Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63results about How to "High force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
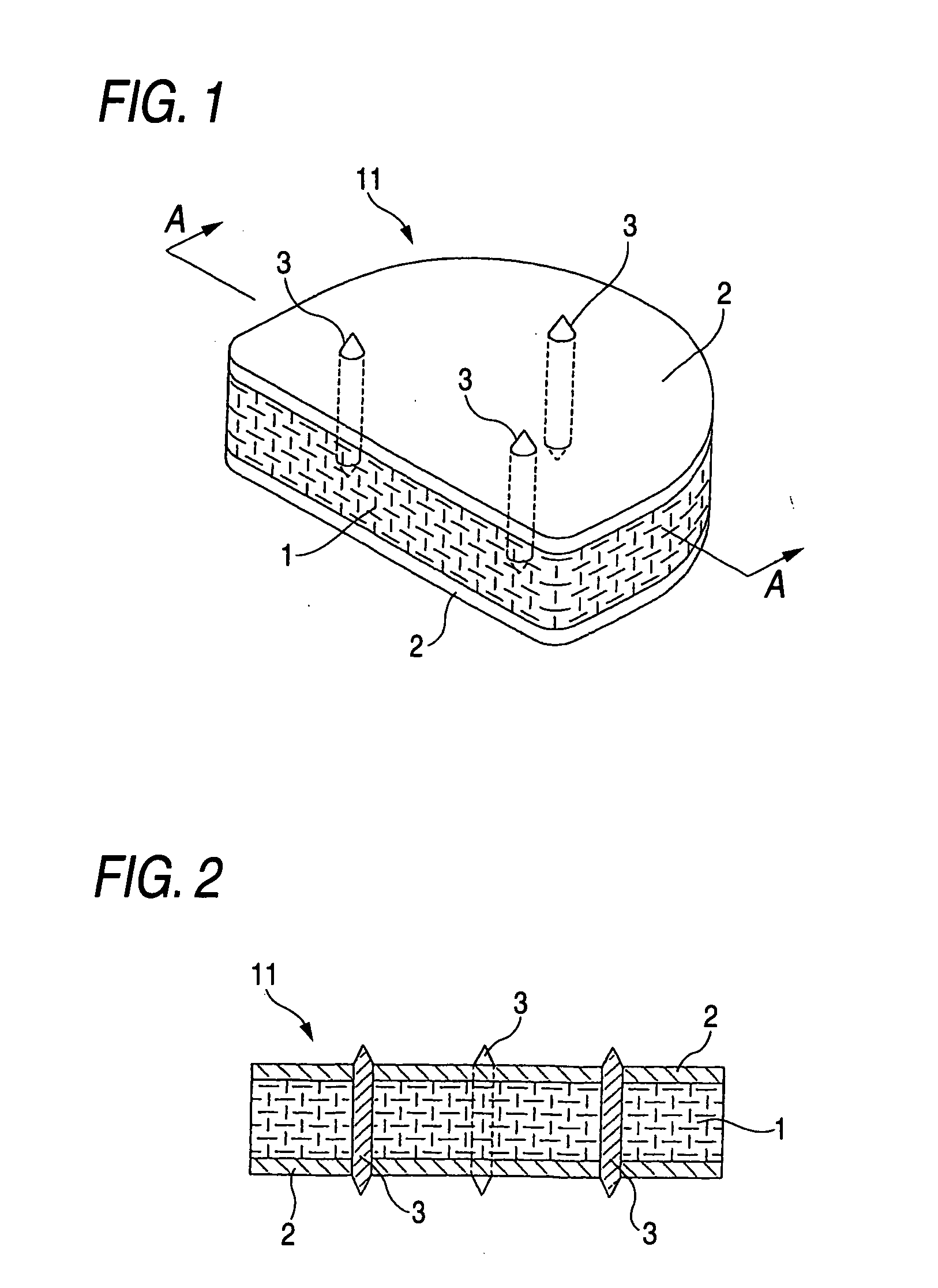
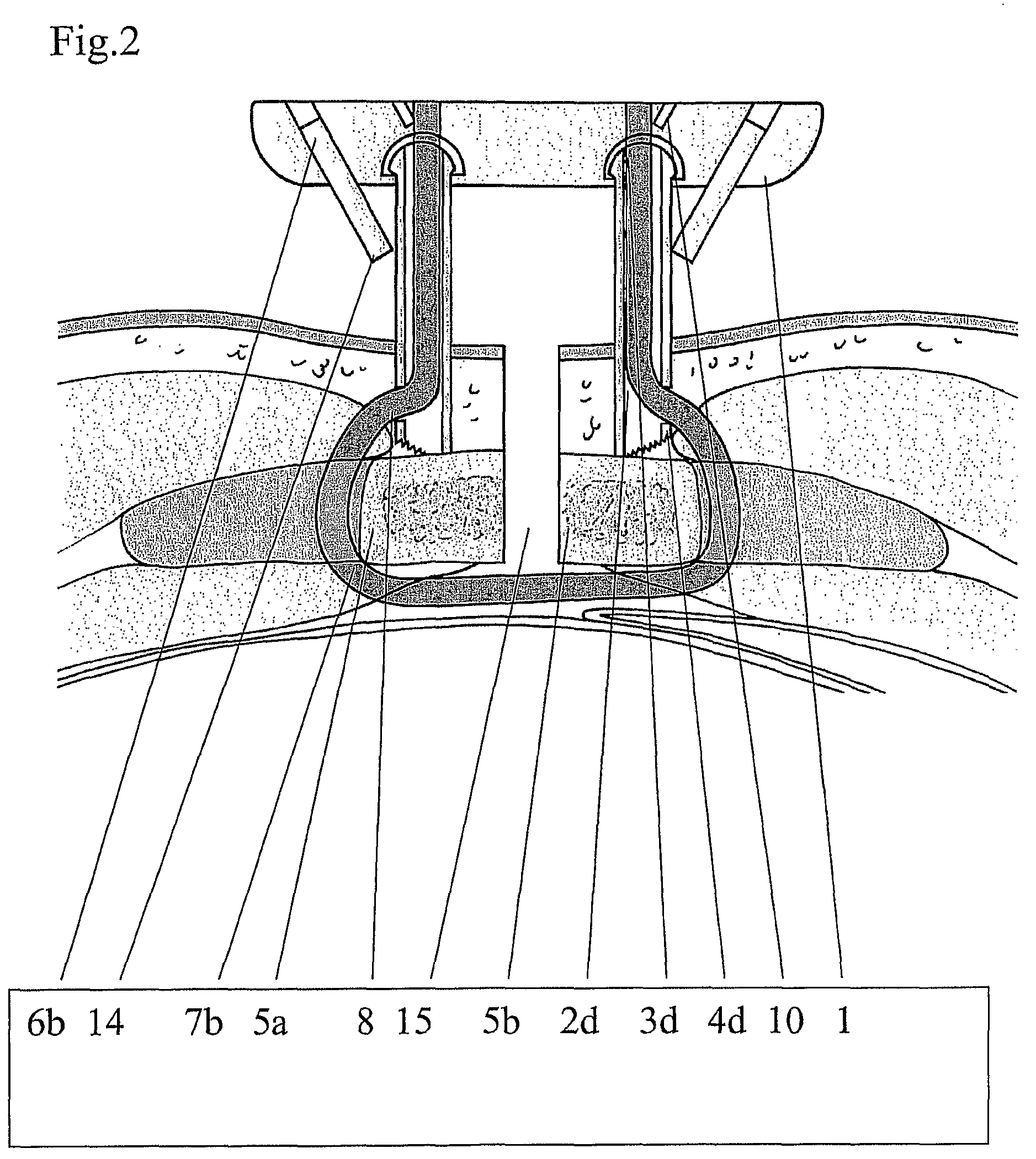
Devices and methods for interstitial injection of biologic agents into tissue
Apparatus and methods for injecting biological agents into tissue. Devices are provided having elongate shafts and distal injection heads for driving needles into tissue and injecting medical agents into the tissue through the needles. A longitudinal force directed along the shaft can be translated to a needle driving force. Some devices provide controllably variable needle penetration depth. Devices include mechanical needle drivers utilizing four link pantographs, rack and pinions, and drive yokes for driving a first needle bearing body toward a second tissue contacting body. Other devices include inflatable members for driving and retracting needles. Still other devices include magnets for biasing the needles in extended and / or retracted positions. The invention includes minimally invasive methods for epicardially injecting cardiocyte precursor cells into infarct myocardial tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Noise reducing footwear
InactiveUS20140373392A1Reduce noise and impact characteristicHigh forceSolesUpperFoot protectionEngineering
The present invention is drawn generally to footwear, and more specifically, to footwear having reduced noise and impact characteristics. According to the invention noise generated by the impact of the footfall when in contact with hard floors is reduced by an outer sole with certain hardness and a sound reducing insole which comprising a material of high indentation forced deflection (IFD) weight having a minimum thickness of ¼ to a maximum ¾ inch, and an optimal thickness of about ½ inch. Also, the footwear comprises an upper portion attached to the outer sole to provide comfort and foot protection.
Owner:CULLEN JOSEPH ROBERT
Biomaterial for artificial cartilage
InactiveUS20060173542A1High forceIdeal deformation propertyBone implantLigamentsBioceramicBiological body
A biomedical material for artificial cartilage is provided which employs a core material comprising a structure made of organic fibers, is flexible and has nearly ideal deformation properties, can be bonded and fixed to living-body bones such as vertebral bodies without fail at a high force, and is free from the generation of fine particles caused by wearing. The biomedical material for artificial cartilage comprises a core material comprising a structure which is either a three-dimensional woven structure or knit structure made of organic fibers arranged along three or more axes or a structure comprising a combination of the woven structure and the knit structure and plates superposed respectively on the upper and lower sides of the core material, the plates being made of a biodegradable and bioabsorbable polymer containing bioactive bioceramic particles.
