Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Spherical nucleic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
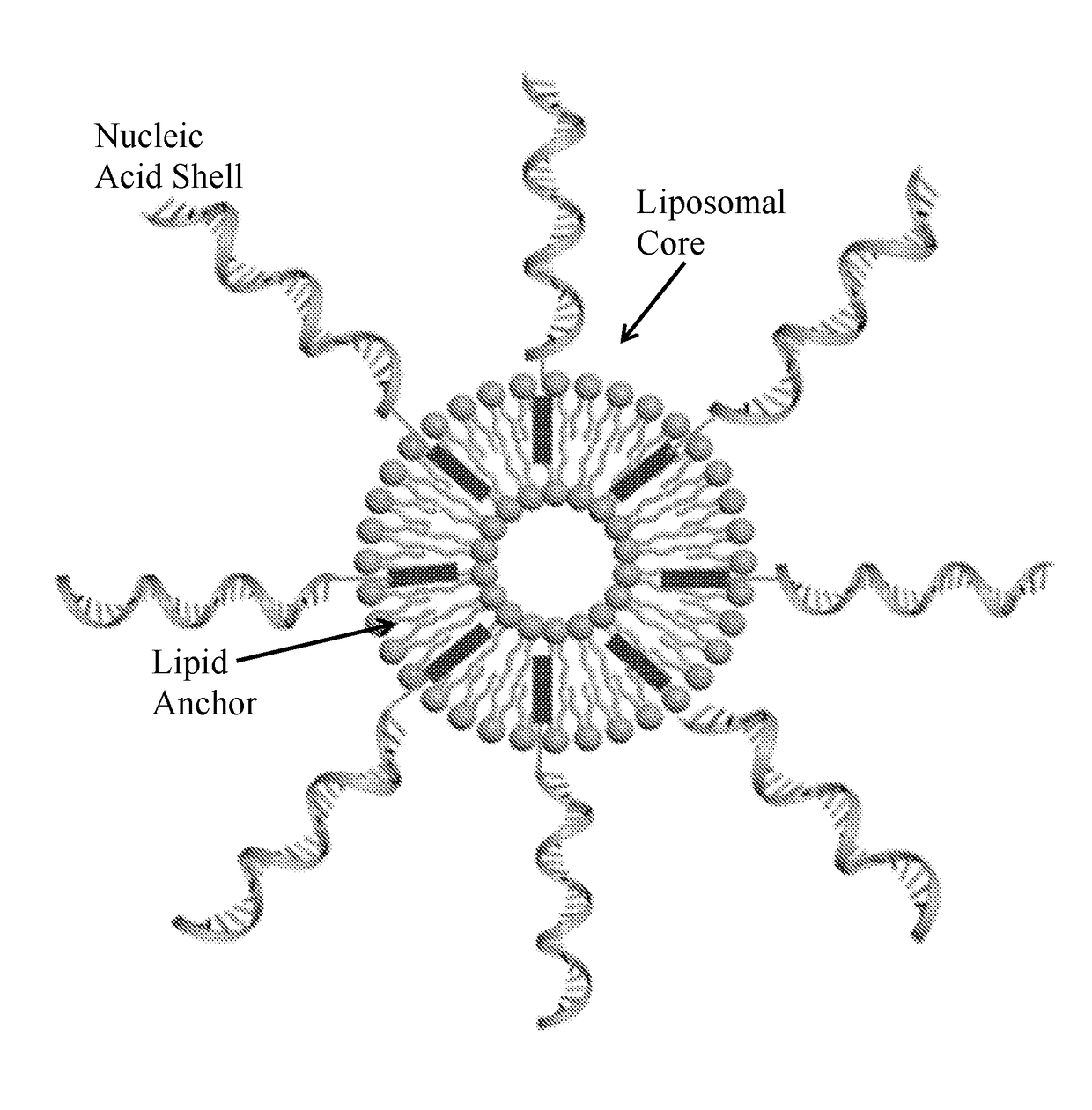
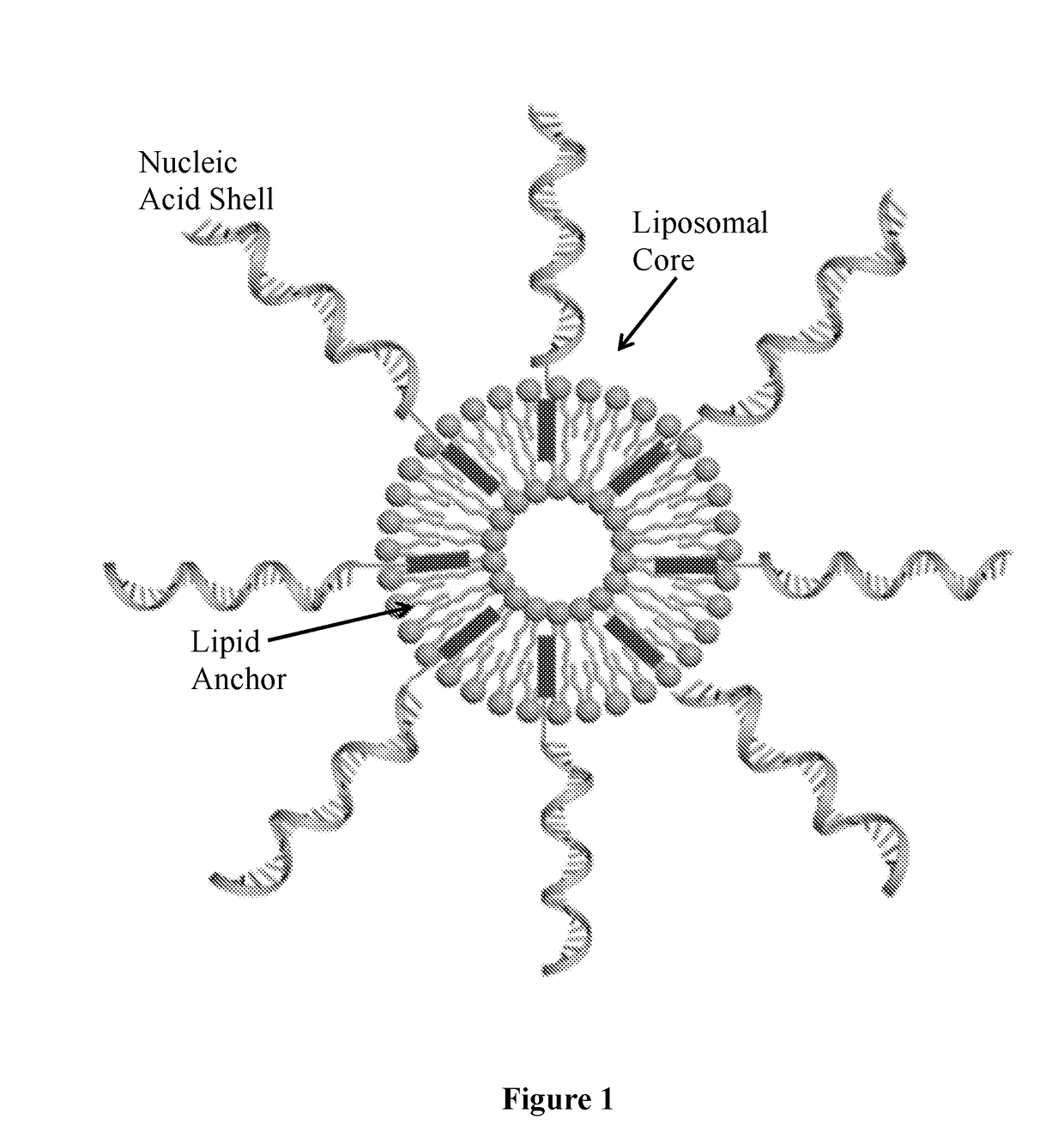
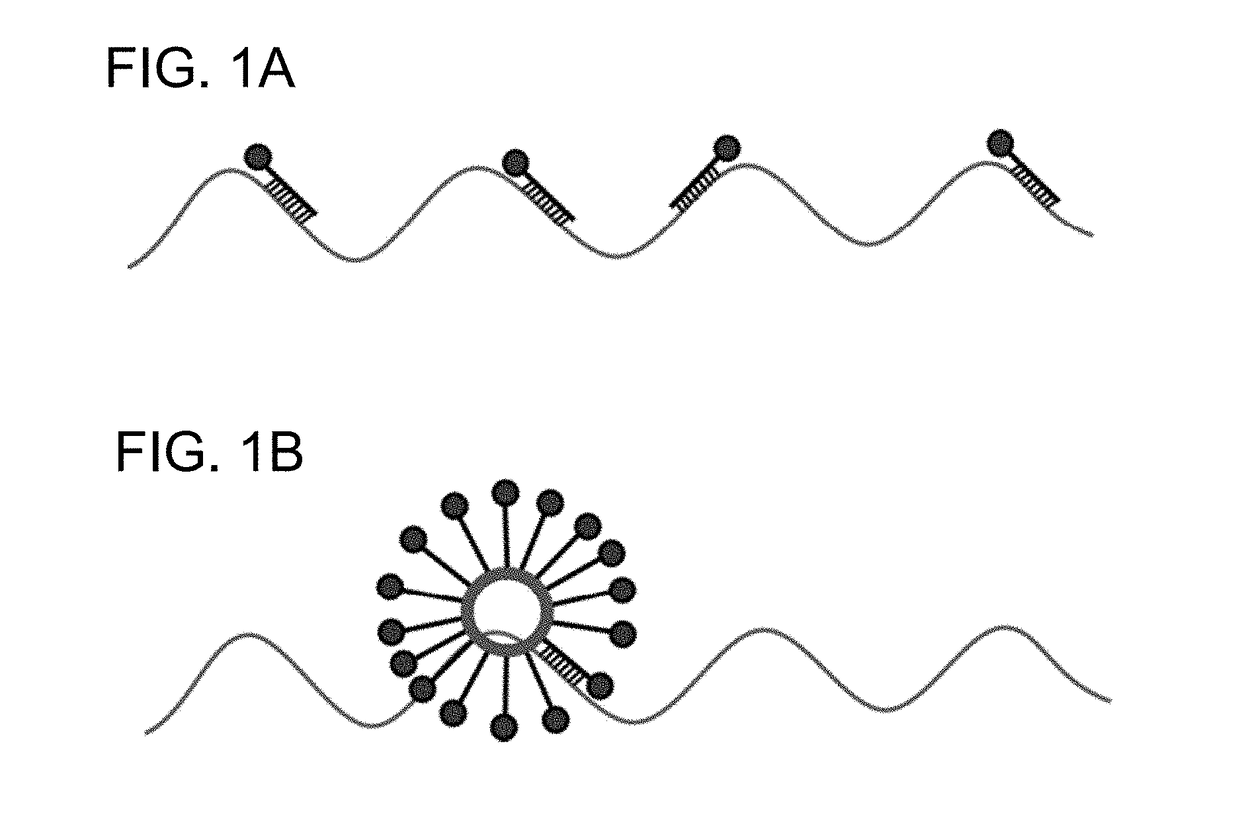
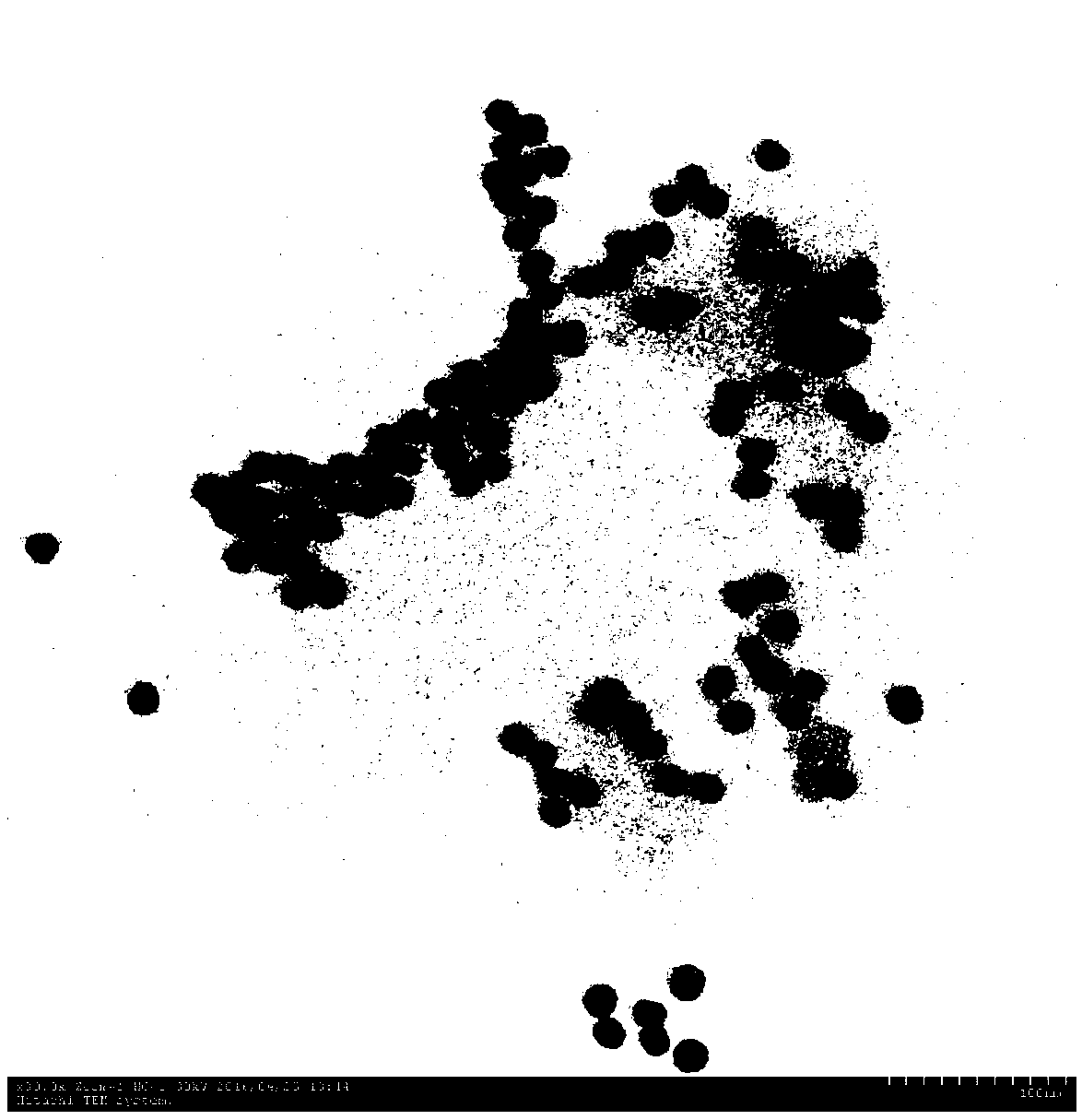
Spherical nucleic acids (SNAs) – defined as structures that are an arrangement of densely packed, highly oriented nucleic acids in a spherical geometry – were first introduced in 1996 by the Mirkin group at Northwestern University. The arrangement and orientation of one-dimensional linear nucleic acids within this three-dimensional framework results in new chemical, biological, and physical properties in the use of nucleic acids for intracellular gene regulation (though this is disputed ), molecular diagnostics, and materials synthesis applications.
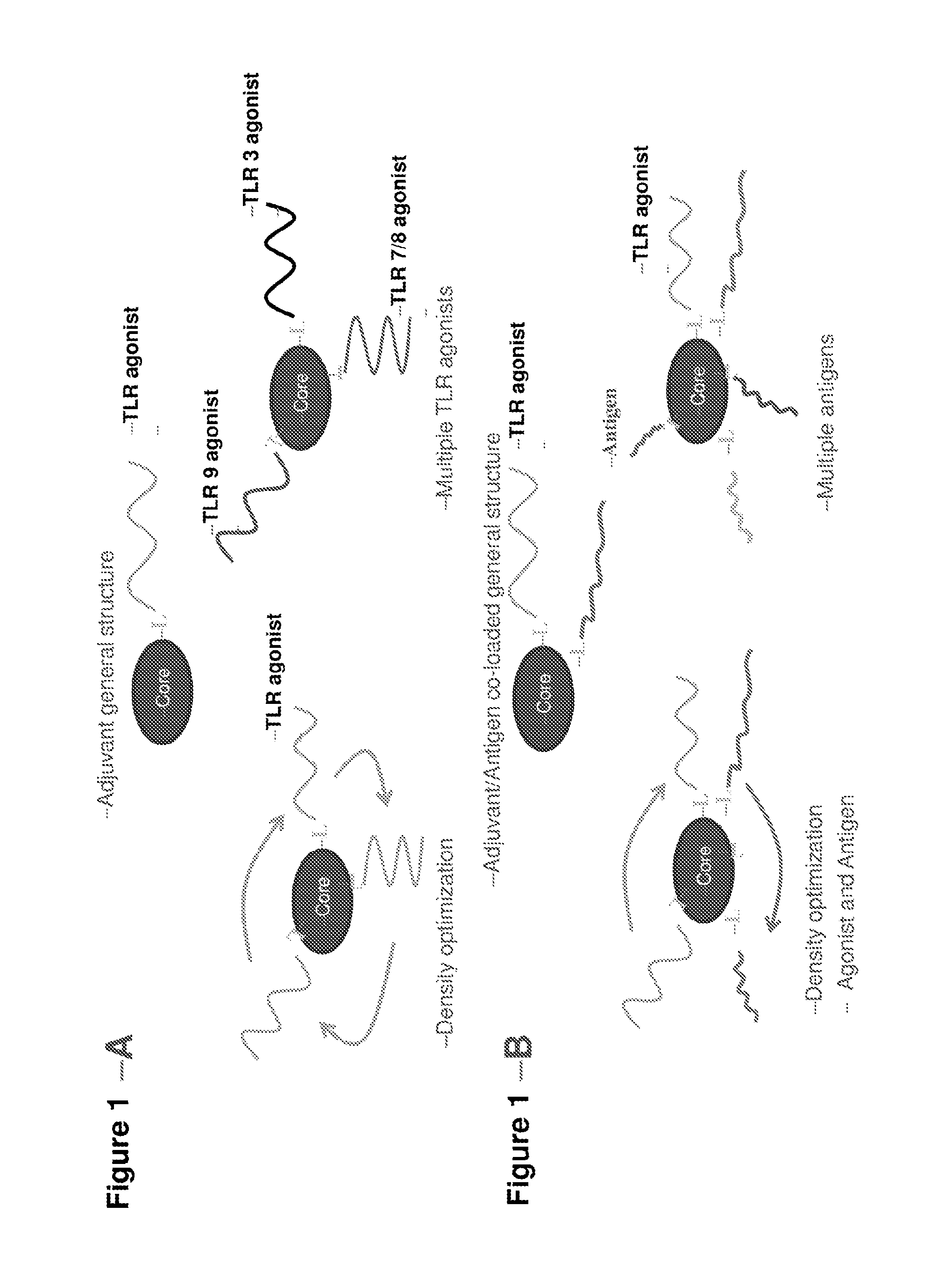
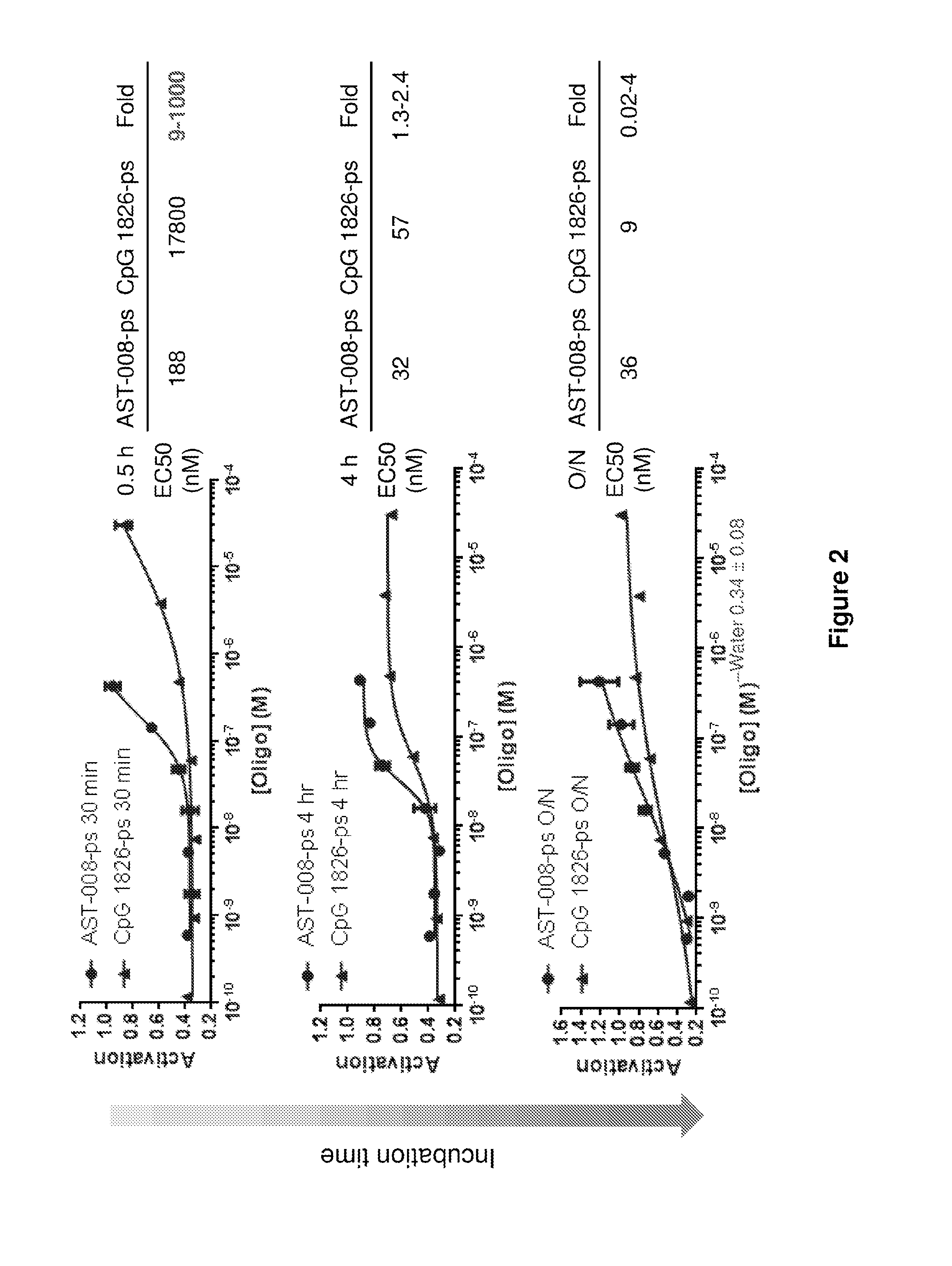
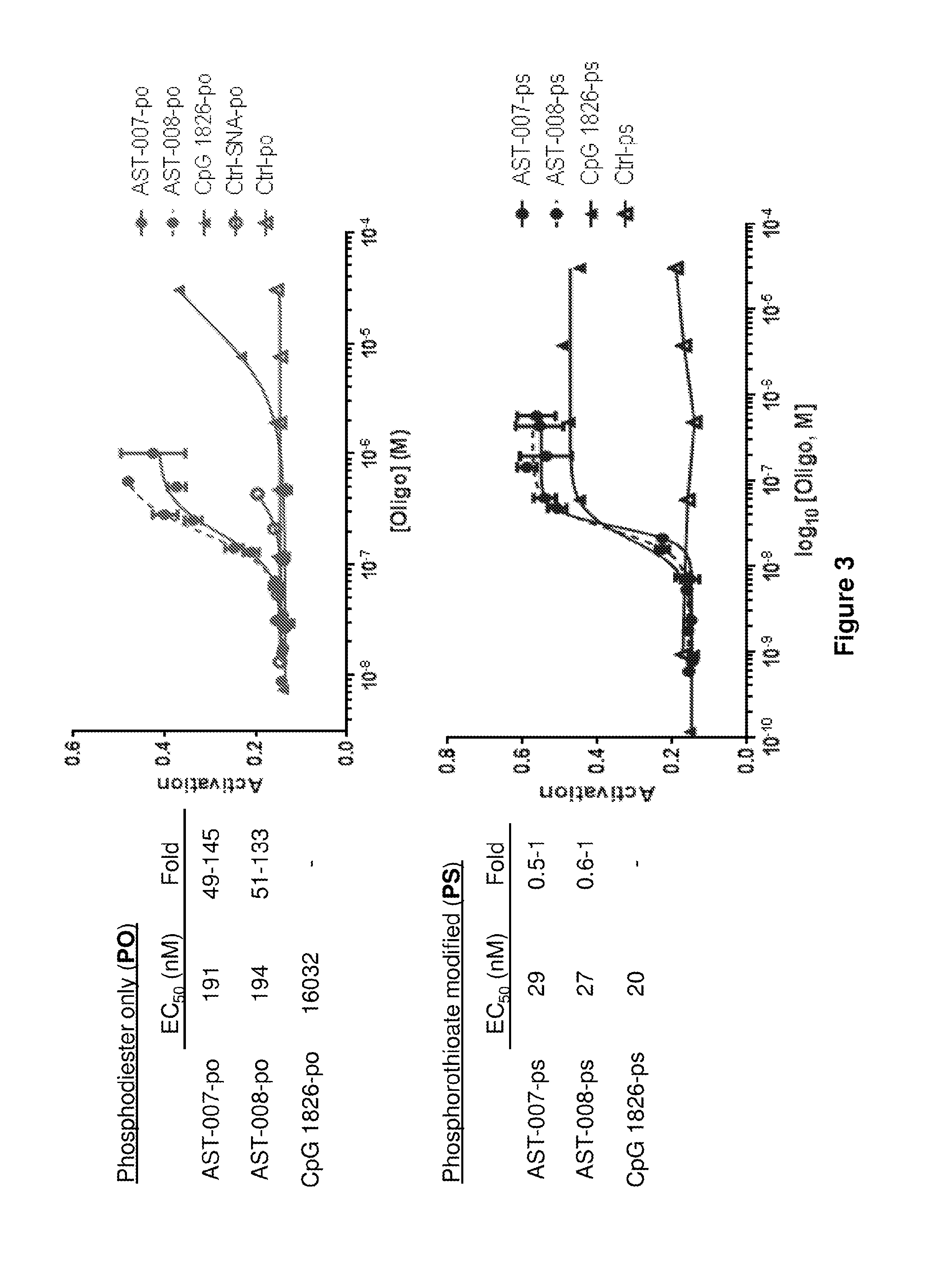
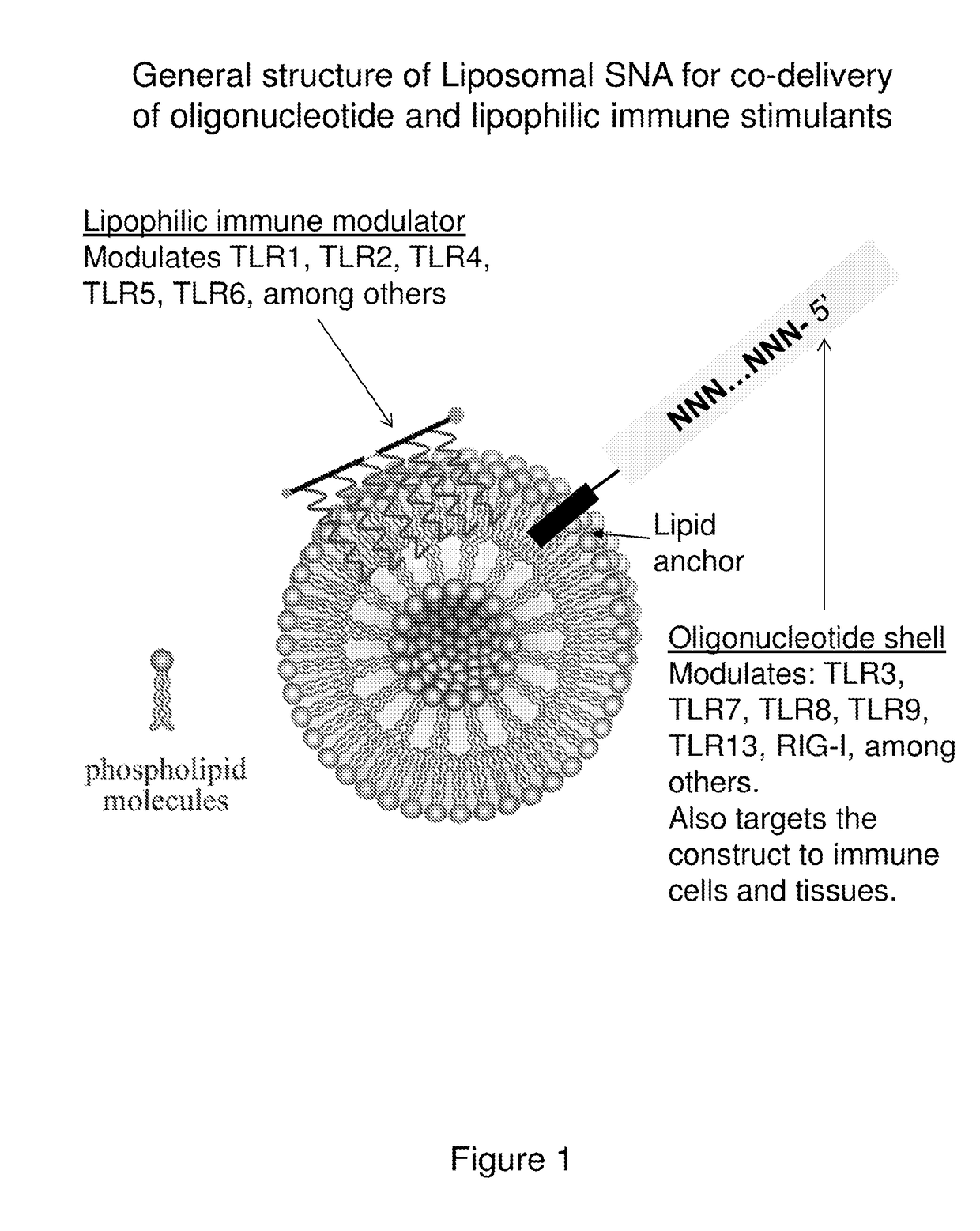
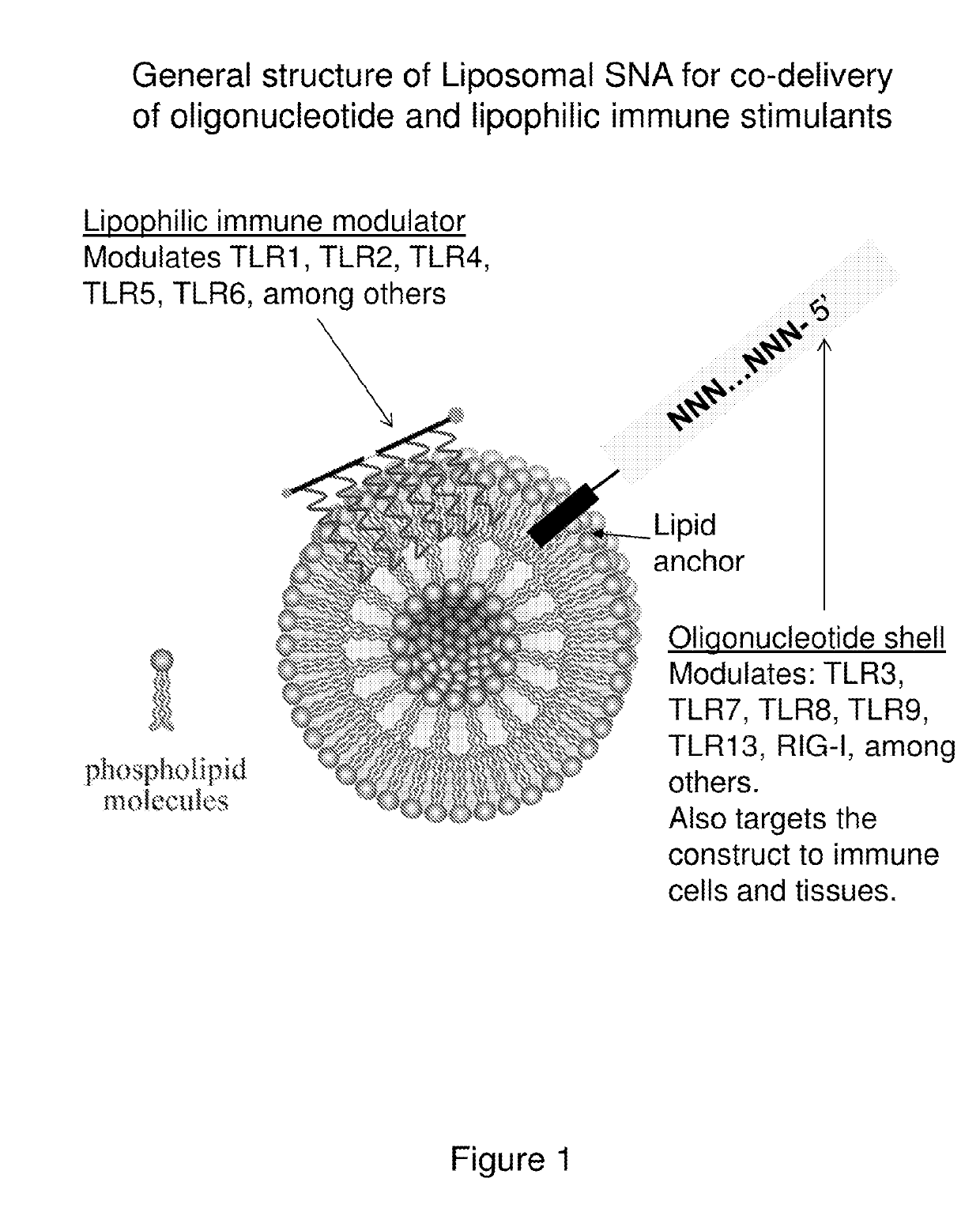
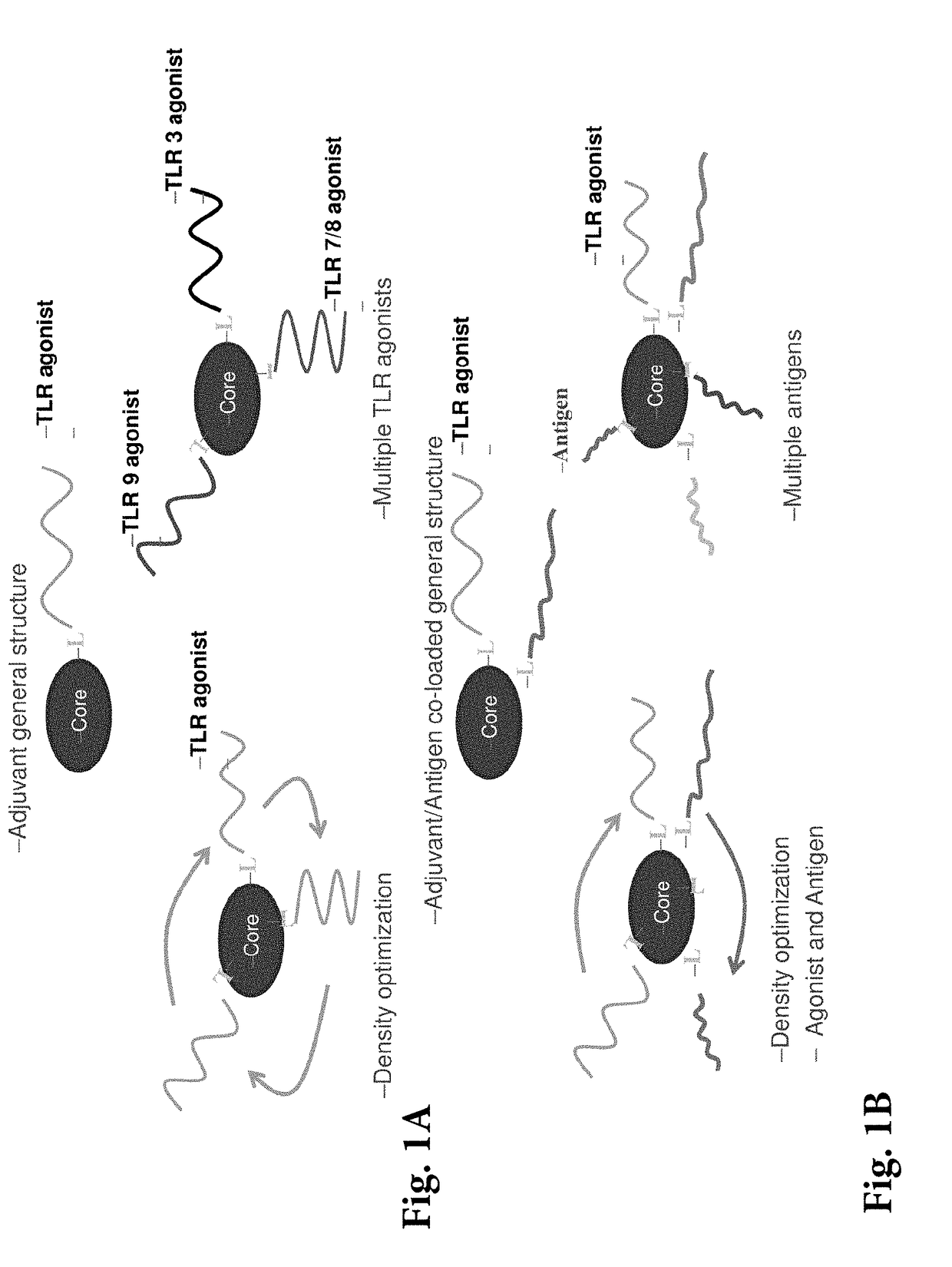
Spherical nucleic acid-based constructs as immunostimulatory agents for prophylactic and therapeutic use
