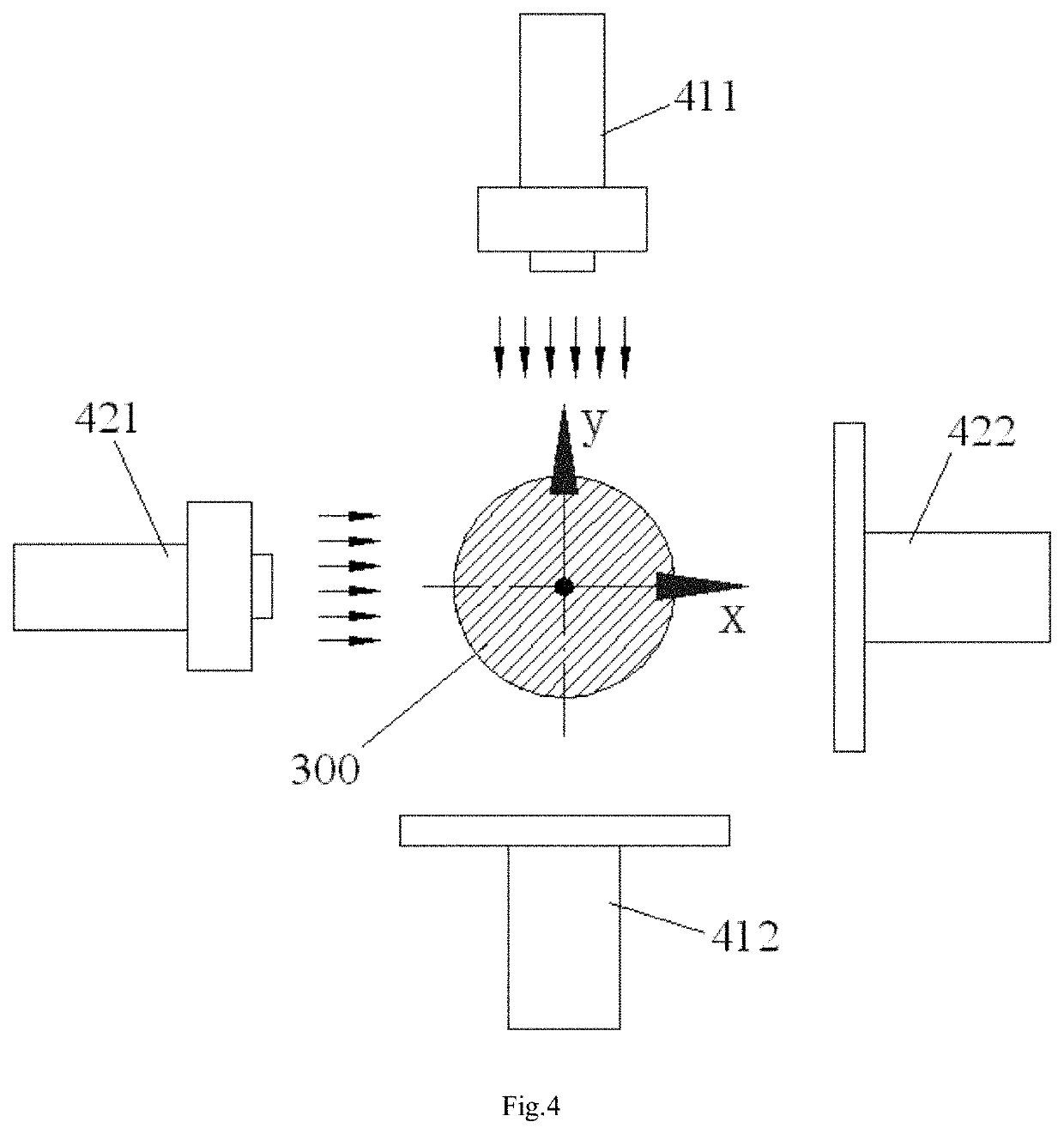
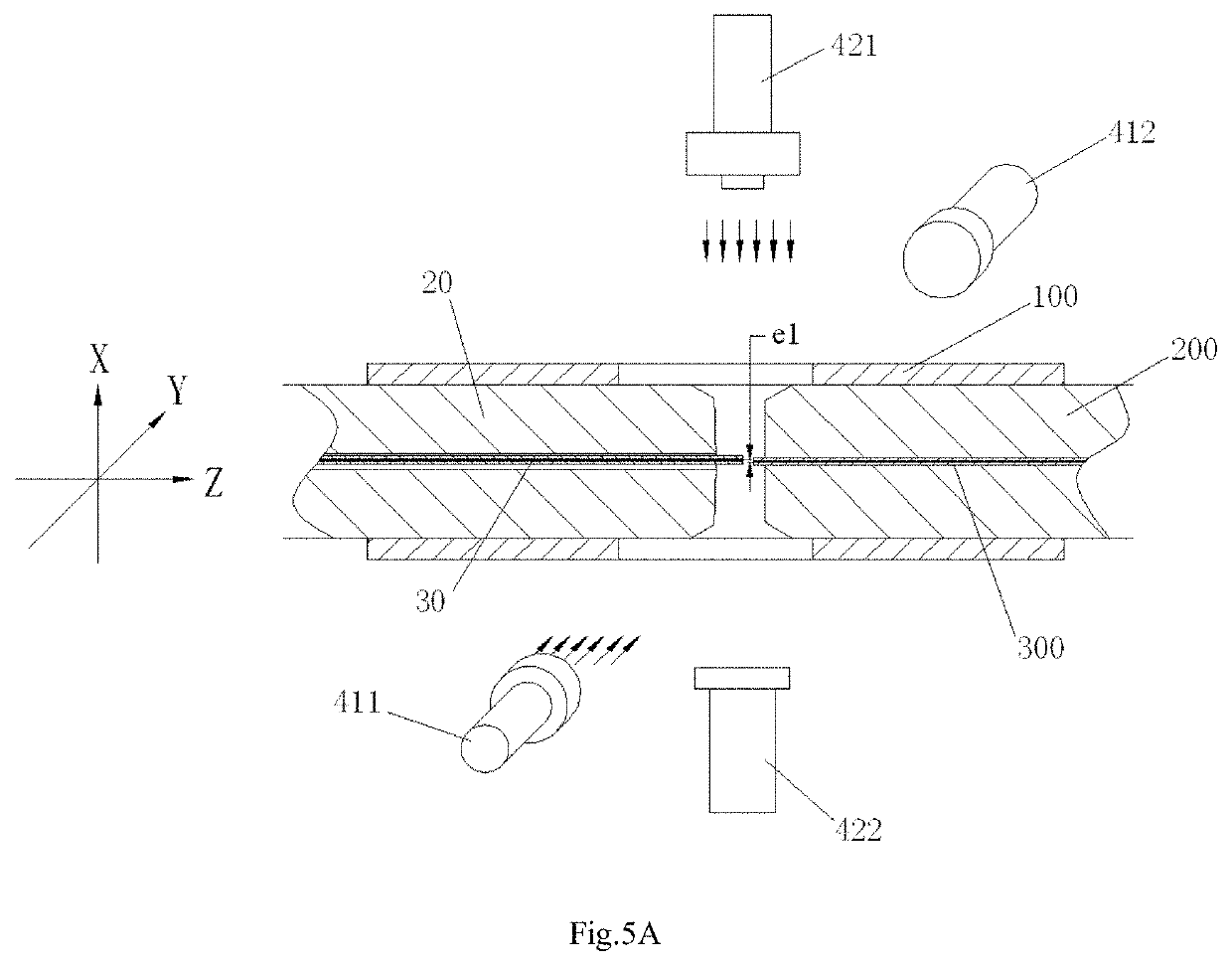
The present invention discloses an alignment system for calibrating a position of an optical fiber (30) in a bore of a ferrule (20), comprising: an outer cylinder alignment element (100) for calibrating a center position of an outer cylinder of the ferrule (20), so that the center of the outer cylinder of the ferrule (20) is aligned with a center of the outer cylinder alignment element (100); a fiber core alignment element (300) comprising a fiber core (302) having a center aligned with the center of the outer cylinder alignment element (100); an optical vision system (411, 412, 421, 422) for identifying a center position of a fiber core (32) of the optical fiber (30) and the center position of the fiber core (302) of the fiber core alignment element (300); and a controlling and moving system for actively adjusting the position of the optical fiber (30) in the bore of the ferrule (20) under the guide of the optical vision system (411, 412, 421, 422), so that the center of the fiber core (32) of the optical fiber (30) is aligned with the center of the fiber core (302) of the fiber core alignment element (300), and so that the center of the fiber core (32) of the optical fiber (30) is aligned with the center of the outer cylinder of the ferrule (20), eliminating the insertion loss of the ferrule (20) due to a radial deviation between the center of the fiber core (32) of the optical fiber (30) and the center of the outer cylinder of the ferrule (20).
Owner:COMMSCOPE TELECOMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Phase coupler for rotating fields
ActiveUS20090261976A1Eliminate insertion lossImprove signal-to-noise ratioLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalMonitoring systemPhase coupling
This invention relates to dynamically controlled, electronic article surveillance (EAS) systems whereby an array of antenna elements is digitally phased and actively driven for concurrent transmission, and digitally phased and combined in the receiver unit to improve detection. In particular, the individual frequency and phase of the plurality of the transmit / receive signals are rapidly varied to allow for automated manipulation (steering) of the transmit field pattern and receive field sensitivity. The invention achieves the following features via means of digital phasing and dynamic computer control: sufficient far-field cancellation, null-free detection and uncompromised detection performance regardless of tag's orientation while using single transmission drivers to drive entire antenna structures, whether loop antenna or ferrite core antenna, using a phase coupler, thereby allowing more efficient system operation or additional features such as deactivator antenna operation.