Owner:TAKIRON CO LTD
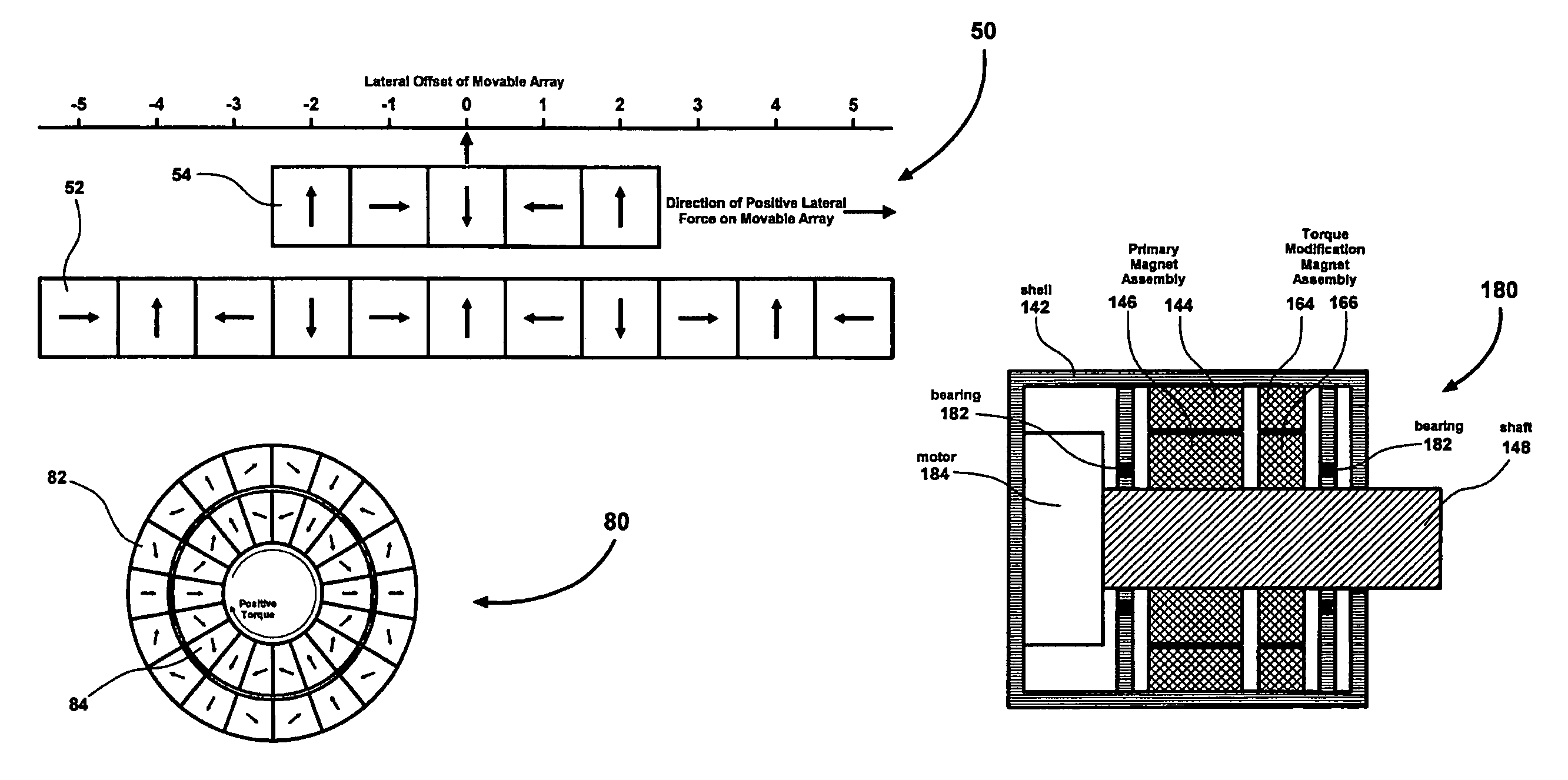
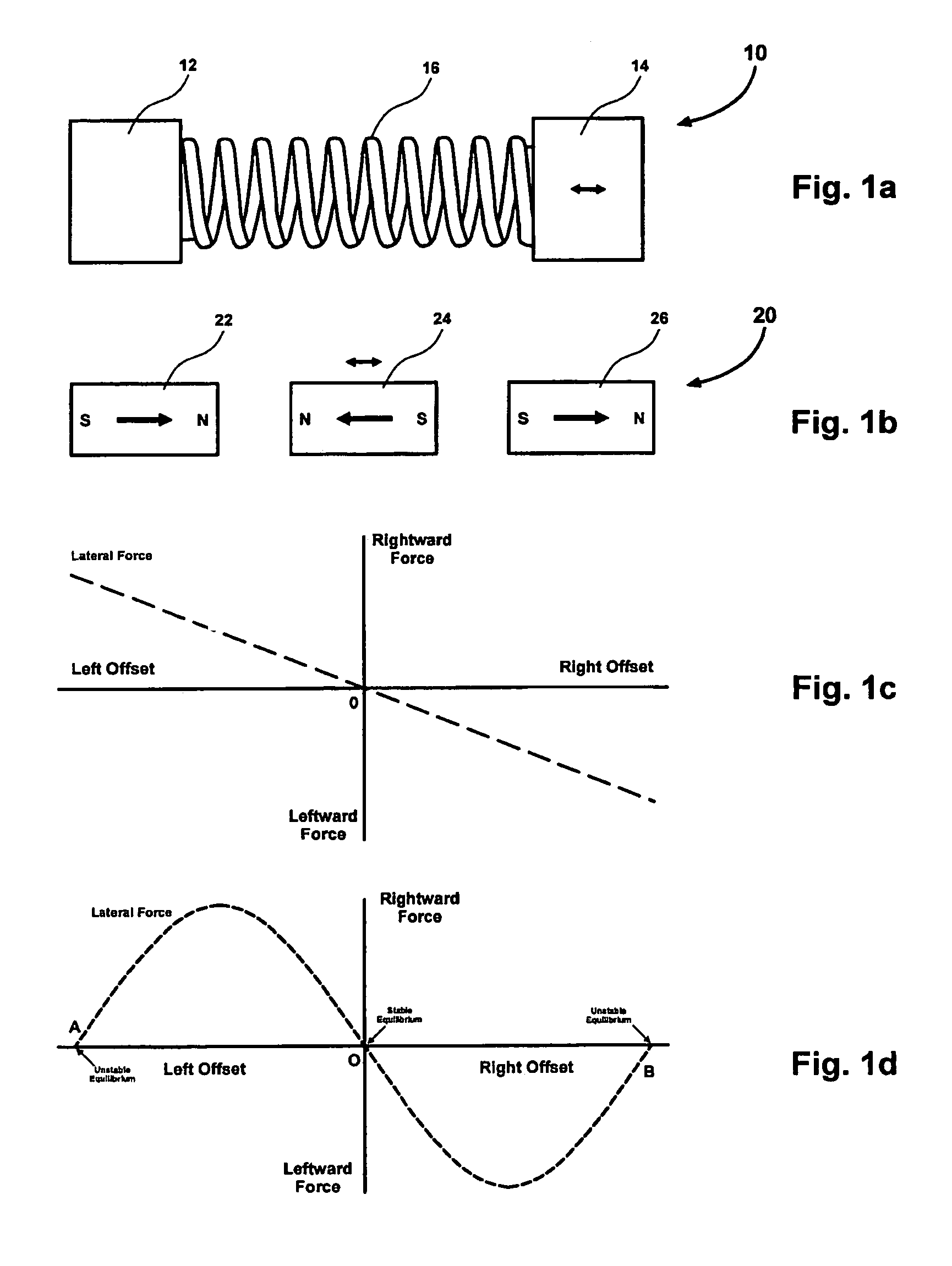
Magnetic spring and actuators with multiple equilibrium positions
ActiveUS7265470B1Move time be shortHigh forceDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic springEquilibrium point
Arrays of magnets configured to create linear or rotary magnetic springs with multiple equilibrium points. Some of the equilibrium points are stable, while others are unstable. No mechanical contact is required between moving and stationary elements of the magnetic springs, resulting in a virtually unlimited lifetime. The magnetic springs can be utilized in conjunction with low force electromagnetic actuators to implement multi-step linear or rotary actuators with high force, very short movement time between unstable equilibrium points, and with near-zero holding power required to maintain actuator position at any unstable equilibrium point. Specific applications that embody the present invention may include, but are not limited to, optical filters, linear valves, or any mechanism that would benefit from an efficient magnetic spring.
Owner:LAUNCHPOINT TECH
Method and apparatus for reversing direction of an article
InactiveUS7703599B2High decelerationHigh forceMechanical working/deformationFunction indicatorsIndustrial engineering
Owner:CURT G JOA
Collaborative robot system and method
InactiveUS20160214261A1Enhanced interactionHigh force capabilityProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl theoryRobot locomotion
A system for robot and human collaboration is provided. The system includes a robot having a programmed path for motion of the robot and a controller in communication with the robot. The controller has a processor and tangible, non-transitory memory on which is recorded instructions for an action to take when an unexpected contact between the robot and an object is detected. The controller is programmed to execute the instructions from the memory via the processor when the unexpected contact is detected, causing the robot to stop motion on a programmed path and to enter a push away mode. In the push away mode, the human can apply a push force having a push force direction to command the robot to move in the push force direction.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Ribbon bonding in an electronic package
InactiveUS20050269694A1Increase the areaIncrease the sectionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A flexible conductive ribbon is ultrasonically bonded to the surface of a die and terminals from a lead frame of a package. Multiple ribbons and / or multiple bonded areas provide various benefits, such as high current capability, reduced spreading resistance, reliable bonds due to large contact areas, lower cost and higher throughput due to less areas to bond and test.
Owner:LUECHINGER CHRISTOPH B
Miniature Piezoelectric Motor and Method of Driving Elements Using Same
InactiveUS20080247059A1Reduce module sizeImprove efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMountingsElectricityLinear motion
The present invention provides a piezoelectric ultrasonic motors and a method of driving a motor with a standing wave. The motors include a thin ring / cylinder-type stator having one or two piezoelectric (ceramic or single crystal) rings / cylinders, coated with a segmented top / outer electrode and a bottom / inner electrode and poled in a thickness / radial direction, a metal ring / cylinder which is laminated with piezoelectric ring(s) / cylinder(s) having several inner threaded protrusions. The motor also includes a power source for supplying an alternating voltage to one group of electrodes of the piezoelectric stator to excite a standing wave vibration along one diameter direction of the stator ring / cylinder. The motor further includes a short cylinder rotor, which may have a lens inside for certain optical applications, or it may include other elements. The rotor is attached to the stator at the threaded surface of the protrusions and is driven to produce a circular motion, which may also be translated into a linear motion by the threaded surface through standing wave deformation at protrusions. Reverse motion of the rotor can be realized by applying the alternating voltage to another group of electrodes of the stator.
