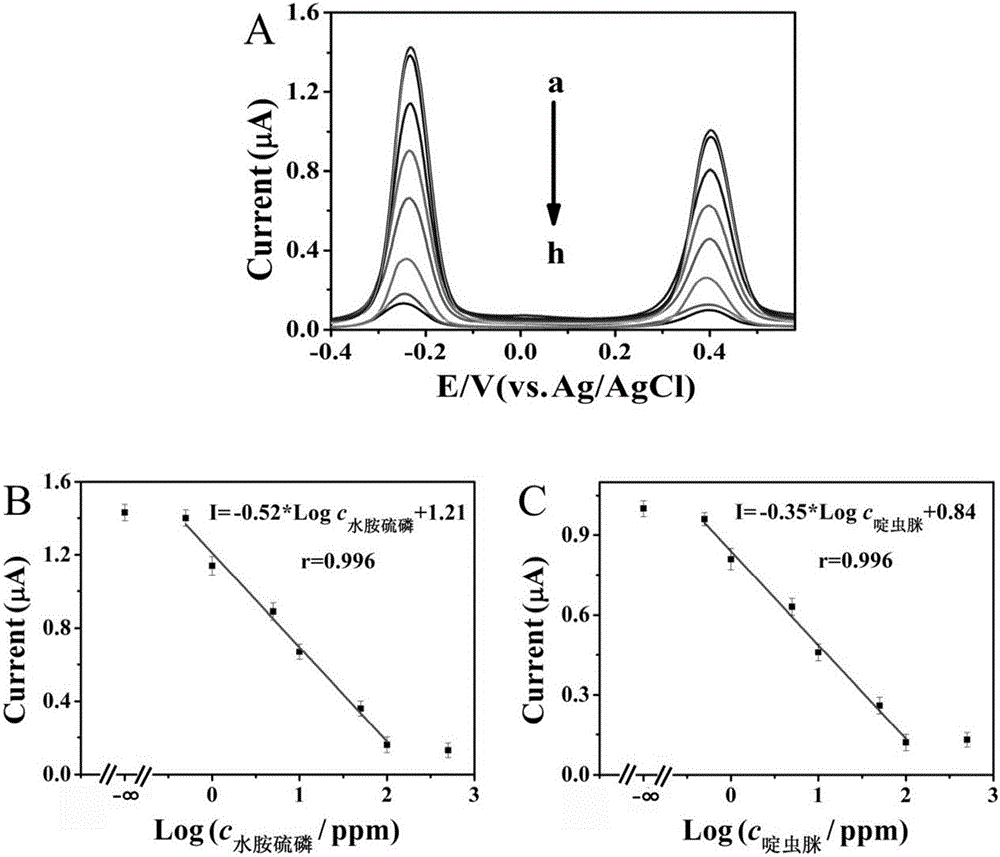
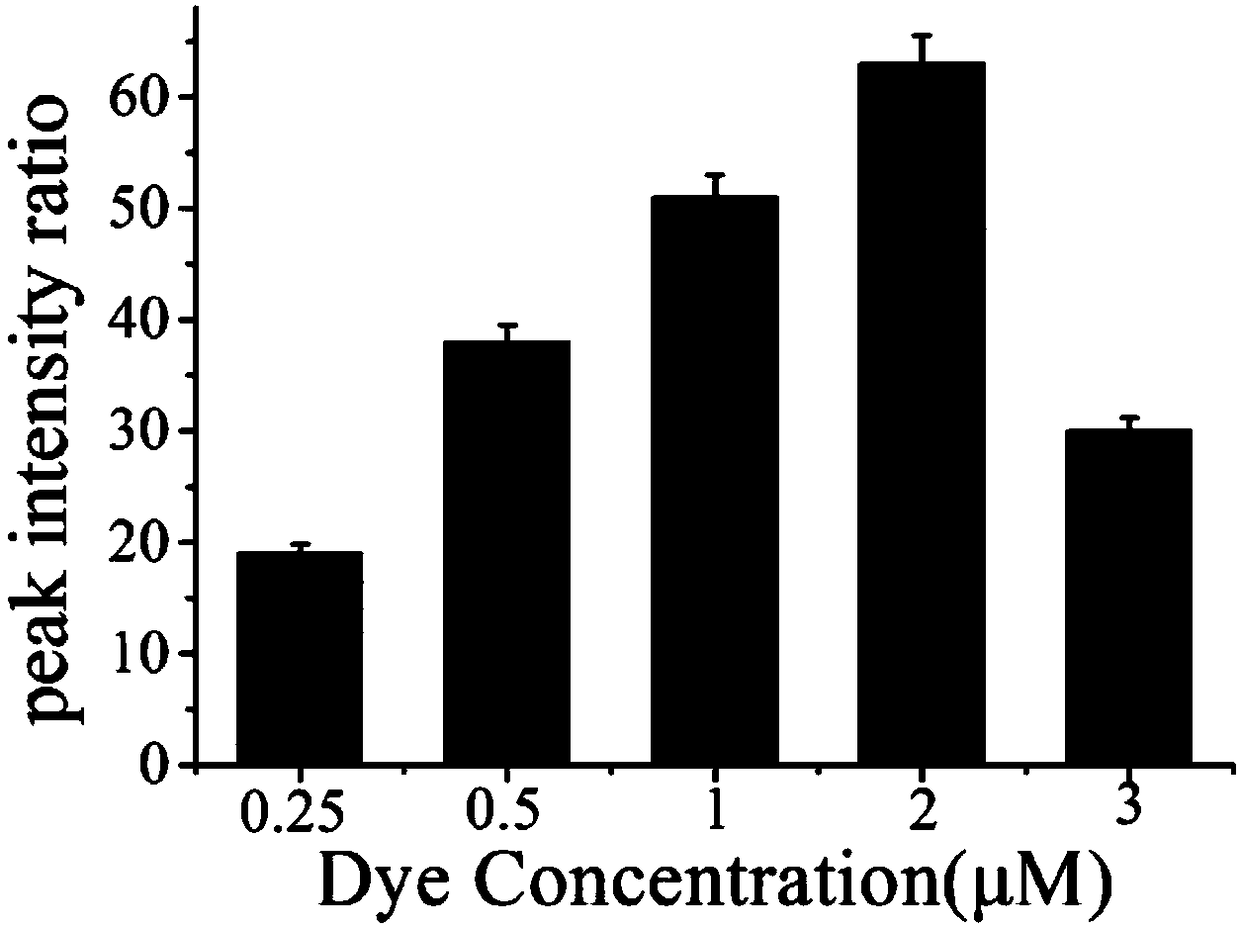
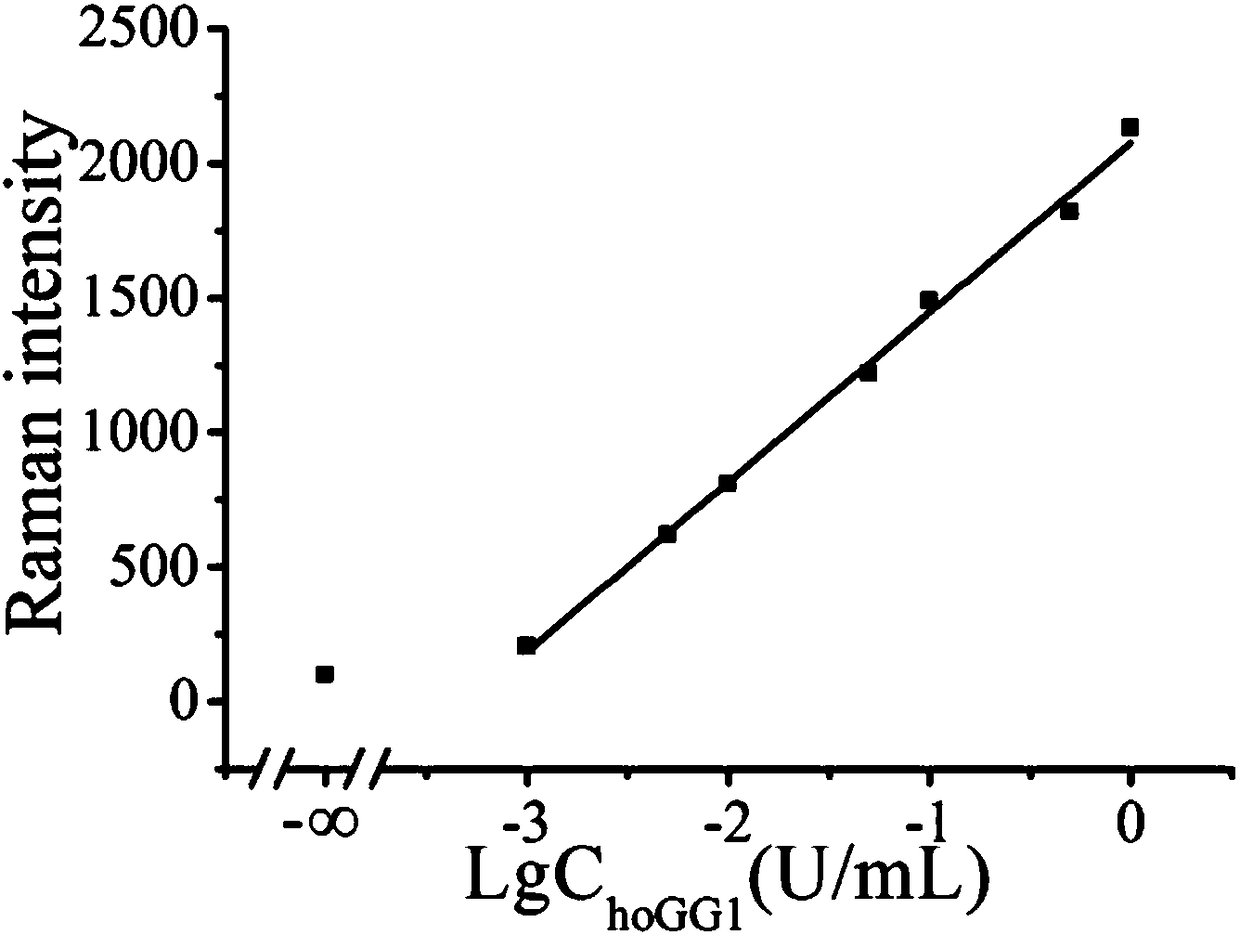
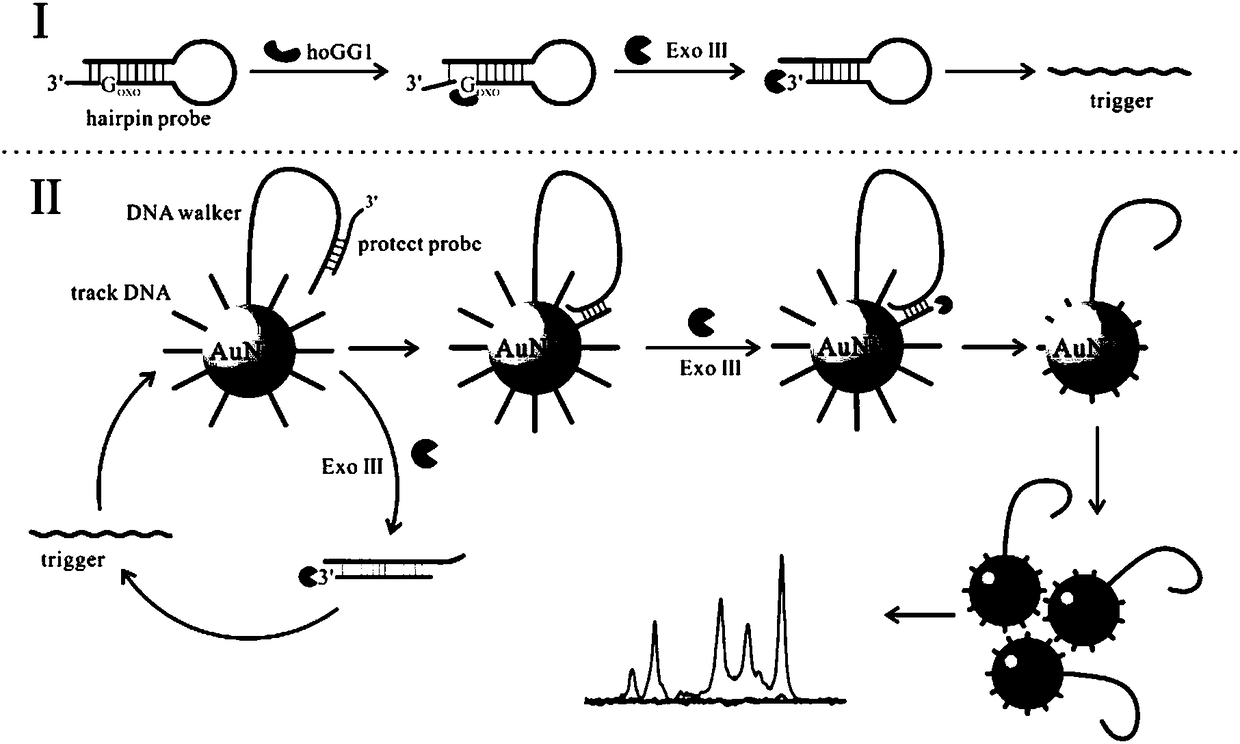
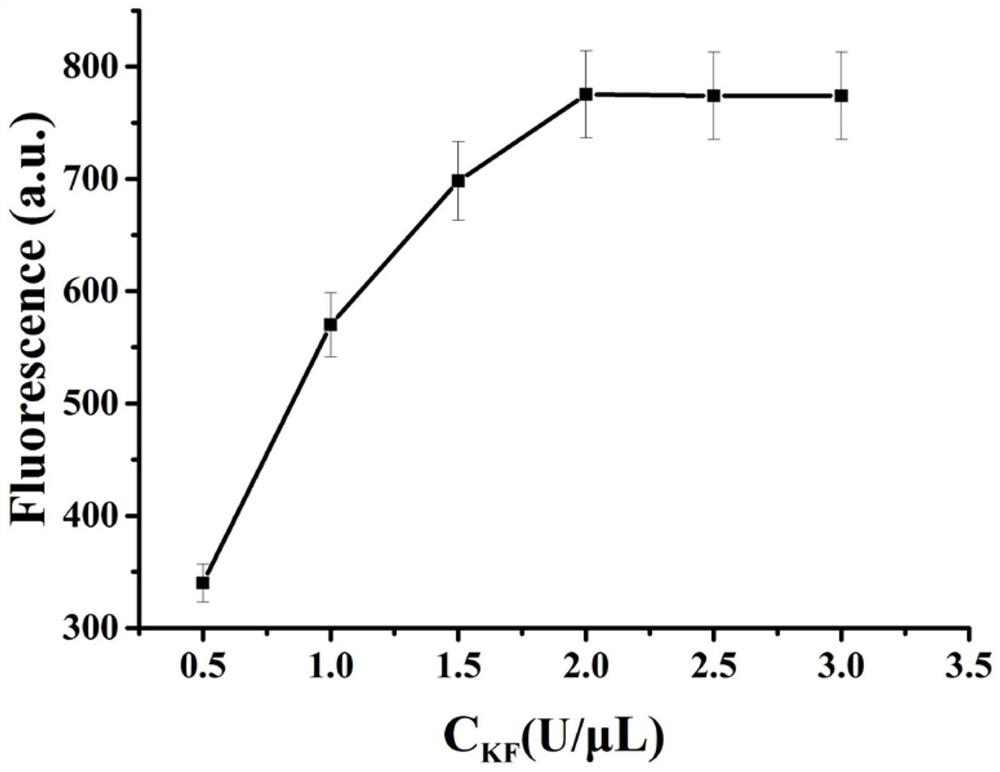
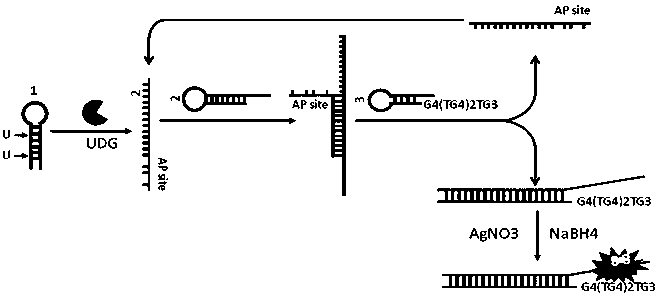
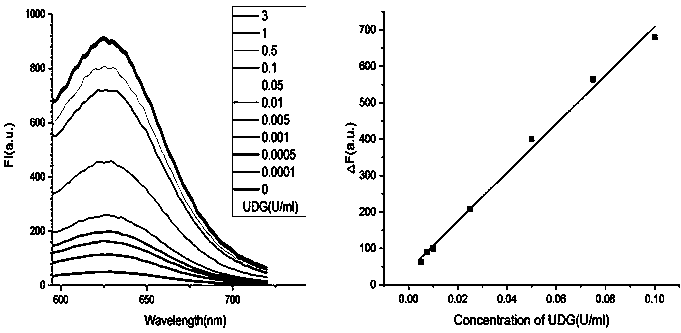
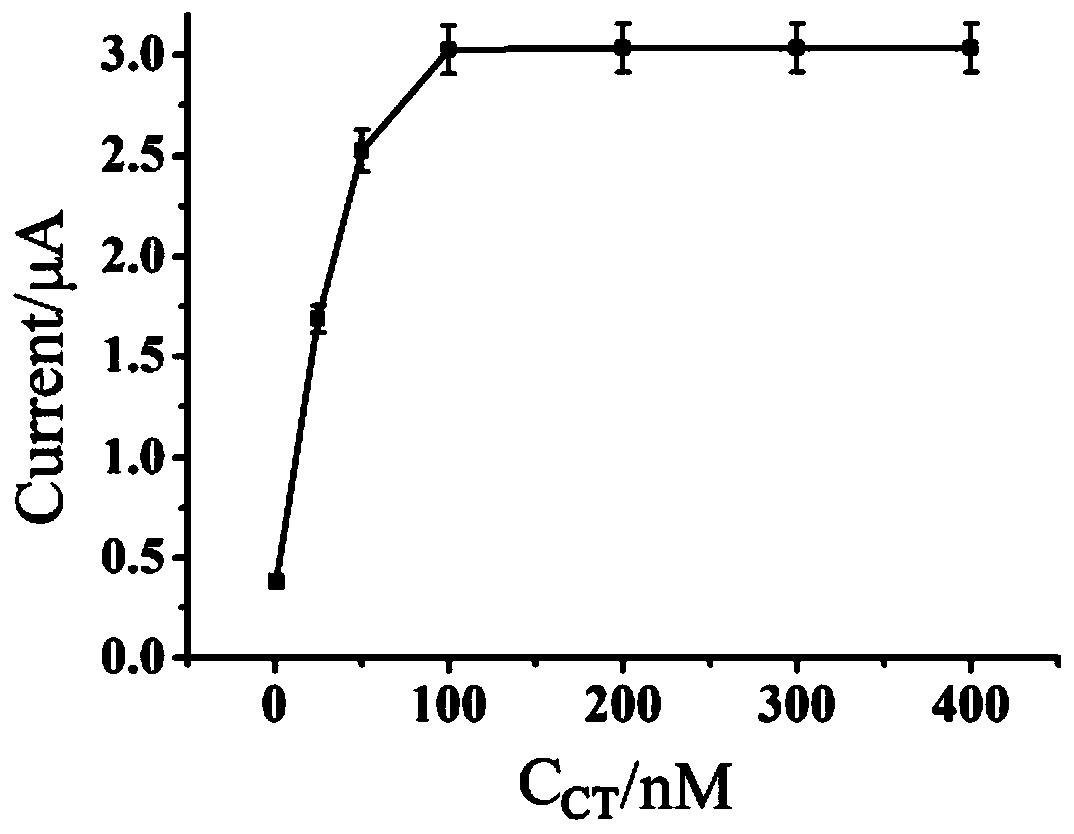
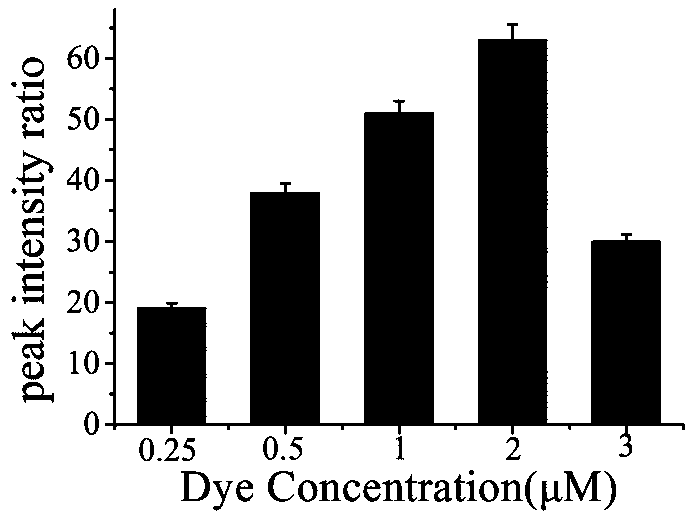
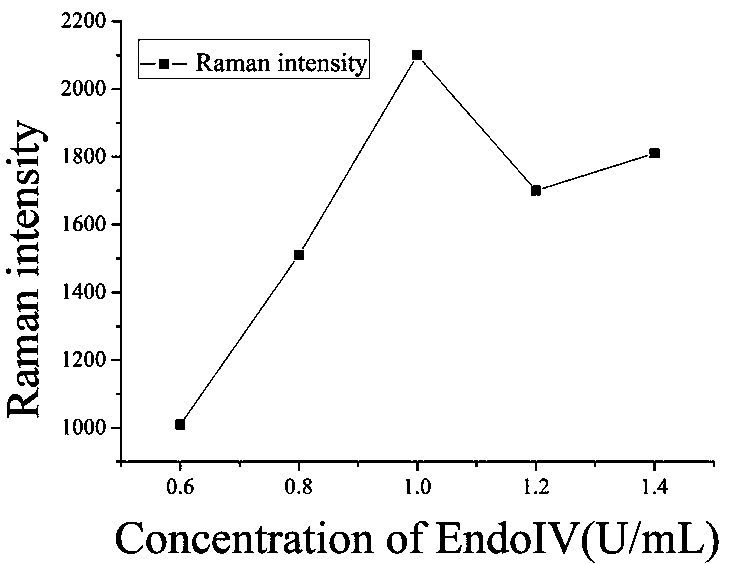
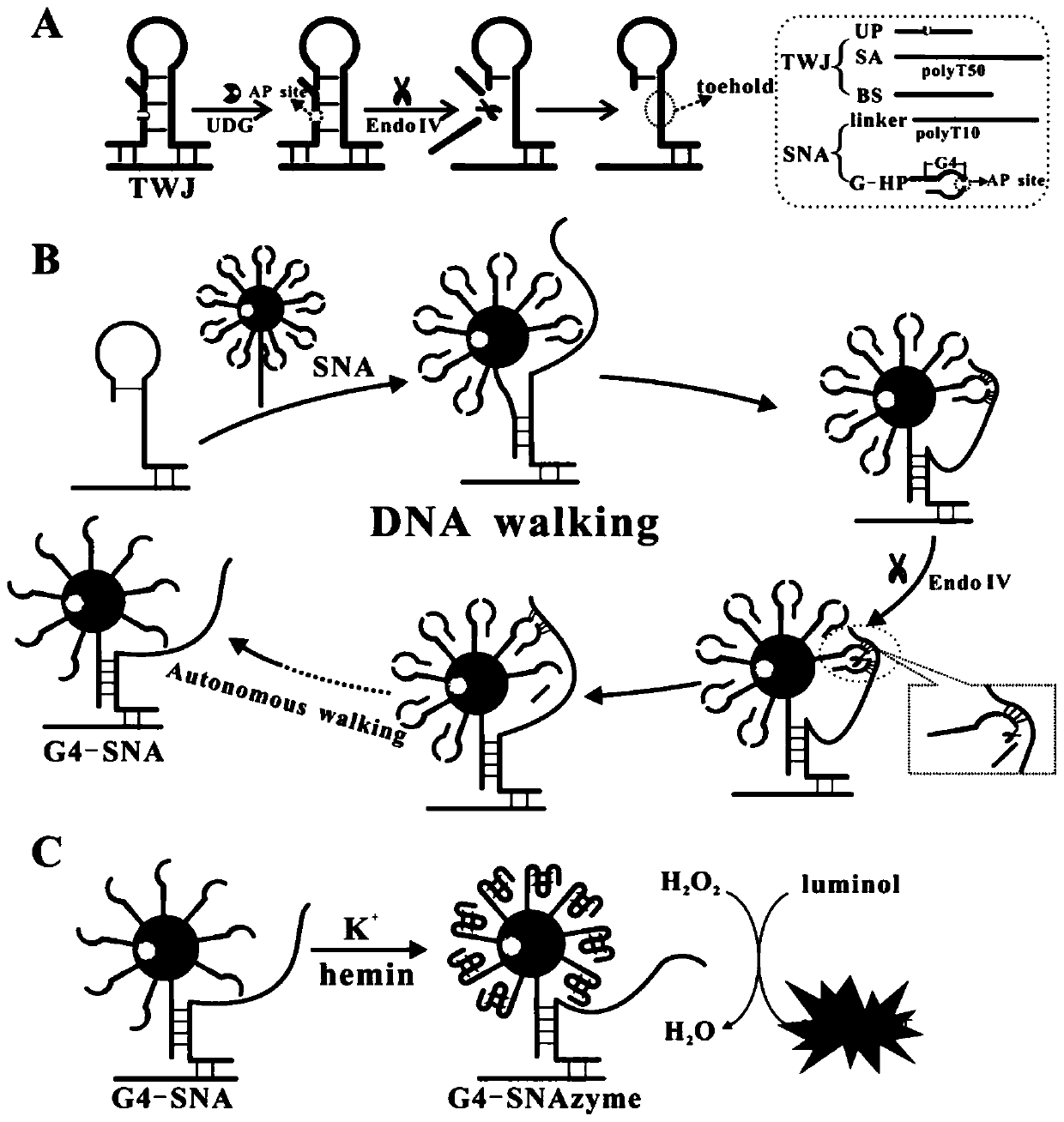
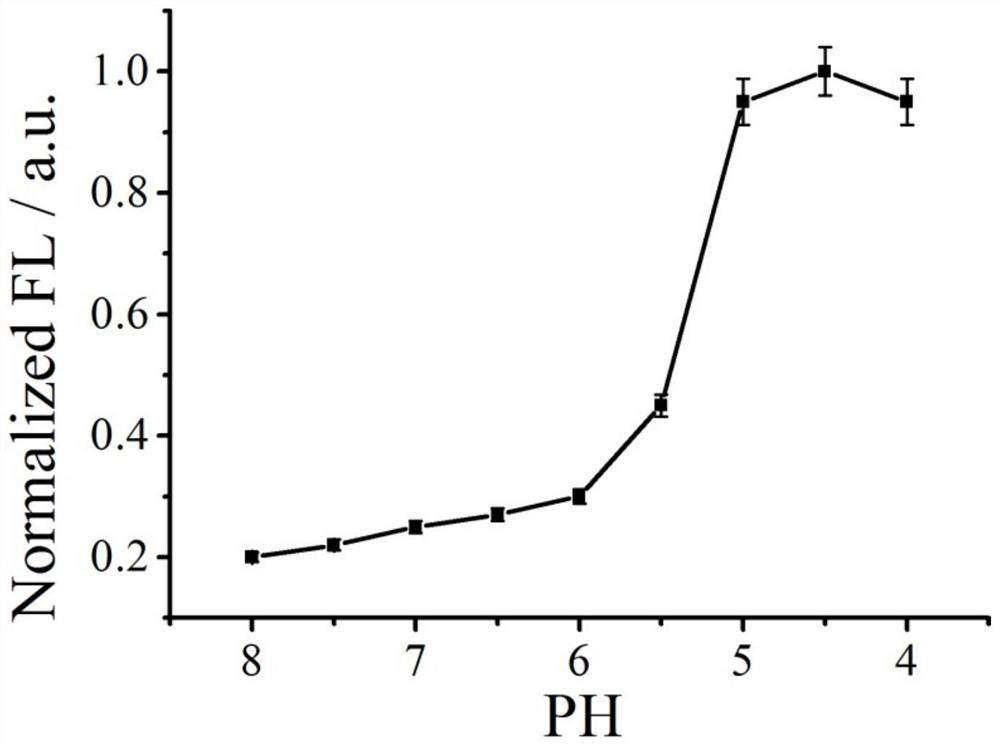
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73results about How to "Inexpensive requirements apply" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
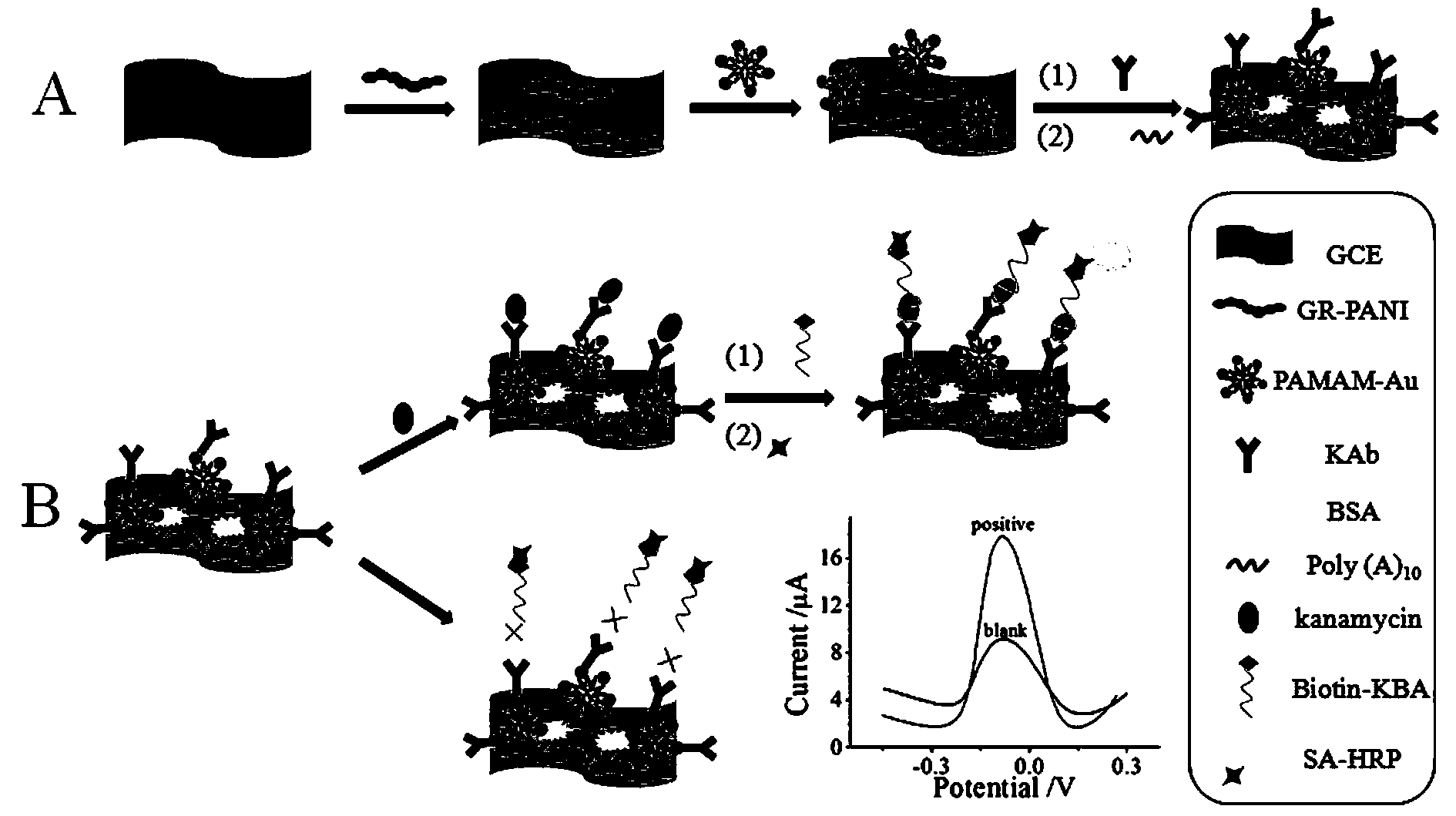
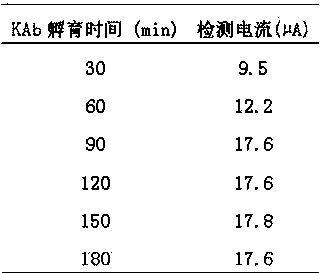
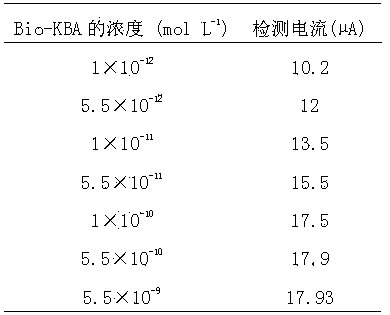
Electrochemical aptamer electrode for kanamycin detection and preparation method of electrochemical aptamer electrode
InactiveCN104237344AEasy to carryConvenient amountMaterial electrochemical variablesKanamycinPolyamide
The invention relates to the technical field of detection sensors and particularly relates to an electrochemical aptamer electrode for kanamycin detection. Graphene-polyaniline compound, polyamide-amine dendritic high molecule-gold nano compound, kanamycin anti-body are modified on a glass carbon electrode in sequence from bottom to up; the surface of the electrode is sealed with BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin) and single chain DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) containing 10 adenine nucleotide. The preparation method is simple, stable in performance and good in electrode repeating performance and is suitable for practical applications of kanamycin detection in food safety and bio-sensor industrialization; the prepared electrode is low in technical cost and is suitable for the requirement of low cost in industrialization; according to a sandwich type electrochemical sensing system fixed by using the glass carbon electrode as a fixing carrier and based on a DNA aptamer, rapid and online kanamycin detection in food is realized and the detection limit is 4.6x10<-6>mu gmL<-1>.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Aptamer electrode for detecting terramycin, and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104777206AConvenient amountIncrease concentrationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAptamerEngineering
The invention provides an aptamer electrode for detecting terramycin. The electrode is characterized in that a glassy carbon electrode is sequentially modified with a graphene-gold nanometer compound and a BSA-OTC compound from bottom to top. A signal layer is methylene blue modified aptamer having a G tetrad structure and folded under an RCA chain amplification reaction, and the content of a target product is reflected through the amount of methylene blue. The invention also provides a manufacturing method of the aptamer electrode. The aptamer electrode has the advantages of simple manufacturing method, stable performances, and good repeatability, and is suitable for terramycin detection in the medicine safety and the industrialized practical application of biosensors.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Electrochemical sensor for detecting isocarbophos and acetamiprid at same time and method system of electrochemical sensor
ActiveCN106841340AAchieve high specificity detectionAchieve recyclingMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical gas sensorFerrocene
The invention discloses an electrochemical sensor for detecting isocarbophos and acetamiprid at same time and a method system of the electrochemical sensor; the electrochemical sensor comprises an electrode, a beacon probe layer, a 6-mercaptohexan-1-ol (MCH) closure layer, and a homogenous reaction product layer sequentially from inside to outside; the beacon probe layer is modified with methylene blue and ferrocene having electrochemical signals not mutually affected; a preparation method comprises: polishing the electrode, treating with H2SO4 and H2O2, and modifying the surface of the electrode with a beacon probe. The electrochemical sensor according to the invention is simple to prepare and has good performance stability, the electrode is highly repeatable, and the electrochemical sensor is applicable to the detection of isocarbophos and acetamiprid in terms of food safety and the actual application of biosensor industrialization; the electrochemical sensor can provide quick online detection for isocarbophos and acetamiprid in food, and isocarbophos and acetamiprid detection limits are 0.12 ppb and 0.37 ppb respectively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Biosensor for detecting hOGG1 activity and use thereof
ActiveCN108169203AMild reaction conditionsFast responseRaman scatteringGlycosidase activityExonuclease III
