Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Data rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
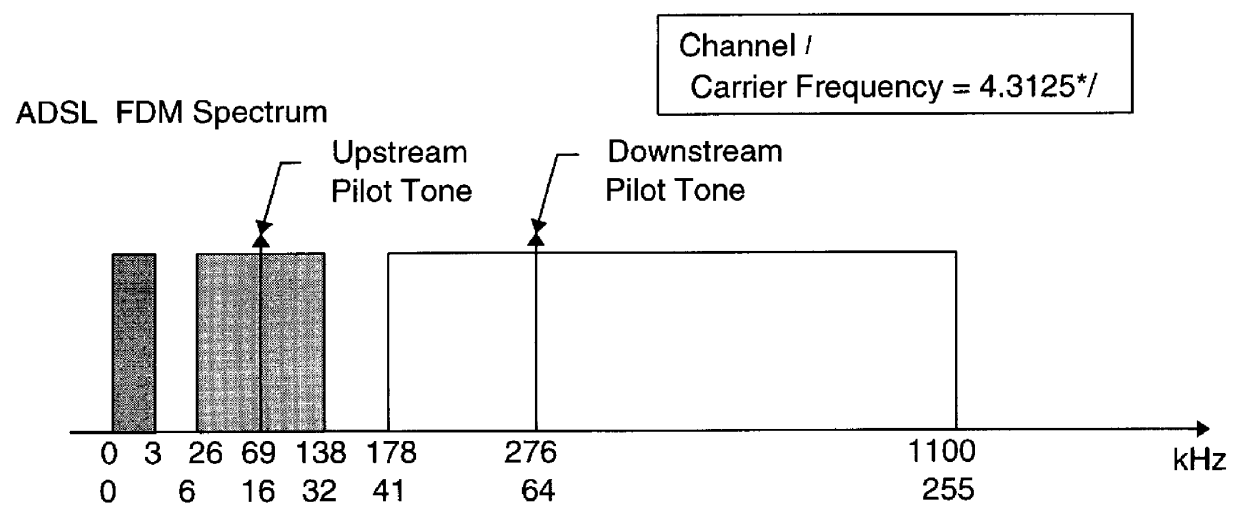
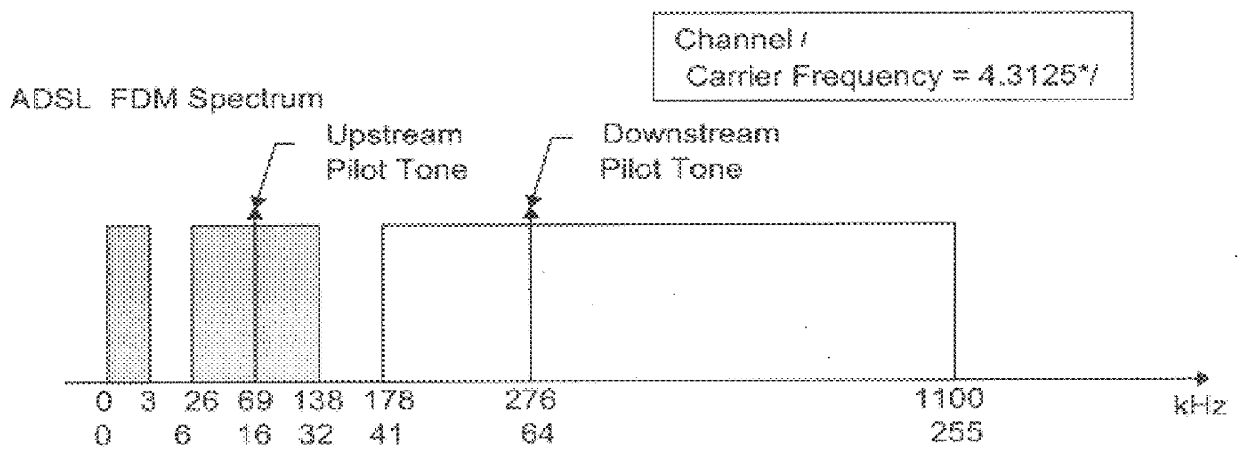
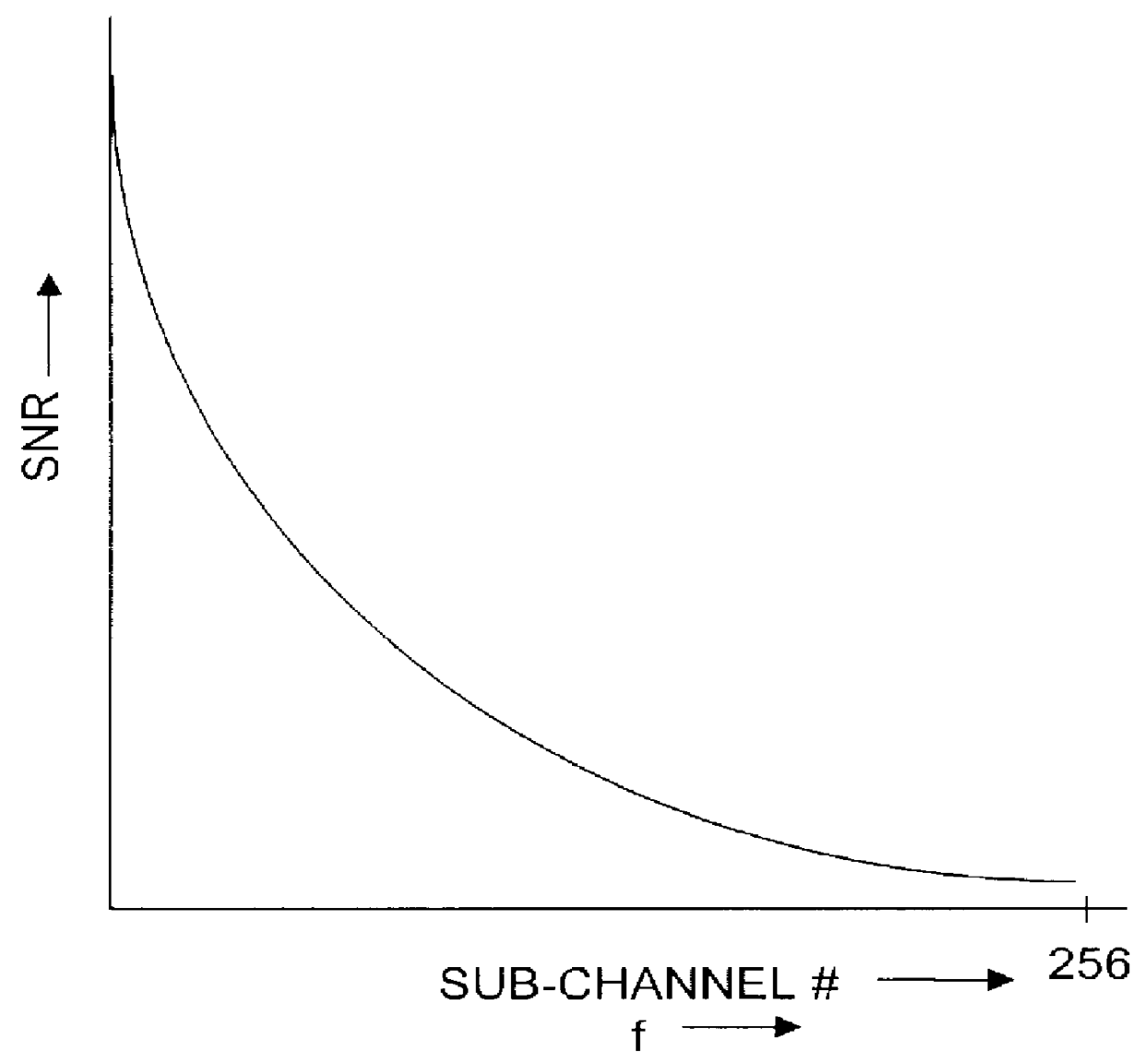
Program for controlling DMT based modem using sub-channel selection to achieve scaleable data rate based on available signal processing resources
InactiveUS6073179ALow costReduce complexityTelephonic communicationTime-division multiplexModem deviceData rate
An applications program is provided for permitting a user of a host processing system to dynamically control a modem having forward compatible and expandable functionality. In a preferred embodiment, the applications program is designed to run on a personal computer running the Windows.RTM. shell, and the modem is compatible with ADSL promulgated standards. As part of such program, initialization and detection routines determine the capabilities of an ADSL modem, including whether the same has been upgraded to have enhanced data throughput. A calibration routine measures the computing power available to the host processor, and based on this information and other relevant parameters determines nominal setup parameters for the modem. These parameters are stored in a Device Parameter Table so that they can be accessed by various application programs that may make use of such modem. A user of such program can at that time or thereafter alter the characteristics of the ADSL modem (including a target data rate) subject to availability of sufficiently powerful analog front end sampling circuitry and processing power.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
Method and apparatus for adaptive transmission control in a high data rate communication system
InactiveUS7088701B1Improve throughputIncrease chanceError prevention/detection by using return channelTime-division multiplexCommunications systemSelf adaptive
In a high data rate communication system, a method and apparatus for improved throughput while transmitting data packets within multiple time slots. In order to avoid unnecessary retransmissions of a packet, a subscriber station sends a Stop-Repeat signal to a base station, causing the base station to cease further transmissions of the packet. In order to enable successful decoding of a packet, a subscriber station sends a Continue-Repeat signal to a base station, causing the base station to send retransmissions of the packet during time slots beyond a predetermined default number of time slots.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
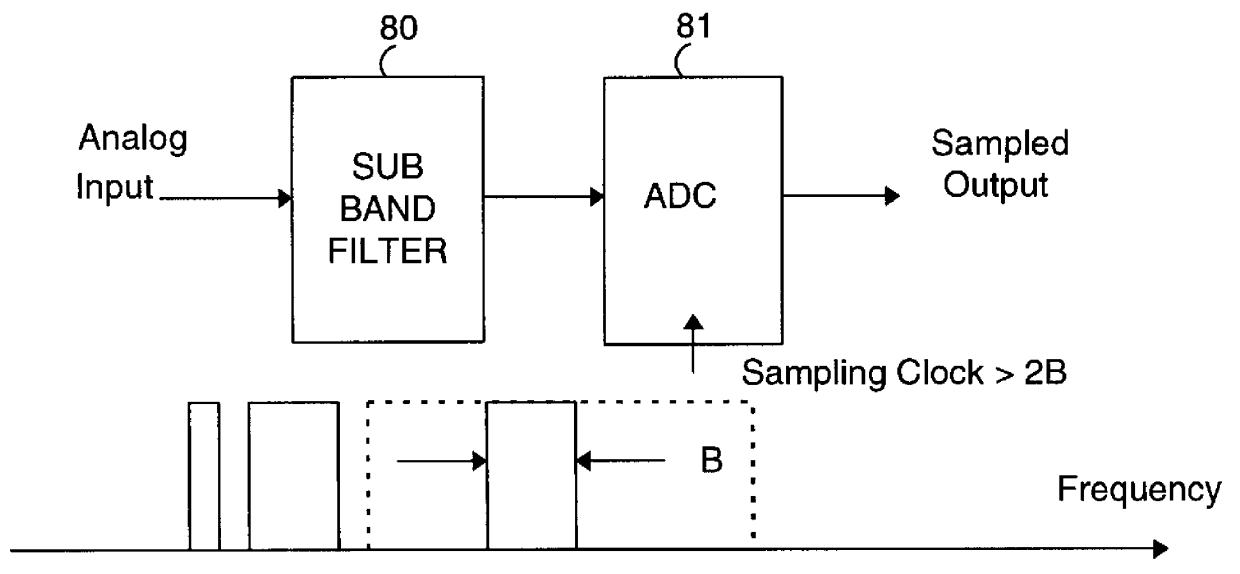
Modular multiplicative data rate modem and method of operation
InactiveUS6065060AReduce in cost and complexitySimple circuitMultiplex system selection arrangementsTelephonic communicationData transmissionModularity
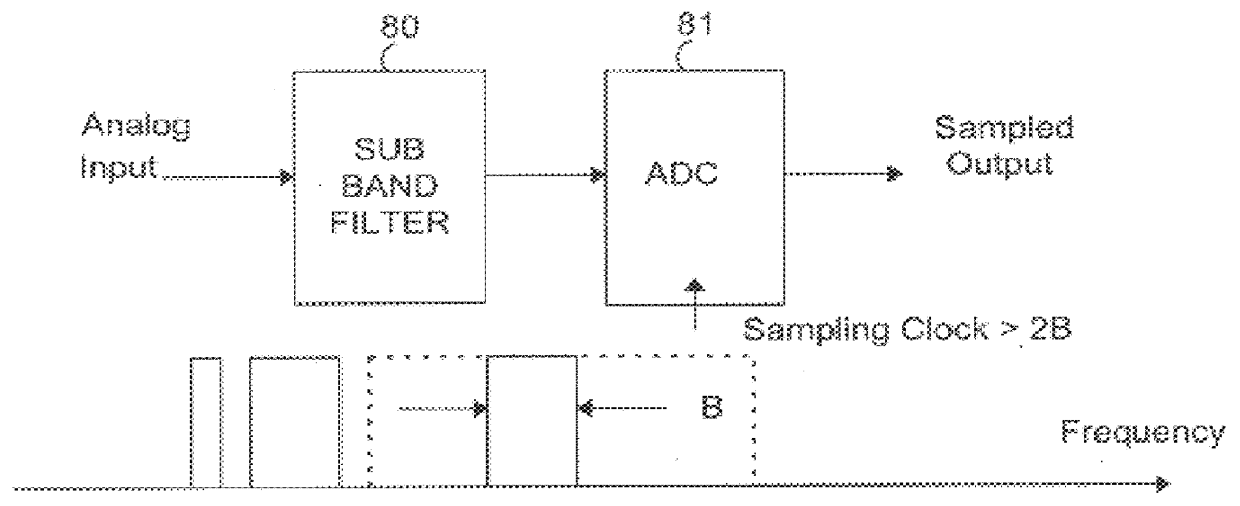
A high speed modem is provided which targets the use of a selectable, desirable portion of the total available bandwidth of a channel for achieving a data rate which nevertheless far exceeds that of conventional voice-band modems. In a preferred embodiment, the invention is implemented in an Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Loop (ADSL), and the nominal data rate is achieved using an analog front end (AFE) with subband filtering which causes an upstream transceiver to use only a selected number of available sub-channels for downstream data transmission and allows slower sampling rate for the AFE. The data rate of the modem is increased in a multiplicative fashion through modular expansion of a bank of AFEs to increase the number of transmitted downstream sub-channels.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
xDSL DMT modem using sub-channel selection to achieve scaleable data rate based on available signal processing resources
InactiveUS6092122AReduce in cost and complexitySimple circuitMultiple-port networksModulated-carrier systemsData transmissionTransceiver
A high speed modem is provided which uses a selectable, desirable portion of the total available bandwidth of a transmission channel. In a preferred embodiment, the invention is incorporated in a dedicated hardware circuit which is connected on one end to a data processor and on the other end to an upstream transceiver through a channel supporting an Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Loop (ADSL) standard. The achievable target data rate of the modem is based on the capabilities of an analog front end (AFE) used in the modem, and a signal processor within the dedicated hardware. In particular, the modem AFE contains subband filtering which causes an upstream transceiver to use only a selected number of available sub-channels for downstream data transmission. The data rate of the modem is increased by upgrading the AFE or the signal processor in order to increase the number of processable transmitted downstream sub-channels.
Owner:ITE TECH INC +1
Triggered packet data rate change in a communication system
InactiveUS7193966B2Effective resourcesIncreased rate capacityTransmission systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementTraffic characteristicTraffic capacity
Communication traffic associated with one or more mobile terminals is monitored to efficiently manage allocated radio resources. A rate management technique dynamically adjusts allocated radio resources to increase or decrease the data rate capacity of allocated radio channels based on actual channel usage. In this manner, radio resources are more efficiently utilized because the amount of excess capacity allocated to individual subscribers is reduced. Monitoring communication traffic may also be used to determine whether additional radio channel resources are allocated to a given subscriber. For example, in a cdma2000 radio access network, subscribers are typically allocated fundamental radio channels and then assigned supplemental channels to access higher data rate services. By monitoring fundament channel traffic characteristics, such as the queue length or packet size of outgoing packet data, the radio access network can determine whether supplemental channel allocation is warranted.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
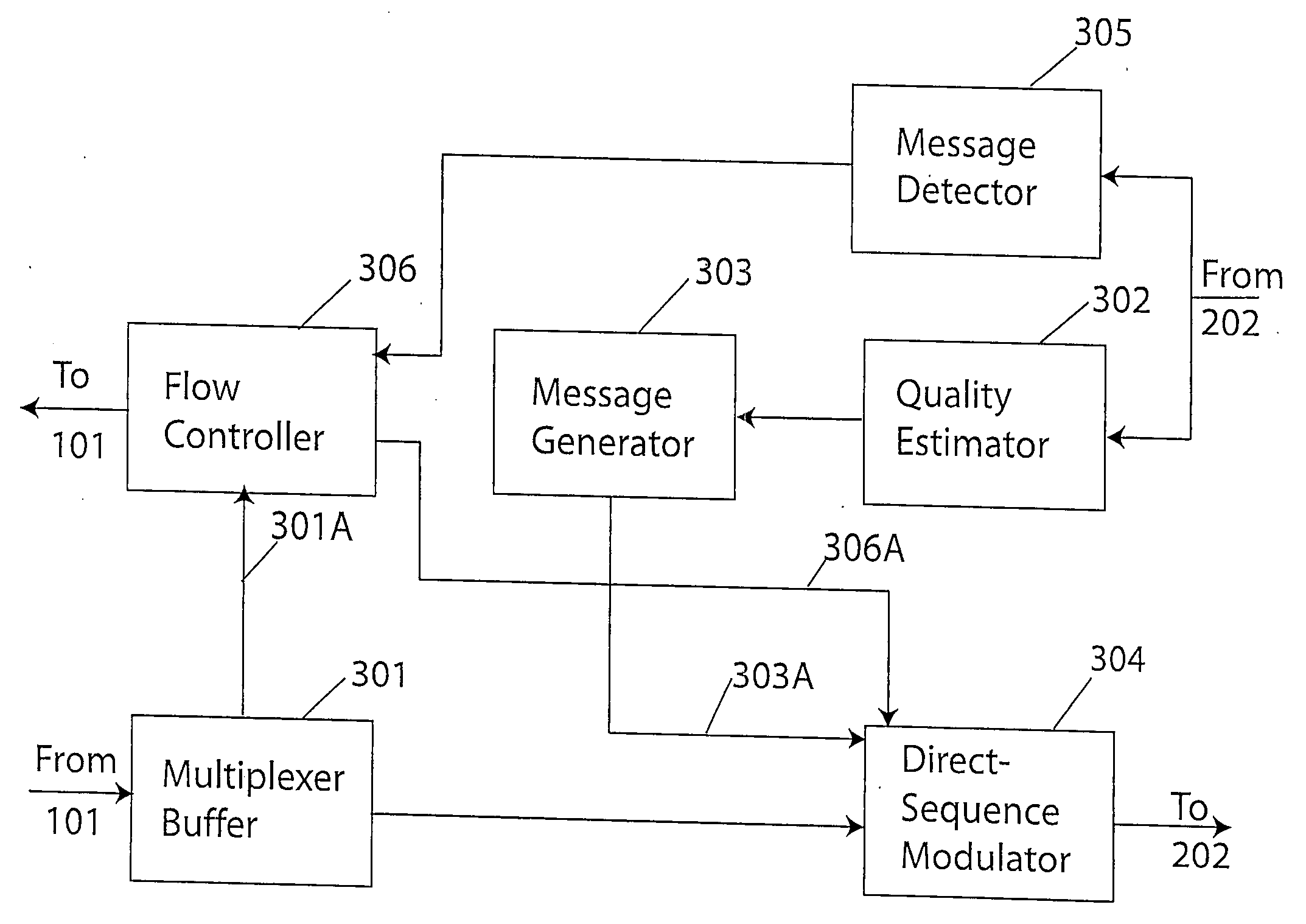
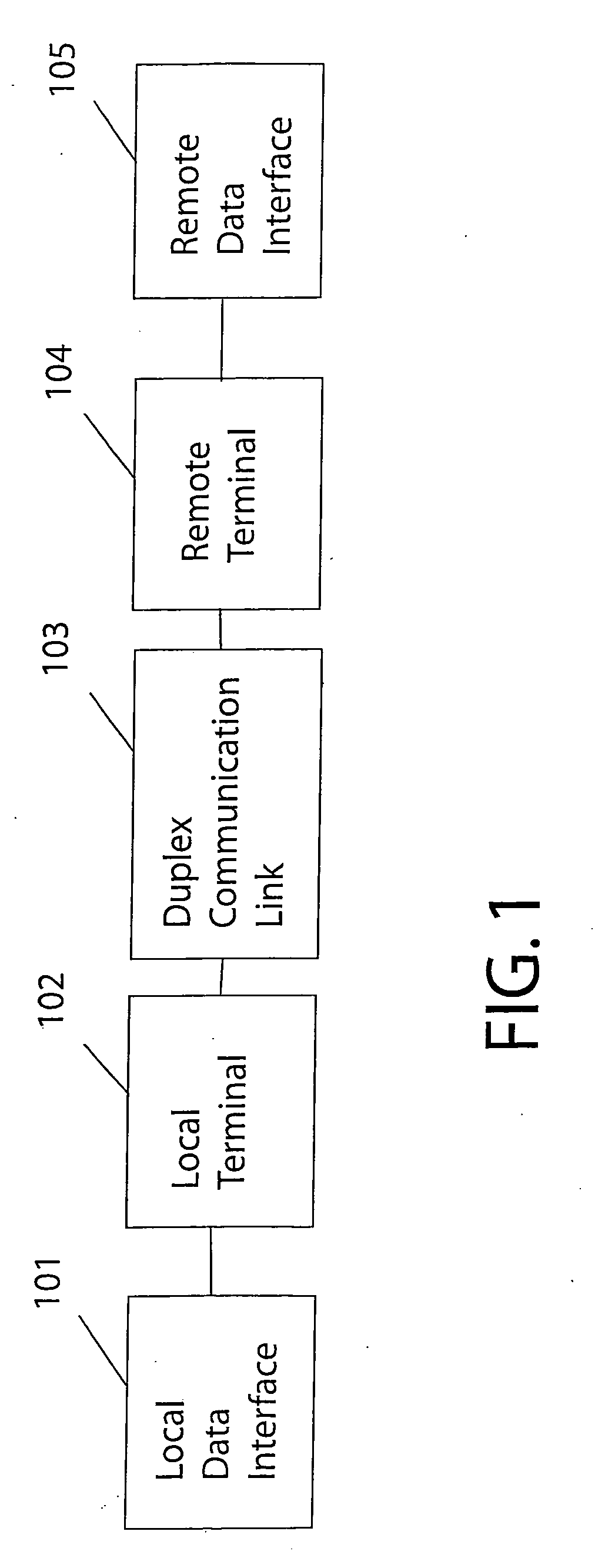
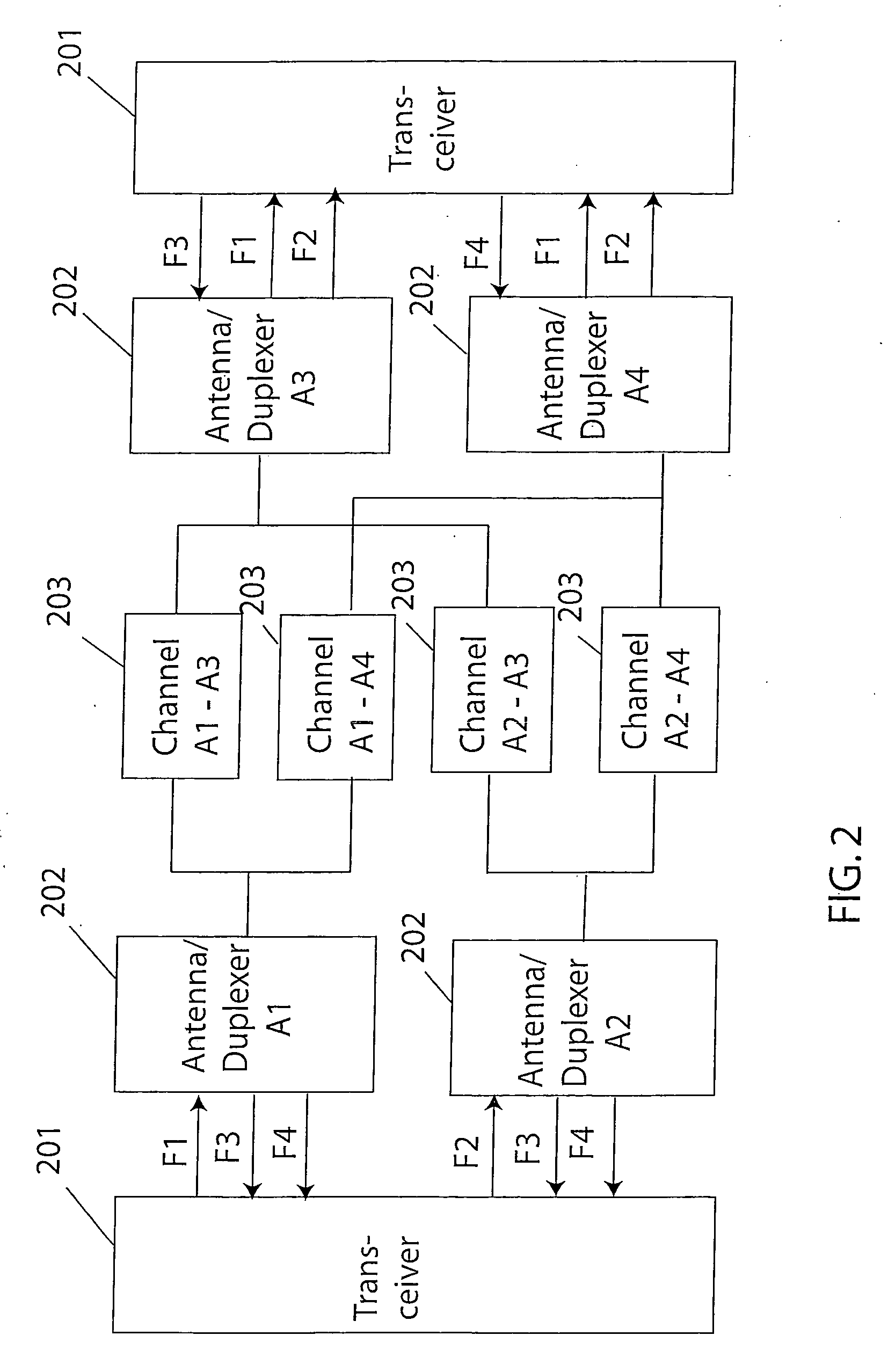
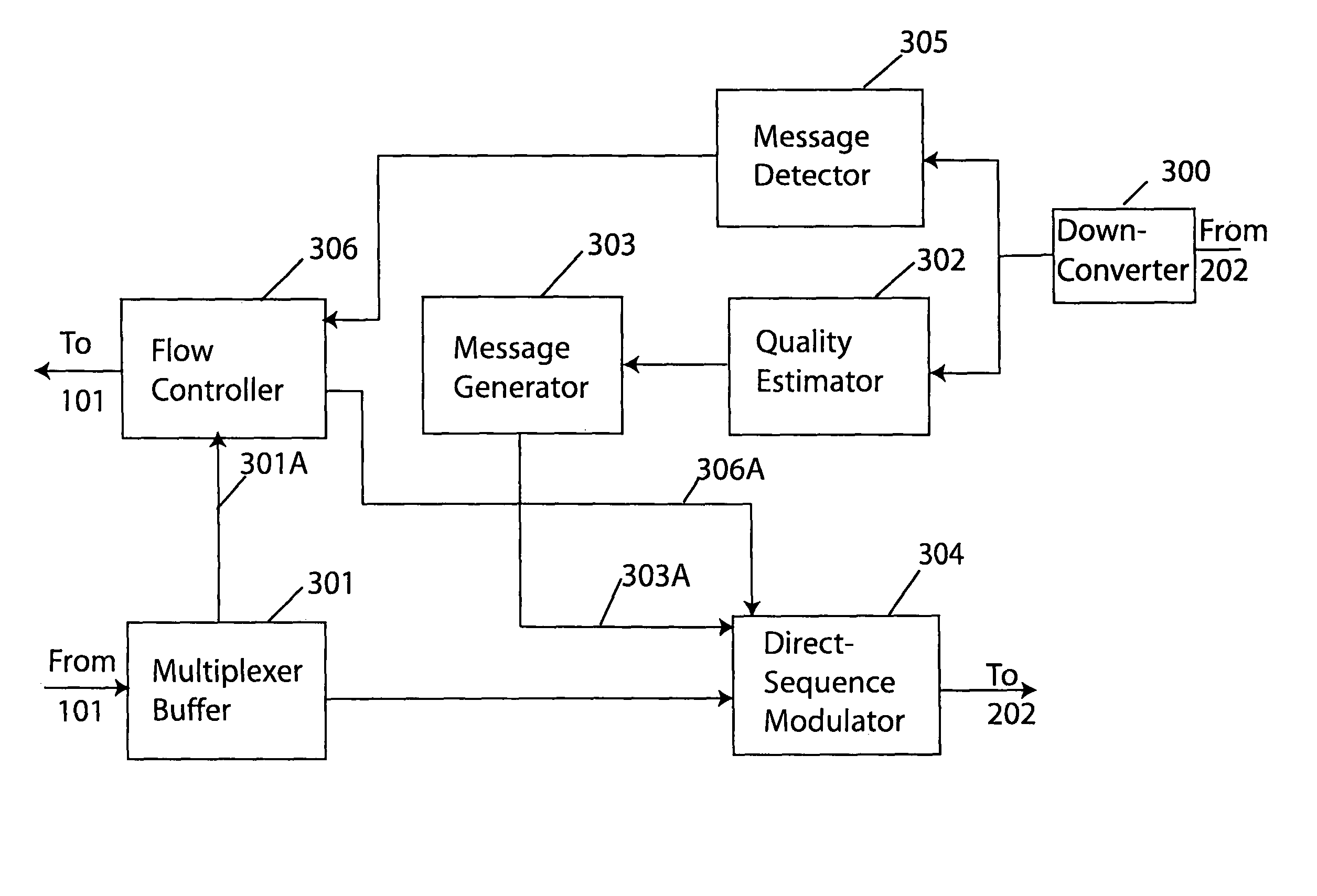
Technique for adaptive data rate communication over fading dispersive channels
ActiveUS20070147251A1Increase capacityMitigate mutual interferenceTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsIndependent dataWave band
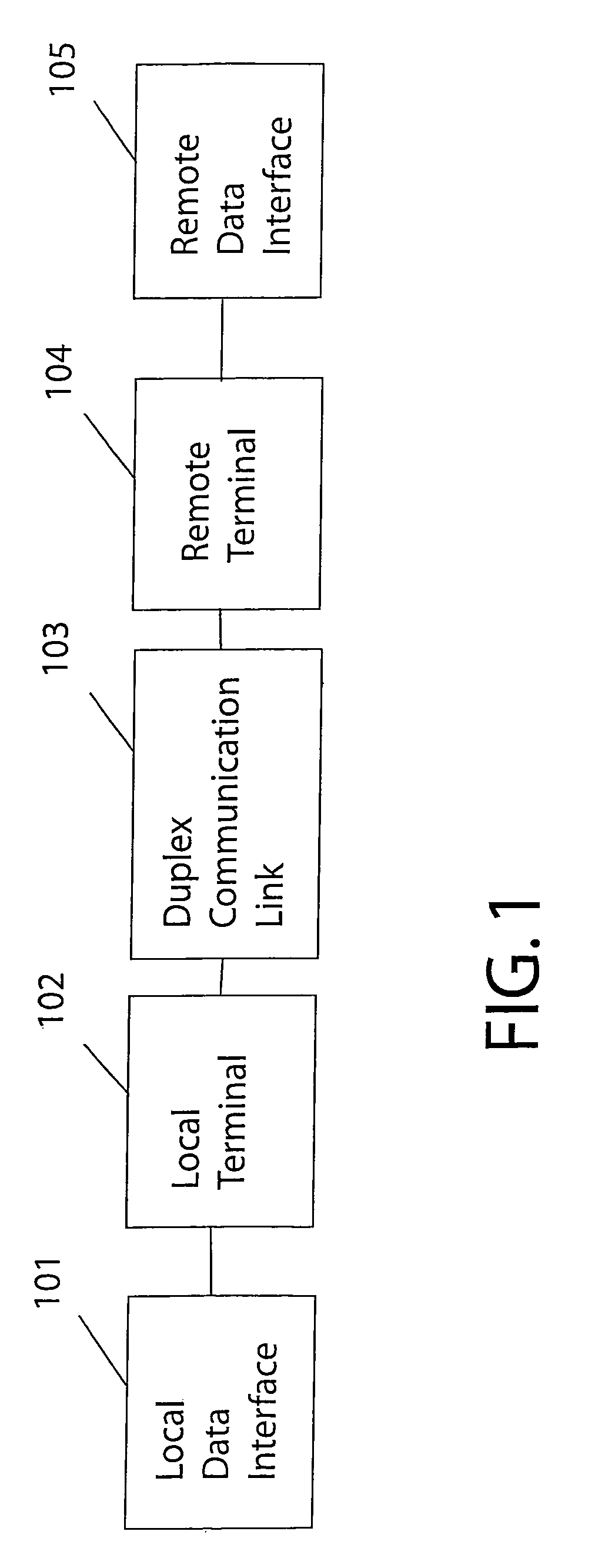
In a duplex radio link wherein digital data information from a data interface is transmitted from a local terminal to a remote terminal over fading dispersive channels, a method and transceiver are described that provide for transmission at an adaptive data rate. The transmission is at a constant symbol rate so that the signal bandwidth can be fixed and at the remote terminal receiver the input sampling rate can be fixed. The digital data information is transmitted over a constant data rate interval in accordance with a selected data rate mode that is a function of direct sequence spreading gain, error correction code rate, and signal constellation type. The data rate is adapted by selecting a data rate mode that is a function of the arrival rate of data packets from the data interface and a link quality measure fed back from the remote terminal. The data packet arrival rate is controlled as a function of the link quality measure and the current data packet arrival rate. In systems with multiple transmit diversity channels, independent data is sent over each of the transmit diversity channels. The adaptive data rate technique utilizes both orthogonal transmit diversities such as frequency and troposcatter polarization diversity as well as nonorthogonal transmit diversities in a Multiple-input Multiple-Output (MIMO) configuration. A single antenna troposcatter link using angle diversity and adaptation of data rate by feedback communications is described. In an idealized feedback communication example, the single antenna system in a Ku-band application is shown to have 15.5 times the data rate capability of a conventional two-antenna system at S-band.