Owner:DONG SHUXIANG
Micromechanical sound transducer
ActiveUS20200100033A1Accurate and reliable detectionPrecise positioningMicrophonesLoudspeakersVertical vibrationMicromachinery
A micromechanical sound transducer according to a first aspect includes a first bending transducer with a free end and a second bending transducer with a free end, the two bending transducers being arranged in a mutual plane, wherein the free end of the first bending transducer is separated from the free end of the second bending transducer via a slit. The second bending transducer is excited in-phase with the vertical vibration of the first bending transducer. A micromechanical sound transducer according to a second aspect includes a first bending transducer that is excited to vibrate vertically and a diaphragm element extending vertically to the first bending transducer, the diaphragm element being separated from a free end of the first bending transducer via a slit.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Ribbon bonding in an electronic package
InactiveUS20070141755A1Increase the areaIncrease the sectionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceLead frame
Owner:ORTHODYNE ELECTRONICS
Generators, transformers and stators containing high-strength, laminated, carbon-fiber windings
InactiveUS20050218741A1Improve the immunityReduce the temperatureMagnetic circuitTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsFiberCarbon fibers
This invention is directed to motors, rotors and stators, transformers, generators and related apparatus comprising carbon fiber windings, and in particular, laminated carbon fiber windings for the generation of electrical energy. The invention is also directed to methods for generating electrical energy from devices of the invention and to methods for reconditioning and repairing conventional apparatus with carbon fiber windings.
Owner:WNOROWSKI EDWARD J JR +1
Electric actuator
InactiveUS7795773B1High materialHigh strengthManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsEngineeringActuator
According to one embodiment, an electric actuator is provided comprising windings constructed from a conductive core of high magnetic permeability material surrounded by an electrical insulator. The conductive core simultaneously carries an electric current and a magnetic field, resulting in an actuator that can develop a high force or torque for its size compared to conventional electric actuators.
Owner:WITTIG MICHAEL
Transverse flux linear motor with permanent magnet excitation
A transverse flux linear motor with permanent magnet excitation having a stator including stator cores and windings respectively wound around the stator cores and supplied with current, and a mover arranged at a central portion of the stator, the mover including mover cores and permanent magnets. Each of the permanent magnets is arranged between adjacent ones of the mover cores. Each stator core has a pair of column portions spaced apart from each other by a desired distance. The windings are arranged in pairs such that each of the winding pairs has two windings wound around respective column portions of an associated one of the stator cores.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Low-voc-emission waterborne coating having high hardness and good adhesion and process for producing the same
A low-VOC-emission waterborne coating is prepared from a waterborne acrylic emulsion, a hydrophilic cross-linking agent, a coalescing agent, additives and a pigment, and the waterborne acrylic emulsion is formed from performing emulsion polymerization on those reactive monomers including an alkyl-group-containing methyl acrylate, a hydroxyl-group-containing methyl acrylate, a carboxyl-group-containing methacrylic acid, a hydroxyl-group-containing acrylic polyester (polyether) polyol, and a methyl acrylate containing alkene-based unsaturated functional groups, which features high hardness, good adhesion, high luster, high acid resistance, high alkali resistance, good weatherability, high solvent resistance, high scrap resistance and high thermal shock resistance.
Owner:NANYA PLASTICS CORP
Method and apparatus for changing speed or direction of an article
InactiveUS8417374B2High decelerationHigh forceDigital data processing detailsFunction indicatorsElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:CURT G JOA
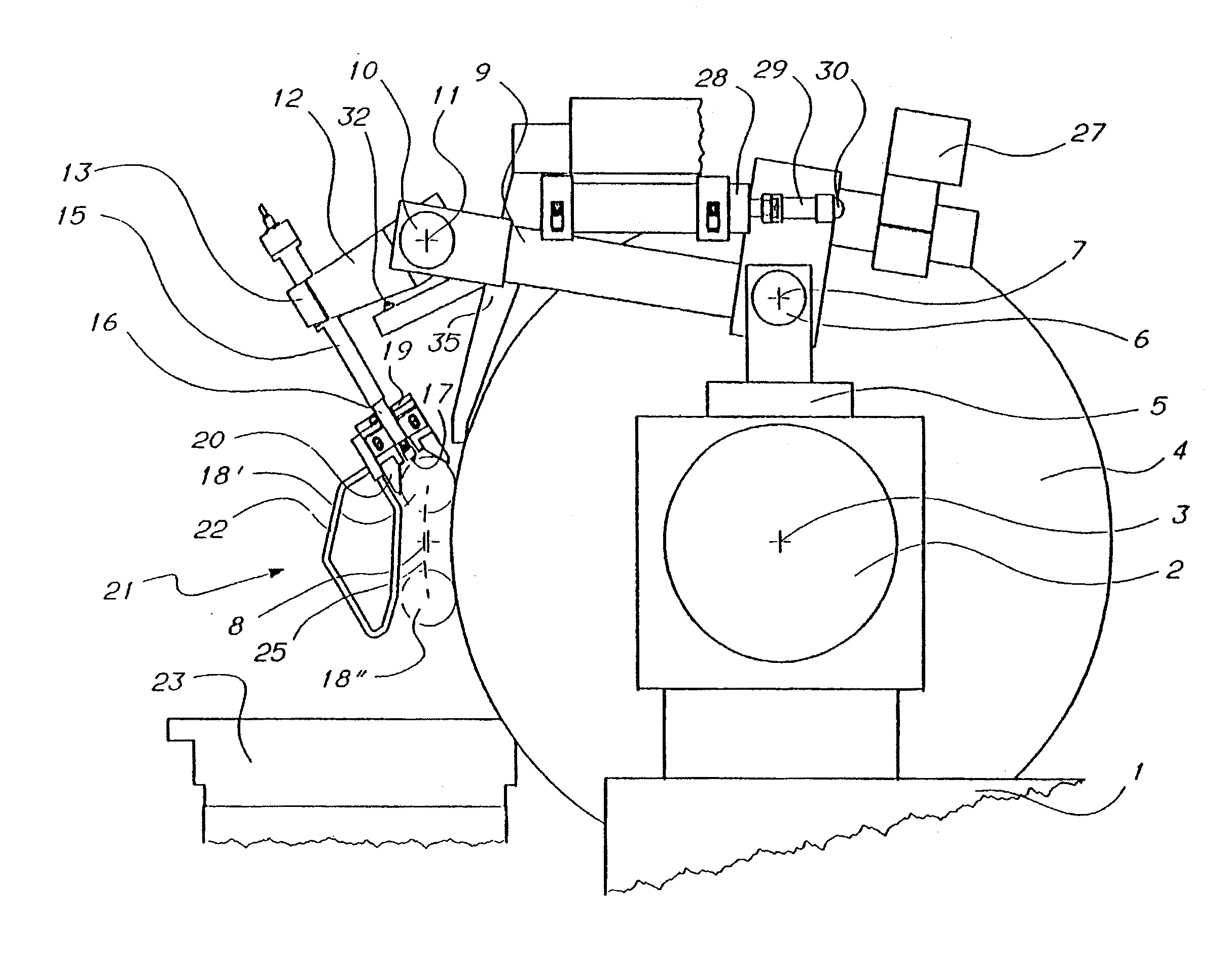
Apparatus for checking diametral dimensions of cylindrical parts rotating with an orbital motion
ActiveUS7607239B2Enabling checkingAvoid interferenceRevolution surface grinding machinesMeasurement/indication equipmentsRest positionReference device
An apparatus for checking the diameter of crankpins (18) of a crankshaft (34) in the course of the machining in a grinding machine comprises a first arm (9) rotating with respect to a support (5) arranged on the grinding-wheel slide (1) of the grinding machine, a second arm (12) rotating with respect to the first, a reference device (20) carried by the second arm and a measuring device (16, 17, 40-45) associated with a reference device. A guide device (21), fixed to the reference device (20), enables the apparatus to engage a crankpin, in the course of the orbital motion of the crankpin, and limit the displacements of the first arm and those of the second arm when a control device (28-30) displaces the apparatus to a rest position.
