Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about How to "Braking achieved" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
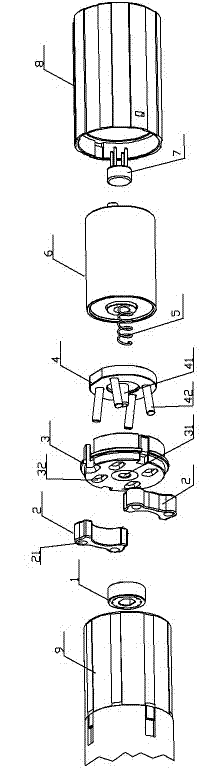
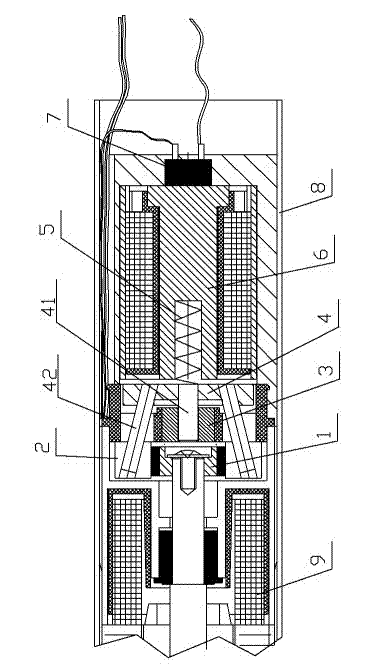
Motor, motor system and charging and braking method
ActiveCN105656243ACompact structureSmall sizeWheel based transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsPower flowElectric machine
The invention relates to a motor used for a vehicle, a motor system comprising the motor and a charging and braking method adopting the motor system. The motor comprises a clutch unit, a planetary gear system, a rotor, magnetic steel and a stator fixedly connected with the magnetic steel, wherein the clutch unit is used for transmitting rotary moment between a wheel axle and the planetary gear system; the planetary gear system is arranged on the wheel axle in a sleeving manner, can utilize force transmitted by the clutch unit to drive the rotor to rotate, or can transmit rotation of the rotor to the clutch unit; when the vehicle travels normally, the motor charges a battery of the vehicle by utilizing induction current which is generated in a coil through relative motion of the stator and the rotor; when the vehicle receives a braking signal, the motor promotes the vehicle to brake by utilizing induction inverse potential which is generated in the coil through relative motion of the stator and the rotor. The motor has the characteristics of compact structure and simple maintenance.
Owner:HANHAI INFORMATION TECH SHANGHAI
Device for switching false urgent accelerator operation into emergency braking during emergency state of vehicle
InactiveCN102501838AOvercome the movePull freelyFoot actuated initiationsPropulsion unit arrangementsEngineeringCentrifugal force
A device for switching false urgent accelerator operation into emergency braking during the emergency state of a vehicle comprises a retractor, a retractable belt-retracting spring and pawls, the retractor is connected with a braking system, a retractable belt of the retractor is connected with an accelerator cable, the principle of the retractable is similar to the principle of an automotive safety belt, the retractable belt-retracting spring is mounted on one side of the retractable belt in the retractor, the pawls are mounted on the other side of the retractable belt, and the pulling speedof the retractable belt controls the centrifugal force of the pawls and adjusts the centrifugal positions of pawl teeth, so that the retractable belt can be freely pulled or stuck and can drive the braking system to carry out braking. The device is characterized in that: the retractor is mounted in a rectangular cavity-shaped emergency brake box, and is normally located at one end in the emergency brake box, which is close to a connecting cable of the braking system, and when the accelerator-stepping speed is over-high, the retractable belt is stuck to pull the retractor and drive a braking cable, so that the braking system is pulled to carry out braking.
Owner:魏伯卿
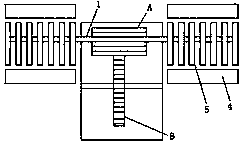
Distribution line pay-off device with braking function
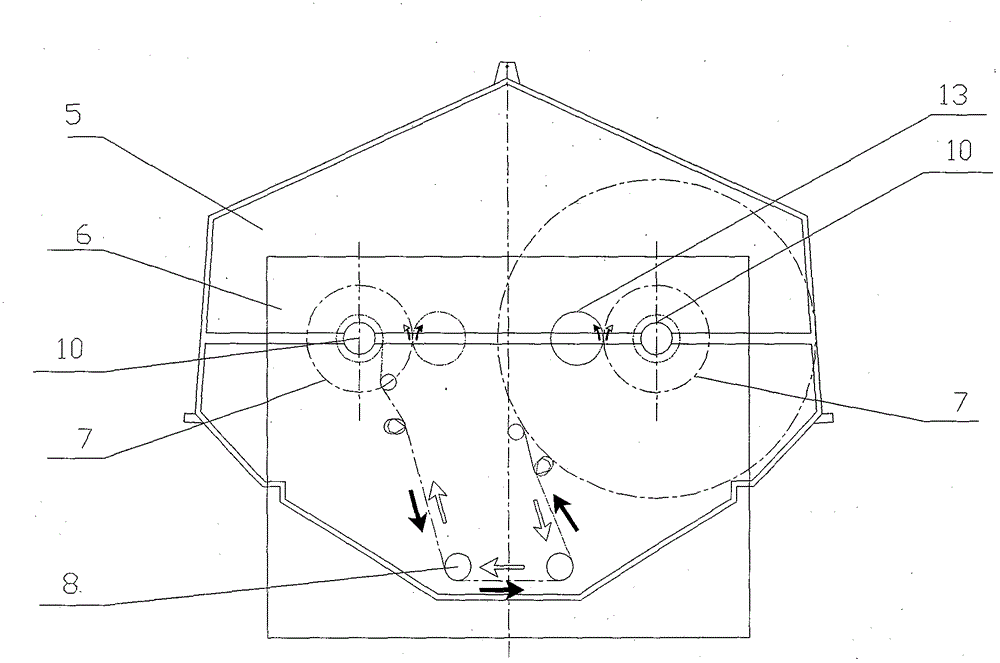
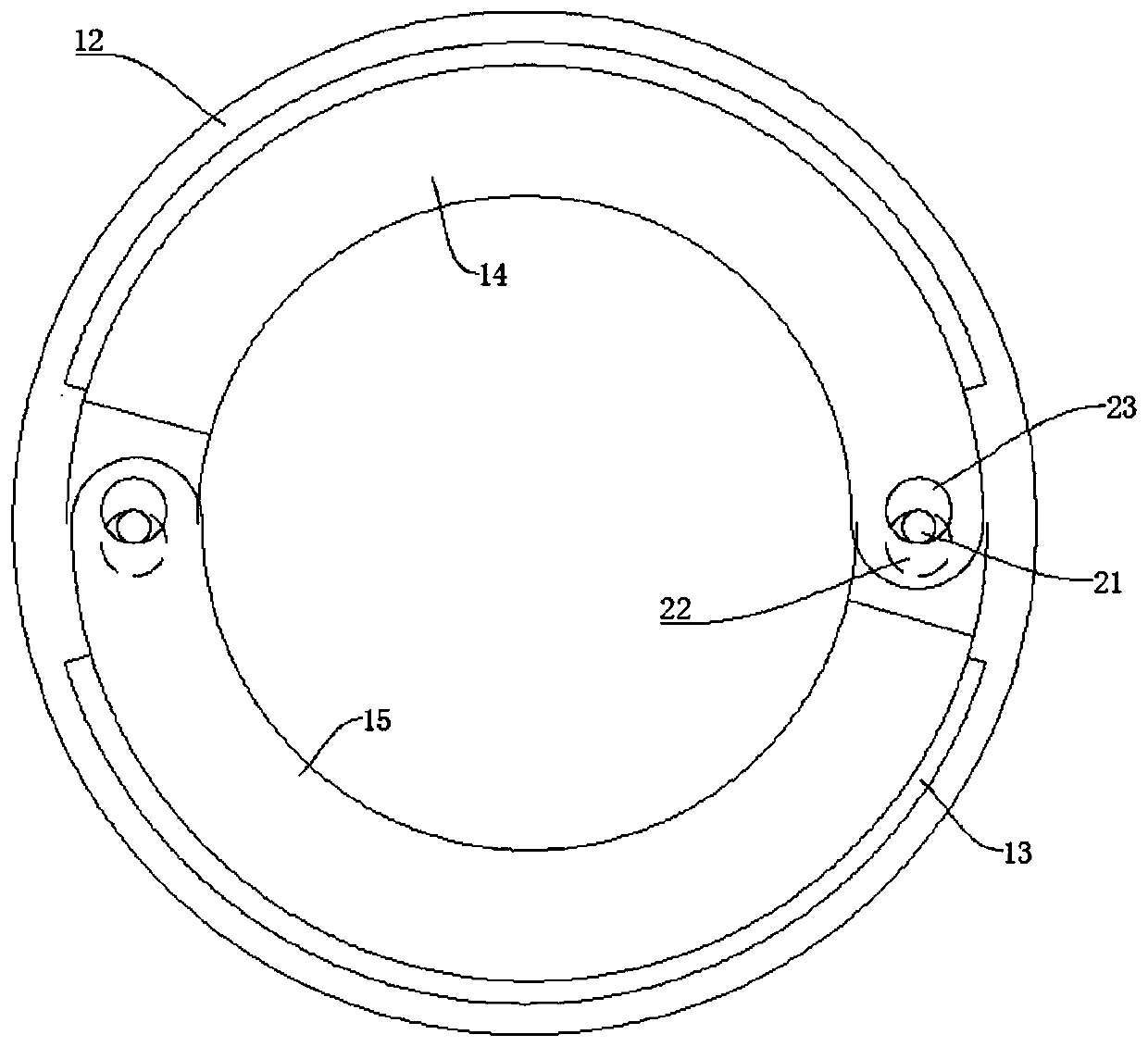
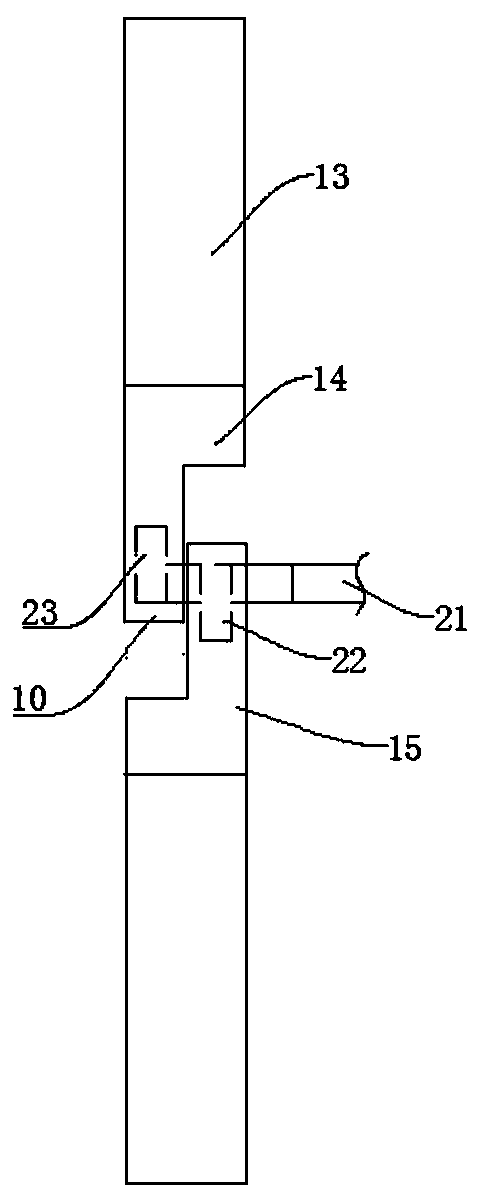
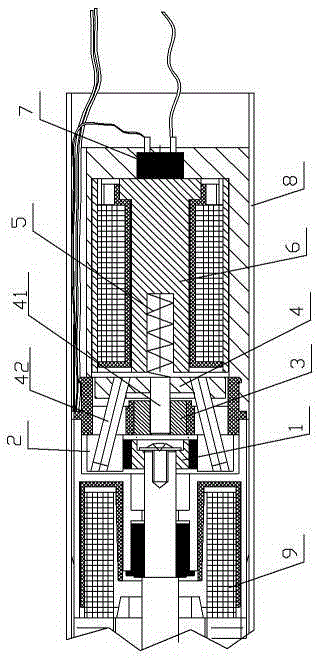
ActiveCN106516859ABraking achievedSimple structureFilament handlingMechanical engineeringBrake control
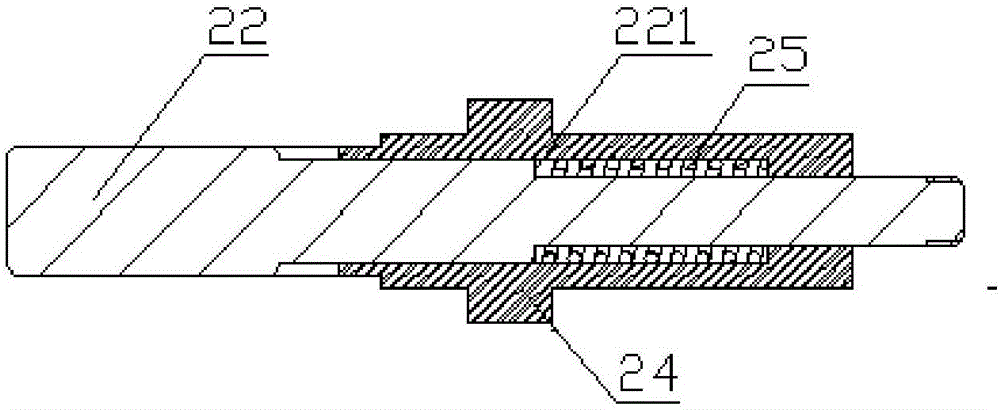
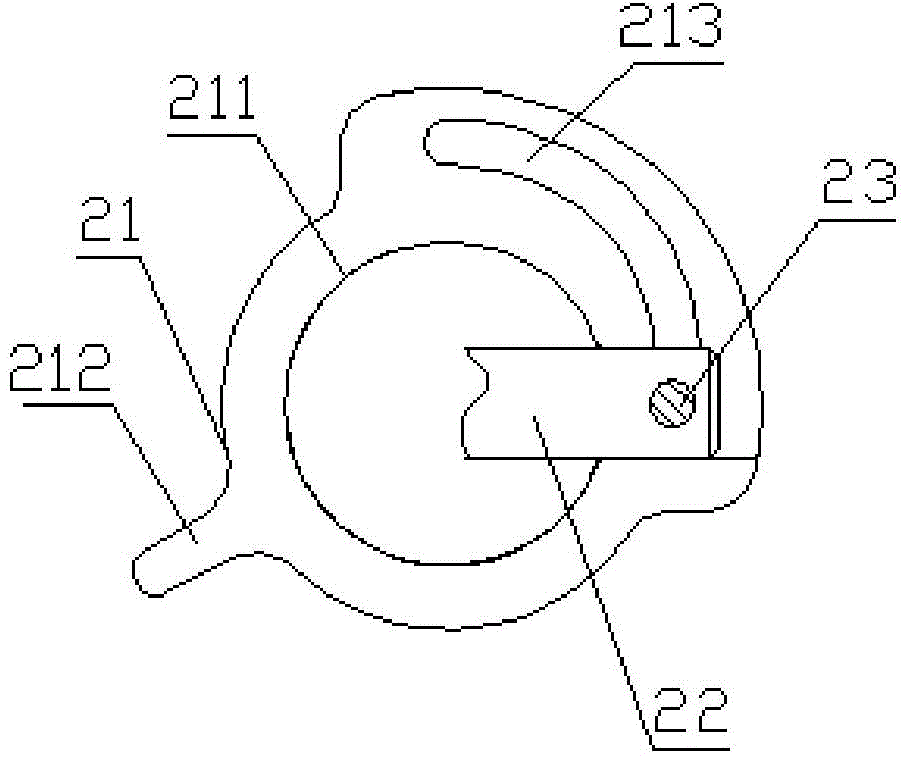
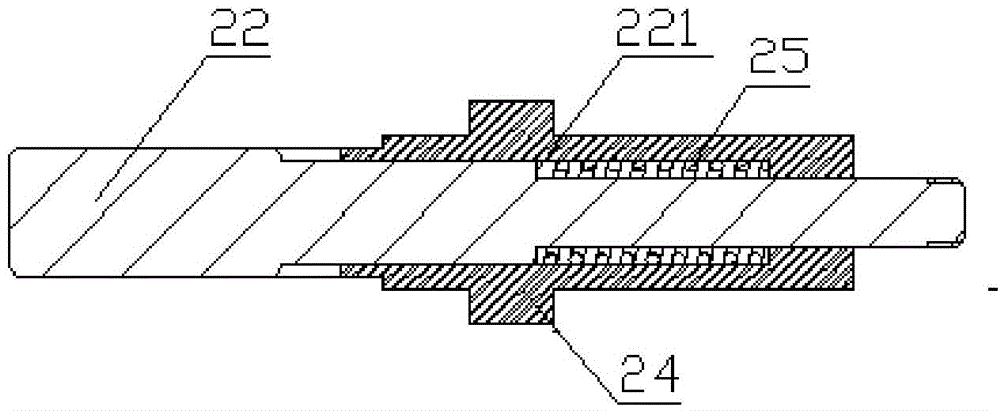
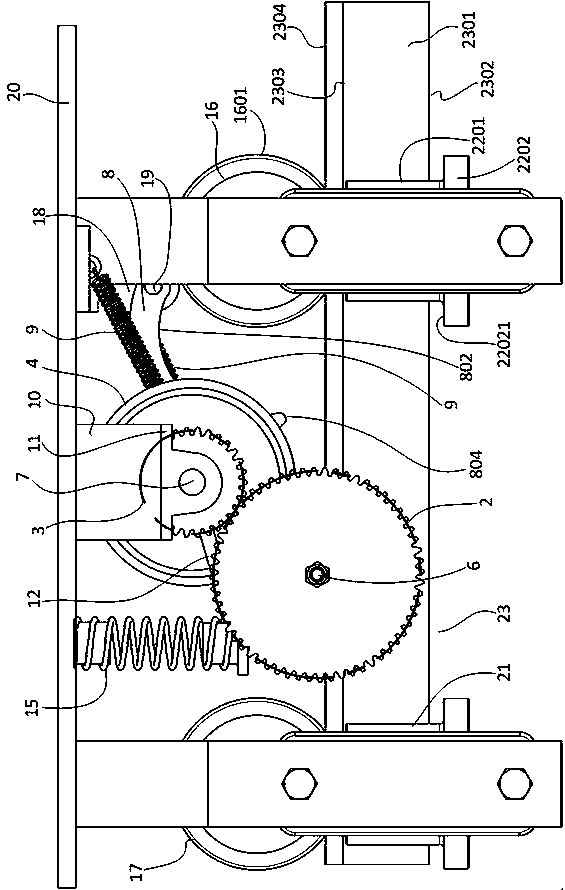
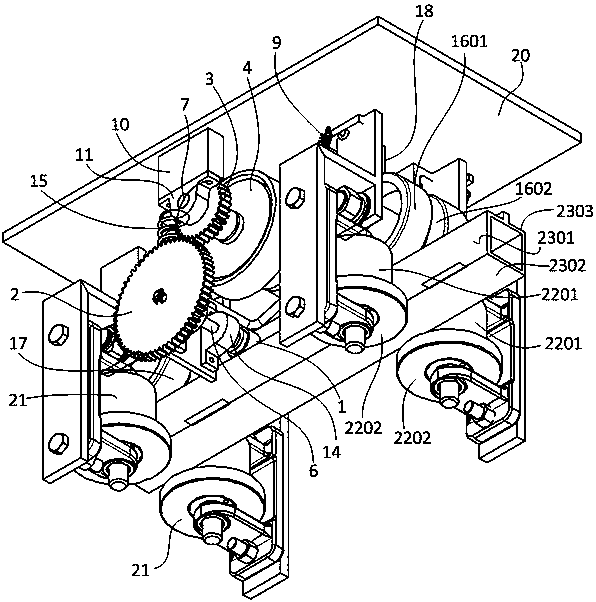
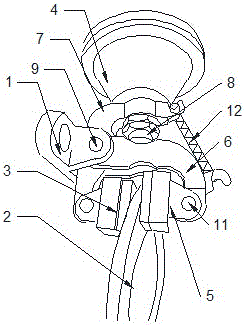
The invention discloses a distribution line pay-off device with the braking function. The device comprises a pay-off rack, the pay-off rack is provided with a pay-off shaft in a rotating mode, a pay-off spool is fixed to the pay-off shaft, the pay-off shaft is fixedly connected to a rotating handle, and the pay-off rack is provided with a braking device braking the pay-off spool rotating inertially. According to the device, the braking device is arranged, by turning a braking control knob to rotate, a braking rod is driven to move axially, a braking contact surface between the braking rod and the pay-off spool is contacted so that the pay-off spool can be braked, the structure is simple and braking is convenient; and a wire arrangement device is arranged so that wires wound around the pay-off spool can be orderly arranged, the structure is simple, and the wire arrangement is convenient.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG PINGHU POWER SUPPLY +2
Numerically controlled electric scooter
