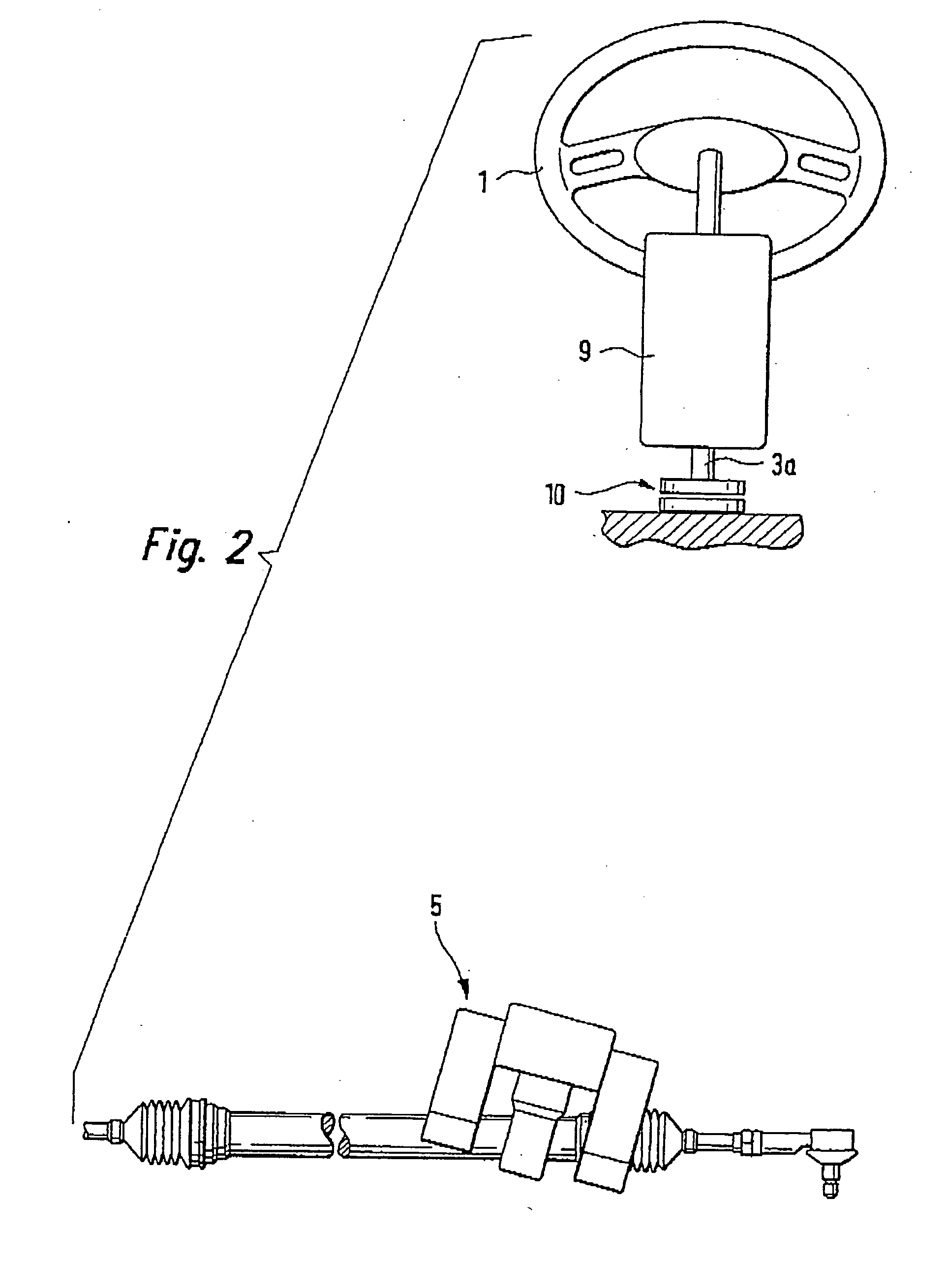
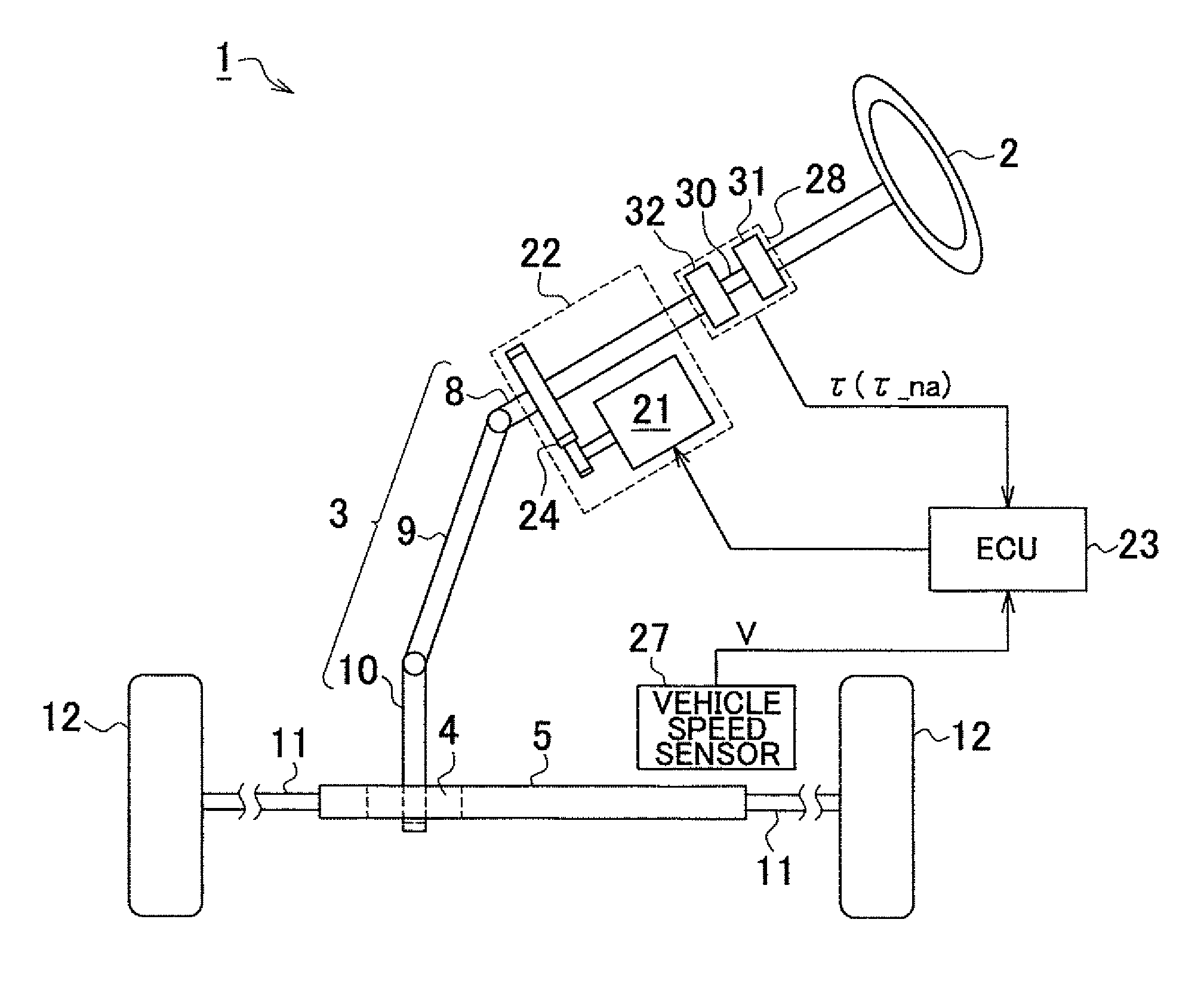
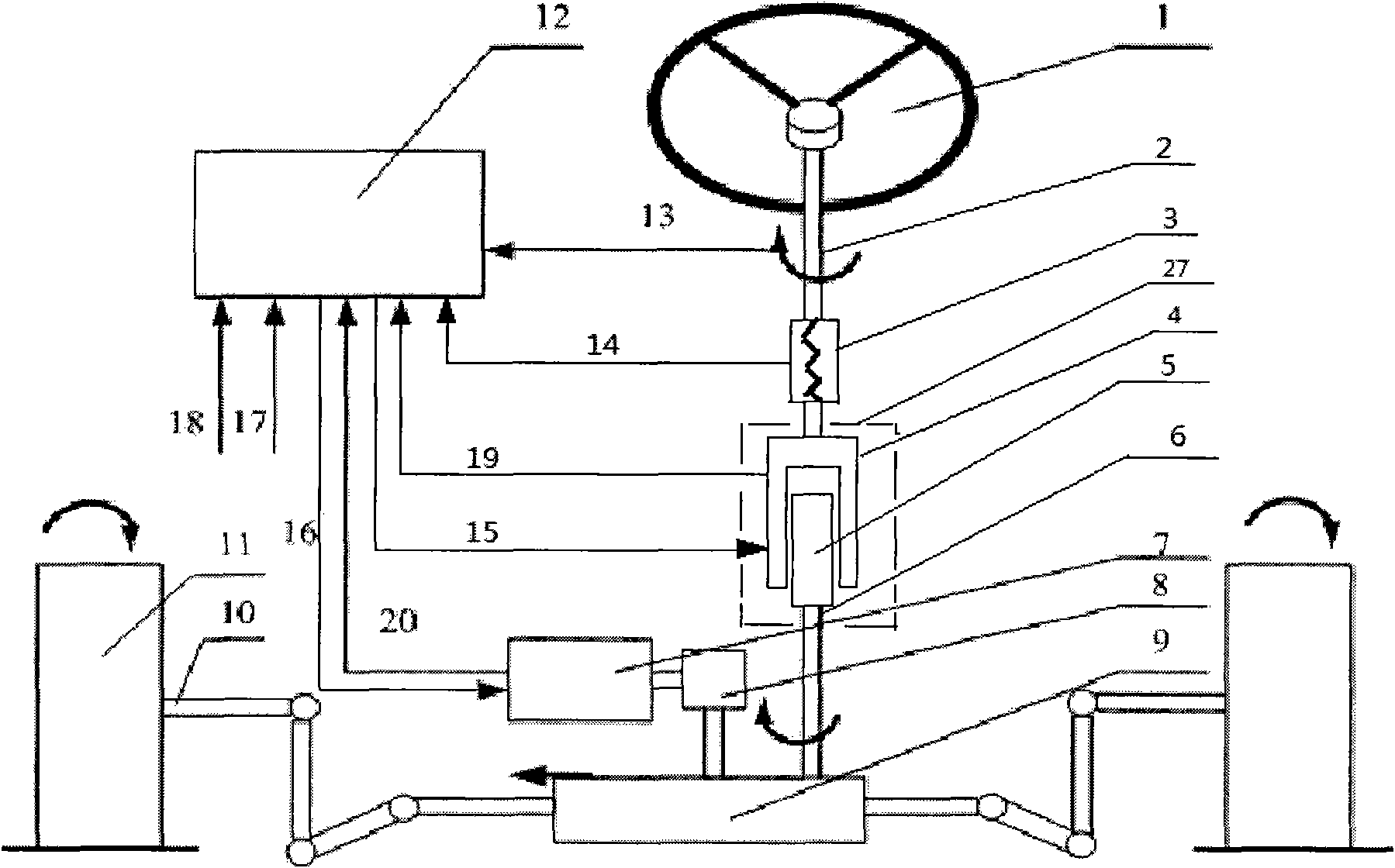
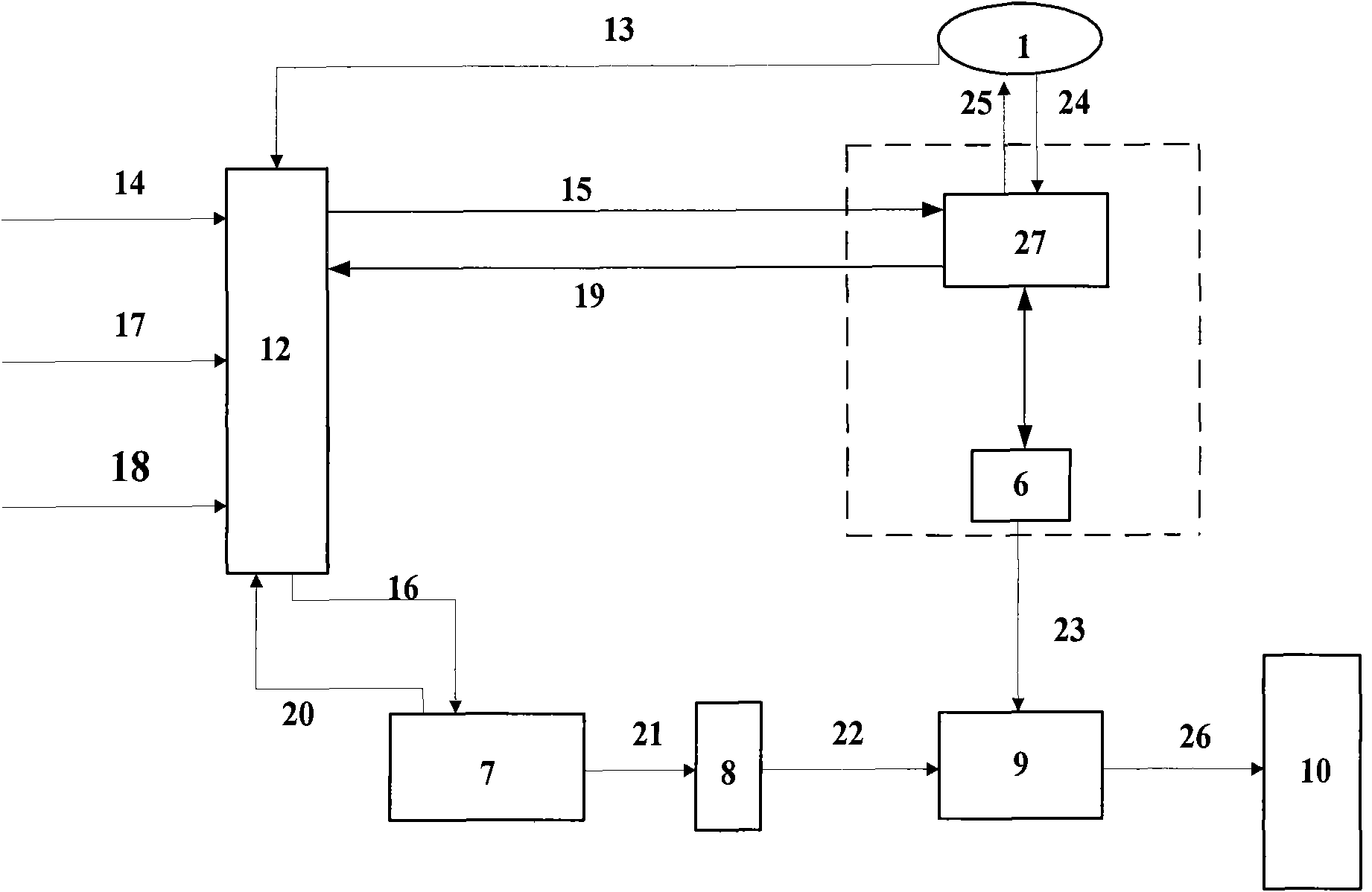
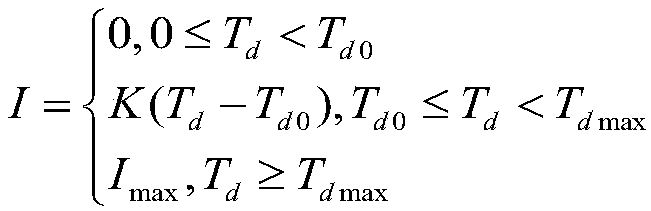Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46results about How to "Good steering feel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Permanent magnet motor
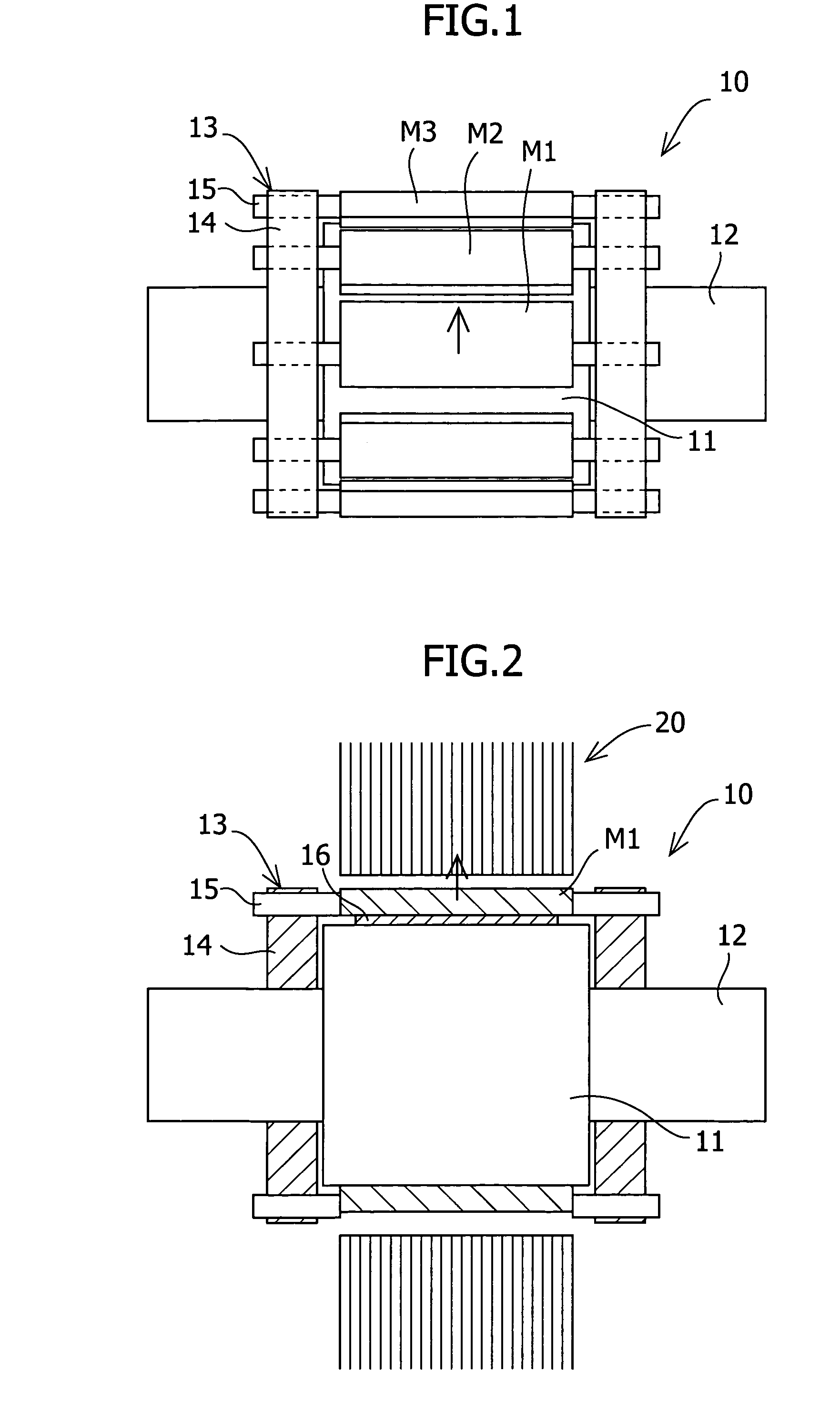
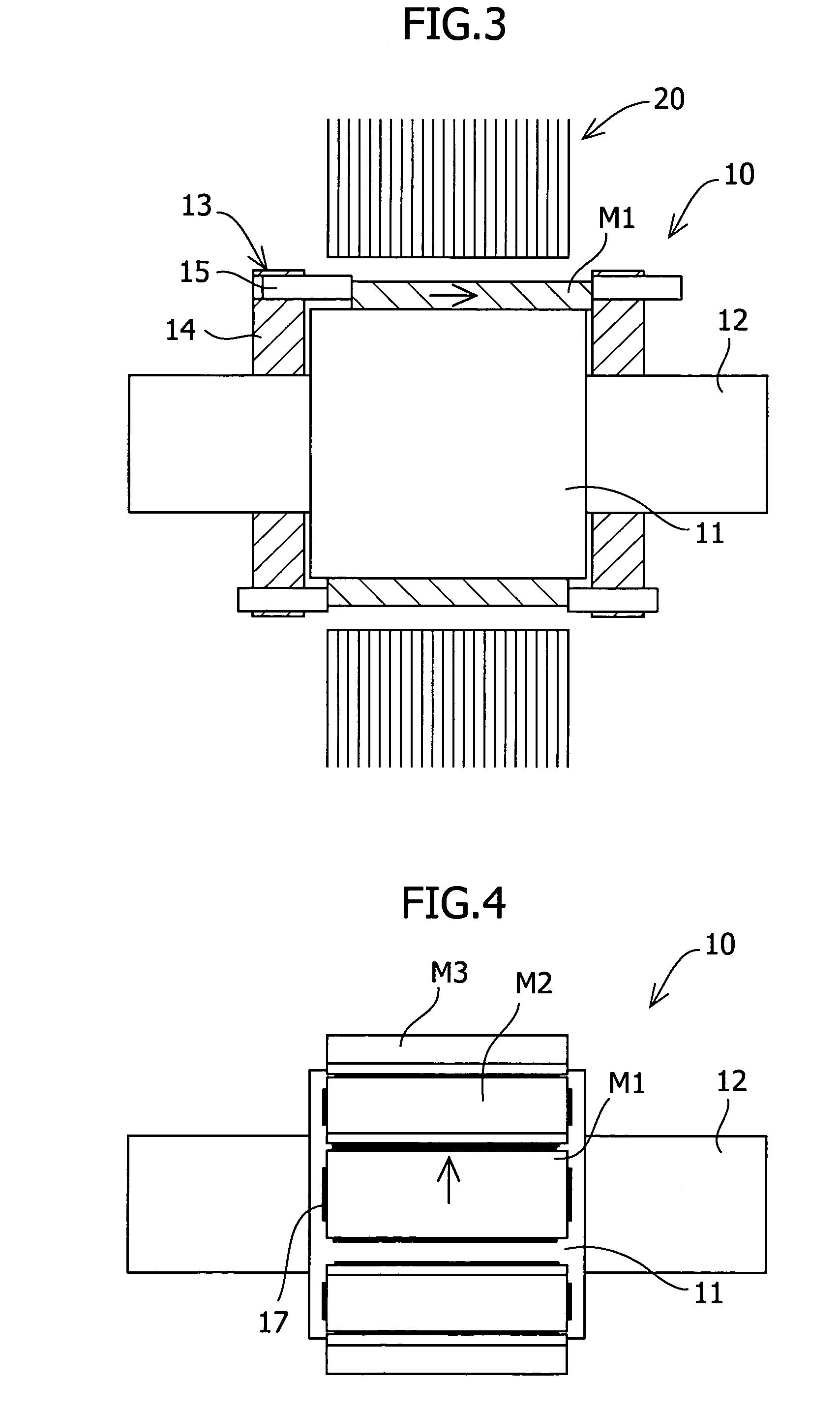
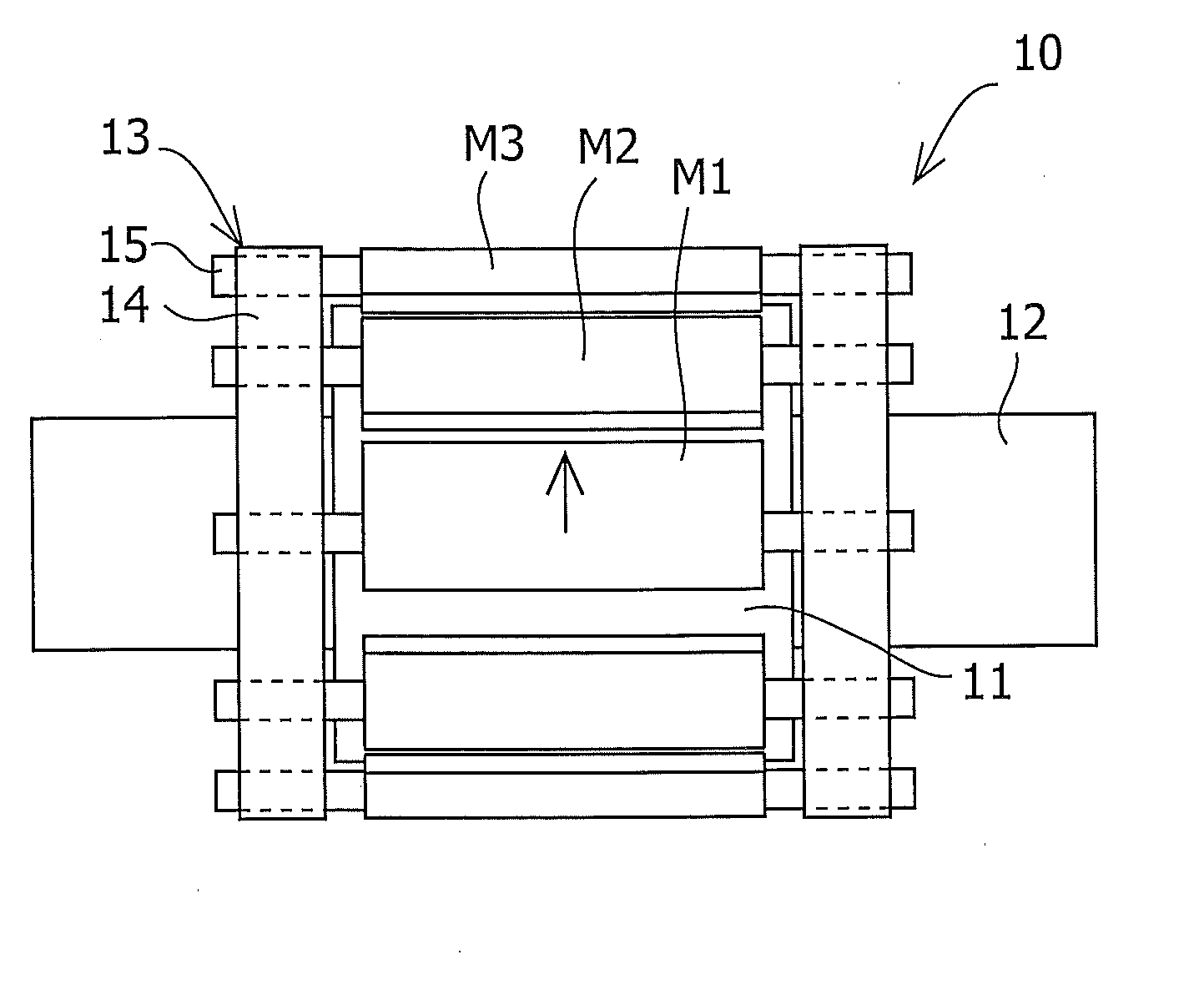
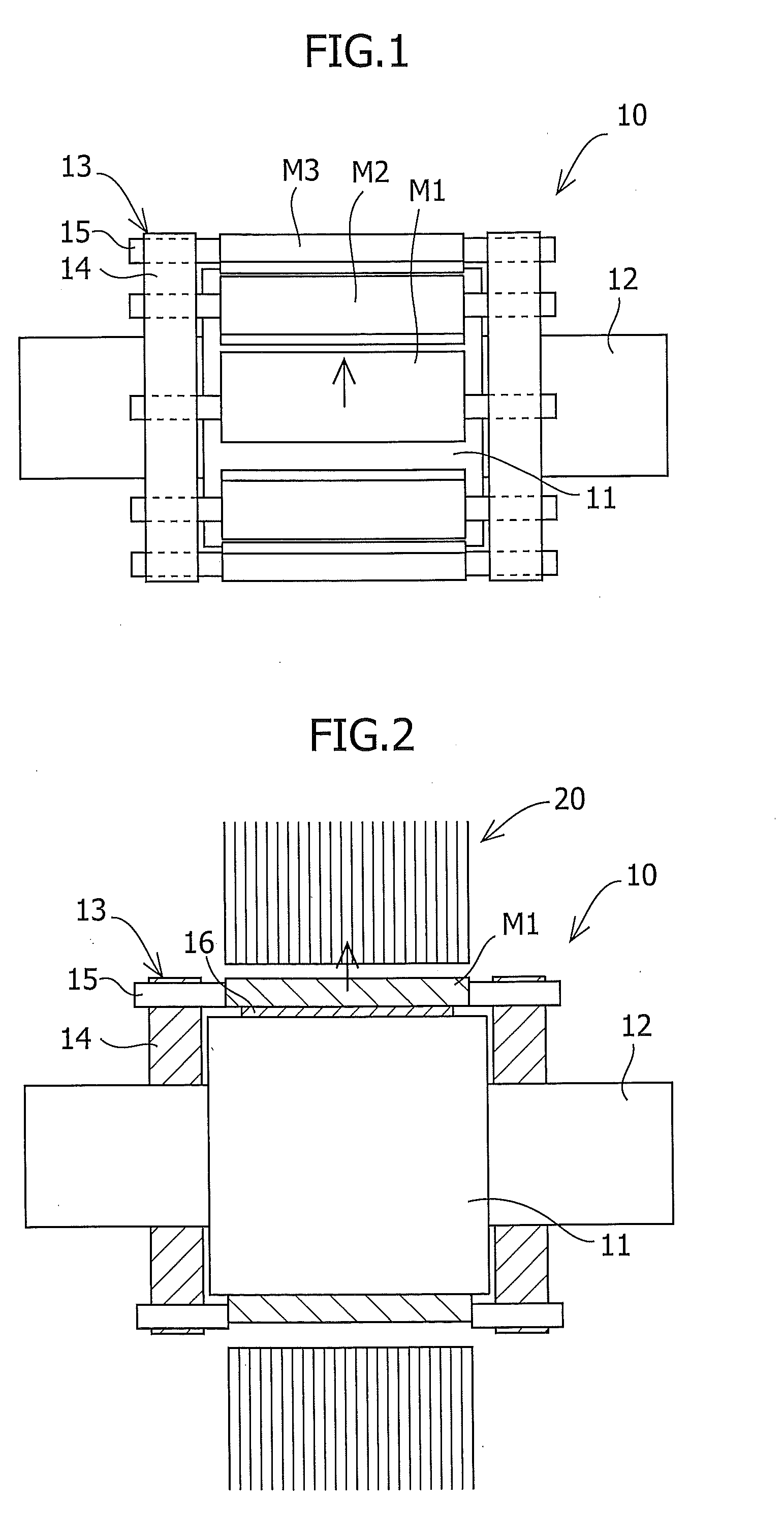
InactiveUS20060038457A1Reduce the cogging torque of servomotorsImprove accuracyMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric power steeringElectric machine
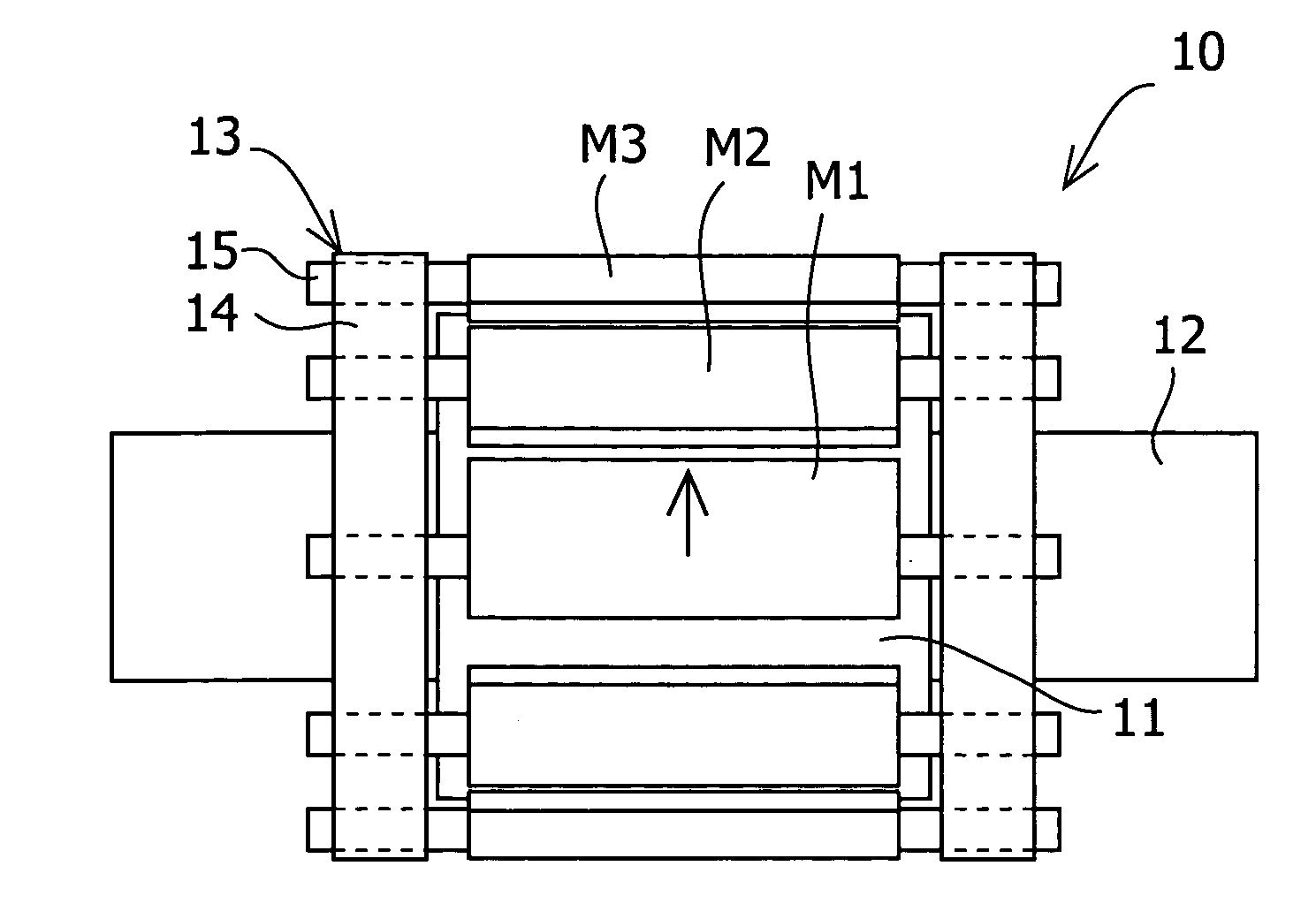
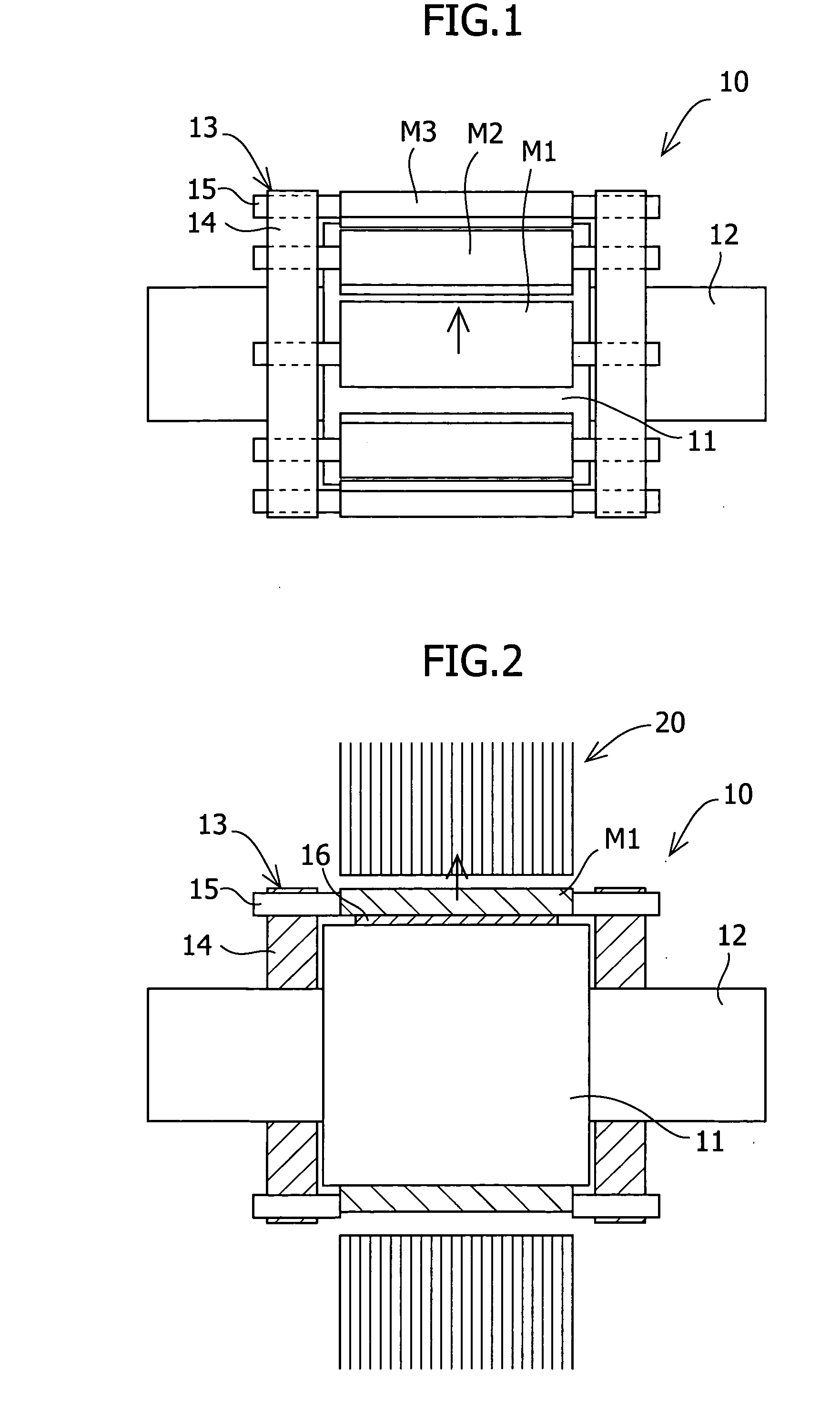
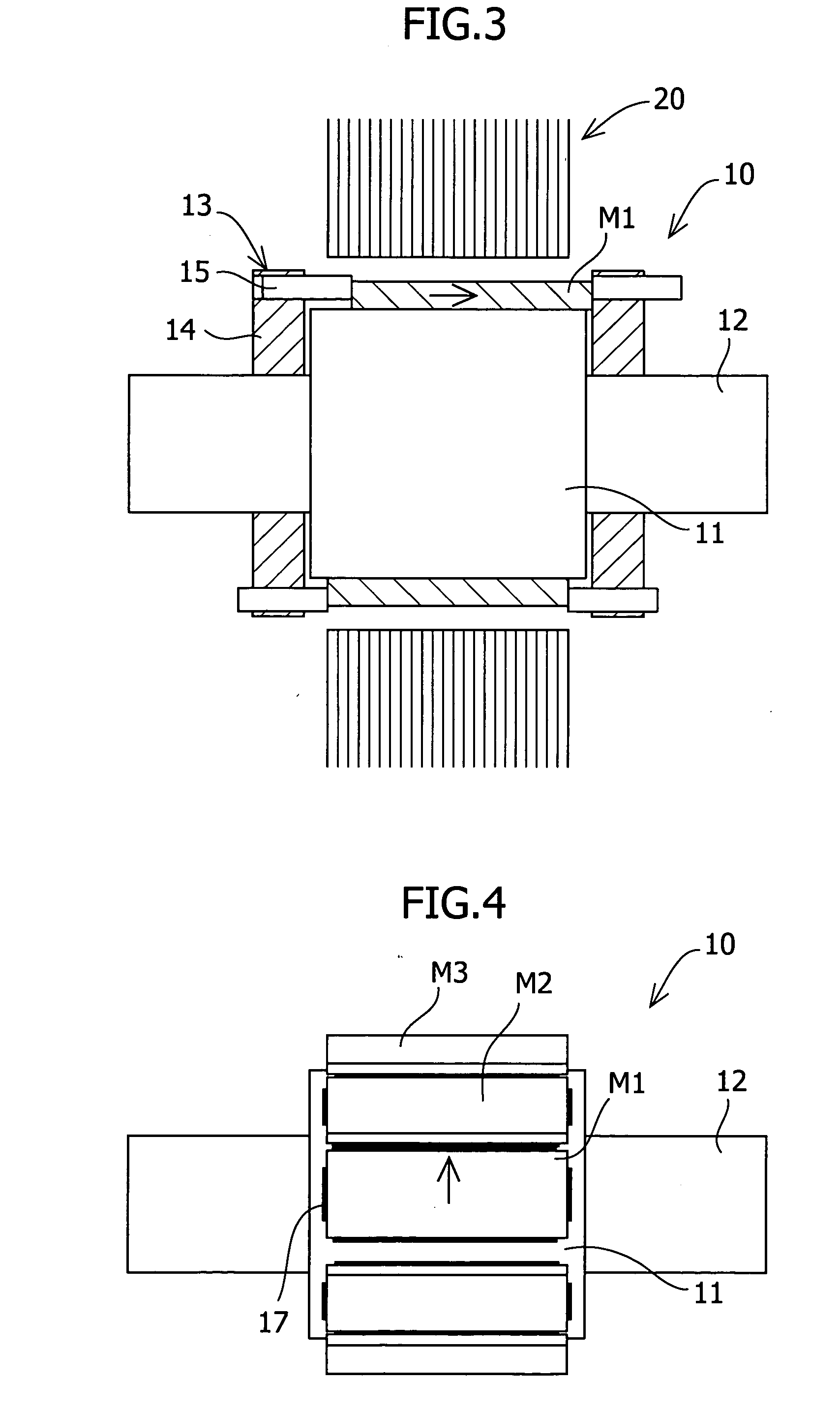
To reduce the cogging torque of servomotors, electric power steering motors, and others, there is provided a permanent magnet motor comprising: a rotor 10 comprising a rotor yoke 11 and a plurality of permanent magnets (M1-M10); and a stator 20 comprising a stator yoke 22, salient magnetic poles 21, and armature windings 23, wherein at least one of the permanent magnets is disposed in an adjustment position that is displaced from a corresponding reference position in at least one of the circumferential, radial, and axial directions of the rotor yoke, and the plurality of permanent magnets excluding the permanent magnet disposed in the adjustment position is disposed in the reference positions, and wherein the adjustment position is set so that the permanent magnet motor in which at least one of the plurality of permanent magnets is disposed in the adjustment position has a smaller cogging torque than a permanent magnet motor in which all of the plurality of permanent magnets are disposed in the reference positions; and a method for adjusting a cogging torque of a permanent magnet motor.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
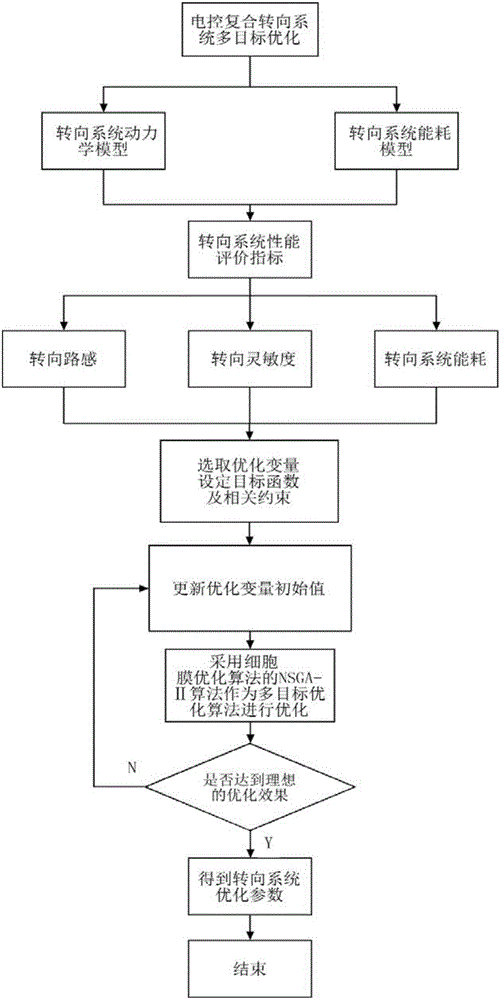
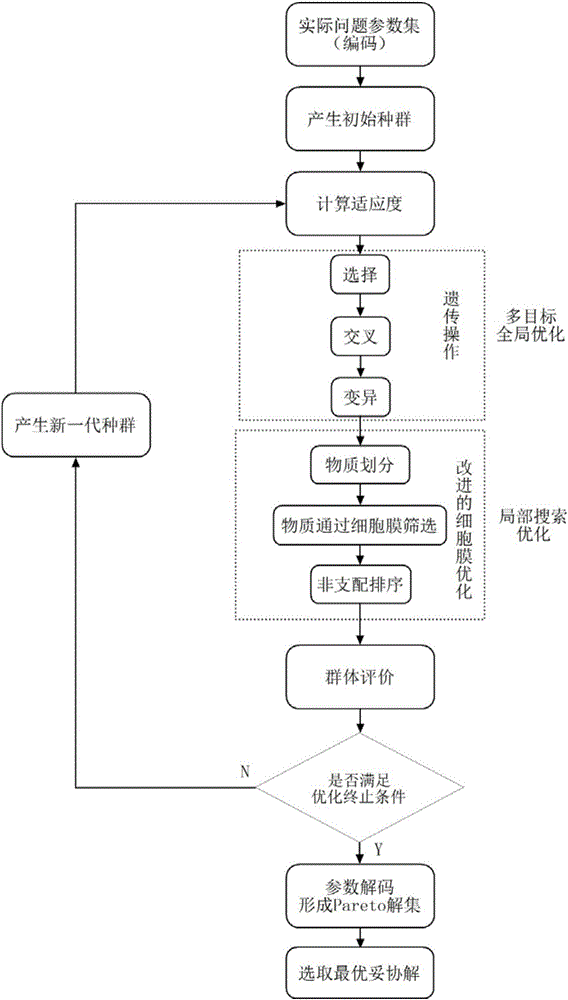
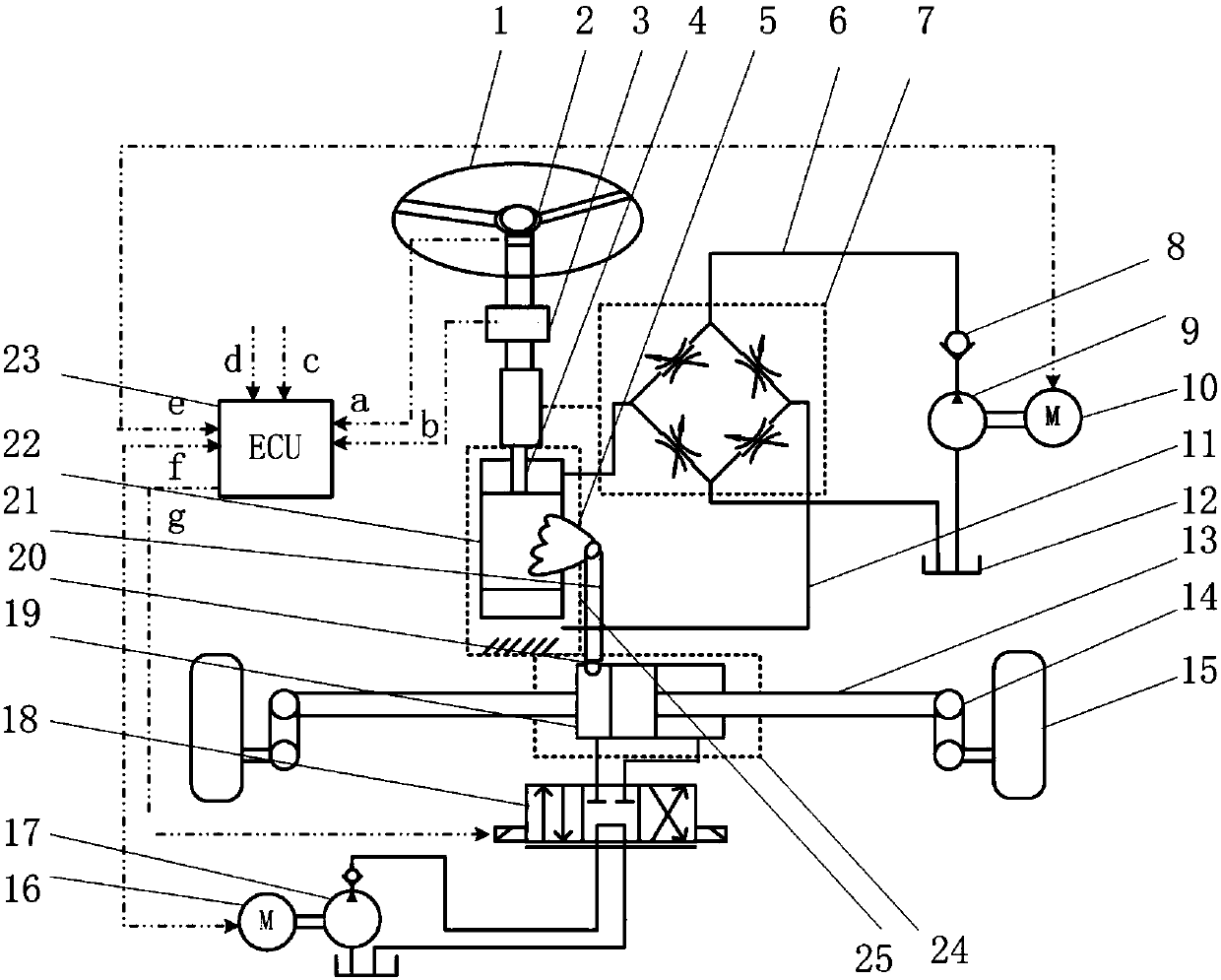
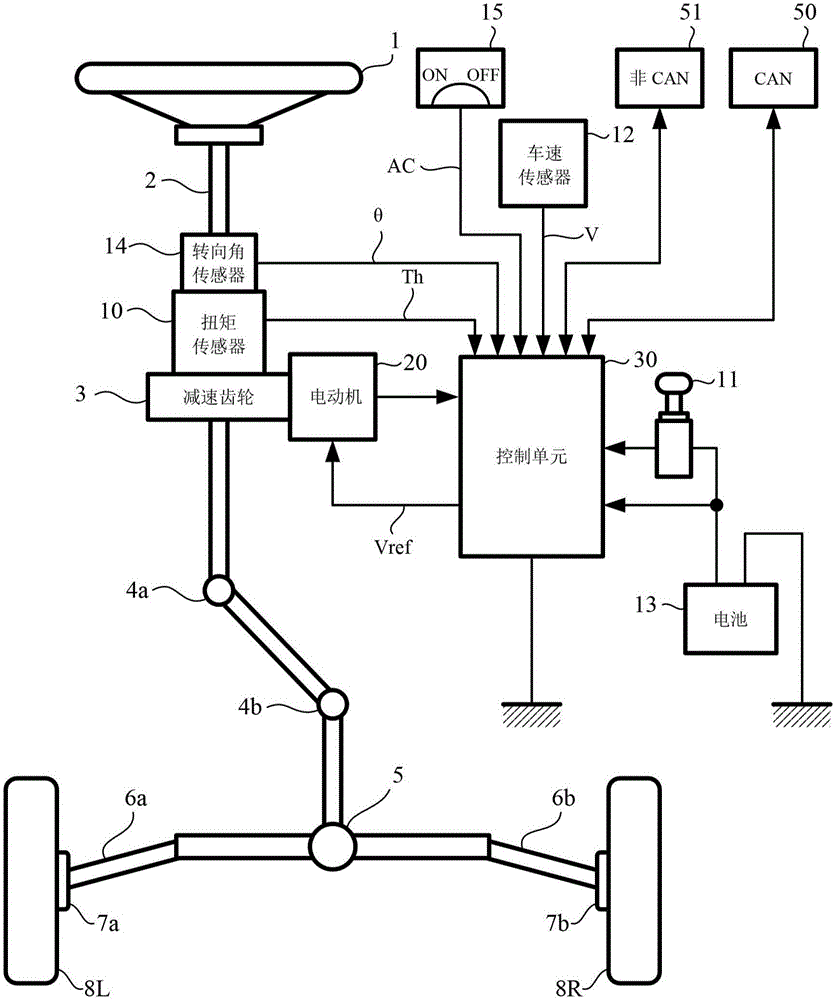
Automobile electric control composite steering system and multi-objective optimization method thereof
ActiveCN106800040AGood road feelAdjustable power steering characteristicsFluid steeringElectrical steeringHydraulic pumpEngineering
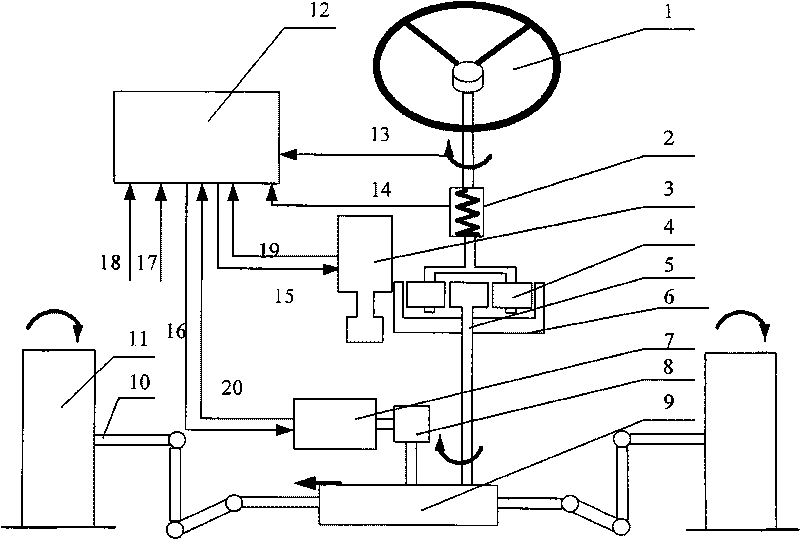
The invention discloses an automobile electric control composite steering system and a multi-objective optimization method thereof. The electric control composite steering system comprises an engine control unit (ECU), a mechanical drive module, an electrically controlled hydraulic power module and an electric power-assisted module. The mechanical drive module comprises a steering wheel, a steering column, a recirculating ball-type steering gear, a steering tie rod and the like; the electrically controlled hydraulic power module comprises a hydraulic tank, a hydraulic pump, a driving motor for the hydraulic pump and a rotary valve and the like; the electric power-assisted module comprises an arc-shaped linear electric motor and the like. According to the driver's preferences, road conditions, vehicle speed, steering angle and rotation speed and the like, the participation mode of the electric power-assisted of the composite steering system is determined. The motor of steering feeling, steering sensitivity and steering power consumption are taken as optimization targets and the steering range is selected as a constraint condition; the important parameters of the composite steering system are optimized through the new multi-objective optimization method and the comprehensive performance of the composite steering system is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system and multi-objective optimization method based on system
InactiveCN105151117AGood followabilitySuitable for the requirements of turning economySteering linkagesFluid steeringSteering wheelDrive motor