Owner:MARPOSS SPA +1
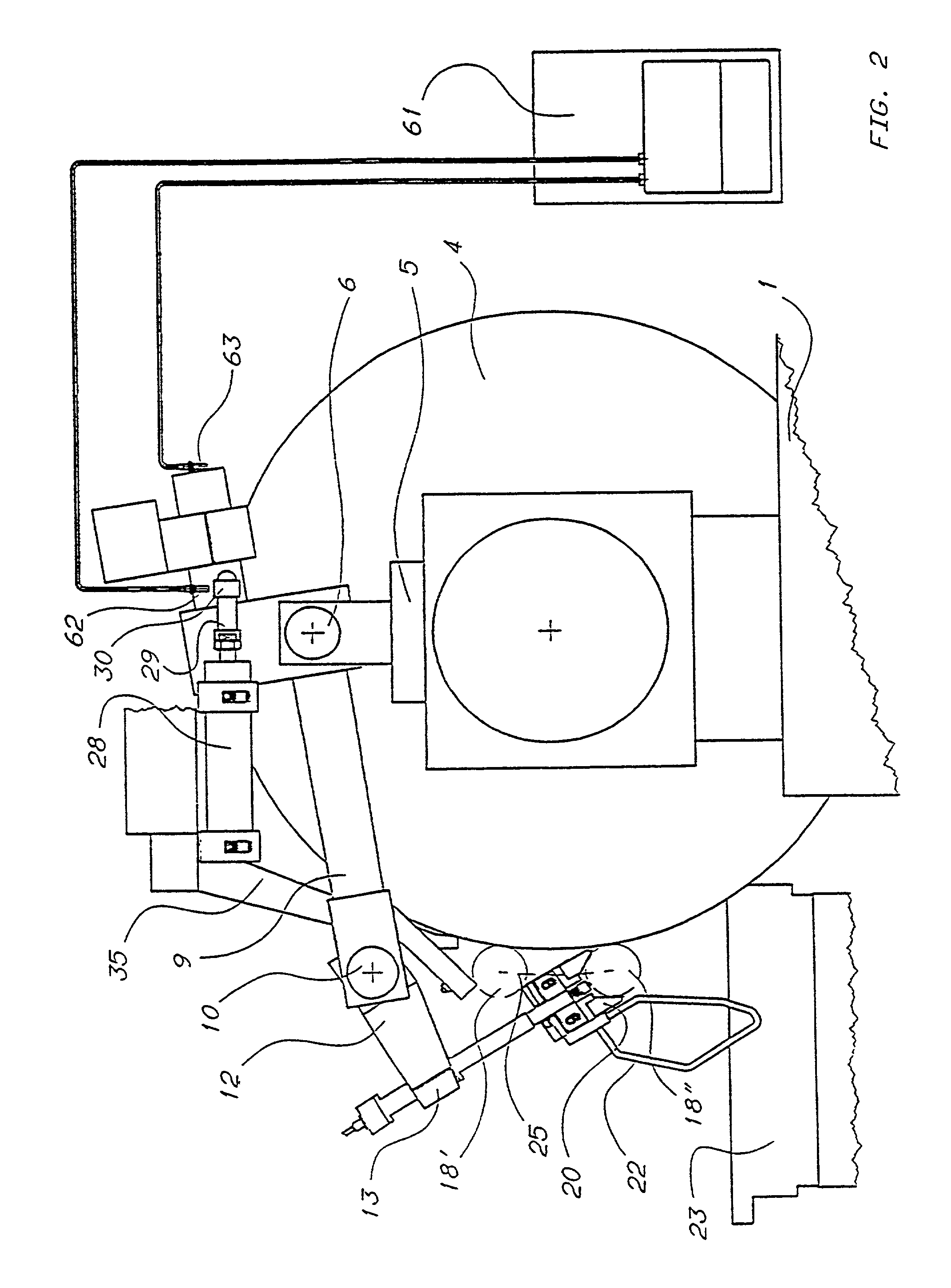
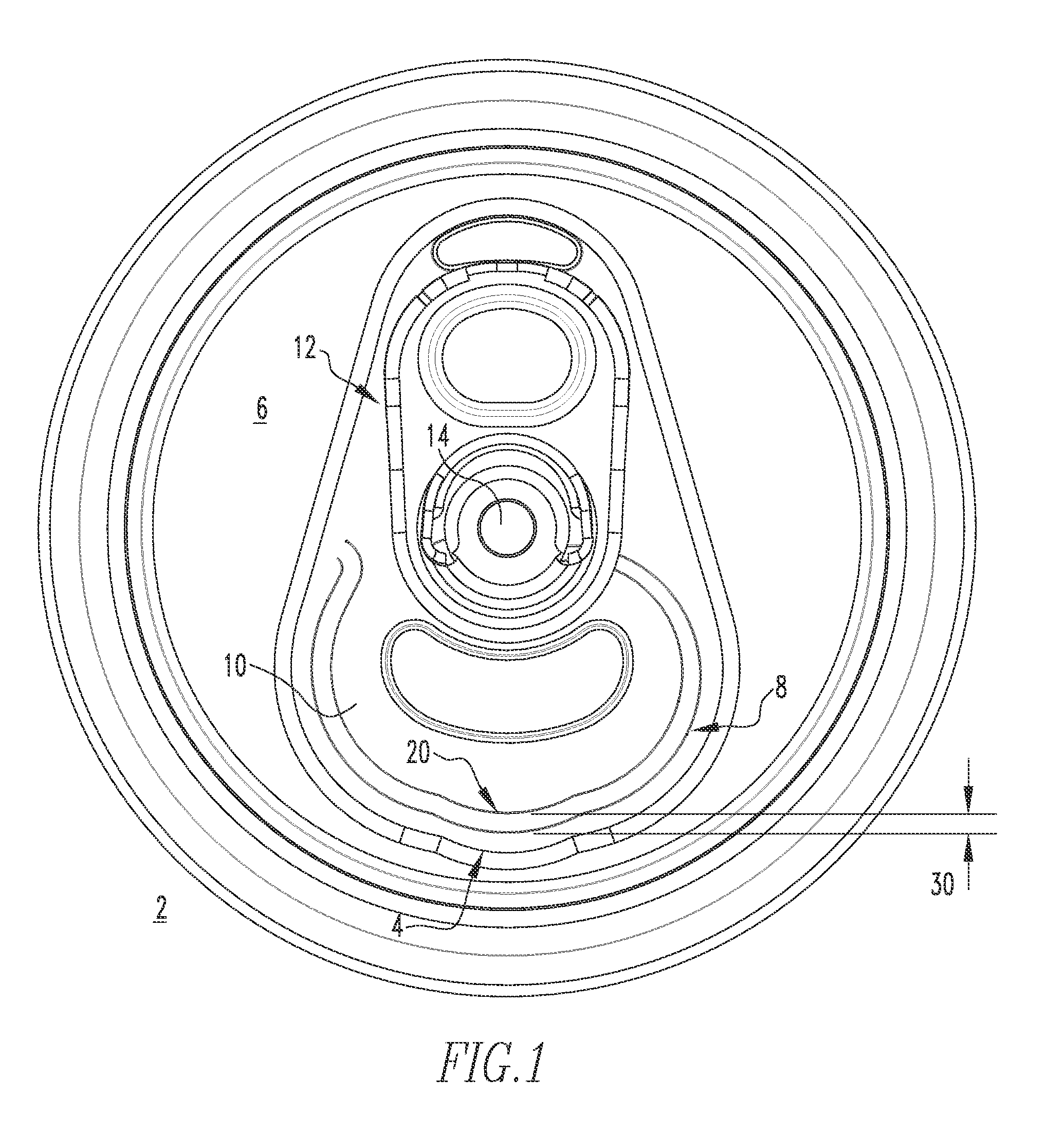
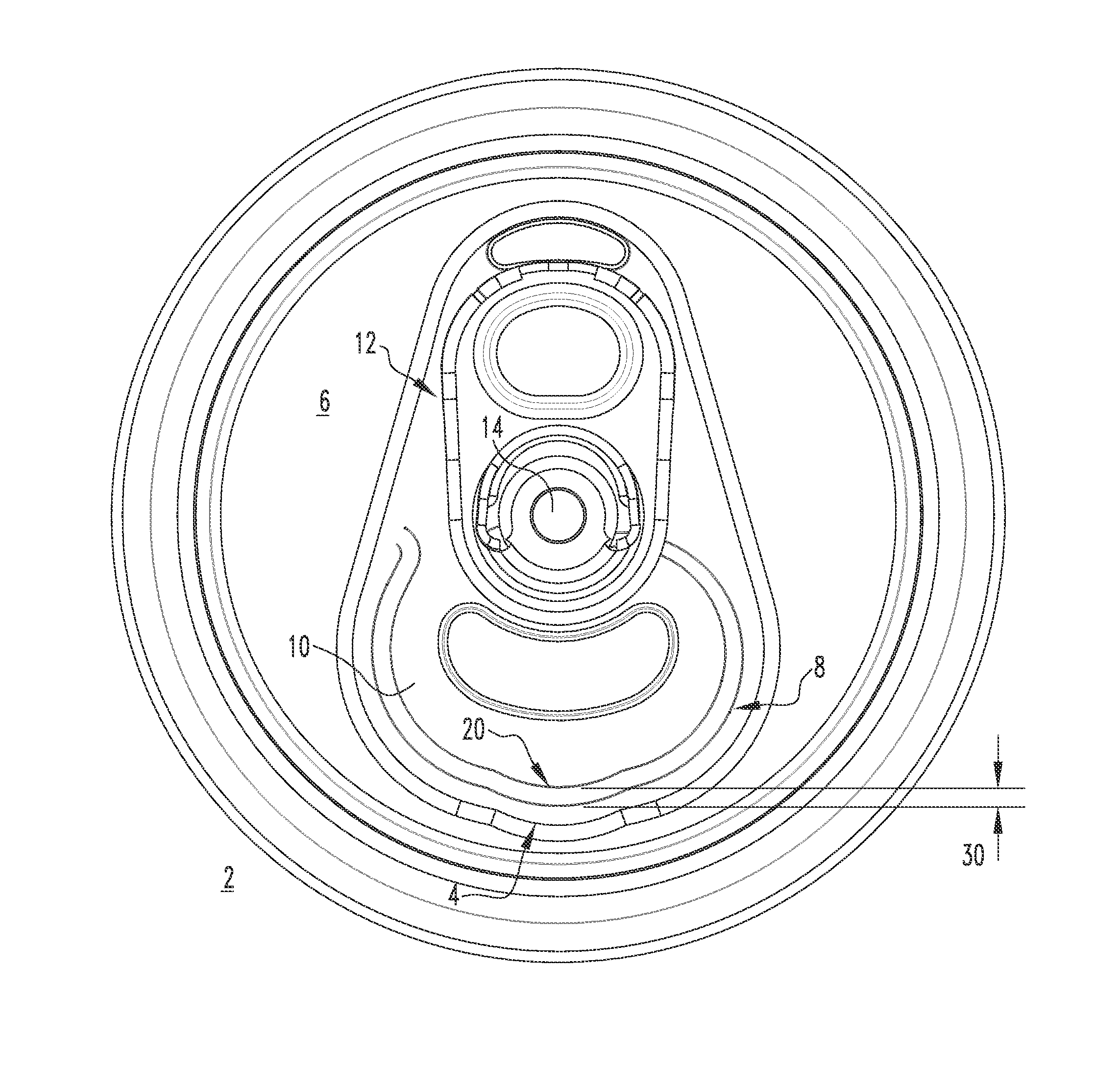
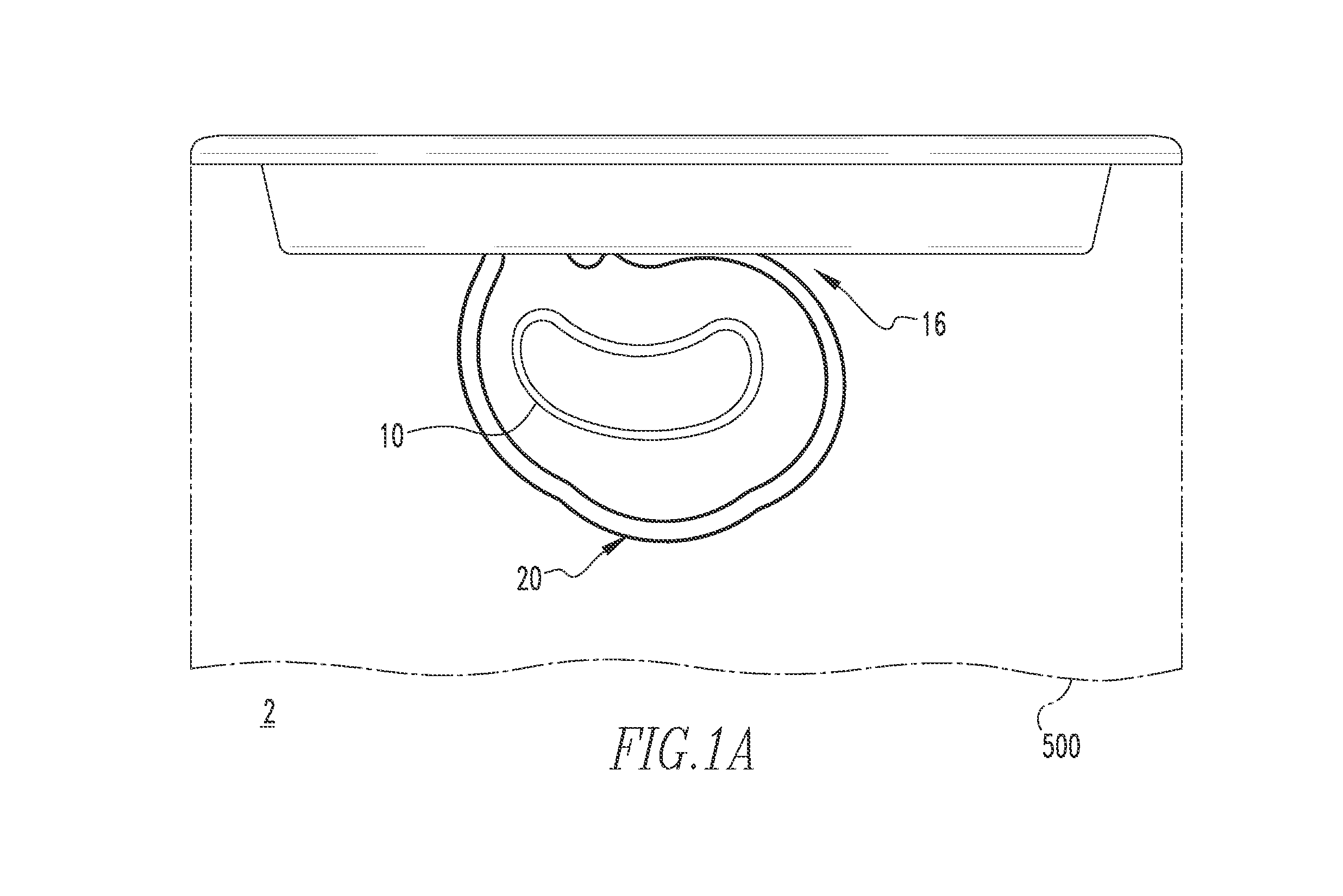
Easy pour spout
A can end is provided, which includes a center panel having a radius, a tab fastened to the center panel, and a scoreline defining a tear panel in the end panel. The tab is operable to sever the scoreline and open the tear panel to provide an opening in the can end. The tear panel includes an enlarged portion extending outwardly toward the center panel radius, thereby enlarging the opening. The enlarged portion forms an easy pour spout.