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
Radio frequency circuit, radio frequency power amplifier, and semiconductor device
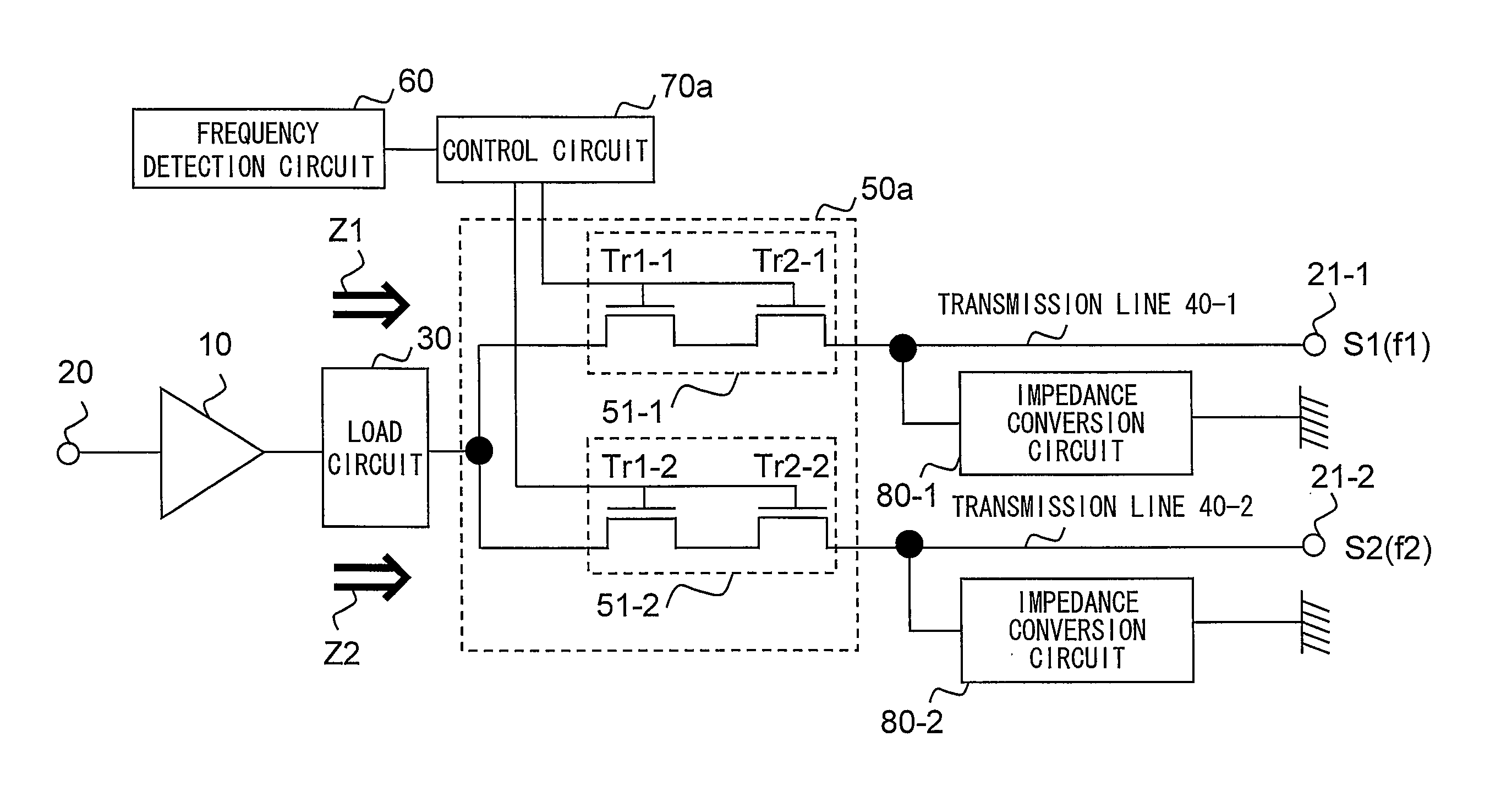
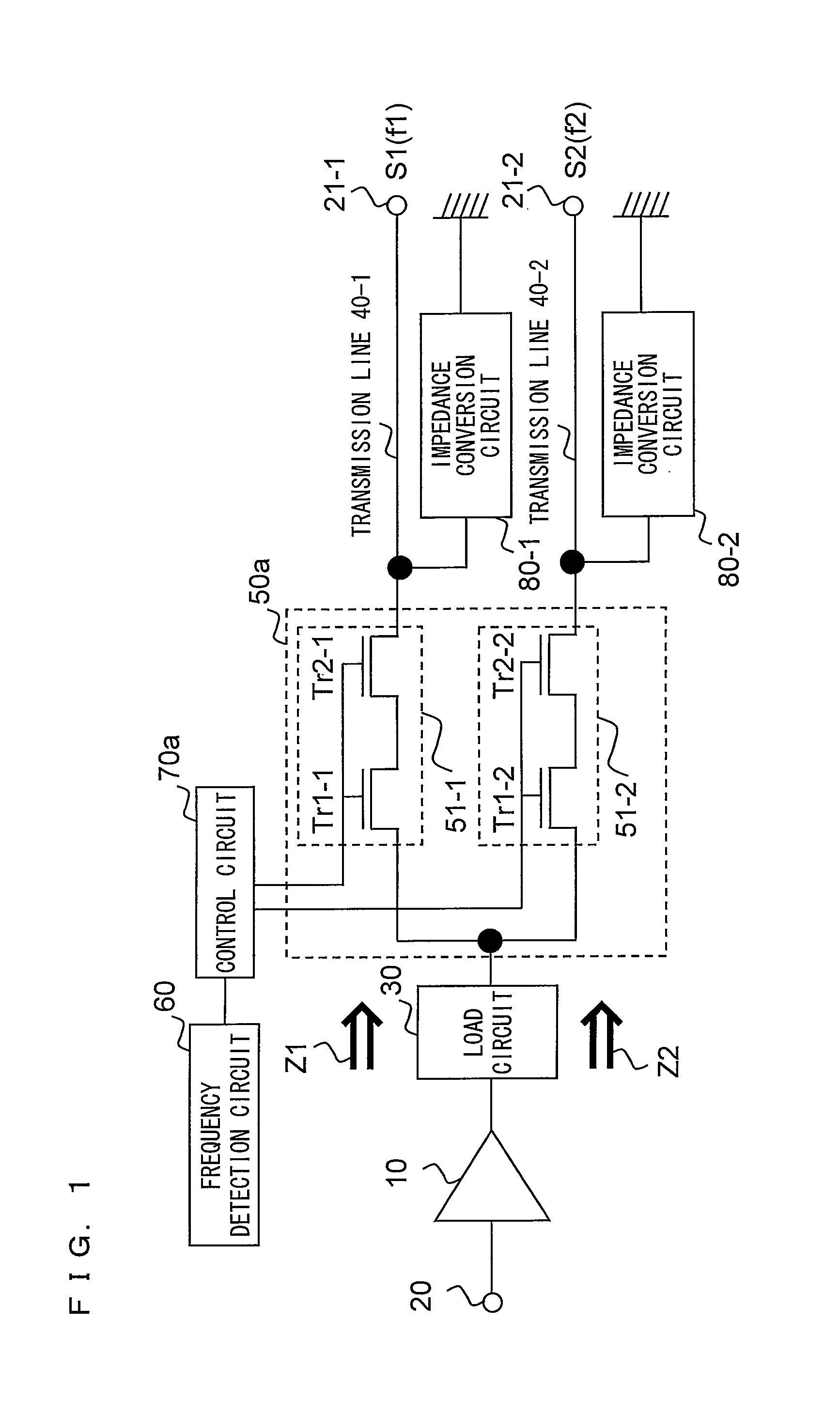
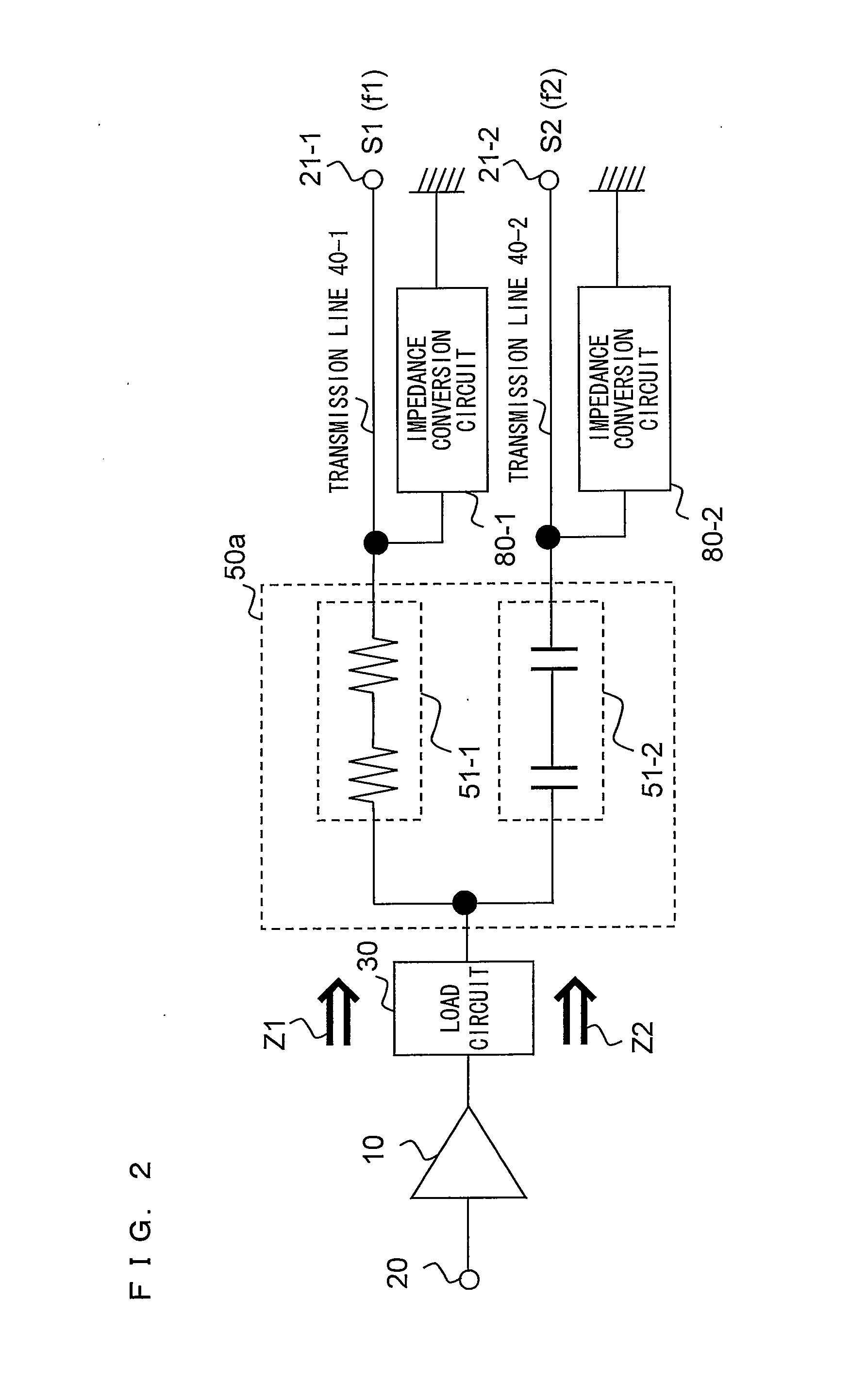
InactiveUS20100081410A1Insertion loss increaseInsertion lossTransmissionLoad circuitRadio frequency power transmission
A radio frequency circuit according to the present invention, is a radio frequency circuit for amplifying a radio frequency signal, the radio frequency circuit comprising: an amplifier circuit for amplifying the radio frequency signal and outputting an amplified signal obtained by the amplification of the radio frequency signal; a load circuit connected to an output of the amplifier circuit; a plurality of transmission lines; a selection circuit for selecting a transmission line among the plurality of transmission lines in accordance with a predetermined parameter of the amplified signal so as to connect the selected transmission line to an output of the load circuit; and a conversion circuit for converting, into a predetermined load impedance, a load impedance looking from the amplifier circuit toward an output side of the amplifier circuit, the conversion being performed in the transmission line selected by the selection circuit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
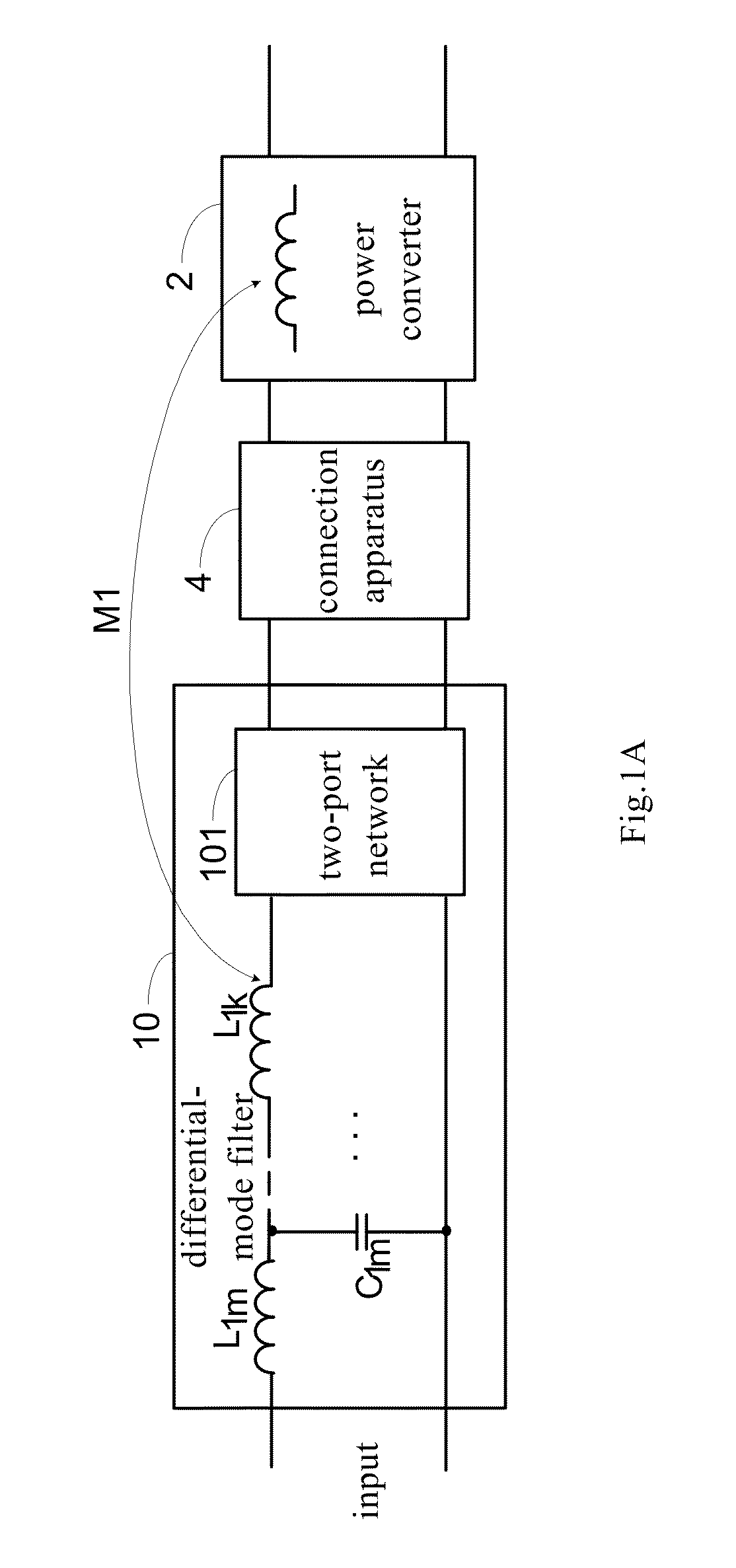
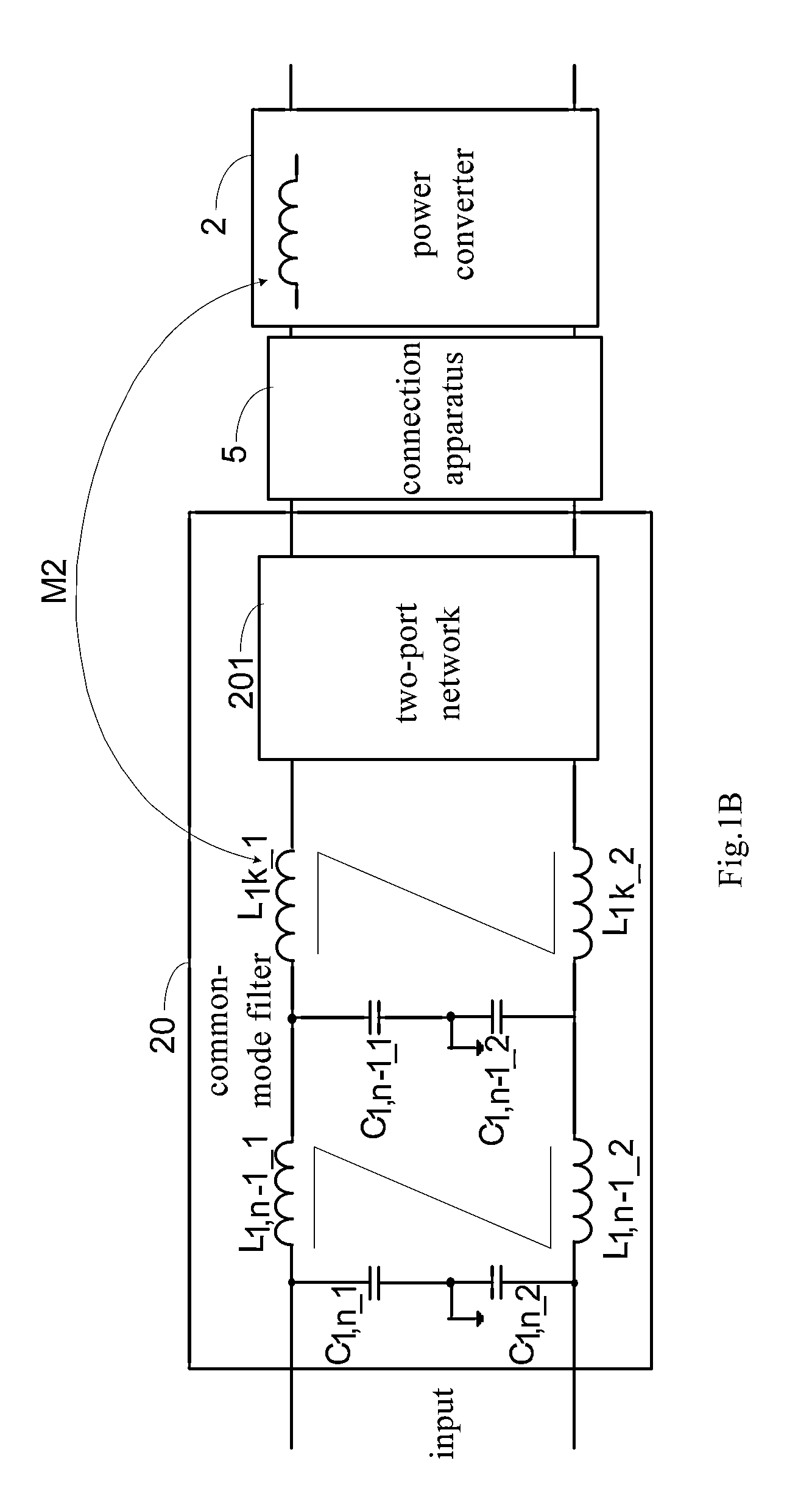
Method for improving performance of filter and power conversion apparatus
ActiveUS20130308352A1Improve filtering effectReduce componentsEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCouplingResonance
A power conversion apparatus is disclosed in the present application. The power conversion apparatus comprises: a power converter comprising an energy-storage magnetic component, and a filter comprising an inductor component and a two-port network connected the energy-storage magnetic component and the inductor component, wherein a series resonance is formed by the two-port network and a mutual inductance which is formed by a coupling between the energy-storage magnetic component and the inductor component.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
