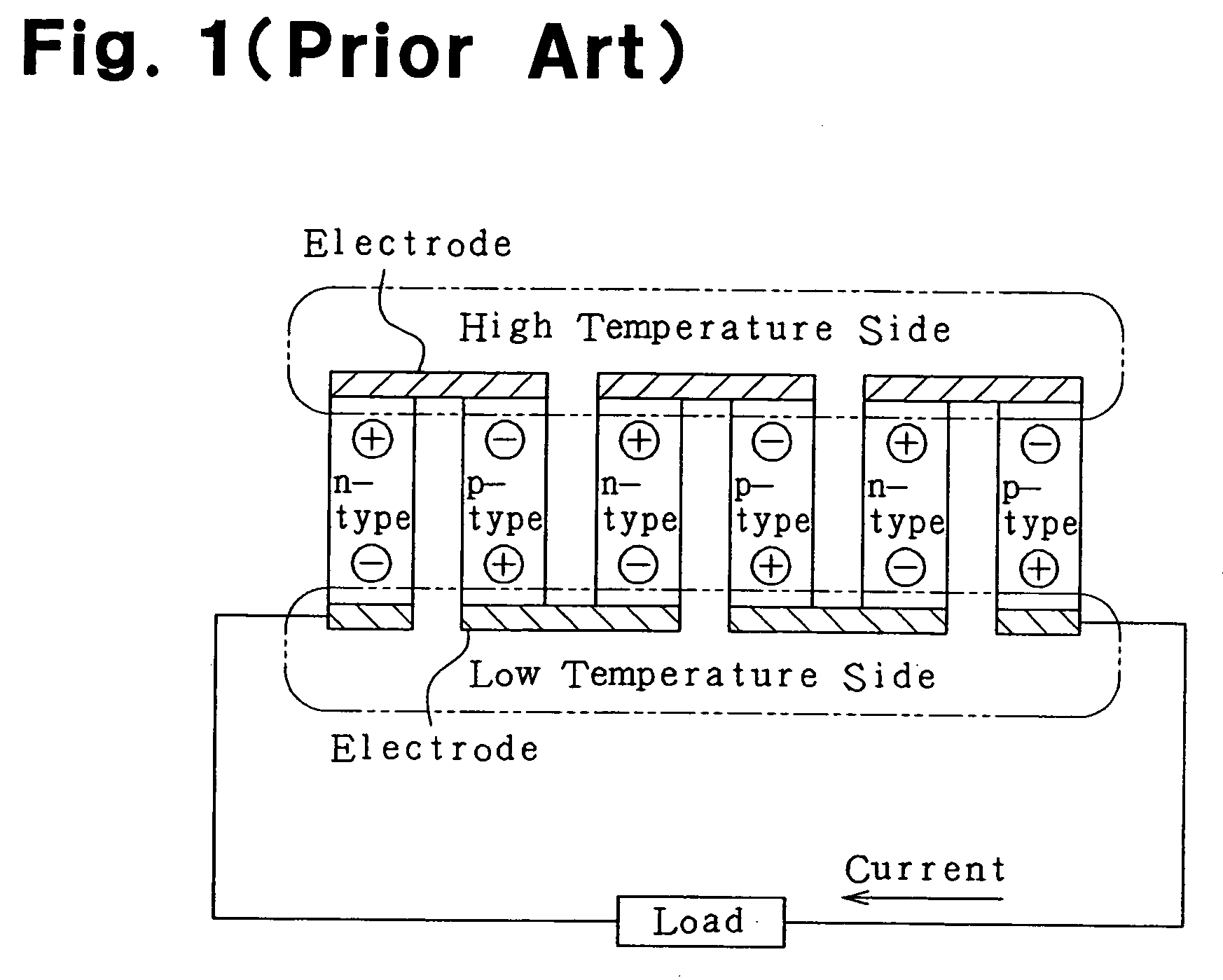
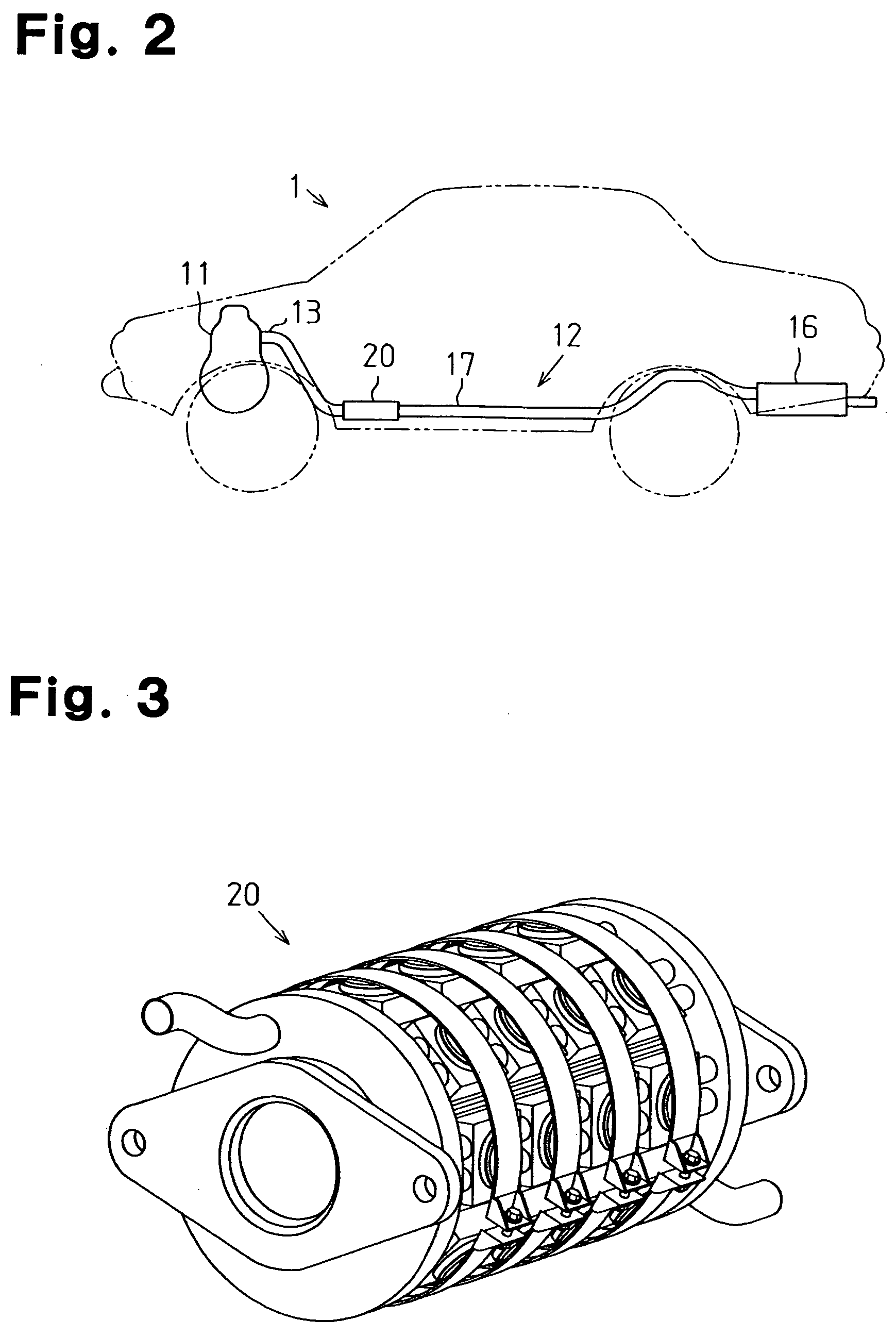
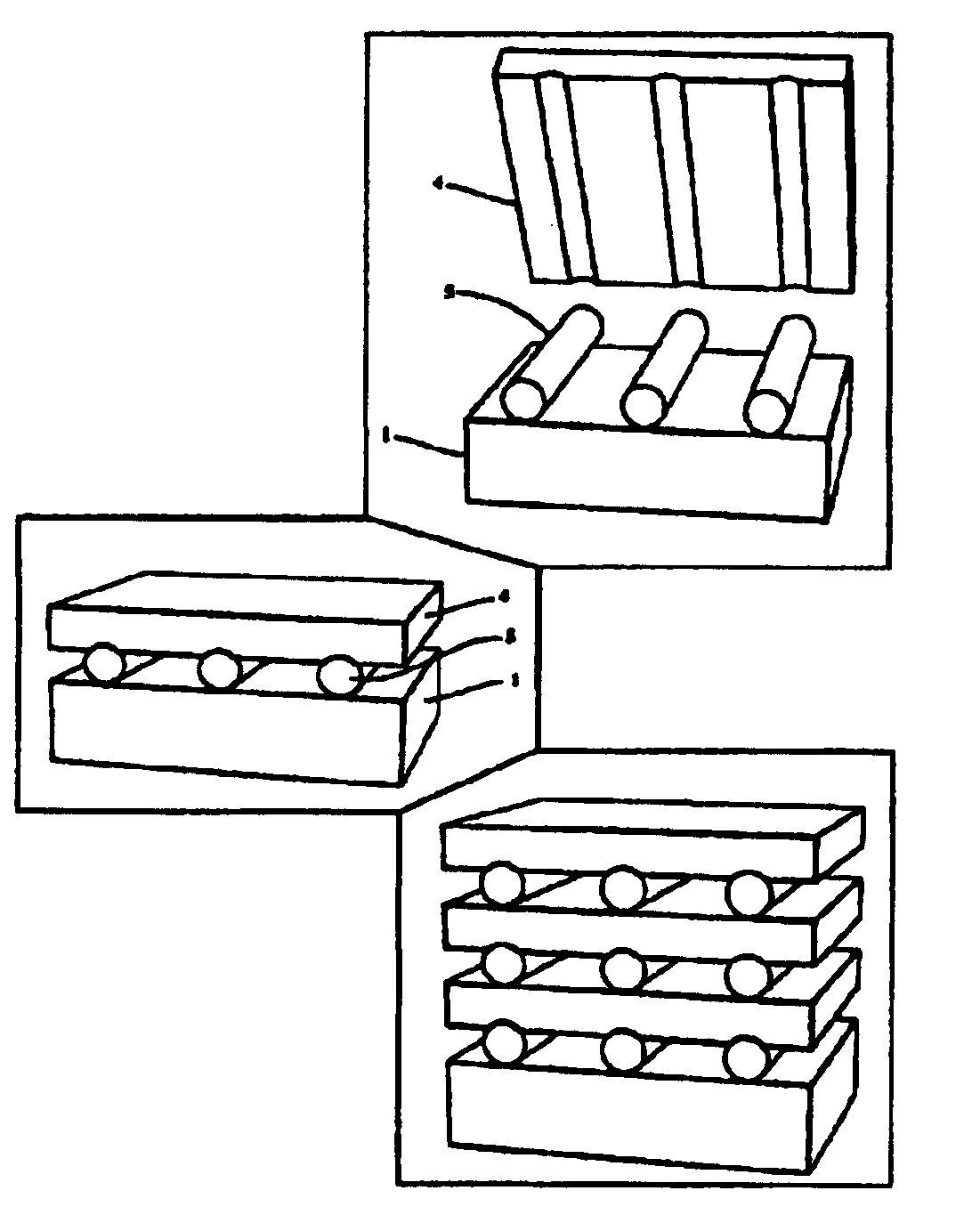
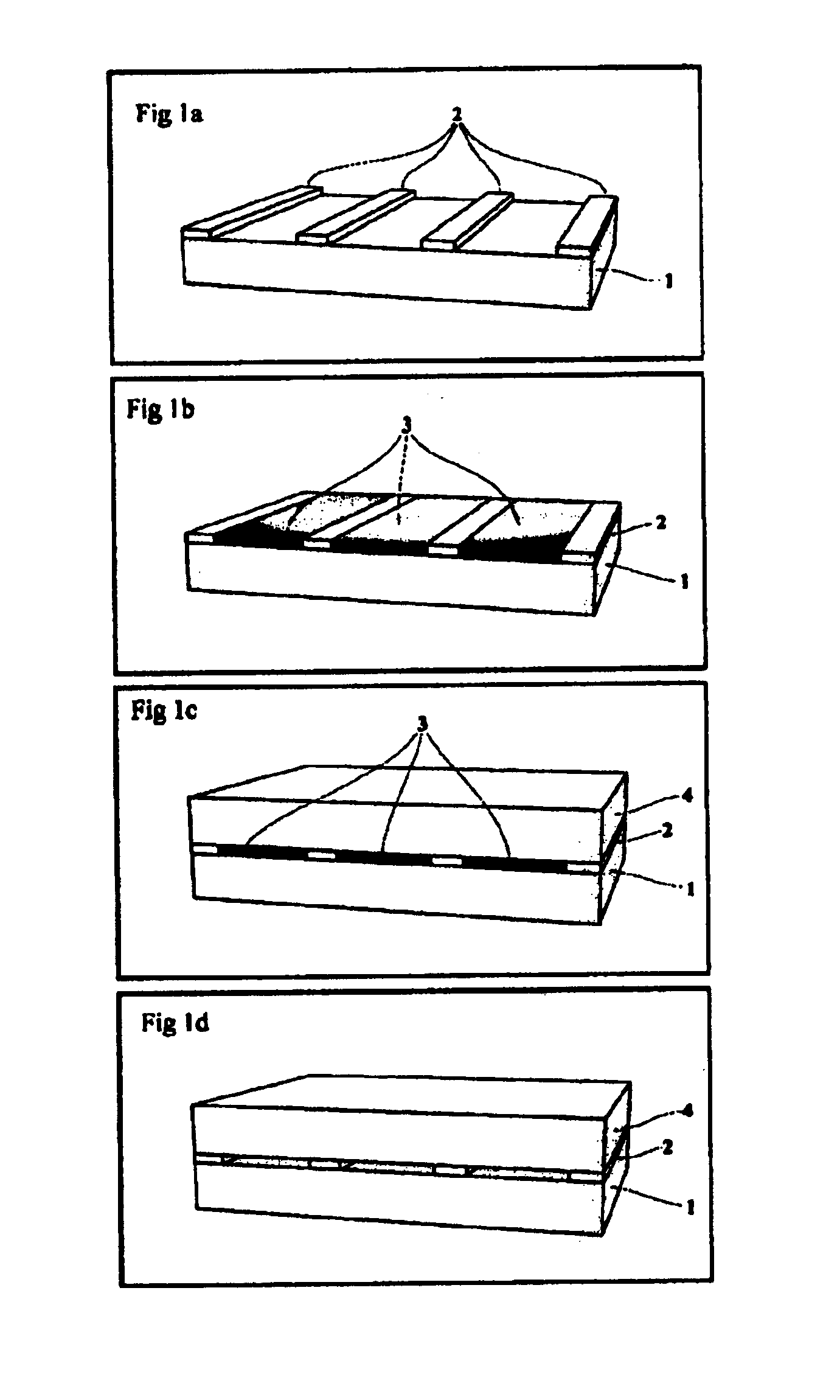
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
408results about "Thermal electric motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
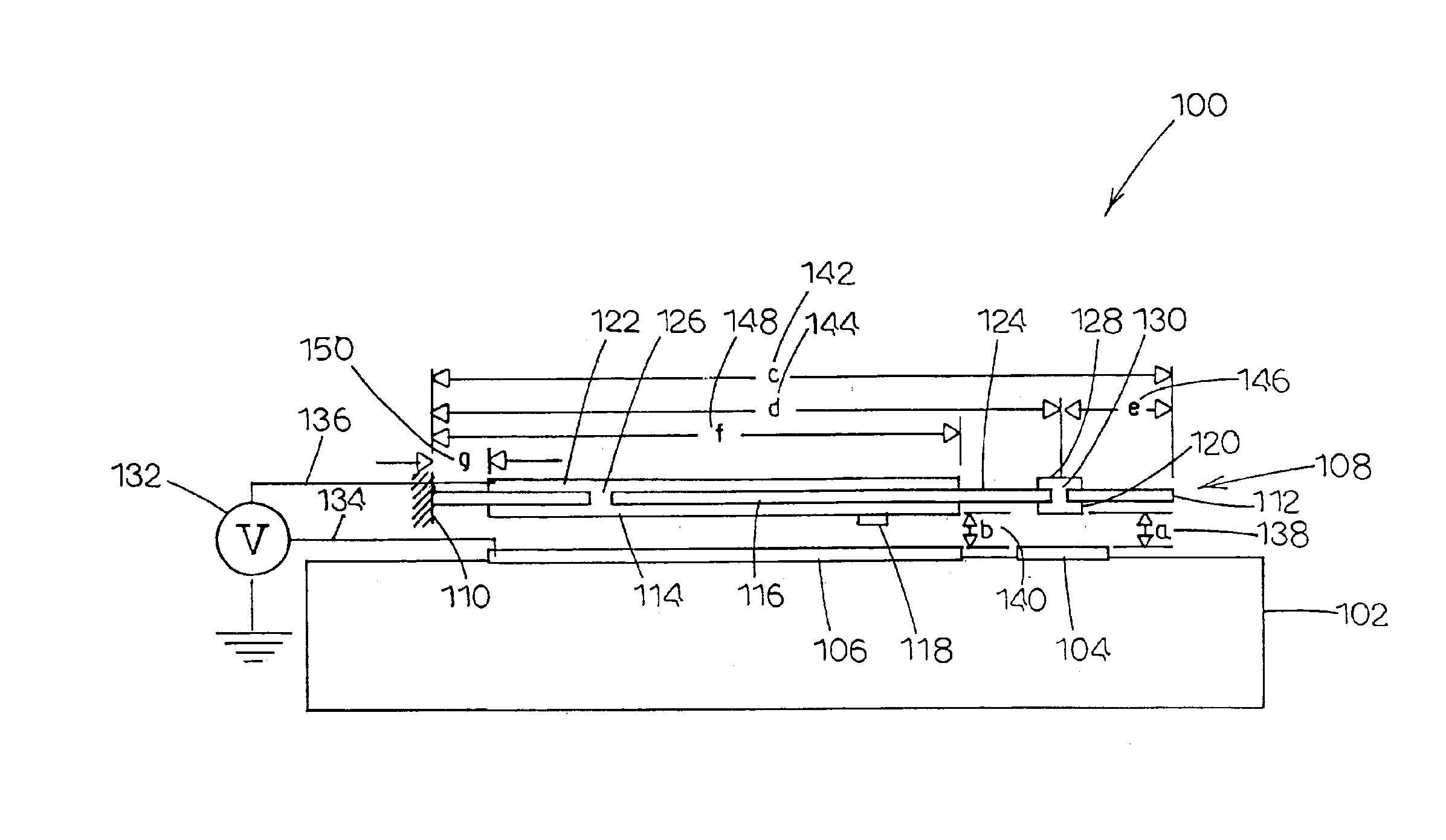
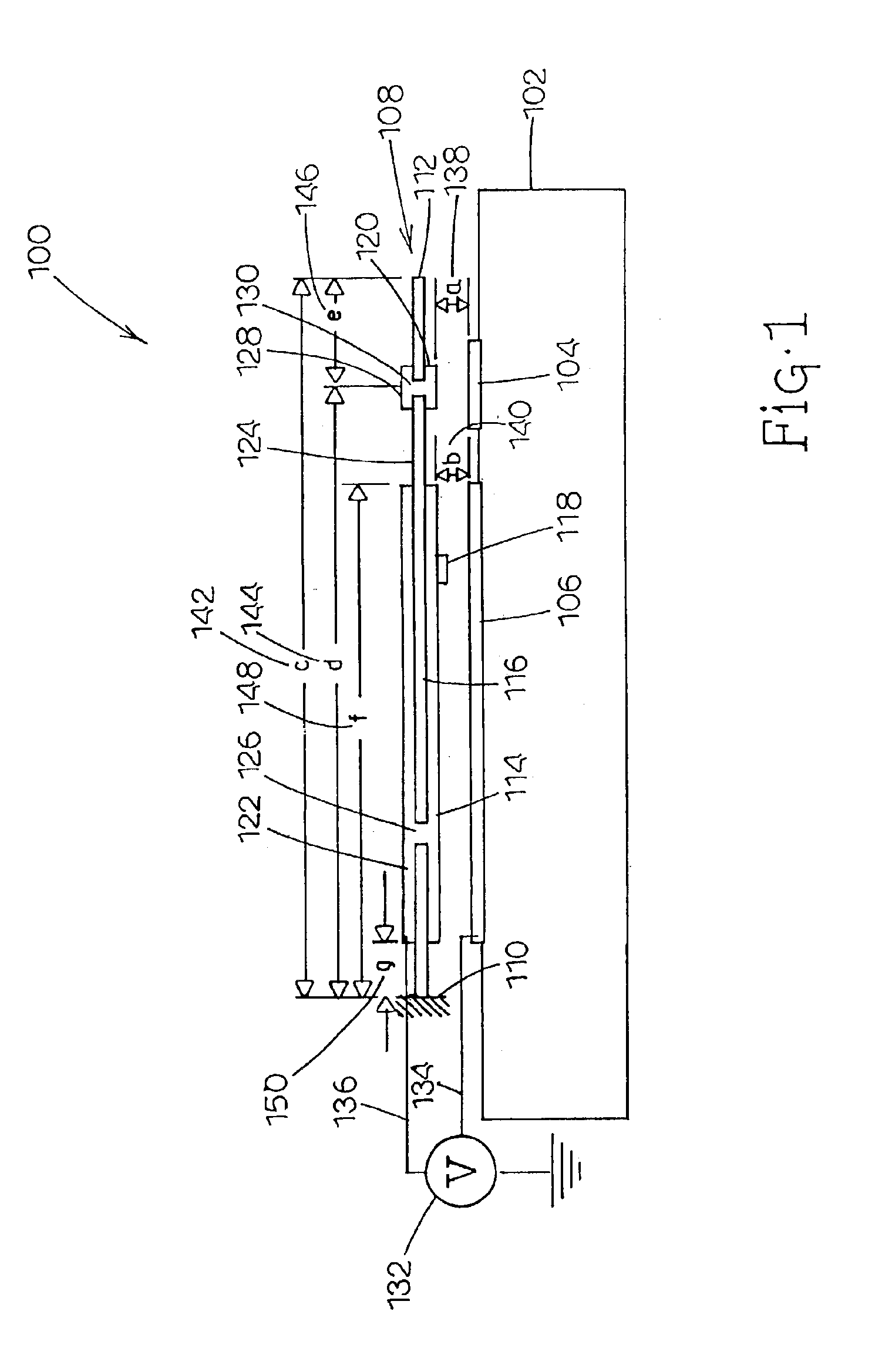
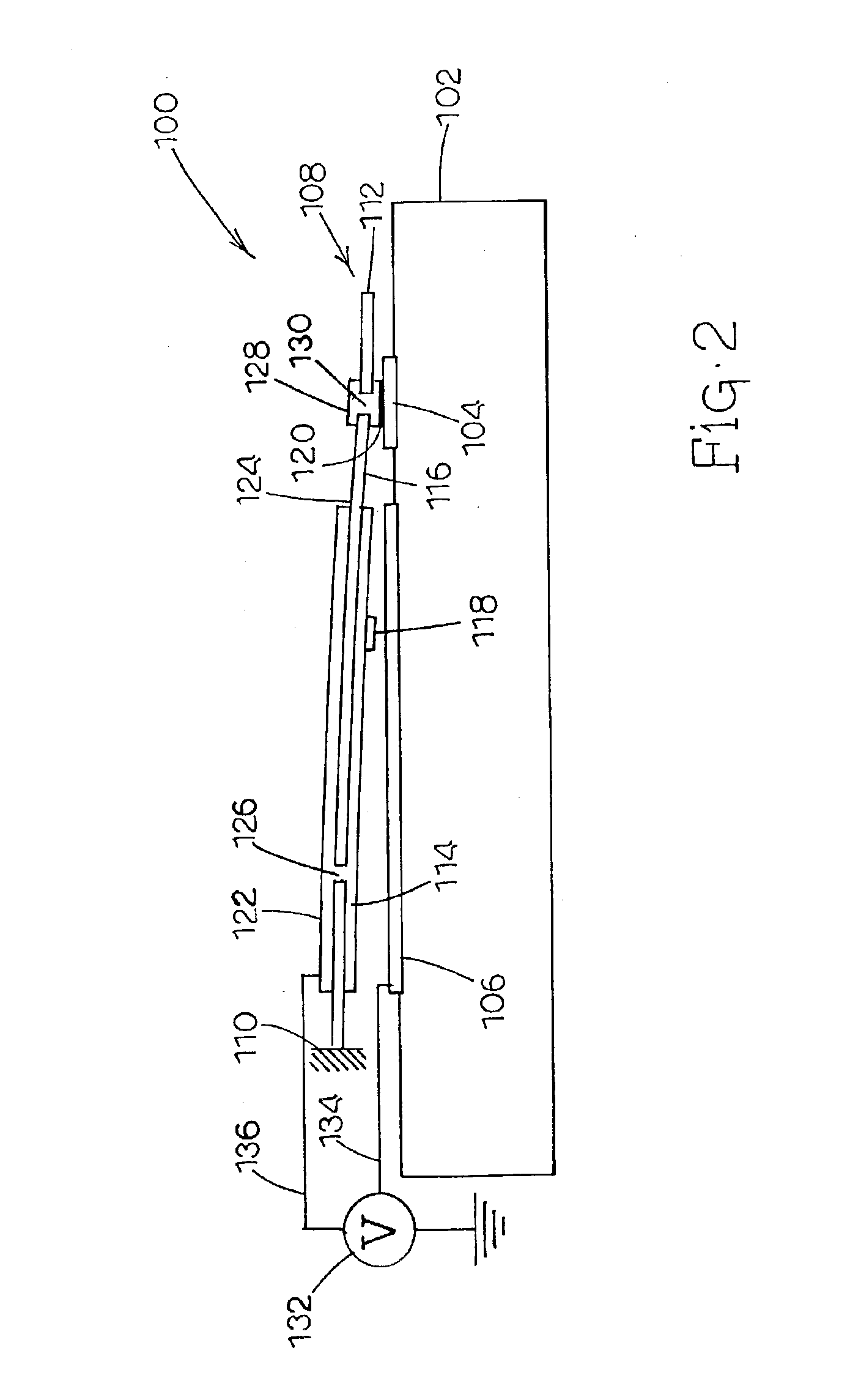
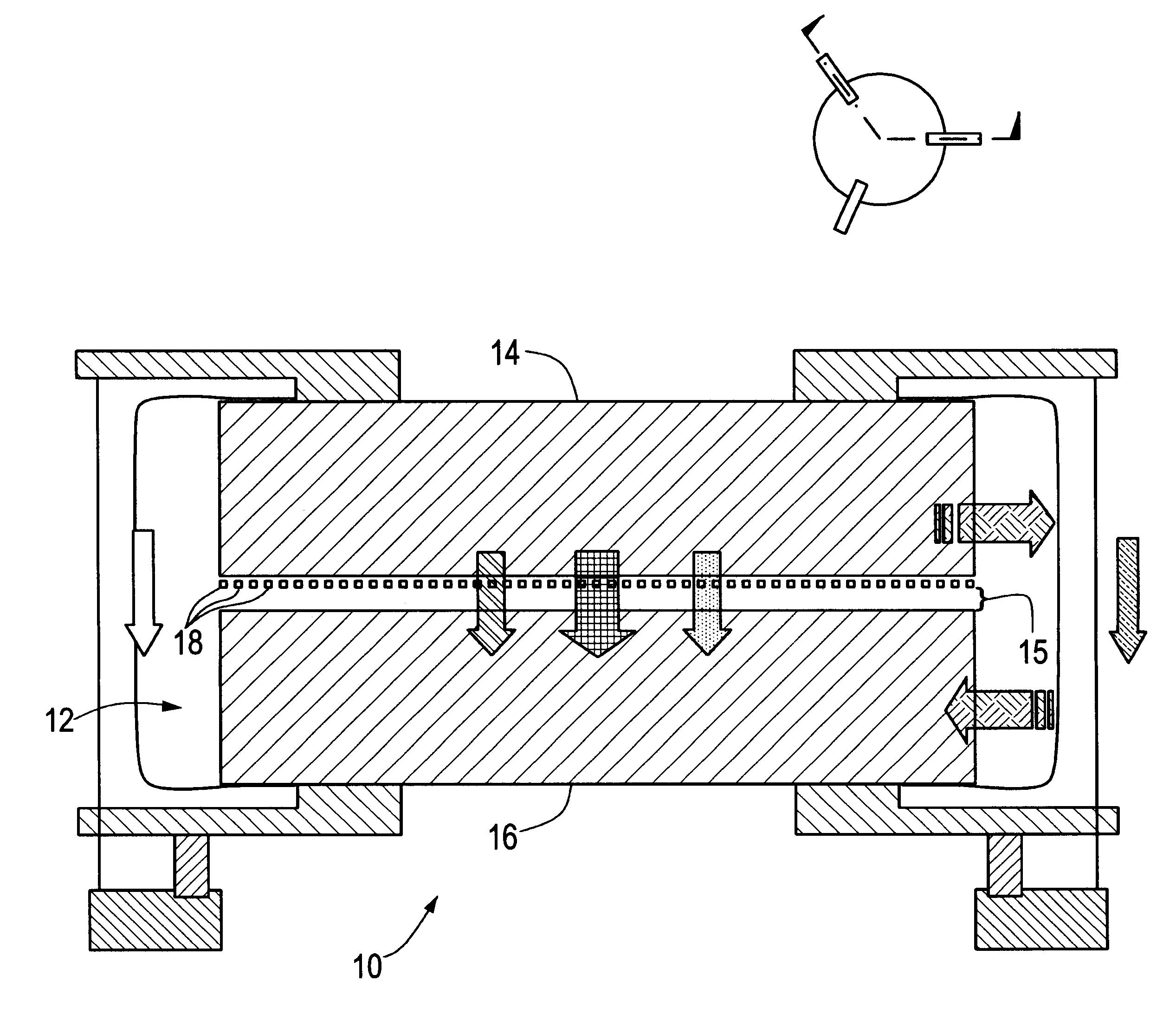
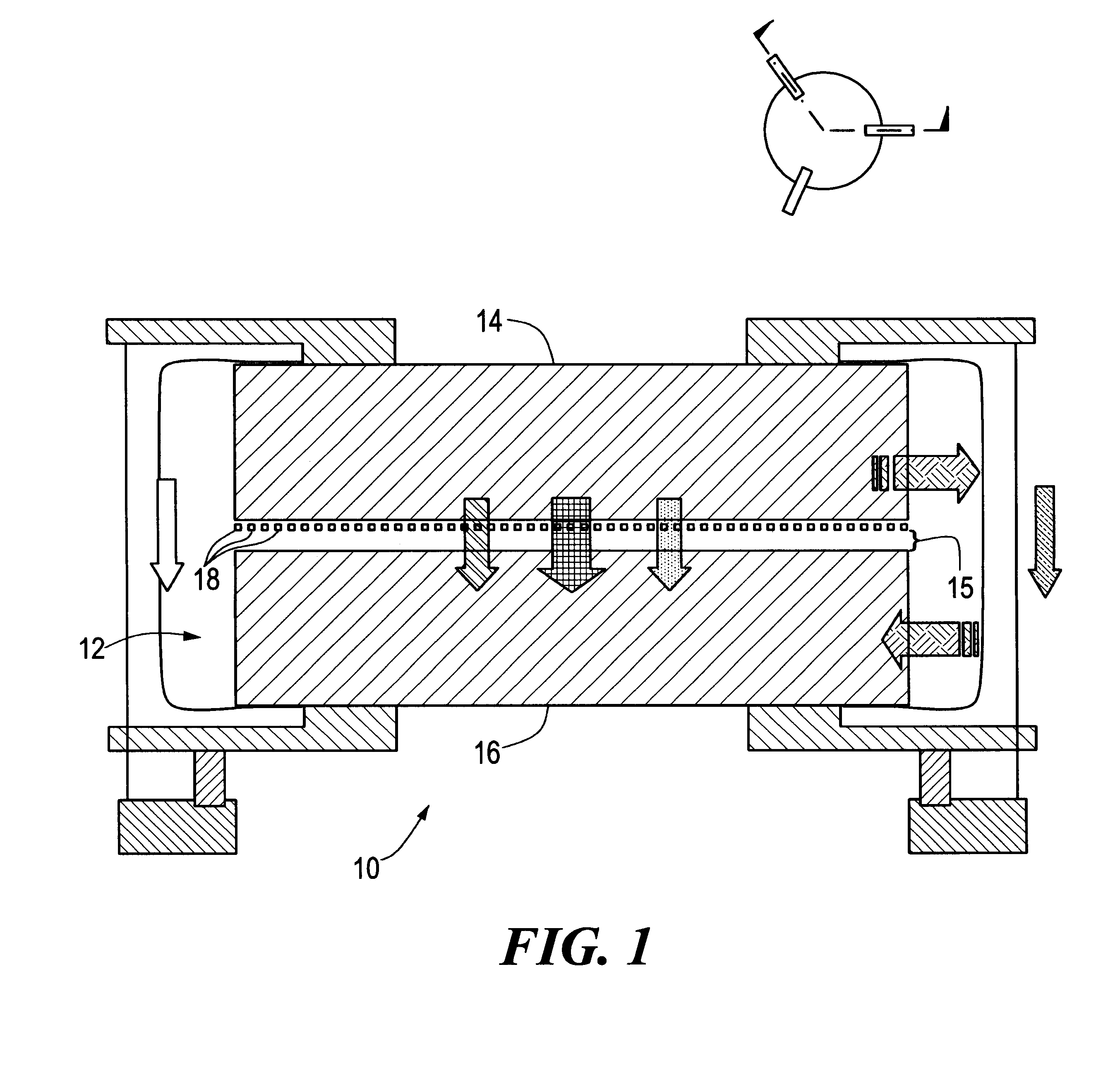
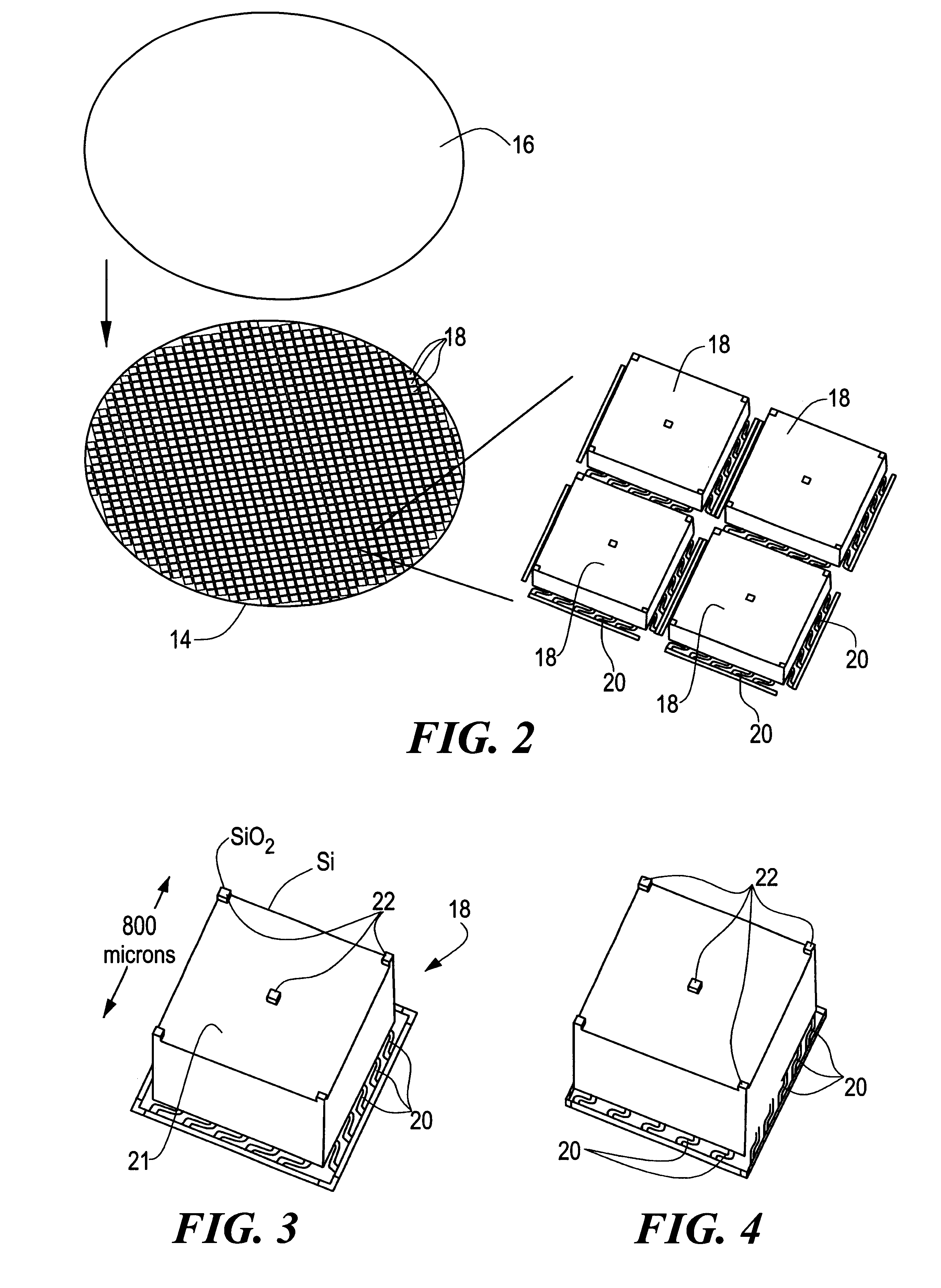
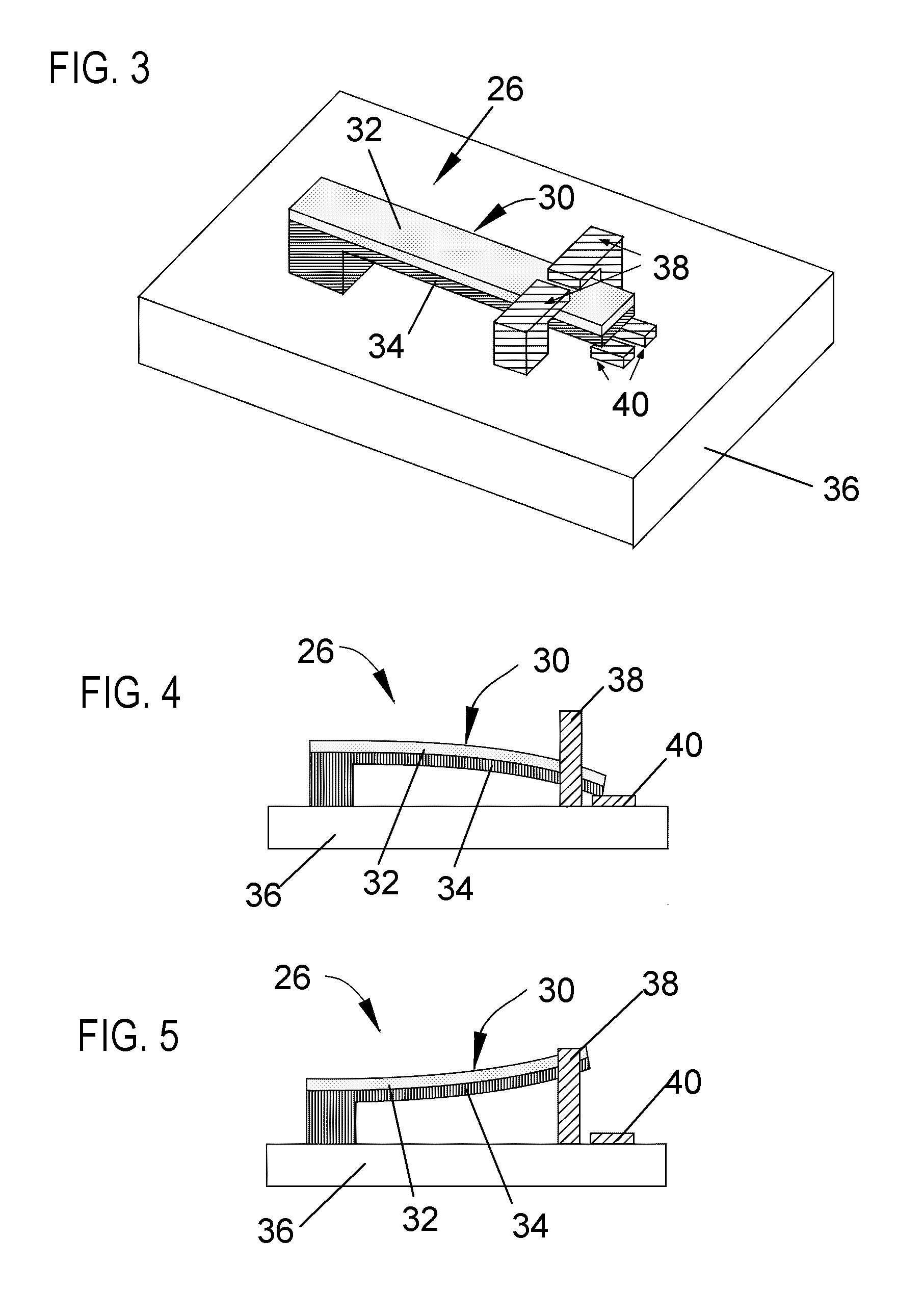
MEMS device having contact and standoff bumps and related methods
InactiveUS6876482B2Avoid contactOptical radiation measurementSolid-state devicesConductive materialsElectrical and Electronics engineering
MEMS Device Having Contact and Standoff Bumps and Related Methods. According to one embodiment, a movable MEMS component suspended over a substrate is provided. The component can include a structural layer having a movable electrode separated from a substrate by a gap. The component can also include at least one standoff bump attached to the structural layer and extending into the gap for preventing contact of the movable electrode with conductive material when the component moves.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD
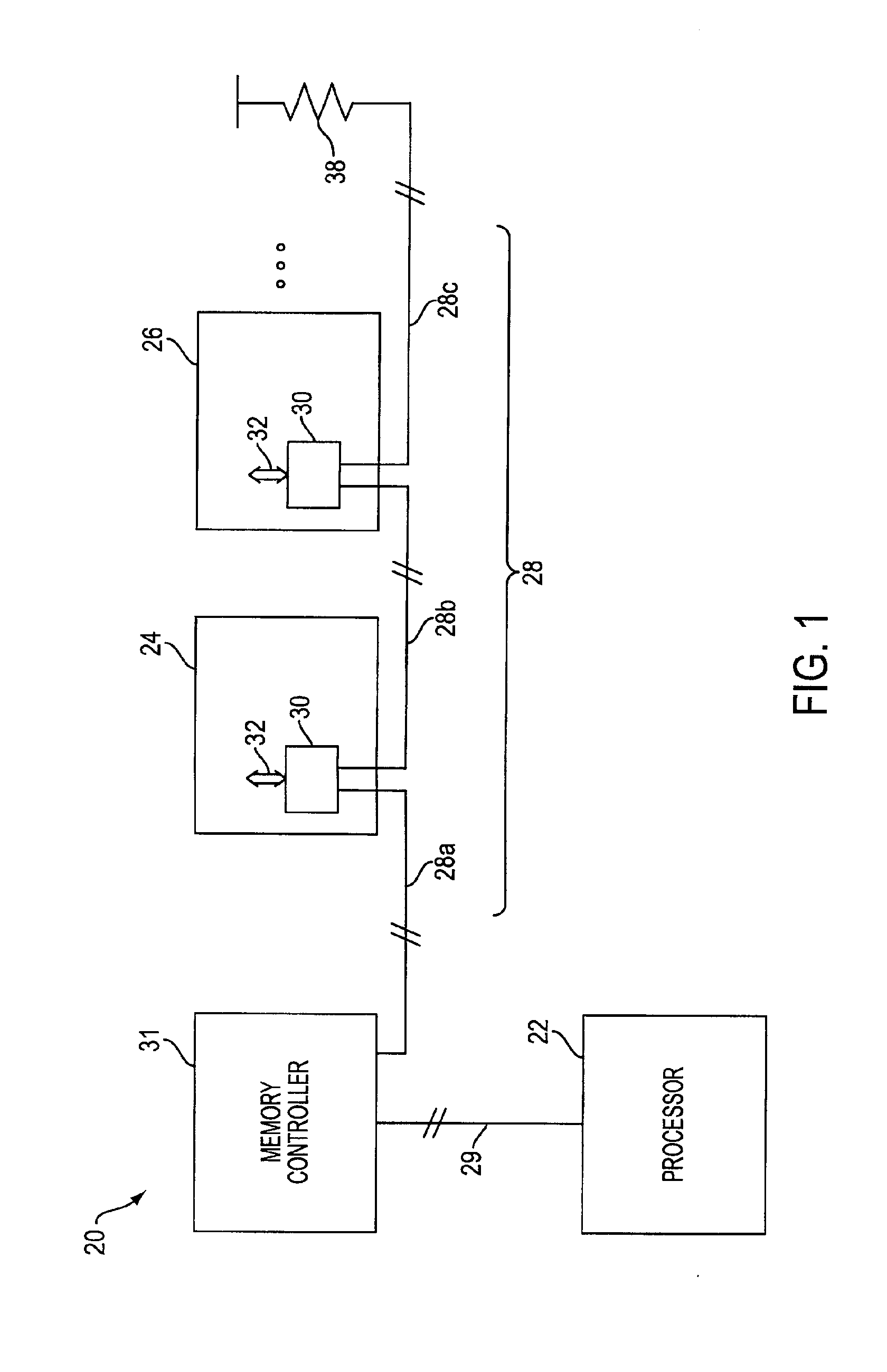
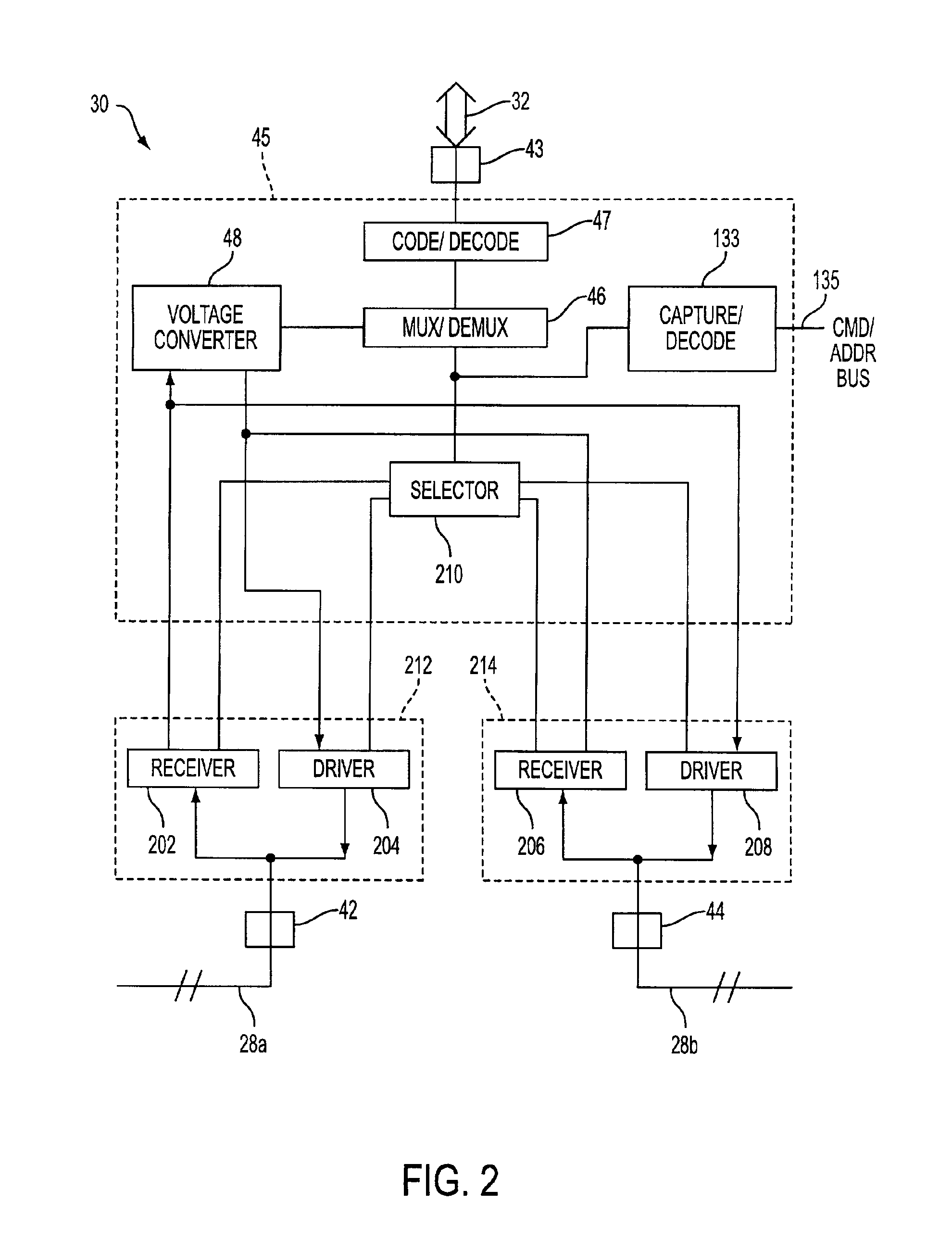
Memory repeater
InactiveUS6882082B2Improve acceleration performanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionCommunications systemMemory bus
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
MEMS device having a trilayered beam and related methods
MEMS Device Having A Trilayered Beam And Related Methods. According to one embodiment, a movable, trilayered microcomponent suspended over a substrate is provided and includes a first electrically conductive layer patterned to define a movable electrode. The first metal layer is separated from the substrate by a gap. The microcomponent further includes a dielectric layer formed on the first metal layer and having an end fixed with respect to the substrate. Furthermore, the microcomponent includes a second electrically conductive layer formed on the dielectric layer and patterned to define an electrode interconnect for electrically communicating with the movable electrode.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD
Driving apparatus
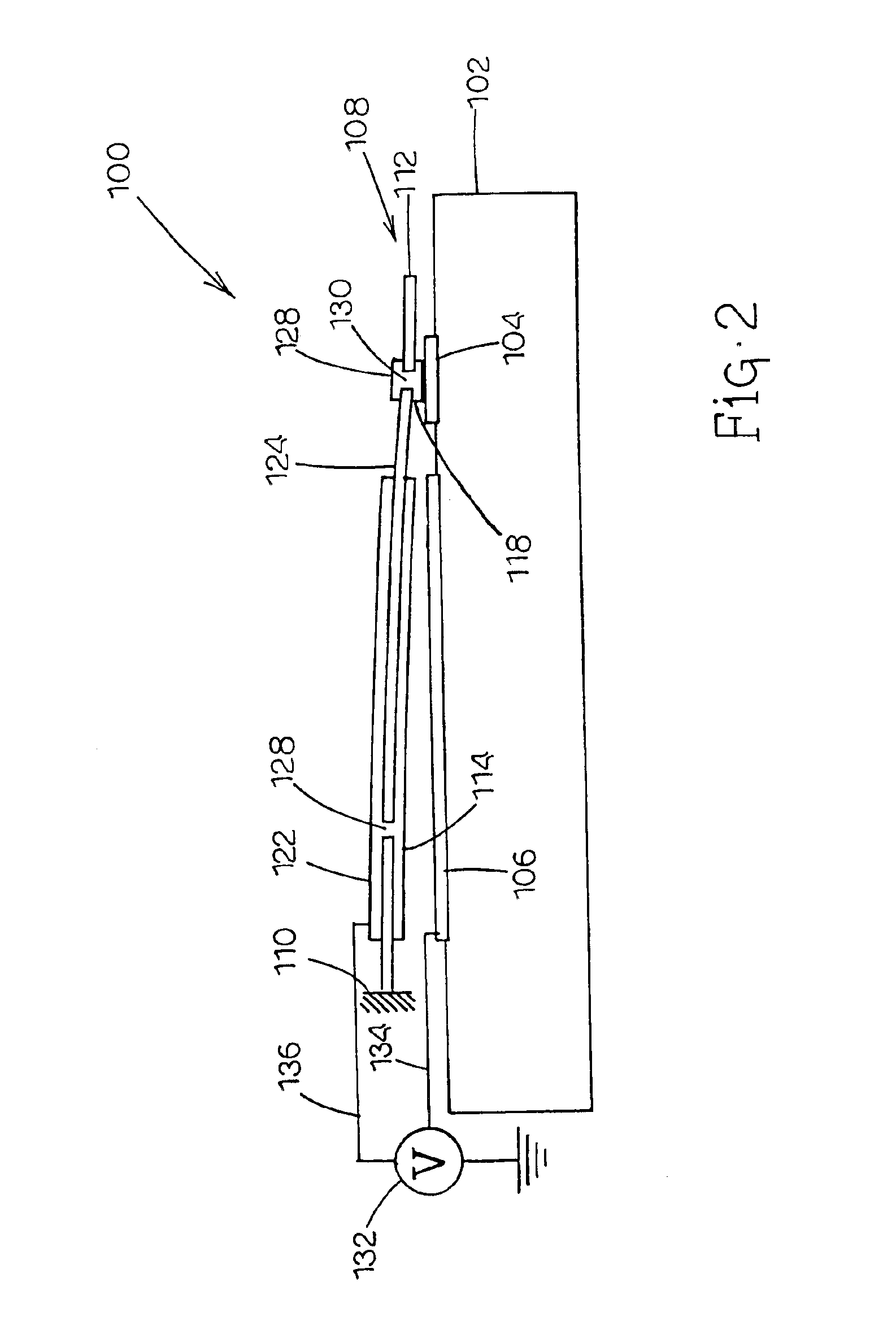
InactiveUS20070109412A1Improve responseImprove cooling effectTelevision system detailsOpticsEllipseImage stabilization
In an auto image stabilization system, a driving member formed as a wire of shape memory alloy (SMA) is retained by a projection of an image capturing unit. A distance Lb from the rotation center of an elastic deforming part to center of gravity (point of application) of the image capturing unit is longer than a distance La from the rotation center of the elastic deforming part to the projection (power point). In the configuration, equivalent mass (apparent mass) of the image capturing unit becomes (Lb / La) times, and it causes deterioration in response. Consequently, the driving member having an ellipse-shaped section in which a value obtained by dividing the width in the longer direction of the section by the width in the shorter direction is 1.3 or larger is employed. As a result, heat dissipation of the driving member increases, so that response in the SMA actuator can be properly improved.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Microcavity apparatus and systems for maintaining a microcavity over a macroscale area