Owner:STOLLE MACHINERY
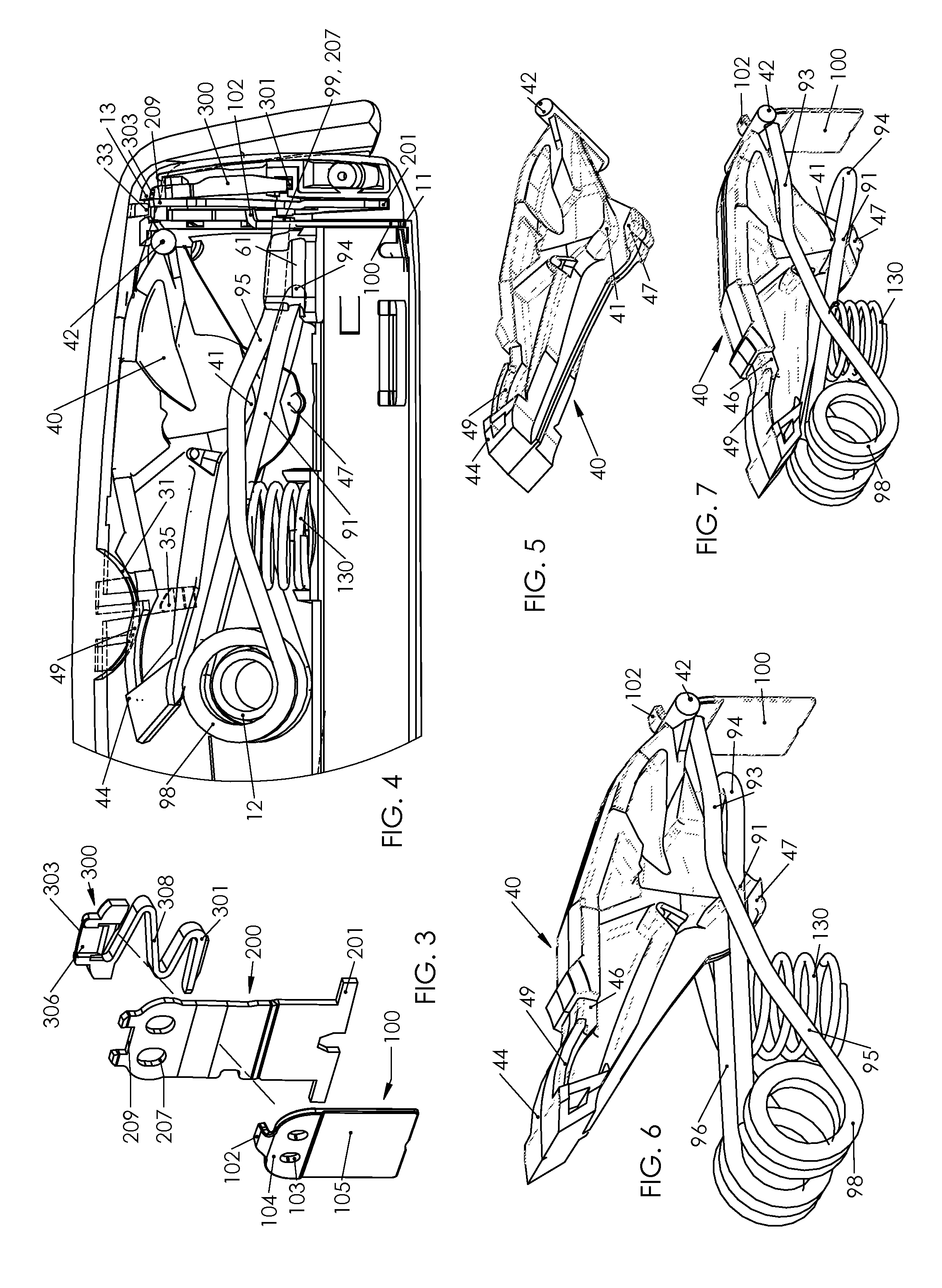
Side bag for motorcycles
ActiveUS20070102469A1Improves theft securityReduce risk of damageLuggage carriersHandbagsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:BAYERISCHE MOTOREN WERKE AG
Hot Melt Adhesive Based On Low Melting Point Polypropylene Homopolymers
ActiveUS20140350155A1Increase setting speedHigh bond strength levelMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesPersonal carePorous substrateWax
A hot melt adhesive for use on porous substrates, wherein the hot melt adhesive hasa) about 10% to about 70% by weight of a polypropylene homopolymer having a DSC melting point of less than 100° C.;b) about 10% to about 60% of a first tackifying resin having a Ring & Ball Softening Point of about 95° C. to about 140° C.;c) about 0% to about 65% of a second tackifying resin that is different than the first tackifying resin;d) about 5% to about 50% of a plasticizer;e) about 1% to about 40% by weight of a secondary polymer which is either a semi-crystalline polymer or wax with an enthalpy of fusion of greater than 30 Joules / gram;f) about 0.1% to about 5% of a stabilizer or antioxidant;wherein the components total 100% by weight of the composition, and the viscosity of the composition is equal to or less than about 20,000 centipoise (cP) at 163° C. (325° F.).
Owner:BOSTIK INC
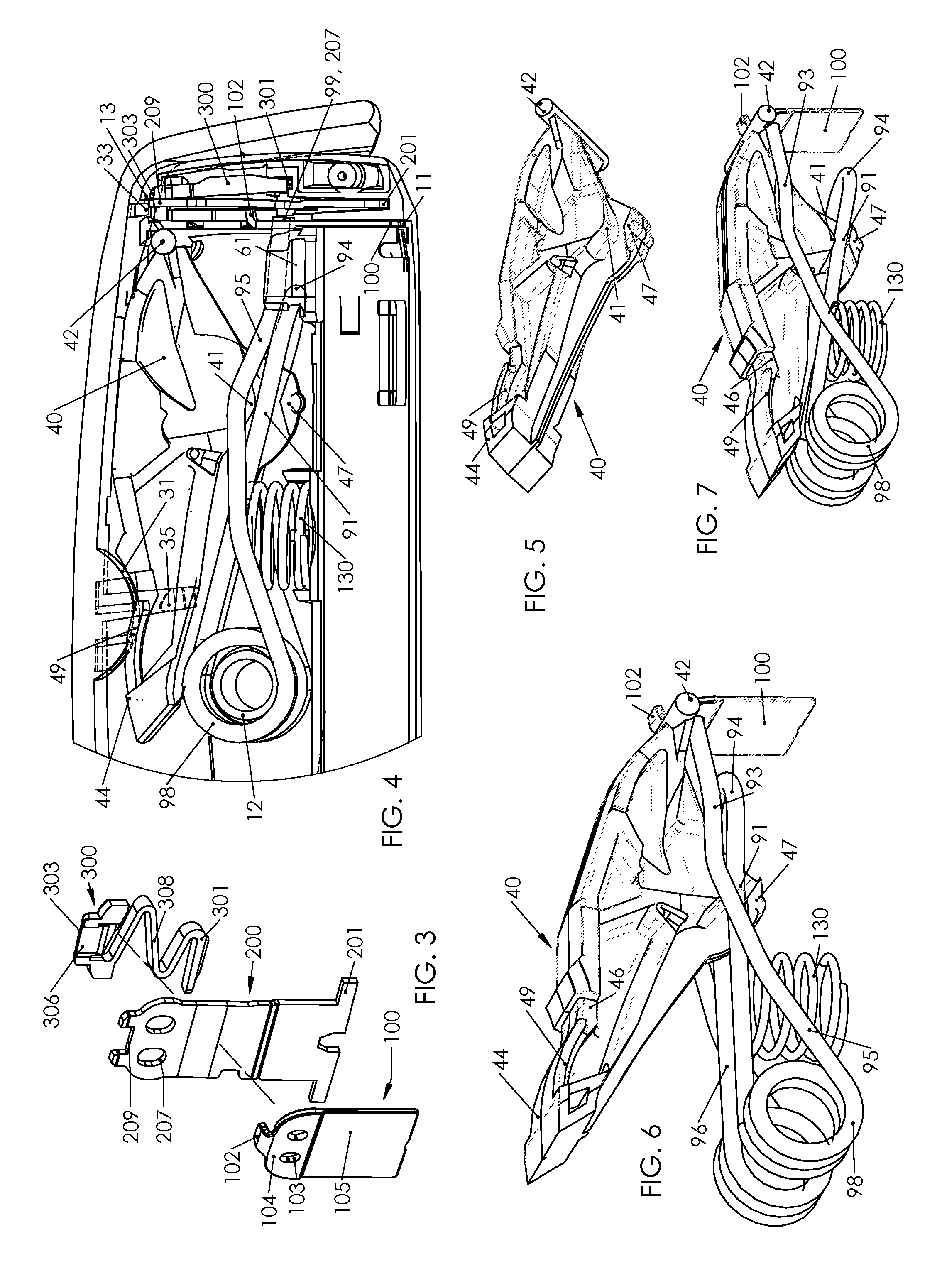
Power spring configurations for a fastening device
ActiveUS20130228607A1Improve efficiencyReduce travel requirementsStapling toolsNailing toolsRest positionEngineering
Power spring configurations for a spring energized fastening device includes a compact double torsion power spring and two opposed compact single torsion springs. Simplified structures to hold the springs in a stable pre-loaded position are disclosed. Each coil has forward extending arms including an angled portion and forward vertically coincident portions. The double torsion spring has a self-locking crossing geometry to hold a pre-loaded rest position. The opposed two springs have a bridge and a mandrel to hold the rest position. A lever presses arms of the spring between a striker and the coil including a compact nesting condition. A tab of the striker extends forward to provide a release edge and a positioning torque bias upon the striker.