InactiveCN102357299ABraking achievedReduce power consumptionSkate-boardsRoller skatesNumerical controlElectric machine
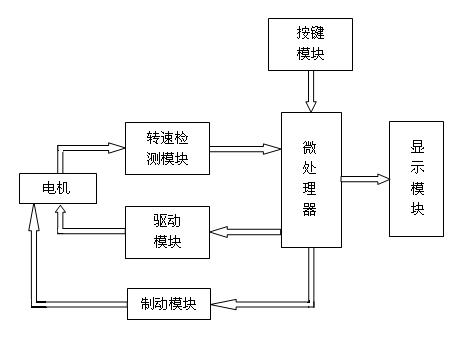
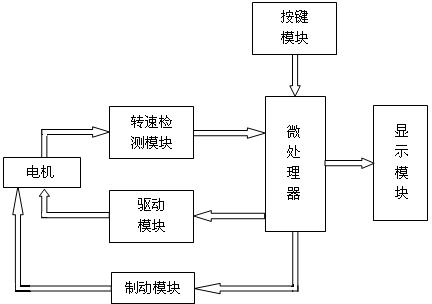
The invention aims at realizing electrification and numerical control of scooters, and discloses a numerically controlled electric scooter. The numerically controlled electric scooter comprises a motor, a driving module, a rotating speed detection module, a brake module, a display module, a button module, a power supply system and a microprocessor. The motor is utilized for transforming electric energy into mechanical energy so that slide wheels of a scooter are driven to rotate. The driving module is utilized for driving the motor to work effectively. The rotating speed detection module is utilized for detecting a current speed of the scooter. The brake module is utilized for brake. The display module is utilized for displaying a current rotating speed and a current system state. The button module is utilized for user data inputting. The power supply system is utilized for whole system power supply. The microprocessor is utilized for receiving and processing data input by users, controlling the driving module to drive the motor to work and controlling the display module to display. The numerically controlled electric scooter has the characteristics of low cost and fast response speed.
Owner:WUXI ADRIAN TECH
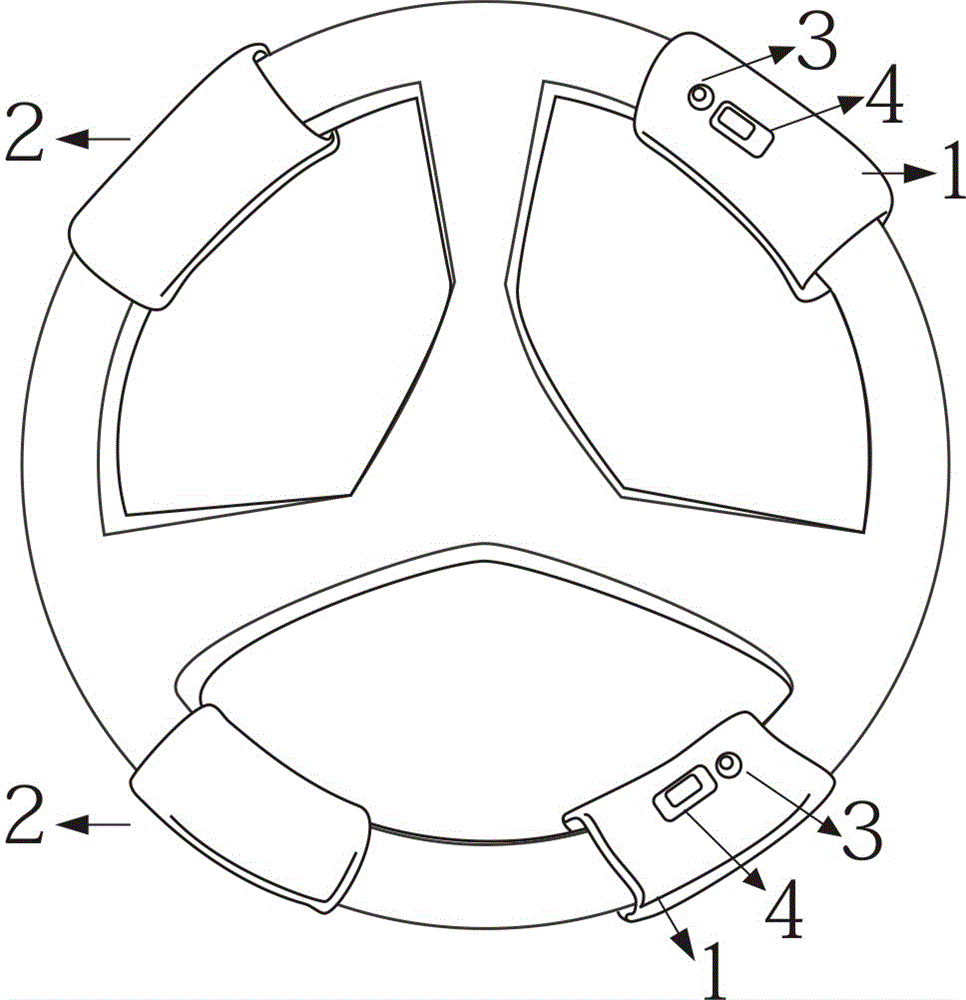
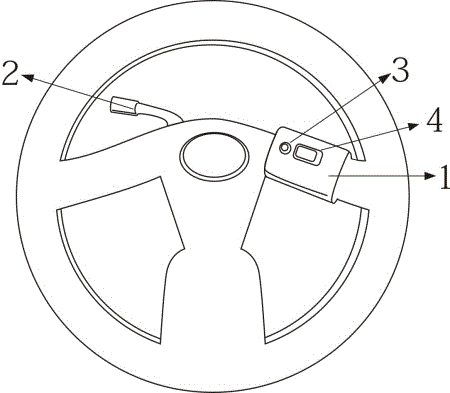
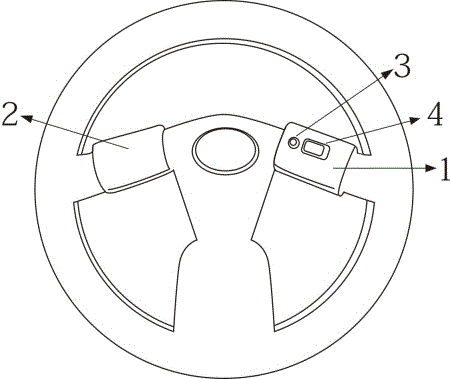
Acceleration and braking device attached to steering wheel
InactiveCN106240538ALow promotion costReduce the burden onHand wheelsHand actuated initiationsEngineeringTreadle
The invention belongs to the field of transportation, and particularly discloses a novel acceleration and braking device. The novel device is attached to a steering wheel of a vehicle. The novel acceleration and braking device can perform acceleration and braking of the vehicle through hand motions. Due to the fact that large burdens are applied to legs when a driver drives a vehicle with an existing pedal type acceleration and brake pedal for a long time, fatigue of legs and joint discomfort are likely to be caused; due to the fact that the design that the acceleration pedal and the brake pedal are stamped by the right foot is adopted, the driver may stamp the acceleration pedal by mistake when the brake pedal needs to be stamped in an emergency, a plurality of painful results are caused. Due to the design of the novel acceleration and brake equipment, working can be transferred to hands when legs are tied, so that switching of hands and legs is achieved, burdens are relieved, and the design is more user-friendly; when in an emergency, a person gets used to clenching the hands, so that the steering wheel is clenched naturally through the motion, the brake effect is achieved naturally, and it is expected that the vicious incidents caused when the driver stamps the acceleration pedal instead of the brake pedal are reduced greatly.
Owner:广州飞速商业管理有限公司
Brake assembly of mute tubular motor
A brake assembly of a mute tubular motor is installed on the tail portion of the tubular motor and comprises a brake disk, brake pads, a fixing base, an armature base, a spring, an electromagnet and a brake cover. The brake cover is meshed with a shell of the tubular motor through teeth, the brake disk is fixed to a rotary shaft of the tubular motor, the brake pads are arranged around the periphery of the brake disk, the spring is installed in a spring groove in the center of the electromagnet, the fixing base is meshed with the inner wall of the brake cover through teeth, one side of the armature base makes contact with the spring, and the spring keeps applying push force to the armature base. A sliding shaft is arranged in the center of the armature base, and the sliding shaft penetrates through a positioning hole of the fixing base. Multiple sets of splayed oblique shafts are arranged on the armature base, and the oblique shafts penetrate through kidney-shaped holes in the fixing base and stretch into oblique holes in the brake pads. The brake assembly is simple in structure and easy to machine; the tubular motor is braked sensitively by a control circuit in the mode that the electromagnet is attracted to the armature base, and the brake pads are further controlled to be unfolded and tightened up through the oblique shafts. Friction plates of the brake assembly are abraded in an integral contact mode, the friction degrees in all positions are the same, and therefore the brake assembly is good in braking effect, longer in service life and low in noise.