InactiveUS6232546B1Efficient transferValid conversionThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentPV power plantsElectricityEnergy transfer
A microcavity apparatus and systems for maintaining microcavity spacing over a macroscopic area. An application of this invention is a microscale generator. This microscale generator includes a first element for receiving energy; a second element, opposite the first element for transferring energy; at least one panel on either of the first element or the second element, the panel facing the other element; a device for controlling the distance between the at least one panel and the facing element to form a predetermined, sub-micron gap between the panel and the facing element for increasing energy transfer to the element for receiving; and a device, responsive to the energy transfer, for generating electricity.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Thermoelectric generator for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20050172993A1Reduce the possibilityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectElectric/fluid circuitEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A thermoelectric generator for an internal combustion engine that prevents a thermoelectric generation element from being damaged. The thermoelectric generator includes a casing, which is arranged in an exhaust passage, and a sleeve. A cooling mechanism is arranged outside the sleeve. Thermoelectric generation elements are arranged between the sleeve and the cooling mechanism in a manner movable relative to both the sleeve and the,cooling mechanism. The thermoelectric generation elements convert heat energy from exhaust in the exhaust passage to electric energy.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Thermotunnel converter with spacers between the electrodes
InactiveUS6876123B2Sufficient efficiencyThe implementation process is simpleThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectElectric discharge tubesEngineeringSmall particles
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Bistable electroactive polymers
ActiveUS8237324B2Improve mechanical energySpeed up the conversion processPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesVitrificationActive polymer
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
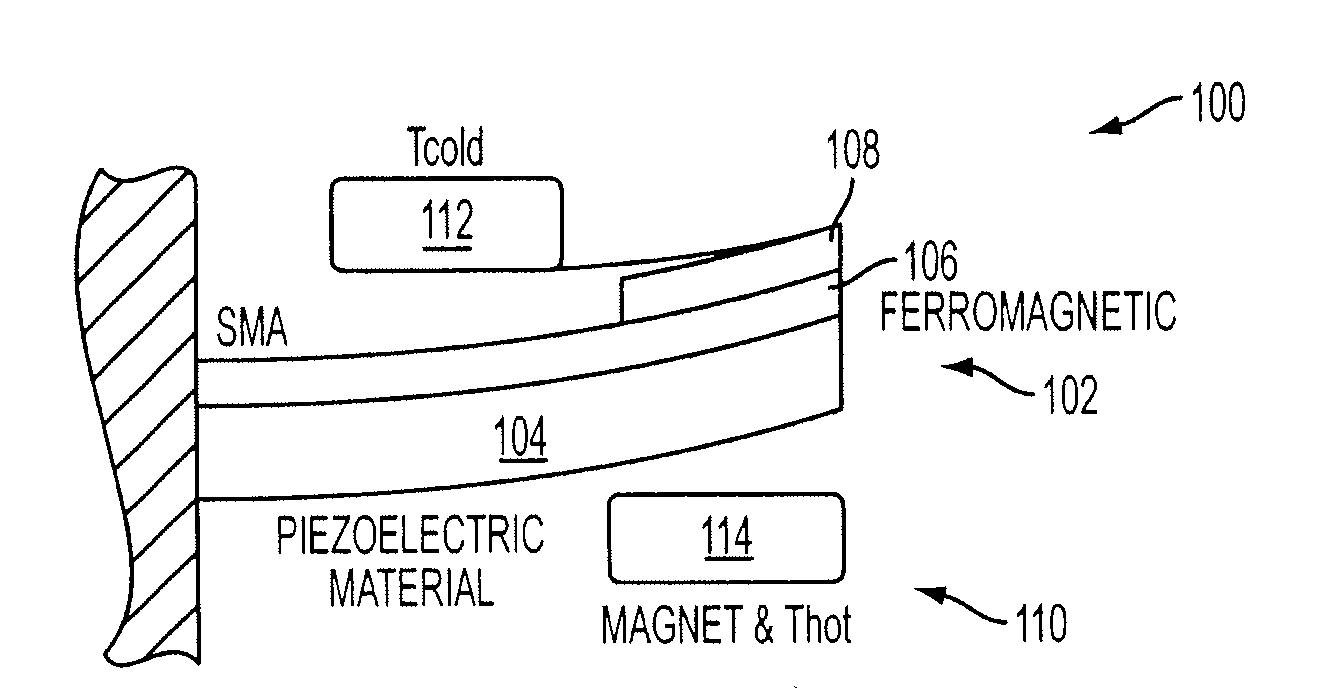
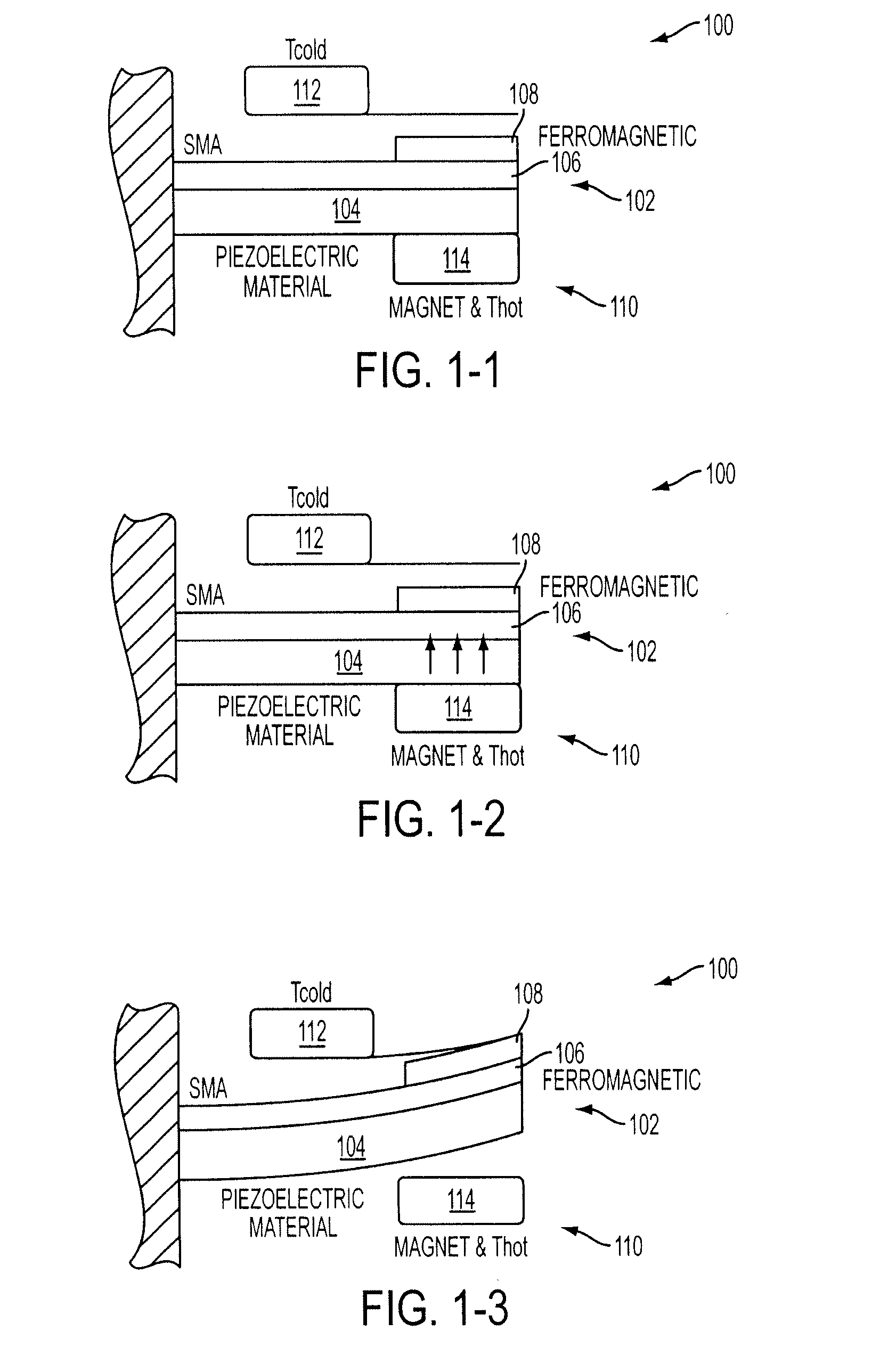
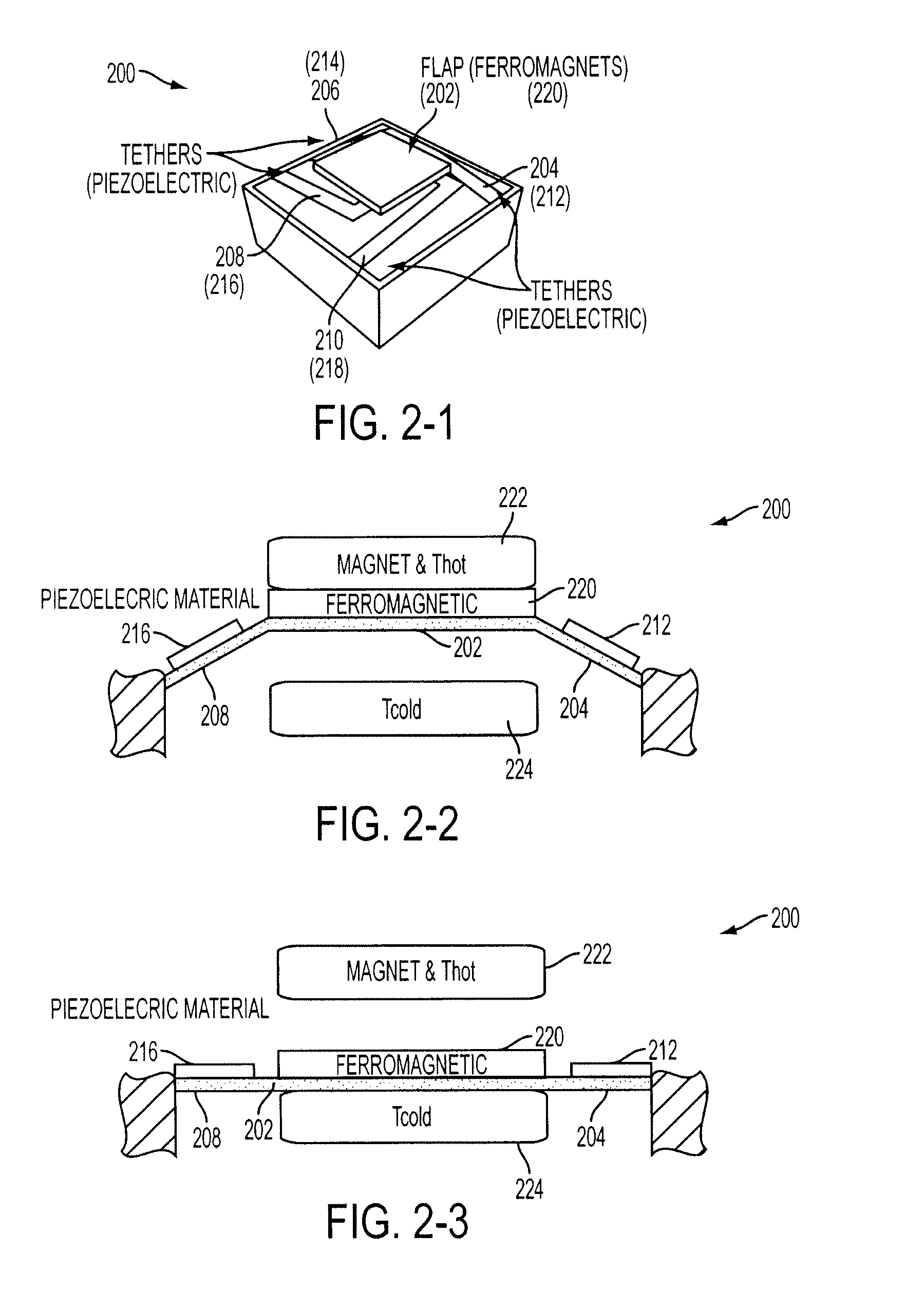
Energy harvesting by means of thermo-mechanical device utilizing bistable ferromagnets
InactiveUS20090315335A1Available energySimple designPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesThermal energyElectricity
An inventive energy harvesting apparatus may include a ferromagnetic material and / or a shape memory alloys to convert thermal energy to mechanical energy to electrical energy. The apparatus is subjected to a thermal gradient to cause beams to bend thus creating stress / strain in a piezoelectric material, or creating magnetic flux in a magnetic path. The charges created in this process can be transferred to electrical batteries.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Thermionic generator
InactiveUS6229083B1Reduce manufacturing costAvoid small quantitiesElectric discharge tubesThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermionic converterEngineering