ActiveUS20160186178A1Enhance immune responseSpecial deliverySnake antigen ingredientsDiseaseSpherical nucleic acid
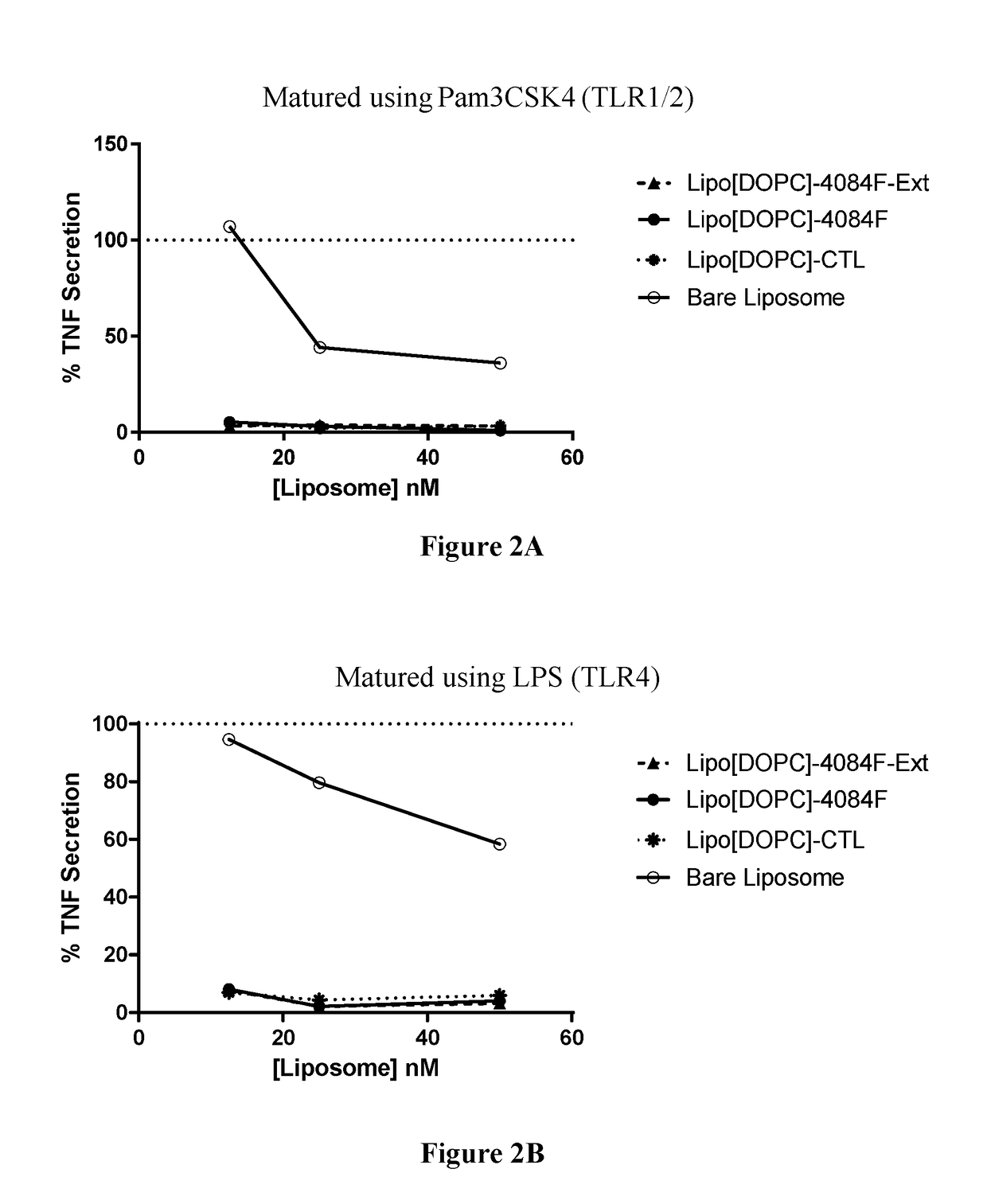
Aspects of the invention relate to spherical nucleic acid-based constructs and related methods and compositions thereof. The compositions of the invention are useful for activating agonists of nucleic acid interacting complexes, such as TLRs, stimulating an immune response, and treating diseases such as infectious disease, cancer, allergies, allergic diseases, and autoimmune disease
Owner:EXICURE INC
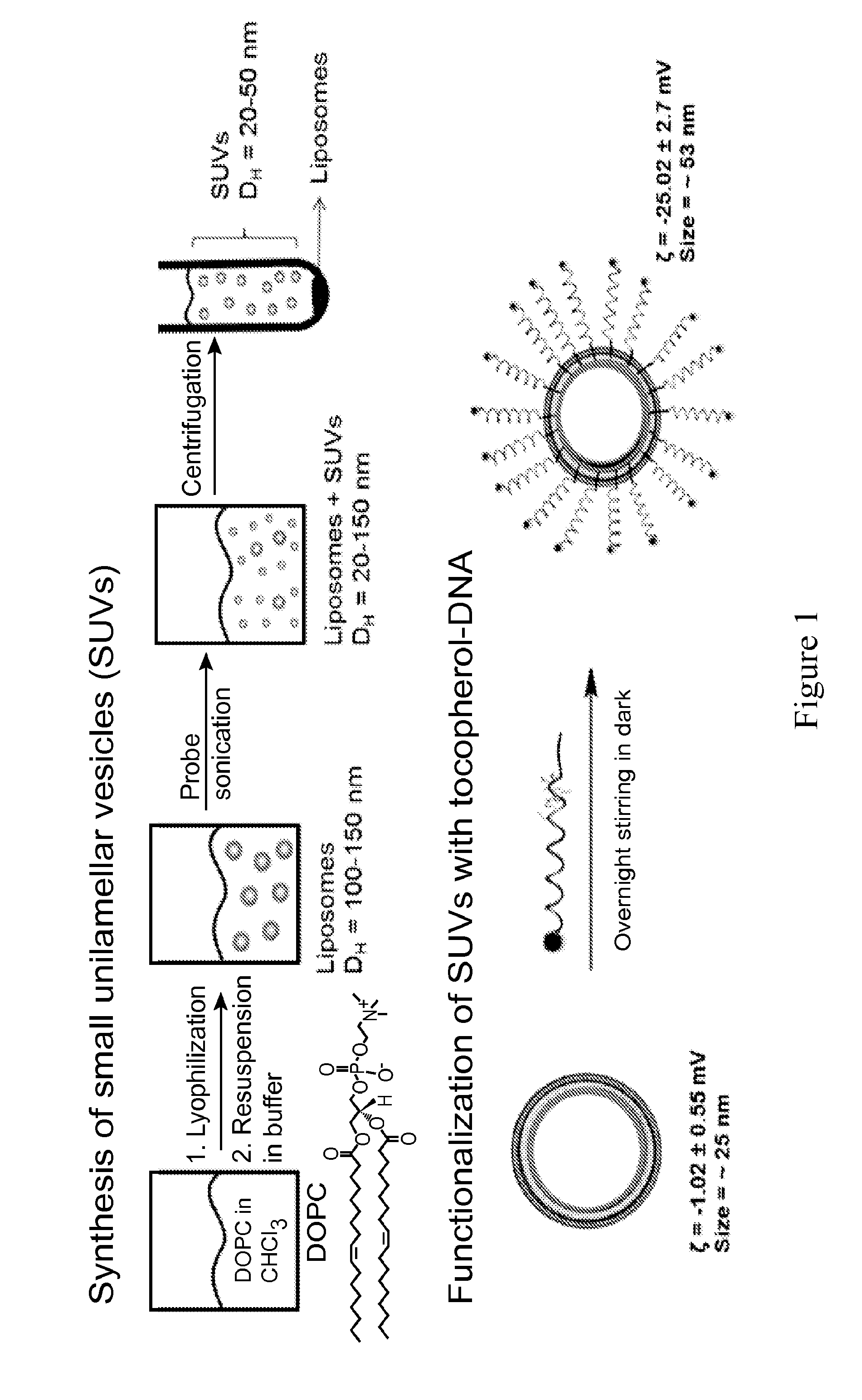
Liposomal particles, methods of making same and uses thereof
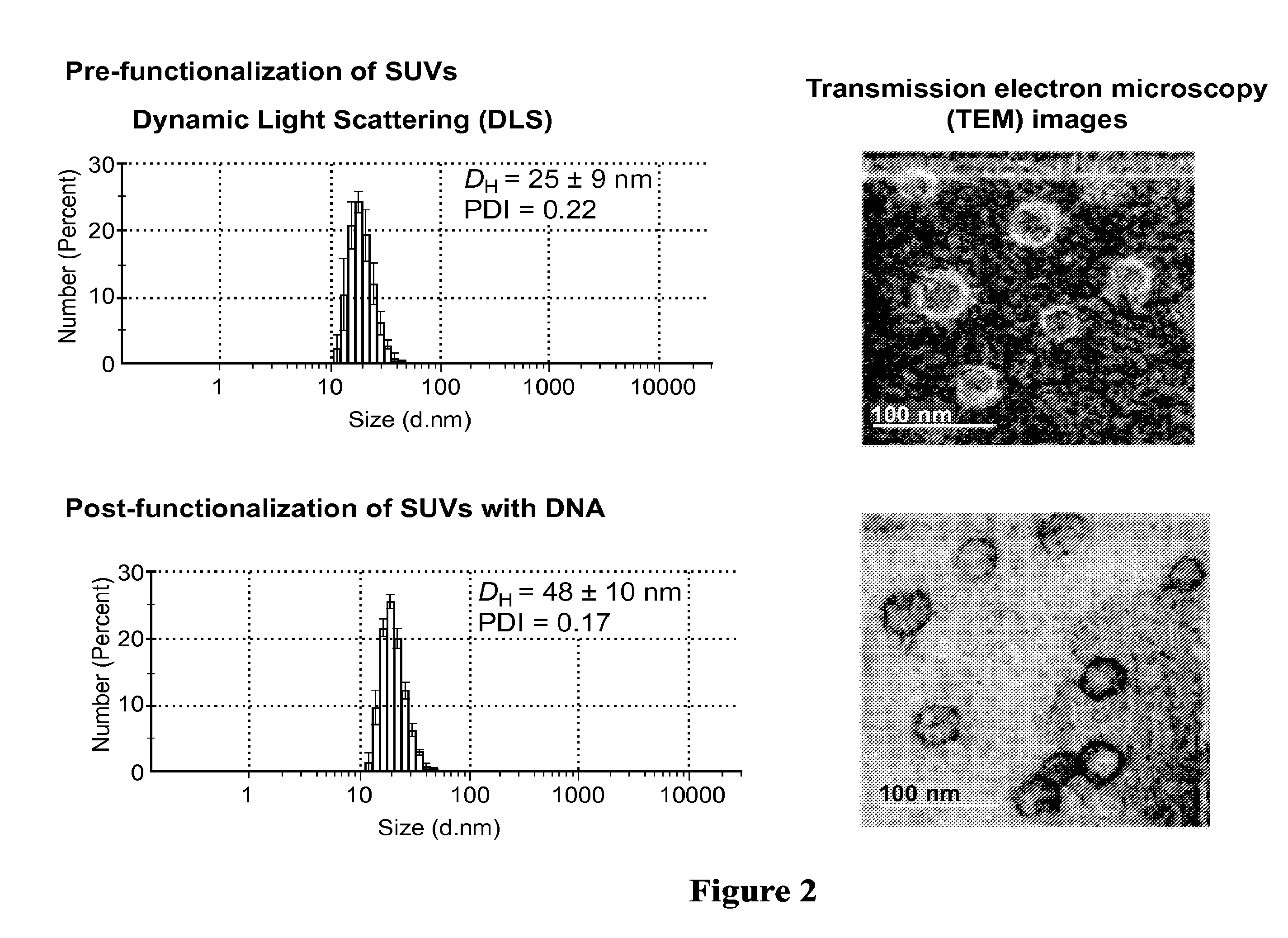
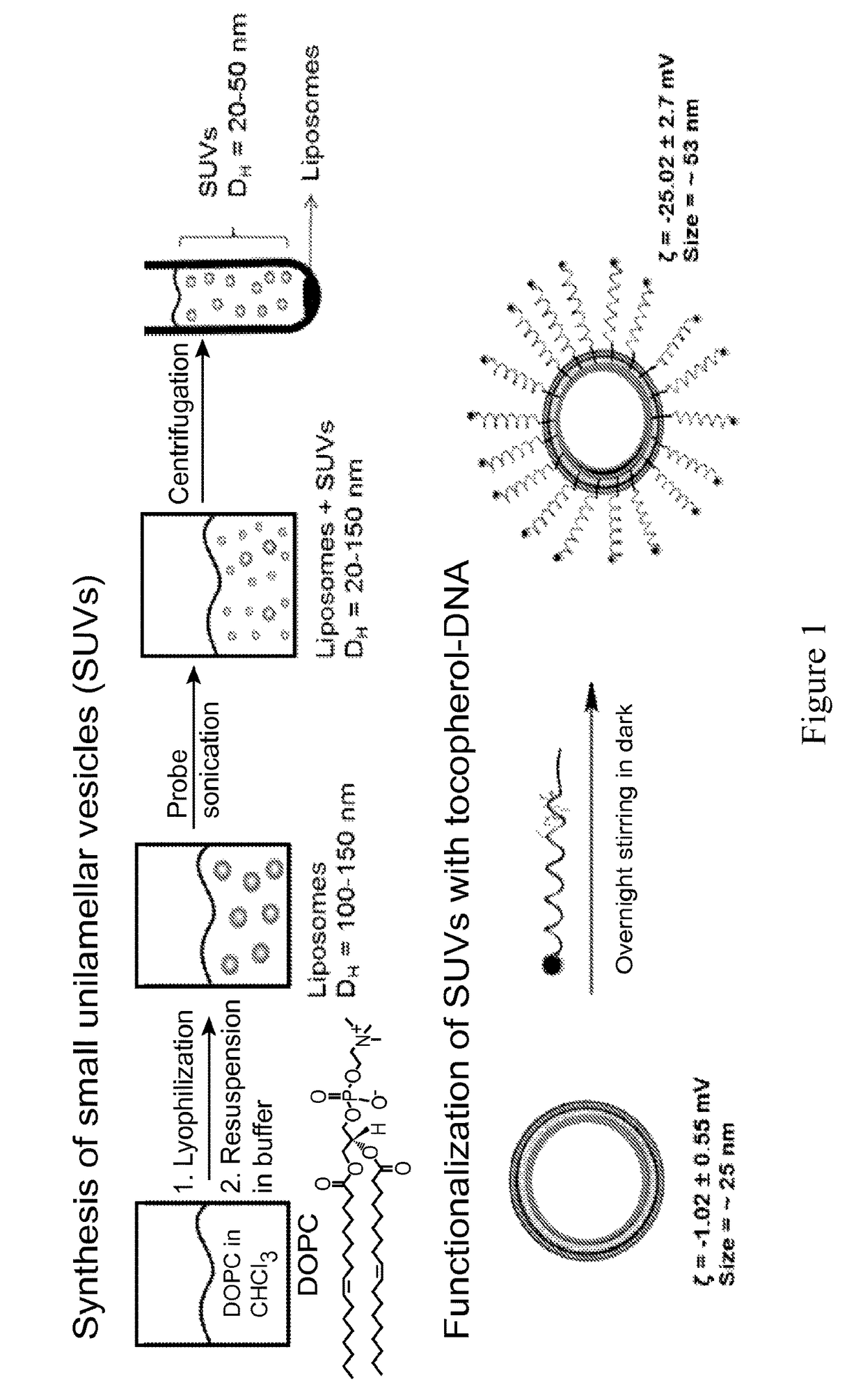
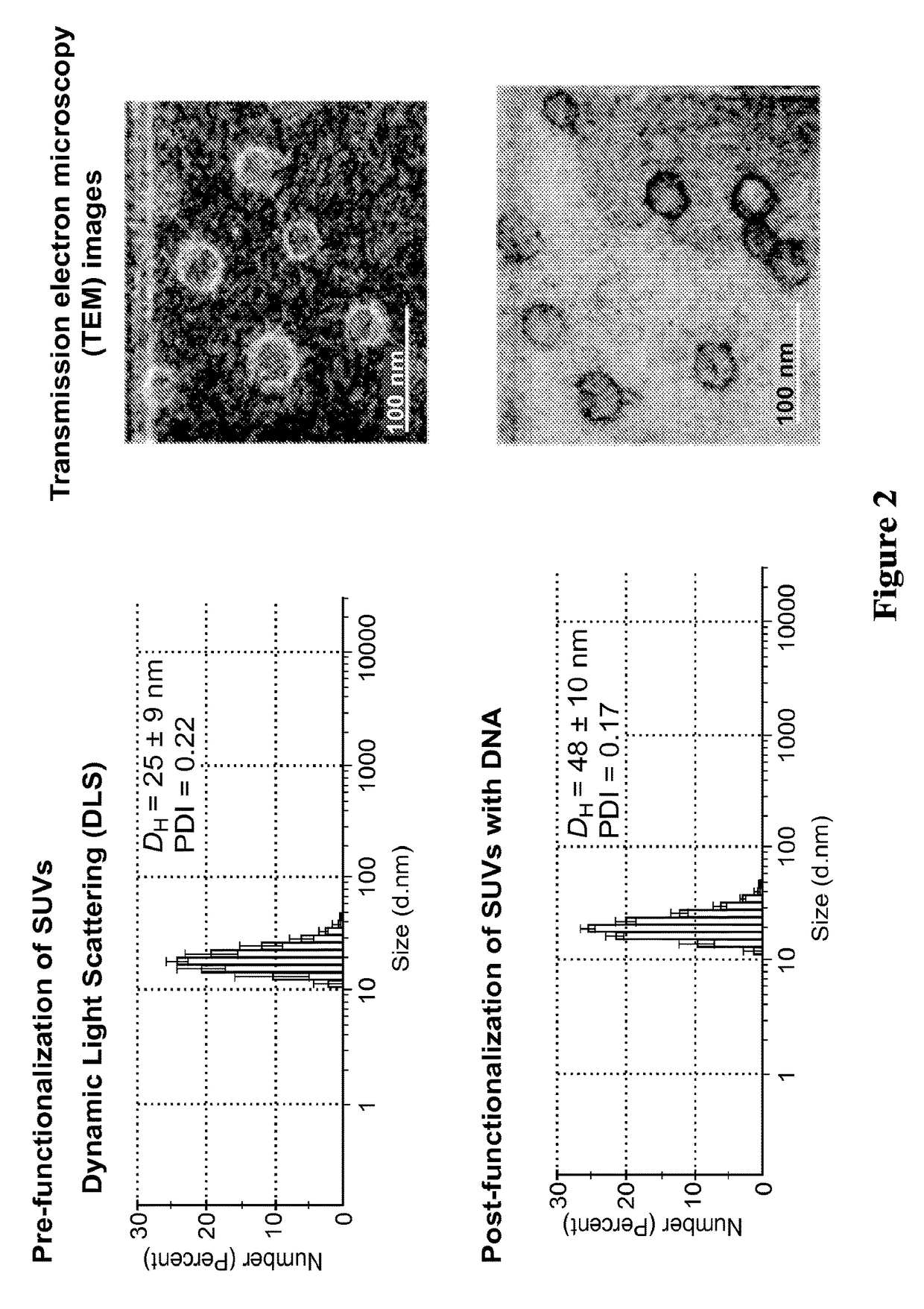
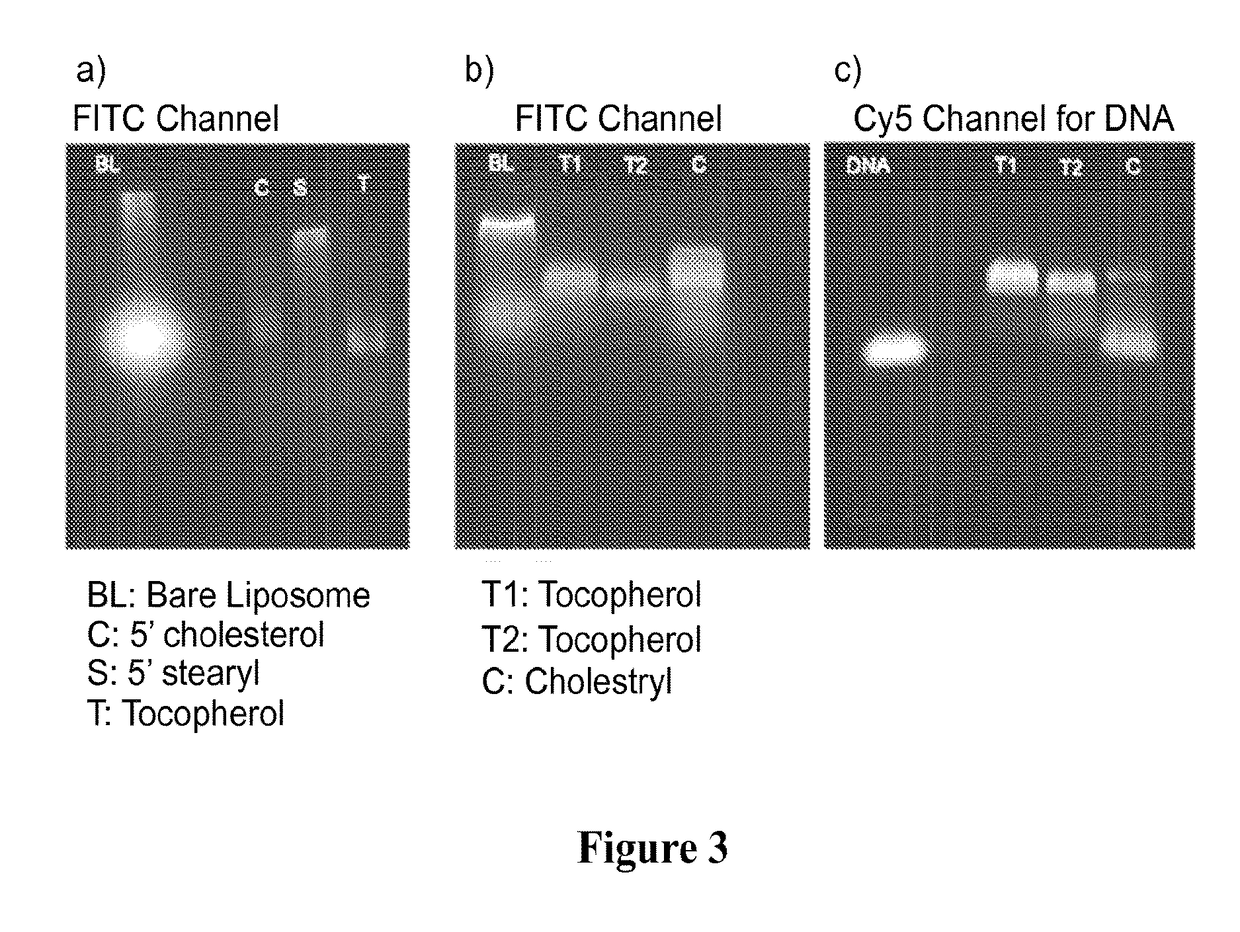
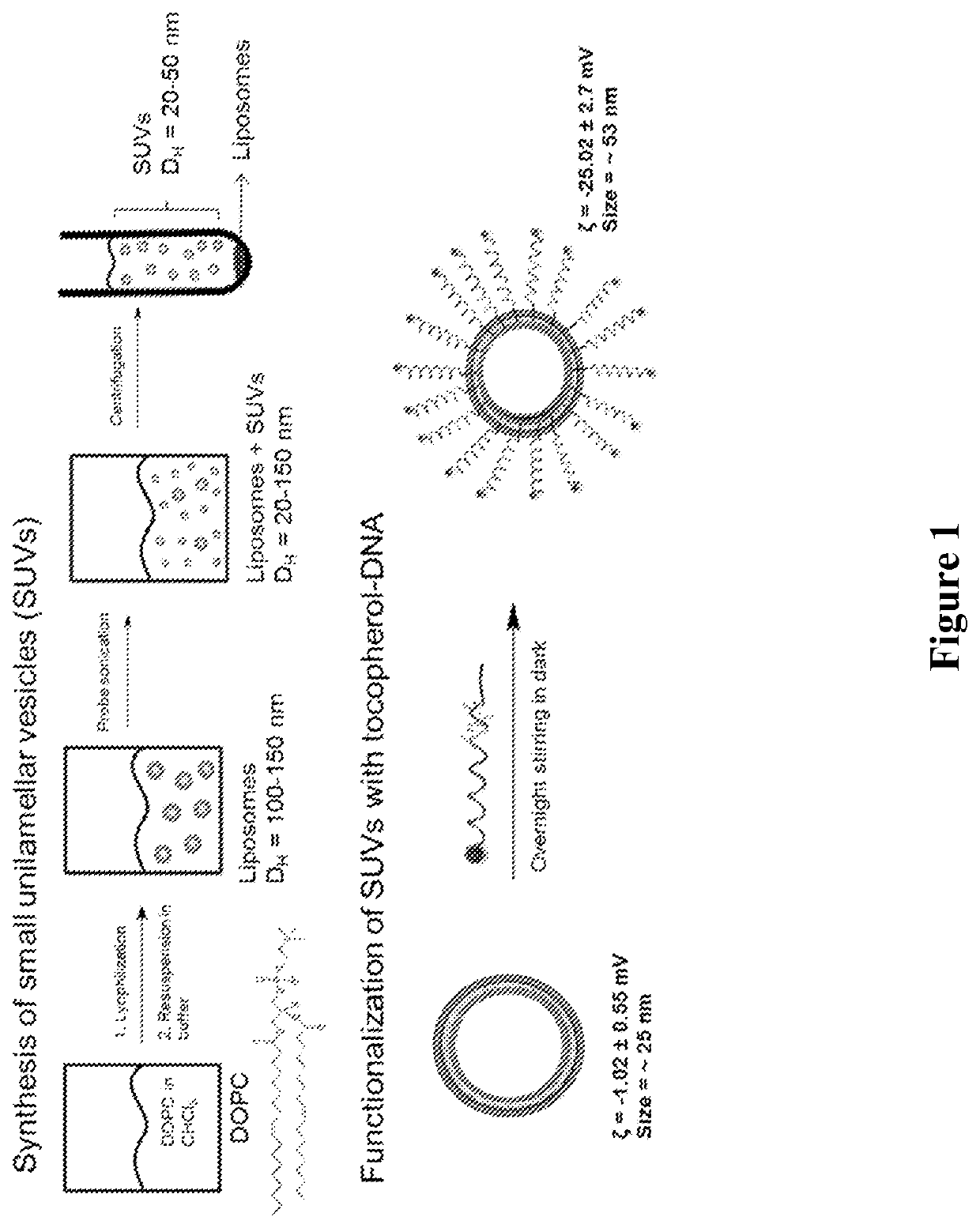
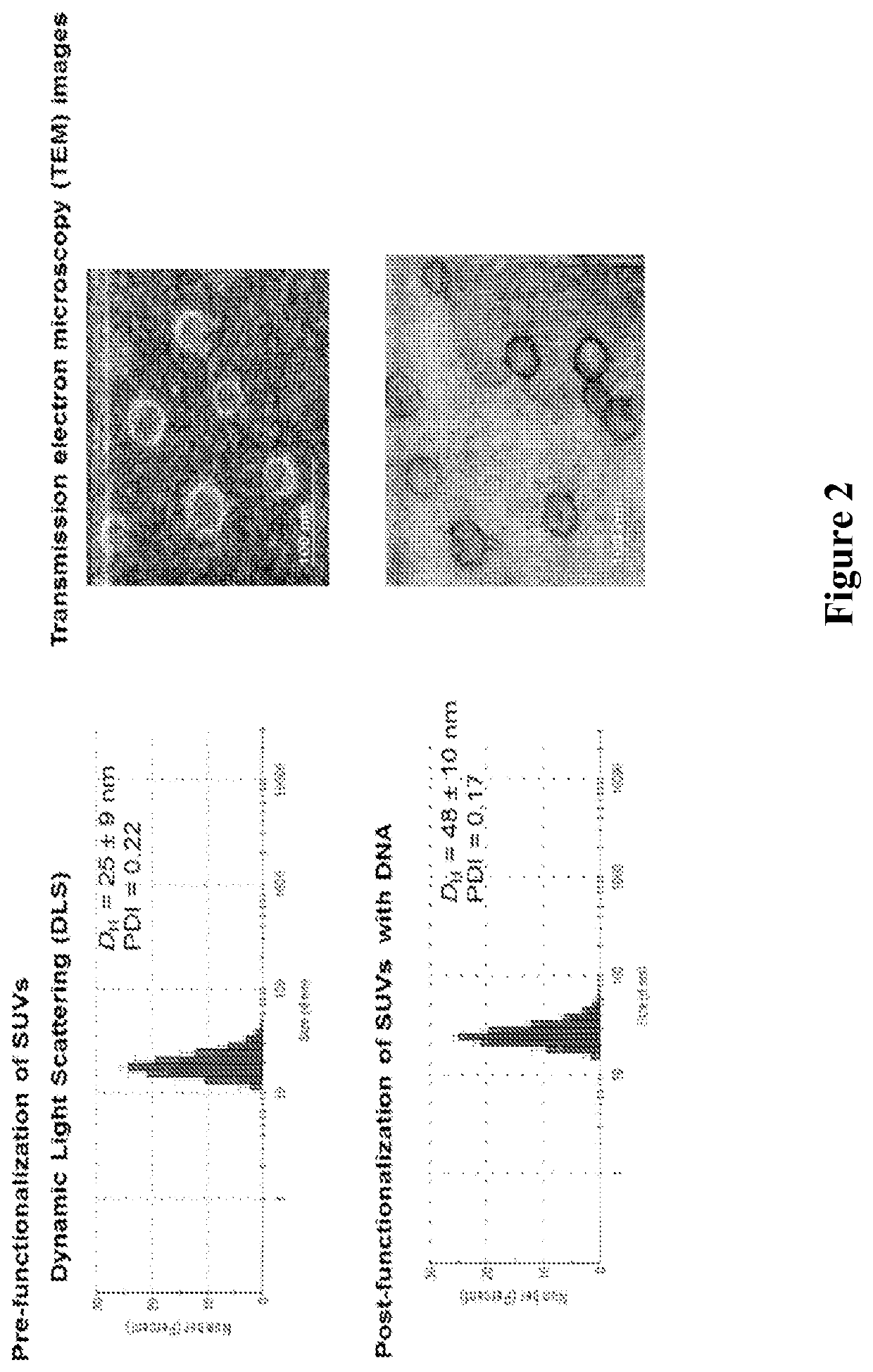
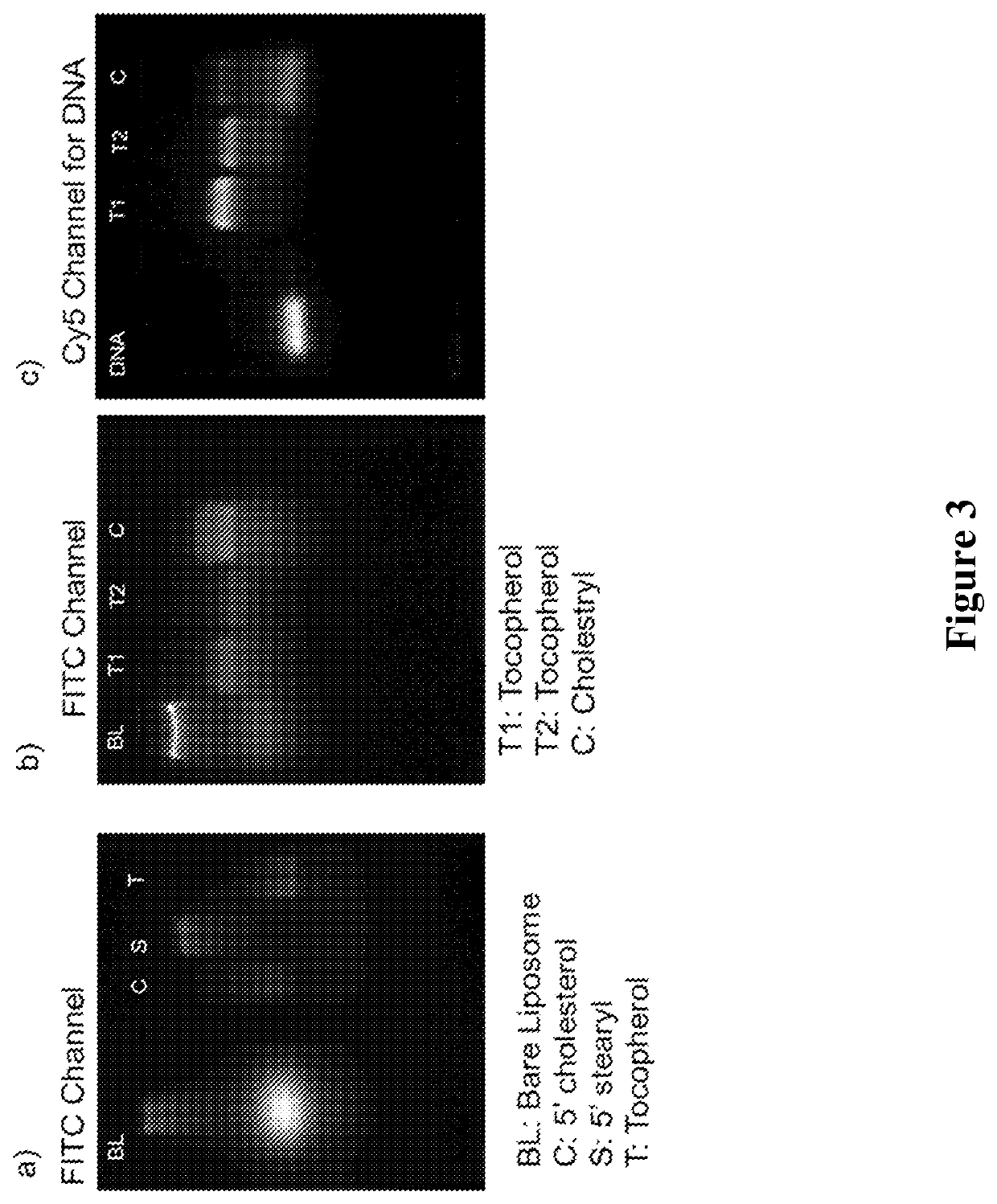
ActiveUS20160310425A1Not stableSpecial deliveryGenetic material ingredientsInstabilityImmunogenicity
Liposomes termed as small unilamellar vesicles (SUVs), can be synthesized in the 20-50 nm size range, but encounter challenges such as instability and aggregation leading to inter-particle fusion. This limits their use as