Owner:MONSEN PETER
Technique for adaptive data rate communication over fading dispersive channels
ActiveUS7751372B2Improve data throughputImprove transmission conditionsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsPacket arrivalDigital data
In a duplex radio link digital data information is transmitted to a remote terminal at a constant symbol rate in accordance with a selected data rate mode that is a function of direct sequence spreading gain, error correction code rate, and signal constellation type. The data rate is adapted by selecting a data rate mode that is a function of a data packet arrival rate and a link quality measure fed back from the remote terminal. The data packet arrival rate is controlled as a function of the link quality measure and the current data packet arrival rate. In systems with multiple transmit diversity channels, independent data is sent over each of the transmit diversity channels. In an idealized feedback communication example, a single antenna troposcatter system in a Ku-band application is shown to have 15.5 times the data rate capability of a conventional two-antenna system at S-band.
Owner:MONSEN PETER
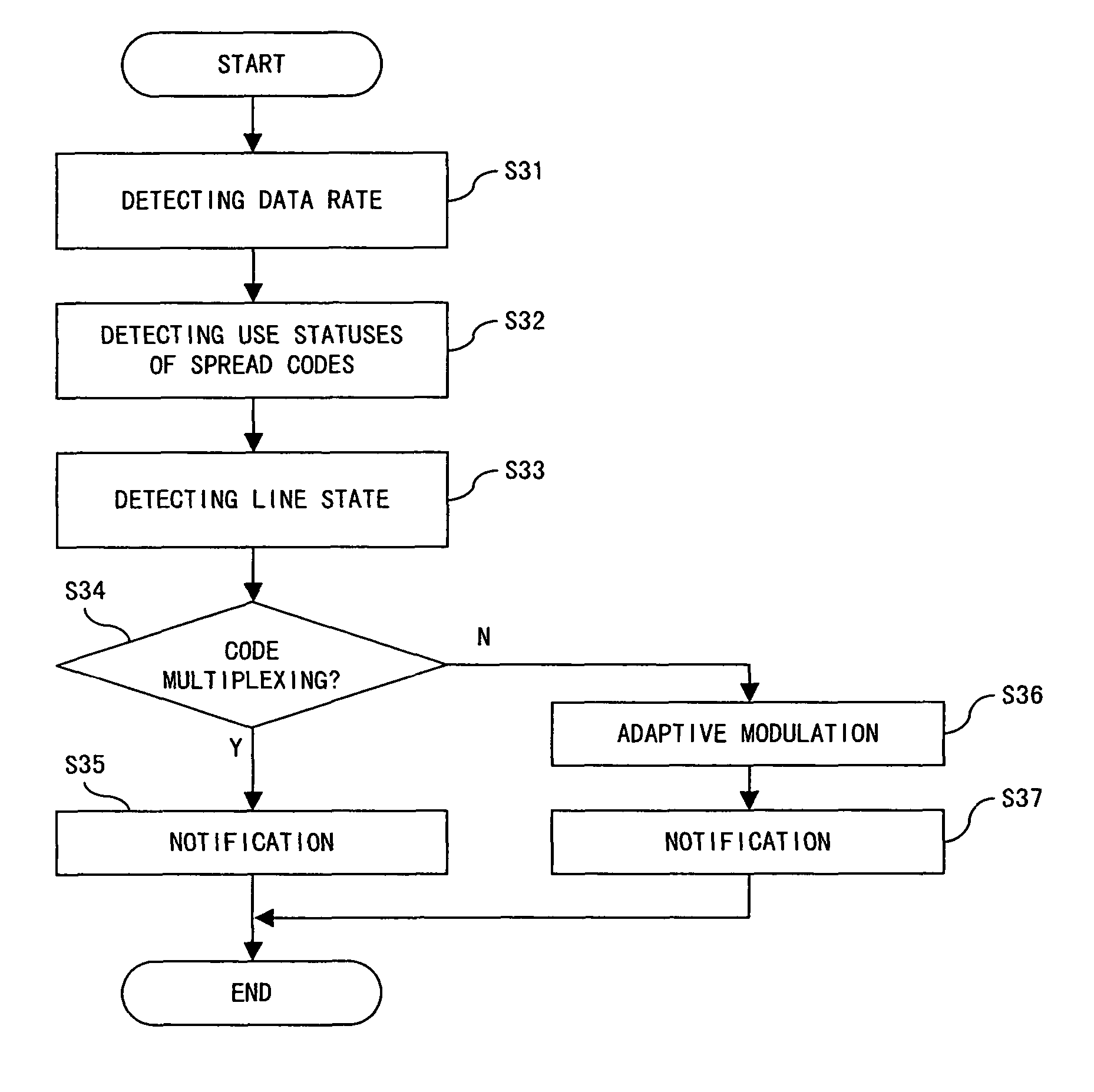
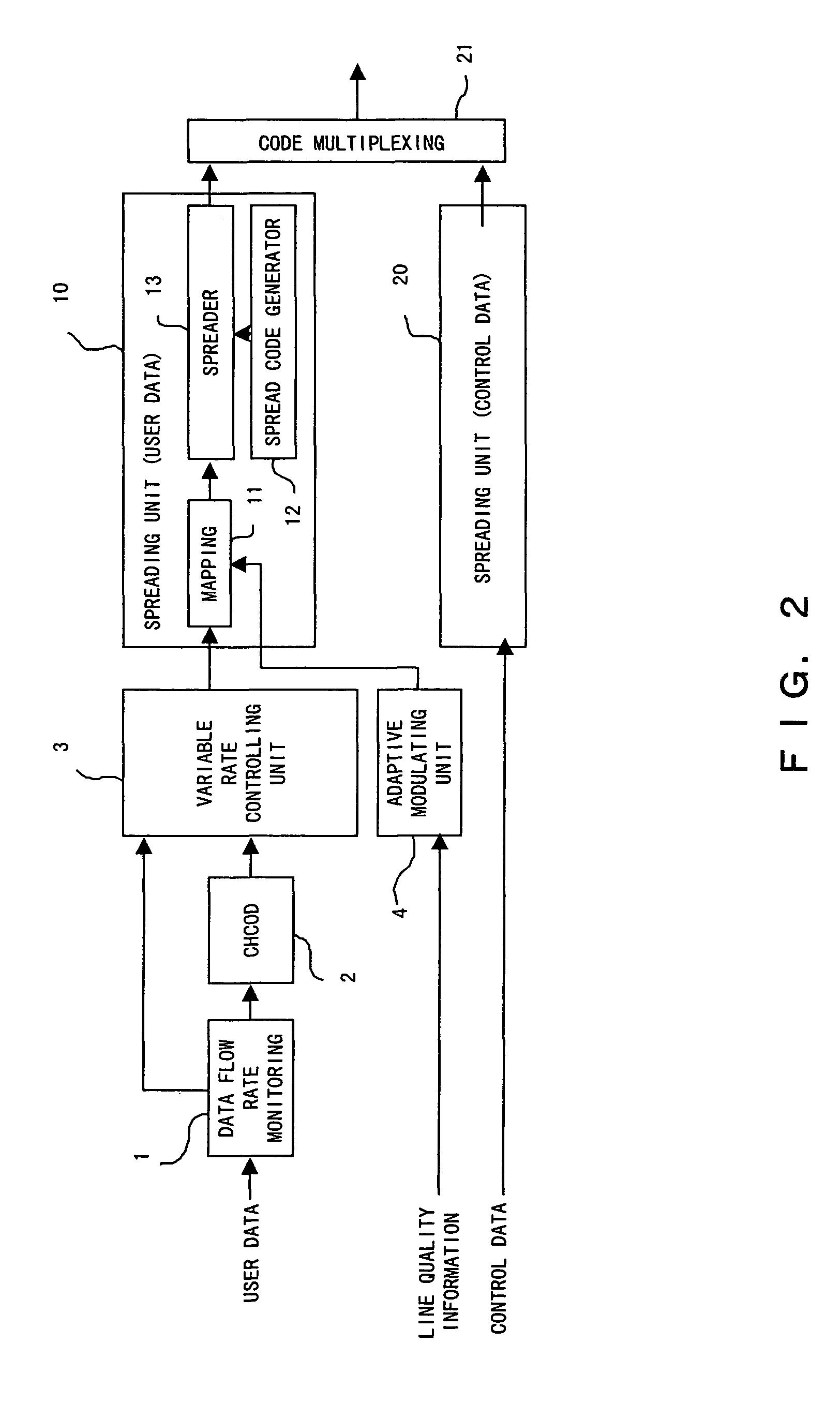
Communications device used in CDMA
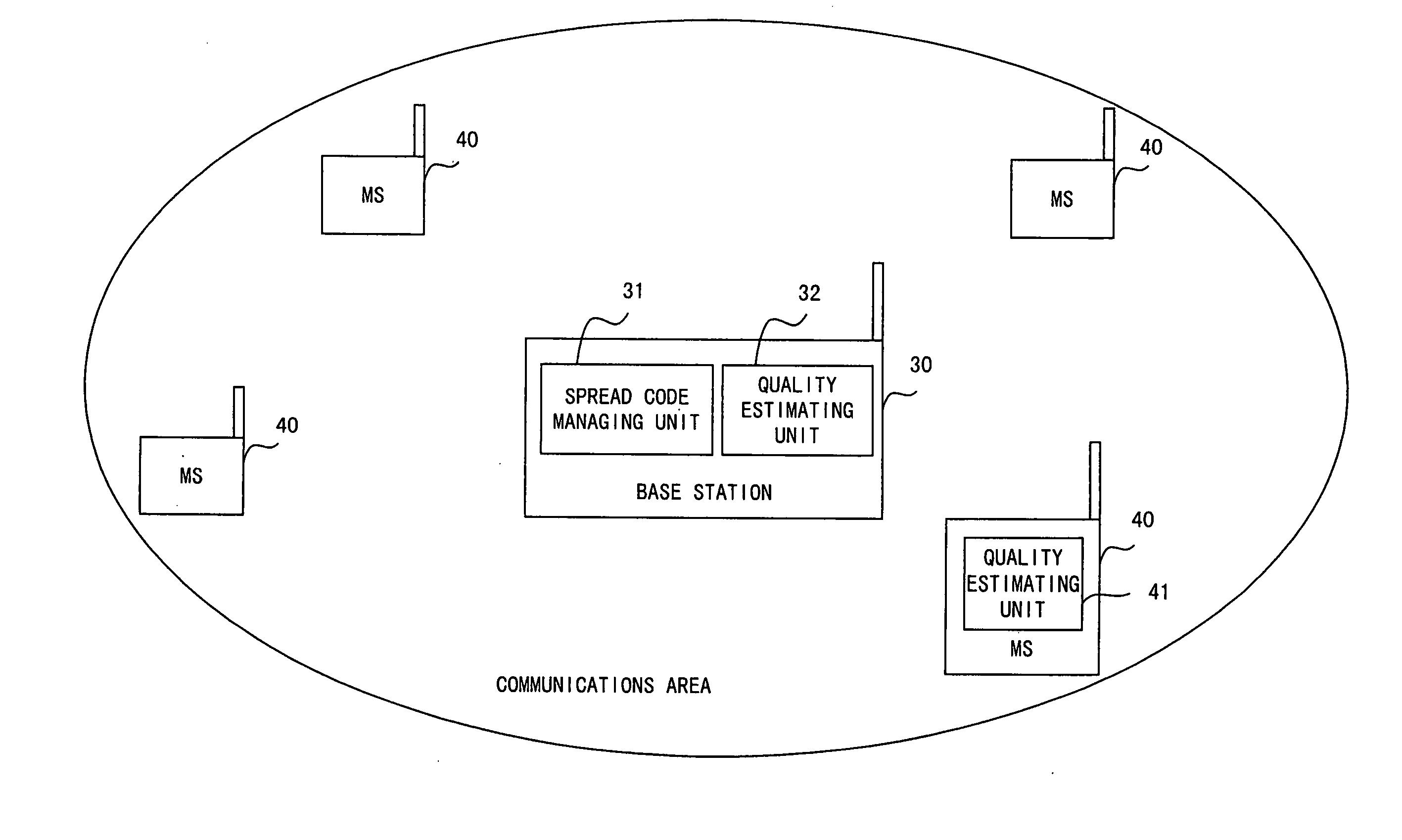
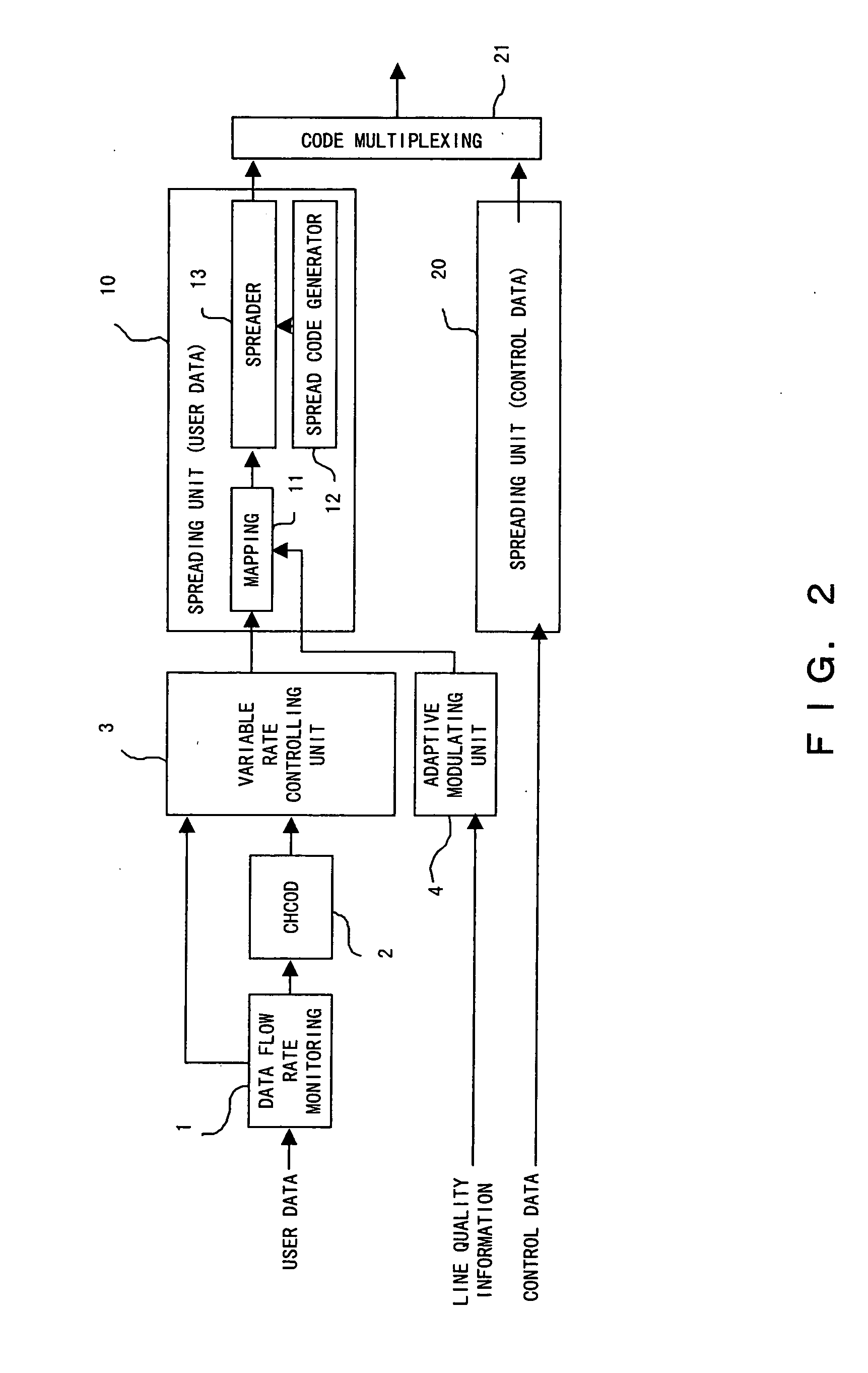
ActiveUS20050018642A1Guaranteed normal transmissionData rateModulated-carrier systemsConnection managementMultiplexingCommunications system
A transmitting device of the present invention is used in a CDMA communications system, and comprises: a plurality of spreading units for spreading user data; a managing unit for managing spread codes; a determining unit for determining a number of codes to be multiplexed based on use statuses of the spread codes managed by said managing unit; and a multiplexing unit for multiplexing the user data spread by spreading units a number of which corresponds to the number of codes to be multiplexed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Analog-to-digital converter having parametric configurablity
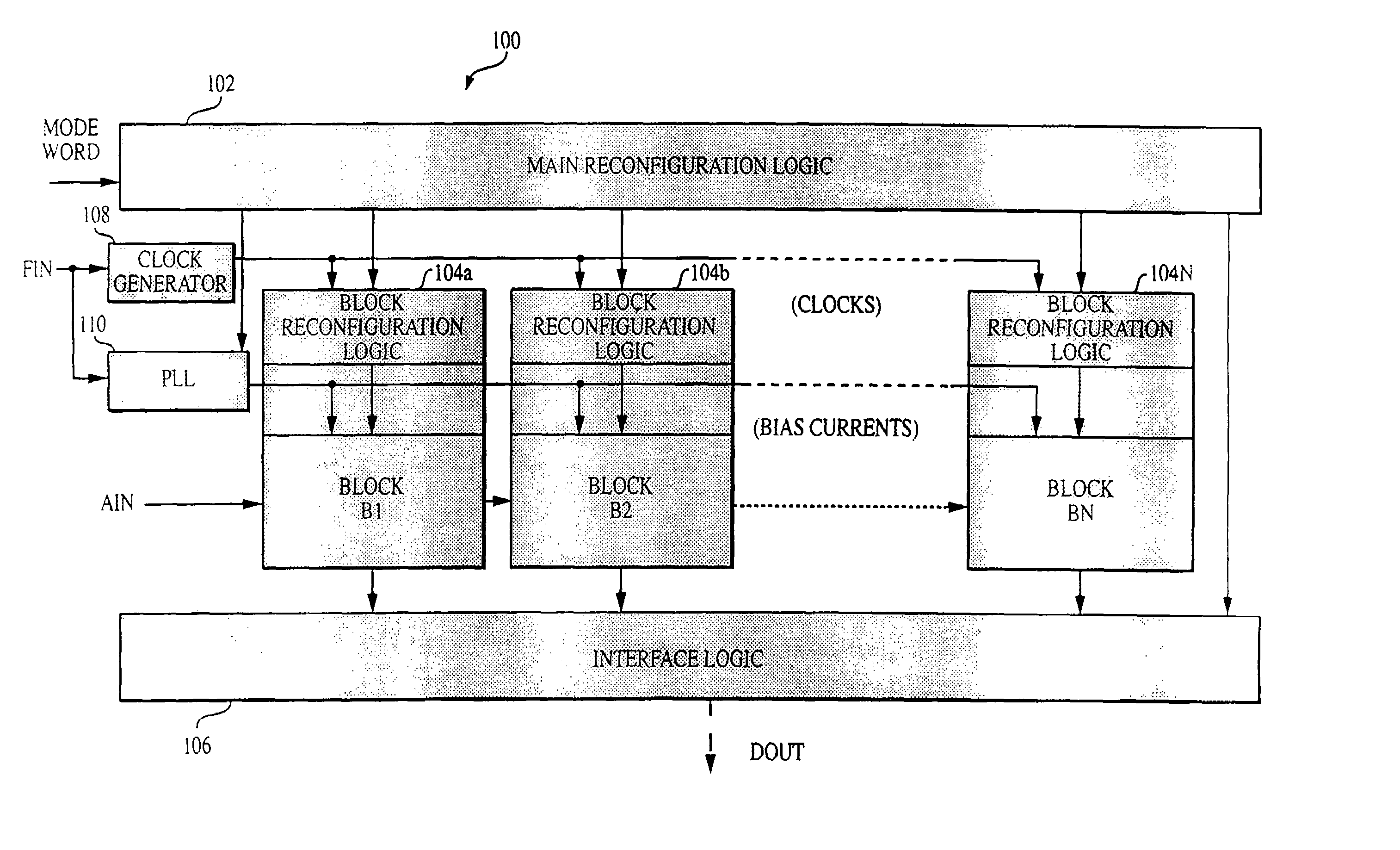
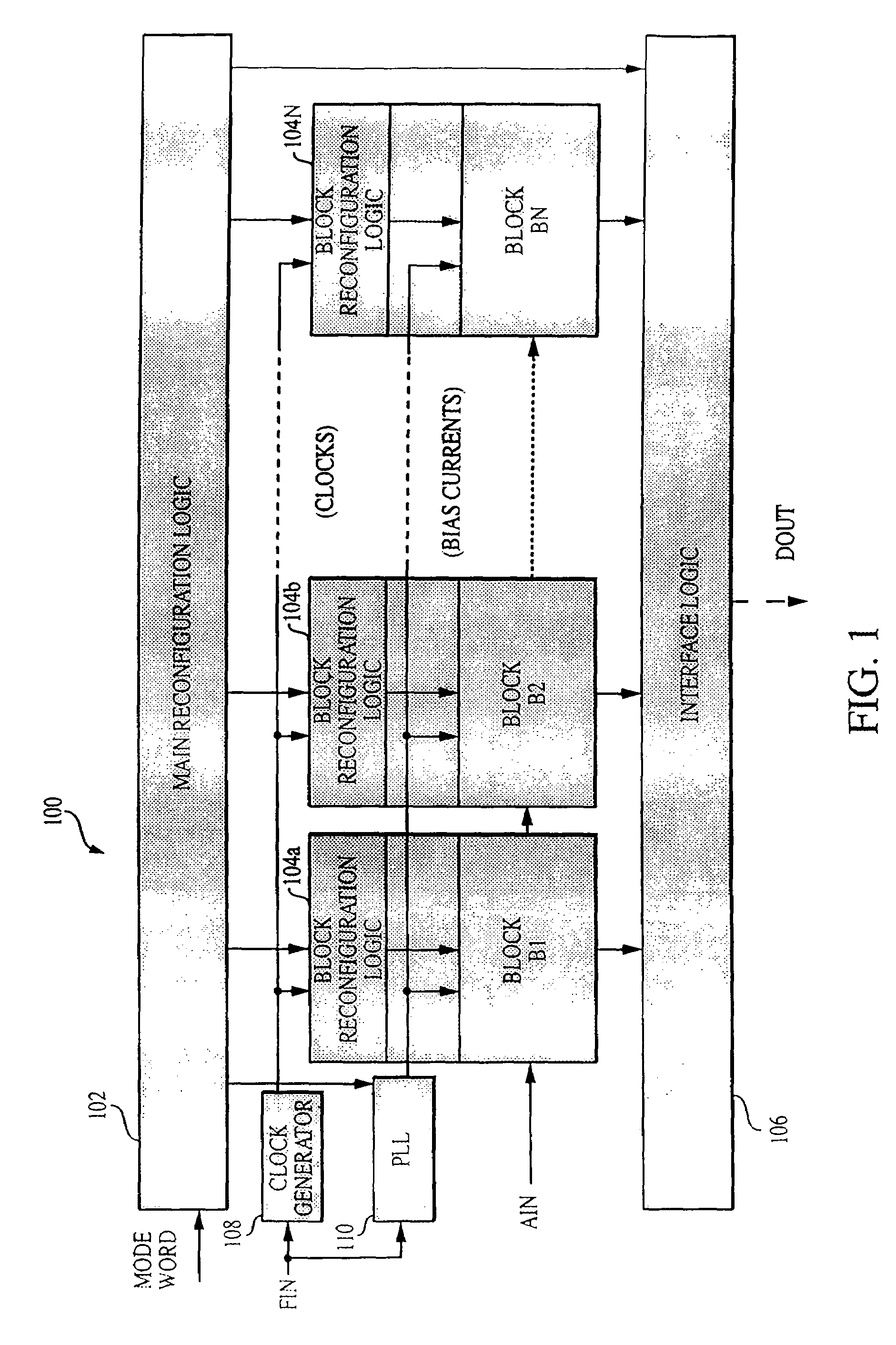
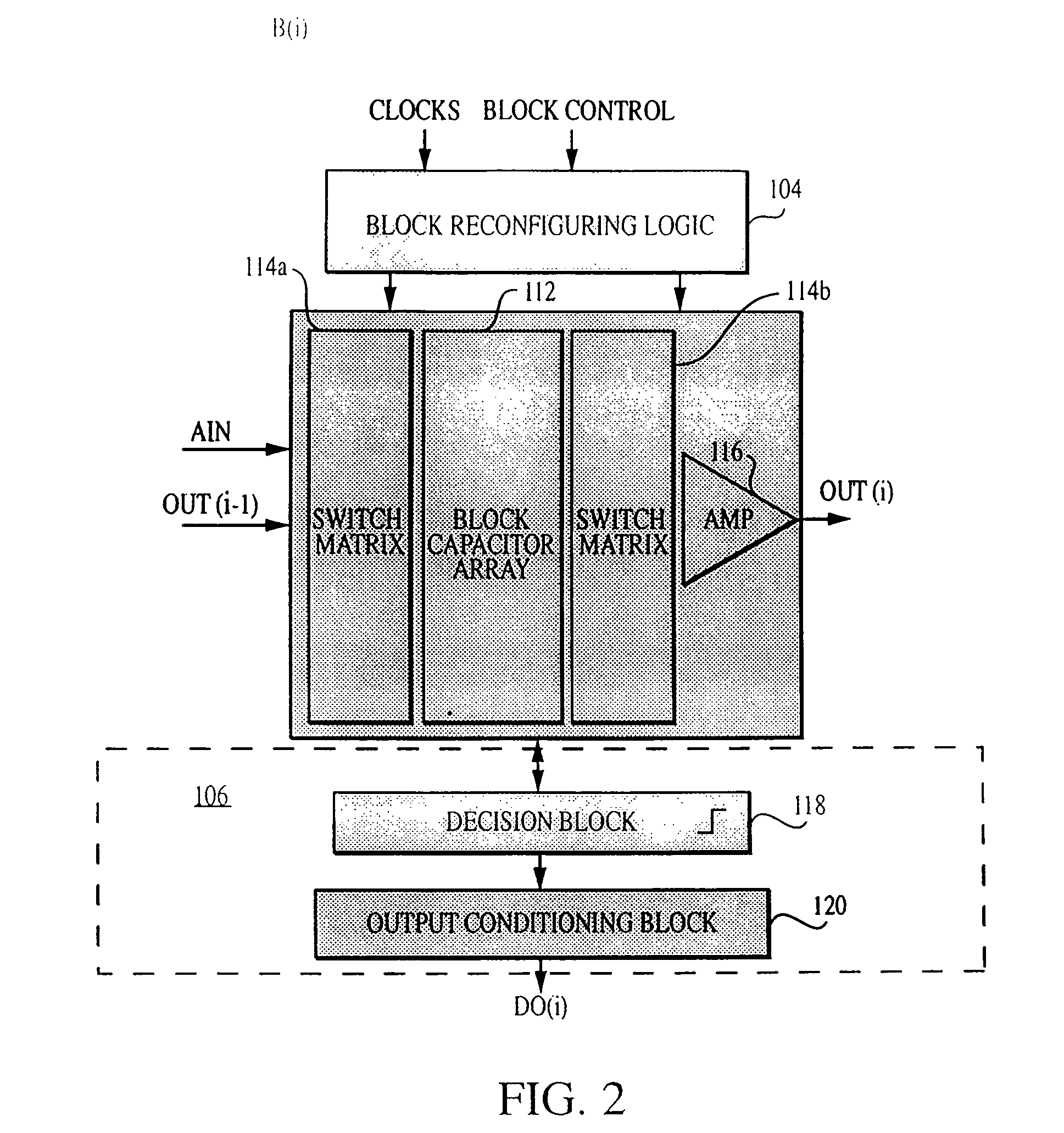
InactiveUS7002501B2High resolutionData rateElectric signal transmission systemsReconfigurable analogue/digital convertersImage resolutionEngineering
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
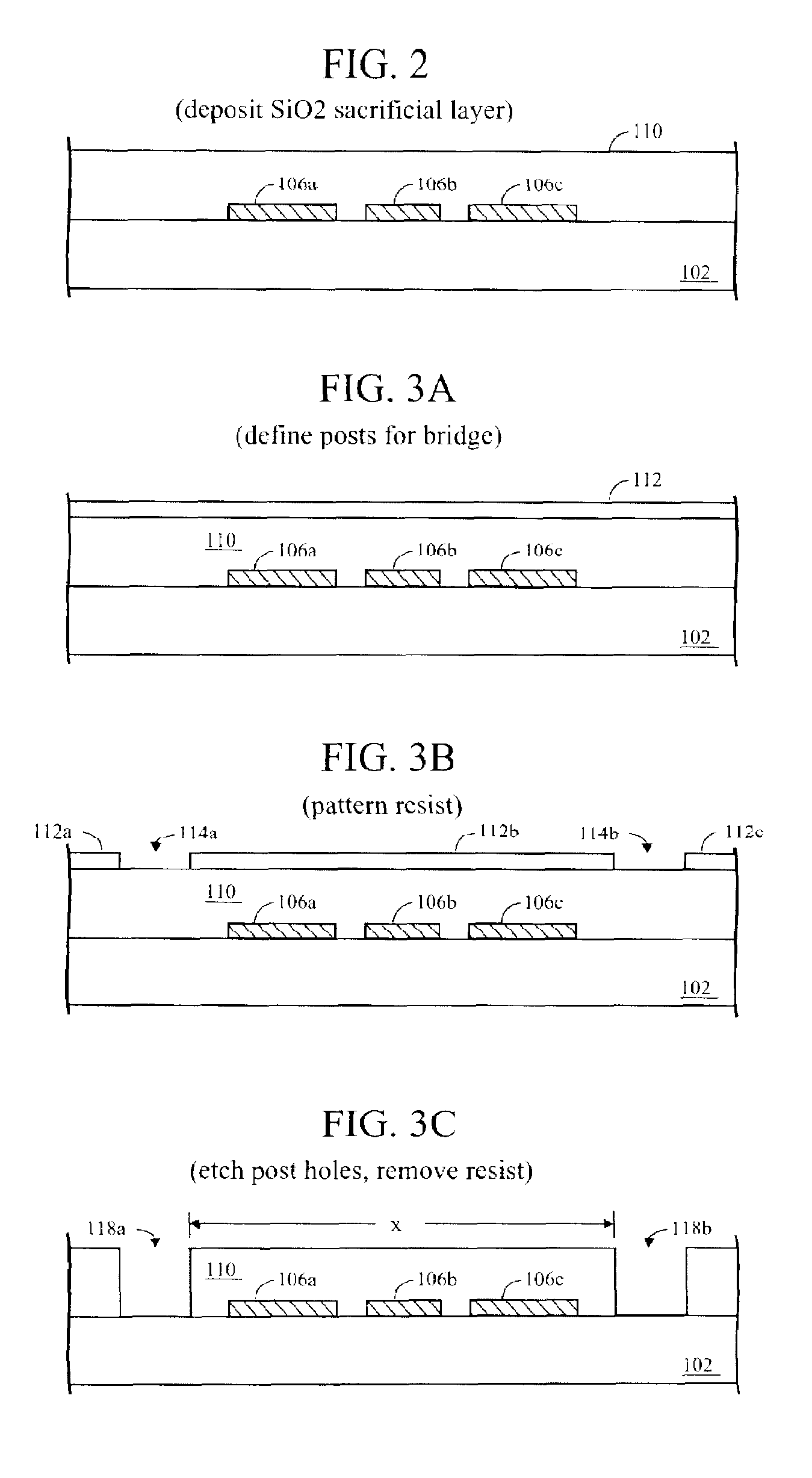
MEMS switches having non-metallic crossbeams
A RF MEMS switch comprising a crossbeam of SiC, supported by at least one leg above a substrate and above a plurality of transmission lines forming a CPW. Bias is provided by at least one layer of metal disposed on a top surface of the SiC crossbeam, such as a layer of chromium followed by a layer of gold, and extending beyond the switch to a biasing pad on the substrate. The switch utilizes stress and conductivity-controlled non-metallic thin cantilevers or bridges, thereby improving the RF characteristics and operational reliability of the switch. The switch can be fabricated with conventional silicon integrated circuit (IC) processing techniques. The design of the switch is very versatile and can be implemented in many transmission line mediums.