Owner:NINGBO HAIYU ELECTROMECHANICAL
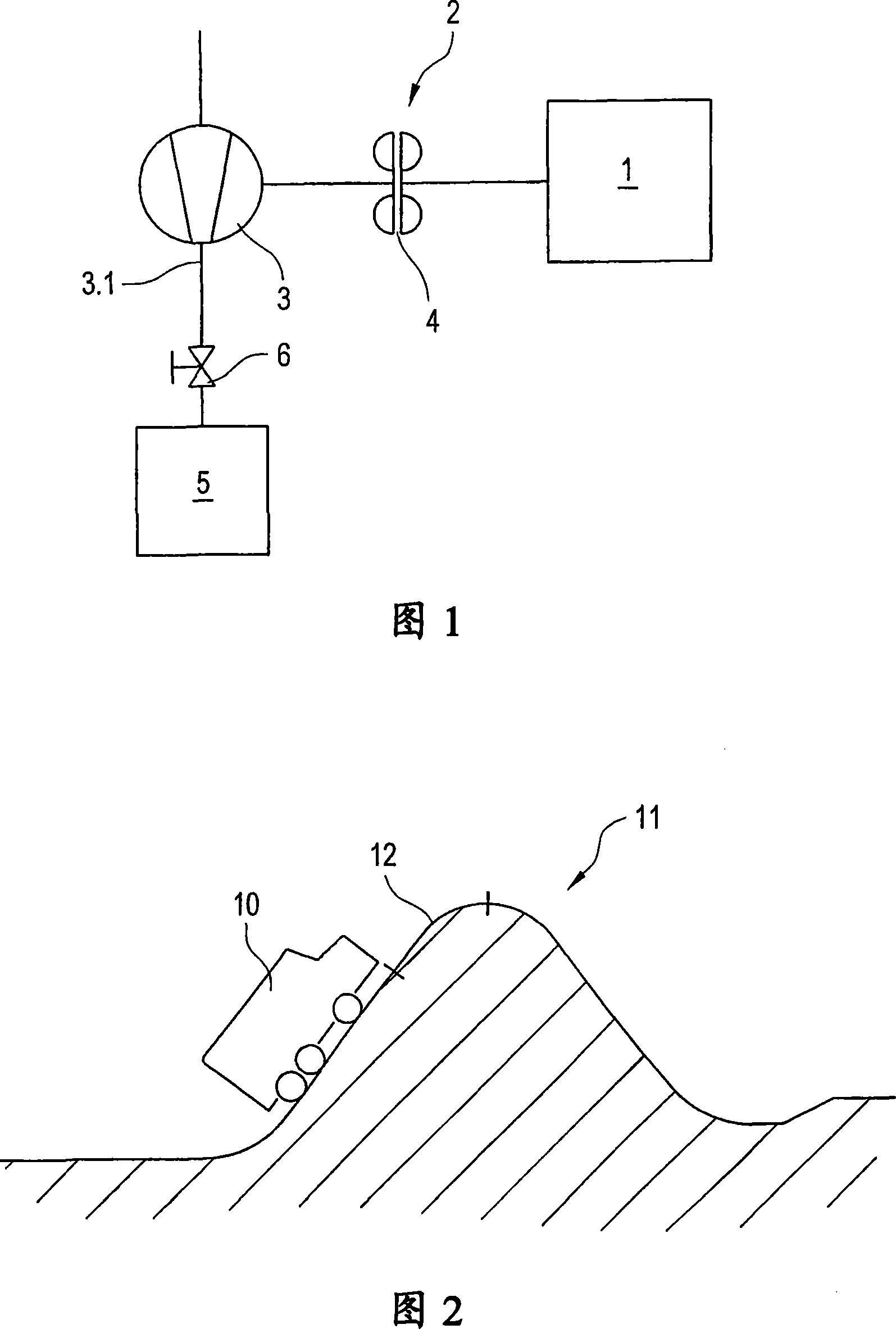
Method for control of a pressurised air supply system for a motor vehicle
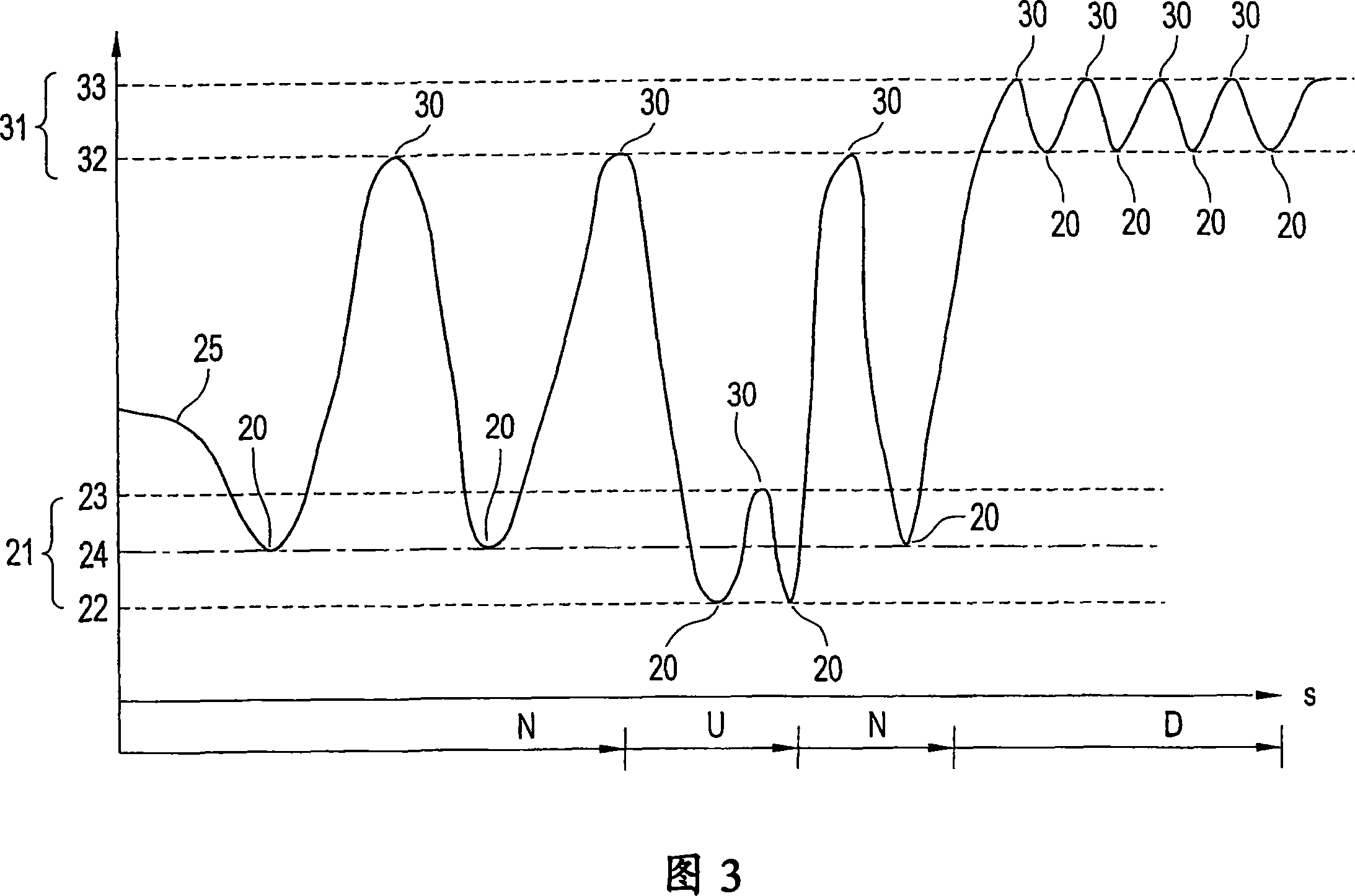
InactiveCN101018697ARealize the shock absorption effectProtect normal operationPump/compressor arrangementsDrive motorAir compressor
The invention relates to a method for control of a pressurised air supply system for a motor vehicle (10), said system comprising a drive motor (1) for driving the motor vehicle, which drives an air compressor (3) by means of a drive connection (2), or said drive connection for driving the air compressor may be switched on. Said method comprises the following method steps: in a supply condition, the air compressor is driven by the drive motor and connected with the air supply side (3.1) thereof to a compressed air system (5) of the motor vehicle (10), such that compressed air is supplied to the compressed air system, in a non-supply condition, the air compressor is not driven and / or is not connected to the compressed air system, whereby the switching of the supply or non-supply condition is carried out on the basis of a comparison of at least one switch pressure value with a pressure (25) in the compressed air system (5) and the topography of the stretch of road (11) on which the motor vehicle (10) is travelling is recorded, said topography includes the profile of the path (12) which the vehicle (10) must cover within a directly following period of time and / or path distance to a given destination. At least one switch pressure value (20,30) is fixed on the basis of the determined topography.
Owner:VOITH TURBO GMBH & CO KG
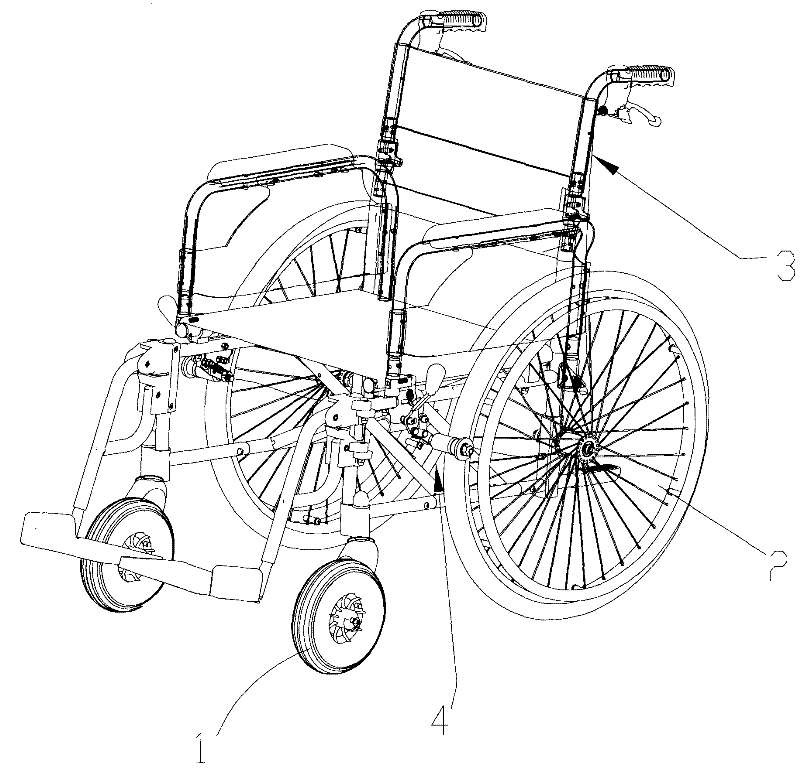
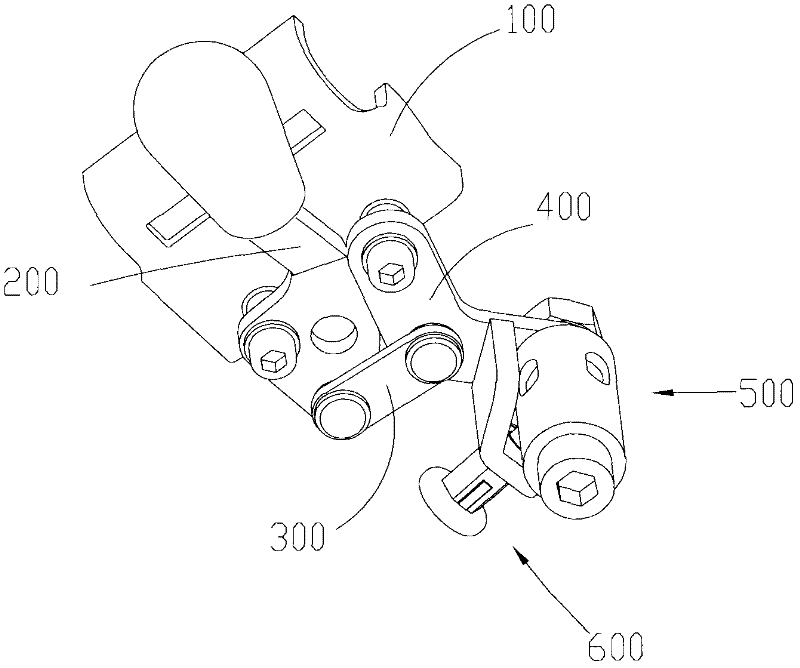
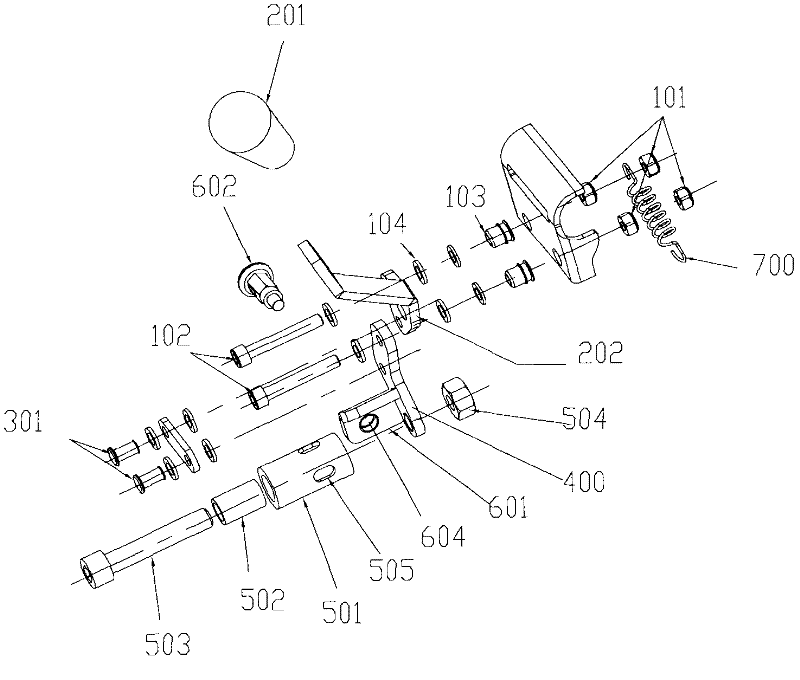
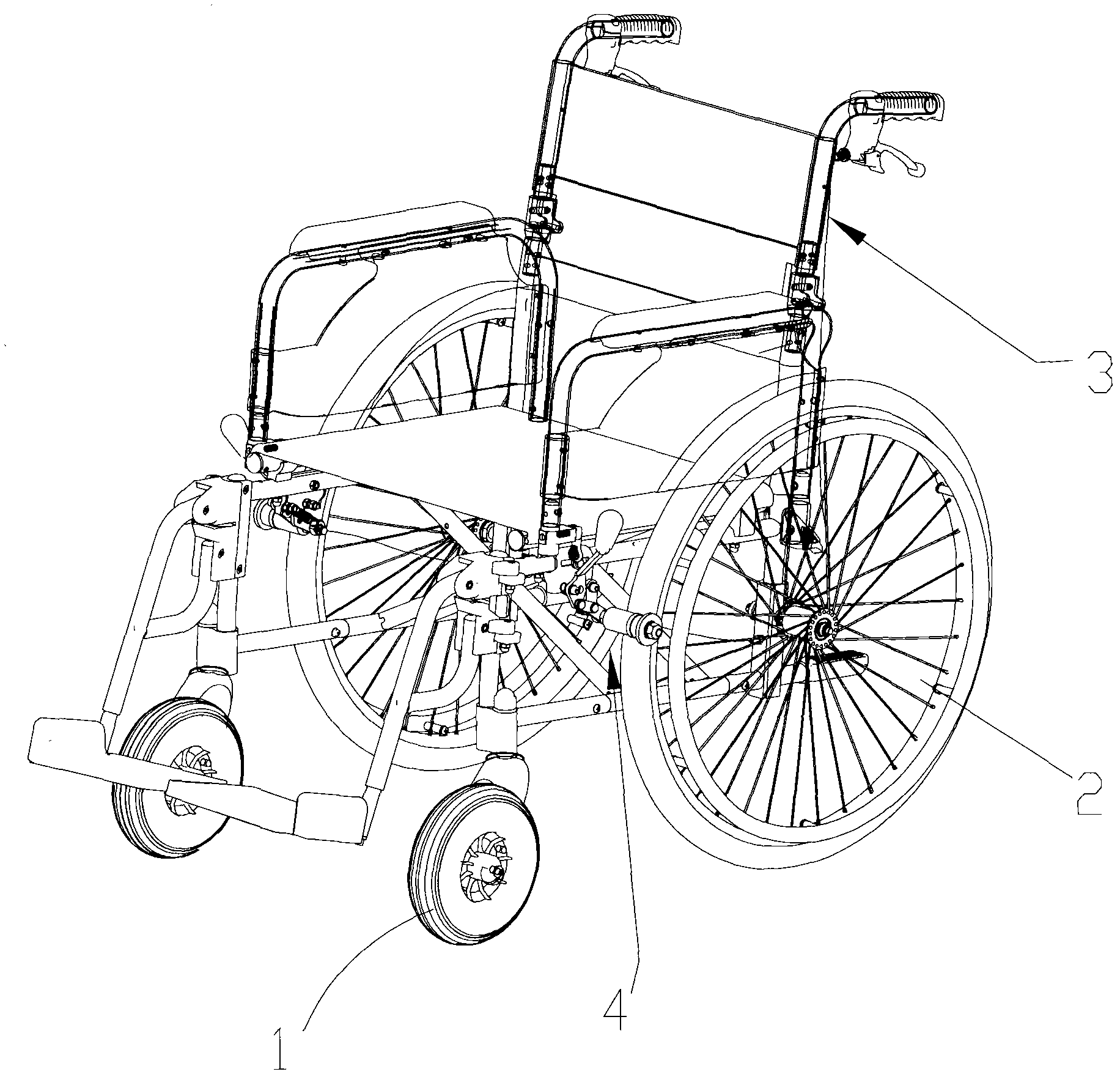
Brake structure and wheelchair comprising same
ActiveCN102398661AImprove securityImprove handlingWheelchairs/patient conveyanceCycle brakesVehicle frameWheelchair
The invention relates to a brake structure and a wheelchair comprising the same. The brake structure comprises a mounting bottom plate and a brake assembly, wherein the mounting bottom plate is fixedly connected with the frame of the wheelchair; the brake assembly is movably arranged on the mounting bottom plate and is used for contacting with and rubbing the rear wheels of the wheelchair. The brake assembly comprises a mandrel, a friction wheel and a locking mechanism, wherein the friction wheel can be unidirectionally and rotatablely sheathed onto the mandrel; the locking mechanism is used for enabling the friction wheel and the mandrel to do relative standstill locking; when the locking mechanism is in a locking state, the friction wheel and the mandrel do the relative standstill locking; and when the locking mechanism is in an unlocking state, the friction wheel only can rotate to the single direction relative to the mandrel. According to the brake structure and the wheelchair comprising the same, half brake and full brake can be realized; the half brake is selected when the wheelchair runs on an abrupt slope, thereby, the forwarding resistance is increased or the wheelchair is prevented from rolling; and when the wheelchair runs on a level road, the full brake of the brake structure can be selected, thereby, the free forwarding or reversing of a user is not influenced.
Owner:卫美恒(苏州)医疗器械有限公司
Distribution line pay-off unit
The invention discloses a distribution line pay-off unit which comprises a pay-off frame. A pay-off shaft is rotationally arranged on the pay-off frame; a pay-off reel is fixedly arranged on the pay-off shaft; the pay-off shaft is fixedly connected with a rotating handle; a brake device for enabling the pay-off reel inertially rotating to brake is arranged on the pay-off frame; meanwhile, a wire arrangement device is arranged on the pay-off frame. According to the invention, on one hand, the distribution line pay-off unit is provided with the brake device, and thus, the distribution line pay-off unit rotates by pulling out a brake control button so as to drive a brake rod to axially move, brake contact surfaces between the brake rod and the pay-off reel are in contact so as to implement brake of the pay-off reel and the distribution line pay-off unit has a simple structure and is convenient to brake; on the other hand, the distribution line pay-off unit is also provided with the wire arrangement device, so that a wire wound on the pay-off reel can be orderly arranged and the distribution line pay-off unit has the simple structure and is convenient to arrange the wire.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Automobile man-machine co-driving mode brake control system and control method