a therapeutic delivery agent. Increasing the surface negative charge of SUVs, via the attachment of anionic entities such as DNA / RNA, increases the colloidal stability of these vesicles. Additionally, the dense spherical arrangement and radial orientation of nucleic acids exhibits unique chemical and biological properties, unlike their linear counterparts. These liposomal particles, are non-toxic and though anionic, can efficiently enter cells without the aid of ancillary cationic transfection agents in a non-immunogenic fashion. These exceptional properties allow their use as delivery agents for gene regulation in different therapies and offer an alternative platform to metal core spherical nucleic acids.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Liposomal particles, methods of making same and uses thereof
Liposomes termed as small unilamellar vesicles (SUVs), can be synthesized in the 20-50 nm size range, but encounter challenges such as instability and aggregation leading to inter-particle fusion. This limits their use as a therapeutic delivery agent. Increasing the surface negative charge of SUVs, via the attachment of anionic entities such as DNA / RNA, increases the colloidal stability of these vesicles. Additionally, the dense spherical arrangement and radial orientation of nucleic acids exhibits unique chemical and biological properties, unlike their linear counterparts. These liposomal particles, are non-toxic and though anionic, can efficiently enter cells without the aid of ancillary cationic transfection agents in a non-immunogenic fashion. These exceptional properties allow their use as delivery agents for gene regulation in different therapies and offer an alternative platform to metal core spherical nucleic acids.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
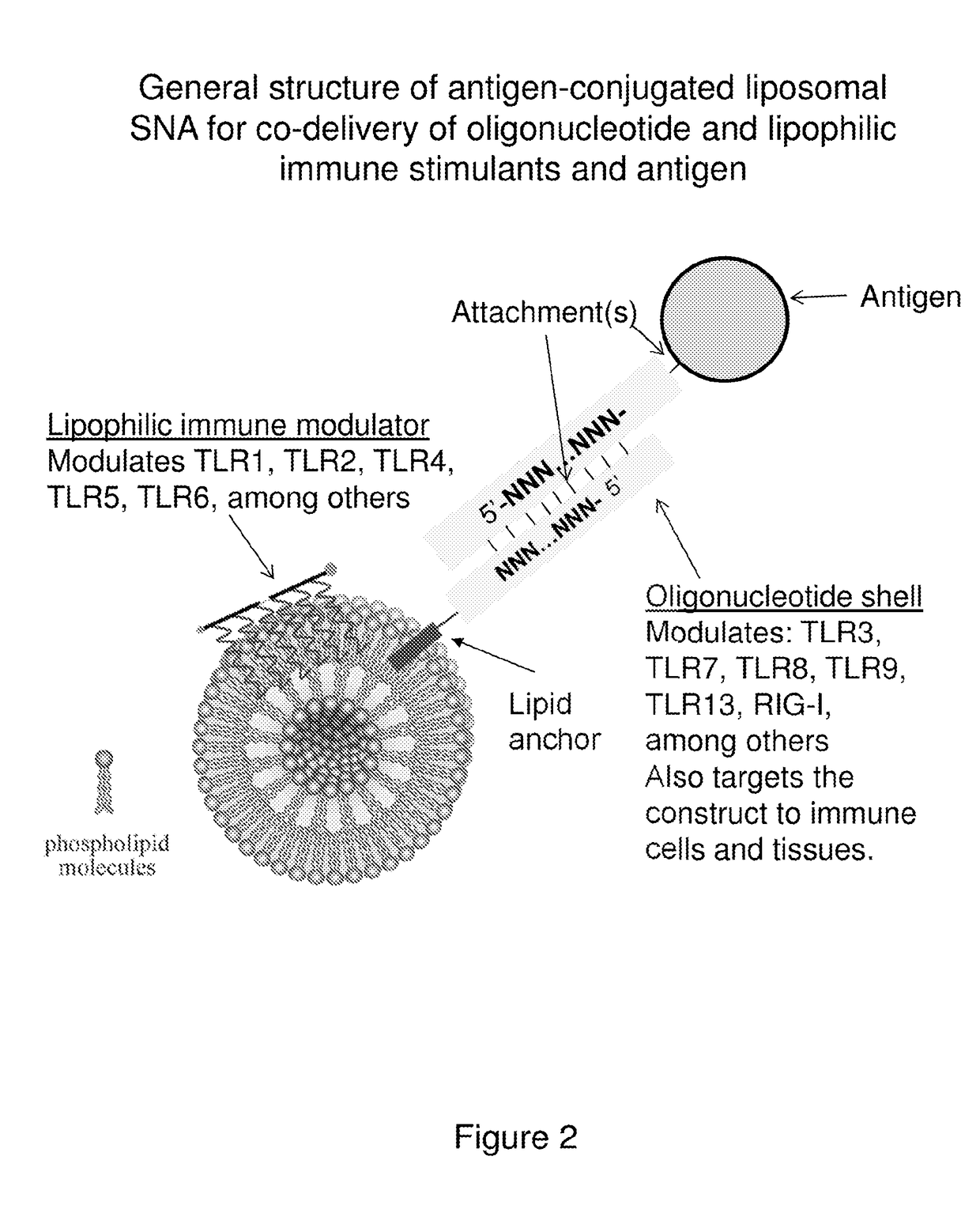
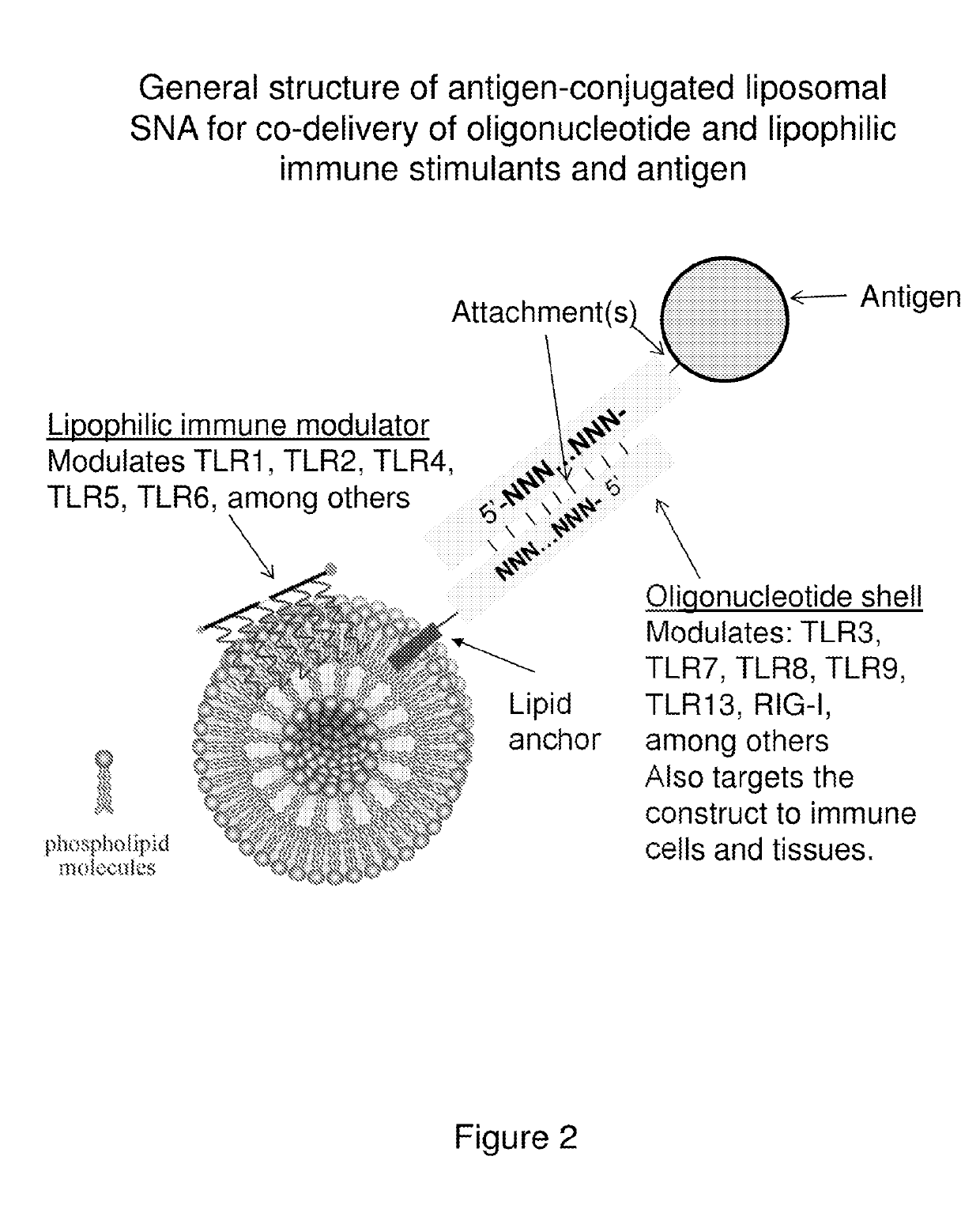
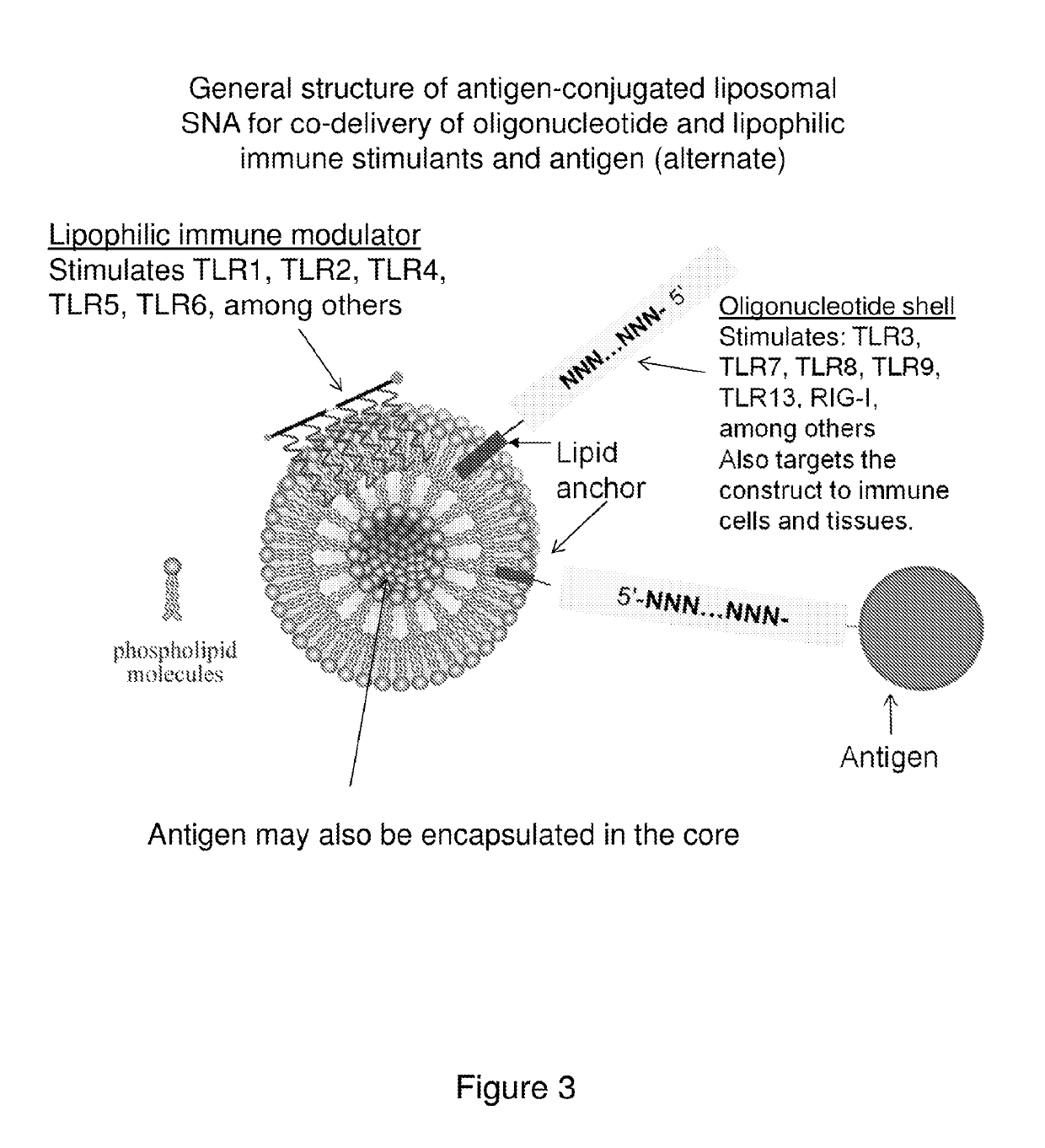
Multivalent delivery of immune modulators by liposomal spherical nucleic acids for prophylactic or therapeutic applications
ActiveUS20170157048A1Antibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsSpherical nucleic acidImmune Modulators
Liposomal spherical nucleic acids that function as multivalent immune modulators are provided according to the invention. The liposomal spherical nucleic acids of the invention are useful prophylactic and therapeutic applications as well as research and diagnostic indications.