The invention provides a biosensor for detecting 8-hydroxylaguanine DNA glycosidase activity. The biosensor comprises an exonuclease III, hairpin probes and gold nanoparticles modified by DNA on the surfaces. Through surface-enhanced Raman detection, the 8-hydroxylaguanine DNA glycosidase activity is detected. The biosensor has mild reaction conditions and a fast reaction rate. A detection methodusing the biosensor is easy to operate, has a short detection period and high detection sensitivity. The main processes based on the detection principle are carried out in a homogeneous phase so thatthe reaction speed is increased and the complexity of operation is reduced. The biosensor realizes fast, simple and sensitive detection of a target. The biosensor realizes a low preparation cost.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Fluorescence biosensor for detecting UDG (Uracil-DNA Glycosylase) and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109444105ARealize highly sensitive detectionLow detection limitFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnergy transferResonance
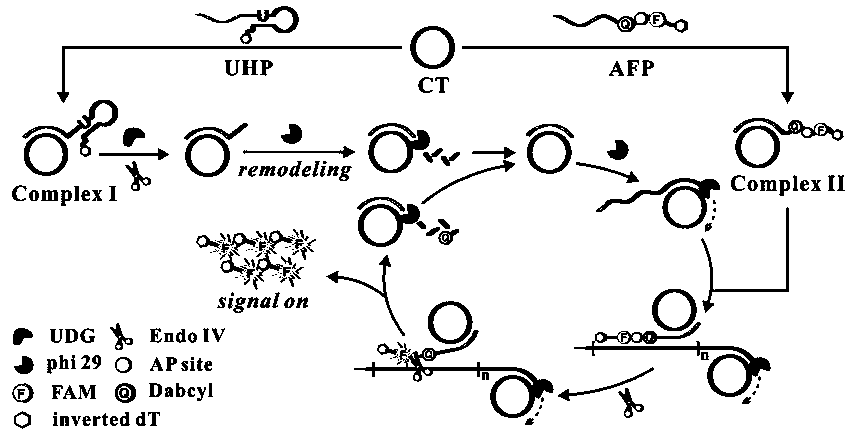
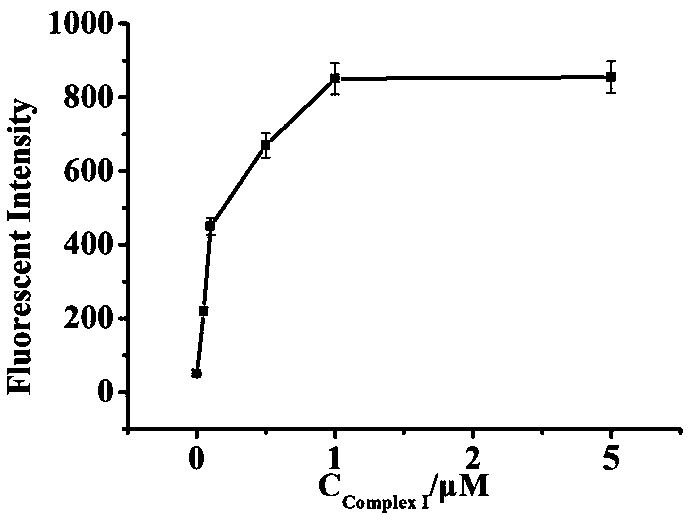
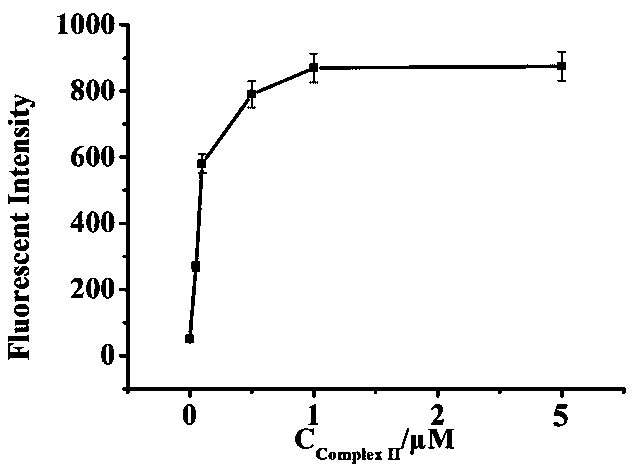
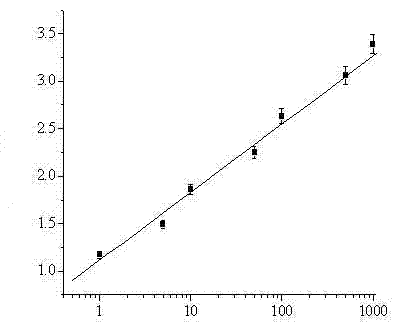
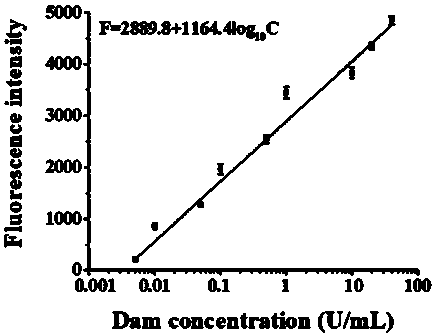
The invention relates to the technical field of a biosensor, and particularly relates to a fluorescence biosensor for detecting UDG (Uracil-DNA Glycosylase) on the basis of a polymerase-assisted feedback rolling circle amplification and endonuclease amplification fluorescence method. The invention aims to solve problems of both low specificity and low sensitivity of a method for detecting UDG in the prior art. The biosensor for detecting the UDG on the basis of a feedback rolling circle amplification technology achieves a rolling circle amplification effect on matching of phi29 polymerase andendonuclease IV, implements fluorescence resonance energy transfer of a fluorophore and a Quenching group and performs a homogeneous reaction on mixed liquid. A preparation method comprises: constructing a circular template and a composite probe; feeding back a rolling circle amplification signal and carrying out fluorescence detection. Specific hydrolysis of the UDG on a basic group U is utilized, and by utilizing such specific reaction, the UDG can be accurately measured and meanwhile, interference can also be avoided; by utilizing endonuclease IV circle amplification, a signal amplificationeffect is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
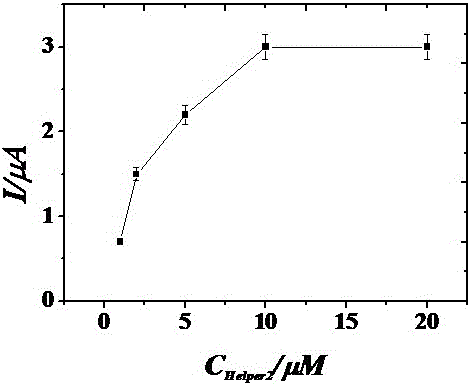
Biosensor for detecting streptomycin based on aptamer and preparation method of biosensor
ActiveCN104764790AHighly specific detectionAchieve recyclingMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerQuantitative determination
The invention provides a biosensor for detecting streptomycin based on an aptamer. The biosensor comprises a gold electrode, wherein an MB capture probe layer, HAP and an ssDNA layer are sequentially modified on the gold electrode. The invention also provides a preparation method of the biosensor. Based on specific recognition of the aptamer and the target, the sensor has the advantages of high detection speed, low detection limit, high specificity and the like, the defects of the conventional streptomycin detection method can be overcome, and rapid and accurate quantitative determination is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
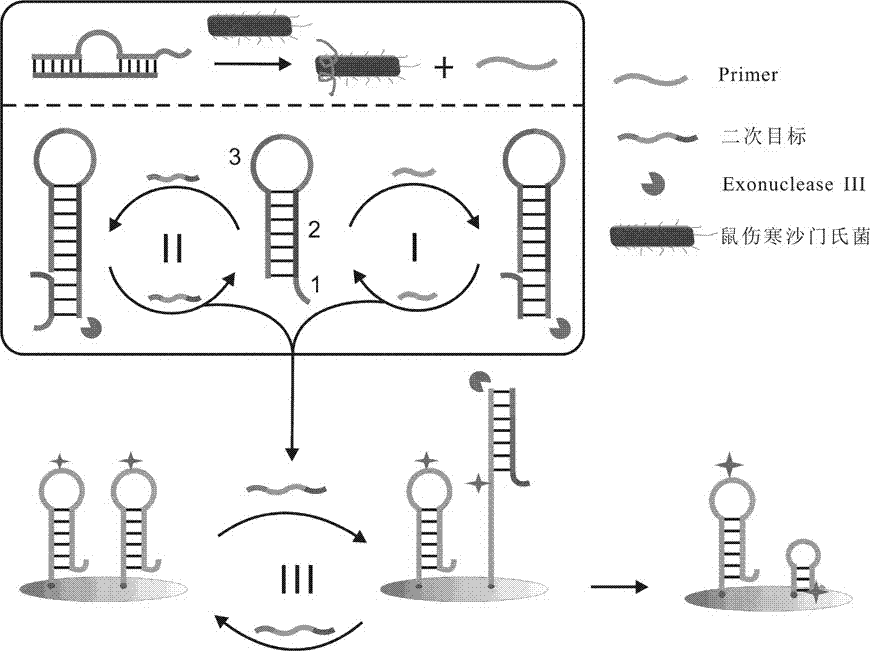
Aptamer based salmonella typhimurium detection biosensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105238852AAchieve high specificity detectionRealize continuous generationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesAptamerSalmonella frintrop
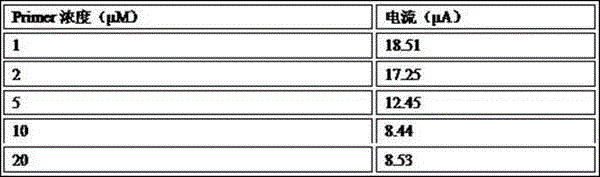
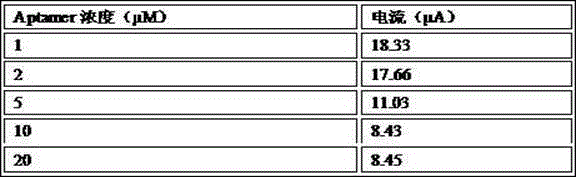
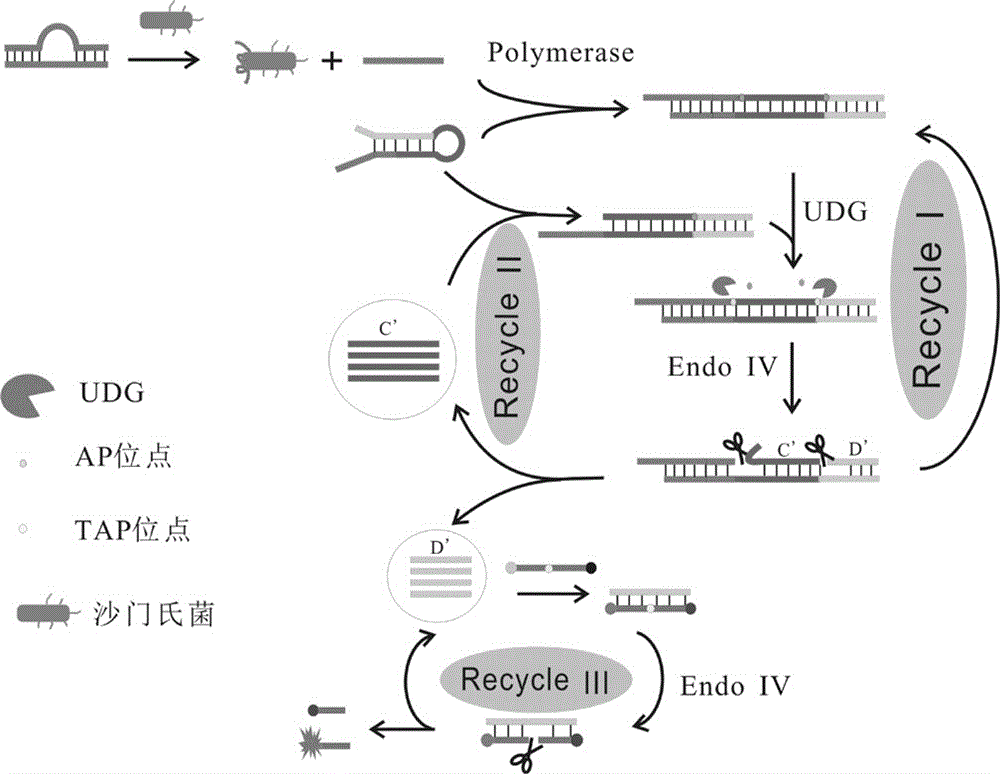
The invention relates to an aptamer based salmonella typhimurium detection biosensor and a preparation method thereof. Signal amplification is realized by continuous generation and cyclic utilization of Primer, and consequently high-sensitivity detection of salmonella typhimurium is realized, and lower detection limit can be acquired. The aptamer based salmonella typhimurium detection biosensor is high in specificity and sensitivity, low in cost and quick in detection. By the detection method, a salmonella typhimurium detection limit is 5-15cfu / mL, and a detection range is 1*10-1*107cfu / mL.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method for detecting salmonella with fluorescence method on basis of enzymatic remediation isothermal cycle amplification
ActiveCN105755124AHighly specific detectionRealize positioning cuttingMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceBiology
The invention relates to the technical field of biological detection, in particular to a fluorescence biological detection method based on enzymatic remediation cycle three-time amplification. The method comprises steps as follows: an arched probe is constructed; enzymatic remediation cycle signal amplification and fluorescence detection are performed; high-specificity detection is performed on a target object, namely, salmonella, by the aid of a nucleic acid aptamer through specific recognition of the nucleic acid aptamer; the signal amplification effect is realized through enzymatic remediation cycle amplification.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Biosensor for detecting salmonella based on aptamer and preparation method thereof and application
ActiveCN110632300ALow detection limitHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFluorescencePeroxidase
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a biosensor for detecting salmonella based on an aptamer. Based on the specific recognition of the aptamer and a target, ahairpin probe HAP is opened, S1 is replaced from a composite probe S by using a fulcrum-mediated strand displacement reaction, a sequence for forming a G-quadruplex is exposed from the replaced S in acatalytic hairpin self-assembly (CHA) amplification manner, and the G-quadruplex / heme DNA enzyme is formed in the presence of heme. Cysteine is oxidized into cystine by using the catalytic performance of G-quadruplex / heme horseradish peroxidase, charge transfer between cysteine and silver clusters via a gold-sulfur bond cannot be realized, fluorescence signal conduction is regulated and controlled, the aptamer biosensor is constructed, and the biosensor only needs one step in reaction, so that the biosensor has the advantages of high detection speed, simplicity and convenience in operation, low price, low detection limit, high specificity and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Biosensor for detecting escherichia coli and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104764774AReduce processing costsInexpensive requirements applyMaterial electrochemical variablesAntiendomysial antibodiesEnterobacteriales
The invention discloses a biosensor for detecting escherichia coli. The biosensor orderly comprises a gold electrode, a glutaraldehyde-escherichia coli antibody layer, a bovine serum albumin sealing layer, an escherichia coli layer and a RCA product layer from inside to outside. The invention discloses a preparation method of the biosensor. The biosensor has stable electrode performances, good repeatability and a detection limit of 1.6*10cfu mL(-1).
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Fluorescent biosensor for detecting ochratoxin A as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109444102AStrong specificityThe detection process is fastFluorescence/phosphorescenceOchratoxin AFluorescence biosensor
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, and particularly relates to a fluorescent biosensor for detecting ochratoxin A based on a rolling ring amplification mediated catalytic hairpin self-assembly and incision enzyme feedback amplification method. According to the fluorescent biosensor, as for a detection mode, a fluorescence method is adopted for detection, and a luminoscopeis utilized; before detection, a padlock probe and a connecting probe form an annular template probe; then a target object is added to a homogeneous solution of a complex probe I, a complex probe II,HP 2 and HP 3, incubating is carried out for 120 minutes at 37 DEG C, and the target object and an aptamer sequence are bound; the multiple feedback amplification process is completed under the actionof a phi29 DNA polymerase and an endonuclease IV, so that signal amplification is realized; and then, the luminoscope is used for setting the excitation wavelength to be 399 nm, the fluorescence intensity at 610 nm is detected, and the detection range is 560-640 nm. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a preparation method for the biosensor. The preparation method has the advantages of beingmild in reaction condition and easy to operate.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Biosensor for detecting glutathione and fabrication method of biosensor
ActiveCN110542674AShort detection cycleHigh sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceNanoparticleEnzyme
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a biosensor for detecting glutathione (GSH) by a gold nanoparticle-based DNA molecule machine. The biosensor comprises a hairpin probe HAP (stem-modified disulfide bond), a composite probe P, a P3 probe, heme, potassium ion, a target object GSH, nanometer gold and a buffer liquid, wherein the composite probe P is modifiedonto a surface of the nanometer gold by polyA modification. A hairpin structure is damaged by a cracking function of the target object GSH on the disulfide bond, a Walker nucleic acid chain is released, P2 can be replaced from the composite probe P through strand displacement reaction of a support point medium by the released Walker nucleic acid chain and the P3 probe, the P2 is a sequence rich with G-quadruplet, G-quadruplet / heme DNA enzyme is formed in the presence of the heme, so that an aptamer biosensor is built. The reaction of the sensor is finished only in one step, thus, the sensor has the advantages of rapid detection speed, low cost, low detection limit, high specificity and the like and is simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
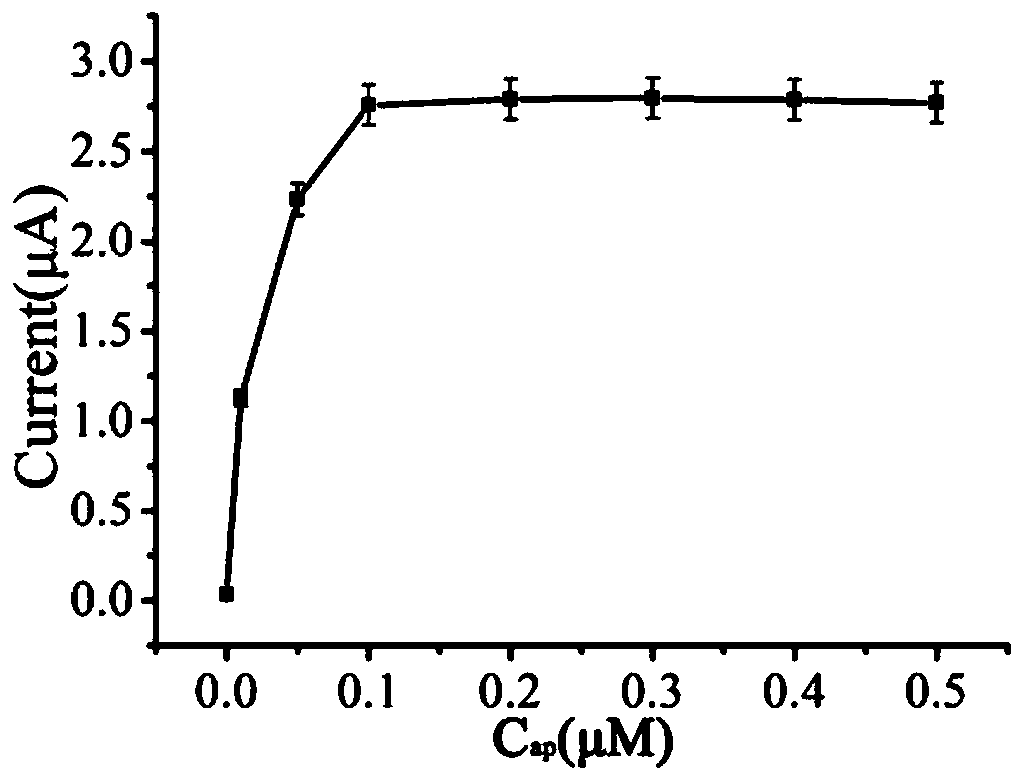
Electrochemical sensor for detecting ATP and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109596685ALow detection limitAchieve recyclingMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerSignal amplification
The invention relates to the technical field of the biosensor, and especially relates to a biosensor for detecting ATP by bringing Apt-1 and Apt-2 closer by ATP and using branch HCR amplification signal. A CP-SH layer, an AP layer, a HP1-HP2-HP3-HP4 layer and a [Ru(NH3)6]3+ layer are orderly modified on an electrode; the preparation method comprises the following steps: pre-treating the electrode,modifying the CP-SH layer to an electrode surface; modifying the AP layer to the electrode surface, and modifying the HP1-HP2-HP3-HP4 layer to the electrode surface, and modifying the[Ru(NH3)6]3+ layer to the electrode surface. The high specificity detection of the target object ATP is realized by utilizing the specificity identification of the aptamer; by utilizing the effect of bring two aptamers closer by the ATP, the cyclic utilization of the target object is realized, and the effect of the first-step signal amplification is achieved. And a signal continuous enhancement effect is realizedby utilizing branch HCR.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
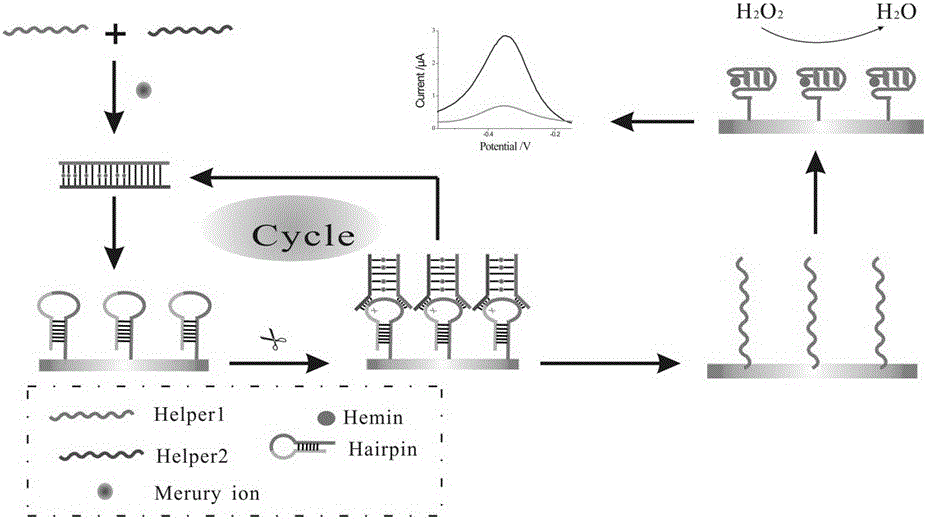
Colorimetric biosensor for detecting mercury ions and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106872682ARealize highly sensitive detectionAchieve improvementMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsNanoparticleSignal amplification
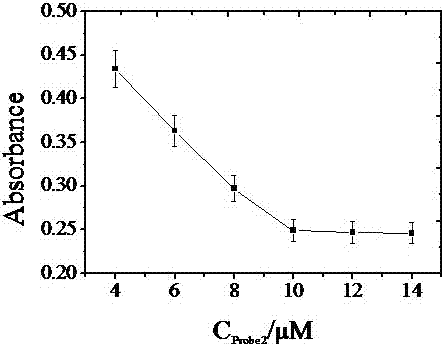
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors and in particular relates to a colorimetric biosensor for detecting mercury ions and a preparation method thereof. The colorimetric biosensor is prepared from the preparation method comprising the following steps: synthesizing gold nanoparticles; modifying Probe4 on surfaces of the gold nanoparticles; mixing a marked nano gold solution and a homogeneous reaction solution. According to the colorimetric biosensor provided by the invention, high-specificity detection on the target object mercury ions is realized by utilizing specific recognition of an aptamer and a T-Hg<2+>-T composite structure; strand displacement is utilized and circulating utilization of Probe2 and Probe3 is realized and the effect of amplifying a signal is realized. The problems of a method for detecting the mercury ions at the prior art that the specificity and sensitivity are relatively low and the cost is high are solved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Fluorescent biosensor for detecting activity of DNA transmethylase and preparation method of fluorescent biosensor
PendingCN109406477AStrong specificityRealize positioning cuttingFluorescence/phosphorescenceDNA methylationNucleic Acid Probes
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a fluorescent biosensor for detecting the activity of DNA transmethylase based on the catalytic hairpin self-assembling. Based on the specific identification of a methylated target object and nucleic acid probe, a three-way circuit structure is formed continuously by utilizing the catalytic hairpin self-assembling, a trigger is circularly amplified, the tail end of the three-way circuit is combined with a signal probe comprising a fluorescent group by virtue of complementary pairing of basic groups, finally a cleavagesite (AP site) of endonuclease IV is used for implementing the positioning cut, and the fluorescent group is released to generate a fluorescent signal of a given intensity. The sensor has the advantages of high detection speed, low detection limit, high specificity and the like, overcomes the defects for detecting the methylation of the DNA at present, and realizes the rapid and accurate quantitative detection for the methylation.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Fluorescent biosensor for detecting mercury ions