The invention relates to an electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system and a multi-objective optimization method based on the system. The electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system comprises a steering mechanical unit, a steering valve opening degree adjusting unit, an oil pump adjusting unit and an electronic control unit (ECU). The problems that in a traditional electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system, steering assistance power can be changed only by changing the rotating speed of an oil pump drive motor, and the opening degree of a steering valve can be linearly adjusted only according to the corner of a steering wheel are solved. Meanwhile, multi-objective optimization is carried out on the electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system, steering road feelings, steering sensitivity and energy consumption are taken as objectives, based on a modified Memetic intelligence algorithm, optimization design is carried out on mechanical parameters and hydraulic system parameters of the electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system, and therefore the system has the good steering road feelings and steering sensitivity with smaller energy consumption.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
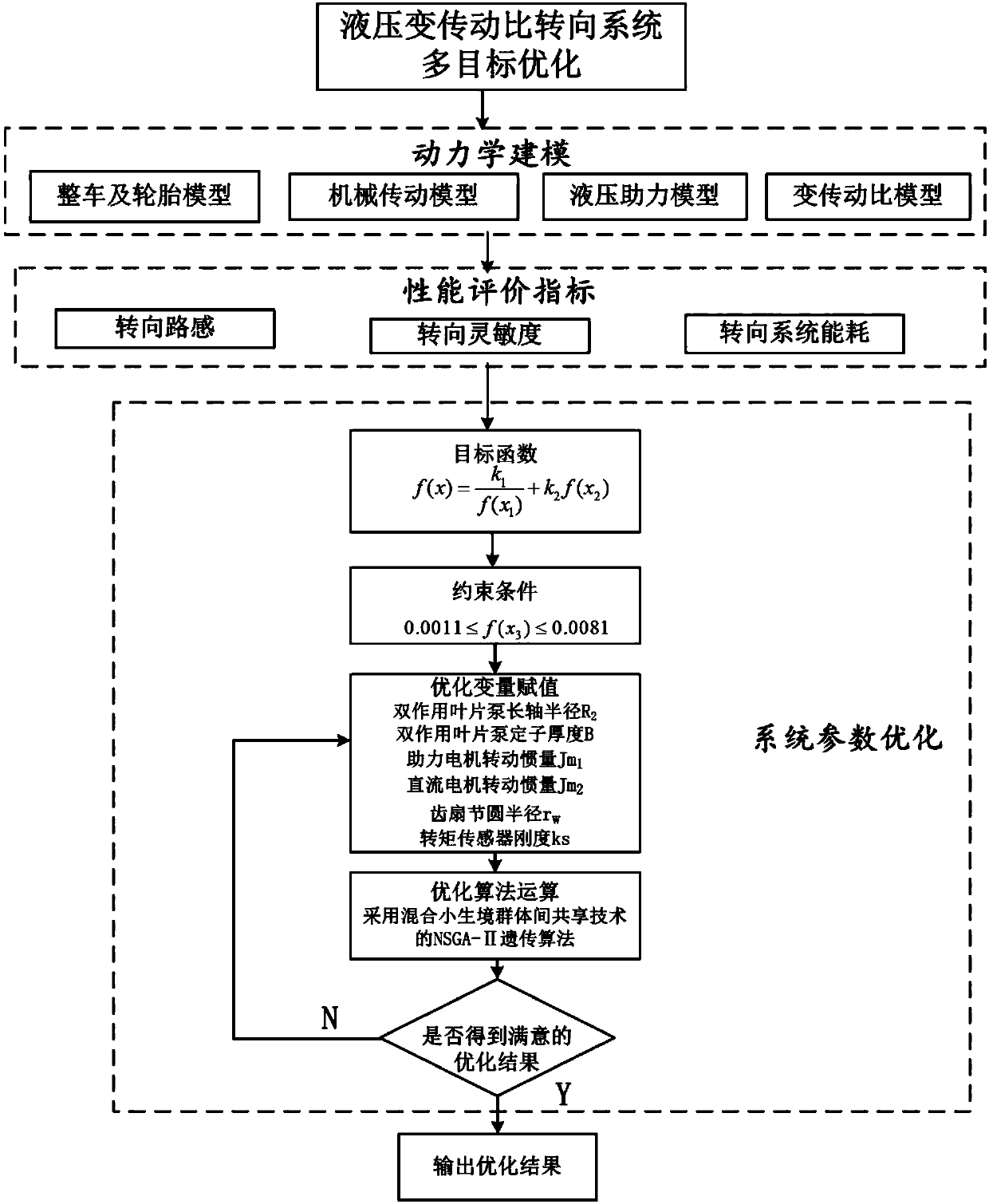
Automobile hydraulic variable-transmission-ratio steering system and multi-objective optimization method thereof
PendingCN107600173AImprove operational stabilityIncrease flexibilitySteering linkagesFluid steeringLow speedGenetic algorithm
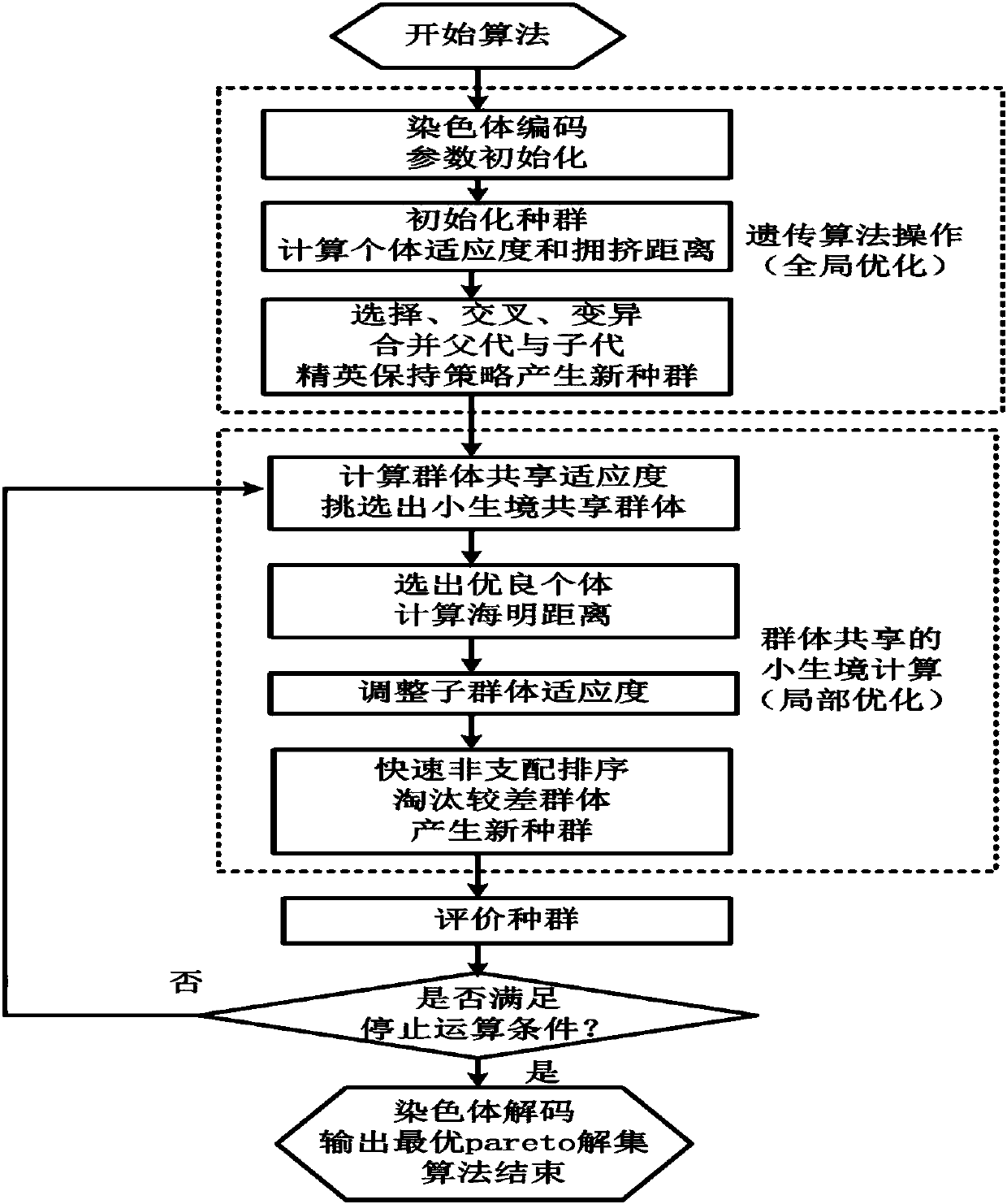
The invention discloses an automobile hydraulic variable-transmission-ratio steering system and a multi-objective optimization method thereof. The automobile hydraulic variable-transmission-ratio steering system comprises a mechanical transmission module, a hydraulic power assisted module, a variable transmission ratio module and a main control module. Aiming at the automobile hydraulic variable-transmission-ratio steering system, mechanical structure parameters and hydraulic parameters which have a great influence on steering performance are selected as optimizing variables, and optimizing objectives are the steering road feel and energy consumption of the steering system; and under the constraint condition of steering sensitivity, multi-objective optimization is conducted through the NSGA-II genetic algorithm of the proposed mixed niche group sharing technology. According to the hydraulic variable-transmission-ratio steering system, the transmission ratio of the steering system can be adjusted according to the automobile travelling working condition, and the characteristics of flexible steering in a low speed and stable steering in a high speed are achieved. After the key parameters of the system are optimized, under the situation of guaranteeing the automobile travelling stability, the good steering road feel can be obtained, meanwhile, the energy consumption of the system is reduced, and the good comprehensive steering performance is obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Electric power-assisted steering system with variable transmission ratio and method for controlling transmission ratio thereof
InactiveCN101722983ARealize variable transmission ratio controlRealize functionSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringElectric power system
The invention relates to an electric power-assisted steering system with a variable transmission ratio and a method for controlling transmission ratio thereof, and belongs to an electric power-assisted steering system. A planetary gear mechanism and a steering motor are arranged between a torque sensor and a gear rack; and on the basis of completing the conventional electric power-assisted steering, the electric power-assisted steering system can realize the functions of variable transmission ratio control and active steering interference.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Brushless DC motor