Owner:EXICURE INC
Liposomal particles, methods of making same and uses thereof
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
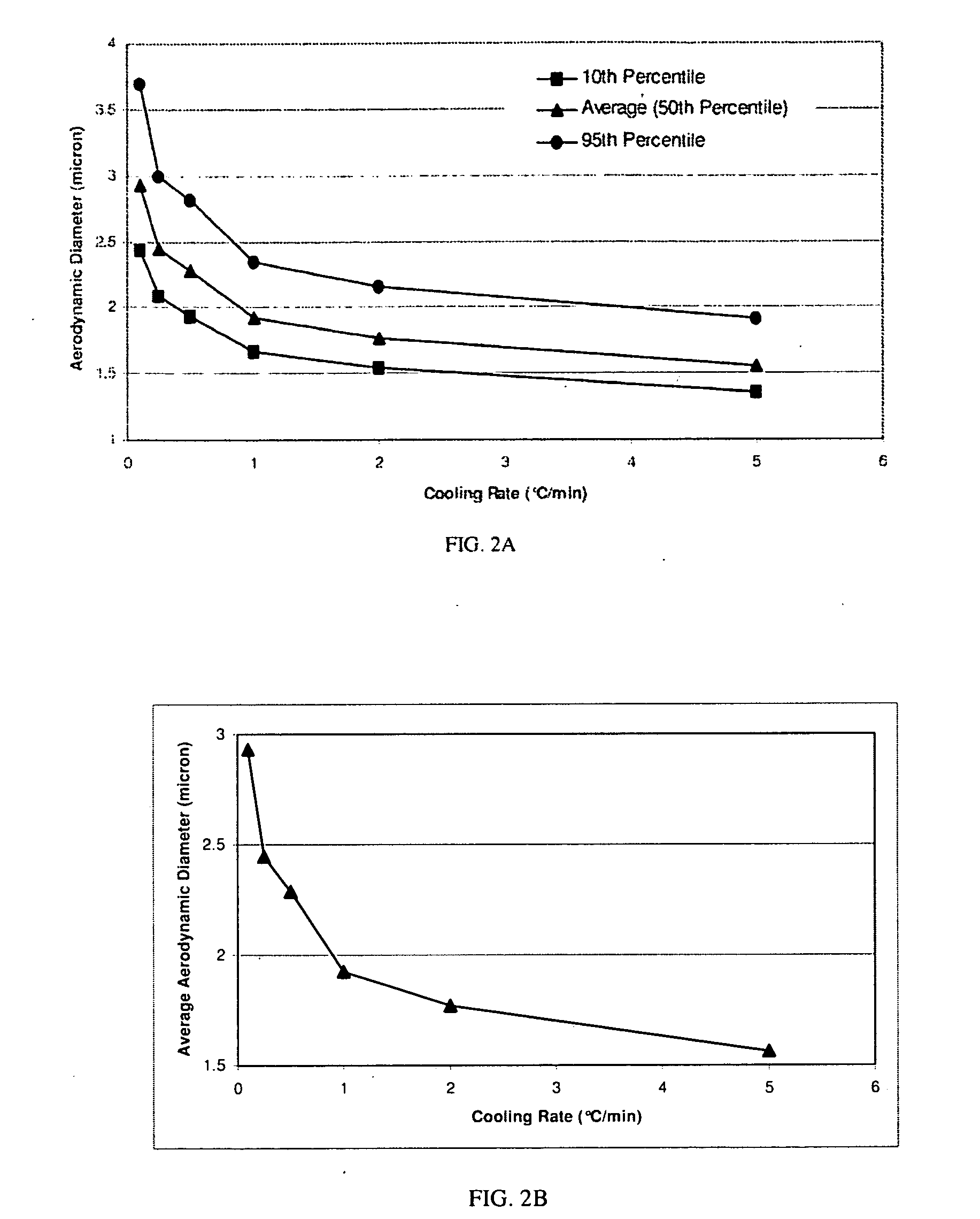
Nucleic Acid Microparticles for Pulmonary Delivery
ActiveUS20090017124A1Powder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsMicroparticle releaseSpherical nucleic acid
The present disclosure is related to microparticle compositions, in which the microparticles are made of nucleic acids and non-polymeric cations, which are suitable for administration to moist or aqueous target locations (e.g., the lung tissue), where the substantially spherical nucleic acid microparticles release the nucleic acids through dissolution, allowing the released nucleic acids to freely interact with the target cells.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Immuno-regulatory lipid containing spherical nucleic acids
InactiveUS20180042848A1Organic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLipid formationSpherical nucleic acid
Immunoregulatory spherical nucleic acids (irSNAs) composed of a lipid containing core and an inert Nucleic non-TLR antagonistic oligonucleotide shell are provided. Acid Shell These it-SNAs are useful for modulating an immune response.
Owner:EXICURE INC
Multivalent delivery of immune modulators by liposomal spherical nucleic acids for prophylactic or therapeutic applications
ActiveUS10434064B2Antibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsImmune modulatorSpherical nucleic acid
Liposomal spherical nucleic acids that function as multivalent immune modulators are provided according to the invention. The liposomal spherical nucleic acids of the invention are useful prophylactic and therapeutic applications as well as research and diagnostic indications.
Owner:EXICURE INC
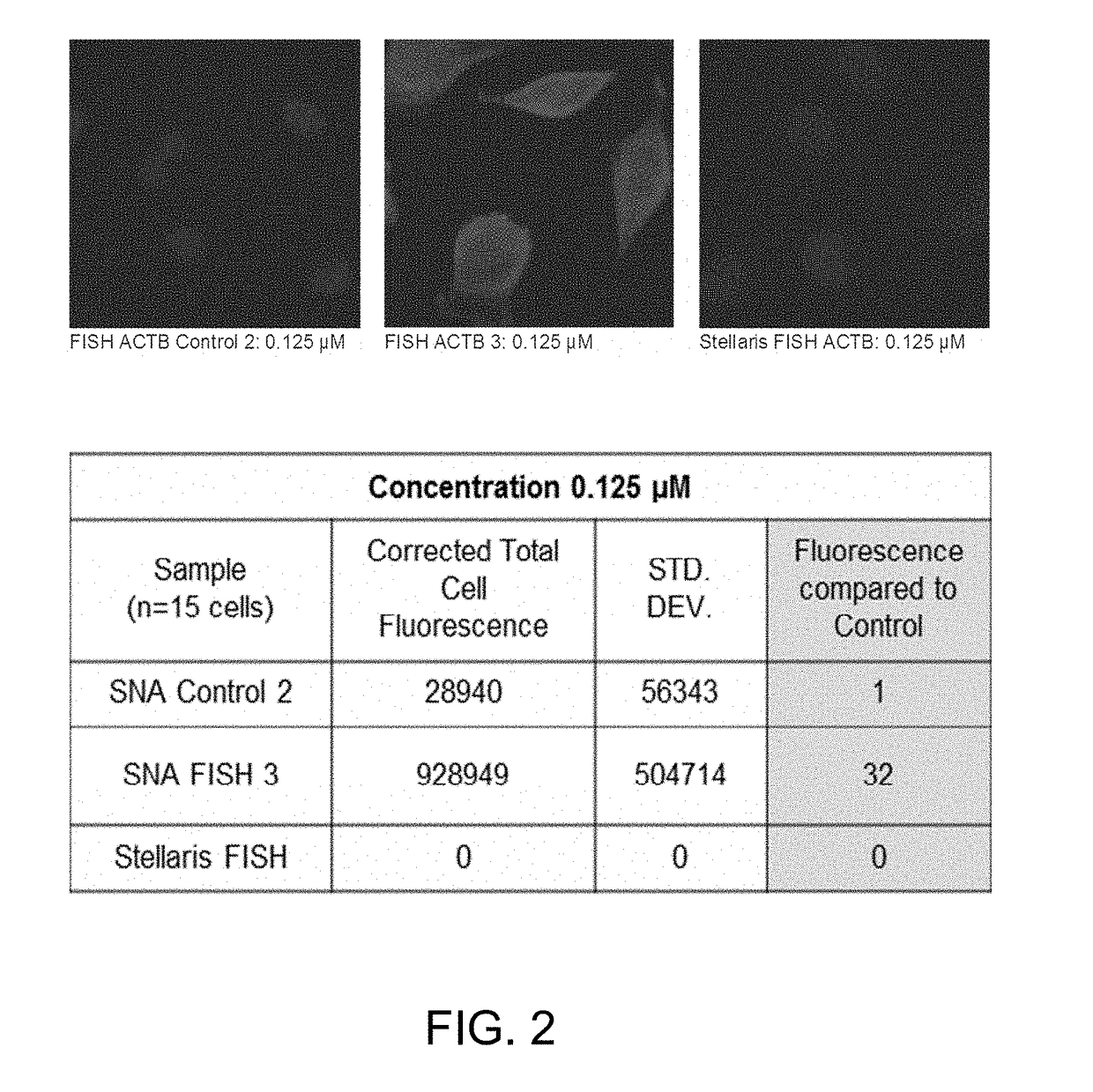
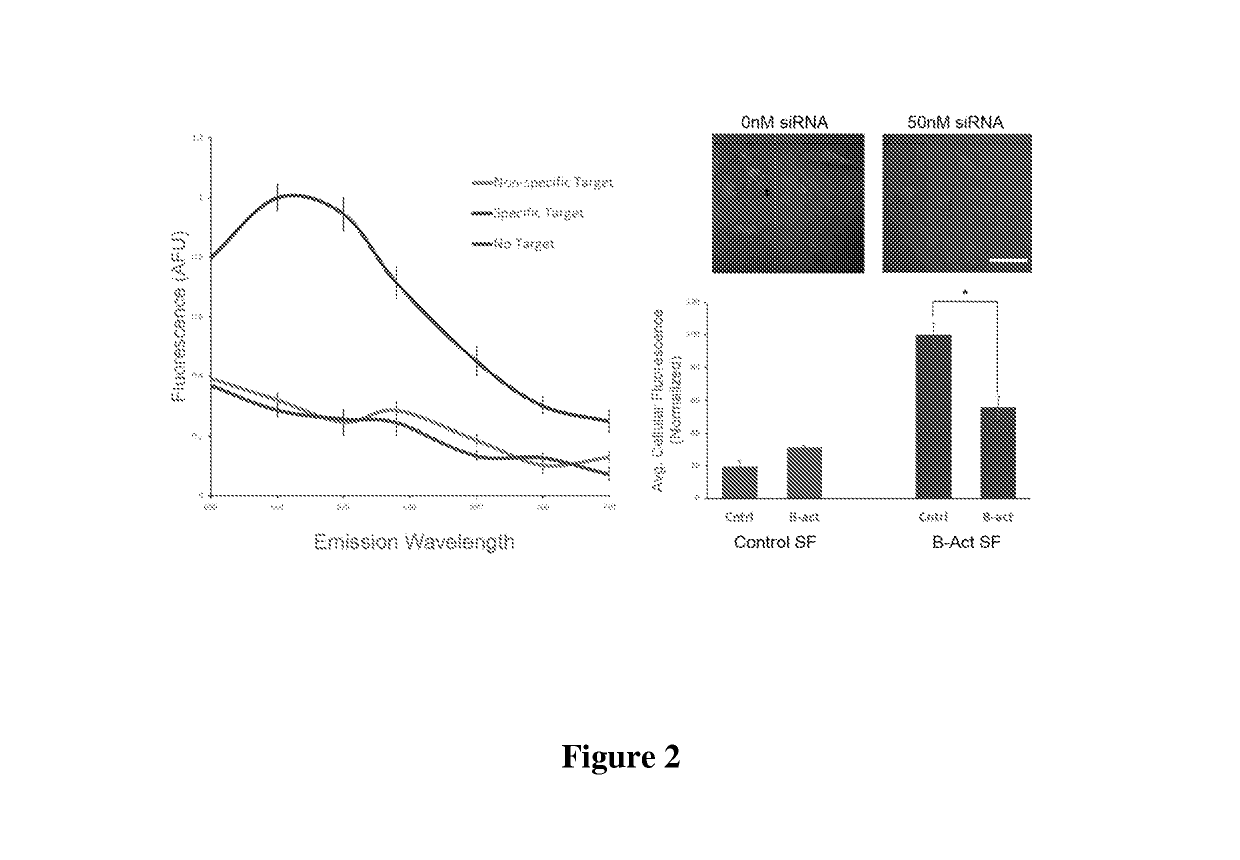
Spherical nucleic acids (SNA) flare based fluorescence in situ hybridization
The invention relates to a method of performing in situ hybridization such as fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) using liposomal spherical nucleic acids (L-SNAs) nanoparticles labeled with dye molecules. The nanoparticles contain one or more nucleic acids that recognize a target of interest in a sample.
Owner:AURASENSE
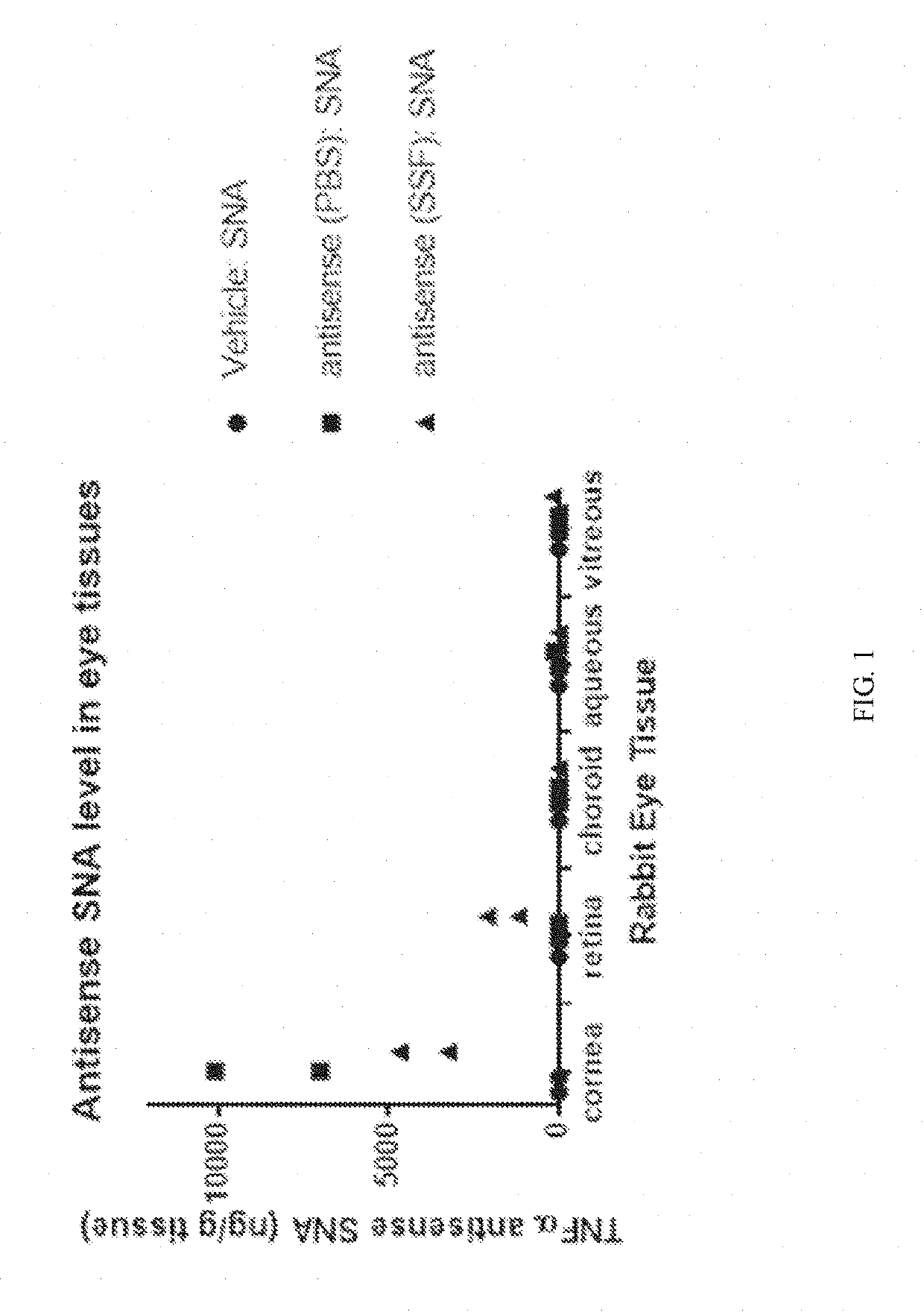
Topical administration of therapeutic agents and oligonucleotide formulations
Aspects of the invention relate to topical and ocular formulations of spherical nucleic acids (SNA), as well as methods of use thereof and compositions thereof. The formulations may include an inhibitor such as an inhibitor of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFa), platelet-derived growth factor subunit A (PDGFA), platelet-derived growth factor subunit B (PDGFB), platelet-derived growth factor subunit C (PDGFC), platelet-derived growth factor subunit D (PDGFD), platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA), platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRB), platelet-derived growth factor receptor like (PDGFRL), vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGFB), vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGFD), vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR1), vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR2), vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR3), beta-2 adrenergic receptor (ADRB2), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), interleukin 1 beta (IL1 β), interleukin 1 receptor-1 (IL1 R1), interleukin 1 receptor-2 (IL1R2), and interleukin 1 receptor-3 (IL1R3). Aspects of the invention further relate to nanostructures comprising self-assembling therapeutic oligonucleotides, such as antisense oligonucleotides, that are linked to a molecular species, wherein the molecular species is positioned in a core of the nanostructure and the oligonucleotides extend radially from the core.