ActiveCN112345506AMild reaction conditionsQuick responseMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMercuric ionFluorescence biosensor
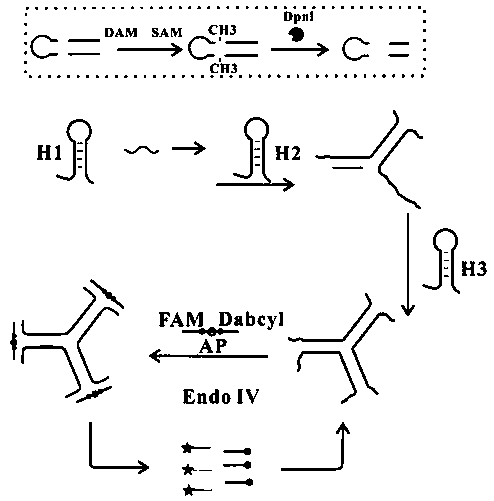
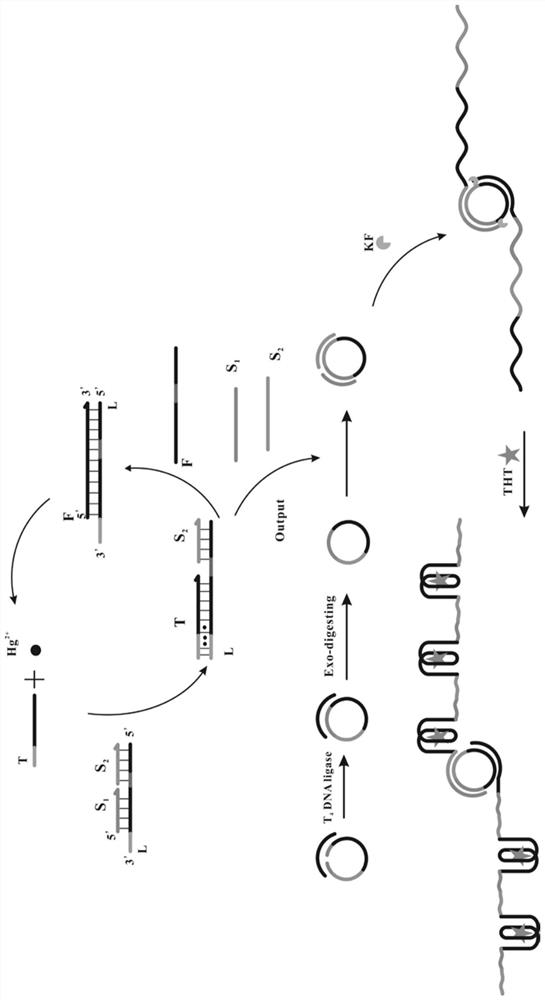
The invention provides a fluorescent biosensor for detecting Hg<2+>. The fluorescent biosensor comprises a composite probe Q, an annular template CP, a trigger chain T, a fuel chain F, a Klenow fragment and thioflavin T; and the trigger chain T, the composite probe Q, the fuel chain F, the annular template CP and the Klenow fragment are uniformly mixed with a mercury ion solution with a series ofconcentrations and a to-be-detected solution respectively, incubating is performed, enzyme is inactivated, the sulfur element T is added, incubating is performed, and the fluorescence intensity is detected. Target cyclic amplification and signal amplification are realized on the basis of the specific binding capacity between basic groups T and Hg<2+> and entropy-driven strand displacement amplification and rolling circle amplification reactions, and the biosensor for sensitive detection of a target object is realized. The sensor has the advantages of high detection speed, low detection limit,high sensitivity and the like, can make up the defects and deficiencies of the existing detection method of Hg<2+>, and realizes rapid and accurate quantitative detection of Hg<2+>.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Nonenzymatic biosensor for detecting activity of uracil-DNA glycosylase
ActiveCN110734961AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisA-DNABio sensor
The invention provides a nonenzymatic biosensor for detecting activity of uracil-DNA glycosylase. The nonenzymatic biosensor comprises a UDG template strand 1, a silver nanocluster DNA template strand2, and a DNA strand 3 rich in cytosine. A fluorescence method is used for detecting the activity of the uracil-DNA glycosylase, the stimulation wave lenagth of fluoroscopic examination is 570nm, thelength of transmitted waves is 630nm, and the detection wave band is 590-720nm. The biosensor provided by the invention is good in specificity, high in sensitivity, mild in reaction condition and highin reaction speed. Because the reaction process is free from addition of external enzymes, and through silver nanocluster fluoroscopic examination, the biosensor is simple to operate, low in reactionrequirements, short in detection cycle, stable in properties, and good in repeatability, and is suitable for detection of UDG in the field of medical health.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Electrochemical biosensor for detecting miRNA as well as preparation method and application of electrochemical biosensor
ActiveCN111440851ARealize highly sensitive detectionAchieve improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a biosensor for detecting miRNA through S specifically recognized by miRNA, conformation change of the S and rolling ring isothermal cycle amplification, and aims to solve the problems of low specificity and sensitivity and high cost of a method for detecting the miRNA in the prior art. According to the biosensor for detecting the miRNA, an electrode is sequentially modified with an S1 layer and an RCA product layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: pretreating the electrode; modifying the S1 layer on the surface of the electrode; and modifying the RCA product layer on the surface of the electrode. The high-specificity detection on a target object is realized by utilizing the specific recognition of the miRNA; and three-step amplification of a target object signal is realized by using a DNAzyme and rolling ring isothermal amplification technology.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
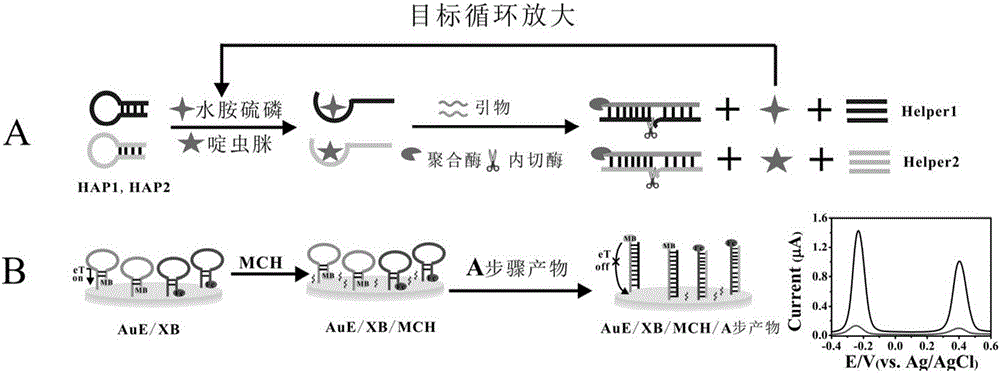
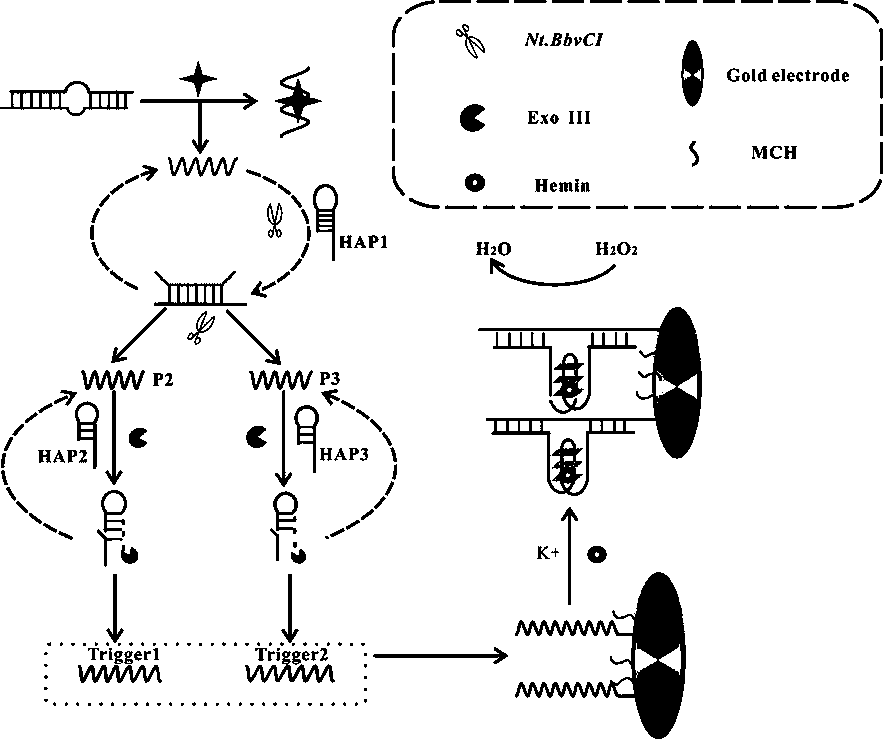
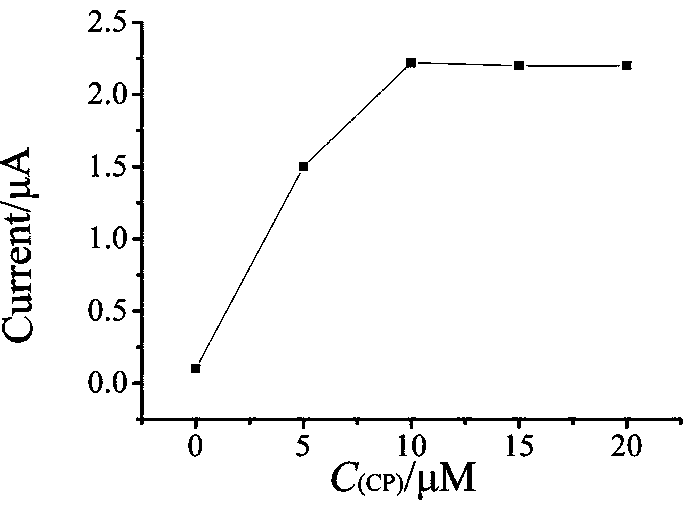
Electrochemical biosensor for detecting kanamycin as well as preparation method and application
ActiveCN109507254AHigh sensitivityAchieve recyclingMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorKanamycin
The invention relates to an electrochemical biosensor for detecting kanamycin based on an aptamer, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical biosensors. By utilizing an Nt.BbvCI incision enzyme with a function of cutting identification, cyclic utilization of a primer is realized, a detection signal is amplified, and the detection sensitivity is improved; by utilizing the specificity idenfitication and the hydrolytic action of an exonuclease III, the circle amplification at a second step is achieved, so that the detection sensitivity is further improved. According to the electrochemical biosensor disclosed by the invention, the specific detection can be improved; the electrochemical biosensor is mild in reaction conditions and high in reaction speed; a process of making an electrode is low in cost, so that the electrochemical biosensor is suitable for the requirement of low cost in industrialization and is also suitable for the detection of the kanamycin in food safety and the actual industrial application of the electrochemical biosensors.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