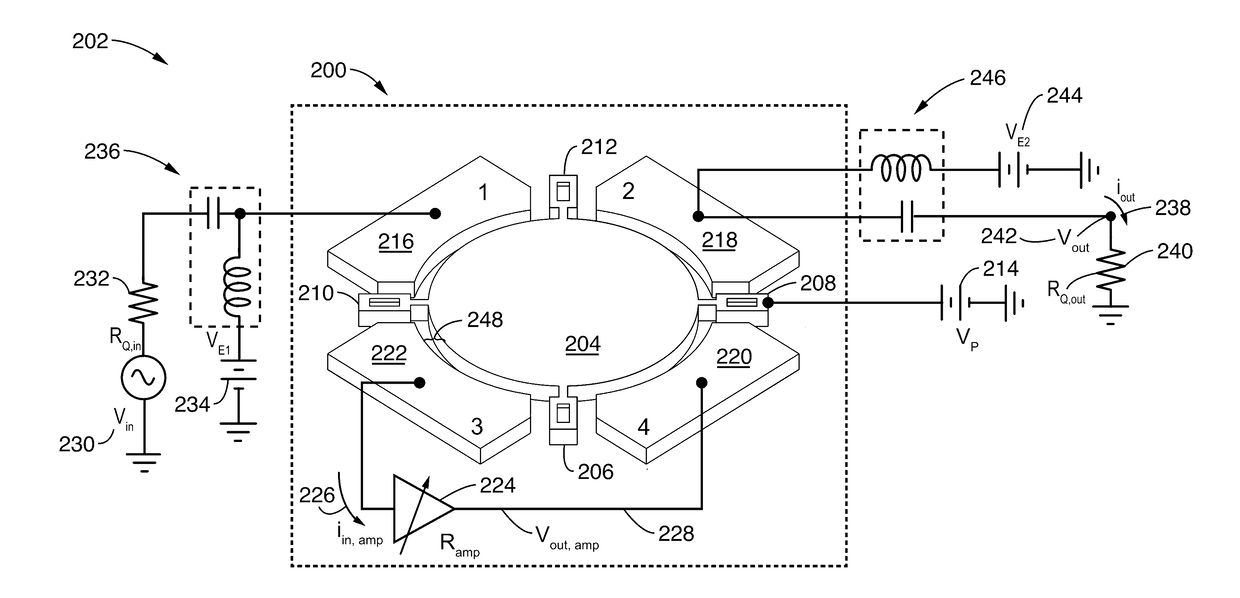
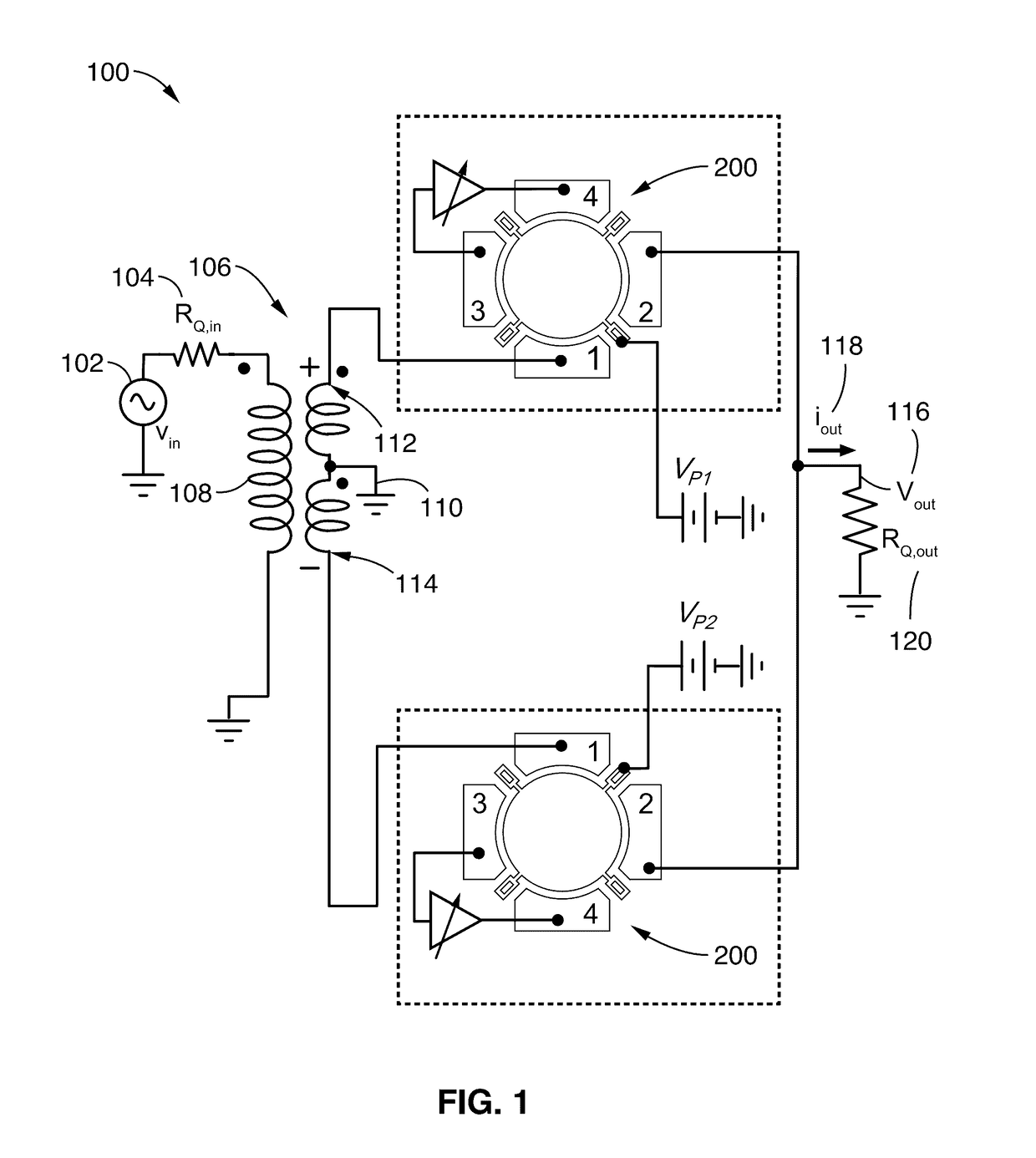
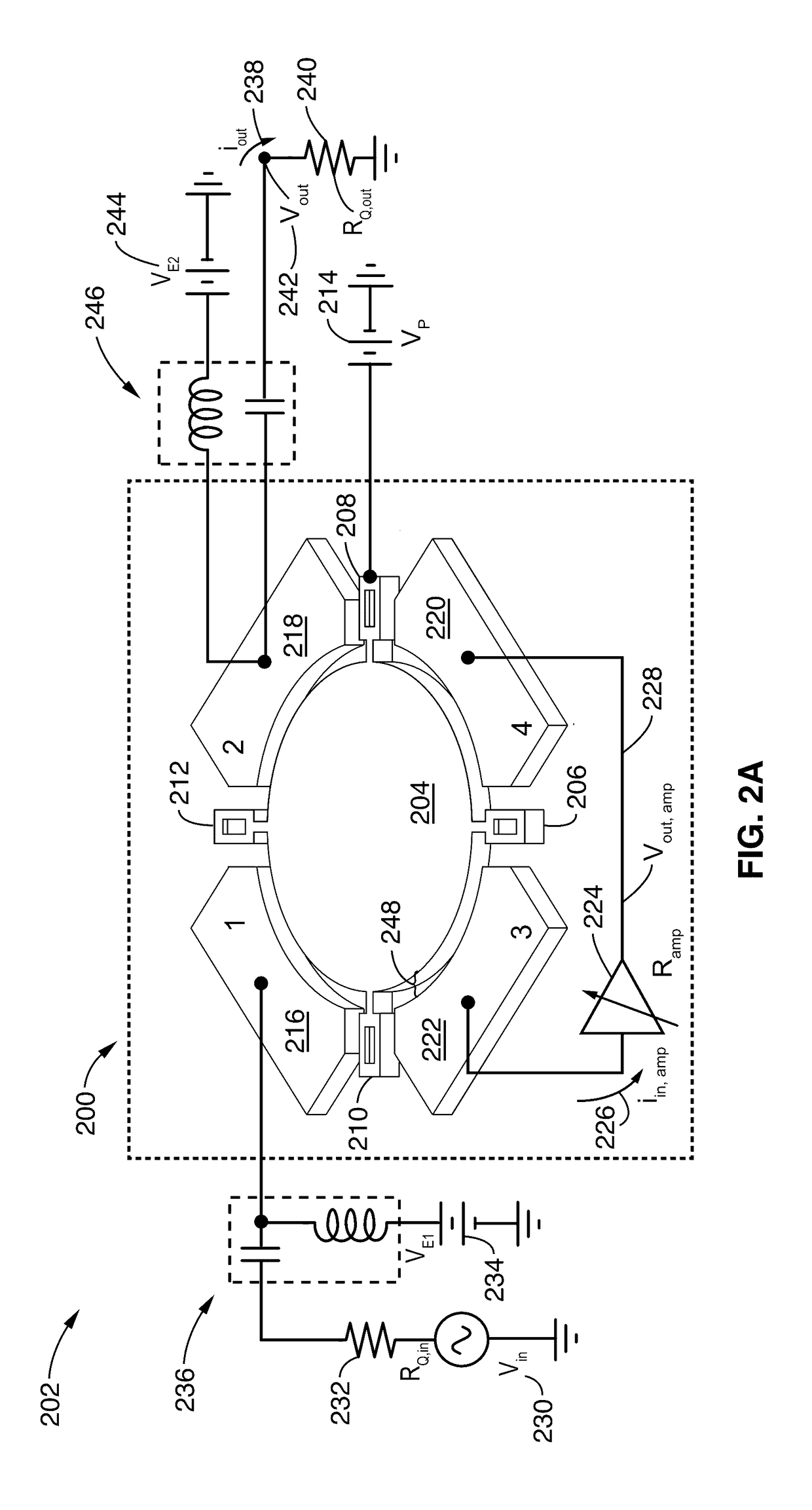
Active resonator system with tunable quality factor, frequency, and impedance
ActiveUS20170126206A1Extend device lifeReduce the required powerTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsFrequency selective two-port networksCapacitanceDynamic range
Active feedback is used with two electrodes of a four-electrode capacitive-gap transduced wine-glass disk resonator to enable boosting of an intrinsic resonator Q and to allow independent control of insertion loss across the two other electrodes. Two such Q-boosted resonators configured as parallel micromechanical filters may achieve a tiny 0.001% bandwidth passband centered around 61 MHz with only 2.7 dB of insertion loss, boosting the intrinsic resonator Q from 57,000, to an active Q of 670,000. The split capacitive coupling electrode design removes amplifier feedback from the signal path, allowing independent control of input-output coupling, Q, and frequency. Controllable resonator Q allows creation of narrow channel-select filters with insertion losses lower than otherwise achievable, and allows maximizing the dynamic range of a communication front-end without the need for a variable gain low noise amplifier.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Miniature multi-decade GHz balun
ActiveUS9071229B1Maximize usable bandwidthMinimize signal lossMultiple-port networksRoboticsWideband balun
A miniature wideband balun is realized wherein a miniature rectangular high permeability ferrite binocular core is wound with a single wire on the first of three legs and a twisted pair of wires on the third of three legs. Each winding is configured from 36 gauge wire to include two turns with precise positioning and spacing on the legs, and precise control over the length and position of the non-wound wire portions. The non-wound wire portions have their ends welded to the conductive terminals of a flat insulating substrate which the core is bonded to. Such an approach results in a wideband response of from 10 MHz to at least 6000 MHz with a substantially flat insertion loss and a low return loss. Additionally, a lid is bonded to the top of the core in order to form a package conducive to handling by standard pick and place robotic assembly machinery.