Owner:NASA
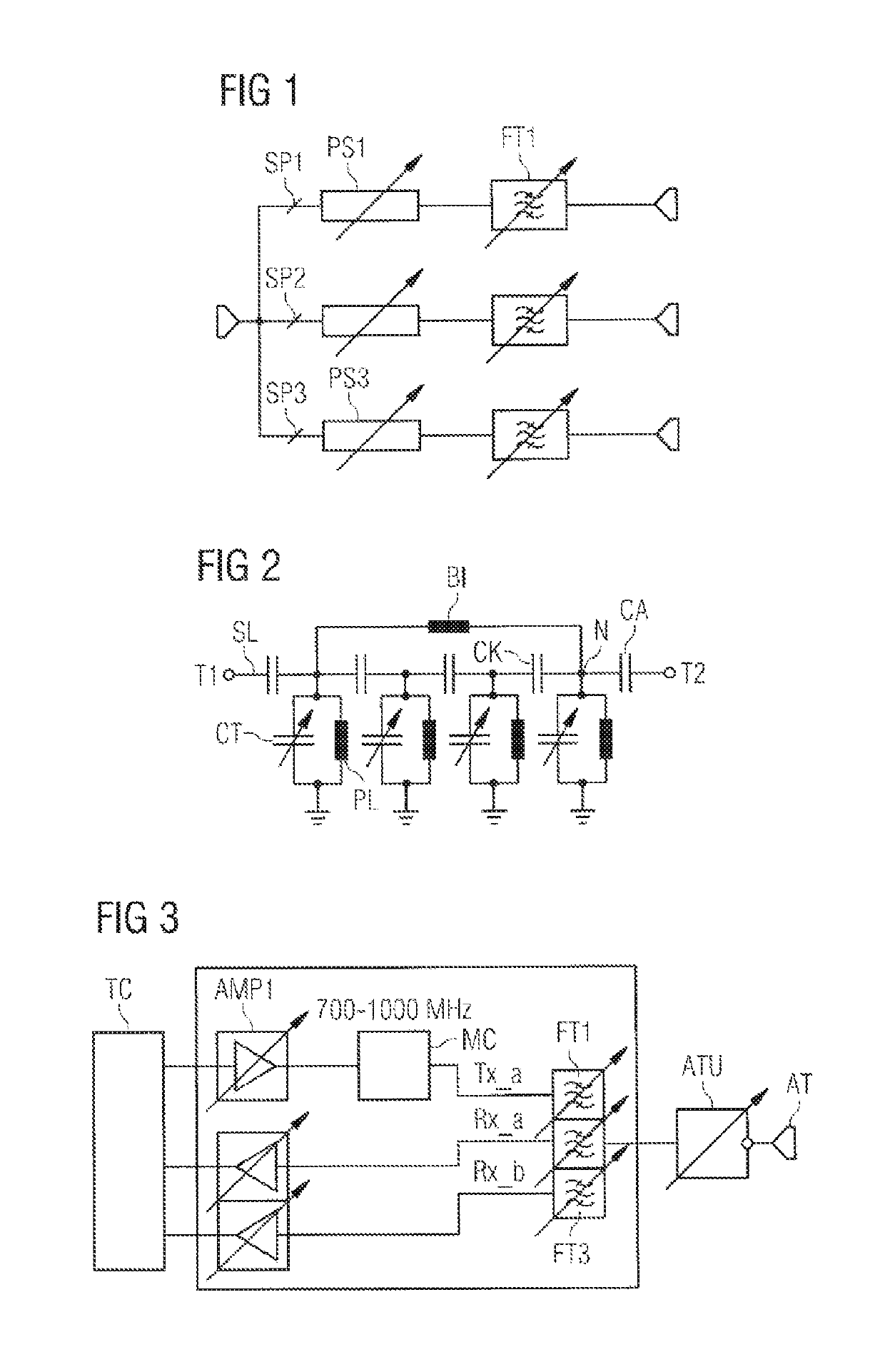
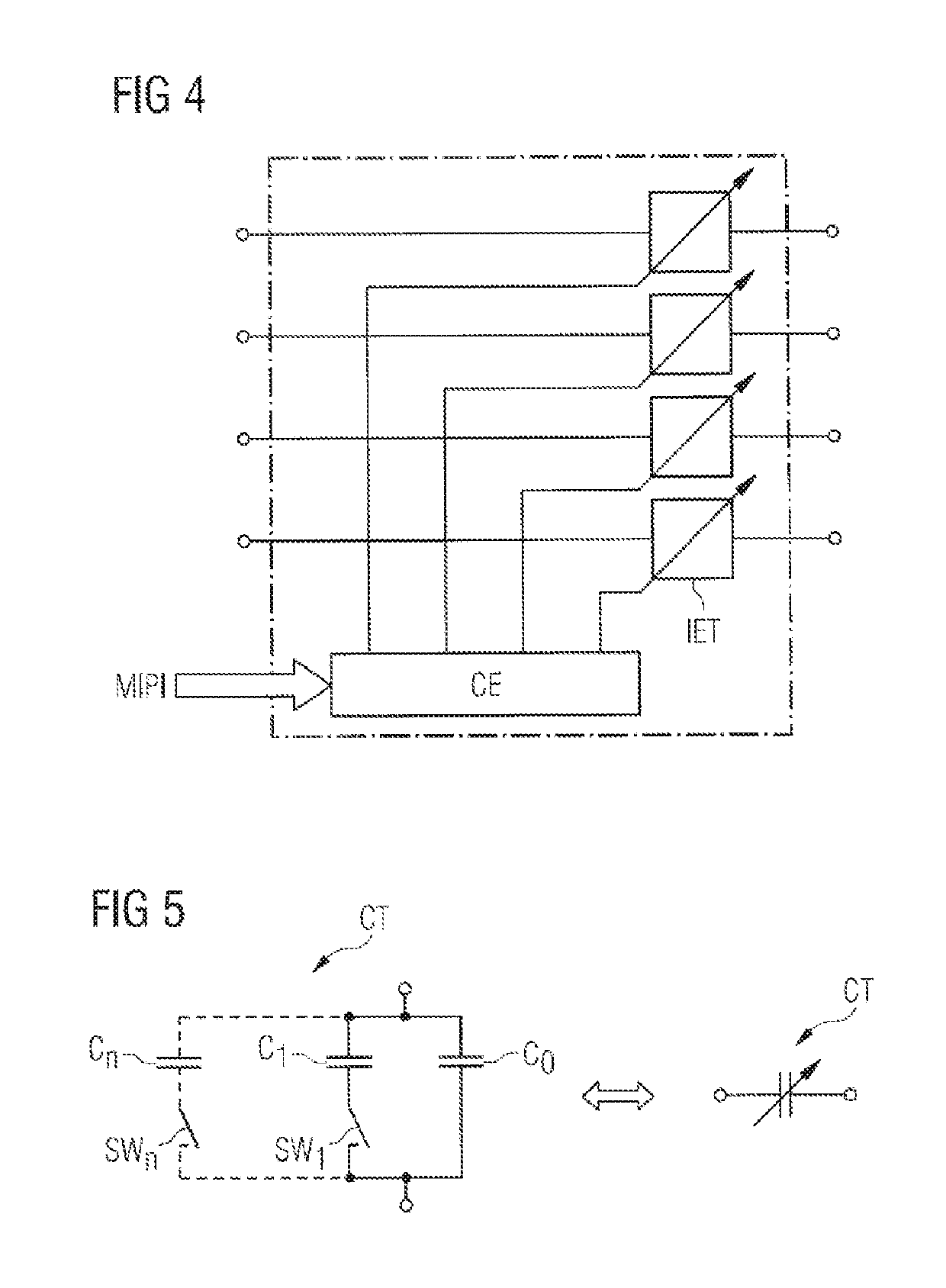
Front-End Circuit for Simultaneous Transmission and Reception Operation
ActiveUS20170012651A1Double data rateData rateMultiple-port networksDuplex signal operationEngineeringControl circuit
A front end circuit is disclosed. In an embodiment, the circuit includes a first antenna connection and first to third signal paths, each of which include a tunable filter and each of which is connected to the first antenna connection. The circuit further includes at least one phase shifter arranged in at least one of the signal paths between a respective filter and the first antenna connection and a control circuit configured to tune frequency bands of the filters, wherein the filters are operable in a FDD operating mode or a TDD operating mode, and wherein the front-end circuit is simultaneous operable in at least one transmission band and at least one reception band using all three filters and the associated signal paths.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
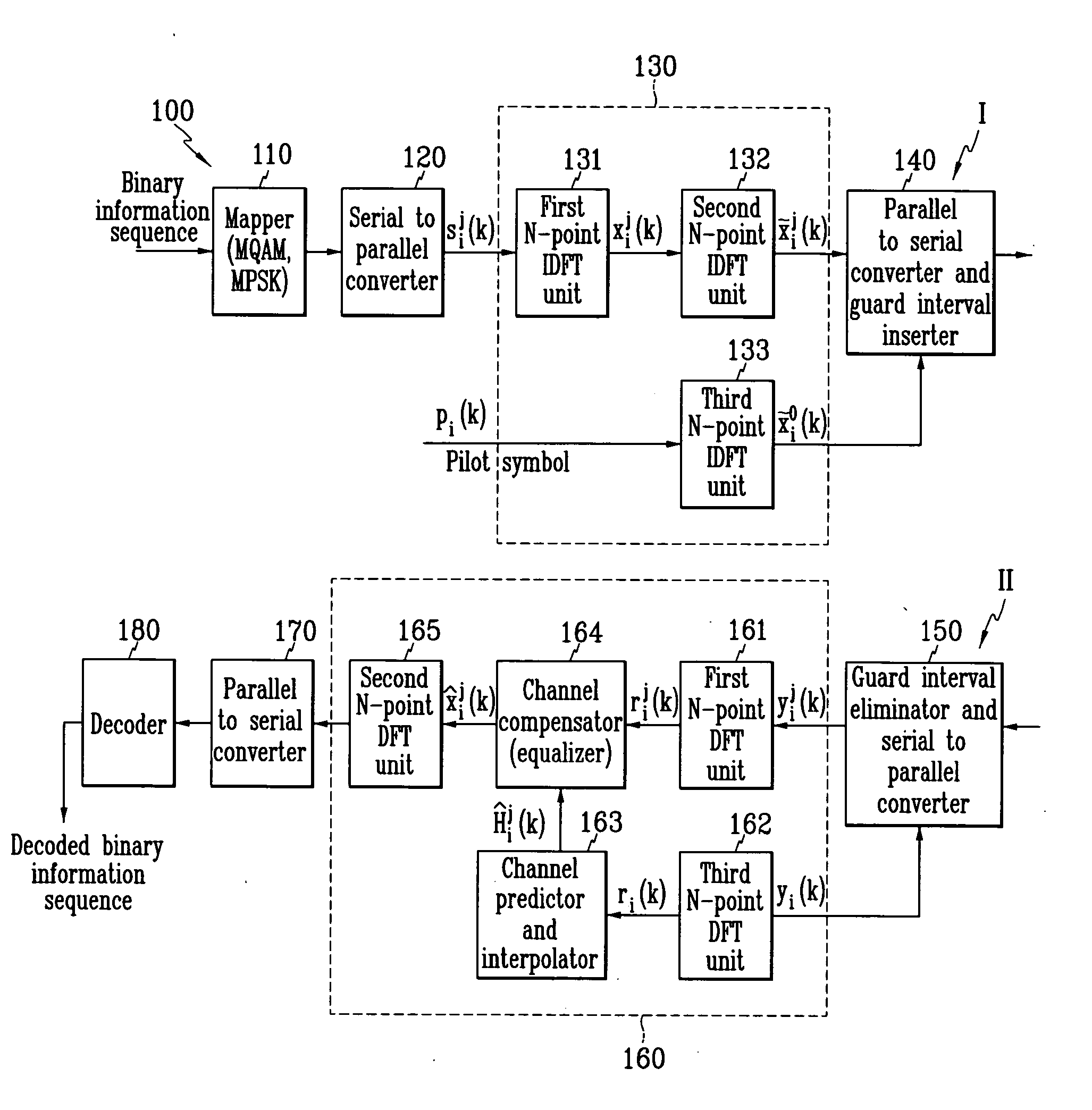
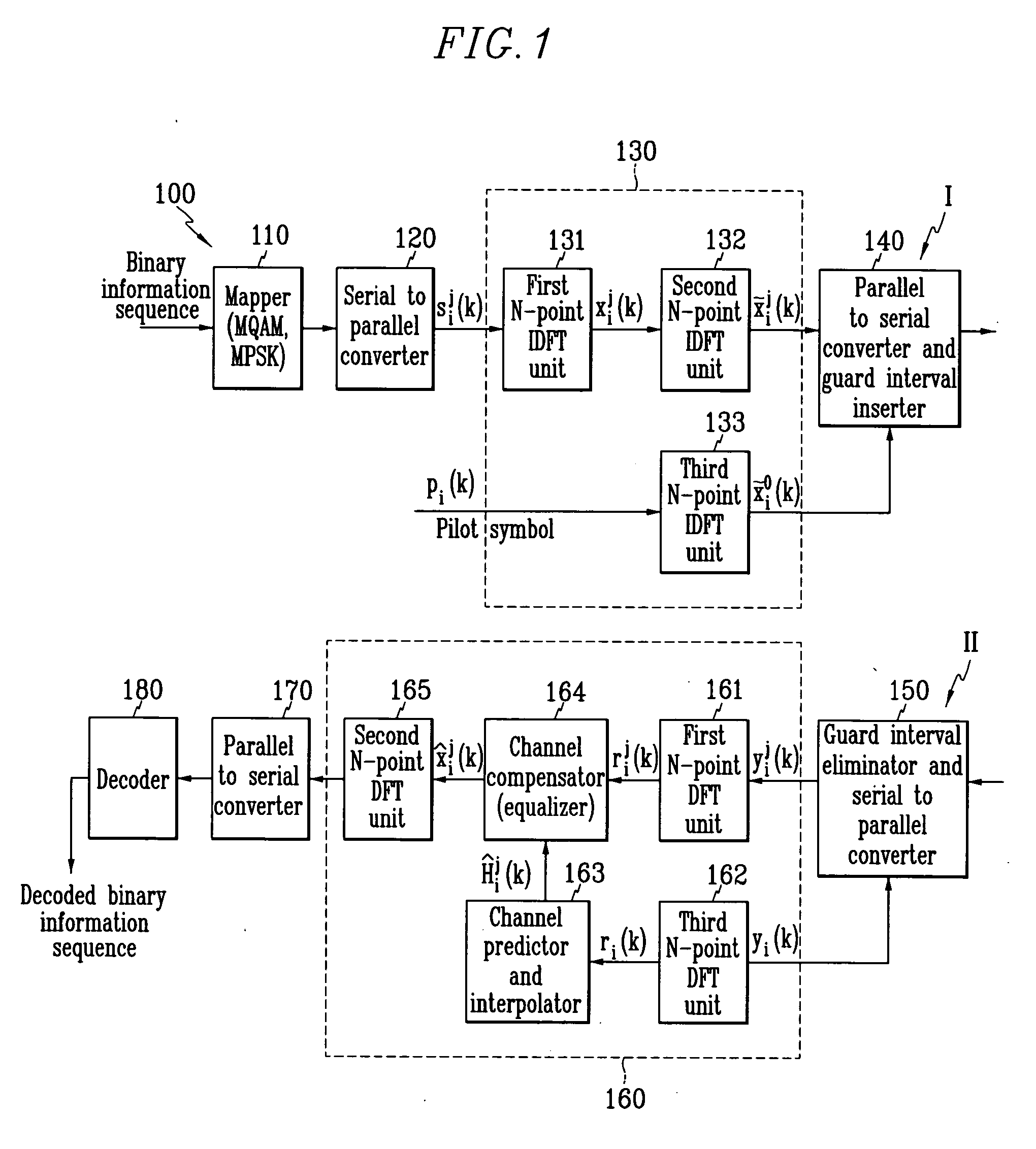
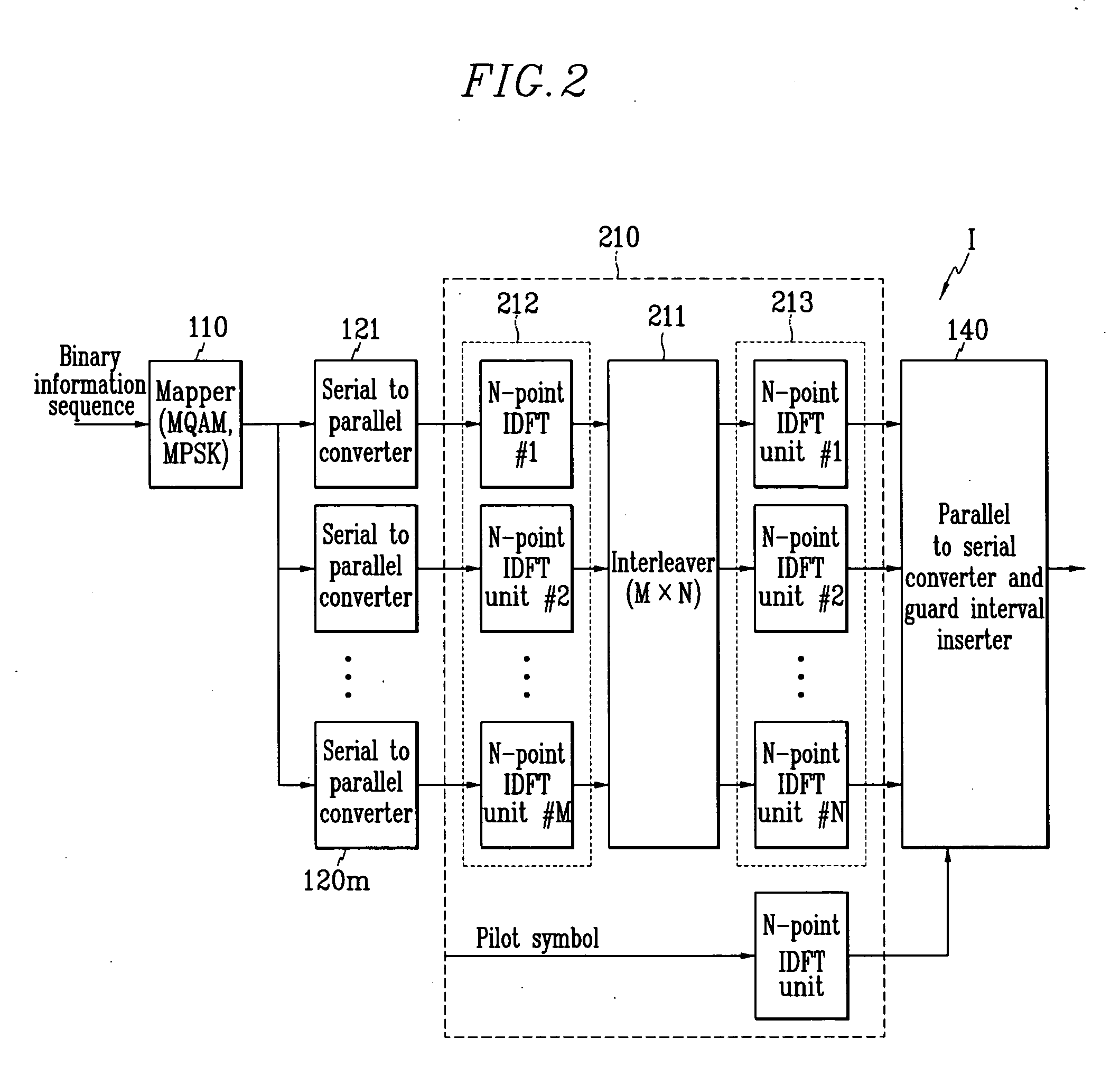
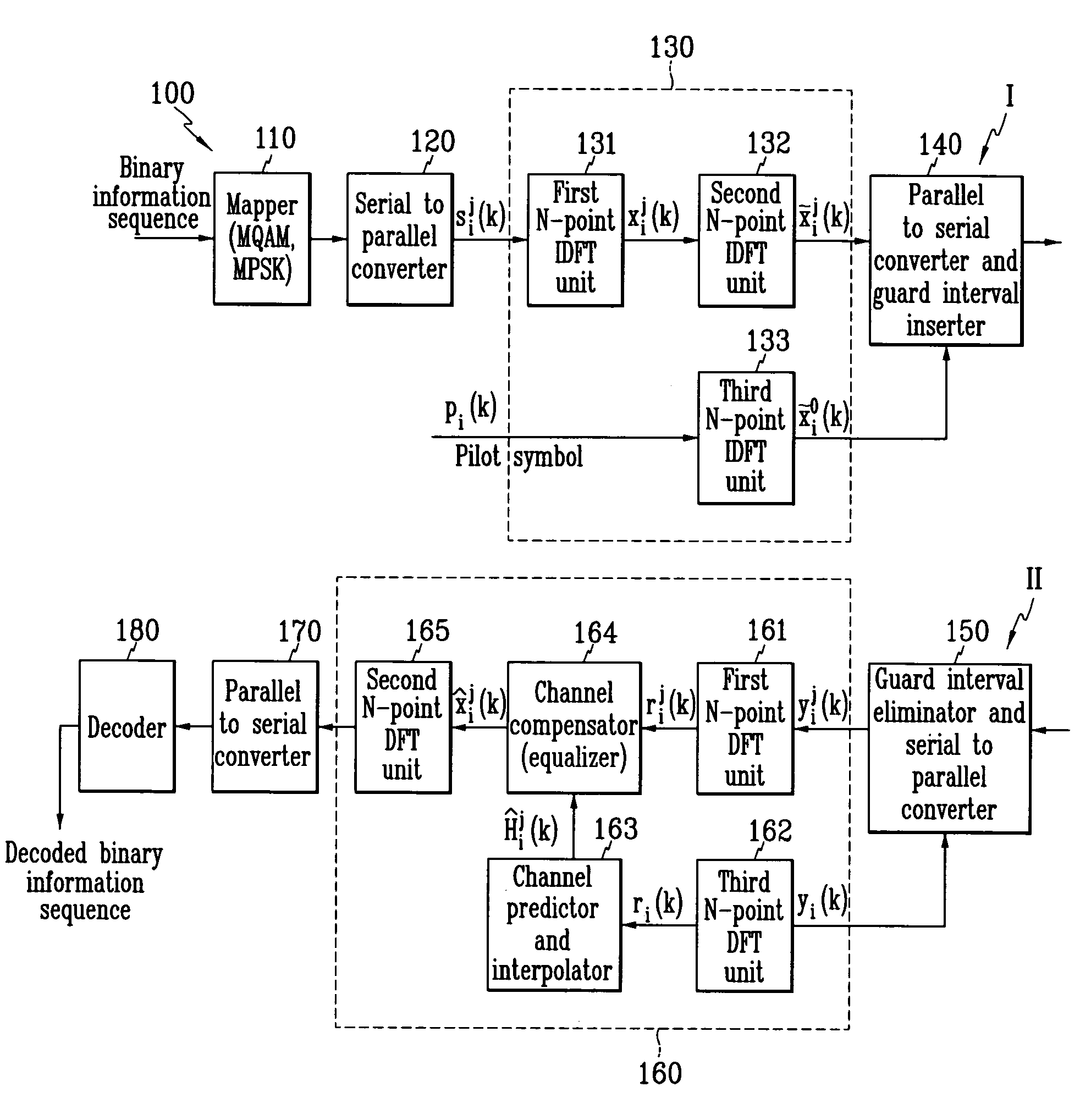
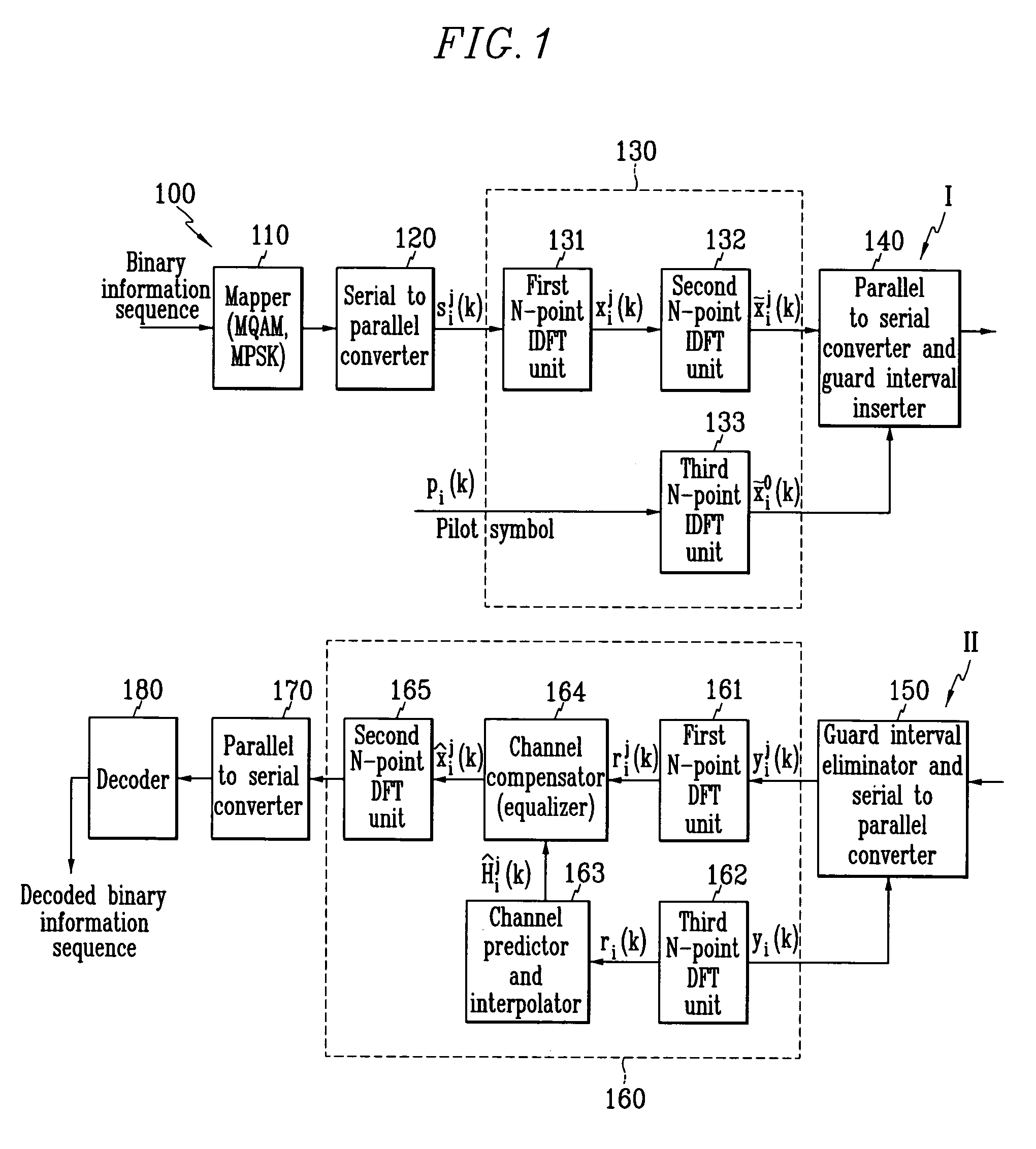
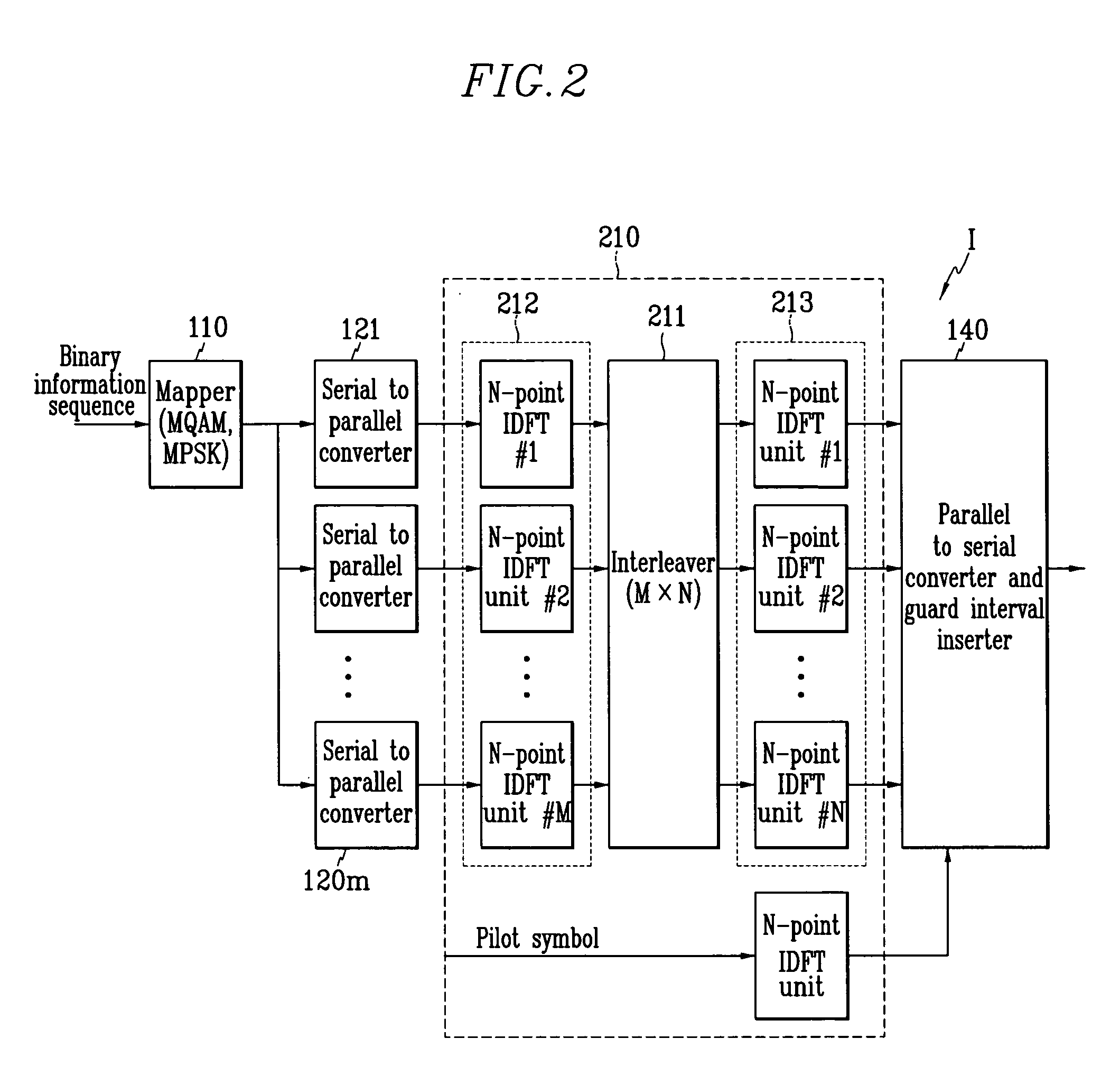
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing wireless communication operable on frequency selective channel, and channel compensation method
InactiveUS20050073948A1Lower BERHigh error rateBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemInverse discrete fourier transform
Disclosed is an OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) wireless communication system operable on a frequency selective channel, and a channel compensation method. An IDFT (inverse discrete Fourier transform) unit of a transmitter includes first through third N-point IDFT units, and performs IDFT on a binary information signal twice. A DFT (discrete Fourier transform) unit of a receiver includes first through third N-point DFT units, a channel predictor and interpolator, and a channel compensator, and performs DFT on the signal received from the transmitter twice.
Owner:KT CORP +1
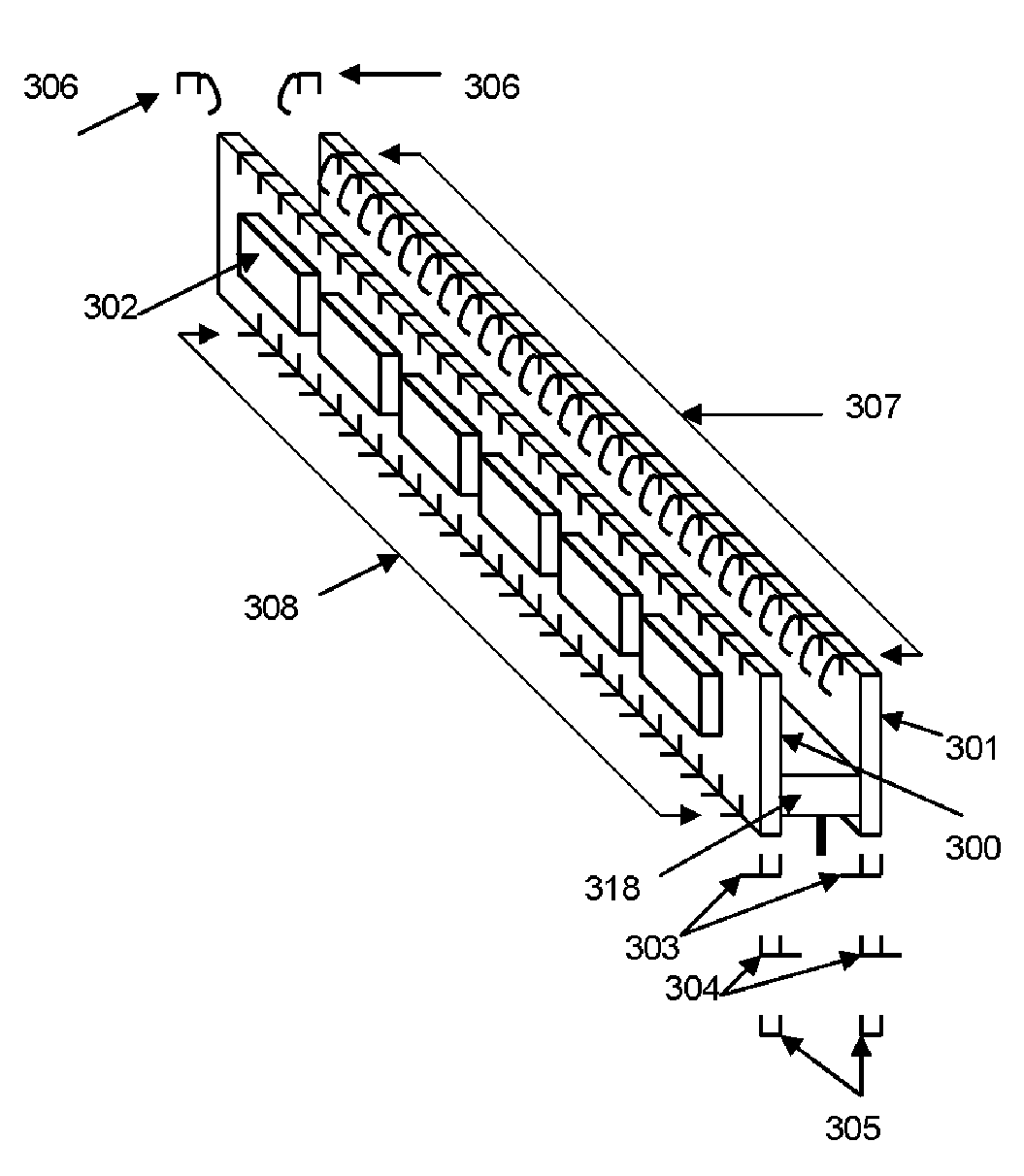
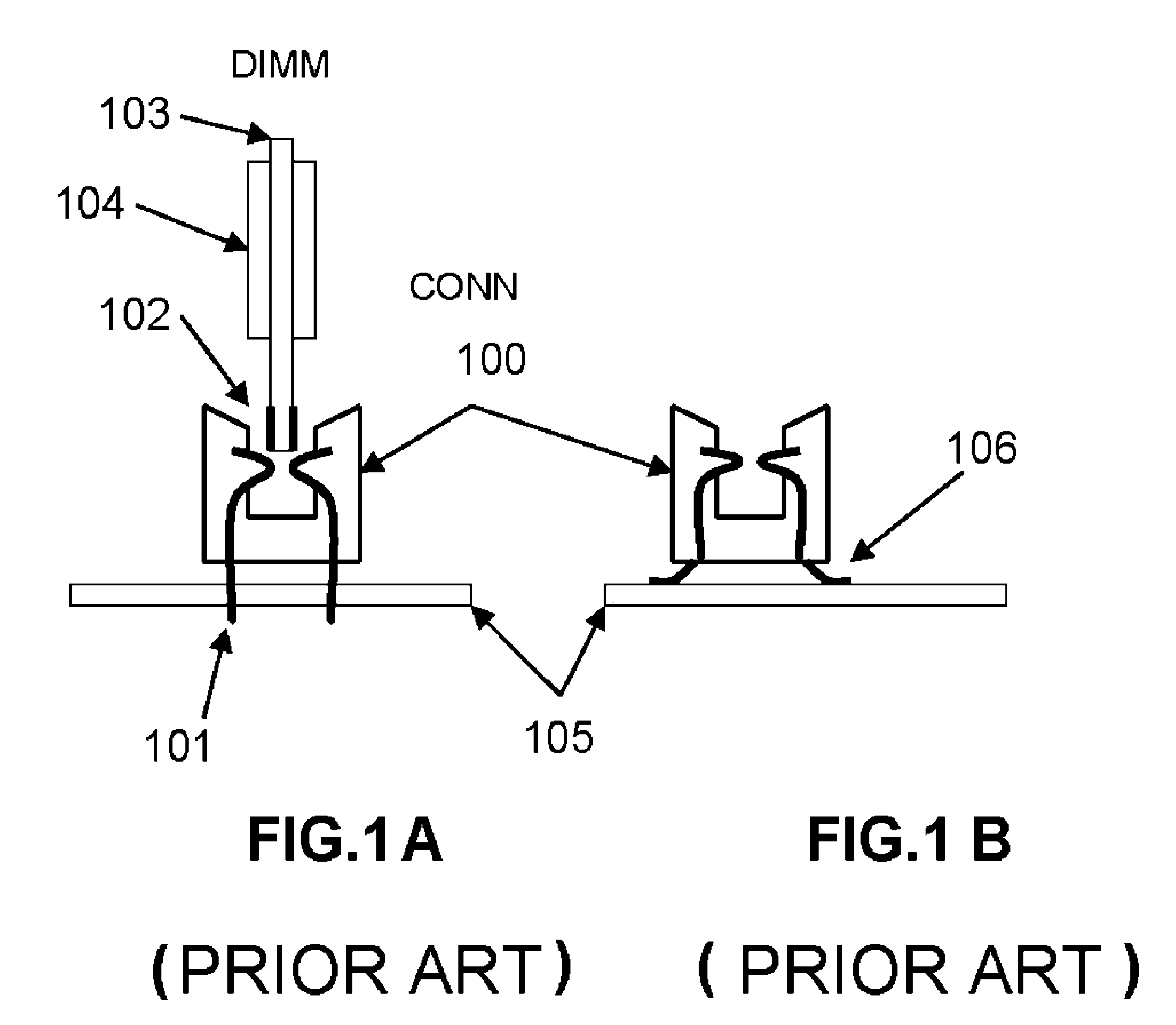
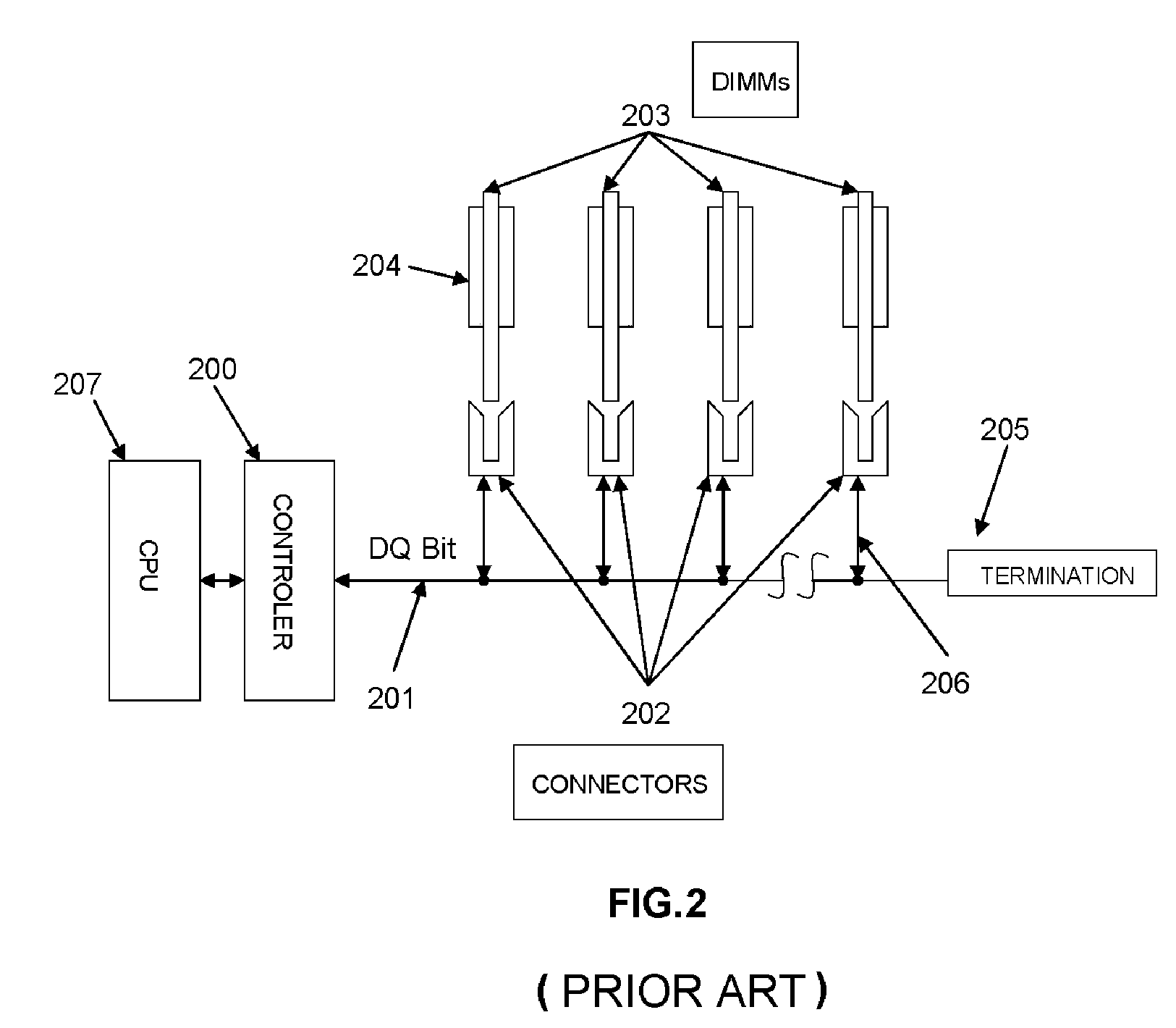
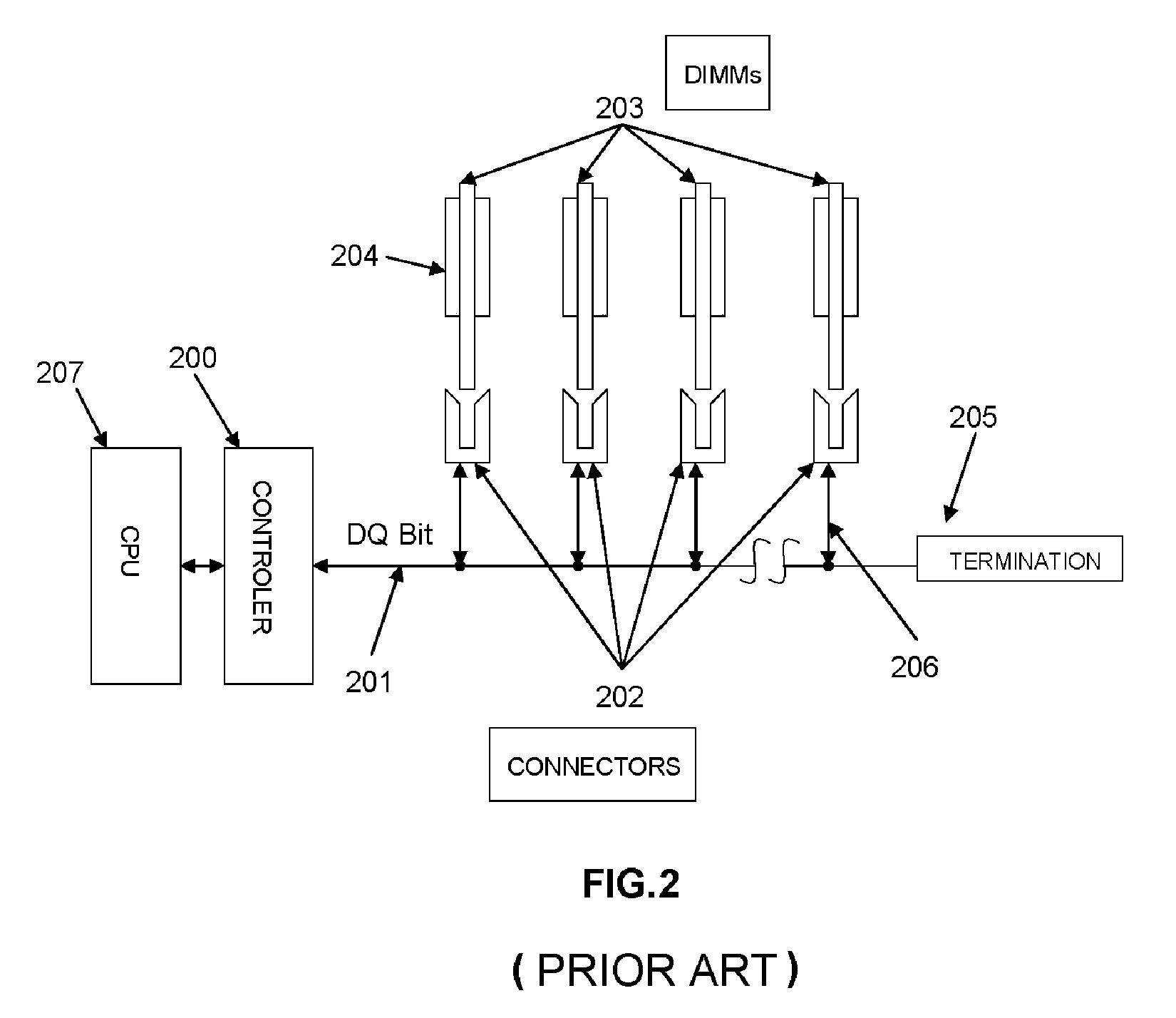
Active Dual in Line Memory Module Connector with Re-driven Propagated Signals
ActiveUS20110143579A1High densityData rateCoupling device detailsPrinted circuit manufactureActive edgeComputer module