InactiveCN101102090AReduce torque fluctuationReduce noiseElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsElectricity
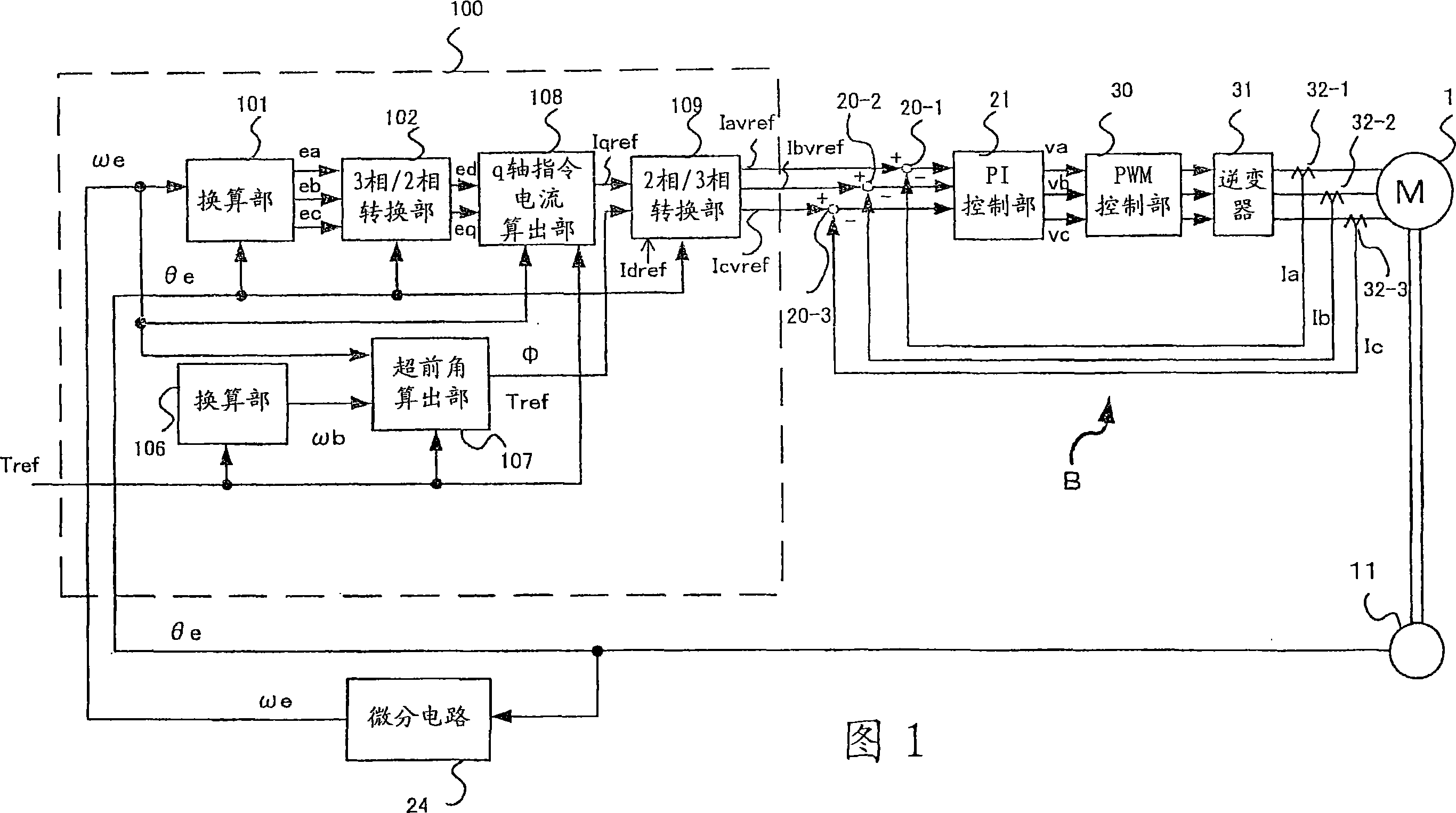
The invention provides a motor for a brushless DC motor, which has small torque ripple even if a trapezoidal wave current is supplied and has a small size and reduced motor noise. Respective phase current command values are calculated on the basis of vector control. Pseudo-vector control for controlling respective phases separately is used as current feedback control.
Owner:NSK LTD
Telescopic shaft for steering a vehicle and motor vehicle steering system
InactiveCN101332828AAvoid plastic deformationSmooth slidingLinear bearingsShaftsRelative phaseCoupling
A telescopic shaft for vehicle steering includes: an inner shaft and a tubular outer shaft fitted with each other; at least three pairs of axial grooves formed on an outer periphery of the inner shaft and an inner periphery of the outer shaft; a rigid coupling element for rigidly connecting the inner shaft and the outer shaft in a circumferential direction (C) of the inner shaft when a relative phase of the inner shaft and the outer shaft with respect to the circumferential direction (C) exceeds a predetermined range; and a plurality of elongate resin rods as elastic coupling elements for elastically connecting the inner shaft and the outer shaft in the circumferential direction (C) when the relative phase is in the predetermined range. Each of the plural resin rods is formed with a groove. A section of the groove is shaped like U opening toward the outside in a radial direction (U) of the inner shaft.
Owner:JTEKT CORP +1
Motor and drive control device therefor
InactiveCN1717860AReduce torque fluctuationReduce noiseElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlElectric power steeringLow noise
The invention provides a motor used for a brushless DC motor, which can not only provide trapezoidal wave electric current, but also achieve small torque fluctuation, minitype and low noise, a drive control device thereof and an electric power steering device using the motor and the drive control device. Current order of each phase is figured out based on vector control; current feedback is controlled by using quasi-vectors of all phases which are individually controlled.
Owner:NSK LTD
Vehicle control apparatus
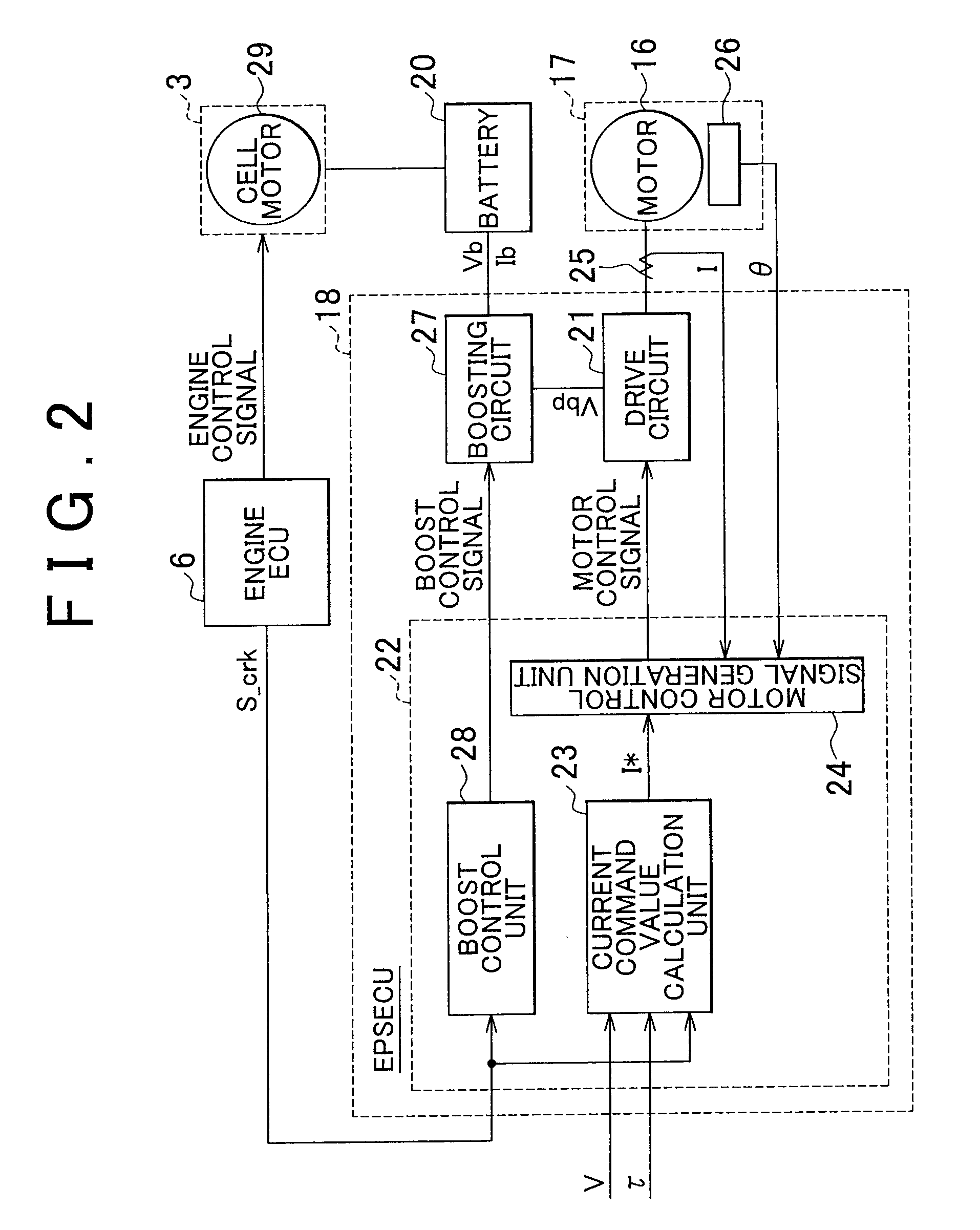
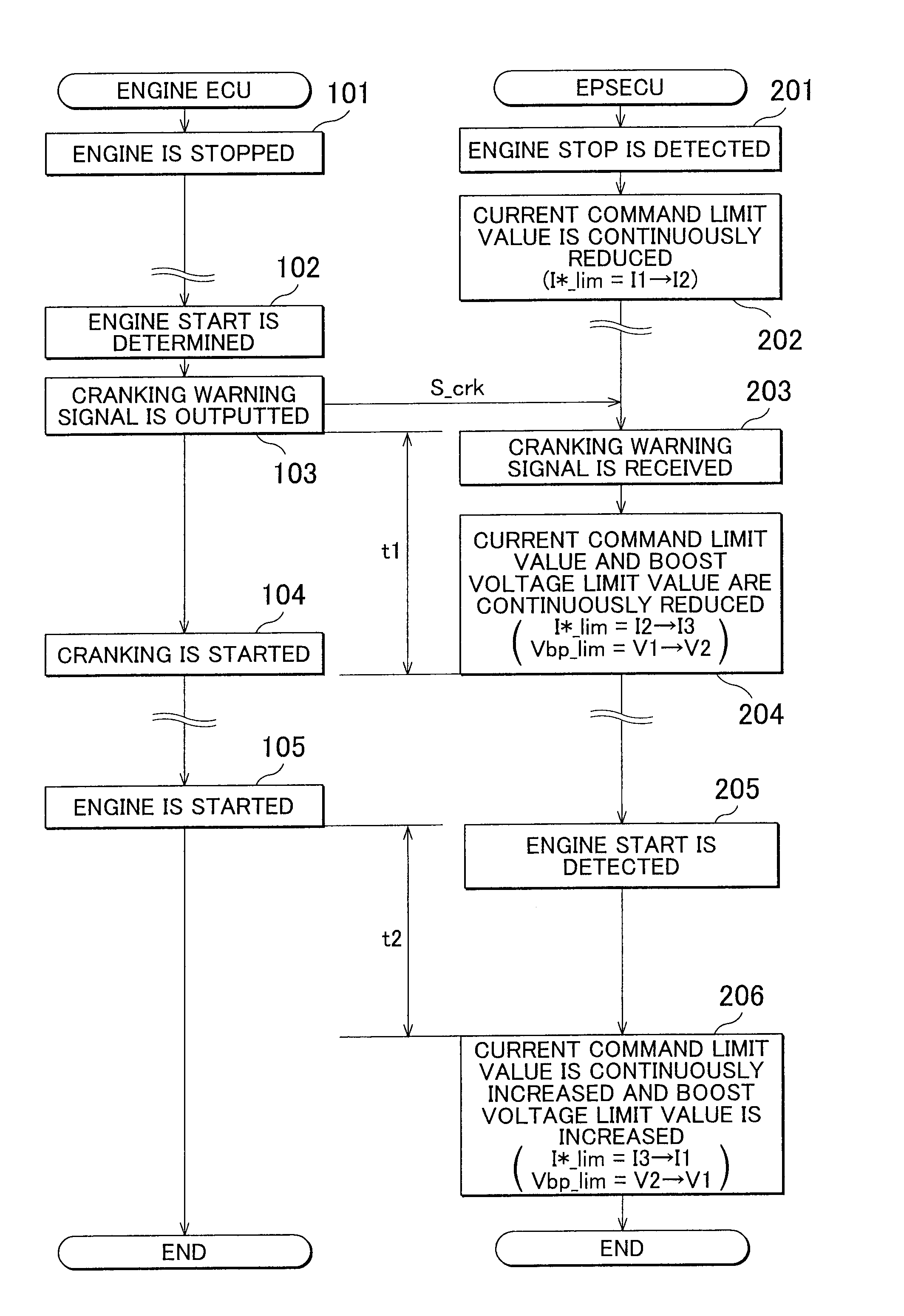
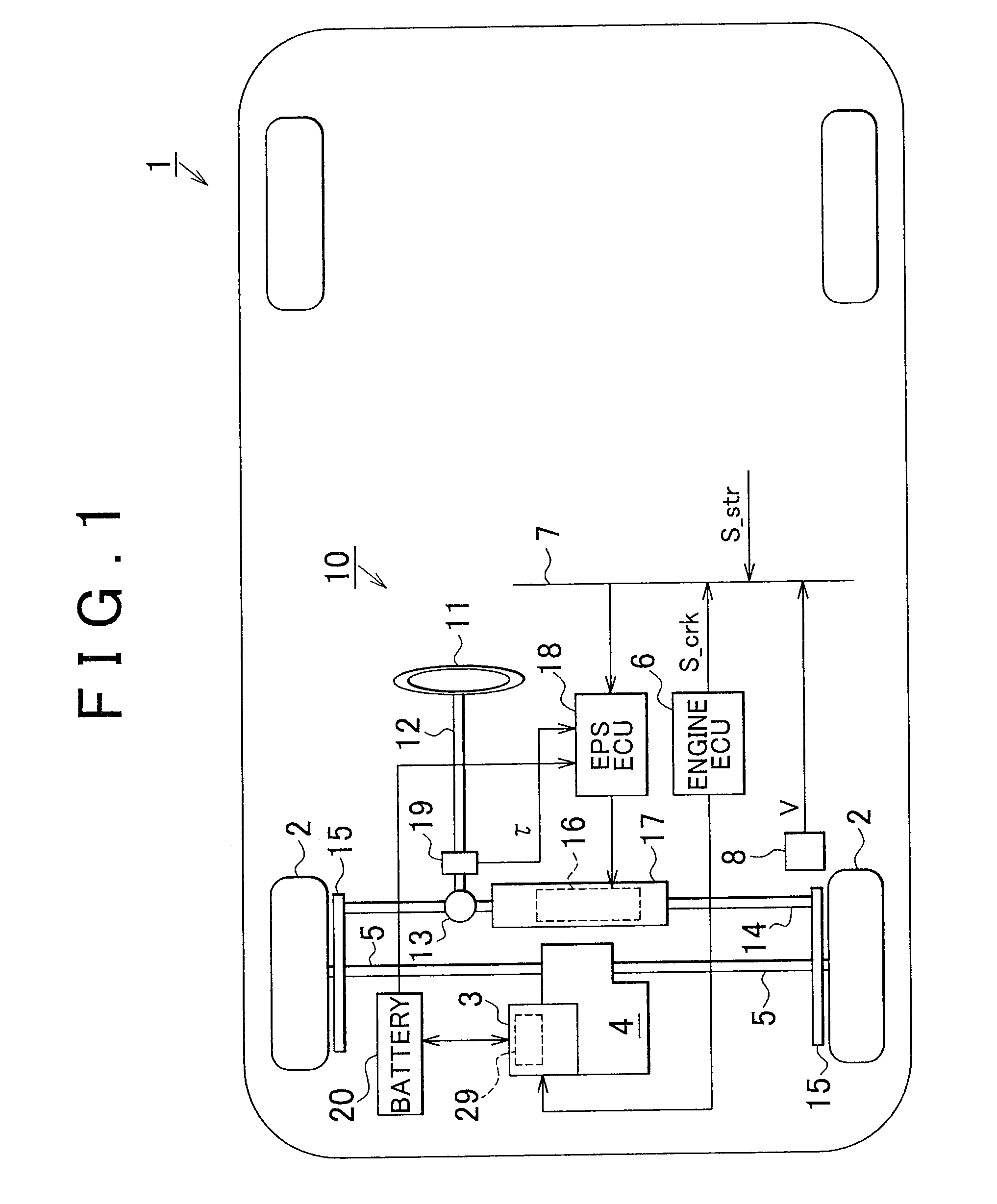
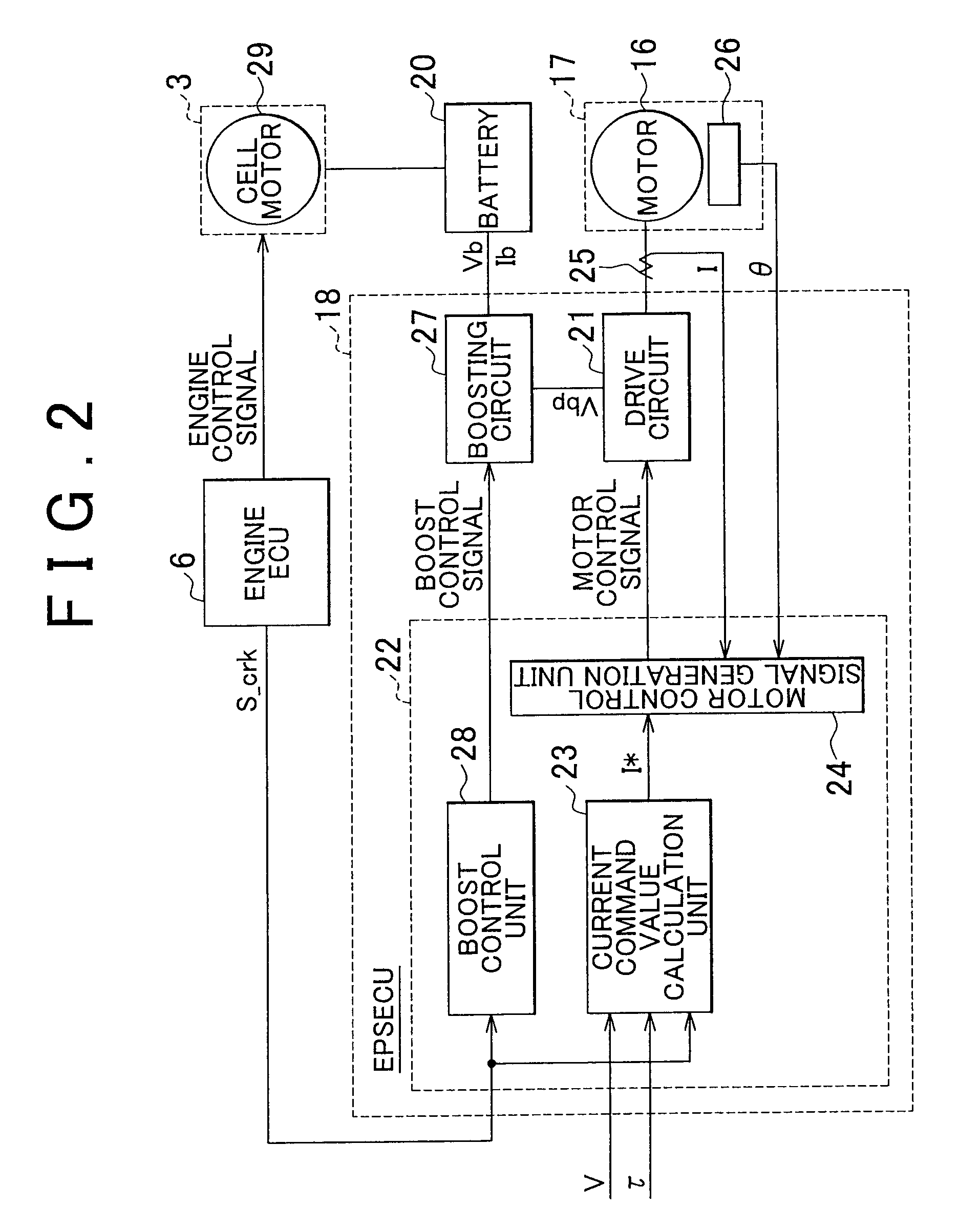
ActiveUS20090292454A1Favorable steering feelingAvoid it happening againDigital data processing detailsElectric motor startersEngineeringLimit value
In a case where an engine ECU determines that the engine is started (restarted), the engine ECU notifies an EPSECU that cranking is to be performed to start the engine before performing the cranking. When such a notification is received, the EPSECU gradually reduces a current command limit value I*_lim and a boost voltage limit value Vbp_lim before the cranking is started.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Motor
InactiveCN101728884AReduce torque rippleGood steering feelElectrical steeringSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsThree-phaseAtomic physics
A motor (40) includes twelve stator teeth (52) arranged at equal intervals in the circumferential direction. A three phase first coil group (Sa) is formed by star-connecting of coils (S 1 , S 3 , S 5 , S 7 , S 9 and S 11 ) formed on the odd-numbered teeth (52), and a three phase second coil group (Sb) is formed by delta-connecting coils (S 2 , S 4 , S 6 , S 8 , S 10 and S 12 ) formed on the even-numbered teeth (52), the first coil group (Sa) and the second coil group (Sb) are connected in parallel.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
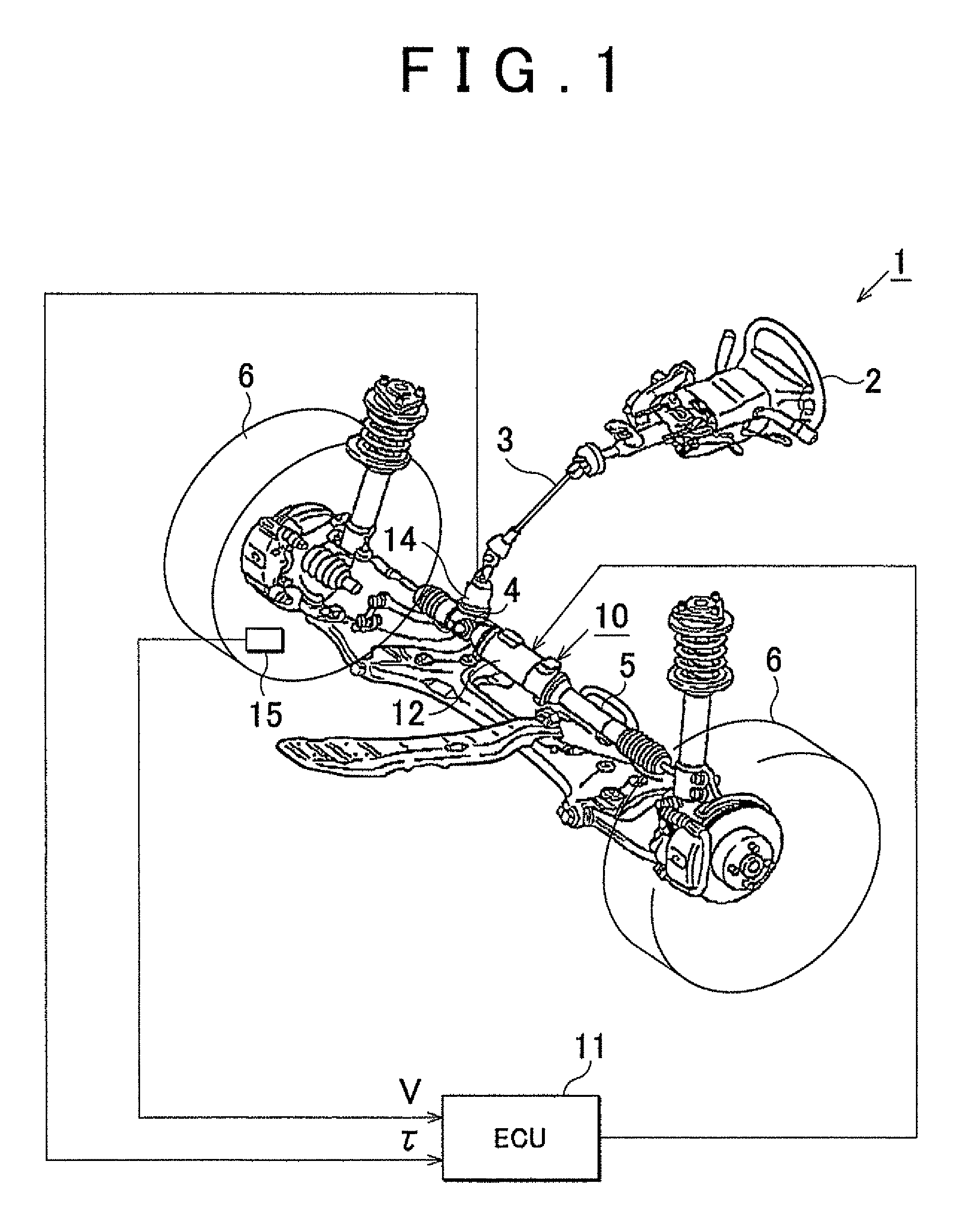
Electric power steering system
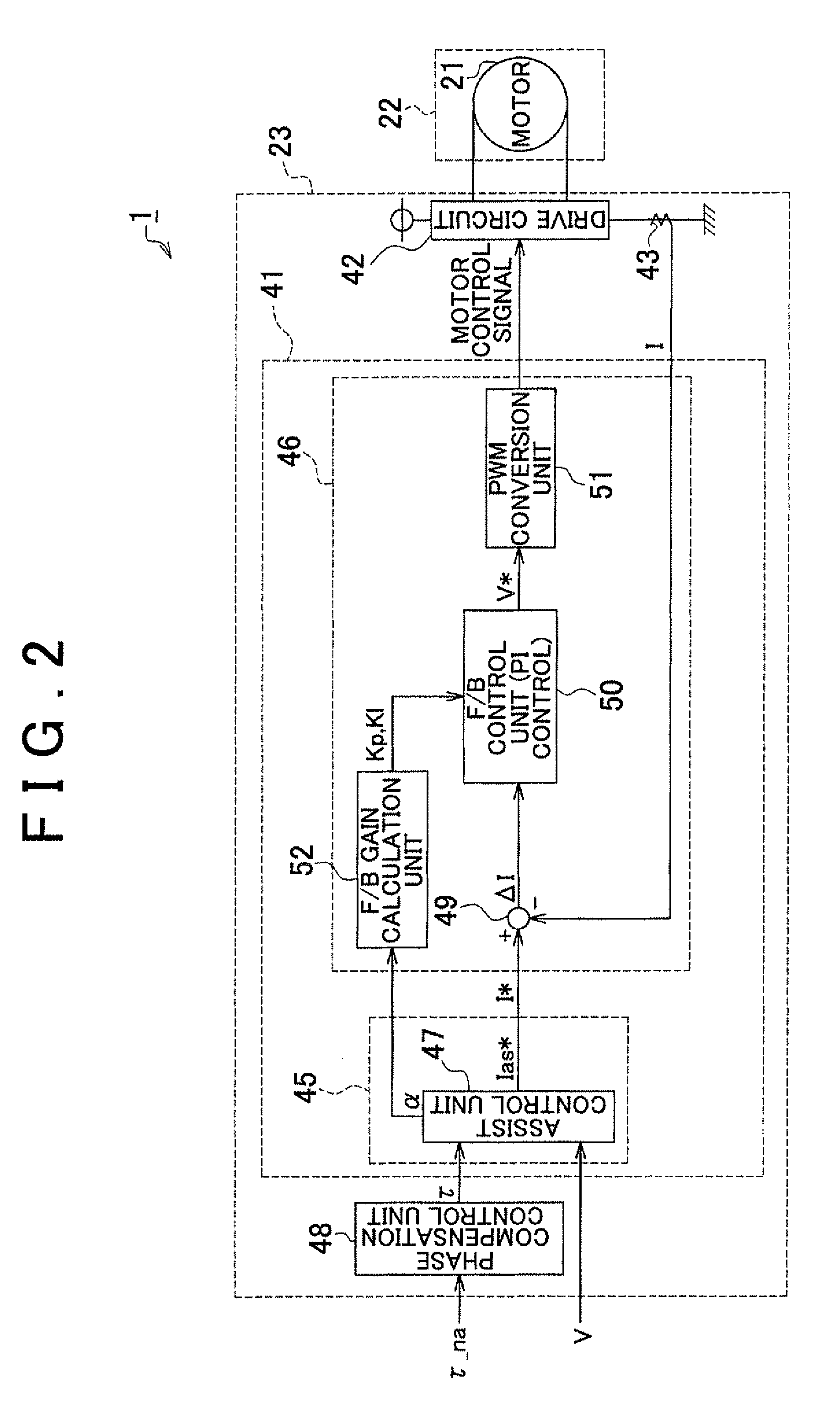