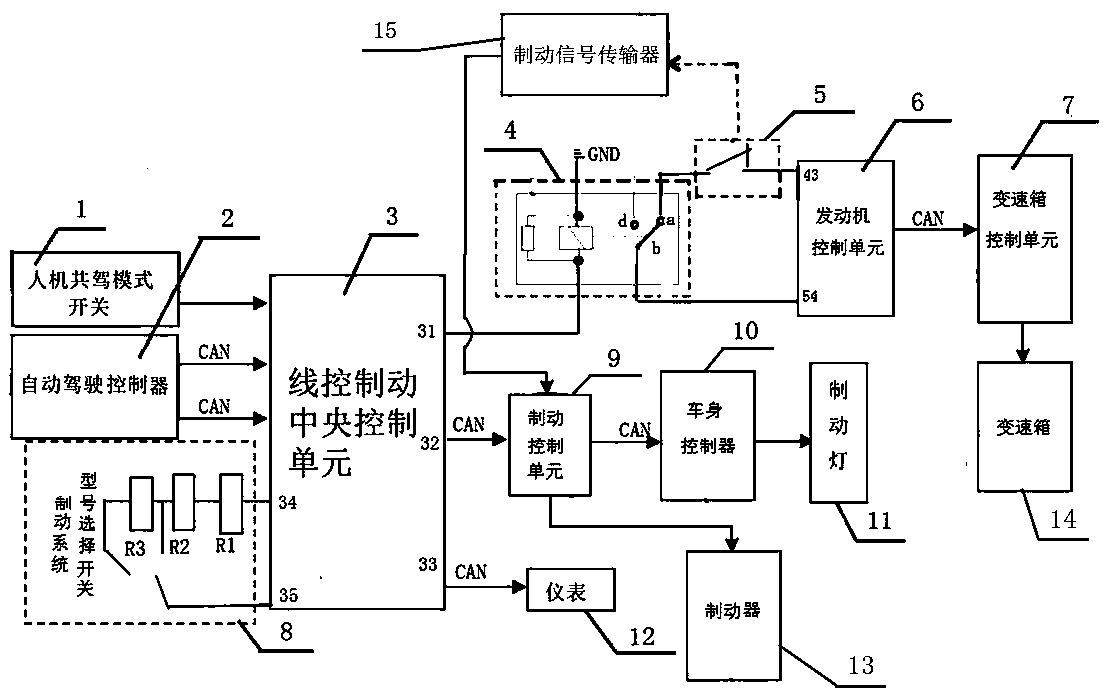
The invention discloses an automobile man-machine co-driving mode brake control system and a control method and belongs to the technical field of automobile manufacturing. The system comprises a brake-by-wire central control unit and a pedal travel switch connected with a brake through a brake control unit, wherein an input end of the brake-by-wire central control unit is correspondingly connectedwith output ends of the man-machine co-driving mode switch and an automatic driving controller, a relay and a pedal travel switch are sequentially connected between a relay power supply control end of the brake-by-wire central control unit and a loop ground end of an engine control unit, a switching signal sampling end of the engine control unit is connected with a common contact end of the relay, and the engine control unit is connected with a gearbox through a gearbox control unit. The system is advantaged in that a problem that the vehicle cannot be stably braked according to the requesteddeceleration in the automatic driving mode of the existing vehicle with both manual driving and automatic driving can be solved.
Owner:DONGFENG LIUZHOU MOTOR
All-weather automobile radar anti-collision driving system
InactiveCN101791981AThe recognition effect is accurateRealize remote temperature measurementOptical rangefindersAcoustic wave reradiationDigital signal processingMatlab language
The invention relates to a radar anti-collision driving system. The system is characterized in that: two sides of the front part of an automobile are provided with anti-side collision laser range finders; the front part is also provided with sonar horns; a sonar transducer is connected with the back of the sonar horns; the sonar transducer is connected with a syndrome all-weather automobile signal processor through an amplifier and a diode detector; a thermal infrared imager is arranged in the front of a cab; a digital signal processor TMS 320240 is adopted in hardware of a driving expert control system and the hardware integrates high-speed signal processing capacity of a DSP and a peripheral circuit suitable for motor control into a whole to directly control speed reduction, steering and braking of the automobile; and a driving expert system adopts an artificial intelligent forward inference engine program and programs by using an artificial intelligent language, namely an LISP language or a MATLAB language. The all-weather automobile radar anti-collision driving system can realize all-weather precise measurement and positioning of targets in front of the automobile, and automatically adjust speed, steering, and braking to fulfill the aim of safe driving.
Owner:成都市猎户座科技有限责任公司
High-precision rotary table with hydraulic brake structure
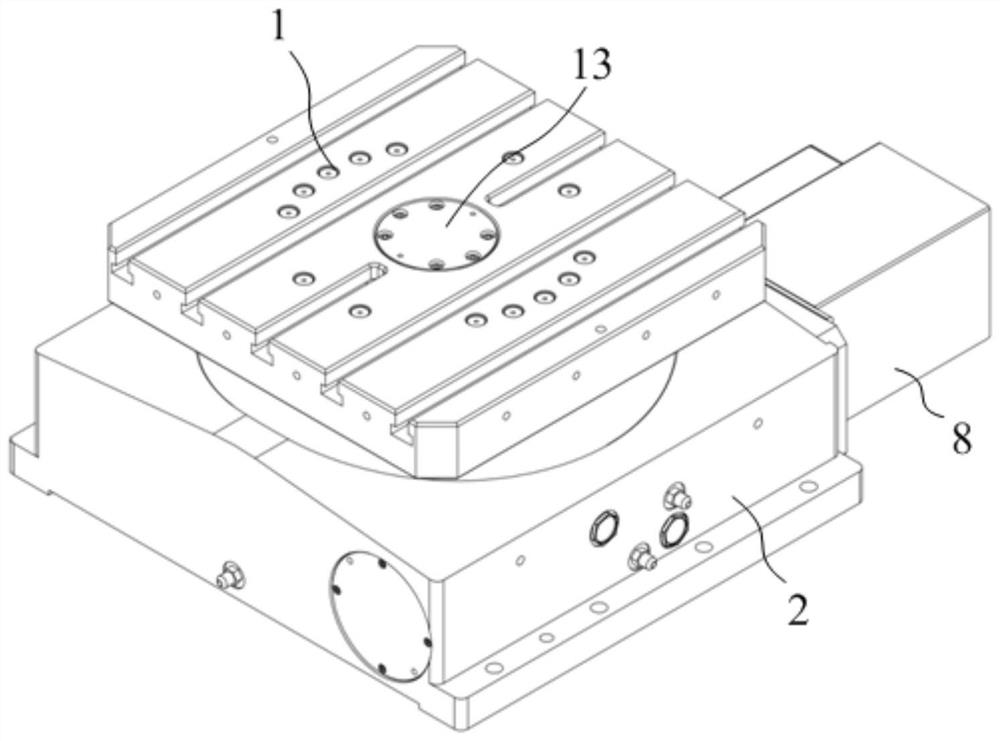
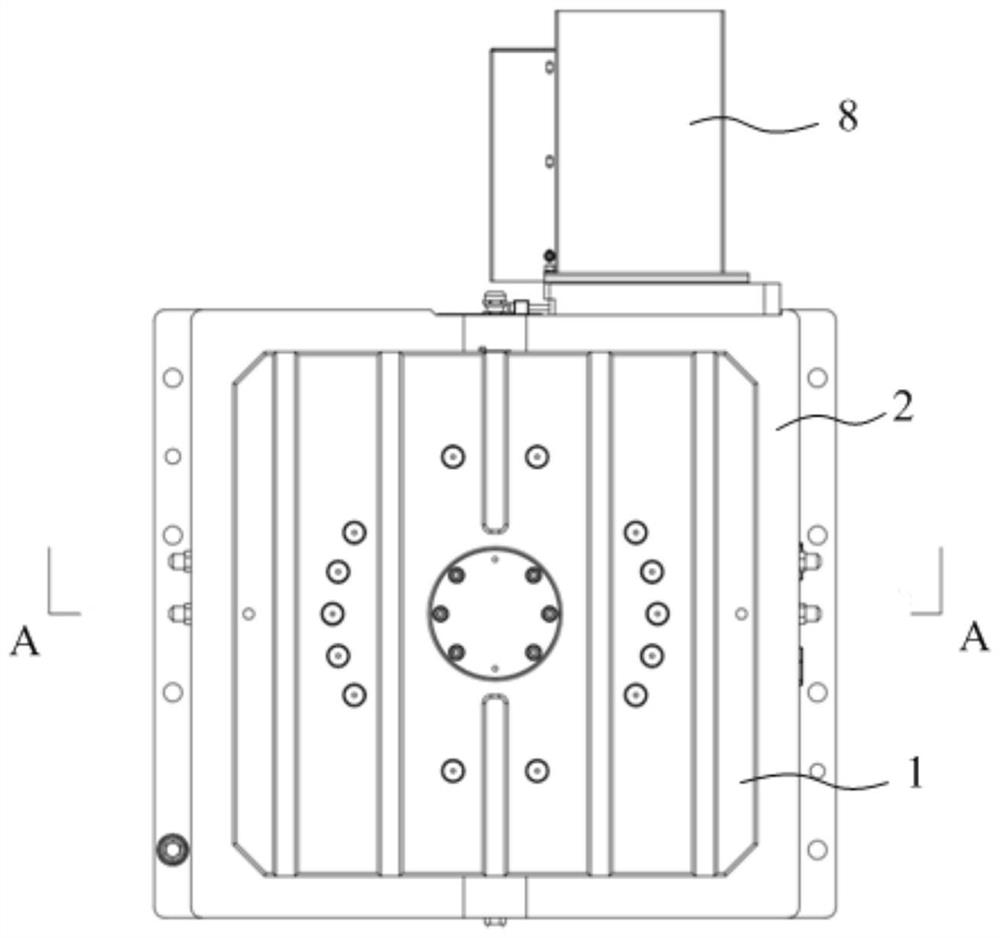
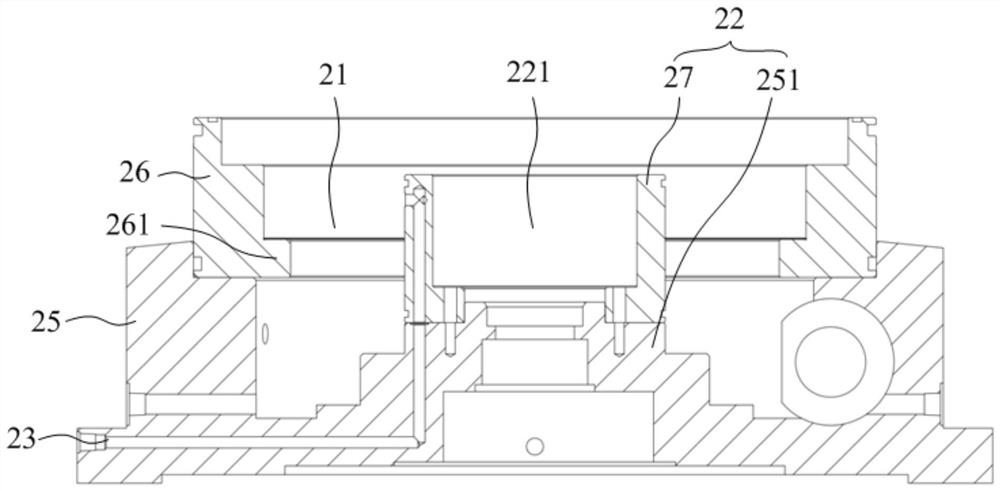
PendingCN114439866ABraking achievedEasy to processBraking membersStands/trestlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The high-precision rotary table with the hydraulic brake structure comprises a rotary table body, a mounting seat, an expansion sleeve, an enclasping sleeve and a rotary driving mechanism, a first mounting cavity is formed in the top of the mounting seat, a mounting column is arranged at the position, in the center of the first mounting cavity, of the mounting seat, and the expansion sleeve, the enclasping sleeve and the rotary driving mechanism are sequentially arranged in the first mounting cavity from inside to outside; the expansion sleeve surrounds the mounting column, an annular sealing oil cavity is formed by the expansion sleeve and the outer wall of the mounting column, and an oil way communicating with the sealing oil cavity is formed in the mounting base. The elastic modulus of the enclasping sleeve is larger than that of the expansion sleeve, the enclasping sleeve is arranged outside the expansion sleeve in a sleeving mode, and when oil does not pass through the sealing oil cavity, the enclasping sleeve is in clearance fit with the rotary driving mechanism; the rotary table body is arranged above the mounting column and covers the first mounting cavity, and the rotary driving mechanism is connected with the rotary table body and used for driving the rotary table body to rotate. The brake energy loss is small, machining is convenient, and positioning is accurate.