A method for building a thermionic converter comprises providing an electrode and creating a central depression of substantially uniform depth on a face of the electrode. A surface of the central depression is coated with a layer comprising a thermionic material. A second electrode comprising a face is also provided, wherein the face of the second electrode comprises a central depression of substantially uniform depth, wherein the central depression is coated with a layer comprising a thermionic material.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Thermoacoustic piezoelectric generator
ActiveUS7081699B2Reduce the oscillation frequencyObstruct passagePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCompression machinesElectricityAlternator
A thermoacoustic generator includes a housing with a thermoacoustic core supported in the housing. The core is operable to introduce acoustical power into the housing to thereby oscillate the pressure of the gas in the housing at a frequency. A piezoelectric alternator is also supported in the housing and has a face that is movable when acted on by the acoustical power. The alternator includes a portion of piezoelectric material operable to produce electrical power when acted upon by a stress. The piezoelectric material is in mechanical communication with the movable face so that movement of the face stresses the piezoelectric material. The alternator has a moving mass that serves as a substantial portion of the resonating mass inside the housing, thereby providing a pressure oscillation frequency in the housing substantially lower than for a similar system with a rigid member replacing the alternator.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
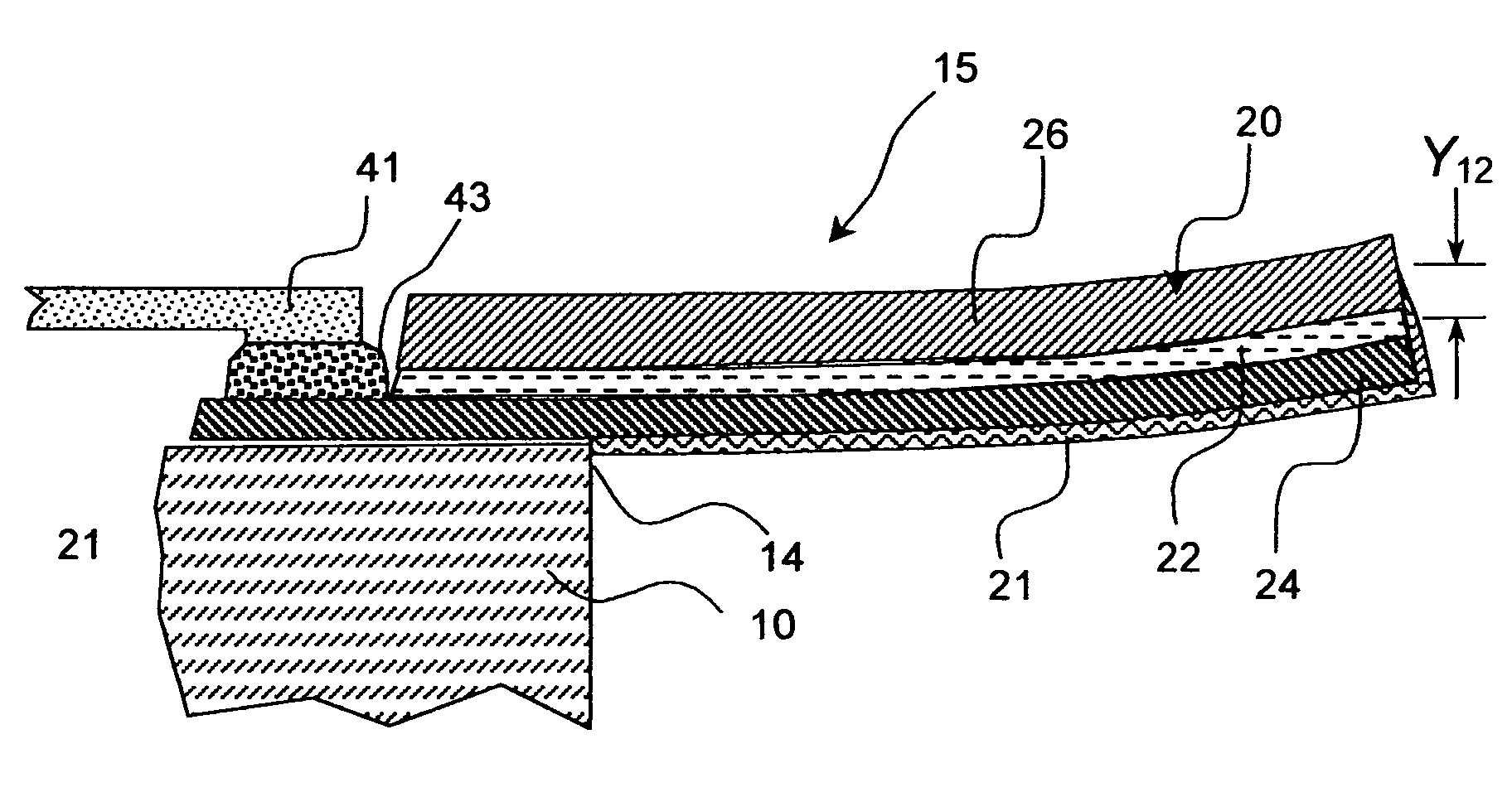
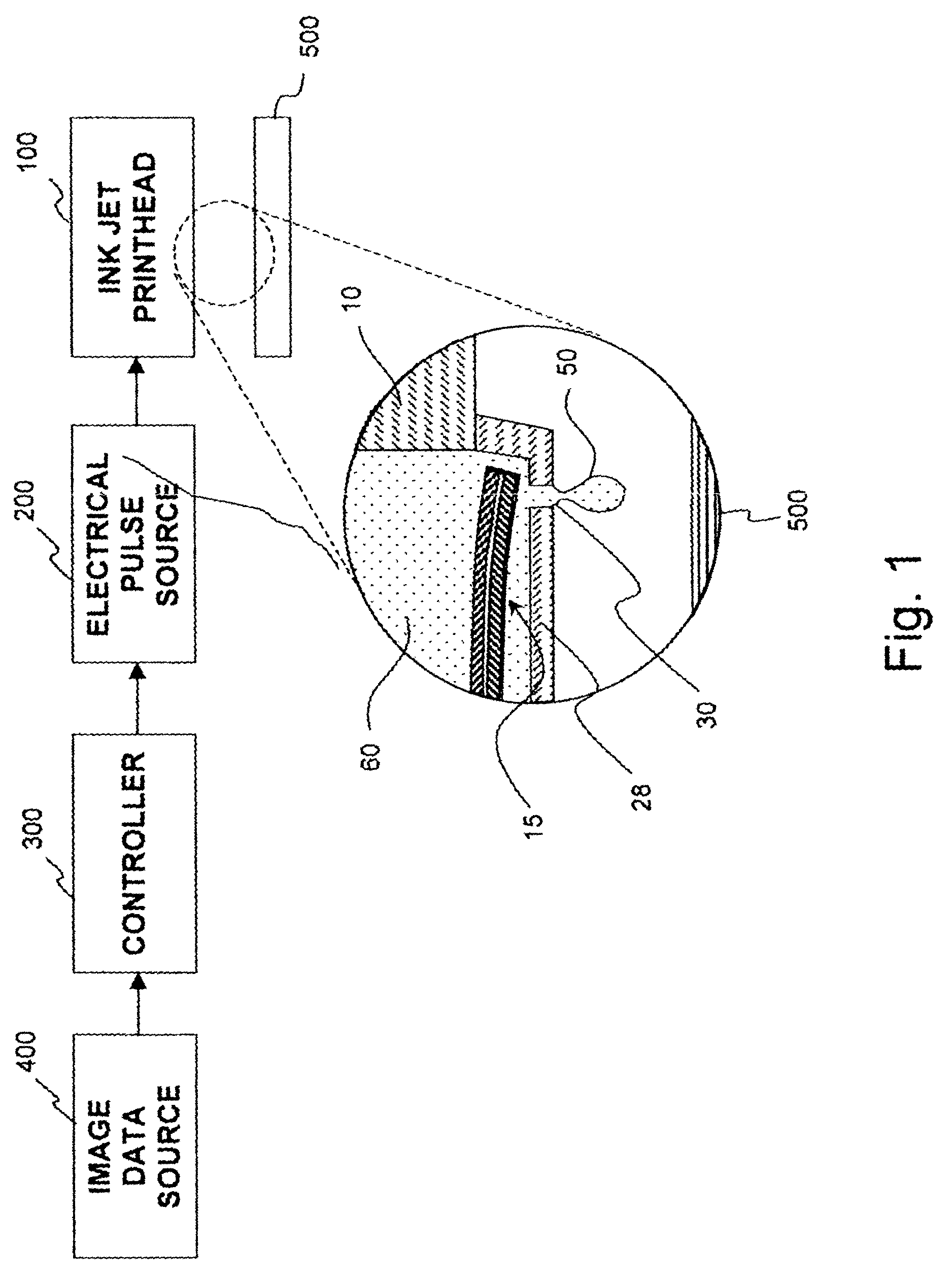
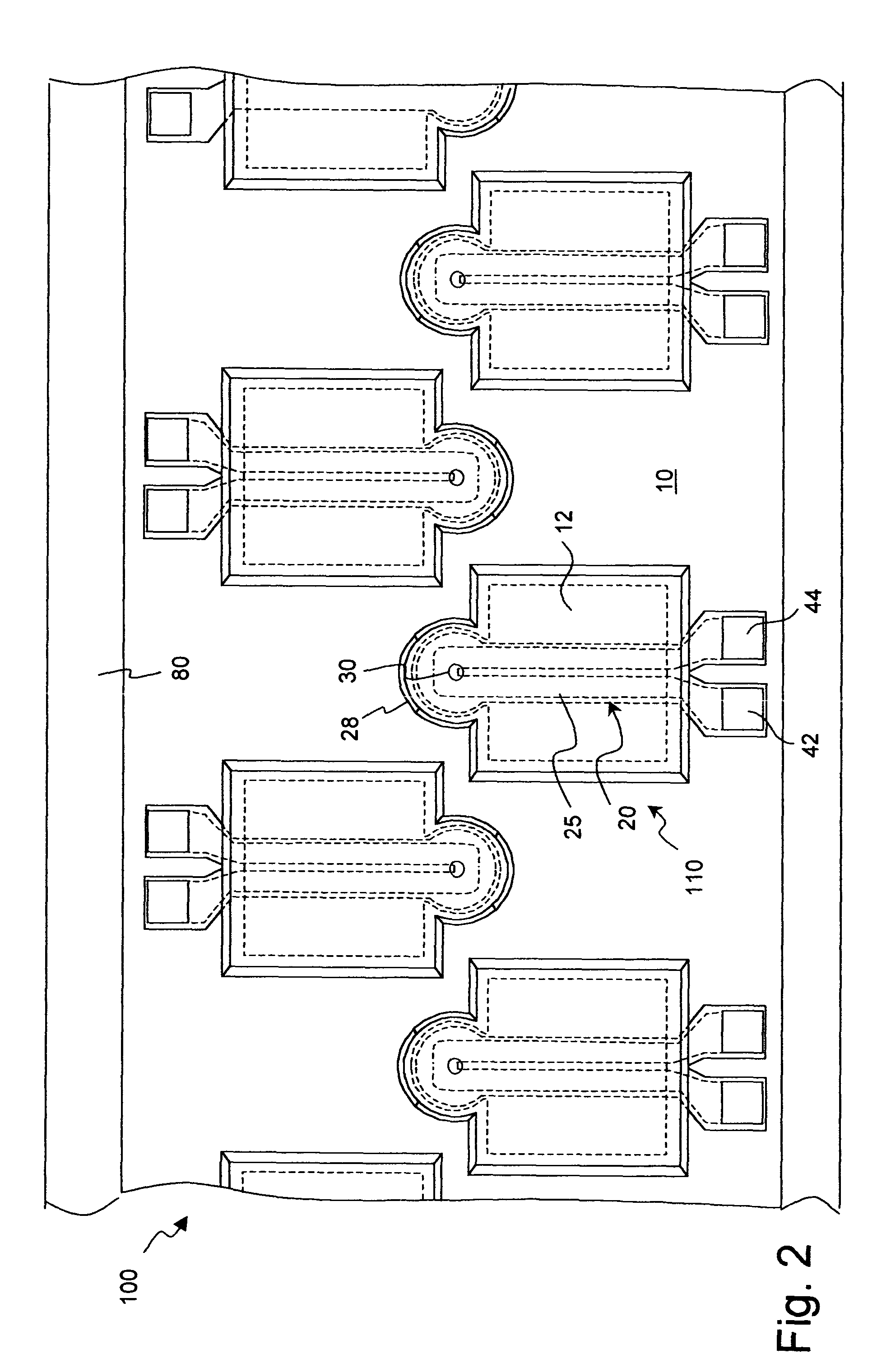
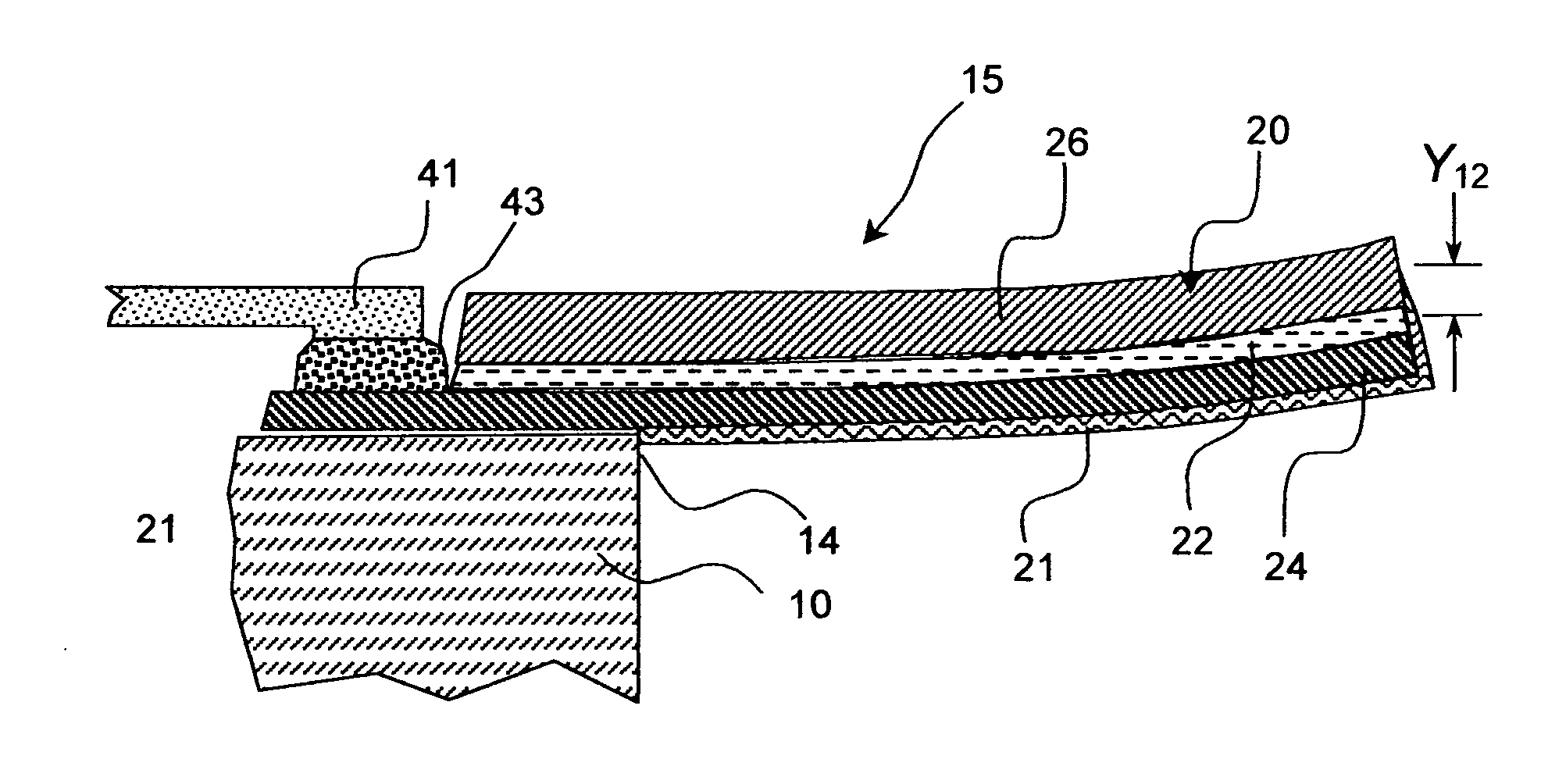
Thermally conductive thermal actuator and liquid drop emitter using same
ActiveUS7073890B2Reduce frequencyWithout excessive riseInking apparatusInfluence generatorsYoung's modulusEngineering
A thermal actuator for a micro-electromechanical device is disclosed. The thermal actuator includes a base element and a movable element extending from the base element and residing at a first position. The movable element includes a barrier layer constructed of a barrier material having low thermal conductivity material, bonded between a first layer and a second layer; wherein the first layer is constructed of a first material having a high coefficient of thermal expansion and the second layer is constructed of a second material having a high thermal conductivity and a high Young's modulus. An apparatus is provided adapted to apply a heat pulse directly to the first layer, causing a thermal expansion of the first layer relative to the second layer and deflection of the movable element to a second position.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Tunneling-effect energy converters
InactiveUS6946596B2Preventive effectThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThermal energyElectricity
Tunneling-effect converters of thermal energy to electricity with an emitter and a collector separated from each other by a distance that is comparable to atomic dimensions and where tunneling effect plays an important role in the charge movement from the emitter to the collector across the gap separating such emitter and collector. At least one of the emitter and collector structures includes a flexible structure. Tunneling-effect converters include devices that convert thermal energy to electrical energy and devices that provide refrigeration when electric power is supplied to such devices.