InactiveUS20110010050A1Favorable steering feelingImprove quietnessSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringMotor control
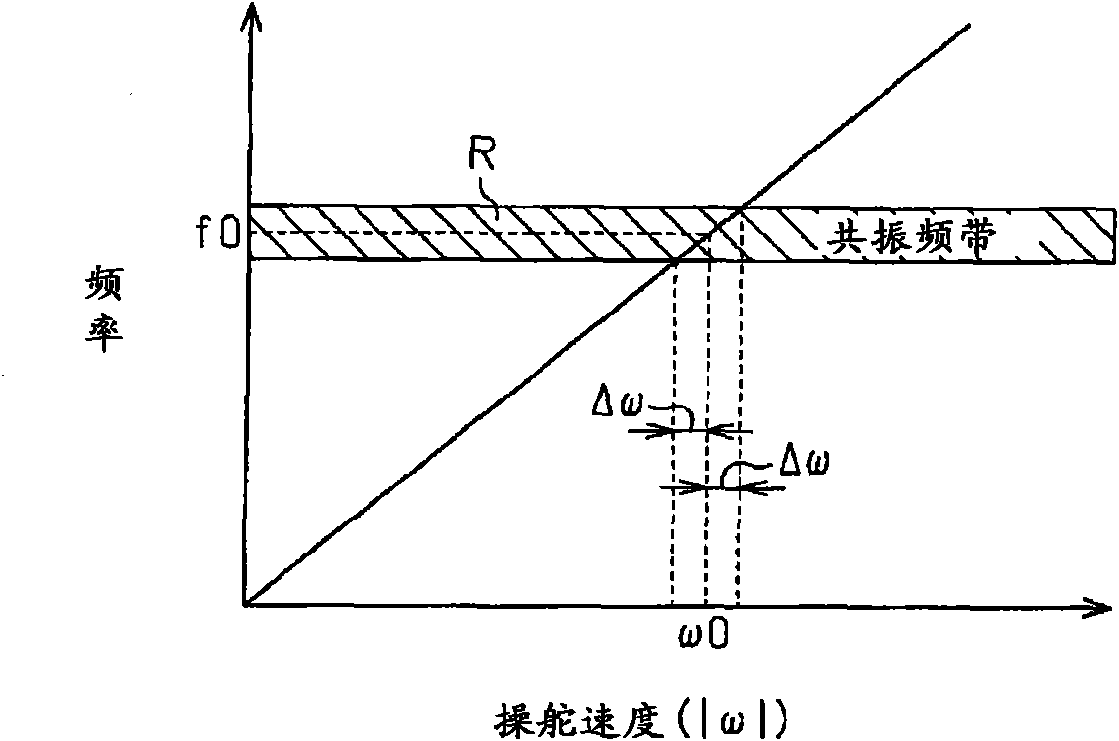
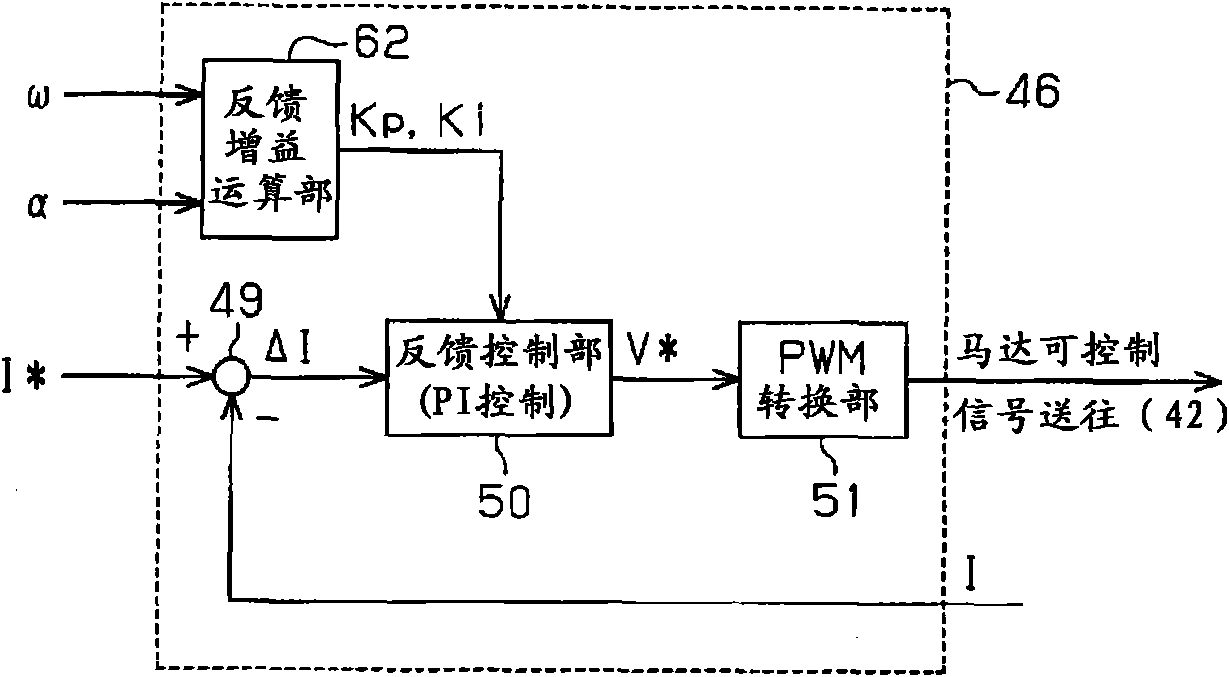
A motor control signal output unit of an electric power steering system includes a feedback gain calculation unit (52), and a feedback control unit executes a feedback control with the use of a proportional gain (Kp) and an integral gain (Ki) that are calculated by the feedback gain calculation unit (52). The feedback gain calculation unit (52) sets the feedback gains to large values (Kp=P0, Ki=I0) when the absolute value of an assist gradient (α) is equal to or smaller than a predetermined value (α0) (|α|≦α0). On the other hand, when the absolute value of the assist gradient (α) exceeds the predetermined value (A) (|α|>α0), the feedback gain calculation unit (52) sets the feedback gains to small values (Kp=p1, Ki=I1:P1<P0, I1<I0).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Electric power steering system
InactiveCN101947973AGood steering feelImprove quietnessSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringControl signal
The invention provides an electric power steering system. A motor control signal output unit of an electric power steering system includes a feedback gain calculation unit (52), and a feedback control unit executes a feedback control with the use of a proportional gain (Kp) and an integral gain (Ki) that are calculated by the feedback gain calculation unit (52). The feedback gain calculation unit (52) sets the feedback gains to large values (Kp=P0, Ki=I0) when the absolute value of an assist gradient ([alpha]) is equal to or smaller than a predetermined value ([alpha]0) (|[alpha]|<=[alpha]0). On the other hand, when the absolute value of the assist gradient ([alpha]) exceeds the predetermined value (A) (|[alpha]|>[alpha]0), the feedback gain calculation unit (52) sets the feedback gains to small values (Kp=p1, Ki=I1:P1<P0, I1<I0).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Clutch for steer-by-wire steering system
InactiveUS20060201733A1Good steering feelSmall fluctuationAnti-theft devicesMechanical steeringFreewheelSteering wheel
A steer-by-wire steering system has a steering wheel actuator and a braking device that acts on the steering column. The braking device is activated when the vehicle steering wheel is to be blocked or at least sharply braked, such as when the steering stop is reached or a wheel goes over the edge of a curb. The braking device functions like a switchable freewheel.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH 50 +1
Electric power steering system
InactiveUS8781682B2Quietness is increasedGood steering feelDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsElectric power steeringElectric machine
A motor control signal output unit of an electric power steering system includes a feedback gain calculation unit (52), and a feedback control unit executes a feedback control with the use of a proportional gain (Kp) and an integral gain (Ki) that are calculated by the feedback gain calculation unit (52). The feedback gain calculation unit (52) sets the feedback gains to large values (Kp=P0, Ki=I0) when the absolute value of an assist gradient (α) is equal to or smaller than a predetermined value (α0) (|α|≦α0). On the other hand, when the absolute value of the assist gradient (α) exceeds the predetermined value (α0) (|α|>α0), the feedback gain calculation unit (52) sets the feedback gains to small values (Kp=p1, Ki=I1:P1<P0, I1<I0).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Electric drive power assisted steering system capable of performing drive ratio variation control by motor and control method thereof
InactiveCN101941459ARealize functionReduce the burden onSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringSteering wheel