Owner:WORKTOOLS
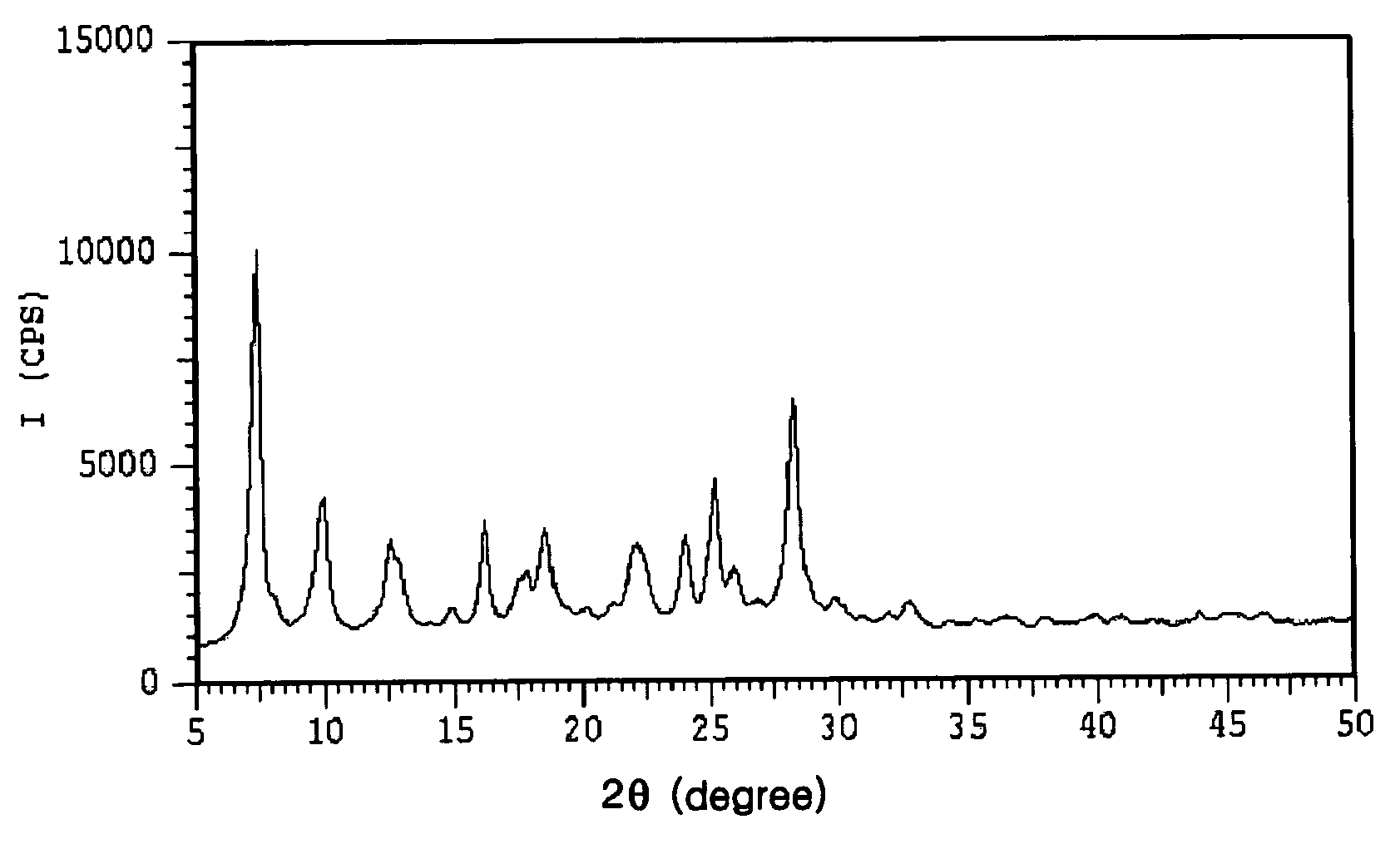
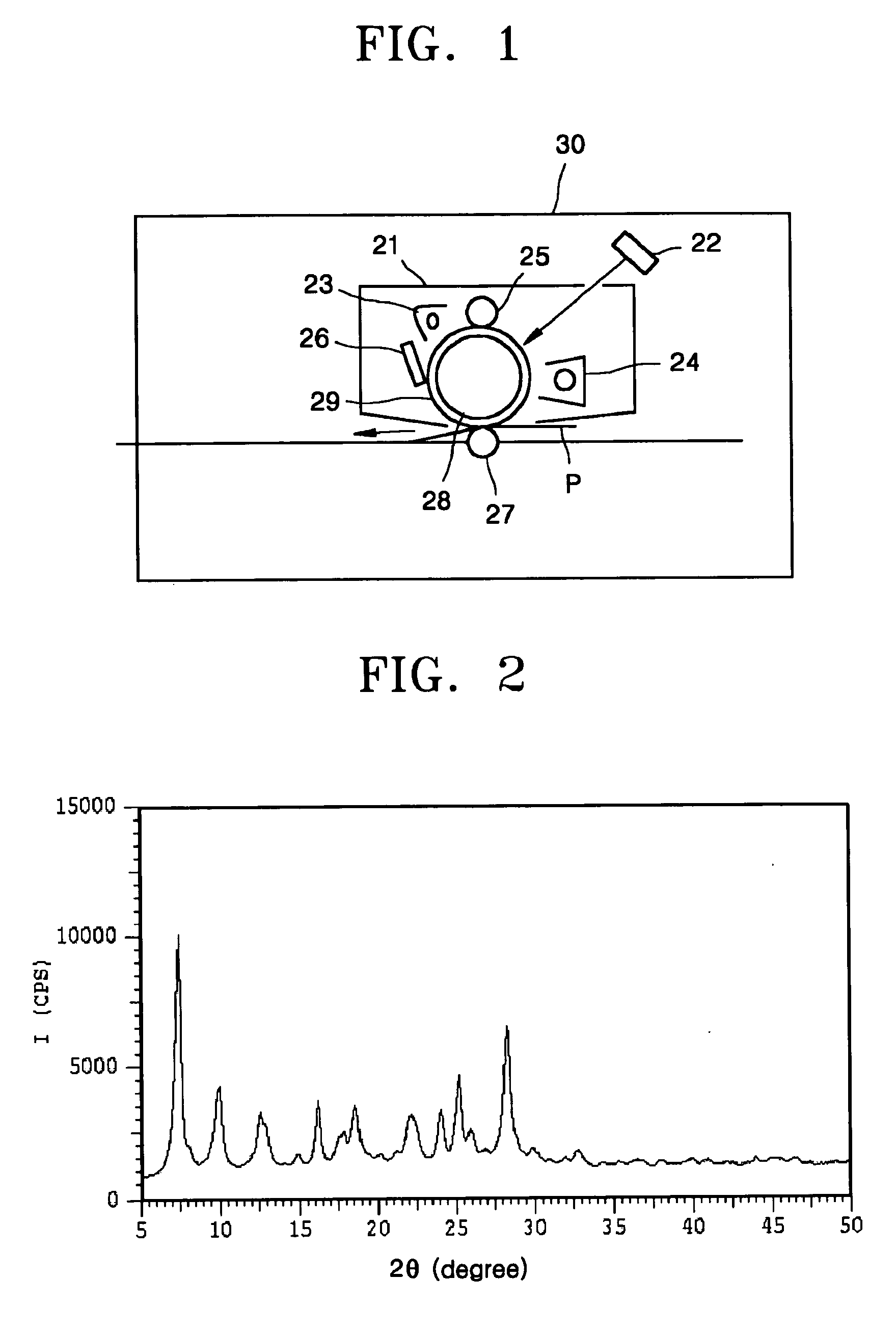
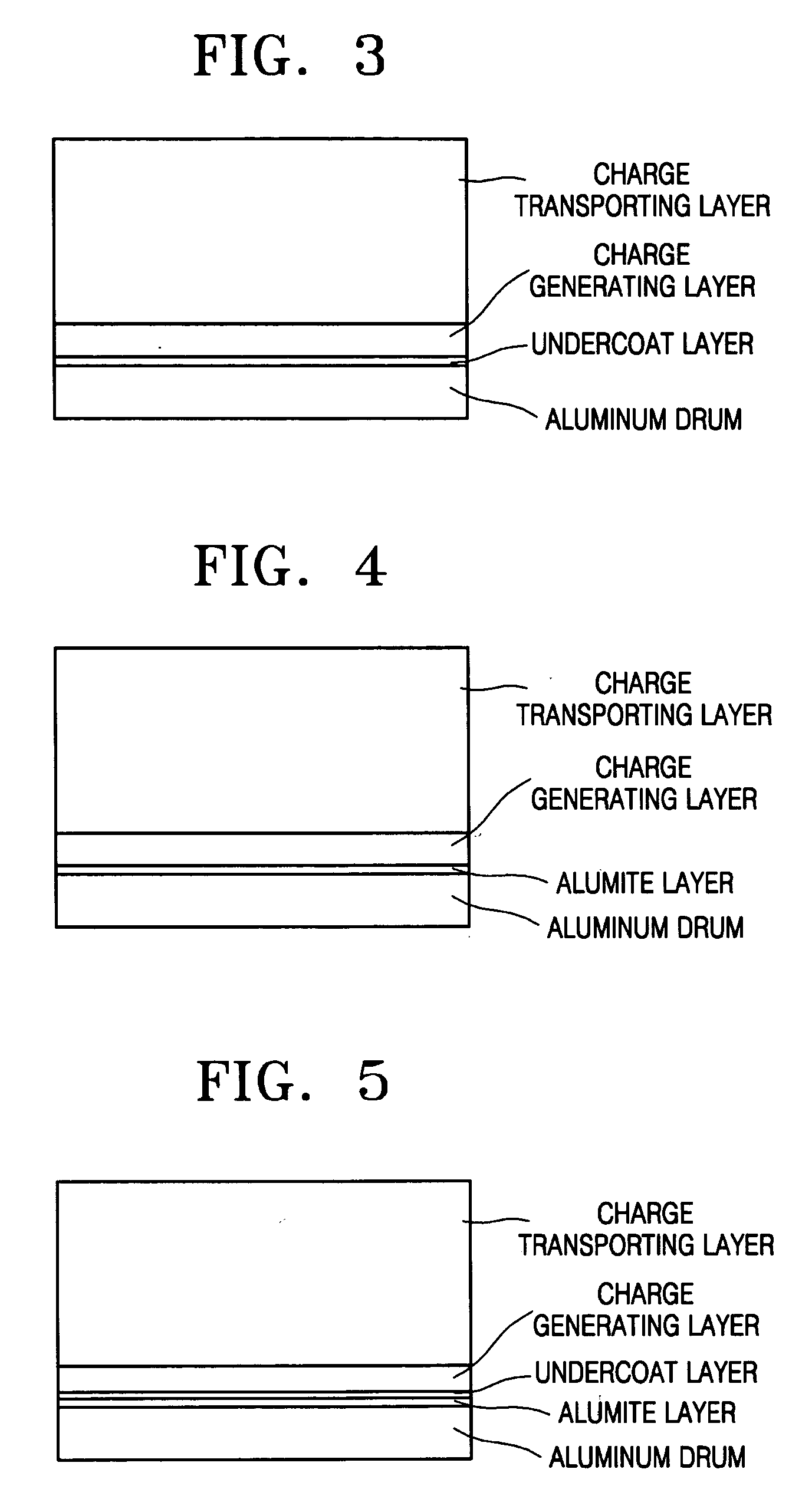
Electrophotographic photoreceptor and electrophotographic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20060154159A1High stability and property and durabilityStable to crystal transition and crystal growthElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeAniline CompoundsElectrically conductive
The invention is directed to an electrophotographic photoreceptor, and an electrophotographic cartridge and an electrophotographic imaging apparatus including the electrophotographic photoreceptor. The electrophotographic photoreceptor includes: an electrically conductive substrate; a charge generating layer formed on the electrically conductive substrate and comprising μ-oxo-gallium phthalocyanine dimer as a charge generating material dispersed in a binder resin; and a charge transporting layer formed on the charge generating layer. The charge transporting layer includes a charge transporting material and a binder resin. The charge transporting material is a combination of (1) a butadiene-based amine compound and a hydrazone compound and (2) a combination of a first benzidine compound and a second benzidine compound. The amount of the charge transporting material is 5-200 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of the binder resin of the charge transporting layer. The electrophotographic photoreceptor has an excellent electrostatic property and a high interlayer adhesive force and resistance to abrasion and can be manufactured at a low cost.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet
InactiveUS20130029147A1High adhesive forceEasy to peelAdhesive processes with adhesive heatingEster polymer adhesivesPolymer scienceNitrogen
Provided is a pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet that maintains a high adhesive force and adhesion reliability (particularly, repulsion resistance and holding power) when the sheet is bonded, and can be easily peeled off from an adherend to easily separate and disassociate a bonded portion when the sheet is peeled off from the adherend.SolutionThe pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet according to the present invention is a pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet having an adhesive layer on at least one surface of a substrate, whereinthe substrate is a heat-shrinkable film, andthe adhesive layer comprises an adhesive composition comprising an acrylic copolymer and a thermally expandable micro particle, the acrylic copolymer comprising a monomer mixture of the following monomers (a1), (a2), and (a3) in the following contents as a constituent:(a1) an alkyl (meth)acrylate monomer having an alkyl group having 4 to 12 carbon atoms and having a glass transition temperature less than 0° C. when the monomer is formed into a homopolymer: 40 to 90% by weight,(a2) a monomer having at least one nitrogen atom and one ethylenically unsaturated bond within the molecule: 5 to 40% by weight, and(a3) a monomer having one ethylenically unsaturated bond within the molecule and having a glass transition temperature of not less than 0° C. when the monomer is formed into a homopolymer ((a2) is excluded): 0 to 40% by weight(the content (% by weight) represents the content of each monomer based on the total weight of the monomers (a1), (a2), and (a3) (100% by weight)).