Owner:MICROPOWER GLOBAL
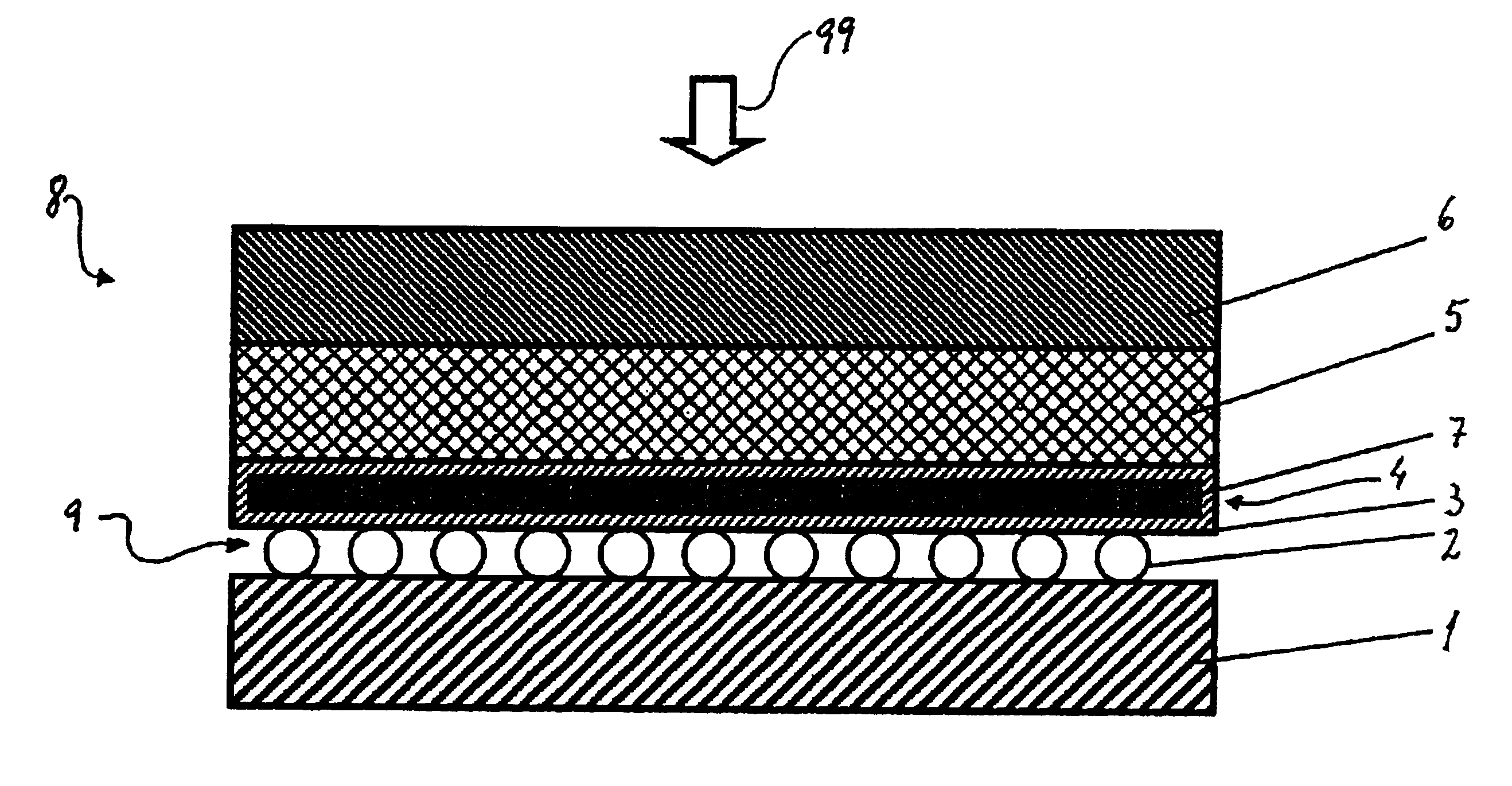
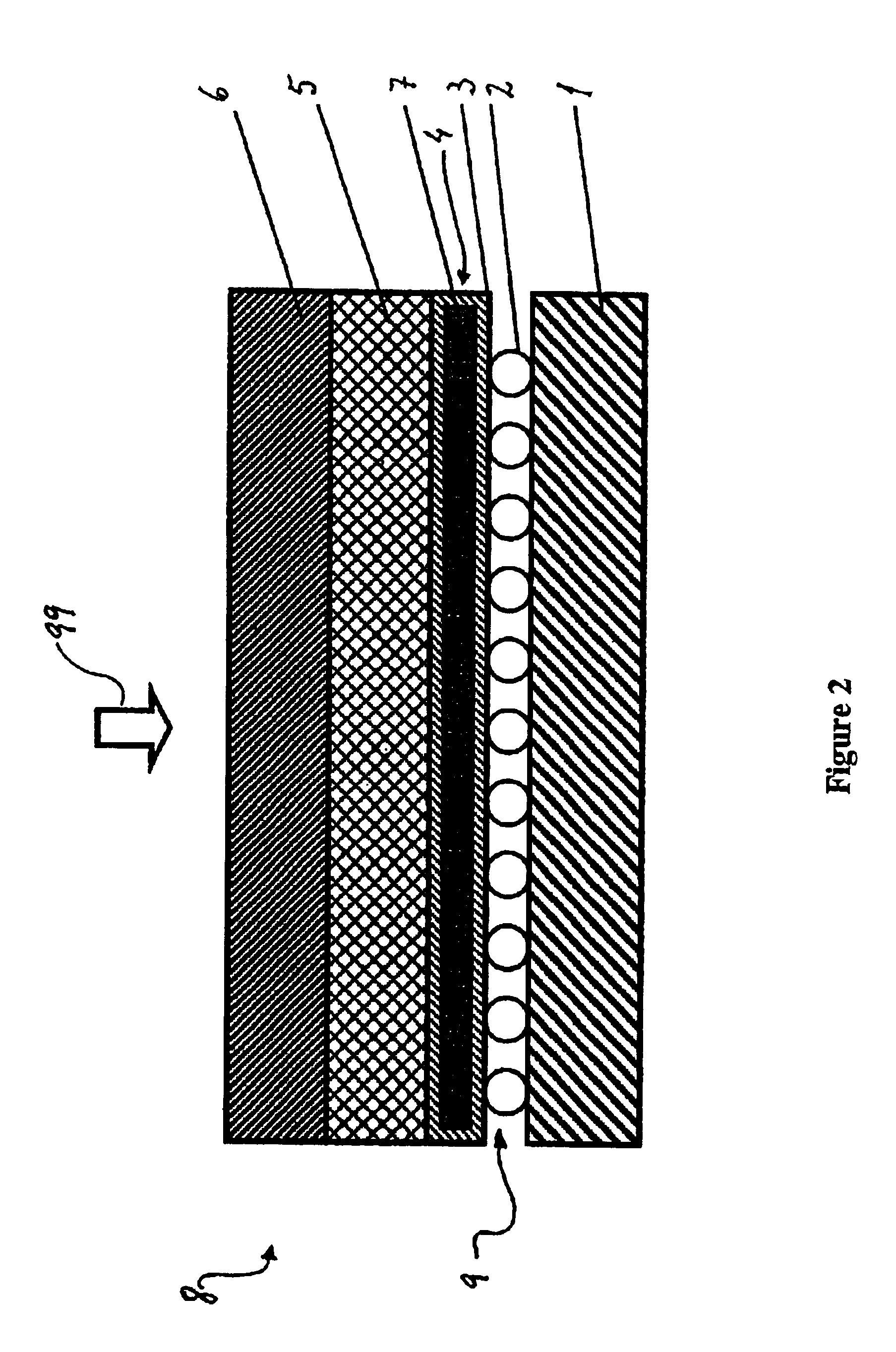
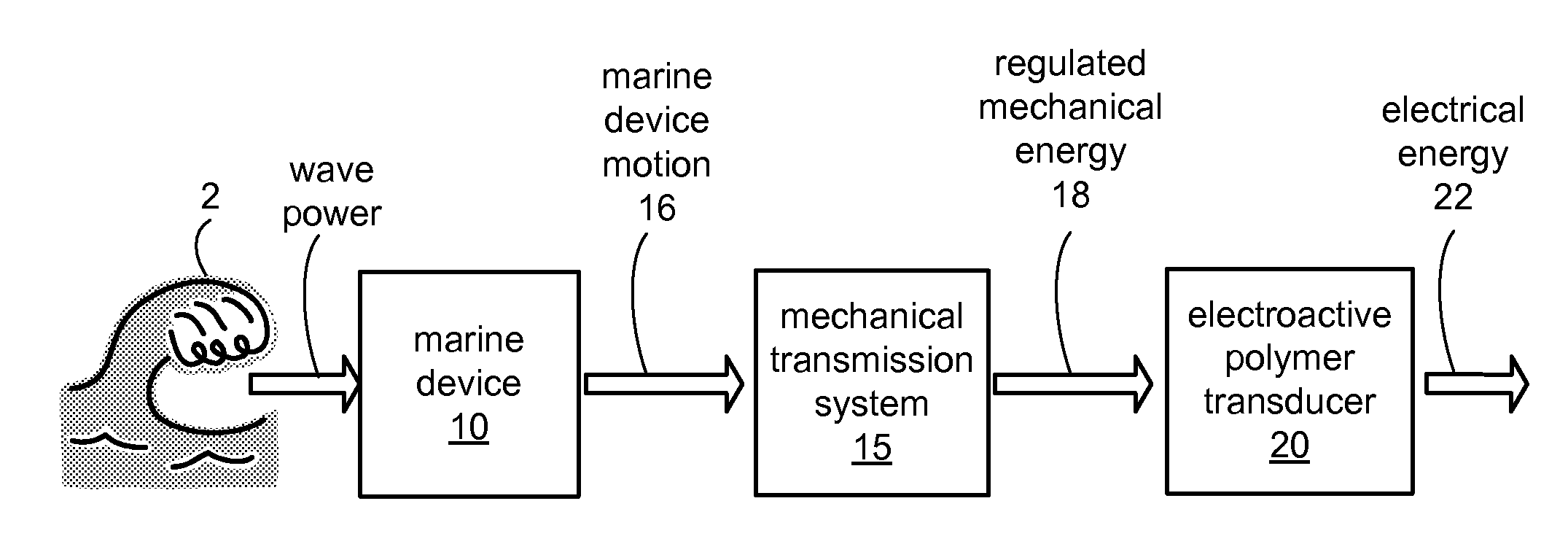
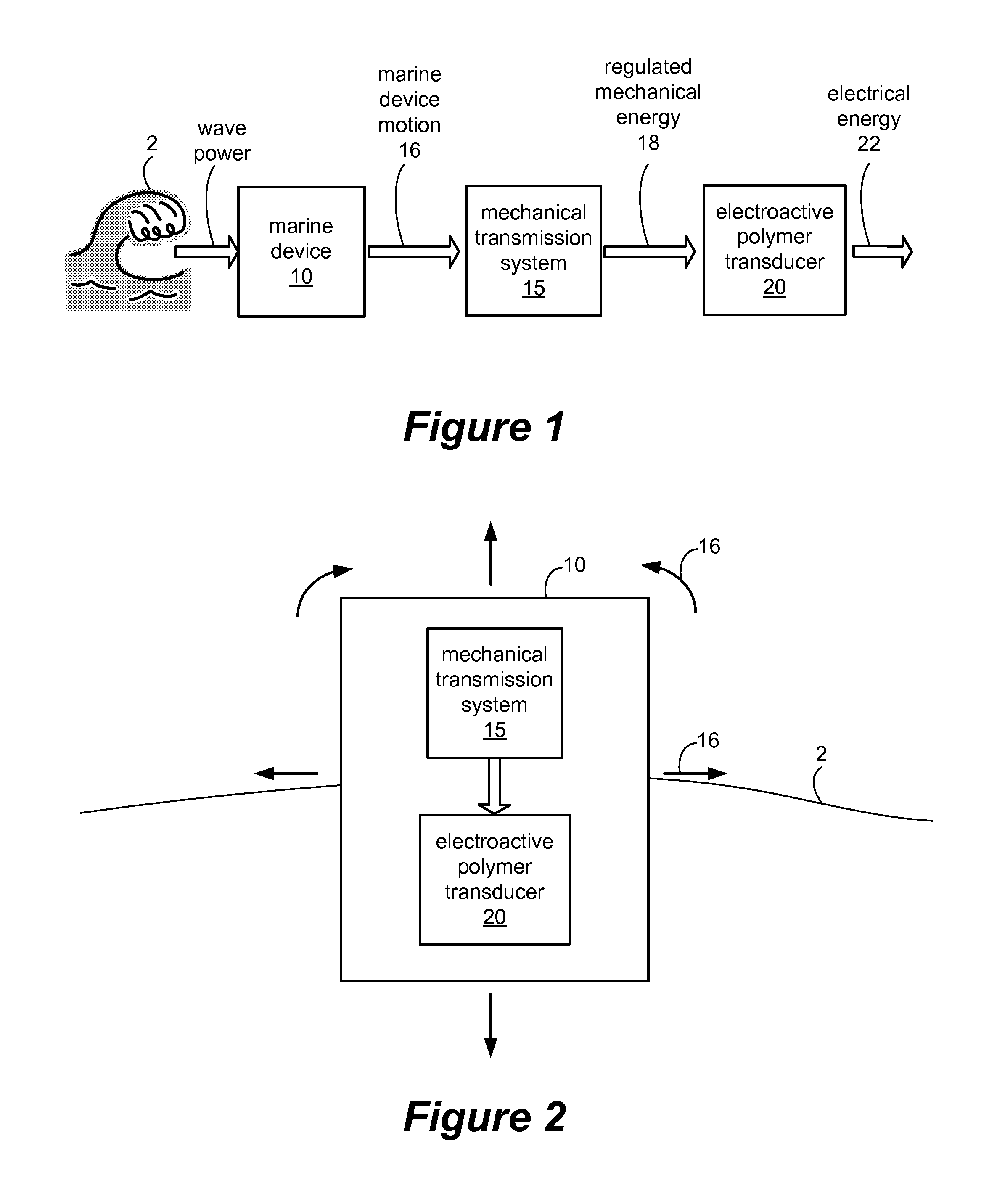
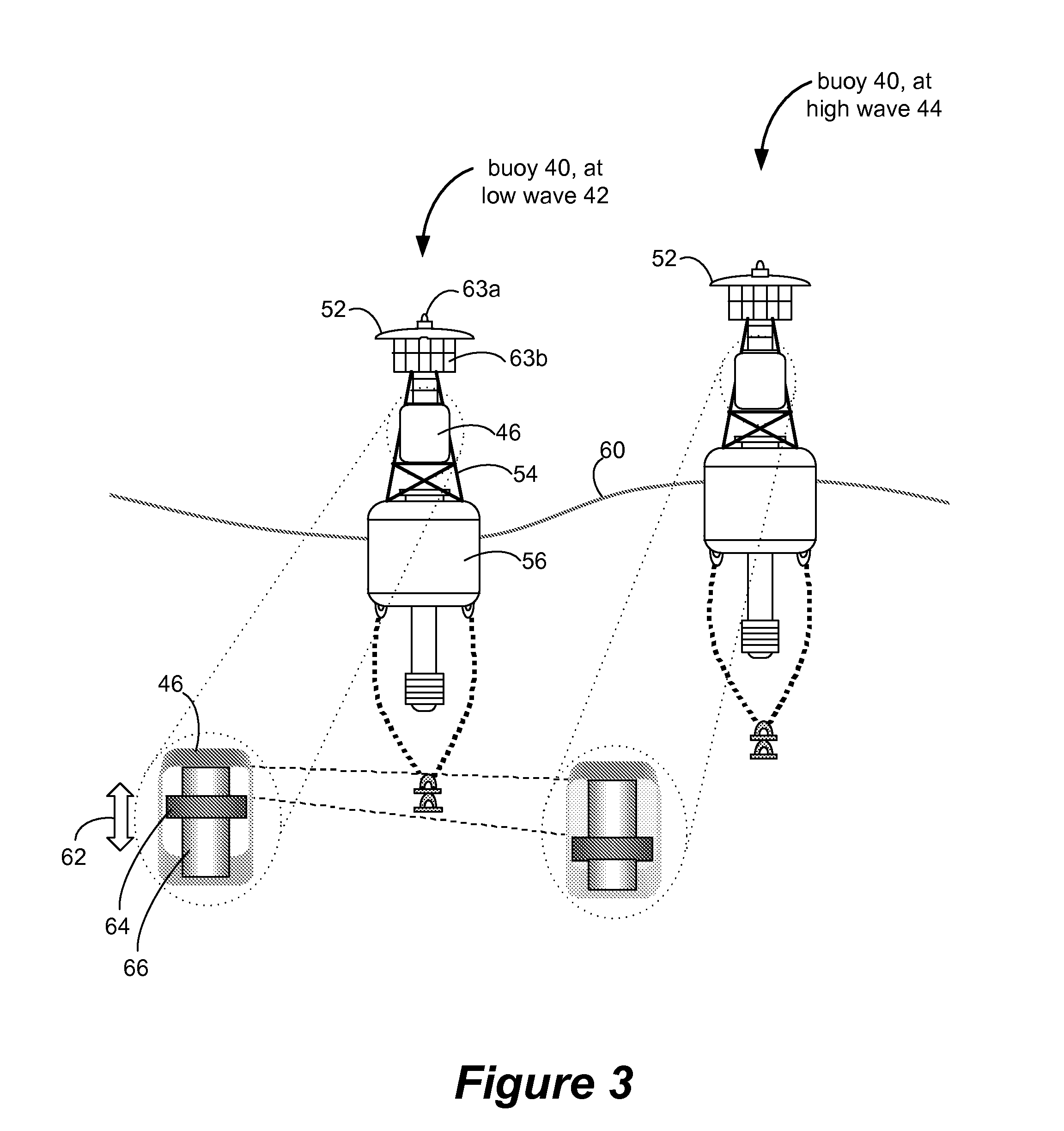
Wave powered generation using electroactive polymers
InactiveUS7557456B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngine fuctionsWave power generationMechanical energy
Described herein are systems and methods that use an electroactive polymer transducer to convert mechanical energy, originally contained in one or more waves, to electrical energy. Marine devices described herein may employ a mechanical energy conversion system that transfers mechanical energy in a wave into mechanical energy suitable for input to the electroactive polymer transducer.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
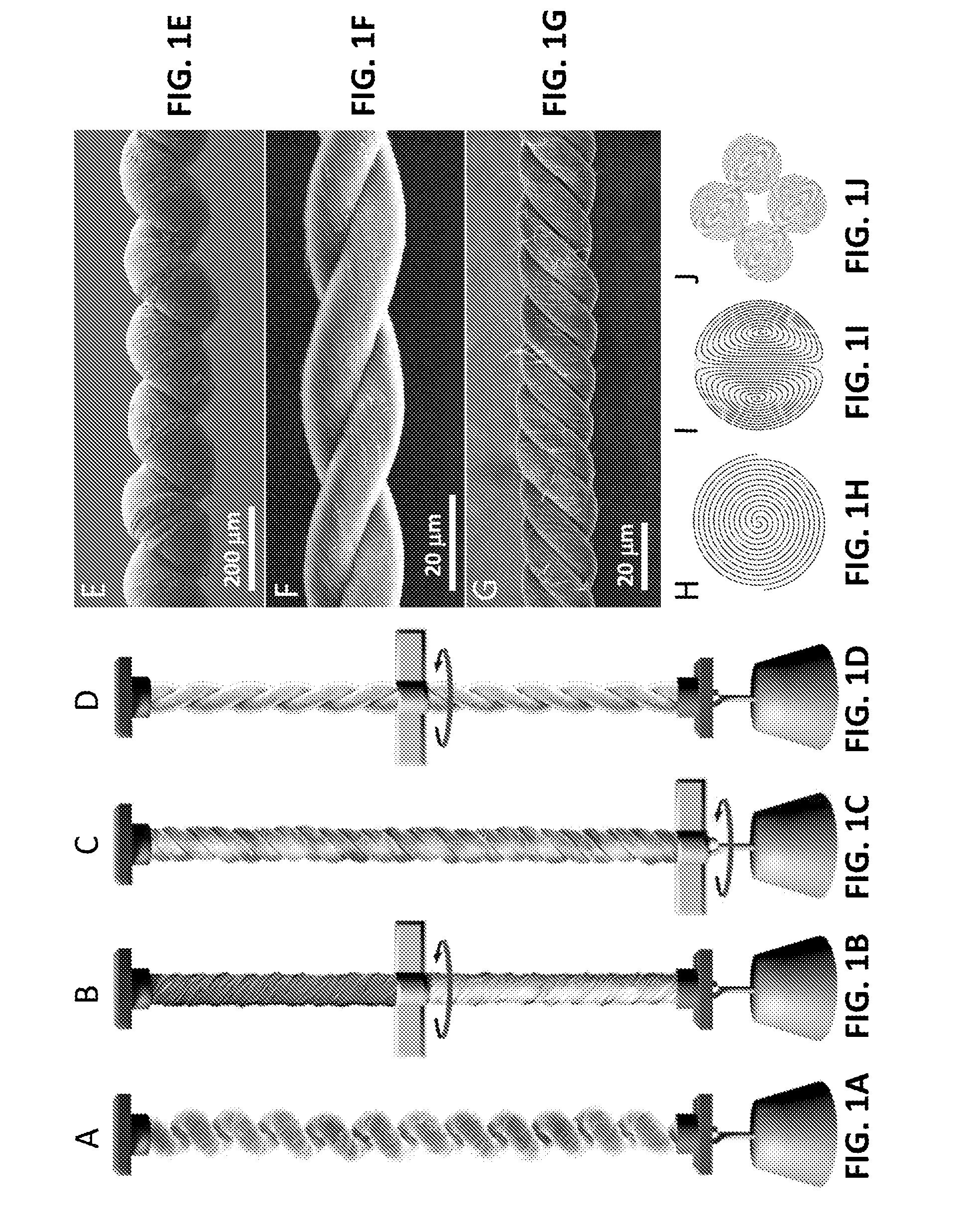
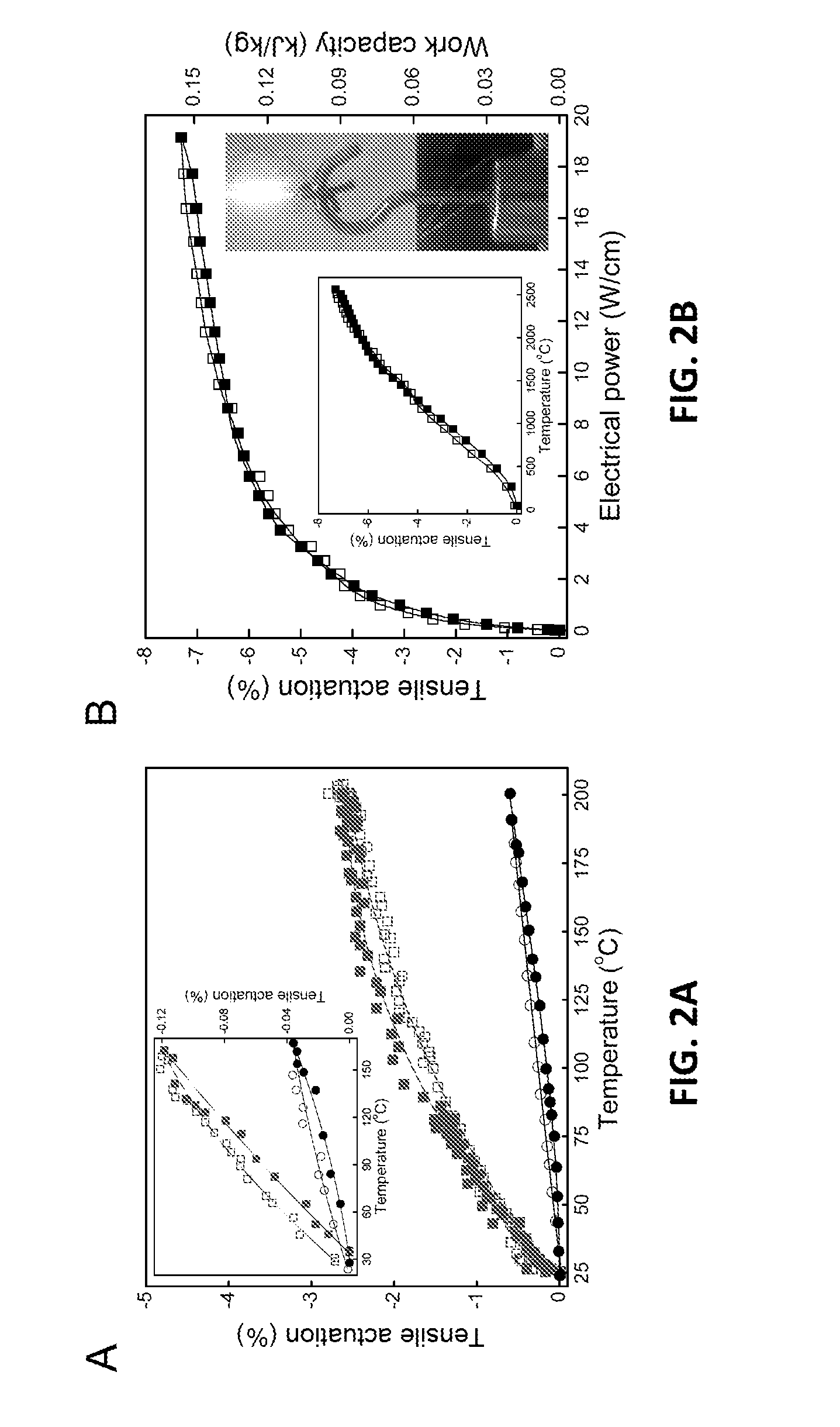
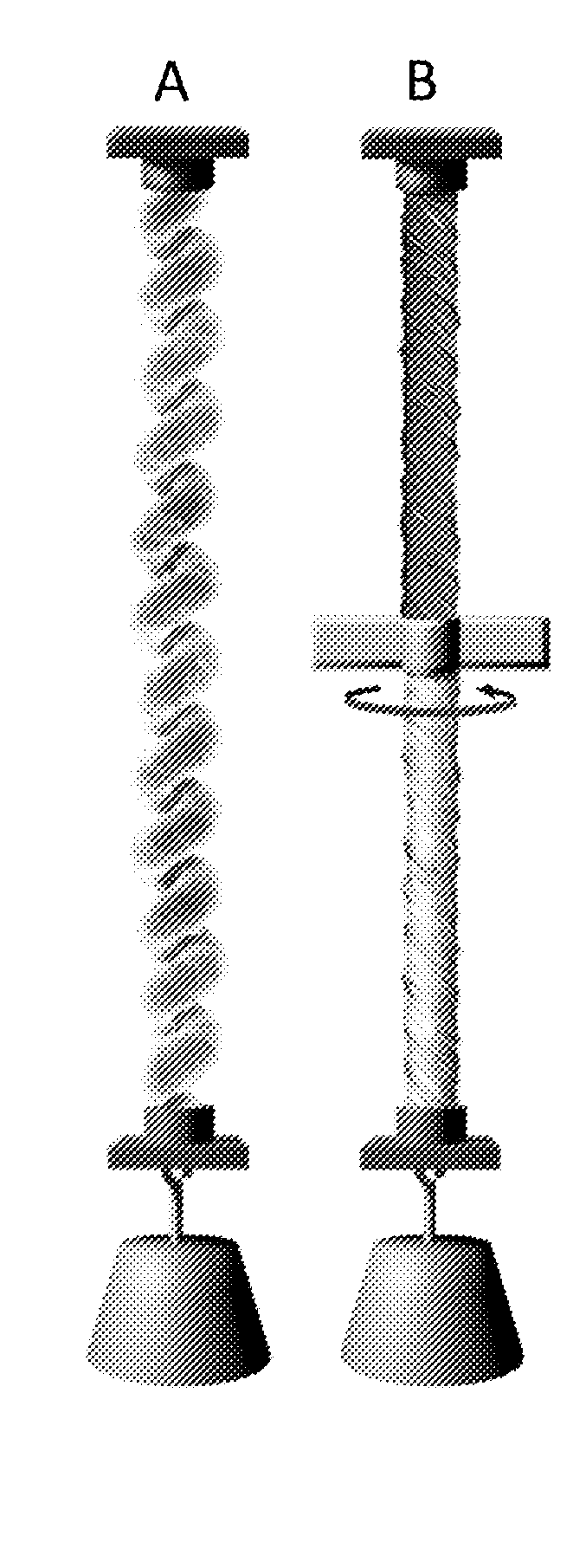
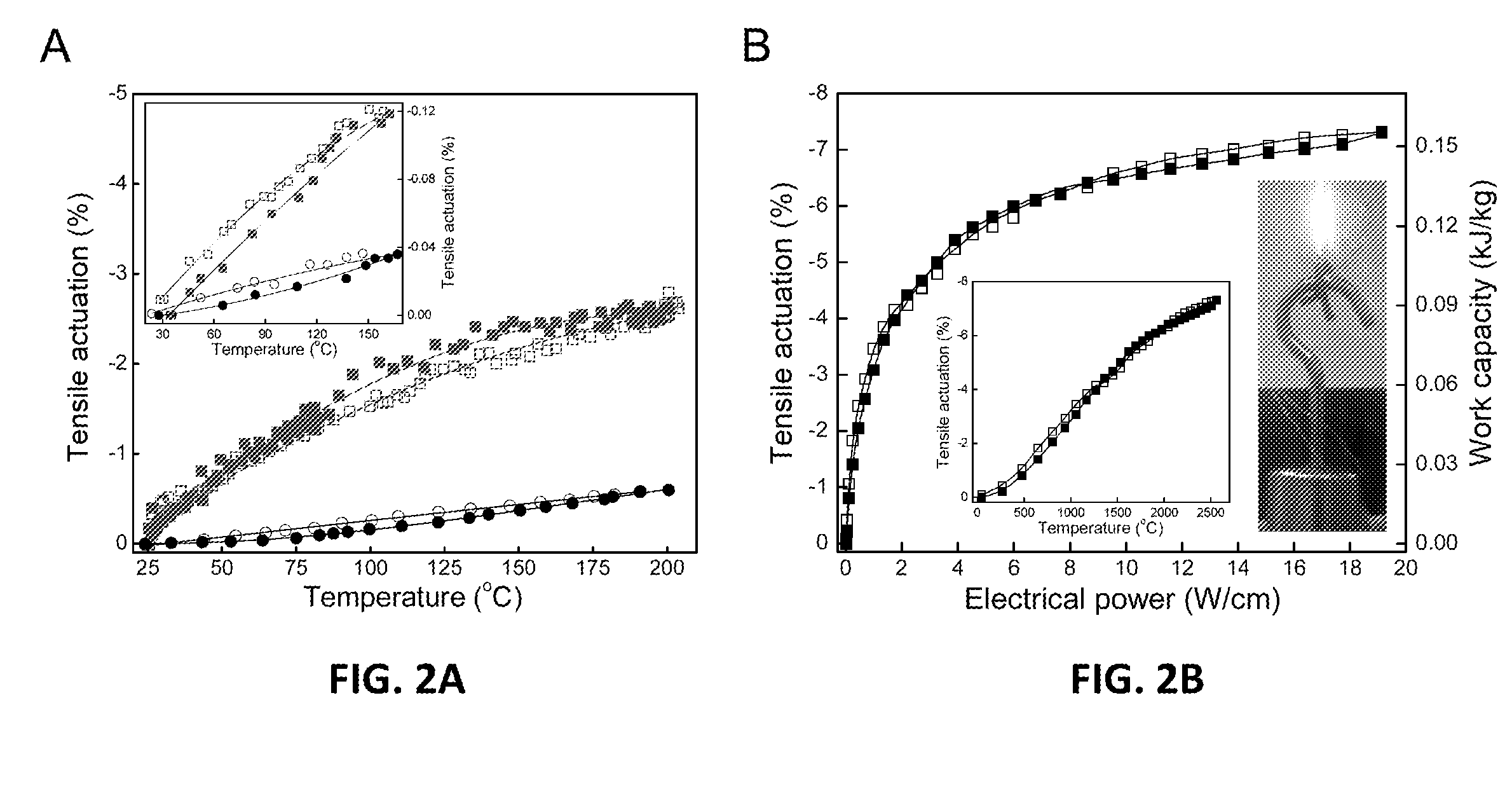
Coiled and non-coiled twisted nanofiber yarn torsional and tensile actuators
Actuators (artificial muscles) comprising twist-spun nanofiber yarn or twist-inserted polymer fibers generate torsional and / or tensile actuation when powered electrically, photonically, chemically, thermally, by absorption, or by other means. These artificial muscles utilize non-coiled or coiled yarns and can be either neat or comprising a guest. Devices comprising these artificial muscles are also described.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Heat-power conversion magnetism devices
InactiveUS20110062821A1Thermal electric motorRefrigeration machinesTemperature differenceHeating power
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Thermomagnetic generator
InactiveUS8729718B2Thermoelectric deivce with magnetic permeability thermal changeVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesEngineeringMagneto
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Apparatus and method for ferroelectric conversion of heat to electrical energy
ActiveUS20100289377A1Robust conversionMaximum polarizationThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changeThermal electric motorThermal energyEngineering
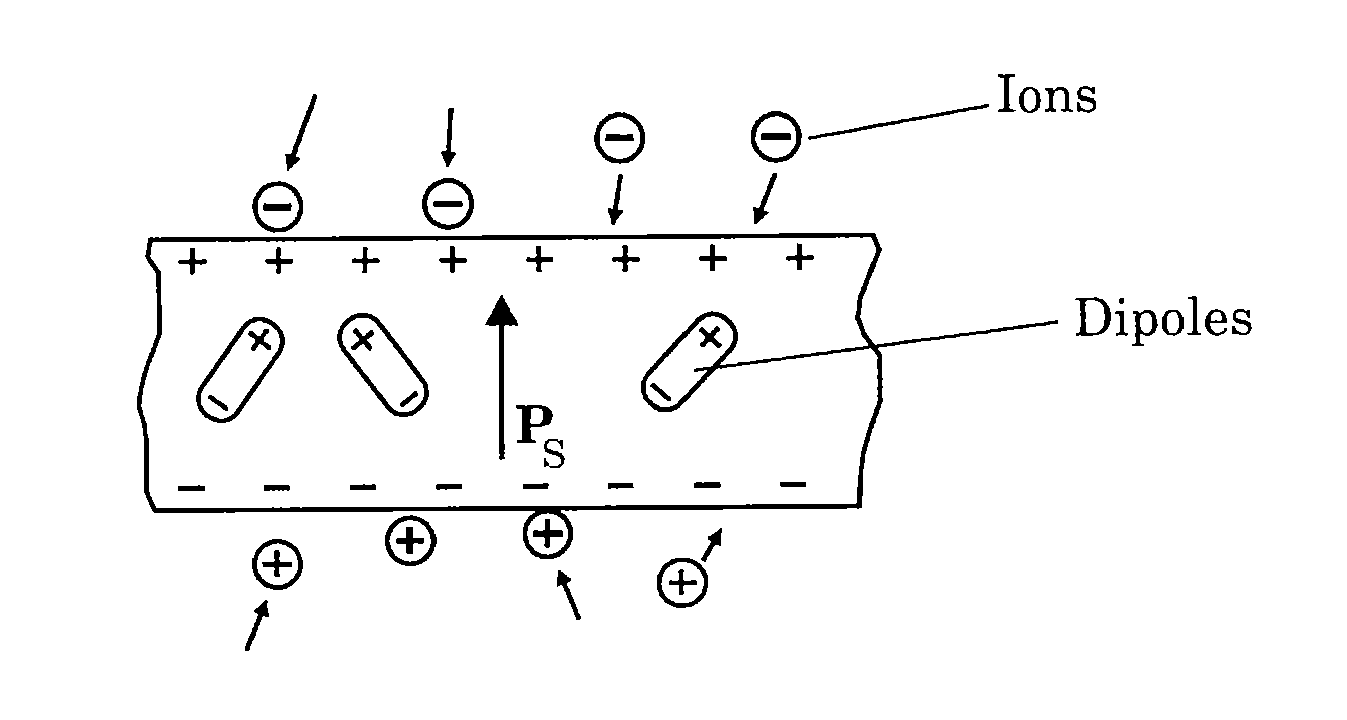
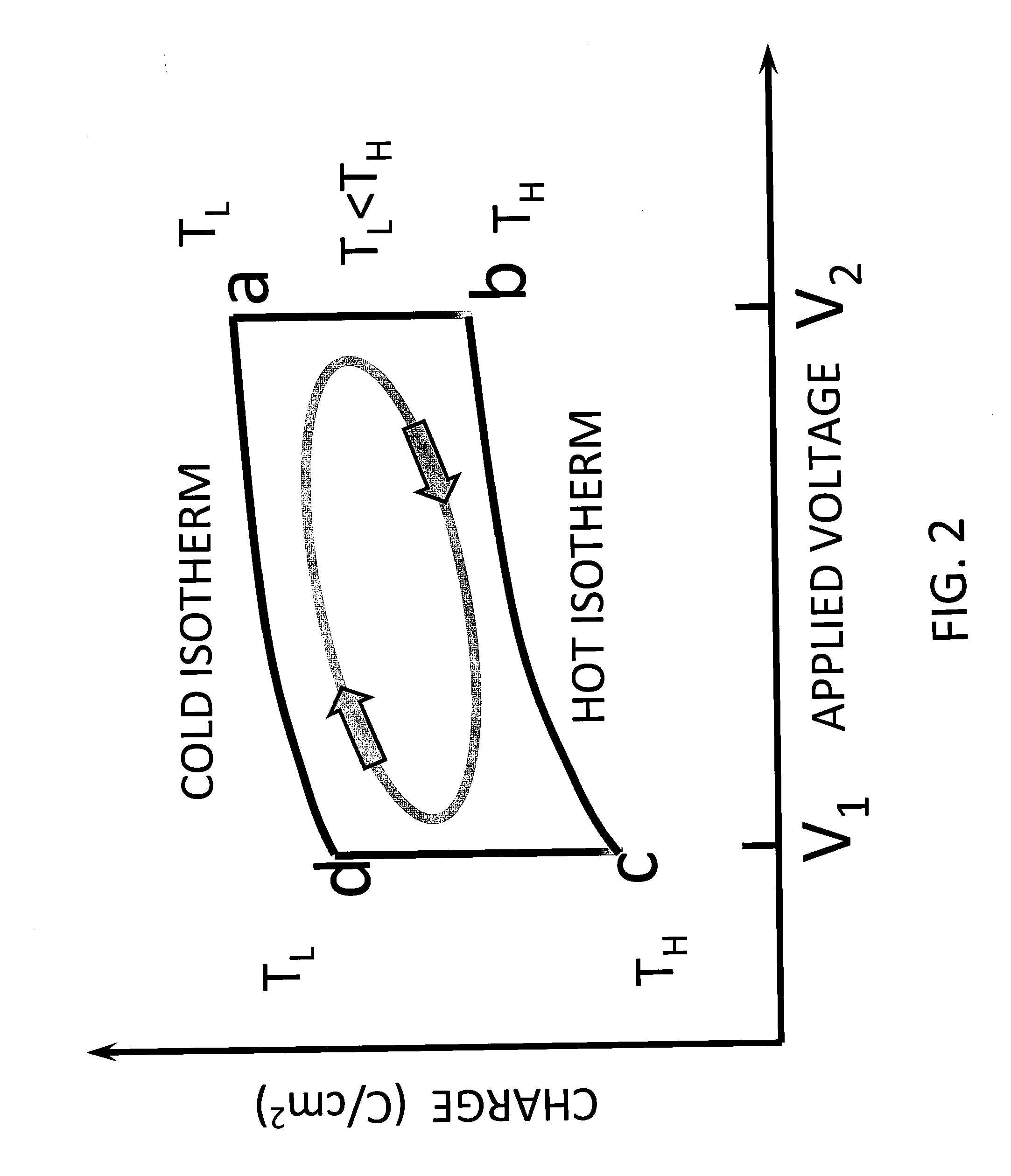