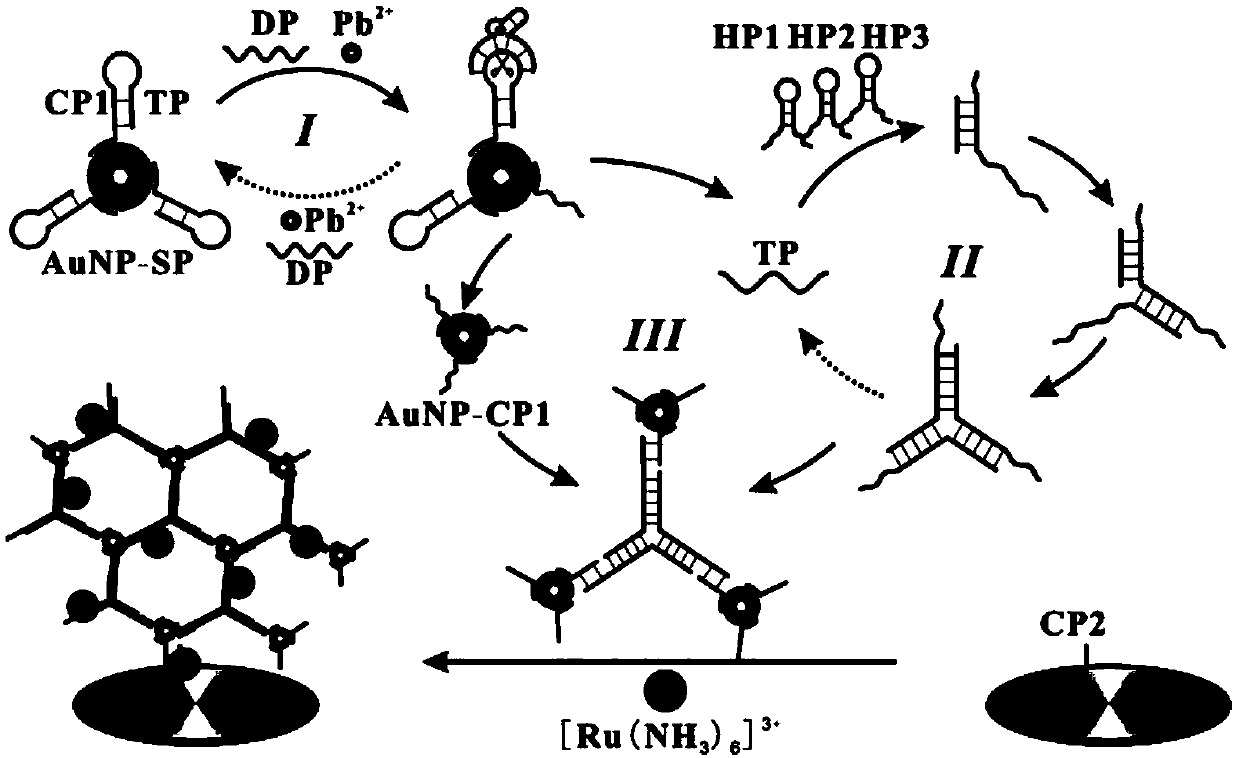
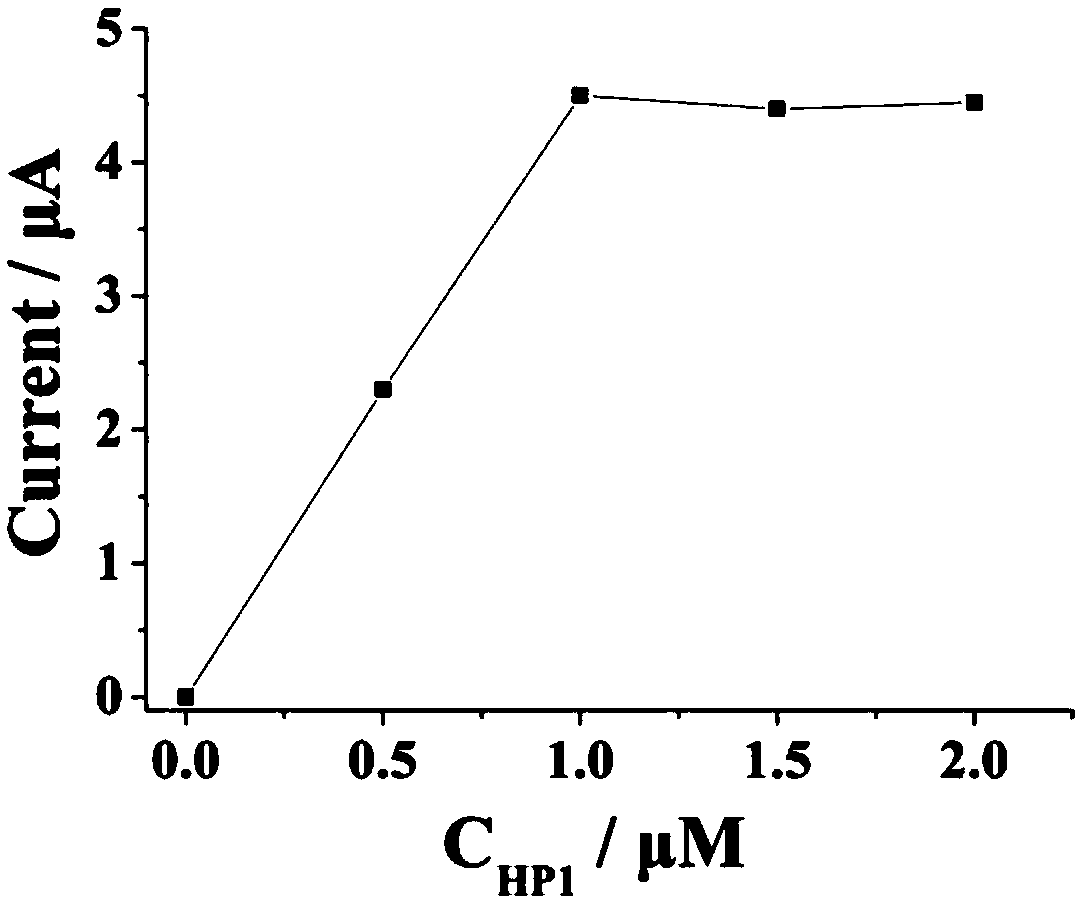
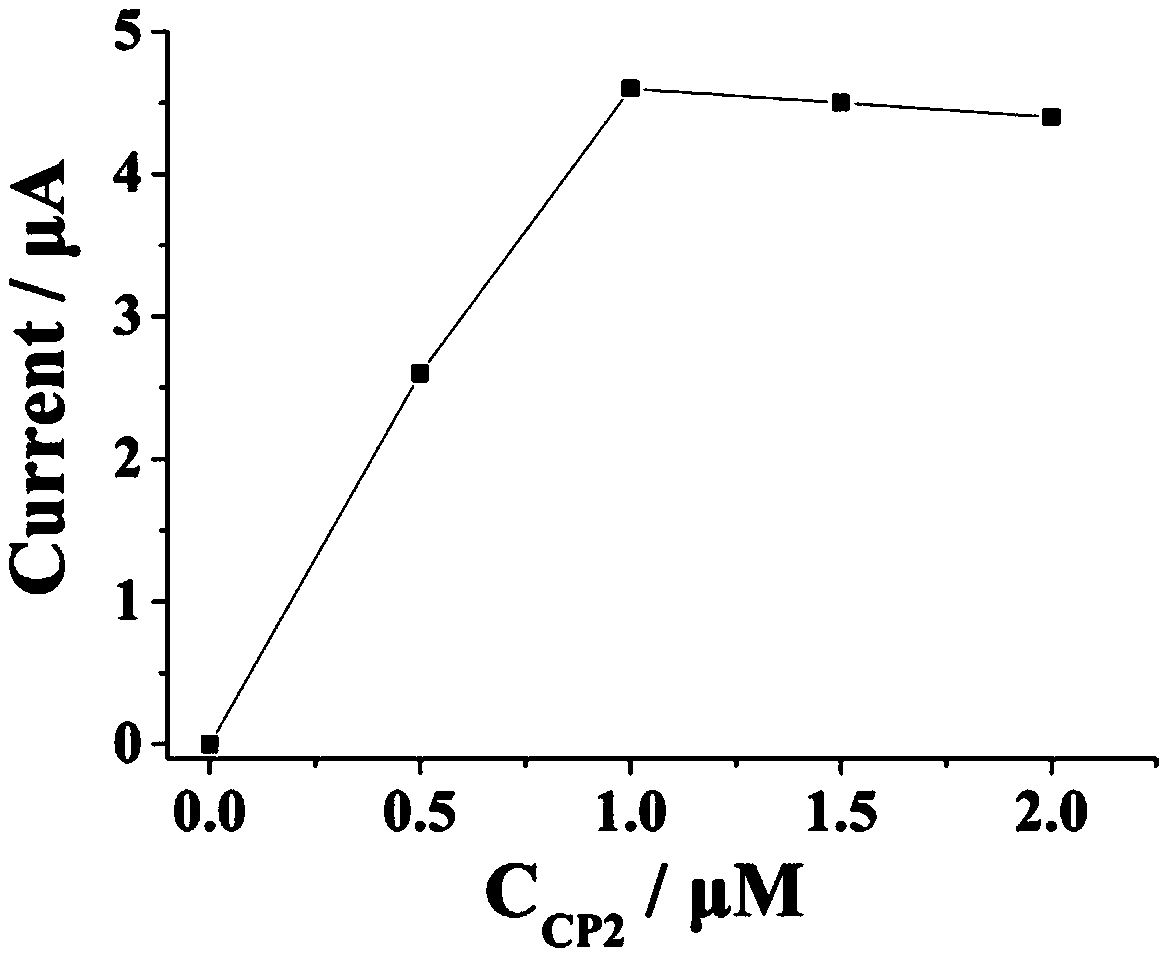
Electrochemical sensor for detecting lead ion and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN109632901AStrong specificityAchieve high specificity detectionMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical gas sensorDNA
The invention relates to the electrochemical sensor technology field and especially relates to an electrochemical sensor for detecting a lead ion. A CP2 layer, a HP1-HP2-HP3-CP1-AuNP layer, and a [Ru(NH3)6]<3+> layer are sequentially modified on an electrode. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of preprocessing the electrode; modifying the CP2 layer to an electrode surface; modifying the HP1-HP2-HP3-CP1-AuNP layer to the electrode surface; and modifying the [Ru(NH3)6]<3+> layer to the electrode surface. The specific identification of a DNA enzyme is used to realize the highspecificity detection of target object lead ions. The cutting effect of the DNA enzyme of lead ion specific identification and a CHA reaction are used to realize the increase of a signal through two-step cycle and one-step amplification modes so as to realize the high-sensitivity detection of lead ions and obtain a lower detection limit. Through the connection performance of nanogold, an effect that the signal is continuously enhanced is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Electrochemical biosensor for detecting Salmonella typhimurium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107037103ARealize highly sensitive detectionAchieve improvementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical biosensorSignal amplification
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to an electrochemical biosensor for detecting Salmonella typhimurium and provides a preparation method of the electrochemical biosensor. The electrochemical biosensor is prepared by modifying an electrode with a HAP2 layer, and homogeneously reacting a mixed liquid. An aptamer of Salmonella typhimurium is used as a recognizing matter to highly specifically detect Salmonella typhimurium in a target by making use of specific recognizing property of the aptamer; the target is recycled through the use of nucleic instrumental enzymes, and signal amplification is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
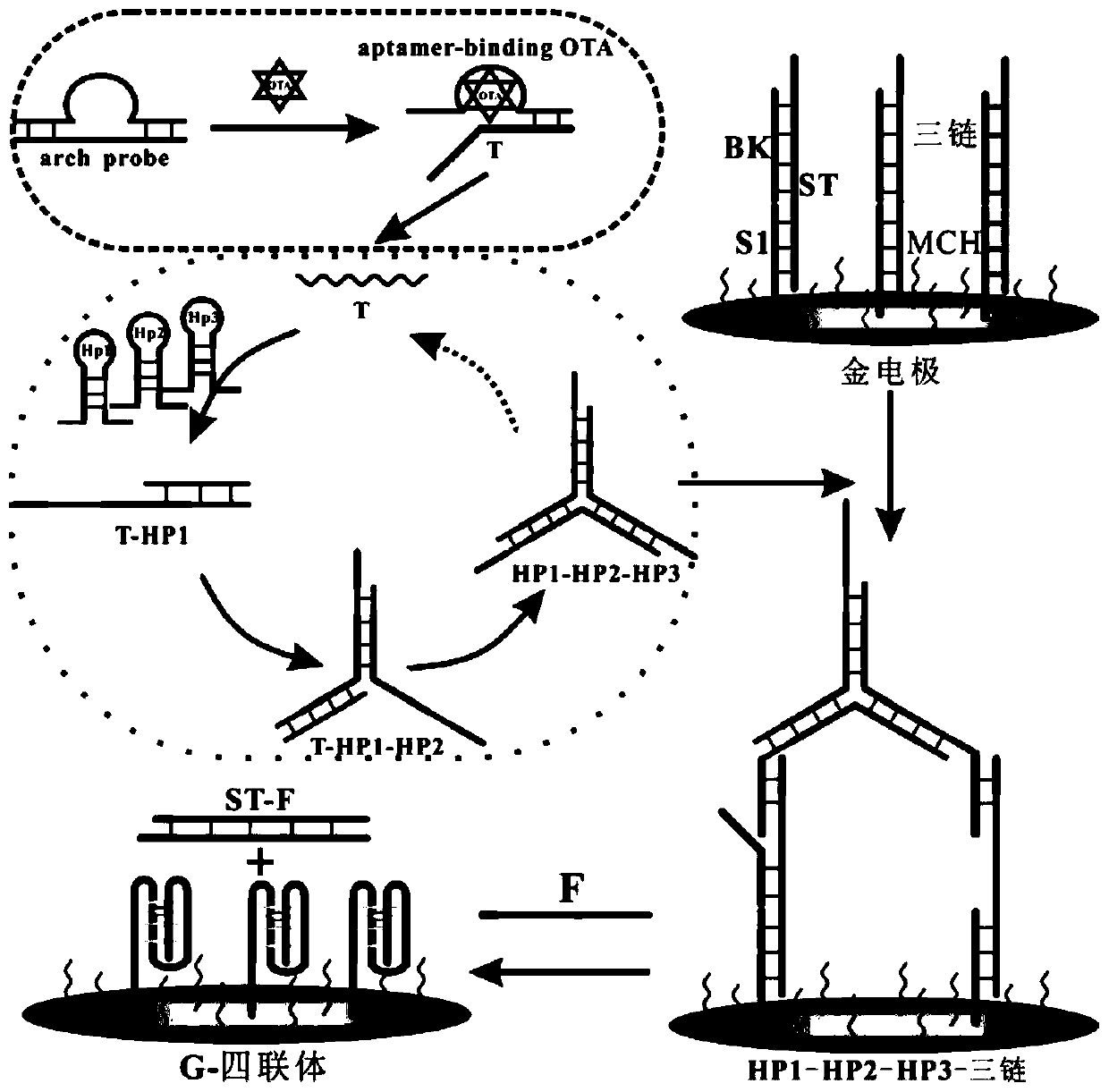
Electrochemical biosensor for detecting ochratoxin A and preparation method of electrochemical biosensor
ActiveCN111424072AStrong specificityThe detection process is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorTarget signal
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, and in particular to an arched probe specifically recognized by ochratoxin A (OTA) and a biosensor for detecting OTA by catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) and chain displacement isothermal cyclic amplification, and aims to solve the problems of low specificity and sensitivity and high cost of a method for detecting OTA in the prior art. According to the biosensor for detecting OTA, an electrode is sequentially modified with an ST-BK-S1 layer, an aptamer-T-HP1-HP2-HP3-F layer and a heme layer. A preparation method comprises the followingsteps: pretreating the electrode; modifying the surface of the electrode with the ST-BK-S1 layer; modifying the surface of the electrode with the aptamer-T-HP1-HP2-HP3-F layer; and modifying the surface of the electrode with the heme layer. High specificity detection of the target OTA is realized by utilizing specificity recognition of the OTA, and two-step amplification of the target signal is realized by utilizing a CHA reaction and the chain displacement isothermal amplification technology.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Salmonella typhimurium detection biosensor
ActiveCN107102047AAchieve high specificity detectionHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpecific detectionOrganism