An Active edge connector for memory modules has a base including two PCB sides and a spacer separating the sides, with driver chips mounted on each side of each side, printed wiring electrically connecting a first set of electrical signals from each of the driver chips to a mother board on which the connector is mounted, and printed wiring for electrically connecting a second set of electrical signals from each of the driver chips to a memory module inserted in the edge connector. When a group of connectors are mounted on a mother board, electrical signals arriving at the first connector are routed to its driver chips, producing re-driven signals to the next connector, and so on. A decoder circuit provides addressing signals determining the last such connector to which the signals are intended, and which prevents the signals from going to any connectors containing memories not addressed.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
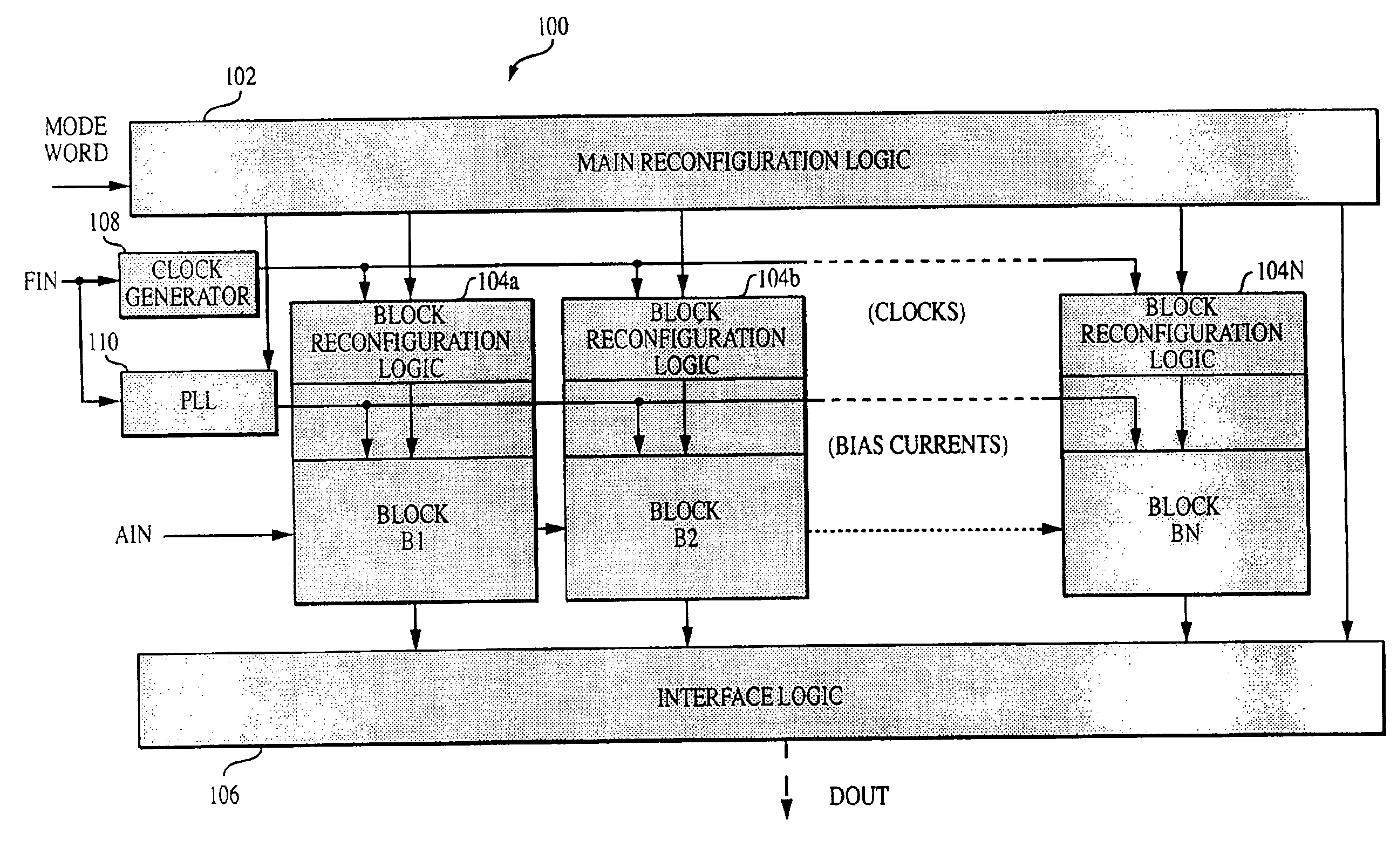
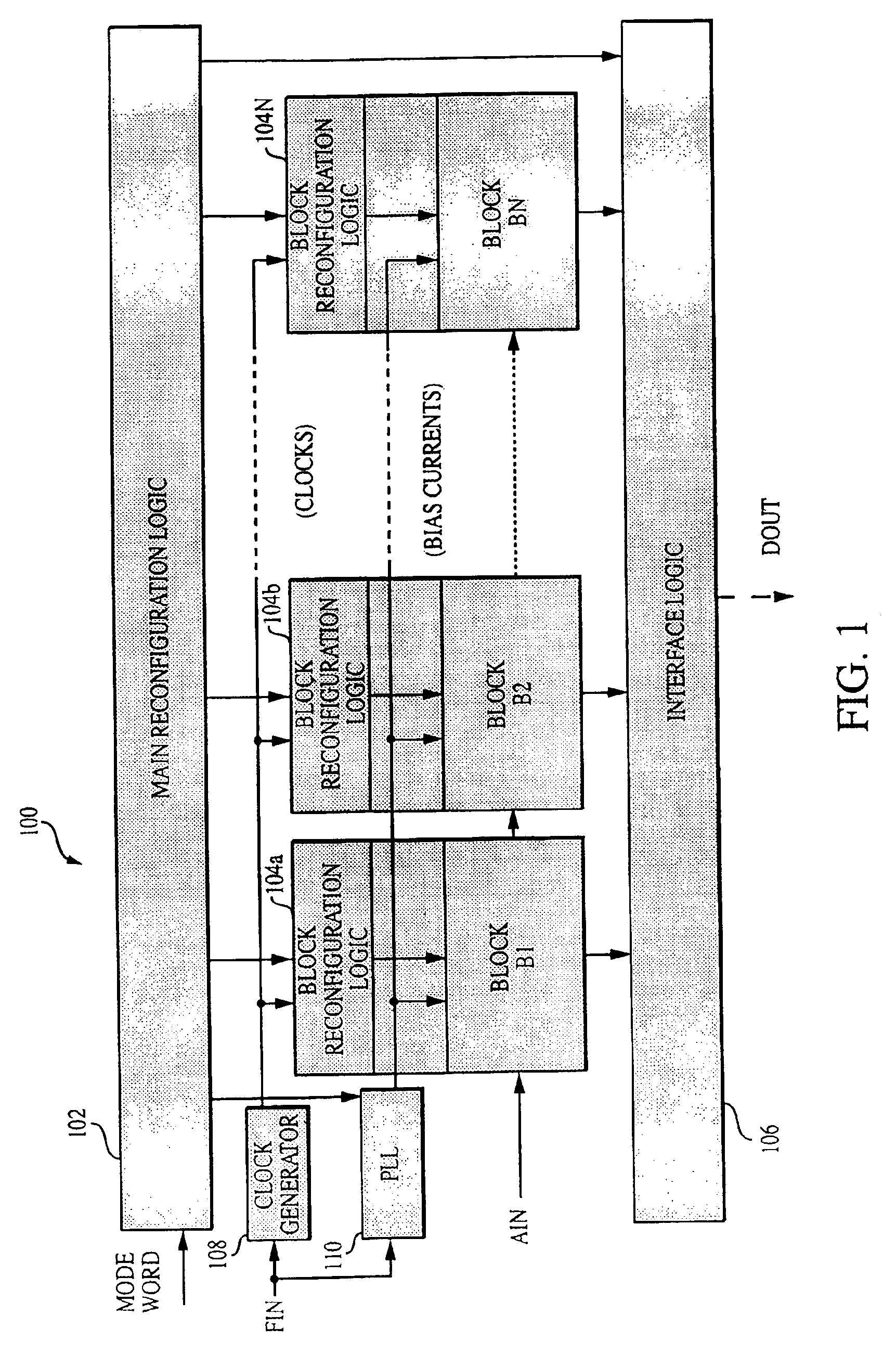
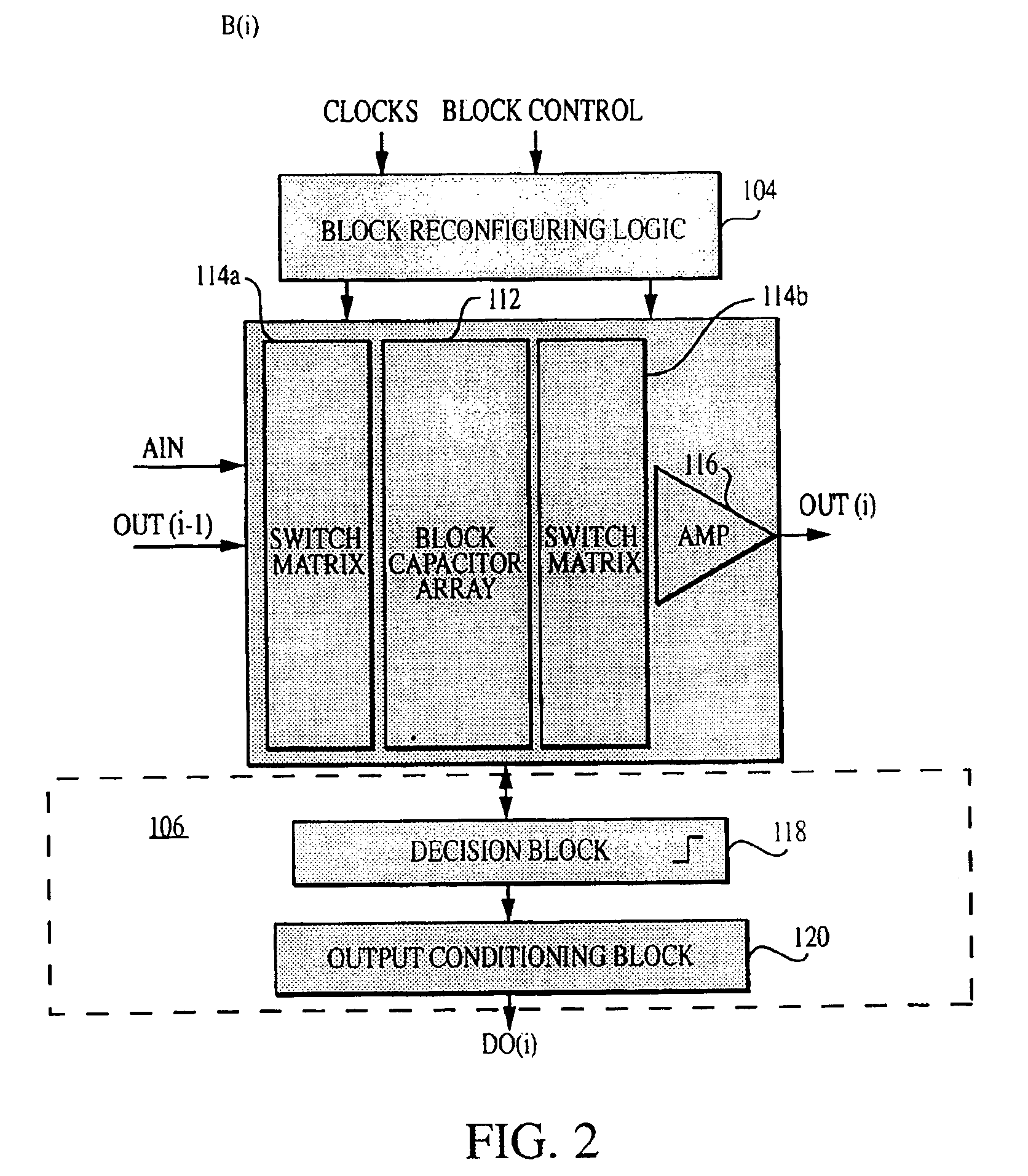
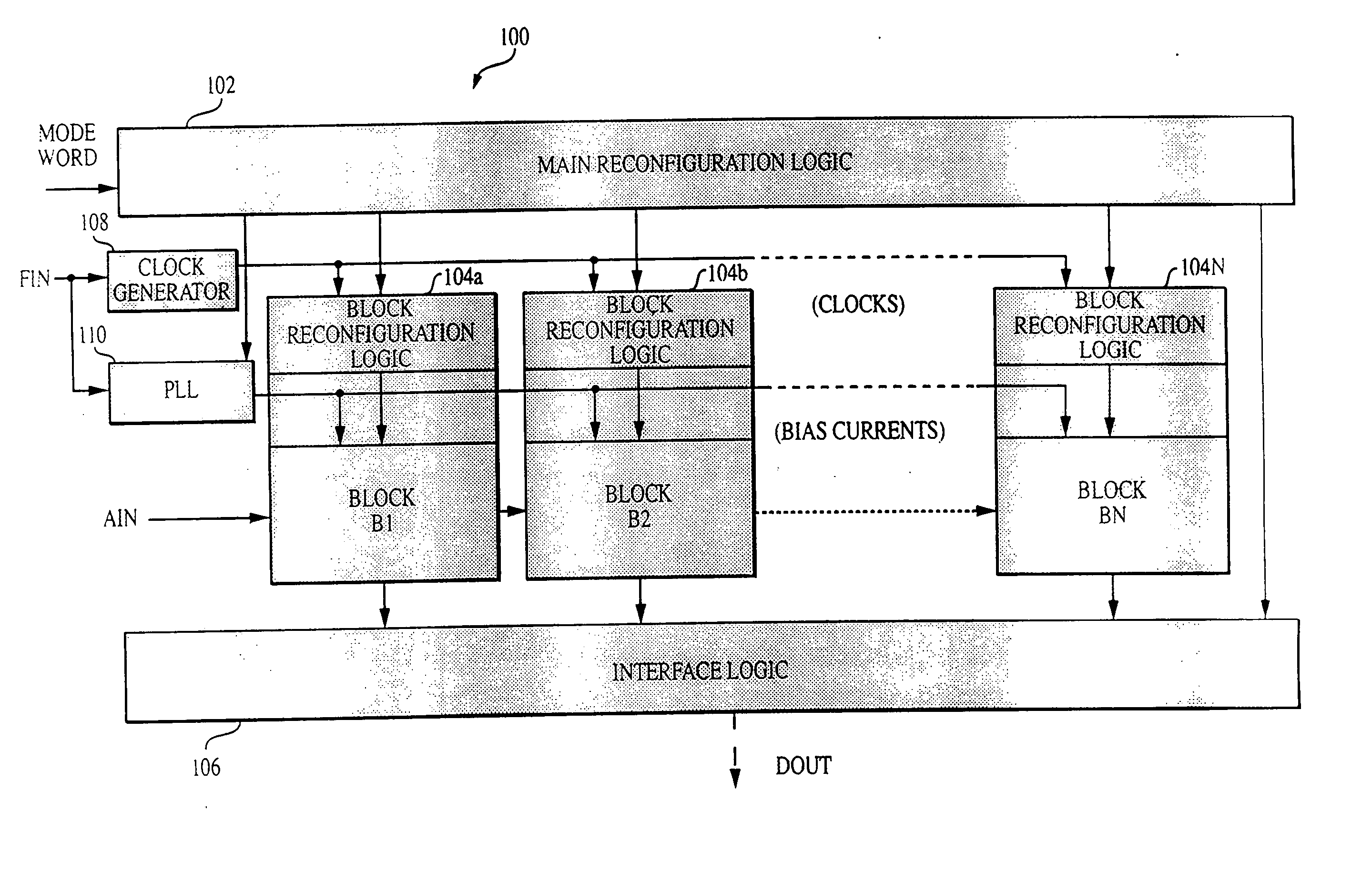
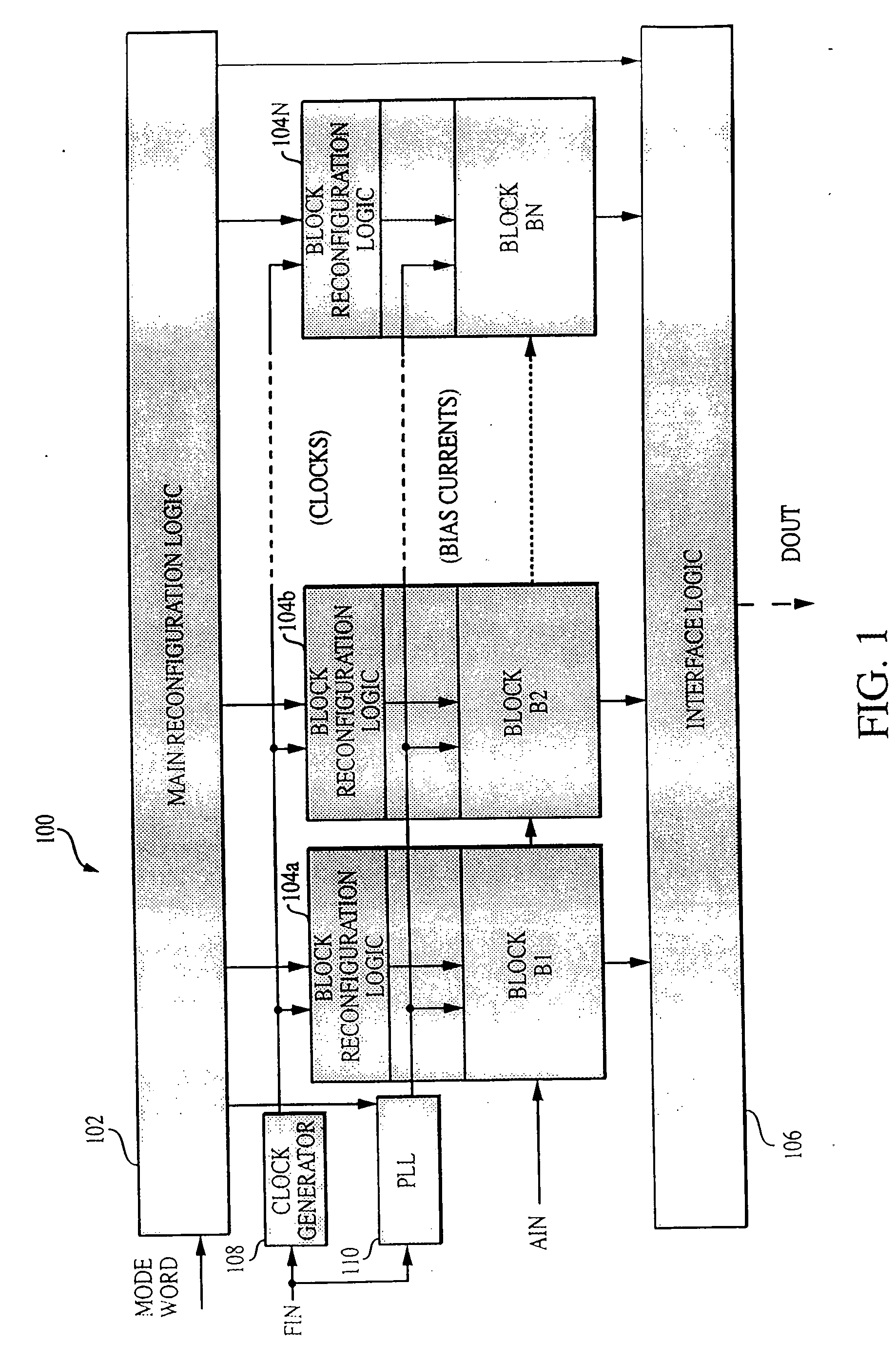
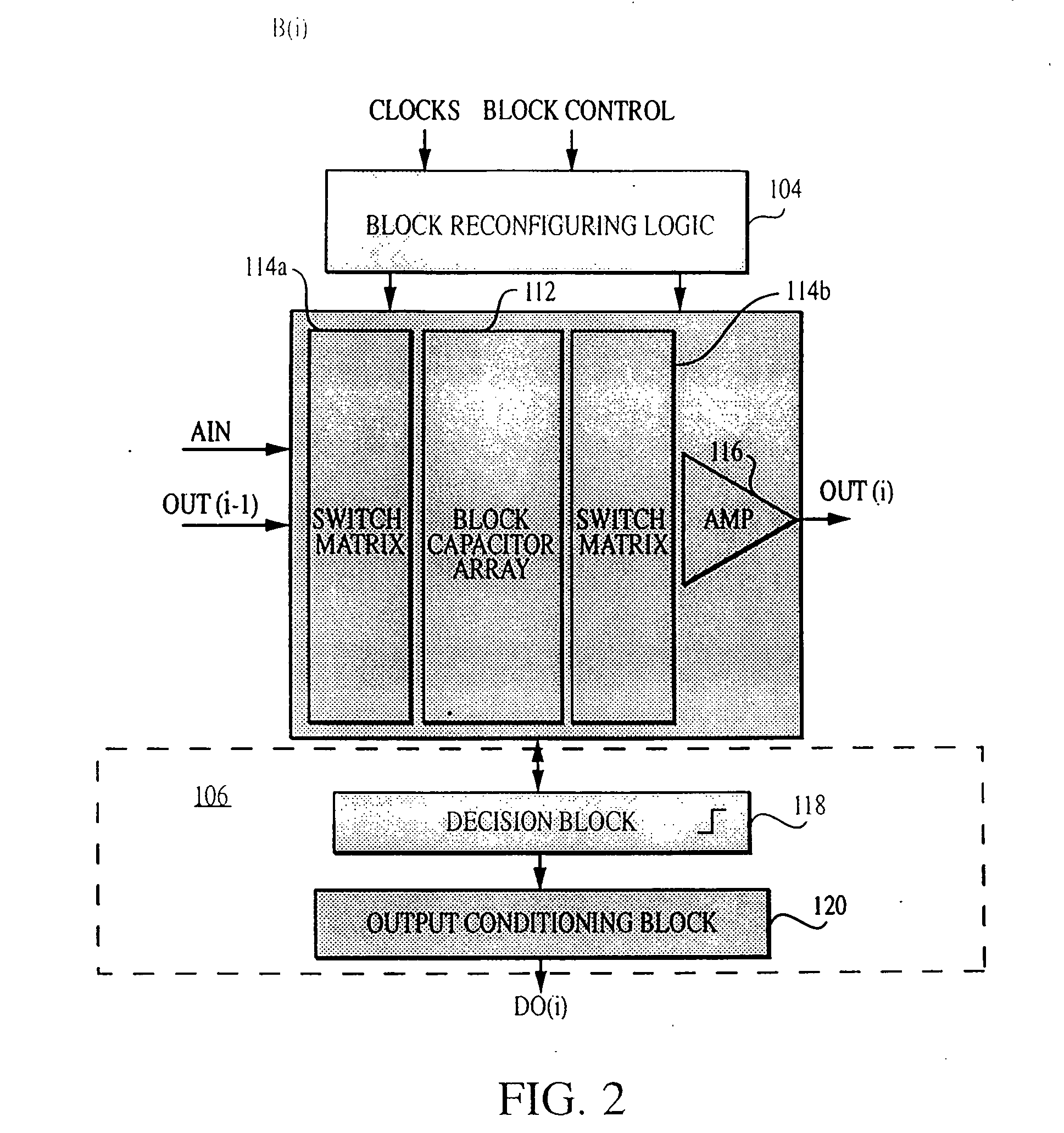
Reconfigurable analog-to-digital converter
InactiveUS6864822B2Improve powerWide rangeElectric signal transmission systemsReconfigurable analogue/digital convertersImage resolutionA d converter
A reconfigurable ADC includes a plurality of reconfigurable blocks for allowing the ADC to provide a plurality of architectures. In one embodiment, the ADC can be configured to operate in a pipeline mode and a sigma-delta mode. This arrangement provides an ADC having a relatively large range of bandwidth and resolution.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Analog-to-Digital Converter Having Parametric Configuirablity
InactiveUS20050190092A1High resolutionData rateElectric signal transmission systemsReconfigurable analogue/digital convertersImage resolutionA d converter
A reconfigurable ADC includes a plurality of reconfigurable blocks for allowing the ADC to provide a plurality of architectures. In one embodiment, the ADC can be configured to operate in a pipeline mode and a sigma-delta mode. This arrangement provides an ADC having a relatively large range of bandwidth and resolution.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Active dual in line memory module connector with re-driven propagated signals
An Active edge connector for memory modules has a base including two PCB sides and a spacer separating the sides, with driver chips mounted on each side of each side, printed wiring electrically connecting a first set of electrical signals from each of the driver chips to a mother board on which the connector is mounted, and printed wiring for electrically connecting a second set of electrical signals from each of the driver chips to a memory