The present invention relates to a new method and apparatus for converting heat to electric energy. The invention exploits the rapid changes in spontaneous polarization that occur in ferroelectric materials during phase change. The invention permits robust and economical generation of electric energy from thermal energy, and it can be used in many different applications. In one aspect, the present invention relates to an apparatus for converting heat to electric energy comprising a pair of electrodes; a ferroelectric layer formed there between with a ferroelectric material characterized with a Curie temperature, Tc, such that when the temperature of the ferroelectric material is lower than Tc, the ferroelectric material is in a ferroelectric phase in which very powerful polarization is established spontaneously in the unit cells of the ferroelectric material, and when the temperature of the ferroelectric material is greater than Tc, spontaneous polarization is not established in the unit cells of the ferroelectric material; and a means for alternately delivering a flow of cold fluid and a flow of hot fluid to the ferroelectric layer so as to alternately cool the ferroelectric layer at a first temperature TL that is lower than Tc, and heat the ferroelectric layer at a second temperature TH that is higher than Tc, thereby the ferroelectric material of the ferroelectric layer undergoes alternating phase transitions between the ferroelectric phase and the paraelectric phase with temperature cycling.
Owner:THE NEOTHERMAL ENERGY
Carbon nanotube MEMS assembly
A carbon nanotube MEMS assembly comprises a plurality of carbon nanotubes oriented into a patterned frame, the patterned frame defining at least two components of a MEMS device. An interstitial material at least partially binds adjacent carbon nanotubes one to another. At least one component of the frame is fixed and at least one component of the frame is movable relative to the fixed component.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
SMA actuator with improved temperature control
InactiveUS6981374B2Improve cooling effectRapid responseEngine componentsMechanical power devicesTemperature controlActive cooling
A SMA actuator having rigid members and SMA wires, in which improved temperature control of the SMA wires of the actuator is provided by a heat sink, which may be the rigid members themselves, in close proximity to at least a central portion of the wires. Optionally, the heat sink is sized and placed such that the end portions of the wires where they are attached to the rigid members are not in close proximity to the heat sink. Where the heat sink is external, it optionally has a cooling element that acts passively as a heat sink during the heating cycle of the actuator and that acts as an active cooling element during the cooling cycle of the actuator. An SMA actuator having a