The invention provides a salmonella typhimurium detection biosensor. The salmonella typhimurium detection biosensor is prepared by sequentially modifying an electrode with an iDNA layer, a Helper layer and homogeneous reaction mixed liquor. The salmonella typhimurium detection biosensor has the beneficial effects that the specific recognition of a nucleic acid aptamer is utilized; the high specific detection of salmonella typhimurium being a target object is realized by using the aptamer of salmonella typhimurium as a recognition substance; and nucleic acid tool enzymes are used for realizing the cyclic utilization of the target object and have a signal amplification effect.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Biosensor for detecting uracil-DNA glycosylase, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109752362ADetection speedLow detection limitRaman scatteringRaman scatteringComputational chemistry
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, and in particular to a biosensor based on a nanogold DNA molecular machine and surface enhanced Raman scattering, in order to solve the problems of relatively low method specificity and sensitivity and high cost in the method for detecting UDG activity in the prior art. A biosensor based on surface enhanced Raman scattering of a DNA molecular machine for detecting UDG activity combines the nanogold molecular machine with the surface enhanced Raman scattering to obtain homogeneous reaction mixed liquor. The preparation method comprisesthe following steps: synthesizing gold nanoparticles; modifying Hairpin Probe,Track DNA and Raman dye onto the surfaces of the gold nanoparticles; and mixing a labeled gold nano solution with a homogeneous reaction solution. The opening of the DNA molecular machine is realized by the specific cutting of incision enzyme IV, and high-sensitivity detection is realized by the surface enhanced Raman scattering; the circulation of the DNA molecular machine is achieved by using excision enzyme III, and a signal amplification role is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Chemiluminescence biosensor for detecting uracil-DNA glycosylase and preparation method and application of chemiluminescence biosensor
ActiveCN110607351ARealize highly sensitive detectionLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpherical nucleic acidDisplacement reactions
The invention relates to the technical field of a biosensor, in particular to detection of uracil-DNA glycosylase based on a chemiluminescence technique for driving a strand displacement reaction based on a tee structure and driving spherical nucleases based on a DNA walker technique. In order to solve the problems of being complex to operate and low in sensitivity for a method for detecting uracil-DNA glycosylase in the prior art, the invention provides a biosensor based on two nanometer technologies of the tee structure and DNA walker, and spherical nucleases are used for catalyzing luminalto be subjected to a chemiluminescence reaction for detection. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing nano-Au, preparing spherical nucleic acid, and forming spherical nucleases in homogeneous phase for catalyzing the chemiluminescence reaction of the luminal. The uracil-DNA glycosylase is used for performing specific recognition and excision on U alkali, so as to realize target specificity detection. Besides, the DNA walker nanometer technology is used for realizing quick and high-sensitivity detection on targets.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Biosensor for targeting cancer cells based on DNA triangular prism structure conformation change
ActiveCN112345507AReduce processing costsMild reaction conditionsFluorescence/phosphorescenceCancer cellFluorescence spectra
The invention belongs to the technical field of biosensors, and relates to a biosensor for targeting cancer cells based on DNA triangular prism structure conformation change. Before detection, a DNA triangular prism nanostructure is firstly constructed; then the pH value of a reaction solution is changed to change the conformation of the triangular prism nanostructure; and a cancer marker ATP is added, proximity reaction is performed to enable two fluorophores to be close to generate FRET, and detection is performed through a fluorescence spectrum. The sensor has the advantages of high detection speed, low detection limit, high specificity and the like, can make up for the defects and deficiencies of the existing detection method, and realizes rapid and accurate quantitative detection.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Electrochemical sensor for detecting mercury ions based on aptamer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106841350ARealize highly sensitive detectionAchieve improvementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAptamerElectrochemistry
The invention provides an electrochemical sensor for detecting mercury ions based on aptamer conformation change. The electrochemical sensor comprises an electrode, wherein the electrode is successively modified with an HAP layer and a Helper layer; the invention also provides a biological preparation method based on specific identification of the aptamer. When the electrochemical sensor provided by the invention is applied to detection, the electrochemical sensor has the characteristics of high specificity, high sensitivity, low cost and rapid detection speed.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Chemiluminescence sensor for detecting acetamiprid and preparation method of sensor
ActiveCN111440850APlay the role of signal amplificationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAptamerNanoparti cles
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a chemical biosensor using a DNAzyme based DNA Walker, aims to solve the problems of relatively low specificity and sensitivity and high cost of acetamiprid detection methods in the prior art, and discloses a chemical biosensor for detecting acetamiprid by the DNAzyme based DNA Walker. DNAzyme cracking is used for assisting in realizing circulating amplification and forming a lot of G-quadruplets simulating the horseradish peroxidase activity on gold nanoparticles. A preparation method comprises the following steps ofpreparing the gold nanoparticles; modifying a Walker chain and a Lock chain to the surfaces of the gold nanoparticles; producing a homogeneous reaction of a labeled gold nanoparticle solution; carrying out a DNAzyme cracking reaction, and chemiluminiscence detection; carrying out high-specificity detection on the acetamiprid as a target object by using a nucleic acid aptamer; and realizing the signal amplification effect by utilizing DNAzyme cracking reaction amplification.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
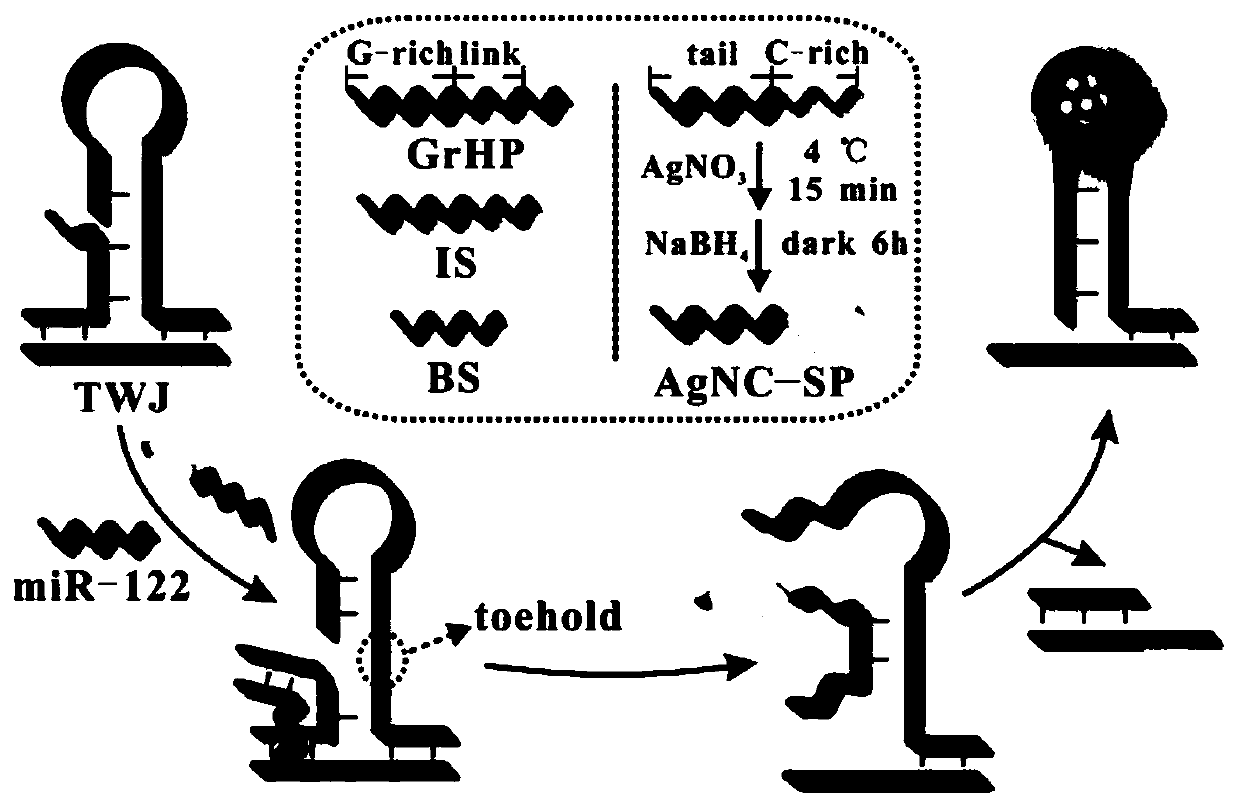
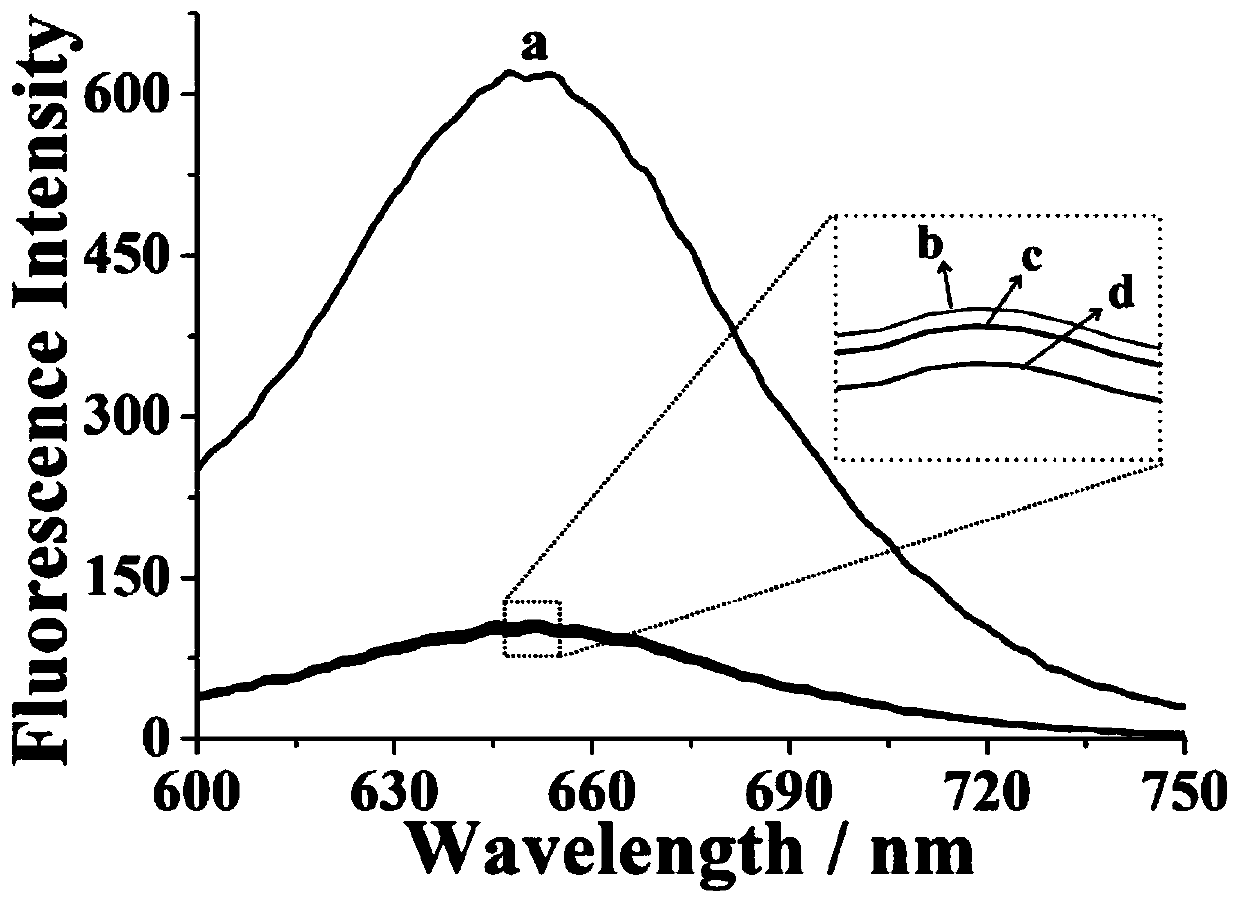
Fluorescence biosensor based on light-up silver cluster probe and application thereof in miR-122 detection
InactiveCN110564817AStrong specificityIncrease migration rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseSilver cluster
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a fluorescence biosensor based on a light-up silver cluster probe and a preparation method of the fluorescence biosensor, and further relates to a G-rich base enhanced silver nano-cluster method. According to the detection mode provided by the invention, miR-122 detection is carried out through generation of a fluorescence signal, the hybridization of the miR-122 and the complementary strand thereof initiates the change of a three-path structure, a toehold end is exposed, and the silver cluster probe is crossed with GrHP clamp by virtue of the toehold end, so that a strand displacement reaction is initiated, the G-rich sequence is close to the silver cluster part, and the fluorescence intensity of the silver cluster is enhanced. The sensor has the advantages of being efficient, high in specificity, easy and convenient to operate, economical and free of marks, enzyme does not need to be used in a system, the defects and deficiencies of an existing detection method of miR-122 can be overcome, and rapid and accurate quantitative detection of miR-122 and early diagnosis of related diseases are achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
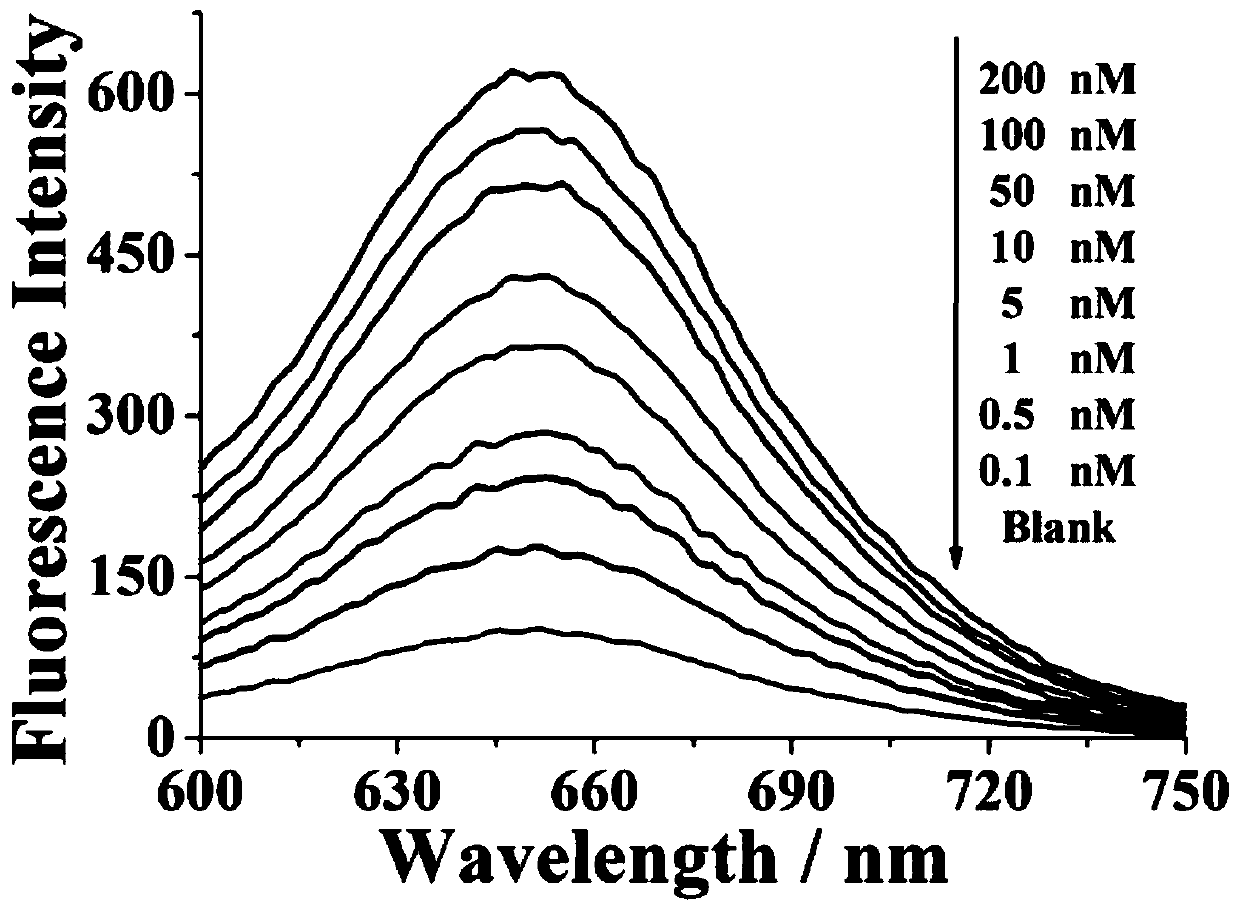
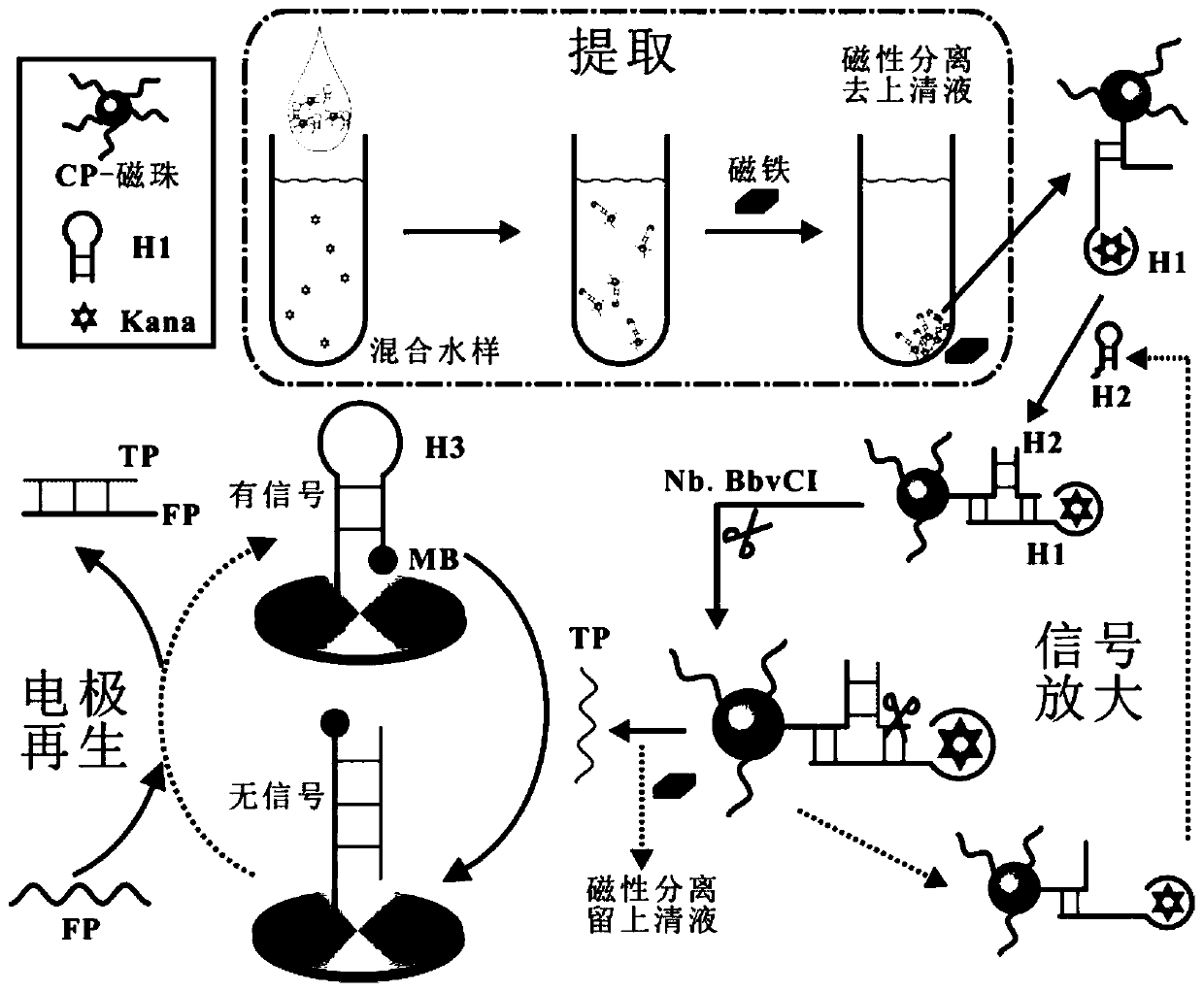
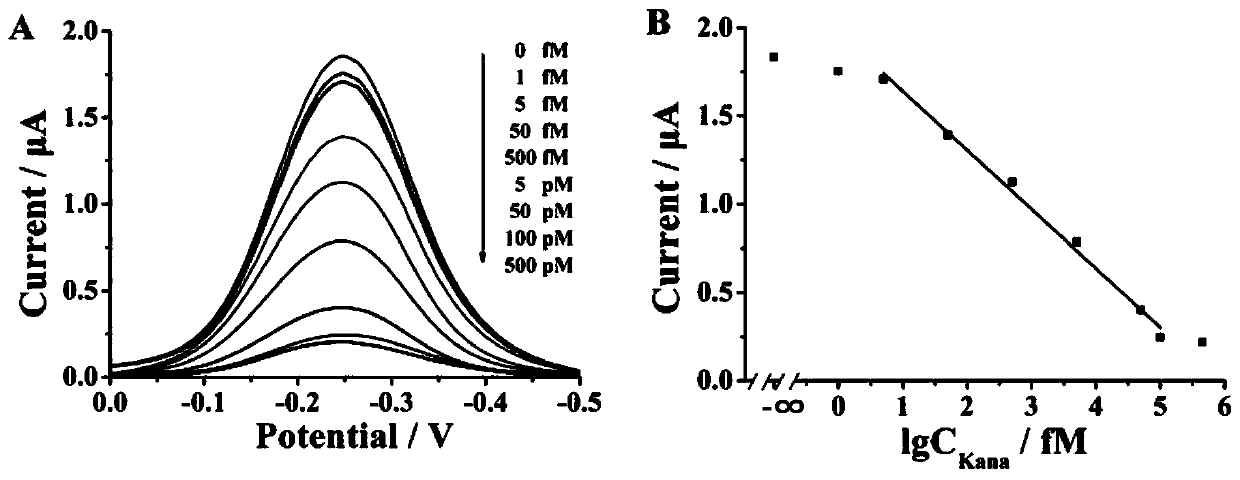
Renewable electrochemical sensor for detecting trace kanamycin, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111474224AStrong specificityThe detection process is fastMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerKanamycin
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, and especially relates to a renewable electrochemical sensor for detecting trace kanamycin, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The invention aims to solve the problems of low specificity and sensitivity and high cost of the Kana detection method in the prior art. The renewable electrochemical sensor for detecting trace kanamycin is characterized in that an electrode is sequentially modified with an H3 layer, a magnetic bead-CP / H1 / H2 layer and an FP layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: pretreating the electrode; modifying the surface of the electrode with the H3 layer; extracting Kana in a water sample by using magnetic beads, and modifying the surface of the electrode with the magnetic bead-CP / H1 / H2 layer; and modifying the surface of the electrode with the FP layer. The specific recognition of an aptamer by Kana is utilized; by utilizing the magnetic beads, the extraction of trace Kana is realized; an Nb.BbvCI enzyme is utilized to realize the effect of signal amplification; and the electrode regeneration process is realized by using FP.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com