Owner:SCI COMPONENTS
Active resonator system with tunable quality factor, frequency, and impedance
ActiveUS10177742B2Increase lossNarrow passbandTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsFrequency selective two-port networksCapacitanceDynamic range
Active feedback is used with two electrodes of a four-electrode capacitive-gap transduced wine-glass disk resonator to enable boosting of an intrinsic resonator Q and to allow independent control of insertion loss across the two other electrodes. Two such Q-boosted resonators configured as parallel micromechanical filters may achieve a tiny 0.001% bandwidth passband centered around 61 MHz with only 2.7 dB of insertion loss, boosting the intrinsic resonator Q from 57,000, to an active Q of 670,000. The split capacitive coupling electrode design removes amplifier feedback from the signal path, allowing independent control of input-output coupling, Q, and frequency. Controllable resonator Q allows creation of narrow channel-select filters with insertion losses lower than otherwise achievable, and allows maximizing the dynamic range of a communication front-end without the need for a variable gain low noise amplifier.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dynamic EAS detection system and method
InactiveUS8587489B2Insertion lossImprove signal-to-noise ratioLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreResonant long antennasAntenna elementField pattern
This invention relates to dynamically controlled, electronic article surveillance (EAS) systems whereby an array of antenna elements is digitally phased and actively driven for concurrent transmission, and digitally phased and combined in the receiver unit to improve security tag detection. In particular, the individual frequency and phase of the plurality of the transmit / receive signals are rapidly varied to allow for automated manipulation (steering) of the transmit field pattern and receive field sensitivity. It is the object of this invention to achieve the following features via means of digital phasing and dynamic computer control: sufficient far-field cancellation, null-free detection and uncompromised detection performance regardless of tag's orientation.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
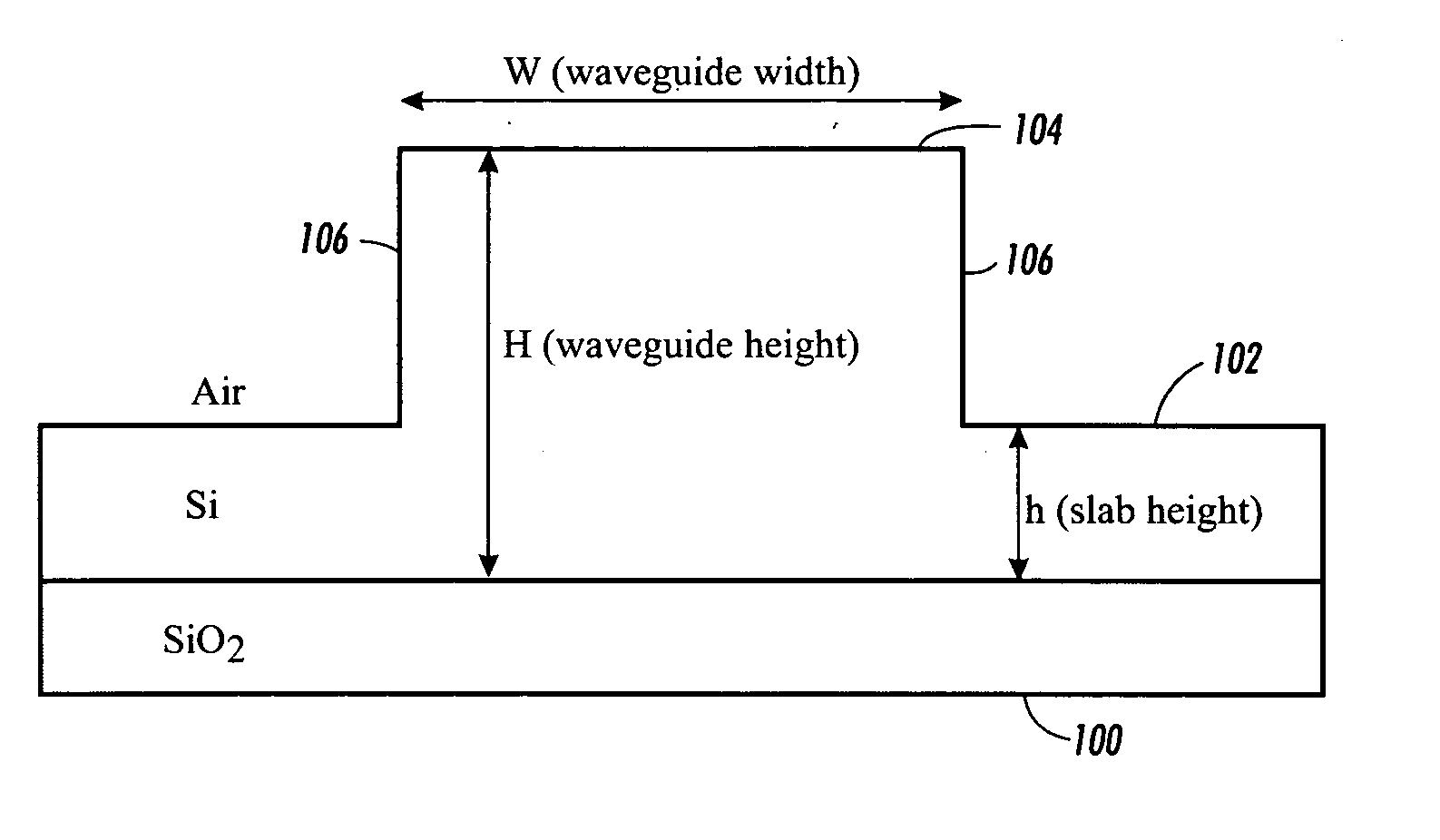
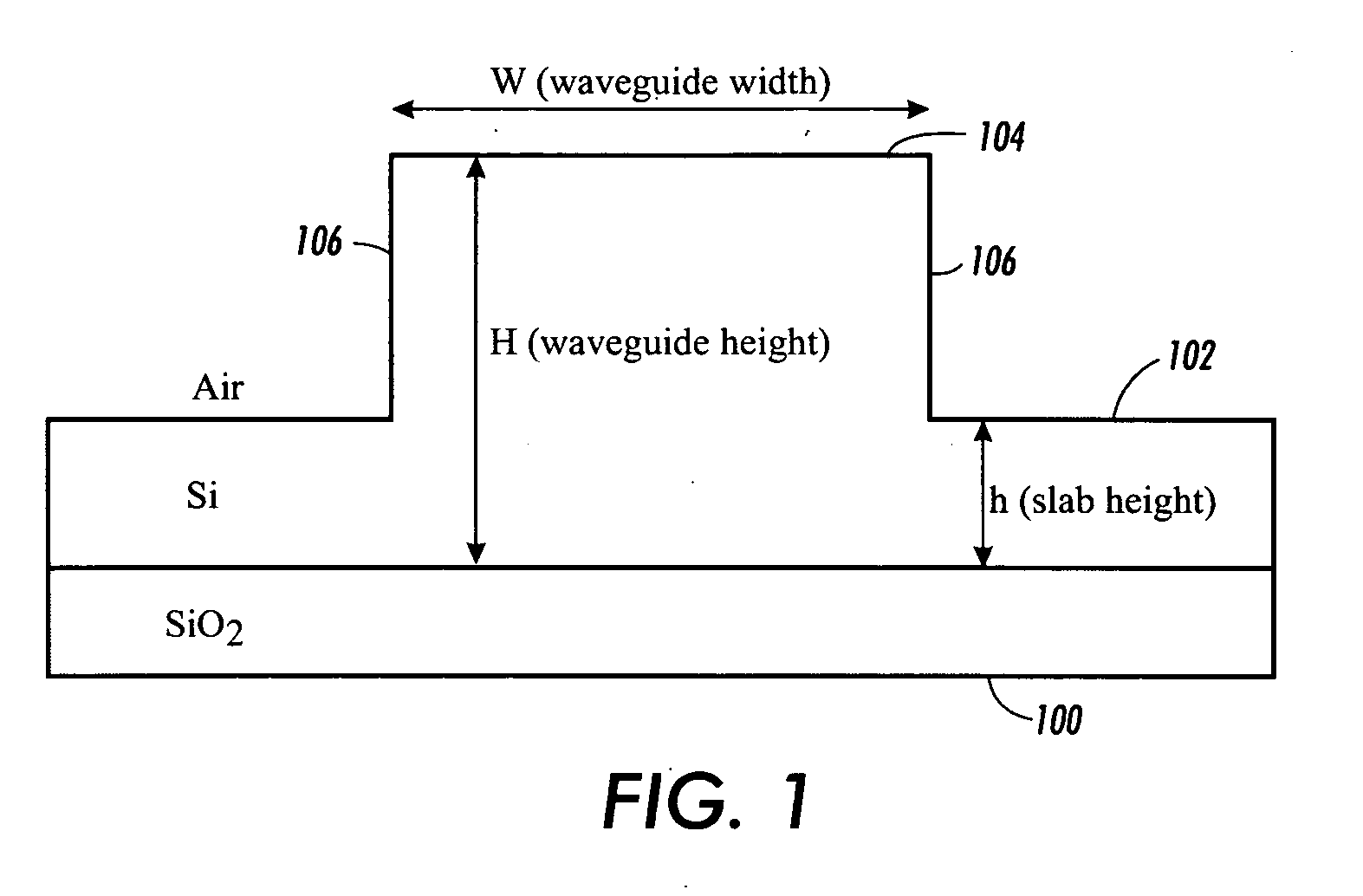
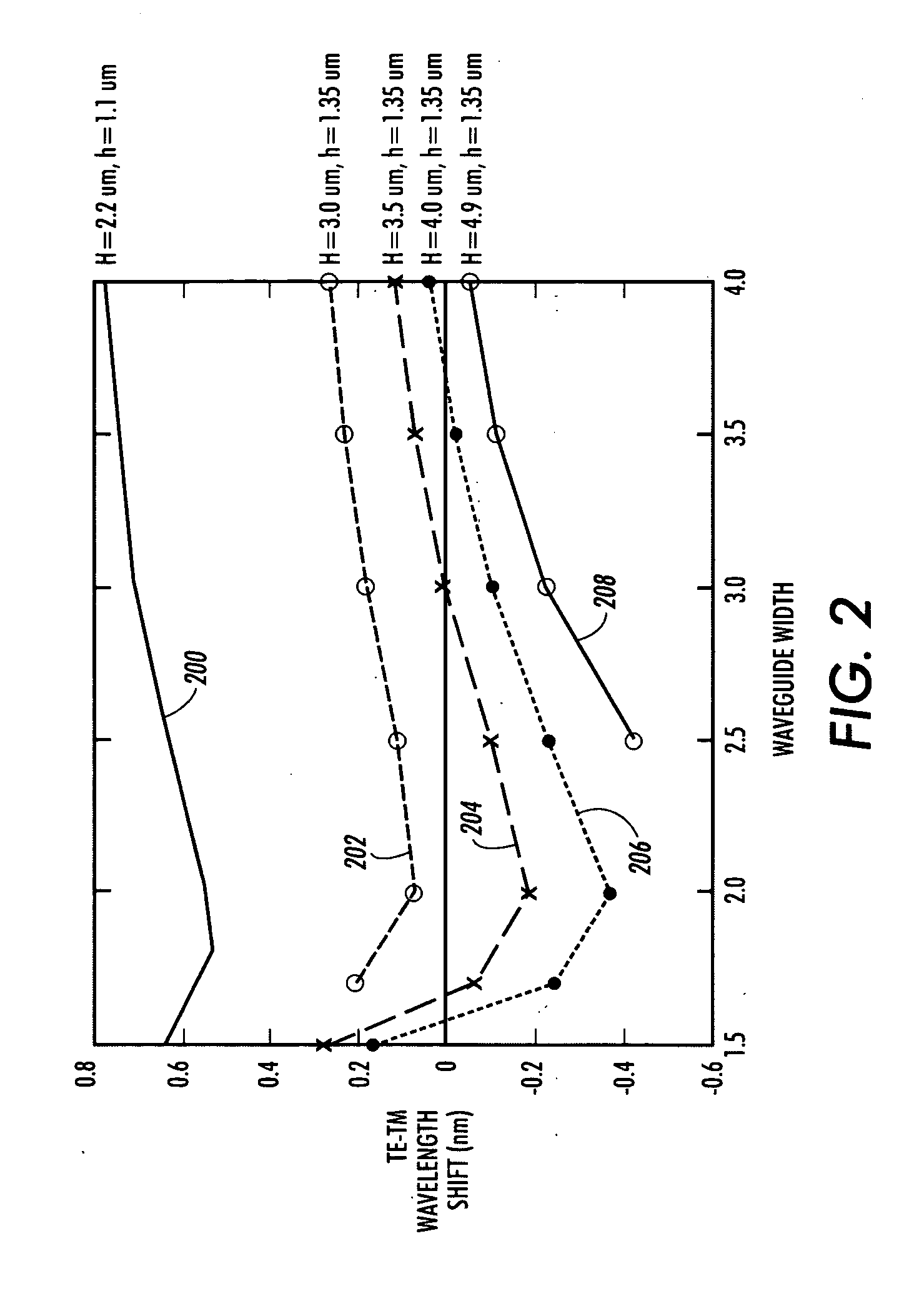
Waveguide structures and methods
InactiveUS20050286850A1Performance deteriorationSmall channel separationOptical articlesOptical waveguide light guideWaveguide
Owner:XEROX CORP
Multiplexer, transmission apparatus, and reception apparatus
ActiveUS20180152210A1Insertion lossFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmissionCapacitanceMultiplexer
A multiplexer includes a common terminal connected to an inductance element at a connection path with an antenna element, filter elements including different pass bands and connected to the antenna element with the common terminal therebetween, and an inductance element arranged in series between a transmission filter with a largest capacitance when viewed from the antenna side among the filter elements and the common terminal. An inductive component of the inductance element and a capacitive component of the transmission filter element define an LC series resonant circuit, and a resonant frequency of the LC series resonant circuit is lower than any of pass bands of the filter elements.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Multiplexer, transmission apparatus, and reception apparatus
ActiveUS9917603B2Insertion lossMultiple-port networksFrequency-division multiplex detailsCapacitanceMultiplexer
A multiplexer includes a common terminal connected to an inductance element at a connection path with an antenna element, filter elements including different pass bands and connected to the antenna element with the common terminal therebetween, and an inductance element arranged in series between a transmission filter with a largest capacitance when viewed from the antenna side among the filter elements and the common terminal. An inductive component of the inductance element and a capacitive component of the transmission filter element define an LC series resonant circuit, and a resonant frequency of the LC series resonant circuit is lower than any of pass bands of the filter elements.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Reflective optical circulator
InactiveUS7826137B2LossStable insertion lossOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingPolarising elementsCatoptricsOptical circulator
Owner:NAMIKI PRECISION JEWEL CO LTD
Balun
ActiveUS20090295495A1Small thicknessHigh quality factorOne-port networksWaveguidesDielectric substrateEngineering
A balun includes a first, second, and third metallic layers, a first dielectric layer disposed between the second and third metallic layers, and a dielectric substrate. The second metallic layer includes a first spiral line having sequentially connected first line segments and a second spiral line having sequentially connected second line segments. A first distance between each two opposite sides of a first region encircled by the innermost first line segments is greater than a second distance between each two adjacent parallel first line segments. A third distance between each two opposite sides of a second region encircled by the innermost second line segments is greater than a fourth distance between each two adjacent parallel second line segments. The third metallic layer includes a third and a fourth spiral lines. The first metallic layer and other elements as a whole are disposed on an opposite surface of the dielectric substrate.