module inserted in the edge connector. When a group of connectors are mounted on a mother board, electrical signals arriving at the first connector are routed to its driver chips, producing re-driven signals to the next connector, and so on. A decoder circuit provides addressing signals determining the last such connector to which the signals are intended, and which prevents the signals from going to any connectors containing memories not addressed.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Active dual in line memory module connector with re-driven propagated signals
ActiveUS7539024B1High operating requirementsHigh densityCoupling device detailsPrinted circuit manufactureActive edgeEngineering
An Active edge connector for memory modules has a base including two PCB sides and a spacer separating the sides, with driver chips mounted on each side of each side, printed wiring electrically connecting a first set of electrical signals from each of the driver chips to a mother board on which the connector is mounted, and printed wiring for electrically connecting a second set of electrical signals from each of the driver chips to a memory module inserted in the edge connector. When a group of connectors are mounted on a mother board, electrical signals arriving at the first connector are routed to its driver chips, producing re-driven signals to the next connector, and so on. A decoder circuit provides addressing signals determining the last such connector to which the signals are intended, and which prevents the signals from going to any connectors containing memories not addressed.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
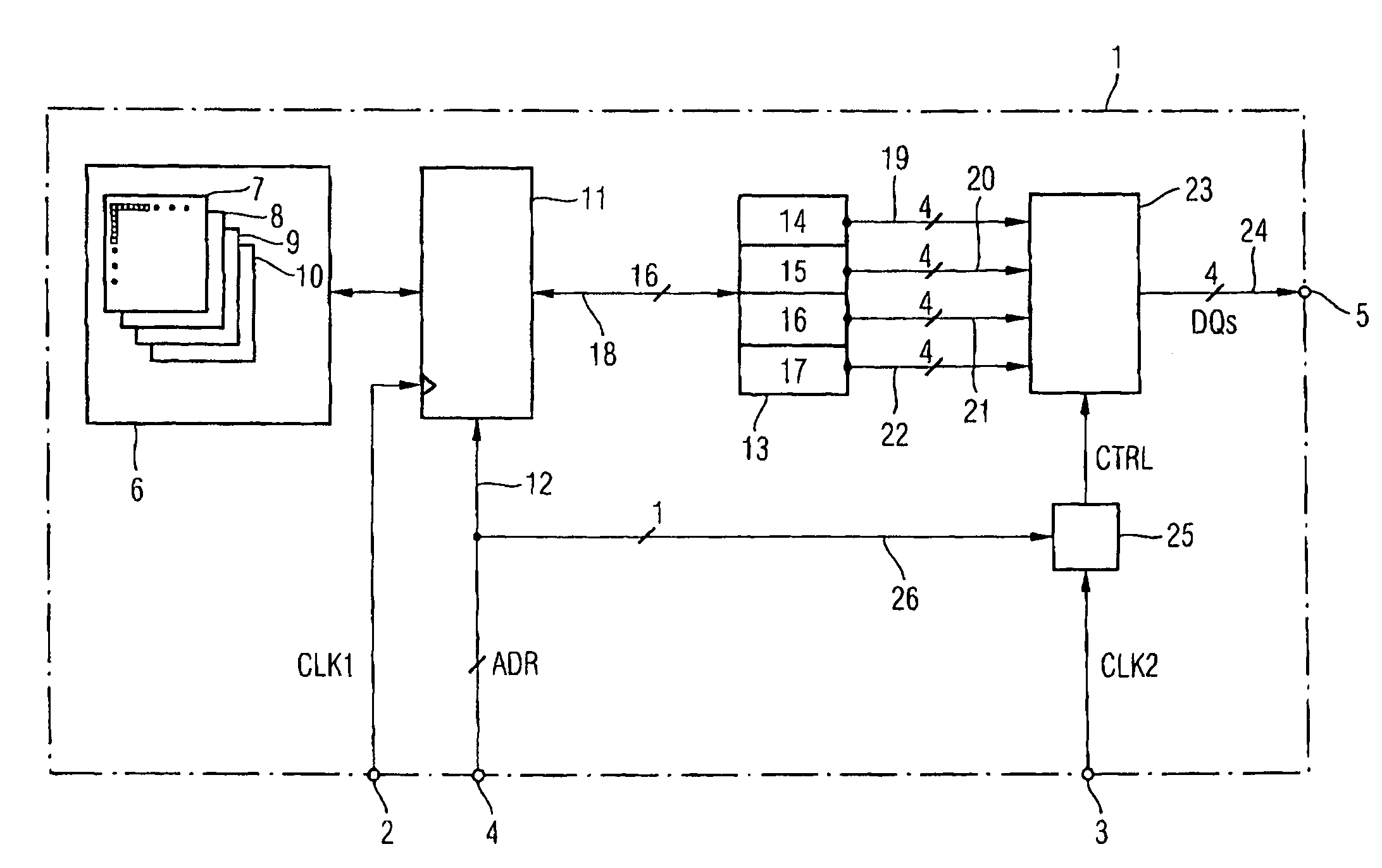
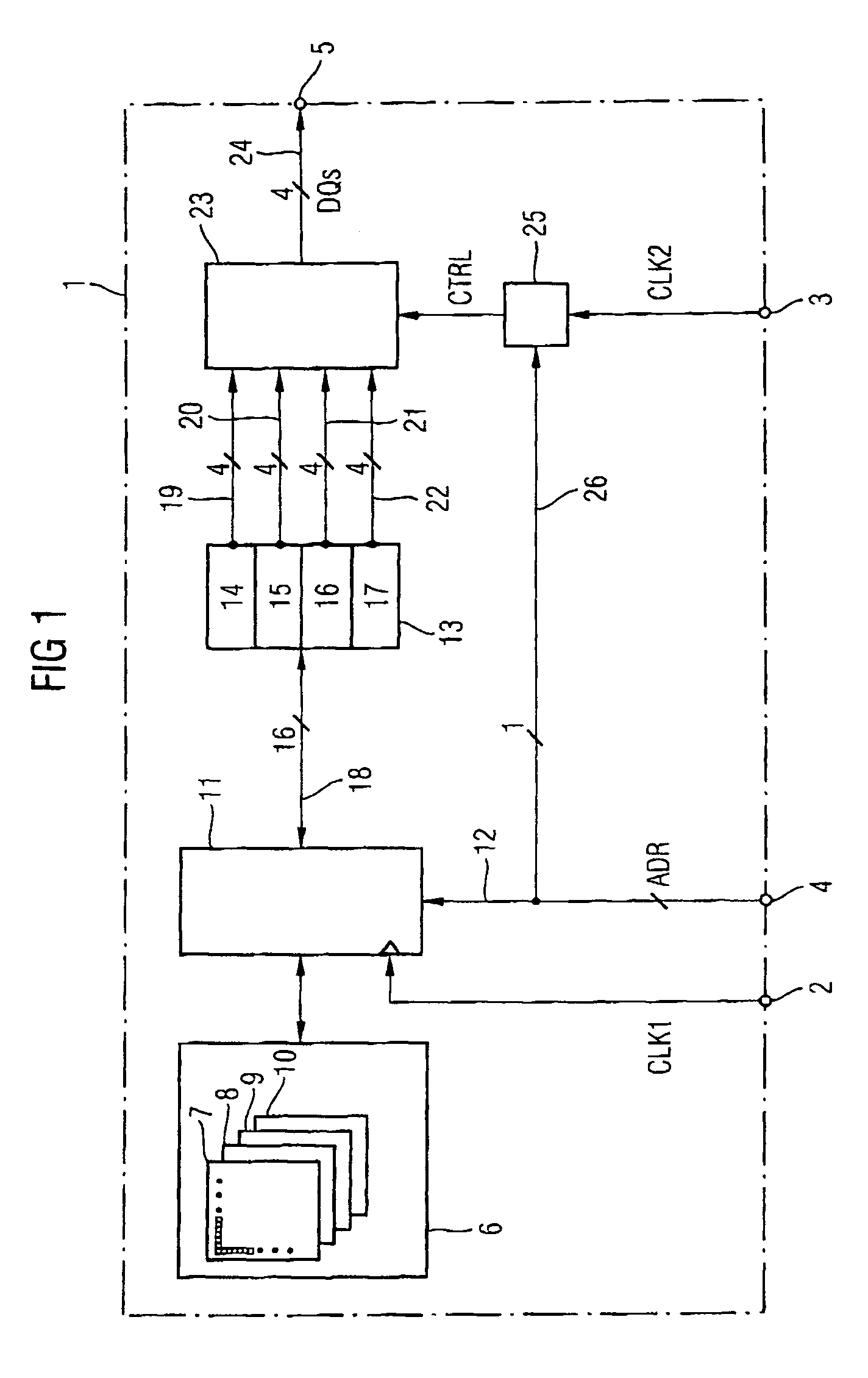
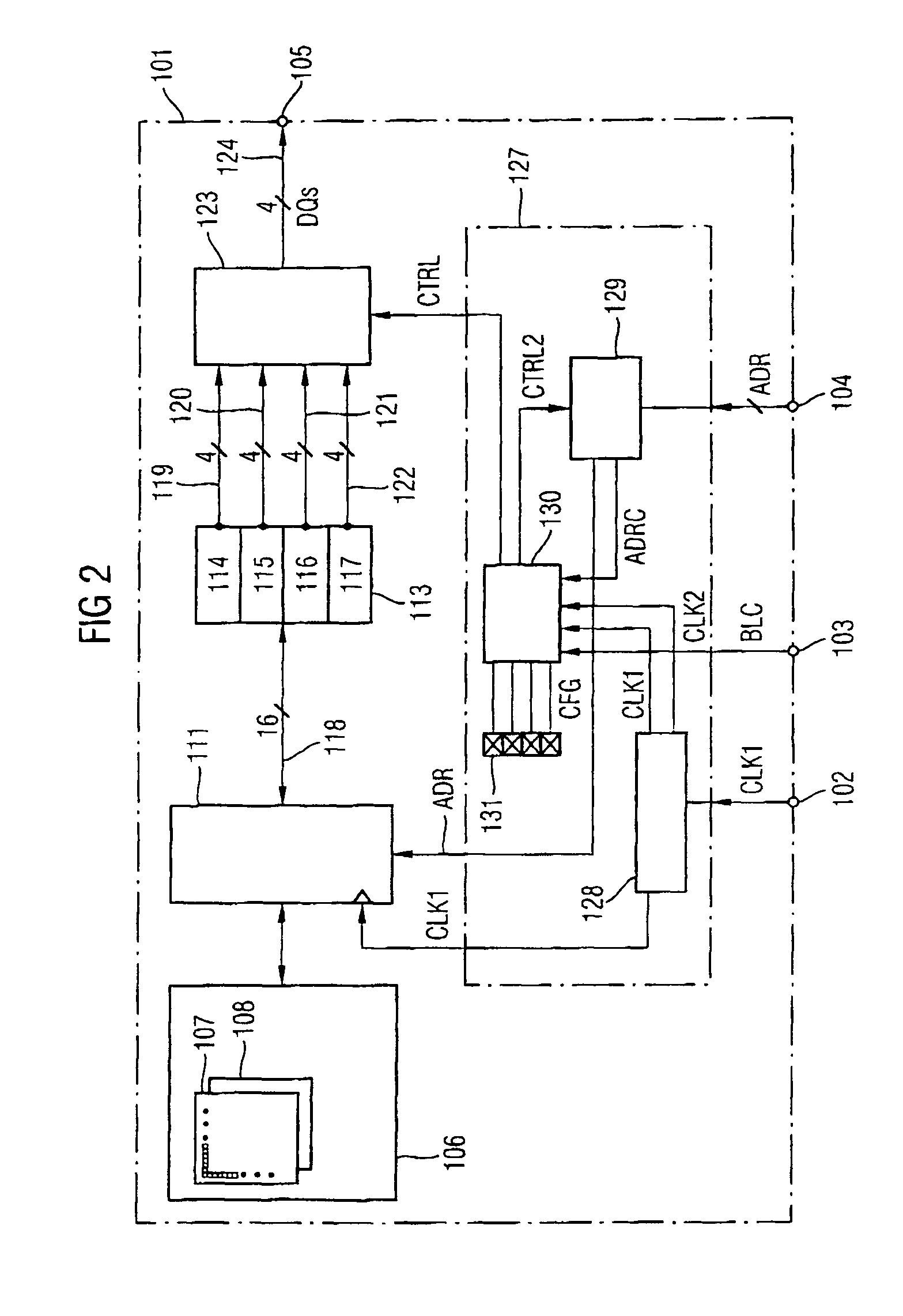
Backwards-compatible memory module
A backwards-compatible memory module is disclosed. According to one aspect, a memory module comprises addressable memory cells organized in organization units having a predetermined number of memory cells, a read / write control device clocked by a first clock signal, a plurality of prefetch registers for initially storing data read from the memory cells wherein the register size corresponds to the predetermined number. In a first operating mode, a switching device clocked by a second clock signal successively couples the prefetch registers to data input / output terminals. The number of data input / output terminals corresponds to the predetermined number. In a second operating mode, the switching device is controlled by at least one address signal and couples at least one of the prefetch registers to the data input / output terminals.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