The invention discloses an electric drive power assisted steering system capable of performing drive ratio variation control by a motor and a control method thereof. The invention relates to an electric drive power assisted steering system. The steering system comprises a steering wheel, a rack connected with the steering wheel by a steering column, a torque sensor positioned below the steering wheel, a power assisted motor connected with the rack by a reducing mechanism, a steering arm connected with the rack, and an electronic control unit (ECU). The steering system is characterized in that: the steering servo motor is arranged on the steering column between the torque sensor and the rack; and a stator and a rotor of the steering servo motor are respectively connected with the torque sensor and the steering column arranged above the gear rack. The invention is capable of realizing the functions of power assisted steering and active steering, and realizing the perfect integration of vehicle safety and mobility.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
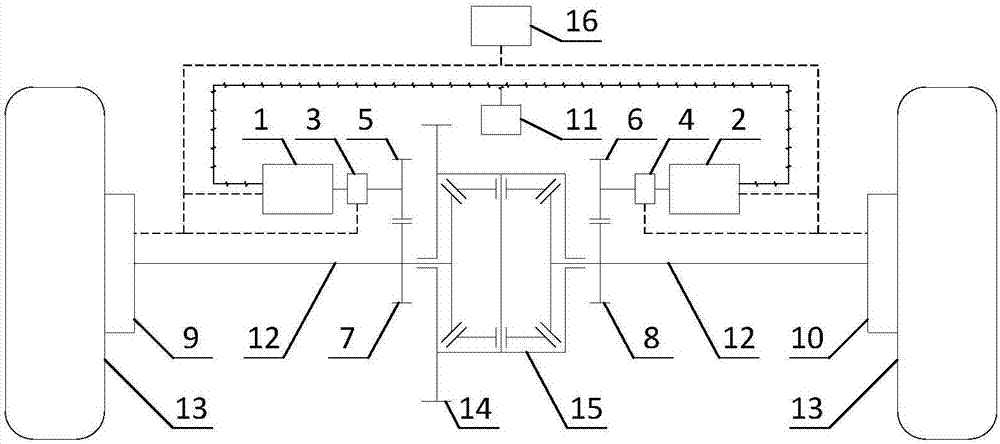
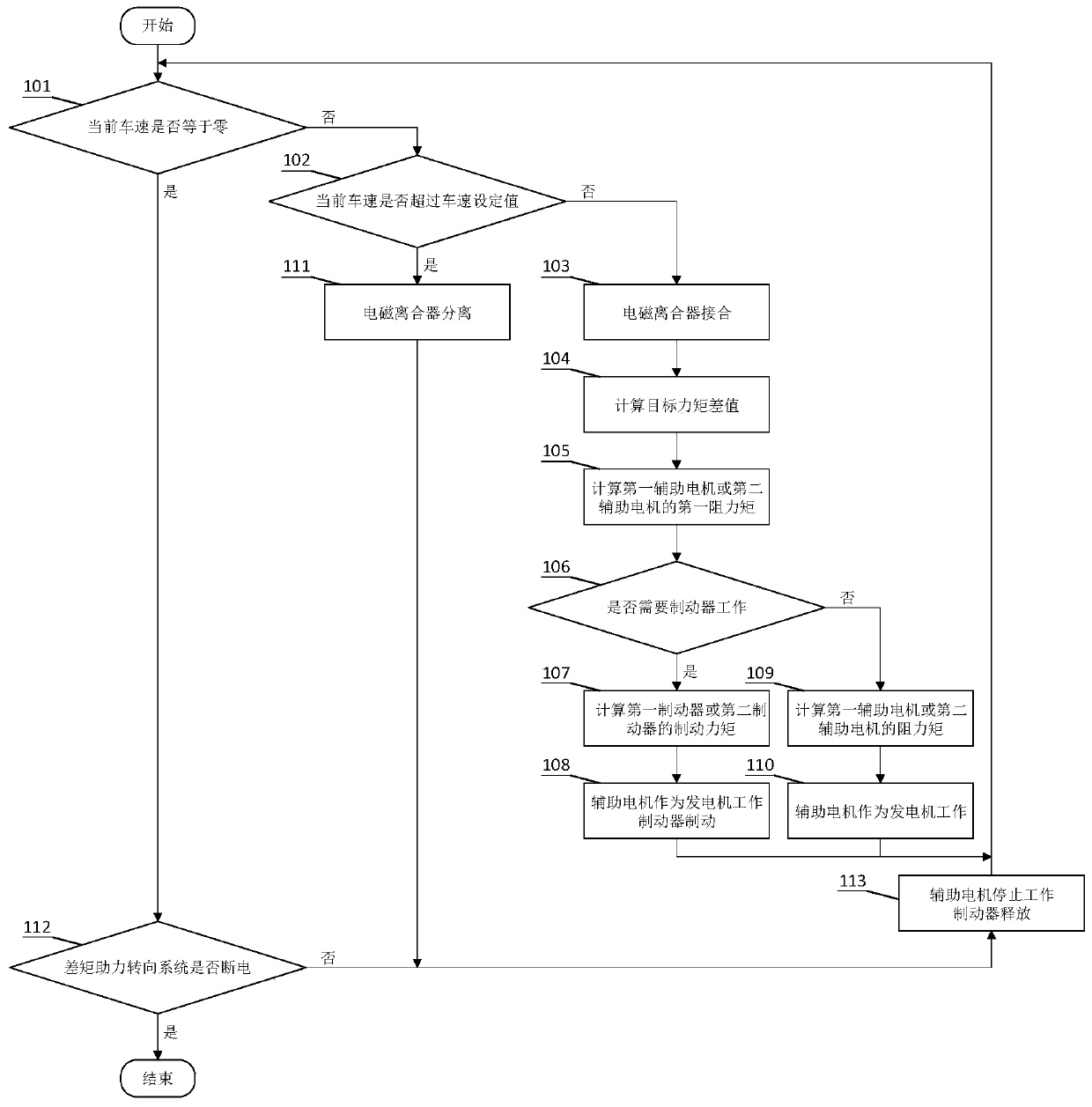
Differential torque power-assisted steering system used for vehicle driving axle and control method of differential torque power-assisted steering system
InactiveCN107117203AAchieve independent controlReduce forceSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlDrive wheelVehicle driving
The invention discloses a differential torque power-assisted steering system used for a vehicle driving axle and a control method of the differential torque power-assisted steering system. A detection mechanism collects steering wheel rotating angle information, steering wheel rotating torque information, wheel speed information, battery voltage information and battery current information, and transmits the information to an electronic control unit; a working mode selection unit allows a driver to select different working modes of the differential torque power-assisted steering system, and transmits the working mode information to the electronic control unit; the electronic control unit controls switching of the working modes and controls an electromagnetic clutch, auxiliary motors and brakes of an execution mechanism to work according to the received information; and the auxiliary motors connected with left and right semi-shafts of the drive axle and the brakes arranged on driving wheels on the left and right sides are utilized, the driving wheels on the left and right sides have different driving torque or braking torque, and the vehicle produces an yaw moment to assist the driver to turn, so that force applied on a steering wheel by the driver is reduced, differential torque power-assisted steering is achieved, and the good steering handing feeling is provided for the driver.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Design method of engineering bridge transport vehicle
ActiveCN101811465ASolve difficult-to-place problemsMeet the requirements of high steering torqueVehicle to carry long loadsOperational systemDriver/operator
The invention relates to a special vehicle for bridge erection and transportation for highways, railways, intercity light rails and the like, and an economically affordable and efficient design method of an engineering bridge transport vehicle. The vehicle at least comprises a front vehicle, a rear vehicle, working devices, a steering system, a transmission system, a hanging system, an anti-overturn bridge, a brake system, an anti-overturn bridge connecting seat, a frame, an operation platform and a connecting piece thereof, and is characterized in that the front vehicle and the rear vehicle are respectively connected with the front part and the rear part of the same bridge via respective working devices, the operation platform is provided with a two-way operation system, and the driver can drive the vehicle forwards or reversely according to different needs so as to make the vehicle driven out of a roadbed quickly after unloading the bridge. The invention can fully meet the technology of bridge transportation construction.