Owner:EXICURE INC
Spherical nucleic acid (SNA)-mediated delivery of lipid-complexes to cells
InactiveUS20180214376A1Organic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSpherical nucleic acidCell biology
Owner:EXICURE INC
Spherical nucleic acid-based constructs as immunostimulatory agents for prophylactic and therapeutic use
Owner:EXICURE INC
Nucleic acid microparticles for pulmonary delivery
ActiveUS8808747B2Powder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroparticle releaseSpherical nucleic acid
The present disclosure is related to microparticle compositions, in which the microparticles are made of nucleic acids and non-polymeric cations, which are suitable for administration to moist or aqueous target locations (e.g., the lung tissue), where the substantially spherical nucleic acid microparticles release the nucleic acids through dissolution, allowing the released nucleic acids to freely interact with the target cells.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
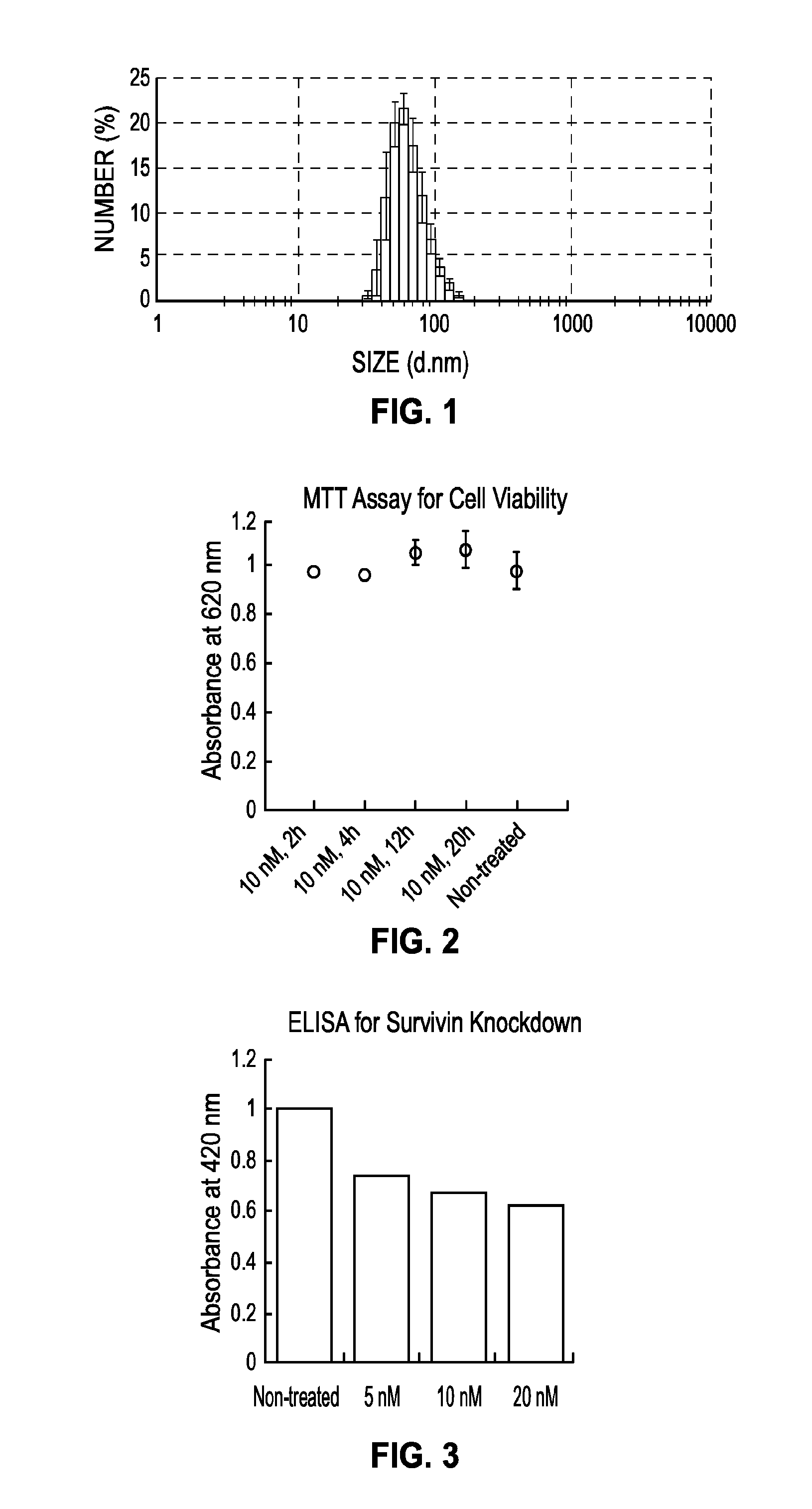
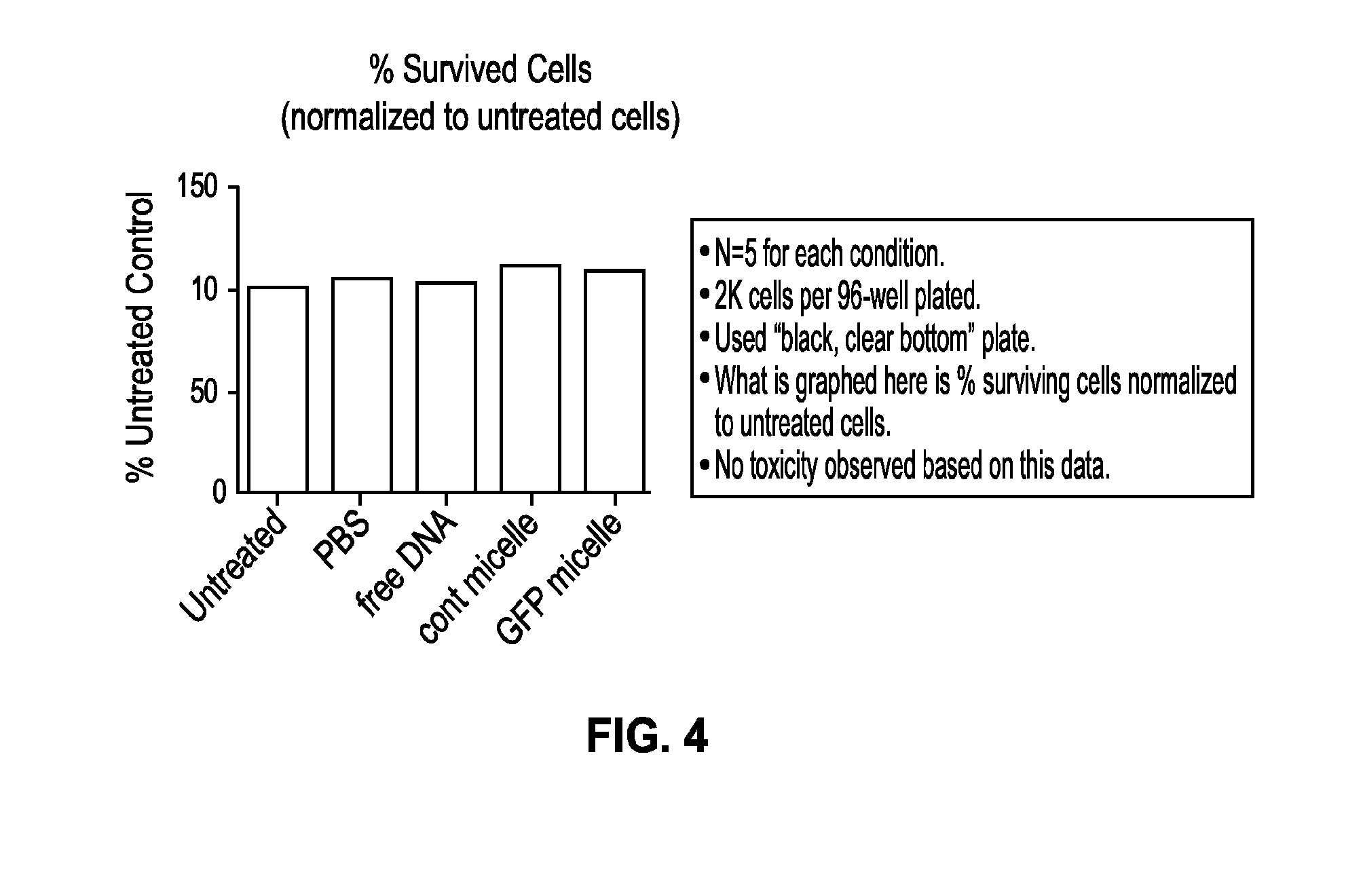
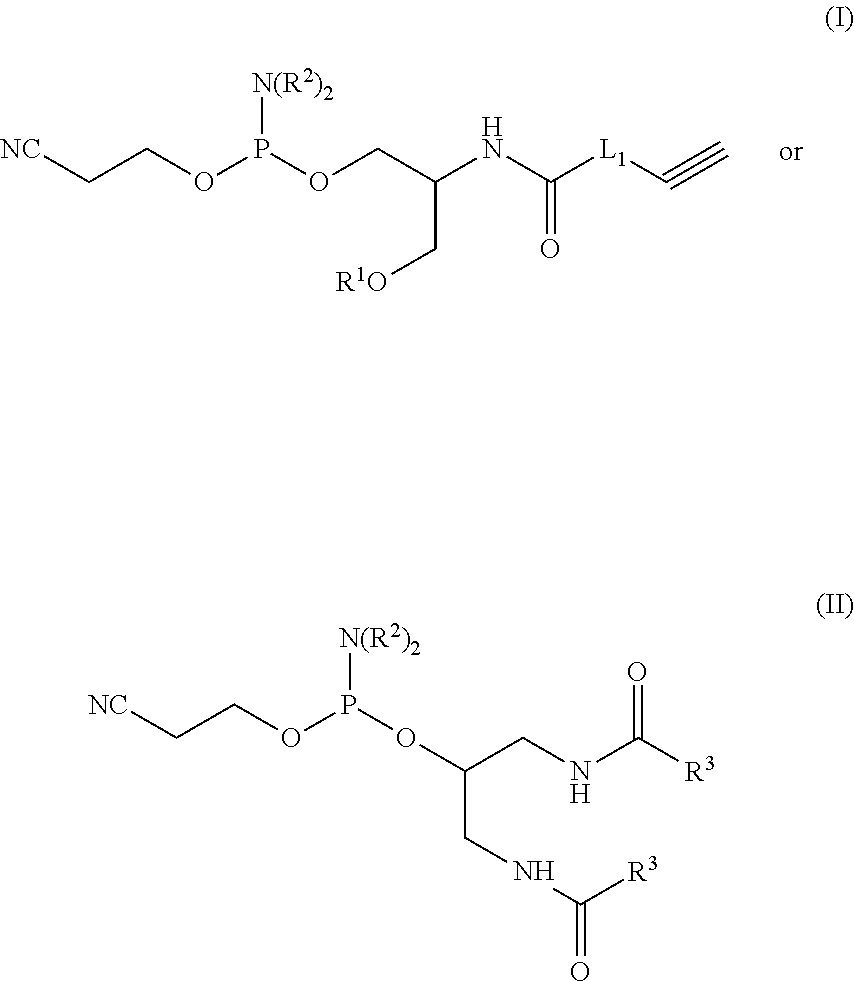
Alkyne phosphoramidites and preparation of spherical nucleic acid constructs
The present disclosure is directed to compositions comprising alkyne oligonucleotides, nanoconjugates prepared from the same, and methods of their use.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Tlr9-targeted spherical nucleic acids having potent antitumor activity
PendingUS20200248183A1Raise the ratioOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseSpherical nucleic acid
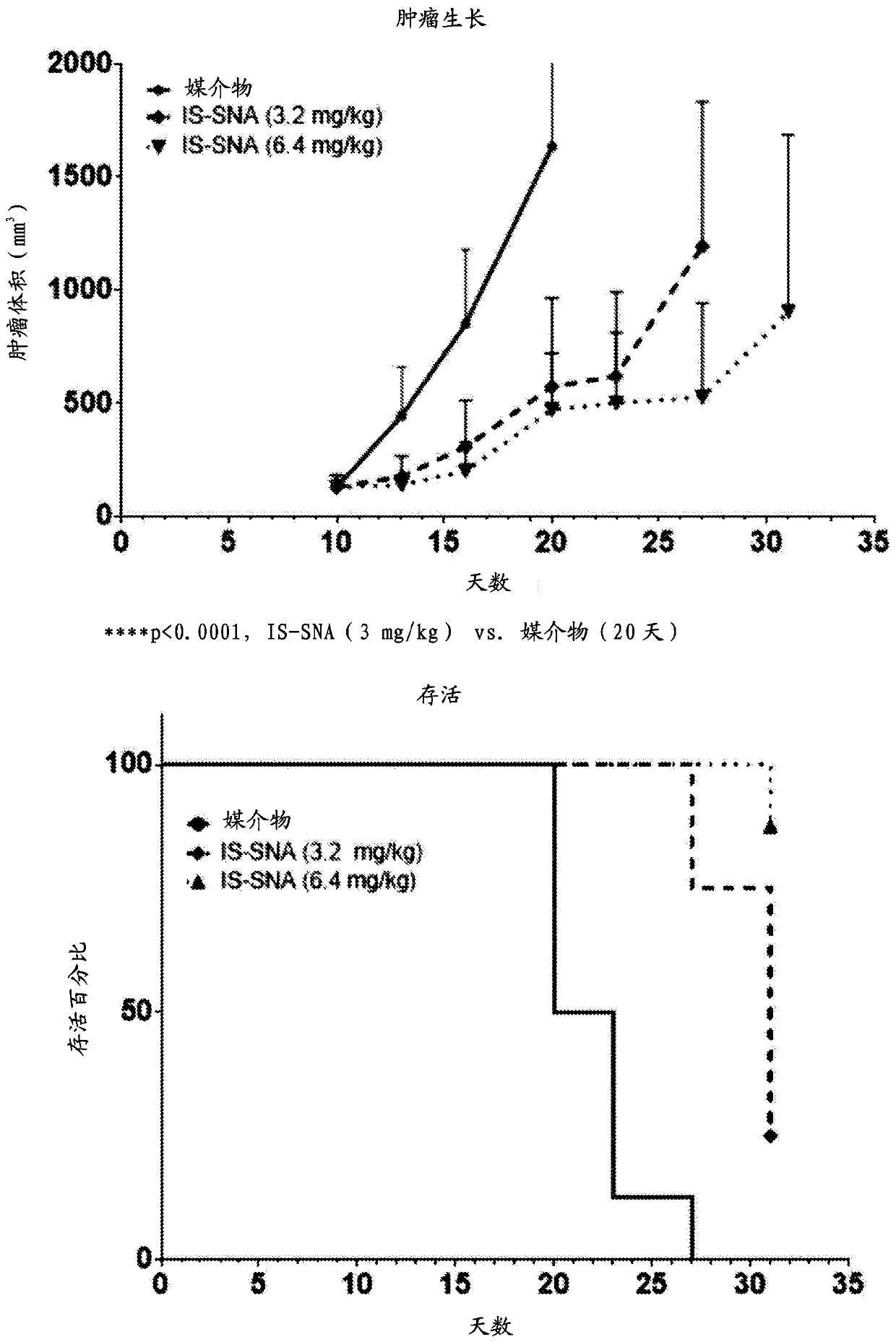
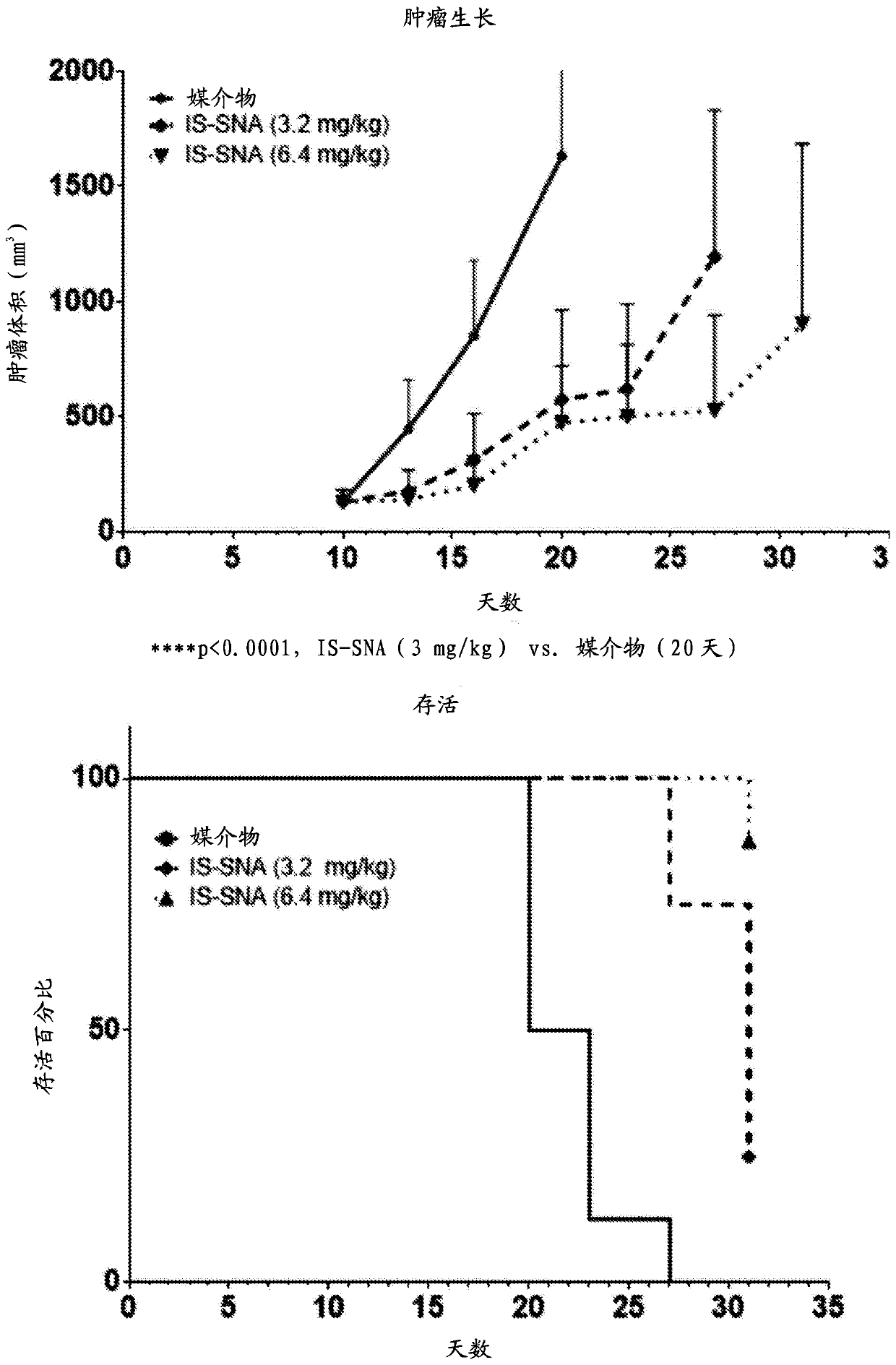
Aspects of the invention relate to immunostimulatory spherical nucleic acids (IS-SNA) for the treatment of a disorder, such as cancer. The IS-SNA may be administered together with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Owner:EXICURE INC
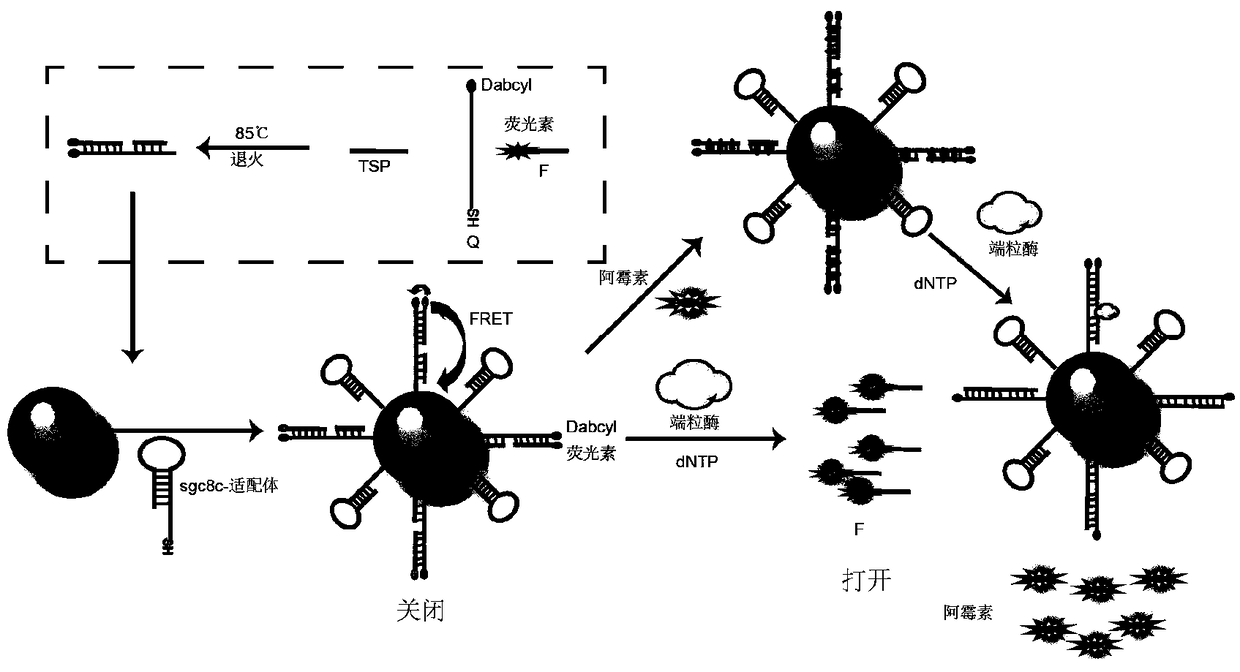
Spherical nucleic acid probe and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108866161AGood biocompatibilityNo side effectsOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseSide effect
The invention discloses a spherical nucleic acid probe and a preparation method and application thereof. The spherical nucleic acid probe uses nanogold as a core of spherical nucleic acid; double-chain DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) formed by hybridizing three chains and an adaptor are assembled to the surface of the nanogold to form an outer shell of the spherical nucleic acid probe. The spherical nucleic acid probe has the advantages that the activity of telomerase can be detected, and the DNA complex at the surface of the probe is rich in CG nucleotide and can carry an anti-drug medicine (adriamycin), so that the spherical nucleic acid probe can be used for treating the cancer cells, and can reach targeting property in the complicated biological environment by utilizing the modified adaptor at the surface of the probe; the stability is good, the biocompatibility is good, the toxic or side effect to the cells is avoided, the detection range is broad, the sensitivity is high, and the like; the detection speed is quick, and the preparation steps are simple.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Synthesis of spherical nucleic acids using lipophilic moieties
Owner:EXICURE OPERATING COMPANY
Surface functionalization of liposomes and liposomal spherical nucleic acids (SNAS)
Owner:EXICURE INC
Nucleic acid microparticles for pulmonary delivery
InactiveCN101686939APowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroparticle releaseSpherical nucleic acid
The present disclosure is related to microparticle compositions, in which the microparticles are made of nucleic acids and non-polymeric cations, which are suitable for administration to moist or aqueous target locations (e.g., the lung tissue), where the substantially spherical nucleic acid microparticles release the nucleic acids through dissolution, allowing the released nucleic acids to freely interact with the target cells.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
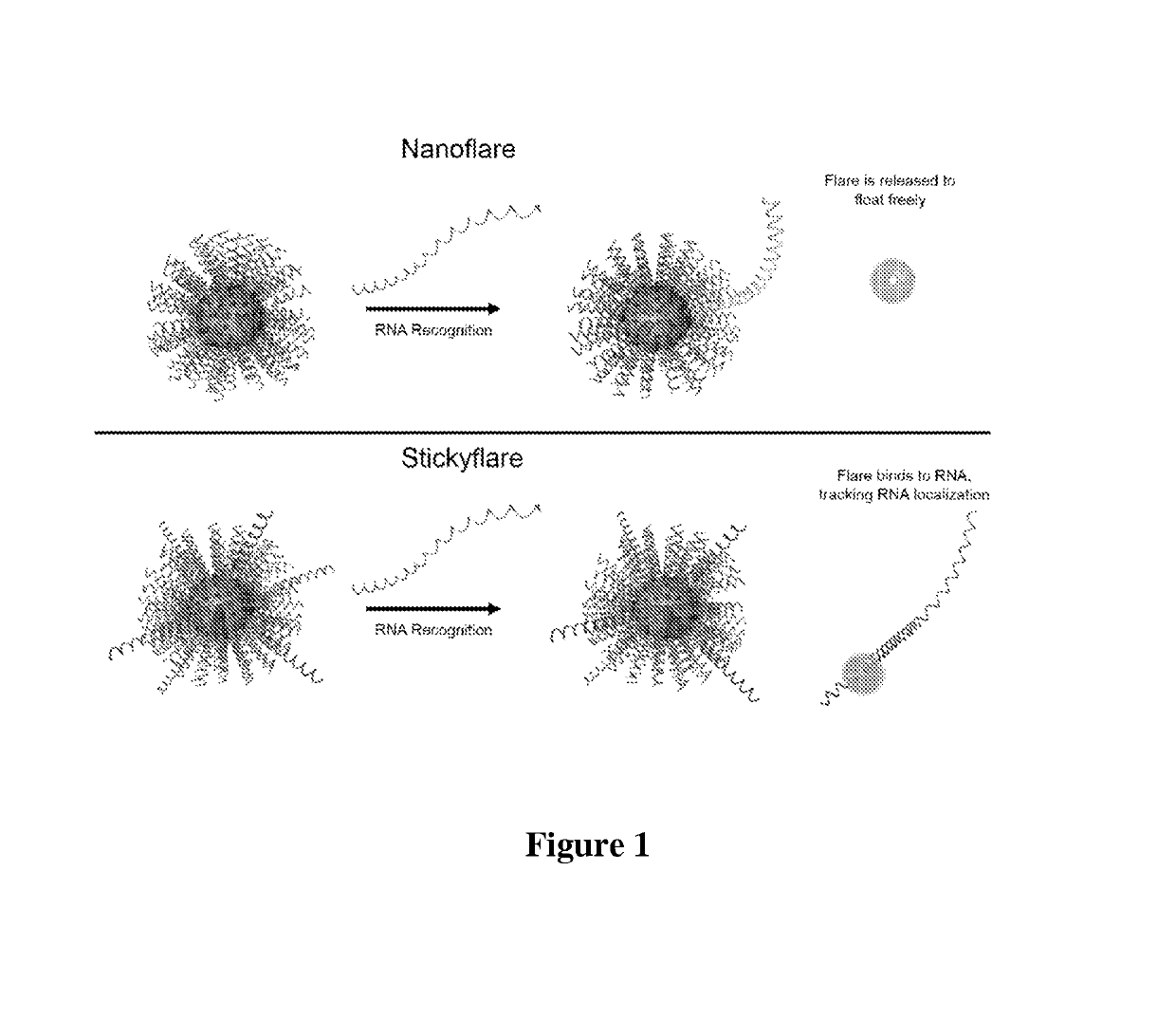
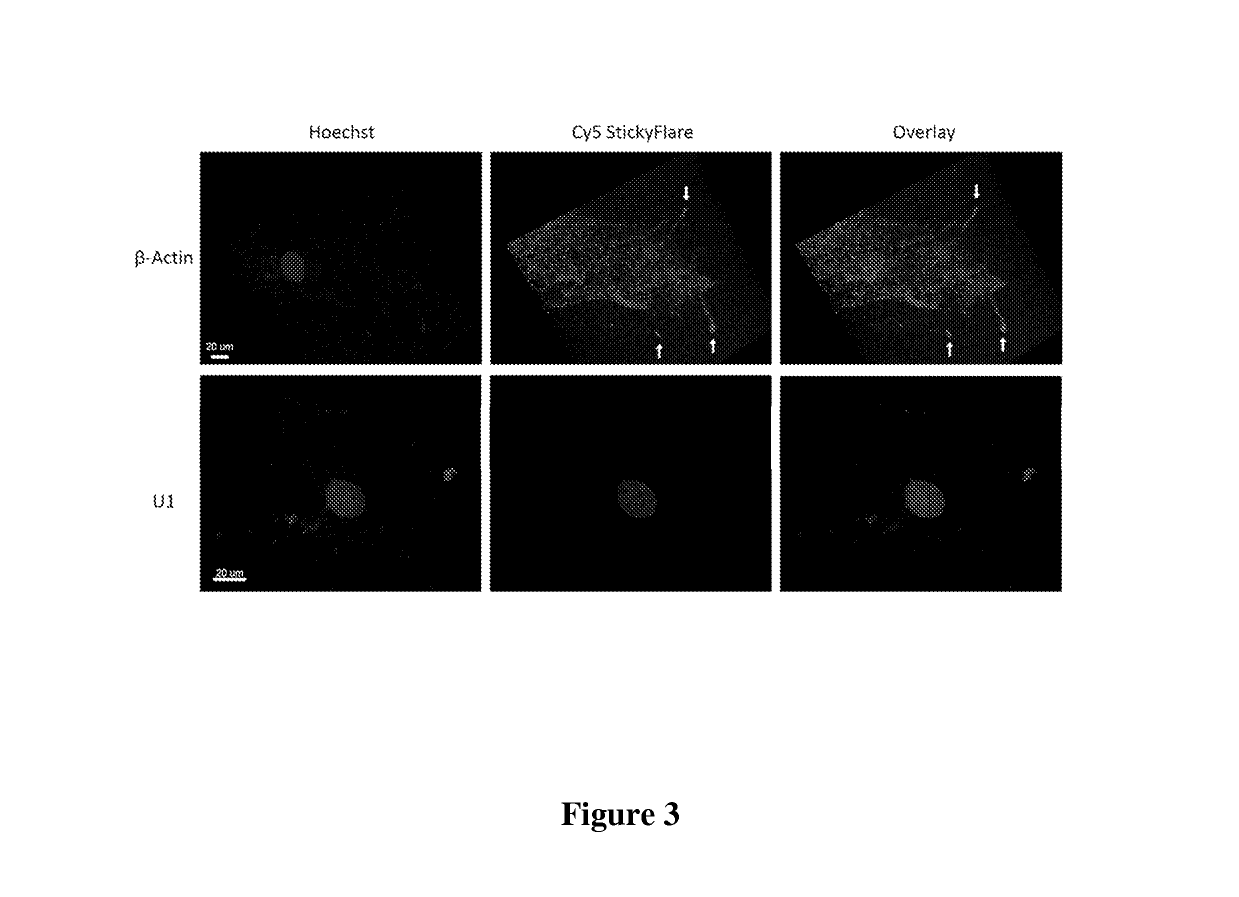
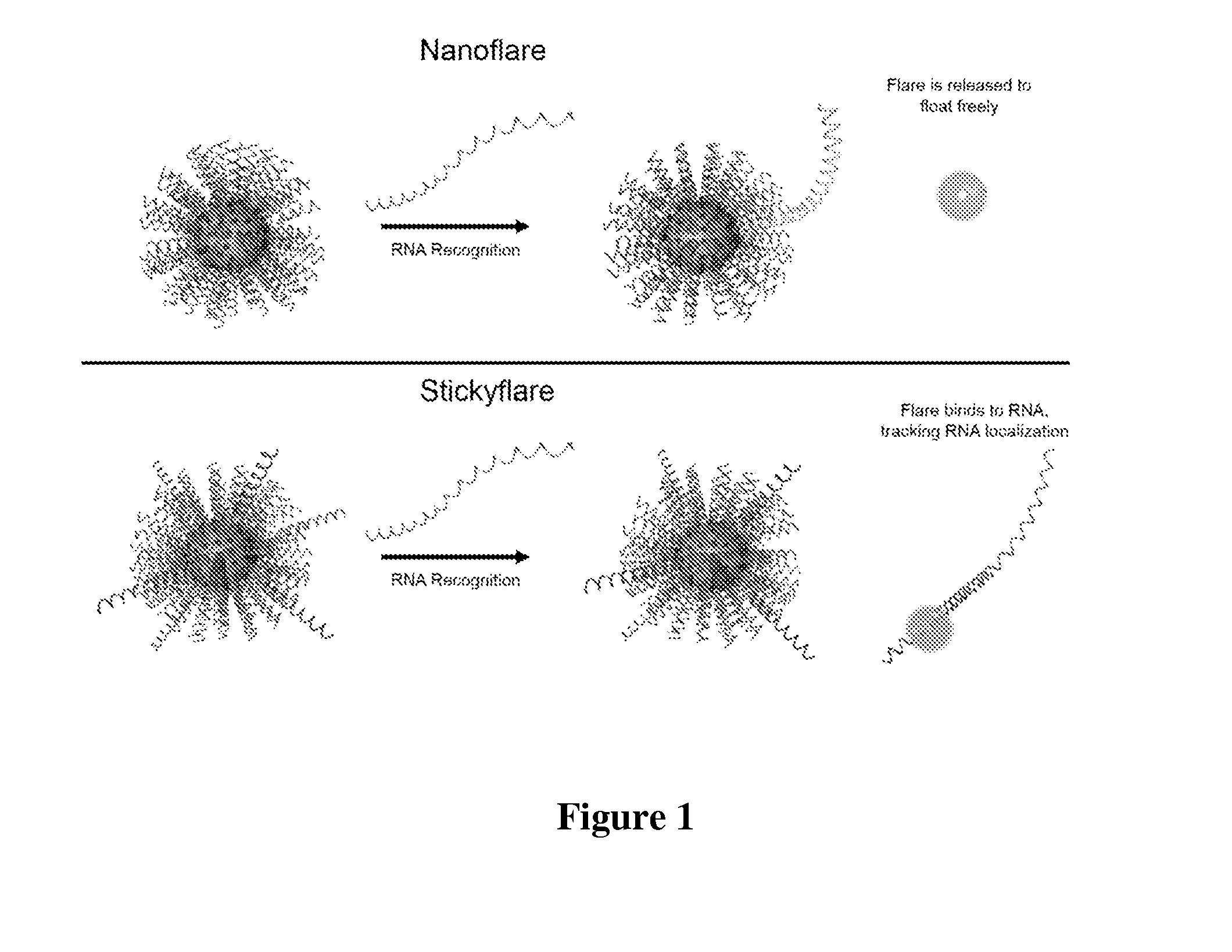
Quantification and spatio-temporal tracking of a target using a spherical nucleic acid (SNA)
The present invention relates to methods of detecting and tracking a target molecule using a nanoparticle wherein the nanoparticle comprises a polynucleotide that can specifically associate with the target molecule, and wherein the association results in a change in a detectable marker that can be measured after association with the target molecule.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
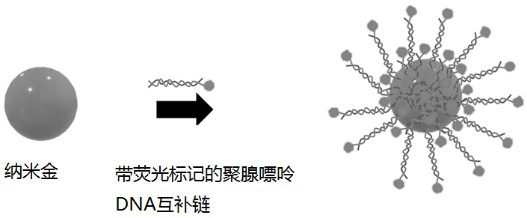
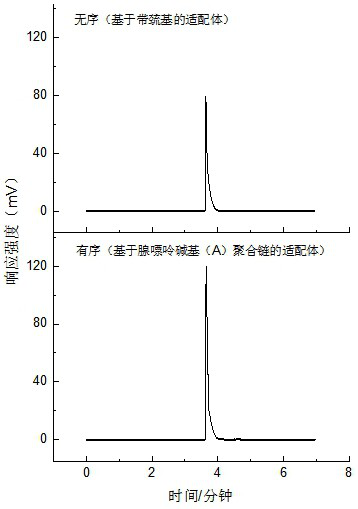
Gold magnetic nanoprobe based on ordered arrangement of aptamers and application of gold magnetic nanoprobe in okadaic acid detection
PendingCN114657185AAchieve saturated coverageInhibition of non-specific adsorptionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingAptamerHigh density