Owner:CYNTEC
Optical isolator
InactiveUS20150185510A1DownsizeIncrease freedomPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsOptical isolatorLanthanide
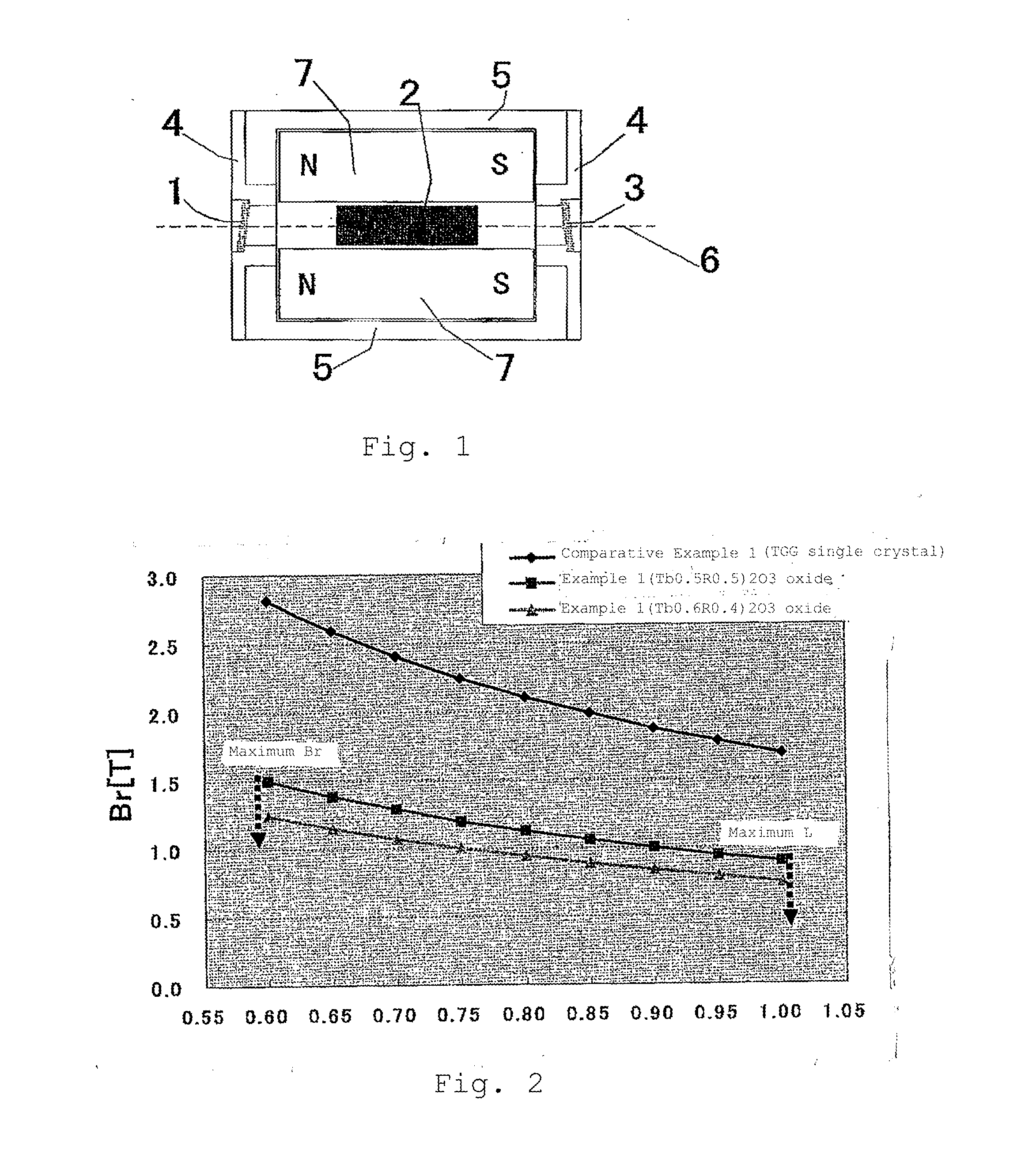
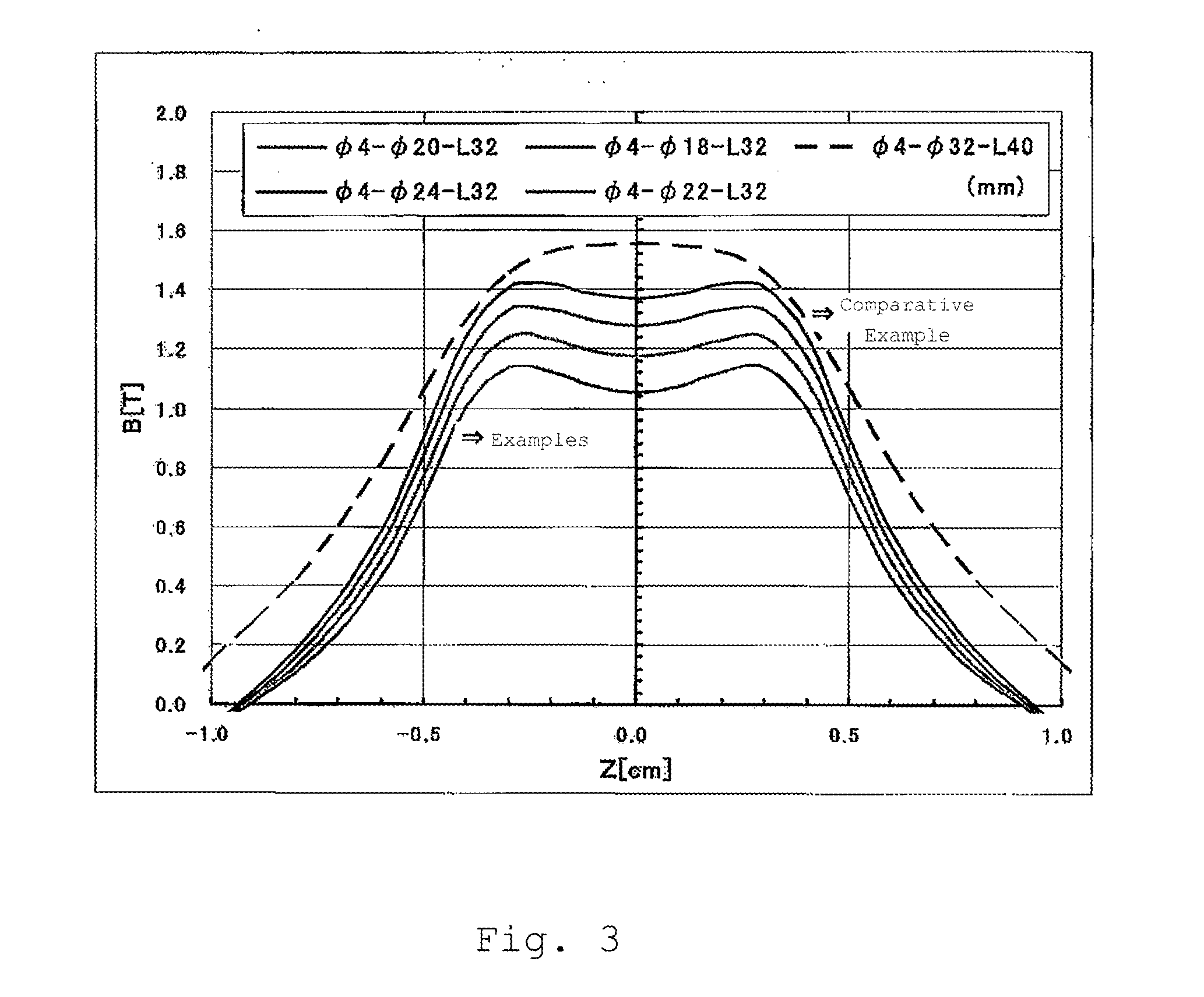
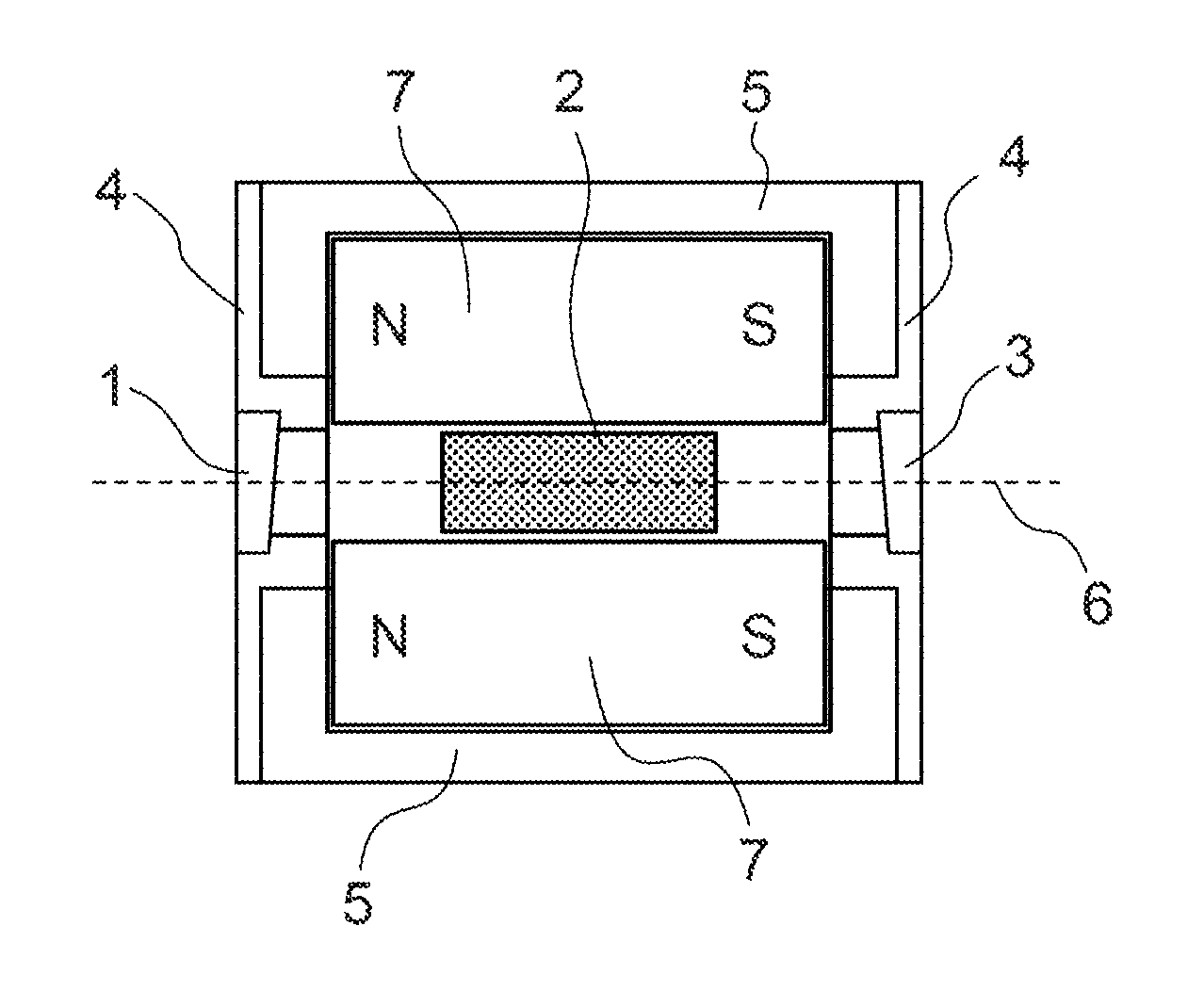
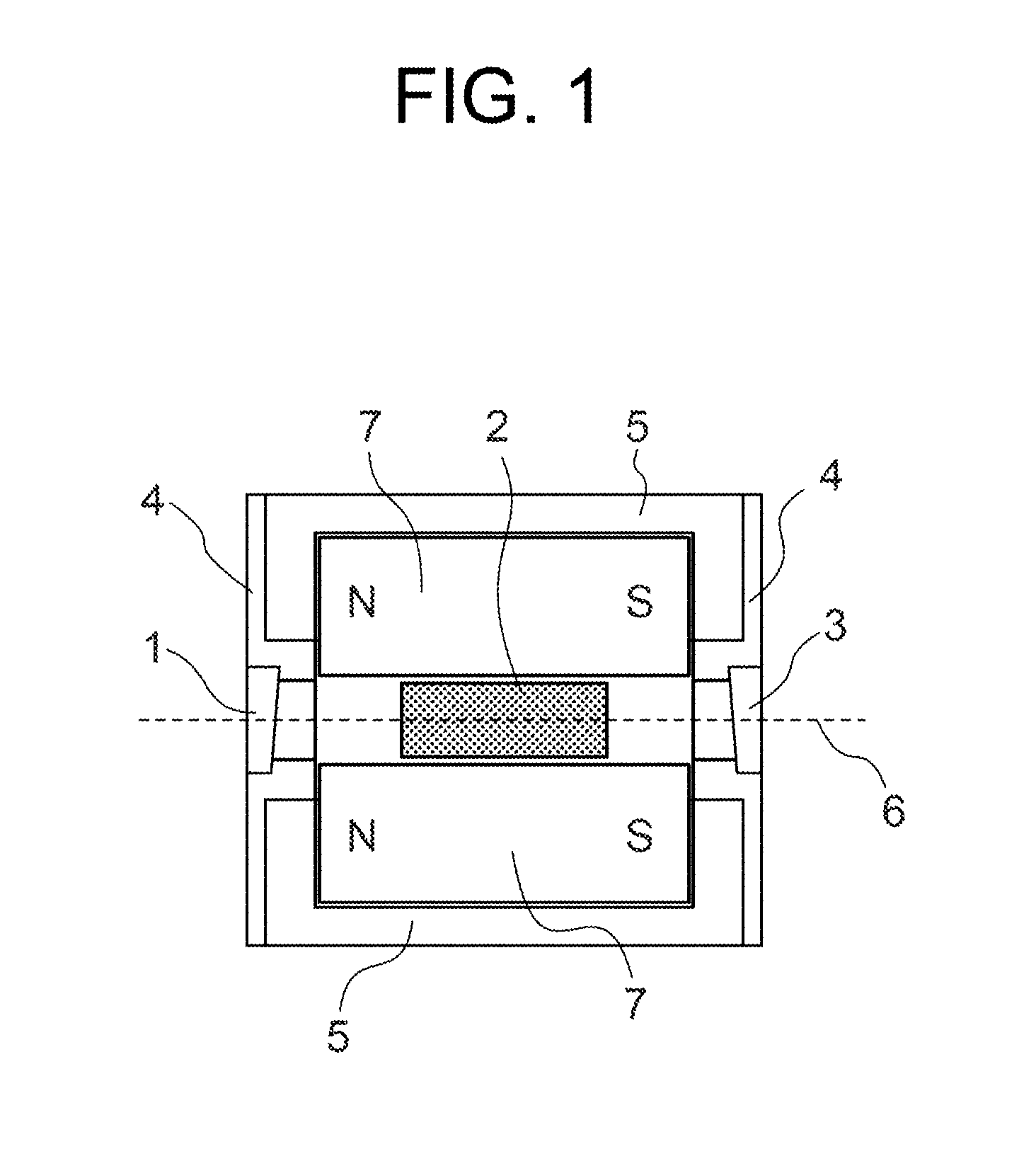
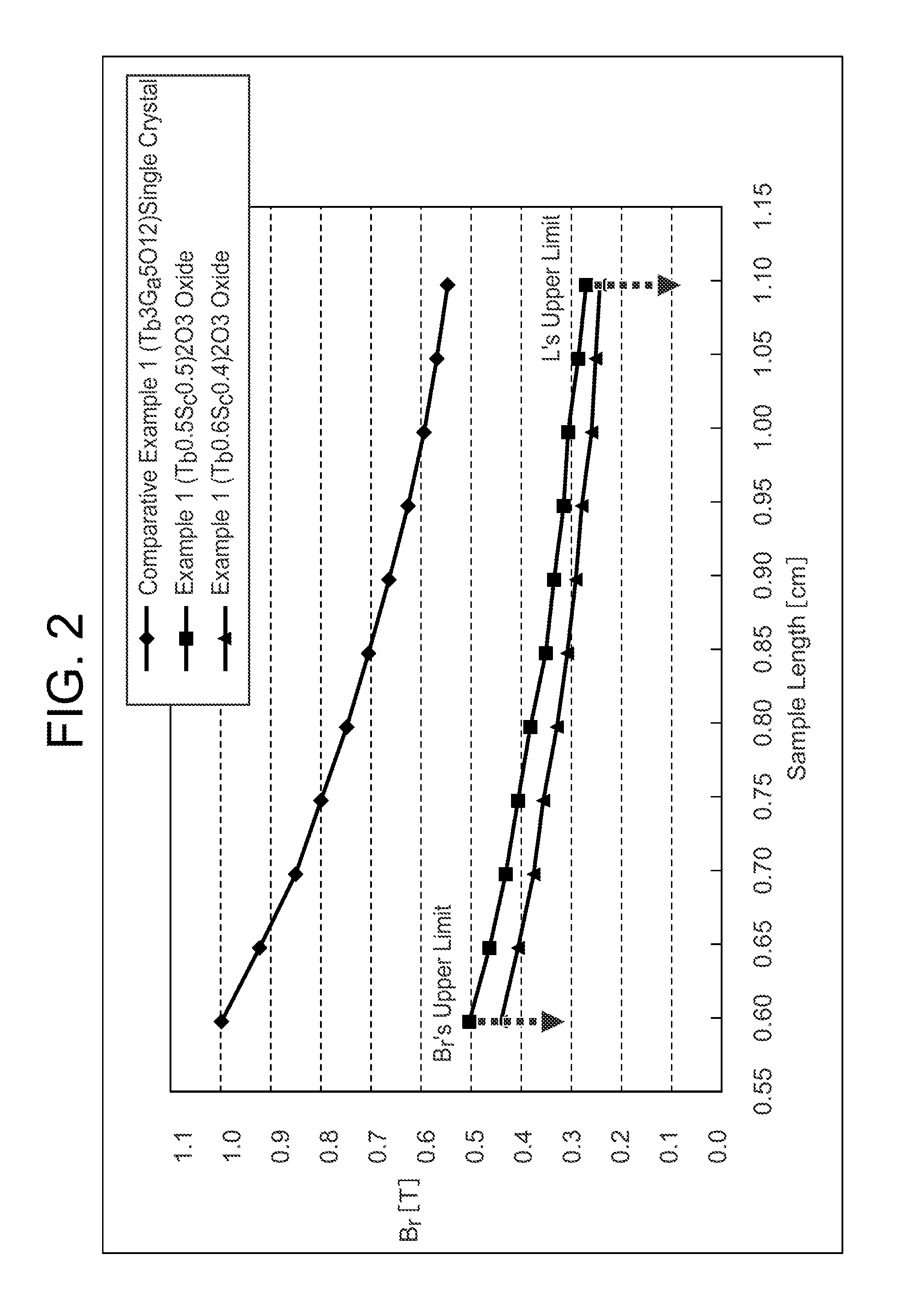
An optical isolator for use with a wavelength band of 970-990 nm is improved in that it has a Faraday rotator made of an oxide material, which contains by 99% or more an oxide (TbxR1−x)2O3 where 0.5≦x≦1.0, and R is scandium, yttrium or any lanthanoid but Tb; the resulting Faraday rotator exhibits a Verdet constant of 0.30 min / Oe·cm or greater in the case of the wavelength band of 970-990 nm; and a hollow magnet is set to sheathe this Faraday rotator; and the sample length L is from 0.6 cm through 1.0 cm.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for improving performance of filter and power conversion apparatus
ActiveUS9350231B2Improve filtering effectReduce componentsEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCouplingResonance
A power conversion apparatus is disclosed in the present application. The power conversion apparatus comprises: a power converter comprising an energy-storage magnetic component, and a filter comprising an inductor component and a two-port network connected the energy-storage magnetic component and the inductor component, wherein a series resonance is formed by the two-port network and a mutual inductance which is formed by a coupling between the energy-storage magnetic component and the inductor component.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Alignment system and method for calibrating position of optical fiber bore ferrule
ActiveUS10215927B2Improve optical performance and random matching performanceReduce or even eliminate various disadvantageous effectsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFiberEngineering
The present invention discloses an alignment system for calibrating a position of an optical fiber (30) in a bore (31) of a ferrule (20), comprising: a calibration ferrule (200) having an alignment guide hole (201) formed therein; an alignment guide element (100) for calibrating a center position of a guide hole (21) of the ferrule, so that a center of the guide hole (21) of the ferrule (20) is aligned with a center of the alignment guide hole (201); a fiber core alignment element (300) comprising a fiber core (302) having a center positioned at a theoretical center relative to a positioning reference defined by the center of the alignment guide hole (201); an optical vision system for identifying a center position of a fiber core (32) of the optical fiber (30) and the center position of the fiber core (302) of the respective fiber core alignment element (300); and a controlling and moving system for actively adjusting the position of the optical fiber (30) in the bore (31) of the ferrule (20) under the guide of the optical vision system, so that the center of the fiber core (32) of the optical fiber (30) is aligned with the center of the fiber core (302) of the respective fiber core alignment element (300), and so that the center of the fiber core (32) of the optical fiber (30) is positioned at a theoretical center relative to a positioning reference defined by the center of the guide hole (21) of the ferrule (20).