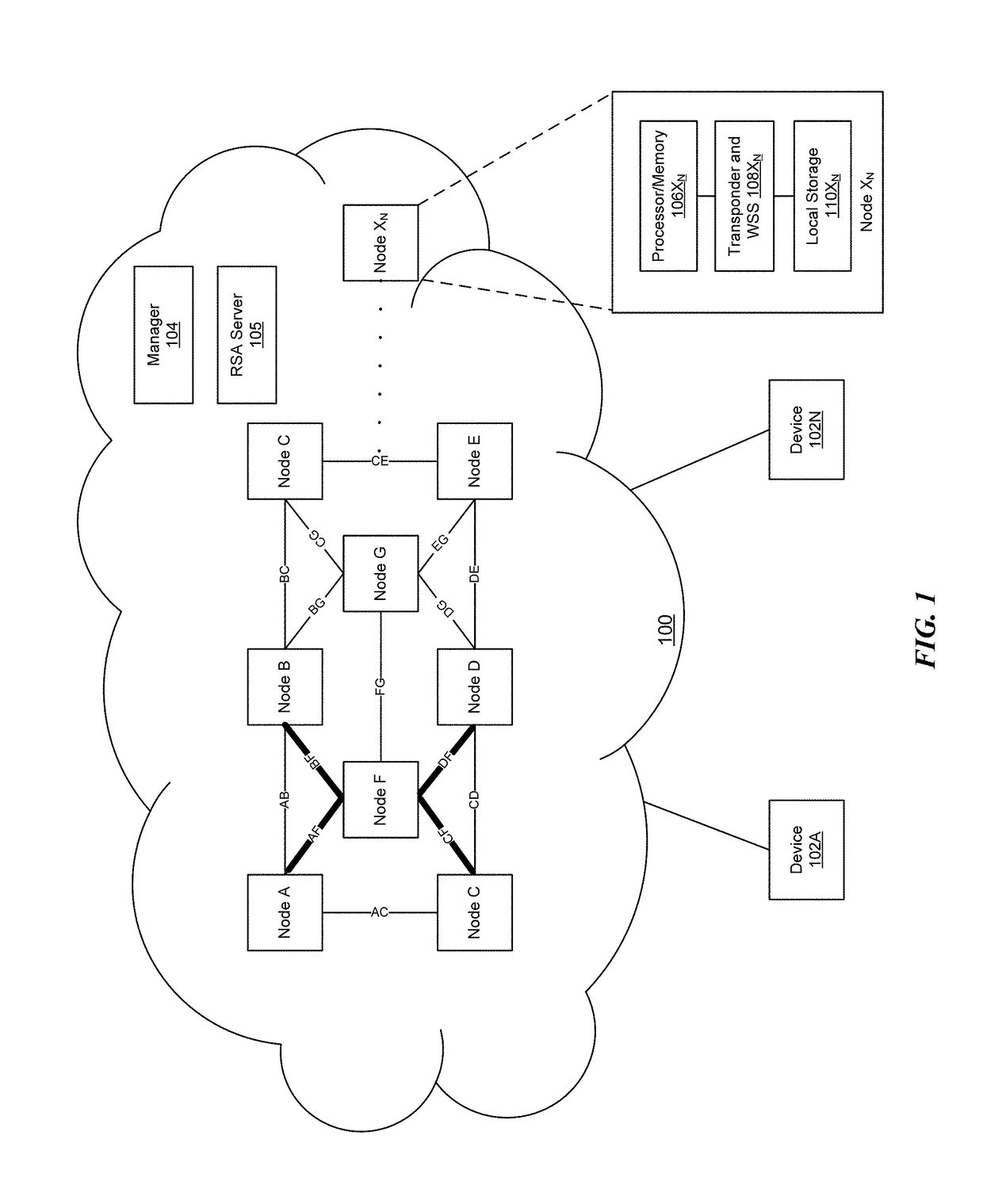
Method and apparatus for efficient network utilization using superchannels
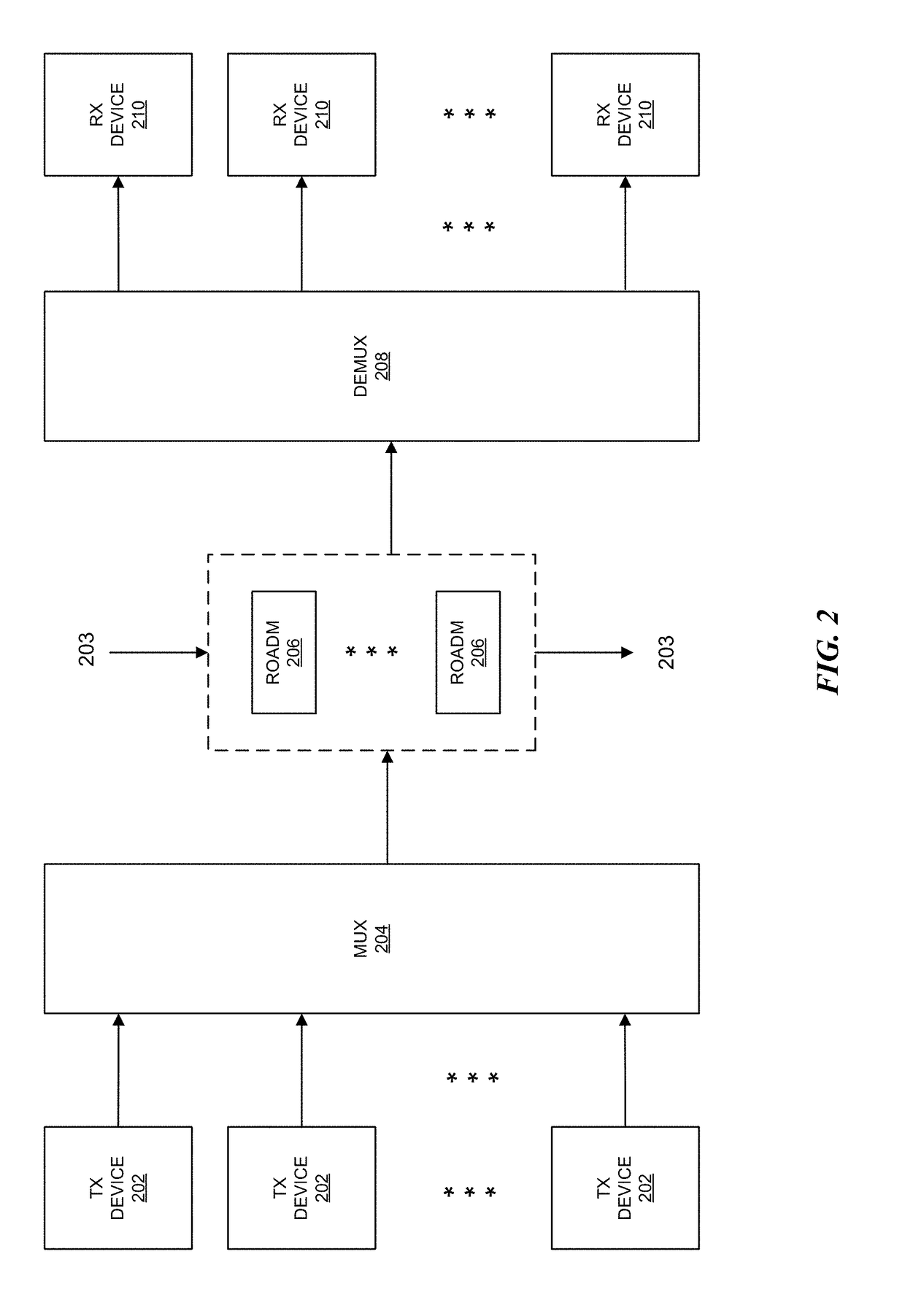
ActiveUS20180076920A1Data rateWell formedMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSuper-channelWavelength selective switching
The disclosure relates to technology for constructing an optical network. A central node is selected among a plurality of nodes in the optical network, and each of the nodes is connected to the central node via a set of superchannels, wherein each of the superchannels includes sub-carriers and has a same data rate. The network resources between the central node and each of the plurality of nodes are managed by dynamically allocating the sub-carrier bandwidths to support communication among the plurality of nodes via the superchannels, and wavelength selective switching is performed among the superchannels at the central node.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
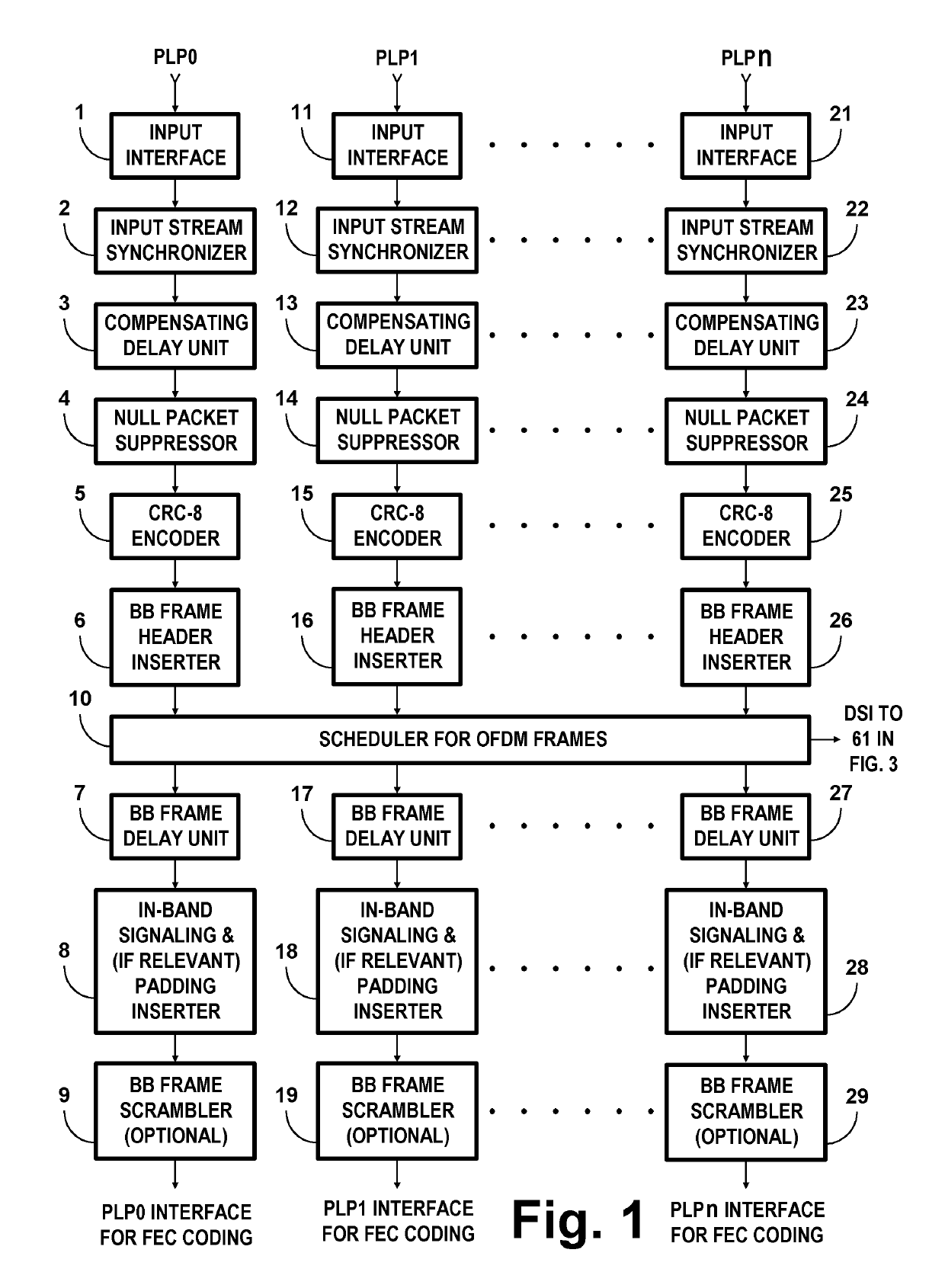
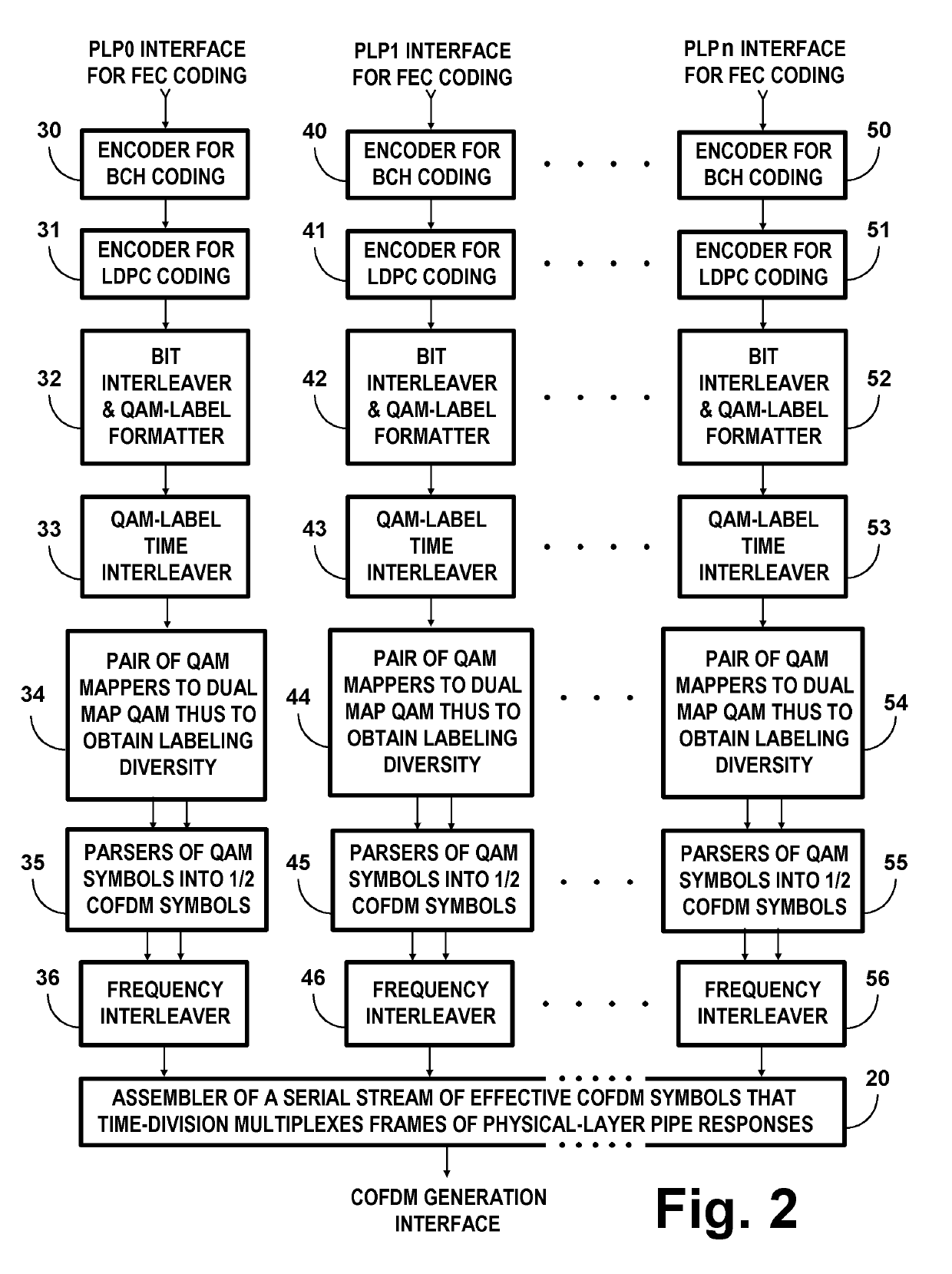
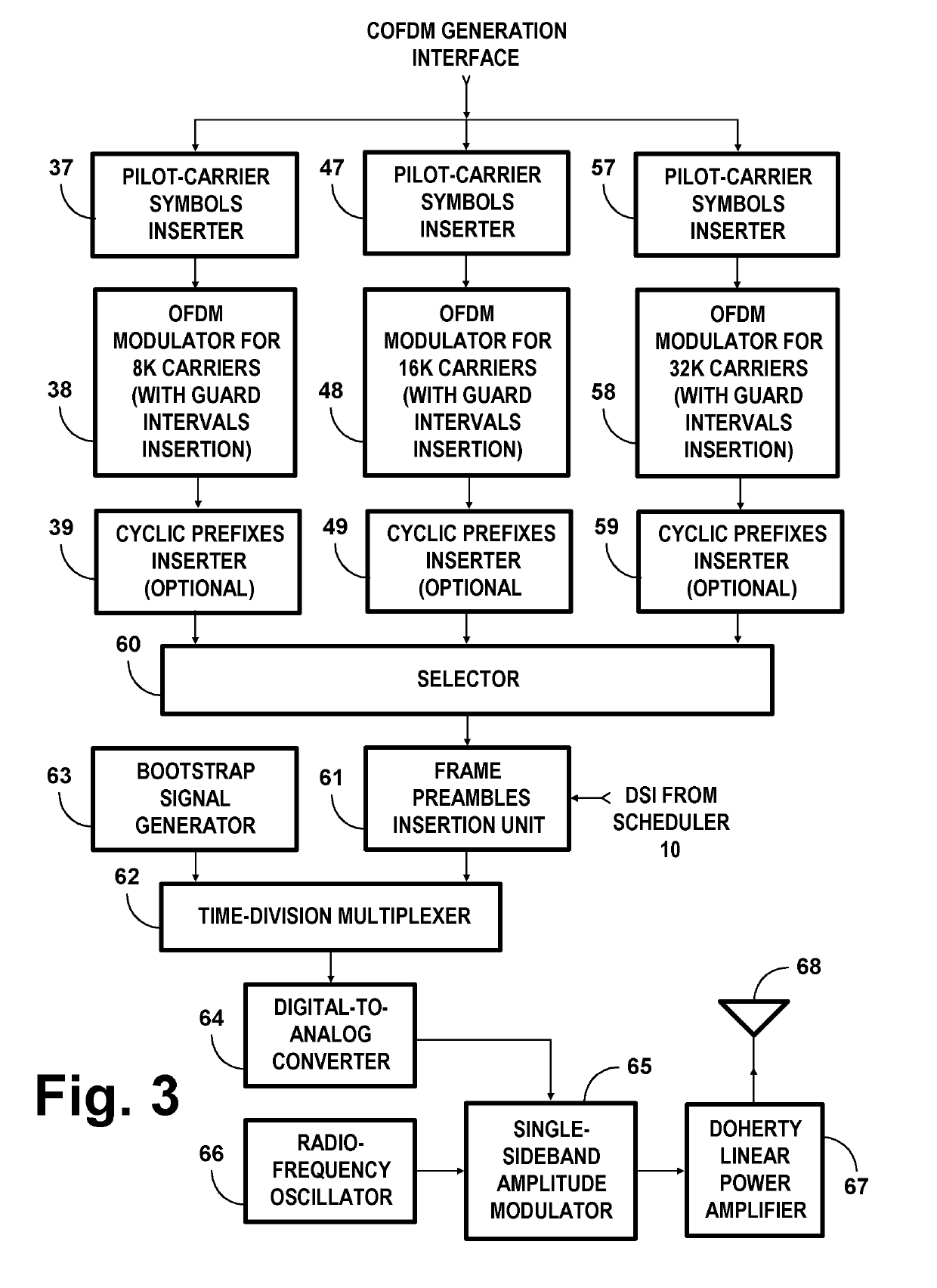
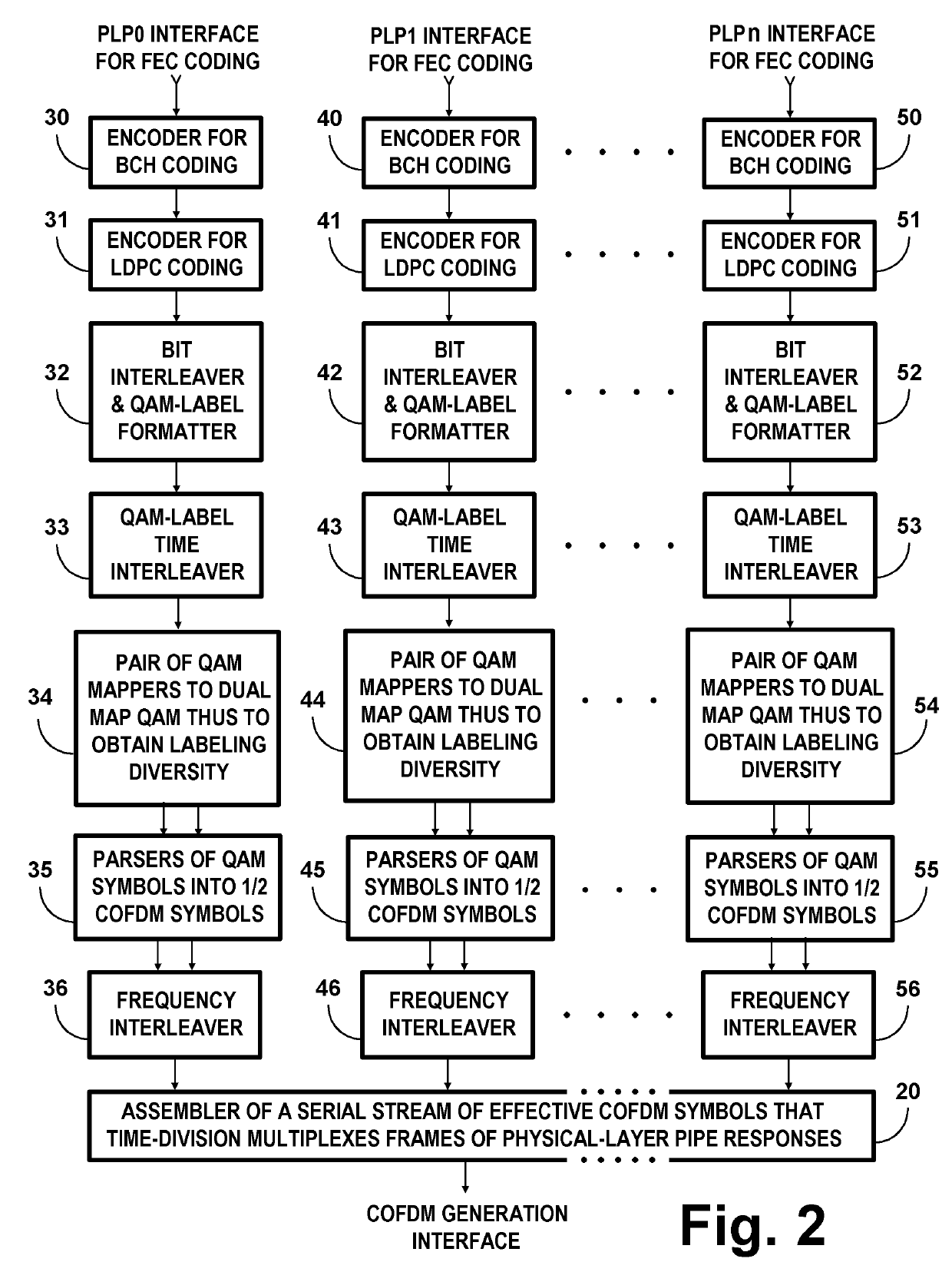
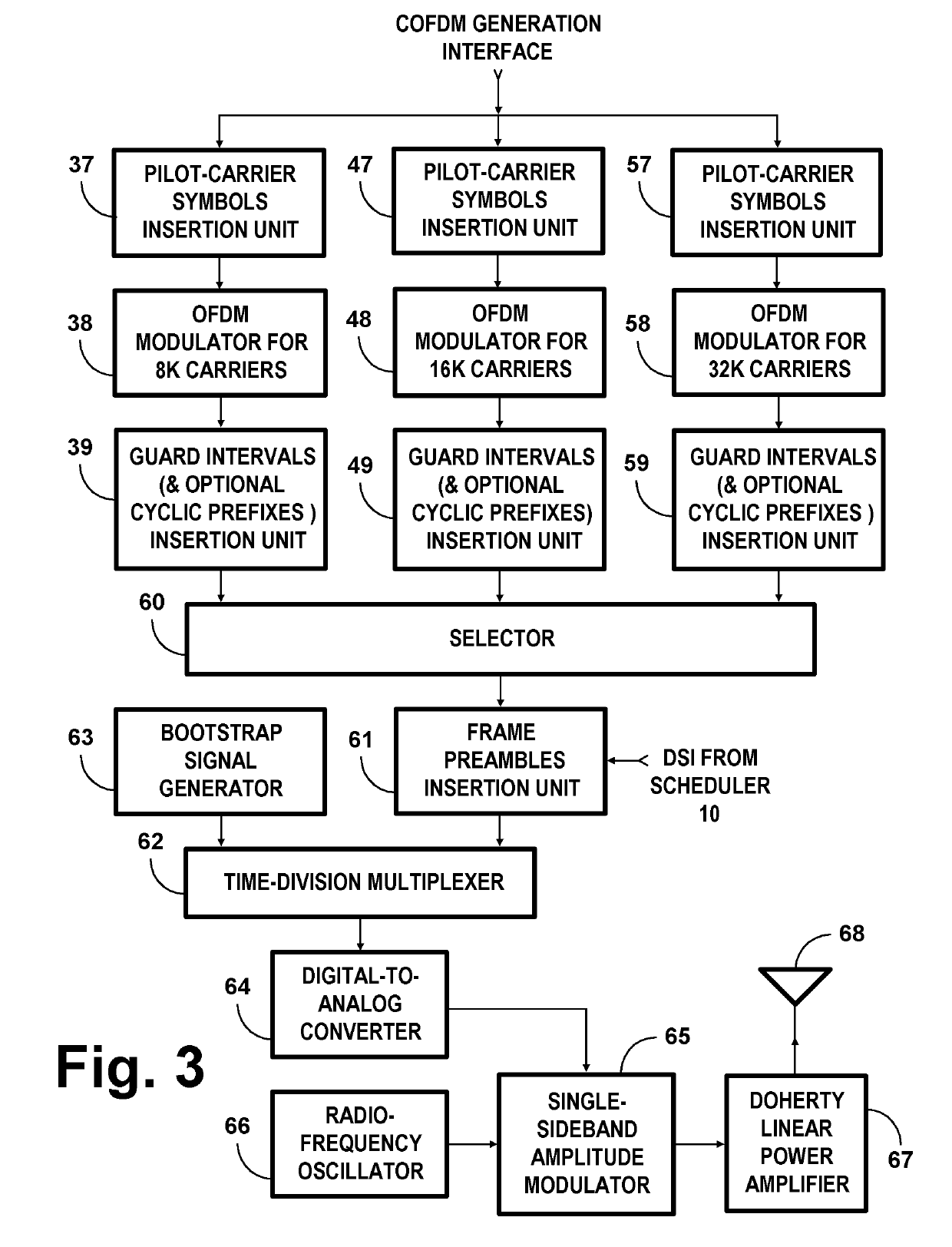
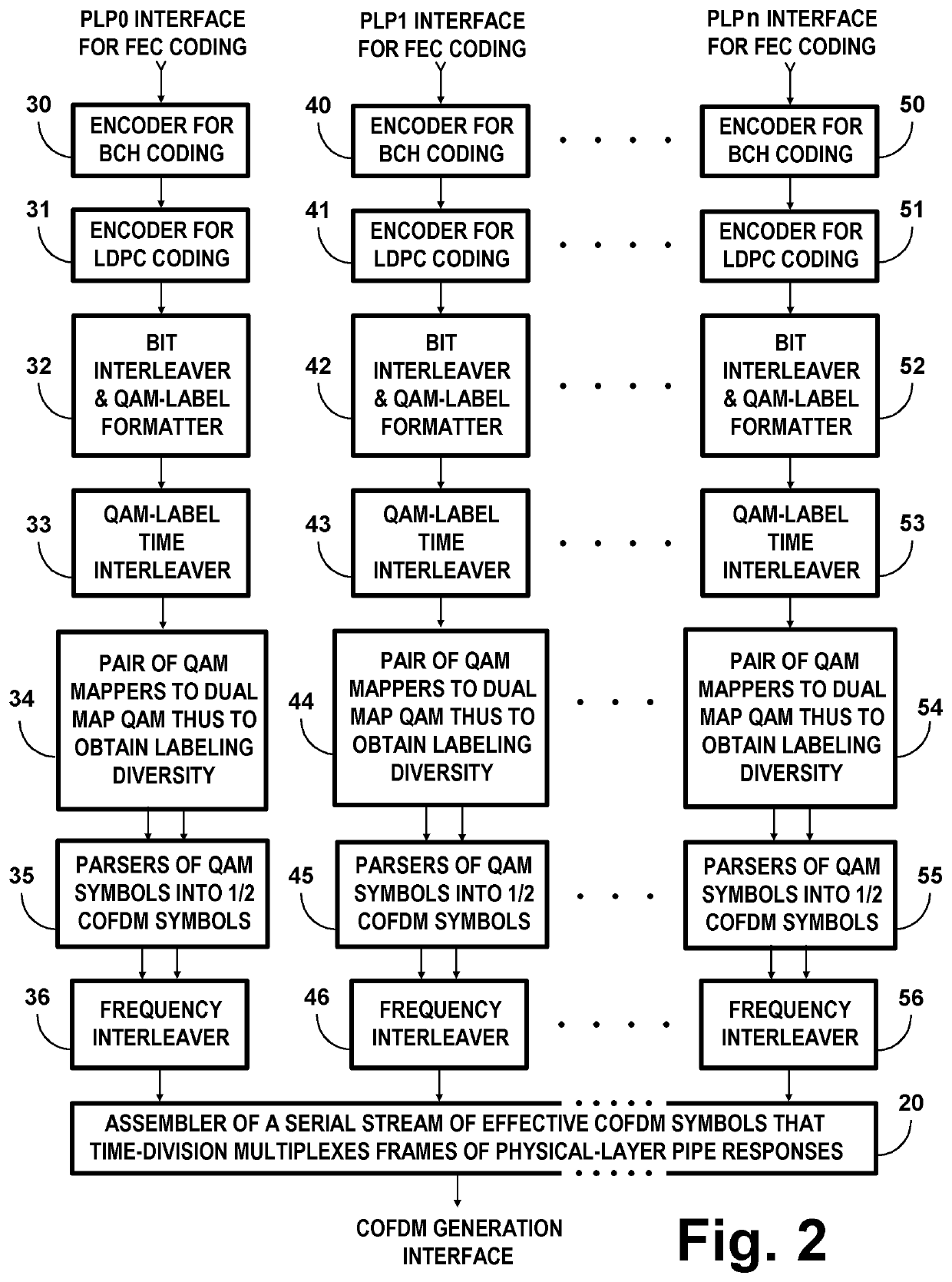
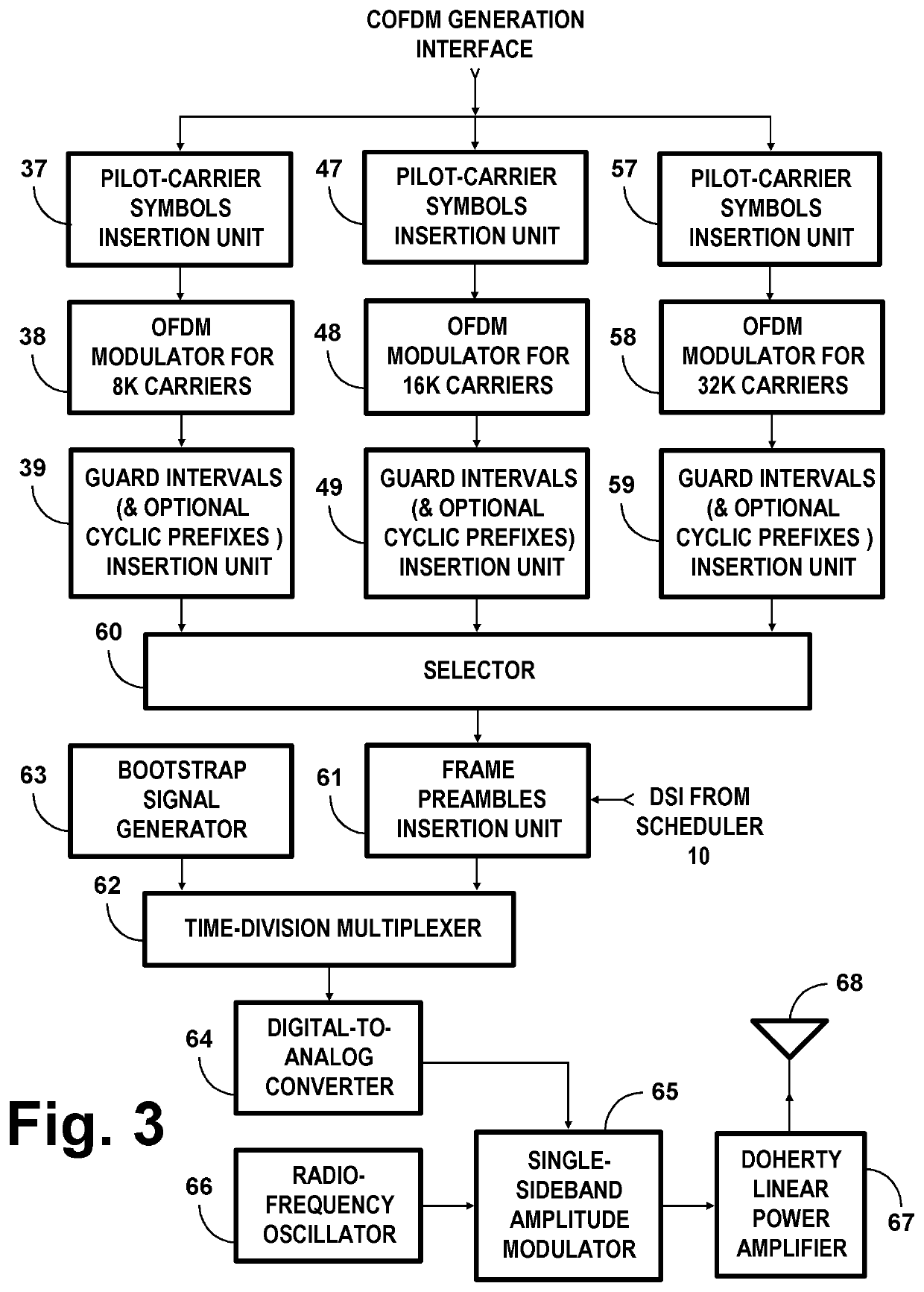
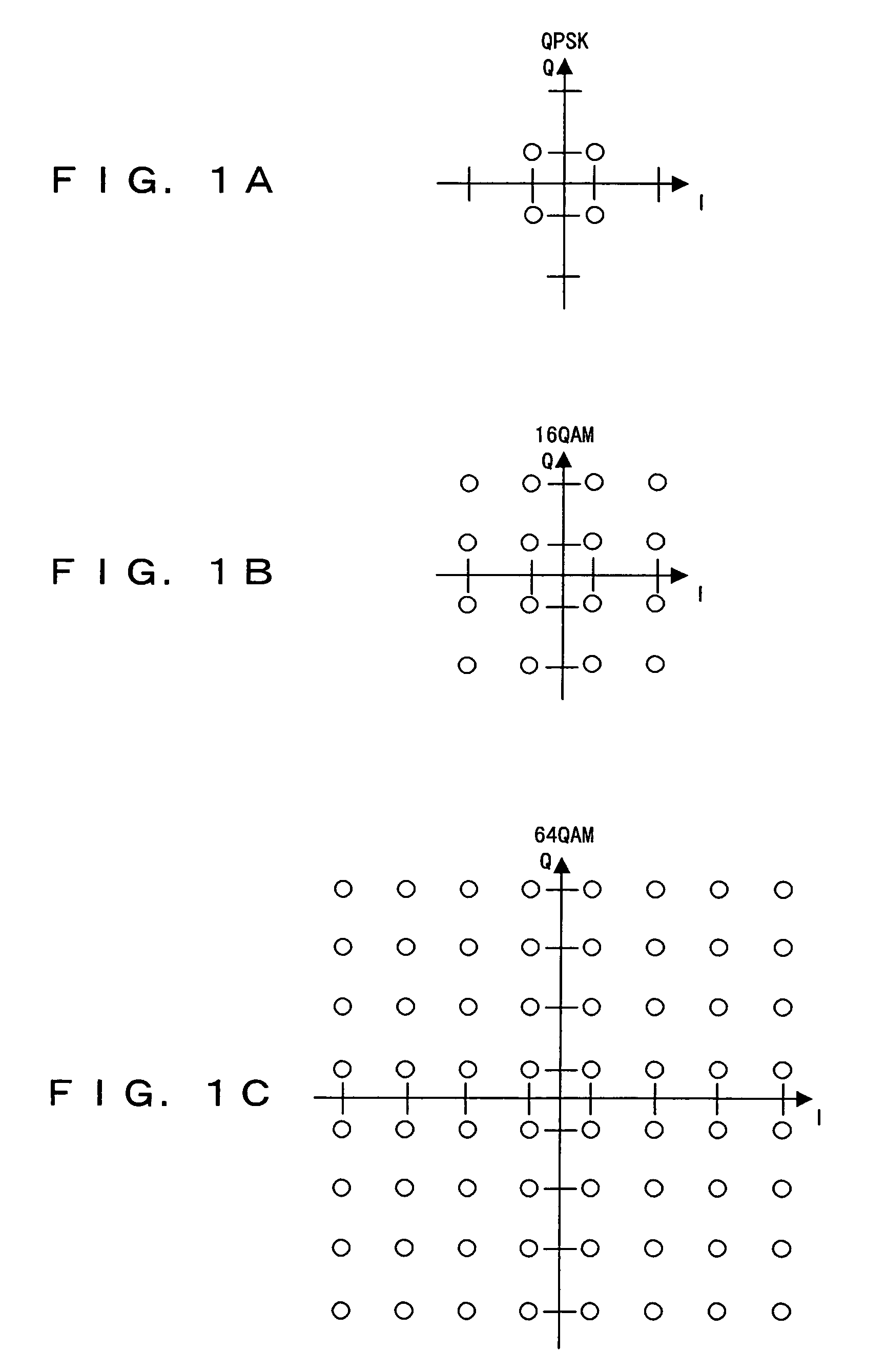
COFDM DCM Communication Systems with Preferred Labeling-Diversity Formats
InactiveUS20190334755A1Improve the receiving signal-to-noise ratioIncrease rangeSpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumCommunications system
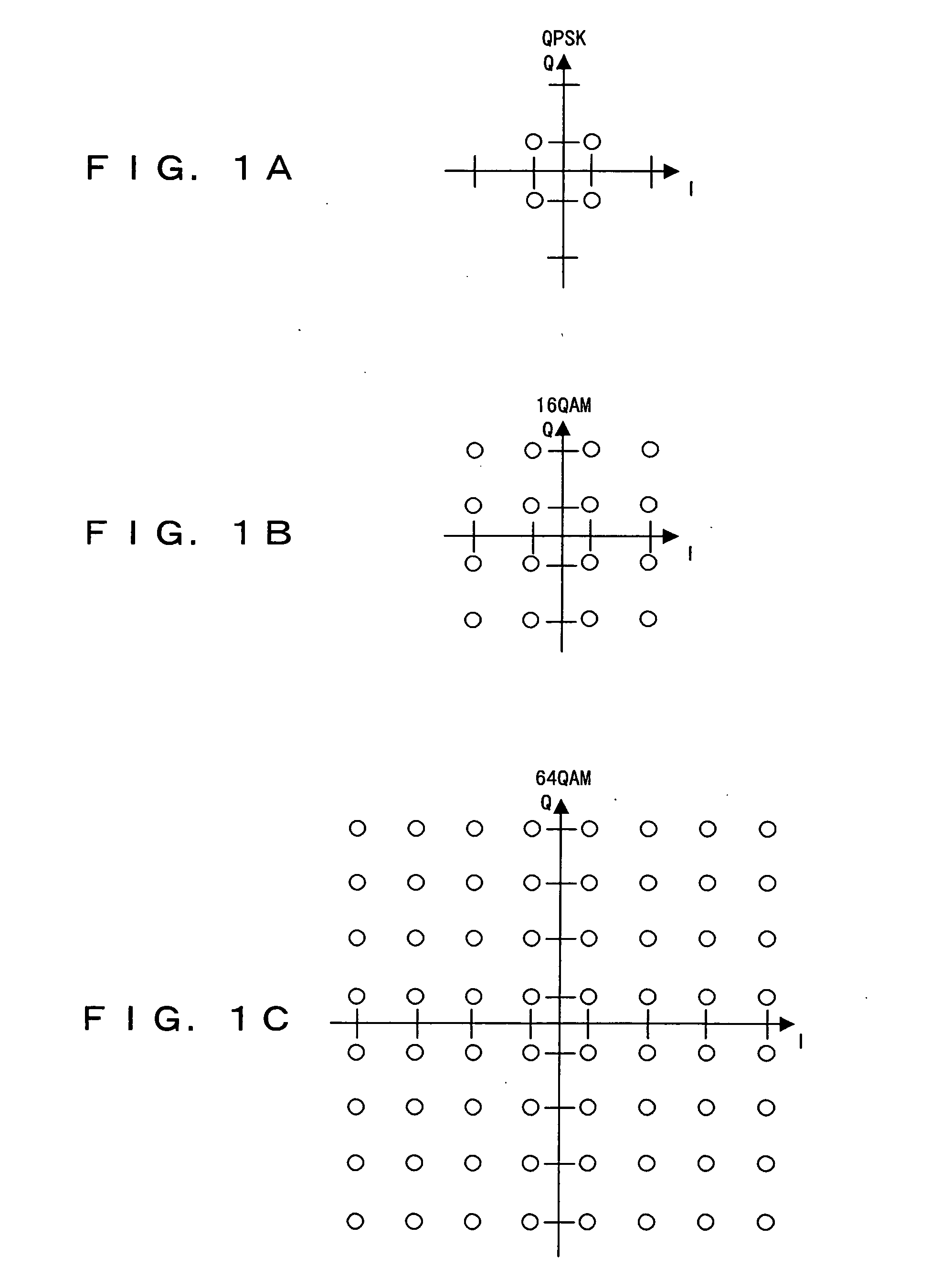
Transmitting apparatus and receiving apparatus for communication systems using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexed (COFDM) dual-subcarrier modulation (DCM) signals. The same coded data is mapped both to COFDM subcarriers located in the lower-frequency half spectrum of the DCM signal and to COFDM subcarriers located in its upper-frequency half spectrum. The mapping of COFDM subcarriers in those half spectra employ labeling diversity. A primary design goal in some preferred labeling diversity formats is to support reception of DCM with less error when accompanied by interfering additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN). A primary design goal in some preferred labeling diversity formats is to reduce the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) of the COFDM DCM signals. In preferred forms of COFDM DCM signal, the quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) of COFDM subcarriers is Gray mapped to position palindromic lattice-point labels along one of the diagonals of each square QAM constellation.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