The invention discloses a gold magnetic nanoprobe based on ordered arrangement of aptamers and application of the gold magnetic nanoprobe in okadaic acid detection (OA). The gold magnetic nanoprobe is formed by combining nanogold spherical nucleic acid and nano magnetic beads, wherein nucleic acid sequences are orderly arranged on the surface of the nanogold spherical nucleic acid; the nucleic acid sequence is formed by an aptamer with an adenine base polymeric chain at the 5'end and a DNA complementary chain with a fluorescent label at the 5 'end. The surface of the gold magnetic nanoprobe is modified with high density and is loaded with orderly arranged aptamers, so that the gold magnetic nanoprobe is high in specific recognition efficiency and simple and convenient to separate a target object, and can react with okadaic acid to release a fluorescently-labeled DNA complementary chain, and laser-induced fluorescence detection is applied, so that high-sensitivity analysis of trace OA is realized.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
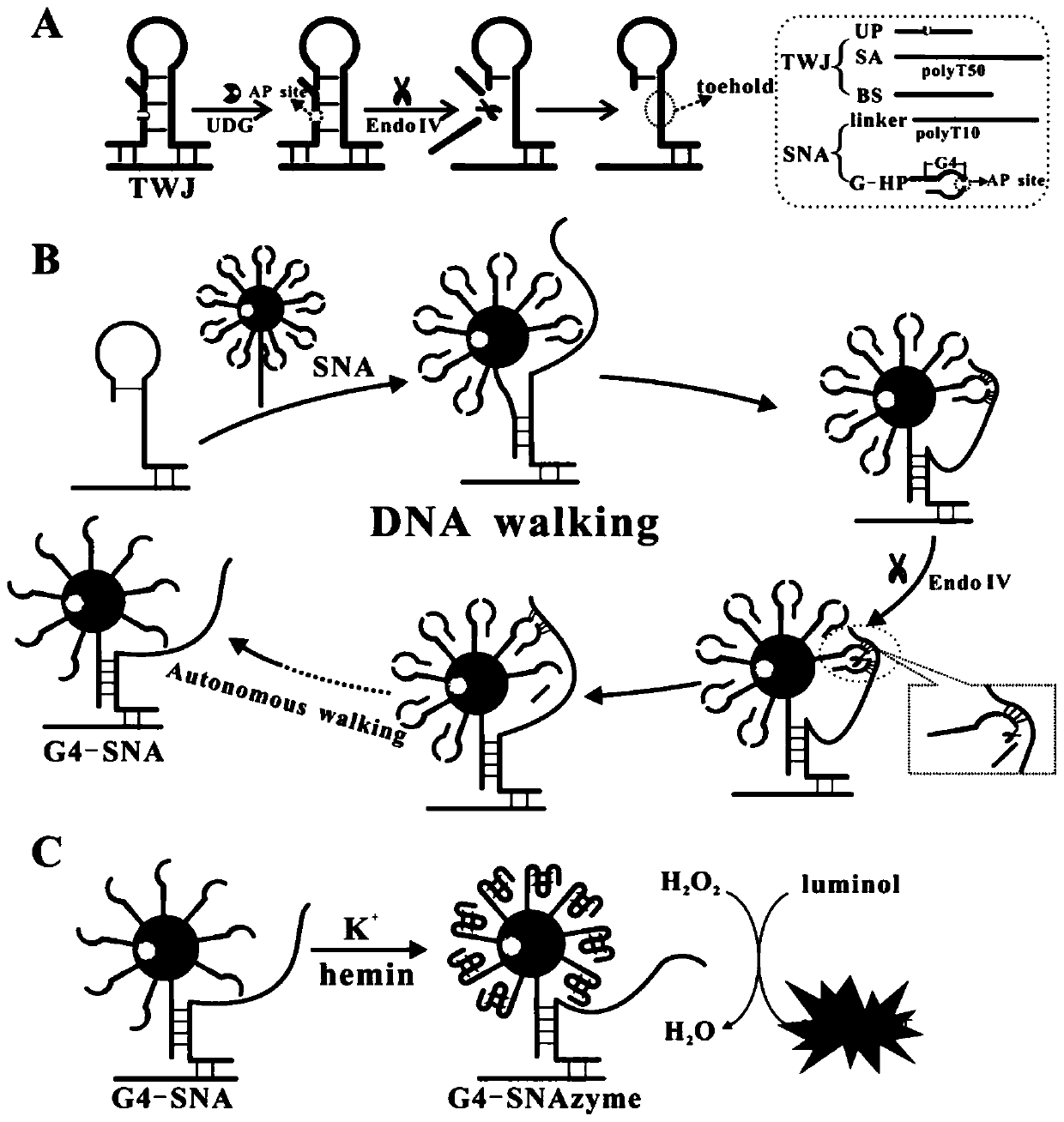
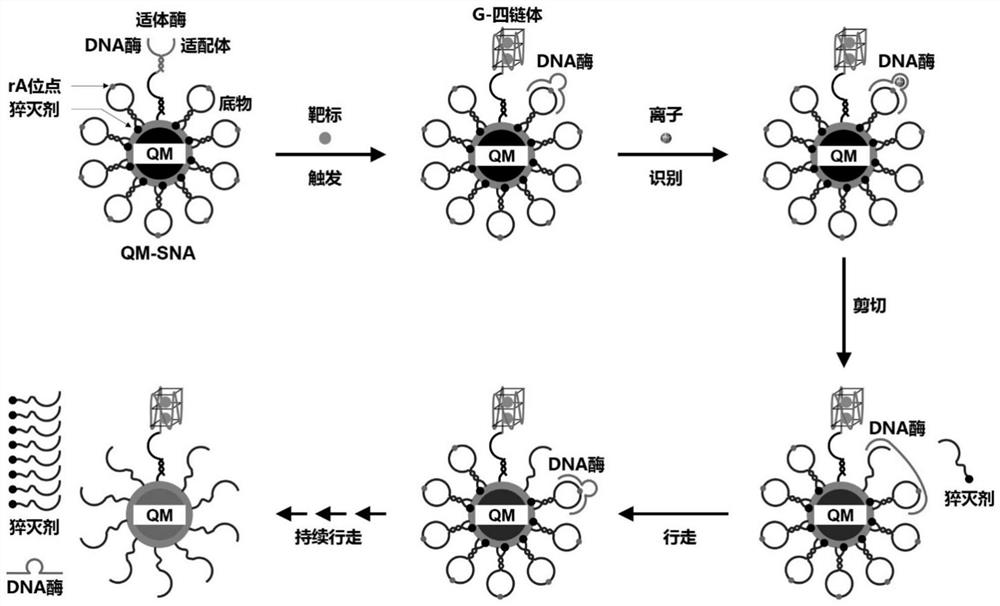
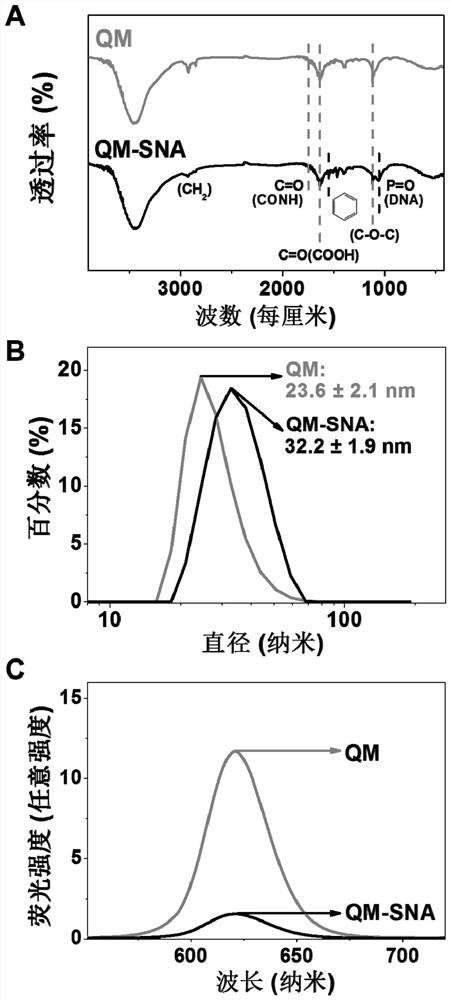
Method for detecting circulating miRNA by using DNA machine based on quantum dot micelle spherical nucleic acid
ActiveCN111593094AHigh sensitivityEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementSpherical nucleic acidCirculating miRNA
The invention discloses a method for detecting circulating miRNA by using a DNA machine based on quantum dot micelle spherical nucleic acid. The specific implementation method comprises the followingthree parts: (1) preparing multicolor quantum dot micelle spherical nucleic acid (QM-SNA) which is loaded with a DNA enzyme sequence and a quenching agent-modified substrate sequence; (2) triggering atarget so as to achieve automatic walking of DNA enzymes along a DNA track (the substrate sequence) on the surface of QM under the assistance of metal ions; and (3) measuring fluorescence signals ofthe multicolor QM through adoption of a fluorospectro photometer after completion of walking so as to realize detection and analysis of miRNA. According to the method for detecting the circulating miRNA by using the DNA machine based on the multicolor QM-SNA, a DNA enzyme walker is used for mediating amplification of the QM fluorescence signals, so that high-sensitivity detection of the miRNA is realized; and multi-element detection of miRNA is realized through adoption of the multi-color QM-SNA, and a new method is provided for accurate detection of the circulating miRNA.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Cystoid type spherical nucleic acid and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108743536AImprove stabilityImprove uniformityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTreatment effectSpherical nucleic acid
The invention provides a cystoid type spherical nucleic acid and a preparation method and application thereof. The cystoid type spherical nucleic acid adopts a PNIPAM-S-S-Py polymer to react with functionalized nucleic acid drugs to obtain a diblock compound, the technology is simple, and the technology is applicable to large-scale production. The cystoid type spherical nucleic acid is of a specific cystoid structure, is high in stability, high in uniformity, high in biocompatibility, tumor targeting and reductive sensitivity inside cells, is degradable, and can be used for efficiently delivering the nucleic acid drugs to specific target cells. The cystoid type spherical nucleic acid can be used as a drug carrier and is high in drug-carrying efficiency, nucleic acid drugs and other drugs can be delivered effectively synchronously, and the cystoid type spherical nucleic acid is of a synergy therapy effect.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Tlr9-targeted spherical nucleic acids having potent antitumor activity
PendingCN109831915AOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsSpherical nucleic acidAntitumor activity
Aspects of the invention relate to immunostimulatory spherical nucleic acids (IS- SNA) for the treatment of a disorder, such as cancer. The IS-SNA may be administered together with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Owner:EXICURE INC
Quantification and spatio-temporal tracking of a target using a spherical nucleic acid (SNA)
ActiveUS20160281086A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsNanoparticleSpherical nucleic acid
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Chemiluminescence biosensor for detecting uracil-DNA glycosylase and preparation method and application of chemiluminescence biosensor
ActiveCN110607351ARealize highly sensitive detectionLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpherical nucleic acidDisplacement reactions
The invention relates to the technical field of a biosensor, in particular to detection of uracil-DNA glycosylase based on a chemiluminescence technique for driving a strand displacement reaction based on a tee structure and driving spherical nucleases based on a DNA walker technique. In order to solve the problems of being complex to operate and low in sensitivity for a method for detecting uracil-DNA glycosylase in the prior art, the invention provides a biosensor based on two nanometer technologies of the tee structure and DNA walker, and spherical nucleases are used for catalyzing luminalto be subjected to a chemiluminescence reaction for detection. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing nano-Au, preparing spherical nucleic acid, and forming spherical nucleases in homogeneous phase for catalyzing the chemiluminescence reaction of the luminal. The uracil-DNA glycosylase is used for performing specific recognition and excision on U alkali, so as to realize target specificity detection. Besides, the DNA walker nanometer technology is used for realizing quick and high-sensitivity detection on targets.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