Owner:FOSHAN PRATIC CNC SCI & TECH
Controllable gasoline-saving semi-axle for vehicle
InactiveCN101016030AGuaranteed uptimeGuaranteed to be in control at any timeControl devicesMagnetic tension forceManufacturing technology
The invention relates to a controllable vehicle fuel-saving semi axle, characterized in that the invention uses inertia theory, arranges inside arc magnetic drawing claw engaged with a Z-type drawing rod with a positioning hole at middle, two symmetry arms of the drawing rod are limited by the axles on two arc drawing claws, the rotation axle of the drawing claw is fixed on a frame support, the clutch frame has a chamber containing a clutch one-way disc whose two sides are arranged with space without spiky, and rollers at angle end, to engage with the clutch, driving tooth and driven tooth, therefore, the invention can on-time control slide and brake, and save fuel, with simple structure, easy operation or the like.
Owner:杨恒道
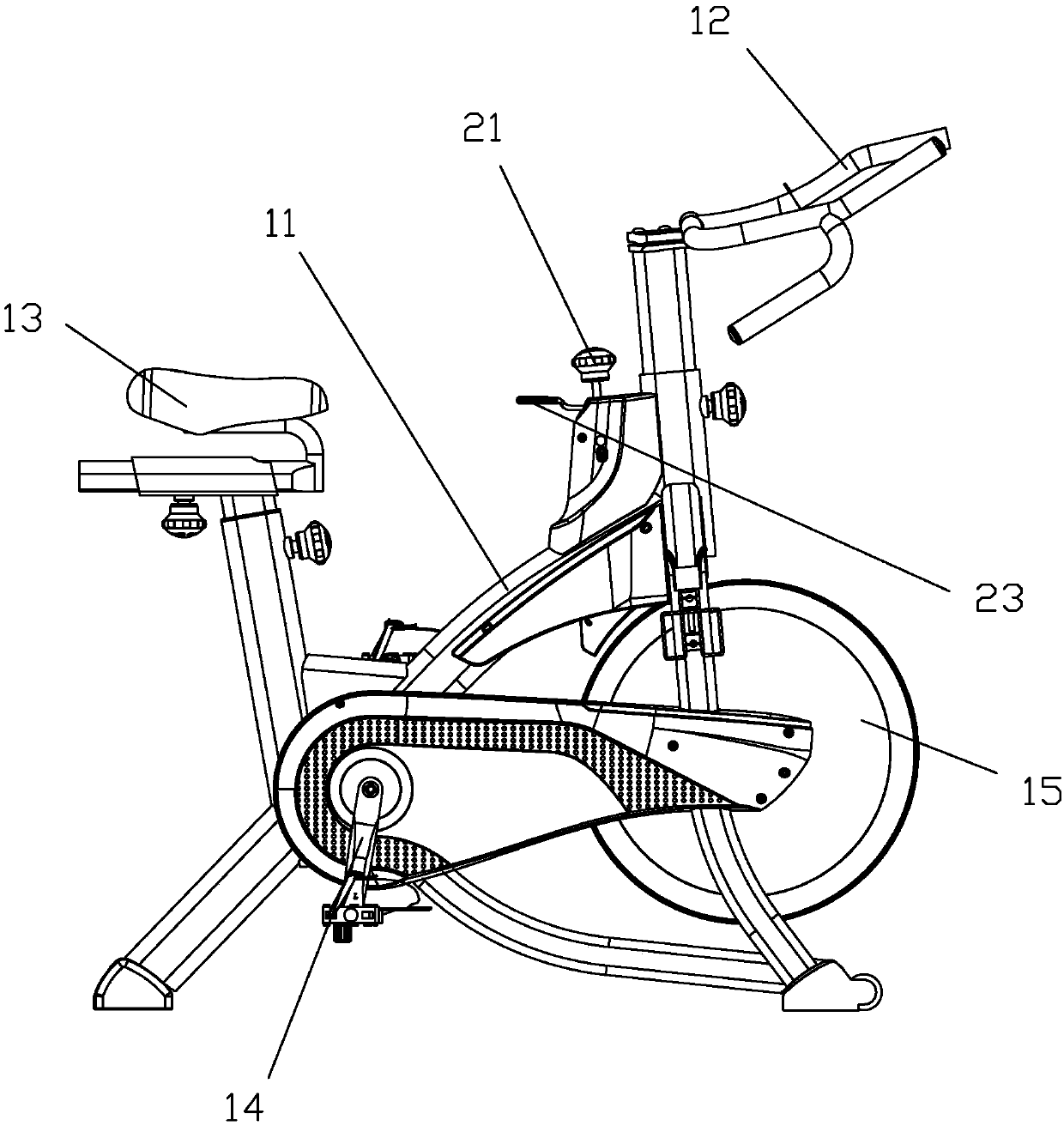
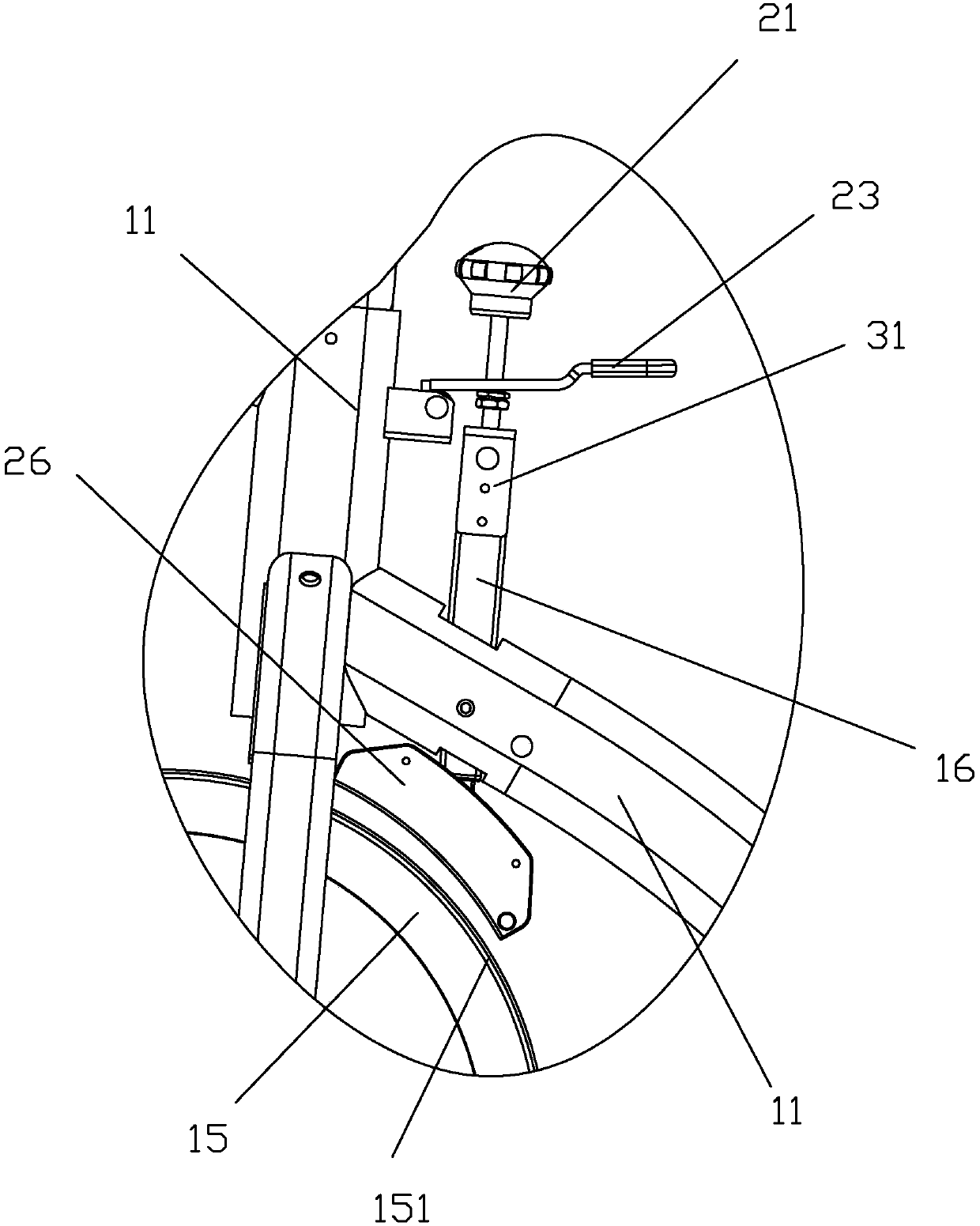
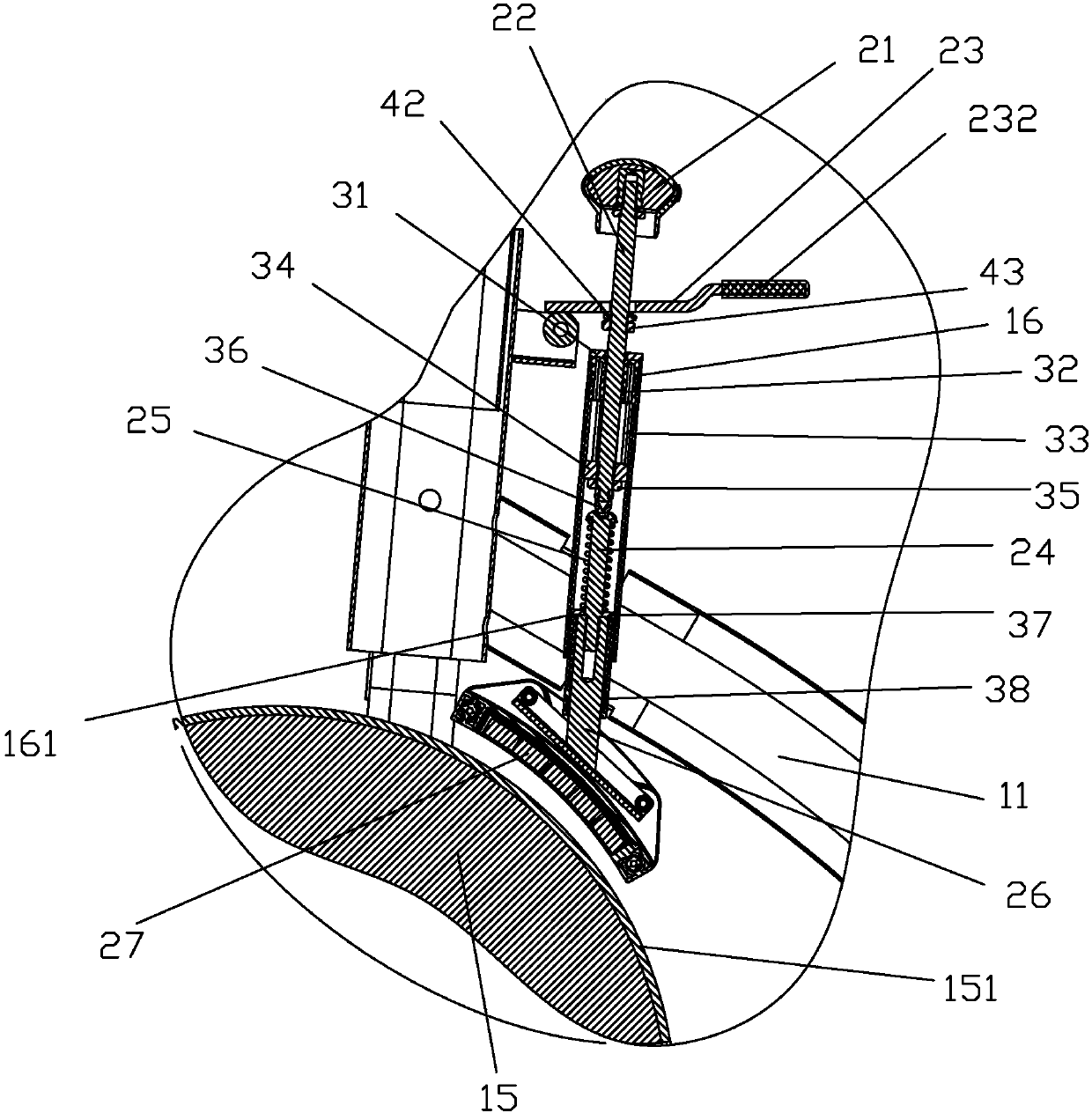
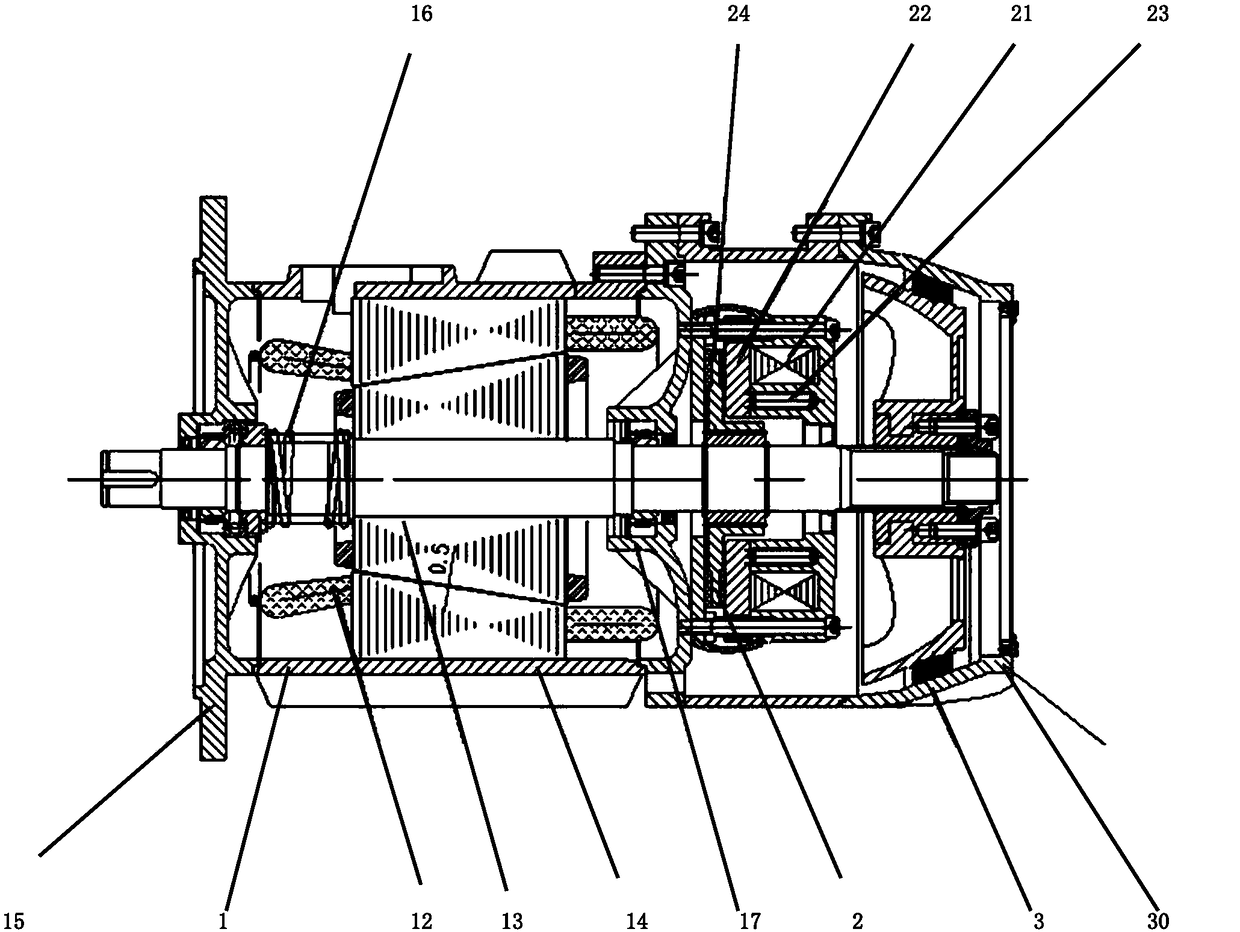
Resistance adjusting mechanism of magnetic control bodybuilding /competition vehicle
InactiveCN109513172AGuaranteed smoothnessSame distanceMovement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesVehicle frameMagnetic reluctance
The invention discloses a resistance adjusting mechanism of a magnetic control bodybuilding / competition vehicle. The resistance adjusting mechanism comprises a sleeve pipe, a brake screw, a limiting piece, a first nut, a bolt, a first pressure spring, a magnetic plate fixing frame and a magnet block. The sleeve pipe is mounted at the position, corresponding to an inertia wheel, of a vehicle frame.The first nut can be accommodated in the sleeve pipe in an up-down moving manner, and an anti-rotation structure is arranged between the first nut and the sleeve pipe, so that the first nut cannot rotate relative to the sleeve pipe. One part of the brake screw extends into the sleeve pipe and is matched with the first nut in a screwing manner. The limiting piece sleeves the brake screw and is positioned between the top of the sleeve pipe and the upper end surface of the first nut. The bottom end of the brake screw is in contact with the top end of the bolt. The first pressure spring is elastically propped between the top of the bolt and the bottom of the sleeve pipe. The lower end of the bolt is connected with the magnetic plate fixing frame with an arc-shaped bottom. The magnetic resistance acting on the inertia wheel by a magnetic plate assembly can be ensured to be uniformly distributed, so that the rotation smoothness of the inertia wheel is ensured.
Owner:XIAMEN AOLRO TECH +1
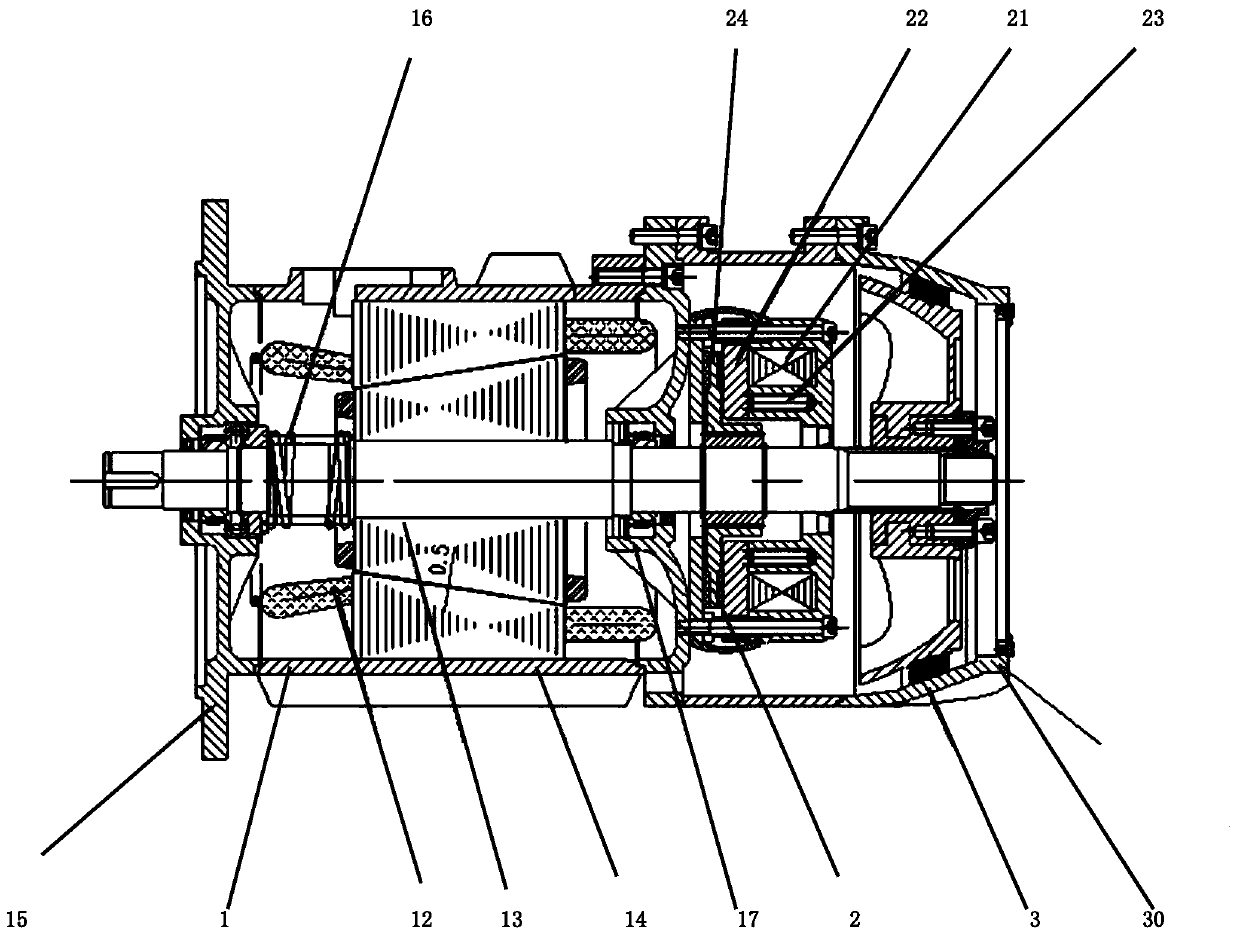
Dual-brake conical motor
ActiveCN108494161AStrong reliabilityImprove securityWinding mechanismsMechanical energy handlingEngineeringMotor shaft