Owner:SHAANXI TONLY HEAVY IND
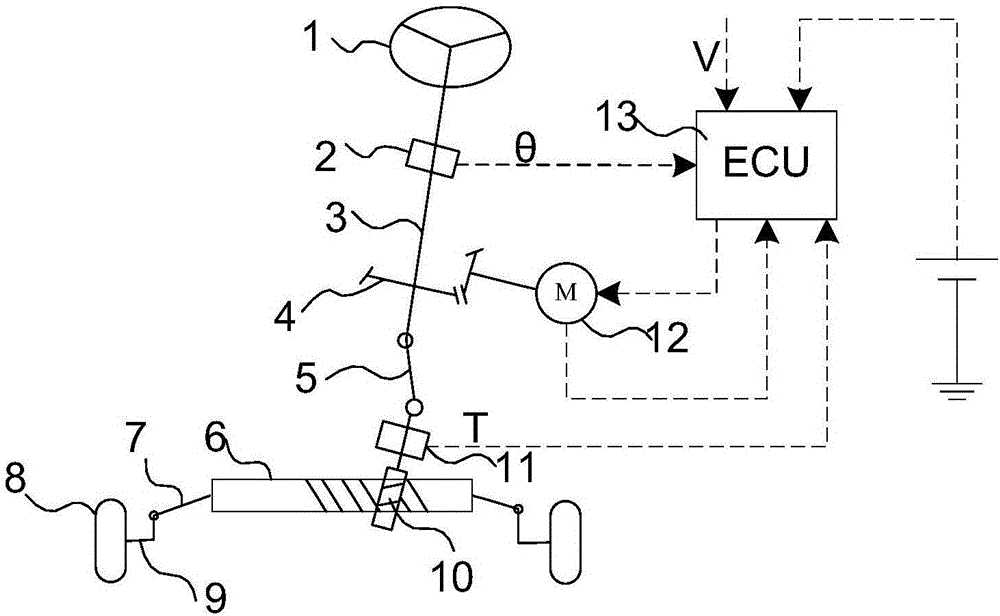
Torque compensation method of power-assisted steering system
InactiveCN107433976AWith frequency gainIt has the function of phase frequency compensationElectrical steeringFrequency compensationSteering wheel
The invention discloses a torque compensation method of a power-assisted steering system. The power-assisted steering system includes a mechanical steering system and an electronic control unit, the input end of the electronic control unit is connected with a torque sensor, and the output end of the electronic control unit is connected with a mechanical steering system through a power-assisted steering motor and a reducing mechanism, wherein the electronic control unit adopts a fourth-order torque compensation method, a steering wheel original torque input signal is input, torque compensation is conducted by adjusting the filtering parameter, and a compensated torque signal is output. According to the torque compensation method of the power-assisted steering system, a fourth-order torque compensator is used for replacing a second-order torque compensator, and the fourth-order torque compensator is also a lead-lag filter, has the amplitude-frequency gaining and phase frequency compensation functions and is more flexible to use; through parameter adjustment, the system can possess various characteristics at the same time, and a better steering feeling is thus obtained.
Owner:上海拿森汽车电子有限公司
Pulse torque method of permanent-magnet synchronous motor for lowering electric power steering
InactiveCN107433978AHigh precisionGood steering feelTorque ripple controlElectrical steeringElectric power steeringSynchronous motor
The invention discloses a pulse torque method of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor for lowering electric power steering. The method comprises the following steps of a, obtaining a tooth groove rotary angle according to an electric rotor angle, and estimating tooth groove torque of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor; b, obtaining a flux harmonic rotary angle according to the electric rotor angle, and estimating flux harmonic torque of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor; c, weakening periodic pulse torque caused by a tooth groove and flux harmonic waves through an iterative control algorithm. Through the iterative learning control algorithm, the periodic pulse torque caused by the tooth groove and the flux harmonic waves is weakened, and the precision of motor controlling is improved, so that an EPS system obtains a better steering hand feeling.
Owner:上海拿森汽车电子有限公司
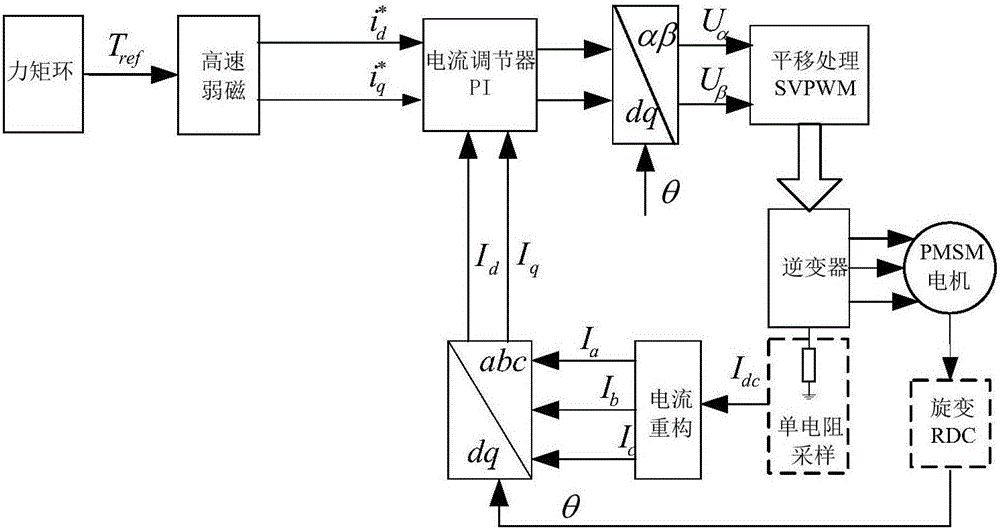
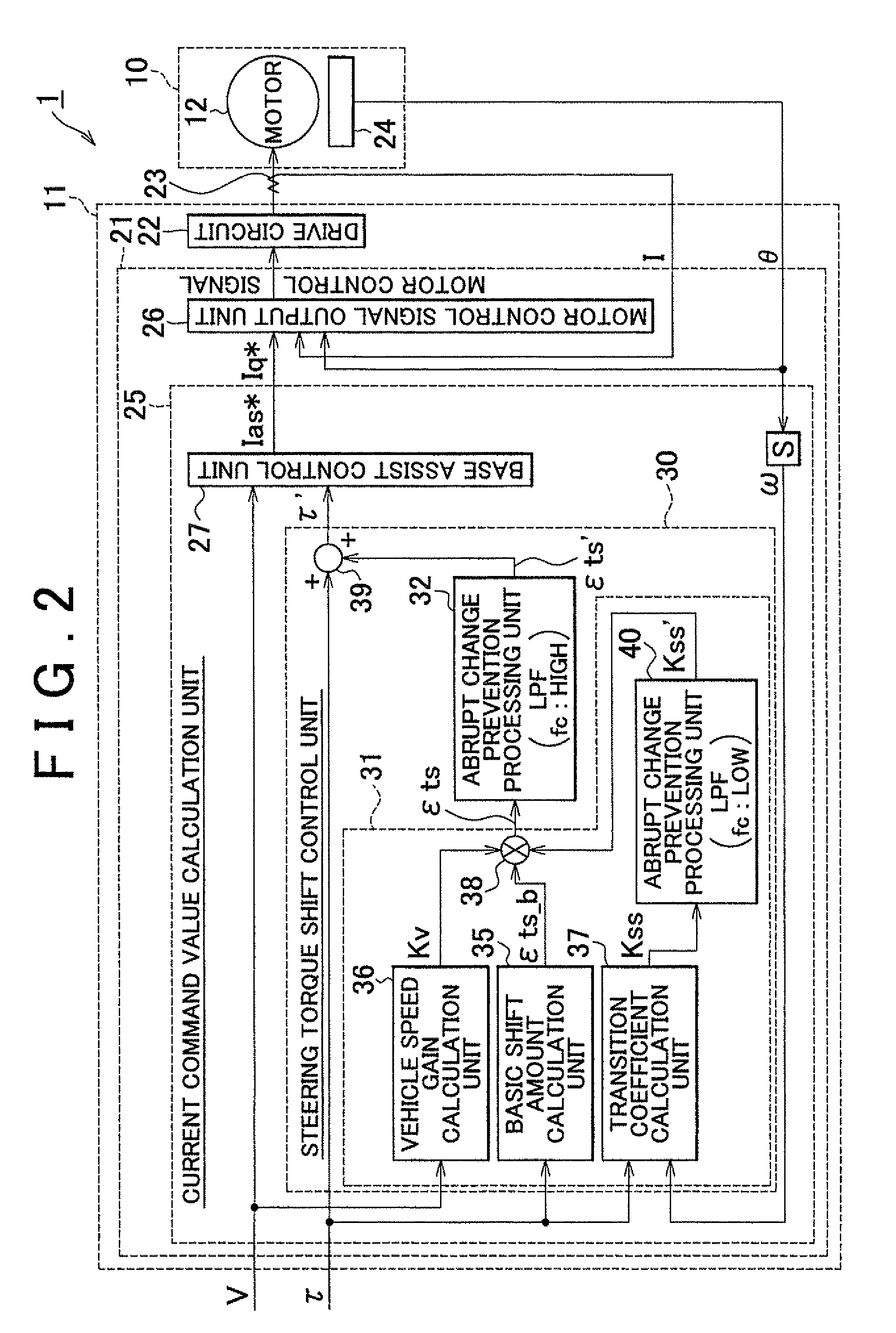
Electric power steering system
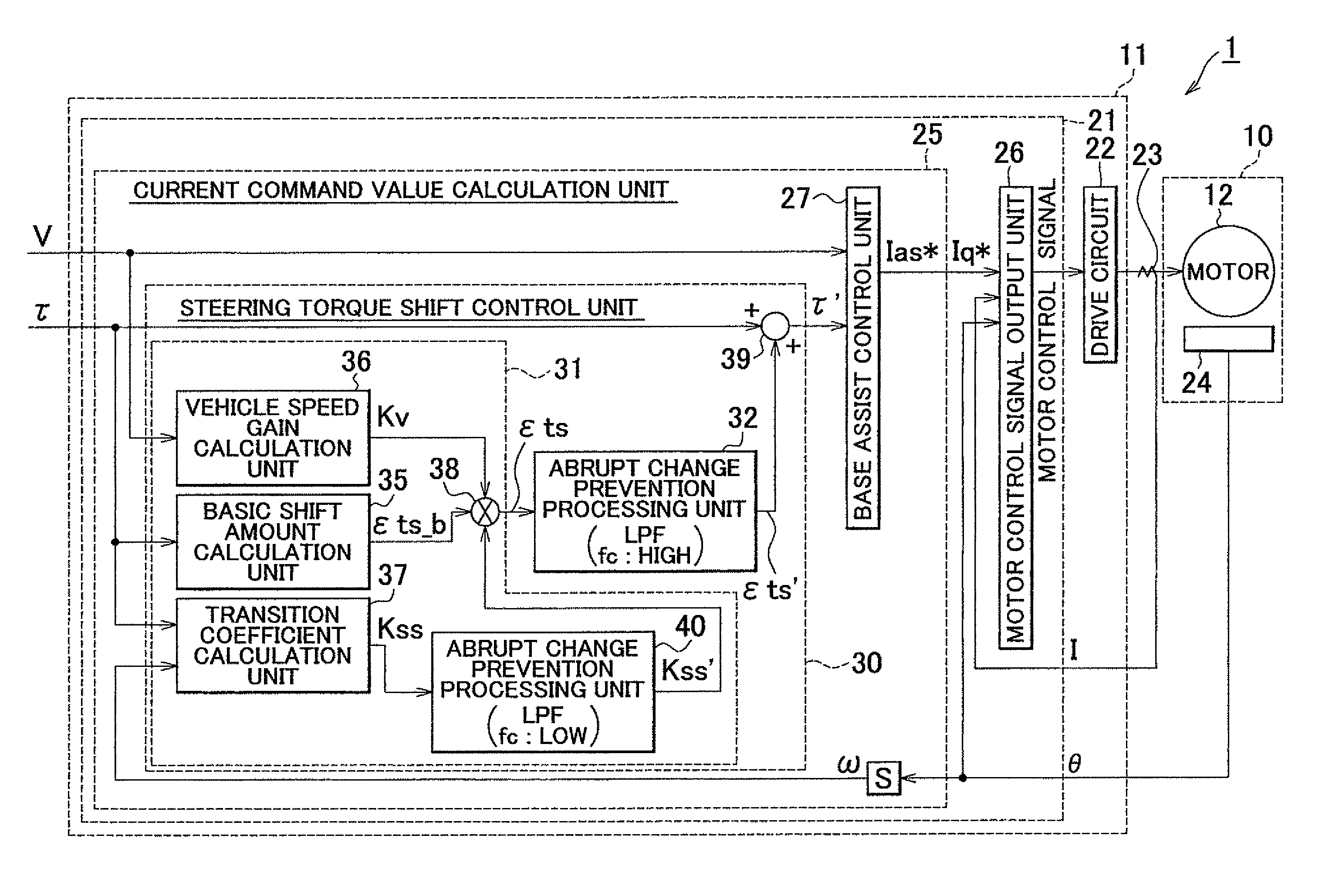
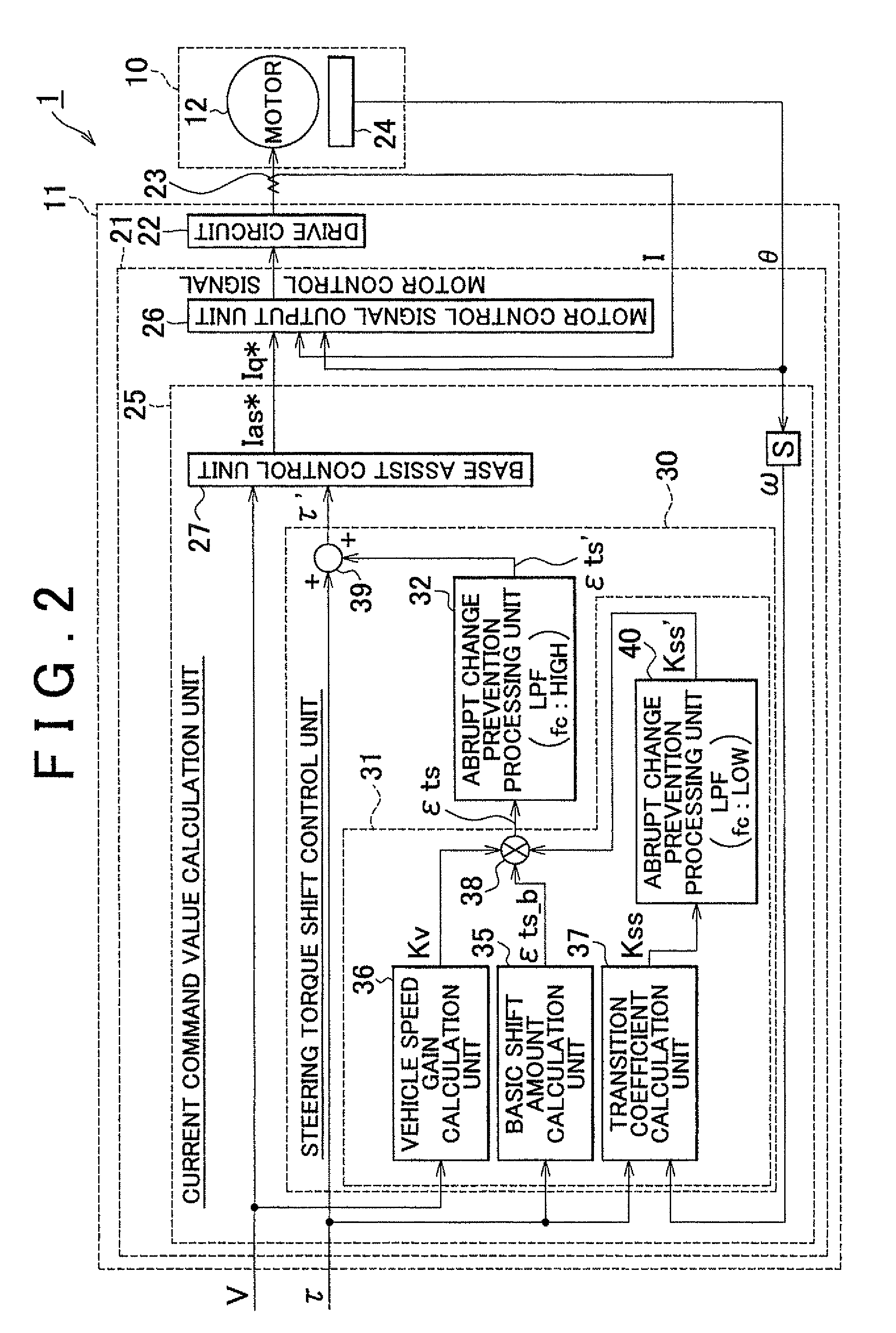
ActiveUS20100324783A1Suppression of drastic changesGood steering feelSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringLow-pass filter
A steering torque shift control amount calculation unit (31) calculates the steering torque shift control amount (εts) by multiplying the basic shift amount (εts_b) used as the basic compensation component by the transition coefficient (Kss). Then, the steering torque shift control amount (εts) is subjected to the low-pass filter process in an abrupt change prevention processing unit (32). An abrupt change prevention processing unit (40) is provided in the steering torque shift control amount calculation unit (31). The transition coefficient (Kss) is subjected to the low-pass filter process in the abrupt change prevention processing unit (40). The cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter that forms the abrupt change prevention processing unit (40) is set to a value lower than the cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter that forms the abrupt change prevention processing unit (32) that executes the low-pass filter process on the torque shift control amount (εts).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Electric power steering system
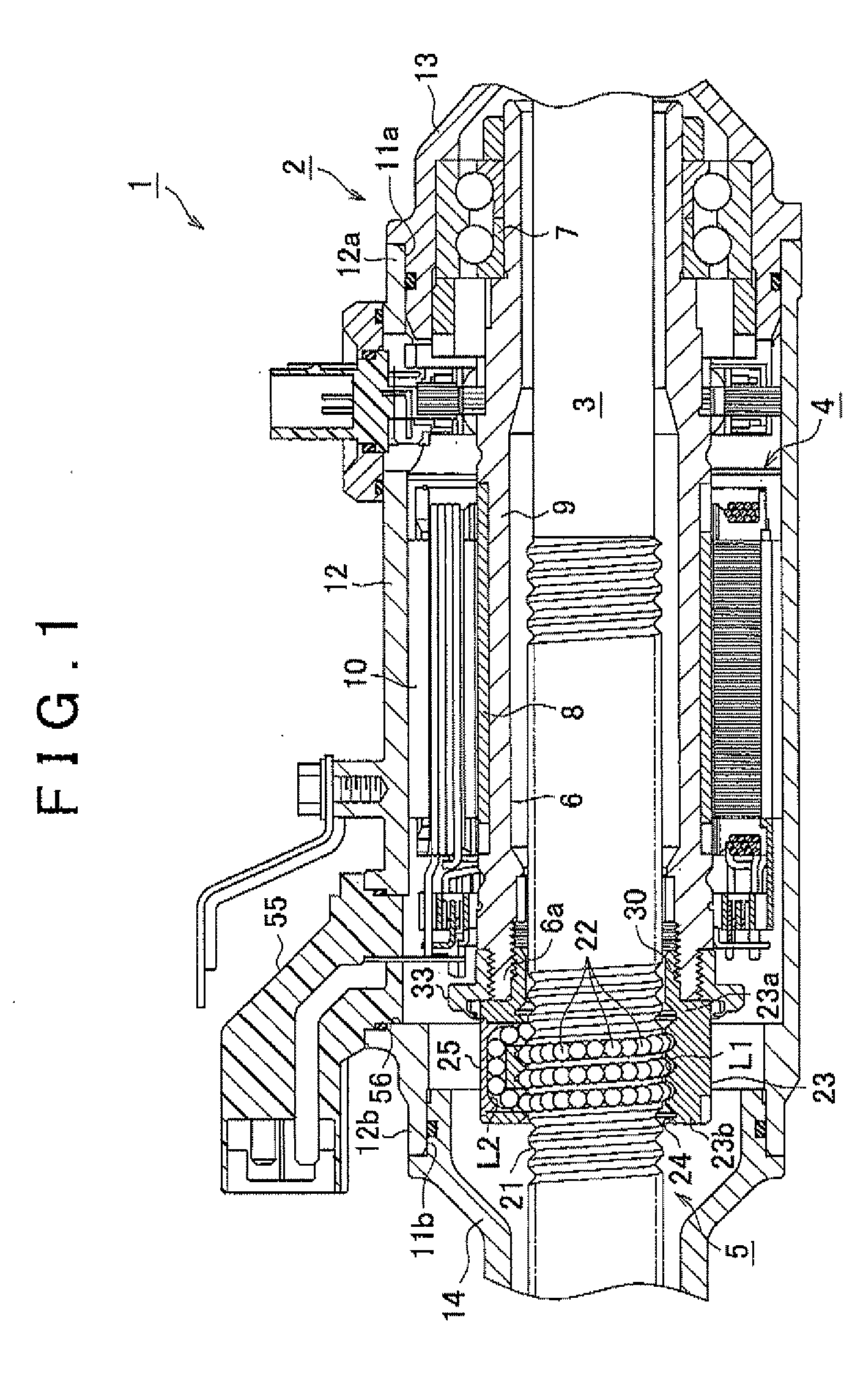
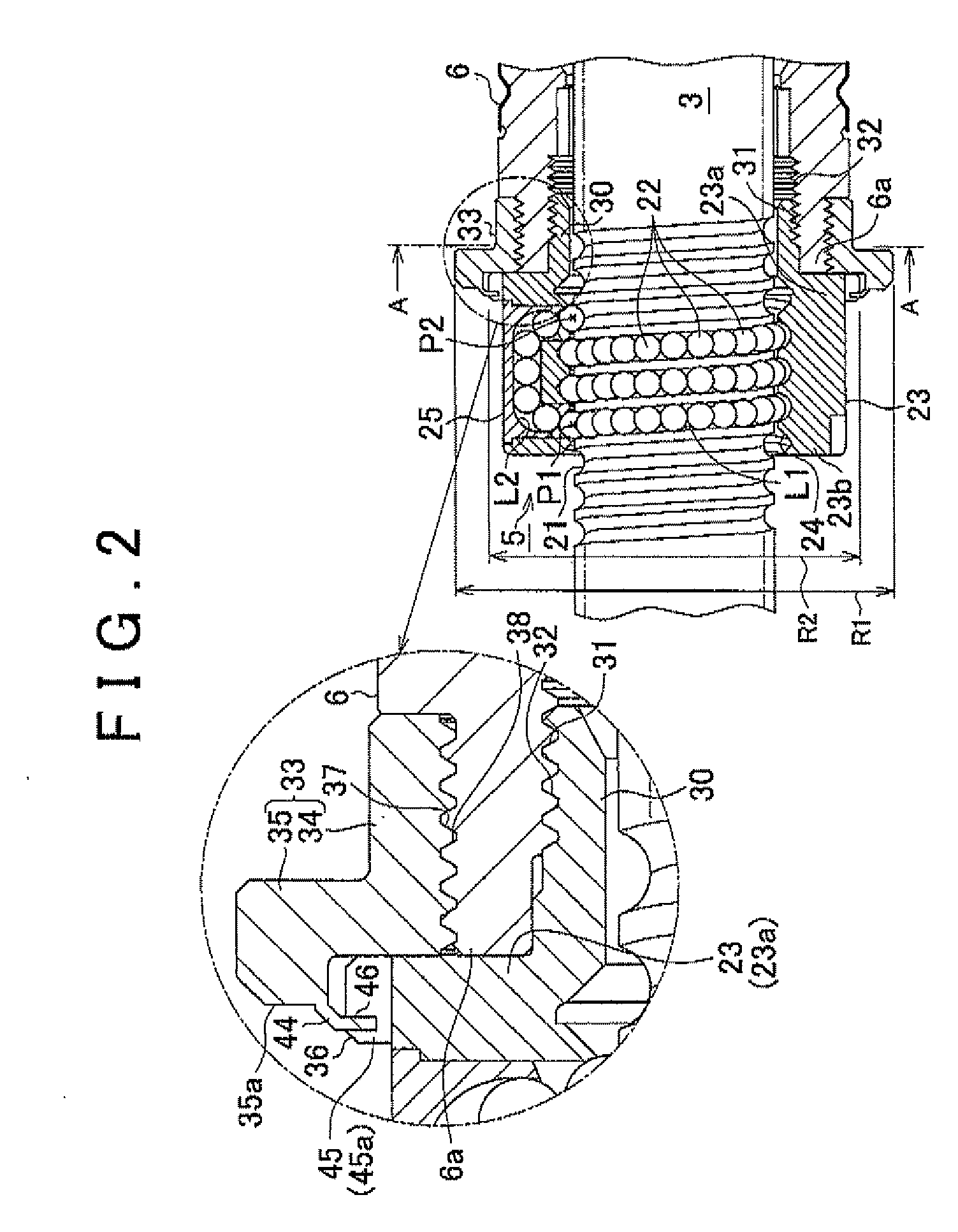
InactiveUS20110048838A1Improve reliabilitySufficient quietnessElectrical steeringElectric power steeringElectric power system
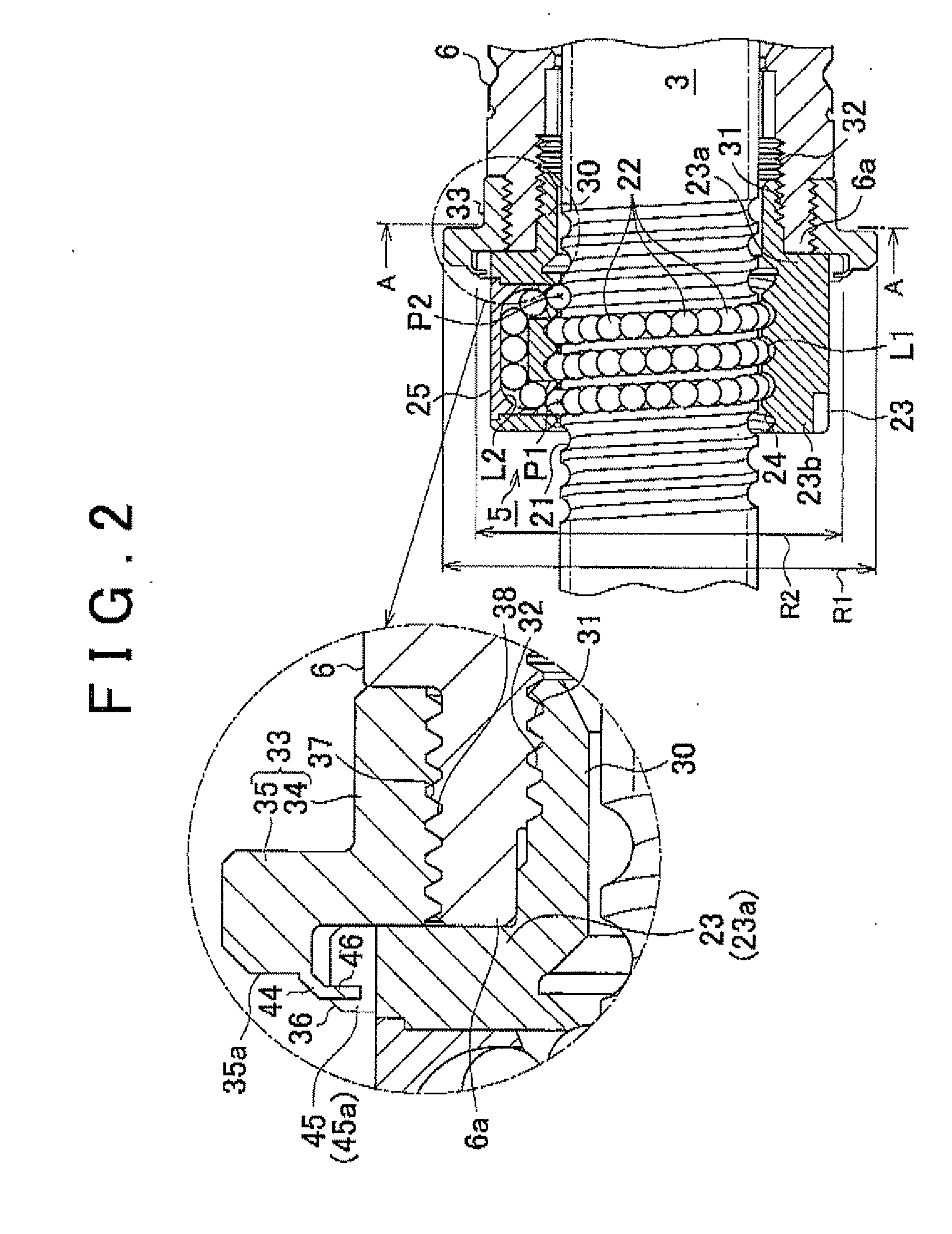
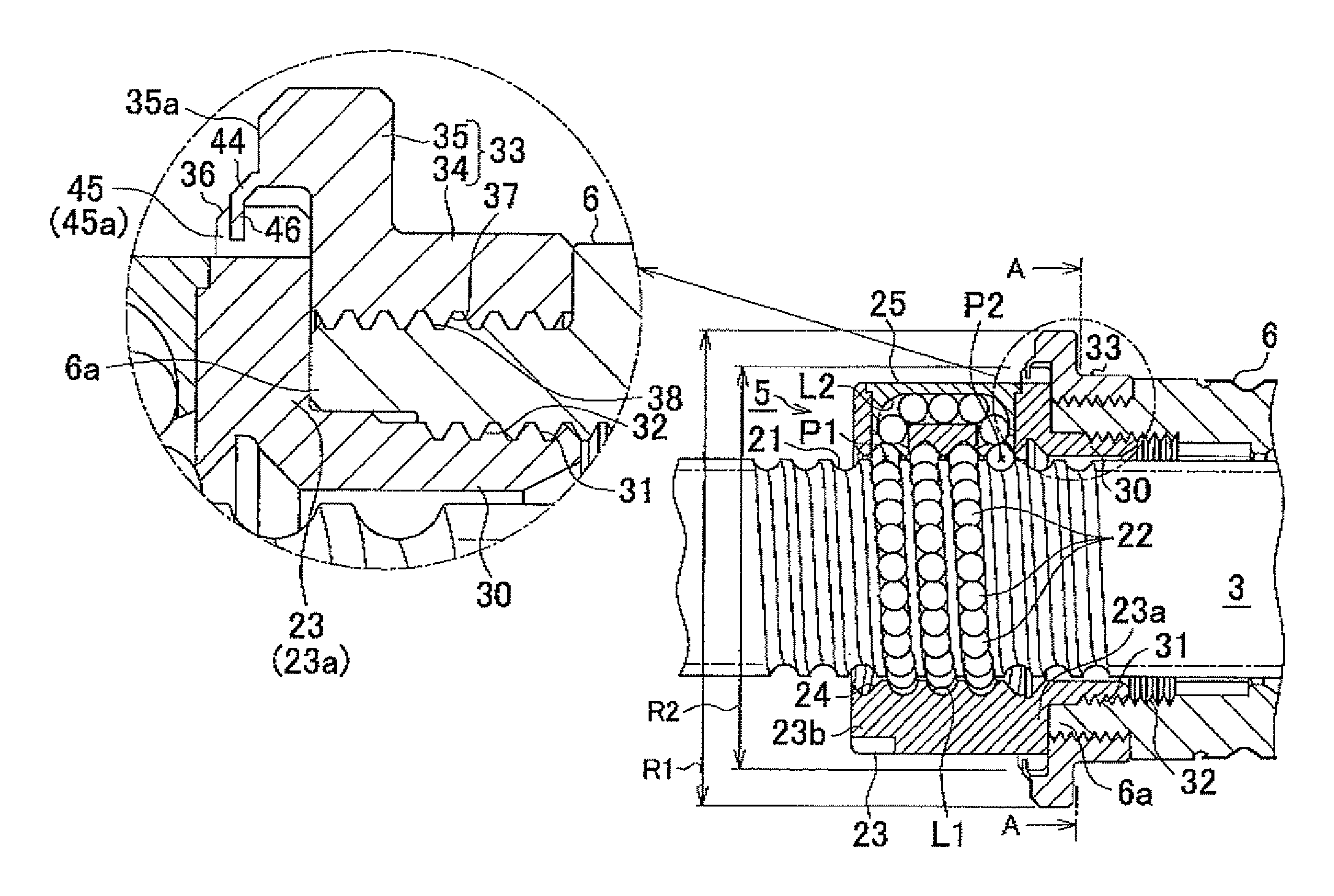
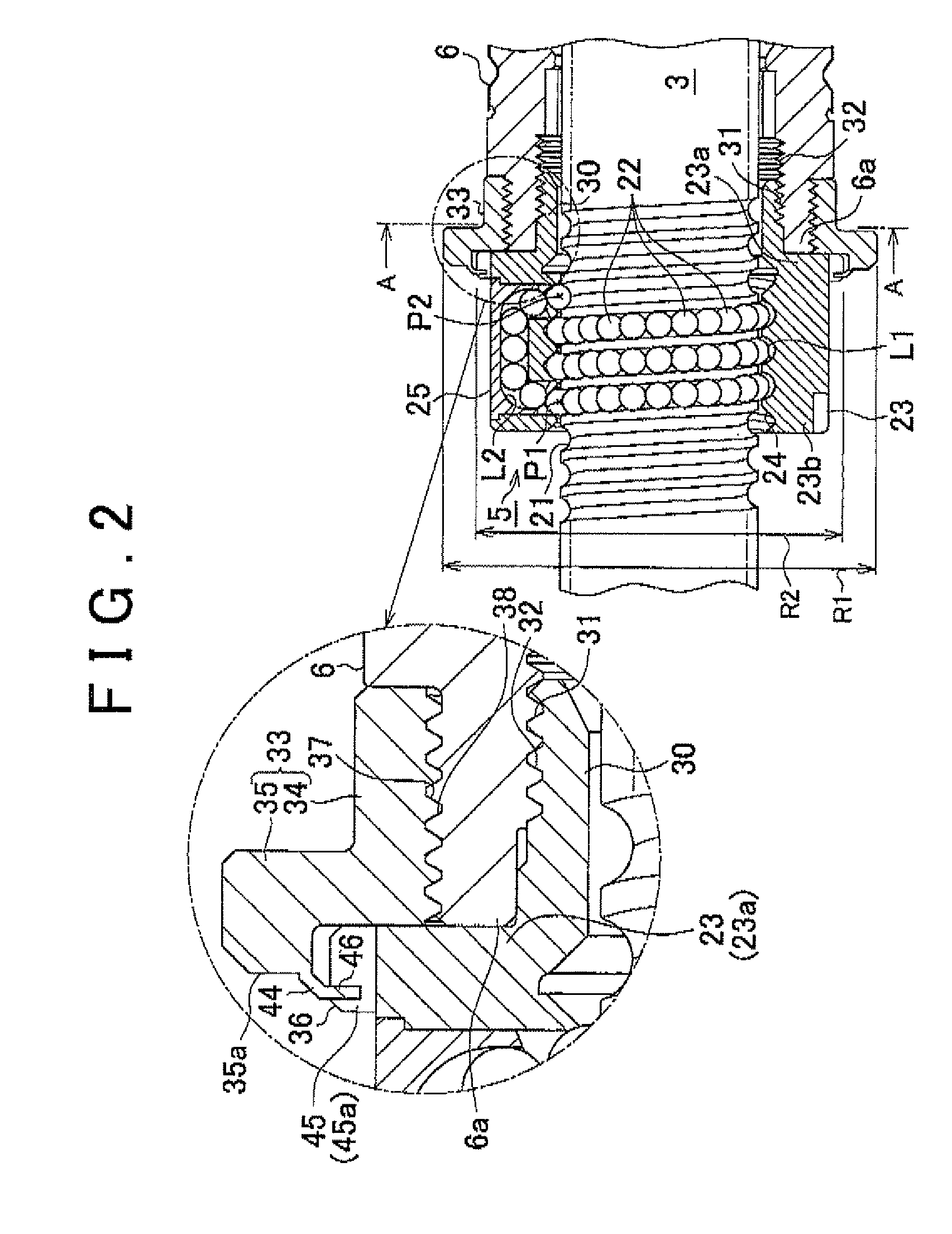
In an electric power steering system, multiple cutouts (45) are formed in a flange portion (36) formed on an axial end portion (23a) of a ball screw nut (23) of a ball screw device that drives a rack shaft. In addition, a motor shaft (6) has a thin-plate portion (44) that extends on the radially outer side of the ball screw nut (23). When the thin-plate portion (44) that extends from the motor shaft (6) is swaged into the cutouts (45) that serve as engagement recesses that have side walls in the circumferential direction, the rotation of the ball screw nut (23) relative to the motor shaft (6) is restricted.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
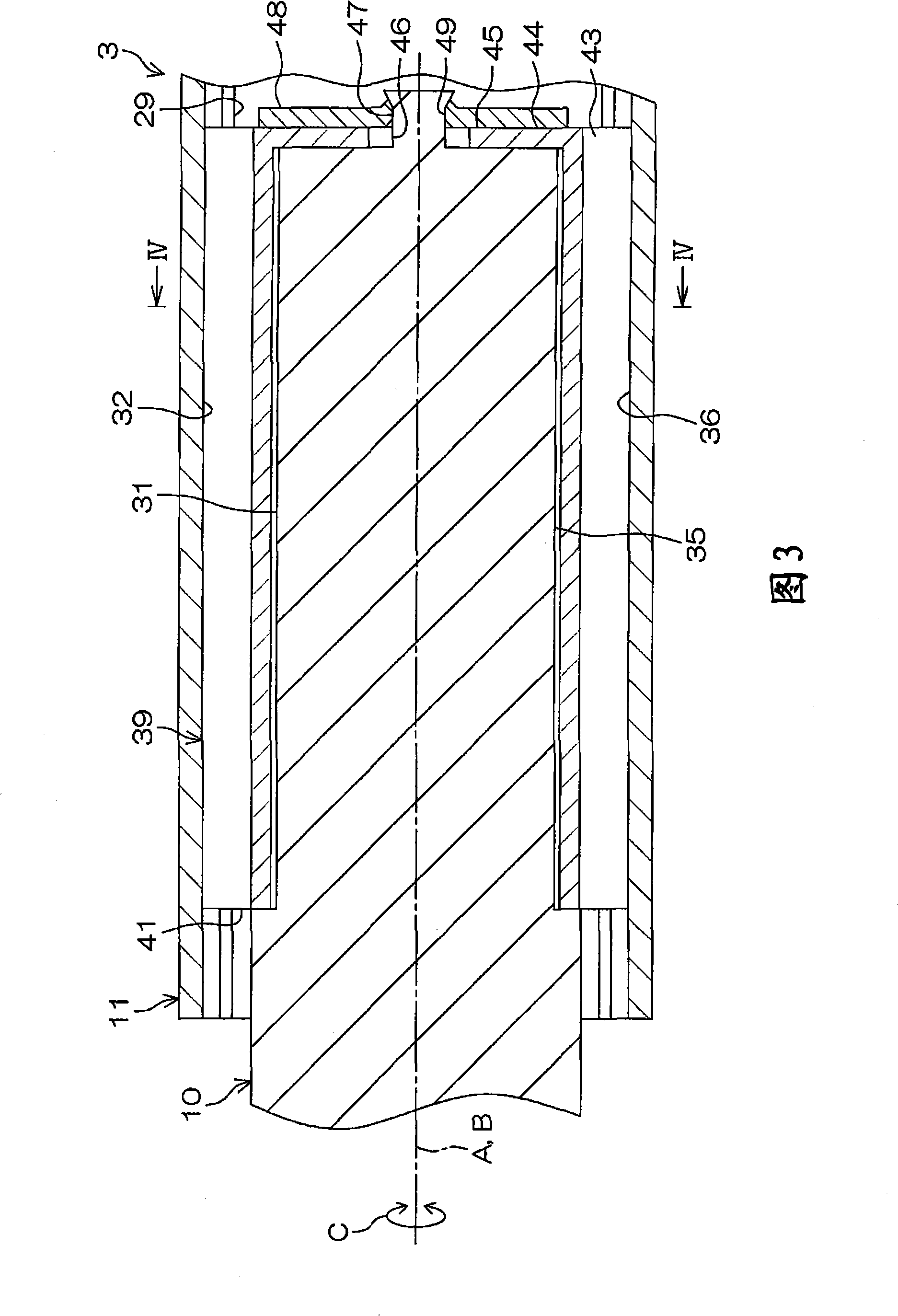
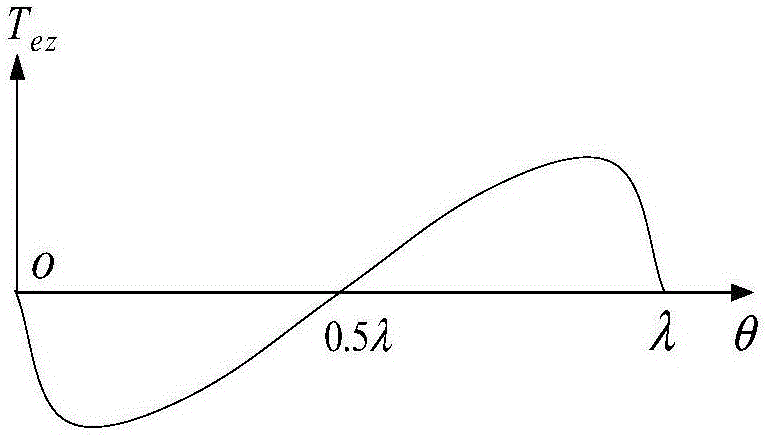
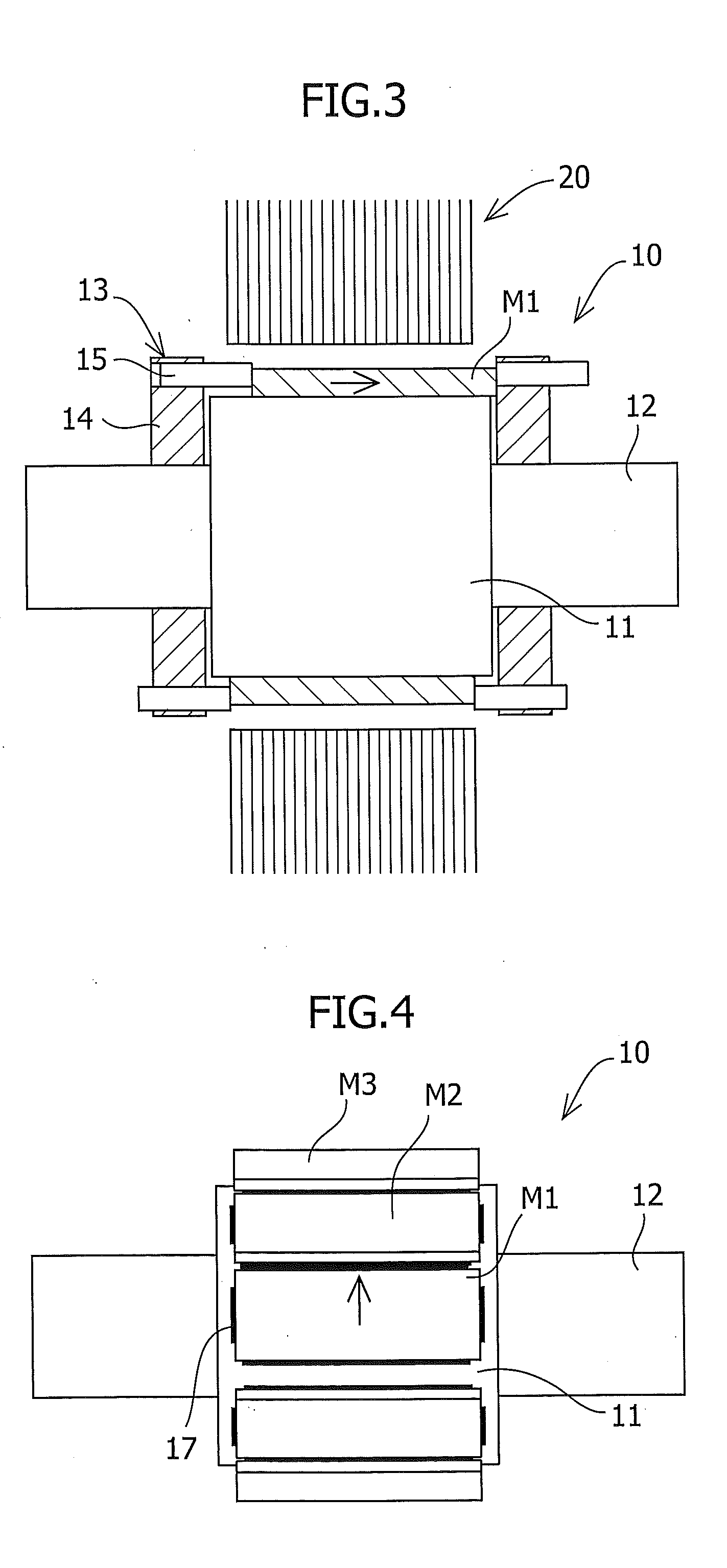
Permanent magnet motor with magnets in an adjusted position to reduce cogging torque