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Compact solenoid valve
InactiveUS20080277501A1Low frictionHigh forceOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLiquid spraying apparatusMagnetic fluxEngineering
A valve is provided having a solenoid coil in an integrally formed magnetic material having a cross-sectional configuration resembling a bundt pan. Such a structure can be stamp-formed and creates an enlarged surface area available for the magnetic flux to the armature at the bottom of the bundt cross-section. However, since the ends of the stamped structure are not relevant to the magnetic circuit, they can be left unfinished. A thin, flat plate armature and an axial flow valve assembly allows for low friction, low mass movement of the valve seal. Placement of the armature and solenoid across a small air gap provides a high force, very fast response time with minimal electrical power consumption.
Owner:EVERETT WILLIAM F +1
Fixing method for a tip winglet and reduced tip leakage blade
InactiveUS20090214355A1Reducing tip leakageHigh forceBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesTurbine bladeMechanical engineering
Reducing the tip leakage for an existing compressor or turbine blade (10), including internally cooled blades, can be achieved by retrofitted the blade with a tip leakage-reducing device in the form of a winglet (12). The winglet (12) can be fixed onto the tip portion by bonding the winglet onto the face or faces of the blade by a key and slot arrangement.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
External Fixator for Osteosynthesis or Bone Gap Manipulation
InactiveUS20080255554A1Avoid burdenHigh forceInternal osteosythesisFractureBones partsBiomedical engineering
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
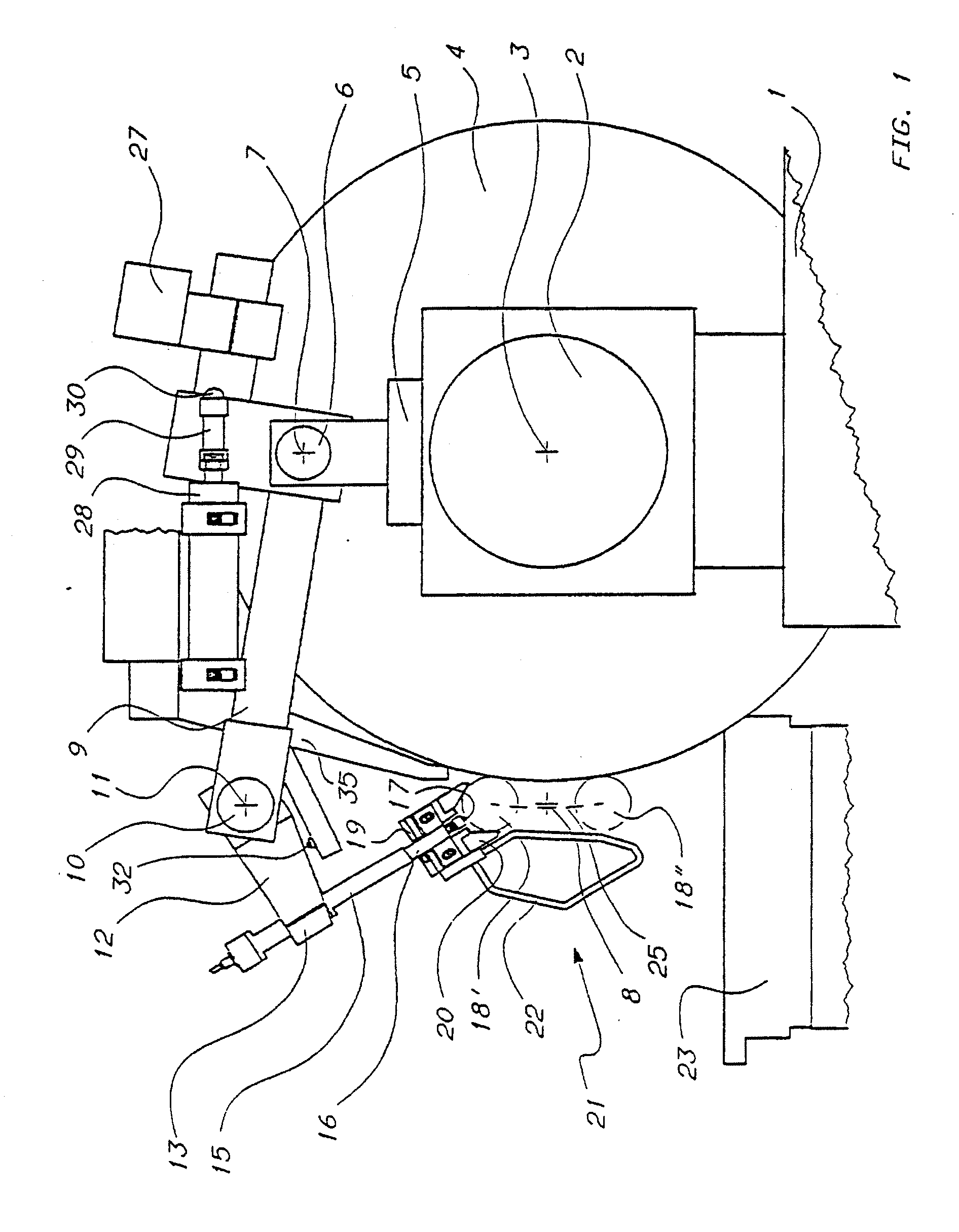
Apparatus for checking diametral dimensions of a rotating cylindrical part during a grinding thereof
InactiveUS20100000109A1Improve Metering PerformanceHigh forceRevolution surface grinding machinesGrinding feed controlRest positionReference device
An apparatus for checking the diameter of crankpins (18) of a crankshaft (34) in the course of the machining in a grinding machine comprises a first arm (9) rotating with respect to a support (5) arranged on the grinding-wheel slide (1) of the grinding machine, a second arm (12) rotating with respect to the first, a reference device (20) carried by the second arm and a measuring device (16, 17, 40-45) associated with a reference device. A guide device (21), fixed to the reference device (20), enables the apparatus to engage a crankpin, in the course of the orbital motion of the crankpin, and limit the displacements of the first arm and those of the second arm when a control device (28-30) displaces the apparatus to a rest position.