Owner:COMMSCOPE TELECOMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Optical isolator for a wavelength band of 600-800 nm
ActiveUS9429778B2Increase freedomDownsize the optical isolatorPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsIsolatorOptical isolator
An optical isolator for use with a wavelength band of 600-800 nm is improved in that it has a Faraday rotator made of an oxide material in which said oxide material contains (TbxR1-x)2O3 such that 0.5≦x≦1.0, and R is scandium, yttrium or any lanthanoid but Tb.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Multiplexer, transmission apparatus, and reception apparatus
ActiveUS10476532B2Insertion lossFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmissionCapacitanceMultiplexer
A multiplexer includes a common terminal connected to an inductance element at a connection path with an antenna element, filter elements including different pass bands and connected to the antenna element with the common terminal therebetween, and an inductance element arranged in series between a transmission filter with a largest capacitance when viewed from the antenna side among the filter elements and the common terminal. An inductive component of the inductance element and a capacitive component of the transmission filter element define an LC series resonant circuit, and a resonant frequency of the LC series resonant circuit is lower than any of pass bands of the filter elements.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
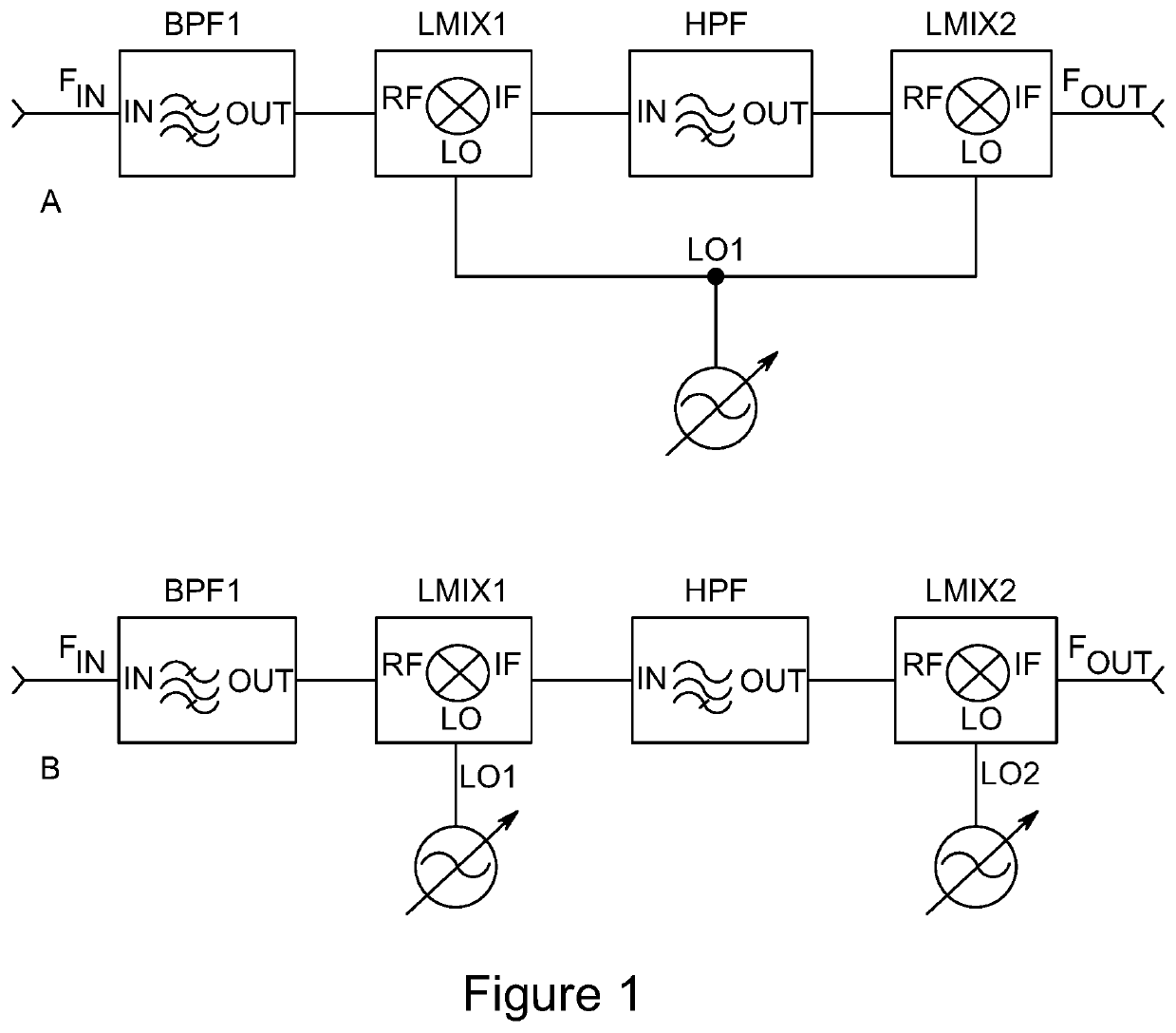
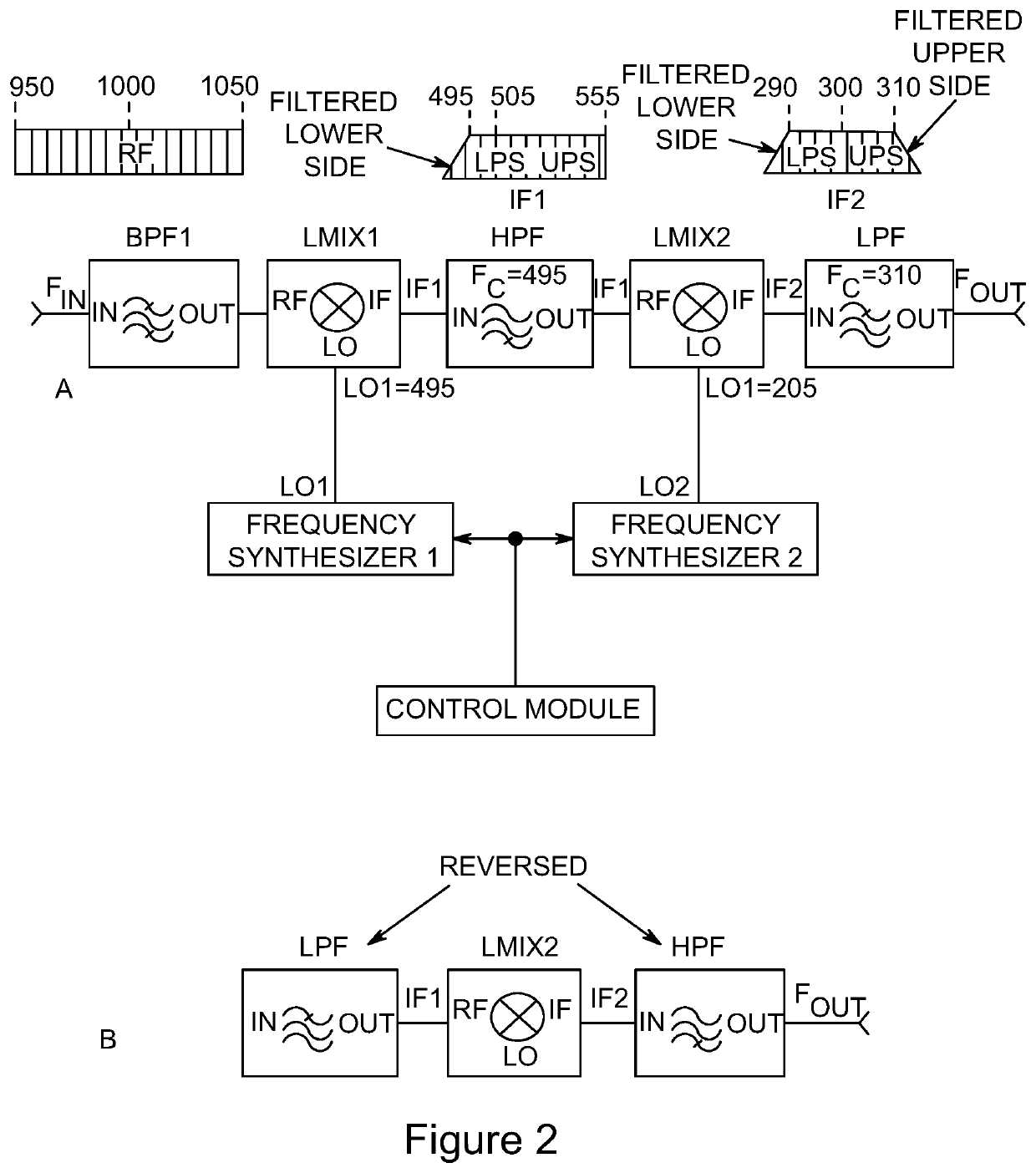
Dynamically tunable radio frequency filter and applications
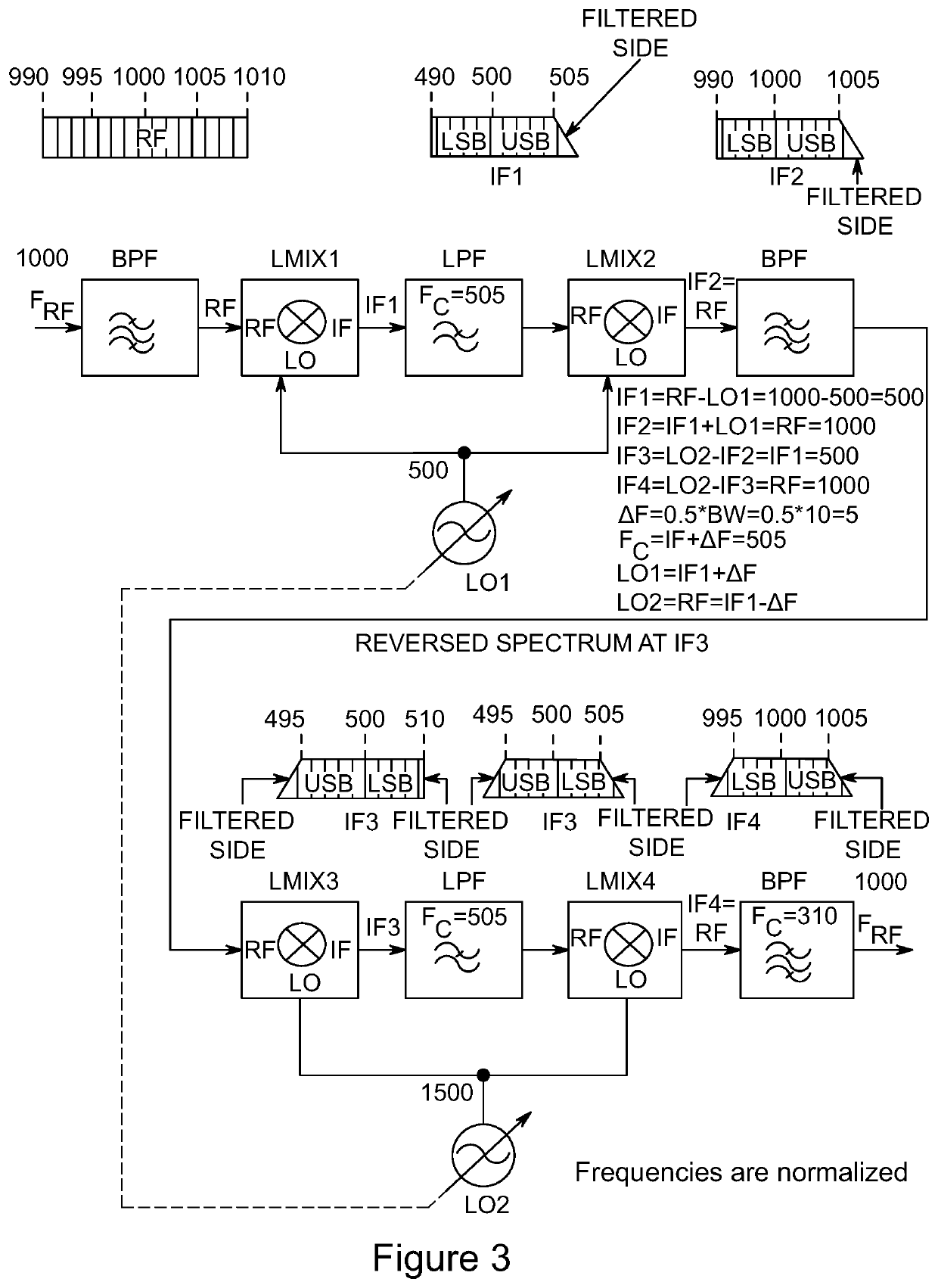
PendingUS20210258025A1Precise processRapid and precise tunabilityTransmissionFrequency spectrumFrequency mixer
A family of radio frequency (RF) filter circuits that use radio frequency linear mixers to controllably separate desired frequency spectrum from undesired frequency spectrum, and convert signals from one frequency to another, permitting inclusion in a closed- or open-loop control circuit that supports rapid dynamic manipulation of the filter circuit's center frequency and bandwidth.