desired contraction limit and a power supply circuit has a switch in the power supply circuit that is normally closed when the actuator is contracted to less than the desired contraction limit and is opened by the actuator reaching the desired contraction limit. This improved temperature control provides greater cooling of the SMA wires for a faster response and an extended working life of the actuator.
Owner:ALFMEIER PRAZISION BAUGRUPPEN & SYSTLOSUNGEN
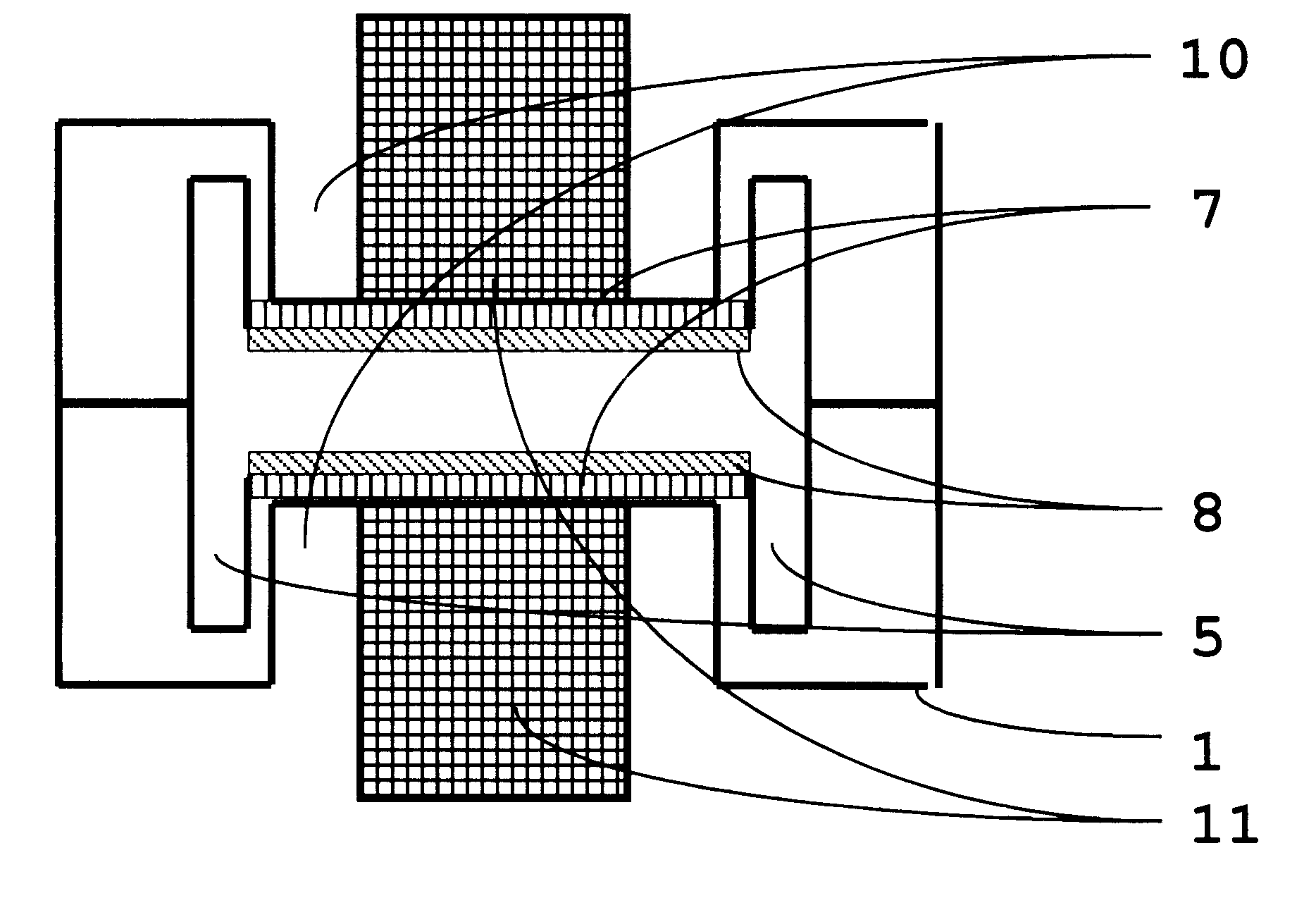
MEMS based pyroelectric thermal energy harvester
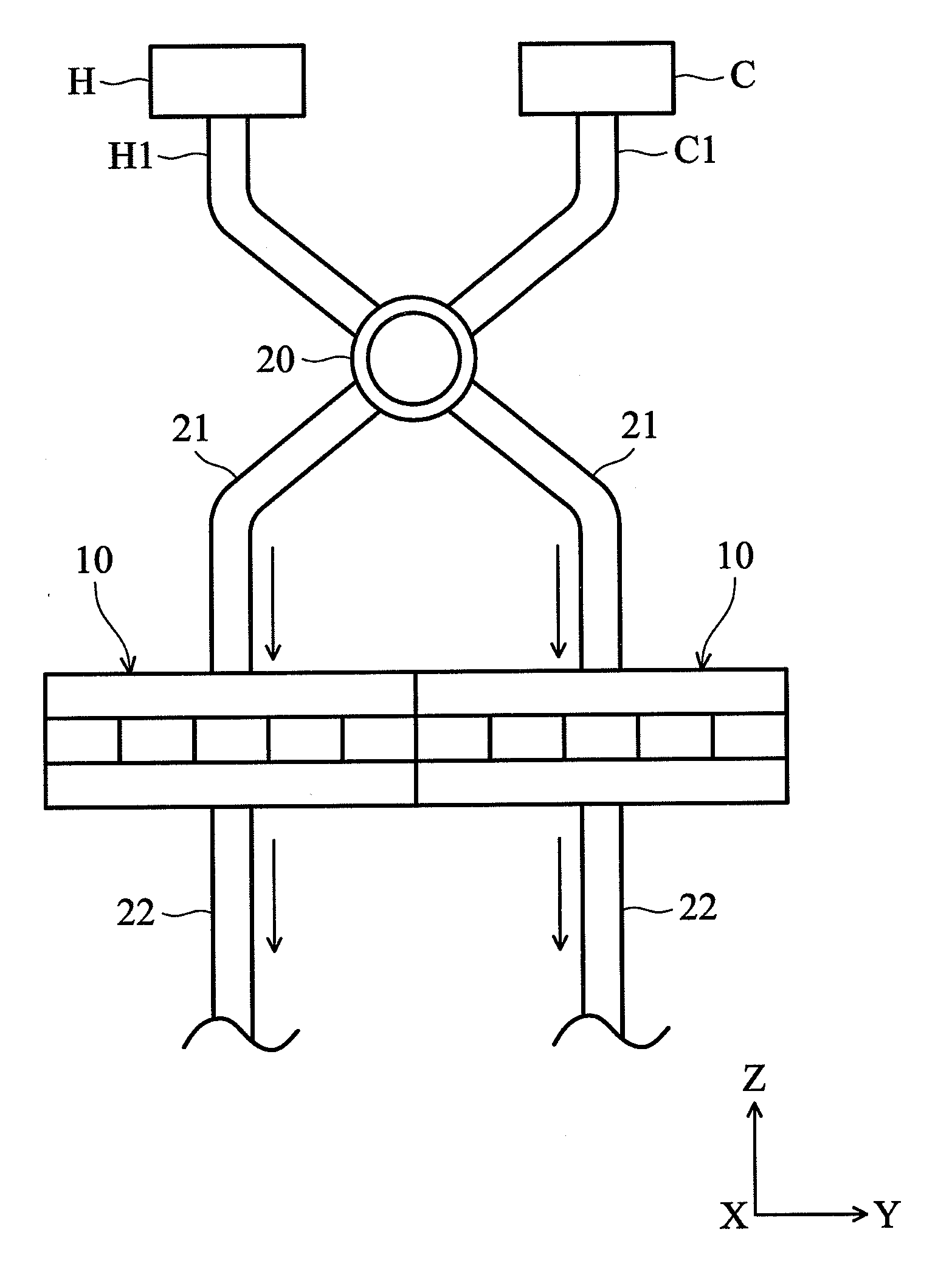
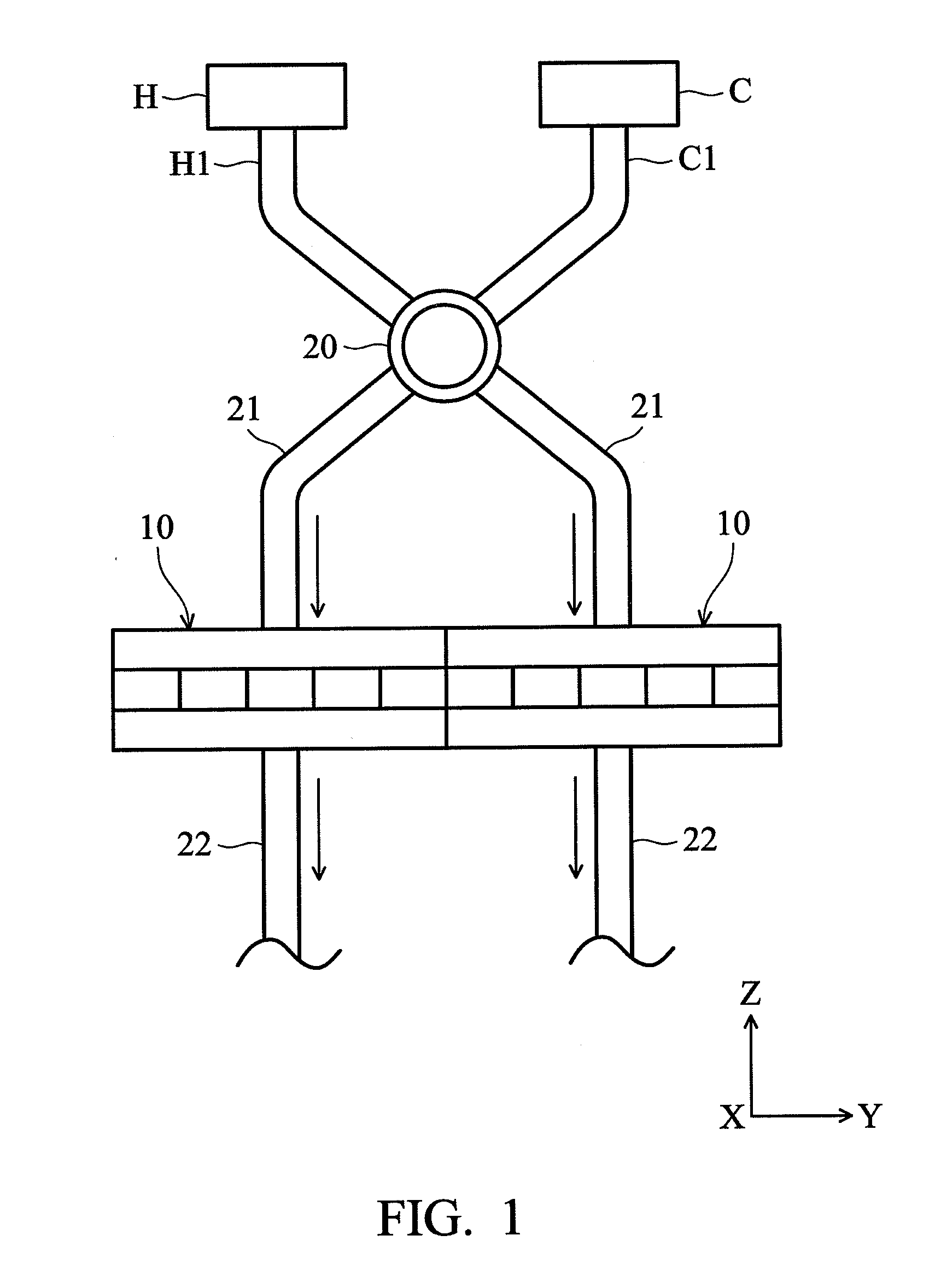
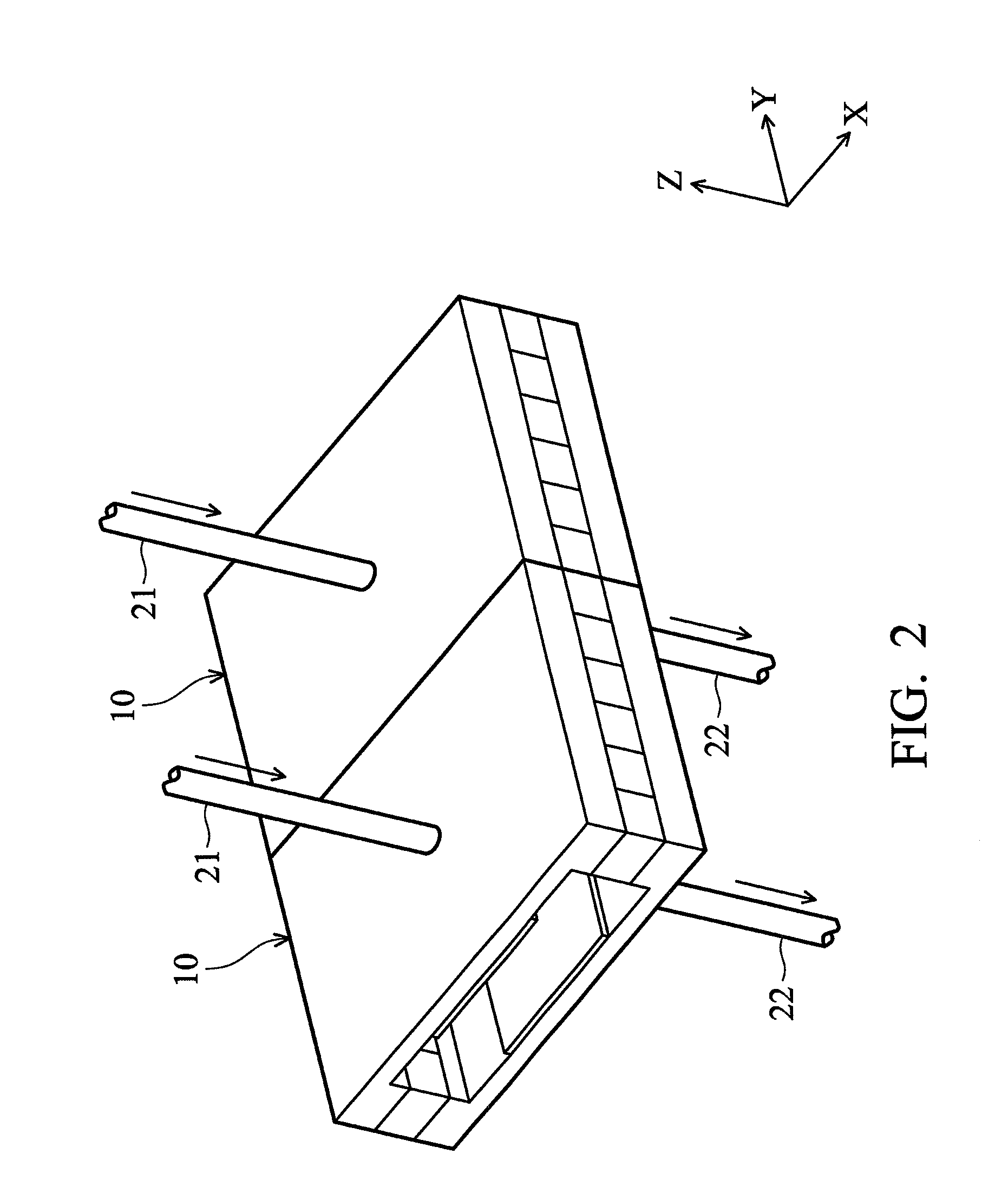
InactiveUS20120056504A1High quality electrical energySignificant reductionThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changeThermal electric motorTemperature differenceDielectric layer
A pyroelectric thermal energy harvesting apparatus for generating an electric current includes a cantilevered layered pyroelectric capacitor extending between a first surface and a second surface, where the first surface includes a temperature difference from the second surface. The layered pyroelectric capacitor includes a conductive, bimetal top electrode layer, an intermediate pyroelectric dielectric layer and a conductive bottom electrode layer. In addition, a pair of proof masses is affixed at a distal end of the layered pyroelectric capacitor to face the first surface and the second surface, wherein the proof masses oscillate between the first surface and the second surface such that a pyroelectric current is generated in the pyroelectric capacitor due to temperature cycling when the proof masses alternately contact the first surface and the second surface.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Thermomagnetic generator
InactiveUS20130106116A1Thermoelectric deivce with magnetic permeability thermal changeVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesEngineeringMagneto
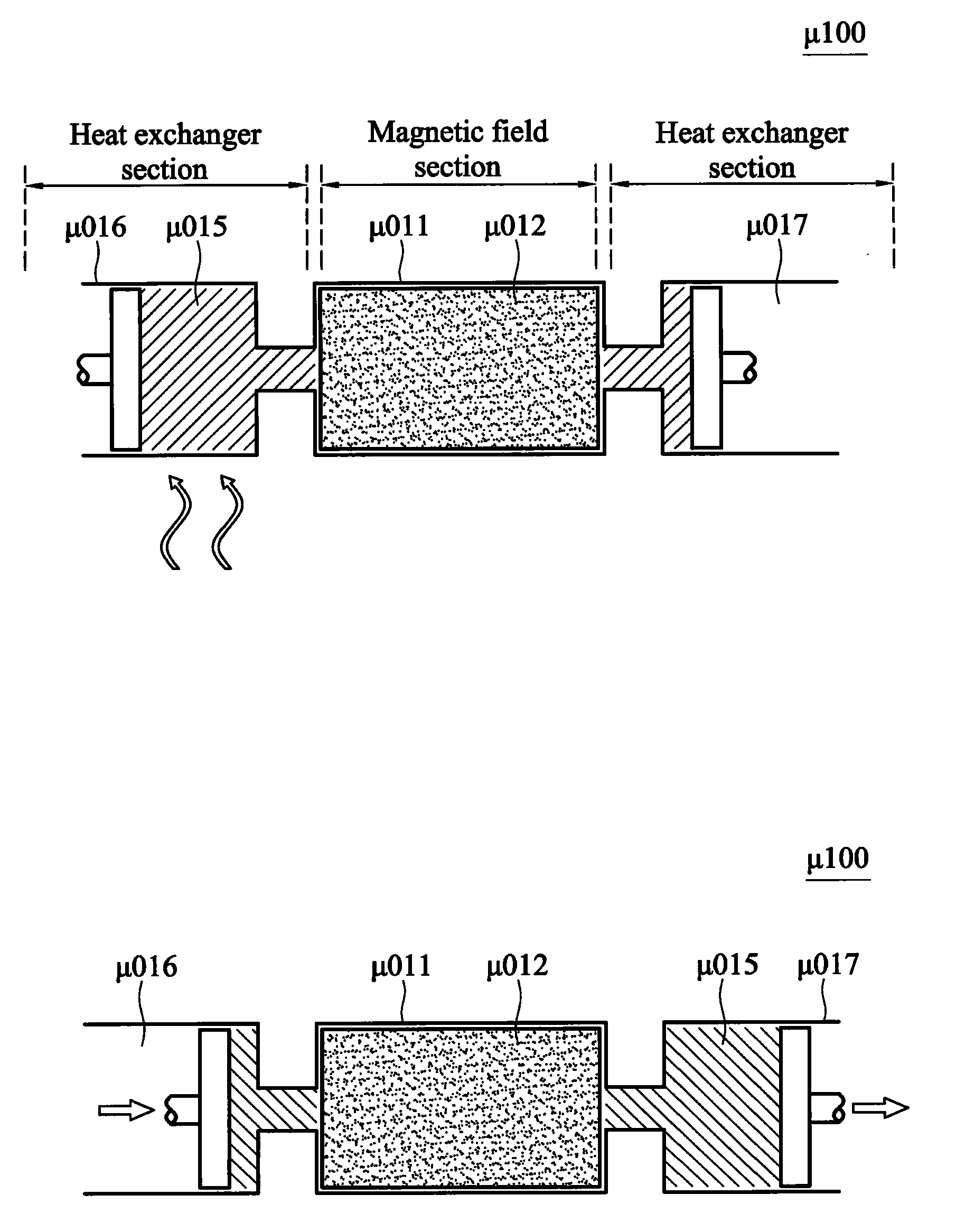
A thermomagnetic generator is provided, including a switch valve, a plurality of magnetic circuit units, a coil, and a plurality of inlet pipes connecting the magnetic circuit units to the switch valve. Each of the magnetic circuit units includes a magneto-caloric member. The switch valve repeatedly and alternatively switches at a predetermined frequency to guide hot and cold fluids to the magnetic circuit units, such that the magneto-caloric members are magnetized and demagnetized, respectively, by the cold and hot fluids. The coil is coupled to at least one of the magnetic circuit units for obtaining an induced voltage.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