InactiveUS7948136B2Reduce the cogging torque of servomotorsImprove accuracyMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric power steeringMagnetic poles
To reduce the cogging torque of servomotors, electric power steering motors, and others, there is provided a permanent magnet motor comprising: a rotor 10 comprising a rotor yoke 11 and a plurality of permanent magnets (M1-M10); and a stator 20 comprising a stator yoke 22, salient magnetic poles 21, and armature windings 23, wherein at least one of the permanent magnets is disposed in an adjustment position that is displaced from a corresponding reference position in at least one of the circumferential, radial, and axial directions of the rotor yoke, and the plurality of permanent magnets excluding the permanent magnet disposed in the adjustment position is disposed in the reference positions, and wherein the adjustment position is set so that the permanent magnet motor in which at least one of the plurality of permanent magnets is disposed in the adjustment position has a smaller cogging torque than a permanent magnet motor in which all of the plurality of permanent magnets are disposed in the reference positions; and a method for adjusting a cogging torque of a permanent magnet motor.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Vehicle control apparatus
ActiveUS8082079B2Avoid it happening againGood steering feelPower operated startersDigital data processing detailsEngineeringLimit value
In a case where an engine ECU determines that the engine is started (restarted), the engine ECU notifies an EPSECU that cranking is to be performed to start the engine before performing the cranking. When such a notification is received, the EPSECU gradually reduces a current command limit value I*_lim and a boost voltage limit value Vbp_lim before the cranking is started.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Method of making a motor with reduced cogging torque
ActiveUS20110192018A1Reduce vibrationReduce the cogging torque of servomotorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectronic circuit testingElectric power steeringElectric machine
To reduce the cogging torque of servomotors, electric power steering motors, and others, there is provided a permanent magnet motor comprising: a rotor 10 comprising a rotor yoke 11 and a plurality of permanent magnets (M1-M10); and a stator 20 comprising a stator yoke 22, salient magnetic poles 21, and armature windings 23, wherein at least one of the permanent magnets is disposed in an adjustment position that is displaced from a corresponding reference position in at least one of the circumferential, radial, and axial directions of the rotor yoke, and the plurality of permanent magnets excluding the permanent magnet disposed in the adjustment position is disposed in the reference positions, and wherein the adjustment position is set so that the permanent magnet motor in which at least one of the plurality of permanent magnets is disposed in the adjustment position has a smaller cogging torque than a permanent magnet motor in which all of the plurality of permanent magnets are disposed in the reference positions; and a method for adjusting a cogging torque of a permanent magnet motor.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Electric power steering system
InactiveUS20110048839A1Improve reliabilitySufficient quietnessElectrical steeringElectric power steeringEngineering
In an electric power steering system, a ball screw nut (23) of a ball screw device that drives a rack shaft is screwed to an axial end portion (6a) of a motor shaft (6) when a threaded portion (31) of a hollow threaded shaft (30) formed at an axial end portion (23a) of the ball screw nut (23) is screwed to a threaded portion (32) formed in the inner periphery of a motor shaft (6). A flange member (33) that is larger in diameter than the ball screw nut (23) is fitted to the outer periphery of the axial end portion (6a) of the motor shaft (6). The flange member (33) is formed in such a manner that when the rotation of the flange member (33) is restricted, the rotation of the ball screw nut (23) and the motor shaft (6) in the same direction is restricted when the ball screw nut (23) is screwed to the motor shaft (6).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Electric power-steering device
InactiveCN106470889AEasing the limitation of correction signalNo sense of incongruitySteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringSteering angle
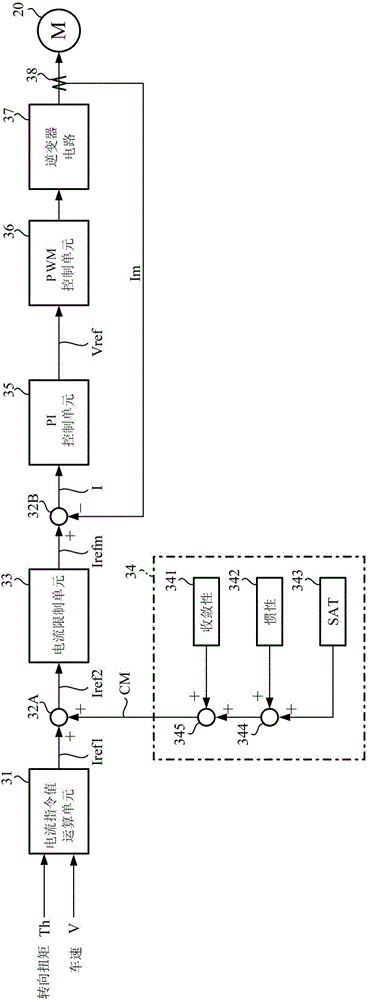
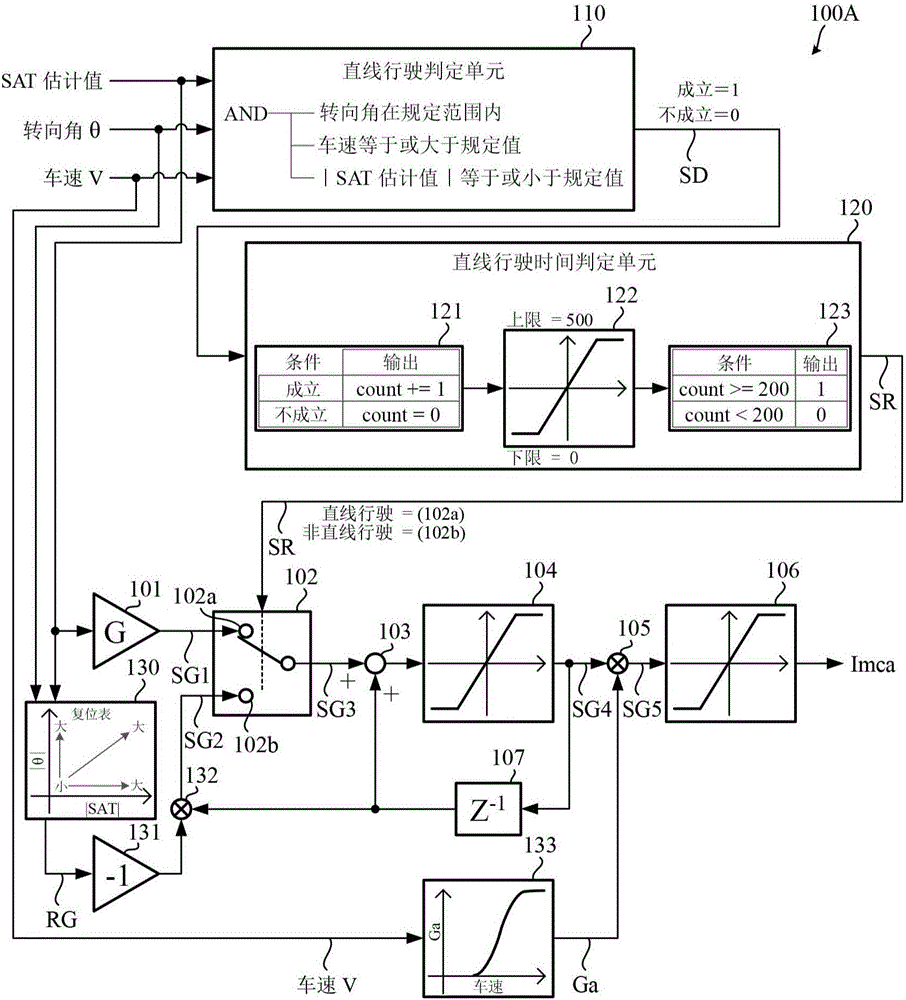
The invention provides a safe electric power-steering device that produces a good steering feel, has the ability to disengage steering-wander suppression or steering-pull suppression, and produces an increased driver-burden reduction effect during steering wander or steering pull. [Solution] A motor-current correction-value computation unit that uses a motor-current correction value based on a motor correction signal to correct a current command value comprises the following: a straight-line-movement determination unit (110, 120) that determines whether a vehicle is moving in a straight line; an adaptive calculation unit that calculates the aforementioned motor correction signal (SG4) in accordance with the result of the straight-line-movement determination, a steering angle (theta), and an applied force (SAT estimate), at least, and outputs said motor correction signal (SG4); a vehicle-speed-sensitive gain unit (133) that outputs a vehicle-speed gain (Ga) that depends on the speed (V) of the vehicle; and an output calculation unit (105, 106) that multiples the motor correction signal (SG4) by the vehicle-speed gain (Ga) and outputs a motor-current correction value (Imc). The motor-current correction-value computation unit also has the ability to set thresholds for the motor correction signal and steering information and disengage steering-wander suppression or steering-pull suppression depending on the result of a condition determination performed on said motor correction signal and steering information and said thresholds.