The invention provides a dual-brake conical motor. The dual-brake conical motor comprises a conical motor, an electromagnetic brake and a conical brake, wherein the electromagnetic brake is connectedwith the conical motor and is arranged between the conical motor and the conical brake, the conical brake comprises a motor shaft, the motor shaft is arranged on the conical motor, and the conical motor, the electromagnetic brake and the conical brake are arranged on the motor shaft. In the dual-brake conical motor provided by the invention, the electromagnetic brake is additionally arranged at afront end at a position where shaft breakage is easy to occur, the motor also can be braked by the electromagnetic brake even shaft breakage phenomenon occurs, an accident is prevented, and the reliability of the motor is improved.
Owner:湖南泰尔汀起重科技有限公司
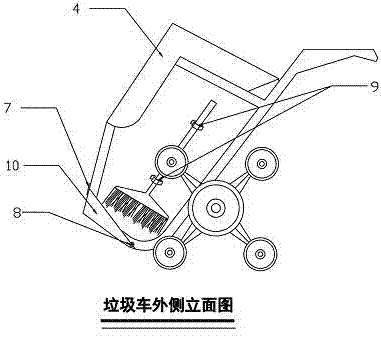
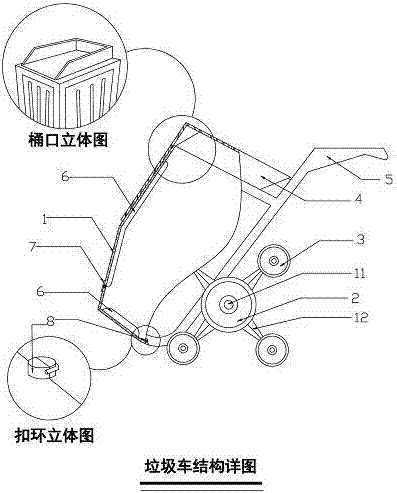
Multifunctional movable garbage can
A multifunctional movable garbage can comprises a can body, an axle, wheels and push handles; and the axle is arranged on the lower half part of the can body in a fixedly combining manner. The multifunctional movable garbage can is characterized in that a movable support base is formed by beveling the bottom of the garbage can, one end of the support base is fixed by a hinge, and the other end of the support base is fixed by a plurality of round lock catches; an inverted modeling dustpan serves as a garbage can top cover, and the side surface of the can body is provided with a device with a broom; and the wheels are a pair of solid ladder stand combined wheels and respectively sleeve two ends of the axle. The garbage can integrates a garbage cart, the broom and the dustpan into a whole, is narrow in shape, changes a traditional garbage inlet and outlet manner, and is suitable for operation of multiple cleaning occasions such as slopes, hollowed ground, step ground, parks, stations, high speed train carriages, and the like.
Owner:刘建宽
Curtain paving tool brake device
PendingCN111734757AAct as a brakeBraking achievedBrake actuating mechanismsActuatorsElectric machineryStructural engineering
The invention discloses a curtain laying tool brake device in the technical field of machinery. The curtain laying tool brake device comprises a linear telescopic cylinder and a guide pipe arranged inparallel with the linear telescopic cylinder, mounting plates are arranged at two ends of the telescopic cylinder,brake pads are arranged on one sides, away from each other, of each mounting plate, and guide parts are arranged on the two mounting plates correspondingly and are in sliding fit in guide pipes in the telescopic direction of the telescopic cylinder. According to the curtain laying tool brake device, when the telescopic cylinder extends out, under the action of acting force and counter-acting force, the brake pads on the mounting plates at the two ends are driven to be synchronously opened towards the two sides, a guide rail is jacked to play a role in braking under the action of friction force, replacing a motor band-type brake is achieved, and braking is achieved.