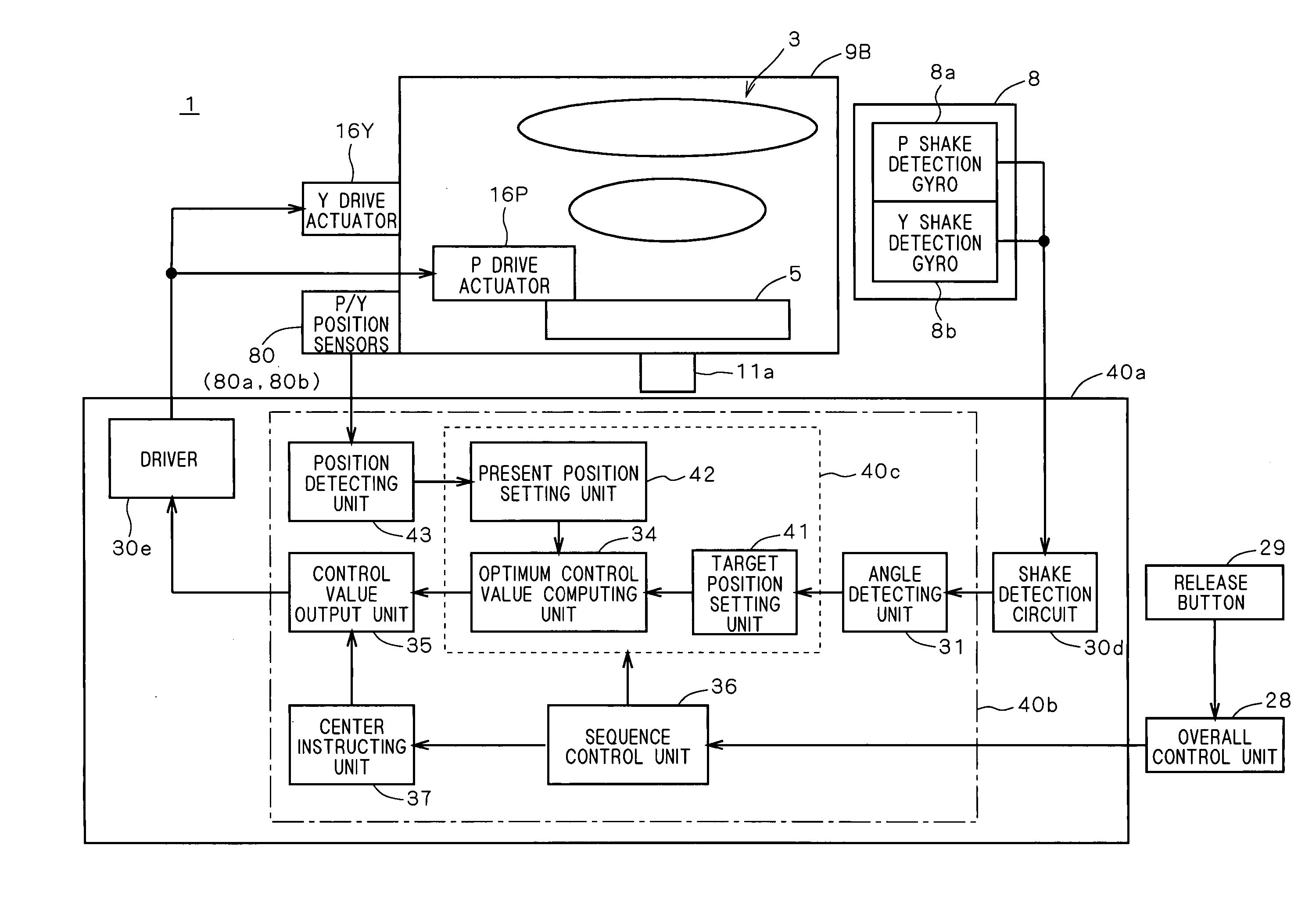
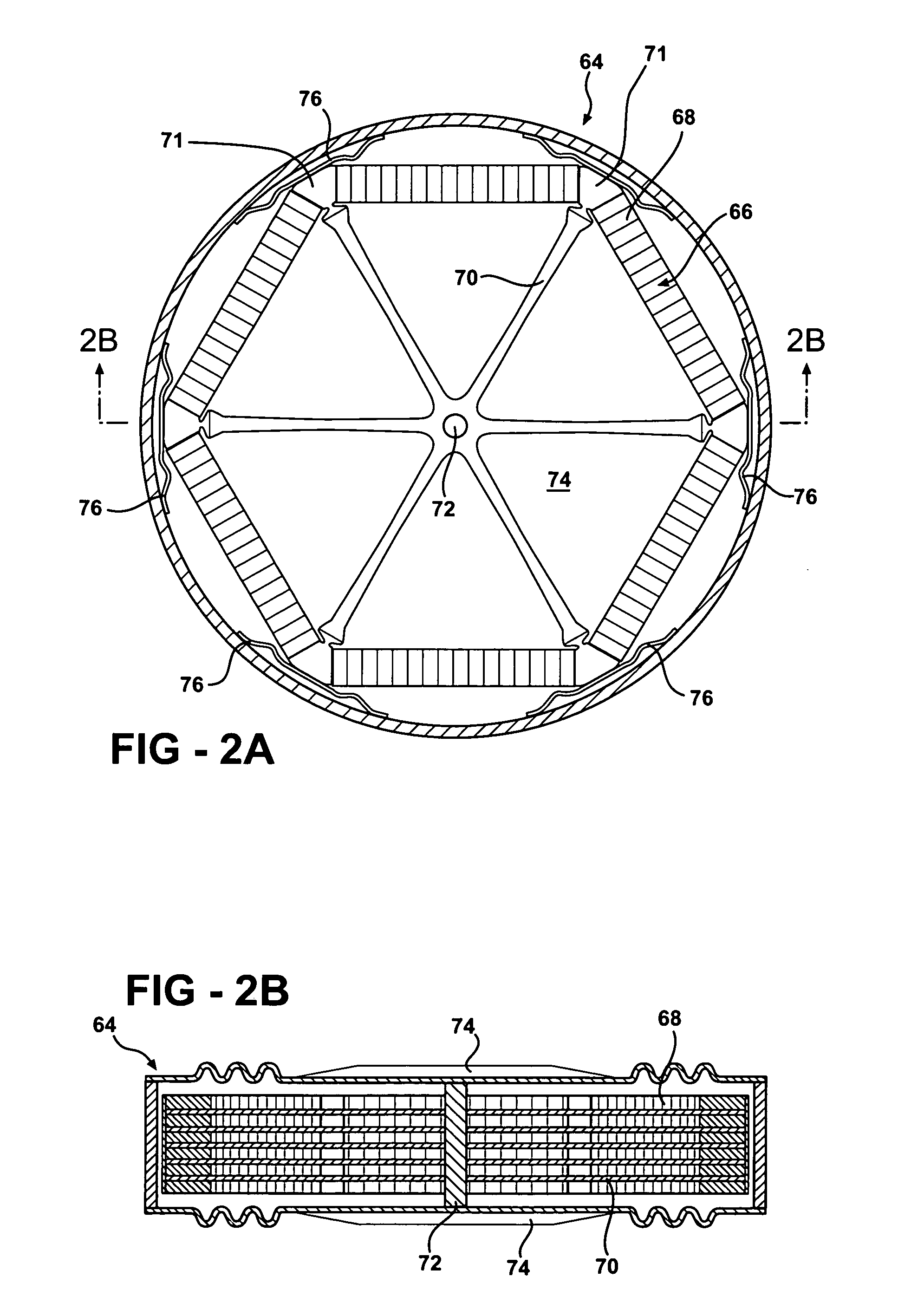
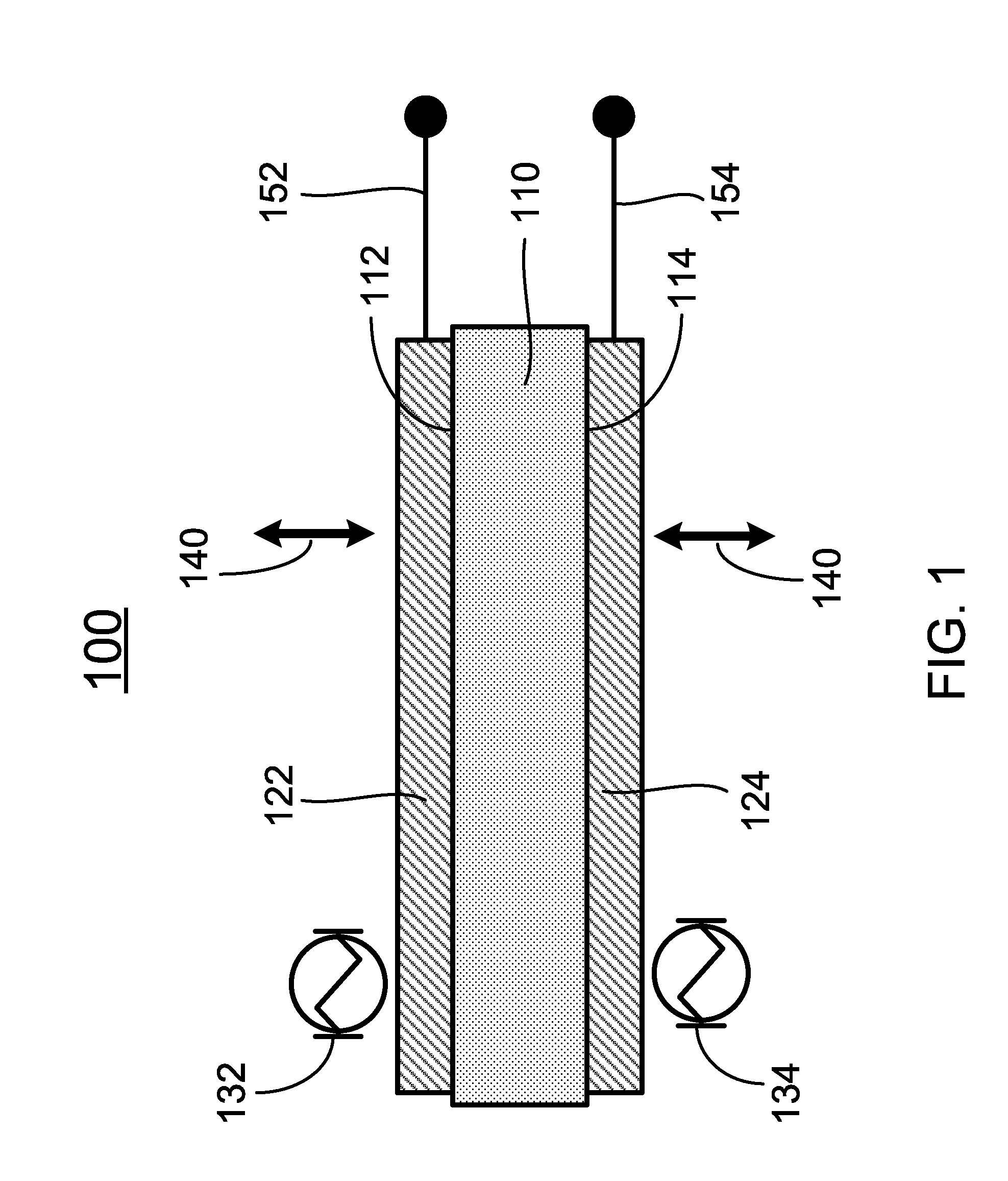
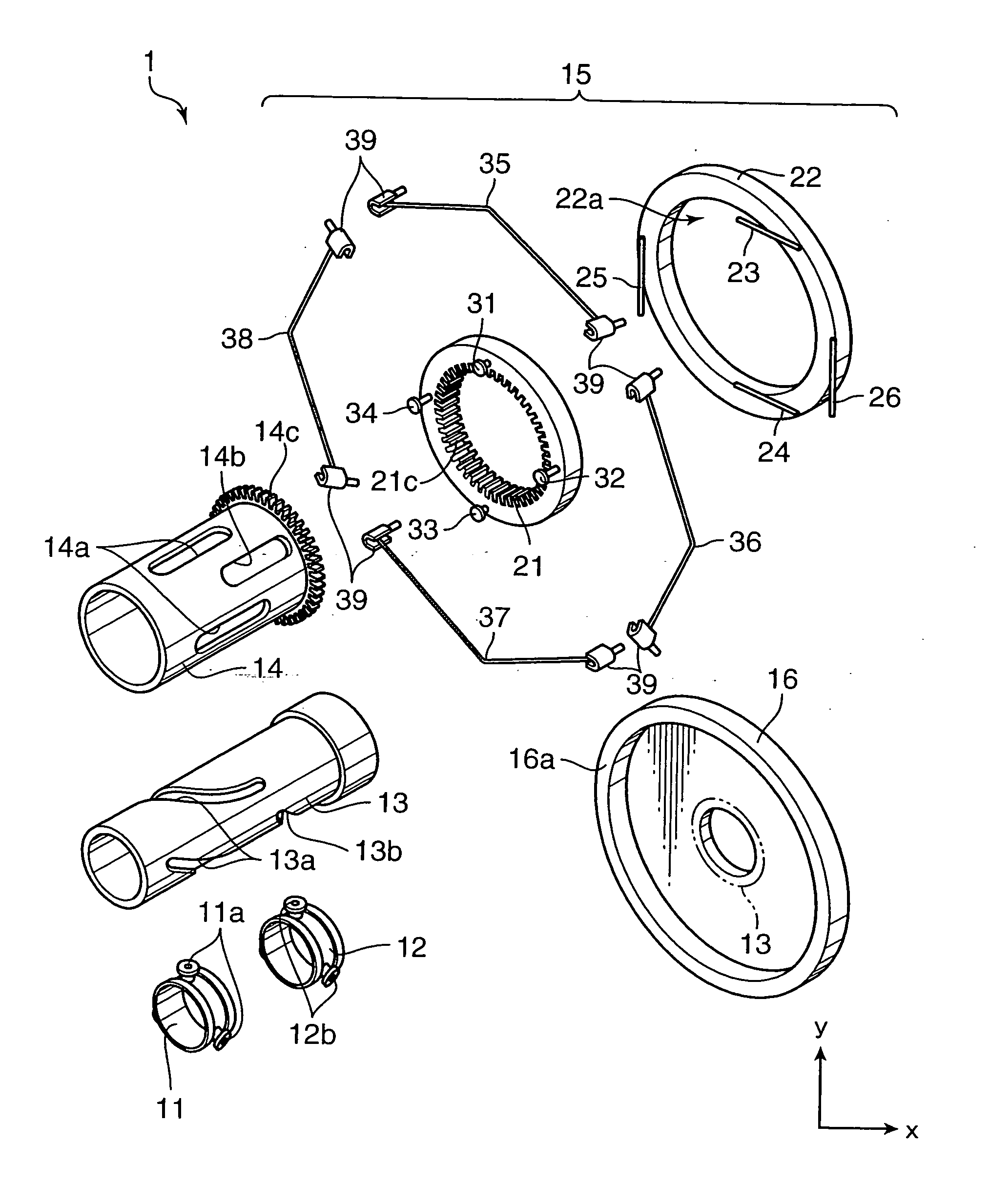
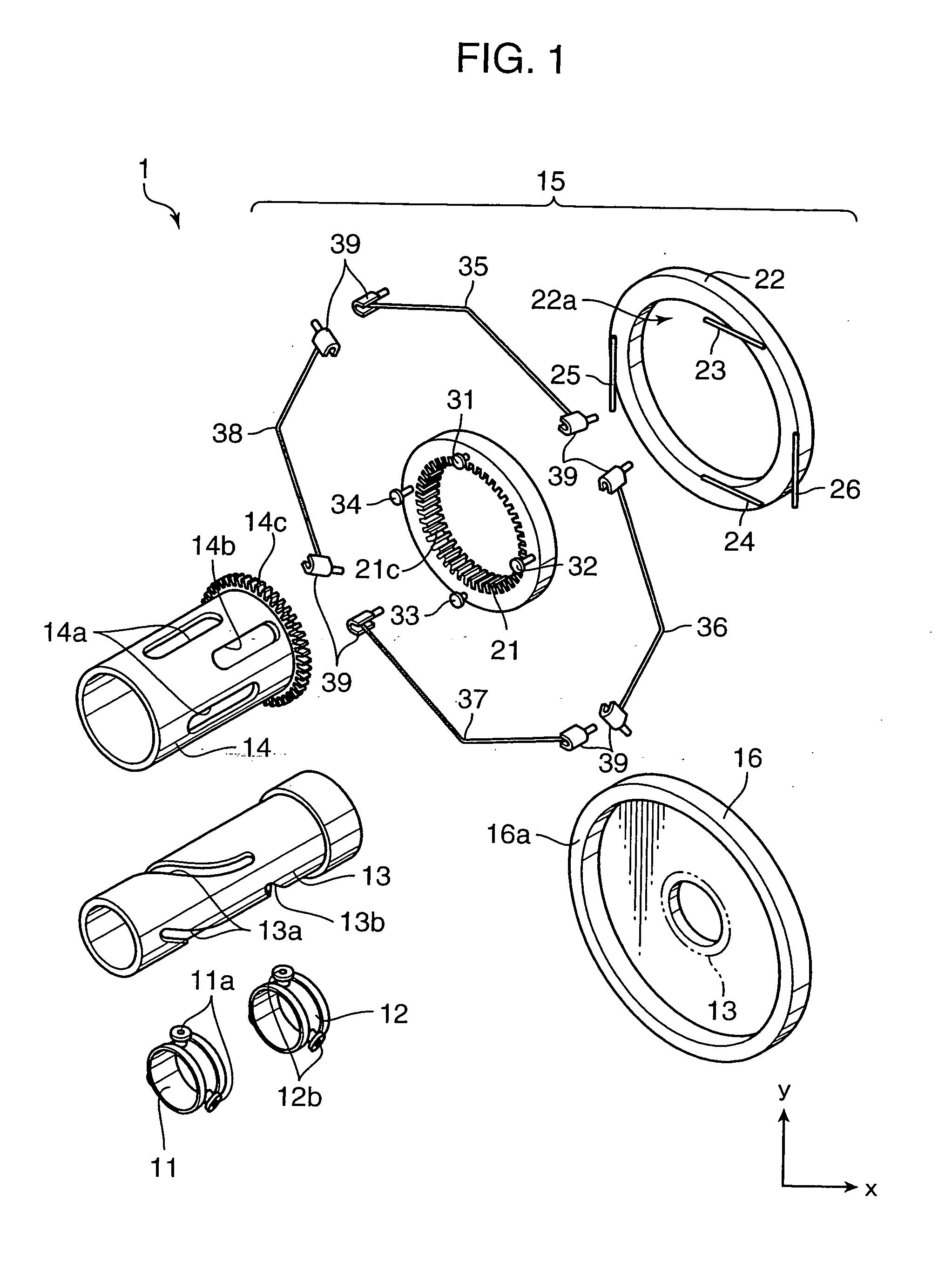
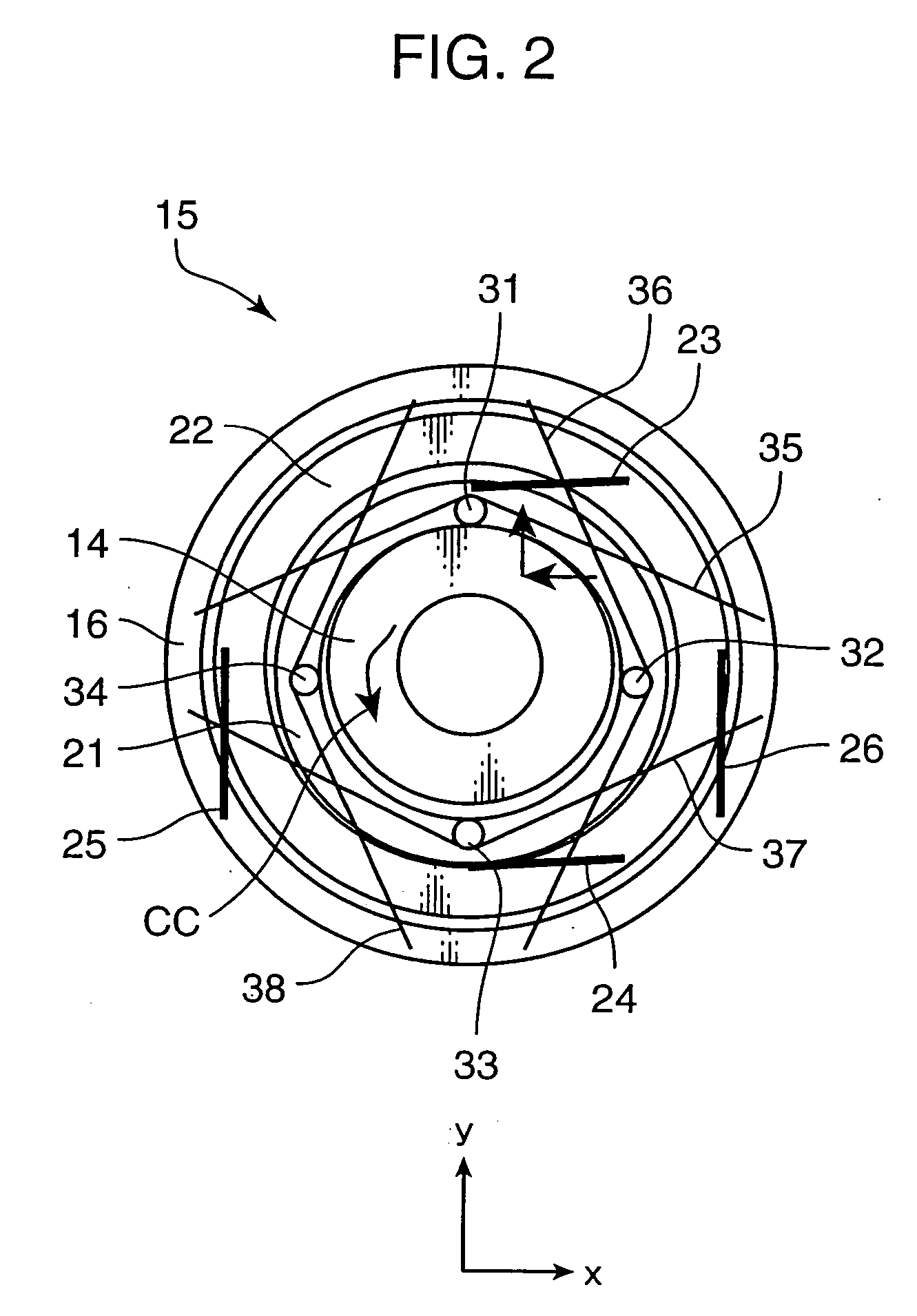
Motor, motor device, and lens drive mechanism using the same
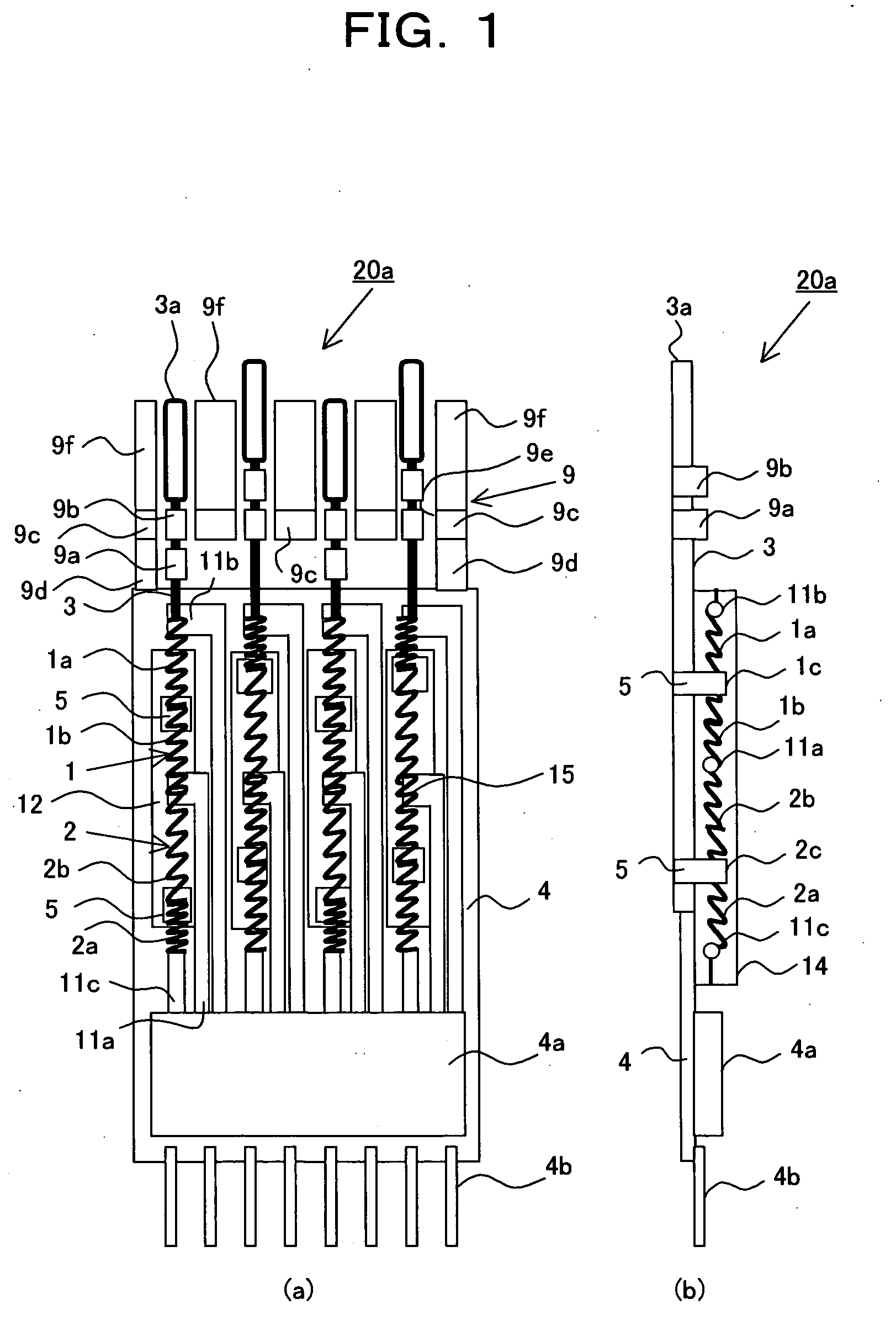
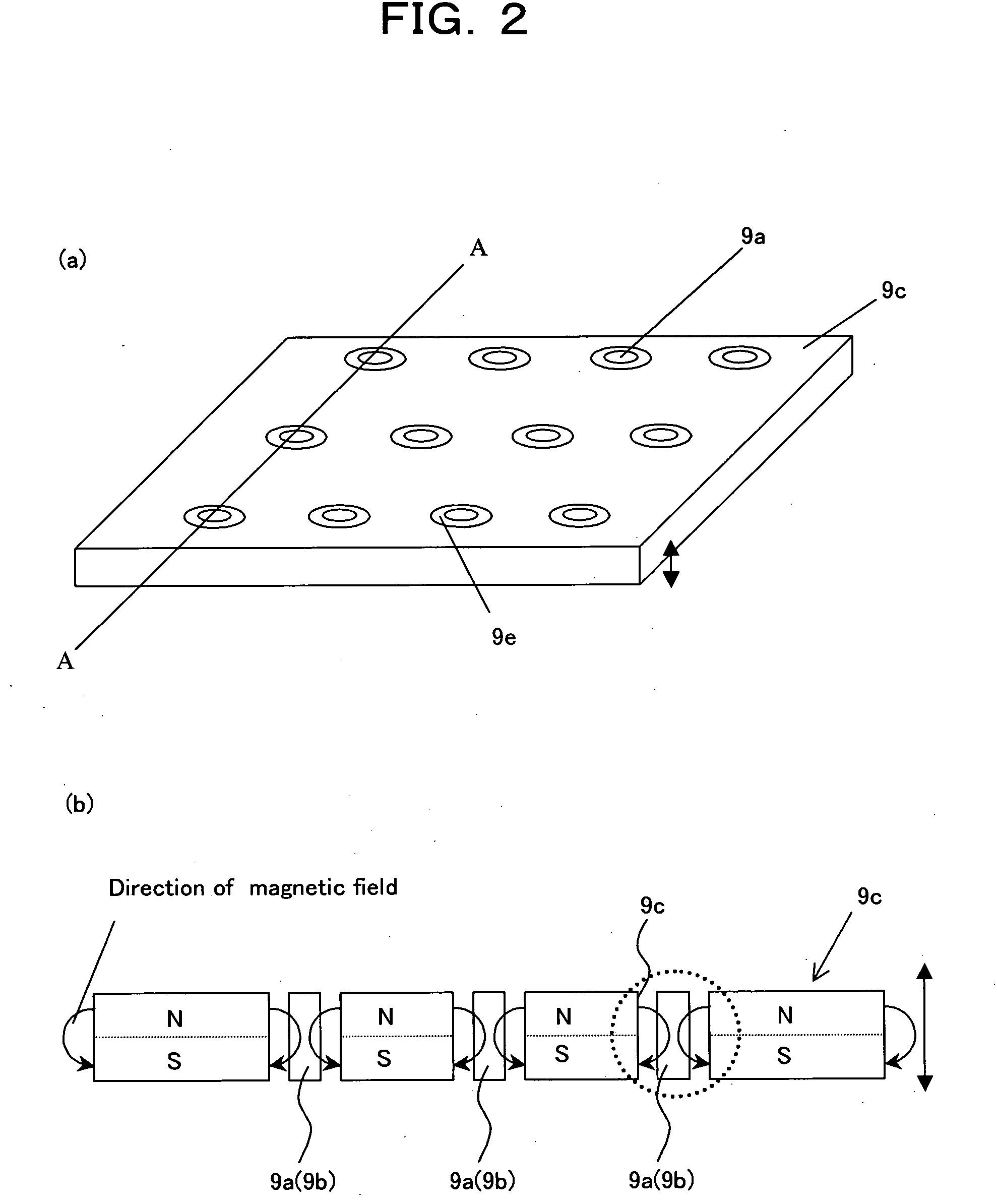
An arrangement of the invention includes a base block 16, a cylindrical cam 14, as a rotary member, which is rotatably supported on the base block 16, and includes a contact portion on an outer periphery thereof for outputting a rotating force, a drive gear 21, as an oscillatory ring, which includes a contact portion on an inner periphery thereof, and is oscillated on a plane perpendicular to a rotation axis of the cylindrical cam 14 in contact with the contact portion of the cylindrical cam 14, parallel springs 23 through 26, as a position retainer, for retaining the position of the drive gear 21, and three or more shape metal alloy actuators (SMA) wires 35 through 38, as expandable and contractible actuators, with both ends of the each SMA wire being fixed to the base block 16 for contact with the drive gear 21.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
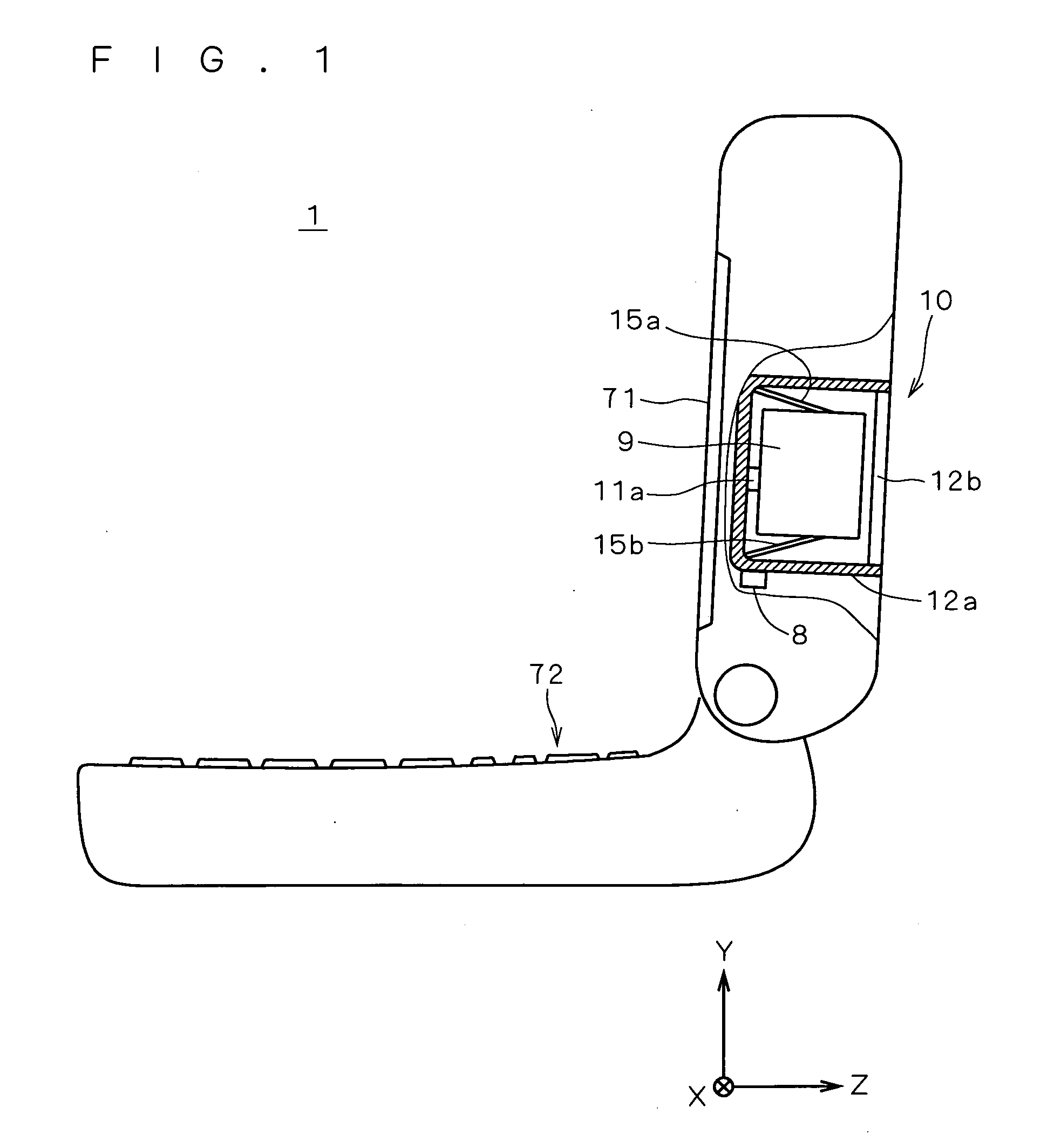
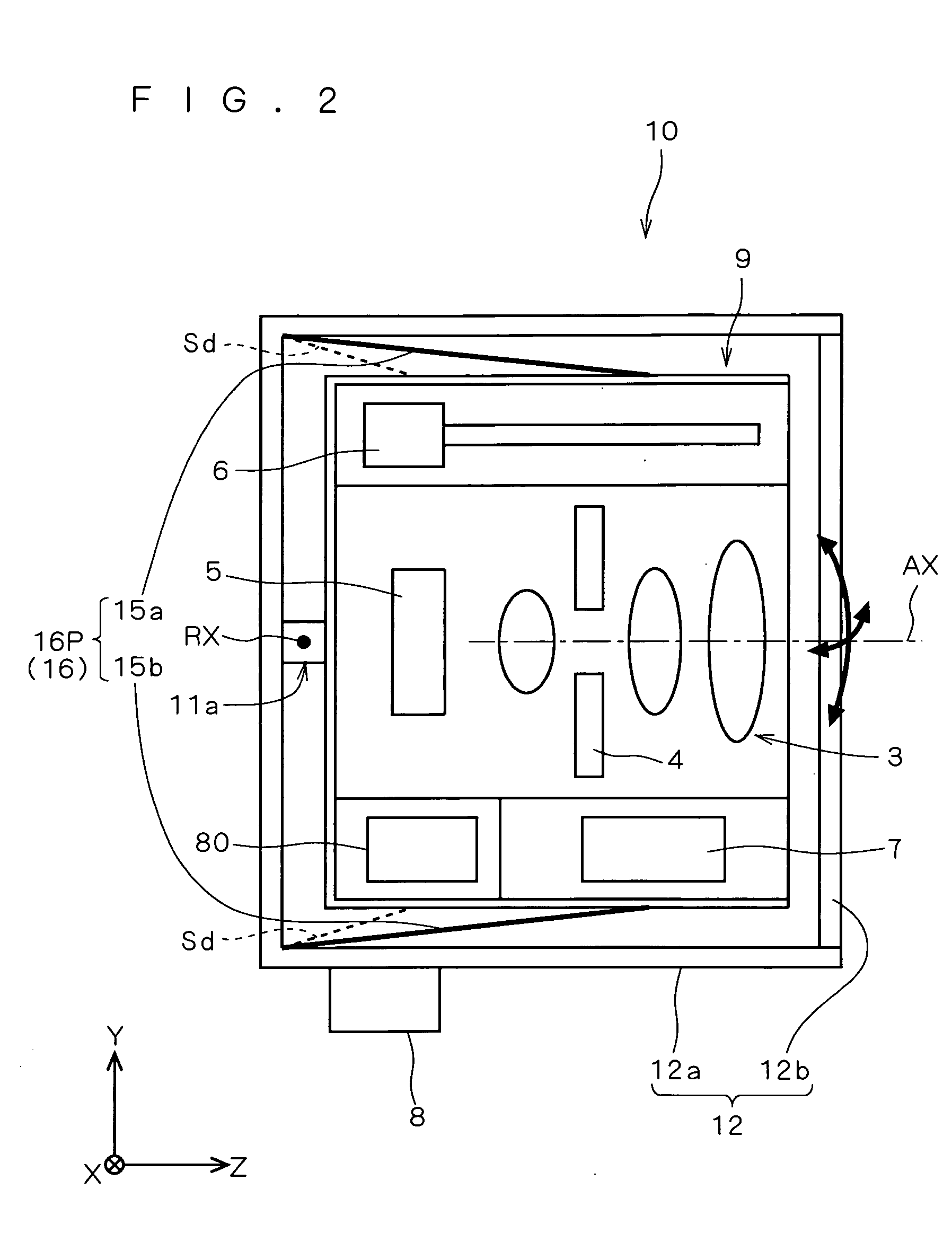
Driving Mechanism Using Shape Memory Alloys And Devices Equipped With The Same
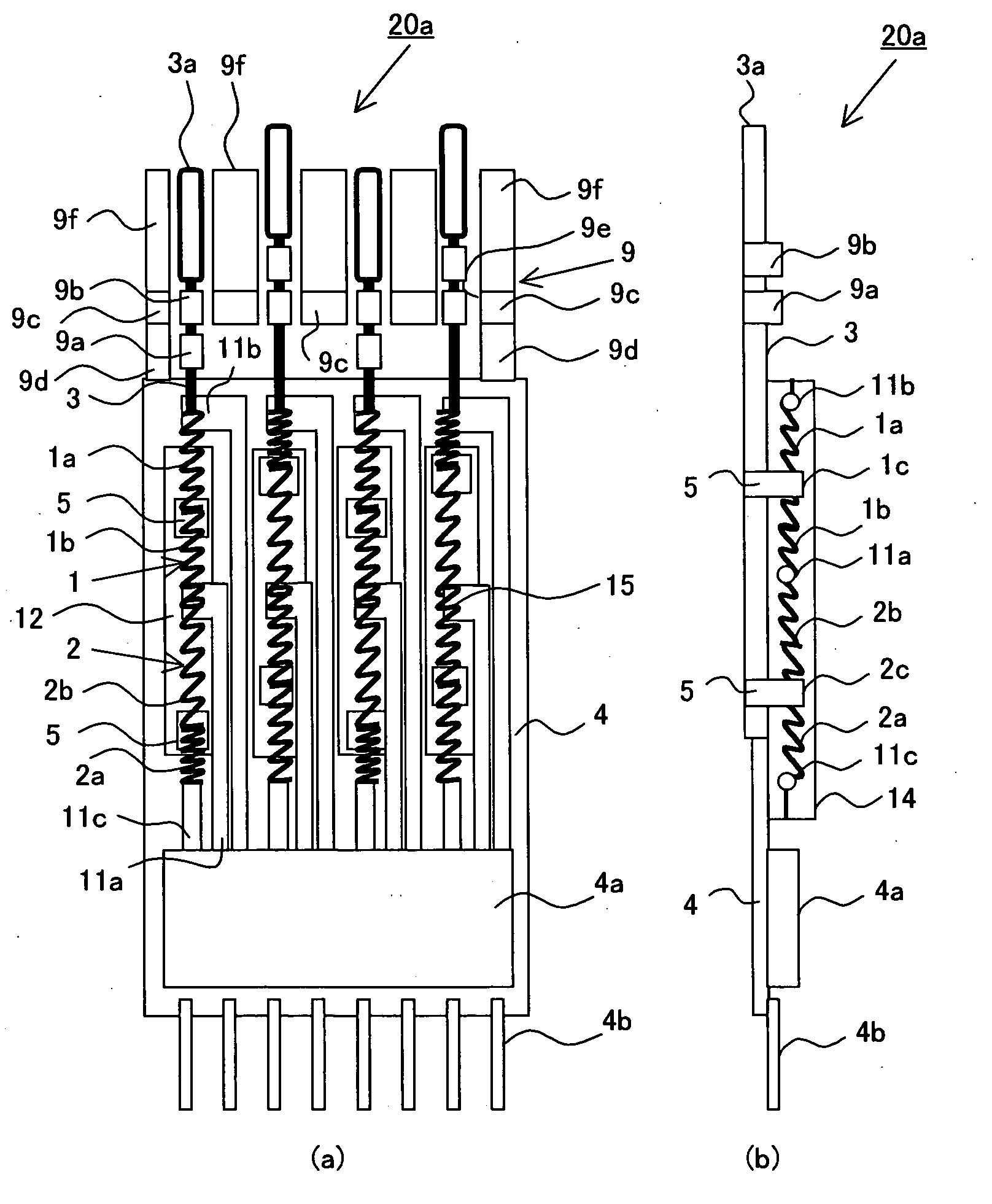
ActiveUS20080227060A1Solve the large power consumptionEasy to integrateMedical devicesCatheterShape-memory alloyAlloy
A driving mechanism using shape memory alloys comprises a first and a second shape memory alloys coils (1, 2), a pin-like drive member (3) connected to each of the shape memory alloys coils (1, 2) extending in the axis direction, a substrate (4) having a wiring pattern (11) and a drive circuit (4a) to supply current to the shape memory alloys coils (1, 2), and a magnetic latch part (9) to hold the drive member (3), and the magnetic latch part (9) has a latch position in the axis direction of the drive member (3), the drive circuit (4a) selectively current-drives the first and the second shape memory alloys coils (1, 2), the driven first or second shape memory alloys coils (1, 2) is heated and compressed to move the drive member (3) in the axis direction, and magnetic bodies (9a, 9b) provided to the drive member (3) is magnetically fixed at the latch position, thereby fixed and held in the axis direction.