Owner:MARPOSS SPA
Power spring configurations for a fastening device
ActiveUS8978952B2Improve efficiencyReduce travel requirementsStapling toolsNailing toolsRest positionSelf locking
Power spring configurations for a spring energized fastening device includes a compact double torsion power spring and two opposed compact single torsion springs. Simplified structures to hold the springs in a stable pre-loaded position are disclosed. Each coil has forward extending arms including an angled portion and forward vertically coincident portions. The double torsion spring has a self-locking crossing geometry to hold a pre-loaded rest position. The opposed two springs have a bridge and a mandrel to hold the rest position. A lever presses arms of the spring between a striker and the coil including a compact nesting condition. A tab of the striker extends forward to provide a release edge and a positioning torque bias upon the striker.
Owner:WORKTOOLS
Hot melt adhesive based on low melting point polypropylene homopolymers
ActiveUS9334431B2Increase speedGood viscosity stabilityMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesPersonal carePorous substratePolymer science
Owner:BOSTIK INC
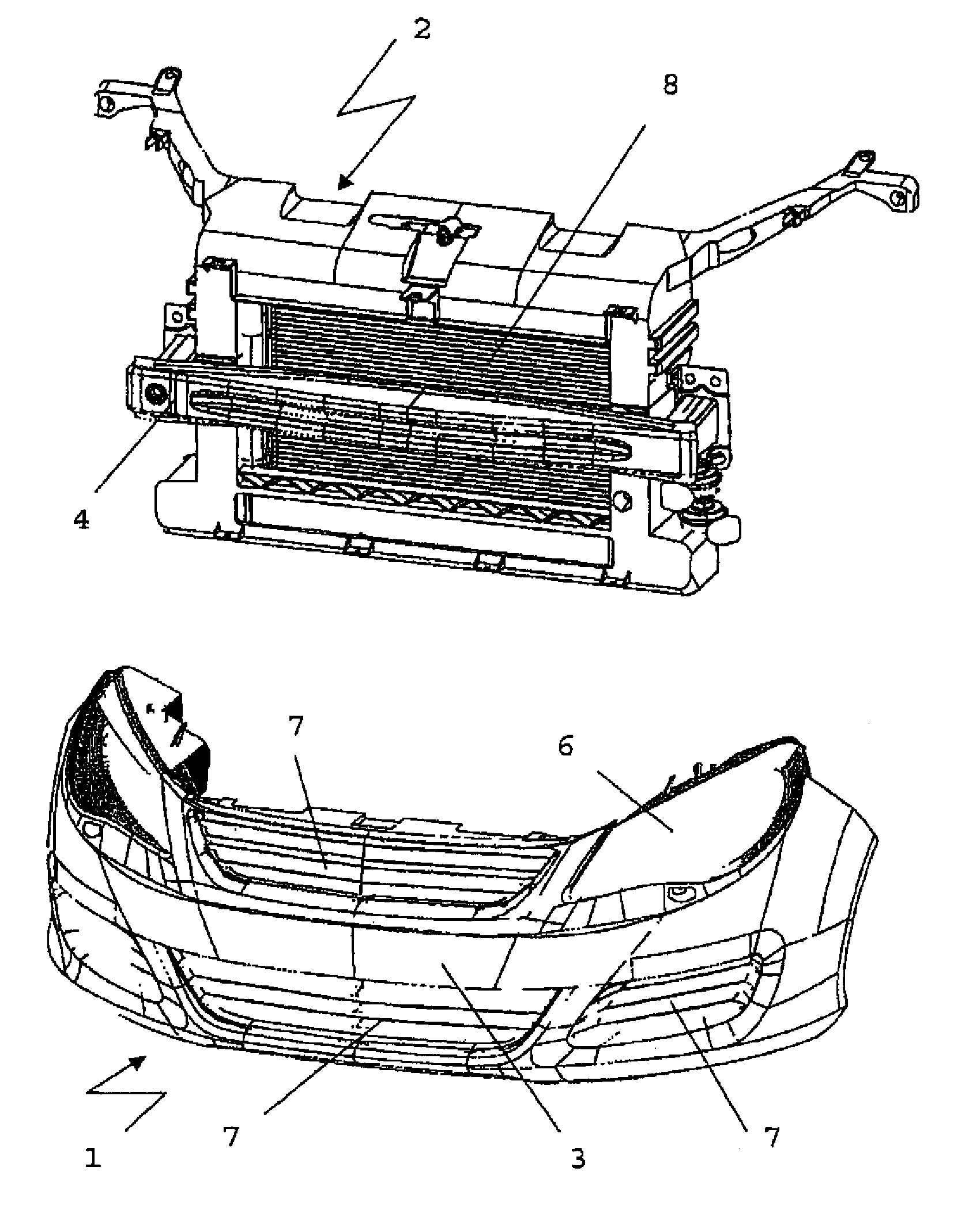
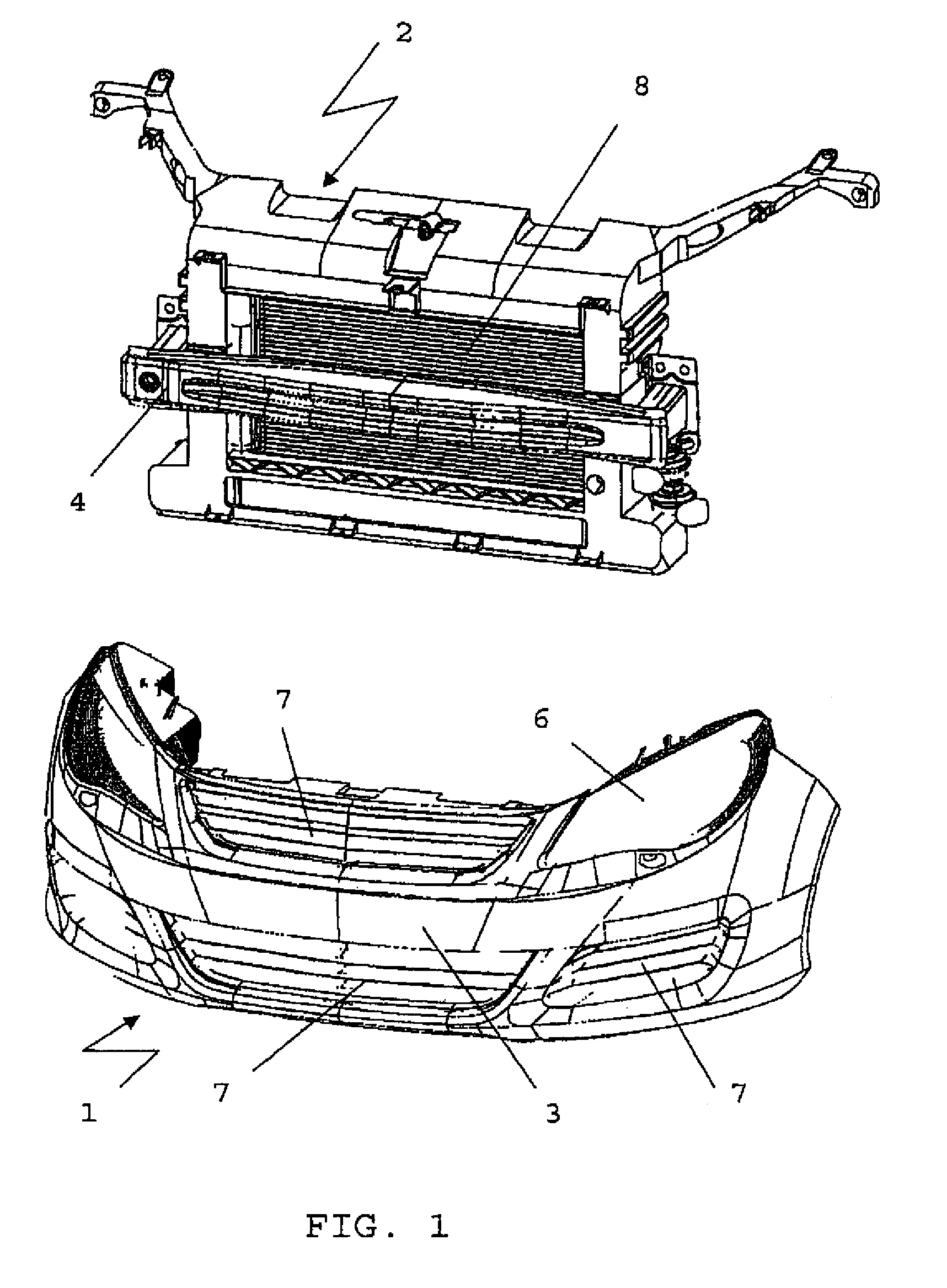
Bumper module
InactiveUS7891850B2Increase flexibilityIncreased valuationVehicle interior lightingLighting elementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:PEGUFORM
Easy pour spout
A can end is provided, which includes a center panel having a radius, a tab fastened to the center panel, and a scoreline defining a tear panel in the end panel. The tab is operable to sever the scoreline and open the tear panel to provide an opening in the can end. The tear panel includes an enlarged portion extending outwardly toward the center panel radius, thereby enlarging the opening. The enlarged portion forms an easy pour spout.
Owner:STOLLE MACHINERY CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com