Owner:HAIXI (FUJIAN) INST CHINA ACAD OF MASCH SCI&TECH GRP
Double-drive speed regulation rotary table of numerical control machine tool
ActiveCN114055193AControl speedRandom combinationLarge fixed membersDriving apparatusNumerical controlEngineering
The invention discloses a double-drive speed regulation rotary table of a numerical control machine tool, and belongs to the technical field of numerical control machine tools. The rotary table comprises a rotary table seat and a rotary table frame rotationally connected to the inner side of the rotary table seat, a table body is mounted in the rotary table frame, and the table body is rotationally connected with a workbench; the rotary table also comprises a planet wheel mechanism, anda workbench is connected with a wheel carrier of the planet wheel mechanism; and a center wheel of the planet wheel mechanism is connected with a first power source, a gear sleeve of the planet wheel mechanism is connected with a second power source, and the workbench is driven to rotate through the first power source and / or the second power source. The two power sources and the planet wheel mechanism are coordinated to synthesize power to be input to the workbench, and control over the speed, torque and position of the rotary table workbench is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG MACHINERY DESIGN INST
Automatic braking device and rail transport vehicle
PendingCN110758353ABraking achievedSimple structureSelf-applying brakesAutomatic initiationsAutomatic brakingEngineering
The invention relates to an automatic braking device and a rail transport vehicle with the automatic braking device. The automatic braking device is characterized by comprising a friction wheel, a first transmission gear, a second transmission gear, a centrifugal clutch and an eccentric wheel, wherein the friction wheel, the first transmission gear, the second transmission gear, the centrifugal clutch and the eccentric wheel are arranged below the vehicle and sequentially driven; the device further comprises a wedge-shaped piece and tension springs symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the wedge-shaped piece, the upper end of the wedge-shaped piece is rotatably connected below the vehicle, the upper ends of the tension springs are fixed below the vehicle, and the lower ends of the tension springs are fixed to the side face of the wedge-shaped piece; under the action of the tension springs, the wedge-shaped piece can be lifted to make contact with the eccentric wheel; and when theeccentric wheel is driven to rotate through a driven piece of the centrifugal clutch, the wedge-shaped piece is pushed down to rotate to be clamped between wheels and the ground. The automatic brakingdevice has wide application range and can be applied to the field of rail transport vehicles, not only is simple in structure, small in size, low in production cost, but also is capable of effectively realizing braking, and is high in reliability and safer.
Owner:武汉励耕果园机械有限公司 +1
Low-voltage line winding braking device for active power distribution network
The invention relates to winding braking, in particular to a low-voltage line winding braking device for an active power distribution network. The low-voltage line winding braking device for the active power distribution network comprises a supporting base, a brake disc and an air cylinder. The low-voltage line winding braking device for the active power distribution network is characterized in that an abrasion-resisting lamination is arranged on each of the two sides of the brake disc, and a supporting frame is arranged at the rear ends of the abrasion-resisting laminations and connected with an L-shaped connecting rod; two bosses are arranged on the supporting base and provided with shaft holes, and a shaft is arranged on the shaft holes and connected with two connecting rods; and the upper end of one connecting rod is connected to a piston rod of the air cylinder, the middle portion of the other connecting rod is arranged at the lower end of the piston rod, and the two abrasion-resisting laminations oppositely move to tightly hold the brake disc under driving of the piston rod. The low-voltage line device has the beneficial effects that the abrasion-resisting laminations on the two sides oppositely move to tightly hold the brake disc under driving of the piston rod to achieve braking, braking is stable and reliable, the braking device is arranged, so that the braking device is good.
Owner:滨州东力电力设计有限公司 +1
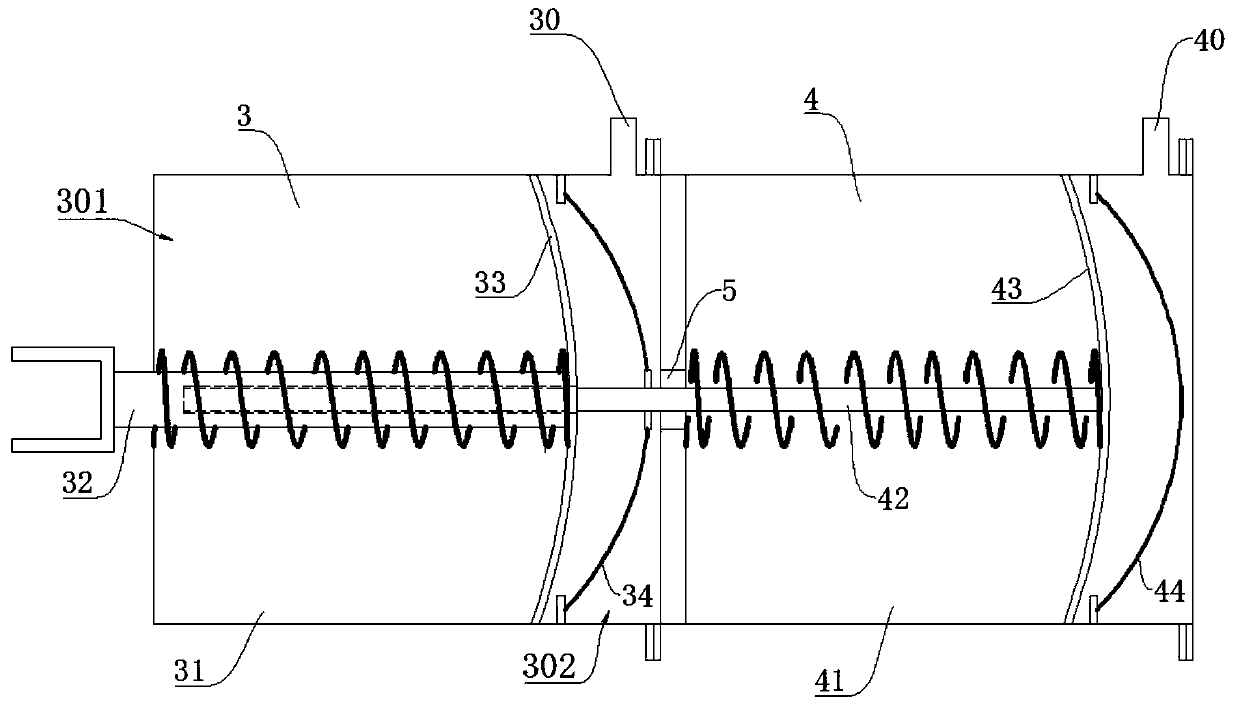
Brake-generator device
InactiveCN102257705BBraking achievedRealize the braking actionMechanical energy handlingDrive shaftEngineering
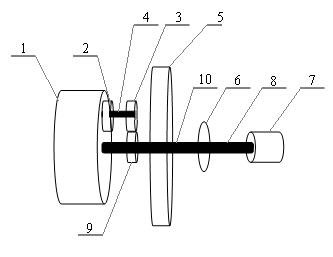
A brake-generator device. The main structure of the device includes: a transmission shaft (1), a transmission gear A, a transmission gear B, rotor modules (2) and stator modules (3). The transmission shaft (1) is laterally set and a transmission gear A is set in the middle of the shaft (1). A transmission mechanism of gear box for vehicles is provided with the output transmission gear B. The gear A is engaged with the gear B. The rotor modules (2) are set in two ends of the shaft (1) and can rotate with the shaft (1). The stator modules (3) are set around the circumference of the rotor modules (2) correspondingly. A generator device consists of the rotor modules (2) and the stator modules (3). The kinetic energy that is output by the transmission mechanism of gear box is transformed to the power energy when the generator device works. In the generating process, a force of gear box is exerted to the transmission shaft (1) to drive the shaft (1) and a reaction force is exerted to the transmission mechanism of gear box to stop rotating and brake. The device can not only brake but also generate power.
Owner:王文晖
Double Brake Cone Motor
ActiveCN108494161BStrong reliabilityImprove securityWinding mechanismsMechanical energy handlingMotor shaftElectromagnetic brake
The invention provides a dual-brake conical motor. The dual-brake conical motor comprises a conical motor, an electromagnetic brake and a conical brake, wherein the electromagnetic brake is connectedwith the conical motor and is arranged between the conical motor and the conical brake, the conical brake comprises a motor shaft, the motor shaft is arranged on the conical motor, and the conical motor, the electromagnetic brake and the conical brake are arranged on the motor shaft. In the dual-brake conical motor provided by the invention, the electromagnetic brake is additionally arranged at afront end at a position where shaft breakage is easy to occur, the motor also can be braked by the electromagnetic brake even shaft breakage phenomenon occurs, an accident is prevented, and the reliability of the motor is improved.
Owner:湖南泰尔汀起重科技有限公司
Brake structure and wheelchair comprising same
ActiveCN102398661BBraking achievedAvoid walking afterWheelchairs/patient conveyanceCycle brakesWheelchairVehicle frame
The invention relates to a brake structure and a wheelchair comprising the same. The brake structure comprises a mounting bottom plate and a brake assembly, wherein the mounting bottom plate is fixedly connected with the frame of the wheelchair; the brake assembly is movably arranged on the mounting bottom plate and is used for contacting with and rubbing the rear wheels of the wheelchair. The brake assembly comprises a mandrel, a friction wheel and a locking mechanism, wherein the friction wheel can be unidirectionally and rotatablely sheathed onto the mandrel; the locking mechanism is used for enabling the friction wheel and the mandrel to do relative standstill locking; when the locking mechanism is in a locking state, the friction wheel and the mandrel do the relative standstill locking; and when the locking mechanism is in an unlocking state, the friction wheel only can rotate to the single direction relative to the mandrel. According to the brake structure and the wheelchair comprising the same, half brake and full brake can be realized; the half brake is selected when the wheelchair runs on an abrupt slope, thereby, the forwarding resistance is increased or the wheelchair is prevented from rolling; and when the wheelchair runs on a level road, the full brake of the brake structure can be selected, thereby, the free forwarding or reversing of a user is not influenced.
Owner:卫美恒(苏州)医疗器械有限公司
Brake device mounted on flight experience device
The invention relates to a brake device mounted on a flight experience device. The brake device mounted on the flight experience device comprises a supporting platform, a combined type brake is symmetrically mounted at the left end and the right end of the supporting platform, and the combined type brake comprises an upper main support, a lower main support and a lateral brake. The lateral brake comprises a lateral shoving and pushing device, a lateral brake shoving and pushing block and a lateral brake cushion. The lateral shoving and pushing device is located between the upper main support and the lower main support, the lateral shoving and pushing device is fixedly connected to a supporting platform, the lateral brake cushion is located between an upper brake cushion and a lower brake cushion, and one side of the lateral brake cushion is connected with the lateral shoving and pushing device through the lateral brake shoving and pushing block. The brake device mounted on the flight experience device has the advantages of being reasonable in structural design, convenient to control, good in brake performance and the like; the occurrence of slipping is avoided by adopting a vertical brake and a transverse brake combining mode and by using the fact that the tooth groove direction of first transverse antiskid zigzag teeth, the tooth groove direction of second transverse antiskid zigzag teeth and the tooth groove direction of vertical antiskid zigzag teeth are all perpendicular to the walking direction of a machine, and rapid braking can be achieved in a flight experience process.
Owner:HUAQIANG FANGTE WUHU CULTURE TECH CO LTD
Powerful balance brake device
PendingCN110067823APlay a guiding roleBraking force is strongBrake actuating mechanismsMechanically actuated drum brakesEngineeringCam
The invention provides a powerful balance brake device comprising a brake drum, a bottom plate, a left brake shoe, a right brake shoe and cam mechanisms. The left brake shoe and the right brake shoe are oppositely arranged to form two pairs of opposite end faces, guiding holes are formed in the two end faces of the left brake shoe and the two end faces of the right brake shoe, and one cam mechanism is arranged between each pair of opposite end faces of the left brake shoe and the right brake shoe; and each cam mechanism comprises a cam shaft, a guide shaft and a cam, the cams are arranged on the cam shafts, through holes are formed in the middle portions of the guide shafts, the cam shafts penetrate through the through holes, one end of each guide shaft is inserted into the corresponding guiding hole of the left brake shoe, and the other end of each guide shaft is inserted into the corresponding guiding hole of the right brake shoe. The technical problems that the braking force is small and braking is not sensitive are solved.