Owner:NSK LTD
Electric power steering system
InactiveUS8397859B2Improve reliabilitySufficient quietnessElectrical steeringElectric power steeringEngineering
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Torque control method and system for electric power-assisted transport vehicle
InactiveCN111017005ASolve the complex calculation processIncrease variabilityElectrical steeringLow speedSteering wheel
The invention relates to a torque control method and system for an electric power-assisted transport vehicle. When the vehicle steers, the torque of a steering wheel is detected, a signal is transmitted to a controller, the controller correspondingly controls the motor after analysis and processing, and the torque output by the motor is transmitted to a gear and rack steering gear through a speedreducing mechanism and finally output to a turning wheel through a transmission shaft. Specifically, a linear power-assisted characteristic curve is adopted and comprises three areas, namely, a non-power-assisted area, a power-assisted change area and a power-assisted constant area; when the vehicle is parked, steered at a low speed or steered during medium-high speed driving, the running speed ofthe vehicle is detected by a running speed sensor, the detected signals are transmitted to the control unit to have corresponding assistance characteristics, and different assistance currents are applied to the motor to change the rotating speed of the motor, so that the variability of the torque during steering is achieved, and good steering control road feel is guaranteed. The problem that an existing torque control method is complex in calculation is solved.
Owner:HENAN BENMA
A differential torque power steering system for automobile drive axle and its control method
InactiveCN107117203BAchieve independent controlReduce forceSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlDrive wheelDriver/operator
The invention discloses a differential torque power-assisted steering system used for a vehicle driving axle and a control method of the differential torque power-assisted steering system. A detection mechanism collects steering wheel rotating angle information, steering wheel rotating torque information, wheel speed information, battery voltage information and battery current information, and transmits the information to an electronic control unit; a working mode selection unit allows a driver to select different working modes of the differential torque power-assisted steering system, and transmits the working mode information to the electronic control unit; the electronic control unit controls switching of the working modes and controls an electromagnetic clutch, auxiliary motors and brakes of an execution mechanism to work according to the received information; and the auxiliary motors connected with left and right semi-shafts of the drive axle and the brakes arranged on driving wheels on the left and right sides are utilized, the driving wheels on the left and right sides have different driving torque or braking torque, and the vehicle produces an yaw moment to assist the driver to turn, so that force applied on a steering wheel by the driver is reduced, differential torque power-assisted steering is achieved, and the good steering handing feeling is provided for the driver.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Electric power steering system
ActiveUS8560174B2Good steering feelSuppression of drastic changesSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringLow-pass filter
A steering torque shift control amount calculation unit (31) calculates the steering torque shift control amount (εts) by multiplying the basic shift amount (εts_b) used as the basic compensation component by the transition coefficient (Kss). Then, the steering torque shift control amount (εts) is subjected to the low-pass filter process in an abrupt change prevention processing unit (32). An abrupt change prevention processing unit (40) is provided in the steering torque shift control amount calculation unit (31). The transition coefficient (Kss) is subjected to the low-pass filter process in the abrupt change prevention processing unit (40). The cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter that forms the abrupt change prevention processing unit (40) is set to a value lower than the cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter that forms the abrupt change prevention processing unit (32) that executes the low-pass filter process on the torque shift control amount (εts).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com