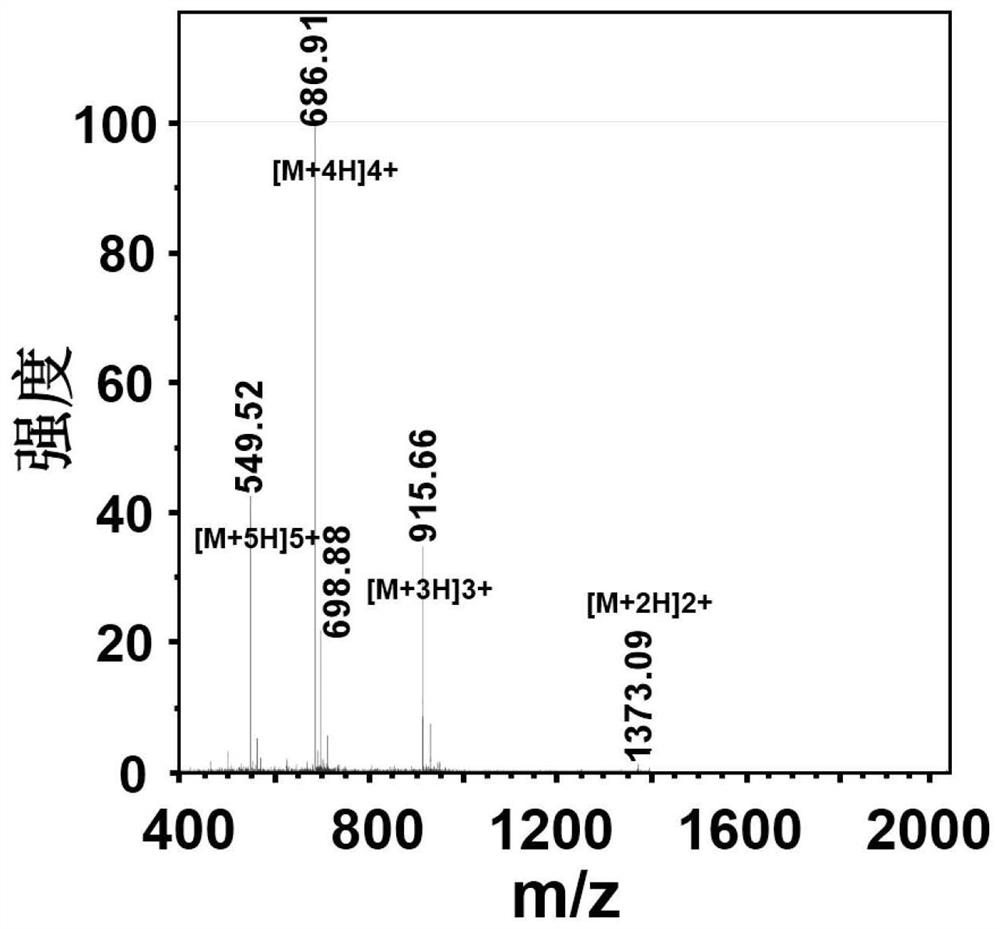
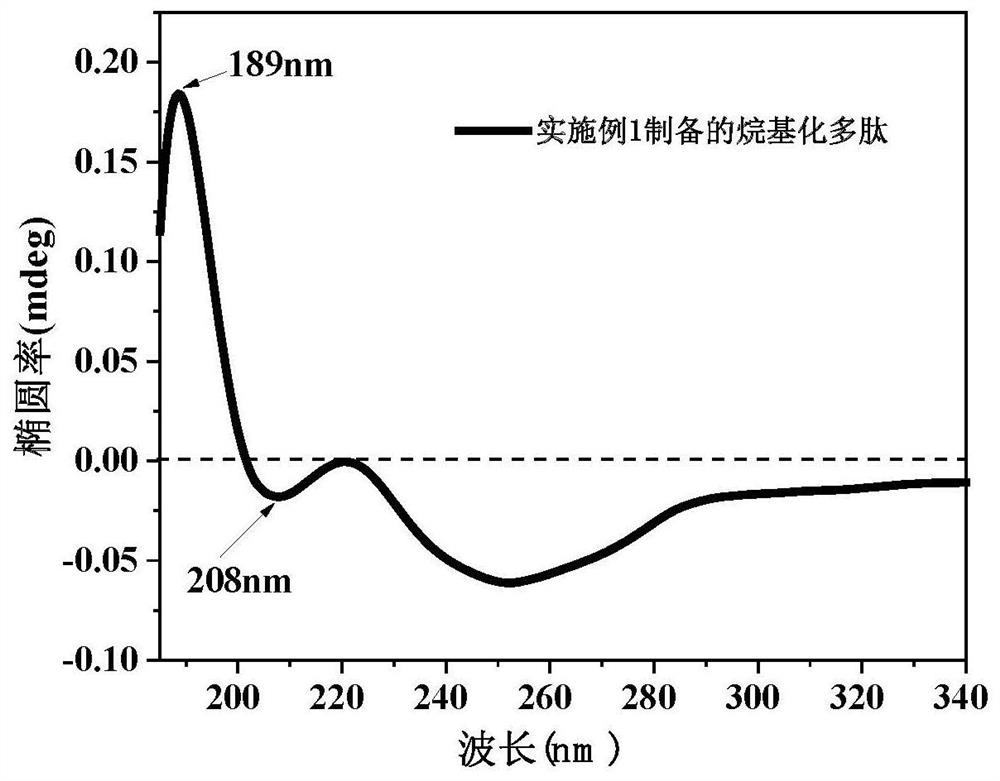
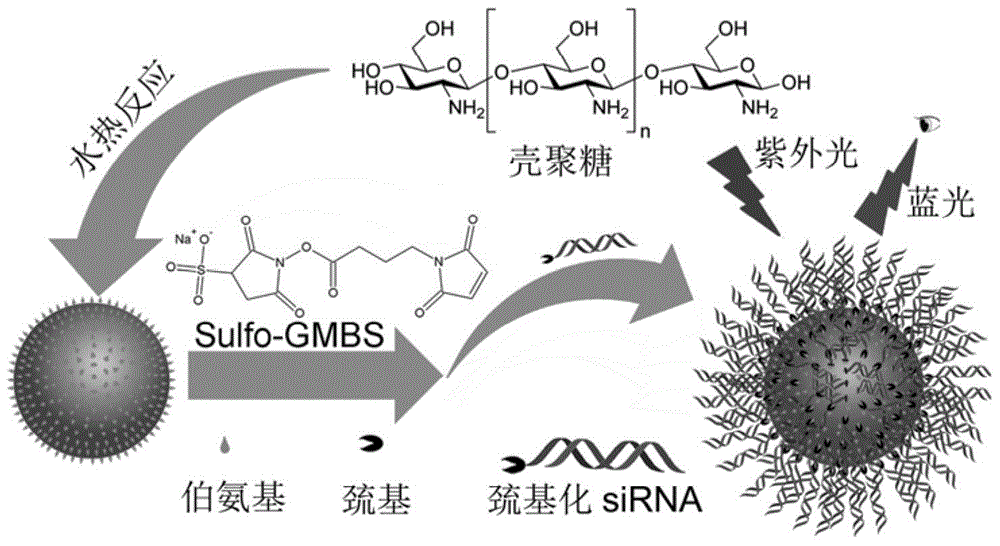
Nucleic acid delivery system based on alkylated polypeptide as well as preparation method and application
InactiveCN113563429AAchieve transmembrane deliveryStable structurePeptide-nucleic acidsOrganic active ingredientsStearic acidDelivery system
The invention discloses a nucleic acid delivery system based on alkylated polypeptide as well as a preparation method and application. The alkylated polypeptide comprises a cationic polypeptide fragment and a hydrophobic fragment, wherein the cationic polypeptide fragment has an alpha-spiral secondary structure; the hydrophobic fragment is a lipid part of any one of palmitic acid, lauric acid, myristic acid and stearic acid; the amino acid sequence of the cationic polypeptide fragment is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1; and the N-end of the cationic polypeptide fragment is connected with the hydrophobic fragment. The alkylated polypeptide can form a spherical nucleic acid delivery system based on the alkylated polypeptide with a proper size and a stable structure with nucleic acid molecules in different N / P proportions in a simple mixing manner, and transmembrane delivery of the nucleic acid molecules can be realized. Compared with the existing lipidosome and polymer transfection reagent, the alkylated polypeptide provided by the invention has the advantage that the preparation process for wrapping a nucleic acid medicine is simplified, and has the advantages of low toxicity, good biocompatibility, low cost and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
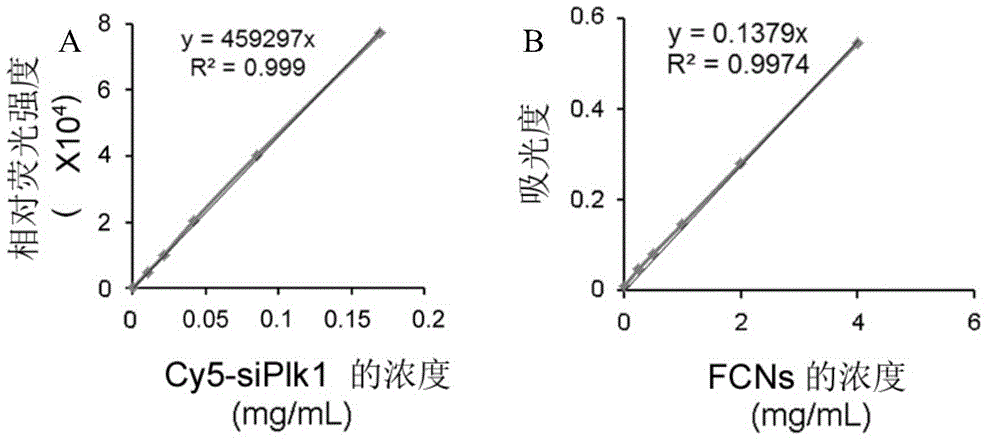
FCN (Fluorescent carbon nano-particle) based visual spherical nucleic acid as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104800859ASimplify complex synthesisEfficient deliveryOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsFluorescenceSpherical nucleic acid
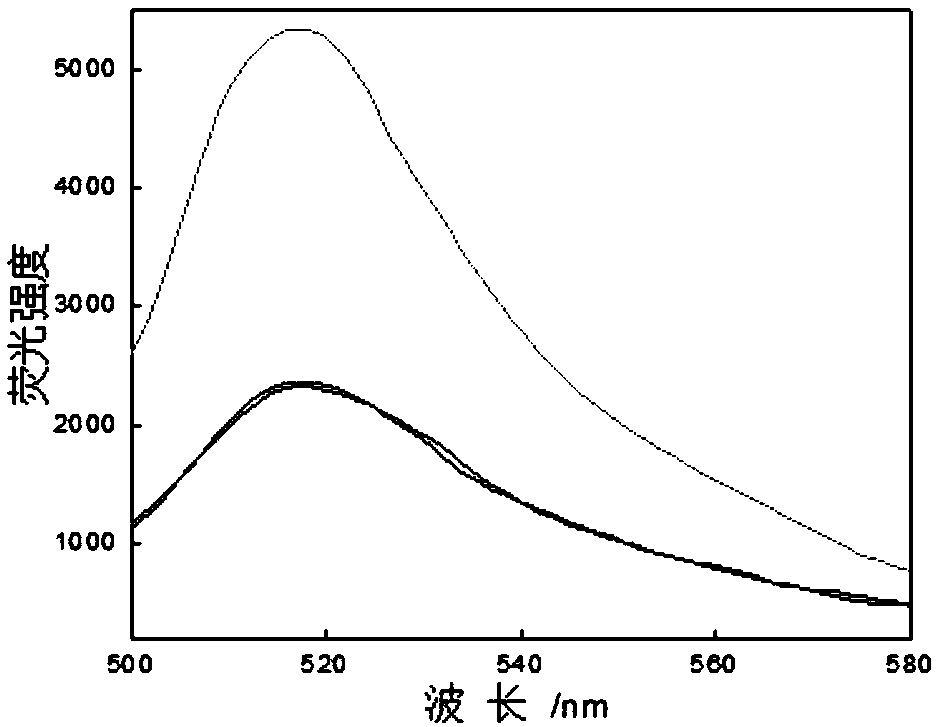
The invention relates to FCN (Fluorescent carbon nano-particle) based visual spherical nucleic acid as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The visual spherical nucleic acid comprises FCNs and oligonucleotide combined on the surfaces of the FCNs. The FCNs with good fluorescence characteristics are obtained with a one-step reaction method and then are combined with oligonucleotide to prepare a visual spherical nucleic acid system; according to the method, a preparation process is simplified, nucleic acid can be effectively delivered into a cell by the visual spherical nucleic acid under the condition of absence of any other transfection reagents, the intake rate and the transfection efficiency of the cell are increased, and important application value is achieved.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
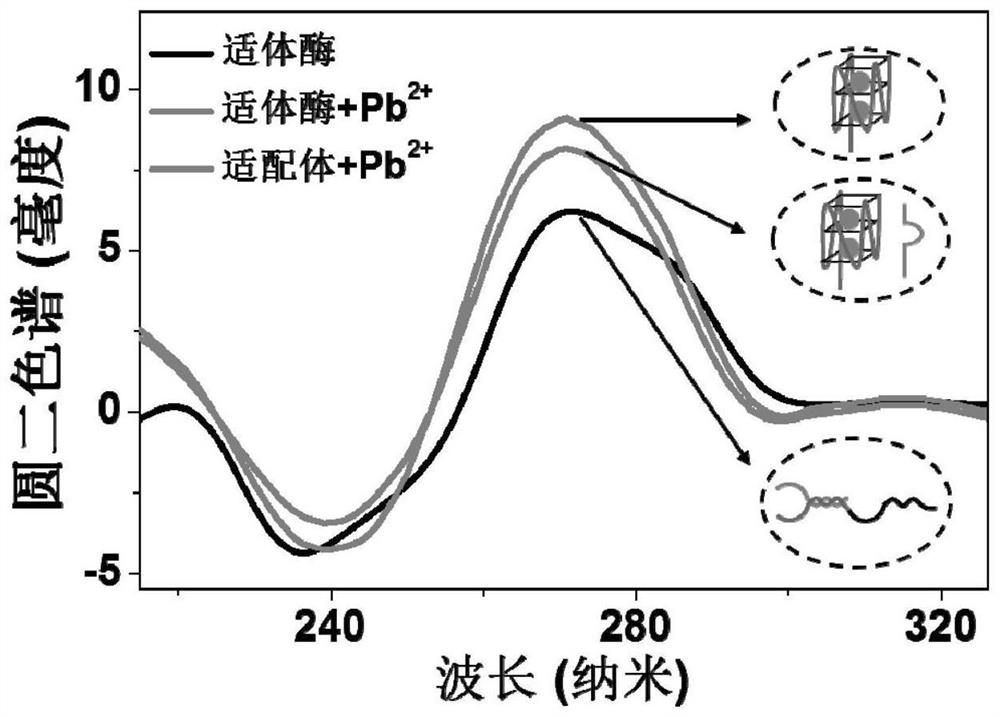
Quantum dot micelle spherical nucleic acid sensor as well as preparation method and application thereof in Pb < 2 + > detection
PendingCN114354912AHigh sensitivityHighly specific detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAptamerSpherical nucleic acid
The invention discloses a quantum dot micelle spherical nucleic acid sensor as well as a preparation method and application thereof in Pb < 2 + > detection. The sensor is formed by coupling two nucleic acid molecules on the surface of a quantum dot micelle, wherein the two nucleic acid molecules are aptamer and an enzyme substrate modified by a quencher; the aptamer enzyme is formed by hybridizing a 5 '-amino modified lead ion aptamer and a DNA enzyme sequence; the enzyme substrate is hairpin structure DNA containing rA site, the 5'end of the DNA is modified with amino, and the 3 'end of the DNA is modified with a quencher. Aptamer enzyme in the sensor is specifically combined with Pb < 2 + > to form a G-quadruplex, DNA enzyme is released, and the DNA enzyme automatically walks by taking an enzyme substrate as a track; and detecting and analyzing Pb < 2 + > by measuring a fluorescence signal of the quantum dot micelle after walking is finished. According to the method for fluorescence amplification detection of Pb < 2 + > based on QM-SNA DNA enzyme walking, high-sensitivity and high-specificity detection of Pb < 2 + > is achieved, and a new detection method is provided for detection of heavy metal ions.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
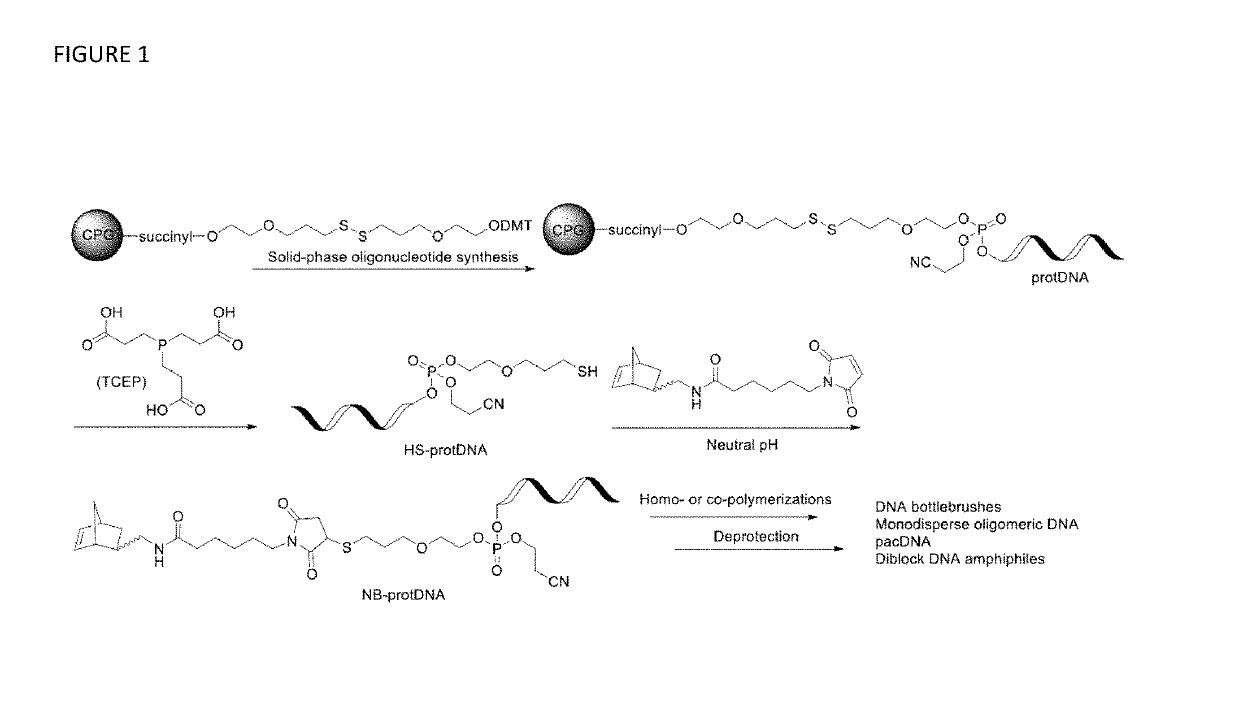
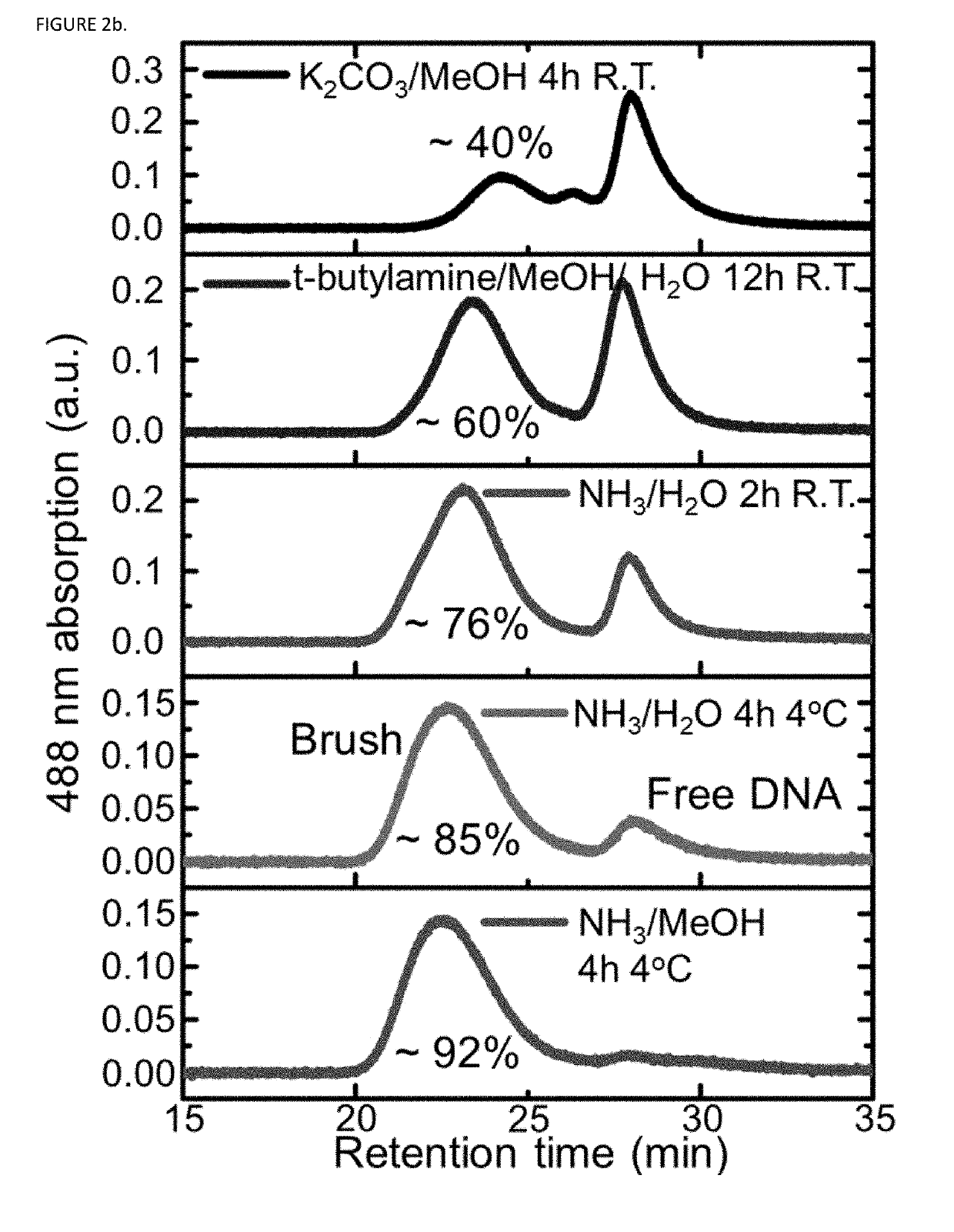
Synthesis of high density molecular DNA brushes via organic-phase ring-opening metathesis (CO)polymerization
InactiveUS20190292310A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh densityOrganic solvent
The invention provides novel synthetic methods for oligonucleotide polymerization reactions that separate the deprotection and cleavage step following solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis into two separate steps, thereby providing fully protected hydrophobic oligonucleotides that can be further manipulated in organic solvents. The disclosed methods enable the synthesis of new structures, such as brush DNA and brush RNA polymers and micellar spherical nucleic acids (SNAs
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com