Owner:BELKIN SAM
Alignment system and method for calibrating position of optical fiber bore ferrule
ActiveUS10634855B2Improve optical performance and random matching performanceReduce or even eliminate various disadvantageous effectsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFiberEngineering
The present invention discloses an alignment system for calibrating a position of an optical fiber in a bore of a ferrule, comprising: an outer cylinder alignment element for calibrating a center position of an outer cylinder of the ferrule, so that the center of the outer cylinder of the ferrule is aligned with a center of the outer cylinder alignment element; a fiber core alignment element comprising a fiber core having a center aligned with the center of the outer cylinder alignment element; an optical vision system for identifying a center position of a fiber core of the optical fiber and the center position of the fiber core of the fiber core alignment element; and a controlling and moving system for actively adjusting the position of the optical fiber in the bore of the ferrule under the guide of the optical vision system.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TELECOMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Power amplifier circuit
ActiveUS10177724B2Reduce lossesIncrease load impedanceTransmission path divisionPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierRadio frequency signal
A power amplifier circuit includes first and second transistors and a first voltage output circuit. A radio frequency signal is input into a base of the first transistor. The first voltage output circuit outputs a first voltage in accordance with a power supply voltage. The first voltage is supplied to a base or a gate of the second transistor. An emitter or a source of the second transistor is connected to a collector of the first transistor. A first amplified signal generated by amplifying the radio frequency signal is output from a collector or a drain of the second transistor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
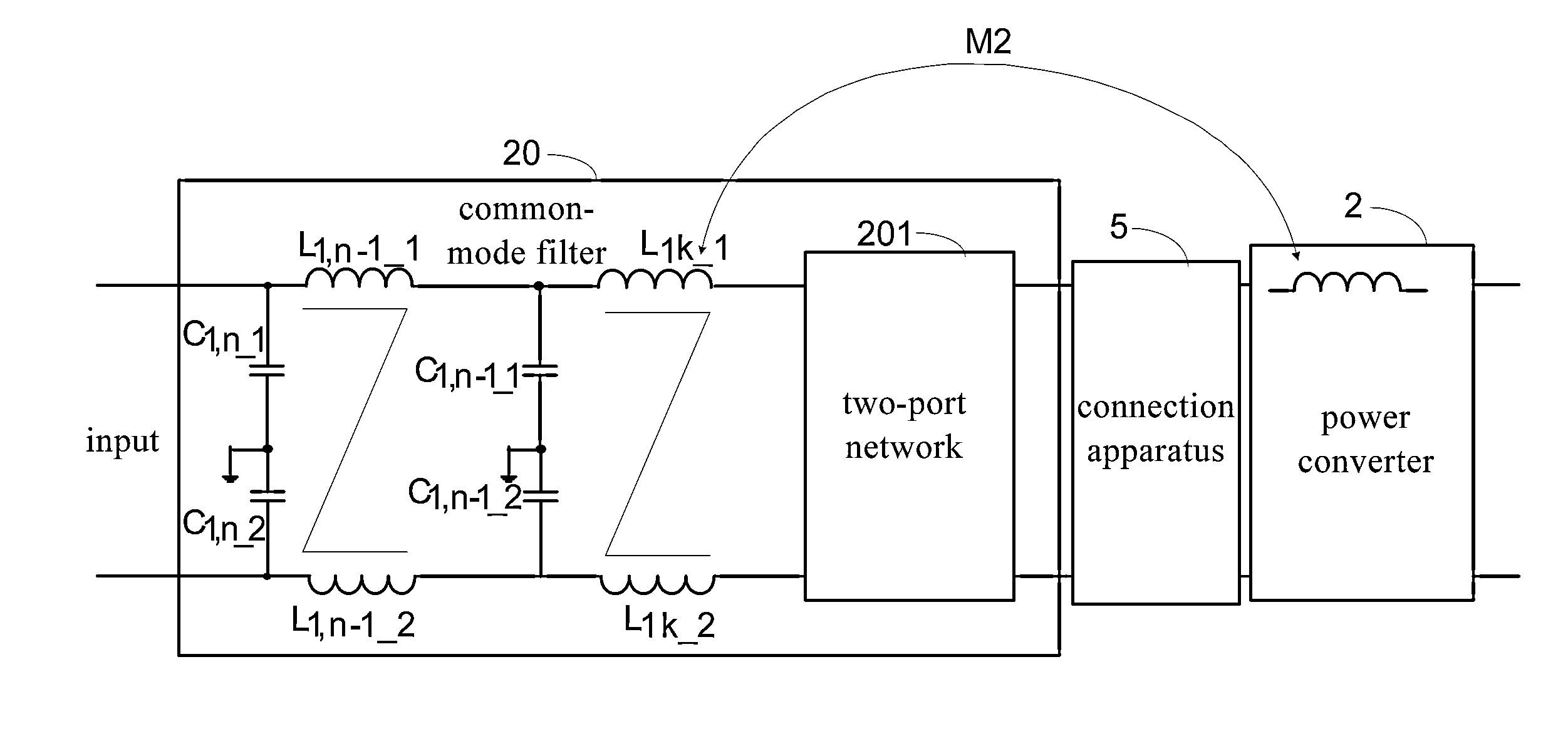
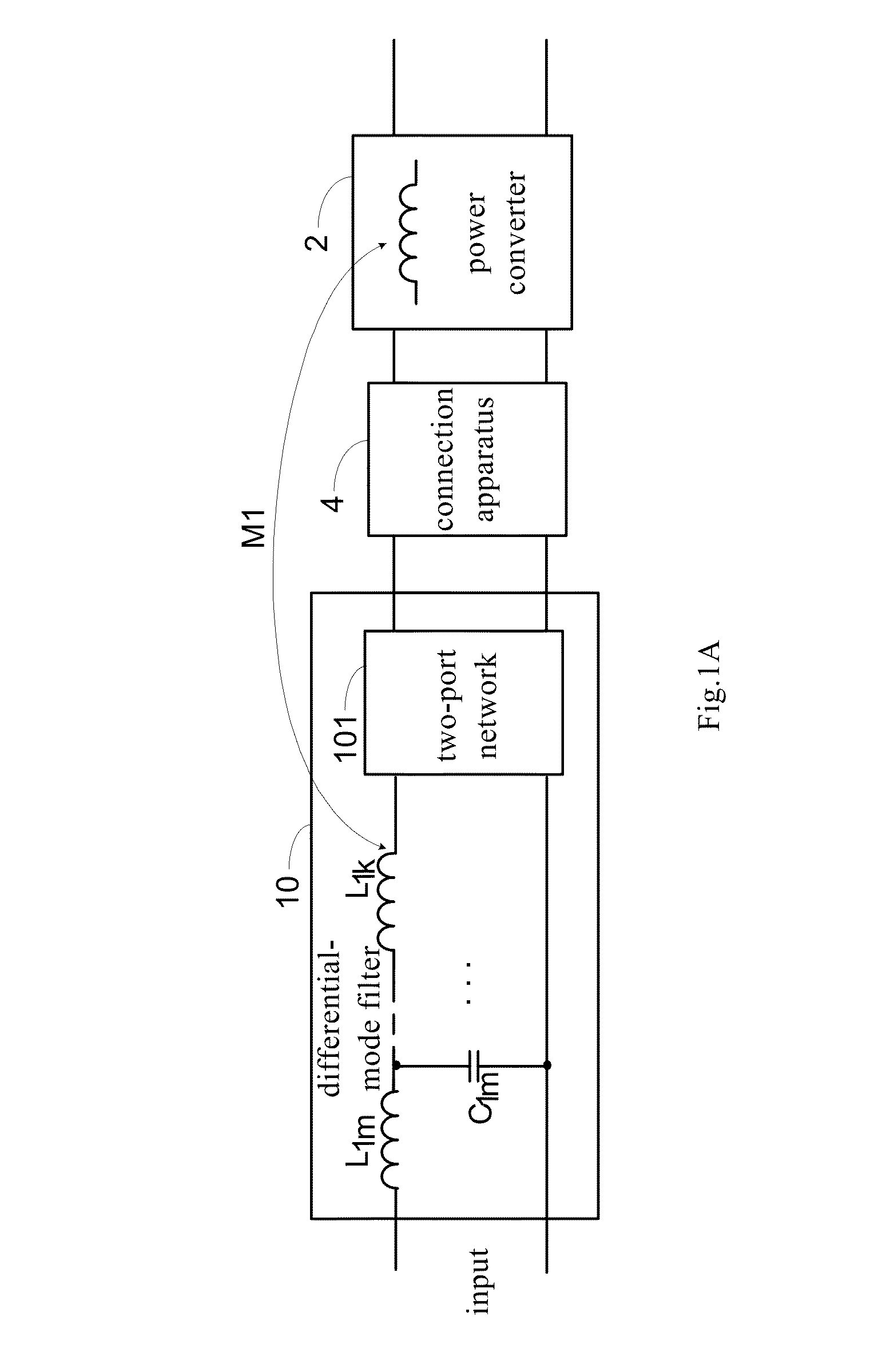
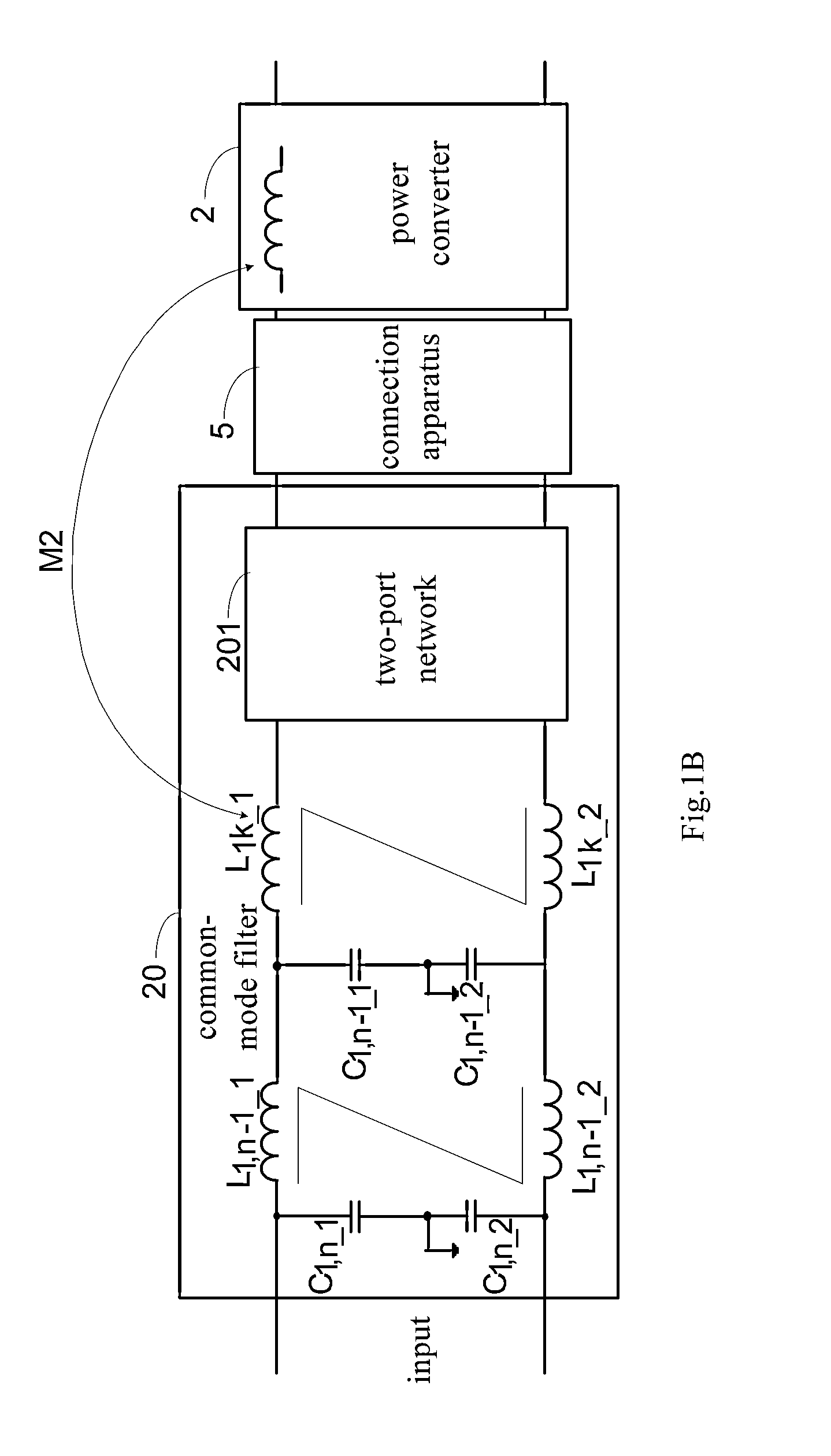
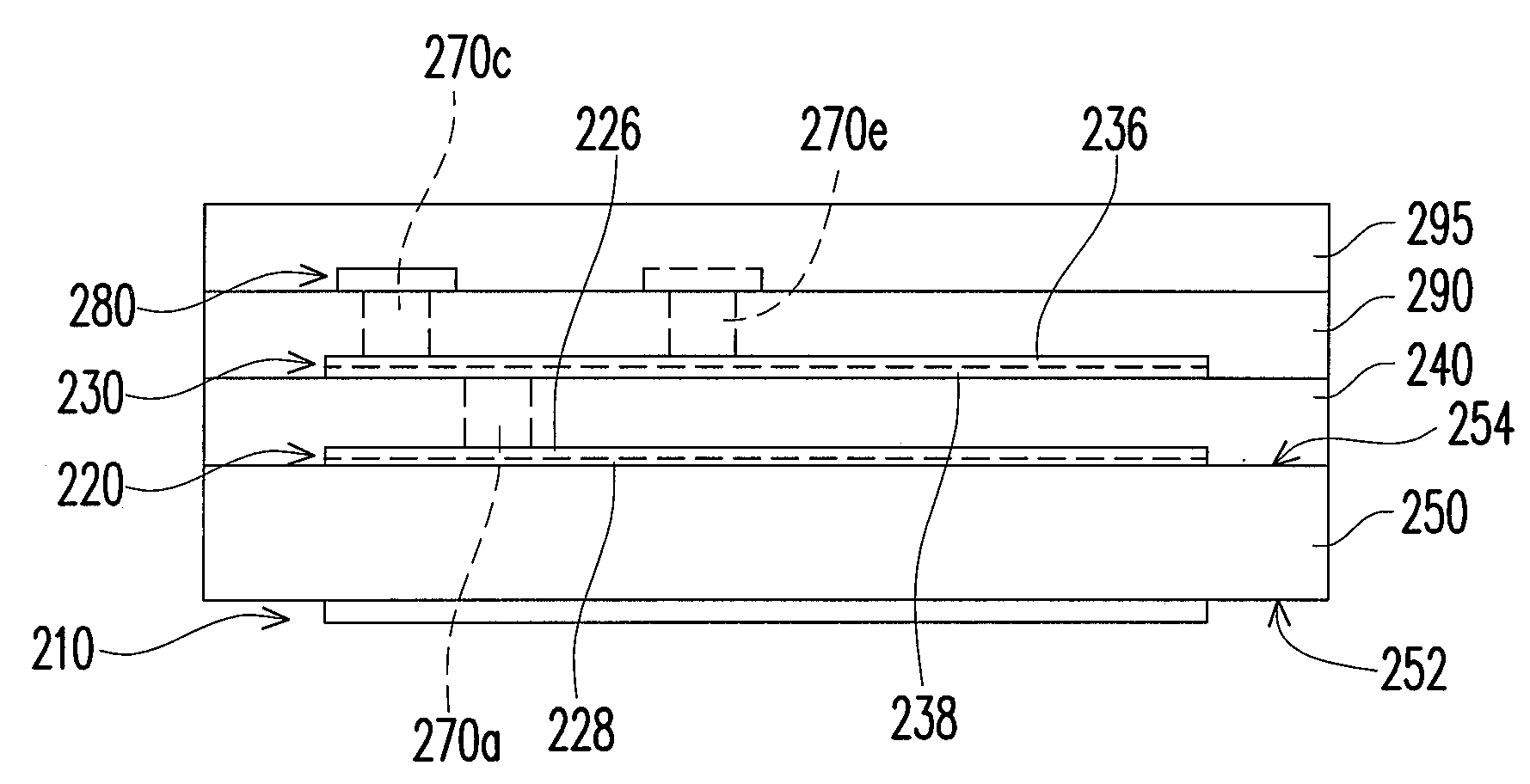
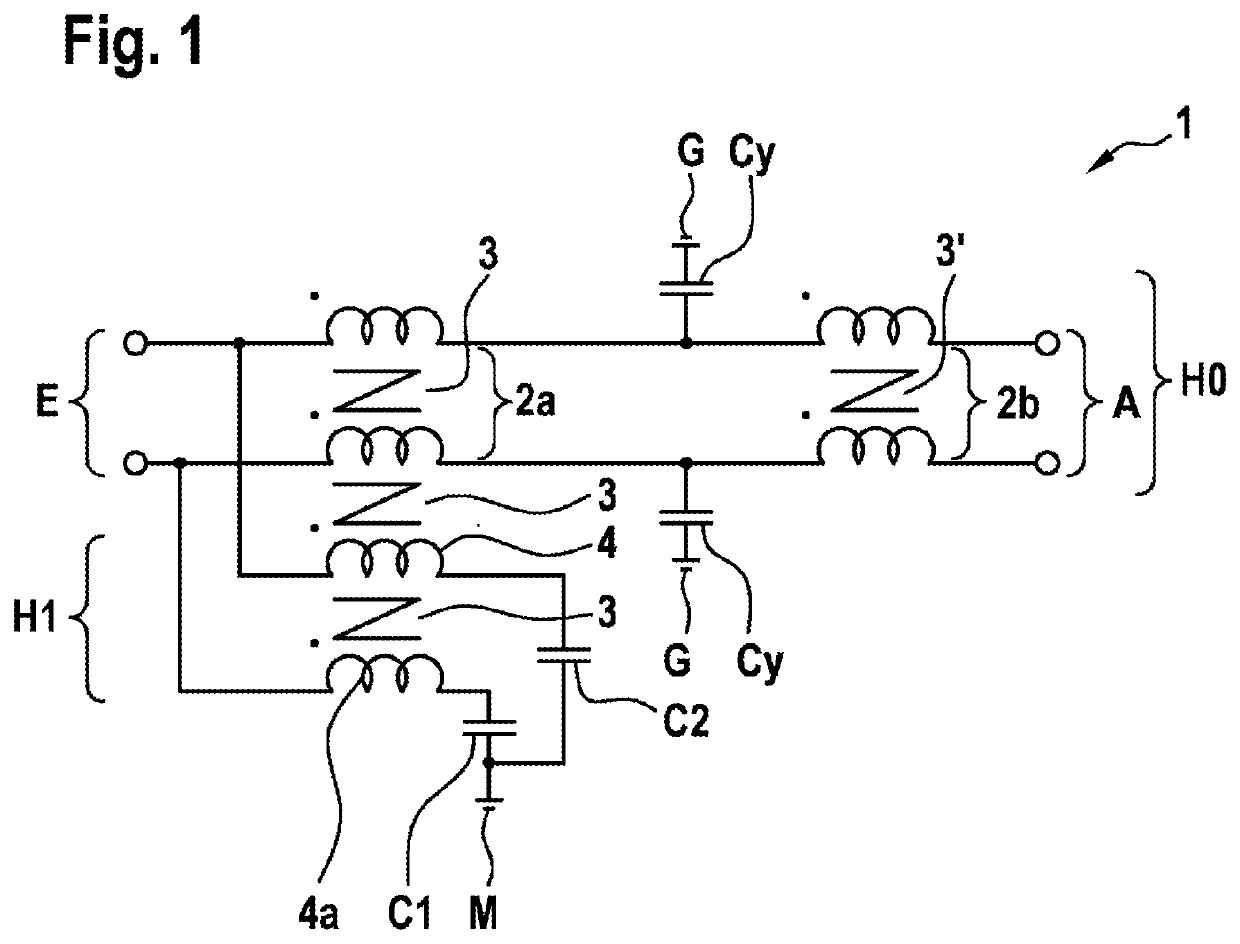
Electrical filter device for filtering a common-mode interference between a current source and a load
ActiveUS20210273550A1Insertion lossLimit capacitanceMultiple-port networksPower conversion systemsInterference resistanceInductor
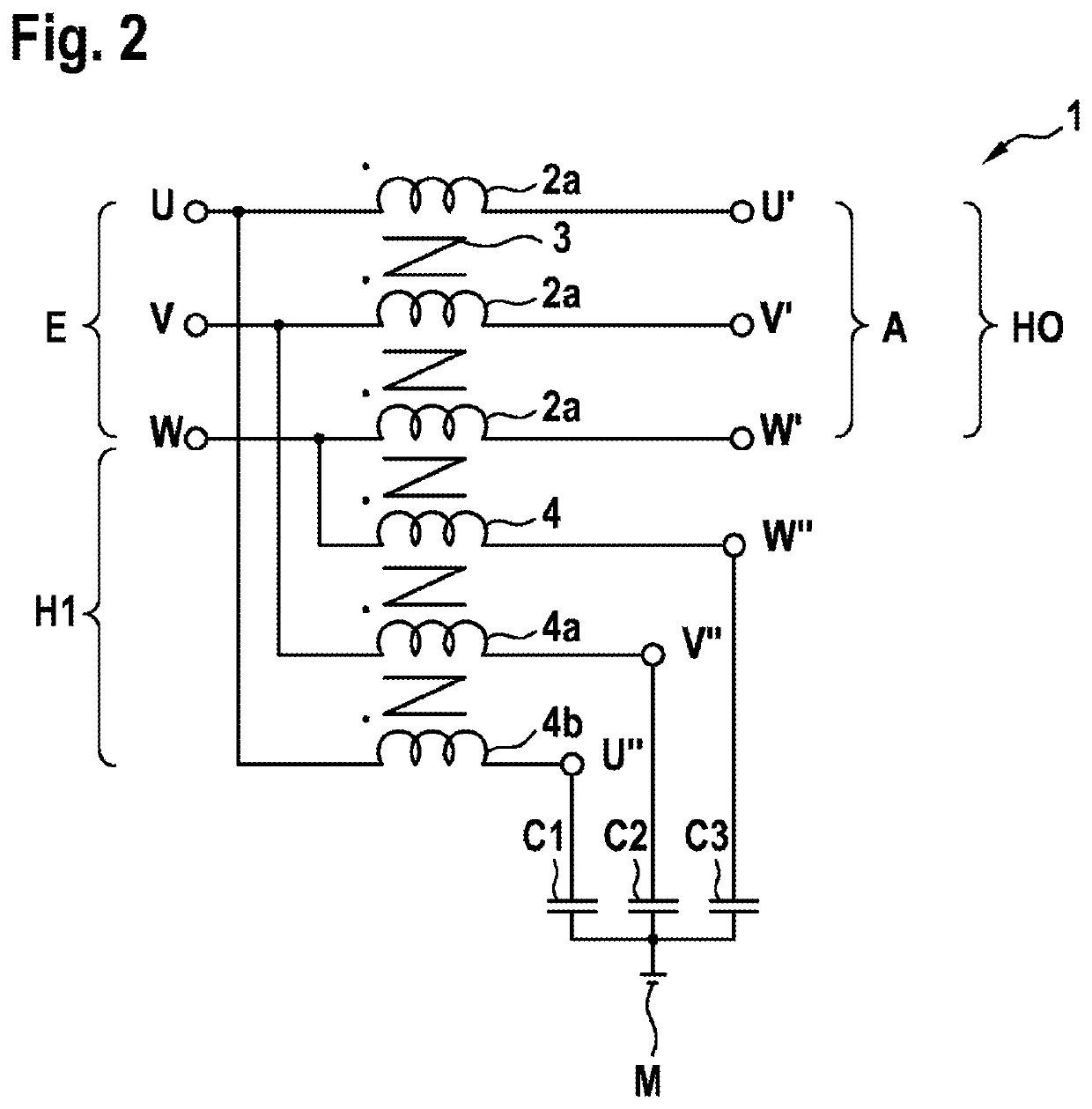
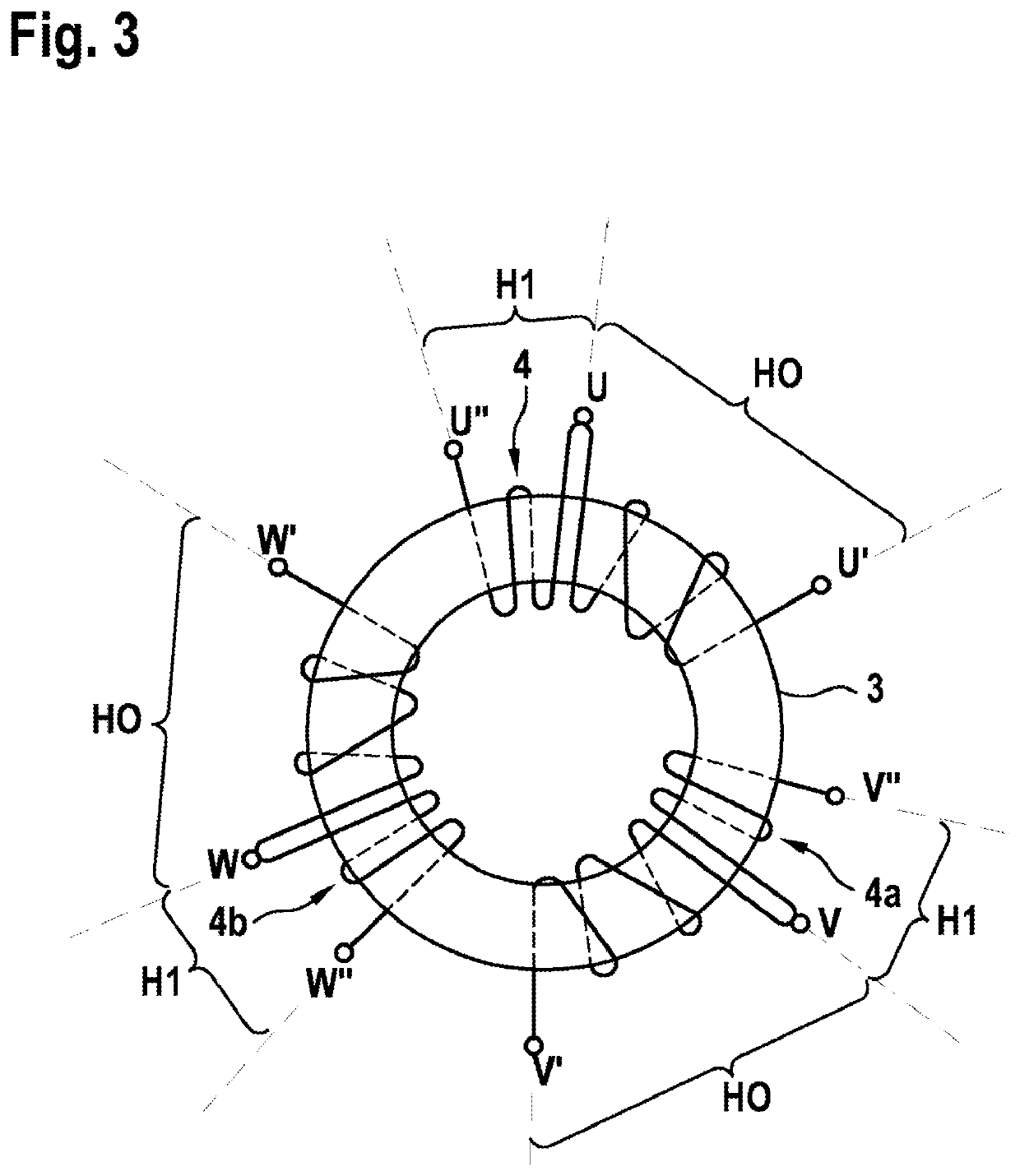
The present invention provides an electrical filter device (1) for filtering a common-mode interference between a current source and a load, comprising:—a signal input (E), which comprises at least one first terminal (E1) and can be connected to the current source;—a signal output (A), which can be connected to the load;—a main stage (H0), having a first main inductor (2a), which comprises a coil with a first core (3), the first main inductor (2a) being connected to the first terminal (E1); and—an auxiliary stage (H1), having at least one first anti-interference capacitor (C1) and one first auxiliary inductor (4), the first auxiliary inductor (4) being connected between the first terminal (E1) and the first anti-interference capacitor (C1), the first auxiliary inductor (4) being inductively coupled to the first main inductor (2a).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com