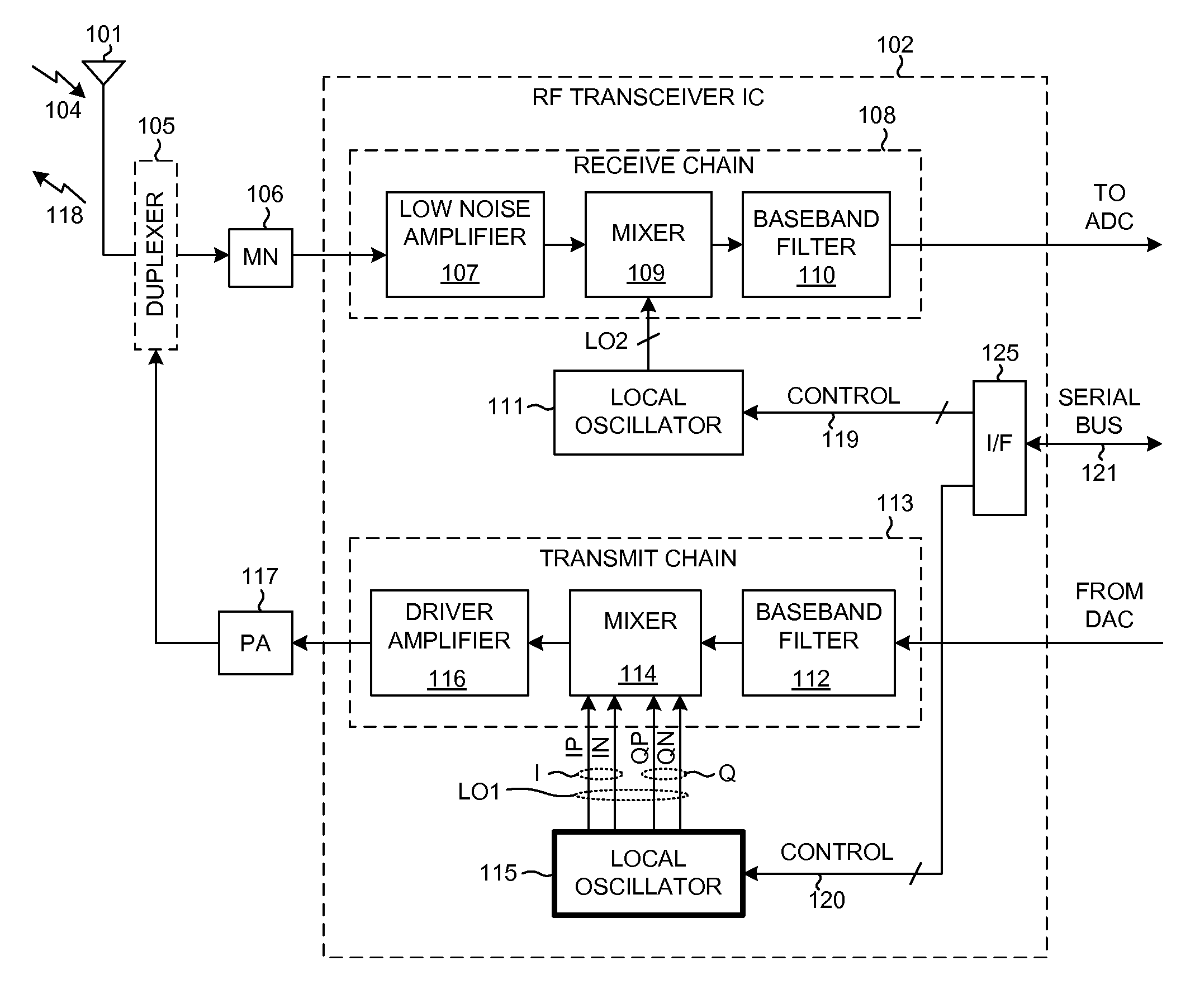
Driving a mixer with a differential lo signal having at least three signal levels
ActiveUS9197161B2Simple designReduce noisePulse generatorFrequency-changer modificationsFrequency spectrumDifferential signaling
The mixer of a transmit chain of a wireless transmitter (such as the transmitter of a cellular telephone handset) is driven with low third harmonic in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) signals. The low third harmonic I and Q signals have three or more signal levels, and transition between the these three or more signal levels at times such that each of the I and Q signals approximates a sine wave and has minimal third harmonic spectral components. In one example, reducing the third harmonic components of the I and Q signals simplifies design of amplifier stages of the transmitter and helps reduce receive band noise.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Front-end circuit for simultaneous transmission and reception operation
ActiveUS10277259B2Data rateSimple adaptationMultiple-port networksDuplex signal operationEngineeringControl circuit
A front end circuit is disclosed. In an embodiment, the circuit includes a first antenna connection and first to third signal paths, each of which include a tunable filter and each of which is connected to the first antenna connection. The circuit further includes at least one phase shifter arranged in at least one of the signal paths between a respective filter and the first antenna connection and a control circuit configured to tune frequency bands of the filters, wherein the filters are operable in a FDD operating mode or a TDD operating mode, and wherein the front-end circuit is simultaneous operable in at least one transmission band and at least one reception band using all three filters and the associated signal paths.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing wireless communication operable on frequency selective channel, and channel compensation method
InactiveUS7548522B2Lower BERHigh error rateBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemInverse discrete fourier transform
Disclosed is an OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) wireless communication system operable on a frequency selective channel, and a channel compensation method. An IDFT (inverse discrete Fourier transform) unit of a transmitter includes first through third N-point IDFT units, and performs IDFT on a binary information signal twice. A DFT (discrete Fourier transform) unit of a receiver includes first through third N-point DFT units, a channel predictor and interpolator, and a channel compensator, and performs DFT on the signal received from the transmitter twice.