Owner:HAGA YOICHI +2
DLC field emission with nano-diamond impregnated metals
InactiveUS20070126312A1Improve electron emission efficiencyCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesDischarge tube/lamp detailsDiamond-like carbonMaterials science
Diamond-like carbon based energy conversion devices and methods of making and using the same which have improved conversion efficiencies and increased reliability are provided. In one aspect, such a device may include a cathode having a plurality of nano-diamond particles disposed in a metal matrix, where the plurality of nano-diamond particles protrude partially from the metal matrix. A layer of diamond-like carbon (DLC) may be deposited on the plurality of nano-diamond particles and the metal matrix. Additionally, an anode may be located in a position to face the plurality of nano-diamond particle protrusions.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
Thermoelectric stack coating for improved solar panel function
InactiveUS20120132256A1Overcome disadvantagesProlong lifePV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationMechanical energyEngineering
Methods and devices for increase power output from solar devices. In one embodiment, the technique enables the front hot solar panel surface to be cooled by attachment of a thermoelectric multilayer stack to the back solar panel surface. The thermoelectric stack cools the solar panel front surface by drawing heat from the front to the back of the panel. That heat is transformed into mechanical vibrations using an inverse Peltier effect and that mechanical energy then transformed into electrical energy using a piezoelectric effect. Power output is first increased by lower operating temperature on front, resulting in a higher power conversion efficiency for the photovoltaic effect taking place in the CIGS / CdS active layers or other thin films, then from an additional power output from secondary electrical energy created from mechanical arising from the temperature-gradient driven occurrence of the thermoelectric effect.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Thermally conductive thermal actuator and liquid drop emitter using same
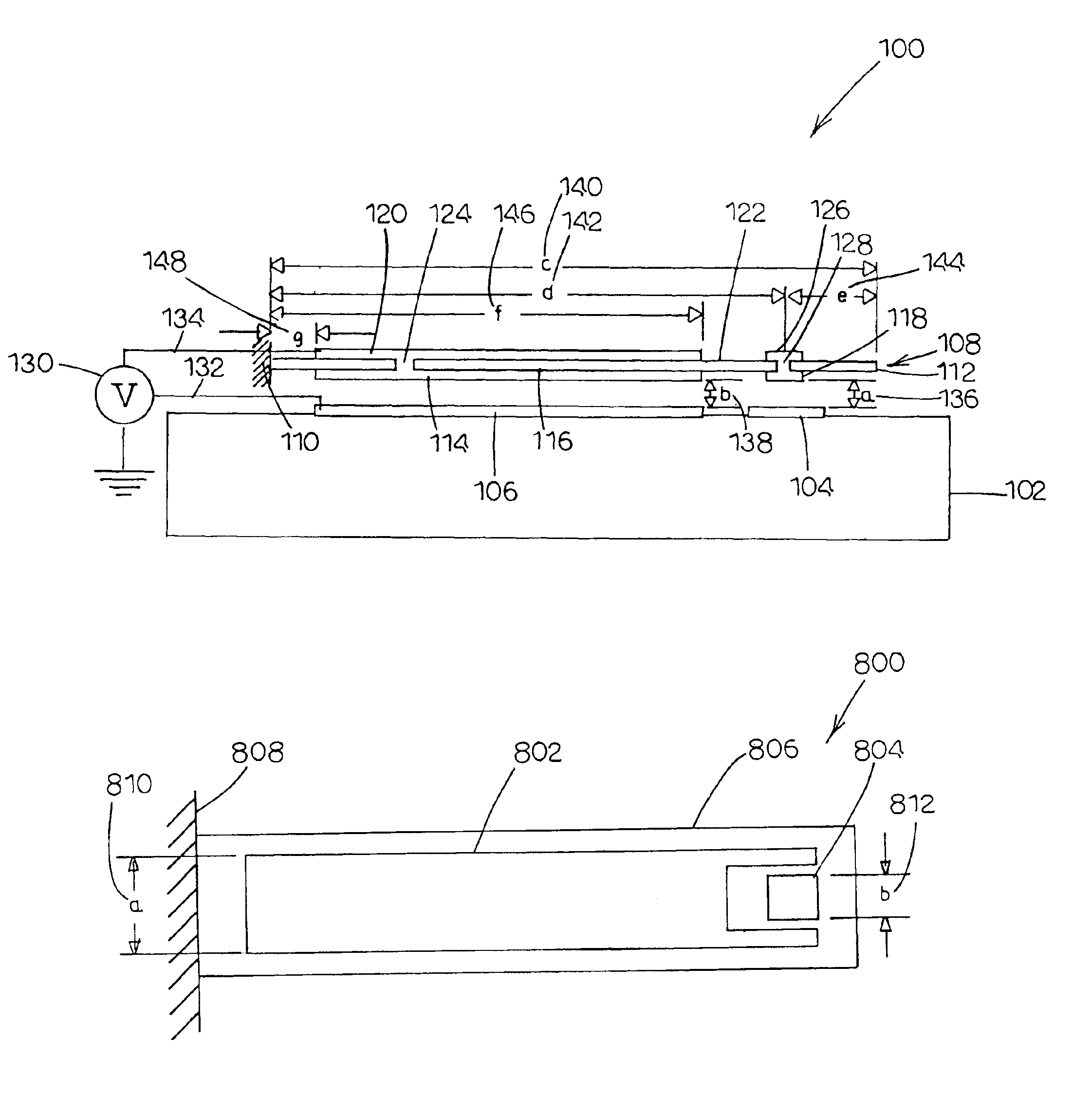
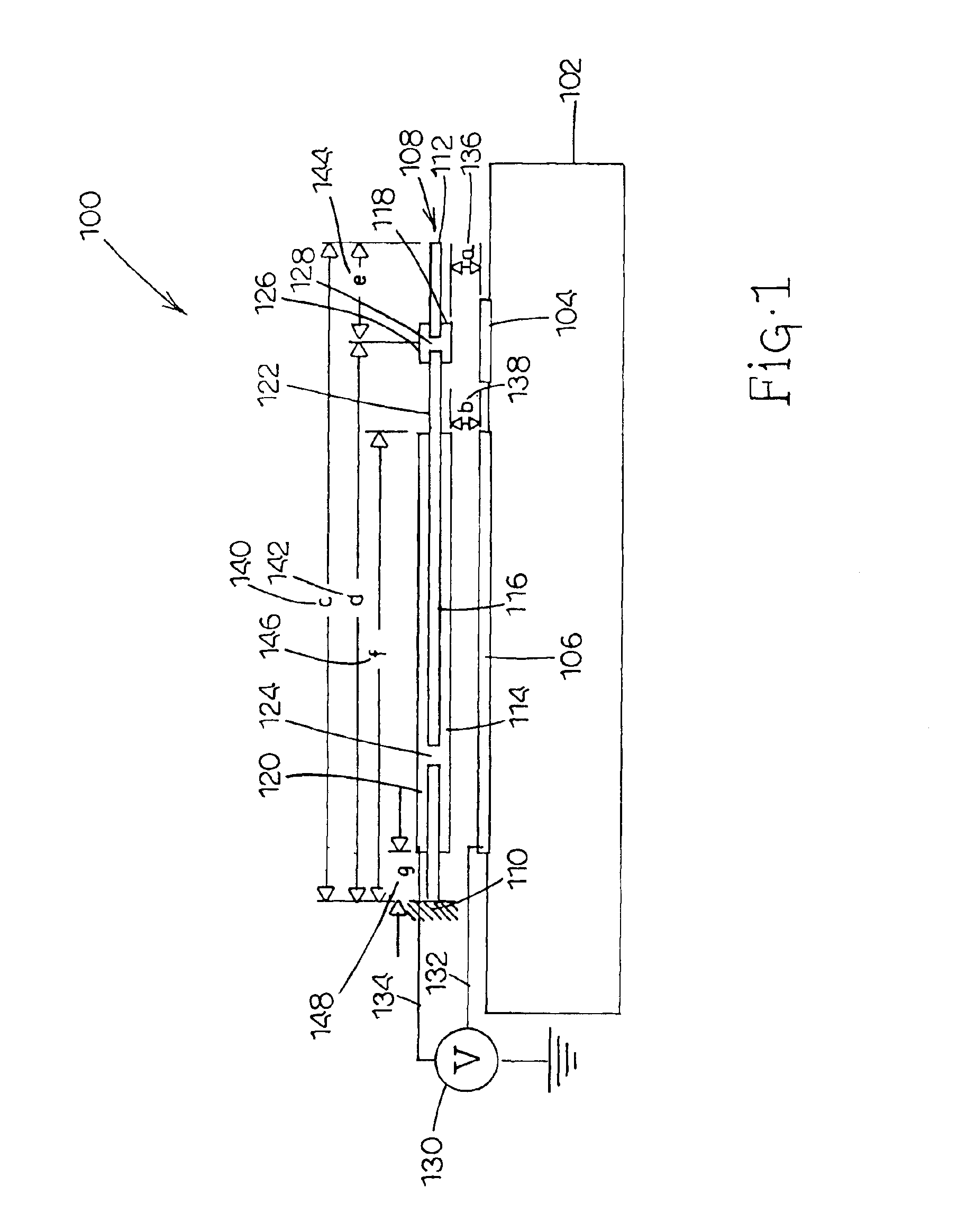
ActiveUS20050046672A1Without excessive riseHigh repetition rateInking apparatusThermal electric motorEngineeringThermal expansion
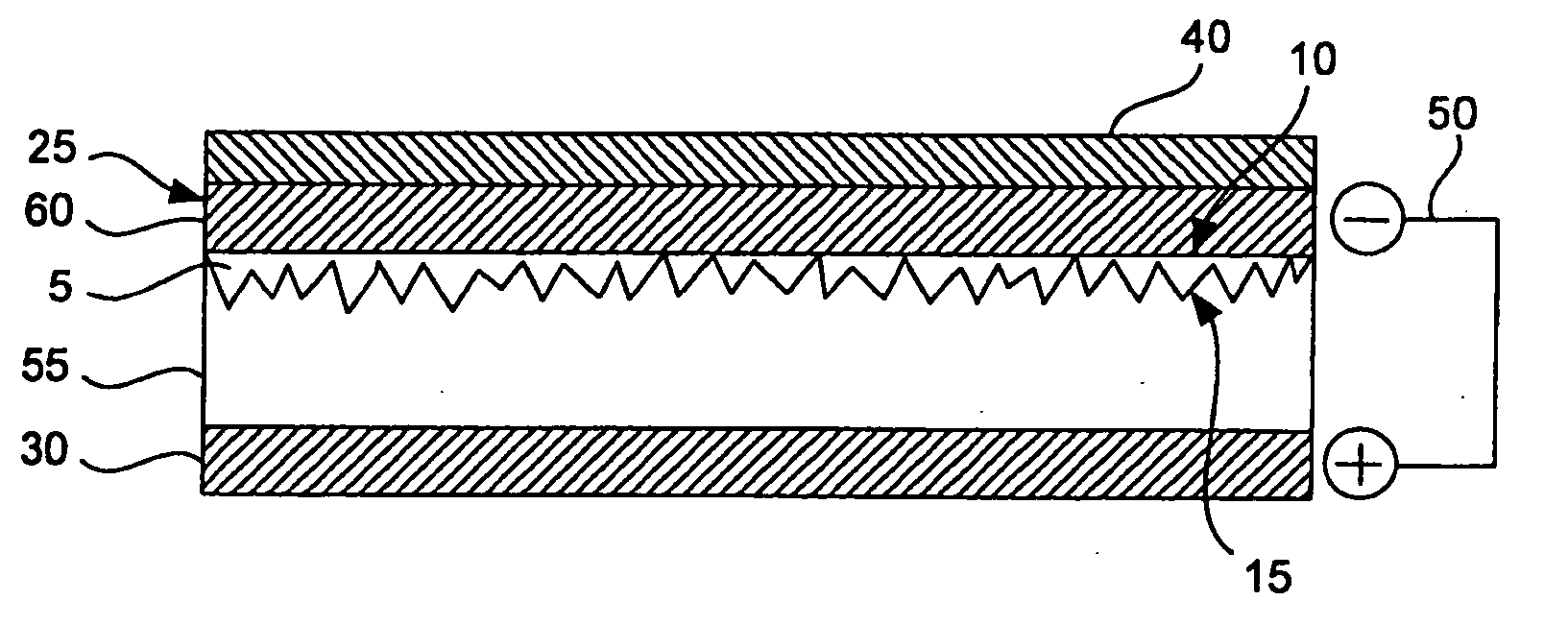
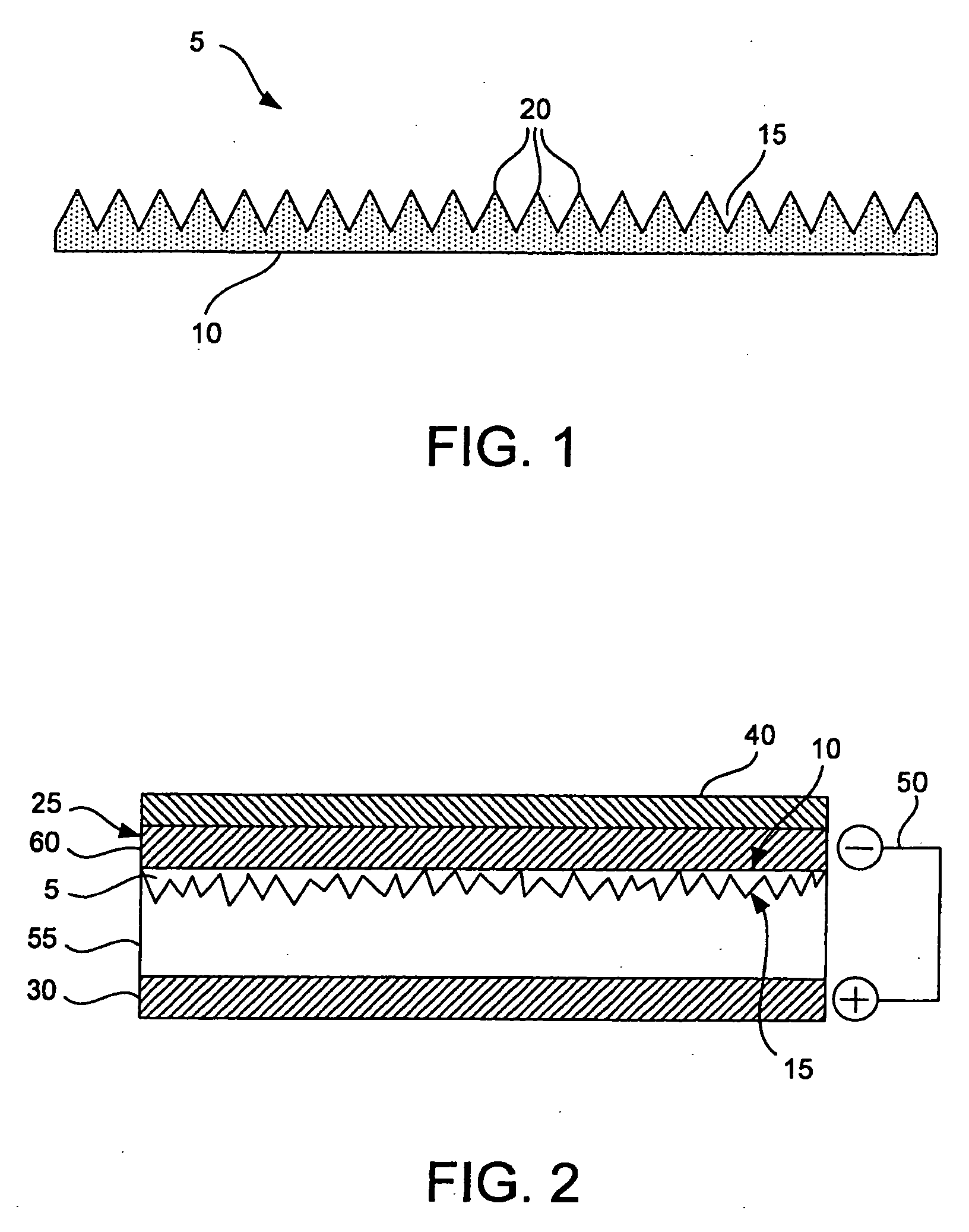
A thermal actuator for a micro-electromechanical device, especially a liquid drop emitter for ink jet printing, is disclosed. The thermal actuator comprises a base element and a movable element extending from the base element and residing at a first position. The movable element includes a barrier layer constructed of a barrier material having low thermal conductivity material, bonded between a first layer and a second layer; wherein the first layer is constructed of a first material having a high coefficient of thermal expansion and the second layer is constructed of a second material having a high thermal conductivity and a high Young's modulus. An apparatus is provided adapted to apply a heat pulse directly to the first layer, causing a thermal expansion of the first layer relative to the second layer and deflection of the movable element to a second position, followed by relaxation of the movable element towards the first position as heat diffuses through the barrier layer to the second layer. Configurations of the movable element as a cantilever, doubly-anchored beam and clamped plate are disclosed. Diamond and silicon carbide materials are well suited for use as the second material. Titanium aluminide is a preferred material for the first material.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Closely spaced electrodes with a uniform gap
InactiveUS20060138896A1Simple inexpensiveLow costFrom solar energyMachines/enginesTunnel diodeEngineering
An improved design for maintaining separation between electrodes in tunneling, diode, thermionic, and other devices is disclosed. At least one electrode is made from flexible material. A magnetic field is present to combine with the current flowing in the flexible electrode and generate a force that counterbalances the electrostatic force between the electrodes. The balancing of forces allows the separation and parallelism between the electrodes to be maintained at a very small spacing without requiring the use of multiple control systems, actuators, or other manipulating means, or spacers. The shape of one or both electrodes is designed to maintain a constant separation over the entire overlapping area of the electrodes. The end result is an electronic device that maintains two closely spaced parallel electrodes in stable equilibrium with a uniform gap therebetween over a large area in a simple configuration for simplified manufacturability and use to convert heat to electricity or electricity to cooling.
Owner:TEMPRONICS INC
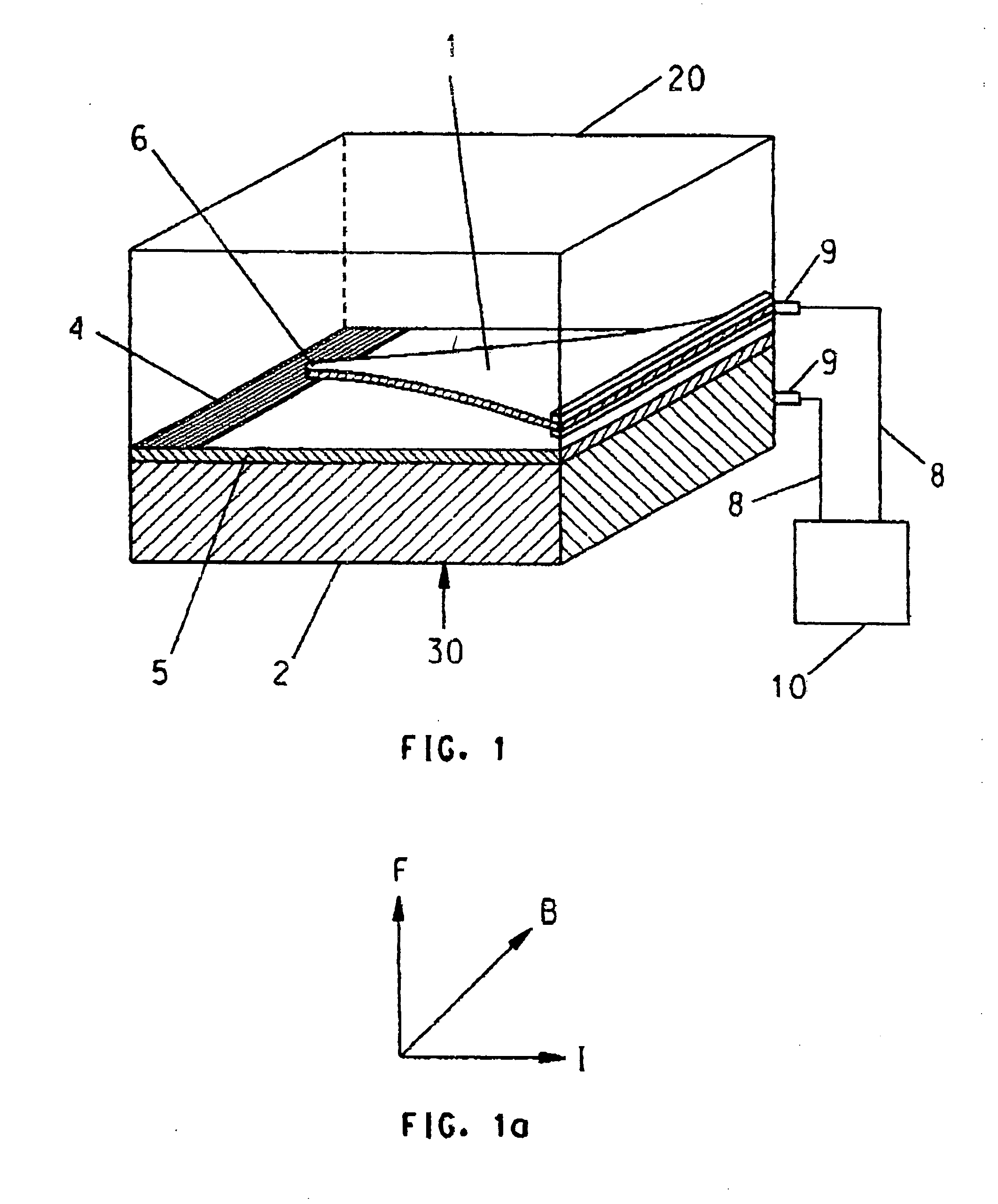
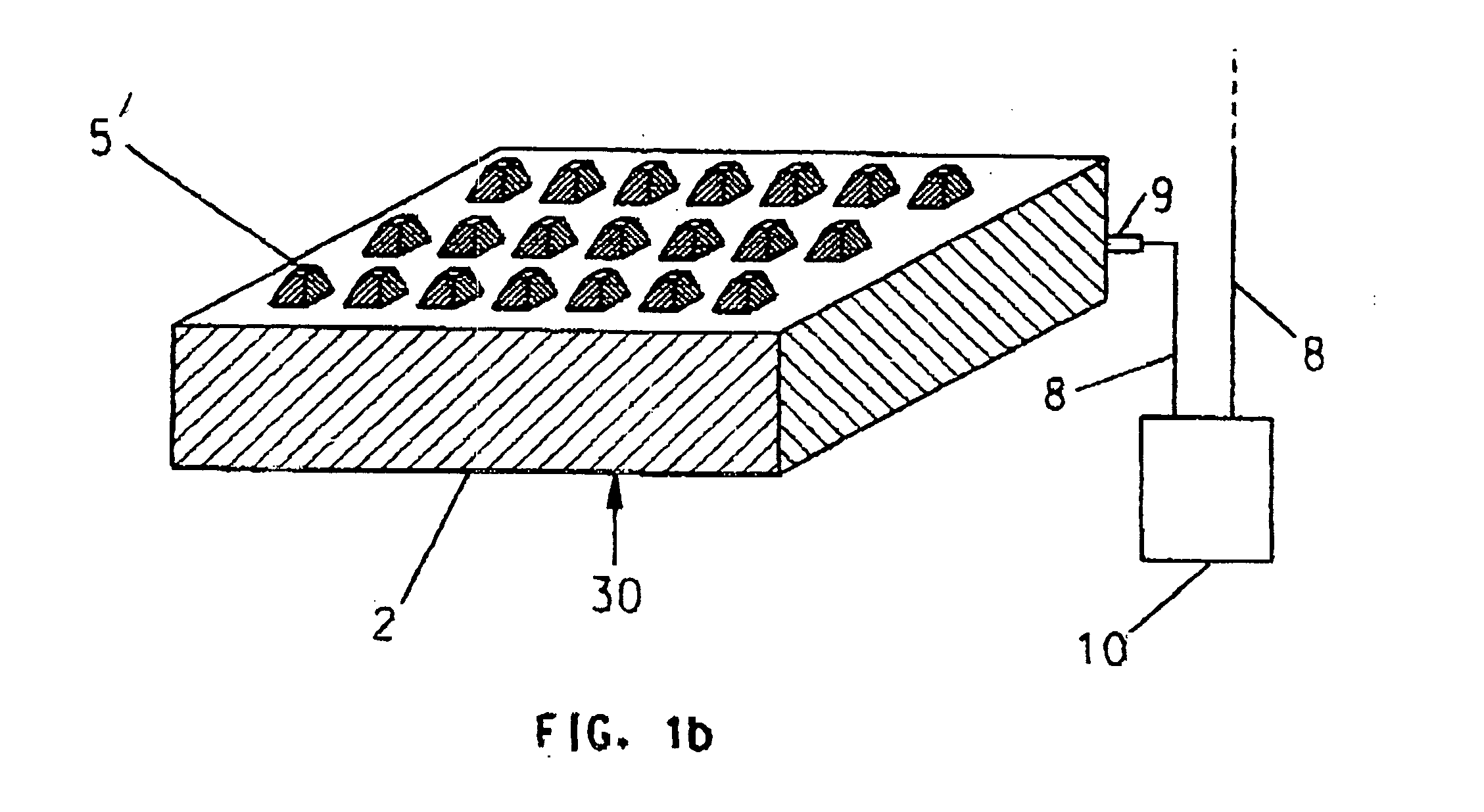
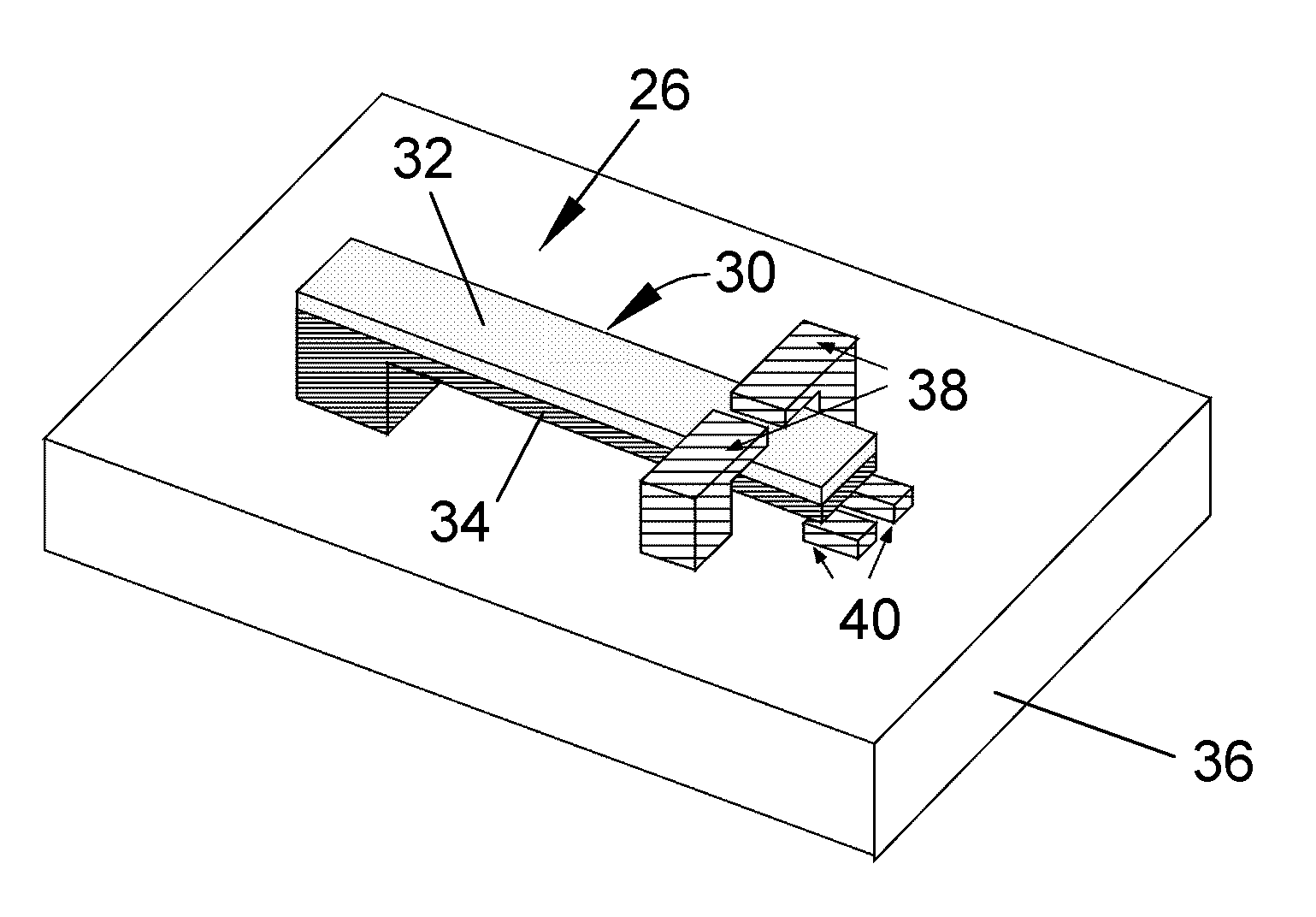
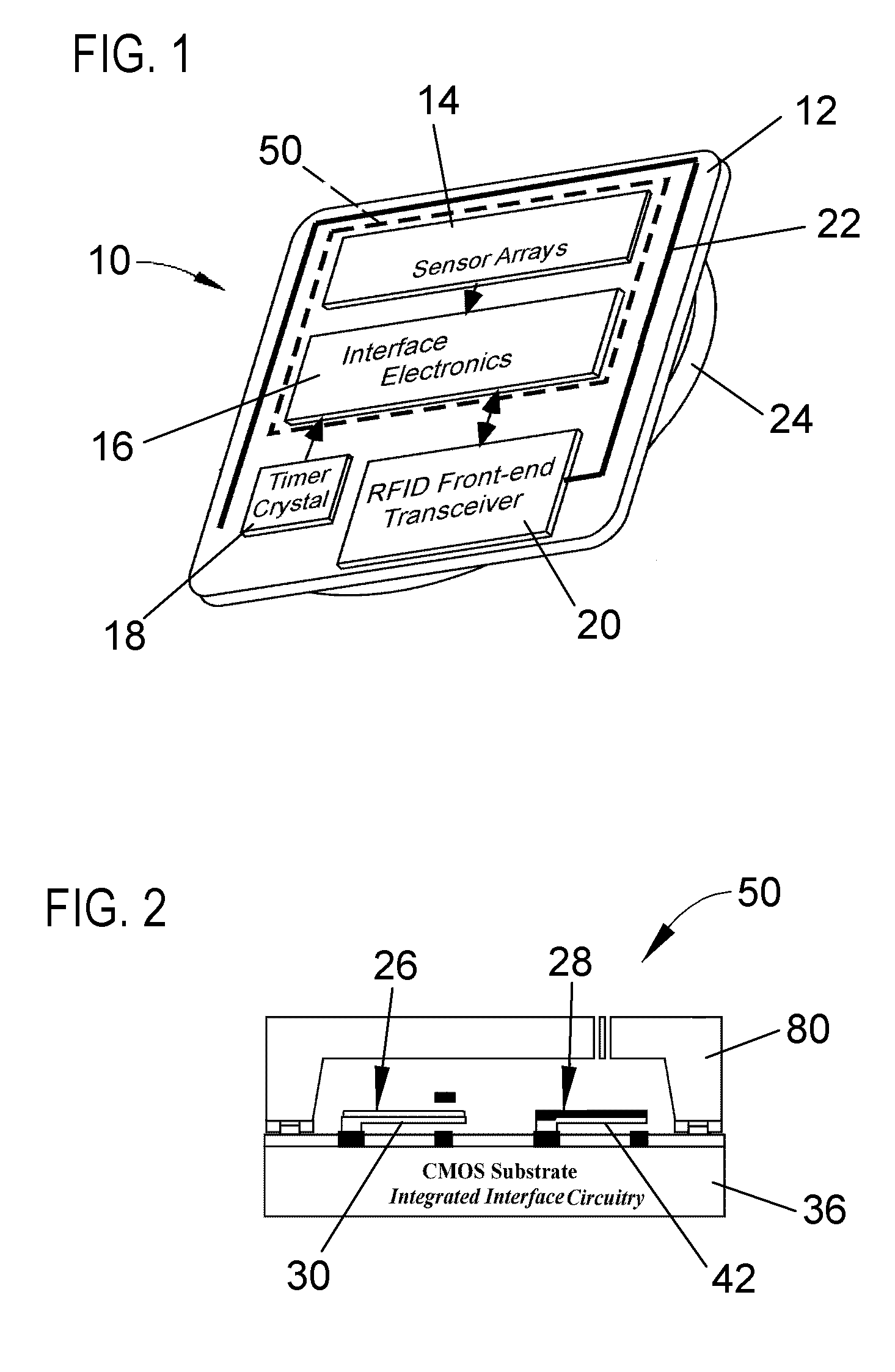
Method and system for monitoring environmental conditions
InactiveUS20070024410A1The testing process is simpleUltra-low power operationThermometer detailsThermometers using mean/integrated valuesEngineeringOpen contact
A sensing system, sensing method, and method of producing a sensing system capable of providing a cumulative measurement capability, such as in the form of a RFID tag capable of measuring cumulative heat and humidity for continuous monitoring of storage and shipping conditions of various goods. The system includes integrated circuitry and a plurality of sensing elements, preferably having cantilevered bimorph beams. Each sensing element is responsive to an environmental condition so as to deflect toward and away from open contacts in response to changes in the environmental condition. Each sensing element produces a digital output when it contacts and closes its open contacts. The integrated circuitry interfaces with the sensing elements so that the digital outputs of the sensing elements are processed to generate a system output of the sensing system.
Owner:BELLUTECH LLC
Coiled and non-coiled twisted polymer fiber torsional and tensile actuators
Actuators (artificial muscles) comprising twist-spun nanofiber yarn or twist-inserted polymer fibers generate torsional and / or tensile actuation when powered electrically, photonically, chemically, thermally, by absorption, or by other means. These artificial muscles utilize non-coiled or coiled yarns and can be either neat or comprising a guest. Devices comprising these artificial muscles are also described.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com