Owner:广西环江航舵汽车科技有限公司
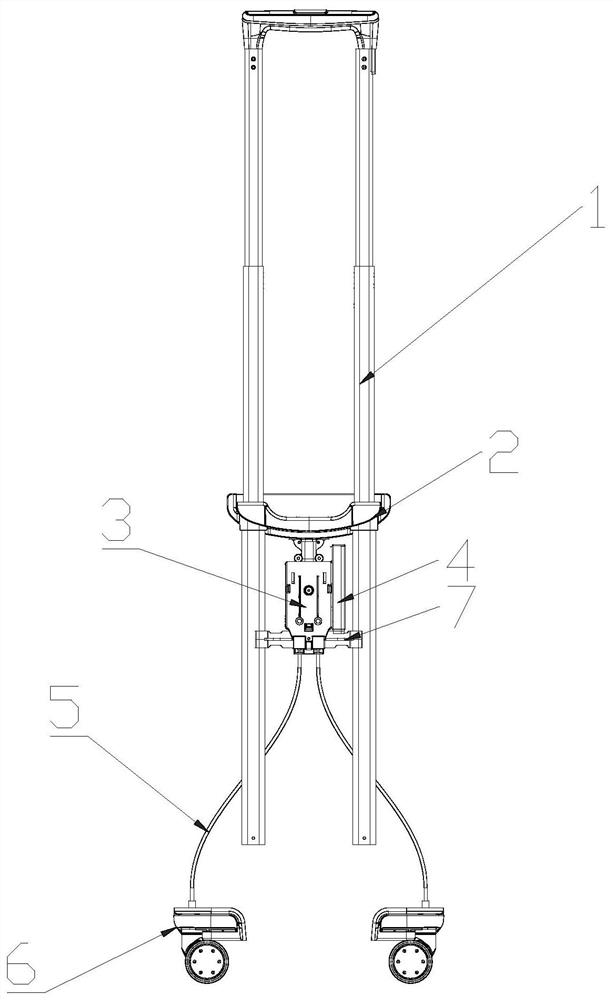
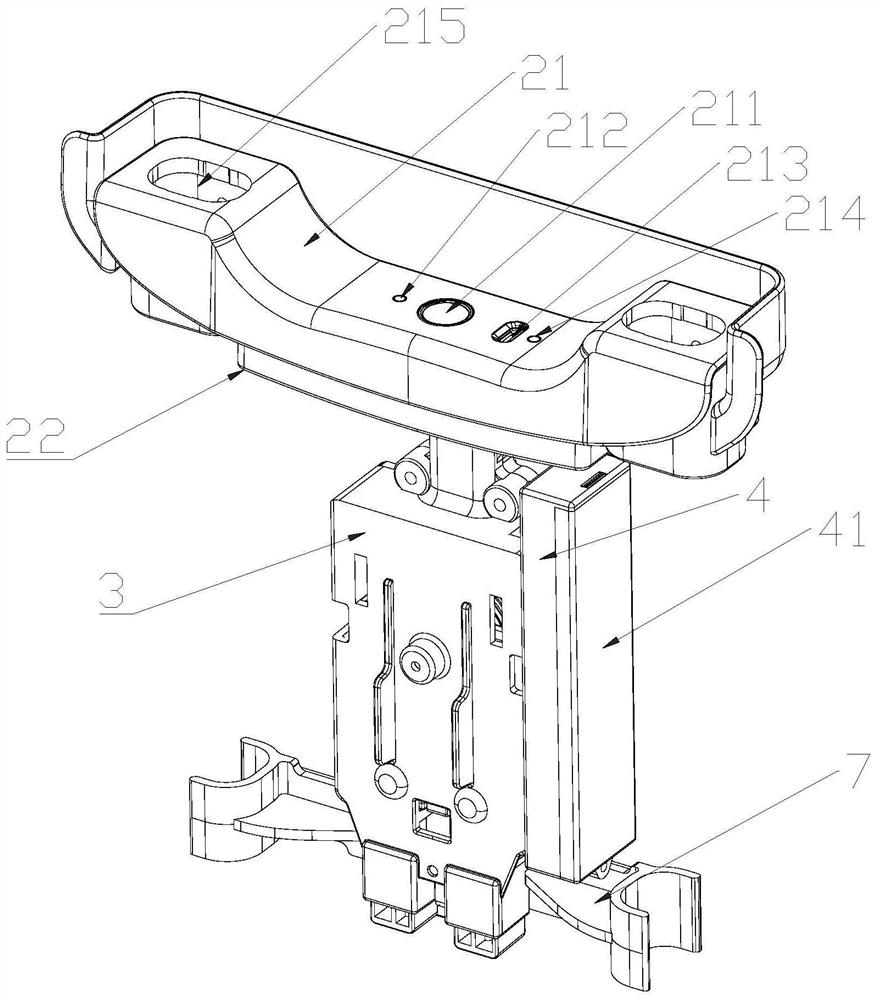
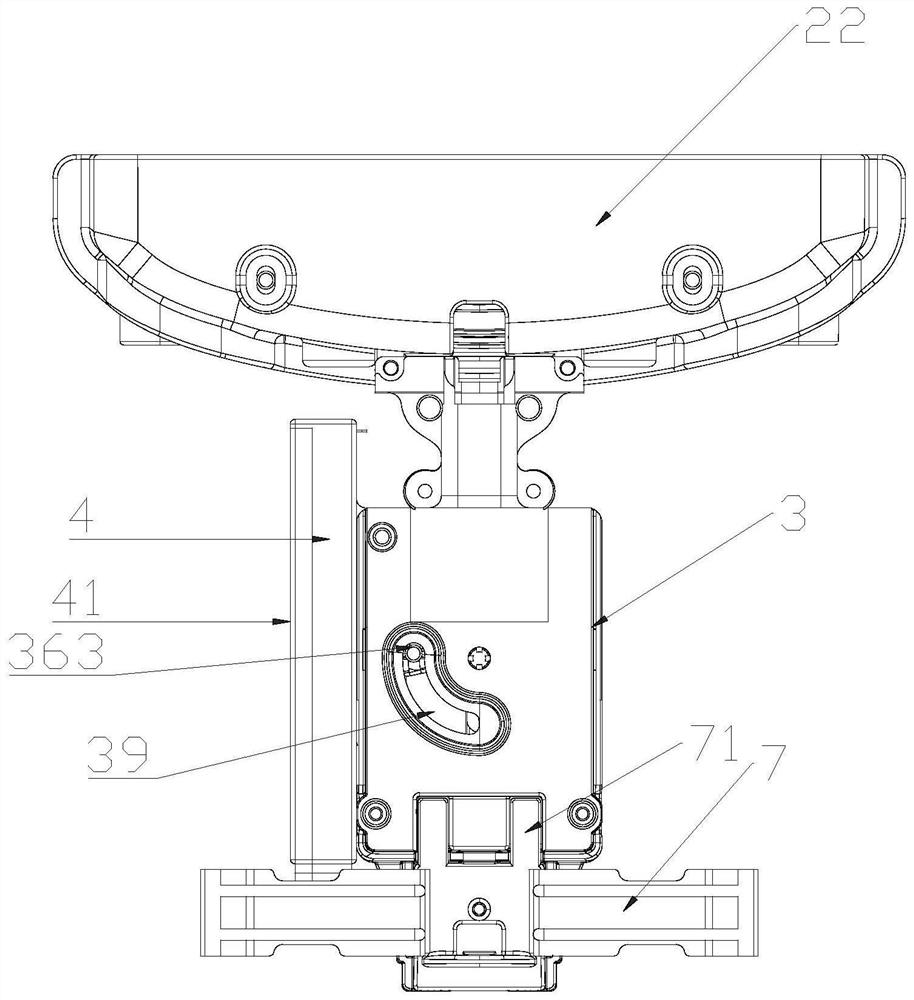
A luggage electric brake device
The present application provides an electric brake device for luggage. In the past, wheel group brakes were all manually operated by pushing buttons to brake, which was laborious. The battery is now used as the energy supply, and the output shaft of the drive motor can be driven to drive the bevel gear to rotate only by lightly pressing the control button. The bevel gear meshes with the sector swing gear and drives the lifting cylinder of the sector swing gear to swing along the sector The circumferential movement of the gear will make the lifting slider move up and drive the transmission line to move up and realize the braking of the brake wheel group; when the brake needs to be released, just press the control button again to drive the output shaft of the drive motor to drive the bevel gear Rotating in the opposite direction, the bevel gear meshes with the sector swing gear and drives the lifting cylinder of the sector swing gear to move along the circumference of the sector swing gear, so that the lift slider moves down to drive the transmission line down and releases the brake wheel Set of brakes. Even the process of braking or releasing the brake is very convenient and labor-saving.
Owner:DONGGUAN JIANG SHUN SUITCASES & HANDBAGS SPARE PARTS
Gear swing-arm single-motor jig dyeing machine
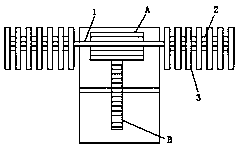
InactiveCN101935927BSimple structureLow powerLiquid/gas/vapor open-width material treatmentTextile treatment machine partsGear wheelEconomic benefits
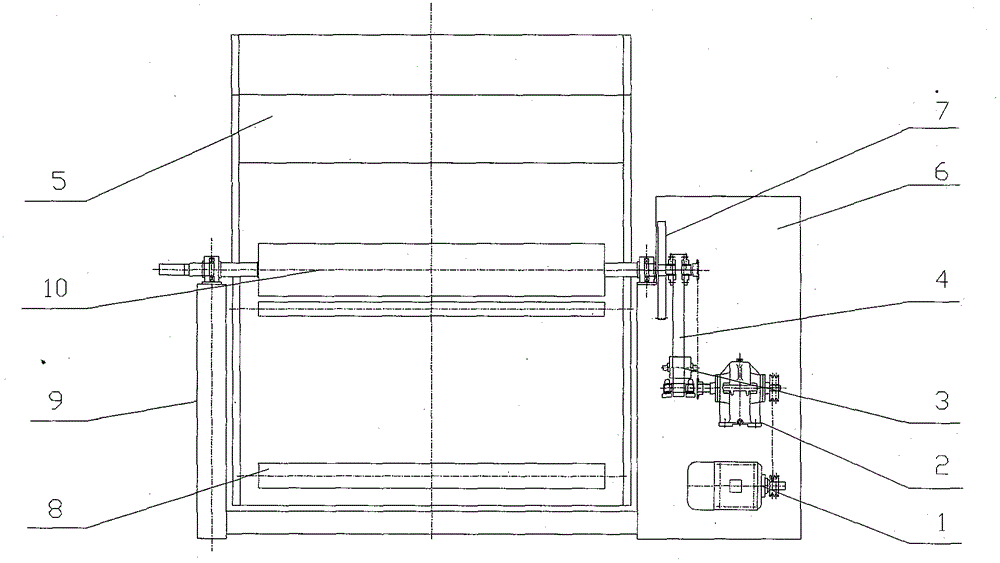
The invention provides a gear swing-arm single-motor jig dyeing machine which relates to a jig dyeing machine in the technical field of weaving and dyeing machines. The invention aims at designing a novel transmission mechanism with the characteristics of simpler structure, device matched investment reduction, motor power reduction, energy saving, stable operation, convenient maintenance, and thelike. Disclosed by adopting a picture 2, a main-drive swing gear 13 is arranged at the upper end of a transmission supporting arm 4, a passive large gear 7 is respectively arranged on one end shafts of a left and a right cloth roller 10, and an air cylinder 3 is connected with the transmission supporting arm 4, has an action of towing an extension function and is in tight contact with the passivelarge gears 7 arranged on the left and right cloth rollers 10. When the right cloth roller 10 reversely operates, the air cylinder 3 has the actions of automatically towing the extension function, isin tight contact with the passive large gear 7 arranged on the right cloth roller 10 and realizes the repeated alternating operation function of the left and right cloth rollers 10. The gear swing-arm single-motor jig dyeing machine is characterized by reducing power of an electric motor 1 and the matched investment of one electric motor 1 and one speed reducer 2, obviously saving electric energyand smoothly operating and can be quickly operated. Owing to the adoption of a novel transmission structure, the structure of the device is more simple and compact, the manufacturing cost of the device is reduced, and more importantly, the gear swing-arm single-motor jig dyeing machine is capable of saving large numbers of energy sources, reducing production cost and increasing economic benefit for users.
Owner:ZAOZHUANG FUYUAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION & ENERGY SAVING MACHINERY MFG CO LTD
Powerful cam brake balancing device
PendingCN110107619ABraking force is strongImprove stability and reliabilityBraking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionBrake shoeCam
The invention provides a powerful cam brake balancing device. The powerful cam brake balancing device comprises a brake drum, a bottom plate, friction plates, a left brake shoe, a right brake shoe andcam mechanisms, wherein the two ends of the left brake shoe and the right brake shoe are separately provided with butt blocks; the butt blocks are provided with cam holes; the left brake shoe is opposite to the right brake shoe to form two pairs of opposite ends; the butt blocks on each pair of opposite ends are arranged in an inner and outer staggered mode; each cam mechanism is arranged betweeneach pair of opposite ends; each cam mechanism comprises a camshaft, an inner cam and an outer cam, wherein the inner cam and the outer cam are separately fixed on the camshaft; the outer cams are eccentrically arranged relative to the inner cams; the outer cams are arranged in cam holes of the outer butt blocks; and the inner cams are arranged in the cam holes of the inner butt blocks. By meansof the powerful cam brake balancing device, the technical problems of low braking force and insensitive braking can be solved.
Owner:广西环江航舵汽车科技有限公司
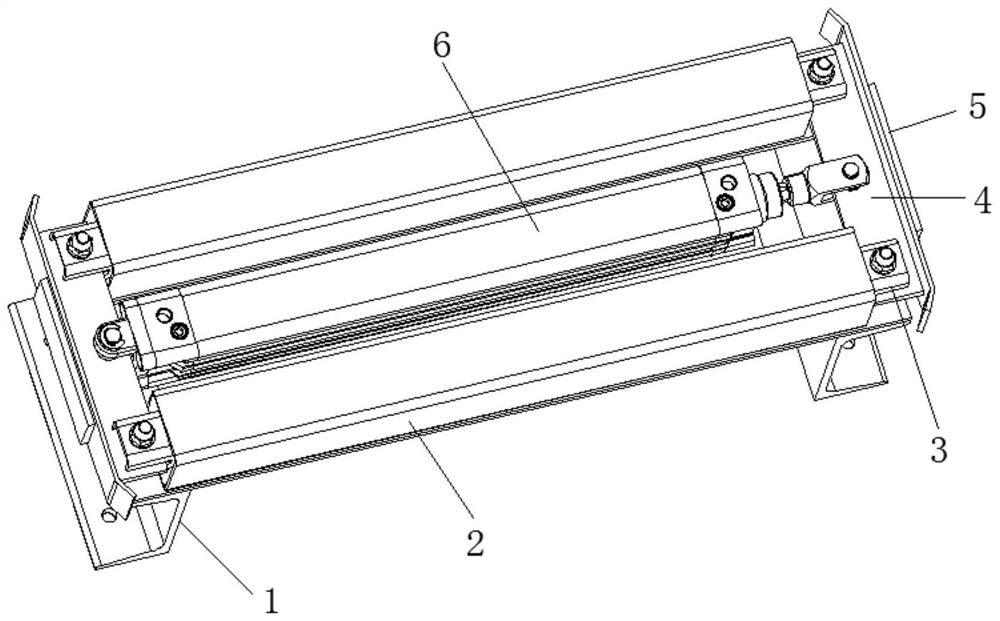
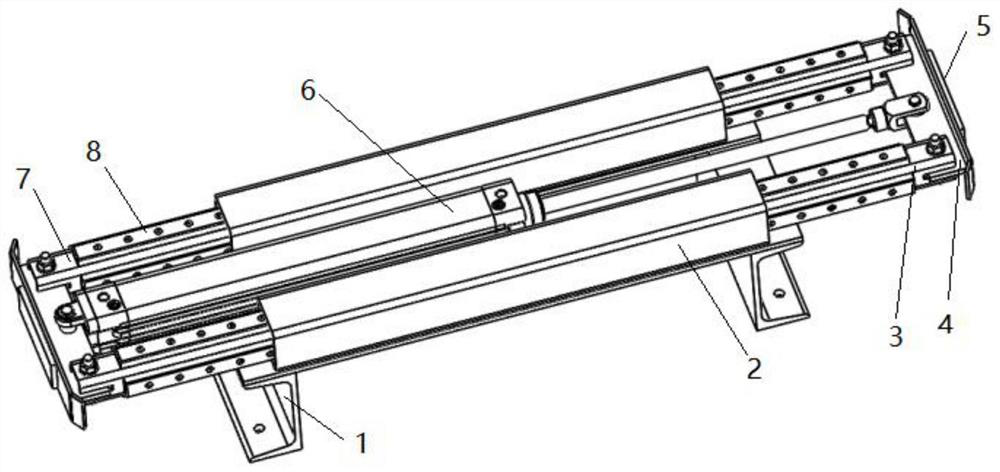
A distribution line pay-off device
ActiveCN104477696BBraking achievedSimple structureFilament handlingActinomycesIndustrial engineering
The invention discloses a distribution line pay-off unit which comprises a pay-off frame. A pay-off shaft is rotationally arranged on the pay-off frame; a pay-off reel is fixedly arranged on the pay-off shaft; the pay-off shaft is fixedly connected with a rotating handle; a brake device for enabling the pay-off reel inertially rotating to brake is arranged on the pay-off frame; meanwhile, a wire arrangement device is arranged on the pay-off frame. According to the invention, on one hand, the distribution line pay-off unit is provided with the brake device, and thus, the distribution line pay-off unit rotates by pulling out a brake control button so as to drive a brake rod to axially move, brake contact surfaces between the brake rod and the pay-off reel are in contact so as to implement brake of the pay-off reel and the distribution line pay-off unit has a simple structure and is convenient to brake; on the other hand, the distribution line pay-off unit is also provided with the wire arrangement device, so that a wire wound on the pay-off reel can be orderly arranged and the distribution line pay-off unit has the simple structure and is convenient to arrange the wire.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Brake assembly for silent tubular motors
Owner:NINGBO HAIYU ELECTROMECHANICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com