Owner:KT CORP +1
COFDM DCM communications systems with preferred labeling diversity formats
ActiveUS20190199572A1Facilitates improvement in receptionImprove signal-to-noise ratioMulti-frequency code systemsPilot signal allocationFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
Transmitting apparatus and receiving apparatus for communication systems using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexed (COFDM) dual-subcarrier modulation (DCM) signals. The same coded data is mapped both to COFDM subcarriers located in the lower-frequency half spectrum of the DCM signal and to COFDM subcarriers located in its upper-frequency half spectrum. The mapping of COFDM subcarriers in those half spectra employ labeling diversity preferred for reception of DCM with less error when accompanied by interfering additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN). In preferred forms of COFDM DCM signal, the quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) of COFDM subcarriers is Gray mapped to position palindromic lattice-point labels along one of the diagonals of each square QAM constellation.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
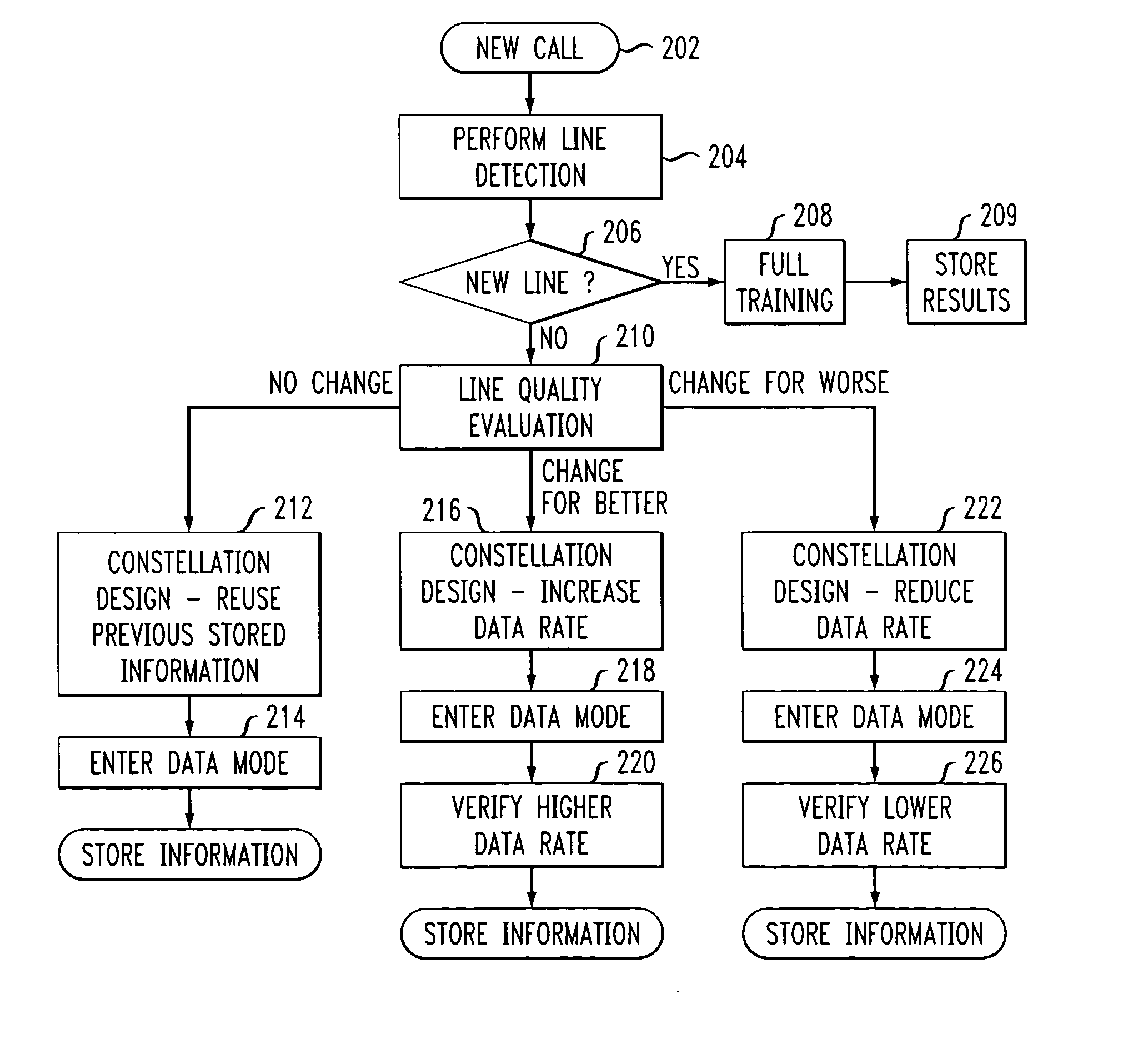
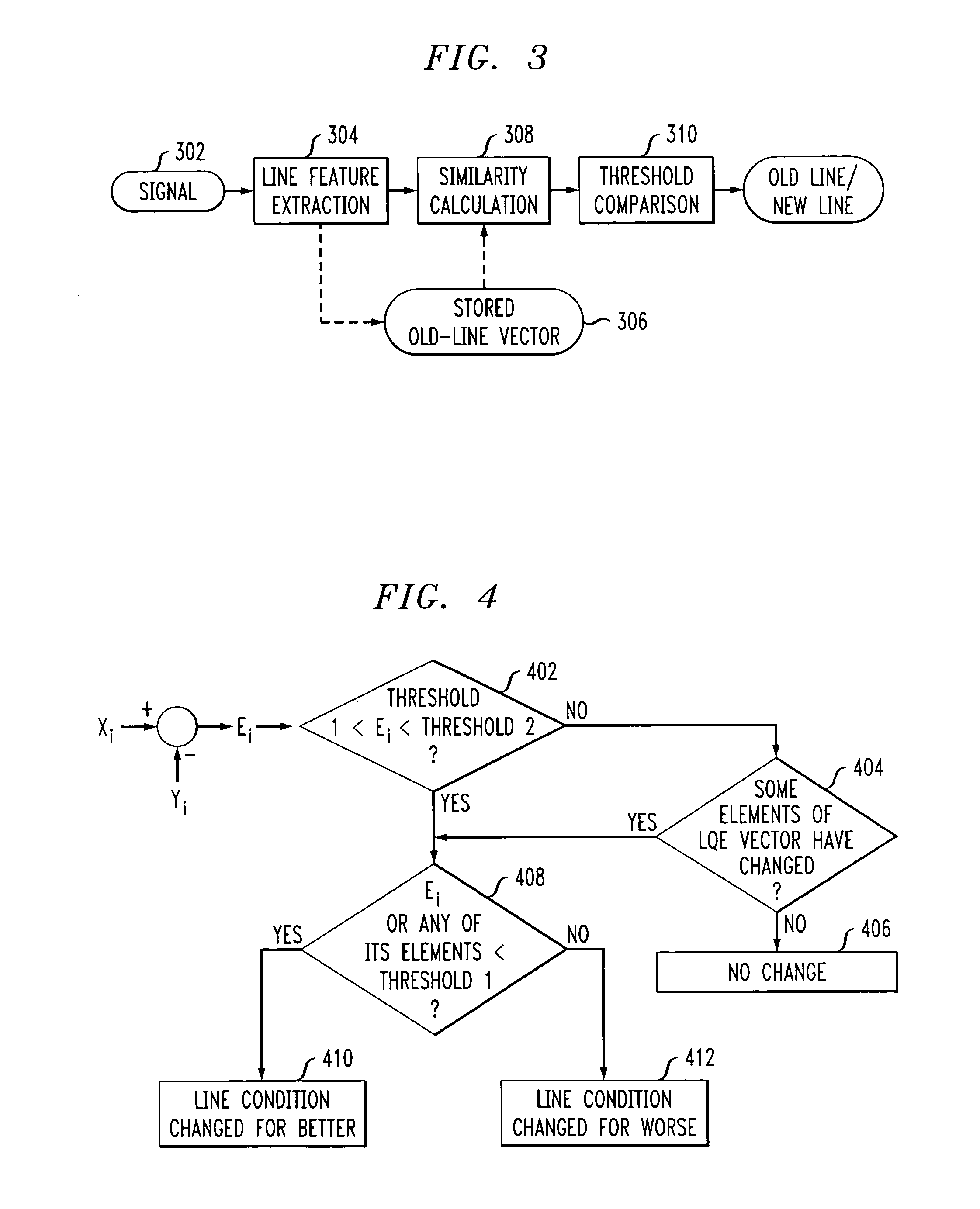
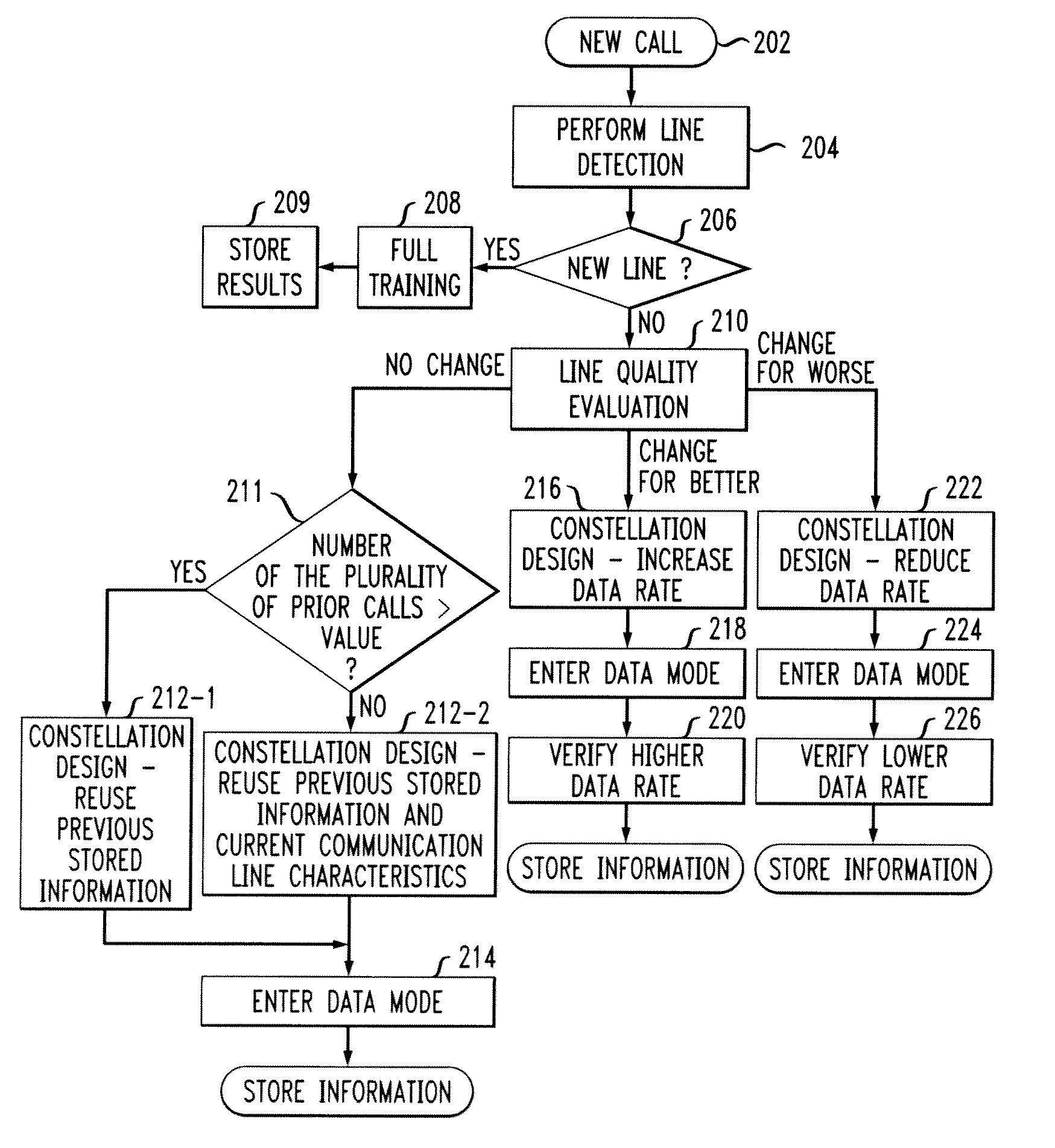
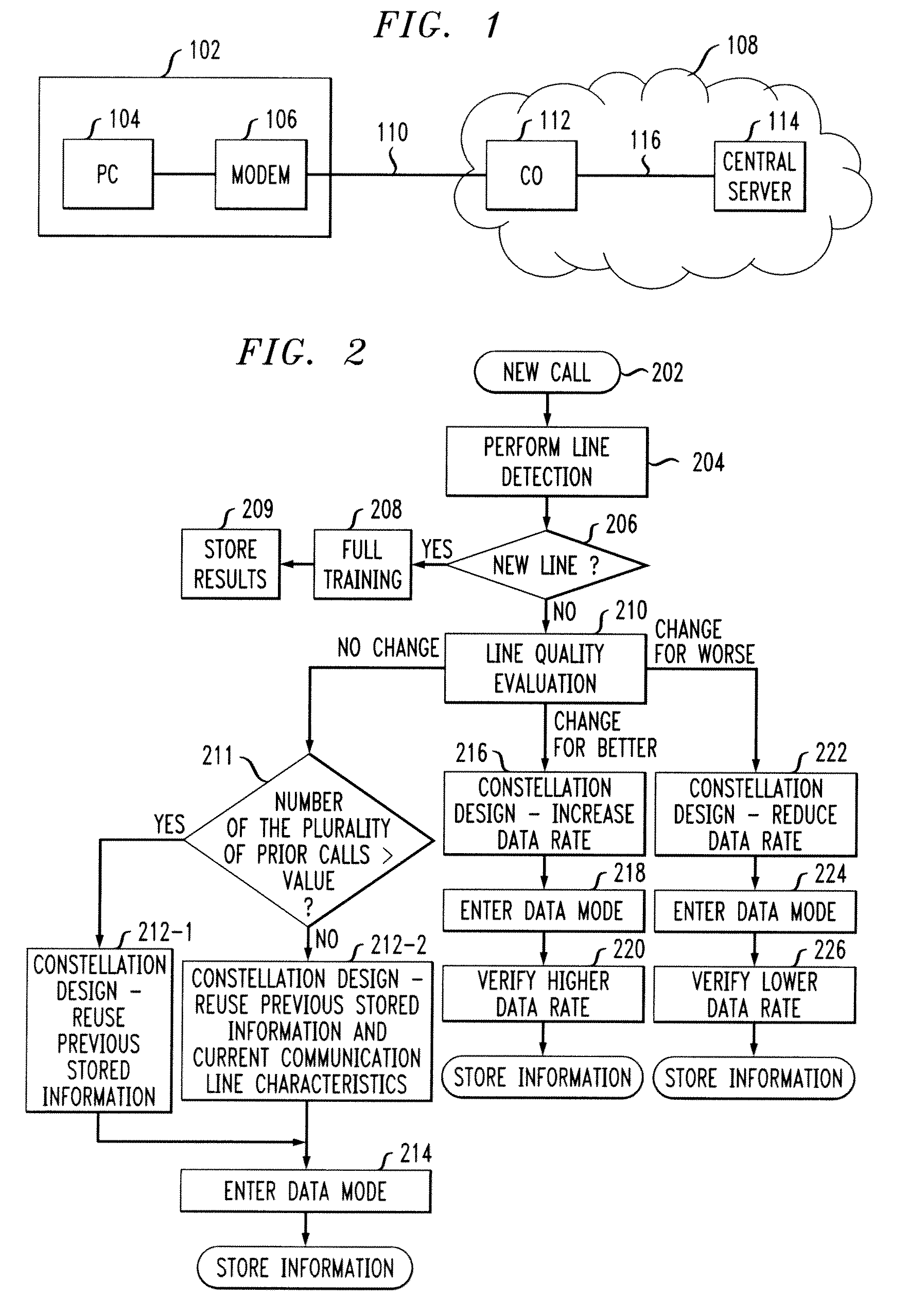
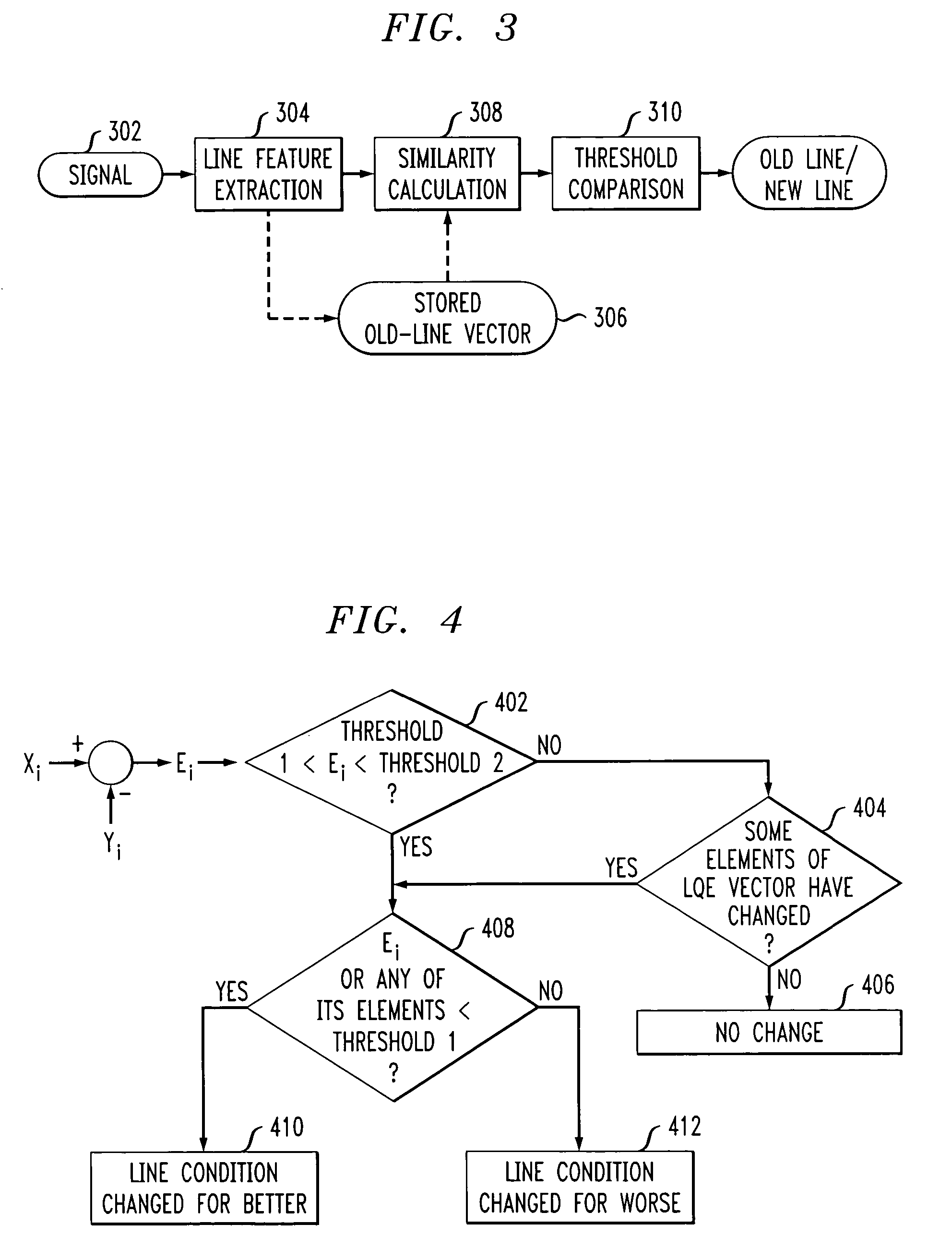
Adaptive modem
InactiveUS20060109894A1Improve performanceIncrease training speedModulated-carrier systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsModem deviceEngineering
Disclosed is a modem that uses information from prior modem calls in a current modem call if the current communication line has the same characteristics as the communication line of a prior call. During modem training, a determination is made as to whether the characteristics of the current communication line is substantially similar to the characteristics of a communication line used during at least one prior call. If the characteristics are substantially similar, the stored data mode information from the prior call(s) is used to design a signal constellation for use during the current call's data mode. If the characteristics are not substantially similar, then full modem training is performed and data mode information is stored for use during subsequent calls. In addition to the communication line similarity test, line quality evaluation may also be performed in order to determine whether there has been a change in the quality of the communication line between the current call and prior call(s). If there has been no change in line quality, then a signal constellation is designed using stored minimal signal distance from one or more prior calls. If there has been a change for the better in line quality, then a signal constellation is designed having a smaller minimal signal distance than the one or more prior call's signal constellation. If there has been a change for the worse in line quality, then a signal constellation is designed having a larger minimal signal distance than the one or more prior call's signal constellation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
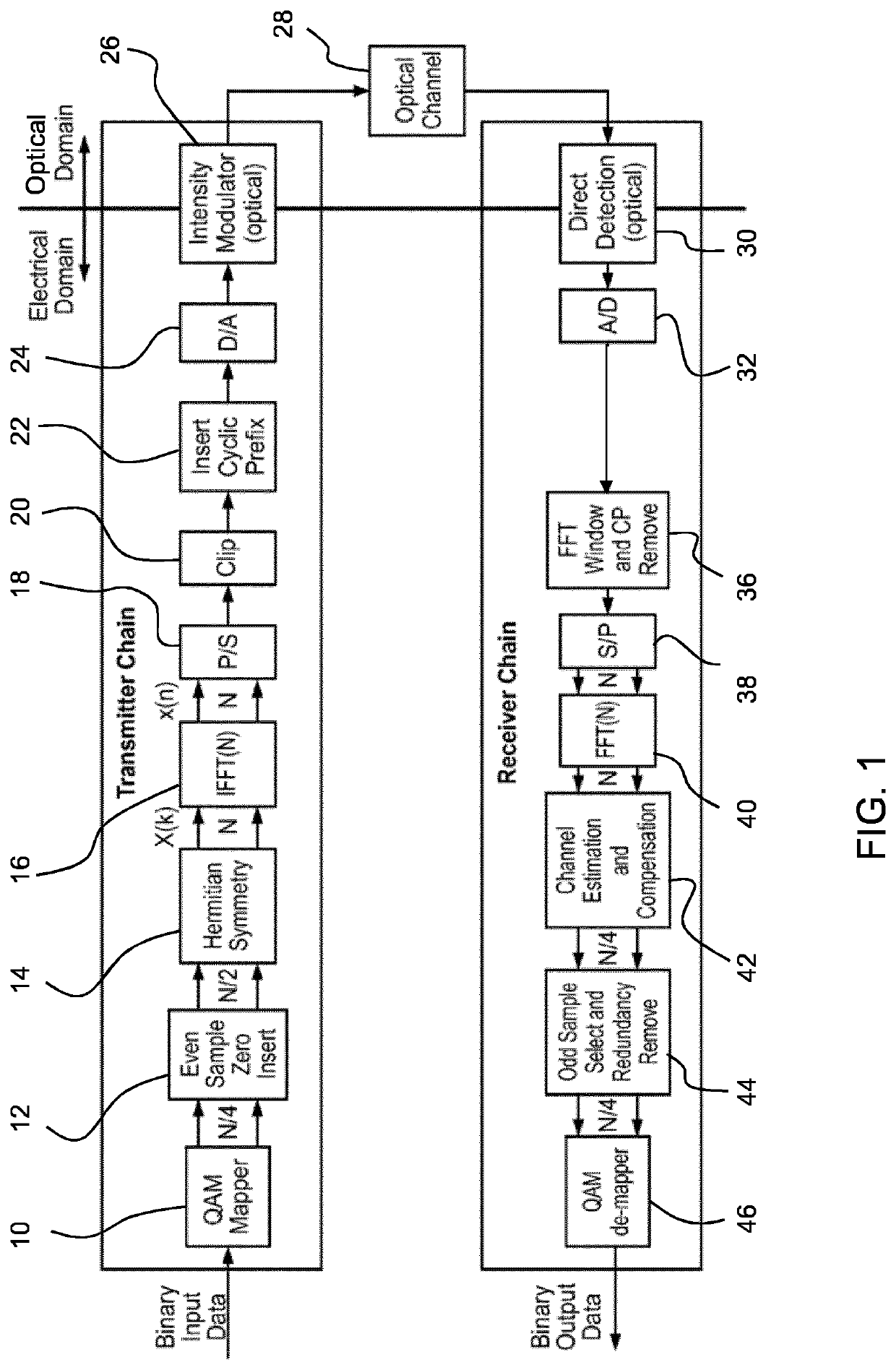
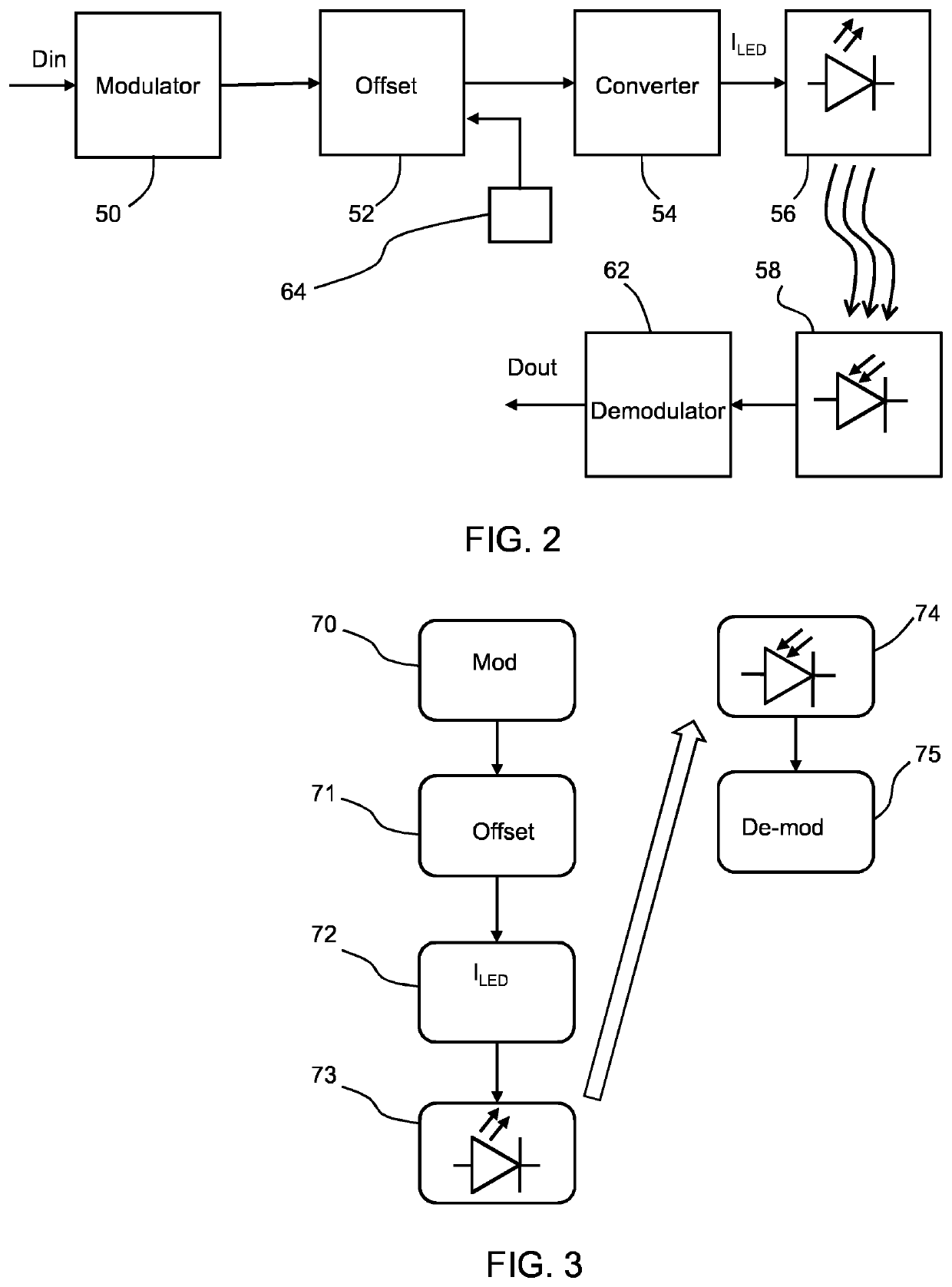
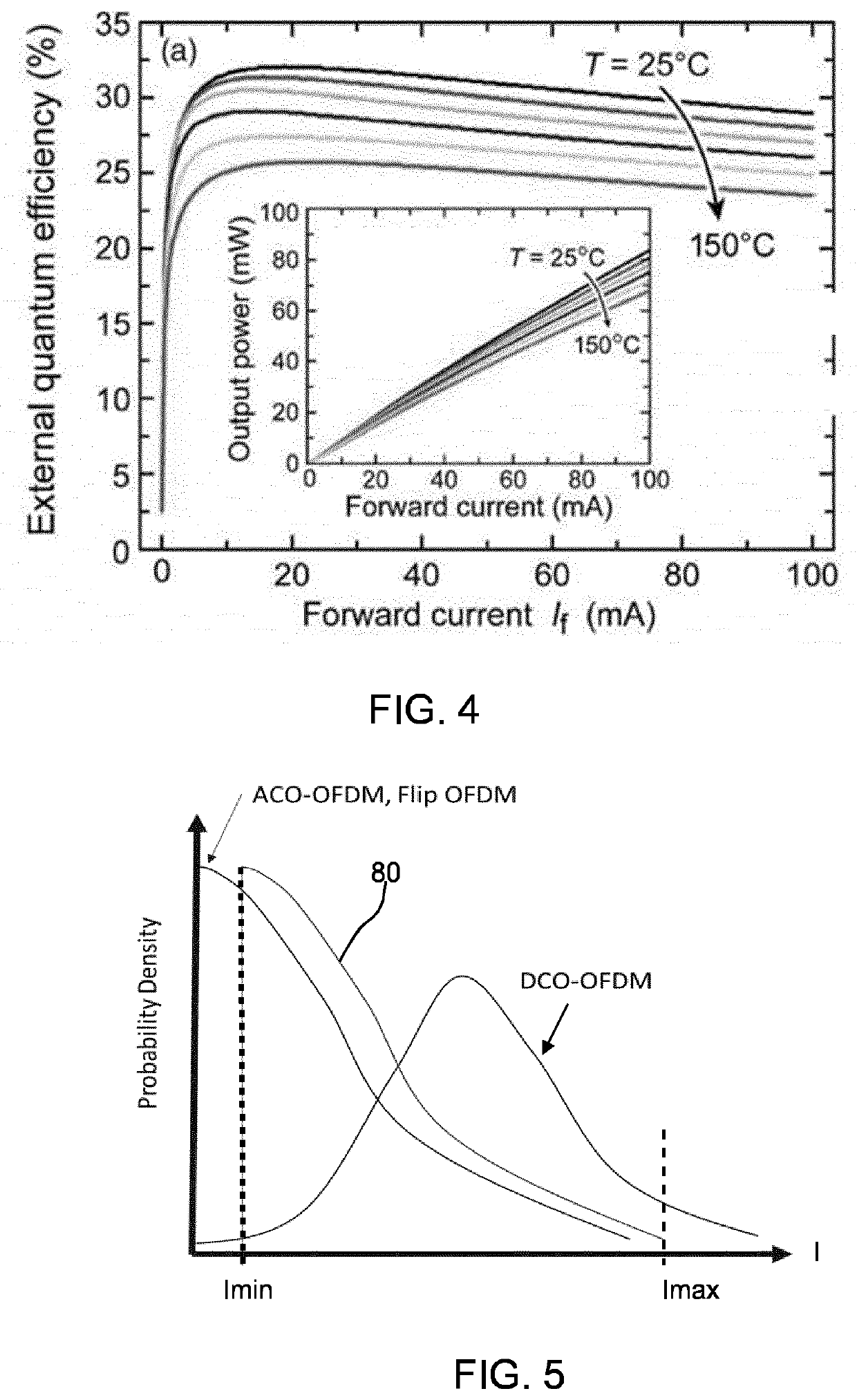
Optical data transmission system and method
ActiveUS20210273729A1Improve relationshipIncrease the number ofClose-range type systemsElectromagnetic transmittersOptical data transmissionHigh data rate
An optical data transmission system and method employs positive only data modulation, with an offset applied to the positive modulated values before generating modulated drive current signals for a light emitting component. The offset is such that the minimum drive current falls in a range where the electron-to-photon efficiency of the light emitting component is substantially constant. The drive current thus falls in a more linear part of its current vs. intensity characteristic. This reduces distortion and hence enables increased data rate.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Communications faster than Shannon rate
ActiveUS9231813B1Faster rateData rateError preventionTransmission path divisionFrequency bandTelecommunications link
This invention introduces a new architecture for quadrature layered modulation (QLM) communications which is faster C / W=npb than the Shannon rate C / W=b by using a data symbol rate npW faster than the Nyquist rate W over a frequency band W where np≧1 is the data symbol rate increase and b is the data symbol information bits, by scaling the signal to compensate for the data symbol inter-symbol interference loss, by using a Shannon bound Eb / No and SNR data symbol metrics, and by using QLM demodulation algorithms. This architecture provides the same performance as the other QLM architectures operating the communications as a layering of Shannon links over W. This new architecture enables existing communications links to exceed the Shannon rate by operating the transmitter at a faster data symbol rate over W, using the QLM metrics, and by implementing QLM demodulation in the receiver as described in this specification.
Owner:VON DER EMBSE URBAIN A
COFDM DCM communications systems with preferred labeling diversity formats
ActiveUS10637711B2Facilitates improvement in receptionImprove signal-to-noise ratioBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumCommunications system
Transmitting apparatus and receiving apparatus for communication systems using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexed (COFDM) dual-subcarrier modulation (DCM) signals. The same coded data is mapped both to COFDM subcarriers located in the lower-frequency half spectrum of the DCM signal and to COFDM subcarriers located in its upper-frequency half spectrum. The mapping of COFDM subcarriers in those half spectra employ labeling diversity preferred for reception of DCM with less error when accompanied by interfering additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN). In preferred forms of COFDM DCM signal, the quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) of COFDM subcarriers is Gray mapped to position palindromic lattice-point labels along one of the diagonals of each square QAM constellation.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
Communications device used in CDMA
InactiveUS8526399B2Data rateSuppress powerModulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexMultiplexingManagement unit
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Adaptive modem
InactiveUS7711040B2Improve performanceIncrease training speedFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsModem deviceEngineering
A modem uses information from prior calls in a current call if the current communication line is similar to the communication line of a prior call. During modem training, the current communication line is compared to a communication line used during at least one prior call. If the characteristics are substantially similar, stored data mode information from the prior call(s) is used to design a signal constellation for use during the current call's data mode. If the number of prior calls exceeds a value, then the signal constellation may be designed using previously stored data mode information without using information from the current call's training mode. If the number of prior calls does not exceed the value, then the signal constellation may be designed using the previously stored data mode information and information from the current call's training mode.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com